User login
COVID at 2 years: Preparing for a different ‘normal’
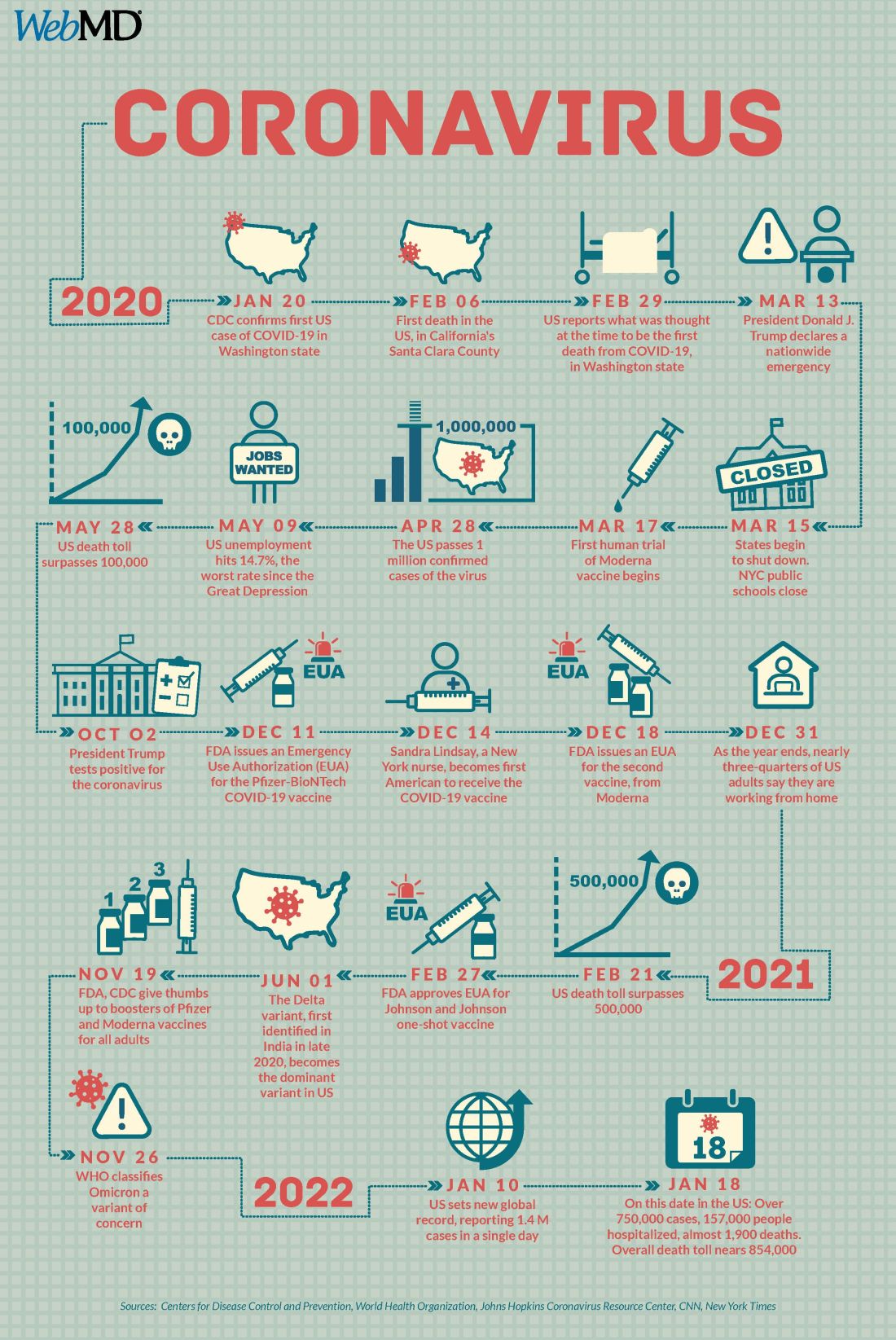
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.

A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.

A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Make America beautiful: Support mask mandates
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
Severe outcomes increased in youth hospitalized after positive COVID-19 test
Approximately 3% of youth who tested positive for COVID-19 in an emergency department setting had severe outcomes after 2 weeks, but this risk was 0.5% among those not admitted to the hospital, based on data from more than 3,000 individuals aged 18 and younger.
In the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, youth younger than 18 years accounted for fewer than 5% of reported cases, but now account for approximately 25% of positive cases, wrote Anna L. Funk, PhD, of the University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada, and colleagues.
However, the risk of severe outcomes of youth with COVID-19 remains poorly understood and data from large studies are lacking, they noted.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from 3,221 children and adolescents who were tested for COVID-19 at one of 41 emergency departments in 10 countries including Argentina, Australia, Canada, Costa Rica, Italy, New Zealand, Paraguay, Singapore, Spain, and the United States between March 2020 and June 2021. Positive infections were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing. At 14 days’ follow-up after a positive test, 735 patients (22.8%), were hospitalized, 107 (3.3%) had severe outcomes, and 4 (0.12%) had died. Severe outcomes were significantly more likely in children aged 5-10 years and 10-18 years vs. less than 1 year (odds ratios, 1.60 and 2.39, respectively), and in children with a self-reported chronic illness (OR, 2.34) or a prior episode of pneumonia (OR, 3.15).
Severe outcomes were more likely in patients who presented with symptoms that started 4-7 days before seeking care, compared with those whose symptoms started 0-3 days before seeking care (OR, 2.22).
The researchers also reviewed data from a subgroup of 2,510 individuals who were discharged home from the ED after initial testing. At 14 days’ follow-up, 50 of these patients (2.0%) were hospitalized and 12 (0.5%) had severe outcomes. In addition, the researchers found that the risk of severe outcomes among hospitalized COVID-19–positive youth was nearly four times higher, compared with hospitalized youth who tested negative for COVID-19 (risk difference, 3.9%).
Previous retrospective studies of severe outcomes in children and adolescents with COVID-19 have yielded varying results, in part because of the variation in study populations, the researchers noted in their discussion of the findings. “Our study population provides a risk estimate for youths brought for ED care.” Therefore, “Our lower estimate of severe disease likely reflects our stringent definition, which required the occurrence of complications or specific invasive interventions,” they said.
The study limitations included the potential overestimation of the risk of severe outcomes because patients were recruited in the ED, the researchers noted. Other limitations included variation in regional case definitions, screening criteria, and testing capacity among different sites and time periods. “Thus, 5% of our SARS-CoV-2–positive participants were asymptomatic – most of whom were tested as they were positive contacts of known cases or as part of routine screening procedures,” they said. The findings also are not generalizable to all community EDs and did not account for variants, they added.
However, the results were strengthened by the ability to compare outcomes for children with positive tests to similar children with negative tests, and add to the literature showing an increased risk of severe outcomes for those hospitalized with positive tests, the researchers concluded.
Data may inform clinical decisions
“The data [in the current study] are concerning for severe outcomes for children even prior to the Omicron strain,” said Margaret Thew, DNP, FP-BC, of Children’s Wisconsin-Milwaukee Hospital, in an interview. “Presently, the number of children infected with the Omicron strain is much higher and hospitalizations among children are at their highest since COVID-19 began,” she said. “For medical providers caring for this population, the study sheds light on pediatric patients who may be at higher risk of severe illness when they become infected with COVID-19,” she added.
“I was surprised by how high the number of pediatric patients hospitalized (22%) and the percentage (3%) with severe disease were during this time,” given that the timeline for these data preceded the spread of the Omicron strain, said Ms. Thew. “The risk of prior pneumonia was quite surprising. I do not recall seeing prior pneumonia as a risk factor for more severe COVID-19 with children or adults,” she added.
The take-home messaging for clinicians caring for children and adolescents is the added knowledge of the risk factors for severe outcomes from COVID-19, including the 10-18 age range, chronic illness, prior pneumonia, and longer symptom duration before seeking care in the ED, Ms. Thew emphasized.
However, additional research is needed on the impact of the new strains of COVID-19 on pediatric and adolescent hospitalizations, Ms. Thew said. Research also is needed on the other illnesses that have resulted from COVID-19, including illness requiring antibiotic use or medical interventions or treatments, and on the risk of combined COVID-19 and influenza viruses, she noted.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Alberta Innovates, the Alberta Health Services University of Calgary Clinical Research Fund, the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, the COVID-19 Research Accelerator Funding Track (CRAFT) Program at the University of California, Davis, and the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center Division of Emergency Medicine Small Grants Program. Lead author Dr. Funk was supported by the University of Calgary Eyes-High Post-Doctoral Research Fund, but had no financial conflicts to disclose. Ms. Thew had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
Approximately 3% of youth who tested positive for COVID-19 in an emergency department setting had severe outcomes after 2 weeks, but this risk was 0.5% among those not admitted to the hospital, based on data from more than 3,000 individuals aged 18 and younger.
In the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, youth younger than 18 years accounted for fewer than 5% of reported cases, but now account for approximately 25% of positive cases, wrote Anna L. Funk, PhD, of the University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada, and colleagues.
However, the risk of severe outcomes of youth with COVID-19 remains poorly understood and data from large studies are lacking, they noted.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from 3,221 children and adolescents who were tested for COVID-19 at one of 41 emergency departments in 10 countries including Argentina, Australia, Canada, Costa Rica, Italy, New Zealand, Paraguay, Singapore, Spain, and the United States between March 2020 and June 2021. Positive infections were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing. At 14 days’ follow-up after a positive test, 735 patients (22.8%), were hospitalized, 107 (3.3%) had severe outcomes, and 4 (0.12%) had died. Severe outcomes were significantly more likely in children aged 5-10 years and 10-18 years vs. less than 1 year (odds ratios, 1.60 and 2.39, respectively), and in children with a self-reported chronic illness (OR, 2.34) or a prior episode of pneumonia (OR, 3.15).
Severe outcomes were more likely in patients who presented with symptoms that started 4-7 days before seeking care, compared with those whose symptoms started 0-3 days before seeking care (OR, 2.22).
The researchers also reviewed data from a subgroup of 2,510 individuals who were discharged home from the ED after initial testing. At 14 days’ follow-up, 50 of these patients (2.0%) were hospitalized and 12 (0.5%) had severe outcomes. In addition, the researchers found that the risk of severe outcomes among hospitalized COVID-19–positive youth was nearly four times higher, compared with hospitalized youth who tested negative for COVID-19 (risk difference, 3.9%).
Previous retrospective studies of severe outcomes in children and adolescents with COVID-19 have yielded varying results, in part because of the variation in study populations, the researchers noted in their discussion of the findings. “Our study population provides a risk estimate for youths brought for ED care.” Therefore, “Our lower estimate of severe disease likely reflects our stringent definition, which required the occurrence of complications or specific invasive interventions,” they said.
The study limitations included the potential overestimation of the risk of severe outcomes because patients were recruited in the ED, the researchers noted. Other limitations included variation in regional case definitions, screening criteria, and testing capacity among different sites and time periods. “Thus, 5% of our SARS-CoV-2–positive participants were asymptomatic – most of whom were tested as they were positive contacts of known cases or as part of routine screening procedures,” they said. The findings also are not generalizable to all community EDs and did not account for variants, they added.
However, the results were strengthened by the ability to compare outcomes for children with positive tests to similar children with negative tests, and add to the literature showing an increased risk of severe outcomes for those hospitalized with positive tests, the researchers concluded.
