User login
Kidney, Cardiovascular Benefits Seen With GLP-1 RA Drugs in SLE, Lupus Nephritis
WASHINGTON — Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) medications appear beneficial for people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis, two new studies suggest.
“The risk of cardiovascular disease is thought to be at least double that for people with lupus ... and we know the risk of progressing to end-stage renal disease [ESKD] for patients with lupus nephritis can be as high as 10%-30%, so there’s clearly a major unmet need for new treatments and approaches to improve these outcomes, perhaps with adjunctive treatment beyond our typical immunosuppressive therapy,” April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The GLP-1 RAs are approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity. They also have proven cardiovascular benefit, along with emerging data suggesting kidney protection independent of glucose lowering. Jorge presented findings from a study using data from the US multicenter electronic health record database TriNetX, showing that, among patients who had both T2D and SLE, those using GLP-1 RAs had lower risks for major adverse cardiac events (MACE), venous thrombosis, kidney disease progression, and all-cause mortality, compared with those using a different class of T2D medication.
A second study using TriNetX, presented at the same ACR meeting session by Anna-Kay Palmer, MD, a third-year internal medicine resident at Jefferson Einstein Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, showed that GLP-1 RAs reduced the risk of progression to ESKD in patients with lupus nephritis, possibly caused by reductions in pro-inflammatory mediators.
Asked to comment, session moderator Diane L. Kamen, MD, professor of medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina Division of Rheumatology, Charleston, said in an interview that she definitely supports the use of GLP-1 RAs for patients who have SLE and/or lupus nephritis and also a drug label indication, either T2D or obesity. “[The GLP-1 RA prescriber] will usually run it by rheumatology to make sure that it doesn’t conflict with any of their other medical treatment, and it’s very reassuring to know that they could actually get a win-win.”
But as far as prescribing off-label for those with SLE/lupus nephritis who don’t have other GLP-1 RA indications, Kamen said, “that’s a black hole at this point. We need to do those prospective studies. But if they have another indication, yes.”
Cardiovascular, Kidney Benefits of GLP-1 RAs
Jorge noted that patients with lupus were excluded from the randomized clinical trials of GLP-1 RAs, so the current study was designed to investigate the potential impact of these medications on cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with SLE and lupus nephritis.
From TriNetX data for 46 healthcare organizations nationwide, a total of 96,511 patients with both SLE and T2D but not ESKD had initiated either a GLP-1 RA or another diabetes drug class, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i), between October 2006 and August 2021. Of those, 29,177 had lupus nephritis.
Propensity score matching for factors such as demographics, lupus severity, comorbidities, and medication use was used to emulate a randomized trial. This yielded 25,838 with SLE and T2D, of whom 910 initiated a GLP-1 RA and 1004 started a DPP4i, and 12,387 with lupus nephritis and T2D, including 267 on a GLP-1 RA and 324 on a DPP4i. After matching, the mean age was 55 years, more than 90% were women, and just under half were White individuals. About one third had chronic kidney disease stages ≥ 3, and about 15% had heart failure.
Over an average follow-up time of 1.2-1.4 years among those with SLE, the hazard ratio (HR) for MACE (a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure) for those taking a GLP-1 RA vs a DPP4i was 0.66, a significant difference. And for venous thrombosis, the HR was also significant at 0.49.
Kidney disease progression, defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate decline of 30% or more or new ESKD, was significantly less likely in the GLP-1 RA group, with a HR of 0.77. All-cause mortality also was dramatically reduced (HR, 0.26). As expected, there was no difference in control outcome, genital infections (HR, 1.02).
In the subgroup with lupus nephritis, there were also lower risks for both MACE (HR, 0.64) and for renal progression (HR, 0.70). “The findings suggest similar cardiac and kidney benefits among patients with SLE and lupus nephritis as have been observed in other populations,” Jorge concluded.
Kamen commented that the study design “was pretty brilliant, because you wouldn’t be able to do a placebo-controlled trial since the indication was diabetes ... but the fact is you do see that the GLP-1 RA gets the benefit whereas the other drug does not.”
Next steps, Jorge said, will be mechanistic studies to better understand the effects of GLP-1 RAs in lupus and other rheumatic diseases, prospective studies of GLP-1 RAs in SLE and lupus nephritis without diabetes, and clarification of ideal timing for GLP-1 RA use in SLE and lupus nephritis.
“Ideally, with our prospective studies with these patients we can try to isolate the effect on patients with lupus and also better understand whether there might be an impact on disease activity through the anti-inflammatory effects of these medications, rather than just the cardioprotective and nephroprotective benefits,” she said.
In Those With Lupus Nephritis, Kidney Protection Seen
In her presentation, Palmer noted that, despite immunosuppressive therapies for SLE, 10%-20% of patients who develop lupus nephritis will progress to ESKD within 5 years of diagnosis.
She added that GLP-1 RAs have been shown to reduce albuminuria in people with diabetes and have been hypothesized to reduce inflammation through multiple pathways, thereby potentially reducing kidney disease independently of the presence of diabetes or weight loss. These pathways include modulating immune cell signaling and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Based on all this, Palmer and colleagues used International Classification of Diseases – 10th edition diagnostic codes in TriNetX to identify 839 patients who had been diagnosed with lupus nephritis between 2014 and 2024 and who were prescribed liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, or exenatide for any time after the lupus nephritis diagnosis. Another 29,840 patients with lupus nephritis had not used GLP-1 RAs.
After 1:1 propensity score matching for age, sex, race, ethnicity, presence of hypertension, diabetes, use of immunosuppressive and diabetes medication, smoking, obesity, and statin use, there were 735 individuals in each group. About two thirds in each had diabetes, whereas the rest had been prescribed the GLP-1 RAs for other indications.
Patients who were not on GLP-1 RAs were twice as likely to develop ESKD or dialysis (8.88% vs 3.971%; odds ratio, 2.35; P = .001).
Kamen pointed out that not including the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers was a study flaw. On the other hand, the fact that not everyone in this study had diabetes was an advantage.
Jorge received grant/research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cabaletta Bio, and the Lupus Clinical Investigator Network. Kamen is an adviser/review panel member for Alpine Immune Sciences. Palmer had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) medications appear beneficial for people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis, two new studies suggest.
“The risk of cardiovascular disease is thought to be at least double that for people with lupus ... and we know the risk of progressing to end-stage renal disease [ESKD] for patients with lupus nephritis can be as high as 10%-30%, so there’s clearly a major unmet need for new treatments and approaches to improve these outcomes, perhaps with adjunctive treatment beyond our typical immunosuppressive therapy,” April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The GLP-1 RAs are approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity. They also have proven cardiovascular benefit, along with emerging data suggesting kidney protection independent of glucose lowering. Jorge presented findings from a study using data from the US multicenter electronic health record database TriNetX, showing that, among patients who had both T2D and SLE, those using GLP-1 RAs had lower risks for major adverse cardiac events (MACE), venous thrombosis, kidney disease progression, and all-cause mortality, compared with those using a different class of T2D medication.
A second study using TriNetX, presented at the same ACR meeting session by Anna-Kay Palmer, MD, a third-year internal medicine resident at Jefferson Einstein Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, showed that GLP-1 RAs reduced the risk of progression to ESKD in patients with lupus nephritis, possibly caused by reductions in pro-inflammatory mediators.
Asked to comment, session moderator Diane L. Kamen, MD, professor of medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina Division of Rheumatology, Charleston, said in an interview that she definitely supports the use of GLP-1 RAs for patients who have SLE and/or lupus nephritis and also a drug label indication, either T2D or obesity. “[The GLP-1 RA prescriber] will usually run it by rheumatology to make sure that it doesn’t conflict with any of their other medical treatment, and it’s very reassuring to know that they could actually get a win-win.”
But as far as prescribing off-label for those with SLE/lupus nephritis who don’t have other GLP-1 RA indications, Kamen said, “that’s a black hole at this point. We need to do those prospective studies. But if they have another indication, yes.”
Cardiovascular, Kidney Benefits of GLP-1 RAs
Jorge noted that patients with lupus were excluded from the randomized clinical trials of GLP-1 RAs, so the current study was designed to investigate the potential impact of these medications on cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with SLE and lupus nephritis.
From TriNetX data for 46 healthcare organizations nationwide, a total of 96,511 patients with both SLE and T2D but not ESKD had initiated either a GLP-1 RA or another diabetes drug class, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i), between October 2006 and August 2021. Of those, 29,177 had lupus nephritis.
Propensity score matching for factors such as demographics, lupus severity, comorbidities, and medication use was used to emulate a randomized trial. This yielded 25,838 with SLE and T2D, of whom 910 initiated a GLP-1 RA and 1004 started a DPP4i, and 12,387 with lupus nephritis and T2D, including 267 on a GLP-1 RA and 324 on a DPP4i. After matching, the mean age was 55 years, more than 90% were women, and just under half were White individuals. About one third had chronic kidney disease stages ≥ 3, and about 15% had heart failure.
Over an average follow-up time of 1.2-1.4 years among those with SLE, the hazard ratio (HR) for MACE (a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure) for those taking a GLP-1 RA vs a DPP4i was 0.66, a significant difference. And for venous thrombosis, the HR was also significant at 0.49.
Kidney disease progression, defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate decline of 30% or more or new ESKD, was significantly less likely in the GLP-1 RA group, with a HR of 0.77. All-cause mortality also was dramatically reduced (HR, 0.26). As expected, there was no difference in control outcome, genital infections (HR, 1.02).
In the subgroup with lupus nephritis, there were also lower risks for both MACE (HR, 0.64) and for renal progression (HR, 0.70). “The findings suggest similar cardiac and kidney benefits among patients with SLE and lupus nephritis as have been observed in other populations,” Jorge concluded.
Kamen commented that the study design “was pretty brilliant, because you wouldn’t be able to do a placebo-controlled trial since the indication was diabetes ... but the fact is you do see that the GLP-1 RA gets the benefit whereas the other drug does not.”
Next steps, Jorge said, will be mechanistic studies to better understand the effects of GLP-1 RAs in lupus and other rheumatic diseases, prospective studies of GLP-1 RAs in SLE and lupus nephritis without diabetes, and clarification of ideal timing for GLP-1 RA use in SLE and lupus nephritis.
“Ideally, with our prospective studies with these patients we can try to isolate the effect on patients with lupus and also better understand whether there might be an impact on disease activity through the anti-inflammatory effects of these medications, rather than just the cardioprotective and nephroprotective benefits,” she said.
In Those With Lupus Nephritis, Kidney Protection Seen
In her presentation, Palmer noted that, despite immunosuppressive therapies for SLE, 10%-20% of patients who develop lupus nephritis will progress to ESKD within 5 years of diagnosis.
She added that GLP-1 RAs have been shown to reduce albuminuria in people with diabetes and have been hypothesized to reduce inflammation through multiple pathways, thereby potentially reducing kidney disease independently of the presence of diabetes or weight loss. These pathways include modulating immune cell signaling and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Based on all this, Palmer and colleagues used International Classification of Diseases – 10th edition diagnostic codes in TriNetX to identify 839 patients who had been diagnosed with lupus nephritis between 2014 and 2024 and who were prescribed liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, or exenatide for any time after the lupus nephritis diagnosis. Another 29,840 patients with lupus nephritis had not used GLP-1 RAs.
After 1:1 propensity score matching for age, sex, race, ethnicity, presence of hypertension, diabetes, use of immunosuppressive and diabetes medication, smoking, obesity, and statin use, there were 735 individuals in each group. About two thirds in each had diabetes, whereas the rest had been prescribed the GLP-1 RAs for other indications.
Patients who were not on GLP-1 RAs were twice as likely to develop ESKD or dialysis (8.88% vs 3.971%; odds ratio, 2.35; P = .001).
Kamen pointed out that not including the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers was a study flaw. On the other hand, the fact that not everyone in this study had diabetes was an advantage.
Jorge received grant/research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cabaletta Bio, and the Lupus Clinical Investigator Network. Kamen is an adviser/review panel member for Alpine Immune Sciences. Palmer had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) medications appear beneficial for people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis, two new studies suggest.
“The risk of cardiovascular disease is thought to be at least double that for people with lupus ... and we know the risk of progressing to end-stage renal disease [ESKD] for patients with lupus nephritis can be as high as 10%-30%, so there’s clearly a major unmet need for new treatments and approaches to improve these outcomes, perhaps with adjunctive treatment beyond our typical immunosuppressive therapy,” April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The GLP-1 RAs are approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity. They also have proven cardiovascular benefit, along with emerging data suggesting kidney protection independent of glucose lowering. Jorge presented findings from a study using data from the US multicenter electronic health record database TriNetX, showing that, among patients who had both T2D and SLE, those using GLP-1 RAs had lower risks for major adverse cardiac events (MACE), venous thrombosis, kidney disease progression, and all-cause mortality, compared with those using a different class of T2D medication.
A second study using TriNetX, presented at the same ACR meeting session by Anna-Kay Palmer, MD, a third-year internal medicine resident at Jefferson Einstein Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, showed that GLP-1 RAs reduced the risk of progression to ESKD in patients with lupus nephritis, possibly caused by reductions in pro-inflammatory mediators.
Asked to comment, session moderator Diane L. Kamen, MD, professor of medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina Division of Rheumatology, Charleston, said in an interview that she definitely supports the use of GLP-1 RAs for patients who have SLE and/or lupus nephritis and also a drug label indication, either T2D or obesity. “[The GLP-1 RA prescriber] will usually run it by rheumatology to make sure that it doesn’t conflict with any of their other medical treatment, and it’s very reassuring to know that they could actually get a win-win.”
But as far as prescribing off-label for those with SLE/lupus nephritis who don’t have other GLP-1 RA indications, Kamen said, “that’s a black hole at this point. We need to do those prospective studies. But if they have another indication, yes.”
Cardiovascular, Kidney Benefits of GLP-1 RAs
Jorge noted that patients with lupus were excluded from the randomized clinical trials of GLP-1 RAs, so the current study was designed to investigate the potential impact of these medications on cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with SLE and lupus nephritis.
From TriNetX data for 46 healthcare organizations nationwide, a total of 96,511 patients with both SLE and T2D but not ESKD had initiated either a GLP-1 RA or another diabetes drug class, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i), between October 2006 and August 2021. Of those, 29,177 had lupus nephritis.
Propensity score matching for factors such as demographics, lupus severity, comorbidities, and medication use was used to emulate a randomized trial. This yielded 25,838 with SLE and T2D, of whom 910 initiated a GLP-1 RA and 1004 started a DPP4i, and 12,387 with lupus nephritis and T2D, including 267 on a GLP-1 RA and 324 on a DPP4i. After matching, the mean age was 55 years, more than 90% were women, and just under half were White individuals. About one third had chronic kidney disease stages ≥ 3, and about 15% had heart failure.
Over an average follow-up time of 1.2-1.4 years among those with SLE, the hazard ratio (HR) for MACE (a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure) for those taking a GLP-1 RA vs a DPP4i was 0.66, a significant difference. And for venous thrombosis, the HR was also significant at 0.49.
Kidney disease progression, defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate decline of 30% or more or new ESKD, was significantly less likely in the GLP-1 RA group, with a HR of 0.77. All-cause mortality also was dramatically reduced (HR, 0.26). As expected, there was no difference in control outcome, genital infections (HR, 1.02).
In the subgroup with lupus nephritis, there were also lower risks for both MACE (HR, 0.64) and for renal progression (HR, 0.70). “The findings suggest similar cardiac and kidney benefits among patients with SLE and lupus nephritis as have been observed in other populations,” Jorge concluded.
Kamen commented that the study design “was pretty brilliant, because you wouldn’t be able to do a placebo-controlled trial since the indication was diabetes ... but the fact is you do see that the GLP-1 RA gets the benefit whereas the other drug does not.”
Next steps, Jorge said, will be mechanistic studies to better understand the effects of GLP-1 RAs in lupus and other rheumatic diseases, prospective studies of GLP-1 RAs in SLE and lupus nephritis without diabetes, and clarification of ideal timing for GLP-1 RA use in SLE and lupus nephritis.
“Ideally, with our prospective studies with these patients we can try to isolate the effect on patients with lupus and also better understand whether there might be an impact on disease activity through the anti-inflammatory effects of these medications, rather than just the cardioprotective and nephroprotective benefits,” she said.
In Those With Lupus Nephritis, Kidney Protection Seen
In her presentation, Palmer noted that, despite immunosuppressive therapies for SLE, 10%-20% of patients who develop lupus nephritis will progress to ESKD within 5 years of diagnosis.
She added that GLP-1 RAs have been shown to reduce albuminuria in people with diabetes and have been hypothesized to reduce inflammation through multiple pathways, thereby potentially reducing kidney disease independently of the presence of diabetes or weight loss. These pathways include modulating immune cell signaling and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Based on all this, Palmer and colleagues used International Classification of Diseases – 10th edition diagnostic codes in TriNetX to identify 839 patients who had been diagnosed with lupus nephritis between 2014 and 2024 and who were prescribed liraglutide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, or exenatide for any time after the lupus nephritis diagnosis. Another 29,840 patients with lupus nephritis had not used GLP-1 RAs.
After 1:1 propensity score matching for age, sex, race, ethnicity, presence of hypertension, diabetes, use of immunosuppressive and diabetes medication, smoking, obesity, and statin use, there were 735 individuals in each group. About two thirds in each had diabetes, whereas the rest had been prescribed the GLP-1 RAs for other indications.
Patients who were not on GLP-1 RAs were twice as likely to develop ESKD or dialysis (8.88% vs 3.971%; odds ratio, 2.35; P = .001).
Kamen pointed out that not including the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers was a study flaw. On the other hand, the fact that not everyone in this study had diabetes was an advantage.
Jorge received grant/research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cabaletta Bio, and the Lupus Clinical Investigator Network. Kamen is an adviser/review panel member for Alpine Immune Sciences. Palmer had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Can New Target Boost Bone Health in Older Women With T2D?
TOPLINE:
In older postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes (T2D), pyridoxamine treatment has potential to prevent fractures and protect bone tissue by targeting advanced glycation end products and also lowers levels of A1c, an early glycation product.
METHODOLOGY:
- Despite greater bone density and low bone turnover, people with T2D have increased fractures risk and higher associated mortality, but previous research linking advanced glycation end products (AGEs) to bone fragility suggests an AGE inhibitor could be a novel therapeutic strategy to prevent the accumulation of AGE in bone tissue.
- This randomized clinical trial, conducted at the Metabolic Bone Disease Unit of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, from December 2017 to February 2021, assessed the efficacy of the vitamin B6 metabolite pyridoxamine, an AGE inhibitor, in promoting bone formation in 55 older postmenopausal women with T2D.
- The participants received either 200 mg of oral pyridoxamine dihydrochloride (n = 27; mean age, 75.6 years) or matching placebo tablets (n = 28; mean age, 73.1 years) twice daily for 1 year.
