User login
Taking a break from TKIs unlikely to shorten survival
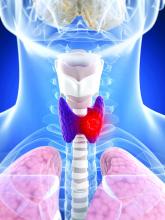
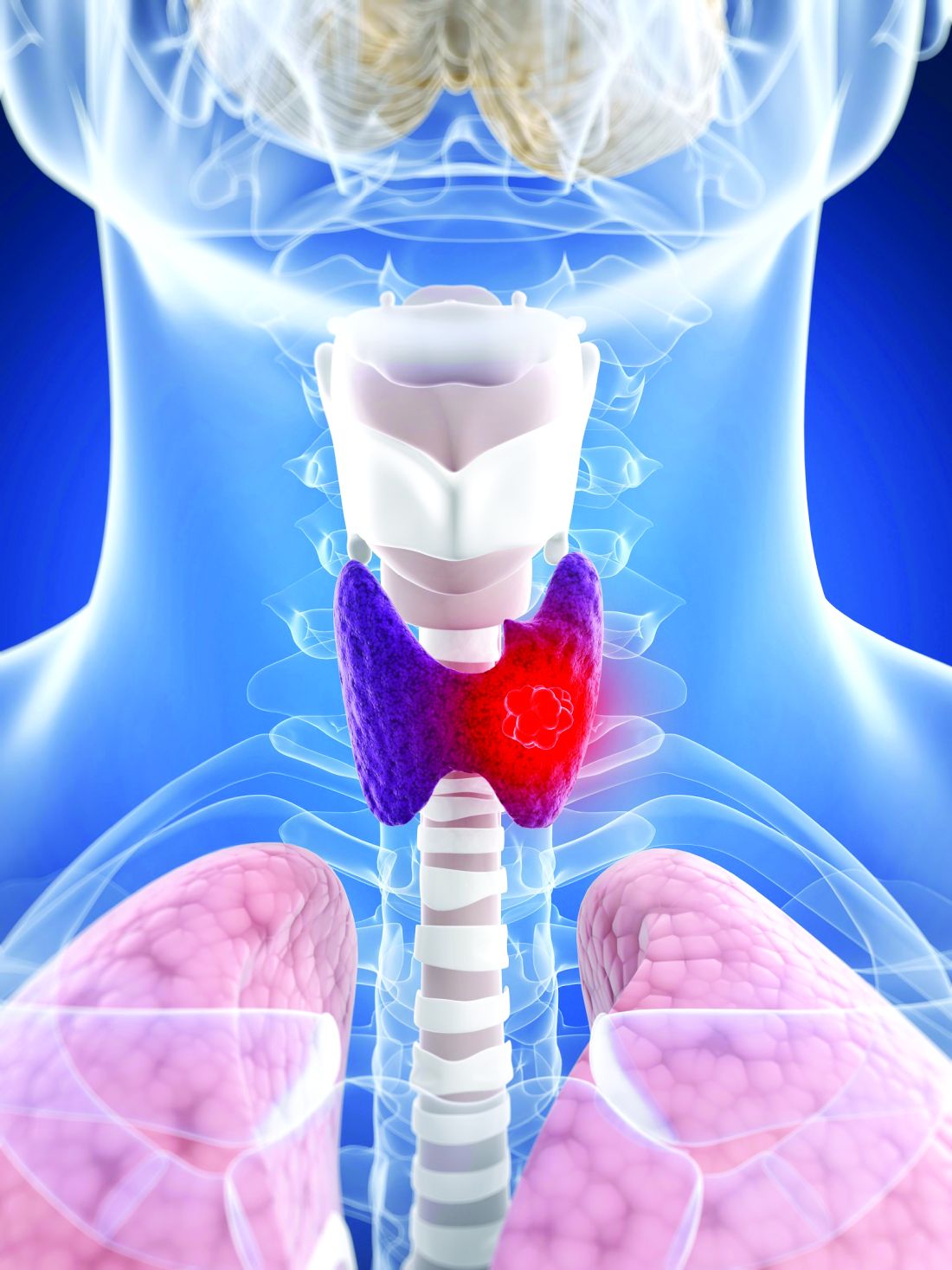
That might soon change with the publication of a unique study. Lasting 10 years, the phase 3 STAR trial involved 920 patients across 60 cancer centers. These patients had advanced kidney cancer and were taking either sunitinib (Sutent) or pazopanib (Votrient).
The results showed that taking an occasional respite from TKI therapy had little impact on the patient’s survival.
The study was published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The study was funded by the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Research because drug companies never run studies on how to reduce the use of their drug, commented lead author Janet Brown, MD, of the University of Sheffield (England).
“We rely on the NIHR to do these important trials that … companies wouldn’t do,” she commented to this news organization.
Commenting on the rationale for STAR, coauthor Jenny Hewison, PhD, of Leeds (England) University School of Medicine, explained that patients often find it difficult to tolerate TKIs. “Although these patients are getting the best treatment that we can offer them, it’s very demanding. … It could make them feel tired, quite unwell. And there can be a range of other effects including sickness and diarrhea.”
As an example, 77% of patients in the pivotal trial of sunitinib in kidney cancer experienced grade 3 or 4 adverse events such as hypertension (13%), fatigue (15%), diarrhea (10%) and hand-foot syndrome (8%).
Both sunitinib and pazopanib carry label warnings of severe and fatal hepatotoxicity.
Also, in contrast to conventional chemotherapy, which is usually given in a finite number of courses, treatment with TKIs carries on indefinitely.
“It feels like you’re taking [TKIs] for the whole of the rest of your life,” said Dr. Brown.
Study details
The STAR trial, an open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled study, is the first phase 3 study of treatment breaks in renal cell carcinoma. The participants had inoperable locoregional or metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and had received no systemic therapy for advanced disease.
They were randomly assigned before TKI treatment to a conventional continuation strategy or a drug-free interval approach. The treating physician decided whether a patient would take sunitinib or pazopanib.
All participants took their drugs for four cycles (6 weeks each cycle). At the 24-week point, those with a complete response, partial response, or stable disease began their randomized assignment.
Individuals who took a break continued until their disease progressed, at which point therapy was resumed. They could take further treatment breaks once their disease was back under control. The group on continuous treatment kept going until disease progression or intolerable toxicities. Median follow up was 58 months.
In both the per-protocol and intent-to-treat (ITT) populations, overall survival was 28 months for the people who received continuous treatment vs. 27 months for those who took a break. Statistical noninferiority was established in the ITT population but not in the per-protocol population.
The median length of all treatment breaks was 87 days. Many people took two or more breaks; one patient took nine breaks overall. The breaks were popular: only 3% of participants who were meant to stop therapy withdrew from the study in order to continue their treatment.
Said Dr. Hewison: “In the very early days of planning the study there were some doubts as to whether it would succeed because of potential unwillingness of people to stop treatment for a while.”
Dr. Brown agreed: “People did worry about that initially, but it actually seemed to be more the other way around. By that time – 6 months – people were relieved to be there. …We actually had some people from the other arm asking, could they also have a break?”
To understand better the benefits of treatment breaks to patients, Janine Bestall, PhD, a senior research fellow in applied health research at the University of Leeds, conducted a qualitative study in parallel with the main trial.
Summing up the patients’ experiences, Dr. Bestall said the drug-free periods “gave them more time.”
Dr. Bestall quoted one patient who said: “I know that things can happen and it grows back, but you’ve always got the buffer there knowing that you can go back and get help. But you actually lead a normal life and the advantage is, yeah, you can go on holiday, you can actually do more things in the garden, cleaning up, painting, whatever needs doing, you do it.”
Dr. Brown said, “I had a lady who, when she was on the trial, had four breaks in total, one when her daughter got married, and [she said] that was really nice for her to do all the shopping and all the normal things that you do, and not be on something that was making her tired and causing sore hands and diarrhea.”
The drug-free interval strategy provided annual cost savings of 3,235 pounds sterling ($3,850) and a noninferior quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) benefit in both the ITT and per-protocol populations.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients in the treatment-break group versus 12% of the continuous-treatment group.
The authors of the study concluded, “Treatment breaks might be a feasible and cost-effective option with lifestyle benefits for patients during tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with renal cell carcinoma.”
Changes in treatment strategies
The STAR trial started recruiting in January 2012.
Since that time, immunotherapy has taken over as first-line treatment for many patients with advanced ccRCC in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
However, TKIs still have a place. The NCCN Kidney Cancer 2022 Guidelines recommend both sunitinib and pazopanib as options for first-line therapy in advanced disease. The 2022 ASCO Metastatic ccRCC guidelines recommend either drug as first-line treatment in combination with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or in monotherapy if there are “coexisting medical problems.”
In the United States, intermittent sunitinib in metastatic RCC was tested in a small study in 2017 with little activity in the literature since then. The authors, led by Moshe Ornstein, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic, concluded at the time that sunitinib treatment breaks were feasible and “clinical efficacy does not seem to be compromised.” Dr. Ornstein was approached for comment on this latest U.K. study but declined.
Back in the United Kingdom, the results of STAR arrived just in time.
Said Dr. Brown: “This has … been really helpful in the U.K. in the pandemic when people said, can these patients have extra breaks? At the worst of the pandemic we were able to say, sure, if it’s stable, we can keep them off for 3-6 months. …And so that’s already had a powerful impact.”
Dr. Brown concluded, “I think what the trial does allow us to do, as individual oncologists, is to look at the patients that this might be suitable for – it won’t be everybody – and to say yes, it’s okay to personalize things.”
The study was funded by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Research. Dr. Bestall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hewison reported funding to her institution from the NIHR Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Brown reports having served as a consultant or adviser for Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; honoraria from Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; research funding paid to their institution from the National Institute for Health and Care Research; and travel expenses from Ipsen. Other coauthors reported numerous relationships with industry.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That might soon change with the publication of a unique study. Lasting 10 years, the phase 3 STAR trial involved 920 patients across 60 cancer centers. These patients had advanced kidney cancer and were taking either sunitinib (Sutent) or pazopanib (Votrient).
The results showed that taking an occasional respite from TKI therapy had little impact on the patient’s survival.
The study was published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The study was funded by the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Research because drug companies never run studies on how to reduce the use of their drug, commented lead author Janet Brown, MD, of the University of Sheffield (England).
“We rely on the NIHR to do these important trials that … companies wouldn’t do,” she commented to this news organization.
Commenting on the rationale for STAR, coauthor Jenny Hewison, PhD, of Leeds (England) University School of Medicine, explained that patients often find it difficult to tolerate TKIs. “Although these patients are getting the best treatment that we can offer them, it’s very demanding. … It could make them feel tired, quite unwell. And there can be a range of other effects including sickness and diarrhea.”
As an example, 77% of patients in the pivotal trial of sunitinib in kidney cancer experienced grade 3 or 4 adverse events such as hypertension (13%), fatigue (15%), diarrhea (10%) and hand-foot syndrome (8%).
Both sunitinib and pazopanib carry label warnings of severe and fatal hepatotoxicity.
Also, in contrast to conventional chemotherapy, which is usually given in a finite number of courses, treatment with TKIs carries on indefinitely.
“It feels like you’re taking [TKIs] for the whole of the rest of your life,” said Dr. Brown.
Study details
The STAR trial, an open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled study, is the first phase 3 study of treatment breaks in renal cell carcinoma. The participants had inoperable locoregional or metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and had received no systemic therapy for advanced disease.
They were randomly assigned before TKI treatment to a conventional continuation strategy or a drug-free interval approach. The treating physician decided whether a patient would take sunitinib or pazopanib.
All participants took their drugs for four cycles (6 weeks each cycle). At the 24-week point, those with a complete response, partial response, or stable disease began their randomized assignment.
Individuals who took a break continued until their disease progressed, at which point therapy was resumed. They could take further treatment breaks once their disease was back under control. The group on continuous treatment kept going until disease progression or intolerable toxicities. Median follow up was 58 months.
In both the per-protocol and intent-to-treat (ITT) populations, overall survival was 28 months for the people who received continuous treatment vs. 27 months for those who took a break. Statistical noninferiority was established in the ITT population but not in the per-protocol population.
The median length of all treatment breaks was 87 days. Many people took two or more breaks; one patient took nine breaks overall. The breaks were popular: only 3% of participants who were meant to stop therapy withdrew from the study in order to continue their treatment.
Said Dr. Hewison: “In the very early days of planning the study there were some doubts as to whether it would succeed because of potential unwillingness of people to stop treatment for a while.”
Dr. Brown agreed: “People did worry about that initially, but it actually seemed to be more the other way around. By that time – 6 months – people were relieved to be there. …We actually had some people from the other arm asking, could they also have a break?”
To understand better the benefits of treatment breaks to patients, Janine Bestall, PhD, a senior research fellow in applied health research at the University of Leeds, conducted a qualitative study in parallel with the main trial.
Summing up the patients’ experiences, Dr. Bestall said the drug-free periods “gave them more time.”
Dr. Bestall quoted one patient who said: “I know that things can happen and it grows back, but you’ve always got the buffer there knowing that you can go back and get help. But you actually lead a normal life and the advantage is, yeah, you can go on holiday, you can actually do more things in the garden, cleaning up, painting, whatever needs doing, you do it.”
Dr. Brown said, “I had a lady who, when she was on the trial, had four breaks in total, one when her daughter got married, and [she said] that was really nice for her to do all the shopping and all the normal things that you do, and not be on something that was making her tired and causing sore hands and diarrhea.”
The drug-free interval strategy provided annual cost savings of 3,235 pounds sterling ($3,850) and a noninferior quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) benefit in both the ITT and per-protocol populations.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients in the treatment-break group versus 12% of the continuous-treatment group.
The authors of the study concluded, “Treatment breaks might be a feasible and cost-effective option with lifestyle benefits for patients during tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with renal cell carcinoma.”
Changes in treatment strategies
The STAR trial started recruiting in January 2012.
Since that time, immunotherapy has taken over as first-line treatment for many patients with advanced ccRCC in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
However, TKIs still have a place. The NCCN Kidney Cancer 2022 Guidelines recommend both sunitinib and pazopanib as options for first-line therapy in advanced disease. The 2022 ASCO Metastatic ccRCC guidelines recommend either drug as first-line treatment in combination with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or in monotherapy if there are “coexisting medical problems.”
In the United States, intermittent sunitinib in metastatic RCC was tested in a small study in 2017 with little activity in the literature since then. The authors, led by Moshe Ornstein, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic, concluded at the time that sunitinib treatment breaks were feasible and “clinical efficacy does not seem to be compromised.” Dr. Ornstein was approached for comment on this latest U.K. study but declined.
Back in the United Kingdom, the results of STAR arrived just in time.
Said Dr. Brown: “This has … been really helpful in the U.K. in the pandemic when people said, can these patients have extra breaks? At the worst of the pandemic we were able to say, sure, if it’s stable, we can keep them off for 3-6 months. …And so that’s already had a powerful impact.”
Dr. Brown concluded, “I think what the trial does allow us to do, as individual oncologists, is to look at the patients that this might be suitable for – it won’t be everybody – and to say yes, it’s okay to personalize things.”
The study was funded by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Research. Dr. Bestall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hewison reported funding to her institution from the NIHR Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Brown reports having served as a consultant or adviser for Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; honoraria from Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; research funding paid to their institution from the National Institute for Health and Care Research; and travel expenses from Ipsen. Other coauthors reported numerous relationships with industry.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That might soon change with the publication of a unique study. Lasting 10 years, the phase 3 STAR trial involved 920 patients across 60 cancer centers. These patients had advanced kidney cancer and were taking either sunitinib (Sutent) or pazopanib (Votrient).
The results showed that taking an occasional respite from TKI therapy had little impact on the patient’s survival.
The study was published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The study was funded by the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Research because drug companies never run studies on how to reduce the use of their drug, commented lead author Janet Brown, MD, of the University of Sheffield (England).
“We rely on the NIHR to do these important trials that … companies wouldn’t do,” she commented to this news organization.
Commenting on the rationale for STAR, coauthor Jenny Hewison, PhD, of Leeds (England) University School of Medicine, explained that patients often find it difficult to tolerate TKIs. “Although these patients are getting the best treatment that we can offer them, it’s very demanding. … It could make them feel tired, quite unwell. And there can be a range of other effects including sickness and diarrhea.”
As an example, 77% of patients in the pivotal trial of sunitinib in kidney cancer experienced grade 3 or 4 adverse events such as hypertension (13%), fatigue (15%), diarrhea (10%) and hand-foot syndrome (8%).
Both sunitinib and pazopanib carry label warnings of severe and fatal hepatotoxicity.
Also, in contrast to conventional chemotherapy, which is usually given in a finite number of courses, treatment with TKIs carries on indefinitely.
“It feels like you’re taking [TKIs] for the whole of the rest of your life,” said Dr. Brown.
Study details
The STAR trial, an open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled study, is the first phase 3 study of treatment breaks in renal cell carcinoma. The participants had inoperable locoregional or metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and had received no systemic therapy for advanced disease.
They were randomly assigned before TKI treatment to a conventional continuation strategy or a drug-free interval approach. The treating physician decided whether a patient would take sunitinib or pazopanib.
All participants took their drugs for four cycles (6 weeks each cycle). At the 24-week point, those with a complete response, partial response, or stable disease began their randomized assignment.
