User login
Erythematous Dermal Facial Plaques in a Neutropenic Patient
THE DIAGNOSIS: Neutrophilic Eccrine Hidradenitis
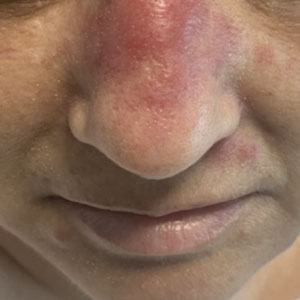
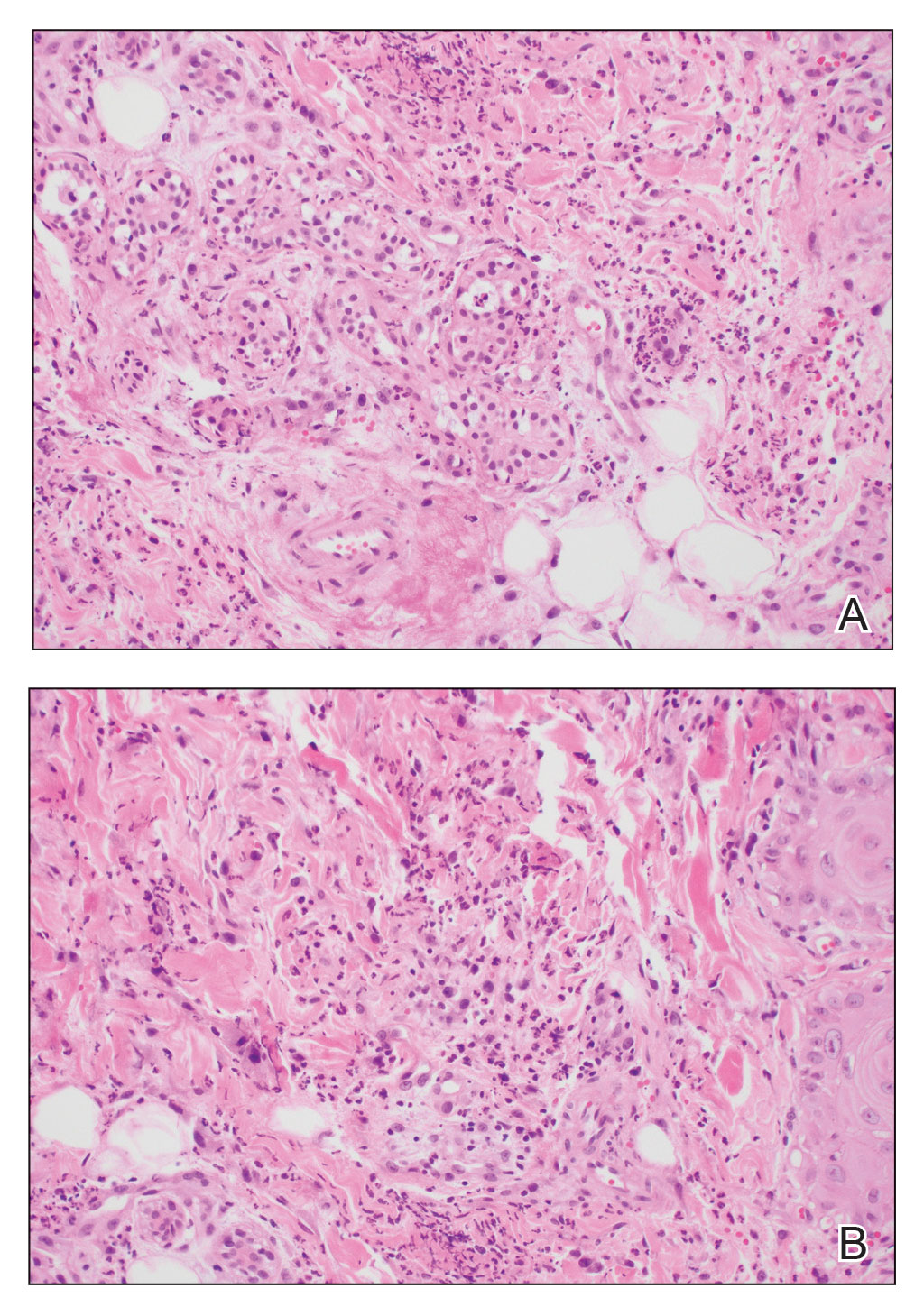
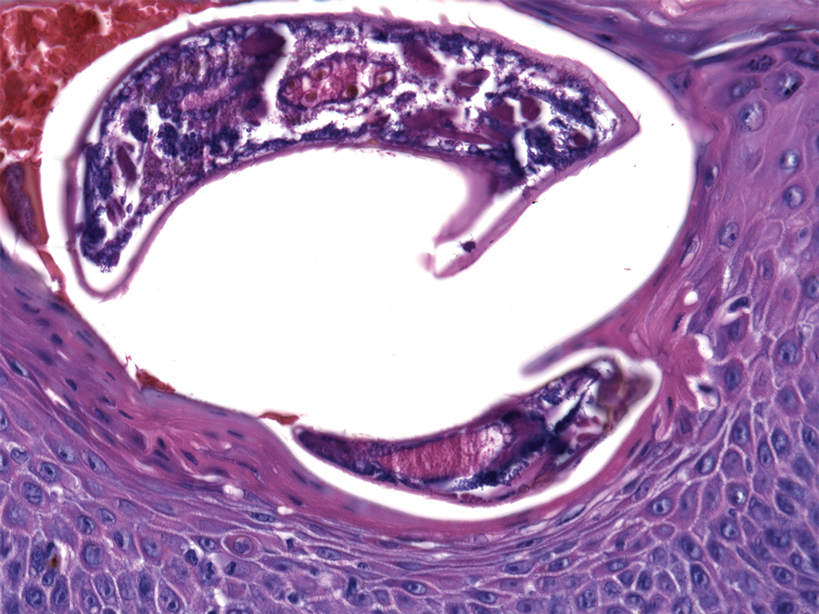
A biopsy from the left preauricular cheek demonstrated dermal neutrophilic inflammation around eccrine coils with focal necrosis (Figure). No notable diffuse dermal neutrophilic infiltrate was present, ruling out Sweet syndrome, and no notable interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate was present, making cellulitis and erysipelas less likely; panculture of tissue also was negative.1,2 Atypical cells in the deep dermis were positive for CD163 and negative for CD117, CD34, CD123, and myeloperoxidase, consistent with a diagnosis of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis (NEH) and reactive histiocytes.3 Treatment with oral prednisone resulted in rapid improvement of symptoms.
Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is a rare reactive neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by eccrine gland involvement. This benign and self-limited condition presents as asymmetric erythematous papules and plaques.2 Among 8 granulocytopenic patients with neutrophilic dermatoses, 5 were diagnosed with NEH.4 Although first identified in 1982, NEH remains poorly understood.2 Initial theories suggested that NEH developed due to cytotoxic substances secreted in sweat glands causing necrosis and neutrophil chemotaxis; however, chemotherapy exposure cannot be linked to every case of NEH. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis can be extremely difficult to differentiate clinically from conditions such as cellulitis and Sweet syndrome.
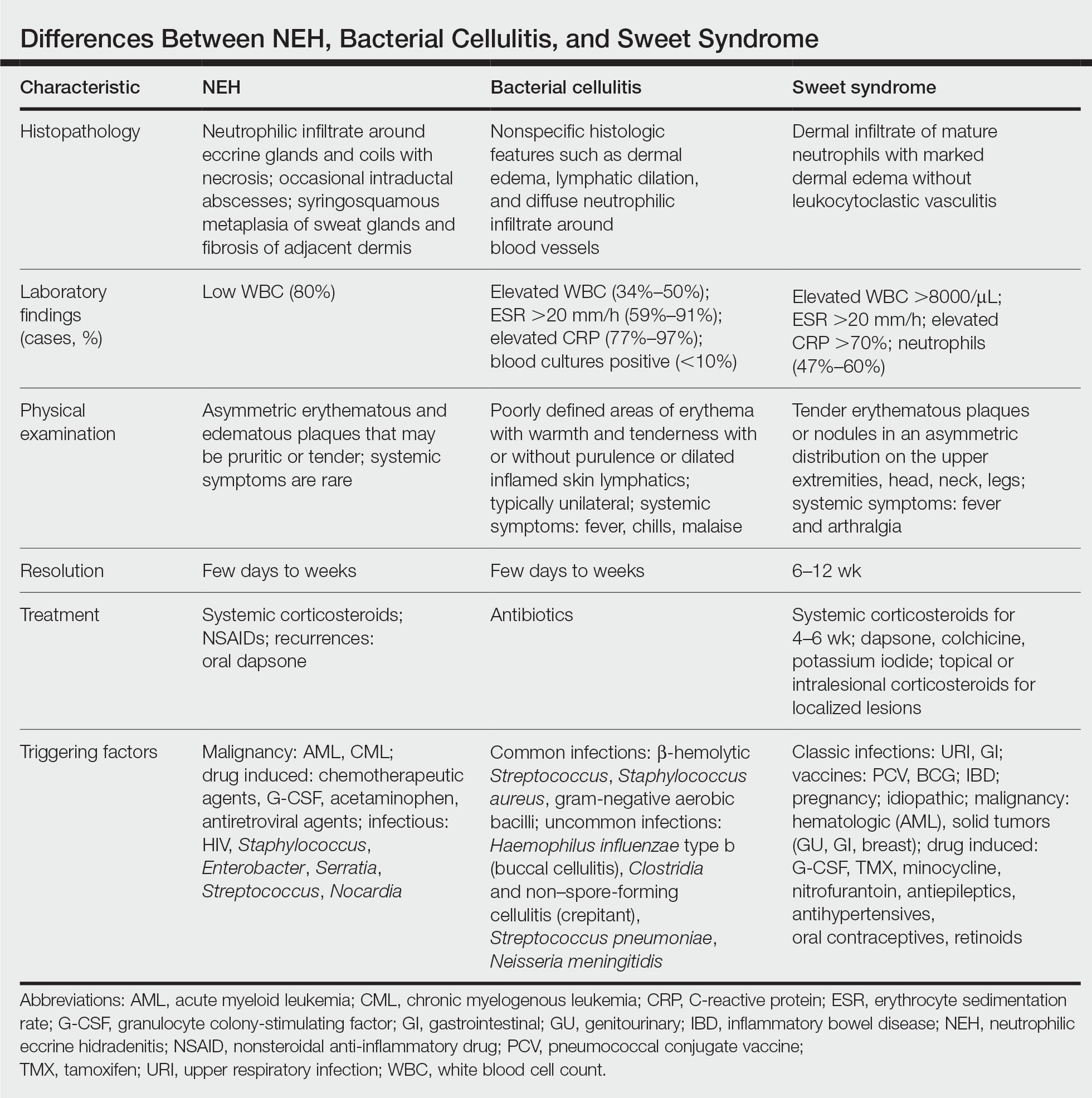
A patient history can be helpful in identifying triggering factors. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis most commonly is associated with malignant, drug-induced, or infectious triggers, while Sweet syndrome has a broad range of associations including infections, vaccines, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, malignancy, and drug-induced etiologies (Table).1 On average, NEH presents 10 days after chemotherapy induction, with 70% of cases presenting after the first chemotherapy cycle.5 Bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas have an infectious etiology, and patients may report symptoms such as fever, chills, or malaise. Immunosuppressed patients are at greater risk for infection; therefore, clinical signs of infection in a granulocytopenic patient should be addressed urgently.
Physical examination may have limited value in differentiating between these diagnoses, as neutrophilic dermatoses notoriously mimic infection. Cutaneous lesions can appear as pruritic or tender erythematous plaques, papules, or nodules in these conditions, though cellulitis and erysipelas tend to be unilateral and may have associated purulence or inflamed skin lymphatics. Given the potential for misdiagnosis, approaching patients with a broad differential can be helpful. In our patient, the differential diagnosis included Sweet syndrome, NEH, bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, leukemia cutis, sarcoid, and eosinophilic cellulitis.
Leukemia cutis refers to the infiltration of neoplastic leukocytes in the skin and often occurs in patients with peripheral leukemia, most often acute myeloid leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Patients with leukemia cutis often have a worse prognosis, as this finding signifies extramedullary spread of disease.6 Clinically, lesions can appear similar to those seen in our patient, though they typically are not symptomatic, can be nodular, tend to exhibit a violaceous hue, and occasionally may be hemorrhagic. Wells syndrome (also known as eosinophilic cellulitis) is an inflammatory dermatosis that presents as painful or pruritic, edematous and erythematous plaques.7,8 A green hue on resolution is present in some cases and may help clinicians differentiate this disease from mimickers.7 Often, eosinophilic cellulitis is misdiagnosed as bacterial cellulitis and treated with antibiotics. The presence of systemic symptoms such as fever or arthralgia is more typical of bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, eosinophilic cellulitis, or Sweet syndrome than of NEH.1 Additionally, inflammatory markers (ie, C-reactive protein) and white blood cell counts tend to be elevated in bacterial cellulitis and Sweet syndrome, while leukopenia often is seen in NEH.
Histopathology is crucial in distinguishing these disease etiologies. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is diagnosed by the characteristic neutrophilic infiltrate and necrosis surrounding eccrine glands and coils. There also may be occasional intraductal abscesses and syringosquamous metaplasia of the sweat glands along with fibrosis of the adjacent dermis. In contrast, histologic sections of Sweet syndrome show numerous mature neutrophils infiltrating the dermis with marked papillary dermal edema. The histopathology of bacterial cellulitis and erysipelas is less specific, but common features include dermal edema, lymphatic dilation, and a diffuse neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding blood vessels. Pathogenic organisms may be seen on histopathology but are not required for the diagnosis of bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas.2 Additionally, blood and tissue culture can assist in identification of both the source of infection and the causative organism, but cultures may not always be positive.
Comparatively, the histopathologic features of eosinophilic cellulitis include dermal edema, eosinophilic infiltration, and flame figures that form when eosinophils degranulate and coat collagen fibers with major basic protein. Flame figures are characteristic but not pathognomonic for eosinophilic cellulitis.7 The histopathology of leukemia cutis varies based on the leukemia classification; generally, in acute myeloid leukemia the infiltrate is composed of neoplastic cells in the early stages of development that are positive for myeloid markers such as myeloperoxidase. Atypical and immature granulocytes within the leukocytic infiltrate differentiate this condition from the other diagnoses. Treatment may entail chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and this diagnosis generally carries the worst prognosis of all the conditions in the differential.6
Differentiating between these conditions is important in guiding treatment, especially in patients with febrile neutropenia. Unnecessary steroids in immunosuppressed patients can be dangerous, especially if the patient has an infection such as bacterial cellulitis. Furthermore, unwarranted antibiotic use for noninfectious conditions may expose patients to substantial side effects and not improve the condition. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis typically is self-limited and treated symptomatically with systemic corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.3 Sweet syndrome often requires a longer course of oral steroids. Leukemia cutis worsens as the leukemia advances, and treatment of the underlying malignancy is the most effective treatment.9
Early and accurate recognition of the diagnosis can prevent harmful diagnostic delay, unnecessary antibiotic use, or extended steroid taper in neutropenic patients. Appreciating the differences between these diagnoses can assist clinicians in investigating and tailoring a broad differential to specific patient presentations, which is especially critical when considering common mimickers for life-threatening conditions.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.0642
- Srivastava M, Scharf S, Meehan SA, et al. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis masquerading as facial cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:693-696. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.032
- Copaescu AM, Castilloux JF, Chababi-Atallah M, et al. A classic clinical case: neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013; 5:340-346. doi:10.1159/000356229
- Aractingi S, Mallet V, Pinquier L, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses during granulocytopenia. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1141-1145.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses occurring in oncology patients. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:106-111. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02605.x
- Wang CX, Pusic I, Anadkat MJ. Association of leukemia cutis with survival in acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:826. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0052
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:908-911.
- Räßler F, Lukács J, Elsner P. Treatment of eosinophilic cellulitis (Wells syndrome): a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1465-1479. doi:10.1111/jdv.13706
- Hobbs LK, Carr PC, Gru AA, et al. Case and review: cutaneous involvement by chronic neutrophilic leukemia vs Sweet syndrome: a diagnostic dilemma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:644-649. doi:10.1111 /cup.13925
THE DIAGNOSIS: Neutrophilic Eccrine Hidradenitis
A biopsy from the left preauricular cheek demonstrated dermal neutrophilic inflammation around eccrine coils with focal necrosis (Figure). No notable diffuse dermal neutrophilic infiltrate was present, ruling out Sweet syndrome, and no notable interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate was present, making cellulitis and erysipelas less likely; panculture of tissue also was negative.1,2 Atypical cells in the deep dermis were positive for CD163 and negative for CD117, CD34, CD123, and myeloperoxidase, consistent with a diagnosis of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis (NEH) and reactive histiocytes.3 Treatment with oral prednisone resulted in rapid improvement of symptoms.

Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is a rare reactive neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by eccrine gland involvement. This benign and self-limited condition presents as asymmetric erythematous papules and plaques.2 Among 8 granulocytopenic patients with neutrophilic dermatoses, 5 were diagnosed with NEH.4 Although first identified in 1982, NEH remains poorly understood.2 Initial theories suggested that NEH developed due to cytotoxic substances secreted in sweat glands causing necrosis and neutrophil chemotaxis; however, chemotherapy exposure cannot be linked to every case of NEH. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis can be extremely difficult to differentiate clinically from conditions such as cellulitis and Sweet syndrome.
A patient history can be helpful in identifying triggering factors. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis most commonly is associated with malignant, drug-induced, or infectious triggers, while Sweet syndrome has a broad range of associations including infections, vaccines, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, malignancy, and drug-induced etiologies (Table).1 On average, NEH presents 10 days after chemotherapy induction, with 70% of cases presenting after the first chemotherapy cycle.5 Bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas have an infectious etiology, and patients may report symptoms such as fever, chills, or malaise. Immunosuppressed patients are at greater risk for infection; therefore, clinical signs of infection in a granulocytopenic patient should be addressed urgently.

Physical examination may have limited value in differentiating between these diagnoses, as neutrophilic dermatoses notoriously mimic infection. Cutaneous lesions can appear as pruritic or tender erythematous plaques, papules, or nodules in these conditions, though cellulitis and erysipelas tend to be unilateral and may have associated purulence or inflamed skin lymphatics. Given the potential for misdiagnosis, approaching patients with a broad differential can be helpful. In our patient, the differential diagnosis included Sweet syndrome, NEH, bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, leukemia cutis, sarcoid, and eosinophilic cellulitis.
Leukemia cutis refers to the infiltration of neoplastic leukocytes in the skin and often occurs in patients with peripheral leukemia, most often acute myeloid leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Patients with leukemia cutis often have a worse prognosis, as this finding signifies extramedullary spread of disease.6 Clinically, lesions can appear similar to those seen in our patient, though they typically are not symptomatic, can be nodular, tend to exhibit a violaceous hue, and occasionally may be hemorrhagic. Wells syndrome (also known as eosinophilic cellulitis) is an inflammatory dermatosis that presents as painful or pruritic, edematous and erythematous plaques.7,8 A green hue on resolution is present in some cases and may help clinicians differentiate this disease from mimickers.7 Often, eosinophilic cellulitis is misdiagnosed as bacterial cellulitis and treated with antibiotics. The presence of systemic symptoms such as fever or arthralgia is more typical of bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, eosinophilic cellulitis, or Sweet syndrome than of NEH.1 Additionally, inflammatory markers (ie, C-reactive protein) and white blood cell counts tend to be elevated in bacterial cellulitis and Sweet syndrome, while leukopenia often is seen in NEH.
Histopathology is crucial in distinguishing these disease etiologies. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is diagnosed by the characteristic neutrophilic infiltrate and necrosis surrounding eccrine glands and coils. There also may be occasional intraductal abscesses and syringosquamous metaplasia of the sweat glands along with fibrosis of the adjacent dermis. In contrast, histologic sections of Sweet syndrome show numerous mature neutrophils infiltrating the dermis with marked papillary dermal edema. The histopathology of bacterial cellulitis and erysipelas is less specific, but common features include dermal edema, lymphatic dilation, and a diffuse neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding blood vessels. Pathogenic organisms may be seen on histopathology but are not required for the diagnosis of bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas.2 Additionally, blood and tissue culture can assist in identification of both the source of infection and the causative organism, but cultures may not always be positive.
Comparatively, the histopathologic features of eosinophilic cellulitis include dermal edema, eosinophilic infiltration, and flame figures that form when eosinophils degranulate and coat collagen fibers with major basic protein. Flame figures are characteristic but not pathognomonic for eosinophilic cellulitis.7 The histopathology of leukemia cutis varies based on the leukemia classification; generally, in acute myeloid leukemia the infiltrate is composed of neoplastic cells in the early stages of development that are positive for myeloid markers such as myeloperoxidase. Atypical and immature granulocytes within the leukocytic infiltrate differentiate this condition from the other diagnoses. Treatment may entail chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and this diagnosis generally carries the worst prognosis of all the conditions in the differential.6
Differentiating between these conditions is important in guiding treatment, especially in patients with febrile neutropenia. Unnecessary steroids in immunosuppressed patients can be dangerous, especially if the patient has an infection such as bacterial cellulitis. Furthermore, unwarranted antibiotic use for noninfectious conditions may expose patients to substantial side effects and not improve the condition. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis typically is self-limited and treated symptomatically with systemic corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.3 Sweet syndrome often requires a longer course of oral steroids. Leukemia cutis worsens as the leukemia advances, and treatment of the underlying malignancy is the most effective treatment.9
Early and accurate recognition of the diagnosis can prevent harmful diagnostic delay, unnecessary antibiotic use, or extended steroid taper in neutropenic patients. Appreciating the differences between these diagnoses can assist clinicians in investigating and tailoring a broad differential to specific patient presentations, which is especially critical when considering common mimickers for life-threatening conditions.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Neutrophilic Eccrine Hidradenitis
A biopsy from the left preauricular cheek demonstrated dermal neutrophilic inflammation around eccrine coils with focal necrosis (Figure). No notable diffuse dermal neutrophilic infiltrate was present, ruling out Sweet syndrome, and no notable interstitial neutrophilic infiltrate was present, making cellulitis and erysipelas less likely; panculture of tissue also was negative.1,2 Atypical cells in the deep dermis were positive for CD163 and negative for CD117, CD34, CD123, and myeloperoxidase, consistent with a diagnosis of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis (NEH) and reactive histiocytes.3 Treatment with oral prednisone resulted in rapid improvement of symptoms.

Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is a rare reactive neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by eccrine gland involvement. This benign and self-limited condition presents as asymmetric erythematous papules and plaques.2 Among 8 granulocytopenic patients with neutrophilic dermatoses, 5 were diagnosed with NEH.4 Although first identified in 1982, NEH remains poorly understood.2 Initial theories suggested that NEH developed due to cytotoxic substances secreted in sweat glands causing necrosis and neutrophil chemotaxis; however, chemotherapy exposure cannot be linked to every case of NEH. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis can be extremely difficult to differentiate clinically from conditions such as cellulitis and Sweet syndrome.
A patient history can be helpful in identifying triggering factors. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis most commonly is associated with malignant, drug-induced, or infectious triggers, while Sweet syndrome has a broad range of associations including infections, vaccines, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, malignancy, and drug-induced etiologies (Table).1 On average, NEH presents 10 days after chemotherapy induction, with 70% of cases presenting after the first chemotherapy cycle.5 Bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas have an infectious etiology, and patients may report symptoms such as fever, chills, or malaise. Immunosuppressed patients are at greater risk for infection; therefore, clinical signs of infection in a granulocytopenic patient should be addressed urgently.

