User login
Seven legal risks of promoting unproven COVID-19 treatments
The emergence of COVID-19 has given the medical world a bewildering array of prevention and treatment protocols. Some physicians are advocating treatments that have not been validated by sound scientific studies. This has already led to licensing issues and other disciplinary actions being taken against physicians, pharmacies, and other health care providers across the country.
Medical professionals try their very best to give sound advice to patients. A medical license does not, however, confer immunity from being misled.
The supporting “science” for alternative prevention and treatments may look legitimate, but these claims are often based on anecdotal evidence. Some studies involve small populations, some are meta-analyses of several small or single-case studies, and others are not properly designed, interpreted, or executed in line with U.S. research and requirements. Yet others have been conducted only in nonhuman analogues, such as frogs or mice.
Many people are refusing a vaccine that has been proven to be relatively safe and effective in numerous repeated and validated studies in the best medical centers across the globe – all in favor of less validated alternatives. This can have serious legal consequences.
The crux of the issue
This is not a question of a physician’s first amendment rights. Nor is it a question of advocating for a scientifically valid minority medical opinion. The point of this article is that promoting unproven products, preventives, treatments, and cures can have dire consequences for licensed medical professionals.
On July 29, 2021, the Federation of State Medical Boards’ Board of Directors released a statement in response to a dramatic increase in the dissemination of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation and disinformation by physicians and other health care professionals on social media platforms, online, and in the media. The statement reads as follows:
“Physicians who generate and spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation or disinformation are risking disciplinary action by state medical boards, including the suspension or revocation of their medical license. Due to their specialized knowledge and training, licensed physicians possess a high degree of public trust and therefore have a powerful platform in society, whether they recognize it or not. They also have an ethical and professional responsibility to practice medicine in the best interests of their patients and must share information that is factual, scientifically grounded, and consensus-driven for the betterment of public health. Spreading inaccurate COVID-19 vaccine information contradicts that responsibility, threatens to further erode public trust in the medical profession, and puts all patients at risk.”
What are the legal consequences?
Medical malpractice
The first consequence to consider is professional liability or medical malpractice. This applies if a patient claims harm as a result of the health care practitioner’s recommendation of an unproven treatment, product, or protocol. For example, strongly discouraging vaccination can result in a wrongful death claim if the patient follows the doctor’s advice, chooses not to vaccinate, contracts COVID-19, and does not recover. Recommending or providing unproven approaches and unapproved treatments is arguably a violation of the standard of care.
The standard of care is grounded in evidence-based medicine: It is commonly defined as the degree of care and skill that would be used by the average physician, who is practicing in his or her relevant specialty, under the same or similar circumstances, given the generally accepted medical knowledge at the time in question.
By way of example, one can see why inhaling peroxide, drinking bleach, or even taking Food and Drug Administration–approved medications that have little or no proven efficacy in treating or preventing COVID-19 is not what the average physician would advocate for under the same or similar circumstances, considering available and commonly accepted medical knowledge. Recommending or providing such treatments can be a breach of the standard of care and can form the basis of a medical malpractice action if, in fact, compensable harm has occurred.
In addition, recommending unproven and unapproved COVID-19 preventives and treatments without appropriate informed consent from patients is arguably also a breach of the standard of care. The claim would be that the patient has not been appropriately informed of the all the known benefits, risks, costs, and other legally required information such as proven efficacy and reasonably available alternatives.
In any event, physicians can rest assured that if a patient is harmed as a result of any of these situations, they’ll probably be answering to someone in the legal system.
Professional licensing action
Regardless of whether there is a medical malpractice action, there is still the potential for a patient complaint to be filed with the state licensing authority on the basis of the same facts and grounds. This can result in an investigation or an administrative complaint against the license of the health care provider.
This is not a mere potential risk. Licensing investigations are underway across the country. Disciplinary licensing actions have already taken place. For example, a Washington Medical Commission panel suspended the license of a physician assistant (PA) on Oct. 12, 2021, after an allegation that his treatment of COVID-19 patients fell below the standard of care. The PA allegedly began a public campaign promoting ivermectin as a curative agent for COVID-19 and prescribed it without adequate examination to at least one person, with no evidence from reliable clinical studies that establish its efficacy in preventing or treating COVID-19.
In licensing claims, alleged violations of failing to comply with the standard of care are usually asserted. These claims may also cite violations of other state statutes that encompass such concepts as negligence; breach of the duty of due care; incompetence; lack of good moral character; and lack of ability to serve the public in a fair, honest, and open manner. A licensing complaint may include alleged violations of statutes that address prescribing protocols, reckless endangerment, failure to supervise, and other issues.
The filing of an administrative complaint is a different animal from a medical malpractice action – they are not even in the same system or branch of government. The focus is not just about what happened to the one patient who complained; it is about protection of the public.
The states’ power to put a clinician on probation, condition, limit, suspend, or revoke the clinician’s license, as well as issue other sanctions such as physician monitoring and fines), is profound. The discipline imposed can upend a clinician’s career and potentially end it entirely.
Administrative discipline determinations are usually available to the public and are required to be reported to all employers (current and future). These discipline determinations are also sent to the National Practitioner Data Bank, other professional clearinghouse organizations (such as the Federation of State Medical Boards), state offices, professional liability insurers, payers with whom the clinician contracts, accreditation and certification organizations, and the clinician’s patients.
Discipline determinations must be promptly reported to licensing agencies in other states where the clinician holds a license, and often results in “sister state” actions because discipline was issued against the clinician in another state. It must be disclosed every time a clinician applies for hospital privileges or new employment. It can result in de-participation from health care insurance programs and can affect board certification, recertification, or accreditation for care programs in which the clinician participates.
In sum, licensing actions can be much worse than medical malpractice judgments and can have longer-term consequences.
Peer review and affected privileges
Recommending, promoting, and providing unapproved or unproven treatments, cures, or preventives to patients may violate hospital/health system, practice group, or surgical center bylaws. This can trigger the peer review process, which serves to improve patient safety and the quality of care.
The peer review process may be commenced because of a concern about the clinician’s compliance with the standard of care; potential patient safety issues; ethical issues; and the clinician’s stability, credibility, or professional competence. Any hospital disciplinary penalty is generally reported to state licensing authorities, which can trigger a licensing investigation. If clinical privileges are affected for a period of more than 30 days, the organization must report the situation to the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Criminal charges
Depending on the facts, a physician or other health care professional could be charged with reckless endangerment, criminal negligence, or manslaughter. If the clinician was assisting someone else who profited from that clinician’s actions, then we can look to a variety of potential federal and state fraud charges as well.
Conviction of a fraud-related felony may also lead to federal health care program and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) exclusion for several years, and then CMS preclusion that can be imposed for years beyond the conclusion of the statutorily required exclusion.
Breach of contract
Some practice groups or other organizational employers have provisions in employment contracts that treat discipline for this type of conduct as a breach of contract. Because of this, the clinician committing breach may be subject to liquidated damages clauses, forfeiture of monies (such as bonuses or other incentives or rewards), termination of employment, forced withdrawal from ownership status, and being sued for breach of contract to recover damages.
Reputation/credibility damage and the attendant consequences
In regard to hospitals and health care system practice groups, another risk is the loss of referrals and revenue. Local media may air or publish exposés. Such stories may widely publicize the media’s version of the facts – true or not. This can cause immediate reputation and credibility damage within the community and may adversely affect a clinician’s patient base. Any information that is publicly broadcast might attract the attention of licensing and law enforcement authorities and taint potential jurors.
Hospitals and health care systems may pull privileges; post on websites; make official statements about the termination of affiliation; or denounce the clinician’s behavior, conduct, and beliefs as being inconsistent with quality care and patient safety. This causes further damage to a physician’s reputation and credibility.
In a group practice, accusations of this sort, licensing discipline, medical malpractice liability, investigations, loss of privileges, and the other sequelae of this conduct can force the withdrawal of the clinician as a member or shareholder in multiprovider groups. Adverse effects on the financial bottom line, patient referrals, and patient volume and bad press are often the basis for voting a clinician out.
Violation of the COVID-19 Consumer Protection Act of 2020
For the duration of the COVID-19 public health emergency, the FTC COVID-19 Consumer Protection Act makes it unlawful for any person, partnership, or corporation (as those terms are defined broadly in the act) to engage in a deceptive act or practice in or affecting commerce associated with the treatment, cure, prevention, mitigation, or diagnosis of COVID-19 or a government benefit related to COVID-19.
The first enforcement action authorized by this act took place in April 2021 against a chiropractor who promised vitamin treatments and cures for COVID-19. The act provides that such a violation shall be treated as a violation of a rule defining an unfair or deceptive act or practice prescribed under the FTC Act.
Under the act, the FTC is authorized to prescribe “rules that define with specificity acts or practices which are unfair or deceptive acts or practices in or affecting commerce.” Deceptive practices are defined as involving a material representation, omission, or practice that is “likely to mislead a consumer acting reasonably in the circumstances.” An act or practice is unfair if it “causes or is likely to cause substantial injury to consumers which is not reasonably avoidable by consumers themselves and not outweighed by countervailing benefits to consumers or to competition.”
After an investigation, the FTC may initiate an enforcement action using either an administrative or judicial process if it has “reason to believe” that the law has been violated. Violations of some laws may result in injunctive relief or civil monetary penalties, which are adjusted annually for inflation.
In addition, many states have deceptive and unfair trade laws that can be enforced in regard to the recommendation, sale, or provision of unproven or unapproved COVID-19 treatments, cures, and preventives as well.
Conclusion
It is difficult even for intelligent, well-intentioned physicians to know precisely what to believe and what to advocate for in the middle of a pandemic. It seems as though new reports and recommendations for preventing and treating COVID-19 are surfacing on a weekly basis. By far, the safest approach for any medical clinician to take is to advocate for positions that are generally accepted in the medical and scientific community at the time advice is given.
Mr. Whitelaw disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Janeway disclosed various associations with the Michigan Association for Healthcare Quality and the Greater Houston Society for Healthcare Risk Management. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The emergence of COVID-19 has given the medical world a bewildering array of prevention and treatment protocols. Some physicians are advocating treatments that have not been validated by sound scientific studies. This has already led to licensing issues and other disciplinary actions being taken against physicians, pharmacies, and other health care providers across the country.
Medical professionals try their very best to give sound advice to patients. A medical license does not, however, confer immunity from being misled.
The supporting “science” for alternative prevention and treatments may look legitimate, but these claims are often based on anecdotal evidence. Some studies involve small populations, some are meta-analyses of several small or single-case studies, and others are not properly designed, interpreted, or executed in line with U.S. research and requirements. Yet others have been conducted only in nonhuman analogues, such as frogs or mice.
Many people are refusing a vaccine that has been proven to be relatively safe and effective in numerous repeated and validated studies in the best medical centers across the globe – all in favor of less validated alternatives. This can have serious legal consequences.
The crux of the issue
This is not a question of a physician’s first amendment rights. Nor is it a question of advocating for a scientifically valid minority medical opinion. The point of this article is that promoting unproven products, preventives, treatments, and cures can have dire consequences for licensed medical professionals.
On July 29, 2021, the Federation of State Medical Boards’ Board of Directors released a statement in response to a dramatic increase in the dissemination of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation and disinformation by physicians and other health care professionals on social media platforms, online, and in the media. The statement reads as follows:
“Physicians who generate and spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation or disinformation are risking disciplinary action by state medical boards, including the suspension or revocation of their medical license. Due to their specialized knowledge and training, licensed physicians possess a high degree of public trust and therefore have a powerful platform in society, whether they recognize it or not. They also have an ethical and professional responsibility to practice medicine in the best interests of their patients and must share information that is factual, scientifically grounded, and consensus-driven for the betterment of public health. Spreading inaccurate COVID-19 vaccine information contradicts that responsibility, threatens to further erode public trust in the medical profession, and puts all patients at risk.”
What are the legal consequences?
Medical malpractice
The first consequence to consider is professional liability or medical malpractice. This applies if a patient claims harm as a result of the health care practitioner’s recommendation of an unproven treatment, product, or protocol. For example, strongly discouraging vaccination can result in a wrongful death claim if the patient follows the doctor’s advice, chooses not to vaccinate, contracts COVID-19, and does not recover. Recommending or providing unproven approaches and unapproved treatments is arguably a violation of the standard of care.
The standard of care is grounded in evidence-based medicine: It is commonly defined as the degree of care and skill that would be used by the average physician, who is practicing in his or her relevant specialty, under the same or similar circumstances, given the generally accepted medical knowledge at the time in question.
By way of example, one can see why inhaling peroxide, drinking bleach, or even taking Food and Drug Administration–approved medications that have little or no proven efficacy in treating or preventing COVID-19 is not what the average physician would advocate for under the same or similar circumstances, considering available and commonly accepted medical knowledge. Recommending or providing such treatments can be a breach of the standard of care and can form the basis of a medical malpractice action if, in fact, compensable harm has occurred.
In addition, recommending unproven and unapproved COVID-19 preventives and treatments without appropriate informed consent from patients is arguably also a breach of the standard of care. The claim would be that the patient has not been appropriately informed of the all the known benefits, risks, costs, and other legally required information such as proven efficacy and reasonably available alternatives.
In any event, physicians can rest assured that if a patient is harmed as a result of any of these situations, they’ll probably be answering to someone in the legal system.
Professional licensing action
Regardless of whether there is a medical malpractice action, there is still the potential for a patient complaint to be filed with the state licensing authority on the basis of the same facts and grounds. This can result in an investigation or an administrative complaint against the license of the health care provider.
This is not a mere potential risk. Licensing investigations are underway across the country. Disciplinary licensing actions have already taken place. For example, a Washington Medical Commission panel suspended the license of a physician assistant (PA) on Oct. 12, 2021, after an allegation that his treatment of COVID-19 patients fell below the standard of care. The PA allegedly began a public campaign promoting ivermectin as a curative agent for COVID-19 and prescribed it without adequate examination to at least one person, with no evidence from reliable clinical studies that establish its efficacy in preventing or treating COVID-19.
In licensing claims, alleged violations of failing to comply with the standard of care are usually asserted. These claims may also cite violations of other state statutes that encompass such concepts as negligence; breach of the duty of due care; incompetence; lack of good moral character; and lack of ability to serve the public in a fair, honest, and open manner. A licensing complaint may include alleged violations of statutes that address prescribing protocols, reckless endangerment, failure to supervise, and other issues.
The filing of an administrative complaint is a different animal from a medical malpractice action – they are not even in the same system or branch of government. The focus is not just about what happened to the one patient who complained; it is about protection of the public.
The states’ power to put a clinician on probation, condition, limit, suspend, or revoke the clinician’s license, as well as issue other sanctions such as physician monitoring and fines), is profound. The discipline imposed can upend a clinician’s career and potentially end it entirely.
Administrative discipline determinations are usually available to the public and are required to be reported to all employers (current and future). These discipline determinations are also sent to the National Practitioner Data Bank, other professional clearinghouse organizations (such as the Federation of State Medical Boards), state offices, professional liability insurers, payers with whom the clinician contracts, accreditation and certification organizations, and the clinician’s patients.
Discipline determinations must be promptly reported to licensing agencies in other states where the clinician holds a license, and often results in “sister state” actions because discipline was issued against the clinician in another state. It must be disclosed every time a clinician applies for hospital privileges or new employment. It can result in de-participation from health care insurance programs and can affect board certification, recertification, or accreditation for care programs in which the clinician participates.
In sum, licensing actions can be much worse than medical malpractice judgments and can have longer-term consequences.
Peer review and affected privileges
Recommending, promoting, and providing unapproved or unproven treatments, cures, or preventives to patients may violate hospital/health system, practice group, or surgical center bylaws. This can trigger the peer review process, which serves to improve patient safety and the quality of care.
The peer review process may be commenced because of a concern about the clinician’s compliance with the standard of care; potential patient safety issues; ethical issues; and the clinician’s stability, credibility, or professional competence. Any hospital disciplinary penalty is generally reported to state licensing authorities, which can trigger a licensing investigation. If clinical privileges are affected for a period of more than 30 days, the organization must report the situation to the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Criminal charges
Depending on the facts, a physician or other health care professional could be charged with reckless endangerment, criminal negligence, or manslaughter. If the clinician was assisting someone else who profited from that clinician’s actions, then we can look to a variety of potential federal and state fraud charges as well.
Conviction of a fraud-related felony may also lead to federal health care program and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) exclusion for several years, and then CMS preclusion that can be imposed for years beyond the conclusion of the statutorily required exclusion.
Breach of contract
Some practice groups or other organizational employers have provisions in employment contracts that treat discipline for this type of conduct as a breach of contract. Because of this, the clinician committing breach may be subject to liquidated damages clauses, forfeiture of monies (such as bonuses or other incentives or rewards), termination of employment, forced withdrawal from ownership status, and being sued for breach of contract to recover damages.
Reputation/credibility damage and the attendant consequences
In regard to hospitals and health care system practice groups, another risk is the loss of referrals and revenue. Local media may air or publish exposés. Such stories may widely publicize the media’s version of the facts – true or not. This can cause immediate reputation and credibility damage within the community and may adversely affect a clinician’s patient base. Any information that is publicly broadcast might attract the attention of licensing and law enforcement authorities and taint potential jurors.
Hospitals and health care systems may pull privileges; post on websites; make official statements about the termination of affiliation; or denounce the clinician’s behavior, conduct, and beliefs as being inconsistent with quality care and patient safety. This causes further damage to a physician’s reputation and credibility.
In a group practice, accusations of this sort, licensing discipline, medical malpractice liability, investigations, loss of privileges, and the other sequelae of this conduct can force the withdrawal of the clinician as a member or shareholder in multiprovider groups. Adverse effects on the financial bottom line, patient referrals, and patient volume and bad press are often the basis for voting a clinician out.
Violation of the COVID-19 Consumer Protection Act of 2020
For the duration of the COVID-19 public health emergency, the FTC COVID-19 Consumer Protection Act makes it unlawful for any person, partnership, or corporation (as those terms are defined broadly in the act) to engage in a deceptive act or practice in or affecting commerce associated with the treatment, cure, prevention, mitigation, or diagnosis of COVID-19 or a government benefit related to COVID-19.
The first enforcement action authorized by this act took place in April 2021 against a chiropractor who promised vitamin treatments and cures for COVID-19. The act provides that such a violation shall be treated as a violation of a rule defining an unfair or deceptive act or practice prescribed under the FTC Act.
Under the act, the FTC is authorized to prescribe “rules that define with specificity acts or practices which are unfair or deceptive acts or practices in or affecting commerce.” Deceptive practices are defined as involving a material representation, omission, or practice that is “likely to mislead a consumer acting reasonably in the circumstances.” An act or practice is unfair if it “causes or is likely to cause substantial injury to consumers which is not reasonably avoidable by consumers themselves and not outweighed by countervailing benefits to consumers or to competition.”
After an investigation, the FTC may initiate an enforcement action using either an administrative or judicial process if it has “reason to believe” that the law has been violated. Violations of some laws may result in injunctive relief or civil monetary penalties, which are adjusted annually for inflation.
In addition, many states have deceptive and unfair trade laws that can be enforced in regard to the recommendation, sale, or provision of unproven or unapproved COVID-19 treatments, cures, and preventives as well.
Conclusion
It is difficult even for intelligent, well-intentioned physicians to know precisely what to believe and what to advocate for in the middle of a pandemic. It seems as though new reports and recommendations for preventing and treating COVID-19 are surfacing on a weekly basis. By far, the safest approach for any medical clinician to take is to advocate for positions that are generally accepted in the medical and scientific community at the time advice is given.
Mr. Whitelaw disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Janeway disclosed various associations with the Michigan Association for Healthcare Quality and the Greater Houston Society for Healthcare Risk Management. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The emergence of COVID-19 has given the medical world a bewildering array of prevention and treatment protocols. Some physicians are advocating treatments that have not been validated by sound scientific studies. This has already led to licensing issues and other disciplinary actions being taken against physicians, pharmacies, and other health care providers across the country.
Medical professionals try their very best to give sound advice to patients. A medical license does not, however, confer immunity from being misled.
The supporting “science” for alternative prevention and treatments may look legitimate, but these claims are often based on anecdotal evidence. Some studies involve small populations, some are meta-analyses of several small or single-case studies, and others are not properly designed, interpreted, or executed in line with U.S. research and requirements. Yet others have been conducted only in nonhuman analogues, such as frogs or mice.
Many people are refusing a vaccine that has been proven to be relatively safe and effective in numerous repeated and validated studies in the best medical centers across the globe – all in favor of less validated alternatives. This can have serious legal consequences.
The crux of the issue
This is not a question of a physician’s first amendment rights. Nor is it a question of advocating for a scientifically valid minority medical opinion. The point of this article is that promoting unproven products, preventives, treatments, and cures can have dire consequences for licensed medical professionals.
On July 29, 2021, the Federation of State Medical Boards’ Board of Directors released a statement in response to a dramatic increase in the dissemination of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation and disinformation by physicians and other health care professionals on social media platforms, online, and in the media. The statement reads as follows:
“Physicians who generate and spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation or disinformation are risking disciplinary action by state medical boards, including the suspension or revocation of their medical license. Due to their specialized knowledge and training, licensed physicians possess a high degree of public trust and therefore have a powerful platform in society, whether they recognize it or not. They also have an ethical and professional responsibility to practice medicine in the best interests of their patients and must share information that is factual, scientifically grounded, and consensus-driven for the betterment of public health. Spreading inaccurate COVID-19 vaccine information contradicts that responsibility, threatens to further erode public trust in the medical profession, and puts all patients at risk.”
What are the legal consequences?
Medical malpractice
The first consequence to consider is professional liability or medical malpractice. This applies if a patient claims harm as a result of the health care practitioner’s recommendation of an unproven treatment, product, or protocol. For example, strongly discouraging vaccination can result in a wrongful death claim if the patient follows the doctor’s advice, chooses not to vaccinate, contracts COVID-19, and does not recover. Recommending or providing unproven approaches and unapproved treatments is arguably a violation of the standard of care.
The standard of care is grounded in evidence-based medicine: It is commonly defined as the degree of care and skill that would be used by the average physician, who is practicing in his or her relevant specialty, under the same or similar circumstances, given the generally accepted medical knowledge at the time in question.
By way of example, one can see why inhaling peroxide, drinking bleach, or even taking Food and Drug Administration–approved medications that have little or no proven efficacy in treating or preventing COVID-19 is not what the average physician would advocate for under the same or similar circumstances, considering available and commonly accepted medical knowledge. Recommending or providing such treatments can be a breach of the standard of care and can form the basis of a medical malpractice action if, in fact, compensable harm has occurred.
In addition, recommending unproven and unapproved COVID-19 preventives and treatments without appropriate informed consent from patients is arguably also a breach of the standard of care. The claim would be that the patient has not been appropriately informed of the all the known benefits, risks, costs, and other legally required information such as proven efficacy and reasonably available alternatives.
In any event, physicians can rest assured that if a patient is harmed as a result of any of these situations, they’ll probably be answering to someone in the legal system.
Professional licensing action
Regardless of whether there is a medical malpractice action, there is still the potential for a patient complaint to be filed with the state licensing authority on the basis of the same facts and grounds. This can result in an investigation or an administrative complaint against the license of the health care provider.
This is not a mere potential risk. Licensing investigations are underway across the country. Disciplinary licensing actions have already taken place. For example, a Washington Medical Commission panel suspended the license of a physician assistant (PA) on Oct. 12, 2021, after an allegation that his treatment of COVID-19 patients fell below the standard of care. The PA allegedly began a public campaign promoting ivermectin as a curative agent for COVID-19 and prescribed it without adequate examination to at least one person, with no evidence from reliable clinical studies that establish its efficacy in preventing or treating COVID-19.
In licensing claims, alleged violations of failing to comply with the standard of care are usually asserted. These claims may also cite violations of other state statutes that encompass such concepts as negligence; breach of the duty of due care; incompetence; lack of good moral character; and lack of ability to serve the public in a fair, honest, and open manner. A licensing complaint may include alleged violations of statutes that address prescribing protocols, reckless endangerment, failure to supervise, and other issues.
The filing of an administrative complaint is a different animal from a medical malpractice action – they are not even in the same system or branch of government. The focus is not just about what happened to the one patient who complained; it is about protection of the public.
The states’ power to put a clinician on probation, condition, limit, suspend, or revoke the clinician’s license, as well as issue other sanctions such as physician monitoring and fines), is profound. The discipline imposed can upend a clinician’s career and potentially end it entirely.
Administrative discipline determinations are usually available to the public and are required to be reported to all employers (current and future). These discipline determinations are also sent to the National Practitioner Data Bank, other professional clearinghouse organizations (such as the Federation of State Medical Boards), state offices, professional liability insurers, payers with whom the clinician contracts, accreditation and certification organizations, and the clinician’s patients.
Discipline determinations must be promptly reported to licensing agencies in other states where the clinician holds a license, and often results in “sister state” actions because discipline was issued against the clinician in another state. It must be disclosed every time a clinician applies for hospital privileges or new employment. It can result in de-participation from health care insurance programs and can affect board certification, recertification, or accreditation for care programs in which the clinician participates.
In sum, licensing actions can be much worse than medical malpractice judgments and can have longer-term consequences.
Peer review and affected privileges
Recommending, promoting, and providing unapproved or unproven treatments, cures, or preventives to patients may violate hospital/health system, practice group, or surgical center bylaws. This can trigger the peer review process, which serves to improve patient safety and the quality of care.
The peer review process may be commenced because of a concern about the clinician’s compliance with the standard of care; potential patient safety issues; ethical issues; and the clinician’s stability, credibility, or professional competence. Any hospital disciplinary penalty is generally reported to state licensing authorities, which can trigger a licensing investigation. If clinical privileges are affected for a period of more than 30 days, the organization must report the situation to the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Criminal charges
Depending on the facts, a physician or other health care professional could be charged with reckless endangerment, criminal negligence, or manslaughter. If the clinician was assisting someone else who profited from that clinician’s actions, then we can look to a variety of potential federal and state fraud charges as well.
Conviction of a fraud-related felony may also lead to federal health care program and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) exclusion for several years, and then CMS preclusion that can be imposed for years beyond the conclusion of the statutorily required exclusion.
Breach of contract
Some practice groups or other organizational employers have provisions in employment contracts that treat discipline for this type of conduct as a breach of contract. Because of this, the clinician committing breach may be subject to liquidated damages clauses, forfeiture of monies (such as bonuses or other incentives or rewards), termination of employment, forced withdrawal from ownership status, and being sued for breach of contract to recover damages.
