User login
‘Deeper dive’ into opioid overdose deaths during COVID pandemic
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid overdose deaths were significantly higher during 2020, but occurrences were not homogeneous across nine states. Male deaths were higher than in the 2 previous years in two states, according to a new, granular examination of data collected by researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General), Boston.
The analysis also showed that synthetic opioids such as fentanyl played an outsized role in most of the states that were reviewed. Additional drugs of abuse found in decedents, such as cocaine and psychostimulants, were more prevalent in some states than in others.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention used provisional death data in its recent report. It found that opioid-related deaths substantially rose in 2020 and that synthetic opioids were a primary driver.
The current Mass General analysis provides a more timely and detailed dive, senior author Mohammad Jalali, PhD, who is a senior scientist at Mass General’s Institute for Technology Assessment, told this news organization.
The findings, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published in MedRxiv.
Shifting sands of opioid use disorder
to analyze and project trends and also to be better prepared to address the shifting sands of opioid use disorder in the United States.
They attempted to collect data on confirmed opioid overdose deaths from all 50 states and Washington, D.C. to assess what might have changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. Only nine states provided enough data for the analysis, which has been submitted to a peer reviewed publication.
These states were Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming.
“Drug overdose data are collected and reported more slowly than COVID-19 data,” Dr. Jalali said in a press release. The data reflected a lag time of about 4 to 8 months in Massachusetts and North Carolina to more than a year in Maryland and Ohio, he noted.
The reporting lag “has clouded the understanding of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on opioid-related overdose deaths,” said Dr. Jalali.
Commenting on the findings, Brandon Marshall, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology at Brown University, Providence, R.I, said that “the overall pattern of what’s being reported here is not surprising,” given the national trends seen in the CDC data.
“This paper adds a deeper dive into some of the sociodemographic trends that we’re starting to observe in specific states,” Dr. Marshall said.
Also commenting for this news organization, Brian Fuehrlein, MD, PhD, director of the psychiatric emergency department at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System in West Haven, Connecticut, noted that the current study “highlights things that we are currently seeing at VA Connecticut.”
Decrease in heroin, rise in fentanyl
The investigators found a significant reduction in overdose deaths that involved heroin in Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Rhode Island. That was a new trend for Alaska, Indiana, and Rhode Island, although with only 3 years of data, it’s hard to say whether it will continue, Dr. Jalali noted.
The decrease in heroin involvement seemed to continue a trend previously observed in Colorado, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and North Carolina.
In Connecticut, heroin was involved in 36% of deaths in 2018, 30% in 2019, and 16% in 2020, according to the study.
“We have begun seeing more and more heroin-negative, fentanyl-positive drug screens,” said Dr. Fuehrlein, who is also associate professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“There is a shift from fentanyl being an adulterant to fentanyl being what is sold and used exclusively,” he added.
In 2020, 92% (n = 887) of deaths in Connecticut involved synthetic opioids, continuing a trend. In Alaska, however, synthetic opioids were involved in 60% (44) of deaths, which is a big jump from 23% (9) in 2018.
Synthetic opioids were involved in the largest percentage of overdoses in all of the states studied. The fewest deaths, 17 (49%), occurred in Wyoming.
Cocaine is also increasingly found in addition to other substances in decedents. In Alaska, about 14% of individuals who overdosed in 2020 also had cocaine in their system, which was a jump from 2% in the prior year.
In Colorado, 19% (94) of those who died also had taken cocaine, up from 13% in 2019. Cocaine was also frequently found in those who died in the northeast: 39% (467) of those who died in Massachusetts, 29% (280) in Connecticut, and 47% (109) in Rhode Island.
There was also an increase in psychostimulants found in those who had died in Massachusetts in 2020.
More male overdoses in 2020
Results also showed that, compared to 2019, significantly more men died from overdoses in 2020 in Colorado (61% vs. 70%, P = .017) and Indiana (62% vs. 70%, P = .026).
This finding was unexpected, said Dr. Marshall, who has observed the same phenomenon in Rhode Island. He is the scientific director of PreventOverdoseRI, Rhode Island’s drug overdose surveillance and information dashboard.
Dr. Marshall and his colleagues conducted a study that also found disproportionate increases in overdoses among men. The findings of that study will be published in September.
“We’re still trying to wrap our head around why that is,” he said. He added that a deeper dive into the Rhode Island data showed that the deaths were increased especially among middle-aged men who had been diagnosed with depression and anxiety.
The same patterns were not seen among women in either Dr. Jalali’s study or his own analysis of the Rhode Island data, said Dr. Marshall.
“That suggests the COVID-19 pandemic impacted men who are at risk for overdose in some particularly severe way,” he noted.
Dr. Fuehrlein said he believes a variety of factors have led to an increase in overdose deaths during the pandemic, including the fact that many patients who would normally seek help avoided care or dropped out of treatment because of COVID fears. In addition, other support systems, such as group therapy and Narcotics Anonymous, were unavailable.
The pandemic increased stress, which can lead to worsening substance use, said Dr. Fuehrlein. He also noted that regular opioid suppliers were often not available, which led some to buy from different dealers, “which can lead to overdose if the fentanyl content is different.”
Identifying at-risk individuals
Dr. Jalali and colleagues note that clinicians and policymakers could use the new study to help identify and treat at-risk individuals.
“Practitioners and policy makers can use our findings to help them anticipate which groups of people might be most affected by opioid overdose and which types of policy interventions might be most effective given each state’s unique situation,” said lead study author Gian-Gabriel P. Garcia, PhD, in a press release. At the time of the study, Dr. Garcia was a postdoctoral fellow at Mass General and Harvard Medical School. He is currently an assistant professor at Georgia Tech, Atlanta.
Dr. Marshall pointed out that Dr. Jalali’s study is also relevant for emergency departments.
ED clinicians “are and will be seeing patients coming in who have no idea they were exposed to an opioid, nevermind fentanyl,” he said. ED clinicians can discuss with patients various harm reduction techniques, including the use of naloxone as well as test strips that can detect fentanyl in the drug supply, he added.
“Given the increasing use of fentanyl, which is very dangerous in overdose, clinicians need to be well versed in a harm reduction/overdose prevention approach to patient care,” Dr. Fuehrlein agreed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases top 200,000, vaccinations down
Weekly pediatric cases of COVID-19 exceeded 200,000 for just the second time during the pandemic, while new vaccinations in children continued to decline.
The weekly count has now increased for 9 consecutive weeks, during which time it has risen by over 2,300%, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Total cases in children number almost 4.8 million since the pandemic started.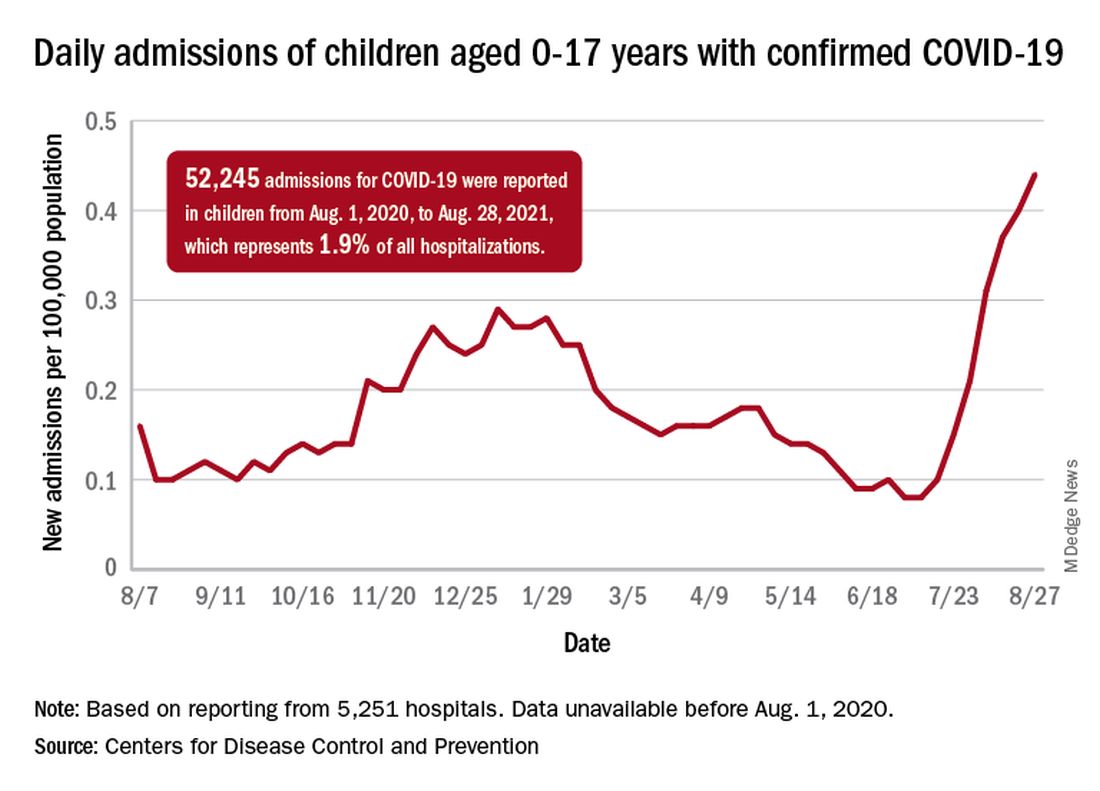
Vaccinations in children are following a different trend. Vaccine initiation has dropped 3 weeks in a row for both of the eligible age groups: First doses administered were down by 29% among 12- to 15-year-olds over that span and by 32% in 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Since vaccination for children aged 12-15 years started in May, 49% had received at least one dose, and just over 36% were fully vaccinated as of Aug. 30. Among children aged 16-17 years, who have been eligible since December, 57.5% had gotten at least one dose of the vaccine and 46% have completed the two-dose regimen. The total number of children with at least one dose, including those under age 12 who are involved in clinical trials, was about 12 million, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalizations are higher than ever
The recent rise in new child cases has been accompanied by an unprecedented increase in hospitalizations. The daily rate in children aged 0-17 years, which did not surpass 0.30 new admissions per 100,000 population during the worst of the winter surge, had risen to 0.45 per 100,000 by Aug. 26. Since July 4, when the new-admission rate was at its low point of 0.07 per 100,000, hospitalizations in children have jumped by 543%, based on data reported to the CDC by 5,251 hospitals.
