User login
COVID-19 Is a Very Weird Virus
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.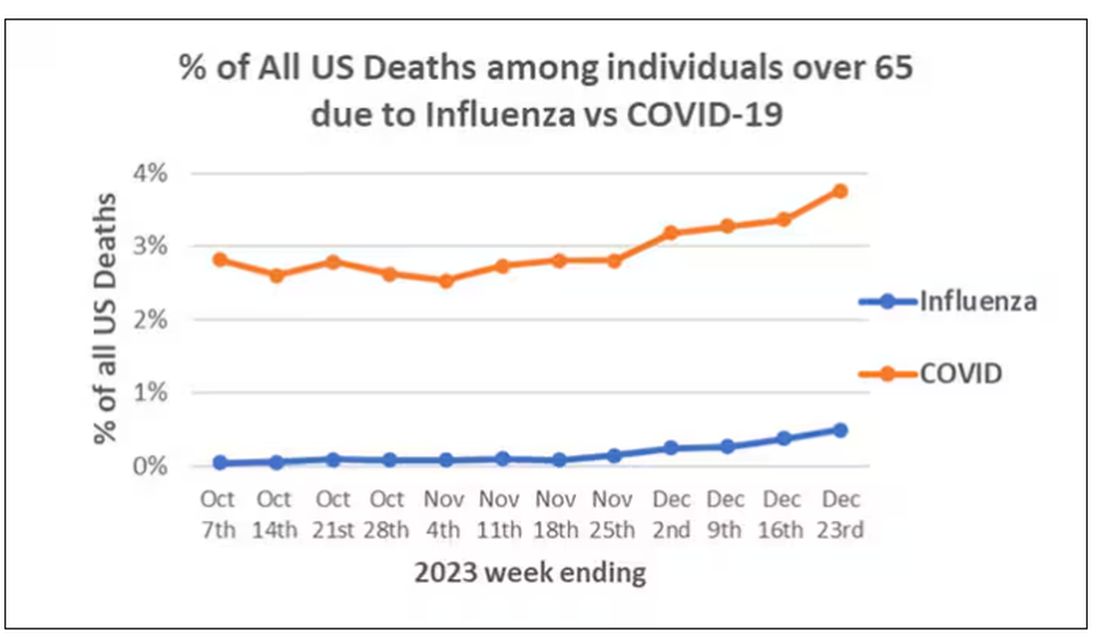
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.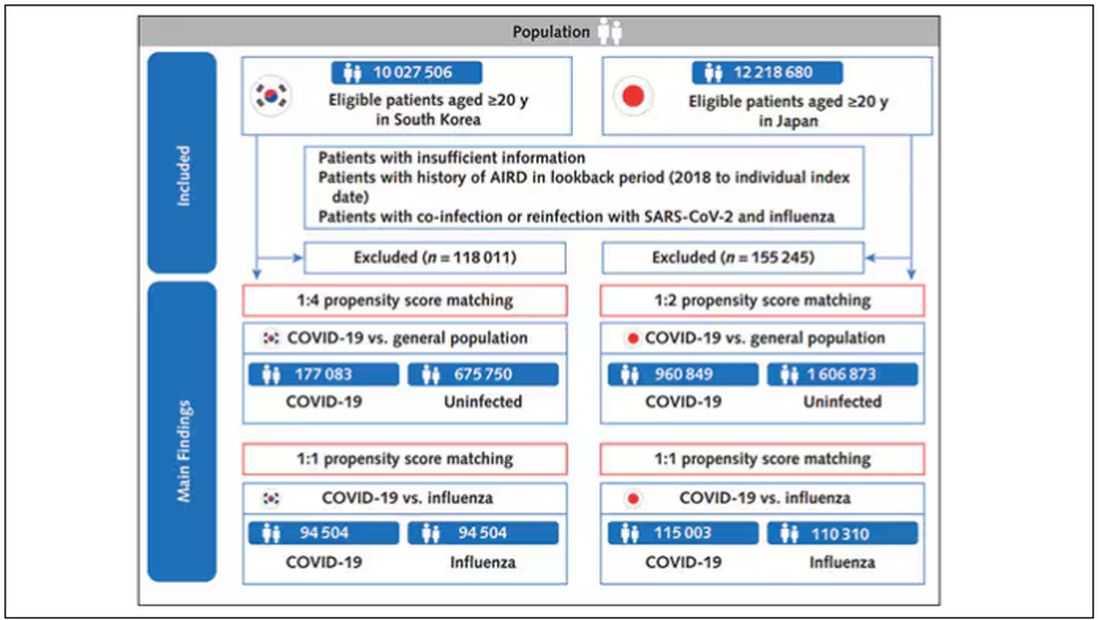
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).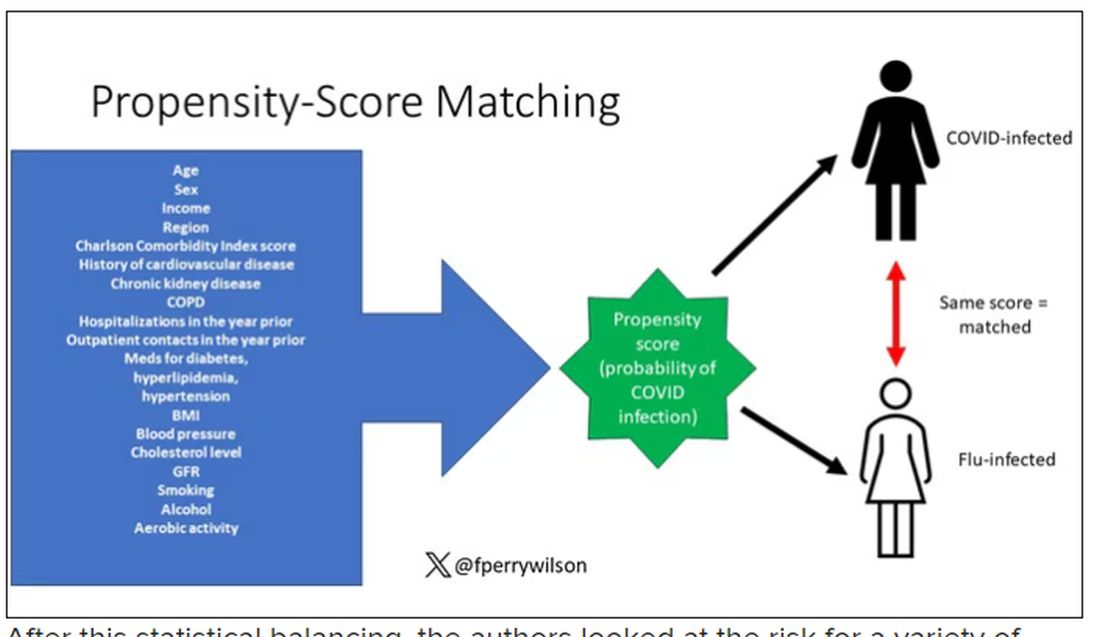
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.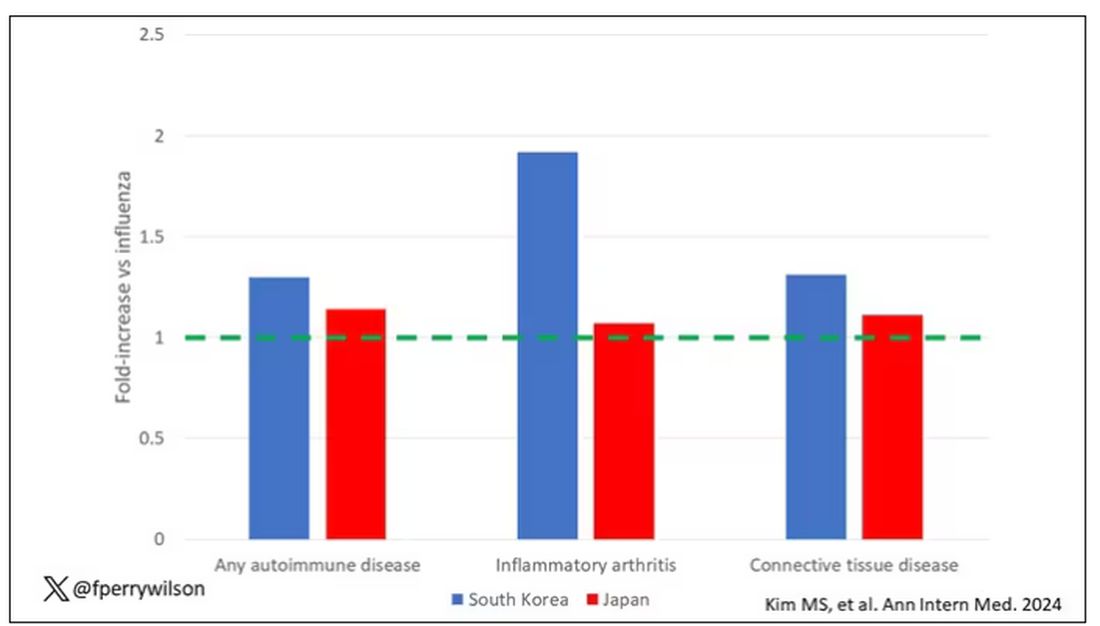
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.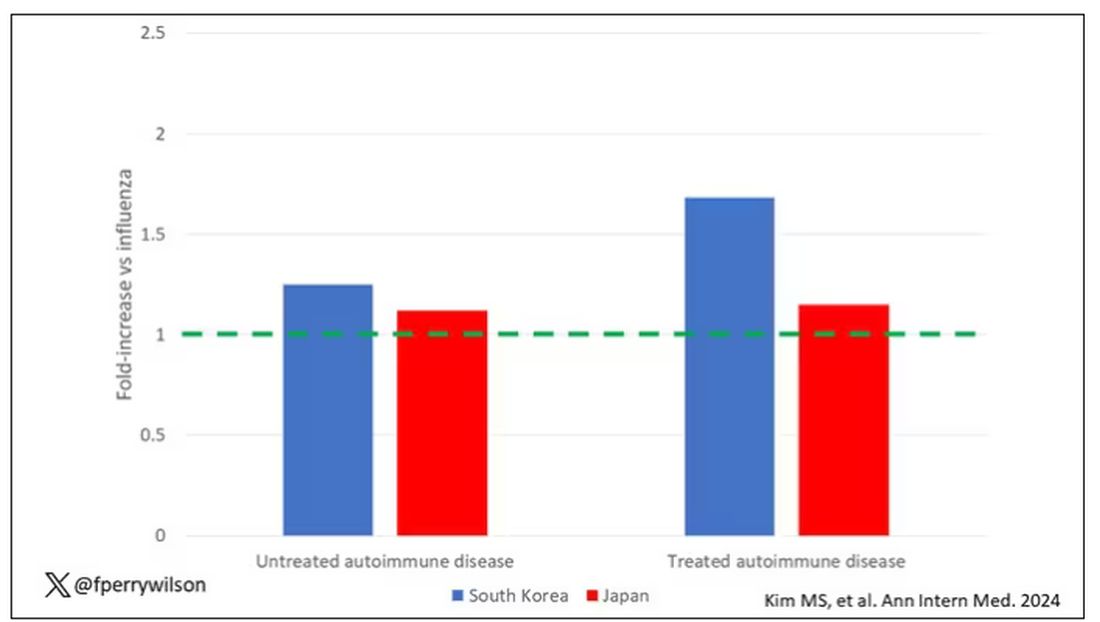
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.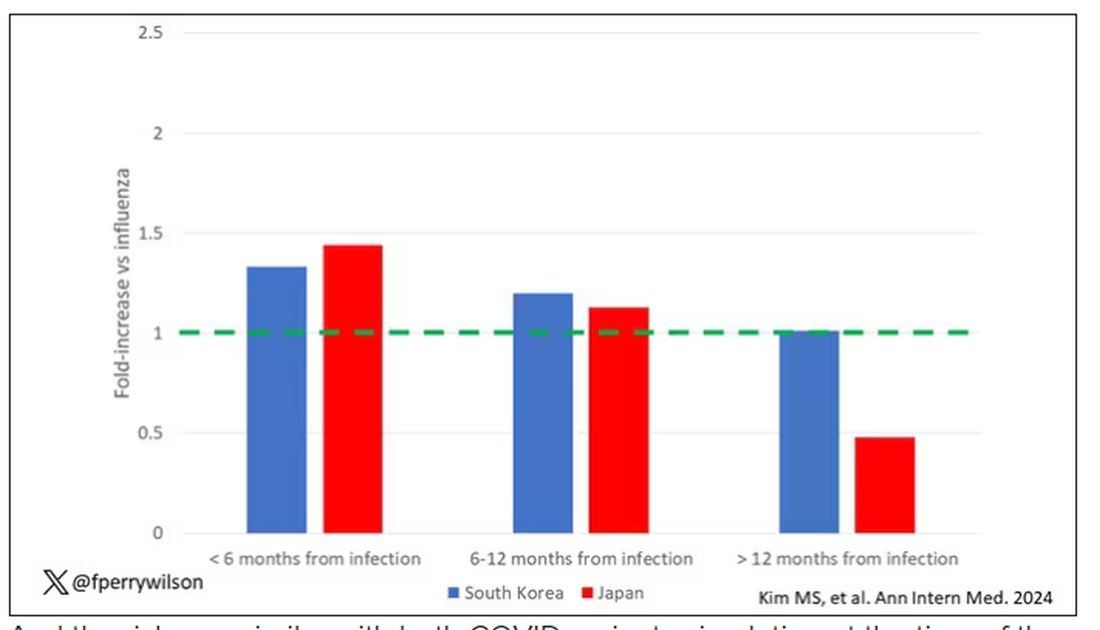
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?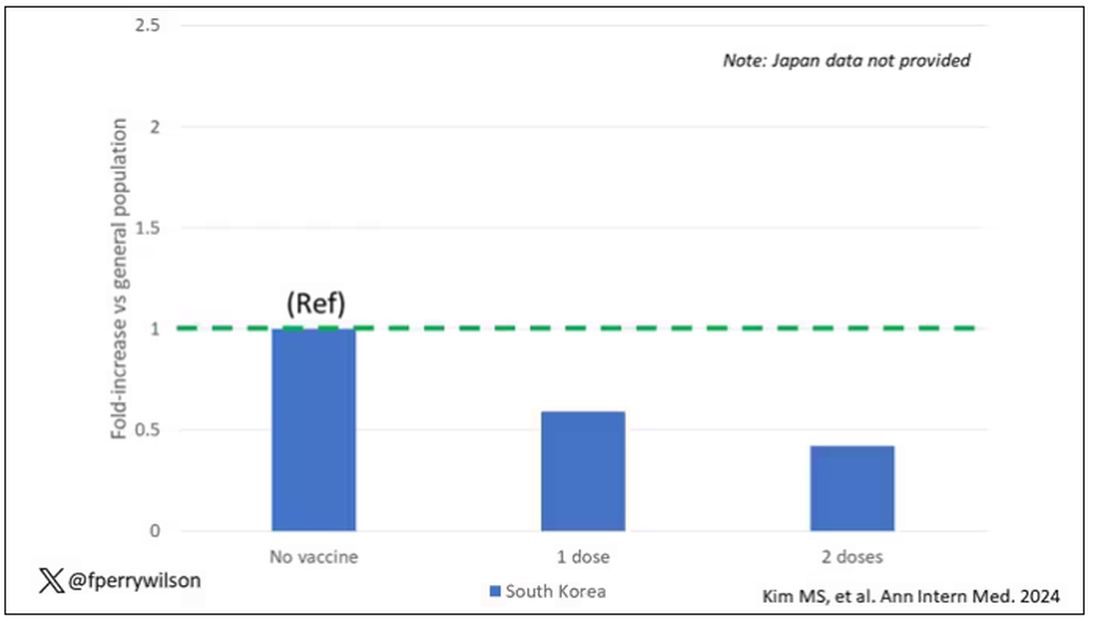
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s Next for the World’s First HIV Vaccine?
When the world needed a COVID vaccine, leading HIV investigators answered the call to intervene in the coronavirus pandemic. Now, efforts to discover the world’s first HIV vaccine are revitalized.