- The primary outcome was the change in the levels of the bone formation marker Procollagen Type I Intact N-terminal Propeptide (P1NP) from baseline to after 12 months of treatment.
- Other outcomes included changes in bone mineral density measured at the lumbar spine, total hip, femoral neck, and 1/3 radius using dual energy x-ray absorptiometry; A1c levels; and skin autofluorescence at 12 months, a surrogate for bone AGEs. The safety of pyridoxamine was evaluated by monitoring neurologic findings and adverse events because high doses of the parent vitamin B6 have been reported to cause neurotoxicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months, pyridoxamine treatment increased P1NP levels by 23% (P = .028) compared with 4.1% with placebo (P = .576), a “nearly significant difference.”
- Bone mineral density at the femoral neck increased by 2.64% with pyridoxamine but decreased by 0.91% with placebo (P = .007), with no changes at the lumbar spine, total hip, or 1/3 radius. The levels of bone resorption markers or skin autofluorescence were not significantly different between the groups.
- A1c levels decreased by 0.38% in the pyridoxamine group and correlated with increased P1NP levels, compared with a 0.05% increase in the placebo group (P = .04).
- Pyridoxamine was well tolerated. Four serious adverse events were reported in the pyridoxamine group and seven in the placebo group; none of these were related to the trial treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“[The study] findings suggest that AGE inhibition might clinically improve the low bone formation state of T2D, and that PM [pyridoxamine] might warrant further investigation as a potential disease mechanism-directed approach for the therapy of T2D bone fragility,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aiden V. Brossfield, Metabolic Bone Disease Unit, Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University Irving Medical Center. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study findings were preliminary. The study’s small sample size and individual variability led to a lack of statistical significance. The exclusion of men may have limited the generalizability of the findings. The short duration of 1 year may have been insufficient for detecting changes in skin AGEs. The levels of circulating AGEs or pyridoxamine were not measured, which could have provided additional insights.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from the US National Institute on Aging. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In older postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes (T2D), pyridoxamine treatment has potential to prevent fractures and protect bone tissue by targeting advanced glycation end products and also lowers levels of A1c, an early glycation product.
METHODOLOGY:
- Despite greater bone density and low bone turnover, people with T2D have increased fractures risk and higher associated mortality, but previous research linking advanced glycation end products (AGEs) to bone fragility suggests an AGE inhibitor could be a novel therapeutic strategy to prevent the accumulation of AGE in bone tissue.
- This randomized clinical trial, conducted at the Metabolic Bone Disease Unit of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, from December 2017 to February 2021, assessed the efficacy of the vitamin B6 metabolite pyridoxamine, an AGE inhibitor, in promoting bone formation in 55 older postmenopausal women with T2D.
- The participants received either 200 mg of oral pyridoxamine dihydrochloride (n = 27; mean age, 75.6 years) or matching placebo tablets (n = 28; mean age, 73.1 years) twice daily for 1 year.
- The primary outcome was the change in the levels of the bone formation marker Procollagen Type I Intact N-terminal Propeptide (P1NP) from baseline to after 12 months of treatment.
- Other outcomes included changes in bone mineral density measured at the lumbar spine, total hip, femoral neck, and 1/3 radius using dual energy x-ray absorptiometry; A1c levels; and skin autofluorescence at 12 months, a surrogate for bone AGEs. The safety of pyridoxamine was evaluated by monitoring neurologic findings and adverse events because high doses of the parent vitamin B6 have been reported to cause neurotoxicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months, pyridoxamine treatment increased P1NP levels by 23% (P = .028) compared with 4.1% with placebo (P = .576), a “nearly significant difference.”
- Bone mineral density at the femoral neck increased by 2.64% with pyridoxamine but decreased by 0.91% with placebo (P = .007), with no changes at the lumbar spine, total hip, or 1/3 radius. The levels of bone resorption markers or skin autofluorescence were not significantly different between the groups.
- A1c levels decreased by 0.38% in the pyridoxamine group and correlated with increased P1NP levels, compared with a 0.05% increase in the placebo group (P = .04).
- Pyridoxamine was well tolerated. Four serious adverse events were reported in the pyridoxamine group and seven in the placebo group; none of these were related to the trial treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“[The study] findings suggest that AGE inhibition might clinically improve the low bone formation state of T2D, and that PM [pyridoxamine] might warrant further investigation as a potential disease mechanism-directed approach for the therapy of T2D bone fragility,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aiden V. Brossfield, Metabolic Bone Disease Unit, Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University Irving Medical Center. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study findings were preliminary. The study’s small sample size and individual variability led to a lack of statistical significance. The exclusion of men may have limited the generalizability of the findings. The short duration of 1 year may have been insufficient for detecting changes in skin AGEs. The levels of circulating AGEs or pyridoxamine were not measured, which could have provided additional insights.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from the US National Institute on Aging. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In older postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes (T2D), pyridoxamine treatment has potential to prevent fractures and protect bone tissue by targeting advanced glycation end products and also lowers levels of A1c, an early glycation product.
METHODOLOGY:
- Despite greater bone density and low bone turnover, people with T2D have increased fractures risk and higher associated mortality, but previous research linking advanced glycation end products (AGEs) to bone fragility suggests an AGE inhibitor could be a novel therapeutic strategy to prevent the accumulation of AGE in bone tissue.
- This randomized clinical trial, conducted at the Metabolic Bone Disease Unit of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, from December 2017 to February 2021, assessed the efficacy of the vitamin B6 metabolite pyridoxamine, an AGE inhibitor, in promoting bone formation in 55 older postmenopausal women with T2D.
- The participants received either 200 mg of oral pyridoxamine dihydrochloride (n = 27; mean age, 75.6 years) or matching placebo tablets (n = 28; mean age, 73.1 years) twice daily for 1 year.
- The primary outcome was the change in the levels of the bone formation marker Procollagen Type I Intact N-terminal Propeptide (P1NP) from baseline to after 12 months of treatment.
- Other outcomes included changes in bone mineral density measured at the lumbar spine, total hip, femoral neck, and 1/3 radius using dual energy x-ray absorptiometry; A1c levels; and skin autofluorescence at 12 months, a surrogate for bone AGEs. The safety of pyridoxamine was evaluated by monitoring neurologic findings and adverse events because high doses of the parent vitamin B6 have been reported to cause neurotoxicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months, pyridoxamine treatment increased P1NP levels by 23% (P = .028) compared with 4.1% with placebo (P = .576), a “nearly significant difference.”
- Bone mineral density at the femoral neck increased by 2.64% with pyridoxamine but decreased by 0.91% with placebo (P = .007), with no changes at the lumbar spine, total hip, or 1/3 radius. The levels of bone resorption markers or skin autofluorescence were not significantly different between the groups.
- A1c levels decreased by 0.38% in the pyridoxamine group and correlated with increased P1NP levels, compared with a 0.05% increase in the placebo group (P = .04).
- Pyridoxamine was well tolerated. Four serious adverse events were reported in the pyridoxamine group and seven in the placebo group; none of these were related to the trial treatment.
IN PRACTICE:
“[The study] findings suggest that AGE inhibition might clinically improve the low bone formation state of T2D, and that PM [pyridoxamine] might warrant further investigation as a potential disease mechanism-directed approach for the therapy of T2D bone fragility,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aiden V. Brossfield, Metabolic Bone Disease Unit, Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University Irving Medical Center. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study findings were preliminary. The study’s small sample size and individual variability led to a lack of statistical significance. The exclusion of men may have limited the generalizability of the findings. The short duration of 1 year may have been insufficient for detecting changes in skin AGEs. The levels of circulating AGEs or pyridoxamine were not measured, which could have provided additional insights.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a grant from the US National Institute on Aging. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fibrosis Risk High in Young Adults With Both Obesity and T2D
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers aimed to assess the prevalence of hepatic steatosis and clinically significant fibrosis (stage ≥ 2) in young adults without a history of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), hypothesizing that the rates would be comparable with those in older adults, especially in the presence of cardiometabolic risk factors.
- Overall, 1420 participants aged 21-79 years with or without T2D (63% or 37%, respectively) were included from outpatient clinics at the University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, and divided into two age groups: < 45 years (n = 243) and ≥ 45 years (n = 1177).
- All the participants underwent assessment of liver stiffness via transient elastography, with magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) or liver biopsy recommended when indicated.
- Participants also underwent a medical history review, physical examination, and fasting blood tests to rule out secondary causes of liver disease.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 52% of participants had hepatic steatosis, and 9.5% had clinically significant fibrosis.
- There were no significant differences in the frequencies of hepatic steatosis (50.2% vs 52.7%; P = .6) or clinically significant hepatic fibrosis (7.5% vs 9.9%; P = .2) observed between young and older adults.
- The presence of either T2D or obesity was linked to an increased prevalence of both hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in both the age groups (P < .01).
- In young and older adults, the presence of both T2D and obesity led to the highest rates of both hepatic steatosis and clinically significant fibrosis, with the latter rate being statistically similar between the groups (15.7% vs 17.3%; P = .2).
- The presence of T2D and obesity was the strongest risk factors for hepatic fibrosis in young adults (odds ratios, 4.33 and 1.16, respectively; P < .05 for both).
IN PRACTICE:
“The clinical implication is that young adults with obesity and T2D carry a high risk of future cirrhosis, possibly as high as older adults, and must be aggressively screened at the first visit and carefully followed,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Anu Sharma, University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, was published online in Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The diagnosis of clinically significant hepatic fibrosis was confirmed via MRE and/or liver biopsy in only 30% of all participants. The study population included a slightly higher proportion of young adults with obesity, T2D, and other cardiometabolic risk factors than that in national averages, which may have limited its generalizability. Genetic variants associated with MASLD were not included in this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded partly by grants from the National Institutes of Health and Echosens. One author disclosed receiving research support and serving as a consultant for various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers aimed to assess the prevalence of hepatic steatosis and clinically significant fibrosis (stage ≥ 2) in young adults without a history of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), hypothesizing that the rates would be comparable with those in older adults, especially in the presence of cardiometabolic risk factors.
- Overall, 1420 participants aged 21-79 years with or without T2D (63% or 37%, respectively) were included from outpatient clinics at the University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, and divided into two age groups: < 45 years (n = 243) and ≥ 45 years (n = 1177).
- All the participants underwent assessment of liver stiffness via transient elastography, with magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) or liver biopsy recommended when indicated.
- Participants also underwent a medical history review, physical examination, and fasting blood tests to rule out secondary causes of liver disease.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 52% of participants had hepatic steatosis, and 9.5% had clinically significant fibrosis.
- There were no significant differences in the frequencies of hepatic steatosis (50.2% vs 52.7%; P = .6) or clinically significant hepatic fibrosis (7.5% vs 9.9%; P = .2) observed between young and older adults.
- The presence of either T2D or obesity was linked to an increased prevalence of both hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in both the age groups (P < .01).
- In young and older adults, the presence of both T2D and obesity led to the highest rates of both hepatic steatosis and clinically significant fibrosis, with the latter rate being statistically similar between the groups (15.7% vs 17.3%; P = .2).
- The presence of T2D and obesity was the strongest risk factors for hepatic fibrosis in young adults (odds ratios, 4.33 and 1.16, respectively; P < .05 for both).
IN PRACTICE:
“The clinical implication is that young adults with obesity and T2D carry a high risk of future cirrhosis, possibly as high as older adults, and must be aggressively screened at the first visit and carefully followed,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Anu Sharma, University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, was published online in Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The diagnosis of clinically significant hepatic fibrosis was confirmed via MRE and/or liver biopsy in only 30% of all participants. The study population included a slightly higher proportion of young adults with obesity, T2D, and other cardiometabolic risk factors than that in national averages, which may have limited its generalizability. Genetic variants associated with MASLD were not included in this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded partly by grants from the National Institutes of Health and Echosens. One author disclosed receiving research support and serving as a consultant for various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers aimed to assess the prevalence of hepatic steatosis and clinically significant fibrosis (stage ≥ 2) in young adults without a history of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), hypothesizing that the rates would be comparable with those in older adults, especially in the presence of cardiometabolic risk factors.
- Overall, 1420 participants aged 21-79 years with or without T2D (63% or 37%, respectively) were included from outpatient clinics at the University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, and divided into two age groups: < 45 years (n = 243) and ≥ 45 years (n = 1177).
- All the participants underwent assessment of liver stiffness via transient elastography, with magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) or liver biopsy recommended when indicated.
- Participants also underwent a medical history review, physical examination, and fasting blood tests to rule out secondary causes of liver disease.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 52% of participants had hepatic steatosis, and 9.5% had clinically significant fibrosis.
- There were no significant differences in the frequencies of hepatic steatosis (50.2% vs 52.7%; P = .6) or clinically significant hepatic fibrosis (7.5% vs 9.9%; P = .2) observed between young and older adults.
- The presence of either T2D or obesity was linked to an increased prevalence of both hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in both the age groups (P < .01).
- In young and older adults, the presence of both T2D and obesity led to the highest rates of both hepatic steatosis and clinically significant fibrosis, with the latter rate being statistically similar between the groups (15.7% vs 17.3%; P = .2).
- The presence of T2D and obesity was the strongest risk factors for hepatic fibrosis in young adults (odds ratios, 4.33 and 1.16, respectively; P < .05 for both).
IN PRACTICE:
“The clinical implication is that young adults with obesity and T2D carry a high risk of future cirrhosis, possibly as high as older adults, and must be aggressively screened at the first visit and carefully followed,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Anu Sharma, University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, was published online in Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The diagnosis of clinically significant hepatic fibrosis was confirmed via MRE and/or liver biopsy in only 30% of all participants. The study population included a slightly higher proportion of young adults with obesity, T2D, and other cardiometabolic risk factors than that in national averages, which may have limited its generalizability. Genetic variants associated with MASLD were not included in this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded partly by grants from the National Institutes of Health and Echosens. One author disclosed receiving research support and serving as a consultant for various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oxidative Stress Marker May Signal Fracture Risk in T2D
TOPLINE:
Elevated levels of plasma F2-isoprostanes, a reliable marker of oxidative stress, are associated with an increased risk for fractures in older ambulatory patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) independently of bone density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with T2D face an increased risk for fractures at any given bone mineral density; oxidative stress levels (reflected in circulating F2-isoprostanes), which are elevated in T2D, are associated with other T2D complications, and may weaken bone integrity.
- Researchers analyzed data from an observational cohort study to investigate the association between the levels of circulating F2-isoprostanes and the risk for clinical fractures in older patients with T2D.
- The data included 703 older ambulatory adults (baseline age, 70-79 years; about half White individuals and half Black individuals ; about half men and half women) from the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study, of whom 132 had T2D.
- Plasma F2-isoprostane levels were measured using baseline serum samples; bone turnover markers were also measured including procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide, osteocalcin, and C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen.
- Incident clinical fractures were tracked over a follow-up period of up to 17.3 years, with fractures verified through radiology reports.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 25.8% patients in the T2D group and 23.5% adults in the non-diabetes group reported an incident clinical fracture during a mean follow-up period of 6.2 and 8.0 years, respectively.
- In patients with T2D, the risk for incident clinical fracture increased by 93% for every standard deviation increase in the log F2-isoprostane serum levels (hazard ratio [HR], 1.93; 95% CI, 1.26-2.95; P = .002) independently of baseline bone density, medication use, and other risk factors, with no such association reported in individuals without T2D (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.81-1.18; P = .79).
- In the T2D group, elevated plasma F2-isoprostane levels were also associated with a decrease in total hip bone mineral density over 4 years (r = −0.28; P = .008), but not in the non-diabetes group.
- No correlation was found between plasma F2-isoprostane levels and circulating advanced glycoxidation end-products, bone turnover markers, or A1c levels in either group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Oxidative stress in T2D may play an important role in the decline of bone quality and not just bone quantity,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Bowen Wang, PhD, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, New York. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was conducted in a well-functioning elderly population with only White and Black participants, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other age groups or less healthy populations. Additionally, the study did not assess prevalent vertebral fracture risk due to the small sample size.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the US National Institute on Aging and the Intramural Research Program of the US National Institutes of Health and the Dr and Ms Sands and Sands Family for Orthopaedic Research. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Elevated levels of plasma F2-isoprostanes, a reliable marker of oxidative stress, are associated with an increased risk for fractures in older ambulatory patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) independently of bone density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with T2D face an increased risk for fractures at any given bone mineral density; oxidative stress levels (reflected in circulating F2-isoprostanes), which are elevated in T2D, are associated with other T2D complications, and may weaken bone integrity.
- Researchers analyzed data from an observational cohort study to investigate the association between the levels of circulating F2-isoprostanes and the risk for clinical fractures in older patients with T2D.
- The data included 703 older ambulatory adults (baseline age, 70-79 years; about half White individuals and half Black individuals ; about half men and half women) from the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study, of whom 132 had T2D.
- Plasma F2-isoprostane levels were measured using baseline serum samples; bone turnover markers were also measured including procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide, osteocalcin, and C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen.
- Incident clinical fractures were tracked over a follow-up period of up to 17.3 years, with fractures verified through radiology reports.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 25.8% patients in the T2D group and 23.5% adults in the non-diabetes group reported an incident clinical fracture during a mean follow-up period of 6.2 and 8.0 years, respectively.
- In patients with T2D, the risk for incident clinical fracture increased by 93% for every standard deviation increase in the log F2-isoprostane serum levels (hazard ratio [HR], 1.93; 95% CI, 1.26-2.95; P = .002) independently of baseline bone density, medication use, and other risk factors, with no such association reported in individuals without T2D (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.81-1.18; P = .79).
- In the T2D group, elevated plasma F2-isoprostane levels were also associated with a decrease in total hip bone mineral density over 4 years (r = −0.28; P = .008), but not in the non-diabetes group.
- No correlation was found between plasma F2-isoprostane levels and circulating advanced glycoxidation end-products, bone turnover markers, or A1c levels in either group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Oxidative stress in T2D may play an important role in the decline of bone quality and not just bone quantity,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Bowen Wang, PhD, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, New York. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was conducted in a well-functioning elderly population with only White and Black participants, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other age groups or less healthy populations. Additionally, the study did not assess prevalent vertebral fracture risk due to the small sample size.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the US National Institute on Aging and the Intramural Research Program of the US National Institutes of Health and the Dr and Ms Sands and Sands Family for Orthopaedic Research. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Elevated levels of plasma F2-isoprostanes, a reliable marker of oxidative stress, are associated with an increased risk for fractures in older ambulatory patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) independently of bone density.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with T2D face an increased risk for fractures at any given bone mineral density; oxidative stress levels (reflected in circulating F2-isoprostanes), which are elevated in T2D, are associated with other T2D complications, and may weaken bone integrity.
- Researchers analyzed data from an observational cohort study to investigate the association between the levels of circulating F2-isoprostanes and the risk for clinical fractures in older patients with T2D.
- The data included 703 older ambulatory adults (baseline age, 70-79 years; about half White individuals and half Black individuals ; about half men and half women) from the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study, of whom 132 had T2D.