Reputation/credibility damage and the attendant consequences
In regard to hospitals and health care system practice groups, another risk is the loss of referrals and revenue. Local media may air or publish exposés. Such stories may widely publicize the media’s version of the facts – true or not. This can cause immediate reputation and credibility damage within the community and may adversely affect a clinician’s patient base. Any information that is publicly broadcast might attract the attention of licensing and law enforcement authorities and taint potential jurors.
Hospitals and health care systems may pull privileges; post on websites; make official statements about the termination of affiliation; or denounce the clinician’s behavior, conduct, and beliefs as being inconsistent with quality care and patient safety. This causes further damage to a physician’s reputation and credibility.
In a group practice, accusations of this sort, licensing discipline, medical malpractice liability, investigations, loss of privileges, and the other sequelae of this conduct can force the withdrawal of the clinician as a member or shareholder in multiprovider groups. Adverse effects on the financial bottom line, patient referrals, and patient volume and bad press are often the basis for voting a clinician out.
Violation of the COVID-19 Consumer Protection Act of 2020
For the duration of the COVID-19 public health emergency, the FTC COVID-19 Consumer Protection Act makes it unlawful for any person, partnership, or corporation (as those terms are defined broadly in the act) to engage in a deceptive act or practice in or affecting commerce associated with the treatment, cure, prevention, mitigation, or diagnosis of COVID-19 or a government benefit related to COVID-19.
The first enforcement action authorized by this act took place in April 2021 against a chiropractor who promised vitamin treatments and cures for COVID-19. The act provides that such a violation shall be treated as a violation of a rule defining an unfair or deceptive act or practice prescribed under the FTC Act.
Under the act, the FTC is authorized to prescribe “rules that define with specificity acts or practices which are unfair or deceptive acts or practices in or affecting commerce.” Deceptive practices are defined as involving a material representation, omission, or practice that is “likely to mislead a consumer acting reasonably in the circumstances.” An act or practice is unfair if it “causes or is likely to cause substantial injury to consumers which is not reasonably avoidable by consumers themselves and not outweighed by countervailing benefits to consumers or to competition.”
After an investigation, the FTC may initiate an enforcement action using either an administrative or judicial process if it has “reason to believe” that the law has been violated. Violations of some laws may result in injunctive relief or civil monetary penalties, which are adjusted annually for inflation.
In addition, many states have deceptive and unfair trade laws that can be enforced in regard to the recommendation, sale, or provision of unproven or unapproved COVID-19 treatments, cures, and preventives as well.
Conclusion
It is difficult even for intelligent, well-intentioned physicians to know precisely what to believe and what to advocate for in the middle of a pandemic. It seems as though new reports and recommendations for preventing and treating COVID-19 are surfacing on a weekly basis. By far, the safest approach for any medical clinician to take is to advocate for positions that are generally accepted in the medical and scientific community at the time advice is given.
Mr. Whitelaw disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Ms. Janeway disclosed various associations with the Michigan Association for Healthcare Quality and the Greater Houston Society for Healthcare Risk Management. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telemedicine, triaging, remote monitoring top list of COVID-era innovations in oncology
When the Winship Cancer Institute at Emory University, Atlanta, faced off against the pandemic in the spring of 2020, it opened a COVID urgent care clinic for Winship oncology patients who had a confirmed or suspected case of COVID, symptoms or a higher risk for the virus. The urgent care clinic, located in a relatively isolated bay of an infusion center, facilitated segregating COVID-suspected patients from other cancer patients while waiting for their polymerase chain reaction test results to show if they were COVID positive.
A strict triage system was also employed to make sure that the right patients were coming in to the new clinic and not those who either could be managed safely at home or were clinically unstable and belonged in the hospital, said Caleb Raine, PA-C, an oncology physician assistant and bone marrow transplant specialist at Winship. Mr. Raine, who manages the COVID urgent care clinic, shared his experience of “innovations worth keeping” from the pandemic for oncology practices during a panel discussion at the Journal of the Advanced Practitioner in Oncology annual conference, held online Oct. 7.
Telephonic triage was conducted by advanced practice providers (APPs) or nurses using an algorithm Mr. Raine developed incorporating COVID exposure with symptoms such as fever or loss of taste or smell. In order to promote consistency in admissions, he made the final decisions about which patients were brought into the clinic for evaluations, services such as supportive care or infusions, or to address cancer symptoms.
Mr. Raine said the triage process helped to enhance communication with other clinical teams at Winship. He hopes to preserve a strict approach to triaging in future program development, including a 14-bed immediate care center, projected to open next spring, building on experience with the COVID urgent care center. It will offer services similar to a day hospital for cancer patients but be open 24 hours with more capabilities than urgent care. It will target those with emergent needs or who otherwise might require a trip to the ED and provide care for those recently discharged from the hospital in need of follow-up.
Remote monitoring
Another conference speaker, Aaron Begue, MS, RN, CNP, vice president for advanced practice providers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, described a pandemic telemedicine intervention for cancer patients implemented by MSKCC during the pandemic. Prior to in-person contact with the care team, patients were asked to complete a questionnaire on their symptoms using MSKCC’s secure online patient portal, MyMSK.
If symptom alerts reached a critical, color-coded threshold, it triggered a nurse or APP from MSKCC to contact the patient at home, typically by phone. APPs also did remote monitoring, including uploaded data from portable home pulse oximeters. A similar symptom tracker was later adapted for monitoring cancer symptoms.
Some APPs took turns working from their own home collecting data needed for inpatient visits and uploading it into the medical record. This helped to deploy clinical teams more efficiently and accommodate some staff who were at high risk of infection because of existing health conditions or quarantined for positive test results.
“We were able to flex our staffing,” Mr. Begue said. Even spending a day staffing a vaccination clinic could provide a break from the intensity of COVID care on the front lines. “All of us are still trying to figure out how to manage staff stress and burnout,” he added, but flexible scheduling seems to be an important strategy.
Early on, things like the crowds coming out in the evening to cheer for New York’s health care workers had a big impact for staff, showing the community’s support. “Later, when public schools were shut down, we worked with two of them to use their outdoor play areas for staff respite – places to sit down outside undisturbed and relax,” he said.
At the height of the COVID surge in New York, telemedicine was an essential component of care, but when it started to recede, Mr. Begue found that a lot of patients wanted in-person visits again. “We had assumed that telemedicine would be the wave of the future and cancer patients would love it,” he said. “We still do thousands of telemedicine visits, but they are no longer the majority.”
MSKCC also does remote telemonitoring visits with patients who live in other states but want to come to New York for surgeries or other procedures or yearly checkups at the hospital. But the logistical headaches of practicing telemedicine across state lines include trying to reconcile varying requirements for medical licensing.
Mr. Begue hopes in the future that some of these state requirements could be relaxed, which might also make it easier to enroll more people from across the country in clinical trials and encourage more collaboration between cancer centers.
“COVID taught us we have to be more forward thinking and prepared for crises,” Mr. Raine said. “In the future we need to be ready for when – not if – the next crisis comes along – although we’re not out of this one yet.”
Mr. Raine and Mr. Begue did not report any disclosures.
When the Winship Cancer Institute at Emory University, Atlanta, faced off against the pandemic in the spring of 2020, it opened a COVID urgent care clinic for Winship oncology patients who had a confirmed or suspected case of COVID, symptoms or a higher risk for the virus. The urgent care clinic, located in a relatively isolated bay of an infusion center, facilitated segregating COVID-suspected patients from other cancer patients while waiting for their polymerase chain reaction test results to show if they were COVID positive.
A strict triage system was also employed to make sure that the right patients were coming in to the new clinic and not those who either could be managed safely at home or were clinically unstable and belonged in the hospital, said Caleb Raine, PA-C, an oncology physician assistant and bone marrow transplant specialist at Winship. Mr. Raine, who manages the COVID urgent care clinic, shared his experience of “innovations worth keeping” from the pandemic for oncology practices during a panel discussion at the Journal of the Advanced Practitioner in Oncology annual conference, held online Oct. 7.
Telephonic triage was conducted by advanced practice providers (APPs) or nurses using an algorithm Mr. Raine developed incorporating COVID exposure with symptoms such as fever or loss of taste or smell. In order to promote consistency in admissions, he made the final decisions about which patients were brought into the clinic for evaluations, services such as supportive care or infusions, or to address cancer symptoms.
Mr. Raine said the triage process helped to enhance communication with other clinical teams at Winship. He hopes to preserve a strict approach to triaging in future program development, including a 14-bed immediate care center, projected to open next spring, building on experience with the COVID urgent care center. It will offer services similar to a day hospital for cancer patients but be open 24 hours with more capabilities than urgent care. It will target those with emergent needs or who otherwise might require a trip to the ED and provide care for those recently discharged from the hospital in need of follow-up.
Remote monitoring
Another conference speaker, Aaron Begue, MS, RN, CNP, vice president for advanced practice providers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, described a pandemic telemedicine intervention for cancer patients implemented by MSKCC during the pandemic. Prior to in-person contact with the care team, patients were asked to complete a questionnaire on their symptoms using MSKCC’s secure online patient portal, MyMSK.
If symptom alerts reached a critical, color-coded threshold, it triggered a nurse or APP from MSKCC to contact the patient at home, typically by phone. APPs also did remote monitoring, including uploaded data from portable home pulse oximeters. A similar symptom tracker was later adapted for monitoring cancer symptoms.
Some APPs took turns working from their own home collecting data needed for inpatient visits and uploading it into the medical record. This helped to deploy clinical teams more efficiently and accommodate some staff who were at high risk of infection because of existing health conditions or quarantined for positive test results.
“We were able to flex our staffing,” Mr. Begue said. Even spending a day staffing a vaccination clinic could provide a break from the intensity of COVID care on the front lines. “All of us are still trying to figure out how to manage staff stress and burnout,” he added, but flexible scheduling seems to be an important strategy.
Early on, things like the crowds coming out in the evening to cheer for New York’s health care workers had a big impact for staff, showing the community’s support. “Later, when public schools were shut down, we worked with two of them to use their outdoor play areas for staff respite – places to sit down outside undisturbed and relax,” he said.
At the height of the COVID surge in New York, telemedicine was an essential component of care, but when it started to recede, Mr. Begue found that a lot of patients wanted in-person visits again. “We had assumed that telemedicine would be the wave of the future and cancer patients would love it,” he said. “We still do thousands of telemedicine visits, but they are no longer the majority.”
MSKCC also does remote telemonitoring visits with patients who live in other states but want to come to New York for surgeries or other procedures or yearly checkups at the hospital. But the logistical headaches of practicing telemedicine across state lines include trying to reconcile varying requirements for medical licensing.
Mr. Begue hopes in the future that some of these state requirements could be relaxed, which might also make it easier to enroll more people from across the country in clinical trials and encourage more collaboration between cancer centers.
“COVID taught us we have to be more forward thinking and prepared for crises,” Mr. Raine said. “In the future we need to be ready for when – not if – the next crisis comes along – although we’re not out of this one yet.”
Mr. Raine and Mr. Begue did not report any disclosures.
When the Winship Cancer Institute at Emory University, Atlanta, faced off against the pandemic in the spring of 2020, it opened a COVID urgent care clinic for Winship oncology patients who had a confirmed or suspected case of COVID, symptoms or a higher risk for the virus. The urgent care clinic, located in a relatively isolated bay of an infusion center, facilitated segregating COVID-suspected patients from other cancer patients while waiting for their polymerase chain reaction test results to show if they were COVID positive.
A strict triage system was also employed to make sure that the right patients were coming in to the new clinic and not those who either could be managed safely at home or were clinically unstable and belonged in the hospital, said Caleb Raine, PA-C, an oncology physician assistant and bone marrow transplant specialist at Winship. Mr. Raine, who manages the COVID urgent care clinic, shared his experience of “innovations worth keeping” from the pandemic for oncology practices during a panel discussion at the Journal of the Advanced Practitioner in Oncology annual conference, held online Oct. 7.
Telephonic triage was conducted by advanced practice providers (APPs) or nurses using an algorithm Mr. Raine developed incorporating COVID exposure with symptoms such as fever or loss of taste or smell. In order to promote consistency in admissions, he made the final decisions about which patients were brought into the clinic for evaluations, services such as supportive care or infusions, or to address cancer symptoms.
Mr. Raine said the triage process helped to enhance communication with other clinical teams at Winship. He hopes to preserve a strict approach to triaging in future program development, including a 14-bed immediate care center, projected to open next spring, building on experience with the COVID urgent care center. It will offer services similar to a day hospital for cancer patients but be open 24 hours with more capabilities than urgent care. It will target those with emergent needs or who otherwise might require a trip to the ED and provide care for those recently discharged from the hospital in need of follow-up.
Remote monitoring
Another conference speaker, Aaron Begue, MS, RN, CNP, vice president for advanced practice providers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, described a pandemic telemedicine intervention for cancer patients implemented by MSKCC during the pandemic. Prior to in-person contact with the care team, patients were asked to complete a questionnaire on their symptoms using MSKCC’s secure online patient portal, MyMSK.
If symptom alerts reached a critical, color-coded threshold, it triggered a nurse or APP from MSKCC to contact the patient at home, typically by phone. APPs also did remote monitoring, including uploaded data from portable home pulse oximeters. A similar symptom tracker was later adapted for monitoring cancer symptoms.
Some APPs took turns working from their own home collecting data needed for inpatient visits and uploading it into the medical record. This helped to deploy clinical teams more efficiently and accommodate some staff who were at high risk of infection because of existing health conditions or quarantined for positive test results.
“We were able to flex our staffing,” Mr. Begue said. Even spending a day staffing a vaccination clinic could provide a break from the intensity of COVID care on the front lines. “All of us are still trying to figure out how to manage staff stress and burnout,” he added, but flexible scheduling seems to be an important strategy.
Early on, things like the crowds coming out in the evening to cheer for New York’s health care workers had a big impact for staff, showing the community’s support. “Later, when public schools were shut down, we worked with two of them to use their outdoor play areas for staff respite – places to sit down outside undisturbed and relax,” he said.
At the height of the COVID surge in New York, telemedicine was an essential component of care, but when it started to recede, Mr. Begue found that a lot of patients wanted in-person visits again. “We had assumed that telemedicine would be the wave of the future and cancer patients would love it,” he said. “We still do thousands of telemedicine visits, but they are no longer the majority.”
MSKCC also does remote telemonitoring visits with patients who live in other states but want to come to New York for surgeries or other procedures or yearly checkups at the hospital. But the logistical headaches of practicing telemedicine across state lines include trying to reconcile varying requirements for medical licensing.
Mr. Begue hopes in the future that some of these state requirements could be relaxed, which might also make it easier to enroll more people from across the country in clinical trials and encourage more collaboration between cancer centers.
“COVID taught us we have to be more forward thinking and prepared for crises,” Mr. Raine said. “In the future we need to be ready for when – not if – the next crisis comes along – although we’re not out of this one yet.”
Mr. Raine and Mr. Begue did not report any disclosures.
FROM JADPRO 2021
Cardiologist positive for Omicron after London conference
Elad Maor, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Sheba Medical Centre near Tel Aviv, posted on Twitter on Nov. 30: “What a mess! Came back from a conference in London. With a mask and 3 Pfizer vaccines I managed to get Omicron.”
Dr. Maor traveled to London on November 19 to attend the PCR London Valves 2021 conference held at the ExCeL Centre Nov. 21-23. He stayed four nights at a hotel in north London and took public transport to and from the ExCeL Centre in East London each day of the meeting. He returned to Israel on the evening of Nov. 23.
Dr. Maor, 45, who has received three doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine, had two PCR tests in the United Kingdom – on November 20 and 21 in line with travel requirements – and another PCR test upon arriving back in Israel in the early hours of Nov. 24. All three tests were negative.
He began experiencing symptoms within days and tested positive on Nov. 27. His symptoms have been mild so far, and he said he was feeling “better” at the time of his tweet on Nov. 30.
Dr. Maor believes he was infected during his trip to London. “The only reasonable explanation is that I got infected on the last day of the meeting – maybe at the airport, maybe at the meeting,” he told The Guardian newspaper.
Although his wife accompanied him to London, neither she nor any of his 3 children have experienced symptoms or tested positive for COVID-19. But Dr. Maor believes he has passed the infection to a 69-year-old colleague in Israel who has since tested positive for the Omicron variant. The colleague, who has also received three vaccine doses, is understood to have mild symptoms at present.
The case suggests that the Omicron variant of COVID-19 may have been circulating in the United Kingdom earlier than previously thought.
Implications for in-person conferences
It will also inevitably lead to questions about the safety of face-to-face conferences, which are only just starting to get underway again.
The PCR Valves 2021 meeting had more than 1,250 on-site attendees as well as 2,400 or more joining online, according to figures on its website. Dr. Maor said he did not have any issues with the conference organizers, who required proof of vaccination before entry. But he posted a photograph on his Twitter account of a crowded auditorium with many delegates not wearing masks.
The conference subsequently posted an announcement on its website alerting delegates that one of the attendees had tested positive for COVID-19 after returning to their home country. It reads: “Since the reported case comes less than a week after the end of PCR London Valves, we want to inform you so that you may decide the best course of action, for yourself, if any.” It does not mention that the case was the Omicron variant.
Patrick Jolly, strategic and market development director of the conference, commented: “As you may imagine, the health, safety and well-being of everyone who visited PCR London Valves was our number-one priority. All protocols mandated by the U.K. government were put in place. Anyone entering the congress center had to present a valid health pass and were requested to wear a mask. Hydro-alcoholic gel and masks were made readily available for all participants and disposal bins for used protective equipment were provided.”
Mr. Jolly also noted: “To date – more than 9 days after the end of PCR London Valves – we have had no report of any other case of participants testing positive who attended PCR London Valves.”
He said the EuroPCR organization believes that medical conferences are safe to be held in person.
“With the above sanitary requirements and protocols, and no complacency in their enforcement, we believe strongly that medical conferences can take place, as the benefits of in-person medical conferences are obvious for the concerned medical communities,” Mr. Jolly added.
But what about other meetings happening imminently and planning in-person attendance?
Eileen Murray, executive director of the American Epilepsy Society (AES), whose annual 5-day meeting starts today at Chicago’s McCormick Place Convention Center, said in an interview that the health, safety, and well-being of everyone attending is a priority.
“Vaccinations are required, with no exceptions, to anyone attending the in-person event,” Ms. Murray said. “AES is using the CLEAR HealthPass to verify identity and vaccination status for our attendees. No one who cannot verify identity and vaccination requirement will be permitted to attend the in-person event.”
She noted that masks will also be required except in limited circumstances when actively eating or drinking, or for a faculty member when actively presenting at a lecture or panel. “Anyone not adhering to the mask policy will be asked to leave the meeting and will be denied readmission to the meeting with no refund,” she said.
“These guidelines were developed in accordance with the latest public health guidance and AES will continue to follow that guidance as any updates are made with the emergence of the Omicron variant,” Ms. Murray added.
Also commenting on this issue, a spokesperson for the American Heart Association, which has its large annual international stroke meeting planned for in-person attendance in New Orleans in February, said: “As we have throughout the pandemic, the American Heart Association is closely monitoring conditions and following the guidance of the CDC as well as state and local health departments related to all in-person meetings.”
“Our upcoming International Stroke Conference, February 9-11, is planned as an in-person and digital experience which allows us the ultimate flexibility to address changing pandemic conditions. The health, safety, and well-being of our volunteers, members, and attendees from around the world remains our number-one priority,” the AHA spokesperson added.
But some COVID-19 experts are taking a more cautious view.
Rowland Kao, PhD, an expert in infectious disease dynamics at the University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, expressed concern about such large in-person conferences.
“We know that the Omicron variant appears to be spreading rapidly, with a recent preprint also telling us that the reinfection rate appears to be higher in South Africa. Should this be borne out, then the evidence would support that our reliance on a combination of vaccine-induced and natural immunity may be compromised by the Omicron variant,” he commented.
“We already know that extended contact indoors provides an additional risk, and so large meetings of this type have the potential to create extended risks. Until we know the extent to which Omicron causes severe illness, we should be extra cautious about these high-risk settings,” Dr. Kao commented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Elad Maor, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Sheba Medical Centre near Tel Aviv, posted on Twitter on Nov. 30: “What a mess! Came back from a conference in London. With a mask and 3 Pfizer vaccines I managed to get Omicron.”
Dr. Maor traveled to London on November 19 to attend the PCR London Valves 2021 conference held at the ExCeL Centre Nov. 21-23. He stayed four nights at a hotel in north London and took public transport to and from the ExCeL Centre in East London each day of the meeting. He returned to Israel on the evening of Nov. 23.
Dr. Maor, 45, who has received three doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine, had two PCR tests in the United Kingdom – on November 20 and 21 in line with travel requirements – and another PCR test upon arriving back in Israel in the early hours of Nov. 24. All three tests were negative.
He began experiencing symptoms within days and tested positive on Nov. 27. His symptoms have been mild so far, and he said he was feeling “better” at the time of his tweet on Nov. 30.
Dr. Maor believes he was infected during his trip to London. “The only reasonable explanation is that I got infected on the last day of the meeting – maybe at the airport, maybe at the meeting,” he told The Guardian newspaper.
Although his wife accompanied him to London, neither she nor any of his 3 children have experienced symptoms or tested positive for COVID-19. But Dr. Maor believes he has passed the infection to a 69-year-old colleague in Israel who has since tested positive for the Omicron variant. The colleague, who has also received three vaccine doses, is understood to have mild symptoms at present.
The case suggests that the Omicron variant of COVID-19 may have been circulating in the United Kingdom earlier than previously thought.
Implications for in-person conferences
It will also inevitably lead to questions about the safety of face-to-face conferences, which are only just starting to get underway again.
The PCR Valves 2021 meeting had more than 1,250 on-site attendees as well as 2,400 or more joining online, according to figures on its website. Dr. Maor said he did not have any issues with the conference organizers, who required proof of vaccination before entry. But he posted a photograph on his Twitter account of a crowded auditorium with many delegates not wearing masks.
The conference subsequently posted an announcement on its website alerting delegates that one of the attendees had tested positive for COVID-19 after returning to their home country. It reads: “Since the reported case comes less than a week after the end of PCR London Valves, we want to inform you so that you may decide the best course of action, for yourself, if any.” It does not mention that the case was the Omicron variant.
Patrick Jolly, strategic and market development director of the conference, commented: “As you may imagine, the health, safety and well-being of everyone who visited PCR London Valves was our number-one priority. All protocols mandated by the U.K. government were put in place. Anyone entering the congress center had to present a valid health pass and were requested to wear a mask. Hydro-alcoholic gel and masks were made readily available for all participants and disposal bins for used protective equipment were provided.”
Mr. Jolly also noted: “To date – more than 9 days after the end of PCR London Valves – we have had no report of any other case of participants testing positive who attended PCR London Valves.”
He said the EuroPCR organization believes that medical conferences are safe to be held in person.
“With the above sanitary requirements and protocols, and no complacency in their enforcement, we believe strongly that medical conferences can take place, as the benefits of in-person medical conferences are obvious for the concerned medical communities,” Mr. Jolly added.
But what about other meetings happening imminently and planning in-person attendance?
Eileen Murray, executive director of the American Epilepsy Society (AES), whose annual 5-day meeting starts today at Chicago’s McCormick Place Convention Center, said in an interview that the health, safety, and well-being of everyone attending is a priority.
“Vaccinations are required, with no exceptions, to anyone attending the in-person event,” Ms. Murray said. “AES is using the CLEAR HealthPass to verify identity and vaccination status for our attendees. No one who cannot verify identity and vaccination requirement will be permitted to attend the in-person event.”
She noted that masks will also be required except in limited circumstances when actively eating or drinking, or for a faculty member when actively presenting at a lecture or panel. “Anyone not adhering to the mask policy will be asked to leave the meeting and will be denied readmission to the meeting with no refund,” she said.
“These guidelines were developed in accordance with the latest public health guidance and AES will continue to follow that guidance as any updates are made with the emergence of the Omicron variant,” Ms. Murray added.
Also commenting on this issue, a spokesperson for the American Heart Association, which has its large annual international stroke meeting planned for in-person attendance in New Orleans in February, said: “As we have throughout the pandemic, the American Heart Association is closely monitoring conditions and following the guidance of the CDC as well as state and local health departments related to all in-person meetings.”
“Our upcoming International Stroke Conference, February 9-11, is planned as an in-person and digital experience which allows us the ultimate flexibility to address changing pandemic conditions. The health, safety, and well-being of our volunteers, members, and attendees from around the world remains our number-one priority,” the AHA spokesperson added.
But some COVID-19 experts are taking a more cautious view.
Rowland Kao, PhD, an expert in infectious disease dynamics at the University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, expressed concern about such large in-person conferences.
“We know that the Omicron variant appears to be spreading rapidly, with a recent preprint also telling us that the reinfection rate appears to be higher in South Africa. Should this be borne out, then the evidence would support that our reliance on a combination of vaccine-induced and natural immunity may be compromised by the Omicron variant,” he commented.
“We already know that extended contact indoors provides an additional risk, and so large meetings of this type have the potential to create extended risks. Until we know the extent to which Omicron causes severe illness, we should be extra cautious about these high-risk settings,” Dr. Kao commented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Elad Maor, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Sheba Medical Centre near Tel Aviv, posted on Twitter on Nov. 30: “What a mess! Came back from a conference in London. With a mask and 3 Pfizer vaccines I managed to get Omicron.”
Dr. Maor traveled to London on November 19 to attend the PCR London Valves 2021 conference held at the ExCeL Centre Nov. 21-23. He stayed four nights at a hotel in north London and took public transport to and from the ExCeL Centre in East London each day of the meeting. He returned to Israel on the evening of Nov. 23.
Dr. Maor, 45, who has received three doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine, had two PCR tests in the United Kingdom – on November 20 and 21 in line with travel requirements – and another PCR test upon arriving back in Israel in the early hours of Nov. 24. All three tests were negative.
He began experiencing symptoms within days and tested positive on Nov. 27. His symptoms have been mild so far, and he said he was feeling “better” at the time of his tweet on Nov. 30.
Dr. Maor believes he was infected during his trip to London. “The only reasonable explanation is that I got infected on the last day of the meeting – maybe at the airport, maybe at the meeting,” he told The Guardian newspaper.
Although his wife accompanied him to London, neither she nor any of his 3 children have experienced symptoms or tested positive for COVID-19. But Dr. Maor believes he has passed the infection to a 69-year-old colleague in Israel who has since tested positive for the Omicron variant. The colleague, who has also received three vaccine doses, is understood to have mild symptoms at present.
