User login
Ancient Viruses in Our DNA Hold Clues to Cancer Treatment
according to a fascinating new study in Science Advances. Targeting these viral remnants still lingering in our DNA could lead to more effective cancer treatment with fewer side effects, the researchers said.
The study “gives a better understanding of how gene regulation can be impacted by these ancient retroviral sequences,” said Dixie Mager, PhD, scientist emeritus at the Terry Fox Laboratory at the British Columbia Cancer Research Institute, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. (Mager was not involved in the study.)
Long thought to be “junk” DNA with no biologic function, “endogenous retroviruses,” which have mutated over time and lost their ability to create the virus, are now known to regulate genes — allowing some genes to turn on and off. Research in recent years suggests they may play a role in diseases like cancer.
But scientists weren’t exactly sure what that role was, said senior study author Edward Chuong, PhD, a genome biologist at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Most studies have looked at whether endogenous retroviruses code for proteins that influence cancer. But these ancient viral strands usually don’t code for proteins at all.
Dr. Chuong took a different approach. Inspired by scientists who’ve studied how viral remnants regulate positive processes (immunity, brain development, or placenta development), he and his team explored whether some might regulate genes that, once activated, help cancer thrive.
Borrowing from epigenomic analysis data (data on molecules that alter gene expression) for 21 cancers mapped by the Cancer Genome Atlas, the researchers identified 19 virus-derived DNA sequences that bind to regulatory proteins more in cancer cells than in healthy cells. All of these could potentially act as gene regulators that promote cancer.
The researchers homed in on one sequence, called LTR10, because it showed especially high activity in several cancers, including lung and colorectal cancer. This DNA segment comes from a virus that entered our ancestors’ genome 30 million years ago, and it’s activated in a third of colorectal cancers.
Using the gene editing technology clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), Dr. Chuong’s team silenced LTR10 in colorectal cancer cells, altering the gene sequence so it couldn’t bind to regulatory proteins. Doing so dampened the activity of nearby cancer-promoting genes.
“They still behaved like cancer cells,” Dr. Chuong said. But “it made the cancer cells more susceptible to radiation. That would imply that the presence of that viral ‘switch’ actually helped those cancer cells survive radiation therapy.”
Previously, two studies had found that viral regulators play a role in promoting two types of cancer: Leukemia and prostate cancer. The new study shows these two cases weren’t flukes. All 21 cancers they looked at had at least one of those 19 viral elements, presumably working as cancer enhancers.
The study also identified what activates LTR10 to make it promote cancer. The culprit is a regulator protein called mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, which is overactivated in about 40% of all human cancers.
Some cancer drugs — MAP kinase inhibitors — already target MAP kinase, and they’re often the first ones prescribed when a patient is diagnosed with cancer, Dr. Chuong said. As with many cancer treatments, doctors don’t know why they work, just that they do.
“By understanding the mechanisms in the cell, we might be able to make them work better or further optimize their treatment,” he said.
“MAP kinase inhibitors are really like a sledgehammer to the cell,” Dr. Chuong said — meaning they affect many cellular processes, not just those related to cancer.
“If we’re able to say that these viral switches are what’s important, then that could potentially help us develop a more targeted therapy that uses something like CRISPR to silence these viral elements,” he said. Or it could help providers choose a MAP kinase inhibitor from among the dozens available best suited to treat an individual patient and avoid side effects.
Still, whether the findings translate to real cancer patients remains to be seen. “It’s very, very hard to go the final step of showing in a patient that these actually make a difference in the cancer,” Dr. Mager said.
More lab research, human trials, and at least a few years will be needed before this discovery could help treat cancer. “Directly targeting these elements as a therapy would be at least 5 years out,” Dr. Chuong said, “partly because that application would rely on CRISPR epigenome editing technology that is still being developed for clinical use.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a fascinating new study in Science Advances. Targeting these viral remnants still lingering in our DNA could lead to more effective cancer treatment with fewer side effects, the researchers said.
The study “gives a better understanding of how gene regulation can be impacted by these ancient retroviral sequences,” said Dixie Mager, PhD, scientist emeritus at the Terry Fox Laboratory at the British Columbia Cancer Research Institute, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. (Mager was not involved in the study.)
Long thought to be “junk” DNA with no biologic function, “endogenous retroviruses,” which have mutated over time and lost their ability to create the virus, are now known to regulate genes — allowing some genes to turn on and off. Research in recent years suggests they may play a role in diseases like cancer.
But scientists weren’t exactly sure what that role was, said senior study author Edward Chuong, PhD, a genome biologist at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Most studies have looked at whether endogenous retroviruses code for proteins that influence cancer. But these ancient viral strands usually don’t code for proteins at all.
Dr. Chuong took a different approach. Inspired by scientists who’ve studied how viral remnants regulate positive processes (immunity, brain development, or placenta development), he and his team explored whether some might regulate genes that, once activated, help cancer thrive.
Borrowing from epigenomic analysis data (data on molecules that alter gene expression) for 21 cancers mapped by the Cancer Genome Atlas, the researchers identified 19 virus-derived DNA sequences that bind to regulatory proteins more in cancer cells than in healthy cells. All of these could potentially act as gene regulators that promote cancer.
The researchers homed in on one sequence, called LTR10, because it showed especially high activity in several cancers, including lung and colorectal cancer. This DNA segment comes from a virus that entered our ancestors’ genome 30 million years ago, and it’s activated in a third of colorectal cancers.
Using the gene editing technology clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), Dr. Chuong’s team silenced LTR10 in colorectal cancer cells, altering the gene sequence so it couldn’t bind to regulatory proteins. Doing so dampened the activity of nearby cancer-promoting genes.
“They still behaved like cancer cells,” Dr. Chuong said. But “it made the cancer cells more susceptible to radiation. That would imply that the presence of that viral ‘switch’ actually helped those cancer cells survive radiation therapy.”
Previously, two studies had found that viral regulators play a role in promoting two types of cancer: Leukemia and prostate cancer. The new study shows these two cases weren’t flukes. All 21 cancers they looked at had at least one of those 19 viral elements, presumably working as cancer enhancers.
The study also identified what activates LTR10 to make it promote cancer. The culprit is a regulator protein called mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, which is overactivated in about 40% of all human cancers.
Some cancer drugs — MAP kinase inhibitors — already target MAP kinase, and they’re often the first ones prescribed when a patient is diagnosed with cancer, Dr. Chuong said. As with many cancer treatments, doctors don’t know why they work, just that they do.
“By understanding the mechanisms in the cell, we might be able to make them work better or further optimize their treatment,” he said.
“MAP kinase inhibitors are really like a sledgehammer to the cell,” Dr. Chuong said — meaning they affect many cellular processes, not just those related to cancer.
“If we’re able to say that these viral switches are what’s important, then that could potentially help us develop a more targeted therapy that uses something like CRISPR to silence these viral elements,” he said. Or it could help providers choose a MAP kinase inhibitor from among the dozens available best suited to treat an individual patient and avoid side effects.
Still, whether the findings translate to real cancer patients remains to be seen. “It’s very, very hard to go the final step of showing in a patient that these actually make a difference in the cancer,” Dr. Mager said.
More lab research, human trials, and at least a few years will be needed before this discovery could help treat cancer. “Directly targeting these elements as a therapy would be at least 5 years out,” Dr. Chuong said, “partly because that application would rely on CRISPR epigenome editing technology that is still being developed for clinical use.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a fascinating new study in Science Advances. Targeting these viral remnants still lingering in our DNA could lead to more effective cancer treatment with fewer side effects, the researchers said.
The study “gives a better understanding of how gene regulation can be impacted by these ancient retroviral sequences,” said Dixie Mager, PhD, scientist emeritus at the Terry Fox Laboratory at the British Columbia Cancer Research Institute, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. (Mager was not involved in the study.)
Long thought to be “junk” DNA with no biologic function, “endogenous retroviruses,” which have mutated over time and lost their ability to create the virus, are now known to regulate genes — allowing some genes to turn on and off. Research in recent years suggests they may play a role in diseases like cancer.
But scientists weren’t exactly sure what that role was, said senior study author Edward Chuong, PhD, a genome biologist at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Most studies have looked at whether endogenous retroviruses code for proteins that influence cancer. But these ancient viral strands usually don’t code for proteins at all.
Dr. Chuong took a different approach. Inspired by scientists who’ve studied how viral remnants regulate positive processes (immunity, brain development, or placenta development), he and his team explored whether some might regulate genes that, once activated, help cancer thrive.
Borrowing from epigenomic analysis data (data on molecules that alter gene expression) for 21 cancers mapped by the Cancer Genome Atlas, the researchers identified 19 virus-derived DNA sequences that bind to regulatory proteins more in cancer cells than in healthy cells. All of these could potentially act as gene regulators that promote cancer.
The researchers homed in on one sequence, called LTR10, because it showed especially high activity in several cancers, including lung and colorectal cancer. This DNA segment comes from a virus that entered our ancestors’ genome 30 million years ago, and it’s activated in a third of colorectal cancers.
Using the gene editing technology clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), Dr. Chuong’s team silenced LTR10 in colorectal cancer cells, altering the gene sequence so it couldn’t bind to regulatory proteins. Doing so dampened the activity of nearby cancer-promoting genes.
“They still behaved like cancer cells,” Dr. Chuong said. But “it made the cancer cells more susceptible to radiation. That would imply that the presence of that viral ‘switch’ actually helped those cancer cells survive radiation therapy.”
Previously, two studies had found that viral regulators play a role in promoting two types of cancer: Leukemia and prostate cancer. The new study shows these two cases weren’t flukes. All 21 cancers they looked at had at least one of those 19 viral elements, presumably working as cancer enhancers.
The study also identified what activates LTR10 to make it promote cancer. The culprit is a regulator protein called mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, which is overactivated in about 40% of all human cancers.
Some cancer drugs — MAP kinase inhibitors — already target MAP kinase, and they’re often the first ones prescribed when a patient is diagnosed with cancer, Dr. Chuong said. As with many cancer treatments, doctors don’t know why they work, just that they do.
“By understanding the mechanisms in the cell, we might be able to make them work better or further optimize their treatment,” he said.
“MAP kinase inhibitors are really like a sledgehammer to the cell,” Dr. Chuong said — meaning they affect many cellular processes, not just those related to cancer.
“If we’re able to say that these viral switches are what’s important, then that could potentially help us develop a more targeted therapy that uses something like CRISPR to silence these viral elements,” he said. Or it could help providers choose a MAP kinase inhibitor from among the dozens available best suited to treat an individual patient and avoid side effects.
Still, whether the findings translate to real cancer patients remains to be seen. “It’s very, very hard to go the final step of showing in a patient that these actually make a difference in the cancer,” Dr. Mager said.
More lab research, human trials, and at least a few years will be needed before this discovery could help treat cancer. “Directly targeting these elements as a therapy would be at least 5 years out,” Dr. Chuong said, “partly because that application would rely on CRISPR epigenome editing technology that is still being developed for clinical use.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
Outcomes with CDK4/6 Inhibitors Vary in BC
Lead investigator Claudio Vernieri, MD, PhD, presented these findings of the PALMARES-2 study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“Along with different safety profiles, drug-drug interactions, and costs of the three available CDK4/6 inhibitor molecules, our efficacy data may help clinicians and patients in choosing the most appropriate CDK4/6 inhibitor in specific clinical contexts,” Dr. Vernieri, who is from the Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan, Italy, said during the meeting.
CDK4/6 inhibitors combined with ET, are the standard of care as first line treatment for this population, noted Dr. Vernieri. However, their efficacy has never been directly compared in a large clinical trial.