- Plasma F2-isoprostane levels were measured using baseline serum samples; bone turnover markers were also measured including procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide, osteocalcin, and C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen.
- Incident clinical fractures were tracked over a follow-up period of up to 17.3 years, with fractures verified through radiology reports.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 25.8% patients in the T2D group and 23.5% adults in the non-diabetes group reported an incident clinical fracture during a mean follow-up period of 6.2 and 8.0 years, respectively.
- In patients with T2D, the risk for incident clinical fracture increased by 93% for every standard deviation increase in the log F2-isoprostane serum levels (hazard ratio [HR], 1.93; 95% CI, 1.26-2.95; P = .002) independently of baseline bone density, medication use, and other risk factors, with no such association reported in individuals without T2D (HR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.81-1.18; P = .79).
- In the T2D group, elevated plasma F2-isoprostane levels were also associated with a decrease in total hip bone mineral density over 4 years (r = −0.28; P = .008), but not in the non-diabetes group.
- No correlation was found between plasma F2-isoprostane levels and circulating advanced glycoxidation end-products, bone turnover markers, or A1c levels in either group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Oxidative stress in T2D may play an important role in the decline of bone quality and not just bone quantity,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Bowen Wang, PhD, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, New York. It was published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was conducted in a well-functioning elderly population with only White and Black participants, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other age groups or less healthy populations. Additionally, the study did not assess prevalent vertebral fracture risk due to the small sample size.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the US National Institute on Aging and the Intramural Research Program of the US National Institutes of Health and the Dr and Ms Sands and Sands Family for Orthopaedic Research. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
US Alcohol-Related Deaths Double Over 2 Decades, With Notable Age and Gender Disparities
TOPLINE:
US alcohol-related mortality rates increased from 10.7 to 21.6 per 100,000 between 1999 and 2020, with the largest rise of 3.8-fold observed in adults aged 25-34 years. Women experienced a 2.5-fold increase, while the Midwest region showed a similar rise in mortality rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- Analysis utilized the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research to examine alcohol-related mortality trends from 1999 to 2020.
- Researchers analyzed data from a total US population of 180,408,769 people aged 25 to 85+ years in 1999 and 226,635,013 people in 2020.
- International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, codes were used to identify deaths with alcohol attribution, including mental and behavioral disorders, alcoholic organ damage, and alcohol-related poisoning.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall mortality rates increased from 10.7 (95% CI, 10.6-10.8) per 100,000 in 1999 to 21.6 (95% CI, 21.4-21.8) per 100,000 in 2020, representing a significant twofold increase.
- Adults aged 55-64 years demonstrated both the steepest increase and highest absolute rates in both 1999 and 2020.
- American Indian and Alaska Native individuals experienced the steepest increase and highest absolute rates among all racial groups.
- The West region maintained the highest absolute rates in both 1999 and 2020, despite the Midwest showing the largest increase.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals who consume large amounts of alcohol tend to have the highest risks of total mortality as well as deaths from cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular disease deaths are predominantly due to myocardial infarction and stroke. To mitigate these risks, health providers may wish to implement screening for alcohol use in primary care and other healthcare settings. By providing brief interventions and referrals to treatment, healthcare providers would be able to achieve the early identification of individuals at risk of alcohol-related harm and offer them the support and resources they need to reduce their alcohol consumption,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexandra Matarazzo, BS, Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton. It was published online in The American Journal of Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
According to the authors, the cross-sectional nature of the data limits the study to descriptive analysis only, making it suitable for hypothesis generation but not hypothesis testing. While the validity and generalizability within the United States are secure because of the use of complete population data, potential bias and uncontrolled confounding may exist because of different population mixes between the two time points.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest. One coauthor disclosed serving as an independent scientist in an advisory role to investigators and sponsors as Chair of Data Monitoring Committees for Amgen and UBC, to the Food and Drug Administration, and to Up to Date. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
US alcohol-related mortality rates increased from 10.7 to 21.6 per 100,000 between 1999 and 2020, with the largest rise of 3.8-fold observed in adults aged 25-34 years. Women experienced a 2.5-fold increase, while the Midwest region showed a similar rise in mortality rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- Analysis utilized the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research to examine alcohol-related mortality trends from 1999 to 2020.
- Researchers analyzed data from a total US population of 180,408,769 people aged 25 to 85+ years in 1999 and 226,635,013 people in 2020.
- International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, codes were used to identify deaths with alcohol attribution, including mental and behavioral disorders, alcoholic organ damage, and alcohol-related poisoning.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall mortality rates increased from 10.7 (95% CI, 10.6-10.8) per 100,000 in 1999 to 21.6 (95% CI, 21.4-21.8) per 100,000 in 2020, representing a significant twofold increase.
- Adults aged 55-64 years demonstrated both the steepest increase and highest absolute rates in both 1999 and 2020.
- American Indian and Alaska Native individuals experienced the steepest increase and highest absolute rates among all racial groups.
- The West region maintained the highest absolute rates in both 1999 and 2020, despite the Midwest showing the largest increase.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals who consume large amounts of alcohol tend to have the highest risks of total mortality as well as deaths from cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular disease deaths are predominantly due to myocardial infarction and stroke. To mitigate these risks, health providers may wish to implement screening for alcohol use in primary care and other healthcare settings. By providing brief interventions and referrals to treatment, healthcare providers would be able to achieve the early identification of individuals at risk of alcohol-related harm and offer them the support and resources they need to reduce their alcohol consumption,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexandra Matarazzo, BS, Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton. It was published online in The American Journal of Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
According to the authors, the cross-sectional nature of the data limits the study to descriptive analysis only, making it suitable for hypothesis generation but not hypothesis testing. While the validity and generalizability within the United States are secure because of the use of complete population data, potential bias and uncontrolled confounding may exist because of different population mixes between the two time points.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest. One coauthor disclosed serving as an independent scientist in an advisory role to investigators and sponsors as Chair of Data Monitoring Committees for Amgen and UBC, to the Food and Drug Administration, and to Up to Date. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
US alcohol-related mortality rates increased from 10.7 to 21.6 per 100,000 between 1999 and 2020, with the largest rise of 3.8-fold observed in adults aged 25-34 years. Women experienced a 2.5-fold increase, while the Midwest region showed a similar rise in mortality rates.
METHODOLOGY:
- Analysis utilized the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Wide-Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research to examine alcohol-related mortality trends from 1999 to 2020.
- Researchers analyzed data from a total US population of 180,408,769 people aged 25 to 85+ years in 1999 and 226,635,013 people in 2020.
- International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, codes were used to identify deaths with alcohol attribution, including mental and behavioral disorders, alcoholic organ damage, and alcohol-related poisoning.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall mortality rates increased from 10.7 (95% CI, 10.6-10.8) per 100,000 in 1999 to 21.6 (95% CI, 21.4-21.8) per 100,000 in 2020, representing a significant twofold increase.
- Adults aged 55-64 years demonstrated both the steepest increase and highest absolute rates in both 1999 and 2020.
- American Indian and Alaska Native individuals experienced the steepest increase and highest absolute rates among all racial groups.
- The West region maintained the highest absolute rates in both 1999 and 2020, despite the Midwest showing the largest increase.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals who consume large amounts of alcohol tend to have the highest risks of total mortality as well as deaths from cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular disease deaths are predominantly due to myocardial infarction and stroke. To mitigate these risks, health providers may wish to implement screening for alcohol use in primary care and other healthcare settings. By providing brief interventions and referrals to treatment, healthcare providers would be able to achieve the early identification of individuals at risk of alcohol-related harm and offer them the support and resources they need to reduce their alcohol consumption,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexandra Matarazzo, BS, Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton. It was published online in The American Journal of Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
According to the authors, the cross-sectional nature of the data limits the study to descriptive analysis only, making it suitable for hypothesis generation but not hypothesis testing. While the validity and generalizability within the United States are secure because of the use of complete population data, potential bias and uncontrolled confounding may exist because of different population mixes between the two time points.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest. One coauthor disclosed serving as an independent scientist in an advisory role to investigators and sponsors as Chair of Data Monitoring Committees for Amgen and UBC, to the Food and Drug Administration, and to Up to Date. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Deprescribe Low-Value Meds to Reduce Polypharmacy Harms
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — While polypharmacy is inevitable for patients with multiple chronic diseases, not all medications improve patient-oriented outcomes, members of the Patients, Experience, Evidence, Research (PEER) team, a group of Canadian primary care professionals who develop evidence-based guidelines, told attendees at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
In a thought-provoking presentation called “Axe the Rx: Deprescribing Chronic Medications with PEER,” the panelists gave examples of medications that may be safely stopped or tapered, particularly for older adults “whose pill bag is heavier than their lunch bag.”
Curbing Cardiovascular Drugs
The 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults call for reaching an LDL-C < 1.8 mmol/L in secondary cardiovascular prevention by potentially adding on medical therapies such as proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors or ezetimibe or both if that target is not reached with the maximal dosage of a statin.
But family physicians do not need to follow this guidance for their patients who have had a myocardial infarction, said Ontario family physician Jennifer Young, MD, a physician advisor in the Canadian College of Family Physicians’ Knowledge Experts and Tools Program.
Treating to below 1.8 mmol/L “means lab testing for the patients,” Young told this news organization. “It means increasing doses [of a statin] to try and get to that level.” If the patient is already on the highest dose of a statin, it means adding other medications that lower cholesterol.
“If that was translating into better outcomes like [preventing] death and another heart attack, then all of that extra effort would be worth it,” said Young. “But we don’t have evidence that it actually does have a benefit for outcomes like death and repeated heart attacks,” compared with putting them on a high dose of a potent statin.
Tapering Opioids
Before placing patients on an opioid taper, clinicians should first assess them for opioid use disorder (OUD), said Jessica Kirkwood, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada. She suggested using the Prescription Opioid Misuse Index questionnaire to do so.
Clinicians should be much more careful in initiating a taper with patients with OUD, said Kirkwood. They must ensure that these patients are motivated to discontinue their opioids. “We’re losing 21 Canadians a day to the opioid crisis. We all know that cutting someone off their opioids and potentially having them seek opioids elsewhere through illicit means can be fatal.”
In addition, clinicians should spend more time counseling patients with OUD than those without, Kirkwood continued. They must explain to these patients how they are being tapered (eg, the intervals and doses) and highlight the benefits of a taper, such as reduced constipation. Opioid agonist therapy (such as methadone or buprenorphine) can be considered in these patients.
Some research has pointed to the importance of patient motivation as a factor in the success of opioid tapers, noted Kirkwood.
Deprescribing Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepine receptor agonists, too, often can be deprescribed. These drugs should not be prescribed to promote sleep on a long-term basis. Yet clinicians commonly encounter patients who have been taking them for more than a year, said pharmacist Betsy Thomas, assistant adjunct professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta.
The medications “are usually fairly effective for the first couple of weeks to about a month, and then the benefits start to decrease, and we start to see more harms,” she said.
Some of the harms that have been associated with continued use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists include delayed reaction time and impaired cognition, which can affect the ability to drive, the risk for falls, and the risk for hip fractures, she noted. Some research suggests that these drugs are not an option for treating insomnia in patients aged 65 years or older.
Clinicians should encourage tapering the use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists to minimize dependence and transition patients to nonpharmacologic approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy to manage insomnia, she said. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of the intervention, and Thomas suggested that family physicians visit the mysleepwell.ca website for more information.
Young, Kirkwood, and Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — While polypharmacy is inevitable for patients with multiple chronic diseases, not all medications improve patient-oriented outcomes, members of the Patients, Experience, Evidence, Research (PEER) team, a group of Canadian primary care professionals who develop evidence-based guidelines, told attendees at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
In a thought-provoking presentation called “Axe the Rx: Deprescribing Chronic Medications with PEER,” the panelists gave examples of medications that may be safely stopped or tapered, particularly for older adults “whose pill bag is heavier than their lunch bag.”
Curbing Cardiovascular Drugs
The 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults call for reaching an LDL-C < 1.8 mmol/L in secondary cardiovascular prevention by potentially adding on medical therapies such as proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors or ezetimibe or both if that target is not reached with the maximal dosage of a statin.
But family physicians do not need to follow this guidance for their patients who have had a myocardial infarction, said Ontario family physician Jennifer Young, MD, a physician advisor in the Canadian College of Family Physicians’ Knowledge Experts and Tools Program.
Treating to below 1.8 mmol/L “means lab testing for the patients,” Young told this news organization. “It means increasing doses [of a statin] to try and get to that level.” If the patient is already on the highest dose of a statin, it means adding other medications that lower cholesterol.
“If that was translating into better outcomes like [preventing] death and another heart attack, then all of that extra effort would be worth it,” said Young. “But we don’t have evidence that it actually does have a benefit for outcomes like death and repeated heart attacks,” compared with putting them on a high dose of a potent statin.
Tapering Opioids
Before placing patients on an opioid taper, clinicians should first assess them for opioid use disorder (OUD), said Jessica Kirkwood, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada. She suggested using the Prescription Opioid Misuse Index questionnaire to do so.
Clinicians should be much more careful in initiating a taper with patients with OUD, said Kirkwood. They must ensure that these patients are motivated to discontinue their opioids. “We’re losing 21 Canadians a day to the opioid crisis. We all know that cutting someone off their opioids and potentially having them seek opioids elsewhere through illicit means can be fatal.”
In addition, clinicians should spend more time counseling patients with OUD than those without, Kirkwood continued. They must explain to these patients how they are being tapered (eg, the intervals and doses) and highlight the benefits of a taper, such as reduced constipation. Opioid agonist therapy (such as methadone or buprenorphine) can be considered in these patients.
Some research has pointed to the importance of patient motivation as a factor in the success of opioid tapers, noted Kirkwood.
Deprescribing Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepine receptor agonists, too, often can be deprescribed. These drugs should not be prescribed to promote sleep on a long-term basis. Yet clinicians commonly encounter patients who have been taking them for more than a year, said pharmacist Betsy Thomas, assistant adjunct professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta.
The medications “are usually fairly effective for the first couple of weeks to about a month, and then the benefits start to decrease, and we start to see more harms,” she said.
Some of the harms that have been associated with continued use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists include delayed reaction time and impaired cognition, which can affect the ability to drive, the risk for falls, and the risk for hip fractures, she noted. Some research suggests that these drugs are not an option for treating insomnia in patients aged 65 years or older.
Clinicians should encourage tapering the use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists to minimize dependence and transition patients to nonpharmacologic approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy to manage insomnia, she said. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of the intervention, and Thomas suggested that family physicians visit the mysleepwell.ca website for more information.
Young, Kirkwood, and Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — While polypharmacy is inevitable for patients with multiple chronic diseases, not all medications improve patient-oriented outcomes, members of the Patients, Experience, Evidence, Research (PEER) team, a group of Canadian primary care professionals who develop evidence-based guidelines, told attendees at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
In a thought-provoking presentation called “Axe the Rx: Deprescribing Chronic Medications with PEER,” the panelists gave examples of medications that may be safely stopped or tapered, particularly for older adults “whose pill bag is heavier than their lunch bag.”
Curbing Cardiovascular Drugs
The 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults call for reaching an LDL-C < 1.8 mmol/L in secondary cardiovascular prevention by potentially adding on medical therapies such as proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors or ezetimibe or both if that target is not reached with the maximal dosage of a statin.
But family physicians do not need to follow this guidance for their patients who have had a myocardial infarction, said Ontario family physician Jennifer Young, MD, a physician advisor in the Canadian College of Family Physicians’ Knowledge Experts and Tools Program.
Treating to below 1.8 mmol/L “means lab testing for the patients,” Young told this news organization. “It means increasing doses [of a statin] to try and get to that level.” If the patient is already on the highest dose of a statin, it means adding other medications that lower cholesterol.
“If that was translating into better outcomes like [preventing] death and another heart attack, then all of that extra effort would be worth it,” said Young. “But we don’t have evidence that it actually does have a benefit for outcomes like death and repeated heart attacks,” compared with putting them on a high dose of a potent statin.
Tapering Opioids
Before placing patients on an opioid taper, clinicians should first assess them for opioid use disorder (OUD), said Jessica Kirkwood, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada. She suggested using the Prescription Opioid Misuse Index questionnaire to do so.
Clinicians should be much more careful in initiating a taper with patients with OUD, said Kirkwood. They must ensure that these patients are motivated to discontinue their opioids. “We’re losing 21 Canadians a day to the opioid crisis. We all know that cutting someone off their opioids and potentially having them seek opioids elsewhere through illicit means can be fatal.”
In addition, clinicians should spend more time counseling patients with OUD than those without, Kirkwood continued. They must explain to these patients how they are being tapered (eg, the intervals and doses) and highlight the benefits of a taper, such as reduced constipation. Opioid agonist therapy (such as methadone or buprenorphine) can be considered in these patients.
Some research has pointed to the importance of patient motivation as a factor in the success of opioid tapers, noted Kirkwood.
Deprescribing Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepine receptor agonists, too, often can be deprescribed. These drugs should not be prescribed to promote sleep on a long-term basis. Yet clinicians commonly encounter patients who have been taking them for more than a year, said pharmacist Betsy Thomas, assistant adjunct professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta.
The medications “are usually fairly effective for the first couple of weeks to about a month, and then the benefits start to decrease, and we start to see more harms,” she said.
Some of the harms that have been associated with continued use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists include delayed reaction time and impaired cognition, which can affect the ability to drive, the risk for falls, and the risk for hip fractures, she noted. Some research suggests that these drugs are not an option for treating insomnia in patients aged 65 years or older.
Clinicians should encourage tapering the use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists to minimize dependence and transition patients to nonpharmacologic approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy to manage insomnia, she said. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of the intervention, and Thomas suggested that family physicians visit the mysleepwell.ca website for more information.
Young, Kirkwood, and Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM FMF 2024
To Hold or Not to Hold GLP-1s Before Surgery
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, there have been two somewhat conflicting recommendations about how to deal with our patients who are on incretin hormone therapy before undergoing elective surgical procedures.
First, the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] has updated the package inserts for all of these incretins, meaning the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic (GIP)/GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide, with a warning about pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation. They instruct patients to let healthcare providers know of any planned surgeries or procedures. This has come about because of postmarketing experience in which patients who are on GLP-1 receptor agonists have had residual gastric contents found despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations.
The problem with this is that the FDA says they don’t really actually know what to tell us to do or not to do because we don’t have knowledge as to how to truly mitigate the risk for pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation. They don’t know if modifying preoperative fasting recommendations should be changed or if temporary discontinuation of the drugs could reduce this problem. They really don’t know what to tell us to do except to tell us that this is a problem we should discuss with our patients.
At about the same time, a society guideline— and this was from a number of different societies, including the American Society of Anesthesiologists — stated that most patients should continue taking their GLP-1 receptor agonist before elective surgery.
This struck me as somewhat discordant from what the FDA said, although the FDA also says they don’t know quite what to tell us to do. This clinical guideline goes into a bit more detail, and what they think might be a good idea is that patients who are at the highest risk for GI side effects should follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure.