“The body is capable of making antibodies to protect us from HIV,” says Yunda Huang, PhD, from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, Washington, who sat down with me before her talk today at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Dr. Huang spoke about the path forward for neutralizing antibody protection after the last attempt in a generation of HIV vaccine development ended in disappointment.
The past two decades marked the rise in HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies, with vaccine strategies to induce them. Promising advances include germline approaches, mRNA, and nanoparticle technologies.
The PrEP vaccine trial testing two experimental prevention regimens in Africa was stopped after investigators reported there is “little to no chance” the trial will show the vaccines are effective.
A Shape-Shifting Virus
HIV has been called the shape-shifting virus because it disguises itself so that even when people are able to make antibodies to it, the virus changes to escape.
But Dr. Huang and others are optimistic that an effective vaccine is still possible.
“We cannot and will not lose hope that the world will have an effective HIV vaccine that is accessible by all who need it, anywhere,” International AIDS Society (IAS) Executive Director Birgit Poniatowski said in a statement in December, when the trial was stopped.
HIV is a still persistent problem in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that reports it has affected an estimated 1.2 million people.
With new people infected every day around the globe, Dr. Huang says she feels a sense of urgency to help. “I think about all the people around the globe and the large number of young girls being hurt and I know our big pool of talent can intervene to change what we see happening.”
Dr. Huang says the clinical trial failures we’ve seen so far will help guide next steps in HIV research as much as successes typically do.
Advances in the Field
With significant advances in protein nanoparticle science, mRNA technology, adjuvant development, and B-cell and antibody analyses, a new wave of clinical trials are on the way.
And with so many new approaches in the works, the HIV Vaccine Trials Network is retooling how it operates to navigate a burgeoning field and identify the most promising regimens.
A new Discovery Medicine Program will help the network assess new vaccine candidates. It will also aim to rule out others earlier on.
For COVID-19 and the flu, multimeric nanoparticles are an important alternative under investigation that could also be adapted for HIV.
Dr. Huang says she is particularly excited to watch the progress in cocktails of combination monoclonals. “I’ve been working in this field for 20 years now and there is a misconception that with pre-exposure prophylaxis, our job is done, but HIV is so far from away from being solved.”
But you just never know, Dr. Huang says. With new research, “we could bump on something at any point that changes everything.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When the world needed a COVID vaccine, leading HIV investigators answered the call to intervene in the coronavirus pandemic. Now, efforts to discover the world’s first HIV vaccine are revitalized.
“The body is capable of making antibodies to protect us from HIV,” says Yunda Huang, PhD, from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, Washington, who sat down with me before her talk today at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Dr. Huang spoke about the path forward for neutralizing antibody protection after the last attempt in a generation of HIV vaccine development ended in disappointment.
The past two decades marked the rise in HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies, with vaccine strategies to induce them. Promising advances include germline approaches, mRNA, and nanoparticle technologies.
The PrEP vaccine trial testing two experimental prevention regimens in Africa was stopped after investigators reported there is “little to no chance” the trial will show the vaccines are effective.
A Shape-Shifting Virus
HIV has been called the shape-shifting virus because it disguises itself so that even when people are able to make antibodies to it, the virus changes to escape.
But Dr. Huang and others are optimistic that an effective vaccine is still possible.
“We cannot and will not lose hope that the world will have an effective HIV vaccine that is accessible by all who need it, anywhere,” International AIDS Society (IAS) Executive Director Birgit Poniatowski said in a statement in December, when the trial was stopped.
HIV is a still persistent problem in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that reports it has affected an estimated 1.2 million people.
With new people infected every day around the globe, Dr. Huang says she feels a sense of urgency to help. “I think about all the people around the globe and the large number of young girls being hurt and I know our big pool of talent can intervene to change what we see happening.”
Dr. Huang says the clinical trial failures we’ve seen so far will help guide next steps in HIV research as much as successes typically do.
Advances in the Field
With significant advances in protein nanoparticle science, mRNA technology, adjuvant development, and B-cell and antibody analyses, a new wave of clinical trials are on the way.
And with so many new approaches in the works, the HIV Vaccine Trials Network is retooling how it operates to navigate a burgeoning field and identify the most promising regimens.
A new Discovery Medicine Program will help the network assess new vaccine candidates. It will also aim to rule out others earlier on.
For COVID-19 and the flu, multimeric nanoparticles are an important alternative under investigation that could also be adapted for HIV.
Dr. Huang says she is particularly excited to watch the progress in cocktails of combination monoclonals. “I’ve been working in this field for 20 years now and there is a misconception that with pre-exposure prophylaxis, our job is done, but HIV is so far from away from being solved.”
But you just never know, Dr. Huang says. With new research, “we could bump on something at any point that changes everything.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When the world needed a COVID vaccine, leading HIV investigators answered the call to intervene in the coronavirus pandemic. Now, efforts to discover the world’s first HIV vaccine are revitalized.
“The body is capable of making antibodies to protect us from HIV,” says Yunda Huang, PhD, from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, Washington, who sat down with me before her talk today at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Dr. Huang spoke about the path forward for neutralizing antibody protection after the last attempt in a generation of HIV vaccine development ended in disappointment.
The past two decades marked the rise in HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies, with vaccine strategies to induce them. Promising advances include germline approaches, mRNA, and nanoparticle technologies.
The PrEP vaccine trial testing two experimental prevention regimens in Africa was stopped after investigators reported there is “little to no chance” the trial will show the vaccines are effective.
A Shape-Shifting Virus
HIV has been called the shape-shifting virus because it disguises itself so that even when people are able to make antibodies to it, the virus changes to escape.
But Dr. Huang and others are optimistic that an effective vaccine is still possible.
“We cannot and will not lose hope that the world will have an effective HIV vaccine that is accessible by all who need it, anywhere,” International AIDS Society (IAS) Executive Director Birgit Poniatowski said in a statement in December, when the trial was stopped.
HIV is a still persistent problem in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that reports it has affected an estimated 1.2 million people.
With new people infected every day around the globe, Dr. Huang says she feels a sense of urgency to help. “I think about all the people around the globe and the large number of young girls being hurt and I know our big pool of talent can intervene to change what we see happening.”
Dr. Huang says the clinical trial failures we’ve seen so far will help guide next steps in HIV research as much as successes typically do.
Advances in the Field
With significant advances in protein nanoparticle science, mRNA technology, adjuvant development, and B-cell and antibody analyses, a new wave of clinical trials are on the way.
And with so many new approaches in the works, the HIV Vaccine Trials Network is retooling how it operates to navigate a burgeoning field and identify the most promising regimens.
A new Discovery Medicine Program will help the network assess new vaccine candidates. It will also aim to rule out others earlier on.
For COVID-19 and the flu, multimeric nanoparticles are an important alternative under investigation that could also be adapted for HIV.
Dr. Huang says she is particularly excited to watch the progress in cocktails of combination monoclonals. “I’ve been working in this field for 20 years now and there is a misconception that with pre-exposure prophylaxis, our job is done, but HIV is so far from away from being solved.”
But you just never know, Dr. Huang says. With new research, “we could bump on something at any point that changes everything.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CROI 2024
Doxy-PEP Cut STIs in San Francisco in Half
Syphilis and chlamydia infections were reduced by half among men who have sex with men and transgender women 1 year after San Francisco rolled out doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (doxy-PEP), according to data presented at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) this week.
After a clinical trial showed that doxy-PEP taken after sex reduced the chance of acquiring syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia by about two-thirds, the San Francisco Department of Public Health released the first guidelines in the country in October 2022.
So far, more than 3700 people in San Francisco have been prescribed doxy-PEP, reports Stephanie Cohen, MD, director of HIV and sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention in the Disease Prevention and Control Branch of Public Health.
Dr. Cohen and her colleagues spent a year monitoring the uptake of doxy-PEP and used a computer model to predict what the rates of sexually transmitted infection would have been without doxy-PEP.
In November 2023, 13 months after the guidelines were introduced, they found that monthly chlamydia and early syphilis infections were 50% and 51% lower, respectively, than what was predicted by the model.
Fewer Infections
The drop in infections is having a tangible effect on patients in San Francisco, and many clinicians are noting that they are seeing far fewer positive tests. “The results that we’re seeing on a city-wide level are absolutely being experienced by individual providers and patients,” Dr. Cohen said.
However, the analysis showed no effect on rates of gonorrhea. It’s not clear why, although Dr. Cohen points out that doxy-PEP was less effective against gonorrhea in the clinical trial. And “there could be other factors in play,” she added. “Adherence might matter more, or it could be affected by the prevalence of tetracycline resistance in the community.”
With rates of STIs, particularly syphilis, quickly rising in recent years, healthcare providers have been scrambling to find effective interventions. So far, doxy-PEP has shown the most promise. “We’ve known for a while that all of the strategies we’ve been employing don’t seem to be working,” noted Chase Cannon, MD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Washington in Seattle. “That’s why doxy-PEP is important. We haven’t had anything that can deflect the curve in a long time.”
What About the Side Effects?
Some concerns remain, however, about the widespread prophylactic use of antibiotics. There are no long-term safety data on the potential side effects of doxy-PEP, and there is still a lot of stigma around interventions that allow people to have sex the way they want, said Dr. Cannon.
But perhaps, the biggest concern is that doxy-PEP could contribute to antibiotic resistance. Those fears are not misplaced, Dr. Cannon added. The results of one study, presented in a poster at CROI, showed that stool samples from people prescribed doxy-PEP had elevated levels of bacterial genes that can confer resistance to tetracyclines, the class of antibiotics to which doxycycline belongs. There was no change in resistance to other classes of antibiotics and no difference in bacterial diversity over the 6 months of the study.
Dr. Cannon cautioned, however, that we can’t extrapolate these results to clinical outcomes. “We can look for signals [of resistance], but we don’t know if this means someone will fail therapy for chlamydia or syphilis,” he said.
There are still many challenges to overcome before doxy-PEP can be rolled out widely, Dr. Cohen explained. There is a lack of consensus among healthcare professionals about who should be offered doxy-PEP. The clinical trial results and the San Fransisco guidelines only apply to men who have sex with men and to transgender women.
Some clinicians argue that the intervention should be provided to a broader population, whereas others want to see more research to ensure that unnecessary antibiotic use is minimized.
So far just one study has tested doxy-PEP in another population — in women in Kenya — and it was found to not be effective. But the data suggest that adherence to the protocol was poor in that study, so the results may not be reliable, Dr. Cohen said.
“We need effective prevention tools for all genders, especially cis women who bear most of the morbidity,” she said. “It stands to reason that this should work for them, but without high-quality evidence, there is insufficient information to make a recommendation for cis women.”
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is currently reviewing public and expert comments and refining final guidelines for release in the coming months, which should alleviate some of the uncertainty. “Many providers are waiting for that guidance before they will feel confident moving forward,” Dr. Cohen noted.
But despite the risks and uncertainty, doxy-PEP looks set to be a major part of the fight against STIs going forward. “Doxy-PEP is essential for us as a nation to be dealing with the syphilis epidemic,” Carl Dieffenbach, PhD, director of the Division of AIDS at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, said in a video introduction to CROI.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Syphilis and chlamydia infections were reduced by half among men who have sex with men and transgender women 1 year after San Francisco rolled out doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (doxy-PEP), according to data presented at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) this week.
After a clinical trial showed that doxy-PEP taken after sex reduced the chance of acquiring syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia by about two-thirds, the San Francisco Department of Public Health released the first guidelines in the country in October 2022.
So far, more than 3700 people in San Francisco have been prescribed doxy-PEP, reports Stephanie Cohen, MD, director of HIV and sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention in the Disease Prevention and Control Branch of Public Health.
Dr. Cohen and her colleagues spent a year monitoring the uptake of doxy-PEP and used a computer model to predict what the rates of sexually transmitted infection would have been without doxy-PEP.
In November 2023, 13 months after the guidelines were introduced, they found that monthly chlamydia and early syphilis infections were 50% and 51% lower, respectively, than what was predicted by the model.
Fewer Infections
The drop in infections is having a tangible effect on patients in San Francisco, and many clinicians are noting that they are seeing far fewer positive tests. “The results that we’re seeing on a city-wide level are absolutely being experienced by individual providers and patients,” Dr. Cohen said.
However, the analysis showed no effect on rates of gonorrhea. It’s not clear why, although Dr. Cohen points out that doxy-PEP was less effective against gonorrhea in the clinical trial. And “there could be other factors in play,” she added. “Adherence might matter more, or it could be affected by the prevalence of tetracycline resistance in the community.”
With rates of STIs, particularly syphilis, quickly rising in recent years, healthcare providers have been scrambling to find effective interventions. So far, doxy-PEP has shown the most promise. “We’ve known for a while that all of the strategies we’ve been employing don’t seem to be working,” noted Chase Cannon, MD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Washington in Seattle. “That’s why doxy-PEP is important. We haven’t had anything that can deflect the curve in a long time.”
What About the Side Effects?
Some concerns remain, however, about the widespread prophylactic use of antibiotics. There are no long-term safety data on the potential side effects of doxy-PEP, and there is still a lot of stigma around interventions that allow people to have sex the way they want, said Dr. Cannon.
But perhaps, the biggest concern is that doxy-PEP could contribute to antibiotic resistance. Those fears are not misplaced, Dr. Cannon added. The results of one study, presented in a poster at CROI, showed that stool samples from people prescribed doxy-PEP had elevated levels of bacterial genes that can confer resistance to tetracyclines, the class of antibiotics to which doxycycline belongs. There was no change in resistance to other classes of antibiotics and no difference in bacterial diversity over the 6 months of the study.
Dr. Cannon cautioned, however, that we can’t extrapolate these results to clinical outcomes. “We can look for signals [of resistance], but we don’t know if this means someone will fail therapy for chlamydia or syphilis,” he said.
There are still many challenges to overcome before doxy-PEP can be rolled out widely, Dr. Cohen explained. There is a lack of consensus among healthcare professionals about who should be offered doxy-PEP. The clinical trial results and the San Fransisco guidelines only apply to men who have sex with men and to transgender women.
Some clinicians argue that the intervention should be provided to a broader population, whereas others want to see more research to ensure that unnecessary antibiotic use is minimized.
So far just one study has tested doxy-PEP in another population — in women in Kenya — and it was found to not be effective. But the data suggest that adherence to the protocol was poor in that study, so the results may not be reliable, Dr. Cohen said.
“We need effective prevention tools for all genders, especially cis women who bear most of the morbidity,” she said. “It stands to reason that this should work for them, but without high-quality evidence, there is insufficient information to make a recommendation for cis women.”
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is currently reviewing public and expert comments and refining final guidelines for release in the coming months, which should alleviate some of the uncertainty. “Many providers are waiting for that guidance before they will feel confident moving forward,” Dr. Cohen noted.
But despite the risks and uncertainty, doxy-PEP looks set to be a major part of the fight against STIs going forward. “Doxy-PEP is essential for us as a nation to be dealing with the syphilis epidemic,” Carl Dieffenbach, PhD, director of the Division of AIDS at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, said in a video introduction to CROI.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Syphilis and chlamydia infections were reduced by half among men who have sex with men and transgender women 1 year after San Francisco rolled out doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (doxy-PEP), according to data presented at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) this week.
After a clinical trial showed that doxy-PEP taken after sex reduced the chance of acquiring syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia by about two-thirds, the San Francisco Department of Public Health released the first guidelines in the country in October 2022.
So far, more than 3700 people in San Francisco have been prescribed doxy-PEP, reports Stephanie Cohen, MD, director of HIV and sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention in the Disease Prevention and Control Branch of Public Health.
Dr. Cohen and her colleagues spent a year monitoring the uptake of doxy-PEP and used a computer model to predict what the rates of sexually transmitted infection would have been without doxy-PEP.
In November 2023, 13 months after the guidelines were introduced, they found that monthly chlamydia and early syphilis infections were 50% and 51% lower, respectively, than what was predicted by the model.
Fewer Infections
The drop in infections is having a tangible effect on patients in San Francisco, and many clinicians are noting that they are seeing far fewer positive tests. “The results that we’re seeing on a city-wide level are absolutely being experienced by individual providers and patients,” Dr. Cohen said.
