User login
Can an ‘unheard of’ approach up adherence to public health advice?
Using principles of psychoanalysis to craft public health messaging may be a novel and effective way of increasing adherence to public health advice during the COVID-19 pandemic, experts say.
In a letter published online Oct. 19 in The Lancet, coauthors Austin Ratner, MD, and Nisarg Gandhi, believe that, as expert communicators, psychoanalysts should be part of the public health care team to help battle the pandemic.
“The idea of using psychoanalysis in a public health setting is relatively unheard of,” Ratner, the author of a book titled “The Psychoanalyst’s Aversion to Proof,” told Medscape Medical News. Ratner earned his MD at John Hopkins School of Medicine but left medicine to become an author. Gandhi is a clinical research intern at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, New Jersey.
Psychoanalysis postulates that defense mechanisms, such as denial, may play an important role in nonadherence to public health guidance regarding the pandemic, Ratner said.
including nonadherence to medical advice regarding COVID-19, as well as climate change and politics.
“By understanding that fear and anxiety underpin a lot of denial, the psychoanalytic viewpoint can help influence public health officials in recognizing the fear and anxiety, how to talk about the threat [of the pandemic], and what can be done about it,” he added.
“A new partnership”
“Psychoanalysts have historically resisted collaboration with disciplines such as social and experimental psychology,” Ratner said. This “insularity” results in “lost opportunities on the path for psychoanalysis to become part of the conversation regarding mass denial and mass nonadherence to medical advice.”
He noted that change is afoot in the psychoanalytic community. The American Psychoanalytic Association (APsaA) has begun to “empower constituents” who seek greater “integration with experimental science and greater involvement with public health.”
To that end, Ratner suggests a “new partnership” between three fields that have until now been disparate: experimental psychology, public health, and psychoanalysis.
Cognitive scientists have studied and documented denial, attributing it to “anxiety’s power to compromise rational thought,” but their approach has not focused on the psychoanalytic model of denial as a defense mechanism, Ratner observed.
Mark Smaller, PhD, past president of APsaA and board member of the International Psychoanalytical Association, elaborated.
“From a psychoanalytic perspective, I am interested in how a defense mechanism functions for individuals and groups,” Smaller told Medscape Medical News.
Denial as a defense mechanism often arises, whether in individuals or groups, from a sense of helplessness, explained Smaller, who is also the chair of the department of public advocacy at APsaA.
“People can only tolerate a certain amount of helplessness – in fact, I would suggest as an analyst that helplessness is the most difficult feeling for humans to come to terms with,” he said.
Helplessness can contribute to trauma and “I think we have a mass case of traumatic helplessness in our country right now because of the pandemic.”
Some people respond to a sense of helplessness with depression or hopelessness, while others “try to integrate the impact of the pandemic by focusing on things over which they have control, like wearing a mask, social distancing, and avoiding places with large numbers of people where the virus can be easily transmitted,” said Smaller.
However, “what seems to have occurred in our country is that, although many people have focused on what we do have control of, a large segment of our population are acting as if COVID-19 doesn’t exist, and we have leadership supporting this denial,” he added.
Is “denial” evidence-based?
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Richard McAnulty, PhD, associate professor of psychology at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte expressed skepticism about the psychoanalytic view of denial, and its potential role in addressing the pandemic.
“A key criticism of psychoanalytic and psychodynamic viewpoints is that many – including the concept of a subconscious mind – are theoretical, not open to empirical research, and not measurable; and one of the most fundamental requirements in science is that all your constructs are measurable.”
For this reason, this approach is “limited in usefulness, although it might be an interesting source of speculation,” said McAnulty.
Ratner disagreed, noting that there is research corroborating the existence of an unconscious mind. Noted analyst Carl Jung, Ratner pointed out, conducted “some great experiments to prove some of the central tenets of psychoanalysis using word associations.”
Jung found that, if individuals were challenged with words that evoked painful associations, it took them longer to arrive at the answer to the test. They also made more mistakes.
Jung’s research “goes back to a core idea of psychoanalysis, which is that painful or difficult thoughts and feelings get distorted, pushed out of consciousness, forgotten, delayed, or suppressed,” Ratner said. These responses might account for “what we’re seeing the U.S. that people are resorting to irrational thinking without being aware of it.”
McAnulty suggested that the psychodynamic idea of denial as a defense mechanism is not relevant to mass nonadherence to pandemic-related medical advice.
Rather, the denial stems from “schemas and belief systems about the world, how people should operate and behave, and the role of government and the medical establishment,” he said.
“When certain recommendations are discrepant with the world view, it creates dissonance or a mismatch and the person will try to reconcile the mismatch,” McAnulty continued. “One way to do that is to say that these recommendations are invalid because they violate the individual’s political beliefs, world view, or religious ideas.”
Ultimately, “it depends on how we define denial,” said McAnulty. “If it means dismissing information that doesn’t fit an existing belief system, that’s denial, but the psychodynamic meaning of ‘denial’ is much deeper than that.”
Smaller, the past president of APsaA, emphasized the importance of empathy when addressing the public. “Psychoanalysts bring empathy to irrationality. Having a psychoanalyst as a team member can help public health officials to communicate better and craft the understanding of anxiety and fear into their message.”
Ratner said he is “not proposing a simplistic silver bullet as an answer to a very complex, multifaceted problem of nonadherence to medical advice.”
Instead, he is “proposing something that hasn’t happened yet, which is more research and more conversation, with psychoanalysis as part of the conversation, because the notion of denial is so relevant, despite how many other factors are involved.”
Ratner, Gandhi, Smaller, and McAnulty have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ratner is the author of The Psychoanalyst’s Aversion to Proof and the medical textbook Concepts in Medical Physiology.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Using principles of psychoanalysis to craft public health messaging may be a novel and effective way of increasing adherence to public health advice during the COVID-19 pandemic, experts say.
In a letter published online Oct. 19 in The Lancet, coauthors Austin Ratner, MD, and Nisarg Gandhi, believe that, as expert communicators, psychoanalysts should be part of the public health care team to help battle the pandemic.
“The idea of using psychoanalysis in a public health setting is relatively unheard of,” Ratner, the author of a book titled “The Psychoanalyst’s Aversion to Proof,” told Medscape Medical News. Ratner earned his MD at John Hopkins School of Medicine but left medicine to become an author. Gandhi is a clinical research intern at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, New Jersey.
Psychoanalysis postulates that defense mechanisms, such as denial, may play an important role in nonadherence to public health guidance regarding the pandemic, Ratner said.
including nonadherence to medical advice regarding COVID-19, as well as climate change and politics.
“By understanding that fear and anxiety underpin a lot of denial, the psychoanalytic viewpoint can help influence public health officials in recognizing the fear and anxiety, how to talk about the threat [of the pandemic], and what can be done about it,” he added.
“A new partnership”
“Psychoanalysts have historically resisted collaboration with disciplines such as social and experimental psychology,” Ratner said. This “insularity” results in “lost opportunities on the path for psychoanalysis to become part of the conversation regarding mass denial and mass nonadherence to medical advice.”
He noted that change is afoot in the psychoanalytic community. The American Psychoanalytic Association (APsaA) has begun to “empower constituents” who seek greater “integration with experimental science and greater involvement with public health.”
To that end, Ratner suggests a “new partnership” between three fields that have until now been disparate: experimental psychology, public health, and psychoanalysis.
Cognitive scientists have studied and documented denial, attributing it to “anxiety’s power to compromise rational thought,” but their approach has not focused on the psychoanalytic model of denial as a defense mechanism, Ratner observed.
Mark Smaller, PhD, past president of APsaA and board member of the International Psychoanalytical Association, elaborated.
“From a psychoanalytic perspective, I am interested in how a defense mechanism functions for individuals and groups,” Smaller told Medscape Medical News.
Denial as a defense mechanism often arises, whether in individuals or groups, from a sense of helplessness, explained Smaller, who is also the chair of the department of public advocacy at APsaA.
“People can only tolerate a certain amount of helplessness – in fact, I would suggest as an analyst that helplessness is the most difficult feeling for humans to come to terms with,” he said.
Helplessness can contribute to trauma and “I think we have a mass case of traumatic helplessness in our country right now because of the pandemic.”
Some people respond to a sense of helplessness with depression or hopelessness, while others “try to integrate the impact of the pandemic by focusing on things over which they have control, like wearing a mask, social distancing, and avoiding places with large numbers of people where the virus can be easily transmitted,” said Smaller.
However, “what seems to have occurred in our country is that, although many people have focused on what we do have control of, a large segment of our population are acting as if COVID-19 doesn’t exist, and we have leadership supporting this denial,” he added.
Is “denial” evidence-based?
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Richard McAnulty, PhD, associate professor of psychology at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte expressed skepticism about the psychoanalytic view of denial, and its potential role in addressing the pandemic.
“A key criticism of psychoanalytic and psychodynamic viewpoints is that many – including the concept of a subconscious mind – are theoretical, not open to empirical research, and not measurable; and one of the most fundamental requirements in science is that all your constructs are measurable.”
For this reason, this approach is “limited in usefulness, although it might be an interesting source of speculation,” said McAnulty.
Ratner disagreed, noting that there is research corroborating the existence of an unconscious mind. Noted analyst Carl Jung, Ratner pointed out, conducted “some great experiments to prove some of the central tenets of psychoanalysis using word associations.”
Jung found that, if individuals were challenged with words that evoked painful associations, it took them longer to arrive at the answer to the test. They also made more mistakes.
Jung’s research “goes back to a core idea of psychoanalysis, which is that painful or difficult thoughts and feelings get distorted, pushed out of consciousness, forgotten, delayed, or suppressed,” Ratner said. These responses might account for “what we’re seeing the U.S. that people are resorting to irrational thinking without being aware of it.”
McAnulty suggested that the psychodynamic idea of denial as a defense mechanism is not relevant to mass nonadherence to pandemic-related medical advice.
Rather, the denial stems from “schemas and belief systems about the world, how people should operate and behave, and the role of government and the medical establishment,” he said.
“When certain recommendations are discrepant with the world view, it creates dissonance or a mismatch and the person will try to reconcile the mismatch,” McAnulty continued. “One way to do that is to say that these recommendations are invalid because they violate the individual’s political beliefs, world view, or religious ideas.”
Ultimately, “it depends on how we define denial,” said McAnulty. “If it means dismissing information that doesn’t fit an existing belief system, that’s denial, but the psychodynamic meaning of ‘denial’ is much deeper than that.”
Smaller, the past president of APsaA, emphasized the importance of empathy when addressing the public. “Psychoanalysts bring empathy to irrationality. Having a psychoanalyst as a team member can help public health officials to communicate better and craft the understanding of anxiety and fear into their message.”
Ratner said he is “not proposing a simplistic silver bullet as an answer to a very complex, multifaceted problem of nonadherence to medical advice.”
Instead, he is “proposing something that hasn’t happened yet, which is more research and more conversation, with psychoanalysis as part of the conversation, because the notion of denial is so relevant, despite how many other factors are involved.”
Ratner, Gandhi, Smaller, and McAnulty have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ratner is the author of The Psychoanalyst’s Aversion to Proof and the medical textbook Concepts in Medical Physiology.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Using principles of psychoanalysis to craft public health messaging may be a novel and effective way of increasing adherence to public health advice during the COVID-19 pandemic, experts say.
In a letter published online Oct. 19 in The Lancet, coauthors Austin Ratner, MD, and Nisarg Gandhi, believe that, as expert communicators, psychoanalysts should be part of the public health care team to help battle the pandemic.
“The idea of using psychoanalysis in a public health setting is relatively unheard of,” Ratner, the author of a book titled “The Psychoanalyst’s Aversion to Proof,” told Medscape Medical News. Ratner earned his MD at John Hopkins School of Medicine but left medicine to become an author. Gandhi is a clinical research intern at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, New Jersey.
Psychoanalysis postulates that defense mechanisms, such as denial, may play an important role in nonadherence to public health guidance regarding the pandemic, Ratner said.
including nonadherence to medical advice regarding COVID-19, as well as climate change and politics.
“By understanding that fear and anxiety underpin a lot of denial, the psychoanalytic viewpoint can help influence public health officials in recognizing the fear and anxiety, how to talk about the threat [of the pandemic], and what can be done about it,” he added.
“A new partnership”
“Psychoanalysts have historically resisted collaboration with disciplines such as social and experimental psychology,” Ratner said. This “insularity” results in “lost opportunities on the path for psychoanalysis to become part of the conversation regarding mass denial and mass nonadherence to medical advice.”
He noted that change is afoot in the psychoanalytic community. The American Psychoanalytic Association (APsaA) has begun to “empower constituents” who seek greater “integration with experimental science and greater involvement with public health.”
To that end, Ratner suggests a “new partnership” between three fields that have until now been disparate: experimental psychology, public health, and psychoanalysis.
Cognitive scientists have studied and documented denial, attributing it to “anxiety’s power to compromise rational thought,” but their approach has not focused on the psychoanalytic model of denial as a defense mechanism, Ratner observed.
Mark Smaller, PhD, past president of APsaA and board member of the International Psychoanalytical Association, elaborated.
“From a psychoanalytic perspective, I am interested in how a defense mechanism functions for individuals and groups,” Smaller told Medscape Medical News.
Denial as a defense mechanism often arises, whether in individuals or groups, from a sense of helplessness, explained Smaller, who is also the chair of the department of public advocacy at APsaA.
“People can only tolerate a certain amount of helplessness – in fact, I would suggest as an analyst that helplessness is the most difficult feeling for humans to come to terms with,” he said.
Helplessness can contribute to trauma and “I think we have a mass case of traumatic helplessness in our country right now because of the pandemic.”
Some people respond to a sense of helplessness with depression or hopelessness, while others “try to integrate the impact of the pandemic by focusing on things over which they have control, like wearing a mask, social distancing, and avoiding places with large numbers of people where the virus can be easily transmitted,” said Smaller.
However, “what seems to have occurred in our country is that, although many people have focused on what we do have control of, a large segment of our population are acting as if COVID-19 doesn’t exist, and we have leadership supporting this denial,” he added.
Is “denial” evidence-based?
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Richard McAnulty, PhD, associate professor of psychology at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte expressed skepticism about the psychoanalytic view of denial, and its potential role in addressing the pandemic.
“A key criticism of psychoanalytic and psychodynamic viewpoints is that many – including the concept of a subconscious mind – are theoretical, not open to empirical research, and not measurable; and one of the most fundamental requirements in science is that all your constructs are measurable.”
For this reason, this approach is “limited in usefulness, although it might be an interesting source of speculation,” said McAnulty.
Ratner disagreed, noting that there is research corroborating the existence of an unconscious mind. Noted analyst Carl Jung, Ratner pointed out, conducted “some great experiments to prove some of the central tenets of psychoanalysis using word associations.”
Jung found that, if individuals were challenged with words that evoked painful associations, it took them longer to arrive at the answer to the test. They also made more mistakes.
Jung’s research “goes back to a core idea of psychoanalysis, which is that painful or difficult thoughts and feelings get distorted, pushed out of consciousness, forgotten, delayed, or suppressed,” Ratner said. These responses might account for “what we’re seeing the U.S. that people are resorting to irrational thinking without being aware of it.”
McAnulty suggested that the psychodynamic idea of denial as a defense mechanism is not relevant to mass nonadherence to pandemic-related medical advice.
Rather, the denial stems from “schemas and belief systems about the world, how people should operate and behave, and the role of government and the medical establishment,” he said.
“When certain recommendations are discrepant with the world view, it creates dissonance or a mismatch and the person will try to reconcile the mismatch,” McAnulty continued. “One way to do that is to say that these recommendations are invalid because they violate the individual’s political beliefs, world view, or religious ideas.”
Ultimately, “it depends on how we define denial,” said McAnulty. “If it means dismissing information that doesn’t fit an existing belief system, that’s denial, but the psychodynamic meaning of ‘denial’ is much deeper than that.”
Smaller, the past president of APsaA, emphasized the importance of empathy when addressing the public. “Psychoanalysts bring empathy to irrationality. Having a psychoanalyst as a team member can help public health officials to communicate better and craft the understanding of anxiety and fear into their message.”
Ratner said he is “not proposing a simplistic silver bullet as an answer to a very complex, multifaceted problem of nonadherence to medical advice.”
Instead, he is “proposing something that hasn’t happened yet, which is more research and more conversation, with psychoanalysis as part of the conversation, because the notion of denial is so relevant, despite how many other factors are involved.”
Ratner, Gandhi, Smaller, and McAnulty have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ratner is the author of The Psychoanalyst’s Aversion to Proof and the medical textbook Concepts in Medical Physiology.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Syphilis: Cutting risk through primary prevention and prenatal screening
CASE Pregnant woman with positive Treponema pallidum antibody test
A 30-year-old primigravida at 10 weeks and 4 days of gestation by her last menstrual period presents to your office for her initial prenatal visit. She expresses no concerns. You order the standard set of laboratory tests, including a sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening panel. Consistent with your institution’s use of the reverse algorithm for syphilis screening, you obtain a Treponema pallidum antibody test, which reflexes to the rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. Three days later, you receive a notification that this patient’s T pallidum antibody result was positive, followed by negative RPR test results. The follow-up T pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA) test also was negative. Given these findings, you consider:
- What is the correct interpretation of the patient’s sequence of test results?
- Is she infected, and does she require treatment?
Meet our perpetrator
Syphilis has plagued society since the late 15th century, although its causative agent, the spirochete T pallidum, was not recognized until 1905.1,2T pallidum bacteria are transmitted via sexual contact, as well as through vertical transmission during pregnancy or delivery. Infection with syphilis is reported in 50% to 60% of sexual partners after a single exposure to an infected individual with early syphilis, and the mean incubation period is 21 days.3T pallidum can cross the placenta and infect a fetus as early as the sixth week of gestation.3 Congenital syphilis infections occur in the neonates of 50% to 80% of women with untreated primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis infections; maternal syphilis is associated with a 21% increased risk of stillbirth, a 6% increased risk of preterm delivery, and a 9% increased risk of neonatal death.4,5 Additionally, syphilis infection is associated with a high risk of HIV infection, as well as coinfection with other STIs.1
Given the highly infective nature of T pallidum, as well as the severity of the potential consequences of infection for both mothers and babies, primary prevention, education of at-risk populations, and early recognition of clinical features of syphilis infection are of utmost importance in preventing morbidity and mortality. In this article, we review the epidemiology and extensive clinical manifestations of syphilis, as well as current screening recommendations and treatment for pregnant women.
The extent of the problem today
Although US rates of syphilis have ebbed and flowed for the past several decades, the current incidence has grown exponentially in recent years, with the number of cases reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) increasing by 71% from 2014 to 2018.6 During this time period, reported cases of primary and secondary syphilis in women more than doubled (172.7% and 165.4%, respectively) according to CDC data, accompanied by a parallel rise in reported cases of congenital syphilis in both live and stillborn infants.6 In 2018, the CDC reported a national rate of congenital syphilis of 33.1 cases per 100,000 live births, a 39.7% rise compared with data from 2017.6
Those most at risk. Risk factors for syphilis infection include age younger than 30 years, low socioeconomic status, substance abuse, HIV infection, concurrent STIs, and high-risk sexual activity (sex with multiple high-risk partners).3 Additionally, reported rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections, as well as congenital syphilis infections, are more elevated among women who identify as Black, American Indian/Alaska Native, and/or Hispanic.6 Congenital infections in the United States are correlated with a lack of prenatal care, which has been similarly linked with racial and socioeconomic disparities, as well as with untreated mental health and substance use disorders and recent immigration to the United States.5,7
Continue to: The many phases of syphilis...
The many phases of syphilis
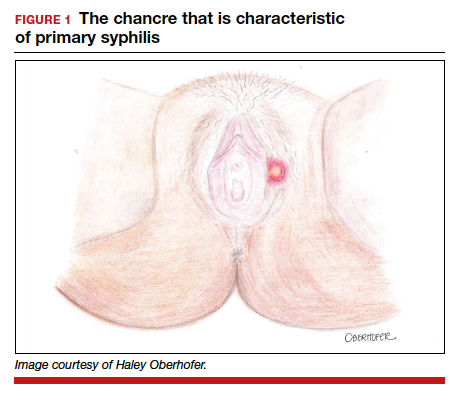
The characteristic lesion of primary syphilis is a chancre, which is a painless, ulcerative lesion with raised borders and a clean, indurated base appearing at the site of spirochete entry (FIGURE 1). Chancres most commonly appear in the genital area, with the most frequent sites in females being within the vaginal canal or on the cervix. Primary chancres tend to heal spontaneously within 3 to 6 weeks, even without treatment, and frequently are accompanied by painless inguinal lymphadenopathy. Given that the most common chancre sites are not immediately apparent, primary infections in women often go undetected.3 In fact, it is essential for clinicians to recognize that, in our routine practice, most patients with syphilis will not be symptomatic at all, and the diagnosis will only be made by serologic screening.
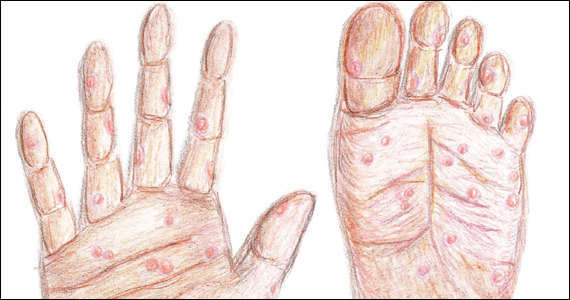
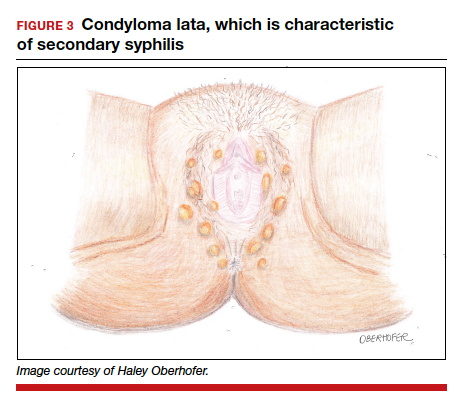
Following resolution of the primary phase, the patient may enter the secondary stage of T pallidum infection. During this stage, spirochetes may disseminate throughout the bloodstream to infect all major organ systems. The principal manifestations of secondary syphilis include a diffuse maculopapular rash that begins on the trunk and proximal extremities and spreads to include the palms and soles (FIGURE 2); mucosal lesions, such as mucous patches and condyloma lata (FIGURE 3); nonscarring alopecia; periostitis; generalized lymphadenopathy; and, in some cases, hepatitis or nephritis.1,3
Secondary syphilis usually clears within 2 to 6 weeks, with the patient then entering the early latent stage of syphilis. During this period, up to 25% of patients are subject to flares of secondary syphilitic lesions but otherwise are asymptomatic.1,3,4 These recurrences tend to occur within 1 year, hence the distinction between early and late latent stages. Once a year has passed, patients are not contagious by sexual transmission and are unlikely to suffer a relapse of secondary symptoms.1,3 However, late latent syphilis is characterized by periods of intermittent bacteremia that allow for seeding of the placenta and infection in about 10% of fetuses.5
Untreated, about 40% of patients will progress to the tertiary stage of syphilis, which is characterized by gummas affecting the skin and mucous membranes (FIGURE 4) and cardiovascular manifestations including arterial aneurysms and aortic insufficiency.3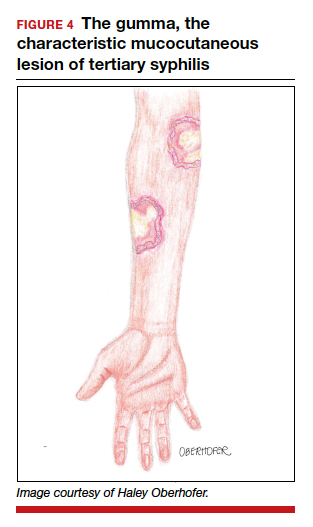
Neurologic manifestations of syphilis may arise during any of the above stages, though the most characteristic manifestations tend to appear decades after the primary infection. Early neurosyphilis may present as meningitis, with or without concomitant ocular syphilis (uveitis, retinitis) and/or as otic syphilis (hearing loss, persistent tinnitus).1,5 Patients with late (tertiary) neurosyphilis tend to exhibit meningovascular symptoms similar to stroke (aphasia, hemiplegia, seizures) and/or parenchymal effects such as general paresis. Tabes dorsalis (manifestations of which include urinary and rectal incontinence, lightning pains, and ataxia) is a late-onset manifestation.1,3
Congenital syphilis can be subdivided into an early and late stage. The first stage, in which clinical findings occur within the first 2 years of life, commonly features a desquamating rash, hepatomegaly, and rhinitis. Anemia, thrombocytopenia, periostitis, and osteomyelitis also have been documented.5 Of note, two-thirds of infants are asymptomatic at birth and may not develop such clinical manifestations for 3 to 8 weeks.3 If untreated, early congenital infection may progress to late manifestations, such as Hutchinson teeth, mulberry molars, interstitial keratitis, deafness, saddle nose, saber shins, and such neurologic abnormalities as developmental delay and general paresis.3
Continue to: Prenatal screening and diagnosis...
Prenatal screening and diagnosis
Current recommendations issued by the CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that all pregnant women should be screened for syphilis infection at their first presentation to care, with repeat screening between 28 and 32 weeks of gestation and at birth, for women living in areas with a high prevalence of syphilis and/or with any of the aforementioned risk factors.3,5 Given that providers may be unfamiliar with the prevalence of syphilis in their area, and that patients may acquire or develop an infection later on in their pregnancy, researchers have begun to investigate the feasibility of universal third-trimester screening. While the cost-effectiveness of such a protocol is disputed, recent studies suggest that it may result in a substantial decrease in adverse maternal and fetal outcomes.8,9
Diagnostic tests
The traditional algorithm for the diagnosis of syphilis infection begins with a nontreponemal screening test, such as the RPR or the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test. If positive, these screening tests are followed by a confirmatory treponemal test, such as the

