User login
Common meds link to sudden cardiac arrest in type 2 diabetes
HAMBURG, Germany – , shows the first such analysis of real-world, primary care data.
People with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD have almost three times the risk of SCA if they take antipsychotic medications and nearly double the risk if they take certain antibiotics that prolong the QT interval, notably, macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
“These data show that commonly prescribed drugs - antipsychotic medications, used by about 3% of people with type 2 diabetes, and antibiotics, taken by 5% to 10%, convey an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest in those without a history of cardiovascular disease,” said Peter Harms, MSc, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Another drug associated with an increase in SCA among patients with diabetes was domperidone, an antinausea medication.
“Perhaps these drugs could be avoided in some cases, and GPs should be more aware of the possible consequences of their use,” he added. “If the patient has type 2 diabetes, then maybe it’s better to avoid some of these medications and try and cope without them, or at least find an alternative antibiotic.”
Mr. Harms, an epidemiologist from Amsterdam University Medical Centers, highlighted that their study was unique because the investigators drew upon primary care data. “These data are extensive, and we find a lot of associations which are very real.”
SCA is associated with 50% of all cardiac deaths and accounts for 20% of all mortality in high-income countries. Of those people who experience SCA, 80% of cases prove fatal.
“As the name suggests, it is difficult to predict because it is sudden, especially in people without a cardiovascular disease history,” Mr. Harms pointed out in an interview with this news organization. He highlighted that “around half of those who experience SCA, often between the ages of 40 and 60 years, have never seen a cardiologist, but many do have type 2 diabetes.
“We need to better understand how to recognize people at risk of SCA, know who to watch and how to prevent these events,” he emphasized.
Vladimira Fejfarova, MD, comoderated the session and commented on the study. “From the clinical point of view, it’s necessary to evaluate risk factors that can contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.”
Overall, the researchers found that, among people with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD, hypoglycemia, severe hypertension, dyslipidemia, and use of QTc-prolonging medications are associated with SCA risk. Among people with type 2 diabetes and CVD, albuminuria and heart failure are associated with SCA risk.
Dr. Fejfarova added: “With type 2 diabetes and also type 1, we need to look more at adverse events, especially when treating infections with macrolides, but also mycotic infections, because antimycotic drugs are known to influence QT intervals that could contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.
“We need to be more cautious with prescribing certain antibiotics that have these side effects in our patients with diabetes,” asserted Dr. Fejfarova, from the Diabetes Centre, Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Prague.
Type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of SCA
The researcher decided to investigate the population of people with type 2 diabetes because their risk of SCD is around twice that of those without type 2 diabetes. Because these patients have relatively frequent checkups with general practitioners, Mr. Harms turned to primary care databases that contained comprehensive and relatively routine information on risk indicators.
Longitudinal associations between clinical characteristics of 3,919 patients with type 2 diabetes – both those with and those without a history of CVD – and SCA (a total of 689 patients) were determined.
Cases were found in the AmsteRdam REsuscitation STtudies (ARREST) registry of out-of-hospital resuscitation attempts by emergency medical services in the Dutch region of Noord-Holland from 2010 to 2019. Case patients were matched with up to five control patients. The control group comprised people with type 2 diabetes who had not experienced an SCA. Control patients were sourced from the same primary care practices who were of similar age and sex. Clinical measurements, including blood pressure and blood glucose readings, medication use, and medical history for the 5 years leading up to an SCA, were obtained from general practice records. A multivariable analysis was performed, and results were stratified for people with and for those without a history of CVD.
Of particular interest were drugs that interfere with cardiac function, including some prokinetic, antibiotic, and antipsychotic medications. All of the drugs are known to be associated with a change in QTc prolongation. Examples include domperidone (QTc-prolonging prokinetic), macrolides and fluoroquinolones (QTc-prolonging antibiotics), and haloperidol (a QTc-prolonging antipsychotic).
Antibiotic and antipsychotic use might contribute to SCA in T2D
Case patients and control patients were similar in age, hemoglobin A1c level, and other characteristics with the exception that more patients with SCA had a history of CVD (40.0% vs. 29.4%).
“Looking at the associations in the overall population, insulin use was strongly associated with SCA risk [hazard ratio, 2.38] and perhaps this was an indicator of severity of type 2 diabetes,” remarked Mr. Harms. “Also, unsurprisingly, a history of arrhythmia [HR, 1.68] and, more surprisingly, prokinetic drug use [HR, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-2.31], specifically those known for QTc-prolongation, were associated with SCA.”
Among people who had experienced an SCA and who did not have a history of CVD (337 case patients/2,023 control patients), QTc-prolonging antipsychotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.87, and antibiotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.66. A low fasting glucose level (< 4.5 mmol/mol) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.5; severely high systolic blood pressure (> 180 mm Hg) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.21; low HDL cholesterol level, with an HR of 1.35; and high LDL cholesterol level (> 2.6 mmol/L), with an HR of 1.64.
Among people with a history of CVD (352 case patients/1,207 control patients), associations between albuminuria and SCA were moderate (HR, 1.54) and severe (HR, 1.55); heart failure was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.85 (95% CI, 1.50-2.29).
Comoderator Dr. Fejfarova added that, in addition to the findings from Dr. Harms’ study, other research presented in the same session highlighted the importance of checking patients for the presence of arrhythmias that could lead to the development of atrioventricular blocks, sinus node diseases, and SCA.
Mr. Harms and Dr. Fejfarova have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, Germany – , shows the first such analysis of real-world, primary care data.
People with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD have almost three times the risk of SCA if they take antipsychotic medications and nearly double the risk if they take certain antibiotics that prolong the QT interval, notably, macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
“These data show that commonly prescribed drugs - antipsychotic medications, used by about 3% of people with type 2 diabetes, and antibiotics, taken by 5% to 10%, convey an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest in those without a history of cardiovascular disease,” said Peter Harms, MSc, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Another drug associated with an increase in SCA among patients with diabetes was domperidone, an antinausea medication.
“Perhaps these drugs could be avoided in some cases, and GPs should be more aware of the possible consequences of their use,” he added. “If the patient has type 2 diabetes, then maybe it’s better to avoid some of these medications and try and cope without them, or at least find an alternative antibiotic.”
Mr. Harms, an epidemiologist from Amsterdam University Medical Centers, highlighted that their study was unique because the investigators drew upon primary care data. “These data are extensive, and we find a lot of associations which are very real.”
SCA is associated with 50% of all cardiac deaths and accounts for 20% of all mortality in high-income countries. Of those people who experience SCA, 80% of cases prove fatal.
“As the name suggests, it is difficult to predict because it is sudden, especially in people without a cardiovascular disease history,” Mr. Harms pointed out in an interview with this news organization. He highlighted that “around half of those who experience SCA, often between the ages of 40 and 60 years, have never seen a cardiologist, but many do have type 2 diabetes.
“We need to better understand how to recognize people at risk of SCA, know who to watch and how to prevent these events,” he emphasized.
Vladimira Fejfarova, MD, comoderated the session and commented on the study. “From the clinical point of view, it’s necessary to evaluate risk factors that can contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.”
Overall, the researchers found that, among people with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD, hypoglycemia, severe hypertension, dyslipidemia, and use of QTc-prolonging medications are associated with SCA risk. Among people with type 2 diabetes and CVD, albuminuria and heart failure are associated with SCA risk.
Dr. Fejfarova added: “With type 2 diabetes and also type 1, we need to look more at adverse events, especially when treating infections with macrolides, but also mycotic infections, because antimycotic drugs are known to influence QT intervals that could contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.
“We need to be more cautious with prescribing certain antibiotics that have these side effects in our patients with diabetes,” asserted Dr. Fejfarova, from the Diabetes Centre, Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Prague.
Type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of SCA
The researcher decided to investigate the population of people with type 2 diabetes because their risk of SCD is around twice that of those without type 2 diabetes. Because these patients have relatively frequent checkups with general practitioners, Mr. Harms turned to primary care databases that contained comprehensive and relatively routine information on risk indicators.
Longitudinal associations between clinical characteristics of 3,919 patients with type 2 diabetes – both those with and those without a history of CVD – and SCA (a total of 689 patients) were determined.
Cases were found in the AmsteRdam REsuscitation STtudies (ARREST) registry of out-of-hospital resuscitation attempts by emergency medical services in the Dutch region of Noord-Holland from 2010 to 2019. Case patients were matched with up to five control patients. The control group comprised people with type 2 diabetes who had not experienced an SCA. Control patients were sourced from the same primary care practices who were of similar age and sex. Clinical measurements, including blood pressure and blood glucose readings, medication use, and medical history for the 5 years leading up to an SCA, were obtained from general practice records. A multivariable analysis was performed, and results were stratified for people with and for those without a history of CVD.
Of particular interest were drugs that interfere with cardiac function, including some prokinetic, antibiotic, and antipsychotic medications. All of the drugs are known to be associated with a change in QTc prolongation. Examples include domperidone (QTc-prolonging prokinetic), macrolides and fluoroquinolones (QTc-prolonging antibiotics), and haloperidol (a QTc-prolonging antipsychotic).
Antibiotic and antipsychotic use might contribute to SCA in T2D
Case patients and control patients were similar in age, hemoglobin A1c level, and other characteristics with the exception that more patients with SCA had a history of CVD (40.0% vs. 29.4%).
“Looking at the associations in the overall population, insulin use was strongly associated with SCA risk [hazard ratio, 2.38] and perhaps this was an indicator of severity of type 2 diabetes,” remarked Mr. Harms. “Also, unsurprisingly, a history of arrhythmia [HR, 1.68] and, more surprisingly, prokinetic drug use [HR, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-2.31], specifically those known for QTc-prolongation, were associated with SCA.”
Among people who had experienced an SCA and who did not have a history of CVD (337 case patients/2,023 control patients), QTc-prolonging antipsychotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.87, and antibiotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.66. A low fasting glucose level (< 4.5 mmol/mol) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.5; severely high systolic blood pressure (> 180 mm Hg) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.21; low HDL cholesterol level, with an HR of 1.35; and high LDL cholesterol level (> 2.6 mmol/L), with an HR of 1.64.
Among people with a history of CVD (352 case patients/1,207 control patients), associations between albuminuria and SCA were moderate (HR, 1.54) and severe (HR, 1.55); heart failure was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.85 (95% CI, 1.50-2.29).
Comoderator Dr. Fejfarova added that, in addition to the findings from Dr. Harms’ study, other research presented in the same session highlighted the importance of checking patients for the presence of arrhythmias that could lead to the development of atrioventricular blocks, sinus node diseases, and SCA.
Mr. Harms and Dr. Fejfarova have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, Germany – , shows the first such analysis of real-world, primary care data.
People with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD have almost three times the risk of SCA if they take antipsychotic medications and nearly double the risk if they take certain antibiotics that prolong the QT interval, notably, macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
“These data show that commonly prescribed drugs - antipsychotic medications, used by about 3% of people with type 2 diabetes, and antibiotics, taken by 5% to 10%, convey an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest in those without a history of cardiovascular disease,” said Peter Harms, MSc, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Another drug associated with an increase in SCA among patients with diabetes was domperidone, an antinausea medication.
“Perhaps these drugs could be avoided in some cases, and GPs should be more aware of the possible consequences of their use,” he added. “If the patient has type 2 diabetes, then maybe it’s better to avoid some of these medications and try and cope without them, or at least find an alternative antibiotic.”
Mr. Harms, an epidemiologist from Amsterdam University Medical Centers, highlighted that their study was unique because the investigators drew upon primary care data. “These data are extensive, and we find a lot of associations which are very real.”
SCA is associated with 50% of all cardiac deaths and accounts for 20% of all mortality in high-income countries. Of those people who experience SCA, 80% of cases prove fatal.
“As the name suggests, it is difficult to predict because it is sudden, especially in people without a cardiovascular disease history,” Mr. Harms pointed out in an interview with this news organization. He highlighted that “around half of those who experience SCA, often between the ages of 40 and 60 years, have never seen a cardiologist, but many do have type 2 diabetes.
“We need to better understand how to recognize people at risk of SCA, know who to watch and how to prevent these events,” he emphasized.
Vladimira Fejfarova, MD, comoderated the session and commented on the study. “From the clinical point of view, it’s necessary to evaluate risk factors that can contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.”
Overall, the researchers found that, among people with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD, hypoglycemia, severe hypertension, dyslipidemia, and use of QTc-prolonging medications are associated with SCA risk. Among people with type 2 diabetes and CVD, albuminuria and heart failure are associated with SCA risk.
Dr. Fejfarova added: “With type 2 diabetes and also type 1, we need to look more at adverse events, especially when treating infections with macrolides, but also mycotic infections, because antimycotic drugs are known to influence QT intervals that could contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.
“We need to be more cautious with prescribing certain antibiotics that have these side effects in our patients with diabetes,” asserted Dr. Fejfarova, from the Diabetes Centre, Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Prague.
Type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of SCA
The researcher decided to investigate the population of people with type 2 diabetes because their risk of SCD is around twice that of those without type 2 diabetes. Because these patients have relatively frequent checkups with general practitioners, Mr. Harms turned to primary care databases that contained comprehensive and relatively routine information on risk indicators.
Longitudinal associations between clinical characteristics of 3,919 patients with type 2 diabetes – both those with and those without a history of CVD – and SCA (a total of 689 patients) were determined.
Cases were found in the AmsteRdam REsuscitation STtudies (ARREST) registry of out-of-hospital resuscitation attempts by emergency medical services in the Dutch region of Noord-Holland from 2010 to 2019. Case patients were matched with up to five control patients. The control group comprised people with type 2 diabetes who had not experienced an SCA. Control patients were sourced from the same primary care practices who were of similar age and sex. Clinical measurements, including blood pressure and blood glucose readings, medication use, and medical history for the 5 years leading up to an SCA, were obtained from general practice records. A multivariable analysis was performed, and results were stratified for people with and for those without a history of CVD.
Of particular interest were drugs that interfere with cardiac function, including some prokinetic, antibiotic, and antipsychotic medications. All of the drugs are known to be associated with a change in QTc prolongation. Examples include domperidone (QTc-prolonging prokinetic), macrolides and fluoroquinolones (QTc-prolonging antibiotics), and haloperidol (a QTc-prolonging antipsychotic).
Antibiotic and antipsychotic use might contribute to SCA in T2D
Case patients and control patients were similar in age, hemoglobin A1c level, and other characteristics with the exception that more patients with SCA had a history of CVD (40.0% vs. 29.4%).
“Looking at the associations in the overall population, insulin use was strongly associated with SCA risk [hazard ratio, 2.38] and perhaps this was an indicator of severity of type 2 diabetes,” remarked Mr. Harms. “Also, unsurprisingly, a history of arrhythmia [HR, 1.68] and, more surprisingly, prokinetic drug use [HR, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-2.31], specifically those known for QTc-prolongation, were associated with SCA.”
Among people who had experienced an SCA and who did not have a history of CVD (337 case patients/2,023 control patients), QTc-prolonging antipsychotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.87, and antibiotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.66. A low fasting glucose level (< 4.5 mmol/mol) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.5; severely high systolic blood pressure (> 180 mm Hg) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.21; low HDL cholesterol level, with an HR of 1.35; and high LDL cholesterol level (> 2.6 mmol/L), with an HR of 1.64.
Among people with a history of CVD (352 case patients/1,207 control patients), associations between albuminuria and SCA were moderate (HR, 1.54) and severe (HR, 1.55); heart failure was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.85 (95% CI, 1.50-2.29).
Comoderator Dr. Fejfarova added that, in addition to the findings from Dr. Harms’ study, other research presented in the same session highlighted the importance of checking patients for the presence of arrhythmias that could lead to the development of atrioventricular blocks, sinus node diseases, and SCA.
Mr. Harms and Dr. Fejfarova have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2023
CMS ‘million hearts’ CVD risk reduction model works
TOPLINE:
The Million Hearts Model, a U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) initiative that encouraged and paid health care organizations to assess and reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, reduced first-time myocardial infarction (MI) and strokes among Medicare beneficiaries without significant changes in Medicare spending, a randomized trial finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the Million Hearts CVD Risk Reduction Model in a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial among 342 health care organizations – half in the intervention group and half in the standard care control group.
- Among 218,684 medium- or high-risk Medicare beneficiaries (median age, 72 years), 130,578 were in the intervention group in which Medicare paid for guideline-concordant care including routine CVD risk assessment, and 88,286 were in the standard care group.
- Outcomes included first time CVD events (for instance, MI, stroke, transient ischemic attack), combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths, and Medicare spending.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up of 4.3 years, the intervention group had a 3.3% lower rate of CVD events than the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.97; 90% confidence interval, 0.93-1.00; P = .09) and a 4.2% lower rate of combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.99; P = .02).
- These relative effects represent an absolute re.duction of 0.3 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event over 5 years (7.8% intervention vs 8.1%) and 0.4 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event or CVD death over 5 years (9.3% intervention vs. 9.7% control).
- The intervention group also had a 4.3% lower death rate (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.98; P = .01; absolute reduction of 0.5 percentage points over 5 years).
- Analyses by cause of death showed the largest relative declines (10.6%) among deaths due to coronary heart disease and CVD.
- There was no significant between-group difference in Medicare spending on CVD events or in overall Medicare Parts A and B spending.
IN PRACTICE:
“The model was unique in paying for overall CVD risk reduction, measured by a novel, longitudinal risk calculator, rather than tying performance-based payments to control of individual risk factors,” the authors write.
“The encouraging findings from the Million Hearts Model suggest that modernized payment models may be an affirmative strategy to [incentivize guideline-concordant CVD preventive care and improve outcomes], though further work is needed to ensure that these models are patient-centric, optimally deployed, and equity-enhancing,” add the editorial writers.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Laura Blue, PhD, Mathematica, Washington, was published online in JAMA, with an accompanying editorial.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitation is nonparticipation of many of the organizations (516 were randomly assigned to one of the study groups, 342 participated) and incomplete entry of beneficiary data into the registry, which could have led to systematic differences between the two groups. Bias due to the selective participation of organizations and beneficiaries cannot be ruled out.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by CMS, Department of Health & Human Services. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The Million Hearts Model, a U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) initiative that encouraged and paid health care organizations to assess and reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, reduced first-time myocardial infarction (MI) and strokes among Medicare beneficiaries without significant changes in Medicare spending, a randomized trial finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the Million Hearts CVD Risk Reduction Model in a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial among 342 health care organizations – half in the intervention group and half in the standard care control group.
- Among 218,684 medium- or high-risk Medicare beneficiaries (median age, 72 years), 130,578 were in the intervention group in which Medicare paid for guideline-concordant care including routine CVD risk assessment, and 88,286 were in the standard care group.
- Outcomes included first time CVD events (for instance, MI, stroke, transient ischemic attack), combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths, and Medicare spending.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up of 4.3 years, the intervention group had a 3.3% lower rate of CVD events than the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.97; 90% confidence interval, 0.93-1.00; P = .09) and a 4.2% lower rate of combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.99; P = .02).
- These relative effects represent an absolute re.duction of 0.3 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event over 5 years (7.8% intervention vs 8.1%) and 0.4 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event or CVD death over 5 years (9.3% intervention vs. 9.7% control).
- The intervention group also had a 4.3% lower death rate (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.98; P = .01; absolute reduction of 0.5 percentage points over 5 years).
- Analyses by cause of death showed the largest relative declines (10.6%) among deaths due to coronary heart disease and CVD.
- There was no significant between-group difference in Medicare spending on CVD events or in overall Medicare Parts A and B spending.
IN PRACTICE:
“The model was unique in paying for overall CVD risk reduction, measured by a novel, longitudinal risk calculator, rather than tying performance-based payments to control of individual risk factors,” the authors write.
“The encouraging findings from the Million Hearts Model suggest that modernized payment models may be an affirmative strategy to [incentivize guideline-concordant CVD preventive care and improve outcomes], though further work is needed to ensure that these models are patient-centric, optimally deployed, and equity-enhancing,” add the editorial writers.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Laura Blue, PhD, Mathematica, Washington, was published online in JAMA, with an accompanying editorial.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitation is nonparticipation of many of the organizations (516 were randomly assigned to one of the study groups, 342 participated) and incomplete entry of beneficiary data into the registry, which could have led to systematic differences between the two groups. Bias due to the selective participation of organizations and beneficiaries cannot be ruled out.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by CMS, Department of Health & Human Services. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The Million Hearts Model, a U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) initiative that encouraged and paid health care organizations to assess and reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, reduced first-time myocardial infarction (MI) and strokes among Medicare beneficiaries without significant changes in Medicare spending, a randomized trial finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the Million Hearts CVD Risk Reduction Model in a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial among 342 health care organizations – half in the intervention group and half in the standard care control group.
- Among 218,684 medium- or high-risk Medicare beneficiaries (median age, 72 years), 130,578 were in the intervention group in which Medicare paid for guideline-concordant care including routine CVD risk assessment, and 88,286 were in the standard care group.
- Outcomes included first time CVD events (for instance, MI, stroke, transient ischemic attack), combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths, and Medicare spending.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up of 4.3 years, the intervention group had a 3.3% lower rate of CVD events than the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.97; 90% confidence interval, 0.93-1.00; P = .09) and a 4.2% lower rate of combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.99; P = .02).
- These relative effects represent an absolute re.duction of 0.3 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event over 5 years (7.8% intervention vs 8.1%) and 0.4 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event or CVD death over 5 years (9.3% intervention vs. 9.7% control).
- The intervention group also had a 4.3% lower death rate (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.98; P = .01; absolute reduction of 0.5 percentage points over 5 years).
- Analyses by cause of death showed the largest relative declines (10.6%) among deaths due to coronary heart disease and CVD.
- There was no significant between-group difference in Medicare spending on CVD events or in overall Medicare Parts A and B spending.
IN PRACTICE:
“The model was unique in paying for overall CVD risk reduction, measured by a novel, longitudinal risk calculator, rather than tying performance-based payments to control of individual risk factors,” the authors write.