However, the analysis showed no effect on rates of gonorrhea. It’s not clear why, although Dr. Cohen points out that doxy-PEP was less effective against gonorrhea in the clinical trial. And “there could be other factors in play,” she added. “Adherence might matter more, or it could be affected by the prevalence of tetracycline resistance in the community.”
With rates of STIs, particularly syphilis, quickly rising in recent years, healthcare providers have been scrambling to find effective interventions. So far, doxy-PEP has shown the most promise. “We’ve known for a while that all of the strategies we’ve been employing don’t seem to be working,” noted Chase Cannon, MD, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Washington in Seattle. “That’s why doxy-PEP is important. We haven’t had anything that can deflect the curve in a long time.”
What About the Side Effects?
Some concerns remain, however, about the widespread prophylactic use of antibiotics. There are no long-term safety data on the potential side effects of doxy-PEP, and there is still a lot of stigma around interventions that allow people to have sex the way they want, said Dr. Cannon.
But perhaps, the biggest concern is that doxy-PEP could contribute to antibiotic resistance. Those fears are not misplaced, Dr. Cannon added. The results of one study, presented in a poster at CROI, showed that stool samples from people prescribed doxy-PEP had elevated levels of bacterial genes that can confer resistance to tetracyclines, the class of antibiotics to which doxycycline belongs. There was no change in resistance to other classes of antibiotics and no difference in bacterial diversity over the 6 months of the study.
Dr. Cannon cautioned, however, that we can’t extrapolate these results to clinical outcomes. “We can look for signals [of resistance], but we don’t know if this means someone will fail therapy for chlamydia or syphilis,” he said.
There are still many challenges to overcome before doxy-PEP can be rolled out widely, Dr. Cohen explained. There is a lack of consensus among healthcare professionals about who should be offered doxy-PEP. The clinical trial results and the San Fransisco guidelines only apply to men who have sex with men and to transgender women.
Some clinicians argue that the intervention should be provided to a broader population, whereas others want to see more research to ensure that unnecessary antibiotic use is minimized.
So far just one study has tested doxy-PEP in another population — in women in Kenya — and it was found to not be effective. But the data suggest that adherence to the protocol was poor in that study, so the results may not be reliable, Dr. Cohen said.
“We need effective prevention tools for all genders, especially cis women who bear most of the morbidity,” she said. “It stands to reason that this should work for them, but without high-quality evidence, there is insufficient information to make a recommendation for cis women.”
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is currently reviewing public and expert comments and refining final guidelines for release in the coming months, which should alleviate some of the uncertainty. “Many providers are waiting for that guidance before they will feel confident moving forward,” Dr. Cohen noted.
But despite the risks and uncertainty, doxy-PEP looks set to be a major part of the fight against STIs going forward. “Doxy-PEP is essential for us as a nation to be dealing with the syphilis epidemic,” Carl Dieffenbach, PhD, director of the Division of AIDS at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, said in a video introduction to CROI.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Bartonella henselae Infection May Occasionally Distract Immune Control of Latent Human Herpesviruses
To the Editor:
We read with interest the September 2023 Cutis article by Swink et al,1 “Cat Scratch Disease Presenting With Concurrent Pityriasis Rosea in a 10-Year-Old Girl.” The authors documented the possibility of Bartonella henselae infection as another causative agent for pityriasis rosea (PR) even though the association of PR with human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and HHV-7 infection is based on several consistent observations and not on occasional findings. The association of PR with endogenous systemic reactivation of HHV-6 and HHV-7 has been identified with different investigations and laboratory techniques. Using polymerase chain reaction, real-time calibrated quantitative polymerase chain reaction, in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy, HHV-6 and HHV-7 have been detected in plasma (a marker of active viral replication), peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and skin lesions from patients with PR.2 In addition, HHV-6 and HHV-7 messenger RNA expression and their specific antigens have been detected in PR skin lesions and herpesvirus virions in various stages of morphogenesis as well as in the supernatant of co-cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with PR.2,3 Lastly, the increased levels of several particular cytokines and chemokinesin the sera of patients with PR support a viral role in its pathogenesis.4
Bartonella henselae is a gram-negative intracellular facultative bacterium that is commonly implicated in causing zoonotic infections worldwide. The incidence of cat-scratch disease (CSD) was reported to be 6.4 cases per 100,000 population in adults and 9.4 cases per 100,000 population in children aged 5 to 9 years globally.5 Approximately 24,000 cases of CSD are reported in the United States every year.6 Therefore, considering these data, if B henselae was a causative agent for PR, the eruption would be observed frequently in many patients with CSD, which is not the case. On the contrary, it is possible that B henselae infection may have reactivated HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 infection. It is well established that B henselae causes a robust cell-mediated immune response by activating natural killer and helper T cells (TH1) and enhancement of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.7 It could be assumed that by strongly stimulating the immune response and polarizing it to a specific antigen cell response, B henselae infection may temporarily distract the T cell-mediated control of the latent infections, such as HHV-6 and HHV-7, which may reactivate and cause PR.
It is important to point out that a case of concomitant B henselae and Epstein-Barr virus infection has been described.8 Even in that case, the B henselae infection may have reactivated Epstein-Barr virus as well as HHV-6 and HHV-7 in the case described by Swink et al.1 Epstein-Barr virus reactivation has been detected in one case8 through serologic testing—IgM, IgG, Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen IgG, and heterophile antibodies—as there were no dermatologic manifestations that may be related to Epstein-Barr virus reactivation from latency.9
In conclusion, a viral or bacterial infection such as Epstein-Barr virus or B henselae may have a transactivating function allowing another (latent) virus such as HHV-6 or HHV-7 to reactivate. Indeed, it has been described that SARS-CoV-2 may act as a transactivator agent triggering HHV-6/HHV-7 reactivation, thereby indirectly causing PR clinical manifestation.10
- Swink SM, Rhodes LP, Levin J. Cat scratch disease presenting with concurrent pityriasis rosea in a 10-year-old girl. Cutis. 2023;112:E24-E26. doi:10.12788/cutis.0861
- Broccolo F, Drago F, Careddu AM, et al. Additional evidence that pityriasis rosea is associated with reactivation of human herpesvirus-6 and -7. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:1234-1240.
- Rebora A, Ciccarese G, Herzum A, et al. Pityriasis rosea and other infectious eruptions during pregnancy: possible life-threatening health conditions for the fetus. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:105-112.
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Broccolo F, et al. The role of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in the pathogenesis of pityriasis rosea. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:438963. doi:10.1155/2015/438963
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73.
- Ackson LA, Perkins BA, Wenger JD. Cat scratch disease in the United States: an analysis of three national databases. Am J Public Health. 1993;83:1707-1711.
- Resto-Ruiz S, Burgess A, Anderson BE. The role of the host immune response in pathogenesis of Bartonella henselae. DNA Cell Biol. 2003; 22:431-440.
- Aparicio-Casares H, Puente-Rico MH, Tomé-Nestal C, et al. A pediatric case of Bartonella henselae and Epstein Barr virus disease with bone and hepatosplenic involvement. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2021;78:467-473.
- Ciccarese G, Trave I, Herzum A, et al. Dermatological manifestations of Epstein-Barr virus systemic infection: a case report and literature review. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1202-1209.
- Drago F, Broccolo F, Ciccarese G. Pityriasis rosea, pityriasis rosea-like eruptions, and herpes zoster in the setting of COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:586-590.
To the Editor:
We read with interest the September 2023 Cutis article by Swink et al,1 “Cat Scratch Disease Presenting With Concurrent Pityriasis Rosea in a 10-Year-Old Girl.” The authors documented the possibility of Bartonella henselae infection as another causative agent for pityriasis rosea (PR) even though the association of PR with human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and HHV-7 infection is based on several consistent observations and not on occasional findings. The association of PR with endogenous systemic reactivation of HHV-6 and HHV-7 has been identified with different investigations and laboratory techniques. Using polymerase chain reaction, real-time calibrated quantitative polymerase chain reaction, in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy, HHV-6 and HHV-7 have been detected in plasma (a marker of active viral replication), peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and skin lesions from patients with PR.2 In addition, HHV-6 and HHV-7 messenger RNA expression and their specific antigens have been detected in PR skin lesions and herpesvirus virions in various stages of morphogenesis as well as in the supernatant of co-cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with PR.2,3 Lastly, the increased levels of several particular cytokines and chemokinesin the sera of patients with PR support a viral role in its pathogenesis.4
Bartonella henselae is a gram-negative intracellular facultative bacterium that is commonly implicated in causing zoonotic infections worldwide. The incidence of cat-scratch disease (CSD) was reported to be 6.4 cases per 100,000 population in adults and 9.4 cases per 100,000 population in children aged 5 to 9 years globally.5 Approximately 24,000 cases of CSD are reported in the United States every year.6 Therefore, considering these data, if B henselae was a causative agent for PR, the eruption would be observed frequently in many patients with CSD, which is not the case. On the contrary, it is possible that B henselae infection may have reactivated HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 infection. It is well established that B henselae causes a robust cell-mediated immune response by activating natural killer and helper T cells (TH1) and enhancement of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.7 It could be assumed that by strongly stimulating the immune response and polarizing it to a specific antigen cell response, B henselae infection may temporarily distract the T cell-mediated control of the latent infections, such as HHV-6 and HHV-7, which may reactivate and cause PR.
It is important to point out that a case of concomitant B henselae and Epstein-Barr virus infection has been described.8 Even in that case, the B henselae infection may have reactivated Epstein-Barr virus as well as HHV-6 and HHV-7 in the case described by Swink et al.1 Epstein-Barr virus reactivation has been detected in one case8 through serologic testing—IgM, IgG, Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen IgG, and heterophile antibodies—as there were no dermatologic manifestations that may be related to Epstein-Barr virus reactivation from latency.9
In conclusion, a viral or bacterial infection such as Epstein-Barr virus or B henselae may have a transactivating function allowing another (latent) virus such as HHV-6 or HHV-7 to reactivate. Indeed, it has been described that SARS-CoV-2 may act as a transactivator agent triggering HHV-6/HHV-7 reactivation, thereby indirectly causing PR clinical manifestation.10
To the Editor:
We read with interest the September 2023 Cutis article by Swink et al,1 “Cat Scratch Disease Presenting With Concurrent Pityriasis Rosea in a 10-Year-Old Girl.” The authors documented the possibility of Bartonella henselae infection as another causative agent for pityriasis rosea (PR) even though the association of PR with human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and HHV-7 infection is based on several consistent observations and not on occasional findings. The association of PR with endogenous systemic reactivation of HHV-6 and HHV-7 has been identified with different investigations and laboratory techniques. Using polymerase chain reaction, real-time calibrated quantitative polymerase chain reaction, in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy, HHV-6 and HHV-7 have been detected in plasma (a marker of active viral replication), peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and skin lesions from patients with PR.2 In addition, HHV-6 and HHV-7 messenger RNA expression and their specific antigens have been detected in PR skin lesions and herpesvirus virions in various stages of morphogenesis as well as in the supernatant of co-cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with PR.2,3 Lastly, the increased levels of several particular cytokines and chemokinesin the sera of patients with PR support a viral role in its pathogenesis.4
Bartonella henselae is a gram-negative intracellular facultative bacterium that is commonly implicated in causing zoonotic infections worldwide. The incidence of cat-scratch disease (CSD) was reported to be 6.4 cases per 100,000 population in adults and 9.4 cases per 100,000 population in children aged 5 to 9 years globally.5 Approximately 24,000 cases of CSD are reported in the United States every year.6 Therefore, considering these data, if B henselae was a causative agent for PR, the eruption would be observed frequently in many patients with CSD, which is not the case. On the contrary, it is possible that B henselae infection may have reactivated HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 infection. It is well established that B henselae causes a robust cell-mediated immune response by activating natural killer and helper T cells (TH1) and enhancement of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.7 It could be assumed that by strongly stimulating the immune response and polarizing it to a specific antigen cell response, B henselae infection may temporarily distract the T cell-mediated control of the latent infections, such as HHV-6 and HHV-7, which may reactivate and cause PR.
It is important to point out that a case of concomitant B henselae and Epstein-Barr virus infection has been described.8 Even in that case, the B henselae infection may have reactivated Epstein-Barr virus as well as HHV-6 and HHV-7 in the case described by Swink et al.1 Epstein-Barr virus reactivation has been detected in one case8 through serologic testing—IgM, IgG, Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen IgG, and heterophile antibodies—as there were no dermatologic manifestations that may be related to Epstein-Barr virus reactivation from latency.9
In conclusion, a viral or bacterial infection such as Epstein-Barr virus or B henselae may have a transactivating function allowing another (latent) virus such as HHV-6 or HHV-7 to reactivate. Indeed, it has been described that SARS-CoV-2 may act as a transactivator agent triggering HHV-6/HHV-7 reactivation, thereby indirectly causing PR clinical manifestation.10
- Swink SM, Rhodes LP, Levin J. Cat scratch disease presenting with concurrent pityriasis rosea in a 10-year-old girl. Cutis. 2023;112:E24-E26. doi:10.12788/cutis.0861
- Broccolo F, Drago F, Careddu AM, et al. Additional evidence that pityriasis rosea is associated with reactivation of human herpesvirus-6 and -7. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:1234-1240.
- Rebora A, Ciccarese G, Herzum A, et al. Pityriasis rosea and other infectious eruptions during pregnancy: possible life-threatening health conditions for the fetus. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:105-112.
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Broccolo F, et al. The role of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in the pathogenesis of pityriasis rosea. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:438963. doi:10.1155/2015/438963
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73.
- Ackson LA, Perkins BA, Wenger JD. Cat scratch disease in the United States: an analysis of three national databases. Am J Public Health. 1993;83:1707-1711.
- Resto-Ruiz S, Burgess A, Anderson BE. The role of the host immune response in pathogenesis of Bartonella henselae. DNA Cell Biol. 2003; 22:431-440.
- Aparicio-Casares H, Puente-Rico MH, Tomé-Nestal C, et al. A pediatric case of Bartonella henselae and Epstein Barr virus disease with bone and hepatosplenic involvement. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2021;78:467-473.
- Ciccarese G, Trave I, Herzum A, et al. Dermatological manifestations of Epstein-Barr virus systemic infection: a case report and literature review. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1202-1209.
- Drago F, Broccolo F, Ciccarese G. Pityriasis rosea, pityriasis rosea-like eruptions, and herpes zoster in the setting of COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:586-590.
- Swink SM, Rhodes LP, Levin J. Cat scratch disease presenting with concurrent pityriasis rosea in a 10-year-old girl. Cutis. 2023;112:E24-E26. doi:10.12788/cutis.0861
- Broccolo F, Drago F, Careddu AM, et al. Additional evidence that pityriasis rosea is associated with reactivation of human herpesvirus-6 and -7. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:1234-1240.
- Rebora A, Ciccarese G, Herzum A, et al. Pityriasis rosea and other infectious eruptions during pregnancy: possible life-threatening health conditions for the fetus. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:105-112.
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Broccolo F, et al. The role of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in the pathogenesis of pityriasis rosea. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:438963. doi:10.1155/2015/438963
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73.
- Ackson LA, Perkins BA, Wenger JD. Cat scratch disease in the United States: an analysis of three national databases. Am J Public Health. 1993;83:1707-1711.
- Resto-Ruiz S, Burgess A, Anderson BE. The role of the host immune response in pathogenesis of Bartonella henselae. DNA Cell Biol. 2003; 22:431-440.
- Aparicio-Casares H, Puente-Rico MH, Tomé-Nestal C, et al. A pediatric case of Bartonella henselae and Epstein Barr virus disease with bone and hepatosplenic involvement. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2021;78:467-473.
- Ciccarese G, Trave I, Herzum A, et al. Dermatological manifestations of Epstein-Barr virus systemic infection: a case report and literature review. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:1202-1209.
- Drago F, Broccolo F, Ciccarese G. Pityriasis rosea, pityriasis rosea-like eruptions, and herpes zoster in the setting of COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:586-590.
Midwife’s Fake Vaccinations Deserve Harsh Punishment: Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan, at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine.
Very recently, a homeopathic midwife in New York was fined $300,000 for giving out phony injections for kids who were looking to get immunized in order to go to school. She gave pellets, which are sometimes called nosodes, I believe, with homeopathic ingredients, meaning next to nothing in them, and then basically certified that these children — and there were over 1500 of them — were compliant with New York State requirements to be vaccinated to go to school.