The case suggests that the Omicron variant of COVID-19 may have been circulating in the United Kingdom earlier than previously thought.
Implications for in-person conferences
It will also inevitably lead to questions about the safety of face-to-face conferences, which are only just starting to get underway again.
The PCR Valves 2021 meeting had more than 1,250 on-site attendees as well as 2,400 or more joining online, according to figures on its website. Dr. Maor said he did not have any issues with the conference organizers, who required proof of vaccination before entry. But he posted a photograph on his Twitter account of a crowded auditorium with many delegates not wearing masks.
The conference subsequently posted an announcement on its website alerting delegates that one of the attendees had tested positive for COVID-19 after returning to their home country. It reads: “Since the reported case comes less than a week after the end of PCR London Valves, we want to inform you so that you may decide the best course of action, for yourself, if any.” It does not mention that the case was the Omicron variant.
Patrick Jolly, strategic and market development director of the conference, commented: “As you may imagine, the health, safety and well-being of everyone who visited PCR London Valves was our number-one priority. All protocols mandated by the U.K. government were put in place. Anyone entering the congress center had to present a valid health pass and were requested to wear a mask. Hydro-alcoholic gel and masks were made readily available for all participants and disposal bins for used protective equipment were provided.”
Mr. Jolly also noted: “To date – more than 9 days after the end of PCR London Valves – we have had no report of any other case of participants testing positive who attended PCR London Valves.”
He said the EuroPCR organization believes that medical conferences are safe to be held in person.
“With the above sanitary requirements and protocols, and no complacency in their enforcement, we believe strongly that medical conferences can take place, as the benefits of in-person medical conferences are obvious for the concerned medical communities,” Mr. Jolly added.
But what about other meetings happening imminently and planning in-person attendance?
Eileen Murray, executive director of the American Epilepsy Society (AES), whose annual 5-day meeting starts today at Chicago’s McCormick Place Convention Center, said in an interview that the health, safety, and well-being of everyone attending is a priority.
“Vaccinations are required, with no exceptions, to anyone attending the in-person event,” Ms. Murray said. “AES is using the CLEAR HealthPass to verify identity and vaccination status for our attendees. No one who cannot verify identity and vaccination requirement will be permitted to attend the in-person event.”
She noted that masks will also be required except in limited circumstances when actively eating or drinking, or for a faculty member when actively presenting at a lecture or panel. “Anyone not adhering to the mask policy will be asked to leave the meeting and will be denied readmission to the meeting with no refund,” she said.
“These guidelines were developed in accordance with the latest public health guidance and AES will continue to follow that guidance as any updates are made with the emergence of the Omicron variant,” Ms. Murray added.
Also commenting on this issue, a spokesperson for the American Heart Association, which has its large annual international stroke meeting planned for in-person attendance in New Orleans in February, said: “As we have throughout the pandemic, the American Heart Association is closely monitoring conditions and following the guidance of the CDC as well as state and local health departments related to all in-person meetings.”
“Our upcoming International Stroke Conference, February 9-11, is planned as an in-person and digital experience which allows us the ultimate flexibility to address changing pandemic conditions. The health, safety, and well-being of our volunteers, members, and attendees from around the world remains our number-one priority,” the AHA spokesperson added.
But some COVID-19 experts are taking a more cautious view.
Rowland Kao, PhD, an expert in infectious disease dynamics at the University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, expressed concern about such large in-person conferences.
“We know that the Omicron variant appears to be spreading rapidly, with a recent preprint also telling us that the reinfection rate appears to be higher in South Africa. Should this be borne out, then the evidence would support that our reliance on a combination of vaccine-induced and natural immunity may be compromised by the Omicron variant,” he commented.
“We already know that extended contact indoors provides an additional risk, and so large meetings of this type have the potential to create extended risks. Until we know the extent to which Omicron causes severe illness, we should be extra cautious about these high-risk settings,” Dr. Kao commented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Successful COVID-19 Surge Management With Monoclonal Antibody Infusion in Emergency Department Patients
From the Center for Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Medicine, University of California, Irvine, CA (Drs. Chow and Chang, Mazaya Soundara), University of California Irvine School of Medicine, Irvine, CA (Ruchi Desai), Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California, Irvine, CA (Dr. Gohil), and the Department of Medicine and Hospital Medicine Program, University of California, Irvine, CA (Dr. Amin).
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has placed substantial strain on hospital resources and has been responsible for more than 733 000 deaths in the United States. The US Food and Drug Administration has granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy in the US for patients with early-stage high-risk COVID-19.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we studied the emergency department (ED) during a massive COVID-19 surge in Orange County, California, from December 4, 2020, to January 29, 2021, as a potential setting for efficient mAb delivery by evaluating the impact of bamlanivimab use in high-risk COVID-19 patients. All patients included in this study had positive results on nucleic acid amplification detection from nasopharyngeal or throat swabs, presented with 1 or more mild or moderate symptom, and met EUA criteria for mAb treatment. The primary outcome analyzed among this cohort of ED patients was overall improvement, which included subsequent ED/hospital visits, inpatient hospitalization, and death related to COVID-19.
Results: We identified 1278 ED patients with COVID-19 not treated with bamlanivimab and 73 patients with COVID-19 treated with bamlanivimab during the treatment period. Of these patients, 239 control patients and 63 treatment patients met EUA criteria. Overall, 7.9% (5/63) of patients receiving bamlanivimab had a subsequent ED/hospital visit, hospitalization, or death compared with 19.2% (46/239) in the control group (P = .03).
Conclusion: Targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 illness and substantially reduce the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths, especially for individuals of underserved populations who may not have access to ambulatory care.
Keywords: COVID-19; mAb; bamlanivimab; surge management.
Since December 2019, the novel pathogen SARS-CoV-2 has spread rapidly, culminating in a pandemic that has caused more than 4.9 million deaths worldwide and claimed more than 733 000 lives in the United States.1 The scale of the COVID-19 pandemic has placed an immense strain on hospital resources, including personal protective equipment (PPE), beds, ventilators and personnel.2,3 A previous analysis demonstrated that hospital capacity strain is associated with increased mortality and worsened health outcomes.4 A more recent analysis in light of the COVID-19 pandemic found that strains on critical care capacity were associated with increased COVID-19 intensive care unit (ICU) mortality.5 While more studies are needed to understand the association between hospital resources and COVID-19 mortality, efforts to decrease COVID-19 hospitalizations by early targeted treatment of patients in outpatient and emergency department (ED) settings may help to relieve the burden on hospital personnel and resources and decrease subsequent mortality.
Current therapeutic options focus on inpatient management of patients who progress to acute respiratory illness while patients with mild presentations are managed with outpatient monitoring, even those at high risk for progression. At the moment, only remdesivir, a viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.6 However, in November 2020, the FDA granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), monotherapy, and combination therapy in a broad range of early-stage, high-risk patients.7-9 Neutralizing mAbs include bamlanivimab (LY-CoV555), etesevimab (LY-CoV016), sotrovimab (VIR-7831), and casirivimab/imdevimab (REGN-COV2). These anti–spike protein antibodies prevent viral attachment to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor (hACE2) and subsequently prevent viral entry.10 mAb therapy has been shown to be effective in substantially reducing viral load, hospitalizations, and ED visits.11
Despite these promising results, uptake of mAb therapy has been slow, with more than 600 000 available doses remaining unused as of mid-January 2021, despite very high infection rates across the United States.12 In addition to the logistical challenges associated with intravenous (IV) therapy in the ambulatory setting, identifying, notifying, and scheduling appointments for ambulatory patients hamper efficient delivery to high-risk patients and limit access to underserved patients without primary care providers. For patients not treated in the ambulatory setting, the ED may serve as an ideal location for early implementation of mAb treatment in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
The University of California, Irvine (UCI) Medical Center is not only the major premium academic medical center in Orange County, California, but also the primary safety net hospital for vulnerable populations in Orange County. During the surge period from December 2020 through January 2021, we were over 100% capacity and had built an onsite mobile hospital to expand the number of beds available. Given the severity of the impact of COVID-19 on our resources, implementing a strategy to reduce hospital admissions, patient death, and subsequent ED visits was imperative. Our goal was to implement a strategy on the front end through the ED to optimize care for patients and reduce the strain on hospital resources.
We sought to study the ED during this massive surge as a potential setting for efficient mAb delivery by evaluating the impact of bamlanivimab use in high risk COVID-19 patients.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study (approved by UCI institutional review board) of sequential COVID-19 adult patients who were evaluated and discharged from the ED between December 4, 2020, and January 29, 2021, and received bamlanivimab treatment (cases) compared with a nontreatment group (control) of ED patients.
Using the UCI electronic medical record (EMR) system, we identified 1278 ED patients with COVID-19 not treated with bamlanivimab and 73 patients with COVID-19 treated with bamlanivimab during the months of December 2020 and January 2021. All patients included in this study met the EUA criteria for mAb therapy. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), during the period of this study, patients met EUA criteria if they had mild to moderate COVID-19, a positive direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing, and a high risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 or hospitalization.13 High risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 and/or hospitalization is defined as meeting at least 1 of the following criteria: a body mass index of 35 or higher, chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes, immunosuppressive disease, currently receiving immunosuppressive treatment, aged 65 years or older, aged 55 years or older and have cardiovascular disease or hypertension, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/other chronic respiratory diseases.13 All patients in the ED who met EUA criteria were offered mAb treatment; those who accepted the treatment were included in the treatment group, and those who refused were included in the control group.
All patients included in this study had positive results on nucleic acid amplification detection from nasopharyngeal or throat swabs and presented with 1 or more mild or moderate symptom, defined as: fever, cough, sore throat, malaise, headache, muscle pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, or shortness of breath. We excluded patients admitted to the hospital on that ED visit and those discharged to hospice. In addition, we excluded patients who presented 2 weeks after symptom onset and those who did not meet EUA criteria. Demographic data (age and gender) and comorbid conditions were obtained by EMR review. Comorbid conditions obtained included diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, coronary artery disease, CKD/end-stage renal disease (ESRD), COPD, obesity, and immunocompromised status.
Bamlanivimab infusion therapy in the ED followed CDC guidelines. Each patient received 700 mg of bamlanivimab diluted in 0.9% sodium chloride and administered as a single IV infusion. We established protocols to give patients IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) infusions directly in the ED.
The primary outcome analyzed among this cohort of ED patients was overall improvement, which included subsequent ED/hospital visits, inpatient hospitalization, and death related to COVID-19 within 90 days of initial ED visit. Each patient was only counted once. Data analysis and statistical tests were conducted using SPSS statistical software (SPSS Inc). Treatment effects were compared using χ2 test with an α level of 0.05. A t test was used for continuous variables, including age. A P value of less than .05 was considered significant.
Results
We screened a total of 1351 patients with COVID-19. Of these, 1278 patients did not receive treatment with bamlanivimab. Two hundred thirty-nine patients met inclusion criteria and were included in the control group. Seventy-three patients were treated with bamlanivimab in the ED; 63 of these patients met EUA criteria and comprised the treatment group (Figure 1).
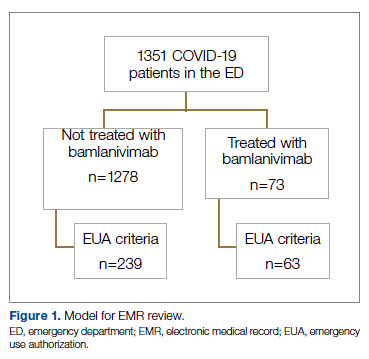
Demographic details of the trial groups are provided in Table 1. The median age of the treatment group was 61 years (interquartile range [IQR], 55-73), while the median age of the control group was 57 years (IQR, 48-68). The difference in median age between the treatment and control individuals was significantly different (P = .03). There was no significant difference found in terms of gender between the control and treatment groups (P = .07). In addition, no significant difference was seen among racial and ethnic groups in the control and treatment groups. Comorbidities and demographics of all patients in the treatment and control groups are provided in Table 1. The only comorbidity that was found to be significantly different between the treatment and control groups was CKD/ESRD. Among those treated with bamlanivimab, 20.6% (13/63) had CKD/ESRD compared with 10.5% (25/239) in the control group (P = .02).
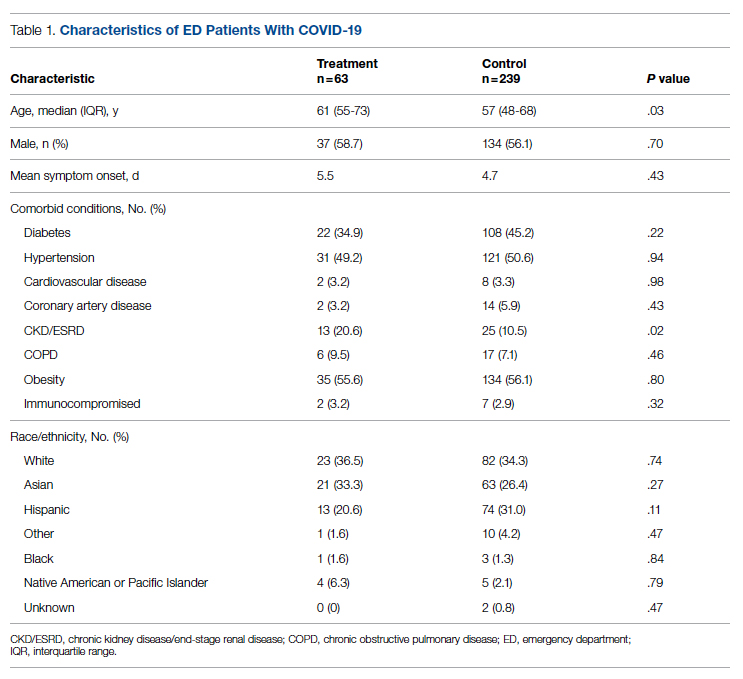
Overall, 7.9% (5/63) of patients receiving bamlanivimab had a subsequent ED/hospital visit, hospitalization, or death compared with 19.2% (46/239) in the control group (P = .03) (Table 2).
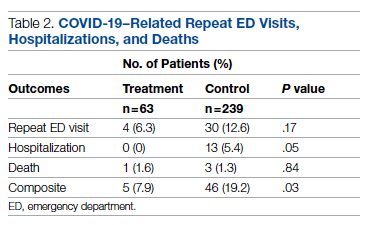
While the primary outcome of overall improvement was significantly different between the 2 groups, comparison of the individual components, including subsequent ED visits, hospitalizations, or death, were not significant. No treatment patients were hospitalized, compared with 5.4% (13/239) in the control group (P = .05). In the treatment group, 6.3% (4/63) returned to the ED compared with 12.6% (30/239) of the control group (P = .17). Finally, 1.6% (1/63) of the treatment group had a subsequent death that was due to COVID-19 compared with 1.3% (3/239) in the control group (P = .84) (Figure 2).
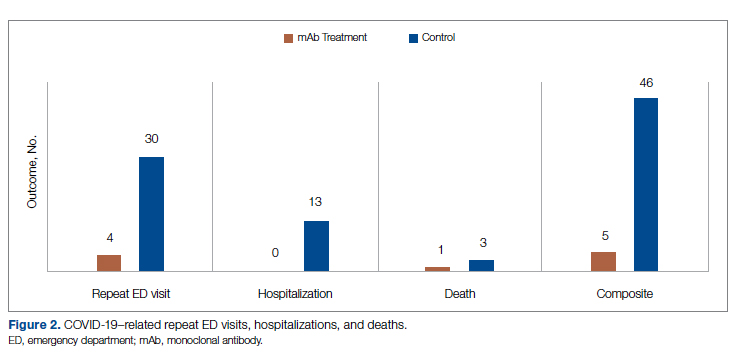
Discussion
In this retrospective cohort study, we observed a significant difference in rates of COVID-19 patients requiring repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths among those who received bamlanivimab compared with those who did not. Our study focused on high-risk patients with mild or moderate COVID-19, a unique subset of individuals who would normally be followed and treated via outpatient monitoring. We propose that treating high-risk patients earlier in their disease process with mAb therapy can have a major impact on overall outcomes, as defined by decreased subsequent hospitalizations, ED visits, and death.
Compared to clinical trials such as BLAZE-1 or REGN-COV2, every patient in this trial had at least 1 high-risk characteristic.9,11 This may explain why a greater proportion of our patients in both the control and treatment groups had subsequent hospitalization, ED visits, and deaths. COVID-19 patients seen in the ED may be a uniquely self-selected population of individuals likely to benefit from mAb therapy since they may be more likely to be sicker, have more comorbidities, or have less readily available primary care access for testing and treatment.14
Despite conducting a thorough literature review, we were unable to find any similar studies describing the ED as an appropriate setting for mAb treatment in patients with COVID-19. Multiple studies have used outpatient clinics as a setting for mAb treatment, and 1 retrospective analysis found that neutralizing mAb treatment in COVID-19 patients in an outpatient setting reduced hospital utilization.15 However, many Americans do not have access to primary care, with 1 study finding that only 75% of Americans had an identified source of primary care in 2015.16 Obstacles to primary care access include disabilities, lack of health insurance, language-related barriers, race/ethnicity, and homelessness.17 Barriers to access for primary care services and timely care make these populations more likely to frequent the ED.17 This makes the ED a unique location for early and targeted treatment of COVID-19 patients with a high risk for progression to severe COVID-19.
During surge periods in the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals met capacity or superseded their capacity for patients, with 4423 hospitals reporting more than 90% of hospital beds occupied and 2591 reporting more than 90% of ICU beds occupied during the peak surge week of January 1, 2021, to January 7, 2021.18 The main goals of lockdowns and masking have been to decrease the transmission of COVID-19 and hopefully flatten the curve to alleviate the burden on hospitals and decrease patient mortality. However, in surge situations when hospitals have already been pushed to their limits, we need to find ways to circumvent these shortages. This was particularly true at our academic medical center during the surge period of December 2020 through January 2021, necessitating the need for an innovative approach to improve patient outcomes and reduce the strain on resources. Utilizing the ED and implementing early treatment strategies with mAbs, especially during a surge crisis, can decrease severity of illness, hospitalizations, and deaths, as demonstrated in our article.
This study had several limitations. First, it is plausible that some ED patients may have gone to a different hospital after discharge from the UCI ED rather than returning to our institution. Given the constraints of using the EMR, we were only able to assess hospitalizations and subsequent ED visits at UCI. Second, there were 2 confounding variables identified when analyzing the demographic differences between the control and treatment group among those who met EUA criteria. The median age among those in the treatment group was greater than those in the control group (P = .03), and the proportion of individuals with CKD/ESRD was also greater in those in the treatment group (P = .02). It is well known that older patients and those with renal disease have higher incidences of morbidity and mortality. Achieving statistically significant differences overall between control and treatment groups despite greater numbers of older individuals and patients with renal disease in the treatment group supports our strategy and the usage of mAb.19,20
Finally, as of April 16, 2021, the FDA revoked EUA for bamlanivimab when administered alone. However, alternative mAb therapies remain available under the EUA, including REGEN-COV (casirivimab and imdevimab), sotrovimab, and the combination therapy of bamlanivimab and etesevimab.21 This decision was made in light of the increased frequency of resistant variants of SARS-CoV-2 with bamlanivimab treatment alone.21 Our study was conducted prior to this announcement. However, as treatment with other mAbs is still permissible, we believe our findings can translate to treatment with mAbs in general. In fact, combination therapy with bamlanivimab and etesevimab has been found to be more effective than monotherapy alone, suggesting that our results may be even more robust with combination mAb therapy.11 Overall, while additional studies are needed with larger sample sizes and combination mAb treatment to fully elucidate the impact of administering mAb treatment in the ED, our results suggest that targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, or deaths.
Conclusion
Targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 illness and substantially reduce the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths, especially for individuals of underserved populations who may not have access to ambulatory care.
Corresponding author: Alpesh Amin, MD, MBA, Department of Medicine and Hospital Medicine Program, University of California, Irvine, 333 City Tower West, Ste 500, Orange, CA 92868; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: This manuscript was generously supported by multiple donors, including the Mehra Family, the Yang Family, and the Chao Family. Dr. Amin reported serving as Principal Investigator or Co-Investigator of clinical trials sponsored by NIH/NIAID, NeuroRX Pharma, Pulmotect, Blade Therapeutics, Novartis, Takeda, Humanigen, Eli Lilly, PTC Therapeutics, OctaPharma, Fulcrum Therapeutics, and Alexion, unrelated to the present study. He has served as speaker and/or consultant for BMS, Pfizer, BI, Portola, Sunovion, Mylan, Salix, Alexion, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Nabriva, Paratek, Bayer, Tetraphase, Achaogen La Jolla, Ferring, Seres, Millennium, PeraHealth, HeartRite, Aseptiscope, and Sprightly, unrelated to the present study.
1. Global map. Johns Hopkins University & Medicine Coronavirus Resource Center. Updated November 9, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
2. Truog RD, Mitchell C, Daley GQ. The toughest triage — allocating ventilators in a pandemic. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(21):1973-1975. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2005689
3. Cavallo JJ, Donoho DA, Forman HP. Hospital capacity and operations in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic—planning for the Nth patient. JAMA Health Forum. 2020;1(3):e200345. doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2020.0345
4. Eriksson CO, Stoner RC, Eden KB, et al. The association between hospital capacity strain and inpatient outcomes in highly developed countries: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(6):686-696. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3936-3
5. Bravata DM, Perkins AJ, Myers LJ, et al. Association of intensive care unit patient load and demand with mortality rates in US Department of Veterans Affairs hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2034266. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34266
6. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(19);1813-1826. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
7. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes monoclonal antibody for treatment of COVID-19. US Food & Drug Administration. November 9, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-monoclonal-antibody-treatment-covid-19
8. Chen P, Nirula A, Heller B, et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):229-237. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2029849
9. Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, et al. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):238-251. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035002
10. Chen X, Li R, Pan Z, et al. Human monoclonal antibodies block the binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17(6):647-649. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0426-7
11. Gottlieb RL, Nirula A, Chen P, et al. Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021;325(7):632-644. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202
12. Toy S, Walker J, Evans M. Highly touted monoclonal antibody therapies sit unused in hospitals The Wall Street Journal. December 27, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.wsj.com/articles/highly-touted-monoclonal-antibody-therapies-sit-unused-in-hospitals-11609087364
13. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies. NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. Updated October 19, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/anti-sars-cov-2-antibody-products/anti-sars-cov-2-monoclonal-antibodies/
14. Langellier BA. Policy recommendations to address high risk of COVID-19 among immigrants. Am J Public Health. 2020;110(8):1137-1139. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2020.305792
15. Verderese J P, Stepanova M, Lam B, et al. Neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment reduces hospitalization for mild and moderate COVID-19: a real-world experience. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;ciab579. doi:10.1093/cid/ciab579
16. Levine DM, Linder JA, Landon BE. Characteristics of Americans with primary care and changes over time, 2002-2015. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(3):463-466. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.6282
17. Rust G, Ye J, Daniels E, et al. Practical barriers to timely primary care access: impact on adult use of emergency department services. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(15):1705-1710. doi:10.1001/archinte.168.15.1705
18. COVID-19 Hospitalization Tracking Project: analysis of HHS data. University of Minnesota. Carlson School of Management. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://carlsonschool.umn.edu/mili-misrc-covid19-tracking-project
19. Zare˛bska-Michaluk D, Jaroszewicz J, Rogalska M, et al. Impact of kidney failure on the severity of COVID-19. J Clin Med. 2021;10(9):2042. doi:10.3390/jcm10092042
20. Shahid Z, Kalayanamitra R, McClafferty B, et al. COVID‐19 and older adults: what we know. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(5):926-929. doi:10.1111/jgs.16472
21. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA revokes emergency use authorization for monoclonal antibody bamlanivimab. US Food & Drug Administration. April 16, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-revokes-emergency-use-authorization-monoclonal-antibody-bamlanivimab
From the Center for Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Medicine, University of California, Irvine, CA (Drs. Chow and Chang, Mazaya Soundara), University of California Irvine School of Medicine, Irvine, CA (Ruchi Desai), Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California, Irvine, CA (Dr. Gohil), and the Department of Medicine and Hospital Medicine Program, University of California, Irvine, CA (Dr. Amin).
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has placed substantial strain on hospital resources and has been responsible for more than 733 000 deaths in the United States. The US Food and Drug Administration has granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy in the US for patients with early-stage high-risk COVID-19.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we studied the emergency department (ED) during a massive COVID-19 surge in Orange County, California, from December 4, 2020, to January 29, 2021, as a potential setting for efficient mAb delivery by evaluating the impact of bamlanivimab use in high-risk COVID-19 patients. All patients included in this study had positive results on nucleic acid amplification detection from nasopharyngeal or throat swabs, presented with 1 or more mild or moderate symptom, and met EUA criteria for mAb treatment. The primary outcome analyzed among this cohort of ED patients was overall improvement, which included subsequent ED/hospital visits, inpatient hospitalization, and death related to COVID-19.
Results: We identified 1278 ED patients with COVID-19 not treated with bamlanivimab and 73 patients with COVID-19 treated with bamlanivimab during the treatment period. Of these patients, 239 control patients and 63 treatment patients met EUA criteria. Overall, 7.9% (5/63) of patients receiving bamlanivimab had a subsequent ED/hospital visit, hospitalization, or death compared with 19.2% (46/239) in the control group (P = .03).
Conclusion: Targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 illness and substantially reduce the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths, especially for individuals of underserved populations who may not have access to ambulatory care.
Keywords: COVID-19; mAb; bamlanivimab; surge management.
Since December 2019, the novel pathogen SARS-CoV-2 has spread rapidly, culminating in a pandemic that has caused more than 4.9 million deaths worldwide and claimed more than 733 000 lives in the United States.1 The scale of the COVID-19 pandemic has placed an immense strain on hospital resources, including personal protective equipment (PPE), beds, ventilators and personnel.2,3 A previous analysis demonstrated that hospital capacity strain is associated with increased mortality and worsened health outcomes.4 A more recent analysis in light of the COVID-19 pandemic found that strains on critical care capacity were associated with increased COVID-19 intensive care unit (ICU) mortality.5 While more studies are needed to understand the association between hospital resources and COVID-19 mortality, efforts to decrease COVID-19 hospitalizations by early targeted treatment of patients in outpatient and emergency department (ED) settings may help to relieve the burden on hospital personnel and resources and decrease subsequent mortality.