“The encouraging findings from the Million Hearts Model suggest that modernized payment models may be an affirmative strategy to [incentivize guideline-concordant CVD preventive care and improve outcomes], though further work is needed to ensure that these models are patient-centric, optimally deployed, and equity-enhancing,” add the editorial writers.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Laura Blue, PhD, Mathematica, Washington, was published online in JAMA, with an accompanying editorial.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitation is nonparticipation of many of the organizations (516 were randomly assigned to one of the study groups, 342 participated) and incomplete entry of beneficiary data into the registry, which could have led to systematic differences between the two groups. Bias due to the selective participation of organizations and beneficiaries cannot be ruled out.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by CMS, Department of Health & Human Services. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stair climbing tied to reduced risk for heart disease
TOPLINE:
new observational data suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- The prospective cohort study used data from 458,860 adults in the UK Biobank cohort who were 38-73 years old at baseline (2006-2010).
- Information about stair climbing, sociodemographic, and lifestyle factors was collected at baseline and 5 years later.
- Cases of ASCVD – defined as coronary artery disease (CAD), ischemic stroke, or acute complications – were identified via hospital records and death registry.
- Associations between stair climbing and ASCVD were examined as hazard ratios from Cox proportional hazards model. Analyses were stratified by susceptibility to ASCVD based on family history, genetic risk, and established risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 39,043 ASCVD, 30,718 CAD, and 10,521 ischemic stroke cases were recorded during a median follow-up of 12.5 years.
- Compared with no-stair climbing, climbing 6-10 flights of stairs daily was associated with a 7% lower ASCVD risk (multivariable-adjusted HR, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.96) and climbing 16-20 flights daily was associated with a 10% lower risk (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94).
- The benefits plateaued at 20 flights daily; comparable results were obtained for CAD and ischemic stroke; the protective effect of stair climbing was attenuated by increasing levels of disease susceptibility.
- Adults who stopped climbing stairs daily during the study had a 32% higher risk of ASCVD (HR, 1.32; 95% CI,1.06-1.65), compared with peers who never reported stair climbing.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings highlight the potential advantages of stair climbing as a primary preventive measure for ASCVD in the general population. Short bursts of high-intensity stair climbing are a time-efficient way to improve cardiorespiratory fitness and lipid profile, especially among those unable to achieve the current physical activity recommendations,” study author Lu Qi, with Tulane University, New Orleans, said in a news release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Atherosclerosis.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational design limits causal inferences. Stair climbing was self-reported via questionnaires and recall bias is a possibility. The UK Biobank participants do not represent the entire population of the country, with a healthy volunteer selection bias previously reported.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
new observational data suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- The prospective cohort study used data from 458,860 adults in the UK Biobank cohort who were 38-73 years old at baseline (2006-2010).
- Information about stair climbing, sociodemographic, and lifestyle factors was collected at baseline and 5 years later.
- Cases of ASCVD – defined as coronary artery disease (CAD), ischemic stroke, or acute complications – were identified via hospital records and death registry.
- Associations between stair climbing and ASCVD were examined as hazard ratios from Cox proportional hazards model. Analyses were stratified by susceptibility to ASCVD based on family history, genetic risk, and established risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 39,043 ASCVD, 30,718 CAD, and 10,521 ischemic stroke cases were recorded during a median follow-up of 12.5 years.
- Compared with no-stair climbing, climbing 6-10 flights of stairs daily was associated with a 7% lower ASCVD risk (multivariable-adjusted HR, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.96) and climbing 16-20 flights daily was associated with a 10% lower risk (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94).
- The benefits plateaued at 20 flights daily; comparable results were obtained for CAD and ischemic stroke; the protective effect of stair climbing was attenuated by increasing levels of disease susceptibility.
- Adults who stopped climbing stairs daily during the study had a 32% higher risk of ASCVD (HR, 1.32; 95% CI,1.06-1.65), compared with peers who never reported stair climbing.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings highlight the potential advantages of stair climbing as a primary preventive measure for ASCVD in the general population. Short bursts of high-intensity stair climbing are a time-efficient way to improve cardiorespiratory fitness and lipid profile, especially among those unable to achieve the current physical activity recommendations,” study author Lu Qi, with Tulane University, New Orleans, said in a news release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Atherosclerosis.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational design limits causal inferences. Stair climbing was self-reported via questionnaires and recall bias is a possibility. The UK Biobank participants do not represent the entire population of the country, with a healthy volunteer selection bias previously reported.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
new observational data suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- The prospective cohort study used data from 458,860 adults in the UK Biobank cohort who were 38-73 years old at baseline (2006-2010).
- Information about stair climbing, sociodemographic, and lifestyle factors was collected at baseline and 5 years later.
- Cases of ASCVD – defined as coronary artery disease (CAD), ischemic stroke, or acute complications – were identified via hospital records and death registry.
- Associations between stair climbing and ASCVD were examined as hazard ratios from Cox proportional hazards model. Analyses were stratified by susceptibility to ASCVD based on family history, genetic risk, and established risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 39,043 ASCVD, 30,718 CAD, and 10,521 ischemic stroke cases were recorded during a median follow-up of 12.5 years.
- Compared with no-stair climbing, climbing 6-10 flights of stairs daily was associated with a 7% lower ASCVD risk (multivariable-adjusted HR, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.96) and climbing 16-20 flights daily was associated with a 10% lower risk (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94).
- The benefits plateaued at 20 flights daily; comparable results were obtained for CAD and ischemic stroke; the protective effect of stair climbing was attenuated by increasing levels of disease susceptibility.
- Adults who stopped climbing stairs daily during the study had a 32% higher risk of ASCVD (HR, 1.32; 95% CI,1.06-1.65), compared with peers who never reported stair climbing.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings highlight the potential advantages of stair climbing as a primary preventive measure for ASCVD in the general population. Short bursts of high-intensity stair climbing are a time-efficient way to improve cardiorespiratory fitness and lipid profile, especially among those unable to achieve the current physical activity recommendations,” study author Lu Qi, with Tulane University, New Orleans, said in a news release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Atherosclerosis.
LIMITATIONS:
The observational design limits causal inferences. Stair climbing was self-reported via questionnaires and recall bias is a possibility. The UK Biobank participants do not represent the entire population of the country, with a healthy volunteer selection bias previously reported.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Diagnosis creep’: Are some AFib patients overtreated?
without those treatments having been validated in those particular groups.
This concern has been highlighted recently in the atrial fibrillation (AF) field, with the recent change in the definition of hypertension in the United States at lower levels of blood pressure causing a lot more patients to become eligible for oral anticoagulation at an earlier stage in their AF course.
U.S. researchers analyzed data from 316,388 patients with AF from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry Practice Innovation and Clinical Excellence outpatient quality improvement registry, and found that at 36 months’ follow-up, 83.5% of patients met the new 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension, while only 53.3% met the previous 140/90 mm Hg definition.
The diagnosis of hypertension gives 1 point in the CHA2DS2-VASc score, which is used to determine risk in AF patients, those with scores of 2 or more being eligible for oral anticoagulation.
The researchers report that in patients with an index CHA2DS2-VASc score of 1 (before the hypertension diagnosis), at 36 months, 83% fulfilled the 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension while the 140/90 mm Hg definition was met by only 50%, giving a large increase in the number of patients who could qualify for oral anticoagulation therapy.
“While the definition of hypertension has changed in response to landmark clinical trials, CHA2DS2-VASc was validated using an older hypertension definition, with limited ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and higher blood pressure goals for treatment,” the authors state.
“Now, patients with AF will meet the CHA2DS2-VASc threshold for oral anticoagulation earlier in their disease course. However, it is not known if patients with scores of 1 or 2 using the new hypertension definition have sufficient stroke risk to offset the bleeding risk of oral anticoagulation and will receive net clinical benefit,” they point out.
This study was published online as a research letter in JAMA Network Open.
Senior author of the report, Mintu Turakhia, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University/iRhythm Technologies Inc., said AF is a good example of how “diagnosis creep” may lead to patients receiving inappropriate treatment.
“Risk scores derived when risk variables were described in one way are starting to be applied based on a diagnosis made in a totally different way,” he said in an interview. “Diagnosis creep is a problem everywhere in medicine. The goal of this study was to quantify what this means for the new definition of hypertension in the context of risk scoring AF patients for anticoagulation treatment. We are calling attention to this issue so clinicians are aware of possible implications.”
Dr. Turakhia explained that the CHA2DS2-VASc score was formulated based on claims data so there was a record of hypertension on the clinical encounter. That hypertension diagnosis would have been based on the old definition of 140/90 mm Hg.
“But now we apply a label of hypertension in the office every time someone has a measurement of elevated blood pressure – treated or untreated – and the blood pressure threshold for a hypertension diagnosis has changed to 130/80 mm Hg,” he said. “We are asking what this means for risk stratification scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc, and how do we quantify what that means for anticoagulation eligibility?”
He said that while identifying hypertension at lower blood pressures may be beneficial with regard to starting antihypertensive treatment earlier with a consequent reduction in cardiovascular outcomes, when this also affects risk scores that determine treatment for other conditions, as is the case for AF, the case is not so clear.
Dr. Turakhia pointed out that with AF, there are additional factors causing diagnosis creep, including earlier detection of AF and identification of shorter episodes due to the use of higher sensitivity tools to detect abnormal rhythms.
“What about the patient who has been identified as having AF based on just a few seconds found on monitoring and who is aged 65 (so just over the age threshold for 1 point on the CHA2DS2-VASc score)?” he asked. “Now we’re going to throw in hypertension with a blood pressure measurement just over 130/80 mm Hg, and they will be eligible for anticoagulation.”
Dr. Turakhia noted that in addition to earlier classification of hypertension, other conditions contributing to the CHA2DS2-VASc score are also being detected earlier, including diabetes and reduced ejection fractions that are considered heart failure.
“I worry about the sum of the parts. We don’t know if the risk score performs equally well when we’re using these different thresholds. We have to be careful that we are not exposing patients to the bleeding risks of anticoagulation unnecessarily. There is a clear issue here,” he said.
What should clinicians do?
In a comment, Gregory Lip, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the University of Liverpool, England, who helped develop the CHA2DS2-VASc score, said clinicians needed to think more broadly when considering hypertension as a risk factor for the score.
He points out that if a patient had a history of hypertension but is now controlled to below 130/80 mm Hg, they would still be considered to be at risk per the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
And for patients without a history of hypertension, and who have a current blood pressure measurement of around 130/80 mm Hg, Dr. Lip advises that it would be premature to diagnose hypertension immediately.
“Hypertension is not a yes/no diagnosis. If you look at the relationship between blood pressure and risk of stroke, it is like a continual dose-response. It doesn’t mean that at 129/79 there is no stroke risk but that at 130/80 there is a stroke risk. It’s not like that,” he said.
“I wouldn’t make a diagnosis on a one-off blood pressure measurement. I would want to monitor that patient and get them to do home measurements,” he commented. “If someone constantly has levels around that 130/80 mm Hg, I don’t necessarily rush in with a definite diagnosis of hypertension and start drug treatment. I would look at lifestyle first. And in such patients, I wouldn’t give them the 1 point for hypertension on the CHA2DS2-VASc score.”
Dr. Lip points out that a hypertension diagnosis is not just about blood pressure numbers. “We have to assess the patients much more completely before giving them a diagnosis and consider factors such as whether there is evidence of hypertension-related end-organ damage, and if lifestyle issues have been addressed.”
Are new risk scores needed?
Dr. Turakhia agreed that clinicians need to look at the bigger picture, but he also suggested that new risk scores may need to be developed.
“All of us in the medical community need to think about whether we should be recalibrating risk prediction with more contemporary evidence – based on our ability to detect disease now,” he commented.
“This could even be a different risk score altogether, possibly incorporating a wider range of parameters or perhaps incorporating machine learning. That’s really the question we need to be asking ourselves,” Dr. Turakhia added.
Dr. Lip noted that there are many stroke risk factors and only those that are most common and have been well validated go into clinical risk scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc.
“These risks scores are by design simplifications, and only have modest predictive value for identifying patients at high risk of stroke. You can always improve on clinical risk scores by adding in other variables,” he said. “There are some risk scores in AF with 26 variables. But the practical application of these more complex scores can be difficult in clinical practice. These risks scores are meant to be simple so that they can be used by busy clinicians in the outpatient clinic or on a ward round. It is not easy to input 26 different variables.”
He also noted that many guidelines are now veering away from categorizing patients at high, medium, or low risk of stroke, which he refers to as “artificial” classifications. “There is now more of a default position that patients should receive stroke prevention normally with a DOAC [direct oral anticoagulant] unless they are low risk.”
Dr. Turakhia agreed that it is imperative to look at the bigger picture when identifying AF patients for anticoagulation. “We have to be careful not to take things at face value. It is more important than ever to use clinical judgment to avoid overtreatment in borderline situations,” he concluded.
This study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s National Cardiovascular Data Registry. Dr. Turakhia reported employment from iRhythm Technologies; equity from AliveCor, Connect America, Evidently, and Forward; grants from U.S. Food and Drug Administration, American Heart Association, Bayer, Sanofi, Gilead, and Bristol Myers Squibb; and personal fees from Pfizer and JAMA Cardiology (prior associate editor) outside the submitted work. Dr. Lip has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
without those treatments having been validated in those particular groups.
This concern has been highlighted recently in the atrial fibrillation (AF) field, with the recent change in the definition of hypertension in the United States at lower levels of blood pressure causing a lot more patients to become eligible for oral anticoagulation at an earlier stage in their AF course.
U.S. researchers analyzed data from 316,388 patients with AF from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry Practice Innovation and Clinical Excellence outpatient quality improvement registry, and found that at 36 months’ follow-up, 83.5% of patients met the new 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension, while only 53.3% met the previous 140/90 mm Hg definition.
The diagnosis of hypertension gives 1 point in the CHA2DS2-VASc score, which is used to determine risk in AF patients, those with scores of 2 or more being eligible for oral anticoagulation.
The researchers report that in patients with an index CHA2DS2-VASc score of 1 (before the hypertension diagnosis), at 36 months, 83% fulfilled the 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension while the 140/90 mm Hg definition was met by only 50%, giving a large increase in the number of patients who could qualify for oral anticoagulation therapy.
“While the definition of hypertension has changed in response to landmark clinical trials, CHA2DS2-VASc was validated using an older hypertension definition, with limited ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and higher blood pressure goals for treatment,” the authors state.
“Now, patients with AF will meet the CHA2DS2-VASc threshold for oral anticoagulation earlier in their disease course. However, it is not known if patients with scores of 1 or 2 using the new hypertension definition have sufficient stroke risk to offset the bleeding risk of oral anticoagulation and will receive net clinical benefit,” they point out.
This study was published online as a research letter in JAMA Network Open.
Senior author of the report, Mintu Turakhia, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University/iRhythm Technologies Inc., said AF is a good example of how “diagnosis creep” may lead to patients receiving inappropriate treatment.
“Risk scores derived when risk variables were described in one way are starting to be applied based on a diagnosis made in a totally different way,” he said in an interview. “Diagnosis creep is a problem everywhere in medicine. The goal of this study was to quantify what this means for the new definition of hypertension in the context of risk scoring AF patients for anticoagulation treatment. We are calling attention to this issue so clinicians are aware of possible implications.”
Dr. Turakhia explained that the CHA2DS2-VASc score was formulated based on claims data so there was a record of hypertension on the clinical encounter. That hypertension diagnosis would have been based on the old definition of 140/90 mm Hg.
“But now we apply a label of hypertension in the office every time someone has a measurement of elevated blood pressure – treated or untreated – and the blood pressure threshold for a hypertension diagnosis has changed to 130/80 mm Hg,” he said. “We are asking what this means for risk stratification scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc, and how do we quantify what that means for anticoagulation eligibility?”
He said that while identifying hypertension at lower blood pressures may be beneficial with regard to starting antihypertensive treatment earlier with a consequent reduction in cardiovascular outcomes, when this also affects risk scores that determine treatment for other conditions, as is the case for AF, the case is not so clear.
Dr. Turakhia pointed out that with AF, there are additional factors causing diagnosis creep, including earlier detection of AF and identification of shorter episodes due to the use of higher sensitivity tools to detect abnormal rhythms.
“What about the patient who has been identified as having AF based on just a few seconds found on monitoring and who is aged 65 (so just over the age threshold for 1 point on the CHA2DS2-VASc score)?” he asked. “Now we’re going to throw in hypertension with a blood pressure measurement just over 130/80 mm Hg, and they will be eligible for anticoagulation.”
Dr. Turakhia noted that in addition to earlier classification of hypertension, other conditions contributing to the CHA2DS2-VASc score are also being detected earlier, including diabetes and reduced ejection fractions that are considered heart failure.
“I worry about the sum of the parts. We don’t know if the risk score performs equally well when we’re using these different thresholds. We have to be careful that we are not exposing patients to the bleeding risks of anticoagulation unnecessarily. There is a clear issue here,” he said.
What should clinicians do?
In a comment, Gregory Lip, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the University of Liverpool, England, who helped develop the CHA2DS2-VASc score, said clinicians needed to think more broadly when considering hypertension as a risk factor for the score.
He points out that if a patient had a history of hypertension but is now controlled to below 130/80 mm Hg, they would still be considered to be at risk per the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
And for patients without a history of hypertension, and who have a current blood pressure measurement of around 130/80 mm Hg, Dr. Lip advises that it would be premature to diagnose hypertension immediately.
“Hypertension is not a yes/no diagnosis. If you look at the relationship between blood pressure and risk of stroke, it is like a continual dose-response. It doesn’t mean that at 129/79 there is no stroke risk but that at 130/80 there is a stroke risk. It’s not like that,” he said.
“I wouldn’t make a diagnosis on a one-off blood pressure measurement. I would want to monitor that patient and get them to do home measurements,” he commented. “If someone constantly has levels around that 130/80 mm Hg, I don’t necessarily rush in with a definite diagnosis of hypertension and start drug treatment. I would look at lifestyle first. And in such patients, I wouldn’t give them the 1 point for hypertension on the CHA2DS2-VASc score.”
Dr. Lip points out that a hypertension diagnosis is not just about blood pressure numbers. “We have to assess the patients much more completely before giving them a diagnosis and consider factors such as whether there is evidence of hypertension-related end-organ damage, and if lifestyle issues have been addressed.”
Are new risk scores needed?
Dr. Turakhia agreed that clinicians need to look at the bigger picture, but he also suggested that new risk scores may need to be developed.
“All of us in the medical community need to think about whether we should be recalibrating risk prediction with more contemporary evidence – based on our ability to detect disease now,” he commented.
“This could even be a different risk score altogether, possibly incorporating a wider range of parameters or perhaps incorporating machine learning. That’s really the question we need to be asking ourselves,” Dr. Turakhia added.
Dr. Lip noted that there are many stroke risk factors and only those that are most common and have been well validated go into clinical risk scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc.
“These risks scores are by design simplifications, and only have modest predictive value for identifying patients at high risk of stroke. You can always improve on clinical risk scores by adding in other variables,” he said. “There are some risk scores in AF with 26 variables. But the practical application of these more complex scores can be difficult in clinical practice. These risks scores are meant to be simple so that they can be used by busy clinicians in the outpatient clinic or on a ward round. It is not easy to input 26 different variables.”
He also noted that many guidelines are now veering away from categorizing patients at high, medium, or low risk of stroke, which he refers to as “artificial” classifications. “There is now more of a default position that patients should receive stroke prevention normally with a DOAC [direct oral anticoagulant] unless they are low risk.”
Dr. Turakhia agreed that it is imperative to look at the bigger picture when identifying AF patients for anticoagulation. “We have to be careful not to take things at face value. It is more important than ever to use clinical judgment to avoid overtreatment in borderline situations,” he concluded.
This study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s National Cardiovascular Data Registry. Dr. Turakhia reported employment from iRhythm Technologies; equity from AliveCor, Connect America, Evidently, and Forward; grants from U.S. Food and Drug Administration, American Heart Association, Bayer, Sanofi, Gilead, and Bristol Myers Squibb; and personal fees from Pfizer and JAMA Cardiology (prior associate editor) outside the submitted work. Dr. Lip has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
without those treatments having been validated in those particular groups.
This concern has been highlighted recently in the atrial fibrillation (AF) field, with the recent change in the definition of hypertension in the United States at lower levels of blood pressure causing a lot more patients to become eligible for oral anticoagulation at an earlier stage in their AF course.
U.S. researchers analyzed data from 316,388 patients with AF from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry Practice Innovation and Clinical Excellence outpatient quality improvement registry, and found that at 36 months’ follow-up, 83.5% of patients met the new 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension, while only 53.3% met the previous 140/90 mm Hg definition.
The diagnosis of hypertension gives 1 point in the CHA2DS2-VASc score, which is used to determine risk in AF patients, those with scores of 2 or more being eligible for oral anticoagulation.
The researchers report that in patients with an index CHA2DS2-VASc score of 1 (before the hypertension diagnosis), at 36 months, 83% fulfilled the 130/80 mm Hg definition of hypertension while the 140/90 mm Hg definition was met by only 50%, giving a large increase in the number of patients who could qualify for oral anticoagulation therapy.
“While the definition of hypertension has changed in response to landmark clinical trials, CHA2DS2-VASc was validated using an older hypertension definition, with limited ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and higher blood pressure goals for treatment,” the authors state.
“Now, patients with AF will meet the CHA2DS2-VASc threshold for oral anticoagulation earlier in their disease course. However, it is not known if patients with scores of 1 or 2 using the new hypertension definition have sufficient stroke risk to offset the bleeding risk of oral anticoagulation and will receive net clinical benefit,” they point out.
This study was published online as a research letter in JAMA Network Open.
Senior author of the report, Mintu Turakhia, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University/iRhythm Technologies Inc., said AF is a good example of how “diagnosis creep” may lead to patients receiving inappropriate treatment.
“Risk scores derived when risk variables were described in one way are starting to be applied based on a diagnosis made in a totally different way,” he said in an interview. “Diagnosis creep is a problem everywhere in medicine. The goal of this study was to quantify what this means for the new definition of hypertension in the context of risk scoring AF patients for anticoagulation treatment. We are calling attention to this issue so clinicians are aware of possible implications.”
