User login
Severe Esophageal Lichen Planus Treated With Tofacitinib
To reach early diagnoses and improve outcomes in cases of mucosal and esophageal lichen planus (ELP), patient education along with a multidisciplinary approach centered on collaboration among dermatologists, gastroenterologists, gynecologists, and dental practitioners should be a priority. Tofacitinib therapy should be considered in the treatment of patients presenting with cutaneous lichen planus (CLP), mucosal lichen planus, and ELP.
Lichen planus is a papulosquamous disease of the skin and mucous membranes that is most common on the skin and oral mucosa. Typical lesions of CLP present as purple, pruritic, polygonal papules and plaques on the flexural surfaces of the wrists and ankles as well as areas of friction or trauma due to scratching such as the shins and lower back. Various subtypes of lichen planus can present simultaneously, resulting in extensive involvement that worsens through koebnerization and affects the oral cavity, esophagus, larynx, sclera, genitalia, scalp, and nails.1,2
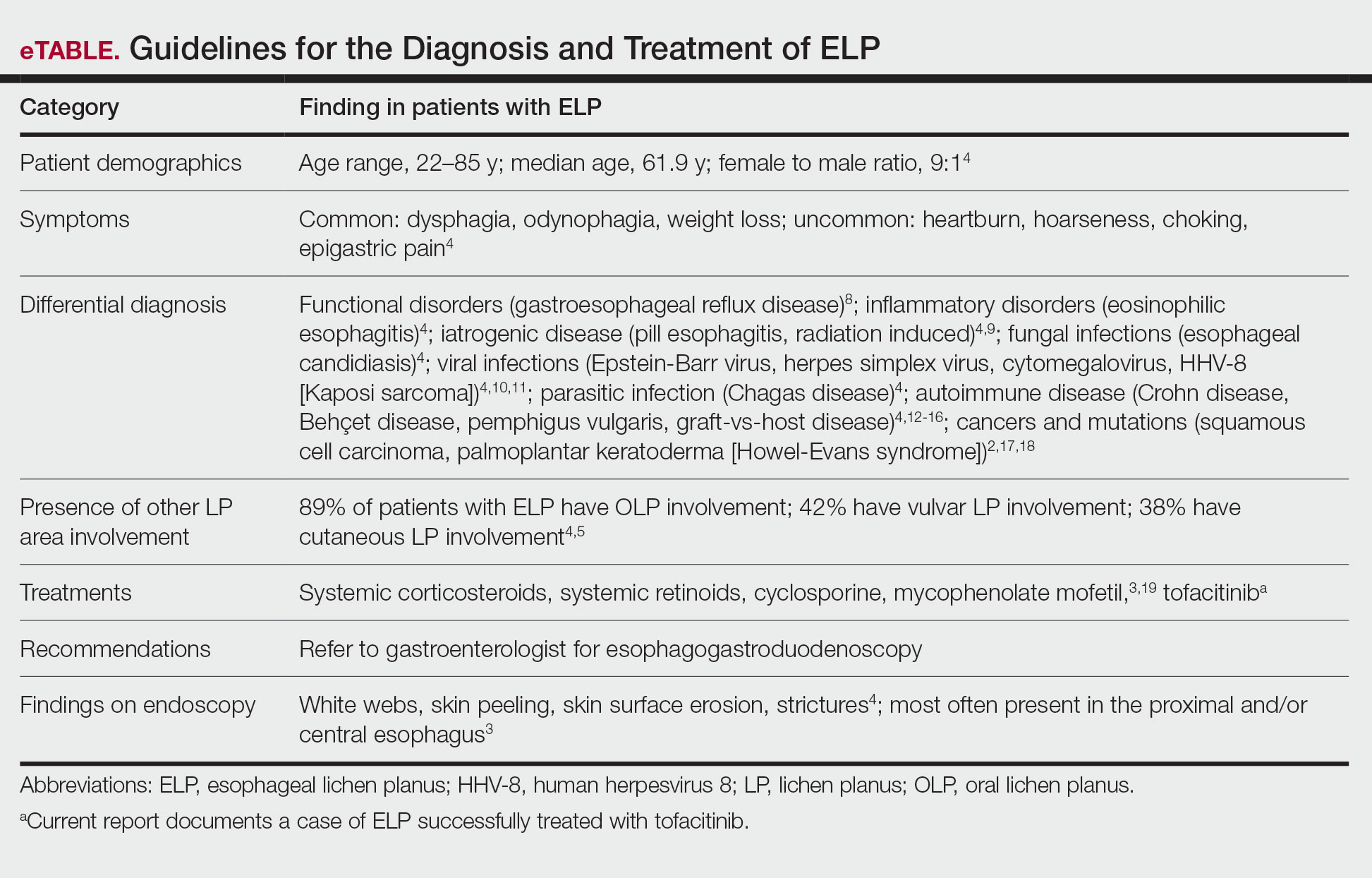
Esophageal lichen planus can develop with or without the presence of CLP, oral lichen planus (OLP), or genital lichen planus.3 It typically affects women older than 50 years and is linked to OLP and vulvar lichen planus, with 1 study reporting that 87% (63/72) of ELP patients were women with a median age of 61.9 years at the time of diagnosis (range, 22–85 years). Almost all ELP patients in the study had lichen planus symptoms in other locations; 89% (64/72) had OLP, and 42% (30/72) had vulvar lichen planus.4 Consequently, a diagnosis of ELP should be followed by a thorough full-body examination to check for lichen planus at other sites. Studies that examined lichen planus patients for ELP found that 25% to 50% of patients diagnosed with orocutaneous lichen planus also had ELP, with ELP frequently presenting without symptoms.3,5 These findings indicate that ELP likely is underdiagnosed and often misdiagnosed, resulting in an underestimation of its prevalence.
Our case highlights a frequently misdiagnosed condition and underscores the importance of close examination of patients presenting with CLP and OLP for signs and symptoms of ELP. Furthermore, we discuss the importance of patient education and collaboration among different specialties in attaining an early diagnosis to improve patient outcomes. Finally, we review the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of CLP, OLP, and ELP, as well as the utility of tofacitinib for ELP.
Case Report
An emaciated 89-year-old woman with an 11-year history of CLP, OLP, and genital lichen planus that had been successfully treated with topicals presented with an OLP recurrence alongside difficulties eating and swallowing. Her symptoms lasted 1 year and would recur when treatment was paused. Her medical history included rheumatoid arthritis, hypothyroidism, and hypertension, and she was taking levothyroxine, olmesartan, and vitamin D supplements. Dentures and olmesartan previously were ruled out as potential triggers following a 2-month elimination. None of her remaining natural teeth had fillings. She also reported that neither she nor her partner had ever smoked or chewed tobacco.
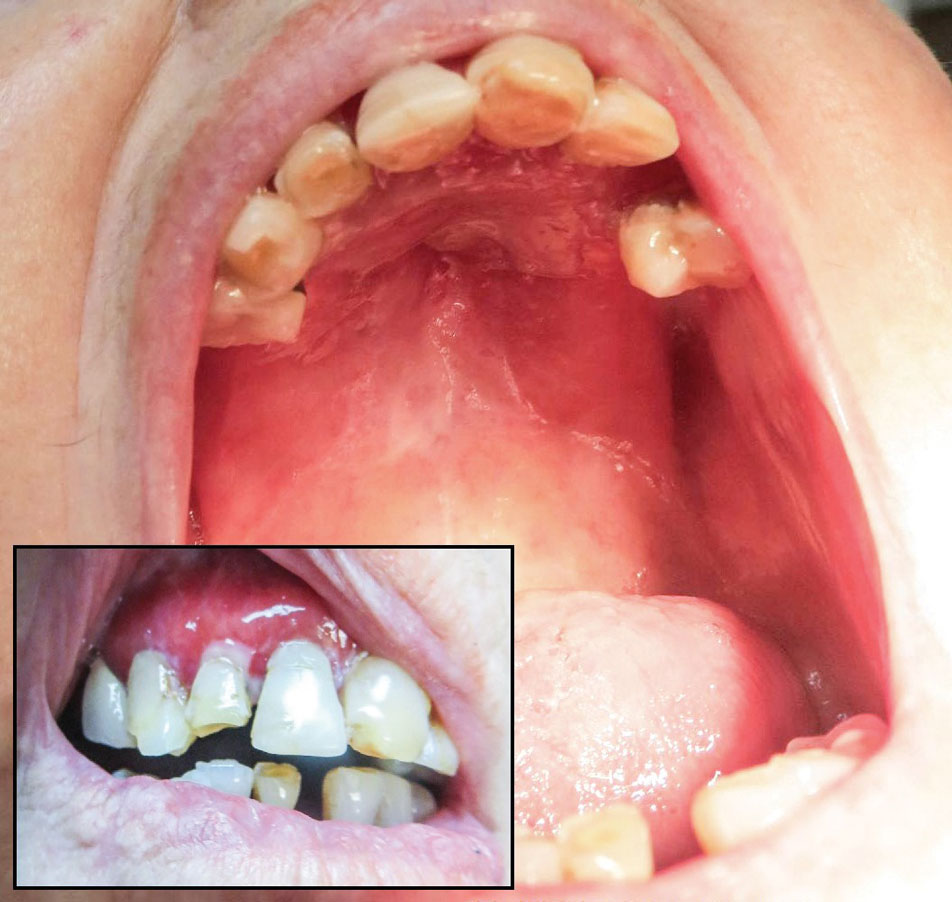
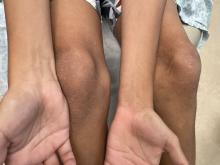
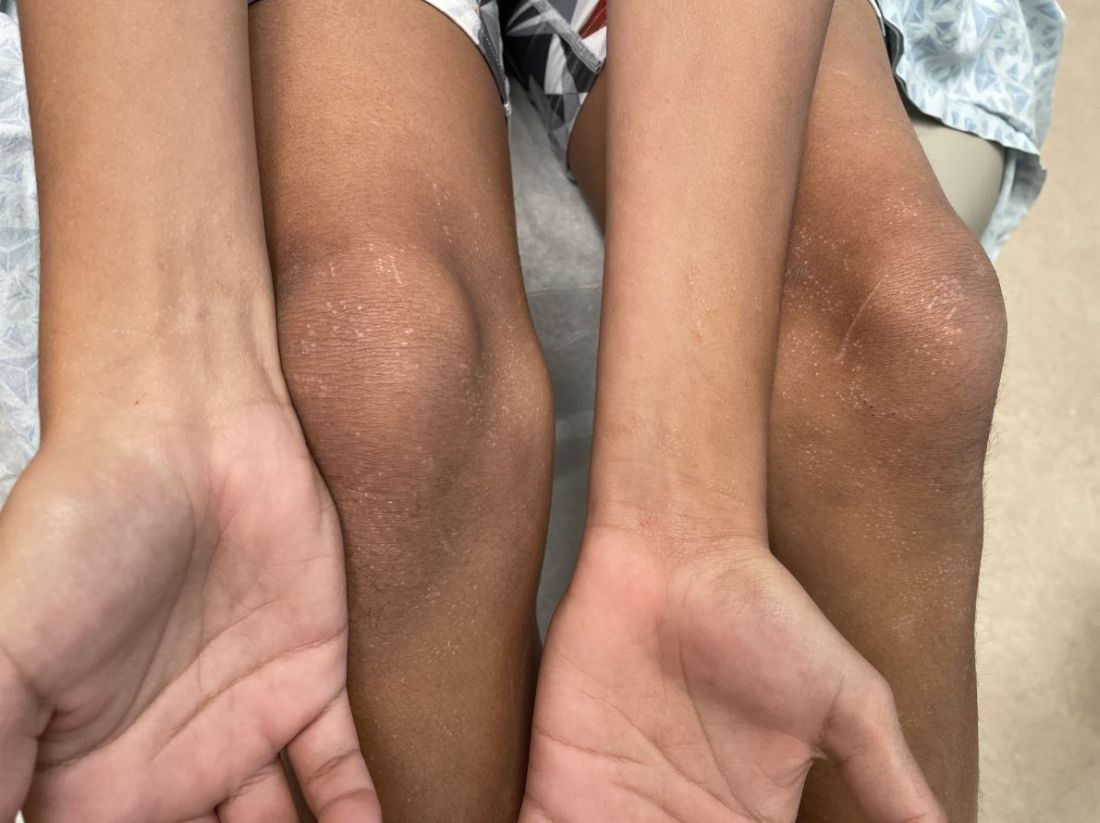
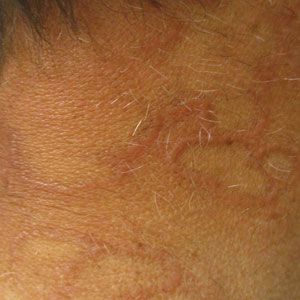
The patient’s lichen planus involvement first manifested as red, itchy, polygonal, lichenoid papules on the superior and inferior mid back 11 years prior to the current presentation (Figure 1). Further examination noted erosions on the genitalia, and a subsequent biopsy of the vulva confirmed a diagnosis of lichen planus (Figure 2). Treatment with halobetasol propionate ointment and tacrolimus ointment 0.1% twice daily (BID) resulted in remission of the CLP and vulvar lichen planus. She presented a year later with oral involvement revealing Wickham striae on the buccal mucosa and erosions on the upper palate that resolved after 2 months of treatment with cyclosporine oral solution mixed with a 5-times-daily nystatin swish-and-spit (Figure 3). The CLP did not recur but OLP was punctuated by remissions and recurrences on a yearly basis, often related to the cessation of mouthwash and topical creams. The OLP and vulvar lichen planus were successfully treated with as-needed use of a cyclosporine mouthwash swish-and-spit 3 times daily as well as halobetasol ointment 0.05% 3 times daily, respectively. Six years later, the patient was hospitalized for unrelated causes and was lost to follow-up for 2 years.
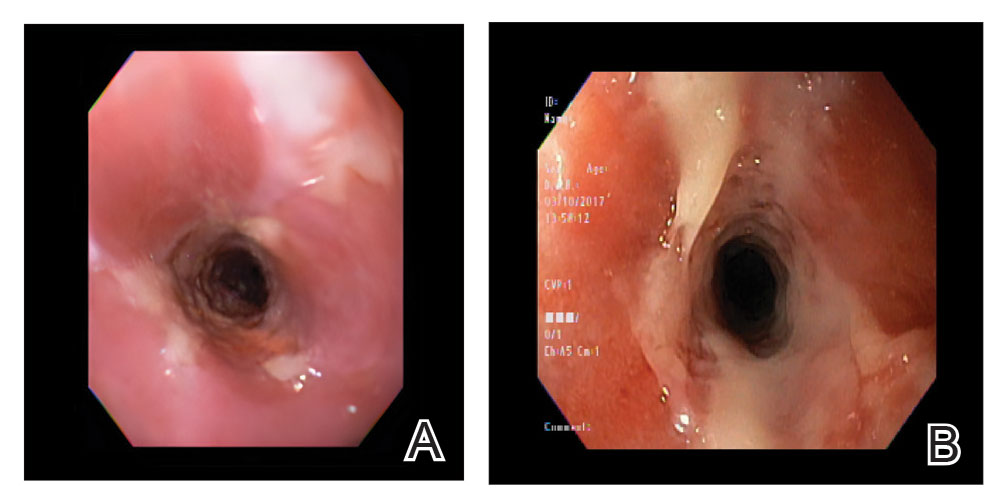
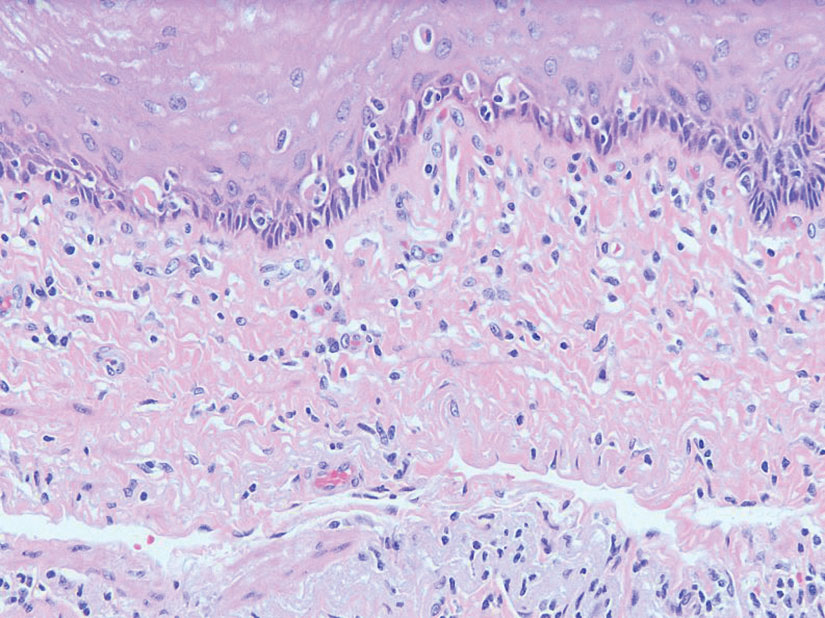
The patient experienced worsening dysphagia and odynophagia over a period of 2 years (mild dysphagia was first recorded 7 years prior to the initial presentation) and reported an unintentional weight loss of 20 pounds. An endoscopy was performed 3 years after the initial report of dysphagia and noted esophageal erosions (Figure 4A) and a stricture (Figure 4B), but all abnormal involvement was attributed to active gastroesophageal reflux disease. She underwent 8 esophageal dilations to treat the stricture but noted that the duration of symptomatic relief decreased with every subsequent dilation. An esophageal stent was placed 4 years after the initial concern of dysphagia, but it was not well tolerated and had to be removed soon thereafter. A year later, the patient underwent an esophageal bypass with a substernal gastric conduit that provided relief for 2 months but failed to permanently resolve the condition. In fact, her condition worsened over the next 1.5 years when she presented with extreme emaciation attributed to a low appetite and pain while eating. A review of the slides from a prior hospital esophageal biopsy revealed lichen planus (Figure 5). She was prescribed tofacitinib 5 mg BID as a dual-purpose treatment for the rheumatoid arthritis and OLP/ELP. At 1-month follow-up she noted that she had only taken one 5-mg pill daily without notable improvement, and after the visit she started the initial recommendation of 5 mg BID. Over the next several months, her condition continued to consistently improve; the odynophagia resolved, and she regained the majority of her lost weight. Tofacitinib was well tolerated across the course of treatment, and no adverse side effects were noted. Furthermore, the patient regained a full range of motion in the previously immobile arthritic right shoulder. She has experienced no recurrence of the genital lichen planus, OLP, or CLP since starting tofacitinib. To date, the patient is still taking only tofacitinib 5 mg BID with no recurrence of the cutaneous, mucosal, or esophageal lichen planus and has experienced no adverse events from the medication.
Comment
Clinical Presentation—Lichen planus—CLP and OLP—most frequently presents between the ages of 40 and 60 years, with a slight female predilection.1,2 The lesions typically present with the 5 P’s—purple, pruritic, polygonal papules and plaques—with some lesions revealing white lacy lines overlying them called Wickham striae.6 The lesions may be red at first before turning purple. They often present on the flexural surfaces of the wrists and ankles as well as the shins and back but rarely affect the face, perhaps because of increased chronic sun exposure.2,6 Less common locations include the scalp, nails, and mucosal areas (eg, oral, vulvar, conjunctival, laryngeal, esophageal, anal).1
If CLP is diagnosed, the patient likely will also have oral lesions, which occur in 50% of patients.2 Once any form of lichen planus is found, it is important to examine all of the most frequently involved locations—mucocutaneous and cutaneous as well as the nails and scalp. Special care should be taken when examining OLP and genital lichen planus, as long-standing lesions have a 2% to 5% chance of transforming into squamous cell carcinoma.2
Although cases of traditional OLP and CLP are ubiquitous in the literature, ELP rarely is documented because of frequent misdiagnoses. Esophageal lichen planus has a closer histopathologic resemblance to OLP compared to CLP, and its highly variable presentation often results in an inconclusive diagnosis.3 A review of 27 patients with lichen planus highlighted the difficult nature of diagnosing ELP; ELP manifested up to 20 years after initial lichen planus diagnosis, and patients underwent an average of 2.5 dilations prior to the successful diagnosis of ELP. Interestingly, 2 patients in the study presented with ELP in isolation, which emphasizes the importance of secondary examination for lichen planus in the presence of esophageal strictures.7 The eTable provides common patient demographics and symptoms to more effectively identify ELP.Differential Diagnosis—Because lichen planus can present anywhere on the body, it may be difficult to differentiate it from other skin conditions. Clinical appearance alone often is insufficient for diagnosing lichen planus, and a punch biopsy often is needed.2,20 Cutaneous lichen planus may resemble eczema, lichen simplex chronicus, pityriasis rosea, prurigo nodularis, and psoriasis, while OLP may resemble bite trauma, leukoplakia, pemphigus, and thrush.20 Dermoscopy of the tissue makes Wickham striae easier to visualize and assists in the diagnosis of lichen planus. Furthermore, thickening of the stratum granulosum, a prevalence of lymphocytes in the dermoepidermal junction, and vacuolar alteration of the stratum basale help to distinguish between lichen planus and other inflammatory dermatoses.20 A diagnosis of lichen planus merits a full-body skin examination—hair, nails, eyes, oral mucosa, and genitalia—to rule out additional involvement.
Esophageal lichen planus most frequently presents as dysphagia, odynophagia, and weight loss, but other symptoms including heartburn, hoarseness, choking, and epigastric pain may suggest esophageal involvement.4 Typically, ELP presents in the proximal and/or central esophagus, assisting in the differentiation between ELP and other esophageal conditions.3 Special consideration should be taken when both ELP and gastroesophageal reflux disease are considered in a differential diagnosis, and it is recommended to pair an upper endoscopy with pH monitoring to avoid misdiagnosis.8 Screening endoscopies also are helpful, as they assist in identifying the characteristic white webs, skin peeling, skin surface erosion, and strictures of ELP.4 Taken together, dermatologists should encourage patients with cutaneous or mucocutaneous lichen planus to undergo an esophagogastroduodenoscopy, especially in the presence of any of ELP’s common symptoms (eTable).
Etiology—Although the exact etiology of lichen planus is not well established, there are several known correlative factors, including hepatitis C; increased stress; dental materials; oral medications, most frequently antihypertensives and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; systemic diseases; and tobacco usage.6,21
Dental materials used in oral treatments such as silver amalgam, gold, cobalt, palladium, chromium, epoxy resins, and dentures can trigger or exacerbate OLP, and patch testing of a patient’s dental materials can help determine if the reaction was caused by the materials.6,22 The removal of material contributing to lesions often will cause OLP to resolve.22
It also has been suggested that the presence of thyroid disorders, autoimmune disease, various cancers, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, oral sedative usage, and/or vitamin D deficiency may be associated with OLP.21,23 Although OLP patients who were initially deficient in vitamin D demonstrated marked improvement with supplementation, it is unlikely that vitamin D supplements impacted our patient’s presentation of OLP, as she had been consistently taking them for more than 5 years with no change in OLP presentation.24
Pathogenesis—Lichen planus is thought to be a cytotoxic CD8+ T cell–mediated autoimmune disease to a virally modified epidermal self-antigen on keratinocytes. The cytotoxic T cells target the modified self-antigens on basal keratinocytes and induce apoptosis.25 The cytokine-mediated lymphocyte homing mechanism is human leukocyte antigen dependent and involves tumor necrosis factor α as well as IFN-γ and IL-1. The latter cytokines lead to upregulation of vascular adhesion molecules on endothelial vessels of subepithelial vascular plexus as well as a cascade of nonspecific mechanisms such as mast cell degranulation and matrix metalloproteinase activation, resulting in increased basement membrane disruption.6
Shao et al19 underscored the role of IFN-γ in CD8+ T cell–mediated cytotoxic cellular responses, noting that the Janus kinase (JAK)–signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway may play a key role in the pathogenesis of lichen planus. They proposed using JAK inhibitors for the treatment of lichen planus, specifically tofacitinib, a JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor, and baricitinib, a JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, as top therapeutic agents for lichen planus (eTable).19 Tofacitinib has been reported to successfully treat conditions such as psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis, sarcoidosis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and lichen planopilaris.26 Additionally, the efficacy of tofacitinib has been established in patients with erosive lichen planus; tofacitinib resulted in marked improvement while prednisone, acitretin, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclosporine treatment failed.27 Although more studies on tofacitinib’s long-term efficacy, cost, and safety are necessary, tofacitinib may soon play an integral role in the battle against inflammatory dermatoses.
Conclusion
Esophageal lichen planus is an underreported form of lichen planus that often is misdiagnosed. It frequently causes dysphagia and odynophagia, resulting in a major decrease in a patient’s quality of life. We present the case of an 89-year-old woman who underwent procedures to dilate her esophagus that worsened her condition. We emphasize the importance of considering ELP in the differential diagnosis of patients presenting with lichen planus in another region. In our patient, tofacitinib 5 mg BID resolved her condition without any adverse effects.
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732. doi:10.1056/nejmcp1103641
- Heath L, Matin R. Lichen planus. InnovAiT. 2017;10:133-138. doi:10.1177/1755738016686804
- Oliveira JP, Uribe NC, Abulafia LA, et al. Esophageal lichenplanus. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:394-396. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153255
- Fox LP, Lightdale CJ, Grossman ME. Lichen planus of the esophagus: what dermatologists need to know. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:175-183. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.029
- Quispel R, van Boxel O, Schipper M, et al. High prevalence of esophageal involvement in lichen planus: a study using magnification chromoendoscopy. Endoscopy. 2009;41:187-193. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1119590
- Gupta S, Jawanda MK. Oral lichen planus: an update on etiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis and management. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:222-229. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.156315
- Katzka DA, Smyrk TC, Bruce AJ, et al. Variations in presentations of esophageal involvement in lichen planus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:777-782. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2010.04.024
- Abraham SC, Ravich WJ, Anhalt GJ, et al. Esophageal lichen planus. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1678-1682. doi:10.1097/00000478-200012000-00014
- Murro D, Jakate S. Radiation esophagitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139:827-830. doi:10.5858/arpa.2014-0111-RS
- Wilcox CM. Infectious esophagitis. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2006;2:567-568.
- Cancio A, Cruz C. A case of Kaposi’s sarcoma of the esophagus presenting with odynophagia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:S995-S996.
- Kokturk A. Clinical and pathological manifestations with differential diagnosis in Behçet’s disease. Patholog Res Int. 2012;2012:690390. doi:10.1155/2012/690390
- Madhusudhan KS, Sharma R. Esophageal lichen planus: a case report and review of literature. Indian J Dermatol. 2008;53:26-27. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.39738
- Bottomley WW, Dakkak M, Walton S, et al. Esophageal involvement in Behçet’s disease. is endoscopy necessary? Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37:594-597. doi:10.1007/BF01307585
- McDonald GB, Sullivan KM, Schuffler MD, et al. Esophageal abnormalities in chronic graft-versus-host disease in humans. Gastroenterology. 1981;80:914-921.
- Trabulo D, Ferreira S, Lage P, et al. Esophageal stenosis with sloughing esophagitis: a curious manifestation of graft-vs-host disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:9217-9222. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9217
- Abbas H, Ghazanfar H, Ul Hussain AN, et al. Atypical presentation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma masquerading as diffuse severe esophagitis. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2021;15:533-538. doi:10.1159/000517129
- Ellis A, Risk JM, Maruthappu T, et al. Tylosis with oesophageal cancer: diagnosis, management and molecular mechanisms. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:126. doi:10.1186/s13023-015-0346-2
- Shao S, Tsoi LC, Sarkar MK, et al. IFN-γ enhances cell-mediated cytotoxicity against keratinocytes via JAK2/STAT1 in lichen planus. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11:eaav7561. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aav7561
- Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
- Dave A, Shariff J, Philipone E. Association between oral lichen planus and systemic conditions and medications: case-control study. Oral Dis. 2020;27:515-524. doi:10.1111/odi.13572
- Krupaa RJ, Sankari SL, Masthan KM, et al. Oral lichen planus: an overview. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015;7(suppl 1):S158-S161. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.155873
- Tak MM, Chalkoo AH. Vitamin D deficiency—a possible contributing factor in the aetiopathogenesis of oral lichen planus. J Evolution Med Dent Sci. 2017;6:4769-4772. doi:10.14260/jemds/2017/1033
- Gupta J, Aggarwal A, Asadullah M, et al. Vitamin D in thetreatment of oral lichen planus: a pilot clinical study. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2019;31:222-227. doi:10.4103/jiaomr.jiaomr_97_19
- Shiohara T, Moriya N, Mochizuki T, et al. Lichenoid tissue reaction (LTR) induced by local transfer of Ia-reactive T-cell clones. II. LTR by epidermal invasion of cytotoxic lymphokine-producing autoreactive T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;89:8-14.
- Sonthalia S, Aggarwal P. Oral tofacitinib: contemporary appraisal of its role in dermatology. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:503-518. doi:10.4103/idoj.idoj_474_18
- Damsky W, Wang A, Olamiju B, et al. Treatment of severe lichen planus with the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:1708-1710.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.01.031
To reach early diagnoses and improve outcomes in cases of mucosal and esophageal lichen planus (ELP), patient education along with a multidisciplinary approach centered on collaboration among dermatologists, gastroenterologists, gynecologists, and dental practitioners should be a priority. Tofacitinib therapy should be considered in the treatment of patients presenting with cutaneous lichen planus (CLP), mucosal lichen planus, and ELP.
Lichen planus is a papulosquamous disease of the skin and mucous membranes that is most common on the skin and oral mucosa. Typical lesions of CLP present as purple, pruritic, polygonal papules and plaques on the flexural surfaces of the wrists and ankles as well as areas of friction or trauma due to scratching such as the shins and lower back. Various subtypes of lichen planus can present simultaneously, resulting in extensive involvement that worsens through koebnerization and affects the oral cavity, esophagus, larynx, sclera, genitalia, scalp, and nails.1,2
Esophageal lichen planus can develop with or without the presence of CLP, oral lichen planus (OLP), or genital lichen planus.3 It typically affects women older than 50 years and is linked to OLP and vulvar lichen planus, with 1 study reporting that 87% (63/72) of ELP patients were women with a median age of 61.9 years at the time of diagnosis (range, 22–85 years). Almost all ELP patients in the study had lichen planus symptoms in other locations; 89% (64/72) had OLP, and 42% (30/72) had vulvar lichen planus.4 Consequently, a diagnosis of ELP should be followed by a thorough full-body examination to check for lichen planus at other sites. Studies that examined lichen planus patients for ELP found that 25% to 50% of patients diagnosed with orocutaneous lichen planus also had ELP, with ELP frequently presenting without symptoms.3,5 These findings indicate that ELP likely is underdiagnosed and often misdiagnosed, resulting in an underestimation of its prevalence.

