User login
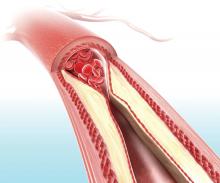
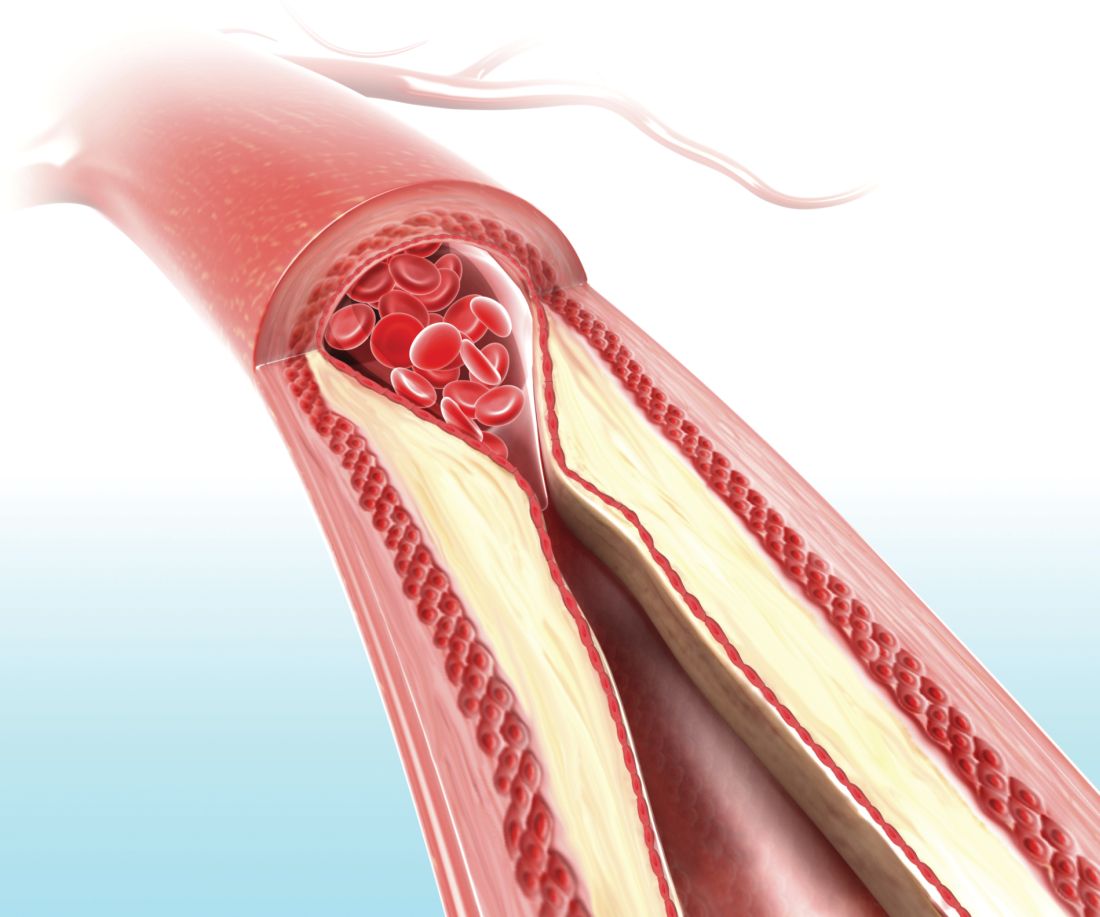
Visual representation of atherosclerosis helps reduce cardiovascular risk
A pictorial representation of carotid ultrasound coupled with a follow-up phone call from a nurse led to reduced cardiovascular disease risk at 1-year follow-up, according to a randomized, controlled study of northern Sweden residents at risk of cardiovascular disease.
“Our study supports further attempts to solve the major problem of prevention failure because of low adherence, despite effective, cost-effective, and evidence-based medications and methods for a healthier lifestyle,” wrote lead author Ulf Näslund, of Umeå (Sweden) University, and his coauthors. The study was published online in the Lancet.
In this trial of 3,532 individuals who were aged 40-60 years with one or more conventional cardiovascular risk factors, the intervention group (1,749) received pictorial information of atherosclerosis as an add-on to normal care. Their primary care physician received the same information, and these participants also received a follow-up phone call from a nurse 2-4 weeks later. The other participants (1,783) received standard care but neither the presentation nor the phone call.
Both the Framingham risk score (FRS) and European Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) were both used to assess outcomes; at 1-year follow-up, the intervention group had an FRS that decreased from baseline (–0.58; 95% confidence interval, –0.86 to –0.30), compared with an increase in the control group (0.35; 95% CI, 0.08-0.63). SCORE values increased twice as much in the control group (0.27; 95% CI, 0.23-0.30), compared with the intervention group (0.13; 95% CI, 0.09-0.18). The authors also observed no differential responses for education level, surmising that “this type of risk communication might contribute to reduction of the social gap in health.”
The authors shared their study’s limitations, including notable differences between dropouts and participants at 1-year follow-up with regard to metabolic risk factors and such fast-developing imaging technologies as CT and MRI out-dating ultrasound findings. They also acknowledged that more research needs to be undertaken to prove that these outcomes are genuine.
This study was funded by Västerbotten County Council, the Swedish Research Council, the Heart and Lung Foundation, and the Swedish Society of Medicine. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Näslund U et al. Lancet. 2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32818-6.
Though improving adherence and outcomes has long eluded clinicians and researchers, this study by Näslund and colleagues provides optimism that cardiovascular risk can be mitigated through educational and motivational factors, according to Richard Kones, MD, of the Cardiometabolic Research Institute in Houston; Umme Rumana, MBBS, of the University of Texas at Houston and the New York Institute of Technology in Old Westbury; and Alberto Morales-Salinas, MD, of the Cardiocentro Ernesto Che Guevara in Villa Clara, Cuba.
The three authors underlined the struggles that low- and middle-income countries go through in terms of “poor adherence and uneven availability and access” for those with high cardiovascular risk; even richer countries like the United States still suffer through a high percentage of hospital admissions that stem from nonadherence to medication. As such, the work of Näslund and colleagues displays the potential of image-based information plus follow-up reinforcement in a manner not often utilized.
“The strengths of the study include size, detail, and the pragmatic, randomized, controlled trial design,” they noted, adding that few other analyses in this area are even comparable. At the same time, lack of resources — including access to transportation and medication — may limit the effectiveness of motivation, especially since the United States differs in prices and health disparities as compared to the study’s Swedish populace.
Coronary heart disease remains one of the world’s leading causes of deaths, and higher adherence will likely lead to “drastic improvements in cardiovascular outcomes.” Yet the three authors state that more research needs to be done to quantify the exact impact of adherence in regard to medication, physical activity, or any reliever of cardiovascular risk: “Whether the results are sustainable and will reduce subsequent major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events requires longer follow-up.”
These comments are adapted from an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]33079-4 ). The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Though improving adherence and outcomes has long eluded clinicians and researchers, this study by Näslund and colleagues provides optimism that cardiovascular risk can be mitigated through educational and motivational factors, according to Richard Kones, MD, of the Cardiometabolic Research Institute in Houston; Umme Rumana, MBBS, of the University of Texas at Houston and the New York Institute of Technology in Old Westbury; and Alberto Morales-Salinas, MD, of the Cardiocentro Ernesto Che Guevara in Villa Clara, Cuba.
The three authors underlined the struggles that low- and middle-income countries go through in terms of “poor adherence and uneven availability and access” for those with high cardiovascular risk; even richer countries like the United States still suffer through a high percentage of hospital admissions that stem from nonadherence to medication. As such, the work of Näslund and colleagues displays the potential of image-based information plus follow-up reinforcement in a manner not often utilized.
“The strengths of the study include size, detail, and the pragmatic, randomized, controlled trial design,” they noted, adding that few other analyses in this area are even comparable. At the same time, lack of resources — including access to transportation and medication — may limit the effectiveness of motivation, especially since the United States differs in prices and health disparities as compared to the study’s Swedish populace.
Coronary heart disease remains one of the world’s leading causes of deaths, and higher adherence will likely lead to “drastic improvements in cardiovascular outcomes.” Yet the three authors state that more research needs to be done to quantify the exact impact of adherence in regard to medication, physical activity, or any reliever of cardiovascular risk: “Whether the results are sustainable and will reduce subsequent major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events requires longer follow-up.”
These comments are adapted from an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]33079-4 ). The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Though improving adherence and outcomes has long eluded clinicians and researchers, this study by Näslund and colleagues provides optimism that cardiovascular risk can be mitigated through educational and motivational factors, according to Richard Kones, MD, of the Cardiometabolic Research Institute in Houston; Umme Rumana, MBBS, of the University of Texas at Houston and the New York Institute of Technology in Old Westbury; and Alberto Morales-Salinas, MD, of the Cardiocentro Ernesto Che Guevara in Villa Clara, Cuba.
The three authors underlined the struggles that low- and middle-income countries go through in terms of “poor adherence and uneven availability and access” for those with high cardiovascular risk; even richer countries like the United States still suffer through a high percentage of hospital admissions that stem from nonadherence to medication. As such, the work of Näslund and colleagues displays the potential of image-based information plus follow-up reinforcement in a manner not often utilized.
“The strengths of the study include size, detail, and the pragmatic, randomized, controlled trial design,” they noted, adding that few other analyses in this area are even comparable. At the same time, lack of resources — including access to transportation and medication — may limit the effectiveness of motivation, especially since the United States differs in prices and health disparities as compared to the study’s Swedish populace.
Coronary heart disease remains one of the world’s leading causes of deaths, and higher adherence will likely lead to “drastic improvements in cardiovascular outcomes.” Yet the three authors state that more research needs to be done to quantify the exact impact of adherence in regard to medication, physical activity, or any reliever of cardiovascular risk: “Whether the results are sustainable and will reduce subsequent major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events requires longer follow-up.”
These comments are adapted from an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]33079-4 ). The authors declared no conflict of interest.
A pictorial representation of carotid ultrasound coupled with a follow-up phone call from a nurse led to reduced cardiovascular disease risk at 1-year follow-up, according to a randomized, controlled study of northern Sweden residents at risk of cardiovascular disease.
“Our study supports further attempts to solve the major problem of prevention failure because of low adherence, despite effective, cost-effective, and evidence-based medications and methods for a healthier lifestyle,” wrote lead author Ulf Näslund, of Umeå (Sweden) University, and his coauthors. The study was published online in the Lancet.
In this trial of 3,532 individuals who were aged 40-60 years with one or more conventional cardiovascular risk factors, the intervention group (1,749) received pictorial information of atherosclerosis as an add-on to normal care. Their primary care physician received the same information, and these participants also received a follow-up phone call from a nurse 2-4 weeks later. The other participants (1,783) received standard care but neither the presentation nor the phone call.
Both the Framingham risk score (FRS) and European Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) were both used to assess outcomes; at 1-year follow-up, the intervention group had an FRS that decreased from baseline (–0.58; 95% confidence interval, –0.86 to –0.30), compared with an increase in the control group (0.35; 95% CI, 0.08-0.63). SCORE values increased twice as much in the control group (0.27; 95% CI, 0.23-0.30), compared with the intervention group (0.13; 95% CI, 0.09-0.18). The authors also observed no differential responses for education level, surmising that “this type of risk communication might contribute to reduction of the social gap in health.”
The authors shared their study’s limitations, including notable differences between dropouts and participants at 1-year follow-up with regard to metabolic risk factors and such fast-developing imaging technologies as CT and MRI out-dating ultrasound findings. They also acknowledged that more research needs to be undertaken to prove that these outcomes are genuine.
This study was funded by Västerbotten County Council, the Swedish Research Council, the Heart and Lung Foundation, and the Swedish Society of Medicine. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Näslund U et al. Lancet. 2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32818-6.
A pictorial representation of carotid ultrasound coupled with a follow-up phone call from a nurse led to reduced cardiovascular disease risk at 1-year follow-up, according to a randomized, controlled study of northern Sweden residents at risk of cardiovascular disease.
“Our study supports further attempts to solve the major problem of prevention failure because of low adherence, despite effective, cost-effective, and evidence-based medications and methods for a healthier lifestyle,” wrote lead author Ulf Näslund, of Umeå (Sweden) University, and his coauthors. The study was published online in the Lancet.
In this trial of 3,532 individuals who were aged 40-60 years with one or more conventional cardiovascular risk factors, the intervention group (1,749) received pictorial information of atherosclerosis as an add-on to normal care. Their primary care physician received the same information, and these participants also received a follow-up phone call from a nurse 2-4 weeks later. The other participants (1,783) received standard care but neither the presentation nor the phone call.
Both the Framingham risk score (FRS) and European Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) were both used to assess outcomes; at 1-year follow-up, the intervention group had an FRS that decreased from baseline (–0.58; 95% confidence interval, –0.86 to –0.30), compared with an increase in the control group (0.35; 95% CI, 0.08-0.63). SCORE values increased twice as much in the control group (0.27; 95% CI, 0.23-0.30), compared with the intervention group (0.13; 95% CI, 0.09-0.18). The authors also observed no differential responses for education level, surmising that “this type of risk communication might contribute to reduction of the social gap in health.”
The authors shared their study’s limitations, including notable differences between dropouts and participants at 1-year follow-up with regard to metabolic risk factors and such fast-developing imaging technologies as CT and MRI out-dating ultrasound findings. They also acknowledged that more research needs to be undertaken to prove that these outcomes are genuine.
This study was funded by Västerbotten County Council, the Swedish Research Council, the Heart and Lung Foundation, and the Swedish Society of Medicine. No conflicts of interest were reported.
SOURCE: Näslund U et al. Lancet. 2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32818-6.
FROM THE LANCET
Key clinical point: Patients who received a pictorial representation of atherosclerosis, plus a nurse-led follow-up phone call, saw reduced cardiovascular disease risk after 1 year.
Major finding: At 1-year follow-up, the intervention group had a Framingham risk score that decreased from baseline (–0.58; 95% confidence interval, –0.86 to –0.30) while the control group saw an increase (0.35; 95% CI, 0.08-0.63).
Study details: A randomized controlled trial of 3,532 participants in a cardiovascular disease prevention program in northern Sweden.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Västerbotten County Council, the Swedish Research Council, the Heart and Lung Foundation, and the Swedish Society of Medicine. No conflicts of interest were reported.
Source: Näslund U et al. Lancet. 2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32818-6.
Lung complications of prescription drug abuse
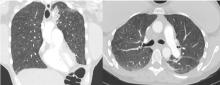
A 39-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with a 2-day history of exertional dyspnea, left-sided chest pain with pleuritic characteristics, and cough without fever or chills. She had a history of severe postprandial nausea and vomiting, weight loss, and malnutrition, which had necessitated placement of a peripherally inserted central catheter in her right arm for total parenteral nutrition.
On physical examination, the patient was afebrile but tachycardic and tachypneic. Her oxygen saturation on room air by pulse oximetry was 91%, though she was not in significant distress. Breath sounds were equal bilaterally and clear, with symmetrical chest wall expansion.
Her white blood cell count was 18.5 × 109/L (reference range 3.5–10.5), with 19.3% eosinophils (reference range 1%–7%); her D-dimer level was also elevated.
Conditions to consider in a patient with these imaging findings in the setting of leukocytosis and eosinophilia include mycobacterial infection, hypersensitivity reaction, diffuse fungal infiltrates, and possibly metastatic disease such as thyroid carcinoma or melanoma. The patient reported having had a purified protein derivative test that was positive for tuberculosis, but she denied having had active disease.
She underwent bronchosocopy. Bronchoalveolar lavage specimen study showed an elevated eosinophil count of 17%. Acid-fast staining detected no organisms. Transbronchial biopsy study revealed foreign-body granulomas from microcrystalline cellulose microemboli deposited in the microvasculature of the patient’s lungs. Upon further questioning the patient admitted she had crushed oral tablets of prescribed opioids and injected them intravenously.
A COMPLICATION OF INJECTING ORAL TABLETS
Oral tablets typically contain talc, cellulose, cornstarch, or combinations of these substances as binding agents. When pulverized, the powder can be combined with water to form an injectable solution with higher and more rapid bioavailability.1,2 The binders, however, are insoluble and accumulate in various tissues.
Intravenous injection of microcellulose has been shown to produce pulmonary and peripheral eosinophilia in birds. In humans, the immune response in foreign body granulomatosis can vary, and case reports have not mentioned eosinophils in the lungs or serum.3,4
Deposition of these particles in pulmonary vessels is common and can trigger a potentially fatal reaction, presenting as acute onset of cough, chest pain, dyspnea, fever, and pulmonary hypertension. The severity of these clinical findings is relative to the degree of pulmonary hypertension created by the arteriolar involvement of these emboli.2,5
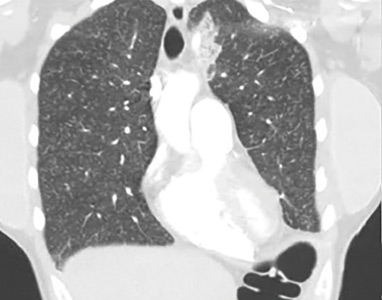
Our patient’s exertional dyspnea and hypoxemia resolved during 1 week of hospitalization with conservative management and supplemental oxygen. She was referred to our pain rehabilitation clinic, where she was successfully weaned from narcotics. Her pulmonary findings on computed tomography were still present 3 years after her initial images, though less prominent.
- Nguyen VT, Chan ES, Chou SH, et al. Pulmonary effects of IV injection of crushed oral tablets: “excipient lung disease.” AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014; 203(5):W506–W515. doi:10.2214/AJR.14.12582
- Bendeck SE, Leung AN, Berry GJ, Daniel D, Ruoss SJ. Cellulose granulomatosis presenting as centrilobular nodules: CT and histologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001; 177(5):1151–1153. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.5.1771151
- Radow SK, Nachamkin I, Morrow C, et al. Foreign body granulomatosis. Clinical and immunologic findings. Am Rev Respir Dis 1983; 127(5):575–580. doi:10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.575
- Wang W, Wideman RF Jr, Bersi TK, Erf GF. Pulmonary and hematological inflammatory responses to intravenous cellulose micro-particles in broilers. Poult Sci 2003; 82(5):771–780. doi:10.1093/ps/82.5.771
- Marchiori E, Lourenco S, Gasparetto TD, Zanetti G, Mano CM, Nobre LF. Pulmonary talcosis: imaging findings. Lung 2010; 188(2):165–171. doi:10.1007/s00408-010-9230-y
A 39-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with a 2-day history of exertional dyspnea, left-sided chest pain with pleuritic characteristics, and cough without fever or chills. She had a history of severe postprandial nausea and vomiting, weight loss, and malnutrition, which had necessitated placement of a peripherally inserted central catheter in her right arm for total parenteral nutrition.
On physical examination, the patient was afebrile but tachycardic and tachypneic. Her oxygen saturation on room air by pulse oximetry was 91%, though she was not in significant distress. Breath sounds were equal bilaterally and clear, with symmetrical chest wall expansion.
Her white blood cell count was 18.5 × 109/L (reference range 3.5–10.5), with 19.3% eosinophils (reference range 1%–7%); her D-dimer level was also elevated.
Conditions to consider in a patient with these imaging findings in the setting of leukocytosis and eosinophilia include mycobacterial infection, hypersensitivity reaction, diffuse fungal infiltrates, and possibly metastatic disease such as thyroid carcinoma or melanoma. The patient reported having had a purified protein derivative test that was positive for tuberculosis, but she denied having had active disease.
She underwent bronchosocopy. Bronchoalveolar lavage specimen study showed an elevated eosinophil count of 17%. Acid-fast staining detected no organisms. Transbronchial biopsy study revealed foreign-body granulomas from microcrystalline cellulose microemboli deposited in the microvasculature of the patient’s lungs. Upon further questioning the patient admitted she had crushed oral tablets of prescribed opioids and injected them intravenously.
A COMPLICATION OF INJECTING ORAL TABLETS
Oral tablets typically contain talc, cellulose, cornstarch, or combinations of these substances as binding agents. When pulverized, the powder can be combined with water to form an injectable solution with higher and more rapid bioavailability.1,2 The binders, however, are insoluble and accumulate in various tissues.
Intravenous injection of microcellulose has been shown to produce pulmonary and peripheral eosinophilia in birds. In humans, the immune response in foreign body granulomatosis can vary, and case reports have not mentioned eosinophils in the lungs or serum.3,4
Deposition of these particles in pulmonary vessels is common and can trigger a potentially fatal reaction, presenting as acute onset of cough, chest pain, dyspnea, fever, and pulmonary hypertension. The severity of these clinical findings is relative to the degree of pulmonary hypertension created by the arteriolar involvement of these emboli.2,5
Our patient’s exertional dyspnea and hypoxemia resolved during 1 week of hospitalization with conservative management and supplemental oxygen. She was referred to our pain rehabilitation clinic, where she was successfully weaned from narcotics. Her pulmonary findings on computed tomography were still present 3 years after her initial images, though less prominent.
A 39-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with a 2-day history of exertional dyspnea, left-sided chest pain with pleuritic characteristics, and cough without fever or chills. She had a history of severe postprandial nausea and vomiting, weight loss, and malnutrition, which had necessitated placement of a peripherally inserted central catheter in her right arm for total parenteral nutrition.
On physical examination, the patient was afebrile but tachycardic and tachypneic. Her oxygen saturation on room air by pulse oximetry was 91%, though she was not in significant distress. Breath sounds were equal bilaterally and clear, with symmetrical chest wall expansion.
Her white blood cell count was 18.5 × 109/L (reference range 3.5–10.5), with 19.3% eosinophils (reference range 1%–7%); her D-dimer level was also elevated.
Conditions to consider in a patient with these imaging findings in the setting of leukocytosis and eosinophilia include mycobacterial infection, hypersensitivity reaction, diffuse fungal infiltrates, and possibly metastatic disease such as thyroid carcinoma or melanoma. The patient reported having had a purified protein derivative test that was positive for tuberculosis, but she denied having had active disease.
She underwent bronchosocopy. Bronchoalveolar lavage specimen study showed an elevated eosinophil count of 17%. Acid-fast staining detected no organisms. Transbronchial biopsy study revealed foreign-body granulomas from microcrystalline cellulose microemboli deposited in the microvasculature of the patient’s lungs. Upon further questioning the patient admitted she had crushed oral tablets of prescribed opioids and injected them intravenously.
A COMPLICATION OF INJECTING ORAL TABLETS
Oral tablets typically contain talc, cellulose, cornstarch, or combinations of these substances as binding agents. When pulverized, the powder can be combined with water to form an injectable solution with higher and more rapid bioavailability.1,2 The binders, however, are insoluble and accumulate in various tissues.