Dr. Turakhia explained that the CHA2DS2-VASc score was formulated based on claims data so there was a record of hypertension on the clinical encounter. That hypertension diagnosis would have been based on the old definition of 140/90 mm Hg.
“But now we apply a label of hypertension in the office every time someone has a measurement of elevated blood pressure – treated or untreated – and the blood pressure threshold for a hypertension diagnosis has changed to 130/80 mm Hg,” he said. “We are asking what this means for risk stratification scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc, and how do we quantify what that means for anticoagulation eligibility?”
He said that while identifying hypertension at lower blood pressures may be beneficial with regard to starting antihypertensive treatment earlier with a consequent reduction in cardiovascular outcomes, when this also affects risk scores that determine treatment for other conditions, as is the case for AF, the case is not so clear.
Dr. Turakhia pointed out that with AF, there are additional factors causing diagnosis creep, including earlier detection of AF and identification of shorter episodes due to the use of higher sensitivity tools to detect abnormal rhythms.
“What about the patient who has been identified as having AF based on just a few seconds found on monitoring and who is aged 65 (so just over the age threshold for 1 point on the CHA2DS2-VASc score)?” he asked. “Now we’re going to throw in hypertension with a blood pressure measurement just over 130/80 mm Hg, and they will be eligible for anticoagulation.”
Dr. Turakhia noted that in addition to earlier classification of hypertension, other conditions contributing to the CHA2DS2-VASc score are also being detected earlier, including diabetes and reduced ejection fractions that are considered heart failure.
“I worry about the sum of the parts. We don’t know if the risk score performs equally well when we’re using these different thresholds. We have to be careful that we are not exposing patients to the bleeding risks of anticoagulation unnecessarily. There is a clear issue here,” he said.
What should clinicians do?
In a comment, Gregory Lip, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the University of Liverpool, England, who helped develop the CHA2DS2-VASc score, said clinicians needed to think more broadly when considering hypertension as a risk factor for the score.
He points out that if a patient had a history of hypertension but is now controlled to below 130/80 mm Hg, they would still be considered to be at risk per the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
And for patients without a history of hypertension, and who have a current blood pressure measurement of around 130/80 mm Hg, Dr. Lip advises that it would be premature to diagnose hypertension immediately.
“Hypertension is not a yes/no diagnosis. If you look at the relationship between blood pressure and risk of stroke, it is like a continual dose-response. It doesn’t mean that at 129/79 there is no stroke risk but that at 130/80 there is a stroke risk. It’s not like that,” he said.
“I wouldn’t make a diagnosis on a one-off blood pressure measurement. I would want to monitor that patient and get them to do home measurements,” he commented. “If someone constantly has levels around that 130/80 mm Hg, I don’t necessarily rush in with a definite diagnosis of hypertension and start drug treatment. I would look at lifestyle first. And in such patients, I wouldn’t give them the 1 point for hypertension on the CHA2DS2-VASc score.”
Dr. Lip points out that a hypertension diagnosis is not just about blood pressure numbers. “We have to assess the patients much more completely before giving them a diagnosis and consider factors such as whether there is evidence of hypertension-related end-organ damage, and if lifestyle issues have been addressed.”
Are new risk scores needed?
Dr. Turakhia agreed that clinicians need to look at the bigger picture, but he also suggested that new risk scores may need to be developed.
“All of us in the medical community need to think about whether we should be recalibrating risk prediction with more contemporary evidence – based on our ability to detect disease now,” he commented.
“This could even be a different risk score altogether, possibly incorporating a wider range of parameters or perhaps incorporating machine learning. That’s really the question we need to be asking ourselves,” Dr. Turakhia added.
Dr. Lip noted that there are many stroke risk factors and only those that are most common and have been well validated go into clinical risk scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc.
“These risks scores are by design simplifications, and only have modest predictive value for identifying patients at high risk of stroke. You can always improve on clinical risk scores by adding in other variables,” he said. “There are some risk scores in AF with 26 variables. But the practical application of these more complex scores can be difficult in clinical practice. These risks scores are meant to be simple so that they can be used by busy clinicians in the outpatient clinic or on a ward round. It is not easy to input 26 different variables.”
He also noted that many guidelines are now veering away from categorizing patients at high, medium, or low risk of stroke, which he refers to as “artificial” classifications. “There is now more of a default position that patients should receive stroke prevention normally with a DOAC [direct oral anticoagulant] unless they are low risk.”
Dr. Turakhia agreed that it is imperative to look at the bigger picture when identifying AF patients for anticoagulation. “We have to be careful not to take things at face value. It is more important than ever to use clinical judgment to avoid overtreatment in borderline situations,” he concluded.
This study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s National Cardiovascular Data Registry. Dr. Turakhia reported employment from iRhythm Technologies; equity from AliveCor, Connect America, Evidently, and Forward; grants from U.S. Food and Drug Administration, American Heart Association, Bayer, Sanofi, Gilead, and Bristol Myers Squibb; and personal fees from Pfizer and JAMA Cardiology (prior associate editor) outside the submitted work. Dr. Lip has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
CKD linked to cardiac arrest in Hispanic, Latinx patients
TOPLINE:
new data show, suggesting early identification of CKD may provide an opportunity to reduce the risk in these groups. Other predictors included heavy drinking, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, heart failure and diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 295 Hispanic or Latinx patients with out-of-hospital SCA from the PRESTO study in Ventura County, California, and 590 frequency-matched controls from the San Diego site of the population-based HCHS/SOL (Hispanic Community Health Survey/Study of Latinos); in both cohorts, men made up 70% of participants, and the median age was about 63 years.
- Researchers collected data on demographics, medical history, and current health conditions. Of note, 51.2% of SCA cases and 8.8% of control participants had CKD, and 20.0% of cases and 0.7% of the control group were on dialysis.
- Pre-SCA echocardiograms were available for 48% of SCA cases and baseline echocardiograms for more than 99% of control participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- In analyses adjusted for age, sex, and clinical variables, predictors significantly associated with higher odds of SCA included: CKD (odds ratio, 7.3; 95% confidence interval, 3.8-14.3; P < .001), heavy drinking (OR, 4.5), stroke (OR, 3.1), atrial fibrillation (OR, 3.7), coronary artery disease (OR, 2.9), heart failure (OR, 2.5), and diabetes (OR, 1.5).
- Hypertension, hyperlipemia, body mass index, and current smoking status were not significantly associated with SCA.
- In adjusted analyses, heart rate (OR, 1.8 per one standard deviation [1-SD] increase), QTc interval (OR, 2.5 per 1-SD increase) and left ventricular ejection fraction (OR, 4.4 per 1-SD decrease) were significantly associated with SCA, suggesting echocardiogram evaluations could help identify Hispanic or Latinx individuals at increased risk for SCA, wrote the authors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study, the first to include feasible numbers of Hispanic or Latino individuals, highlights the importance of renal dysfunction as a risk factor for SCA in the community,” the authors wrote, adding that early identification and management of chronic kidney disease could reduce risk for SCA in this population.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Kyndaron Reinier, PhD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Health System, Los Angeles, and colleagues. It was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
LIMITATIONS:
Most participants from the HCHS/SOL study were born outside the United States, compared with about half the SCA cases, which could have influenced cardiovascular disease risk, although results did not change considerably when models were adjusted for place of birth. Study participants were predominantly of Mexican heritage, so results may not be generalizable to Hispanic or Latinx individuals from other regions. As medical history was assessed differently in the two studies, there could be some error in estimating the strength of associations. Results from echocardiographic data should be viewed as hypothesis generating because of the potential for residual bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The Ventura PRESTO study was funded, in part, by the National Institutes of Health, and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The HCHS/SOL was carried out as a collaborative study supported by contracts from the NHLBI.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
new data show, suggesting early identification of CKD may provide an opportunity to reduce the risk in these groups. Other predictors included heavy drinking, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, heart failure and diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 295 Hispanic or Latinx patients with out-of-hospital SCA from the PRESTO study in Ventura County, California, and 590 frequency-matched controls from the San Diego site of the population-based HCHS/SOL (Hispanic Community Health Survey/Study of Latinos); in both cohorts, men made up 70% of participants, and the median age was about 63 years.
- Researchers collected data on demographics, medical history, and current health conditions. Of note, 51.2% of SCA cases and 8.8% of control participants had CKD, and 20.0% of cases and 0.7% of the control group were on dialysis.
- Pre-SCA echocardiograms were available for 48% of SCA cases and baseline echocardiograms for more than 99% of control participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- In analyses adjusted for age, sex, and clinical variables, predictors significantly associated with higher odds of SCA included: CKD (odds ratio, 7.3; 95% confidence interval, 3.8-14.3; P < .001), heavy drinking (OR, 4.5), stroke (OR, 3.1), atrial fibrillation (OR, 3.7), coronary artery disease (OR, 2.9), heart failure (OR, 2.5), and diabetes (OR, 1.5).
- Hypertension, hyperlipemia, body mass index, and current smoking status were not significantly associated with SCA.
- In adjusted analyses, heart rate (OR, 1.8 per one standard deviation [1-SD] increase), QTc interval (OR, 2.5 per 1-SD increase) and left ventricular ejection fraction (OR, 4.4 per 1-SD decrease) were significantly associated with SCA, suggesting echocardiogram evaluations could help identify Hispanic or Latinx individuals at increased risk for SCA, wrote the authors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study, the first to include feasible numbers of Hispanic or Latino individuals, highlights the importance of renal dysfunction as a risk factor for SCA in the community,” the authors wrote, adding that early identification and management of chronic kidney disease could reduce risk for SCA in this population.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Kyndaron Reinier, PhD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Health System, Los Angeles, and colleagues. It was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
LIMITATIONS:
Most participants from the HCHS/SOL study were born outside the United States, compared with about half the SCA cases, which could have influenced cardiovascular disease risk, although results did not change considerably when models were adjusted for place of birth. Study participants were predominantly of Mexican heritage, so results may not be generalizable to Hispanic or Latinx individuals from other regions. As medical history was assessed differently in the two studies, there could be some error in estimating the strength of associations. Results from echocardiographic data should be viewed as hypothesis generating because of the potential for residual bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The Ventura PRESTO study was funded, in part, by the National Institutes of Health, and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The HCHS/SOL was carried out as a collaborative study supported by contracts from the NHLBI.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
new data show, suggesting early identification of CKD may provide an opportunity to reduce the risk in these groups. Other predictors included heavy drinking, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, heart failure and diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 295 Hispanic or Latinx patients with out-of-hospital SCA from the PRESTO study in Ventura County, California, and 590 frequency-matched controls from the San Diego site of the population-based HCHS/SOL (Hispanic Community Health Survey/Study of Latinos); in both cohorts, men made up 70% of participants, and the median age was about 63 years.
- Researchers collected data on demographics, medical history, and current health conditions. Of note, 51.2% of SCA cases and 8.8% of control participants had CKD, and 20.0% of cases and 0.7% of the control group were on dialysis.
- Pre-SCA echocardiograms were available for 48% of SCA cases and baseline echocardiograms for more than 99% of control participants.
TAKEAWAY:
- In analyses adjusted for age, sex, and clinical variables, predictors significantly associated with higher odds of SCA included: CKD (odds ratio, 7.3; 95% confidence interval, 3.8-14.3; P < .001), heavy drinking (OR, 4.5), stroke (OR, 3.1), atrial fibrillation (OR, 3.7), coronary artery disease (OR, 2.9), heart failure (OR, 2.5), and diabetes (OR, 1.5).
- Hypertension, hyperlipemia, body mass index, and current smoking status were not significantly associated with SCA.
- In adjusted analyses, heart rate (OR, 1.8 per one standard deviation [1-SD] increase), QTc interval (OR, 2.5 per 1-SD increase) and left ventricular ejection fraction (OR, 4.4 per 1-SD decrease) were significantly associated with SCA, suggesting echocardiogram evaluations could help identify Hispanic or Latinx individuals at increased risk for SCA, wrote the authors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study, the first to include feasible numbers of Hispanic or Latino individuals, highlights the importance of renal dysfunction as a risk factor for SCA in the community,” the authors wrote, adding that early identification and management of chronic kidney disease could reduce risk for SCA in this population.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Kyndaron Reinier, PhD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Health System, Los Angeles, and colleagues. It was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
LIMITATIONS:
Most participants from the HCHS/SOL study were born outside the United States, compared with about half the SCA cases, which could have influenced cardiovascular disease risk, although results did not change considerably when models were adjusted for place of birth. Study participants were predominantly of Mexican heritage, so results may not be generalizable to Hispanic or Latinx individuals from other regions. As medical history was assessed differently in the two studies, there could be some error in estimating the strength of associations. Results from echocardiographic data should be viewed as hypothesis generating because of the potential for residual bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The Ventura PRESTO study was funded, in part, by the National Institutes of Health, and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The HCHS/SOL was carried out as a collaborative study supported by contracts from the NHLBI.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
EMA warns that omega-3-acid ethyl esters may cause AFib
In its September meeting, the Should atrial fibrillation develop, intake of the medication must be stopped permanently.
Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are used to treat hypertriglyceridemia if lifestyle changes, particularly those related to nutrition, have not been sufficient to lower the blood triglyceride level. Hypertriglyceridemia is a risk factor for coronary heart disease.
During a Periodic Safety Update Single Assessment Procedure, the EMA safety committee analyzed systematic overviews and meta-analyses of randomized, controlled clinical studies. Experts found a dose-dependent increase in the risk for atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiovascular diseases or cardiovascular risk factors who were being treated with omega-3-acid ethyl esters, compared with those treated with placebo. The observed risk was at its highest at a dose of 4 g/d.
The PRAC will recommend an update to the Summary of Product Characteristics for preparations that contain omega-3-acid ethyl esters. The aim is to inform physicians, pharmacists, and patients of the risk for atrial fibrillation. A notification will be sent to health care professionals soon to inform them of further details.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In its September meeting, the Should atrial fibrillation develop, intake of the medication must be stopped permanently.
Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are used to treat hypertriglyceridemia if lifestyle changes, particularly those related to nutrition, have not been sufficient to lower the blood triglyceride level. Hypertriglyceridemia is a risk factor for coronary heart disease.
During a Periodic Safety Update Single Assessment Procedure, the EMA safety committee analyzed systematic overviews and meta-analyses of randomized, controlled clinical studies. Experts found a dose-dependent increase in the risk for atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiovascular diseases or cardiovascular risk factors who were being treated with omega-3-acid ethyl esters, compared with those treated with placebo. The observed risk was at its highest at a dose of 4 g/d.
The PRAC will recommend an update to the Summary of Product Characteristics for preparations that contain omega-3-acid ethyl esters. The aim is to inform physicians, pharmacists, and patients of the risk for atrial fibrillation. A notification will be sent to health care professionals soon to inform them of further details.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In its September meeting, the Should atrial fibrillation develop, intake of the medication must be stopped permanently.
Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are used to treat hypertriglyceridemia if lifestyle changes, particularly those related to nutrition, have not been sufficient to lower the blood triglyceride level. Hypertriglyceridemia is a risk factor for coronary heart disease.
During a Periodic Safety Update Single Assessment Procedure, the EMA safety committee analyzed systematic overviews and meta-analyses of randomized, controlled clinical studies. Experts found a dose-dependent increase in the risk for atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiovascular diseases or cardiovascular risk factors who were being treated with omega-3-acid ethyl esters, compared with those treated with placebo. The observed risk was at its highest at a dose of 4 g/d.
The PRAC will recommend an update to the Summary of Product Characteristics for preparations that contain omega-3-acid ethyl esters. The aim is to inform physicians, pharmacists, and patients of the risk for atrial fibrillation. A notification will be sent to health care professionals soon to inform them of further details.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
High and low HDL cholesterol levels linked to dementia risk
TOPLINE:
High and low levels of HDL cholesterol but not levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk for dementia in older adults, a new study found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Electronic health record and survey data on 184,367 Kaiser Permanente Northern California participants (median age, 69.5 years) with no history of dementia were taken.
- Cholesterol levels were measured within 2 years of survey completion.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 25,214 incident cases of dementia reported over an average follow-up of 8.77 years.
- Dementia risk was significantly higher in people with low HDL cholesterol (11-41 mg/dL; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.07; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.11) and high HDL cholesterol (> 65 mg/dL; aHR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.11-1.20).
- The study demonstrates an association between low and high levels of “good” cholesterol but not a causal link.
- There was no significant association between LDL cholesterol and dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the conclusion that some lipoproteins may be modifiable risk factors for dementia, even in late life,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Erin L. Ferguson, MPH, department of epidemiology & biostatistics, University of California, San Francisco, and was funded by the National Institutes of Health. It was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
There were no adjustments for apo E status and confounding and selection bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
High and low levels of HDL cholesterol but not levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk for dementia in older adults, a new study found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Electronic health record and survey data on 184,367 Kaiser Permanente Northern California participants (median age, 69.5 years) with no history of dementia were taken.
- Cholesterol levels were measured within 2 years of survey completion.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 25,214 incident cases of dementia reported over an average follow-up of 8.77 years.
- Dementia risk was significantly higher in people with low HDL cholesterol (11-41 mg/dL; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.07; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.11) and high HDL cholesterol (> 65 mg/dL; aHR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.11-1.20).
- The study demonstrates an association between low and high levels of “good” cholesterol but not a causal link.
- There was no significant association between LDL cholesterol and dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the conclusion that some lipoproteins may be modifiable risk factors for dementia, even in late life,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Erin L. Ferguson, MPH, department of epidemiology & biostatistics, University of California, San Francisco, and was funded by the National Institutes of Health. It was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
There were no adjustments for apo E status and confounding and selection bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
High and low levels of HDL cholesterol but not levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk for dementia in older adults, a new study found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Electronic health record and survey data on 184,367 Kaiser Permanente Northern California participants (median age, 69.5 years) with no history of dementia were taken.
- Cholesterol levels were measured within 2 years of survey completion.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 25,214 incident cases of dementia reported over an average follow-up of 8.77 years.
- Dementia risk was significantly higher in people with low HDL cholesterol (11-41 mg/dL; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.07; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.11) and high HDL cholesterol (> 65 mg/dL; aHR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.11-1.20).
- The study demonstrates an association between low and high levels of “good” cholesterol but not a causal link.
- There was no significant association between LDL cholesterol and dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the conclusion that some lipoproteins may be modifiable risk factors for dementia, even in late life,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Erin L. Ferguson, MPH, department of epidemiology & biostatistics, University of California, San Francisco, and was funded by the National Institutes of Health. It was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
There were no adjustments for apo E status and confounding and selection bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pragmatic solutions to ‘catastrophic’ global stroke burden
Deaths and disability because of stroke are expected to rise alarmingly over the next 30 years, with almost 10 million stroke deaths forecast annually by 2050, according to a new report from the World Stroke Organization–Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group.
“This highlights the need for urgent measures to reduce stroke burden worldwide, with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries,” the report authors stated.
These measures include an increase in trained health care workers who can implement effective primary prevention strategies, including the early detection and adequate management of hypertension.
On the basis of a review of evidence-based guidelines, recent surveys, and in-depth interviews with stroke experts around the world, the WSO–Lancet Neurology Commission made evidence-based pragmatic recommendations to reduce the global burden of stroke, including measures to improve surveillance, prevention, acute care, and rehabilitation.
The report was announced on Oct. 10 by WSO President, Sheila Martins, MD, at the World Stroke Conference in Toronto. The report was also published online in The Lancet Neurology.
“Stroke care has changed a lot in the last few years,” said Dr. Martins, who is chief of neurology and neurosurgery at Hospital Moinhos de Vento, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and founder and president of the Brazilian Stroke Network. “We know what we need to do to reduce the global burden of stroke, and high-income countries are making progress in that regard. But the situation in low- and middle-income countries is catastrophic, with mortality rates of up to 80% in individuals who have had a stroke in some countries. There is a very large gap between knowledge and implementation.”
Dr. Martins said that the commission is offering potential innovative suggestions on how to change this reality.
“While we have the knowledge on the strategies needed to reduce stroke burden, the mechanisms needed to implement this knowledge will be different in different countries and cultures. Our commission includes several representatives from low- and middle-income countries, and we will be working with local stakeholders in these countries to try and implement our recommendations,” Dr. Martins explained.
Stroke mortality and disability is on the rise
In the report, the authors pointed out that the global burden of stroke is “huge.” In 2020, stroke was the second leading cause of death (6.6 million deaths) and the third leading cause of disability – responsible for 143 million disability-adjusted life-years – after neonatal disorders and ischemic heart disease. Stroke is also a leading cause of depression and dementia.
The absolute number of people affected by stroke, which includes those who die or remain disabled, has almost doubled in the past 30 years, the report authors noted. Most of the contemporary stroke burden is in low- and middle-income countries, and the burden of disability after a stroke is increasing at a faster pace in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries. Alarmingly, the incidence of stroke is increasing in young and middle-aged people globally.
The commission forecasts the burden of stroke from 2020 to 2050, with projections estimating that stroke mortality will increase by 50% to 9.7 million and disability-adjusted life-years growing to over 189.3 million by 2050.
“Stroke exerts an enormous toll on the world’s population, leading to the death and permanent disability of millions of people each year, and costing billions of dollars,” said Valery L. Feigin, MD, of Auckland (New Zealand) University of Technology, and commission cochair. “Precisely forecasting the health and economic impacts of stroke decades into the future is inherently challenging given the levels of uncertainty involved, but these estimates are indicative of the ever-increasing burden we will see in the years ahead unless urgent, effective action is taken.”
The report authors explained that multiple factors contribute to the high burden of stroke in low- and middle-income countries, including undetected and uncontrolled hypertension; lack of easily accessible, high-quality health services; insufficient attention to and investment in prevention, air pollution; population growth; unhealthy lifestyles (for example, poor diet, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, obesity); an earlier age of stroke onset and greater proportion of hemorrhagic strokes than in high-income countries; and the burden of infectious diseases resulting in competition for limited health care resources.