“Since these compounds have different pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety profiles, costs, and drug-drug interactions, identifying which of the three CDK4/6 inhibitors may be more effective in specific clinical contexts is a highly clinically relevant issue,” he said. “Real-world data represent a key source to perform direct comparisons.”
The PALMARES-2 study was a retrospective, multicenter, population-based study, in 18 Italian cancer centers. Its two main objectives were to compare the real-world PFS of abemaciclib versus ribociclib versus palbociclib, in combination with ET, in the whole study cohort, as well as in various subgroups including patients with endocrine-resistant disease, luminal B-like disease, or in premenopausal women.
A total of 1,850 patients (median age, 63 years) were enrolled between January 1, 2016 and September 1, 2023, with 750 (40.6%) receiving palbociclib, and 676 (36.5%) and 424 (22.9%) receiving ribociclib and abemaciclib, respectively.
Baseline imbalance
Importantly, there were significant imbalances in baseline characteristics of the patients, with those receiving abemaciclib being more likely to have endocrine-resistant disease, low progesterone receptor expression, and liver metastasis, and less likely to have de novo metastatic disease, compared with other patients, said Dr. Vernieri.
The analysis showed that across the entire cohort, the median real-world PFS and overall survival (OS) were 34.7 months and 66.6 months, respectively, by a January 1, 2024, data cutoff date. “I believe that the overall survival data are still immature to make a definitive conclusion,” he commented, noting that at enrollment only about half of patients had undergone disease progression, and at the close of the study only about 25% had died.
After adjusting for clinically relevant patient- and tumor-related covariates, “we found that both abemaciclib and ribociclib were more effective than palbociclib, whereas we did not find statistically significant differences between abemaciclib and ribociclib,” he reported.
Specifically, the adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for PFS was 0.71 for abemaciclib versus palbociclib (95% CI, 0.56-0.90; P = .005), 0.81 for ribociclib versus palbociclib (95% CI, 0.65-0.99; P = .048), and 0.91 for abemaciclib versus ribociclib (95% CI, 0.70-1.19; P = .505).
“Regarding subgroup analysis, we found that abemaciclib and ribociclib were more effective than palbociclib in patients with endocrine-resistant or luminal B-like disease, as well as in premenopausal women. Abemaciclib was superior to palbociclib in patients with poorer ECOG [Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group] performance status and to both palbociclib and ribociclib in patients with de novo metastatic disease. Both ribociclib and abemaciclib showed a trend toward higher efficacy in patients with liver metastases. However, this difference only reached statistical significance in patients treated with ribociclib. And finally, the three CDK4/6 inhibitors were similarly effective in patients who were older or at bone-only disease,” he concluded.
Justifying adjustment
Speaking during the audience question period Giuseppe Del Priore, MD, from Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, said he preferred unadjusted results when examining real-world data, “because that’s the benefit,” and he questioned why the researchers had adjusted their numbers.
Dr. Vernieri explained that the adjustments were made to account for the important imbalances in the baseline characteristics of the patients.
“When we plotted unadjusted curves, we did not find statistically significant differences between these three drugs, only a trend toward the direction that I showed you today,” he said. “However, as you saw from the tables showing the characteristics of patients, there were important imbalances in terms of important prognostic factors in the three patient cohorts. So, I think that, for this kind of data and based on this level of imbalance, adjustment is necessary.
“To reinforce our conclusions, what we did was also to perform a propensity score match–based analysis,” Dr. Vernieri continued. “I did not have the time to show the results today, but these data were fully in line with the study conclusions. And we also performed a backward selection of variables. So, we basically selected variables more likely to be associated with patient prognosis. And also those models confirm the study conclusion. So I think the conclusions are quite solid.”
Dr. Del Priore, an adjunct professor of obstetrics and gynecology with a specialty in oncology, on the other hand, said he was not convinced that any of the drugs might be better or worse in the actual population treated.
“I still maintain that unadjusted real-world data should be presented and then only a limited adjusted analysis performed using the most unbalanced variables,” he said. “To do more elaborate adjustments may falsely imply a difference in drug choice and outcomes which never should be the conclusion with observational studies. Instead, the conclusions should be that, with typical use, the following similarities in PFS and OS were observed. Then point out how drug choice and important prognostic variables might be linked, thus limiting the generalizable conclusions even further.
“I would conclude that prospective studies should balance for the variables used in the PALMARES-2 analyses, which actually may have been chosen for adjustment post hoc,” Dr. Del Priore said.
The study was funded by the Italian Association for Cancer Research, the European Research Council, the Ministero della Salute, the Scientific Directorate of Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Giuliani’s Foundation and Roche. Dr. Vernieri reported consulting or advisory roles with Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca, Novartis, and Pfizer; speakers’ bureau roles with Accademia Nazionale Di Medicina (ACCMED), Istituto Gentili, Lilly and Novartis; and research funding from Roche. Dr. Del Priore reported no conflicts of interest and disclosed that he is chief medical officer at BriaCell.
Lead investigator Claudio Vernieri, MD, PhD, presented these findings of the PALMARES-2 study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“Along with different safety profiles, drug-drug interactions, and costs of the three available CDK4/6 inhibitor molecules, our efficacy data may help clinicians and patients in choosing the most appropriate CDK4/6 inhibitor in specific clinical contexts,” Dr. Vernieri, who is from the Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan, Italy, said during the meeting.
CDK4/6 inhibitors combined with ET, are the standard of care as first line treatment for this population, noted Dr. Vernieri. However, their efficacy has never been directly compared in a large clinical trial.
“Since these compounds have different pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety profiles, costs, and drug-drug interactions, identifying which of the three CDK4/6 inhibitors may be more effective in specific clinical contexts is a highly clinically relevant issue,” he said. “Real-world data represent a key source to perform direct comparisons.”
The PALMARES-2 study was a retrospective, multicenter, population-based study, in 18 Italian cancer centers. Its two main objectives were to compare the real-world PFS of abemaciclib versus ribociclib versus palbociclib, in combination with ET, in the whole study cohort, as well as in various subgroups including patients with endocrine-resistant disease, luminal B-like disease, or in premenopausal women.
A total of 1,850 patients (median age, 63 years) were enrolled between January 1, 2016 and September 1, 2023, with 750 (40.6%) receiving palbociclib, and 676 (36.5%) and 424 (22.9%) receiving ribociclib and abemaciclib, respectively.
Baseline imbalance
Importantly, there were significant imbalances in baseline characteristics of the patients, with those receiving abemaciclib being more likely to have endocrine-resistant disease, low progesterone receptor expression, and liver metastasis, and less likely to have de novo metastatic disease, compared with other patients, said Dr. Vernieri.
The analysis showed that across the entire cohort, the median real-world PFS and overall survival (OS) were 34.7 months and 66.6 months, respectively, by a January 1, 2024, data cutoff date. “I believe that the overall survival data are still immature to make a definitive conclusion,” he commented, noting that at enrollment only about half of patients had undergone disease progression, and at the close of the study only about 25% had died.
After adjusting for clinically relevant patient- and tumor-related covariates, “we found that both abemaciclib and ribociclib were more effective than palbociclib, whereas we did not find statistically significant differences between abemaciclib and ribociclib,” he reported.
Specifically, the adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for PFS was 0.71 for abemaciclib versus palbociclib (95% CI, 0.56-0.90; P = .005), 0.81 for ribociclib versus palbociclib (95% CI, 0.65-0.99; P = .048), and 0.91 for abemaciclib versus ribociclib (95% CI, 0.70-1.19; P = .505).
“Regarding subgroup analysis, we found that abemaciclib and ribociclib were more effective than palbociclib in patients with endocrine-resistant or luminal B-like disease, as well as in premenopausal women. Abemaciclib was superior to palbociclib in patients with poorer ECOG [Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group] performance status and to both palbociclib and ribociclib in patients with de novo metastatic disease. Both ribociclib and abemaciclib showed a trend toward higher efficacy in patients with liver metastases. However, this difference only reached statistical significance in patients treated with ribociclib. And finally, the three CDK4/6 inhibitors were similarly effective in patients who were older or at bone-only disease,” he concluded.
Justifying adjustment
Speaking during the audience question period Giuseppe Del Priore, MD, from Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, said he preferred unadjusted results when examining real-world data, “because that’s the benefit,” and he questioned why the researchers had adjusted their numbers.
Dr. Vernieri explained that the adjustments were made to account for the important imbalances in the baseline characteristics of the patients.
“When we plotted unadjusted curves, we did not find statistically significant differences between these three drugs, only a trend toward the direction that I showed you today,” he said. “However, as you saw from the tables showing the characteristics of patients, there were important imbalances in terms of important prognostic factors in the three patient cohorts. So, I think that, for this kind of data and based on this level of imbalance, adjustment is necessary.
“To reinforce our conclusions, what we did was also to perform a propensity score match–based analysis,” Dr. Vernieri continued. “I did not have the time to show the results today, but these data were fully in line with the study conclusions. And we also performed a backward selection of variables. So, we basically selected variables more likely to be associated with patient prognosis. And also those models confirm the study conclusion. So I think the conclusions are quite solid.”
Dr. Del Priore, an adjunct professor of obstetrics and gynecology with a specialty in oncology, on the other hand, said he was not convinced that any of the drugs might be better or worse in the actual population treated.
“I still maintain that unadjusted real-world data should be presented and then only a limited adjusted analysis performed using the most unbalanced variables,” he said. “To do more elaborate adjustments may falsely imply a difference in drug choice and outcomes which never should be the conclusion with observational studies. Instead, the conclusions should be that, with typical use, the following similarities in PFS and OS were observed. Then point out how drug choice and important prognostic variables might be linked, thus limiting the generalizable conclusions even further.
“I would conclude that prospective studies should balance for the variables used in the PALMARES-2 analyses, which actually may have been chosen for adjustment post hoc,” Dr. Del Priore said.
The study was funded by the Italian Association for Cancer Research, the European Research Council, the Ministero della Salute, the Scientific Directorate of Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Giuliani’s Foundation and Roche. Dr. Vernieri reported consulting or advisory roles with Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca, Novartis, and Pfizer; speakers’ bureau roles with Accademia Nazionale Di Medicina (ACCMED), Istituto Gentili, Lilly and Novartis; and research funding from Roche. Dr. Del Priore reported no conflicts of interest and disclosed that he is chief medical officer at BriaCell.
Lead investigator Claudio Vernieri, MD, PhD, presented these findings of the PALMARES-2 study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“Along with different safety profiles, drug-drug interactions, and costs of the three available CDK4/6 inhibitor molecules, our efficacy data may help clinicians and patients in choosing the most appropriate CDK4/6 inhibitor in specific clinical contexts,” Dr. Vernieri, who is from the Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan, Italy, said during the meeting.
CDK4/6 inhibitors combined with ET, are the standard of care as first line treatment for this population, noted Dr. Vernieri. However, their efficacy has never been directly compared in a large clinical trial.
“Since these compounds have different pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety profiles, costs, and drug-drug interactions, identifying which of the three CDK4/6 inhibitors may be more effective in specific clinical contexts is a highly clinically relevant issue,” he said. “Real-world data represent a key source to perform direct comparisons.”
The PALMARES-2 study was a retrospective, multicenter, population-based study, in 18 Italian cancer centers. Its two main objectives were to compare the real-world PFS of abemaciclib versus ribociclib versus palbociclib, in combination with ET, in the whole study cohort, as well as in various subgroups including patients with endocrine-resistant disease, luminal B-like disease, or in premenopausal women.
A total of 1,850 patients (median age, 63 years) were enrolled between January 1, 2016 and September 1, 2023, with 750 (40.6%) receiving palbociclib, and 676 (36.5%) and 424 (22.9%) receiving ribociclib and abemaciclib, respectively.