Data may inform clinical decisions
“The data [in the current study] are concerning for severe outcomes for children even prior to the Omicron strain,” said Margaret Thew, DNP, FP-BC, of Children’s Wisconsin-Milwaukee Hospital, in an interview. “Presently, the number of children infected with the Omicron strain is much higher and hospitalizations among children are at their highest since COVID-19 began,” she said. “For medical providers caring for this population, the study sheds light on pediatric patients who may be at higher risk of severe illness when they become infected with COVID-19,” she added.
“I was surprised by how high the number of pediatric patients hospitalized (22%) and the percentage (3%) with severe disease were during this time,” given that the timeline for these data preceded the spread of the Omicron strain, said Ms. Thew. “The risk of prior pneumonia was quite surprising. I do not recall seeing prior pneumonia as a risk factor for more severe COVID-19 with children or adults,” she added.
The take-home messaging for clinicians caring for children and adolescents is the added knowledge of the risk factors for severe outcomes from COVID-19, including the 10-18 age range, chronic illness, prior pneumonia, and longer symptom duration before seeking care in the ED, Ms. Thew emphasized.
However, additional research is needed on the impact of the new strains of COVID-19 on pediatric and adolescent hospitalizations, Ms. Thew said. Research also is needed on the other illnesses that have resulted from COVID-19, including illness requiring antibiotic use or medical interventions or treatments, and on the risk of combined COVID-19 and influenza viruses, she noted.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Alberta Innovates, the Alberta Health Services University of Calgary Clinical Research Fund, the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, the COVID-19 Research Accelerator Funding Track (CRAFT) Program at the University of California, Davis, and the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center Division of Emergency Medicine Small Grants Program. Lead author Dr. Funk was supported by the University of Calgary Eyes-High Post-Doctoral Research Fund, but had no financial conflicts to disclose. Ms. Thew had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
Approximately 3% of youth who tested positive for COVID-19 in an emergency department setting had severe outcomes after 2 weeks, but this risk was 0.5% among those not admitted to the hospital, based on data from more than 3,000 individuals aged 18 and younger.
In the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, youth younger than 18 years accounted for fewer than 5% of reported cases, but now account for approximately 25% of positive cases, wrote Anna L. Funk, PhD, of the University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada, and colleagues.
However, the risk of severe outcomes of youth with COVID-19 remains poorly understood and data from large studies are lacking, they noted.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from 3,221 children and adolescents who were tested for COVID-19 at one of 41 emergency departments in 10 countries including Argentina, Australia, Canada, Costa Rica, Italy, New Zealand, Paraguay, Singapore, Spain, and the United States between March 2020 and June 2021. Positive infections were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing. At 14 days’ follow-up after a positive test, 735 patients (22.8%), were hospitalized, 107 (3.3%) had severe outcomes, and 4 (0.12%) had died. Severe outcomes were significantly more likely in children aged 5-10 years and 10-18 years vs. less than 1 year (odds ratios, 1.60 and 2.39, respectively), and in children with a self-reported chronic illness (OR, 2.34) or a prior episode of pneumonia (OR, 3.15).
Severe outcomes were more likely in patients who presented with symptoms that started 4-7 days before seeking care, compared with those whose symptoms started 0-3 days before seeking care (OR, 2.22).
The researchers also reviewed data from a subgroup of 2,510 individuals who were discharged home from the ED after initial testing. At 14 days’ follow-up, 50 of these patients (2.0%) were hospitalized and 12 (0.5%) had severe outcomes. In addition, the researchers found that the risk of severe outcomes among hospitalized COVID-19–positive youth was nearly four times higher, compared with hospitalized youth who tested negative for COVID-19 (risk difference, 3.9%).
Previous retrospective studies of severe outcomes in children and adolescents with COVID-19 have yielded varying results, in part because of the variation in study populations, the researchers noted in their discussion of the findings. “Our study population provides a risk estimate for youths brought for ED care.” Therefore, “Our lower estimate of severe disease likely reflects our stringent definition, which required the occurrence of complications or specific invasive interventions,” they said.
The study limitations included the potential overestimation of the risk of severe outcomes because patients were recruited in the ED, the researchers noted. Other limitations included variation in regional case definitions, screening criteria, and testing capacity among different sites and time periods. “Thus, 5% of our SARS-CoV-2–positive participants were asymptomatic – most of whom were tested as they were positive contacts of known cases or as part of routine screening procedures,” they said. The findings also are not generalizable to all community EDs and did not account for variants, they added.
However, the results were strengthened by the ability to compare outcomes for children with positive tests to similar children with negative tests, and add to the literature showing an increased risk of severe outcomes for those hospitalized with positive tests, the researchers concluded.
Data may inform clinical decisions
“The data [in the current study] are concerning for severe outcomes for children even prior to the Omicron strain,” said Margaret Thew, DNP, FP-BC, of Children’s Wisconsin-Milwaukee Hospital, in an interview. “Presently, the number of children infected with the Omicron strain is much higher and hospitalizations among children are at their highest since COVID-19 began,” she said. “For medical providers caring for this population, the study sheds light on pediatric patients who may be at higher risk of severe illness when they become infected with COVID-19,” she added.
“I was surprised by how high the number of pediatric patients hospitalized (22%) and the percentage (3%) with severe disease were during this time,” given that the timeline for these data preceded the spread of the Omicron strain, said Ms. Thew. “The risk of prior pneumonia was quite surprising. I do not recall seeing prior pneumonia as a risk factor for more severe COVID-19 with children or adults,” she added.
The take-home messaging for clinicians caring for children and adolescents is the added knowledge of the risk factors for severe outcomes from COVID-19, including the 10-18 age range, chronic illness, prior pneumonia, and longer symptom duration before seeking care in the ED, Ms. Thew emphasized.
However, additional research is needed on the impact of the new strains of COVID-19 on pediatric and adolescent hospitalizations, Ms. Thew said. Research also is needed on the other illnesses that have resulted from COVID-19, including illness requiring antibiotic use or medical interventions or treatments, and on the risk of combined COVID-19 and influenza viruses, she noted.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Alberta Innovates, the Alberta Health Services University of Calgary Clinical Research Fund, the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, the COVID-19 Research Accelerator Funding Track (CRAFT) Program at the University of California, Davis, and the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center Division of Emergency Medicine Small Grants Program. Lead author Dr. Funk was supported by the University of Calgary Eyes-High Post-Doctoral Research Fund, but had no financial conflicts to disclose. Ms. Thew had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Cardiac function normalizes by 3 months in MIS-C in study
While 80%-85% of children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome have cardiovascular involvement, “lack of knowledge about the short-term consequences of MIS-C has led to uncertainty among physicians in making recommendations about follow-up,” Daisuke Matsubara, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in their paper, which was published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Dr. Matsubara, of the department of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues examined cardiac outcomes among 60 patients aged 18 years or under admitted to two Philadelphia hospitals with MIS-C between April 2020 and January 2021. They compared those with outcomes in 60 age-matched healthy children who had undergone echocardiography for a range of non–COVID-related conditions such as chest pain or syncope.
The study used echocardiography, MRI, biochemistry, and functional and clinical parameters to assess the degree of change and damage to the heart at 3 months after admission.
When the patients first presented to a hospital, 42 had biochemical signs of myocardial injury, such as elevated brain-type natriuretic peptide and troponin levels. However, most patients’ symptoms were no longer present by the time they were discharged from hospital.
The researchers found that 81% of patients who presented with myocardial injury had lost the left atrial contraction phase. This dropped to 51% during the subacute phase, then 30% at 1 month. By 3-4 months, all patients achieved normal left atrial contraction phase.
At 1 month after admission, all MIS-C patients had significant signs of cardiac strain, compared with controls, including changes to global longitudinal strain, global circumferential strain, circumferential early diastolic strain rate, and right ventricular free wall longitudinal strain.
Parameters of strain normalized by 3 months
All parameters of strain had normalized, compared with controls, by 3 months. In the case of global longitudinal strain and left atrial strain, the median time to normalization was 6 days. For left ventricular ejection fraction the median time to normalization was 8 days and for right ventricular free wall longitudinal strain it was 9 days.
A small difference persisted with global longitudinal strain, but the authors said the difference was within the range of normal published values and not clinically relevant. The dysfunction appeared to be spread evenly across the heart rather than varying between segments, they noted.
“Deformation analysis could detect subtle myocardial changes; therefore, our study suggests the absence of persistent subclinical myocardial dysfunction after 3-4 months,” Dr. Matsubara said in an interview.
Four patients experienced small coronary aneurysms during the acute phase of MIS-C, but all had resolved within 2 months and none experienced any further lesions.
Among the 14 patients who underwent cardiac MRI at presentation, 2 had evidence of myocardial edema and fibrosis during the subacute phase of illness, despite having normal left ventricular systolic function and conventional echocardiography.
At follow-up, only one patient had residual edema; this individual had no evidence of fibrosis and had normal systolic function.
Study provides reassurance, but longer follow-up needed
Commenting on the study, pediatric cardiologist Devyani Chowdhury, MD, director of Cardiology Care for Children in Lancaster, Pa., said that overall it provided reassurance that most children do recover from MIS-C – and fits with her own clinical experience of the condition – but cautioned that longer-term follow-up was still needed.
“Three months is really not long term for a child,” Dr. Chowdhury said in an interview. “I’ve had a couple of patients whose MRIs have not normalized even after 1 year.”
Dr. Chowdhury also noted that it was a relatively small sample size, and it was also not yet possible to work out what host factors might play a role in increasing the risk of longer-term effects of MIS-C.
“I think it is a disease in evolution and we have to give it time, but in the very short term at least these kids are not dying, they are recovering, going home, and returning to activity and the heart is getting better,” she said.
The study authors suggested their findings could provide an evidence base for recommendations on when children with MIS-C can return to sports and physical activity, given that current consensus statements on the issue treat MIS-C as being equivalent to myocarditis in adults.
Dr. Matsubara noted that the cardiac outcomes of MIS-C were very different from those in COVID-19–affected adults, where echocardiography and MRI show longer-term evidence of myocardial impairments.
“This finding is also different from that of adult COVID-19, where the high troponin is reported to be the prognostic factor,” he said, suggesting this could explain different mechanisms of myocardial injury between MIS-C and COVID-19 myocarditis.
One author was supported by the National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
While 80%-85% of children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome have cardiovascular involvement, “lack of knowledge about the short-term consequences of MIS-C has led to uncertainty among physicians in making recommendations about follow-up,” Daisuke Matsubara, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in their paper, which was published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Dr. Matsubara, of the department of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues examined cardiac outcomes among 60 patients aged 18 years or under admitted to two Philadelphia hospitals with MIS-C between April 2020 and January 2021. They compared those with outcomes in 60 age-matched healthy children who had undergone echocardiography for a range of non–COVID-related conditions such as chest pain or syncope.
The study used echocardiography, MRI, biochemistry, and functional and clinical parameters to assess the degree of change and damage to the heart at 3 months after admission.
When the patients first presented to a hospital, 42 had biochemical signs of myocardial injury, such as elevated brain-type natriuretic peptide and troponin levels. However, most patients’ symptoms were no longer present by the time they were discharged from hospital.