Intravenous injection of microcellulose has been shown to produce pulmonary and peripheral eosinophilia in birds. In humans, the immune response in foreign body granulomatosis can vary, and case reports have not mentioned eosinophils in the lungs or serum.3,4
Deposition of these particles in pulmonary vessels is common and can trigger a potentially fatal reaction, presenting as acute onset of cough, chest pain, dyspnea, fever, and pulmonary hypertension. The severity of these clinical findings is relative to the degree of pulmonary hypertension created by the arteriolar involvement of these emboli.2,5
Our patient’s exertional dyspnea and hypoxemia resolved during 1 week of hospitalization with conservative management and supplemental oxygen. She was referred to our pain rehabilitation clinic, where she was successfully weaned from narcotics. Her pulmonary findings on computed tomography were still present 3 years after her initial images, though less prominent.
- Nguyen VT, Chan ES, Chou SH, et al. Pulmonary effects of IV injection of crushed oral tablets: “excipient lung disease.” AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014; 203(5):W506–W515. doi:10.2214/AJR.14.12582
- Bendeck SE, Leung AN, Berry GJ, Daniel D, Ruoss SJ. Cellulose granulomatosis presenting as centrilobular nodules: CT and histologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001; 177(5):1151–1153. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.5.1771151
- Radow SK, Nachamkin I, Morrow C, et al. Foreign body granulomatosis. Clinical and immunologic findings. Am Rev Respir Dis 1983; 127(5):575–580. doi:10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.575
- Wang W, Wideman RF Jr, Bersi TK, Erf GF. Pulmonary and hematological inflammatory responses to intravenous cellulose micro-particles in broilers. Poult Sci 2003; 82(5):771–780. doi:10.1093/ps/82.5.771
- Marchiori E, Lourenco S, Gasparetto TD, Zanetti G, Mano CM, Nobre LF. Pulmonary talcosis: imaging findings. Lung 2010; 188(2):165–171. doi:10.1007/s00408-010-9230-y
- Nguyen VT, Chan ES, Chou SH, et al. Pulmonary effects of IV injection of crushed oral tablets: “excipient lung disease.” AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014; 203(5):W506–W515. doi:10.2214/AJR.14.12582
- Bendeck SE, Leung AN, Berry GJ, Daniel D, Ruoss SJ. Cellulose granulomatosis presenting as centrilobular nodules: CT and histologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001; 177(5):1151–1153. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.5.1771151
- Radow SK, Nachamkin I, Morrow C, et al. Foreign body granulomatosis. Clinical and immunologic findings. Am Rev Respir Dis 1983; 127(5):575–580. doi:10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.575
- Wang W, Wideman RF Jr, Bersi TK, Erf GF. Pulmonary and hematological inflammatory responses to intravenous cellulose micro-particles in broilers. Poult Sci 2003; 82(5):771–780. doi:10.1093/ps/82.5.771
- Marchiori E, Lourenco S, Gasparetto TD, Zanetti G, Mano CM, Nobre LF. Pulmonary talcosis: imaging findings. Lung 2010; 188(2):165–171. doi:10.1007/s00408-010-9230-y
Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) for Small Bowel Obstruction in the ED
Small bowel obstruction (SBO) accounts for 2% of all cases of abdominal pain presenting to the ED and 15% of abdominal pain admissions to surgical units from the ED.1,2 SBO can be a difficult diagnosis; the most common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, obstipation, and constipation. The symptomatology depends on multiple factors: the area of the blockage, length of obstruction, and degree of the obstruction (either partial or complete).3 An upper gastrointestinal (GI) blockage classically presents with nausea and vomiting, while a lower GI blockage often presents with abdominal pain, constipation, and obstipation. Complications of obstruction range from significant morbidity—such as bowel strangulation (23%) and sepsis (31%)—to mortality (9%).4 ED POCUS allows for rapid and accurate diagnosis of SBO.
CASE
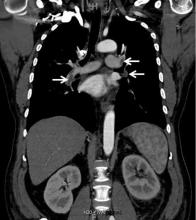
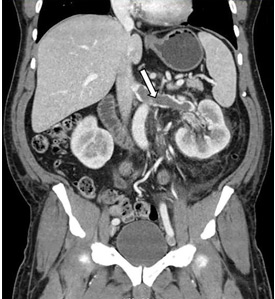
A 60-year-old female with a past medical history of peptic ulcer disease and multiple abdominal surgeries, including umbilical hernia repair, appendectomy, and total abdominal hysterectomy, presented to the ED with an 8-hour history of nausea and vomiting. She reported that her abdomen felt bloated. She had experienced non-bloody, watery stools for the prior 3 weeks. She also reported three to four weeks of epigastric abdominal pain similar to her previous “ulcer pain.” Of note, she was evaluated in GI clinic one day prior to her ED visit for dysphagia, abdominal distention, and diarrhea and was scheduled for an outpatient upper endoscopy. Initial vitals were significant for a heart rate of 100 beats/min. Physical exam was significant for a mildly distended abdomen, tender to palpation at epigastrium without rebound or guarding. Labs showed a white blood cell count of 11.8 K/uL and otherwise unremarkable complete blood count, basic metabolic panel, liver function tests, and lactate measurement. Given the patient’s history of multiple abdominal surgeries and clinical presentation, POCUS was performed to evaluate for SBO. Dilated loops of small bowel were visualized in the lower abdomen gas, suggestive of SBO.
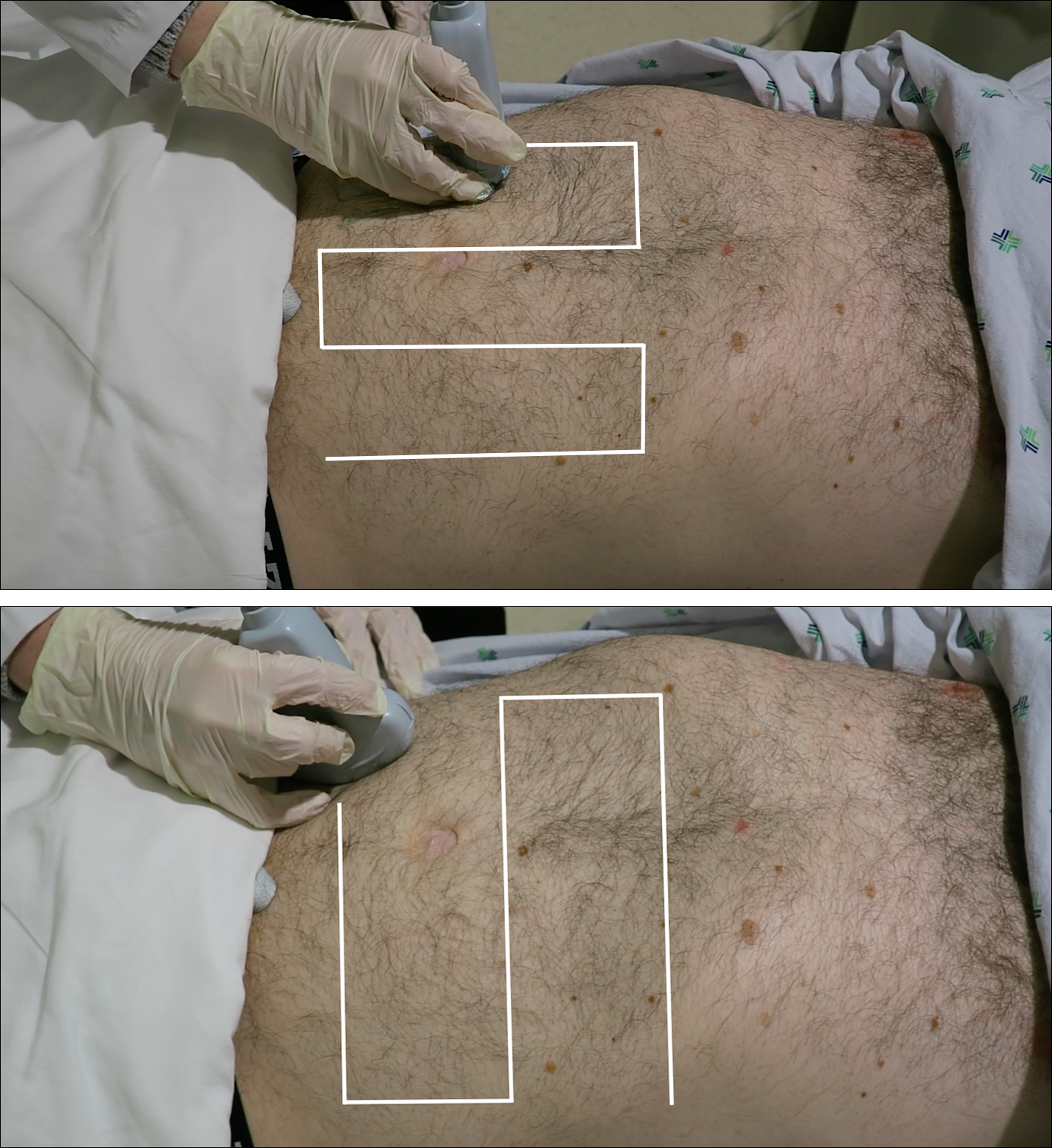
Since the small bowel encompasses a large portion of the abdomen, to fully evaluate for SBO, multiple views are necessary. These include the epigastrium, bilateral colic gutters, and suprapubic regions.5 Use the low-frequency curvilinear transducer to obtain these views, scanning in the transverse and sagittal planes (see Figures 1 and 2). Scan while moving the transducer in columns (ie, “mowing the lawn”), making sure to cover the entire abdomen. To assure that you are evaluating the small bowel, and not the large bowel, look for the characteristic plicae circularis of the small bowel (shown in Figure 3). In children and very slender adults, the high-frequency linear probe may provide enough depth to obtain adequate views.
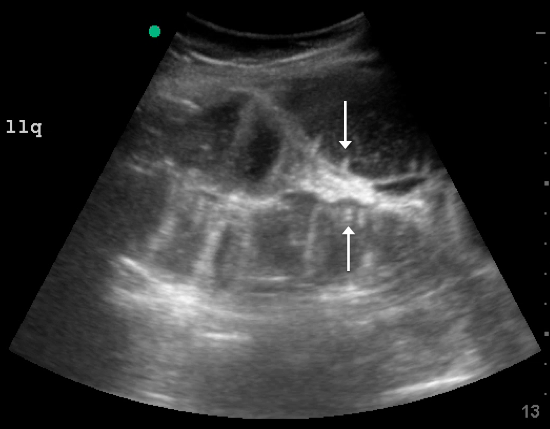
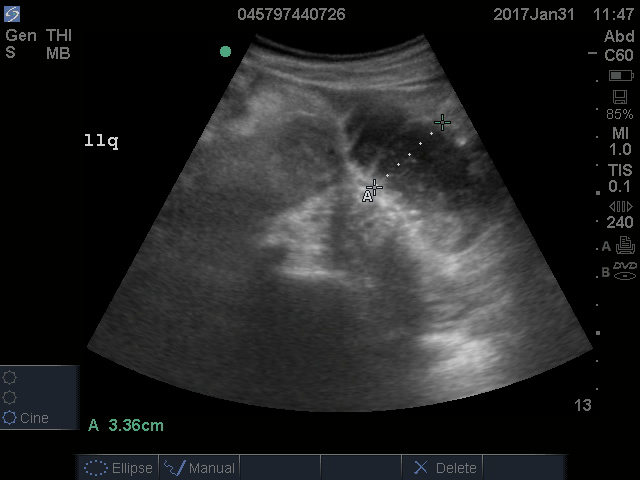
A fluid-filled small intestinal segment >2.5 cm is consistent with a diagnosis of SBO. Measuring the diameter of the small bowel is both the most sensitive and specific sign; a measurement of greater than 2.5 cm is diagnostic, with a sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 91% (see Figure 4).6 This can be somewhat difficult to visualize, as bowel loops are multidirectional and diameters can mistakenly be taken on an indirect cut; to avoid over- or underestimation of bowel diameter, you may want to measure in the short axis using a transverse cross-sectional view of the bowel.
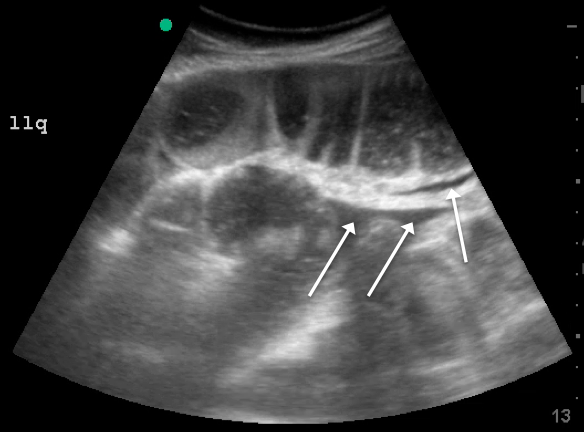
Lack of peristalsis is suggestive of a closed-loop obstruction. However, this finding may be more difficult to visualize, as it requires several continuous minutes of scanning or repeated exams to truly establish absent peristalsis. In prolonged courses of SBO, the bowel wall can measure >3 mm, which suggests necrosis, warranting accelerated surgical intervention. In addition, the detection of extraluminal peritoneal fluid can help determine the severity of the SBO, and small versus large fluid amounts can help determine whether medical or surgical management is warranted (see Figure 5).7
DISCUSSION
Increased time to diagnosis of SBO can lead to prolonged patient suffering and greater complication rates. The gold standard for diagnosing SBO—CT with intravenous and oral contrast—can take hours, requiring patients, who are often nauseated, to ingest and tolerate oral contrast. In the past, an “obstructive series” of x-rays would have been used early in the work-up of possible SBO.6
Recent literature suggests that POCUS is not only faster, more cost effective, and advantageous (involving no ionizing radiation), but also more accurate than x-rays. Specifically, a meta-analysis by Taylor et al showed pooled estimates for obstructive series x-rays have a sensitivity (Sn) of 75%, a specificity (Sp) of 66%, a positive likelihood ratio (+LR) of 1.6, and a negative likelihood ratio (-LR) of 0.43.1 On the other hand, pooled results from ED studies of emergency medicine (EM) residents performing POCUS in patients with signs and symptoms suspicious for SBO showed POCUS had a Sn of 97%, Sp of 90%, +LR of 9.5, and a -LR of 0.04.1,5,8 While detractors point to the operator-dependent nature of POCUS, literature suggests that with EM residents novice to POCUS for SBO (defined as less than 5 previous scans for SBO) were given a 10-minute didactic session and yielded Sn 94%, Sp 81%, +LR 5.0, -LR 0.07.5 Unluer et al trained novice EM residents for 6 hours and found them to yield Sn 98%, Sp 95%, +LR 19.5, and -LR 0.02.8 Thus, while it is no surprise that those with more training attain better results, both studies show it does not take much time for EM providers to surpass the accuracy of x-rays with POCUS.
CASE CONCLUSION
The findings on POCUS highly suggested the diagnosis of an SBO. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous and oral contrast was ordered to further evaluate obstruction, transition point, and possible complications, including signs of ischemia per surgical request. CT demonstrated dilated loops of small bowel with transition point in the right lower quadrant, with a small amount of mesenteric fluid consistent with SBO with possible early bowel compromise due to ischemia. General surgery admitted the patient; conservative treatment with serial abdominal exams, nasogastric tube, NPO and bowel rest was ordered. The patient’s diet was gradually advanced, and she was discharged on the eleventh day of hospitalization.
SUMMARY
POCUS is a useful non-invasive tool that can accurately diagnose SBO. POCUS has increased sensitivity and specificity when compared to abdominal X-rays. This bedside imaging will not only give the ED provider rapid diagnostic information but also lead to expedited surgical intervention.
- Taylor MR, Lalani N. Adult small bowel obstruction. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20(6):528-544.
- Hastings RS, Powers RD. Abdominal pain in the ED: a 35-year retrospective. Am J Emerg Med.2011;29:711-716.
- Markogiannakis H, Messaris E, Dardamanis D, et al. Acute mechanical bowel obstruction: clinical presentation, etiology, management and outcome. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:432.
- Bickell N, Federman A, Aufses A. Influence of time on risk of bowel resection in complete small bowel obstruction. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;201(6):847-854.
- Jang TB, Chandler D, Kaji AH. Bedside ultrasonography for the detection of small bowel obstruction in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2011;28:676-678.
- Carpenter CR, Pines JM. The end of X-rays for suspected small bowel obstruction? Using evidence-based diagnostics to inform best practices in emergency medicine. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20:618-20.
- Grassi R, Romano S, D’Amario F, et al. The relevance of free fluid between intestinal loops detected by sonography in the clinical assessment of small bowel obstruction in adults. Eur J Radiol. 2004;50(1):5-14.
- Unlüer E, Yavaşi O, Eroğlu O, Yilmaz C, Akarca F. Ultrasonography by emergency medicine and radiology residents for the diagnosis of small bowel obstruction. Eur J Emerg Med. 2010;17(5):260-264.
Small bowel obstruction (SBO) accounts for 2% of all cases of abdominal pain presenting to the ED and 15% of abdominal pain admissions to surgical units from the ED.1,2 SBO can be a difficult diagnosis; the most common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, obstipation, and constipation. The symptomatology depends on multiple factors: the area of the blockage, length of obstruction, and degree of the obstruction (either partial or complete).3 An upper gastrointestinal (GI) blockage classically presents with nausea and vomiting, while a lower GI blockage often presents with abdominal pain, constipation, and obstipation. Complications of obstruction range from significant morbidity—such as bowel strangulation (23%) and sepsis (31%)—to mortality (9%).4 ED POCUS allows for rapid and accurate diagnosis of SBO.
CASE
A 60-year-old female with a past medical history of peptic ulcer disease and multiple abdominal surgeries, including umbilical hernia repair, appendectomy, and total abdominal hysterectomy, presented to the ED with an 8-hour history of nausea and vomiting. She reported that her abdomen felt bloated. She had experienced non-bloody, watery stools for the prior 3 weeks. She also reported three to four weeks of epigastric abdominal pain similar to her previous “ulcer pain.” Of note, she was evaluated in GI clinic one day prior to her ED visit for dysphagia, abdominal distention, and diarrhea and was scheduled for an outpatient upper endoscopy. Initial vitals were significant for a heart rate of 100 beats/min. Physical exam was significant for a mildly distended abdomen, tender to palpation at epigastrium without rebound or guarding. Labs showed a white blood cell count of 11.8 K/uL and otherwise unremarkable complete blood count, basic metabolic panel, liver function tests, and lactate measurement. Given the patient’s history of multiple abdominal surgeries and clinical presentation, POCUS was performed to evaluate for SBO. Dilated loops of small bowel were visualized in the lower abdomen gas, suggestive of SBO.
Since the small bowel encompasses a large portion of the abdomen, to fully evaluate for SBO, multiple views are necessary. These include the epigastrium, bilateral colic gutters, and suprapubic regions.5 Use the low-frequency curvilinear transducer to obtain these views, scanning in the transverse and sagittal planes (see Figures 1 and 2). Scan while moving the transducer in columns (ie, “mowing the lawn”), making sure to cover the entire abdomen. To assure that you are evaluating the small bowel, and not the large bowel, look for the characteristic plicae circularis of the small bowel (shown in Figure 3). In children and very slender adults, the high-frequency linear probe may provide enough depth to obtain adequate views.


A fluid-filled small intestinal segment >2.5 cm is consistent with a diagnosis of SBO. Measuring the diameter of the small bowel is both the most sensitive and specific sign; a measurement of greater than 2.5 cm is diagnostic, with a sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 91% (see Figure 4).6 This can be somewhat difficult to visualize, as bowel loops are multidirectional and diameters can mistakenly be taken on an indirect cut; to avoid over- or underestimation of bowel diameter, you may want to measure in the short axis using a transverse cross-sectional view of the bowel.

Lack of peristalsis is suggestive of a closed-loop obstruction. However, this finding may be more difficult to visualize, as it requires several continuous minutes of scanning or repeated exams to truly establish absent peristalsis. In prolonged courses of SBO, the bowel wall can measure >3 mm, which suggests necrosis, warranting accelerated surgical intervention. In addition, the detection of extraluminal peritoneal fluid can help determine the severity of the SBO, and small versus large fluid amounts can help determine whether medical or surgical management is warranted (see Figure 5).7

DISCUSSION
Increased time to diagnosis of SBO can lead to prolonged patient suffering and greater complication rates. The gold standard for diagnosing SBO—CT with intravenous and oral contrast—can take hours, requiring patients, who are often nauseated, to ingest and tolerate oral contrast. In the past, an “obstructive series” of x-rays would have been used early in the work-up of possible SBO.6
Recent literature suggests that POCUS is not only faster, more cost effective, and advantageous (involving no ionizing radiation), but also more accurate than x-rays. Specifically, a meta-analysis by Taylor et al showed pooled estimates for obstructive series x-rays have a sensitivity (Sn) of 75%, a specificity (Sp) of 66%, a positive likelihood ratio (+LR) of 1.6, and a negative likelihood ratio (-LR) of 0.43.1 On the other hand, pooled results from ED studies of emergency medicine (EM) residents performing POCUS in patients with signs and symptoms suspicious for SBO showed POCUS had a Sn of 97%, Sp of 90%, +LR of 9.5, and a -LR of 0.04.1,5,8 While detractors point to the operator-dependent nature of POCUS, literature suggests that with EM residents novice to POCUS for SBO (defined as less than 5 previous scans for SBO) were given a 10-minute didactic session and yielded Sn 94%, Sp 81%, +LR 5.0, -LR 0.07.5 Unluer et al trained novice EM residents for 6 hours and found them to yield Sn 98%, Sp 95%, +LR 19.5, and -LR 0.02.8 Thus, while it is no surprise that those with more training attain better results, both studies show it does not take much time for EM providers to surpass the accuracy of x-rays with POCUS.
CASE CONCLUSION
The findings on POCUS highly suggested the diagnosis of an SBO. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous and oral contrast was ordered to further evaluate obstruction, transition point, and possible complications, including signs of ischemia per surgical request. CT demonstrated dilated loops of small bowel with transition point in the right lower quadrant, with a small amount of mesenteric fluid consistent with SBO with possible early bowel compromise due to ischemia. General surgery admitted the patient; conservative treatment with serial abdominal exams, nasogastric tube, NPO and bowel rest was ordered. The patient’s diet was gradually advanced, and she was discharged on the eleventh day of hospitalization.
SUMMARY
POCUS is a useful non-invasive tool that can accurately diagnose SBO. POCUS has increased sensitivity and specificity when compared to abdominal X-rays. This bedside imaging will not only give the ED provider rapid diagnostic information but also lead to expedited surgical intervention.