A total of 52,245 children were admitted with confirmed COVID-19 from Aug. 1, 2020, when the CDC dataset begins, to Aug. 28, 2021. Those children represent 1.9% of all COVID admissions (2.7 million) in the United States over that period, the CDC said.
Total COVID-related deaths in children are up to 425 in the 48 jurisdictions (45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide mortality data by age, the AAP and the CHA said.
Record-high numbers for the previous 2 reporting weeks – 23 deaths during Aug. 20-26 and 24 deaths during Aug. 13-19, when the previous weekly high was 16 – at least partially reflect the recent addition of South Carolina and New Mexico to the AAP/CHA database, as the two states just started reporting age-related data.
Weekly pediatric cases of COVID-19 exceeded 200,000 for just the second time during the pandemic, while new vaccinations in children continued to decline.
The weekly count has now increased for 9 consecutive weeks, during which time it has risen by over 2,300%, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Total cases in children number almost 4.8 million since the pandemic started.
Vaccinations in children are following a different trend. Vaccine initiation has dropped 3 weeks in a row for both of the eligible age groups: First doses administered were down by 29% among 12- to 15-year-olds over that span and by 32% in 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Since vaccination for children aged 12-15 years started in May, 49% had received at least one dose, and just over 36% were fully vaccinated as of Aug. 30. Among children aged 16-17 years, who have been eligible since December, 57.5% had gotten at least one dose of the vaccine and 46% have completed the two-dose regimen. The total number of children with at least one dose, including those under age 12 who are involved in clinical trials, was about 12 million, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalizations are higher than ever
The recent rise in new child cases has been accompanied by an unprecedented increase in hospitalizations. The daily rate in children aged 0-17 years, which did not surpass 0.30 new admissions per 100,000 population during the worst of the winter surge, had risen to 0.45 per 100,000 by Aug. 26. Since July 4, when the new-admission rate was at its low point of 0.07 per 100,000, hospitalizations in children have jumped by 543%, based on data reported to the CDC by 5,251 hospitals.
A total of 52,245 children were admitted with confirmed COVID-19 from Aug. 1, 2020, when the CDC dataset begins, to Aug. 28, 2021. Those children represent 1.9% of all COVID admissions (2.7 million) in the United States over that period, the CDC said.
Total COVID-related deaths in children are up to 425 in the 48 jurisdictions (45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide mortality data by age, the AAP and the CHA said.
Record-high numbers for the previous 2 reporting weeks – 23 deaths during Aug. 20-26 and 24 deaths during Aug. 13-19, when the previous weekly high was 16 – at least partially reflect the recent addition of South Carolina and New Mexico to the AAP/CHA database, as the two states just started reporting age-related data.
Weekly pediatric cases of COVID-19 exceeded 200,000 for just the second time during the pandemic, while new vaccinations in children continued to decline.
The weekly count has now increased for 9 consecutive weeks, during which time it has risen by over 2,300%, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report. Total cases in children number almost 4.8 million since the pandemic started.
Vaccinations in children are following a different trend. Vaccine initiation has dropped 3 weeks in a row for both of the eligible age groups: First doses administered were down by 29% among 12- to 15-year-olds over that span and by 32% in 16- to 17-year-olds, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Since vaccination for children aged 12-15 years started in May, 49% had received at least one dose, and just over 36% were fully vaccinated as of Aug. 30. Among children aged 16-17 years, who have been eligible since December, 57.5% had gotten at least one dose of the vaccine and 46% have completed the two-dose regimen. The total number of children with at least one dose, including those under age 12 who are involved in clinical trials, was about 12 million, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalizations are higher than ever
The recent rise in new child cases has been accompanied by an unprecedented increase in hospitalizations. The daily rate in children aged 0-17 years, which did not surpass 0.30 new admissions per 100,000 population during the worst of the winter surge, had risen to 0.45 per 100,000 by Aug. 26. Since July 4, when the new-admission rate was at its low point of 0.07 per 100,000, hospitalizations in children have jumped by 543%, based on data reported to the CDC by 5,251 hospitals.
A total of 52,245 children were admitted with confirmed COVID-19 from Aug. 1, 2020, when the CDC dataset begins, to Aug. 28, 2021. Those children represent 1.9% of all COVID admissions (2.7 million) in the United States over that period, the CDC said.
Total COVID-related deaths in children are up to 425 in the 48 jurisdictions (45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that provide mortality data by age, the AAP and the CHA said.
Record-high numbers for the previous 2 reporting weeks – 23 deaths during Aug. 20-26 and 24 deaths during Aug. 13-19, when the previous weekly high was 16 – at least partially reflect the recent addition of South Carolina and New Mexico to the AAP/CHA database, as the two states just started reporting age-related data.
Reassuring data on long-term outcomes among kids with MIS-C
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID symptoms can persist for more than 1 year, study shows
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC panel unanimously backs Pfizer vax, fortifying FDA approval
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
An independent expert panel within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has studied the potential benefits and risks of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and voted unanimously to recommend the shots for all Americans ages 16 and older.
The vaccine was fully approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) last week.
The inoculation is still available to teens ages 12 to 15 under an emergency use authorization from the FDA.
ACIP now sends its recommendation to the CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, for her sign off.
After reviewing the evidence behind the vaccine, panel member Sarah Long, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, said she couldn’t recall another instance where panelists had so much data on which to base their recommendation.
“This vaccine is worthy of the trust of the American people,” she said.
Doctors across the country use vaccines in line with the recommendations made by the ACIP. Their approval typically means that private and government insurers will cover the cost of the shots. In the case of the COVID-19 vaccines, the government is already picking up the tab.
Few surprises
The panel’s independent review of the vaccine’s effectiveness from nine studies held few surprises.
They found the Pfizer vaccine prevented a COVID infection with symptoms about 90%–92% of the time, at least for the first 4 months after the second shot. Protection against hospitalization and death was even higher.
The vaccine was about 89% effective at preventing a COVID infection without symptoms, according to a pooled estimate of five studies.
The data included in the review was updated only through March 13 of this year, however, and does not reflect the impact of further waning of immunity or the impact of the Delta variant.
In making their recommendation, the panel got an update on the safety of the vaccines, which have now been used in the United States for about 9 months.
The rate of anaphylaxis has settled at around five cases for every million shots given, according to the ACIP’s review of the evidence.
Cases of myocarditis and pericarditis were more common after getting a Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than would be expected to happen naturally in the general population, but the risk was still very rare, and elevated primarily for men younger than age 30.
Out of 17 million second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines in the United States, there have been 327 confirmed cases of myocarditis reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System in people who are younger than age 30. The average hospital stay for a myocarditis cases is 1 to 2 days.
So far, no one in the United States diagnosed with myocarditis after vaccination has died.
What’s more, the risk of myocarditis after vaccination was dwarfed by the risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection. The risk of myocarditis after a COVID infection was 6 to 34 times higher than the risk after receiving an mRNA vaccine.
About 11% of people who get the vaccine experience a serious reaction to the shot, compared with about 3% in the placebo group. Serious reactions were defined as pain; swelling or redness at the injection site that interferes with activity; needing to visit the hospital or ER for pain; tissue necrosis, or having skin slough off; high fever; vomiting that requires hydration; persistent diarrhea; severe headache; or muscle pain/severe joint pain.
“Safe and effective”
After hearing a presentation on the state of the pandemic in the US, some panel members were struck and shaken that 38% of Americans who are eligible are still not fully vaccinated.
Pablo Sanchez, MD, a pediatrician at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said, “We’re doing an abysmal job vaccinating the American people. The message has to go out that the vaccines are safe and effective.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children’s upper airways primed to combat SARS-CoV-2 infection
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways of children are preactivated and primed to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection, which may contribute to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection than adults, new research suggests.
The findings may help to explain why children have a lower risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness or becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place, the researchers say.
The study was published online Aug. 18 in Nature Biotechnology.