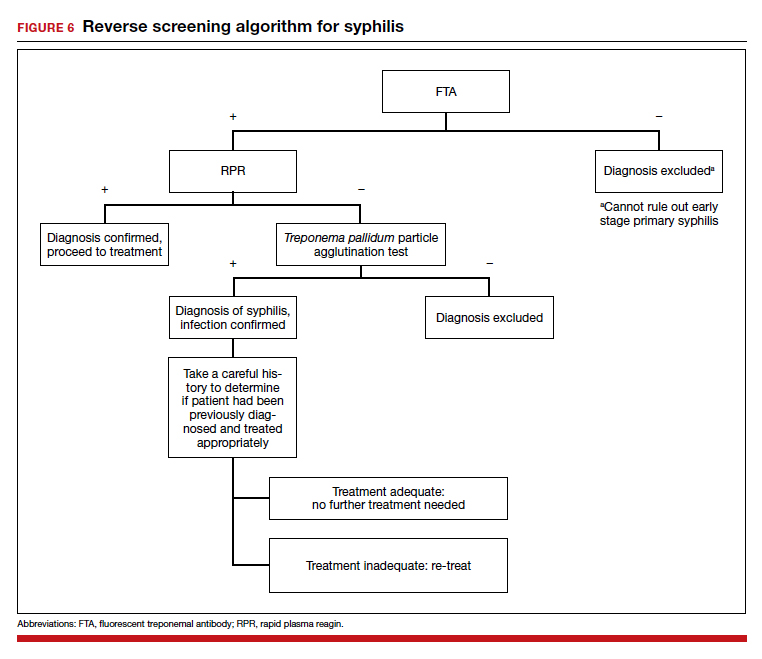
The “reverse” screening algorithm begins with the FTA and, if positive, reflexes to the RPR. A reactive RPR indicates an active infection, and the patient should be treated. A negative RPR should be followed by the TP-PA to rule out a false-positive immunoglobulin G test. If the TP-PA test result is positive, the diagnosis of syphilis is confirmed (FIGURE 6). It is crucial to understand, however, that treponemal antibodies will remain positive for a patient’s lifetime, and someone who may have been treated for syphilis in the past also will screen positive. Once 2 treponemal tests are positive, physicians should take a careful history to assess prior infection risk and treatment status. A negative TP-PA excludes a diagnosis of syphilis.
Advantages of the reverse screening algorithm. Nontreponemal tests are inexpensive and easy to perform, and titers allow for identification of a baseline to evaluate response to treatment.11 However, given the fluctuation of RPR sensitivity (depending on stage of disease and a decreased ability to detect primary and latent stages of syphilis), there has been a resurgence of interest in the reverse algorithm.11 While reverse screening has been found to incur higher costs, and may result in overtreatment and increased stress due to false-positive results,12 there is evidence to suggest that this algorithm is more sensitive for primary and latent infections.8,11,13-15
Given the rise in prevalence of syphilis infections in the United States over the past decade, and therefore a higher pretest probability of syphilis in the population, we favor the reverse screening algorithm in obstetrics, particularly given the risks of adverse maternal and fetal outcomes.
Treating syphilis in pregnancy
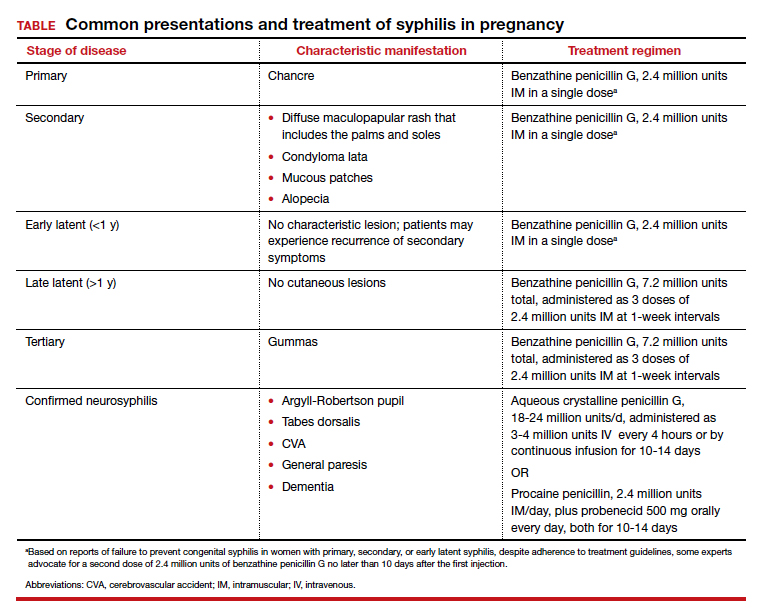
Parenteral benzathine penicillin G is the only currently recommended medication for the treatment of syphilis in pregnancy. This drug is effective in treating maternal infection and in preventing fetal infections, as well as in treating established fetal infections.3,5 Regimens differ depending on the stage of syphilis infection (TABLE). Treatment for presumed early syphilis is recommended for women who have had sexual contact with a partner diagnosed with primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis within 3 months of their current pregnancy.5 Any patient with diagnosed syphilis who demonstrates clinical signs of neurologic involvement should undergo lumbar puncture to assess for evidence of neurosyphilis.3 CDC guidelines recommend that patients who report an allergy to penicillin undergo desensitization therapy in a controlled setting, as other antibiotics that have been investigated in the treatment of syphilis are either not appropriate due to teratogenicity or due to suboptimal fetal treatment.3,5
Syphilotherapy may lead to the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction, which is an acute systemic reaction to inflammatory cytokines produced in response to lipopolysaccharide released by dying spirochetes.5 This reaction is characterized by fever, chills, myalgia, headache, hypotension, and worsening of cutaneous lesions. Preterm labor and delivery and fetal heart rate tracing abnormalities also have been documented in pregnant women experiencing this reaction, particularly during the second half of pregnancy.16 Prior to the start of treatment, a detailed sonographic assessment should be performed to assess the fetus for signs of early syphilis, including hepatomegaly, elevated peak systolic velocity of the middle cerebral artery (indicative of fetal anemia), polyhydramnios, placentomegaly, or hydrops.5,7
CASE Resolved
The combination of the patient’s test results—positive FTA, negative RPR, and negative TP-PA—suggest a false-positive treponemal assay. This sequence of tests excludes a diagnosis of syphilis; therefore, no treatment is necessary. Depending on the prevalence of syphilis in the patient’s geographic location, as well as her sexual history, rescreening between 28 and 32 weeks may be warranted. ●
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Barnett R. Syphilis. Lancet. 2018;391:1471.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore T, et al. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:862-919.
- Gomez GB, Kamb ML, Newman LM, et al. Untreated maternal syphilis and adverse outcomes of pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ. 2013;91:217-226.
- Adhikari EH. Syphilis in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1121-1135.
- Syphilis. CDC website. https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats18/syphilis.htm. Published October 1, 2019. Accessed October 6, 2020.
- Rac MF, Revell PA, Eppes CS. Syphilis during pregnancy: a preventable threat to maternal-fetal health. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;4:352-363.
- Dunseth CD, Ford BA, Krasowski MD. Traditional versus reverse syphilis algorithms: a comparison at a large academic medical center. Pract Lab Med. 2017;8:52-59.
- Hersh AR, Megli CJ, Caughey AB. Repeat screening for syphilis in the third trimester of pregnancy: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:699-706.
- Albright CM, Emerson JB, Werner EF, et al. Third trimester prenatal syphilis screening: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:479-485.
- Seña AC, White BL, Sparling PF. Novel Treponema pallidum serologic tests: a paradigm shift in syphilis screening for the 21st century. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:700-708.
- Owusu-Edusei K Jr, Peterman TA, Ballard RC. Serologic testing for syphilis in the United States: a cost-effectiveness analysis of two screening algorithms. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38:1-7.
- Huh HJ, Chung JW, Park SY, et al. Comparison of automated treponemal and nontreponemal test algorithms as first-line syphilis screening assays. Ann Lab Med. 2016;36:23-27.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Syphilis testing algorithms using treponemal test for initial screening-four laboratories. New York City, 2005-2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008;57:872-875.
- Mishra S, Boily MC, Ng V, et al. The laboratory impact of changing syphilis screening from the rapid-plasma reagin to a treponemal enzyme immunoassay: a case-study from the greater Toronto area. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38:190-196.
- Klein VR, Cox SM, Mitchell MD, et al. The Jarisch-Herzheimer reaction complicating syphilotherapy in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1990;75:375-380.
CASE Pregnant woman with positive Treponema pallidum antibody test
A 30-year-old primigravida at 10 weeks and 4 days of gestation by her last menstrual period presents to your office for her initial prenatal visit. She expresses no concerns. You order the standard set of laboratory tests, including a sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening panel. Consistent with your institution’s use of the reverse algorithm for syphilis screening, you obtain a Treponema pallidum antibody test, which reflexes to the rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. Three days later, you receive a notification that this patient’s T pallidum antibody result was positive, followed by negative RPR test results. The follow-up T pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA) test also was negative. Given these findings, you consider:
- What is the correct interpretation of the patient’s sequence of test results?
- Is she infected, and does she require treatment?
Meet our perpetrator
Syphilis has plagued society since the late 15th century, although its causative agent, the spirochete T pallidum, was not recognized until 1905.1,2T pallidum bacteria are transmitted via sexual contact, as well as through vertical transmission during pregnancy or delivery. Infection with syphilis is reported in 50% to 60% of sexual partners after a single exposure to an infected individual with early syphilis, and the mean incubation period is 21 days.3T pallidum can cross the placenta and infect a fetus as early as the sixth week of gestation.3 Congenital syphilis infections occur in the neonates of 50% to 80% of women with untreated primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis infections; maternal syphilis is associated with a 21% increased risk of stillbirth, a 6% increased risk of preterm delivery, and a 9% increased risk of neonatal death.4,5 Additionally, syphilis infection is associated with a high risk of HIV infection, as well as coinfection with other STIs.1
Given the highly infective nature of T pallidum, as well as the severity of the potential consequences of infection for both mothers and babies, primary prevention, education of at-risk populations, and early recognition of clinical features of syphilis infection are of utmost importance in preventing morbidity and mortality. In this article, we review the epidemiology and extensive clinical manifestations of syphilis, as well as current screening recommendations and treatment for pregnant women.
The extent of the problem today
Although US rates of syphilis have ebbed and flowed for the past several decades, the current incidence has grown exponentially in recent years, with the number of cases reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) increasing by 71% from 2014 to 2018.6 During this time period, reported cases of primary and secondary syphilis in women more than doubled (172.7% and 165.4%, respectively) according to CDC data, accompanied by a parallel rise in reported cases of congenital syphilis in both live and stillborn infants.6 In 2018, the CDC reported a national rate of congenital syphilis of 33.1 cases per 100,000 live births, a 39.7% rise compared with data from 2017.6
Those most at risk. Risk factors for syphilis infection include age younger than 30 years, low socioeconomic status, substance abuse, HIV infection, concurrent STIs, and high-risk sexual activity (sex with multiple high-risk partners).3 Additionally, reported rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections, as well as congenital syphilis infections, are more elevated among women who identify as Black, American Indian/Alaska Native, and/or Hispanic.6 Congenital infections in the United States are correlated with a lack of prenatal care, which has been similarly linked with racial and socioeconomic disparities, as well as with untreated mental health and substance use disorders and recent immigration to the United States.5,7
Continue to: The many phases of syphilis...
The many phases of syphilis
The characteristic lesion of primary syphilis is a chancre, which is a painless, ulcerative lesion with raised borders and a clean, indurated base appearing at the site of spirochete entry (FIGURE 1). Chancres most commonly appear in the genital area, with the most frequent sites in females being within the vaginal canal or on the cervix. Primary chancres tend to heal spontaneously within 3 to 6 weeks, even without treatment, and frequently are accompanied by painless inguinal lymphadenopathy. Given that the most common chancre sites are not immediately apparent, primary infections in women often go undetected.3 In fact, it is essential for clinicians to recognize that, in our routine practice, most patients with syphilis will not be symptomatic at all, and the diagnosis will only be made by serologic screening.

Following resolution of the primary phase, the patient may enter the secondary stage of T pallidum infection. During this stage, spirochetes may disseminate throughout the bloodstream to infect all major organ systems. The principal manifestations of secondary syphilis include a diffuse maculopapular rash that begins on the trunk and proximal extremities and spreads to include the palms and soles (FIGURE 2); mucosal lesions, such as mucous patches and condyloma lata (FIGURE 3); nonscarring alopecia; periostitis; generalized lymphadenopathy; and, in some cases, hepatitis or nephritis.1,3

Secondary syphilis usually clears within 2 to 6 weeks, with the patient then entering the early latent stage of syphilis. During this period, up to 25% of patients are subject to flares of secondary syphilitic lesions but otherwise are asymptomatic.1,3,4 These recurrences tend to occur within 1 year, hence the distinction between early and late latent stages. Once a year has passed, patients are not contagious by sexual transmission and are unlikely to suffer a relapse of secondary symptoms.1,3 However, late latent syphilis is characterized by periods of intermittent bacteremia that allow for seeding of the placenta and infection in about 10% of fetuses.5
Untreated, about 40% of patients will progress to the tertiary stage of syphilis, which is characterized by gummas affecting the skin and mucous membranes (FIGURE 4) and cardiovascular manifestations including arterial aneurysms and aortic insufficiency.3
Neurologic manifestations of syphilis may arise during any of the above stages, though the most characteristic manifestations tend to appear decades after the primary infection. Early neurosyphilis may present as meningitis, with or without concomitant ocular syphilis (uveitis, retinitis) and/or as otic syphilis (hearing loss, persistent tinnitus).1,5 Patients with late (tertiary) neurosyphilis tend to exhibit meningovascular symptoms similar to stroke (aphasia, hemiplegia, seizures) and/or parenchymal effects such as general paresis. Tabes dorsalis (manifestations of which include urinary and rectal incontinence, lightning pains, and ataxia) is a late-onset manifestation.1,3
Congenital syphilis can be subdivided into an early and late stage. The first stage, in which clinical findings occur within the first 2 years of life, commonly features a desquamating rash, hepatomegaly, and rhinitis. Anemia, thrombocytopenia, periostitis, and osteomyelitis also have been documented.5 Of note, two-thirds of infants are asymptomatic at birth and may not develop such clinical manifestations for 3 to 8 weeks.3 If untreated, early congenital infection may progress to late manifestations, such as Hutchinson teeth, mulberry molars, interstitial keratitis, deafness, saddle nose, saber shins, and such neurologic abnormalities as developmental delay and general paresis.3
Continue to: Prenatal screening and diagnosis...
Prenatal screening and diagnosis
Current recommendations issued by the CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that all pregnant women should be screened for syphilis infection at their first presentation to care, with repeat screening between 28 and 32 weeks of gestation and at birth, for women living in areas with a high prevalence of syphilis and/or with any of the aforementioned risk factors.3,5 Given that providers may be unfamiliar with the prevalence of syphilis in their area, and that patients may acquire or develop an infection later on in their pregnancy, researchers have begun to investigate the feasibility of universal third-trimester screening. While the cost-effectiveness of such a protocol is disputed, recent studies suggest that it may result in a substantial decrease in adverse maternal and fetal outcomes.8,9
Diagnostic tests
The traditional algorithm for the diagnosis of syphilis infection begins with a nontreponemal screening test, such as the RPR or the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test. If positive, these screening tests are followed by a confirmatory treponemal test, such as the

The “reverse” screening algorithm begins with the FTA and, if positive, reflexes to the RPR. A reactive RPR indicates an active infection, and the patient should be treated. A negative RPR should be followed by the TP-PA to rule out a false-positive immunoglobulin G test. If the TP-PA test result is positive, the diagnosis of syphilis is confirmed (FIGURE 6). It is crucial to understand, however, that treponemal antibodies will remain positive for a patient’s lifetime, and someone who may have been treated for syphilis in the past also will screen positive. Once 2 treponemal tests are positive, physicians should take a careful history to assess prior infection risk and treatment status. A negative TP-PA excludes a diagnosis of syphilis.

