User login
Malaria: Testing parasite DNA in travelers’ blood may help predict drug resistance
Testing the DNA of antimicrobial-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in the blood of travelers from malaria-endemic regions may help researchers monitor how drug resistance changes over time, a study from Canada reports.
“Malaria remains the deadliest vector-borne infectious disease worldwide. Plasmodium spp., most commonly P. falciparum, are responsible for [approximately] 229 million cases and 500,000 deaths from malaria annually,” the authors write in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
“Our findings demonstrate an absence of genetic markers of resistance to the most powerful antimalarials on the planet – the artemisinins – in potentially deadly malaria imported primarily from sub-Saharan Africa over time. This is good news,” senior study author Andrea K. Boggild, MD, MSc, DTMH, told this news organization.
“We also showed that over 90% of falciparum malaria imports were resistant to the proguanil component of the fixed drug combination atovaquone-proguanil, a popular oral antimalarial that is first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria in Canada,” Dr. Boggild, an associate professor in the department of medicine at the University of Toronto, Canada, added in an email. “We documented no genetic markers of atovaquone resistance.”
Search for global patterns of emerging drug resistance
Dr. Boggild, the medical director of the tropical disease unit at Toronto General Hospital, and colleagues analyzed 243 whole-blood specimens that contained P. falciparum and no other Plasmodium species from the malaria biobank at the Public Health Ontario Laboratory in Toronto. They analyzed specimens from the years 2008-2009, 2013-2014, and 2017-2018 from patients ranging in age from 3 to 88 years. Of the 186 patients with a documented travel history, 81 had traveled in West Africa, the most common region, and 40 in Nigeria, the most common country. Five specimens came from travelers to Southeast Asia, and one came from a traveler to the Caribbean.
The researchers extracted DNA from whole blood and detected the parasite’s DNA by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). They analyzed 23 different single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in six genes, and quantified the prevalence of resistance markers, including genes that provoke resistance to the most common antimalarial drugs: chloroquine, mefloquine, atovaquone/proguanil, and the artemisinins.
They analyzed SNPs at atpase6 (pfATPase6), pfcrt (chloroquine resistance transporter, cytb (cytochrome b), dhfr (dihydrofolate reductase), dhps (dihydropteroate synthetase), mdr1 (multidrug resistance protein) and mdr1 copy number, and kelch13 (kelch protein gene on chromosome 13).
Over time, they detected increasing mutant genotypes for dhfr S108N (P = .001) and dhps A613T (P = .029) but decreasing mutant genotypes for mdr1 N86Y (P < .001), D1246Y (P = .003), pfcrt K76T (P = .011), and pfcrt 74-75 (P = .014). They found no kelch13 mutations. They detected fewer mutations indicating chloroquine resistance over time, suggesting less chloroquine pressure in specimens from travelers to Africa, but mutations that provided proguanil resistance increased.
“Antimalarial resistance – particularly resistance to the powerful artemisinins – continues to expand globally, and it is important to conduct routine surveillance for resistant parasites in order to inform appropriate prevention and treatment guidelines,” Dr. Boggild explained. “It cannot be presumed that a drug’s efficacy will be durable over time given the global landscape of antimalarial resistance.”
Dr. Boggild acknowledged limitations to the study, including incomplete travel history in about half of the patients, relatively few patients from Southeast Asia, and the small sample set.
“Clinicians caring for travelers before or after travel should familiarize themselves with the options for malaria prevention and treatment and understand the risk–benefit profile of each drug,” Dr. Boggild advised.
“Resistance to proguanil means that we are reliant on the partner drug atovaquone for the antimalarial action of this formulation, which is effective only when taken with food,” she added.
Anne N. Cowell, MD, MPH, of the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Diego, was not surprised by the findings.
“The study demonstrates how quickly malaria parasites adapt and evolve to survive changes in malaria treatment,” Dr. Cowell, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
“These changes reflect changing malaria treatment and thus drug pressure during the time period,” she said in an email. “Because the majority of the clinical samples with a known travel history came from West Africa, and there was no clear evidence of artemisinin resistance in the area during the final time period studied, it is not surprising that they did not find kelch13 resistance mutations.
“The increase in mutations associated with proguanil resistance is concerning because atovaquone-proguanil is frequently used for prophylaxis during travel,” Dr. Cowell added. “There is no widespread evidence of resistance in travelers at this time, but it warrants monitoring.”
Sean C. Murphy, MD, PhD, an associate professor of laboratory medicine and the director of the malaria molecular diagnostic laboratory at the University of Washington in Seattle, also was not surprised by the study’s results.
“It may be just a matter of time before evidence of artemisinin resistance crops up among returning travelers,” he said in an email. “When that happens, we may lose the opportunity to easily use common go-to drugs like atovaquone/proguanil to treat these patients.
“The biggest takeaway of this study is the reminder that drug-resistant malaria (including the future potential for artemisinin-resistant malaria) is just an airplane flight or two away from nonendemic places like Canada and the United States,” Dr. Murphy noted. He was not involved with this Canadian study.
“Continued investment is needed to support malaria control, drug resistance monitoring, and vaccine efforts in order to fight this relentless, terrible parasite,” he urged.
The Project Initiation Fund of Public Health Ontario funded the study. The study authors, Dr. Cowell, and Dr. Murphy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Testing the DNA of antimicrobial-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in the blood of travelers from malaria-endemic regions may help researchers monitor how drug resistance changes over time, a study from Canada reports.
“Malaria remains the deadliest vector-borne infectious disease worldwide. Plasmodium spp., most commonly P. falciparum, are responsible for [approximately] 229 million cases and 500,000 deaths from malaria annually,” the authors write in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
“Our findings demonstrate an absence of genetic markers of resistance to the most powerful antimalarials on the planet – the artemisinins – in potentially deadly malaria imported primarily from sub-Saharan Africa over time. This is good news,” senior study author Andrea K. Boggild, MD, MSc, DTMH, told this news organization.
“We also showed that over 90% of falciparum malaria imports were resistant to the proguanil component of the fixed drug combination atovaquone-proguanil, a popular oral antimalarial that is first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria in Canada,” Dr. Boggild, an associate professor in the department of medicine at the University of Toronto, Canada, added in an email. “We documented no genetic markers of atovaquone resistance.”
Search for global patterns of emerging drug resistance
Dr. Boggild, the medical director of the tropical disease unit at Toronto General Hospital, and colleagues analyzed 243 whole-blood specimens that contained P. falciparum and no other Plasmodium species from the malaria biobank at the Public Health Ontario Laboratory in Toronto. They analyzed specimens from the years 2008-2009, 2013-2014, and 2017-2018 from patients ranging in age from 3 to 88 years. Of the 186 patients with a documented travel history, 81 had traveled in West Africa, the most common region, and 40 in Nigeria, the most common country. Five specimens came from travelers to Southeast Asia, and one came from a traveler to the Caribbean.
The researchers extracted DNA from whole blood and detected the parasite’s DNA by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). They analyzed 23 different single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in six genes, and quantified the prevalence of resistance markers, including genes that provoke resistance to the most common antimalarial drugs: chloroquine, mefloquine, atovaquone/proguanil, and the artemisinins.
They analyzed SNPs at atpase6 (pfATPase6), pfcrt (chloroquine resistance transporter, cytb (cytochrome b), dhfr (dihydrofolate reductase), dhps (dihydropteroate synthetase), mdr1 (multidrug resistance protein) and mdr1 copy number, and kelch13 (kelch protein gene on chromosome 13).
Over time, they detected increasing mutant genotypes for dhfr S108N (P = .001) and dhps A613T (P = .029) but decreasing mutant genotypes for mdr1 N86Y (P < .001), D1246Y (P = .003), pfcrt K76T (P = .011), and pfcrt 74-75 (P = .014). They found no kelch13 mutations. They detected fewer mutations indicating chloroquine resistance over time, suggesting less chloroquine pressure in specimens from travelers to Africa, but mutations that provided proguanil resistance increased.
“Antimalarial resistance – particularly resistance to the powerful artemisinins – continues to expand globally, and it is important to conduct routine surveillance for resistant parasites in order to inform appropriate prevention and treatment guidelines,” Dr. Boggild explained. “It cannot be presumed that a drug’s efficacy will be durable over time given the global landscape of antimalarial resistance.”
Dr. Boggild acknowledged limitations to the study, including incomplete travel history in about half of the patients, relatively few patients from Southeast Asia, and the small sample set.
“Clinicians caring for travelers before or after travel should familiarize themselves with the options for malaria prevention and treatment and understand the risk–benefit profile of each drug,” Dr. Boggild advised.
“Resistance to proguanil means that we are reliant on the partner drug atovaquone for the antimalarial action of this formulation, which is effective only when taken with food,” she added.
Anne N. Cowell, MD, MPH, of the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Diego, was not surprised by the findings.
“The study demonstrates how quickly malaria parasites adapt and evolve to survive changes in malaria treatment,” Dr. Cowell, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
“These changes reflect changing malaria treatment and thus drug pressure during the time period,” she said in an email. “Because the majority of the clinical samples with a known travel history came from West Africa, and there was no clear evidence of artemisinin resistance in the area during the final time period studied, it is not surprising that they did not find kelch13 resistance mutations.
“The increase in mutations associated with proguanil resistance is concerning because atovaquone-proguanil is frequently used for prophylaxis during travel,” Dr. Cowell added. “There is no widespread evidence of resistance in travelers at this time, but it warrants monitoring.”
Sean C. Murphy, MD, PhD, an associate professor of laboratory medicine and the director of the malaria molecular diagnostic laboratory at the University of Washington in Seattle, also was not surprised by the study’s results.
“It may be just a matter of time before evidence of artemisinin resistance crops up among returning travelers,” he said in an email. “When that happens, we may lose the opportunity to easily use common go-to drugs like atovaquone/proguanil to treat these patients.
“The biggest takeaway of this study is the reminder that drug-resistant malaria (including the future potential for artemisinin-resistant malaria) is just an airplane flight or two away from nonendemic places like Canada and the United States,” Dr. Murphy noted. He was not involved with this Canadian study.
“Continued investment is needed to support malaria control, drug resistance monitoring, and vaccine efforts in order to fight this relentless, terrible parasite,” he urged.
The Project Initiation Fund of Public Health Ontario funded the study. The study authors, Dr. Cowell, and Dr. Murphy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Testing the DNA of antimicrobial-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in the blood of travelers from malaria-endemic regions may help researchers monitor how drug resistance changes over time, a study from Canada reports.
“Malaria remains the deadliest vector-borne infectious disease worldwide. Plasmodium spp., most commonly P. falciparum, are responsible for [approximately] 229 million cases and 500,000 deaths from malaria annually,” the authors write in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
“Our findings demonstrate an absence of genetic markers of resistance to the most powerful antimalarials on the planet – the artemisinins – in potentially deadly malaria imported primarily from sub-Saharan Africa over time. This is good news,” senior study author Andrea K. Boggild, MD, MSc, DTMH, told this news organization.
“We also showed that over 90% of falciparum malaria imports were resistant to the proguanil component of the fixed drug combination atovaquone-proguanil, a popular oral antimalarial that is first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria in Canada,” Dr. Boggild, an associate professor in the department of medicine at the University of Toronto, Canada, added in an email. “We documented no genetic markers of atovaquone resistance.”
Search for global patterns of emerging drug resistance
Dr. Boggild, the medical director of the tropical disease unit at Toronto General Hospital, and colleagues analyzed 243 whole-blood specimens that contained P. falciparum and no other Plasmodium species from the malaria biobank at the Public Health Ontario Laboratory in Toronto. They analyzed specimens from the years 2008-2009, 2013-2014, and 2017-2018 from patients ranging in age from 3 to 88 years. Of the 186 patients with a documented travel history, 81 had traveled in West Africa, the most common region, and 40 in Nigeria, the most common country. Five specimens came from travelers to Southeast Asia, and one came from a traveler to the Caribbean.
The researchers extracted DNA from whole blood and detected the parasite’s DNA by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). They analyzed 23 different single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in six genes, and quantified the prevalence of resistance markers, including genes that provoke resistance to the most common antimalarial drugs: chloroquine, mefloquine, atovaquone/proguanil, and the artemisinins.
They analyzed SNPs at atpase6 (pfATPase6), pfcrt (chloroquine resistance transporter, cytb (cytochrome b), dhfr (dihydrofolate reductase), dhps (dihydropteroate synthetase), mdr1 (multidrug resistance protein) and mdr1 copy number, and kelch13 (kelch protein gene on chromosome 13).
Over time, they detected increasing mutant genotypes for dhfr S108N (P = .001) and dhps A613T (P = .029) but decreasing mutant genotypes for mdr1 N86Y (P < .001), D1246Y (P = .003), pfcrt K76T (P = .011), and pfcrt 74-75 (P = .014). They found no kelch13 mutations. They detected fewer mutations indicating chloroquine resistance over time, suggesting less chloroquine pressure in specimens from travelers to Africa, but mutations that provided proguanil resistance increased.
“Antimalarial resistance – particularly resistance to the powerful artemisinins – continues to expand globally, and it is important to conduct routine surveillance for resistant parasites in order to inform appropriate prevention and treatment guidelines,” Dr. Boggild explained. “It cannot be presumed that a drug’s efficacy will be durable over time given the global landscape of antimalarial resistance.”
Dr. Boggild acknowledged limitations to the study, including incomplete travel history in about half of the patients, relatively few patients from Southeast Asia, and the small sample set.
“Clinicians caring for travelers before or after travel should familiarize themselves with the options for malaria prevention and treatment and understand the risk–benefit profile of each drug,” Dr. Boggild advised.
“Resistance to proguanil means that we are reliant on the partner drug atovaquone for the antimalarial action of this formulation, which is effective only when taken with food,” she added.
Anne N. Cowell, MD, MPH, of the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Diego, was not surprised by the findings.
“The study demonstrates how quickly malaria parasites adapt and evolve to survive changes in malaria treatment,” Dr. Cowell, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
“These changes reflect changing malaria treatment and thus drug pressure during the time period,” she said in an email. “Because the majority of the clinical samples with a known travel history came from West Africa, and there was no clear evidence of artemisinin resistance in the area during the final time period studied, it is not surprising that they did not find kelch13 resistance mutations.
“The increase in mutations associated with proguanil resistance is concerning because atovaquone-proguanil is frequently used for prophylaxis during travel,” Dr. Cowell added. “There is no widespread evidence of resistance in travelers at this time, but it warrants monitoring.”
Sean C. Murphy, MD, PhD, an associate professor of laboratory medicine and the director of the malaria molecular diagnostic laboratory at the University of Washington in Seattle, also was not surprised by the study’s results.
“It may be just a matter of time before evidence of artemisinin resistance crops up among returning travelers,” he said in an email. “When that happens, we may lose the opportunity to easily use common go-to drugs like atovaquone/proguanil to treat these patients.
“The biggest takeaway of this study is the reminder that drug-resistant malaria (including the future potential for artemisinin-resistant malaria) is just an airplane flight or two away from nonendemic places like Canada and the United States,” Dr. Murphy noted. He was not involved with this Canadian study.
“Continued investment is needed to support malaria control, drug resistance monitoring, and vaccine efforts in order to fight this relentless, terrible parasite,” he urged.
The Project Initiation Fund of Public Health Ontario funded the study. The study authors, Dr. Cowell, and Dr. Murphy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Experts decry CDC’s long pause on neglected tropical disease testing
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has long been the premier reference lab for the United States and, for some diseases, internationally.
In September 2021, the CDC stated on its website that it would stop testing for parasites, herpesvirus encephalitis, human herpesvirus 6 and 7, Epstein-Barr virus, and other viruses, saying, “We are working diligently to implement laboratory system improvements.”
At the time, the CDC said testing would be halted only for a few months.
In response to a query from this news organization, a CDC spokesperson replied, “While at present we are unable to share a detailed timeline, our highest priority is to resume high-quality testing operations in a phased, prioritized approach as soon as possible and to offer the same tests that were available before the pause.”
Several global health clinicians told this news organization that they were not aware of the halt and that they are now uncertain about the specific diagnosis and best treatment for some patients. Other patients have been lost to follow-up.
In response, a group of tropical disease specialists who focus on neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) wrote an editorial, “Neglected Testing for Neglected Tropical Diseases at the CDC,” which recently appeared in the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (AJTMH).
NTDs are caused by viruses, bacteria, and parasites. They include leprosy and worms; many such diseases are disfiguring, such as filariasis (which causes the hugely swollen extremities of elephantiasis) and onchocerciasis (river blindness). They also include some viral and bacterial diseases. Their common denominator is that they are diseases of poverty, primarily in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, so they garner little attention from “first world” countries.
The loss of testing for two devastating parasites – Chagas and Leishmania – was particularly significant. Few other labs in the United States test for these, and the tests can be expensive and of variable quality, experts said.
Norman Beatty, MD, a global health physician at the University of Florida, told this news organization, “Chagas confirmatory testing is only available at the CDC and is the most reliable testing we have access to in the United States. Leishmania species identification is also only available at the CDC and is important in determining which antiparasitic medications we will use.”
Chagas disease is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi and is transmitted by triatomine bugs, also known as kissing bugs. Chagas is a major cause of an enlarged heart and congestive heart failure, as well as a dramatically enlarged esophagus or colon.
Prior to the cuts and before COVID-19, the CDC reported that they ran 10,000 to 15,000 tests for parasitic diseases annually. Testing requests declined during COVID. In 2021, they ran 1,003 tests for Chagas.
Dr. Beatty said that he first became aware of the CDC’s testing cuts last fall when he sought care for a patient. He was first told the delay would be 2-3 weeks, then another 2-3 weeks. It’s now been 7 months, and only three tests have been resumed.
Dr. Beatty added that for Chagas disease in particular, there is urgency in testing because cardiac complications can be life-threatening. He said that “a lot of these diseases can be considered rare, but they also have a tremendous ability to cause morbidity and mortality.”
Leishmania infections are also serious. Following the bite of an infected sandfly, they can cause disfiguring skin infections, but, more importantly, they can affect the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Dr. Beatty said that since testing was dropped at the CDC, some colleagues had to send specimens outside of the country.
Dr. Beatty emphasized that the cuts in testing at the CDC highlight disparities in our society. “There are other commercial reference laboratories who may have some of these tests available, but the vast majority of people who suffer from diseases are underserved and vulnerable. [My patients] most definitely will not have access to advanced testing commercial laboratories,” Dr. Beatty said. Those laboratories include Associated Regional University Pathologists laboratories, Quest Diagnostics, and LabCorp Diagnostics. But for some parasitic infections, there will simply be no testing, and patients will not receive appropriate therapy.
The CDC’s website says, “USAID and CDC work together on a shared agenda to advance global progress towards the control and elimination of NTDs that can be addressed with preventive chemotherapy. ... CDC has strong working relationships with WHO, regional reference laboratories/bodies, [and] national NTD programs ... working with these partners through the provision of unique laboratory, diagnostic, and epidemiological technical assistance.”
The WHO Roadmap for 2030 aims to prevent and control many NTDs, in part by “providing new interventions and effective, standardized, and affordable diagnostics.” Last year, the CDC said that they “will continue working with WHO and other global partners to meet the established goals.”