Primed for action
Children appear to be better able than adults to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, but, until now, the exact molecular mechanisms have been unclear.
A team of investigators from Germany did an in-depth analysis of nasal swab samples obtained from 24 children and 21 adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as well as a control group of 18 children and 23 adults who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2.
“We wanted to understand why viral defense appears to work so much better in children than in adults,” Irina Lehmann, PhD, head of the molecular epidemiology unit at the Berlin Institute of Health Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, explained in a news release.
Single-cell sequencing showed that children had higher baseline levels of certain RNA-sensing receptors that are relevant to SARS-CoV-2 detection, such as MDA5 and RIG-I, in the epithelial and immune cells of their noses.
This differential expression led to stronger early immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children than in adults.
Children were also more likely than adults to have distinct immune cell subpopulations, including KLRC1+ cytotoxic T cells, involved in fighting infection, and memory CD8+ T cells, associated with the development of long-lasting immunity.
‘Clear evidence’
The study provides “clear evidence” that upper-airway immune cells of children are “primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults,” the investigators say.
Primed virus sensing and a preactivated innate immune response in children leads to efficient early production of interferons (IFNs) in the infected airways, likely mediating substantial antiviral effects, they note.
Ultimately, this may lead to lower viral replication and faster clearance in children. In fact, several studies have already shown that children eliminate the virus more quickly than adults, consistent with the concept that they shut down viral replication earlier, the study team says.
Weighing in on the findings for this news organization, John Wherry, PhD, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said this “interesting study highlights potential differences in innate immunity and possibly geographic immunity in the upper respiratory tract in children versus adults.”
“We know there are differences in innate immunity over a lifespan, but exactly how these differences might relate to viral infection remains unclear,” said Dr. Wherry, who was not involved in the study.
“Children, of course, often have more respiratory infections than adults [but] whether this is due to exposure [i.e., daycare, schools, etc.] or susceptibility [lack of accumulated adaptive immunity over a greater number of years of exposure] is unclear,” Dr. Wherry noted.
“These data may help reveal what kinds of innate immune responses in the upper respiratory tract might help restrain SARS-CoV-2 and [perhaps partially] explain why children typically have milder COVID-19 disease,” he added.
The study was supported by the Berlin Institute of Health COVID-19 research program and fightCOVID@DKFZ initiative, European Commission, German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), and German Research Foundation. Dr. Lehmann and Dr. Wherry have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antidepressant helps prevent hospitalization in COVID patients: Study
A handful of studies have suggested that for newly infected COVID-19 patients, risk for serious illness may be reduced with a short course of fluvoxamine (Luvox), a decades-old pill typically prescribed for depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). But those were small studies involving just a few hundred people.
This week, researchers reported promising data from a large, randomized phase 3 trial that enrolled COVID-19 patients from 11 sites in Brazil. In this study, in which 1,472 people were assigned to receive either a 10-day course of fluvoxamine or placebo pills, the antidepressant cut emergency department and hospital admissions by 29%.
Findings from the new study, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published August 23 in MedRxiv.
Around the globe, particularly in countries without access to vaccines, “treatment options that are cheap and available and supported by good-quality evidence are the only hope we’ve got to reduce mortality within high-risk populations,” said Edward Mills, PhD, professor in the department of health research methods, evidence, and impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The new findings came from TOGETHER, a large platform trial coordinated by Dr. Mills and colleagues to evaluate the use of fluvoxamine and other repurposed drug candidates for symptomatic, high-risk, adult outpatients with confirmed cases of COVID-19.
The trial’s adaptive format allows multiple agents to be added and tested alongside placebo in a single master protocol – similar to the United Kingdom’s Recovery trial, which found that the common steroid dexamethasone could reduce deaths among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
In platform trials, treatment arms can be dropped for futility, as was the case with hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir-ritonavir, neither of which did better than placebo at preventing hospitalization in an earlier TOGETHER trial analysis.
Study details
In the newly reported analysis, patients were randomly assigned to receive fluvoxamine or placebo between January and August 2021. Participants took fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily for 10 days. By comparison, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends a maximum daily dose of 300 mg of fluvoxamine for patients with OCD; full psychiatric benefits occur after 6 weeks.
For the primary outcome, the investigators assessed whether the conditions of patients with COVID worsened over a 28-day period so as to require either hospitalization or observation in the emergency department for more than 6 hours. In the placebo group, 108 of 733 patients’ conditions deteriorated to this extent (14.7%); by contrast, only 77 of 739 patients in the fluvoxamine group (10.4%) met these primary criteria – a relative risk reduction of 29%.
The treatment effect was greater (34%) in the per protocol analysis of participants who completed their course of pills.
The investigators also collected data on vital signs, including temperature and oxygen saturation, as well as adverse events reported at clinic visits or through video conferencing, phone calls, or social media applications. Side effects were mild, most commonly nausea and fatigue, and did not differ significantly between active treatment and control groups, Dr. Mills said in an interview.
Amid scores of studies evaluating repurposed drugs for COVID-19, the data on fluvoxamine are “looking much more favorable than anyone could have guessed – at least anyone in infectious disease,” said Paul Sax, MD, clinical director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The new TOGETHER trial results augment supportive data published in JAMA last November from a phase 2 randomized trial that was small but “very well done,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Those results got a boost from a subsequent study of 65 racetrack workers who chose to take fluvoxamine during a COVID-19 outbreak in the San Francisco Bay area. Forty-eight persons opted against taking the drug. In this small, nonrandomized study, “the people who chose to be treated with fluvoxamine were sicker [at baseline] than the people who didn’t go on it, and yet the [treated group] ended up better,” said Dr. Sax, who discussed accumulating data on the use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 in a recent New England Journal of Medicine blog post.
Anti-inflammatory effect?
After reviewing the new findings, Frank Domino, MD, professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said he would encourage patients with high-risk COVID-19 to consider taking fluvoxamine to lower their risk of being hospitalized. “But I would make it clear this was not a ‘cure,’ “ he said, “and we are unsure how it helps.”
At this point, U.S. treatment guidelines do not recommend fluvoxamine as the standard of care for nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but the National Institutes of Health is “very aware of the data,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) – a class of drugs that includes the more commonly prescribed antidepressant fluoxetine (Prozac). If prescribed off-label to COVID-19 patients, fluvoxamine should not be used within 2 weeks of starting treatment with other SSRI or monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants and should be used with caution with other QT-interval prolonging medications, Dr. Sax said.
In addition, fluvoxamine can enhance the effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs, potentially triggering bleeding.
On the basis of in vitro and mouse studies of fluvoxamine, “we think it has an anti-inflammatory effect,” said child psychiatrist Angela Reiersen, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who came up with the idea for testing fluvoxamine in last year’s phase 2 trial and coauthored a recent article describing the drug’s potential mechanisms of action in COVID-19.
She and other researchers believe fluvoxamine’s anti-inflammatory effects derive from the molecule’s binding to the sigma-1 receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum, which regulates cellular responses to stress and infection.
Fluvoxamine also inhibits the activation of platelets. “In COVID-19, there does seem to be a problem with hyperactivation of platelets and excessive blood clots forming, so it is possible this could be another mechanism where it might be helping,” Dr. Reiersen said.
If sigma-1 activation turns out to be the main mechanism underlying fluvoxamine’s benefits in COVID-19, other sigma-1 agonists, such as fluoxetine, may also help. In a retrospective analysis of thousands of adults hospitalized for COVID-19 in France early in the pandemic, those who were taking antidepressants had a 44% lower risk for intubation or death.
And in a study under review, researchers at Stanford (Calif.) University and the University of California, San Francisco, analyzed electronic health records to explore a potential link between fluoxetine use and COVID outcomes among more than 80,000 patients from over 80 institutions across the United States. Other research suggests that antipsychotics could also have protective effects for patients with COVID-19.
Long COVID, long-term challenges
On the basis of its potential mechanisms of action, fluvoxamine may be able to prevent or treat long COVID, Dr. Reiersen said. That possibility will be assessed among other secondary endpoints in two ongoing studies of repurposed drugs: the NIH’s ACTIV-6, and the University of Minnesota’s COVID-OUT, an at-home trial of ivermectin, metformin, and fluvoxamine.
Dr. Reiersen and Washington University colleagues are also analyzing longer-term outcomes of participants in their own phase 3 trial of fluvoxamine (Stop COVID 2), which was discontinued when enrollment slowed to a trickle during the U.S. vaccine rollout. Logistical hurdles and scant funding have greatly hampered efforts to test the use of off-patent drugs for COVID-19 outpatients during the pandemic.
U.S. efforts face other obstacles as well. Elsewhere in the world – including Brazil, where the TOGETHER trial was run – vaccines are scarce, and there are no monoclonal antibodies.
“People have a great sense of community duty, and they’re participating in the trials,” Dr. Mills said. “You’re in a much more political environment in the U.S. on these outpatient trials.”
The TOGETHER trial was funded by Fast Grants and the Rainwater Foundation. Dr. Reiersen is an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, which was filed by Washington University, St. Louis. Dr. Mills, Dr. Domino, and Dr. Sax report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A handful of studies have suggested that for newly infected COVID-19 patients, risk for serious illness may be reduced with a short course of fluvoxamine (Luvox), a decades-old pill typically prescribed for depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). But those were small studies involving just a few hundred people.