Advantages of the reverse screening algorithm. Nontreponemal tests are inexpensive and easy to perform, and titers allow for identification of a baseline to evaluate response to treatment.11 However, given the fluctuation of RPR sensitivity (depending on stage of disease and a decreased ability to detect primary and latent stages of syphilis), there has been a resurgence of interest in the reverse algorithm.11 While reverse screening has been found to incur higher costs, and may result in overtreatment and increased stress due to false-positive results,12 there is evidence to suggest that this algorithm is more sensitive for primary and latent infections.8,11,13-15
Given the rise in prevalence of syphilis infections in the United States over the past decade, and therefore a higher pretest probability of syphilis in the population, we favor the reverse screening algorithm in obstetrics, particularly given the risks of adverse maternal and fetal outcomes.
Treating syphilis in pregnancy
Parenteral benzathine penicillin G is the only currently recommended medication for the treatment of syphilis in pregnancy. This drug is effective in treating maternal infection and in preventing fetal infections, as well as in treating established fetal infections.3,5 Regimens differ depending on the stage of syphilis infection (TABLE). Treatment for presumed early syphilis is recommended for women who have had sexual contact with a partner diagnosed with primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis within 3 months of their current pregnancy.5 Any patient with diagnosed syphilis who demonstrates clinical signs of neurologic involvement should undergo lumbar puncture to assess for evidence of neurosyphilis.3 CDC guidelines recommend that patients who report an allergy to penicillin undergo desensitization therapy in a controlled setting, as other antibiotics that have been investigated in the treatment of syphilis are either not appropriate due to teratogenicity or due to suboptimal fetal treatment.3,5

Syphilotherapy may lead to the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction, which is an acute systemic reaction to inflammatory cytokines produced in response to lipopolysaccharide released by dying spirochetes.5 This reaction is characterized by fever, chills, myalgia, headache, hypotension, and worsening of cutaneous lesions. Preterm labor and delivery and fetal heart rate tracing abnormalities also have been documented in pregnant women experiencing this reaction, particularly during the second half of pregnancy.16 Prior to the start of treatment, a detailed sonographic assessment should be performed to assess the fetus for signs of early syphilis, including hepatomegaly, elevated peak systolic velocity of the middle cerebral artery (indicative of fetal anemia), polyhydramnios, placentomegaly, or hydrops.5,7
CASE Resolved
The combination of the patient’s test results—positive FTA, negative RPR, and negative TP-PA—suggest a false-positive treponemal assay. This sequence of tests excludes a diagnosis of syphilis; therefore, no treatment is necessary. Depending on the prevalence of syphilis in the patient’s geographic location, as well as her sexual history, rescreening between 28 and 32 weeks may be warranted. ●
CASE Pregnant woman with positive Treponema pallidum antibody test
A 30-year-old primigravida at 10 weeks and 4 days of gestation by her last menstrual period presents to your office for her initial prenatal visit. She expresses no concerns. You order the standard set of laboratory tests, including a sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening panel. Consistent with your institution’s use of the reverse algorithm for syphilis screening, you obtain a Treponema pallidum antibody test, which reflexes to the rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. Three days later, you receive a notification that this patient’s T pallidum antibody result was positive, followed by negative RPR test results. The follow-up T pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA) test also was negative. Given these findings, you consider:
- What is the correct interpretation of the patient’s sequence of test results?
- Is she infected, and does she require treatment?
Meet our perpetrator
Syphilis has plagued society since the late 15th century, although its causative agent, the spirochete T pallidum, was not recognized until 1905.1,2T pallidum bacteria are transmitted via sexual contact, as well as through vertical transmission during pregnancy or delivery. Infection with syphilis is reported in 50% to 60% of sexual partners after a single exposure to an infected individual with early syphilis, and the mean incubation period is 21 days.3T pallidum can cross the placenta and infect a fetus as early as the sixth week of gestation.3 Congenital syphilis infections occur in the neonates of 50% to 80% of women with untreated primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis infections; maternal syphilis is associated with a 21% increased risk of stillbirth, a 6% increased risk of preterm delivery, and a 9% increased risk of neonatal death.4,5 Additionally, syphilis infection is associated with a high risk of HIV infection, as well as coinfection with other STIs.1
Given the highly infective nature of T pallidum, as well as the severity of the potential consequences of infection for both mothers and babies, primary prevention, education of at-risk populations, and early recognition of clinical features of syphilis infection are of utmost importance in preventing morbidity and mortality. In this article, we review the epidemiology and extensive clinical manifestations of syphilis, as well as current screening recommendations and treatment for pregnant women.
The extent of the problem today
Although US rates of syphilis have ebbed and flowed for the past several decades, the current incidence has grown exponentially in recent years, with the number of cases reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) increasing by 71% from 2014 to 2018.6 During this time period, reported cases of primary and secondary syphilis in women more than doubled (172.7% and 165.4%, respectively) according to CDC data, accompanied by a parallel rise in reported cases of congenital syphilis in both live and stillborn infants.6 In 2018, the CDC reported a national rate of congenital syphilis of 33.1 cases per 100,000 live births, a 39.7% rise compared with data from 2017.6
Those most at risk. Risk factors for syphilis infection include age younger than 30 years, low socioeconomic status, substance abuse, HIV infection, concurrent STIs, and high-risk sexual activity (sex with multiple high-risk partners).3 Additionally, reported rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections, as well as congenital syphilis infections, are more elevated among women who identify as Black, American Indian/Alaska Native, and/or Hispanic.6 Congenital infections in the United States are correlated with a lack of prenatal care, which has been similarly linked with racial and socioeconomic disparities, as well as with untreated mental health and substance use disorders and recent immigration to the United States.5,7
Continue to: The many phases of syphilis...
The many phases of syphilis
The characteristic lesion of primary syphilis is a chancre, which is a painless, ulcerative lesion with raised borders and a clean, indurated base appearing at the site of spirochete entry (FIGURE 1). Chancres most commonly appear in the genital area, with the most frequent sites in females being within the vaginal canal or on the cervix. Primary chancres tend to heal spontaneously within 3 to 6 weeks, even without treatment, and frequently are accompanied by painless inguinal lymphadenopathy. Given that the most common chancre sites are not immediately apparent, primary infections in women often go undetected.3 In fact, it is essential for clinicians to recognize that, in our routine practice, most patients with syphilis will not be symptomatic at all, and the diagnosis will only be made by serologic screening.

Following resolution of the primary phase, the patient may enter the secondary stage of T pallidum infection. During this stage, spirochetes may disseminate throughout the bloodstream to infect all major organ systems. The principal manifestations of secondary syphilis include a diffuse maculopapular rash that begins on the trunk and proximal extremities and spreads to include the palms and soles (FIGURE 2); mucosal lesions, such as mucous patches and condyloma lata (FIGURE 3); nonscarring alopecia; periostitis; generalized lymphadenopathy; and, in some cases, hepatitis or nephritis.1,3

Secondary syphilis usually clears within 2 to 6 weeks, with the patient then entering the early latent stage of syphilis. During this period, up to 25% of patients are subject to flares of secondary syphilitic lesions but otherwise are asymptomatic.1,3,4 These recurrences tend to occur within 1 year, hence the distinction between early and late latent stages. Once a year has passed, patients are not contagious by sexual transmission and are unlikely to suffer a relapse of secondary symptoms.1,3 However, late latent syphilis is characterized by periods of intermittent bacteremia that allow for seeding of the placenta and infection in about 10% of fetuses.5
Untreated, about 40% of patients will progress to the tertiary stage of syphilis, which is characterized by gummas affecting the skin and mucous membranes (FIGURE 4) and cardiovascular manifestations including arterial aneurysms and aortic insufficiency.3
Neurologic manifestations of syphilis may arise during any of the above stages, though the most characteristic manifestations tend to appear decades after the primary infection. Early neurosyphilis may present as meningitis, with or without concomitant ocular syphilis (uveitis, retinitis) and/or as otic syphilis (hearing loss, persistent tinnitus).1,5 Patients with late (tertiary) neurosyphilis tend to exhibit meningovascular symptoms similar to stroke (aphasia, hemiplegia, seizures) and/or parenchymal effects such as general paresis. Tabes dorsalis (manifestations of which include urinary and rectal incontinence, lightning pains, and ataxia) is a late-onset manifestation.1,3
Congenital syphilis can be subdivided into an early and late stage. The first stage, in which clinical findings occur within the first 2 years of life, commonly features a desquamating rash, hepatomegaly, and rhinitis. Anemia, thrombocytopenia, periostitis, and osteomyelitis also have been documented.5 Of note, two-thirds of infants are asymptomatic at birth and may not develop such clinical manifestations for 3 to 8 weeks.3 If untreated, early congenital infection may progress to late manifestations, such as Hutchinson teeth, mulberry molars, interstitial keratitis, deafness, saddle nose, saber shins, and such neurologic abnormalities as developmental delay and general paresis.3
Continue to: Prenatal screening and diagnosis...
Prenatal screening and diagnosis
Current recommendations issued by the CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that all pregnant women should be screened for syphilis infection at their first presentation to care, with repeat screening between 28 and 32 weeks of gestation and at birth, for women living in areas with a high prevalence of syphilis and/or with any of the aforementioned risk factors.3,5 Given that providers may be unfamiliar with the prevalence of syphilis in their area, and that patients may acquire or develop an infection later on in their pregnancy, researchers have begun to investigate the feasibility of universal third-trimester screening. While the cost-effectiveness of such a protocol is disputed, recent studies suggest that it may result in a substantial decrease in adverse maternal and fetal outcomes.8,9
Diagnostic tests
The traditional algorithm for the diagnosis of syphilis infection begins with a nontreponemal screening test, such as the RPR or the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test. If positive, these screening tests are followed by a confirmatory treponemal test, such as the

The “reverse” screening algorithm begins with the FTA and, if positive, reflexes to the RPR. A reactive RPR indicates an active infection, and the patient should be treated. A negative RPR should be followed by the TP-PA to rule out a false-positive immunoglobulin G test. If the TP-PA test result is positive, the diagnosis of syphilis is confirmed (FIGURE 6). It is crucial to understand, however, that treponemal antibodies will remain positive for a patient’s lifetime, and someone who may have been treated for syphilis in the past also will screen positive. Once 2 treponemal tests are positive, physicians should take a careful history to assess prior infection risk and treatment status. A negative TP-PA excludes a diagnosis of syphilis.

Advantages of the reverse screening algorithm. Nontreponemal tests are inexpensive and easy to perform, and titers allow for identification of a baseline to evaluate response to treatment.11 However, given the fluctuation of RPR sensitivity (depending on stage of disease and a decreased ability to detect primary and latent stages of syphilis), there has been a resurgence of interest in the reverse algorithm.11 While reverse screening has been found to incur higher costs, and may result in overtreatment and increased stress due to false-positive results,12 there is evidence to suggest that this algorithm is more sensitive for primary and latent infections.8,11,13-15
Given the rise in prevalence of syphilis infections in the United States over the past decade, and therefore a higher pretest probability of syphilis in the population, we favor the reverse screening algorithm in obstetrics, particularly given the risks of adverse maternal and fetal outcomes.
Treating syphilis in pregnancy
Parenteral benzathine penicillin G is the only currently recommended medication for the treatment of syphilis in pregnancy. This drug is effective in treating maternal infection and in preventing fetal infections, as well as in treating established fetal infections.3,5 Regimens differ depending on the stage of syphilis infection (TABLE). Treatment for presumed early syphilis is recommended for women who have had sexual contact with a partner diagnosed with primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis within 3 months of their current pregnancy.5 Any patient with diagnosed syphilis who demonstrates clinical signs of neurologic involvement should undergo lumbar puncture to assess for evidence of neurosyphilis.3 CDC guidelines recommend that patients who report an allergy to penicillin undergo desensitization therapy in a controlled setting, as other antibiotics that have been investigated in the treatment of syphilis are either not appropriate due to teratogenicity or due to suboptimal fetal treatment.3,5