Small bowel obstruction (SBO) accounts for 2% of all cases of abdominal pain presenting to the ED and 15% of abdominal pain admissions to surgical units from the ED.1,2 SBO can be a difficult diagnosis; the most common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, obstipation, and constipation. The symptomatology depends on multiple factors: the area of the blockage, length of obstruction, and degree of the obstruction (either partial or complete).3 An upper gastrointestinal (GI) blockage classically presents with nausea and vomiting, while a lower GI blockage often presents with abdominal pain, constipation, and obstipation. Complications of obstruction range from significant morbidity—such as bowel strangulation (23%) and sepsis (31%)—to mortality (9%).4 ED POCUS allows for rapid and accurate diagnosis of SBO.
CASE
A 60-year-old female with a past medical history of peptic ulcer disease and multiple abdominal surgeries, including umbilical hernia repair, appendectomy, and total abdominal hysterectomy, presented to the ED with an 8-hour history of nausea and vomiting. She reported that her abdomen felt bloated. She had experienced non-bloody, watery stools for the prior 3 weeks. She also reported three to four weeks of epigastric abdominal pain similar to her previous “ulcer pain.” Of note, she was evaluated in GI clinic one day prior to her ED visit for dysphagia, abdominal distention, and diarrhea and was scheduled for an outpatient upper endoscopy. Initial vitals were significant for a heart rate of 100 beats/min. Physical exam was significant for a mildly distended abdomen, tender to palpation at epigastrium without rebound or guarding. Labs showed a white blood cell count of 11.8 K/uL and otherwise unremarkable complete blood count, basic metabolic panel, liver function tests, and lactate measurement. Given the patient’s history of multiple abdominal surgeries and clinical presentation, POCUS was performed to evaluate for SBO. Dilated loops of small bowel were visualized in the lower abdomen gas, suggestive of SBO.
Since the small bowel encompasses a large portion of the abdomen, to fully evaluate for SBO, multiple views are necessary. These include the epigastrium, bilateral colic gutters, and suprapubic regions.5 Use the low-frequency curvilinear transducer to obtain these views, scanning in the transverse and sagittal planes (see Figures 1 and 2). Scan while moving the transducer in columns (ie, “mowing the lawn”), making sure to cover the entire abdomen. To assure that you are evaluating the small bowel, and not the large bowel, look for the characteristic plicae circularis of the small bowel (shown in Figure 3). In children and very slender adults, the high-frequency linear probe may provide enough depth to obtain adequate views.


A fluid-filled small intestinal segment >2.5 cm is consistent with a diagnosis of SBO. Measuring the diameter of the small bowel is both the most sensitive and specific sign; a measurement of greater than 2.5 cm is diagnostic, with a sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 91% (see Figure 4).6 This can be somewhat difficult to visualize, as bowel loops are multidirectional and diameters can mistakenly be taken on an indirect cut; to avoid over- or underestimation of bowel diameter, you may want to measure in the short axis using a transverse cross-sectional view of the bowel.

Lack of peristalsis is suggestive of a closed-loop obstruction. However, this finding may be more difficult to visualize, as it requires several continuous minutes of scanning or repeated exams to truly establish absent peristalsis. In prolonged courses of SBO, the bowel wall can measure >3 mm, which suggests necrosis, warranting accelerated surgical intervention. In addition, the detection of extraluminal peritoneal fluid can help determine the severity of the SBO, and small versus large fluid amounts can help determine whether medical or surgical management is warranted (see Figure 5).7

DISCUSSION
Increased time to diagnosis of SBO can lead to prolonged patient suffering and greater complication rates. The gold standard for diagnosing SBO—CT with intravenous and oral contrast—can take hours, requiring patients, who are often nauseated, to ingest and tolerate oral contrast. In the past, an “obstructive series” of x-rays would have been used early in the work-up of possible SBO.6
Recent literature suggests that POCUS is not only faster, more cost effective, and advantageous (involving no ionizing radiation), but also more accurate than x-rays. Specifically, a meta-analysis by Taylor et al showed pooled estimates for obstructive series x-rays have a sensitivity (Sn) of 75%, a specificity (Sp) of 66%, a positive likelihood ratio (+LR) of 1.6, and a negative likelihood ratio (-LR) of 0.43.1 On the other hand, pooled results from ED studies of emergency medicine (EM) residents performing POCUS in patients with signs and symptoms suspicious for SBO showed POCUS had a Sn of 97%, Sp of 90%, +LR of 9.5, and a -LR of 0.04.1,5,8 While detractors point to the operator-dependent nature of POCUS, literature suggests that with EM residents novice to POCUS for SBO (defined as less than 5 previous scans for SBO) were given a 10-minute didactic session and yielded Sn 94%, Sp 81%, +LR 5.0, -LR 0.07.5 Unluer et al trained novice EM residents for 6 hours and found them to yield Sn 98%, Sp 95%, +LR 19.5, and -LR 0.02.8 Thus, while it is no surprise that those with more training attain better results, both studies show it does not take much time for EM providers to surpass the accuracy of x-rays with POCUS.
CASE CONCLUSION
The findings on POCUS highly suggested the diagnosis of an SBO. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous and oral contrast was ordered to further evaluate obstruction, transition point, and possible complications, including signs of ischemia per surgical request. CT demonstrated dilated loops of small bowel with transition point in the right lower quadrant, with a small amount of mesenteric fluid consistent with SBO with possible early bowel compromise due to ischemia. General surgery admitted the patient; conservative treatment with serial abdominal exams, nasogastric tube, NPO and bowel rest was ordered. The patient’s diet was gradually advanced, and she was discharged on the eleventh day of hospitalization.
SUMMARY
POCUS is a useful non-invasive tool that can accurately diagnose SBO. POCUS has increased sensitivity and specificity when compared to abdominal X-rays. This bedside imaging will not only give the ED provider rapid diagnostic information but also lead to expedited surgical intervention.
- Taylor MR, Lalani N. Adult small bowel obstruction. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20(6):528-544.
- Hastings RS, Powers RD. Abdominal pain in the ED: a 35-year retrospective. Am J Emerg Med.2011;29:711-716.
- Markogiannakis H, Messaris E, Dardamanis D, et al. Acute mechanical bowel obstruction: clinical presentation, etiology, management and outcome. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:432.
- Bickell N, Federman A, Aufses A. Influence of time on risk of bowel resection in complete small bowel obstruction. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;201(6):847-854.
- Jang TB, Chandler D, Kaji AH. Bedside ultrasonography for the detection of small bowel obstruction in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2011;28:676-678.
- Carpenter CR, Pines JM. The end of X-rays for suspected small bowel obstruction? Using evidence-based diagnostics to inform best practices in emergency medicine. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20:618-20.
- Grassi R, Romano S, D’Amario F, et al. The relevance of free fluid between intestinal loops detected by sonography in the clinical assessment of small bowel obstruction in adults. Eur J Radiol. 2004;50(1):5-14.
- Unlüer E, Yavaşi O, Eroğlu O, Yilmaz C, Akarca F. Ultrasonography by emergency medicine and radiology residents for the diagnosis of small bowel obstruction. Eur J Emerg Med. 2010;17(5):260-264.
- Taylor MR, Lalani N. Adult small bowel obstruction. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20(6):528-544.
- Hastings RS, Powers RD. Abdominal pain in the ED: a 35-year retrospective. Am J Emerg Med.2011;29:711-716.
- Markogiannakis H, Messaris E, Dardamanis D, et al. Acute mechanical bowel obstruction: clinical presentation, etiology, management and outcome. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:432.
- Bickell N, Federman A, Aufses A. Influence of time on risk of bowel resection in complete small bowel obstruction. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;201(6):847-854.
- Jang TB, Chandler D, Kaji AH. Bedside ultrasonography for the detection of small bowel obstruction in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2011;28:676-678.
- Carpenter CR, Pines JM. The end of X-rays for suspected small bowel obstruction? Using evidence-based diagnostics to inform best practices in emergency medicine. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20:618-20.
- Grassi R, Romano S, D’Amario F, et al. The relevance of free fluid between intestinal loops detected by sonography in the clinical assessment of small bowel obstruction in adults. Eur J Radiol. 2004;50(1):5-14.
- Unlüer E, Yavaşi O, Eroğlu O, Yilmaz C, Akarca F. Ultrasonography by emergency medicine and radiology residents for the diagnosis of small bowel obstruction. Eur J Emerg Med. 2010;17(5):260-264.
CAC scores in type 1 diabetes no higher than general population
CHICAGO – Roughly 70% of some 1,200 adult patients with type 1 diabetes screened for coronary artery calcium had a score of zero, about the same prevalence as in the general, U.S. adult population, suggesting the unexpected conclusion that a majority of middle-aged patients with type 1 diabetes do not have an elevated risk for coronary artery disease, in contrast to patients with type 2 diabetes.
Among 1,205 asymptomatic people with type 1 diabetes who underwent coronary artery calcium (CAC) measurement and were followed for an average of about 11 years, 71% had a CAC score of zero at baseline followed by a cardiovascular disease event rate of 5.6 events/1,000 patient years of follow-up, a “very low” event rate that made these patients no more likely to have an event than any adult of similar age and sex in the general U.S. population, Matthew J. Budoff, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
In prior reports, about half of patients with type 2 diabetes had a CAC score of zero, noted Dr. Budoff, professor of medicine and a specialist in cardiac CT imaging and preventive cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. In a general adult population that’s about 45 years old roughly three-quarters would have a CAC score of zero, he noted.
Until now, little has been known about CAC scores in asymptomatic, middle-aged adults with type 1 diabetes. The findings reported by Dr. Budoff raise questions about the 2018 revision of the cholesterol guideline from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association, released during the meeting (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.003), which lumps type 1 and type 2 diabetes together as a special high-risk category for cholesterol management.
The guideline should instead “advocate for more therapy with a CAC score of more than 100 and less therapy with a CAC score of zero in patients with type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Budoff suggested. “A statin for someone with a CAC score of zero probably won’t result in event reduction. The 70% of patients with type 1 diabetes who have a CAC score of zero potentially may not benefit from a statin,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Budoff and his associates used CAC scores and outcomes data collected on 1,205 asymptomatic people with type 1 diabetes enrolled in the EDIC (Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications) trial who underwent CAC scoring as part of the study protocol when they averaged 43 years of age. Follow-up tracked the incidence of cardiovascular disease events in 1,156 of these patients for an average of about 11 years. During follow-up, 105 patients had a cardiovascular disease event, an overall rate of 8.5 events/1,000 patient years of follow-up.
The results also confirmed the prognostic power of the CAC score in these patients. Compared with the very low event rate among those with a zero score, patients with a score of 1-100 had 71% more events, patients with a CAC score of 101-300 had a 5.4-fold higher event rate as those with no coronary calcium, and patients with a CAC score of greater than 300 had a 6.9-fold higher event rate than those with no coronary calcium, Dr. Budoff reported.
Coronary calcium deposits, a direct reflection of atheroma load, can change over time, but somewhat slowly. A CAC score of zero is very reliable for predicting a very low rate of cardiovascular disease events over the subsequent 5 years, and in many people it can reliably predict for as long as 10 years, Dr. Budoff said. Beyond that, follow-up CAC scoring is necessary to check for changes in coronary status, “especially in patients with type 1 diabetes,”
SOURCE: Budoff M et al. Abstract 13133.
CHICAGO – Roughly 70% of some 1,200 adult patients with type 1 diabetes screened for coronary artery calcium had a score of zero, about the same prevalence as in the general, U.S. adult population, suggesting the unexpected conclusion that a majority of middle-aged patients with type 1 diabetes do not have an elevated risk for coronary artery disease, in contrast to patients with type 2 diabetes.
Among 1,205 asymptomatic people with type 1 diabetes who underwent coronary artery calcium (CAC) measurement and were followed for an average of about 11 years, 71% had a CAC score of zero at baseline followed by a cardiovascular disease event rate of 5.6 events/1,000 patient years of follow-up, a “very low” event rate that made these patients no more likely to have an event than any adult of similar age and sex in the general U.S. population, Matthew J. Budoff, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
In prior reports, about half of patients with type 2 diabetes had a CAC score of zero, noted Dr. Budoff, professor of medicine and a specialist in cardiac CT imaging and preventive cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. In a general adult population that’s about 45 years old roughly three-quarters would have a CAC score of zero, he noted.
Until now, little has been known about CAC scores in asymptomatic, middle-aged adults with type 1 diabetes. The findings reported by Dr. Budoff raise questions about the 2018 revision of the cholesterol guideline from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association, released during the meeting (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.003), which lumps type 1 and type 2 diabetes together as a special high-risk category for cholesterol management.
The guideline should instead “advocate for more therapy with a CAC score of more than 100 and less therapy with a CAC score of zero in patients with type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Budoff suggested. “A statin for someone with a CAC score of zero probably won’t result in event reduction. The 70% of patients with type 1 diabetes who have a CAC score of zero potentially may not benefit from a statin,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Budoff and his associates used CAC scores and outcomes data collected on 1,205 asymptomatic people with type 1 diabetes enrolled in the EDIC (Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications) trial who underwent CAC scoring as part of the study protocol when they averaged 43 years of age. Follow-up tracked the incidence of cardiovascular disease events in 1,156 of these patients for an average of about 11 years. During follow-up, 105 patients had a cardiovascular disease event, an overall rate of 8.5 events/1,000 patient years of follow-up.
The results also confirmed the prognostic power of the CAC score in these patients. Compared with the very low event rate among those with a zero score, patients with a score of 1-100 had 71% more events, patients with a CAC score of 101-300 had a 5.4-fold higher event rate as those with no coronary calcium, and patients with a CAC score of greater than 300 had a 6.9-fold higher event rate than those with no coronary calcium, Dr. Budoff reported.
Coronary calcium deposits, a direct reflection of atheroma load, can change over time, but somewhat slowly. A CAC score of zero is very reliable for predicting a very low rate of cardiovascular disease events over the subsequent 5 years, and in many people it can reliably predict for as long as 10 years, Dr. Budoff said. Beyond that, follow-up CAC scoring is necessary to check for changes in coronary status, “especially in patients with type 1 diabetes,”
SOURCE: Budoff M et al. Abstract 13133.
CHICAGO – Roughly 70% of some 1,200 adult patients with type 1 diabetes screened for coronary artery calcium had a score of zero, about the same prevalence as in the general, U.S. adult population, suggesting the unexpected conclusion that a majority of middle-aged patients with type 1 diabetes do not have an elevated risk for coronary artery disease, in contrast to patients with type 2 diabetes.
Among 1,205 asymptomatic people with type 1 diabetes who underwent coronary artery calcium (CAC) measurement and were followed for an average of about 11 years, 71% had a CAC score of zero at baseline followed by a cardiovascular disease event rate of 5.6 events/1,000 patient years of follow-up, a “very low” event rate that made these patients no more likely to have an event than any adult of similar age and sex in the general U.S. population, Matthew J. Budoff, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
In prior reports, about half of patients with type 2 diabetes had a CAC score of zero, noted Dr. Budoff, professor of medicine and a specialist in cardiac CT imaging and preventive cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. In a general adult population that’s about 45 years old roughly three-quarters would have a CAC score of zero, he noted.
Until now, little has been known about CAC scores in asymptomatic, middle-aged adults with type 1 diabetes. The findings reported by Dr. Budoff raise questions about the 2018 revision of the cholesterol guideline from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association, released during the meeting (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.003), which lumps type 1 and type 2 diabetes together as a special high-risk category for cholesterol management.
The guideline should instead “advocate for more therapy with a CAC score of more than 100 and less therapy with a CAC score of zero in patients with type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Budoff suggested. “A statin for someone with a CAC score of zero probably won’t result in event reduction. The 70% of patients with type 1 diabetes who have a CAC score of zero potentially may not benefit from a statin,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Budoff and his associates used CAC scores and outcomes data collected on 1,205 asymptomatic people with type 1 diabetes enrolled in the EDIC (Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications) trial who underwent CAC scoring as part of the study protocol when they averaged 43 years of age. Follow-up tracked the incidence of cardiovascular disease events in 1,156 of these patients for an average of about 11 years. During follow-up, 105 patients had a cardiovascular disease event, an overall rate of 8.5 events/1,000 patient years of follow-up.
The results also confirmed the prognostic power of the CAC score in these patients. Compared with the very low event rate among those with a zero score, patients with a score of 1-100 had 71% more events, patients with a CAC score of 101-300 had a 5.4-fold higher event rate as those with no coronary calcium, and patients with a CAC score of greater than 300 had a 6.9-fold higher event rate than those with no coronary calcium, Dr. Budoff reported.
Coronary calcium deposits, a direct reflection of atheroma load, can change over time, but somewhat slowly. A CAC score of zero is very reliable for predicting a very low rate of cardiovascular disease events over the subsequent 5 years, and in many people it can reliably predict for as long as 10 years, Dr. Budoff said. Beyond that, follow-up CAC scoring is necessary to check for changes in coronary status, “especially in patients with type 1 diabetes,”
SOURCE: Budoff M et al. Abstract 13133.
REPORTING FROM THE AHA SCIENTIFIC SESSIONS
Key clinical point: .
Major finding: Seventy-one percent of patients with type 1 diabetes had a coronary artery calcium score of zero.
Study details: Review of data collected from 1,205 patients in the EDIC trial.
Disclosures: The EDIC trial had no commercial funding. Dr. Budoff has received research funding from General Electric.
Source: Budoff M et al. AHA 2018, Abstract 13133.
New cholesterol guidelines expand options for primary care
CHICAGO – New U.S. cholesterol guidelines spell out the role for ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors, expand the scope of individualized risk assessment, and cite the potential value of a coronary artery calcium score as an additional risk determinant.
Neil J. Stone MD, vice chair of the of the 2018 Cholesterol Guidelines Committee, sat down for an interview and detailed the research behind the guidelines and how new features can help guide treatment decisions for patients at risk for a cardiovascular event.
CHICAGO – New U.S. cholesterol guidelines spell out the role for ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors, expand the scope of individualized risk assessment, and cite the potential value of a coronary artery calcium score as an additional risk determinant.
Neil J. Stone MD, vice chair of the of the 2018 Cholesterol Guidelines Committee, sat down for an interview and detailed the research behind the guidelines and how new features can help guide treatment decisions for patients at risk for a cardiovascular event.
CHICAGO – New U.S. cholesterol guidelines spell out the role for ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors, expand the scope of individualized risk assessment, and cite the potential value of a coronary artery calcium score as an additional risk determinant.
Neil J. Stone MD, vice chair of the of the 2018 Cholesterol Guidelines Committee, sat down for an interview and detailed the research behind the guidelines and how new features can help guide treatment decisions for patients at risk for a cardiovascular event.
REPORTING FROM THE AHA SCIENTIFIC SESSIONS
Ultrasound excels for assessing shoulder dislocation
SAN DIEGO – Point-of-care ultrasound should be the go-to approach for the routine assessment of suspected shoulder dislocations in the ED, based on data from a prospective, multicenter study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
In the observational study, the average time needed to diagnose shoulder dislocation using ultrasound was 18 seconds, far faster than time from triage to x-ray, according to Michael Secko, MD, director of the emergency ultrasound division at Stony Brook University (NY).
The results from this study, called MUDDS (Musculoskeletal Ultrasound to Diagnose Dislocated Shoulders), support point-of-care ultrasound as a faster and more readily performed alternative to x-ray. Of the 46 adult patients enrolled so far in the ongoing study, ultrasound’s sensitivity has been 96% and its specificity 100% when validated by x-ray findings.
In the study, adults presenting to the ED are evaluated with point-of-care ultrasound from a posterior approach using either a curvilinear or linear transducer in the transverse plane. About half of the patients enrolled so far had injuries caused by falls, and many of the others had a shoulder complaint related to being pulled. Slightly more than one-third had a previous shoulder dislocation.
When evaluated with point-of-care ultrasound and x-ray, 23 of the 42 evaluable patients had a dislocation. The time from triage to ultrasound evaluation averaged 60 minutes, 40 minutes faster than the average of 100 minutes from triage to x-ray. Both tests were ordered at the same time.
Ultrasound performed less well for the diagnosis of a fracture, with a sensitivity of only 53%. Dr. Secko said the anterior approach would not be expected to provide a comprehensive assessment for fracture. He noted, for example, that there was no attempt in this study to evaluate patients for the presence of Bankart lesions. However, in those found to have a fracture on point-of-care ultrasound, the specificity of this imaging tool was 96%.
Ultimately, a major goal of this study was to determine whether a posterior point-of-care ultrasound could provide a quick answer to the question, “is it in or out?” Although patients are still being enrolled, Dr. Secko believed there is already good evidence that ultrasound is fast and effective for diagnosing dislocations.
Others have addressed this same question. Citing a meta-analysis published last year, Dr. Secko reported that all but one of four studies evaluating ultrasound for shoulder dislocations found a sensitivity and specificity of 100% (Gottlieb M et al. West J Emerg Med. 2017 Aug;18[5]:937-942).
Many centers have already switched to ultrasound for the evaluation of shoulder dislocations, according to Andrew S. Liteplo, MD, who moderated the ACEP session in which Dr. Secko presented his data. “If you are not already doing this for suspected shoulder dislocation, start right away because it is easy and awesome,” said Dr. Liteplo, who is chief of the division of ultrasound in emergency medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. He also advised that ultrasound can also can be performed after reduction to confirm the efficacy of treatment.
Dr. Secko reported no financial relationships relevant to this study.
SAN DIEGO – Point-of-care ultrasound should be the go-to approach for the routine assessment of suspected shoulder dislocations in the ED, based on data from a prospective, multicenter study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
In the observational study, the average time needed to diagnose shoulder dislocation using ultrasound was 18 seconds, far faster than time from triage to x-ray, according to Michael Secko, MD, director of the emergency ultrasound division at Stony Brook University (NY).
The results from this study, called MUDDS (Musculoskeletal Ultrasound to Diagnose Dislocated Shoulders), support point-of-care ultrasound as a faster and more readily performed alternative to x-ray. Of the 46 adult patients enrolled so far in the ongoing study, ultrasound’s sensitivity has been 96% and its specificity 100% when validated by x-ray findings.
In the study, adults presenting to the ED are evaluated with point-of-care ultrasound from a posterior approach using either a curvilinear or linear transducer in the transverse plane. About half of the patients enrolled so far had injuries caused by falls, and many of the others had a shoulder complaint related to being pulled. Slightly more than one-third had a previous shoulder dislocation.
When evaluated with point-of-care ultrasound and x-ray, 23 of the 42 evaluable patients had a dislocation. The time from triage to ultrasound evaluation averaged 60 minutes, 40 minutes faster than the average of 100 minutes from triage to x-ray. Both tests were ordered at the same time.