Individuals who took a break continued until their disease progressed, at which point therapy was resumed. They could take further treatment breaks once their disease was back under control. The group on continuous treatment kept going until disease progression or intolerable toxicities. Median follow up was 58 months.
In both the per-protocol and intent-to-treat (ITT) populations, overall survival was 28 months for the people who received continuous treatment vs. 27 months for those who took a break. Statistical noninferiority was established in the ITT population but not in the per-protocol population.
The median length of all treatment breaks was 87 days. Many people took two or more breaks; one patient took nine breaks overall. The breaks were popular: only 3% of participants who were meant to stop therapy withdrew from the study in order to continue their treatment.
Said Dr. Hewison: “In the very early days of planning the study there were some doubts as to whether it would succeed because of potential unwillingness of people to stop treatment for a while.”
Dr. Brown agreed: “People did worry about that initially, but it actually seemed to be more the other way around. By that time – 6 months – people were relieved to be there. …We actually had some people from the other arm asking, could they also have a break?”
To understand better the benefits of treatment breaks to patients, Janine Bestall, PhD, a senior research fellow in applied health research at the University of Leeds, conducted a qualitative study in parallel with the main trial.
Summing up the patients’ experiences, Dr. Bestall said the drug-free periods “gave them more time.”
Dr. Bestall quoted one patient who said: “I know that things can happen and it grows back, but you’ve always got the buffer there knowing that you can go back and get help. But you actually lead a normal life and the advantage is, yeah, you can go on holiday, you can actually do more things in the garden, cleaning up, painting, whatever needs doing, you do it.”
Dr. Brown said, “I had a lady who, when she was on the trial, had four breaks in total, one when her daughter got married, and [she said] that was really nice for her to do all the shopping and all the normal things that you do, and not be on something that was making her tired and causing sore hands and diarrhea.”
The drug-free interval strategy provided annual cost savings of 3,235 pounds sterling ($3,850) and a noninferior quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) benefit in both the ITT and per-protocol populations.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients in the treatment-break group versus 12% of the continuous-treatment group.
The authors of the study concluded, “Treatment breaks might be a feasible and cost-effective option with lifestyle benefits for patients during tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with renal cell carcinoma.”
Changes in treatment strategies
The STAR trial started recruiting in January 2012.
Since that time, immunotherapy has taken over as first-line treatment for many patients with advanced ccRCC in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
However, TKIs still have a place. The NCCN Kidney Cancer 2022 Guidelines recommend both sunitinib and pazopanib as options for first-line therapy in advanced disease. The 2022 ASCO Metastatic ccRCC guidelines recommend either drug as first-line treatment in combination with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or in monotherapy if there are “coexisting medical problems.”
In the United States, intermittent sunitinib in metastatic RCC was tested in a small study in 2017 with little activity in the literature since then. The authors, led by Moshe Ornstein, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic, concluded at the time that sunitinib treatment breaks were feasible and “clinical efficacy does not seem to be compromised.” Dr. Ornstein was approached for comment on this latest U.K. study but declined.
Back in the United Kingdom, the results of STAR arrived just in time.
Said Dr. Brown: “This has … been really helpful in the U.K. in the pandemic when people said, can these patients have extra breaks? At the worst of the pandemic we were able to say, sure, if it’s stable, we can keep them off for 3-6 months. …And so that’s already had a powerful impact.”
Dr. Brown concluded, “I think what the trial does allow us to do, as individual oncologists, is to look at the patients that this might be suitable for – it won’t be everybody – and to say yes, it’s okay to personalize things.”
The study was funded by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Research. Dr. Bestall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hewison reported funding to her institution from the NIHR Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Brown reports having served as a consultant or adviser for Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; honoraria from Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; research funding paid to their institution from the National Institute for Health and Care Research; and travel expenses from Ipsen. Other coauthors reported numerous relationships with industry.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY
Who’s at higher risk for breast cancer recurrence?
New research shows that patients with ER-negative disease have a higher risk of a second breast cancer within a 5-year window post diagnosis, compared with patients with ER-positive disease.
“Our findings suggest that primary breast cancer ER status could be used to identify women at highest risk of second breast cancer events during the early post-treatment period and should be a consideration for guidelines and decision-making regarding surveillance imaging regimens for breast cancer survivors,” the study authors, led by Kathryn P. Lowry, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, concluded.
The study was published online in Cancer.
Breast cancer survivors are at risk for a second breast cancer, making ongoing surveillance essential. Surveillance could be informed by better understanding an individual’s recurrence risk, but whether differences exist for women with ER‐positive vs. ER‐negative cancers remains unclear.
Dr. Lowry and colleagues analyzed women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer between 2000 and 2017, drawing from six Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium registries. The team collected information on patients’ ER status as well as second breast cancer events detectable by surveillance imaging. Second breast cancer rates were assessed 1-5 years and 6-10 years after diagnosis. The final study cohort included 23,139 women with ER-positive disease and 4,605 with ER-negative disease.
The researchers found that, at the 5-year mark, the cumulative breast cancer incidence was 7.1% for ER‐negative disease and 3.6% for ER‐positive disease. At the 10-year mark, the cumulative breast cancer incidence was still higher for women with ER-negative disease – 11.8% vs. 7.5% among those with ER-positive disease.
Patients with ER-negative disease also had higher rates of second breast cancers within the first 5 years of follow-ups – 16.0 per 1,000 person‐years vs. 7.8 per 1,000 person‐years for those with ER‐positive breast cancer – though after 5 years, the rates by ER status were similar among the two groups (12.1 per 1,000 vs. 9.3 per 1,000 person‐years, respectively).
Overall, the findings indicate that the “ER status of the primary invasive cancer was an important prognostic factor for both the magnitude and the timing of second breast cancer events,” the authors concluded.
The team noted several limitations to their study, including that information on the presence of pathogenic variants, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, were not available. Given that these variants tend to be more common among women with ER-negative breast cancers, this could represent a confounder.
Marisa C. Weiss, MD, chief medical officer and founder of Breastcancer.org, who was not involved in the research, highlighted two important details to keep in mind.
“We do know that triple negative breast cancers are associated with a higher risk of having an inherited genetic abnormality like BRCA1, which predicts a higher risk of second malignancies,” said Dr. Weiss, a breast oncologist at Lankenau Medical Center in Wynnewood, Pa. “Also, it should be noted that patients with HR-positive breast cancer have a higher incidence of local recurrence spread out over 10-plus years.”
What might these results mean for practice and following patients over the long term?
According to the researchers, “further study is needed to evaluate whether women with ER‐negative primary cancers may potentially benefit from more intensive surveillance in the early postdiagnosis period.”
Dr. Weiss noted as well that “each person’s situation is unique,” and it is “very important to develop a customized survivorship care plan with close surveillance,” which includes genetic testing.
Dr. Lowry reported grants from the American Cancer Society and personal fees from the Radiological Society of North America outside the submitted work. Several coauthors also reported disclosures. Dr. Weiss reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research shows that patients with ER-negative disease have a higher risk of a second breast cancer within a 5-year window post diagnosis, compared with patients with ER-positive disease.
“Our findings suggest that primary breast cancer ER status could be used to identify women at highest risk of second breast cancer events during the early post-treatment period and should be a consideration for guidelines and decision-making regarding surveillance imaging regimens for breast cancer survivors,” the study authors, led by Kathryn P. Lowry, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, concluded.
The study was published online in Cancer.
Breast cancer survivors are at risk for a second breast cancer, making ongoing surveillance essential. Surveillance could be informed by better understanding an individual’s recurrence risk, but whether differences exist for women with ER‐positive vs. ER‐negative cancers remains unclear.
Dr. Lowry and colleagues analyzed women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer between 2000 and 2017, drawing from six Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium registries. The team collected information on patients’ ER status as well as second breast cancer events detectable by surveillance imaging. Second breast cancer rates were assessed 1-5 years and 6-10 years after diagnosis. The final study cohort included 23,139 women with ER-positive disease and 4,605 with ER-negative disease.
The researchers found that, at the 5-year mark, the cumulative breast cancer incidence was 7.1% for ER‐negative disease and 3.6% for ER‐positive disease. At the 10-year mark, the cumulative breast cancer incidence was still higher for women with ER-negative disease – 11.8% vs. 7.5% among those with ER-positive disease.
Patients with ER-negative disease also had higher rates of second breast cancers within the first 5 years of follow-ups – 16.0 per 1,000 person‐years vs. 7.8 per 1,000 person‐years for those with ER‐positive breast cancer – though after 5 years, the rates by ER status were similar among the two groups (12.1 per 1,000 vs. 9.3 per 1,000 person‐years, respectively).
Overall, the findings indicate that the “ER status of the primary invasive cancer was an important prognostic factor for both the magnitude and the timing of second breast cancer events,” the authors concluded.
The team noted several limitations to their study, including that information on the presence of pathogenic variants, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, were not available. Given that these variants tend to be more common among women with ER-negative breast cancers, this could represent a confounder.
Marisa C. Weiss, MD, chief medical officer and founder of Breastcancer.org, who was not involved in the research, highlighted two important details to keep in mind.
“We do know that triple negative breast cancers are associated with a higher risk of having an inherited genetic abnormality like BRCA1, which predicts a higher risk of second malignancies,” said Dr. Weiss, a breast oncologist at Lankenau Medical Center in Wynnewood, Pa. “Also, it should be noted that patients with HR-positive breast cancer have a higher incidence of local recurrence spread out over 10-plus years.”
What might these results mean for practice and following patients over the long term?
According to the researchers, “further study is needed to evaluate whether women with ER‐negative primary cancers may potentially benefit from more intensive surveillance in the early postdiagnosis period.”
Dr. Weiss noted as well that “each person’s situation is unique,” and it is “very important to develop a customized survivorship care plan with close surveillance,” which includes genetic testing.
Dr. Lowry reported grants from the American Cancer Society and personal fees from the Radiological Society of North America outside the submitted work. Several coauthors also reported disclosures. Dr. Weiss reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research shows that patients with ER-negative disease have a higher risk of a second breast cancer within a 5-year window post diagnosis, compared with patients with ER-positive disease.
“Our findings suggest that primary breast cancer ER status could be used to identify women at highest risk of second breast cancer events during the early post-treatment period and should be a consideration for guidelines and decision-making regarding surveillance imaging regimens for breast cancer survivors,” the study authors, led by Kathryn P. Lowry, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, concluded.
The study was published online in Cancer.
Breast cancer survivors are at risk for a second breast cancer, making ongoing surveillance essential. Surveillance could be informed by better understanding an individual’s recurrence risk, but whether differences exist for women with ER‐positive vs. ER‐negative cancers remains unclear.
Dr. Lowry and colleagues analyzed women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer between 2000 and 2017, drawing from six Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium registries. The team collected information on patients’ ER status as well as second breast cancer events detectable by surveillance imaging. Second breast cancer rates were assessed 1-5 years and 6-10 years after diagnosis. The final study cohort included 23,139 women with ER-positive disease and 4,605 with ER-negative disease.
The researchers found that, at the 5-year mark, the cumulative breast cancer incidence was 7.1% for ER‐negative disease and 3.6% for ER‐positive disease. At the 10-year mark, the cumulative breast cancer incidence was still higher for women with ER-negative disease – 11.8% vs. 7.5% among those with ER-positive disease.
Patients with ER-negative disease also had higher rates of second breast cancers within the first 5 years of follow-ups – 16.0 per 1,000 person‐years vs. 7.8 per 1,000 person‐years for those with ER‐positive breast cancer – though after 5 years, the rates by ER status were similar among the two groups (12.1 per 1,000 vs. 9.3 per 1,000 person‐years, respectively).
Overall, the findings indicate that the “ER status of the primary invasive cancer was an important prognostic factor for both the magnitude and the timing of second breast cancer events,” the authors concluded.
The team noted several limitations to their study, including that information on the presence of pathogenic variants, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, were not available. Given that these variants tend to be more common among women with ER-negative breast cancers, this could represent a confounder.
Marisa C. Weiss, MD, chief medical officer and founder of Breastcancer.org, who was not involved in the research, highlighted two important details to keep in mind.
“We do know that triple negative breast cancers are associated with a higher risk of having an inherited genetic abnormality like BRCA1, which predicts a higher risk of second malignancies,” said Dr. Weiss, a breast oncologist at Lankenau Medical Center in Wynnewood, Pa. “Also, it should be noted that patients with HR-positive breast cancer have a higher incidence of local recurrence spread out over 10-plus years.”
What might these results mean for practice and following patients over the long term?
According to the researchers, “further study is needed to evaluate whether women with ER‐negative primary cancers may potentially benefit from more intensive surveillance in the early postdiagnosis period.”
Dr. Weiss noted as well that “each person’s situation is unique,” and it is “very important to develop a customized survivorship care plan with close surveillance,” which includes genetic testing.
Dr. Lowry reported grants from the American Cancer Society and personal fees from the Radiological Society of North America outside the submitted work. Several coauthors also reported disclosures. Dr. Weiss reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CANCER
Rucaparib benefit in BRCA+ prostate cancer confirmed
The finding, which comes from the TRITON3 clinical trial, provides evidence of clinical benefit for an indication for rucaparib that was granted an accelerated approval in May 2020.
“Rucaparib reduced the risk of progression or death by half in patients with BRCA alterations,” said lead author Alan H. Bryce, MD, medical director of the Genomic Oncology Clinic at Mayo Clinic Arizona, in Phoenix.
For the subgroup of patients with BRCA alterations, the median PFS was 11.2 months with rucaparib vs. 6.4 months (hazard ratio, 0.50; P < .001) among those who received physician’s choice of therapy, which included docetaxel or a second-generation ARPI, such as abiraterone or enzalutamide.
In another subgroup of patients whose disease had ATM alterations, the median PFS was 8.1 months with rucaparib vs. 6.8 months with physician’s choice of drug. The difference was not statistically significant.
However, the difference was significant in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population (comprising both subgroups), for whom the median PFS was 10.2 months with rucaparib vs. 6.4 months with physician’s choice of drug (HR, 0.61; P < .001 by log-rank test).
Dr. Bryce pointed out that three-quarters of the patients in the physician’s-choice arm who had progressive disease crossed over to rucaparib upon progression and that overall survival (OS) results are immature. At 62 months, median OS did not significantly differ in the BRCA subgroup (24.3 vs. 20.8 months favoring rucaparib; P = .21) or in the ITT group (23.6 vs. 20.9 months; P = .67).
Importantly, rucaparib was well tolerated. In all treatment groups, the most frequent adverse events were asthenia and fatigue, Bryce said. “There were no cases of myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia reported.”
These results from the TRITON3 trial were presented at the 2023 ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium and were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Suggested benefit
Rucaparib is the first PARP inhibitor approved for use in patients with mCRPC that harbors deleterious BRCA mutations (germline and/or somatic) who have already been treated with androgen receptor–directed therapy and a taxane-based chemotherapy. This prostate cancer indication was granted an accelerated approval in May 2020 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on the basis of response rates and effect on levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) from the TRITON2 clinical trial, the forerunner of the current study.
The TRITON2 study was a single-arm clinical trial that involved three cohorts: 62 patients with a BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable disease; 115 patients with a BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable or nonmeasurable disease; and 209 patients with homologous recombination deficiency–positive mCRPC.
In an analysis of 115 patients with a deleterious BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable or nonmeasurable disease, the confirmed PSA response rate was 55%. For the patients with measurable disease and a BRCA mutation, the objective response rate was 44%. The objective response rate was similar for those with a germline BRCA mutation.
Study details
The current phase 3 randomized TRITON3 clinical trial was conducted to confirm the earlier findings and to expand upon the data in mCRPC. The participants in this trial were patients with mCRPC who had specific gene alterations, including BRCA and ATM alterations, who had experienced disease progression after androgen receptor–directed therapy but who had not yet received chemotherapy.
A total of 270 men were assigned to receive rucaparib (600 mg twice daily); 135 patients received their physician’s choice of medication. Within the two study arms, 302 patients had a BRCA alteration, and 103 patients had an ATM alteration. The ITT population consisted of all the patients who had been randomly assigned to either of the two groups. A prespecified subgroup included patients with a BRCA alteration.
The primary outcome was the median duration of imaging-based PSF, as determined through independent review. Key secondary outcomes were overall survival and objective response rate.
The most common adverse events in the rucaparib group were fatigue, nausea, and anemia or decreased hemoglobin. In the control group, the most common adverse events were fatigue, diarrhea, and neuropathy. The most common events of grade 3 or higher were anemia or decreased hemoglobin, neutropenia or a decreased neutrophil count, and fatigue in the rucaparib group, and fatigue and neutropenia or a decreased neutrophil count among control patients.
No changes in standard of care
In a discussion of the study, Elena Castro, MD, PhD, of the Instituto de Investigación Biomédica de Málaga, Campanillas, Spain, emphasized that there is a clear benefit from the use of PARP inhibitors (such as rucaparib) for patients with BRCA alterations.
However, she highlighted the absence of convincing overall survival data and the absence of a clear benefit on PFS in the subgroup of patients with ATM alterations.