This week, researchers reported promising data from a large, randomized phase 3 trial that enrolled COVID-19 patients from 11 sites in Brazil. In this study, in which 1,472 people were assigned to receive either a 10-day course of fluvoxamine or placebo pills, the antidepressant cut emergency department and hospital admissions by 29%.
Findings from the new study, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published August 23 in MedRxiv.
Around the globe, particularly in countries without access to vaccines, “treatment options that are cheap and available and supported by good-quality evidence are the only hope we’ve got to reduce mortality within high-risk populations,” said Edward Mills, PhD, professor in the department of health research methods, evidence, and impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The new findings came from TOGETHER, a large platform trial coordinated by Dr. Mills and colleagues to evaluate the use of fluvoxamine and other repurposed drug candidates for symptomatic, high-risk, adult outpatients with confirmed cases of COVID-19.
The trial’s adaptive format allows multiple agents to be added and tested alongside placebo in a single master protocol – similar to the United Kingdom’s Recovery trial, which found that the common steroid dexamethasone could reduce deaths among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
In platform trials, treatment arms can be dropped for futility, as was the case with hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir-ritonavir, neither of which did better than placebo at preventing hospitalization in an earlier TOGETHER trial analysis.
Study details
In the newly reported analysis, patients were randomly assigned to receive fluvoxamine or placebo between January and August 2021. Participants took fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily for 10 days. By comparison, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends a maximum daily dose of 300 mg of fluvoxamine for patients with OCD; full psychiatric benefits occur after 6 weeks.
For the primary outcome, the investigators assessed whether the conditions of patients with COVID worsened over a 28-day period so as to require either hospitalization or observation in the emergency department for more than 6 hours. In the placebo group, 108 of 733 patients’ conditions deteriorated to this extent (14.7%); by contrast, only 77 of 739 patients in the fluvoxamine group (10.4%) met these primary criteria – a relative risk reduction of 29%.
The treatment effect was greater (34%) in the per protocol analysis of participants who completed their course of pills.
The investigators also collected data on vital signs, including temperature and oxygen saturation, as well as adverse events reported at clinic visits or through video conferencing, phone calls, or social media applications. Side effects were mild, most commonly nausea and fatigue, and did not differ significantly between active treatment and control groups, Dr. Mills said in an interview.
Amid scores of studies evaluating repurposed drugs for COVID-19, the data on fluvoxamine are “looking much more favorable than anyone could have guessed – at least anyone in infectious disease,” said Paul Sax, MD, clinical director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The new TOGETHER trial results augment supportive data published in JAMA last November from a phase 2 randomized trial that was small but “very well done,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Those results got a boost from a subsequent study of 65 racetrack workers who chose to take fluvoxamine during a COVID-19 outbreak in the San Francisco Bay area. Forty-eight persons opted against taking the drug. In this small, nonrandomized study, “the people who chose to be treated with fluvoxamine were sicker [at baseline] than the people who didn’t go on it, and yet the [treated group] ended up better,” said Dr. Sax, who discussed accumulating data on the use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 in a recent New England Journal of Medicine blog post.
Anti-inflammatory effect?
After reviewing the new findings, Frank Domino, MD, professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said he would encourage patients with high-risk COVID-19 to consider taking fluvoxamine to lower their risk of being hospitalized. “But I would make it clear this was not a ‘cure,’ “ he said, “and we are unsure how it helps.”
At this point, U.S. treatment guidelines do not recommend fluvoxamine as the standard of care for nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but the National Institutes of Health is “very aware of the data,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) – a class of drugs that includes the more commonly prescribed antidepressant fluoxetine (Prozac). If prescribed off-label to COVID-19 patients, fluvoxamine should not be used within 2 weeks of starting treatment with other SSRI or monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants and should be used with caution with other QT-interval prolonging medications, Dr. Sax said.
In addition, fluvoxamine can enhance the effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs, potentially triggering bleeding.
On the basis of in vitro and mouse studies of fluvoxamine, “we think it has an anti-inflammatory effect,” said child psychiatrist Angela Reiersen, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who came up with the idea for testing fluvoxamine in last year’s phase 2 trial and coauthored a recent article describing the drug’s potential mechanisms of action in COVID-19.
She and other researchers believe fluvoxamine’s anti-inflammatory effects derive from the molecule’s binding to the sigma-1 receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum, which regulates cellular responses to stress and infection.
Fluvoxamine also inhibits the activation of platelets. “In COVID-19, there does seem to be a problem with hyperactivation of platelets and excessive blood clots forming, so it is possible this could be another mechanism where it might be helping,” Dr. Reiersen said.
If sigma-1 activation turns out to be the main mechanism underlying fluvoxamine’s benefits in COVID-19, other sigma-1 agonists, such as fluoxetine, may also help. In a retrospective analysis of thousands of adults hospitalized for COVID-19 in France early in the pandemic, those who were taking antidepressants had a 44% lower risk for intubation or death.
And in a study under review, researchers at Stanford (Calif.) University and the University of California, San Francisco, analyzed electronic health records to explore a potential link between fluoxetine use and COVID outcomes among more than 80,000 patients from over 80 institutions across the United States. Other research suggests that antipsychotics could also have protective effects for patients with COVID-19.
Long COVID, long-term challenges
On the basis of its potential mechanisms of action, fluvoxamine may be able to prevent or treat long COVID, Dr. Reiersen said. That possibility will be assessed among other secondary endpoints in two ongoing studies of repurposed drugs: the NIH’s ACTIV-6, and the University of Minnesota’s COVID-OUT, an at-home trial of ivermectin, metformin, and fluvoxamine.
Dr. Reiersen and Washington University colleagues are also analyzing longer-term outcomes of participants in their own phase 3 trial of fluvoxamine (Stop COVID 2), which was discontinued when enrollment slowed to a trickle during the U.S. vaccine rollout. Logistical hurdles and scant funding have greatly hampered efforts to test the use of off-patent drugs for COVID-19 outpatients during the pandemic.
U.S. efforts face other obstacles as well. Elsewhere in the world – including Brazil, where the TOGETHER trial was run – vaccines are scarce, and there are no monoclonal antibodies.
“People have a great sense of community duty, and they’re participating in the trials,” Dr. Mills said. “You’re in a much more political environment in the U.S. on these outpatient trials.”
The TOGETHER trial was funded by Fast Grants and the Rainwater Foundation. Dr. Reiersen is an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, which was filed by Washington University, St. Louis. Dr. Mills, Dr. Domino, and Dr. Sax report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A handful of studies have suggested that for newly infected COVID-19 patients, risk for serious illness may be reduced with a short course of fluvoxamine (Luvox), a decades-old pill typically prescribed for depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). But those were small studies involving just a few hundred people.
This week, researchers reported promising data from a large, randomized phase 3 trial that enrolled COVID-19 patients from 11 sites in Brazil. In this study, in which 1,472 people were assigned to receive either a 10-day course of fluvoxamine or placebo pills, the antidepressant cut emergency department and hospital admissions by 29%.
Findings from the new study, which have not yet been peer reviewed, were published August 23 in MedRxiv.
Around the globe, particularly in countries without access to vaccines, “treatment options that are cheap and available and supported by good-quality evidence are the only hope we’ve got to reduce mortality within high-risk populations,” said Edward Mills, PhD, professor in the department of health research methods, evidence, and impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
The new findings came from TOGETHER, a large platform trial coordinated by Dr. Mills and colleagues to evaluate the use of fluvoxamine and other repurposed drug candidates for symptomatic, high-risk, adult outpatients with confirmed cases of COVID-19.
The trial’s adaptive format allows multiple agents to be added and tested alongside placebo in a single master protocol – similar to the United Kingdom’s Recovery trial, which found that the common steroid dexamethasone could reduce deaths among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
In platform trials, treatment arms can be dropped for futility, as was the case with hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir-ritonavir, neither of which did better than placebo at preventing hospitalization in an earlier TOGETHER trial analysis.
Study details
In the newly reported analysis, patients were randomly assigned to receive fluvoxamine or placebo between January and August 2021. Participants took fluvoxamine 100 mg twice daily for 10 days. By comparison, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends a maximum daily dose of 300 mg of fluvoxamine for patients with OCD; full psychiatric benefits occur after 6 weeks.
For the primary outcome, the investigators assessed whether the conditions of patients with COVID worsened over a 28-day period so as to require either hospitalization or observation in the emergency department for more than 6 hours. In the placebo group, 108 of 733 patients’ conditions deteriorated to this extent (14.7%); by contrast, only 77 of 739 patients in the fluvoxamine group (10.4%) met these primary criteria – a relative risk reduction of 29%.
The treatment effect was greater (34%) in the per protocol analysis of participants who completed their course of pills.
The investigators also collected data on vital signs, including temperature and oxygen saturation, as well as adverse events reported at clinic visits or through video conferencing, phone calls, or social media applications. Side effects were mild, most commonly nausea and fatigue, and did not differ significantly between active treatment and control groups, Dr. Mills said in an interview.