However, homeopathy is straight-up bunk. We have seen it again and again discredited as just something that doesn’t work. It has a tradition, but it’s basically nonsense. It certainly doesn’t work as a way to vaccinate anybody.
This midwife basically lied and gave phony certification to the parents of these kids. I’m not talking about the COVID-19 vaccine. I’m talking measles, mumps, rubella, flu, and polio — the childhood immunization schedule. For whatever reason, they put their faith in her and she went along with this fraud.
I think the fine is appropriate, but I think she should be penalized further. Why? When you send 1500 kids to school, mostly in Long Island, New York, but to schools all over the place, you are setting up conditions to bring back epidemic diseases like measles.
We’re already seeing measles outbreaks. At least five states have them. There’s a significant measles outbreak in Philadelphia. Although I can’t say for sure, I believe those outbreaks are directly linked to parents, post–COVID-19, becoming vaccine hesitant and either not vaccinating and lying or going to alternative practitioners like this midwife and claiming that they have been vaccinated.
You’re doing harm not only to the children who you allow to go to school under phony pretenses, but also you’re putting their classmates at risk. We all know that measles is very, very contagious. You’re risking the return of a disease that leads to hospitalization and sometimes even death. That is basically unconscionable.
I think her license should be taken away and she should not be practicing anymore. I believe that anyone who is involved in this kind of phony, dangerous, fraudulent practice ought to be severely punished.
Pre–COVID-19, we had just about gotten rid of measles and mumps. We didn’t see these diseases. Sometimes parents got a bit lazy in childhood vaccination basically because we had used immunization to get rid of the diseases.
Going to alternative healers and allowing people to get away with fraudulent nonsense risks bringing back disabling and deadly killers is not fair to you, me, and other people who are put at risk. It’s not fair to the kids who go to school with other kids who they think are vaccinated but aren’t.
I’m Art Caplan, at the Division of Medical Ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position); serves as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan, at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine.
Very recently, a homeopathic midwife in New York was fined $300,000 for giving out phony injections for kids who were looking to get immunized in order to go to school. She gave pellets, which are sometimes called nosodes, I believe, with homeopathic ingredients, meaning next to nothing in them, and then basically certified that these children — and there were over 1500 of them — were compliant with New York State requirements to be vaccinated to go to school.
However, homeopathy is straight-up bunk. We have seen it again and again discredited as just something that doesn’t work. It has a tradition, but it’s basically nonsense. It certainly doesn’t work as a way to vaccinate anybody.
This midwife basically lied and gave phony certification to the parents of these kids. I’m not talking about the COVID-19 vaccine. I’m talking measles, mumps, rubella, flu, and polio — the childhood immunization schedule. For whatever reason, they put their faith in her and she went along with this fraud.
I think the fine is appropriate, but I think she should be penalized further. Why? When you send 1500 kids to school, mostly in Long Island, New York, but to schools all over the place, you are setting up conditions to bring back epidemic diseases like measles.
We’re already seeing measles outbreaks. At least five states have them. There’s a significant measles outbreak in Philadelphia. Although I can’t say for sure, I believe those outbreaks are directly linked to parents, post–COVID-19, becoming vaccine hesitant and either not vaccinating and lying or going to alternative practitioners like this midwife and claiming that they have been vaccinated.
You’re doing harm not only to the children who you allow to go to school under phony pretenses, but also you’re putting their classmates at risk. We all know that measles is very, very contagious. You’re risking the return of a disease that leads to hospitalization and sometimes even death. That is basically unconscionable.
I think her license should be taken away and she should not be practicing anymore. I believe that anyone who is involved in this kind of phony, dangerous, fraudulent practice ought to be severely punished.
Pre–COVID-19, we had just about gotten rid of measles and mumps. We didn’t see these diseases. Sometimes parents got a bit lazy in childhood vaccination basically because we had used immunization to get rid of the diseases.
Going to alternative healers and allowing people to get away with fraudulent nonsense risks bringing back disabling and deadly killers is not fair to you, me, and other people who are put at risk. It’s not fair to the kids who go to school with other kids who they think are vaccinated but aren’t.
I’m Art Caplan, at the Division of Medical Ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position); serves as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan, at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine.
Very recently, a homeopathic midwife in New York was fined $300,000 for giving out phony injections for kids who were looking to get immunized in order to go to school. She gave pellets, which are sometimes called nosodes, I believe, with homeopathic ingredients, meaning next to nothing in them, and then basically certified that these children — and there were over 1500 of them — were compliant with New York State requirements to be vaccinated to go to school.
However, homeopathy is straight-up bunk. We have seen it again and again discredited as just something that doesn’t work. It has a tradition, but it’s basically nonsense. It certainly doesn’t work as a way to vaccinate anybody.
This midwife basically lied and gave phony certification to the parents of these kids. I’m not talking about the COVID-19 vaccine. I’m talking measles, mumps, rubella, flu, and polio — the childhood immunization schedule. For whatever reason, they put their faith in her and she went along with this fraud.
I think the fine is appropriate, but I think she should be penalized further. Why? When you send 1500 kids to school, mostly in Long Island, New York, but to schools all over the place, you are setting up conditions to bring back epidemic diseases like measles.
We’re already seeing measles outbreaks. At least five states have them. There’s a significant measles outbreak in Philadelphia. Although I can’t say for sure, I believe those outbreaks are directly linked to parents, post–COVID-19, becoming vaccine hesitant and either not vaccinating and lying or going to alternative practitioners like this midwife and claiming that they have been vaccinated.
You’re doing harm not only to the children who you allow to go to school under phony pretenses, but also you’re putting their classmates at risk. We all know that measles is very, very contagious. You’re risking the return of a disease that leads to hospitalization and sometimes even death. That is basically unconscionable.
I think her license should be taken away and she should not be practicing anymore. I believe that anyone who is involved in this kind of phony, dangerous, fraudulent practice ought to be severely punished.
Pre–COVID-19, we had just about gotten rid of measles and mumps. We didn’t see these diseases. Sometimes parents got a bit lazy in childhood vaccination basically because we had used immunization to get rid of the diseases.
Going to alternative healers and allowing people to get away with fraudulent nonsense risks bringing back disabling and deadly killers is not fair to you, me, and other people who are put at risk. It’s not fair to the kids who go to school with other kids who they think are vaccinated but aren’t.
I’m Art Caplan, at the Division of Medical Ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position); serves as a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Increased Risk of New Rheumatic Disease Follows COVID-19 Infection
The risk of developing a new autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease (AIRD) is greater following a COVID-19 infection than after an influenza infection or in the general population, according to a study published March 5 in Annals of Internal Medicine. More severe COVID-19 infections were linked to a greater risk of incident rheumatic disease, but vaccination appeared protective against development of a new AIRD.
“Importantly, this study shows the value of vaccination to prevent severe disease and these types of sequelae,” Anne Davidson, MBBS, a professor in the Institute of Molecular Medicine at The Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in Manhasset, New York, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
Previous research had already identified the likelihood of an association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent development of a new AIRD. This new study, however, includes much larger cohorts from two different countries and relies on more robust methodology than previous studies, experts said.
“Unique steps were taken by the study authors to make sure that what they were looking at in terms of signal was most likely true,” Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine in rheumatology at Washington University in St. Louis, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. Dr. Davidson agreed, noting that these authors “were a bit more rigorous with ascertainment of the autoimmune diagnosis, using two codes and also checking that appropriate medications were administered.”
More Robust and Rigorous Research
Past cohort studies finding an increased risk of rheumatic disease after COVID-19 “based their findings solely on comparisons between infected and uninfected groups, which could be influenced by ascertainment bias due to disparities in care, differences in health-seeking tendencies, and inherent risks among the groups,” Min Seo Kim, MD, of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, Massachusetts, and his colleagues reported. Their study, however, required at least two claims with codes for rheumatic disease and compared patients with COVID-19 to those with flu “to adjust for the potentially heightened detection of AIRD in SARS-CoV-2–infected persons owing to their interactions with the health care system.”
Dr. Alfred Kim said the fact that they used at least two claims codes “gives a little more credence that the patients were actually experiencing some sort of autoimmune inflammatory condition as opposed to a very transient issue post COVID that just went away on its own.”
He acknowledged that the previous research was reasonably strong, “especially in light of the fact that there has been so much work done on a molecular level demonstrating that COVID-19 is associated with a substantial increase in autoantibodies in a significant proportion of patients, so this always opened up the possibility that this could associate with some sort of autoimmune disease downstream.”
While the study is well done with a large population, “it still has limitations that might overestimate the effect,” Kevin W. Byram, MD, associate professor of medicine in rheumatology and immunology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “We certainly have seen individual cases of new rheumatic disease where COVID-19 infection is likely the trigger,” but the phenomenon is not new, he added.
“Many autoimmune diseases are spurred by a loss of tolerance that might be induced by a pathogen of some sort,” Dr. Byram said. “The study is right to point out different forms of bias that might be at play. One in particular that is important to consider in a study like this is the lack of case-level adjudication regarding the diagnosis of rheumatic disease” since the study relied on available ICD-10 codes and medication prescriptions.
The researchers used national claims data to compare risk of incident AIRD in 10,027,506 South Korean and 12,218,680 Japanese adults, aged 20 and older, at 1 month, 6 months, and 12 months after COVID-19 infection, influenza infection, or a matched index date for uninfected control participants. Only patients with at least two claims for AIRD were considered to have a new diagnosis.
Patients who had COVID-19 between January 2020 and December 2021, confirmed by PCR or antigen testing, were matched 1:1 with patients who had test-confirmed influenza during that time and 1:4 with uninfected control participants, whose index date was set to the infection date of their matched COVID-19 patient.
The propensity score matching was based on age, sex, household income, urban versus rural residence, and various clinical characteristics and history: body mass index; blood pressure; fasting blood glucose; glomerular filtration rate; smoking status; alcohol consumption; weekly aerobic physical activity; comorbidity index; hospitalizations and outpatient visits in the previous year; past use of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, or hypertension medication; and history of cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or respiratory infectious disease.
Patients with a history of AIRD or with coinfection or reinfection of COVID-19 and influenza were excluded, as were patients diagnosed with rheumatic disease within a month of COVID-19 infection.
Risk Varied With Disease Severity and Vaccination Status
Among the Korean patients, 3.9% had a COVID-19 infection and 0.98% had an influenza infection. After matching, the comparison populations included 94,504 patients with COVID-19 versus 94,504 patients with flu, and 177,083 patients with COVID-19 versus 675,750 uninfected controls.
The risk of developing an AIRD at least 1 month after infection in South Korean patients with COVID-19 was 25% higher than in uninfected control participants (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.18–1.31; P < .05) and 30% higher than in influenza patients (aHR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.02–1.59; P < .05). Specifically, risk in South Korean patients with COVID-19 was significantly increased for connective tissue disease and both treated and untreated AIRD but not for inflammatory arthritis.
Among the Japanese patients, 8.2% had COVID-19 and 0.99% had flu, resulting in matched populations of 115,003 with COVID-19 versus 110,310 with flu, and 960,849 with COVID-19 versus 1,606,873 uninfected patients. The effect size was larger in Japanese patients, with a 79% increased risk for AIRD in patients with COVID-19, compared with the general population (aHR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.77–1.82; P < .05) and a 14% increased risk, compared with patients with influenza infection (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.10–1.17; P < .05). In Japanese patients, risk was increased across all four categories, including a doubled risk for inflammatory arthritis (aHR, 2.02; 95% CI, 1.96–2.07; P < .05), compared with the general population.
The researchers had data only from the South Korean cohort to calculate risk based on vaccination status, SARS-CoV-2 variant (wild type versus Delta), and COVID-19 severity. Researchers determined a COVID-19 infection to be moderate-to-severe based on billing codes for ICU admission or requiring oxygen therapy, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, renal replacement, or CPR.
Infection with both the original strain and the Delta variant were linked to similar increased risks for AIRD, but moderate to severe COVID-19 infections had greater risk of subsequent AIRD (aHR, 1.42; P < .05) than mild infections (aHR, 1.22; P < .05). Vaccination was linked to a lower risk of AIRD within the COVID-19 patient population: One dose was linked to a 41% reduced risk (HR, 0.59; P < .05) and two doses were linked to a 58% reduced risk (HR, 0.42; P < .05), regardless of the vaccine type, compared with unvaccinated patients with COVID-19. The apparent protective effect of vaccination was true only for patients with mild COVID-19, not those with moderate to severe infection.
“One has to wonder whether or not these people were at much higher risk of developing autoimmune disease that just got exposed because they got COVID, so that a fraction of these would have gotten an autoimmune disease downstream,” Dr. Alfred Kim said. Regardless, one clinical implication of the findings is the reduced risk in vaccinated patients, regardless of the vaccine type, given the fact that “mRNA vaccination in particular has not been associated with any autoantibody development,” he said.
Though the correlations in the study cannot translate to causation, several mechanisms might be at play in a viral infection contributing to autoimmune risk, Dr. Davidson said. Given that viral nucleic acids also recognize self-nucleic acids, “a large load of viral nucleic acid may break tolerance,” or “viral proteins could also mimic self-proteins,” she said. “In addition, tolerance may be broken by a highly inflammatory environment associated with the release of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators.”
The association between new-onset autoimmune disease and severe COVID-19 infection suggests multiple mechanisms may be involved in excess immune stimulation, Dr. Davidson said. But she added that it’s unclear how these findings, involving the original strain and Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2, might relate to currently circulating variants.
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of the Republic of Korea. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships with industry. Dr. Alfred Kim has sponsored research agreements with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novartis; receives royalties from a patent with Kypha Inc.; and has done consulting or speaking for Amgen, ANI Pharmaceuticals, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Exagen Diagnostics, GlaxoSmithKline, Kypha, Miltenyi Biotech, Pfizer, Rheumatology & Arthritis Learning Network, Synthekine, Techtonic Therapeutics, and UpToDate. Dr. Byram reported consulting for TenSixteen Bio. Dr. Davidson had no disclosures.
The risk of developing a new autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease (AIRD) is greater following a COVID-19 infection than after an influenza infection or in the general population, according to a study published March 5 in Annals of Internal Medicine. More severe COVID-19 infections were linked to a greater risk of incident rheumatic disease, but vaccination appeared protective against development of a new AIRD.
“Importantly, this study shows the value of vaccination to prevent severe disease and these types of sequelae,” Anne Davidson, MBBS, a professor in the Institute of Molecular Medicine at The Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in Manhasset, New York, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
Previous research had already identified the likelihood of an association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent development of a new AIRD. This new study, however, includes much larger cohorts from two different countries and relies on more robust methodology than previous studies, experts said.
“Unique steps were taken by the study authors to make sure that what they were looking at in terms of signal was most likely true,” Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine in rheumatology at Washington University in St. Louis, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. Dr. Davidson agreed, noting that these authors “were a bit more rigorous with ascertainment of the autoimmune diagnosis, using two codes and also checking that appropriate medications were administered.”
More Robust and Rigorous Research
Past cohort studies finding an increased risk of rheumatic disease after COVID-19 “based their findings solely on comparisons between infected and uninfected groups, which could be influenced by ascertainment bias due to disparities in care, differences in health-seeking tendencies, and inherent risks among the groups,” Min Seo Kim, MD, of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, Massachusetts, and his colleagues reported. Their study, however, required at least two claims with codes for rheumatic disease and compared patients with COVID-19 to those with flu “to adjust for the potentially heightened detection of AIRD in SARS-CoV-2–infected persons owing to their interactions with the health care system.”
Dr. Alfred Kim said the fact that they used at least two claims codes “gives a little more credence that the patients were actually experiencing some sort of autoimmune inflammatory condition as opposed to a very transient issue post COVID that just went away on its own.”
He acknowledged that the previous research was reasonably strong, “especially in light of the fact that there has been so much work done on a molecular level demonstrating that COVID-19 is associated with a substantial increase in autoantibodies in a significant proportion of patients, so this always opened up the possibility that this could associate with some sort of autoimmune disease downstream.”
While the study is well done with a large population, “it still has limitations that might overestimate the effect,” Kevin W. Byram, MD, associate professor of medicine in rheumatology and immunology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “We certainly have seen individual cases of new rheumatic disease where COVID-19 infection is likely the trigger,” but the phenomenon is not new, he added.