The researchers found that 81% of patients who presented with myocardial injury had lost the left atrial contraction phase. This dropped to 51% during the subacute phase, then 30% at 1 month. By 3-4 months, all patients achieved normal left atrial contraction phase.
At 1 month after admission, all MIS-C patients had significant signs of cardiac strain, compared with controls, including changes to global longitudinal strain, global circumferential strain, circumferential early diastolic strain rate, and right ventricular free wall longitudinal strain.
Parameters of strain normalized by 3 months
All parameters of strain had normalized, compared with controls, by 3 months. In the case of global longitudinal strain and left atrial strain, the median time to normalization was 6 days. For left ventricular ejection fraction the median time to normalization was 8 days and for right ventricular free wall longitudinal strain it was 9 days.
A small difference persisted with global longitudinal strain, but the authors said the difference was within the range of normal published values and not clinically relevant. The dysfunction appeared to be spread evenly across the heart rather than varying between segments, they noted.
“Deformation analysis could detect subtle myocardial changes; therefore, our study suggests the absence of persistent subclinical myocardial dysfunction after 3-4 months,” Dr. Matsubara said in an interview.
Four patients experienced small coronary aneurysms during the acute phase of MIS-C, but all had resolved within 2 months and none experienced any further lesions.
Among the 14 patients who underwent cardiac MRI at presentation, 2 had evidence of myocardial edema and fibrosis during the subacute phase of illness, despite having normal left ventricular systolic function and conventional echocardiography.
At follow-up, only one patient had residual edema; this individual had no evidence of fibrosis and had normal systolic function.
Study provides reassurance, but longer follow-up needed
Commenting on the study, pediatric cardiologist Devyani Chowdhury, MD, director of Cardiology Care for Children in Lancaster, Pa., said that overall it provided reassurance that most children do recover from MIS-C – and fits with her own clinical experience of the condition – but cautioned that longer-term follow-up was still needed.
“Three months is really not long term for a child,” Dr. Chowdhury said in an interview. “I’ve had a couple of patients whose MRIs have not normalized even after 1 year.”
Dr. Chowdhury also noted that it was a relatively small sample size, and it was also not yet possible to work out what host factors might play a role in increasing the risk of longer-term effects of MIS-C.
“I think it is a disease in evolution and we have to give it time, but in the very short term at least these kids are not dying, they are recovering, going home, and returning to activity and the heart is getting better,” she said.
The study authors suggested their findings could provide an evidence base for recommendations on when children with MIS-C can return to sports and physical activity, given that current consensus statements on the issue treat MIS-C as being equivalent to myocarditis in adults.
Dr. Matsubara noted that the cardiac outcomes of MIS-C were very different from those in COVID-19–affected adults, where echocardiography and MRI show longer-term evidence of myocardial impairments.
“This finding is also different from that of adult COVID-19, where the high troponin is reported to be the prognostic factor,” he said, suggesting this could explain different mechanisms of myocardial injury between MIS-C and COVID-19 myocarditis.
One author was supported by the National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
While 80%-85% of children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome have cardiovascular involvement, “lack of knowledge about the short-term consequences of MIS-C has led to uncertainty among physicians in making recommendations about follow-up,” Daisuke Matsubara, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in their paper, which was published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Dr. Matsubara, of the department of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues examined cardiac outcomes among 60 patients aged 18 years or under admitted to two Philadelphia hospitals with MIS-C between April 2020 and January 2021. They compared those with outcomes in 60 age-matched healthy children who had undergone echocardiography for a range of non–COVID-related conditions such as chest pain or syncope.
The study used echocardiography, MRI, biochemistry, and functional and clinical parameters to assess the degree of change and damage to the heart at 3 months after admission.
When the patients first presented to a hospital, 42 had biochemical signs of myocardial injury, such as elevated brain-type natriuretic peptide and troponin levels. However, most patients’ symptoms were no longer present by the time they were discharged from hospital.
The researchers found that 81% of patients who presented with myocardial injury had lost the left atrial contraction phase. This dropped to 51% during the subacute phase, then 30% at 1 month. By 3-4 months, all patients achieved normal left atrial contraction phase.
At 1 month after admission, all MIS-C patients had significant signs of cardiac strain, compared with controls, including changes to global longitudinal strain, global circumferential strain, circumferential early diastolic strain rate, and right ventricular free wall longitudinal strain.
Parameters of strain normalized by 3 months
All parameters of strain had normalized, compared with controls, by 3 months. In the case of global longitudinal strain and left atrial strain, the median time to normalization was 6 days. For left ventricular ejection fraction the median time to normalization was 8 days and for right ventricular free wall longitudinal strain it was 9 days.
A small difference persisted with global longitudinal strain, but the authors said the difference was within the range of normal published values and not clinically relevant. The dysfunction appeared to be spread evenly across the heart rather than varying between segments, they noted.
“Deformation analysis could detect subtle myocardial changes; therefore, our study suggests the absence of persistent subclinical myocardial dysfunction after 3-4 months,” Dr. Matsubara said in an interview.
Four patients experienced small coronary aneurysms during the acute phase of MIS-C, but all had resolved within 2 months and none experienced any further lesions.
Among the 14 patients who underwent cardiac MRI at presentation, 2 had evidence of myocardial edema and fibrosis during the subacute phase of illness, despite having normal left ventricular systolic function and conventional echocardiography.
At follow-up, only one patient had residual edema; this individual had no evidence of fibrosis and had normal systolic function.
Study provides reassurance, but longer follow-up needed
Commenting on the study, pediatric cardiologist Devyani Chowdhury, MD, director of Cardiology Care for Children in Lancaster, Pa., said that overall it provided reassurance that most children do recover from MIS-C – and fits with her own clinical experience of the condition – but cautioned that longer-term follow-up was still needed.
“Three months is really not long term for a child,” Dr. Chowdhury said in an interview. “I’ve had a couple of patients whose MRIs have not normalized even after 1 year.”
Dr. Chowdhury also noted that it was a relatively small sample size, and it was also not yet possible to work out what host factors might play a role in increasing the risk of longer-term effects of MIS-C.
“I think it is a disease in evolution and we have to give it time, but in the very short term at least these kids are not dying, they are recovering, going home, and returning to activity and the heart is getting better,” she said.
The study authors suggested their findings could provide an evidence base for recommendations on when children with MIS-C can return to sports and physical activity, given that current consensus statements on the issue treat MIS-C as being equivalent to myocarditis in adults.
Dr. Matsubara noted that the cardiac outcomes of MIS-C were very different from those in COVID-19–affected adults, where echocardiography and MRI show longer-term evidence of myocardial impairments.
“This finding is also different from that of adult COVID-19, where the high troponin is reported to be the prognostic factor,” he said, suggesting this could explain different mechanisms of myocardial injury between MIS-C and COVID-19 myocarditis.
One author was supported by the National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Mental health problems in kids linked with school closures
Behavior problems, anxiety, and depression in youths were associated with these individuals participating in remote schooling during broader social lockdowns in a new study.
The systematic review, which was published in JAMA Pediatrics on Jan. 18, 2022, was based on data from 36 studies from 11 countries on mental health, physical health, and well-being in children and adolescents aged 0-18 years. The total population included 79,781 children and 18,028 parents or caregivers. The studies reflected the first wave of pandemic school closures and lockdowns from February to July 2020, with the duration of school closure ranging from 1 week to 3 months.
“There are strong theoretical reasons to suggest that school closures may have contributed to a considerable proportion of the harms identified here, particularly mental health harms, through reduction in social contacts with peers and teachers,” Russell Viner, PhD, of UCL Great Ormond St Institute of Child Health, London, and colleagues wrote in their paper.
The researchers included 9 longitudinal pre-post studies, 5 cohort studies, 21 cross-sectional studies, and 1 modeling study in their analysis. Overall, approximately one-third of the studies (36%) were considered high quality, and approximately two-thirds (64%) of the studies were published in journals. Twenty-five of the reports analyzed focused on mental health and well-being.
Schools provide not only education, but also services including meals, health care, and health supplies. Schools also serve as a safety net and source of social support for children, the researchers noted.
The losses children may have experienced during school closures occurred during a time when more than 167,000 children younger than 18 years lost a parent or caregiver to COVID-19, according to a recent report titled “Hidden Pain” by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania, Nemours Children’s Health, and the COVID Collaborative. Although not addressed in the current study, school closures would prevent bereaved children from receiving social-emotional support from friends and teachers. This crisis of loss also prompted the American Academy of Pediatrics to issue a National State of Emergency in Children’s Mental Health in October 2021.
New study results
These studies identified associations between school closures during broader lockdowns and increased emotional and behavioral problems, as well as increased restlessness and inattention. Across these studies, 18%-60% of children and adolescents scored higher than the risk thresholds for diagnoses of distress, especially depressive symptoms and anxiety.
Although two studies showed no significant association with suicide in response to school closures during lockdowns, three studies suggested increased use of screen time, two studies reported increased social media use, and six studies reported lower levels of physical activity.
Three studies of child abuse showed decreases in notifications during lockdowns, likely driven by lack of referrals from schools, the authors noted. A total of 10 studies on sleep and 5 studies on diet showed inconsistent evidence of harm during the specific period of school closures and social lockdowns.
“The contrast of rises in distress with decreases in presentations suggests that there was an escalation of unmet mental health need during lockdowns in already vulnerable children and adolescents,” the researchers wrote. “More troubling still is evidence of a reduction in the ability of the health and social care systems to protect children in many countries, as shown by the large falls in child protection referrals seen in high-quality cohort studies.”
‘Study presents concrete assessments rather than speculation’
“Concerns have been widely expressed in the lay media and beyond that school closures could negatively impact the mental and physical health of children and adolescents,” M. Susan Jay, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said in an interview. “The authors presented a narrative synthesis summarizing available evidence for the first wave of COVID-19 on school closures during the broader social lockdown occurring during this period.”
The “importance” of this research is that “it is not a single convenience sample study, but a systematic review from 11 countries including the United States, United Kingdom, China, and Turkey, among others, and that the quality of the information was graded,” Dr. Jay said. “Although not a meta-analysis, the study presents concrete assessments rather than speculation and overviews its limitations so that the clinician can weigh this information. Importantly, the authors excluded closure of schools with transmission of infection.
“Clearly, school lockdowns as a measure of controlling infectious disease needs balance with potential of negative health behaviors in children and adolescents. Ongoing prospective longitudinal studies are needed as sequential waves of the pandemic continue,” she emphasized.
“Clinically, this study highlights the need for clinicians to consider [asking] about the impact of school closures and remote versus hybrid versus in-person education [as part of their] patients and families question inventory,” Dr. Jay said. “Also, the use of depression inventories can be offered to youth to assess their mental health state at a visit, either via telemedicine or in person, and ideally at sequential visits for a more in-depth assessment.”
Schools play key role in social and emotional development
“It was important to conduct this study now, because this current time is unprecedented,” Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, of the University of South Carolina, Columbia, said in an interview. “We know based on evolutionary biology, anthropology, and developmental psychology, among other disciplines, that meaningful interpersonal interactions embedded in the context of community are vital to supporting human well-being.
“In our current time, the primary framework of community for our children is the school setting; it is the predominant space where they engage in the interpersonal interactions necessary for developing resilience, their sense of purpose, belonging, and fidelity,” he emphasized.