Amid scores of studies evaluating repurposed drugs for COVID-19, the data on fluvoxamine are “looking much more favorable than anyone could have guessed – at least anyone in infectious disease,” said Paul Sax, MD, clinical director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The new TOGETHER trial results augment supportive data published in JAMA last November from a phase 2 randomized trial that was small but “very well done,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Those results got a boost from a subsequent study of 65 racetrack workers who chose to take fluvoxamine during a COVID-19 outbreak in the San Francisco Bay area. Forty-eight persons opted against taking the drug. In this small, nonrandomized study, “the people who chose to be treated with fluvoxamine were sicker [at baseline] than the people who didn’t go on it, and yet the [treated group] ended up better,” said Dr. Sax, who discussed accumulating data on the use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 in a recent New England Journal of Medicine blog post.
Anti-inflammatory effect?
After reviewing the new findings, Frank Domino, MD, professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said he would encourage patients with high-risk COVID-19 to consider taking fluvoxamine to lower their risk of being hospitalized. “But I would make it clear this was not a ‘cure,’ “ he said, “and we are unsure how it helps.”
At this point, U.S. treatment guidelines do not recommend fluvoxamine as the standard of care for nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients, but the National Institutes of Health is “very aware of the data,” Dr. Sax told this news organization.
Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) – a class of drugs that includes the more commonly prescribed antidepressant fluoxetine (Prozac). If prescribed off-label to COVID-19 patients, fluvoxamine should not be used within 2 weeks of starting treatment with other SSRI or monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants and should be used with caution with other QT-interval prolonging medications, Dr. Sax said.
In addition, fluvoxamine can enhance the effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs, potentially triggering bleeding.
On the basis of in vitro and mouse studies of fluvoxamine, “we think it has an anti-inflammatory effect,” said child psychiatrist Angela Reiersen, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who came up with the idea for testing fluvoxamine in last year’s phase 2 trial and coauthored a recent article describing the drug’s potential mechanisms of action in COVID-19.
She and other researchers believe fluvoxamine’s anti-inflammatory effects derive from the molecule’s binding to the sigma-1 receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum, which regulates cellular responses to stress and infection.
Fluvoxamine also inhibits the activation of platelets. “In COVID-19, there does seem to be a problem with hyperactivation of platelets and excessive blood clots forming, so it is possible this could be another mechanism where it might be helping,” Dr. Reiersen said.
If sigma-1 activation turns out to be the main mechanism underlying fluvoxamine’s benefits in COVID-19, other sigma-1 agonists, such as fluoxetine, may also help. In a retrospective analysis of thousands of adults hospitalized for COVID-19 in France early in the pandemic, those who were taking antidepressants had a 44% lower risk for intubation or death.
And in a study under review, researchers at Stanford (Calif.) University and the University of California, San Francisco, analyzed electronic health records to explore a potential link between fluoxetine use and COVID outcomes among more than 80,000 patients from over 80 institutions across the United States. Other research suggests that antipsychotics could also have protective effects for patients with COVID-19.
Long COVID, long-term challenges
On the basis of its potential mechanisms of action, fluvoxamine may be able to prevent or treat long COVID, Dr. Reiersen said. That possibility will be assessed among other secondary endpoints in two ongoing studies of repurposed drugs: the NIH’s ACTIV-6, and the University of Minnesota’s COVID-OUT, an at-home trial of ivermectin, metformin, and fluvoxamine.
Dr. Reiersen and Washington University colleagues are also analyzing longer-term outcomes of participants in their own phase 3 trial of fluvoxamine (Stop COVID 2), which was discontinued when enrollment slowed to a trickle during the U.S. vaccine rollout. Logistical hurdles and scant funding have greatly hampered efforts to test the use of off-patent drugs for COVID-19 outpatients during the pandemic.
U.S. efforts face other obstacles as well. Elsewhere in the world – including Brazil, where the TOGETHER trial was run – vaccines are scarce, and there are no monoclonal antibodies.
“People have a great sense of community duty, and they’re participating in the trials,” Dr. Mills said. “You’re in a much more political environment in the U.S. on these outpatient trials.”
The TOGETHER trial was funded by Fast Grants and the Rainwater Foundation. Dr. Reiersen is an inventor on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, which was filed by Washington University, St. Louis. Dr. Mills, Dr. Domino, and Dr. Sax report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Advocates seek to reframe masks as a disability accommodation
As governors and legislatures in states such as Texas, Florida, South Carolina, and Arkansas have banned schools and other entities from implementing mask mandates, disability rights advocates have pushed back. In federal civil rights lawsuits, they argue that bans on mask mandates violate antidiscrimination laws protecting people with disabilities.
For unvaccinated and immunosuppressed individuals, masks can provide crucial protection from SARS-CoV-2.
argues Mical Raz, MD, PhD, a professor at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) and a physician at Strong Memorial Hospital, also in Rochester, New York, in an article published in JAMA with coauthor Doron Dorfman, LLB, JSD.
This news organization talked with Dr. Raz about approaching mask requirements as disability accommodation during the COVID-19 pandemic. The following interview was lightly edited for length and clarity.
How did you come to think about mask requirements as a form of disability accommodation?
I saw a tweet from a professor at a university who said they couldn’t ask students about their vaccination status or to wear a mask. All agency was removed from the professor to take care of and protect themselves. I thought, well, that can’t be right. And ostensibly, that would be particularly dangerous for somebody with immunosuppression for whom the vaccine is not adequately protective. So, I called my friend, Doron Dorfman, and asked him to help me think through the legal part of this. We fleshed it out and wrote the article that same night.
How novel is it to view accommodations for people who are immunosuppressed through the lens of disability accommodation?
I think there has not been enough focus during the pandemic on individuals with disabilities or on how disability law can be mobilized during this pandemic to help supplement the public health law. This framework should be used a lot more because it’s good for everybody, not just for individuals with disabilities.
For example, take what’s called the “curb effect.” If you expand sidewalks, yes, it helps individuals who use a wheelchair. But it also helps me as a mom with a stroller. It helps somebody with a shopping cart, or a kid with a bike. If we adopt policies that are inclusive to those who are disadvantaged, it’s good for everybody. We should always strive to be an inclusive society, not just because it’s the right thing to do but because it really makes our society better.
How can mask requirements be used as a form of disability accommodation, as you argue in the JAMA article?
The ADA requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for disability. In this case, the disability is your immunosuppressive status. We have an abundance of evidence showing individuals who are immunocompromised and vaccinated are still inadequately protected from the SARS-CoV-2 virus. So, there is absolute data to show individuals with immunosuppression have a disability that requires accommodation.
The ADA has a mandate requiring employers to adjust or modify policies in order to accommodate a disability. There are certain situations in which you cannot or do not need to accommodate a disability, when it would fundamentally alter the kind of employment you offer or if it’s an undue burden or hardship. But given that we’ve been wearing masks and working remotely for a year now, arguing that somehow these accommodations are no longer possible seems disingenuous.
In that way, allowing a person who’s immunocompromised to require those around them to mask is a form of modified protective policies. And in this case, those policies line up with a public health good, masking in the face of the highly contagious Delta variant ravaging our country right now.
In your view, can this argument be used in the mask debates happening right now across the country?
This argument can and should be useful for a couple of different lawsuits that are now underway in different states. I hope our article will provide further support for those suits. And I hope in school board hearings, when parents and teachers are talking about their concerns, this could be one way to argue for why we should allow mask mandates in classes. I’ve received emails from parents who said they’re going to bring this article to their school board hearing.
I also hope this could shift the narrative around the pandemic. Instead of focusing on individual responsibility – I got my vaccine shot so I’m fine – let’s focus on how we create an inclusive environment where we protect everybody, including those who cannot be vaccinated because of age or disability, or those who are vaccinated but inadequately protected because of their underlying conditions.
In the JAMA article, you talk about how our pandemic response has focused on individual health and how that individual focus can be ableist. Can you explain that point?
I think this idea that we just make our choices – like whether to get vaccinated or wear a mask, or not – and live with it really perpetuates a highly individualistic and ableist mindset. It doesn’t consider the people I admit to the hospital who are vaccinated but have a heart transplant and didn’t mount the sufficient immune response. Or even the people who chose not to be vaccinated because they were exposed to hours and hours of misinformation on TV.
We like to individualize everything, focusing on personal responsibility and choices, but a pandemic is one of those moments where everybody’s choices affect everybody else. Laying responsibility at the doorstep of each person, rather than thinking about what steps we as a society could be taking, is cheap and politically expedient. There is no public health rationale behind the bans on mask requirements in states like Texas, Iowa, and Florida. These choices are about politics. And the price is always borne by the most disadvantaged among us.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As governors and legislatures in states such as Texas, Florida, South Carolina, and Arkansas have banned schools and other entities from implementing mask mandates, disability rights advocates have pushed back. In federal civil rights lawsuits, they argue that bans on mask mandates violate antidiscrimination laws protecting people with disabilities.
For unvaccinated and immunosuppressed individuals, masks can provide crucial protection from SARS-CoV-2.
argues Mical Raz, MD, PhD, a professor at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) and a physician at Strong Memorial Hospital, also in Rochester, New York, in an article published in JAMA with coauthor Doron Dorfman, LLB, JSD.