“Many autoimmune diseases are spurred by a loss of tolerance that might be induced by a pathogen of some sort,” Dr. Byram said. “The study is right to point out different forms of bias that might be at play. One in particular that is important to consider in a study like this is the lack of case-level adjudication regarding the diagnosis of rheumatic disease” since the study relied on available ICD-10 codes and medication prescriptions.
The researchers used national claims data to compare risk of incident AIRD in 10,027,506 South Korean and 12,218,680 Japanese adults, aged 20 and older, at 1 month, 6 months, and 12 months after COVID-19 infection, influenza infection, or a matched index date for uninfected control participants. Only patients with at least two claims for AIRD were considered to have a new diagnosis.
Patients who had COVID-19 between January 2020 and December 2021, confirmed by PCR or antigen testing, were matched 1:1 with patients who had test-confirmed influenza during that time and 1:4 with uninfected control participants, whose index date was set to the infection date of their matched COVID-19 patient.
The propensity score matching was based on age, sex, household income, urban versus rural residence, and various clinical characteristics and history: body mass index; blood pressure; fasting blood glucose; glomerular filtration rate; smoking status; alcohol consumption; weekly aerobic physical activity; comorbidity index; hospitalizations and outpatient visits in the previous year; past use of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, or hypertension medication; and history of cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or respiratory infectious disease.
Patients with a history of AIRD or with coinfection or reinfection of COVID-19 and influenza were excluded, as were patients diagnosed with rheumatic disease within a month of COVID-19 infection.
Risk Varied With Disease Severity and Vaccination Status
Among the Korean patients, 3.9% had a COVID-19 infection and 0.98% had an influenza infection. After matching, the comparison populations included 94,504 patients with COVID-19 versus 94,504 patients with flu, and 177,083 patients with COVID-19 versus 675,750 uninfected controls.
The risk of developing an AIRD at least 1 month after infection in South Korean patients with COVID-19 was 25% higher than in uninfected control participants (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.18–1.31; P < .05) and 30% higher than in influenza patients (aHR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.02–1.59; P < .05). Specifically, risk in South Korean patients with COVID-19 was significantly increased for connective tissue disease and both treated and untreated AIRD but not for inflammatory arthritis.
Among the Japanese patients, 8.2% had COVID-19 and 0.99% had flu, resulting in matched populations of 115,003 with COVID-19 versus 110,310 with flu, and 960,849 with COVID-19 versus 1,606,873 uninfected patients. The effect size was larger in Japanese patients, with a 79% increased risk for AIRD in patients with COVID-19, compared with the general population (aHR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.77–1.82; P < .05) and a 14% increased risk, compared with patients with influenza infection (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.10–1.17; P < .05). In Japanese patients, risk was increased across all four categories, including a doubled risk for inflammatory arthritis (aHR, 2.02; 95% CI, 1.96–2.07; P < .05), compared with the general population.
The researchers had data only from the South Korean cohort to calculate risk based on vaccination status, SARS-CoV-2 variant (wild type versus Delta), and COVID-19 severity. Researchers determined a COVID-19 infection to be moderate-to-severe based on billing codes for ICU admission or requiring oxygen therapy, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, renal replacement, or CPR.
Infection with both the original strain and the Delta variant were linked to similar increased risks for AIRD, but moderate to severe COVID-19 infections had greater risk of subsequent AIRD (aHR, 1.42; P < .05) than mild infections (aHR, 1.22; P < .05). Vaccination was linked to a lower risk of AIRD within the COVID-19 patient population: One dose was linked to a 41% reduced risk (HR, 0.59; P < .05) and two doses were linked to a 58% reduced risk (HR, 0.42; P < .05), regardless of the vaccine type, compared with unvaccinated patients with COVID-19. The apparent protective effect of vaccination was true only for patients with mild COVID-19, not those with moderate to severe infection.
“One has to wonder whether or not these people were at much higher risk of developing autoimmune disease that just got exposed because they got COVID, so that a fraction of these would have gotten an autoimmune disease downstream,” Dr. Alfred Kim said. Regardless, one clinical implication of the findings is the reduced risk in vaccinated patients, regardless of the vaccine type, given the fact that “mRNA vaccination in particular has not been associated with any autoantibody development,” he said.
Though the correlations in the study cannot translate to causation, several mechanisms might be at play in a viral infection contributing to autoimmune risk, Dr. Davidson said. Given that viral nucleic acids also recognize self-nucleic acids, “a large load of viral nucleic acid may break tolerance,” or “viral proteins could also mimic self-proteins,” she said. “In addition, tolerance may be broken by a highly inflammatory environment associated with the release of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators.”
The association between new-onset autoimmune disease and severe COVID-19 infection suggests multiple mechanisms may be involved in excess immune stimulation, Dr. Davidson said. But she added that it’s unclear how these findings, involving the original strain and Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2, might relate to currently circulating variants.
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of the Republic of Korea. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships with industry. Dr. Alfred Kim has sponsored research agreements with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novartis; receives royalties from a patent with Kypha Inc.; and has done consulting or speaking for Amgen, ANI Pharmaceuticals, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Exagen Diagnostics, GlaxoSmithKline, Kypha, Miltenyi Biotech, Pfizer, Rheumatology & Arthritis Learning Network, Synthekine, Techtonic Therapeutics, and UpToDate. Dr. Byram reported consulting for TenSixteen Bio. Dr. Davidson had no disclosures.
The risk of developing a new autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease (AIRD) is greater following a COVID-19 infection than after an influenza infection or in the general population, according to a study published March 5 in Annals of Internal Medicine. More severe COVID-19 infections were linked to a greater risk of incident rheumatic disease, but vaccination appeared protective against development of a new AIRD.
“Importantly, this study shows the value of vaccination to prevent severe disease and these types of sequelae,” Anne Davidson, MBBS, a professor in the Institute of Molecular Medicine at The Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in Manhasset, New York, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
Previous research had already identified the likelihood of an association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent development of a new AIRD. This new study, however, includes much larger cohorts from two different countries and relies on more robust methodology than previous studies, experts said.
“Unique steps were taken by the study authors to make sure that what they were looking at in terms of signal was most likely true,” Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine in rheumatology at Washington University in St. Louis, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. Dr. Davidson agreed, noting that these authors “were a bit more rigorous with ascertainment of the autoimmune diagnosis, using two codes and also checking that appropriate medications were administered.”
More Robust and Rigorous Research
Past cohort studies finding an increased risk of rheumatic disease after COVID-19 “based their findings solely on comparisons between infected and uninfected groups, which could be influenced by ascertainment bias due to disparities in care, differences in health-seeking tendencies, and inherent risks among the groups,” Min Seo Kim, MD, of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, Massachusetts, and his colleagues reported. Their study, however, required at least two claims with codes for rheumatic disease and compared patients with COVID-19 to those with flu “to adjust for the potentially heightened detection of AIRD in SARS-CoV-2–infected persons owing to their interactions with the health care system.”
Dr. Alfred Kim said the fact that they used at least two claims codes “gives a little more credence that the patients were actually experiencing some sort of autoimmune inflammatory condition as opposed to a very transient issue post COVID that just went away on its own.”
He acknowledged that the previous research was reasonably strong, “especially in light of the fact that there has been so much work done on a molecular level demonstrating that COVID-19 is associated with a substantial increase in autoantibodies in a significant proportion of patients, so this always opened up the possibility that this could associate with some sort of autoimmune disease downstream.”
While the study is well done with a large population, “it still has limitations that might overestimate the effect,” Kevin W. Byram, MD, associate professor of medicine in rheumatology and immunology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “We certainly have seen individual cases of new rheumatic disease where COVID-19 infection is likely the trigger,” but the phenomenon is not new, he added.
“Many autoimmune diseases are spurred by a loss of tolerance that might be induced by a pathogen of some sort,” Dr. Byram said. “The study is right to point out different forms of bias that might be at play. One in particular that is important to consider in a study like this is the lack of case-level adjudication regarding the diagnosis of rheumatic disease” since the study relied on available ICD-10 codes and medication prescriptions.
The researchers used national claims data to compare risk of incident AIRD in 10,027,506 South Korean and 12,218,680 Japanese adults, aged 20 and older, at 1 month, 6 months, and 12 months after COVID-19 infection, influenza infection, or a matched index date for uninfected control participants. Only patients with at least two claims for AIRD were considered to have a new diagnosis.
Patients who had COVID-19 between January 2020 and December 2021, confirmed by PCR or antigen testing, were matched 1:1 with patients who had test-confirmed influenza during that time and 1:4 with uninfected control participants, whose index date was set to the infection date of their matched COVID-19 patient.
The propensity score matching was based on age, sex, household income, urban versus rural residence, and various clinical characteristics and history: body mass index; blood pressure; fasting blood glucose; glomerular filtration rate; smoking status; alcohol consumption; weekly aerobic physical activity; comorbidity index; hospitalizations and outpatient visits in the previous year; past use of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, or hypertension medication; and history of cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or respiratory infectious disease.
Patients with a history of AIRD or with coinfection or reinfection of COVID-19 and influenza were excluded, as were patients diagnosed with rheumatic disease within a month of COVID-19 infection.
Risk Varied With Disease Severity and Vaccination Status
Among the Korean patients, 3.9% had a COVID-19 infection and 0.98% had an influenza infection. After matching, the comparison populations included 94,504 patients with COVID-19 versus 94,504 patients with flu, and 177,083 patients with COVID-19 versus 675,750 uninfected controls.
The risk of developing an AIRD at least 1 month after infection in South Korean patients with COVID-19 was 25% higher than in uninfected control participants (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.18–1.31; P < .05) and 30% higher than in influenza patients (aHR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.02–1.59; P < .05). Specifically, risk in South Korean patients with COVID-19 was significantly increased for connective tissue disease and both treated and untreated AIRD but not for inflammatory arthritis.
Among the Japanese patients, 8.2% had COVID-19 and 0.99% had flu, resulting in matched populations of 115,003 with COVID-19 versus 110,310 with flu, and 960,849 with COVID-19 versus 1,606,873 uninfected patients. The effect size was larger in Japanese patients, with a 79% increased risk for AIRD in patients with COVID-19, compared with the general population (aHR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.77–1.82; P < .05) and a 14% increased risk, compared with patients with influenza infection (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.10–1.17; P < .05). In Japanese patients, risk was increased across all four categories, including a doubled risk for inflammatory arthritis (aHR, 2.02; 95% CI, 1.96–2.07; P < .05), compared with the general population.
The researchers had data only from the South Korean cohort to calculate risk based on vaccination status, SARS-CoV-2 variant (wild type versus Delta), and COVID-19 severity. Researchers determined a COVID-19 infection to be moderate-to-severe based on billing codes for ICU admission or requiring oxygen therapy, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, renal replacement, or CPR.
Infection with both the original strain and the Delta variant were linked to similar increased risks for AIRD, but moderate to severe COVID-19 infections had greater risk of subsequent AIRD (aHR, 1.42; P < .05) than mild infections (aHR, 1.22; P < .05). Vaccination was linked to a lower risk of AIRD within the COVID-19 patient population: One dose was linked to a 41% reduced risk (HR, 0.59; P < .05) and two doses were linked to a 58% reduced risk (HR, 0.42; P < .05), regardless of the vaccine type, compared with unvaccinated patients with COVID-19. The apparent protective effect of vaccination was true only for patients with mild COVID-19, not those with moderate to severe infection.
“One has to wonder whether or not these people were at much higher risk of developing autoimmune disease that just got exposed because they got COVID, so that a fraction of these would have gotten an autoimmune disease downstream,” Dr. Alfred Kim said. Regardless, one clinical implication of the findings is the reduced risk in vaccinated patients, regardless of the vaccine type, given the fact that “mRNA vaccination in particular has not been associated with any autoantibody development,” he said.
Though the correlations in the study cannot translate to causation, several mechanisms might be at play in a viral infection contributing to autoimmune risk, Dr. Davidson said. Given that viral nucleic acids also recognize self-nucleic acids, “a large load of viral nucleic acid may break tolerance,” or “viral proteins could also mimic self-proteins,” she said. “In addition, tolerance may be broken by a highly inflammatory environment associated with the release of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators.”
The association between new-onset autoimmune disease and severe COVID-19 infection suggests multiple mechanisms may be involved in excess immune stimulation, Dr. Davidson said. But she added that it’s unclear how these findings, involving the original strain and Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2, might relate to currently circulating variants.
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of the Republic of Korea. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships with industry. Dr. Alfred Kim has sponsored research agreements with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Novartis; receives royalties from a patent with Kypha Inc.; and has done consulting or speaking for Amgen, ANI Pharmaceuticals, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Exagen Diagnostics, GlaxoSmithKline, Kypha, Miltenyi Biotech, Pfizer, Rheumatology & Arthritis Learning Network, Synthekine, Techtonic Therapeutics, and UpToDate. Dr. Byram reported consulting for TenSixteen Bio. Dr. Davidson had no disclosures.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Oral Transmission of Chagas Disease Has Severe Effects
Thanks to decades of successful vector control strategies, vector-borne transmission of Chagas disease has significantly decreased in many regions. Oral ingestion of Trypanosoma cruzi through contaminated food and beverages, however, is increasing. Unlike vector transmission, oral transmission of Chagas disease entails high lethality in pediatric and adult populations.
“The oral transmission of Chagas disease is becoming a much more recognized route, and it is crucial to understand that people can die from this type of transmission,” Norman L. Beatty, MD, assistant professor of infectious diseases and global medicine at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, Florida, told this news organization. Dr. Beatty is the lead author of a recent article on the subject.
In regions where the parasite circulates in the environment, people are consuming foods, fruit juices, and possibly wild animal meat that may be contaminated. “As we experience changes in our environment and in the way we consume food, it is crucial to consider how food preparation is carried out in areas where T cruzi transmission occurs in the environment,” said Dr. Beatty. “And as organic farming methods without insecticides become increasingly common, more research is needed in these areas, both in Latin America and in the United States, to understand if oral transmission of T cruzi is occurring.”
In the Amazon basin, foodborne transmission is already the leading cause of acute Chagas disease. It has been described in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, and Venezuela.
Dr. Beatty’s colleagues recently treated a Brazilian patient at the hospital in Florida. “He came to our hospital very ill, with acute myocarditis after consuming contaminated açaí.” Clarifying that there is widespread awareness about oral transmission in Brazil, he stated, “We are concerned that it may not be recognized in other areas of Latin America.”
Mexico and regions of Central America have little to no information on oral transmission, but it is likely occurring, and cases may be going undetected in the region, said Dr. Beatty.
He investigated the issue in Colombia as part of an international collaboration involving the University of Antioquia, aiming to find ways to mitigate oral transmission and create a model that can be used throughout Latin America and the United States. For the Colombia study, they reviewed all cases reported to the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, and oral transmission turned out to be more common than the research group expected. “Still, I imagine that in certain areas with limited resources…there are many more cases that are not being reported.
“A myth I would like to dispel is that Chagas disease is not being transmitted in the United States,” Dr. Beatty added. He mentioned that at least 30 American states have vectors, and in Florida, it was documented that triatomines invaded homes and bit residents. In addition, 30% of these insects are infected with T cruzi. Research is underway to determine whether Floridians are becoming infected and if they are also at risk of contracting Chagas disease orally, said Dr. Beatty. “In the United States, we know very little about how many people are infected and what the infection routes are. Much more research is needed.”
Roberto Chuit, MD, PhD, a doctor in public health and an external consultant for the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), agreed that this route of food contamination, which occurs because of vector-borne parasites, was until recently masked or hidden by the predominance of vector presence. Just as it began to gain importance as other transmission routes were controlled, “it now has extremely high importance in the Americas, as does vertical transmission,” he said.
In 2023, more than 50 years after the first description of oral transmission, the PAHO expert meeting proposed to alert health services and the broader community about the severity and potential lethality of oral Chagas disease outbreaks to elicit immediate responses and mitigation measures. The body also proposed conducting studies to provide detailed information on the contamination source and the wild vectors present in oral transmission foci.