They basically look at who is at highest risk, and they say the following: Patients in the escalation phase of their incretin therapy — that is, early in treatment when the dose is increasing — are most likely to have delays in gastric emptying because that effect is lessened over time. They say that the elective surgery should be deferred until the escalation phase has passed and the GI symptoms have dissipated.
They’re very clear that patients who have significant GI symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, and shortness of breath, should wait until their symptoms have dissipated.
They think this is something that would be good no matter what dose of drug these patients are on. They do say that you tend to see more issues with gastric emptying in patients at the highest dose of a GLP-1 receptor agonist. They also mention other medical conditions that may slow gastric emptying, such as Parkinson’s disease, which may further modify the perioperative management plan.
Their proposed solutions that sort of correspond with my proposed solutions include assessing the patient. Obviously, if a patient is going up on the dose of these drugs or having many GI side effects, that’s someone who you probably don’t want to send for elective surgery if you don’t have to. However, if you need to — and possibly in everybody — you might want to withhold the drug for 10-14 days preoperatively to make sure they don’t have significant GI side effects as they’re preparing for their procedure.
One of the things the anesthesiology group was worried about was that glucose levels would go up and patients would have hyperglycemia going into surgery. I’m not so worried about holding a dose or two of one of these agents. I don’t see much hyperglycemia occurring. If it does, you can treat it in other ways.
If it’s somebody where you think they’re having symptoms but they want to have the procedure anyway, you can put them on a liquid diet for 24 hours or so, so that there’s less of a risk for retained gastric contents, at least solid gastric contents. Anesthesiologists can help with this as well because in many cases, they can do a point-of-care gastric ultrasound to check for retained food or fluid.
I know this is sort of vague because I don’t have clear recommendations, but I do think it’s important to talk with your patients to assess whether they’re having signs or symptoms of gastroparesis. I think it’s not unreasonable to hold the incretin hormone therapy for one or two doses before a procedure if you have that opportunity, and be sure that the anesthesiologist and surgery team are aware of the fact that the patient has been on one of these agents so that they’re a little more aware of the risk for aspiration.
Anne L. Peters, Professor, Department of Clinical Medicine, Keck School of Medicine; Director, University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) on the advisory board for Abbott Diabetes Care; Becton Dickinson; Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Eli Lilly and Company; Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Livongo; Medscape; Merck & Co., Inc.; Novo Nordisk; Omada Health; OptumHealth; sanofi; Zafgen Received research support from: Dexcom; MannKind Corporation; Astra Zeneca. Serve(d) as a member of a speakers bureau for: Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, there have been two somewhat conflicting recommendations about how to deal with our patients who are on incretin hormone therapy before undergoing elective surgical procedures.
First, the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] has updated the package inserts for all of these incretins, meaning the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic (GIP)/GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide, with a warning about pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation. They instruct patients to let healthcare providers know of any planned surgeries or procedures. This has come about because of postmarketing experience in which patients who are on GLP-1 receptor agonists have had residual gastric contents found despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations.
The problem with this is that the FDA says they don’t really actually know what to tell us to do or not to do because we don’t have knowledge as to how to truly mitigate the risk for pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation. They don’t know if modifying preoperative fasting recommendations should be changed or if temporary discontinuation of the drugs could reduce this problem. They really don’t know what to tell us to do except to tell us that this is a problem we should discuss with our patients.
At about the same time, a society guideline— and this was from a number of different societies, including the American Society of Anesthesiologists — stated that most patients should continue taking their GLP-1 receptor agonist before elective surgery.
This struck me as somewhat discordant from what the FDA said, although the FDA also says they don’t know quite what to tell us to do. This clinical guideline goes into a bit more detail, and what they think might be a good idea is that patients who are at the highest risk for GI side effects should follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure.
They basically look at who is at highest risk, and they say the following: Patients in the escalation phase of their incretin therapy — that is, early in treatment when the dose is increasing — are most likely to have delays in gastric emptying because that effect is lessened over time. They say that the elective surgery should be deferred until the escalation phase has passed and the GI symptoms have dissipated.
They’re very clear that patients who have significant GI symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, and shortness of breath, should wait until their symptoms have dissipated.
They think this is something that would be good no matter what dose of drug these patients are on. They do say that you tend to see more issues with gastric emptying in patients at the highest dose of a GLP-1 receptor agonist. They also mention other medical conditions that may slow gastric emptying, such as Parkinson’s disease, which may further modify the perioperative management plan.
Their proposed solutions that sort of correspond with my proposed solutions include assessing the patient. Obviously, if a patient is going up on the dose of these drugs or having many GI side effects, that’s someone who you probably don’t want to send for elective surgery if you don’t have to. However, if you need to — and possibly in everybody — you might want to withhold the drug for 10-14 days preoperatively to make sure they don’t have significant GI side effects as they’re preparing for their procedure.
One of the things the anesthesiology group was worried about was that glucose levels would go up and patients would have hyperglycemia going into surgery. I’m not so worried about holding a dose or two of one of these agents. I don’t see much hyperglycemia occurring. If it does, you can treat it in other ways.
If it’s somebody where you think they’re having symptoms but they want to have the procedure anyway, you can put them on a liquid diet for 24 hours or so, so that there’s less of a risk for retained gastric contents, at least solid gastric contents. Anesthesiologists can help with this as well because in many cases, they can do a point-of-care gastric ultrasound to check for retained food or fluid.
I know this is sort of vague because I don’t have clear recommendations, but I do think it’s important to talk with your patients to assess whether they’re having signs or symptoms of gastroparesis. I think it’s not unreasonable to hold the incretin hormone therapy for one or two doses before a procedure if you have that opportunity, and be sure that the anesthesiologist and surgery team are aware of the fact that the patient has been on one of these agents so that they’re a little more aware of the risk for aspiration.
Anne L. Peters, Professor, Department of Clinical Medicine, Keck School of Medicine; Director, University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) on the advisory board for Abbott Diabetes Care; Becton Dickinson; Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Eli Lilly and Company; Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Livongo; Medscape; Merck & Co., Inc.; Novo Nordisk; Omada Health; OptumHealth; sanofi; Zafgen Received research support from: Dexcom; MannKind Corporation; Astra Zeneca. Serve(d) as a member of a speakers bureau for: Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, there have been two somewhat conflicting recommendations about how to deal with our patients who are on incretin hormone therapy before undergoing elective surgical procedures.
First, the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] has updated the package inserts for all of these incretins, meaning the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic (GIP)/GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide, with a warning about pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation. They instruct patients to let healthcare providers know of any planned surgeries or procedures. This has come about because of postmarketing experience in which patients who are on GLP-1 receptor agonists have had residual gastric contents found despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations.
The problem with this is that the FDA says they don’t really actually know what to tell us to do or not to do because we don’t have knowledge as to how to truly mitigate the risk for pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation. They don’t know if modifying preoperative fasting recommendations should be changed or if temporary discontinuation of the drugs could reduce this problem. They really don’t know what to tell us to do except to tell us that this is a problem we should discuss with our patients.
At about the same time, a society guideline— and this was from a number of different societies, including the American Society of Anesthesiologists — stated that most patients should continue taking their GLP-1 receptor agonist before elective surgery.
This struck me as somewhat discordant from what the FDA said, although the FDA also says they don’t know quite what to tell us to do. This clinical guideline goes into a bit more detail, and what they think might be a good idea is that patients who are at the highest risk for GI side effects should follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure.
They basically look at who is at highest risk, and they say the following: Patients in the escalation phase of their incretin therapy — that is, early in treatment when the dose is increasing — are most likely to have delays in gastric emptying because that effect is lessened over time. They say that the elective surgery should be deferred until the escalation phase has passed and the GI symptoms have dissipated.
They’re very clear that patients who have significant GI symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, and shortness of breath, should wait until their symptoms have dissipated.
They think this is something that would be good no matter what dose of drug these patients are on. They do say that you tend to see more issues with gastric emptying in patients at the highest dose of a GLP-1 receptor agonist. They also mention other medical conditions that may slow gastric emptying, such as Parkinson’s disease, which may further modify the perioperative management plan.
Their proposed solutions that sort of correspond with my proposed solutions include assessing the patient. Obviously, if a patient is going up on the dose of these drugs or having many GI side effects, that’s someone who you probably don’t want to send for elective surgery if you don’t have to. However, if you need to — and possibly in everybody — you might want to withhold the drug for 10-14 days preoperatively to make sure they don’t have significant GI side effects as they’re preparing for their procedure.
One of the things the anesthesiology group was worried about was that glucose levels would go up and patients would have hyperglycemia going into surgery. I’m not so worried about holding a dose or two of one of these agents. I don’t see much hyperglycemia occurring. If it does, you can treat it in other ways.
If it’s somebody where you think they’re having symptoms but they want to have the procedure anyway, you can put them on a liquid diet for 24 hours or so, so that there’s less of a risk for retained gastric contents, at least solid gastric contents. Anesthesiologists can help with this as well because in many cases, they can do a point-of-care gastric ultrasound to check for retained food or fluid.
I know this is sort of vague because I don’t have clear recommendations, but I do think it’s important to talk with your patients to assess whether they’re having signs or symptoms of gastroparesis. I think it’s not unreasonable to hold the incretin hormone therapy for one or two doses before a procedure if you have that opportunity, and be sure that the anesthesiologist and surgery team are aware of the fact that the patient has been on one of these agents so that they’re a little more aware of the risk for aspiration.
Anne L. Peters, Professor, Department of Clinical Medicine, Keck School of Medicine; Director, University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) on the advisory board for Abbott Diabetes Care; Becton Dickinson; Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Eli Lilly and Company; Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Livongo; Medscape; Merck & Co., Inc.; Novo Nordisk; Omada Health; OptumHealth; sanofi; Zafgen Received research support from: Dexcom; MannKind Corporation; Astra Zeneca. Serve(d) as a member of a speakers bureau for: Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As Populations Age, Occam’s Razor Loses Its Diagnostic Edge
The principle of parsimony, often referred to as “Occam’s razor,” favors a unifying explanation over multiple ones, as long as both explain the data equally well. This heuristic, widely used in medical practice, advocates for simpler explanations rather than complex theories. However, its application in modern medicine has sparked debate.
“Hickam’s dictum,” a counterargument to Occam’s razor, asserts that patients — especially as populations grow older and more fragile — can simultaneously have multiple, unrelated diagnoses. These contrasting perspectives on clinical reasoning, balancing diagnostic simplicity and complexity, are both used in daily medical practice.
But are these two axioms truly in conflict, or is this a false dichotomy?
Occam’s Razor and Simple Diagnoses
Interpersonal variability in diagnostic approaches, shaped by the subjective nature of many judgments, complicates the formal evaluation of diagnostic parsimony (Occam’s razor). Indirect evidence suggests that prioritizing simplicity in diagnosis can result in under-detection of secondary conditions, particularly in patients with chronic illnesses.
For example, older patients with a known chronic illness were found to have a 30%-60% lower likelihood of being treated for an unrelated secondary diagnosis than matched peers without the chronic condition. Other studies indicate that a readily available, simple diagnosis can lead clinicians to prematurely close their diagnostic reasoning, overlooking other significant illnesses.
Beyond Hickam’s Dictum and Occam’s Razor
A recent study explored the phenomenon of multiple diagnoses by examining the supposed conflict between Hickam’s dictum and Occam’s razor, as well as the ambiguities in how they are interpreted and used by physicians in clinical reasoning.
Part 1: Researchers identified articles on PubMed related to Hickam’s dictum or conflicting with Occam’s razor, categorizing instances into four models of Hickam’s dictum:
1. Incidentaloma: An asymptomatic condition discovered accidentally.
2. Preexisting diagnosis: A known condition in the patient’s medical history.
3. Causally related disease: A complication, association, epiphenomenon, or underlying cause connected to the primary diagnosis.
4. Coincidental and independent disease: A symptomatic condition unrelated to the primary diagnosis.
Part 2: Researchers analyzed 220 case records from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and clinical problem-solving reports published in The New England Journal of Medicine between 2017 and 2023. They found no cases where the final diagnosis was not a unifying one.
Part 3: In an online survey of 265 physicians, 79% identified coincidental symptomatic conditions (category 4) as the least likely type of multiple diagnoses. Preexisting conditions (category 2) emerged as the most common, reflecting the tendency to add new diagnoses to a patient’s existing health profile. Almost one third of instances referencing Hickam’s dictum or violations of Occam’s razor fell into category 2.
Causally related diseases (category 3) were probabilistically dependent, meaning that the presence of one condition increased the likelihood of the other, based on the strength (often unknown) of the causal relationship.
Practical Insights
The significant finding of this work was that multiple diagnoses occur in predictable patterns, informed by causal connections between conditions, symptom onset timing, and likelihood. The principle of common causation supports the search for a unifying diagnosis for coincidental symptoms. It is not surprising that causally related phenomena often co-occur, as reflected by the fact that 40% of multiple diagnoses in the study’s first part were causally linked.
Thus, understanding multiple diagnoses goes beyond Hickam’s dictum and Occam’s razor. It requires not only identifying diseases but also examining their causal relationships and the timing of symptom onset. A unifying diagnosis is not equivalent to a single diagnosis; rather, it represents a causal pathway linking underlying pathologic changes to acute presentations.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The principle of parsimony, often referred to as “Occam’s razor,” favors a unifying explanation over multiple ones, as long as both explain the data equally well. This heuristic, widely used in medical practice, advocates for simpler explanations rather than complex theories. However, its application in modern medicine has sparked debate.
“Hickam’s dictum,” a counterargument to Occam’s razor, asserts that patients — especially as populations grow older and more fragile — can simultaneously have multiple, unrelated diagnoses. These contrasting perspectives on clinical reasoning, balancing diagnostic simplicity and complexity, are both used in daily medical practice.
But are these two axioms truly in conflict, or is this a false dichotomy?
Occam’s Razor and Simple Diagnoses
Interpersonal variability in diagnostic approaches, shaped by the subjective nature of many judgments, complicates the formal evaluation of diagnostic parsimony (Occam’s razor). Indirect evidence suggests that prioritizing simplicity in diagnosis can result in under-detection of secondary conditions, particularly in patients with chronic illnesses.
For example, older patients with a known chronic illness were found to have a 30%-60% lower likelihood of being treated for an unrelated secondary diagnosis than matched peers without the chronic condition. Other studies indicate that a readily available, simple diagnosis can lead clinicians to prematurely close their diagnostic reasoning, overlooking other significant illnesses.
Beyond Hickam’s Dictum and Occam’s Razor
A recent study explored the phenomenon of multiple diagnoses by examining the supposed conflict between Hickam’s dictum and Occam’s razor, as well as the ambiguities in how they are interpreted and used by physicians in clinical reasoning.
Part 1: Researchers identified articles on PubMed related to Hickam’s dictum or conflicting with Occam’s razor, categorizing instances into four models of Hickam’s dictum:
1. Incidentaloma: An asymptomatic condition discovered accidentally.
2. Preexisting diagnosis: A known condition in the patient’s medical history.
3. Causally related disease: A complication, association, epiphenomenon, or underlying cause connected to the primary diagnosis.
4. Coincidental and independent disease: A symptomatic condition unrelated to the primary diagnosis.
Part 2: Researchers analyzed 220 case records from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and clinical problem-solving reports published in The New England Journal of Medicine between 2017 and 2023. They found no cases where the final diagnosis was not a unifying one.
Part 3: In an online survey of 265 physicians, 79% identified coincidental symptomatic conditions (category 4) as the least likely type of multiple diagnoses. Preexisting conditions (category 2) emerged as the most common, reflecting the tendency to add new diagnoses to a patient’s existing health profile. Almost one third of instances referencing Hickam’s dictum or violations of Occam’s razor fell into category 2.
Causally related diseases (category 3) were probabilistically dependent, meaning that the presence of one condition increased the likelihood of the other, based on the strength (often unknown) of the causal relationship.
Practical Insights
The significant finding of this work was that multiple diagnoses occur in predictable patterns, informed by causal connections between conditions, symptom onset timing, and likelihood. The principle of common causation supports the search for a unifying diagnosis for coincidental symptoms. It is not surprising that causally related phenomena often co-occur, as reflected by the fact that 40% of multiple diagnoses in the study’s first part were causally linked.
Thus, understanding multiple diagnoses goes beyond Hickam’s dictum and Occam’s razor. It requires not only identifying diseases but also examining their causal relationships and the timing of symptom onset. A unifying diagnosis is not equivalent to a single diagnosis; rather, it represents a causal pathway linking underlying pathologic changes to acute presentations.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The principle of parsimony, often referred to as “Occam’s razor,” favors a unifying explanation over multiple ones, as long as both explain the data equally well. This heuristic, widely used in medical practice, advocates for simpler explanations rather than complex theories. However, its application in modern medicine has sparked debate.
“Hickam’s dictum,” a counterargument to Occam’s razor, asserts that patients — especially as populations grow older and more fragile — can simultaneously have multiple, unrelated diagnoses. These contrasting perspectives on clinical reasoning, balancing diagnostic simplicity and complexity, are both used in daily medical practice.
But are these two axioms truly in conflict, or is this a false dichotomy?
Occam’s Razor and Simple Diagnoses
Interpersonal variability in diagnostic approaches, shaped by the subjective nature of many judgments, complicates the formal evaluation of diagnostic parsimony (Occam’s razor). Indirect evidence suggests that prioritizing simplicity in diagnosis can result in under-detection of secondary conditions, particularly in patients with chronic illnesses.
For example, older patients with a known chronic illness were found to have a 30%-60% lower likelihood of being treated for an unrelated secondary diagnosis than matched peers without the chronic condition. Other studies indicate that a readily available, simple diagnosis can lead clinicians to prematurely close their diagnostic reasoning, overlooking other significant illnesses.
Beyond Hickam’s Dictum and Occam’s Razor
A recent study explored the phenomenon of multiple diagnoses by examining the supposed conflict between Hickam’s dictum and Occam’s razor, as well as the ambiguities in how they are interpreted and used by physicians in clinical reasoning.
Part 1: Researchers identified articles on PubMed related to Hickam’s dictum or conflicting with Occam’s razor, categorizing instances into four models of Hickam’s dictum:
1. Incidentaloma: An asymptomatic condition discovered accidentally.
2. Preexisting diagnosis: A known condition in the patient’s medical history.
3. Causally related disease: A complication, association, epiphenomenon, or underlying cause connected to the primary diagnosis.
4. Coincidental and independent disease: A symptomatic condition unrelated to the primary diagnosis.
Part 2: Researchers analyzed 220 case records from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and clinical problem-solving reports published in The New England Journal of Medicine between 2017 and 2023. They found no cases where the final diagnosis was not a unifying one.
Part 3: In an online survey of 265 physicians, 79% identified coincidental symptomatic conditions (category 4) as the least likely type of multiple diagnoses. Preexisting conditions (category 2) emerged as the most common, reflecting the tendency to add new diagnoses to a patient’s existing health profile. Almost one third of instances referencing Hickam’s dictum or violations of Occam’s razor fell into category 2.