“These data raise several questions,” she noted, “such as, do patients with ATM alterations benefit at all? And should PARP inhibitors [such as rucaparib] precede or follow docetaxel therapy?”
Because of the high crossover rate, it may be possible to evaluate the directionality of docetaxel followed by PARP inhibitors and the other way around, she suggested.
Dr. Castro said that patients with BRCA alterations benefit from PARP inhibitors and are likely to derive more benefit from them than from taxanes.
“But those with ATM alterations are unlikely to benefit from rucaparib more than from taxanes,” she said.
In a comment, Hank Ng, MD, medical oncologist, NYU Langone Perlmutter Cancer Center, New York, said he is not convinced that the findings from TRITON 3 represent a new standard of care in BRCA 1/2 mutations or ATM.
“Currently, we know that, for patients with prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 or ATM, the standard of care is an androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI), such as abiraterone or enzalutamide, then docetaxel, and then a PARP inhibitor like rucaparib,” he said.
(Currently, rucaparib is indicated for use in patients with mCRPC with BRCA alterations after they have already received an ARPI and taxane-based chemotherapy.)
Dr. Ng also questioned the control arm of the TRITON 3 trial. All the participants in the trial had already experienced disease progression after treatment with a second-generation ARPI. But the physician’s choice of therapy allowed them to move on to another ARPI or to docetaxel.
Dr. NG commented that, “in almost all cases, after progression of one ARPI, switching to another ARPI does not provide much benefit – from what is visible from this abstract – and only 56% patients received docetaxel, and thus 44% received a not-beneficial treatment,” he said.
“I am not sure what the docetaxel subgroup showed, but potentially, if those numbers are convincing, we could move this [rucaparib] ahead of docetaxel,” he speculated.
However, he also pointed out that an overall survival benefit has not yet been shown; so far, the benefit that has been shown is with respect to imaging-based PFS.
Dr. Ng does agree that rucaparib is indicated in the second line after progression with one ARPI for patients who are not candidates for chemotherapy. “But this has not yet shown me that we should absolutely be offering rucaparib before docetaxel,” he said.
TRITON3 was supported by Clovis Oncology, manufacturer of rucaparib. Dr. Bryce has relationships with Bayer, Foundation Medicine, Janssen, Merck, Myovant Sciences, and Novartis and holds a patent for therapeutic targeting of cancer patients with NRG1 rearrangements. Dr. Castro has relationships with Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Clovis Oncology, Janssen-Cilag, Merck, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The finding, which comes from the TRITON3 clinical trial, provides evidence of clinical benefit for an indication for rucaparib that was granted an accelerated approval in May 2020.
“Rucaparib reduced the risk of progression or death by half in patients with BRCA alterations,” said lead author Alan H. Bryce, MD, medical director of the Genomic Oncology Clinic at Mayo Clinic Arizona, in Phoenix.
For the subgroup of patients with BRCA alterations, the median PFS was 11.2 months with rucaparib vs. 6.4 months (hazard ratio, 0.50; P < .001) among those who received physician’s choice of therapy, which included docetaxel or a second-generation ARPI, such as abiraterone or enzalutamide.
In another subgroup of patients whose disease had ATM alterations, the median PFS was 8.1 months with rucaparib vs. 6.8 months with physician’s choice of drug. The difference was not statistically significant.
However, the difference was significant in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population (comprising both subgroups), for whom the median PFS was 10.2 months with rucaparib vs. 6.4 months with physician’s choice of drug (HR, 0.61; P < .001 by log-rank test).
Dr. Bryce pointed out that three-quarters of the patients in the physician’s-choice arm who had progressive disease crossed over to rucaparib upon progression and that overall survival (OS) results are immature. At 62 months, median OS did not significantly differ in the BRCA subgroup (24.3 vs. 20.8 months favoring rucaparib; P = .21) or in the ITT group (23.6 vs. 20.9 months; P = .67).
Importantly, rucaparib was well tolerated. In all treatment groups, the most frequent adverse events were asthenia and fatigue, Bryce said. “There were no cases of myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia reported.”
These results from the TRITON3 trial were presented at the 2023 ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium and were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Suggested benefit
Rucaparib is the first PARP inhibitor approved for use in patients with mCRPC that harbors deleterious BRCA mutations (germline and/or somatic) who have already been treated with androgen receptor–directed therapy and a taxane-based chemotherapy. This prostate cancer indication was granted an accelerated approval in May 2020 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on the basis of response rates and effect on levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) from the TRITON2 clinical trial, the forerunner of the current study.
The TRITON2 study was a single-arm clinical trial that involved three cohorts: 62 patients with a BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable disease; 115 patients with a BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable or nonmeasurable disease; and 209 patients with homologous recombination deficiency–positive mCRPC.
In an analysis of 115 patients with a deleterious BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable or nonmeasurable disease, the confirmed PSA response rate was 55%. For the patients with measurable disease and a BRCA mutation, the objective response rate was 44%. The objective response rate was similar for those with a germline BRCA mutation.
Study details
The current phase 3 randomized TRITON3 clinical trial was conducted to confirm the earlier findings and to expand upon the data in mCRPC. The participants in this trial were patients with mCRPC who had specific gene alterations, including BRCA and ATM alterations, who had experienced disease progression after androgen receptor–directed therapy but who had not yet received chemotherapy.
A total of 270 men were assigned to receive rucaparib (600 mg twice daily); 135 patients received their physician’s choice of medication. Within the two study arms, 302 patients had a BRCA alteration, and 103 patients had an ATM alteration. The ITT population consisted of all the patients who had been randomly assigned to either of the two groups. A prespecified subgroup included patients with a BRCA alteration.
The primary outcome was the median duration of imaging-based PSF, as determined through independent review. Key secondary outcomes were overall survival and objective response rate.
The most common adverse events in the rucaparib group were fatigue, nausea, and anemia or decreased hemoglobin. In the control group, the most common adverse events were fatigue, diarrhea, and neuropathy. The most common events of grade 3 or higher were anemia or decreased hemoglobin, neutropenia or a decreased neutrophil count, and fatigue in the rucaparib group, and fatigue and neutropenia or a decreased neutrophil count among control patients.
No changes in standard of care
In a discussion of the study, Elena Castro, MD, PhD, of the Instituto de Investigación Biomédica de Málaga, Campanillas, Spain, emphasized that there is a clear benefit from the use of PARP inhibitors (such as rucaparib) for patients with BRCA alterations.
However, she highlighted the absence of convincing overall survival data and the absence of a clear benefit on PFS in the subgroup of patients with ATM alterations.
“These data raise several questions,” she noted, “such as, do patients with ATM alterations benefit at all? And should PARP inhibitors [such as rucaparib] precede or follow docetaxel therapy?”
Because of the high crossover rate, it may be possible to evaluate the directionality of docetaxel followed by PARP inhibitors and the other way around, she suggested.
Dr. Castro said that patients with BRCA alterations benefit from PARP inhibitors and are likely to derive more benefit from them than from taxanes.
“But those with ATM alterations are unlikely to benefit from rucaparib more than from taxanes,” she said.
In a comment, Hank Ng, MD, medical oncologist, NYU Langone Perlmutter Cancer Center, New York, said he is not convinced that the findings from TRITON 3 represent a new standard of care in BRCA 1/2 mutations or ATM.
“Currently, we know that, for patients with prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 or ATM, the standard of care is an androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI), such as abiraterone or enzalutamide, then docetaxel, and then a PARP inhibitor like rucaparib,” he said.
(Currently, rucaparib is indicated for use in patients with mCRPC with BRCA alterations after they have already received an ARPI and taxane-based chemotherapy.)
Dr. Ng also questioned the control arm of the TRITON 3 trial. All the participants in the trial had already experienced disease progression after treatment with a second-generation ARPI. But the physician’s choice of therapy allowed them to move on to another ARPI or to docetaxel.
Dr. NG commented that, “in almost all cases, after progression of one ARPI, switching to another ARPI does not provide much benefit – from what is visible from this abstract – and only 56% patients received docetaxel, and thus 44% received a not-beneficial treatment,” he said.
“I am not sure what the docetaxel subgroup showed, but potentially, if those numbers are convincing, we could move this [rucaparib] ahead of docetaxel,” he speculated.
However, he also pointed out that an overall survival benefit has not yet been shown; so far, the benefit that has been shown is with respect to imaging-based PFS.
Dr. Ng does agree that rucaparib is indicated in the second line after progression with one ARPI for patients who are not candidates for chemotherapy. “But this has not yet shown me that we should absolutely be offering rucaparib before docetaxel,” he said.
TRITON3 was supported by Clovis Oncology, manufacturer of rucaparib. Dr. Bryce has relationships with Bayer, Foundation Medicine, Janssen, Merck, Myovant Sciences, and Novartis and holds a patent for therapeutic targeting of cancer patients with NRG1 rearrangements. Dr. Castro has relationships with Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Clovis Oncology, Janssen-Cilag, Merck, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The finding, which comes from the TRITON3 clinical trial, provides evidence of clinical benefit for an indication for rucaparib that was granted an accelerated approval in May 2020.
“Rucaparib reduced the risk of progression or death by half in patients with BRCA alterations,” said lead author Alan H. Bryce, MD, medical director of the Genomic Oncology Clinic at Mayo Clinic Arizona, in Phoenix.
For the subgroup of patients with BRCA alterations, the median PFS was 11.2 months with rucaparib vs. 6.4 months (hazard ratio, 0.50; P < .001) among those who received physician’s choice of therapy, which included docetaxel or a second-generation ARPI, such as abiraterone or enzalutamide.
In another subgroup of patients whose disease had ATM alterations, the median PFS was 8.1 months with rucaparib vs. 6.8 months with physician’s choice of drug. The difference was not statistically significant.
However, the difference was significant in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population (comprising both subgroups), for whom the median PFS was 10.2 months with rucaparib vs. 6.4 months with physician’s choice of drug (HR, 0.61; P < .001 by log-rank test).
Dr. Bryce pointed out that three-quarters of the patients in the physician’s-choice arm who had progressive disease crossed over to rucaparib upon progression and that overall survival (OS) results are immature. At 62 months, median OS did not significantly differ in the BRCA subgroup (24.3 vs. 20.8 months favoring rucaparib; P = .21) or in the ITT group (23.6 vs. 20.9 months; P = .67).
Importantly, rucaparib was well tolerated. In all treatment groups, the most frequent adverse events were asthenia and fatigue, Bryce said. “There were no cases of myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia reported.”
These results from the TRITON3 trial were presented at the 2023 ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium and were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Suggested benefit
Rucaparib is the first PARP inhibitor approved for use in patients with mCRPC that harbors deleterious BRCA mutations (germline and/or somatic) who have already been treated with androgen receptor–directed therapy and a taxane-based chemotherapy. This prostate cancer indication was granted an accelerated approval in May 2020 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on the basis of response rates and effect on levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) from the TRITON2 clinical trial, the forerunner of the current study.
The TRITON2 study was a single-arm clinical trial that involved three cohorts: 62 patients with a BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable disease; 115 patients with a BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable or nonmeasurable disease; and 209 patients with homologous recombination deficiency–positive mCRPC.
In an analysis of 115 patients with a deleterious BRCA mutation (germline and/or somatic) and measurable or nonmeasurable disease, the confirmed PSA response rate was 55%. For the patients with measurable disease and a BRCA mutation, the objective response rate was 44%. The objective response rate was similar for those with a germline BRCA mutation.
Study details
The current phase 3 randomized TRITON3 clinical trial was conducted to confirm the earlier findings and to expand upon the data in mCRPC. The participants in this trial were patients with mCRPC who had specific gene alterations, including BRCA and ATM alterations, who had experienced disease progression after androgen receptor–directed therapy but who had not yet received chemotherapy.
A total of 270 men were assigned to receive rucaparib (600 mg twice daily); 135 patients received their physician’s choice of medication. Within the two study arms, 302 patients had a BRCA alteration, and 103 patients had an ATM alteration. The ITT population consisted of all the patients who had been randomly assigned to either of the two groups. A prespecified subgroup included patients with a BRCA alteration.
The primary outcome was the median duration of imaging-based PSF, as determined through independent review. Key secondary outcomes were overall survival and objective response rate.
The most common adverse events in the rucaparib group were fatigue, nausea, and anemia or decreased hemoglobin. In the control group, the most common adverse events were fatigue, diarrhea, and neuropathy. The most common events of grade 3 or higher were anemia or decreased hemoglobin, neutropenia or a decreased neutrophil count, and fatigue in the rucaparib group, and fatigue and neutropenia or a decreased neutrophil count among control patients.
No changes in standard of care
In a discussion of the study, Elena Castro, MD, PhD, of the Instituto de Investigación Biomédica de Málaga, Campanillas, Spain, emphasized that there is a clear benefit from the use of PARP inhibitors (such as rucaparib) for patients with BRCA alterations.
However, she highlighted the absence of convincing overall survival data and the absence of a clear benefit on PFS in the subgroup of patients with ATM alterations.
“These data raise several questions,” she noted, “such as, do patients with ATM alterations benefit at all? And should PARP inhibitors [such as rucaparib] precede or follow docetaxel therapy?”
Because of the high crossover rate, it may be possible to evaluate the directionality of docetaxel followed by PARP inhibitors and the other way around, she suggested.
Dr. Castro said that patients with BRCA alterations benefit from PARP inhibitors and are likely to derive more benefit from them than from taxanes.
“But those with ATM alterations are unlikely to benefit from rucaparib more than from taxanes,” she said.
In a comment, Hank Ng, MD, medical oncologist, NYU Langone Perlmutter Cancer Center, New York, said he is not convinced that the findings from TRITON 3 represent a new standard of care in BRCA 1/2 mutations or ATM.
“Currently, we know that, for patients with prostate cancer with BRCA1/2 or ATM, the standard of care is an androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI), such as abiraterone or enzalutamide, then docetaxel, and then a PARP inhibitor like rucaparib,” he said.
(Currently, rucaparib is indicated for use in patients with mCRPC with BRCA alterations after they have already received an ARPI and taxane-based chemotherapy.)
Dr. Ng also questioned the control arm of the TRITON 3 trial. All the participants in the trial had already experienced disease progression after treatment with a second-generation ARPI. But the physician’s choice of therapy allowed them to move on to another ARPI or to docetaxel.
Dr. NG commented that, “in almost all cases, after progression of one ARPI, switching to another ARPI does not provide much benefit – from what is visible from this abstract – and only 56% patients received docetaxel, and thus 44% received a not-beneficial treatment,” he said.
“I am not sure what the docetaxel subgroup showed, but potentially, if those numbers are convincing, we could move this [rucaparib] ahead of docetaxel,” he speculated.
However, he also pointed out that an overall survival benefit has not yet been shown; so far, the benefit that has been shown is with respect to imaging-based PFS.
Dr. Ng does agree that rucaparib is indicated in the second line after progression with one ARPI for patients who are not candidates for chemotherapy. “But this has not yet shown me that we should absolutely be offering rucaparib before docetaxel,” he said.
TRITON3 was supported by Clovis Oncology, manufacturer of rucaparib. Dr. Bryce has relationships with Bayer, Foundation Medicine, Janssen, Merck, Myovant Sciences, and Novartis and holds a patent for therapeutic targeting of cancer patients with NRG1 rearrangements. Dr. Castro has relationships with Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Clovis Oncology, Janssen-Cilag, Merck, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO GU 2023
Genomic clues to poor outcomes in young breast cancer patients
and offer clues about molecular targets for future trials.
Compared with older women with early stage HR-positive breast cancer, women under 40 years of age had significantly higher frequencies of certain mutations, such as GATA3, as well as genomic features associated with a poor prognosis. Notably, the researchers found that women with such poor prognostic features vs. those with none had a significantly worse 8-year distant recurrence-free interval and overall survival.
“We have demonstrated age-related differences in genomic profiles with enrichment of genomic features associated with poor prognosis in these younger premenopausal women compared with older premenopausal and postmenopausal women,” the authors wrote in the study, published in the Annals of Oncology. Importantly, the genomic features highlight “the potential for age-focused treatment strategies.”
Charis Eng, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute, Ohio, noted that the findings are promising but need further validation.
“With time and the appropriate clinical trials in place, I envision that these findings will enable the personalized genomics-driven management of these cancers – not only treatment, but also toward prevention,” said Dr. Eng, who was not involved in the study.
Young premenopausal women, particularly those with HR-positive, luminal breast cancer, are known to have significantly higher recurrence rates and worse survival, compared with older women, but the reasons have remained unclear.
Although previous studies have identified key gene expression signatures linked to worse outcomes in younger patients with breast cancer, there are limited data on this younger patient population, especially by breast cancer subtype. Given that breast cancer treatment strategies are often similar across age groups, such evidence gaps could represent missed opportunities for developing more targeted treatment strategies for this high-risk population of young women.
To further investigate the cancer-specific genetic profiles in younger women, Sherene Loi, MD, PhD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, University of Melbourne, and colleagues turned to data from the pivotal, multicenter Suppression of Ovarian Function Trial (SOFT).
Using next-generation sequencing, Dr. Loi and colleagues evaluated HR-positive, HER2-negative tumors among a subset of 1,276 premenopausal women who were diagnosed with early stage breast cancer. The study employed deep-targeted sequencing for most patients (n = 1,258) as well as whole-exome sequencing in a matched case-control subsample of young women with a median age of 38 years (n = 82).