But testing for a number of NTDs is not currently available at the CDC. In response to questions from this news organization, a CDC spokesperson said the agency “supports the development of country capacity for NTD testing required ... but does not perform testing related to the WHO Roadmap.”
A group of CDC officials wrote an editorial response that was published in AJTMH, saying the agency has “three main priorities: reducing parasitic disease-related death, illness, and disability in the United States; reducing the global burden of malaria; and eliminating targeted neglected tropical diseases.”
In response to this news organization’s interview request, a CDC spokesperson wrote, “CDC is unwavering in our commitment to provide the highest quality laboratory diagnostic services for parasitic diseases. We understand the concerns expressed in the editorial and the challenges the pause in testing for parasitic diseases presents for health care providers, particularly those treating people at elevated risk for parasitic diseases.”
Michael Reich, PhD, Dr. Beatty’s co-author, is an international health policy expert at Harvard. He and the physicians had approached CDC about the elimination of services. He said in an interview, “We’re still unable to get clear responses except for something along the lines of, ‘We are working on it. It is complicated. It takes time. We’re doing our best.’”
Dr. Reich added, “For me, this raises troubling issues both of transparency and accountability – transparency about what is going on and what the problems are, and accountability in terms of who’s being held responsible for the closures and the impacts on both public health and patient treatment.”
Dr. Beatty concluded, “I think the goal of our group was to bring more awareness to the importance of having a national laboratory that can service all people, even the most underserved and vulnerable populations.” He added, “Chagas disease is a disease of inequity in Latin Americans. Without having access to an appropriate laboratory such as the CDC, we would be taking a backwards approach to tackle neglected tropical diseases in our country and worldwide.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Reich report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has long been the premier reference lab for the United States and, for some diseases, internationally.
In September 2021, the CDC stated on its website that it would stop testing for parasites, herpesvirus encephalitis, human herpesvirus 6 and 7, Epstein-Barr virus, and other viruses, saying, “We are working diligently to implement laboratory system improvements.”
At the time, the CDC said testing would be halted only for a few months.
In response to a query from this news organization, a CDC spokesperson replied, “While at present we are unable to share a detailed timeline, our highest priority is to resume high-quality testing operations in a phased, prioritized approach as soon as possible and to offer the same tests that were available before the pause.”
Several global health clinicians told this news organization that they were not aware of the halt and that they are now uncertain about the specific diagnosis and best treatment for some patients. Other patients have been lost to follow-up.
In response, a group of tropical disease specialists who focus on neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) wrote an editorial, “Neglected Testing for Neglected Tropical Diseases at the CDC,” which recently appeared in the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (AJTMH).
NTDs are caused by viruses, bacteria, and parasites. They include leprosy and worms; many such diseases are disfiguring, such as filariasis (which causes the hugely swollen extremities of elephantiasis) and onchocerciasis (river blindness). They also include some viral and bacterial diseases. Their common denominator is that they are diseases of poverty, primarily in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, so they garner little attention from “first world” countries.
The loss of testing for two devastating parasites – Chagas and Leishmania – was particularly significant. Few other labs in the United States test for these, and the tests can be expensive and of variable quality, experts said.
Norman Beatty, MD, a global health physician at the University of Florida, told this news organization, “Chagas confirmatory testing is only available at the CDC and is the most reliable testing we have access to in the United States. Leishmania species identification is also only available at the CDC and is important in determining which antiparasitic medications we will use.”
Chagas disease is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi and is transmitted by triatomine bugs, also known as kissing bugs. Chagas is a major cause of an enlarged heart and congestive heart failure, as well as a dramatically enlarged esophagus or colon.
Prior to the cuts and before COVID-19, the CDC reported that they ran 10,000 to 15,000 tests for parasitic diseases annually. Testing requests declined during COVID. In 2021, they ran 1,003 tests for Chagas.
Dr. Beatty said that he first became aware of the CDC’s testing cuts last fall when he sought care for a patient. He was first told the delay would be 2-3 weeks, then another 2-3 weeks. It’s now been 7 months, and only three tests have been resumed.
Dr. Beatty added that for Chagas disease in particular, there is urgency in testing because cardiac complications can be life-threatening. He said that “a lot of these diseases can be considered rare, but they also have a tremendous ability to cause morbidity and mortality.”
Leishmania infections are also serious. Following the bite of an infected sandfly, they can cause disfiguring skin infections, but, more importantly, they can affect the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Dr. Beatty said that since testing was dropped at the CDC, some colleagues had to send specimens outside of the country.
Dr. Beatty emphasized that the cuts in testing at the CDC highlight disparities in our society. “There are other commercial reference laboratories who may have some of these tests available, but the vast majority of people who suffer from diseases are underserved and vulnerable. [My patients] most definitely will not have access to advanced testing commercial laboratories,” Dr. Beatty said. Those laboratories include Associated Regional University Pathologists laboratories, Quest Diagnostics, and LabCorp Diagnostics. But for some parasitic infections, there will simply be no testing, and patients will not receive appropriate therapy.
The CDC’s website says, “USAID and CDC work together on a shared agenda to advance global progress towards the control and elimination of NTDs that can be addressed with preventive chemotherapy. ... CDC has strong working relationships with WHO, regional reference laboratories/bodies, [and] national NTD programs ... working with these partners through the provision of unique laboratory, diagnostic, and epidemiological technical assistance.”
The WHO Roadmap for 2030 aims to prevent and control many NTDs, in part by “providing new interventions and effective, standardized, and affordable diagnostics.” Last year, the CDC said that they “will continue working with WHO and other global partners to meet the established goals.”
But testing for a number of NTDs is not currently available at the CDC. In response to questions from this news organization, a CDC spokesperson said the agency “supports the development of country capacity for NTD testing required ... but does not perform testing related to the WHO Roadmap.”
A group of CDC officials wrote an editorial response that was published in AJTMH, saying the agency has “three main priorities: reducing parasitic disease-related death, illness, and disability in the United States; reducing the global burden of malaria; and eliminating targeted neglected tropical diseases.”
In response to this news organization’s interview request, a CDC spokesperson wrote, “CDC is unwavering in our commitment to provide the highest quality laboratory diagnostic services for parasitic diseases. We understand the concerns expressed in the editorial and the challenges the pause in testing for parasitic diseases presents for health care providers, particularly those treating people at elevated risk for parasitic diseases.”
Michael Reich, PhD, Dr. Beatty’s co-author, is an international health policy expert at Harvard. He and the physicians had approached CDC about the elimination of services. He said in an interview, “We’re still unable to get clear responses except for something along the lines of, ‘We are working on it. It is complicated. It takes time. We’re doing our best.’”
Dr. Reich added, “For me, this raises troubling issues both of transparency and accountability – transparency about what is going on and what the problems are, and accountability in terms of who’s being held responsible for the closures and the impacts on both public health and patient treatment.”
Dr. Beatty concluded, “I think the goal of our group was to bring more awareness to the importance of having a national laboratory that can service all people, even the most underserved and vulnerable populations.” He added, “Chagas disease is a disease of inequity in Latin Americans. Without having access to an appropriate laboratory such as the CDC, we would be taking a backwards approach to tackle neglected tropical diseases in our country and worldwide.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Reich report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has long been the premier reference lab for the United States and, for some diseases, internationally.
In September 2021, the CDC stated on its website that it would stop testing for parasites, herpesvirus encephalitis, human herpesvirus 6 and 7, Epstein-Barr virus, and other viruses, saying, “We are working diligently to implement laboratory system improvements.”
At the time, the CDC said testing would be halted only for a few months.
In response to a query from this news organization, a CDC spokesperson replied, “While at present we are unable to share a detailed timeline, our highest priority is to resume high-quality testing operations in a phased, prioritized approach as soon as possible and to offer the same tests that were available before the pause.”
Several global health clinicians told this news organization that they were not aware of the halt and that they are now uncertain about the specific diagnosis and best treatment for some patients. Other patients have been lost to follow-up.
In response, a group of tropical disease specialists who focus on neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) wrote an editorial, “Neglected Testing for Neglected Tropical Diseases at the CDC,” which recently appeared in the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (AJTMH).
NTDs are caused by viruses, bacteria, and parasites. They include leprosy and worms; many such diseases are disfiguring, such as filariasis (which causes the hugely swollen extremities of elephantiasis) and onchocerciasis (river blindness). They also include some viral and bacterial diseases. Their common denominator is that they are diseases of poverty, primarily in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, so they garner little attention from “first world” countries.
The loss of testing for two devastating parasites – Chagas and Leishmania – was particularly significant. Few other labs in the United States test for these, and the tests can be expensive and of variable quality, experts said.
Norman Beatty, MD, a global health physician at the University of Florida, told this news organization, “Chagas confirmatory testing is only available at the CDC and is the most reliable testing we have access to in the United States. Leishmania species identification is also only available at the CDC and is important in determining which antiparasitic medications we will use.”
Chagas disease is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi and is transmitted by triatomine bugs, also known as kissing bugs. Chagas is a major cause of an enlarged heart and congestive heart failure, as well as a dramatically enlarged esophagus or colon.
Prior to the cuts and before COVID-19, the CDC reported that they ran 10,000 to 15,000 tests for parasitic diseases annually. Testing requests declined during COVID. In 2021, they ran 1,003 tests for Chagas.
Dr. Beatty said that he first became aware of the CDC’s testing cuts last fall when he sought care for a patient. He was first told the delay would be 2-3 weeks, then another 2-3 weeks. It’s now been 7 months, and only three tests have been resumed.
Dr. Beatty added that for Chagas disease in particular, there is urgency in testing because cardiac complications can be life-threatening. He said that “a lot of these diseases can be considered rare, but they also have a tremendous ability to cause morbidity and mortality.”
Leishmania infections are also serious. Following the bite of an infected sandfly, they can cause disfiguring skin infections, but, more importantly, they can affect the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Dr. Beatty said that since testing was dropped at the CDC, some colleagues had to send specimens outside of the country.
Dr. Beatty emphasized that the cuts in testing at the CDC highlight disparities in our society. “There are other commercial reference laboratories who may have some of these tests available, but the vast majority of people who suffer from diseases are underserved and vulnerable. [My patients] most definitely will not have access to advanced testing commercial laboratories,” Dr. Beatty said. Those laboratories include Associated Regional University Pathologists laboratories, Quest Diagnostics, and LabCorp Diagnostics. But for some parasitic infections, there will simply be no testing, and patients will not receive appropriate therapy.
The CDC’s website says, “USAID and CDC work together on a shared agenda to advance global progress towards the control and elimination of NTDs that can be addressed with preventive chemotherapy. ... CDC has strong working relationships with WHO, regional reference laboratories/bodies, [and] national NTD programs ... working with these partners through the provision of unique laboratory, diagnostic, and epidemiological technical assistance.”
The WHO Roadmap for 2030 aims to prevent and control many NTDs, in part by “providing new interventions and effective, standardized, and affordable diagnostics.” Last year, the CDC said that they “will continue working with WHO and other global partners to meet the established goals.”
But testing for a number of NTDs is not currently available at the CDC. In response to questions from this news organization, a CDC spokesperson said the agency “supports the development of country capacity for NTD testing required ... but does not perform testing related to the WHO Roadmap.”
A group of CDC officials wrote an editorial response that was published in AJTMH, saying the agency has “three main priorities: reducing parasitic disease-related death, illness, and disability in the United States; reducing the global burden of malaria; and eliminating targeted neglected tropical diseases.”
In response to this news organization’s interview request, a CDC spokesperson wrote, “CDC is unwavering in our commitment to provide the highest quality laboratory diagnostic services for parasitic diseases. We understand the concerns expressed in the editorial and the challenges the pause in testing for parasitic diseases presents for health care providers, particularly those treating people at elevated risk for parasitic diseases.”
Michael Reich, PhD, Dr. Beatty’s co-author, is an international health policy expert at Harvard. He and the physicians had approached CDC about the elimination of services. He said in an interview, “We’re still unable to get clear responses except for something along the lines of, ‘We are working on it. It is complicated. It takes time. We’re doing our best.’”
Dr. Reich added, “For me, this raises troubling issues both of transparency and accountability – transparency about what is going on and what the problems are, and accountability in terms of who’s being held responsible for the closures and the impacts on both public health and patient treatment.”
Dr. Beatty concluded, “I think the goal of our group was to bring more awareness to the importance of having a national laboratory that can service all people, even the most underserved and vulnerable populations.” He added, “Chagas disease is a disease of inequity in Latin Americans. Without having access to an appropriate laboratory such as the CDC, we would be taking a backwards approach to tackle neglected tropical diseases in our country and worldwide.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Reich report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging tick-borne pathogen has spread to state of Georgia
Heartland virus (HRTV), an emerging infection first detected in lone star ticks in Missouri in 2009, has spread to lone star ticks in Georgia, a study published in Emerging Infectious Diseases reports.
HRTV disease is transmitted by the bite of an infected Amblyomma americanum tick, named “lone star” because of the silver-white spot on the female scutum (back).
“By … sampling … in an area with reported exposure to HRTV in wildlife and humans and testing for infection in thousands of ticks from multiple sites and physiologic stages, we confirmed the presence of HRTV in Georgia,” the authors write.
“This information about the expanding geographic range of lone star ticks, combined with increased human presence in tick-infested habitats, can be used to improve strategies for preventing tick bites and to alert physicians about this emerging tickborne virus infection,” a press release by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes.
Persistent field and lab work led to HRTV discovery in Georgia
The search for infected lone star ticks began after a retroactive analysis confirmed that a person who died in Georgia in 2005 from an unidentified illness was infected with HRTV. A subsequent analysis of serum samples collected earlier from local white-tailed deer showed that the deer had been exposed to HRTV since at least 2001, according to a press release by Emory University.
These discoveries prompted local researchers to investigate whether lone star ticks in rural, woodsy central Georgia were carrying HRTV.
Lead study author Yamila Romer, MD, an infectious disease clinician and microbiologist in the department of environmental sciences at Emory University in Atlanta, and her colleagues collected samples of ticks in 2018 at 26 sites near the location of the patient who died and the seropositive deer. In 2019, they focused their collections on the two sites that had provided the most ticks in 2018.
From April to October in both years, the research team visited sites weekly to swish white flannel flags through underbrush. They picked off adult and nymph Amblyomma americanum ticks, placed them into vials, and transported them to their lab. They sorted 9,294 ticks by sex, life stage, and collection site. Then they crushed the ticks and extracted their RNA.
To confirm viral infection, the team tested RNA extracted from cell culture supernatants using a real-time polymerase chain reaction test specific for HRTV.
In the three pools of ticks that tested positive for HRTV, the researchers found a minimum infection rate of 0.46/1,000 ticks, suggesting that about 1 of every 2,000 ticks carried HRTV. They sequenced the genome of the three isolates and found that the genomes were similar to one another but were very different from the genomes from HRTV samples taken outside Georgia.
Catherine A. Hill, PhD, a professor of entomology and vector biology and the interim head of the department of entomology at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Ind., was impressed with the researchers’ discovery.
“Heartland virus is difficult to detect,” she said in an email. “The prevalence of human cases is low, and the virus appears to be present at very low levels in populations of lone star tick. The investigators went to some lengths to survey for the virus, collect, and process thousands of ticks – and they found the needle in the haystack.” Dr. Hill was not involved in the study.
Georgia data help researchers monitor HRTV spread
HRTV was first identified in 2009 in Missouri in two people hospitalized with fever, muscle pain, diarrhea, and low white blood cell and platelet counts. Researchers traced the infections to lone star ticks, and they found antibodies to the virus in blood samples from deer and other wild mammals.
According to the CDC, U.S. cases of tick-borne diseases more than doubled between 2004 and 2016. As of January 2021, more than 50 human cases of HRTV disease had been reported in 11 Midwestern and Southeastern states: Arkansas, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, and Tennessee.
Precautions, signs, symptoms, testing, and treatment
“The lone star tick is aggressive and will actively seek out a human host to bite,” Dr. Hill noted.
She recommends that health care providers advise patients to avoid tick habitat, wear protective clothing, apply repellants, know the signs and symptoms of tick-borne disease, and seek immediate medical care if they become ill.
Common symptoms of HRTV disease include fatigue, fever, nausea, diarrhea, and anorexia. Treatment is supportive. Many patients have been hospitalized, and some with comorbidities have died.
HRTV infection is rarely tested for, and the disease burden is unknown. With no commercial tests available in the United States, the CDC performs molecular and serologic testing for HRTV infection. The agency advises doctors to contact their state health department if they suspect a patient may have HRTV disease.
Further research is needed
Samantha M. Wisely, PhD, a professor of wildlife ecology and the director of the Cervidae Health Research Initiative at the University of Florida in Gainesville, was not surprised by the study finding.
“The more we look for heartland virus, the more places we find it,” Dr. Wisely told this news organization in an email.
“Little is known about which wildlife play a role in maintaining the virus on the landscape,” said Dr. Wisely, who was not involved in the study. “White-tailed deer have been shown to produce antibodies, meaning they have been exposed to the virus, but no one has actually found the virus in a wildlife species.”
The whole-genome sequencing of the virus was particularly important, Dr. Wisely explained. “Whole-genome data allow researchers to better understand viral evolution, pathogenicity, and viral dynamics across space and time – how it is evolving.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Emory University Research Council. The authors, Dr. Wisely, and Dr. Hill have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heartland virus (HRTV), an emerging infection first detected in lone star ticks in Missouri in 2009, has spread to lone star ticks in Georgia, a study published in Emerging Infectious Diseases reports.
HRTV disease is transmitted by the bite of an infected Amblyomma americanum tick, named “lone star” because of the silver-white spot on the female scutum (back).
“By … sampling … in an area with reported exposure to HRTV in wildlife and humans and testing for infection in thousands of ticks from multiple sites and physiologic stages, we confirmed the presence of HRTV in Georgia,” the authors write.
“This information about the expanding geographic range of lone star ticks, combined with increased human presence in tick-infested habitats, can be used to improve strategies for preventing tick bites and to alert physicians about this emerging tickborne virus infection,” a press release by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes.
Persistent field and lab work led to HRTV discovery in Georgia
The search for infected lone star ticks began after a retroactive analysis confirmed that a person who died in Georgia in 2005 from an unidentified illness was infected with HRTV. A subsequent analysis of serum samples collected earlier from local white-tailed deer showed that the deer had been exposed to HRTV since at least 2001, according to a press release by Emory University.
These discoveries prompted local researchers to investigate whether lone star ticks in rural, woodsy central Georgia were carrying HRTV.
Lead study author Yamila Romer, MD, an infectious disease clinician and microbiologist in the department of environmental sciences at Emory University in Atlanta, and her colleagues collected samples of ticks in 2018 at 26 sites near the location of the patient who died and the seropositive deer. In 2019, they focused their collections on the two sites that had provided the most ticks in 2018.
From April to October in both years, the research team visited sites weekly to swish white flannel flags through underbrush. They picked off adult and nymph Amblyomma americanum ticks, placed them into vials, and transported them to their lab. They sorted 9,294 ticks by sex, life stage, and collection site. Then they crushed the ticks and extracted their RNA.
To confirm viral infection, the team tested RNA extracted from cell culture supernatants using a real-time polymerase chain reaction test specific for HRTV.