“Rarely in the course of human existence have kids been removed from the broader context of community to this extent and for this duration,” Dr. Loper said. “This study capitalizes on this unprecedented moment to begin to further understand how compromises in our sociocultural infrastructure of community, like school closures and lockdowns, may manifest as mental health problems in children and adolescents. More importantly, it contributes to the exploration of potential unintended consequences of our current infection control measures so we can adapt to support the overall well-being of our children in this ‘new normal.’ ”
Dr. Loper added that he was not surprised by the new study’s findings.
“We were already seeing a decline in pediatric mental health and overall well-being in the years preceding COVID-19 because of the ‘isolation epidemic’ involving many of the factors that this study explored,” he said. “I think this review further illustrates the vital necessity of community to support the health and well-being of humans, and specifically children and adolescents.”
From a clinical standpoint, “we need to be intentional and consistent in balancing infection control measures with our kids’ fundamental psychosocial needs,” Dr. Loper said.
“We need to recognize that, when children and adolescents are isolated from community, their fundamental psychosocial needs go unmet,” he emphasized. “If children and adolescents cannot access the meaningful interpersonal interactions necessary for resilience, then they cannot overcome or navigate distress. They will exhibit the avoidance and withdrawal behaviors that accumulate to manifest as adverse mental health symptoms like anxiety and depression.
“Additional research is needed to further explore how compromises in the psychosocial infrastructure of community manifest as downstream symptom indicators such as anxiety and depression,” which are often manifestations of unmet needs, Dr. Loper said.
Limitations and strengths, according to authors
The findings were limited by several factors, including a lack of examination of school closures’ effects on mental health independent of broader social lockdowns, according to the researchers. Other limitations included the authors potentially having missed studies, inclusion of cross-sectional studies with relatively weak evidence, potential bias from studies using parent reports, and a focus on the first COVID-19 wave, during which many school closures were of limited duration. Also, the researchers said they did not include studies focused on particular groups, such as children with learning difficulties or autism.
The use of large databases from education as well as health care in studies analyzed were strengths of the new research, they said. The investigators received no outside funding for their study. The researchers, Dr. Jay, and Dr. Loper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Jay serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Behavior problems, anxiety, and depression in youths were associated with these individuals participating in remote schooling during broader social lockdowns in a new study.
The systematic review, which was published in JAMA Pediatrics on Jan. 18, 2022, was based on data from 36 studies from 11 countries on mental health, physical health, and well-being in children and adolescents aged 0-18 years. The total population included 79,781 children and 18,028 parents or caregivers. The studies reflected the first wave of pandemic school closures and lockdowns from February to July 2020, with the duration of school closure ranging from 1 week to 3 months.
“There are strong theoretical reasons to suggest that school closures may have contributed to a considerable proportion of the harms identified here, particularly mental health harms, through reduction in social contacts with peers and teachers,” Russell Viner, PhD, of UCL Great Ormond St Institute of Child Health, London, and colleagues wrote in their paper.
The researchers included 9 longitudinal pre-post studies, 5 cohort studies, 21 cross-sectional studies, and 1 modeling study in their analysis. Overall, approximately one-third of the studies (36%) were considered high quality, and approximately two-thirds (64%) of the studies were published in journals. Twenty-five of the reports analyzed focused on mental health and well-being.
Schools provide not only education, but also services including meals, health care, and health supplies. Schools also serve as a safety net and source of social support for children, the researchers noted.
The losses children may have experienced during school closures occurred during a time when more than 167,000 children younger than 18 years lost a parent or caregiver to COVID-19, according to a recent report titled “Hidden Pain” by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania, Nemours Children’s Health, and the COVID Collaborative. Although not addressed in the current study, school closures would prevent bereaved children from receiving social-emotional support from friends and teachers. This crisis of loss also prompted the American Academy of Pediatrics to issue a National State of Emergency in Children’s Mental Health in October 2021.
New study results
These studies identified associations between school closures during broader lockdowns and increased emotional and behavioral problems, as well as increased restlessness and inattention. Across these studies, 18%-60% of children and adolescents scored higher than the risk thresholds for diagnoses of distress, especially depressive symptoms and anxiety.
Although two studies showed no significant association with suicide in response to school closures during lockdowns, three studies suggested increased use of screen time, two studies reported increased social media use, and six studies reported lower levels of physical activity.
Three studies of child abuse showed decreases in notifications during lockdowns, likely driven by lack of referrals from schools, the authors noted. A total of 10 studies on sleep and 5 studies on diet showed inconsistent evidence of harm during the specific period of school closures and social lockdowns.
“The contrast of rises in distress with decreases in presentations suggests that there was an escalation of unmet mental health need during lockdowns in already vulnerable children and adolescents,” the researchers wrote. “More troubling still is evidence of a reduction in the ability of the health and social care systems to protect children in many countries, as shown by the large falls in child protection referrals seen in high-quality cohort studies.”
‘Study presents concrete assessments rather than speculation’
“Concerns have been widely expressed in the lay media and beyond that school closures could negatively impact the mental and physical health of children and adolescents,” M. Susan Jay, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said in an interview. “The authors presented a narrative synthesis summarizing available evidence for the first wave of COVID-19 on school closures during the broader social lockdown occurring during this period.”
The “importance” of this research is that “it is not a single convenience sample study, but a systematic review from 11 countries including the United States, United Kingdom, China, and Turkey, among others, and that the quality of the information was graded,” Dr. Jay said. “Although not a meta-analysis, the study presents concrete assessments rather than speculation and overviews its limitations so that the clinician can weigh this information. Importantly, the authors excluded closure of schools with transmission of infection.
“Clearly, school lockdowns as a measure of controlling infectious disease needs balance with potential of negative health behaviors in children and adolescents. Ongoing prospective longitudinal studies are needed as sequential waves of the pandemic continue,” she emphasized.
“Clinically, this study highlights the need for clinicians to consider [asking] about the impact of school closures and remote versus hybrid versus in-person education [as part of their] patients and families question inventory,” Dr. Jay said. “Also, the use of depression inventories can be offered to youth to assess their mental health state at a visit, either via telemedicine or in person, and ideally at sequential visits for a more in-depth assessment.”
Schools play key role in social and emotional development
“It was important to conduct this study now, because this current time is unprecedented,” Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, of the University of South Carolina, Columbia, said in an interview. “We know based on evolutionary biology, anthropology, and developmental psychology, among other disciplines, that meaningful interpersonal interactions embedded in the context of community are vital to supporting human well-being.
“In our current time, the primary framework of community for our children is the school setting; it is the predominant space where they engage in the interpersonal interactions necessary for developing resilience, their sense of purpose, belonging, and fidelity,” he emphasized.
“Rarely in the course of human existence have kids been removed from the broader context of community to this extent and for this duration,” Dr. Loper said. “This study capitalizes on this unprecedented moment to begin to further understand how compromises in our sociocultural infrastructure of community, like school closures and lockdowns, may manifest as mental health problems in children and adolescents. More importantly, it contributes to the exploration of potential unintended consequences of our current infection control measures so we can adapt to support the overall well-being of our children in this ‘new normal.’ ”
Dr. Loper added that he was not surprised by the new study’s findings.
“We were already seeing a decline in pediatric mental health and overall well-being in the years preceding COVID-19 because of the ‘isolation epidemic’ involving many of the factors that this study explored,” he said. “I think this review further illustrates the vital necessity of community to support the health and well-being of humans, and specifically children and adolescents.”
From a clinical standpoint, “we need to be intentional and consistent in balancing infection control measures with our kids’ fundamental psychosocial needs,” Dr. Loper said.
“We need to recognize that, when children and adolescents are isolated from community, their fundamental psychosocial needs go unmet,” he emphasized. “If children and adolescents cannot access the meaningful interpersonal interactions necessary for resilience, then they cannot overcome or navigate distress. They will exhibit the avoidance and withdrawal behaviors that accumulate to manifest as adverse mental health symptoms like anxiety and depression.
“Additional research is needed to further explore how compromises in the psychosocial infrastructure of community manifest as downstream symptom indicators such as anxiety and depression,” which are often manifestations of unmet needs, Dr. Loper said.
Limitations and strengths, according to authors
The findings were limited by several factors, including a lack of examination of school closures’ effects on mental health independent of broader social lockdowns, according to the researchers. Other limitations included the authors potentially having missed studies, inclusion of cross-sectional studies with relatively weak evidence, potential bias from studies using parent reports, and a focus on the first COVID-19 wave, during which many school closures were of limited duration. Also, the researchers said they did not include studies focused on particular groups, such as children with learning difficulties or autism.
The use of large databases from education as well as health care in studies analyzed were strengths of the new research, they said. The investigators received no outside funding for their study. The researchers, Dr. Jay, and Dr. Loper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Jay serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Behavior problems, anxiety, and depression in youths were associated with these individuals participating in remote schooling during broader social lockdowns in a new study.
The systematic review, which was published in JAMA Pediatrics on Jan. 18, 2022, was based on data from 36 studies from 11 countries on mental health, physical health, and well-being in children and adolescents aged 0-18 years. The total population included 79,781 children and 18,028 parents or caregivers. The studies reflected the first wave of pandemic school closures and lockdowns from February to July 2020, with the duration of school closure ranging from 1 week to 3 months.
“There are strong theoretical reasons to suggest that school closures may have contributed to a considerable proportion of the harms identified here, particularly mental health harms, through reduction in social contacts with peers and teachers,” Russell Viner, PhD, of UCL Great Ormond St Institute of Child Health, London, and colleagues wrote in their paper.
The researchers included 9 longitudinal pre-post studies, 5 cohort studies, 21 cross-sectional studies, and 1 modeling study in their analysis. Overall, approximately one-third of the studies (36%) were considered high quality, and approximately two-thirds (64%) of the studies were published in journals. Twenty-five of the reports analyzed focused on mental health and well-being.
Schools provide not only education, but also services including meals, health care, and health supplies. Schools also serve as a safety net and source of social support for children, the researchers noted.
The losses children may have experienced during school closures occurred during a time when more than 167,000 children younger than 18 years lost a parent or caregiver to COVID-19, according to a recent report titled “Hidden Pain” by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania, Nemours Children’s Health, and the COVID Collaborative. Although not addressed in the current study, school closures would prevent bereaved children from receiving social-emotional support from friends and teachers. This crisis of loss also prompted the American Academy of Pediatrics to issue a National State of Emergency in Children’s Mental Health in October 2021.
New study results
These studies identified associations between school closures during broader lockdowns and increased emotional and behavioral problems, as well as increased restlessness and inattention. Across these studies, 18%-60% of children and adolescents scored higher than the risk thresholds for diagnoses of distress, especially depressive symptoms and anxiety.
Although two studies showed no significant association with suicide in response to school closures during lockdowns, three studies suggested increased use of screen time, two studies reported increased social media use, and six studies reported lower levels of physical activity.
Three studies of child abuse showed decreases in notifications during lockdowns, likely driven by lack of referrals from schools, the authors noted. A total of 10 studies on sleep and 5 studies on diet showed inconsistent evidence of harm during the specific period of school closures and social lockdowns.
“The contrast of rises in distress with decreases in presentations suggests that there was an escalation of unmet mental health need during lockdowns in already vulnerable children and adolescents,” the researchers wrote. “More troubling still is evidence of a reduction in the ability of the health and social care systems to protect children in many countries, as shown by the large falls in child protection referrals seen in high-quality cohort studies.”