Syphilotherapy may lead to the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction, which is an acute systemic reaction to inflammatory cytokines produced in response to lipopolysaccharide released by dying spirochetes.5 This reaction is characterized by fever, chills, myalgia, headache, hypotension, and worsening of cutaneous lesions. Preterm labor and delivery and fetal heart rate tracing abnormalities also have been documented in pregnant women experiencing this reaction, particularly during the second half of pregnancy.16 Prior to the start of treatment, a detailed sonographic assessment should be performed to assess the fetus for signs of early syphilis, including hepatomegaly, elevated peak systolic velocity of the middle cerebral artery (indicative of fetal anemia), polyhydramnios, placentomegaly, or hydrops.5,7
CASE Resolved
The combination of the patient’s test results—positive FTA, negative RPR, and negative TP-PA—suggest a false-positive treponemal assay. This sequence of tests excludes a diagnosis of syphilis; therefore, no treatment is necessary. Depending on the prevalence of syphilis in the patient’s geographic location, as well as her sexual history, rescreening between 28 and 32 weeks may be warranted. ●
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Barnett R. Syphilis. Lancet. 2018;391:1471.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore T, et al. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:862-919.
- Gomez GB, Kamb ML, Newman LM, et al. Untreated maternal syphilis and adverse outcomes of pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ. 2013;91:217-226.
- Adhikari EH. Syphilis in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1121-1135.
- Syphilis. CDC website. https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats18/syphilis.htm. Published October 1, 2019. Accessed October 6, 2020.
- Rac MF, Revell PA, Eppes CS. Syphilis during pregnancy: a preventable threat to maternal-fetal health. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;4:352-363.
- Dunseth CD, Ford BA, Krasowski MD. Traditional versus reverse syphilis algorithms: a comparison at a large academic medical center. Pract Lab Med. 2017;8:52-59.
- Hersh AR, Megli CJ, Caughey AB. Repeat screening for syphilis in the third trimester of pregnancy: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:699-706.
- Albright CM, Emerson JB, Werner EF, et al. Third trimester prenatal syphilis screening: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:479-485.
- Seña AC, White BL, Sparling PF. Novel Treponema pallidum serologic tests: a paradigm shift in syphilis screening for the 21st century. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:700-708.
- Owusu-Edusei K Jr, Peterman TA, Ballard RC. Serologic testing for syphilis in the United States: a cost-effectiveness analysis of two screening algorithms. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38:1-7.
- Huh HJ, Chung JW, Park SY, et al. Comparison of automated treponemal and nontreponemal test algorithms as first-line syphilis screening assays. Ann Lab Med. 2016;36:23-27.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Syphilis testing algorithms using treponemal test for initial screening-four laboratories. New York City, 2005-2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008;57:872-875.
- Mishra S, Boily MC, Ng V, et al. The laboratory impact of changing syphilis screening from the rapid-plasma reagin to a treponemal enzyme immunoassay: a case-study from the greater Toronto area. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38:190-196.
- Klein VR, Cox SM, Mitchell MD, et al. The Jarisch-Herzheimer reaction complicating syphilotherapy in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1990;75:375-380.
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Barnett R. Syphilis. Lancet. 2018;391:1471.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infections. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore T, et al. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:862-919.
- Gomez GB, Kamb ML, Newman LM, et al. Untreated maternal syphilis and adverse outcomes of pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ. 2013;91:217-226.
- Adhikari EH. Syphilis in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1121-1135.
- Syphilis. CDC website. https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats18/syphilis.htm. Published October 1, 2019. Accessed October 6, 2020.
- Rac MF, Revell PA, Eppes CS. Syphilis during pregnancy: a preventable threat to maternal-fetal health. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;4:352-363.
- Dunseth CD, Ford BA, Krasowski MD. Traditional versus reverse syphilis algorithms: a comparison at a large academic medical center. Pract Lab Med. 2017;8:52-59.
- Hersh AR, Megli CJ, Caughey AB. Repeat screening for syphilis in the third trimester of pregnancy: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:699-706.
- Albright CM, Emerson JB, Werner EF, et al. Third trimester prenatal syphilis screening: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:479-485.
- Seña AC, White BL, Sparling PF. Novel Treponema pallidum serologic tests: a paradigm shift in syphilis screening for the 21st century. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:700-708.
- Owusu-Edusei K Jr, Peterman TA, Ballard RC. Serologic testing for syphilis in the United States: a cost-effectiveness analysis of two screening algorithms. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38:1-7.
- Huh HJ, Chung JW, Park SY, et al. Comparison of automated treponemal and nontreponemal test algorithms as first-line syphilis screening assays. Ann Lab Med. 2016;36:23-27.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Syphilis testing algorithms using treponemal test for initial screening-four laboratories. New York City, 2005-2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008;57:872-875.
- Mishra S, Boily MC, Ng V, et al. The laboratory impact of changing syphilis screening from the rapid-plasma reagin to a treponemal enzyme immunoassay: a case-study from the greater Toronto area. Sex Transm Dis. 2011;38:190-196.
- Klein VR, Cox SM, Mitchell MD, et al. The Jarisch-Herzheimer reaction complicating syphilotherapy in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1990;75:375-380.
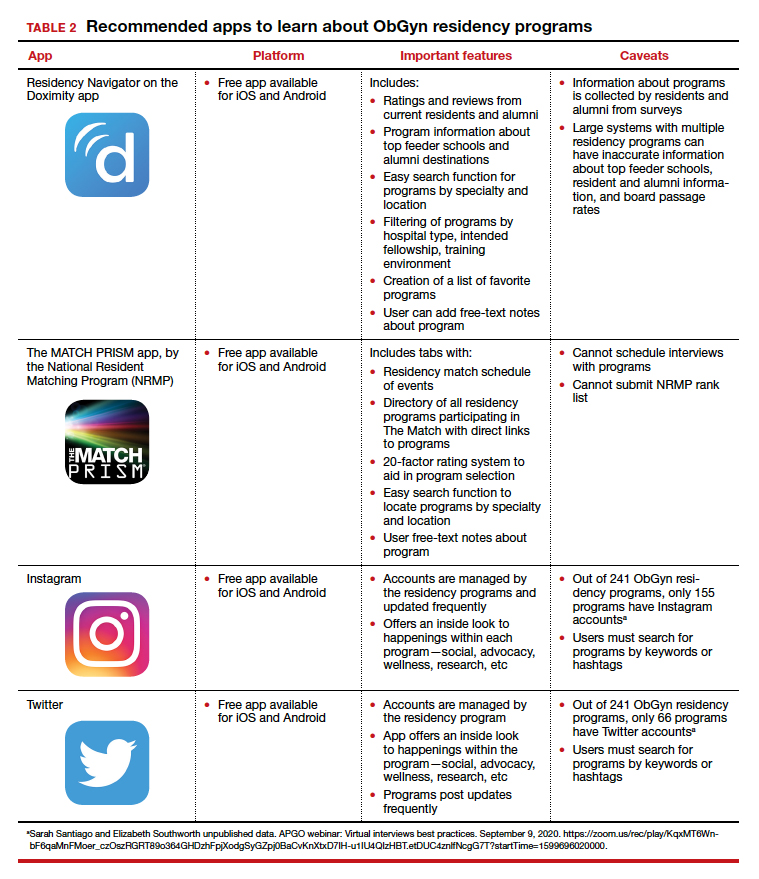
Apps for applying to ObGyn residency programs in the era of virtual interviews
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has upended the traditional 2020–2021 application season for ObGyn residency programs. In May 2020, the 2 national ObGyn education organizations, the Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics (APGO) and Council on Resident Education in ObGyn (CREOG), issued guidelines to ensure a fair and equitable application process.1 These guidelines are consistent with recommendations from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) and the Coalition for Physician Accountability. Important recommendations include:
- limiting away rotations
- being flexible in the number of specialty-specific letters of recommendation required
- encouraging residency programs to develop alternate means of conveying information about their curriculum.
In addition, these statements provide timing on when programs should release interview offers and when to begin interviews. Finally, programs are required to commit to online interviews and virtual visits for all applicants, including local students, rather than in-person interviews.
Here, we focus on identifying apps that students can use to help them with the application process—apps for the nuts and bolts of applying and interviewing and apps to learn more about individual programs.
Students must use the Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) platform from AAMC to enter their information and register with the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP). Students also must use the ERAS to submit their applications to their selected residency programs. The ERAS platform does not include an app to aid in the completion or submission of an application. The NRMP has developed the MATCH PRISM app, but this does not allow students to register for the match or submit their rank list. To learn about how to schedule interviews, residency programs may use one of the following sources: ERAS, Interview Broker, or Thalamus. Moreover, APGO/CREOG has partnered with Thalamus for the upcoming application cycle, which provides residency programs and applicants tools for application management, interview scheduling, and itinerary building. Thalamus offers a free app.
This year offers some unique challenges. The application process for ObGyn residencies is likely to be more competitive, and students face the added stress of having to navigate the interview season:
- without away rotations (audition interviews)
- without in-person visits of the city/hospital/program or social events before or after interview day
- with an all-virtual interview day.
Continue to: To find information on individual residency programs...
To find information on individual residency programs, the APGO website lists the FREIDA and APGO Residency Directories, which are not apps. Students are also aware of the Doximity Residency Navigator, which does include an app. The NRMP MATCH PRISM app is another resource, as it provides students with a directory of residency programs and information about each program.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recognizes that residency program websites and social media will be crucial in helping applicants learn about individual programs, faculty, and residents. As such, ACOG hosted a Virtual Residency Showcase in September 2020 in which programs posted content on Instagram and Twitter using the hashtag #ACOG-ResWeek20.2 Similarly, APGO and CREOG produced a report containing a social media directory, which lists individual residency programs and whether or not they have a social media handle/account.3 In a recent webinar,4 Drs. Sarah Santiago and Elizabeth Southworth noted that the number of residency programs that have an Instagram account more than doubled (from 60 to 128) between May and September 2020.
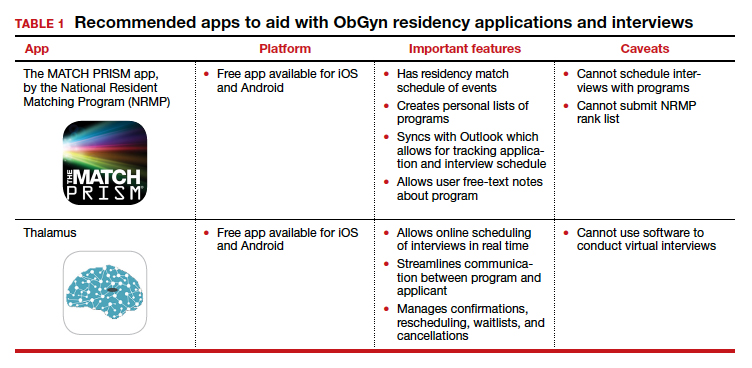
We present 2 tables describing the important features and caveats of apps available to students to assist them with residency applications this year—TABLE 1 summarizes apps to aid with applications and interviews; TABLE 2 lists apps designed for students to learn more about individual residency programs. We wish all of this year’s students every success in their search for the right program. ●
- Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Council on Resident Education in ObGyn. Updated APGO and CREOG Residency Application Response to COVID-19. https://www.apgo.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/05 /Updated-APGO-CREOG-Residency-Response-to -COVID-19-.pdf. Accessed October 27, 2020.
- https://www.acog.org/education-and-events/webinars /virtual-residency-showcase. Accessed October 4, 2020.
- Social media directory-ObGyn. https://docs.google.com /spreadsheets/d/e/2PACX-1vQ6boyn7FWV9tEhfQp1o3 XJgNIPNBQ3qCYf4IpV-rOPcd212J-HNR84p0r85nXrAz MvOmcNlgjywDP/pubhtml?gid=1472916499&single =true. Accessed October 27, 2020.
- APGO webinar: Virtual interviews best practices. September 9, 2020. https://zoom.us/rec/play/KqxMT6Wnb F6qaMnFMoer_czOszRGRT89o364GHDzhFpjXodgSyGZpj 0BaCvKnXtxD7IH-u1IU4QIzHBT.etDUC4znlfNcgG7T?start Time=1599696020000. Accessed October 4, 2020.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has upended the traditional 2020–2021 application season for ObGyn residency programs. In May 2020, the 2 national ObGyn education organizations, the Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics (APGO) and Council on Resident Education in ObGyn (CREOG), issued guidelines to ensure a fair and equitable application process.1 These guidelines are consistent with recommendations from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) and the Coalition for Physician Accountability. Important recommendations include:
- limiting away rotations
- being flexible in the number of specialty-specific letters of recommendation required
- encouraging residency programs to develop alternate means of conveying information about their curriculum.
In addition, these statements provide timing on when programs should release interview offers and when to begin interviews. Finally, programs are required to commit to online interviews and virtual visits for all applicants, including local students, rather than in-person interviews.
Here, we focus on identifying apps that students can use to help them with the application process—apps for the nuts and bolts of applying and interviewing and apps to learn more about individual programs.
Students must use the Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) platform from AAMC to enter their information and register with the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP). Students also must use the ERAS to submit their applications to their selected residency programs. The ERAS platform does not include an app to aid in the completion or submission of an application. The NRMP has developed the MATCH PRISM app, but this does not allow students to register for the match or submit their rank list. To learn about how to schedule interviews, residency programs may use one of the following sources: ERAS, Interview Broker, or Thalamus. Moreover, APGO/CREOG has partnered with Thalamus for the upcoming application cycle, which provides residency programs and applicants tools for application management, interview scheduling, and itinerary building. Thalamus offers a free app.
This year offers some unique challenges. The application process for ObGyn residencies is likely to be more competitive, and students face the added stress of having to navigate the interview season:
- without away rotations (audition interviews)
- without in-person visits of the city/hospital/program or social events before or after interview day
- with an all-virtual interview day.
Continue to: To find information on individual residency programs...
To find information on individual residency programs, the APGO website lists the FREIDA and APGO Residency Directories, which are not apps. Students are also aware of the Doximity Residency Navigator, which does include an app. The NRMP MATCH PRISM app is another resource, as it provides students with a directory of residency programs and information about each program.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recognizes that residency program websites and social media will be crucial in helping applicants learn about individual programs, faculty, and residents. As such, ACOG hosted a Virtual Residency Showcase in September 2020 in which programs posted content on Instagram and Twitter using the hashtag #ACOG-ResWeek20.2 Similarly, APGO and CREOG produced a report containing a social media directory, which lists individual residency programs and whether or not they have a social media handle/account.3 In a recent webinar,4 Drs. Sarah Santiago and Elizabeth Southworth noted that the number of residency programs that have an Instagram account more than doubled (from 60 to 128) between May and September 2020.

We present 2 tables describing the important features and caveats of apps available to students to assist them with residency applications this year—TABLE 1 summarizes apps to aid with applications and interviews; TABLE 2 lists apps designed for students to learn more about individual residency programs. We wish all of this year’s students every success in their search for the right program. ●

The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has upended the traditional 2020–2021 application season for ObGyn residency programs. In May 2020, the 2 national ObGyn education organizations, the Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics (APGO) and Council on Resident Education in ObGyn (CREOG), issued guidelines to ensure a fair and equitable application process.1 These guidelines are consistent with recommendations from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) and the Coalition for Physician Accountability. Important recommendations include:
- limiting away rotations
- being flexible in the number of specialty-specific letters of recommendation required
- encouraging residency programs to develop alternate means of conveying information about their curriculum.
In addition, these statements provide timing on when programs should release interview offers and when to begin interviews. Finally, programs are required to commit to online interviews and virtual visits for all applicants, including local students, rather than in-person interviews.
Here, we focus on identifying apps that students can use to help them with the application process—apps for the nuts and bolts of applying and interviewing and apps to learn more about individual programs.
Students must use the Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) platform from AAMC to enter their information and register with the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP). Students also must use the ERAS to submit their applications to their selected residency programs. The ERAS platform does not include an app to aid in the completion or submission of an application. The NRMP has developed the MATCH PRISM app, but this does not allow students to register for the match or submit their rank list. To learn about how to schedule interviews, residency programs may use one of the following sources: ERAS, Interview Broker, or Thalamus. Moreover, APGO/CREOG has partnered with Thalamus for the upcoming application cycle, which provides residency programs and applicants tools for application management, interview scheduling, and itinerary building. Thalamus offers a free app.
This year offers some unique challenges. The application process for ObGyn residencies is likely to be more competitive, and students face the added stress of having to navigate the interview season:
- without away rotations (audition interviews)
- without in-person visits of the city/hospital/program or social events before or after interview day
- with an all-virtual interview day.
Continue to: To find information on individual residency programs...
To find information on individual residency programs, the APGO website lists the FREIDA and APGO Residency Directories, which are not apps. Students are also aware of the Doximity Residency Navigator, which does include an app. The NRMP MATCH PRISM app is another resource, as it provides students with a directory of residency programs and information about each program.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recognizes that residency program websites and social media will be crucial in helping applicants learn about individual programs, faculty, and residents. As such, ACOG hosted a Virtual Residency Showcase in September 2020 in which programs posted content on Instagram and Twitter using the hashtag #ACOG-ResWeek20.2 Similarly, APGO and CREOG produced a report containing a social media directory, which lists individual residency programs and whether or not they have a social media handle/account.3 In a recent webinar,4 Drs. Sarah Santiago and Elizabeth Southworth noted that the number of residency programs that have an Instagram account more than doubled (from 60 to 128) between May and September 2020.

We present 2 tables describing the important features and caveats of apps available to students to assist them with residency applications this year—TABLE 1 summarizes apps to aid with applications and interviews; TABLE 2 lists apps designed for students to learn more about individual residency programs. We wish all of this year’s students every success in their search for the right program. ●

- Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Council on Resident Education in ObGyn. Updated APGO and CREOG Residency Application Response to COVID-19. https://www.apgo.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/05 /Updated-APGO-CREOG-Residency-Response-to -COVID-19-.pdf. Accessed October 27, 2020.
- https://www.acog.org/education-and-events/webinars /virtual-residency-showcase. Accessed October 4, 2020.
- Social media directory-ObGyn. https://docs.google.com /spreadsheets/d/e/2PACX-1vQ6boyn7FWV9tEhfQp1o3 XJgNIPNBQ3qCYf4IpV-rOPcd212J-HNR84p0r85nXrAz MvOmcNlgjywDP/pubhtml?gid=1472916499&single =true. Accessed October 27, 2020.
- APGO webinar: Virtual interviews best practices. September 9, 2020. https://zoom.us/rec/play/KqxMT6Wnb F6qaMnFMoer_czOszRGRT89o364GHDzhFpjXodgSyGZpj 0BaCvKnXtxD7IH-u1IU4QIzHBT.etDUC4znlfNcgG7T?start Time=1599696020000. Accessed October 4, 2020.
- Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Council on Resident Education in ObGyn. Updated APGO and CREOG Residency Application Response to COVID-19. https://www.apgo.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/05 /Updated-APGO-CREOG-Residency-Response-to -COVID-19-.pdf. Accessed October 27, 2020.
- https://www.acog.org/education-and-events/webinars /virtual-residency-showcase. Accessed October 4, 2020.
- Social media directory-ObGyn. https://docs.google.com /spreadsheets/d/e/2PACX-1vQ6boyn7FWV9tEhfQp1o3 XJgNIPNBQ3qCYf4IpV-rOPcd212J-HNR84p0r85nXrAz MvOmcNlgjywDP/pubhtml?gid=1472916499&single =true. Accessed October 27, 2020.
- APGO webinar: Virtual interviews best practices. September 9, 2020. https://zoom.us/rec/play/KqxMT6Wnb F6qaMnFMoer_czOszRGRT89o364GHDzhFpjXodgSyGZpj 0BaCvKnXtxD7IH-u1IU4QIzHBT.etDUC4znlfNcgG7T?start Time=1599696020000. Accessed October 4, 2020.
How mental health care would look under a Trump vs. Biden administration
The COVID-19 pandemic is one of the most pressing public health challenges the United States has ever faced, and the resulting financial ruin and social isolation are creating a mental health pandemic that will continue well after COVID-19 lockdowns end. To understand which presidential candidate would best lead the mental health recovery, we identified three of the most critical issues in mental health and compared the plans of the two candidates.
Fighting the opioid epidemic
Over the last several years, the opioid epidemic has devastated American families and communities. Prior to the pandemic, drug overdoses were the leading cause of death for American adults under 50 years of age. The effects of COVID-19–enabled overdose deaths to rise even higher. Multiple elements of the pandemic – isolation, unemployment, and increased anxiety and depression – make those struggling with substance use even more vulnerable, and immediate and comprehensive action is needed to address this national tragedy.
Donald J. Trump: President Trump has been vocal and active in addressing this problem since he took office. One of the Trump administration’s successes is launching the Opioid and Drug Abuse Commission and rolling out a five-point strategy built around improving services, data, research, overdose-reversing drugs, and pain management. Last year, the Trump administration funded $10 billion over 5 years to combat both the opioid epidemic and mental health issues by building upon the 21st Century CURES Act. However, in this same budget, the administration proposed cutting funding by $600 million for SAMHSA, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, which is the top government agency for addressing and providing care for substance use.
President Trump also created an assistant secretary for mental health and substance use position in the Department of Health & Human Services, and appointed Elinore F. McCance-Katz, MD, PhD, a psychiatrist with a strong track record on fighting opioid abuse in Rhode Island, to the post.
Joe Biden: Former Vice President Biden emphasizes that substance use is “a disease of the brain,” refuting the long-held misconception that addiction is an issue of willpower. This stigmatization is very personal given that his own son Hunter reportedly suffered through mental health and substance use issues since his teenage years. However, Biden also had a major role in pushing forward the federal “war on drugs,” including his role in crafting the “Len Bias law.”
Mr. Biden has since released a multifaceted plan for reducing substance use, aiming to make prevention and treatment services more available through a $125 billion federal investment. There are also measures to hold pharmaceutical companies accountable for triggering the crisis, stop the flow of fentanyl to the United States, and restrict incentive payments from manufacturers to doctors so as to limit the dosing and usage of powerful opioids.
Accessing health care
One of the main dividing lines in this election has been the battle to either gut or build upon the Affordable Care Act (ACA). This will have deep ramifications on people’s access to health mental health services. Since COVID-19 started, more than 50% of Americans have reported worsening mental health. This makes it crucial that each candidate’s mental health plan is judged by how they would expand access to insurance, address unenforced parity laws, and protect those who have a mental health disorder as a preexisting condition.
Mr. Trump: Following a failed Senate vote to repeal this law, the Trump administration took a piecemeal approach to dismantling the ACA that included removing the individual mandate, enabling states to introduce Medicaid work requirements, and reducing cost-sharing subsidies to insurers.
If a re-elected Trump administration pursued a complete repeal of the ACA law, many individuals with previous access to mental health and substance abuse treatment via Medicaid expansion may lose access altogether. In addition, key mechanisms aimed at making sure that mental health services are covered by private health plans may be lost, which could undermine policies to address opioids and suicide. On the other hand, the Trump administration’s move during the pandemic to expand telemedicine services has also expanded access to mental health services.
Mr. Biden: Mr. Biden’s plan would build upon the ACA by working to achieve parity between the treatment of mental health and physical health. The ACA itself strengthened the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (federal parity law), which Mr. Biden championed as vice president, by mandating that all private insurance cover mental health and substance abuse treatment. This act still exempts some health plans, such as larger employers; and many insurers have used loopholes in the policy to illegally deny what could be life-saving coverage.
It follows that those who can afford Mr. Biden’s proposed public option Medicare buy-in would receive more comprehensive mental health benefits. He also says he would invest in school and college mental health professionals, an important opportunity for early intervention given 75% of lifetime mental illness starts by age 24 years. While Mr. Biden has not stated a specific plan for addressing minority groups, whose mental health has been disproportionately affected by COVID-19, he has acknowledged that this unmet need should be targeted.
Addressing suicide
More than 3,000 Americans attempt suicide every day. Suicide is the second leading cause of death for America’s youth and one of the top 10 leading causes of death across the population. Numerous strategies are necessary to address suicide, but one of the most decisive is gun control. Gun violence is inextricably tied to suicide: States where gun prevalence is higher see about four times the number of suicides because of guns, whereas nonfirearm suicide rates are the same as those seen elsewhere. In 2017, of the nearly 40,000 people who died of gun violence, 60% were attributable to suicides. Since the pandemic started, there have been increases in reported suicidal thoughts and a nearly 1,000% increase in use of the national crisis hotline. This is especially concerning given the uptick during the pandemic of gun purchases; as of September, more guns have been purchased this year than any year before.
Mr. Trump: Prior to coronavirus, the Trump administration was unwilling to enact gun control legislation. In early 2017, Mr. Trump removed an Obama-era bill that would have expanded the background check database. It would have added those deemed legally unfit to handle their own funds and those who received Social Security funds for mental health reasons. During the lockdown, the administration made an advisory ruling declaring gun shops as essential businesses that states should keep open.
Mr. Biden: The former vice president has a history of supporting gun control measures in his time as a senator and vice president. In the Senate, Mr. Biden supported both the Brady handgun bill in 1993 and a ban on assault weapons in 1994. As vice president, he was tasked by President Obama to push for a renewed assault weapons ban and a background check bill (Manchin-Toomey bill).
During his 2020 presidential campaign, Mr. Biden has suggested creating universal background checks and reinstating bans on assault rifle sales. He has said that he is also open to having a federal buyback program for assault rifles from gun owners.
Why this matters
The winner of the 2020 election will lead an electorate that is reeling from the health, economic, and social consequences COVID-19. The next administration needs to act swiftly to address the mental health pandemic and have a keen awareness of what is ahead. As Americans make their voting decision, consider who has the best plans not only to contain the virus but also the mental health crises that are ravaging our nation.
Dr. Vasan is a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry at Stanford (Calif.) University, where she is founder and executive director of Brainstorm: The Stanford Lab for Mental Health Innovation. She also serves as chief medical officer of Real, and chair of the American Psychiatric Association Committee on Innovation. Dr. Vasan has no conflicts of interest. Mr. Agbafe is a fellow at Stanford Brainstorm and a first-year medical student at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He has no conflicts of interest. Ms. Li is a policy intern at Stanford Brainstorm and an undergraduate student in the department of economics at the University of California, Berkeley. She has no conflicts of interest.
The COVID-19 pandemic is one of the most pressing public health challenges the United States has ever faced, and the resulting financial ruin and social isolation are creating a mental health pandemic that will continue well after COVID-19 lockdowns end. To understand which presidential candidate would best lead the mental health recovery, we identified three of the most critical issues in mental health and compared the plans of the two candidates.
Fighting the opioid epidemic
Over the last several years, the opioid epidemic has devastated American families and communities. Prior to the pandemic, drug overdoses were the leading cause of death for American adults under 50 years of age. The effects of COVID-19–enabled overdose deaths to rise even higher. Multiple elements of the pandemic – isolation, unemployment, and increased anxiety and depression – make those struggling with substance use even more vulnerable, and immediate and comprehensive action is needed to address this national tragedy.
Donald J. Trump: President Trump has been vocal and active in addressing this problem since he took office. One of the Trump administration’s successes is launching the Opioid and Drug Abuse Commission and rolling out a five-point strategy built around improving services, data, research, overdose-reversing drugs, and pain management. Last year, the Trump administration funded $10 billion over 5 years to combat both the opioid epidemic and mental health issues by building upon the 21st Century CURES Act. However, in this same budget, the administration proposed cutting funding by $600 million for SAMHSA, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, which is the top government agency for addressing and providing care for substance use.
President Trump also created an assistant secretary for mental health and substance use position in the Department of Health & Human Services, and appointed Elinore F. McCance-Katz, MD, PhD, a psychiatrist with a strong track record on fighting opioid abuse in Rhode Island, to the post.
Joe Biden: Former Vice President Biden emphasizes that substance use is “a disease of the brain,” refuting the long-held misconception that addiction is an issue of willpower. This stigmatization is very personal given that his own son Hunter reportedly suffered through mental health and substance use issues since his teenage years. However, Biden also had a major role in pushing forward the federal “war on drugs,” including his role in crafting the “Len Bias law.”
Mr. Biden has since released a multifaceted plan for reducing substance use, aiming to make prevention and treatment services more available through a $125 billion federal investment. There are also measures to hold pharmaceutical companies accountable for triggering the crisis, stop the flow of fentanyl to the United States, and restrict incentive payments from manufacturers to doctors so as to limit the dosing and usage of powerful opioids.
Accessing health care
One of the main dividing lines in this election has been the battle to either gut or build upon the Affordable Care Act (ACA). This will have deep ramifications on people’s access to health mental health services. Since COVID-19 started, more than 50% of Americans have reported worsening mental health. This makes it crucial that each candidate’s mental health plan is judged by how they would expand access to insurance, address unenforced parity laws, and protect those who have a mental health disorder as a preexisting condition.
Mr. Trump: Following a failed Senate vote to repeal this law, the Trump administration took a piecemeal approach to dismantling the ACA that included removing the individual mandate, enabling states to introduce Medicaid work requirements, and reducing cost-sharing subsidies to insurers.
If a re-elected Trump administration pursued a complete repeal of the ACA law, many individuals with previous access to mental health and substance abuse treatment via Medicaid expansion may lose access altogether. In addition, key mechanisms aimed at making sure that mental health services are covered by private health plans may be lost, which could undermine policies to address opioids and suicide. On the other hand, the Trump administration’s move during the pandemic to expand telemedicine services has also expanded access to mental health services.
Mr. Biden: Mr. Biden’s plan would build upon the ACA by working to achieve parity between the treatment of mental health and physical health. The ACA itself strengthened the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (federal parity law), which Mr. Biden championed as vice president, by mandating that all private insurance cover mental health and substance abuse treatment. This act still exempts some health plans, such as larger employers; and many insurers have used loopholes in the policy to illegally deny what could be life-saving coverage.
It follows that those who can afford Mr. Biden’s proposed public option Medicare buy-in would receive more comprehensive mental health benefits. He also says he would invest in school and college mental health professionals, an important opportunity for early intervention given 75% of lifetime mental illness starts by age 24 years. While Mr. Biden has not stated a specific plan for addressing minority groups, whose mental health has been disproportionately affected by COVID-19, he has acknowledged that this unmet need should be targeted.
Addressing suicide
More than 3,000 Americans attempt suicide every day. Suicide is the second leading cause of death for America’s youth and one of the top 10 leading causes of death across the population. Numerous strategies are necessary to address suicide, but one of the most decisive is gun control. Gun violence is inextricably tied to suicide: States where gun prevalence is higher see about four times the number of suicides because of guns, whereas nonfirearm suicide rates are the same as those seen elsewhere. In 2017, of the nearly 40,000 people who died of gun violence, 60% were attributable to suicides. Since the pandemic started, there have been increases in reported suicidal thoughts and a nearly 1,000% increase in use of the national crisis hotline. This is especially concerning given the uptick during the pandemic of gun purchases; as of September, more guns have been purchased this year than any year before.
Mr. Trump: Prior to coronavirus, the Trump administration was unwilling to enact gun control legislation. In early 2017, Mr. Trump removed an Obama-era bill that would have expanded the background check database. It would have added those deemed legally unfit to handle their own funds and those who received Social Security funds for mental health reasons. During the lockdown, the administration made an advisory ruling declaring gun shops as essential businesses that states should keep open.
Mr. Biden: The former vice president has a history of supporting gun control measures in his time as a senator and vice president. In the Senate, Mr. Biden supported both the Brady handgun bill in 1993 and a ban on assault weapons in 1994. As vice president, he was tasked by President Obama to push for a renewed assault weapons ban and a background check bill (Manchin-Toomey bill).
During his 2020 presidential campaign, Mr. Biden has suggested creating universal background checks and reinstating bans on assault rifle sales. He has said that he is also open to having a federal buyback program for assault rifles from gun owners.
Why this matters
The winner of the 2020 election will lead an electorate that is reeling from the health, economic, and social consequences COVID-19. The next administration needs to act swiftly to address the mental health pandemic and have a keen awareness of what is ahead. As Americans make their voting decision, consider who has the best plans not only to contain the virus but also the mental health crises that are ravaging our nation.
Dr. Vasan is a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry at Stanford (Calif.) University, where she is founder and executive director of Brainstorm: The Stanford Lab for Mental Health Innovation. She also serves as chief medical officer of Real, and chair of the American Psychiatric Association Committee on Innovation. Dr. Vasan has no conflicts of interest. Mr. Agbafe is a fellow at Stanford Brainstorm and a first-year medical student at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He has no conflicts of interest. Ms. Li is a policy intern at Stanford Brainstorm and an undergraduate student in the department of economics at the University of California, Berkeley. She has no conflicts of interest.
The COVID-19 pandemic is one of the most pressing public health challenges the United States has ever faced, and the resulting financial ruin and social isolation are creating a mental health pandemic that will continue well after COVID-19 lockdowns end. To understand which presidential candidate would best lead the mental health recovery, we identified three of the most critical issues in mental health and compared the plans of the two candidates.
Fighting the opioid epidemic
Over the last several years, the opioid epidemic has devastated American families and communities. Prior to the pandemic, drug overdoses were the leading cause of death for American adults under 50 years of age. The effects of COVID-19–enabled overdose deaths to rise even higher. Multiple elements of the pandemic – isolation, unemployment, and increased anxiety and depression – make those struggling with substance use even more vulnerable, and immediate and comprehensive action is needed to address this national tragedy.
Donald J. Trump: President Trump has been vocal and active in addressing this problem since he took office. One of the Trump administration’s successes is launching the Opioid and Drug Abuse Commission and rolling out a five-point strategy built around improving services, data, research, overdose-reversing drugs, and pain management. Last year, the Trump administration funded $10 billion over 5 years to combat both the opioid epidemic and mental health issues by building upon the 21st Century CURES Act. However, in this same budget, the administration proposed cutting funding by $600 million for SAMHSA, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, which is the top government agency for addressing and providing care for substance use.
President Trump also created an assistant secretary for mental health and substance use position in the Department of Health & Human Services, and appointed Elinore F. McCance-Katz, MD, PhD, a psychiatrist with a strong track record on fighting opioid abuse in Rhode Island, to the post.
Joe Biden: Former Vice President Biden emphasizes that substance use is “a disease of the brain,” refuting the long-held misconception that addiction is an issue of willpower. This stigmatization is very personal given that his own son Hunter reportedly suffered through mental health and substance use issues since his teenage years. However, Biden also had a major role in pushing forward the federal “war on drugs,” including his role in crafting the “Len Bias law.”
Mr. Biden has since released a multifaceted plan for reducing substance use, aiming to make prevention and treatment services more available through a $125 billion federal investment. There are also measures to hold pharmaceutical companies accountable for triggering the crisis, stop the flow of fentanyl to the United States, and restrict incentive payments from manufacturers to doctors so as to limit the dosing and usage of powerful opioids.
Accessing health care
One of the main dividing lines in this election has been the battle to either gut or build upon the Affordable Care Act (ACA). This will have deep ramifications on people’s access to health mental health services. Since COVID-19 started, more than 50% of Americans have reported worsening mental health. This makes it crucial that each candidate’s mental health plan is judged by how they would expand access to insurance, address unenforced parity laws, and protect those who have a mental health disorder as a preexisting condition.
Mr. Trump: Following a failed Senate vote to repeal this law, the Trump administration took a piecemeal approach to dismantling the ACA that included removing the individual mandate, enabling states to introduce Medicaid work requirements, and reducing cost-sharing subsidies to insurers.
If a re-elected Trump administration pursued a complete repeal of the ACA law, many individuals with previous access to mental health and substance abuse treatment via Medicaid expansion may lose access altogether. In addition, key mechanisms aimed at making sure that mental health services are covered by private health plans may be lost, which could undermine policies to address opioids and suicide. On the other hand, the Trump administration’s move during the pandemic to expand telemedicine services has also expanded access to mental health services.
Mr. Biden: Mr. Biden’s plan would build upon the ACA by working to achieve parity between the treatment of mental health and physical health. The ACA itself strengthened the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (federal parity law), which Mr. Biden championed as vice president, by mandating that all private insurance cover mental health and substance abuse treatment. This act still exempts some health plans, such as larger employers; and many insurers have used loopholes in the policy to illegally deny what could be life-saving coverage.
It follows that those who can afford Mr. Biden’s proposed public option Medicare buy-in would receive more comprehensive mental health benefits. He also says he would invest in school and college mental health professionals, an important opportunity for early intervention given 75% of lifetime mental illness starts by age 24 years. While Mr. Biden has not stated a specific plan for addressing minority groups, whose mental health has been disproportionately affected by COVID-19, he has acknowledged that this unmet need should be targeted.
Addressing suicide
More than 3,000 Americans attempt suicide every day. Suicide is the second leading cause of death for America’s youth and one of the top 10 leading causes of death across the population. Numerous strategies are necessary to address suicide, but one of the most decisive is gun control. Gun violence is inextricably tied to suicide: States where gun prevalence is higher see about four times the number of suicides because of guns, whereas nonfirearm suicide rates are the same as those seen elsewhere. In 2017, of the nearly 40,000 people who died of gun violence, 60% were attributable to suicides. Since the pandemic started, there have been increases in reported suicidal thoughts and a nearly 1,000% increase in use of the national crisis hotline. This is especially concerning given the uptick during the pandemic of gun purchases; as of September, more guns have been purchased this year than any year before.
Mr. Trump: Prior to coronavirus, the Trump administration was unwilling to enact gun control legislation. In early 2017, Mr. Trump removed an Obama-era bill that would have expanded the background check database. It would have added those deemed legally unfit to handle their own funds and those who received Social Security funds for mental health reasons. During the lockdown, the administration made an advisory ruling declaring gun shops as essential businesses that states should keep open.
Mr. Biden: The former vice president has a history of supporting gun control measures in his time as a senator and vice president. In the Senate, Mr. Biden supported both the Brady handgun bill in 1993 and a ban on assault weapons in 1994. As vice president, he was tasked by President Obama to push for a renewed assault weapons ban and a background check bill (Manchin-Toomey bill).
During his 2020 presidential campaign, Mr. Biden has suggested creating universal background checks and reinstating bans on assault rifle sales. He has said that he is also open to having a federal buyback program for assault rifles from gun owners.
Why this matters
The winner of the 2020 election will lead an electorate that is reeling from the health, economic, and social consequences COVID-19. The next administration needs to act swiftly to address the mental health pandemic and have a keen awareness of what is ahead. As Americans make their voting decision, consider who has the best plans not only to contain the virus but also the mental health crises that are ravaging our nation.
Dr. Vasan is a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry at Stanford (Calif.) University, where she is founder and executive director of Brainstorm: The Stanford Lab for Mental Health Innovation. She also serves as chief medical officer of Real, and chair of the American Psychiatric Association Committee on Innovation. Dr. Vasan has no conflicts of interest. Mr. Agbafe is a fellow at Stanford Brainstorm and a first-year medical student at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He has no conflicts of interest. Ms. Li is a policy intern at Stanford Brainstorm and an undergraduate student in the department of economics at the University of California, Berkeley. She has no conflicts of interest.
Health sector has spent $464 million on lobbying in 2020
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.
PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.

PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.

PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
CDC panel takes on COVID vaccine rollout, risks, and side effects
Federal advisers who will help determine which Americans get the first COVID vaccines took an in-depth look Oct. 30 at the challenges they face in selecting priority groups.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will face two key decisions once a COVID vaccine wins clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
ACIP will need to decide whether to recommend its use in adults (the age group in which vaccines are currently being tested). The group will also need to offer direction on which groups should get priority in vaccine allocation, inasmuch as early supplies will not be sufficient to vaccinate everyone.
At the Oct. 30 meeting, CDC’s Kathleen Dooling, MD, MPH, suggested that ACIP plan on tackling these issues as two separate questions when it comes time to weigh in on an approved vaccine. Although there was no formal vote among ACIP members at the meeting, Dooling’s proposal for tackling a future recommendation in a two-part fashion drew positive feedback.
ACIP member Katherine A. Poehling, MD, MPH, suggested that the panel and CDC be ready to reexamine the situation frequently regarding COVID vaccination. “Perhaps we could think about reviewing data on a monthly basis and updating the recommendation, so that we can account for the concerns and balance both the benefits and the [potential] harm,” Poehling said.
Dooling agreed. “Both the vaccine recommendation and allocation will be revisited in what is a very dynamic situation,” Dooling replied to Poehling. “So all new evidence will be brought to ACIP, and certainly the allocation as vaccine distribution proceeds will need to be adjusted accordingly.”
Ethics and limited evidence
During the meeting, ACIP members repeatedly expressed discomfort with the prospect of having to weigh in on widespread use of COVID vaccines on the basis of limited evidence.
Within months, FDA may opt for a special clearance, known as an emergency use authorization (EUA), for one or more of the experimental COVID vaccines now in advanced testing. Many of FDA’s past EUA clearances were granted for test kits. For those EUA approvals, the agency considered risks of false results but not longer-term, direct harm to patients from these products.
With a COVID vaccine, there will be strong pressure to distribute doses as quickly as possible with the hope of curbing the pandemic, which has already led to more than 229,000 deaths in the United States alone and has disrupted lives and economies around the world. But questions will persist about the possibility of serious complications from these vaccines, ACIP members noted.
“My personal struggle is the ethical side and how to balance these two,” said ACIP member Robert L. Atmar, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, who noted that he expects his fellow panelists to share this concern.
Currently, four experimental COVID vaccines likely to be used in the United States have advanced to phase 3 testing. Pfizer Inc and BioNtech have enrolled more than 42,000 participants in a test of their candidate, BNT162b2 vaccine, and rival Moderna has enrolled about 30,000 participants in a test of its mRNA-1273 vaccine, CDC staff said.
The other two advanced COVID vaccine candidates have overcome recent hurdles. AstraZeneca Plc on Oct. 23 announced that FDA had removed a hold on the testing of its AZD1222 vaccine candidate; the trial will enroll approximately 30,000 people. Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen unit also announced that day the lifting of a safety pause for its Ad26.COV2.S vaccine; the phase 3 trial for that vaccine will enroll approximately 60,000 volunteers. Federal agencies, states, and territories have developed plans for future distribution of COVID vaccines, CDC staff said in briefing materials for today’s ACIP meeting.
Several ACIP members raised many of the same concerns that members of an FDA advisory committee raised at a meeting earlier in October. ACIP and FDA advisers honed in on the FDA’s decision to set a median follow-up duration of 2 months in phase 3 trials in connection with expected EUA applications for COVID-19 vaccines.
“I struggle with following people for 2 months after their second vaccination as a time point to start making final decisions about safety,” said ACIP member Sharon E. Frey, MD, a professor at St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri. “I just want to put that out there.”
Medical front line, then who?
There is consensus that healthcare workers be in the first stage ― Phase 1 ― of distribution. That recommendation was made in a report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM). Phase 1A would include first responders; Phase 1B might include people of all ages who have two or more comorbidities that put them at significantly higher risk for COVID-19 or death, as well as older adults living in congregate or overcrowded settings, the NASEM report said.
A presentation from the CDC’s Matthew Biggerstaff, ScD, MPH, underscored challenges in distributing what are expected to be limited initial supplies of COVID vaccines.
Biggerstaff showed several scenarios the CDC’s Data, Analytics, and Modeling Task Force had studied. The initial allocation of vaccines would be for healthcare workers, followed by what the CDC called Phase 1B.
Choices for a rollout may include next giving COVID vaccines to people at high risk, such as persons who have one or more chronic medical conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, kidney disease, or obesity. Other options for the rollout could be to vaccinate people aged 65 years and older or essential workers whose employment puts them in contact with the public, thus raising the risk of contracting the virus.
The CDC’s research found that the greatest impact in preventing death was to initially vaccinate adults aged 65 and older in Phase 1B. The agency staff described this approach as likely to result in an about “1 to 11% increase in averted deaths across the scenarios.”
Initially vaccinating essential workers or high-risk adults in Phase 1B would avert the most infections. The agency staff described this approach as yielding about “1 to 5% increase in averted infections across the scenarios,” Biggerstaff said during his presentation.
The following are other findings of the CDC staff:
The earlier the vaccine rollout relative to increasing transmission, the greater the averted percentage and differences between the strategies.
Differences were not substantial in some scenarios.
The need to continue efforts to slow the spread of COVID-19 should be emphasized.
Adverse effects
ACIP members also heard about strategies for tracking potential side effects of future vaccines. A presentation by Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Task Force/Vaccine Safety Team, included details about a new smartphone-based active surveillance program for COVID-19 vaccine safety.
Known as v-safe, this system would use Web-based survey monitoring and incorporate text messaging. It would conduct electronic health checks on vaccine recipients, which would occur daily during the first week post vaccination and weekly thereafter for 6 weeks from the time of vaccination.
Clinicians “can play an important role in helping CDC enroll patients in v-safe at the time of vaccination,” Shimabukuro noted in his presentation. This would add another task, though, for clinicians, the CDC staff noted.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are special concerns
Of special concern with the rollout of a COVID vaccine are recommendations regarding pregnancy and breastfeeding. Women constitute about 75% of the healthcare workforce, CDC staff noted.
At the time the initial ACIP COVID vaccination recommendations are made, there could be approximately 330,000 healthcare personnel who are pregnant or who have recently given birth. Available data indicate potentially increased risks for severe maternal illness and preterm birth associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, said CDC’s Megan Wallace, DrPH, MPH, in a presentation for the Friday meeting.
In an Oct. 27 letter to ACIP, Chair Jose Romero, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), urged the panel to ensure that pregnant women and new mothers in the healthcare workforce have priority access to a COVID vaccine. Pregnant and lactating women were “noticeably and alarmingly absent from the NASEM vaccine allocation plan for COVID-19,” wrote Christopher M. Zahn, MD, vice president for practice activities at ACOG, in the letter to Romero.
“ACOG urges ACIP to incorporate pregnant and lactating women clearly and explicitly into its COVID-19 vaccine allocation and prioritization framework,” Zahn wrote. “Should an Emergency Use Authorization be executed for one or more COVID-19 vaccines and provide a permissive recommendation for pregnant and lactating women, pregnant health care workers, pregnant first responders, and pregnant individuals with underlying conditions should be prioritized for vaccination alongside their non-pregnant peers.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal advisers who will help determine which Americans get the first COVID vaccines took an in-depth look Oct. 30 at the challenges they face in selecting priority groups.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will face two key decisions once a COVID vaccine wins clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
ACIP will need to decide whether to recommend its use in adults (the age group in which vaccines are currently being tested). The group will also need to offer direction on which groups should get priority in vaccine allocation, inasmuch as early supplies will not be sufficient to vaccinate everyone.
At the Oct. 30 meeting, CDC’s Kathleen Dooling, MD, MPH, suggested that ACIP plan on tackling these issues as two separate questions when it comes time to weigh in on an approved vaccine. Although there was no formal vote among ACIP members at the meeting, Dooling’s proposal for tackling a future recommendation in a two-part fashion drew positive feedback.
ACIP member Katherine A. Poehling, MD, MPH, suggested that the panel and CDC be ready to reexamine the situation frequently regarding COVID vaccination. “Perhaps we could think about reviewing data on a monthly basis and updating the recommendation, so that we can account for the concerns and balance both the benefits and the [potential] harm,” Poehling said.
Dooling agreed. “Both the vaccine recommendation and allocation will be revisited in what is a very dynamic situation,” Dooling replied to Poehling. “So all new evidence will be brought to ACIP, and certainly the allocation as vaccine distribution proceeds will need to be adjusted accordingly.”
Ethics and limited evidence
During the meeting, ACIP members repeatedly expressed discomfort with the prospect of having to weigh in on widespread use of COVID vaccines on the basis of limited evidence.
Within months, FDA may opt for a special clearance, known as an emergency use authorization (EUA), for one or more of the experimental COVID vaccines now in advanced testing. Many of FDA’s past EUA clearances were granted for test kits. For those EUA approvals, the agency considered risks of false results but not longer-term, direct harm to patients from these products.
With a COVID vaccine, there will be strong pressure to distribute doses as quickly as possible with the hope of curbing the pandemic, which has already led to more than 229,000 deaths in the United States alone and has disrupted lives and economies around the world. But questions will persist about the possibility of serious complications from these vaccines, ACIP members noted.
“My personal struggle is the ethical side and how to balance these two,” said ACIP member Robert L. Atmar, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, who noted that he expects his fellow panelists to share this concern.
Currently, four experimental COVID vaccines likely to be used in the United States have advanced to phase 3 testing. Pfizer Inc and BioNtech have enrolled more than 42,000 participants in a test of their candidate, BNT162b2 vaccine, and rival Moderna has enrolled about 30,000 participants in a test of its mRNA-1273 vaccine, CDC staff said.
The other two advanced COVID vaccine candidates have overcome recent hurdles. AstraZeneca Plc on Oct. 23 announced that FDA had removed a hold on the testing of its AZD1222 vaccine candidate; the trial will enroll approximately 30,000 people. Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen unit also announced that day the lifting of a safety pause for its Ad26.COV2.S vaccine; the phase 3 trial for that vaccine will enroll approximately 60,000 volunteers. Federal agencies, states, and territories have developed plans for future distribution of COVID vaccines, CDC staff said in briefing materials for today’s ACIP meeting.
Several ACIP members raised many of the same concerns that members of an FDA advisory committee raised at a meeting earlier in October. ACIP and FDA advisers honed in on the FDA’s decision to set a median follow-up duration of 2 months in phase 3 trials in connection with expected EUA applications for COVID-19 vaccines.
“I struggle with following people for 2 months after their second vaccination as a time point to start making final decisions about safety,” said ACIP member Sharon E. Frey, MD, a professor at St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri. “I just want to put that out there.”
Medical front line, then who?
There is consensus that healthcare workers be in the first stage ― Phase 1 ― of distribution. That recommendation was made in a report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM). Phase 1A would include first responders; Phase 1B might include people of all ages who have two or more comorbidities that put them at significantly higher risk for COVID-19 or death, as well as older adults living in congregate or overcrowded settings, the NASEM report said.
A presentation from the CDC’s Matthew Biggerstaff, ScD, MPH, underscored challenges in distributing what are expected to be limited initial supplies of COVID vaccines.
Biggerstaff showed several scenarios the CDC’s Data, Analytics, and Modeling Task Force had studied. The initial allocation of vaccines would be for healthcare workers, followed by what the CDC called Phase 1B.
Choices for a rollout may include next giving COVID vaccines to people at high risk, such as persons who have one or more chronic medical conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, kidney disease, or obesity. Other options for the rollout could be to vaccinate people aged 65 years and older or essential workers whose employment puts them in contact with the public, thus raising the risk of contracting the virus.
The CDC’s research found that the greatest impact in preventing death was to initially vaccinate adults aged 65 and older in Phase 1B. The agency staff described this approach as likely to result in an about “1 to 11% increase in averted deaths across the scenarios.”
Initially vaccinating essential workers or high-risk adults in Phase 1B would avert the most infections. The agency staff described this approach as yielding about “1 to 5% increase in averted infections across the scenarios,” Biggerstaff said during his presentation.
The following are other findings of the CDC staff:
The earlier the vaccine rollout relative to increasing transmission, the greater the averted percentage and differences between the strategies.
Differences were not substantial in some scenarios.
The need to continue efforts to slow the spread of COVID-19 should be emphasized.
Adverse effects
ACIP members also heard about strategies for tracking potential side effects of future vaccines. A presentation by Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Task Force/Vaccine Safety Team, included details about a new smartphone-based active surveillance program for COVID-19 vaccine safety.
Known as v-safe, this system would use Web-based survey monitoring and incorporate text messaging. It would conduct electronic health checks on vaccine recipients, which would occur daily during the first week post vaccination and weekly thereafter for 6 weeks from the time of vaccination.
Clinicians “can play an important role in helping CDC enroll patients in v-safe at the time of vaccination,” Shimabukuro noted in his presentation. This would add another task, though, for clinicians, the CDC staff noted.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are special concerns
Of special concern with the rollout of a COVID vaccine are recommendations regarding pregnancy and breastfeeding. Women constitute about 75% of the healthcare workforce, CDC staff noted.
At the time the initial ACIP COVID vaccination recommendations are made, there could be approximately 330,000 healthcare personnel who are pregnant or who have recently given birth. Available data indicate potentially increased risks for severe maternal illness and preterm birth associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, said CDC’s Megan Wallace, DrPH, MPH, in a presentation for the Friday meeting.
In an Oct. 27 letter to ACIP, Chair Jose Romero, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), urged the panel to ensure that pregnant women and new mothers in the healthcare workforce have priority access to a COVID vaccine. Pregnant and lactating women were “noticeably and alarmingly absent from the NASEM vaccine allocation plan for COVID-19,” wrote Christopher M. Zahn, MD, vice president for practice activities at ACOG, in the letter to Romero.
“ACOG urges ACIP to incorporate pregnant and lactating women clearly and explicitly into its COVID-19 vaccine allocation and prioritization framework,” Zahn wrote. “Should an Emergency Use Authorization be executed for one or more COVID-19 vaccines and provide a permissive recommendation for pregnant and lactating women, pregnant health care workers, pregnant first responders, and pregnant individuals with underlying conditions should be prioritized for vaccination alongside their non-pregnant peers.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal advisers who will help determine which Americans get the first COVID vaccines took an in-depth look Oct. 30 at the challenges they face in selecting priority groups.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will face two key decisions once a COVID vaccine wins clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
ACIP will need to decide whether to recommend its use in adults (the age group in which vaccines are currently being tested). The group will also need to offer direction on which groups should get priority in vaccine allocation, inasmuch as early supplies will not be sufficient to vaccinate everyone.
At the Oct. 30 meeting, CDC’s Kathleen Dooling, MD, MPH, suggested that ACIP plan on tackling these issues as two separate questions when it comes time to weigh in on an approved vaccine. Although there was no formal vote among ACIP members at the meeting, Dooling’s proposal for tackling a future recommendation in a two-part fashion drew positive feedback.
ACIP member Katherine A. Poehling, MD, MPH, suggested that the panel and CDC be ready to reexamine the situation frequently regarding COVID vaccination. “Perhaps we could think about reviewing data on a monthly basis and updating the recommendation, so that we can account for the concerns and balance both the benefits and the [potential] harm,” Poehling said.
Dooling agreed. “Both the vaccine recommendation and allocation will be revisited in what is a very dynamic situation,” Dooling replied to Poehling. “So all new evidence will be brought to ACIP, and certainly the allocation as vaccine distribution proceeds will need to be adjusted accordingly.”
Ethics and limited evidence
During the meeting, ACIP members repeatedly expressed discomfort with the prospect of having to weigh in on widespread use of COVID vaccines on the basis of limited evidence.
Within months, FDA may opt for a special clearance, known as an emergency use authorization (EUA), for one or more of the experimental COVID vaccines now in advanced testing. Many of FDA’s past EUA clearances were granted for test kits. For those EUA approvals, the agency considered risks of false results but not longer-term, direct harm to patients from these products.
With a COVID vaccine, there will be strong pressure to distribute doses as quickly as possible with the hope of curbing the pandemic, which has already led to more than 229,000 deaths in the United States alone and has disrupted lives and economies around the world. But questions will persist about the possibility of serious complications from these vaccines, ACIP members noted.
“My personal struggle is the ethical side and how to balance these two,” said ACIP member Robert L. Atmar, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, who noted that he expects his fellow panelists to share this concern.
Currently, four experimental COVID vaccines likely to be used in the United States have advanced to phase 3 testing. Pfizer Inc and BioNtech have enrolled more than 42,000 participants in a test of their candidate, BNT162b2 vaccine, and rival Moderna has enrolled about 30,000 participants in a test of its mRNA-1273 vaccine, CDC staff said.
The other two advanced COVID vaccine candidates have overcome recent hurdles. AstraZeneca Plc on Oct. 23 announced that FDA had removed a hold on the testing of its AZD1222 vaccine candidate; the trial will enroll approximately 30,000 people. Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen unit also announced that day the lifting of a safety pause for its Ad26.COV2.S vaccine; the phase 3 trial for that vaccine will enroll approximately 60,000 volunteers. Federal agencies, states, and territories have developed plans for future distribution of COVID vaccines, CDC staff said in briefing materials for today’s ACIP meeting.
Several ACIP members raised many of the same concerns that members of an FDA advisory committee raised at a meeting earlier in October. ACIP and FDA advisers honed in on the FDA’s decision to set a median follow-up duration of 2 months in phase 3 trials in connection with expected EUA applications for COVID-19 vaccines.
“I struggle with following people for 2 months after their second vaccination as a time point to start making final decisions about safety,” said ACIP member Sharon E. Frey, MD, a professor at St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri. “I just want to put that out there.”
Medical front line, then who?
There is consensus that healthcare workers be in the first stage ― Phase 1 ― of distribution. That recommendation was made in a report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM). Phase 1A would include first responders; Phase 1B might include people of all ages who have two or more comorbidities that put them at significantly higher risk for COVID-19 or death, as well as older adults living in congregate or overcrowded settings, the NASEM report said.
A presentation from the CDC’s Matthew Biggerstaff, ScD, MPH, underscored challenges in distributing what are expected to be limited initial supplies of COVID vaccines.
Biggerstaff showed several scenarios the CDC’s Data, Analytics, and Modeling Task Force had studied. The initial allocation of vaccines would be for healthcare workers, followed by what the CDC called Phase 1B.
Choices for a rollout may include next giving COVID vaccines to people at high risk, such as persons who have one or more chronic medical conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, kidney disease, or obesity. Other options for the rollout could be to vaccinate people aged 65 years and older or essential workers whose employment puts them in contact with the public, thus raising the risk of contracting the virus.
The CDC’s research found that the greatest impact in preventing death was to initially vaccinate adults aged 65 and older in Phase 1B. The agency staff described this approach as likely to result in an about “1 to 11% increase in averted deaths across the scenarios.”
Initially vaccinating essential workers or high-risk adults in Phase 1B would avert the most infections. The agency staff described this approach as yielding about “1 to 5% increase in averted infections across the scenarios,” Biggerstaff said during his presentation.
The following are other findings of the CDC staff:
The earlier the vaccine rollout relative to increasing transmission, the greater the averted percentage and differences between the strategies.
Differences were not substantial in some scenarios.
The need to continue efforts to slow the spread of COVID-19 should be emphasized.
Adverse effects
ACIP members also heard about strategies for tracking potential side effects of future vaccines. A presentation by Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Task Force/Vaccine Safety Team, included details about a new smartphone-based active surveillance program for COVID-19 vaccine safety.
Known as v-safe, this system would use Web-based survey monitoring and incorporate text messaging. It would conduct electronic health checks on vaccine recipients, which would occur daily during the first week post vaccination and weekly thereafter for 6 weeks from the time of vaccination.
Clinicians “can play an important role in helping CDC enroll patients in v-safe at the time of vaccination,” Shimabukuro noted in his presentation. This would add another task, though, for clinicians, the CDC staff noted.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are special concerns
Of special concern with the rollout of a COVID vaccine are recommendations regarding pregnancy and breastfeeding. Women constitute about 75% of the healthcare workforce, CDC staff noted.
At the time the initial ACIP COVID vaccination recommendations are made, there could be approximately 330,000 healthcare personnel who are pregnant or who have recently given birth. Available data indicate potentially increased risks for severe maternal illness and preterm birth associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, said CDC’s Megan Wallace, DrPH, MPH, in a presentation for the Friday meeting.
In an Oct. 27 letter to ACIP, Chair Jose Romero, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), urged the panel to ensure that pregnant women and new mothers in the healthcare workforce have priority access to a COVID vaccine. Pregnant and lactating women were “noticeably and alarmingly absent from the NASEM vaccine allocation plan for COVID-19,” wrote Christopher M. Zahn, MD, vice president for practice activities at ACOG, in the letter to Romero.
“ACOG urges ACIP to incorporate pregnant and lactating women clearly and explicitly into its COVID-19 vaccine allocation and prioritization framework,” Zahn wrote. “Should an Emergency Use Authorization be executed for one or more COVID-19 vaccines and provide a permissive recommendation for pregnant and lactating women, pregnant health care workers, pregnant first responders, and pregnant individuals with underlying conditions should be prioritized for vaccination alongside their non-pregnant peers.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HHS extends deadline for patient access to your clinical notes
The Department of Health & Human Services on Oct. 29 extended the deadline for health care groups to provide patients with immediate electronic access to their doctors’ clinical notes as well as test results and reports from pathology and imaging.
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, and will now go into effect April 5.
The announcement comes just 4 days before the previously established Nov. 2 deadline and gives the pandemic as the reason for the delay.
“We are hearing that, while there is strong support for advancing patient access … stakeholders also must manage the needs being experienced during the current pandemic,” Don Rucker, MD, national coordinator for health information technology at HHS, said in a press statement.
“To be clear, the Office of the National Coordinator is not removing the requirements advancing patient access to their health information,” he added.
‘What you make of it’
Scott MacDonald, MD, electronic health record medical director at the University of California, Davis, said his organization is proceeding anyway. “UC Davis is going to start releasing notes and test results on Nov. 12,” he said in an interview.
Other organizations and practices now have more time, he said, but the law stays the same. “There’s no change to the what or why – only to the when,” Dr. MacDonald pointed out.
Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., will take advantage of the extra time, Trent Rosenbloom, MD, MPH, director of patient portals, said in an interview.
“Given the super-short time frame we had to work under as this emerged out from dealing with COVID, we feel that we have not addressed all the potential legal-edge cases such as dealing with adolescent medicine and child abuse,” he said.
On Oct. 21, this news organization reported on the then-imminent start of the new law, which irked many readers. They cited, among other things, the likelihood of patient confusion with fast patient access to all clinical notes.
“To me, the biggest issue is that we speak a foreign language that most outside of medicine don’t speak. Our job is to explain it to the patient at a level they can understand. What will 100% happen now is that a patient will not be able to reconcile what is in the note to what they’ve been told,” Andrew White, MD, wrote in a reader comment.