This news organization talked with Dr. Raz about approaching mask requirements as disability accommodation during the COVID-19 pandemic. The following interview was lightly edited for length and clarity.
How did you come to think about mask requirements as a form of disability accommodation?
I saw a tweet from a professor at a university who said they couldn’t ask students about their vaccination status or to wear a mask. All agency was removed from the professor to take care of and protect themselves. I thought, well, that can’t be right. And ostensibly, that would be particularly dangerous for somebody with immunosuppression for whom the vaccine is not adequately protective. So, I called my friend, Doron Dorfman, and asked him to help me think through the legal part of this. We fleshed it out and wrote the article that same night.
How novel is it to view accommodations for people who are immunosuppressed through the lens of disability accommodation?
I think there has not been enough focus during the pandemic on individuals with disabilities or on how disability law can be mobilized during this pandemic to help supplement the public health law. This framework should be used a lot more because it’s good for everybody, not just for individuals with disabilities.
For example, take what’s called the “curb effect.” If you expand sidewalks, yes, it helps individuals who use a wheelchair. But it also helps me as a mom with a stroller. It helps somebody with a shopping cart, or a kid with a bike. If we adopt policies that are inclusive to those who are disadvantaged, it’s good for everybody. We should always strive to be an inclusive society, not just because it’s the right thing to do but because it really makes our society better.
How can mask requirements be used as a form of disability accommodation, as you argue in the JAMA article?
The ADA requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for disability. In this case, the disability is your immunosuppressive status. We have an abundance of evidence showing individuals who are immunocompromised and vaccinated are still inadequately protected from the SARS-CoV-2 virus. So, there is absolute data to show individuals with immunosuppression have a disability that requires accommodation.
The ADA has a mandate requiring employers to adjust or modify policies in order to accommodate a disability. There are certain situations in which you cannot or do not need to accommodate a disability, when it would fundamentally alter the kind of employment you offer or if it’s an undue burden or hardship. But given that we’ve been wearing masks and working remotely for a year now, arguing that somehow these accommodations are no longer possible seems disingenuous.
In that way, allowing a person who’s immunocompromised to require those around them to mask is a form of modified protective policies. And in this case, those policies line up with a public health good, masking in the face of the highly contagious Delta variant ravaging our country right now.
In your view, can this argument be used in the mask debates happening right now across the country?
This argument can and should be useful for a couple of different lawsuits that are now underway in different states. I hope our article will provide further support for those suits. And I hope in school board hearings, when parents and teachers are talking about their concerns, this could be one way to argue for why we should allow mask mandates in classes. I’ve received emails from parents who said they’re going to bring this article to their school board hearing.
I also hope this could shift the narrative around the pandemic. Instead of focusing on individual responsibility – I got my vaccine shot so I’m fine – let’s focus on how we create an inclusive environment where we protect everybody, including those who cannot be vaccinated because of age or disability, or those who are vaccinated but inadequately protected because of their underlying conditions.
In the JAMA article, you talk about how our pandemic response has focused on individual health and how that individual focus can be ableist. Can you explain that point?
I think this idea that we just make our choices – like whether to get vaccinated or wear a mask, or not – and live with it really perpetuates a highly individualistic and ableist mindset. It doesn’t consider the people I admit to the hospital who are vaccinated but have a heart transplant and didn’t mount the sufficient immune response. Or even the people who chose not to be vaccinated because they were exposed to hours and hours of misinformation on TV.
We like to individualize everything, focusing on personal responsibility and choices, but a pandemic is one of those moments where everybody’s choices affect everybody else. Laying responsibility at the doorstep of each person, rather than thinking about what steps we as a society could be taking, is cheap and politically expedient. There is no public health rationale behind the bans on mask requirements in states like Texas, Iowa, and Florida. These choices are about politics. And the price is always borne by the most disadvantaged among us.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As governors and legislatures in states such as Texas, Florida, South Carolina, and Arkansas have banned schools and other entities from implementing mask mandates, disability rights advocates have pushed back. In federal civil rights lawsuits, they argue that bans on mask mandates violate antidiscrimination laws protecting people with disabilities.
For unvaccinated and immunosuppressed individuals, masks can provide crucial protection from SARS-CoV-2.
argues Mical Raz, MD, PhD, a professor at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) and a physician at Strong Memorial Hospital, also in Rochester, New York, in an article published in JAMA with coauthor Doron Dorfman, LLB, JSD.
This news organization talked with Dr. Raz about approaching mask requirements as disability accommodation during the COVID-19 pandemic. The following interview was lightly edited for length and clarity.
How did you come to think about mask requirements as a form of disability accommodation?
I saw a tweet from a professor at a university who said they couldn’t ask students about their vaccination status or to wear a mask. All agency was removed from the professor to take care of and protect themselves. I thought, well, that can’t be right. And ostensibly, that would be particularly dangerous for somebody with immunosuppression for whom the vaccine is not adequately protective. So, I called my friend, Doron Dorfman, and asked him to help me think through the legal part of this. We fleshed it out and wrote the article that same night.
How novel is it to view accommodations for people who are immunosuppressed through the lens of disability accommodation?
I think there has not been enough focus during the pandemic on individuals with disabilities or on how disability law can be mobilized during this pandemic to help supplement the public health law. This framework should be used a lot more because it’s good for everybody, not just for individuals with disabilities.
For example, take what’s called the “curb effect.” If you expand sidewalks, yes, it helps individuals who use a wheelchair. But it also helps me as a mom with a stroller. It helps somebody with a shopping cart, or a kid with a bike. If we adopt policies that are inclusive to those who are disadvantaged, it’s good for everybody. We should always strive to be an inclusive society, not just because it’s the right thing to do but because it really makes our society better.
How can mask requirements be used as a form of disability accommodation, as you argue in the JAMA article?
The ADA requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations for disability. In this case, the disability is your immunosuppressive status. We have an abundance of evidence showing individuals who are immunocompromised and vaccinated are still inadequately protected from the SARS-CoV-2 virus. So, there is absolute data to show individuals with immunosuppression have a disability that requires accommodation.
The ADA has a mandate requiring employers to adjust or modify policies in order to accommodate a disability. There are certain situations in which you cannot or do not need to accommodate a disability, when it would fundamentally alter the kind of employment you offer or if it’s an undue burden or hardship. But given that we’ve been wearing masks and working remotely for a year now, arguing that somehow these accommodations are no longer possible seems disingenuous.
In that way, allowing a person who’s immunocompromised to require those around them to mask is a form of modified protective policies. And in this case, those policies line up with a public health good, masking in the face of the highly contagious Delta variant ravaging our country right now.
In your view, can this argument be used in the mask debates happening right now across the country?
This argument can and should be useful for a couple of different lawsuits that are now underway in different states. I hope our article will provide further support for those suits. And I hope in school board hearings, when parents and teachers are talking about their concerns, this could be one way to argue for why we should allow mask mandates in classes. I’ve received emails from parents who said they’re going to bring this article to their school board hearing.
I also hope this could shift the narrative around the pandemic. Instead of focusing on individual responsibility – I got my vaccine shot so I’m fine – let’s focus on how we create an inclusive environment where we protect everybody, including those who cannot be vaccinated because of age or disability, or those who are vaccinated but inadequately protected because of their underlying conditions.
In the JAMA article, you talk about how our pandemic response has focused on individual health and how that individual focus can be ableist. Can you explain that point?
I think this idea that we just make our choices – like whether to get vaccinated or wear a mask, or not – and live with it really perpetuates a highly individualistic and ableist mindset. It doesn’t consider the people I admit to the hospital who are vaccinated but have a heart transplant and didn’t mount the sufficient immune response. Or even the people who chose not to be vaccinated because they were exposed to hours and hours of misinformation on TV.
We like to individualize everything, focusing on personal responsibility and choices, but a pandemic is one of those moments where everybody’s choices affect everybody else. Laying responsibility at the doorstep of each person, rather than thinking about what steps we as a society could be taking, is cheap and politically expedient. There is no public health rationale behind the bans on mask requirements in states like Texas, Iowa, and Florida. These choices are about politics. And the price is always borne by the most disadvantaged among us.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ACR updates COVID vaccine guidance with booster schedule
Patients on immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory therapy should receive a third dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine at least 28 days after the second dose of either of these two mRNA vaccines, according to updated recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology.
The update follows the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation that certain immunocompromised patients receive a third dose of an mRNA vaccine to reduce their risk of contracting COVID-19.
Individuals receiving the Pfizer vaccine must be aged 12 years and older, while those receiving the Moderna vaccine must be 18 years and older, the ACR emphasized.
“These statements were based upon a dearth of high-quality data and are not intended to replace clinical judgment,” the authors wrote. “Modifications made to treatment plans, particularly in complex rheumatic disease patients, are highly disease, patient, geography, and time specific and, therefore, must be individualized as part of a shared decision-making process.”
The task force recommended using the same mRNA vaccine booster as the patient received for their initial two-dose series when possible, but notes that either mRNA vaccine is acceptable, and recommends the mRNA vaccine for patients who have yet to receive any vaccine because of the availability of the booster. The task force emphasized that they achieved no consensus on recommending a booster mRNA vaccine to patients who received a single dose of Johnson & Johnson vaccine because the safety data are uncertain.