Causally related diseases (category 3) were probabilistically dependent, meaning that the presence of one condition increased the likelihood of the other, based on the strength (often unknown) of the causal relationship.
Practical Insights
The significant finding of this work was that multiple diagnoses occur in predictable patterns, informed by causal connections between conditions, symptom onset timing, and likelihood. The principle of common causation supports the search for a unifying diagnosis for coincidental symptoms. It is not surprising that causally related phenomena often co-occur, as reflected by the fact that 40% of multiple diagnoses in the study’s first part were causally linked.
Thus, understanding multiple diagnoses goes beyond Hickam’s dictum and Occam’s razor. It requires not only identifying diseases but also examining their causal relationships and the timing of symptom onset. A unifying diagnosis is not equivalent to a single diagnosis; rather, it represents a causal pathway linking underlying pathologic changes to acute presentations.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Semaglutide Increase Risk for Optic Neuropathy?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the TriNetX Analytics Network to investigate the potential risk for NAION associated with semaglutide use in a broader population worldwide.
- They included Caucasians aged ≥ 18 years with only type 2 diabetes (n = 37,245) , only obesity (n = 138,391), or both (n = 64,989) who visited healthcare facilities three or more times.
- The participants were further grouped into those prescribed semaglutide and those using non–GLP-1 RA medications.
- Propensity score matching was performed to balance age, sex, body mass index, A1C levels, medications, and underlying comorbidities between the participants using semaglutide or non–GLP-1 RAs.
- The main outcome measure was the occurrence of NAION, evaluated at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up.
TAKEAWAY:
- The use of semaglutide vs non–GLP-1 RAs was not associated with an increased risk for NAION in people with only type 2 diabetes during the 1-year (hazard ratio [HR], 2.32; 95% CI, 0.60-8.97), 2-year (HR, 2.31; 95% CI, 0.86-6.17), and 3-year (HR, 1.51; 0.71-3.25) follow-up periods.
- Similarly, in the obesity-only cohort, use of semaglutide was not linked to the development of NAION across 1-year (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.08-2.09), 2-year (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.20-2.24), and 3-year (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.24-2.17) follow-up periods.
- The patients with both diabetes and obesity also showed no significant association between use of semaglutide and the risk for NAION across each follow-up period.
- Sensitivity analysis confirmed the prescription of semaglutide was not associated with an increased risk for NAION compared with non–GLP-1 RA medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our large, multinational, population-based, real-world study found that semaglutide is not associated with an increased risk of NAION in the general population,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Chien-Chih Chou, MD, PhD, of National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, in Taipei City, Taiwan, and was published online on November 02, 2024, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have limited the ability to establish causality between the use of semaglutide and the risk for NAION. The reliance on diagnosis coding for NAION may have introduced a potential misclassification of cases. Moreover, approximately half of the healthcare organizations in the TriNetX network are based in the United States, potentially limiting the diversity of the data.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from Taichung Veterans General Hospital. The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the TriNetX Analytics Network to investigate the potential risk for NAION associated with semaglutide use in a broader population worldwide.
- They included Caucasians aged ≥ 18 years with only type 2 diabetes (n = 37,245) , only obesity (n = 138,391), or both (n = 64,989) who visited healthcare facilities three or more times.
- The participants were further grouped into those prescribed semaglutide and those using non–GLP-1 RA medications.
- Propensity score matching was performed to balance age, sex, body mass index, A1C levels, medications, and underlying comorbidities between the participants using semaglutide or non–GLP-1 RAs.
- The main outcome measure was the occurrence of NAION, evaluated at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up.
TAKEAWAY:
- The use of semaglutide vs non–GLP-1 RAs was not associated with an increased risk for NAION in people with only type 2 diabetes during the 1-year (hazard ratio [HR], 2.32; 95% CI, 0.60-8.97), 2-year (HR, 2.31; 95% CI, 0.86-6.17), and 3-year (HR, 1.51; 0.71-3.25) follow-up periods.
- Similarly, in the obesity-only cohort, use of semaglutide was not linked to the development of NAION across 1-year (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.08-2.09), 2-year (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.20-2.24), and 3-year (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.24-2.17) follow-up periods.
- The patients with both diabetes and obesity also showed no significant association between use of semaglutide and the risk for NAION across each follow-up period.
- Sensitivity analysis confirmed the prescription of semaglutide was not associated with an increased risk for NAION compared with non–GLP-1 RA medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our large, multinational, population-based, real-world study found that semaglutide is not associated with an increased risk of NAION in the general population,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Chien-Chih Chou, MD, PhD, of National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, in Taipei City, Taiwan, and was published online on November 02, 2024, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have limited the ability to establish causality between the use of semaglutide and the risk for NAION. The reliance on diagnosis coding for NAION may have introduced a potential misclassification of cases. Moreover, approximately half of the healthcare organizations in the TriNetX network are based in the United States, potentially limiting the diversity of the data.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from Taichung Veterans General Hospital. The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the TriNetX Analytics Network to investigate the potential risk for NAION associated with semaglutide use in a broader population worldwide.
- They included Caucasians aged ≥ 18 years with only type 2 diabetes (n = 37,245) , only obesity (n = 138,391), or both (n = 64,989) who visited healthcare facilities three or more times.
- The participants were further grouped into those prescribed semaglutide and those using non–GLP-1 RA medications.
- Propensity score matching was performed to balance age, sex, body mass index, A1C levels, medications, and underlying comorbidities between the participants using semaglutide or non–GLP-1 RAs.
- The main outcome measure was the occurrence of NAION, evaluated at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up.
TAKEAWAY:
- The use of semaglutide vs non–GLP-1 RAs was not associated with an increased risk for NAION in people with only type 2 diabetes during the 1-year (hazard ratio [HR], 2.32; 95% CI, 0.60-8.97), 2-year (HR, 2.31; 95% CI, 0.86-6.17), and 3-year (HR, 1.51; 0.71-3.25) follow-up periods.
- Similarly, in the obesity-only cohort, use of semaglutide was not linked to the development of NAION across 1-year (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.08-2.09), 2-year (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.20-2.24), and 3-year (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.24-2.17) follow-up periods.
- The patients with both diabetes and obesity also showed no significant association between use of semaglutide and the risk for NAION across each follow-up period.
- Sensitivity analysis confirmed the prescription of semaglutide was not associated with an increased risk for NAION compared with non–GLP-1 RA medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our large, multinational, population-based, real-world study found that semaglutide is not associated with an increased risk of NAION in the general population,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Chien-Chih Chou, MD, PhD, of National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, in Taipei City, Taiwan, and was published online on November 02, 2024, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have limited the ability to establish causality between the use of semaglutide and the risk for NAION. The reliance on diagnosis coding for NAION may have introduced a potential misclassification of cases. Moreover, approximately half of the healthcare organizations in the TriNetX network are based in the United States, potentially limiting the diversity of the data.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from Taichung Veterans General Hospital. The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Satisfaction With Department of Veterans Affairs Prosthetics and Support Services as Reported by Women and Men Veterans
Satisfaction With Department of Veterans Affairs Prosthetics and Support Services as Reported by Women and Men Veterans
Limb loss is a significant and growing concern in the United States. Nearly 2 million Americans are living with limb loss, and up to 185,000 people undergo amputations annually.1-4 Of these patients, about 35% are women.5 The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides about 10% of US amputations.6-8 Between 2015 and 2019, the number of prosthetic devices provided to female veterans increased from 3.3 million to 4.6 million.5,9,10
Previous research identified disparities in prosthetic care between men and women, both within and outside the VHA. These disparities include slower prosthesis prescription and receipt among women, in addition to differences in self-reported mobility, satisfaction, rates of prosthesis rejection, and challenges related to prosthesis appearance and fit.5,10,11 Recent studies suggest women tend to have worse outcomes following amputation, and are underrepresented in amputation research.12,13 However, these disparities are poorly described in a large, national sample. Because women represent a growing portion of patients with limb loss in the VHA, understanding their needs is critical.14
The Johnny Isakson and David P. Roe, MD Veterans Health Care and Benefits Improvement Act of 2020 was enacted, in part, to improve the care provided to women veterans.15 The law required the VHA to conduct a survey of ≥ 50,000 veterans to assess the satisfaction of women veterans with prostheses provided by the VHA. To comply with this legislation and understand how women veterans rate their prostheses and related care in the VHA, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Center for Collaborative Evaluation (VACE) conducted a large national survey of veterans with limb loss that oversampled women veterans. This article describes the survey results, including characteristics of female veterans with limb loss receiving care from the VHA, assesses their satisfaction with prostheses and prosthetic care, and highlights where their responses differ from those of male veterans.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional, mixedmode survey of eligible amputees in the VHA Support Service Capital Assets Amputee Data Cube. We identified a cohort of veterans with any major amputation (above the ankle or wrist) or partial hand or foot amputation who received VHA care between October 1, 2019, and September 30, 2020. The final cohort yielded 46,646 potentially eligible veterans. Thirty-three had invalid contact information, leaving 46,613 veterans who were asked to participate, including 1356 women.
Survey
We created a survey instrument de novo that included questions from validated instruments, including the Trinity Amputation Prosthesis and Experience Scales to assess prosthetic device satisfaction, the Prosthesis Evaluation Questionnaire to assess quality of life (QOL) satisfaction, and the Orthotics Prosthetics Users Survey to assess prosthesis-related care satisfaction. 16-18 Additional questions were incorporated from a survey of veterans with upper limb amputation to assess the importance of cosmetic considerations related to the prosthesis and comfort with prosthesis use in intimate relationships.19 Questions were also included to assess amputation type, year of amputation, if a prosthesis was currently used, reasons for ceasing use of a prosthesis, reasons for never using a prosthesis, the types of prostheses used, intensity of prosthesis use, satisfaction with time required to receive a prosthetic limb, and if the prosthesis reflected the veteran’s selfidentified gender. Veterans were asked to answer questions based on their most recent amputation.
We tested the survey using cognitive interviews with 6 veterans to refine the survey and better understand how veterans interpreted the questions. Pilot testers completed the survey and participated in individual interviews with experienced interviewers (CL and RRK) to describe how they selected their responses.20 This feedback was used to refine the survey. The online survey was programmed using Qualtrics Software and manually translated into Spanish.
Given the multimodal design, surveys were distributed by email, text message, and US Postal Service (USPS). Surveys were emailed to all veterans for whom a valid email address was available. If emails were undeliverable, veterans were contacted via text message or the USPS. Surveys were distributed by text message to all veterans without an email address but with a cellphone number. We were unable to consistently identify invalid numbers among all text message recipients. Invitations with a survey URL and QR code were sent via USPS to veterans who had no valid email address or cellphone number. Targeted efforts were made to increase the response rate for women. A random sample of 200 women who had not completed the survey 2 weeks prior to the closing date (15% of women in sample) was selected to receive personal phone calls. Another random sample of 400 women was selected to receive personalized outreach emails. The survey data were confidential, and responses could not be traced to identifying information.
Data Analyses
We conducted a descriptive analysis, including percentages and means for responses to variables focused on describing amputation characteristics, prosthesis characteristics, and QOL. All data, including missing values, were used to document the percentage of respondents for each question. Removing missing data from the denominator when calculating percentages could introduce bias to the analysis because we cannot be certain data are missing at random. Missing variables were removed to avoid underinflation of mean scores.
We compared responses across 2 groups: individuals who self-identified as men and individuals who self-identified as women. For each question, we assessed whether each of these groups differed significantly from the remaining sample. For example, we examined whether the percentage of men who answered affirmatively to a question was significantly higher or lower than that of individuals not identifying as male, and whether the percentage of women who answered affirmatively was significantly higher or lower than that of individuals not identifying as female. We utilized x2 tests to determine significant differences for percentage calculations and t tests to determine significant differences in means across gender.
Since conducting multiple comparisons within a dataset may result in inflating statistical significance (type 1 errors), we used a more conservative estimate of statistical significance (α = 0.01) and high significance (α = 0.001). This study was deemed quality improvement by the VHA Rehabilitation and Prosthetic Services (12RPS) and acknowledged by the VA Research Office at Eastern Colorado Health Care System and was not subject to institutional review board review.
Results
Surveys were distributed to 46,613 veterans and were completed by 4981 respondents for a 10.7% overall response rate. Survey respondents were generally similar to the eligible population invited to participate, but the proportion of women who completed the survey was higher than the proportion of women eligible to participate (2.0% of eligible population vs 16.7% of respondents), likely due to specific efforts to target women. Survey respondents were slightly younger than the general population (67.3 years vs 68.7 years), less likely to be male (97.1% vs 83.3%), showed similar representation of Operation Enduring Freedom/Operation Iraqi Freedom (OEF/OIF) veterans (4.4% vs 4.1%), and were less likely to have diabetes (58.0% vs 52.7% had diabetes) (Table 1).
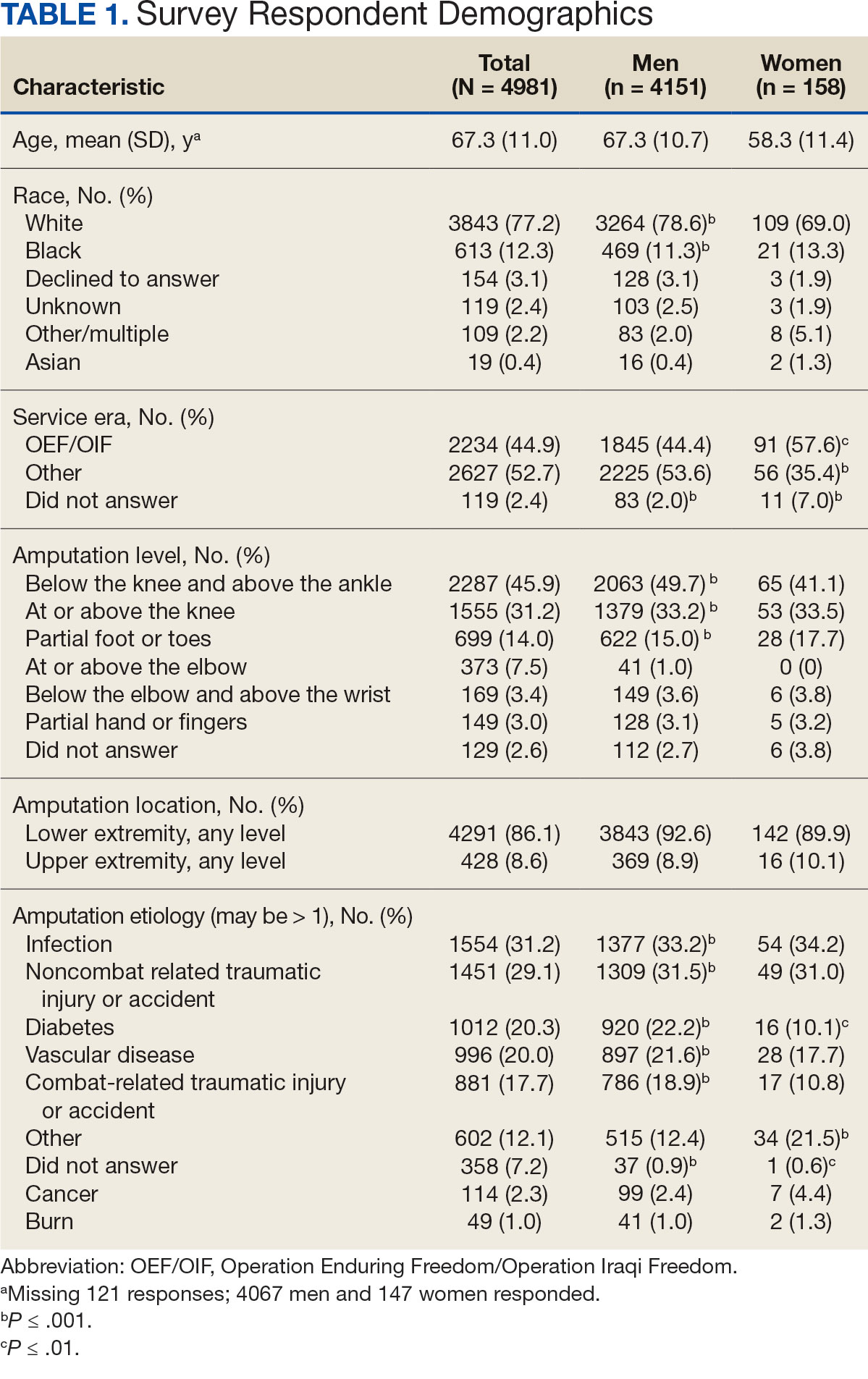
The mean age of male respondents was 67.3 years, while the mean age of female respondents was 58.3 years. The majority of respondents were male (83.3%) and White (77.2%). Female respondents were less likely to have diabetes (35.4% of women vs 53.5% of men) and less likely to report that their most recent amputation resulted from diabetes (10.1% of women vs 22.2% of men). Women respondents were more likely to report an amputation due to other causes, such as adverse results of surgery, neurologic disease, suicide attempt, blood clots, tumors, rheumatoid arthritis, and revisions of previous amputations. Most women respondents did not serve during the OEF or OIF eras. The most common amputation site for women respondents was lower limb, either below the knee and above the ankle or above the knee.
Most participants use an everyday prosthesis, but women were more likely to report using a sports-specific prosthesis (Table 2). Overall, most respondents report using a prosthesis (87.7%); however, women were more likely to report not using a prosthesis (19.4% of women vs 11.1% of men; P ≤ .01). Additionally, a lower proportion of women report using a prosthesis for < 12 hours per day (30.6% of women vs 46.4% of men; P ≤ .01) or using a prosthesis every day (54.8% of women vs 74.6% of men; P ≤ .001).