In the three pools of ticks that tested positive for HRTV, the researchers found a minimum infection rate of 0.46/1,000 ticks, suggesting that about 1 of every 2,000 ticks carried HRTV. They sequenced the genome of the three isolates and found that the genomes were similar to one another but were very different from the genomes from HRTV samples taken outside Georgia.
Catherine A. Hill, PhD, a professor of entomology and vector biology and the interim head of the department of entomology at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Ind., was impressed with the researchers’ discovery.
“Heartland virus is difficult to detect,” she said in an email. “The prevalence of human cases is low, and the virus appears to be present at very low levels in populations of lone star tick. The investigators went to some lengths to survey for the virus, collect, and process thousands of ticks – and they found the needle in the haystack.” Dr. Hill was not involved in the study.
Georgia data help researchers monitor HRTV spread
HRTV was first identified in 2009 in Missouri in two people hospitalized with fever, muscle pain, diarrhea, and low white blood cell and platelet counts. Researchers traced the infections to lone star ticks, and they found antibodies to the virus in blood samples from deer and other wild mammals.
According to the CDC, U.S. cases of tick-borne diseases more than doubled between 2004 and 2016. As of January 2021, more than 50 human cases of HRTV disease had been reported in 11 Midwestern and Southeastern states: Arkansas, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, and Tennessee.
Precautions, signs, symptoms, testing, and treatment
“The lone star tick is aggressive and will actively seek out a human host to bite,” Dr. Hill noted.
She recommends that health care providers advise patients to avoid tick habitat, wear protective clothing, apply repellants, know the signs and symptoms of tick-borne disease, and seek immediate medical care if they become ill.
Common symptoms of HRTV disease include fatigue, fever, nausea, diarrhea, and anorexia. Treatment is supportive. Many patients have been hospitalized, and some with comorbidities have died.
HRTV infection is rarely tested for, and the disease burden is unknown. With no commercial tests available in the United States, the CDC performs molecular and serologic testing for HRTV infection. The agency advises doctors to contact their state health department if they suspect a patient may have HRTV disease.
Further research is needed
Samantha M. Wisely, PhD, a professor of wildlife ecology and the director of the Cervidae Health Research Initiative at the University of Florida in Gainesville, was not surprised by the study finding.
“The more we look for heartland virus, the more places we find it,” Dr. Wisely told this news organization in an email.
“Little is known about which wildlife play a role in maintaining the virus on the landscape,” said Dr. Wisely, who was not involved in the study. “White-tailed deer have been shown to produce antibodies, meaning they have been exposed to the virus, but no one has actually found the virus in a wildlife species.”
The whole-genome sequencing of the virus was particularly important, Dr. Wisely explained. “Whole-genome data allow researchers to better understand viral evolution, pathogenicity, and viral dynamics across space and time – how it is evolving.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Emory University Research Council. The authors, Dr. Wisely, and Dr. Hill have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heartland virus (HRTV), an emerging infection first detected in lone star ticks in Missouri in 2009, has spread to lone star ticks in Georgia, a study published in Emerging Infectious Diseases reports.
HRTV disease is transmitted by the bite of an infected Amblyomma americanum tick, named “lone star” because of the silver-white spot on the female scutum (back).
“By … sampling … in an area with reported exposure to HRTV in wildlife and humans and testing for infection in thousands of ticks from multiple sites and physiologic stages, we confirmed the presence of HRTV in Georgia,” the authors write.
“This information about the expanding geographic range of lone star ticks, combined with increased human presence in tick-infested habitats, can be used to improve strategies for preventing tick bites and to alert physicians about this emerging tickborne virus infection,” a press release by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes.
Persistent field and lab work led to HRTV discovery in Georgia
The search for infected lone star ticks began after a retroactive analysis confirmed that a person who died in Georgia in 2005 from an unidentified illness was infected with HRTV. A subsequent analysis of serum samples collected earlier from local white-tailed deer showed that the deer had been exposed to HRTV since at least 2001, according to a press release by Emory University.
These discoveries prompted local researchers to investigate whether lone star ticks in rural, woodsy central Georgia were carrying HRTV.
Lead study author Yamila Romer, MD, an infectious disease clinician and microbiologist in the department of environmental sciences at Emory University in Atlanta, and her colleagues collected samples of ticks in 2018 at 26 sites near the location of the patient who died and the seropositive deer. In 2019, they focused their collections on the two sites that had provided the most ticks in 2018.
From April to October in both years, the research team visited sites weekly to swish white flannel flags through underbrush. They picked off adult and nymph Amblyomma americanum ticks, placed them into vials, and transported them to their lab. They sorted 9,294 ticks by sex, life stage, and collection site. Then they crushed the ticks and extracted their RNA.
To confirm viral infection, the team tested RNA extracted from cell culture supernatants using a real-time polymerase chain reaction test specific for HRTV.
In the three pools of ticks that tested positive for HRTV, the researchers found a minimum infection rate of 0.46/1,000 ticks, suggesting that about 1 of every 2,000 ticks carried HRTV. They sequenced the genome of the three isolates and found that the genomes were similar to one another but were very different from the genomes from HRTV samples taken outside Georgia.
Catherine A. Hill, PhD, a professor of entomology and vector biology and the interim head of the department of entomology at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Ind., was impressed with the researchers’ discovery.
“Heartland virus is difficult to detect,” she said in an email. “The prevalence of human cases is low, and the virus appears to be present at very low levels in populations of lone star tick. The investigators went to some lengths to survey for the virus, collect, and process thousands of ticks – and they found the needle in the haystack.” Dr. Hill was not involved in the study.
Georgia data help researchers monitor HRTV spread
HRTV was first identified in 2009 in Missouri in two people hospitalized with fever, muscle pain, diarrhea, and low white blood cell and platelet counts. Researchers traced the infections to lone star ticks, and they found antibodies to the virus in blood samples from deer and other wild mammals.
According to the CDC, U.S. cases of tick-borne diseases more than doubled between 2004 and 2016. As of January 2021, more than 50 human cases of HRTV disease had been reported in 11 Midwestern and Southeastern states: Arkansas, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, and Tennessee.
Precautions, signs, symptoms, testing, and treatment
“The lone star tick is aggressive and will actively seek out a human host to bite,” Dr. Hill noted.
She recommends that health care providers advise patients to avoid tick habitat, wear protective clothing, apply repellants, know the signs and symptoms of tick-borne disease, and seek immediate medical care if they become ill.
Common symptoms of HRTV disease include fatigue, fever, nausea, diarrhea, and anorexia. Treatment is supportive. Many patients have been hospitalized, and some with comorbidities have died.
HRTV infection is rarely tested for, and the disease burden is unknown. With no commercial tests available in the United States, the CDC performs molecular and serologic testing for HRTV infection. The agency advises doctors to contact their state health department if they suspect a patient may have HRTV disease.
Further research is needed
Samantha M. Wisely, PhD, a professor of wildlife ecology and the director of the Cervidae Health Research Initiative at the University of Florida in Gainesville, was not surprised by the study finding.
“The more we look for heartland virus, the more places we find it,” Dr. Wisely told this news organization in an email.
“Little is known about which wildlife play a role in maintaining the virus on the landscape,” said Dr. Wisely, who was not involved in the study. “White-tailed deer have been shown to produce antibodies, meaning they have been exposed to the virus, but no one has actually found the virus in a wildlife species.”
The whole-genome sequencing of the virus was particularly important, Dr. Wisely explained. “Whole-genome data allow researchers to better understand viral evolution, pathogenicity, and viral dynamics across space and time – how it is evolving.”
The study was supported by a grant from the Emory University Research Council. The authors, Dr. Wisely, and Dr. Hill have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Children and COVID: Decline in new cases comes to an end
It was a good run while it lasted.
according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The number of reported pediatric cases for the week was 33,146, and the actual increase from the previous week was just 7,231 cases, the AAP and CHA said, but some reports suggest that the new COVID variants and subvariants are starting to have an effect on incidence in some areas while mask mandates continue to fall.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that, over the last week or two, the 7-day average for percentage of emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID has risen from 0.5% to 0.6% in children aged 0-11 years, from 0.3% to 0.5% among 12- to 15-year-olds, and from 0.3% to 0.4% in 16- and 17-year-olds. Small increases, to be sure, but increases nonetheless.
A somewhat similar scenario is playing out for new admissions of children aged 0-17, which have leveled out after dropping from a high of 1.25 per 100,000 population in mid-January to 0.13 per 100,000 in early April. Over the last 2 weeks, the rate has been alternating between 0.13 and 0.14 per 100,000, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The latest news on the vaccination front came from Pfizer and BIoNTech, which announced that a third dose of its COVID-19 vaccine boosted immune protection in children aged 5-11 years in a phase 2/3 trial. Protection against the Omicron strain was 36 times higher than the two previous doses, the companies said, adding that they plan to submit a request for emergency use authorization of a booster dose in the near future.
The ongoing vaccination effort, however, produced mixed results in the last week. Initial vaccinations among children aged 5-11 years fell 14.5% to another new low while initial doses were up 9.3% for those aged 12-17, the AAP said. Overall, just 28.2% of the country’s 5- to 11-year-olds are fully vaccinated, compared with 58.7% of those aged 12-17, the CDC reported.
It was a good run while it lasted.
according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The number of reported pediatric cases for the week was 33,146, and the actual increase from the previous week was just 7,231 cases, the AAP and CHA said, but some reports suggest that the new COVID variants and subvariants are starting to have an effect on incidence in some areas while mask mandates continue to fall.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that, over the last week or two, the 7-day average for percentage of emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID has risen from 0.5% to 0.6% in children aged 0-11 years, from 0.3% to 0.5% among 12- to 15-year-olds, and from 0.3% to 0.4% in 16- and 17-year-olds. Small increases, to be sure, but increases nonetheless.
A somewhat similar scenario is playing out for new admissions of children aged 0-17, which have leveled out after dropping from a high of 1.25 per 100,000 population in mid-January to 0.13 per 100,000 in early April. Over the last 2 weeks, the rate has been alternating between 0.13 and 0.14 per 100,000, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The latest news on the vaccination front came from Pfizer and BIoNTech, which announced that a third dose of its COVID-19 vaccine boosted immune protection in children aged 5-11 years in a phase 2/3 trial. Protection against the Omicron strain was 36 times higher than the two previous doses, the companies said, adding that they plan to submit a request for emergency use authorization of a booster dose in the near future.
The ongoing vaccination effort, however, produced mixed results in the last week. Initial vaccinations among children aged 5-11 years fell 14.5% to another new low while initial doses were up 9.3% for those aged 12-17, the AAP said. Overall, just 28.2% of the country’s 5- to 11-year-olds are fully vaccinated, compared with 58.7% of those aged 12-17, the CDC reported.
It was a good run while it lasted.
according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The number of reported pediatric cases for the week was 33,146, and the actual increase from the previous week was just 7,231 cases, the AAP and CHA said, but some reports suggest that the new COVID variants and subvariants are starting to have an effect on incidence in some areas while mask mandates continue to fall.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that, over the last week or two, the 7-day average for percentage of emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID has risen from 0.5% to 0.6% in children aged 0-11 years, from 0.3% to 0.5% among 12- to 15-year-olds, and from 0.3% to 0.4% in 16- and 17-year-olds. Small increases, to be sure, but increases nonetheless.
A somewhat similar scenario is playing out for new admissions of children aged 0-17, which have leveled out after dropping from a high of 1.25 per 100,000 population in mid-January to 0.13 per 100,000 in early April. Over the last 2 weeks, the rate has been alternating between 0.13 and 0.14 per 100,000, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The latest news on the vaccination front came from Pfizer and BIoNTech, which announced that a third dose of its COVID-19 vaccine boosted immune protection in children aged 5-11 years in a phase 2/3 trial. Protection against the Omicron strain was 36 times higher than the two previous doses, the companies said, adding that they plan to submit a request for emergency use authorization of a booster dose in the near future.
The ongoing vaccination effort, however, produced mixed results in the last week. Initial vaccinations among children aged 5-11 years fell 14.5% to another new low while initial doses were up 9.3% for those aged 12-17, the AAP said. Overall, just 28.2% of the country’s 5- to 11-year-olds are fully vaccinated, compared with 58.7% of those aged 12-17, the CDC reported.
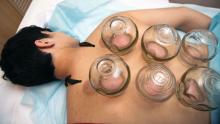
Cupping in dermatology
My inspiration to write about cupping this month stems from the perception that everyone seems to be talking about it, from a facialist who suggested it for me to a coworker who swears by cupping to treat her allergies. Cupping is by no means a novel procedure. Its use as a health therapy dates back thousands of years to ancient Egypt (1500 BCE), ancient Greece (described by Hippocrates), ancient Rome (described by the Greek physician Galen), China (during the Han dynasty, 206 BCE to 220 CE) and traditional Islamic culture.1 Over the past decade, the popularity of this ancient procedure has been increasing in the United States.1 Cupping has been applied as a remedy for various dermatologic and medical conditions, including herpes zoster, headaches, diminished appetite, maldigestion, abscess evacuation, narcolepsy, pain, fever, dysmenorrhea, and gout.1,2
Theories on the mechanism(s) of action
The practice of cupping is differentiated into dry and wet cupping.1,2 Traditionally, with dry cupping, a flame is applied to heat the air inside a thick glass cup (rather than the cup itself).1 The cup is placed on the skin surface, and negative pressure suctions the skin into the cup. Wet cupping differs mainly from dry cupping in that it involves blood-letting. Cups made of either silicone or glass of varying size and shapes are used. Modern adaptations to cupping include needle, herbal, and pulsatile cupping, as well as a “moving cupping” technique (vs. traditionally stationary cups).1
There are several theories, many of which are derived from the nondermatologic literature (that is, pain management), as to how cupping may deliver a clinical benefit. Some theories are based in scientific and medical principles, whereas other theories are more whimsical – specifically, that cupping draws out evil spirits.2 Studies of dry cupping have suggested that the procedure results in increased oxygenation of muscles via a local increase in oxygenated hemoglobin, which may help improve muscular activity and reduce pain.1 As theorized by Lowe in 2017, negative pressure exerted by dry cupping leads to stretching and dilation of capillaries, which increases blood flow.3 Wet cupping has been shown to increase heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and beta-endorphin expression in rat models, which is thought to facilitate pain management.1 Removal of oxidants and reduction of reactive oxygen species in the blood is believed to be among the benefits of wet cupping.1
Cupping in general dermatology
While , as well as various inflammatory conditions.
Herpes zoster
In 2010, Cao et al. reported on their systematic review of wet cupping after completing searches of multiple databases (that is, PubMed, the Cochrane Library [Issue 3, 2008], China Network Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Scientific Journal Database, and Wan Fang Database). They identified eight randomized controlled trials involving 651 patients, with meta-analyses revealing that wet cupping performed better than medications in terms of the number of “cured” patients, number of patients with improved symptoms, and a lower incidence of postherpetic neuralgia. Wet cupping, in addition to medication, was also found to be superior to medication alone in multiple patients. The researchers concluded that wet cupping appears to effectively treat herpes zoster.4 However, the study failed to identify which medications were used to treat herpes zoster. In the United States, common medications for herpes zoster include acyclovir, valacyclovir, steroids, gabapentin, and other neuromodulators. Without knowing which medications were used, it is difficult to compare cupping to medication in terms of efficacy in treating herpes zoster.
Urticaria
Urticaria (hives) is an inflammatory skin condition that can be very uncomfortable for patients but often resolves without intervention within several months after onset. In 2001, Li and Ding reported on the treatment with cupping of 40 patients with urticaria. The cure rate among the treatment group was cited as 55%, compared with 30% in the control group, who were treated with a traditional Chinese remedy and an unidentified first-generation antihistamine.1,5 In 2020, Xiao et al. conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of cupping therapy for patients with chronic urticaria. They identified 13 comparisons from 12 randomized controlled trials involving 842 subjects. The investigators found no significant differences between wet cupping and medication usage. They also found that cupping combined with antihistamine treatment was superior to antihistamines alone, and cupping therapy with acupuncture was more effective than acupuncture alone. The investigators did call for caution, citing the poor quality of the studies reviewed.6
It is important to note that it is difficult to attribute resolution of urticaria to the use of cupping given the self-resolution often associated with this condition. Antihistamines are the mainstay of therapy for urticaria, but in my personal experience, patients are not entirely satisfied with the level of symptom control with antihistamines alone and often search for alternative therapies to control the pesky hives and associated itch. In 2014, omalizumab (Xolair) was approved for treating chronic idiopathic urticaria, which has helped patients control symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria without needing to take antihistamines. There was no indication that the studies reviewed by Xiao et al. compared cupping against this new effective treatment. Therefore, these studies comparing cupping to medical management are outdated.
Acne, eczema, and psoriasis
Soliman’s 2018 review of cupping in dermatology included a few studies on these common cutaneous conditions. For instance, a 2013 single-blind prospective study by Xu et al. reported on the results of patients with moderate acne who received wet cupping (in the form of prickling bloodletting) twice weekly for 6 weeks.7 They reported that patients demonstrated improvement in the global acne grading system (GAGS) score by the end of the trial.1,7 Unfortunately, cupping was not compared with standard acne treatments (that is, benzoyl peroxide, topical and oral antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, spironolactone).
In evaluating cupping for acute eczema, wet cupping was compared with oral loratadine and topical ointments in a 2007 study by Yao and Li. They divided 88 cases into treatment and control groups, with the former group (n = 46) receiving bloodletting puncturing and cupping and the control group (n = 42) receiving oral loratadine and topical Pairuisong (an herbal ointment used in Chinese medicine). The investigators observed no significant difference in total effective rates but a superior difference in the rates of responses that were considered “cured” and “markedly effective” in favor of the cupping treatment.1,8 However, a case report by Hon et al. has indicated that cupping therapy may be associated with more harm than benefit when used as an eczema treatment.1,9
In addition, it is important to note that the past 5 years have been gamechanging in the management of chronic eczema in terms of the array of novel and effective therapies (e.g., dupilumab and JAK inhibitors) and chronic moderate-to-severe eczema has become very treatable. Similarly, acute eczema is often successfully managed with topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and emollients. As such, there is no compelling reason to consider an unproven treatment such as cupping.
In 2020, Xing et al. reviewed 16 randomized controlled trials assessing the use of “moving cupping” for plaque psoriasis, with 1,164 patients meeting inclusion criteria. Moving cupping was found to be significantly more effective than “no-moving” cupping therapy, and moving cupping, combined with medications, performed better than medications alone.10 None of the trials evaluated in this study included randomized controlled trials that compared patients using any of the more modern psoriasis medications, specifically biologics. And, again, the studies evaluated were not of the highest quality.
The data that support cupping, as summarized above, are based mostly on case reports, and strong double-blind prospective studies are lacking. Additionally, most of the studies cited gauged the efficacy of cupping using qualitative endpoints, rather than standardized quantitative endpoints and scales. Moreover, spontaneous remission of various dermatoses can occur, or they can improve over time, including acute eczema, psoriasis, and, especially, urticaria.