Baseline imbalance
Importantly, there were significant imbalances in baseline characteristics of the patients, with those receiving abemaciclib being more likely to have endocrine-resistant disease, low progesterone receptor expression, and liver metastasis, and less likely to have de novo metastatic disease, compared with other patients, said Dr. Vernieri.
The analysis showed that across the entire cohort, the median real-world PFS and overall survival (OS) were 34.7 months and 66.6 months, respectively, by a January 1, 2024, data cutoff date. “I believe that the overall survival data are still immature to make a definitive conclusion,” he commented, noting that at enrollment only about half of patients had undergone disease progression, and at the close of the study only about 25% had died.
After adjusting for clinically relevant patient- and tumor-related covariates, “we found that both abemaciclib and ribociclib were more effective than palbociclib, whereas we did not find statistically significant differences between abemaciclib and ribociclib,” he reported.
Specifically, the adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for PFS was 0.71 for abemaciclib versus palbociclib (95% CI, 0.56-0.90; P = .005), 0.81 for ribociclib versus palbociclib (95% CI, 0.65-0.99; P = .048), and 0.91 for abemaciclib versus ribociclib (95% CI, 0.70-1.19; P = .505).
“Regarding subgroup analysis, we found that abemaciclib and ribociclib were more effective than palbociclib in patients with endocrine-resistant or luminal B-like disease, as well as in premenopausal women. Abemaciclib was superior to palbociclib in patients with poorer ECOG [Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group] performance status and to both palbociclib and ribociclib in patients with de novo metastatic disease. Both ribociclib and abemaciclib showed a trend toward higher efficacy in patients with liver metastases. However, this difference only reached statistical significance in patients treated with ribociclib. And finally, the three CDK4/6 inhibitors were similarly effective in patients who were older or at bone-only disease,” he concluded.
Justifying adjustment
Speaking during the audience question period Giuseppe Del Priore, MD, from Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, said he preferred unadjusted results when examining real-world data, “because that’s the benefit,” and he questioned why the researchers had adjusted their numbers.
Dr. Vernieri explained that the adjustments were made to account for the important imbalances in the baseline characteristics of the patients.
“When we plotted unadjusted curves, we did not find statistically significant differences between these three drugs, only a trend toward the direction that I showed you today,” he said. “However, as you saw from the tables showing the characteristics of patients, there were important imbalances in terms of important prognostic factors in the three patient cohorts. So, I think that, for this kind of data and based on this level of imbalance, adjustment is necessary.
“To reinforce our conclusions, what we did was also to perform a propensity score match–based analysis,” Dr. Vernieri continued. “I did not have the time to show the results today, but these data were fully in line with the study conclusions. And we also performed a backward selection of variables. So, we basically selected variables more likely to be associated with patient prognosis. And also those models confirm the study conclusion. So I think the conclusions are quite solid.”
Dr. Del Priore, an adjunct professor of obstetrics and gynecology with a specialty in oncology, on the other hand, said he was not convinced that any of the drugs might be better or worse in the actual population treated.
“I still maintain that unadjusted real-world data should be presented and then only a limited adjusted analysis performed using the most unbalanced variables,” he said. “To do more elaborate adjustments may falsely imply a difference in drug choice and outcomes which never should be the conclusion with observational studies. Instead, the conclusions should be that, with typical use, the following similarities in PFS and OS were observed. Then point out how drug choice and important prognostic variables might be linked, thus limiting the generalizable conclusions even further.
“I would conclude that prospective studies should balance for the variables used in the PALMARES-2 analyses, which actually may have been chosen for adjustment post hoc,” Dr. Del Priore said.
The study was funded by the Italian Association for Cancer Research, the European Research Council, the Ministero della Salute, the Scientific Directorate of Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Giuliani’s Foundation and Roche. Dr. Vernieri reported consulting or advisory roles with Daiichi Sankyo/Astra Zeneca, Novartis, and Pfizer; speakers’ bureau roles with Accademia Nazionale Di Medicina (ACCMED), Istituto Gentili, Lilly and Novartis; and research funding from Roche. Dr. Del Priore reported no conflicts of interest and disclosed that he is chief medical officer at BriaCell.
FROM ASCO 2024
Which Patients With Early TNBC Can Avoid Chemotherapy?
TOPLINE:
which suggest that stromal TILs could be a useful biomarker to optimize treatment decisions in this patient population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The absolute benefit of chemotherapy remains unclear among patients with stage I TNBC. High levels of stromal TILs, a promising biomarker, have been linked to better survival in patients with TNBC, but data focused on stage I disease are lacking.
- In the current analysis, researchers identified a cohort of 1041 women (mean age at diagnosis, 64.4 years) from the Netherlands Cancer Registry with stage I TNBC who had an available TIL score and had undergone a lumpectomy or a mastectomy but had not received neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
- Patients’ clinical data were matched to their corresponding pathologic data provided by the Dutch Pathology Registry, and a pathologist blinded to outcomes scored stromal TIL levels according to the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group guidelines.
- The primary endpoint was breast cancer–specific survival at prespecified stromal TIL cutoffs of 30%, 50%, and 75%. Secondary outcomes included specific survival by pathologic tumor stage and overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 8.6% of women had a pT1a tumor, 38.7% had a pT1b tumor, and 52.6% had a pT1c tumor. In the cohort, 25.6% of patients had stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher, 19.5% had levels of 50% or higher, and 13.5% had levels of 75% or higher.
- Over a median follow-up of 11.4 years, 335 patients died, 107 (32%) of whom died from breast cancer. Patients with smaller tumors (pT1abNO) had better survival outcomes than those with larger tumors (pT1cNO) — a 10-year breast cancer–specific survival of 92% vs 86%, respectively.
- In the overall cohort, stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher were associated with better breast cancer–specific survival than those with stromal TIL levels below 30% (96% vs 87%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.45). Stromal TIL levels of 50% or greater were also associated with better 10-year breast cancer–specific survival than those with levels below 50% (92% vs 88%; HR, 0.59). A similar pattern was observed for stromal TIL levels and overall survival.
- In patients with pT1c tumors, the 10-year breast cancer–specific survival among those with stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher was 95% vs 83% for levels below the 30% cutoff (HR, 0.24). Similarly, the 10-year breast cancer–specific survival for those in the 50% or higher group was 95% vs 84% for levels below that cutoff (HR, 0.27). The 10-year breast cancer–specific survival improved to 98% among patients with stromal TIL levels of 75% or higher (HR, 0.09).
IN PRACTICE:
The results supported the establishment of “treatment-optimization clinical trials in patients with stage I TNBC, using [stromal] TIL level as an integral biomarker to prospectively confirm the observed excellent survival when neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy is not administered,” the authors wrote. Assessing stromal TILs is also “inexpensive,” the authors added.
SOURCE:
The research, conducted by Marleen Kok, MD, PhD, Department of Medical Oncology, the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, and colleagues, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors noted that the study was limited by its observational nature. The patients were drawn from a larger cohort, about half of whom received adjuvant chemotherapy, and the patients who did not receive chemotherapy may have had favorable tumor characteristics. There were also no data on BRCA1 or BRCA2 germline mutation status and recurrences and/or distant metastases. The database did not include data on patient ethnicity because most Dutch patients were White.
DISCLOSURES:
Research at the Netherlands Cancer Institute was supported by institutional grants from the Dutch Cancer Society and the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport. Dr. Kok declared financial relationships with several organizations including Gilead and Domain Therapeutics, as well as institutional grants from AstraZeneca, BMS, and Roche. Other authors also declared numerous financial relationships for themselves and their institutions with pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which suggest that stromal TILs could be a useful biomarker to optimize treatment decisions in this patient population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The absolute benefit of chemotherapy remains unclear among patients with stage I TNBC. High levels of stromal TILs, a promising biomarker, have been linked to better survival in patients with TNBC, but data focused on stage I disease are lacking.
- In the current analysis, researchers identified a cohort of 1041 women (mean age at diagnosis, 64.4 years) from the Netherlands Cancer Registry with stage I TNBC who had an available TIL score and had undergone a lumpectomy or a mastectomy but had not received neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
- Patients’ clinical data were matched to their corresponding pathologic data provided by the Dutch Pathology Registry, and a pathologist blinded to outcomes scored stromal TIL levels according to the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group guidelines.
- The primary endpoint was breast cancer–specific survival at prespecified stromal TIL cutoffs of 30%, 50%, and 75%. Secondary outcomes included specific survival by pathologic tumor stage and overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 8.6% of women had a pT1a tumor, 38.7% had a pT1b tumor, and 52.6% had a pT1c tumor. In the cohort, 25.6% of patients had stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher, 19.5% had levels of 50% or higher, and 13.5% had levels of 75% or higher.
- Over a median follow-up of 11.4 years, 335 patients died, 107 (32%) of whom died from breast cancer. Patients with smaller tumors (pT1abNO) had better survival outcomes than those with larger tumors (pT1cNO) — a 10-year breast cancer–specific survival of 92% vs 86%, respectively.
- In the overall cohort, stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher were associated with better breast cancer–specific survival than those with stromal TIL levels below 30% (96% vs 87%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.45). Stromal TIL levels of 50% or greater were also associated with better 10-year breast cancer–specific survival than those with levels below 50% (92% vs 88%; HR, 0.59). A similar pattern was observed for stromal TIL levels and overall survival.
- In patients with pT1c tumors, the 10-year breast cancer–specific survival among those with stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher was 95% vs 83% for levels below the 30% cutoff (HR, 0.24). Similarly, the 10-year breast cancer–specific survival for those in the 50% or higher group was 95% vs 84% for levels below that cutoff (HR, 0.27). The 10-year breast cancer–specific survival improved to 98% among patients with stromal TIL levels of 75% or higher (HR, 0.09).
IN PRACTICE:
The results supported the establishment of “treatment-optimization clinical trials in patients with stage I TNBC, using [stromal] TIL level as an integral biomarker to prospectively confirm the observed excellent survival when neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy is not administered,” the authors wrote. Assessing stromal TILs is also “inexpensive,” the authors added.
SOURCE:
The research, conducted by Marleen Kok, MD, PhD, Department of Medical Oncology, the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, and colleagues, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors noted that the study was limited by its observational nature. The patients were drawn from a larger cohort, about half of whom received adjuvant chemotherapy, and the patients who did not receive chemotherapy may have had favorable tumor characteristics. There were also no data on BRCA1 or BRCA2 germline mutation status and recurrences and/or distant metastases. The database did not include data on patient ethnicity because most Dutch patients were White.
DISCLOSURES:
Research at the Netherlands Cancer Institute was supported by institutional grants from the Dutch Cancer Society and the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport. Dr. Kok declared financial relationships with several organizations including Gilead and Domain Therapeutics, as well as institutional grants from AstraZeneca, BMS, and Roche. Other authors also declared numerous financial relationships for themselves and their institutions with pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which suggest that stromal TILs could be a useful biomarker to optimize treatment decisions in this patient population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The absolute benefit of chemotherapy remains unclear among patients with stage I TNBC. High levels of stromal TILs, a promising biomarker, have been linked to better survival in patients with TNBC, but data focused on stage I disease are lacking.
- In the current analysis, researchers identified a cohort of 1041 women (mean age at diagnosis, 64.4 years) from the Netherlands Cancer Registry with stage I TNBC who had an available TIL score and had undergone a lumpectomy or a mastectomy but had not received neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
- Patients’ clinical data were matched to their corresponding pathologic data provided by the Dutch Pathology Registry, and a pathologist blinded to outcomes scored stromal TIL levels according to the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group guidelines.
- The primary endpoint was breast cancer–specific survival at prespecified stromal TIL cutoffs of 30%, 50%, and 75%. Secondary outcomes included specific survival by pathologic tumor stage and overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 8.6% of women had a pT1a tumor, 38.7% had a pT1b tumor, and 52.6% had a pT1c tumor. In the cohort, 25.6% of patients had stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher, 19.5% had levels of 50% or higher, and 13.5% had levels of 75% or higher.