Unique Clinical Manifestations
The exacerbated signs and symptoms of oral infection (see sidebar) are attributed to the high parasite loads in contaminated food and beverages. A single crushed triatomine along with a food or beverage harboring T cruzi can contain an estimated 600,000 metacyclic trypomastigotes, compared with 3000-4000 per µL when infection occurs by triatomine fecal matter. The robust systemic immune response observed in patients with acute oral Chagas disease is thought to result from more efficient transmission after penetration through the oral, pharyngeal, and gastric mucosae.
Seven Things to Know About Orally Transmitted Chagas Disease
1. It presents with exacerbated symptoms and rapid disease progression in immunocompetent individuals. This presentation is not common in vector-borne, congenital, or transfusion-related transmission. It can cause fulminant myocarditis and heart failure, meningoencephalitis, or potentially fatal shock due to parasitemia.
2. Most patients (71%-100%) with acute oral Chagas present with fever.
3. Electrocardiographic abnormalities, specifically ventricular depolarization alterations and pericardial involvement, are observed in most patients.
4. Facial edema, which typically affects the entire face and parts of the lips, is present in 57%-100% of patients with acute oral Chagas disease. In those with acute symptoms from vector transmission, unilateral periorbital swelling (Romaña’s sign) is more common.
5. Other notable systemic symptoms include edema of the lower extremities, myalgia, generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal discomfort, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, headache, chest pain, cutaneous erythematous rash, jaundice, arthralgia, epistaxis, hematemesis, melena, and palpitations.
6. The incubation period after oral ingestion of products contaminated with Trypanosoma cruzi is approximately 3-22 days, in contrast to 4-15 days for vector-borne transmission and 8-160 days for transfusion and transplant-related transmission.
7. Patients need antiparasitic drugs immediately.
Thinking Epidemiologically
Dr. Chuit recalled that suspicion of food contamination should be based on epidemiology, especially in outbreaks affecting several people and in regions where Chagas vectors have been described. Sometimes, however, a single careless tourist consumes contaminated products.
“The difficulty is that many times it is not considered, and if it is not considered, the search for the parasite is not requested,” said Dr. Chuit. He added that it is common for the professional to consider Chagas disease only if viral and bacterial isolation tests are negative. Clinicians sometimes consider Chagas disease because the patient has not responded to regular treatments for other causes, such as antibiotics and hydration.
Epidemiology is important, especially when Chagas disease is diagnosed in groups or a family, because they are usually not isolated cases but outbreaks of 3-40 cases, according to Dr. Chuit. “Under these conditions, it must be quickly considered…that this parasite may be involved.”
One of the difficulties is that the source of these oral transmissions is not recognized most of the time. In general, the sources are usually foods that are more likely to be contaminated by insects or insect feces, such as orange juice or sugarcane. But in fact, any food or beverage left unattended could be contaminated by vectors or possible secretions from infected marsupial odoriferous glands.
An analysis of 32 outbreaks from 1965 to 2022 showed that the main foods involved in oral transmission were homemade fruit juices. But different vector species were identified, and the reservoirs were mainly dogs, rodents, and large American opossums (Didelphis).
The largest oral Chagas outbreak was linked to the consumption of contaminated guava juice in a primary school in Caracas, Venezuela. Nonindustrially produced açaí is a common source of orally acquired Chagas disease in Brazil. In Colombia, Chagas disease has been associated with the consumption of palm wine, sugar cane, and tangerine juice. Other oral transmission routes include consuming meat from wild animals and ingesting blood from infected armadillos, which is related to a traditional medicine practice.
Deadly Yet Easily Treatable
In the outbreak of 119 confirmed and suspected cases in Venezuela, 20.3% required hospitalization, and a 5-year-old child died of acute myocarditis. These percentages differ from those reported in vector transmission, which is asymptomatic in the acute phase for 95%-99% of cases or will only develop a mild febrile illness that resolves on its own.
“Not all cases will present as severe, because depending on the inoculum, there may be individuals with subclinical situations. But any food poisoning that occurs in endemic areas, where food is not properly controlled, and these street foods are associated with processes in jungle areas, raises the possibility that T cruzi is involved and should be considered as a differential diagnosis,» noted Dr. Chuit. “The treatment is highly effective, and people recover quickly.”
“The most important thing about oral transmission of Chagas is that someone infected in this way needs antiparasitic drugs immediately. We can cure them if we treat them immediately,” said Dr. Beatty, adding that treatment is sometimes delayed due to lack of access to appropriate antiparasitic drugs. “Here in the United States and in Latin America, it is quite common for healthcare professionals not to understand the differences between vector, vertical, and oral transmission. By not treating these patients, they become ill quickly.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Chuit declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Thanks to decades of successful vector control strategies, vector-borne transmission of Chagas disease has significantly decreased in many regions. Oral ingestion of Trypanosoma cruzi through contaminated food and beverages, however, is increasing. Unlike vector transmission, oral transmission of Chagas disease entails high lethality in pediatric and adult populations.
“The oral transmission of Chagas disease is becoming a much more recognized route, and it is crucial to understand that people can die from this type of transmission,” Norman L. Beatty, MD, assistant professor of infectious diseases and global medicine at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, Florida, told this news organization. Dr. Beatty is the lead author of a recent article on the subject.
In regions where the parasite circulates in the environment, people are consuming foods, fruit juices, and possibly wild animal meat that may be contaminated. “As we experience changes in our environment and in the way we consume food, it is crucial to consider how food preparation is carried out in areas where T cruzi transmission occurs in the environment,” said Dr. Beatty. “And as organic farming methods without insecticides become increasingly common, more research is needed in these areas, both in Latin America and in the United States, to understand if oral transmission of T cruzi is occurring.”
In the Amazon basin, foodborne transmission is already the leading cause of acute Chagas disease. It has been described in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, and Venezuela.
Dr. Beatty’s colleagues recently treated a Brazilian patient at the hospital in Florida. “He came to our hospital very ill, with acute myocarditis after consuming contaminated açaí.” Clarifying that there is widespread awareness about oral transmission in Brazil, he stated, “We are concerned that it may not be recognized in other areas of Latin America.”
Mexico and regions of Central America have little to no information on oral transmission, but it is likely occurring, and cases may be going undetected in the region, said Dr. Beatty.
He investigated the issue in Colombia as part of an international collaboration involving the University of Antioquia, aiming to find ways to mitigate oral transmission and create a model that can be used throughout Latin America and the United States. For the Colombia study, they reviewed all cases reported to the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, and oral transmission turned out to be more common than the research group expected. “Still, I imagine that in certain areas with limited resources…there are many more cases that are not being reported.
“A myth I would like to dispel is that Chagas disease is not being transmitted in the United States,” Dr. Beatty added. He mentioned that at least 30 American states have vectors, and in Florida, it was documented that triatomines invaded homes and bit residents. In addition, 30% of these insects are infected with T cruzi. Research is underway to determine whether Floridians are becoming infected and if they are also at risk of contracting Chagas disease orally, said Dr. Beatty. “In the United States, we know very little about how many people are infected and what the infection routes are. Much more research is needed.”
Roberto Chuit, MD, PhD, a doctor in public health and an external consultant for the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), agreed that this route of food contamination, which occurs because of vector-borne parasites, was until recently masked or hidden by the predominance of vector presence. Just as it began to gain importance as other transmission routes were controlled, “it now has extremely high importance in the Americas, as does vertical transmission,” he said.
In 2023, more than 50 years after the first description of oral transmission, the PAHO expert meeting proposed to alert health services and the broader community about the severity and potential lethality of oral Chagas disease outbreaks to elicit immediate responses and mitigation measures. The body also proposed conducting studies to provide detailed information on the contamination source and the wild vectors present in oral transmission foci.
Unique Clinical Manifestations
The exacerbated signs and symptoms of oral infection (see sidebar) are attributed to the high parasite loads in contaminated food and beverages. A single crushed triatomine along with a food or beverage harboring T cruzi can contain an estimated 600,000 metacyclic trypomastigotes, compared with 3000-4000 per µL when infection occurs by triatomine fecal matter. The robust systemic immune response observed in patients with acute oral Chagas disease is thought to result from more efficient transmission after penetration through the oral, pharyngeal, and gastric mucosae.
Seven Things to Know About Orally Transmitted Chagas Disease
1. It presents with exacerbated symptoms and rapid disease progression in immunocompetent individuals. This presentation is not common in vector-borne, congenital, or transfusion-related transmission. It can cause fulminant myocarditis and heart failure, meningoencephalitis, or potentially fatal shock due to parasitemia.
2. Most patients (71%-100%) with acute oral Chagas present with fever.
3. Electrocardiographic abnormalities, specifically ventricular depolarization alterations and pericardial involvement, are observed in most patients.
4. Facial edema, which typically affects the entire face and parts of the lips, is present in 57%-100% of patients with acute oral Chagas disease. In those with acute symptoms from vector transmission, unilateral periorbital swelling (Romaña’s sign) is more common.
5. Other notable systemic symptoms include edema of the lower extremities, myalgia, generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal discomfort, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, headache, chest pain, cutaneous erythematous rash, jaundice, arthralgia, epistaxis, hematemesis, melena, and palpitations.
6. The incubation period after oral ingestion of products contaminated with Trypanosoma cruzi is approximately 3-22 days, in contrast to 4-15 days for vector-borne transmission and 8-160 days for transfusion and transplant-related transmission.
7. Patients need antiparasitic drugs immediately.
Thinking Epidemiologically
Dr. Chuit recalled that suspicion of food contamination should be based on epidemiology, especially in outbreaks affecting several people and in regions where Chagas vectors have been described. Sometimes, however, a single careless tourist consumes contaminated products.
“The difficulty is that many times it is not considered, and if it is not considered, the search for the parasite is not requested,” said Dr. Chuit. He added that it is common for the professional to consider Chagas disease only if viral and bacterial isolation tests are negative. Clinicians sometimes consider Chagas disease because the patient has not responded to regular treatments for other causes, such as antibiotics and hydration.
Epidemiology is important, especially when Chagas disease is diagnosed in groups or a family, because they are usually not isolated cases but outbreaks of 3-40 cases, according to Dr. Chuit. “Under these conditions, it must be quickly considered…that this parasite may be involved.”
One of the difficulties is that the source of these oral transmissions is not recognized most of the time. In general, the sources are usually foods that are more likely to be contaminated by insects or insect feces, such as orange juice or sugarcane. But in fact, any food or beverage left unattended could be contaminated by vectors or possible secretions from infected marsupial odoriferous glands.
An analysis of 32 outbreaks from 1965 to 2022 showed that the main foods involved in oral transmission were homemade fruit juices. But different vector species were identified, and the reservoirs were mainly dogs, rodents, and large American opossums (Didelphis).
The largest oral Chagas outbreak was linked to the consumption of contaminated guava juice in a primary school in Caracas, Venezuela. Nonindustrially produced açaí is a common source of orally acquired Chagas disease in Brazil. In Colombia, Chagas disease has been associated with the consumption of palm wine, sugar cane, and tangerine juice. Other oral transmission routes include consuming meat from wild animals and ingesting blood from infected armadillos, which is related to a traditional medicine practice.
Deadly Yet Easily Treatable
In the outbreak of 119 confirmed and suspected cases in Venezuela, 20.3% required hospitalization, and a 5-year-old child died of acute myocarditis. These percentages differ from those reported in vector transmission, which is asymptomatic in the acute phase for 95%-99% of cases or will only develop a mild febrile illness that resolves on its own.
“Not all cases will present as severe, because depending on the inoculum, there may be individuals with subclinical situations. But any food poisoning that occurs in endemic areas, where food is not properly controlled, and these street foods are associated with processes in jungle areas, raises the possibility that T cruzi is involved and should be considered as a differential diagnosis,» noted Dr. Chuit. “The treatment is highly effective, and people recover quickly.”
“The most important thing about oral transmission of Chagas is that someone infected in this way needs antiparasitic drugs immediately. We can cure them if we treat them immediately,” said Dr. Beatty, adding that treatment is sometimes delayed due to lack of access to appropriate antiparasitic drugs. “Here in the United States and in Latin America, it is quite common for healthcare professionals not to understand the differences between vector, vertical, and oral transmission. By not treating these patients, they become ill quickly.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Chuit declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Thanks to decades of successful vector control strategies, vector-borne transmission of Chagas disease has significantly decreased in many regions. Oral ingestion of Trypanosoma cruzi through contaminated food and beverages, however, is increasing. Unlike vector transmission, oral transmission of Chagas disease entails high lethality in pediatric and adult populations.
“The oral transmission of Chagas disease is becoming a much more recognized route, and it is crucial to understand that people can die from this type of transmission,” Norman L. Beatty, MD, assistant professor of infectious diseases and global medicine at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, Florida, told this news organization. Dr. Beatty is the lead author of a recent article on the subject.
In regions where the parasite circulates in the environment, people are consuming foods, fruit juices, and possibly wild animal meat that may be contaminated. “As we experience changes in our environment and in the way we consume food, it is crucial to consider how food preparation is carried out in areas where T cruzi transmission occurs in the environment,” said Dr. Beatty. “And as organic farming methods without insecticides become increasingly common, more research is needed in these areas, both in Latin America and in the United States, to understand if oral transmission of T cruzi is occurring.”
In the Amazon basin, foodborne transmission is already the leading cause of acute Chagas disease. It has been described in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, and Venezuela.
Dr. Beatty’s colleagues recently treated a Brazilian patient at the hospital in Florida. “He came to our hospital very ill, with acute myocarditis after consuming contaminated açaí.” Clarifying that there is widespread awareness about oral transmission in Brazil, he stated, “We are concerned that it may not be recognized in other areas of Latin America.”
Mexico and regions of Central America have little to no information on oral transmission, but it is likely occurring, and cases may be going undetected in the region, said Dr. Beatty.
He investigated the issue in Colombia as part of an international collaboration involving the University of Antioquia, aiming to find ways to mitigate oral transmission and create a model that can be used throughout Latin America and the United States. For the Colombia study, they reviewed all cases reported to the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, and oral transmission turned out to be more common than the research group expected. “Still, I imagine that in certain areas with limited resources…there are many more cases that are not being reported.
“A myth I would like to dispel is that Chagas disease is not being transmitted in the United States,” Dr. Beatty added. He mentioned that at least 30 American states have vectors, and in Florida, it was documented that triatomines invaded homes and bit residents. In addition, 30% of these insects are infected with T cruzi. Research is underway to determine whether Floridians are becoming infected and if they are also at risk of contracting Chagas disease orally, said Dr. Beatty. “In the United States, we know very little about how many people are infected and what the infection routes are. Much more research is needed.”
Roberto Chuit, MD, PhD, a doctor in public health and an external consultant for the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), agreed that this route of food contamination, which occurs because of vector-borne parasites, was until recently masked or hidden by the predominance of vector presence. Just as it began to gain importance as other transmission routes were controlled, “it now has extremely high importance in the Americas, as does vertical transmission,” he said.
In 2023, more than 50 years after the first description of oral transmission, the PAHO expert meeting proposed to alert health services and the broader community about the severity and potential lethality of oral Chagas disease outbreaks to elicit immediate responses and mitigation measures. The body also proposed conducting studies to provide detailed information on the contamination source and the wild vectors present in oral transmission foci.
Unique Clinical Manifestations
The exacerbated signs and symptoms of oral infection (see sidebar) are attributed to the high parasite loads in contaminated food and beverages. A single crushed triatomine along with a food or beverage harboring T cruzi can contain an estimated 600,000 metacyclic trypomastigotes, compared with 3000-4000 per µL when infection occurs by triatomine fecal matter. The robust systemic immune response observed in patients with acute oral Chagas disease is thought to result from more efficient transmission after penetration through the oral, pharyngeal, and gastric mucosae.
Seven Things to Know About Orally Transmitted Chagas Disease
1. It presents with exacerbated symptoms and rapid disease progression in immunocompetent individuals. This presentation is not common in vector-borne, congenital, or transfusion-related transmission. It can cause fulminant myocarditis and heart failure, meningoencephalitis, or potentially fatal shock due to parasitemia.
2. Most patients (71%-100%) with acute oral Chagas present with fever.
3. Electrocardiographic abnormalities, specifically ventricular depolarization alterations and pericardial involvement, are observed in most patients.