Adverse effects of cupping
Often alternative therapies are seen as “benign” and without adverse effects. However, complications can result from cupping. Trauma can be induced from the cupping itself by damaging superficial blood vessels and causing bruising.1,11 Blistering can also occur secondary to the suction effect, and the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin can be separated.1,11 Further, burns and discoloration have also been noted secondary to heat, trauma, and post inflammatory pigmentary changes.1,11 Another risk of cupping is the Koebner phenomenon, which occurs with psoriasis, with new lesions appearing in traumatized skin.12 Other adverse outcomes that have been reported with cupping include reactivation of herpes simplex virus secondary to skin trauma, iron deficiency anemia (secondary to blood loss), panniculitis, infections, and residual marks mistaken for signs of child abuse.1,11
Cupping in aesthetic dermatology
Facial cupping, a distinct practice from body cupping used to treat general dermatology conditions described previously, is also increasing in popularity. This practice is usually conducted in association with a facial or facial acupuncture by an aesthetician or other licensed professional. It can also be performed using at-home kits. The marketing claims for facial cupping cite improved tightening and contouring of facial skin, increased facial microcirculation and collagen synthesis, and enhanced lymphatic flow to aid with facial puffiness or swelling. One supposed mechanism for these benefits is that cupping increases blood flow. Interestingly, there was a 2020 animal study in which photoacoustic imaging of a mouse ear revealed increased temporary blood flow in the cupping microenvironment.13 Currently, however, there is no evidence in the English scientific literature that supports facial cupping. The benefits attributed to facial cupping for aesthetic purposes have emerged only in personal anecdotes. The temporary increase in blood flow may induce inflammation and swelling that adds volume to the face and temporarily diminishes wrinkles. However, this temporary plumpness may be associated with adverse effects, such as local trauma, irritation, bruising, postinflammatory pigmentary alteration, or even herpes reactivation. In my opinion, the possible adverse effects of cupping outweigh any potential benefit, especially given the insufficient evidence supporting the utility of cupping for cosmetic enhancement.
Summary
There is increasing interest among patients to incorporate complementary and alternative medicine – including the ancient tradition of cupping – in managing medical dermatologic conditions. However, current evidence supporting cupping as an effective therapeutic strategy is not strong, with most studies to date appearing to be of poor quality or not sufficiently convincing to displace standard therapies. Our medical strategies for managing chronic dermatologic conditions, particularly inflammatory disorders, continue to improve from both a safety and a proven efficacy standpoint. Therefore, I would not forgo medical management in favor of cupping. While cupping can be used as an adjunct therapy, I would caution patients about possible adverse side effects. In the aesthetic world, cupping is also gaining popularity, but this trend is also not supported by current evidence or studies, at least in the Western literature.
Dr. Goldman is a dermatologist in private practice in Miami and specializes in cosmetic and general dermatology. She practices at Baumann Cosmetic & Research Institute and is also opening a general dermatology practice. Write to her at [email protected] or message her on Instragram @DrChloeGoldman. Dr. Goldman receives compensation to create social media content for Replenix, a skin care company. She has no other disclosures.
References
1. Soliman Y et al. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018 Jun;27(2):103-7.
2. França K and Lotti T. Advances in Integrative Dermatology. John Wiley & Sons, 2019.
3. Lowe DT. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017 Nov;29:162-8.
4.Cao H et al. Altern Ther Health Med. 2010 Nov-Dec;16(6):48-54.
5. Li L and Ding J. J Tradit Chin Med. 2001 Mar;21(1):37-8.
6. Xiao XJ et al. J Integr Med. 2020 Jul;18(4):303-12.
7. Xu J et al. J Tradit Chin Med. 2013 Dec;33(6):752-6.
8. Yao J et al. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2007; Jun;27(6):424-6.
9. Hon KL et al. Case Rep Pediatr. 2013;2013:605829.
10. Xing M et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 9;99(41):e22539.
11. Kim TH et al. Eur J Integr Med. 2014 Aug 1;6(4):434-40.
12. Vender R and Vender R. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015 May-Jun;19(3):320-2.
13. Zhou Y et al. Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Apr 6;11(5):2394-401.
This article was updated 4/25/22.
My inspiration to write about cupping this month stems from the perception that everyone seems to be talking about it, from a facialist who suggested it for me to a coworker who swears by cupping to treat her allergies. Cupping is by no means a novel procedure. Its use as a health therapy dates back thousands of years to ancient Egypt (1500 BCE), ancient Greece (described by Hippocrates), ancient Rome (described by the Greek physician Galen), China (during the Han dynasty, 206 BCE to 220 CE) and traditional Islamic culture.1 Over the past decade, the popularity of this ancient procedure has been increasing in the United States.1 Cupping has been applied as a remedy for various dermatologic and medical conditions, including herpes zoster, headaches, diminished appetite, maldigestion, abscess evacuation, narcolepsy, pain, fever, dysmenorrhea, and gout.1,2
Theories on the mechanism(s) of action
The practice of cupping is differentiated into dry and wet cupping.1,2 Traditionally, with dry cupping, a flame is applied to heat the air inside a thick glass cup (rather than the cup itself).1 The cup is placed on the skin surface, and negative pressure suctions the skin into the cup. Wet cupping differs mainly from dry cupping in that it involves blood-letting. Cups made of either silicone or glass of varying size and shapes are used. Modern adaptations to cupping include needle, herbal, and pulsatile cupping, as well as a “moving cupping” technique (vs. traditionally stationary cups).1
There are several theories, many of which are derived from the nondermatologic literature (that is, pain management), as to how cupping may deliver a clinical benefit. Some theories are based in scientific and medical principles, whereas other theories are more whimsical – specifically, that cupping draws out evil spirits.2 Studies of dry cupping have suggested that the procedure results in increased oxygenation of muscles via a local increase in oxygenated hemoglobin, which may help improve muscular activity and reduce pain.1 As theorized by Lowe in 2017, negative pressure exerted by dry cupping leads to stretching and dilation of capillaries, which increases blood flow.3 Wet cupping has been shown to increase heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and beta-endorphin expression in rat models, which is thought to facilitate pain management.1 Removal of oxidants and reduction of reactive oxygen species in the blood is believed to be among the benefits of wet cupping.1
Cupping in general dermatology
While , as well as various inflammatory conditions.
Herpes zoster
In 2010, Cao et al. reported on their systematic review of wet cupping after completing searches of multiple databases (that is, PubMed, the Cochrane Library [Issue 3, 2008], China Network Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Scientific Journal Database, and Wan Fang Database). They identified eight randomized controlled trials involving 651 patients, with meta-analyses revealing that wet cupping performed better than medications in terms of the number of “cured” patients, number of patients with improved symptoms, and a lower incidence of postherpetic neuralgia. Wet cupping, in addition to medication, was also found to be superior to medication alone in multiple patients. The researchers concluded that wet cupping appears to effectively treat herpes zoster.4 However, the study failed to identify which medications were used to treat herpes zoster. In the United States, common medications for herpes zoster include acyclovir, valacyclovir, steroids, gabapentin, and other neuromodulators. Without knowing which medications were used, it is difficult to compare cupping to medication in terms of efficacy in treating herpes zoster.
Urticaria
Urticaria (hives) is an inflammatory skin condition that can be very uncomfortable for patients but often resolves without intervention within several months after onset. In 2001, Li and Ding reported on the treatment with cupping of 40 patients with urticaria. The cure rate among the treatment group was cited as 55%, compared with 30% in the control group, who were treated with a traditional Chinese remedy and an unidentified first-generation antihistamine.1,5 In 2020, Xiao et al. conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of cupping therapy for patients with chronic urticaria. They identified 13 comparisons from 12 randomized controlled trials involving 842 subjects. The investigators found no significant differences between wet cupping and medication usage. They also found that cupping combined with antihistamine treatment was superior to antihistamines alone, and cupping therapy with acupuncture was more effective than acupuncture alone. The investigators did call for caution, citing the poor quality of the studies reviewed.6
It is important to note that it is difficult to attribute resolution of urticaria to the use of cupping given the self-resolution often associated with this condition. Antihistamines are the mainstay of therapy for urticaria, but in my personal experience, patients are not entirely satisfied with the level of symptom control with antihistamines alone and often search for alternative therapies to control the pesky hives and associated itch. In 2014, omalizumab (Xolair) was approved for treating chronic idiopathic urticaria, which has helped patients control symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria without needing to take antihistamines. There was no indication that the studies reviewed by Xiao et al. compared cupping against this new effective treatment. Therefore, these studies comparing cupping to medical management are outdated.
Acne, eczema, and psoriasis
Soliman’s 2018 review of cupping in dermatology included a few studies on these common cutaneous conditions. For instance, a 2013 single-blind prospective study by Xu et al. reported on the results of patients with moderate acne who received wet cupping (in the form of prickling bloodletting) twice weekly for 6 weeks.7 They reported that patients demonstrated improvement in the global acne grading system (GAGS) score by the end of the trial.1,7 Unfortunately, cupping was not compared with standard acne treatments (that is, benzoyl peroxide, topical and oral antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, spironolactone).
In evaluating cupping for acute eczema, wet cupping was compared with oral loratadine and topical ointments in a 2007 study by Yao and Li. They divided 88 cases into treatment and control groups, with the former group (n = 46) receiving bloodletting puncturing and cupping and the control group (n = 42) receiving oral loratadine and topical Pairuisong (an herbal ointment used in Chinese medicine). The investigators observed no significant difference in total effective rates but a superior difference in the rates of responses that were considered “cured” and “markedly effective” in favor of the cupping treatment.1,8 However, a case report by Hon et al. has indicated that cupping therapy may be associated with more harm than benefit when used as an eczema treatment.1,9
In addition, it is important to note that the past 5 years have been gamechanging in the management of chronic eczema in terms of the array of novel and effective therapies (e.g., dupilumab and JAK inhibitors) and chronic moderate-to-severe eczema has become very treatable. Similarly, acute eczema is often successfully managed with topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and emollients. As such, there is no compelling reason to consider an unproven treatment such as cupping.
In 2020, Xing et al. reviewed 16 randomized controlled trials assessing the use of “moving cupping” for plaque psoriasis, with 1,164 patients meeting inclusion criteria. Moving cupping was found to be significantly more effective than “no-moving” cupping therapy, and moving cupping, combined with medications, performed better than medications alone.10 None of the trials evaluated in this study included randomized controlled trials that compared patients using any of the more modern psoriasis medications, specifically biologics. And, again, the studies evaluated were not of the highest quality.
The data that support cupping, as summarized above, are based mostly on case reports, and strong double-blind prospective studies are lacking. Additionally, most of the studies cited gauged the efficacy of cupping using qualitative endpoints, rather than standardized quantitative endpoints and scales. Moreover, spontaneous remission of various dermatoses can occur, or they can improve over time, including acute eczema, psoriasis, and, especially, urticaria.
Adverse effects of cupping
Often alternative therapies are seen as “benign” and without adverse effects. However, complications can result from cupping. Trauma can be induced from the cupping itself by damaging superficial blood vessels and causing bruising.1,11 Blistering can also occur secondary to the suction effect, and the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin can be separated.1,11 Further, burns and discoloration have also been noted secondary to heat, trauma, and post inflammatory pigmentary changes.1,11 Another risk of cupping is the Koebner phenomenon, which occurs with psoriasis, with new lesions appearing in traumatized skin.12 Other adverse outcomes that have been reported with cupping include reactivation of herpes simplex virus secondary to skin trauma, iron deficiency anemia (secondary to blood loss), panniculitis, infections, and residual marks mistaken for signs of child abuse.1,11
Cupping in aesthetic dermatology
Facial cupping, a distinct practice from body cupping used to treat general dermatology conditions described previously, is also increasing in popularity. This practice is usually conducted in association with a facial or facial acupuncture by an aesthetician or other licensed professional. It can also be performed using at-home kits. The marketing claims for facial cupping cite improved tightening and contouring of facial skin, increased facial microcirculation and collagen synthesis, and enhanced lymphatic flow to aid with facial puffiness or swelling. One supposed mechanism for these benefits is that cupping increases blood flow. Interestingly, there was a 2020 animal study in which photoacoustic imaging of a mouse ear revealed increased temporary blood flow in the cupping microenvironment.13 Currently, however, there is no evidence in the English scientific literature that supports facial cupping. The benefits attributed to facial cupping for aesthetic purposes have emerged only in personal anecdotes. The temporary increase in blood flow may induce inflammation and swelling that adds volume to the face and temporarily diminishes wrinkles. However, this temporary plumpness may be associated with adverse effects, such as local trauma, irritation, bruising, postinflammatory pigmentary alteration, or even herpes reactivation. In my opinion, the possible adverse effects of cupping outweigh any potential benefit, especially given the insufficient evidence supporting the utility of cupping for cosmetic enhancement.
Summary
There is increasing interest among patients to incorporate complementary and alternative medicine – including the ancient tradition of cupping – in managing medical dermatologic conditions. However, current evidence supporting cupping as an effective therapeutic strategy is not strong, with most studies to date appearing to be of poor quality or not sufficiently convincing to displace standard therapies. Our medical strategies for managing chronic dermatologic conditions, particularly inflammatory disorders, continue to improve from both a safety and a proven efficacy standpoint. Therefore, I would not forgo medical management in favor of cupping. While cupping can be used as an adjunct therapy, I would caution patients about possible adverse side effects. In the aesthetic world, cupping is also gaining popularity, but this trend is also not supported by current evidence or studies, at least in the Western literature.
Dr. Goldman is a dermatologist in private practice in Miami and specializes in cosmetic and general dermatology. She practices at Baumann Cosmetic & Research Institute and is also opening a general dermatology practice. Write to her at [email protected] or message her on Instragram @DrChloeGoldman. Dr. Goldman receives compensation to create social media content for Replenix, a skin care company. She has no other disclosures.
References
1. Soliman Y et al. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018 Jun;27(2):103-7.
2. França K and Lotti T. Advances in Integrative Dermatology. John Wiley & Sons, 2019.
3. Lowe DT. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017 Nov;29:162-8.
4.Cao H et al. Altern Ther Health Med. 2010 Nov-Dec;16(6):48-54.
5. Li L and Ding J. J Tradit Chin Med. 2001 Mar;21(1):37-8.
6. Xiao XJ et al. J Integr Med. 2020 Jul;18(4):303-12.
7. Xu J et al. J Tradit Chin Med. 2013 Dec;33(6):752-6.
8. Yao J et al. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2007; Jun;27(6):424-6.
9. Hon KL et al. Case Rep Pediatr. 2013;2013:605829.
10. Xing M et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 9;99(41):e22539.
11. Kim TH et al. Eur J Integr Med. 2014 Aug 1;6(4):434-40.
12. Vender R and Vender R. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015 May-Jun;19(3):320-2.
13. Zhou Y et al. Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Apr 6;11(5):2394-401.
This article was updated 4/25/22.
My inspiration to write about cupping this month stems from the perception that everyone seems to be talking about it, from a facialist who suggested it for me to a coworker who swears by cupping to treat her allergies. Cupping is by no means a novel procedure. Its use as a health therapy dates back thousands of years to ancient Egypt (1500 BCE), ancient Greece (described by Hippocrates), ancient Rome (described by the Greek physician Galen), China (during the Han dynasty, 206 BCE to 220 CE) and traditional Islamic culture.1 Over the past decade, the popularity of this ancient procedure has been increasing in the United States.1 Cupping has been applied as a remedy for various dermatologic and medical conditions, including herpes zoster, headaches, diminished appetite, maldigestion, abscess evacuation, narcolepsy, pain, fever, dysmenorrhea, and gout.1,2
Theories on the mechanism(s) of action
The practice of cupping is differentiated into dry and wet cupping.1,2 Traditionally, with dry cupping, a flame is applied to heat the air inside a thick glass cup (rather than the cup itself).1 The cup is placed on the skin surface, and negative pressure suctions the skin into the cup. Wet cupping differs mainly from dry cupping in that it involves blood-letting. Cups made of either silicone or glass of varying size and shapes are used. Modern adaptations to cupping include needle, herbal, and pulsatile cupping, as well as a “moving cupping” technique (vs. traditionally stationary cups).1
There are several theories, many of which are derived from the nondermatologic literature (that is, pain management), as to how cupping may deliver a clinical benefit. Some theories are based in scientific and medical principles, whereas other theories are more whimsical – specifically, that cupping draws out evil spirits.2 Studies of dry cupping have suggested that the procedure results in increased oxygenation of muscles via a local increase in oxygenated hemoglobin, which may help improve muscular activity and reduce pain.1 As theorized by Lowe in 2017, negative pressure exerted by dry cupping leads to stretching and dilation of capillaries, which increases blood flow.3 Wet cupping has been shown to increase heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and beta-endorphin expression in rat models, which is thought to facilitate pain management.1 Removal of oxidants and reduction of reactive oxygen species in the blood is believed to be among the benefits of wet cupping.1
Cupping in general dermatology
While , as well as various inflammatory conditions.
Herpes zoster
In 2010, Cao et al. reported on their systematic review of wet cupping after completing searches of multiple databases (that is, PubMed, the Cochrane Library [Issue 3, 2008], China Network Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Scientific Journal Database, and Wan Fang Database). They identified eight randomized controlled trials involving 651 patients, with meta-analyses revealing that wet cupping performed better than medications in terms of the number of “cured” patients, number of patients with improved symptoms, and a lower incidence of postherpetic neuralgia. Wet cupping, in addition to medication, was also found to be superior to medication alone in multiple patients. The researchers concluded that wet cupping appears to effectively treat herpes zoster.4 However, the study failed to identify which medications were used to treat herpes zoster. In the United States, common medications for herpes zoster include acyclovir, valacyclovir, steroids, gabapentin, and other neuromodulators. Without knowing which medications were used, it is difficult to compare cupping to medication in terms of efficacy in treating herpes zoster.
Urticaria
Urticaria (hives) is an inflammatory skin condition that can be very uncomfortable for patients but often resolves without intervention within several months after onset. In 2001, Li and Ding reported on the treatment with cupping of 40 patients with urticaria. The cure rate among the treatment group was cited as 55%, compared with 30% in the control group, who were treated with a traditional Chinese remedy and an unidentified first-generation antihistamine.1,5 In 2020, Xiao et al. conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of cupping therapy for patients with chronic urticaria. They identified 13 comparisons from 12 randomized controlled trials involving 842 subjects. The investigators found no significant differences between wet cupping and medication usage. They also found that cupping combined with antihistamine treatment was superior to antihistamines alone, and cupping therapy with acupuncture was more effective than acupuncture alone. The investigators did call for caution, citing the poor quality of the studies reviewed.6
It is important to note that it is difficult to attribute resolution of urticaria to the use of cupping given the self-resolution often associated with this condition. Antihistamines are the mainstay of therapy for urticaria, but in my personal experience, patients are not entirely satisfied with the level of symptom control with antihistamines alone and often search for alternative therapies to control the pesky hives and associated itch. In 2014, omalizumab (Xolair) was approved for treating chronic idiopathic urticaria, which has helped patients control symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria without needing to take antihistamines. There was no indication that the studies reviewed by Xiao et al. compared cupping against this new effective treatment. Therefore, these studies comparing cupping to medical management are outdated.