The enormous financial cost of stroke
The total cost of stroke (both direct treatment and rehabilitation costs and indirect costs due to loss of income) is estimated to rise from $891 billion per year in 2017 to as much as $2.31 trillion by 2050. “These substantial increases in the costs associated with stroke will cause distressing financial circumstances for many communities and national health systems,” the authors said.
However, this increase can be avoided because stroke is highly preventable and treatable, they stressed. “These unsustainable trends in burden and costs of stroke underline the importance of identifying interventions to prevent and manage stroke more effectively.”
The Commission pointed out that population-wide primary prevention across the lifespan is extremely cost effective. It has been estimated that for every $1 spent on the prevention of stroke and cardiovascular disease, there is a more than $10 return on investment.
Additionally, primary prevention efforts directed at stroke would probably yield large gains because of the secondary effects of reducing the risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, dementia, and some types of cancer that share common risk factors, the authors noted.
“One of the most common problems in implementing stroke prevention and care recommendations is the lack of funding. Our commission recommends introducing legislative regulations and taxations of unhealthy products (such as salt, alcohol, sugary drinks, trans fats) by each and every government in the world,” Dr. Feigin said.
“Such taxation would not only reduce consumption of these products – and therefore lead to the reduction of burden from stroke and major other noncommunicable diseases – but also generate a large revenue sufficient to fund not only prevention programs and services for stroke and other major disorders, but also reduce poverty, inequality in health service provision, and improve wellbeing of the population,” he added.
Recommendations
The commission authors made the following recommendations for key priorities to reduce the burden of stroke:
Surveillance and prevention
- Incorporate stroke events and risk factor surveillance into national stroke action plans.
- Establish a system for population-wide primary and secondary stroke prevention, with emphasis on lifestyle modification for people at any level of risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
- Primary and secondary stroke prevention services should be freely accessible and supported by universal health coverage, with access to affordable drugs for management of hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and clotting disorders.
- Governments must allocate a fixed proportion of their annual health care funding for prevention of stroke and related noncommunicable diseases. This funding could come from taxation of tobacco, salt, alcohol, and sugar.
- Raise public awareness and take action to encourage a healthy lifestyle and prevent stroke via population-wide deployment of digital technologies with simple, inexpensive screening for cardiovascular disease and modifiable risk factors.
- Establish protocol-based shifting of tasks from highly trained health care professionals to supervised paramedical health care workers, to facilitate population-wide primary stroke prevention interventions across rural and urban settings.
Acute care
- Prioritize effective planning of acute stroke care services; capacity building, training, and certification of a multidisciplinary workforce; provision of evidence-based equipment and affordable medicines; and adequate resource allocation at national and regional levels.
- Establish regional networks and protocol-driven services, including community-wide awareness campaigns for early recognition of a stroke, regionally coordinated prehospital services, telemedicine networks, and stroke centers that can triage and treat all cases of acute stroke, and facilitate timely access to reperfusion therapy.
- Integrate acute care networks into the four pillars of the stroke “quadrangle” of resources, including surveillance, prevention, and rehabilitation services, by involving all relevant stakeholders (that is, communities, policy makers, nongovernmental organizations, national and regional stroke organizations, and public and private health care providers) in the stroke care continuum.
Rehabilitation
- Establish multidisciplinary rehabilitation services and adapt evidence-based recommendations to the local context, including the training, support, and supervision of community health care workers and caregivers to assist in long-term care.
- Invest in research to generate innovative low-cost interventions, in public awareness to improve demand for rehabilitation services, and in advocacy to mobilize resources for multidisciplinary rehabilitation.
- Promote the training of stroke rehabilitation professionals. Use digital portals to improve training and to extend the use of assessment tools – such as the Modified Rankin Scale and the U.S. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale – and quality of life measures to assess functional impairment and monitor recovery.
The commission concluded that, “overall, if the recommendations of this Commission are implemented, the burden of stroke will be reduced substantially ... which will improve brain health and overall wellbeing worldwide.”
Dr. Martins said that the WSO is committed to supporting and accelerating the implementation of these recommendations globally through the WSO Implementation Task Force, with stroke experts to advise the establishment of stroke prevention and care and to contribute with educational programs, and through Global Stroke Alliance meetings facilitating the discussions between stroke experts and policy makers, giving technical support to governments to elaborate national plans for stroke and to include stroke care in universal health coverage packages.
The Commission received funding from the WSO, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Health Research Council of New Zealand, and National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia and was supported by the NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Deaths and disability because of stroke are expected to rise alarmingly over the next 30 years, with almost 10 million stroke deaths forecast annually by 2050, according to a new report from the World Stroke Organization–Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group.
“This highlights the need for urgent measures to reduce stroke burden worldwide, with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries,” the report authors stated.
These measures include an increase in trained health care workers who can implement effective primary prevention strategies, including the early detection and adequate management of hypertension.
On the basis of a review of evidence-based guidelines, recent surveys, and in-depth interviews with stroke experts around the world, the WSO–Lancet Neurology Commission made evidence-based pragmatic recommendations to reduce the global burden of stroke, including measures to improve surveillance, prevention, acute care, and rehabilitation.
The report was announced on Oct. 10 by WSO President, Sheila Martins, MD, at the World Stroke Conference in Toronto. The report was also published online in The Lancet Neurology.
“Stroke care has changed a lot in the last few years,” said Dr. Martins, who is chief of neurology and neurosurgery at Hospital Moinhos de Vento, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and founder and president of the Brazilian Stroke Network. “We know what we need to do to reduce the global burden of stroke, and high-income countries are making progress in that regard. But the situation in low- and middle-income countries is catastrophic, with mortality rates of up to 80% in individuals who have had a stroke in some countries. There is a very large gap between knowledge and implementation.”
Dr. Martins said that the commission is offering potential innovative suggestions on how to change this reality.
“While we have the knowledge on the strategies needed to reduce stroke burden, the mechanisms needed to implement this knowledge will be different in different countries and cultures. Our commission includes several representatives from low- and middle-income countries, and we will be working with local stakeholders in these countries to try and implement our recommendations,” Dr. Martins explained.
Stroke mortality and disability is on the rise
In the report, the authors pointed out that the global burden of stroke is “huge.” In 2020, stroke was the second leading cause of death (6.6 million deaths) and the third leading cause of disability – responsible for 143 million disability-adjusted life-years – after neonatal disorders and ischemic heart disease. Stroke is also a leading cause of depression and dementia.
The absolute number of people affected by stroke, which includes those who die or remain disabled, has almost doubled in the past 30 years, the report authors noted. Most of the contemporary stroke burden is in low- and middle-income countries, and the burden of disability after a stroke is increasing at a faster pace in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries. Alarmingly, the incidence of stroke is increasing in young and middle-aged people globally.
The commission forecasts the burden of stroke from 2020 to 2050, with projections estimating that stroke mortality will increase by 50% to 9.7 million and disability-adjusted life-years growing to over 189.3 million by 2050.
“Stroke exerts an enormous toll on the world’s population, leading to the death and permanent disability of millions of people each year, and costing billions of dollars,” said Valery L. Feigin, MD, of Auckland (New Zealand) University of Technology, and commission cochair. “Precisely forecasting the health and economic impacts of stroke decades into the future is inherently challenging given the levels of uncertainty involved, but these estimates are indicative of the ever-increasing burden we will see in the years ahead unless urgent, effective action is taken.”
The report authors explained that multiple factors contribute to the high burden of stroke in low- and middle-income countries, including undetected and uncontrolled hypertension; lack of easily accessible, high-quality health services; insufficient attention to and investment in prevention, air pollution; population growth; unhealthy lifestyles (for example, poor diet, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, obesity); an earlier age of stroke onset and greater proportion of hemorrhagic strokes than in high-income countries; and the burden of infectious diseases resulting in competition for limited health care resources.
The enormous financial cost of stroke
The total cost of stroke (both direct treatment and rehabilitation costs and indirect costs due to loss of income) is estimated to rise from $891 billion per year in 2017 to as much as $2.31 trillion by 2050. “These substantial increases in the costs associated with stroke will cause distressing financial circumstances for many communities and national health systems,” the authors said.
However, this increase can be avoided because stroke is highly preventable and treatable, they stressed. “These unsustainable trends in burden and costs of stroke underline the importance of identifying interventions to prevent and manage stroke more effectively.”
The Commission pointed out that population-wide primary prevention across the lifespan is extremely cost effective. It has been estimated that for every $1 spent on the prevention of stroke and cardiovascular disease, there is a more than $10 return on investment.
Additionally, primary prevention efforts directed at stroke would probably yield large gains because of the secondary effects of reducing the risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, dementia, and some types of cancer that share common risk factors, the authors noted.
“One of the most common problems in implementing stroke prevention and care recommendations is the lack of funding. Our commission recommends introducing legislative regulations and taxations of unhealthy products (such as salt, alcohol, sugary drinks, trans fats) by each and every government in the world,” Dr. Feigin said.
“Such taxation would not only reduce consumption of these products – and therefore lead to the reduction of burden from stroke and major other noncommunicable diseases – but also generate a large revenue sufficient to fund not only prevention programs and services for stroke and other major disorders, but also reduce poverty, inequality in health service provision, and improve wellbeing of the population,” he added.
Recommendations
The commission authors made the following recommendations for key priorities to reduce the burden of stroke:
Surveillance and prevention
- Incorporate stroke events and risk factor surveillance into national stroke action plans.
- Establish a system for population-wide primary and secondary stroke prevention, with emphasis on lifestyle modification for people at any level of risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
- Primary and secondary stroke prevention services should be freely accessible and supported by universal health coverage, with access to affordable drugs for management of hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and clotting disorders.
- Governments must allocate a fixed proportion of their annual health care funding for prevention of stroke and related noncommunicable diseases. This funding could come from taxation of tobacco, salt, alcohol, and sugar.
- Raise public awareness and take action to encourage a healthy lifestyle and prevent stroke via population-wide deployment of digital technologies with simple, inexpensive screening for cardiovascular disease and modifiable risk factors.
- Establish protocol-based shifting of tasks from highly trained health care professionals to supervised paramedical health care workers, to facilitate population-wide primary stroke prevention interventions across rural and urban settings.
Acute care
- Prioritize effective planning of acute stroke care services; capacity building, training, and certification of a multidisciplinary workforce; provision of evidence-based equipment and affordable medicines; and adequate resource allocation at national and regional levels.
- Establish regional networks and protocol-driven services, including community-wide awareness campaigns for early recognition of a stroke, regionally coordinated prehospital services, telemedicine networks, and stroke centers that can triage and treat all cases of acute stroke, and facilitate timely access to reperfusion therapy.
- Integrate acute care networks into the four pillars of the stroke “quadrangle” of resources, including surveillance, prevention, and rehabilitation services, by involving all relevant stakeholders (that is, communities, policy makers, nongovernmental organizations, national and regional stroke organizations, and public and private health care providers) in the stroke care continuum.
Rehabilitation
- Establish multidisciplinary rehabilitation services and adapt evidence-based recommendations to the local context, including the training, support, and supervision of community health care workers and caregivers to assist in long-term care.
- Invest in research to generate innovative low-cost interventions, in public awareness to improve demand for rehabilitation services, and in advocacy to mobilize resources for multidisciplinary rehabilitation.
- Promote the training of stroke rehabilitation professionals. Use digital portals to improve training and to extend the use of assessment tools – such as the Modified Rankin Scale and the U.S. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale – and quality of life measures to assess functional impairment and monitor recovery.
The commission concluded that, “overall, if the recommendations of this Commission are implemented, the burden of stroke will be reduced substantially ... which will improve brain health and overall wellbeing worldwide.”
Dr. Martins said that the WSO is committed to supporting and accelerating the implementation of these recommendations globally through the WSO Implementation Task Force, with stroke experts to advise the establishment of stroke prevention and care and to contribute with educational programs, and through Global Stroke Alliance meetings facilitating the discussions between stroke experts and policy makers, giving technical support to governments to elaborate national plans for stroke and to include stroke care in universal health coverage packages.
The Commission received funding from the WSO, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Health Research Council of New Zealand, and National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia and was supported by the NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Deaths and disability because of stroke are expected to rise alarmingly over the next 30 years, with almost 10 million stroke deaths forecast annually by 2050, according to a new report from the World Stroke Organization–Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group.
“This highlights the need for urgent measures to reduce stroke burden worldwide, with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries,” the report authors stated.
These measures include an increase in trained health care workers who can implement effective primary prevention strategies, including the early detection and adequate management of hypertension.
On the basis of a review of evidence-based guidelines, recent surveys, and in-depth interviews with stroke experts around the world, the WSO–Lancet Neurology Commission made evidence-based pragmatic recommendations to reduce the global burden of stroke, including measures to improve surveillance, prevention, acute care, and rehabilitation.
The report was announced on Oct. 10 by WSO President, Sheila Martins, MD, at the World Stroke Conference in Toronto. The report was also published online in The Lancet Neurology.
“Stroke care has changed a lot in the last few years,” said Dr. Martins, who is chief of neurology and neurosurgery at Hospital Moinhos de Vento, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and founder and president of the Brazilian Stroke Network. “We know what we need to do to reduce the global burden of stroke, and high-income countries are making progress in that regard. But the situation in low- and middle-income countries is catastrophic, with mortality rates of up to 80% in individuals who have had a stroke in some countries. There is a very large gap between knowledge and implementation.”
Dr. Martins said that the commission is offering potential innovative suggestions on how to change this reality.
“While we have the knowledge on the strategies needed to reduce stroke burden, the mechanisms needed to implement this knowledge will be different in different countries and cultures. Our commission includes several representatives from low- and middle-income countries, and we will be working with local stakeholders in these countries to try and implement our recommendations,” Dr. Martins explained.
Stroke mortality and disability is on the rise
In the report, the authors pointed out that the global burden of stroke is “huge.” In 2020, stroke was the second leading cause of death (6.6 million deaths) and the third leading cause of disability – responsible for 143 million disability-adjusted life-years – after neonatal disorders and ischemic heart disease. Stroke is also a leading cause of depression and dementia.
The absolute number of people affected by stroke, which includes those who die or remain disabled, has almost doubled in the past 30 years, the report authors noted. Most of the contemporary stroke burden is in low- and middle-income countries, and the burden of disability after a stroke is increasing at a faster pace in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income countries. Alarmingly, the incidence of stroke is increasing in young and middle-aged people globally.
The commission forecasts the burden of stroke from 2020 to 2050, with projections estimating that stroke mortality will increase by 50% to 9.7 million and disability-adjusted life-years growing to over 189.3 million by 2050.
“Stroke exerts an enormous toll on the world’s population, leading to the death and permanent disability of millions of people each year, and costing billions of dollars,” said Valery L. Feigin, MD, of Auckland (New Zealand) University of Technology, and commission cochair. “Precisely forecasting the health and economic impacts of stroke decades into the future is inherently challenging given the levels of uncertainty involved, but these estimates are indicative of the ever-increasing burden we will see in the years ahead unless urgent, effective action is taken.”
The report authors explained that multiple factors contribute to the high burden of stroke in low- and middle-income countries, including undetected and uncontrolled hypertension; lack of easily accessible, high-quality health services; insufficient attention to and investment in prevention, air pollution; population growth; unhealthy lifestyles (for example, poor diet, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, obesity); an earlier age of stroke onset and greater proportion of hemorrhagic strokes than in high-income countries; and the burden of infectious diseases resulting in competition for limited health care resources.
The enormous financial cost of stroke
The total cost of stroke (both direct treatment and rehabilitation costs and indirect costs due to loss of income) is estimated to rise from $891 billion per year in 2017 to as much as $2.31 trillion by 2050. “These substantial increases in the costs associated with stroke will cause distressing financial circumstances for many communities and national health systems,” the authors said.
However, this increase can be avoided because stroke is highly preventable and treatable, they stressed. “These unsustainable trends in burden and costs of stroke underline the importance of identifying interventions to prevent and manage stroke more effectively.”
The Commission pointed out that population-wide primary prevention across the lifespan is extremely cost effective. It has been estimated that for every $1 spent on the prevention of stroke and cardiovascular disease, there is a more than $10 return on investment.
Additionally, primary prevention efforts directed at stroke would probably yield large gains because of the secondary effects of reducing the risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, dementia, and some types of cancer that share common risk factors, the authors noted.
“One of the most common problems in implementing stroke prevention and care recommendations is the lack of funding. Our commission recommends introducing legislative regulations and taxations of unhealthy products (such as salt, alcohol, sugary drinks, trans fats) by each and every government in the world,” Dr. Feigin said.
“Such taxation would not only reduce consumption of these products – and therefore lead to the reduction of burden from stroke and major other noncommunicable diseases – but also generate a large revenue sufficient to fund not only prevention programs and services for stroke and other major disorders, but also reduce poverty, inequality in health service provision, and improve wellbeing of the population,” he added.
Recommendations
The commission authors made the following recommendations for key priorities to reduce the burden of stroke:
Surveillance and prevention
- Incorporate stroke events and risk factor surveillance into national stroke action plans.
- Establish a system for population-wide primary and secondary stroke prevention, with emphasis on lifestyle modification for people at any level of risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease.
- Primary and secondary stroke prevention services should be freely accessible and supported by universal health coverage, with access to affordable drugs for management of hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and clotting disorders.
- Governments must allocate a fixed proportion of their annual health care funding for prevention of stroke and related noncommunicable diseases. This funding could come from taxation of tobacco, salt, alcohol, and sugar.
- Raise public awareness and take action to encourage a healthy lifestyle and prevent stroke via population-wide deployment of digital technologies with simple, inexpensive screening for cardiovascular disease and modifiable risk factors.
- Establish protocol-based shifting of tasks from highly trained health care professionals to supervised paramedical health care workers, to facilitate population-wide primary stroke prevention interventions across rural and urban settings.
Acute care
- Prioritize effective planning of acute stroke care services; capacity building, training, and certification of a multidisciplinary workforce; provision of evidence-based equipment and affordable medicines; and adequate resource allocation at national and regional levels.
- Establish regional networks and protocol-driven services, including community-wide awareness campaigns for early recognition of a stroke, regionally coordinated prehospital services, telemedicine networks, and stroke centers that can triage and treat all cases of acute stroke, and facilitate timely access to reperfusion therapy.
- Integrate acute care networks into the four pillars of the stroke “quadrangle” of resources, including surveillance, prevention, and rehabilitation services, by involving all relevant stakeholders (that is, communities, policy makers, nongovernmental organizations, national and regional stroke organizations, and public and private health care providers) in the stroke care continuum.
Rehabilitation
- Establish multidisciplinary rehabilitation services and adapt evidence-based recommendations to the local context, including the training, support, and supervision of community health care workers and caregivers to assist in long-term care.
- Invest in research to generate innovative low-cost interventions, in public awareness to improve demand for rehabilitation services, and in advocacy to mobilize resources for multidisciplinary rehabilitation.
- Promote the training of stroke rehabilitation professionals. Use digital portals to improve training and to extend the use of assessment tools – such as the Modified Rankin Scale and the U.S. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale – and quality of life measures to assess functional impairment and monitor recovery.
The commission concluded that, “overall, if the recommendations of this Commission are implemented, the burden of stroke will be reduced substantially ... which will improve brain health and overall wellbeing worldwide.”
Dr. Martins said that the WSO is committed to supporting and accelerating the implementation of these recommendations globally through the WSO Implementation Task Force, with stroke experts to advise the establishment of stroke prevention and care and to contribute with educational programs, and through Global Stroke Alliance meetings facilitating the discussions between stroke experts and policy makers, giving technical support to governments to elaborate national plans for stroke and to include stroke care in universal health coverage packages.
The Commission received funding from the WSO, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Health Research Council of New Zealand, and National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia and was supported by the NIH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET NEUROLOGY
How best to diagnose and manage abdominal aortic aneurysms
Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) caused about 6000 deaths annually in the United States between 2014 and 20201 and are associated with a pooled mortality rate of 81%.2 They result from a distinct degenerative process of the layers of the aortic wall.2 An AAA is defined as an abdominal aorta whose dilation is > 50% normal (more commonly, a diameter > 3 cm).3,4 The risk for rupture correlates closely with size; most ruptures occur in aneurysms > 5.5 cm3,4 (TABLE 15).
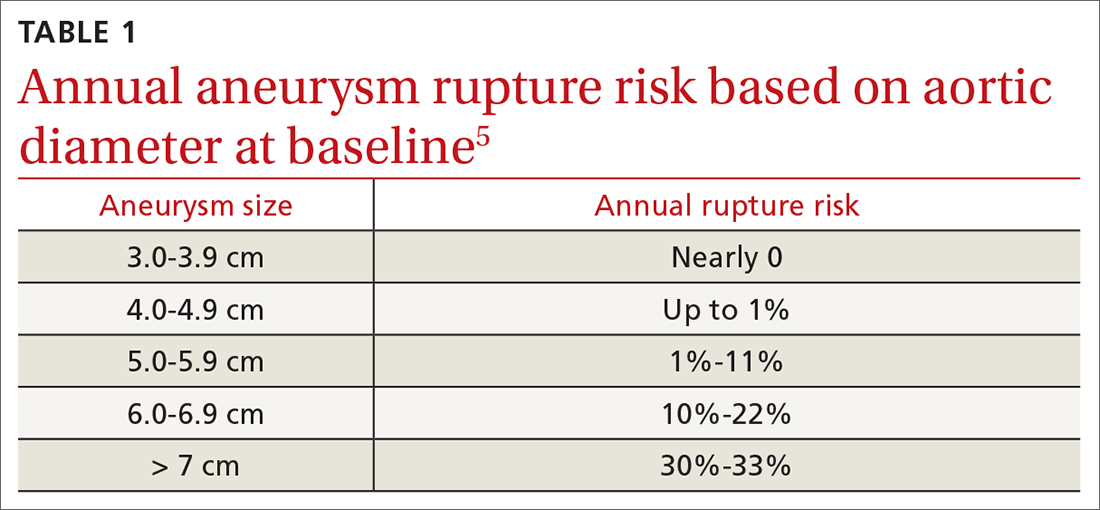
Most AAAs are asymptomatic and often go undetected until rupture, resulting in poor outcomes. Because of a low and declining prevalence of AAA and ruptured AAA in developed countries, screening recommendations target high-risk groups rather than the general population.4,6-8 This review summarizes risk factors, prevalence, and current evidence-based screening and management recommendations for AAA.