Physical examination may have limited value in differentiating between these diagnoses, as neutrophilic dermatoses notoriously mimic infection. Cutaneous lesions can appear as pruritic or tender erythematous plaques, papules, or nodules in these conditions, though cellulitis and erysipelas tend to be unilateral and may have associated purulence or inflamed skin lymphatics. Given the potential for misdiagnosis, approaching patients with a broad differential can be helpful. In our patient, the differential diagnosis included Sweet syndrome, NEH, bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, leukemia cutis, sarcoid, and eosinophilic cellulitis.
Leukemia cutis refers to the infiltration of neoplastic leukocytes in the skin and often occurs in patients with peripheral leukemia, most often acute myeloid leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Patients with leukemia cutis often have a worse prognosis, as this finding signifies extramedullary spread of disease.6 Clinically, lesions can appear similar to those seen in our patient, though they typically are not symptomatic, can be nodular, tend to exhibit a violaceous hue, and occasionally may be hemorrhagic. Wells syndrome (also known as eosinophilic cellulitis) is an inflammatory dermatosis that presents as painful or pruritic, edematous and erythematous plaques.7,8 A green hue on resolution is present in some cases and may help clinicians differentiate this disease from mimickers.7 Often, eosinophilic cellulitis is misdiagnosed as bacterial cellulitis and treated with antibiotics. The presence of systemic symptoms such as fever or arthralgia is more typical of bacterial cellulitis, erysipelas, eosinophilic cellulitis, or Sweet syndrome than of NEH.1 Additionally, inflammatory markers (ie, C-reactive protein) and white blood cell counts tend to be elevated in bacterial cellulitis and Sweet syndrome, while leukopenia often is seen in NEH.
Histopathology is crucial in distinguishing these disease etiologies. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis is diagnosed by the characteristic neutrophilic infiltrate and necrosis surrounding eccrine glands and coils. There also may be occasional intraductal abscesses and syringosquamous metaplasia of the sweat glands along with fibrosis of the adjacent dermis. In contrast, histologic sections of Sweet syndrome show numerous mature neutrophils infiltrating the dermis with marked papillary dermal edema. The histopathology of bacterial cellulitis and erysipelas is less specific, but common features include dermal edema, lymphatic dilation, and a diffuse neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding blood vessels. Pathogenic organisms may be seen on histopathology but are not required for the diagnosis of bacterial cellulitis or erysipelas.2 Additionally, blood and tissue culture can assist in identification of both the source of infection and the causative organism, but cultures may not always be positive.
Comparatively, the histopathologic features of eosinophilic cellulitis include dermal edema, eosinophilic infiltration, and flame figures that form when eosinophils degranulate and coat collagen fibers with major basic protein. Flame figures are characteristic but not pathognomonic for eosinophilic cellulitis.7 The histopathology of leukemia cutis varies based on the leukemia classification; generally, in acute myeloid leukemia the infiltrate is composed of neoplastic cells in the early stages of development that are positive for myeloid markers such as myeloperoxidase. Atypical and immature granulocytes within the leukocytic infiltrate differentiate this condition from the other diagnoses. Treatment may entail chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and this diagnosis generally carries the worst prognosis of all the conditions in the differential.6
Differentiating between these conditions is important in guiding treatment, especially in patients with febrile neutropenia. Unnecessary steroids in immunosuppressed patients can be dangerous, especially if the patient has an infection such as bacterial cellulitis. Furthermore, unwarranted antibiotic use for noninfectious conditions may expose patients to substantial side effects and not improve the condition. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis typically is self-limited and treated symptomatically with systemic corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.3 Sweet syndrome often requires a longer course of oral steroids. Leukemia cutis worsens as the leukemia advances, and treatment of the underlying malignancy is the most effective treatment.9
Early and accurate recognition of the diagnosis can prevent harmful diagnostic delay, unnecessary antibiotic use, or extended steroid taper in neutropenic patients. Appreciating the differences between these diagnoses can assist clinicians in investigating and tailoring a broad differential to specific patient presentations, which is especially critical when considering common mimickers for life-threatening conditions.
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.0642
- Srivastava M, Scharf S, Meehan SA, et al. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis masquerading as facial cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:693-696. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.032
- Copaescu AM, Castilloux JF, Chababi-Atallah M, et al. A classic clinical case: neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013; 5:340-346. doi:10.1159/000356229
- Aractingi S, Mallet V, Pinquier L, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses during granulocytopenia. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1141-1145.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses occurring in oncology patients. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:106-111. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02605.x
- Wang CX, Pusic I, Anadkat MJ. Association of leukemia cutis with survival in acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:826. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0052
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:908-911.
- Räßler F, Lukács J, Elsner P. Treatment of eosinophilic cellulitis (Wells syndrome): a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1465-1479. doi:10.1111/jdv.13706
- Hobbs LK, Carr PC, Gru AA, et al. Case and review: cutaneous involvement by chronic neutrophilic leukemia vs Sweet syndrome: a diagnostic dilemma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:644-649. doi:10.1111 /cup.13925
- Nelson CA, Stephen S, Ashchyan HJ, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:987-1006. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.11.0642
- Srivastava M, Scharf S, Meehan SA, et al. Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis masquerading as facial cellulitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:693-696. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.07.032
- Copaescu AM, Castilloux JF, Chababi-Atallah M, et al. A classic clinical case: neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013; 5:340-346. doi:10.1159/000356229
- Aractingi S, Mallet V, Pinquier L, et al. Neutrophilic dermatoses during granulocytopenia. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1141-1145.
- Cohen PR. Neutrophilic dermatoses occurring in oncology patients. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:106-111. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02605.x
- Wang CX, Pusic I, Anadkat MJ. Association of leukemia cutis with survival in acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:826. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0052
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:908-911.
- Räßler F, Lukács J, Elsner P. Treatment of eosinophilic cellulitis (Wells syndrome): a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1465-1479. doi:10.1111/jdv.13706
- Hobbs LK, Carr PC, Gru AA, et al. Case and review: cutaneous involvement by chronic neutrophilic leukemia vs Sweet syndrome: a diagnostic dilemma. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:644-649. doi:10.1111 /cup.13925
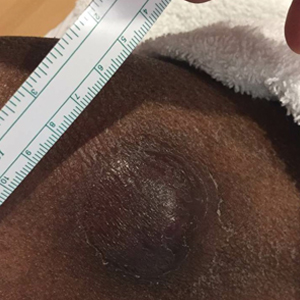
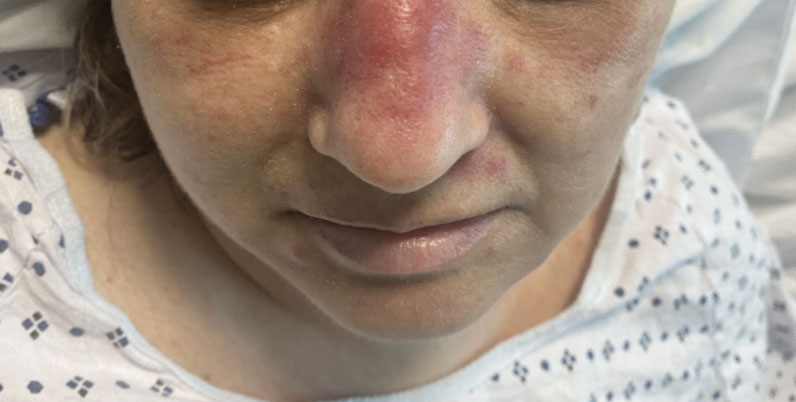
A 50-year-old woman undergoing cytarabine induction therapy for acute myeloid leukemia developed tender, erythematous, dermal plaques on the nasal dorsum, left medial eyebrow, left preauricular cheek, and right cheek. The rash erupted 7 days after receiving the cytarabine induction regimen. She had a fever (temperature, 39.9 °C [103.8 °F]) and also was neutropenic.
Extensive Erosions and Ulcerations on the Trunk and Extremities in a Neonate
The Diagnosis: Dominant Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
Blisters in a neonate may be caused by infectious, traumatic, autoimmune, or congenital etiologies. Biopsy findings correlated with clinical findings usually can establish a prompt diagnosis when the clinical diagnosis is uncertain. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) as well as indirect immunofluorescence studies are useful when autoimmune blistering disease or congenital or heritable disorders of skin fragility are in the differential diagnosis. Many genetic abnormalities of skin fragility are associated with marked morbidity and mortality, and prompt diagnosis is essential to provide proper care. Our patient’s parents had no history of skin disorders, and there was no known family history of blistering disease or traumatic birth. A heritable disorder of skin fragility was still a top consideration because of the extensive blistering in the absence of any other symptoms.
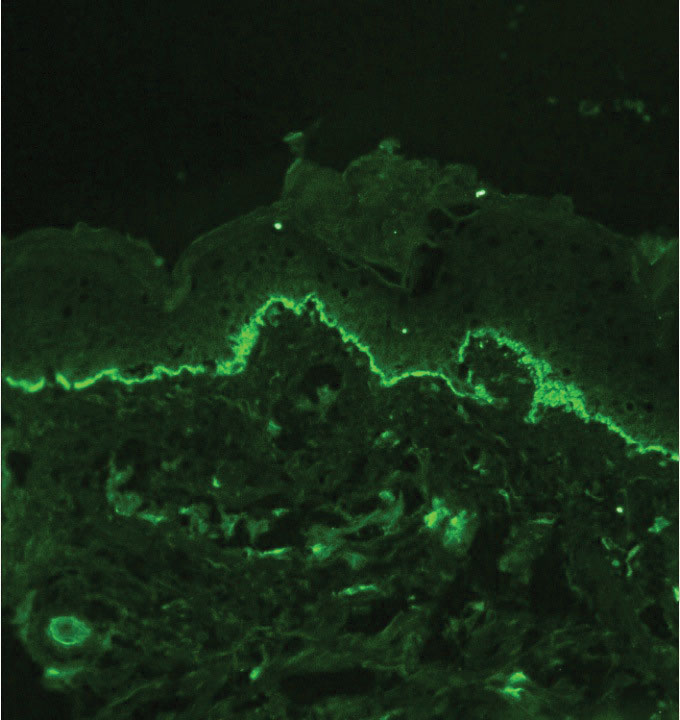
Although dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is an uncommon cause of skin fragility in neonates, our patient’s presentation was typical because of the extensive blistering and increased fragility of the skin at pressure points. Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa has both dominant and recessive presentations that span a spectrum from mild and focal skin blistering to extensive blistering with esophageal involvement.1 Early diagnosis and treatment can mitigate potential failure to thrive or premature death. Inherited mutations in the type VII collagen gene, COL7A1, are causative.2 Dominant DEB may be associated with dental caries, swallowing problems secondary to esophageal scarring, and constipation, as well as dystrophic or absent nails. Immunomapping studies of the skin often reveal type VII collagen cytoplasmic granules in the epidermis and weaker reaction in the roof of the subepidermal separation (quiz image).3 Abnormalities in type VII collagen impact the production of anchoring fibrils. Blister cleavage occurs in the sublamina densa with type VII collagen staining evident on the blister roof (quiz image).4 Patients with severe generalized recessive DEB may have barely detectable type VII collagen. In our patient, the cytoplasmic staining and weak staining in the epidermal roof of the separation confirmed the clinical impression of dominant DEB.
Autoimmune blistering disease should be considered in the histologic differential diagnosis, but it usually is associated with obvious disease in the mother. Direct immunofluorescence of pemphigoid gestationis reveals linear deposition of C3 at the basement membrane zone, which also can be associated with IgG (Figure 1). Neonates receiving passive transfer of antibodies may develop annular erythema, vesicles, and even dyshidroticlike changes on the soles.5
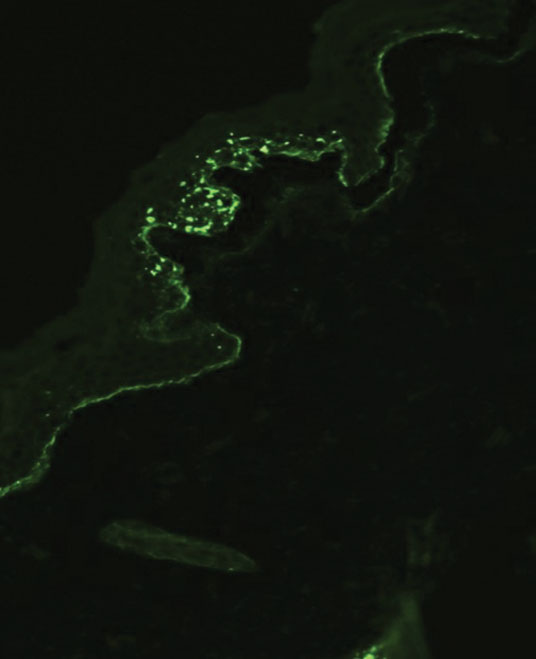
Suction blisters are subepithelial.6,7 When they occur in the neonatal period, they often are localized and are thought to be the result of vigorous sucking in utero.6 They quickly resolve without treatment and do not reveal abnormalities on DIF. If immunomapping is done for type VII collagen, it will be located at the floor of the suction blister (Figure 2).
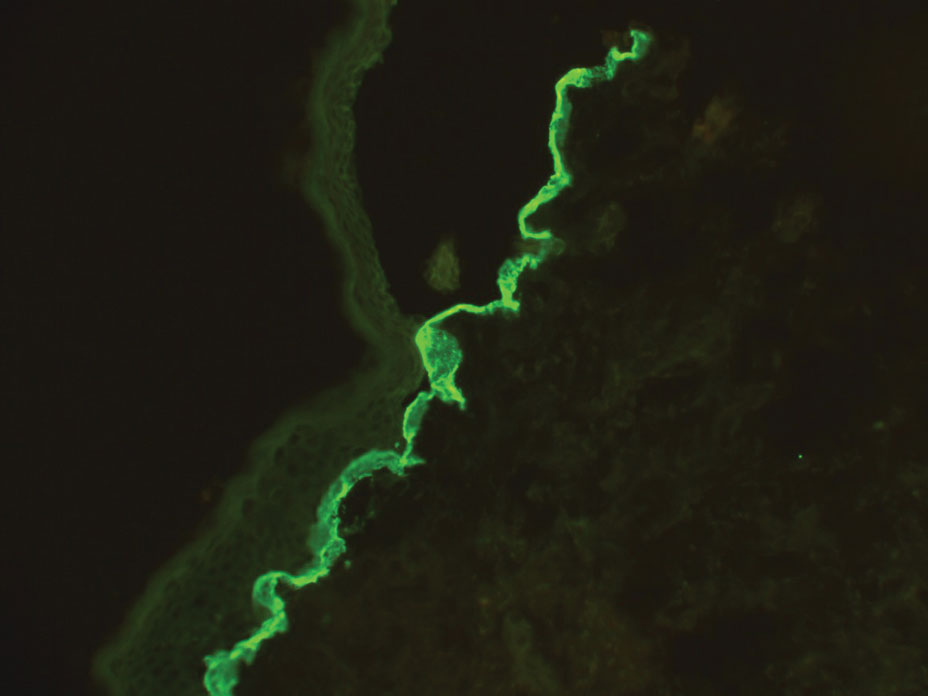
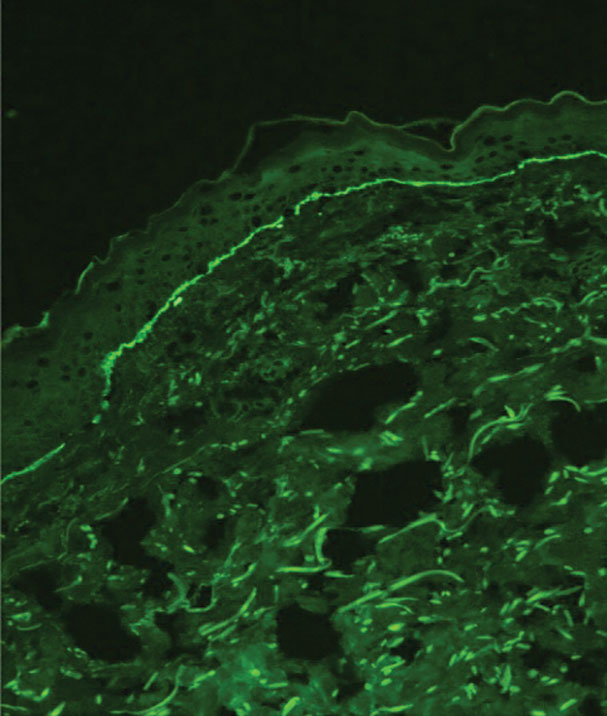
Bullous pemphigoid is associated with deposition of linear IgG along the dermoepidermal junction—IgG4 is most common—and/or C3 (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence on split-skin biopsy reveals IgG on the epidermal side of the blister in bullous pemphigoid in contrast to epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, where the immune deposits are found on the dermal side of the split.8,9 Linear IgA bullous disease is associated with IgA deposition (Figure 4).10,11 Secretory IgA derived from breast milk can be causative.11 Neonatal linear IgA bullous disease is a serious condition associated with marked mucosal involvement that can eventuate in respiratory compromise. Prompt recognition is important; breastfeeding must be stopped and supportive therapy must be provided.

Other types of vesicular or pustular eruptions in the newborn usually are easily diagnosed by their typical clinical presentation without biopsy. Erythema toxicum neonatorum usually presents within 1 to 2 days of birth. It is self-limited and often resembles acne, but it also occurs on the trunk and extremities. Transient neonatal pustular melanosis may be present at birth and predominantly is seen in newborns with skin of color. Lesions easily rupture and usually resolve within 1 to 2 days. Infectious causes of blistering often can be identified on clinical examination and confirmed by culture. Herpes simplex virus infection is associated with characteristic multinucleated giant cells as well as steel grey nuclei evident on routine histologic evaluation. Bullous impetigo reveals superficial acantholysis and will have negative findings on DIF.12
When a neonate presents with widespread blistering, both genetic disorders of skin fragility as well as passive transfer of antibodies from maternal autoimmune disease need to be considered. Direct immunofluorescence and indirect immunofluorescence immunomapping findings can be useful in clarifying the diagnosis when heritable disorders of skin fragility or autoimmune blistering diseases are a clinical consideration.
- Has C, Bauer JW, Bodemer C, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:614-627. doi:10.1111/bjd.18921
- Dang N, Murrell DF. Mutation analysis and characterization of COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Exp Dermatol. 2008;17:553-568. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00723.x
- Has C, He Y. Research techniques made simple: immunofluorescence antigen mapping in epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:E65-E71. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2016.05.093
- Rao R, Mellerio J, Bhogal BS, et al. Immunofluorescence antigen mapping for hereditary epidermolysis bullosa. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:692-697.
- Aoyama Y, Asai K, Hioki K, et al. Herpes gestationis in a mother and newborn: immunoclinical perspectives based on a weekly followup of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay index of a bullous pemphigoid antigen noncollagenous domain. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1168-1172. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.9.1168
- Afsar FS, Cun S, Seremet S. Neonatal sucking blister [published online November 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030 /qt33b1w59j.
- Yu WY, Wei ML. Suction blisters. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:237. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3277
- Gupta R, Woodley DT, Chen M. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:60-69.
- Reis-Filho EG, Silva Tde A, Aguirre LH, et al. Bullous pemphigoid in a 3-month-old infant: case report and literature review of this dermatosis in childhood. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:961-965. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20132378
- Hruza LL, Mallory SB, Fitzgibbons J, et al. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis in a neonate. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:171-176. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470
- Egami S, Suzuki C, Kurihara Y, et al. Neonatal linear IgA bullous dermatosis mediated by breast milk–borne maternal IgA. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1107-1111. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2392
- Ligtenberg KG, Hu JK, Panse G, et al. Bullous impetigo masquerading as pemphigus foliaceus in an adult patient. JAAD Case Rep. 2020; 6:428-430. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.040
The Diagnosis: Dominant Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
Blisters in a neonate may be caused by infectious, traumatic, autoimmune, or congenital etiologies. Biopsy findings correlated with clinical findings usually can establish a prompt diagnosis when the clinical diagnosis is uncertain. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) as well as indirect immunofluorescence studies are useful when autoimmune blistering disease or congenital or heritable disorders of skin fragility are in the differential diagnosis. Many genetic abnormalities of skin fragility are associated with marked morbidity and mortality, and prompt diagnosis is essential to provide proper care. Our patient’s parents had no history of skin disorders, and there was no known family history of blistering disease or traumatic birth. A heritable disorder of skin fragility was still a top consideration because of the extensive blistering in the absence of any other symptoms.
Although dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is an uncommon cause of skin fragility in neonates, our patient’s presentation was typical because of the extensive blistering and increased fragility of the skin at pressure points. Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa has both dominant and recessive presentations that span a spectrum from mild and focal skin blistering to extensive blistering with esophageal involvement.1 Early diagnosis and treatment can mitigate potential failure to thrive or premature death. Inherited mutations in the type VII collagen gene, COL7A1, are causative.2 Dominant DEB may be associated with dental caries, swallowing problems secondary to esophageal scarring, and constipation, as well as dystrophic or absent nails. Immunomapping studies of the skin often reveal type VII collagen cytoplasmic granules in the epidermis and weaker reaction in the roof of the subepidermal separation (quiz image).3 Abnormalities in type VII collagen impact the production of anchoring fibrils. Blister cleavage occurs in the sublamina densa with type VII collagen staining evident on the blister roof (quiz image).4 Patients with severe generalized recessive DEB may have barely detectable type VII collagen. In our patient, the cytoplasmic staining and weak staining in the epidermal roof of the separation confirmed the clinical impression of dominant DEB.
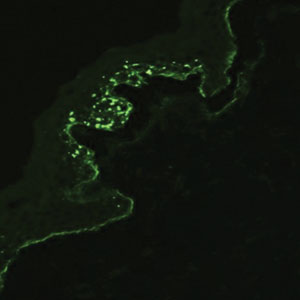
Autoimmune blistering disease should be considered in the histologic differential diagnosis, but it usually is associated with obvious disease in the mother. Direct immunofluorescence of pemphigoid gestationis reveals linear deposition of C3 at the basement membrane zone, which also can be associated with IgG (Figure 1). Neonates receiving passive transfer of antibodies may develop annular erythema, vesicles, and even dyshidroticlike changes on the soles.5

Suction blisters are subepithelial.6,7 When they occur in the neonatal period, they often are localized and are thought to be the result of vigorous sucking in utero.6 They quickly resolve without treatment and do not reveal abnormalities on DIF. If immunomapping is done for type VII collagen, it will be located at the floor of the suction blister (Figure 2).

Bullous pemphigoid is associated with deposition of linear IgG along the dermoepidermal junction—IgG4 is most common—and/or C3 (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence on split-skin biopsy reveals IgG on the epidermal side of the blister in bullous pemphigoid in contrast to epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, where the immune deposits are found on the dermal side of the split.8,9 Linear IgA bullous disease is associated with IgA deposition (Figure 4).10,11 Secretory IgA derived from breast milk can be causative.11 Neonatal linear IgA bullous disease is a serious condition associated with marked mucosal involvement that can eventuate in respiratory compromise. Prompt recognition is important; breastfeeding must be stopped and supportive therapy must be provided.

Other types of vesicular or pustular eruptions in the newborn usually are easily diagnosed by their typical clinical presentation without biopsy. Erythema toxicum neonatorum usually presents within 1 to 2 days of birth. It is self-limited and often resembles acne, but it also occurs on the trunk and extremities. Transient neonatal pustular melanosis may be present at birth and predominantly is seen in newborns with skin of color. Lesions easily rupture and usually resolve within 1 to 2 days. Infectious causes of blistering often can be identified on clinical examination and confirmed by culture. Herpes simplex virus infection is associated with characteristic multinucleated giant cells as well as steel grey nuclei evident on routine histologic evaluation. Bullous impetigo reveals superficial acantholysis and will have negative findings on DIF.12

When a neonate presents with widespread blistering, both genetic disorders of skin fragility as well as passive transfer of antibodies from maternal autoimmune disease need to be considered. Direct immunofluorescence and indirect immunofluorescence immunomapping findings can be useful in clarifying the diagnosis when heritable disorders of skin fragility or autoimmune blistering diseases are a clinical consideration.
The Diagnosis: Dominant Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
Blisters in a neonate may be caused by infectious, traumatic, autoimmune, or congenital etiologies. Biopsy findings correlated with clinical findings usually can establish a prompt diagnosis when the clinical diagnosis is uncertain. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) as well as indirect immunofluorescence studies are useful when autoimmune blistering disease or congenital or heritable disorders of skin fragility are in the differential diagnosis. Many genetic abnormalities of skin fragility are associated with marked morbidity and mortality, and prompt diagnosis is essential to provide proper care. Our patient’s parents had no history of skin disorders, and there was no known family history of blistering disease or traumatic birth. A heritable disorder of skin fragility was still a top consideration because of the extensive blistering in the absence of any other symptoms.
Although dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is an uncommon cause of skin fragility in neonates, our patient’s presentation was typical because of the extensive blistering and increased fragility of the skin at pressure points. Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa has both dominant and recessive presentations that span a spectrum from mild and focal skin blistering to extensive blistering with esophageal involvement.1 Early diagnosis and treatment can mitigate potential failure to thrive or premature death. Inherited mutations in the type VII collagen gene, COL7A1, are causative.2 Dominant DEB may be associated with dental caries, swallowing problems secondary to esophageal scarring, and constipation, as well as dystrophic or absent nails. Immunomapping studies of the skin often reveal type VII collagen cytoplasmic granules in the epidermis and weaker reaction in the roof of the subepidermal separation (quiz image).3 Abnormalities in type VII collagen impact the production of anchoring fibrils. Blister cleavage occurs in the sublamina densa with type VII collagen staining evident on the blister roof (quiz image).4 Patients with severe generalized recessive DEB may have barely detectable type VII collagen. In our patient, the cytoplasmic staining and weak staining in the epidermal roof of the separation confirmed the clinical impression of dominant DEB.
Autoimmune blistering disease should be considered in the histologic differential diagnosis, but it usually is associated with obvious disease in the mother. Direct immunofluorescence of pemphigoid gestationis reveals linear deposition of C3 at the basement membrane zone, which also can be associated with IgG (Figure 1). Neonates receiving passive transfer of antibodies may develop annular erythema, vesicles, and even dyshidroticlike changes on the soles.5

Suction blisters are subepithelial.6,7 When they occur in the neonatal period, they often are localized and are thought to be the result of vigorous sucking in utero.6 They quickly resolve without treatment and do not reveal abnormalities on DIF. If immunomapping is done for type VII collagen, it will be located at the floor of the suction blister (Figure 2).

Bullous pemphigoid is associated with deposition of linear IgG along the dermoepidermal junction—IgG4 is most common—and/or C3 (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence on split-skin biopsy reveals IgG on the epidermal side of the blister in bullous pemphigoid in contrast to epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, where the immune deposits are found on the dermal side of the split.8,9 Linear IgA bullous disease is associated with IgA deposition (Figure 4).10,11 Secretory IgA derived from breast milk can be causative.11 Neonatal linear IgA bullous disease is a serious condition associated with marked mucosal involvement that can eventuate in respiratory compromise. Prompt recognition is important; breastfeeding must be stopped and supportive therapy must be provided.