But benefits of open notes outweigh the risks, say proponents, who claim that doctor-patient communication and trust actually improve with information access and that research indicates other benefits such as improved medication adherence.
Open notes are “what you make of it,” said Marlene Millen, MD, an internist at UC San Diego Health, which has had a pilot open-notes program for 3 years.
“I actually end all of my appointments with: ‘Don’t forget to read your note later,’ ” she said in an interview.
Dr. Millen feared open notes initially but, within the first 3 months of usage, about 15 patients gave her direct feedback on how much they appreciated her notes. “It seemed to really reassure them that they were getting good care.”
Dr. MacDonald and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Department of Health & Human Services on Oct. 29 extended the deadline for health care groups to provide patients with immediate electronic access to their doctors’ clinical notes as well as test results and reports from pathology and imaging.
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, and will now go into effect April 5.
The announcement comes just 4 days before the previously established Nov. 2 deadline and gives the pandemic as the reason for the delay.
“We are hearing that, while there is strong support for advancing patient access … stakeholders also must manage the needs being experienced during the current pandemic,” Don Rucker, MD, national coordinator for health information technology at HHS, said in a press statement.
“To be clear, the Office of the National Coordinator is not removing the requirements advancing patient access to their health information,” he added.
‘What you make of it’
Scott MacDonald, MD, electronic health record medical director at the University of California, Davis, said his organization is proceeding anyway. “UC Davis is going to start releasing notes and test results on Nov. 12,” he said in an interview.
Other organizations and practices now have more time, he said, but the law stays the same. “There’s no change to the what or why – only to the when,” Dr. MacDonald pointed out.
Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., will take advantage of the extra time, Trent Rosenbloom, MD, MPH, director of patient portals, said in an interview.
“Given the super-short time frame we had to work under as this emerged out from dealing with COVID, we feel that we have not addressed all the potential legal-edge cases such as dealing with adolescent medicine and child abuse,” he said.
On Oct. 21, this news organization reported on the then-imminent start of the new law, which irked many readers. They cited, among other things, the likelihood of patient confusion with fast patient access to all clinical notes.
“To me, the biggest issue is that we speak a foreign language that most outside of medicine don’t speak. Our job is to explain it to the patient at a level they can understand. What will 100% happen now is that a patient will not be able to reconcile what is in the note to what they’ve been told,” Andrew White, MD, wrote in a reader comment.
But benefits of open notes outweigh the risks, say proponents, who claim that doctor-patient communication and trust actually improve with information access and that research indicates other benefits such as improved medication adherence.
Open notes are “what you make of it,” said Marlene Millen, MD, an internist at UC San Diego Health, which has had a pilot open-notes program for 3 years.
“I actually end all of my appointments with: ‘Don’t forget to read your note later,’ ” she said in an interview.
Dr. Millen feared open notes initially but, within the first 3 months of usage, about 15 patients gave her direct feedback on how much they appreciated her notes. “It seemed to really reassure them that they were getting good care.”
Dr. MacDonald and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Department of Health & Human Services on Oct. 29 extended the deadline for health care groups to provide patients with immediate electronic access to their doctors’ clinical notes as well as test results and reports from pathology and imaging.
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, and will now go into effect April 5.
The announcement comes just 4 days before the previously established Nov. 2 deadline and gives the pandemic as the reason for the delay.
“We are hearing that, while there is strong support for advancing patient access … stakeholders also must manage the needs being experienced during the current pandemic,” Don Rucker, MD, national coordinator for health information technology at HHS, said in a press statement.
“To be clear, the Office of the National Coordinator is not removing the requirements advancing patient access to their health information,” he added.
‘What you make of it’
Scott MacDonald, MD, electronic health record medical director at the University of California, Davis, said his organization is proceeding anyway. “UC Davis is going to start releasing notes and test results on Nov. 12,” he said in an interview.
Other organizations and practices now have more time, he said, but the law stays the same. “There’s no change to the what or why – only to the when,” Dr. MacDonald pointed out.
Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., will take advantage of the extra time, Trent Rosenbloom, MD, MPH, director of patient portals, said in an interview.
“Given the super-short time frame we had to work under as this emerged out from dealing with COVID, we feel that we have not addressed all the potential legal-edge cases such as dealing with adolescent medicine and child abuse,” he said.
On Oct. 21, this news organization reported on the then-imminent start of the new law, which irked many readers. They cited, among other things, the likelihood of patient confusion with fast patient access to all clinical notes.
“To me, the biggest issue is that we speak a foreign language that most outside of medicine don’t speak. Our job is to explain it to the patient at a level they can understand. What will 100% happen now is that a patient will not be able to reconcile what is in the note to what they’ve been told,” Andrew White, MD, wrote in a reader comment.
But benefits of open notes outweigh the risks, say proponents, who claim that doctor-patient communication and trust actually improve with information access and that research indicates other benefits such as improved medication adherence.
Open notes are “what you make of it,” said Marlene Millen, MD, an internist at UC San Diego Health, which has had a pilot open-notes program for 3 years.
“I actually end all of my appointments with: ‘Don’t forget to read your note later,’ ” she said in an interview.
Dr. Millen feared open notes initially but, within the first 3 months of usage, about 15 patients gave her direct feedback on how much they appreciated her notes. “It seemed to really reassure them that they were getting good care.”
Dr. MacDonald and Dr. Millen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Florida will investigate all COVID-19 deaths
The Florida Department of Health will investigate the state’s 16,000 coronavirus deaths due to questions about the integrity of the data, according to an announcement issued Wednesday.
State health department officials said the “fatality data reported to the state consistently presents confusion and warrants a rigorous review.” The review is meant to “ensure data integrity.”
“During a pandemic, the public must be able to rely on accurate public health data to make informed decisions,” Scott Rivkees, the surgeon general for Florida, said in the statement.
Among the 95 deaths reported Wednesday for instance, 16 had more than a 2-month separation between the time of testing positive for COVID-19 and passing away, and 5 cases had a 3-month gap. In addition, 11 of the deaths occurred more than a month ago.
The health department then listed data for all 95 cases, including the age, gender, county and the dates of test positivity and death. Palm Beach County had 50 of the COVID-19 deaths.
“To ensure the accuracy of COVID-19 related deaths, the department will be performing additional reviews of all deaths,” Rivkees said. “Timely and accurate data remains a top priority of the Department of Health.”
Last week, Jose Oliva, speaker of the Florida House of Representatives, said medical examiner reports were “often lacking in rigor.” House Democrats then said Republicans were trying to “downplay the death toll,” according to the South Florida Sun Sentinel .
Fred Piccolo Jr., a spokesman for Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, told the newspaper Wednesday that officials have struggled to obtain timely data. Labs sometimes report test results from weeks before, he added.
“It’s really one of those things that you gotta know if someone is dying of COVID or if they’re not,” Piccolo said. “Then you can legitimately say, here are the numbers.”
Sources
Florida Department of Health, “Florida Surgeon General Implements Additional Review Process for Fatalities Attributed to COVID-19 to Ensure Data Integrity.”
South Florida Sun Sentinel, “Florida to investigate all COVID-19 deaths after questions about ‘integrity’ of data.”
WebMD Health News © 2020
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Florida Department of Health will investigate the state’s 16,000 coronavirus deaths due to questions about the integrity of the data, according to an announcement issued Wednesday.
State health department officials said the “fatality data reported to the state consistently presents confusion and warrants a rigorous review.” The review is meant to “ensure data integrity.”
“During a pandemic, the public must be able to rely on accurate public health data to make informed decisions,” Scott Rivkees, the surgeon general for Florida, said in the statement.
Among the 95 deaths reported Wednesday for instance, 16 had more than a 2-month separation between the time of testing positive for COVID-19 and passing away, and 5 cases had a 3-month gap. In addition, 11 of the deaths occurred more than a month ago.
The health department then listed data for all 95 cases, including the age, gender, county and the dates of test positivity and death. Palm Beach County had 50 of the COVID-19 deaths.
“To ensure the accuracy of COVID-19 related deaths, the department will be performing additional reviews of all deaths,” Rivkees said. “Timely and accurate data remains a top priority of the Department of Health.”
Last week, Jose Oliva, speaker of the Florida House of Representatives, said medical examiner reports were “often lacking in rigor.” House Democrats then said Republicans were trying to “downplay the death toll,” according to the South Florida Sun Sentinel .
Fred Piccolo Jr., a spokesman for Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, told the newspaper Wednesday that officials have struggled to obtain timely data. Labs sometimes report test results from weeks before, he added.
“It’s really one of those things that you gotta know if someone is dying of COVID or if they’re not,” Piccolo said. “Then you can legitimately say, here are the numbers.”
Sources
Florida Department of Health, “Florida Surgeon General Implements Additional Review Process for Fatalities Attributed to COVID-19 to Ensure Data Integrity.”
South Florida Sun Sentinel, “Florida to investigate all COVID-19 deaths after questions about ‘integrity’ of data.”
WebMD Health News © 2020
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Florida Department of Health will investigate the state’s 16,000 coronavirus deaths due to questions about the integrity of the data, according to an announcement issued Wednesday.
State health department officials said the “fatality data reported to the state consistently presents confusion and warrants a rigorous review.” The review is meant to “ensure data integrity.”
“During a pandemic, the public must be able to rely on accurate public health data to make informed decisions,” Scott Rivkees, the surgeon general for Florida, said in the statement.
Among the 95 deaths reported Wednesday for instance, 16 had more than a 2-month separation between the time of testing positive for COVID-19 and passing away, and 5 cases had a 3-month gap. In addition, 11 of the deaths occurred more than a month ago.
The health department then listed data for all 95 cases, including the age, gender, county and the dates of test positivity and death. Palm Beach County had 50 of the COVID-19 deaths.
“To ensure the accuracy of COVID-19 related deaths, the department will be performing additional reviews of all deaths,” Rivkees said. “Timely and accurate data remains a top priority of the Department of Health.”
Last week, Jose Oliva, speaker of the Florida House of Representatives, said medical examiner reports were “often lacking in rigor.” House Democrats then said Republicans were trying to “downplay the death toll,” according to the South Florida Sun Sentinel .
Fred Piccolo Jr., a spokesman for Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, told the newspaper Wednesday that officials have struggled to obtain timely data. Labs sometimes report test results from weeks before, he added.
“It’s really one of those things that you gotta know if someone is dying of COVID or if they’re not,” Piccolo said. “Then you can legitimately say, here are the numbers.”
Sources
Florida Department of Health, “Florida Surgeon General Implements Additional Review Process for Fatalities Attributed to COVID-19 to Ensure Data Integrity.”
South Florida Sun Sentinel, “Florida to investigate all COVID-19 deaths after questions about ‘integrity’ of data.”
WebMD Health News © 2020
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccine standards questioned at FDA advisory meeting
The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee met for a wide-ranging discussion beginning around 10 am. The FDA did not ask the panel to weigh in on any particular vaccine. Instead, the FDA asked for the panel’s feedback on a series of questions, including considerations for continuing phase 3 trials if a product were to get an interim clearance known as an emergency use authorization (EUA).
Speakers at the hearing made a variety of requests, including asking for data showing COVID-19 vaccines can prevent serious illness and urging transparency about the agency’s deliberations for each product to be considered.
FDA staff are closely tracking the crop of experimental vaccines that have made it into advanced stages of testing, including products from Pfizer Inc, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Moderna.
‘Time for a reset’
Among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Lurie, MD, who served as an FDA associate commissioner from 2014 to 2017. Now the president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, Lurie was among the speakers who asked the agency to make its independence clear.
President Donald Trump has for months been making predictions about COVID-19 vaccine approvals that have been overly optimistic. In one example, the president, who is seeking re-election on November 3, last month spoke about being able to begin distributing a vaccine in October.
“Until now the process of developing candidate vaccines has been inappropriately politicized with an eye on the election calendar, rather than the deliberate timeframe science requires,” Lurie told the FDA advisory panel. “Now is the time for a reset. This committee has a unique opportunity to set a new tone for vaccine deliberations going forward.”
Lurie asked the panel to press the FDA to commit to hold an advisory committee meeting on requests by drugmakers for EUAs. He also asked the panel to demand that informed consent forms and minutes from institutional review board (IRB) discussions of COVID-19 vaccines trials be made public.
Also among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Doshi, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, who argued that the current trials won’t answer the right questions about the COVID-19 vaccines.
“We could end up with approved vaccines that reduce the risk of mild infection, but do not decrease the risk of hospitalization, ICU use, or death — either at all or by a clinically relevant amount,” Doshi told the panel.
In his presentation, he reiterated points he had made previously, including in an October 21 article in the BMJ, for which he is an associate editor. Doshi also raised these concerns in a September opinion article in The New York Times, co-authored with Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape.
Risks of a ‘rushed vaccine’
Other complaints about the FDA’s approach included criticism of a 2-month follow-up time after vaccination, which was seen as too short. ECRI, a nonprofit organization that seeks to improve the safety, quality, and cost-effectiveness of medicines, has argued that approving a weak COVID-19 vaccine might worsen the pandemic.
In an October 21 statement, ECRI noted the risk of a partially effective vaccine, which could be welcomed as a means of slowing transmission of the virus. But public response and attitudes over the past 9 months in the United States suggest that people would relax their precautions as soon as a vaccine is available.
“Resulting infections may offset the vaccine’s impact and end up increasing the mortality and morbidity burden,” ECRI said in the brief.
“The risks and consequences of a rushed vaccine could be very severe if the review is anything shy of thorough,” ECRI Chief Executive Officer Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, said in a statement prepared for the hearing.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee met for a wide-ranging discussion beginning around 10 am. The FDA did not ask the panel to weigh in on any particular vaccine. Instead, the FDA asked for the panel’s feedback on a series of questions, including considerations for continuing phase 3 trials if a product were to get an interim clearance known as an emergency use authorization (EUA).
Speakers at the hearing made a variety of requests, including asking for data showing COVID-19 vaccines can prevent serious illness and urging transparency about the agency’s deliberations for each product to be considered.
FDA staff are closely tracking the crop of experimental vaccines that have made it into advanced stages of testing, including products from Pfizer Inc, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Moderna.
‘Time for a reset’
Among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Lurie, MD, who served as an FDA associate commissioner from 2014 to 2017. Now the president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, Lurie was among the speakers who asked the agency to make its independence clear.
President Donald Trump has for months been making predictions about COVID-19 vaccine approvals that have been overly optimistic. In one example, the president, who is seeking re-election on November 3, last month spoke about being able to begin distributing a vaccine in October.
“Until now the process of developing candidate vaccines has been inappropriately politicized with an eye on the election calendar, rather than the deliberate timeframe science requires,” Lurie told the FDA advisory panel. “Now is the time for a reset. This committee has a unique opportunity to set a new tone for vaccine deliberations going forward.”
Lurie asked the panel to press the FDA to commit to hold an advisory committee meeting on requests by drugmakers for EUAs. He also asked the panel to demand that informed consent forms and minutes from institutional review board (IRB) discussions of COVID-19 vaccines trials be made public.
Also among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Doshi, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, who argued that the current trials won’t answer the right questions about the COVID-19 vaccines.
“We could end up with approved vaccines that reduce the risk of mild infection, but do not decrease the risk of hospitalization, ICU use, or death — either at all or by a clinically relevant amount,” Doshi told the panel.
In his presentation, he reiterated points he had made previously, including in an October 21 article in the BMJ, for which he is an associate editor. Doshi also raised these concerns in a September opinion article in The New York Times, co-authored with Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape.
Risks of a ‘rushed vaccine’
Other complaints about the FDA’s approach included criticism of a 2-month follow-up time after vaccination, which was seen as too short. ECRI, a nonprofit organization that seeks to improve the safety, quality, and cost-effectiveness of medicines, has argued that approving a weak COVID-19 vaccine might worsen the pandemic.
In an October 21 statement, ECRI noted the risk of a partially effective vaccine, which could be welcomed as a means of slowing transmission of the virus. But public response and attitudes over the past 9 months in the United States suggest that people would relax their precautions as soon as a vaccine is available.
“Resulting infections may offset the vaccine’s impact and end up increasing the mortality and morbidity burden,” ECRI said in the brief.
“The risks and consequences of a rushed vaccine could be very severe if the review is anything shy of thorough,” ECRI Chief Executive Officer Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, said in a statement prepared for the hearing.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee met for a wide-ranging discussion beginning around 10 am. The FDA did not ask the panel to weigh in on any particular vaccine. Instead, the FDA asked for the panel’s feedback on a series of questions, including considerations for continuing phase 3 trials if a product were to get an interim clearance known as an emergency use authorization (EUA).
Speakers at the hearing made a variety of requests, including asking for data showing COVID-19 vaccines can prevent serious illness and urging transparency about the agency’s deliberations for each product to be considered.
FDA staff are closely tracking the crop of experimental vaccines that have made it into advanced stages of testing, including products from Pfizer Inc, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, and Moderna.
‘Time for a reset’
Among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Lurie, MD, who served as an FDA associate commissioner from 2014 to 2017. Now the president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, Lurie was among the speakers who asked the agency to make its independence clear.
President Donald Trump has for months been making predictions about COVID-19 vaccine approvals that have been overly optimistic. In one example, the president, who is seeking re-election on November 3, last month spoke about being able to begin distributing a vaccine in October.
“Until now the process of developing candidate vaccines has been inappropriately politicized with an eye on the election calendar, rather than the deliberate timeframe science requires,” Lurie told the FDA advisory panel. “Now is the time for a reset. This committee has a unique opportunity to set a new tone for vaccine deliberations going forward.”
Lurie asked the panel to press the FDA to commit to hold an advisory committee meeting on requests by drugmakers for EUAs. He also asked the panel to demand that informed consent forms and minutes from institutional review board (IRB) discussions of COVID-19 vaccines trials be made public.
Also among the speakers at the public hearing was Peter Doshi, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland School of Pharmacy, who argued that the current trials won’t answer the right questions about the COVID-19 vaccines.
“We could end up with approved vaccines that reduce the risk of mild infection, but do not decrease the risk of hospitalization, ICU use, or death — either at all or by a clinically relevant amount,” Doshi told the panel.
In his presentation, he reiterated points he had made previously, including in an October 21 article in the BMJ, for which he is an associate editor. Doshi also raised these concerns in a September opinion article in The New York Times, co-authored with Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief of Medscape.
Risks of a ‘rushed vaccine’
Other complaints about the FDA’s approach included criticism of a 2-month follow-up time after vaccination, which was seen as too short. ECRI, a nonprofit organization that seeks to improve the safety, quality, and cost-effectiveness of medicines, has argued that approving a weak COVID-19 vaccine might worsen the pandemic.
In an October 21 statement, ECRI noted the risk of a partially effective vaccine, which could be welcomed as a means of slowing transmission of the virus. But public response and attitudes over the past 9 months in the United States suggest that people would relax their precautions as soon as a vaccine is available.
“Resulting infections may offset the vaccine’s impact and end up increasing the mortality and morbidity burden,” ECRI said in the brief.
“The risks and consequences of a rushed vaccine could be very severe if the review is anything shy of thorough,” ECRI Chief Executive Officer Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, said in a statement prepared for the hearing.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Human Papillomavirus Vaccination in LGBTQ Patients: The Need for Dermatologists on the Front Lines
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the United States. It is the causative agent of genital warts, as well as cervical, anal, penile, vulvar, vaginal, and some head and neck cancers.1 Development of the HPV vaccine and its introduction into the scheduled vaccine series recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) represented a major public health milestone. The CDC recommends the HPV vaccine for all children beginning at 11 or 12 years of age, even as early as 9 years, regardless of gender identity or sexuality. As of late 2016, the 9-valent formulation (Gardasil 9 [Merck]) is the only HPV vaccine distributed in the United States, and the vaccination schedule depends specifically on age. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC revised its recommendations in 2019 to include “shared clinical decision-making regarding HPV vaccination . . . for some adults aged 27 through 45 years.”2 This change in policy has notable implications for sexual and gender minority populations, such as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer or questioning (LGBTQ) patients, especially in the context of dermatologic care. Herein, we discuss HPV-related conditions for LGBTQ patients, barriers to vaccine administration, and the role of dermatologists in promoting an increased vaccination rate in the LGBTQ community.
HPV-Related Conditions
A 2019 review of dermatologic care for LGBTQ patients identified many specific health disparities of HPV.3 Specifically, men who have sex with men (MSM) are more likely than heterosexual men to have oral, anal, and penile HPV infections, including high-risk HPV types.3 From 2011 to 2014, 18% and 13% of MSM had oral HPV infection and high-risk oral HPV infection, respectively, compared to only 11% and 7%, respectively, of men who reported never having had a same-sex sexual partner.4
Similarly, despite the CDC’s position that patients with perianal warts might benefit from digital anal examination or referral for standard or high-resolution anoscopy to detect intra-anal warts, improvements in morbidity have not yet been realized. In 2017, anal cancer incidence was 45.9 cases for every 100,000 person-years among human immunodeficiency (HIV)–positive MSM and 5.1 cases for every 100,000 person-years among HIV-negative MSM vs only 1.5 cases for every 100,000 person-years among men in the United States overall.3 Yet the CDC states that there is insufficient evidence to recommend routine anal cancer screening among MSM, even when a patient is HIV positive. Therefore, current screening practices and treatments are insufficient as MSM continue to have a disproportionately higher rate of HPV-associated disease compared to other populations.
Barriers to HPV Vaccine Administration
The HPV vaccination rate among MSM in adolescent populations varies across reports.5-7 Interestingly, a 2016 survey study found that MSM had approximately 2-times greater odds of initiating the HPV vaccine than heterosexual men.8 However, a study specifically sampling young gay and bisexual men (N=428) found that only 13% had received any doses of the HPV vaccine.6
Regardless, HPV vaccination is much less common among all males than it is among all females, and the low rate of vaccination among sexual minority men has a disproportionate impact, given their higher risk for HPV infection.4 Although the HPV vaccination rate increased from 2014 to 2017, the HPV vaccination rate in MSM overall is less than half of the Healthy People 2020 goal of 80%.9 A 2018 review determined that HPV vaccination is a cost-effective strategy for preventing anal cancer in MSM10; yet male patients might still view the HPV vaccine as a “women’s issue” and are less likely to be vaccinated if they are not prompted by health care providers. Additionally, HPV vaccination is remarkably less likely in MSM when patients are older, uninsured, of lower socioeconomic status, or have not disclosed their sexual identity to their health care provider.9 Dermatologists should be mindful of these barriers to promote HPV vaccination in MSM before, or soon after, sexual debut.