Ultrasound performed less well for the diagnosis of a fracture, with a sensitivity of only 53%. Dr. Secko said the anterior approach would not be expected to provide a comprehensive assessment for fracture. He noted, for example, that there was no attempt in this study to evaluate patients for the presence of Bankart lesions. However, in those found to have a fracture on point-of-care ultrasound, the specificity of this imaging tool was 96%.
Ultimately, a major goal of this study was to determine whether a posterior point-of-care ultrasound could provide a quick answer to the question, “is it in or out?” Although patients are still being enrolled, Dr. Secko believed there is already good evidence that ultrasound is fast and effective for diagnosing dislocations.
Others have addressed this same question. Citing a meta-analysis published last year, Dr. Secko reported that all but one of four studies evaluating ultrasound for shoulder dislocations found a sensitivity and specificity of 100% (Gottlieb M et al. West J Emerg Med. 2017 Aug;18[5]:937-942).
Many centers have already switched to ultrasound for the evaluation of shoulder dislocations, according to Andrew S. Liteplo, MD, who moderated the ACEP session in which Dr. Secko presented his data. “If you are not already doing this for suspected shoulder dislocation, start right away because it is easy and awesome,” said Dr. Liteplo, who is chief of the division of ultrasound in emergency medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. He also advised that ultrasound can also can be performed after reduction to confirm the efficacy of treatment.
Dr. Secko reported no financial relationships relevant to this study.
SAN DIEGO – Point-of-care ultrasound should be the go-to approach for the routine assessment of suspected shoulder dislocations in the ED, based on data from a prospective, multicenter study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
In the observational study, the average time needed to diagnose shoulder dislocation using ultrasound was 18 seconds, far faster than time from triage to x-ray, according to Michael Secko, MD, director of the emergency ultrasound division at Stony Brook University (NY).
The results from this study, called MUDDS (Musculoskeletal Ultrasound to Diagnose Dislocated Shoulders), support point-of-care ultrasound as a faster and more readily performed alternative to x-ray. Of the 46 adult patients enrolled so far in the ongoing study, ultrasound’s sensitivity has been 96% and its specificity 100% when validated by x-ray findings.
In the study, adults presenting to the ED are evaluated with point-of-care ultrasound from a posterior approach using either a curvilinear or linear transducer in the transverse plane. About half of the patients enrolled so far had injuries caused by falls, and many of the others had a shoulder complaint related to being pulled. Slightly more than one-third had a previous shoulder dislocation.
When evaluated with point-of-care ultrasound and x-ray, 23 of the 42 evaluable patients had a dislocation. The time from triage to ultrasound evaluation averaged 60 minutes, 40 minutes faster than the average of 100 minutes from triage to x-ray. Both tests were ordered at the same time.
Ultrasound performed less well for the diagnosis of a fracture, with a sensitivity of only 53%. Dr. Secko said the anterior approach would not be expected to provide a comprehensive assessment for fracture. He noted, for example, that there was no attempt in this study to evaluate patients for the presence of Bankart lesions. However, in those found to have a fracture on point-of-care ultrasound, the specificity of this imaging tool was 96%.
Ultimately, a major goal of this study was to determine whether a posterior point-of-care ultrasound could provide a quick answer to the question, “is it in or out?” Although patients are still being enrolled, Dr. Secko believed there is already good evidence that ultrasound is fast and effective for diagnosing dislocations.
Others have addressed this same question. Citing a meta-analysis published last year, Dr. Secko reported that all but one of four studies evaluating ultrasound for shoulder dislocations found a sensitivity and specificity of 100% (Gottlieb M et al. West J Emerg Med. 2017 Aug;18[5]:937-942).
Many centers have already switched to ultrasound for the evaluation of shoulder dislocations, according to Andrew S. Liteplo, MD, who moderated the ACEP session in which Dr. Secko presented his data. “If you are not already doing this for suspected shoulder dislocation, start right away because it is easy and awesome,” said Dr. Liteplo, who is chief of the division of ultrasound in emergency medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. He also advised that ultrasound can also can be performed after reduction to confirm the efficacy of treatment.
Dr. Secko reported no financial relationships relevant to this study.
REPORTING FROM ACEP18
Key clinical point: Point-of-care ultrasound is accurate, simple, and fast, relative to x-ray, for the evaluation of shoulder dislocation.
Major finding: Based on results from 42 patients, time from triage to ultrasound, which had a sensitivity of 96% and specificity of 100%, was 60 minutes versus 100 minutes for x-ray.
Study details: An ongoing prospective, multicenter, observational study.
Disclosures: Dr. Secko reported no financial relationships relevant to this study.
Funding for NIH BRAIN Initiative reaches new heights
The National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) Initiative will finish 2018 with its largest round of grant funding ever, giving $220 million to more than 200 research awards, and bringing this year’s total to more than $400 million, according to an announcement from the agency.
The BRAIN Initiative began in 2013 with the objective of revolutionizing our understanding of the human brain by accelerating the development and application of innovative technologies that will allow researchers to show how individual cells and complex neural circuits interact in both time and space and thereby seek new ways to treat, cure, and prevent brain disorders.
In the current round of funding that was authorized by Congress through the regular appropriations process and the 21st Century Cures Act, new projects include the creation of a wireless optical tomography cap for scanning human brain activity; the development of a noninvasive brain-computer interface system for improving the lives of paralysis patients; and the testing of noninvasive brain stimulation devices for treating schizophrenia, attention deficit disorders, and other brain diseases; the development of self-growing biological electrodes for recording brain activity; and the creation of an indestructible hydrogel system to help map neural circuits, according to the announcement.
Not all of the research involves technological advancement. In fact, one line of funding involves neuroethics. For instance, for epilepsy syndromes in the latest round of funding for 2018, researchers aim to explore ethical issues confronting families and clinicians when considering new treatment options for drug-resistant epilepsy in children.
The NIH is also leveraging some of the BRAIN Initiative funding toward finding new, nonaddictive pain treatments as part of the its HEAL (Helping to End Addiction Long-term) Initiative, such as support for research on the fundamental neurobiology of endogenous opioid systems.
The National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) Initiative will finish 2018 with its largest round of grant funding ever, giving $220 million to more than 200 research awards, and bringing this year’s total to more than $400 million, according to an announcement from the agency.
The BRAIN Initiative began in 2013 with the objective of revolutionizing our understanding of the human brain by accelerating the development and application of innovative technologies that will allow researchers to show how individual cells and complex neural circuits interact in both time and space and thereby seek new ways to treat, cure, and prevent brain disorders.
In the current round of funding that was authorized by Congress through the regular appropriations process and the 21st Century Cures Act, new projects include the creation of a wireless optical tomography cap for scanning human brain activity; the development of a noninvasive brain-computer interface system for improving the lives of paralysis patients; and the testing of noninvasive brain stimulation devices for treating schizophrenia, attention deficit disorders, and other brain diseases; the development of self-growing biological electrodes for recording brain activity; and the creation of an indestructible hydrogel system to help map neural circuits, according to the announcement.
Not all of the research involves technological advancement. In fact, one line of funding involves neuroethics. For instance, for epilepsy syndromes in the latest round of funding for 2018, researchers aim to explore ethical issues confronting families and clinicians when considering new treatment options for drug-resistant epilepsy in children.
The NIH is also leveraging some of the BRAIN Initiative funding toward finding new, nonaddictive pain treatments as part of the its HEAL (Helping to End Addiction Long-term) Initiative, such as support for research on the fundamental neurobiology of endogenous opioid systems.
The National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) Initiative will finish 2018 with its largest round of grant funding ever, giving $220 million to more than 200 research awards, and bringing this year’s total to more than $400 million, according to an announcement from the agency.
The BRAIN Initiative began in 2013 with the objective of revolutionizing our understanding of the human brain by accelerating the development and application of innovative technologies that will allow researchers to show how individual cells and complex neural circuits interact in both time and space and thereby seek new ways to treat, cure, and prevent brain disorders.
In the current round of funding that was authorized by Congress through the regular appropriations process and the 21st Century Cures Act, new projects include the creation of a wireless optical tomography cap for scanning human brain activity; the development of a noninvasive brain-computer interface system for improving the lives of paralysis patients; and the testing of noninvasive brain stimulation devices for treating schizophrenia, attention deficit disorders, and other brain diseases; the development of self-growing biological electrodes for recording brain activity; and the creation of an indestructible hydrogel system to help map neural circuits, according to the announcement.
Not all of the research involves technological advancement. In fact, one line of funding involves neuroethics. For instance, for epilepsy syndromes in the latest round of funding for 2018, researchers aim to explore ethical issues confronting families and clinicians when considering new treatment options for drug-resistant epilepsy in children.
The NIH is also leveraging some of the BRAIN Initiative funding toward finding new, nonaddictive pain treatments as part of the its HEAL (Helping to End Addiction Long-term) Initiative, such as support for research on the fundamental neurobiology of endogenous opioid systems.
Bisphosphonate-related atypical femoral fracture: Managing a rare but serious complication
Bisphosphonate therapy minimizes bone loss and reduces fracture risk by up to 50% in patients with osteoporosis,1 but it is also associated with increased risks of osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fracture. Although atypical femoral fractures are rare, they can have a devastating effect. Patient concern about this complication has contributed to a decrease in bisphosphonate use by about half in the last decade or so,2,3 and we fear this could result in an increase in hip fracture rates.
In this article, we examine the evidence on bisphosphonate-associated atypical femoral fractures, including risks, pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention.
ATYPICAL FRACTURES INVOLVE THE FEMORAL SHAFT, NOT THE HEAD
An atypical femoral fracture is a transverse fracture of the femoral shaft (diaphysis), defined by both clinical criteria and radiographic appearance.
To be defined as atypical, a femoral fracture must meet 4 of the following 5 criteria4:
- Occurs with minimal or no trauma
- Has a predominantly transverse fracture line, originating at the lateral cortex and sometimes becoming oblique as it progresses medially across the femur
- Extends through both cortices and may be associated with a medial spike (complete fractures); or involves only the lateral cortex (incomplete fractures)
- Is noncomminuted or minimally comminuted
- Shows localized periosteal or endosteal thickening (termed “beaking” or “flaring”) of the lateral cortex at the fracture site.
Several minor features are also important but are not required, eg:
- Cortical thickening of the femoral shaft
- Unilateral or bilateral prodromal pain preceding the fracture
- Bilateral incomplete or complete femoral diaphysis fractures
- Delayed fracture healing.
Atypical femoral fracture can occur anywhere along the shaft, from just distal to the lesser trochanter to just proximal to the supracondylar flare. However, most occur in 2 areas, with 1 cluster centered at about 41 mm from the lesser trochanter (more common in relatively younger patients) and the other at 187 mm.5
ABSOLUTE RISK IS LOW BUT INCREASES WITH LONGER USE
Atypical femoral fractures are rare. Schilcher et al6 reviewed radiographs of 1,234 women who had a subtrochanteric or shaft fracture and found 59 (4.6%) of fractures were atypical. In a systematic review of 14 studies,7 the incidence ranged from 3.0 to 9.8 cases per 100,000 patient-years.
Furthermore, not all atypical femoral fractures are in bisphosphonate users: 7.4% were in nonusers in 1 series8 and 22% in another.9
Nevertheless, most studies show that bisphosphonate use increases the incidence of atypical femoral fracture, and the incidence increases with duration of use, especially after 3 years.7
An international task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research listed the absolute risk as between 3.2 and 50 cases per 100,000 patient-years, with longer use (> 5 years) increasing the risk to about 100 per 100,000 patient-years.4 After stopping bisphosphonate therapy, the risk diminished by 70% per year.9
In another study, for 0.1 to 1.9 years of therapy, the age-adjusted atypical fracture rates were 1.78 per 100,000 per year (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.5–2.0), increasing to 113.1 per 100,000 per year (95% CI 69.3–156.8) with exposure from 8 to 9.9 years.10
A case-control study found that more than 5 years of bisphosphonate use increased the fracture risk by an odds ratio of 2.74 (95% CI 1.25–6.02).11
The incidence of typical femoral fracture was higher in those who adhered better to their oral bisphosphonate regimen in some studies,12 but the opposite was true in others.13
The benefits of bisphosphonate therapy in reducing fracture risk, however, outweigh the risk of atypical fracture.4
We do not know whether the rate of atypical femoral fracture is increasing. A review of Kaiser Permanente Northwest records found that the rates of atypical femoral shaft fracture had remained stable from 1996 to 2009. However, 61.9% of patients who met the strict radiographic criteria had taken oral bisphosphonates.14 These data suggest that bisphosphonate use has not increased the overall population-based risk for subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures, but that bisphosphonates and other risk factors may have increased the likelihood that such fractures will exhibit atypical radiographic features.
A population-based study in Denmark13 found that alendronate use longer than 10 years was associated with an adjusted 30% lower risk of hip fracture and no increase in the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fracture. In addition, the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fracture was lower with high adherence to alendronate treatment (based on medication possession ratio > 80%) compared with low adherence (ratio < 50%) (odds ratio 0.88, 95% CI 0.77–0.99). The risk was not increased in current vs past users.
The Danish study13 used the coding of the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10) to identify subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures without radiologic review for atypical radiographic features. The lack of specific ICD-10 coding for subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures with atypical radiographic features has limited our knowledge of their incidence.
Contralateral fracture in more than one-fourth of cases
After an atypical femoral fracture, patients have a significant risk of fracture on the contralateral side. In a case-control study, 28% of patients with atypical femoral fracture suffered a contralateral fracture, compared with 0.9% of patients presenting with a typical fracture pattern (odds ratio 42.6, 95% CI 12.8–142.4).15
Contralateral fracture occurs from 1 month to 4 years after the index atypical femoral fracture.16
There are reports of bisphosphonate-related low-impact fractures in other sites such as the tibia17 and forearm.18 However, they may be too rare to warrant screening.
Mortality rates
A Swedish database study found that patients with atypical femoral fractures, whether bisphosphonate users or nonusers, do not have higher mortality rates than patients with ordinary subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures.19 Furthermore, the mortality rates for those with atypical femoral fracture were similar to rates in the general population. In contrast, patients with an ordinary femoral fracture had a higher mortality risk than the general population.19
Other studies suggest that atypical femoral fracture may be associated with a less favorable prognosis in older patients,20 but this could be due to differences in demographics, treatment adherence, or postfracture care.21
In addition, functional outcomes as measured by independent mobility at discharge and at 3 months were comparable between patients with atypical fracture and those with typical fracture.22
IMAGING STUDIES
If a long-term bisphosphonate user presents with hip, thigh, or groin pain, imaging studies are recommended.
Plain radiography
Radiography is usually the first step and should include a frontal view of the pelvis (Figure 1) and 2 views of the full length of each femur. If radiography is not conclusive, bone scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) should be considered.
A linear cortex transverse fracture pattern and focal lateral cortical thickening are the most sensitive and specific radiographic features.23,24 Because of the risk of fracture on the contralateral side, radiographic study of that side is recommended as well.
Computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT) is not sensitive for early stress fractures and, given the radiation burden, is not recommended in the workup of atypical fracture.
Bone scanning
Bone scanning using technetium 99m-labeled methylene diphosphonate with a gamma camera shows active bone turnover. Stress fractures and atypical femoral fractures are most easily identified in the third (delayed) phase of the bone scan. Although bone scanning is highly sensitive, the specificity is limited by lack of spatial resolution. Atypical femoral fracture appears as increased activity in the subtrochanteric region with a predilection for the lateral cortex.
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
Conventional dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) extends only to 1 to 2 cm below the lesser trochanter and can therefore miss atypical fractures, which usually occur farther down. The overall detection rate for DXA was 61% in a sample of 33 patients.25
Newer scanners can look at the entire femoral shaft.26 In addition, newer software can quantify focal thickening (beaking) of the lateral cortex and screen patients who have no symptoms. The results of serial measurements can be graphed so that the practitioner can view trends to help assess or rule out potential asymptomatic atypical femoral fracture.
A localized reaction (periosteal thickening of the lateral cortex or beaking) often precedes atypical femoral fracture. A 2017 study reported that patients with high localized reaction (mean height 3.3 mm) that was of the pointed type and was accompanied by prodromal pain had an increased risk of complete or incomplete atypical femoral fracture at that site.27 This finding is used by the newer DXA software. The predictive value of beaking on extended femoral DXA may be as high as 83%.26
Magnetic resonance imaging
The MRI characteristics of atypical femoral fracture are similar to those of other stress fractures except that there is a lateral-to-medial pattern rather than a medial pattern. The earliest findings include periosteal reaction about the lateral cortex with a normal marrow signal.
MRI may be of particular benefit in patients with known atypical femoral fracture to screen the contralateral leg. It should image the entire length of both femurs. Contrast enhancement is not needed.
Regardless of whether initial findings were discovered on conventional radiographs or DXA, MRI confirmation is needed. Radionuclide bone scanning is currently not recommended because it lacks specificity. Combination imaging is recommended, with either radiography plus MRI or DXA plus MRI.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
The differential diagnosis of atypical femoral fracture includes stress fracture, pathologic fracture, hypophosphatasia, and osteogenesis imperfecta.28 Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia can cause Looser zones, which can be confused with atypical femoral fractures but usually occur on the medial side.4 Stress fracture of the femur can occur below the lesser trochanter but usually begins in the medial, not the lateral, cortex.
Pathologic fractures from underlying osseous lesions can mimic the cortical beaking of bisphosphonate-related fracture, but they usually show the associated underlying lucent lesion and poorly defined margins. A sinus tract along the region of a chronic osteomyelitis may also appear similar.
Hypophosphatasia is an inborn error of metabolism caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the gene encoding alkaline phosphatase, resulting in pyrophosphate accumulation and causing osteomalacia from impaired mineralization. This can result in femoral pseudofracture that is often bilateral and occurs in the subtrochanteric region.29
ADDITIONAL RISK FACTORS
Patients with atypical femoral fracture are generally a heterogeneous group, but there are risk factors to note other than bisphosphonate exposure.
Asian women had a risk 8 times higher than white women in 1 study.30
Bone geometry. Mahjoub et al8 reported that compared with controls, patients with atypical femoral fracture had greater offset of the femoral shaft from the center of rotation of the femoral head, a more acute angle between the femoral neck and shaft, and greater proximal cortical thickness.
Medications. In addition to bisphosphonates, other drugs associated with atypical femoral fracture include RANK-ligand inhibitors such as denosumab (another drug for osteoporosis),31 glucocorticoids,32,33 and proton pump inhibitors.32,33
Genetics. Three sisters with atypical femoral fracture were found to have 37 rare mutations in 34 genes, including one in the GGPS1 gene, which codes for geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase—an enzyme that bisphosphonates inhibit.34
Medical conditions other than osteoporosis include collagen diseases, chronic pulmonary disease, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes.35
Clinical recommendations
Current recommendations are to reevaluate bisphosphonate use in patients with osteoporosis after 5 or more years of therapy.36
Given that patients with osteoporosis are at increased risk of typical fracture, those at higher risk should be considered for continued bisphosphonate therapy. Factors for high risk include the following:
- History of fracture on therapy
- Hip T score –2.5 or lower
- Older age (≥ 70)
- Other strong risk factors for fracture such as smoking, alcohol use, corticosteroid use, rheumatoid arthritis, and family history
- World Health Organization FRAX fracture risk score above the country-specific threshold.
Those at lower risk should be considered for a 2- to 3-year bisphosphonate holiday with periodic reevaluation of bone density and, possibly, bone markers.36
WHAT IS THE UNDERLYING PATHOPHYSIOLOGY?
The mechanism by which bisphosphonates increase the risk of atypical femoral fracture is not clear. These drugs work by suppressing bone turnover; however, in theory, prolonged use could suppress it too much and increase bone fragility.
One hypothesis is that bisphosphonates impair the toughening of cortical bone, an important barrier to clinical fracture. This is supported by a study that found bisphosphonate users with atypical femoral fracture had deficits in intrinsic and extrinsic bone toughness, perhaps due to treatment-related increases in matrix mineralization.37 Although this study and others showed an increase in matrix mineralization and reduced mineralization heterogeneity with bisphosphonate use,38,39 it is unclear whether such changes contributed to reduced toughness or to atypical femoral fracture.
Changes in the skeletal geometry of the lower limb such as femoral neck-shaft angle and femoral curvature alter the stresses and strains experienced by the femoral diaphysis with loading. Because the incidence of incomplete atypical femoral fracture is much greater than that of complete fracture, most incomplete atypical femoral fractures heal before the fracture progresses.
Ultimately, all fractures, including atypical femoral fractures, occur when mechanical stress and strain exceed bone strength.
Antiresorptive drugs such as bisphosphonates, estrogen, calcitonin, and RANK ligand inhibitors prevent hip fracture by increasing the strength of the proximal femur—perhaps at the expense of the strength (or toughness) of the subtrochanteric shaft. It is also possible that treatment-related increases in hip strength (and reduced hip fracture rates) promote or sustain the transfer of stress and strain to femoral regions that experience lesser or no increases in strength from treatment, which likely includes the shaft.40,41
CT studies in Japanese women with osteoporosis have shown that 2 years of zoledronate therapy had greater effects in the hip than in the femoral shaft, with significant increases in cortical thickness and volumetric bone mineral density at the femoral neck and intertrochanteric region compared with baseline.42 But zoledronate did not increase femoral shaft cortical thickness and caused only a minor increase in femoral shaft volumetric bone mineral density. Fracture patterns may have depended on damage and effects of bone turnover on mass and structure.
This hypothetical scenario portrays a possible “hip survival bias” mechanism for atypical femoral fracture, with the association with antiresorptive drugs arising from greater stress and strain in cortical regions where these fractures occur rather than from treatment-related reductions in cortical bone strength or toughness.
PRODROMAL PAIN IS COMMON
From 32% to 76% of patients who have incomplete or developing atypical femoral fracture present with a prodrome of groin or hip pain.4,43 Prodromal pain occurs any time from 2 weeks to several years before the fracture, presenting as pain in the anterior or lateral thigh or in the groin.
Prodromal pain in a patient on antiresorptive therapy should be a signal for the clinician to obtain a radiograph of the hip and to look for contralateral symptoms and fractures. The most common mechanism of injury appears to be a ground-level fall or even a nontraumatic activity such as walking or stepping off a curb.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
In bisphosphonate users with radiographic evidence of atypical femoral fracture, the bisphosphonate should be discontinued and the patient assessed for calcium and vitamin D deficiency, with supplements prescribed if needed.4
For patients with incomplete fracture and persistent pain after 3 months of medical management, prophylactic surgical nail fixation is recommended to prevent complete fracture.
Teriparatide, which has been associated with enhanced bone fracture healing, is a possible treatment to promote healing of atypical femoral fracture, either alone or as an adjunct to surgical fixation. A systematic review published in 2015 supported the use of teriparatide for enhancing fracture healing in atypical femoral fracture.44 In addition, a 10-patient series45 showed that incomplete fractures without radiolucent lines responded to teriparatide alone, whereas those with radiolucent lines needed intramedullary nailing.