Compared with women aged 40 and older, those under 40 years of age (n = 359) had significantly higher frequencies of mutations in GATA3 (19% vs. 16%) and copy number-amplifications (47% vs. 26%).
Younger women also had significantly higher features suggestive of homologous recombination deficiency (27% vs. 21% in older women), and a higher proportion of PIK3CA mutations with concurrent copy number-amplifications (23% vs. 11%, respectively), all considered to be poor prognostic features.
In addition, younger women had significantly lower frequencies of certain mutations, including PIK3CA (32% vs. 47%), CDH1 (3% vs. 9%), and MAP3K1 (7% vs. 12%), compared with older women.
Overall, 46% of women had poor prognostic features. These poor prognostic features were observed in 72% of patients under age 35, compared with 54% aged 35-39, and 40% of those 40 and over.
Compared with women without those features, women with poor prognostic features had a lower 8-year distant recurrence-free interval of 84% vs. 94% (hazard ratio, 1.85), and worse 8-year overall survival of 88% vs. 96%, respectively (HR, 2.20). Notably, younger women under age 40 had the poorest outcomes, with an 8-year distant recurrence-free interval rate of 74% vs. 85% in older women, and an 8-year overall survival of 80% vs. 93%, respectively.
How might these results inform potential therapeutics?
Drugs targeting the homologous recombination deficiency pathway are well established, and up to 36% of very young patients in the study showed genomic features of homologous recombination deficiency, the authors noted.
In addition, Dr. Eng explained, there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments that can target the copy number amplified, PIK3CA-mutated tumors, including therapies that target PIK3CA itself, or proteins downstream of it. However, use of such therapies would need “to be tested experimentally, especially since pathway inhibition sometimes may result in rebound signaling to promote tumor growth,” Dr. Eng said.
An important caveat is that patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be underrepresented in the SOFT clinical trial, as the trial excluded patients who already had bilateral oophorectomy or planned to within 5 years, the authors noted.
Nevertheless, Dr. Loi said that the study is important because “there are no other datasets as large or with this long follow-up for very young women with breast cancer.”
Furthermore, “the SOFT clinical trial was practice-changing, so using the tumor samples associated with this study is more impactful than smaller cohorts with no outcome data or institutional retrospective cohorts,” she said.
Dr. Eng agreed that the study’s size is an important attribute, allowing the authors to “identify differences that would have been missed in a smaller and more heterogeneous series.”
She added that future research should also include ancestry and racial diversity.
“While young women have higher occurrences of aggressive breast cancers, mortality is twice as likely in young Black women, compared to young White women,” Dr. Eng said.
The study received funding from a Susan G. Komen for the Cure Promise Grant, the National Health and Research Council of Australia, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the National Breast Cancer Foundation of Australia, and support from the family of Judy Eisman in Australia. Dr. Loi and Dr. Eng report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
and offer clues about molecular targets for future trials.
Compared with older women with early stage HR-positive breast cancer, women under 40 years of age had significantly higher frequencies of certain mutations, such as GATA3, as well as genomic features associated with a poor prognosis. Notably, the researchers found that women with such poor prognostic features vs. those with none had a significantly worse 8-year distant recurrence-free interval and overall survival.
“We have demonstrated age-related differences in genomic profiles with enrichment of genomic features associated with poor prognosis in these younger premenopausal women compared with older premenopausal and postmenopausal women,” the authors wrote in the study, published in the Annals of Oncology. Importantly, the genomic features highlight “the potential for age-focused treatment strategies.”
Charis Eng, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute, Ohio, noted that the findings are promising but need further validation.
“With time and the appropriate clinical trials in place, I envision that these findings will enable the personalized genomics-driven management of these cancers – not only treatment, but also toward prevention,” said Dr. Eng, who was not involved in the study.
Young premenopausal women, particularly those with HR-positive, luminal breast cancer, are known to have significantly higher recurrence rates and worse survival, compared with older women, but the reasons have remained unclear.
Although previous studies have identified key gene expression signatures linked to worse outcomes in younger patients with breast cancer, there are limited data on this younger patient population, especially by breast cancer subtype. Given that breast cancer treatment strategies are often similar across age groups, such evidence gaps could represent missed opportunities for developing more targeted treatment strategies for this high-risk population of young women.
To further investigate the cancer-specific genetic profiles in younger women, Sherene Loi, MD, PhD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, University of Melbourne, and colleagues turned to data from the pivotal, multicenter Suppression of Ovarian Function Trial (SOFT).
Using next-generation sequencing, Dr. Loi and colleagues evaluated HR-positive, HER2-negative tumors among a subset of 1,276 premenopausal women who were diagnosed with early stage breast cancer. The study employed deep-targeted sequencing for most patients (n = 1,258) as well as whole-exome sequencing in a matched case-control subsample of young women with a median age of 38 years (n = 82).
Compared with women aged 40 and older, those under 40 years of age (n = 359) had significantly higher frequencies of mutations in GATA3 (19% vs. 16%) and copy number-amplifications (47% vs. 26%).
Younger women also had significantly higher features suggestive of homologous recombination deficiency (27% vs. 21% in older women), and a higher proportion of PIK3CA mutations with concurrent copy number-amplifications (23% vs. 11%, respectively), all considered to be poor prognostic features.
In addition, younger women had significantly lower frequencies of certain mutations, including PIK3CA (32% vs. 47%), CDH1 (3% vs. 9%), and MAP3K1 (7% vs. 12%), compared with older women.
Overall, 46% of women had poor prognostic features. These poor prognostic features were observed in 72% of patients under age 35, compared with 54% aged 35-39, and 40% of those 40 and over.
Compared with women without those features, women with poor prognostic features had a lower 8-year distant recurrence-free interval of 84% vs. 94% (hazard ratio, 1.85), and worse 8-year overall survival of 88% vs. 96%, respectively (HR, 2.20). Notably, younger women under age 40 had the poorest outcomes, with an 8-year distant recurrence-free interval rate of 74% vs. 85% in older women, and an 8-year overall survival of 80% vs. 93%, respectively.
How might these results inform potential therapeutics?
Drugs targeting the homologous recombination deficiency pathway are well established, and up to 36% of very young patients in the study showed genomic features of homologous recombination deficiency, the authors noted.
In addition, Dr. Eng explained, there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments that can target the copy number amplified, PIK3CA-mutated tumors, including therapies that target PIK3CA itself, or proteins downstream of it. However, use of such therapies would need “to be tested experimentally, especially since pathway inhibition sometimes may result in rebound signaling to promote tumor growth,” Dr. Eng said.
An important caveat is that patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be underrepresented in the SOFT clinical trial, as the trial excluded patients who already had bilateral oophorectomy or planned to within 5 years, the authors noted.
Nevertheless, Dr. Loi said that the study is important because “there are no other datasets as large or with this long follow-up for very young women with breast cancer.”
Furthermore, “the SOFT clinical trial was practice-changing, so using the tumor samples associated with this study is more impactful than smaller cohorts with no outcome data or institutional retrospective cohorts,” she said.
Dr. Eng agreed that the study’s size is an important attribute, allowing the authors to “identify differences that would have been missed in a smaller and more heterogeneous series.”
She added that future research should also include ancestry and racial diversity.
“While young women have higher occurrences of aggressive breast cancers, mortality is twice as likely in young Black women, compared to young White women,” Dr. Eng said.
The study received funding from a Susan G. Komen for the Cure Promise Grant, the National Health and Research Council of Australia, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the National Breast Cancer Foundation of Australia, and support from the family of Judy Eisman in Australia. Dr. Loi and Dr. Eng report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
and offer clues about molecular targets for future trials.
Compared with older women with early stage HR-positive breast cancer, women under 40 years of age had significantly higher frequencies of certain mutations, such as GATA3, as well as genomic features associated with a poor prognosis. Notably, the researchers found that women with such poor prognostic features vs. those with none had a significantly worse 8-year distant recurrence-free interval and overall survival.
“We have demonstrated age-related differences in genomic profiles with enrichment of genomic features associated with poor prognosis in these younger premenopausal women compared with older premenopausal and postmenopausal women,” the authors wrote in the study, published in the Annals of Oncology. Importantly, the genomic features highlight “the potential for age-focused treatment strategies.”
Charis Eng, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute, Ohio, noted that the findings are promising but need further validation.
“With time and the appropriate clinical trials in place, I envision that these findings will enable the personalized genomics-driven management of these cancers – not only treatment, but also toward prevention,” said Dr. Eng, who was not involved in the study.
Young premenopausal women, particularly those with HR-positive, luminal breast cancer, are known to have significantly higher recurrence rates and worse survival, compared with older women, but the reasons have remained unclear.
Although previous studies have identified key gene expression signatures linked to worse outcomes in younger patients with breast cancer, there are limited data on this younger patient population, especially by breast cancer subtype. Given that breast cancer treatment strategies are often similar across age groups, such evidence gaps could represent missed opportunities for developing more targeted treatment strategies for this high-risk population of young women.
To further investigate the cancer-specific genetic profiles in younger women, Sherene Loi, MD, PhD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, University of Melbourne, and colleagues turned to data from the pivotal, multicenter Suppression of Ovarian Function Trial (SOFT).
Using next-generation sequencing, Dr. Loi and colleagues evaluated HR-positive, HER2-negative tumors among a subset of 1,276 premenopausal women who were diagnosed with early stage breast cancer. The study employed deep-targeted sequencing for most patients (n = 1,258) as well as whole-exome sequencing in a matched case-control subsample of young women with a median age of 38 years (n = 82).
Compared with women aged 40 and older, those under 40 years of age (n = 359) had significantly higher frequencies of mutations in GATA3 (19% vs. 16%) and copy number-amplifications (47% vs. 26%).
Younger women also had significantly higher features suggestive of homologous recombination deficiency (27% vs. 21% in older women), and a higher proportion of PIK3CA mutations with concurrent copy number-amplifications (23% vs. 11%, respectively), all considered to be poor prognostic features.
In addition, younger women had significantly lower frequencies of certain mutations, including PIK3CA (32% vs. 47%), CDH1 (3% vs. 9%), and MAP3K1 (7% vs. 12%), compared with older women.
Overall, 46% of women had poor prognostic features. These poor prognostic features were observed in 72% of patients under age 35, compared with 54% aged 35-39, and 40% of those 40 and over.
Compared with women without those features, women with poor prognostic features had a lower 8-year distant recurrence-free interval of 84% vs. 94% (hazard ratio, 1.85), and worse 8-year overall survival of 88% vs. 96%, respectively (HR, 2.20). Notably, younger women under age 40 had the poorest outcomes, with an 8-year distant recurrence-free interval rate of 74% vs. 85% in older women, and an 8-year overall survival of 80% vs. 93%, respectively.
How might these results inform potential therapeutics?
Drugs targeting the homologous recombination deficiency pathway are well established, and up to 36% of very young patients in the study showed genomic features of homologous recombination deficiency, the authors noted.
In addition, Dr. Eng explained, there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments that can target the copy number amplified, PIK3CA-mutated tumors, including therapies that target PIK3CA itself, or proteins downstream of it. However, use of such therapies would need “to be tested experimentally, especially since pathway inhibition sometimes may result in rebound signaling to promote tumor growth,” Dr. Eng said.
An important caveat is that patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be underrepresented in the SOFT clinical trial, as the trial excluded patients who already had bilateral oophorectomy or planned to within 5 years, the authors noted.
Nevertheless, Dr. Loi said that the study is important because “there are no other datasets as large or with this long follow-up for very young women with breast cancer.”
Furthermore, “the SOFT clinical trial was practice-changing, so using the tumor samples associated with this study is more impactful than smaller cohorts with no outcome data or institutional retrospective cohorts,” she said.
Dr. Eng agreed that the study’s size is an important attribute, allowing the authors to “identify differences that would have been missed in a smaller and more heterogeneous series.”
She added that future research should also include ancestry and racial diversity.
“While young women have higher occurrences of aggressive breast cancers, mortality is twice as likely in young Black women, compared to young White women,” Dr. Eng said.
The study received funding from a Susan G. Komen for the Cure Promise Grant, the National Health and Research Council of Australia, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the National Breast Cancer Foundation of Australia, and support from the family of Judy Eisman in Australia. Dr. Loi and Dr. Eng report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF ONCOLOGY
The 5-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer is increasing
John Whyte, MD: Hello, I’m Dr. John Whyte, the Chief Medical Officer of WebMD. One of those cancers was pancreatic cancer, which historically has had a very low survival rate. What’s going on here? Are we doing better with diagnosis, treatment, a combination?
Joining me today is Dr. Lynn Matrisian. She is PanCAN’s chief science officer. Dr. Matrisian, thanks for joining me today. It’s great to see you.
Lynn Matrisian, PhD, MBA: Great to be here. Thank you.
Dr. Whyte: Well, tell me what your first reaction was when you saw the recent data from the American Cancer Society. What one word would you use?
Dr. Matrisian: Hopeful. I think hopeful in general that survival rates are increasing, not for all cancers, but for many cancers. We continue to make progress. Research is making a difference. And we’re making progress against cancer in general.
Dr. Whyte: You’re passionate, as our viewers know, about pancreatic cancer. And that’s been one of the hardest cancers to treat, and one of the lowest survival rates. But there’s some encouraging news that we saw, didn’t we?
Dr. Matrisian: Yes. So the 5-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer went up a whole percentage. It’s at 12% now. And what’s really good is it was at 11% last year. It was at 10% the year before. So that’s 2 years in a row that we’ve had an increase in the 5-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer. So we’re hopeful that’s a trajectory that we can really capitalize on is how fast we’re making progress in this disease.
Dr. Whyte: I want to put it into context, Lynn. Because some people might be thinking, 1%? Like you’re excited about 1%? That doesn’t seem that much. But correct me if I’m wrong. A one percentage point increase means 641 more loved ones will enjoy life’s moments, as you put it, 5 years after their diagnosis that otherwise wouldn’t have. What does that practically mean to viewers?
Dr. Matrisian: That means that more than 600 people in the United States will hug a loved one 5 years after that diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. It is a very deadly disease. But we’re going to, by continuing to make progress, it gives those moments to those people. And it means that we’re making progress against the disease in general.
Dr. Whyte: So even 1%, and 1% each year, does have value.
Dr. Matrisian: It has a lot of value.
Dr. Whyte: What’s driving this improvement? Is it better screening? And we’re not so great still in screening a pancreatic cancer. Is it the innovation in cancer treatments? What do you think is accounting for what we hope is this trajectory of increases in 5-year survival?
Dr. Matrisian: Right, so the nice thing the reason that we like looking at 5-year survival rates is because it takes into account all of those things. And we have actually made progress in all of those things. So by looking at those that are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer in general as a whole, and looking at their survival, we are looking at better treatments. People who are getting pancreatic cancer later are living longer as a result of better treatments.
But it’s not just that. It’s also, if you’re diagnosed earlier, your 5-year survival rate is higher. More people who are diagnosed early live to five years than those that are diagnosed later. So within that statistic, there are more people who are diagnosed earlier. And those people also live longer. So it takes into account all of those things, which is why we really like to look at that five-year survival rate for a disease like pancreatic cancer.
Dr. Whyte: Where are we on screening? Because we always want to catch people early. That gives them that greatest chance of survival. Have we made much improvements there? And if we have, what are they?
Dr. Matrisian: Well we have made improvements there are more people that are now diagnosed with localized disease than there were 20 years ago. So that is increasing. And we’re still doing it really by being aware of the symptoms right now. Being aware that kind of chronic indigestion, lower back pain that won’t go away, these are signs and symptoms. And especially things like jaundice ...
Dr. Whyte: That yellow color that they might see.
Dr. Matrisian: Yes, that yellow colors in your eye, that’s a really important symptom that would certainly send people to the doctor in order to look at this. So some of it is being more aware and finding the disease earlier. But what we’re really hoping for is some sort of blood test or some sort of other way of looking through medical records and identifying those people that need to go and be checked.
Dr. Whyte: Now we chatted about that almost two years ago. So tell me the progress that we’ve made. How are we doing?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah, well there’s a number of companies now that have blood tests that are available. They still need more work. They still need more studies to really understand how good they are at finding pancreatic cancer early. But we didn’t have them a couple of years ago. And so it’s really a very exciting time in the field, that there’s companies that were taking advantage of research for many years and actually turning it into a commercial product that is available for people to check.
Dr. Whyte: And then what about treatments? More treatment options today than there were just a few years ago, but still a lot of progress to be made. So when we talk about even 12% 5-year survival, we’d love to see it much more. And you talk about, I don’t want to misquote, so correct me if I’m wrong. Your goal is 20%. Five-year survival by 2030. That’s not too far. So, Lynn, how are we going to get there?
Dr. Matrisian: Okay, well this is our mission. And that’s exactly our goal, 20% by 2030. So we’ve got some work to do. And we are working at both fronts. You’re right, we need better treatments. And so we’ve set up a clinical trial platform where we can look at a lot of different treatments much more efficiently, much faster, kind of taking advantage of an infrastructure to do that. And that’s called Precision Promise. And we’re excited about that as a way to get new treatments for advanced pancreatic cancer.