Our case highlights a frequently misdiagnosed condition and underscores the importance of close examination of patients presenting with CLP and OLP for signs and symptoms of ELP. Furthermore, we discuss the importance of patient education and collaboration among different specialties in attaining an early diagnosis to improve patient outcomes. Finally, we review the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of CLP, OLP, and ELP, as well as the utility of tofacitinib for ELP.

Case Report
An emaciated 89-year-old woman with an 11-year history of CLP, OLP, and genital lichen planus that had been successfully treated with topicals presented with an OLP recurrence alongside difficulties eating and swallowing. Her symptoms lasted 1 year and would recur when treatment was paused. Her medical history included rheumatoid arthritis, hypothyroidism, and hypertension, and she was taking levothyroxine, olmesartan, and vitamin D supplements. Dentures and olmesartan previously were ruled out as potential triggers following a 2-month elimination. None of her remaining natural teeth had fillings. She also reported that neither she nor her partner had ever smoked or chewed tobacco.

The patient’s lichen planus involvement first manifested as red, itchy, polygonal, lichenoid papules on the superior and inferior mid back 11 years prior to the current presentation (Figure 1). Further examination noted erosions on the genitalia, and a subsequent biopsy of the vulva confirmed a diagnosis of lichen planus (Figure 2). Treatment with halobetasol propionate ointment and tacrolimus ointment 0.1% twice daily (BID) resulted in remission of the CLP and vulvar lichen planus. She presented a year later with oral involvement revealing Wickham striae on the buccal mucosa and erosions on the upper palate that resolved after 2 months of treatment with cyclosporine oral solution mixed with a 5-times-daily nystatin swish-and-spit (Figure 3). The CLP did not recur but OLP was punctuated by remissions and recurrences on a yearly basis, often related to the cessation of mouthwash and topical creams. The OLP and vulvar lichen planus were successfully treated with as-needed use of a cyclosporine mouthwash swish-and-spit 3 times daily as well as halobetasol ointment 0.05% 3 times daily, respectively. Six years later, the patient was hospitalized for unrelated causes and was lost to follow-up for 2 years.

The patient experienced worsening dysphagia and odynophagia over a period of 2 years (mild dysphagia was first recorded 7 years prior to the initial presentation) and reported an unintentional weight loss of 20 pounds. An endoscopy was performed 3 years after the initial report of dysphagia and noted esophageal erosions (Figure 4A) and a stricture (Figure 4B), but all abnormal involvement was attributed to active gastroesophageal reflux disease. She underwent 8 esophageal dilations to treat the stricture but noted that the duration of symptomatic relief decreased with every subsequent dilation. An esophageal stent was placed 4 years after the initial concern of dysphagia, but it was not well tolerated and had to be removed soon thereafter. A year later, the patient underwent an esophageal bypass with a substernal gastric conduit that provided relief for 2 months but failed to permanently resolve the condition. In fact, her condition worsened over the next 1.5 years when she presented with extreme emaciation attributed to a low appetite and pain while eating. A review of the slides from a prior hospital esophageal biopsy revealed lichen planus (Figure 5). She was prescribed tofacitinib 5 mg BID as a dual-purpose treatment for the rheumatoid arthritis and OLP/ELP. At 1-month follow-up she noted that she had only taken one 5-mg pill daily without notable improvement, and after the visit she started the initial recommendation of 5 mg BID. Over the next several months, her condition continued to consistently improve; the odynophagia resolved, and she regained the majority of her lost weight. Tofacitinib was well tolerated across the course of treatment, and no adverse side effects were noted. Furthermore, the patient regained a full range of motion in the previously immobile arthritic right shoulder. She has experienced no recurrence of the genital lichen planus, OLP, or CLP since starting tofacitinib. To date, the patient is still taking only tofacitinib 5 mg BID with no recurrence of the cutaneous, mucosal, or esophageal lichen planus and has experienced no adverse events from the medication.

Comment
Clinical Presentation—Lichen planus—CLP and OLP—most frequently presents between the ages of 40 and 60 years, with a slight female predilection.1,2 The lesions typically present with the 5 P’s—purple, pruritic, polygonal papules and plaques—with some lesions revealing white lacy lines overlying them called Wickham striae.6 The lesions may be red at first before turning purple. They often present on the flexural surfaces of the wrists and ankles as well as the shins and back but rarely affect the face, perhaps because of increased chronic sun exposure.2,6 Less common locations include the scalp, nails, and mucosal areas (eg, oral, vulvar, conjunctival, laryngeal, esophageal, anal).1
If CLP is diagnosed, the patient likely will also have oral lesions, which occur in 50% of patients.2 Once any form of lichen planus is found, it is important to examine all of the most frequently involved locations—mucocutaneous and cutaneous as well as the nails and scalp. Special care should be taken when examining OLP and genital lichen planus, as long-standing lesions have a 2% to 5% chance of transforming into squamous cell carcinoma.2
Although cases of traditional OLP and CLP are ubiquitous in the literature, ELP rarely is documented because of frequent misdiagnoses. Esophageal lichen planus has a closer histopathologic resemblance to OLP compared to CLP, and its highly variable presentation often results in an inconclusive diagnosis.3 A review of 27 patients with lichen planus highlighted the difficult nature of diagnosing ELP; ELP manifested up to 20 years after initial lichen planus diagnosis, and patients underwent an average of 2.5 dilations prior to the successful diagnosis of ELP. Interestingly, 2 patients in the study presented with ELP in isolation, which emphasizes the importance of secondary examination for lichen planus in the presence of esophageal strictures.7 The eTable provides common patient demographics and symptoms to more effectively identify ELP.Differential Diagnosis—Because lichen planus can present anywhere on the body, it may be difficult to differentiate it from other skin conditions. Clinical appearance alone often is insufficient for diagnosing lichen planus, and a punch biopsy often is needed.2,20 Cutaneous lichen planus may resemble eczema, lichen simplex chronicus, pityriasis rosea, prurigo nodularis, and psoriasis, while OLP may resemble bite trauma, leukoplakia, pemphigus, and thrush.20 Dermoscopy of the tissue makes Wickham striae easier to visualize and assists in the diagnosis of lichen planus. Furthermore, thickening of the stratum granulosum, a prevalence of lymphocytes in the dermoepidermal junction, and vacuolar alteration of the stratum basale help to distinguish between lichen planus and other inflammatory dermatoses.20 A diagnosis of lichen planus merits a full-body skin examination—hair, nails, eyes, oral mucosa, and genitalia—to rule out additional involvement.
Esophageal lichen planus most frequently presents as dysphagia, odynophagia, and weight loss, but other symptoms including heartburn, hoarseness, choking, and epigastric pain may suggest esophageal involvement.4 Typically, ELP presents in the proximal and/or central esophagus, assisting in the differentiation between ELP and other esophageal conditions.3 Special consideration should be taken when both ELP and gastroesophageal reflux disease are considered in a differential diagnosis, and it is recommended to pair an upper endoscopy with pH monitoring to avoid misdiagnosis.8 Screening endoscopies also are helpful, as they assist in identifying the characteristic white webs, skin peeling, skin surface erosion, and strictures of ELP.4 Taken together, dermatologists should encourage patients with cutaneous or mucocutaneous lichen planus to undergo an esophagogastroduodenoscopy, especially in the presence of any of ELP’s common symptoms (eTable).
Etiology—Although the exact etiology of lichen planus is not well established, there are several known correlative factors, including hepatitis C; increased stress; dental materials; oral medications, most frequently antihypertensives and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; systemic diseases; and tobacco usage.6,21
Dental materials used in oral treatments such as silver amalgam, gold, cobalt, palladium, chromium, epoxy resins, and dentures can trigger or exacerbate OLP, and patch testing of a patient’s dental materials can help determine if the reaction was caused by the materials.6,22 The removal of material contributing to lesions often will cause OLP to resolve.22
It also has been suggested that the presence of thyroid disorders, autoimmune disease, various cancers, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, oral sedative usage, and/or vitamin D deficiency may be associated with OLP.21,23 Although OLP patients who were initially deficient in vitamin D demonstrated marked improvement with supplementation, it is unlikely that vitamin D supplements impacted our patient’s presentation of OLP, as she had been consistently taking them for more than 5 years with no change in OLP presentation.24
Pathogenesis—Lichen planus is thought to be a cytotoxic CD8+ T cell–mediated autoimmune disease to a virally modified epidermal self-antigen on keratinocytes. The cytotoxic T cells target the modified self-antigens on basal keratinocytes and induce apoptosis.25 The cytokine-mediated lymphocyte homing mechanism is human leukocyte antigen dependent and involves tumor necrosis factor α as well as IFN-γ and IL-1. The latter cytokines lead to upregulation of vascular adhesion molecules on endothelial vessels of subepithelial vascular plexus as well as a cascade of nonspecific mechanisms such as mast cell degranulation and matrix metalloproteinase activation, resulting in increased basement membrane disruption.6
Shao et al19 underscored the role of IFN-γ in CD8+ T cell–mediated cytotoxic cellular responses, noting that the Janus kinase (JAK)–signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway may play a key role in the pathogenesis of lichen planus. They proposed using JAK inhibitors for the treatment of lichen planus, specifically tofacitinib, a JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor, and baricitinib, a JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, as top therapeutic agents for lichen planus (eTable).19 Tofacitinib has been reported to successfully treat conditions such as psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis, sarcoidosis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and lichen planopilaris.26 Additionally, the efficacy of tofacitinib has been established in patients with erosive lichen planus; tofacitinib resulted in marked improvement while prednisone, acitretin, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclosporine treatment failed.27 Although more studies on tofacitinib’s long-term efficacy, cost, and safety are necessary, tofacitinib may soon play an integral role in the battle against inflammatory dermatoses.

Conclusion
Esophageal lichen planus is an underreported form of lichen planus that often is misdiagnosed. It frequently causes dysphagia and odynophagia, resulting in a major decrease in a patient’s quality of life. We present the case of an 89-year-old woman who underwent procedures to dilate her esophagus that worsened her condition. We emphasize the importance of considering ELP in the differential diagnosis of patients presenting with lichen planus in another region. In our patient, tofacitinib 5 mg BID resolved her condition without any adverse effects.
To reach early diagnoses and improve outcomes in cases of mucosal and esophageal lichen planus (ELP), patient education along with a multidisciplinary approach centered on collaboration among dermatologists, gastroenterologists, gynecologists, and dental practitioners should be a priority. Tofacitinib therapy should be considered in the treatment of patients presenting with cutaneous lichen planus (CLP), mucosal lichen planus, and ELP.
Lichen planus is a papulosquamous disease of the skin and mucous membranes that is most common on the skin and oral mucosa. Typical lesions of CLP present as purple, pruritic, polygonal papules and plaques on the flexural surfaces of the wrists and ankles as well as areas of friction or trauma due to scratching such as the shins and lower back. Various subtypes of lichen planus can present simultaneously, resulting in extensive involvement that worsens through koebnerization and affects the oral cavity, esophagus, larynx, sclera, genitalia, scalp, and nails.1,2
Esophageal lichen planus can develop with or without the presence of CLP, oral lichen planus (OLP), or genital lichen planus.3 It typically affects women older than 50 years and is linked to OLP and vulvar lichen planus, with 1 study reporting that 87% (63/72) of ELP patients were women with a median age of 61.9 years at the time of diagnosis (range, 22–85 years). Almost all ELP patients in the study had lichen planus symptoms in other locations; 89% (64/72) had OLP, and 42% (30/72) had vulvar lichen planus.4 Consequently, a diagnosis of ELP should be followed by a thorough full-body examination to check for lichen planus at other sites. Studies that examined lichen planus patients for ELP found that 25% to 50% of patients diagnosed with orocutaneous lichen planus also had ELP, with ELP frequently presenting without symptoms.3,5 These findings indicate that ELP likely is underdiagnosed and often misdiagnosed, resulting in an underestimation of its prevalence.

Our case highlights a frequently misdiagnosed condition and underscores the importance of close examination of patients presenting with CLP and OLP for signs and symptoms of ELP. Furthermore, we discuss the importance of patient education and collaboration among different specialties in attaining an early diagnosis to improve patient outcomes. Finally, we review the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of CLP, OLP, and ELP, as well as the utility of tofacitinib for ELP.

Case Report
An emaciated 89-year-old woman with an 11-year history of CLP, OLP, and genital lichen planus that had been successfully treated with topicals presented with an OLP recurrence alongside difficulties eating and swallowing. Her symptoms lasted 1 year and would recur when treatment was paused. Her medical history included rheumatoid arthritis, hypothyroidism, and hypertension, and she was taking levothyroxine, olmesartan, and vitamin D supplements. Dentures and olmesartan previously were ruled out as potential triggers following a 2-month elimination. None of her remaining natural teeth had fillings. She also reported that neither she nor her partner had ever smoked or chewed tobacco.

The patient’s lichen planus involvement first manifested as red, itchy, polygonal, lichenoid papules on the superior and inferior mid back 11 years prior to the current presentation (Figure 1). Further examination noted erosions on the genitalia, and a subsequent biopsy of the vulva confirmed a diagnosis of lichen planus (Figure 2). Treatment with halobetasol propionate ointment and tacrolimus ointment 0.1% twice daily (BID) resulted in remission of the CLP and vulvar lichen planus. She presented a year later with oral involvement revealing Wickham striae on the buccal mucosa and erosions on the upper palate that resolved after 2 months of treatment with cyclosporine oral solution mixed with a 5-times-daily nystatin swish-and-spit (Figure 3). The CLP did not recur but OLP was punctuated by remissions and recurrences on a yearly basis, often related to the cessation of mouthwash and topical creams. The OLP and vulvar lichen planus were successfully treated with as-needed use of a cyclosporine mouthwash swish-and-spit 3 times daily as well as halobetasol ointment 0.05% 3 times daily, respectively. Six years later, the patient was hospitalized for unrelated causes and was lost to follow-up for 2 years.

The patient experienced worsening dysphagia and odynophagia over a period of 2 years (mild dysphagia was first recorded 7 years prior to the initial presentation) and reported an unintentional weight loss of 20 pounds. An endoscopy was performed 3 years after the initial report of dysphagia and noted esophageal erosions (Figure 4A) and a stricture (Figure 4B), but all abnormal involvement was attributed to active gastroesophageal reflux disease. She underwent 8 esophageal dilations to treat the stricture but noted that the duration of symptomatic relief decreased with every subsequent dilation. An esophageal stent was placed 4 years after the initial concern of dysphagia, but it was not well tolerated and had to be removed soon thereafter. A year later, the patient underwent an esophageal bypass with a substernal gastric conduit that provided relief for 2 months but failed to permanently resolve the condition. In fact, her condition worsened over the next 1.5 years when she presented with extreme emaciation attributed to a low appetite and pain while eating. A review of the slides from a prior hospital esophageal biopsy revealed lichen planus (Figure 5). She was prescribed tofacitinib 5 mg BID as a dual-purpose treatment for the rheumatoid arthritis and OLP/ELP. At 1-month follow-up she noted that she had only taken one 5-mg pill daily without notable improvement, and after the visit she started the initial recommendation of 5 mg BID. Over the next several months, her condition continued to consistently improve; the odynophagia resolved, and she regained the majority of her lost weight. Tofacitinib was well tolerated across the course of treatment, and no adverse side effects were noted. Furthermore, the patient regained a full range of motion in the previously immobile arthritic right shoulder. She has experienced no recurrence of the genital lichen planus, OLP, or CLP since starting tofacitinib. To date, the patient is still taking only tofacitinib 5 mg BID with no recurrence of the cutaneous, mucosal, or esophageal lichen planus and has experienced no adverse events from the medication.

Comment
Clinical Presentation—Lichen planus—CLP and OLP—most frequently presents between the ages of 40 and 60 years, with a slight female predilection.1,2 The lesions typically present with the 5 P’s—purple, pruritic, polygonal papules and plaques—with some lesions revealing white lacy lines overlying them called Wickham striae.6 The lesions may be red at first before turning purple. They often present on the flexural surfaces of the wrists and ankles as well as the shins and back but rarely affect the face, perhaps because of increased chronic sun exposure.2,6 Less common locations include the scalp, nails, and mucosal areas (eg, oral, vulvar, conjunctival, laryngeal, esophageal, anal).1
If CLP is diagnosed, the patient likely will also have oral lesions, which occur in 50% of patients.2 Once any form of lichen planus is found, it is important to examine all of the most frequently involved locations—mucocutaneous and cutaneous as well as the nails and scalp. Special care should be taken when examining OLP and genital lichen planus, as long-standing lesions have a 2% to 5% chance of transforming into squamous cell carcinoma.2
Although cases of traditional OLP and CLP are ubiquitous in the literature, ELP rarely is documented because of frequent misdiagnoses. Esophageal lichen planus has a closer histopathologic resemblance to OLP compared to CLP, and its highly variable presentation often results in an inconclusive diagnosis.3 A review of 27 patients with lichen planus highlighted the difficult nature of diagnosing ELP; ELP manifested up to 20 years after initial lichen planus diagnosis, and patients underwent an average of 2.5 dilations prior to the successful diagnosis of ELP. Interestingly, 2 patients in the study presented with ELP in isolation, which emphasizes the importance of secondary examination for lichen planus in the presence of esophageal strictures.7 The eTable provides common patient demographics and symptoms to more effectively identify ELP.Differential Diagnosis—Because lichen planus can present anywhere on the body, it may be difficult to differentiate it from other skin conditions. Clinical appearance alone often is insufficient for diagnosing lichen planus, and a punch biopsy often is needed.2,20 Cutaneous lichen planus may resemble eczema, lichen simplex chronicus, pityriasis rosea, prurigo nodularis, and psoriasis, while OLP may resemble bite trauma, leukoplakia, pemphigus, and thrush.20 Dermoscopy of the tissue makes Wickham striae easier to visualize and assists in the diagnosis of lichen planus. Furthermore, thickening of the stratum granulosum, a prevalence of lymphocytes in the dermoepidermal junction, and vacuolar alteration of the stratum basale help to distinguish between lichen planus and other inflammatory dermatoses.20 A diagnosis of lichen planus merits a full-body skin examination—hair, nails, eyes, oral mucosa, and genitalia—to rule out additional involvement.
Esophageal lichen planus most frequently presents as dysphagia, odynophagia, and weight loss, but other symptoms including heartburn, hoarseness, choking, and epigastric pain may suggest esophageal involvement.4 Typically, ELP presents in the proximal and/or central esophagus, assisting in the differentiation between ELP and other esophageal conditions.3 Special consideration should be taken when both ELP and gastroesophageal reflux disease are considered in a differential diagnosis, and it is recommended to pair an upper endoscopy with pH monitoring to avoid misdiagnosis.8 Screening endoscopies also are helpful, as they assist in identifying the characteristic white webs, skin peeling, skin surface erosion, and strictures of ELP.4 Taken together, dermatologists should encourage patients with cutaneous or mucocutaneous lichen planus to undergo an esophagogastroduodenoscopy, especially in the presence of any of ELP’s common symptoms (eTable).
Etiology—Although the exact etiology of lichen planus is not well established, there are several known correlative factors, including hepatitis C; increased stress; dental materials; oral medications, most frequently antihypertensives and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; systemic diseases; and tobacco usage.6,21
Dental materials used in oral treatments such as silver amalgam, gold, cobalt, palladium, chromium, epoxy resins, and dentures can trigger or exacerbate OLP, and patch testing of a patient’s dental materials can help determine if the reaction was caused by the materials.6,22 The removal of material contributing to lesions often will cause OLP to resolve.22
It also has been suggested that the presence of thyroid disorders, autoimmune disease, various cancers, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, oral sedative usage, and/or vitamin D deficiency may be associated with OLP.21,23 Although OLP patients who were initially deficient in vitamin D demonstrated marked improvement with supplementation, it is unlikely that vitamin D supplements impacted our patient’s presentation of OLP, as she had been consistently taking them for more than 5 years with no change in OLP presentation.24
Pathogenesis—Lichen planus is thought to be a cytotoxic CD8+ T cell–mediated autoimmune disease to a virally modified epidermal self-antigen on keratinocytes. The cytotoxic T cells target the modified self-antigens on basal keratinocytes and induce apoptosis.25 The cytokine-mediated lymphocyte homing mechanism is human leukocyte antigen dependent and involves tumor necrosis factor α as well as IFN-γ and IL-1. The latter cytokines lead to upregulation of vascular adhesion molecules on endothelial vessels of subepithelial vascular plexus as well as a cascade of nonspecific mechanisms such as mast cell degranulation and matrix metalloproteinase activation, resulting in increased basement membrane disruption.6
Shao et al19 underscored the role of IFN-γ in CD8+ T cell–mediated cytotoxic cellular responses, noting that the Janus kinase (JAK)–signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway may play a key role in the pathogenesis of lichen planus. They proposed using JAK inhibitors for the treatment of lichen planus, specifically tofacitinib, a JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor, and baricitinib, a JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, as top therapeutic agents for lichen planus (eTable).19 Tofacitinib has been reported to successfully treat conditions such as psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis, sarcoidosis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and lichen planopilaris.26 Additionally, the efficacy of tofacitinib has been established in patients with erosive lichen planus; tofacitinib resulted in marked improvement while prednisone, acitretin, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclosporine treatment failed.27 Although more studies on tofacitinib’s long-term efficacy, cost, and safety are necessary, tofacitinib may soon play an integral role in the battle against inflammatory dermatoses.