- Over a median follow-up of 11.4 years, 335 patients died, 107 (32%) of whom died from breast cancer. Patients with smaller tumors (pT1abNO) had better survival outcomes than those with larger tumors (pT1cNO) — a 10-year breast cancer–specific survival of 92% vs 86%, respectively.
- In the overall cohort, stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher were associated with better breast cancer–specific survival than those with stromal TIL levels below 30% (96% vs 87%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.45). Stromal TIL levels of 50% or greater were also associated with better 10-year breast cancer–specific survival than those with levels below 50% (92% vs 88%; HR, 0.59). A similar pattern was observed for stromal TIL levels and overall survival.
- In patients with pT1c tumors, the 10-year breast cancer–specific survival among those with stromal TIL levels of 30% or higher was 95% vs 83% for levels below the 30% cutoff (HR, 0.24). Similarly, the 10-year breast cancer–specific survival for those in the 50% or higher group was 95% vs 84% for levels below that cutoff (HR, 0.27). The 10-year breast cancer–specific survival improved to 98% among patients with stromal TIL levels of 75% or higher (HR, 0.09).
IN PRACTICE:
The results supported the establishment of “treatment-optimization clinical trials in patients with stage I TNBC, using [stromal] TIL level as an integral biomarker to prospectively confirm the observed excellent survival when neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy is not administered,” the authors wrote. Assessing stromal TILs is also “inexpensive,” the authors added.
SOURCE:
The research, conducted by Marleen Kok, MD, PhD, Department of Medical Oncology, the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, and colleagues, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors noted that the study was limited by its observational nature. The patients were drawn from a larger cohort, about half of whom received adjuvant chemotherapy, and the patients who did not receive chemotherapy may have had favorable tumor characteristics. There were also no data on BRCA1 or BRCA2 germline mutation status and recurrences and/or distant metastases. The database did not include data on patient ethnicity because most Dutch patients were White.
DISCLOSURES:
Research at the Netherlands Cancer Institute was supported by institutional grants from the Dutch Cancer Society and the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport. Dr. Kok declared financial relationships with several organizations including Gilead and Domain Therapeutics, as well as institutional grants from AstraZeneca, BMS, and Roche. Other authors also declared numerous financial relationships for themselves and their institutions with pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What Does Hormone Receptor Mean in BRCA-Associated BC?
CHICAGO — Being hormone receptor positive is generally a favorable prognostic factor in breast cancer, but that doesn’t seem to be the case in women with BRCA-associated tumors, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
The conclusion is based on a large international study on how hormone receptor status impacts breast cancer outcomes in young women with germline BRCA pathological variants (PVs).
Overall, “hormone receptor positivity did not seem to have a strong positive prognostic value in young BRCA carriers” with early breast cancer, lead investigator Luca Arecco, MD, an oncology resident at the University of Genoa, Italy, said at the meeting.
Investigators reviewed the records of 4709 women ages 40 years or younger with stage 1-3 BRCA-associated invasive breast cancer treated from 2000 to 2020 at 78 centers in 28 countries across four continents. Median follow-up was about 8 years.
Weaker Prognostic Value in Hormone Receptor Status
They found, in general, that hormone receptor–positive breast cancer appears to be biologically more aggressive in patients with BRCA PVs than in the general breast cancer population, generating outcomes similar to those with hormone receptor-negative BRCA tumors.
Specifically, among patients with germline BRCA PVs, while hormone receptor–positive patients had a higher distant recurrence rate (13.1% vs. 9.6%) than hormone receptor–negative patients, 8-year disease free survival (65.8% and 63.4% respectively) and overall survival (a bit under 90% in both groups) were similar.
Hormone receptor–positive patients did have a lower rate of second primary breast cancers (9.1% versus 14.7%).
In the formal write-up of the results published shortly after the meeting in Annals of Oncology, the investigators concluded that “in young BRCA carriers, differences in recurrence pattern and second primary breast cancer among hormone receptor–positive versus negative disease warrant consideration in counseling patients on treatment, follow-up, and risk-reducing surgery.”
The team also found other differences between BRCA-associated breast cancer and sporadic disease. For instance, in the BRCA cohort, luminal A-like breast cancer had a worse long-term prognosis in their BRCA cohort than triple-negative or HER2-positive disease. Luminal A-like tumors are generally considered less aggressive, but in patients with BRCA PVs, “improving neoadjuvant chemotherapy … could be worthwhile,” the investigators said.
Also, although the risk of recurrence for sporadic hormone receptor–negative tumors is highest in the first few years, the team found that the risk in the hormone negative BRCA cohort progressively increased with longer follow-up, driven by the occurrence of second primary breast cancers, especially in patients with BRCA 1 PVs.
Greater Clarity in Prognosis in BRCA-Associated Breast Cancer
Overall, study discussant Lisa A. Carey, MD, a breast cancer specialist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “we now know much more clearly the issues of prognosis in women who are very young and have germline BRCA-associated breast cancer,” about 12% of newly diagnosed cases.
“Young patients with germline BRCA-associated breast cancers have high relapse and high new primary risks, warranting comprehensive multimodality therapy,” she said.
A bit fewer than half of women in the study were hormone receptor–positive, and they tended to be patients with BRCA 2 PVs. The rest were hormone receptor–negative and tended to have BRCA 1 PVs.
Patients with hormone receptor–positive disease had grade 3 cancers in about 50% of cases, while patients with hormone receptor–negative disease had a grade 3 disease in over 80%.
Hormone receptor–positive patients were more likely to have nodal involvement and undergo mastectomies but less likely to receive chemotherapy than hormone receptor–negative patients. It’s likely that few patients in the review received PARP inhibitors, Dr. Carey noted.
Although overall survival at 8 years was similar in both groups, after that point “the prognosis of patients with hormone receptor–positive disease appeared to be worse … This appeared to occur earlier than that described in sporadic disease,” in which the worsening of survival in hormone receptor–positive disease occurs after a follow-up of at least 14-15 years, the investigators noted in their journal report.
The work was funded by the Italian Association for Cancer Research, Institut Jules Bordet, Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Australian National Health and Medical Council, Cancer Australia, US National Institute of Health, and others. Dr. Arecco had no disclosures. Dr. Carey and other coauthors disclosed research funding, speaker honoraria, and other financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Lilly, and other pharmaceutical companies.
CHICAGO — Being hormone receptor positive is generally a favorable prognostic factor in breast cancer, but that doesn’t seem to be the case in women with BRCA-associated tumors, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
The conclusion is based on a large international study on how hormone receptor status impacts breast cancer outcomes in young women with germline BRCA pathological variants (PVs).
Overall, “hormone receptor positivity did not seem to have a strong positive prognostic value in young BRCA carriers” with early breast cancer, lead investigator Luca Arecco, MD, an oncology resident at the University of Genoa, Italy, said at the meeting.
Investigators reviewed the records of 4709 women ages 40 years or younger with stage 1-3 BRCA-associated invasive breast cancer treated from 2000 to 2020 at 78 centers in 28 countries across four continents. Median follow-up was about 8 years.
Weaker Prognostic Value in Hormone Receptor Status
They found, in general, that hormone receptor–positive breast cancer appears to be biologically more aggressive in patients with BRCA PVs than in the general breast cancer population, generating outcomes similar to those with hormone receptor-negative BRCA tumors.
Specifically, among patients with germline BRCA PVs, while hormone receptor–positive patients had a higher distant recurrence rate (13.1% vs. 9.6%) than hormone receptor–negative patients, 8-year disease free survival (65.8% and 63.4% respectively) and overall survival (a bit under 90% in both groups) were similar.
Hormone receptor–positive patients did have a lower rate of second primary breast cancers (9.1% versus 14.7%).
In the formal write-up of the results published shortly after the meeting in Annals of Oncology, the investigators concluded that “in young BRCA carriers, differences in recurrence pattern and second primary breast cancer among hormone receptor–positive versus negative disease warrant consideration in counseling patients on treatment, follow-up, and risk-reducing surgery.”
The team also found other differences between BRCA-associated breast cancer and sporadic disease. For instance, in the BRCA cohort, luminal A-like breast cancer had a worse long-term prognosis in their BRCA cohort than triple-negative or HER2-positive disease. Luminal A-like tumors are generally considered less aggressive, but in patients with BRCA PVs, “improving neoadjuvant chemotherapy … could be worthwhile,” the investigators said.
Also, although the risk of recurrence for sporadic hormone receptor–negative tumors is highest in the first few years, the team found that the risk in the hormone negative BRCA cohort progressively increased with longer follow-up, driven by the occurrence of second primary breast cancers, especially in patients with BRCA 1 PVs.
Greater Clarity in Prognosis in BRCA-Associated Breast Cancer
Overall, study discussant Lisa A. Carey, MD, a breast cancer specialist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “we now know much more clearly the issues of prognosis in women who are very young and have germline BRCA-associated breast cancer,” about 12% of newly diagnosed cases.
“Young patients with germline BRCA-associated breast cancers have high relapse and high new primary risks, warranting comprehensive multimodality therapy,” she said.
A bit fewer than half of women in the study were hormone receptor–positive, and they tended to be patients with BRCA 2 PVs. The rest were hormone receptor–negative and tended to have BRCA 1 PVs.
Patients with hormone receptor–positive disease had grade 3 cancers in about 50% of cases, while patients with hormone receptor–negative disease had a grade 3 disease in over 80%.
Hormone receptor–positive patients were more likely to have nodal involvement and undergo mastectomies but less likely to receive chemotherapy than hormone receptor–negative patients. It’s likely that few patients in the review received PARP inhibitors, Dr. Carey noted.
Although overall survival at 8 years was similar in both groups, after that point “the prognosis of patients with hormone receptor–positive disease appeared to be worse … This appeared to occur earlier than that described in sporadic disease,” in which the worsening of survival in hormone receptor–positive disease occurs after a follow-up of at least 14-15 years, the investigators noted in their journal report.
The work was funded by the Italian Association for Cancer Research, Institut Jules Bordet, Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Australian National Health and Medical Council, Cancer Australia, US National Institute of Health, and others. Dr. Arecco had no disclosures. Dr. Carey and other coauthors disclosed research funding, speaker honoraria, and other financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Lilly, and other pharmaceutical companies.
CHICAGO — Being hormone receptor positive is generally a favorable prognostic factor in breast cancer, but that doesn’t seem to be the case in women with BRCA-associated tumors, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
The conclusion is based on a large international study on how hormone receptor status impacts breast cancer outcomes in young women with germline BRCA pathological variants (PVs).
Overall, “hormone receptor positivity did not seem to have a strong positive prognostic value in young BRCA carriers” with early breast cancer, lead investigator Luca Arecco, MD, an oncology resident at the University of Genoa, Italy, said at the meeting.
Investigators reviewed the records of 4709 women ages 40 years or younger with stage 1-3 BRCA-associated invasive breast cancer treated from 2000 to 2020 at 78 centers in 28 countries across four continents. Median follow-up was about 8 years.
Weaker Prognostic Value in Hormone Receptor Status
They found, in general, that hormone receptor–positive breast cancer appears to be biologically more aggressive in patients with BRCA PVs than in the general breast cancer population, generating outcomes similar to those with hormone receptor-negative BRCA tumors.
Specifically, among patients with germline BRCA PVs, while hormone receptor–positive patients had a higher distant recurrence rate (13.1% vs. 9.6%) than hormone receptor–negative patients, 8-year disease free survival (65.8% and 63.4% respectively) and overall survival (a bit under 90% in both groups) were similar.
Hormone receptor–positive patients did have a lower rate of second primary breast cancers (9.1% versus 14.7%).