Other types of vesicular or pustular eruptions in the newborn usually are easily diagnosed by their typical clinical presentation without biopsy. Erythema toxicum neonatorum usually presents within 1 to 2 days of birth. It is self-limited and often resembles acne, but it also occurs on the trunk and extremities. Transient neonatal pustular melanosis may be present at birth and predominantly is seen in newborns with skin of color. Lesions easily rupture and usually resolve within 1 to 2 days. Infectious causes of blistering often can be identified on clinical examination and confirmed by culture. Herpes simplex virus infection is associated with characteristic multinucleated giant cells as well as steel grey nuclei evident on routine histologic evaluation. Bullous impetigo reveals superficial acantholysis and will have negative findings on DIF.12

When a neonate presents with widespread blistering, both genetic disorders of skin fragility as well as passive transfer of antibodies from maternal autoimmune disease need to be considered. Direct immunofluorescence and indirect immunofluorescence immunomapping findings can be useful in clarifying the diagnosis when heritable disorders of skin fragility or autoimmune blistering diseases are a clinical consideration.
- Has C, Bauer JW, Bodemer C, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:614-627. doi:10.1111/bjd.18921
- Dang N, Murrell DF. Mutation analysis and characterization of COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Exp Dermatol. 2008;17:553-568. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00723.x
- Has C, He Y. Research techniques made simple: immunofluorescence antigen mapping in epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:E65-E71. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2016.05.093
- Rao R, Mellerio J, Bhogal BS, et al. Immunofluorescence antigen mapping for hereditary epidermolysis bullosa. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:692-697.
- Aoyama Y, Asai K, Hioki K, et al. Herpes gestationis in a mother and newborn: immunoclinical perspectives based on a weekly followup of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay index of a bullous pemphigoid antigen noncollagenous domain. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1168-1172. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.9.1168
- Afsar FS, Cun S, Seremet S. Neonatal sucking blister [published online November 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030 /qt33b1w59j.
- Yu WY, Wei ML. Suction blisters. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:237. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3277
- Gupta R, Woodley DT, Chen M. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:60-69.
- Reis-Filho EG, Silva Tde A, Aguirre LH, et al. Bullous pemphigoid in a 3-month-old infant: case report and literature review of this dermatosis in childhood. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:961-965. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20132378
- Hruza LL, Mallory SB, Fitzgibbons J, et al. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis in a neonate. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:171-176. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470
- Egami S, Suzuki C, Kurihara Y, et al. Neonatal linear IgA bullous dermatosis mediated by breast milk–borne maternal IgA. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1107-1111. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2392
- Ligtenberg KG, Hu JK, Panse G, et al. Bullous impetigo masquerading as pemphigus foliaceus in an adult patient. JAAD Case Rep. 2020; 6:428-430. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.040
- Has C, Bauer JW, Bodemer C, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:614-627. doi:10.1111/bjd.18921
- Dang N, Murrell DF. Mutation analysis and characterization of COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Exp Dermatol. 2008;17:553-568. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00723.x
- Has C, He Y. Research techniques made simple: immunofluorescence antigen mapping in epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:E65-E71. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2016.05.093
- Rao R, Mellerio J, Bhogal BS, et al. Immunofluorescence antigen mapping for hereditary epidermolysis bullosa. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:692-697.
- Aoyama Y, Asai K, Hioki K, et al. Herpes gestationis in a mother and newborn: immunoclinical perspectives based on a weekly followup of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay index of a bullous pemphigoid antigen noncollagenous domain. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1168-1172. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.9.1168
- Afsar FS, Cun S, Seremet S. Neonatal sucking blister [published online November 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030 /qt33b1w59j.
- Yu WY, Wei ML. Suction blisters. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:237. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3277
- Gupta R, Woodley DT, Chen M. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:60-69.
- Reis-Filho EG, Silva Tde A, Aguirre LH, et al. Bullous pemphigoid in a 3-month-old infant: case report and literature review of this dermatosis in childhood. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:961-965. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20132378
- Hruza LL, Mallory SB, Fitzgibbons J, et al. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis in a neonate. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:171-176. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470
- Egami S, Suzuki C, Kurihara Y, et al. Neonatal linear IgA bullous dermatosis mediated by breast milk–borne maternal IgA. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1107-1111. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2392
- Ligtenberg KG, Hu JK, Panse G, et al. Bullous impetigo masquerading as pemphigus foliaceus in an adult patient. JAAD Case Rep. 2020; 6:428-430. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.040
A neonate was born with extensive erosions and ulcerations on the trunk and extremities. The eroded areas had a beefy red appearance. A biopsy taken from a small blister was stained for type VII collagen by indirect immunofluorescence.
Glitter Effects of Nail Art on Optical Coherence Tomography
Practice Gap
Nail art can skew the results of optical coherence tomography (OCT), a noninvasive imaging technology that is used to visualize nail morphology in diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and onychomycosis, with a penetration depth of 2 mm and high-resolution images.1 Few studies have evaluated the effects of nail art on OCT. Saleah and colleagues1 found that clear, semitransparent, and red nail polishes do not interfere with visualization of the nail plate, whereas nontransparent gel polish and art stones obscure the image. They did not comment on the effect of glitter nail art in their study, though they did test 1 nail that contained glitter.1 Monpeurt et al2 compared matte and glossy nail polishes. They found that matte polish was readily identifiable from the nail plate, whereas glossy polish presented a greater number of artifacts.2
The Solution
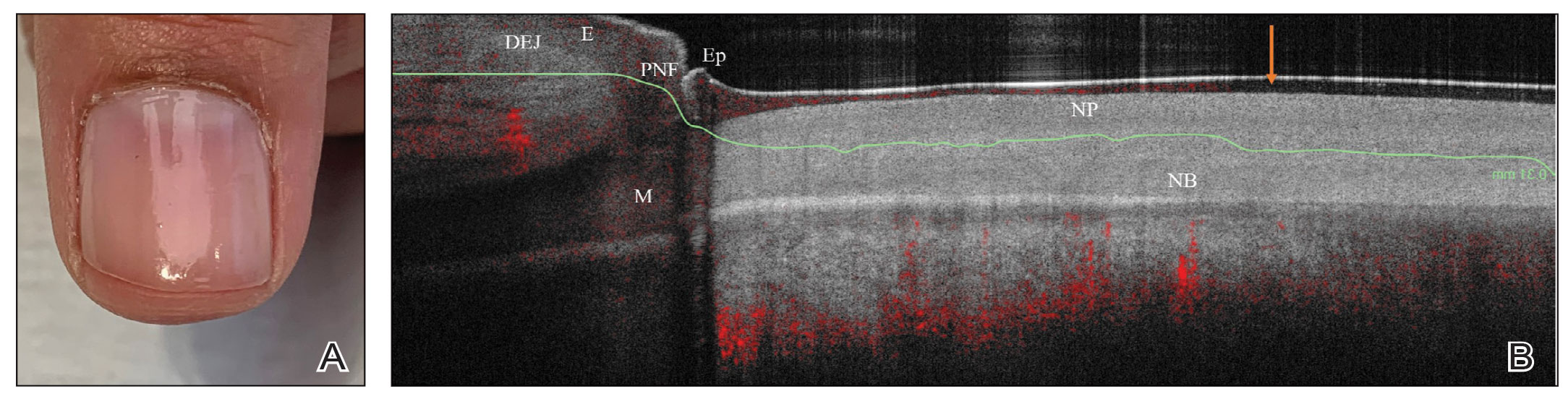
We looked at 3 glitter nail polishes—gold, pink, and silver—that were scanned by OCT to assess the effect of the polish on the resulting image. We determined that glitter particles completely obscured the nail bed and nail plate, regardless of color (Figure 1). Glossy clear polish imparted a distinct film on the top of the nail plate that did not obscure the nail plate or the nail bed (Figure 2).
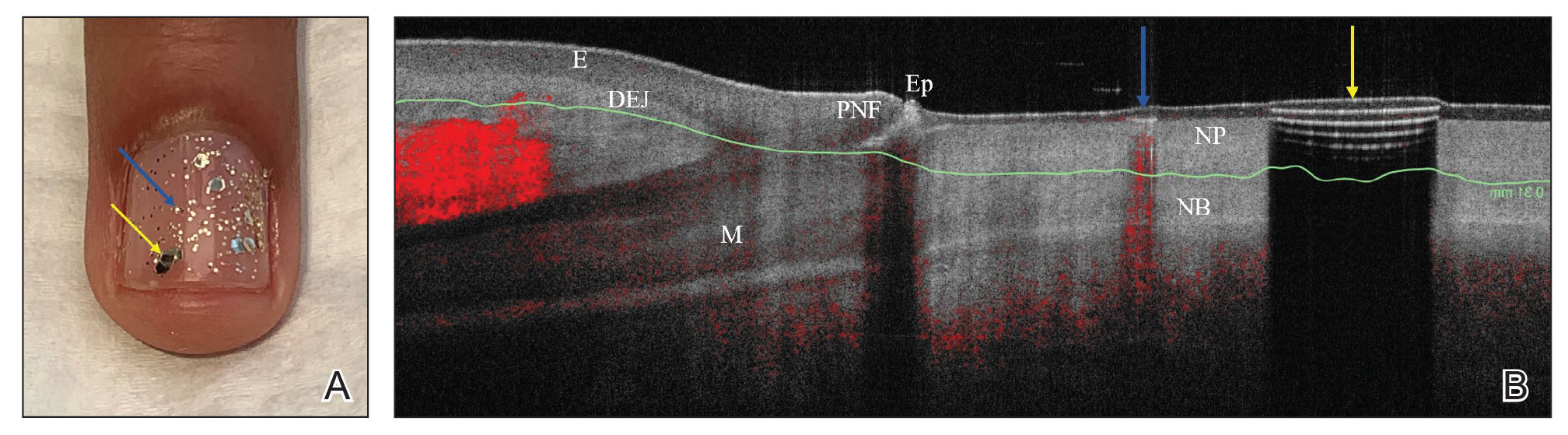
We conclude that glitter nail polish contains numerous reflective solid particles that interfere with OCT imaging of the nail plate and nail bed. As a result, we recommend removal of nail art to properly assess nail pathology. Because removal may need to be conducted by a nail technician, the treating clinician should inform the patient ahead of time to come to the appointment with bare (ie, unpolished) nails.
Practice Implications
Bringing awareness to the necessity of removing nail art prior to OCT imaging is crucial because many patients partake in its application, and removal may require the involvement of a professional nail technician. If a patient can be made aware that they should remove all nail art in advance, they will be better prepared for an OCT imaging session. Such a protocol increases efficiency, decreases diagnostic delay, and reduces cost associated with multiple office visits.
- Saleah S, Kim P, Seong D, et al. A preliminary study of post-progressive nail-art effects on in vivo nail plate using optical coherence tomography-based intensity profiling assessment. Sci Rep. 2021;11:666. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79497-3
- Monpeurt C, Cinotti E, Hebert M, et al. Thickness and morphology assessment of nail polishes applied on nails by high-definition optical coherence tomography. Skin Res Technol. 2018;24:156-157. doi:10.1111/srt.12406
Practice Gap
Nail art can skew the results of optical coherence tomography (OCT), a noninvasive imaging technology that is used to visualize nail morphology in diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and onychomycosis, with a penetration depth of 2 mm and high-resolution images.1 Few studies have evaluated the effects of nail art on OCT. Saleah and colleagues1 found that clear, semitransparent, and red nail polishes do not interfere with visualization of the nail plate, whereas nontransparent gel polish and art stones obscure the image. They did not comment on the effect of glitter nail art in their study, though they did test 1 nail that contained glitter.1 Monpeurt et al2 compared matte and glossy nail polishes. They found that matte polish was readily identifiable from the nail plate, whereas glossy polish presented a greater number of artifacts.2
The Solution
We looked at 3 glitter nail polishes—gold, pink, and silver—that were scanned by OCT to assess the effect of the polish on the resulting image. We determined that glitter particles completely obscured the nail bed and nail plate, regardless of color (Figure 1). Glossy clear polish imparted a distinct film on the top of the nail plate that did not obscure the nail plate or the nail bed (Figure 2).

We conclude that glitter nail polish contains numerous reflective solid particles that interfere with OCT imaging of the nail plate and nail bed. As a result, we recommend removal of nail art to properly assess nail pathology. Because removal may need to be conducted by a nail technician, the treating clinician should inform the patient ahead of time to come to the appointment with bare (ie, unpolished) nails.

Practice Implications
Bringing awareness to the necessity of removing nail art prior to OCT imaging is crucial because many patients partake in its application, and removal may require the involvement of a professional nail technician. If a patient can be made aware that they should remove all nail art in advance, they will be better prepared for an OCT imaging session. Such a protocol increases efficiency, decreases diagnostic delay, and reduces cost associated with multiple office visits.
Practice Gap
Nail art can skew the results of optical coherence tomography (OCT), a noninvasive imaging technology that is used to visualize nail morphology in diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and onychomycosis, with a penetration depth of 2 mm and high-resolution images.1 Few studies have evaluated the effects of nail art on OCT. Saleah and colleagues1 found that clear, semitransparent, and red nail polishes do not interfere with visualization of the nail plate, whereas nontransparent gel polish and art stones obscure the image. They did not comment on the effect of glitter nail art in their study, though they did test 1 nail that contained glitter.1 Monpeurt et al2 compared matte and glossy nail polishes. They found that matte polish was readily identifiable from the nail plate, whereas glossy polish presented a greater number of artifacts.2
The Solution
We looked at 3 glitter nail polishes—gold, pink, and silver—that were scanned by OCT to assess the effect of the polish on the resulting image. We determined that glitter particles completely obscured the nail bed and nail plate, regardless of color (Figure 1). Glossy clear polish imparted a distinct film on the top of the nail plate that did not obscure the nail plate or the nail bed (Figure 2).

We conclude that glitter nail polish contains numerous reflective solid particles that interfere with OCT imaging of the nail plate and nail bed. As a result, we recommend removal of nail art to properly assess nail pathology. Because removal may need to be conducted by a nail technician, the treating clinician should inform the patient ahead of time to come to the appointment with bare (ie, unpolished) nails.

Practice Implications
Bringing awareness to the necessity of removing nail art prior to OCT imaging is crucial because many patients partake in its application, and removal may require the involvement of a professional nail technician. If a patient can be made aware that they should remove all nail art in advance, they will be better prepared for an OCT imaging session. Such a protocol increases efficiency, decreases diagnostic delay, and reduces cost associated with multiple office visits.
- Saleah S, Kim P, Seong D, et al. A preliminary study of post-progressive nail-art effects on in vivo nail plate using optical coherence tomography-based intensity profiling assessment. Sci Rep. 2021;11:666. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79497-3
- Monpeurt C, Cinotti E, Hebert M, et al. Thickness and morphology assessment of nail polishes applied on nails by high-definition optical coherence tomography. Skin Res Technol. 2018;24:156-157. doi:10.1111/srt.12406
- Saleah S, Kim P, Seong D, et al. A preliminary study of post-progressive nail-art effects on in vivo nail plate using optical coherence tomography-based intensity profiling assessment. Sci Rep. 2021;11:666. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79497-3
- Monpeurt C, Cinotti E, Hebert M, et al. Thickness and morphology assessment of nail polishes applied on nails by high-definition optical coherence tomography. Skin Res Technol. 2018;24:156-157. doi:10.1111/srt.12406
Oval Brown Plaque on the Palm
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.
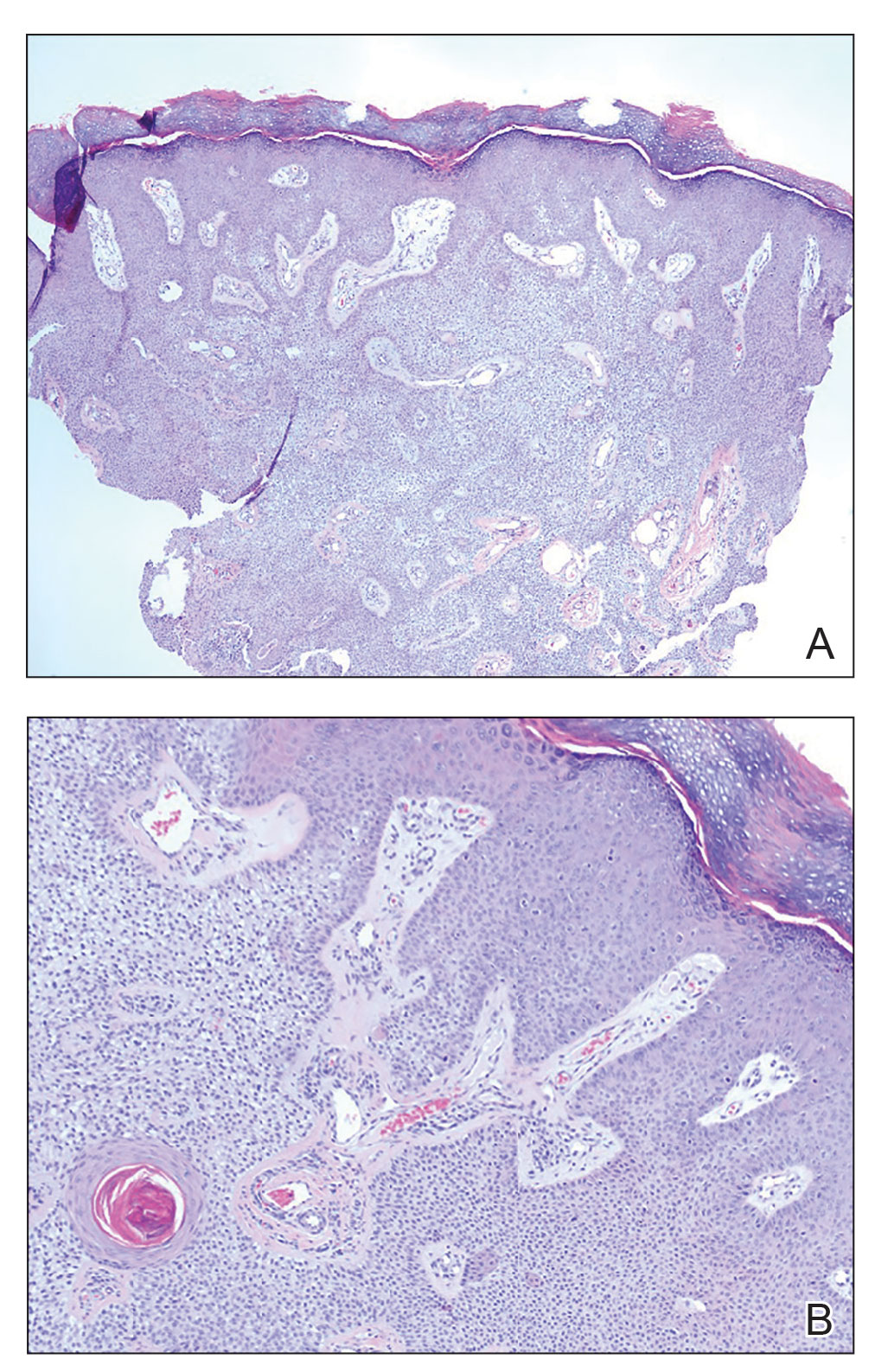
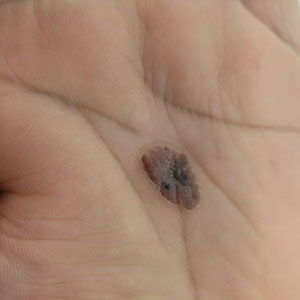
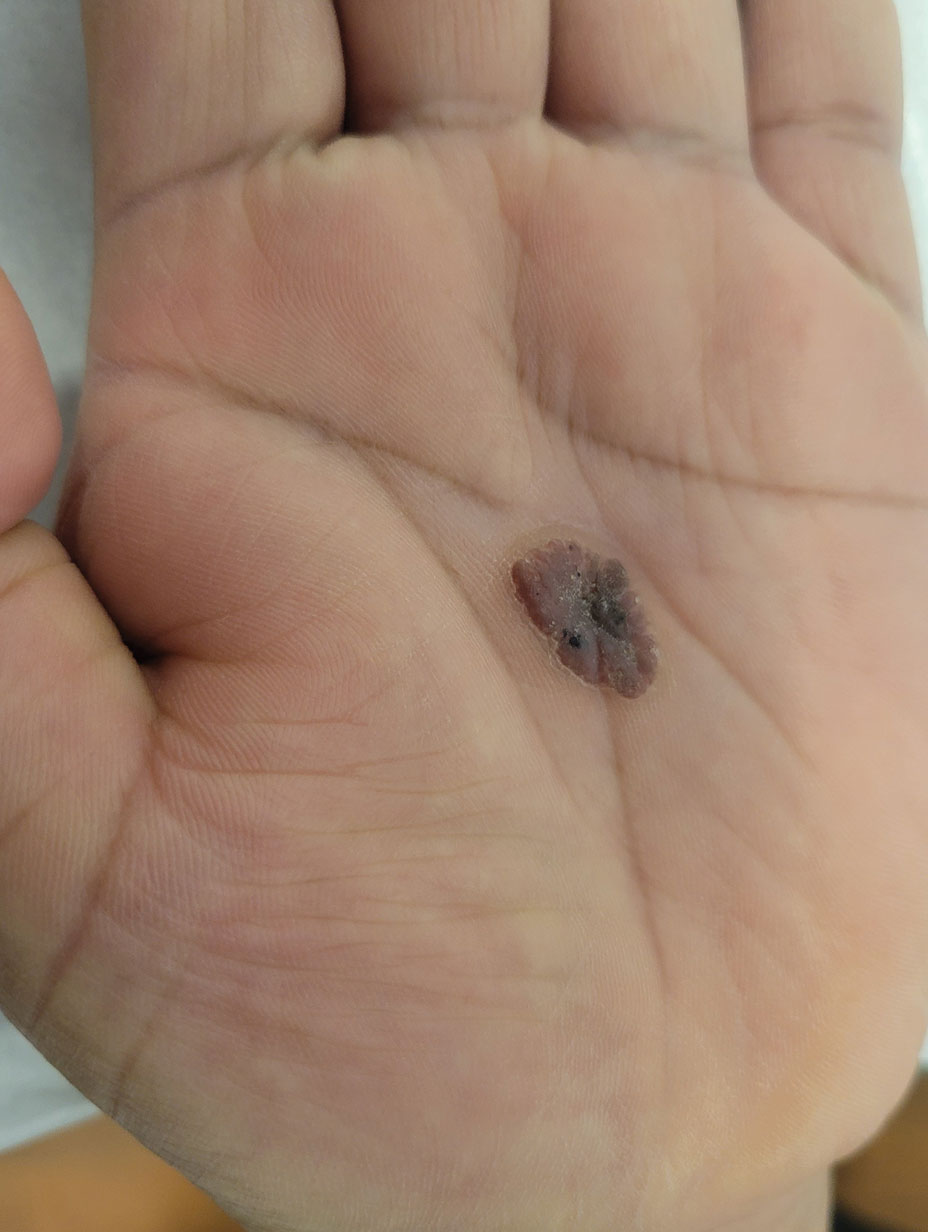
Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.

Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.

Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
A 43-year-old woman presented with a painful lesion on the palm of 30 years’ duration that had grown in size. Physical examination revealed an oval, brown, lobulated plaque with a hyperkeratotic rim on the left palm. She reported bleeding and pain. A shallow cup-shaped depression was noted within the plaque. A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed.
Crusted Scabies Presenting as Erythroderma in a Patient With Iatrogenic Immunosuppression for Treatment of Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
Scabies is caused by cutaneous ectoparasitic infection by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis. The infection is highly contagious via direct skin-to-skin contact or indirectly through infested bedding, clothing or fomites.1,2 Scabies occurs at all ages, in all ethnic groups, and at all socioeconomic levels.1 Analysis by the Global Burden of Disease estimates that 200 million individuals have been infected with scabies worldwide. The World Health Organization has declared scabies a neglected tropical disease.3
Crusted scabies is a severe and rare form of scabies, with hyperinfestation of thousands to millions of mites, and more commonly is associated with immunosuppressed states, including HIV and hematologic malignancies.1,2,4 Crusted scabies has a high mortality rate due to sepsis when left untreated.3,5
Occasionally, iatrogenic immunosuppression contributes to the development of crusted scabies.1,2 Iatrogenic immunosuppression leading to crusted scabies most commonly occurs secondary to immunosuppression after bone marrow or solid organ transplantation.6 Less often, crusted scabies is caused by iatrogenic immunosuppression from other clinical scenarios.1,2
We describe a patient with iatrogenic immunosuppression due to azathioprine-induced myelosuppression for the treatment of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) who developed crusted scabies that clinically presented as erythroderma. Crusted scabies should be included in the differential diagnosis of erythroderma, especially in the setting of iatrogenic immunosuppression, for timely and appropriate management.
Case Report
An 84-year-old man presented with worsening pruritus, erythema, and thick yellow scale that progressed to erythroderma over the last 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with GPA 6 months prior to presentation and was treated with azathioprine 150 mg/d, prednisone 10 mg/d, and sulfamethoxazole 800 mg plus trimethoprim 160 mg twice weekly for prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
Three weeks prior to presentation, the patient was hospitalized for pancytopenia attributed to azathioprine-induced myelosuppression (hemoglobin, 6.1 g/dL [reference range, 13.5–18.0 g/dL]; hematocrit, 17.5% [reference range, 42%–52%]; white blood cell count, 1.66×103/μL [reference range, 4.0–10.5×103/μL]; platelet count, 146×103/μL [reference range, 150–450×103/μL]; absolute neutrophil count, 1.29×103/μL [reference range, 1.4–6.5×103/μL]). He was transferred to a skilled nursing facility after discharge and referred to dermatology for evaluation of the worsening pruritic rash.
At the current presentation, the patient denied close contact with anyone who had a similar rash at home or at the skilled nursing facility. Physical examination revealed diffuse erythroderma with yellow scale on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs (Figure 1). The palms showed scattered 2- to 3-mm pustules. The mucosal surfaces did not have lesions. A punch biopsy of a pustule from the right arm revealed focal spongiosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis, as well as a perivascular and interstitial mixed inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils. Organisms morphologically compatible with scabies were found in the stratum corneum (Figure 2). Another punch biopsy of a pustule from the right arm was performed for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) and was negative for immunoglobulin deposition. Mineral oil preparation from pustules on the palm was positive for mites.
The patient was treated with permethrin cream 5% and oral ivermectin 200 μg/kg on day 1 and day 10. The prednisone dosage was increased from 10 mg/d to 50 mg/d and tapered over 2 weeks to treat the symptomatic rash and GPA. He remains on maintenance rituximab for GPA, without recurrence of scabies.
Comment
Pathogenesis—As an obligate parasite, S scabiei spends its entire life cycle within the host. Impregnated female mites burrow into the epidermis after mating and lay eggs daily for 1 to 2 months. Eggs hatch 2 or 3 days later. Larvae then migrate to the skin surface; burrow into the stratum corneum, where they mature into adults; and then mate on the skin surface.1,4
Clinical Presentation and Sequelae—Typically, scabies presents 2 to 6 weeks after initial exposure with generalized and intense itching and inflammatory pruritic papules on the finger webs, wrists, elbows, axillae, buttocks, umbilicus, genitalia, and areolae.1 Burrows are specific for scabies but may not always be present. Often, there are nonspecific secondary lesions, including excoriations, dermatitis, and impetiginization.
Complications of scabies can be severe, with initial colonization and infection of the skin resulting in impetigo and cellulitis. Systematic sequelae from local skin infection include post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, rheumatic fever, and sepsis. Mortality from sepsis in scabies can be high.3,5
Classic Crusted Scabies and Other Variants—Crusted scabies presents with psoriasiform hyperkeratotic plaques involving the hands and feet with potential nail involvement that can become more generalized.1 Alterations in CD4+ T-cell function have been implicated in the development of crusted scabies, in which an excessive helper T cell (TH2) response is elicited against the ectoparasite, which may help explain the intense pruritus of scabies.6 Occasionally, iatrogenic immunosuppression contributes to development of crusted scabies,1 as was the case with our patient. However, it is rare for crusted scabies to present with erythroderma.7
Other atypical presentations of scabies include a seborrheic dermatitis–like presentation in infants, nodular lesions in the groin and axillae in more chronic scabies, and vesicles or bullous lesions.1
Diagnosis—Identification of mites, eggs, or feces is necessary for definitive diagnosis of scabies.8 These materials can be obtained through skin scrapings with mineral oil and observed under light microscopy or direct dermoscopy. Multiple scrapings on many lesions should be performed because failure to identify mites can be common and does not rule out scabies. Dermoscopic examination of active lesions under low power also can be helpful, given that identification of dark brown triangular structures can correspond to visualization of the pigmented anterior section of the mite.9-11 A skin biopsy can help identify mites, but histopathology often shows a nonspecific hypersensitivity reaction.12 Therefore, empiric treatment often is necessary.
Differential Diagnosis—The differential diagnosis of erythroderma is broad and includes a drug eruption; Sézary syndrome; and pre-existing skin diseases, including psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis rubra pilaris, pemphigus foliaceus, and bullous pemphigoid. Histopathology is critical to differentiate these diagnoses. Bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus foliaceus are immunobullous diseases that typically are positive for immunoglobulin deposition on DIF. In rare cases, scabies also can present with bullae and positive DIF test results.13
Treatment—First-line treatment of crusted scabies in the United States is permethrin cream 5%, followed by oral ivermectin 200 μg/kg.4,5,14,15 Other scabicides include topicals such as benzyl benzoate 10% to 25%; precipitated sulfur 2% to 10%; crotamiton 10%; malathion 0.5%; and lindane 1%.5 The association of neurotoxicity with lindane has considerably reduced the drug’s use.1
During treatment of scabies, it is important to isolate patients to mitigate the possibility of spread.4 Pruritus can persist for a few weeks after completion of therapy.5 Patients should be closely monitored to ensure that this symptom is secondary to skin inflammation and not incomplete treatment.
Treatment of crusted scabies may require repeated treatments to decrease the notable mite burden as well as the associated crusting and scale. Adding a keratolytic such as 5% to 10% salicylic acid in petrolatum to the treatment regimen may be useful for breaking up thick scale.5
Immunosuppression—With numerous immunomodulatory drugs for treating autoimmunity comes an increased risk for iatrogenic immunosuppression that may contribute to the development of crusted scabies.16 In a number of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,17-19 psoriasis,20,21 pemphigus vulgaris,22 systemic lupus erythematosus,23 systemic sclerosis,22,24 bullous pemphigoid,25,26 and dermatomyositis,27 patients have developed crusted scabies secondary to treatment-related immunosuppression. These immunosuppressive therapies include systemic steroids,22-24,26-31 methotrexate,23 infliximab,18 adalimumab,21 toclizumab,19 and etanercept.20 In a case of drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome, the patient developed crusted scabies during long-term use of oral steroids.22
Patients with a malignancy who are being treated with chemotherapy also can develop crusted scabies.28 Crusted scabies has even been associated with long-term topical steroid32-34 and topical calcineurin inhibitor use.16
Iatrogenic immunosuppression in our patient resulted from treatment of GPA with azathioprine, an immunosuppressive drug that acts as an antagonist of the breakdown of purines, leading to inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis.35 On occasion, azathioprine can induce immunosuppression in the form of myelosuppression and resulting pancytopenia, as was the case with our patient.
Conclusion
Although scabies is designated as a neglected tropical disease by the World Health Organization, it still causes a notable burden worldwide, regardless of the economics. Our case highlights an unusual presentation of scabies as erythroderma in the setting of iatrogenic immunosuppression from azathioprine use. Dermatologists should consider crusted scabies in the differential diagnosis of erythroderma, especially in immunocompromised patients, to avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment. Immunosuppressive therapy is an important mainstay in the treatment of many conditions, but it is important to consider that these medications can place patients at an increased risk for rare opportunistic infections. Therefore, patients receiving such treatment should be closely monitored.
- Chosidow O. Clinical practices. Scabies. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1718-1727. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp052784
- Salgado F, Elston DM. What’s eating you? scabies in the developing world. Cutis. 2017;100:287-289.
- Karimkhani C, Colombara DV, Drucker AM, et al. The global burden of scabies: a cross-sectional analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:1247-1254. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30483-8
- Currie BJ, McCarthy JS. Permethrin and ivermectin for scabies. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:717-725. doi:10.1056/NEJMct0910329
- Thomas C, Coates SJ, Engelman D, et al. Ectoparasites: scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:533-548. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.05.109
- Roberts LJ, Huffam SE, Walton SF, et al. Crusted scabies: clinical and immunological findings in seventy-eight patients and a review of the literature. J Infect. 2005;50:375-381. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2004.08.033
- Wang X-D, Shen H, Liu Z-H. Contagious erythroderma. J Emerg Med. 2016;51:180-181. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2016.05.027
- Johnston G, Sladden M. Scabies: diagnosis and treatment. BMJ. 2005;331:619-622. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7517.619
- Micali G, Lacarrubba F, Massimino D, et al. Dermatoscopy: alternative uses in daily clinical practice. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1135-1146. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.010
- Bollea Garlatti LA, Torre AC, Bollea Garlatti ML, et al.. Dermoscopy aids the diagnosis of crusted scabies in an erythrodermic patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E93-E95. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.04.061
- Tang J, You Z, Ran Y. Simple methods to enhance the diagnosis of scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:E99-E100. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.07.038
- Falk ES, Eide TJ. Histologic and clinical findings in human scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1981;20:600-605. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1981.tb00844.x
- Shahab RKA, Loo DS. Bullous scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:346-350. doi:10.1067/s0190-9622(03)00876-4
- Strong M, Johnstone P. Interventions for treating scabies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD000320. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000320.pub2
- Rosumeck S, Nast A, Dressler C. Evaluation of ivermectin vs permethrin for treating scabies—summary of a Cochrane Review. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:730-732. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0279
- Ruiz-Maldonado R. Pimecrolimus related crusted scabies in an infant. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:299-300. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2006.00241.x
- Bu X, Fan J, Hu X, et al. Norwegian scabies in a patient treated with Tripterygium glycoside for rheumatoid arthritis. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:556-558. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20174946
- Pipitone MA, Adams B, Sheth A, et al. Crusted scabies in a patient being treated with infliximab for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:719-720. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.12.039
- Baccouche K, Sellam J, Guegan S, et al. Crusted Norwegian scabies, an opportunistic infection, with tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2011;78:402-404. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.02.008
- Saillard C, Darrieux L, Safa G. Crusted scabies complicates etanercept therapy in a patient with severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:E138-E139. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.09.049
- Belvisi V, Orsi GB, Del Borgo C, et al. Large nosocomial outbreakassociated with a Norwegian scabies index case undergoing TNF-α inhibitor treatment: management and control. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2015;36:1358-1360. doi:10.1017/ice.2015.188
- Nofal A. Variable response of crusted scabies to oral ivermectin: report on eight Egyptian patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:793-797. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03177.x
- Yee BE, Carlos CA, Hata T. Crusted scabies of the scalp in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt9dm891gd.
- Bumb RA, Mehta RD. Crusted scabies in a patient of systemic sclerosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2000;66:143-144.
- Hylwa SA, Loss L, Grassi M. Crusted scabies and tinea corporis after treatment of presumed bullous pemphigoid. Cutis. 2013;92:193-198.
- Svecova D, Chmurova N, Pallova A, et al. Norwegian scabies in immunosuppressed patient misdiagnosed as an adverse drug reaction. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2009;58:121-123.
- Dourmishev AL, Serafimova DK, Dourmishev LA, et al. Crusted scabies of the scalp in dermatomyositis patients: three cases treated with oral ivermectin. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:231-234. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.1998.00330.x
- Mortazavi H, Abedini R, Sadri F, et al. Crusted scabies in a patient with brain astrocytoma: report of a case. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:E526-E527. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2009.06.011
- Lima FCDR, Cerqueira AMM, MBS, et al. Crusted scabies due to indiscriminate use of glucocorticoid therapy in infant. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:383-385. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20174433
- Binic´ I, Jankovic´ A, Jovanovic´ D, et al. Crusted (Norwegian) scabies following systemic and topical corticosteroid therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25:188-191. doi:10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.188
- Ohtaki N, Taniguchi H, Ohtomo H. Oral ivermectin treatment in two cases of scabies: effective in crusted scabies induced by corticosteroid but ineffective in nail scabies. J Dermatol. 2003;30:411-416. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2003.tb00408.x
- Bilan P, Colin-Gorski AM, Chapelon E, et al. Crusted scabies induced by topical corticosteroids: a case report [in French]. Arch Pediatr. 2015;22:1292-1294. doi:10.1016/j.arcped.2015.09.004
- Marlière V, Roul S, C, et al. Crusted (Norwegian) scabies induced by use of topical corticosteroids and treated successfully with ivermectin. J Pediatr. 1999;135:122-124. doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70342-2
- Jaramillo-Ayerbe F, J. Ivermectin for crusted Norwegian scabies induced by use of topical steroids. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:143-145. doi:10.1001/archderm.134.2.143
- Elion GB. The purine path to chemotherapy. Science. 1989;244:41-47. doi:10.1126/science.2649979
Scabies is caused by cutaneous ectoparasitic infection by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis. The infection is highly contagious via direct skin-to-skin contact or indirectly through infested bedding, clothing or fomites.1,2 Scabies occurs at all ages, in all ethnic groups, and at all socioeconomic levels.1 Analysis by the Global Burden of Disease estimates that 200 million individuals have been infected with scabies worldwide. The World Health Organization has declared scabies a neglected tropical disease.3
Crusted scabies is a severe and rare form of scabies, with hyperinfestation of thousands to millions of mites, and more commonly is associated with immunosuppressed states, including HIV and hematologic malignancies.1,2,4 Crusted scabies has a high mortality rate due to sepsis when left untreated.3,5
Occasionally, iatrogenic immunosuppression contributes to the development of crusted scabies.1,2 Iatrogenic immunosuppression leading to crusted scabies most commonly occurs secondary to immunosuppression after bone marrow or solid organ transplantation.6 Less often, crusted scabies is caused by iatrogenic immunosuppression from other clinical scenarios.1,2
We describe a patient with iatrogenic immunosuppression due to azathioprine-induced myelosuppression for the treatment of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) who developed crusted scabies that clinically presented as erythroderma. Crusted scabies should be included in the differential diagnosis of erythroderma, especially in the setting of iatrogenic immunosuppression, for timely and appropriate management.
Case Report
An 84-year-old man presented with worsening pruritus, erythema, and thick yellow scale that progressed to erythroderma over the last 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with GPA 6 months prior to presentation and was treated with azathioprine 150 mg/d, prednisone 10 mg/d, and sulfamethoxazole 800 mg plus trimethoprim 160 mg twice weekly for prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
Three weeks prior to presentation, the patient was hospitalized for pancytopenia attributed to azathioprine-induced myelosuppression (hemoglobin, 6.1 g/dL [reference range, 13.5–18.0 g/dL]; hematocrit, 17.5% [reference range, 42%–52%]; white blood cell count, 1.66×103/μL [reference range, 4.0–10.5×103/μL]; platelet count, 146×103/μL [reference range, 150–450×103/μL]; absolute neutrophil count, 1.29×103/μL [reference range, 1.4–6.5×103/μL]). He was transferred to a skilled nursing facility after discharge and referred to dermatology for evaluation of the worsening pruritic rash.

At the current presentation, the patient denied close contact with anyone who had a similar rash at home or at the skilled nursing facility. Physical examination revealed diffuse erythroderma with yellow scale on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs (Figure 1). The palms showed scattered 2- to 3-mm pustules. The mucosal surfaces did not have lesions. A punch biopsy of a pustule from the right arm revealed focal spongiosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis, as well as a perivascular and interstitial mixed inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils. Organisms morphologically compatible with scabies were found in the stratum corneum (Figure 2). Another punch biopsy of a pustule from the right arm was performed for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) and was negative for immunoglobulin deposition. Mineral oil preparation from pustules on the palm was positive for mites.

The patient was treated with permethrin cream 5% and oral ivermectin 200 μg/kg on day 1 and day 10. The prednisone dosage was increased from 10 mg/d to 50 mg/d and tapered over 2 weeks to treat the symptomatic rash and GPA. He remains on maintenance rituximab for GPA, without recurrence of scabies.
Comment
Pathogenesis—As an obligate parasite, S scabiei spends its entire life cycle within the host. Impregnated female mites burrow into the epidermis after mating and lay eggs daily for 1 to 2 months. Eggs hatch 2 or 3 days later. Larvae then migrate to the skin surface; burrow into the stratum corneum, where they mature into adults; and then mate on the skin surface.1,4
Clinical Presentation and Sequelae—Typically, scabies presents 2 to 6 weeks after initial exposure with generalized and intense itching and inflammatory pruritic papules on the finger webs, wrists, elbows, axillae, buttocks, umbilicus, genitalia, and areolae.1 Burrows are specific for scabies but may not always be present. Often, there are nonspecific secondary lesions, including excoriations, dermatitis, and impetiginization.
Complications of scabies can be severe, with initial colonization and infection of the skin resulting in impetigo and cellulitis. Systematic sequelae from local skin infection include post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, rheumatic fever, and sepsis. Mortality from sepsis in scabies can be high.3,5
Classic Crusted Scabies and Other Variants—Crusted scabies presents with psoriasiform hyperkeratotic plaques involving the hands and feet with potential nail involvement that can become more generalized.1 Alterations in CD4+ T-cell function have been implicated in the development of crusted scabies, in which an excessive helper T cell (TH2) response is elicited against the ectoparasite, which may help explain the intense pruritus of scabies.6 Occasionally, iatrogenic immunosuppression contributes to development of crusted scabies,1 as was the case with our patient. However, it is rare for crusted scabies to present with erythroderma.7
Other atypical presentations of scabies include a seborrheic dermatitis–like presentation in infants, nodular lesions in the groin and axillae in more chronic scabies, and vesicles or bullous lesions.1
Diagnosis—Identification of mites, eggs, or feces is necessary for definitive diagnosis of scabies.8 These materials can be obtained through skin scrapings with mineral oil and observed under light microscopy or direct dermoscopy. Multiple scrapings on many lesions should be performed because failure to identify mites can be common and does not rule out scabies. Dermoscopic examination of active lesions under low power also can be helpful, given that identification of dark brown triangular structures can correspond to visualization of the pigmented anterior section of the mite.9-11 A skin biopsy can help identify mites, but histopathology often shows a nonspecific hypersensitivity reaction.12 Therefore, empiric treatment often is necessary.
Differential Diagnosis—The differential diagnosis of erythroderma is broad and includes a drug eruption; Sézary syndrome; and pre-existing skin diseases, including psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis rubra pilaris, pemphigus foliaceus, and bullous pemphigoid. Histopathology is critical to differentiate these diagnoses. Bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus foliaceus are immunobullous diseases that typically are positive for immunoglobulin deposition on DIF. In rare cases, scabies also can present with bullae and positive DIF test results.13
Treatment—First-line treatment of crusted scabies in the United States is permethrin cream 5%, followed by oral ivermectin 200 μg/kg.4,5,14,15 Other scabicides include topicals such as benzyl benzoate 10% to 25%; precipitated sulfur 2% to 10%; crotamiton 10%; malathion 0.5%; and lindane 1%.5 The association of neurotoxicity with lindane has considerably reduced the drug’s use.1
During treatment of scabies, it is important to isolate patients to mitigate the possibility of spread.4 Pruritus can persist for a few weeks after completion of therapy.5 Patients should be closely monitored to ensure that this symptom is secondary to skin inflammation and not incomplete treatment.
Treatment of crusted scabies may require repeated treatments to decrease the notable mite burden as well as the associated crusting and scale. Adding a keratolytic such as 5% to 10% salicylic acid in petrolatum to the treatment regimen may be useful for breaking up thick scale.5
Immunosuppression—With numerous immunomodulatory drugs for treating autoimmunity comes an increased risk for iatrogenic immunosuppression that may contribute to the development of crusted scabies.16 In a number of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,17-19 psoriasis,20,21 pemphigus vulgaris,22 systemic lupus erythematosus,23 systemic sclerosis,22,24 bullous pemphigoid,25,26 and dermatomyositis,27 patients have developed crusted scabies secondary to treatment-related immunosuppression. These immunosuppressive therapies include systemic steroids,22-24,26-31 methotrexate,23 infliximab,18 adalimumab,21 toclizumab,19 and etanercept.20 In a case of drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome, the patient developed crusted scabies during long-term use of oral steroids.22
Patients with a malignancy who are being treated with chemotherapy also can develop crusted scabies.28 Crusted scabies has even been associated with long-term topical steroid32-34 and topical calcineurin inhibitor use.16
Iatrogenic immunosuppression in our patient resulted from treatment of GPA with azathioprine, an immunosuppressive drug that acts as an antagonist of the breakdown of purines, leading to inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis.35 On occasion, azathioprine can induce immunosuppression in the form of myelosuppression and resulting pancytopenia, as was the case with our patient.
Conclusion
Although scabies is designated as a neglected tropical disease by the World Health Organization, it still causes a notable burden worldwide, regardless of the economics. Our case highlights an unusual presentation of scabies as erythroderma in the setting of iatrogenic immunosuppression from azathioprine use. Dermatologists should consider crusted scabies in the differential diagnosis of erythroderma, especially in immunocompromised patients, to avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment. Immunosuppressive therapy is an important mainstay in the treatment of many conditions, but it is important to consider that these medications can place patients at an increased risk for rare opportunistic infections. Therefore, patients receiving such treatment should be closely monitored.
Scabies is caused by cutaneous ectoparasitic infection by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis. The infection is highly contagious via direct skin-to-skin contact or indirectly through infested bedding, clothing or fomites.1,2 Scabies occurs at all ages, in all ethnic groups, and at all socioeconomic levels.1 Analysis by the Global Burden of Disease estimates that 200 million individuals have been infected with scabies worldwide. The World Health Organization has declared scabies a neglected tropical disease.3
Crusted scabies is a severe and rare form of scabies, with hyperinfestation of thousands to millions of mites, and more commonly is associated with immunosuppressed states, including HIV and hematologic malignancies.1,2,4 Crusted scabies has a high mortality rate due to sepsis when left untreated.3,5
Occasionally, iatrogenic immunosuppression contributes to the development of crusted scabies.1,2 Iatrogenic immunosuppression leading to crusted scabies most commonly occurs secondary to immunosuppression after bone marrow or solid organ transplantation.6 Less often, crusted scabies is caused by iatrogenic immunosuppression from other clinical scenarios.1,2
We describe a patient with iatrogenic immunosuppression due to azathioprine-induced myelosuppression for the treatment of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) who developed crusted scabies that clinically presented as erythroderma. Crusted scabies should be included in the differential diagnosis of erythroderma, especially in the setting of iatrogenic immunosuppression, for timely and appropriate management.
Case Report
An 84-year-old man presented with worsening pruritus, erythema, and thick yellow scale that progressed to erythroderma over the last 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with GPA 6 months prior to presentation and was treated with azathioprine 150 mg/d, prednisone 10 mg/d, and sulfamethoxazole 800 mg plus trimethoprim 160 mg twice weekly for prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
Three weeks prior to presentation, the patient was hospitalized for pancytopenia attributed to azathioprine-induced myelosuppression (hemoglobin, 6.1 g/dL [reference range, 13.5–18.0 g/dL]; hematocrit, 17.5% [reference range, 42%–52%]; white blood cell count, 1.66×103/μL [reference range, 4.0–10.5×103/μL]; platelet count, 146×103/μL [reference range, 150–450×103/μL]; absolute neutrophil count, 1.29×103/μL [reference range, 1.4–6.5×103/μL]). He was transferred to a skilled nursing facility after discharge and referred to dermatology for evaluation of the worsening pruritic rash.

At the current presentation, the patient denied close contact with anyone who had a similar rash at home or at the skilled nursing facility. Physical examination revealed diffuse erythroderma with yellow scale on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs (Figure 1). The palms showed scattered 2- to 3-mm pustules. The mucosal surfaces did not have lesions. A punch biopsy of a pustule from the right arm revealed focal spongiosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis, as well as a perivascular and interstitial mixed inflammatory infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils. Organisms morphologically compatible with scabies were found in the stratum corneum (Figure 2). Another punch biopsy of a pustule from the right arm was performed for direct immunofluorescence (DIF) and was negative for immunoglobulin deposition. Mineral oil preparation from pustules on the palm was positive for mites.