Acne, eczema, and psoriasis
Soliman’s 2018 review of cupping in dermatology included a few studies on these common cutaneous conditions. For instance, a 2013 single-blind prospective study by Xu et al. reported on the results of patients with moderate acne who received wet cupping (in the form of prickling bloodletting) twice weekly for 6 weeks.7 They reported that patients demonstrated improvement in the global acne grading system (GAGS) score by the end of the trial.1,7 Unfortunately, cupping was not compared with standard acne treatments (that is, benzoyl peroxide, topical and oral antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, spironolactone).
In evaluating cupping for acute eczema, wet cupping was compared with oral loratadine and topical ointments in a 2007 study by Yao and Li. They divided 88 cases into treatment and control groups, with the former group (n = 46) receiving bloodletting puncturing and cupping and the control group (n = 42) receiving oral loratadine and topical Pairuisong (an herbal ointment used in Chinese medicine). The investigators observed no significant difference in total effective rates but a superior difference in the rates of responses that were considered “cured” and “markedly effective” in favor of the cupping treatment.1,8 However, a case report by Hon et al. has indicated that cupping therapy may be associated with more harm than benefit when used as an eczema treatment.1,9
In addition, it is important to note that the past 5 years have been gamechanging in the management of chronic eczema in terms of the array of novel and effective therapies (e.g., dupilumab and JAK inhibitors) and chronic moderate-to-severe eczema has become very treatable. Similarly, acute eczema is often successfully managed with topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and emollients. As such, there is no compelling reason to consider an unproven treatment such as cupping.
In 2020, Xing et al. reviewed 16 randomized controlled trials assessing the use of “moving cupping” for plaque psoriasis, with 1,164 patients meeting inclusion criteria. Moving cupping was found to be significantly more effective than “no-moving” cupping therapy, and moving cupping, combined with medications, performed better than medications alone.10 None of the trials evaluated in this study included randomized controlled trials that compared patients using any of the more modern psoriasis medications, specifically biologics. And, again, the studies evaluated were not of the highest quality.
The data that support cupping, as summarized above, are based mostly on case reports, and strong double-blind prospective studies are lacking. Additionally, most of the studies cited gauged the efficacy of cupping using qualitative endpoints, rather than standardized quantitative endpoints and scales. Moreover, spontaneous remission of various dermatoses can occur, or they can improve over time, including acute eczema, psoriasis, and, especially, urticaria.
Adverse effects of cupping
Often alternative therapies are seen as “benign” and without adverse effects. However, complications can result from cupping. Trauma can be induced from the cupping itself by damaging superficial blood vessels and causing bruising.1,11 Blistering can also occur secondary to the suction effect, and the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin can be separated.1,11 Further, burns and discoloration have also been noted secondary to heat, trauma, and post inflammatory pigmentary changes.1,11 Another risk of cupping is the Koebner phenomenon, which occurs with psoriasis, with new lesions appearing in traumatized skin.12 Other adverse outcomes that have been reported with cupping include reactivation of herpes simplex virus secondary to skin trauma, iron deficiency anemia (secondary to blood loss), panniculitis, infections, and residual marks mistaken for signs of child abuse.1,11
Cupping in aesthetic dermatology
Facial cupping, a distinct practice from body cupping used to treat general dermatology conditions described previously, is also increasing in popularity. This practice is usually conducted in association with a facial or facial acupuncture by an aesthetician or other licensed professional. It can also be performed using at-home kits. The marketing claims for facial cupping cite improved tightening and contouring of facial skin, increased facial microcirculation and collagen synthesis, and enhanced lymphatic flow to aid with facial puffiness or swelling. One supposed mechanism for these benefits is that cupping increases blood flow. Interestingly, there was a 2020 animal study in which photoacoustic imaging of a mouse ear revealed increased temporary blood flow in the cupping microenvironment.13 Currently, however, there is no evidence in the English scientific literature that supports facial cupping. The benefits attributed to facial cupping for aesthetic purposes have emerged only in personal anecdotes. The temporary increase in blood flow may induce inflammation and swelling that adds volume to the face and temporarily diminishes wrinkles. However, this temporary plumpness may be associated with adverse effects, such as local trauma, irritation, bruising, postinflammatory pigmentary alteration, or even herpes reactivation. In my opinion, the possible adverse effects of cupping outweigh any potential benefit, especially given the insufficient evidence supporting the utility of cupping for cosmetic enhancement.
Summary
There is increasing interest among patients to incorporate complementary and alternative medicine – including the ancient tradition of cupping – in managing medical dermatologic conditions. However, current evidence supporting cupping as an effective therapeutic strategy is not strong, with most studies to date appearing to be of poor quality or not sufficiently convincing to displace standard therapies. Our medical strategies for managing chronic dermatologic conditions, particularly inflammatory disorders, continue to improve from both a safety and a proven efficacy standpoint. Therefore, I would not forgo medical management in favor of cupping. While cupping can be used as an adjunct therapy, I would caution patients about possible adverse side effects. In the aesthetic world, cupping is also gaining popularity, but this trend is also not supported by current evidence or studies, at least in the Western literature.
Dr. Goldman is a dermatologist in private practice in Miami and specializes in cosmetic and general dermatology. She practices at Baumann Cosmetic & Research Institute and is also opening a general dermatology practice. Write to her at [email protected] or message her on Instragram @DrChloeGoldman. Dr. Goldman receives compensation to create social media content for Replenix, a skin care company. She has no other disclosures.
References
1. Soliman Y et al. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018 Jun;27(2):103-7.
2. França K and Lotti T. Advances in Integrative Dermatology. John Wiley & Sons, 2019.
3. Lowe DT. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017 Nov;29:162-8.
4.Cao H et al. Altern Ther Health Med. 2010 Nov-Dec;16(6):48-54.
5. Li L and Ding J. J Tradit Chin Med. 2001 Mar;21(1):37-8.
6. Xiao XJ et al. J Integr Med. 2020 Jul;18(4):303-12.
7. Xu J et al. J Tradit Chin Med. 2013 Dec;33(6):752-6.
8. Yao J et al. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2007; Jun;27(6):424-6.
9. Hon KL et al. Case Rep Pediatr. 2013;2013:605829.
10. Xing M et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 9;99(41):e22539.
11. Kim TH et al. Eur J Integr Med. 2014 Aug 1;6(4):434-40.
12. Vender R and Vender R. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015 May-Jun;19(3):320-2.
13. Zhou Y et al. Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Apr 6;11(5):2394-401.
This article was updated 4/25/22.
Pediatric hepatitis cases may be linked to adenovirus, CDC says
Internationally, 108 cases have been reported in the United Kingdom, with 79 cases occurring in England. There are three documented cases in Spain, and similar cases are being reported in Denmark and the Netherlands, according to an article in Science. In the United Kingdom, cases have been reported in children up to 16 years old, but most affected children are between 2 and 5 years old. Eight children in the United Kingdom have required liver transplants.
On April 14, the CDC said that nine cases have been recorded in Alabama since the fall of 2021. All of these cases have been in children between 1 and 6 years old, and two children have needed liver transplants. Two additional cases have been reported in North Carolina, according to Stat News, and both children have since recovered.
Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viruses—common causes of hepatitis—have been ruled out in the U.K. and Spanish cases. More than three-fourths (77%) of the children sickened in the United Kingdom and all nine cases in Alabama have tested positive for a form of the adenovirus. While adenovirus can cause hepatitis in children, it is usually in those who are immunocompromised.
The CDC health alert advises clinicians who have cases of unexplained hepatitis in children to test for adenovirus and report these cases to the CDC as well as state public health authorities. The agency recommends nucleic acid amplification testing to detect adenovirus using respiratory swabs, stool samples or rectal swabs, or blood.
Officials are exploring whether these cases are linked to a version of the virus called adenovirus 41, which is associated with gut inflammation. The most recent case in Alabama was reported in February, and five of the nine children in the state with these puzzling cases of hepatitis have tested positive for adenovirus 41.
There have yet to be any links among the cases in Alabama or North Carolina, and investigators in the United Kingdom have also not found any connections in their cases, STAT News reports.
“CDC is working with state health departments to see if there are additional U.S. cases and what may be causing these cases,” said Kristen Nordlund, a CDC spokesperson, in a statement to STAT News. “At this time, adenovirus may be the cause for these, but investigators are still learning more – including ruling out the more common causes of hepatitis.”
Looking for other explanations
None of the children in the United States with hepatitis had COVID-19, but a few children in the United Kingdom have tested positive for the virus; none of these children have received the COVID-19 vaccine.
While the U.K. Health Security Agency says their investigation “continues to point toward a link to adenovirus infection,” they are also considering other contributing factors such as an environmental cause or COVID-19.
“COVID has been consistently shown to increase liver test numbers,” Nancy Reau, MD, the section chief of hepatology at Rush University in Chicago, said in an interview with this news organization. “It has been shown to cause other organ involvement besides just pulmonary symptoms and respiratory failure. As this virus evolves, it might be that in children, it is more able to present as hepatitis.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 4/22/22.
Internationally, 108 cases have been reported in the United Kingdom, with 79 cases occurring in England. There are three documented cases in Spain, and similar cases are being reported in Denmark and the Netherlands, according to an article in Science. In the United Kingdom, cases have been reported in children up to 16 years old, but most affected children are between 2 and 5 years old. Eight children in the United Kingdom have required liver transplants.
On April 14, the CDC said that nine cases have been recorded in Alabama since the fall of 2021. All of these cases have been in children between 1 and 6 years old, and two children have needed liver transplants. Two additional cases have been reported in North Carolina, according to Stat News, and both children have since recovered.
Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viruses—common causes of hepatitis—have been ruled out in the U.K. and Spanish cases. More than three-fourths (77%) of the children sickened in the United Kingdom and all nine cases in Alabama have tested positive for a form of the adenovirus. While adenovirus can cause hepatitis in children, it is usually in those who are immunocompromised.
The CDC health alert advises clinicians who have cases of unexplained hepatitis in children to test for adenovirus and report these cases to the CDC as well as state public health authorities. The agency recommends nucleic acid amplification testing to detect adenovirus using respiratory swabs, stool samples or rectal swabs, or blood.
Officials are exploring whether these cases are linked to a version of the virus called adenovirus 41, which is associated with gut inflammation. The most recent case in Alabama was reported in February, and five of the nine children in the state with these puzzling cases of hepatitis have tested positive for adenovirus 41.
There have yet to be any links among the cases in Alabama or North Carolina, and investigators in the United Kingdom have also not found any connections in their cases, STAT News reports.
“CDC is working with state health departments to see if there are additional U.S. cases and what may be causing these cases,” said Kristen Nordlund, a CDC spokesperson, in a statement to STAT News. “At this time, adenovirus may be the cause for these, but investigators are still learning more – including ruling out the more common causes of hepatitis.”
Looking for other explanations
None of the children in the United States with hepatitis had COVID-19, but a few children in the United Kingdom have tested positive for the virus; none of these children have received the COVID-19 vaccine.
While the U.K. Health Security Agency says their investigation “continues to point toward a link to adenovirus infection,” they are also considering other contributing factors such as an environmental cause or COVID-19.
“COVID has been consistently shown to increase liver test numbers,” Nancy Reau, MD, the section chief of hepatology at Rush University in Chicago, said in an interview with this news organization. “It has been shown to cause other organ involvement besides just pulmonary symptoms and respiratory failure. As this virus evolves, it might be that in children, it is more able to present as hepatitis.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 4/22/22.
Internationally, 108 cases have been reported in the United Kingdom, with 79 cases occurring in England. There are three documented cases in Spain, and similar cases are being reported in Denmark and the Netherlands, according to an article in Science. In the United Kingdom, cases have been reported in children up to 16 years old, but most affected children are between 2 and 5 years old. Eight children in the United Kingdom have required liver transplants.
On April 14, the CDC said that nine cases have been recorded in Alabama since the fall of 2021. All of these cases have been in children between 1 and 6 years old, and two children have needed liver transplants. Two additional cases have been reported in North Carolina, according to Stat News, and both children have since recovered.
Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viruses—common causes of hepatitis—have been ruled out in the U.K. and Spanish cases. More than three-fourths (77%) of the children sickened in the United Kingdom and all nine cases in Alabama have tested positive for a form of the adenovirus. While adenovirus can cause hepatitis in children, it is usually in those who are immunocompromised.
The CDC health alert advises clinicians who have cases of unexplained hepatitis in children to test for adenovirus and report these cases to the CDC as well as state public health authorities. The agency recommends nucleic acid amplification testing to detect adenovirus using respiratory swabs, stool samples or rectal swabs, or blood.
Officials are exploring whether these cases are linked to a version of the virus called adenovirus 41, which is associated with gut inflammation. The most recent case in Alabama was reported in February, and five of the nine children in the state with these puzzling cases of hepatitis have tested positive for adenovirus 41.
There have yet to be any links among the cases in Alabama or North Carolina, and investigators in the United Kingdom have also not found any connections in their cases, STAT News reports.
“CDC is working with state health departments to see if there are additional U.S. cases and what may be causing these cases,” said Kristen Nordlund, a CDC spokesperson, in a statement to STAT News. “At this time, adenovirus may be the cause for these, but investigators are still learning more – including ruling out the more common causes of hepatitis.”
Looking for other explanations
None of the children in the United States with hepatitis had COVID-19, but a few children in the United Kingdom have tested positive for the virus; none of these children have received the COVID-19 vaccine.
While the U.K. Health Security Agency says their investigation “continues to point toward a link to adenovirus infection,” they are also considering other contributing factors such as an environmental cause or COVID-19.
“COVID has been consistently shown to increase liver test numbers,” Nancy Reau, MD, the section chief of hepatology at Rush University in Chicago, said in an interview with this news organization. “It has been shown to cause other organ involvement besides just pulmonary symptoms and respiratory failure. As this virus evolves, it might be that in children, it is more able to present as hepatitis.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 4/22/22.
Omicron BA.2: What do we know so far?
Omicron has 30 mutations of the spike protein, compared with the original Wuhan-Hu-1 variant, with 15 mutations of the receptor-binding domain (which are linked to a decrease in antibody binding), mutations at the furin S1/S2 site (which improves furin binding and increases infectiousness), and mutations of the amino terminal domain (which is the main binding site for some of the therapeutic antibodies used to treat COVID-19 infections).
Omicron’s functional characteristics
Non–peer-reviewed studies have shown a replication of Omicron in pulmonary epithelial cells, which was shown to be less efficient, when compared with Delta and Wuhan-Hu-1. The number of viral copies from an Omicron infection in pulmonary epithelial cells was significantly lower, compared with infection with the Delta or Wuhan-Hu-1 variants. The association of these characteristics found an increase in the number of viral copies in human epithelial cells (taken from the nasal airways) infected with Omicron. This supports the understanding that Omicron is more transmissible but results in a less severe manifestation of the disease.
As for the phenotypic expression of the infection, attention has been focused on Omicron’s reduced capacity to cause syncytia in pulmonary tissue cultures, information which is relevant to its clinical significance, if we consider that the formation of syncytia has been associated with a more severe manifestation of the disease. Furthermore, it has emerged that Omicron can use different cellular entry routes, with a preference for endosomal fusion over superficial cellular fusion. This characteristic allows Omicron to significantly increase the number of types of cells it can infect.
Omicron BA.2 evolves
Between November and December 2021, Omicron progressed, evolving into a variant with characteristics similar to those of its predecessors (that is, it underwent a gradual and progressive increase in transmissibility). Early studies on the Omicron variant were mainly based on the BA.1 subvariant. Since the start of January 2022, there has been an unexpected increase in BA.2 in Europe and Asia. Since then, continued surveillance on the evolution of Omicron has shown an increased prevalence of two subvariants: BA.1 with a R346K mutation (BA.1 + R346K) and B.1.1.529.2 (BA.2), with the latter containing eight unique spike mutations and 13 missing spike mutations, compared with those found in BA.1.
From these differences, we cannot presume that their antigenic properties are similar or different, but they seem to be antigenically equidistant from wild-type SARS-CoV-2, likely jeopardizing in equal measures the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines. Furthermore, BA.2 shows significant resistance to 17 out of 19 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies tested in this study, demonstrating that current monoclonal antibody therapy may have significant limitations in terms of adequate coverage for all subvariants of the Omicron variant.
Omicron BA.2 and reinfection
BA.2 initially represented only 13% of Omicron sequences at a global level, quickly becoming the dominant form in some countries, such as Denmark. At the end of 2021, BA.2 represented around 20% of all Danish cases of SARS-CoV-2. Halfway through January 2022, this had increased to around 45%, data that indicate that BA.2 carries an advantage over BA.1 within the highly vaccinated population of Denmark.
BA.2 is associated with an increased susceptibility of infection for unvaccinated individuals (odds ratio, 2.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.58-3.04), fully vaccinated individuals (OR, 2.45; 95% CI, 1.77-3.40), and booster-vaccinated individuals (OR, 2.99; 95% CI, 2.11-4.24), compared with BA.1. The pattern of increased transmissibility in BA.2 households was not observed for fully vaccinated and booster-vaccinated primary cases, where the OR of transmission was below 1 for BA.2, compared with BA.1. These data confirm the immune-evasive properties of BA.2 that further reduce the protective effect of vaccination against infection, but do not increase its transmissibility from vaccinated individuals with breakthrough infections.
Omicron, BA.2, and vaccination
The understanding of serum neutralizing activity, in correlation to the efficacy of a vaccine, is a priority of research because of the growing epidemiological significance of BA.2. There is evidence to support the claim that the immune-evasive nature of BA.2 doesn›t seem to be as severe as that of BA.1, and it is possible that there are other viral or host factors that are enabling the rapid diffusion of BA.2. A study published in Science Immunology investigated humoral and cellular immune responses to Omicron and other variants of concern (VOCs), looking to understand how, and to what degree, vaccinated individuals are protected against Omicron. From the results, a very low level of antibody cross-neutralization of Omicron, or a lack thereof, was seen when compared with wild type, Beta, and Delta variants, which could be partially restored by a third booster vaccination. Furthermore, T lymphocytes were shown to recognize Omicron with the same efficacy as seen for the other VOCs, suggesting that vaccinated individuals maintain T lymphocyte immunity, an element that is capable of providing protection in the absence of neutralizing antibodies, limiting the chance of serious disease.
These results are consistent with those available from a study performed in a population from Qatar made up of 2,239,193 people who had received at least two doses of a BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 vaccine. The efficacy of the booster against a symptomatic Omicron infection, compared with that from the primary series, was 49.4% (95% CI, 47.1-51.6). The efficacy of the booster against hospitalization for COVID-19 and the death rate from Omicron infection, compared with the primary series, was 76.5% (95% CI, 55.9-87.5). The efficacy of the BNT162b2 booster against a symptomatic Delta variant infection (or B.1.617.2), compared with the primary series, was 86.1% (95% CI, 67.3-94.1).
To summarize, the constant increase in the prevalence of BA.2 in more countries over the world has confirmed the growth advantage that this variant has compared with others. BA.2 reduces the protective effect of vaccination against infection. Omicron antibody cross-neutralization can be partially restored by a third booster vaccination, an aspect that becomes problematic in the context of a low vaccination rate, where peaks of Omicron may increase the likelihood of infection in the elderly and in other groups at a higher risk of severe disease. Omicron BA.2 opens up new evolution channels, but what do the experts think will happen?