In the formal write-up of the results published shortly after the meeting in Annals of Oncology, the investigators concluded that “in young BRCA carriers, differences in recurrence pattern and second primary breast cancer among hormone receptor–positive versus negative disease warrant consideration in counseling patients on treatment, follow-up, and risk-reducing surgery.”
The team also found other differences between BRCA-associated breast cancer and sporadic disease. For instance, in the BRCA cohort, luminal A-like breast cancer had a worse long-term prognosis in their BRCA cohort than triple-negative or HER2-positive disease. Luminal A-like tumors are generally considered less aggressive, but in patients with BRCA PVs, “improving neoadjuvant chemotherapy … could be worthwhile,” the investigators said.
Also, although the risk of recurrence for sporadic hormone receptor–negative tumors is highest in the first few years, the team found that the risk in the hormone negative BRCA cohort progressively increased with longer follow-up, driven by the occurrence of second primary breast cancers, especially in patients with BRCA 1 PVs.
Greater Clarity in Prognosis in BRCA-Associated Breast Cancer
Overall, study discussant Lisa A. Carey, MD, a breast cancer specialist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “we now know much more clearly the issues of prognosis in women who are very young and have germline BRCA-associated breast cancer,” about 12% of newly diagnosed cases.
“Young patients with germline BRCA-associated breast cancers have high relapse and high new primary risks, warranting comprehensive multimodality therapy,” she said.
A bit fewer than half of women in the study were hormone receptor–positive, and they tended to be patients with BRCA 2 PVs. The rest were hormone receptor–negative and tended to have BRCA 1 PVs.
Patients with hormone receptor–positive disease had grade 3 cancers in about 50% of cases, while patients with hormone receptor–negative disease had a grade 3 disease in over 80%.
Hormone receptor–positive patients were more likely to have nodal involvement and undergo mastectomies but less likely to receive chemotherapy than hormone receptor–negative patients. It’s likely that few patients in the review received PARP inhibitors, Dr. Carey noted.
Although overall survival at 8 years was similar in both groups, after that point “the prognosis of patients with hormone receptor–positive disease appeared to be worse … This appeared to occur earlier than that described in sporadic disease,” in which the worsening of survival in hormone receptor–positive disease occurs after a follow-up of at least 14-15 years, the investigators noted in their journal report.
The work was funded by the Italian Association for Cancer Research, Institut Jules Bordet, Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Australian National Health and Medical Council, Cancer Australia, US National Institute of Health, and others. Dr. Arecco had no disclosures. Dr. Carey and other coauthors disclosed research funding, speaker honoraria, and other financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Lilly, and other pharmaceutical companies.
FROM ASCO 2024
Black Women With Breast Cancer Face Clinical Inequities
Black metastatic breast cancer patients with PIK3CA mutations were less likely to receive targeted therapy and less likely to be enrolled in clinical trials than White patients and had shorter overall survival, according to a retrospective cohort study. Black and White patients were equally likely to receive other drugs that did not require genomic testing.
“These clinical inequities in the use of targeted therapies and clinical trials ... must be a focus going forward,” said lead investigator Emily Podany, MD, a clinical fellow in hematology-oncology at Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. “Our consortium is looking for paths forward in order to try and decrease these striking inequities. And it’s a focus of future research for us and future implementation [of] science interventions, hopefully, across the country.”
The study results were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Black Women Underrepresented
Black women are generally underrepresented in clinical trials, noted Dr. Podany. “They make up about 2%-5% of the patients in breast cancer clinical trials, and there are documented inequities in treatment and in outcomes for Black patients with metastatic breast cancer. This includes longer treatment delays, it includes fewer sentinel lymph node biopsies, and unfortunately, they’re more likely to discontinue treatment early.”
In terms of PI3K inhibition, PIK3CA mutations are found in about 40% of patients with HR-positive HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Alpelisib is FDA-approved as a targeted therapy for these patients, she said.
The study evaluated records of 1327 patients with metastatic breast cancer who also had circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) results and were treated at Washington University, Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and Northwestern University in Chicago. Of these, 795 had an ER-positive, HER2-negative subtype and were included in the analysis. Most (89%) of the patients were White (n = 708), while 11% (n = 87) were Black, and the only baseline difference between patients was that Black patients had significantly more de novo metastatic breast cancer (31% versus 22%).
Use of PI3K, CDK4/6, or mTOR inhibitors was evaluated using manual electronic medical review, and genomic differences were evaluated using logistic regression.
The analysis showed inequities in both treatment and clinical trial enrollment. There were no differences between groups in the use of CDK4/6 or mTOR inhibitors, which do not require a genomic profile, the researchers noted, but Black patients with PIK3CA single nucleotide variants (SNV) were significantly less likely than White patients to use PI3K inhibitors (5.9% versus 28.8%; P = .045), despite no difference in PIK3CA mutations between groups (36% and 34% respectively). Similarly, 11% of White patients with PIK3CA mutations were enrolled in clinical trials, but none of the Black patients was.
Genomic differences were also found, Dr. Podany reported. Black patients with estrogen/progesterone receptor (ER/PR) positive, HER2-negative disease were more likely to have a CCND1 copy number variant. And for ER-positive PR-negative HER2-negative patients, Black patients were more likely to have a GATA3 SNV, while White patients were more likely to have a KRAS copy number variant.
Black Survival Less Than Half
The analysis also found significant differences in overall survival from the time of the first liquid biopsy, with White ER-positive, PR-negative, HER2-negative patients living a median of 21 months, versus 9.1 months for Black patients.
There were several limitations to the study beyond its retrospective nature, “so, we may be underestimating the true inequity,” noted Dr. Podany. “These are large urban academic centers, so our patients have access to these treatments. They have access to care. They have access to ctDNA liquid biopsy testing. And the timing of ctDNA, especially the first ctDNA test, is variable and provider-dependant. We were also unable to assess receipt of PI3 kinase inhibitors at future time points after the end of this cohort study.”
Asked for comment, Giuseppe Del Priore, MD, MPH, from Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, approved of the study design “with subjects limited to three distinctive institutions. That parameter alone can control for several unknown variables among the studied comparison groups, ie, Black women versus others.”
However, Dr. Del Priore, who is adjunct professor of obstetrics and gynecology, with a specialty in oncology, added, “retrospective studies are not reliable except for generating hypotheses. Therefore, I would like to see a rapid implementation of an intervention trial at these same institutions to ensure equal consideration of, and access to, targeted therapies. Too often a retrospective correlation is reported, but the solution is elusive due to unknown factors. In this case, knowing there is a mutation is far from alleviating the disproportionate burden of disease that many communities face.”
Dr. Podany had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Del Priore reported no conflicts of interest and disclosed that he is chief medical officer at BriaCell.
Black metastatic breast cancer patients with PIK3CA mutations were less likely to receive targeted therapy and less likely to be enrolled in clinical trials than White patients and had shorter overall survival, according to a retrospective cohort study. Black and White patients were equally likely to receive other drugs that did not require genomic testing.
“These clinical inequities in the use of targeted therapies and clinical trials ... must be a focus going forward,” said lead investigator Emily Podany, MD, a clinical fellow in hematology-oncology at Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. “Our consortium is looking for paths forward in order to try and decrease these striking inequities. And it’s a focus of future research for us and future implementation [of] science interventions, hopefully, across the country.”
The study results were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Black Women Underrepresented
Black women are generally underrepresented in clinical trials, noted Dr. Podany. “They make up about 2%-5% of the patients in breast cancer clinical trials, and there are documented inequities in treatment and in outcomes for Black patients with metastatic breast cancer. This includes longer treatment delays, it includes fewer sentinel lymph node biopsies, and unfortunately, they’re more likely to discontinue treatment early.”
In terms of PI3K inhibition, PIK3CA mutations are found in about 40% of patients with HR-positive HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Alpelisib is FDA-approved as a targeted therapy for these patients, she said.
The study evaluated records of 1327 patients with metastatic breast cancer who also had circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) results and were treated at Washington University, Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and Northwestern University in Chicago. Of these, 795 had an ER-positive, HER2-negative subtype and were included in the analysis. Most (89%) of the patients were White (n = 708), while 11% (n = 87) were Black, and the only baseline difference between patients was that Black patients had significantly more de novo metastatic breast cancer (31% versus 22%).
Use of PI3K, CDK4/6, or mTOR inhibitors was evaluated using manual electronic medical review, and genomic differences were evaluated using logistic regression.
The analysis showed inequities in both treatment and clinical trial enrollment. There were no differences between groups in the use of CDK4/6 or mTOR inhibitors, which do not require a genomic profile, the researchers noted, but Black patients with PIK3CA single nucleotide variants (SNV) were significantly less likely than White patients to use PI3K inhibitors (5.9% versus 28.8%; P = .045), despite no difference in PIK3CA mutations between groups (36% and 34% respectively). Similarly, 11% of White patients with PIK3CA mutations were enrolled in clinical trials, but none of the Black patients was.
Genomic differences were also found, Dr. Podany reported. Black patients with estrogen/progesterone receptor (ER/PR) positive, HER2-negative disease were more likely to have a CCND1 copy number variant. And for ER-positive PR-negative HER2-negative patients, Black patients were more likely to have a GATA3 SNV, while White patients were more likely to have a KRAS copy number variant.
Black Survival Less Than Half
The analysis also found significant differences in overall survival from the time of the first liquid biopsy, with White ER-positive, PR-negative, HER2-negative patients living a median of 21 months, versus 9.1 months for Black patients.
There were several limitations to the study beyond its retrospective nature, “so, we may be underestimating the true inequity,” noted Dr. Podany. “These are large urban academic centers, so our patients have access to these treatments. They have access to care. They have access to ctDNA liquid biopsy testing. And the timing of ctDNA, especially the first ctDNA test, is variable and provider-dependant. We were also unable to assess receipt of PI3 kinase inhibitors at future time points after the end of this cohort study.”
Asked for comment, Giuseppe Del Priore, MD, MPH, from Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, approved of the study design “with subjects limited to three distinctive institutions. That parameter alone can control for several unknown variables among the studied comparison groups, ie, Black women versus others.”
However, Dr. Del Priore, who is adjunct professor of obstetrics and gynecology, with a specialty in oncology, added, “retrospective studies are not reliable except for generating hypotheses. Therefore, I would like to see a rapid implementation of an intervention trial at these same institutions to ensure equal consideration of, and access to, targeted therapies. Too often a retrospective correlation is reported, but the solution is elusive due to unknown factors. In this case, knowing there is a mutation is far from alleviating the disproportionate burden of disease that many communities face.”
Dr. Podany had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Del Priore reported no conflicts of interest and disclosed that he is chief medical officer at BriaCell.
Black metastatic breast cancer patients with PIK3CA mutations were less likely to receive targeted therapy and less likely to be enrolled in clinical trials than White patients and had shorter overall survival, according to a retrospective cohort study. Black and White patients were equally likely to receive other drugs that did not require genomic testing.
“These clinical inequities in the use of targeted therapies and clinical trials ... must be a focus going forward,” said lead investigator Emily Podany, MD, a clinical fellow in hematology-oncology at Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. “Our consortium is looking for paths forward in order to try and decrease these striking inequities. And it’s a focus of future research for us and future implementation [of] science interventions, hopefully, across the country.”
The study results were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Black Women Underrepresented
Black women are generally underrepresented in clinical trials, noted Dr. Podany. “They make up about 2%-5% of the patients in breast cancer clinical trials, and there are documented inequities in treatment and in outcomes for Black patients with metastatic breast cancer. This includes longer treatment delays, it includes fewer sentinel lymph node biopsies, and unfortunately, they’re more likely to discontinue treatment early.”