The patient was treated with permethrin cream 5% and oral ivermectin 200 μg/kg on day 1 and day 10. The prednisone dosage was increased from 10 mg/d to 50 mg/d and tapered over 2 weeks to treat the symptomatic rash and GPA. He remains on maintenance rituximab for GPA, without recurrence of scabies.
Comment
Pathogenesis—As an obligate parasite, S scabiei spends its entire life cycle within the host. Impregnated female mites burrow into the epidermis after mating and lay eggs daily for 1 to 2 months. Eggs hatch 2 or 3 days later. Larvae then migrate to the skin surface; burrow into the stratum corneum, where they mature into adults; and then mate on the skin surface.1,4
Clinical Presentation and Sequelae—Typically, scabies presents 2 to 6 weeks after initial exposure with generalized and intense itching and inflammatory pruritic papules on the finger webs, wrists, elbows, axillae, buttocks, umbilicus, genitalia, and areolae.1 Burrows are specific for scabies but may not always be present. Often, there are nonspecific secondary lesions, including excoriations, dermatitis, and impetiginization.
Complications of scabies can be severe, with initial colonization and infection of the skin resulting in impetigo and cellulitis. Systematic sequelae from local skin infection include post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, rheumatic fever, and sepsis. Mortality from sepsis in scabies can be high.3,5
Classic Crusted Scabies and Other Variants—Crusted scabies presents with psoriasiform hyperkeratotic plaques involving the hands and feet with potential nail involvement that can become more generalized.1 Alterations in CD4+ T-cell function have been implicated in the development of crusted scabies, in which an excessive helper T cell (TH2) response is elicited against the ectoparasite, which may help explain the intense pruritus of scabies.6 Occasionally, iatrogenic immunosuppression contributes to development of crusted scabies,1 as was the case with our patient. However, it is rare for crusted scabies to present with erythroderma.7
Other atypical presentations of scabies include a seborrheic dermatitis–like presentation in infants, nodular lesions in the groin and axillae in more chronic scabies, and vesicles or bullous lesions.1
Diagnosis—Identification of mites, eggs, or feces is necessary for definitive diagnosis of scabies.8 These materials can be obtained through skin scrapings with mineral oil and observed under light microscopy or direct dermoscopy. Multiple scrapings on many lesions should be performed because failure to identify mites can be common and does not rule out scabies. Dermoscopic examination of active lesions under low power also can be helpful, given that identification of dark brown triangular structures can correspond to visualization of the pigmented anterior section of the mite.9-11 A skin biopsy can help identify mites, but histopathology often shows a nonspecific hypersensitivity reaction.12 Therefore, empiric treatment often is necessary.
Differential Diagnosis—The differential diagnosis of erythroderma is broad and includes a drug eruption; Sézary syndrome; and pre-existing skin diseases, including psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis rubra pilaris, pemphigus foliaceus, and bullous pemphigoid. Histopathology is critical to differentiate these diagnoses. Bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus foliaceus are immunobullous diseases that typically are positive for immunoglobulin deposition on DIF. In rare cases, scabies also can present with bullae and positive DIF test results.13
Treatment—First-line treatment of crusted scabies in the United States is permethrin cream 5%, followed by oral ivermectin 200 μg/kg.4,5,14,15 Other scabicides include topicals such as benzyl benzoate 10% to 25%; precipitated sulfur 2% to 10%; crotamiton 10%; malathion 0.5%; and lindane 1%.5 The association of neurotoxicity with lindane has considerably reduced the drug’s use.1
During treatment of scabies, it is important to isolate patients to mitigate the possibility of spread.4 Pruritus can persist for a few weeks after completion of therapy.5 Patients should be closely monitored to ensure that this symptom is secondary to skin inflammation and not incomplete treatment.
Treatment of crusted scabies may require repeated treatments to decrease the notable mite burden as well as the associated crusting and scale. Adding a keratolytic such as 5% to 10% salicylic acid in petrolatum to the treatment regimen may be useful for breaking up thick scale.5
Immunosuppression—With numerous immunomodulatory drugs for treating autoimmunity comes an increased risk for iatrogenic immunosuppression that may contribute to the development of crusted scabies.16 In a number of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,17-19 psoriasis,20,21 pemphigus vulgaris,22 systemic lupus erythematosus,23 systemic sclerosis,22,24 bullous pemphigoid,25,26 and dermatomyositis,27 patients have developed crusted scabies secondary to treatment-related immunosuppression. These immunosuppressive therapies include systemic steroids,22-24,26-31 methotrexate,23 infliximab,18 adalimumab,21 toclizumab,19 and etanercept.20 In a case of drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome, the patient developed crusted scabies during long-term use of oral steroids.22
Patients with a malignancy who are being treated with chemotherapy also can develop crusted scabies.28 Crusted scabies has even been associated with long-term topical steroid32-34 and topical calcineurin inhibitor use.16
Iatrogenic immunosuppression in our patient resulted from treatment of GPA with azathioprine, an immunosuppressive drug that acts as an antagonist of the breakdown of purines, leading to inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis.35 On occasion, azathioprine can induce immunosuppression in the form of myelosuppression and resulting pancytopenia, as was the case with our patient.
Conclusion
Although scabies is designated as a neglected tropical disease by the World Health Organization, it still causes a notable burden worldwide, regardless of the economics. Our case highlights an unusual presentation of scabies as erythroderma in the setting of iatrogenic immunosuppression from azathioprine use. Dermatologists should consider crusted scabies in the differential diagnosis of erythroderma, especially in immunocompromised patients, to avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment. Immunosuppressive therapy is an important mainstay in the treatment of many conditions, but it is important to consider that these medications can place patients at an increased risk for rare opportunistic infections. Therefore, patients receiving such treatment should be closely monitored.
- Chosidow O. Clinical practices. Scabies. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1718-1727. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp052784
- Salgado F, Elston DM. What’s eating you? scabies in the developing world. Cutis. 2017;100:287-289.
- Karimkhani C, Colombara DV, Drucker AM, et al. The global burden of scabies: a cross-sectional analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:1247-1254. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30483-8
- Currie BJ, McCarthy JS. Permethrin and ivermectin for scabies. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:717-725. doi:10.1056/NEJMct0910329
- Thomas C, Coates SJ, Engelman D, et al. Ectoparasites: scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:533-548. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.05.109
- Roberts LJ, Huffam SE, Walton SF, et al. Crusted scabies: clinical and immunological findings in seventy-eight patients and a review of the literature. J Infect. 2005;50:375-381. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2004.08.033
- Wang X-D, Shen H, Liu Z-H. Contagious erythroderma. J Emerg Med. 2016;51:180-181. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2016.05.027
- Johnston G, Sladden M. Scabies: diagnosis and treatment. BMJ. 2005;331:619-622. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7517.619
- Micali G, Lacarrubba F, Massimino D, et al. Dermatoscopy: alternative uses in daily clinical practice. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1135-1146. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.010
- Bollea Garlatti LA, Torre AC, Bollea Garlatti ML, et al.. Dermoscopy aids the diagnosis of crusted scabies in an erythrodermic patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E93-E95. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.04.061
- Tang J, You Z, Ran Y. Simple methods to enhance the diagnosis of scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:E99-E100. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.07.038
- Falk ES, Eide TJ. Histologic and clinical findings in human scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1981;20:600-605. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1981.tb00844.x
- Shahab RKA, Loo DS. Bullous scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:346-350. doi:10.1067/s0190-9622(03)00876-4
- Strong M, Johnstone P. Interventions for treating scabies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD000320. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000320.pub2
- Rosumeck S, Nast A, Dressler C. Evaluation of ivermectin vs permethrin for treating scabies—summary of a Cochrane Review. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:730-732. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0279
- Ruiz-Maldonado R. Pimecrolimus related crusted scabies in an infant. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:299-300. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2006.00241.x
- Bu X, Fan J, Hu X, et al. Norwegian scabies in a patient treated with Tripterygium glycoside for rheumatoid arthritis. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:556-558. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20174946
- Pipitone MA, Adams B, Sheth A, et al. Crusted scabies in a patient being treated with infliximab for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:719-720. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.12.039
- Baccouche K, Sellam J, Guegan S, et al. Crusted Norwegian scabies, an opportunistic infection, with tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2011;78:402-404. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.02.008
- Saillard C, Darrieux L, Safa G. Crusted scabies complicates etanercept therapy in a patient with severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:E138-E139. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.09.049
- Belvisi V, Orsi GB, Del Borgo C, et al. Large nosocomial outbreakassociated with a Norwegian scabies index case undergoing TNF-α inhibitor treatment: management and control. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2015;36:1358-1360. doi:10.1017/ice.2015.188
- Nofal A. Variable response of crusted scabies to oral ivermectin: report on eight Egyptian patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:793-797. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03177.x
- Yee BE, Carlos CA, Hata T. Crusted scabies of the scalp in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt9dm891gd.
- Bumb RA, Mehta RD. Crusted scabies in a patient of systemic sclerosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2000;66:143-144.
- Hylwa SA, Loss L, Grassi M. Crusted scabies and tinea corporis after treatment of presumed bullous pemphigoid. Cutis. 2013;92:193-198.
- Svecova D, Chmurova N, Pallova A, et al. Norwegian scabies in immunosuppressed patient misdiagnosed as an adverse drug reaction. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2009;58:121-123.
- Dourmishev AL, Serafimova DK, Dourmishev LA, et al. Crusted scabies of the scalp in dermatomyositis patients: three cases treated with oral ivermectin. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:231-234. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.1998.00330.x
- Mortazavi H, Abedini R, Sadri F, et al. Crusted scabies in a patient with brain astrocytoma: report of a case. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:E526-E527. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2009.06.011
- Lima FCDR, Cerqueira AMM, MBS, et al. Crusted scabies due to indiscriminate use of glucocorticoid therapy in infant. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:383-385. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20174433
- Binic´ I, Jankovic´ A, Jovanovic´ D, et al. Crusted (Norwegian) scabies following systemic and topical corticosteroid therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25:188-191. doi:10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.188
- Ohtaki N, Taniguchi H, Ohtomo H. Oral ivermectin treatment in two cases of scabies: effective in crusted scabies induced by corticosteroid but ineffective in nail scabies. J Dermatol. 2003;30:411-416. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2003.tb00408.x
- Bilan P, Colin-Gorski AM, Chapelon E, et al. Crusted scabies induced by topical corticosteroids: a case report [in French]. Arch Pediatr. 2015;22:1292-1294. doi:10.1016/j.arcped.2015.09.004
- Marlière V, Roul S, C, et al. Crusted (Norwegian) scabies induced by use of topical corticosteroids and treated successfully with ivermectin. J Pediatr. 1999;135:122-124. doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70342-2
- Jaramillo-Ayerbe F, J. Ivermectin for crusted Norwegian scabies induced by use of topical steroids. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:143-145. doi:10.1001/archderm.134.2.143
- Elion GB. The purine path to chemotherapy. Science. 1989;244:41-47. doi:10.1126/science.2649979
- Chosidow O. Clinical practices. Scabies. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1718-1727. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp052784
- Salgado F, Elston DM. What’s eating you? scabies in the developing world. Cutis. 2017;100:287-289.
- Karimkhani C, Colombara DV, Drucker AM, et al. The global burden of scabies: a cross-sectional analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:1247-1254. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30483-8
- Currie BJ, McCarthy JS. Permethrin and ivermectin for scabies. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:717-725. doi:10.1056/NEJMct0910329
- Thomas C, Coates SJ, Engelman D, et al. Ectoparasites: scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:533-548. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.05.109
- Roberts LJ, Huffam SE, Walton SF, et al. Crusted scabies: clinical and immunological findings in seventy-eight patients and a review of the literature. J Infect. 2005;50:375-381. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2004.08.033
- Wang X-D, Shen H, Liu Z-H. Contagious erythroderma. J Emerg Med. 2016;51:180-181. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2016.05.027
- Johnston G, Sladden M. Scabies: diagnosis and treatment. BMJ. 2005;331:619-622. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7517.619
- Micali G, Lacarrubba F, Massimino D, et al. Dermatoscopy: alternative uses in daily clinical practice. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1135-1146. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.010
- Bollea Garlatti LA, Torre AC, Bollea Garlatti ML, et al.. Dermoscopy aids the diagnosis of crusted scabies in an erythrodermic patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E93-E95. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.04.061
- Tang J, You Z, Ran Y. Simple methods to enhance the diagnosis of scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:E99-E100. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.07.038
- Falk ES, Eide TJ. Histologic and clinical findings in human scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1981;20:600-605. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1981.tb00844.x
- Shahab RKA, Loo DS. Bullous scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:346-350. doi:10.1067/s0190-9622(03)00876-4
- Strong M, Johnstone P. Interventions for treating scabies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD000320. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000320.pub2
- Rosumeck S, Nast A, Dressler C. Evaluation of ivermectin vs permethrin for treating scabies—summary of a Cochrane Review. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:730-732. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.0279
- Ruiz-Maldonado R. Pimecrolimus related crusted scabies in an infant. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:299-300. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2006.00241.x
- Bu X, Fan J, Hu X, et al. Norwegian scabies in a patient treated with Tripterygium glycoside for rheumatoid arthritis. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:556-558. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20174946
- Pipitone MA, Adams B, Sheth A, et al. Crusted scabies in a patient being treated with infliximab for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:719-720. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.12.039
- Baccouche K, Sellam J, Guegan S, et al. Crusted Norwegian scabies, an opportunistic infection, with tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2011;78:402-404. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.02.008
- Saillard C, Darrieux L, Safa G. Crusted scabies complicates etanercept therapy in a patient with severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:E138-E139. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.09.049
- Belvisi V, Orsi GB, Del Borgo C, et al. Large nosocomial outbreakassociated with a Norwegian scabies index case undergoing TNF-α inhibitor treatment: management and control. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2015;36:1358-1360. doi:10.1017/ice.2015.188
- Nofal A. Variable response of crusted scabies to oral ivermectin: report on eight Egyptian patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:793-797. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03177.x
- Yee BE, Carlos CA, Hata T. Crusted scabies of the scalp in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:13030/qt9dm891gd.
- Bumb RA, Mehta RD. Crusted scabies in a patient of systemic sclerosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2000;66:143-144.
- Hylwa SA, Loss L, Grassi M. Crusted scabies and tinea corporis after treatment of presumed bullous pemphigoid. Cutis. 2013;92:193-198.
- Svecova D, Chmurova N, Pallova A, et al. Norwegian scabies in immunosuppressed patient misdiagnosed as an adverse drug reaction. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2009;58:121-123.
- Dourmishev AL, Serafimova DK, Dourmishev LA, et al. Crusted scabies of the scalp in dermatomyositis patients: three cases treated with oral ivermectin. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:231-234. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.1998.00330.x
- Mortazavi H, Abedini R, Sadri F, et al. Crusted scabies in a patient with brain astrocytoma: report of a case. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:E526-E527. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2009.06.011
- Lima FCDR, Cerqueira AMM, MBS, et al. Crusted scabies due to indiscriminate use of glucocorticoid therapy in infant. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:383-385. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20174433
- Binic´ I, Jankovic´ A, Jovanovic´ D, et al. Crusted (Norwegian) scabies following systemic and topical corticosteroid therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25:188-191. doi:10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.188
- Ohtaki N, Taniguchi H, Ohtomo H. Oral ivermectin treatment in two cases of scabies: effective in crusted scabies induced by corticosteroid but ineffective in nail scabies. J Dermatol. 2003;30:411-416. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2003.tb00408.x
- Bilan P, Colin-Gorski AM, Chapelon E, et al. Crusted scabies induced by topical corticosteroids: a case report [in French]. Arch Pediatr. 2015;22:1292-1294. doi:10.1016/j.arcped.2015.09.004
- Marlière V, Roul S, C, et al. Crusted (Norwegian) scabies induced by use of topical corticosteroids and treated successfully with ivermectin. J Pediatr. 1999;135:122-124. doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70342-2
- Jaramillo-Ayerbe F, J. Ivermectin for crusted Norwegian scabies induced by use of topical steroids. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:143-145. doi:10.1001/archderm.134.2.143
- Elion GB. The purine path to chemotherapy. Science. 1989;244:41-47. doi:10.1126/science.2649979
Practice Points
- Crusted scabies is a highly contagious, severe cutaneous ectoparasitic infection that can present atypically in the form of erythroderma.
- Immunomodulatory drugs for the treatment of autoimmune disease can predispose patients to infection, including ectoparasitic infection.
- Dermatologists should be familiar with the full scope of the clinical presentations of scabies and should especially consider this condition in the differential diagnosis of patients who present in an immunosuppressed state.
Primary Effusion Lymphoma: An Infiltrative Plaque in a Patient With HIV
To the Editor:
A 47-year-old man presented to the dermatology service with an asymptomatic plaque on the right thigh of 2 months’ duration. He had a medical history of HIV and Kaposi sarcoma as well as a recently relapsed primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) subsequent to an allogeneic bone marrow transplant. He initially was diagnosed with PEL 3 years prior to the current presentation during a workup for fever and weight loss. Imaging at the time demonstrated a bladder mass, which was biopsied and demonstrated PEL. Further imaging demonstrated both sinus and bone marrow involvement. Prior to dermatologic consultation, he had been treated with 6 cycles of etoposide, prednisolone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH); 6 cycles of brentuximab; 4 cycles of rituximab with gemcitabine and oxaliplatin; and 2 cycles of ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide. Despite these therapies, he had 3 relapses, and oncology determined the need for a matched unrelated donor allogeneic stem cell transplant for his PEL.
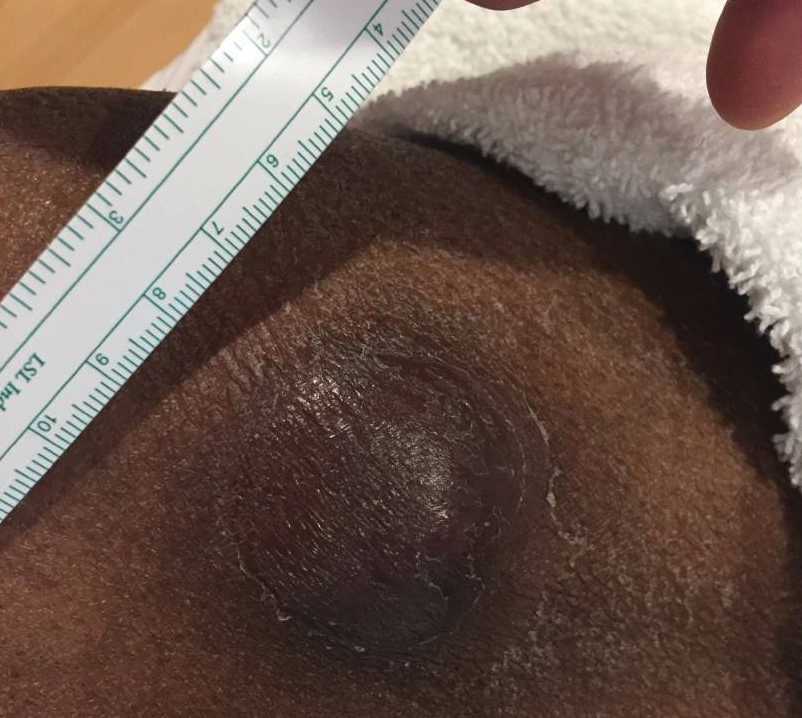
At the time of dermatology consultation, the patient was being managed on daratumumab and bortezomib. Physical examination revealed an infiltrative plaque on the right inferomedial thigh measuring approximately 6.0 cm (largest dimension) with a small amount of peripheral scale (Figure 1). An ultrasound revealed notable subcutaneous tissue edema and increased vascularity without a discrete mass or fluid collection. A 4-mm punch biopsy demonstrated a dense infiltrate comprised of collections of histiocytes admixed with scattered plasma cells and mature lymphoid aggregates. Additionally, rare enlarged plasmablastic cells with scant basophilic cytoplasm and slightly irregular nuclear contours were visualized (Figure 2A). Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD3 with a normal CD4:CD8 ratio, CD68-highlighted histiocytes within the lymphoid aggregates, and human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)(or Kaposi sarcoma–associated herpesvirus) demonstrated stippled nuclear staining within the scattered large cells (Figure 2B). Epstein-Barr virus–encoded RNA staining was negative, though the area of interest was lost on deeper sectioning of the tissue block. The histopathologic findings were consistent with cutaneous extracavitary PEL. Shortly after this diagnosis, he died from disease complications.
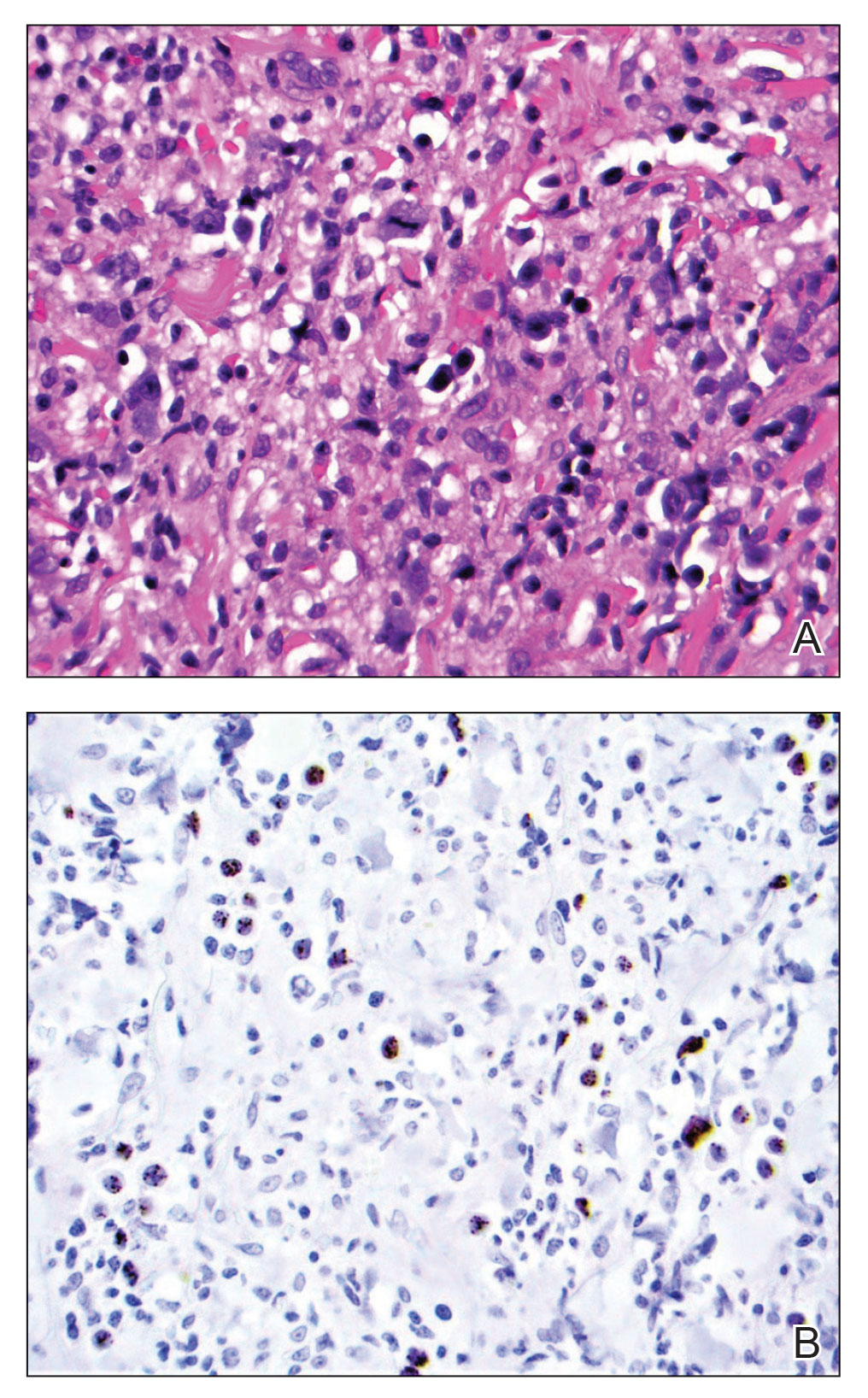
Primary effusion lymphoma is an aggressive non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma that was first described by Knowles et al1 in 1989. Primary effusion lymphoma occurs exclusively in the setting of HHV-8 infection and typically is associated with chronic immunosuppression related to HIV/AIDS. Cases that are negative for HIV-1 are rare but have been reported in organ transplant recipients and elderly men from areas with a high prevalence of HHV-8 infections. Most HIV-associated cases show concurrent Epstein-Barr virus infection, though the pathogenic meaning of this co-infection remains unclear.2,3
Primary effusion lymphoma classically presents as an isolated effusion of malignant lymphoid cells within body cavities in the absence of solid tumor masses. The pleural, peritoneal, and pericardial spaces most commonly are involved. Extracavitary PEL, a rare variant, may present as a solid mass without effusion. In general, extracavitary tumors may occur in the setting of de novo malignancy or recurrent PEL.4 Cutaneous manifestations associated with extracavitary PEL are rare; 4 cases have been described in which skin lesions were the heralding sign of the disease.3 Interestingly, despite obligatory underlying HHV-8 infection, a review by Pielasinski et al3 noted only 2 patients with cutaneous PEL who had prior or concurrent Kaposi sarcoma. This heterogeneity in HHV-8–related phenotypes may be related to differences in microRNA expression, but further study is needed.5
The diagnosis of PEL relies on histologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular analysis of the affected tissue. The malignant cells typically are large with round to irregular nuclei. These cells may demonstrate a variety of appearances, including anaplastic, plasmablastic, and immunoblastic morphologies.6,7 The immunophenotype displays CD45 positivity and markers of lymphocyte activation (CD30, CD38, CD71), while typical B-cell (CD19, CD20, CD79a) and T-cell (CD3, CD4, CD8) markers often are absent.6-8 Human herpesvirus 8 detection by polymerase chain reaction testing of the peripheral blood or by immunohistochemistry staining of the affected tissue is required for diagnosis.6,7 Epstein-Barr virus infection may be detected via in situ hybridization, though it is not required for diagnosis.
The overall prognosis for PEL is poor; Brimo et al6 reported a median survival of less than 6 months, and Guillet et al9 reported 5-year overall survival (OS) for PEL vs extracavitary PEL to be 43% vs 39%. Another review noted variation in survival contingent on the number of body cavities involved; patients with a single body cavity involved experienced a median OS of 18 months, whereas patients with multiple involved cavities experienced a median OS of 4 months,7 possibly due to the limited study of treatment regimens or disease aggressiveness. Even in cases of successful initial treatment, relapse within 6 to 8 months is common. Extracavitary PEL may have improved disease-free survival relative to classic PEL, though the data were less clear for OS.9 Limitations of the Guillet et al9 study included a small sample size, the impossibility to randomize to disease type, and loss of power on the log-rank test for OS in the setting of possible nonproportional hazards (crossing survival curves). Overall, prognostic differences between the groups may be challenging to ascertain until further data are obtained.
As with many HIV-associated neoplasms, antiretroviral treatment (ART) for HIV-positive patients affords a better prognosis when used in addition to therapy directed at malignancy.7 The general approach is for concurrent ART with systemic therapies such as rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone for the rare CD20+ cases, and cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) or dose-adjusted EPOCH therapy in the more common CD20− PEL cases. Narkhede et al7 suggested avoidance of methotrexate in patients with effusions because of increased toxicity, but it is unclear if this recommendation is applicable in extracavitary PEL patients without an effusion. Additionally, second-line treatment modalities include radiation for solid PEL masses, HHV-8–targeted antivirals, and stem cell transplantation, though evidence is limited. Of note, there is a phase I-II trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02911142) ongoing for treatment-naïve PEL patients involving the experimental treatment DA-EPOCH-R plus lenalidomide, but the trial is ongoing.10
We report a case of cutaneous PEL in a patient with a history of Kaposi sarcoma. The patient’s deterioration and ultimate death despite initial treatment with EPOCH and bone marrow transplantation followed by final management with daratumumab and bortezomib confirm other reports that PEL has a poor prognosis and that optimal treatments are not well delineated for these patients. In general, the current approach is to utilize ART for HIV-positive patients and to then implement chemotherapy such as CHOP. Without continued research and careful planning of treatments, data will remain limited on how best to serve patients with PEL.
- Knowles DM, Inghirami G, Ubriaco A, et al. Molecular genetic analysis of three AIDS-associated neoplasms of uncertain lineage demonstrates their B-cell derivation and the possible pathogenetic role of the Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1989;73:792-799.
- Kugasia IAR, Kumar A, Khatri A, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma of the pleural space: report of a rare complication of cardiac transplant with review of the literature. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019;21:E13005.
- Pielasinski U, Santonja C, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, et al. Extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma presenting as a cutaneous tumor: a case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2014;41:745-753.
- Boulanger E, Meignin V, Afonso PV, et al. Extracavitary tumor after primary effusion lymphoma: relapse or second distinct lymphoma? Haematologica. 2007;92:1275-1276.
- Goncalves PH, Uldrick TS, Yarchoan R. HIV-associated Kaposi sarcoma and related diseases. AIDS. 2017;31:1903-1916.
- Brimo F, Michel RP, Khetani K, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma: a series of 4 cases and review of the literature with emphasis on cytomorphologic and immunocytochemical differential diagnosis. Cancer. 2007;111:224-233.
- Narkhede M, Arora S, Ujjani C. Primary effusion lymphoma: current perspectives. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:3747-3754.
- Chen YB, Rahemtullah A, Hochberg E. Primary effusion lymphoma. Oncologist. 2007;12:569-576.
- Guillet S, Gerard L, Meignin V, et al. Classic and extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma in 51 HIV-infected patients from a single institution. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:233-237.
To the Editor:
A 47-year-old man presented to the dermatology service with an asymptomatic plaque on the right thigh of 2 months’ duration. He had a medical history of HIV and Kaposi sarcoma as well as a recently relapsed primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) subsequent to an allogeneic bone marrow transplant. He initially was diagnosed with PEL 3 years prior to the current presentation during a workup for fever and weight loss. Imaging at the time demonstrated a bladder mass, which was biopsied and demonstrated PEL. Further imaging demonstrated both sinus and bone marrow involvement. Prior to dermatologic consultation, he had been treated with 6 cycles of etoposide, prednisolone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH); 6 cycles of brentuximab; 4 cycles of rituximab with gemcitabine and oxaliplatin; and 2 cycles of ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide. Despite these therapies, he had 3 relapses, and oncology determined the need for a matched unrelated donor allogeneic stem cell transplant for his PEL.

At the time of dermatology consultation, the patient was being managed on daratumumab and bortezomib. Physical examination revealed an infiltrative plaque on the right inferomedial thigh measuring approximately 6.0 cm (largest dimension) with a small amount of peripheral scale (Figure 1). An ultrasound revealed notable subcutaneous tissue edema and increased vascularity without a discrete mass or fluid collection. A 4-mm punch biopsy demonstrated a dense infiltrate comprised of collections of histiocytes admixed with scattered plasma cells and mature lymphoid aggregates. Additionally, rare enlarged plasmablastic cells with scant basophilic cytoplasm and slightly irregular nuclear contours were visualized (Figure 2A). Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD3 with a normal CD4:CD8 ratio, CD68-highlighted histiocytes within the lymphoid aggregates, and human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)(or Kaposi sarcoma–associated herpesvirus) demonstrated stippled nuclear staining within the scattered large cells (Figure 2B). Epstein-Barr virus–encoded RNA staining was negative, though the area of interest was lost on deeper sectioning of the tissue block. The histopathologic findings were consistent with cutaneous extracavitary PEL. Shortly after this diagnosis, he died from disease complications.

Primary effusion lymphoma is an aggressive non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma that was first described by Knowles et al1 in 1989. Primary effusion lymphoma occurs exclusively in the setting of HHV-8 infection and typically is associated with chronic immunosuppression related to HIV/AIDS. Cases that are negative for HIV-1 are rare but have been reported in organ transplant recipients and elderly men from areas with a high prevalence of HHV-8 infections. Most HIV-associated cases show concurrent Epstein-Barr virus infection, though the pathogenic meaning of this co-infection remains unclear.2,3
Primary effusion lymphoma classically presents as an isolated effusion of malignant lymphoid cells within body cavities in the absence of solid tumor masses. The pleural, peritoneal, and pericardial spaces most commonly are involved. Extracavitary PEL, a rare variant, may present as a solid mass without effusion. In general, extracavitary tumors may occur in the setting of de novo malignancy or recurrent PEL.4 Cutaneous manifestations associated with extracavitary PEL are rare; 4 cases have been described in which skin lesions were the heralding sign of the disease.3 Interestingly, despite obligatory underlying HHV-8 infection, a review by Pielasinski et al3 noted only 2 patients with cutaneous PEL who had prior or concurrent Kaposi sarcoma. This heterogeneity in HHV-8–related phenotypes may be related to differences in microRNA expression, but further study is needed.5
The diagnosis of PEL relies on histologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular analysis of the affected tissue. The malignant cells typically are large with round to irregular nuclei. These cells may demonstrate a variety of appearances, including anaplastic, plasmablastic, and immunoblastic morphologies.6,7 The immunophenotype displays CD45 positivity and markers of lymphocyte activation (CD30, CD38, CD71), while typical B-cell (CD19, CD20, CD79a) and T-cell (CD3, CD4, CD8) markers often are absent.6-8 Human herpesvirus 8 detection by polymerase chain reaction testing of the peripheral blood or by immunohistochemistry staining of the affected tissue is required for diagnosis.6,7 Epstein-Barr virus infection may be detected via in situ hybridization, though it is not required for diagnosis.
The overall prognosis for PEL is poor; Brimo et al6 reported a median survival of less than 6 months, and Guillet et al9 reported 5-year overall survival (OS) for PEL vs extracavitary PEL to be 43% vs 39%. Another review noted variation in survival contingent on the number of body cavities involved; patients with a single body cavity involved experienced a median OS of 18 months, whereas patients with multiple involved cavities experienced a median OS of 4 months,7 possibly due to the limited study of treatment regimens or disease aggressiveness. Even in cases of successful initial treatment, relapse within 6 to 8 months is common. Extracavitary PEL may have improved disease-free survival relative to classic PEL, though the data were less clear for OS.9 Limitations of the Guillet et al9 study included a small sample size, the impossibility to randomize to disease type, and loss of power on the log-rank test for OS in the setting of possible nonproportional hazards (crossing survival curves). Overall, prognostic differences between the groups may be challenging to ascertain until further data are obtained.
As with many HIV-associated neoplasms, antiretroviral treatment (ART) for HIV-positive patients affords a better prognosis when used in addition to therapy directed at malignancy.7 The general approach is for concurrent ART with systemic therapies such as rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone for the rare CD20+ cases, and cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) or dose-adjusted EPOCH therapy in the more common CD20− PEL cases. Narkhede et al7 suggested avoidance of methotrexate in patients with effusions because of increased toxicity, but it is unclear if this recommendation is applicable in extracavitary PEL patients without an effusion. Additionally, second-line treatment modalities include radiation for solid PEL masses, HHV-8–targeted antivirals, and stem cell transplantation, though evidence is limited. Of note, there is a phase I-II trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02911142) ongoing for treatment-naïve PEL patients involving the experimental treatment DA-EPOCH-R plus lenalidomide, but the trial is ongoing.10
We report a case of cutaneous PEL in a patient with a history of Kaposi sarcoma. The patient’s deterioration and ultimate death despite initial treatment with EPOCH and bone marrow transplantation followed by final management with daratumumab and bortezomib confirm other reports that PEL has a poor prognosis and that optimal treatments are not well delineated for these patients. In general, the current approach is to utilize ART for HIV-positive patients and to then implement chemotherapy such as CHOP. Without continued research and careful planning of treatments, data will remain limited on how best to serve patients with PEL.
To the Editor:
A 47-year-old man presented to the dermatology service with an asymptomatic plaque on the right thigh of 2 months’ duration. He had a medical history of HIV and Kaposi sarcoma as well as a recently relapsed primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) subsequent to an allogeneic bone marrow transplant. He initially was diagnosed with PEL 3 years prior to the current presentation during a workup for fever and weight loss. Imaging at the time demonstrated a bladder mass, which was biopsied and demonstrated PEL. Further imaging demonstrated both sinus and bone marrow involvement. Prior to dermatologic consultation, he had been treated with 6 cycles of etoposide, prednisolone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH); 6 cycles of brentuximab; 4 cycles of rituximab with gemcitabine and oxaliplatin; and 2 cycles of ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide. Despite these therapies, he had 3 relapses, and oncology determined the need for a matched unrelated donor allogeneic stem cell transplant for his PEL.