Who’s at risk?
Age is the most significant nonmodifiable risk factor, with AAA rupture uncommon in patients younger than 55 years.9 One retrospective study found the odds ratio (OR) for diagnosing AAA was 9.41 in adults ages 65 to 69 years (95% CI, 8.76-10.12; P < .0001) and 14.46 (95% CI, 13.45-15.55; P < .0001) in adults ages 70 to 74 years, compared to adults younger than 55 years.10
Smoking is the most potent modifiable risk factor for AAA. Among patients with AAA, > 90% have a history of smoking.4 The association between smoking and AAA is dose dependent, with an OR of 2.61 (95% CI, 2.47-2.74) in patients with a pack-per-year history < 5 years and 12.13 (95% CI, 11.66-12.61) in patients with a pack-per-year history > 35 years, compared to nonsmokers.10 The risk for AAA increases with smoking duration but decreases with cessation duration.4,10 Smoking cessation remains an important intervention, as active smokers have higher AAA rupture rates.11
Other risk factors for AAA include concomitant cardiovascular disease (CVD) such as coronary artery disease (CAD), cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerosis, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.10 Factors associated with reduced risk for AAA include African American race, Hispanic ethnicity, Asian ethnicity, diabetes, smoking cessation, consuming fruits and vegetables > 3 times per week, and exercising more than once per week.6,10
Prevalence declines but sex-based disparities in outcomes persist
The prevalence of AAA has declined in the United States and Europe in recent decades, correlating with declining rates of smoking.4,12 Reports published between 2011 and 2019 estimate that AAA prevalence in men older than 60 years has declined over time, with a prevalence of 1.2% to 3.3%.6 The prevalence of AAA has also decreased in women,6,13,14 estimated in 1 study to be as low as 0.74%.13 Similarly, deaths from ruptured AAA have declined markedly in the United States—by 70% between 1999 and 2016 according to 1 analysis.9
One striking difference in the male-female data is that although AAAs are more common in men, there is a 2- to 4-fold higher risk for rupture in women, who account for nearly half of all AAA-related deaths.9,10,15-17 The reasons for this heightened risk to women despite lower prevalence are not fully understood but are likely multifactorial and related to a general lack of screening for AAA in women, tendency for AAA to rupture at smaller diameters in women, rupture at an older age in women, and a history of worse surgical outcomes in women than men (though the gap in surgical outcomes appears to be closing).9,10,18
Continue to: While declines in AAA and AAA-related...
While declines in AAA and AAA-related death are largely attributed to lower smoking rates, other likely contributing factors include the implementation of screening programs, incidental detection during cross-sectional imaging, and improved surgical techniques and management of CV risk factors (eg, hypertension, hyperlipidemia).9,10
The benefits of screening older men
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have demonstrated the benefits of AAA screening programs. A meta-analysis of 4 populationbased RCTs of AAA screening in men ≥ 65 years demonstrated statistically significant reductions in AAA rupture (OR = 0.62; 95% CI, 0.55-0.70) and death from AAA (OR = 0.65; 95% CI, 0.57-0.74) over 12 to 15 years, with a number needed to screen (NNS) of 305 (95% CI, 248-411) to prevent 1 AAA-related death.18 The study also found screening decreases the rate of emergent surgeries for AAA (OR = 0.57; 95% CI, 0.48-0.68) while increasing the number of elective surgeries (OR = 1.44; 95% CI, 1.34-1.55) over 4 to 15 years.18
Only 1 study has demonstrated an improvement in all-cause mortality with screening programs, with a relatively small benefit (OR = 0.97; 95% CI, 0.94-0.99).19 Only 1 of the studies included women and, while underpowered, showed no difference in AAA-related death or rupture.20 Guidelines and recommendations of various countries and professional societies focus screening on subgroups at highest risk for AAA.4,6-8,18
Screening recommendations from USPSTF and others
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) currently recommends one-time ultrasound screening for AAA in men ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked (commonly defined as having smoked > 100 cigarettes) in their lifetime.6 This grade “B” recommendation, initially made in 2005 and reaffirmed in the 2014 and 2019 USPSTF updates, recommends screening the highest-risk segment of the population (ie, older male smokers).
In men ages 65 to 75 years with no smoking history, rather than routine screening, the USPSTF recommends selectively offering screening based on the patient’s medical history, family history, risk factors, and personal values (with a “C” grade).6 The USPSTF continues to recommend against screening for AAA in women with no smoking history and no family history of AAA.6 According to the USPSTF, the evidence is insufficient to recommend for or against screening women ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked or have a family history of AAA (“I” statement).6
Continue to: One critique of the USPSTF recommendations
One critique of the USPSTF recommendations is that they fail to detect a significant portion of patients with AAA and AAA rupture. For example, in a retrospective analysis of 55,197 patients undergoing AAA repair, only 33% would have been detected by the USPSTF grade “B” recommendation to screen male smokers ages 65 to 75 years, and an analysis of AAA-related fatalities found 43% would be missed by USPSTF criteria.9,21
Screening guidelines from the Society for Vascular Surgery (SVS) are broader than those of the USPSTF, in an attempt to capture a larger percentage of the population at risk for AAA-related disease by extrapolating from epidemiologic data. The SVS guidelines include screening for women ages 65 to 75 years with a smoking history, screening men and women ages 65 to 75 years who have a first-degree relative with AAA, and consideration of screening patients older than 75 years if they are in good health and have a first-degree relative with AAA or a smoking history and have not been previously screened.4 However, these expanded recommendations are not supported by patient-oriented evidence.6
Attempts to broaden screening guidelines must be tempered by potential risks for harm, primarily overdiagnosis (ie, diagnosing AAAs that would not otherwise rise to clinical significance) and overtreatment (ie, resulting in unnecessary imaging, appointments, anxiety, or surgery). Negative psychological effects on quality of life after a diagnosis of AAA have not been shown to cause significant harm.6,18
A recent UK analysis found that screening programs for AAA in women modeled after those in men are not cost effective, with an NNS to prevent 1 death of 3900 in women vs 700 in men.15,18 Another recent trial of ultrasound screening in 5200 high-risk women ages 65 to 74 years found an AAA incidence of 0.29% (95% CI, 0.18%-0.48%) in which only 3 large aneurysms were identified.22
In the United States, rates of screening for AAA remain low.23 One study has shown electronic medical record–based reminders increased screening rates from 48% to 80%.24 Point-of-care bedside ultrasound performed by clinicians also could improve screening rates. Multiple studies have demonstrated that screening and diagnosis of AAA can be performed safely and effectively at the bedside by nonradiologists such as family physicians and emergency physicians.25-28 In 1 study, such exams added < 4 minutes to the patient encounter.26 Follow-up surveillance schedules for those identified as having a AAA are summarized in TABLE 2.4
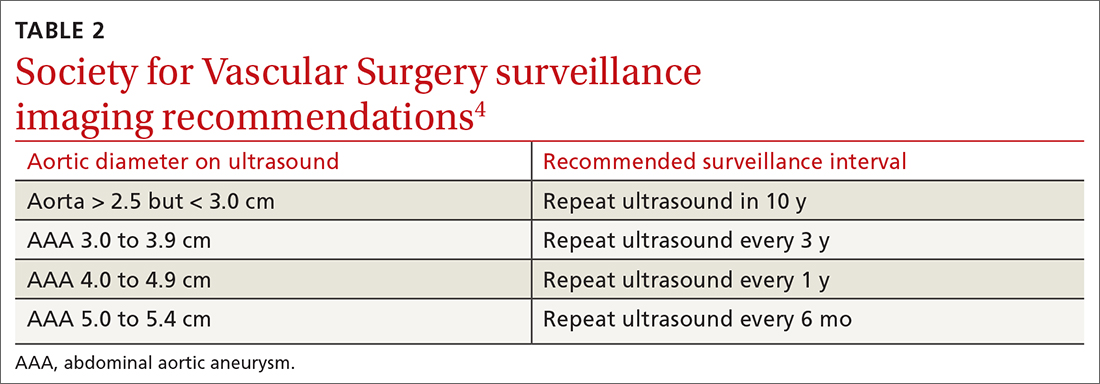
Continue to: Management options
Management options: Immediate repair or surveillance?
After diagnosing AAA, important decisions must be made regarding management, including indications for surgical repair, appropriate follow-up surveillance, and medications for secondary prevention and cardiovascular risk reduction.
EVAR vs open repair
The 2 main surgical strategies for aneurysm repair are open repair and endovascular repair (EVAR). In the United States, EVAR is becoming the more common approach and was used to repair asymptomatic aneurysms in > 80% of patients and ruptured aneurysms in 50% of patients.6 There have been multiple RCTs assessing EVAR and open repair for large and small aneurysms.29-34 Findings across these studies consistently show EVAR is associated with lower immediate (ie, 30-day) morbidity and mortality but no longer-term survival benefit compared to open repair.
EVAR procedures require ongoing long-term surveillance for endovascular leakage and other complications, resulting in an increased need for re-intervention.31,33,35 For these reasons, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines suggest open repair as the preferred modality.7 However, SVS and the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association guidance support either EVAR or open repair, noting that open repair may be preferable in patients unable to engage in long-term follow-up surveillance.36

Indications for repair. In general, repair is indicated when an aneurysm reaches or exceeds 5.5 cm.4,7 Both SVS and NICE also recommend clinicians consider surgical repair of smaller, rapidly expanding aneurysms (> 1 cm over a 1-year period).4,7 Based on evidence suggesting a higher risk for rupture in women with smaller aneurysms,14,37 SVS recommends clinicians consider surgical repair in women with an AAA ≥ 5.0 cm. Several RCTs evaluating the benefits of immediate repair for smaller-sized aneurysms (4.0-5.5 cm) favored surveillance.38,39 Accepted indications for surgical repair are summarized in TABLE 3.4,7,34Surgical repair recommendations also are based on aneurysm morphology, which can be fusiform or saccular (FIGURE). More than 90% of AAAs are fusiform.40 Although saccular AAAs are less common, some studies suggest they are more prone to rupture than fusiform AAAs, and SVS guidelines suggest surgical repair of saccular aneurysms regardless of size.4,41,42
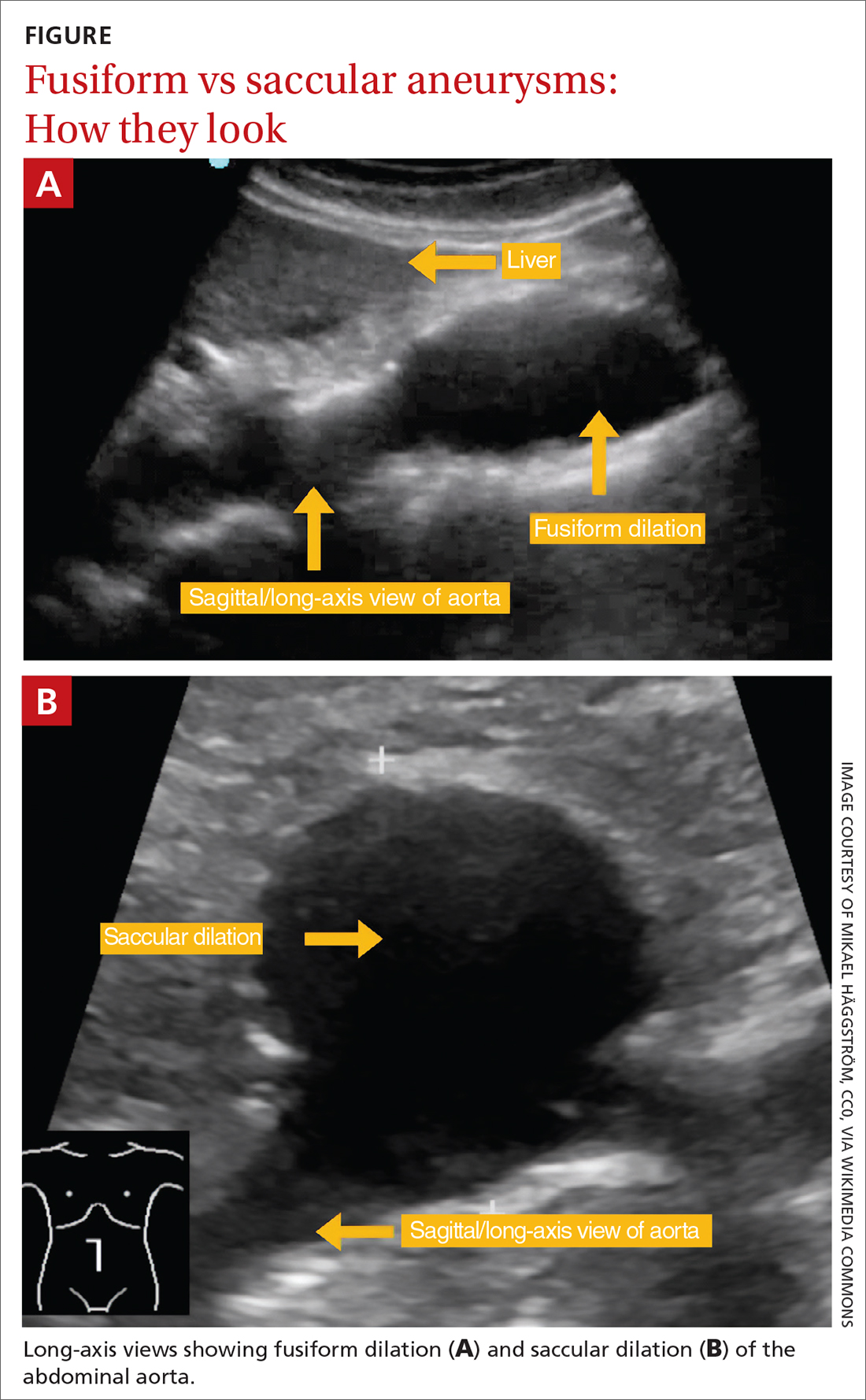
Perioperative and long-term risks. Both EVAR and open repair of AAA carry a high perioperative and long-term risk for death, as patients often have multiple comorbidities. A 2019 trial comparing EVAR to open repair with 14 years of follow-up reported death in 68% of patients in the EVAR group and 70% in the open repair group. 31 Among these deaths, 2.7% in the EVAR group and 3.7% in the open repair group were aneurysm related.31 The study also found a second surgical intervention was required in 19.8% of patients in the open repair group and 26.7% in the EVAR group.31
Continue to: When assessing perioperative risk...
When assessing perioperative risk, SVS guidelines recommend clinicians employ a shared decision-making approach with patients that incorporates Vascular Quality Initiative (VQI) mortality risk score.4 (VQI risk calculators are available at https://qxmd.com/vascular-study-group-new-england-decision-support-tools.43)
Medication management
Based on the close association of aortic aneurysm with atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD), professional societies such as the European Society of Cardiology and European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) have suggested aortic aneurysm is equivalent to ASCVD and should be managed medically in a similar manner to peripheral arterial disease.44 Indeed, many patients with AAA may have concomitant CAD or other arterial vascular diseases (eg, carotid, lower extremity).
Statins. In its guidelines, the ESC/EAS consider patients with AAA at “very high risk” for adverse CV events and suggest pharmacotherapy with high-intensity statins, adding ezetimibe or proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors if needed, to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥ 50% from baseline, with a goal of < 55 mg/dL.44 Statin therapy additionally lowers all-cause postoperative mortality in patients undergoing AAA repair but does not affect the rate of aneurysm expansion.45
Aspirin and other anticoagulants. Although aspirin therapy may be indicated for the secondary prevention of other cardiovascular events that may coexist with AAA, it does not appear to affect the rate of growth or prevent rupture of aneurysms.46,47 In addition to aspirin, anticoagulants such as clopidogrel, enoxaparin, and warfarin are not recommended when the presence of AAA is the only indication.4
Other medications. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, and antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) have been studied as a treatment for AAA. However, none has shown benefit in reducing aneurysm growth or rupture and they are not recommended for that sole purpose.4,48
Metformin. There is a negative association between diabetes and AAA expansion and rupture. Several cohort studies have indicated that this may be an independent effect driven primarily by exposure to metformin. While it is not unreasonable to consider this another important indication for metformin use in patients with diabetes, RCT evidence has yet to establish a role for metformin in patients without diabetes who have AAA.48,49
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank Gwen Wilson, MLS, AHIP, for her assistance with the literature searches performed in the preparation of this manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Nicholas LeFevre, MD, Family and Community Medicine, University of Missouri–Columbia School of Medicine, One Hospital Drive, M224 Medical Science Building, Columbia, MO 65212; [email protected]
1. CDC. Wide-ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research (WONDER) database. Accessed August 30, 2023. https://wonder.cdc.gov/ucd-icd10.html
2. Reimerink JJ, van der Laan MJ, Koelemay MJ, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2013;100:1405-1413. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9235
3. Kent KC. Clinical practice. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
4. Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
5. Moll FL, Powell JT, Fraedrich G, et al. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms clinical practice guidelines of the European society for vascular surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;41 suppl 1:S1-S58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.09.011
6. Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2019;322:2211-2218. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18928
7. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG156]. March 19, 2020. Accessed June 30, 2023. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156/chapter/recommendations
8. Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Recommendations on screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm in primary care. CMAJ. 2017;189:E1137-E1145. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.170118
9. Abdulameer H, Al Taii H, Al-Kindi SG, et al. Epidemiology of fatal ruptured aortic aneurysms in the United States (1999-2016). J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:378-384.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.03.435
10. Kent KC, Zwolak RM, Egorova NN, et al. Analysis of risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in a cohort of more than 3 million individuals. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:539-548. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.05.090
11. [No authors listed] Smoking, lung function and the prognosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm. The UK Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2000;19:636-642. doi: 10.1053/ejvs.2000.1066
12. Oliver-Williams C, Sweeting MJ, Turton G, et al. Lessons learned about prevalence and growth rates of abdominal aortic aneurysms from a 25-year ultrasound population screening programme. Br J Surg. 2018;105:68-74. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10715
13. Ulug P, Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, et al. Meta-analysis of the current prevalence of screen-detected abdominal aortic aneurysm in women. Br J Surg. 2016;103:1097-1104. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10225
14. Chabok M, Nicolaides A, Aslam M, et al. Risk factors associated with increased prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysm in women. Br J Surg. 2016;103:1132-1138. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10179
15. Sweeting, MJ, Masconi KL, Jones E, et al. Analysis of clinical benefit, harms, and cost-effectiveness of screening women for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Lancet. 2018;392:487-495. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31222-4
16. Sweeting MJ, Thompson SG, Brown LC, et al; RESCAN collaborators. Meta-analysis of individual patient data to examine factors affecting growth and rupture of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2012;99:655-665. doi: 10.1002/bjs.8707
17. Skibba AA, Evans JR, Hopkins SP, et al. Reconsidering gender relative to risk of rupture in the contemporary management of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2015;62:1429-1436. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.07.079
18. Guirguis-Blake JM, Beil TL, Senger CA, et al. Primary care screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2019;322:2219-2238. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17021
19. Thompson SG, Ashton HA, Gao L, et al; Multicentre Aneurysm Screening Study (MASS) Group. Final follow-up of the Multicentre Aneurysm Screening Study (MASS) randomized trial of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening. Br J Surg. 2012;99:1649-1656. doi: 10.1002/bjs.8897
20. Ashton HA, Gao L, Kim LG, et al. Fifteen-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial of ultrasonographic screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2007;94:696-701. doi: 10.1002/bjs.5780
21. Carnevale ML, Koleilat I, Lipsitz EC, et al. Extended screening guidelines for the diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72:1917-1926. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.03.047
22. Duncan A, Maslen C, Gibson C, et al. Ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm in high-risk women. Br J Surg. 2021;108:1192-1198. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znab220
23. Shreibati JB, Baker LC, Hlatky MA, et al. Impact of the Screening Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Very Efficiently (SAAAVE) Act on abdominal ultrasonography use among Medicare beneficiaries. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:1456-1462. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.4268
24. Hye RJ, Smith AE, Wong GH, et al. Leveraging the electronic medical record to implement an abdominal aortic aneurysm screening program. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59:1535-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.12.016
25. Rubano E, Mehta N, Caputo W, et al., Systematic review: emergency department bedside ultrasonography for diagnosing suspected abdominal aortic aneurysm. Acad Emerg Med. 2013. 20:128-138. doi: 10.1111/acem.12080
26. Blois B. Office-based ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:e172-e178.
27. Arnold MJ, Jonas CE, Carter RE. Point-of-care ultrasonography. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101:275-285.