Conclusion
Esophageal lichen planus is an underreported form of lichen planus that often is misdiagnosed. It frequently causes dysphagia and odynophagia, resulting in a major decrease in a patient’s quality of life. We present the case of an 89-year-old woman who underwent procedures to dilate her esophagus that worsened her condition. We emphasize the importance of considering ELP in the differential diagnosis of patients presenting with lichen planus in another region. In our patient, tofacitinib 5 mg BID resolved her condition without any adverse effects.
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732. doi:10.1056/nejmcp1103641
- Heath L, Matin R. Lichen planus. InnovAiT. 2017;10:133-138. doi:10.1177/1755738016686804
- Oliveira JP, Uribe NC, Abulafia LA, et al. Esophageal lichenplanus. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:394-396. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153255
- Fox LP, Lightdale CJ, Grossman ME. Lichen planus of the esophagus: what dermatologists need to know. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:175-183. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.029
- Quispel R, van Boxel O, Schipper M, et al. High prevalence of esophageal involvement in lichen planus: a study using magnification chromoendoscopy. Endoscopy. 2009;41:187-193. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1119590
- Gupta S, Jawanda MK. Oral lichen planus: an update on etiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis and management. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:222-229. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.156315
- Katzka DA, Smyrk TC, Bruce AJ, et al. Variations in presentations of esophageal involvement in lichen planus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:777-782. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2010.04.024
- Abraham SC, Ravich WJ, Anhalt GJ, et al. Esophageal lichen planus. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1678-1682. doi:10.1097/00000478-200012000-00014
- Murro D, Jakate S. Radiation esophagitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139:827-830. doi:10.5858/arpa.2014-0111-RS
- Wilcox CM. Infectious esophagitis. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2006;2:567-568.
- Cancio A, Cruz C. A case of Kaposi’s sarcoma of the esophagus presenting with odynophagia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:S995-S996.
- Kokturk A. Clinical and pathological manifestations with differential diagnosis in Behçet’s disease. Patholog Res Int. 2012;2012:690390. doi:10.1155/2012/690390
- Madhusudhan KS, Sharma R. Esophageal lichen planus: a case report and review of literature. Indian J Dermatol. 2008;53:26-27. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.39738
- Bottomley WW, Dakkak M, Walton S, et al. Esophageal involvement in Behçet’s disease. is endoscopy necessary? Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37:594-597. doi:10.1007/BF01307585
- McDonald GB, Sullivan KM, Schuffler MD, et al. Esophageal abnormalities in chronic graft-versus-host disease in humans. Gastroenterology. 1981;80:914-921.
- Trabulo D, Ferreira S, Lage P, et al. Esophageal stenosis with sloughing esophagitis: a curious manifestation of graft-vs-host disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:9217-9222. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9217
- Abbas H, Ghazanfar H, Ul Hussain AN, et al. Atypical presentation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma masquerading as diffuse severe esophagitis. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2021;15:533-538. doi:10.1159/000517129
- Ellis A, Risk JM, Maruthappu T, et al. Tylosis with oesophageal cancer: diagnosis, management and molecular mechanisms. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:126. doi:10.1186/s13023-015-0346-2
- Shao S, Tsoi LC, Sarkar MK, et al. IFN-γ enhances cell-mediated cytotoxicity against keratinocytes via JAK2/STAT1 in lichen planus. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11:eaav7561. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aav7561
- Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
- Dave A, Shariff J, Philipone E. Association between oral lichen planus and systemic conditions and medications: case-control study. Oral Dis. 2020;27:515-524. doi:10.1111/odi.13572
- Krupaa RJ, Sankari SL, Masthan KM, et al. Oral lichen planus: an overview. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015;7(suppl 1):S158-S161. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.155873
- Tak MM, Chalkoo AH. Vitamin D deficiency—a possible contributing factor in the aetiopathogenesis of oral lichen planus. J Evolution Med Dent Sci. 2017;6:4769-4772. doi:10.14260/jemds/2017/1033
- Gupta J, Aggarwal A, Asadullah M, et al. Vitamin D in thetreatment of oral lichen planus: a pilot clinical study. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2019;31:222-227. doi:10.4103/jiaomr.jiaomr_97_19
- Shiohara T, Moriya N, Mochizuki T, et al. Lichenoid tissue reaction (LTR) induced by local transfer of Ia-reactive T-cell clones. II. LTR by epidermal invasion of cytotoxic lymphokine-producing autoreactive T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;89:8-14.
- Sonthalia S, Aggarwal P. Oral tofacitinib: contemporary appraisal of its role in dermatology. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:503-518. doi:10.4103/idoj.idoj_474_18
- Damsky W, Wang A, Olamiju B, et al. Treatment of severe lichen planus with the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:1708-1710.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.01.031
- Le Cleach L, Chosidow O. Lichen planus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:723-732. doi:10.1056/nejmcp1103641
- Heath L, Matin R. Lichen planus. InnovAiT. 2017;10:133-138. doi:10.1177/1755738016686804
- Oliveira JP, Uribe NC, Abulafia LA, et al. Esophageal lichenplanus. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:394-396. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153255
- Fox LP, Lightdale CJ, Grossman ME. Lichen planus of the esophagus: what dermatologists need to know. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:175-183. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.029
- Quispel R, van Boxel O, Schipper M, et al. High prevalence of esophageal involvement in lichen planus: a study using magnification chromoendoscopy. Endoscopy. 2009;41:187-193. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1119590
- Gupta S, Jawanda MK. Oral lichen planus: an update on etiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis and management. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:222-229. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.156315
- Katzka DA, Smyrk TC, Bruce AJ, et al. Variations in presentations of esophageal involvement in lichen planus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:777-782. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2010.04.024
- Abraham SC, Ravich WJ, Anhalt GJ, et al. Esophageal lichen planus. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1678-1682. doi:10.1097/00000478-200012000-00014
- Murro D, Jakate S. Radiation esophagitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139:827-830. doi:10.5858/arpa.2014-0111-RS
- Wilcox CM. Infectious esophagitis. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2006;2:567-568.
- Cancio A, Cruz C. A case of Kaposi’s sarcoma of the esophagus presenting with odynophagia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:S995-S996.
- Kokturk A. Clinical and pathological manifestations with differential diagnosis in Behçet’s disease. Patholog Res Int. 2012;2012:690390. doi:10.1155/2012/690390
- Madhusudhan KS, Sharma R. Esophageal lichen planus: a case report and review of literature. Indian J Dermatol. 2008;53:26-27. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.39738
- Bottomley WW, Dakkak M, Walton S, et al. Esophageal involvement in Behçet’s disease. is endoscopy necessary? Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37:594-597. doi:10.1007/BF01307585
- McDonald GB, Sullivan KM, Schuffler MD, et al. Esophageal abnormalities in chronic graft-versus-host disease in humans. Gastroenterology. 1981;80:914-921.
- Trabulo D, Ferreira S, Lage P, et al. Esophageal stenosis with sloughing esophagitis: a curious manifestation of graft-vs-host disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:9217-9222. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9217
- Abbas H, Ghazanfar H, Ul Hussain AN, et al. Atypical presentation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma masquerading as diffuse severe esophagitis. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2021;15:533-538. doi:10.1159/000517129
- Ellis A, Risk JM, Maruthappu T, et al. Tylosis with oesophageal cancer: diagnosis, management and molecular mechanisms. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:126. doi:10.1186/s13023-015-0346-2
- Shao S, Tsoi LC, Sarkar MK, et al. IFN-γ enhances cell-mediated cytotoxicity against keratinocytes via JAK2/STAT1 in lichen planus. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11:eaav7561. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aav7561
- Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
- Dave A, Shariff J, Philipone E. Association between oral lichen planus and systemic conditions and medications: case-control study. Oral Dis. 2020;27:515-524. doi:10.1111/odi.13572
- Krupaa RJ, Sankari SL, Masthan KM, et al. Oral lichen planus: an overview. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015;7(suppl 1):S158-S161. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.155873
- Tak MM, Chalkoo AH. Vitamin D deficiency—a possible contributing factor in the aetiopathogenesis of oral lichen planus. J Evolution Med Dent Sci. 2017;6:4769-4772. doi:10.14260/jemds/2017/1033
- Gupta J, Aggarwal A, Asadullah M, et al. Vitamin D in thetreatment of oral lichen planus: a pilot clinical study. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2019;31:222-227. doi:10.4103/jiaomr.jiaomr_97_19
- Shiohara T, Moriya N, Mochizuki T, et al. Lichenoid tissue reaction (LTR) induced by local transfer of Ia-reactive T-cell clones. II. LTR by epidermal invasion of cytotoxic lymphokine-producing autoreactive T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1987;89:8-14.
- Sonthalia S, Aggarwal P. Oral tofacitinib: contemporary appraisal of its role in dermatology. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:503-518. doi:10.4103/idoj.idoj_474_18
- Damsky W, Wang A, Olamiju B, et al. Treatment of severe lichen planus with the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:1708-1710.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.01.031
Practice Points
- Patients diagnosed with lichen planus should be informed about the signs of esophageal lichen planus (ELP).
- Twenty-five percent to 50% of patients with oral lichen planus (OLP) have been shown to have concomitant ELP.
- Esophageal lichen planus may be asymptomatic and often is misdiagnosed.
- Tofacitinib should be considered for the treatment of ELP, OLP, and cutaneous lichen planus.
Violaceous Nodules on the Leg in a Patient with HIV
The Diagnosis: Plasmablastic Lymphoma
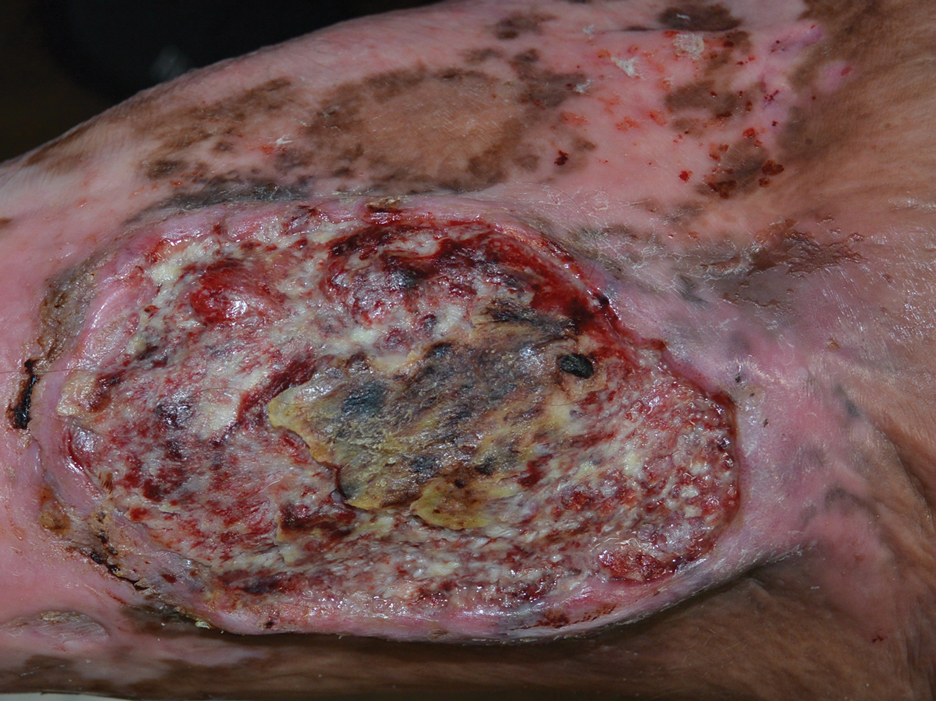
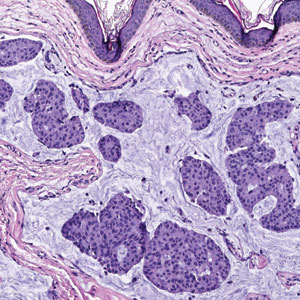
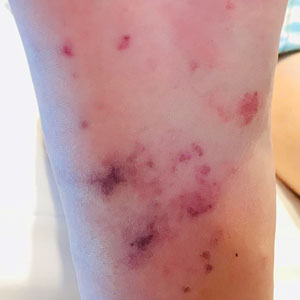
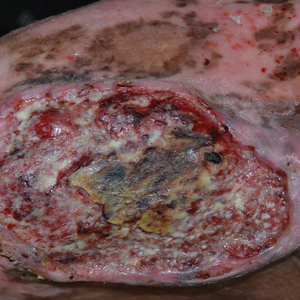
A punch biopsy of one of the leg nodules with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed sheets of medium to large cells with plasmacytic differentiation (Figure, A and B). Immunohistochemistry showed CD79, epithelial membrane antigen, multiple myeloma 1, and CD138 positivity, as well as CD-19 negativity and positive staining on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (Figure, C). Ki-67 stained greater than 90% of the neoplastic cells. Neoplastic cells were found to be λ restricted on κ and λ immunohistochemistry. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD3, and CD20 stains were negative. Subsequent fluorescent in situ hybridization was positive for MYC/immunoglobulin heavy chain (MYC/IGH) rearrangement t(8;14), confirming a diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL).
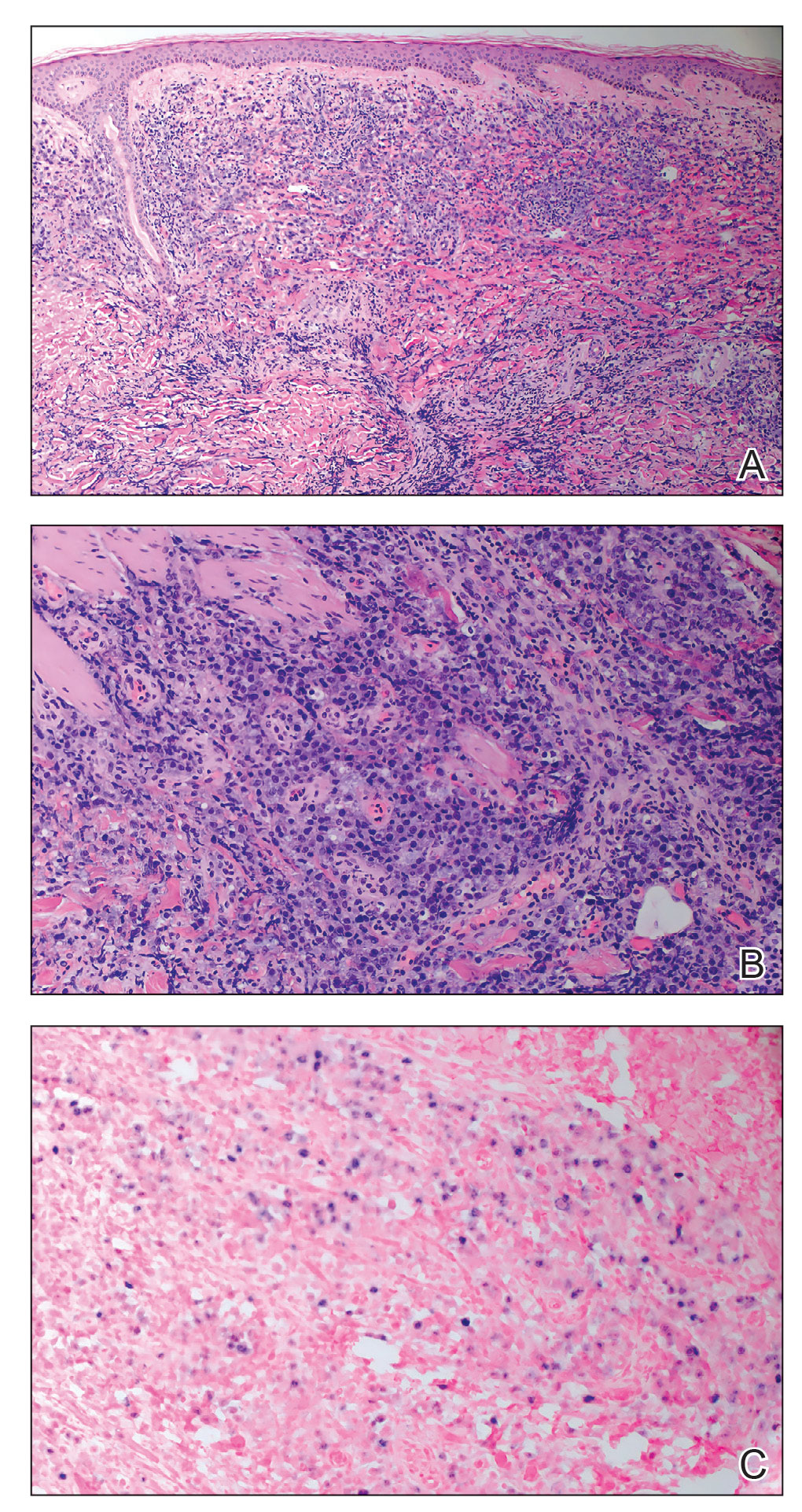
A bone marrow biopsy revealed normocellular bone marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis and no morphologic, immunophenotypic, or fluorescent in situ hybridization evidence of plasmablastic lymphoma or other pathology in the bone marrow. Our patient was started on hyper-CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin hydrochloride, dexamethasone) chemotherapy and was doing well with plans for a fourth course of chemotherapy. There is no standardized treatment course for cutaneous PBL, though excision with adjunctive chemotherapy treatment commonly has been reported in the literature.1
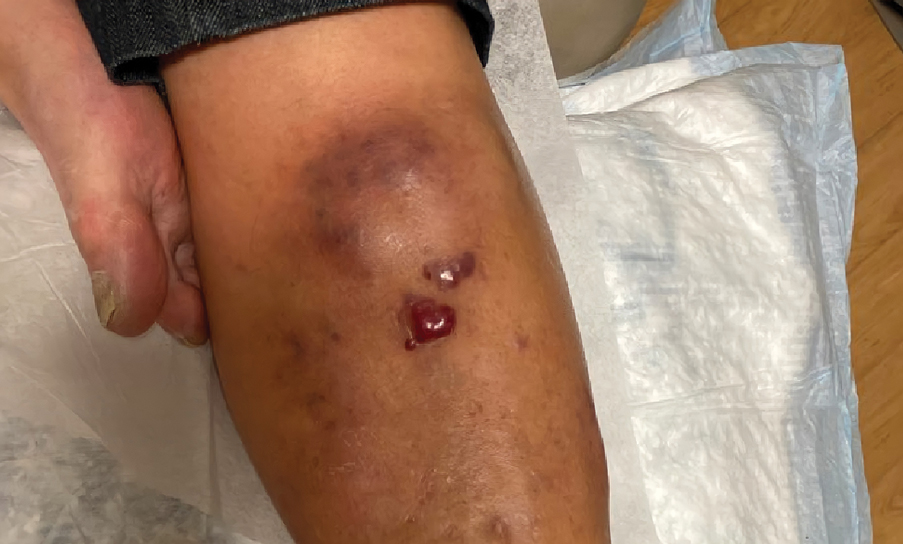
Plasmablastic lymphoma is a rare and aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with EBV infection that compromises approximately 2% to 3% of all HIV-related lymphomas.1,2 It frequently is associated with immunosuppression in patients with HIV or in transplant recipients on immunosuppression; however, it has been reported in immunocompetent individuals such as elderly patients.2 Plasmablastic lymphoma most commonly presents on the buccal mucosa but also can affect the gastrointestinal tract and occasionally has cutaneous manifestations.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations of PBL range from erythematous infiltrated plaques to ulcerated nodules presenting in an array of colors from flesh colored to violaceous.2 Primary cutaneous lesions can be seen on the legs, as in our patient.
Histopathologic examination reveals sheets of plasmablasts or large cells with eccentric nuclei and abundant basophilic cytoplasm.1 Plasmablastic lymphoma frequently is positive for mature B-cell markers such as CD38, CD138, multiple myeloma 1, and B lymphocyte–induced maturation protein 1.2,3 Uncommonly, PBL expresses paired box protein Pax-5 and CD20 markers.3 Although pathogenesis is poorly understood, it has been speculated that EBV infection is a common pathogenic factor. Epstein-Barr virus positivity has been noted in 60% of cases.2
Plasmablastic lymphoma and other malignant plasma cell processes such as plasmablastic myeloma (PBM) are morphologically similar. Proliferation of plasmablasts with rare plasmacytic cells is common in PBL, while plasmacytic cells are predominant in PBM. MYC rearrangement/ immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement t(8;14) was used to differentiate PBL from PBM in our patient; however, more cases of PBM with MYC/IGH rearrangement t(8;14) have been reported, making it an unreliable differentiating factor.4 A detailed clinical, pathologic, and genetic survey remains necessary for confirmatory diagnosis of PBL. Compared to other malignant plasma cell processes, PBL more commonly is seen in immunocompromised patients or those with HIV, such as our patient. Additionally, EBV testing is more likely to be positive in patients with PBL, further supporting this diagnosis in our patient.4
Presentations of bacillary angiomatosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and cutaneous lymphoma may be clinically similar; therefore, careful immunohistopathologic differentiation is necessary. Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative disorder that develops from HHV-8 infection and commonly is associated with HIV. It presents as painless vascular lesions in a range of colors with typical progression from patch to plaque to nodules, frequently on the lower extremities. Histologically, admixtures of bland spindle cells, slitlike small vessel proliferation, and lymphocytic infiltration are typical. Neoplastic vessels lack basement membrane zones, resulting in microhemorrhages and hemosiderin deposition. Neoplastic vessels label with CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers in addition to HHV-8 antibodies, which is highly specific for Kaposi sarcoma and differentiates it from PBL.5
Bacillary angiomatosis is an infectious neovascular proliferation characterized by papular lesions that may resemble the lesions of PBL. Mixed cell infiltration in inflammatory cells with clumping of granular material is characteristic. Under Warthin-Starry staining, the granular material is abundant in gram-negative rods representing Bartonella species, which is the implicated infectious agent in bacillary angiomatosis.
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) is the most common CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder and also may present with exophytic nodules. The etiology of LyP remains unknown, but it is suspected that overexpression of CD30 plays a role. Lymphomatoid papulosis presents as red-violaceous papules and nodules in various stages of healing. Although variable histology among types of LyP exists, CD30+ T-cell lymphocytes remain the hallmark of LyP. Type A LyP, which accounts for 80% of LyP cases, reveals CD4+ and CD30+ cells scattered among neutrophils, eosinophils, and small lymphocytes.5 Lymphomatoid papulosis typically is self-healing, recurrent, and carries an excellent prognosis.
Plasmablastic lymphoma remains a rare and aggressive type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that can have primary cutaneous manifestations. It is prudent to consider PBL in the differential diagnosis of nodular lower extremity lesions, especially in immunosuppressed patients.
- Jambusaria A, Shafer D, Wu H, et al. Cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:676-678.
- Marques SA, Abbade LP, Guiotoku MM, et al. Primary cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma revealing clinically unsuspected HIV infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:507-509.
- Bhatt R, Desai DS. Plasmablastic lymphoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532975/
- Morris A, Monohan G. Plasmablastic myeloma versus plasmablastic lymphoma: different yet related diseases. Hematol Transfus Int J. 2018;6:25-28. doi:10.15406/htij.2018.06.00146
- Prieto-Torres L, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Onaindia A, et al. CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies. Haematologica. 2019;104:226-235.
The Diagnosis: Plasmablastic Lymphoma
A punch biopsy of one of the leg nodules with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed sheets of medium to large cells with plasmacytic differentiation (Figure, A and B). Immunohistochemistry showed CD79, epithelial membrane antigen, multiple myeloma 1, and CD138 positivity, as well as CD-19 negativity and positive staining on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (Figure, C). Ki-67 stained greater than 90% of the neoplastic cells. Neoplastic cells were found to be λ restricted on κ and λ immunohistochemistry. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD3, and CD20 stains were negative. Subsequent fluorescent in situ hybridization was positive for MYC/immunoglobulin heavy chain (MYC/IGH) rearrangement t(8;14), confirming a diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL).

A bone marrow biopsy revealed normocellular bone marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis and no morphologic, immunophenotypic, or fluorescent in situ hybridization evidence of plasmablastic lymphoma or other pathology in the bone marrow. Our patient was started on hyper-CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin hydrochloride, dexamethasone) chemotherapy and was doing well with plans for a fourth course of chemotherapy. There is no standardized treatment course for cutaneous PBL, though excision with adjunctive chemotherapy treatment commonly has been reported in the literature.1
Plasmablastic lymphoma is a rare and aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with EBV infection that compromises approximately 2% to 3% of all HIV-related lymphomas.1,2 It frequently is associated with immunosuppression in patients with HIV or in transplant recipients on immunosuppression; however, it has been reported in immunocompetent individuals such as elderly patients.2 Plasmablastic lymphoma most commonly presents on the buccal mucosa but also can affect the gastrointestinal tract and occasionally has cutaneous manifestations.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations of PBL range from erythematous infiltrated plaques to ulcerated nodules presenting in an array of colors from flesh colored to violaceous.2 Primary cutaneous lesions can be seen on the legs, as in our patient.
Histopathologic examination reveals sheets of plasmablasts or large cells with eccentric nuclei and abundant basophilic cytoplasm.1 Plasmablastic lymphoma frequently is positive for mature B-cell markers such as CD38, CD138, multiple myeloma 1, and B lymphocyte–induced maturation protein 1.2,3 Uncommonly, PBL expresses paired box protein Pax-5 and CD20 markers.3 Although pathogenesis is poorly understood, it has been speculated that EBV infection is a common pathogenic factor. Epstein-Barr virus positivity has been noted in 60% of cases.2
Plasmablastic lymphoma and other malignant plasma cell processes such as plasmablastic myeloma (PBM) are morphologically similar. Proliferation of plasmablasts with rare plasmacytic cells is common in PBL, while plasmacytic cells are predominant in PBM. MYC rearrangement/ immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement t(8;14) was used to differentiate PBL from PBM in our patient; however, more cases of PBM with MYC/IGH rearrangement t(8;14) have been reported, making it an unreliable differentiating factor.4 A detailed clinical, pathologic, and genetic survey remains necessary for confirmatory diagnosis of PBL. Compared to other malignant plasma cell processes, PBL more commonly is seen in immunocompromised patients or those with HIV, such as our patient. Additionally, EBV testing is more likely to be positive in patients with PBL, further supporting this diagnosis in our patient.4
Presentations of bacillary angiomatosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and cutaneous lymphoma may be clinically similar; therefore, careful immunohistopathologic differentiation is necessary. Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative disorder that develops from HHV-8 infection and commonly is associated with HIV. It presents as painless vascular lesions in a range of colors with typical progression from patch to plaque to nodules, frequently on the lower extremities. Histologically, admixtures of bland spindle cells, slitlike small vessel proliferation, and lymphocytic infiltration are typical. Neoplastic vessels lack basement membrane zones, resulting in microhemorrhages and hemosiderin deposition. Neoplastic vessels label with CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers in addition to HHV-8 antibodies, which is highly specific for Kaposi sarcoma and differentiates it from PBL.5
Bacillary angiomatosis is an infectious neovascular proliferation characterized by papular lesions that may resemble the lesions of PBL. Mixed cell infiltration in inflammatory cells with clumping of granular material is characteristic. Under Warthin-Starry staining, the granular material is abundant in gram-negative rods representing Bartonella species, which is the implicated infectious agent in bacillary angiomatosis.
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) is the most common CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder and also may present with exophytic nodules. The etiology of LyP remains unknown, but it is suspected that overexpression of CD30 plays a role. Lymphomatoid papulosis presents as red-violaceous papules and nodules in various stages of healing. Although variable histology among types of LyP exists, CD30+ T-cell lymphocytes remain the hallmark of LyP. Type A LyP, which accounts for 80% of LyP cases, reveals CD4+ and CD30+ cells scattered among neutrophils, eosinophils, and small lymphocytes.5 Lymphomatoid papulosis typically is self-healing, recurrent, and carries an excellent prognosis.
Plasmablastic lymphoma remains a rare and aggressive type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that can have primary cutaneous manifestations. It is prudent to consider PBL in the differential diagnosis of nodular lower extremity lesions, especially in immunosuppressed patients.
The Diagnosis: Plasmablastic Lymphoma
A punch biopsy of one of the leg nodules with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed sheets of medium to large cells with plasmacytic differentiation (Figure, A and B). Immunohistochemistry showed CD79, epithelial membrane antigen, multiple myeloma 1, and CD138 positivity, as well as CD-19 negativity and positive staining on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (Figure, C). Ki-67 stained greater than 90% of the neoplastic cells. Neoplastic cells were found to be λ restricted on κ and λ immunohistochemistry. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD3, and CD20 stains were negative. Subsequent fluorescent in situ hybridization was positive for MYC/immunoglobulin heavy chain (MYC/IGH) rearrangement t(8;14), confirming a diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL).