The updated guidance also identifies the Food and Drug Administration’s emergency use authorization in August for the use of REGEN-COV monoclonal antibody treatment for emergency postexposure prophylaxis for COVID-19 in adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older who weigh at least 40 kg and are at increased risk for severe COVID-19, which includes patients receiving immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory therapies other than hydroxychloroquine. Patients who have been exposed to an individual with COVID-19 should discuss this treatment with their health care provider as an added precaution; however, the guidance emphasized that the prophylactic treatment is not a substitute for COVID-19 vaccination.
The recommendations advise clinicians to counsel their patients to refrain from taking certain immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications for 1-2 weeks after booster vaccination if disease activity allows, with the exception of glucocorticoids and anticytokines such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and others including interleukin-17, IL-12/23, IL-23, IL-1R, IL-6R antagonists, for which the task force did not achieve a consensus recommendation.
The guidance notes that patients on rituximab or other anti-CD20 medications “should discuss the optimal timing [of the booster] with their rheumatology provider” and that some practitioners measure CD19 B cells as a tool with which to time the booster and subsequent rituximab dosing. For those who elect to dose without such information, or for whom such measurement is not available or feasible, provide the booster 2-4 weeks before next anticipated rituximab dose (e.g., at month 5.0 or 5.5 for patients on an every-6-month rituximab dosing schedule).”
There was strong consensus from the task force that health care providers “should not routinely order any lab testing (e.g., antibody tests for IgM and/or IgG to spike or nucleocapsid proteins) to assess immunity to COVID-19 post vaccination, nor to assess the need for vaccination in a yet-unvaccinated person.”
“The updated information from the ACR addresses not only booster vaccination but also other important and practical issues facing rheumatology providers and their patients related to the pandemic,” said task force chair Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, in an ACR statement announcing the updates.
“Although the guidance is issued in light of the best evidence available, the science regarding COVID-19 vaccination as it affects the practice of rheumatology is undergoing rapid evolution,” he noted. “We need direct evidence such as that from randomized trials to inform the best practices of what we can do to protect our patients from SARS-CoV-2.”
The update retains the current recommendations that rheumatology patients follow all public health guidelines regarding physical distancing and other preventive measures following vaccination, but the task force did not recommend exceeding current public health guidance. “The appropriateness for continued preventive measures (e.g., masking, physical distancing) should be discussed with patients as their rheumatology providers deem appropriate,” they wrote.
The full updated version of the ACR’s COVID-19 Vaccine Clinical Guidance for Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases will be published in Arthritis & Rheumatology. The summary was developed by the ACR COVID-19 Vaccine Clinical Guidance Task Force, which included 9 rheumatologists, 2 infectious disease specialists, and 2 public health experts with current or past employment history with the CDC.
The ACR encourages clinicians with questions or concerns to email [email protected] for support.
Patients on immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory therapy should receive a third dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine at least 28 days after the second dose of either of these two mRNA vaccines, according to updated recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology.
The update follows the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation that certain immunocompromised patients receive a third dose of an mRNA vaccine to reduce their risk of contracting COVID-19.
Individuals receiving the Pfizer vaccine must be aged 12 years and older, while those receiving the Moderna vaccine must be 18 years and older, the ACR emphasized.
“These statements were based upon a dearth of high-quality data and are not intended to replace clinical judgment,” the authors wrote. “Modifications made to treatment plans, particularly in complex rheumatic disease patients, are highly disease, patient, geography, and time specific and, therefore, must be individualized as part of a shared decision-making process.”
The task force recommended using the same mRNA vaccine booster as the patient received for their initial two-dose series when possible, but notes that either mRNA vaccine is acceptable, and recommends the mRNA vaccine for patients who have yet to receive any vaccine because of the availability of the booster. The task force emphasized that they achieved no consensus on recommending a booster mRNA vaccine to patients who received a single dose of Johnson & Johnson vaccine because the safety data are uncertain.
The updated guidance also identifies the Food and Drug Administration’s emergency use authorization in August for the use of REGEN-COV monoclonal antibody treatment for emergency postexposure prophylaxis for COVID-19 in adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older who weigh at least 40 kg and are at increased risk for severe COVID-19, which includes patients receiving immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory therapies other than hydroxychloroquine. Patients who have been exposed to an individual with COVID-19 should discuss this treatment with their health care provider as an added precaution; however, the guidance emphasized that the prophylactic treatment is not a substitute for COVID-19 vaccination.
The recommendations advise clinicians to counsel their patients to refrain from taking certain immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications for 1-2 weeks after booster vaccination if disease activity allows, with the exception of glucocorticoids and anticytokines such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and others including interleukin-17, IL-12/23, IL-23, IL-1R, IL-6R antagonists, for which the task force did not achieve a consensus recommendation.
The guidance notes that patients on rituximab or other anti-CD20 medications “should discuss the optimal timing [of the booster] with their rheumatology provider” and that some practitioners measure CD19 B cells as a tool with which to time the booster and subsequent rituximab dosing. For those who elect to dose without such information, or for whom such measurement is not available or feasible, provide the booster 2-4 weeks before next anticipated rituximab dose (e.g., at month 5.0 or 5.5 for patients on an every-6-month rituximab dosing schedule).”
There was strong consensus from the task force that health care providers “should not routinely order any lab testing (e.g., antibody tests for IgM and/or IgG to spike or nucleocapsid proteins) to assess immunity to COVID-19 post vaccination, nor to assess the need for vaccination in a yet-unvaccinated person.”
“The updated information from the ACR addresses not only booster vaccination but also other important and practical issues facing rheumatology providers and their patients related to the pandemic,” said task force chair Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, in an ACR statement announcing the updates.
“Although the guidance is issued in light of the best evidence available, the science regarding COVID-19 vaccination as it affects the practice of rheumatology is undergoing rapid evolution,” he noted. “We need direct evidence such as that from randomized trials to inform the best practices of what we can do to protect our patients from SARS-CoV-2.”
The update retains the current recommendations that rheumatology patients follow all public health guidelines regarding physical distancing and other preventive measures following vaccination, but the task force did not recommend exceeding current public health guidance. “The appropriateness for continued preventive measures (e.g., masking, physical distancing) should be discussed with patients as their rheumatology providers deem appropriate,” they wrote.
The full updated version of the ACR’s COVID-19 Vaccine Clinical Guidance for Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases will be published in Arthritis & Rheumatology. The summary was developed by the ACR COVID-19 Vaccine Clinical Guidance Task Force, which included 9 rheumatologists, 2 infectious disease specialists, and 2 public health experts with current or past employment history with the CDC.
The ACR encourages clinicians with questions or concerns to email [email protected] for support.
Patients on immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory therapy should receive a third dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine at least 28 days after the second dose of either of these two mRNA vaccines, according to updated recommendations from the American College of Rheumatology.
The update follows the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation that certain immunocompromised patients receive a third dose of an mRNA vaccine to reduce their risk of contracting COVID-19.
Individuals receiving the Pfizer vaccine must be aged 12 years and older, while those receiving the Moderna vaccine must be 18 years and older, the ACR emphasized.
“These statements were based upon a dearth of high-quality data and are not intended to replace clinical judgment,” the authors wrote. “Modifications made to treatment plans, particularly in complex rheumatic disease patients, are highly disease, patient, geography, and time specific and, therefore, must be individualized as part of a shared decision-making process.”
The task force recommended using the same mRNA vaccine booster as the patient received for their initial two-dose series when possible, but notes that either mRNA vaccine is acceptable, and recommends the mRNA vaccine for patients who have yet to receive any vaccine because of the availability of the booster. The task force emphasized that they achieved no consensus on recommending a booster mRNA vaccine to patients who received a single dose of Johnson & Johnson vaccine because the safety data are uncertain.
The updated guidance also identifies the Food and Drug Administration’s emergency use authorization in August for the use of REGEN-COV monoclonal antibody treatment for emergency postexposure prophylaxis for COVID-19 in adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older who weigh at least 40 kg and are at increased risk for severe COVID-19, which includes patients receiving immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory therapies other than hydroxychloroquine. Patients who have been exposed to an individual with COVID-19 should discuss this treatment with their health care provider as an added precaution; however, the guidance emphasized that the prophylactic treatment is not a substitute for COVID-19 vaccination.
The recommendations advise clinicians to counsel their patients to refrain from taking certain immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications for 1-2 weeks after booster vaccination if disease activity allows, with the exception of glucocorticoids and anticytokines such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and others including interleukin-17, IL-12/23, IL-23, IL-1R, IL-6R antagonists, for which the task force did not achieve a consensus recommendation.
The guidance notes that patients on rituximab or other anti-CD20 medications “should discuss the optimal timing [of the booster] with their rheumatology provider” and that some practitioners measure CD19 B cells as a tool with which to time the booster and subsequent rituximab dosing. For those who elect to dose without such information, or for whom such measurement is not available or feasible, provide the booster 2-4 weeks before next anticipated rituximab dose (e.g., at month 5.0 or 5.5 for patients on an every-6-month rituximab dosing schedule).”