And then we’re also working on the early detection end. We think an important symptom of pancreatic cancer that isn’t often recognized is new onset diabetes, sudden diabetes in those over 50 where that person did not have diabetes before. So it’s new, looks like type 2 diabetes, but it’s actually caused by pancreatic cancer.
And so we have an initiative, The Early Detection Initiative, that is taking advantage of that. And seeing if we image people right away based on that symptom, can we find pancreatic cancer early? So we think it’s important to look both at trying to diagnose it earlier, as well as trying to treat it better for advanced disease.
Dr. Whyte: Yeah. You know, at WebMD we’re always trying to empower people with better information so they can also become advocates for their health. You’re an expert in advocacy on pancreatic cancer. So what’s your advice to listeners as to how they become good advocates for themselves or advocates in general for loved ones who have pancreatic cancer?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah. Yeah. Well certainly, knowledge is power. And so the real thing to do is to call the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. This is what we do. We stay up on the most current information. We have very experienced case managers who can help navigate the complexities of pancreatic cancer at every stage of the journey.
Or if you have questions about pancreatic cancer, call PanCAN. Go to PanCAN.org and give us a call. Because it’s really that knowledge, knowing what it is that you need to get more knowledge about, how to advocate for yourself is very important in a disease, in any disease, but in particular a disease like pancreatic cancer.
Dr. Whyte: And I don’t want to dismiss the progress that we’ve made, that you’ve just referenced in terms of the increased survival. But there’s still a long way to go. We need a lot more dollars for research. We need a lot more clinical trials to take place. What’s your message to a viewer who’s been diagnosed with pancreatic cancer or a loved one? What’s your message, Lynn, today for them?
Dr. Matrisian: Well, first, get as much knowledge as you can. Call PanCAN, and let us help you help your loved one. But then help us. Let’s do research. Let’s do more research. Let’s understand this disease better so we can make those kinds of progress in both treatment and early detection.
And PanCAN works very hard at understanding the disease and setting up research programs that are going to make a difference, that are going to get us to that aggressive goal of 20% survival by 2030. So there is a lot of things that can be done, raise awareness to your friends and neighbors about the disease, lots of things that will help this whole field.
Dr. Whyte: What’s your feeling on second opinions? Given that this can be a difficult cancer to treat, given that there’s emerging therapies that are always developing, when you have a diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, is it important to consider getting a second opinion?
Dr. Matrisian: Yes. Yes, it is. And our case managers will help with that process. We do think it’s important.
Dr. Whyte: Because sometimes, Lynn, people just want to get started, right? Get it out of me. Get treatment. And sometimes getting a second opinion, doing some genomic testing can take time. So what’s your response to that?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah. Yeah. Well we say, your care team is very important. Who is on your care team, and it may take a little time to find the right people on your care team. But that is an incredibly important step. Sometimes it’s not just one person. Sometimes you need more than one doctor, more than one nurse, more than one type of specialty to help you deal with this. And taking the time to do that is incredibly important.
Yes, you need to – you do need to act. But act smart. And do it with knowledge. Do it really understanding what your options are, and advocate for yourself.
Dr. Whyte: And surround yourself as you reference with that right care team for you, because that’s the most important thing when you have any type of cancer diagnosis. Dr. Lynn Matrisian, I want to thank you for taking time today.
Dr. Matrisian: Thank you so much, John.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
John Whyte, MD: Hello, I’m Dr. John Whyte, the Chief Medical Officer of WebMD. One of those cancers was pancreatic cancer, which historically has had a very low survival rate. What’s going on here? Are we doing better with diagnosis, treatment, a combination?
Joining me today is Dr. Lynn Matrisian. She is PanCAN’s chief science officer. Dr. Matrisian, thanks for joining me today. It’s great to see you.
Lynn Matrisian, PhD, MBA: Great to be here. Thank you.
Dr. Whyte: Well, tell me what your first reaction was when you saw the recent data from the American Cancer Society. What one word would you use?
Dr. Matrisian: Hopeful. I think hopeful in general that survival rates are increasing, not for all cancers, but for many cancers. We continue to make progress. Research is making a difference. And we’re making progress against cancer in general.
Dr. Whyte: You’re passionate, as our viewers know, about pancreatic cancer. And that’s been one of the hardest cancers to treat, and one of the lowest survival rates. But there’s some encouraging news that we saw, didn’t we?
Dr. Matrisian: Yes. So the 5-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer went up a whole percentage. It’s at 12% now. And what’s really good is it was at 11% last year. It was at 10% the year before. So that’s 2 years in a row that we’ve had an increase in the 5-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer. So we’re hopeful that’s a trajectory that we can really capitalize on is how fast we’re making progress in this disease.
Dr. Whyte: I want to put it into context, Lynn. Because some people might be thinking, 1%? Like you’re excited about 1%? That doesn’t seem that much. But correct me if I’m wrong. A one percentage point increase means 641 more loved ones will enjoy life’s moments, as you put it, 5 years after their diagnosis that otherwise wouldn’t have. What does that practically mean to viewers?
Dr. Matrisian: That means that more than 600 people in the United States will hug a loved one 5 years after that diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. It is a very deadly disease. But we’re going to, by continuing to make progress, it gives those moments to those people. And it means that we’re making progress against the disease in general.
Dr. Whyte: So even 1%, and 1% each year, does have value.
Dr. Matrisian: It has a lot of value.
Dr. Whyte: What’s driving this improvement? Is it better screening? And we’re not so great still in screening a pancreatic cancer. Is it the innovation in cancer treatments? What do you think is accounting for what we hope is this trajectory of increases in 5-year survival?
Dr. Matrisian: Right, so the nice thing the reason that we like looking at 5-year survival rates is because it takes into account all of those things. And we have actually made progress in all of those things. So by looking at those that are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer in general as a whole, and looking at their survival, we are looking at better treatments. People who are getting pancreatic cancer later are living longer as a result of better treatments.
But it’s not just that. It’s also, if you’re diagnosed earlier, your 5-year survival rate is higher. More people who are diagnosed early live to five years than those that are diagnosed later. So within that statistic, there are more people who are diagnosed earlier. And those people also live longer. So it takes into account all of those things, which is why we really like to look at that five-year survival rate for a disease like pancreatic cancer.
Dr. Whyte: Where are we on screening? Because we always want to catch people early. That gives them that greatest chance of survival. Have we made much improvements there? And if we have, what are they?
Dr. Matrisian: Well we have made improvements there are more people that are now diagnosed with localized disease than there were 20 years ago. So that is increasing. And we’re still doing it really by being aware of the symptoms right now. Being aware that kind of chronic indigestion, lower back pain that won’t go away, these are signs and symptoms. And especially things like jaundice ...
Dr. Whyte: That yellow color that they might see.
Dr. Matrisian: Yes, that yellow colors in your eye, that’s a really important symptom that would certainly send people to the doctor in order to look at this. So some of it is being more aware and finding the disease earlier. But what we’re really hoping for is some sort of blood test or some sort of other way of looking through medical records and identifying those people that need to go and be checked.
Dr. Whyte: Now we chatted about that almost two years ago. So tell me the progress that we’ve made. How are we doing?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah, well there’s a number of companies now that have blood tests that are available. They still need more work. They still need more studies to really understand how good they are at finding pancreatic cancer early. But we didn’t have them a couple of years ago. And so it’s really a very exciting time in the field, that there’s companies that were taking advantage of research for many years and actually turning it into a commercial product that is available for people to check.
Dr. Whyte: And then what about treatments? More treatment options today than there were just a few years ago, but still a lot of progress to be made. So when we talk about even 12% 5-year survival, we’d love to see it much more. And you talk about, I don’t want to misquote, so correct me if I’m wrong. Your goal is 20%. Five-year survival by 2030. That’s not too far. So, Lynn, how are we going to get there?
Dr. Matrisian: Okay, well this is our mission. And that’s exactly our goal, 20% by 2030. So we’ve got some work to do. And we are working at both fronts. You’re right, we need better treatments. And so we’ve set up a clinical trial platform where we can look at a lot of different treatments much more efficiently, much faster, kind of taking advantage of an infrastructure to do that. And that’s called Precision Promise. And we’re excited about that as a way to get new treatments for advanced pancreatic cancer.
And then we’re also working on the early detection end. We think an important symptom of pancreatic cancer that isn’t often recognized is new onset diabetes, sudden diabetes in those over 50 where that person did not have diabetes before. So it’s new, looks like type 2 diabetes, but it’s actually caused by pancreatic cancer.
And so we have an initiative, The Early Detection Initiative, that is taking advantage of that. And seeing if we image people right away based on that symptom, can we find pancreatic cancer early? So we think it’s important to look both at trying to diagnose it earlier, as well as trying to treat it better for advanced disease.
Dr. Whyte: Yeah. You know, at WebMD we’re always trying to empower people with better information so they can also become advocates for their health. You’re an expert in advocacy on pancreatic cancer. So what’s your advice to listeners as to how they become good advocates for themselves or advocates in general for loved ones who have pancreatic cancer?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah. Yeah. Well certainly, knowledge is power. And so the real thing to do is to call the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. This is what we do. We stay up on the most current information. We have very experienced case managers who can help navigate the complexities of pancreatic cancer at every stage of the journey.
Or if you have questions about pancreatic cancer, call PanCAN. Go to PanCAN.org and give us a call. Because it’s really that knowledge, knowing what it is that you need to get more knowledge about, how to advocate for yourself is very important in a disease, in any disease, but in particular a disease like pancreatic cancer.
Dr. Whyte: And I don’t want to dismiss the progress that we’ve made, that you’ve just referenced in terms of the increased survival. But there’s still a long way to go. We need a lot more dollars for research. We need a lot more clinical trials to take place. What’s your message to a viewer who’s been diagnosed with pancreatic cancer or a loved one? What’s your message, Lynn, today for them?
Dr. Matrisian: Well, first, get as much knowledge as you can. Call PanCAN, and let us help you help your loved one. But then help us. Let’s do research. Let’s do more research. Let’s understand this disease better so we can make those kinds of progress in both treatment and early detection.
And PanCAN works very hard at understanding the disease and setting up research programs that are going to make a difference, that are going to get us to that aggressive goal of 20% survival by 2030. So there is a lot of things that can be done, raise awareness to your friends and neighbors about the disease, lots of things that will help this whole field.
Dr. Whyte: What’s your feeling on second opinions? Given that this can be a difficult cancer to treat, given that there’s emerging therapies that are always developing, when you have a diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, is it important to consider getting a second opinion?
Dr. Matrisian: Yes. Yes, it is. And our case managers will help with that process. We do think it’s important.
Dr. Whyte: Because sometimes, Lynn, people just want to get started, right? Get it out of me. Get treatment. And sometimes getting a second opinion, doing some genomic testing can take time. So what’s your response to that?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah. Yeah. Well we say, your care team is very important. Who is on your care team, and it may take a little time to find the right people on your care team. But that is an incredibly important step. Sometimes it’s not just one person. Sometimes you need more than one doctor, more than one nurse, more than one type of specialty to help you deal with this. And taking the time to do that is incredibly important.
Yes, you need to – you do need to act. But act smart. And do it with knowledge. Do it really understanding what your options are, and advocate for yourself.
Dr. Whyte: And surround yourself as you reference with that right care team for you, because that’s the most important thing when you have any type of cancer diagnosis. Dr. Lynn Matrisian, I want to thank you for taking time today.
Dr. Matrisian: Thank you so much, John.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
John Whyte, MD: Hello, I’m Dr. John Whyte, the Chief Medical Officer of WebMD. One of those cancers was pancreatic cancer, which historically has had a very low survival rate. What’s going on here? Are we doing better with diagnosis, treatment, a combination?
Joining me today is Dr. Lynn Matrisian. She is PanCAN’s chief science officer. Dr. Matrisian, thanks for joining me today. It’s great to see you.
Lynn Matrisian, PhD, MBA: Great to be here. Thank you.
Dr. Whyte: Well, tell me what your first reaction was when you saw the recent data from the American Cancer Society. What one word would you use?
Dr. Matrisian: Hopeful. I think hopeful in general that survival rates are increasing, not for all cancers, but for many cancers. We continue to make progress. Research is making a difference. And we’re making progress against cancer in general.
Dr. Whyte: You’re passionate, as our viewers know, about pancreatic cancer. And that’s been one of the hardest cancers to treat, and one of the lowest survival rates. But there’s some encouraging news that we saw, didn’t we?
Dr. Matrisian: Yes. So the 5-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer went up a whole percentage. It’s at 12% now. And what’s really good is it was at 11% last year. It was at 10% the year before. So that’s 2 years in a row that we’ve had an increase in the 5-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer. So we’re hopeful that’s a trajectory that we can really capitalize on is how fast we’re making progress in this disease.
Dr. Whyte: I want to put it into context, Lynn. Because some people might be thinking, 1%? Like you’re excited about 1%? That doesn’t seem that much. But correct me if I’m wrong. A one percentage point increase means 641 more loved ones will enjoy life’s moments, as you put it, 5 years after their diagnosis that otherwise wouldn’t have. What does that practically mean to viewers?
Dr. Matrisian: That means that more than 600 people in the United States will hug a loved one 5 years after that diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. It is a very deadly disease. But we’re going to, by continuing to make progress, it gives those moments to those people. And it means that we’re making progress against the disease in general.
Dr. Whyte: So even 1%, and 1% each year, does have value.
Dr. Matrisian: It has a lot of value.
Dr. Whyte: What’s driving this improvement? Is it better screening? And we’re not so great still in screening a pancreatic cancer. Is it the innovation in cancer treatments? What do you think is accounting for what we hope is this trajectory of increases in 5-year survival?
Dr. Matrisian: Right, so the nice thing the reason that we like looking at 5-year survival rates is because it takes into account all of those things. And we have actually made progress in all of those things. So by looking at those that are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer in general as a whole, and looking at their survival, we are looking at better treatments. People who are getting pancreatic cancer later are living longer as a result of better treatments.
But it’s not just that. It’s also, if you’re diagnosed earlier, your 5-year survival rate is higher. More people who are diagnosed early live to five years than those that are diagnosed later. So within that statistic, there are more people who are diagnosed earlier. And those people also live longer. So it takes into account all of those things, which is why we really like to look at that five-year survival rate for a disease like pancreatic cancer.
Dr. Whyte: Where are we on screening? Because we always want to catch people early. That gives them that greatest chance of survival. Have we made much improvements there? And if we have, what are they?
Dr. Matrisian: Well we have made improvements there are more people that are now diagnosed with localized disease than there were 20 years ago. So that is increasing. And we’re still doing it really by being aware of the symptoms right now. Being aware that kind of chronic indigestion, lower back pain that won’t go away, these are signs and symptoms. And especially things like jaundice ...
Dr. Whyte: That yellow color that they might see.
Dr. Matrisian: Yes, that yellow colors in your eye, that’s a really important symptom that would certainly send people to the doctor in order to look at this. So some of it is being more aware and finding the disease earlier. But what we’re really hoping for is some sort of blood test or some sort of other way of looking through medical records and identifying those people that need to go and be checked.
Dr. Whyte: Now we chatted about that almost two years ago. So tell me the progress that we’ve made. How are we doing?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah, well there’s a number of companies now that have blood tests that are available. They still need more work. They still need more studies to really understand how good they are at finding pancreatic cancer early. But we didn’t have them a couple of years ago. And so it’s really a very exciting time in the field, that there’s companies that were taking advantage of research for many years and actually turning it into a commercial product that is available for people to check.
Dr. Whyte: And then what about treatments? More treatment options today than there were just a few years ago, but still a lot of progress to be made. So when we talk about even 12% 5-year survival, we’d love to see it much more. And you talk about, I don’t want to misquote, so correct me if I’m wrong. Your goal is 20%. Five-year survival by 2030. That’s not too far. So, Lynn, how are we going to get there?
Dr. Matrisian: Okay, well this is our mission. And that’s exactly our goal, 20% by 2030. So we’ve got some work to do. And we are working at both fronts. You’re right, we need better treatments. And so we’ve set up a clinical trial platform where we can look at a lot of different treatments much more efficiently, much faster, kind of taking advantage of an infrastructure to do that. And that’s called Precision Promise. And we’re excited about that as a way to get new treatments for advanced pancreatic cancer.
And then we’re also working on the early detection end. We think an important symptom of pancreatic cancer that isn’t often recognized is new onset diabetes, sudden diabetes in those over 50 where that person did not have diabetes before. So it’s new, looks like type 2 diabetes, but it’s actually caused by pancreatic cancer.
And so we have an initiative, The Early Detection Initiative, that is taking advantage of that. And seeing if we image people right away based on that symptom, can we find pancreatic cancer early? So we think it’s important to look both at trying to diagnose it earlier, as well as trying to treat it better for advanced disease.
Dr. Whyte: Yeah. You know, at WebMD we’re always trying to empower people with better information so they can also become advocates for their health. You’re an expert in advocacy on pancreatic cancer. So what’s your advice to listeners as to how they become good advocates for themselves or advocates in general for loved ones who have pancreatic cancer?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah. Yeah. Well certainly, knowledge is power. And so the real thing to do is to call the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. This is what we do. We stay up on the most current information. We have very experienced case managers who can help navigate the complexities of pancreatic cancer at every stage of the journey.