‘Study presents concrete assessments rather than speculation’
“Concerns have been widely expressed in the lay media and beyond that school closures could negatively impact the mental and physical health of children and adolescents,” M. Susan Jay, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, said in an interview. “The authors presented a narrative synthesis summarizing available evidence for the first wave of COVID-19 on school closures during the broader social lockdown occurring during this period.”
The “importance” of this research is that “it is not a single convenience sample study, but a systematic review from 11 countries including the United States, United Kingdom, China, and Turkey, among others, and that the quality of the information was graded,” Dr. Jay said. “Although not a meta-analysis, the study presents concrete assessments rather than speculation and overviews its limitations so that the clinician can weigh this information. Importantly, the authors excluded closure of schools with transmission of infection.
“Clearly, school lockdowns as a measure of controlling infectious disease needs balance with potential of negative health behaviors in children and adolescents. Ongoing prospective longitudinal studies are needed as sequential waves of the pandemic continue,” she emphasized.
“Clinically, this study highlights the need for clinicians to consider [asking] about the impact of school closures and remote versus hybrid versus in-person education [as part of their] patients and families question inventory,” Dr. Jay said. “Also, the use of depression inventories can be offered to youth to assess their mental health state at a visit, either via telemedicine or in person, and ideally at sequential visits for a more in-depth assessment.”
Schools play key role in social and emotional development
“It was important to conduct this study now, because this current time is unprecedented,” Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, of the University of South Carolina, Columbia, said in an interview. “We know based on evolutionary biology, anthropology, and developmental psychology, among other disciplines, that meaningful interpersonal interactions embedded in the context of community are vital to supporting human well-being.
“In our current time, the primary framework of community for our children is the school setting; it is the predominant space where they engage in the interpersonal interactions necessary for developing resilience, their sense of purpose, belonging, and fidelity,” he emphasized.
“Rarely in the course of human existence have kids been removed from the broader context of community to this extent and for this duration,” Dr. Loper said. “This study capitalizes on this unprecedented moment to begin to further understand how compromises in our sociocultural infrastructure of community, like school closures and lockdowns, may manifest as mental health problems in children and adolescents. More importantly, it contributes to the exploration of potential unintended consequences of our current infection control measures so we can adapt to support the overall well-being of our children in this ‘new normal.’ ”
Dr. Loper added that he was not surprised by the new study’s findings.
“We were already seeing a decline in pediatric mental health and overall well-being in the years preceding COVID-19 because of the ‘isolation epidemic’ involving many of the factors that this study explored,” he said. “I think this review further illustrates the vital necessity of community to support the health and well-being of humans, and specifically children and adolescents.”
From a clinical standpoint, “we need to be intentional and consistent in balancing infection control measures with our kids’ fundamental psychosocial needs,” Dr. Loper said.
“We need to recognize that, when children and adolescents are isolated from community, their fundamental psychosocial needs go unmet,” he emphasized. “If children and adolescents cannot access the meaningful interpersonal interactions necessary for resilience, then they cannot overcome or navigate distress. They will exhibit the avoidance and withdrawal behaviors that accumulate to manifest as adverse mental health symptoms like anxiety and depression.
“Additional research is needed to further explore how compromises in the psychosocial infrastructure of community manifest as downstream symptom indicators such as anxiety and depression,” which are often manifestations of unmet needs, Dr. Loper said.
Limitations and strengths, according to authors
The findings were limited by several factors, including a lack of examination of school closures’ effects on mental health independent of broader social lockdowns, according to the researchers. Other limitations included the authors potentially having missed studies, inclusion of cross-sectional studies with relatively weak evidence, potential bias from studies using parent reports, and a focus on the first COVID-19 wave, during which many school closures were of limited duration. Also, the researchers said they did not include studies focused on particular groups, such as children with learning difficulties or autism.
The use of large databases from education as well as health care in studies analyzed were strengths of the new research, they said. The investigators received no outside funding for their study. The researchers, Dr. Jay, and Dr. Loper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Jay serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Study finds genetic factor for COVID smell and taste loss
, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Genetics
The finding could eventually help the 1.6 million people in the United States who still can’t smell or have had a change in their ability to smell more than 6 months after getting the coronavirus. The exact cause related to COVID-19 is still unknown, but researchers believe it could be because of damage in a part of the nose called the olfactory epithelium.
“How we get from infection to smell loss remains unclear,” Justin Turner, MD, an associate professor of otolaryngology at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., told NBC News. Dr. Turner was not part of the research team.
“Early data suggest that supporting cells of the olfactory epithelium are the ones mostly being infected by the virus, and presumably this leads to the death of the neurons themselves,” he said. “But we don’t really, really know why and when that happens, and why it seems to preferentially happen in certain individuals.”
Researchers at 23andMe, a genomics and biotechnology company, did the study as part of a larger COVID-19 project, which includes people in the United States and the United Kingdom. They analyzed data from nearly 70,000 people who took online surveys after receiving a positive coronavirus test. Among those, 68% reported a loss of smell or taste as a symptom.
The study team compared the genetic differences between those who lost their sense of smell and taste and those who didn’t. They found that a location near two olfactory genes – UGT2A1 and UGT2A2 – is associated with COVID-19 loss of smell and taste. The genetic risk factor makes it 11% more likely for a person with COVID-19 to lose their sense of smell or taste.
The research team also found that women were 11% more likely than men to report a loss of smell and taste. About 73% of those who reported a loss of smell and taste were ages 26-35.
The researchers aren’t sure how the genes are involved, though they suspect that infected cells could lead to smell loss. Typically, the genes are expressed in tissue inside the nose involved with smell and play a role in processing things that have an odor. To use the findings, researchers need to learn more about the genes, how they are expressed, and what their functions are, NBC News reported.
The findings could help lead to treatments. Other research has shown that the loss of taste and smell is related to a “failure to protect the sensory cells of the nose and tongue from viral infection,” Danielle Reed, PhD, associate director of the Monell Chemical Senses Center in Philadelphia, told NBC News. She was not part of the research team but studies person-to-person differences in the loss of these senses because of COVID-19.
“This study suggests a different direction,” she said. “The pathways that break down the chemicals that cause taste and smell in the first place might be over or underactive, reducing or distorting the ability to taste and smell.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Genetics
The finding could eventually help the 1.6 million people in the United States who still can’t smell or have had a change in their ability to smell more than 6 months after getting the coronavirus. The exact cause related to COVID-19 is still unknown, but researchers believe it could be because of damage in a part of the nose called the olfactory epithelium.
“How we get from infection to smell loss remains unclear,” Justin Turner, MD, an associate professor of otolaryngology at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., told NBC News. Dr. Turner was not part of the research team.
“Early data suggest that supporting cells of the olfactory epithelium are the ones mostly being infected by the virus, and presumably this leads to the death of the neurons themselves,” he said. “But we don’t really, really know why and when that happens, and why it seems to preferentially happen in certain individuals.”
Researchers at 23andMe, a genomics and biotechnology company, did the study as part of a larger COVID-19 project, which includes people in the United States and the United Kingdom. They analyzed data from nearly 70,000 people who took online surveys after receiving a positive coronavirus test. Among those, 68% reported a loss of smell or taste as a symptom.
The study team compared the genetic differences between those who lost their sense of smell and taste and those who didn’t. They found that a location near two olfactory genes – UGT2A1 and UGT2A2 – is associated with COVID-19 loss of smell and taste. The genetic risk factor makes it 11% more likely for a person with COVID-19 to lose their sense of smell or taste.
The research team also found that women were 11% more likely than men to report a loss of smell and taste. About 73% of those who reported a loss of smell and taste were ages 26-35.
The researchers aren’t sure how the genes are involved, though they suspect that infected cells could lead to smell loss. Typically, the genes are expressed in tissue inside the nose involved with smell and play a role in processing things that have an odor. To use the findings, researchers need to learn more about the genes, how they are expressed, and what their functions are, NBC News reported.
The findings could help lead to treatments. Other research has shown that the loss of taste and smell is related to a “failure to protect the sensory cells of the nose and tongue from viral infection,” Danielle Reed, PhD, associate director of the Monell Chemical Senses Center in Philadelphia, told NBC News. She was not part of the research team but studies person-to-person differences in the loss of these senses because of COVID-19.
“This study suggests a different direction,” she said. “The pathways that break down the chemicals that cause taste and smell in the first place might be over or underactive, reducing or distorting the ability to taste and smell.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Genetics
The finding could eventually help the 1.6 million people in the United States who still can’t smell or have had a change in their ability to smell more than 6 months after getting the coronavirus. The exact cause related to COVID-19 is still unknown, but researchers believe it could be because of damage in a part of the nose called the olfactory epithelium.
“How we get from infection to smell loss remains unclear,” Justin Turner, MD, an associate professor of otolaryngology at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., told NBC News. Dr. Turner was not part of the research team.
“Early data suggest that supporting cells of the olfactory epithelium are the ones mostly being infected by the virus, and presumably this leads to the death of the neurons themselves,” he said. “But we don’t really, really know why and when that happens, and why it seems to preferentially happen in certain individuals.”
Researchers at 23andMe, a genomics and biotechnology company, did the study as part of a larger COVID-19 project, which includes people in the United States and the United Kingdom. They analyzed data from nearly 70,000 people who took online surveys after receiving a positive coronavirus test. Among those, 68% reported a loss of smell or taste as a symptom.
The study team compared the genetic differences between those who lost their sense of smell and taste and those who didn’t. They found that a location near two olfactory genes – UGT2A1 and UGT2A2 – is associated with COVID-19 loss of smell and taste. The genetic risk factor makes it 11% more likely for a person with COVID-19 to lose their sense of smell or taste.
The research team also found that women were 11% more likely than men to report a loss of smell and taste. About 73% of those who reported a loss of smell and taste were ages 26-35.
The researchers aren’t sure how the genes are involved, though they suspect that infected cells could lead to smell loss. Typically, the genes are expressed in tissue inside the nose involved with smell and play a role in processing things that have an odor. To use the findings, researchers need to learn more about the genes, how they are expressed, and what their functions are, NBC News reported.
The findings could help lead to treatments. Other research has shown that the loss of taste and smell is related to a “failure to protect the sensory cells of the nose and tongue from viral infection,” Danielle Reed, PhD, associate director of the Monell Chemical Senses Center in Philadelphia, told NBC News. She was not part of the research team but studies person-to-person differences in the loss of these senses because of COVID-19.
“This study suggests a different direction,” she said. “The pathways that break down the chemicals that cause taste and smell in the first place might be over or underactive, reducing or distorting the ability to taste and smell.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE GENETICS
Fourth vaccine shot less effective against Omicron, Israeli study says
, according to new research at an Israeli hospital.
The preliminary results, released on Jan. 17, challenge the idea of giving a second booster dose to slow the spread of the coronavirus, according to USA Today.
“Despite increased antibody levels, the fourth vaccine only offers a partial defense against the virus,” Gili Regev-Yochay, MD, director of the hospital’s infection prevention and control units, told reporters.
“The vaccines, which were more effective against previous variants, offer less protection versus Omicron,” she said.
In a clinical trial, 274 medical workers at Sheba Medical Center near Tel Aviv received a fourth vaccine dose in December – 154 got the Pfizer vaccine and 120 got the Moderna vaccine – after previously getting three Pfizer shots.