These results suggest that teriparatide works best when the fracture site is stable, either inherently or with surgical fixation.
ORTHOPEDIC CARE
Orthopedic care for atypical femoral fracture differs depending on whether the patient experiences pain and whether the fracture is incomplete or complete. Figure 2 shows a treatment algorithm for atypical femoral fracture.
These are difficult fractures to manage, complicated by delayed healing in the elderly, complex displacement patterns, altered bone geometry, and risk of fracture in the opposite limb, all of which raise questions about recommending protected weight-bearing exercise.
Furthermore, atypical femoral fracture is often associated with increased anterolateral bowing of the femur, making it difficult to insert an intramedullary nail: the radius of curvature of the bone is shorter than that of a standard femoral nail. This mismatch can lead to intraoperative complications such as iatrogenic fracture during prophylactic nailing, malunion from excess straightening of the femur (which can itself lead to leg length discrepancy), and gapping of the fracture site, particularly on the medial side.
Intramedullary nailing for complete fracture
Intramedullary nailing is the first-line treatment for complete atypical femoral fracture, although the risk of delayed healing and revision surgery may be somewhat higher than with typical femoral fracture.46 Prophylactic intramedullary nailing should be considered for a patient with intractable pain.2
A radiograph of the opposite leg should be obtained routinely, looking for an asymptomatic fracture. Bisphosphonates should be discontinued and calcium and vitamin D continued. Teriparatide therapy can be considered as an alternative treatment.
Conservative management for incomplete fracture without pain
Incomplete atypical femoral fracture unaccompanied by pain can be followed conservatively.47 In addition to stopping antiresorptive therapy, patients need to avoid high-impact and repetitive-impact activities such as jumping or running. If pain occurs, patients should begin protected weight-bearing exercise.
Treatment is uncertain for incomplete fracture with pain
For patients with incomplete atypical femoral fracture and pain, treatment is controversial. Regimens that include 2 to 3 months of protected weight-bearing exercise, a full metabolic bone workup, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and anabolic bone agents have produced some success. Some authors have reported poor results from conservative care, with few patients achieving pain relief or signs of complete healing.48,49 Additionally, if an incomplete fracture is found in the opposite femur, protected weight-bearing of both legs may not be possible.
Patients with incomplete fracture should be monitored regularly with radiography and physical examination. If there is progression of the fracture, escalation of pain, or failure to heal within 2 to 3 months, then surgical treatment is necessary.
Prophylactic placement of an intramedullary nail to prevent completion of the fracture and allow a return to full weight-bearing is generally advised.50 A long locking plate can be used if bone deformities make it difficult to place an intramedullary nail; however, nails are preferred because they allow formation of endochondral callus, which can be helpful in these difficult-to-heal fractures.
Results from retrospective reviews have shown that surgically treated patients with bisphosphonate-associated incomplete atypical femoral fracture were more likely than those treated nonsurgically to be pain-free (81% vs 64%) and have radiographic healing (100% vs 18% at final follow-up).46 Results have also been positive for those with complete atypical femoral fracture. At 6 months, 64% of surgically treated patients were pain-free and 98% were radiographically healed.51
The unusual geometry of the femur in patients with atypical femoral fracture and the presence of intramedullary cortical callus makes the placement of an intramedullary femoral rod more complex than in typical femoral fracture.8
Intramedullary nailing of atypical femoral fracture is a challenge for even the most experienced surgeon, and vigilance is imperative to avoid iatrogenic fracture and malunion.
MANY QUESTIONS REMAIN
We need more studies on the pathophysiology of bisphosphonate-associated atypical femoral fracture, the value of periodic screening with DXA, and which factors predict high risk (eg, Asian ethnicity, use of certain medications, femoral geometry). In addition, we need more data on the success of conservative management of incomplete fracture, including use of teriparatide.
- Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, et al. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet 1996; 348(9041):1535–1541. pmid:8950879
- Jha S, Wang Z, Laucis N, Bhattacharyya T. Trends in media reports, oral bisphosphonate prescriptions, and hip fractures 1996–2012: an ecological analysis. J Bone Miner Res 2015; 30(12):2179–2187. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2565
- Solomon DH, Johnston SS, Boytsov NN, McMorrow D, Lane JM, Krohn KD. Osteoporosis medication use after hip fracture in US patients between 2002 and 2011. J Bone Miner Res 2014; 29(9):1929–1937. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2202
- Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 2014; 29(1):1–23. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1998
- Koeppen VA, Schilcher J, Aspenberg P. Dichotomous location of 160 atypical femoral fractures. Acta Orthop 2013; 84(6):561–564. doi:10.3109/17453674.2013.866193
- Schilcher J, Koeppen V, Aspenberg P, Michäelsson K. Risk of atypical femoral fracture during and after bisphosphonate use. Acta Orthop 2015; 86(1):100–107. doi:10.3109/17453674.2015.1004149
- Khow KS, Shibu P, Yu SC, Chehade MJ, Visvanathan R. Epidemiology and postoperative outcomes of atypical femoral fractures in older adults: a systematic review. J Nutr Health Aging 2017; 21(1):83–91. doi:10.1007/s12603-015-0652-3
- Mahjoub Z, Jean S, Leclerc JT, et al. Incidence and characteristics of atypical femoral fractures: clinical and geometrical data. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(4):767–776. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2748
- Schilcher J, Michaelsson K, Aspenberg P. Bisphosphonate use and atypical fractures of the femoral shaft. N Engl J Med 2011; 364(18):1728–1737. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1010650
- Dell RM, Adams AL, Greene DF, et al. Incidence of atypical nontraumatic diaphyseal fractures of the femur. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27(12):2544–2550. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1719
- Park-Wyllie LY, Mamdani MM, Juurlink DN, et al. Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older women. JAMA 2011; 305(8):783–789. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.190
- Wang Z, Ward MM, Chan L, Bhattacharyya T. Adherence to oral bisphosphonates and the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures among female Medicare beneficiaries. Osteoporos Int 2014; 25(8):2109–2116. doi:10.1007/s00198-014-2738-x
- Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Prieto-Alhambra D, Eastell R. Risk of hip, subtrochanteric, and femoral shaft fractures among mid and long term users of alendronate: nationwide cohort and nested case-control study. BMJ 2016; 353:i3365. doi:10.1136/bmj.i3365
- Feldstein AC, Black D, Perrin N, et al. Incidence and demography of femur fractures with and without atypical features. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27(5):977–986. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1550
- Meier RP, Perneger TV, Stern R, Rizzoli R, Peter RE. Increasing occurrence of atypical femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use. Arch Intern Med 2012; 172(12):930–936. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2012.1796
- La Rocca Vieira R, Rosenberg ZS, Allison MB, Im SA, Babb J, Peck V. Frequency of incomplete atypical femoral fractures in asymptomatic patients on long term bisphosphonate therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012; 198(5):1144–1151. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7442
- Bissonnette L, April PM, Dumais R, Boire G, Roux S. Atypical fracture of the tibial diaphysis associated with bisphosphonate therapy: a case report. Bone 2013; 56(2):406–409. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.07.012
- Moon J, Bither N, Lee T. Atypical forearm fractures associated with long-term use of bisphosphonate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2013; 133(7):889–892. doi:10.1007/s00402-013-1760-3
- Kharazmi M, Hallberg P, Schilcher J, Aspenberg P, Michaëlsson K. Mortality after atypical femoral fractures: a cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(3):491–497. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2767
- Medin E, Goude F, Melberg HO, Tediosi F, Belicza E, Peltola M; EuroHOPE Study Group. European regional differences in all-cause mortality and length of stay for patients with hip fracture. Health Econ 2015; 24(suppl 2):53–64. doi:10.1002/hec.3278
- Abrahamsen B, Prieto-Alhambra D. Patients with atypical femur fractures have the same mortality as the background population-drug channeling bias, bisphosphonate effects and public health implications. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(3):488–490. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2801
- Khow KS, Paterson F, Shibu P, Yu SC, Chehade MJ, Visvanathan R. Outcomes between older adults with atypical and typical femoral fractures are comparable. Injury 2017; 48(2):394–398. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2016.10.035
- Adams AL, Xue F, Chantra JQ, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of radiographic characteristics in atypical femoral fractures. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(1):413–417. doi:10.1007/s00198-016-3809-y
- Rosenberg ZS, La Rocca Vieira R, Chan SS, et al. Bisphosphonate-related complete atypical subtrochanteric femoral fractures: diagnostic utility of radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011; 197(4):954–960. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.6262
- Kim S, Yang KH, Lim H, et al. Detection of prefracture hip lesions in atypical subtrochanteric fracture with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry images. Radiology 2014; 270(2):487–495. doi:10.1148/radiol.13122691
- van de Laarschot DM, Smits AA, Buitendijk SK, Stegenga MT, Zillikens MC. Screening for atypical femur fractures using extended femur scans by DXA. J Bone Miner Res 2017; 32(8):1632–1639. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3164
- Sato H, Kondo N, Nakatsue T, et al. High and pointed type of femoral localized reaction frequently extends to complete an incomplete atypical femoral fracture in patients with autoimmune diseases on long-term glucocorticoids and bisphosphonates. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(8):2367–2376. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-4038-8
- Giaconi JC, Watterson CT. Bisphosphonate-related atypical femur fractures and the radiographic features. In: Silverman SL, Abrahamsen B, eds. The Duration and Safety of Osteoporosis Treatment. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:107–124. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-23639-1
- Whyte MP. Atypical femoral fractures, bisphosphonates, and adult hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Res 2009; 24(6):1132–1134. doi:10.1359/jbmr.081253
- Lo JC, Hui RL, Grimsrud CD, et al. The association of race/ethnicity and risk of atypical femoral fracture among older women receiving oral bisphosphonate therapy. Bone 2016; 85:142–147. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2016.01.002
- Bone HG, Wagman RB, Brandi ML, et al. 10 years of denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from the phase 3 randomised FREEDOM trial and open-label extension. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017; 5(7):513–523. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30138-9
- Koh JH, Myong JP, Yoo J, et al. Predisposing factors associated with atypical femur fracture among postmenopausal Korean women receiving bisphosphonate therapy: 8 years' experience in a single center. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(11):3251–3259. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-4169-y
- Kim D, Sung YK, Cho SK, Han M, Kim YS. Factors associated with atypical femoral fracture. Rheumatol Int 2016; 36(1):65–71. doi:10.1007/s00296-015-3323-0
- Roca-Ayats N, Balcells S, Garcia-Giralt N, et al. GGPS1 mutation and atypical femoral fractures with bisphosphonates. N Engl J Med 2017; 376(18):1794–1795. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1612804
- Giusti A, Hamdy NA, Dekkers OM, Ramautar SR, Dijkstra S, Papapoulos SE. Atypical fractures and bisphosphonate therapy: a cohort study of patients with femoral fracture with radiographic adjudication of fracture site and features. Bone 2011; 48(5):966–971. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2010.12.033
- Adler RA, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Bauer DC, et al. Managing osteoporosis in patients on long-term bisphosphonate treatment: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(1):16–35. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2708
- Lloyd AA, Gludovatz B, Riedel C, et al. Atypical fracture with long-term bisphosphonate therapy is associated with altered cortical composition and reduced fracture resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2017; 114(33):8722–8727. doi:10.1073/pnas.1704460114
- Ettinger B, Burr DB, Ritchie RO. Proposed pathogenesis for atypical femoral fractures; lessons from materials research. Bone 2013; 55(2):495–500. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.02.004
- Burr DB, Liu Z, Allen MR. Duration-dependent effects of clinically relevant oral alendronate doses on cortical bone toughness in beagle dogs. Bone 2015; 71:58–62. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2014.10.010
- Sasaki S, Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, Kasukawa Y, Shimada Y. Low-energy diaphyseal femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use and severe curved femur: a case series. J Bone Miner Metab 2012; 30(5):561–567. doi:10.1007/s00774-012-0358-0
- Pulkkinen P, Gluer C, Jamsa T. Investigation of differences between hip fracture types: a worthy strategy of improved risk assessment and fracture prevention. Bone 2011; 49(4):600–604. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2011.07.022
- Ito M, Sone T, Shiraki M, et al. The effect of once-yearly zoledronic acid on hip structural and biomechanical properties derived using computed tomography (CT) in Japanese women with osteoporosis. Bone 2018; 106:179–186. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2017.10.013
- Bogdan Y, Einhorn TA. Clinical presentation of atypical femur fractures. In: Silverman SL, Abrahamsen B, eds. The Duration and Safety of Osteoporosis Treatment. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:137–140. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-23639-1
- Im GI, Lee SH. Effect of teriparatide on healing of atypical femoral fractures: a systemic review. J Bone Metab 2015; 22(4):183–189. doi:10.11005/jbm.2015.22.4.183
- Saleh A, Hegde VV, Potty AG, Schneider R, Cornell CN, Lane JM. Management strategy for symptomatic bisphosphonate-associated incomplete atypical femoral fractures. HSS J 2012; 8(2):103–110. doi:10.1007/s11420-012-9275-y
- Egol KA, Park JH, Prensky C, Rosenberg ZS, Peck V, Tejwani NC. Surgical treatment improves clinical and functional outcomes for patients who sustain incomplete bisphosphonate-related femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2013; 27(6):331–335. doi:10.1097/BOT.0b013e31827240ae
- Koh A, Guerado E, Giannoudis PV. Atypical femoral fractures related to bisphosphonate treatment: issues and controversies related to their surgical management. Bone Joint J 2017; 99-B(3):295–302. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B3.BJJ-2016-0276.R2
- Oh CW, Oh JK, Park KC, Kim JW, Yoon YC. Prophylactic nailing of incomplete atypical femoral fractures. ScientificWorldJournal 2013; 2013:450148. doi:10.1155/2013/450148
- Ha YC, Cho MR, Park KH, Kim SY, Koo KH. Is surgery necessary for femoral insufficiency fractures after long-term bisphosphonate therapy? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010; 468(12):3393–3398. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1583-2
- Tosounidis TH, Lampropoulou-Adamidou, Kanakaris NK. Intramedullary nailing of sequential bilateral atypical subtrochanteric fractures and the management of distal femoral intraoperative fracture. J Orthop Trauma 2015 Jun 11. Epub ahead of print. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000370
- Egol KA, Park JH, Rosenberg ZS, Peck V, Tejwani NC. Healing delayed but generally reliable after bisphosphonate-associated complete femur fractures treated with IM nails. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014; 472(9):2728–2734. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-2963-1
Bisphosphonate therapy minimizes bone loss and reduces fracture risk by up to 50% in patients with osteoporosis,1 but it is also associated with increased risks of osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fracture. Although atypical femoral fractures are rare, they can have a devastating effect. Patient concern about this complication has contributed to a decrease in bisphosphonate use by about half in the last decade or so,2,3 and we fear this could result in an increase in hip fracture rates.
In this article, we examine the evidence on bisphosphonate-associated atypical femoral fractures, including risks, pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention.
ATYPICAL FRACTURES INVOLVE THE FEMORAL SHAFT, NOT THE HEAD
An atypical femoral fracture is a transverse fracture of the femoral shaft (diaphysis), defined by both clinical criteria and radiographic appearance.
To be defined as atypical, a femoral fracture must meet 4 of the following 5 criteria4:
- Occurs with minimal or no trauma
- Has a predominantly transverse fracture line, originating at the lateral cortex and sometimes becoming oblique as it progresses medially across the femur
- Extends through both cortices and may be associated with a medial spike (complete fractures); or involves only the lateral cortex (incomplete fractures)
- Is noncomminuted or minimally comminuted
- Shows localized periosteal or endosteal thickening (termed “beaking” or “flaring”) of the lateral cortex at the fracture site.
Several minor features are also important but are not required, eg:
- Cortical thickening of the femoral shaft
- Unilateral or bilateral prodromal pain preceding the fracture
- Bilateral incomplete or complete femoral diaphysis fractures
- Delayed fracture healing.
Atypical femoral fracture can occur anywhere along the shaft, from just distal to the lesser trochanter to just proximal to the supracondylar flare. However, most occur in 2 areas, with 1 cluster centered at about 41 mm from the lesser trochanter (more common in relatively younger patients) and the other at 187 mm.5
ABSOLUTE RISK IS LOW BUT INCREASES WITH LONGER USE
Atypical femoral fractures are rare. Schilcher et al6 reviewed radiographs of 1,234 women who had a subtrochanteric or shaft fracture and found 59 (4.6%) of fractures were atypical. In a systematic review of 14 studies,7 the incidence ranged from 3.0 to 9.8 cases per 100,000 patient-years.
Furthermore, not all atypical femoral fractures are in bisphosphonate users: 7.4% were in nonusers in 1 series8 and 22% in another.9
Nevertheless, most studies show that bisphosphonate use increases the incidence of atypical femoral fracture, and the incidence increases with duration of use, especially after 3 years.7
An international task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research listed the absolute risk as between 3.2 and 50 cases per 100,000 patient-years, with longer use (> 5 years) increasing the risk to about 100 per 100,000 patient-years.4 After stopping bisphosphonate therapy, the risk diminished by 70% per year.9
In another study, for 0.1 to 1.9 years of therapy, the age-adjusted atypical fracture rates were 1.78 per 100,000 per year (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.5–2.0), increasing to 113.1 per 100,000 per year (95% CI 69.3–156.8) with exposure from 8 to 9.9 years.10
A case-control study found that more than 5 years of bisphosphonate use increased the fracture risk by an odds ratio of 2.74 (95% CI 1.25–6.02).11
The incidence of typical femoral fracture was higher in those who adhered better to their oral bisphosphonate regimen in some studies,12 but the opposite was true in others.13
The benefits of bisphosphonate therapy in reducing fracture risk, however, outweigh the risk of atypical fracture.4
We do not know whether the rate of atypical femoral fracture is increasing. A review of Kaiser Permanente Northwest records found that the rates of atypical femoral shaft fracture had remained stable from 1996 to 2009. However, 61.9% of patients who met the strict radiographic criteria had taken oral bisphosphonates.14 These data suggest that bisphosphonate use has not increased the overall population-based risk for subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures, but that bisphosphonates and other risk factors may have increased the likelihood that such fractures will exhibit atypical radiographic features.
A population-based study in Denmark13 found that alendronate use longer than 10 years was associated with an adjusted 30% lower risk of hip fracture and no increase in the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fracture. In addition, the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fracture was lower with high adherence to alendronate treatment (based on medication possession ratio > 80%) compared with low adherence (ratio < 50%) (odds ratio 0.88, 95% CI 0.77–0.99). The risk was not increased in current vs past users.
The Danish study13 used the coding of the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10) to identify subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures without radiologic review for atypical radiographic features. The lack of specific ICD-10 coding for subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures with atypical radiographic features has limited our knowledge of their incidence.
Contralateral fracture in more than one-fourth of cases
After an atypical femoral fracture, patients have a significant risk of fracture on the contralateral side. In a case-control study, 28% of patients with atypical femoral fracture suffered a contralateral fracture, compared with 0.9% of patients presenting with a typical fracture pattern (odds ratio 42.6, 95% CI 12.8–142.4).15
Contralateral fracture occurs from 1 month to 4 years after the index atypical femoral fracture.16
There are reports of bisphosphonate-related low-impact fractures in other sites such as the tibia17 and forearm.18 However, they may be too rare to warrant screening.
Mortality rates
A Swedish database study found that patients with atypical femoral fractures, whether bisphosphonate users or nonusers, do not have higher mortality rates than patients with ordinary subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures.19 Furthermore, the mortality rates for those with atypical femoral fracture were similar to rates in the general population. In contrast, patients with an ordinary femoral fracture had a higher mortality risk than the general population.19
Other studies suggest that atypical femoral fracture may be associated with a less favorable prognosis in older patients,20 but this could be due to differences in demographics, treatment adherence, or postfracture care.21
In addition, functional outcomes as measured by independent mobility at discharge and at 3 months were comparable between patients with atypical fracture and those with typical fracture.22
IMAGING STUDIES
If a long-term bisphosphonate user presents with hip, thigh, or groin pain, imaging studies are recommended.
Plain radiography
Radiography is usually the first step and should include a frontal view of the pelvis (Figure 1) and 2 views of the full length of each femur. If radiography is not conclusive, bone scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) should be considered.
A linear cortex transverse fracture pattern and focal lateral cortical thickening are the most sensitive and specific radiographic features.23,24 Because of the risk of fracture on the contralateral side, radiographic study of that side is recommended as well.
Computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT) is not sensitive for early stress fractures and, given the radiation burden, is not recommended in the workup of atypical fracture.
Bone scanning
Bone scanning using technetium 99m-labeled methylene diphosphonate with a gamma camera shows active bone turnover. Stress fractures and atypical femoral fractures are most easily identified in the third (delayed) phase of the bone scan. Although bone scanning is highly sensitive, the specificity is limited by lack of spatial resolution. Atypical femoral fracture appears as increased activity in the subtrochanteric region with a predilection for the lateral cortex.
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
Conventional dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) extends only to 1 to 2 cm below the lesser trochanter and can therefore miss atypical fractures, which usually occur farther down. The overall detection rate for DXA was 61% in a sample of 33 patients.25
Newer scanners can look at the entire femoral shaft.26 In addition, newer software can quantify focal thickening (beaking) of the lateral cortex and screen patients who have no symptoms. The results of serial measurements can be graphed so that the practitioner can view trends to help assess or rule out potential asymptomatic atypical femoral fracture.
A localized reaction (periosteal thickening of the lateral cortex or beaking) often precedes atypical femoral fracture. A 2017 study reported that patients with high localized reaction (mean height 3.3 mm) that was of the pointed type and was accompanied by prodromal pain had an increased risk of complete or incomplete atypical femoral fracture at that site.27 This finding is used by the newer DXA software. The predictive value of beaking on extended femoral DXA may be as high as 83%.26
Magnetic resonance imaging
The MRI characteristics of atypical femoral fracture are similar to those of other stress fractures except that there is a lateral-to-medial pattern rather than a medial pattern. The earliest findings include periosteal reaction about the lateral cortex with a normal marrow signal.
MRI may be of particular benefit in patients with known atypical femoral fracture to screen the contralateral leg. It should image the entire length of both femurs. Contrast enhancement is not needed.
Regardless of whether initial findings were discovered on conventional radiographs or DXA, MRI confirmation is needed. Radionuclide bone scanning is currently not recommended because it lacks specificity. Combination imaging is recommended, with either radiography plus MRI or DXA plus MRI.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
The differential diagnosis of atypical femoral fracture includes stress fracture, pathologic fracture, hypophosphatasia, and osteogenesis imperfecta.28 Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia can cause Looser zones, which can be confused with atypical femoral fractures but usually occur on the medial side.4 Stress fracture of the femur can occur below the lesser trochanter but usually begins in the medial, not the lateral, cortex.