Or if you have questions about pancreatic cancer, call PanCAN. Go to PanCAN.org and give us a call. Because it’s really that knowledge, knowing what it is that you need to get more knowledge about, how to advocate for yourself is very important in a disease, in any disease, but in particular a disease like pancreatic cancer.
Dr. Whyte: And I don’t want to dismiss the progress that we’ve made, that you’ve just referenced in terms of the increased survival. But there’s still a long way to go. We need a lot more dollars for research. We need a lot more clinical trials to take place. What’s your message to a viewer who’s been diagnosed with pancreatic cancer or a loved one? What’s your message, Lynn, today for them?
Dr. Matrisian: Well, first, get as much knowledge as you can. Call PanCAN, and let us help you help your loved one. But then help us. Let’s do research. Let’s do more research. Let’s understand this disease better so we can make those kinds of progress in both treatment and early detection.
And PanCAN works very hard at understanding the disease and setting up research programs that are going to make a difference, that are going to get us to that aggressive goal of 20% survival by 2030. So there is a lot of things that can be done, raise awareness to your friends and neighbors about the disease, lots of things that will help this whole field.
Dr. Whyte: What’s your feeling on second opinions? Given that this can be a difficult cancer to treat, given that there’s emerging therapies that are always developing, when you have a diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, is it important to consider getting a second opinion?
Dr. Matrisian: Yes. Yes, it is. And our case managers will help with that process. We do think it’s important.
Dr. Whyte: Because sometimes, Lynn, people just want to get started, right? Get it out of me. Get treatment. And sometimes getting a second opinion, doing some genomic testing can take time. So what’s your response to that?
Dr. Matrisian: Yeah. Yeah. Well we say, your care team is very important. Who is on your care team, and it may take a little time to find the right people on your care team. But that is an incredibly important step. Sometimes it’s not just one person. Sometimes you need more than one doctor, more than one nurse, more than one type of specialty to help you deal with this. And taking the time to do that is incredibly important.
Yes, you need to – you do need to act. But act smart. And do it with knowledge. Do it really understanding what your options are, and advocate for yourself.
Dr. Whyte: And surround yourself as you reference with that right care team for you, because that’s the most important thing when you have any type of cancer diagnosis. Dr. Lynn Matrisian, I want to thank you for taking time today.
Dr. Matrisian: Thank you so much, John.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lifestyle choices could curb genetic risk for thyroid cancer
A healthier lifestyle mitigated the impact of genetic factors on the risk of thyroid cancer, in a study based on data from more than 260,000 individuals.
Thyroid cancer has increased globally in recent years and ranks 9th among 36 cancers worldwide, at a considerable cost to health care systems, wrote Xiuming Feng of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China, and colleagues.
Both genetic and lifestyle factors are related to thyroid cancer; previous research suggests a heritability of about 50%, but data on the impact of modifiable lifestyle factors on thyroid cancer are limited, the researchers said.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers used data from the UK Biobank and recruited adults aged 40-69 years during March 2006–October 2010. The final study population included 264,956 individuals of European descent. The median age of the participants was 57 years, and 52% were women.
Data on lifestyle behaviors were collected using interviews and questionnaires. The researchers constructed a total lifestyle score based on five variables: diet, physical activity, weight, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Each variable was assigned a score of 0 or 1, with 1 being favorable lifestyle behavior. Lifestyle was divided into three categories: unfavorable (scores 0-1), intermediate (score 2), and favorable (scores 3-5).
Each individual’s polygenic risk score (PRS) was categorized as low, intermediate, or high based on a meta–genome-wide association study of three cohorts.
The main outcome was the development of thyroid cancer.
The researchers identified 423 incident thyroid cancer cases over a median follow-up of 11.1 years.
Overall, higher PRSs were significantly associated with thyroid cancer (hazard ratio, 2.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.91-2.64; P < .00001) as was an unfavorable lifestyle score (HR, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.50-2.49; P < .001 for trend).
An unfavorable lifestyle was significantly associated with thyroid cancer in the highest PRS group, and individuals with high PRS and unfavorable lifestyle had a nearly fivefold increased risk of thyroid cancer (HR, 4.89; 95% CI, 3.03-7.91; P < .001). By extension, “Adherence to a healthier lifestyle could decrease the incidence of thyroid cancer in individuals with a higher PRS,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the availability of only baseline lifestyle data, and lack of data on iodine intake, radiation exposure, experience, and family history, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the potential lack of generalizability to populations other than the individuals of European descent in the current study, they said.
However, the study is the first known to address the association among lifestyle, genetic factors, and risk of thyroid cancer, and was strengthened by the large study population, and the results suggest that lifestyle interventions may help reduce the risk of thyroid cancer in those with a genetic predisposition, they concluded.
Healthy living can make a difference
The incidence of thyroid cancer has increased annually, and exploring the possible risk factors could prevent the occurrence of thyroid cancer, corresponding author Xiaobo Yang, PhD, said in an interview.
Previous studies have reported that thyroid cancer is related to genetics and lifestyle, said Dr. Yang. “However, whether healthy lifestyle was associated with thyroid cancer risk and could attenuate the impact of genetic variants on thyroid cancer remains equivocal; therefore, it is crucial to determine the associations between genetic and lifestyle with thyroid cancer,” he said.
“To our surprise, we found that adherence to healthier lifestyle also could reduce the risk of thyroid cancer in those with high genetic predispositions,” said Dr. Yang. “The findings highlight the potential role of lifestyle interventions on thyroid cancer, especially in those with high genetic risk, because the heritability of thyroid cancer was very high, approximately 50%,” he said. “More attention should be paid to the role of healthier lifestyle in the prevention of cancer,” he added.
“Adherence to a healthier lifestyle could decrease the risk of thyroid cancer, which is the important message for clinicians,” said Dr. Yang. “It is not too soon to comment on implications for clinical practice, because many studies have maintained the consistent comment that healthier lifestyle could prevent the occurrence of cancer,” he said.
The relationship between sex-specific lifestyle factors such as smoking and alcohol use and thyroid cancer remains uncertain, and more research is needed to validate these associations, Dr. Yang said. More research also is needed to confirm the complex mechanism between lifestyle and genetics in thyroid cancer, he added.
The study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A healthier lifestyle mitigated the impact of genetic factors on the risk of thyroid cancer, in a study based on data from more than 260,000 individuals.
Thyroid cancer has increased globally in recent years and ranks 9th among 36 cancers worldwide, at a considerable cost to health care systems, wrote Xiuming Feng of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China, and colleagues.
Both genetic and lifestyle factors are related to thyroid cancer; previous research suggests a heritability of about 50%, but data on the impact of modifiable lifestyle factors on thyroid cancer are limited, the researchers said.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers used data from the UK Biobank and recruited adults aged 40-69 years during March 2006–October 2010. The final study population included 264,956 individuals of European descent. The median age of the participants was 57 years, and 52% were women.
Data on lifestyle behaviors were collected using interviews and questionnaires. The researchers constructed a total lifestyle score based on five variables: diet, physical activity, weight, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Each variable was assigned a score of 0 or 1, with 1 being favorable lifestyle behavior. Lifestyle was divided into three categories: unfavorable (scores 0-1), intermediate (score 2), and favorable (scores 3-5).
Each individual’s polygenic risk score (PRS) was categorized as low, intermediate, or high based on a meta–genome-wide association study of three cohorts.
The main outcome was the development of thyroid cancer.
The researchers identified 423 incident thyroid cancer cases over a median follow-up of 11.1 years.
Overall, higher PRSs were significantly associated with thyroid cancer (hazard ratio, 2.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.91-2.64; P < .00001) as was an unfavorable lifestyle score (HR, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.50-2.49; P < .001 for trend).
An unfavorable lifestyle was significantly associated with thyroid cancer in the highest PRS group, and individuals with high PRS and unfavorable lifestyle had a nearly fivefold increased risk of thyroid cancer (HR, 4.89; 95% CI, 3.03-7.91; P < .001). By extension, “Adherence to a healthier lifestyle could decrease the incidence of thyroid cancer in individuals with a higher PRS,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the availability of only baseline lifestyle data, and lack of data on iodine intake, radiation exposure, experience, and family history, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the potential lack of generalizability to populations other than the individuals of European descent in the current study, they said.
However, the study is the first known to address the association among lifestyle, genetic factors, and risk of thyroid cancer, and was strengthened by the large study population, and the results suggest that lifestyle interventions may help reduce the risk of thyroid cancer in those with a genetic predisposition, they concluded.
Healthy living can make a difference
The incidence of thyroid cancer has increased annually, and exploring the possible risk factors could prevent the occurrence of thyroid cancer, corresponding author Xiaobo Yang, PhD, said in an interview.
Previous studies have reported that thyroid cancer is related to genetics and lifestyle, said Dr. Yang. “However, whether healthy lifestyle was associated with thyroid cancer risk and could attenuate the impact of genetic variants on thyroid cancer remains equivocal; therefore, it is crucial to determine the associations between genetic and lifestyle with thyroid cancer,” he said.
“To our surprise, we found that adherence to healthier lifestyle also could reduce the risk of thyroid cancer in those with high genetic predispositions,” said Dr. Yang. “The findings highlight the potential role of lifestyle interventions on thyroid cancer, especially in those with high genetic risk, because the heritability of thyroid cancer was very high, approximately 50%,” he said. “More attention should be paid to the role of healthier lifestyle in the prevention of cancer,” he added.
“Adherence to a healthier lifestyle could decrease the risk of thyroid cancer, which is the important message for clinicians,” said Dr. Yang. “It is not too soon to comment on implications for clinical practice, because many studies have maintained the consistent comment that healthier lifestyle could prevent the occurrence of cancer,” he said.
The relationship between sex-specific lifestyle factors such as smoking and alcohol use and thyroid cancer remains uncertain, and more research is needed to validate these associations, Dr. Yang said. More research also is needed to confirm the complex mechanism between lifestyle and genetics in thyroid cancer, he added.
The study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A healthier lifestyle mitigated the impact of genetic factors on the risk of thyroid cancer, in a study based on data from more than 260,000 individuals.
Thyroid cancer has increased globally in recent years and ranks 9th among 36 cancers worldwide, at a considerable cost to health care systems, wrote Xiuming Feng of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China, and colleagues.
Both genetic and lifestyle factors are related to thyroid cancer; previous research suggests a heritability of about 50%, but data on the impact of modifiable lifestyle factors on thyroid cancer are limited, the researchers said.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers used data from the UK Biobank and recruited adults aged 40-69 years during March 2006–October 2010. The final study population included 264,956 individuals of European descent. The median age of the participants was 57 years, and 52% were women.
Data on lifestyle behaviors were collected using interviews and questionnaires. The researchers constructed a total lifestyle score based on five variables: diet, physical activity, weight, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Each variable was assigned a score of 0 or 1, with 1 being favorable lifestyle behavior. Lifestyle was divided into three categories: unfavorable (scores 0-1), intermediate (score 2), and favorable (scores 3-5).
Each individual’s polygenic risk score (PRS) was categorized as low, intermediate, or high based on a meta–genome-wide association study of three cohorts.
The main outcome was the development of thyroid cancer.
The researchers identified 423 incident thyroid cancer cases over a median follow-up of 11.1 years.
Overall, higher PRSs were significantly associated with thyroid cancer (hazard ratio, 2.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.91-2.64; P < .00001) as was an unfavorable lifestyle score (HR, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.50-2.49; P < .001 for trend).
An unfavorable lifestyle was significantly associated with thyroid cancer in the highest PRS group, and individuals with high PRS and unfavorable lifestyle had a nearly fivefold increased risk of thyroid cancer (HR, 4.89; 95% CI, 3.03-7.91; P < .001). By extension, “Adherence to a healthier lifestyle could decrease the incidence of thyroid cancer in individuals with a higher PRS,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the availability of only baseline lifestyle data, and lack of data on iodine intake, radiation exposure, experience, and family history, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the potential lack of generalizability to populations other than the individuals of European descent in the current study, they said.
However, the study is the first known to address the association among lifestyle, genetic factors, and risk of thyroid cancer, and was strengthened by the large study population, and the results suggest that lifestyle interventions may help reduce the risk of thyroid cancer in those with a genetic predisposition, they concluded.
Healthy living can make a difference
The incidence of thyroid cancer has increased annually, and exploring the possible risk factors could prevent the occurrence of thyroid cancer, corresponding author Xiaobo Yang, PhD, said in an interview.
Previous studies have reported that thyroid cancer is related to genetics and lifestyle, said Dr. Yang. “However, whether healthy lifestyle was associated with thyroid cancer risk and could attenuate the impact of genetic variants on thyroid cancer remains equivocal; therefore, it is crucial to determine the associations between genetic and lifestyle with thyroid cancer,” he said.
“To our surprise, we found that adherence to healthier lifestyle also could reduce the risk of thyroid cancer in those with high genetic predispositions,” said Dr. Yang. “The findings highlight the potential role of lifestyle interventions on thyroid cancer, especially in those with high genetic risk, because the heritability of thyroid cancer was very high, approximately 50%,” he said. “More attention should be paid to the role of healthier lifestyle in the prevention of cancer,” he added.
“Adherence to a healthier lifestyle could decrease the risk of thyroid cancer, which is the important message for clinicians,” said Dr. Yang. “It is not too soon to comment on implications for clinical practice, because many studies have maintained the consistent comment that healthier lifestyle could prevent the occurrence of cancer,” he said.
The relationship between sex-specific lifestyle factors such as smoking and alcohol use and thyroid cancer remains uncertain, and more research is needed to validate these associations, Dr. Yang said. More research also is needed to confirm the complex mechanism between lifestyle and genetics in thyroid cancer, he added.
The study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
‘Game changer’: Thyroid cancer recurrence no higher with lobectomy
Patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer and lymph node metastasis show no significant increase in tumor recurrence when undergoing lobectomy compared with a total thyroidectomy, new research shows.
“Results of this cohort study suggest that patients with ipsilateral clinical lateral neck metastasis (cN1b) papillary thyroid cancer who underwent lobectomy exhibited recurrence-free survival rates similar to those who underwent total thyroidectomy after controlling for major prognostic factors,” the authors conclude in the study published online in JAMA Surgery.
“These findings suggest that cN1b alone should not be an absolute indication for total thyroidectomy,” they note.
The study, involving the largest cohort to date to compare patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer treated with lobectomy versus total thyroidectomy, “challenged the current guidelines and pushed the boundary of limited surgical treatment even further,” say Michelle B. Mulder, MD, and Quan-Yang Duh, MD, of the department of surgery, University of California, San Francisco, in an accompanying editorial.
“It can be a game changer if confirmed by future prospective and multicenter studies,” they add.
Guidelines still recommend total thyroidectomy with subsequent RAI
While lower-intensity treatment options, with a lower risk of complications, have gained favor in the treatment of low-risk papillary thyroid cancer, guidelines still recommend the consideration of total thyroidectomy and subsequent radioactive iodine ablation (RAI) for intermediate-risk cancers because of the higher chance of recurrence, particularly among those with clinically positive nodes.
However, data on the superiority of a total thyroidectomy, with or without RAI, versus lobectomy is inconsistent, prompting first author Siyuan Xu, MD, of the department of head and neck surgical oncology, National Cancer Center, Beijing, and colleagues to compare the risk of recurrence with the two approaches.
For the study, patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer treated at the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Cancer Hospital in Beijing between January 2000 and December 2017, who had a lobectomy or total thyroidectomy, were paired 1:1 in a propensity score matching analysis.
Other than treatment type, the 265 pairs of patients were matched based on all other potential prognostic factors, including age, sex, primary tumor size, minor extrathyroidal extension, multifocality, number of lymph node metastases, and lymph node ratio.
Participants were a mean age of 37 years and 66% were female.
With a median follow-up of 60 months in the lobectomy group and 58 months in the total thyroidectomy group, structural recurrences occurred in 7.9% (21) and 6.4% (17) of patients, respectively, which was not significantly different.
The primary endpoint, 5-year rate of recurrence-free survival, was also not significantly different between the lobectomy (92.3%) and total thyroidectomy groups (93.7%) (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.10; P = .77).
In a further stratified analysis of patients treated with total thyroidectomy along with RAI (n = 75), the lack of a significant difference in recurrence-free survival versus lobectomy remained (aHR, 0.59; P = .46).
The results were similar in unadjusted as well as adjusted analyses, and a power analysis indicated that the study had a 90% power to detect a more than 4.9% difference in recurrence-free survival.
“Given the lower complication rate of lobectomy, a maximal 4.9% recurrence-free survival difference is acceptable, which enhances the reliability of the study results,” the authors say.
They conclude that “our findings call into question whether cN1b alone [ipsilateral clinical lateral neck metastasis papillary thyroid cancer] should be an absolute determinant for deciding the optimal extent of thyroid surgery for papillary thyroid cancer.”
With total thyroidectomy, RAI can be given
An important argument in favor of total thyroidectomy is that with the complete resection of thyroid tissue, RAI ablation can then be used for postoperative detection of residual or metastatic disease, as well as for treatment, the authors note.