Both groups received a boost in antibodies that was “slightly higher” than after the third shot, Dr. Regev-Yochay said. But when compared with a control group that didn’t receive the fourth dose, the extra boost didn’t prevent the spread of Omicron.
“We see many infected with Omicron who received the fourth dose,” Dr. Regev-Yochay said. “Granted, a bit less than in the control group, but still a lot of infections.”
Some public health officials in Israel say the campaign for fourth doses is still worthwhile, according to The Times of Israel. The vaccine still works well against the Alpha and Delta variants, Dr. Regev-Yochay said, and a fourth shot should go to older adults and those who face higher risks for severe COVID-19.
Hours after releasing the preliminary results, Sheba Medical Center published a statement calling for “continuing the vaccination drive for risk groups at this time, even though the vaccine doesn’t provide optimal protection against getting infected with the variant.” News outlets reported that the hospital was pressured into issuing the statement after Israel’s Health Ministry didn’t like the release of the early study results, The Times of Israel reported.
The second booster “returns the level of antibodies to what it was at the beginning of the third booster,” Nachman Ash, MD, director of Israel’s Health Ministry, told Channel 13 TV in Israel, according to The Associated Press.
“That has great importance, especially among the older population,” he said.
As of Sunday, more than 500,000 people in Israel had received fourth doses since the country began offering them last month to medical workers, immunocompromised patients, and people ages 60 years and older, the AP reported. At the same time, the country has faced a recent coronavirus surge that has led to record-breaking numbers of cases and rising hospitalizations.
On Tuesday, the Israeli government said it would shorten the mandatory quarantine period from 7 days to 5 days, the AP reported.
“This decision will enable us to continue safeguarding public health on the one hand and to keep the economy going at this time on the other, even though it is difficult, so that we can get through this wave safely,” Prime Minister Naftali Bennett said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to new research at an Israeli hospital.
The preliminary results, released on Jan. 17, challenge the idea of giving a second booster dose to slow the spread of the coronavirus, according to USA Today.
“Despite increased antibody levels, the fourth vaccine only offers a partial defense against the virus,” Gili Regev-Yochay, MD, director of the hospital’s infection prevention and control units, told reporters.
“The vaccines, which were more effective against previous variants, offer less protection versus Omicron,” she said.
In a clinical trial, 274 medical workers at Sheba Medical Center near Tel Aviv received a fourth vaccine dose in December – 154 got the Pfizer vaccine and 120 got the Moderna vaccine – after previously getting three Pfizer shots.
Both groups received a boost in antibodies that was “slightly higher” than after the third shot, Dr. Regev-Yochay said. But when compared with a control group that didn’t receive the fourth dose, the extra boost didn’t prevent the spread of Omicron.
“We see many infected with Omicron who received the fourth dose,” Dr. Regev-Yochay said. “Granted, a bit less than in the control group, but still a lot of infections.”
Some public health officials in Israel say the campaign for fourth doses is still worthwhile, according to The Times of Israel. The vaccine still works well against the Alpha and Delta variants, Dr. Regev-Yochay said, and a fourth shot should go to older adults and those who face higher risks for severe COVID-19.
Hours after releasing the preliminary results, Sheba Medical Center published a statement calling for “continuing the vaccination drive for risk groups at this time, even though the vaccine doesn’t provide optimal protection against getting infected with the variant.” News outlets reported that the hospital was pressured into issuing the statement after Israel’s Health Ministry didn’t like the release of the early study results, The Times of Israel reported.
The second booster “returns the level of antibodies to what it was at the beginning of the third booster,” Nachman Ash, MD, director of Israel’s Health Ministry, told Channel 13 TV in Israel, according to The Associated Press.
“That has great importance, especially among the older population,” he said.
As of Sunday, more than 500,000 people in Israel had received fourth doses since the country began offering them last month to medical workers, immunocompromised patients, and people ages 60 years and older, the AP reported. At the same time, the country has faced a recent coronavirus surge that has led to record-breaking numbers of cases and rising hospitalizations.
On Tuesday, the Israeli government said it would shorten the mandatory quarantine period from 7 days to 5 days, the AP reported.
“This decision will enable us to continue safeguarding public health on the one hand and to keep the economy going at this time on the other, even though it is difficult, so that we can get through this wave safely,” Prime Minister Naftali Bennett said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to new research at an Israeli hospital.
The preliminary results, released on Jan. 17, challenge the idea of giving a second booster dose to slow the spread of the coronavirus, according to USA Today.
“Despite increased antibody levels, the fourth vaccine only offers a partial defense against the virus,” Gili Regev-Yochay, MD, director of the hospital’s infection prevention and control units, told reporters.
“The vaccines, which were more effective against previous variants, offer less protection versus Omicron,” she said.
In a clinical trial, 274 medical workers at Sheba Medical Center near Tel Aviv received a fourth vaccine dose in December – 154 got the Pfizer vaccine and 120 got the Moderna vaccine – after previously getting three Pfizer shots.
Both groups received a boost in antibodies that was “slightly higher” than after the third shot, Dr. Regev-Yochay said. But when compared with a control group that didn’t receive the fourth dose, the extra boost didn’t prevent the spread of Omicron.
“We see many infected with Omicron who received the fourth dose,” Dr. Regev-Yochay said. “Granted, a bit less than in the control group, but still a lot of infections.”
Some public health officials in Israel say the campaign for fourth doses is still worthwhile, according to The Times of Israel. The vaccine still works well against the Alpha and Delta variants, Dr. Regev-Yochay said, and a fourth shot should go to older adults and those who face higher risks for severe COVID-19.
Hours after releasing the preliminary results, Sheba Medical Center published a statement calling for “continuing the vaccination drive for risk groups at this time, even though the vaccine doesn’t provide optimal protection against getting infected with the variant.” News outlets reported that the hospital was pressured into issuing the statement after Israel’s Health Ministry didn’t like the release of the early study results, The Times of Israel reported.
The second booster “returns the level of antibodies to what it was at the beginning of the third booster,” Nachman Ash, MD, director of Israel’s Health Ministry, told Channel 13 TV in Israel, according to The Associated Press.
“That has great importance, especially among the older population,” he said.
As of Sunday, more than 500,000 people in Israel had received fourth doses since the country began offering them last month to medical workers, immunocompromised patients, and people ages 60 years and older, the AP reported. At the same time, the country has faced a recent coronavirus surge that has led to record-breaking numbers of cases and rising hospitalizations.
On Tuesday, the Israeli government said it would shorten the mandatory quarantine period from 7 days to 5 days, the AP reported.
“This decision will enable us to continue safeguarding public health on the one hand and to keep the economy going at this time on the other, even though it is difficult, so that we can get through this wave safely,” Prime Minister Naftali Bennett said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: U.S. sees almost 1 million new cases
Another record week for COVID-19 brought almost 1 million new cases to the children of the United States, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The pre-Omicron high for new cases in a week – 252,000 during the Delta surge of the late summer and early fall – has been surpassed each of the last 3 weeks and now stands at 981,000 (Jan. 7-13), according to the AAP/CHA weekly COVID-19 report. Over the 3-week stretch from Dec. 17 to Jan. 13, weekly cases increased by 394%.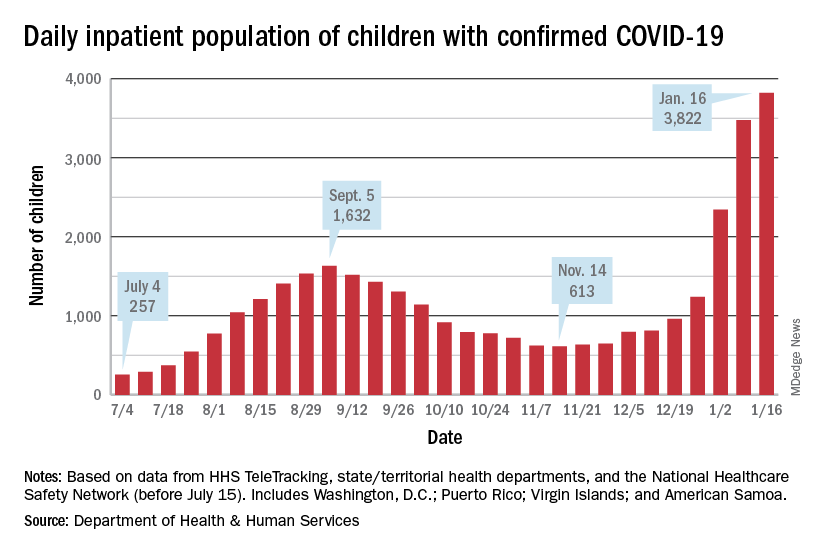
Hospitalizations also climbed to new heights, as daily admissions reached 1.23 per 100,000 children on Jan. 14, an increase of 547% since Nov. 30, when the rate was 0.19 per 100,000. Before Omicron, the highest rate for children was 0.47 per 100,000, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The inpatient population count, meanwhile, has followed suit. On Jan. 16, there were 3,822 children hospitalized in pediatric inpatient beds with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19, which is 523% higher than the 613 children who were hospitalized on Nov. 14, according to the Department of Health & Human Services. In the last week, though, the population was up by just 10%.
The one thing that has not surged in the last few weeks is vaccination. Among children aged 5-11 years, the weekly count of those who have received at least one dose dropped by 34% over the last 5 weeks, falling from 527,000 for Dec.11-17 to 347,000 during Jan. 8-14, the CDC said on the COVID Data Tracker, which also noted that just 18.4% of this age group is fully vaccinated.
The situation was reversed in children aged 12-15, who were up by 36% over that same time, but their numbers were much smaller: 78,000 for the week of Dec. 11-17 and 106,000 for Jan. 8-14. Those aged 16-17 were up by just 4% over that 5-week span, the CDC data show.
Over the course of the entire pandemic, almost 9.5 million cases of COVID-19 in children have been reported, and children represent 17.8% of all cases reported in 49 states (excluding New York but including New York City), the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Three states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas) stopped public reporting over the summer, but many states count individuals up to age 19 as children, and others (South Carolina, Tennessee, and West Virginia) go up to age 20, the AAP and CHA noted. The CDC, by comparison, puts the number of cases for those aged 0-17 at 8.3 million, but that estimate is based on only 51 million of the nearly 67 million U.S. cases as of Jan. 18.
Another record week for COVID-19 brought almost 1 million new cases to the children of the United States, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The pre-Omicron high for new cases in a week – 252,000 during the Delta surge of the late summer and early fall – has been surpassed each of the last 3 weeks and now stands at 981,000 (Jan. 7-13), according to the AAP/CHA weekly COVID-19 report. Over the 3-week stretch from Dec. 17 to Jan. 13, weekly cases increased by 394%.
Hospitalizations also climbed to new heights, as daily admissions reached 1.23 per 100,000 children on Jan. 14, an increase of 547% since Nov. 30, when the rate was 0.19 per 100,000. Before Omicron, the highest rate for children was 0.47 per 100,000, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The inpatient population count, meanwhile, has followed suit. On Jan. 16, there were 3,822 children hospitalized in pediatric inpatient beds with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19, which is 523% higher than the 613 children who were hospitalized on Nov. 14, according to the Department of Health & Human Services. In the last week, though, the population was up by just 10%.
The one thing that has not surged in the last few weeks is vaccination. Among children aged 5-11 years, the weekly count of those who have received at least one dose dropped by 34% over the last 5 weeks, falling from 527,000 for Dec.11-17 to 347,000 during Jan. 8-14, the CDC said on the COVID Data Tracker, which also noted that just 18.4% of this age group is fully vaccinated.