Current therapeutic options focus on inpatient management of patients who progress to acute respiratory illness while patients with mild presentations are managed with outpatient monitoring, even those at high risk for progression. At the moment, only remdesivir, a viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.6 However, in November 2020, the FDA granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), monotherapy, and combination therapy in a broad range of early-stage, high-risk patients.7-9 Neutralizing mAbs include bamlanivimab (LY-CoV555), etesevimab (LY-CoV016), sotrovimab (VIR-7831), and casirivimab/imdevimab (REGN-COV2). These anti–spike protein antibodies prevent viral attachment to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor (hACE2) and subsequently prevent viral entry.10 mAb therapy has been shown to be effective in substantially reducing viral load, hospitalizations, and ED visits.11
Despite these promising results, uptake of mAb therapy has been slow, with more than 600 000 available doses remaining unused as of mid-January 2021, despite very high infection rates across the United States.12 In addition to the logistical challenges associated with intravenous (IV) therapy in the ambulatory setting, identifying, notifying, and scheduling appointments for ambulatory patients hamper efficient delivery to high-risk patients and limit access to underserved patients without primary care providers. For patients not treated in the ambulatory setting, the ED may serve as an ideal location for early implementation of mAb treatment in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
The University of California, Irvine (UCI) Medical Center is not only the major premium academic medical center in Orange County, California, but also the primary safety net hospital for vulnerable populations in Orange County. During the surge period from December 2020 through January 2021, we were over 100% capacity and had built an onsite mobile hospital to expand the number of beds available. Given the severity of the impact of COVID-19 on our resources, implementing a strategy to reduce hospital admissions, patient death, and subsequent ED visits was imperative. Our goal was to implement a strategy on the front end through the ED to optimize care for patients and reduce the strain on hospital resources.
We sought to study the ED during this massive surge as a potential setting for efficient mAb delivery by evaluating the impact of bamlanivimab use in high risk COVID-19 patients.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study (approved by UCI institutional review board) of sequential COVID-19 adult patients who were evaluated and discharged from the ED between December 4, 2020, and January 29, 2021, and received bamlanivimab treatment (cases) compared with a nontreatment group (control) of ED patients.
Using the UCI electronic medical record (EMR) system, we identified 1278 ED patients with COVID-19 not treated with bamlanivimab and 73 patients with COVID-19 treated with bamlanivimab during the months of December 2020 and January 2021. All patients included in this study met the EUA criteria for mAb therapy. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), during the period of this study, patients met EUA criteria if they had mild to moderate COVID-19, a positive direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing, and a high risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 or hospitalization.13 High risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 and/or hospitalization is defined as meeting at least 1 of the following criteria: a body mass index of 35 or higher, chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes, immunosuppressive disease, currently receiving immunosuppressive treatment, aged 65 years or older, aged 55 years or older and have cardiovascular disease or hypertension, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/other chronic respiratory diseases.13 All patients in the ED who met EUA criteria were offered mAb treatment; those who accepted the treatment were included in the treatment group, and those who refused were included in the control group.
All patients included in this study had positive results on nucleic acid amplification detection from nasopharyngeal or throat swabs and presented with 1 or more mild or moderate symptom, defined as: fever, cough, sore throat, malaise, headache, muscle pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, or shortness of breath. We excluded patients admitted to the hospital on that ED visit and those discharged to hospice. In addition, we excluded patients who presented 2 weeks after symptom onset and those who did not meet EUA criteria. Demographic data (age and gender) and comorbid conditions were obtained by EMR review. Comorbid conditions obtained included diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, coronary artery disease, CKD/end-stage renal disease (ESRD), COPD, obesity, and immunocompromised status.
Bamlanivimab infusion therapy in the ED followed CDC guidelines. Each patient received 700 mg of bamlanivimab diluted in 0.9% sodium chloride and administered as a single IV infusion. We established protocols to give patients IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) infusions directly in the ED.
The primary outcome analyzed among this cohort of ED patients was overall improvement, which included subsequent ED/hospital visits, inpatient hospitalization, and death related to COVID-19 within 90 days of initial ED visit. Each patient was only counted once. Data analysis and statistical tests were conducted using SPSS statistical software (SPSS Inc). Treatment effects were compared using χ2 test with an α level of 0.05. A t test was used for continuous variables, including age. A P value of less than .05 was considered significant.
Results
We screened a total of 1351 patients with COVID-19. Of these, 1278 patients did not receive treatment with bamlanivimab. Two hundred thirty-nine patients met inclusion criteria and were included in the control group. Seventy-three patients were treated with bamlanivimab in the ED; 63 of these patients met EUA criteria and comprised the treatment group (Figure 1).

Demographic details of the trial groups are provided in Table 1. The median age of the treatment group was 61 years (interquartile range [IQR], 55-73), while the median age of the control group was 57 years (IQR, 48-68). The difference in median age between the treatment and control individuals was significantly different (P = .03). There was no significant difference found in terms of gender between the control and treatment groups (P = .07). In addition, no significant difference was seen among racial and ethnic groups in the control and treatment groups. Comorbidities and demographics of all patients in the treatment and control groups are provided in Table 1. The only comorbidity that was found to be significantly different between the treatment and control groups was CKD/ESRD. Among those treated with bamlanivimab, 20.6% (13/63) had CKD/ESRD compared with 10.5% (25/239) in the control group (P = .02).

Overall, 7.9% (5/63) of patients receiving bamlanivimab had a subsequent ED/hospital visit, hospitalization, or death compared with 19.2% (46/239) in the control group (P = .03) (Table 2).

While the primary outcome of overall improvement was significantly different between the 2 groups, comparison of the individual components, including subsequent ED visits, hospitalizations, or death, were not significant. No treatment patients were hospitalized, compared with 5.4% (13/239) in the control group (P = .05). In the treatment group, 6.3% (4/63) returned to the ED compared with 12.6% (30/239) of the control group (P = .17). Finally, 1.6% (1/63) of the treatment group had a subsequent death that was due to COVID-19 compared with 1.3% (3/239) in the control group (P = .84) (Figure 2).

Discussion
In this retrospective cohort study, we observed a significant difference in rates of COVID-19 patients requiring repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths among those who received bamlanivimab compared with those who did not. Our study focused on high-risk patients with mild or moderate COVID-19, a unique subset of individuals who would normally be followed and treated via outpatient monitoring. We propose that treating high-risk patients earlier in their disease process with mAb therapy can have a major impact on overall outcomes, as defined by decreased subsequent hospitalizations, ED visits, and death.
Compared to clinical trials such as BLAZE-1 or REGN-COV2, every patient in this trial had at least 1 high-risk characteristic.9,11 This may explain why a greater proportion of our patients in both the control and treatment groups had subsequent hospitalization, ED visits, and deaths. COVID-19 patients seen in the ED may be a uniquely self-selected population of individuals likely to benefit from mAb therapy since they may be more likely to be sicker, have more comorbidities, or have less readily available primary care access for testing and treatment.14
Despite conducting a thorough literature review, we were unable to find any similar studies describing the ED as an appropriate setting for mAb treatment in patients with COVID-19. Multiple studies have used outpatient clinics as a setting for mAb treatment, and 1 retrospective analysis found that neutralizing mAb treatment in COVID-19 patients in an outpatient setting reduced hospital utilization.15 However, many Americans do not have access to primary care, with 1 study finding that only 75% of Americans had an identified source of primary care in 2015.16 Obstacles to primary care access include disabilities, lack of health insurance, language-related barriers, race/ethnicity, and homelessness.17 Barriers to access for primary care services and timely care make these populations more likely to frequent the ED.17 This makes the ED a unique location for early and targeted treatment of COVID-19 patients with a high risk for progression to severe COVID-19.
During surge periods in the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals met capacity or superseded their capacity for patients, with 4423 hospitals reporting more than 90% of hospital beds occupied and 2591 reporting more than 90% of ICU beds occupied during the peak surge week of January 1, 2021, to January 7, 2021.18 The main goals of lockdowns and masking have been to decrease the transmission of COVID-19 and hopefully flatten the curve to alleviate the burden on hospitals and decrease patient mortality. However, in surge situations when hospitals have already been pushed to their limits, we need to find ways to circumvent these shortages. This was particularly true at our academic medical center during the surge period of December 2020 through January 2021, necessitating the need for an innovative approach to improve patient outcomes and reduce the strain on resources. Utilizing the ED and implementing early treatment strategies with mAbs, especially during a surge crisis, can decrease severity of illness, hospitalizations, and deaths, as demonstrated in our article.
This study had several limitations. First, it is plausible that some ED patients may have gone to a different hospital after discharge from the UCI ED rather than returning to our institution. Given the constraints of using the EMR, we were only able to assess hospitalizations and subsequent ED visits at UCI. Second, there were 2 confounding variables identified when analyzing the demographic differences between the control and treatment group among those who met EUA criteria. The median age among those in the treatment group was greater than those in the control group (P = .03), and the proportion of individuals with CKD/ESRD was also greater in those in the treatment group (P = .02). It is well known that older patients and those with renal disease have higher incidences of morbidity and mortality. Achieving statistically significant differences overall between control and treatment groups despite greater numbers of older individuals and patients with renal disease in the treatment group supports our strategy and the usage of mAb.19,20
Finally, as of April 16, 2021, the FDA revoked EUA for bamlanivimab when administered alone. However, alternative mAb therapies remain available under the EUA, including REGEN-COV (casirivimab and imdevimab), sotrovimab, and the combination therapy of bamlanivimab and etesevimab.21 This decision was made in light of the increased frequency of resistant variants of SARS-CoV-2 with bamlanivimab treatment alone.21 Our study was conducted prior to this announcement. However, as treatment with other mAbs is still permissible, we believe our findings can translate to treatment with mAbs in general. In fact, combination therapy with bamlanivimab and etesevimab has been found to be more effective than monotherapy alone, suggesting that our results may be even more robust with combination mAb therapy.11 Overall, while additional studies are needed with larger sample sizes and combination mAb treatment to fully elucidate the impact of administering mAb treatment in the ED, our results suggest that targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, or deaths.
Conclusion
Targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 illness and substantially reduce the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths, especially for individuals of underserved populations who may not have access to ambulatory care.
Corresponding author: Alpesh Amin, MD, MBA, Department of Medicine and Hospital Medicine Program, University of California, Irvine, 333 City Tower West, Ste 500, Orange, CA 92868; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: This manuscript was generously supported by multiple donors, including the Mehra Family, the Yang Family, and the Chao Family. Dr. Amin reported serving as Principal Investigator or Co-Investigator of clinical trials sponsored by NIH/NIAID, NeuroRX Pharma, Pulmotect, Blade Therapeutics, Novartis, Takeda, Humanigen, Eli Lilly, PTC Therapeutics, OctaPharma, Fulcrum Therapeutics, and Alexion, unrelated to the present study. He has served as speaker and/or consultant for BMS, Pfizer, BI, Portola, Sunovion, Mylan, Salix, Alexion, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Nabriva, Paratek, Bayer, Tetraphase, Achaogen La Jolla, Ferring, Seres, Millennium, PeraHealth, HeartRite, Aseptiscope, and Sprightly, unrelated to the present study.
From the Center for Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Medicine, University of California, Irvine, CA (Drs. Chow and Chang, Mazaya Soundara), University of California Irvine School of Medicine, Irvine, CA (Ruchi Desai), Division of Infectious Diseases, University of California, Irvine, CA (Dr. Gohil), and the Department of Medicine and Hospital Medicine Program, University of California, Irvine, CA (Dr. Amin).
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has placed substantial strain on hospital resources and has been responsible for more than 733 000 deaths in the United States. The US Food and Drug Administration has granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy in the US for patients with early-stage high-risk COVID-19.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we studied the emergency department (ED) during a massive COVID-19 surge in Orange County, California, from December 4, 2020, to January 29, 2021, as a potential setting for efficient mAb delivery by evaluating the impact of bamlanivimab use in high-risk COVID-19 patients. All patients included in this study had positive results on nucleic acid amplification detection from nasopharyngeal or throat swabs, presented with 1 or more mild or moderate symptom, and met EUA criteria for mAb treatment. The primary outcome analyzed among this cohort of ED patients was overall improvement, which included subsequent ED/hospital visits, inpatient hospitalization, and death related to COVID-19.
Results: We identified 1278 ED patients with COVID-19 not treated with bamlanivimab and 73 patients with COVID-19 treated with bamlanivimab during the treatment period. Of these patients, 239 control patients and 63 treatment patients met EUA criteria. Overall, 7.9% (5/63) of patients receiving bamlanivimab had a subsequent ED/hospital visit, hospitalization, or death compared with 19.2% (46/239) in the control group (P = .03).
Conclusion: Targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 illness and substantially reduce the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths, especially for individuals of underserved populations who may not have access to ambulatory care.
Keywords: COVID-19; mAb; bamlanivimab; surge management.
Since December 2019, the novel pathogen SARS-CoV-2 has spread rapidly, culminating in a pandemic that has caused more than 4.9 million deaths worldwide and claimed more than 733 000 lives in the United States.1 The scale of the COVID-19 pandemic has placed an immense strain on hospital resources, including personal protective equipment (PPE), beds, ventilators and personnel.2,3 A previous analysis demonstrated that hospital capacity strain is associated with increased mortality and worsened health outcomes.4 A more recent analysis in light of the COVID-19 pandemic found that strains on critical care capacity were associated with increased COVID-19 intensive care unit (ICU) mortality.5 While more studies are needed to understand the association between hospital resources and COVID-19 mortality, efforts to decrease COVID-19 hospitalizations by early targeted treatment of patients in outpatient and emergency department (ED) settings may help to relieve the burden on hospital personnel and resources and decrease subsequent mortality.
Current therapeutic options focus on inpatient management of patients who progress to acute respiratory illness while patients with mild presentations are managed with outpatient monitoring, even those at high risk for progression. At the moment, only remdesivir, a viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.6 However, in November 2020, the FDA granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), monotherapy, and combination therapy in a broad range of early-stage, high-risk patients.7-9 Neutralizing mAbs include bamlanivimab (LY-CoV555), etesevimab (LY-CoV016), sotrovimab (VIR-7831), and casirivimab/imdevimab (REGN-COV2). These anti–spike protein antibodies prevent viral attachment to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor (hACE2) and subsequently prevent viral entry.10 mAb therapy has been shown to be effective in substantially reducing viral load, hospitalizations, and ED visits.11
Despite these promising results, uptake of mAb therapy has been slow, with more than 600 000 available doses remaining unused as of mid-January 2021, despite very high infection rates across the United States.12 In addition to the logistical challenges associated with intravenous (IV) therapy in the ambulatory setting, identifying, notifying, and scheduling appointments for ambulatory patients hamper efficient delivery to high-risk patients and limit access to underserved patients without primary care providers. For patients not treated in the ambulatory setting, the ED may serve as an ideal location for early implementation of mAb treatment in high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
The University of California, Irvine (UCI) Medical Center is not only the major premium academic medical center in Orange County, California, but also the primary safety net hospital for vulnerable populations in Orange County. During the surge period from December 2020 through January 2021, we were over 100% capacity and had built an onsite mobile hospital to expand the number of beds available. Given the severity of the impact of COVID-19 on our resources, implementing a strategy to reduce hospital admissions, patient death, and subsequent ED visits was imperative. Our goal was to implement a strategy on the front end through the ED to optimize care for patients and reduce the strain on hospital resources.
We sought to study the ED during this massive surge as a potential setting for efficient mAb delivery by evaluating the impact of bamlanivimab use in high risk COVID-19 patients.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study (approved by UCI institutional review board) of sequential COVID-19 adult patients who were evaluated and discharged from the ED between December 4, 2020, and January 29, 2021, and received bamlanivimab treatment (cases) compared with a nontreatment group (control) of ED patients.
Using the UCI electronic medical record (EMR) system, we identified 1278 ED patients with COVID-19 not treated with bamlanivimab and 73 patients with COVID-19 treated with bamlanivimab during the months of December 2020 and January 2021. All patients included in this study met the EUA criteria for mAb therapy. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), during the period of this study, patients met EUA criteria if they had mild to moderate COVID-19, a positive direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing, and a high risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 or hospitalization.13 High risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 and/or hospitalization is defined as meeting at least 1 of the following criteria: a body mass index of 35 or higher, chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes, immunosuppressive disease, currently receiving immunosuppressive treatment, aged 65 years or older, aged 55 years or older and have cardiovascular disease or hypertension, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/other chronic respiratory diseases.13 All patients in the ED who met EUA criteria were offered mAb treatment; those who accepted the treatment were included in the treatment group, and those who refused were included in the control group.
All patients included in this study had positive results on nucleic acid amplification detection from nasopharyngeal or throat swabs and presented with 1 or more mild or moderate symptom, defined as: fever, cough, sore throat, malaise, headache, muscle pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, or shortness of breath. We excluded patients admitted to the hospital on that ED visit and those discharged to hospice. In addition, we excluded patients who presented 2 weeks after symptom onset and those who did not meet EUA criteria. Demographic data (age and gender) and comorbid conditions were obtained by EMR review. Comorbid conditions obtained included diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, coronary artery disease, CKD/end-stage renal disease (ESRD), COPD, obesity, and immunocompromised status.
Bamlanivimab infusion therapy in the ED followed CDC guidelines. Each patient received 700 mg of bamlanivimab diluted in 0.9% sodium chloride and administered as a single IV infusion. We established protocols to give patients IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) infusions directly in the ED.
The primary outcome analyzed among this cohort of ED patients was overall improvement, which included subsequent ED/hospital visits, inpatient hospitalization, and death related to COVID-19 within 90 days of initial ED visit. Each patient was only counted once. Data analysis and statistical tests were conducted using SPSS statistical software (SPSS Inc). Treatment effects were compared using χ2 test with an α level of 0.05. A t test was used for continuous variables, including age. A P value of less than .05 was considered significant.
Results
We screened a total of 1351 patients with COVID-19. Of these, 1278 patients did not receive treatment with bamlanivimab. Two hundred thirty-nine patients met inclusion criteria and were included in the control group. Seventy-three patients were treated with bamlanivimab in the ED; 63 of these patients met EUA criteria and comprised the treatment group (Figure 1).

Demographic details of the trial groups are provided in Table 1. The median age of the treatment group was 61 years (interquartile range [IQR], 55-73), while the median age of the control group was 57 years (IQR, 48-68). The difference in median age between the treatment and control individuals was significantly different (P = .03). There was no significant difference found in terms of gender between the control and treatment groups (P = .07). In addition, no significant difference was seen among racial and ethnic groups in the control and treatment groups. Comorbidities and demographics of all patients in the treatment and control groups are provided in Table 1. The only comorbidity that was found to be significantly different between the treatment and control groups was CKD/ESRD. Among those treated with bamlanivimab, 20.6% (13/63) had CKD/ESRD compared with 10.5% (25/239) in the control group (P = .02).

Overall, 7.9% (5/63) of patients receiving bamlanivimab had a subsequent ED/hospital visit, hospitalization, or death compared with 19.2% (46/239) in the control group (P = .03) (Table 2).

While the primary outcome of overall improvement was significantly different between the 2 groups, comparison of the individual components, including subsequent ED visits, hospitalizations, or death, were not significant. No treatment patients were hospitalized, compared with 5.4% (13/239) in the control group (P = .05). In the treatment group, 6.3% (4/63) returned to the ED compared with 12.6% (30/239) of the control group (P = .17). Finally, 1.6% (1/63) of the treatment group had a subsequent death that was due to COVID-19 compared with 1.3% (3/239) in the control group (P = .84) (Figure 2).

Discussion
In this retrospective cohort study, we observed a significant difference in rates of COVID-19 patients requiring repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths among those who received bamlanivimab compared with those who did not. Our study focused on high-risk patients with mild or moderate COVID-19, a unique subset of individuals who would normally be followed and treated via outpatient monitoring. We propose that treating high-risk patients earlier in their disease process with mAb therapy can have a major impact on overall outcomes, as defined by decreased subsequent hospitalizations, ED visits, and death.
Compared to clinical trials such as BLAZE-1 or REGN-COV2, every patient in this trial had at least 1 high-risk characteristic.9,11 This may explain why a greater proportion of our patients in both the control and treatment groups had subsequent hospitalization, ED visits, and deaths. COVID-19 patients seen in the ED may be a uniquely self-selected population of individuals likely to benefit from mAb therapy since they may be more likely to be sicker, have more comorbidities, or have less readily available primary care access for testing and treatment.14
Despite conducting a thorough literature review, we were unable to find any similar studies describing the ED as an appropriate setting for mAb treatment in patients with COVID-19. Multiple studies have used outpatient clinics as a setting for mAb treatment, and 1 retrospective analysis found that neutralizing mAb treatment in COVID-19 patients in an outpatient setting reduced hospital utilization.15 However, many Americans do not have access to primary care, with 1 study finding that only 75% of Americans had an identified source of primary care in 2015.16 Obstacles to primary care access include disabilities, lack of health insurance, language-related barriers, race/ethnicity, and homelessness.17 Barriers to access for primary care services and timely care make these populations more likely to frequent the ED.17 This makes the ED a unique location for early and targeted treatment of COVID-19 patients with a high risk for progression to severe COVID-19.
During surge periods in the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals met capacity or superseded their capacity for patients, with 4423 hospitals reporting more than 90% of hospital beds occupied and 2591 reporting more than 90% of ICU beds occupied during the peak surge week of January 1, 2021, to January 7, 2021.18 The main goals of lockdowns and masking have been to decrease the transmission of COVID-19 and hopefully flatten the curve to alleviate the burden on hospitals and decrease patient mortality. However, in surge situations when hospitals have already been pushed to their limits, we need to find ways to circumvent these shortages. This was particularly true at our academic medical center during the surge period of December 2020 through January 2021, necessitating the need for an innovative approach to improve patient outcomes and reduce the strain on resources. Utilizing the ED and implementing early treatment strategies with mAbs, especially during a surge crisis, can decrease severity of illness, hospitalizations, and deaths, as demonstrated in our article.
This study had several limitations. First, it is plausible that some ED patients may have gone to a different hospital after discharge from the UCI ED rather than returning to our institution. Given the constraints of using the EMR, we were only able to assess hospitalizations and subsequent ED visits at UCI. Second, there were 2 confounding variables identified when analyzing the demographic differences between the control and treatment group among those who met EUA criteria. The median age among those in the treatment group was greater than those in the control group (P = .03), and the proportion of individuals with CKD/ESRD was also greater in those in the treatment group (P = .02). It is well known that older patients and those with renal disease have higher incidences of morbidity and mortality. Achieving statistically significant differences overall between control and treatment groups despite greater numbers of older individuals and patients with renal disease in the treatment group supports our strategy and the usage of mAb.19,20
Finally, as of April 16, 2021, the FDA revoked EUA for bamlanivimab when administered alone. However, alternative mAb therapies remain available under the EUA, including REGEN-COV (casirivimab and imdevimab), sotrovimab, and the combination therapy of bamlanivimab and etesevimab.21 This decision was made in light of the increased frequency of resistant variants of SARS-CoV-2 with bamlanivimab treatment alone.21 Our study was conducted prior to this announcement. However, as treatment with other mAbs is still permissible, we believe our findings can translate to treatment with mAbs in general. In fact, combination therapy with bamlanivimab and etesevimab has been found to be more effective than monotherapy alone, suggesting that our results may be even more robust with combination mAb therapy.11 Overall, while additional studies are needed with larger sample sizes and combination mAb treatment to fully elucidate the impact of administering mAb treatment in the ED, our results suggest that targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, or deaths.
Conclusion
Targeting ED patients for mAb treatment may be an effective strategy to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 illness and substantially reduce the composite end point of repeat ED visits, hospitalizations, and deaths, especially for individuals of underserved populations who may not have access to ambulatory care.
Corresponding author: Alpesh Amin, MD, MBA, Department of Medicine and Hospital Medicine Program, University of California, Irvine, 333 City Tower West, Ste 500, Orange, CA 92868; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: This manuscript was generously supported by multiple donors, including the Mehra Family, the Yang Family, and the Chao Family. Dr. Amin reported serving as Principal Investigator or Co-Investigator of clinical trials sponsored by NIH/NIAID, NeuroRX Pharma, Pulmotect, Blade Therapeutics, Novartis, Takeda, Humanigen, Eli Lilly, PTC Therapeutics, OctaPharma, Fulcrum Therapeutics, and Alexion, unrelated to the present study. He has served as speaker and/or consultant for BMS, Pfizer, BI, Portola, Sunovion, Mylan, Salix, Alexion, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Nabriva, Paratek, Bayer, Tetraphase, Achaogen La Jolla, Ferring, Seres, Millennium, PeraHealth, HeartRite, Aseptiscope, and Sprightly, unrelated to the present study.