Other members of the LGBTQ community, such as women who have sex with women, face notable HPV-related health disparities and would benefit from increased vaccination efforts by dermatologists. Adolescent and young adult women who have sex with women are less likely than heterosexual adolescent and young adult women to receive routine Papanicolaou tests and initiate HPV vaccination, despite having a higher number of lifetime sexual partners and a higher risk for HPV exposure.11 A 2015 survey study (N=3253) found that after adjusting for covariates, only 8.5% of lesbians and 33.2% of bisexual women and girls who had heard of the HPV vaccine had initiated vaccination compared to 28.4% of their heterosexual counterparts.11 The HPV vaccine is an effective public health tool for the prevention of cervical cancer in these populations. A study of women aged 15 to 19 years in the HPV vaccination era (2007-2014) found significant (P<.05) observed population-level decreases in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia incidence across all grades.12
Transgender women also face a high rate of HPV infection, HIV infection, and other structural and financial disparities, such as low insurance coverage, that can limit their access to vaccination. Transgender men have a higher rate of HPV infection than cisgender men, and those with female internal reproductive organs are less likely to receive routine Papanicolaou tests. A 2018 survey study found that approximately one-third of transgender men and women reported initiating the HPV vaccination series,13 but further investigation is required to make balanced comparisons to cisgender patients.
The Role of the Dermatologist
Collectively, these disparities emphasize the need for increased involvement by dermatologists in HPV vaccination efforts for all LGBTQ patients. Adult patients may have concerns about ties of the HPV vaccine to drug manufacturers and the general safety of vaccination. For pediatric patients, parents/guardians also may be concerned about an assumed but not evidence-based increase in sexual promiscuity following HPV vaccination.14 These topics can be challenging to discuss, but dermatologists have the duty to be proactive and initiate conversation about HPV vaccination, as opposed to waiting for patients to express interest. Dermatologists should stress the safety of the vaccine as well as its potential to protect against multiple, even life-threatening diseases. Providers also can explain that the ACIP recommends catch-up vaccination for all individuals through 26 years of age, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity.
With the ACIP having recently expanded the appropriate age range for HPV vaccination, we encourage dermatologists to engage in education and shared decision-making to ensure that adult patients with specific risk factors receive the HPV vaccine. Because the expanded ACIP recommendations are aimed at vaccination before HPV exposure, vaccination might not be appropriate for all LGBTQ patients. However, eliciting a sexual history with routine patient intake forms or during the clinical encounter ensures equal access to the HPV vaccine.
Greater awareness of HPV-related disparities and barriers to vaccination in LGBTQ populations has the potential to notably decrease HPV-associated mortality and morbidity. Increased involvement by dermatologists contributes to the efforts of other specialties in universal HPV vaccination, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity—ideally in younger age groups, such that patients receive the vaccine prior to coitarche.
There are many ways that dermatologists can advocate for HPV vaccination. Those in a multispecialty or academic practice can readily refer patients to an associated internist, primary care physician, or vaccination clinic in the same building or institution. Dermatologists in private practice might be able to administer the HPV vaccine themselves or can advocate for patients to receive the vaccine at a local facility of the Department of Health or at a nonprofit organization, such as a Planned Parenthood center. Although pediatricians and family physicians remain front-line providers of these services, dermatologists represent an additional member of a patient’s care team, capable of advocating for this important intervention.
- Brianti P, De Flammineis E, Mercuri SR. Review of HPV-related diseases and cancers. New Microbiol. 2017;40:80-85.
- Meites E, Szilagyi PG, Chesson HW, et al. Human papillomavirus vaccination for adults: updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:698-702.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Sonawane K, Suk R, Chiao EY, et al. Oral human papillomavirus infection: differences in prevalence between sexes and concordance with genital human papillomavirus infection, NHANES 2011 to 2014. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167:714-724.
- Kosche C, Mansh M, Luskus M, et al. Dermatologic care of sexual and gender minority/LGBTQIA youth, part 2: recognition and management of the unique dermatologic needs of SGM adolescents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;35:587-593.
- Reiter PL, McRee A-L, Katz ML, et al. Human papillomavirus vaccination among young adult gay and bisexual men in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105:96-102.
- Charlton BM, Reisner SL, Ag
énor M, et al. Sexual orientation disparities in human papillomavirus vaccination in a longitudinal cohort of U.S. males and females. LGBT Health. 2017;4:202-209. - Agénor M, Peitzmeier SM, Gordon AR, et al. Sexual orientation identity disparities in human papillomavirus vaccination initiation and completion among young adult US women and men. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:1187-1196.
- Loretan C, Chamberlain AT, Sanchez T, et al. Trends and characteristics associated with human papillomavirus vaccination uptake among men who have sex with men in the United States, 2014-2017. Sex Transm Dis. 2019;46:465-473.
- Setiawan D, Wondimu A, Ong K, et al. Cost effectiveness of human papillomavirus vaccination for men who have sex with men; reviewing the available evidence. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018;36:929-939.
- Agénor M, Peitzmeier S, Gordon AR, et al. Sexual orientation identity disparities in awareness and initiation of the human papillomavirus vaccine among U.S. women and girls: a national survey. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163:99-106.
- Benard VB, Castle PE, Jenison SA, et al. Population-based incidence rates of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in the human papillomavirus vaccine era. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:833-837.
- McRee A-L, Gower AL, Reiter PL. Preventive healthcare services use among transgender young adults. Int J Transgend. 2018;19:417-423.
- Trinidad J. Policy focus: promoting human papilloma virus vaccine to prevent genital warts and cancer. Boston, MA: The Fenway Institute; 2012. https://fenwayhealth.org/documents/the-fenway-institute/policy-briefs/PolicyFocus_HPV_v4_10.09.12.pdf. Accessed September 15, 2020.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the United States. It is the causative agent of genital warts, as well as cervical, anal, penile, vulvar, vaginal, and some head and neck cancers.1 Development of the HPV vaccine and its introduction into the scheduled vaccine series recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) represented a major public health milestone. The CDC recommends the HPV vaccine for all children beginning at 11 or 12 years of age, even as early as 9 years, regardless of gender identity or sexuality. As of late 2016, the 9-valent formulation (Gardasil 9 [Merck]) is the only HPV vaccine distributed in the United States, and the vaccination schedule depends specifically on age. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC revised its recommendations in 2019 to include “shared clinical decision-making regarding HPV vaccination . . . for some adults aged 27 through 45 years.”2 This change in policy has notable implications for sexual and gender minority populations, such as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer or questioning (LGBTQ) patients, especially in the context of dermatologic care. Herein, we discuss HPV-related conditions for LGBTQ patients, barriers to vaccine administration, and the role of dermatologists in promoting an increased vaccination rate in the LGBTQ community.
HPV-Related Conditions
A 2019 review of dermatologic care for LGBTQ patients identified many specific health disparities of HPV.3 Specifically, men who have sex with men (MSM) are more likely than heterosexual men to have oral, anal, and penile HPV infections, including high-risk HPV types.3 From 2011 to 2014, 18% and 13% of MSM had oral HPV infection and high-risk oral HPV infection, respectively, compared to only 11% and 7%, respectively, of men who reported never having had a same-sex sexual partner.4
Similarly, despite the CDC’s position that patients with perianal warts might benefit from digital anal examination or referral for standard or high-resolution anoscopy to detect intra-anal warts, improvements in morbidity have not yet been realized. In 2017, anal cancer incidence was 45.9 cases for every 100,000 person-years among human immunodeficiency (HIV)–positive MSM and 5.1 cases for every 100,000 person-years among HIV-negative MSM vs only 1.5 cases for every 100,000 person-years among men in the United States overall.3 Yet the CDC states that there is insufficient evidence to recommend routine anal cancer screening among MSM, even when a patient is HIV positive. Therefore, current screening practices and treatments are insufficient as MSM continue to have a disproportionately higher rate of HPV-associated disease compared to other populations.
Barriers to HPV Vaccine Administration
The HPV vaccination rate among MSM in adolescent populations varies across reports.5-7 Interestingly, a 2016 survey study found that MSM had approximately 2-times greater odds of initiating the HPV vaccine than heterosexual men.8 However, a study specifically sampling young gay and bisexual men (N=428) found that only 13% had received any doses of the HPV vaccine.6
Regardless, HPV vaccination is much less common among all males than it is among all females, and the low rate of vaccination among sexual minority men has a disproportionate impact, given their higher risk for HPV infection.4 Although the HPV vaccination rate increased from 2014 to 2017, the HPV vaccination rate in MSM overall is less than half of the Healthy People 2020 goal of 80%.9 A 2018 review determined that HPV vaccination is a cost-effective strategy for preventing anal cancer in MSM10; yet male patients might still view the HPV vaccine as a “women’s issue” and are less likely to be vaccinated if they are not prompted by health care providers. Additionally, HPV vaccination is remarkably less likely in MSM when patients are older, uninsured, of lower socioeconomic status, or have not disclosed their sexual identity to their health care provider.9 Dermatologists should be mindful of these barriers to promote HPV vaccination in MSM before, or soon after, sexual debut.
Other members of the LGBTQ community, such as women who have sex with women, face notable HPV-related health disparities and would benefit from increased vaccination efforts by dermatologists. Adolescent and young adult women who have sex with women are less likely than heterosexual adolescent and young adult women to receive routine Papanicolaou tests and initiate HPV vaccination, despite having a higher number of lifetime sexual partners and a higher risk for HPV exposure.11 A 2015 survey study (N=3253) found that after adjusting for covariates, only 8.5% of lesbians and 33.2% of bisexual women and girls who had heard of the HPV vaccine had initiated vaccination compared to 28.4% of their heterosexual counterparts.11 The HPV vaccine is an effective public health tool for the prevention of cervical cancer in these populations. A study of women aged 15 to 19 years in the HPV vaccination era (2007-2014) found significant (P<.05) observed population-level decreases in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia incidence across all grades.12
Transgender women also face a high rate of HPV infection, HIV infection, and other structural and financial disparities, such as low insurance coverage, that can limit their access to vaccination. Transgender men have a higher rate of HPV infection than cisgender men, and those with female internal reproductive organs are less likely to receive routine Papanicolaou tests. A 2018 survey study found that approximately one-third of transgender men and women reported initiating the HPV vaccination series,13 but further investigation is required to make balanced comparisons to cisgender patients.
The Role of the Dermatologist
Collectively, these disparities emphasize the need for increased involvement by dermatologists in HPV vaccination efforts for all LGBTQ patients. Adult patients may have concerns about ties of the HPV vaccine to drug manufacturers and the general safety of vaccination. For pediatric patients, parents/guardians also may be concerned about an assumed but not evidence-based increase in sexual promiscuity following HPV vaccination.14 These topics can be challenging to discuss, but dermatologists have the duty to be proactive and initiate conversation about HPV vaccination, as opposed to waiting for patients to express interest. Dermatologists should stress the safety of the vaccine as well as its potential to protect against multiple, even life-threatening diseases. Providers also can explain that the ACIP recommends catch-up vaccination for all individuals through 26 years of age, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity.
With the ACIP having recently expanded the appropriate age range for HPV vaccination, we encourage dermatologists to engage in education and shared decision-making to ensure that adult patients with specific risk factors receive the HPV vaccine. Because the expanded ACIP recommendations are aimed at vaccination before HPV exposure, vaccination might not be appropriate for all LGBTQ patients. However, eliciting a sexual history with routine patient intake forms or during the clinical encounter ensures equal access to the HPV vaccine.
Greater awareness of HPV-related disparities and barriers to vaccination in LGBTQ populations has the potential to notably decrease HPV-associated mortality and morbidity. Increased involvement by dermatologists contributes to the efforts of other specialties in universal HPV vaccination, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity—ideally in younger age groups, such that patients receive the vaccine prior to coitarche.
There are many ways that dermatologists can advocate for HPV vaccination. Those in a multispecialty or academic practice can readily refer patients to an associated internist, primary care physician, or vaccination clinic in the same building or institution. Dermatologists in private practice might be able to administer the HPV vaccine themselves or can advocate for patients to receive the vaccine at a local facility of the Department of Health or at a nonprofit organization, such as a Planned Parenthood center. Although pediatricians and family physicians remain front-line providers of these services, dermatologists represent an additional member of a patient’s care team, capable of advocating for this important intervention.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the United States. It is the causative agent of genital warts, as well as cervical, anal, penile, vulvar, vaginal, and some head and neck cancers.1 Development of the HPV vaccine and its introduction into the scheduled vaccine series recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) represented a major public health milestone. The CDC recommends the HPV vaccine for all children beginning at 11 or 12 years of age, even as early as 9 years, regardless of gender identity or sexuality. As of late 2016, the 9-valent formulation (Gardasil 9 [Merck]) is the only HPV vaccine distributed in the United States, and the vaccination schedule depends specifically on age. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC revised its recommendations in 2019 to include “shared clinical decision-making regarding HPV vaccination . . . for some adults aged 27 through 45 years.”2 This change in policy has notable implications for sexual and gender minority populations, such as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer or questioning (LGBTQ) patients, especially in the context of dermatologic care. Herein, we discuss HPV-related conditions for LGBTQ patients, barriers to vaccine administration, and the role of dermatologists in promoting an increased vaccination rate in the LGBTQ community.
HPV-Related Conditions
A 2019 review of dermatologic care for LGBTQ patients identified many specific health disparities of HPV.3 Specifically, men who have sex with men (MSM) are more likely than heterosexual men to have oral, anal, and penile HPV infections, including high-risk HPV types.3 From 2011 to 2014, 18% and 13% of MSM had oral HPV infection and high-risk oral HPV infection, respectively, compared to only 11% and 7%, respectively, of men who reported never having had a same-sex sexual partner.4
Similarly, despite the CDC’s position that patients with perianal warts might benefit from digital anal examination or referral for standard or high-resolution anoscopy to detect intra-anal warts, improvements in morbidity have not yet been realized. In 2017, anal cancer incidence was 45.9 cases for every 100,000 person-years among human immunodeficiency (HIV)–positive MSM and 5.1 cases for every 100,000 person-years among HIV-negative MSM vs only 1.5 cases for every 100,000 person-years among men in the United States overall.3 Yet the CDC states that there is insufficient evidence to recommend routine anal cancer screening among MSM, even when a patient is HIV positive. Therefore, current screening practices and treatments are insufficient as MSM continue to have a disproportionately higher rate of HPV-associated disease compared to other populations.
Barriers to HPV Vaccine Administration
The HPV vaccination rate among MSM in adolescent populations varies across reports.5-7 Interestingly, a 2016 survey study found that MSM had approximately 2-times greater odds of initiating the HPV vaccine than heterosexual men.8 However, a study specifically sampling young gay and bisexual men (N=428) found that only 13% had received any doses of the HPV vaccine.6
Regardless, HPV vaccination is much less common among all males than it is among all females, and the low rate of vaccination among sexual minority men has a disproportionate impact, given their higher risk for HPV infection.4 Although the HPV vaccination rate increased from 2014 to 2017, the HPV vaccination rate in MSM overall is less than half of the Healthy People 2020 goal of 80%.9 A 2018 review determined that HPV vaccination is a cost-effective strategy for preventing anal cancer in MSM10; yet male patients might still view the HPV vaccine as a “women’s issue” and are less likely to be vaccinated if they are not prompted by health care providers. Additionally, HPV vaccination is remarkably less likely in MSM when patients are older, uninsured, of lower socioeconomic status, or have not disclosed their sexual identity to their health care provider.9 Dermatologists should be mindful of these barriers to promote HPV vaccination in MSM before, or soon after, sexual debut.
Other members of the LGBTQ community, such as women who have sex with women, face notable HPV-related health disparities and would benefit from increased vaccination efforts by dermatologists. Adolescent and young adult women who have sex with women are less likely than heterosexual adolescent and young adult women to receive routine Papanicolaou tests and initiate HPV vaccination, despite having a higher number of lifetime sexual partners and a higher risk for HPV exposure.11 A 2015 survey study (N=3253) found that after adjusting for covariates, only 8.5% of lesbians and 33.2% of bisexual women and girls who had heard of the HPV vaccine had initiated vaccination compared to 28.4% of their heterosexual counterparts.11 The HPV vaccine is an effective public health tool for the prevention of cervical cancer in these populations. A study of women aged 15 to 19 years in the HPV vaccination era (2007-2014) found significant (P<.05) observed population-level decreases in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia incidence across all grades.12
Transgender women also face a high rate of HPV infection, HIV infection, and other structural and financial disparities, such as low insurance coverage, that can limit their access to vaccination. Transgender men have a higher rate of HPV infection than cisgender men, and those with female internal reproductive organs are less likely to receive routine Papanicolaou tests. A 2018 survey study found that approximately one-third of transgender men and women reported initiating the HPV vaccination series,13 but further investigation is required to make balanced comparisons to cisgender patients.
The Role of the Dermatologist
Collectively, these disparities emphasize the need for increased involvement by dermatologists in HPV vaccination efforts for all LGBTQ patients. Adult patients may have concerns about ties of the HPV vaccine to drug manufacturers and the general safety of vaccination. For pediatric patients, parents/guardians also may be concerned about an assumed but not evidence-based increase in sexual promiscuity following HPV vaccination.14 These topics can be challenging to discuss, but dermatologists have the duty to be proactive and initiate conversation about HPV vaccination, as opposed to waiting for patients to express interest. Dermatologists should stress the safety of the vaccine as well as its potential to protect against multiple, even life-threatening diseases. Providers also can explain that the ACIP recommends catch-up vaccination for all individuals through 26 years of age, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity.
With the ACIP having recently expanded the appropriate age range for HPV vaccination, we encourage dermatologists to engage in education and shared decision-making to ensure that adult patients with specific risk factors receive the HPV vaccine. Because the expanded ACIP recommendations are aimed at vaccination before HPV exposure, vaccination might not be appropriate for all LGBTQ patients. However, eliciting a sexual history with routine patient intake forms or during the clinical encounter ensures equal access to the HPV vaccine.
Greater awareness of HPV-related disparities and barriers to vaccination in LGBTQ populations has the potential to notably decrease HPV-associated mortality and morbidity. Increased involvement by dermatologists contributes to the efforts of other specialties in universal HPV vaccination, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity—ideally in younger age groups, such that patients receive the vaccine prior to coitarche.
There are many ways that dermatologists can advocate for HPV vaccination. Those in a multispecialty or academic practice can readily refer patients to an associated internist, primary care physician, or vaccination clinic in the same building or institution. Dermatologists in private practice might be able to administer the HPV vaccine themselves or can advocate for patients to receive the vaccine at a local facility of the Department of Health or at a nonprofit organization, such as a Planned Parenthood center. Although pediatricians and family physicians remain front-line providers of these services, dermatologists represent an additional member of a patient’s care team, capable of advocating for this important intervention.
- Brianti P, De Flammineis E, Mercuri SR. Review of HPV-related diseases and cancers. New Microbiol. 2017;40:80-85.
- Meites E, Szilagyi PG, Chesson HW, et al. Human papillomavirus vaccination for adults: updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:698-702.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Sonawane K, Suk R, Chiao EY, et al. Oral human papillomavirus infection: differences in prevalence between sexes and concordance with genital human papillomavirus infection, NHANES 2011 to 2014. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167:714-724.
- Kosche C, Mansh M, Luskus M, et al. Dermatologic care of sexual and gender minority/LGBTQIA youth, part 2: recognition and management of the unique dermatologic needs of SGM adolescents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;35:587-593.
- Reiter PL, McRee A-L, Katz ML, et al. Human papillomavirus vaccination among young adult gay and bisexual men in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105:96-102.
- Charlton BM, Reisner SL, Ag
énor M, et al. Sexual orientation disparities in human papillomavirus vaccination in a longitudinal cohort of U.S. males and females. LGBT Health. 2017;4:202-209. - Agénor M, Peitzmeier SM, Gordon AR, et al. Sexual orientation identity disparities in human papillomavirus vaccination initiation and completion among young adult US women and men. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:1187-1196.
- Loretan C, Chamberlain AT, Sanchez T, et al. Trends and characteristics associated with human papillomavirus vaccination uptake among men who have sex with men in the United States, 2014-2017. Sex Transm Dis. 2019;46:465-473.
- Setiawan D, Wondimu A, Ong K, et al. Cost effectiveness of human papillomavirus vaccination for men who have sex with men; reviewing the available evidence. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018;36:929-939.
- Agénor M, Peitzmeier S, Gordon AR, et al. Sexual orientation identity disparities in awareness and initiation of the human papillomavirus vaccine among U.S. women and girls: a national survey. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163:99-106.
- Benard VB, Castle PE, Jenison SA, et al. Population-based incidence rates of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in the human papillomavirus vaccine era. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:833-837.
- McRee A-L, Gower AL, Reiter PL. Preventive healthcare services use among transgender young adults. Int J Transgend. 2018;19:417-423.
- Trinidad J. Policy focus: promoting human papilloma virus vaccine to prevent genital warts and cancer. Boston, MA: The Fenway Institute; 2012. https://fenwayhealth.org/documents/the-fenway-institute/policy-briefs/PolicyFocus_HPV_v4_10.09.12.pdf. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Brianti P, De Flammineis E, Mercuri SR. Review of HPV-related diseases and cancers. New Microbiol. 2017;40:80-85.
- Meites E, Szilagyi PG, Chesson HW, et al. Human papillomavirus vaccination for adults: updated recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:698-702.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Sonawane K, Suk R, Chiao EY, et al. Oral human papillomavirus infection: differences in prevalence between sexes and concordance with genital human papillomavirus infection, NHANES 2011 to 2014. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167:714-724.
- Kosche C, Mansh M, Luskus M, et al. Dermatologic care of sexual and gender minority/LGBTQIA youth, part 2: recognition and management of the unique dermatologic needs of SGM adolescents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;35:587-593.
- Reiter PL, McRee A-L, Katz ML, et al. Human papillomavirus vaccination among young adult gay and bisexual men in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105:96-102.
- Charlton BM, Reisner SL, Ag
énor M, et al. Sexual orientation disparities in human papillomavirus vaccination in a longitudinal cohort of U.S. males and females. LGBT Health. 2017;4:202-209. - Agénor M, Peitzmeier SM, Gordon AR, et al. Sexual orientation identity disparities in human papillomavirus vaccination initiation and completion among young adult US women and men. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:1187-1196.
- Loretan C, Chamberlain AT, Sanchez T, et al. Trends and characteristics associated with human papillomavirus vaccination uptake among men who have sex with men in the United States, 2014-2017. Sex Transm Dis. 2019;46:465-473.
- Setiawan D, Wondimu A, Ong K, et al. Cost effectiveness of human papillomavirus vaccination for men who have sex with men; reviewing the available evidence. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018;36:929-939.
- Agénor M, Peitzmeier S, Gordon AR, et al. Sexual orientation identity disparities in awareness and initiation of the human papillomavirus vaccine among U.S. women and girls: a national survey. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163:99-106.
- Benard VB, Castle PE, Jenison SA, et al. Population-based incidence rates of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in the human papillomavirus vaccine era. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:833-837.
- McRee A-L, Gower AL, Reiter PL. Preventive healthcare services use among transgender young adults. Int J Transgend. 2018;19:417-423.
- Trinidad J. Policy focus: promoting human papilloma virus vaccine to prevent genital warts and cancer. Boston, MA: The Fenway Institute; 2012. https://fenwayhealth.org/documents/the-fenway-institute/policy-briefs/PolicyFocus_HPV_v4_10.09.12.pdf. Accessed September 15, 2020.