The situation was reversed in children aged 12-15, who were up by 36% over that same time, but their numbers were much smaller: 78,000 for the week of Dec. 11-17 and 106,000 for Jan. 8-14. Those aged 16-17 were up by just 4% over that 5-week span, the CDC data show.
Over the course of the entire pandemic, almost 9.5 million cases of COVID-19 in children have been reported, and children represent 17.8% of all cases reported in 49 states (excluding New York but including New York City), the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Three states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas) stopped public reporting over the summer, but many states count individuals up to age 19 as children, and others (South Carolina, Tennessee, and West Virginia) go up to age 20, the AAP and CHA noted. The CDC, by comparison, puts the number of cases for those aged 0-17 at 8.3 million, but that estimate is based on only 51 million of the nearly 67 million U.S. cases as of Jan. 18.
Another record week for COVID-19 brought almost 1 million new cases to the children of the United States, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The pre-Omicron high for new cases in a week – 252,000 during the Delta surge of the late summer and early fall – has been surpassed each of the last 3 weeks and now stands at 981,000 (Jan. 7-13), according to the AAP/CHA weekly COVID-19 report. Over the 3-week stretch from Dec. 17 to Jan. 13, weekly cases increased by 394%.
Hospitalizations also climbed to new heights, as daily admissions reached 1.23 per 100,000 children on Jan. 14, an increase of 547% since Nov. 30, when the rate was 0.19 per 100,000. Before Omicron, the highest rate for children was 0.47 per 100,000, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The inpatient population count, meanwhile, has followed suit. On Jan. 16, there were 3,822 children hospitalized in pediatric inpatient beds with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19, which is 523% higher than the 613 children who were hospitalized on Nov. 14, according to the Department of Health & Human Services. In the last week, though, the population was up by just 10%.
The one thing that has not surged in the last few weeks is vaccination. Among children aged 5-11 years, the weekly count of those who have received at least one dose dropped by 34% over the last 5 weeks, falling from 527,000 for Dec.11-17 to 347,000 during Jan. 8-14, the CDC said on the COVID Data Tracker, which also noted that just 18.4% of this age group is fully vaccinated.
The situation was reversed in children aged 12-15, who were up by 36% over that same time, but their numbers were much smaller: 78,000 for the week of Dec. 11-17 and 106,000 for Jan. 8-14. Those aged 16-17 were up by just 4% over that 5-week span, the CDC data show.
Over the course of the entire pandemic, almost 9.5 million cases of COVID-19 in children have been reported, and children represent 17.8% of all cases reported in 49 states (excluding New York but including New York City), the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Three states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas) stopped public reporting over the summer, but many states count individuals up to age 19 as children, and others (South Carolina, Tennessee, and West Virginia) go up to age 20, the AAP and CHA noted. The CDC, by comparison, puts the number of cases for those aged 0-17 at 8.3 million, but that estimate is based on only 51 million of the nearly 67 million U.S. cases as of Jan. 18.
Negative home COVID test no ‘free pass’ for kids, study finds
With the country looking increasingly to rapid testing as an off-ramp from the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study shows that the performance of the tests in children falls below standards set by regulatory agencies in the United States and elsewhere for diagnostic accuracy.
Experts said the findings, from a meta-analysis by researchers in the United Kingdom and Germany, underscore that, while a positive result on a rapid test is almost certainly an indicator of infection, negative results often are unreliable and can lead to a false sense of security.
“Real-life performance of current antigen tests for professional use in pediatric populations is below the minimum performance criteria set by WHO, the United States Food and Drug Administration, or the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (U.K.),” according to Naomi Fujita-Rohwerder, PhD, a research associate at the Cologne-based German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), and her colleagues, whose study appears in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
The researchers said that the study suggests that performance of rapid testing in a pediatric population is comparable to that in adults. However, they said they could not identify any studies investigating self-testing in children, which also could affect test performance.
Egon Ozer, MD, PhD, director of the center for pathogen genomics and microbial evolution at Northwestern University in Chicago, said the finding that specificity was high but sensitivity was middling “suggests that we should be very careful about interpreting negative antigen test results in children and recognize that there is a fair amount of uncertainty in the tests in this situation.”
Researchers from IQWiG, which examines the advantages and disadvantages of medical interventions, and the University of Manchester (England), conducted the systematic review and meta-analysis, which they described as the first of its kind to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for current SARS-CoV-2 infections in children.
They compiled information from 17 studies with a total 6,355 participants. They compared all antigen tests to reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The studies compared eight antigen tests from six different brands. The rapid antigen tests, available from pharmacies and online stores, are widely used for self-testing in schools and testing toddlers before kindergarten.
The pooled diagnostic sensitivity of antigen tests was 64.2% and specificity was 99.1%.
Dr. Ozer noted that the analysis “was not able to address important outstanding questions such as the likelihood of transmitting infection with a false-negative antigen test versus a true-negative antigen test or how much repeated testing can increase the sensitivity.”
“In Europe, we don’t know how most tests perform in real life,” Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said. “And even in countries like the United States, where market access is more stringent, we don’t know whether self-testing performed by children or sample collection in toddlers by laypersons has a significant impact on the diagnostic accuracy. Also, diagnostic accuracy estimates reported in our study may not apply to the current omicron or future variants of SARS-CoV-2 or vaccinated children. Hopefully, these essential gaps in the evidence will get addressed soon.”
Dr. Ozer said one takeaway from this study is negative antigen tests should not be considered a “free pass” in children, especially if the child is symptomatic, has been recently exposed to COVID-19, or is planning to spend time with individuals with conditions that place them at high risk for complications of COVID-19 infection. “In such cases, consider getting PCR testing or at least performing a repeat antigen test 36-48 hours after the first negative,” he said.
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said the low diagnostic sensitivity may affect the use of the tests. The gaps in evidence her group found in their study point to research needed to support evidence-based decision-making. “In particular, evidence is needed on real-life performance of tests in schools, self-testing performed by children, and kindergarten, [particularly] sample collection in toddlers by laypersons,” she said.
However, she stressed, testing is only a single measure. “Effectively reducing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the current pandemic requires multilayered mitigation measures,” she said. “Rapid testing represents one single layer. It can have its use at the population level, even though the sensitivity of antigen tests is lower than expected. However, antigen-based rapid testing is not a magic bullet: If your kid tests negative, do not disregard other mitigation measures.”
Edward Campbell, PhD, a virologist at Loyola University of Chicago, who serves on the board of LaGrange Elementary School District 102 outside Chicago, said the findings were unsurprising.
“This study generally looks consistent with what is known for adults. These rapid antigen tests are less sensitive than other tests,” said Dr. Campbell, who also runs a testing company for private schools in the Chicago area using reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. Even so, he said, “These tests are still effective at identifying people who are infectious to some degree. Never miss an opportunity to test.”
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Campbell owns Safeguard Surveillance.
With the country looking increasingly to rapid testing as an off-ramp from the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study shows that the performance of the tests in children falls below standards set by regulatory agencies in the United States and elsewhere for diagnostic accuracy.
Experts said the findings, from a meta-analysis by researchers in the United Kingdom and Germany, underscore that, while a positive result on a rapid test is almost certainly an indicator of infection, negative results often are unreliable and can lead to a false sense of security.
“Real-life performance of current antigen tests for professional use in pediatric populations is below the minimum performance criteria set by WHO, the United States Food and Drug Administration, or the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (U.K.),” according to Naomi Fujita-Rohwerder, PhD, a research associate at the Cologne-based German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), and her colleagues, whose study appears in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
The researchers said that the study suggests that performance of rapid testing in a pediatric population is comparable to that in adults. However, they said they could not identify any studies investigating self-testing in children, which also could affect test performance.
Egon Ozer, MD, PhD, director of the center for pathogen genomics and microbial evolution at Northwestern University in Chicago, said the finding that specificity was high but sensitivity was middling “suggests that we should be very careful about interpreting negative antigen test results in children and recognize that there is a fair amount of uncertainty in the tests in this situation.”
Researchers from IQWiG, which examines the advantages and disadvantages of medical interventions, and the University of Manchester (England), conducted the systematic review and meta-analysis, which they described as the first of its kind to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for current SARS-CoV-2 infections in children.
They compiled information from 17 studies with a total 6,355 participants. They compared all antigen tests to reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The studies compared eight antigen tests from six different brands. The rapid antigen tests, available from pharmacies and online stores, are widely used for self-testing in schools and testing toddlers before kindergarten.
The pooled diagnostic sensitivity of antigen tests was 64.2% and specificity was 99.1%.
Dr. Ozer noted that the analysis “was not able to address important outstanding questions such as the likelihood of transmitting infection with a false-negative antigen test versus a true-negative antigen test or how much repeated testing can increase the sensitivity.”
“In Europe, we don’t know how most tests perform in real life,” Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said. “And even in countries like the United States, where market access is more stringent, we don’t know whether self-testing performed by children or sample collection in toddlers by laypersons has a significant impact on the diagnostic accuracy. Also, diagnostic accuracy estimates reported in our study may not apply to the current omicron or future variants of SARS-CoV-2 or vaccinated children. Hopefully, these essential gaps in the evidence will get addressed soon.”
Dr. Ozer said one takeaway from this study is negative antigen tests should not be considered a “free pass” in children, especially if the child is symptomatic, has been recently exposed to COVID-19, or is planning to spend time with individuals with conditions that place them at high risk for complications of COVID-19 infection. “In such cases, consider getting PCR testing or at least performing a repeat antigen test 36-48 hours after the first negative,” he said.
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said the low diagnostic sensitivity may affect the use of the tests. The gaps in evidence her group found in their study point to research needed to support evidence-based decision-making. “In particular, evidence is needed on real-life performance of tests in schools, self-testing performed by children, and kindergarten, [particularly] sample collection in toddlers by laypersons,” she said.
However, she stressed, testing is only a single measure. “Effectively reducing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the current pandemic requires multilayered mitigation measures,” she said. “Rapid testing represents one single layer. It can have its use at the population level, even though the sensitivity of antigen tests is lower than expected. However, antigen-based rapid testing is not a magic bullet: If your kid tests negative, do not disregard other mitigation measures.”
Edward Campbell, PhD, a virologist at Loyola University of Chicago, who serves on the board of LaGrange Elementary School District 102 outside Chicago, said the findings were unsurprising.
“This study generally looks consistent with what is known for adults. These rapid antigen tests are less sensitive than other tests,” said Dr. Campbell, who also runs a testing company for private schools in the Chicago area using reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. Even so, he said, “These tests are still effective at identifying people who are infectious to some degree. Never miss an opportunity to test.”
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Campbell owns Safeguard Surveillance.
With the country looking increasingly to rapid testing as an off-ramp from the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study shows that the performance of the tests in children falls below standards set by regulatory agencies in the United States and elsewhere for diagnostic accuracy.
Experts said the findings, from a meta-analysis by researchers in the United Kingdom and Germany, underscore that, while a positive result on a rapid test is almost certainly an indicator of infection, negative results often are unreliable and can lead to a false sense of security.