Pathologic fractures from underlying osseous lesions can mimic the cortical beaking of bisphosphonate-related fracture, but they usually show the associated underlying lucent lesion and poorly defined margins. A sinus tract along the region of a chronic osteomyelitis may also appear similar.
Hypophosphatasia is an inborn error of metabolism caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the gene encoding alkaline phosphatase, resulting in pyrophosphate accumulation and causing osteomalacia from impaired mineralization. This can result in femoral pseudofracture that is often bilateral and occurs in the subtrochanteric region.29
ADDITIONAL RISK FACTORS
Patients with atypical femoral fracture are generally a heterogeneous group, but there are risk factors to note other than bisphosphonate exposure.
Asian women had a risk 8 times higher than white women in 1 study.30
Bone geometry. Mahjoub et al8 reported that compared with controls, patients with atypical femoral fracture had greater offset of the femoral shaft from the center of rotation of the femoral head, a more acute angle between the femoral neck and shaft, and greater proximal cortical thickness.
Medications. In addition to bisphosphonates, other drugs associated with atypical femoral fracture include RANK-ligand inhibitors such as denosumab (another drug for osteoporosis),31 glucocorticoids,32,33 and proton pump inhibitors.32,33
Genetics. Three sisters with atypical femoral fracture were found to have 37 rare mutations in 34 genes, including one in the GGPS1 gene, which codes for geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase—an enzyme that bisphosphonates inhibit.34
Medical conditions other than osteoporosis include collagen diseases, chronic pulmonary disease, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes.35
Clinical recommendations
Current recommendations are to reevaluate bisphosphonate use in patients with osteoporosis after 5 or more years of therapy.36
Given that patients with osteoporosis are at increased risk of typical fracture, those at higher risk should be considered for continued bisphosphonate therapy. Factors for high risk include the following:
- History of fracture on therapy
- Hip T score –2.5 or lower
- Older age (≥ 70)
- Other strong risk factors for fracture such as smoking, alcohol use, corticosteroid use, rheumatoid arthritis, and family history
- World Health Organization FRAX fracture risk score above the country-specific threshold.
Those at lower risk should be considered for a 2- to 3-year bisphosphonate holiday with periodic reevaluation of bone density and, possibly, bone markers.36
WHAT IS THE UNDERLYING PATHOPHYSIOLOGY?
The mechanism by which bisphosphonates increase the risk of atypical femoral fracture is not clear. These drugs work by suppressing bone turnover; however, in theory, prolonged use could suppress it too much and increase bone fragility.
One hypothesis is that bisphosphonates impair the toughening of cortical bone, an important barrier to clinical fracture. This is supported by a study that found bisphosphonate users with atypical femoral fracture had deficits in intrinsic and extrinsic bone toughness, perhaps due to treatment-related increases in matrix mineralization.37 Although this study and others showed an increase in matrix mineralization and reduced mineralization heterogeneity with bisphosphonate use,38,39 it is unclear whether such changes contributed to reduced toughness or to atypical femoral fracture.
Changes in the skeletal geometry of the lower limb such as femoral neck-shaft angle and femoral curvature alter the stresses and strains experienced by the femoral diaphysis with loading. Because the incidence of incomplete atypical femoral fracture is much greater than that of complete fracture, most incomplete atypical femoral fractures heal before the fracture progresses.
Ultimately, all fractures, including atypical femoral fractures, occur when mechanical stress and strain exceed bone strength.
Antiresorptive drugs such as bisphosphonates, estrogen, calcitonin, and RANK ligand inhibitors prevent hip fracture by increasing the strength of the proximal femur—perhaps at the expense of the strength (or toughness) of the subtrochanteric shaft. It is also possible that treatment-related increases in hip strength (and reduced hip fracture rates) promote or sustain the transfer of stress and strain to femoral regions that experience lesser or no increases in strength from treatment, which likely includes the shaft.40,41
CT studies in Japanese women with osteoporosis have shown that 2 years of zoledronate therapy had greater effects in the hip than in the femoral shaft, with significant increases in cortical thickness and volumetric bone mineral density at the femoral neck and intertrochanteric region compared with baseline.42 But zoledronate did not increase femoral shaft cortical thickness and caused only a minor increase in femoral shaft volumetric bone mineral density. Fracture patterns may have depended on damage and effects of bone turnover on mass and structure.
This hypothetical scenario portrays a possible “hip survival bias” mechanism for atypical femoral fracture, with the association with antiresorptive drugs arising from greater stress and strain in cortical regions where these fractures occur rather than from treatment-related reductions in cortical bone strength or toughness.
PRODROMAL PAIN IS COMMON
From 32% to 76% of patients who have incomplete or developing atypical femoral fracture present with a prodrome of groin or hip pain.4,43 Prodromal pain occurs any time from 2 weeks to several years before the fracture, presenting as pain in the anterior or lateral thigh or in the groin.
Prodromal pain in a patient on antiresorptive therapy should be a signal for the clinician to obtain a radiograph of the hip and to look for contralateral symptoms and fractures. The most common mechanism of injury appears to be a ground-level fall or even a nontraumatic activity such as walking or stepping off a curb.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
In bisphosphonate users with radiographic evidence of atypical femoral fracture, the bisphosphonate should be discontinued and the patient assessed for calcium and vitamin D deficiency, with supplements prescribed if needed.4
For patients with incomplete fracture and persistent pain after 3 months of medical management, prophylactic surgical nail fixation is recommended to prevent complete fracture.
Teriparatide, which has been associated with enhanced bone fracture healing, is a possible treatment to promote healing of atypical femoral fracture, either alone or as an adjunct to surgical fixation. A systematic review published in 2015 supported the use of teriparatide for enhancing fracture healing in atypical femoral fracture.44 In addition, a 10-patient series45 showed that incomplete fractures without radiolucent lines responded to teriparatide alone, whereas those with radiolucent lines needed intramedullary nailing.
These results suggest that teriparatide works best when the fracture site is stable, either inherently or with surgical fixation.
ORTHOPEDIC CARE
Orthopedic care for atypical femoral fracture differs depending on whether the patient experiences pain and whether the fracture is incomplete or complete. Figure 2 shows a treatment algorithm for atypical femoral fracture.
These are difficult fractures to manage, complicated by delayed healing in the elderly, complex displacement patterns, altered bone geometry, and risk of fracture in the opposite limb, all of which raise questions about recommending protected weight-bearing exercise.
Furthermore, atypical femoral fracture is often associated with increased anterolateral bowing of the femur, making it difficult to insert an intramedullary nail: the radius of curvature of the bone is shorter than that of a standard femoral nail. This mismatch can lead to intraoperative complications such as iatrogenic fracture during prophylactic nailing, malunion from excess straightening of the femur (which can itself lead to leg length discrepancy), and gapping of the fracture site, particularly on the medial side.
Intramedullary nailing for complete fracture
Intramedullary nailing is the first-line treatment for complete atypical femoral fracture, although the risk of delayed healing and revision surgery may be somewhat higher than with typical femoral fracture.46 Prophylactic intramedullary nailing should be considered for a patient with intractable pain.2
A radiograph of the opposite leg should be obtained routinely, looking for an asymptomatic fracture. Bisphosphonates should be discontinued and calcium and vitamin D continued. Teriparatide therapy can be considered as an alternative treatment.
Conservative management for incomplete fracture without pain
Incomplete atypical femoral fracture unaccompanied by pain can be followed conservatively.47 In addition to stopping antiresorptive therapy, patients need to avoid high-impact and repetitive-impact activities such as jumping or running. If pain occurs, patients should begin protected weight-bearing exercise.
Treatment is uncertain for incomplete fracture with pain
For patients with incomplete atypical femoral fracture and pain, treatment is controversial. Regimens that include 2 to 3 months of protected weight-bearing exercise, a full metabolic bone workup, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and anabolic bone agents have produced some success. Some authors have reported poor results from conservative care, with few patients achieving pain relief or signs of complete healing.48,49 Additionally, if an incomplete fracture is found in the opposite femur, protected weight-bearing of both legs may not be possible.
Patients with incomplete fracture should be monitored regularly with radiography and physical examination. If there is progression of the fracture, escalation of pain, or failure to heal within 2 to 3 months, then surgical treatment is necessary.
Prophylactic placement of an intramedullary nail to prevent completion of the fracture and allow a return to full weight-bearing is generally advised.50 A long locking plate can be used if bone deformities make it difficult to place an intramedullary nail; however, nails are preferred because they allow formation of endochondral callus, which can be helpful in these difficult-to-heal fractures.
Results from retrospective reviews have shown that surgically treated patients with bisphosphonate-associated incomplete atypical femoral fracture were more likely than those treated nonsurgically to be pain-free (81% vs 64%) and have radiographic healing (100% vs 18% at final follow-up).46 Results have also been positive for those with complete atypical femoral fracture. At 6 months, 64% of surgically treated patients were pain-free and 98% were radiographically healed.51
The unusual geometry of the femur in patients with atypical femoral fracture and the presence of intramedullary cortical callus makes the placement of an intramedullary femoral rod more complex than in typical femoral fracture.8
Intramedullary nailing of atypical femoral fracture is a challenge for even the most experienced surgeon, and vigilance is imperative to avoid iatrogenic fracture and malunion.
MANY QUESTIONS REMAIN
We need more studies on the pathophysiology of bisphosphonate-associated atypical femoral fracture, the value of periodic screening with DXA, and which factors predict high risk (eg, Asian ethnicity, use of certain medications, femoral geometry). In addition, we need more data on the success of conservative management of incomplete fracture, including use of teriparatide.
Bisphosphonate therapy minimizes bone loss and reduces fracture risk by up to 50% in patients with osteoporosis,1 but it is also associated with increased risks of osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fracture. Although atypical femoral fractures are rare, they can have a devastating effect. Patient concern about this complication has contributed to a decrease in bisphosphonate use by about half in the last decade or so,2,3 and we fear this could result in an increase in hip fracture rates.
In this article, we examine the evidence on bisphosphonate-associated atypical femoral fractures, including risks, pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention.
ATYPICAL FRACTURES INVOLVE THE FEMORAL SHAFT, NOT THE HEAD
An atypical femoral fracture is a transverse fracture of the femoral shaft (diaphysis), defined by both clinical criteria and radiographic appearance.
To be defined as atypical, a femoral fracture must meet 4 of the following 5 criteria4:
- Occurs with minimal or no trauma
- Has a predominantly transverse fracture line, originating at the lateral cortex and sometimes becoming oblique as it progresses medially across the femur
- Extends through both cortices and may be associated with a medial spike (complete fractures); or involves only the lateral cortex (incomplete fractures)
- Is noncomminuted or minimally comminuted
- Shows localized periosteal or endosteal thickening (termed “beaking” or “flaring”) of the lateral cortex at the fracture site.
Several minor features are also important but are not required, eg:
- Cortical thickening of the femoral shaft
- Unilateral or bilateral prodromal pain preceding the fracture
- Bilateral incomplete or complete femoral diaphysis fractures
- Delayed fracture healing.
Atypical femoral fracture can occur anywhere along the shaft, from just distal to the lesser trochanter to just proximal to the supracondylar flare. However, most occur in 2 areas, with 1 cluster centered at about 41 mm from the lesser trochanter (more common in relatively younger patients) and the other at 187 mm.5
ABSOLUTE RISK IS LOW BUT INCREASES WITH LONGER USE
Atypical femoral fractures are rare. Schilcher et al6 reviewed radiographs of 1,234 women who had a subtrochanteric or shaft fracture and found 59 (4.6%) of fractures were atypical. In a systematic review of 14 studies,7 the incidence ranged from 3.0 to 9.8 cases per 100,000 patient-years.
Furthermore, not all atypical femoral fractures are in bisphosphonate users: 7.4% were in nonusers in 1 series8 and 22% in another.9
Nevertheless, most studies show that bisphosphonate use increases the incidence of atypical femoral fracture, and the incidence increases with duration of use, especially after 3 years.7
An international task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research listed the absolute risk as between 3.2 and 50 cases per 100,000 patient-years, with longer use (> 5 years) increasing the risk to about 100 per 100,000 patient-years.4 After stopping bisphosphonate therapy, the risk diminished by 70% per year.9
In another study, for 0.1 to 1.9 years of therapy, the age-adjusted atypical fracture rates were 1.78 per 100,000 per year (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.5–2.0), increasing to 113.1 per 100,000 per year (95% CI 69.3–156.8) with exposure from 8 to 9.9 years.10
A case-control study found that more than 5 years of bisphosphonate use increased the fracture risk by an odds ratio of 2.74 (95% CI 1.25–6.02).11
The incidence of typical femoral fracture was higher in those who adhered better to their oral bisphosphonate regimen in some studies,12 but the opposite was true in others.13
The benefits of bisphosphonate therapy in reducing fracture risk, however, outweigh the risk of atypical fracture.4
We do not know whether the rate of atypical femoral fracture is increasing. A review of Kaiser Permanente Northwest records found that the rates of atypical femoral shaft fracture had remained stable from 1996 to 2009. However, 61.9% of patients who met the strict radiographic criteria had taken oral bisphosphonates.14 These data suggest that bisphosphonate use has not increased the overall population-based risk for subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures, but that bisphosphonates and other risk factors may have increased the likelihood that such fractures will exhibit atypical radiographic features.
A population-based study in Denmark13 found that alendronate use longer than 10 years was associated with an adjusted 30% lower risk of hip fracture and no increase in the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fracture. In addition, the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fracture was lower with high adherence to alendronate treatment (based on medication possession ratio > 80%) compared with low adherence (ratio < 50%) (odds ratio 0.88, 95% CI 0.77–0.99). The risk was not increased in current vs past users.
The Danish study13 used the coding of the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10) to identify subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures without radiologic review for atypical radiographic features. The lack of specific ICD-10 coding for subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures with atypical radiographic features has limited our knowledge of their incidence.
Contralateral fracture in more than one-fourth of cases
After an atypical femoral fracture, patients have a significant risk of fracture on the contralateral side. In a case-control study, 28% of patients with atypical femoral fracture suffered a contralateral fracture, compared with 0.9% of patients presenting with a typical fracture pattern (odds ratio 42.6, 95% CI 12.8–142.4).15
Contralateral fracture occurs from 1 month to 4 years after the index atypical femoral fracture.16
There are reports of bisphosphonate-related low-impact fractures in other sites such as the tibia17 and forearm.18 However, they may be too rare to warrant screening.
Mortality rates
A Swedish database study found that patients with atypical femoral fractures, whether bisphosphonate users or nonusers, do not have higher mortality rates than patients with ordinary subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures.19 Furthermore, the mortality rates for those with atypical femoral fracture were similar to rates in the general population. In contrast, patients with an ordinary femoral fracture had a higher mortality risk than the general population.19
Other studies suggest that atypical femoral fracture may be associated with a less favorable prognosis in older patients,20 but this could be due to differences in demographics, treatment adherence, or postfracture care.21
In addition, functional outcomes as measured by independent mobility at discharge and at 3 months were comparable between patients with atypical fracture and those with typical fracture.22
IMAGING STUDIES
If a long-term bisphosphonate user presents with hip, thigh, or groin pain, imaging studies are recommended.
Plain radiography
Radiography is usually the first step and should include a frontal view of the pelvis (Figure 1) and 2 views of the full length of each femur. If radiography is not conclusive, bone scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) should be considered.
A linear cortex transverse fracture pattern and focal lateral cortical thickening are the most sensitive and specific radiographic features.23,24 Because of the risk of fracture on the contralateral side, radiographic study of that side is recommended as well.
Computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT) is not sensitive for early stress fractures and, given the radiation burden, is not recommended in the workup of atypical fracture.
Bone scanning
Bone scanning using technetium 99m-labeled methylene diphosphonate with a gamma camera shows active bone turnover. Stress fractures and atypical femoral fractures are most easily identified in the third (delayed) phase of the bone scan. Although bone scanning is highly sensitive, the specificity is limited by lack of spatial resolution. Atypical femoral fracture appears as increased activity in the subtrochanteric region with a predilection for the lateral cortex.
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
Conventional dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) extends only to 1 to 2 cm below the lesser trochanter and can therefore miss atypical fractures, which usually occur farther down. The overall detection rate for DXA was 61% in a sample of 33 patients.25
Newer scanners can look at the entire femoral shaft.26 In addition, newer software can quantify focal thickening (beaking) of the lateral cortex and screen patients who have no symptoms. The results of serial measurements can be graphed so that the practitioner can view trends to help assess or rule out potential asymptomatic atypical femoral fracture.
A localized reaction (periosteal thickening of the lateral cortex or beaking) often precedes atypical femoral fracture. A 2017 study reported that patients with high localized reaction (mean height 3.3 mm) that was of the pointed type and was accompanied by prodromal pain had an increased risk of complete or incomplete atypical femoral fracture at that site.27 This finding is used by the newer DXA software. The predictive value of beaking on extended femoral DXA may be as high as 83%.26
Magnetic resonance imaging
The MRI characteristics of atypical femoral fracture are similar to those of other stress fractures except that there is a lateral-to-medial pattern rather than a medial pattern. The earliest findings include periosteal reaction about the lateral cortex with a normal marrow signal.
MRI may be of particular benefit in patients with known atypical femoral fracture to screen the contralateral leg. It should image the entire length of both femurs. Contrast enhancement is not needed.
Regardless of whether initial findings were discovered on conventional radiographs or DXA, MRI confirmation is needed. Radionuclide bone scanning is currently not recommended because it lacks specificity. Combination imaging is recommended, with either radiography plus MRI or DXA plus MRI.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
The differential diagnosis of atypical femoral fracture includes stress fracture, pathologic fracture, hypophosphatasia, and osteogenesis imperfecta.28 Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia can cause Looser zones, which can be confused with atypical femoral fractures but usually occur on the medial side.4 Stress fracture of the femur can occur below the lesser trochanter but usually begins in the medial, not the lateral, cortex.
Pathologic fractures from underlying osseous lesions can mimic the cortical beaking of bisphosphonate-related fracture, but they usually show the associated underlying lucent lesion and poorly defined margins. A sinus tract along the region of a chronic osteomyelitis may also appear similar.
Hypophosphatasia is an inborn error of metabolism caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the gene encoding alkaline phosphatase, resulting in pyrophosphate accumulation and causing osteomalacia from impaired mineralization. This can result in femoral pseudofracture that is often bilateral and occurs in the subtrochanteric region.29
ADDITIONAL RISK FACTORS
Patients with atypical femoral fracture are generally a heterogeneous group, but there are risk factors to note other than bisphosphonate exposure.
Asian women had a risk 8 times higher than white women in 1 study.30
Bone geometry. Mahjoub et al8 reported that compared with controls, patients with atypical femoral fracture had greater offset of the femoral shaft from the center of rotation of the femoral head, a more acute angle between the femoral neck and shaft, and greater proximal cortical thickness.
Medications. In addition to bisphosphonates, other drugs associated with atypical femoral fracture include RANK-ligand inhibitors such as denosumab (another drug for osteoporosis),31 glucocorticoids,32,33 and proton pump inhibitors.32,33
Genetics. Three sisters with atypical femoral fracture were found to have 37 rare mutations in 34 genes, including one in the GGPS1 gene, which codes for geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase—an enzyme that bisphosphonates inhibit.34
Medical conditions other than osteoporosis include collagen diseases, chronic pulmonary disease, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes.35
Clinical recommendations
Current recommendations are to reevaluate bisphosphonate use in patients with osteoporosis after 5 or more years of therapy.36
Given that patients with osteoporosis are at increased risk of typical fracture, those at higher risk should be considered for continued bisphosphonate therapy. Factors for high risk include the following:
- History of fracture on therapy
- Hip T score –2.5 or lower
- Older age (≥ 70)
- Other strong risk factors for fracture such as smoking, alcohol use, corticosteroid use, rheumatoid arthritis, and family history
- World Health Organization FRAX fracture risk score above the country-specific threshold.
Those at lower risk should be considered for a 2- to 3-year bisphosphonate holiday with periodic reevaluation of bone density and, possibly, bone markers.36
WHAT IS THE UNDERLYING PATHOPHYSIOLOGY?
The mechanism by which bisphosphonates increase the risk of atypical femoral fracture is not clear. These drugs work by suppressing bone turnover; however, in theory, prolonged use could suppress it too much and increase bone fragility.
One hypothesis is that bisphosphonates impair the toughening of cortical bone, an important barrier to clinical fracture. This is supported by a study that found bisphosphonate users with atypical femoral fracture had deficits in intrinsic and extrinsic bone toughness, perhaps due to treatment-related increases in matrix mineralization.37 Although this study and others showed an increase in matrix mineralization and reduced mineralization heterogeneity with bisphosphonate use,38,39 it is unclear whether such changes contributed to reduced toughness or to atypical femoral fracture.
Changes in the skeletal geometry of the lower limb such as femoral neck-shaft angle and femoral curvature alter the stresses and strains experienced by the femoral diaphysis with loading. Because the incidence of incomplete atypical femoral fracture is much greater than that of complete fracture, most incomplete atypical femoral fractures heal before the fracture progresses.
Ultimately, all fractures, including atypical femoral fractures, occur when mechanical stress and strain exceed bone strength.
Antiresorptive drugs such as bisphosphonates, estrogen, calcitonin, and RANK ligand inhibitors prevent hip fracture by increasing the strength of the proximal femur—perhaps at the expense of the strength (or toughness) of the subtrochanteric shaft. It is also possible that treatment-related increases in hip strength (and reduced hip fracture rates) promote or sustain the transfer of stress and strain to femoral regions that experience lesser or no increases in strength from treatment, which likely includes the shaft.40,41
CT studies in Japanese women with osteoporosis have shown that 2 years of zoledronate therapy had greater effects in the hip than in the femoral shaft, with significant increases in cortical thickness and volumetric bone mineral density at the femoral neck and intertrochanteric region compared with baseline.42 But zoledronate did not increase femoral shaft cortical thickness and caused only a minor increase in femoral shaft volumetric bone mineral density. Fracture patterns may have depended on damage and effects of bone turnover on mass and structure.
This hypothetical scenario portrays a possible “hip survival bias” mechanism for atypical femoral fracture, with the association with antiresorptive drugs arising from greater stress and strain in cortical regions where these fractures occur rather than from treatment-related reductions in cortical bone strength or toughness.
PRODROMAL PAIN IS COMMON
From 32% to 76% of patients who have incomplete or developing atypical femoral fracture present with a prodrome of groin or hip pain.4,43 Prodromal pain occurs any time from 2 weeks to several years before the fracture, presenting as pain in the anterior or lateral thigh or in the groin.