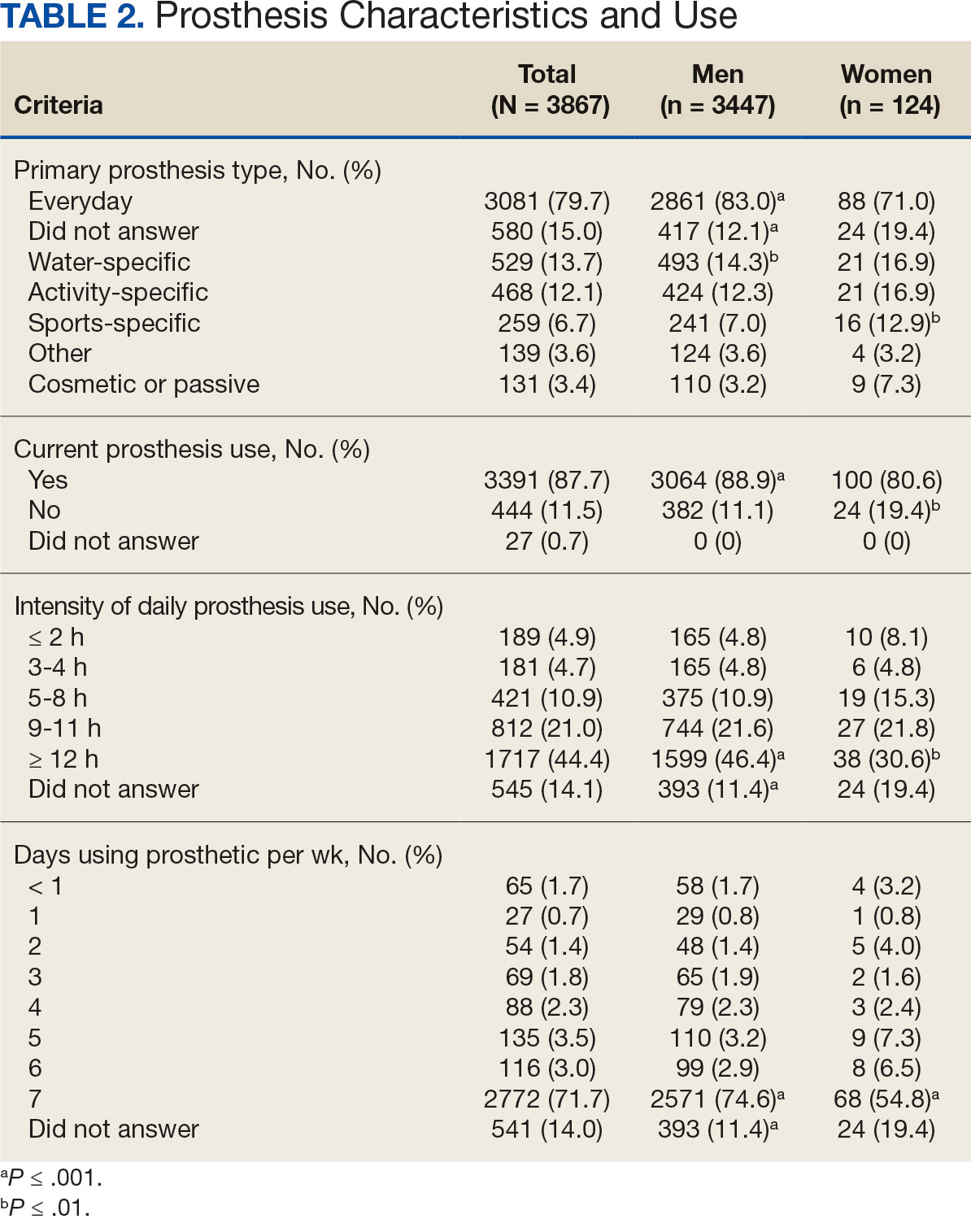
In the overall sample, the mean satisfaction score with a prosthesis was 2.7 on a 5-point scale, and women had slightly lower overall satisfaction scores (2.6 for women vs 2.7 for men; P ≤ .001) (Table 3). Women also had lower satisfaction scores related to appearance, usefulness, reliability, and comfort. Women were more likely to indicate that it was very important to be able to wear jewelry and accessories (20.2% of women vs 11.6% of men; P ≤ .01), while men were less likely to indicate that it was somewhat or very important that the prosthesis not restrict clothing or shoes (95.2% of women vs 82.9% of men; P ≤ .001). Men were more likely than women to report being comfortable or very comfortable using their prosthesis in intimate contact: 40.5% vs 29.0%, respectively (P ≤ .001).
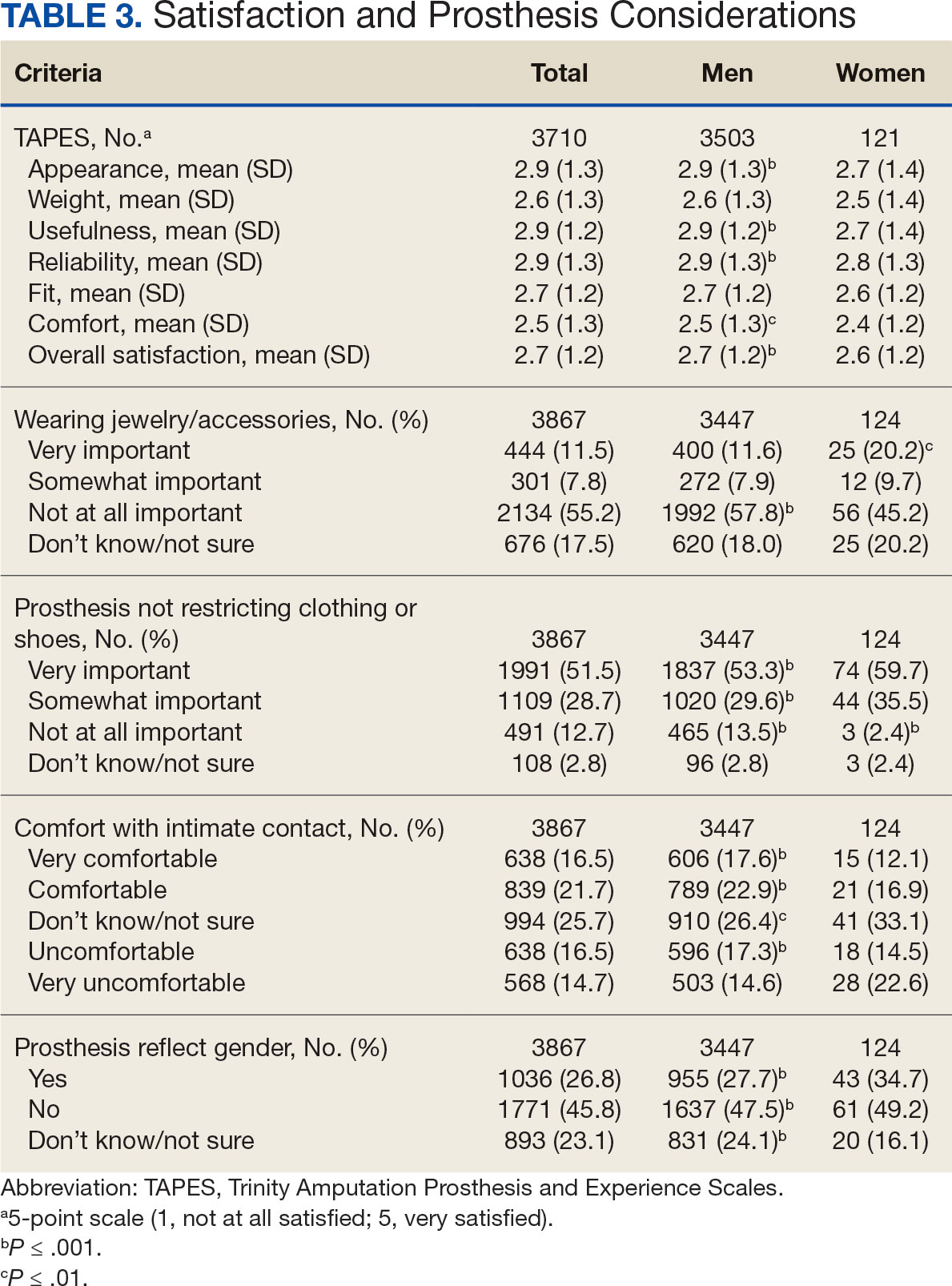
Overall, participants reported high satisfaction with appointment times, wait times, courteous treatment, opportunities to express concerns, and staff responsiveness. Men were slightly more likely than women to be satisfied with training (P ≤ 0.001) and problem discussion (P ≤ 0.01) (Table 4). There were no statistically significant differences in satisfaction or QOL ratings between women and men. The overall sample rated both QOL and satisfaction with QOL 6.7 on a 10-point scale.
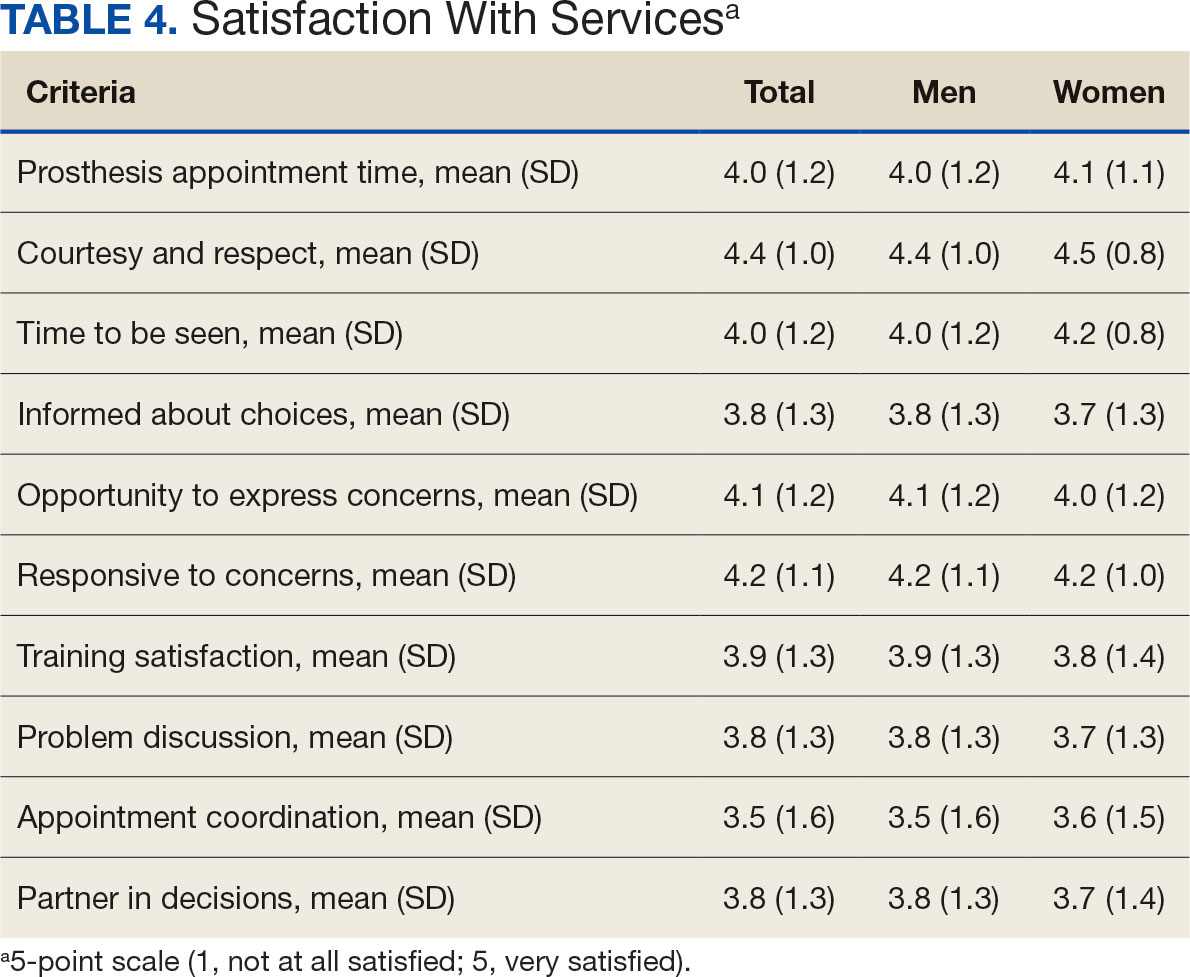
Discussion
The goal of this study was to characterize the experience of veterans with limb loss receiving care in the VHA and assess their satisfaction with prostheses and prosthetic care. We received responses from nearly 5000 veterans, 158 of whom were women. Women veteran respondents were slightly younger and less likely to have an amputation due to diabetes. We did not observe significant differences in amputation level between men and women but women were less likely to use a prosthesis, reported lower intensity of prosthesis use, and were less satisfied with certain aspects of their prostheses. Women may also be less satisfied with prosthesis training and problem discussion. However, we found no differences in QOL ratings between men and women.
Findings indicating women were more likely to report not using a prosthesis and that a lower proportion of women report using a prosthesis for > 12 hours a day or every day are consistent with previous research. 21,22 Interestingly, women were more likely to report using a sports-specific prosthesis. This is notable because prior research suggests that individuals with amputations may avoid participating in sports and exercise, and a lack of access to sports-specific prostheses may inhibit physical activity.23,24 Women in this sample were slightly less satisfied with their prostheses overall and reported lower satisfaction scores regarding appearance, usefulness, reliability, and comfort, consistent with previous findings.25
A lower percentage of women in this sample reported being comfortable or very comfortable using their prosthesis during intimate contact. Previous research on prosthesis satisfaction suggests individuals who rate prosthesis satisfaction lower also report lower body image across genders. 26 While women in this sample did not rate their prosthesis satisfaction lower than men, they did report lower intensity of prosthesis use, suggesting potential issues with their prostheses this survey did not evaluate. Women indicated the importance of prostheses not restricting jewelry, accessories, clothing, or shoes. These results have significant clinical and social implications. A recent qualitative study emphasizes that women veterans feel prostheses are primarily designed for men and may not work well with their physiological needs.9 Research focused on limbs better suited to women’s bodies could result in better fitting sockets, lightweight limbs, or less bulky designs. Additional research has also explored the difficulties in accommodating a range of footwear for patients with lower limb amputation. One study found that varying footwear heights affect the function of adjustable prosthetic feet in ways that may not be optimal.27
Ratings of satisfaction with prosthesisrelated services between men and women in this sample are consistent with a recent study showing that women veterans do not have significant differences in satisfaction with prosthesis-related services.28 However, this study focused specifically on lower limb amputations, while the respondents of this study include those with both upper and lower limb amputations. Importantly, our findings that women are less likely to be satisfied with prosthesis training and problem discussions support recent qualitative findings in which women expressed a desire to work with prosthetists who listen to them, take their concerns seriously, and seek solutions that fit their needs. We did not observe a difference in QOL ratings between men and women in the sample despite lower satisfaction among women with some elements of prosthesis-related services. Previous research suggests many factors impact QOL after amputation, most notably time since amputation.16,29
Limitations
This survey was deployed in a short timeline that did not allow for careful sample selection or implementing strategies to increase response rate. Additionally, the study was conducted among veterans receiving care in the VHA, and findings may not be generalizable to limb loss in other settings. Finally, the discrepancy in number of respondents who identified as men vs women made it difficult to compare differences between the 2 groups.
Conclusions
This is the largest sample of survey respondents of veterans with limb loss to date. While the findings suggest veterans are generally satisfied with prosthetic-related services overall, they also highlight several areas for improvement with services or prostheses. Given that most veterans with limb loss are men, there is a significant discrepancy between the number of women and men respondents. Additional studies with more comparable numbers of men and women have found similar ratings of satisfaction with prostheses and services.28 Further research specifically focused on improving the experiences of women should focus on better characterizing their experiences and identifying how they differ from those of male veterans. For example, understanding how to engage female veterans with limb loss in prosthesis training and problem discussions may improve their experience with their care teams and improve their use of prostheses. Understanding experiences and needs that are specific to women could lead to the development of processes, resources, or devices that are tailored to the unique requirements of women with limb loss.
- Ziegler-Graham K, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim PL, Travison TG, Brookmeyer R. Estimating the prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(3):422-429. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.11.005
- Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Limb amputation and limb deficiency: epidemiology and recent trends in the united states. South Med J. 2002;95(8):875-883. doi:10.1097/00007611-200208000-00018
- Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, Shore AD. Reamputation, mortality, and health care costs among persons with dysvascular lower-limb amputations. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(3):480-486. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.06.072
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ambulatory and inpatient procedures in the United States. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/pressroom/98facts/ambulat.htm
- Ljung J, Iacangelo A. Identifying and acknowledging a sex gap in lower-limb prosthetics. JPO. 2024;36(1):e18-e24. doi:10.1097/JPO.0000000000000470
- Feinglass J, Brown JL, LoSasso A, et al. Rates of lower-extremity amputation and arterial reconstruction in the united states, 1979 to 1996. Am J Public Health. 1999;89(8):1222- 1227. doi:10.2105/ajph.89.8.1222
- Mayfield JA, Reiber GE, Maynard C, Czerniecki JM, Caps MT, Sangeorzan BJ. Trends in lower limb amputation in the Veterans Health Administration, 1989-1998. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2000;37(1):23-30.
- Feinglass J, Pearce WH, Martin GJ, et al. Postoperative and late survival outcomes after major amputation: findings from the department of veterans affairs national surgical quality improvement program. Surgery. 2001;130(1):21-29. doi:10.1067/msy.2001.115359
- Lehavot K, Young JP, Thomas RM, et al. Voices of women veterans with lower limb prostheses: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(3):799-805. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07572-8
- US Government Accountability Office. COVID-19: Opportunities to improve federal response. GAO-21-60. Published November 12, 2020. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-21-60
- Littman AJ, Peterson AC, Korpak A, et al. Differences in prosthetic prescription between men and women veterans after transtibial or transfemoral lowerextremity amputation: a longitudinal cohort study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(8)1274-1281. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2023.02.011
- Cimino SR, Vijayakumar A, MacKay C, Mayo AL, Hitzig SL, Guilcher SJT. Sex and gender differences in quality of life and related domains for individuals with adult acquired lower-limb amputation: a scoping review. Disabil Rehabil. 2022 Oct 23;44(22):6899-6925. doi:10.1080/09638288.2021.1974106
- DadeMatthews OO, Roper JA, Vazquez A, Shannon DM, Sefton JM. Prosthetic device and service satisfaction, quality of life, and functional performance in lower limb prosthesis clients. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2024;48(4):422-430. doi:10.1097/PXR.0000000000000285
- Hamilton AB, Schwarz EB, Thomas HN, Goldstein KM. Moving women veterans’ health research forward: a special supplement. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(Suppl3):665– 667. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07606-1
- US Congress. Public Law 116-315: An Act to Improve the Lives of Veterans, S 5108 (2) (F). 116th Congress; 2021. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.congress.gov/116/plaws/publ315/PLAW-116publ315.pdf
- Gallagher P, MacLachlan M. The Trinity amputation and prosthesis experience scales and quality of life in people with lower-limb amputation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(5):730-736. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2003.07.009
- Legro MW, Reiber GD, Smith DG, del Aguila M, Larsen J, Boone D. Prosthesis evaluation questionnaire for persons with lower limb amputations: assessing prosthesis-related quality of life. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(8):931-938. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90090-9
- Legro MW, Reiber GD, Smith DG, del Aguila M, Larsen J, Boone D. Prosthesis evaluation questionnaire for persons with lower limb amputations: assessing prosthesis-related quality of life. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(8):931-938. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90090-9
- Heinemann AW, Bode RK, O’Reilly C. Development and measurement properties of the orthotics and prosthetics users’ survey (OPUS): a comprehensive set of clinical outcome instruments. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2003;27(3):191-206. doi:10.1080/03093640308726682
- Resnik LJ, Borgia ML, Clark MA. A national survey of prosthesis use in veterans with major upper limb amputation: comparisons by gender. PM R. 2020;12(11):1086-1098. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12351
- Collins D. Pretesting survey instruments: an overview of cognitive methods. Qual Life Res. 2003;12(3):229-238. doi:10.1023/a:1023254226592
- Østlie K, Lesjø IM, Franklin RJ, Garfelt B, Skjeldal OH, Magnus P. Prosthesis rejection in acquired major upper-limb amputees: a population-based survey. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2012;7(4):294-303. doi:10.3109/17483107.2011.635405
- Pezzin LE, Dillingham TR, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim P, Rossbach P. Use and satisfaction with prosthetic limb devices and related services. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(5):723-729. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2003.06.002
- Deans S, Burns D, McGarry A, Murray K, Mutrie N. Motivations and barriers to prosthesis users participation in physical activity, exercise and sport: a review of the literature. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2012;36(3):260-269. doi:10.1177/0309364612437905
- McDonald CL, Kahn A, Hafner BJ, Morgan SJ. Prevalence of secondary prosthesis use in lower limb prosthesis users. Disabil Rehabil. 2023;46(5):1016-1022. doi:10.1080/09638288.2023.2182919
- Baars EC, Schrier E, Dijkstra PU, Geertzen JHB. Prosthesis satisfaction in lower limb amputees: a systematic review of associated factors and questionnaires. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(39):e12296. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000012296
- Murray CD, Fox J. Body image and prosthesis satisfaction in the lower limb amputee. Disabil Rehabil. 2002;24(17):925–931. doi:10.1080/09638280210150014
- Major MJ, Quinlan J, Hansen AH, Esposito ER. Effects of women’s footwear on the mechanical function of heel-height accommodating prosthetic feet. PLoS One. 2022;17(1). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0262910.