A bone marrow biopsy revealed normocellular bone marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis and no morphologic, immunophenotypic, or fluorescent in situ hybridization evidence of plasmablastic lymphoma or other pathology in the bone marrow. Our patient was started on hyper-CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin hydrochloride, dexamethasone) chemotherapy and was doing well with plans for a fourth course of chemotherapy. There is no standardized treatment course for cutaneous PBL, though excision with adjunctive chemotherapy treatment commonly has been reported in the literature.1
Plasmablastic lymphoma is a rare and aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with EBV infection that compromises approximately 2% to 3% of all HIV-related lymphomas.1,2 It frequently is associated with immunosuppression in patients with HIV or in transplant recipients on immunosuppression; however, it has been reported in immunocompetent individuals such as elderly patients.2 Plasmablastic lymphoma most commonly presents on the buccal mucosa but also can affect the gastrointestinal tract and occasionally has cutaneous manifestations.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations of PBL range from erythematous infiltrated plaques to ulcerated nodules presenting in an array of colors from flesh colored to violaceous.2 Primary cutaneous lesions can be seen on the legs, as in our patient.
Histopathologic examination reveals sheets of plasmablasts or large cells with eccentric nuclei and abundant basophilic cytoplasm.1 Plasmablastic lymphoma frequently is positive for mature B-cell markers such as CD38, CD138, multiple myeloma 1, and B lymphocyte–induced maturation protein 1.2,3 Uncommonly, PBL expresses paired box protein Pax-5 and CD20 markers.3 Although pathogenesis is poorly understood, it has been speculated that EBV infection is a common pathogenic factor. Epstein-Barr virus positivity has been noted in 60% of cases.2
Plasmablastic lymphoma and other malignant plasma cell processes such as plasmablastic myeloma (PBM) are morphologically similar. Proliferation of plasmablasts with rare plasmacytic cells is common in PBL, while plasmacytic cells are predominant in PBM. MYC rearrangement/ immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement t(8;14) was used to differentiate PBL from PBM in our patient; however, more cases of PBM with MYC/IGH rearrangement t(8;14) have been reported, making it an unreliable differentiating factor.4 A detailed clinical, pathologic, and genetic survey remains necessary for confirmatory diagnosis of PBL. Compared to other malignant plasma cell processes, PBL more commonly is seen in immunocompromised patients or those with HIV, such as our patient. Additionally, EBV testing is more likely to be positive in patients with PBL, further supporting this diagnosis in our patient.4
Presentations of bacillary angiomatosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and cutaneous lymphoma may be clinically similar; therefore, careful immunohistopathologic differentiation is necessary. Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative disorder that develops from HHV-8 infection and commonly is associated with HIV. It presents as painless vascular lesions in a range of colors with typical progression from patch to plaque to nodules, frequently on the lower extremities. Histologically, admixtures of bland spindle cells, slitlike small vessel proliferation, and lymphocytic infiltration are typical. Neoplastic vessels lack basement membrane zones, resulting in microhemorrhages and hemosiderin deposition. Neoplastic vessels label with CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers in addition to HHV-8 antibodies, which is highly specific for Kaposi sarcoma and differentiates it from PBL.5
Bacillary angiomatosis is an infectious neovascular proliferation characterized by papular lesions that may resemble the lesions of PBL. Mixed cell infiltration in inflammatory cells with clumping of granular material is characteristic. Under Warthin-Starry staining, the granular material is abundant in gram-negative rods representing Bartonella species, which is the implicated infectious agent in bacillary angiomatosis.
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) is the most common CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder and also may present with exophytic nodules. The etiology of LyP remains unknown, but it is suspected that overexpression of CD30 plays a role. Lymphomatoid papulosis presents as red-violaceous papules and nodules in various stages of healing. Although variable histology among types of LyP exists, CD30+ T-cell lymphocytes remain the hallmark of LyP. Type A LyP, which accounts for 80% of LyP cases, reveals CD4+ and CD30+ cells scattered among neutrophils, eosinophils, and small lymphocytes.5 Lymphomatoid papulosis typically is self-healing, recurrent, and carries an excellent prognosis.
Plasmablastic lymphoma remains a rare and aggressive type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that can have primary cutaneous manifestations. It is prudent to consider PBL in the differential diagnosis of nodular lower extremity lesions, especially in immunosuppressed patients.
- Jambusaria A, Shafer D, Wu H, et al. Cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:676-678.
- Marques SA, Abbade LP, Guiotoku MM, et al. Primary cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma revealing clinically unsuspected HIV infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:507-509.
- Bhatt R, Desai DS. Plasmablastic lymphoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532975/
- Morris A, Monohan G. Plasmablastic myeloma versus plasmablastic lymphoma: different yet related diseases. Hematol Transfus Int J. 2018;6:25-28. doi:10.15406/htij.2018.06.00146
- Prieto-Torres L, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Onaindia A, et al. CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies. Haematologica. 2019;104:226-235.
- Jambusaria A, Shafer D, Wu H, et al. Cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:676-678.
- Marques SA, Abbade LP, Guiotoku MM, et al. Primary cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma revealing clinically unsuspected HIV infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:507-509.
- Bhatt R, Desai DS. Plasmablastic lymphoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532975/
- Morris A, Monohan G. Plasmablastic myeloma versus plasmablastic lymphoma: different yet related diseases. Hematol Transfus Int J. 2018;6:25-28. doi:10.15406/htij.2018.06.00146
- Prieto-Torres L, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Onaindia A, et al. CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies. Haematologica. 2019;104:226-235.
A 67-year-old man with long-standing hepatitis B virus and HIV managed with chronic antiretroviral therapy presented to an urgent care facility with worsening erythema and edema of the legs of 2 weeks’ duration. He was prescribed a 7-day course of cephalexin for presumed cellulitis. Two months later, he developed nodules on the lower extremities. He was seen by podiatry and prescribed a course of amoxicillin–clavulanic acid for presumed infection. Despite 2 courses of antibiotics, his symptoms progressed. The nodules expanded in number and some developed ulceration. Three months into his clinical course, he presented to our dermatology clinic. Physical examination revealed two 2- to 3-cm, violaceous, exophytic, tender nodules. He reported tactile allodynia of the lower extremities and denied fever, chills, night sweats, or weight loss. He also denied exposure to infectious or chemical agents and reported no recent travel. The patient was chronically taking lisinopril/hydrochlorothiazide, escitalopram, elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide, bupropion, and aspirin with no recent changes. A complete hematologic and biochemical survey largely was unremarkable. His HIV viral load was undetectable with a CD4 count greater than 400/mm3 (reference range, 490–1436/mm3). Lactate dehydrogenase was elevated at 568 IU/L (reference range, 135–225 IU/L). The lower leg lesions were biopsied for confirmatory diagnosis.
Expert discusses pros, cons of molecular tests for melanoma
SAN DIEGO – , according to Gregory A. Hosler, MD, PhD.
At the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update, Dr. Hosler, director of dermatopathology for ProPath, highlighted the following molecular tests currently used for the diagnosis of challenging melanocytic lesions:
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). This technique allows for the detection of chromosomal copy number changes throughout the tumor genome. “With CGH, test (tumor) DNA and normal DNA are differentially labeled and compared to a reference library. Gains and losses of portions of the tumor genome are determined by comparing the relative signals from these two groups,” said Dr. Hosler, clinical professor of pathology and dermatology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“In the past, your library was a metaphase of spread of chromosomes, which introduced technical challenges and made performance of the assay labor intensive. Because of this, CGH is not routinely performed by clinical laboratories and is used more as an exploratory/research technique.”
Array CGH (also known as SNP array). Newer versions of CGH use short DNA sequences that are tiled onto a chip. “The interesting thing about these chips is that you can purchase them or design them on your own,” Dr. Hosler said. “The chips may cover the entire genome or cover specific areas of the genome at higher resolution.” One upside of array CGH, he continued, is that it allows one to detect essentially all gains or losses of chromosomal material in a single reaction. “It is not subject to the artifacts associated with cutting thin sections like with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH); it can detect copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity, and it is more scalable,” Dr. Hosler said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center.
One downside of array CGH is that does not allow one to analyze specific cells, “so if you have a tumor that’s heterogeneous, the assay is agnostic to this and spits out a result based on all the material provided,” he said. “You can’t parse out different areas of the lesion. It also does not track balanced translocations.” In addition, he said, “there are also questions about reimbursement and these are lab-developed tests, so each lab’s assay is different. Finally, it requires specialized equipment and expertise for interpretation.”
FISH. First-generation melanoma FISH assays, which became available in 2009, used six probes and four colors and had a sensitivity of about 87% and specificity of about 95%, Dr. Hosler said, but there were problems with those assays, particularly related to Spitz nevi. Spitz nevi often duplicate their chromosomes, “so instead of being diploid they’re tetraploid,” he said.
“The second-generation melanoma FISH assays addressed this by adding centromeres to the assay, and targeted probes could be compared to the centromeres on the same chromosome to determine if these were true copy number gains, due to genetic instability, or gains or losses of entire arms or whole chromosomes. This modification and the addition of new targets really improved upon the sensitivity and specificity (94% and 98%, respectively),” he said, noting that this assay is widely used.
Upsides of melanoma FISH assays are that they are a “fairly routine methodology” in large clinical laboratories, he said, and that many labs are familiar with interpretation. “I would say the biggest advantage to FISH is its ability to analyze specific cells, which is useful with small or heterogeneous tumors,” Dr. Hosler said. “Also, there is a genetic reimbursement code for it, and it yields diagnostic and potentially prognostic information.” For example, certain copy number changes have shown to portend a worse prognosis if they’re present in a melanocytic tumor, including alterations in CDKN2A, CCND1, MYC, topoisomerase, and BAP1.
Downsides of melanoma FISH assays are that they are expensive, labor-intensive, and require experts to interpret the results. “The stacking and truncation of cell nuclei innate to paraffin-embedded FISH make interpretation difficult,” he said. “Also, all colors cannot be viewed simultaneously, and each lab’s assay potentially is different, requiring validation. These are not [Food and Drug Administration]-approved tests.”
Next generation sequencing (NGS). Also known as high-throughput sequencing, this technique allows for the generation of millions of sequencing reads that are aligned to a standard human genome, and likely represents the wave of the future. “With NGS you can increase breadth, so you can sequence the entire genome if you want, but you can also increase depth, meaning increasing the number of reads over a single target of the genome,” Dr. Hosler said. “That’s useful if you’re looking for a low frequency mutation.”
For example, NGS allows one to detect alterations of BRAF and KIT and other potentially actionable alterations. It can also be used to detect mutations in benign and malignant melanocytic lesions, including historically diagnostically challenging Spitz and desmoplastic subgroups. Several different NGS technologies exist, and there are different strategies behind each assay, including whole genome sequencing, whole exome sequencing, transcriptome sequencing, and targeted panels. “I’ve seen panels of 10 and I’ve seen panels of 1,500; there’s a wide range,” Dr. Hosler said. “The biggest challenge with NGS, currently, is that it’s difficult to interpret. Trying to figure out what’s important and what’s not important can be challenging. Often you need a team of people who are experts in bioinformatics to interpret these results.”
Slow turnaround time is another downside. “It can take a month to get results, and sometimes clinicians don’t want to wait that long, especially if they think a lesion is melanoma, so that’s an area of focus for NGS laboratories,” he said. “And there are questions on reimbursement. If you run NGS on every unusual melanocytic lesion, that’s not a good use of health care dollars. Who’s paying for it? I don’t have an answer for you. It’s all over the map right now. Each lab’s test and billing practice is different.”
Dr. Hosler reported having no relevant financial disclosures. ProPath is a nationwide pathology practice.
SAN DIEGO – , according to Gregory A. Hosler, MD, PhD.
At the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update, Dr. Hosler, director of dermatopathology for ProPath, highlighted the following molecular tests currently used for the diagnosis of challenging melanocytic lesions:
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). This technique allows for the detection of chromosomal copy number changes throughout the tumor genome. “With CGH, test (tumor) DNA and normal DNA are differentially labeled and compared to a reference library. Gains and losses of portions of the tumor genome are determined by comparing the relative signals from these two groups,” said Dr. Hosler, clinical professor of pathology and dermatology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“In the past, your library was a metaphase of spread of chromosomes, which introduced technical challenges and made performance of the assay labor intensive. Because of this, CGH is not routinely performed by clinical laboratories and is used more as an exploratory/research technique.”
Array CGH (also known as SNP array). Newer versions of CGH use short DNA sequences that are tiled onto a chip. “The interesting thing about these chips is that you can purchase them or design them on your own,” Dr. Hosler said. “The chips may cover the entire genome or cover specific areas of the genome at higher resolution.” One upside of array CGH, he continued, is that it allows one to detect essentially all gains or losses of chromosomal material in a single reaction. “It is not subject to the artifacts associated with cutting thin sections like with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH); it can detect copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity, and it is more scalable,” Dr. Hosler said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center.
One downside of array CGH is that does not allow one to analyze specific cells, “so if you have a tumor that’s heterogeneous, the assay is agnostic to this and spits out a result based on all the material provided,” he said. “You can’t parse out different areas of the lesion. It also does not track balanced translocations.” In addition, he said, “there are also questions about reimbursement and these are lab-developed tests, so each lab’s assay is different. Finally, it requires specialized equipment and expertise for interpretation.”
FISH. First-generation melanoma FISH assays, which became available in 2009, used six probes and four colors and had a sensitivity of about 87% and specificity of about 95%, Dr. Hosler said, but there were problems with those assays, particularly related to Spitz nevi. Spitz nevi often duplicate their chromosomes, “so instead of being diploid they’re tetraploid,” he said.
“The second-generation melanoma FISH assays addressed this by adding centromeres to the assay, and targeted probes could be compared to the centromeres on the same chromosome to determine if these were true copy number gains, due to genetic instability, or gains or losses of entire arms or whole chromosomes. This modification and the addition of new targets really improved upon the sensitivity and specificity (94% and 98%, respectively),” he said, noting that this assay is widely used.
Upsides of melanoma FISH assays are that they are a “fairly routine methodology” in large clinical laboratories, he said, and that many labs are familiar with interpretation. “I would say the biggest advantage to FISH is its ability to analyze specific cells, which is useful with small or heterogeneous tumors,” Dr. Hosler said. “Also, there is a genetic reimbursement code for it, and it yields diagnostic and potentially prognostic information.” For example, certain copy number changes have shown to portend a worse prognosis if they’re present in a melanocytic tumor, including alterations in CDKN2A, CCND1, MYC, topoisomerase, and BAP1.
Downsides of melanoma FISH assays are that they are expensive, labor-intensive, and require experts to interpret the results. “The stacking and truncation of cell nuclei innate to paraffin-embedded FISH make interpretation difficult,” he said. “Also, all colors cannot be viewed simultaneously, and each lab’s assay potentially is different, requiring validation. These are not [Food and Drug Administration]-approved tests.”
Next generation sequencing (NGS). Also known as high-throughput sequencing, this technique allows for the generation of millions of sequencing reads that are aligned to a standard human genome, and likely represents the wave of the future. “With NGS you can increase breadth, so you can sequence the entire genome if you want, but you can also increase depth, meaning increasing the number of reads over a single target of the genome,” Dr. Hosler said. “That’s useful if you’re looking for a low frequency mutation.”
For example, NGS allows one to detect alterations of BRAF and KIT and other potentially actionable alterations. It can also be used to detect mutations in benign and malignant melanocytic lesions, including historically diagnostically challenging Spitz and desmoplastic subgroups. Several different NGS technologies exist, and there are different strategies behind each assay, including whole genome sequencing, whole exome sequencing, transcriptome sequencing, and targeted panels. “I’ve seen panels of 10 and I’ve seen panels of 1,500; there’s a wide range,” Dr. Hosler said. “The biggest challenge with NGS, currently, is that it’s difficult to interpret. Trying to figure out what’s important and what’s not important can be challenging. Often you need a team of people who are experts in bioinformatics to interpret these results.”
Slow turnaround time is another downside. “It can take a month to get results, and sometimes clinicians don’t want to wait that long, especially if they think a lesion is melanoma, so that’s an area of focus for NGS laboratories,” he said. “And there are questions on reimbursement. If you run NGS on every unusual melanocytic lesion, that’s not a good use of health care dollars. Who’s paying for it? I don’t have an answer for you. It’s all over the map right now. Each lab’s test and billing practice is different.”
Dr. Hosler reported having no relevant financial disclosures. ProPath is a nationwide pathology practice.
SAN DIEGO – , according to Gregory A. Hosler, MD, PhD.
At the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update, Dr. Hosler, director of dermatopathology for ProPath, highlighted the following molecular tests currently used for the diagnosis of challenging melanocytic lesions:
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). This technique allows for the detection of chromosomal copy number changes throughout the tumor genome. “With CGH, test (tumor) DNA and normal DNA are differentially labeled and compared to a reference library. Gains and losses of portions of the tumor genome are determined by comparing the relative signals from these two groups,” said Dr. Hosler, clinical professor of pathology and dermatology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“In the past, your library was a metaphase of spread of chromosomes, which introduced technical challenges and made performance of the assay labor intensive. Because of this, CGH is not routinely performed by clinical laboratories and is used more as an exploratory/research technique.”
Array CGH (also known as SNP array). Newer versions of CGH use short DNA sequences that are tiled onto a chip. “The interesting thing about these chips is that you can purchase them or design them on your own,” Dr. Hosler said. “The chips may cover the entire genome or cover specific areas of the genome at higher resolution.” One upside of array CGH, he continued, is that it allows one to detect essentially all gains or losses of chromosomal material in a single reaction. “It is not subject to the artifacts associated with cutting thin sections like with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH); it can detect copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity, and it is more scalable,” Dr. Hosler said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center.
One downside of array CGH is that does not allow one to analyze specific cells, “so if you have a tumor that’s heterogeneous, the assay is agnostic to this and spits out a result based on all the material provided,” he said. “You can’t parse out different areas of the lesion. It also does not track balanced translocations.” In addition, he said, “there are also questions about reimbursement and these are lab-developed tests, so each lab’s assay is different. Finally, it requires specialized equipment and expertise for interpretation.”
FISH. First-generation melanoma FISH assays, which became available in 2009, used six probes and four colors and had a sensitivity of about 87% and specificity of about 95%, Dr. Hosler said, but there were problems with those assays, particularly related to Spitz nevi. Spitz nevi often duplicate their chromosomes, “so instead of being diploid they’re tetraploid,” he said.
“The second-generation melanoma FISH assays addressed this by adding centromeres to the assay, and targeted probes could be compared to the centromeres on the same chromosome to determine if these were true copy number gains, due to genetic instability, or gains or losses of entire arms or whole chromosomes. This modification and the addition of new targets really improved upon the sensitivity and specificity (94% and 98%, respectively),” he said, noting that this assay is widely used.
Upsides of melanoma FISH assays are that they are a “fairly routine methodology” in large clinical laboratories, he said, and that many labs are familiar with interpretation. “I would say the biggest advantage to FISH is its ability to analyze specific cells, which is useful with small or heterogeneous tumors,” Dr. Hosler said. “Also, there is a genetic reimbursement code for it, and it yields diagnostic and potentially prognostic information.” For example, certain copy number changes have shown to portend a worse prognosis if they’re present in a melanocytic tumor, including alterations in CDKN2A, CCND1, MYC, topoisomerase, and BAP1.
Downsides of melanoma FISH assays are that they are expensive, labor-intensive, and require experts to interpret the results. “The stacking and truncation of cell nuclei innate to paraffin-embedded FISH make interpretation difficult,” he said. “Also, all colors cannot be viewed simultaneously, and each lab’s assay potentially is different, requiring validation. These are not [Food and Drug Administration]-approved tests.”
Next generation sequencing (NGS). Also known as high-throughput sequencing, this technique allows for the generation of millions of sequencing reads that are aligned to a standard human genome, and likely represents the wave of the future. “With NGS you can increase breadth, so you can sequence the entire genome if you want, but you can also increase depth, meaning increasing the number of reads over a single target of the genome,” Dr. Hosler said. “That’s useful if you’re looking for a low frequency mutation.”
For example, NGS allows one to detect alterations of BRAF and KIT and other potentially actionable alterations. It can also be used to detect mutations in benign and malignant melanocytic lesions, including historically diagnostically challenging Spitz and desmoplastic subgroups. Several different NGS technologies exist, and there are different strategies behind each assay, including whole genome sequencing, whole exome sequencing, transcriptome sequencing, and targeted panels. “I’ve seen panels of 10 and I’ve seen panels of 1,500; there’s a wide range,” Dr. Hosler said. “The biggest challenge with NGS, currently, is that it’s difficult to interpret. Trying to figure out what’s important and what’s not important can be challenging. Often you need a team of people who are experts in bioinformatics to interpret these results.”
Slow turnaround time is another downside. “It can take a month to get results, and sometimes clinicians don’t want to wait that long, especially if they think a lesion is melanoma, so that’s an area of focus for NGS laboratories,” he said. “And there are questions on reimbursement. If you run NGS on every unusual melanocytic lesion, that’s not a good use of health care dollars. Who’s paying for it? I don’t have an answer for you. It’s all over the map right now. Each lab’s test and billing practice is different.”
Dr. Hosler reported having no relevant financial disclosures. ProPath is a nationwide pathology practice.
AT MELANOMA 2023
Asymptomatic Soft Tumor on the Forearm
The Diagnosis: Aneurysmal Dermatofibroma
A shave biopsy of the entire tumor was performed at the initial visit. Histologic examination with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed a fibrohistiocytic infiltrate containing cleftlike cavernous spaces lined by epithelial cells (Figure, A). Immunohistochemical staining revealed factor XIIIa expression on fibrohistiocytic cells (Figure, B). CD34 was expressed on vascular endothelial cells, but it failed to highlight the fibrohistiocytic space (Figure, C). Overall, these findings supported the diagnosis of aneurysmal dermatofibroma. The lesion healed without complications, and the patient was counseled on the risk for recurrence. He was offered localized excision but opted for conservative management without excision and close follow-up and monitoring.
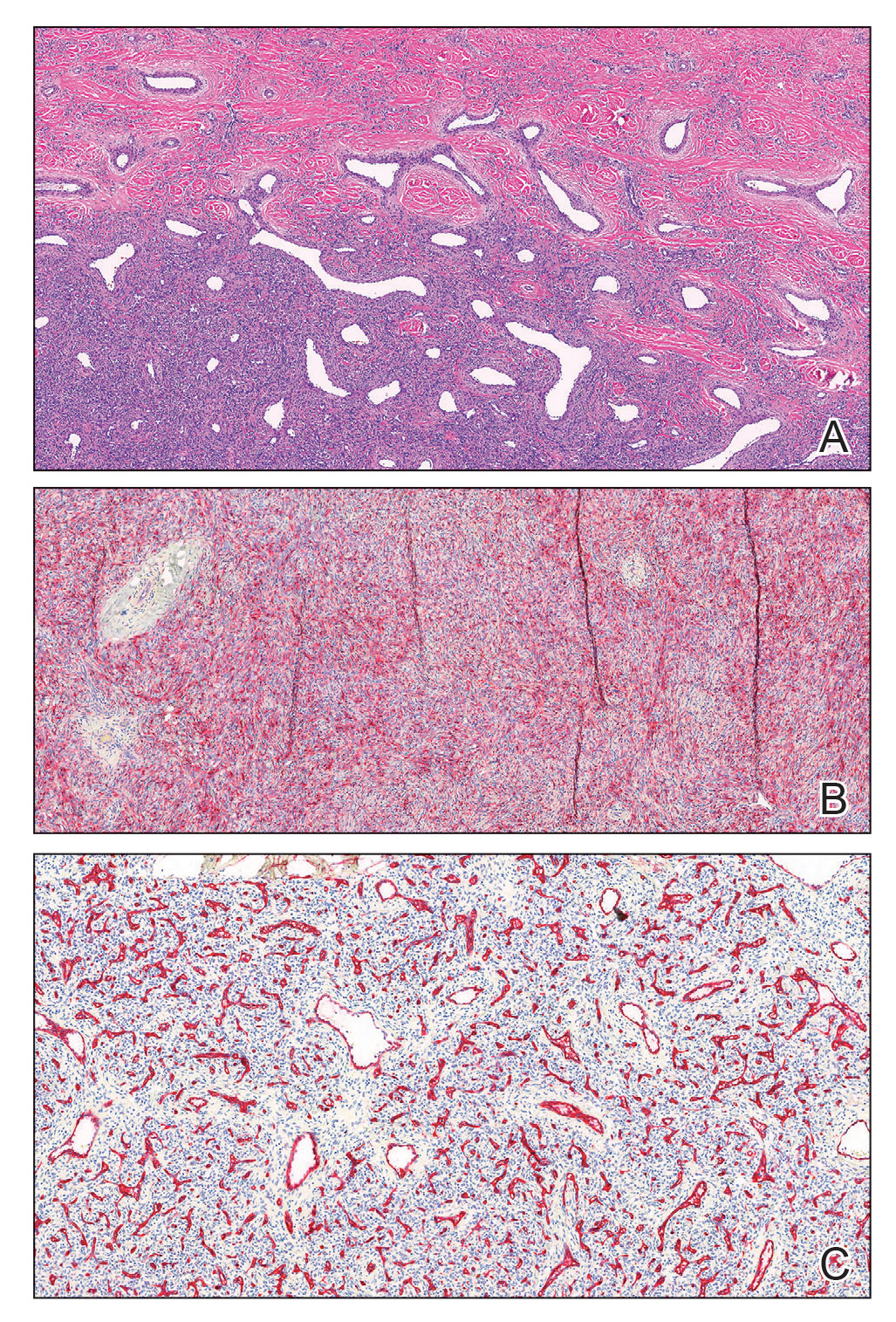
Dermatofibromas are common benign cutaneous nodules that often are asymptomatic and occur on the extremities. Dermatofibromas also are known as cutaneous fibrous histiocytomas and have numerous histologic variants. Aneurysmal dermatofibroma (also called aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma) is a rare histologic variant of dermatofibroma presenting as a slow-growing exophytic tumor that can be purple, red, brown, or blue. Although classic dermatofibromas typically constitute a straightforward diagnosis, aneurysmal dermatofibromas often are more challenging to clinically differentiate from other cutaneous neoplasms. Additionally, due to the exophytic nature and larger size (0.5–4.0 cm), aneurysmal dermatofibromas do not exhibit the characteristic dimple (Fitzpatrick) sign found in many dermatofibromas. Aneurysmal dermatofibromas are 10 times more likely to recur than classic dermatofibromas.1-4
Aneurysmal dermatofibromas can mimic other cutaneous neoplasms, some indolent and others more aggressive. Similar to aneurysmal dermatofibromas, solitary neurofibromas and nevi lipomatosus can appear as asymptomatic exophytic nodules with a similar spectrum of color and indolent clinical courses. In nevus lipomatosus, the dermis is almost entirely replaced by mature adipose tissue.5 Solitary neurofibromas represent a proliferation of neuromesenchymal cells with haphazardly arranged, wavy nuclei characteristic of nerve cells.6 Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans can be distinguished from aneurysmal dermatofibroma by lack of factor XIIIa expression and diffuse positivity for CD34.7 Finally, aneurysmal dermatofibromas may resemble vascular tumors such as nodular Kaposi sarcoma. Kaposi sarcoma can be differentiated from an aneurysmal dermatofibroma by the presence of characteristic vascular wrapping, the absence of fibrohistiocytic cells, and expression of human herpesvirus 8 latent nuclear antigen-1.1,8 Although aneurysmal dermatofibromas are of low malignant potential, they are associated with a higher rate of recurrence compared to common dermatofibromas.9 Definitive treatment involves complete excision with follow-up to ensure no signs of recurrence.10 Incomplete excision can increase the likelihood of recurrence, especially for larger aneurysmal dermatofibromas. Aneurysmal dermatofibromas are one of the subtypes of dermatofibromas that may extend into the subcutaneous tissue. Han et al2 found that 77.8% of aneurysmal dermatofibromas extended into subcutaneous tissue. Recognizing the clinical and pathological features of this rare subtype of dermatofibroma can aid dermatologists in appropriate recognition and management.
- Burr DM, Peterson WA, Peterson MW. Aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Am Osteopath. June 2018;40. Accessed February 14, 2023. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.aocd.org/resource/resmgr/jaocd/contents/volume40/40-04.pdf
- Han TY, Chang HS, Lee JHK, et al. A clinical and histopathological study of 122 cases of dermatofibroma (benign fibrous histiocytoma). Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:185-192.
- Morariu SH, Suciu M, Vartolomei MD, et al. Aneurysmal dermatofibroma mimicking both clinical and dermoscopic malignant melanoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55:1221-1224.
- Calonje E, Fletcher CDM. Aneurysmal benign fibrous histiocytoma: clinicopathological analysis of 40 cases of a tumour frequently misdiagnosed as a vascular neoplasm. Histopathology. 1995;26:323-331.
- Pujani M, Choudhury M, Garg T, et al. Nevus lipomatosus superficialis: a rare cutaneous hamartoma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:109-110.
- Strike SA, Puhaindran ME. Nerve tumors of the upper extremity. Clin Plast Surg. 2019;46:347-350.
- Cohen PR, Rapini RP, Farhood AI. Dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: differential expression of CD34 and factor XIIIa. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:573-574.
- Kandal S, Ozmen S, Demir HY, et al. Aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma of the skin: a rare variant of dermatofibroma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116:2050-2051.
- Hornick JL. Cutaneous soft tissue tumors: how do we make sense of fibrous and “fibrohistiocytic” tumors with confusing names and similar appearances? Mod Pathol. 2020;33:56-65.
- Das A, Das A, Bandyopadhyay D, et al. Aneurysmal benign fibrous histiocytoma presenting as a giant acrochordon on thigh. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:436.
The Diagnosis: Aneurysmal Dermatofibroma
A shave biopsy of the entire tumor was performed at the initial visit. Histologic examination with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed a fibrohistiocytic infiltrate containing cleftlike cavernous spaces lined by epithelial cells (Figure, A). Immunohistochemical staining revealed factor XIIIa expression on fibrohistiocytic cells (Figure, B). CD34 was expressed on vascular endothelial cells, but it failed to highlight the fibrohistiocytic space (Figure, C). Overall, these findings supported the diagnosis of aneurysmal dermatofibroma. The lesion healed without complications, and the patient was counseled on the risk for recurrence. He was offered localized excision but opted for conservative management without excision and close follow-up and monitoring.

Dermatofibromas are common benign cutaneous nodules that often are asymptomatic and occur on the extremities. Dermatofibromas also are known as cutaneous fibrous histiocytomas and have numerous histologic variants. Aneurysmal dermatofibroma (also called aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma) is a rare histologic variant of dermatofibroma presenting as a slow-growing exophytic tumor that can be purple, red, brown, or blue. Although classic dermatofibromas typically constitute a straightforward diagnosis, aneurysmal dermatofibromas often are more challenging to clinically differentiate from other cutaneous neoplasms. Additionally, due to the exophytic nature and larger size (0.5–4.0 cm), aneurysmal dermatofibromas do not exhibit the characteristic dimple (Fitzpatrick) sign found in many dermatofibromas. Aneurysmal dermatofibromas are 10 times more likely to recur than classic dermatofibromas.1-4
Aneurysmal dermatofibromas can mimic other cutaneous neoplasms, some indolent and others more aggressive. Similar to aneurysmal dermatofibromas, solitary neurofibromas and nevi lipomatosus can appear as asymptomatic exophytic nodules with a similar spectrum of color and indolent clinical courses. In nevus lipomatosus, the dermis is almost entirely replaced by mature adipose tissue.5 Solitary neurofibromas represent a proliferation of neuromesenchymal cells with haphazardly arranged, wavy nuclei characteristic of nerve cells.6 Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans can be distinguished from aneurysmal dermatofibroma by lack of factor XIIIa expression and diffuse positivity for CD34.7 Finally, aneurysmal dermatofibromas may resemble vascular tumors such as nodular Kaposi sarcoma. Kaposi sarcoma can be differentiated from an aneurysmal dermatofibroma by the presence of characteristic vascular wrapping, the absence of fibrohistiocytic cells, and expression of human herpesvirus 8 latent nuclear antigen-1.1,8 Although aneurysmal dermatofibromas are of low malignant potential, they are associated with a higher rate of recurrence compared to common dermatofibromas.9 Definitive treatment involves complete excision with follow-up to ensure no signs of recurrence.10 Incomplete excision can increase the likelihood of recurrence, especially for larger aneurysmal dermatofibromas. Aneurysmal dermatofibromas are one of the subtypes of dermatofibromas that may extend into the subcutaneous tissue. Han et al2 found that 77.8% of aneurysmal dermatofibromas extended into subcutaneous tissue. Recognizing the clinical and pathological features of this rare subtype of dermatofibroma can aid dermatologists in appropriate recognition and management.
The Diagnosis: Aneurysmal Dermatofibroma
A shave biopsy of the entire tumor was performed at the initial visit. Histologic examination with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed a fibrohistiocytic infiltrate containing cleftlike cavernous spaces lined by epithelial cells (Figure, A). Immunohistochemical staining revealed factor XIIIa expression on fibrohistiocytic cells (Figure, B). CD34 was expressed on vascular endothelial cells, but it failed to highlight the fibrohistiocytic space (Figure, C). Overall, these findings supported the diagnosis of aneurysmal dermatofibroma. The lesion healed without complications, and the patient was counseled on the risk for recurrence. He was offered localized excision but opted for conservative management without excision and close follow-up and monitoring.