1. Global map. Johns Hopkins University & Medicine Coronavirus Resource Center. Updated November 9, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
2. Truog RD, Mitchell C, Daley GQ. The toughest triage — allocating ventilators in a pandemic. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(21):1973-1975. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2005689
3. Cavallo JJ, Donoho DA, Forman HP. Hospital capacity and operations in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic—planning for the Nth patient. JAMA Health Forum. 2020;1(3):e200345. doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2020.0345
4. Eriksson CO, Stoner RC, Eden KB, et al. The association between hospital capacity strain and inpatient outcomes in highly developed countries: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(6):686-696. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3936-3
5. Bravata DM, Perkins AJ, Myers LJ, et al. Association of intensive care unit patient load and demand with mortality rates in US Department of Veterans Affairs hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2034266. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34266
6. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(19);1813-1826. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
7. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes monoclonal antibody for treatment of COVID-19. US Food & Drug Administration. November 9, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-monoclonal-antibody-treatment-covid-19
8. Chen P, Nirula A, Heller B, et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):229-237. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2029849
9. Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, et al. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):238-251. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035002
10. Chen X, Li R, Pan Z, et al. Human monoclonal antibodies block the binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17(6):647-649. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0426-7
11. Gottlieb RL, Nirula A, Chen P, et al. Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021;325(7):632-644. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202
12. Toy S, Walker J, Evans M. Highly touted monoclonal antibody therapies sit unused in hospitals The Wall Street Journal. December 27, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.wsj.com/articles/highly-touted-monoclonal-antibody-therapies-sit-unused-in-hospitals-11609087364
13. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies. NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. Updated October 19, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/anti-sars-cov-2-antibody-products/anti-sars-cov-2-monoclonal-antibodies/
14. Langellier BA. Policy recommendations to address high risk of COVID-19 among immigrants. Am J Public Health. 2020;110(8):1137-1139. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2020.305792
15. Verderese J P, Stepanova M, Lam B, et al. Neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment reduces hospitalization for mild and moderate COVID-19: a real-world experience. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;ciab579. doi:10.1093/cid/ciab579
16. Levine DM, Linder JA, Landon BE. Characteristics of Americans with primary care and changes over time, 2002-2015. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(3):463-466. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.6282
17. Rust G, Ye J, Daniels E, et al. Practical barriers to timely primary care access: impact on adult use of emergency department services. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(15):1705-1710. doi:10.1001/archinte.168.15.1705
18. COVID-19 Hospitalization Tracking Project: analysis of HHS data. University of Minnesota. Carlson School of Management. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://carlsonschool.umn.edu/mili-misrc-covid19-tracking-project
19. Zare˛bska-Michaluk D, Jaroszewicz J, Rogalska M, et al. Impact of kidney failure on the severity of COVID-19. J Clin Med. 2021;10(9):2042. doi:10.3390/jcm10092042
20. Shahid Z, Kalayanamitra R, McClafferty B, et al. COVID‐19 and older adults: what we know. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(5):926-929. doi:10.1111/jgs.16472
21. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA revokes emergency use authorization for monoclonal antibody bamlanivimab. US Food & Drug Administration. April 16, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-revokes-emergency-use-authorization-monoclonal-antibody-bamlanivimab
1. Global map. Johns Hopkins University & Medicine Coronavirus Resource Center. Updated November 9, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
2. Truog RD, Mitchell C, Daley GQ. The toughest triage — allocating ventilators in a pandemic. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(21):1973-1975. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2005689
3. Cavallo JJ, Donoho DA, Forman HP. Hospital capacity and operations in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic—planning for the Nth patient. JAMA Health Forum. 2020;1(3):e200345. doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2020.0345
4. Eriksson CO, Stoner RC, Eden KB, et al. The association between hospital capacity strain and inpatient outcomes in highly developed countries: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(6):686-696. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3936-3
5. Bravata DM, Perkins AJ, Myers LJ, et al. Association of intensive care unit patient load and demand with mortality rates in US Department of Veterans Affairs hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2034266. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34266
6. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(19);1813-1826. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
7. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes monoclonal antibody for treatment of COVID-19. US Food & Drug Administration. November 9, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-monoclonal-antibody-treatment-covid-19
8. Chen P, Nirula A, Heller B, et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):229-237. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2029849
9. Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, et al. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):238-251. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035002
10. Chen X, Li R, Pan Z, et al. Human monoclonal antibodies block the binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17(6):647-649. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0426-7
11. Gottlieb RL, Nirula A, Chen P, et al. Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021;325(7):632-644. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202
12. Toy S, Walker J, Evans M. Highly touted monoclonal antibody therapies sit unused in hospitals The Wall Street Journal. December 27, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.wsj.com/articles/highly-touted-monoclonal-antibody-therapies-sit-unused-in-hospitals-11609087364
13. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies. NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. Updated October 19, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/anti-sars-cov-2-antibody-products/anti-sars-cov-2-monoclonal-antibodies/
14. Langellier BA. Policy recommendations to address high risk of COVID-19 among immigrants. Am J Public Health. 2020;110(8):1137-1139. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2020.305792
15. Verderese J P, Stepanova M, Lam B, et al. Neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment reduces hospitalization for mild and moderate COVID-19: a real-world experience. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;ciab579. doi:10.1093/cid/ciab579
16. Levine DM, Linder JA, Landon BE. Characteristics of Americans with primary care and changes over time, 2002-2015. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(3):463-466. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.6282
17. Rust G, Ye J, Daniels E, et al. Practical barriers to timely primary care access: impact on adult use of emergency department services. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(15):1705-1710. doi:10.1001/archinte.168.15.1705
18. COVID-19 Hospitalization Tracking Project: analysis of HHS data. University of Minnesota. Carlson School of Management. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://carlsonschool.umn.edu/mili-misrc-covid19-tracking-project
19. Zare˛bska-Michaluk D, Jaroszewicz J, Rogalska M, et al. Impact of kidney failure on the severity of COVID-19. J Clin Med. 2021;10(9):2042. doi:10.3390/jcm10092042
20. Shahid Z, Kalayanamitra R, McClafferty B, et al. COVID‐19 and older adults: what we know. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(5):926-929. doi:10.1111/jgs.16472
21. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA revokes emergency use authorization for monoclonal antibody bamlanivimab. US Food & Drug Administration. April 16, 2021. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-revokes-emergency-use-authorization-monoclonal-antibody-bamlanivimab
Residency programs readjust during COVID
Hospitalist-honed agility proves invaluable
It could be argued that hospital medicine in the United States was made vital by a major infectious disease epidemic – the HIV/AIDS crisis – said Emily Gottenborg, MD, a hospitalist and program director of hospitalist training at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Certainly, it was born out of the need for change, for physicians who could coordinate complex patient care plans and serve as the “quarterbacks” of the hospital. “As a result, we have always been very nimble and ready to embrace change,” said Dr. Gottenborg.
That hospitalist-honed agility and penchant for innovation has proven to be invaluable during the current COVID-19 pandemic as hospital medicine–focused residency programs have been forced to pivot quickly and modify their agendas. From managing the pandemic’s impact on residents’ day-to-day experiences, to carefully balancing educational needs and goals, program leaders have worked tirelessly to ensure that residents continue to receive excellent training.
The overarching theme across U.S.-based residency programs is that the educational changes and challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic have often been one and the same.
Service versus education
At the beginning of the pandemic, trainees at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center were limited in seeing COVID patients in order to curb exposure. But now that COVID appears to be the new normal, “I think the question becomes: ‘How do we incorporate our trainees to take care of COVID patients since it seems it will be staying around for a while?’ ” said Rachna Rawal, MD, a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine at UPMC.
This dilemma highlights the conflict between service and education. Residents have been motivated and eager to help, which has been beneficial whenever there is a surge. “At the same time, you want to preserve their education, and it’s a very difficult balance at times,” said Dr. Rawal. It’s also challenging to figure out the safest way for residents to see patients, as well as how to include medical students, since interns and residents serve as important educational resources for them.
Keeping trainees involved with daily virtual conferences rather than in-person interactions raises the question of whether or not the engagement is equivalent. “It’s harder to keep them accountable when they’re not in person, but it’s also not worth the risk given the COVID numbers at times,” Dr. Rawal said. The goal has become to make sure residents stay safe while still feeling that they are getting a good education.
A balancing act
“I think early on, there was a lot of pride in what we were doing, that we were on the front line managing this thing that was emerging,” said Daniel Ricotta, MD, a hospitalist and associate program director of the internal medicine residency at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. “And now I think people are starting to feel a little bit weary.”
It has been demanding trying to manage ongoing educational needs through this time. “At the end of the day, residents are still trainees and have to be trained and educated. They’re not just worker bees taking care of patients,” Dr. Ricotta said. Residents need a well-rounded clinical experience – “they can’t just take care of COVID patients and then be able to graduate as general internists,” he said – but that becomes onerous when the hospital is full of patients with COVID.
Along with balancing residents’ clinical immersion, Dr. Ricotta said there has been the challenge of doing “the content-based teaching from didactics that occur in the context of clinical work, but are somewhat separated when you need to limit the number of people in the rooms and try to keep as many people at home as possible when they’re not taking care of patients in order to limit their level of risk.” Adjusting and readjusting both of these aspects has had a major impact on residents’ day-to-day education.
“A big part of residency is community,” noted Dr. Ricotta, but the sense of community has been disrupted because some of the bonding experiences residents used to do outside the hospital to build that community have necessarily gone by the wayside. This particularly affects interns from around the country who are meeting each other for the first time. “We actually had a normal intern orientation this year, but last year, when everything was virtual, we were trying to find ways to bridge relationships in a way that was safe and socially distanced,” he said.
Improving quality
UC Denver is unique in that they have a 3-year program specifically for hospital medicine residents, said Dr. Gottenborg. Right away, “our residents rose to the challenge and wanted to be part of the workforce that helps care for this critical population of [COVID] patients.” The residents were able to run the ICUs and take care of COVID patients, but in exchange, they had to give up some of their elective rotation time.
One aspect of the UC Denver hospital medicine residency program is participation in projects that focus on how to improve the health care system. Over the past year, the residents worked on one project in particular that focused on restructuring the guidelines for consulting physical therapists. Since many patients end up needing a physical therapist for a variety of reasons, a full hospital puts increased strain on their workload, making their time more precious.
“[The project] forced us to think about the right criteria to consult them,” explained Dr. Gottenborg. “We cut down essentially all the inappropriate consults to PT, opening their time. That project was driven by how the residents were experiencing the pandemic in the hospital.”
Learning to adapt
“The training environment during this pandemic has been tumultuous for both our residents and medical students,” said Alan M. Hall, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and pediatrics and assistant dean of curriculum integration at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Along with treating patients with COVID-19, he said trainees have also had to cope with anxiety about getting the virus themselves or inadvertently bringing it home to their families.
Like most medical schools, University of Kentucky students were shifted away from clinical rotations and into alternative and online education for a time. When they returned to in-person education, the students were initially restricted from seeing patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 in order to reduce their personal risk and to conserve personal protective equipment.
This especially impacted certain rotations, such as pediatrics. Because respiratory symptoms are common in this population, students were greatly limited in the number of new patients they could see. Now they are given the option to see patients with COVID-19 if they want to.
“Our residents have had to adapt to seemingly endless changes during this pandemic,” Dr. Hall said. For example, at the beginning of the surge, the internal medicine residents trained for a completely new clinical model, though this ultimately never needed to be implemented. Then they had to adjust to extremely high census numbers that continue to have an effect on almost all of their rotations.
Conversely, the pediatrics residents saw far fewer inpatients last winter than they typically would. This made it more difficult for them to feel comfortable when census numbers increased with common diagnoses like bronchiolitis. “However, those respiratory viruses that were hibernating last winter caused an unusual and challenging summer surge,” Dr. Hall said.
The biggest challenge though “is knowing that there is not a perfect solution for this global pandemic’s effect on medical education,” said Dr. Hall. “We can’t possibly perfectly balance the safety of our learners and their families with the dangers of COVID-19.”
Leadership discussions
As a residency program leader, Dr. Ricotta said there are conversations about multiple topics, including maintaining a safe learning environment; providing important aspects of residency training; whether to go back to full in-person teaching, keep doing virtual teaching, or implement a hybrid model; and how to help residents understand the balance between their personal and professional lives, especially in terms of safety.
“They have to their lives outside of the hospital, but we also are trying to instill ... what their responsibility is to society, to their patients, and to each other,” said Dr. Ricotta.
A more recent discussion has been about how to manage the COVID vaccine boosters. “We can’t have everyone getting vaccines at the same time because they might have symptoms afterward, and then be out sick – you’re missing half your workforce,” Dr. Ricotta said. But staggering residents’ booster shots created yet another dilemma around deciding who received the booster sooner rather than later.
The biggest consideration for Dr. Gottenborg’s leadership team was deciding whether to use their residents to help with the COVID surges or keep them in a traditional residency experience. While the residents wanted to be part of the pandemic response, there were many factors to consider. Ultimately, they came up with a balance between the amount of time residents should spend taking care of COVID patients while also assuring that they leave the program with all the skills and experiences they need.
Though Dr. Hall works more closely with medical students than residents, he sees the challenges and effects as being similar. Creating harmony between a safe learning environment and students’ educational goals has been the topic of endless discussions. This includes decisions as to whether or not students should be involved in person in certain activities such as large classroom didactics, written exams, seeing patients in clinical settings, and small group discussions.
Recruitment effects
When it comes to recruiting during a global pandemic, the experiences and predictions are mixed. Dr. Hall believes virtual interviews are making recruitment easier, but in turn, the fact that they are virtual also makes it harder for the applicant to get a good feel for the program and the people involved in it.
Dr. Ricotta reported that recruitment numbers have been fairly steady at Beth Israel Deaconess over the last few years. “In addition to the critical care physicians, hospital medicine was really the front line of this pandemic and so in some ways, we gained some recognition that we may not have had otherwise,” said Dr. Ricotta. He believes this has the benefit of attracting some residents, but at the same time, it could potentially scare others away from what they perceive as a demanding, grueling job. “I think it has been mixed. It’s dependent on the person.”
At UC Denver, Dr. Gottenborg said they are seeing a rapid rise in the number of applications and interest in their programs. Still, “I think this could go both ways,” she acknowledged. With the focus on hospital medicine in the media, medical students are more aware of the specialty and what it involves. “I think the sense of mission is really exemplified and everyone is talking about it,” she said. This is evident in the arrival this summer of the first new class of interns since the pandemic. “They’re incredibly passionate about the work,” said Dr. Gottenborg.
However, there is also the notable increase in physician burnout since the pandemic started. That this has been regularly featured in the media leaves Dr. Gottenborg to wonder if prospective residents will shy away from hospital medicine because they believe it is an area that leads to burnout. “I hope that’s not the case,” she said.
“I would actually argue [recruitment] is easier,” said Dr. Rawal. Like Dr. Hall, she sees virtual interviews as a big benefit to prospective trainees because they don’t have to spend a large amount of money on travel, food, and other expenses like they did before, a welcome relief for residents with significant debt. “I think that is one very big positive from the pandemic,” she said. Her trainees were advised to make a final list and consider going to see the top two or three in person, but “at this point, there’s really no expectation to go see all 15 places that you look into.”
Dr. Rawal also pointed out that recruitment is affected by whether or not trainees are expected to see COVID patients. “I know in some places they aren’t and in some places they are, so it just depends on where you are and what you’re looking for,” she said.
Shifts in education
It remains to be seen if all the educational changes will be permanent, though it appears that many will remain. Dr. Hall hopes that virtual visits to provide care to patients who have difficulty getting to physical clinics will continue to be a focus for hospital medicine trainees. “For medical students, I think this will allow us to better assess what content can best be delivered in person, synchronously online, or asynchronously through recorded content,” he said.
Dr. Ricotta predicts that virtual conferences will become more pervasive as academic hospitals continue to acquire more community hospitals, especially for grand rounds. “The virtual teaching that occurred in the residency program because it’s required by the [Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education] has, I think, informed how academic centers do ongoing faculty development, professional development, and obviously education for the residents,” Dr. Ricotta said. “I think virtual teaching is here to stay.” This includes telehealth training, which had not been a widespread part of residency education before now.
Trainees have been given tools to handle high patient censuses and learned a whole new set of communication skills, thanks to the pandemic, said Dr. Rawal. There has been a focus on learning how to advocate for the vaccine, along with education on situations like how to have conversations with patients who don’t believe they have COVID, even when their tests are positive. “Learning to handle these situations and still be a physician and provide appropriate care regardless of the patient’s views is very important. This is not something I learned in my training because it never came up,” she said.
Dr. Gottenborg has been impressed by the resident workforce’s response across all specialties throughout these difficult days. “They were universally ready to dive in and work long hours and care for these very sick patients and ultimately share their experiences so that we could do it better as these patients continue to flow through our systems,” she said. “It has been very invigorating.”
The pandemic has also put a spotlight on the importance of being flexible, as well as various problems with how health care systems operate, “which, for people in our field, gets us both excited and gives us a lot of work to do,” said Dr. Gottenborg. “Our residents see that and feel that and will hopefully continue to hold that torch in hospital medicine.”
In spite of everything, Dr. Rawal believes this is an exhilarating time to be a trainee. “They’re getting an opportunity that none of us got. Usually, when policies are made, we really don’t see the immediate impact.” But with recent mandates like masks and social distancing, “the rate of change that they get to see things happen is exciting. They’re going to be a very exciting group of physicians.”
Hospitalist-honed agility proves invaluable
Hospitalist-honed agility proves invaluable
It could be argued that hospital medicine in the United States was made vital by a major infectious disease epidemic – the HIV/AIDS crisis – said Emily Gottenborg, MD, a hospitalist and program director of hospitalist training at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Certainly, it was born out of the need for change, for physicians who could coordinate complex patient care plans and serve as the “quarterbacks” of the hospital. “As a result, we have always been very nimble and ready to embrace change,” said Dr. Gottenborg.
That hospitalist-honed agility and penchant for innovation has proven to be invaluable during the current COVID-19 pandemic as hospital medicine–focused residency programs have been forced to pivot quickly and modify their agendas. From managing the pandemic’s impact on residents’ day-to-day experiences, to carefully balancing educational needs and goals, program leaders have worked tirelessly to ensure that residents continue to receive excellent training.
The overarching theme across U.S.-based residency programs is that the educational changes and challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic have often been one and the same.
Service versus education
At the beginning of the pandemic, trainees at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center were limited in seeing COVID patients in order to curb exposure. But now that COVID appears to be the new normal, “I think the question becomes: ‘How do we incorporate our trainees to take care of COVID patients since it seems it will be staying around for a while?’ ” said Rachna Rawal, MD, a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine at UPMC.
This dilemma highlights the conflict between service and education. Residents have been motivated and eager to help, which has been beneficial whenever there is a surge. “At the same time, you want to preserve their education, and it’s a very difficult balance at times,” said Dr. Rawal. It’s also challenging to figure out the safest way for residents to see patients, as well as how to include medical students, since interns and residents serve as important educational resources for them.
Keeping trainees involved with daily virtual conferences rather than in-person interactions raises the question of whether or not the engagement is equivalent. “It’s harder to keep them accountable when they’re not in person, but it’s also not worth the risk given the COVID numbers at times,” Dr. Rawal said. The goal has become to make sure residents stay safe while still feeling that they are getting a good education.
A balancing act
“I think early on, there was a lot of pride in what we were doing, that we were on the front line managing this thing that was emerging,” said Daniel Ricotta, MD, a hospitalist and associate program director of the internal medicine residency at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. “And now I think people are starting to feel a little bit weary.”
It has been demanding trying to manage ongoing educational needs through this time. “At the end of the day, residents are still trainees and have to be trained and educated. They’re not just worker bees taking care of patients,” Dr. Ricotta said. Residents need a well-rounded clinical experience – “they can’t just take care of COVID patients and then be able to graduate as general internists,” he said – but that becomes onerous when the hospital is full of patients with COVID.
Along with balancing residents’ clinical immersion, Dr. Ricotta said there has been the challenge of doing “the content-based teaching from didactics that occur in the context of clinical work, but are somewhat separated when you need to limit the number of people in the rooms and try to keep as many people at home as possible when they’re not taking care of patients in order to limit their level of risk.” Adjusting and readjusting both of these aspects has had a major impact on residents’ day-to-day education.
“A big part of residency is community,” noted Dr. Ricotta, but the sense of community has been disrupted because some of the bonding experiences residents used to do outside the hospital to build that community have necessarily gone by the wayside. This particularly affects interns from around the country who are meeting each other for the first time. “We actually had a normal intern orientation this year, but last year, when everything was virtual, we were trying to find ways to bridge relationships in a way that was safe and socially distanced,” he said.
Improving quality
UC Denver is unique in that they have a 3-year program specifically for hospital medicine residents, said Dr. Gottenborg. Right away, “our residents rose to the challenge and wanted to be part of the workforce that helps care for this critical population of [COVID] patients.” The residents were able to run the ICUs and take care of COVID patients, but in exchange, they had to give up some of their elective rotation time.
One aspect of the UC Denver hospital medicine residency program is participation in projects that focus on how to improve the health care system. Over the past year, the residents worked on one project in particular that focused on restructuring the guidelines for consulting physical therapists. Since many patients end up needing a physical therapist for a variety of reasons, a full hospital puts increased strain on their workload, making their time more precious.
“[The project] forced us to think about the right criteria to consult them,” explained Dr. Gottenborg. “We cut down essentially all the inappropriate consults to PT, opening their time. That project was driven by how the residents were experiencing the pandemic in the hospital.”
Learning to adapt
“The training environment during this pandemic has been tumultuous for both our residents and medical students,” said Alan M. Hall, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and pediatrics and assistant dean of curriculum integration at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Along with treating patients with COVID-19, he said trainees have also had to cope with anxiety about getting the virus themselves or inadvertently bringing it home to their families.
Like most medical schools, University of Kentucky students were shifted away from clinical rotations and into alternative and online education for a time. When they returned to in-person education, the students were initially restricted from seeing patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 in order to reduce their personal risk and to conserve personal protective equipment.
This especially impacted certain rotations, such as pediatrics. Because respiratory symptoms are common in this population, students were greatly limited in the number of new patients they could see. Now they are given the option to see patients with COVID-19 if they want to.
“Our residents have had to adapt to seemingly endless changes during this pandemic,” Dr. Hall said. For example, at the beginning of the surge, the internal medicine residents trained for a completely new clinical model, though this ultimately never needed to be implemented. Then they had to adjust to extremely high census numbers that continue to have an effect on almost all of their rotations.
Conversely, the pediatrics residents saw far fewer inpatients last winter than they typically would. This made it more difficult for them to feel comfortable when census numbers increased with common diagnoses like bronchiolitis. “However, those respiratory viruses that were hibernating last winter caused an unusual and challenging summer surge,” Dr. Hall said.
The biggest challenge though “is knowing that there is not a perfect solution for this global pandemic’s effect on medical education,” said Dr. Hall. “We can’t possibly perfectly balance the safety of our learners and their families with the dangers of COVID-19.”
Leadership discussions
As a residency program leader, Dr. Ricotta said there are conversations about multiple topics, including maintaining a safe learning environment; providing important aspects of residency training; whether to go back to full in-person teaching, keep doing virtual teaching, or implement a hybrid model; and how to help residents understand the balance between their personal and professional lives, especially in terms of safety.
“They have to their lives outside of the hospital, but we also are trying to instill ... what their responsibility is to society, to their patients, and to each other,” said Dr. Ricotta.
A more recent discussion has been about how to manage the COVID vaccine boosters. “We can’t have everyone getting vaccines at the same time because they might have symptoms afterward, and then be out sick – you’re missing half your workforce,” Dr. Ricotta said. But staggering residents’ booster shots created yet another dilemma around deciding who received the booster sooner rather than later.
The biggest consideration for Dr. Gottenborg’s leadership team was deciding whether to use their residents to help with the COVID surges or keep them in a traditional residency experience. While the residents wanted to be part of the pandemic response, there were many factors to consider. Ultimately, they came up with a balance between the amount of time residents should spend taking care of COVID patients while also assuring that they leave the program with all the skills and experiences they need.
Though Dr. Hall works more closely with medical students than residents, he sees the challenges and effects as being similar. Creating harmony between a safe learning environment and students’ educational goals has been the topic of endless discussions. This includes decisions as to whether or not students should be involved in person in certain activities such as large classroom didactics, written exams, seeing patients in clinical settings, and small group discussions.
Recruitment effects
When it comes to recruiting during a global pandemic, the experiences and predictions are mixed. Dr. Hall believes virtual interviews are making recruitment easier, but in turn, the fact that they are virtual also makes it harder for the applicant to get a good feel for the program and the people involved in it.
Dr. Ricotta reported that recruitment numbers have been fairly steady at Beth Israel Deaconess over the last few years. “In addition to the critical care physicians, hospital medicine was really the front line of this pandemic and so in some ways, we gained some recognition that we may not have had otherwise,” said Dr. Ricotta. He believes this has the benefit of attracting some residents, but at the same time, it could potentially scare others away from what they perceive as a demanding, grueling job. “I think it has been mixed. It’s dependent on the person.”
At UC Denver, Dr. Gottenborg said they are seeing a rapid rise in the number of applications and interest in their programs. Still, “I think this could go both ways,” she acknowledged. With the focus on hospital medicine in the media, medical students are more aware of the specialty and what it involves. “I think the sense of mission is really exemplified and everyone is talking about it,” she said. This is evident in the arrival this summer of the first new class of interns since the pandemic. “They’re incredibly passionate about the work,” said Dr. Gottenborg.
However, there is also the notable increase in physician burnout since the pandemic started. That this has been regularly featured in the media leaves Dr. Gottenborg to wonder if prospective residents will shy away from hospital medicine because they believe it is an area that leads to burnout. “I hope that’s not the case,” she said.
“I would actually argue [recruitment] is easier,” said Dr. Rawal. Like Dr. Hall, she sees virtual interviews as a big benefit to prospective trainees because they don’t have to spend a large amount of money on travel, food, and other expenses like they did before, a welcome relief for residents with significant debt. “I think that is one very big positive from the pandemic,” she said. Her trainees were advised to make a final list and consider going to see the top two or three in person, but “at this point, there’s really no expectation to go see all 15 places that you look into.”
Dr. Rawal also pointed out that recruitment is affected by whether or not trainees are expected to see COVID patients. “I know in some places they aren’t and in some places they are, so it just depends on where you are and what you’re looking for,” she said.
Shifts in education
It remains to be seen if all the educational changes will be permanent, though it appears that many will remain. Dr. Hall hopes that virtual visits to provide care to patients who have difficulty getting to physical clinics will continue to be a focus for hospital medicine trainees. “For medical students, I think this will allow us to better assess what content can best be delivered in person, synchronously online, or asynchronously through recorded content,” he said.
Dr. Ricotta predicts that virtual conferences will become more pervasive as academic hospitals continue to acquire more community hospitals, especially for grand rounds. “The virtual teaching that occurred in the residency program because it’s required by the [Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education] has, I think, informed how academic centers do ongoing faculty development, professional development, and obviously education for the residents,” Dr. Ricotta said. “I think virtual teaching is here to stay.” This includes telehealth training, which had not been a widespread part of residency education before now.
Trainees have been given tools to handle high patient censuses and learned a whole new set of communication skills, thanks to the pandemic, said Dr. Rawal. There has been a focus on learning how to advocate for the vaccine, along with education on situations like how to have conversations with patients who don’t believe they have COVID, even when their tests are positive. “Learning to handle these situations and still be a physician and provide appropriate care regardless of the patient’s views is very important. This is not something I learned in my training because it never came up,” she said.
Dr. Gottenborg has been impressed by the resident workforce’s response across all specialties throughout these difficult days. “They were universally ready to dive in and work long hours and care for these very sick patients and ultimately share their experiences so that we could do it better as these patients continue to flow through our systems,” she said. “It has been very invigorating.”
The pandemic has also put a spotlight on the importance of being flexible, as well as various problems with how health care systems operate, “which, for people in our field, gets us both excited and gives us a lot of work to do,” said Dr. Gottenborg. “Our residents see that and feel that and will hopefully continue to hold that torch in hospital medicine.”
In spite of everything, Dr. Rawal believes this is an exhilarating time to be a trainee. “They’re getting an opportunity that none of us got. Usually, when policies are made, we really don’t see the immediate impact.” But with recent mandates like masks and social distancing, “the rate of change that they get to see things happen is exciting. They’re going to be a very exciting group of physicians.”