- Kuo PB, Lehavot K, Thomas RM, et al. Gender differences in prosthesis-related outcomes among veterans: results of a national survey of U.S. veterans. PM R. 2024;16(3):239- 249. doi:10.1002/pmrj.13028
- Asano M, Rushton P, Miller WC, Deathe BA. Predictors of quality of life among individuals who have a lower limb amputation. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2008;32(2):231-243. doi:10.1080/03093640802024955
Limb loss is a significant and growing concern in the United States. Nearly 2 million Americans are living with limb loss, and up to 185,000 people undergo amputations annually.1-4 Of these patients, about 35% are women.5 The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides about 10% of US amputations.6-8 Between 2015 and 2019, the number of prosthetic devices provided to female veterans increased from 3.3 million to 4.6 million.5,9,10
Previous research identified disparities in prosthetic care between men and women, both within and outside the VHA. These disparities include slower prosthesis prescription and receipt among women, in addition to differences in self-reported mobility, satisfaction, rates of prosthesis rejection, and challenges related to prosthesis appearance and fit.5,10,11 Recent studies suggest women tend to have worse outcomes following amputation, and are underrepresented in amputation research.12,13 However, these disparities are poorly described in a large, national sample. Because women represent a growing portion of patients with limb loss in the VHA, understanding their needs is critical.14
The Johnny Isakson and David P. Roe, MD Veterans Health Care and Benefits Improvement Act of 2020 was enacted, in part, to improve the care provided to women veterans.15 The law required the VHA to conduct a survey of ≥ 50,000 veterans to assess the satisfaction of women veterans with prostheses provided by the VHA. To comply with this legislation and understand how women veterans rate their prostheses and related care in the VHA, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Center for Collaborative Evaluation (VACE) conducted a large national survey of veterans with limb loss that oversampled women veterans. This article describes the survey results, including characteristics of female veterans with limb loss receiving care from the VHA, assesses their satisfaction with prostheses and prosthetic care, and highlights where their responses differ from those of male veterans.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional, mixedmode survey of eligible amputees in the VHA Support Service Capital Assets Amputee Data Cube. We identified a cohort of veterans with any major amputation (above the ankle or wrist) or partial hand or foot amputation who received VHA care between October 1, 2019, and September 30, 2020. The final cohort yielded 46,646 potentially eligible veterans. Thirty-three had invalid contact information, leaving 46,613 veterans who were asked to participate, including 1356 women.
Survey
We created a survey instrument de novo that included questions from validated instruments, including the Trinity Amputation Prosthesis and Experience Scales to assess prosthetic device satisfaction, the Prosthesis Evaluation Questionnaire to assess quality of life (QOL) satisfaction, and the Orthotics Prosthetics Users Survey to assess prosthesis-related care satisfaction. 16-18 Additional questions were incorporated from a survey of veterans with upper limb amputation to assess the importance of cosmetic considerations related to the prosthesis and comfort with prosthesis use in intimate relationships.19 Questions were also included to assess amputation type, year of amputation, if a prosthesis was currently used, reasons for ceasing use of a prosthesis, reasons for never using a prosthesis, the types of prostheses used, intensity of prosthesis use, satisfaction with time required to receive a prosthetic limb, and if the prosthesis reflected the veteran’s selfidentified gender. Veterans were asked to answer questions based on their most recent amputation.
We tested the survey using cognitive interviews with 6 veterans to refine the survey and better understand how veterans interpreted the questions. Pilot testers completed the survey and participated in individual interviews with experienced interviewers (CL and RRK) to describe how they selected their responses.20 This feedback was used to refine the survey. The online survey was programmed using Qualtrics Software and manually translated into Spanish.
Given the multimodal design, surveys were distributed by email, text message, and US Postal Service (USPS). Surveys were emailed to all veterans for whom a valid email address was available. If emails were undeliverable, veterans were contacted via text message or the USPS. Surveys were distributed by text message to all veterans without an email address but with a cellphone number. We were unable to consistently identify invalid numbers among all text message recipients. Invitations with a survey URL and QR code were sent via USPS to veterans who had no valid email address or cellphone number. Targeted efforts were made to increase the response rate for women. A random sample of 200 women who had not completed the survey 2 weeks prior to the closing date (15% of women in sample) was selected to receive personal phone calls. Another random sample of 400 women was selected to receive personalized outreach emails. The survey data were confidential, and responses could not be traced to identifying information.
Data Analyses
We conducted a descriptive analysis, including percentages and means for responses to variables focused on describing amputation characteristics, prosthesis characteristics, and QOL. All data, including missing values, were used to document the percentage of respondents for each question. Removing missing data from the denominator when calculating percentages could introduce bias to the analysis because we cannot be certain data are missing at random. Missing variables were removed to avoid underinflation of mean scores.
We compared responses across 2 groups: individuals who self-identified as men and individuals who self-identified as women. For each question, we assessed whether each of these groups differed significantly from the remaining sample. For example, we examined whether the percentage of men who answered affirmatively to a question was significantly higher or lower than that of individuals not identifying as male, and whether the percentage of women who answered affirmatively was significantly higher or lower than that of individuals not identifying as female. We utilized x2 tests to determine significant differences for percentage calculations and t tests to determine significant differences in means across gender.
Since conducting multiple comparisons within a dataset may result in inflating statistical significance (type 1 errors), we used a more conservative estimate of statistical significance (α = 0.01) and high significance (α = 0.001). This study was deemed quality improvement by the VHA Rehabilitation and Prosthetic Services (12RPS) and acknowledged by the VA Research Office at Eastern Colorado Health Care System and was not subject to institutional review board review.
Results
Surveys were distributed to 46,613 veterans and were completed by 4981 respondents for a 10.7% overall response rate. Survey respondents were generally similar to the eligible population invited to participate, but the proportion of women who completed the survey was higher than the proportion of women eligible to participate (2.0% of eligible population vs 16.7% of respondents), likely due to specific efforts to target women. Survey respondents were slightly younger than the general population (67.3 years vs 68.7 years), less likely to be male (97.1% vs 83.3%), showed similar representation of Operation Enduring Freedom/Operation Iraqi Freedom (OEF/OIF) veterans (4.4% vs 4.1%), and were less likely to have diabetes (58.0% vs 52.7% had diabetes) (Table 1).

The mean age of male respondents was 67.3 years, while the mean age of female respondents was 58.3 years. The majority of respondents were male (83.3%) and White (77.2%). Female respondents were less likely to have diabetes (35.4% of women vs 53.5% of men) and less likely to report that their most recent amputation resulted from diabetes (10.1% of women vs 22.2% of men). Women respondents were more likely to report an amputation due to other causes, such as adverse results of surgery, neurologic disease, suicide attempt, blood clots, tumors, rheumatoid arthritis, and revisions of previous amputations. Most women respondents did not serve during the OEF or OIF eras. The most common amputation site for women respondents was lower limb, either below the knee and above the ankle or above the knee.
Most participants use an everyday prosthesis, but women were more likely to report using a sports-specific prosthesis (Table 2). Overall, most respondents report using a prosthesis (87.7%); however, women were more likely to report not using a prosthesis (19.4% of women vs 11.1% of men; P ≤ .01). Additionally, a lower proportion of women report using a prosthesis for < 12 hours per day (30.6% of women vs 46.4% of men; P ≤ .01) or using a prosthesis every day (54.8% of women vs 74.6% of men; P ≤ .001).

In the overall sample, the mean satisfaction score with a prosthesis was 2.7 on a 5-point scale, and women had slightly lower overall satisfaction scores (2.6 for women vs 2.7 for men; P ≤ .001) (Table 3). Women also had lower satisfaction scores related to appearance, usefulness, reliability, and comfort. Women were more likely to indicate that it was very important to be able to wear jewelry and accessories (20.2% of women vs 11.6% of men; P ≤ .01), while men were less likely to indicate that it was somewhat or very important that the prosthesis not restrict clothing or shoes (95.2% of women vs 82.9% of men; P ≤ .001). Men were more likely than women to report being comfortable or very comfortable using their prosthesis in intimate contact: 40.5% vs 29.0%, respectively (P ≤ .001).

Overall, participants reported high satisfaction with appointment times, wait times, courteous treatment, opportunities to express concerns, and staff responsiveness. Men were slightly more likely than women to be satisfied with training (P ≤ 0.001) and problem discussion (P ≤ 0.01) (Table 4). There were no statistically significant differences in satisfaction or QOL ratings between women and men. The overall sample rated both QOL and satisfaction with QOL 6.7 on a 10-point scale.

Discussion
The goal of this study was to characterize the experience of veterans with limb loss receiving care in the VHA and assess their satisfaction with prostheses and prosthetic care. We received responses from nearly 5000 veterans, 158 of whom were women. Women veteran respondents were slightly younger and less likely to have an amputation due to diabetes. We did not observe significant differences in amputation level between men and women but women were less likely to use a prosthesis, reported lower intensity of prosthesis use, and were less satisfied with certain aspects of their prostheses. Women may also be less satisfied with prosthesis training and problem discussion. However, we found no differences in QOL ratings between men and women.
Findings indicating women were more likely to report not using a prosthesis and that a lower proportion of women report using a prosthesis for > 12 hours a day or every day are consistent with previous research. 21,22 Interestingly, women were more likely to report using a sports-specific prosthesis. This is notable because prior research suggests that individuals with amputations may avoid participating in sports and exercise, and a lack of access to sports-specific prostheses may inhibit physical activity.23,24 Women in this sample were slightly less satisfied with their prostheses overall and reported lower satisfaction scores regarding appearance, usefulness, reliability, and comfort, consistent with previous findings.25
A lower percentage of women in this sample reported being comfortable or very comfortable using their prosthesis during intimate contact. Previous research on prosthesis satisfaction suggests individuals who rate prosthesis satisfaction lower also report lower body image across genders. 26 While women in this sample did not rate their prosthesis satisfaction lower than men, they did report lower intensity of prosthesis use, suggesting potential issues with their prostheses this survey did not evaluate. Women indicated the importance of prostheses not restricting jewelry, accessories, clothing, or shoes. These results have significant clinical and social implications. A recent qualitative study emphasizes that women veterans feel prostheses are primarily designed for men and may not work well with their physiological needs.9 Research focused on limbs better suited to women’s bodies could result in better fitting sockets, lightweight limbs, or less bulky designs. Additional research has also explored the difficulties in accommodating a range of footwear for patients with lower limb amputation. One study found that varying footwear heights affect the function of adjustable prosthetic feet in ways that may not be optimal.27
Ratings of satisfaction with prosthesisrelated services between men and women in this sample are consistent with a recent study showing that women veterans do not have significant differences in satisfaction with prosthesis-related services.28 However, this study focused specifically on lower limb amputations, while the respondents of this study include those with both upper and lower limb amputations. Importantly, our findings that women are less likely to be satisfied with prosthesis training and problem discussions support recent qualitative findings in which women expressed a desire to work with prosthetists who listen to them, take their concerns seriously, and seek solutions that fit their needs. We did not observe a difference in QOL ratings between men and women in the sample despite lower satisfaction among women with some elements of prosthesis-related services. Previous research suggests many factors impact QOL after amputation, most notably time since amputation.16,29
Limitations
This survey was deployed in a short timeline that did not allow for careful sample selection or implementing strategies to increase response rate. Additionally, the study was conducted among veterans receiving care in the VHA, and findings may not be generalizable to limb loss in other settings. Finally, the discrepancy in number of respondents who identified as men vs women made it difficult to compare differences between the 2 groups.
Conclusions
This is the largest sample of survey respondents of veterans with limb loss to date. While the findings suggest veterans are generally satisfied with prosthetic-related services overall, they also highlight several areas for improvement with services or prostheses. Given that most veterans with limb loss are men, there is a significant discrepancy between the number of women and men respondents. Additional studies with more comparable numbers of men and women have found similar ratings of satisfaction with prostheses and services.28 Further research specifically focused on improving the experiences of women should focus on better characterizing their experiences and identifying how they differ from those of male veterans. For example, understanding how to engage female veterans with limb loss in prosthesis training and problem discussions may improve their experience with their care teams and improve their use of prostheses. Understanding experiences and needs that are specific to women could lead to the development of processes, resources, or devices that are tailored to the unique requirements of women with limb loss.
Limb loss is a significant and growing concern in the United States. Nearly 2 million Americans are living with limb loss, and up to 185,000 people undergo amputations annually.1-4 Of these patients, about 35% are women.5 The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) provides about 10% of US amputations.6-8 Between 2015 and 2019, the number of prosthetic devices provided to female veterans increased from 3.3 million to 4.6 million.5,9,10
Previous research identified disparities in prosthetic care between men and women, both within and outside the VHA. These disparities include slower prosthesis prescription and receipt among women, in addition to differences in self-reported mobility, satisfaction, rates of prosthesis rejection, and challenges related to prosthesis appearance and fit.5,10,11 Recent studies suggest women tend to have worse outcomes following amputation, and are underrepresented in amputation research.12,13 However, these disparities are poorly described in a large, national sample. Because women represent a growing portion of patients with limb loss in the VHA, understanding their needs is critical.14
The Johnny Isakson and David P. Roe, MD Veterans Health Care and Benefits Improvement Act of 2020 was enacted, in part, to improve the care provided to women veterans.15 The law required the VHA to conduct a survey of ≥ 50,000 veterans to assess the satisfaction of women veterans with prostheses provided by the VHA. To comply with this legislation and understand how women veterans rate their prostheses and related care in the VHA, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Center for Collaborative Evaluation (VACE) conducted a large national survey of veterans with limb loss that oversampled women veterans. This article describes the survey results, including characteristics of female veterans with limb loss receiving care from the VHA, assesses their satisfaction with prostheses and prosthetic care, and highlights where their responses differ from those of male veterans.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional, mixedmode survey of eligible amputees in the VHA Support Service Capital Assets Amputee Data Cube. We identified a cohort of veterans with any major amputation (above the ankle or wrist) or partial hand or foot amputation who received VHA care between October 1, 2019, and September 30, 2020. The final cohort yielded 46,646 potentially eligible veterans. Thirty-three had invalid contact information, leaving 46,613 veterans who were asked to participate, including 1356 women.
Survey
We created a survey instrument de novo that included questions from validated instruments, including the Trinity Amputation Prosthesis and Experience Scales to assess prosthetic device satisfaction, the Prosthesis Evaluation Questionnaire to assess quality of life (QOL) satisfaction, and the Orthotics Prosthetics Users Survey to assess prosthesis-related care satisfaction. 16-18 Additional questions were incorporated from a survey of veterans with upper limb amputation to assess the importance of cosmetic considerations related to the prosthesis and comfort with prosthesis use in intimate relationships.19 Questions were also included to assess amputation type, year of amputation, if a prosthesis was currently used, reasons for ceasing use of a prosthesis, reasons for never using a prosthesis, the types of prostheses used, intensity of prosthesis use, satisfaction with time required to receive a prosthetic limb, and if the prosthesis reflected the veteran’s selfidentified gender. Veterans were asked to answer questions based on their most recent amputation.
We tested the survey using cognitive interviews with 6 veterans to refine the survey and better understand how veterans interpreted the questions. Pilot testers completed the survey and participated in individual interviews with experienced interviewers (CL and RRK) to describe how they selected their responses.20 This feedback was used to refine the survey. The online survey was programmed using Qualtrics Software and manually translated into Spanish.
Given the multimodal design, surveys were distributed by email, text message, and US Postal Service (USPS). Surveys were emailed to all veterans for whom a valid email address was available. If emails were undeliverable, veterans were contacted via text message or the USPS. Surveys were distributed by text message to all veterans without an email address but with a cellphone number. We were unable to consistently identify invalid numbers among all text message recipients. Invitations with a survey URL and QR code were sent via USPS to veterans who had no valid email address or cellphone number. Targeted efforts were made to increase the response rate for women. A random sample of 200 women who had not completed the survey 2 weeks prior to the closing date (15% of women in sample) was selected to receive personal phone calls. Another random sample of 400 women was selected to receive personalized outreach emails. The survey data were confidential, and responses could not be traced to identifying information.
Data Analyses
We conducted a descriptive analysis, including percentages and means for responses to variables focused on describing amputation characteristics, prosthesis characteristics, and QOL. All data, including missing values, were used to document the percentage of respondents for each question. Removing missing data from the denominator when calculating percentages could introduce bias to the analysis because we cannot be certain data are missing at random. Missing variables were removed to avoid underinflation of mean scores.
We compared responses across 2 groups: individuals who self-identified as men and individuals who self-identified as women. For each question, we assessed whether each of these groups differed significantly from the remaining sample. For example, we examined whether the percentage of men who answered affirmatively to a question was significantly higher or lower than that of individuals not identifying as male, and whether the percentage of women who answered affirmatively was significantly higher or lower than that of individuals not identifying as female. We utilized x2 tests to determine significant differences for percentage calculations and t tests to determine significant differences in means across gender.
Since conducting multiple comparisons within a dataset may result in inflating statistical significance (type 1 errors), we used a more conservative estimate of statistical significance (α = 0.01) and high significance (α = 0.001). This study was deemed quality improvement by the VHA Rehabilitation and Prosthetic Services (12RPS) and acknowledged by the VA Research Office at Eastern Colorado Health Care System and was not subject to institutional review board review.