Dermatofibromas are common benign cutaneous nodules that often are asymptomatic and occur on the extremities. Dermatofibromas also are known as cutaneous fibrous histiocytomas and have numerous histologic variants. Aneurysmal dermatofibroma (also called aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma) is a rare histologic variant of dermatofibroma presenting as a slow-growing exophytic tumor that can be purple, red, brown, or blue. Although classic dermatofibromas typically constitute a straightforward diagnosis, aneurysmal dermatofibromas often are more challenging to clinically differentiate from other cutaneous neoplasms. Additionally, due to the exophytic nature and larger size (0.5–4.0 cm), aneurysmal dermatofibromas do not exhibit the characteristic dimple (Fitzpatrick) sign found in many dermatofibromas. Aneurysmal dermatofibromas are 10 times more likely to recur than classic dermatofibromas.1-4
Aneurysmal dermatofibromas can mimic other cutaneous neoplasms, some indolent and others more aggressive. Similar to aneurysmal dermatofibromas, solitary neurofibromas and nevi lipomatosus can appear as asymptomatic exophytic nodules with a similar spectrum of color and indolent clinical courses. In nevus lipomatosus, the dermis is almost entirely replaced by mature adipose tissue.5 Solitary neurofibromas represent a proliferation of neuromesenchymal cells with haphazardly arranged, wavy nuclei characteristic of nerve cells.6 Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans can be distinguished from aneurysmal dermatofibroma by lack of factor XIIIa expression and diffuse positivity for CD34.7 Finally, aneurysmal dermatofibromas may resemble vascular tumors such as nodular Kaposi sarcoma. Kaposi sarcoma can be differentiated from an aneurysmal dermatofibroma by the presence of characteristic vascular wrapping, the absence of fibrohistiocytic cells, and expression of human herpesvirus 8 latent nuclear antigen-1.1,8 Although aneurysmal dermatofibromas are of low malignant potential, they are associated with a higher rate of recurrence compared to common dermatofibromas.9 Definitive treatment involves complete excision with follow-up to ensure no signs of recurrence.10 Incomplete excision can increase the likelihood of recurrence, especially for larger aneurysmal dermatofibromas. Aneurysmal dermatofibromas are one of the subtypes of dermatofibromas that may extend into the subcutaneous tissue. Han et al2 found that 77.8% of aneurysmal dermatofibromas extended into subcutaneous tissue. Recognizing the clinical and pathological features of this rare subtype of dermatofibroma can aid dermatologists in appropriate recognition and management.
- Burr DM, Peterson WA, Peterson MW. Aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Am Osteopath. June 2018;40. Accessed February 14, 2023. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.aocd.org/resource/resmgr/jaocd/contents/volume40/40-04.pdf
- Han TY, Chang HS, Lee JHK, et al. A clinical and histopathological study of 122 cases of dermatofibroma (benign fibrous histiocytoma). Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:185-192.
- Morariu SH, Suciu M, Vartolomei MD, et al. Aneurysmal dermatofibroma mimicking both clinical and dermoscopic malignant melanoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55:1221-1224.
- Calonje E, Fletcher CDM. Aneurysmal benign fibrous histiocytoma: clinicopathological analysis of 40 cases of a tumour frequently misdiagnosed as a vascular neoplasm. Histopathology. 1995;26:323-331.
- Pujani M, Choudhury M, Garg T, et al. Nevus lipomatosus superficialis: a rare cutaneous hamartoma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:109-110.
- Strike SA, Puhaindran ME. Nerve tumors of the upper extremity. Clin Plast Surg. 2019;46:347-350.
- Cohen PR, Rapini RP, Farhood AI. Dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: differential expression of CD34 and factor XIIIa. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:573-574.
- Kandal S, Ozmen S, Demir HY, et al. Aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma of the skin: a rare variant of dermatofibroma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116:2050-2051.
- Hornick JL. Cutaneous soft tissue tumors: how do we make sense of fibrous and “fibrohistiocytic” tumors with confusing names and similar appearances? Mod Pathol. 2020;33:56-65.
- Das A, Das A, Bandyopadhyay D, et al. Aneurysmal benign fibrous histiocytoma presenting as a giant acrochordon on thigh. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:436.
- Burr DM, Peterson WA, Peterson MW. Aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Am Osteopath. June 2018;40. Accessed February 14, 2023. https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.aocd.org/resource/resmgr/jaocd/contents/volume40/40-04.pdf
- Han TY, Chang HS, Lee JHK, et al. A clinical and histopathological study of 122 cases of dermatofibroma (benign fibrous histiocytoma). Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:185-192.
- Morariu SH, Suciu M, Vartolomei MD, et al. Aneurysmal dermatofibroma mimicking both clinical and dermoscopic malignant melanoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55:1221-1224.
- Calonje E, Fletcher CDM. Aneurysmal benign fibrous histiocytoma: clinicopathological analysis of 40 cases of a tumour frequently misdiagnosed as a vascular neoplasm. Histopathology. 1995;26:323-331.
- Pujani M, Choudhury M, Garg T, et al. Nevus lipomatosus superficialis: a rare cutaneous hamartoma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:109-110.
- Strike SA, Puhaindran ME. Nerve tumors of the upper extremity. Clin Plast Surg. 2019;46:347-350.
- Cohen PR, Rapini RP, Farhood AI. Dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: differential expression of CD34 and factor XIIIa. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:573-574.
- Kandal S, Ozmen S, Demir HY, et al. Aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma of the skin: a rare variant of dermatofibroma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116:2050-2051.
- Hornick JL. Cutaneous soft tissue tumors: how do we make sense of fibrous and “fibrohistiocytic” tumors with confusing names and similar appearances? Mod Pathol. 2020;33:56-65.
- Das A, Das A, Bandyopadhyay D, et al. Aneurysmal benign fibrous histiocytoma presenting as a giant acrochordon on thigh. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:436.
A 43-year-old Black man with no notable medical history presented to our clinic with a progressively enlarging tumor on the right forearm of 12 months’ duration. Despite its progressive growth, the tumor was asymptomatic. Physical examination of the right forearm revealed a 3.7×3.0-cm, well-circumscribed, exophytic tumor with a mildly erythematous hue, scaly surface, and rubbery consistency. There was no surrounding erythema, edema, localized lymphadenopathy, or concurrent lymphedema.
An 11-year-old boy presents with small itchy bumps on the wrists, face, arms, and legs
The patient was diagnosed with lichen nitidus, given the characteristic clinical presentation.
Lichen nitidus is a rare chronic inflammatory condition of the skin that most commonly presents in children and young adults and does not seem to be restricted to any sex or race. The classic lesions are described as asymptomatic to slightly pruritic, small (1 mm), skin-colored to hypopigmented flat-topped papules.
Koebner phenomenon is usually seen in which the skin lesions appear in areas of traumatized healthy skin. The extremities, abdomen, chest, and penis are common locations for the lesions to occur. Rarely, the oral mucosa or nails can be involved. It has been described in patients with a diagnosis of Crohn’s disease, Niemann-Pick disease, Down syndrome, and HIV. The rare, generalized purpuric variant has been reported in a few cases associated with interferon and ribavirin treatment for hepatitis C infection and nivolumab treatment for cancer. The pathophysiology of lichen nitidus is unknown.
Lichen nitidus can occur in the presence of other skin conditions like lichen planus, atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, erythema nodosum, and lichen spinulosus. Histopathologic characteristics of lichen nitidus are described as a “ball and claw” of epidermal rete around a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Parakeratosis overlying epidermal atrophy and focal basal liquefaction degeneration is also seen.
The differential diagnosis of lichen nitidus includes flat warts, which can present as clusters of small flat-topped papules that can show a pseudo-Koebner phenomenon (where the virus is seeded in traumatized skin). The morphological difference between the condition is that lichen nitidus lesions are usually monomorphic, compared with flat warts, which usually present with different sizes and shapes.
Patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis may present with a generalized monomorphic eruption of skin-colored papules (known as ID reaction) that can sometimes be very similar to lichen nitidus. Allergic contact dermatitis tends to respond fairly quickly to topical or systemic corticosteroids, unlike lichen nitidus. There are a few reports that consider lichen nitidus to be a variant of lichen planus, although they have different histopathologic findings. Lichen planus lesions are described as polygonal, pruritic, purple to pink papules most commonly seen on the wrists, lower back, and ankles. Lichen planus can be seen in patients with hepatitis C and may also occur secondary to medication.
Milia are small keratin cysts on the skin that are commonly seen in babies as primary milia and can be seen in older children secondary to trauma (commonly on the eyelids) or medications. Given their size and monomorphic appearance, they can sometimes be confused with lichen nitidus.
Lichen nitidus is often asymptomatic and the lesions resolve within a few months to years. Topical corticosteroids can be helpful to alleviate the symptoms in patients who present with pruritus. In more persistent and generalized cases, phototherapy, systemic corticosteroids, acitretin, isotretinoin, or cyclosporine can be considered.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Chu J and Lam JM. CMAJ. 2014 Dec 9;186(18):E688.
Lestringant G et al. Dermatology 1996;192:171-3.
Peterson JA et al. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2021 Aug 25;35(1):70-2.
Schwartz C and Goodman MB. “Lichen nitidus,” in StatPearls. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
The patient was diagnosed with lichen nitidus, given the characteristic clinical presentation.
Lichen nitidus is a rare chronic inflammatory condition of the skin that most commonly presents in children and young adults and does not seem to be restricted to any sex or race. The classic lesions are described as asymptomatic to slightly pruritic, small (1 mm), skin-colored to hypopigmented flat-topped papules.
Koebner phenomenon is usually seen in which the skin lesions appear in areas of traumatized healthy skin. The extremities, abdomen, chest, and penis are common locations for the lesions to occur. Rarely, the oral mucosa or nails can be involved. It has been described in patients with a diagnosis of Crohn’s disease, Niemann-Pick disease, Down syndrome, and HIV. The rare, generalized purpuric variant has been reported in a few cases associated with interferon and ribavirin treatment for hepatitis C infection and nivolumab treatment for cancer. The pathophysiology of lichen nitidus is unknown.
Lichen nitidus can occur in the presence of other skin conditions like lichen planus, atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, erythema nodosum, and lichen spinulosus. Histopathologic characteristics of lichen nitidus are described as a “ball and claw” of epidermal rete around a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Parakeratosis overlying epidermal atrophy and focal basal liquefaction degeneration is also seen.
The differential diagnosis of lichen nitidus includes flat warts, which can present as clusters of small flat-topped papules that can show a pseudo-Koebner phenomenon (where the virus is seeded in traumatized skin). The morphological difference between the condition is that lichen nitidus lesions are usually monomorphic, compared with flat warts, which usually present with different sizes and shapes.
Patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis may present with a generalized monomorphic eruption of skin-colored papules (known as ID reaction) that can sometimes be very similar to lichen nitidus. Allergic contact dermatitis tends to respond fairly quickly to topical or systemic corticosteroids, unlike lichen nitidus. There are a few reports that consider lichen nitidus to be a variant of lichen planus, although they have different histopathologic findings. Lichen planus lesions are described as polygonal, pruritic, purple to pink papules most commonly seen on the wrists, lower back, and ankles. Lichen planus can be seen in patients with hepatitis C and may also occur secondary to medication.
Milia are small keratin cysts on the skin that are commonly seen in babies as primary milia and can be seen in older children secondary to trauma (commonly on the eyelids) or medications. Given their size and monomorphic appearance, they can sometimes be confused with lichen nitidus.
Lichen nitidus is often asymptomatic and the lesions resolve within a few months to years. Topical corticosteroids can be helpful to alleviate the symptoms in patients who present with pruritus. In more persistent and generalized cases, phototherapy, systemic corticosteroids, acitretin, isotretinoin, or cyclosporine can be considered.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Chu J and Lam JM. CMAJ. 2014 Dec 9;186(18):E688.
Lestringant G et al. Dermatology 1996;192:171-3.
Peterson JA et al. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2021 Aug 25;35(1):70-2.
Schwartz C and Goodman MB. “Lichen nitidus,” in StatPearls. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
The patient was diagnosed with lichen nitidus, given the characteristic clinical presentation.
Lichen nitidus is a rare chronic inflammatory condition of the skin that most commonly presents in children and young adults and does not seem to be restricted to any sex or race. The classic lesions are described as asymptomatic to slightly pruritic, small (1 mm), skin-colored to hypopigmented flat-topped papules.
Koebner phenomenon is usually seen in which the skin lesions appear in areas of traumatized healthy skin. The extremities, abdomen, chest, and penis are common locations for the lesions to occur. Rarely, the oral mucosa or nails can be involved. It has been described in patients with a diagnosis of Crohn’s disease, Niemann-Pick disease, Down syndrome, and HIV. The rare, generalized purpuric variant has been reported in a few cases associated with interferon and ribavirin treatment for hepatitis C infection and nivolumab treatment for cancer. The pathophysiology of lichen nitidus is unknown.
Lichen nitidus can occur in the presence of other skin conditions like lichen planus, atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, erythema nodosum, and lichen spinulosus. Histopathologic characteristics of lichen nitidus are described as a “ball and claw” of epidermal rete around a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Parakeratosis overlying epidermal atrophy and focal basal liquefaction degeneration is also seen.
The differential diagnosis of lichen nitidus includes flat warts, which can present as clusters of small flat-topped papules that can show a pseudo-Koebner phenomenon (where the virus is seeded in traumatized skin). The morphological difference between the condition is that lichen nitidus lesions are usually monomorphic, compared with flat warts, which usually present with different sizes and shapes.
Patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis may present with a generalized monomorphic eruption of skin-colored papules (known as ID reaction) that can sometimes be very similar to lichen nitidus. Allergic contact dermatitis tends to respond fairly quickly to topical or systemic corticosteroids, unlike lichen nitidus. There are a few reports that consider lichen nitidus to be a variant of lichen planus, although they have different histopathologic findings. Lichen planus lesions are described as polygonal, pruritic, purple to pink papules most commonly seen on the wrists, lower back, and ankles. Lichen planus can be seen in patients with hepatitis C and may also occur secondary to medication.
Milia are small keratin cysts on the skin that are commonly seen in babies as primary milia and can be seen in older children secondary to trauma (commonly on the eyelids) or medications. Given their size and monomorphic appearance, they can sometimes be confused with lichen nitidus.
Lichen nitidus is often asymptomatic and the lesions resolve within a few months to years. Topical corticosteroids can be helpful to alleviate the symptoms in patients who present with pruritus. In more persistent and generalized cases, phototherapy, systemic corticosteroids, acitretin, isotretinoin, or cyclosporine can be considered.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Chu J and Lam JM. CMAJ. 2014 Dec 9;186(18):E688.
Lestringant G et al. Dermatology 1996;192:171-3.
Peterson JA et al. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2021 Aug 25;35(1):70-2.
Schwartz C and Goodman MB. “Lichen nitidus,” in StatPearls. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
An 11-year-old male with a prior history of atopic dermatitis as a young child, presents with 6 months of slightly itchy, small bumps on the wrists, face, arms, and legs. Has been treated with fluocinolone oil and hydrocortisone 2.5% for a month with no change in the lesions. Besides the use of topical corticosteroids, he has not been taking any other medications.
On physical examination he has multiple skin-colored, flat-topped papules that coalesce into plaques on the arms, legs, chest, and back (Photo 1). Koebner phenomenon was also seen on the knees and arms. There were no lesions in the mouth or on the nails.
Dome-Shaped Periorbital Papule
The Diagnosis: Endocrine Mucin-Producing Sweat Gland Carcinoma
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) is a rare cutaneous adnexal tumor that characteristically presents as slowgrowing, flesh-colored papules, nodules, or cystic lesions around the periorbital skin in elderly female patients.1 Histopathology of EMPSGCs reveals well-circumscribed multinodular dermal lesions that can be either cystic or solid and often are arranged in papillary and cribriform patterns (quiz image). Nests of uniform tumor cells are composed of small- to medium-sized epithelial cells with monomorphic nuclei showing fine to stippled chromatin.2 Histologically, EMPSGC resembles a solid papillary carcinoma of the breast, which is attributed to their common embryologic origin.3 Intracytoplasmic and extracellular mucin often are seen on hematoxylin and eosin staining.2 Variable immunohistochemical stain expression has been reported, including positive staining with synaptophysin and chromogranin. Other markers include cytokeratin CAM 5.2, epithelial membrane antigen, estrogen or progesterone receptors, and cytokeratin 7.4 Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma is thought to be a precursor to invasive neuroendocrine-type primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma has been associated with EMPSGC in approximately 35.7% of cases. Histologically, primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma that has transformed from EMPSGC would show an infiltration of tumor nests with desmoplastic stroma or mucin pools with clusters of tumor cells.2
Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare malignant tumor that often presents on the head and neck. It usually appears as a single, slowly growing subcutaneous nodule or multinodular plaque.5,6 Histologic features include basaloid cells in alternating tubular and cribriform patterns. The cribriform areas are composed of pseudoglandular adenoid spaces that contain mucin, basement membrane zone material, and cellular debris from necrotic neoplastic cells (Figure 1).7 Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma predominantly is dermal with extension to the subcutaneous tissue. True ductal structures that demonstrate decapitation secretion also may be present.7
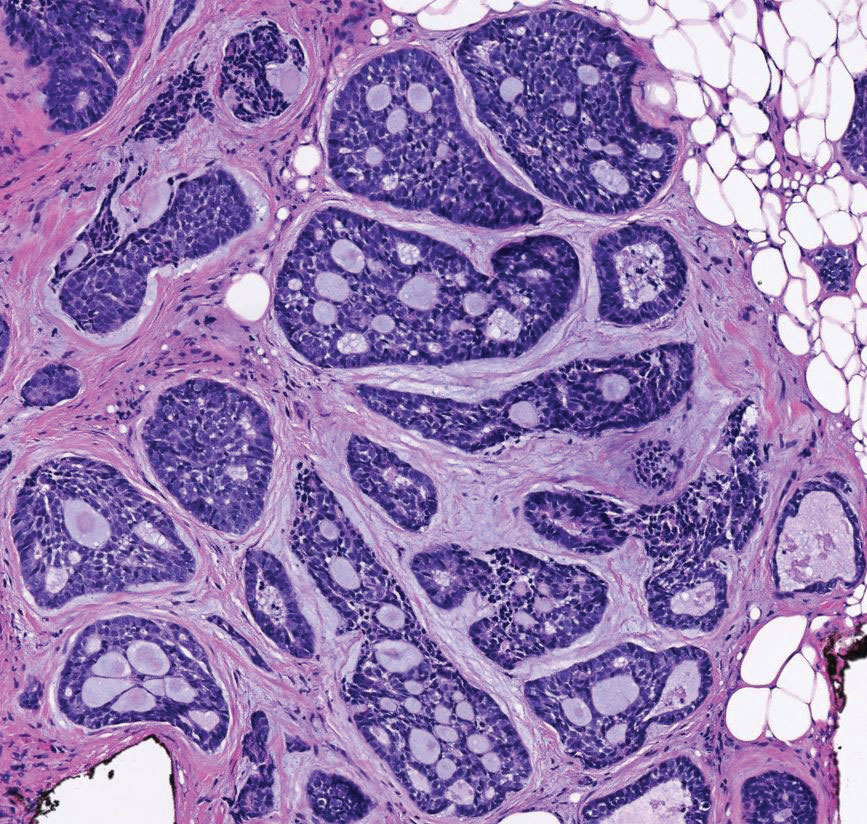
Basal cell carcinoma (adenoid type) presents as a pigmented or nonpigmented nodule or ulcer on sunexposed areas of the head and neck. Histopathology reveals basaloid cells surrounding islands of connective tissue resulting in a lacelike pattern (Figure 2). The lumina may contain a colloidal substance or amorphous granular material.8 The characteristic features of basal cell carcinomas, such as nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading cells, retraction of adjacent stroma, increased apoptosis and mitotic figures, and connection to the epidermis, can be helpful to distinguish basal cell carcinoma histologically from EMPSGC.2
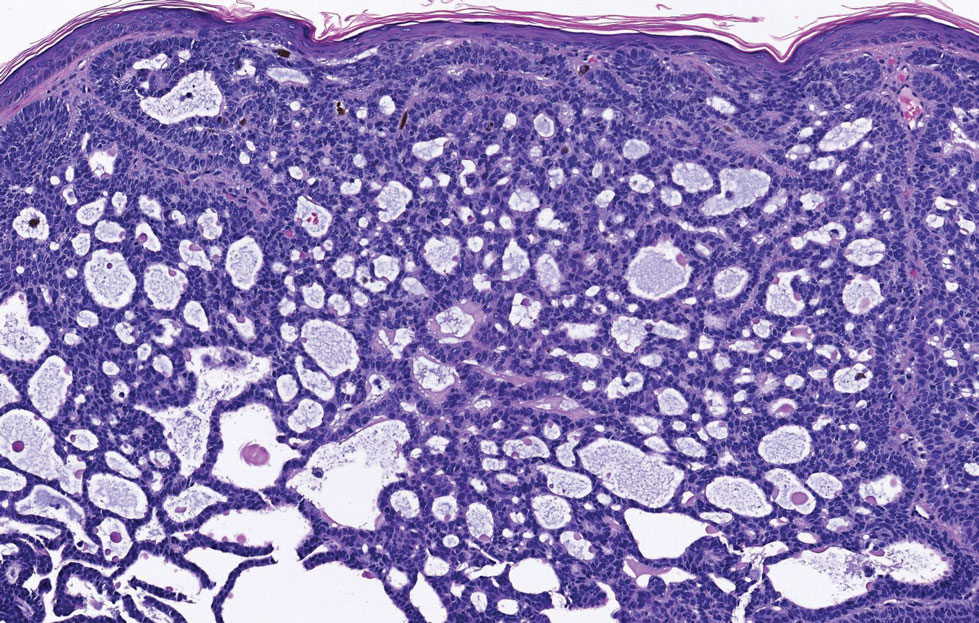
Apocrine hidrocystomas clinically present as round, flesh-colored, shiny or translucent, dome-shaped papules or nodules near the eyelid margin or lateral canthus.9 Histologically, they are composed of proliferating apocrine secretory coils with an epithelial side of cuboidal or columnar cells and a luminal side exhibiting decapitation secretion (Figure 3).2 An epidermal connection is absent.9 Apocrine hidrocystomas may exhibit complex architecture and papillary ductal hyperplasia that are difficult to distinguish from EMPSGC, especially if EMPSGC presents with cystic morphology. Apocrine cytomorphology and the lack of neuroendocrine marker expression and mucin production distinguish apocrine hidrocystomas. Furthermore, hidrocystomas infrequently demonstrate the nodular, solid, cribriform areas appreciated in EMPSGC.2
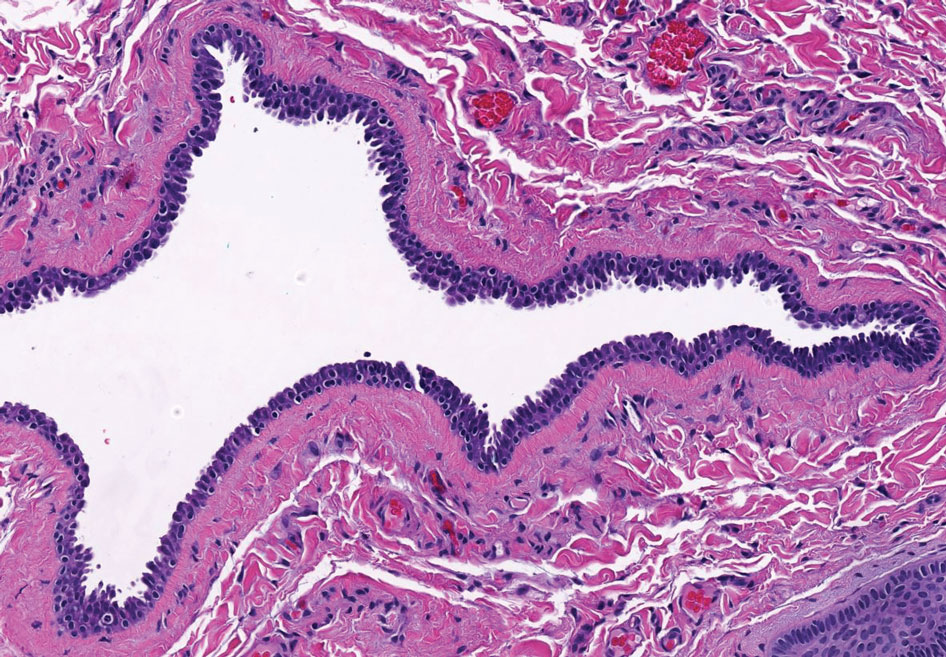
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a rare, slowly growing, locally aggressive sweat gland tumor that commonly presents as a flesh-colored to yellow papule, nodule, or plaque on the central face.10 Histopathologic examination reveals both eccrine and follicular differentiation. Keratin cysts, bland keratinocyte cords, and epithelium with ductal differentiation is observed in the superficial layers (Figure 4). Deep invasion into the subcutis and perineural invasion frequently is observed.
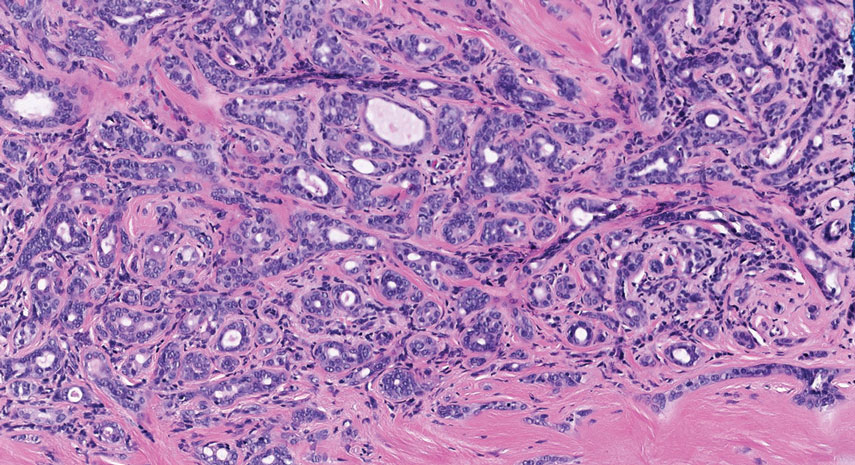
- Mulay K, Menon V, Lahane S, et al. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) of the eyelid: clinicopathologic features, immunohistochemical findings and review of literature. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1374-1377. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1745_18
- Au RTM, Bundele MM. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and associated primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:1156-1165. doi:10.1111/cup.13983
- Flieder A, Koerner FC, Pilch BZ, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: a cutaneous neoplasm analogous to solid papillary carcinoma of breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1501-1506. doi:10.1097/00000478-199712000-00014
- Shimizu I, Dufresne R, Robinson-Bostom L. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma. Cutis. 2014;93:47-49.
- Ahn CS, Sangüeza OP. Malignant sweat gland tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:53-71. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2018.09.002
- Tonev ID, Pirgova YS, Conev NV. Primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the skin with multiple local recurrences. Case Rep Oncol. 2015;8:251-255. doi:10.1159/000431082
- Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck—an update. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:652-661. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.005
- Tambe SA, Ghate SS, Jerajani HR. Adenoid type of basal cell carcinoma: rare histopathological variant at an unusual location. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:159. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.108080
- Kikuchi K, Fukunaga S, Inoue H, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the lower lip: a case report and literature review. Head Neck Pathol. 2014;8:117-121. doi:10.1007/s12105-013-0451-2
- Zito PM, Mazzoni T. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
The Diagnosis: Endocrine Mucin-Producing Sweat Gland Carcinoma
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) is a rare cutaneous adnexal tumor that characteristically presents as slowgrowing, flesh-colored papules, nodules, or cystic lesions around the periorbital skin in elderly female patients.1 Histopathology of EMPSGCs reveals well-circumscribed multinodular dermal lesions that can be either cystic or solid and often are arranged in papillary and cribriform patterns (quiz image). Nests of uniform tumor cells are composed of small- to medium-sized epithelial cells with monomorphic nuclei showing fine to stippled chromatin.2 Histologically, EMPSGC resembles a solid papillary carcinoma of the breast, which is attributed to their common embryologic origin.3 Intracytoplasmic and extracellular mucin often are seen on hematoxylin and eosin staining.2 Variable immunohistochemical stain expression has been reported, including positive staining with synaptophysin and chromogranin. Other markers include cytokeratin CAM 5.2, epithelial membrane antigen, estrogen or progesterone receptors, and cytokeratin 7.4 Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma is thought to be a precursor to invasive neuroendocrine-type primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma has been associated with EMPSGC in approximately 35.7% of cases. Histologically, primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma that has transformed from EMPSGC would show an infiltration of tumor nests with desmoplastic stroma or mucin pools with clusters of tumor cells.2
Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare malignant tumor that often presents on the head and neck. It usually appears as a single, slowly growing subcutaneous nodule or multinodular plaque.5,6 Histologic features include basaloid cells in alternating tubular and cribriform patterns. The cribriform areas are composed of pseudoglandular adenoid spaces that contain mucin, basement membrane zone material, and cellular debris from necrotic neoplastic cells (Figure 1).7 Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma predominantly is dermal with extension to the subcutaneous tissue. True ductal structures that demonstrate decapitation secretion also may be present.7

Basal cell carcinoma (adenoid type) presents as a pigmented or nonpigmented nodule or ulcer on sunexposed areas of the head and neck. Histopathology reveals basaloid cells surrounding islands of connective tissue resulting in a lacelike pattern (Figure 2). The lumina may contain a colloidal substance or amorphous granular material.8 The characteristic features of basal cell carcinomas, such as nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading cells, retraction of adjacent stroma, increased apoptosis and mitotic figures, and connection to the epidermis, can be helpful to distinguish basal cell carcinoma histologically from EMPSGC.2

Apocrine hidrocystomas clinically present as round, flesh-colored, shiny or translucent, dome-shaped papules or nodules near the eyelid margin or lateral canthus.9 Histologically, they are composed of proliferating apocrine secretory coils with an epithelial side of cuboidal or columnar cells and a luminal side exhibiting decapitation secretion (Figure 3).2 An epidermal connection is absent.9 Apocrine hidrocystomas may exhibit complex architecture and papillary ductal hyperplasia that are difficult to distinguish from EMPSGC, especially if EMPSGC presents with cystic morphology. Apocrine cytomorphology and the lack of neuroendocrine marker expression and mucin production distinguish apocrine hidrocystomas. Furthermore, hidrocystomas infrequently demonstrate the nodular, solid, cribriform areas appreciated in EMPSGC.2

Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a rare, slowly growing, locally aggressive sweat gland tumor that commonly presents as a flesh-colored to yellow papule, nodule, or plaque on the central face.10 Histopathologic examination reveals both eccrine and follicular differentiation. Keratin cysts, bland keratinocyte cords, and epithelium with ductal differentiation is observed in the superficial layers (Figure 4). Deep invasion into the subcutis and perineural invasion frequently is observed.