In terms of PI3K inhibition, PIK3CA mutations are found in about 40% of patients with HR-positive HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Alpelisib is FDA-approved as a targeted therapy for these patients, she said.
The study evaluated records of 1327 patients with metastatic breast cancer who also had circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) results and were treated at Washington University, Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and Northwestern University in Chicago. Of these, 795 had an ER-positive, HER2-negative subtype and were included in the analysis. Most (89%) of the patients were White (n = 708), while 11% (n = 87) were Black, and the only baseline difference between patients was that Black patients had significantly more de novo metastatic breast cancer (31% versus 22%).
Use of PI3K, CDK4/6, or mTOR inhibitors was evaluated using manual electronic medical review, and genomic differences were evaluated using logistic regression.
The analysis showed inequities in both treatment and clinical trial enrollment. There were no differences between groups in the use of CDK4/6 or mTOR inhibitors, which do not require a genomic profile, the researchers noted, but Black patients with PIK3CA single nucleotide variants (SNV) were significantly less likely than White patients to use PI3K inhibitors (5.9% versus 28.8%; P = .045), despite no difference in PIK3CA mutations between groups (36% and 34% respectively). Similarly, 11% of White patients with PIK3CA mutations were enrolled in clinical trials, but none of the Black patients was.
Genomic differences were also found, Dr. Podany reported. Black patients with estrogen/progesterone receptor (ER/PR) positive, HER2-negative disease were more likely to have a CCND1 copy number variant. And for ER-positive PR-negative HER2-negative patients, Black patients were more likely to have a GATA3 SNV, while White patients were more likely to have a KRAS copy number variant.
Black Survival Less Than Half
The analysis also found significant differences in overall survival from the time of the first liquid biopsy, with White ER-positive, PR-negative, HER2-negative patients living a median of 21 months, versus 9.1 months for Black patients.
There were several limitations to the study beyond its retrospective nature, “so, we may be underestimating the true inequity,” noted Dr. Podany. “These are large urban academic centers, so our patients have access to these treatments. They have access to care. They have access to ctDNA liquid biopsy testing. And the timing of ctDNA, especially the first ctDNA test, is variable and provider-dependant. We were also unable to assess receipt of PI3 kinase inhibitors at future time points after the end of this cohort study.”
Asked for comment, Giuseppe Del Priore, MD, MPH, from Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, approved of the study design “with subjects limited to three distinctive institutions. That parameter alone can control for several unknown variables among the studied comparison groups, ie, Black women versus others.”
However, Dr. Del Priore, who is adjunct professor of obstetrics and gynecology, with a specialty in oncology, added, “retrospective studies are not reliable except for generating hypotheses. Therefore, I would like to see a rapid implementation of an intervention trial at these same institutions to ensure equal consideration of, and access to, targeted therapies. Too often a retrospective correlation is reported, but the solution is elusive due to unknown factors. In this case, knowing there is a mutation is far from alleviating the disproportionate burden of disease that many communities face.”
Dr. Podany had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Del Priore reported no conflicts of interest and disclosed that he is chief medical officer at BriaCell.
FROM ASCO 2024
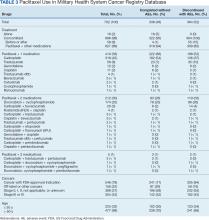
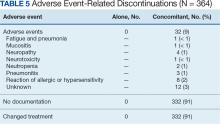
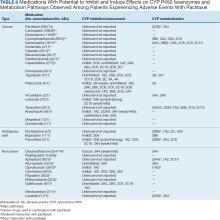
Paclitaxel Drug-Drug Interactions in the Military Health System
Background
Paclitaxel was first derived from the bark of the yew tree (Taxus brevifolia). It was discovered as part of a National Cancer Institute program screen of plants and natural products with putative anticancer activity during the 1960s.1-9 Paclitaxel works by suppressing spindle microtube dynamics, which results in the blockage of the metaphase-anaphase transitions, inhibition of mitosis, and induction of apoptosis in a broad spectrum of cancer cells. Paclitaxel also displayed additional anticancer activities, including the suppression of cell proliferation and antiangiogenic effects. However, since the growth of normal body cells may also be affected, other adverse effects (AEs) will also occur.8-18
Two different chemotherapy drugs contain paclitaxel—paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel—and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes them as separate entities.19-21 Taxol (paclitaxel) was approved by the FDA in 1992 for treating advanced ovarian cancer.20 It has since been approved for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma (as an orphan drug), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and cervical cancers (in combination withbevacizumab) in 1994, 1997, 1999, and 2014, respectively.21 Since 2002, a generic version of Taxol, known as paclitaxel injectable, has been FDA-approved from different manufacturers. According to the National Cancer Institute, a combination of carboplatin and Taxol is approved to treat carcinoma of unknown primary, cervical, endometrial, NSCLC, ovarian, and thymoma cancers.19 Abraxane (nab-paclitaxel) was FDA-approved to treat metastatic breast cancer in 2005. It was later approved for first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC and late-stage pancreatic cancer in 2012 and 2013, respectively. In 2018 and 2020, both Taxol and Abraxane were approved for first-line treatment of metastatic squamous cell NSCLC in combination with carboplatin and pembrolizumab and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer in combination with pembrolizumab, respectively.22-26 In 2019, Abraxane was approved with atezolizumab to treat metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, but this approval was withdrawn in 2021. In 2022, a generic version of Abraxane, known as paclitaxel protein-bound, was released in the United States. Furthermore, paclitaxel-containing formulations also are being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.19-32
One of the main limitations of paclitaxel is its low solubility in water, which complicates its drug supply. To distribute this hydrophobic anticancer drug efficiently, paclitaxel is formulated and administered to patients via polyethoxylated castor oil or albumin-bound (nab-paclitaxel). However, polyethoxylated castor oil induces complement activation and is the cause of common hypersensitivity reactions related to paclitaxel use.2,17,33-38 Therefore, many alternatives to polyethoxylated castor oil have been researched.
Since 2000, new paclitaxel formulations have emerged using nanomedicine techniques. The difference between these formulations is the drug vehicle. Different paclitaxel-based nanotechnological vehicles have been developed and approved, such as albumin-based nanoparticles, polymeric lipidic nanoparticles, polymeric micelles, and liposomes, with many others in clinical trial phases.3,37 Albumin-based nanoparticles have a high response rate (33%), whereas the response rate for polyethoxylated castor oil is 25% in patients with metastatic breast cancer.33,39-52 The use of paclitaxel dimer nanoparticles also has been proposed as a method for increasing drug solubility.33,53
Paclitaxel is metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes 2C8 and 3A4. When administering paclitaxel with known inhibitors, inducers, or substrates of CYP2C8 or CYP3A4, caution is required.19-22 Regulations for CYP research were not issued until 2008, so potential interactions between paclitaxel and other drugs have not been extensively evaluated in clinical trials. A study of 12 kinase inhibitors showed strong inhibition of CYP2C8 and/or CYP3A4 pathways by these inhibitors, which could alter the ratio of paclitaxel metabolites in vivo, leading to clinically relevant changes.54 Differential metabolism has been linked to paclitaxel-induced neurotoxicity in patients with cancer.55 Nonetheless, variants in the CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 genes do not account for significant interindividual variability in paclitaxel pharmacokinetics.56 In liver microsomes, losartan inhibited paclitaxel metabolism when used at concentrations > 50 µmol/L.57 Many drug-drug interaction (DDI) studies of CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 have shown similar results for paclitaxel.58-64
The goals of this study are to investigate prescribed drugs used with paclitaxel and determine patient outcomes through several Military Health System (MHS) databases. The investigation focused on (1) the functions of paclitaxel; (2) identifying AEs that patients experienced; (3) evaluating differences when paclitaxel is used alone vs concomitantly and between the completed vs discontinued treatment groups; (4) identifying all drugs used during paclitaxel treatment; and (5) evaluating DDIs with antidepressants (that have an FDA boxed warning and are known to have DDIs confirmed in previous publications) and other drugs.65-67
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, institutionalreview board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and MHS data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and the Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
METHODS
The DoD Cancer Registry Program was established in 1986 and currently contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in the CAPER record represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER includes data from 2003 to 2024.
Each observation in the PDTS record represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary at an MTF through the TRICARE mail-order program or a US retail pharmacy. Missing from this record are prescriptions filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions. The MHS Data Repository PDTS record is available from 2002 to 2024. The legacy Composite Health Care System is being replaced by GENESIS at MTFs.
Data Extraction Design
The study design involved a cross-sectional analysis. We requested data extraction for paclitaxel from 1998 to 2022. Data from the DoD Cancer Registry Program were used to identify patients who received cancer treatment. Once patients were identified, the CAPER database was searched for diagnoses to identify other health conditions, whereas the PDTS database was used to populate a list of prescription medications filled during chemotherapy treatment.
Data collected from the JPC included cancer treatment, cancer information, demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. Collected data from the MHS include diagnosis and filled prescription history from initiation to completion of the therapy period (or 2 years after the diagnosis date). For the analysis of the DoD Cancer Registry Program and CAPER databases, we used all collected data without excluding any. When analyzing PDTS data, we excluded patients with PDTS data but without a record of paclitaxel being filled, or medications filled outside the chemotherapy period (by evaluating the dispensed date and day of supply).
Data Extraction Analysis
The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual 2016 and the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.68,69 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the paclitaxel groups divided by the total number of patients or data variables. The subgroup percentage was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients in that subgroup.
In alone vs concomitant and completed vs discontinued treatment groups, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to statistical significance (P < .05) using a statistics website.70 Concomitant was defined as paclitaxel taken with other antineoplastic agent(s) before, after, or at the same time as cancer therapy. For the retrospective data analysis, physicians’ notes with a period, comma, forward slash, semicolon, or space between medication names were interpreted as concurrent, whereas plus (+), minus/plus (-/+), or “and” between drug names that were dispensed on the same day were interpreted as combined with known common combinations: 2 drugs (DM886 paclitaxel and carboplatin and DM881-TC-1 paclitaxel and cisplatin) or 3 drugs (DM887-ACT doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and paclitaxel). Completed treatment was defined as paclitaxel as the last medication the patient took without recorded AEs; switching or experiencing AEs was defined as discontinued treatment.
RESULTS
The JPC provided 702 entries for 687 patients with a mean age of 56 years (range, 2 months to 88 years) who were treated with paclitaxel from March 1996 to October 2021. Fifteen patients had duplicate entries because they had multiple cancer sites or occurrences. There were 623 patients (89%) who received paclitaxel for FDA-approved indications. The most common types of cancer identified were 344 patients with breast cancer (49%), 91 patients with lung cancer (13%), 79 patients with ovarian cancer (11%), and 75 patients with endometrial cancer (11%) (Table 1). Seventy-nine patients (11%) received paclitaxel for cancers that were not for FDA-approved indications, including 19 for cancers of the fallopian tube (3%) and 17 for esophageal cancer (2%) (Table 2).
There were 477 patients (68%) aged > 50 years. A total of 304 patients (43%) had a stage III or IV cancer diagnosis and 398 (57%) had stage II or lower (combination of data for stages 0, I, and II; not applicable; and unknown) cancer diagnosis. For systemic treatment, 16 patients (2%) were treated with paclitaxel alone and 686 patients (98%) received paclitaxel concomitantly with additional chemotherapy: 59 patients (9%) in the before or after group, 410 patients (58%) had a 2-drug combination, 212 patients (30%) had a 3-drug combination, and 5 patients (1%) had a 4-drug combination. In addition, for doublet therapies, paclitaxel combined with carboplatin, trastuzumab, gemcitabine, or cisplatin had more patients (318, 58, 12, and 11, respectively) than other combinations (≤ 4 patients). For triplet therapies, paclitaxel combined withdoxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide or carboplatin plus bevacizumab had more patients (174 and 20, respectively) than other combinations, including quadruplet therapies (≤ 4 patients) (Table 3).