28. Nixon G, Blattner K, Muirhead J, et al. Point-of-care ultrasound for FAST and AAA in rural New Zealand: quality and impact on patient care. Rural Remote Health. 2019;19:5027. doi: 10.22605/RRH5027
29. Lederle FA, Wilson SE, Johnson GR, et al. Immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1437-1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012573
30. Filardo G, Lederle FA, Ballard DJ, et al. Immediate open repair vs surveillance in patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms: survival differences by aneurysm size. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013;88:910-919. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.05.014
31. Lederle FA, Kyriakides TC, Stroupe KT, et al. Open versus endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2126-2135. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1715955
32. Patel R, Sweeting MJ, Powell JT, et al., Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in 15-years’ follow-up of the UK endovascular aneurysm repair trial 1 (EVAR trial 1): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2366-2374. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31135-7
33. van Schaik TG, Yeung KK, Verhagen HJ, et al. Long-term survival and secondary procedures after open or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2017;66:1379-1389. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.05.122
34. Powell JT, Brady AR, Brown, LC, et al; United Kingdom Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Long-term outcomes of immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1445-1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa013527
35. Paravastu SC, Jayarajasingam R, Cottam R, et al. Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD004178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004178.pub2
36. Rooke TW, Hirsch AT, Misra S, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA focused update of the guideline for the management of patients with peripheral artery disease (updating the 2005 guideline): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:2020-2045. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.08.023
37. Bhak RH, Wininger M, Johnson GR, et al. Factors associated with small abdominal aortic aneurysm expansion rate. JAMA Surg. 2015;150:44-50. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2014.2025
38. Ouriel K, Clair DG, Kent KC, et al; Positive Impact of Endovascular Options for treating Aneurysms Early (PIVOTAL) Investigators. Endovascular repair compared with surveillance for patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2010;51:1081-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2009.10.113
39. Cao P, De Rango P, Verzini F, et al. Comparison of surveillance versus aortic endografting for small aneurysm repair (CAESAR): results from a randomised trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;41:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.08.026
40. Karthaus EG, Tong TML, Vahl A, et al; Dutch Society of Vascular Surgery, the Steering Committee of the Dutch Surgical Aneurysm Audit and the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing. Saccular abdominal aortic aneurysms: patient characteristics, clinical presentation, treatment, and outcomes in the Netherlands. Ann Surg. 2019;270:852-858. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003529
41. Nathan DP, Xu C, Pouch AM, et al. Increased wall stress of saccular versus fusiform aneurysms of the descending thoracic aorta. Ann Vasc Surg. 2011;25:1129-2237. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2011.07.008
42. Durojaye MS, Adeniyi TO, Alagbe OA. Multiple saccular aneurysms of the abdominal aorta: a case report and short review of risk factors for rupture on CT Scan. Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2020;18:178-180.
43. Bertges DJ, Neal D, Schanzer A, et al. The Vascular Quality Initiative Cardiac Risk Index for prediction of myocardial infarction after vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64:1411-1421.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.04.045
44. Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:111-188. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455
45. Twine CP, Williams IM. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of statin therapy on abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2011;98:346-353. doi: 10.1002/bjs.7343
46. Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:e596-e646. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
47. Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2873-2926. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu281
48. Lederle FA, Noorbaloochi S, Nugent S, et al. Multicentre study of abdominal aortic aneurysm measurement and enlargement. Br J Surg. 2015;102:1480-1487. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9895
49. Itoga NK, Rothenberg KA, Suarez P, et al. Metformin prescription status and abdominal aortic aneurysm disease progression in the U.S. veteran population. J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:710-716.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.06.19
Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) caused about 6000 deaths annually in the United States between 2014 and 20201 and are associated with a pooled mortality rate of 81%.2 They result from a distinct degenerative process of the layers of the aortic wall.2 An AAA is defined as an abdominal aorta whose dilation is > 50% normal (more commonly, a diameter > 3 cm).3,4 The risk for rupture correlates closely with size; most ruptures occur in aneurysms > 5.5 cm3,4 (TABLE 15).

Most AAAs are asymptomatic and often go undetected until rupture, resulting in poor outcomes. Because of a low and declining prevalence of AAA and ruptured AAA in developed countries, screening recommendations target high-risk groups rather than the general population.4,6-8 This review summarizes risk factors, prevalence, and current evidence-based screening and management recommendations for AAA.
Who’s at risk?
Age is the most significant nonmodifiable risk factor, with AAA rupture uncommon in patients younger than 55 years.9 One retrospective study found the odds ratio (OR) for diagnosing AAA was 9.41 in adults ages 65 to 69 years (95% CI, 8.76-10.12; P < .0001) and 14.46 (95% CI, 13.45-15.55; P < .0001) in adults ages 70 to 74 years, compared to adults younger than 55 years.10
Smoking is the most potent modifiable risk factor for AAA. Among patients with AAA, > 90% have a history of smoking.4 The association between smoking and AAA is dose dependent, with an OR of 2.61 (95% CI, 2.47-2.74) in patients with a pack-per-year history < 5 years and 12.13 (95% CI, 11.66-12.61) in patients with a pack-per-year history > 35 years, compared to nonsmokers.10 The risk for AAA increases with smoking duration but decreases with cessation duration.4,10 Smoking cessation remains an important intervention, as active smokers have higher AAA rupture rates.11
Other risk factors for AAA include concomitant cardiovascular disease (CVD) such as coronary artery disease (CAD), cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerosis, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.10 Factors associated with reduced risk for AAA include African American race, Hispanic ethnicity, Asian ethnicity, diabetes, smoking cessation, consuming fruits and vegetables > 3 times per week, and exercising more than once per week.6,10
Prevalence declines but sex-based disparities in outcomes persist
The prevalence of AAA has declined in the United States and Europe in recent decades, correlating with declining rates of smoking.4,12 Reports published between 2011 and 2019 estimate that AAA prevalence in men older than 60 years has declined over time, with a prevalence of 1.2% to 3.3%.6 The prevalence of AAA has also decreased in women,6,13,14 estimated in 1 study to be as low as 0.74%.13 Similarly, deaths from ruptured AAA have declined markedly in the United States—by 70% between 1999 and 2016 according to 1 analysis.9
One striking difference in the male-female data is that although AAAs are more common in men, there is a 2- to 4-fold higher risk for rupture in women, who account for nearly half of all AAA-related deaths.9,10,15-17 The reasons for this heightened risk to women despite lower prevalence are not fully understood but are likely multifactorial and related to a general lack of screening for AAA in women, tendency for AAA to rupture at smaller diameters in women, rupture at an older age in women, and a history of worse surgical outcomes in women than men (though the gap in surgical outcomes appears to be closing).9,10,18
Continue to: While declines in AAA and AAA-related...
While declines in AAA and AAA-related death are largely attributed to lower smoking rates, other likely contributing factors include the implementation of screening programs, incidental detection during cross-sectional imaging, and improved surgical techniques and management of CV risk factors (eg, hypertension, hyperlipidemia).9,10
The benefits of screening older men
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have demonstrated the benefits of AAA screening programs. A meta-analysis of 4 populationbased RCTs of AAA screening in men ≥ 65 years demonstrated statistically significant reductions in AAA rupture (OR = 0.62; 95% CI, 0.55-0.70) and death from AAA (OR = 0.65; 95% CI, 0.57-0.74) over 12 to 15 years, with a number needed to screen (NNS) of 305 (95% CI, 248-411) to prevent 1 AAA-related death.18 The study also found screening decreases the rate of emergent surgeries for AAA (OR = 0.57; 95% CI, 0.48-0.68) while increasing the number of elective surgeries (OR = 1.44; 95% CI, 1.34-1.55) over 4 to 15 years.18
Only 1 study has demonstrated an improvement in all-cause mortality with screening programs, with a relatively small benefit (OR = 0.97; 95% CI, 0.94-0.99).19 Only 1 of the studies included women and, while underpowered, showed no difference in AAA-related death or rupture.20 Guidelines and recommendations of various countries and professional societies focus screening on subgroups at highest risk for AAA.4,6-8,18
Screening recommendations from USPSTF and others
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) currently recommends one-time ultrasound screening for AAA in men ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked (commonly defined as having smoked > 100 cigarettes) in their lifetime.6 This grade “B” recommendation, initially made in 2005 and reaffirmed in the 2014 and 2019 USPSTF updates, recommends screening the highest-risk segment of the population (ie, older male smokers).
In men ages 65 to 75 years with no smoking history, rather than routine screening, the USPSTF recommends selectively offering screening based on the patient’s medical history, family history, risk factors, and personal values (with a “C” grade).6 The USPSTF continues to recommend against screening for AAA in women with no smoking history and no family history of AAA.6 According to the USPSTF, the evidence is insufficient to recommend for or against screening women ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked or have a family history of AAA (“I” statement).6
Continue to: One critique of the USPSTF recommendations
One critique of the USPSTF recommendations is that they fail to detect a significant portion of patients with AAA and AAA rupture. For example, in a retrospective analysis of 55,197 patients undergoing AAA repair, only 33% would have been detected by the USPSTF grade “B” recommendation to screen male smokers ages 65 to 75 years, and an analysis of AAA-related fatalities found 43% would be missed by USPSTF criteria.9,21
Screening guidelines from the Society for Vascular Surgery (SVS) are broader than those of the USPSTF, in an attempt to capture a larger percentage of the population at risk for AAA-related disease by extrapolating from epidemiologic data. The SVS guidelines include screening for women ages 65 to 75 years with a smoking history, screening men and women ages 65 to 75 years who have a first-degree relative with AAA, and consideration of screening patients older than 75 years if they are in good health and have a first-degree relative with AAA or a smoking history and have not been previously screened.4 However, these expanded recommendations are not supported by patient-oriented evidence.6
Attempts to broaden screening guidelines must be tempered by potential risks for harm, primarily overdiagnosis (ie, diagnosing AAAs that would not otherwise rise to clinical significance) and overtreatment (ie, resulting in unnecessary imaging, appointments, anxiety, or surgery). Negative psychological effects on quality of life after a diagnosis of AAA have not been shown to cause significant harm.6,18
A recent UK analysis found that screening programs for AAA in women modeled after those in men are not cost effective, with an NNS to prevent 1 death of 3900 in women vs 700 in men.15,18 Another recent trial of ultrasound screening in 5200 high-risk women ages 65 to 74 years found an AAA incidence of 0.29% (95% CI, 0.18%-0.48%) in which only 3 large aneurysms were identified.22
In the United States, rates of screening for AAA remain low.23 One study has shown electronic medical record–based reminders increased screening rates from 48% to 80%.24 Point-of-care bedside ultrasound performed by clinicians also could improve screening rates. Multiple studies have demonstrated that screening and diagnosis of AAA can be performed safely and effectively at the bedside by nonradiologists such as family physicians and emergency physicians.25-28 In 1 study, such exams added < 4 minutes to the patient encounter.26 Follow-up surveillance schedules for those identified as having a AAA are summarized in TABLE 2.4

Continue to: Management options
Management options: Immediate repair or surveillance?
After diagnosing AAA, important decisions must be made regarding management, including indications for surgical repair, appropriate follow-up surveillance, and medications for secondary prevention and cardiovascular risk reduction.
EVAR vs open repair
The 2 main surgical strategies for aneurysm repair are open repair and endovascular repair (EVAR). In the United States, EVAR is becoming the more common approach and was used to repair asymptomatic aneurysms in > 80% of patients and ruptured aneurysms in 50% of patients.6 There have been multiple RCTs assessing EVAR and open repair for large and small aneurysms.29-34 Findings across these studies consistently show EVAR is associated with lower immediate (ie, 30-day) morbidity and mortality but no longer-term survival benefit compared to open repair.
EVAR procedures require ongoing long-term surveillance for endovascular leakage and other complications, resulting in an increased need for re-intervention.31,33,35 For these reasons, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines suggest open repair as the preferred modality.7 However, SVS and the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association guidance support either EVAR or open repair, noting that open repair may be preferable in patients unable to engage in long-term follow-up surveillance.36

Indications for repair. In general, repair is indicated when an aneurysm reaches or exceeds 5.5 cm.4,7 Both SVS and NICE also recommend clinicians consider surgical repair of smaller, rapidly expanding aneurysms (> 1 cm over a 1-year period).4,7 Based on evidence suggesting a higher risk for rupture in women with smaller aneurysms,14,37 SVS recommends clinicians consider surgical repair in women with an AAA ≥ 5.0 cm. Several RCTs evaluating the benefits of immediate repair for smaller-sized aneurysms (4.0-5.5 cm) favored surveillance.38,39 Accepted indications for surgical repair are summarized in TABLE 3.4,7,34Surgical repair recommendations also are based on aneurysm morphology, which can be fusiform or saccular (FIGURE). More than 90% of AAAs are fusiform.40 Although saccular AAAs are less common, some studies suggest they are more prone to rupture than fusiform AAAs, and SVS guidelines suggest surgical repair of saccular aneurysms regardless of size.4,41,42

Perioperative and long-term risks. Both EVAR and open repair of AAA carry a high perioperative and long-term risk for death, as patients often have multiple comorbidities. A 2019 trial comparing EVAR to open repair with 14 years of follow-up reported death in 68% of patients in the EVAR group and 70% in the open repair group. 31 Among these deaths, 2.7% in the EVAR group and 3.7% in the open repair group were aneurysm related.31 The study also found a second surgical intervention was required in 19.8% of patients in the open repair group and 26.7% in the EVAR group.31
Continue to: When assessing perioperative risk...
When assessing perioperative risk, SVS guidelines recommend clinicians employ a shared decision-making approach with patients that incorporates Vascular Quality Initiative (VQI) mortality risk score.4 (VQI risk calculators are available at https://qxmd.com/vascular-study-group-new-england-decision-support-tools.43)
Medication management
Based on the close association of aortic aneurysm with atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD), professional societies such as the European Society of Cardiology and European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) have suggested aortic aneurysm is equivalent to ASCVD and should be managed medically in a similar manner to peripheral arterial disease.44 Indeed, many patients with AAA may have concomitant CAD or other arterial vascular diseases (eg, carotid, lower extremity).
Statins. In its guidelines, the ESC/EAS consider patients with AAA at “very high risk” for adverse CV events and suggest pharmacotherapy with high-intensity statins, adding ezetimibe or proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors if needed, to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥ 50% from baseline, with a goal of < 55 mg/dL.44 Statin therapy additionally lowers all-cause postoperative mortality in patients undergoing AAA repair but does not affect the rate of aneurysm expansion.45
Aspirin and other anticoagulants. Although aspirin therapy may be indicated for the secondary prevention of other cardiovascular events that may coexist with AAA, it does not appear to affect the rate of growth or prevent rupture of aneurysms.46,47 In addition to aspirin, anticoagulants such as clopidogrel, enoxaparin, and warfarin are not recommended when the presence of AAA is the only indication.4
Other medications. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, and antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) have been studied as a treatment for AAA. However, none has shown benefit in reducing aneurysm growth or rupture and they are not recommended for that sole purpose.4,48
Metformin. There is a negative association between diabetes and AAA expansion and rupture. Several cohort studies have indicated that this may be an independent effect driven primarily by exposure to metformin. While it is not unreasonable to consider this another important indication for metformin use in patients with diabetes, RCT evidence has yet to establish a role for metformin in patients without diabetes who have AAA.48,49
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank Gwen Wilson, MLS, AHIP, for her assistance with the literature searches performed in the preparation of this manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Nicholas LeFevre, MD, Family and Community Medicine, University of Missouri–Columbia School of Medicine, One Hospital Drive, M224 Medical Science Building, Columbia, MO 65212; [email protected]
Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) caused about 6000 deaths annually in the United States between 2014 and 20201 and are associated with a pooled mortality rate of 81%.2 They result from a distinct degenerative process of the layers of the aortic wall.2 An AAA is defined as an abdominal aorta whose dilation is > 50% normal (more commonly, a diameter > 3 cm).3,4 The risk for rupture correlates closely with size; most ruptures occur in aneurysms > 5.5 cm3,4 (TABLE 15).

Most AAAs are asymptomatic and often go undetected until rupture, resulting in poor outcomes. Because of a low and declining prevalence of AAA and ruptured AAA in developed countries, screening recommendations target high-risk groups rather than the general population.4,6-8 This review summarizes risk factors, prevalence, and current evidence-based screening and management recommendations for AAA.
Who’s at risk?
Age is the most significant nonmodifiable risk factor, with AAA rupture uncommon in patients younger than 55 years.9 One retrospective study found the odds ratio (OR) for diagnosing AAA was 9.41 in adults ages 65 to 69 years (95% CI, 8.76-10.12; P < .0001) and 14.46 (95% CI, 13.45-15.55; P < .0001) in adults ages 70 to 74 years, compared to adults younger than 55 years.10
Smoking is the most potent modifiable risk factor for AAA. Among patients with AAA, > 90% have a history of smoking.4 The association between smoking and AAA is dose dependent, with an OR of 2.61 (95% CI, 2.47-2.74) in patients with a pack-per-year history < 5 years and 12.13 (95% CI, 11.66-12.61) in patients with a pack-per-year history > 35 years, compared to nonsmokers.10 The risk for AAA increases with smoking duration but decreases with cessation duration.4,10 Smoking cessation remains an important intervention, as active smokers have higher AAA rupture rates.11
Other risk factors for AAA include concomitant cardiovascular disease (CVD) such as coronary artery disease (CAD), cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerosis, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.10 Factors associated with reduced risk for AAA include African American race, Hispanic ethnicity, Asian ethnicity, diabetes, smoking cessation, consuming fruits and vegetables > 3 times per week, and exercising more than once per week.6,10
Prevalence declines but sex-based disparities in outcomes persist
The prevalence of AAA has declined in the United States and Europe in recent decades, correlating with declining rates of smoking.4,12 Reports published between 2011 and 2019 estimate that AAA prevalence in men older than 60 years has declined over time, with a prevalence of 1.2% to 3.3%.6 The prevalence of AAA has also decreased in women,6,13,14 estimated in 1 study to be as low as 0.74%.13 Similarly, deaths from ruptured AAA have declined markedly in the United States—by 70% between 1999 and 2016 according to 1 analysis.9
One striking difference in the male-female data is that although AAAs are more common in men, there is a 2- to 4-fold higher risk for rupture in women, who account for nearly half of all AAA-related deaths.9,10,15-17 The reasons for this heightened risk to women despite lower prevalence are not fully understood but are likely multifactorial and related to a general lack of screening for AAA in women, tendency for AAA to rupture at smaller diameters in women, rupture at an older age in women, and a history of worse surgical outcomes in women than men (though the gap in surgical outcomes appears to be closing).9,10,18
Continue to: While declines in AAA and AAA-related...
While declines in AAA and AAA-related death are largely attributed to lower smoking rates, other likely contributing factors include the implementation of screening programs, incidental detection during cross-sectional imaging, and improved surgical techniques and management of CV risk factors (eg, hypertension, hyperlipidemia).9,10
The benefits of screening older men
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have demonstrated the benefits of AAA screening programs. A meta-analysis of 4 populationbased RCTs of AAA screening in men ≥ 65 years demonstrated statistically significant reductions in AAA rupture (OR = 0.62; 95% CI, 0.55-0.70) and death from AAA (OR = 0.65; 95% CI, 0.57-0.74) over 12 to 15 years, with a number needed to screen (NNS) of 305 (95% CI, 248-411) to prevent 1 AAA-related death.18 The study also found screening decreases the rate of emergent surgeries for AAA (OR = 0.57; 95% CI, 0.48-0.68) while increasing the number of elective surgeries (OR = 1.44; 95% CI, 1.34-1.55) over 4 to 15 years.18
Only 1 study has demonstrated an improvement in all-cause mortality with screening programs, with a relatively small benefit (OR = 0.97; 95% CI, 0.94-0.99).19 Only 1 of the studies included women and, while underpowered, showed no difference in AAA-related death or rupture.20 Guidelines and recommendations of various countries and professional societies focus screening on subgroups at highest risk for AAA.4,6-8,18
Screening recommendations from USPSTF and others
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) currently recommends one-time ultrasound screening for AAA in men ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked (commonly defined as having smoked > 100 cigarettes) in their lifetime.6 This grade “B” recommendation, initially made in 2005 and reaffirmed in the 2014 and 2019 USPSTF updates, recommends screening the highest-risk segment of the population (ie, older male smokers).
In men ages 65 to 75 years with no smoking history, rather than routine screening, the USPSTF recommends selectively offering screening based on the patient’s medical history, family history, risk factors, and personal values (with a “C” grade).6 The USPSTF continues to recommend against screening for AAA in women with no smoking history and no family history of AAA.6 According to the USPSTF, the evidence is insufficient to recommend for or against screening women ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked or have a family history of AAA (“I” statement).6
Continue to: One critique of the USPSTF recommendations
One critique of the USPSTF recommendations is that they fail to detect a significant portion of patients with AAA and AAA rupture. For example, in a retrospective analysis of 55,197 patients undergoing AAA repair, only 33% would have been detected by the USPSTF grade “B” recommendation to screen male smokers ages 65 to 75 years, and an analysis of AAA-related fatalities found 43% would be missed by USPSTF criteria.9,21
Screening guidelines from the Society for Vascular Surgery (SVS) are broader than those of the USPSTF, in an attempt to capture a larger percentage of the population at risk for AAA-related disease by extrapolating from epidemiologic data. The SVS guidelines include screening for women ages 65 to 75 years with a smoking history, screening men and women ages 65 to 75 years who have a first-degree relative with AAA, and consideration of screening patients older than 75 years if they are in good health and have a first-degree relative with AAA or a smoking history and have not been previously screened.4 However, these expanded recommendations are not supported by patient-oriented evidence.6
Attempts to broaden screening guidelines must be tempered by potential risks for harm, primarily overdiagnosis (ie, diagnosing AAAs that would not otherwise rise to clinical significance) and overtreatment (ie, resulting in unnecessary imaging, appointments, anxiety, or surgery). Negative psychological effects on quality of life after a diagnosis of AAA have not been shown to cause significant harm.6,18
A recent UK analysis found that screening programs for AAA in women modeled after those in men are not cost effective, with an NNS to prevent 1 death of 3900 in women vs 700 in men.15,18 Another recent trial of ultrasound screening in 5200 high-risk women ages 65 to 74 years found an AAA incidence of 0.29% (95% CI, 0.18%-0.48%) in which only 3 large aneurysms were identified.22
In the United States, rates of screening for AAA remain low.23 One study has shown electronic medical record–based reminders increased screening rates from 48% to 80%.24 Point-of-care bedside ultrasound performed by clinicians also could improve screening rates. Multiple studies have demonstrated that screening and diagnosis of AAA can be performed safely and effectively at the bedside by nonradiologists such as family physicians and emergency physicians.25-28 In 1 study, such exams added < 4 minutes to the patient encounter.26 Follow-up surveillance schedules for those identified as having a AAA are summarized in TABLE 2.4

Continue to: Management options
Management options: Immediate repair or surveillance?
After diagnosing AAA, important decisions must be made regarding management, including indications for surgical repair, appropriate follow-up surveillance, and medications for secondary prevention and cardiovascular risk reduction.