The Diagnosis: Endocrine Mucin-Producing Sweat Gland Carcinoma
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) is a rare cutaneous adnexal tumor that characteristically presents as slowgrowing, flesh-colored papules, nodules, or cystic lesions around the periorbital skin in elderly female patients.1 Histopathology of EMPSGCs reveals well-circumscribed multinodular dermal lesions that can be either cystic or solid and often are arranged in papillary and cribriform patterns (quiz image). Nests of uniform tumor cells are composed of small- to medium-sized epithelial cells with monomorphic nuclei showing fine to stippled chromatin.2 Histologically, EMPSGC resembles a solid papillary carcinoma of the breast, which is attributed to their common embryologic origin.3 Intracytoplasmic and extracellular mucin often are seen on hematoxylin and eosin staining.2 Variable immunohistochemical stain expression has been reported, including positive staining with synaptophysin and chromogranin. Other markers include cytokeratin CAM 5.2, epithelial membrane antigen, estrogen or progesterone receptors, and cytokeratin 7.4 Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma is thought to be a precursor to invasive neuroendocrine-type primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma has been associated with EMPSGC in approximately 35.7% of cases. Histologically, primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma that has transformed from EMPSGC would show an infiltration of tumor nests with desmoplastic stroma or mucin pools with clusters of tumor cells.2
Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare malignant tumor that often presents on the head and neck. It usually appears as a single, slowly growing subcutaneous nodule or multinodular plaque.5,6 Histologic features include basaloid cells in alternating tubular and cribriform patterns. The cribriform areas are composed of pseudoglandular adenoid spaces that contain mucin, basement membrane zone material, and cellular debris from necrotic neoplastic cells (Figure 1).7 Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma predominantly is dermal with extension to the subcutaneous tissue. True ductal structures that demonstrate decapitation secretion also may be present.7

Basal cell carcinoma (adenoid type) presents as a pigmented or nonpigmented nodule or ulcer on sunexposed areas of the head and neck. Histopathology reveals basaloid cells surrounding islands of connective tissue resulting in a lacelike pattern (Figure 2). The lumina may contain a colloidal substance or amorphous granular material.8 The characteristic features of basal cell carcinomas, such as nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading cells, retraction of adjacent stroma, increased apoptosis and mitotic figures, and connection to the epidermis, can be helpful to distinguish basal cell carcinoma histologically from EMPSGC.2

Apocrine hidrocystomas clinically present as round, flesh-colored, shiny or translucent, dome-shaped papules or nodules near the eyelid margin or lateral canthus.9 Histologically, they are composed of proliferating apocrine secretory coils with an epithelial side of cuboidal or columnar cells and a luminal side exhibiting decapitation secretion (Figure 3).2 An epidermal connection is absent.9 Apocrine hidrocystomas may exhibit complex architecture and papillary ductal hyperplasia that are difficult to distinguish from EMPSGC, especially if EMPSGC presents with cystic morphology. Apocrine cytomorphology and the lack of neuroendocrine marker expression and mucin production distinguish apocrine hidrocystomas. Furthermore, hidrocystomas infrequently demonstrate the nodular, solid, cribriform areas appreciated in EMPSGC.2

Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is a rare, slowly growing, locally aggressive sweat gland tumor that commonly presents as a flesh-colored to yellow papule, nodule, or plaque on the central face.10 Histopathologic examination reveals both eccrine and follicular differentiation. Keratin cysts, bland keratinocyte cords, and epithelium with ductal differentiation is observed in the superficial layers (Figure 4). Deep invasion into the subcutis and perineural invasion frequently is observed.

- Mulay K, Menon V, Lahane S, et al. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) of the eyelid: clinicopathologic features, immunohistochemical findings and review of literature. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1374-1377. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1745_18
- Au RTM, Bundele MM. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and associated primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:1156-1165. doi:10.1111/cup.13983
- Flieder A, Koerner FC, Pilch BZ, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: a cutaneous neoplasm analogous to solid papillary carcinoma of breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1501-1506. doi:10.1097/00000478-199712000-00014
- Shimizu I, Dufresne R, Robinson-Bostom L. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma. Cutis. 2014;93:47-49.
- Ahn CS, Sangüeza OP. Malignant sweat gland tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:53-71. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2018.09.002
- Tonev ID, Pirgova YS, Conev NV. Primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the skin with multiple local recurrences. Case Rep Oncol. 2015;8:251-255. doi:10.1159/000431082
- Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck—an update. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:652-661. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.005
- Tambe SA, Ghate SS, Jerajani HR. Adenoid type of basal cell carcinoma: rare histopathological variant at an unusual location. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:159. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.108080
- Kikuchi K, Fukunaga S, Inoue H, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the lower lip: a case report and literature review. Head Neck Pathol. 2014;8:117-121. doi:10.1007/s12105-013-0451-2
- Zito PM, Mazzoni T. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Mulay K, Menon V, Lahane S, et al. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) of the eyelid: clinicopathologic features, immunohistochemical findings and review of literature. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67:1374-1377. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1745_18
- Au RTM, Bundele MM. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and associated primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:1156-1165. doi:10.1111/cup.13983
- Flieder A, Koerner FC, Pilch BZ, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: a cutaneous neoplasm analogous to solid papillary carcinoma of breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1501-1506. doi:10.1097/00000478-199712000-00014
- Shimizu I, Dufresne R, Robinson-Bostom L. Endocrine mucinproducing sweat gland carcinoma. Cutis. 2014;93:47-49.
- Ahn CS, Sangüeza OP. Malignant sweat gland tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:53-71. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2018.09.002
- Tonev ID, Pirgova YS, Conev NV. Primary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the skin with multiple local recurrences. Case Rep Oncol. 2015;8:251-255. doi:10.1159/000431082
- Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck—an update. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:652-661. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.005
- Tambe SA, Ghate SS, Jerajani HR. Adenoid type of basal cell carcinoma: rare histopathological variant at an unusual location. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:159. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.108080
- Kikuchi K, Fukunaga S, Inoue H, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma of the lower lip: a case report and literature review. Head Neck Pathol. 2014;8:117-121. doi:10.1007/s12105-013-0451-2
- Zito PM, Mazzoni T. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
A 76-year-old woman presented with a slowly growing, asymptomatic, 5-mm, pink-brown, dome-shaped papule adjacent to the left lateral canthus of several years’ duration. Dermoscopic examination revealed fine linear peripheral blood vessels. The lesional cells were positive with cytokeratin 7, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, chromogranin, synaptophysin, and neuron-specific enolase. Cytokeratin 20 and p63 were negative, and the Ki-67 proliferative index was less than 5%.
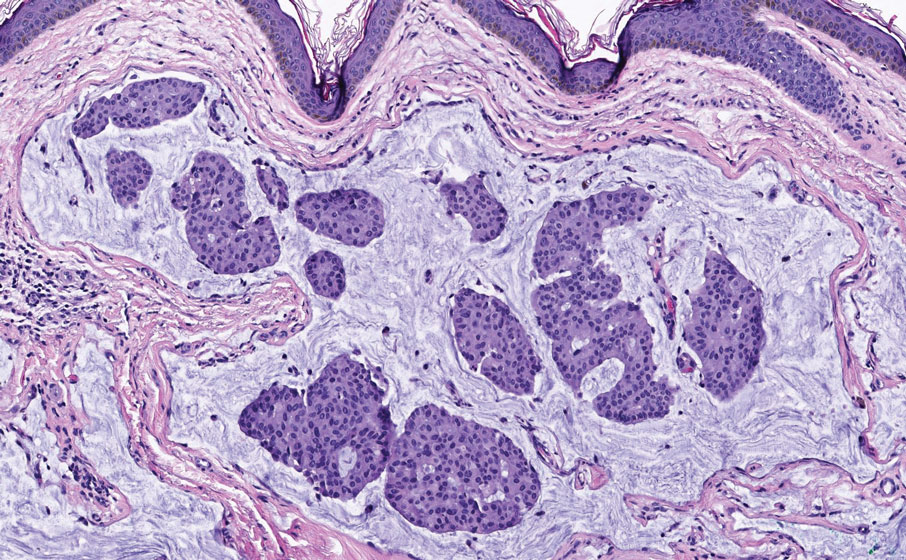
Fungal Osler Nodes Indicate Candidal Infective Endocarditis
To the Editor:
A 44-year-old woman presented with a low-grade fever (temperature, 38.0 °C) and painful acral lesions of 1 week’s duration. She had a history of hepatitis C viral infection and intravenous (IV) drug use, as well as polymicrobial infective endocarditis that involved the tricuspid and aortic valves; pathogenic organisms were identified via blood culture as Enterococcus faecalis, Serratia species, Streptococcus viridans, and Candida albicans. The patient had received a mechanical aortic valve and bioprosthetic tricuspid valve replacement 5 months prior with warfarin therapy and had completed a postsurgical 6-week course of high-dose micafungin. She reported that she had developed painful, violaceous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the left foot 2 weeks prior to presentation. Her symptoms improved with a short systemic steroid taper; however, within a week she developed new tender, erythematous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the right foot and the palmar surface of the left hand with associated lower extremity swelling. She denied other symptoms, including fever, chills, neurologic symptoms, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, hematuria, and hematochezia. Due to worsening cutaneous findings, the patient presented to the emergency department, prompting hospital admission for empiric antibacterial therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam for suspected infectious endocarditis. Dermatology was consulted after 1 day of antibacterial therapy without improvement to determine the etiology of the patient’s skin findings.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile with partially blanching violaceous to purpuric, tender, edematous papules on the left fourth and fifth finger pads, as well as scattered, painful, purpuric patches with stellate borders on the right plantar foot (Figure 1). Laboratory test results revealed mild anemia (hemoglobin, 11.9 g/dL [reference range, 12.0–15.0 g/dL], mild neutrophilia (neutrophils, 8.4×109/L [reference range, 1.9–7.9×109/L], elevated acute-phase reactants (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 71 mm/h [reference range, 0–20 mm/h]; C-reactive protein, 5.7 mg/dL [reference range, 0.0–0.5 mg/dL]), and positive hepatitis C virus antibody with an undetectable viral load. At the time of dermatologic evaluation, admission blood cultures and transthoracic echocardiogram were negative. Additionally, a transesophageal echocardiogram, limited by artifact from the mechanical aortic valve, was equivocal for valvular pathology. Subsequent ophthalmologic evaluation was negative for lesions associated with endocarditis, such as retinal hemorrhages.
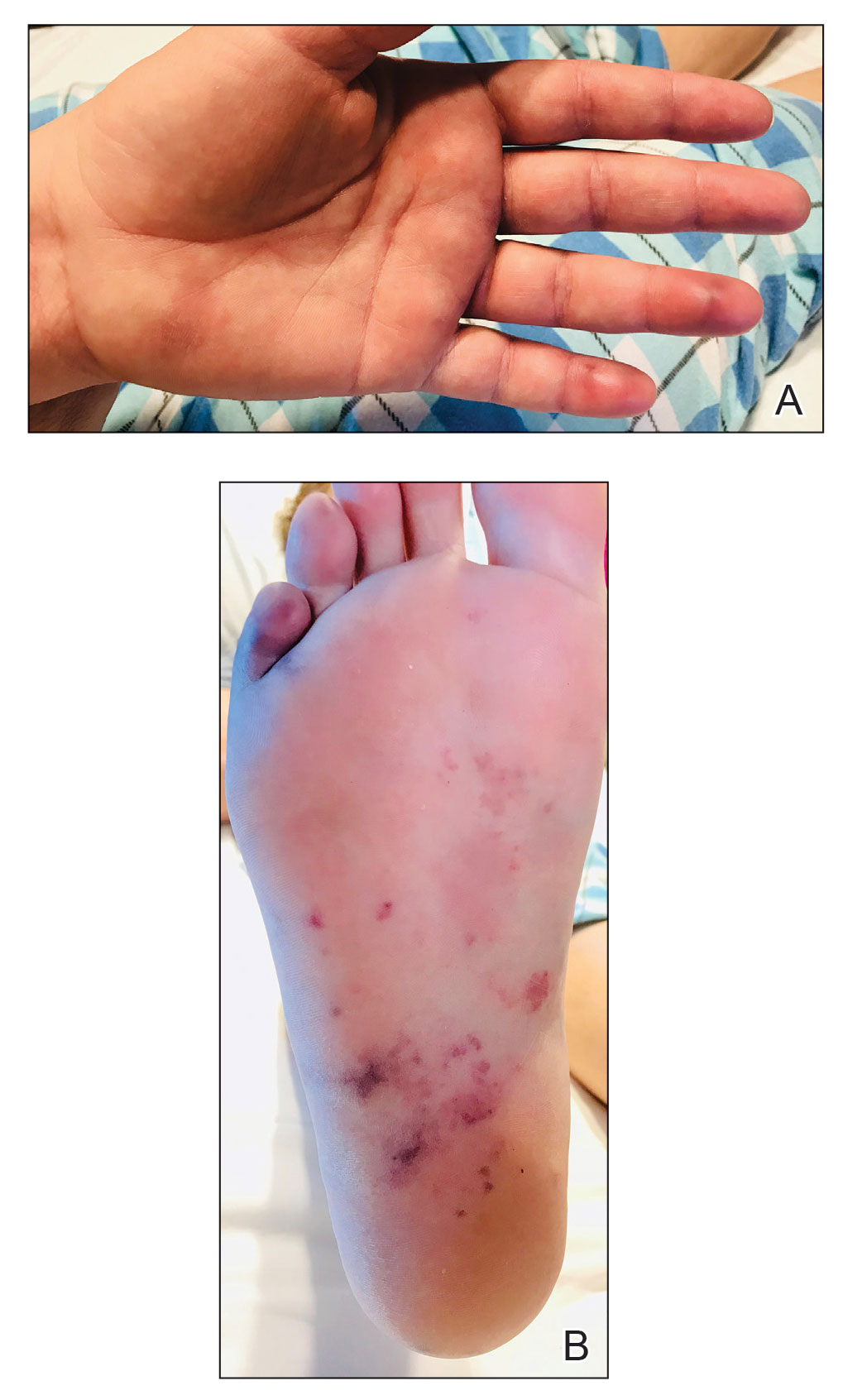
Punch biopsies of the left fourth finger pad were submitted for histopathologic analysis and tissue cultures. Histopathology demonstrated deep dermal perivascular neutrophilic inflammation with multiple intravascular thrombi, perivascular fibrin, and karyorrhectic debris (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stains revealed fungal spores with rare pseudohyphae within the thrombosed vascular spaces and the perivascular dermis, consistent with fungal septic emboli (Figure 3).
Empiric systemic antifungal coverage composed of IV liposomal amphotericin B and oral flucytosine was initiated, and the patient’s tender acral papules rapidly improved. Within 48 hours of biopsy, skin tissue culture confirmed the presence of C albicans. Four days after the preliminary dermatopathology report, confirmatory blood cultures resulted with pansensitive C albicans. Final tissue and blood cultures were negative for bacteria including mycobacteria. In addition to a 6-week course of IV amphotericin B and flucytosine, repeat surgical intervention was considered, and lifelong suppressive antifungal oral therapy was recommended. Unfortunately, the patient did not present for follow-up. Three months later, she presented to the emergency department with peritonitis; in the operating room, she was found to have ischemia of the entirety of the small and large intestines and died shortly thereafter.
Fungal endocarditis is rare, tending to develop in patient populations with particular risk factors such as immune compromise, structural heart defects or prosthetic valves, and IV drug use. Candida infective endocarditis (CIE) represents less than 2% of infective endocarditis cases and carries a high mortality rate (30%–80%).1-3 Diagnosis may be challenging, as the clinical presentation varies widely. Although some patients may present with classic features of infective endocarditis, including fever, cardiac murmurs, and positive blood cultures, many cases of infective endocarditis present with nonspecific symptoms, raising a broad clinical differential diagnosis. Delay in diagnosis, which is seen in 82% of patients with fungal endocarditis, may be attributed to the slow progression of symptoms, inconclusive cardiac imaging, or negative blood cultures seen in almost one-third of cases.2,3 The feared complication of systemic embolization via infective endocarditis may occur in up to one-half of cases, with the highest rates associated with staphylococcal or fungal pathogens.2 The risk for embolization in fungal endocarditis is independent of the size of the cardiac valve vegetations; accordingly, sequelae of embolic complications may arise despite negative cardiac imaging.4 Embolic complications, which typically are seen within the first 2 to 4 weeks of treatment, may serve as the presenting feature of endocarditis and may even occur after completion of antimicrobial therapy.
Detection of cutaneous manifestations of infective endocarditis, including Janeway lesions, Osler nodes, and splinter hemorrhages, may allow for earlier diagnosis. Despite eponymous recognition, Janeway lesions and Osler nodes are relatively uncommon manifestations of infective endocarditis and may be found in only 5% to 15% of cases.5 Biopsies of suspected Janeway lesions and Osler nodes may allow for recognition of relevant vascular pathology, identification of the causative pathogen, and strong support for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis.4-7
The initial photomicrograph of corresponding Janeway lesion histopathology was published by Kerr in 1955 and revealed dermal microabscesses posited to be secondary to bacterial emboli.8,9 Additional cases through the years have reported overlapping histopathologic features of Janeway lesions and Osler nodes, with the latter often defined by the presence of vasculitis.4 Although there appears to be ongoing debate and overlap between the 2 integumentary findings, a general consensus on differentiation takes into account both the clinical signs and symptoms as well as the histopathologic findings.10,11
Osler nodes present as tender, violaceous, subcutaneous nodules on the acral surfaces, usually on the pads of the fingers and toes.5 The pathogenesis involves the deposition of immune complexes as a sequela of vascular occlusion by microthrombi classically seen in the late phase of subacute endocarditis. Janeway lesions present as nontender erythematous macules on the acral surfaces and are thought to represent microthrombi with dermal microabscesses, more common in acute endocarditis. Our patient demonstrated features of both Osler nodes and Janeway lesions. Despite the presence of fungal thrombi—a pathophysiology closer to that of Janeway lesions—the clinical presentation of painful acral nodules affecting finger pads and histologic features of vasculitis may be better characterized as Osler nodes. Regardless of pathogenesis, these cutaneous findings serve as a minor clinical criterion in the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis when present.12
Candida infective endocarditis should be suspected in a patient with a history of valvular disease or prior infective endocarditis with fungemia, unexplained neurologic signs, or manifestations of peripheral embolization despite negative blood cultures.3 Particularly in the setting of negative cardiac imaging, recognition of CIE requires heightened diagnostic acumen and clinicopathologic correlation. Although culture and pathologic examination of valvular vegetations represents the gold standard for diagnosis of CIE, aspiration and culture of easily accessible septic emboli may provide rapid identification of the etiologic pathogen. In 1976, Alpert et al13 identified C albicans from an aspirated Osler node. Postmortem examination revealed extensive involvement of the homograft valve and aortic root with C albicans.13 Many other examples exist in the literature demonstrating matching pathogenic isolates from microbiologic cultures of skin and blood.4,9,14,15 Thadepalli and Francis7 investigated 26 cases of endocarditis in heroin users in which the admitting diagnosis was endocarditis in only 4 cases. The etiologic pathogen was aspirated from secondary sites of localized infections secondary to emboli, including cutaneous lesions in 10 of the cases. Gram stain and culture revealed the causative organism leading to the ultimate diagnosis and management in 17 of 26 patients with endocarditis.7
The incidence of fungal endocarditis is increasing, with a reported 67% of cases caused by nosocomial infection.1 Given the rising incidence of fungal endocarditis and its accompanying diagnostic difficulties, including frequently negative blood cultures and cardiac imaging, clinicians must perform careful skin examinations, employ judicious use of skin biopsy, and carefully correlate clinical and pathologic findings to improve recognition of this disease and guide patient care.
- Arnold CJ, Johnson M, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis: an observational cohort study with a focus on therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:2365. doi:10.1128/AAC.04867-14
- Chaudhary SC, Sawlani KK, Arora R, et al. Native aortic valve fungal endocarditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2012007144. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007144
- Ellis ME, Al-Abdely H, Sandridge A, et al. Fungal endocarditis: evidence in the world literature, 1965–1995. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:50-62. doi:10.1086/317550
- Gil MP, Velasco M, Botella R, et al. Janeway lesions: differential diagnosis with Osler’s nodes. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:673-674. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1993.tb04025.x
- Gomes RT, Tiberto LR, Bello VNM, et al. Dermatologic manifestations of infective endocarditis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:92-94.
- Yee JM. Osler’s nodes and the recognition of infective endocarditis: a lesion of diagnostic importance. South Med J. 1987;80:753-757.
- Thadepalli H, Francis C. Diagnostic clues in metastatic lesions of endocarditia in addicts. West J Med. 1978;128:1-5.
- Kerr A Jr. Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis. Charles C. Thomas; 1955.
- Kerr A Jr, Tan JS. Biopsies of the Janeway lesion of infective endocarditis. J Cutan Pathol. 1979;6:124-129. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1979.tb01113.x
- Marrie TJ. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Am J Med. 2008;121:105-106. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.035
- Gunson TH, Oliver GF. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Australas J Dermatol. 2007;48:251-255. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2007.00397.x
- Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK, et al. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am J Med. 1994;96:200-209.
- Alpert JS, Krous HF, Dalen JE, et al. Pathogenesis of Osler’s nodes. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85:471-473. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-471
- Cardullo AC, Silvers DN, Grossman ME. Janeway lesions and Osler’s nodes: a review of histopathologic findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1088-1090. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(90)70157-D
- Vinson RP, Chung A, Elston DM, et al. Septic microemboli in a Janeway lesion of bacterial endocarditis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:984-985. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(96)90125-5
To the Editor:
A 44-year-old woman presented with a low-grade fever (temperature, 38.0 °C) and painful acral lesions of 1 week’s duration. She had a history of hepatitis C viral infection and intravenous (IV) drug use, as well as polymicrobial infective endocarditis that involved the tricuspid and aortic valves; pathogenic organisms were identified via blood culture as Enterococcus faecalis, Serratia species, Streptococcus viridans, and Candida albicans. The patient had received a mechanical aortic valve and bioprosthetic tricuspid valve replacement 5 months prior with warfarin therapy and had completed a postsurgical 6-week course of high-dose micafungin. She reported that she had developed painful, violaceous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the left foot 2 weeks prior to presentation. Her symptoms improved with a short systemic steroid taper; however, within a week she developed new tender, erythematous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the right foot and the palmar surface of the left hand with associated lower extremity swelling. She denied other symptoms, including fever, chills, neurologic symptoms, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, hematuria, and hematochezia. Due to worsening cutaneous findings, the patient presented to the emergency department, prompting hospital admission for empiric antibacterial therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam for suspected infectious endocarditis. Dermatology was consulted after 1 day of antibacterial therapy without improvement to determine the etiology of the patient’s skin findings.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile with partially blanching violaceous to purpuric, tender, edematous papules on the left fourth and fifth finger pads, as well as scattered, painful, purpuric patches with stellate borders on the right plantar foot (Figure 1). Laboratory test results revealed mild anemia (hemoglobin, 11.9 g/dL [reference range, 12.0–15.0 g/dL], mild neutrophilia (neutrophils, 8.4×109/L [reference range, 1.9–7.9×109/L], elevated acute-phase reactants (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 71 mm/h [reference range, 0–20 mm/h]; C-reactive protein, 5.7 mg/dL [reference range, 0.0–0.5 mg/dL]), and positive hepatitis C virus antibody with an undetectable viral load. At the time of dermatologic evaluation, admission blood cultures and transthoracic echocardiogram were negative. Additionally, a transesophageal echocardiogram, limited by artifact from the mechanical aortic valve, was equivocal for valvular pathology. Subsequent ophthalmologic evaluation was negative for lesions associated with endocarditis, such as retinal hemorrhages.

Punch biopsies of the left fourth finger pad were submitted for histopathologic analysis and tissue cultures. Histopathology demonstrated deep dermal perivascular neutrophilic inflammation with multiple intravascular thrombi, perivascular fibrin, and karyorrhectic debris (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stains revealed fungal spores with rare pseudohyphae within the thrombosed vascular spaces and the perivascular dermis, consistent with fungal septic emboli (Figure 3).

Empiric systemic antifungal coverage composed of IV liposomal amphotericin B and oral flucytosine was initiated, and the patient’s tender acral papules rapidly improved. Within 48 hours of biopsy, skin tissue culture confirmed the presence of C albicans. Four days after the preliminary dermatopathology report, confirmatory blood cultures resulted with pansensitive C albicans. Final tissue and blood cultures were negative for bacteria including mycobacteria. In addition to a 6-week course of IV amphotericin B and flucytosine, repeat surgical intervention was considered, and lifelong suppressive antifungal oral therapy was recommended. Unfortunately, the patient did not present for follow-up. Three months later, she presented to the emergency department with peritonitis; in the operating room, she was found to have ischemia of the entirety of the small and large intestines and died shortly thereafter.