Prodromal pain in a patient on antiresorptive therapy should be a signal for the clinician to obtain a radiograph of the hip and to look for contralateral symptoms and fractures. The most common mechanism of injury appears to be a ground-level fall or even a nontraumatic activity such as walking or stepping off a curb.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
In bisphosphonate users with radiographic evidence of atypical femoral fracture, the bisphosphonate should be discontinued and the patient assessed for calcium and vitamin D deficiency, with supplements prescribed if needed.4
For patients with incomplete fracture and persistent pain after 3 months of medical management, prophylactic surgical nail fixation is recommended to prevent complete fracture.
Teriparatide, which has been associated with enhanced bone fracture healing, is a possible treatment to promote healing of atypical femoral fracture, either alone or as an adjunct to surgical fixation. A systematic review published in 2015 supported the use of teriparatide for enhancing fracture healing in atypical femoral fracture.44 In addition, a 10-patient series45 showed that incomplete fractures without radiolucent lines responded to teriparatide alone, whereas those with radiolucent lines needed intramedullary nailing.
These results suggest that teriparatide works best when the fracture site is stable, either inherently or with surgical fixation.
ORTHOPEDIC CARE
Orthopedic care for atypical femoral fracture differs depending on whether the patient experiences pain and whether the fracture is incomplete or complete. Figure 2 shows a treatment algorithm for atypical femoral fracture.
These are difficult fractures to manage, complicated by delayed healing in the elderly, complex displacement patterns, altered bone geometry, and risk of fracture in the opposite limb, all of which raise questions about recommending protected weight-bearing exercise.
Furthermore, atypical femoral fracture is often associated with increased anterolateral bowing of the femur, making it difficult to insert an intramedullary nail: the radius of curvature of the bone is shorter than that of a standard femoral nail. This mismatch can lead to intraoperative complications such as iatrogenic fracture during prophylactic nailing, malunion from excess straightening of the femur (which can itself lead to leg length discrepancy), and gapping of the fracture site, particularly on the medial side.
Intramedullary nailing for complete fracture
Intramedullary nailing is the first-line treatment for complete atypical femoral fracture, although the risk of delayed healing and revision surgery may be somewhat higher than with typical femoral fracture.46 Prophylactic intramedullary nailing should be considered for a patient with intractable pain.2
A radiograph of the opposite leg should be obtained routinely, looking for an asymptomatic fracture. Bisphosphonates should be discontinued and calcium and vitamin D continued. Teriparatide therapy can be considered as an alternative treatment.
Conservative management for incomplete fracture without pain
Incomplete atypical femoral fracture unaccompanied by pain can be followed conservatively.47 In addition to stopping antiresorptive therapy, patients need to avoid high-impact and repetitive-impact activities such as jumping or running. If pain occurs, patients should begin protected weight-bearing exercise.
Treatment is uncertain for incomplete fracture with pain
For patients with incomplete atypical femoral fracture and pain, treatment is controversial. Regimens that include 2 to 3 months of protected weight-bearing exercise, a full metabolic bone workup, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and anabolic bone agents have produced some success. Some authors have reported poor results from conservative care, with few patients achieving pain relief or signs of complete healing.48,49 Additionally, if an incomplete fracture is found in the opposite femur, protected weight-bearing of both legs may not be possible.
Patients with incomplete fracture should be monitored regularly with radiography and physical examination. If there is progression of the fracture, escalation of pain, or failure to heal within 2 to 3 months, then surgical treatment is necessary.
Prophylactic placement of an intramedullary nail to prevent completion of the fracture and allow a return to full weight-bearing is generally advised.50 A long locking plate can be used if bone deformities make it difficult to place an intramedullary nail; however, nails are preferred because they allow formation of endochondral callus, which can be helpful in these difficult-to-heal fractures.
Results from retrospective reviews have shown that surgically treated patients with bisphosphonate-associated incomplete atypical femoral fracture were more likely than those treated nonsurgically to be pain-free (81% vs 64%) and have radiographic healing (100% vs 18% at final follow-up).46 Results have also been positive for those with complete atypical femoral fracture. At 6 months, 64% of surgically treated patients were pain-free and 98% were radiographically healed.51
The unusual geometry of the femur in patients with atypical femoral fracture and the presence of intramedullary cortical callus makes the placement of an intramedullary femoral rod more complex than in typical femoral fracture.8
Intramedullary nailing of atypical femoral fracture is a challenge for even the most experienced surgeon, and vigilance is imperative to avoid iatrogenic fracture and malunion.
MANY QUESTIONS REMAIN
We need more studies on the pathophysiology of bisphosphonate-associated atypical femoral fracture, the value of periodic screening with DXA, and which factors predict high risk (eg, Asian ethnicity, use of certain medications, femoral geometry). In addition, we need more data on the success of conservative management of incomplete fracture, including use of teriparatide.
- Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, et al. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet 1996; 348(9041):1535–1541. pmid:8950879
- Jha S, Wang Z, Laucis N, Bhattacharyya T. Trends in media reports, oral bisphosphonate prescriptions, and hip fractures 1996–2012: an ecological analysis. J Bone Miner Res 2015; 30(12):2179–2187. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2565
- Solomon DH, Johnston SS, Boytsov NN, McMorrow D, Lane JM, Krohn KD. Osteoporosis medication use after hip fracture in US patients between 2002 and 2011. J Bone Miner Res 2014; 29(9):1929–1937. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2202
- Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 2014; 29(1):1–23. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1998
- Koeppen VA, Schilcher J, Aspenberg P. Dichotomous location of 160 atypical femoral fractures. Acta Orthop 2013; 84(6):561–564. doi:10.3109/17453674.2013.866193
- Schilcher J, Koeppen V, Aspenberg P, Michäelsson K. Risk of atypical femoral fracture during and after bisphosphonate use. Acta Orthop 2015; 86(1):100–107. doi:10.3109/17453674.2015.1004149
- Khow KS, Shibu P, Yu SC, Chehade MJ, Visvanathan R. Epidemiology and postoperative outcomes of atypical femoral fractures in older adults: a systematic review. J Nutr Health Aging 2017; 21(1):83–91. doi:10.1007/s12603-015-0652-3
- Mahjoub Z, Jean S, Leclerc JT, et al. Incidence and characteristics of atypical femoral fractures: clinical and geometrical data. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(4):767–776. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2748
- Schilcher J, Michaelsson K, Aspenberg P. Bisphosphonate use and atypical fractures of the femoral shaft. N Engl J Med 2011; 364(18):1728–1737. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1010650
- Dell RM, Adams AL, Greene DF, et al. Incidence of atypical nontraumatic diaphyseal fractures of the femur. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27(12):2544–2550. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1719
- Park-Wyllie LY, Mamdani MM, Juurlink DN, et al. Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older women. JAMA 2011; 305(8):783–789. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.190
- Wang Z, Ward MM, Chan L, Bhattacharyya T. Adherence to oral bisphosphonates and the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures among female Medicare beneficiaries. Osteoporos Int 2014; 25(8):2109–2116. doi:10.1007/s00198-014-2738-x
- Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Prieto-Alhambra D, Eastell R. Risk of hip, subtrochanteric, and femoral shaft fractures among mid and long term users of alendronate: nationwide cohort and nested case-control study. BMJ 2016; 353:i3365. doi:10.1136/bmj.i3365
- Feldstein AC, Black D, Perrin N, et al. Incidence and demography of femur fractures with and without atypical features. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27(5):977–986. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1550
- Meier RP, Perneger TV, Stern R, Rizzoli R, Peter RE. Increasing occurrence of atypical femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use. Arch Intern Med 2012; 172(12):930–936. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2012.1796
- La Rocca Vieira R, Rosenberg ZS, Allison MB, Im SA, Babb J, Peck V. Frequency of incomplete atypical femoral fractures in asymptomatic patients on long term bisphosphonate therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012; 198(5):1144–1151. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7442
- Bissonnette L, April PM, Dumais R, Boire G, Roux S. Atypical fracture of the tibial diaphysis associated with bisphosphonate therapy: a case report. Bone 2013; 56(2):406–409. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.07.012
- Moon J, Bither N, Lee T. Atypical forearm fractures associated with long-term use of bisphosphonate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2013; 133(7):889–892. doi:10.1007/s00402-013-1760-3
- Kharazmi M, Hallberg P, Schilcher J, Aspenberg P, Michaëlsson K. Mortality after atypical femoral fractures: a cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(3):491–497. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2767
- Medin E, Goude F, Melberg HO, Tediosi F, Belicza E, Peltola M; EuroHOPE Study Group. European regional differences in all-cause mortality and length of stay for patients with hip fracture. Health Econ 2015; 24(suppl 2):53–64. doi:10.1002/hec.3278
- Abrahamsen B, Prieto-Alhambra D. Patients with atypical femur fractures have the same mortality as the background population-drug channeling bias, bisphosphonate effects and public health implications. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(3):488–490. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2801
- Khow KS, Paterson F, Shibu P, Yu SC, Chehade MJ, Visvanathan R. Outcomes between older adults with atypical and typical femoral fractures are comparable. Injury 2017; 48(2):394–398. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2016.10.035
- Adams AL, Xue F, Chantra JQ, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of radiographic characteristics in atypical femoral fractures. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(1):413–417. doi:10.1007/s00198-016-3809-y
- Rosenberg ZS, La Rocca Vieira R, Chan SS, et al. Bisphosphonate-related complete atypical subtrochanteric femoral fractures: diagnostic utility of radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011; 197(4):954–960. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.6262
- Kim S, Yang KH, Lim H, et al. Detection of prefracture hip lesions in atypical subtrochanteric fracture with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry images. Radiology 2014; 270(2):487–495. doi:10.1148/radiol.13122691
- van de Laarschot DM, Smits AA, Buitendijk SK, Stegenga MT, Zillikens MC. Screening for atypical femur fractures using extended femur scans by DXA. J Bone Miner Res 2017; 32(8):1632–1639. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3164
- Sato H, Kondo N, Nakatsue T, et al. High and pointed type of femoral localized reaction frequently extends to complete an incomplete atypical femoral fracture in patients with autoimmune diseases on long-term glucocorticoids and bisphosphonates. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(8):2367–2376. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-4038-8
- Giaconi JC, Watterson CT. Bisphosphonate-related atypical femur fractures and the radiographic features. In: Silverman SL, Abrahamsen B, eds. The Duration and Safety of Osteoporosis Treatment. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:107–124. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-23639-1
- Whyte MP. Atypical femoral fractures, bisphosphonates, and adult hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Res 2009; 24(6):1132–1134. doi:10.1359/jbmr.081253
- Lo JC, Hui RL, Grimsrud CD, et al. The association of race/ethnicity and risk of atypical femoral fracture among older women receiving oral bisphosphonate therapy. Bone 2016; 85:142–147. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2016.01.002
- Bone HG, Wagman RB, Brandi ML, et al. 10 years of denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from the phase 3 randomised FREEDOM trial and open-label extension. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017; 5(7):513–523. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30138-9
- Koh JH, Myong JP, Yoo J, et al. Predisposing factors associated with atypical femur fracture among postmenopausal Korean women receiving bisphosphonate therapy: 8 years' experience in a single center. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(11):3251–3259. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-4169-y
- Kim D, Sung YK, Cho SK, Han M, Kim YS. Factors associated with atypical femoral fracture. Rheumatol Int 2016; 36(1):65–71. doi:10.1007/s00296-015-3323-0
- Roca-Ayats N, Balcells S, Garcia-Giralt N, et al. GGPS1 mutation and atypical femoral fractures with bisphosphonates. N Engl J Med 2017; 376(18):1794–1795. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1612804
- Giusti A, Hamdy NA, Dekkers OM, Ramautar SR, Dijkstra S, Papapoulos SE. Atypical fractures and bisphosphonate therapy: a cohort study of patients with femoral fracture with radiographic adjudication of fracture site and features. Bone 2011; 48(5):966–971. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2010.12.033
- Adler RA, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Bauer DC, et al. Managing osteoporosis in patients on long-term bisphosphonate treatment: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(1):16–35. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2708
- Lloyd AA, Gludovatz B, Riedel C, et al. Atypical fracture with long-term bisphosphonate therapy is associated with altered cortical composition and reduced fracture resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2017; 114(33):8722–8727. doi:10.1073/pnas.1704460114
- Ettinger B, Burr DB, Ritchie RO. Proposed pathogenesis for atypical femoral fractures; lessons from materials research. Bone 2013; 55(2):495–500. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.02.004
- Burr DB, Liu Z, Allen MR. Duration-dependent effects of clinically relevant oral alendronate doses on cortical bone toughness in beagle dogs. Bone 2015; 71:58–62. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2014.10.010
- Sasaki S, Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, Kasukawa Y, Shimada Y. Low-energy diaphyseal femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use and severe curved femur: a case series. J Bone Miner Metab 2012; 30(5):561–567. doi:10.1007/s00774-012-0358-0
- Pulkkinen P, Gluer C, Jamsa T. Investigation of differences between hip fracture types: a worthy strategy of improved risk assessment and fracture prevention. Bone 2011; 49(4):600–604. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2011.07.022
- Ito M, Sone T, Shiraki M, et al. The effect of once-yearly zoledronic acid on hip structural and biomechanical properties derived using computed tomography (CT) in Japanese women with osteoporosis. Bone 2018; 106:179–186. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2017.10.013
- Bogdan Y, Einhorn TA. Clinical presentation of atypical femur fractures. In: Silverman SL, Abrahamsen B, eds. The Duration and Safety of Osteoporosis Treatment. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:137–140. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-23639-1
- Im GI, Lee SH. Effect of teriparatide on healing of atypical femoral fractures: a systemic review. J Bone Metab 2015; 22(4):183–189. doi:10.11005/jbm.2015.22.4.183
- Saleh A, Hegde VV, Potty AG, Schneider R, Cornell CN, Lane JM. Management strategy for symptomatic bisphosphonate-associated incomplete atypical femoral fractures. HSS J 2012; 8(2):103–110. doi:10.1007/s11420-012-9275-y
- Egol KA, Park JH, Prensky C, Rosenberg ZS, Peck V, Tejwani NC. Surgical treatment improves clinical and functional outcomes for patients who sustain incomplete bisphosphonate-related femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2013; 27(6):331–335. doi:10.1097/BOT.0b013e31827240ae
- Koh A, Guerado E, Giannoudis PV. Atypical femoral fractures related to bisphosphonate treatment: issues and controversies related to their surgical management. Bone Joint J 2017; 99-B(3):295–302. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B3.BJJ-2016-0276.R2
- Oh CW, Oh JK, Park KC, Kim JW, Yoon YC. Prophylactic nailing of incomplete atypical femoral fractures. ScientificWorldJournal 2013; 2013:450148. doi:10.1155/2013/450148
- Ha YC, Cho MR, Park KH, Kim SY, Koo KH. Is surgery necessary for femoral insufficiency fractures after long-term bisphosphonate therapy? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010; 468(12):3393–3398. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1583-2
- Tosounidis TH, Lampropoulou-Adamidou, Kanakaris NK. Intramedullary nailing of sequential bilateral atypical subtrochanteric fractures and the management of distal femoral intraoperative fracture. J Orthop Trauma 2015 Jun 11. Epub ahead of print. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000370
- Egol KA, Park JH, Rosenberg ZS, Peck V, Tejwani NC. Healing delayed but generally reliable after bisphosphonate-associated complete femur fractures treated with IM nails. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014; 472(9):2728–2734. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-2963-1
- Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, et al. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet 1996; 348(9041):1535–1541. pmid:8950879
- Jha S, Wang Z, Laucis N, Bhattacharyya T. Trends in media reports, oral bisphosphonate prescriptions, and hip fractures 1996–2012: an ecological analysis. J Bone Miner Res 2015; 30(12):2179–2187. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2565
- Solomon DH, Johnston SS, Boytsov NN, McMorrow D, Lane JM, Krohn KD. Osteoporosis medication use after hip fracture in US patients between 2002 and 2011. J Bone Miner Res 2014; 29(9):1929–1937. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2202
- Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 2014; 29(1):1–23. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1998
- Koeppen VA, Schilcher J, Aspenberg P. Dichotomous location of 160 atypical femoral fractures. Acta Orthop 2013; 84(6):561–564. doi:10.3109/17453674.2013.866193
- Schilcher J, Koeppen V, Aspenberg P, Michäelsson K. Risk of atypical femoral fracture during and after bisphosphonate use. Acta Orthop 2015; 86(1):100–107. doi:10.3109/17453674.2015.1004149
- Khow KS, Shibu P, Yu SC, Chehade MJ, Visvanathan R. Epidemiology and postoperative outcomes of atypical femoral fractures in older adults: a systematic review. J Nutr Health Aging 2017; 21(1):83–91. doi:10.1007/s12603-015-0652-3
- Mahjoub Z, Jean S, Leclerc JT, et al. Incidence and characteristics of atypical femoral fractures: clinical and geometrical data. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(4):767–776. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2748
- Schilcher J, Michaelsson K, Aspenberg P. Bisphosphonate use and atypical fractures of the femoral shaft. N Engl J Med 2011; 364(18):1728–1737. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1010650
- Dell RM, Adams AL, Greene DF, et al. Incidence of atypical nontraumatic diaphyseal fractures of the femur. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27(12):2544–2550. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1719
- Park-Wyllie LY, Mamdani MM, Juurlink DN, et al. Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older women. JAMA 2011; 305(8):783–789. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.190
- Wang Z, Ward MM, Chan L, Bhattacharyya T. Adherence to oral bisphosphonates and the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures among female Medicare beneficiaries. Osteoporos Int 2014; 25(8):2109–2116. doi:10.1007/s00198-014-2738-x
- Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Prieto-Alhambra D, Eastell R. Risk of hip, subtrochanteric, and femoral shaft fractures among mid and long term users of alendronate: nationwide cohort and nested case-control study. BMJ 2016; 353:i3365. doi:10.1136/bmj.i3365
- Feldstein AC, Black D, Perrin N, et al. Incidence and demography of femur fractures with and without atypical features. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27(5):977–986. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1550
- Meier RP, Perneger TV, Stern R, Rizzoli R, Peter RE. Increasing occurrence of atypical femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use. Arch Intern Med 2012; 172(12):930–936. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2012.1796
- La Rocca Vieira R, Rosenberg ZS, Allison MB, Im SA, Babb J, Peck V. Frequency of incomplete atypical femoral fractures in asymptomatic patients on long term bisphosphonate therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012; 198(5):1144–1151. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7442
- Bissonnette L, April PM, Dumais R, Boire G, Roux S. Atypical fracture of the tibial diaphysis associated with bisphosphonate therapy: a case report. Bone 2013; 56(2):406–409. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.07.012
- Moon J, Bither N, Lee T. Atypical forearm fractures associated with long-term use of bisphosphonate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2013; 133(7):889–892. doi:10.1007/s00402-013-1760-3
- Kharazmi M, Hallberg P, Schilcher J, Aspenberg P, Michaëlsson K. Mortality after atypical femoral fractures: a cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(3):491–497. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2767
- Medin E, Goude F, Melberg HO, Tediosi F, Belicza E, Peltola M; EuroHOPE Study Group. European regional differences in all-cause mortality and length of stay for patients with hip fracture. Health Econ 2015; 24(suppl 2):53–64. doi:10.1002/hec.3278
- Abrahamsen B, Prieto-Alhambra D. Patients with atypical femur fractures have the same mortality as the background population-drug channeling bias, bisphosphonate effects and public health implications. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(3):488–490. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2801
- Khow KS, Paterson F, Shibu P, Yu SC, Chehade MJ, Visvanathan R. Outcomes between older adults with atypical and typical femoral fractures are comparable. Injury 2017; 48(2):394–398. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2016.10.035
- Adams AL, Xue F, Chantra JQ, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of radiographic characteristics in atypical femoral fractures. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(1):413–417. doi:10.1007/s00198-016-3809-y
- Rosenberg ZS, La Rocca Vieira R, Chan SS, et al. Bisphosphonate-related complete atypical subtrochanteric femoral fractures: diagnostic utility of radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011; 197(4):954–960. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.6262
- Kim S, Yang KH, Lim H, et al. Detection of prefracture hip lesions in atypical subtrochanteric fracture with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry images. Radiology 2014; 270(2):487–495. doi:10.1148/radiol.13122691
- van de Laarschot DM, Smits AA, Buitendijk SK, Stegenga MT, Zillikens MC. Screening for atypical femur fractures using extended femur scans by DXA. J Bone Miner Res 2017; 32(8):1632–1639. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3164
- Sato H, Kondo N, Nakatsue T, et al. High and pointed type of femoral localized reaction frequently extends to complete an incomplete atypical femoral fracture in patients with autoimmune diseases on long-term glucocorticoids and bisphosphonates. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(8):2367–2376. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-4038-8
- Giaconi JC, Watterson CT. Bisphosphonate-related atypical femur fractures and the radiographic features. In: Silverman SL, Abrahamsen B, eds. The Duration and Safety of Osteoporosis Treatment. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:107–124. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-23639-1
- Whyte MP. Atypical femoral fractures, bisphosphonates, and adult hypophosphatasia. J Bone Miner Res 2009; 24(6):1132–1134. doi:10.1359/jbmr.081253
- Lo JC, Hui RL, Grimsrud CD, et al. The association of race/ethnicity and risk of atypical femoral fracture among older women receiving oral bisphosphonate therapy. Bone 2016; 85:142–147. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2016.01.002
- Bone HG, Wagman RB, Brandi ML, et al. 10 years of denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from the phase 3 randomised FREEDOM trial and open-label extension. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017; 5(7):513–523. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30138-9
- Koh JH, Myong JP, Yoo J, et al. Predisposing factors associated with atypical femur fracture among postmenopausal Korean women receiving bisphosphonate therapy: 8 years' experience in a single center. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(11):3251–3259. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-4169-y
- Kim D, Sung YK, Cho SK, Han M, Kim YS. Factors associated with atypical femoral fracture. Rheumatol Int 2016; 36(1):65–71. doi:10.1007/s00296-015-3323-0
- Roca-Ayats N, Balcells S, Garcia-Giralt N, et al. GGPS1 mutation and atypical femoral fractures with bisphosphonates. N Engl J Med 2017; 376(18):1794–1795. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1612804
- Giusti A, Hamdy NA, Dekkers OM, Ramautar SR, Dijkstra S, Papapoulos SE. Atypical fractures and bisphosphonate therapy: a cohort study of patients with femoral fracture with radiographic adjudication of fracture site and features. Bone 2011; 48(5):966–971. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2010.12.033
- Adler RA, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Bauer DC, et al. Managing osteoporosis in patients on long-term bisphosphonate treatment: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(1):16–35. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2708
- Lloyd AA, Gludovatz B, Riedel C, et al. Atypical fracture with long-term bisphosphonate therapy is associated with altered cortical composition and reduced fracture resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2017; 114(33):8722–8727. doi:10.1073/pnas.1704460114
- Ettinger B, Burr DB, Ritchie RO. Proposed pathogenesis for atypical femoral fractures; lessons from materials research. Bone 2013; 55(2):495–500. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.02.004
- Burr DB, Liu Z, Allen MR. Duration-dependent effects of clinically relevant oral alendronate doses on cortical bone toughness in beagle dogs. Bone 2015; 71:58–62. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2014.10.010
- Sasaki S, Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, Kasukawa Y, Shimada Y. Low-energy diaphyseal femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use and severe curved femur: a case series. J Bone Miner Metab 2012; 30(5):561–567. doi:10.1007/s00774-012-0358-0
- Pulkkinen P, Gluer C, Jamsa T. Investigation of differences between hip fracture types: a worthy strategy of improved risk assessment and fracture prevention. Bone 2011; 49(4):600–604. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2011.07.022
- Ito M, Sone T, Shiraki M, et al. The effect of once-yearly zoledronic acid on hip structural and biomechanical properties derived using computed tomography (CT) in Japanese women with osteoporosis. Bone 2018; 106:179–186. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2017.10.013
- Bogdan Y, Einhorn TA. Clinical presentation of atypical femur fractures. In: Silverman SL, Abrahamsen B, eds. The Duration and Safety of Osteoporosis Treatment. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2016:137–140. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-23639-1
- Im GI, Lee SH. Effect of teriparatide on healing of atypical femoral fractures: a systemic review. J Bone Metab 2015; 22(4):183–189. doi:10.11005/jbm.2015.22.4.183
- Saleh A, Hegde VV, Potty AG, Schneider R, Cornell CN, Lane JM. Management strategy for symptomatic bisphosphonate-associated incomplete atypical femoral fractures. HSS J 2012; 8(2):103–110. doi:10.1007/s11420-012-9275-y
- Egol KA, Park JH, Prensky C, Rosenberg ZS, Peck V, Tejwani NC. Surgical treatment improves clinical and functional outcomes for patients who sustain incomplete bisphosphonate-related femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2013; 27(6):331–335. doi:10.1097/BOT.0b013e31827240ae
- Koh A, Guerado E, Giannoudis PV. Atypical femoral fractures related to bisphosphonate treatment: issues and controversies related to their surgical management. Bone Joint J 2017; 99-B(3):295–302. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B3.BJJ-2016-0276.R2
- Oh CW, Oh JK, Park KC, Kim JW, Yoon YC. Prophylactic nailing of incomplete atypical femoral fractures. ScientificWorldJournal 2013; 2013:450148. doi:10.1155/2013/450148
- Ha YC, Cho MR, Park KH, Kim SY, Koo KH. Is surgery necessary for femoral insufficiency fractures after long-term bisphosphonate therapy? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010; 468(12):3393–3398. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1583-2
- Tosounidis TH, Lampropoulou-Adamidou, Kanakaris NK. Intramedullary nailing of sequential bilateral atypical subtrochanteric fractures and the management of distal femoral intraoperative fracture. J Orthop Trauma 2015 Jun 11. Epub ahead of print. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000370
- Egol KA, Park JH, Rosenberg ZS, Peck V, Tejwani NC. Healing delayed but generally reliable after bisphosphonate-associated complete femur fractures treated with IM nails. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014; 472(9):2728–2734. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-2963-1
KEY POINTS
- The benefits of bisphosphonate therapy in reducing fracture risk outweigh the risk of atypical fracture.