Results
Surveys were distributed to 46,613 veterans and were completed by 4981 respondents for a 10.7% overall response rate. Survey respondents were generally similar to the eligible population invited to participate, but the proportion of women who completed the survey was higher than the proportion of women eligible to participate (2.0% of eligible population vs 16.7% of respondents), likely due to specific efforts to target women. Survey respondents were slightly younger than the general population (67.3 years vs 68.7 years), less likely to be male (97.1% vs 83.3%), showed similar representation of Operation Enduring Freedom/Operation Iraqi Freedom (OEF/OIF) veterans (4.4% vs 4.1%), and were less likely to have diabetes (58.0% vs 52.7% had diabetes) (Table 1).

The mean age of male respondents was 67.3 years, while the mean age of female respondents was 58.3 years. The majority of respondents were male (83.3%) and White (77.2%). Female respondents were less likely to have diabetes (35.4% of women vs 53.5% of men) and less likely to report that their most recent amputation resulted from diabetes (10.1% of women vs 22.2% of men). Women respondents were more likely to report an amputation due to other causes, such as adverse results of surgery, neurologic disease, suicide attempt, blood clots, tumors, rheumatoid arthritis, and revisions of previous amputations. Most women respondents did not serve during the OEF or OIF eras. The most common amputation site for women respondents was lower limb, either below the knee and above the ankle or above the knee.
Most participants use an everyday prosthesis, but women were more likely to report using a sports-specific prosthesis (Table 2). Overall, most respondents report using a prosthesis (87.7%); however, women were more likely to report not using a prosthesis (19.4% of women vs 11.1% of men; P ≤ .01). Additionally, a lower proportion of women report using a prosthesis for < 12 hours per day (30.6% of women vs 46.4% of men; P ≤ .01) or using a prosthesis every day (54.8% of women vs 74.6% of men; P ≤ .001).

In the overall sample, the mean satisfaction score with a prosthesis was 2.7 on a 5-point scale, and women had slightly lower overall satisfaction scores (2.6 for women vs 2.7 for men; P ≤ .001) (Table 3). Women also had lower satisfaction scores related to appearance, usefulness, reliability, and comfort. Women were more likely to indicate that it was very important to be able to wear jewelry and accessories (20.2% of women vs 11.6% of men; P ≤ .01), while men were less likely to indicate that it was somewhat or very important that the prosthesis not restrict clothing or shoes (95.2% of women vs 82.9% of men; P ≤ .001). Men were more likely than women to report being comfortable or very comfortable using their prosthesis in intimate contact: 40.5% vs 29.0%, respectively (P ≤ .001).

Overall, participants reported high satisfaction with appointment times, wait times, courteous treatment, opportunities to express concerns, and staff responsiveness. Men were slightly more likely than women to be satisfied with training (P ≤ 0.001) and problem discussion (P ≤ 0.01) (Table 4). There were no statistically significant differences in satisfaction or QOL ratings between women and men. The overall sample rated both QOL and satisfaction with QOL 6.7 on a 10-point scale.

Discussion
The goal of this study was to characterize the experience of veterans with limb loss receiving care in the VHA and assess their satisfaction with prostheses and prosthetic care. We received responses from nearly 5000 veterans, 158 of whom were women. Women veteran respondents were slightly younger and less likely to have an amputation due to diabetes. We did not observe significant differences in amputation level between men and women but women were less likely to use a prosthesis, reported lower intensity of prosthesis use, and were less satisfied with certain aspects of their prostheses. Women may also be less satisfied with prosthesis training and problem discussion. However, we found no differences in QOL ratings between men and women.
Findings indicating women were more likely to report not using a prosthesis and that a lower proportion of women report using a prosthesis for > 12 hours a day or every day are consistent with previous research. 21,22 Interestingly, women were more likely to report using a sports-specific prosthesis. This is notable because prior research suggests that individuals with amputations may avoid participating in sports and exercise, and a lack of access to sports-specific prostheses may inhibit physical activity.23,24 Women in this sample were slightly less satisfied with their prostheses overall and reported lower satisfaction scores regarding appearance, usefulness, reliability, and comfort, consistent with previous findings.25
A lower percentage of women in this sample reported being comfortable or very comfortable using their prosthesis during intimate contact. Previous research on prosthesis satisfaction suggests individuals who rate prosthesis satisfaction lower also report lower body image across genders. 26 While women in this sample did not rate their prosthesis satisfaction lower than men, they did report lower intensity of prosthesis use, suggesting potential issues with their prostheses this survey did not evaluate. Women indicated the importance of prostheses not restricting jewelry, accessories, clothing, or shoes. These results have significant clinical and social implications. A recent qualitative study emphasizes that women veterans feel prostheses are primarily designed for men and may not work well with their physiological needs.9 Research focused on limbs better suited to women’s bodies could result in better fitting sockets, lightweight limbs, or less bulky designs. Additional research has also explored the difficulties in accommodating a range of footwear for patients with lower limb amputation. One study found that varying footwear heights affect the function of adjustable prosthetic feet in ways that may not be optimal.27
Ratings of satisfaction with prosthesisrelated services between men and women in this sample are consistent with a recent study showing that women veterans do not have significant differences in satisfaction with prosthesis-related services.28 However, this study focused specifically on lower limb amputations, while the respondents of this study include those with both upper and lower limb amputations. Importantly, our findings that women are less likely to be satisfied with prosthesis training and problem discussions support recent qualitative findings in which women expressed a desire to work with prosthetists who listen to them, take their concerns seriously, and seek solutions that fit their needs. We did not observe a difference in QOL ratings between men and women in the sample despite lower satisfaction among women with some elements of prosthesis-related services. Previous research suggests many factors impact QOL after amputation, most notably time since amputation.16,29
Limitations
This survey was deployed in a short timeline that did not allow for careful sample selection or implementing strategies to increase response rate. Additionally, the study was conducted among veterans receiving care in the VHA, and findings may not be generalizable to limb loss in other settings. Finally, the discrepancy in number of respondents who identified as men vs women made it difficult to compare differences between the 2 groups.
Conclusions
This is the largest sample of survey respondents of veterans with limb loss to date. While the findings suggest veterans are generally satisfied with prosthetic-related services overall, they also highlight several areas for improvement with services or prostheses. Given that most veterans with limb loss are men, there is a significant discrepancy between the number of women and men respondents. Additional studies with more comparable numbers of men and women have found similar ratings of satisfaction with prostheses and services.28 Further research specifically focused on improving the experiences of women should focus on better characterizing their experiences and identifying how they differ from those of male veterans. For example, understanding how to engage female veterans with limb loss in prosthesis training and problem discussions may improve their experience with their care teams and improve their use of prostheses. Understanding experiences and needs that are specific to women could lead to the development of processes, resources, or devices that are tailored to the unique requirements of women with limb loss.
- Ziegler-Graham K, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim PL, Travison TG, Brookmeyer R. Estimating the prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(3):422-429. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.11.005
- Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Limb amputation and limb deficiency: epidemiology and recent trends in the united states. South Med J. 2002;95(8):875-883. doi:10.1097/00007611-200208000-00018
- Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, Shore AD. Reamputation, mortality, and health care costs among persons with dysvascular lower-limb amputations. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(3):480-486. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.06.072
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ambulatory and inpatient procedures in the United States. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/pressroom/98facts/ambulat.htm
- Ljung J, Iacangelo A. Identifying and acknowledging a sex gap in lower-limb prosthetics. JPO. 2024;36(1):e18-e24. doi:10.1097/JPO.0000000000000470
- Feinglass J, Brown JL, LoSasso A, et al. Rates of lower-extremity amputation and arterial reconstruction in the united states, 1979 to 1996. Am J Public Health. 1999;89(8):1222- 1227. doi:10.2105/ajph.89.8.1222
- Mayfield JA, Reiber GE, Maynard C, Czerniecki JM, Caps MT, Sangeorzan BJ. Trends in lower limb amputation in the Veterans Health Administration, 1989-1998. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2000;37(1):23-30.
- Feinglass J, Pearce WH, Martin GJ, et al. Postoperative and late survival outcomes after major amputation: findings from the department of veterans affairs national surgical quality improvement program. Surgery. 2001;130(1):21-29. doi:10.1067/msy.2001.115359
- Lehavot K, Young JP, Thomas RM, et al. Voices of women veterans with lower limb prostheses: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(3):799-805. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07572-8
- US Government Accountability Office. COVID-19: Opportunities to improve federal response. GAO-21-60. Published November 12, 2020. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-21-60
- Littman AJ, Peterson AC, Korpak A, et al. Differences in prosthetic prescription between men and women veterans after transtibial or transfemoral lowerextremity amputation: a longitudinal cohort study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(8)1274-1281. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2023.02.011
- Cimino SR, Vijayakumar A, MacKay C, Mayo AL, Hitzig SL, Guilcher SJT. Sex and gender differences in quality of life and related domains for individuals with adult acquired lower-limb amputation: a scoping review. Disabil Rehabil. 2022 Oct 23;44(22):6899-6925. doi:10.1080/09638288.2021.1974106
- DadeMatthews OO, Roper JA, Vazquez A, Shannon DM, Sefton JM. Prosthetic device and service satisfaction, quality of life, and functional performance in lower limb prosthesis clients. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2024;48(4):422-430. doi:10.1097/PXR.0000000000000285
- Hamilton AB, Schwarz EB, Thomas HN, Goldstein KM. Moving women veterans’ health research forward: a special supplement. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(Suppl3):665– 667. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07606-1
- US Congress. Public Law 116-315: An Act to Improve the Lives of Veterans, S 5108 (2) (F). 116th Congress; 2021. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.congress.gov/116/plaws/publ315/PLAW-116publ315.pdf
- Gallagher P, MacLachlan M. The Trinity amputation and prosthesis experience scales and quality of life in people with lower-limb amputation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(5):730-736. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2003.07.009
- Legro MW, Reiber GD, Smith DG, del Aguila M, Larsen J, Boone D. Prosthesis evaluation questionnaire for persons with lower limb amputations: assessing prosthesis-related quality of life. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(8):931-938. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90090-9
- Legro MW, Reiber GD, Smith DG, del Aguila M, Larsen J, Boone D. Prosthesis evaluation questionnaire for persons with lower limb amputations: assessing prosthesis-related quality of life. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(8):931-938. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90090-9
- Heinemann AW, Bode RK, O’Reilly C. Development and measurement properties of the orthotics and prosthetics users’ survey (OPUS): a comprehensive set of clinical outcome instruments. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2003;27(3):191-206. doi:10.1080/03093640308726682
- Resnik LJ, Borgia ML, Clark MA. A national survey of prosthesis use in veterans with major upper limb amputation: comparisons by gender. PM R. 2020;12(11):1086-1098. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12351
- Collins D. Pretesting survey instruments: an overview of cognitive methods. Qual Life Res. 2003;12(3):229-238. doi:10.1023/a:1023254226592
- Østlie K, Lesjø IM, Franklin RJ, Garfelt B, Skjeldal OH, Magnus P. Prosthesis rejection in acquired major upper-limb amputees: a population-based survey. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2012;7(4):294-303. doi:10.3109/17483107.2011.635405
- Pezzin LE, Dillingham TR, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim P, Rossbach P. Use and satisfaction with prosthetic limb devices and related services. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(5):723-729. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2003.06.002
- Deans S, Burns D, McGarry A, Murray K, Mutrie N. Motivations and barriers to prosthesis users participation in physical activity, exercise and sport: a review of the literature. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2012;36(3):260-269. doi:10.1177/0309364612437905
- McDonald CL, Kahn A, Hafner BJ, Morgan SJ. Prevalence of secondary prosthesis use in lower limb prosthesis users. Disabil Rehabil. 2023;46(5):1016-1022. doi:10.1080/09638288.2023.2182919
- Baars EC, Schrier E, Dijkstra PU, Geertzen JHB. Prosthesis satisfaction in lower limb amputees: a systematic review of associated factors and questionnaires. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(39):e12296. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000012296
- Murray CD, Fox J. Body image and prosthesis satisfaction in the lower limb amputee. Disabil Rehabil. 2002;24(17):925–931. doi:10.1080/09638280210150014
- Major MJ, Quinlan J, Hansen AH, Esposito ER. Effects of women’s footwear on the mechanical function of heel-height accommodating prosthetic feet. PLoS One. 2022;17(1). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0262910.
- Kuo PB, Lehavot K, Thomas RM, et al. Gender differences in prosthesis-related outcomes among veterans: results of a national survey of U.S. veterans. PM R. 2024;16(3):239- 249. doi:10.1002/pmrj.13028
- Asano M, Rushton P, Miller WC, Deathe BA. Predictors of quality of life among individuals who have a lower limb amputation. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2008;32(2):231-243. doi:10.1080/03093640802024955
- Ziegler-Graham K, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim PL, Travison TG, Brookmeyer R. Estimating the prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(3):422-429. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.11.005
- Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, MacKenzie EJ. Limb amputation and limb deficiency: epidemiology and recent trends in the united states. South Med J. 2002;95(8):875-883. doi:10.1097/00007611-200208000-00018
- Dillingham TR, Pezzin LE, Shore AD. Reamputation, mortality, and health care costs among persons with dysvascular lower-limb amputations. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(3):480-486. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.06.072
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ambulatory and inpatient procedures in the United States. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/pressroom/98facts/ambulat.htm
- Ljung J, Iacangelo A. Identifying and acknowledging a sex gap in lower-limb prosthetics. JPO. 2024;36(1):e18-e24. doi:10.1097/JPO.0000000000000470
- Feinglass J, Brown JL, LoSasso A, et al. Rates of lower-extremity amputation and arterial reconstruction in the united states, 1979 to 1996. Am J Public Health. 1999;89(8):1222- 1227. doi:10.2105/ajph.89.8.1222
- Mayfield JA, Reiber GE, Maynard C, Czerniecki JM, Caps MT, Sangeorzan BJ. Trends in lower limb amputation in the Veterans Health Administration, 1989-1998. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2000;37(1):23-30.
- Feinglass J, Pearce WH, Martin GJ, et al. Postoperative and late survival outcomes after major amputation: findings from the department of veterans affairs national surgical quality improvement program. Surgery. 2001;130(1):21-29. doi:10.1067/msy.2001.115359
- Lehavot K, Young JP, Thomas RM, et al. Voices of women veterans with lower limb prostheses: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(3):799-805. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07572-8
- US Government Accountability Office. COVID-19: Opportunities to improve federal response. GAO-21-60. Published November 12, 2020. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-21-60
- Littman AJ, Peterson AC, Korpak A, et al. Differences in prosthetic prescription between men and women veterans after transtibial or transfemoral lowerextremity amputation: a longitudinal cohort study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(8)1274-1281. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2023.02.011
- Cimino SR, Vijayakumar A, MacKay C, Mayo AL, Hitzig SL, Guilcher SJT. Sex and gender differences in quality of life and related domains for individuals with adult acquired lower-limb amputation: a scoping review. Disabil Rehabil. 2022 Oct 23;44(22):6899-6925. doi:10.1080/09638288.2021.1974106
- DadeMatthews OO, Roper JA, Vazquez A, Shannon DM, Sefton JM. Prosthetic device and service satisfaction, quality of life, and functional performance in lower limb prosthesis clients. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2024;48(4):422-430. doi:10.1097/PXR.0000000000000285
- Hamilton AB, Schwarz EB, Thomas HN, Goldstein KM. Moving women veterans’ health research forward: a special supplement. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(Suppl3):665– 667. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07606-1
- US Congress. Public Law 116-315: An Act to Improve the Lives of Veterans, S 5108 (2) (F). 116th Congress; 2021. Accessed September 30, 2024. https://www.congress.gov/116/plaws/publ315/PLAW-116publ315.pdf
- Gallagher P, MacLachlan M. The Trinity amputation and prosthesis experience scales and quality of life in people with lower-limb amputation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(5):730-736. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2003.07.009
- Legro MW, Reiber GD, Smith DG, del Aguila M, Larsen J, Boone D. Prosthesis evaluation questionnaire for persons with lower limb amputations: assessing prosthesis-related quality of life. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(8):931-938. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90090-9
- Legro MW, Reiber GD, Smith DG, del Aguila M, Larsen J, Boone D. Prosthesis evaluation questionnaire for persons with lower limb amputations: assessing prosthesis-related quality of life. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(8):931-938. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90090-9
- Heinemann AW, Bode RK, O’Reilly C. Development and measurement properties of the orthotics and prosthetics users’ survey (OPUS): a comprehensive set of clinical outcome instruments. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2003;27(3):191-206. doi:10.1080/03093640308726682
- Resnik LJ, Borgia ML, Clark MA. A national survey of prosthesis use in veterans with major upper limb amputation: comparisons by gender. PM R. 2020;12(11):1086-1098. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12351
- Collins D. Pretesting survey instruments: an overview of cognitive methods. Qual Life Res. 2003;12(3):229-238. doi:10.1023/a:1023254226592
- Østlie K, Lesjø IM, Franklin RJ, Garfelt B, Skjeldal OH, Magnus P. Prosthesis rejection in acquired major upper-limb amputees: a population-based survey. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2012;7(4):294-303. doi:10.3109/17483107.2011.635405
- Pezzin LE, Dillingham TR, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim P, Rossbach P. Use and satisfaction with prosthetic limb devices and related services. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(5):723-729. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2003.06.002
- Deans S, Burns D, McGarry A, Murray K, Mutrie N. Motivations and barriers to prosthesis users participation in physical activity, exercise and sport: a review of the literature. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2012;36(3):260-269. doi:10.1177/0309364612437905
- McDonald CL, Kahn A, Hafner BJ, Morgan SJ. Prevalence of secondary prosthesis use in lower limb prosthesis users. Disabil Rehabil. 2023;46(5):1016-1022. doi:10.1080/09638288.2023.2182919
- Baars EC, Schrier E, Dijkstra PU, Geertzen JHB. Prosthesis satisfaction in lower limb amputees: a systematic review of associated factors and questionnaires. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(39):e12296. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000012296
- Murray CD, Fox J. Body image and prosthesis satisfaction in the lower limb amputee. Disabil Rehabil. 2002;24(17):925–931. doi:10.1080/09638280210150014
- Major MJ, Quinlan J, Hansen AH, Esposito ER. Effects of women’s footwear on the mechanical function of heel-height accommodating prosthetic feet. PLoS One. 2022;17(1). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0262910.
- Kuo PB, Lehavot K, Thomas RM, et al. Gender differences in prosthesis-related outcomes among veterans: results of a national survey of U.S. veterans. PM R. 2024;16(3):239- 249. doi:10.1002/pmrj.13028
- Asano M, Rushton P, Miller WC, Deathe BA. Predictors of quality of life among individuals who have a lower limb amputation. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2008;32(2):231-243. doi:10.1080/03093640802024955
Satisfaction With Department of Veterans Affairs Prosthetics and Support Services as Reported by Women and Men Veterans
Satisfaction With Department of Veterans Affairs Prosthetics and Support Services as Reported by Women and Men Veterans