There was strong consensus from the task force that health care providers “should not routinely order any lab testing (e.g., antibody tests for IgM and/or IgG to spike or nucleocapsid proteins) to assess immunity to COVID-19 post vaccination, nor to assess the need for vaccination in a yet-unvaccinated person.”
“The updated information from the ACR addresses not only booster vaccination but also other important and practical issues facing rheumatology providers and their patients related to the pandemic,” said task force chair Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, in an ACR statement announcing the updates.
“Although the guidance is issued in light of the best evidence available, the science regarding COVID-19 vaccination as it affects the practice of rheumatology is undergoing rapid evolution,” he noted. “We need direct evidence such as that from randomized trials to inform the best practices of what we can do to protect our patients from SARS-CoV-2.”
The update retains the current recommendations that rheumatology patients follow all public health guidelines regarding physical distancing and other preventive measures following vaccination, but the task force did not recommend exceeding current public health guidance. “The appropriateness for continued preventive measures (e.g., masking, physical distancing) should be discussed with patients as their rheumatology providers deem appropriate,” they wrote.
The full updated version of the ACR’s COVID-19 Vaccine Clinical Guidance for Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases will be published in Arthritis & Rheumatology. The summary was developed by the ACR COVID-19 Vaccine Clinical Guidance Task Force, which included 9 rheumatologists, 2 infectious disease specialists, and 2 public health experts with current or past employment history with the CDC.
The ACR encourages clinicians with questions or concerns to email [email protected] for support.
NIH to study COVID vaccine booster in people with autoimmune disease
In the wake of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation for a third COVID-19 mRNA vaccine dose for immunocompromised people and the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization of the third dose, the according to an announcement.
The investigators of the trial, called COVID‐19 Booster Vaccine in Autoimmune Disease Non‐Responders, also want to determine if pausing immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune disease improves the antibody response to an extra dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
The trial will specifically look at the effects of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or mycophenolic acid (MPA), and methotrexate (MTX), or receipt of B cell–depletion therapy such as rituximab within the past 12 months on immune response to a booster dose in people with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic sclerosis, or pemphigus. They have to have either no serologic response to their initial COVID-19 vaccine regimen or a suboptimal response, defined as a Roche Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (RBD) result greater than or equal to 50 U/mL.
The results of studies conducted in solid-organ transplant recipients who take immunosuppressants showed that an extra dose of vaccine could improve the immune response to the vaccine in many of the individuals, which suggests that the same approach might work in people with autoimmune disease who need treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. Improving the immune response of people with autoimmune disease to COVID-19 vaccines is important because higher rates of severe COVID-19 and death have been reported in this group of patients than in the general population, and it is unclear whether this is attributable to the autoimmune disease, the immunosuppressive medications taken to treat it, or both.
The open-label trial, conducted by the NIAID-funded Autoimmunity Centers of Excellence, aims to enroll 600 people aged 18 years and older with those conditions at 15-20 sites in the United States.
Because medications commonly taken by people with these conditions have been associated with poorer immune responses to vaccines, the trial will randomize the following two cohorts to stop or continue taking their immunosuppressive medication(s) or stop them before and after the booster according to protocol:
- Cohort 1 includes people who are taking MMF or MPA, without additional B cell–depleting medications or MTX.
- Cohort 2 includes people who are taking MTX without additional B cell–depleting medications or MMF/MPA.
A third, nonrandomized cohort consists of people who have received B cell–depletion therapy within the past 12 months regardless of whether they are also taking MMF/MPA or MTX.
Besides the cohort-specific exclusions, other rheumatic disease medications, including biologics, are allowed in the groups.
The primary outcome of the trial is the proportion of participants who have a protective antibody response at week 4. Secondary outcomes will examine various antibody responses at intervals, changes in disease activity across autoimmune diseases, adverse events, and SARS-CoV-2 infections out to 48 weeks.
Study participants will be followed for a total of 13 months. Preliminary results are expected in November 2021, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The trial is being led by Judith James, MD, PhD; Meggan Mackay, MD, MS; Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc; and Amit Bar-Or, MD.
In the wake of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation for a third COVID-19 mRNA vaccine dose for immunocompromised people and the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization of the third dose, the according to an announcement.
The investigators of the trial, called COVID‐19 Booster Vaccine in Autoimmune Disease Non‐Responders, also want to determine if pausing immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune disease improves the antibody response to an extra dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
The trial will specifically look at the effects of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or mycophenolic acid (MPA), and methotrexate (MTX), or receipt of B cell–depletion therapy such as rituximab within the past 12 months on immune response to a booster dose in people with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic sclerosis, or pemphigus. They have to have either no serologic response to their initial COVID-19 vaccine regimen or a suboptimal response, defined as a Roche Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (RBD) result greater than or equal to 50 U/mL.
The results of studies conducted in solid-organ transplant recipients who take immunosuppressants showed that an extra dose of vaccine could improve the immune response to the vaccine in many of the individuals, which suggests that the same approach might work in people with autoimmune disease who need treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. Improving the immune response of people with autoimmune disease to COVID-19 vaccines is important because higher rates of severe COVID-19 and death have been reported in this group of patients than in the general population, and it is unclear whether this is attributable to the autoimmune disease, the immunosuppressive medications taken to treat it, or both.
The open-label trial, conducted by the NIAID-funded Autoimmunity Centers of Excellence, aims to enroll 600 people aged 18 years and older with those conditions at 15-20 sites in the United States.
Because medications commonly taken by people with these conditions have been associated with poorer immune responses to vaccines, the trial will randomize the following two cohorts to stop or continue taking their immunosuppressive medication(s) or stop them before and after the booster according to protocol:
- Cohort 1 includes people who are taking MMF or MPA, without additional B cell–depleting medications or MTX.
- Cohort 2 includes people who are taking MTX without additional B cell–depleting medications or MMF/MPA.
A third, nonrandomized cohort consists of people who have received B cell–depletion therapy within the past 12 months regardless of whether they are also taking MMF/MPA or MTX.
Besides the cohort-specific exclusions, other rheumatic disease medications, including biologics, are allowed in the groups.
The primary outcome of the trial is the proportion of participants who have a protective antibody response at week 4. Secondary outcomes will examine various antibody responses at intervals, changes in disease activity across autoimmune diseases, adverse events, and SARS-CoV-2 infections out to 48 weeks.
Study participants will be followed for a total of 13 months. Preliminary results are expected in November 2021, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The trial is being led by Judith James, MD, PhD; Meggan Mackay, MD, MS; Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc; and Amit Bar-Or, MD.
In the wake of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendation for a third COVID-19 mRNA vaccine dose for immunocompromised people and the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization of the third dose, the according to an announcement.
The investigators of the trial, called COVID‐19 Booster Vaccine in Autoimmune Disease Non‐Responders, also want to determine if pausing immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune disease improves the antibody response to an extra dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
The trial will specifically look at the effects of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or mycophenolic acid (MPA), and methotrexate (MTX), or receipt of B cell–depletion therapy such as rituximab within the past 12 months on immune response to a booster dose in people with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic sclerosis, or pemphigus. They have to have either no serologic response to their initial COVID-19 vaccine regimen or a suboptimal response, defined as a Roche Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (RBD) result greater than or equal to 50 U/mL.
The results of studies conducted in solid-organ transplant recipients who take immunosuppressants showed that an extra dose of vaccine could improve the immune response to the vaccine in many of the individuals, which suggests that the same approach might work in people with autoimmune disease who need treatment with immunosuppressive drugs. Improving the immune response of people with autoimmune disease to COVID-19 vaccines is important because higher rates of severe COVID-19 and death have been reported in this group of patients than in the general population, and it is unclear whether this is attributable to the autoimmune disease, the immunosuppressive medications taken to treat it, or both.
The open-label trial, conducted by the NIAID-funded Autoimmunity Centers of Excellence, aims to enroll 600 people aged 18 years and older with those conditions at 15-20 sites in the United States.
Because medications commonly taken by people with these conditions have been associated with poorer immune responses to vaccines, the trial will randomize the following two cohorts to stop or continue taking their immunosuppressive medication(s) or stop them before and after the booster according to protocol:
- Cohort 1 includes people who are taking MMF or MPA, without additional B cell–depleting medications or MTX.
- Cohort 2 includes people who are taking MTX without additional B cell–depleting medications or MMF/MPA.
A third, nonrandomized cohort consists of people who have received B cell–depletion therapy within the past 12 months regardless of whether they are also taking MMF/MPA or MTX.
Besides the cohort-specific exclusions, other rheumatic disease medications, including biologics, are allowed in the groups.
The primary outcome of the trial is the proportion of participants who have a protective antibody response at week 4. Secondary outcomes will examine various antibody responses at intervals, changes in disease activity across autoimmune diseases, adverse events, and SARS-CoV-2 infections out to 48 weeks.
Study participants will be followed for a total of 13 months. Preliminary results are expected in November 2021, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The trial is being led by Judith James, MD, PhD; Meggan Mackay, MD, MS; Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, MSc; and Amit Bar-Or, MD.