At the time of dermatology consultation, the patient was being managed on daratumumab and bortezomib. Physical examination revealed an infiltrative plaque on the right inferomedial thigh measuring approximately 6.0 cm (largest dimension) with a small amount of peripheral scale (Figure 1). An ultrasound revealed notable subcutaneous tissue edema and increased vascularity without a discrete mass or fluid collection. A 4-mm punch biopsy demonstrated a dense infiltrate comprised of collections of histiocytes admixed with scattered plasma cells and mature lymphoid aggregates. Additionally, rare enlarged plasmablastic cells with scant basophilic cytoplasm and slightly irregular nuclear contours were visualized (Figure 2A). Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD3 with a normal CD4:CD8 ratio, CD68-highlighted histiocytes within the lymphoid aggregates, and human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)(or Kaposi sarcoma–associated herpesvirus) demonstrated stippled nuclear staining within the scattered large cells (Figure 2B). Epstein-Barr virus–encoded RNA staining was negative, though the area of interest was lost on deeper sectioning of the tissue block. The histopathologic findings were consistent with cutaneous extracavitary PEL. Shortly after this diagnosis, he died from disease complications.

Primary effusion lymphoma is an aggressive non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma that was first described by Knowles et al1 in 1989. Primary effusion lymphoma occurs exclusively in the setting of HHV-8 infection and typically is associated with chronic immunosuppression related to HIV/AIDS. Cases that are negative for HIV-1 are rare but have been reported in organ transplant recipients and elderly men from areas with a high prevalence of HHV-8 infections. Most HIV-associated cases show concurrent Epstein-Barr virus infection, though the pathogenic meaning of this co-infection remains unclear.2,3
Primary effusion lymphoma classically presents as an isolated effusion of malignant lymphoid cells within body cavities in the absence of solid tumor masses. The pleural, peritoneal, and pericardial spaces most commonly are involved. Extracavitary PEL, a rare variant, may present as a solid mass without effusion. In general, extracavitary tumors may occur in the setting of de novo malignancy or recurrent PEL.4 Cutaneous manifestations associated with extracavitary PEL are rare; 4 cases have been described in which skin lesions were the heralding sign of the disease.3 Interestingly, despite obligatory underlying HHV-8 infection, a review by Pielasinski et al3 noted only 2 patients with cutaneous PEL who had prior or concurrent Kaposi sarcoma. This heterogeneity in HHV-8–related phenotypes may be related to differences in microRNA expression, but further study is needed.5
The diagnosis of PEL relies on histologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular analysis of the affected tissue. The malignant cells typically are large with round to irregular nuclei. These cells may demonstrate a variety of appearances, including anaplastic, plasmablastic, and immunoblastic morphologies.6,7 The immunophenotype displays CD45 positivity and markers of lymphocyte activation (CD30, CD38, CD71), while typical B-cell (CD19, CD20, CD79a) and T-cell (CD3, CD4, CD8) markers often are absent.6-8 Human herpesvirus 8 detection by polymerase chain reaction testing of the peripheral blood or by immunohistochemistry staining of the affected tissue is required for diagnosis.6,7 Epstein-Barr virus infection may be detected via in situ hybridization, though it is not required for diagnosis.
The overall prognosis for PEL is poor; Brimo et al6 reported a median survival of less than 6 months, and Guillet et al9 reported 5-year overall survival (OS) for PEL vs extracavitary PEL to be 43% vs 39%. Another review noted variation in survival contingent on the number of body cavities involved; patients with a single body cavity involved experienced a median OS of 18 months, whereas patients with multiple involved cavities experienced a median OS of 4 months,7 possibly due to the limited study of treatment regimens or disease aggressiveness. Even in cases of successful initial treatment, relapse within 6 to 8 months is common. Extracavitary PEL may have improved disease-free survival relative to classic PEL, though the data were less clear for OS.9 Limitations of the Guillet et al9 study included a small sample size, the impossibility to randomize to disease type, and loss of power on the log-rank test for OS in the setting of possible nonproportional hazards (crossing survival curves). Overall, prognostic differences between the groups may be challenging to ascertain until further data are obtained.
As with many HIV-associated neoplasms, antiretroviral treatment (ART) for HIV-positive patients affords a better prognosis when used in addition to therapy directed at malignancy.7 The general approach is for concurrent ART with systemic therapies such as rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone for the rare CD20+ cases, and cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) or dose-adjusted EPOCH therapy in the more common CD20− PEL cases. Narkhede et al7 suggested avoidance of methotrexate in patients with effusions because of increased toxicity, but it is unclear if this recommendation is applicable in extracavitary PEL patients without an effusion. Additionally, second-line treatment modalities include radiation for solid PEL masses, HHV-8–targeted antivirals, and stem cell transplantation, though evidence is limited. Of note, there is a phase I-II trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02911142) ongoing for treatment-naïve PEL patients involving the experimental treatment DA-EPOCH-R plus lenalidomide, but the trial is ongoing.10
We report a case of cutaneous PEL in a patient with a history of Kaposi sarcoma. The patient’s deterioration and ultimate death despite initial treatment with EPOCH and bone marrow transplantation followed by final management with daratumumab and bortezomib confirm other reports that PEL has a poor prognosis and that optimal treatments are not well delineated for these patients. In general, the current approach is to utilize ART for HIV-positive patients and to then implement chemotherapy such as CHOP. Without continued research and careful planning of treatments, data will remain limited on how best to serve patients with PEL.
- Knowles DM, Inghirami G, Ubriaco A, et al. Molecular genetic analysis of three AIDS-associated neoplasms of uncertain lineage demonstrates their B-cell derivation and the possible pathogenetic role of the Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1989;73:792-799.
- Kugasia IAR, Kumar A, Khatri A, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma of the pleural space: report of a rare complication of cardiac transplant with review of the literature. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019;21:E13005.
- Pielasinski U, Santonja C, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, et al. Extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma presenting as a cutaneous tumor: a case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2014;41:745-753.
- Boulanger E, Meignin V, Afonso PV, et al. Extracavitary tumor after primary effusion lymphoma: relapse or second distinct lymphoma? Haematologica. 2007;92:1275-1276.
- Goncalves PH, Uldrick TS, Yarchoan R. HIV-associated Kaposi sarcoma and related diseases. AIDS. 2017;31:1903-1916.
- Brimo F, Michel RP, Khetani K, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma: a series of 4 cases and review of the literature with emphasis on cytomorphologic and immunocytochemical differential diagnosis. Cancer. 2007;111:224-233.
- Narkhede M, Arora S, Ujjani C. Primary effusion lymphoma: current perspectives. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:3747-3754.
- Chen YB, Rahemtullah A, Hochberg E. Primary effusion lymphoma. Oncologist. 2007;12:569-576.
- Guillet S, Gerard L, Meignin V, et al. Classic and extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma in 51 HIV-infected patients from a single institution. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:233-237.
- Knowles DM, Inghirami G, Ubriaco A, et al. Molecular genetic analysis of three AIDS-associated neoplasms of uncertain lineage demonstrates their B-cell derivation and the possible pathogenetic role of the Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1989;73:792-799.
- Kugasia IAR, Kumar A, Khatri A, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma of the pleural space: report of a rare complication of cardiac transplant with review of the literature. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019;21:E13005.
- Pielasinski U, Santonja C, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, et al. Extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma presenting as a cutaneous tumor: a case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2014;41:745-753.
- Boulanger E, Meignin V, Afonso PV, et al. Extracavitary tumor after primary effusion lymphoma: relapse or second distinct lymphoma? Haematologica. 2007;92:1275-1276.
- Goncalves PH, Uldrick TS, Yarchoan R. HIV-associated Kaposi sarcoma and related diseases. AIDS. 2017;31:1903-1916.
- Brimo F, Michel RP, Khetani K, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma: a series of 4 cases and review of the literature with emphasis on cytomorphologic and immunocytochemical differential diagnosis. Cancer. 2007;111:224-233.
- Narkhede M, Arora S, Ujjani C. Primary effusion lymphoma: current perspectives. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:3747-3754.
- Chen YB, Rahemtullah A, Hochberg E. Primary effusion lymphoma. Oncologist. 2007;12:569-576.
- Guillet S, Gerard L, Meignin V, et al. Classic and extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma in 51 HIV-infected patients from a single institution. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:233-237.
Practice Points
- Extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma is an aggressive non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma that occurs solely in the presence of human herpesvirus 8 infection and typically is associated with HIV/AIDS.
- Diagnosis necessitates a thorough workup and correlation of histologic, molecular, and immunophenotypic analysis.
- Antiretroviral therapy in HIV-positive patients and intensive chemotherapy regimens are the current recommended treatments. Despite newer targeted agents, the prognosis remains poor.
Papular Acneform Eruption With Mucositis
The Diagnosis: Syphilis
Histopathology revealed psoriasiform hyperplasia, endothelial cell swelling, and a brisk lichenoid inflammation with plasma cells (Figure, A). There also was pustular folliculitis in association with well-formed granulomatous inflammation and a prominent number of plasma cells (Figure, B). Treponema pallidum immunostaining showed numerous organisms in the epidermal and follicular epithelium. Rapid plasma reagin was found to be positive with a titer of 1:128. Evaluation for neurosyphilis through lumbar puncture was negative; the patient also was HIV negative. All of our patient’s skin lesions cleared after a 3-week course of weekly intramuscular benzathine G injections. Due to his substantial clinical improvement, the patient was subsequently lost to follow-up.
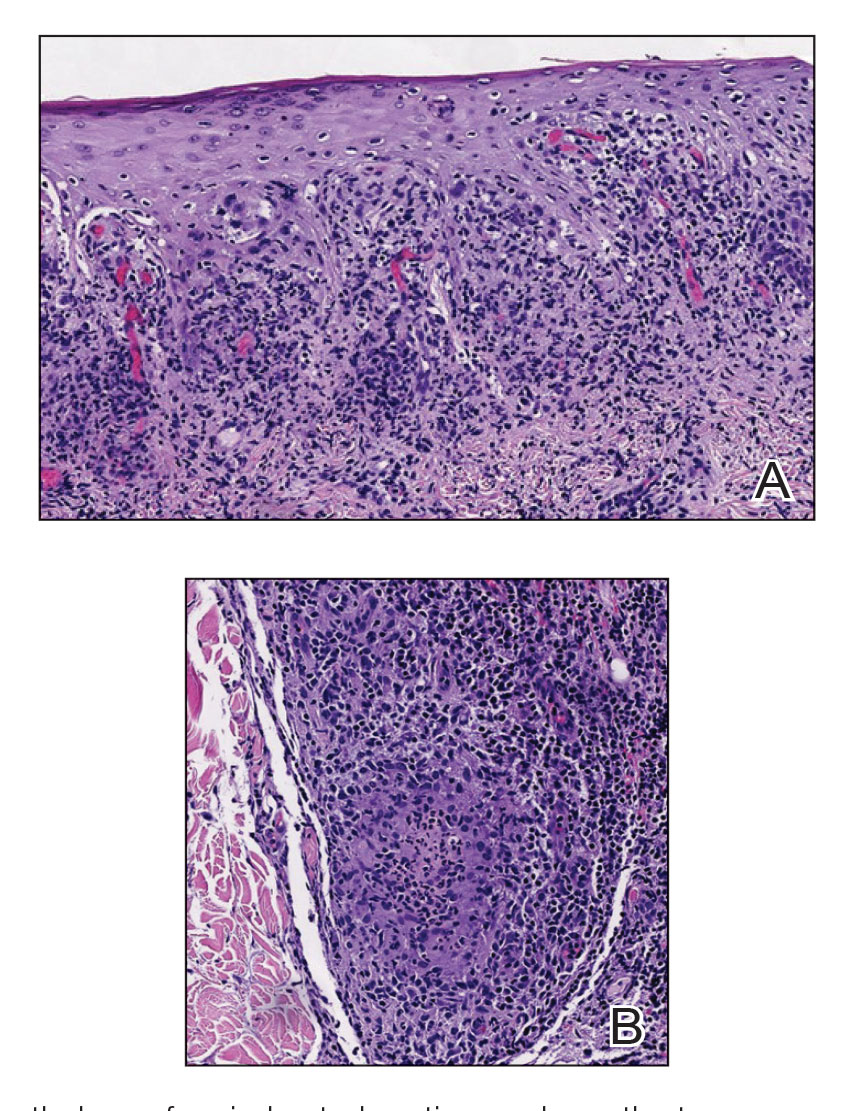
Syphilis, an infectious disease caused by the spirochete bacterium T pallidum, has a well-known natural history defined by various stages classically categorized as primary, secondary, latent, or late (tertiary).1 The classic lesion in primary syphilis is the chancre, a painless ulcer with raised borders that develops within approximately 3 weeks following the initial inoculation.2 Secondary syphilis manifests with mucocutaneous findings in up to 97% of patients, and untreated patients develop secondary syphilis at a rate of approximately 25%.3 Although mucocutaneous findings in secondary syphilis can vary widely, patients most commonly develop a diffuse maculopapular exanthem, and 40% develop mucosal findings including genital ulcers, mucous patches, and condylomata lata.1 In latent syphilis, there is seroreactivity, but otherwise there are no clinical symptoms. A clear symptomatic history of prior primary or secondary syphilis may be known or unknown. Latent syphilis is divided into early and late phases, and the World Health Organization designates 2 years after the first suspected exposure as the cutoff point for early and late latency.4 During the first 4 years of latent syphilis, patients may exhibit mucocutaneous relapses. Our patient denied any sexual activity for more than 3 years prior to presentation. Because of the start of iatrogenic immunosuppression during this period, this case was classified as late latent syphilis with mucocutaneous reactivation.
Behçet disease was included within the differential diagnosis but is characterized by multiorgan systemic vasculitis that causes various mucocutaneous findings including aphthous ulcers, papulopustular lesions, and genital ulcers.5 Histopathologic features are nonspecific, and the clinical finding of recurrent genital and oral ulceration should be present for diagnosis. This disease predominantly occurs in East Asian or Mediterranean populations and is otherwise rare in White individuals.
SAPHO (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis) syndrome is a rare disorder consisting of skin, joint, and bone manifestations.6 Severe acne generally is accompanied by palmoplantar pustulosis along with pain and joint tenderness involving the anterior chest and axial skeleton, both of which were absent in our patient.
Pustular psoriasis can be localized or generalized. Localized presentations frequently are acral and may be associated with a variable degree of nail dystrophy and arthritis. Generalized presentations are characterized by hyperemic, well-defined patches with variable numbers of pustules.7 The pustules are the consequence of exuberate neutrophilic exocytosis into the epidermis and are nonfollicular.
Steroid-induced acne may be considered in the proper clinical setting of an acneform eruption with a prior history of systemic steroid treatment. However, additional findings of mucositis would not be expected, and although our patient was prescribed prednisone from his primary care physician prior to presentation to our clinic, this medication was given after the onset of the cutaneous eruption.
Syphilis commonly is referred to as the great mimicker due to its potential diverse morphologic presentations, which can involve acneform eruptions, though rare.8 In the setting of mucositis, generalized acneform eruptions should raise suspicion for the possibility of syphilis, even in the absence of other more classic cutaneous features.
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: historical aspects, microbiology, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1-14.
- Sparling PF. Natural history of syphilis. In: Holmes KK, Mardh PA, Sparling PF, et al, eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. McGraw Hill; 1990:213.
- Clark EG, Danbolt N. The Oslo study of the natural course of untreated syphilis: an epidemiologic investigation based on a re-study of the Boeck-Bruusgaard material. Med Clin North Am. 1964;48:613.
- Sule RR, Deshpande SG, Dharmadhikari NJ, et al. Late cutaneous syphilis. Cutis. 1997;59:135-137.
- Wilder EG, Frieder J, Sulhan S, et al. Spectrum of orocutaneous disease associations: genodermatoses and inflammatory conditions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:809-830.
- Carneiro S, Sampaio-Barros PD. SAPHO syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2013;39:401-418.
- Bachelez H. Pustular psoriasis and related pustular skin diseases. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:614-618.
- Domantay-Apostol GP, Handog EB, Gabriel MT. Syphilis: the international challenge of the great imitator. Dermatol Clin. 2008; 26:191-202, v. doi:10.1016/j.det.2007.12.001
The Diagnosis: Syphilis
Histopathology revealed psoriasiform hyperplasia, endothelial cell swelling, and a brisk lichenoid inflammation with plasma cells (Figure, A). There also was pustular folliculitis in association with well-formed granulomatous inflammation and a prominent number of plasma cells (Figure, B). Treponema pallidum immunostaining showed numerous organisms in the epidermal and follicular epithelium. Rapid plasma reagin was found to be positive with a titer of 1:128. Evaluation for neurosyphilis through lumbar puncture was negative; the patient also was HIV negative. All of our patient’s skin lesions cleared after a 3-week course of weekly intramuscular benzathine G injections. Due to his substantial clinical improvement, the patient was subsequently lost to follow-up.

Syphilis, an infectious disease caused by the spirochete bacterium T pallidum, has a well-known natural history defined by various stages classically categorized as primary, secondary, latent, or late (tertiary).1 The classic lesion in primary syphilis is the chancre, a painless ulcer with raised borders that develops within approximately 3 weeks following the initial inoculation.2 Secondary syphilis manifests with mucocutaneous findings in up to 97% of patients, and untreated patients develop secondary syphilis at a rate of approximately 25%.3 Although mucocutaneous findings in secondary syphilis can vary widely, patients most commonly develop a diffuse maculopapular exanthem, and 40% develop mucosal findings including genital ulcers, mucous patches, and condylomata lata.1 In latent syphilis, there is seroreactivity, but otherwise there are no clinical symptoms. A clear symptomatic history of prior primary or secondary syphilis may be known or unknown. Latent syphilis is divided into early and late phases, and the World Health Organization designates 2 years after the first suspected exposure as the cutoff point for early and late latency.4 During the first 4 years of latent syphilis, patients may exhibit mucocutaneous relapses. Our patient denied any sexual activity for more than 3 years prior to presentation. Because of the start of iatrogenic immunosuppression during this period, this case was classified as late latent syphilis with mucocutaneous reactivation.
Behçet disease was included within the differential diagnosis but is characterized by multiorgan systemic vasculitis that causes various mucocutaneous findings including aphthous ulcers, papulopustular lesions, and genital ulcers.5 Histopathologic features are nonspecific, and the clinical finding of recurrent genital and oral ulceration should be present for diagnosis. This disease predominantly occurs in East Asian or Mediterranean populations and is otherwise rare in White individuals.
SAPHO (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis) syndrome is a rare disorder consisting of skin, joint, and bone manifestations.6 Severe acne generally is accompanied by palmoplantar pustulosis along with pain and joint tenderness involving the anterior chest and axial skeleton, both of which were absent in our patient.
Pustular psoriasis can be localized or generalized. Localized presentations frequently are acral and may be associated with a variable degree of nail dystrophy and arthritis. Generalized presentations are characterized by hyperemic, well-defined patches with variable numbers of pustules.7 The pustules are the consequence of exuberate neutrophilic exocytosis into the epidermis and are nonfollicular.
Steroid-induced acne may be considered in the proper clinical setting of an acneform eruption with a prior history of systemic steroid treatment. However, additional findings of mucositis would not be expected, and although our patient was prescribed prednisone from his primary care physician prior to presentation to our clinic, this medication was given after the onset of the cutaneous eruption.
Syphilis commonly is referred to as the great mimicker due to its potential diverse morphologic presentations, which can involve acneform eruptions, though rare.8 In the setting of mucositis, generalized acneform eruptions should raise suspicion for the possibility of syphilis, even in the absence of other more classic cutaneous features.
The Diagnosis: Syphilis
Histopathology revealed psoriasiform hyperplasia, endothelial cell swelling, and a brisk lichenoid inflammation with plasma cells (Figure, A). There also was pustular folliculitis in association with well-formed granulomatous inflammation and a prominent number of plasma cells (Figure, B). Treponema pallidum immunostaining showed numerous organisms in the epidermal and follicular epithelium. Rapid plasma reagin was found to be positive with a titer of 1:128. Evaluation for neurosyphilis through lumbar puncture was negative; the patient also was HIV negative. All of our patient’s skin lesions cleared after a 3-week course of weekly intramuscular benzathine G injections. Due to his substantial clinical improvement, the patient was subsequently lost to follow-up.