EVAR vs open repair
The 2 main surgical strategies for aneurysm repair are open repair and endovascular repair (EVAR). In the United States, EVAR is becoming the more common approach and was used to repair asymptomatic aneurysms in > 80% of patients and ruptured aneurysms in 50% of patients.6 There have been multiple RCTs assessing EVAR and open repair for large and small aneurysms.29-34 Findings across these studies consistently show EVAR is associated with lower immediate (ie, 30-day) morbidity and mortality but no longer-term survival benefit compared to open repair.
EVAR procedures require ongoing long-term surveillance for endovascular leakage and other complications, resulting in an increased need for re-intervention.31,33,35 For these reasons, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines suggest open repair as the preferred modality.7 However, SVS and the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association guidance support either EVAR or open repair, noting that open repair may be preferable in patients unable to engage in long-term follow-up surveillance.36

Indications for repair. In general, repair is indicated when an aneurysm reaches or exceeds 5.5 cm.4,7 Both SVS and NICE also recommend clinicians consider surgical repair of smaller, rapidly expanding aneurysms (> 1 cm over a 1-year period).4,7 Based on evidence suggesting a higher risk for rupture in women with smaller aneurysms,14,37 SVS recommends clinicians consider surgical repair in women with an AAA ≥ 5.0 cm. Several RCTs evaluating the benefits of immediate repair for smaller-sized aneurysms (4.0-5.5 cm) favored surveillance.38,39 Accepted indications for surgical repair are summarized in TABLE 3.4,7,34Surgical repair recommendations also are based on aneurysm morphology, which can be fusiform or saccular (FIGURE). More than 90% of AAAs are fusiform.40 Although saccular AAAs are less common, some studies suggest they are more prone to rupture than fusiform AAAs, and SVS guidelines suggest surgical repair of saccular aneurysms regardless of size.4,41,42

Perioperative and long-term risks. Both EVAR and open repair of AAA carry a high perioperative and long-term risk for death, as patients often have multiple comorbidities. A 2019 trial comparing EVAR to open repair with 14 years of follow-up reported death in 68% of patients in the EVAR group and 70% in the open repair group. 31 Among these deaths, 2.7% in the EVAR group and 3.7% in the open repair group were aneurysm related.31 The study also found a second surgical intervention was required in 19.8% of patients in the open repair group and 26.7% in the EVAR group.31
Continue to: When assessing perioperative risk...
When assessing perioperative risk, SVS guidelines recommend clinicians employ a shared decision-making approach with patients that incorporates Vascular Quality Initiative (VQI) mortality risk score.4 (VQI risk calculators are available at https://qxmd.com/vascular-study-group-new-england-decision-support-tools.43)
Medication management
Based on the close association of aortic aneurysm with atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD), professional societies such as the European Society of Cardiology and European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) have suggested aortic aneurysm is equivalent to ASCVD and should be managed medically in a similar manner to peripheral arterial disease.44 Indeed, many patients with AAA may have concomitant CAD or other arterial vascular diseases (eg, carotid, lower extremity).
Statins. In its guidelines, the ESC/EAS consider patients with AAA at “very high risk” for adverse CV events and suggest pharmacotherapy with high-intensity statins, adding ezetimibe or proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors if needed, to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥ 50% from baseline, with a goal of < 55 mg/dL.44 Statin therapy additionally lowers all-cause postoperative mortality in patients undergoing AAA repair but does not affect the rate of aneurysm expansion.45
Aspirin and other anticoagulants. Although aspirin therapy may be indicated for the secondary prevention of other cardiovascular events that may coexist with AAA, it does not appear to affect the rate of growth or prevent rupture of aneurysms.46,47 In addition to aspirin, anticoagulants such as clopidogrel, enoxaparin, and warfarin are not recommended when the presence of AAA is the only indication.4
Other medications. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, and antibiotics (eg, doxycycline) have been studied as a treatment for AAA. However, none has shown benefit in reducing aneurysm growth or rupture and they are not recommended for that sole purpose.4,48
Metformin. There is a negative association between diabetes and AAA expansion and rupture. Several cohort studies have indicated that this may be an independent effect driven primarily by exposure to metformin. While it is not unreasonable to consider this another important indication for metformin use in patients with diabetes, RCT evidence has yet to establish a role for metformin in patients without diabetes who have AAA.48,49
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank Gwen Wilson, MLS, AHIP, for her assistance with the literature searches performed in the preparation of this manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Nicholas LeFevre, MD, Family and Community Medicine, University of Missouri–Columbia School of Medicine, One Hospital Drive, M224 Medical Science Building, Columbia, MO 65212; [email protected]
1. CDC. Wide-ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research (WONDER) database. Accessed August 30, 2023. https://wonder.cdc.gov/ucd-icd10.html
2. Reimerink JJ, van der Laan MJ, Koelemay MJ, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2013;100:1405-1413. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9235
3. Kent KC. Clinical practice. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
4. Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
5. Moll FL, Powell JT, Fraedrich G, et al. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms clinical practice guidelines of the European society for vascular surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;41 suppl 1:S1-S58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.09.011
6. Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2019;322:2211-2218. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18928
7. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG156]. March 19, 2020. Accessed June 30, 2023. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156/chapter/recommendations
8. Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Recommendations on screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm in primary care. CMAJ. 2017;189:E1137-E1145. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.170118
9. Abdulameer H, Al Taii H, Al-Kindi SG, et al. Epidemiology of fatal ruptured aortic aneurysms in the United States (1999-2016). J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:378-384.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.03.435
10. Kent KC, Zwolak RM, Egorova NN, et al. Analysis of risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in a cohort of more than 3 million individuals. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:539-548. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.05.090
11. [No authors listed] Smoking, lung function and the prognosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm. The UK Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2000;19:636-642. doi: 10.1053/ejvs.2000.1066
12. Oliver-Williams C, Sweeting MJ, Turton G, et al. Lessons learned about prevalence and growth rates of abdominal aortic aneurysms from a 25-year ultrasound population screening programme. Br J Surg. 2018;105:68-74. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10715
13. Ulug P, Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, et al. Meta-analysis of the current prevalence of screen-detected abdominal aortic aneurysm in women. Br J Surg. 2016;103:1097-1104. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10225
14. Chabok M, Nicolaides A, Aslam M, et al. Risk factors associated with increased prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysm in women. Br J Surg. 2016;103:1132-1138. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10179
15. Sweeting, MJ, Masconi KL, Jones E, et al. Analysis of clinical benefit, harms, and cost-effectiveness of screening women for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Lancet. 2018;392:487-495. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31222-4
16. Sweeting MJ, Thompson SG, Brown LC, et al; RESCAN collaborators. Meta-analysis of individual patient data to examine factors affecting growth and rupture of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2012;99:655-665. doi: 10.1002/bjs.8707
17. Skibba AA, Evans JR, Hopkins SP, et al. Reconsidering gender relative to risk of rupture in the contemporary management of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2015;62:1429-1436. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.07.079
18. Guirguis-Blake JM, Beil TL, Senger CA, et al. Primary care screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2019;322:2219-2238. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17021
19. Thompson SG, Ashton HA, Gao L, et al; Multicentre Aneurysm Screening Study (MASS) Group. Final follow-up of the Multicentre Aneurysm Screening Study (MASS) randomized trial of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening. Br J Surg. 2012;99:1649-1656. doi: 10.1002/bjs.8897
20. Ashton HA, Gao L, Kim LG, et al. Fifteen-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial of ultrasonographic screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2007;94:696-701. doi: 10.1002/bjs.5780
21. Carnevale ML, Koleilat I, Lipsitz EC, et al. Extended screening guidelines for the diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72:1917-1926. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.03.047
22. Duncan A, Maslen C, Gibson C, et al. Ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm in high-risk women. Br J Surg. 2021;108:1192-1198. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znab220
23. Shreibati JB, Baker LC, Hlatky MA, et al. Impact of the Screening Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Very Efficiently (SAAAVE) Act on abdominal ultrasonography use among Medicare beneficiaries. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:1456-1462. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.4268
24. Hye RJ, Smith AE, Wong GH, et al. Leveraging the electronic medical record to implement an abdominal aortic aneurysm screening program. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59:1535-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.12.016
25. Rubano E, Mehta N, Caputo W, et al., Systematic review: emergency department bedside ultrasonography for diagnosing suspected abdominal aortic aneurysm. Acad Emerg Med. 2013. 20:128-138. doi: 10.1111/acem.12080
26. Blois B. Office-based ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:e172-e178.
27. Arnold MJ, Jonas CE, Carter RE. Point-of-care ultrasonography. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101:275-285.
28. Nixon G, Blattner K, Muirhead J, et al. Point-of-care ultrasound for FAST and AAA in rural New Zealand: quality and impact on patient care. Rural Remote Health. 2019;19:5027. doi: 10.22605/RRH5027
29. Lederle FA, Wilson SE, Johnson GR, et al. Immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1437-1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012573
30. Filardo G, Lederle FA, Ballard DJ, et al. Immediate open repair vs surveillance in patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms: survival differences by aneurysm size. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013;88:910-919. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.05.014
31. Lederle FA, Kyriakides TC, Stroupe KT, et al. Open versus endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2126-2135. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1715955
32. Patel R, Sweeting MJ, Powell JT, et al., Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in 15-years’ follow-up of the UK endovascular aneurysm repair trial 1 (EVAR trial 1): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2366-2374. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31135-7
33. van Schaik TG, Yeung KK, Verhagen HJ, et al. Long-term survival and secondary procedures after open or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2017;66:1379-1389. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.05.122
34. Powell JT, Brady AR, Brown, LC, et al; United Kingdom Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Long-term outcomes of immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1445-1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa013527
35. Paravastu SC, Jayarajasingam R, Cottam R, et al. Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD004178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004178.pub2
36. Rooke TW, Hirsch AT, Misra S, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA focused update of the guideline for the management of patients with peripheral artery disease (updating the 2005 guideline): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:2020-2045. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.08.023
37. Bhak RH, Wininger M, Johnson GR, et al. Factors associated with small abdominal aortic aneurysm expansion rate. JAMA Surg. 2015;150:44-50. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2014.2025
38. Ouriel K, Clair DG, Kent KC, et al; Positive Impact of Endovascular Options for treating Aneurysms Early (PIVOTAL) Investigators. Endovascular repair compared with surveillance for patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2010;51:1081-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2009.10.113
39. Cao P, De Rango P, Verzini F, et al. Comparison of surveillance versus aortic endografting for small aneurysm repair (CAESAR): results from a randomised trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;41:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.08.026
40. Karthaus EG, Tong TML, Vahl A, et al; Dutch Society of Vascular Surgery, the Steering Committee of the Dutch Surgical Aneurysm Audit and the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing. Saccular abdominal aortic aneurysms: patient characteristics, clinical presentation, treatment, and outcomes in the Netherlands. Ann Surg. 2019;270:852-858. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003529
41. Nathan DP, Xu C, Pouch AM, et al. Increased wall stress of saccular versus fusiform aneurysms of the descending thoracic aorta. Ann Vasc Surg. 2011;25:1129-2237. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2011.07.008
42. Durojaye MS, Adeniyi TO, Alagbe OA. Multiple saccular aneurysms of the abdominal aorta: a case report and short review of risk factors for rupture on CT Scan. Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2020;18:178-180.
43. Bertges DJ, Neal D, Schanzer A, et al. The Vascular Quality Initiative Cardiac Risk Index for prediction of myocardial infarction after vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64:1411-1421.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.04.045
44. Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:111-188. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455
45. Twine CP, Williams IM. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of statin therapy on abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2011;98:346-353. doi: 10.1002/bjs.7343
46. Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:e596-e646. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
47. Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2873-2926. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu281
48. Lederle FA, Noorbaloochi S, Nugent S, et al. Multicentre study of abdominal aortic aneurysm measurement and enlargement. Br J Surg. 2015;102:1480-1487. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9895
49. Itoga NK, Rothenberg KA, Suarez P, et al. Metformin prescription status and abdominal aortic aneurysm disease progression in the U.S. veteran population. J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:710-716.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.06.19
1. CDC. Wide-ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research (WONDER) database. Accessed August 30, 2023. https://wonder.cdc.gov/ucd-icd10.html
2. Reimerink JJ, van der Laan MJ, Koelemay MJ, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2013;100:1405-1413. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9235
3. Kent KC. Clinical practice. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
4. Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
5. Moll FL, Powell JT, Fraedrich G, et al. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms clinical practice guidelines of the European society for vascular surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;41 suppl 1:S1-S58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.09.011
6. Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2019;322:2211-2218. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18928
7. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline [NG156]. March 19, 2020. Accessed June 30, 2023. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156/chapter/recommendations
8. Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Recommendations on screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm in primary care. CMAJ. 2017;189:E1137-E1145. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.170118
9. Abdulameer H, Al Taii H, Al-Kindi SG, et al. Epidemiology of fatal ruptured aortic aneurysms in the United States (1999-2016). J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:378-384.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.03.435
10. Kent KC, Zwolak RM, Egorova NN, et al. Analysis of risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in a cohort of more than 3 million individuals. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:539-548. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.05.090
11. [No authors listed] Smoking, lung function and the prognosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm. The UK Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2000;19:636-642. doi: 10.1053/ejvs.2000.1066
12. Oliver-Williams C, Sweeting MJ, Turton G, et al. Lessons learned about prevalence and growth rates of abdominal aortic aneurysms from a 25-year ultrasound population screening programme. Br J Surg. 2018;105:68-74. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10715
13. Ulug P, Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, et al. Meta-analysis of the current prevalence of screen-detected abdominal aortic aneurysm in women. Br J Surg. 2016;103:1097-1104. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10225
14. Chabok M, Nicolaides A, Aslam M, et al. Risk factors associated with increased prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysm in women. Br J Surg. 2016;103:1132-1138. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10179
15. Sweeting, MJ, Masconi KL, Jones E, et al. Analysis of clinical benefit, harms, and cost-effectiveness of screening women for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Lancet. 2018;392:487-495. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31222-4
16. Sweeting MJ, Thompson SG, Brown LC, et al; RESCAN collaborators. Meta-analysis of individual patient data to examine factors affecting growth and rupture of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2012;99:655-665. doi: 10.1002/bjs.8707
17. Skibba AA, Evans JR, Hopkins SP, et al. Reconsidering gender relative to risk of rupture in the contemporary management of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2015;62:1429-1436. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.07.079
18. Guirguis-Blake JM, Beil TL, Senger CA, et al. Primary care screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2019;322:2219-2238. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17021
19. Thompson SG, Ashton HA, Gao L, et al; Multicentre Aneurysm Screening Study (MASS) Group. Final follow-up of the Multicentre Aneurysm Screening Study (MASS) randomized trial of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening. Br J Surg. 2012;99:1649-1656. doi: 10.1002/bjs.8897
20. Ashton HA, Gao L, Kim LG, et al. Fifteen-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial of ultrasonographic screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2007;94:696-701. doi: 10.1002/bjs.5780
21. Carnevale ML, Koleilat I, Lipsitz EC, et al. Extended screening guidelines for the diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72:1917-1926. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.03.047
22. Duncan A, Maslen C, Gibson C, et al. Ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm in high-risk women. Br J Surg. 2021;108:1192-1198. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znab220
23. Shreibati JB, Baker LC, Hlatky MA, et al. Impact of the Screening Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Very Efficiently (SAAAVE) Act on abdominal ultrasonography use among Medicare beneficiaries. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:1456-1462. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.4268
24. Hye RJ, Smith AE, Wong GH, et al. Leveraging the electronic medical record to implement an abdominal aortic aneurysm screening program. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59:1535-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.12.016
25. Rubano E, Mehta N, Caputo W, et al., Systematic review: emergency department bedside ultrasonography for diagnosing suspected abdominal aortic aneurysm. Acad Emerg Med. 2013. 20:128-138. doi: 10.1111/acem.12080
26. Blois B. Office-based ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:e172-e178.
27. Arnold MJ, Jonas CE, Carter RE. Point-of-care ultrasonography. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101:275-285.
28. Nixon G, Blattner K, Muirhead J, et al. Point-of-care ultrasound for FAST and AAA in rural New Zealand: quality and impact on patient care. Rural Remote Health. 2019;19:5027. doi: 10.22605/RRH5027
29. Lederle FA, Wilson SE, Johnson GR, et al. Immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1437-1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012573
30. Filardo G, Lederle FA, Ballard DJ, et al. Immediate open repair vs surveillance in patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms: survival differences by aneurysm size. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013;88:910-919. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.05.014
31. Lederle FA, Kyriakides TC, Stroupe KT, et al. Open versus endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2126-2135. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1715955
32. Patel R, Sweeting MJ, Powell JT, et al., Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in 15-years’ follow-up of the UK endovascular aneurysm repair trial 1 (EVAR trial 1): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2366-2374. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31135-7
33. van Schaik TG, Yeung KK, Verhagen HJ, et al. Long-term survival and secondary procedures after open or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2017;66:1379-1389. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.05.122
34. Powell JT, Brady AR, Brown, LC, et al; United Kingdom Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Long-term outcomes of immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1445-1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa013527
35. Paravastu SC, Jayarajasingam R, Cottam R, et al. Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD004178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004178.pub2
36. Rooke TW, Hirsch AT, Misra S, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA focused update of the guideline for the management of patients with peripheral artery disease (updating the 2005 guideline): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:2020-2045. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.08.023
37. Bhak RH, Wininger M, Johnson GR, et al. Factors associated with small abdominal aortic aneurysm expansion rate. JAMA Surg. 2015;150:44-50. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2014.2025
38. Ouriel K, Clair DG, Kent KC, et al; Positive Impact of Endovascular Options for treating Aneurysms Early (PIVOTAL) Investigators. Endovascular repair compared with surveillance for patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2010;51:1081-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2009.10.113
39. Cao P, De Rango P, Verzini F, et al. Comparison of surveillance versus aortic endografting for small aneurysm repair (CAESAR): results from a randomised trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;41:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.08.026
40. Karthaus EG, Tong TML, Vahl A, et al; Dutch Society of Vascular Surgery, the Steering Committee of the Dutch Surgical Aneurysm Audit and the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing. Saccular abdominal aortic aneurysms: patient characteristics, clinical presentation, treatment, and outcomes in the Netherlands. Ann Surg. 2019;270:852-858. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003529
41. Nathan DP, Xu C, Pouch AM, et al. Increased wall stress of saccular versus fusiform aneurysms of the descending thoracic aorta. Ann Vasc Surg. 2011;25:1129-2237. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2011.07.008
42. Durojaye MS, Adeniyi TO, Alagbe OA. Multiple saccular aneurysms of the abdominal aorta: a case report and short review of risk factors for rupture on CT Scan. Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2020;18:178-180.
43. Bertges DJ, Neal D, Schanzer A, et al. The Vascular Quality Initiative Cardiac Risk Index for prediction of myocardial infarction after vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64:1411-1421.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.04.045
44. Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:111-188. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455
45. Twine CP, Williams IM. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of statin therapy on abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 2011;98:346-353. doi: 10.1002/bjs.7343
46. Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:e596-e646. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
47. Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2873-2926. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu281
48. Lederle FA, Noorbaloochi S, Nugent S, et al. Multicentre study of abdominal aortic aneurysm measurement and enlargement. Br J Surg. 2015;102:1480-1487. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9895
49. Itoga NK, Rothenberg KA, Suarez P, et al. Metformin prescription status and abdominal aortic aneurysm disease progression in the U.S. veteran population. J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:710-716.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.06.19
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Perform a one-time abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) screening ultrasound in men ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked. B
› Consider performing a one-time AAA screening ultrasound in women ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked. C
› Prescribe high-intensity statin therapy for men and women with atherosclerotic AAA. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Can these salt substitutes prevent complications of hypertension?
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 47-year-old man in generally good health presents to a family medicine clinic for a well visit. He does not use tobacco products and had a benign colonoscopy last year. He reports walking for 30 minutes 3 to 4 times per week for exercise, althoug h he has gained 3 lbs over the past 2 years. He has no family history of early coronary artery disease, but his father and older brother have hypertension. His mother has a history of diabetes and hyperlipidemia.
The patient’s physical exam is unremarkable except for an elevated BP reading of 151/82 mm Hg. A review of his chart indicates he has had multiple elevated readings in the past that have ranged from 132/72 mm Hg to 139/89 mm Hg. The patient is interested in antihypertensive treatment but wants to know if modifying his diet and replacing his regular table salt with a salt substitute will lower his high BP. What can you recommend?
Hypertension is a leading cause of CV morbidity and mortality worldwide and is linked to increased dietary sodium intake. An estimated 1.28 billion people worldwide have hypertension; however, more than half of cases are undiagnosed.2 The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for hypertension in adults older than 18 years and confirming elevated measurements conducted in a nonclinical setting before starting medication (grade “A”).3
Cut-points for the diagnosis of hypertension vary. The American Academy of Family Physicians, 4 the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8), 5 the International Society of Hypertension, 6 and the European Society of Cardiology 7 use ≥ 140 mm Hg systolic BP (SBP) or ≥ 90 mm Hg diastolic BP (DBP) to define hypertension. The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines use ≥ 130/80 mm Hg. 8
When treating patients with hypertension, primary care physicians often recommend lifestyle modifications such as the
Systematic reviews have shown a measurable improvement in BP with sodium reduction and potassium substitution. 10-12 More importantly, high-quality evidence demonstrates a decreased risk for CV disease, kidney disease, and all-cause mortality with lower dietary sodium intake. 13 Previous studies have shown that potassium-enriched salt substitutes lower BP, but their impact on CV morbidity and mortality is not well defined. Although lowering BP is associated with improved clinical impact, there is a lack of patient-oriented evidence that demonstrates improvement in CV disease and mortality.
The Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS), published in 2021, demonstrated the protective effect of salt substitution against stroke, other CV events, and death. 14 Furthermore, this 5-year, cluster-randomized controlled trial of 20,995 participants across 600 villages in China demonstrated reduced CV mortality and BP reduction similar to standard pharmacologic treatment. Prior to SSaSS, 17 randomized controlled trials demonstrated a BP-lowering effect of salt substitutes but did not directly study the impact on clinical outcomes. 13
Continue to: In this 2022 systematic review...