4. Facial edema, which typically affects the entire face and parts of the lips, is present in 57%-100% of patients with acute oral Chagas disease. In those with acute symptoms from vector transmission, unilateral periorbital swelling (Romaña’s sign) is more common.
5. Other notable systemic symptoms include edema of the lower extremities, myalgia, generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal discomfort, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, headache, chest pain, cutaneous erythematous rash, jaundice, arthralgia, epistaxis, hematemesis, melena, and palpitations.
6. The incubation period after oral ingestion of products contaminated with Trypanosoma cruzi is approximately 3-22 days, in contrast to 4-15 days for vector-borne transmission and 8-160 days for transfusion and transplant-related transmission.
7. Patients need antiparasitic drugs immediately.
Thinking Epidemiologically
Dr. Chuit recalled that suspicion of food contamination should be based on epidemiology, especially in outbreaks affecting several people and in regions where Chagas vectors have been described. Sometimes, however, a single careless tourist consumes contaminated products.
“The difficulty is that many times it is not considered, and if it is not considered, the search for the parasite is not requested,” said Dr. Chuit. He added that it is common for the professional to consider Chagas disease only if viral and bacterial isolation tests are negative. Clinicians sometimes consider Chagas disease because the patient has not responded to regular treatments for other causes, such as antibiotics and hydration.
Epidemiology is important, especially when Chagas disease is diagnosed in groups or a family, because they are usually not isolated cases but outbreaks of 3-40 cases, according to Dr. Chuit. “Under these conditions, it must be quickly considered…that this parasite may be involved.”
One of the difficulties is that the source of these oral transmissions is not recognized most of the time. In general, the sources are usually foods that are more likely to be contaminated by insects or insect feces, such as orange juice or sugarcane. But in fact, any food or beverage left unattended could be contaminated by vectors or possible secretions from infected marsupial odoriferous glands.
An analysis of 32 outbreaks from 1965 to 2022 showed that the main foods involved in oral transmission were homemade fruit juices. But different vector species were identified, and the reservoirs were mainly dogs, rodents, and large American opossums (Didelphis).
The largest oral Chagas outbreak was linked to the consumption of contaminated guava juice in a primary school in Caracas, Venezuela. Nonindustrially produced açaí is a common source of orally acquired Chagas disease in Brazil. In Colombia, Chagas disease has been associated with the consumption of palm wine, sugar cane, and tangerine juice. Other oral transmission routes include consuming meat from wild animals and ingesting blood from infected armadillos, which is related to a traditional medicine practice.
Deadly Yet Easily Treatable
In the outbreak of 119 confirmed and suspected cases in Venezuela, 20.3% required hospitalization, and a 5-year-old child died of acute myocarditis. These percentages differ from those reported in vector transmission, which is asymptomatic in the acute phase for 95%-99% of cases or will only develop a mild febrile illness that resolves on its own.
“Not all cases will present as severe, because depending on the inoculum, there may be individuals with subclinical situations. But any food poisoning that occurs in endemic areas, where food is not properly controlled, and these street foods are associated with processes in jungle areas, raises the possibility that T cruzi is involved and should be considered as a differential diagnosis,» noted Dr. Chuit. “The treatment is highly effective, and people recover quickly.”
“The most important thing about oral transmission of Chagas is that someone infected in this way needs antiparasitic drugs immediately. We can cure them if we treat them immediately,” said Dr. Beatty, adding that treatment is sometimes delayed due to lack of access to appropriate antiparasitic drugs. “Here in the United States and in Latin America, it is quite common for healthcare professionals not to understand the differences between vector, vertical, and oral transmission. By not treating these patients, they become ill quickly.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Chuit declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Oral Herpes Tied to Double Dementia Risk in Older Adults
TOPLINE:
A history of herpes simplex virus (HSV) is associated with a more than doubling of the risk for dementia in older people, results of a prospective epidemiological study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 1002 dementia-free 70-year-olds from the Prospective Investigation of Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors cohort who were assessed at baseline and at age 75 and 80 years and followed through medical records at age 85 years.
- Researchers collected and analyzed blood samples to detect anti-HSV and anti-HSV-1 immunoglobulin (Ig) G, anti-cytomegalovirus (CMV) IgG, anti-HSV IgM, and anti-HSV and anti-CMV IgG levels and apolipoprotein epsilon 4 (APOE 4) status of participants.
- Investigators collected information on anti-herpesvirus drug treatment and reviewed dementia diagnoses obtained from medical records to classify as established or probable dementia or Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
TAKEAWAY:
- 82% of participants were anti-HSV IgG carriers, of which 6% had received drug treatment for herpes virus, and 7% of participants developed all-cause dementia and 4% AD during the median 15-year follow up.
- In HSV and HSV-1 subsamples, treatment for herpes virus was not significantly associated with lower risks for AD (HR, 1.46, P = .532 and HR, 1.64; P = .419, respectively) or dementia (HR 1.70; P = .222 and HR, 1.60; P = .320, respectively).
- There was no significant interaction between anti-HSV IgG seroprevalence and APOE 4 with regard to dementia risk, likely due to underpowering, and there were no associations between anti-CMV IgG positivity or anti-HSV IgM positivity and AD or dementia.
IN PRACTICE:
“What’s special about this particular study is that the participants are roughly the same age, which makes the results even more reliable since age differences, which are otherwise linked to the development of dementia, cannot confuse the results,” lead author Erika Vestin, a medical student in the Department of Public Health and Caring Sciences, Clinical Geriatrics, Uppsala University, Sweden, said in a press release. Findings may drive dementia research further towards treating the illness at an early stage using common anti-herpes virus drugs, Ms. Vestin added.
SOURCE:
The study, with Ms. Vestin as lead author, was published online on February 14, 2024, in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
LIMITATIONS:
The study underrepresented people with diabetes, heart failure, and stroke and lacked information on treatment compliance, dosage, and length and number of prescriptions, which prevented analysis of dose dependency. Since dementia data collection relied on medical records, dementia cases may be underreported. Some cases of AD could have been misclassified as vascular dementia or other dementia.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Gun and Bertil Stohne’s Foundation, Swedish Dementia Association, Swedish Society of Medicine, Märta Lundqvist Foundation, Thureus Foundation, Region Uppsala, Gamla Tjänarinnor Foundation, and Swedish Brain Foundation. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A history of herpes simplex virus (HSV) is associated with a more than doubling of the risk for dementia in older people, results of a prospective epidemiological study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 1002 dementia-free 70-year-olds from the Prospective Investigation of Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors cohort who were assessed at baseline and at age 75 and 80 years and followed through medical records at age 85 years.
- Researchers collected and analyzed blood samples to detect anti-HSV and anti-HSV-1 immunoglobulin (Ig) G, anti-cytomegalovirus (CMV) IgG, anti-HSV IgM, and anti-HSV and anti-CMV IgG levels and apolipoprotein epsilon 4 (APOE 4) status of participants.
- Investigators collected information on anti-herpesvirus drug treatment and reviewed dementia diagnoses obtained from medical records to classify as established or probable dementia or Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
TAKEAWAY:
- 82% of participants were anti-HSV IgG carriers, of which 6% had received drug treatment for herpes virus, and 7% of participants developed all-cause dementia and 4% AD during the median 15-year follow up.
- In HSV and HSV-1 subsamples, treatment for herpes virus was not significantly associated with lower risks for AD (HR, 1.46, P = .532 and HR, 1.64; P = .419, respectively) or dementia (HR 1.70; P = .222 and HR, 1.60; P = .320, respectively).
- There was no significant interaction between anti-HSV IgG seroprevalence and APOE 4 with regard to dementia risk, likely due to underpowering, and there were no associations between anti-CMV IgG positivity or anti-HSV IgM positivity and AD or dementia.
IN PRACTICE:
“What’s special about this particular study is that the participants are roughly the same age, which makes the results even more reliable since age differences, which are otherwise linked to the development of dementia, cannot confuse the results,” lead author Erika Vestin, a medical student in the Department of Public Health and Caring Sciences, Clinical Geriatrics, Uppsala University, Sweden, said in a press release. Findings may drive dementia research further towards treating the illness at an early stage using common anti-herpes virus drugs, Ms. Vestin added.
SOURCE:
The study, with Ms. Vestin as lead author, was published online on February 14, 2024, in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
LIMITATIONS:
The study underrepresented people with diabetes, heart failure, and stroke and lacked information on treatment compliance, dosage, and length and number of prescriptions, which prevented analysis of dose dependency. Since dementia data collection relied on medical records, dementia cases may be underreported. Some cases of AD could have been misclassified as vascular dementia or other dementia.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Gun and Bertil Stohne’s Foundation, Swedish Dementia Association, Swedish Society of Medicine, Märta Lundqvist Foundation, Thureus Foundation, Region Uppsala, Gamla Tjänarinnor Foundation, and Swedish Brain Foundation. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A history of herpes simplex virus (HSV) is associated with a more than doubling of the risk for dementia in older people, results of a prospective epidemiological study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 1002 dementia-free 70-year-olds from the Prospective Investigation of Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors cohort who were assessed at baseline and at age 75 and 80 years and followed through medical records at age 85 years.
- Researchers collected and analyzed blood samples to detect anti-HSV and anti-HSV-1 immunoglobulin (Ig) G, anti-cytomegalovirus (CMV) IgG, anti-HSV IgM, and anti-HSV and anti-CMV IgG levels and apolipoprotein epsilon 4 (APOE 4) status of participants.
- Investigators collected information on anti-herpesvirus drug treatment and reviewed dementia diagnoses obtained from medical records to classify as established or probable dementia or Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
TAKEAWAY:
- 82% of participants were anti-HSV IgG carriers, of which 6% had received drug treatment for herpes virus, and 7% of participants developed all-cause dementia and 4% AD during the median 15-year follow up.
- In HSV and HSV-1 subsamples, treatment for herpes virus was not significantly associated with lower risks for AD (HR, 1.46, P = .532 and HR, 1.64; P = .419, respectively) or dementia (HR 1.70; P = .222 and HR, 1.60; P = .320, respectively).
- There was no significant interaction between anti-HSV IgG seroprevalence and APOE 4 with regard to dementia risk, likely due to underpowering, and there were no associations between anti-CMV IgG positivity or anti-HSV IgM positivity and AD or dementia.
IN PRACTICE:
“What’s special about this particular study is that the participants are roughly the same age, which makes the results even more reliable since age differences, which are otherwise linked to the development of dementia, cannot confuse the results,” lead author Erika Vestin, a medical student in the Department of Public Health and Caring Sciences, Clinical Geriatrics, Uppsala University, Sweden, said in a press release. Findings may drive dementia research further towards treating the illness at an early stage using common anti-herpes virus drugs, Ms. Vestin added.
SOURCE:
The study, with Ms. Vestin as lead author, was published online on February 14, 2024, in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
LIMITATIONS:
The study underrepresented people with diabetes, heart failure, and stroke and lacked information on treatment compliance, dosage, and length and number of prescriptions, which prevented analysis of dose dependency. Since dementia data collection relied on medical records, dementia cases may be underreported. Some cases of AD could have been misclassified as vascular dementia or other dementia.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Gun and Bertil Stohne’s Foundation, Swedish Dementia Association, Swedish Society of Medicine, Märta Lundqvist Foundation, Thureus Foundation, Region Uppsala, Gamla Tjänarinnor Foundation, and Swedish Brain Foundation. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ebola Vaccine Saves Lives Even After Exposure
The Ervebo vaccine not only reduces the risk for Ebola infection but also halves mortality rates. This is the result of a study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases.
Rebecca Coulborn, an epidemiologist at Epicentre in Paris, France, and colleagues analyzed data collected during the 10th Ebola epidemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Their analysis revealed that among the 2279 patients with confirmed Ebola who were admitted to an Ebola health facility between July 27, 2018, and April 27, 2020, the mortality risk was 56% for unvaccinated patients. In vaccinated patients, however, it was only 25%. The reduced mortality applied to all patients, regardless of age and gender.
The study was funded by Doctors Without Borders. For data collection, Epicentre, the epidemiological division of Doctors Without Borders, collaborated with the Institut National de Recherche Biomédicale and the Ministry of Health of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The study authors focused on the Ervebo vaccine, which is approved for use against Zaire ebolavirus in the European Union, the United States, and some African countries, among others. It is the only Ebola vaccine currently recommended for use during an epidemic. It is administered intramuscularly as a single dose and is approved for adults aged 18 years and older.
The vaccine is primarily recommended for ring vaccination of individuals at a high risk for infection during an epidemic. In studies, the vaccine has been used for ring vaccinations among contacts of diagnosed cases since the end of the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014 and 2015 and since 2018 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The preliminary estimated vaccine effectiveness 10 days after vaccination is 97.5%-100%. The duration of protection is unknown. Individuals who became ill despite vaccination typically experienced a milder course of illness.
Although people should be vaccinated as early as possible during Ebola outbreaks, the results of the Epicentre study showed that the vaccine still protects against the risk for infection even when administered after exposure to the virus.
Furthermore, Dr. Coulborn and her team found no antagonistic effect between vaccination and Ebola treatment in their analysis. “Vaccination following exposure to a person infected with Ebola still provides significant protection against death, even if administered shortly before the onset of symptoms,” said study author Dr. Coulborn in a press release from Doctors Without Borders.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Ervebo vaccine not only reduces the risk for Ebola infection but also halves mortality rates. This is the result of a study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases.
Rebecca Coulborn, an epidemiologist at Epicentre in Paris, France, and colleagues analyzed data collected during the 10th Ebola epidemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Their analysis revealed that among the 2279 patients with confirmed Ebola who were admitted to an Ebola health facility between July 27, 2018, and April 27, 2020, the mortality risk was 56% for unvaccinated patients. In vaccinated patients, however, it was only 25%. The reduced mortality applied to all patients, regardless of age and gender.
The study was funded by Doctors Without Borders. For data collection, Epicentre, the epidemiological division of Doctors Without Borders, collaborated with the Institut National de Recherche Biomédicale and the Ministry of Health of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The study authors focused on the Ervebo vaccine, which is approved for use against Zaire ebolavirus in the European Union, the United States, and some African countries, among others. It is the only Ebola vaccine currently recommended for use during an epidemic. It is administered intramuscularly as a single dose and is approved for adults aged 18 years and older.
The vaccine is primarily recommended for ring vaccination of individuals at a high risk for infection during an epidemic. In studies, the vaccine has been used for ring vaccinations among contacts of diagnosed cases since the end of the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014 and 2015 and since 2018 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The preliminary estimated vaccine effectiveness 10 days after vaccination is 97.5%-100%. The duration of protection is unknown. Individuals who became ill despite vaccination typically experienced a milder course of illness.
Although people should be vaccinated as early as possible during Ebola outbreaks, the results of the Epicentre study showed that the vaccine still protects against the risk for infection even when administered after exposure to the virus.
Furthermore, Dr. Coulborn and her team found no antagonistic effect between vaccination and Ebola treatment in their analysis. “Vaccination following exposure to a person infected with Ebola still provides significant protection against death, even if administered shortly before the onset of symptoms,” said study author Dr. Coulborn in a press release from Doctors Without Borders.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Ervebo vaccine not only reduces the risk for Ebola infection but also halves mortality rates. This is the result of a study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases.
Rebecca Coulborn, an epidemiologist at Epicentre in Paris, France, and colleagues analyzed data collected during the 10th Ebola epidemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Their analysis revealed that among the 2279 patients with confirmed Ebola who were admitted to an Ebola health facility between July 27, 2018, and April 27, 2020, the mortality risk was 56% for unvaccinated patients. In vaccinated patients, however, it was only 25%. The reduced mortality applied to all patients, regardless of age and gender.
The study was funded by Doctors Without Borders. For data collection, Epicentre, the epidemiological division of Doctors Without Borders, collaborated with the Institut National de Recherche Biomédicale and the Ministry of Health of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The study authors focused on the Ervebo vaccine, which is approved for use against Zaire ebolavirus in the European Union, the United States, and some African countries, among others. It is the only Ebola vaccine currently recommended for use during an epidemic. It is administered intramuscularly as a single dose and is approved for adults aged 18 years and older.