“Real-life performance of current antigen tests for professional use in pediatric populations is below the minimum performance criteria set by WHO, the United States Food and Drug Administration, or the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (U.K.),” according to Naomi Fujita-Rohwerder, PhD, a research associate at the Cologne-based German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), and her colleagues, whose study appears in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
The researchers said that the study suggests that performance of rapid testing in a pediatric population is comparable to that in adults. However, they said they could not identify any studies investigating self-testing in children, which also could affect test performance.
Egon Ozer, MD, PhD, director of the center for pathogen genomics and microbial evolution at Northwestern University in Chicago, said the finding that specificity was high but sensitivity was middling “suggests that we should be very careful about interpreting negative antigen test results in children and recognize that there is a fair amount of uncertainty in the tests in this situation.”
Researchers from IQWiG, which examines the advantages and disadvantages of medical interventions, and the University of Manchester (England), conducted the systematic review and meta-analysis, which they described as the first of its kind to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for current SARS-CoV-2 infections in children.
They compiled information from 17 studies with a total 6,355 participants. They compared all antigen tests to reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The studies compared eight antigen tests from six different brands. The rapid antigen tests, available from pharmacies and online stores, are widely used for self-testing in schools and testing toddlers before kindergarten.
The pooled diagnostic sensitivity of antigen tests was 64.2% and specificity was 99.1%.
Dr. Ozer noted that the analysis “was not able to address important outstanding questions such as the likelihood of transmitting infection with a false-negative antigen test versus a true-negative antigen test or how much repeated testing can increase the sensitivity.”
“In Europe, we don’t know how most tests perform in real life,” Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said. “And even in countries like the United States, where market access is more stringent, we don’t know whether self-testing performed by children or sample collection in toddlers by laypersons has a significant impact on the diagnostic accuracy. Also, diagnostic accuracy estimates reported in our study may not apply to the current omicron or future variants of SARS-CoV-2 or vaccinated children. Hopefully, these essential gaps in the evidence will get addressed soon.”
Dr. Ozer said one takeaway from this study is negative antigen tests should not be considered a “free pass” in children, especially if the child is symptomatic, has been recently exposed to COVID-19, or is planning to spend time with individuals with conditions that place them at high risk for complications of COVID-19 infection. “In such cases, consider getting PCR testing or at least performing a repeat antigen test 36-48 hours after the first negative,” he said.
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said the low diagnostic sensitivity may affect the use of the tests. The gaps in evidence her group found in their study point to research needed to support evidence-based decision-making. “In particular, evidence is needed on real-life performance of tests in schools, self-testing performed by children, and kindergarten, [particularly] sample collection in toddlers by laypersons,” she said.
However, she stressed, testing is only a single measure. “Effectively reducing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the current pandemic requires multilayered mitigation measures,” she said. “Rapid testing represents one single layer. It can have its use at the population level, even though the sensitivity of antigen tests is lower than expected. However, antigen-based rapid testing is not a magic bullet: If your kid tests negative, do not disregard other mitigation measures.”
Edward Campbell, PhD, a virologist at Loyola University of Chicago, who serves on the board of LaGrange Elementary School District 102 outside Chicago, said the findings were unsurprising.
“This study generally looks consistent with what is known for adults. These rapid antigen tests are less sensitive than other tests,” said Dr. Campbell, who also runs a testing company for private schools in the Chicago area using reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. Even so, he said, “These tests are still effective at identifying people who are infectious to some degree. Never miss an opportunity to test.”
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Campbell owns Safeguard Surveillance.
BMJ EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE
Feds’ website for free at-home COVID tests launches day early
The Biden administration’s new no-cost, at-home testing program launched Jan. 18, a day ahead of schedule.
The administration said 500 million tests are available to be delivered to homes across the country. This accounts for half of the president’s recent pledge to purchase 1 billion free at-home COVID-19 tests to distribute to the American public.
On a Jan. 14 call with reporters, senior White House officials offered some details about the new program.
Here’s what we know so far.
How do I order my free tests?
Americans can visit COVIDtests.gov to order their rapid at-home tests. You can also order directly from the U.S. Postal Service website. After you order, you’ll receive a confirmation email that promises to send tracking information once your order ships.
What information do I need to order the tests?
You only need your name and home mailing address.
There is also an option to provide your email address to get updates on the status of your order.
What if someone needs help ordering the tests?
There will be a free call-in line for people needing more help, including those having trouble accessing the internet, according to White House officials.
What tests will be available?
There are nine at-home tests available through FDA emergency use authorization. According to the Frequently Asked Questions section of COVIDtests.gov, "You will not be able to choose the brand you order as part of this program.”
How long will it take to get the tests once I order them?
Tests are expected to ship 7 to 12 days after you order them.
But White House officials say that the time frame will likely shorten as the program gains steam.
How many can I order?
There’s a limit of four tests per residential mailing address.
For larger families, White House officials suggest trying other free testing options, like visiting COVID-19 testing sites or your local health center.
Is this a one-time opportunity?
The White House doesn’t say, but officials did mention that if you run out of your four free tests, there are many other ways to access free at-home tests, such as COVID-19 testing sites, pharmacies, and community health centers.
The free tests available through COVIDtests.gov are in addition to an estimated 375 million at-home rapid tests on the market in the U.S. this month.
When should people use a rapid at-home test?
The CDC and experts with other public health groups agree that Americans should consider using at-home rapid tests in the following situations:
- If they begin to have symptoms consistent with COVID-19;
- At least 5 days after close contact with someone who has COVID;
- If someone is indoors with a group of people who are at risk of severe disease or are unvaccinated.
Are at-home rapid tests accurate?
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and other federal officials confirmed through studies that all tests distributed through this program can detect the Omicron variant. These agencies also confirmed that their performance is consistent with the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
Is the website designed to handle high demand?
After the original website to sign up for health insurance under the Affordable Care Act crashed repeatedly at launch, the government says it has prepared for high demand for ordering at-home rapid tests.
The U.S. Digital Service (USDS), an organization founded after Healthcare.gov, has partnered with the Postal Service to plan for the launch.
The Postal Service has expanded its staffing, similar to what’s done during the holidays.
All orders in the continental United States will be shipped through first-class mail, with shipments to Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. territories, and military and overseas addresses sent through priority mail.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Biden administration’s new no-cost, at-home testing program launched Jan. 18, a day ahead of schedule.
The administration said 500 million tests are available to be delivered to homes across the country. This accounts for half of the president’s recent pledge to purchase 1 billion free at-home COVID-19 tests to distribute to the American public.
On a Jan. 14 call with reporters, senior White House officials offered some details about the new program.
Here’s what we know so far.
How do I order my free tests?
Americans can visit COVIDtests.gov to order their rapid at-home tests. You can also order directly from the U.S. Postal Service website. After you order, you’ll receive a confirmation email that promises to send tracking information once your order ships.
What information do I need to order the tests?
You only need your name and home mailing address.
There is also an option to provide your email address to get updates on the status of your order.
What if someone needs help ordering the tests?
There will be a free call-in line for people needing more help, including those having trouble accessing the internet, according to White House officials.
What tests will be available?
There are nine at-home tests available through FDA emergency use authorization. According to the Frequently Asked Questions section of COVIDtests.gov, "You will not be able to choose the brand you order as part of this program.”
How long will it take to get the tests once I order them?
Tests are expected to ship 7 to 12 days after you order them.
But White House officials say that the time frame will likely shorten as the program gains steam.
How many can I order?
There’s a limit of four tests per residential mailing address.
For larger families, White House officials suggest trying other free testing options, like visiting COVID-19 testing sites or your local health center.
Is this a one-time opportunity?
The White House doesn’t say, but officials did mention that if you run out of your four free tests, there are many other ways to access free at-home tests, such as COVID-19 testing sites, pharmacies, and community health centers.
The free tests available through COVIDtests.gov are in addition to an estimated 375 million at-home rapid tests on the market in the U.S. this month.
When should people use a rapid at-home test?
The CDC and experts with other public health groups agree that Americans should consider using at-home rapid tests in the following situations:
- If they begin to have symptoms consistent with COVID-19;
- At least 5 days after close contact with someone who has COVID;
- If someone is indoors with a group of people who are at risk of severe disease or are unvaccinated.
Are at-home rapid tests accurate?
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and other federal officials confirmed through studies that all tests distributed through this program can detect the Omicron variant. These agencies also confirmed that their performance is consistent with the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
Is the website designed to handle high demand?
After the original website to sign up for health insurance under the Affordable Care Act crashed repeatedly at launch, the government says it has prepared for high demand for ordering at-home rapid tests.
The U.S. Digital Service (USDS), an organization founded after Healthcare.gov, has partnered with the Postal Service to plan for the launch.
The Postal Service has expanded its staffing, similar to what’s done during the holidays.
All orders in the continental United States will be shipped through first-class mail, with shipments to Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. territories, and military and overseas addresses sent through priority mail.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Biden administration’s new no-cost, at-home testing program launched Jan. 18, a day ahead of schedule.
The administration said 500 million tests are available to be delivered to homes across the country. This accounts for half of the president’s recent pledge to purchase 1 billion free at-home COVID-19 tests to distribute to the American public.
On a Jan. 14 call with reporters, senior White House officials offered some details about the new program.
Here’s what we know so far.
How do I order my free tests?
Americans can visit COVIDtests.gov to order their rapid at-home tests. You can also order directly from the U.S. Postal Service website. After you order, you’ll receive a confirmation email that promises to send tracking information once your order ships.
What information do I need to order the tests?
You only need your name and home mailing address.
There is also an option to provide your email address to get updates on the status of your order.
What if someone needs help ordering the tests?
There will be a free call-in line for people needing more help, including those having trouble accessing the internet, according to White House officials.
What tests will be available?
There are nine at-home tests available through FDA emergency use authorization. According to the Frequently Asked Questions section of COVIDtests.gov, "You will not be able to choose the brand you order as part of this program.”
How long will it take to get the tests once I order them?
Tests are expected to ship 7 to 12 days after you order them.
But White House officials say that the time frame will likely shorten as the program gains steam.
How many can I order?
There’s a limit of four tests per residential mailing address.
For larger families, White House officials suggest trying other free testing options, like visiting COVID-19 testing sites or your local health center.
Is this a one-time opportunity?
The White House doesn’t say, but officials did mention that if you run out of your four free tests, there are many other ways to access free at-home tests, such as COVID-19 testing sites, pharmacies, and community health centers.
The free tests available through COVIDtests.gov are in addition to an estimated 375 million at-home rapid tests on the market in the U.S. this month.
When should people use a rapid at-home test?
The CDC and experts with other public health groups agree that Americans should consider using at-home rapid tests in the following situations:
- If they begin to have symptoms consistent with COVID-19;
- At least 5 days after close contact with someone who has COVID;
- If someone is indoors with a group of people who are at risk of severe disease or are unvaccinated.
Are at-home rapid tests accurate?
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and other federal officials confirmed through studies that all tests distributed through this program can detect the Omicron variant. These agencies also confirmed that their performance is consistent with the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
Is the website designed to handle high demand?
After the original website to sign up for health insurance under the Affordable Care Act crashed repeatedly at launch, the government says it has prepared for high demand for ordering at-home rapid tests.
The U.S. Digital Service (USDS), an organization founded after Healthcare.gov, has partnered with the Postal Service to plan for the launch.
The Postal Service has expanded its staffing, similar to what’s done during the holidays.
All orders in the continental United States will be shipped through first-class mail, with shipments to Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. territories, and military and overseas addresses sent through priority mail.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.