It could be argued that hospital medicine in the United States was made vital by a major infectious disease epidemic – the HIV/AIDS crisis – said Emily Gottenborg, MD, a hospitalist and program director of hospitalist training at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Certainly, it was born out of the need for change, for physicians who could coordinate complex patient care plans and serve as the “quarterbacks” of the hospital. “As a result, we have always been very nimble and ready to embrace change,” said Dr. Gottenborg.
That hospitalist-honed agility and penchant for innovation has proven to be invaluable during the current COVID-19 pandemic as hospital medicine–focused residency programs have been forced to pivot quickly and modify their agendas. From managing the pandemic’s impact on residents’ day-to-day experiences, to carefully balancing educational needs and goals, program leaders have worked tirelessly to ensure that residents continue to receive excellent training.
The overarching theme across U.S.-based residency programs is that the educational changes and challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic have often been one and the same.
Service versus education
At the beginning of the pandemic, trainees at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center were limited in seeing COVID patients in order to curb exposure. But now that COVID appears to be the new normal, “I think the question becomes: ‘How do we incorporate our trainees to take care of COVID patients since it seems it will be staying around for a while?’ ” said Rachna Rawal, MD, a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine at UPMC.
This dilemma highlights the conflict between service and education. Residents have been motivated and eager to help, which has been beneficial whenever there is a surge. “At the same time, you want to preserve their education, and it’s a very difficult balance at times,” said Dr. Rawal. It’s also challenging to figure out the safest way for residents to see patients, as well as how to include medical students, since interns and residents serve as important educational resources for them.
Keeping trainees involved with daily virtual conferences rather than in-person interactions raises the question of whether or not the engagement is equivalent. “It’s harder to keep them accountable when they’re not in person, but it’s also not worth the risk given the COVID numbers at times,” Dr. Rawal said. The goal has become to make sure residents stay safe while still feeling that they are getting a good education.
A balancing act
“I think early on, there was a lot of pride in what we were doing, that we were on the front line managing this thing that was emerging,” said Daniel Ricotta, MD, a hospitalist and associate program director of the internal medicine residency at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. “And now I think people are starting to feel a little bit weary.”
It has been demanding trying to manage ongoing educational needs through this time. “At the end of the day, residents are still trainees and have to be trained and educated. They’re not just worker bees taking care of patients,” Dr. Ricotta said. Residents need a well-rounded clinical experience – “they can’t just take care of COVID patients and then be able to graduate as general internists,” he said – but that becomes onerous when the hospital is full of patients with COVID.
Along with balancing residents’ clinical immersion, Dr. Ricotta said there has been the challenge of doing “the content-based teaching from didactics that occur in the context of clinical work, but are somewhat separated when you need to limit the number of people in the rooms and try to keep as many people at home as possible when they’re not taking care of patients in order to limit their level of risk.” Adjusting and readjusting both of these aspects has had a major impact on residents’ day-to-day education.
“A big part of residency is community,” noted Dr. Ricotta, but the sense of community has been disrupted because some of the bonding experiences residents used to do outside the hospital to build that community have necessarily gone by the wayside. This particularly affects interns from around the country who are meeting each other for the first time. “We actually had a normal intern orientation this year, but last year, when everything was virtual, we were trying to find ways to bridge relationships in a way that was safe and socially distanced,” he said.
Improving quality
UC Denver is unique in that they have a 3-year program specifically for hospital medicine residents, said Dr. Gottenborg. Right away, “our residents rose to the challenge and wanted to be part of the workforce that helps care for this critical population of [COVID] patients.” The residents were able to run the ICUs and take care of COVID patients, but in exchange, they had to give up some of their elective rotation time.
One aspect of the UC Denver hospital medicine residency program is participation in projects that focus on how to improve the health care system. Over the past year, the residents worked on one project in particular that focused on restructuring the guidelines for consulting physical therapists. Since many patients end up needing a physical therapist for a variety of reasons, a full hospital puts increased strain on their workload, making their time more precious.
“[The project] forced us to think about the right criteria to consult them,” explained Dr. Gottenborg. “We cut down essentially all the inappropriate consults to PT, opening their time. That project was driven by how the residents were experiencing the pandemic in the hospital.”
Learning to adapt
“The training environment during this pandemic has been tumultuous for both our residents and medical students,” said Alan M. Hall, MD, associate professor of internal medicine and pediatrics and assistant dean of curriculum integration at the University of Kentucky, Lexington. Along with treating patients with COVID-19, he said trainees have also had to cope with anxiety about getting the virus themselves or inadvertently bringing it home to their families.
Like most medical schools, University of Kentucky students were shifted away from clinical rotations and into alternative and online education for a time. When they returned to in-person education, the students were initially restricted from seeing patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 in order to reduce their personal risk and to conserve personal protective equipment.
This especially impacted certain rotations, such as pediatrics. Because respiratory symptoms are common in this population, students were greatly limited in the number of new patients they could see. Now they are given the option to see patients with COVID-19 if they want to.
“Our residents have had to adapt to seemingly endless changes during this pandemic,” Dr. Hall said. For example, at the beginning of the surge, the internal medicine residents trained for a completely new clinical model, though this ultimately never needed to be implemented. Then they had to adjust to extremely high census numbers that continue to have an effect on almost all of their rotations.
Conversely, the pediatrics residents saw far fewer inpatients last winter than they typically would. This made it more difficult for them to feel comfortable when census numbers increased with common diagnoses like bronchiolitis. “However, those respiratory viruses that were hibernating last winter caused an unusual and challenging summer surge,” Dr. Hall said.
The biggest challenge though “is knowing that there is not a perfect solution for this global pandemic’s effect on medical education,” said Dr. Hall. “We can’t possibly perfectly balance the safety of our learners and their families with the dangers of COVID-19.”
Leadership discussions
As a residency program leader, Dr. Ricotta said there are conversations about multiple topics, including maintaining a safe learning environment; providing important aspects of residency training; whether to go back to full in-person teaching, keep doing virtual teaching, or implement a hybrid model; and how to help residents understand the balance between their personal and professional lives, especially in terms of safety.
“They have to their lives outside of the hospital, but we also are trying to instill ... what their responsibility is to society, to their patients, and to each other,” said Dr. Ricotta.
A more recent discussion has been about how to manage the COVID vaccine boosters. “We can’t have everyone getting vaccines at the same time because they might have symptoms afterward, and then be out sick – you’re missing half your workforce,” Dr. Ricotta said. But staggering residents’ booster shots created yet another dilemma around deciding who received the booster sooner rather than later.
The biggest consideration for Dr. Gottenborg’s leadership team was deciding whether to use their residents to help with the COVID surges or keep them in a traditional residency experience. While the residents wanted to be part of the pandemic response, there were many factors to consider. Ultimately, they came up with a balance between the amount of time residents should spend taking care of COVID patients while also assuring that they leave the program with all the skills and experiences they need.
Though Dr. Hall works more closely with medical students than residents, he sees the challenges and effects as being similar. Creating harmony between a safe learning environment and students’ educational goals has been the topic of endless discussions. This includes decisions as to whether or not students should be involved in person in certain activities such as large classroom didactics, written exams, seeing patients in clinical settings, and small group discussions.
Recruitment effects
When it comes to recruiting during a global pandemic, the experiences and predictions are mixed. Dr. Hall believes virtual interviews are making recruitment easier, but in turn, the fact that they are virtual also makes it harder for the applicant to get a good feel for the program and the people involved in it.
Dr. Ricotta reported that recruitment numbers have been fairly steady at Beth Israel Deaconess over the last few years. “In addition to the critical care physicians, hospital medicine was really the front line of this pandemic and so in some ways, we gained some recognition that we may not have had otherwise,” said Dr. Ricotta. He believes this has the benefit of attracting some residents, but at the same time, it could potentially scare others away from what they perceive as a demanding, grueling job. “I think it has been mixed. It’s dependent on the person.”
At UC Denver, Dr. Gottenborg said they are seeing a rapid rise in the number of applications and interest in their programs. Still, “I think this could go both ways,” she acknowledged. With the focus on hospital medicine in the media, medical students are more aware of the specialty and what it involves. “I think the sense of mission is really exemplified and everyone is talking about it,” she said. This is evident in the arrival this summer of the first new class of interns since the pandemic. “They’re incredibly passionate about the work,” said Dr. Gottenborg.
However, there is also the notable increase in physician burnout since the pandemic started. That this has been regularly featured in the media leaves Dr. Gottenborg to wonder if prospective residents will shy away from hospital medicine because they believe it is an area that leads to burnout. “I hope that’s not the case,” she said.
“I would actually argue [recruitment] is easier,” said Dr. Rawal. Like Dr. Hall, she sees virtual interviews as a big benefit to prospective trainees because they don’t have to spend a large amount of money on travel, food, and other expenses like they did before, a welcome relief for residents with significant debt. “I think that is one very big positive from the pandemic,” she said. Her trainees were advised to make a final list and consider going to see the top two or three in person, but “at this point, there’s really no expectation to go see all 15 places that you look into.”
Dr. Rawal also pointed out that recruitment is affected by whether or not trainees are expected to see COVID patients. “I know in some places they aren’t and in some places they are, so it just depends on where you are and what you’re looking for,” she said.
Shifts in education
It remains to be seen if all the educational changes will be permanent, though it appears that many will remain. Dr. Hall hopes that virtual visits to provide care to patients who have difficulty getting to physical clinics will continue to be a focus for hospital medicine trainees. “For medical students, I think this will allow us to better assess what content can best be delivered in person, synchronously online, or asynchronously through recorded content,” he said.
Dr. Ricotta predicts that virtual conferences will become more pervasive as academic hospitals continue to acquire more community hospitals, especially for grand rounds. “The virtual teaching that occurred in the residency program because it’s required by the [Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education] has, I think, informed how academic centers do ongoing faculty development, professional development, and obviously education for the residents,” Dr. Ricotta said. “I think virtual teaching is here to stay.” This includes telehealth training, which had not been a widespread part of residency education before now.
Trainees have been given tools to handle high patient censuses and learned a whole new set of communication skills, thanks to the pandemic, said Dr. Rawal. There has been a focus on learning how to advocate for the vaccine, along with education on situations like how to have conversations with patients who don’t believe they have COVID, even when their tests are positive. “Learning to handle these situations and still be a physician and provide appropriate care regardless of the patient’s views is very important. This is not something I learned in my training because it never came up,” she said.
Dr. Gottenborg has been impressed by the resident workforce’s response across all specialties throughout these difficult days. “They were universally ready to dive in and work long hours and care for these very sick patients and ultimately share their experiences so that we could do it better as these patients continue to flow through our systems,” she said. “It has been very invigorating.”
The pandemic has also put a spotlight on the importance of being flexible, as well as various problems with how health care systems operate, “which, for people in our field, gets us both excited and gives us a lot of work to do,” said Dr. Gottenborg. “Our residents see that and feel that and will hopefully continue to hold that torch in hospital medicine.”
In spite of everything, Dr. Rawal believes this is an exhilarating time to be a trainee. “They’re getting an opportunity that none of us got. Usually, when policies are made, we really don’t see the immediate impact.” But with recent mandates like masks and social distancing, “the rate of change that they get to see things happen is exciting. They’re going to be a very exciting group of physicians.”
Hospitals refused to give patients ivermectin. Lockdowns and political pressure followed.
Officials of another Montana hospital accused public officials of threatening and harassing their health care workers for refusing to treat a politically connected COVID-19 patient with that antiparasitic drug or hydroxychloroquine, another drug unauthorized by the Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID.
And in neighboring Idaho, a medical resident said police had to be called to a hospital after a COVID patient’s relative verbally abused her and threatened physical violence because she would not prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine, “drugs that are not beneficial in the treatment of COVID-19,” she wrote.
These three conflicts, which occurred from September to November, underline the pressure on health care workers to provide unauthorized COVID treatments, particularly in parts of the country where vaccination rates are low, government skepticism is high, and conservative leaders have championed the treatments.
“You’re going to have this from time to time, but it’s not the norm,” said Rich Rasmussen, president and CEO of the Montana Hospital Association. “The vast majority of patients are completely compliant and have good, robust conversations with their medical care team. But you’re going to have these outliers.”
Even before the pandemic, the health care and social assistance industry — which includes residential care facilities and child daycare, among other services — led all U.S. industries in nonfatal workplace violence, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. COVID has made the problem worse, leading to hospital security upgrades, staff training, and calls for increased federal regulation.
Ivermectin and other unauthorized covid treatments have become a major source of dispute in recent months. Lawsuits over hospitals’ refusals to provide ivermectin to patients have been filed in Texas, Florida, Illinois, and elsewhere. The ivermectin harassment extends beyond U.S. borders to providers and public health officials worldwide, in such countries as Australia, Brazil, and the United Kingdom. Even so, reports of threats of violence and harassment like those recently seen in the Northern Rocky Mountains region have been relatively rare.
Ivermectin is approved to treat parasites in animals, and low doses of the drug are approved to treat worms, head lice, and certain skin conditions in humans. But the FDA has not authorized the drug to treat COVID. The agency says that clinical trials are ongoing but that the current data does not show it is an effective COVID treatment and taking higher-than-approved levels can lead to overdose.
Likewise, hydroxychloroquine can cause serious health problems and the drug does not help speed recovery or decrease the chance of dying of COVID, according to the FDA.
In Missoula, Montana, the Community Medical Center was placed on lockdown, and police were called on Nov. 17 after a woman reportedly threatened violence over how her relative was being treated, according to a Police Department statement. Nobody was arrested.
“The family member was upset the patient was not treated with ivermectin,” Lt. Eddie McLean said Nov. 30.
Hospital spokesperson Megan Condra confirmed Dec. 1 that the patient’s relative demanded ivermectin, but she said the patient was not there for COVID, though she declined to disclose the patient’s medical issue. The main entrance of the hospital was locked to control who entered the building, Ms. Condra added, but the hospital’s formal lockdown procedures were not implemented.
The scare was reminiscent of one that happened in Idaho in September. Dr. Ashley Carvalho, who is completing her medical residency training in Boise, wrote in an op-ed in the Idaho Capital Sun that she was verbally abused and threatened with both physical violence and a lawsuit by a patient’s relative after she refused to prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine.
“My patient was struggling to breathe, but the family refused to allow me to provide care,” Dr. Carvalho wrote. “A call to the police was the only solution.”
An 82-year-old woman who was active in Montana Republican politics was admitted to St. Peter’s Health, the hospital in Helena, with COVID in October. According to a November report by a special counsel appointed by state lawmakers, a family friend contacted Chief Deputy Attorney General Kris Hansen, a former Republican state senator, with multiple complaints: Hospital officials had not delivered a power-of-attorney document left by relatives for the patient to sign, she was denied her preferred medical treatment, she was cut off from her family, and the family worried hospital officials might prevent her from leaving. The patient later died.
That complaint led to the involvement of Republican Attorney General Austin Knudsen, who texted a lobbyist for the Montana Hospital Association who is also on St. Peter’s board of directors. An image of the exchange was included in the report.
“I’m about to send law enforcement in and file unlawful restraint charges,” Mr. Knudsen wrote to Mark Taylor, who responded that he would make inquiries.
“This has been going on since yesterday and I was hoping the hospital would do the right thing. But my patience is wearing thin,” the attorney general added.
A Montana Highway Patrol trooper was sent to the hospital to take the statement of the patient’s family members. Ms. Hansen also participated in a conference call with multiple health care providers in which she talked about the “legal ramifications” of withholding documents and the patient’s preferred treatment, which included ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine.
Public Service Commissioner Jennifer Fielder, a former Republican state senator, left a three-minute voicemail on a hospital line saying the patient’s friends in the Senate would not be too happy to learn of the care St. Peter’s was providing, according to the special counsel’s report.
Ms. Fielder and the patient’s daughter also cited a “right to try” law that Montana legislators passed in 2015 that allows terminally ill patients to seek experimental treatments. But a legal analysis written for the Montana Medical Association says that while the law does not require a provider to prescribe a particular medication if a patient demands it, it could give a provider legal immunity if the provider decides to prescribe the treatment, according to the Montana State News Bureau.
The report did not offer any conclusions or allegations of wrongdoing.
Hospital officials said before and after the report’s release that their health care providers were threatened and harassed when they refused to administer certain treatments for COVID.
“We stand by our assertion that the involvement of public officials in clinical care is inappropriate; that individuals leveraged their official positions in an attempt to influence clinical care; and that some of the exchanges that took place were threatening or harassing,” spokesperson Katie Gallagher said in a statement.
“Further, we reviewed all medical and legal records related to this patient’s care and verified that our teams provided care in accordance with clinical best practice, hospital policy, and patient rights,” Ms. Gallagher added.
The attorney general’s office did not respond to a request for comment but told the Montana Free Press in a statement that nobody at the state agency threatened anyone.
Mr. Rasmussen, the head of the Montana Hospital Association, said St. Peter’s officials have not reached out to the group for assistance. He downplayed the attorney general’s intervention in Helena, saying it often happens that people who know medical leaders or trustees will advocate on behalf of a relative or friend.
“Is this situation different? Certainly, because it’s from the attorney general,” Mr. Rasmussen said. “But I think the AG was responding to a constituent. Others would reach out to whoever they know on the hospital board.”
He added that hospitals have procedures in place that allow family members of patients to take their complaints to a supervisor or other hospital leader without resorting to threats.
Hospitals in the region that have watched the allegations of threats and harassment unfold declined to comment on their procedures to handle such conflicts.
“We respect the independent medical judgment of our providers who practice medicine consistent with approved, authorized treatment and recognized clinical standards,” said Bozeman Health spokesperson Lauren Brendel.
Tanner Gooch, a spokesperson for SCL Health Montana, which operates hospitals in Billings, Butte, and Miles City, said SCL does not endorse ivermectin or other COVID treatments that haven’t been approved by the FDA but doesn’t ban them, either.
“Ultimately, the treatment decisions are at the discretion of the provider,” Mr. Gooch said. “To our knowledge, no COVID-19 patients have been treated with ivermectin at our hospitals.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Officials of another Montana hospital accused public officials of threatening and harassing their health care workers for refusing to treat a politically connected COVID-19 patient with that antiparasitic drug or hydroxychloroquine, another drug unauthorized by the Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID.
And in neighboring Idaho, a medical resident said police had to be called to a hospital after a COVID patient’s relative verbally abused her and threatened physical violence because she would not prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine, “drugs that are not beneficial in the treatment of COVID-19,” she wrote.
These three conflicts, which occurred from September to November, underline the pressure on health care workers to provide unauthorized COVID treatments, particularly in parts of the country where vaccination rates are low, government skepticism is high, and conservative leaders have championed the treatments.
“You’re going to have this from time to time, but it’s not the norm,” said Rich Rasmussen, president and CEO of the Montana Hospital Association. “The vast majority of patients are completely compliant and have good, robust conversations with their medical care team. But you’re going to have these outliers.”
Even before the pandemic, the health care and social assistance industry — which includes residential care facilities and child daycare, among other services — led all U.S. industries in nonfatal workplace violence, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. COVID has made the problem worse, leading to hospital security upgrades, staff training, and calls for increased federal regulation.
Ivermectin and other unauthorized covid treatments have become a major source of dispute in recent months. Lawsuits over hospitals’ refusals to provide ivermectin to patients have been filed in Texas, Florida, Illinois, and elsewhere. The ivermectin harassment extends beyond U.S. borders to providers and public health officials worldwide, in such countries as Australia, Brazil, and the United Kingdom. Even so, reports of threats of violence and harassment like those recently seen in the Northern Rocky Mountains region have been relatively rare.
Ivermectin is approved to treat parasites in animals, and low doses of the drug are approved to treat worms, head lice, and certain skin conditions in humans. But the FDA has not authorized the drug to treat COVID. The agency says that clinical trials are ongoing but that the current data does not show it is an effective COVID treatment and taking higher-than-approved levels can lead to overdose.
Likewise, hydroxychloroquine can cause serious health problems and the drug does not help speed recovery or decrease the chance of dying of COVID, according to the FDA.
In Missoula, Montana, the Community Medical Center was placed on lockdown, and police were called on Nov. 17 after a woman reportedly threatened violence over how her relative was being treated, according to a Police Department statement. Nobody was arrested.
“The family member was upset the patient was not treated with ivermectin,” Lt. Eddie McLean said Nov. 30.
Hospital spokesperson Megan Condra confirmed Dec. 1 that the patient’s relative demanded ivermectin, but she said the patient was not there for COVID, though she declined to disclose the patient’s medical issue. The main entrance of the hospital was locked to control who entered the building, Ms. Condra added, but the hospital’s formal lockdown procedures were not implemented.
The scare was reminiscent of one that happened in Idaho in September. Dr. Ashley Carvalho, who is completing her medical residency training in Boise, wrote in an op-ed in the Idaho Capital Sun that she was verbally abused and threatened with both physical violence and a lawsuit by a patient’s relative after she refused to prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine.
“My patient was struggling to breathe, but the family refused to allow me to provide care,” Dr. Carvalho wrote. “A call to the police was the only solution.”
An 82-year-old woman who was active in Montana Republican politics was admitted to St. Peter’s Health, the hospital in Helena, with COVID in October. According to a November report by a special counsel appointed by state lawmakers, a family friend contacted Chief Deputy Attorney General Kris Hansen, a former Republican state senator, with multiple complaints: Hospital officials had not delivered a power-of-attorney document left by relatives for the patient to sign, she was denied her preferred medical treatment, she was cut off from her family, and the family worried hospital officials might prevent her from leaving. The patient later died.
That complaint led to the involvement of Republican Attorney General Austin Knudsen, who texted a lobbyist for the Montana Hospital Association who is also on St. Peter’s board of directors. An image of the exchange was included in the report.
“I’m about to send law enforcement in and file unlawful restraint charges,” Mr. Knudsen wrote to Mark Taylor, who responded that he would make inquiries.
“This has been going on since yesterday and I was hoping the hospital would do the right thing. But my patience is wearing thin,” the attorney general added.
A Montana Highway Patrol trooper was sent to the hospital to take the statement of the patient’s family members. Ms. Hansen also participated in a conference call with multiple health care providers in which she talked about the “legal ramifications” of withholding documents and the patient’s preferred treatment, which included ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine.
Public Service Commissioner Jennifer Fielder, a former Republican state senator, left a three-minute voicemail on a hospital line saying the patient’s friends in the Senate would not be too happy to learn of the care St. Peter’s was providing, according to the special counsel’s report.
Ms. Fielder and the patient’s daughter also cited a “right to try” law that Montana legislators passed in 2015 that allows terminally ill patients to seek experimental treatments. But a legal analysis written for the Montana Medical Association says that while the law does not require a provider to prescribe a particular medication if a patient demands it, it could give a provider legal immunity if the provider decides to prescribe the treatment, according to the Montana State News Bureau.
The report did not offer any conclusions or allegations of wrongdoing.
Hospital officials said before and after the report’s release that their health care providers were threatened and harassed when they refused to administer certain treatments for COVID.
“We stand by our assertion that the involvement of public officials in clinical care is inappropriate; that individuals leveraged their official positions in an attempt to influence clinical care; and that some of the exchanges that took place were threatening or harassing,” spokesperson Katie Gallagher said in a statement.
“Further, we reviewed all medical and legal records related to this patient’s care and verified that our teams provided care in accordance with clinical best practice, hospital policy, and patient rights,” Ms. Gallagher added.
The attorney general’s office did not respond to a request for comment but told the Montana Free Press in a statement that nobody at the state agency threatened anyone.
Mr. Rasmussen, the head of the Montana Hospital Association, said St. Peter’s officials have not reached out to the group for assistance. He downplayed the attorney general’s intervention in Helena, saying it often happens that people who know medical leaders or trustees will advocate on behalf of a relative or friend.
“Is this situation different? Certainly, because it’s from the attorney general,” Mr. Rasmussen said. “But I think the AG was responding to a constituent. Others would reach out to whoever they know on the hospital board.”
He added that hospitals have procedures in place that allow family members of patients to take their complaints to a supervisor or other hospital leader without resorting to threats.
Hospitals in the region that have watched the allegations of threats and harassment unfold declined to comment on their procedures to handle such conflicts.
“We respect the independent medical judgment of our providers who practice medicine consistent with approved, authorized treatment and recognized clinical standards,” said Bozeman Health spokesperson Lauren Brendel.
Tanner Gooch, a spokesperson for SCL Health Montana, which operates hospitals in Billings, Butte, and Miles City, said SCL does not endorse ivermectin or other COVID treatments that haven’t been approved by the FDA but doesn’t ban them, either.
“Ultimately, the treatment decisions are at the discretion of the provider,” Mr. Gooch said. “To our knowledge, no COVID-19 patients have been treated with ivermectin at our hospitals.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Officials of another Montana hospital accused public officials of threatening and harassing their health care workers for refusing to treat a politically connected COVID-19 patient with that antiparasitic drug or hydroxychloroquine, another drug unauthorized by the Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID.
And in neighboring Idaho, a medical resident said police had to be called to a hospital after a COVID patient’s relative verbally abused her and threatened physical violence because she would not prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine, “drugs that are not beneficial in the treatment of COVID-19,” she wrote.
These three conflicts, which occurred from September to November, underline the pressure on health care workers to provide unauthorized COVID treatments, particularly in parts of the country where vaccination rates are low, government skepticism is high, and conservative leaders have championed the treatments.
“You’re going to have this from time to time, but it’s not the norm,” said Rich Rasmussen, president and CEO of the Montana Hospital Association. “The vast majority of patients are completely compliant and have good, robust conversations with their medical care team. But you’re going to have these outliers.”
Even before the pandemic, the health care and social assistance industry — which includes residential care facilities and child daycare, among other services — led all U.S. industries in nonfatal workplace violence, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. COVID has made the problem worse, leading to hospital security upgrades, staff training, and calls for increased federal regulation.
Ivermectin and other unauthorized covid treatments have become a major source of dispute in recent months. Lawsuits over hospitals’ refusals to provide ivermectin to patients have been filed in Texas, Florida, Illinois, and elsewhere. The ivermectin harassment extends beyond U.S. borders to providers and public health officials worldwide, in such countries as Australia, Brazil, and the United Kingdom. Even so, reports of threats of violence and harassment like those recently seen in the Northern Rocky Mountains region have been relatively rare.
Ivermectin is approved to treat parasites in animals, and low doses of the drug are approved to treat worms, head lice, and certain skin conditions in humans. But the FDA has not authorized the drug to treat COVID. The agency says that clinical trials are ongoing but that the current data does not show it is an effective COVID treatment and taking higher-than-approved levels can lead to overdose.