A version of this article was originally published in Italian on Univadis.
Omicron has 30 mutations of the spike protein, compared with the original Wuhan-Hu-1 variant, with 15 mutations of the receptor-binding domain (which are linked to a decrease in antibody binding), mutations at the furin S1/S2 site (which improves furin binding and increases infectiousness), and mutations of the amino terminal domain (which is the main binding site for some of the therapeutic antibodies used to treat COVID-19 infections).
Omicron’s functional characteristics
Non–peer-reviewed studies have shown a replication of Omicron in pulmonary epithelial cells, which was shown to be less efficient, when compared with Delta and Wuhan-Hu-1. The number of viral copies from an Omicron infection in pulmonary epithelial cells was significantly lower, compared with infection with the Delta or Wuhan-Hu-1 variants. The association of these characteristics found an increase in the number of viral copies in human epithelial cells (taken from the nasal airways) infected with Omicron. This supports the understanding that Omicron is more transmissible but results in a less severe manifestation of the disease.
As for the phenotypic expression of the infection, attention has been focused on Omicron’s reduced capacity to cause syncytia in pulmonary tissue cultures, information which is relevant to its clinical significance, if we consider that the formation of syncytia has been associated with a more severe manifestation of the disease. Furthermore, it has emerged that Omicron can use different cellular entry routes, with a preference for endosomal fusion over superficial cellular fusion. This characteristic allows Omicron to significantly increase the number of types of cells it can infect.
Omicron BA.2 evolves
Between November and December 2021, Omicron progressed, evolving into a variant with characteristics similar to those of its predecessors (that is, it underwent a gradual and progressive increase in transmissibility). Early studies on the Omicron variant were mainly based on the BA.1 subvariant. Since the start of January 2022, there has been an unexpected increase in BA.2 in Europe and Asia. Since then, continued surveillance on the evolution of Omicron has shown an increased prevalence of two subvariants: BA.1 with a R346K mutation (BA.1 + R346K) and B.1.1.529.2 (BA.2), with the latter containing eight unique spike mutations and 13 missing spike mutations, compared with those found in BA.1.
From these differences, we cannot presume that their antigenic properties are similar or different, but they seem to be antigenically equidistant from wild-type SARS-CoV-2, likely jeopardizing in equal measures the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines. Furthermore, BA.2 shows significant resistance to 17 out of 19 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies tested in this study, demonstrating that current monoclonal antibody therapy may have significant limitations in terms of adequate coverage for all subvariants of the Omicron variant.
Omicron BA.2 and reinfection
BA.2 initially represented only 13% of Omicron sequences at a global level, quickly becoming the dominant form in some countries, such as Denmark. At the end of 2021, BA.2 represented around 20% of all Danish cases of SARS-CoV-2. Halfway through January 2022, this had increased to around 45%, data that indicate that BA.2 carries an advantage over BA.1 within the highly vaccinated population of Denmark.
BA.2 is associated with an increased susceptibility of infection for unvaccinated individuals (odds ratio, 2.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.58-3.04), fully vaccinated individuals (OR, 2.45; 95% CI, 1.77-3.40), and booster-vaccinated individuals (OR, 2.99; 95% CI, 2.11-4.24), compared with BA.1. The pattern of increased transmissibility in BA.2 households was not observed for fully vaccinated and booster-vaccinated primary cases, where the OR of transmission was below 1 for BA.2, compared with BA.1. These data confirm the immune-evasive properties of BA.2 that further reduce the protective effect of vaccination against infection, but do not increase its transmissibility from vaccinated individuals with breakthrough infections.
Omicron, BA.2, and vaccination
The understanding of serum neutralizing activity, in correlation to the efficacy of a vaccine, is a priority of research because of the growing epidemiological significance of BA.2. There is evidence to support the claim that the immune-evasive nature of BA.2 doesn›t seem to be as severe as that of BA.1, and it is possible that there are other viral or host factors that are enabling the rapid diffusion of BA.2. A study published in Science Immunology investigated humoral and cellular immune responses to Omicron and other variants of concern (VOCs), looking to understand how, and to what degree, vaccinated individuals are protected against Omicron. From the results, a very low level of antibody cross-neutralization of Omicron, or a lack thereof, was seen when compared with wild type, Beta, and Delta variants, which could be partially restored by a third booster vaccination. Furthermore, T lymphocytes were shown to recognize Omicron with the same efficacy as seen for the other VOCs, suggesting that vaccinated individuals maintain T lymphocyte immunity, an element that is capable of providing protection in the absence of neutralizing antibodies, limiting the chance of serious disease.
These results are consistent with those available from a study performed in a population from Qatar made up of 2,239,193 people who had received at least two doses of a BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 vaccine. The efficacy of the booster against a symptomatic Omicron infection, compared with that from the primary series, was 49.4% (95% CI, 47.1-51.6). The efficacy of the booster against hospitalization for COVID-19 and the death rate from Omicron infection, compared with the primary series, was 76.5% (95% CI, 55.9-87.5). The efficacy of the BNT162b2 booster against a symptomatic Delta variant infection (or B.1.617.2), compared with the primary series, was 86.1% (95% CI, 67.3-94.1).
To summarize, the constant increase in the prevalence of BA.2 in more countries over the world has confirmed the growth advantage that this variant has compared with others. BA.2 reduces the protective effect of vaccination against infection. Omicron antibody cross-neutralization can be partially restored by a third booster vaccination, an aspect that becomes problematic in the context of a low vaccination rate, where peaks of Omicron may increase the likelihood of infection in the elderly and in other groups at a higher risk of severe disease. Omicron BA.2 opens up new evolution channels, but what do the experts think will happen?
A version of this article was originally published in Italian on Univadis.
Omicron has 30 mutations of the spike protein, compared with the original Wuhan-Hu-1 variant, with 15 mutations of the receptor-binding domain (which are linked to a decrease in antibody binding), mutations at the furin S1/S2 site (which improves furin binding and increases infectiousness), and mutations of the amino terminal domain (which is the main binding site for some of the therapeutic antibodies used to treat COVID-19 infections).
Omicron’s functional characteristics
Non–peer-reviewed studies have shown a replication of Omicron in pulmonary epithelial cells, which was shown to be less efficient, when compared with Delta and Wuhan-Hu-1. The number of viral copies from an Omicron infection in pulmonary epithelial cells was significantly lower, compared with infection with the Delta or Wuhan-Hu-1 variants. The association of these characteristics found an increase in the number of viral copies in human epithelial cells (taken from the nasal airways) infected with Omicron. This supports the understanding that Omicron is more transmissible but results in a less severe manifestation of the disease.
As for the phenotypic expression of the infection, attention has been focused on Omicron’s reduced capacity to cause syncytia in pulmonary tissue cultures, information which is relevant to its clinical significance, if we consider that the formation of syncytia has been associated with a more severe manifestation of the disease. Furthermore, it has emerged that Omicron can use different cellular entry routes, with a preference for endosomal fusion over superficial cellular fusion. This characteristic allows Omicron to significantly increase the number of types of cells it can infect.
Omicron BA.2 evolves
Between November and December 2021, Omicron progressed, evolving into a variant with characteristics similar to those of its predecessors (that is, it underwent a gradual and progressive increase in transmissibility). Early studies on the Omicron variant were mainly based on the BA.1 subvariant. Since the start of January 2022, there has been an unexpected increase in BA.2 in Europe and Asia. Since then, continued surveillance on the evolution of Omicron has shown an increased prevalence of two subvariants: BA.1 with a R346K mutation (BA.1 + R346K) and B.1.1.529.2 (BA.2), with the latter containing eight unique spike mutations and 13 missing spike mutations, compared with those found in BA.1.
From these differences, we cannot presume that their antigenic properties are similar or different, but they seem to be antigenically equidistant from wild-type SARS-CoV-2, likely jeopardizing in equal measures the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines. Furthermore, BA.2 shows significant resistance to 17 out of 19 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies tested in this study, demonstrating that current monoclonal antibody therapy may have significant limitations in terms of adequate coverage for all subvariants of the Omicron variant.
Omicron BA.2 and reinfection
BA.2 initially represented only 13% of Omicron sequences at a global level, quickly becoming the dominant form in some countries, such as Denmark. At the end of 2021, BA.2 represented around 20% of all Danish cases of SARS-CoV-2. Halfway through January 2022, this had increased to around 45%, data that indicate that BA.2 carries an advantage over BA.1 within the highly vaccinated population of Denmark.
BA.2 is associated with an increased susceptibility of infection for unvaccinated individuals (odds ratio, 2.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.58-3.04), fully vaccinated individuals (OR, 2.45; 95% CI, 1.77-3.40), and booster-vaccinated individuals (OR, 2.99; 95% CI, 2.11-4.24), compared with BA.1. The pattern of increased transmissibility in BA.2 households was not observed for fully vaccinated and booster-vaccinated primary cases, where the OR of transmission was below 1 for BA.2, compared with BA.1. These data confirm the immune-evasive properties of BA.2 that further reduce the protective effect of vaccination against infection, but do not increase its transmissibility from vaccinated individuals with breakthrough infections.
Omicron, BA.2, and vaccination
The understanding of serum neutralizing activity, in correlation to the efficacy of a vaccine, is a priority of research because of the growing epidemiological significance of BA.2. There is evidence to support the claim that the immune-evasive nature of BA.2 doesn›t seem to be as severe as that of BA.1, and it is possible that there are other viral or host factors that are enabling the rapid diffusion of BA.2. A study published in Science Immunology investigated humoral and cellular immune responses to Omicron and other variants of concern (VOCs), looking to understand how, and to what degree, vaccinated individuals are protected against Omicron. From the results, a very low level of antibody cross-neutralization of Omicron, or a lack thereof, was seen when compared with wild type, Beta, and Delta variants, which could be partially restored by a third booster vaccination. Furthermore, T lymphocytes were shown to recognize Omicron with the same efficacy as seen for the other VOCs, suggesting that vaccinated individuals maintain T lymphocyte immunity, an element that is capable of providing protection in the absence of neutralizing antibodies, limiting the chance of serious disease.
These results are consistent with those available from a study performed in a population from Qatar made up of 2,239,193 people who had received at least two doses of a BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 vaccine. The efficacy of the booster against a symptomatic Omicron infection, compared with that from the primary series, was 49.4% (95% CI, 47.1-51.6). The efficacy of the booster against hospitalization for COVID-19 and the death rate from Omicron infection, compared with the primary series, was 76.5% (95% CI, 55.9-87.5). The efficacy of the BNT162b2 booster against a symptomatic Delta variant infection (or B.1.617.2), compared with the primary series, was 86.1% (95% CI, 67.3-94.1).
To summarize, the constant increase in the prevalence of BA.2 in more countries over the world has confirmed the growth advantage that this variant has compared with others. BA.2 reduces the protective effect of vaccination against infection. Omicron antibody cross-neutralization can be partially restored by a third booster vaccination, an aspect that becomes problematic in the context of a low vaccination rate, where peaks of Omicron may increase the likelihood of infection in the elderly and in other groups at a higher risk of severe disease. Omicron BA.2 opens up new evolution channels, but what do the experts think will happen?
A version of this article was originally published in Italian on Univadis.
Babies die as congenital syphilis continues a decade-long surge across the U.S.
For a decade, the number of babies born with syphilis in the United States has surged, undeterred. Data released Apr. 12 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows just how dire the outbreak has become.
In 2012, 332 babies were born infected with the disease. In 2021, that number had climbed nearly sevenfold, to at least 2,268, according to preliminary estimates. And 166 of those babies died.
About 7% of babies diagnosed with syphilis in recent years have died; thousands of others born with the disease have faced problems that include brain and bone malformations, blindness, and organ damage.
For public health officials, the situation is all the more heartbreaking, considering that congenital syphilis rates reached near-historic modern lows from 2000 to 2012 amid ambitious prevention and education efforts. By 2020, following a sharp erosion in funding and attention, the nationwide case rate was more than seven times that of 2012.
“The really depressing thing about it is we had this thing virtually eradicated back in the year 2000,” said William Andrews, a public information officer for Oklahoma’s sexual health and harm reduction service. “Now it’s back with a vengeance. We are really trying to get the message out that sexual health is health. It’s nothing to be ashamed of.”
Even as caseloads soar, the CDC budget for STD prevention – the primary funding source for most public health departments – has been largely stagnant for two decades, its purchasing power dragged even lower by inflation.
The CDC report on STD trends provides official data on congenital syphilis cases for 2020, as well as preliminary case counts for 2021 that are expected to increase. CDC data shows that congenital syphilis rates in 2020 continued to climb in already overwhelmed states like Texas, California, and Nevada and that the disease is now present in almost every state in the nation. All but three states – Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont – reported congenital syphilis cases in 2020.
From 2011 to 2020, congenital syphilis resulted in 633 documented stillbirths and infant deaths, according to the new CDC data.
Preventing congenital syphilis – the term used when syphilis is transferred to a fetus in utero – is from a medical standpoint exceedingly simple: If a pregnant woman is diagnosed at least a month before giving birth, just a few shots of penicillin have a near-perfect cure rate for mother and baby. But funding cuts and competing priorities in the nation’s fragmented public health care system have vastly narrowed access to such services.
The reasons pregnant people with syphilis go undiagnosed or untreated vary geographically, according to data collected by states and analyzed by the CDC.
In Western states, the largest share of cases involve women who have received little to no prenatal care and aren’t tested for syphilis until they give birth. Many have substance use disorders, primarily related to methamphetamines. “They’ve felt a lot of judgment and stigma by the medical community,” said Stephanie Pierce, MD, a maternal fetal medicine specialist at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, who runs a clinic for women with high-risk pregnancies.
In Southern states, a CDC study of 2018 data found that the largest share of congenital syphilis cases were among women who had been tested and diagnosed but hadn’t received treatment. That year, among Black moms who gave birth to a baby with syphilis, 37% had not been treated adequately even though they’d received a timely diagnosis. Among white moms, that number was 24%. Longstanding racism in medical care, poverty, transportation issues, poorly funded public health departments, and crowded clinics whose employees are too overworked to follow up with patients all contribute to the problem, according to infectious disease experts.
Doctors are also noticing a growing number of women who are treated for syphilis but reinfected during pregnancy. Amid rising cases and stagnant resources, some states have focused disease investigations on pregnant women of childbearing age; they can no longer prioritize treating sexual partners who are also infected.
Eric McGrath, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Wayne State University, Detroit, said that he’d seen several newborns in recent years whose mothers had been treated for syphilis but then were re-exposed during pregnancy by partners who hadn’t been treated.
Treating a newborn baby for syphilis isn’t trivial. Penicillin carries little risk, but delivering it to a baby often involves a lumbar puncture and other painful procedures. And treatment typically means keeping the baby in the hospital for 10 days, interrupting an important time for family bonding.
Dr. McGrath has seen a couple of babies in his career who weren’t diagnosed or treated at birth and later came to him with full-blown syphilis complications, including full-body rashes and inflamed livers. It was an awful experience he doesn’t want to repeat. The preferred course, he said, is to spare the baby the ordeal and treat parents early in the pregnancy.
But in some places, providers aren’t routinely testing for syphilis. Although most states mandate testing at some point during pregnancy, as of last year just 14 required it for everyone in the third trimester. The CDC recommends third-trimester testing in areas with high rates of syphilis, a growing share of the United States.
After Arizona declared a statewide outbreak in 2018, state health officials wanted to know whether widespread testing in the third trimester could have prevented infections. Looking at 18 months of data, analysts found that nearly three-quarters of the more than 200 pregnant women diagnosed with syphilis in 2017 and the first half of 2018 got treatment. That left 57 babies born with syphilis, nine of whom died. The analysts estimated that a third of the infections could have been prevented with testing in the third trimester.
Based on the numbers they saw in those 18 months, officials estimated that screening all women on Medicaid in the third trimester would cost the state $113,300 annually, and that treating all cases of syphilis that screening would catch could be done for just $113. Factoring in the hospitalization costs for infected infants, the officials concluded the additional testing would save the state money.
And yet prevention money has been hard to come by. Taking inflation into account, CDC prevention funding for STDs has fallen 41% since 2003, according to an analysis by the National Coalition of STD Directors. That’s even as cases have risen, leaving public health departments saddled with more work and far less money.
Janine Waters, STD program manager for the state of New Mexico, has watched the unraveling. When Ms. Waters started her career more than 20 years ago, she and her colleagues followed up on every case of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reported, not only making sure that people got treatment but also getting in touch with their sexual partners, with the aim of stopping the spread of infection. In a 2019 interview with Kaiser Health News, she said her team was struggling to keep up with syphilis alone, even as they registered with dread congenital syphilis cases surging in neighboring Texas and Arizona.
By 2020, New Mexico had the highest rate of congenital syphilis in the country.
The COVID-19 pandemic drained the remaining resources. Half of health departments across the country discontinued STD fieldwork altogether, diverting their resources to COVID. In California, which for years has struggled with high rates of congenital syphilis, three-quarters of local health departments dispatched more than half of their STD staffers to work on COVID.
As the pandemic ebbs – at least in the short term – many public health departments are turning their attention back to syphilis and other diseases. And they are doing it with reinforcements. Although the Biden administration’s proposed STD prevention budget for 2023 remains flat, the American Rescue Plan Act included $200 million to help health departments boost contact tracing and surveillance for covid and other infectious diseases. Many departments are funneling that money toward STDs.
The money is an infusion that state health officials say will make a difference. But when taking inflation into account, it essentially brings STD prevention funding back to what it was in 2003, said Stephanie Arnold Pang of the National Coalition of STD Directors. And the American Rescue Plan money doesn’t cover some aspects of STD prevention, including clinical services.
The coalition wants to revive dedicated STD clinics, where people can drop in for testing and treatment at little to no cost. Advocates say that would fill a void that has plagued treatment efforts since public clinics closed en masse in the wake of the 2008 recession.
Texas, battling its own pervasive outbreak, will use its share of American Rescue Plan money to fill 94 new positions focused on various aspects of STD prevention. Those hires will bolster a range of measures the state put in place before the pandemic, including an updated data system to track infections, review boards in major cities that examine what went wrong for every case of congenital syphilis, and a requirement that providers test for syphilis during the third trimester of pregnancy. The suite of interventions seems to be working, but it could be a while before cases go down, said Amy Carter, the state’s congenital syphilis coordinator.
“The growth didn’t happen overnight,” Ms. Carter said. “So our prevention efforts aren’t going to have a direct impact overnight either.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation
For a decade, the number of babies born with syphilis in the United States has surged, undeterred. Data released Apr. 12 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows just how dire the outbreak has become.
In 2012, 332 babies were born infected with the disease. In 2021, that number had climbed nearly sevenfold, to at least 2,268, according to preliminary estimates. And 166 of those babies died.
About 7% of babies diagnosed with syphilis in recent years have died; thousands of others born with the disease have faced problems that include brain and bone malformations, blindness, and organ damage.
For public health officials, the situation is all the more heartbreaking, considering that congenital syphilis rates reached near-historic modern lows from 2000 to 2012 amid ambitious prevention and education efforts. By 2020, following a sharp erosion in funding and attention, the nationwide case rate was more than seven times that of 2012.