- Bisphosphonate use for longer than 5 years greatly increases the risk of atypical femoral fracture.
- Treatment of atypical femoral fracture varies depending on whether the patient has pain and whether the fracture is complete or incomplete.
Renal vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
A 49-year-old man developed nephrotic-range proteinuria (urine protein–creatinine ratio 4.1 g/g), and primary membranous nephropathy was diagnosed by kidney biopsy. He declined therapy apart from angiotensin receptor blockade.
Five months after undergoing the biopsy, he presented to the emergency room with marked dyspnea, cough, and epigastric discomfort. His blood pressure was 160/100 mm Hg, heart rate 95 beats/minute, and oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry 97% at rest on ambient air, decreasing to 92% with ambulation.
Initial laboratory testing results were as follows:
- Sodium 135 mmol/L (reference range 136–144)
- Potassium 3.9 mmol/L (3.7–5.1)
- Chloride 104 mmol/L (97–105)
- Bicarbonate 21 mmol/L (22–30)
- Blood urea nitrogen 14 mg/dL (9–24)
- Serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dL (0.73–1.22)
- Albumin 2.1 g/dL (3.4–4.9).
Urinalysis revealed the following:
- 5 red blood cells per high-power field, compared with 1 to 2 previously
- 3+ proteinuria
- Urine protein–creatinine ratio 11 g/g
- No glucosuria.
Electrocardiography revealed normal sinus rhythm without ischemic changes. Chest radiography did not show consolidation.
At 7 months after the thrombotic event, there was no evidence of residual renal vein thrombosis on magnetic resonance venography, and at 14 months his serum creatinine level was 0.9 mg/dL, albumin 4.0 g/dL, and urine protein–creatinine ratio 0.8 g/g.
RENAL VEIN THROMBOSIS: RISK FACTORS AND CLINICAL FEATURES
Severe hypoalbuminemia in the setting of nephrotic syndrome due to membranous nephropathy is associated with the highest risk of venous thromboembolic events, with renal vein thrombus being the classic complication.1 Venous thromboembolic events also occur in other nephrotic syndromes, albeit at a lower frequency.2
Venous thromboembolic events are estimated to occur in 7% to 33% of patients with membranous glomerulopathy, with albumin levels less than 2.8 g/dL considered a notable risk factor.1,2
While often a chronic complication, acute renal vein thrombosis may present with flank pain and hematuria.3 In our patient, the dramatic increase in proteinuria and possibly the increase in hematuria suggested renal vein thrombosis. Proximal tubular dysfunction, such as glucosuria, can be seen on occasion.
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Screening asymptomatic patients for renal vein thrombosis is not recommended, and the decision to start prophylactic anticoagulation must be individualized.4
Although renal venography historically was the gold standard test to diagnose renal vein thrombosis, it has been replaced by noninvasive imaging such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance venography.
While anticoagulation remains the treatment of choice, catheter-directed thrombectomy or surgical thrombectomy can be considered for some patients with acute renal vein thrombosis.5
- Couser WG. Primary membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017; 12(6):983–997. doi:10.2215/CJN.11761116
- Barbour SJ, Greenwald A, Djurdjev O, et al. Disease-specific risk of venous thromboembolic events is increased in idiopathic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2012; 81(2):190–195. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.312
- Lionaki S, Derebail VK, Hogan SL, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients with membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 7(1):43–51. doi:10.2215/CJN.04250511
- Lee T, Biddle AK, Lionaki S, et al. Personalized prophylactic anticoagulation decision analysis in patients with membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 2014; 85(6):1412–1420. doi:10.1038/ki.2013.476
- Jaar BG, Kim HS, Samaniego MD, Lund GB, Atta MG. Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy: a new approach in the treatment of acute renal-vein thrombosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002; 17(6):1122–1125. pmid:12032209
A 49-year-old man developed nephrotic-range proteinuria (urine protein–creatinine ratio 4.1 g/g), and primary membranous nephropathy was diagnosed by kidney biopsy. He declined therapy apart from angiotensin receptor blockade.
Five months after undergoing the biopsy, he presented to the emergency room with marked dyspnea, cough, and epigastric discomfort. His blood pressure was 160/100 mm Hg, heart rate 95 beats/minute, and oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry 97% at rest on ambient air, decreasing to 92% with ambulation.
Initial laboratory testing results were as follows:
- Sodium 135 mmol/L (reference range 136–144)
- Potassium 3.9 mmol/L (3.7–5.1)
- Chloride 104 mmol/L (97–105)
- Bicarbonate 21 mmol/L (22–30)
- Blood urea nitrogen 14 mg/dL (9–24)
- Serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dL (0.73–1.22)
- Albumin 2.1 g/dL (3.4–4.9).
Urinalysis revealed the following:
- 5 red blood cells per high-power field, compared with 1 to 2 previously
- 3+ proteinuria
- Urine protein–creatinine ratio 11 g/g
- No glucosuria.
Electrocardiography revealed normal sinus rhythm without ischemic changes. Chest radiography did not show consolidation.
At 7 months after the thrombotic event, there was no evidence of residual renal vein thrombosis on magnetic resonance venography, and at 14 months his serum creatinine level was 0.9 mg/dL, albumin 4.0 g/dL, and urine protein–creatinine ratio 0.8 g/g.
RENAL VEIN THROMBOSIS: RISK FACTORS AND CLINICAL FEATURES
Severe hypoalbuminemia in the setting of nephrotic syndrome due to membranous nephropathy is associated with the highest risk of venous thromboembolic events, with renal vein thrombus being the classic complication.1 Venous thromboembolic events also occur in other nephrotic syndromes, albeit at a lower frequency.2
Venous thromboembolic events are estimated to occur in 7% to 33% of patients with membranous glomerulopathy, with albumin levels less than 2.8 g/dL considered a notable risk factor.1,2
While often a chronic complication, acute renal vein thrombosis may present with flank pain and hematuria.3 In our patient, the dramatic increase in proteinuria and possibly the increase in hematuria suggested renal vein thrombosis. Proximal tubular dysfunction, such as glucosuria, can be seen on occasion.
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Screening asymptomatic patients for renal vein thrombosis is not recommended, and the decision to start prophylactic anticoagulation must be individualized.4
Although renal venography historically was the gold standard test to diagnose renal vein thrombosis, it has been replaced by noninvasive imaging such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance venography.
While anticoagulation remains the treatment of choice, catheter-directed thrombectomy or surgical thrombectomy can be considered for some patients with acute renal vein thrombosis.5
A 49-year-old man developed nephrotic-range proteinuria (urine protein–creatinine ratio 4.1 g/g), and primary membranous nephropathy was diagnosed by kidney biopsy. He declined therapy apart from angiotensin receptor blockade.
Five months after undergoing the biopsy, he presented to the emergency room with marked dyspnea, cough, and epigastric discomfort. His blood pressure was 160/100 mm Hg, heart rate 95 beats/minute, and oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry 97% at rest on ambient air, decreasing to 92% with ambulation.
Initial laboratory testing results were as follows:
- Sodium 135 mmol/L (reference range 136–144)
- Potassium 3.9 mmol/L (3.7–5.1)
- Chloride 104 mmol/L (97–105)
- Bicarbonate 21 mmol/L (22–30)
- Blood urea nitrogen 14 mg/dL (9–24)
- Serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dL (0.73–1.22)
- Albumin 2.1 g/dL (3.4–4.9).
Urinalysis revealed the following:
- 5 red blood cells per high-power field, compared with 1 to 2 previously
- 3+ proteinuria
- Urine protein–creatinine ratio 11 g/g
- No glucosuria.
Electrocardiography revealed normal sinus rhythm without ischemic changes. Chest radiography did not show consolidation.
At 7 months after the thrombotic event, there was no evidence of residual renal vein thrombosis on magnetic resonance venography, and at 14 months his serum creatinine level was 0.9 mg/dL, albumin 4.0 g/dL, and urine protein–creatinine ratio 0.8 g/g.
RENAL VEIN THROMBOSIS: RISK FACTORS AND CLINICAL FEATURES
Severe hypoalbuminemia in the setting of nephrotic syndrome due to membranous nephropathy is associated with the highest risk of venous thromboembolic events, with renal vein thrombus being the classic complication.1 Venous thromboembolic events also occur in other nephrotic syndromes, albeit at a lower frequency.2
Venous thromboembolic events are estimated to occur in 7% to 33% of patients with membranous glomerulopathy, with albumin levels less than 2.8 g/dL considered a notable risk factor.1,2
While often a chronic complication, acute renal vein thrombosis may present with flank pain and hematuria.3 In our patient, the dramatic increase in proteinuria and possibly the increase in hematuria suggested renal vein thrombosis. Proximal tubular dysfunction, such as glucosuria, can be seen on occasion.
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Screening asymptomatic patients for renal vein thrombosis is not recommended, and the decision to start prophylactic anticoagulation must be individualized.4
Although renal venography historically was the gold standard test to diagnose renal vein thrombosis, it has been replaced by noninvasive imaging such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance venography.
While anticoagulation remains the treatment of choice, catheter-directed thrombectomy or surgical thrombectomy can be considered for some patients with acute renal vein thrombosis.5
- Couser WG. Primary membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017; 12(6):983–997. doi:10.2215/CJN.11761116
- Barbour SJ, Greenwald A, Djurdjev O, et al. Disease-specific risk of venous thromboembolic events is increased in idiopathic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2012; 81(2):190–195. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.312
- Lionaki S, Derebail VK, Hogan SL, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients with membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 7(1):43–51. doi:10.2215/CJN.04250511
- Lee T, Biddle AK, Lionaki S, et al. Personalized prophylactic anticoagulation decision analysis in patients with membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 2014; 85(6):1412–1420. doi:10.1038/ki.2013.476
- Jaar BG, Kim HS, Samaniego MD, Lund GB, Atta MG. Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy: a new approach in the treatment of acute renal-vein thrombosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002; 17(6):1122–1125. pmid:12032209
- Couser WG. Primary membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017; 12(6):983–997. doi:10.2215/CJN.11761116
- Barbour SJ, Greenwald A, Djurdjev O, et al. Disease-specific risk of venous thromboembolic events is increased in idiopathic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2012; 81(2):190–195. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.312
- Lionaki S, Derebail VK, Hogan SL, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients with membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 7(1):43–51. doi:10.2215/CJN.04250511
- Lee T, Biddle AK, Lionaki S, et al. Personalized prophylactic anticoagulation decision analysis in patients with membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 2014; 85(6):1412–1420. doi:10.1038/ki.2013.476
- Jaar BG, Kim HS, Samaniego MD, Lund GB, Atta MG. Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy: a new approach in the treatment of acute renal-vein thrombosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002; 17(6):1122–1125. pmid:12032209
Back pain as a sign of inferior vena cava filter complications
A 63-year-old woman presented with an acute exacerbation of chronic back pain after a fall. She was taking warfarin because of a history of factor V Leiden, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism, for which a temporary inferior vena cava (IVC) filter had been placed 8 years ago. Her physicians had subsequently tried to remove the filter, without success. Some time after that, 1 of the filter struts had been removed after it migrated through her abdominal wall.
Laboratory testing revealed a supratherapeutic international normalized ratio of 8.5.
The patient underwent endovascular aneurysm repair with adequate placement of a vascular graft. She was discharged on therapeutic anticoagulation, and her back pain had notably improved.
COMPLICATIONS OF IVC FILTERS
In the United States, the use of IVC filters has increased significantly over the last decade, with placement rates ranging from 12% to 17% in patients with venous thromboembolism.1
The American Heart Association recommends filter placement for patients with venous thromboembolism for whom anticoagulation has failed or is contraindicated, patients unable to withstand pulmonary embolism, and patients who are hemodynamically unstable.2 While indications vary in the guidelines released by different societies, filters are most often placed in patients who have an acute bleed, significant surgery after admission for venous thromboembolism, metastatic cancer, and severe illness.3
Complications can occur during and after insertion and during removal. They are more frequent with temporary than with permanent filters, and include filter movement and fracture as well as occlusion and penetration.4,5
In our patient, we believe that the 3 remaining filter struts likely penetrated the wall of the IVC to the extent that they encountered adjacent structures (aorta, duodenum, kidney).
Of cases of IVC filter penetration reported to a US Food and Drug Administration database, 13.1% involved small bowel perforation, 6.5% involved aortic perforation, and 4.2% involved retroperitoneal bleeding. Symptoms such as abdominal and back pain were present in 38.3% of cases involving IVC penetration.5
Therefore, the differential diagnosis for patients with a history of IVC filter placement presenting with these symptoms should address filter complications, including occlusion, incorrect placement, fracture, migration, and penetration of the filter.4 If complications occur, treatment options include anticoagulation, endovascular repair, and surgical intervention.
- Alkhouli M, Bashir R. Inferior vena cava filters in the United States: less is more. Int J Cardiol 2014; 177(3):742–743. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.08.010
- Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, et al; American Heart Association Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and Resuscitation; American Heart Association Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; American Heart Association Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011; 123(16):1788–1830. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e318214914f
- White RH, Geraghty EM, Brunson A, et al. High variation between hospitals in vena cava filter use for venous thromboembolism. JAMA Intern Med 2013; 173(7):506–512. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.2352
- Sella DM, Oldenburg WA. Complications of inferior vena cava filters. Semin Vasc Surg 2013; 26(1):23–28. doi:10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2013.04.005
- Andreoli JM, Lewandowski RJ, Vogelzang RL, Ryu RK. Comparison of complication rates associated with permanent and retrievable inferior vena cava filters: a review of the MAUDE database. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2014; 25(8):1181–1185. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2014.04.016
A 63-year-old woman presented with an acute exacerbation of chronic back pain after a fall. She was taking warfarin because of a history of factor V Leiden, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism, for which a temporary inferior vena cava (IVC) filter had been placed 8 years ago. Her physicians had subsequently tried to remove the filter, without success. Some time after that, 1 of the filter struts had been removed after it migrated through her abdominal wall.
Laboratory testing revealed a supratherapeutic international normalized ratio of 8.5.
The patient underwent endovascular aneurysm repair with adequate placement of a vascular graft. She was discharged on therapeutic anticoagulation, and her back pain had notably improved.
COMPLICATIONS OF IVC FILTERS
In the United States, the use of IVC filters has increased significantly over the last decade, with placement rates ranging from 12% to 17% in patients with venous thromboembolism.1
The American Heart Association recommends filter placement for patients with venous thromboembolism for whom anticoagulation has failed or is contraindicated, patients unable to withstand pulmonary embolism, and patients who are hemodynamically unstable.2 While indications vary in the guidelines released by different societies, filters are most often placed in patients who have an acute bleed, significant surgery after admission for venous thromboembolism, metastatic cancer, and severe illness.3
Complications can occur during and after insertion and during removal. They are more frequent with temporary than with permanent filters, and include filter movement and fracture as well as occlusion and penetration.4,5
In our patient, we believe that the 3 remaining filter struts likely penetrated the wall of the IVC to the extent that they encountered adjacent structures (aorta, duodenum, kidney).
Of cases of IVC filter penetration reported to a US Food and Drug Administration database, 13.1% involved small bowel perforation, 6.5% involved aortic perforation, and 4.2% involved retroperitoneal bleeding. Symptoms such as abdominal and back pain were present in 38.3% of cases involving IVC penetration.5
Therefore, the differential diagnosis for patients with a history of IVC filter placement presenting with these symptoms should address filter complications, including occlusion, incorrect placement, fracture, migration, and penetration of the filter.4 If complications occur, treatment options include anticoagulation, endovascular repair, and surgical intervention.
A 63-year-old woman presented with an acute exacerbation of chronic back pain after a fall. She was taking warfarin because of a history of factor V Leiden, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism, for which a temporary inferior vena cava (IVC) filter had been placed 8 years ago. Her physicians had subsequently tried to remove the filter, without success. Some time after that, 1 of the filter struts had been removed after it migrated through her abdominal wall.
Laboratory testing revealed a supratherapeutic international normalized ratio of 8.5.
The patient underwent endovascular aneurysm repair with adequate placement of a vascular graft. She was discharged on therapeutic anticoagulation, and her back pain had notably improved.
COMPLICATIONS OF IVC FILTERS
In the United States, the use of IVC filters has increased significantly over the last decade, with placement rates ranging from 12% to 17% in patients with venous thromboembolism.1
The American Heart Association recommends filter placement for patients with venous thromboembolism for whom anticoagulation has failed or is contraindicated, patients unable to withstand pulmonary embolism, and patients who are hemodynamically unstable.2 While indications vary in the guidelines released by different societies, filters are most often placed in patients who have an acute bleed, significant surgery after admission for venous thromboembolism, metastatic cancer, and severe illness.3
Complications can occur during and after insertion and during removal. They are more frequent with temporary than with permanent filters, and include filter movement and fracture as well as occlusion and penetration.4,5
In our patient, we believe that the 3 remaining filter struts likely penetrated the wall of the IVC to the extent that they encountered adjacent structures (aorta, duodenum, kidney).
Of cases of IVC filter penetration reported to a US Food and Drug Administration database, 13.1% involved small bowel perforation, 6.5% involved aortic perforation, and 4.2% involved retroperitoneal bleeding. Symptoms such as abdominal and back pain were present in 38.3% of cases involving IVC penetration.5
Therefore, the differential diagnosis for patients with a history of IVC filter placement presenting with these symptoms should address filter complications, including occlusion, incorrect placement, fracture, migration, and penetration of the filter.4 If complications occur, treatment options include anticoagulation, endovascular repair, and surgical intervention.
- Alkhouli M, Bashir R. Inferior vena cava filters in the United States: less is more. Int J Cardiol 2014; 177(3):742–743. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.08.010
- Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, et al; American Heart Association Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and Resuscitation; American Heart Association Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; American Heart Association Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011; 123(16):1788–1830. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e318214914f
- White RH, Geraghty EM, Brunson A, et al. High variation between hospitals in vena cava filter use for venous thromboembolism. JAMA Intern Med 2013; 173(7):506–512. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.2352
- Sella DM, Oldenburg WA. Complications of inferior vena cava filters. Semin Vasc Surg 2013; 26(1):23–28. doi:10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2013.04.005
- Andreoli JM, Lewandowski RJ, Vogelzang RL, Ryu RK. Comparison of complication rates associated with permanent and retrievable inferior vena cava filters: a review of the MAUDE database. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2014; 25(8):1181–1185. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2014.04.016
- Alkhouli M, Bashir R. Inferior vena cava filters in the United States: less is more. Int J Cardiol 2014; 177(3):742–743. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.08.010
- Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, et al; American Heart Association Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and Resuscitation; American Heart Association Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease; American Heart Association Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011; 123(16):1788–1830. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e318214914f
- White RH, Geraghty EM, Brunson A, et al. High variation between hospitals in vena cava filter use for venous thromboembolism. JAMA Intern Med 2013; 173(7):506–512. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.2352
- Sella DM, Oldenburg WA. Complications of inferior vena cava filters. Semin Vasc Surg 2013; 26(1):23–28. doi:10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2013.04.005
- Andreoli JM, Lewandowski RJ, Vogelzang RL, Ryu RK. Comparison of complication rates associated with permanent and retrievable inferior vena cava filters: a review of the MAUDE database. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2014; 25(8):1181–1185. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2014.04.016