Likewise, hydroxychloroquine can cause serious health problems and the drug does not help speed recovery or decrease the chance of dying of COVID, according to the FDA.
In Missoula, Montana, the Community Medical Center was placed on lockdown, and police were called on Nov. 17 after a woman reportedly threatened violence over how her relative was being treated, according to a Police Department statement. Nobody was arrested.
“The family member was upset the patient was not treated with ivermectin,” Lt. Eddie McLean said Nov. 30.
Hospital spokesperson Megan Condra confirmed Dec. 1 that the patient’s relative demanded ivermectin, but she said the patient was not there for COVID, though she declined to disclose the patient’s medical issue. The main entrance of the hospital was locked to control who entered the building, Ms. Condra added, but the hospital’s formal lockdown procedures were not implemented.
The scare was reminiscent of one that happened in Idaho in September. Dr. Ashley Carvalho, who is completing her medical residency training in Boise, wrote in an op-ed in the Idaho Capital Sun that she was verbally abused and threatened with both physical violence and a lawsuit by a patient’s relative after she refused to prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine.
“My patient was struggling to breathe, but the family refused to allow me to provide care,” Dr. Carvalho wrote. “A call to the police was the only solution.”
An 82-year-old woman who was active in Montana Republican politics was admitted to St. Peter’s Health, the hospital in Helena, with COVID in October. According to a November report by a special counsel appointed by state lawmakers, a family friend contacted Chief Deputy Attorney General Kris Hansen, a former Republican state senator, with multiple complaints: Hospital officials had not delivered a power-of-attorney document left by relatives for the patient to sign, she was denied her preferred medical treatment, she was cut off from her family, and the family worried hospital officials might prevent her from leaving. The patient later died.
That complaint led to the involvement of Republican Attorney General Austin Knudsen, who texted a lobbyist for the Montana Hospital Association who is also on St. Peter’s board of directors. An image of the exchange was included in the report.
“I’m about to send law enforcement in and file unlawful restraint charges,” Mr. Knudsen wrote to Mark Taylor, who responded that he would make inquiries.
“This has been going on since yesterday and I was hoping the hospital would do the right thing. But my patience is wearing thin,” the attorney general added.
A Montana Highway Patrol trooper was sent to the hospital to take the statement of the patient’s family members. Ms. Hansen also participated in a conference call with multiple health care providers in which she talked about the “legal ramifications” of withholding documents and the patient’s preferred treatment, which included ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine.
Public Service Commissioner Jennifer Fielder, a former Republican state senator, left a three-minute voicemail on a hospital line saying the patient’s friends in the Senate would not be too happy to learn of the care St. Peter’s was providing, according to the special counsel’s report.
Ms. Fielder and the patient’s daughter also cited a “right to try” law that Montana legislators passed in 2015 that allows terminally ill patients to seek experimental treatments. But a legal analysis written for the Montana Medical Association says that while the law does not require a provider to prescribe a particular medication if a patient demands it, it could give a provider legal immunity if the provider decides to prescribe the treatment, according to the Montana State News Bureau.
The report did not offer any conclusions or allegations of wrongdoing.
Hospital officials said before and after the report’s release that their health care providers were threatened and harassed when they refused to administer certain treatments for COVID.
“We stand by our assertion that the involvement of public officials in clinical care is inappropriate; that individuals leveraged their official positions in an attempt to influence clinical care; and that some of the exchanges that took place were threatening or harassing,” spokesperson Katie Gallagher said in a statement.
“Further, we reviewed all medical and legal records related to this patient’s care and verified that our teams provided care in accordance with clinical best practice, hospital policy, and patient rights,” Ms. Gallagher added.
The attorney general’s office did not respond to a request for comment but told the Montana Free Press in a statement that nobody at the state agency threatened anyone.
Mr. Rasmussen, the head of the Montana Hospital Association, said St. Peter’s officials have not reached out to the group for assistance. He downplayed the attorney general’s intervention in Helena, saying it often happens that people who know medical leaders or trustees will advocate on behalf of a relative or friend.
“Is this situation different? Certainly, because it’s from the attorney general,” Mr. Rasmussen said. “But I think the AG was responding to a constituent. Others would reach out to whoever they know on the hospital board.”
He added that hospitals have procedures in place that allow family members of patients to take their complaints to a supervisor or other hospital leader without resorting to threats.
Hospitals in the region that have watched the allegations of threats and harassment unfold declined to comment on their procedures to handle such conflicts.
“We respect the independent medical judgment of our providers who practice medicine consistent with approved, authorized treatment and recognized clinical standards,” said Bozeman Health spokesperson Lauren Brendel.
Tanner Gooch, a spokesperson for SCL Health Montana, which operates hospitals in Billings, Butte, and Miles City, said SCL does not endorse ivermectin or other COVID treatments that haven’t been approved by the FDA but doesn’t ban them, either.
“Ultimately, the treatment decisions are at the discretion of the provider,” Mr. Gooch said. “To our knowledge, no COVID-19 patients have been treated with ivermectin at our hospitals.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
No serious CV risks for elderly after Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine
A French population-based study provides further evidence that the BNT162b2 Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine does not increase the short-term risk for serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people.
The study showed no increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, or pulmonary embolism (PE) following vaccination in adults aged 75 years or older in the 14 days following vaccination.
“These findings regarding the BNT162b2 vaccine’s short-term cardiovascular safety profile in older people are reassuring. They should be taken into account by doctors when considering implementing a third dose of the vaccine in older people,” Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, PhD, with the French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety, Saint-Denis, France, said in an interview.
The study was published as a research letter online Nov. 22 in JAMA.
The Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine was the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccine authorized in France and has been widely used in older people. The phase 3 trials of the vaccine showed no increase in cardiovascular events, but older people were underrepresented in the trials.
As of April 30, 2021, nearly 3.9 million French adults aged 75 or older had received at least one dose of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine and 3.2 million had received two doses.
Using the French National Health Data System linked to the national COVID-19 vaccination database, Dr. Jabagi and her colleagues identified all unvaccinated or vaccinated adults aged 75 and older who were hospitalized between Dec. 15, 2020, and April 30, 2021, for acute MI, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, or PE.
During the 4.5-month study period, 11,113 elderly were hospitalized for acute MI, 17,014 for ischemic stroke, 4,804 for hemorrhagic stroke, and 7,221 for PE. Of these, 58.6%, 54.0%, 42.7%, and 55.3%, respectively, had received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the 14 days following receipt of either dose, no significant increased risk was found for any outcome, the investigators report.
The relative incidence (RI) for MI after the first and second dose was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.88-1.06) and 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16), respectively.
For ischemic stroke, the RI was 0.90 after the first dose (95% CI, 0.84-0.98) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.84-1.02) after the second; for hemorrhagic stroke, the RI was 0.90 (95% CI, 0.78-1.04) and 0.97 (95% CI, 0.81-1.15), respectively.
For PE, the RI was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.75-0.96) after the first dose and 1.10 (95% CI, 0.95-1.26) after the second dose.
There was also no significant increase for any of the cardiovascular events when the exposure risk window was subdivided into 1 to 7 days and 8 to 14 days.
“Evaluating the short-term risk of hospitalization for severe cardiovascular events after the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in older people was a priority, especially after signals for hypertension and cardiovascular, thromboembolic, and hemorrhagic events have been issued from spontaneous notification data,” Dr. Jabagi said in an interview.
“The results of this nationwide study provide further solid evidence regarding the lack of increase of serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people in the 14 days following both doses of the vaccine,” Dr. Jabagi said.
The French study supports a recent U.S. study of more than 6 million people demonstrating that serious health risks were no more common in the first 3 weeks after Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccination compared with 22 to 42 days later.
As previously reported by this news organization, mRNA vaccination was not associated with greater risks for Guillain-Barré syndrome, myocarditis/pericarditis, stroke, or 20 other serious outcomes.
The current study had no specific funding. Dr. Jabagi and colleagues have declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A French population-based study provides further evidence that the BNT162b2 Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine does not increase the short-term risk for serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people.
The study showed no increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, or pulmonary embolism (PE) following vaccination in adults aged 75 years or older in the 14 days following vaccination.
“These findings regarding the BNT162b2 vaccine’s short-term cardiovascular safety profile in older people are reassuring. They should be taken into account by doctors when considering implementing a third dose of the vaccine in older people,” Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, PhD, with the French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety, Saint-Denis, France, said in an interview.
The study was published as a research letter online Nov. 22 in JAMA.
The Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine was the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccine authorized in France and has been widely used in older people. The phase 3 trials of the vaccine showed no increase in cardiovascular events, but older people were underrepresented in the trials.
As of April 30, 2021, nearly 3.9 million French adults aged 75 or older had received at least one dose of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine and 3.2 million had received two doses.
Using the French National Health Data System linked to the national COVID-19 vaccination database, Dr. Jabagi and her colleagues identified all unvaccinated or vaccinated adults aged 75 and older who were hospitalized between Dec. 15, 2020, and April 30, 2021, for acute MI, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, or PE.
During the 4.5-month study period, 11,113 elderly were hospitalized for acute MI, 17,014 for ischemic stroke, 4,804 for hemorrhagic stroke, and 7,221 for PE. Of these, 58.6%, 54.0%, 42.7%, and 55.3%, respectively, had received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the 14 days following receipt of either dose, no significant increased risk was found for any outcome, the investigators report.
The relative incidence (RI) for MI after the first and second dose was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.88-1.06) and 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16), respectively.
For ischemic stroke, the RI was 0.90 after the first dose (95% CI, 0.84-0.98) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.84-1.02) after the second; for hemorrhagic stroke, the RI was 0.90 (95% CI, 0.78-1.04) and 0.97 (95% CI, 0.81-1.15), respectively.
For PE, the RI was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.75-0.96) after the first dose and 1.10 (95% CI, 0.95-1.26) after the second dose.
There was also no significant increase for any of the cardiovascular events when the exposure risk window was subdivided into 1 to 7 days and 8 to 14 days.
“Evaluating the short-term risk of hospitalization for severe cardiovascular events after the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in older people was a priority, especially after signals for hypertension and cardiovascular, thromboembolic, and hemorrhagic events have been issued from spontaneous notification data,” Dr. Jabagi said in an interview.
“The results of this nationwide study provide further solid evidence regarding the lack of increase of serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people in the 14 days following both doses of the vaccine,” Dr. Jabagi said.
The French study supports a recent U.S. study of more than 6 million people demonstrating that serious health risks were no more common in the first 3 weeks after Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccination compared with 22 to 42 days later.
As previously reported by this news organization, mRNA vaccination was not associated with greater risks for Guillain-Barré syndrome, myocarditis/pericarditis, stroke, or 20 other serious outcomes.
The current study had no specific funding. Dr. Jabagi and colleagues have declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A French population-based study provides further evidence that the BNT162b2 Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine does not increase the short-term risk for serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people.
The study showed no increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, or pulmonary embolism (PE) following vaccination in adults aged 75 years or older in the 14 days following vaccination.
“These findings regarding the BNT162b2 vaccine’s short-term cardiovascular safety profile in older people are reassuring. They should be taken into account by doctors when considering implementing a third dose of the vaccine in older people,” Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, PhD, with the French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety, Saint-Denis, France, said in an interview.
The study was published as a research letter online Nov. 22 in JAMA.
The Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine was the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccine authorized in France and has been widely used in older people. The phase 3 trials of the vaccine showed no increase in cardiovascular events, but older people were underrepresented in the trials.
As of April 30, 2021, nearly 3.9 million French adults aged 75 or older had received at least one dose of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine and 3.2 million had received two doses.
Using the French National Health Data System linked to the national COVID-19 vaccination database, Dr. Jabagi and her colleagues identified all unvaccinated or vaccinated adults aged 75 and older who were hospitalized between Dec. 15, 2020, and April 30, 2021, for acute MI, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, or PE.
During the 4.5-month study period, 11,113 elderly were hospitalized for acute MI, 17,014 for ischemic stroke, 4,804 for hemorrhagic stroke, and 7,221 for PE. Of these, 58.6%, 54.0%, 42.7%, and 55.3%, respectively, had received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the 14 days following receipt of either dose, no significant increased risk was found for any outcome, the investigators report.
The relative incidence (RI) for MI after the first and second dose was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.88-1.06) and 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16), respectively.
For ischemic stroke, the RI was 0.90 after the first dose (95% CI, 0.84-0.98) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.84-1.02) after the second; for hemorrhagic stroke, the RI was 0.90 (95% CI, 0.78-1.04) and 0.97 (95% CI, 0.81-1.15), respectively.
For PE, the RI was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.75-0.96) after the first dose and 1.10 (95% CI, 0.95-1.26) after the second dose.
There was also no significant increase for any of the cardiovascular events when the exposure risk window was subdivided into 1 to 7 days and 8 to 14 days.
“Evaluating the short-term risk of hospitalization for severe cardiovascular events after the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in older people was a priority, especially after signals for hypertension and cardiovascular, thromboembolic, and hemorrhagic events have been issued from spontaneous notification data,” Dr. Jabagi said in an interview.
“The results of this nationwide study provide further solid evidence regarding the lack of increase of serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people in the 14 days following both doses of the vaccine,” Dr. Jabagi said.
The French study supports a recent U.S. study of more than 6 million people demonstrating that serious health risks were no more common in the first 3 weeks after Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccination compared with 22 to 42 days later.
As previously reported by this news organization, mRNA vaccination was not associated with greater risks for Guillain-Barré syndrome, myocarditis/pericarditis, stroke, or 20 other serious outcomes.
The current study had no specific funding. Dr. Jabagi and colleagues have declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It feels like COVID is closing in
Like so many of you, I have weathered COVID-19 for the last almost 2 years. We’ve dealt with anxiety in our patients and ourselves, ever conflicting directives over masks, and uncertainty and hope over vaccinations.
In the beginning, it seemed elsewhere. Wuhan, China, the state of Washington, New York City.
In the beginning, I awoke with rising anxiety every morning at 4 a.m.
Now, it is part of life. We know how to do this.
I work in a D.C. hospital that takes care of COVID-19 patients. I don’t intubate or come into direct contact with patients’ secretions.
I felt lucky.
Last summer, I felt relief, after being fully vaccinated. We thought we were almost over it. But the numbers abroad and in the United States keep rising.
We have developed protocols. We test every patient for COVID-19 before admitting them to psychiatry, which is now routine. COVID-19–positive patients with suicidal ideation go to our medicine-psychiatric unit. We are single-room occupancy. No visitors.
Now, it feels like COVID is closing in. Lots of my patients on consultation-liaison psychiatry had COVID-19 or do now. The number of patients with long COVID is increasing. My elderly mother-in-law picked it up from a hospital. My young, healthy adult son got it but is now doing relatively OK. We will see if his ADHD worsens.
I received contact tracing recently for going into a patient room with contact precautions. I had put on the gown and gloves, but did I wear my goggles? I keep them on my forehead but could not remember if I had slipped them over my eyes.
I get tested weekly. My nose runs inside my mask. I sneeze. Is this COVID?
Of course, I am vaccinated with a booster shot. But breakthrough infections occur.
I am lucky, I keep reminding myself. I have a job and income and good PPE.
So, we are learning how to manage this disease. But it still closes in. My brain screams: “I do not want to catch this disease. I do not want to get sick. I do not want to get long COVID.”
“Calm down, Cam,” I tell myself. “You can do this!” I have learned how to do all the PPE, including tying the plastic ties along the backs of the plastic gowns.
All psychiatry meetings are virtual now. I cannot do virtual with enthusiasm. I say I will, but then do not log on. I miss the camaraderie.
All appointments are mainly telehealth. That has its pros and cons.
So bottom line – I will keep keeping on.
But I really want others to get vaccinated and wear masks. More than that, how can we as a psychiatric community get us through this pandemic?
Here are a few suggestions, some of which I have made before:
- Focus on what we can control, especially exercise and sleep. Walk during times when the sun is shining. Rake the gorgeous autumn yellow and orange leaves.
- Give small (or large) gifts of kindness to others. Give to food banks, provide large tips to those who bring you takeout, help out at an animal shelter.
- Talk through established media about self-care and therapy for anxiety and depression.
- Clean out your closets. Give clothes to Afghan refugees.
- Read good books about trying times – such as World War II and the long wars in Afghanistan and Iraq.
- Take care of veterans and the elderly and homeless.
- Take care of yourself and your family.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center. She has no conflicts of interest.
Like so many of you, I have weathered COVID-19 for the last almost 2 years. We’ve dealt with anxiety in our patients and ourselves, ever conflicting directives over masks, and uncertainty and hope over vaccinations.
In the beginning, it seemed elsewhere. Wuhan, China, the state of Washington, New York City.
In the beginning, I awoke with rising anxiety every morning at 4 a.m.
Now, it is part of life. We know how to do this.
I work in a D.C. hospital that takes care of COVID-19 patients. I don’t intubate or come into direct contact with patients’ secretions.
I felt lucky.
Last summer, I felt relief, after being fully vaccinated. We thought we were almost over it. But the numbers abroad and in the United States keep rising.
We have developed protocols. We test every patient for COVID-19 before admitting them to psychiatry, which is now routine. COVID-19–positive patients with suicidal ideation go to our medicine-psychiatric unit. We are single-room occupancy. No visitors.
Now, it feels like COVID is closing in. Lots of my patients on consultation-liaison psychiatry had COVID-19 or do now. The number of patients with long COVID is increasing. My elderly mother-in-law picked it up from a hospital. My young, healthy adult son got it but is now doing relatively OK. We will see if his ADHD worsens.
I received contact tracing recently for going into a patient room with contact precautions. I had put on the gown and gloves, but did I wear my goggles? I keep them on my forehead but could not remember if I had slipped them over my eyes.
I get tested weekly. My nose runs inside my mask. I sneeze. Is this COVID?
Of course, I am vaccinated with a booster shot. But breakthrough infections occur.
I am lucky, I keep reminding myself. I have a job and income and good PPE.
So, we are learning how to manage this disease. But it still closes in. My brain screams: “I do not want to catch this disease. I do not want to get sick. I do not want to get long COVID.”
“Calm down, Cam,” I tell myself. “You can do this!” I have learned how to do all the PPE, including tying the plastic ties along the backs of the plastic gowns.
All psychiatry meetings are virtual now. I cannot do virtual with enthusiasm. I say I will, but then do not log on. I miss the camaraderie.
All appointments are mainly telehealth. That has its pros and cons.
So bottom line – I will keep keeping on.
But I really want others to get vaccinated and wear masks. More than that, how can we as a psychiatric community get us through this pandemic?
Here are a few suggestions, some of which I have made before:
- Focus on what we can control, especially exercise and sleep. Walk during times when the sun is shining. Rake the gorgeous autumn yellow and orange leaves.
- Give small (or large) gifts of kindness to others. Give to food banks, provide large tips to those who bring you takeout, help out at an animal shelter.
- Talk through established media about self-care and therapy for anxiety and depression.
- Clean out your closets. Give clothes to Afghan refugees.
- Read good books about trying times – such as World War II and the long wars in Afghanistan and Iraq.
- Take care of veterans and the elderly and homeless.
- Take care of yourself and your family.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center. She has no conflicts of interest.
Like so many of you, I have weathered COVID-19 for the last almost 2 years. We’ve dealt with anxiety in our patients and ourselves, ever conflicting directives over masks, and uncertainty and hope over vaccinations.
In the beginning, it seemed elsewhere. Wuhan, China, the state of Washington, New York City.
In the beginning, I awoke with rising anxiety every morning at 4 a.m.
Now, it is part of life. We know how to do this.
I work in a D.C. hospital that takes care of COVID-19 patients. I don’t intubate or come into direct contact with patients’ secretions.
I felt lucky.
Last summer, I felt relief, after being fully vaccinated. We thought we were almost over it. But the numbers abroad and in the United States keep rising.
We have developed protocols. We test every patient for COVID-19 before admitting them to psychiatry, which is now routine. COVID-19–positive patients with suicidal ideation go to our medicine-psychiatric unit. We are single-room occupancy. No visitors.
Now, it feels like COVID is closing in. Lots of my patients on consultation-liaison psychiatry had COVID-19 or do now. The number of patients with long COVID is increasing. My elderly mother-in-law picked it up from a hospital. My young, healthy adult son got it but is now doing relatively OK. We will see if his ADHD worsens.
I received contact tracing recently for going into a patient room with contact precautions. I had put on the gown and gloves, but did I wear my goggles? I keep them on my forehead but could not remember if I had slipped them over my eyes.
I get tested weekly. My nose runs inside my mask. I sneeze. Is this COVID?
Of course, I am vaccinated with a booster shot. But breakthrough infections occur.
I am lucky, I keep reminding myself. I have a job and income and good PPE.
So, we are learning how to manage this disease. But it still closes in. My brain screams: “I do not want to catch this disease. I do not want to get sick. I do not want to get long COVID.”
“Calm down, Cam,” I tell myself. “You can do this!” I have learned how to do all the PPE, including tying the plastic ties along the backs of the plastic gowns.
All psychiatry meetings are virtual now. I cannot do virtual with enthusiasm. I say I will, but then do not log on. I miss the camaraderie.
All appointments are mainly telehealth. That has its pros and cons.
So bottom line – I will keep keeping on.
But I really want others to get vaccinated and wear masks. More than that, how can we as a psychiatric community get us through this pandemic?
Here are a few suggestions, some of which I have made before:
- Focus on what we can control, especially exercise and sleep. Walk during times when the sun is shining. Rake the gorgeous autumn yellow and orange leaves.
- Give small (or large) gifts of kindness to others. Give to food banks, provide large tips to those who bring you takeout, help out at an animal shelter.
- Talk through established media about self-care and therapy for anxiety and depression.
- Clean out your closets. Give clothes to Afghan refugees.
- Read good books about trying times – such as World War II and the long wars in Afghanistan and Iraq.
- Take care of veterans and the elderly and homeless.
- Take care of yourself and your family.
Dr. Ritchie is chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center. She has no conflicts of interest.
COVID-19 and the immunocompromised physician
Working feverishly to complete the myriad patient notes accumulated throughout a hectic day, my phone vibrated – alerting me to a number that, over the past several years, has wrought uncertainty, grief, and overwhelming relief. Answering hesitantly, I listened to my physician’s pharmacist inform me of unexpected and alarming news.
Since COVID-19 was first identified more than 1 year ago, more than 770,000 people have died in the United States. In the wake of those losses, countless grieve while attempting to navigate a future without their loved ones. Meanwhile, scientists worked feverishly to combat a pandemic relentless in contagion. As health care professionals, we work tirelessly against the sharpened scythe of death, toiling day after day without an identifiable end. All the while, advocacy has prevailed as the need for personal protective equipment, improved ventilation systems, sanitization measures, and other mitigation measures, such as mask wearing and social distancing, echoed swiftly across the nation and around the world.
But, as the months have progressed, and life has seemingly transitioned toward a parallel version of reality, subsections of communities have grown restless. Several nontherapeutic, ineffective, and falsely touted regimens have been promoted. Amid the chaos of misinformation, most medical professionals have sought support from respected journals and infectious disease experts to filter out jargon and piece together scientifically sound protocols. Although many lives have prevailed by way of those advancements, mixed messages about interventions have emerged – and in many quarters across the country, anger, resistance, and outright refusal have prevailed.
Yet, we – the medical community – have forged ever onward as the cases continued and the death toll steadily climbed. In many cases, physicians who are years removed from critical care training have been thrust into COVID units, while residents have shifted toward working outside of their chosen specialty. Outpatient offices have closed, salaries have been cut, and furloughs have loomed as days fade into months. Beset with exhaustion and uncertainty, sacrifice has become a common thread that intrinsically united us against an unrelenting foe.
Most people continued navigating the many changes and made concerted efforts to mimic our prepandemic lives. Working from home in makeshift offices, dusting off math skills to assist children through the doldrums of distance learning, and mastering various audiovisual platforms, we reinforced social bonds and forged new connections echoing the hallmark resilience reminiscent of our shared distant ancestry.
As of this writing, thanks to our work – and that of scientists and policy makers – about 69% of Americans have received at least one dose of vaccine, and vaccines are widely available to children 5 and older. But it has been disheartening to watch misinformation about vaccine research and development propagated by political figures, social media, and lay people.
Processing the phone call
While listening to my physician’s pharmacist, I slowed my breaths in an effort to find calm. Years of navigating the American health care industry had left me both equipped and ill-prepared for the unexpected. I listened intently to the pharmacist’s words while staring blankly at a computer screen – uncertain of what had felt so assured not 10 minutes earlier.
That’s when I got the news. The intravenous medication that aided in my stabilization had suffered a critical shortage because of its successful use in the treatment of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia – patients who, in a majority of cases, had likely refused the vaccines. As result, the medication that had enabled my return to work, active engagement in nonwork pursuits, and most importantly, equipped my body to thrive despite the damage it had suffered, suddenly vanished.
Gently placing my phone on the desk, my heart beat rapidly as tears steadily streamed down my face. Staring blankly ahead, my hands gradually balled into fists as I let out a sound of fear, agony, and uncertainty. Screaming at everything and nothing, nausea swelled as panic flooded my body. In that moment, I ruminated on the conversation with the pharmacist. There had been no discussion, no option for me to maintain accessibility to this valuable medicine. Consequently, I felt helpless. Although the same medication, albeit a different mechanism of delivery, was promptly chosen as an adequate substitute, there was no guarantee of it bestowing the same degree of efficacy. So I was terrified, envisioning the progress made over several years as plummeting into an abyss of pain and despair. What are those of us who have chosen medicine as our profession but are immunocompromised expected to make of this?
Over the next several weeks, I diligently adhered to the new regimen and focused on positive mentation. Nevertheless, day by day, the symptoms worsened; eventually, I became bed ridden. I tried to gather what little composure remained to reschedule patients and justify the resounding guilt of perceived failure. I remember the sweet and gentle look of my child as I once again could not summon the strength to play pretend. This felt overwhelming. Would I ever go back to work? Would I see my child grow? No amount of pleading or screaming would change the fact that a medical system chose to roll the dice on my health. In a haze of discomfort and betrayal, I wondered how a physician or medical facility could justify removing medication from someone reliant upon it. How do we choose the appropriate allocation of resources when the consequences are potentially catastrophic?