Patients were more likely to discontinue paclitaxel if they received concomitant treatment. None of the 16 patients receiving paclitaxel monotherapy experienced AEs, whereas 364 of 686 patients (53%) treated concomitantly discontinued (P < .001). Comparisons of 1 drug vs combination (2 to 4 drugs) and use for treating cancers that were FDA-approved indications vs off-label use were significant (P < .001), whereas comparisons of stage II or lower vs stage III and IV cancer and of those aged ≤ 50 years vs aged > 50 years were not significant (P = .50 andP = .30, respectively) (Table 4).
Among the 364 patients who had concomitant treatment and had discontinued their treatment, 332 (91%) switched treatments with no AEs documented and 32 (9%) experienced fatigue with pneumonia, mucositis, neuropathy, neurotoxicity, neutropenia, pneumonitis, allergic or hypersensitivity reaction, or an unknown AE. Patients who discontinued treatment because of unknown AEs had a physician’s note that detailed progressive disease, a significant decline in performance status, and another unknown adverse effect due to a previous sinus tract infection and infectious colitis (Table 5).
Management Analysis and Reporting Tool Database
MHS data analysts provided data on diagnoses for 639 patients among 687 submitteddiagnoses, with 294 patients completing and 345 discontinuing paclitaxel treatment. Patients in the completed treatment group had 3 to 258 unique health conditions documented, while patients in the discontinued treatment group had 4 to 181 unique health conditions documented. The MHS reported 3808 unique diagnosis conditions for the completed group and 3714 for the discontinued group (P = .02).
The mean (SD) number of diagnoses was 51 (31) for the completed and 55 (28) for the discontinued treatment groups (Figure). Among 639 patients who received paclitaxel, the top 5 diagnoses were administrative, including encounters for other administrative examinations; antineoplastic chemotherapy; administrative examination for unspecified; other specified counseling; and adjustment and management of vascular access device. The database does not differentiate between administrative and clinically significant diagnoses.
MHS data analysts provided data for 336 of 687 submitted patients who were prescribed paclitaxel; 46 patients had no PDTS data, and 305 patients had PDTS data without paclitaxel, Taxol, or Abraxane dispensed. Medications that were filled outside the chemotherapy period were removed by evaluating the dispensed date and day of supply. Among these 336 patients, 151 completed the treatment and 185 discontinued, with 14 patients experiencing documented AEs. Patients in the completed treatment group filled 9 to 56 prescriptions while patients in the discontinued treatment group filled 6 to 70 prescriptions.Patients in the discontinued group filled more prescriptions than those who completed treatment: 793 vs 591, respectively (P = .34).
The mean (SD) number of filled prescription drugs was 24 (9) for the completed and 34 (12) for the discontinued treatment group. The 5 most filled prescriptions with paclitaxel from 336 patients with PDTS data were dexamethasone (324 prescriptions with 14 recorded AEs), diphenhydramine (296 prescriptions with 12 recorded AEs), ondansetron (277 prescriptions with 11 recorded AEs), prochlorperazine (265 prescriptions with 12 recorded AEs), and sodium chloride (232 prescriptions with 11 recorded AEs).
DISCUSSION
As a retrospective review, this study is more limited in the strength of its conclusions when compared to randomized control trials. The DoD Cancer Registry Program only contains information about cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes. Therefore, noncancer drugs are based solely on the PDTS database. In most cases, physicians' notes on AEs were not detailed. There was no distinction between initial vs later lines of therapy and dosage reductions. The change in status or appearance of a new medical condition did not indicate whether paclitaxel caused the changes to develop or directly worsen a pre-existing condition. The PDTS records prescriptions filled, but that may not reflect patients taking prescriptions.
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel has a long list of both approved and off-label uses in malignancies as a primary agent and in conjunction with other drugs. The FDA prescribing information for Taxol and Abraxane was last updated in April 2011 and September 2020, respectively.20,21 The National Institutes of Health National Library of Medicine has the current update for paclitaxel on July 2023.19,22 Thus, the prescribed information for paclitaxel referenced in the database may not always be up to date. The combinations of paclitaxel with bevacizumab, carboplatin, or carboplatin and pembrolizumab were not in the Taxol prescribing information. Likewise, a combination of nab-paclitaxel with atezolizumab or carboplatin and pembrolizumab is missing in the Abraxane prescribing information.22-27
The generic name is not the same as a generic drug, which may have slight differences from the brand name product.71 The generic drug versions of Taxol and Abraxane have been approved by the FDA as paclitaxel injectable and paclitaxel-protein bound, respectively. There was a global shortage of nab-paclitaxel from October 2021 to June 2022 because of a manufacturing problem.72 During this shortage, data showed similar comments from physician documents that treatment switched to Taxol due to the Abraxane shortage.
Of 336 patients in the PDTS database with dispensed paclitaxel prescriptions, 276 received paclitaxel (year dispensed, 2013-2022), 27 received Abraxane (year dispensed, 2013-2022), 47 received Taxol (year dispensed, 2004-2015), 8 received both Abraxane and paclitaxel, and 6 received both Taxol and paclitaxel. Based on this information, it appears that the distinction between the drugs was not made in the PDTS until after 2015, 10 years after Abraxane received FDA approval. Abraxane was prescribed in the MHS in 2013, 8 years after FDA approval. There were a few comparison studies of Abraxane and Taxol.73-76
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established for paclitaxel. According to the DoD Cancer Registry Program, the youngest patient was aged 2 months. In 2021, this patient was diagnosed with corpus uteri and treated with carboplatin and Taxol in course 1; in course 2, the patient reacted to Taxol; in course 3, Taxol was replaced with Abraxane; in courses 4 to 7, the patient was treated with carboplatin only.
Discontinued Treatment
Ten patients had prescribed Taxol that was changed due to AEs: 1 was switched to Abraxane and atezolizumab, 3 switched to Abraxane, 2 switched to docetaxel, 1 switched to doxorubicin, and 3 switched to pembrolizumab (based on physician’s comments). Of the 10 patients, 7 had Taxol reaction, 2 experienced disease progression, and 1 experienced high programmed death–ligand 1 expression (this patient with breast cancer was switched to Abraxane and atezolizumab during the accelerated FDA approval phase for atezolizumab, which was later revoked). Five patients were treated with carboplatin and Taxol for cancer of the anal canal (changed to pembrolizumab after disease progression), lung not otherwise specified (changed to carboplatin and pembrolizumab due to Taxol reaction), lower inner quadrant of the breast (changed to doxorubicin due to hypersensitivity reaction), corpus uteri (changed to Abraxane due to Taxol reaction), and ovary (changed to docetaxel due to Taxol reaction). Three patients were treated with doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and Taxol for breast cancer; 2 patients with breast cancer not otherwise specified switched to Abraxane due to cardiopulmonary hypersensitivity and Taxol reaction and 1 patient with cancer of the upper outer quadrant of the breast changed to docetaxel due to allergic reaction. One patient, who was treated with paclitaxel, ifosfamide, and cisplatin for metastasis of the lower lobe of the lung and kidney cancer, experienced complications due to infectious colitis (treated with ciprofloxacin) and then switched to pembrolizumab after the disease progressed. These AEs are known in paclitaxel medical literature on paclitaxel AEs.19-24,77-81
Combining 2 or more treatments to target cancer-inducing or cell-sustaining pathways is a cornerstone of chemotherapy.82-84 Most combinations are given on the same day, but some are not. For 3- or 4-drug combinations, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide were given first, followed by paclitaxel with or withouttrastuzumab, carboplatin, or pembrolizumab. Only 16 patients (2%) were treated with paclitaxel alone; therefore, the completed and discontinued treatment groups are mostly concomitant treatment. As a result, the comparisons of the completed and discontinued treatment groups were almost the same for the diagnosis. The PDTS data have a better result because 2 exclusion criteria were applied before narrowing the analysis down to paclitaxel treatment specifically.
Antidepressants and Other Drugs
Drug response can vary from person to person and can lead to treatment failure related to AEs. One major factor in drug metabolism is CYP.85 CYP2C8 is the major pathway for paclitaxel and CYP3A4 is the minor pathway. When evaluating the noncancer drugs, there were no reports of CYP2C8 inhibition or induction.Over the years, many DDI warnings have been issued for paclitaxel with different drugs in various electronic resources.
Oncologists follow guidelines to prevent DDIs, as paclitaxel is known to have severe, moderate, and minor interactions with other drugs. Among 687 patients, 261 (38%) were prescribed any of 14 antidepressants. Eight of these antidepressants (amitriptyline, citalopram, desipramine, doxepin, venlafaxine, escitalopram, nortriptyline, and trazodone) are metabolized, 3 (mirtazapine, sertraline, and fluoxetine) are metabolized and inhibited, 2 (bupropion and duloxetine) are neither metabolized nor inhibited, and 1 (paroxetine) is inhibited by CYP3A4. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, and trazodone were more commonly dispensed (84, 78, and 42 patients, respectively) than others (≤ 33 patients).
Of 32 patients with documented AEs,14 (44%) had 168 dispensed drugs in the PDTS database. Six patients (19%) were treated with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel for breast cancer; 6 (19%) were treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel for cancer of the lung (n = 3), corpus uteri (n = 2), and ovary (n = 1); 1 patient (3%) was treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel, then switched to carboplatin, bevacizumab, and paclitaxel, and then completed treatment with carboplatin and paclitaxel for an unspecified female genital cancer; and 1 patient (3%) was treated with cisplatin, ifosfamide, and paclitaxel for metastasis of the lower lobe lung and kidney cancer.
The 14 patients with PDTS data had 18 cancer drugs dispensed. Eleven had moderate interaction reports and 7 had no interaction reports. A total of 165 noncancer drugs were dispensed, of which 3 were antidepressants and had no interactions reported, 8 had moderate interactions reported, and 2 had minor interactions with Taxol and Abraxane, respectively (Table 6).86-129
Of 3 patients who were dispensed bupropion, nortriptyline, or paroxetine, 1 patient with breast cancer was treated with doxorubicin andcyclophosphamide, followed by paclitaxel with bupropion, nortriptyline, pegfilgrastim,dexamethasone, and 17 other noncancer drugs that had no interaction report dispensed during paclitaxel treatment. Of 2 patients with lung cancer, 1 patient was treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel with nortriptyline, dexamethasone, and 13 additional medications, and the second patient was treated with paroxetine, cimetidine, dexamethasone, and 12 other medications. Patients were dispensed up to6 noncancer medications on the same day as paclitaxel administration to control the AEs, not including the prodrugs filled before the treatments. Paroxetine and cimetidine have weak inhibition, and dexamethasone has weak induction of CYP3A4. Therefore, while 1:1 DDIs might have little or no effect with weak inhibit/induce CYP3A4 drugs, 1:1:1 or more combinations could have a different outcome (confirmed in previous publications).65-67
Dispensed on the same day may not mean taken at the same time. One patient experienced an AE with dispensed 50 mg losartan, carboplatin plus paclitaxel, dexamethasone, and 6 other noncancer drugs. Losartan inhibits paclitaxel, which can lead to negative AEs.57,66,67 However, there were no blood or plasma samples taken to confirm the losartan was taken at the same time as the paclitaxel given this was not a clinical trial.