The vaccine is primarily recommended for ring vaccination of individuals at a high risk for infection during an epidemic. In studies, the vaccine has been used for ring vaccinations among contacts of diagnosed cases since the end of the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014 and 2015 and since 2018 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The preliminary estimated vaccine effectiveness 10 days after vaccination is 97.5%-100%. The duration of protection is unknown. Individuals who became ill despite vaccination typically experienced a milder course of illness.
Although people should be vaccinated as early as possible during Ebola outbreaks, the results of the Epicentre study showed that the vaccine still protects against the risk for infection even when administered after exposure to the virus.
Furthermore, Dr. Coulborn and her team found no antagonistic effect between vaccination and Ebola treatment in their analysis. “Vaccination following exposure to a person infected with Ebola still provides significant protection against death, even if administered shortly before the onset of symptoms,” said study author Dr. Coulborn in a press release from Doctors Without Borders.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Florida’s Stance on Measles Upends Expert Guidance
Amid an ongoing measles outbreak in Florida possibly sparked by vaccine hesitancy, the state’s surgeon general Joseph Ladapo, MD, is contradicting public health guidance of encouraging quarantine of unvaccinated children.
Rather than requesting that parents keep children unvaccinated against measles home from school or to get their children vaccinated, both critical tools in containing an outbreak, Dr. Ladapo has advised parents to do whatever they think is best. Pediatricians and infectious disease specialists fear a free-for-all will fuel the spread of the highly infectious virus, including in their own clinics.
The outbreak has been traced to an elementary school in Weston and has so far sickened at least eight children, one of whom is younger than 5 years. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, roughly 91% of the 230,000-odd kindergarteners in Florida had received the requisite doses of the MMR vaccine, which also protects against mumps and rubella, for the 2022-2023 school year, below the 95% vaccination level which public health authorities believes confers herd immunity against measles. An estimated 4.5% of kindergarteners in the state have received an exemption for the vaccine, which prevents measles in 97% of the people who get the shots, for a lifetime. The first dose is given around age 13 months and the second when people are age 4 or 5 years and soon to enter school.
“If you’re vaccinated you have a very slim chance of getting the virus,” said Rana Alissa, MD, a pediatrician at University of Florida Health in Jacksonville.
An unvaccinated child has no protection against measles, and could spread it to others merely by sneezing or touching a surface. In a school setting, infection could spread to a teacher who cannot receive the measles vaccine due to a weakened immune system, or the unvaccinated child could spread the virus at a pediatric clinic or hospital when seeking care for measles unless the clinic staff takes rigorous steps to separate the child from other children. Some children at the clinic won’t be able to get the measles vaccine either because of immunodeficiency or perhaps having had a bone marrow transplant.
Assuming the unvaccinated child is healthy, the measles infection will run its course, and the child will then be immune to the disease, Dr. Alissa said. But meanwhile, the child could pose a significant risk to others.
“We’re not worried about the unvaccinated kids who are very healthy. We’re worried about the adults who did not get vaccinated and who are very sick,” said Dr. Alissa, vice president of the Florida chapter of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). “We’re worried about the little kids who are less than 13 months old. We’re worried about the kids with immunodeficiency disorders.” The Florida chapter of the AAP encourages parents to get their children vaccinated against measles amid the ongoing outbreak.
“I wish our surgeon general was on the same page as us,” Dr. Alissa added, noting that she thinks misplaced vaccine hesitancy has caused some parents to forego a safe and effective vaccine for their children.
Never Too Late to Vaxx
Measles symptoms appear 10-14 days after exposure and can include sore throat, cough, runny nose, inflamed eyes, fever, and blotchy skin rashes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 20% of people who are unvaccinated against measles will be hospitalized for the virus if they contract it.
Given the incubation period for the virus, clinicians and public health officials recommend unvaccinated children isolate for 21 days after being exposed to measles at school. The advice applies to any unvaccinated child, whether because their parent opted against the vaccine or because they cannot safely receive the immunization.
This is the guidance that Surgeon General Ladapo is flouting.
“We have a public health system. They’re awesome. They’re the experts. Let’s use them,” Dr. Alissa noted. “Their recommendation is to keep the unvaccinated kids at home for 21 days when you have an outbreak.”
“We’re not calling him doctor anymore,” said Andrew Pavia, MD, chief of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
“Getting your kids immunized before they enter school is so critical,” added Dr. Pavia, because the 21-day quarantine period is onerous for children and parents alike.
In a February 26 statement, Marcus Plescia, MD, MPH, chief medical officer of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, said “well-established public health practice recommends that unvaccinated persons exposed to measles stay home for at least 21 days to prevent further growth of the outbreak. While this is undoubtedly disruptive to the persons impacted, imagine how much more disruptive it would be if measles takes hold again in the United States, spreading widely, and impacting children and communities across the entire nation.”
During an outbreak, it’s still possible to give a measles vaccine to a child who has not yet received the shots, Dr. Pavia stressed. But time is of the essence: Vaccination should occur within 72 hours of the first known measles case in a school.
“It’s not perfect, they may still get measles, but it will greatly decrease the severity,” Dr. Pavia said.
If some children won’t get vaccinated during an outbreak, their parents may call a pediatrician or hospital staff for help as measles symptoms take hold. Clinicians should advise everyone in the home who is older than 2 years to begin wearing N95 masks and gloves, Dr. Alissa said. And when the child comes into the clinic he or she should be examined in a separate room, ideally one with negative air pressure and frequent filtration, Dr. Alissa added. If not, any private room will do if nobody else uses the room for at least 2 hours afterward.
“Measles is phenomenally transmissible,” Dr. Pavia said. A person with the virus can infect 12 to 18 others who are not protected against the pathogen.
Someone with a severe reaction to measles could get an injection of intramuscular immunoglobulin, Dr. Pavia said, although this tends to be uncomfortable and expensive.
“The vaccine works. We almost got rid of measles,” Dr. Alissa said, although parents who choose to send their unvaccinated children to school can do so if they choose to.
“The fear of every pediatrician is to have a child die from this,” she said. “People who are sick, please stay at home.”
Dr. Pavia reported an advisory relationship with Sanofi Pasteur regarding an RSV vaccine. Dr. Alissa reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Amid an ongoing measles outbreak in Florida possibly sparked by vaccine hesitancy, the state’s surgeon general Joseph Ladapo, MD, is contradicting public health guidance of encouraging quarantine of unvaccinated children.
Rather than requesting that parents keep children unvaccinated against measles home from school or to get their children vaccinated, both critical tools in containing an outbreak, Dr. Ladapo has advised parents to do whatever they think is best. Pediatricians and infectious disease specialists fear a free-for-all will fuel the spread of the highly infectious virus, including in their own clinics.
The outbreak has been traced to an elementary school in Weston and has so far sickened at least eight children, one of whom is younger than 5 years. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, roughly 91% of the 230,000-odd kindergarteners in Florida had received the requisite doses of the MMR vaccine, which also protects against mumps and rubella, for the 2022-2023 school year, below the 95% vaccination level which public health authorities believes confers herd immunity against measles. An estimated 4.5% of kindergarteners in the state have received an exemption for the vaccine, which prevents measles in 97% of the people who get the shots, for a lifetime. The first dose is given around age 13 months and the second when people are age 4 or 5 years and soon to enter school.
“If you’re vaccinated you have a very slim chance of getting the virus,” said Rana Alissa, MD, a pediatrician at University of Florida Health in Jacksonville.
An unvaccinated child has no protection against measles, and could spread it to others merely by sneezing or touching a surface. In a school setting, infection could spread to a teacher who cannot receive the measles vaccine due to a weakened immune system, or the unvaccinated child could spread the virus at a pediatric clinic or hospital when seeking care for measles unless the clinic staff takes rigorous steps to separate the child from other children. Some children at the clinic won’t be able to get the measles vaccine either because of immunodeficiency or perhaps having had a bone marrow transplant.
Assuming the unvaccinated child is healthy, the measles infection will run its course, and the child will then be immune to the disease, Dr. Alissa said. But meanwhile, the child could pose a significant risk to others.
“We’re not worried about the unvaccinated kids who are very healthy. We’re worried about the adults who did not get vaccinated and who are very sick,” said Dr. Alissa, vice president of the Florida chapter of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). “We’re worried about the little kids who are less than 13 months old. We’re worried about the kids with immunodeficiency disorders.” The Florida chapter of the AAP encourages parents to get their children vaccinated against measles amid the ongoing outbreak.
“I wish our surgeon general was on the same page as us,” Dr. Alissa added, noting that she thinks misplaced vaccine hesitancy has caused some parents to forego a safe and effective vaccine for their children.
Never Too Late to Vaxx
Measles symptoms appear 10-14 days after exposure and can include sore throat, cough, runny nose, inflamed eyes, fever, and blotchy skin rashes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 20% of people who are unvaccinated against measles will be hospitalized for the virus if they contract it.
Given the incubation period for the virus, clinicians and public health officials recommend unvaccinated children isolate for 21 days after being exposed to measles at school. The advice applies to any unvaccinated child, whether because their parent opted against the vaccine or because they cannot safely receive the immunization.
This is the guidance that Surgeon General Ladapo is flouting.
“We have a public health system. They’re awesome. They’re the experts. Let’s use them,” Dr. Alissa noted. “Their recommendation is to keep the unvaccinated kids at home for 21 days when you have an outbreak.”
“We’re not calling him doctor anymore,” said Andrew Pavia, MD, chief of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
“Getting your kids immunized before they enter school is so critical,” added Dr. Pavia, because the 21-day quarantine period is onerous for children and parents alike.
In a February 26 statement, Marcus Plescia, MD, MPH, chief medical officer of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, said “well-established public health practice recommends that unvaccinated persons exposed to measles stay home for at least 21 days to prevent further growth of the outbreak. While this is undoubtedly disruptive to the persons impacted, imagine how much more disruptive it would be if measles takes hold again in the United States, spreading widely, and impacting children and communities across the entire nation.”
During an outbreak, it’s still possible to give a measles vaccine to a child who has not yet received the shots, Dr. Pavia stressed. But time is of the essence: Vaccination should occur within 72 hours of the first known measles case in a school.
“It’s not perfect, they may still get measles, but it will greatly decrease the severity,” Dr. Pavia said.
If some children won’t get vaccinated during an outbreak, their parents may call a pediatrician or hospital staff for help as measles symptoms take hold. Clinicians should advise everyone in the home who is older than 2 years to begin wearing N95 masks and gloves, Dr. Alissa said. And when the child comes into the clinic he or she should be examined in a separate room, ideally one with negative air pressure and frequent filtration, Dr. Alissa added. If not, any private room will do if nobody else uses the room for at least 2 hours afterward.
“Measles is phenomenally transmissible,” Dr. Pavia said. A person with the virus can infect 12 to 18 others who are not protected against the pathogen.
Someone with a severe reaction to measles could get an injection of intramuscular immunoglobulin, Dr. Pavia said, although this tends to be uncomfortable and expensive.
“The vaccine works. We almost got rid of measles,” Dr. Alissa said, although parents who choose to send their unvaccinated children to school can do so if they choose to.
“The fear of every pediatrician is to have a child die from this,” she said. “People who are sick, please stay at home.”
Dr. Pavia reported an advisory relationship with Sanofi Pasteur regarding an RSV vaccine. Dr. Alissa reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Amid an ongoing measles outbreak in Florida possibly sparked by vaccine hesitancy, the state’s surgeon general Joseph Ladapo, MD, is contradicting public health guidance of encouraging quarantine of unvaccinated children.
Rather than requesting that parents keep children unvaccinated against measles home from school or to get their children vaccinated, both critical tools in containing an outbreak, Dr. Ladapo has advised parents to do whatever they think is best. Pediatricians and infectious disease specialists fear a free-for-all will fuel the spread of the highly infectious virus, including in their own clinics.
The outbreak has been traced to an elementary school in Weston and has so far sickened at least eight children, one of whom is younger than 5 years. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, roughly 91% of the 230,000-odd kindergarteners in Florida had received the requisite doses of the MMR vaccine, which also protects against mumps and rubella, for the 2022-2023 school year, below the 95% vaccination level which public health authorities believes confers herd immunity against measles. An estimated 4.5% of kindergarteners in the state have received an exemption for the vaccine, which prevents measles in 97% of the people who get the shots, for a lifetime. The first dose is given around age 13 months and the second when people are age 4 or 5 years and soon to enter school.
“If you’re vaccinated you have a very slim chance of getting the virus,” said Rana Alissa, MD, a pediatrician at University of Florida Health in Jacksonville.
An unvaccinated child has no protection against measles, and could spread it to others merely by sneezing or touching a surface. In a school setting, infection could spread to a teacher who cannot receive the measles vaccine due to a weakened immune system, or the unvaccinated child could spread the virus at a pediatric clinic or hospital when seeking care for measles unless the clinic staff takes rigorous steps to separate the child from other children. Some children at the clinic won’t be able to get the measles vaccine either because of immunodeficiency or perhaps having had a bone marrow transplant.
Assuming the unvaccinated child is healthy, the measles infection will run its course, and the child will then be immune to the disease, Dr. Alissa said. But meanwhile, the child could pose a significant risk to others.
“We’re not worried about the unvaccinated kids who are very healthy. We’re worried about the adults who did not get vaccinated and who are very sick,” said Dr. Alissa, vice president of the Florida chapter of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). “We’re worried about the little kids who are less than 13 months old. We’re worried about the kids with immunodeficiency disorders.” The Florida chapter of the AAP encourages parents to get their children vaccinated against measles amid the ongoing outbreak.
“I wish our surgeon general was on the same page as us,” Dr. Alissa added, noting that she thinks misplaced vaccine hesitancy has caused some parents to forego a safe and effective vaccine for their children.
Never Too Late to Vaxx
Measles symptoms appear 10-14 days after exposure and can include sore throat, cough, runny nose, inflamed eyes, fever, and blotchy skin rashes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 20% of people who are unvaccinated against measles will be hospitalized for the virus if they contract it.
Given the incubation period for the virus, clinicians and public health officials recommend unvaccinated children isolate for 21 days after being exposed to measles at school. The advice applies to any unvaccinated child, whether because their parent opted against the vaccine or because they cannot safely receive the immunization.
This is the guidance that Surgeon General Ladapo is flouting.
“We have a public health system. They’re awesome. They’re the experts. Let’s use them,” Dr. Alissa noted. “Their recommendation is to keep the unvaccinated kids at home for 21 days when you have an outbreak.”
“We’re not calling him doctor anymore,” said Andrew Pavia, MD, chief of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
“Getting your kids immunized before they enter school is so critical,” added Dr. Pavia, because the 21-day quarantine period is onerous for children and parents alike.
In a February 26 statement, Marcus Plescia, MD, MPH, chief medical officer of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, said “well-established public health practice recommends that unvaccinated persons exposed to measles stay home for at least 21 days to prevent further growth of the outbreak. While this is undoubtedly disruptive to the persons impacted, imagine how much more disruptive it would be if measles takes hold again in the United States, spreading widely, and impacting children and communities across the entire nation.”
During an outbreak, it’s still possible to give a measles vaccine to a child who has not yet received the shots, Dr. Pavia stressed. But time is of the essence: Vaccination should occur within 72 hours of the first known measles case in a school.
“It’s not perfect, they may still get measles, but it will greatly decrease the severity,” Dr. Pavia said.
If some children won’t get vaccinated during an outbreak, their parents may call a pediatrician or hospital staff for help as measles symptoms take hold. Clinicians should advise everyone in the home who is older than 2 years to begin wearing N95 masks and gloves, Dr. Alissa said. And when the child comes into the clinic he or she should be examined in a separate room, ideally one with negative air pressure and frequent filtration, Dr. Alissa added. If not, any private room will do if nobody else uses the room for at least 2 hours afterward.
“Measles is phenomenally transmissible,” Dr. Pavia said. A person with the virus can infect 12 to 18 others who are not protected against the pathogen.
Someone with a severe reaction to measles could get an injection of intramuscular immunoglobulin, Dr. Pavia said, although this tends to be uncomfortable and expensive.
“The vaccine works. We almost got rid of measles,” Dr. Alissa said, although parents who choose to send their unvaccinated children to school can do so if they choose to.
“The fear of every pediatrician is to have a child die from this,” she said. “People who are sick, please stay at home.”
Dr. Pavia reported an advisory relationship with Sanofi Pasteur regarding an RSV vaccine. Dr. Alissa reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.