Searching for context
When a country is founded on the mission of rising as a leading world power built upon the concepts of freedom, basic human rights, and individuality while supporting an infrastructure of capitalism, power, and control, crises – particularly those related to public health – can fan deep divisions. Here in the United States, we have seen misinterpretation, misunderstanding, and bitter indignation fuel the flames of provocation as protests of mask mandates, distance learning, and social distancing were touted as violating the very core upon which the country was established. Frustration, palpable among health care professionals, grew ever greater as the importance of vaccination in quelling virus mutations and decreasing morbidity and mortality were openly disparaged and ignored.
Not only have we watched people refuse the vaccines, but some are ignoring other mitigation measures. So the question becomes: How are we, as health care professionals trying to maintain a therapeutic alliance with those who reject lifesaving practices, expected to process this? Sitting in appointments and attempting interventions without judgment feels impractical and nearly impossible – particularly when the behaviors of these patients have the potential of violating our own health and well-being. How do we remain altruistic in our endeavors when those who seek our care seem callously indifferent to our lives – and to those of our families?
Measuring the value of life
Within the fevered haze of this past year, many stories highlighting grim realities have captured the media spotlight. From individuals unable to have emergency evaluations because of facilities being inundated by COVID-19 patients to individuals prematurely discharged, hospital bed shortages, and financial pressures from insurance companies. In reciting the phrase “Primum non noncere,” we physicians are committing to providing fair and competent medical treatment. At times, urgent decisions are necessary but are always made in the best interest of the patient(s). Ultimately, I am left debating how these agonizing weeks served any meaningful purpose. Moreover, when choosing the many over the few, what are the determinant factors? I am left asking: What is the value of a life?
Philosophically, this ethical dilemma is captured succinctly via the “trolley problem,” formulated in 1967 by Philippa Foot, MD. This is how Dr. Foot’s formulation unfolds: Close your eyes, and imagine you are inside a trolley careening unhindered down the rumbling tracks. Straight ahead you see five people bound to the tracks in imminent danger of being struck, and on the other side, one person is tied to the tracks. Do you continue the same course – thereby condemning five innocent people to death – or do you make the active decision to switch tracks, therefore consigning the one to their fate? Envision the people what do they look like? How old are they? If the one were a small child or a close friend, would that alter your decision? How does one make such a harrowing choice knowing the irreversible consequences? Depending on your action, this quandary falls within two primary schools of thought: Utilitarianism, which posits that the best action is the greatest good for the greatest number of people, and deontologicalism, which suggests that action is inherently right or wrong regardless of the consequences. Therefore, the decision to save the five is not favored.
However simplistic those scenarios may read, such principles when viewed through different lenses, they form the basis of medical ethics. In effect, every acute decision, every aspect of treatment is predicated upon the principles of nonmaleficence, beneficence, utility, distributive justice, and autonomy. Yet, the manner in which they are applied is highly contingent upon myriad variables. For example, sociopolitical factors, including population size (rural versus urban), economics (impoverished versus wealthy), as well as demographic factors (age, ethnicity, gender, sexuality) can highly influence and sometimes unknowingly influence interpretation and allocation of health care resources. This dilemma does not yield easily applicable and universal solutions. Nevertheless, it is paramount to evaluate policies effectively and tediously, particularly those with detrimental ramifications. Likewise, remaining flexible in our willingness to explore alternative solutions and encourage open discord among those with opposing viewpoints is key to instituting individual or institutional change that values the one as it values the many.
After several weeks of acute illness and a variety of short-acting interventions, I received approval to resume intravenous therapy. While the saga has ultimately reached a satisfactory conclusion, I am left with stupefied disbelief toward the people who took a gamble on my health. I am facing a battle between understanding the obligation of medicine to provide ethical and reasonable care without hesitation or judgment versus embittered resentment when faced with those who openly campaign against lifesaving interventions, such as the COVID-19 vaccine. For me, each day and the one that follows is riddled with complicated emotion. Every time I prematurely cease activity out of discomfort and weariness, I worry about my increasingly foreboding workload. In those moments, in that place of questions without answers, I remember that someone somewhere ultimately decided to switch the trolley’s track.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with interests in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. Dr. Thomas has no conflicts of interest.
Working feverishly to complete the myriad patient notes accumulated throughout a hectic day, my phone vibrated – alerting me to a number that, over the past several years, has wrought uncertainty, grief, and overwhelming relief. Answering hesitantly, I listened to my physician’s pharmacist inform me of unexpected and alarming news.
Since COVID-19 was first identified more than 1 year ago, more than 770,000 people have died in the United States. In the wake of those losses, countless grieve while attempting to navigate a future without their loved ones. Meanwhile, scientists worked feverishly to combat a pandemic relentless in contagion. As health care professionals, we work tirelessly against the sharpened scythe of death, toiling day after day without an identifiable end. All the while, advocacy has prevailed as the need for personal protective equipment, improved ventilation systems, sanitization measures, and other mitigation measures, such as mask wearing and social distancing, echoed swiftly across the nation and around the world.
But, as the months have progressed, and life has seemingly transitioned toward a parallel version of reality, subsections of communities have grown restless. Several nontherapeutic, ineffective, and falsely touted regimens have been promoted. Amid the chaos of misinformation, most medical professionals have sought support from respected journals and infectious disease experts to filter out jargon and piece together scientifically sound protocols. Although many lives have prevailed by way of those advancements, mixed messages about interventions have emerged – and in many quarters across the country, anger, resistance, and outright refusal have prevailed.
Yet, we – the medical community – have forged ever onward as the cases continued and the death toll steadily climbed. In many cases, physicians who are years removed from critical care training have been thrust into COVID units, while residents have shifted toward working outside of their chosen specialty. Outpatient offices have closed, salaries have been cut, and furloughs have loomed as days fade into months. Beset with exhaustion and uncertainty, sacrifice has become a common thread that intrinsically united us against an unrelenting foe.
Most people continued navigating the many changes and made concerted efforts to mimic our prepandemic lives. Working from home in makeshift offices, dusting off math skills to assist children through the doldrums of distance learning, and mastering various audiovisual platforms, we reinforced social bonds and forged new connections echoing the hallmark resilience reminiscent of our shared distant ancestry.
As of this writing, thanks to our work – and that of scientists and policy makers – about 69% of Americans have received at least one dose of vaccine, and vaccines are widely available to children 5 and older. But it has been disheartening to watch misinformation about vaccine research and development propagated by political figures, social media, and lay people.
Processing the phone call
While listening to my physician’s pharmacist, I slowed my breaths in an effort to find calm. Years of navigating the American health care industry had left me both equipped and ill-prepared for the unexpected. I listened intently to the pharmacist’s words while staring blankly at a computer screen – uncertain of what had felt so assured not 10 minutes earlier.
That’s when I got the news. The intravenous medication that aided in my stabilization had suffered a critical shortage because of its successful use in the treatment of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia – patients who, in a majority of cases, had likely refused the vaccines. As result, the medication that had enabled my return to work, active engagement in nonwork pursuits, and most importantly, equipped my body to thrive despite the damage it had suffered, suddenly vanished.
Gently placing my phone on the desk, my heart beat rapidly as tears steadily streamed down my face. Staring blankly ahead, my hands gradually balled into fists as I let out a sound of fear, agony, and uncertainty. Screaming at everything and nothing, nausea swelled as panic flooded my body. In that moment, I ruminated on the conversation with the pharmacist. There had been no discussion, no option for me to maintain accessibility to this valuable medicine. Consequently, I felt helpless. Although the same medication, albeit a different mechanism of delivery, was promptly chosen as an adequate substitute, there was no guarantee of it bestowing the same degree of efficacy. So I was terrified, envisioning the progress made over several years as plummeting into an abyss of pain and despair. What are those of us who have chosen medicine as our profession but are immunocompromised expected to make of this?
Over the next several weeks, I diligently adhered to the new regimen and focused on positive mentation. Nevertheless, day by day, the symptoms worsened; eventually, I became bed ridden. I tried to gather what little composure remained to reschedule patients and justify the resounding guilt of perceived failure. I remember the sweet and gentle look of my child as I once again could not summon the strength to play pretend. This felt overwhelming. Would I ever go back to work? Would I see my child grow? No amount of pleading or screaming would change the fact that a medical system chose to roll the dice on my health. In a haze of discomfort and betrayal, I wondered how a physician or medical facility could justify removing medication from someone reliant upon it. How do we choose the appropriate allocation of resources when the consequences are potentially catastrophic?
Searching for context
When a country is founded on the mission of rising as a leading world power built upon the concepts of freedom, basic human rights, and individuality while supporting an infrastructure of capitalism, power, and control, crises – particularly those related to public health – can fan deep divisions. Here in the United States, we have seen misinterpretation, misunderstanding, and bitter indignation fuel the flames of provocation as protests of mask mandates, distance learning, and social distancing were touted as violating the very core upon which the country was established. Frustration, palpable among health care professionals, grew ever greater as the importance of vaccination in quelling virus mutations and decreasing morbidity and mortality were openly disparaged and ignored.
Not only have we watched people refuse the vaccines, but some are ignoring other mitigation measures. So the question becomes: How are we, as health care professionals trying to maintain a therapeutic alliance with those who reject lifesaving practices, expected to process this? Sitting in appointments and attempting interventions without judgment feels impractical and nearly impossible – particularly when the behaviors of these patients have the potential of violating our own health and well-being. How do we remain altruistic in our endeavors when those who seek our care seem callously indifferent to our lives – and to those of our families?
Measuring the value of life
Within the fevered haze of this past year, many stories highlighting grim realities have captured the media spotlight. From individuals unable to have emergency evaluations because of facilities being inundated by COVID-19 patients to individuals prematurely discharged, hospital bed shortages, and financial pressures from insurance companies. In reciting the phrase “Primum non noncere,” we physicians are committing to providing fair and competent medical treatment. At times, urgent decisions are necessary but are always made in the best interest of the patient(s). Ultimately, I am left debating how these agonizing weeks served any meaningful purpose. Moreover, when choosing the many over the few, what are the determinant factors? I am left asking: What is the value of a life?
Philosophically, this ethical dilemma is captured succinctly via the “trolley problem,” formulated in 1967 by Philippa Foot, MD. This is how Dr. Foot’s formulation unfolds: Close your eyes, and imagine you are inside a trolley careening unhindered down the rumbling tracks. Straight ahead you see five people bound to the tracks in imminent danger of being struck, and on the other side, one person is tied to the tracks. Do you continue the same course – thereby condemning five innocent people to death – or do you make the active decision to switch tracks, therefore consigning the one to their fate? Envision the people what do they look like? How old are they? If the one were a small child or a close friend, would that alter your decision? How does one make such a harrowing choice knowing the irreversible consequences? Depending on your action, this quandary falls within two primary schools of thought: Utilitarianism, which posits that the best action is the greatest good for the greatest number of people, and deontologicalism, which suggests that action is inherently right or wrong regardless of the consequences. Therefore, the decision to save the five is not favored.
However simplistic those scenarios may read, such principles when viewed through different lenses, they form the basis of medical ethics. In effect, every acute decision, every aspect of treatment is predicated upon the principles of nonmaleficence, beneficence, utility, distributive justice, and autonomy. Yet, the manner in which they are applied is highly contingent upon myriad variables. For example, sociopolitical factors, including population size (rural versus urban), economics (impoverished versus wealthy), as well as demographic factors (age, ethnicity, gender, sexuality) can highly influence and sometimes unknowingly influence interpretation and allocation of health care resources. This dilemma does not yield easily applicable and universal solutions. Nevertheless, it is paramount to evaluate policies effectively and tediously, particularly those with detrimental ramifications. Likewise, remaining flexible in our willingness to explore alternative solutions and encourage open discord among those with opposing viewpoints is key to instituting individual or institutional change that values the one as it values the many.
After several weeks of acute illness and a variety of short-acting interventions, I received approval to resume intravenous therapy. While the saga has ultimately reached a satisfactory conclusion, I am left with stupefied disbelief toward the people who took a gamble on my health. I am facing a battle between understanding the obligation of medicine to provide ethical and reasonable care without hesitation or judgment versus embittered resentment when faced with those who openly campaign against lifesaving interventions, such as the COVID-19 vaccine. For me, each day and the one that follows is riddled with complicated emotion. Every time I prematurely cease activity out of discomfort and weariness, I worry about my increasingly foreboding workload. In those moments, in that place of questions without answers, I remember that someone somewhere ultimately decided to switch the trolley’s track.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with interests in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. Dr. Thomas has no conflicts of interest.
Working feverishly to complete the myriad patient notes accumulated throughout a hectic day, my phone vibrated – alerting me to a number that, over the past several years, has wrought uncertainty, grief, and overwhelming relief. Answering hesitantly, I listened to my physician’s pharmacist inform me of unexpected and alarming news.
Since COVID-19 was first identified more than 1 year ago, more than 770,000 people have died in the United States. In the wake of those losses, countless grieve while attempting to navigate a future without their loved ones. Meanwhile, scientists worked feverishly to combat a pandemic relentless in contagion. As health care professionals, we work tirelessly against the sharpened scythe of death, toiling day after day without an identifiable end. All the while, advocacy has prevailed as the need for personal protective equipment, improved ventilation systems, sanitization measures, and other mitigation measures, such as mask wearing and social distancing, echoed swiftly across the nation and around the world.
But, as the months have progressed, and life has seemingly transitioned toward a parallel version of reality, subsections of communities have grown restless. Several nontherapeutic, ineffective, and falsely touted regimens have been promoted. Amid the chaos of misinformation, most medical professionals have sought support from respected journals and infectious disease experts to filter out jargon and piece together scientifically sound protocols. Although many lives have prevailed by way of those advancements, mixed messages about interventions have emerged – and in many quarters across the country, anger, resistance, and outright refusal have prevailed.
Yet, we – the medical community – have forged ever onward as the cases continued and the death toll steadily climbed. In many cases, physicians who are years removed from critical care training have been thrust into COVID units, while residents have shifted toward working outside of their chosen specialty. Outpatient offices have closed, salaries have been cut, and furloughs have loomed as days fade into months. Beset with exhaustion and uncertainty, sacrifice has become a common thread that intrinsically united us against an unrelenting foe.
Most people continued navigating the many changes and made concerted efforts to mimic our prepandemic lives. Working from home in makeshift offices, dusting off math skills to assist children through the doldrums of distance learning, and mastering various audiovisual platforms, we reinforced social bonds and forged new connections echoing the hallmark resilience reminiscent of our shared distant ancestry.
As of this writing, thanks to our work – and that of scientists and policy makers – about 69% of Americans have received at least one dose of vaccine, and vaccines are widely available to children 5 and older. But it has been disheartening to watch misinformation about vaccine research and development propagated by political figures, social media, and lay people.
Processing the phone call
While listening to my physician’s pharmacist, I slowed my breaths in an effort to find calm. Years of navigating the American health care industry had left me both equipped and ill-prepared for the unexpected. I listened intently to the pharmacist’s words while staring blankly at a computer screen – uncertain of what had felt so assured not 10 minutes earlier.
That’s when I got the news. The intravenous medication that aided in my stabilization had suffered a critical shortage because of its successful use in the treatment of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia – patients who, in a majority of cases, had likely refused the vaccines. As result, the medication that had enabled my return to work, active engagement in nonwork pursuits, and most importantly, equipped my body to thrive despite the damage it had suffered, suddenly vanished.
Gently placing my phone on the desk, my heart beat rapidly as tears steadily streamed down my face. Staring blankly ahead, my hands gradually balled into fists as I let out a sound of fear, agony, and uncertainty. Screaming at everything and nothing, nausea swelled as panic flooded my body. In that moment, I ruminated on the conversation with the pharmacist. There had been no discussion, no option for me to maintain accessibility to this valuable medicine. Consequently, I felt helpless. Although the same medication, albeit a different mechanism of delivery, was promptly chosen as an adequate substitute, there was no guarantee of it bestowing the same degree of efficacy. So I was terrified, envisioning the progress made over several years as plummeting into an abyss of pain and despair. What are those of us who have chosen medicine as our profession but are immunocompromised expected to make of this?
Over the next several weeks, I diligently adhered to the new regimen and focused on positive mentation. Nevertheless, day by day, the symptoms worsened; eventually, I became bed ridden. I tried to gather what little composure remained to reschedule patients and justify the resounding guilt of perceived failure. I remember the sweet and gentle look of my child as I once again could not summon the strength to play pretend. This felt overwhelming. Would I ever go back to work? Would I see my child grow? No amount of pleading or screaming would change the fact that a medical system chose to roll the dice on my health. In a haze of discomfort and betrayal, I wondered how a physician or medical facility could justify removing medication from someone reliant upon it. How do we choose the appropriate allocation of resources when the consequences are potentially catastrophic?
Searching for context
When a country is founded on the mission of rising as a leading world power built upon the concepts of freedom, basic human rights, and individuality while supporting an infrastructure of capitalism, power, and control, crises – particularly those related to public health – can fan deep divisions. Here in the United States, we have seen misinterpretation, misunderstanding, and bitter indignation fuel the flames of provocation as protests of mask mandates, distance learning, and social distancing were touted as violating the very core upon which the country was established. Frustration, palpable among health care professionals, grew ever greater as the importance of vaccination in quelling virus mutations and decreasing morbidity and mortality were openly disparaged and ignored.
Not only have we watched people refuse the vaccines, but some are ignoring other mitigation measures. So the question becomes: How are we, as health care professionals trying to maintain a therapeutic alliance with those who reject lifesaving practices, expected to process this? Sitting in appointments and attempting interventions without judgment feels impractical and nearly impossible – particularly when the behaviors of these patients have the potential of violating our own health and well-being. How do we remain altruistic in our endeavors when those who seek our care seem callously indifferent to our lives – and to those of our families?
Measuring the value of life
Within the fevered haze of this past year, many stories highlighting grim realities have captured the media spotlight. From individuals unable to have emergency evaluations because of facilities being inundated by COVID-19 patients to individuals prematurely discharged, hospital bed shortages, and financial pressures from insurance companies. In reciting the phrase “Primum non noncere,” we physicians are committing to providing fair and competent medical treatment. At times, urgent decisions are necessary but are always made in the best interest of the patient(s). Ultimately, I am left debating how these agonizing weeks served any meaningful purpose. Moreover, when choosing the many over the few, what are the determinant factors? I am left asking: What is the value of a life?
Philosophically, this ethical dilemma is captured succinctly via the “trolley problem,” formulated in 1967 by Philippa Foot, MD. This is how Dr. Foot’s formulation unfolds: Close your eyes, and imagine you are inside a trolley careening unhindered down the rumbling tracks. Straight ahead you see five people bound to the tracks in imminent danger of being struck, and on the other side, one person is tied to the tracks. Do you continue the same course – thereby condemning five innocent people to death – or do you make the active decision to switch tracks, therefore consigning the one to their fate? Envision the people what do they look like? How old are they? If the one were a small child or a close friend, would that alter your decision? How does one make such a harrowing choice knowing the irreversible consequences? Depending on your action, this quandary falls within two primary schools of thought: Utilitarianism, which posits that the best action is the greatest good for the greatest number of people, and deontologicalism, which suggests that action is inherently right or wrong regardless of the consequences. Therefore, the decision to save the five is not favored.
However simplistic those scenarios may read, such principles when viewed through different lenses, they form the basis of medical ethics. In effect, every acute decision, every aspect of treatment is predicated upon the principles of nonmaleficence, beneficence, utility, distributive justice, and autonomy. Yet, the manner in which they are applied is highly contingent upon myriad variables. For example, sociopolitical factors, including population size (rural versus urban), economics (impoverished versus wealthy), as well as demographic factors (age, ethnicity, gender, sexuality) can highly influence and sometimes unknowingly influence interpretation and allocation of health care resources. This dilemma does not yield easily applicable and universal solutions. Nevertheless, it is paramount to evaluate policies effectively and tediously, particularly those with detrimental ramifications. Likewise, remaining flexible in our willingness to explore alternative solutions and encourage open discord among those with opposing viewpoints is key to instituting individual or institutional change that values the one as it values the many.
After several weeks of acute illness and a variety of short-acting interventions, I received approval to resume intravenous therapy. While the saga has ultimately reached a satisfactory conclusion, I am left with stupefied disbelief toward the people who took a gamble on my health. I am facing a battle between understanding the obligation of medicine to provide ethical and reasonable care without hesitation or judgment versus embittered resentment when faced with those who openly campaign against lifesaving interventions, such as the COVID-19 vaccine. For me, each day and the one that follows is riddled with complicated emotion. Every time I prematurely cease activity out of discomfort and weariness, I worry about my increasingly foreboding workload. In those moments, in that place of questions without answers, I remember that someone somewhere ultimately decided to switch the trolley’s track.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with interests in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. Dr. Thomas has no conflicts of interest.
COVID-19 antibody drug likely works against Omicron, companies say
The companies said Dec. 2 that they tested the drug, called sotrovimab, against individual mutations found in the Omicron variant, according to The Wall Street Journal. The preliminary findings haven’t yet been peer-reviewed, and the drug will need to be tested against the whole spike protein on the virus to confirm results.
GlaxoSmithKline and Vir have previously tested sotrovimab against mutations on other variants, the newspaper reported. When the Omicron variant was identified, the companies looked at earlier research to find the tests they had done against mutations that are also found in Omicron.
Sotrovimab targets a spot on the spike protein that is found in other coronaviruses and is thought to be less likely to mutate, according to the newspaper. Omicron has at least two mutations that overlap with the drug’s target site, but researchers at the companies don’t think the mutations will affect the treatment’s ability to bind to the spike protein.
GlaxoSmithKline expects to see results from testing the drug against the full mutated spike protein in the next 2 to 3 weeks, the Journal reported.
Sotrovimab has been authorized in about a dozen countries, including the United States, which paid about $1 billion for hundreds of thousands of doses.
Other companies have also been testing their antibody treatments against the Omicron variant.
Regeneron announced Nov. 30 that its drug could be less effective, and it said further analyses will determine how much less effective by using the actual Omicron genetic sequence, according to Reuters.
Outside scientists have also said the antibody drug from Eli Lilly & Co. isn’t as effective against Omicron. The company told Reuters that it is still testing the treatment against the variant.
Another experimental antibody therapy developed by Adagio Therapeutics appears to work well against the new variant, the Journal reported, but the treatment is in late-stage clinical trials and isn’t yet authorized.
Antiviral drugs could also help prevent hospitalization and may be less vulnerable to new variants because they target a different part of the virus, the newspaper reported. Merck and Pfizer have developed antiviral pills, which still require FDA approval.
In addition, Gilead believes its approved IV therapy, called remdesivir, will continue to be effective against the variant, Reuters reported.
The FDA said Nov. 30 that it is looking at the effect that authorized COVID-19 vaccines can have on Omicron and expects to have more information in coming weeks, Reuters reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The companies said Dec. 2 that they tested the drug, called sotrovimab, against individual mutations found in the Omicron variant, according to The Wall Street Journal. The preliminary findings haven’t yet been peer-reviewed, and the drug will need to be tested against the whole spike protein on the virus to confirm results.
GlaxoSmithKline and Vir have previously tested sotrovimab against mutations on other variants, the newspaper reported. When the Omicron variant was identified, the companies looked at earlier research to find the tests they had done against mutations that are also found in Omicron.
Sotrovimab targets a spot on the spike protein that is found in other coronaviruses and is thought to be less likely to mutate, according to the newspaper. Omicron has at least two mutations that overlap with the drug’s target site, but researchers at the companies don’t think the mutations will affect the treatment’s ability to bind to the spike protein.
GlaxoSmithKline expects to see results from testing the drug against the full mutated spike protein in the next 2 to 3 weeks, the Journal reported.
Sotrovimab has been authorized in about a dozen countries, including the United States, which paid about $1 billion for hundreds of thousands of doses.
Other companies have also been testing their antibody treatments against the Omicron variant.
Regeneron announced Nov. 30 that its drug could be less effective, and it said further analyses will determine how much less effective by using the actual Omicron genetic sequence, according to Reuters.
Outside scientists have also said the antibody drug from Eli Lilly & Co. isn’t as effective against Omicron. The company told Reuters that it is still testing the treatment against the variant.
Another experimental antibody therapy developed by Adagio Therapeutics appears to work well against the new variant, the Journal reported, but the treatment is in late-stage clinical trials and isn’t yet authorized.
Antiviral drugs could also help prevent hospitalization and may be less vulnerable to new variants because they target a different part of the virus, the newspaper reported. Merck and Pfizer have developed antiviral pills, which still require FDA approval.
In addition, Gilead believes its approved IV therapy, called remdesivir, will continue to be effective against the variant, Reuters reported.
The FDA said Nov. 30 that it is looking at the effect that authorized COVID-19 vaccines can have on Omicron and expects to have more information in coming weeks, Reuters reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The companies said Dec. 2 that they tested the drug, called sotrovimab, against individual mutations found in the Omicron variant, according to The Wall Street Journal. The preliminary findings haven’t yet been peer-reviewed, and the drug will need to be tested against the whole spike protein on the virus to confirm results.
GlaxoSmithKline and Vir have previously tested sotrovimab against mutations on other variants, the newspaper reported. When the Omicron variant was identified, the companies looked at earlier research to find the tests they had done against mutations that are also found in Omicron.
Sotrovimab targets a spot on the spike protein that is found in other coronaviruses and is thought to be less likely to mutate, according to the newspaper. Omicron has at least two mutations that overlap with the drug’s target site, but researchers at the companies don’t think the mutations will affect the treatment’s ability to bind to the spike protein.
GlaxoSmithKline expects to see results from testing the drug against the full mutated spike protein in the next 2 to 3 weeks, the Journal reported.
Sotrovimab has been authorized in about a dozen countries, including the United States, which paid about $1 billion for hundreds of thousands of doses.
Other companies have also been testing their antibody treatments against the Omicron variant.
Regeneron announced Nov. 30 that its drug could be less effective, and it said further analyses will determine how much less effective by using the actual Omicron genetic sequence, according to Reuters.
Outside scientists have also said the antibody drug from Eli Lilly & Co. isn’t as effective against Omicron. The company told Reuters that it is still testing the treatment against the variant.
Another experimental antibody therapy developed by Adagio Therapeutics appears to work well against the new variant, the Journal reported, but the treatment is in late-stage clinical trials and isn’t yet authorized.
Antiviral drugs could also help prevent hospitalization and may be less vulnerable to new variants because they target a different part of the virus, the newspaper reported. Merck and Pfizer have developed antiviral pills, which still require FDA approval.
In addition, Gilead believes its approved IV therapy, called remdesivir, will continue to be effective against the variant, Reuters reported.
The FDA said Nov. 30 that it is looking at the effect that authorized COVID-19 vaccines can have on Omicron and expects to have more information in coming weeks, Reuters reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.