“The really depressing thing about it is we had this thing virtually eradicated back in the year 2000,” said William Andrews, a public information officer for Oklahoma’s sexual health and harm reduction service. “Now it’s back with a vengeance. We are really trying to get the message out that sexual health is health. It’s nothing to be ashamed of.”
Even as caseloads soar, the CDC budget for STD prevention – the primary funding source for most public health departments – has been largely stagnant for two decades, its purchasing power dragged even lower by inflation.
The CDC report on STD trends provides official data on congenital syphilis cases for 2020, as well as preliminary case counts for 2021 that are expected to increase. CDC data shows that congenital syphilis rates in 2020 continued to climb in already overwhelmed states like Texas, California, and Nevada and that the disease is now present in almost every state in the nation. All but three states – Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont – reported congenital syphilis cases in 2020.
From 2011 to 2020, congenital syphilis resulted in 633 documented stillbirths and infant deaths, according to the new CDC data.
Preventing congenital syphilis – the term used when syphilis is transferred to a fetus in utero – is from a medical standpoint exceedingly simple: If a pregnant woman is diagnosed at least a month before giving birth, just a few shots of penicillin have a near-perfect cure rate for mother and baby. But funding cuts and competing priorities in the nation’s fragmented public health care system have vastly narrowed access to such services.
The reasons pregnant people with syphilis go undiagnosed or untreated vary geographically, according to data collected by states and analyzed by the CDC.
In Western states, the largest share of cases involve women who have received little to no prenatal care and aren’t tested for syphilis until they give birth. Many have substance use disorders, primarily related to methamphetamines. “They’ve felt a lot of judgment and stigma by the medical community,” said Stephanie Pierce, MD, a maternal fetal medicine specialist at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, who runs a clinic for women with high-risk pregnancies.
In Southern states, a CDC study of 2018 data found that the largest share of congenital syphilis cases were among women who had been tested and diagnosed but hadn’t received treatment. That year, among Black moms who gave birth to a baby with syphilis, 37% had not been treated adequately even though they’d received a timely diagnosis. Among white moms, that number was 24%. Longstanding racism in medical care, poverty, transportation issues, poorly funded public health departments, and crowded clinics whose employees are too overworked to follow up with patients all contribute to the problem, according to infectious disease experts.
Doctors are also noticing a growing number of women who are treated for syphilis but reinfected during pregnancy. Amid rising cases and stagnant resources, some states have focused disease investigations on pregnant women of childbearing age; they can no longer prioritize treating sexual partners who are also infected.
Eric McGrath, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Wayne State University, Detroit, said that he’d seen several newborns in recent years whose mothers had been treated for syphilis but then were re-exposed during pregnancy by partners who hadn’t been treated.
Treating a newborn baby for syphilis isn’t trivial. Penicillin carries little risk, but delivering it to a baby often involves a lumbar puncture and other painful procedures. And treatment typically means keeping the baby in the hospital for 10 days, interrupting an important time for family bonding.
Dr. McGrath has seen a couple of babies in his career who weren’t diagnosed or treated at birth and later came to him with full-blown syphilis complications, including full-body rashes and inflamed livers. It was an awful experience he doesn’t want to repeat. The preferred course, he said, is to spare the baby the ordeal and treat parents early in the pregnancy.
But in some places, providers aren’t routinely testing for syphilis. Although most states mandate testing at some point during pregnancy, as of last year just 14 required it for everyone in the third trimester. The CDC recommends third-trimester testing in areas with high rates of syphilis, a growing share of the United States.
After Arizona declared a statewide outbreak in 2018, state health officials wanted to know whether widespread testing in the third trimester could have prevented infections. Looking at 18 months of data, analysts found that nearly three-quarters of the more than 200 pregnant women diagnosed with syphilis in 2017 and the first half of 2018 got treatment. That left 57 babies born with syphilis, nine of whom died. The analysts estimated that a third of the infections could have been prevented with testing in the third trimester.
Based on the numbers they saw in those 18 months, officials estimated that screening all women on Medicaid in the third trimester would cost the state $113,300 annually, and that treating all cases of syphilis that screening would catch could be done for just $113. Factoring in the hospitalization costs for infected infants, the officials concluded the additional testing would save the state money.
And yet prevention money has been hard to come by. Taking inflation into account, CDC prevention funding for STDs has fallen 41% since 2003, according to an analysis by the National Coalition of STD Directors. That’s even as cases have risen, leaving public health departments saddled with more work and far less money.
Janine Waters, STD program manager for the state of New Mexico, has watched the unraveling. When Ms. Waters started her career more than 20 years ago, she and her colleagues followed up on every case of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reported, not only making sure that people got treatment but also getting in touch with their sexual partners, with the aim of stopping the spread of infection. In a 2019 interview with Kaiser Health News, she said her team was struggling to keep up with syphilis alone, even as they registered with dread congenital syphilis cases surging in neighboring Texas and Arizona.
By 2020, New Mexico had the highest rate of congenital syphilis in the country.
The COVID-19 pandemic drained the remaining resources. Half of health departments across the country discontinued STD fieldwork altogether, diverting their resources to COVID. In California, which for years has struggled with high rates of congenital syphilis, three-quarters of local health departments dispatched more than half of their STD staffers to work on COVID.
As the pandemic ebbs – at least in the short term – many public health departments are turning their attention back to syphilis and other diseases. And they are doing it with reinforcements. Although the Biden administration’s proposed STD prevention budget for 2023 remains flat, the American Rescue Plan Act included $200 million to help health departments boost contact tracing and surveillance for covid and other infectious diseases. Many departments are funneling that money toward STDs.
The money is an infusion that state health officials say will make a difference. But when taking inflation into account, it essentially brings STD prevention funding back to what it was in 2003, said Stephanie Arnold Pang of the National Coalition of STD Directors. And the American Rescue Plan money doesn’t cover some aspects of STD prevention, including clinical services.
The coalition wants to revive dedicated STD clinics, where people can drop in for testing and treatment at little to no cost. Advocates say that would fill a void that has plagued treatment efforts since public clinics closed en masse in the wake of the 2008 recession.
Texas, battling its own pervasive outbreak, will use its share of American Rescue Plan money to fill 94 new positions focused on various aspects of STD prevention. Those hires will bolster a range of measures the state put in place before the pandemic, including an updated data system to track infections, review boards in major cities that examine what went wrong for every case of congenital syphilis, and a requirement that providers test for syphilis during the third trimester of pregnancy. The suite of interventions seems to be working, but it could be a while before cases go down, said Amy Carter, the state’s congenital syphilis coordinator.
“The growth didn’t happen overnight,” Ms. Carter said. “So our prevention efforts aren’t going to have a direct impact overnight either.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation
For a decade, the number of babies born with syphilis in the United States has surged, undeterred. Data released Apr. 12 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows just how dire the outbreak has become.
In 2012, 332 babies were born infected with the disease. In 2021, that number had climbed nearly sevenfold, to at least 2,268, according to preliminary estimates. And 166 of those babies died.
About 7% of babies diagnosed with syphilis in recent years have died; thousands of others born with the disease have faced problems that include brain and bone malformations, blindness, and organ damage.
For public health officials, the situation is all the more heartbreaking, considering that congenital syphilis rates reached near-historic modern lows from 2000 to 2012 amid ambitious prevention and education efforts. By 2020, following a sharp erosion in funding and attention, the nationwide case rate was more than seven times that of 2012.
“The really depressing thing about it is we had this thing virtually eradicated back in the year 2000,” said William Andrews, a public information officer for Oklahoma’s sexual health and harm reduction service. “Now it’s back with a vengeance. We are really trying to get the message out that sexual health is health. It’s nothing to be ashamed of.”
Even as caseloads soar, the CDC budget for STD prevention – the primary funding source for most public health departments – has been largely stagnant for two decades, its purchasing power dragged even lower by inflation.
The CDC report on STD trends provides official data on congenital syphilis cases for 2020, as well as preliminary case counts for 2021 that are expected to increase. CDC data shows that congenital syphilis rates in 2020 continued to climb in already overwhelmed states like Texas, California, and Nevada and that the disease is now present in almost every state in the nation. All but three states – Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont – reported congenital syphilis cases in 2020.
From 2011 to 2020, congenital syphilis resulted in 633 documented stillbirths and infant deaths, according to the new CDC data.
Preventing congenital syphilis – the term used when syphilis is transferred to a fetus in utero – is from a medical standpoint exceedingly simple: If a pregnant woman is diagnosed at least a month before giving birth, just a few shots of penicillin have a near-perfect cure rate for mother and baby. But funding cuts and competing priorities in the nation’s fragmented public health care system have vastly narrowed access to such services.
The reasons pregnant people with syphilis go undiagnosed or untreated vary geographically, according to data collected by states and analyzed by the CDC.
In Western states, the largest share of cases involve women who have received little to no prenatal care and aren’t tested for syphilis until they give birth. Many have substance use disorders, primarily related to methamphetamines. “They’ve felt a lot of judgment and stigma by the medical community,” said Stephanie Pierce, MD, a maternal fetal medicine specialist at the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, who runs a clinic for women with high-risk pregnancies.
In Southern states, a CDC study of 2018 data found that the largest share of congenital syphilis cases were among women who had been tested and diagnosed but hadn’t received treatment. That year, among Black moms who gave birth to a baby with syphilis, 37% had not been treated adequately even though they’d received a timely diagnosis. Among white moms, that number was 24%. Longstanding racism in medical care, poverty, transportation issues, poorly funded public health departments, and crowded clinics whose employees are too overworked to follow up with patients all contribute to the problem, according to infectious disease experts.
Doctors are also noticing a growing number of women who are treated for syphilis but reinfected during pregnancy. Amid rising cases and stagnant resources, some states have focused disease investigations on pregnant women of childbearing age; they can no longer prioritize treating sexual partners who are also infected.
Eric McGrath, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Wayne State University, Detroit, said that he’d seen several newborns in recent years whose mothers had been treated for syphilis but then were re-exposed during pregnancy by partners who hadn’t been treated.
Treating a newborn baby for syphilis isn’t trivial. Penicillin carries little risk, but delivering it to a baby often involves a lumbar puncture and other painful procedures. And treatment typically means keeping the baby in the hospital for 10 days, interrupting an important time for family bonding.
Dr. McGrath has seen a couple of babies in his career who weren’t diagnosed or treated at birth and later came to him with full-blown syphilis complications, including full-body rashes and inflamed livers. It was an awful experience he doesn’t want to repeat. The preferred course, he said, is to spare the baby the ordeal and treat parents early in the pregnancy.
But in some places, providers aren’t routinely testing for syphilis. Although most states mandate testing at some point during pregnancy, as of last year just 14 required it for everyone in the third trimester. The CDC recommends third-trimester testing in areas with high rates of syphilis, a growing share of the United States.
After Arizona declared a statewide outbreak in 2018, state health officials wanted to know whether widespread testing in the third trimester could have prevented infections. Looking at 18 months of data, analysts found that nearly three-quarters of the more than 200 pregnant women diagnosed with syphilis in 2017 and the first half of 2018 got treatment. That left 57 babies born with syphilis, nine of whom died. The analysts estimated that a third of the infections could have been prevented with testing in the third trimester.
Based on the numbers they saw in those 18 months, officials estimated that screening all women on Medicaid in the third trimester would cost the state $113,300 annually, and that treating all cases of syphilis that screening would catch could be done for just $113. Factoring in the hospitalization costs for infected infants, the officials concluded the additional testing would save the state money.
And yet prevention money has been hard to come by. Taking inflation into account, CDC prevention funding for STDs has fallen 41% since 2003, according to an analysis by the National Coalition of STD Directors. That’s even as cases have risen, leaving public health departments saddled with more work and far less money.
Janine Waters, STD program manager for the state of New Mexico, has watched the unraveling. When Ms. Waters started her career more than 20 years ago, she and her colleagues followed up on every case of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reported, not only making sure that people got treatment but also getting in touch with their sexual partners, with the aim of stopping the spread of infection. In a 2019 interview with Kaiser Health News, she said her team was struggling to keep up with syphilis alone, even as they registered with dread congenital syphilis cases surging in neighboring Texas and Arizona.
By 2020, New Mexico had the highest rate of congenital syphilis in the country.
The COVID-19 pandemic drained the remaining resources. Half of health departments across the country discontinued STD fieldwork altogether, diverting their resources to COVID. In California, which for years has struggled with high rates of congenital syphilis, three-quarters of local health departments dispatched more than half of their STD staffers to work on COVID.
As the pandemic ebbs – at least in the short term – many public health departments are turning their attention back to syphilis and other diseases. And they are doing it with reinforcements. Although the Biden administration’s proposed STD prevention budget for 2023 remains flat, the American Rescue Plan Act included $200 million to help health departments boost contact tracing and surveillance for covid and other infectious diseases. Many departments are funneling that money toward STDs.
The money is an infusion that state health officials say will make a difference. But when taking inflation into account, it essentially brings STD prevention funding back to what it was in 2003, said Stephanie Arnold Pang of the National Coalition of STD Directors. And the American Rescue Plan money doesn’t cover some aspects of STD prevention, including clinical services.
The coalition wants to revive dedicated STD clinics, where people can drop in for testing and treatment at little to no cost. Advocates say that would fill a void that has plagued treatment efforts since public clinics closed en masse in the wake of the 2008 recession.
Texas, battling its own pervasive outbreak, will use its share of American Rescue Plan money to fill 94 new positions focused on various aspects of STD prevention. Those hires will bolster a range of measures the state put in place before the pandemic, including an updated data system to track infections, review boards in major cities that examine what went wrong for every case of congenital syphilis, and a requirement that providers test for syphilis during the third trimester of pregnancy. The suite of interventions seems to be working, but it could be a while before cases go down, said Amy Carter, the state’s congenital syphilis coordinator.
“The growth didn’t happen overnight,” Ms. Carter said. “So our prevention efforts aren’t going to have a direct impact overnight either.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation
To engage injection drug users in HCV care, go to where they are
For injection drug users with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, providing treatment opportunities within a local needle exchange program can provide care to more patients and eventually cure more patients, a new study suggests.
The study’s findings help “counteract the implicit belief within the medical community that people who inject drugs can’t or don’t want to engage in health care,” lead author Benjamin Eckhardt, MD, with NYU Grossman School of Medicine, told this news organization.
“By simply focusing on patient accompaniment, limiting stigma, and removing the punitive response for missed appointments, we can effectively engage people who inject drugs in health care and more specifically cure their infection, making significant inroads to HCV elimination,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Nonjudgmental, patient-centered approach
Researchers included 165 injection drug users with HCV (mean age, 42 years; 78% men); 82 were randomly allocated to the accessible care intervention and 83 to a usual care control group.
The accessible care model provides HCV treatment within a community-based needle exchange program in a comfortable, nonjudgmental atmosphere, “without fear of shame or stigma that people who inject drugs often experience in mainstream institutions,” the investigators explain.
Control participants were connected to a patient navigator who facilitated referrals to community direct antigen antiviral therapy programs that were not at a syringe service program.
In an intent-to-treat analysis, those enrolled in the accessible care group achieved sustained viral eradication at 12 months at significantly higher rates than those in the control group (67% vs. 23%; P < .001).
Once patients initiated treatment, cure rates were the same in both groups (86%), indicating that the major benefit of the accessible care program was in facilitating treatment, rather than increasing adherence to or response to treatment, the researchers noted.
This is reflected in the fact that the percentage of participants who advanced along the care cascade was significantly higher at each step for the accessible care group than the control group, from referral to an HCV clinician (93% vs. 45%), attendance of the initial HCV clinical visit (87% vs. 37%), completion of baseline laboratory testing (87% vs. 31%), and treatment initiation (78% vs. 27%).
Getting to the population in need
“The most surprising aspect of the study was how successful we were at recruiting, engaging, and treating people who inject drugs who lived outside the immediate community where the syringe exchange program was located and had no prior connection to the program,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
“We had numerous individuals travel 45-plus minutes on the subway from the South Bronx, passing four major medical centers with robust hepatitis C treatment programs, to seek care for hepatitis C in a small, dark office – but also an office they’d heard can be trusted – without fear of stigma or preconditions,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
Commenting on the study’s findings, Nancy Reau, MD, section chief of hepatology at Rush Medical College, Chicago, said, “This is another successful example of making therapy accessible to the population who is in need versus trying to move them into a tertiary care model.”
Dr. Reau noted that similar care models exist in the United States but are not always accessible to the population in need.
“The safety and efficacy of current therapy and the simplified care cascade make HCV an appropriate disease for this delivery,” she said, adding that this study “highlights not just the importance of these programs but also the necessity of engaging the medical community, changing policy, and using patient navigators and monetary support/prioritization to provide appropriate HCV management to those who are at high risk for the disease and for transmission.”
Accessible care beyond HCV
The coauthors of an accompanying editor’s note point out that the treatment for HCV has improved substantially, but it can be a real challenge to provide treatment to injection drug users because the U.S. health care system is not oriented toward the needs of this population.
“It is not surprising that the accessible care arm achieved a higher rate of viral eradication, as it created a patient-focused experience,” write Asha Choudhury, MD, MPH, with the University of California, San Francisco, and Mitchell Katz, MD, with NYC Health and Hospitals. “Creating inviting and engaging environments is particularly important when caring for patients from stigmatized groups. Having more sites that are accessible and inclusive like this for treating patients will likely increase treatment of hepatitis C.”
In their view, the study raises “two dueling questions: Is this model replicable across the U.S.? And, conversely, why isn’t all medical care offered in friendly, nonjudgmental settings with the intention of meeting patient goals?”
They conclude that the study’s lessons extend beyond this particular population and have implications for the field at large.
“The model is replicable to the extent that health care systems are prepared to provide nonjudgmental supportive care for persons who inject drugs,” they write. “However, all patients would benefit from a health care system that provided more patient-centered environments.”
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Eckhardt reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and Gilead during the conduct of the study. Dr. Choudhury, Dr. Katz, and Dr. Reau report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For injection drug users with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, providing treatment opportunities within a local needle exchange program can provide care to more patients and eventually cure more patients, a new study suggests.
The study’s findings help “counteract the implicit belief within the medical community that people who inject drugs can’t or don’t want to engage in health care,” lead author Benjamin Eckhardt, MD, with NYU Grossman School of Medicine, told this news organization.
“By simply focusing on patient accompaniment, limiting stigma, and removing the punitive response for missed appointments, we can effectively engage people who inject drugs in health care and more specifically cure their infection, making significant inroads to HCV elimination,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Nonjudgmental, patient-centered approach
Researchers included 165 injection drug users with HCV (mean age, 42 years; 78% men); 82 were randomly allocated to the accessible care intervention and 83 to a usual care control group.
The accessible care model provides HCV treatment within a community-based needle exchange program in a comfortable, nonjudgmental atmosphere, “without fear of shame or stigma that people who inject drugs often experience in mainstream institutions,” the investigators explain.
Control participants were connected to a patient navigator who facilitated referrals to community direct antigen antiviral therapy programs that were not at a syringe service program.
In an intent-to-treat analysis, those enrolled in the accessible care group achieved sustained viral eradication at 12 months at significantly higher rates than those in the control group (67% vs. 23%; P < .001).