Syphilis, an infectious disease caused by the spirochete bacterium T pallidum, has a well-known natural history defined by various stages classically categorized as primary, secondary, latent, or late (tertiary).1 The classic lesion in primary syphilis is the chancre, a painless ulcer with raised borders that develops within approximately 3 weeks following the initial inoculation.2 Secondary syphilis manifests with mucocutaneous findings in up to 97% of patients, and untreated patients develop secondary syphilis at a rate of approximately 25%.3 Although mucocutaneous findings in secondary syphilis can vary widely, patients most commonly develop a diffuse maculopapular exanthem, and 40% develop mucosal findings including genital ulcers, mucous patches, and condylomata lata.1 In latent syphilis, there is seroreactivity, but otherwise there are no clinical symptoms. A clear symptomatic history of prior primary or secondary syphilis may be known or unknown. Latent syphilis is divided into early and late phases, and the World Health Organization designates 2 years after the first suspected exposure as the cutoff point for early and late latency.4 During the first 4 years of latent syphilis, patients may exhibit mucocutaneous relapses. Our patient denied any sexual activity for more than 3 years prior to presentation. Because of the start of iatrogenic immunosuppression during this period, this case was classified as late latent syphilis with mucocutaneous reactivation.
Behçet disease was included within the differential diagnosis but is characterized by multiorgan systemic vasculitis that causes various mucocutaneous findings including aphthous ulcers, papulopustular lesions, and genital ulcers.5 Histopathologic features are nonspecific, and the clinical finding of recurrent genital and oral ulceration should be present for diagnosis. This disease predominantly occurs in East Asian or Mediterranean populations and is otherwise rare in White individuals.
SAPHO (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis) syndrome is a rare disorder consisting of skin, joint, and bone manifestations.6 Severe acne generally is accompanied by palmoplantar pustulosis along with pain and joint tenderness involving the anterior chest and axial skeleton, both of which were absent in our patient.
Pustular psoriasis can be localized or generalized. Localized presentations frequently are acral and may be associated with a variable degree of nail dystrophy and arthritis. Generalized presentations are characterized by hyperemic, well-defined patches with variable numbers of pustules.7 The pustules are the consequence of exuberate neutrophilic exocytosis into the epidermis and are nonfollicular.
Steroid-induced acne may be considered in the proper clinical setting of an acneform eruption with a prior history of systemic steroid treatment. However, additional findings of mucositis would not be expected, and although our patient was prescribed prednisone from his primary care physician prior to presentation to our clinic, this medication was given after the onset of the cutaneous eruption.
Syphilis commonly is referred to as the great mimicker due to its potential diverse morphologic presentations, which can involve acneform eruptions, though rare.8 In the setting of mucositis, generalized acneform eruptions should raise suspicion for the possibility of syphilis, even in the absence of other more classic cutaneous features.
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: historical aspects, microbiology, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1-14.
- Sparling PF. Natural history of syphilis. In: Holmes KK, Mardh PA, Sparling PF, et al, eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. McGraw Hill; 1990:213.
- Clark EG, Danbolt N. The Oslo study of the natural course of untreated syphilis: an epidemiologic investigation based on a re-study of the Boeck-Bruusgaard material. Med Clin North Am. 1964;48:613.
- Sule RR, Deshpande SG, Dharmadhikari NJ, et al. Late cutaneous syphilis. Cutis. 1997;59:135-137.
- Wilder EG, Frieder J, Sulhan S, et al. Spectrum of orocutaneous disease associations: genodermatoses and inflammatory conditions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:809-830.
- Carneiro S, Sampaio-Barros PD. SAPHO syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2013;39:401-418.
- Bachelez H. Pustular psoriasis and related pustular skin diseases. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:614-618.
- Domantay-Apostol GP, Handog EB, Gabriel MT. Syphilis: the international challenge of the great imitator. Dermatol Clin. 2008; 26:191-202, v. doi:10.1016/j.det.2007.12.001
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: historical aspects, microbiology, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1-14.
- Sparling PF. Natural history of syphilis. In: Holmes KK, Mardh PA, Sparling PF, et al, eds. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. McGraw Hill; 1990:213.
- Clark EG, Danbolt N. The Oslo study of the natural course of untreated syphilis: an epidemiologic investigation based on a re-study of the Boeck-Bruusgaard material. Med Clin North Am. 1964;48:613.
- Sule RR, Deshpande SG, Dharmadhikari NJ, et al. Late cutaneous syphilis. Cutis. 1997;59:135-137.
- Wilder EG, Frieder J, Sulhan S, et al. Spectrum of orocutaneous disease associations: genodermatoses and inflammatory conditions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:809-830.
- Carneiro S, Sampaio-Barros PD. SAPHO syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2013;39:401-418.
- Bachelez H. Pustular psoriasis and related pustular skin diseases. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:614-618.
- Domantay-Apostol GP, Handog EB, Gabriel MT. Syphilis: the international challenge of the great imitator. Dermatol Clin. 2008; 26:191-202, v. doi:10.1016/j.det.2007.12.001
A 48-year-old man with a history of ulcerative colitis that was well-controlled with adalimumab presented with a generalized acneform eruption involving the face, chest (top) and back, as well as a well-defined ovoid ulcer on the anterior aspect of the tongue (bottom) of 2 months’ duration. Prior treatment with prednisone 60 mg daily for 14 days resulted in no improvement. He denied unintentional weight loss, cyclic fever, or arthritis. A complete blood cell count with differential showed mild anemia (hemoglobin, 11.6 g/dL [reference range, 13.2–16.6 g/dL]) with a differential cell count that was within reference range for each cell type. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was elevated at 44 mm/h (reference range, 0–22 mm/h). A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen of an indurated cystic papule on the torso was obtained.
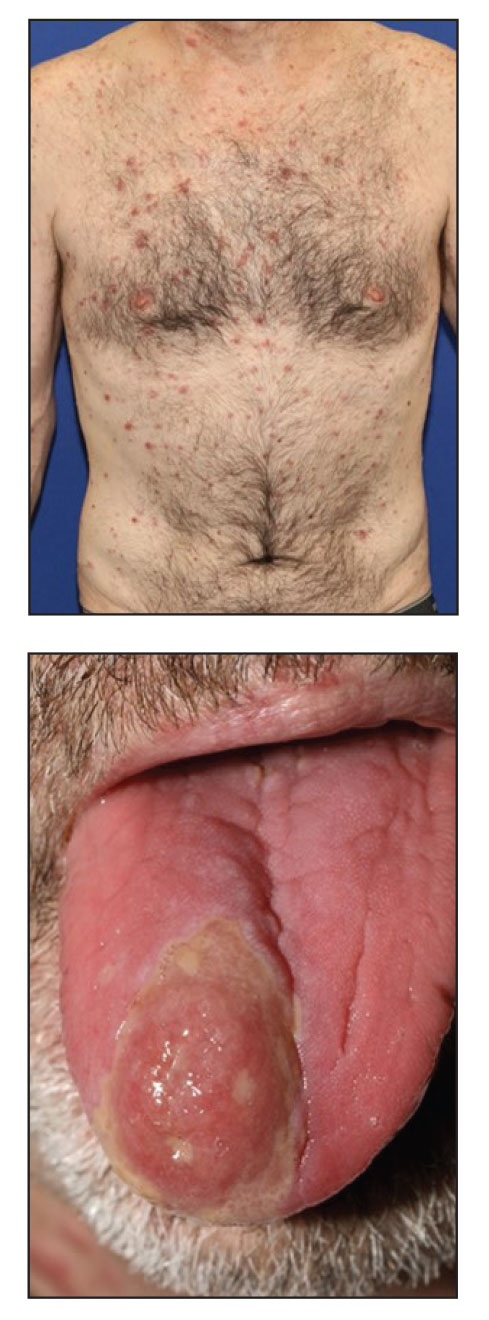
Expunging ‘penicillin allergy’: Your questions answered
Last month, I described a 28-year-old patient with a history of injection drug use who presented with pain in his left forearm. His history showed that, within the past 2 years, he’d been seen for cutaneous infections multiple times as an outpatient and in the emergency department. His records indicated that he was diagnosed with a penicillin allergy as a child when he developed a rash after receiving amoxicillin. I believed the next course of action should be to test for a penicillin allergy with an oral amoxicillin challenge.
Thank you for your excellent questions regarding this case. Great to hear the enthusiasm for testing for penicillin allergy!
One question focused on the course of action in the case of a mild or moderate IgE-mediated reaction after a single dose test with amoxicillin. Treatment for these reactions should include an antihistamine. I would reserve intravenous antihistamines for more severe cases, which also require treatment with a course of corticosteroids. However, the risk for a moderate to severe reaction to amoxicillin on retesting is quite low.
Clinicians need to exercise caution in the use of systemic corticosteroids. These drugs can be lifesaving, but even short courses of corticosteroids are associated with potentially serious adverse events. In a review of adverse events associated with short-course systemic corticosteroids among children, the rate of vomiting was 5.4%; behavioral change, 4.7%; and sleep disturbance, 4.3%. One child died after contracting herpes zoster, more than one-third of children developed elevated blood pressure, and 81.1% had evidence of suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
Among adults, short courses of systemic corticosteroids are associated with acute increases in the risks for gastrointestinal bleeding and hypertension. Cumulative exposure to short courses of corticosteroids over time results in higher risks for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and osteoporosis.
Another question prompted by this young man’s case focused on the durability of IgE reactions against penicillin. The IgE response to penicillin does indeed wane over time; 80% of patients with a previous true penicillin allergy can tolerate the antibiotic after 10 years. Thus, about 95% of patients with a remote history of penicillin allergy are tolerant of penicillin, and testing can be performed using the algorithm described.
Clinicians should avoid applying current guidelines for the evaluation of patients with penicillin allergy to other common drug allergies. The overall prevalence of sulfonamide allergy is 3%-8%, and the vast majority of these reactions follow treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Sulfa allergy is even more common among persons living with HIV infection. The natural history of sulfa allergy is not as well established as penicillin allergy. Allergy testing is encouraged in these cases. Graded oral challenge testing is best reserved for patients who are unlikely to have a true sulfa allergy based on their history.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, I described a 28-year-old patient with a history of injection drug use who presented with pain in his left forearm. His history showed that, within the past 2 years, he’d been seen for cutaneous infections multiple times as an outpatient and in the emergency department. His records indicated that he was diagnosed with a penicillin allergy as a child when he developed a rash after receiving amoxicillin. I believed the next course of action should be to test for a penicillin allergy with an oral amoxicillin challenge.
Thank you for your excellent questions regarding this case. Great to hear the enthusiasm for testing for penicillin allergy!
One question focused on the course of action in the case of a mild or moderate IgE-mediated reaction after a single dose test with amoxicillin. Treatment for these reactions should include an antihistamine. I would reserve intravenous antihistamines for more severe cases, which also require treatment with a course of corticosteroids. However, the risk for a moderate to severe reaction to amoxicillin on retesting is quite low.
Clinicians need to exercise caution in the use of systemic corticosteroids. These drugs can be lifesaving, but even short courses of corticosteroids are associated with potentially serious adverse events. In a review of adverse events associated with short-course systemic corticosteroids among children, the rate of vomiting was 5.4%; behavioral change, 4.7%; and sleep disturbance, 4.3%. One child died after contracting herpes zoster, more than one-third of children developed elevated blood pressure, and 81.1% had evidence of suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
Among adults, short courses of systemic corticosteroids are associated with acute increases in the risks for gastrointestinal bleeding and hypertension. Cumulative exposure to short courses of corticosteroids over time results in higher risks for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and osteoporosis.
Another question prompted by this young man’s case focused on the durability of IgE reactions against penicillin. The IgE response to penicillin does indeed wane over time; 80% of patients with a previous true penicillin allergy can tolerate the antibiotic after 10 years. Thus, about 95% of patients with a remote history of penicillin allergy are tolerant of penicillin, and testing can be performed using the algorithm described.
Clinicians should avoid applying current guidelines for the evaluation of patients with penicillin allergy to other common drug allergies. The overall prevalence of sulfonamide allergy is 3%-8%, and the vast majority of these reactions follow treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Sulfa allergy is even more common among persons living with HIV infection. The natural history of sulfa allergy is not as well established as penicillin allergy. Allergy testing is encouraged in these cases. Graded oral challenge testing is best reserved for patients who are unlikely to have a true sulfa allergy based on their history.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, I described a 28-year-old patient with a history of injection drug use who presented with pain in his left forearm. His history showed that, within the past 2 years, he’d been seen for cutaneous infections multiple times as an outpatient and in the emergency department. His records indicated that he was diagnosed with a penicillin allergy as a child when he developed a rash after receiving amoxicillin. I believed the next course of action should be to test for a penicillin allergy with an oral amoxicillin challenge.
Thank you for your excellent questions regarding this case. Great to hear the enthusiasm for testing for penicillin allergy!
One question focused on the course of action in the case of a mild or moderate IgE-mediated reaction after a single dose test with amoxicillin. Treatment for these reactions should include an antihistamine. I would reserve intravenous antihistamines for more severe cases, which also require treatment with a course of corticosteroids. However, the risk for a moderate to severe reaction to amoxicillin on retesting is quite low.
Clinicians need to exercise caution in the use of systemic corticosteroids. These drugs can be lifesaving, but even short courses of corticosteroids are associated with potentially serious adverse events. In a review of adverse events associated with short-course systemic corticosteroids among children, the rate of vomiting was 5.4%; behavioral change, 4.7%; and sleep disturbance, 4.3%. One child died after contracting herpes zoster, more than one-third of children developed elevated blood pressure, and 81.1% had evidence of suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
Among adults, short courses of systemic corticosteroids are associated with acute increases in the risks for gastrointestinal bleeding and hypertension. Cumulative exposure to short courses of corticosteroids over time results in higher risks for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and osteoporosis.
Another question prompted by this young man’s case focused on the durability of IgE reactions against penicillin. The IgE response to penicillin does indeed wane over time; 80% of patients with a previous true penicillin allergy can tolerate the antibiotic after 10 years. Thus, about 95% of patients with a remote history of penicillin allergy are tolerant of penicillin, and testing can be performed using the algorithm described.
Clinicians should avoid applying current guidelines for the evaluation of patients with penicillin allergy to other common drug allergies. The overall prevalence of sulfonamide allergy is 3%-8%, and the vast majority of these reactions follow treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Sulfa allergy is even more common among persons living with HIV infection. The natural history of sulfa allergy is not as well established as penicillin allergy. Allergy testing is encouraged in these cases. Graded oral challenge testing is best reserved for patients who are unlikely to have a true sulfa allergy based on their history.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Papular Reticulated Rash
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
Histopathology of the punch biopsy revealed subcorneal collections of neutrophils flanked by a spongiotic epidermis with neutrophil and eosinophil exocytosis. Rare dyskeratotic keratinocytes were identified at the dermoepidermal junction, and grampositive bacterial organisms were seen in a follicular infundibulum with purulent inflammation. The dermis demonstrated a mildly dense superficial perivascular and interstitial infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, scattered neutrophils, and eosinophils (Figure).
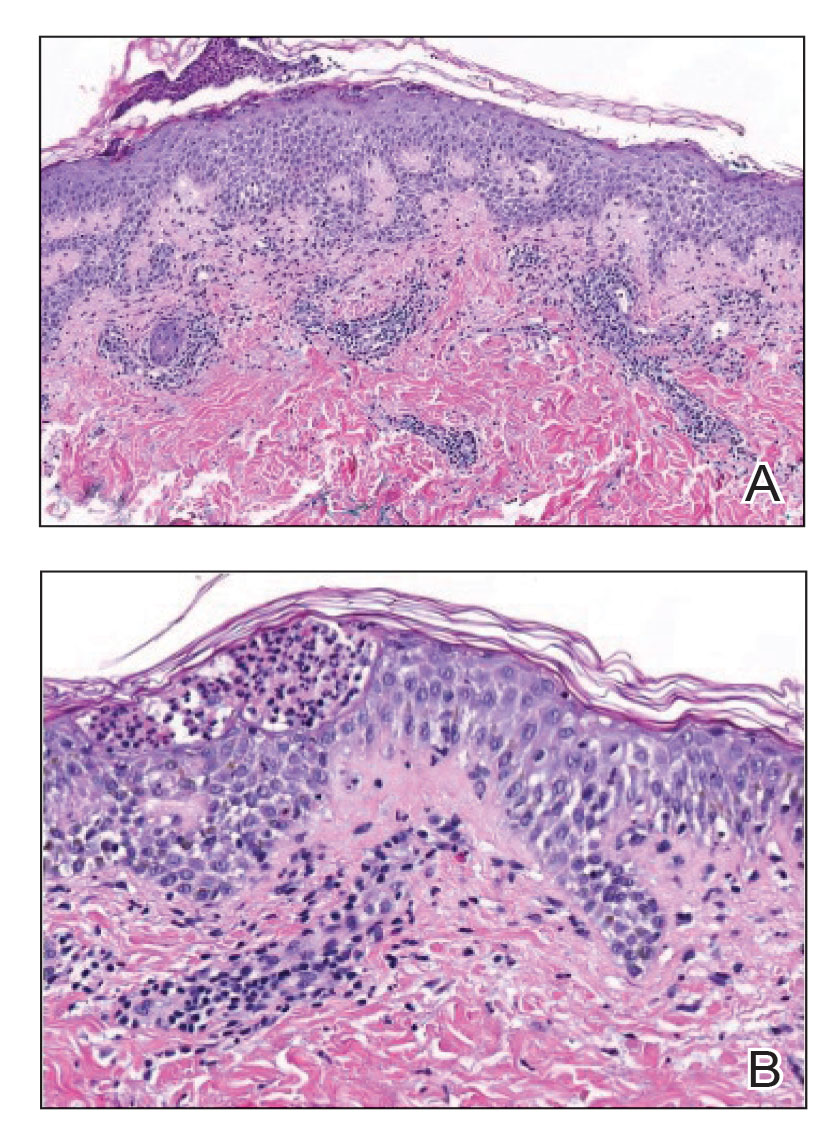
Given the combination of clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa (PP) was rendered and a urinalysis was ordered, which confirmed ketonuria. The patient was started on minocycline 100 mg twice daily and was advised to reintroduce carbohydrates into her diet. Resolution of the inflammatory component of the rash was achieved at 3-week follow-up, with residual reticulated postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare, albeit globally underrecognized, inflammatory dermatosis characterized by pruritic, symmetric, erythematous papules and plaques on the chest, back, neck, and rarely the arms and forehead that subsequently involute, leaving reticular postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.1 Prurigo pigmentosa is predominant in females (2.6:1 ratio). The mean age at presentation is 24.4 years, and it most commonly has been documented among populations in Asian countries, though it is unclear if a genetic predilection exists, as reports of PP are increasing globally with improved clinical awareness.1,2
The etiology of PP remains unknown; however, associations are well documented between PP and a ketogenic state secondary to uncontrolled diabetes, a low-carbohydrate diet, anorexia nervosa, or bariatric surgery.3 It is theorized that high serum ketones lead to perivascular ketone deposition, which induces neutrophil migration and chemotaxis,4 as substantiated by evidence of rash resolution with correction of the ketogenic state and improvement after administration of tetracyclines, a drug class known for neutrophil chemotaxis inhibition.5 Improvement of PP via these treatment mechanisms suggests that ketone bodies may play a role in the pathogenesis of PP.
Interestingly, Kafle et al6 reported that patients with PP commonly have bacterial colonies and associated inflammatory sequelae at the level of the hair follicles, which suggests that follicular involvement plays a role in the pathogenesis of PP. These findings are consistent with our patient’s histopathology consisting of gram-positive organisms and purulent inflammation at the infundibulum. The histopathologic features of PP are stage specific.1 Early stages are characterized by a superficial perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils that then spread to dermal papillae. Neutrophils then quickly sweep through the epidermis, causing spongiosis, ballooning, necrotic keratocytes, and consequent surface epithelium abscess formation. Over time, the dermal infiltrate assumes a lichenoid pattern as eosinophils and lymphocytes invade and predominate over neutrophils. Eventually, melanophages appear in the dermis as the epidermis undergoes hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and hyperpigmentation.1 The histologic differential diagnosis for PP is broad and varies based on the stage-specific progression of clinical and histopathologic findings.
Similar to PP, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus has a female predominance and resolves with subsequent dyspigmentation; however, it initially is characterized by annular plaques with central clearing or papulosquamous lesions restricted to sun-exposed skin. Photosensitivity is a prominent feature, and roughly 50% of patients meet diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus.7 Histopathology shows interface changes with increased dermal mucin and a perivascular lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate.
Papular pityriasis rosea can present as a pruritic papular rash on the back and chest; however, it most commonly is associated with a herald patch and typically follows a flulike prodrome.8 Biopsy reveals mounds of parakeratosis with mild spongiosis, perivascular inflammation, and extravasated erythrocytes.
Galli-Galli disease can present as a pruritic rash with follicular papules under the breasts and other flexural areas but histopathologically shows elongated rete ridges with dermal melanosis and acantholysis.9
Hailey-Hailey disease commonly presents in the third decade of life and can manifest as painful, pruritic, vesicular lesions on erythematous skin distributed on the back, neck, and inframammary region, as seen in our case; however, it is histopathologically associated with widespread epidermal acantholysis unlike the findings seen in our patient.10
First-line treatment of PP includes antibiotics such as minocycline, doxycycline, and dapsone due to their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis. In patients with nutritional deficiencies or ketosis, reintroduction of carbohydrates alone has been effective.5,11
Prurigo pigmentosa is an underrecognized inflammatory dermatosis with a complex stage-dependent clinicopathologic presentation. Clinicians should be aware of the etiologic and histopathologic patterns of this unique dermatosis. Rash presentation in the context of a low-carbohydrate diet should prompt biopsy as well as treatment with antibiotics and dietary reintroduction of carbohydrates.
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- de Sousa Vargas TJ, Abreu Raposo CM, Lima RB, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: report of 3 cases from Brazil and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:267-274. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000643
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79. doi:10.1016/J .JDIN.2021.03.003
- Beutler BD, Cohen PR, Lee RA. Prurigo pigmentosa: literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015;16:533-543. doi:10.1007/S40257-015-0154-4
- Chiam LYT, Goh BK, Lim KS, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a report of two cases that responded to minocycline. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2230.2009.03253.X
- Kafle SU, Swe SM, Hsiao PF, et al. Folliculitis in prurigo pigmentosa: a proposed pathogenesis based on clinical and pathological observation. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:20-27. doi:10.1111/CUP.12829
- Sontheimer RD. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: 25-year evolution of a prototypic subset (subphenotype) of lupus erythematosus defined by characteristic cutaneous, pathological, immunological, and genetic findings. Autoimmun Rev. 2005;4:253-263. doi:10.1016/J .AUTREV.2004.10.00
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Pityriasis rosea: an updated review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2021;17:201-211. doi:10.2174/15733963166662 00923161330
- Sprecher E, Indelman M, Khamaysi Z, et al. Galli-Galli disease is an acantholytic variant of Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:572-574. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.2006.07703.X
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.1992.TB00658
- Lu L-Y, Chen C-B. Keto rash: ketoacidosis-induced prurigo pigmentosa. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022;97:20-21. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.11.019
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
Histopathology of the punch biopsy revealed subcorneal collections of neutrophils flanked by a spongiotic epidermis with neutrophil and eosinophil exocytosis. Rare dyskeratotic keratinocytes were identified at the dermoepidermal junction, and grampositive bacterial organisms were seen in a follicular infundibulum with purulent inflammation. The dermis demonstrated a mildly dense superficial perivascular and interstitial infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, scattered neutrophils, and eosinophils (Figure).

Given the combination of clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa (PP) was rendered and a urinalysis was ordered, which confirmed ketonuria. The patient was started on minocycline 100 mg twice daily and was advised to reintroduce carbohydrates into her diet. Resolution of the inflammatory component of the rash was achieved at 3-week follow-up, with residual reticulated postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare, albeit globally underrecognized, inflammatory dermatosis characterized by pruritic, symmetric, erythematous papules and plaques on the chest, back, neck, and rarely the arms and forehead that subsequently involute, leaving reticular postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.1 Prurigo pigmentosa is predominant in females (2.6:1 ratio). The mean age at presentation is 24.4 years, and it most commonly has been documented among populations in Asian countries, though it is unclear if a genetic predilection exists, as reports of PP are increasing globally with improved clinical awareness.1,2
The etiology of PP remains unknown; however, associations are well documented between PP and a ketogenic state secondary to uncontrolled diabetes, a low-carbohydrate diet, anorexia nervosa, or bariatric surgery.3 It is theorized that high serum ketones lead to perivascular ketone deposition, which induces neutrophil migration and chemotaxis,4 as substantiated by evidence of rash resolution with correction of the ketogenic state and improvement after administration of tetracyclines, a drug class known for neutrophil chemotaxis inhibition.5 Improvement of PP via these treatment mechanisms suggests that ketone bodies may play a role in the pathogenesis of PP.
Interestingly, Kafle et al6 reported that patients with PP commonly have bacterial colonies and associated inflammatory sequelae at the level of the hair follicles, which suggests that follicular involvement plays a role in the pathogenesis of PP. These findings are consistent with our patient’s histopathology consisting of gram-positive organisms and purulent inflammation at the infundibulum. The histopathologic features of PP are stage specific.1 Early stages are characterized by a superficial perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils that then spread to dermal papillae. Neutrophils then quickly sweep through the epidermis, causing spongiosis, ballooning, necrotic keratocytes, and consequent surface epithelium abscess formation. Over time, the dermal infiltrate assumes a lichenoid pattern as eosinophils and lymphocytes invade and predominate over neutrophils. Eventually, melanophages appear in the dermis as the epidermis undergoes hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and hyperpigmentation.1 The histologic differential diagnosis for PP is broad and varies based on the stage-specific progression of clinical and histopathologic findings.
Similar to PP, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus has a female predominance and resolves with subsequent dyspigmentation; however, it initially is characterized by annular plaques with central clearing or papulosquamous lesions restricted to sun-exposed skin. Photosensitivity is a prominent feature, and roughly 50% of patients meet diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus.7 Histopathology shows interface changes with increased dermal mucin and a perivascular lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate.
Papular pityriasis rosea can present as a pruritic papular rash on the back and chest; however, it most commonly is associated with a herald patch and typically follows a flulike prodrome.8 Biopsy reveals mounds of parakeratosis with mild spongiosis, perivascular inflammation, and extravasated erythrocytes.
Galli-Galli disease can present as a pruritic rash with follicular papules under the breasts and other flexural areas but histopathologically shows elongated rete ridges with dermal melanosis and acantholysis.9
Hailey-Hailey disease commonly presents in the third decade of life and can manifest as painful, pruritic, vesicular lesions on erythematous skin distributed on the back, neck, and inframammary region, as seen in our case; however, it is histopathologically associated with widespread epidermal acantholysis unlike the findings seen in our patient.10
First-line treatment of PP includes antibiotics such as minocycline, doxycycline, and dapsone due to their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis. In patients with nutritional deficiencies or ketosis, reintroduction of carbohydrates alone has been effective.5,11
Prurigo pigmentosa is an underrecognized inflammatory dermatosis with a complex stage-dependent clinicopathologic presentation. Clinicians should be aware of the etiologic and histopathologic patterns of this unique dermatosis. Rash presentation in the context of a low-carbohydrate diet should prompt biopsy as well as treatment with antibiotics and dietary reintroduction of carbohydrates.
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
Histopathology of the punch biopsy revealed subcorneal collections of neutrophils flanked by a spongiotic epidermis with neutrophil and eosinophil exocytosis. Rare dyskeratotic keratinocytes were identified at the dermoepidermal junction, and grampositive bacterial organisms were seen in a follicular infundibulum with purulent inflammation. The dermis demonstrated a mildly dense superficial perivascular and interstitial infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, scattered neutrophils, and eosinophils (Figure).