Indeed, a study using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database showed RAI ablation is associated with a 29% reduction in the risk of death in patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer, with a hazard risk of 0.71.
However, conflicting data from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, suggests no significant benefit with total thyroidectomy and RAI ablation.
The current study’s analysis of patients treated with RAI, though limited in size, supports the latter study’s findings, the authors note.
“When we performed further stratified analyses in patients treated with total thyroidectomy plus RAI ablation and their counterparts, no significant difference was found, which conformed with [the] result from the whole cohort.”
“Certainly, the stratified comparison did not have enough power to examine the effect of RAI ablation on tumor recurrence subject to the limitation of sample size and case selection [and] further study is needed on this topic,” they write.
Some limitations warrant cautious interpretation
In their editorial, Dr. Mulder and Dr. Duh note that while some previous studies have shown similar outcomes relating to tumor size, thyroid hormone suppression therapy, and multifocality, “few have addressed lateral neck involvement.”
They suggest cautious interpretation, however, due to limitations, acknowledged by the authors, including the single-center nature of the study.
“Appropriate propensity matching may mitigate selection bias but cannot eliminate it entirely and their findings may not be replicated in other institutions by other surgeons,” they note.
Other limitations include that changes in clinical practice and patient selection were likely over the course of the study because of significant changes in American Thyroid Association (ATA) guidelines between 2009 and 2017, and characteristics including molecular genetic testing, which could have influenced final results, were not taken into consideration.
Furthermore, for patients with intermediate-risk cancer, modifications in postoperative follow-up are necessary following lobectomy versus total thyroidectomy; “the role of radioiodine is limited and the levels of thyroglobulin more complicated to interpret,” they note.
The study and editorial authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer and lymph node metastasis show no significant increase in tumor recurrence when undergoing lobectomy compared with a total thyroidectomy, new research shows.
“Results of this cohort study suggest that patients with ipsilateral clinical lateral neck metastasis (cN1b) papillary thyroid cancer who underwent lobectomy exhibited recurrence-free survival rates similar to those who underwent total thyroidectomy after controlling for major prognostic factors,” the authors conclude in the study published online in JAMA Surgery.
“These findings suggest that cN1b alone should not be an absolute indication for total thyroidectomy,” they note.
The study, involving the largest cohort to date to compare patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer treated with lobectomy versus total thyroidectomy, “challenged the current guidelines and pushed the boundary of limited surgical treatment even further,” say Michelle B. Mulder, MD, and Quan-Yang Duh, MD, of the department of surgery, University of California, San Francisco, in an accompanying editorial.
“It can be a game changer if confirmed by future prospective and multicenter studies,” they add.
Guidelines still recommend total thyroidectomy with subsequent RAI
While lower-intensity treatment options, with a lower risk of complications, have gained favor in the treatment of low-risk papillary thyroid cancer, guidelines still recommend the consideration of total thyroidectomy and subsequent radioactive iodine ablation (RAI) for intermediate-risk cancers because of the higher chance of recurrence, particularly among those with clinically positive nodes.
However, data on the superiority of a total thyroidectomy, with or without RAI, versus lobectomy is inconsistent, prompting first author Siyuan Xu, MD, of the department of head and neck surgical oncology, National Cancer Center, Beijing, and colleagues to compare the risk of recurrence with the two approaches.
For the study, patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer treated at the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Cancer Hospital in Beijing between January 2000 and December 2017, who had a lobectomy or total thyroidectomy, were paired 1:1 in a propensity score matching analysis.
Other than treatment type, the 265 pairs of patients were matched based on all other potential prognostic factors, including age, sex, primary tumor size, minor extrathyroidal extension, multifocality, number of lymph node metastases, and lymph node ratio.
Participants were a mean age of 37 years and 66% were female.
With a median follow-up of 60 months in the lobectomy group and 58 months in the total thyroidectomy group, structural recurrences occurred in 7.9% (21) and 6.4% (17) of patients, respectively, which was not significantly different.
The primary endpoint, 5-year rate of recurrence-free survival, was also not significantly different between the lobectomy (92.3%) and total thyroidectomy groups (93.7%) (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.10; P = .77).
In a further stratified analysis of patients treated with total thyroidectomy along with RAI (n = 75), the lack of a significant difference in recurrence-free survival versus lobectomy remained (aHR, 0.59; P = .46).
The results were similar in unadjusted as well as adjusted analyses, and a power analysis indicated that the study had a 90% power to detect a more than 4.9% difference in recurrence-free survival.
“Given the lower complication rate of lobectomy, a maximal 4.9% recurrence-free survival difference is acceptable, which enhances the reliability of the study results,” the authors say.
They conclude that “our findings call into question whether cN1b alone [ipsilateral clinical lateral neck metastasis papillary thyroid cancer] should be an absolute determinant for deciding the optimal extent of thyroid surgery for papillary thyroid cancer.”
With total thyroidectomy, RAI can be given
An important argument in favor of total thyroidectomy is that with the complete resection of thyroid tissue, RAI ablation can then be used for postoperative detection of residual or metastatic disease, as well as for treatment, the authors note.
Indeed, a study using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database showed RAI ablation is associated with a 29% reduction in the risk of death in patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer, with a hazard risk of 0.71.
However, conflicting data from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, suggests no significant benefit with total thyroidectomy and RAI ablation.
The current study’s analysis of patients treated with RAI, though limited in size, supports the latter study’s findings, the authors note.
“When we performed further stratified analyses in patients treated with total thyroidectomy plus RAI ablation and their counterparts, no significant difference was found, which conformed with [the] result from the whole cohort.”
“Certainly, the stratified comparison did not have enough power to examine the effect of RAI ablation on tumor recurrence subject to the limitation of sample size and case selection [and] further study is needed on this topic,” they write.
Some limitations warrant cautious interpretation
In their editorial, Dr. Mulder and Dr. Duh note that while some previous studies have shown similar outcomes relating to tumor size, thyroid hormone suppression therapy, and multifocality, “few have addressed lateral neck involvement.”
They suggest cautious interpretation, however, due to limitations, acknowledged by the authors, including the single-center nature of the study.
“Appropriate propensity matching may mitigate selection bias but cannot eliminate it entirely and their findings may not be replicated in other institutions by other surgeons,” they note.
Other limitations include that changes in clinical practice and patient selection were likely over the course of the study because of significant changes in American Thyroid Association (ATA) guidelines between 2009 and 2017, and characteristics including molecular genetic testing, which could have influenced final results, were not taken into consideration.
Furthermore, for patients with intermediate-risk cancer, modifications in postoperative follow-up are necessary following lobectomy versus total thyroidectomy; “the role of radioiodine is limited and the levels of thyroglobulin more complicated to interpret,” they note.
The study and editorial authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer and lymph node metastasis show no significant increase in tumor recurrence when undergoing lobectomy compared with a total thyroidectomy, new research shows.
“Results of this cohort study suggest that patients with ipsilateral clinical lateral neck metastasis (cN1b) papillary thyroid cancer who underwent lobectomy exhibited recurrence-free survival rates similar to those who underwent total thyroidectomy after controlling for major prognostic factors,” the authors conclude in the study published online in JAMA Surgery.
“These findings suggest that cN1b alone should not be an absolute indication for total thyroidectomy,” they note.
The study, involving the largest cohort to date to compare patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer treated with lobectomy versus total thyroidectomy, “challenged the current guidelines and pushed the boundary of limited surgical treatment even further,” say Michelle B. Mulder, MD, and Quan-Yang Duh, MD, of the department of surgery, University of California, San Francisco, in an accompanying editorial.
“It can be a game changer if confirmed by future prospective and multicenter studies,” they add.
Guidelines still recommend total thyroidectomy with subsequent RAI
While lower-intensity treatment options, with a lower risk of complications, have gained favor in the treatment of low-risk papillary thyroid cancer, guidelines still recommend the consideration of total thyroidectomy and subsequent radioactive iodine ablation (RAI) for intermediate-risk cancers because of the higher chance of recurrence, particularly among those with clinically positive nodes.
However, data on the superiority of a total thyroidectomy, with or without RAI, versus lobectomy is inconsistent, prompting first author Siyuan Xu, MD, of the department of head and neck surgical oncology, National Cancer Center, Beijing, and colleagues to compare the risk of recurrence with the two approaches.
For the study, patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer treated at the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Cancer Hospital in Beijing between January 2000 and December 2017, who had a lobectomy or total thyroidectomy, were paired 1:1 in a propensity score matching analysis.
Other than treatment type, the 265 pairs of patients were matched based on all other potential prognostic factors, including age, sex, primary tumor size, minor extrathyroidal extension, multifocality, number of lymph node metastases, and lymph node ratio.
Participants were a mean age of 37 years and 66% were female.
With a median follow-up of 60 months in the lobectomy group and 58 months in the total thyroidectomy group, structural recurrences occurred in 7.9% (21) and 6.4% (17) of patients, respectively, which was not significantly different.
The primary endpoint, 5-year rate of recurrence-free survival, was also not significantly different between the lobectomy (92.3%) and total thyroidectomy groups (93.7%) (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.10; P = .77).
In a further stratified analysis of patients treated with total thyroidectomy along with RAI (n = 75), the lack of a significant difference in recurrence-free survival versus lobectomy remained (aHR, 0.59; P = .46).
The results were similar in unadjusted as well as adjusted analyses, and a power analysis indicated that the study had a 90% power to detect a more than 4.9% difference in recurrence-free survival.
“Given the lower complication rate of lobectomy, a maximal 4.9% recurrence-free survival difference is acceptable, which enhances the reliability of the study results,” the authors say.
They conclude that “our findings call into question whether cN1b alone [ipsilateral clinical lateral neck metastasis papillary thyroid cancer] should be an absolute determinant for deciding the optimal extent of thyroid surgery for papillary thyroid cancer.”
With total thyroidectomy, RAI can be given
An important argument in favor of total thyroidectomy is that with the complete resection of thyroid tissue, RAI ablation can then be used for postoperative detection of residual or metastatic disease, as well as for treatment, the authors note.
Indeed, a study using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database showed RAI ablation is associated with a 29% reduction in the risk of death in patients with intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer, with a hazard risk of 0.71.
However, conflicting data from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, suggests no significant benefit with total thyroidectomy and RAI ablation.
The current study’s analysis of patients treated with RAI, though limited in size, supports the latter study’s findings, the authors note.
“When we performed further stratified analyses in patients treated with total thyroidectomy plus RAI ablation and their counterparts, no significant difference was found, which conformed with [the] result from the whole cohort.”
“Certainly, the stratified comparison did not have enough power to examine the effect of RAI ablation on tumor recurrence subject to the limitation of sample size and case selection [and] further study is needed on this topic,” they write.
Some limitations warrant cautious interpretation
In their editorial, Dr. Mulder and Dr. Duh note that while some previous studies have shown similar outcomes relating to tumor size, thyroid hormone suppression therapy, and multifocality, “few have addressed lateral neck involvement.”
They suggest cautious interpretation, however, due to limitations, acknowledged by the authors, including the single-center nature of the study.
“Appropriate propensity matching may mitigate selection bias but cannot eliminate it entirely and their findings may not be replicated in other institutions by other surgeons,” they note.
Other limitations include that changes in clinical practice and patient selection were likely over the course of the study because of significant changes in American Thyroid Association (ATA) guidelines between 2009 and 2017, and characteristics including molecular genetic testing, which could have influenced final results, were not taken into consideration.
Furthermore, for patients with intermediate-risk cancer, modifications in postoperative follow-up are necessary following lobectomy versus total thyroidectomy; “the role of radioiodine is limited and the levels of thyroglobulin more complicated to interpret,” they note.
The study and editorial authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Link between PCOS and increased risk of pancreatic cancer?
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Safe to expand limits of active surveillance in thyroid cancer?
Expanding eligibility for active surveillance in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer appears to be safe, a new prospective trial indicates.
Researchers found that doubling the limits for tumor size to 2 cm and nearly doubling the limits for tumor growth in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer showed no increased risk of adverse outcomes or mortality for patients undergoing active surveillance versus surgery.
“The results of this nonrandomized controlled trial suggest the basis of a more permissive strategy for thyroid cancer management, strengthening the evidence for active surveillance and broadening potential candidacy to most diagnosed thyroid cancers,” the authors conclude. “By extending [tumor] size/growth limits, these study results potentially broaden the potential candidacy for active surveillance and reduce the likelihood of surgery by lengthening the window of observation.”
However, “the expanded parameters are quite controversial,” first author Allen S. Ho, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told this news organization. Prior studies have only examined tumor size limits up to 1 cm and “clinicians rarely recommend active surveillance up to 2 cm,” Dr. Ho noted. “As far as we know, Cedars-Sinai is the only place that will consider it.”
In addition, the ultimate decision surrounding active surveillance versus surgery may depend on the patient’s level of anxiety, researchers found.
The research was published in JAMA Oncology.
The potential to expand criteria for thyroid cancer active surveillance comes amid ongoing concerns surrounding overtreatment. Advances in technology have led to increased detection of small, often indolent thyroid cancers that can likely be monitored safely through active surveillance but may present decision-making challenges for clinicians about whether to treat or watch and wait.
Similar challenges in prostate cancer have been addressed with tiered risk stratification, but such guidelines have not been as firmly established in thyroid cancer.
Guidelines from the American Thyroid Association in 2015 suggest active surveillance as an alternative for very low-risk tumors; however, studies in general have recommended the approach for initial tumor sizes of only up to 1 cm and with growth of less than 3 mm. And overall, active surveillance has not been broadly adopted as an option in thyroid cancer, the authors explained.
To determine if criteria for active surveillance can be safely expanded to tumors up to 2 cm and for those with growth up to 5 mm, Dr. Ho and colleagues compared outcomes among 222 patients with Bethesda 5 or 6 nodules of 2 cm or smaller who received either active surveillance or immediate surgery.
The patients were recruited from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center between 2014 and 2021. Patients were a median 46.8 years old; 76% were female.
The median size of tumors was 11 mm, with about 60% representing larger tumors (10.1 to 20 mm) and 20.6% measuring 15.1 to 20 mm.
About half of patients (n = 112) chose active surveillance. The median size of tumors in this group was smaller than those in the surgery group (10.1 mm vs. 12 mm). Tumor growth exceeded 5 mm in 3.6% of cases, and tumor volume increases of more than 100% occurred in 7% of cases.
With a mean follow-up of 37 months, 90% (101) of those on active surveillance continued with that approach. Notably, 41% of these patients demonstrated a decrease in tumor size, and no cases of metastatic lymph nodes or distant metastases emerged.
Of the 110 patients who elected to undergo immediate surgery, 19% (21) had equivocal-risk or undetermined features on final pathology, but the disease severity for these patients remained classified as stage I thyroid cancer.
The disease-specific survival and overall survival rates were the same in both groups, at 100%.
Although a general concern is that larger tumors may be more likely to grow, it’s important to note that “papillary thyroid cancer exists in a spectrum,” Dr. Ho explained. What that means is “some smaller cancers grow quickly, while some larger cancers are stable for decades.”
“We believe that a 1 cm cutoff is arbitrary,” Dr. Ho said, adding that 2 cm cancers that grow will still be within the therapeutic window for safe surgery.
However, a key factor in treatment decisions is patient fear. The authors also looked at the anxiety levels in both groups, using the 18-item Thyroid Cancer Modified Anxiety Scale.
Among the 59 patients who participated, those who chose immediate surgery had significantly higher baseline anxiety levels, compared with those who opted for active surveillance. Notably, these higher rates of anxiety endured over time, including after the intervention.
“It is unsurprising that patients choosing surgery possess a higher baseline level of worry,” Dr. Ho said. “However, we were astonished to find that such patients retained high levels of worry, even after surgery and presumed cure of their cancer.”
The role of the anxiety, however, underscores the need for clinicians to be mindful of the often profound psychological impacts of cancer, even low-risk disease.
“We always encourage clinicians to educate patients on active surveillance, especially as it gets highlighted more in official guidelines,” Dr. Ho noted. “However, we certainly acknowledge that cancer is a life-changing diagnosis, and the term can carry enormous psychological weight.”
The authors also acknowledged several study limitations, including the single-center, nonrandomized design and small sample size, and urge follow-up analyses to “independently verify our findings.”
In an accompanying editorial, Andrea L. Merrill, MD, from Boston Medical Center, and Priya H. Dedhia, MD, PhD, with Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, said the findings have important clinical implications.
“This provocative study not only lays the groundwork for expanding active surveillance criteria for low-risk papillary thyroid cancer but may also improve use of current American Thyroid Association guidelines for active surveillance by demonstrating that use of active surveillance for Bethesda 5 or 6 nodules 20 mm or smaller was not associated with an increase in staging or disease-specific mortality,” they write.
The study is also notable for being among the first to assess the role of patient anxiety in the selection of immediate surgery versus active surveillance, Dr. Merrill and Dr. Dedhia added.
“These findings imply that patient anxiety should be an essential component of shared decision-making and selection of strategies for low-risk papillary thyroid cancer,” they say.