Once patients initiated treatment, cure rates were the same in both groups (86%), indicating that the major benefit of the accessible care program was in facilitating treatment, rather than increasing adherence to or response to treatment, the researchers noted.
This is reflected in the fact that the percentage of participants who advanced along the care cascade was significantly higher at each step for the accessible care group than the control group, from referral to an HCV clinician (93% vs. 45%), attendance of the initial HCV clinical visit (87% vs. 37%), completion of baseline laboratory testing (87% vs. 31%), and treatment initiation (78% vs. 27%).
Getting to the population in need
“The most surprising aspect of the study was how successful we were at recruiting, engaging, and treating people who inject drugs who lived outside the immediate community where the syringe exchange program was located and had no prior connection to the program,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
“We had numerous individuals travel 45-plus minutes on the subway from the South Bronx, passing four major medical centers with robust hepatitis C treatment programs, to seek care for hepatitis C in a small, dark office – but also an office they’d heard can be trusted – without fear of stigma or preconditions,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
Commenting on the study’s findings, Nancy Reau, MD, section chief of hepatology at Rush Medical College, Chicago, said, “This is another successful example of making therapy accessible to the population who is in need versus trying to move them into a tertiary care model.”
Dr. Reau noted that similar care models exist in the United States but are not always accessible to the population in need.
“The safety and efficacy of current therapy and the simplified care cascade make HCV an appropriate disease for this delivery,” she said, adding that this study “highlights not just the importance of these programs but also the necessity of engaging the medical community, changing policy, and using patient navigators and monetary support/prioritization to provide appropriate HCV management to those who are at high risk for the disease and for transmission.”
Accessible care beyond HCV
The coauthors of an accompanying editor’s note point out that the treatment for HCV has improved substantially, but it can be a real challenge to provide treatment to injection drug users because the U.S. health care system is not oriented toward the needs of this population.
“It is not surprising that the accessible care arm achieved a higher rate of viral eradication, as it created a patient-focused experience,” write Asha Choudhury, MD, MPH, with the University of California, San Francisco, and Mitchell Katz, MD, with NYC Health and Hospitals. “Creating inviting and engaging environments is particularly important when caring for patients from stigmatized groups. Having more sites that are accessible and inclusive like this for treating patients will likely increase treatment of hepatitis C.”
In their view, the study raises “two dueling questions: Is this model replicable across the U.S.? And, conversely, why isn’t all medical care offered in friendly, nonjudgmental settings with the intention of meeting patient goals?”
They conclude that the study’s lessons extend beyond this particular population and have implications for the field at large.
“The model is replicable to the extent that health care systems are prepared to provide nonjudgmental supportive care for persons who inject drugs,” they write. “However, all patients would benefit from a health care system that provided more patient-centered environments.”
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Eckhardt reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and Gilead during the conduct of the study. Dr. Choudhury, Dr. Katz, and Dr. Reau report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For injection drug users with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, providing treatment opportunities within a local needle exchange program can provide care to more patients and eventually cure more patients, a new study suggests.
The study’s findings help “counteract the implicit belief within the medical community that people who inject drugs can’t or don’t want to engage in health care,” lead author Benjamin Eckhardt, MD, with NYU Grossman School of Medicine, told this news organization.
“By simply focusing on patient accompaniment, limiting stigma, and removing the punitive response for missed appointments, we can effectively engage people who inject drugs in health care and more specifically cure their infection, making significant inroads to HCV elimination,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Nonjudgmental, patient-centered approach
Researchers included 165 injection drug users with HCV (mean age, 42 years; 78% men); 82 were randomly allocated to the accessible care intervention and 83 to a usual care control group.
The accessible care model provides HCV treatment within a community-based needle exchange program in a comfortable, nonjudgmental atmosphere, “without fear of shame or stigma that people who inject drugs often experience in mainstream institutions,” the investigators explain.
Control participants were connected to a patient navigator who facilitated referrals to community direct antigen antiviral therapy programs that were not at a syringe service program.
In an intent-to-treat analysis, those enrolled in the accessible care group achieved sustained viral eradication at 12 months at significantly higher rates than those in the control group (67% vs. 23%; P < .001).
Once patients initiated treatment, cure rates were the same in both groups (86%), indicating that the major benefit of the accessible care program was in facilitating treatment, rather than increasing adherence to or response to treatment, the researchers noted.
This is reflected in the fact that the percentage of participants who advanced along the care cascade was significantly higher at each step for the accessible care group than the control group, from referral to an HCV clinician (93% vs. 45%), attendance of the initial HCV clinical visit (87% vs. 37%), completion of baseline laboratory testing (87% vs. 31%), and treatment initiation (78% vs. 27%).
Getting to the population in need
“The most surprising aspect of the study was how successful we were at recruiting, engaging, and treating people who inject drugs who lived outside the immediate community where the syringe exchange program was located and had no prior connection to the program,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
“We had numerous individuals travel 45-plus minutes on the subway from the South Bronx, passing four major medical centers with robust hepatitis C treatment programs, to seek care for hepatitis C in a small, dark office – but also an office they’d heard can be trusted – without fear of stigma or preconditions,” Dr. Eckhardt said.
Commenting on the study’s findings, Nancy Reau, MD, section chief of hepatology at Rush Medical College, Chicago, said, “This is another successful example of making therapy accessible to the population who is in need versus trying to move them into a tertiary care model.”
Dr. Reau noted that similar care models exist in the United States but are not always accessible to the population in need.
“The safety and efficacy of current therapy and the simplified care cascade make HCV an appropriate disease for this delivery,” she said, adding that this study “highlights not just the importance of these programs but also the necessity of engaging the medical community, changing policy, and using patient navigators and monetary support/prioritization to provide appropriate HCV management to those who are at high risk for the disease and for transmission.”
Accessible care beyond HCV
The coauthors of an accompanying editor’s note point out that the treatment for HCV has improved substantially, but it can be a real challenge to provide treatment to injection drug users because the U.S. health care system is not oriented toward the needs of this population.
“It is not surprising that the accessible care arm achieved a higher rate of viral eradication, as it created a patient-focused experience,” write Asha Choudhury, MD, MPH, with the University of California, San Francisco, and Mitchell Katz, MD, with NYC Health and Hospitals. “Creating inviting and engaging environments is particularly important when caring for patients from stigmatized groups. Having more sites that are accessible and inclusive like this for treating patients will likely increase treatment of hepatitis C.”
In their view, the study raises “two dueling questions: Is this model replicable across the U.S.? And, conversely, why isn’t all medical care offered in friendly, nonjudgmental settings with the intention of meeting patient goals?”
They conclude that the study’s lessons extend beyond this particular population and have implications for the field at large.
“The model is replicable to the extent that health care systems are prepared to provide nonjudgmental supportive care for persons who inject drugs,” they write. “However, all patients would benefit from a health care system that provided more patient-centered environments.”
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Eckhardt reports receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and Gilead during the conduct of the study. Dr. Choudhury, Dr. Katz, and Dr. Reau report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Asymptomatic C. difficile carriers may infect the people they live with after hospitalization
Hospitalized patients who are asymptomatic Clostridioides difficile carriers may infect people they live with after they return home, a study based on U.S. insurance claim data suggests.
Although C. difficile infection (CDI) is considered to be a common hospital-acquired infection, reports of community-associated CDI in patients who have not been hospitalized are increasing, the authors wrote in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
“Individuals in households where another family member was recently hospitalized but not diagnosed with a CDI appear to be at increased risk for CDI,” said lead author Aaron C. Miller, PhD, a research assistant professor in the department of internal medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City. “When individuals are hospitalized, they may become colonized with C. difficile without developing symptoms and subsequently transmit the pathogen to other family members after they return home,” he said by email.
Dr. Miller and colleagues analyzed insurance claims data from 2001 through 2017 using the U.S. Commercial Claims and Medicare Supplemental datasets of IBM MarketScan Research Databases. Over that period, they searched employer-sponsored commercial insurance claims and Medicare supplemental claims of 194,424 enrollees, and they linked claims from multiple family members in the same enrollment plan.
They identified 224,818 CDI cases, and 3,871 of them were considered potential asymptomatic C. difficile transmissions from a recently hospitalized family member.
The researchers gathered monthly C. difficile incidence data from households with a family member who had been hospitalized within the past 60 days and compared them with data from households without a hospitalized family member.
Enrollees exposed to a recently hospitalized family member had a 73% greater incidence of CDI compared with enrollees who were not exposed. The longer the family member’s hospital stay, the greater the risk that someone in the household became infected.
Compared with people whose family members were hospitalized less than 1 day, people whose family members were hospitalized from 1 to 3 days had an incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 1.30 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.19-1.41), and those whose family members were hospitalized for more than 30 days had an IRR of 2.45 (95% CI, 1.66-3.60).
CDI incidence increased with age. Compared with people 17 years of age or younger, the IRR increased to 9.32 (95% CI, 8.92-9.73) for those over 65.
Females had higher CDI incidence than males (IRR 1.30; 95% CI, 1.28-1.33).
Households with an infant also had higher CDI incidence than those without (IRR 1.5; 95% CI, 1.44-1.58).
People taking antimicrobials had higher CDI IRRs: 2.69 (95% CI, 2.59-2.79) for low-CDI-risk antibiotics and 8.83 (95% CI, 8.63-9.03) for high-CDI-risk antibiotics.
People taking proton-pump inhibitors had an IRR of 2.23 (95% CI, 2.15-2.30).
Reactions from four experts
Douglas S. Paauw MD, MACP, professor of medicine and the chair for patient-centered clinical education at the University of Washington, Seattle, was not surprised by the findings. “We have wondered for a while how community-acquired CDI occurs,” he said in an email. “This important study offers a plausible explanation for some cases.”
Dr. Paauw advises doctors to consider CDI in their patients who have been exposed to hospitalized people.
David M. Aronoff, MD, FIDSA, FAAM, professor of medicine and the chair of the department of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis, advises providers to educate hospital patients being discharged about how CDI is spread and how they can practice good hand hygiene at home.
“An open question of this strong study is whether we should be testing certain hospital patients for asymptomatic C. difficile carriage before they are discharged,” he added in an email.
In a phone interview, Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, professor of medicine and clinical director of the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, noted that community-acquired CDI is frequent enough that his institution performs routine C. difficile testing on all patients with unexplained severe diarrhea.
“This intriguing study bears additional research and follow-up because clearly these spores are hardy,” he said. “But a key point in this billings- and claims-based study is that no one knows where household members acquired CDI, whether it was actually through household transmission.”
Ramin Asgary, MD, MPH, FASTMH, associate professor of global health in the Milken Institute School of Public Health at George Washington University, Washington, cautioned about “an increasing issue with drug-resistant CDI.
“This important, timely study provides another step in the right direction to better understanding and addressing CDI and other hospital-based infections that have become increasing threats to the safety of our patients, their families, and health care in general,” he said in an email.
Dr. Miller said that the scale and scope of the data are strengths of the study, and he acknowledged that its basis in claims and billing data is a limitation. He and his group plan to explore genetic relationships involved in CDI transmission.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All authors and independent experts have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalized patients who are asymptomatic Clostridioides difficile carriers may infect people they live with after they return home, a study based on U.S. insurance claim data suggests.
Although C. difficile infection (CDI) is considered to be a common hospital-acquired infection, reports of community-associated CDI in patients who have not been hospitalized are increasing, the authors wrote in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
“Individuals in households where another family member was recently hospitalized but not diagnosed with a CDI appear to be at increased risk for CDI,” said lead author Aaron C. Miller, PhD, a research assistant professor in the department of internal medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City. “When individuals are hospitalized, they may become colonized with C. difficile without developing symptoms and subsequently transmit the pathogen to other family members after they return home,” he said by email.
Dr. Miller and colleagues analyzed insurance claims data from 2001 through 2017 using the U.S. Commercial Claims and Medicare Supplemental datasets of IBM MarketScan Research Databases. Over that period, they searched employer-sponsored commercial insurance claims and Medicare supplemental claims of 194,424 enrollees, and they linked claims from multiple family members in the same enrollment plan.
They identified 224,818 CDI cases, and 3,871 of them were considered potential asymptomatic C. difficile transmissions from a recently hospitalized family member.
The researchers gathered monthly C. difficile incidence data from households with a family member who had been hospitalized within the past 60 days and compared them with data from households without a hospitalized family member.
Enrollees exposed to a recently hospitalized family member had a 73% greater incidence of CDI compared with enrollees who were not exposed. The longer the family member’s hospital stay, the greater the risk that someone in the household became infected.
Compared with people whose family members were hospitalized less than 1 day, people whose family members were hospitalized from 1 to 3 days had an incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 1.30 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.19-1.41), and those whose family members were hospitalized for more than 30 days had an IRR of 2.45 (95% CI, 1.66-3.60).
CDI incidence increased with age. Compared with people 17 years of age or younger, the IRR increased to 9.32 (95% CI, 8.92-9.73) for those over 65.
Females had higher CDI incidence than males (IRR 1.30; 95% CI, 1.28-1.33).
Households with an infant also had higher CDI incidence than those without (IRR 1.5; 95% CI, 1.44-1.58).
People taking antimicrobials had higher CDI IRRs: 2.69 (95% CI, 2.59-2.79) for low-CDI-risk antibiotics and 8.83 (95% CI, 8.63-9.03) for high-CDI-risk antibiotics.
People taking proton-pump inhibitors had an IRR of 2.23 (95% CI, 2.15-2.30).
Reactions from four experts
Douglas S. Paauw MD, MACP, professor of medicine and the chair for patient-centered clinical education at the University of Washington, Seattle, was not surprised by the findings. “We have wondered for a while how community-acquired CDI occurs,” he said in an email. “This important study offers a plausible explanation for some cases.”
Dr. Paauw advises doctors to consider CDI in their patients who have been exposed to hospitalized people.
David M. Aronoff, MD, FIDSA, FAAM, professor of medicine and the chair of the department of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis, advises providers to educate hospital patients being discharged about how CDI is spread and how they can practice good hand hygiene at home.
“An open question of this strong study is whether we should be testing certain hospital patients for asymptomatic C. difficile carriage before they are discharged,” he added in an email.
In a phone interview, Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, professor of medicine and clinical director of the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, noted that community-acquired CDI is frequent enough that his institution performs routine C. difficile testing on all patients with unexplained severe diarrhea.
“This intriguing study bears additional research and follow-up because clearly these spores are hardy,” he said. “But a key point in this billings- and claims-based study is that no one knows where household members acquired CDI, whether it was actually through household transmission.”
Ramin Asgary, MD, MPH, FASTMH, associate professor of global health in the Milken Institute School of Public Health at George Washington University, Washington, cautioned about “an increasing issue with drug-resistant CDI.
“This important, timely study provides another step in the right direction to better understanding and addressing CDI and other hospital-based infections that have become increasing threats to the safety of our patients, their families, and health care in general,” he said in an email.
Dr. Miller said that the scale and scope of the data are strengths of the study, and he acknowledged that its basis in claims and billing data is a limitation. He and his group plan to explore genetic relationships involved in CDI transmission.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All authors and independent experts have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalized patients who are asymptomatic Clostridioides difficile carriers may infect people they live with after they return home, a study based on U.S. insurance claim data suggests.
Although C. difficile infection (CDI) is considered to be a common hospital-acquired infection, reports of community-associated CDI in patients who have not been hospitalized are increasing, the authors wrote in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
“Individuals in households where another family member was recently hospitalized but not diagnosed with a CDI appear to be at increased risk for CDI,” said lead author Aaron C. Miller, PhD, a research assistant professor in the department of internal medicine at the University of Iowa, Iowa City. “When individuals are hospitalized, they may become colonized with C. difficile without developing symptoms and subsequently transmit the pathogen to other family members after they return home,” he said by email.
Dr. Miller and colleagues analyzed insurance claims data from 2001 through 2017 using the U.S. Commercial Claims and Medicare Supplemental datasets of IBM MarketScan Research Databases. Over that period, they searched employer-sponsored commercial insurance claims and Medicare supplemental claims of 194,424 enrollees, and they linked claims from multiple family members in the same enrollment plan.
They identified 224,818 CDI cases, and 3,871 of them were considered potential asymptomatic C. difficile transmissions from a recently hospitalized family member.
The researchers gathered monthly C. difficile incidence data from households with a family member who had been hospitalized within the past 60 days and compared them with data from households without a hospitalized family member.
Enrollees exposed to a recently hospitalized family member had a 73% greater incidence of CDI compared with enrollees who were not exposed. The longer the family member’s hospital stay, the greater the risk that someone in the household became infected.
Compared with people whose family members were hospitalized less than 1 day, people whose family members were hospitalized from 1 to 3 days had an incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 1.30 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.19-1.41), and those whose family members were hospitalized for more than 30 days had an IRR of 2.45 (95% CI, 1.66-3.60).
CDI incidence increased with age. Compared with people 17 years of age or younger, the IRR increased to 9.32 (95% CI, 8.92-9.73) for those over 65.
Females had higher CDI incidence than males (IRR 1.30; 95% CI, 1.28-1.33).
Households with an infant also had higher CDI incidence than those without (IRR 1.5; 95% CI, 1.44-1.58).
People taking antimicrobials had higher CDI IRRs: 2.69 (95% CI, 2.59-2.79) for low-CDI-risk antibiotics and 8.83 (95% CI, 8.63-9.03) for high-CDI-risk antibiotics.
People taking proton-pump inhibitors had an IRR of 2.23 (95% CI, 2.15-2.30).
Reactions from four experts
Douglas S. Paauw MD, MACP, professor of medicine and the chair for patient-centered clinical education at the University of Washington, Seattle, was not surprised by the findings. “We have wondered for a while how community-acquired CDI occurs,” he said in an email. “This important study offers a plausible explanation for some cases.”
Dr. Paauw advises doctors to consider CDI in their patients who have been exposed to hospitalized people.
David M. Aronoff, MD, FIDSA, FAAM, professor of medicine and the chair of the department of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis, advises providers to educate hospital patients being discharged about how CDI is spread and how they can practice good hand hygiene at home.
“An open question of this strong study is whether we should be testing certain hospital patients for asymptomatic C. difficile carriage before they are discharged,” he added in an email.
In a phone interview, Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, professor of medicine and clinical director of the division of infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, noted that community-acquired CDI is frequent enough that his institution performs routine C. difficile testing on all patients with unexplained severe diarrhea.
“This intriguing study bears additional research and follow-up because clearly these spores are hardy,” he said. “But a key point in this billings- and claims-based study is that no one knows where household members acquired CDI, whether it was actually through household transmission.”
Ramin Asgary, MD, MPH, FASTMH, associate professor of global health in the Milken Institute School of Public Health at George Washington University, Washington, cautioned about “an increasing issue with drug-resistant CDI.
“This important, timely study provides another step in the right direction to better understanding and addressing CDI and other hospital-based infections that have become increasing threats to the safety of our patients, their families, and health care in general,” he said in an email.
Dr. Miller said that the scale and scope of the data are strengths of the study, and he acknowledged that its basis in claims and billing data is a limitation. He and his group plan to explore genetic relationships involved in CDI transmission.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All authors and independent experts have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.