Given the combination of clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa (PP) was rendered and a urinalysis was ordered, which confirmed ketonuria. The patient was started on minocycline 100 mg twice daily and was advised to reintroduce carbohydrates into her diet. Resolution of the inflammatory component of the rash was achieved at 3-week follow-up, with residual reticulated postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare, albeit globally underrecognized, inflammatory dermatosis characterized by pruritic, symmetric, erythematous papules and plaques on the chest, back, neck, and rarely the arms and forehead that subsequently involute, leaving reticular postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.1 Prurigo pigmentosa is predominant in females (2.6:1 ratio). The mean age at presentation is 24.4 years, and it most commonly has been documented among populations in Asian countries, though it is unclear if a genetic predilection exists, as reports of PP are increasing globally with improved clinical awareness.1,2
The etiology of PP remains unknown; however, associations are well documented between PP and a ketogenic state secondary to uncontrolled diabetes, a low-carbohydrate diet, anorexia nervosa, or bariatric surgery.3 It is theorized that high serum ketones lead to perivascular ketone deposition, which induces neutrophil migration and chemotaxis,4 as substantiated by evidence of rash resolution with correction of the ketogenic state and improvement after administration of tetracyclines, a drug class known for neutrophil chemotaxis inhibition.5 Improvement of PP via these treatment mechanisms suggests that ketone bodies may play a role in the pathogenesis of PP.
Interestingly, Kafle et al6 reported that patients with PP commonly have bacterial colonies and associated inflammatory sequelae at the level of the hair follicles, which suggests that follicular involvement plays a role in the pathogenesis of PP. These findings are consistent with our patient’s histopathology consisting of gram-positive organisms and purulent inflammation at the infundibulum. The histopathologic features of PP are stage specific.1 Early stages are characterized by a superficial perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils that then spread to dermal papillae. Neutrophils then quickly sweep through the epidermis, causing spongiosis, ballooning, necrotic keratocytes, and consequent surface epithelium abscess formation. Over time, the dermal infiltrate assumes a lichenoid pattern as eosinophils and lymphocytes invade and predominate over neutrophils. Eventually, melanophages appear in the dermis as the epidermis undergoes hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and hyperpigmentation.1 The histologic differential diagnosis for PP is broad and varies based on the stage-specific progression of clinical and histopathologic findings.
Similar to PP, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus has a female predominance and resolves with subsequent dyspigmentation; however, it initially is characterized by annular plaques with central clearing or papulosquamous lesions restricted to sun-exposed skin. Photosensitivity is a prominent feature, and roughly 50% of patients meet diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus.7 Histopathology shows interface changes with increased dermal mucin and a perivascular lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate.
Papular pityriasis rosea can present as a pruritic papular rash on the back and chest; however, it most commonly is associated with a herald patch and typically follows a flulike prodrome.8 Biopsy reveals mounds of parakeratosis with mild spongiosis, perivascular inflammation, and extravasated erythrocytes.
Galli-Galli disease can present as a pruritic rash with follicular papules under the breasts and other flexural areas but histopathologically shows elongated rete ridges with dermal melanosis and acantholysis.9
Hailey-Hailey disease commonly presents in the third decade of life and can manifest as painful, pruritic, vesicular lesions on erythematous skin distributed on the back, neck, and inframammary region, as seen in our case; however, it is histopathologically associated with widespread epidermal acantholysis unlike the findings seen in our patient.10
First-line treatment of PP includes antibiotics such as minocycline, doxycycline, and dapsone due to their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis. In patients with nutritional deficiencies or ketosis, reintroduction of carbohydrates alone has been effective.5,11
Prurigo pigmentosa is an underrecognized inflammatory dermatosis with a complex stage-dependent clinicopathologic presentation. Clinicians should be aware of the etiologic and histopathologic patterns of this unique dermatosis. Rash presentation in the context of a low-carbohydrate diet should prompt biopsy as well as treatment with antibiotics and dietary reintroduction of carbohydrates.
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- de Sousa Vargas TJ, Abreu Raposo CM, Lima RB, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: report of 3 cases from Brazil and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:267-274. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000643
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79. doi:10.1016/J .JDIN.2021.03.003
- Beutler BD, Cohen PR, Lee RA. Prurigo pigmentosa: literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015;16:533-543. doi:10.1007/S40257-015-0154-4
- Chiam LYT, Goh BK, Lim KS, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a report of two cases that responded to minocycline. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2230.2009.03253.X
- Kafle SU, Swe SM, Hsiao PF, et al. Folliculitis in prurigo pigmentosa: a proposed pathogenesis based on clinical and pathological observation. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:20-27. doi:10.1111/CUP.12829
- Sontheimer RD. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: 25-year evolution of a prototypic subset (subphenotype) of lupus erythematosus defined by characteristic cutaneous, pathological, immunological, and genetic findings. Autoimmun Rev. 2005;4:253-263. doi:10.1016/J .AUTREV.2004.10.00
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Pityriasis rosea: an updated review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2021;17:201-211. doi:10.2174/15733963166662 00923161330
- Sprecher E, Indelman M, Khamaysi Z, et al. Galli-Galli disease is an acantholytic variant of Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:572-574. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.2006.07703.X
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.1992.TB00658
- Lu L-Y, Chen C-B. Keto rash: ketoacidosis-induced prurigo pigmentosa. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022;97:20-21. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.11.019
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- de Sousa Vargas TJ, Abreu Raposo CM, Lima RB, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: report of 3 cases from Brazil and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:267-274. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000643
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79. doi:10.1016/J .JDIN.2021.03.003
- Beutler BD, Cohen PR, Lee RA. Prurigo pigmentosa: literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015;16:533-543. doi:10.1007/S40257-015-0154-4
- Chiam LYT, Goh BK, Lim KS, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a report of two cases that responded to minocycline. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2230.2009.03253.X
- Kafle SU, Swe SM, Hsiao PF, et al. Folliculitis in prurigo pigmentosa: a proposed pathogenesis based on clinical and pathological observation. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:20-27. doi:10.1111/CUP.12829
- Sontheimer RD. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: 25-year evolution of a prototypic subset (subphenotype) of lupus erythematosus defined by characteristic cutaneous, pathological, immunological, and genetic findings. Autoimmun Rev. 2005;4:253-263. doi:10.1016/J .AUTREV.2004.10.00
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Pityriasis rosea: an updated review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2021;17:201-211. doi:10.2174/15733963166662 00923161330
- Sprecher E, Indelman M, Khamaysi Z, et al. Galli-Galli disease is an acantholytic variant of Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:572-574. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.2006.07703.X
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.1992.TB00658
- Lu L-Y, Chen C-B. Keto rash: ketoacidosis-induced prurigo pigmentosa. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022;97:20-21. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.11.019
An otherwise healthy 22-year-old woman presented with a painful eruption with burning and pruritus that had been slowly worsening as it spread over the last 4 weeks. The rash first appeared on the lower chest and inframammary folds (top) and spread to the upper chest, neck, back (bottom), arms, and lower face. Physical examination revealed multiple illdefined, erythematous papules, patches, and plaques on the chest, back, neck, and upper abdomen. Individual lesions coalesced into plaques that displayed a reticular configuration. There were no lesions in the axillae. The patient had been following a low-carbohydrate diet for 4 months. A punch biopsy was performed.
Miliarial Gout in an Immunocompromised Patient
To the Editor:
Miliarial gout is a rare intradermal manifestation of tophaceous gout. It was first described in 2007 when a patient presented with multiple small papules with a red base containing a white- to cream-colored substance,1 which has rarely been reported,1-6 according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from 2007 to 2023 using the term miliarial gout. We describe a case of miliarial gout in a patient with a history of gout, uric acid levels within reference range, and immunocompromised status due to a prior orthotopic heart transplant.
A 59-year-old man presented with innumerable subcutaneous, firm, popcornlike clustered papules on the posterior surfaces of the upper arms and thighs of 5 years’ duration (Figure 1). The involved areas were sometimes painful on manipulation, but the patient was otherwise asymptomatic. His medical history was notable for tophaceous gout of more than 10 years’ duration, calcinosis cutis, adrenal insufficiency, essential hypertension, and an orthotopic heart transplant 2 years prior to the current presentation. At the current presentation he was taking tacrolimus, colchicine, febuxostat, and low-dose prednisone. The patient denied any other skin changes such as ulceration or bullae. In addition to the innumerable subcutaneous papules, he had much larger firm deep nodules bilaterally on the elbow (Figure 2). A complete blood cell count with differential and comprehensive metabolic panel results were within reference range. A 4-mm punch biopsy of the right posterior arm revealed dermal deposits consistent with gout on hematoxylin and eosin staining (Figure 3) but no calcium deposits on von Kossa staining, consistent with miliarial gout.
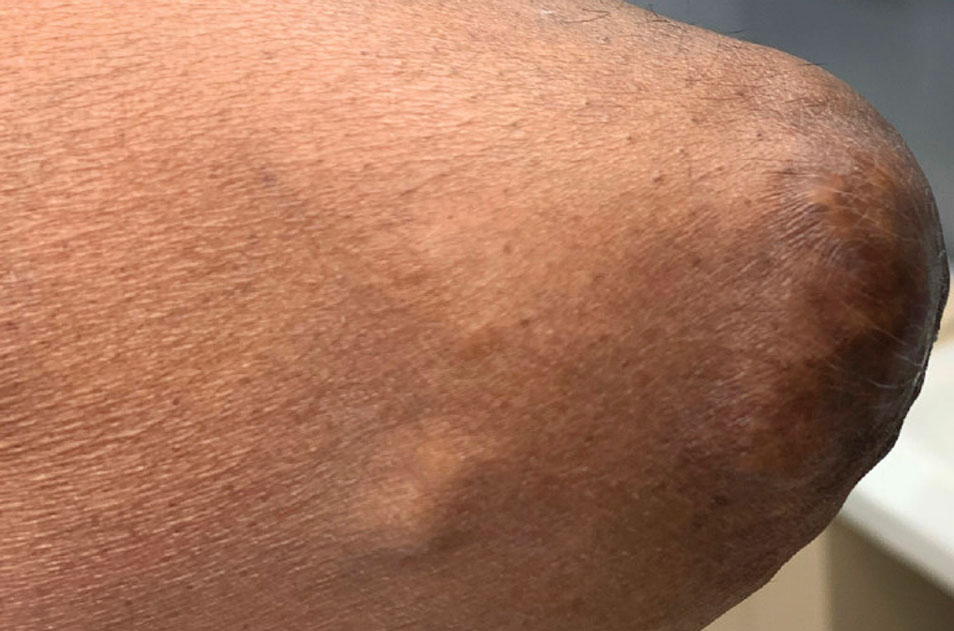
He was treated with 0.6 mg of colchicine daily, 80 mg of febuxostat twice daily, and 2.5 mg of prednisone daily. Unfortunately, the patient had difficulty affording his medications and therefore experienced frequent flares.
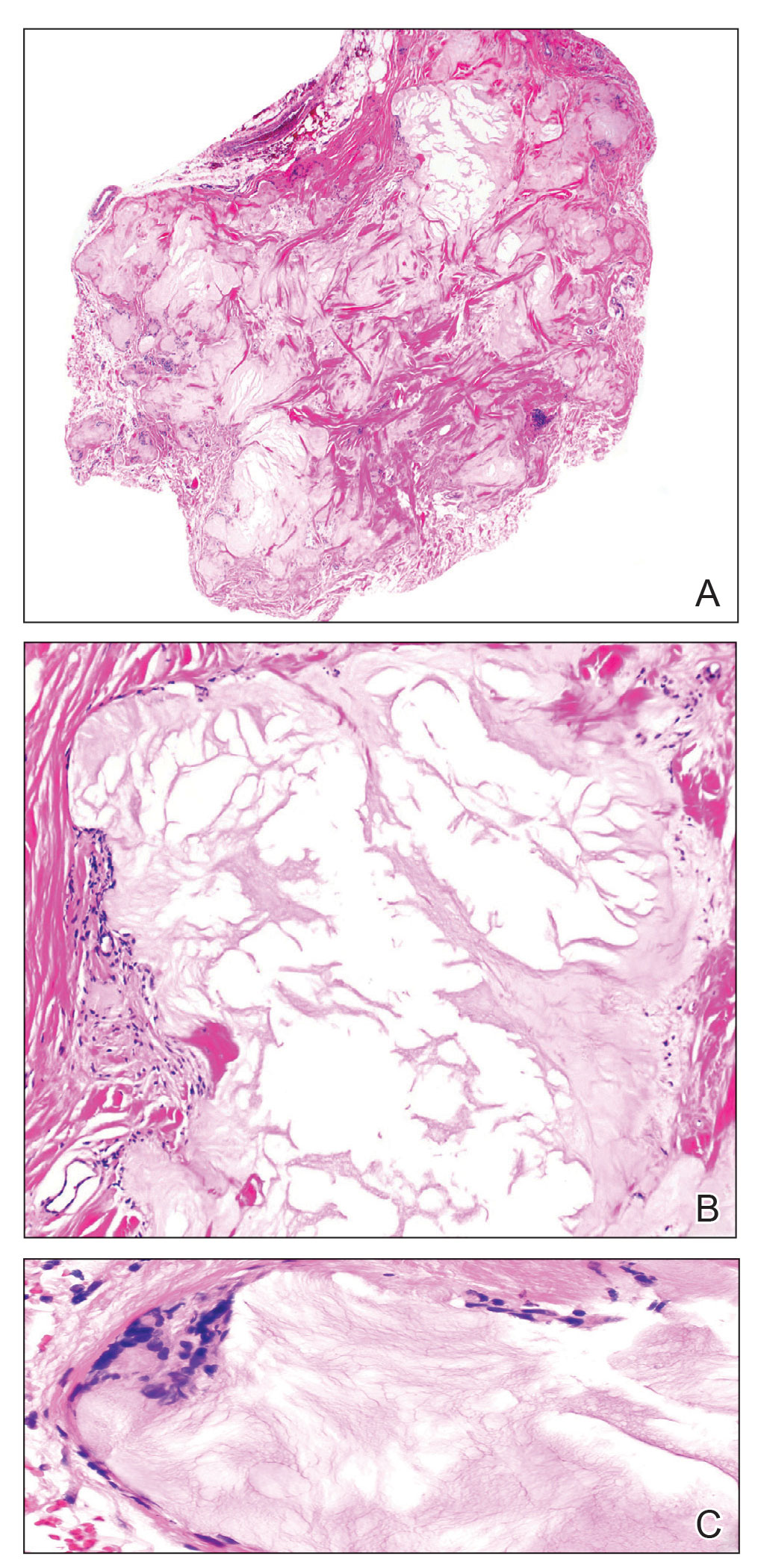
Gout is caused by inflammation that occurs from deposition of monosodium urate crystals in tissues, most commonly occurring in the skin and joints. Gout affects8.3 million individuals and is one of the most common rheumatic diseases of adulthood. The classic presentation of the acute form is monoarticular with associated swelling, erythema, and pain. The chronic form (also known as tophaceous gout) affects soft tissue and presents with smooth or multilobulated nodules.2 Miliarial gout is a rare variant of chronic tophaceous gout, and the diagnosis is based on atypical location, size, and distribution of tophi deposition.
In the updated American College of Rheumatology criteria for gout published in 2020, tophi are defined as draining or chalklike subcutaneous nodules that typically are located in joints, ears, olecranon bursae, finger pads, and tendons.3 The term miliarial gout, which is not universally defined, is used to describe the morphology and distribution of tophi deposition in areas outside of the typical locations defined by the American College of Rheumatology criteria. Miliarial refers to the small, multilobulated, and disseminated presentation of tophi. The involvement of atypical locations distinguishes miliarial gout from chronic tophaceous gout.
The cause of tophi deposition in atypical locations is unknown. It is thought that patients with a history of sustained hyperuricemia have a much greater burden of urate crystal deposition, which can lead to involvement of atypical locations. Our patient had innumerable, discrete, 1- to 5-mm, multilobulated tophi located on the posterior upper arms and thighs even though his uric acid levels were within reference range over the last 5 years.
Miliarial gout is a rare entity.1 In 2007, Shukla et al1 coined the term miliarial gout when reporting the first known presentation of a patient with multiple tiny papules containing a white or creamlike substance scattered on an erythematous base. Other cases of miliarial gout have commonly involved the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hands, knees, abdomen, extensor forearms, and thighs.5 Similarly, our patient had disease involvement of the posterior upper arms and thighs. Furthermore, miliarial gout has been associated with carpal tunnel syndrome; monosodium urate crystal deposition in this space can lead to a clinical diagnosis of this condition.6
With a history of orthotopic heart transplant, it is possible that our patient’s immunocompromised status could have increased his susceptibility for the miliarial form of chronic tophaceous gout. Gout reportedly is the most common inflammatory arthritis in transplant recipients, with the highest prevalence following renal and heart transplantation.7 Pretransplant hyperuricemia is correlated with higher probabilities of posttransplant gout.8 In patients with a heart transplant, hyperuricemia may be due to diuretic use. Additionally, the presence of a gout diagnosis before transplant nearly triples the likelihood of posttransplant gout, which often is more severe than de novo gout, as seen in our patient. Calcineurin inhibitors, including tacrolimus, also can predispose patients to hyperuricemia and more severe forms of gout in the posttransplant phase by limiting fractional urate excretion within the first 3 months of therapy.7 Treatment with oral steroids, as in our patient, also has been identified as a potential inciting factor for the development of cutaneous tophaceous gout.9
Treatment with allopurinol and colchicine has been effective in patients with miliarial gout. Obesity and long-term treatment with furosemide (which our patient was not taking) are considered risk factors for the deposition of dermal and hypodermal urates.9 Our patient had a body mass index of 35 (≥30 indicates obesity); therefore, he also should be counseled on lifestyle modifications for optimal disease control.
- Shukla R, Vender RB, Alhabeeb A, et al. Miliarial gout (a new entity). J Cutan Med Surg. 2007;11:31-34.
- Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:3136-3141.
- Neogi T, Jansen, TL, Dalbeth N, et al. 2015 gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:2557-2568.
- Hung TL, Wang WM, Chiang CP. Miliarial gout: a rare presentation of extensive cutaneous tophi. QJM. 2016;109:811-812.
- Mireku KA, Burgy JR, Davis LS. Miliarial gout: a rare clinical presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E17-E18.
- Sadovici-Bobeica V, Mazur-Nicorici L, Nicorici A, et al. Chronic miliarial gout associated with carpal tunnel syndrome: a very rare clinical presentation. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2018;5:000926.
- Schwab P, Lipton S, Kerr GS. Rheumatologic sequelae and challenges in organ transplantation. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24:329-340.
- Hernández-Molina G, Cachafeiro-Vilar A, Villa AR, et al. Gout in renal allograft recipients according to the pretransplant hyperuricemic status. Transplantation. 2008;86:1543-1547.
- Aguayo RS, Baradad M, Soria X, et al. Unilateral milia‐type intradermal tophi associated with underlying urate subcutaneous deposition: an uncommon cutaneous presentation of gout. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:622-625.
To the Editor:
Miliarial gout is a rare intradermal manifestation of tophaceous gout. It was first described in 2007 when a patient presented with multiple small papules with a red base containing a white- to cream-colored substance,1 which has rarely been reported,1-6 according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from 2007 to 2023 using the term miliarial gout. We describe a case of miliarial gout in a patient with a history of gout, uric acid levels within reference range, and immunocompromised status due to a prior orthotopic heart transplant.

A 59-year-old man presented with innumerable subcutaneous, firm, popcornlike clustered papules on the posterior surfaces of the upper arms and thighs of 5 years’ duration (Figure 1). The involved areas were sometimes painful on manipulation, but the patient was otherwise asymptomatic. His medical history was notable for tophaceous gout of more than 10 years’ duration, calcinosis cutis, adrenal insufficiency, essential hypertension, and an orthotopic heart transplant 2 years prior to the current presentation. At the current presentation he was taking tacrolimus, colchicine, febuxostat, and low-dose prednisone. The patient denied any other skin changes such as ulceration or bullae. In addition to the innumerable subcutaneous papules, he had much larger firm deep nodules bilaterally on the elbow (Figure 2). A complete blood cell count with differential and comprehensive metabolic panel results were within reference range. A 4-mm punch biopsy of the right posterior arm revealed dermal deposits consistent with gout on hematoxylin and eosin staining (Figure 3) but no calcium deposits on von Kossa staining, consistent with miliarial gout.

He was treated with 0.6 mg of colchicine daily, 80 mg of febuxostat twice daily, and 2.5 mg of prednisone daily. Unfortunately, the patient had difficulty affording his medications and therefore experienced frequent flares.

Gout is caused by inflammation that occurs from deposition of monosodium urate crystals in tissues, most commonly occurring in the skin and joints. Gout affects8.3 million individuals and is one of the most common rheumatic diseases of adulthood. The classic presentation of the acute form is monoarticular with associated swelling, erythema, and pain. The chronic form (also known as tophaceous gout) affects soft tissue and presents with smooth or multilobulated nodules.2 Miliarial gout is a rare variant of chronic tophaceous gout, and the diagnosis is based on atypical location, size, and distribution of tophi deposition.
In the updated American College of Rheumatology criteria for gout published in 2020, tophi are defined as draining or chalklike subcutaneous nodules that typically are located in joints, ears, olecranon bursae, finger pads, and tendons.3 The term miliarial gout, which is not universally defined, is used to describe the morphology and distribution of tophi deposition in areas outside of the typical locations defined by the American College of Rheumatology criteria. Miliarial refers to the small, multilobulated, and disseminated presentation of tophi. The involvement of atypical locations distinguishes miliarial gout from chronic tophaceous gout.
The cause of tophi deposition in atypical locations is unknown. It is thought that patients with a history of sustained hyperuricemia have a much greater burden of urate crystal deposition, which can lead to involvement of atypical locations. Our patient had innumerable, discrete, 1- to 5-mm, multilobulated tophi located on the posterior upper arms and thighs even though his uric acid levels were within reference range over the last 5 years.
Miliarial gout is a rare entity.1 In 2007, Shukla et al1 coined the term miliarial gout when reporting the first known presentation of a patient with multiple tiny papules containing a white or creamlike substance scattered on an erythematous base. Other cases of miliarial gout have commonly involved the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hands, knees, abdomen, extensor forearms, and thighs.5 Similarly, our patient had disease involvement of the posterior upper arms and thighs. Furthermore, miliarial gout has been associated with carpal tunnel syndrome; monosodium urate crystal deposition in this space can lead to a clinical diagnosis of this condition.6
With a history of orthotopic heart transplant, it is possible that our patient’s immunocompromised status could have increased his susceptibility for the miliarial form of chronic tophaceous gout. Gout reportedly is the most common inflammatory arthritis in transplant recipients, with the highest prevalence following renal and heart transplantation.7 Pretransplant hyperuricemia is correlated with higher probabilities of posttransplant gout.8 In patients with a heart transplant, hyperuricemia may be due to diuretic use. Additionally, the presence of a gout diagnosis before transplant nearly triples the likelihood of posttransplant gout, which often is more severe than de novo gout, as seen in our patient. Calcineurin inhibitors, including tacrolimus, also can predispose patients to hyperuricemia and more severe forms of gout in the posttransplant phase by limiting fractional urate excretion within the first 3 months of therapy.7 Treatment with oral steroids, as in our patient, also has been identified as a potential inciting factor for the development of cutaneous tophaceous gout.9
Treatment with allopurinol and colchicine has been effective in patients with miliarial gout. Obesity and long-term treatment with furosemide (which our patient was not taking) are considered risk factors for the deposition of dermal and hypodermal urates.9 Our patient had a body mass index of 35 (≥30 indicates obesity); therefore, he also should be counseled on lifestyle modifications for optimal disease control.
To the Editor:
Miliarial gout is a rare intradermal manifestation of tophaceous gout. It was first described in 2007 when a patient presented with multiple small papules with a red base containing a white- to cream-colored substance,1 which has rarely been reported,1-6 according to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from 2007 to 2023 using the term miliarial gout. We describe a case of miliarial gout in a patient with a history of gout, uric acid levels within reference range, and immunocompromised status due to a prior orthotopic heart transplant.

A 59-year-old man presented with innumerable subcutaneous, firm, popcornlike clustered papules on the posterior surfaces of the upper arms and thighs of 5 years’ duration (Figure 1). The involved areas were sometimes painful on manipulation, but the patient was otherwise asymptomatic. His medical history was notable for tophaceous gout of more than 10 years’ duration, calcinosis cutis, adrenal insufficiency, essential hypertension, and an orthotopic heart transplant 2 years prior to the current presentation. At the current presentation he was taking tacrolimus, colchicine, febuxostat, and low-dose prednisone. The patient denied any other skin changes such as ulceration or bullae. In addition to the innumerable subcutaneous papules, he had much larger firm deep nodules bilaterally on the elbow (Figure 2). A complete blood cell count with differential and comprehensive metabolic panel results were within reference range. A 4-mm punch biopsy of the right posterior arm revealed dermal deposits consistent with gout on hematoxylin and eosin staining (Figure 3) but no calcium deposits on von Kossa staining, consistent with miliarial gout.

He was treated with 0.6 mg of colchicine daily, 80 mg of febuxostat twice daily, and 2.5 mg of prednisone daily. Unfortunately, the patient had difficulty affording his medications and therefore experienced frequent flares.

Gout is caused by inflammation that occurs from deposition of monosodium urate crystals in tissues, most commonly occurring in the skin and joints. Gout affects8.3 million individuals and is one of the most common rheumatic diseases of adulthood. The classic presentation of the acute form is monoarticular with associated swelling, erythema, and pain. The chronic form (also known as tophaceous gout) affects soft tissue and presents with smooth or multilobulated nodules.2 Miliarial gout is a rare variant of chronic tophaceous gout, and the diagnosis is based on atypical location, size, and distribution of tophi deposition.
In the updated American College of Rheumatology criteria for gout published in 2020, tophi are defined as draining or chalklike subcutaneous nodules that typically are located in joints, ears, olecranon bursae, finger pads, and tendons.3 The term miliarial gout, which is not universally defined, is used to describe the morphology and distribution of tophi deposition in areas outside of the typical locations defined by the American College of Rheumatology criteria. Miliarial refers to the small, multilobulated, and disseminated presentation of tophi. The involvement of atypical locations distinguishes miliarial gout from chronic tophaceous gout.
The cause of tophi deposition in atypical locations is unknown. It is thought that patients with a history of sustained hyperuricemia have a much greater burden of urate crystal deposition, which can lead to involvement of atypical locations. Our patient had innumerable, discrete, 1- to 5-mm, multilobulated tophi located on the posterior upper arms and thighs even though his uric acid levels were within reference range over the last 5 years.
Miliarial gout is a rare entity.1 In 2007, Shukla et al1 coined the term miliarial gout when reporting the first known presentation of a patient with multiple tiny papules containing a white or creamlike substance scattered on an erythematous base. Other cases of miliarial gout have commonly involved the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hands, knees, abdomen, extensor forearms, and thighs.5 Similarly, our patient had disease involvement of the posterior upper arms and thighs. Furthermore, miliarial gout has been associated with carpal tunnel syndrome; monosodium urate crystal deposition in this space can lead to a clinical diagnosis of this condition.6
With a history of orthotopic heart transplant, it is possible that our patient’s immunocompromised status could have increased his susceptibility for the miliarial form of chronic tophaceous gout. Gout reportedly is the most common inflammatory arthritis in transplant recipients, with the highest prevalence following renal and heart transplantation.7 Pretransplant hyperuricemia is correlated with higher probabilities of posttransplant gout.8 In patients with a heart transplant, hyperuricemia may be due to diuretic use. Additionally, the presence of a gout diagnosis before transplant nearly triples the likelihood of posttransplant gout, which often is more severe than de novo gout, as seen in our patient. Calcineurin inhibitors, including tacrolimus, also can predispose patients to hyperuricemia and more severe forms of gout in the posttransplant phase by limiting fractional urate excretion within the first 3 months of therapy.7 Treatment with oral steroids, as in our patient, also has been identified as a potential inciting factor for the development of cutaneous tophaceous gout.9
Treatment with allopurinol and colchicine has been effective in patients with miliarial gout. Obesity and long-term treatment with furosemide (which our patient was not taking) are considered risk factors for the deposition of dermal and hypodermal urates.9 Our patient had a body mass index of 35 (≥30 indicates obesity); therefore, he also should be counseled on lifestyle modifications for optimal disease control.
- Shukla R, Vender RB, Alhabeeb A, et al. Miliarial gout (a new entity). J Cutan Med Surg. 2007;11:31-34.
- Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:3136-3141.
- Neogi T, Jansen, TL, Dalbeth N, et al. 2015 gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:2557-2568.
- Hung TL, Wang WM, Chiang CP. Miliarial gout: a rare presentation of extensive cutaneous tophi. QJM. 2016;109:811-812.
- Mireku KA, Burgy JR, Davis LS. Miliarial gout: a rare clinical presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E17-E18.
- Sadovici-Bobeica V, Mazur-Nicorici L, Nicorici A, et al. Chronic miliarial gout associated with carpal tunnel syndrome: a very rare clinical presentation. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2018;5:000926.
- Schwab P, Lipton S, Kerr GS. Rheumatologic sequelae and challenges in organ transplantation. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24:329-340.
- Hernández-Molina G, Cachafeiro-Vilar A, Villa AR, et al. Gout in renal allograft recipients according to the pretransplant hyperuricemic status. Transplantation. 2008;86:1543-1547.
- Aguayo RS, Baradad M, Soria X, et al. Unilateral milia‐type intradermal tophi associated with underlying urate subcutaneous deposition: an uncommon cutaneous presentation of gout. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:622-625.
- Shukla R, Vender RB, Alhabeeb A, et al. Miliarial gout (a new entity). J Cutan Med Surg. 2007;11:31-34.
- Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:3136-3141.
- Neogi T, Jansen, TL, Dalbeth N, et al. 2015 gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:2557-2568.
- Hung TL, Wang WM, Chiang CP. Miliarial gout: a rare presentation of extensive cutaneous tophi. QJM. 2016;109:811-812.
- Mireku KA, Burgy JR, Davis LS. Miliarial gout: a rare clinical presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E17-E18.
- Sadovici-Bobeica V, Mazur-Nicorici L, Nicorici A, et al. Chronic miliarial gout associated with carpal tunnel syndrome: a very rare clinical presentation. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2018;5:000926.
- Schwab P, Lipton S, Kerr GS. Rheumatologic sequelae and challenges in organ transplantation. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24:329-340.
- Hernández-Molina G, Cachafeiro-Vilar A, Villa AR, et al. Gout in renal allograft recipients according to the pretransplant hyperuricemic status. Transplantation. 2008;86:1543-1547.
- Aguayo RS, Baradad M, Soria X, et al. Unilateral milia‐type intradermal tophi associated with underlying urate subcutaneous deposition: an uncommon cutaneous presentation of gout. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:622-625.
Practice Points
- Miliarial gout is a rare intradermal manifestation of tophaceous gout and often presents as multiple small papules containing a white- to cream-colored substance.
- Immunocompromised status may be a risk factor for miliarial gout, especially in patients with a history of gout or hyperuricemia.
- Effective treatments for miliarial gout include allopurinol and colchicine.