In this 2022 systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 Yin et al evaluated 21 trials, including SSaSS, for the effect of salt substitutes on BP and other clinical outcomes, and the generalizability of the study results to diverse populations. The systematic review included parallel-group, step-wedge, and cluster-randomized controlled trials reporting the effect of salt substitutes on BP or clinical outcomes.
STUDY SUMMARY
Salt substitutes reduced BP across diverse populations
This systematic review and meta-analysis reviewed existing literature for randomized controlled trials investigating the effects of potassium-enriched salt substitutes on clinical outcomes for patients without kidney disease. The most commonly used salt substitute was potassium chloride, at 25% to 65% potassium.
The systematic review identified 21 trials comprising 31,949 study participants from 15 different countries with 1 to 60 months’ duration. Meta-analyses were performed using 19 trials for BP outcomes and 5 trials for vascular outcomes. Eleven trials were rated as having low risk for bias, 8 were deemed to have some concern, and 2 were rated as high risk for bias. Comparisons of data excluding studies with high risk for bias yielded results similar to comparisons of all studies.
The meta-analysis of 19 trials demonstrated reduced SBP (–4.6 mm Hg; 95% CI, –6.1 to –3.1) and DBP (–1.6 mm Hg; 95% CI, –2.4 to –0.8) in participants using potassium-enriched salt substitutes. However, the authors noted substantial heterogeneity among the studies (I 2 > 70%) for both SBP and DBP outcomes. Although there were no subgroup differences for age, sex, hypertension history, or other biomarkers, outcome differences were associated with trial duration, baseline potassium intake, and composition of the salt substitute.
Potassium-enriched salt substitutes were associated with reduced total mortality (risk ratio [RR] = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94), CV mortality (RR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.81-0.94), and CV events (RR = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94). In a meta-regression, each 10% reduction in the sodium content of the salt substitute was associated with a 1.5–mm Hg greater reduction in SBP (95% CI, –3.0 to –0.03) and a 1.0–mm Hg greater reduction in DBP (95% CI, –1.8 to –0.1). However, the authors suggest interpreting meta-regression results with caution.
Continue to: Only 2 of the studes...
Only 2 of the studies in the systematic review explicitly reported the adverse effect of hyperkalemia, and there was no statistical difference in events between randomized groups. Eight other studies reported no serious adverse events related to hyperkalemia , and 11 studies did not report on the risk for hyperkalemia.
WHAT’S NEW
High-quality data demonstrate beneficial outcomes
Previous observational and interventional studies demonstrated a BP-lowering effect of salt substitutes, but limited data with poor-quality evidence existed for the impact of salt substitutes on clinical outcomes such as mortality and CV events. This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that potassium-supplemented salt may reduce BP and secondarily reduce the risk for CV events, CV mortality, and total mortality, without clear harmful effects reported.
CAVEATS
Some patient populations, comorbidities excluded from study
The study did not include patients with kidney disease or those taking potassium-sparing diuretics. Furthermore, the available data do not include primary prevention participants.
Subgroup analyses should be interpreted with caution due to the small number of trials available for individual subgroups. In addition, funnel plot asymmetry for studies reporting DBP suggests at least some effect of publication bias for that outcome.
Although BP reduction due to salt substitutes may be small at an individual level, these levels of reduction may be important at a population level.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
For appropriate patients, no challenges anticipated
There are no significant challenges to implementing conclusions from this study in the primary care setting. Family physicians should be able to recommend potassium-enriched salt substitutes to patients with hypertension who are not at risk for hyperkalemia, including those with kidney disease, on potassium-sparing diuretics, or with a history of hyperkalemia/hyperkalemic conditions. Salt substitutes, including potassium-enriched salts, are readily available in stores.
1. Yin X, Rodgers A, Perkovic A, et al. Effects of salt substitutes on clinical outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart. 2022;108:1608-1615. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2022-321332
2. NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. 2021;398:957-980. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1
3. USPSTF. Hypertension in adults: screening. Final recommendation statement. Published April 27, 2021. Accessed September 18, 2023. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/hypertension-in-adults-screening
4. Coles S, Fisher L, Lin KW, et al. Blood pressure targets in adults with hypertension: a clinical practice guideline from the AAFP. Published November 4, 2022. Accessed September 18, 2023. www.aafp.org/dam/AAFP/documents/journals/afp/AAFPHypertensionGuideline.pdf
5. James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014;311:507-520. doi: 10.1001/jama. 2013.284427
6. Unger T, Borgi C, Charchar F, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2020;75:1334-1357. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15026
7. Mancia G, Kreutz R, Brunstrom M, et al; the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Endorsed by the European Renal Association (ERA) and the International Society of Hypertension (ISH). J Hypertens. 2023; Jun 21. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003480
8. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:e13-e115. 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000065
9. National Center for Health Statistics. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2014 state and national summary tables. Accessed June 27, 2023. www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ahcd/namcs_summary/2014_namcs_web_tables.pdf
10. Huang L, Trieu K, Yoshimura S, et al. Effect of dose and duration of reduction in dietary sodium on blood pressure levels: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ. 2020;368:m315. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m315
11. Filippini T, Violi F, D’Amico R, et al. The effect of potassium supplementation on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2017;230:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.12.048
12. Brand A, Visser ME, Schoonees A, et al. Replacing salt with low-sodium salt substitutes (LSSS) for cardiovascular health in adults, children and pregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;8:CD015207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015207
13. He FJ, Tan M, Ma Y, et al. Salt reduction to prevent hypertension and cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:632-647. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.11.055
14. Neal B, Wu Y, Feng X, et al. Effect of salt substitution on cardiovascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1067-1077. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105675
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 47-year-old man in generally good health presents to a family medicine clinic for a well visit. He does not use tobacco products and had a benign colonoscopy last year. He reports walking for 30 minutes 3 to 4 times per week for exercise, althoug h he has gained 3 lbs over the past 2 years. He has no family history of early coronary artery disease, but his father and older brother have hypertension. His mother has a history of diabetes and hyperlipidemia.
The patient’s physical exam is unremarkable except for an elevated BP reading of 151/82 mm Hg. A review of his chart indicates he has had multiple elevated readings in the past that have ranged from 132/72 mm Hg to 139/89 mm Hg. The patient is interested in antihypertensive treatment but wants to know if modifying his diet and replacing his regular table salt with a salt substitute will lower his high BP. What can you recommend?
Hypertension is a leading cause of CV morbidity and mortality worldwide and is linked to increased dietary sodium intake. An estimated 1.28 billion people worldwide have hypertension; however, more than half of cases are undiagnosed.2 The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for hypertension in adults older than 18 years and confirming elevated measurements conducted in a nonclinical setting before starting medication (grade “A”).3
Cut-points for the diagnosis of hypertension vary. The American Academy of Family Physicians, 4 the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8), 5 the International Society of Hypertension, 6 and the European Society of Cardiology 7 use ≥ 140 mm Hg systolic BP (SBP) or ≥ 90 mm Hg diastolic BP (DBP) to define hypertension. The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines use ≥ 130/80 mm Hg. 8
When treating patients with hypertension, primary care physicians often recommend lifestyle modifications such as the
Systematic reviews have shown a measurable improvement in BP with sodium reduction and potassium substitution. 10-12 More importantly, high-quality evidence demonstrates a decreased risk for CV disease, kidney disease, and all-cause mortality with lower dietary sodium intake. 13 Previous studies have shown that potassium-enriched salt substitutes lower BP, but their impact on CV morbidity and mortality is not well defined. Although lowering BP is associated with improved clinical impact, there is a lack of patient-oriented evidence that demonstrates improvement in CV disease and mortality.
The Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS), published in 2021, demonstrated the protective effect of salt substitution against stroke, other CV events, and death. 14 Furthermore, this 5-year, cluster-randomized controlled trial of 20,995 participants across 600 villages in China demonstrated reduced CV mortality and BP reduction similar to standard pharmacologic treatment. Prior to SSaSS, 17 randomized controlled trials demonstrated a BP-lowering effect of salt substitutes but did not directly study the impact on clinical outcomes. 13
Continue to: In this 2022 systematic review...
In this 2022 systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 Yin et al evaluated 21 trials, including SSaSS, for the effect of salt substitutes on BP and other clinical outcomes, and the generalizability of the study results to diverse populations. The systematic review included parallel-group, step-wedge, and cluster-randomized controlled trials reporting the effect of salt substitutes on BP or clinical outcomes.
STUDY SUMMARY
Salt substitutes reduced BP across diverse populations
This systematic review and meta-analysis reviewed existing literature for randomized controlled trials investigating the effects of potassium-enriched salt substitutes on clinical outcomes for patients without kidney disease. The most commonly used salt substitute was potassium chloride, at 25% to 65% potassium.
The systematic review identified 21 trials comprising 31,949 study participants from 15 different countries with 1 to 60 months’ duration. Meta-analyses were performed using 19 trials for BP outcomes and 5 trials for vascular outcomes. Eleven trials were rated as having low risk for bias, 8 were deemed to have some concern, and 2 were rated as high risk for bias. Comparisons of data excluding studies with high risk for bias yielded results similar to comparisons of all studies.
The meta-analysis of 19 trials demonstrated reduced SBP (–4.6 mm Hg; 95% CI, –6.1 to –3.1) and DBP (–1.6 mm Hg; 95% CI, –2.4 to –0.8) in participants using potassium-enriched salt substitutes. However, the authors noted substantial heterogeneity among the studies (I 2 > 70%) for both SBP and DBP outcomes. Although there were no subgroup differences for age, sex, hypertension history, or other biomarkers, outcome differences were associated with trial duration, baseline potassium intake, and composition of the salt substitute.
Potassium-enriched salt substitutes were associated with reduced total mortality (risk ratio [RR] = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94), CV mortality (RR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.81-0.94), and CV events (RR = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94). In a meta-regression, each 10% reduction in the sodium content of the salt substitute was associated with a 1.5–mm Hg greater reduction in SBP (95% CI, –3.0 to –0.03) and a 1.0–mm Hg greater reduction in DBP (95% CI, –1.8 to –0.1). However, the authors suggest interpreting meta-regression results with caution.
Continue to: Only 2 of the studes...
Only 2 of the studies in the systematic review explicitly reported the adverse effect of hyperkalemia, and there was no statistical difference in events between randomized groups. Eight other studies reported no serious adverse events related to hyperkalemia , and 11 studies did not report on the risk for hyperkalemia.
WHAT’S NEW
High-quality data demonstrate beneficial outcomes
Previous observational and interventional studies demonstrated a BP-lowering effect of salt substitutes, but limited data with poor-quality evidence existed for the impact of salt substitutes on clinical outcomes such as mortality and CV events. This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that potassium-supplemented salt may reduce BP and secondarily reduce the risk for CV events, CV mortality, and total mortality, without clear harmful effects reported.
CAVEATS
Some patient populations, comorbidities excluded from study
The study did not include patients with kidney disease or those taking potassium-sparing diuretics. Furthermore, the available data do not include primary prevention participants.
Subgroup analyses should be interpreted with caution due to the small number of trials available for individual subgroups. In addition, funnel plot asymmetry for studies reporting DBP suggests at least some effect of publication bias for that outcome.
Although BP reduction due to salt substitutes may be small at an individual level, these levels of reduction may be important at a population level.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
For appropriate patients, no challenges anticipated
There are no significant challenges to implementing conclusions from this study in the primary care setting. Family physicians should be able to recommend potassium-enriched salt substitutes to patients with hypertension who are not at risk for hyperkalemia, including those with kidney disease, on potassium-sparing diuretics, or with a history of hyperkalemia/hyperkalemic conditions. Salt substitutes, including potassium-enriched salts, are readily available in stores.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 47-year-old man in generally good health presents to a family medicine clinic for a well visit. He does not use tobacco products and had a benign colonoscopy last year. He reports walking for 30 minutes 3 to 4 times per week for exercise, althoug h he has gained 3 lbs over the past 2 years. He has no family history of early coronary artery disease, but his father and older brother have hypertension. His mother has a history of diabetes and hyperlipidemia.
The patient’s physical exam is unremarkable except for an elevated BP reading of 151/82 mm Hg. A review of his chart indicates he has had multiple elevated readings in the past that have ranged from 132/72 mm Hg to 139/89 mm Hg. The patient is interested in antihypertensive treatment but wants to know if modifying his diet and replacing his regular table salt with a salt substitute will lower his high BP. What can you recommend?
Hypertension is a leading cause of CV morbidity and mortality worldwide and is linked to increased dietary sodium intake. An estimated 1.28 billion people worldwide have hypertension; however, more than half of cases are undiagnosed.2 The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for hypertension in adults older than 18 years and confirming elevated measurements conducted in a nonclinical setting before starting medication (grade “A”).3
Cut-points for the diagnosis of hypertension vary. The American Academy of Family Physicians, 4 the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8), 5 the International Society of Hypertension, 6 and the European Society of Cardiology 7 use ≥ 140 mm Hg systolic BP (SBP) or ≥ 90 mm Hg diastolic BP (DBP) to define hypertension. The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines use ≥ 130/80 mm Hg. 8
When treating patients with hypertension, primary care physicians often recommend lifestyle modifications such as the
Systematic reviews have shown a measurable improvement in BP with sodium reduction and potassium substitution. 10-12 More importantly, high-quality evidence demonstrates a decreased risk for CV disease, kidney disease, and all-cause mortality with lower dietary sodium intake. 13 Previous studies have shown that potassium-enriched salt substitutes lower BP, but their impact on CV morbidity and mortality is not well defined. Although lowering BP is associated with improved clinical impact, there is a lack of patient-oriented evidence that demonstrates improvement in CV disease and mortality.
The Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS), published in 2021, demonstrated the protective effect of salt substitution against stroke, other CV events, and death. 14 Furthermore, this 5-year, cluster-randomized controlled trial of 20,995 participants across 600 villages in China demonstrated reduced CV mortality and BP reduction similar to standard pharmacologic treatment. Prior to SSaSS, 17 randomized controlled trials demonstrated a BP-lowering effect of salt substitutes but did not directly study the impact on clinical outcomes. 13
Continue to: In this 2022 systematic review...
In this 2022 systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 Yin et al evaluated 21 trials, including SSaSS, for the effect of salt substitutes on BP and other clinical outcomes, and the generalizability of the study results to diverse populations. The systematic review included parallel-group, step-wedge, and cluster-randomized controlled trials reporting the effect of salt substitutes on BP or clinical outcomes.
STUDY SUMMARY
Salt substitutes reduced BP across diverse populations
This systematic review and meta-analysis reviewed existing literature for randomized controlled trials investigating the effects of potassium-enriched salt substitutes on clinical outcomes for patients without kidney disease. The most commonly used salt substitute was potassium chloride, at 25% to 65% potassium.
The systematic review identified 21 trials comprising 31,949 study participants from 15 different countries with 1 to 60 months’ duration. Meta-analyses were performed using 19 trials for BP outcomes and 5 trials for vascular outcomes. Eleven trials were rated as having low risk for bias, 8 were deemed to have some concern, and 2 were rated as high risk for bias. Comparisons of data excluding studies with high risk for bias yielded results similar to comparisons of all studies.
The meta-analysis of 19 trials demonstrated reduced SBP (–4.6 mm Hg; 95% CI, –6.1 to –3.1) and DBP (–1.6 mm Hg; 95% CI, –2.4 to –0.8) in participants using potassium-enriched salt substitutes. However, the authors noted substantial heterogeneity among the studies (I 2 > 70%) for both SBP and DBP outcomes. Although there were no subgroup differences for age, sex, hypertension history, or other biomarkers, outcome differences were associated with trial duration, baseline potassium intake, and composition of the salt substitute.
Potassium-enriched salt substitutes were associated with reduced total mortality (risk ratio [RR] = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94), CV mortality (RR = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.81-0.94), and CV events (RR = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.85-0.94). In a meta-regression, each 10% reduction in the sodium content of the salt substitute was associated with a 1.5–mm Hg greater reduction in SBP (95% CI, –3.0 to –0.03) and a 1.0–mm Hg greater reduction in DBP (95% CI, –1.8 to –0.1). However, the authors suggest interpreting meta-regression results with caution.
Continue to: Only 2 of the studes...
Only 2 of the studies in the systematic review explicitly reported the adverse effect of hyperkalemia, and there was no statistical difference in events between randomized groups. Eight other studies reported no serious adverse events related to hyperkalemia , and 11 studies did not report on the risk for hyperkalemia.
WHAT’S NEW
High-quality data demonstrate beneficial outcomes
Previous observational and interventional studies demonstrated a BP-lowering effect of salt substitutes, but limited data with poor-quality evidence existed for the impact of salt substitutes on clinical outcomes such as mortality and CV events. This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that potassium-supplemented salt may reduce BP and secondarily reduce the risk for CV events, CV mortality, and total mortality, without clear harmful effects reported.
CAVEATS
Some patient populations, comorbidities excluded from study
The study did not include patients with kidney disease or those taking potassium-sparing diuretics. Furthermore, the available data do not include primary prevention participants.
Subgroup analyses should be interpreted with caution due to the small number of trials available for individual subgroups. In addition, funnel plot asymmetry for studies reporting DBP suggests at least some effect of publication bias for that outcome.
Although BP reduction due to salt substitutes may be small at an individual level, these levels of reduction may be important at a population level.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
For appropriate patients, no challenges anticipated
There are no significant challenges to implementing conclusions from this study in the primary care setting. Family physicians should be able to recommend potassium-enriched salt substitutes to patients with hypertension who are not at risk for hyperkalemia, including those with kidney disease, on potassium-sparing diuretics, or with a history of hyperkalemia/hyperkalemic conditions. Salt substitutes, including potassium-enriched salts, are readily available in stores.
1. Yin X, Rodgers A, Perkovic A, et al. Effects of salt substitutes on clinical outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart. 2022;108:1608-1615. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2022-321332
2. NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. 2021;398:957-980. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1
3. USPSTF. Hypertension in adults: screening. Final recommendation statement. Published April 27, 2021. Accessed September 18, 2023. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/hypertension-in-adults-screening
4. Coles S, Fisher L, Lin KW, et al. Blood pressure targets in adults with hypertension: a clinical practice guideline from the AAFP. Published November 4, 2022. Accessed September 18, 2023. www.aafp.org/dam/AAFP/documents/journals/afp/AAFPHypertensionGuideline.pdf
5. James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014;311:507-520. doi: 10.1001/jama. 2013.284427
6. Unger T, Borgi C, Charchar F, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2020;75:1334-1357. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15026
7. Mancia G, Kreutz R, Brunstrom M, et al; the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Endorsed by the European Renal Association (ERA) and the International Society of Hypertension (ISH). J Hypertens. 2023; Jun 21. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003480
8. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:e13-e115. 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000065
9. National Center for Health Statistics. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2014 state and national summary tables. Accessed June 27, 2023. www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ahcd/namcs_summary/2014_namcs_web_tables.pdf
10. Huang L, Trieu K, Yoshimura S, et al. Effect of dose and duration of reduction in dietary sodium on blood pressure levels: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ. 2020;368:m315. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m315
11. Filippini T, Violi F, D’Amico R, et al. The effect of potassium supplementation on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2017;230:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.12.048
12. Brand A, Visser ME, Schoonees A, et al. Replacing salt with low-sodium salt substitutes (LSSS) for cardiovascular health in adults, children and pregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;8:CD015207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015207
13. He FJ, Tan M, Ma Y, et al. Salt reduction to prevent hypertension and cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:632-647. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.11.055
14. Neal B, Wu Y, Feng X, et al. Effect of salt substitution on cardiovascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1067-1077. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105675
1. Yin X, Rodgers A, Perkovic A, et al. Effects of salt substitutes on clinical outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart. 2022;108:1608-1615. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2022-321332
2. NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. 2021;398:957-980. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1
3. USPSTF. Hypertension in adults: screening. Final recommendation statement. Published April 27, 2021. Accessed September 18, 2023. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/hypertension-in-adults-screening
4. Coles S, Fisher L, Lin KW, et al. Blood pressure targets in adults with hypertension: a clinical practice guideline from the AAFP. Published November 4, 2022. Accessed September 18, 2023. www.aafp.org/dam/AAFP/documents/journals/afp/AAFPHypertensionGuideline.pdf
5. James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014;311:507-520. doi: 10.1001/jama. 2013.284427
6. Unger T, Borgi C, Charchar F, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2020;75:1334-1357. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15026
7. Mancia G, Kreutz R, Brunstrom M, et al; the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Endorsed by the European Renal Association (ERA) and the International Society of Hypertension (ISH). J Hypertens. 2023; Jun 21. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003480
8. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:e13-e115. 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000065
9. National Center for Health Statistics. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2014 state and national summary tables. Accessed June 27, 2023. www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ahcd/namcs_summary/2014_namcs_web_tables.pdf
10. Huang L, Trieu K, Yoshimura S, et al. Effect of dose and duration of reduction in dietary sodium on blood pressure levels: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ. 2020;368:m315. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m315
11. Filippini T, Violi F, D’Amico R, et al. The effect of potassium supplementation on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2017;230:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.12.048
12. Brand A, Visser ME, Schoonees A, et al. Replacing salt with low-sodium salt substitutes (LSSS) for cardiovascular health in adults, children and pregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;8:CD015207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015207
13. He FJ, Tan M, Ma Y, et al. Salt reduction to prevent hypertension and cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:632-647. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.11.055
14. Neal B, Wu Y, Feng X, et al. Effect of salt substitution on cardiovascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1067-1077. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105675
PRACTICE CHANGER
Consider recommending potassium-enriched salt substitutes for appropriate patients with hypertension to reduce blood pressure (BP) and risk for related cardiovascular (CV) events or mortality.
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
A: Based on a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. 1
Yin X, Rodgers A, Perkovic A, et al. Effects of salt substitutes on clinical outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart . 2022;108:1608-1615. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2022-321332