Fungal endocarditis is rare, tending to develop in patient populations with particular risk factors such as immune compromise, structural heart defects or prosthetic valves, and IV drug use. Candida infective endocarditis (CIE) represents less than 2% of infective endocarditis cases and carries a high mortality rate (30%–80%).1-3 Diagnosis may be challenging, as the clinical presentation varies widely. Although some patients may present with classic features of infective endocarditis, including fever, cardiac murmurs, and positive blood cultures, many cases of infective endocarditis present with nonspecific symptoms, raising a broad clinical differential diagnosis. Delay in diagnosis, which is seen in 82% of patients with fungal endocarditis, may be attributed to the slow progression of symptoms, inconclusive cardiac imaging, or negative blood cultures seen in almost one-third of cases.2,3 The feared complication of systemic embolization via infective endocarditis may occur in up to one-half of cases, with the highest rates associated with staphylococcal or fungal pathogens.2 The risk for embolization in fungal endocarditis is independent of the size of the cardiac valve vegetations; accordingly, sequelae of embolic complications may arise despite negative cardiac imaging.4 Embolic complications, which typically are seen within the first 2 to 4 weeks of treatment, may serve as the presenting feature of endocarditis and may even occur after completion of antimicrobial therapy.
Detection of cutaneous manifestations of infective endocarditis, including Janeway lesions, Osler nodes, and splinter hemorrhages, may allow for earlier diagnosis. Despite eponymous recognition, Janeway lesions and Osler nodes are relatively uncommon manifestations of infective endocarditis and may be found in only 5% to 15% of cases.5 Biopsies of suspected Janeway lesions and Osler nodes may allow for recognition of relevant vascular pathology, identification of the causative pathogen, and strong support for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis.4-7
The initial photomicrograph of corresponding Janeway lesion histopathology was published by Kerr in 1955 and revealed dermal microabscesses posited to be secondary to bacterial emboli.8,9 Additional cases through the years have reported overlapping histopathologic features of Janeway lesions and Osler nodes, with the latter often defined by the presence of vasculitis.4 Although there appears to be ongoing debate and overlap between the 2 integumentary findings, a general consensus on differentiation takes into account both the clinical signs and symptoms as well as the histopathologic findings.10,11
Osler nodes present as tender, violaceous, subcutaneous nodules on the acral surfaces, usually on the pads of the fingers and toes.5 The pathogenesis involves the deposition of immune complexes as a sequela of vascular occlusion by microthrombi classically seen in the late phase of subacute endocarditis. Janeway lesions present as nontender erythematous macules on the acral surfaces and are thought to represent microthrombi with dermal microabscesses, more common in acute endocarditis. Our patient demonstrated features of both Osler nodes and Janeway lesions. Despite the presence of fungal thrombi—a pathophysiology closer to that of Janeway lesions—the clinical presentation of painful acral nodules affecting finger pads and histologic features of vasculitis may be better characterized as Osler nodes. Regardless of pathogenesis, these cutaneous findings serve as a minor clinical criterion in the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis when present.12
Candida infective endocarditis should be suspected in a patient with a history of valvular disease or prior infective endocarditis with fungemia, unexplained neurologic signs, or manifestations of peripheral embolization despite negative blood cultures.3 Particularly in the setting of negative cardiac imaging, recognition of CIE requires heightened diagnostic acumen and clinicopathologic correlation. Although culture and pathologic examination of valvular vegetations represents the gold standard for diagnosis of CIE, aspiration and culture of easily accessible septic emboli may provide rapid identification of the etiologic pathogen. In 1976, Alpert et al13 identified C albicans from an aspirated Osler node. Postmortem examination revealed extensive involvement of the homograft valve and aortic root with C albicans.13 Many other examples exist in the literature demonstrating matching pathogenic isolates from microbiologic cultures of skin and blood.4,9,14,15 Thadepalli and Francis7 investigated 26 cases of endocarditis in heroin users in which the admitting diagnosis was endocarditis in only 4 cases. The etiologic pathogen was aspirated from secondary sites of localized infections secondary to emboli, including cutaneous lesions in 10 of the cases. Gram stain and culture revealed the causative organism leading to the ultimate diagnosis and management in 17 of 26 patients with endocarditis.7
The incidence of fungal endocarditis is increasing, with a reported 67% of cases caused by nosocomial infection.1 Given the rising incidence of fungal endocarditis and its accompanying diagnostic difficulties, including frequently negative blood cultures and cardiac imaging, clinicians must perform careful skin examinations, employ judicious use of skin biopsy, and carefully correlate clinical and pathologic findings to improve recognition of this disease and guide patient care.
To the Editor:
A 44-year-old woman presented with a low-grade fever (temperature, 38.0 °C) and painful acral lesions of 1 week’s duration. She had a history of hepatitis C viral infection and intravenous (IV) drug use, as well as polymicrobial infective endocarditis that involved the tricuspid and aortic valves; pathogenic organisms were identified via blood culture as Enterococcus faecalis, Serratia species, Streptococcus viridans, and Candida albicans. The patient had received a mechanical aortic valve and bioprosthetic tricuspid valve replacement 5 months prior with warfarin therapy and had completed a postsurgical 6-week course of high-dose micafungin. She reported that she had developed painful, violaceous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the left foot 2 weeks prior to presentation. Her symptoms improved with a short systemic steroid taper; however, within a week she developed new tender, erythematous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the right foot and the palmar surface of the left hand with associated lower extremity swelling. She denied other symptoms, including fever, chills, neurologic symptoms, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, hematuria, and hematochezia. Due to worsening cutaneous findings, the patient presented to the emergency department, prompting hospital admission for empiric antibacterial therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam for suspected infectious endocarditis. Dermatology was consulted after 1 day of antibacterial therapy without improvement to determine the etiology of the patient’s skin findings.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile with partially blanching violaceous to purpuric, tender, edematous papules on the left fourth and fifth finger pads, as well as scattered, painful, purpuric patches with stellate borders on the right plantar foot (Figure 1). Laboratory test results revealed mild anemia (hemoglobin, 11.9 g/dL [reference range, 12.0–15.0 g/dL], mild neutrophilia (neutrophils, 8.4×109/L [reference range, 1.9–7.9×109/L], elevated acute-phase reactants (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 71 mm/h [reference range, 0–20 mm/h]; C-reactive protein, 5.7 mg/dL [reference range, 0.0–0.5 mg/dL]), and positive hepatitis C virus antibody with an undetectable viral load. At the time of dermatologic evaluation, admission blood cultures and transthoracic echocardiogram were negative. Additionally, a transesophageal echocardiogram, limited by artifact from the mechanical aortic valve, was equivocal for valvular pathology. Subsequent ophthalmologic evaluation was negative for lesions associated with endocarditis, such as retinal hemorrhages.

Punch biopsies of the left fourth finger pad were submitted for histopathologic analysis and tissue cultures. Histopathology demonstrated deep dermal perivascular neutrophilic inflammation with multiple intravascular thrombi, perivascular fibrin, and karyorrhectic debris (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stains revealed fungal spores with rare pseudohyphae within the thrombosed vascular spaces and the perivascular dermis, consistent with fungal septic emboli (Figure 3).

Empiric systemic antifungal coverage composed of IV liposomal amphotericin B and oral flucytosine was initiated, and the patient’s tender acral papules rapidly improved. Within 48 hours of biopsy, skin tissue culture confirmed the presence of C albicans. Four days after the preliminary dermatopathology report, confirmatory blood cultures resulted with pansensitive C albicans. Final tissue and blood cultures were negative for bacteria including mycobacteria. In addition to a 6-week course of IV amphotericin B and flucytosine, repeat surgical intervention was considered, and lifelong suppressive antifungal oral therapy was recommended. Unfortunately, the patient did not present for follow-up. Three months later, she presented to the emergency department with peritonitis; in the operating room, she was found to have ischemia of the entirety of the small and large intestines and died shortly thereafter.

Fungal endocarditis is rare, tending to develop in patient populations with particular risk factors such as immune compromise, structural heart defects or prosthetic valves, and IV drug use. Candida infective endocarditis (CIE) represents less than 2% of infective endocarditis cases and carries a high mortality rate (30%–80%).1-3 Diagnosis may be challenging, as the clinical presentation varies widely. Although some patients may present with classic features of infective endocarditis, including fever, cardiac murmurs, and positive blood cultures, many cases of infective endocarditis present with nonspecific symptoms, raising a broad clinical differential diagnosis. Delay in diagnosis, which is seen in 82% of patients with fungal endocarditis, may be attributed to the slow progression of symptoms, inconclusive cardiac imaging, or negative blood cultures seen in almost one-third of cases.2,3 The feared complication of systemic embolization via infective endocarditis may occur in up to one-half of cases, with the highest rates associated with staphylococcal or fungal pathogens.2 The risk for embolization in fungal endocarditis is independent of the size of the cardiac valve vegetations; accordingly, sequelae of embolic complications may arise despite negative cardiac imaging.4 Embolic complications, which typically are seen within the first 2 to 4 weeks of treatment, may serve as the presenting feature of endocarditis and may even occur after completion of antimicrobial therapy.
Detection of cutaneous manifestations of infective endocarditis, including Janeway lesions, Osler nodes, and splinter hemorrhages, may allow for earlier diagnosis. Despite eponymous recognition, Janeway lesions and Osler nodes are relatively uncommon manifestations of infective endocarditis and may be found in only 5% to 15% of cases.5 Biopsies of suspected Janeway lesions and Osler nodes may allow for recognition of relevant vascular pathology, identification of the causative pathogen, and strong support for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis.4-7
The initial photomicrograph of corresponding Janeway lesion histopathology was published by Kerr in 1955 and revealed dermal microabscesses posited to be secondary to bacterial emboli.8,9 Additional cases through the years have reported overlapping histopathologic features of Janeway lesions and Osler nodes, with the latter often defined by the presence of vasculitis.4 Although there appears to be ongoing debate and overlap between the 2 integumentary findings, a general consensus on differentiation takes into account both the clinical signs and symptoms as well as the histopathologic findings.10,11
Osler nodes present as tender, violaceous, subcutaneous nodules on the acral surfaces, usually on the pads of the fingers and toes.5 The pathogenesis involves the deposition of immune complexes as a sequela of vascular occlusion by microthrombi classically seen in the late phase of subacute endocarditis. Janeway lesions present as nontender erythematous macules on the acral surfaces and are thought to represent microthrombi with dermal microabscesses, more common in acute endocarditis. Our patient demonstrated features of both Osler nodes and Janeway lesions. Despite the presence of fungal thrombi—a pathophysiology closer to that of Janeway lesions—the clinical presentation of painful acral nodules affecting finger pads and histologic features of vasculitis may be better characterized as Osler nodes. Regardless of pathogenesis, these cutaneous findings serve as a minor clinical criterion in the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis when present.12
Candida infective endocarditis should be suspected in a patient with a history of valvular disease or prior infective endocarditis with fungemia, unexplained neurologic signs, or manifestations of peripheral embolization despite negative blood cultures.3 Particularly in the setting of negative cardiac imaging, recognition of CIE requires heightened diagnostic acumen and clinicopathologic correlation. Although culture and pathologic examination of valvular vegetations represents the gold standard for diagnosis of CIE, aspiration and culture of easily accessible septic emboli may provide rapid identification of the etiologic pathogen. In 1976, Alpert et al13 identified C albicans from an aspirated Osler node. Postmortem examination revealed extensive involvement of the homograft valve and aortic root with C albicans.13 Many other examples exist in the literature demonstrating matching pathogenic isolates from microbiologic cultures of skin and blood.4,9,14,15 Thadepalli and Francis7 investigated 26 cases of endocarditis in heroin users in which the admitting diagnosis was endocarditis in only 4 cases. The etiologic pathogen was aspirated from secondary sites of localized infections secondary to emboli, including cutaneous lesions in 10 of the cases. Gram stain and culture revealed the causative organism leading to the ultimate diagnosis and management in 17 of 26 patients with endocarditis.7
The incidence of fungal endocarditis is increasing, with a reported 67% of cases caused by nosocomial infection.1 Given the rising incidence of fungal endocarditis and its accompanying diagnostic difficulties, including frequently negative blood cultures and cardiac imaging, clinicians must perform careful skin examinations, employ judicious use of skin biopsy, and carefully correlate clinical and pathologic findings to improve recognition of this disease and guide patient care.
- Arnold CJ, Johnson M, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis: an observational cohort study with a focus on therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:2365. doi:10.1128/AAC.04867-14
- Chaudhary SC, Sawlani KK, Arora R, et al. Native aortic valve fungal endocarditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2012007144. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007144
- Ellis ME, Al-Abdely H, Sandridge A, et al. Fungal endocarditis: evidence in the world literature, 1965–1995. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:50-62. doi:10.1086/317550
- Gil MP, Velasco M, Botella R, et al. Janeway lesions: differential diagnosis with Osler’s nodes. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:673-674. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1993.tb04025.x
- Gomes RT, Tiberto LR, Bello VNM, et al. Dermatologic manifestations of infective endocarditis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:92-94.
- Yee JM. Osler’s nodes and the recognition of infective endocarditis: a lesion of diagnostic importance. South Med J. 1987;80:753-757.
- Thadepalli H, Francis C. Diagnostic clues in metastatic lesions of endocarditia in addicts. West J Med. 1978;128:1-5.
- Kerr A Jr. Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis. Charles C. Thomas; 1955.
- Kerr A Jr, Tan JS. Biopsies of the Janeway lesion of infective endocarditis. J Cutan Pathol. 1979;6:124-129. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1979.tb01113.x
- Marrie TJ. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Am J Med. 2008;121:105-106. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.035
- Gunson TH, Oliver GF. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Australas J Dermatol. 2007;48:251-255. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2007.00397.x
- Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK, et al. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am J Med. 1994;96:200-209.
- Alpert JS, Krous HF, Dalen JE, et al. Pathogenesis of Osler’s nodes. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85:471-473. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-471
- Cardullo AC, Silvers DN, Grossman ME. Janeway lesions and Osler’s nodes: a review of histopathologic findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1088-1090. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(90)70157-D
- Vinson RP, Chung A, Elston DM, et al. Septic microemboli in a Janeway lesion of bacterial endocarditis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:984-985. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(96)90125-5
- Arnold CJ, Johnson M, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis: an observational cohort study with a focus on therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:2365. doi:10.1128/AAC.04867-14
- Chaudhary SC, Sawlani KK, Arora R, et al. Native aortic valve fungal endocarditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2012007144. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007144
- Ellis ME, Al-Abdely H, Sandridge A, et al. Fungal endocarditis: evidence in the world literature, 1965–1995. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:50-62. doi:10.1086/317550
- Gil MP, Velasco M, Botella R, et al. Janeway lesions: differential diagnosis with Osler’s nodes. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:673-674. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1993.tb04025.x
- Gomes RT, Tiberto LR, Bello VNM, et al. Dermatologic manifestations of infective endocarditis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:92-94.
- Yee JM. Osler’s nodes and the recognition of infective endocarditis: a lesion of diagnostic importance. South Med J. 1987;80:753-757.
- Thadepalli H, Francis C. Diagnostic clues in metastatic lesions of endocarditia in addicts. West J Med. 1978;128:1-5.
- Kerr A Jr. Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis. Charles C. Thomas; 1955.
- Kerr A Jr, Tan JS. Biopsies of the Janeway lesion of infective endocarditis. J Cutan Pathol. 1979;6:124-129. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1979.tb01113.x
- Marrie TJ. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Am J Med. 2008;121:105-106. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.035
- Gunson TH, Oliver GF. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Australas J Dermatol. 2007;48:251-255. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2007.00397.x
- Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK, et al. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am J Med. 1994;96:200-209.
- Alpert JS, Krous HF, Dalen JE, et al. Pathogenesis of Osler’s nodes. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85:471-473. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-471
- Cardullo AC, Silvers DN, Grossman ME. Janeway lesions and Osler’s nodes: a review of histopathologic findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1088-1090. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(90)70157-D
- Vinson RP, Chung A, Elston DM, et al. Septic microemboli in a Janeway lesion of bacterial endocarditis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:984-985. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(96)90125-5
PRACTICE POINTS
- Fungal infective endocarditis is rare, and diagnostic tests such as blood cultures and echocardiography may not detect the disease.
- The mortality rate of fungal endocarditis is high, with improved clinical outcomes if diagnosed and treated early.
- Clinicopathologic correlation between integumentary examination and skin biopsy findings may provide timely diagnosis, thereby guiding appropriate therapy.
Annular Plaques Overlying Hyperpigmented Telangiectatic Patches on the Neck
The Diagnosis: Annular Elastolytic Giant Cell Granuloma
Histologic examination of the shave biopsies showed a granulomatous infiltrate of small lymphocytes, histiocytes, and multinucleated giant cells. The giant cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, with several also containing fragments of basophilic elastic fibers (elastophagocytosis)(Figure). Additionally, the granulomas revealed no signs of necrosis, making an infectious source unlikely, and examination under polarized light was negative for foreign material. These clinical and histologic findings were diagnostic for annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG).
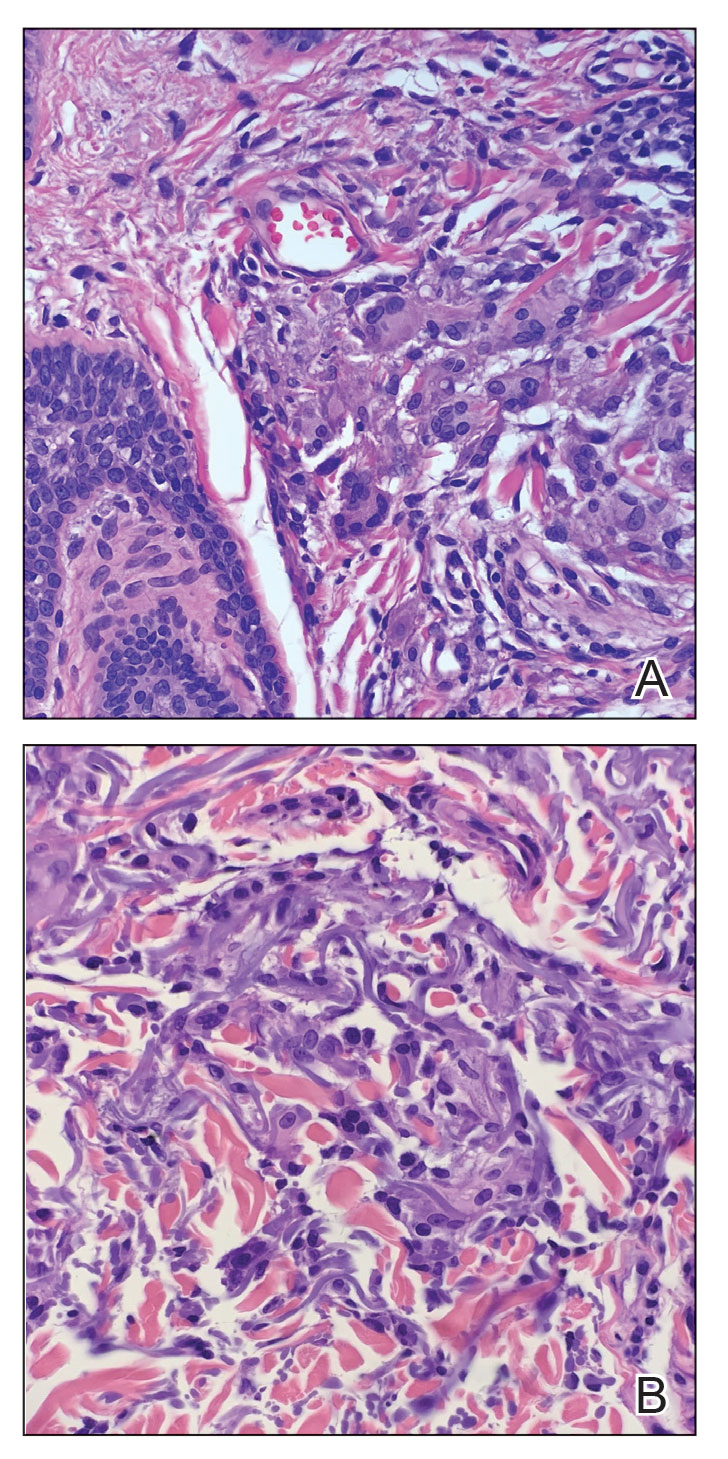
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma is a rare chronic inflammatory disorder that classically presents on sun-exposed skin as annular plaques with elevated borders and atrophic centers.1-4 Histologically, AEGCG is characterized by diffuse granulomatous infiltrates composed of multinucleated giant cells, histiocytes, and lymphocytes in the dermis, along with phagocytosis of elastic fibers by multinucleated giant cells.5 The underlying etiology and pathogenesis of AEGCG remains unknown.6
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma commonly affects females aged 35 to 75 years; however, cases have been reported in the male and pediatric patient populations.1,2 Documented cases are known to last from 1 month to 10 years.7,8 Although the mechanisms underlying the development of AEGCG remain to be elucidated, studies have determined that the skin disorder is associated with sarcoidosis, molluscum contagiosum, amyloidosis, diabetes mellitus, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.9 Diabetes mellitus is the most common comorbidity associated with AEGCG, and it is theorized that diabetes contributes to the increased incidence of AEGCG in this population by inducing damage to elastic fibers in the skin.10 One study that examined 50 cases of AEGCG found that 38 patients had serum glucose levels evaluated, with 8 cases being subsequently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and 6 cases with apparent impaired glucose tolerance, indicating that 37% of the sample population with AEGCG who were evaluated for metabolic disease were found to have definitive or latent type 2 diabetes mellitus.11 Although AEGCG is a rare disorder, a substantial number of patients diagnosed with AEGCG also have diabetes mellitus, making it important to consider screening all patients with AEGCG for diabetes given the ease and widely available resources to check glucose levels.
Actinic granuloma, granuloma annulare, atypical facial necrobiosis lipoidica, granuloma multiforme, secondary syphilis, tinea corporis, and erythema annulare centrifugum most commonly are included in the differential diagnosis with AEGCG; histopathology is the key determinant in discerning between these conditions.12 Our patient presented with typical annular plaques overlying hyperpigmented telangiectatic patches. With known type 2 diabetes mellitus and the clinical findings, granuloma annulare, erythema annulare centrifugum, and AEGCG remained high on the differential.
No standard of care exists for AEGCG due to its rare nature and tendency to spontaneously resolve. The most common first-line treatment includes topical and intralesional steroids, topical pimecrolimus, and the use of sunscreen and other sun-protective measures. UV radiation, specifically UVA, has been determined to be a causal factor for AEGCG by changing the antigenicity of elastic fibers and producing an immune response in individuals with fair skin.13 Further, resistant cases of AEGCG successfully have been treated with cyclosporine, systemic steroids, antimalarials, dapsone, and oral retinoids.14,15 Some studies reported partial regression or full resolution with topical tretinoin; adalimumab; clobetasol ointment; or a combination of corticosteroids, antihistamines, and hydroxychloroquine.2 Only 1 case series using sulfasalazine reported worsening symptoms after treatment initiation.16 Our patient deferred systemic medications and was treated with 4 weeks of topical triamcinolone followed by 4 weeks of topical tacrolimus with minimal improvement. At the time of diagnosis, our patient also was encouraged to use sun-protective measures. At 6-month follow-up, the lesions remained stable, and the decision was made to continue with photoprotection.
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456. doi:10.7759/cureus.11456
- Chen WT, Hsiao PF, Wu YH. Spectrum and clinical variants of giant cell elastolytic granuloma. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:738-745. doi:10.1111/ijd.13502
- Raposo I, Mota F, Lobo I, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a “visible” diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt9rq3j927
- Klemke CD, Siebold D, Dippel E, et al. Generalised annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Dermatology. 2003;207:420-422. doi:10.1159/000074132
- Hassan R, Arunprasath P, Padmavathy L, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in association with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:107-110. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.178087
- Kaya Erdog˘ an H, Arık D, Acer E, et al. Clinicopathological features of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma patients. Turkish J Dermatol. 2018;12:85-89.
- Can B, Kavala M, Türkog˘ lu Z, et al. Successful treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with hydroxychloroquine. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:509-511. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2011.04941.x
- Arora S, Malik A, Patil C, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a report of 10 cases. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6(suppl 1):S17-S20. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.171055
- Doulaveri G, Tsagroni E, Giannadaki M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in a 70-year-old woman. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:290-291. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01767.x
- Marmon S, O’Reilly KE, Fischer M, et al. Papular variant of annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:23.
- Aso Y, Izaki S, Teraki Y. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the Japanese literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36:917-919. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-2230.2011.04094.x
- Liu X, Zhang W, Liu Y, et al. A case of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with syphilis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018; 10:158-161. doi:10.1159/000489910
- Gutiérrez-González E, Pereiro M Jr, Toribio J. Elastolytic actinic giant cell granuloma. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:331-341. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.002
- de Oliveira FL, de Barros Silveira LK, Machado Ade M, et al. Hybrid clinical and histopathological pattern in annular lesions: an overlap between annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma and granuloma annulare? Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2012;2012:102915. doi:10.1155/2012/102915
- Wagenseller A, Larocca C, Vashi NA. Treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with topical tretinoin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:699-700.
- Yang YW, Lehrer MD, Mangold AR, et al. Treatment of granuloma annulare and related granulomatous diseases with sulphasalazine: a series of 16 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:211-215. doi:10.1111/jdv.16356
The Diagnosis: Annular Elastolytic Giant Cell Granuloma
Histologic examination of the shave biopsies showed a granulomatous infiltrate of small lymphocytes, histiocytes, and multinucleated giant cells. The giant cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, with several also containing fragments of basophilic elastic fibers (elastophagocytosis)(Figure). Additionally, the granulomas revealed no signs of necrosis, making an infectious source unlikely, and examination under polarized light was negative for foreign material. These clinical and histologic findings were diagnostic for annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG).

Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma is a rare chronic inflammatory disorder that classically presents on sun-exposed skin as annular plaques with elevated borders and atrophic centers.1-4 Histologically, AEGCG is characterized by diffuse granulomatous infiltrates composed of multinucleated giant cells, histiocytes, and lymphocytes in the dermis, along with phagocytosis of elastic fibers by multinucleated giant cells.5 The underlying etiology and pathogenesis of AEGCG remains unknown.6
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma commonly affects females aged 35 to 75 years; however, cases have been reported in the male and pediatric patient populations.1,2 Documented cases are known to last from 1 month to 10 years.7,8 Although the mechanisms underlying the development of AEGCG remain to be elucidated, studies have determined that the skin disorder is associated with sarcoidosis, molluscum contagiosum, amyloidosis, diabetes mellitus, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.9 Diabetes mellitus is the most common comorbidity associated with AEGCG, and it is theorized that diabetes contributes to the increased incidence of AEGCG in this population by inducing damage to elastic fibers in the skin.10 One study that examined 50 cases of AEGCG found that 38 patients had serum glucose levels evaluated, with 8 cases being subsequently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and 6 cases with apparent impaired glucose tolerance, indicating that 37% of the sample population with AEGCG who were evaluated for metabolic disease were found to have definitive or latent type 2 diabetes mellitus.11 Although AEGCG is a rare disorder, a substantial number of patients diagnosed with AEGCG also have diabetes mellitus, making it important to consider screening all patients with AEGCG for diabetes given the ease and widely available resources to check glucose levels.
Actinic granuloma, granuloma annulare, atypical facial necrobiosis lipoidica, granuloma multiforme, secondary syphilis, tinea corporis, and erythema annulare centrifugum most commonly are included in the differential diagnosis with AEGCG; histopathology is the key determinant in discerning between these conditions.12 Our patient presented with typical annular plaques overlying hyperpigmented telangiectatic patches. With known type 2 diabetes mellitus and the clinical findings, granuloma annulare, erythema annulare centrifugum, and AEGCG remained high on the differential.
No standard of care exists for AEGCG due to its rare nature and tendency to spontaneously resolve. The most common first-line treatment includes topical and intralesional steroids, topical pimecrolimus, and the use of sunscreen and other sun-protective measures. UV radiation, specifically UVA, has been determined to be a causal factor for AEGCG by changing the antigenicity of elastic fibers and producing an immune response in individuals with fair skin.13 Further, resistant cases of AEGCG successfully have been treated with cyclosporine, systemic steroids, antimalarials, dapsone, and oral retinoids.14,15 Some studies reported partial regression or full resolution with topical tretinoin; adalimumab; clobetasol ointment; or a combination of corticosteroids, antihistamines, and hydroxychloroquine.2 Only 1 case series using sulfasalazine reported worsening symptoms after treatment initiation.16 Our patient deferred systemic medications and was treated with 4 weeks of topical triamcinolone followed by 4 weeks of topical tacrolimus with minimal improvement. At the time of diagnosis, our patient also was encouraged to use sun-protective measures. At 6-month follow-up, the lesions remained stable, and the decision was made to continue with photoprotection.
The Diagnosis: Annular Elastolytic Giant Cell Granuloma
Histologic examination of the shave biopsies showed a granulomatous infiltrate of small lymphocytes, histiocytes, and multinucleated giant cells. The giant cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, with several also containing fragments of basophilic elastic fibers (elastophagocytosis)(Figure). Additionally, the granulomas revealed no signs of necrosis, making an infectious source unlikely, and examination under polarized light was negative for foreign material. These clinical and histologic findings were diagnostic for annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG).

Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma is a rare chronic inflammatory disorder that classically presents on sun-exposed skin as annular plaques with elevated borders and atrophic centers.1-4 Histologically, AEGCG is characterized by diffuse granulomatous infiltrates composed of multinucleated giant cells, histiocytes, and lymphocytes in the dermis, along with phagocytosis of elastic fibers by multinucleated giant cells.5 The underlying etiology and pathogenesis of AEGCG remains unknown.6
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma commonly affects females aged 35 to 75 years; however, cases have been reported in the male and pediatric patient populations.1,2 Documented cases are known to last from 1 month to 10 years.7,8 Although the mechanisms underlying the development of AEGCG remain to be elucidated, studies have determined that the skin disorder is associated with sarcoidosis, molluscum contagiosum, amyloidosis, diabetes mellitus, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.9 Diabetes mellitus is the most common comorbidity associated with AEGCG, and it is theorized that diabetes contributes to the increased incidence of AEGCG in this population by inducing damage to elastic fibers in the skin.10 One study that examined 50 cases of AEGCG found that 38 patients had serum glucose levels evaluated, with 8 cases being subsequently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and 6 cases with apparent impaired glucose tolerance, indicating that 37% of the sample population with AEGCG who were evaluated for metabolic disease were found to have definitive or latent type 2 diabetes mellitus.11 Although AEGCG is a rare disorder, a substantial number of patients diagnosed with AEGCG also have diabetes mellitus, making it important to consider screening all patients with AEGCG for diabetes given the ease and widely available resources to check glucose levels.
Actinic granuloma, granuloma annulare, atypical facial necrobiosis lipoidica, granuloma multiforme, secondary syphilis, tinea corporis, and erythema annulare centrifugum most commonly are included in the differential diagnosis with AEGCG; histopathology is the key determinant in discerning between these conditions.12 Our patient presented with typical annular plaques overlying hyperpigmented telangiectatic patches. With known type 2 diabetes mellitus and the clinical findings, granuloma annulare, erythema annulare centrifugum, and AEGCG remained high on the differential.
No standard of care exists for AEGCG due to its rare nature and tendency to spontaneously resolve. The most common first-line treatment includes topical and intralesional steroids, topical pimecrolimus, and the use of sunscreen and other sun-protective measures. UV radiation, specifically UVA, has been determined to be a causal factor for AEGCG by changing the antigenicity of elastic fibers and producing an immune response in individuals with fair skin.13 Further, resistant cases of AEGCG successfully have been treated with cyclosporine, systemic steroids, antimalarials, dapsone, and oral retinoids.14,15 Some studies reported partial regression or full resolution with topical tretinoin; adalimumab; clobetasol ointment; or a combination of corticosteroids, antihistamines, and hydroxychloroquine.2 Only 1 case series using sulfasalazine reported worsening symptoms after treatment initiation.16 Our patient deferred systemic medications and was treated with 4 weeks of topical triamcinolone followed by 4 weeks of topical tacrolimus with minimal improvement. At the time of diagnosis, our patient also was encouraged to use sun-protective measures. At 6-month follow-up, the lesions remained stable, and the decision was made to continue with photoprotection.
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456. doi:10.7759/cureus.11456
- Chen WT, Hsiao PF, Wu YH. Spectrum and clinical variants of giant cell elastolytic granuloma. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:738-745. doi:10.1111/ijd.13502
- Raposo I, Mota F, Lobo I, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a “visible” diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt9rq3j927
- Klemke CD, Siebold D, Dippel E, et al. Generalised annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Dermatology. 2003;207:420-422. doi:10.1159/000074132
- Hassan R, Arunprasath P, Padmavathy L, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in association with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:107-110. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.178087
- Kaya Erdog˘ an H, Arık D, Acer E, et al. Clinicopathological features of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma patients. Turkish J Dermatol. 2018;12:85-89.
- Can B, Kavala M, Türkog˘ lu Z, et al. Successful treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with hydroxychloroquine. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:509-511. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2011.04941.x
- Arora S, Malik A, Patil C, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a report of 10 cases. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6(suppl 1):S17-S20. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.171055
- Doulaveri G, Tsagroni E, Giannadaki M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in a 70-year-old woman. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:290-291. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01767.x
- Marmon S, O’Reilly KE, Fischer M, et al. Papular variant of annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:23.
- Aso Y, Izaki S, Teraki Y. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the Japanese literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36:917-919. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-2230.2011.04094.x
- Liu X, Zhang W, Liu Y, et al. A case of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with syphilis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018; 10:158-161. doi:10.1159/000489910
- Gutiérrez-González E, Pereiro M Jr, Toribio J. Elastolytic actinic giant cell granuloma. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:331-341. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.002
- de Oliveira FL, de Barros Silveira LK, Machado Ade M, et al. Hybrid clinical and histopathological pattern in annular lesions: an overlap between annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma and granuloma annulare? Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2012;2012:102915. doi:10.1155/2012/102915
- Wagenseller A, Larocca C, Vashi NA. Treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with topical tretinoin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:699-700.
- Yang YW, Lehrer MD, Mangold AR, et al. Treatment of granuloma annulare and related granulomatous diseases with sulphasalazine: a series of 16 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:211-215. doi:10.1111/jdv.16356
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456. doi:10.7759/cureus.11456
- Chen WT, Hsiao PF, Wu YH. Spectrum and clinical variants of giant cell elastolytic granuloma. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:738-745. doi:10.1111/ijd.13502
- Raposo I, Mota F, Lobo I, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a “visible” diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt9rq3j927
- Klemke CD, Siebold D, Dippel E, et al. Generalised annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Dermatology. 2003;207:420-422. doi:10.1159/000074132
- Hassan R, Arunprasath P, Padmavathy L, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in association with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:107-110. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.178087
- Kaya Erdog˘ an H, Arık D, Acer E, et al. Clinicopathological features of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma patients. Turkish J Dermatol. 2018;12:85-89.
- Can B, Kavala M, Türkog˘ lu Z, et al. Successful treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with hydroxychloroquine. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:509-511. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2011.04941.x
- Arora S, Malik A, Patil C, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma: a report of 10 cases. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6(suppl 1):S17-S20. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.171055
- Doulaveri G, Tsagroni E, Giannadaki M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma in a 70-year-old woman. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:290-291. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01767.x
- Marmon S, O’Reilly KE, Fischer M, et al. Papular variant of annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:23.
- Aso Y, Izaki S, Teraki Y. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the Japanese literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011;36:917-919. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-2230.2011.04094.x
- Liu X, Zhang W, Liu Y, et al. A case of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma associated with syphilis. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018; 10:158-161. doi:10.1159/000489910
- Gutiérrez-González E, Pereiro M Jr, Toribio J. Elastolytic actinic giant cell granuloma. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:331-341. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.002
- de Oliveira FL, de Barros Silveira LK, Machado Ade M, et al. Hybrid clinical and histopathological pattern in annular lesions: an overlap between annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma and granuloma annulare? Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2012;2012:102915. doi:10.1155/2012/102915
- Wagenseller A, Larocca C, Vashi NA. Treatment of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma with topical tretinoin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:699-700.
- Yang YW, Lehrer MD, Mangold AR, et al. Treatment of granuloma annulare and related granulomatous diseases with sulphasalazine: a series of 16 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:211-215. doi:10.1111/jdv.16356
A 58-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, nephrolithiasis, hypovitaminosis D, and hypercholesterolemia presented to our dermatology clinic for a follow-up total-body skin examination after a prior diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma on the vertex of the scalp. Physical examination revealed extensive photodamage and annular plaques overlying hyperpigmented telangiectatic patches on the dorsal portion of the neck. The eruption persisted for 1 year and failed to improve with clotrimazole cream. His medications included simvastatin, metformin, chlorthalidone, vitamin D, and tamsulosin. Two shave biopsies from the posterior neck were performed.

How should PRAME be used to evaluate melanocytic lesions?
SAN DIEGO – , according to Cora Humberson, MD.
“I’m a fan, but there are issues with it,” Dr. Humberson, dermatopathology coordinator in the department of pathology at Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “It’s all in how you use it.”
PRAME is part of the cancer/testis (CT) antigens, of which more than 40 have now been identified. They are encoded by genes that are normally expressed only in the human germ line, but are also expressed in various tumor types, including melanoma and carcinomas of the bladder, lung, and liver. “The biological function of these antigens is not fully understood, but they may act as a repressor of retinoic acid, potentially inhibiting differentiation, inhibiting proliferation arrest – things that we associate with malignancy,” she said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center. “These immunogenic proteins are being pursued as targets for therapeutic cancer vaccines,” she noted.
CT antigens are also being evaluated for their role in oncogenesis, she added. Recapitulation of portions of the germline gene-expression might contribute characteristic features to the neoplastic phenotype, including immortality, invasiveness, immune evasion, and metastatic capacity.
According to Dr. Humberson, PRAME can be used to differentiate comingled nevus and melanoma, to distinguish between nevoid melanoma and nevus, and for melanoma margin assessment in sun-damaged skin. One potential pitfall is that sun-damaged melanocytes may express PRAME. “The older the person and the more sun damage [they have], the more likely you are to see this, but the melanocytes won’t be grouped, they’ll be scattered,” she said.
Another pitfall is that less than 15% of nevi may express PRAME. “PRAME can be expressed in scars, so if you’re looking at a spindle cell lesion, be aware that you might be looking at a scar if you’re seeing PRAME expression,” she added. She also noted that PRAME immunohistochemistry (IHC) expression is not a prognostic biomarker in thin melanomas.
If fewer than 25% of cells in a melanocytic lesion express PRAME, most published assessments of PRAME IHC favor nevi as the diagnosis. “If more than 75% are expressing it, it favors melanoma,” Dr. Humberson said. “There’s a big category in between. It’s not that 30% is more likely benign or that 60% is more likely malignant; you can’t really depend upon [PRAME] if you’re in this range.”
A diagnostic accuracy study found that when more than 75% of cells express PRAME, the marker has a sensitivity of 0.63 and a specificity of 0.97.
Selected PRAME-related published references she recommended include: J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48(9):1115-23; Diagnostics. 2022 Sep 9; 12(9):2197, and J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49(9):829-32.
Dr. Humberson reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – , according to Cora Humberson, MD.
“I’m a fan, but there are issues with it,” Dr. Humberson, dermatopathology coordinator in the department of pathology at Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “It’s all in how you use it.”
PRAME is part of the cancer/testis (CT) antigens, of which more than 40 have now been identified. They are encoded by genes that are normally expressed only in the human germ line, but are also expressed in various tumor types, including melanoma and carcinomas of the bladder, lung, and liver. “The biological function of these antigens is not fully understood, but they may act as a repressor of retinoic acid, potentially inhibiting differentiation, inhibiting proliferation arrest – things that we associate with malignancy,” she said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center. “These immunogenic proteins are being pursued as targets for therapeutic cancer vaccines,” she noted.
CT antigens are also being evaluated for their role in oncogenesis, she added. Recapitulation of portions of the germline gene-expression might contribute characteristic features to the neoplastic phenotype, including immortality, invasiveness, immune evasion, and metastatic capacity.
According to Dr. Humberson, PRAME can be used to differentiate comingled nevus and melanoma, to distinguish between nevoid melanoma and nevus, and for melanoma margin assessment in sun-damaged skin. One potential pitfall is that sun-damaged melanocytes may express PRAME. “The older the person and the more sun damage [they have], the more likely you are to see this, but the melanocytes won’t be grouped, they’ll be scattered,” she said.
Another pitfall is that less than 15% of nevi may express PRAME. “PRAME can be expressed in scars, so if you’re looking at a spindle cell lesion, be aware that you might be looking at a scar if you’re seeing PRAME expression,” she added. She also noted that PRAME immunohistochemistry (IHC) expression is not a prognostic biomarker in thin melanomas.
If fewer than 25% of cells in a melanocytic lesion express PRAME, most published assessments of PRAME IHC favor nevi as the diagnosis. “If more than 75% are expressing it, it favors melanoma,” Dr. Humberson said. “There’s a big category in between. It’s not that 30% is more likely benign or that 60% is more likely malignant; you can’t really depend upon [PRAME] if you’re in this range.”
A diagnostic accuracy study found that when more than 75% of cells express PRAME, the marker has a sensitivity of 0.63 and a specificity of 0.97.
Selected PRAME-related published references she recommended include: J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48(9):1115-23; Diagnostics. 2022 Sep 9; 12(9):2197, and J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49(9):829-32.
Dr. Humberson reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – , according to Cora Humberson, MD.
“I’m a fan, but there are issues with it,” Dr. Humberson, dermatopathology coordinator in the department of pathology at Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center, San Diego, said at the annual Cutaneous Malignancy Update. “It’s all in how you use it.”
PRAME is part of the cancer/testis (CT) antigens, of which more than 40 have now been identified. They are encoded by genes that are normally expressed only in the human germ line, but are also expressed in various tumor types, including melanoma and carcinomas of the bladder, lung, and liver. “The biological function of these antigens is not fully understood, but they may act as a repressor of retinoic acid, potentially inhibiting differentiation, inhibiting proliferation arrest – things that we associate with malignancy,” she said at the meeting, which was hosted by Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center. “These immunogenic proteins are being pursued as targets for therapeutic cancer vaccines,” she noted.
CT antigens are also being evaluated for their role in oncogenesis, she added. Recapitulation of portions of the germline gene-expression might contribute characteristic features to the neoplastic phenotype, including immortality, invasiveness, immune evasion, and metastatic capacity.
According to Dr. Humberson, PRAME can be used to differentiate comingled nevus and melanoma, to distinguish between nevoid melanoma and nevus, and for melanoma margin assessment in sun-damaged skin. One potential pitfall is that sun-damaged melanocytes may express PRAME. “The older the person and the more sun damage [they have], the more likely you are to see this, but the melanocytes won’t be grouped, they’ll be scattered,” she said.
Another pitfall is that less than 15% of nevi may express PRAME. “PRAME can be expressed in scars, so if you’re looking at a spindle cell lesion, be aware that you might be looking at a scar if you’re seeing PRAME expression,” she added. She also noted that PRAME immunohistochemistry (IHC) expression is not a prognostic biomarker in thin melanomas.
If fewer than 25% of cells in a melanocytic lesion express PRAME, most published assessments of PRAME IHC favor nevi as the diagnosis. “If more than 75% are expressing it, it favors melanoma,” Dr. Humberson said. “There’s a big category in between. It’s not that 30% is more likely benign or that 60% is more likely malignant; you can’t really depend upon [PRAME] if you’re in this range.”
A diagnostic accuracy study found that when more than 75% of cells express PRAME, the marker has a sensitivity of 0.63 and a specificity of 0.97.
Selected PRAME-related published references she recommended include: J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48(9):1115-23; Diagnostics. 2022 Sep 9; 12(9):2197, and J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49(9):829-32.
Dr. Humberson reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT MELANOMA 2023
Chronic Ulcerative Lesion
The Diagnosis: Marjolin Ulcer
A skin biopsy during his prior hospital admission demonstrated an ulcer with granulation tissue and mixed inflammation, and the patient was discharged with close outpatient follow-up. Two repeat skin biopsies from the peripheral margin at the time of the outpatient follow-up confirmed an invasive, well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (Figure), consistent with a Marjolin ulcer. Radiography demonstrated multiple left iliac chain and inguinal lymphadenopathies with extensive subcutaneous disease overlying the left medial tibia. After tumor board discussion, surgery was not recommended due to the size and likely penetration into the muscle. The patient began treatment with cemiplimab-rwlc, a PD-1 inhibitor. Within 4 cycles of treatment, he had improved pain and ambulation, and a 3-month follow-up positron emission tomography scan revealed decreased lymph node and cutaneous metabolic activity as well as clinical improvement.
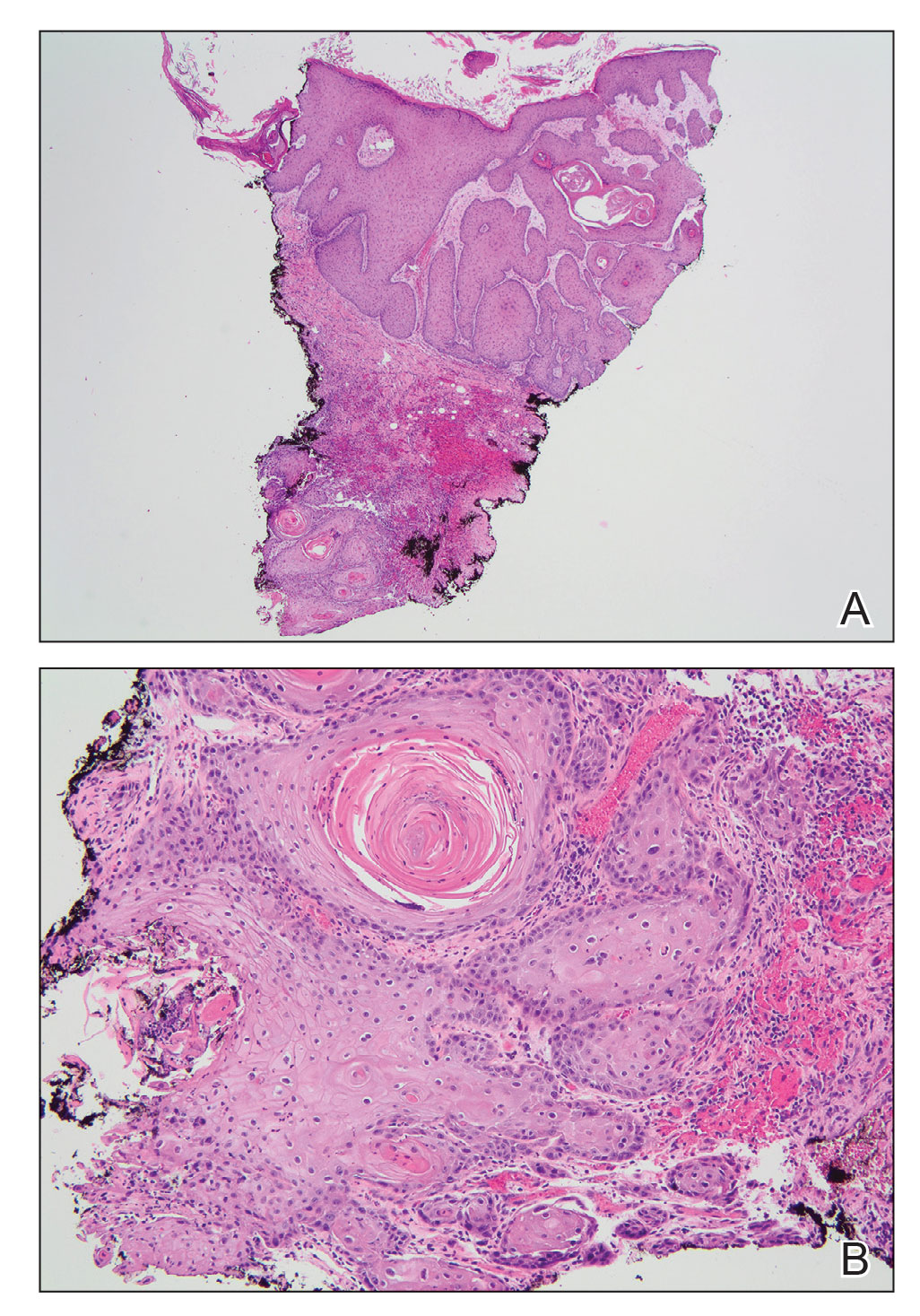
Marjolin ulcers are rare and aggressive squamous cell carcinomas that arise from chronic wounds such as burn scars or pressure ulcers.1 Although an underlying well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma is the most common etiology, patients also may present with underlying basal cell carcinomas, melanomas, or angiosarcomas.2 The exact pathogenesis underlying the malignant degeneration is unclear but appears to be driven by chronic inflammation. Patients classically present with a nonhealing ulcer associated with raised, friable, or crusty borders, as well as surrounding scar tissue. There is a median latency of 30 years after the trauma, though acute transformation within 12 months of an injury is possible.3 The diagnosis is confirmed with a peripheral wound biopsy. Surgical excision with wide margins remains the most common and effective intervention, especially for localized disease.1 The addition of lymph node dissection remains controversial, but treatment decisions can be guided by radiographic staging.4
The prognosis of Marjolin ulcers remains poor, with a predicted 5-year survival rate ranging from 43% to 58%.1 Dermatologists and trainees should be aware of Marjolin ulcers, especially as a mimicker of other chronic ulcerating conditions. Among the differential diagnosis, ulcerative lichen planus is a condition that commonly affects the oral and genital regions; however, patients with erosive lichen planus may develop an increased risk for the subsequent development of squamous cell carcinoma in the region.5 Furthermore, arterial ulcers typically develop on the distal lower extremities with other signs of chronic ischemia, including absent peripheral pulses, atrophic skin, hair loss, and ankle-brachial indices less than 0.5. Conversely, a venous ulcer classically affects the medial malleolus and will have evidence of venous insufficiency, including stasis dermatitis and peripheral edema.6
- Iqbal FM, Sinha Y, Jaffe W. Marjolin’s ulcer: a rare entity with a call for early diagnosis [published online July 15, 2015]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-208176
- Kanth AM, Heiman AJ, Nair L, et al. Current trends in management of Marjolin’s ulcer: a systematic review. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:144-151. doi:10.1093/jbcr/iraa128
- Copcu E. Marjolin’s ulcer: a preventable complication of burns? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:E156-E164. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181a8082e
- Pekarek B, Buck S, Osher L. A comprehensive review on Marjolin’s ulcers: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Coll Certif Wound Spec. 2011; 3:60-64. doi:10.1016/j.jcws.2012.04.001
- Tziotzios C, Lee JYW, Brier T, et al. Lichen planus and lichenoid dermatoses: clinical overview and molecular basis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:789-804.
- Spentzouris G, Labropoulos N. The evaluation of lower-extremity ulcers. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2009;26:286-295. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242204
The Diagnosis: Marjolin Ulcer
A skin biopsy during his prior hospital admission demonstrated an ulcer with granulation tissue and mixed inflammation, and the patient was discharged with close outpatient follow-up. Two repeat skin biopsies from the peripheral margin at the time of the outpatient follow-up confirmed an invasive, well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (Figure), consistent with a Marjolin ulcer. Radiography demonstrated multiple left iliac chain and inguinal lymphadenopathies with extensive subcutaneous disease overlying the left medial tibia. After tumor board discussion, surgery was not recommended due to the size and likely penetration into the muscle. The patient began treatment with cemiplimab-rwlc, a PD-1 inhibitor. Within 4 cycles of treatment, he had improved pain and ambulation, and a 3-month follow-up positron emission tomography scan revealed decreased lymph node and cutaneous metabolic activity as well as clinical improvement.

Marjolin ulcers are rare and aggressive squamous cell carcinomas that arise from chronic wounds such as burn scars or pressure ulcers.1 Although an underlying well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma is the most common etiology, patients also may present with underlying basal cell carcinomas, melanomas, or angiosarcomas.2 The exact pathogenesis underlying the malignant degeneration is unclear but appears to be driven by chronic inflammation. Patients classically present with a nonhealing ulcer associated with raised, friable, or crusty borders, as well as surrounding scar tissue. There is a median latency of 30 years after the trauma, though acute transformation within 12 months of an injury is possible.3 The diagnosis is confirmed with a peripheral wound biopsy. Surgical excision with wide margins remains the most common and effective intervention, especially for localized disease.1 The addition of lymph node dissection remains controversial, but treatment decisions can be guided by radiographic staging.4
The prognosis of Marjolin ulcers remains poor, with a predicted 5-year survival rate ranging from 43% to 58%.1 Dermatologists and trainees should be aware of Marjolin ulcers, especially as a mimicker of other chronic ulcerating conditions. Among the differential diagnosis, ulcerative lichen planus is a condition that commonly affects the oral and genital regions; however, patients with erosive lichen planus may develop an increased risk for the subsequent development of squamous cell carcinoma in the region.5 Furthermore, arterial ulcers typically develop on the distal lower extremities with other signs of chronic ischemia, including absent peripheral pulses, atrophic skin, hair loss, and ankle-brachial indices less than 0.5. Conversely, a venous ulcer classically affects the medial malleolus and will have evidence of venous insufficiency, including stasis dermatitis and peripheral edema.6
The Diagnosis: Marjolin Ulcer
A skin biopsy during his prior hospital admission demonstrated an ulcer with granulation tissue and mixed inflammation, and the patient was discharged with close outpatient follow-up. Two repeat skin biopsies from the peripheral margin at the time of the outpatient follow-up confirmed an invasive, well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (Figure), consistent with a Marjolin ulcer. Radiography demonstrated multiple left iliac chain and inguinal lymphadenopathies with extensive subcutaneous disease overlying the left medial tibia. After tumor board discussion, surgery was not recommended due to the size and likely penetration into the muscle. The patient began treatment with cemiplimab-rwlc, a PD-1 inhibitor. Within 4 cycles of treatment, he had improved pain and ambulation, and a 3-month follow-up positron emission tomography scan revealed decreased lymph node and cutaneous metabolic activity as well as clinical improvement.

Marjolin ulcers are rare and aggressive squamous cell carcinomas that arise from chronic wounds such as burn scars or pressure ulcers.1 Although an underlying well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma is the most common etiology, patients also may present with underlying basal cell carcinomas, melanomas, or angiosarcomas.2 The exact pathogenesis underlying the malignant degeneration is unclear but appears to be driven by chronic inflammation. Patients classically present with a nonhealing ulcer associated with raised, friable, or crusty borders, as well as surrounding scar tissue. There is a median latency of 30 years after the trauma, though acute transformation within 12 months of an injury is possible.3 The diagnosis is confirmed with a peripheral wound biopsy. Surgical excision with wide margins remains the most common and effective intervention, especially for localized disease.1 The addition of lymph node dissection remains controversial, but treatment decisions can be guided by radiographic staging.4
The prognosis of Marjolin ulcers remains poor, with a predicted 5-year survival rate ranging from 43% to 58%.1 Dermatologists and trainees should be aware of Marjolin ulcers, especially as a mimicker of other chronic ulcerating conditions. Among the differential diagnosis, ulcerative lichen planus is a condition that commonly affects the oral and genital regions; however, patients with erosive lichen planus may develop an increased risk for the subsequent development of squamous cell carcinoma in the region.5 Furthermore, arterial ulcers typically develop on the distal lower extremities with other signs of chronic ischemia, including absent peripheral pulses, atrophic skin, hair loss, and ankle-brachial indices less than 0.5. Conversely, a venous ulcer classically affects the medial malleolus and will have evidence of venous insufficiency, including stasis dermatitis and peripheral edema.6
- Iqbal FM, Sinha Y, Jaffe W. Marjolin’s ulcer: a rare entity with a call for early diagnosis [published online July 15, 2015]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-208176
- Kanth AM, Heiman AJ, Nair L, et al. Current trends in management of Marjolin’s ulcer: a systematic review. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:144-151. doi:10.1093/jbcr/iraa128
- Copcu E. Marjolin’s ulcer: a preventable complication of burns? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:E156-E164. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181a8082e
- Pekarek B, Buck S, Osher L. A comprehensive review on Marjolin’s ulcers: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Coll Certif Wound Spec. 2011; 3:60-64. doi:10.1016/j.jcws.2012.04.001
- Tziotzios C, Lee JYW, Brier T, et al. Lichen planus and lichenoid dermatoses: clinical overview and molecular basis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:789-804.
- Spentzouris G, Labropoulos N. The evaluation of lower-extremity ulcers. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2009;26:286-295. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242204
- Iqbal FM, Sinha Y, Jaffe W. Marjolin’s ulcer: a rare entity with a call for early diagnosis [published online July 15, 2015]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-208176
- Kanth AM, Heiman AJ, Nair L, et al. Current trends in management of Marjolin’s ulcer: a systematic review. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42:144-151. doi:10.1093/jbcr/iraa128
- Copcu E. Marjolin’s ulcer: a preventable complication of burns? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:E156-E164. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181a8082e
- Pekarek B, Buck S, Osher L. A comprehensive review on Marjolin’s ulcers: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Coll Certif Wound Spec. 2011; 3:60-64. doi:10.1016/j.jcws.2012.04.001
- Tziotzios C, Lee JYW, Brier T, et al. Lichen planus and lichenoid dermatoses: clinical overview and molecular basis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:789-804.
- Spentzouris G, Labropoulos N. The evaluation of lower-extremity ulcers. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2009;26:286-295. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242204
A 46-year-old man with a history of a left leg burn during childhood that was unsuccessfully treated with multiple skin grafts presented as a hospital follow-up for outpatient management of an ulcer. The patient had an ulcer that gradually increased in size over 7 years. Over the course of 2 weeks prior to the hospital presentation, he noted increased pain and severe difficulty with ambulation but remained afebrile without other systemic symptoms. Prior to the outpatient follow-up, he had been admitted to the hospital where he underwent imaging, laboratory studies, and skin biopsy, as well as treatment with empiric vancomycin. Physical examination revealed a large undermined ulcer with an elevated peripheral margin and crusting on the left lower leg with surrounding chronic scarring.