The study authors and editorial authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Expanding eligibility for active surveillance in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer appears to be safe, a new prospective trial indicates.
Researchers found that doubling the limits for tumor size to 2 cm and nearly doubling the limits for tumor growth in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer showed no increased risk of adverse outcomes or mortality for patients undergoing active surveillance versus surgery.
“The results of this nonrandomized controlled trial suggest the basis of a more permissive strategy for thyroid cancer management, strengthening the evidence for active surveillance and broadening potential candidacy to most diagnosed thyroid cancers,” the authors conclude. “By extending [tumor] size/growth limits, these study results potentially broaden the potential candidacy for active surveillance and reduce the likelihood of surgery by lengthening the window of observation.”
However, “the expanded parameters are quite controversial,” first author Allen S. Ho, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told this news organization. Prior studies have only examined tumor size limits up to 1 cm and “clinicians rarely recommend active surveillance up to 2 cm,” Dr. Ho noted. “As far as we know, Cedars-Sinai is the only place that will consider it.”
In addition, the ultimate decision surrounding active surveillance versus surgery may depend on the patient’s level of anxiety, researchers found.
The research was published in JAMA Oncology.
The potential to expand criteria for thyroid cancer active surveillance comes amid ongoing concerns surrounding overtreatment. Advances in technology have led to increased detection of small, often indolent thyroid cancers that can likely be monitored safely through active surveillance but may present decision-making challenges for clinicians about whether to treat or watch and wait.
Similar challenges in prostate cancer have been addressed with tiered risk stratification, but such guidelines have not been as firmly established in thyroid cancer.
Guidelines from the American Thyroid Association in 2015 suggest active surveillance as an alternative for very low-risk tumors; however, studies in general have recommended the approach for initial tumor sizes of only up to 1 cm and with growth of less than 3 mm. And overall, active surveillance has not been broadly adopted as an option in thyroid cancer, the authors explained.
To determine if criteria for active surveillance can be safely expanded to tumors up to 2 cm and for those with growth up to 5 mm, Dr. Ho and colleagues compared outcomes among 222 patients with Bethesda 5 or 6 nodules of 2 cm or smaller who received either active surveillance or immediate surgery.
The patients were recruited from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center between 2014 and 2021. Patients were a median 46.8 years old; 76% were female.
The median size of tumors was 11 mm, with about 60% representing larger tumors (10.1 to 20 mm) and 20.6% measuring 15.1 to 20 mm.
About half of patients (n = 112) chose active surveillance. The median size of tumors in this group was smaller than those in the surgery group (10.1 mm vs. 12 mm). Tumor growth exceeded 5 mm in 3.6% of cases, and tumor volume increases of more than 100% occurred in 7% of cases.
With a mean follow-up of 37 months, 90% (101) of those on active surveillance continued with that approach. Notably, 41% of these patients demonstrated a decrease in tumor size, and no cases of metastatic lymph nodes or distant metastases emerged.
Of the 110 patients who elected to undergo immediate surgery, 19% (21) had equivocal-risk or undetermined features on final pathology, but the disease severity for these patients remained classified as stage I thyroid cancer.
The disease-specific survival and overall survival rates were the same in both groups, at 100%.
Although a general concern is that larger tumors may be more likely to grow, it’s important to note that “papillary thyroid cancer exists in a spectrum,” Dr. Ho explained. What that means is “some smaller cancers grow quickly, while some larger cancers are stable for decades.”
“We believe that a 1 cm cutoff is arbitrary,” Dr. Ho said, adding that 2 cm cancers that grow will still be within the therapeutic window for safe surgery.
However, a key factor in treatment decisions is patient fear. The authors also looked at the anxiety levels in both groups, using the 18-item Thyroid Cancer Modified Anxiety Scale.
Among the 59 patients who participated, those who chose immediate surgery had significantly higher baseline anxiety levels, compared with those who opted for active surveillance. Notably, these higher rates of anxiety endured over time, including after the intervention.
“It is unsurprising that patients choosing surgery possess a higher baseline level of worry,” Dr. Ho said. “However, we were astonished to find that such patients retained high levels of worry, even after surgery and presumed cure of their cancer.”
The role of the anxiety, however, underscores the need for clinicians to be mindful of the often profound psychological impacts of cancer, even low-risk disease.
“We always encourage clinicians to educate patients on active surveillance, especially as it gets highlighted more in official guidelines,” Dr. Ho noted. “However, we certainly acknowledge that cancer is a life-changing diagnosis, and the term can carry enormous psychological weight.”
The authors also acknowledged several study limitations, including the single-center, nonrandomized design and small sample size, and urge follow-up analyses to “independently verify our findings.”
In an accompanying editorial, Andrea L. Merrill, MD, from Boston Medical Center, and Priya H. Dedhia, MD, PhD, with Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, said the findings have important clinical implications.
“This provocative study not only lays the groundwork for expanding active surveillance criteria for low-risk papillary thyroid cancer but may also improve use of current American Thyroid Association guidelines for active surveillance by demonstrating that use of active surveillance for Bethesda 5 or 6 nodules 20 mm or smaller was not associated with an increase in staging or disease-specific mortality,” they write.
The study is also notable for being among the first to assess the role of patient anxiety in the selection of immediate surgery versus active surveillance, Dr. Merrill and Dr. Dedhia added.
“These findings imply that patient anxiety should be an essential component of shared decision-making and selection of strategies for low-risk papillary thyroid cancer,” they say.
The study authors and editorial authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Expanding eligibility for active surveillance in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer appears to be safe, a new prospective trial indicates.
Researchers found that doubling the limits for tumor size to 2 cm and nearly doubling the limits for tumor growth in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer showed no increased risk of adverse outcomes or mortality for patients undergoing active surveillance versus surgery.
“The results of this nonrandomized controlled trial suggest the basis of a more permissive strategy for thyroid cancer management, strengthening the evidence for active surveillance and broadening potential candidacy to most diagnosed thyroid cancers,” the authors conclude. “By extending [tumor] size/growth limits, these study results potentially broaden the potential candidacy for active surveillance and reduce the likelihood of surgery by lengthening the window of observation.”
However, “the expanded parameters are quite controversial,” first author Allen S. Ho, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told this news organization. Prior studies have only examined tumor size limits up to 1 cm and “clinicians rarely recommend active surveillance up to 2 cm,” Dr. Ho noted. “As far as we know, Cedars-Sinai is the only place that will consider it.”
In addition, the ultimate decision surrounding active surveillance versus surgery may depend on the patient’s level of anxiety, researchers found.
The research was published in JAMA Oncology.
The potential to expand criteria for thyroid cancer active surveillance comes amid ongoing concerns surrounding overtreatment. Advances in technology have led to increased detection of small, often indolent thyroid cancers that can likely be monitored safely through active surveillance but may present decision-making challenges for clinicians about whether to treat or watch and wait.
Similar challenges in prostate cancer have been addressed with tiered risk stratification, but such guidelines have not been as firmly established in thyroid cancer.
Guidelines from the American Thyroid Association in 2015 suggest active surveillance as an alternative for very low-risk tumors; however, studies in general have recommended the approach for initial tumor sizes of only up to 1 cm and with growth of less than 3 mm. And overall, active surveillance has not been broadly adopted as an option in thyroid cancer, the authors explained.
To determine if criteria for active surveillance can be safely expanded to tumors up to 2 cm and for those with growth up to 5 mm, Dr. Ho and colleagues compared outcomes among 222 patients with Bethesda 5 or 6 nodules of 2 cm or smaller who received either active surveillance or immediate surgery.
The patients were recruited from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center between 2014 and 2021. Patients were a median 46.8 years old; 76% were female.
The median size of tumors was 11 mm, with about 60% representing larger tumors (10.1 to 20 mm) and 20.6% measuring 15.1 to 20 mm.
About half of patients (n = 112) chose active surveillance. The median size of tumors in this group was smaller than those in the surgery group (10.1 mm vs. 12 mm). Tumor growth exceeded 5 mm in 3.6% of cases, and tumor volume increases of more than 100% occurred in 7% of cases.
With a mean follow-up of 37 months, 90% (101) of those on active surveillance continued with that approach. Notably, 41% of these patients demonstrated a decrease in tumor size, and no cases of metastatic lymph nodes or distant metastases emerged.
Of the 110 patients who elected to undergo immediate surgery, 19% (21) had equivocal-risk or undetermined features on final pathology, but the disease severity for these patients remained classified as stage I thyroid cancer.
The disease-specific survival and overall survival rates were the same in both groups, at 100%.
Although a general concern is that larger tumors may be more likely to grow, it’s important to note that “papillary thyroid cancer exists in a spectrum,” Dr. Ho explained. What that means is “some smaller cancers grow quickly, while some larger cancers are stable for decades.”
“We believe that a 1 cm cutoff is arbitrary,” Dr. Ho said, adding that 2 cm cancers that grow will still be within the therapeutic window for safe surgery.
However, a key factor in treatment decisions is patient fear. The authors also looked at the anxiety levels in both groups, using the 18-item Thyroid Cancer Modified Anxiety Scale.
Among the 59 patients who participated, those who chose immediate surgery had significantly higher baseline anxiety levels, compared with those who opted for active surveillance. Notably, these higher rates of anxiety endured over time, including after the intervention.
“It is unsurprising that patients choosing surgery possess a higher baseline level of worry,” Dr. Ho said. “However, we were astonished to find that such patients retained high levels of worry, even after surgery and presumed cure of their cancer.”
The role of the anxiety, however, underscores the need for clinicians to be mindful of the often profound psychological impacts of cancer, even low-risk disease.
“We always encourage clinicians to educate patients on active surveillance, especially as it gets highlighted more in official guidelines,” Dr. Ho noted. “However, we certainly acknowledge that cancer is a life-changing diagnosis, and the term can carry enormous psychological weight.”
The authors also acknowledged several study limitations, including the single-center, nonrandomized design and small sample size, and urge follow-up analyses to “independently verify our findings.”
In an accompanying editorial, Andrea L. Merrill, MD, from Boston Medical Center, and Priya H. Dedhia, MD, PhD, with Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, said the findings have important clinical implications.
“This provocative study not only lays the groundwork for expanding active surveillance criteria for low-risk papillary thyroid cancer but may also improve use of current American Thyroid Association guidelines for active surveillance by demonstrating that use of active surveillance for Bethesda 5 or 6 nodules 20 mm or smaller was not associated with an increase in staging or disease-specific mortality,” they write.
The study is also notable for being among the first to assess the role of patient anxiety in the selection of immediate surgery versus active surveillance, Dr. Merrill and Dr. Dedhia added.
“These findings imply that patient anxiety should be an essential component of shared decision-making and selection of strategies for low-risk papillary thyroid cancer,” they say.
The study authors and editorial authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientists find microplastics in human lung tissue
U.K. scientists said microplastics may pose even more of a threat than previously thought after confirming their presence in lung tissue taken from living people.
Microplastics were identified in all lung regions, but significantly higher levels were found in the lower lung.
The results supported inhalation as an exposure risk, according to the team from the University of Hull and Hull York Medical School (England), who said their findings could support further investigations into the effects of airborne microplastics on respiratory health.
The study, published in Science of the Total Environment, used lung tissue collected from surgical procedures on patients during routine medical care at Castle Hill Hospital in East Yorkshire.
Polypropylene and polyethylene
It found 39 microplastics in 11 of the 13 lung tissue samples tested using micro-Fourier-transform infrared (μFTIR) analysis, which the scientists said was considerably higher than results from previous laboratory tests.
Of microplastics detected, 12 polymer types were identified, of which the most common were polypropylene, (23%) polyethylene terephthalate (18%), and resin (15%). The fibers are commonly found in packaging, bottles, clothing, rope and twine manufacture, and other industries, the scientists said.
Microplastics with dimensions as small as 4 μm were found, but the scientists said they were surprised to discover samples as large as greater than 2 mm within all lung region samples, with the majority being fibrous and fragmented.
The study identified 11 microplastics in the upper part of the lung, seven in the mid part, and 21 in the lower part of the lung.
Laura Sadofsky, the study’s lead author, said: “Microplastics have previously been found in human cadaver autopsy samples. This is the first robust study to show microplastics in lungs from live people. It also shows that they are in the lower parts of the lung. Lung airways are very narrow, so no one thought they could possibly get there, but they clearly have.”
There were also considerably higher levels of microplastics found in male patients, compared with female patients.
Future investigations into health implications
“The characterization of types and levels of microplastics we have found can now inform realistic conditions for laboratory exposure experiments with the aim of determining health impacts,” said Laura Sadofsky, who is a senior lecturer in respiratory medicine in the Centre for Atherothrombotic and Metabolic Research at Hull York Medical School.
The latest investigation followed previous research by the medical school and the University of Hull, which found high levels of atmospheric microplastics within the Humber region.
That study, published in Atmosphere, identified resins, which could have originated from degraded roads, paint marking, or tire rubber, as well as polyethylene fibers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
U.K. scientists said microplastics may pose even more of a threat than previously thought after confirming their presence in lung tissue taken from living people.
Microplastics were identified in all lung regions, but significantly higher levels were found in the lower lung.
The results supported inhalation as an exposure risk, according to the team from the University of Hull and Hull York Medical School (England), who said their findings could support further investigations into the effects of airborne microplastics on respiratory health.
The study, published in Science of the Total Environment, used lung tissue collected from surgical procedures on patients during routine medical care at Castle Hill Hospital in East Yorkshire.
Polypropylene and polyethylene
It found 39 microplastics in 11 of the 13 lung tissue samples tested using micro-Fourier-transform infrared (μFTIR) analysis, which the scientists said was considerably higher than results from previous laboratory tests.
Of microplastics detected, 12 polymer types were identified, of which the most common were polypropylene, (23%) polyethylene terephthalate (18%), and resin (15%). The fibers are commonly found in packaging, bottles, clothing, rope and twine manufacture, and other industries, the scientists said.
Microplastics with dimensions as small as 4 μm were found, but the scientists said they were surprised to discover samples as large as greater than 2 mm within all lung region samples, with the majority being fibrous and fragmented.
The study identified 11 microplastics in the upper part of the lung, seven in the mid part, and 21 in the lower part of the lung.
Laura Sadofsky, the study’s lead author, said: “Microplastics have previously been found in human cadaver autopsy samples. This is the first robust study to show microplastics in lungs from live people. It also shows that they are in the lower parts of the lung. Lung airways are very narrow, so no one thought they could possibly get there, but they clearly have.”
There were also considerably higher levels of microplastics found in male patients, compared with female patients.
Future investigations into health implications
“The characterization of types and levels of microplastics we have found can now inform realistic conditions for laboratory exposure experiments with the aim of determining health impacts,” said Laura Sadofsky, who is a senior lecturer in respiratory medicine in the Centre for Atherothrombotic and Metabolic Research at Hull York Medical School.
The latest investigation followed previous research by the medical school and the University of Hull, which found high levels of atmospheric microplastics within the Humber region.
That study, published in Atmosphere, identified resins, which could have originated from degraded roads, paint marking, or tire rubber, as well as polyethylene fibers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
U.K. scientists said microplastics may pose even more of a threat than previously thought after confirming their presence in lung tissue taken from living people.
Microplastics were identified in all lung regions, but significantly higher levels were found in the lower lung.
The results supported inhalation as an exposure risk, according to the team from the University of Hull and Hull York Medical School (England), who said their findings could support further investigations into the effects of airborne microplastics on respiratory health.
The study, published in Science of the Total Environment, used lung tissue collected from surgical procedures on patients during routine medical care at Castle Hill Hospital in East Yorkshire.
Polypropylene and polyethylene
It found 39 microplastics in 11 of the 13 lung tissue samples tested using micro-Fourier-transform infrared (μFTIR) analysis, which the scientists said was considerably higher than results from previous laboratory tests.
Of microplastics detected, 12 polymer types were identified, of which the most common were polypropylene, (23%) polyethylene terephthalate (18%), and resin (15%). The fibers are commonly found in packaging, bottles, clothing, rope and twine manufacture, and other industries, the scientists said.
Microplastics with dimensions as small as 4 μm were found, but the scientists said they were surprised to discover samples as large as greater than 2 mm within all lung region samples, with the majority being fibrous and fragmented.
The study identified 11 microplastics in the upper part of the lung, seven in the mid part, and 21 in the lower part of the lung.
Laura Sadofsky, the study’s lead author, said: “Microplastics have previously been found in human cadaver autopsy samples. This is the first robust study to show microplastics in lungs from live people. It also shows that they are in the lower parts of the lung. Lung airways are very narrow, so no one thought they could possibly get there, but they clearly have.”
There were also considerably higher levels of microplastics found in male patients, compared with female patients.
Future investigations into health implications
“The characterization of types and levels of microplastics we have found can now inform realistic conditions for laboratory exposure experiments with the aim of determining health impacts,” said Laura Sadofsky, who is a senior lecturer in respiratory medicine in the Centre for Atherothrombotic and Metabolic Research at Hull York Medical School.
The latest investigation followed previous research by the medical school and the University of Hull, which found high levels of atmospheric microplastics within the Humber region.
That study, published in Atmosphere, identified resins, which could have originated from degraded roads, paint marking, or tire rubber, as well as polyethylene fibers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.