Conclusions
This retrospective study discusses the use of paclitaxel in the MHS and the potential DDIs associated with it. The study population consisted mostly of active-duty personnel, who are required to be healthy or have controlled or nonactive medical diagnoses and be physically fit. This group is mixed with dependents and retirees that are more reflective of the average US population. As a result, this patient population is healthier than the general population, with a lower prevalence of common illnesses such as diabetes and obesity. The study aimed to identify drugs used alongside paclitaxel treatment. While further research is needed to identify potential DDIs among patients who experienced AEs, in vitro testing will need to be conducted before confirming causality. The low number of AEs experienced by only 32 of 702 patients (5%), with no deaths during paclitaxel treatment, indicates that the drug is generally well tolerated. Although this study cannot conclude that concomitant use with noncancer drugs led to the discontinuation of paclitaxel, we can conclude that there seems to be no significant DDIsidentified between paclitaxel and antidepressants. This comprehensive overview provides clinicians with a complete picture of paclitaxel use for 27 years (1996-2022), enabling them to make informed decisions about paclitaxel treatment.
Acknowledgments
The Department of Research Program funds at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center supported this protocol. We sincerely appreciate the contribution of data extraction from the Joint Pathology Center teams (Francisco J. Rentas, John D. McGeeney, Beatriz A. Hallo, and Johnny P. Beason) and the MHS database personnel (Maj Ryan Costantino, Brandon E. Jenkins, and Alexander G. Rittel). We gratefully thank you for the protocol support from the Department of Research programs: CDR Martin L. Boese, CDR Wesley R. Campbell, Maj. Abhimanyu Chandel, CDR Ling Ye, Chelsea N. Powers, Yaling Zhou, Elizabeth Schafer, Micah Stretch, Diane Beaner, and Adrienne Woodard.
1. American Chemical Society. Discovery of camptothecin and taxol. acs.org. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.acs.org/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/camptothecintaxol.html
2. Bocci G, Di Paolo A, Danesi R. The pharmacological bases of the antiangiogenic activity of paclitaxel. Angiogenesis. 2013;16(3):481-492. doi:10.1007/s10456-013-9334-0.
3. Meštrovic T. Paclitaxel history. News Medical Life Sciences. Updated March 11, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Paclitaxel-History.aspx
4. Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC. Paclitaxel (taxol). N Engl J Med. 1995;332(15):1004-1014. doi:10.1056/NEJM199504133321507
5. Walsh V, Goodman J. The billion dollar molecule: Taxol in historical and theoretical perspective. Clio Med. 2002;66:245-267. doi:10.1163/9789004333499_013
6. Perdue RE, Jr, Hartwell JL. The search for plant sources of anticancer drugs. Morris Arboretum Bull. 1969;20:35-53.
7. Wall ME, Wani MC. Camptothecin and taxol: discovery to clinic—thirteenth Bruce F. Cain Memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 1995;55:753-760.
8. Wani MC, Taylor HL, Wall ME, Coggon P, McPhail AT. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971;93(9):2325-2327. doi:10.1021/ja00738a045
9. Weaver BA. How taxol/paclitaxel kills cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2014;25(18):2677-2681. doi:10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0916
10. Chen JG, Horwitz SB. Differential mitotic responses to microtubule-stabilizing and-destabilizing drugs. Cancer Res. 2002;62(7):1935-1938.
11. Singh S, Dash AK. Paclitaxel in cancer treatment: perspectives and prospects of its delivery challenges. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2009;26(4):333-372. doi:10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.v26.i4.10
12. Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979;277(5698):665-667. doi:10.1038/277665a0
13. Fuchs DA, Johnson RK. Cytologic evidence that taxol, an antineoplastic agent from taxus brevifolia, acts as a mitotic spindle poison. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978;62(8):1219-1222.
14. Walsh V, Goodman J. From taxol to taxol: the changing identities and ownership of an anti-cancer drug. Med Anthropol. 2002;21(3-4):307-336. doi:10.1080/01459740214074
15. Walsh V, Goodman J. Cancer chemotherapy, biodiversity, public and private property: the case of the anti-cancer drug taxol. Soc Sci Med. 1999;49(9):1215-1225. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00161-6
16. Jordan MA, Wendell K, Gardiner S, Derry WB, Copp H, Wilson L. Mitotic block induced in HeLa cells by low concentrations of paclitaxel (taxol) results in abnormal mitotic exit and apoptotic cell death. Cancer Res. 1996;56(4):816-825.
17. Picard M, Castells MC. Re-visiting hypersensitivity reactions to taxanes: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015;49(2):177-191. doi:10.1007/s12016-014-8416-0
18. Zasadil LM, Andersen KA, Yeum D, et al. Cytotoxicity of paclitaxel in breast cancer is due to chromosome missegregation on multipolar spindles. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:229ra243. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007965
19. National Cancer Institute. Carboplatin-Taxol. Published May 30, 2012. Updated March 22, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/carboplatin-taxol
20. Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb; 2011. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
21. Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2021. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
22. Awosika AO, Farrar MC, Jacobs TF. Paclitaxel. StatPearls. Updated November 18, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536917/
23. Gerriets V, Kasi A. Bevacizumab. StatPearls. Updated September 1, 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482126/
24. American Cancer Society. Chemotherapy for endometrial cancer. Updated March 27, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/endometrial-cancer/treating/chemotherapy.html
25. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy for first-line treatment of metastatic squamous NSCLC. October 30, 2018. Updated December 14, 2018. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-combination-chemotherapy-first-line-treatment-metastatic-squamous-nsclc
26. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for locally recurrent unresectable or metastatic triple negative breast cancer. November 13, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-pembrolizumab-locally-recurrent-unresectable-or-metastatic-triple
27. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves atezolizumab for PD-L1 positive unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast. March 8, 2019. Updated March 18, 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-approves-atezolizumab-pd-l1-positive-unresectable-locally-advanced-or-metastatic-triple-negative
28. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA issues alert about efficacy and potential safety concerns with atezolizumab in combination with paclitaxel for treatment of breast cancer. September 8, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-issues-alert-about-efficacy-and-potential-safety-concerns-atezolizumab-combination-paclitaxel
29. Tan AR. Chemoimmunotherapy: still the standard of care for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. ASCO Daily News. February 23, 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://dailynews.ascopubs.org/do/chemoimmunotherapy-still-standard-care-metastatic-triple-negative-breast-cancer
30. McGuire WP, Rowinsky EK, Rosenshein NB, et al. Taxol: a unique antineoplastic agent with significant activity in advanced ovarian epithelial neoplasms. Ann Intern Med. 1989;111(4):273-279. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-111-4-273
31. Milas L, Hunter NR, Kurdoglu B, et al. Kinetics of mitotic arrest and apoptosis in murine mammary and ovarian tumors treated with taxol. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;35(4):297-303. doi:10.1007/BF00689448
32. Searle J, Collins DJ, Harmon B, Kerr JF. The spontaneous occurrence of apoptosis in squamous carcinomas of the uterine cervix. Pathology. 1973;5(2):163-169. doi:10.3109/00313027309060831
33. Gallego-Jara J, Lozano-Terol G, Sola-Martínez RA, Cánovas-Díaz M, de Diego Puente T. A compressive review about taxol®: history and future challenges. Molecules. 2020;25(24):5986. doi:10.3390/molecules25245986
34. Bernabeu E, Cagel M, Lagomarsino E, Moretton M, Chiappetta DA. Paclitaxel: What has been done and the challenges remain ahead. Int J Pharm. 2017;526(1-2):474-495. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.016
35. Nehate C, Jain S, Saneja A, et al. Paclitaxel formulations: challenges and novel delivery options. Curr Drug Deliv. 2014;11(6):666-686. doi:10.2174/1567201811666140609154949
36. Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Sparreboom A, Cremophor EL. The drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(13):1590-1598. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(01)00171-x
37. Chowdhury MR, Moshikur RM, Wakabayashi R, et al. In vivo biocompatibility, pharmacokinetics, antitumor efficacy, and hypersensitivity evaluation of ionic liquid-mediated paclitaxel formulations. Int J Pharm. 2019;565:219-226. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.05.020
38. Borgå O, Henriksson R, Bjermo H, Lilienberg E, Heldring N, Loman N. Maximum tolerated dose and pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel micellar in patients with recurrent malignant solid tumours: a dose-escalation study. Adv Ther. 2019;36(5):1150-1163. doi:10.1007/s12325-019-00909-6
39. Rouzier R, Rajan R, Wagner P, et al. Microtubule-associated protein tau: a marker of paclitaxel sensitivity in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(23):8315-8320. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408974102
40. Choudhury H, Gorain B, Tekade RK, Pandey M, Karmakar S, Pal TK. Safety against nephrotoxicity in paclitaxel treatment: oral nanocarrier as an effective tool in preclinical evaluation with marked in vivo antitumor activity. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017;91:179-189. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.10.023
41. Barkat MA, Beg S, Pottoo FH, Ahmad FJ. Nanopaclitaxel therapy: an evidence based review on the battle for next-generation formulation challenges. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2019;14(10):1323-1341. doi:10.2217/nnm-2018-0313
42. Sofias AM, Dunne M, Storm G, Allen C. The battle of “nano” paclitaxel. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;122:20-30. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2017.02.003
43. Yang N, Wang C, Wang J, et al. Aurora inase a stabilizes FOXM1 to enhance paclitaxel resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(9):6442-6453. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14538
44. Chowdhury MR, Moshikur RM, Wakabayashi R, et al. Ionic-liquid-based paclitaxel preparation: a new potential formulation for cancer treatment. Mol Pharm. 2018;15(16):2484-2488. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00305
45. Chung HJ, Kim HJ, Hong ST. Tumor-specific delivery of a paclitaxel-loading HSA-haemin nanoparticle for cancer treatment. Nanomedicine. 2020;23:102089. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2019.102089
46. Ye L, He J, Hu Z, et al. Antitumor effect and toxicity of lipusu in rat ovarian cancer xenografts. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;52:200-206. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.11.004
47. Ma WW, Lam ET, Dy GK, et al. A pharmacokinetic and dose-escalating study of paclitaxel injection concentrate for nano-dispersion (PICN) alone and with arboplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2557. doi:10.1200/jco.2013.31.15_suppl.2557
48. Micha JP, Goldstein BH, Birk CL, Rettenmaier MA, Brown JV. Abraxane in the treatment of ovarian cancer: the absence of hypersensitivity reactions. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;100(2):437-438. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.09.012
49. Ingle SG, Pai RV, Monpara JD, Vavia PR. Liposils: an effective strategy for stabilizing paclitaxel loaded liposomes by surface coating with silica. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;122:51-63. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2018.06.025
50. Abriata JP, Turatti RC, Luiz MT, et al. Development, characterization and biological in vitro assays of paclitaxel-loaded PCL polymeric nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:347-355. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.035
51. Hu J, Fu S, Peng Q, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded polymeric nanoparticles combined with chronomodulated chemotherapy on lung cancer: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2017;516(1-2):313-322. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.11.047
52. Dranitsaris G, Yu B, Wang L, et al. Abraxane® vs Taxol® for patients with advanced breast cancer: a prospective time and motion analysis from a chinese health care perspective. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016;22(2):205-211. doi:10.1177/1078155214556008
53. Pei Q, Hu X, Liu S, Li Y, Xie Z, Jing X. Paclitaxel dimers assembling nanomedicines for treatment of cervix carcinoma. J Control Release. 2017;254:23-33. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.03.391
54. Wang Y, Wang M, Qi H, et al. Pathway-dependent inhibition of paclitaxel hydroxylation by kinase inhibitors and assessment of drug-drug interaction potentials. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42(4):782-795. doi:10.1124/dmd.113.053793
55. Shen F, Jiang G, Philips S, et al. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (POR) associated with severe paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients of european ancestry from ECOG-ACRIN E5103. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29(13):2494-2500. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2431
56. Henningsson A, Marsh S, Loos WJ, et al. Association of CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 polymorphisms with the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(22):8097-8104. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1152
57. Mukai Y, Senda A, Toda T, et al. Drug-drug interaction between losartan and paclitaxel in human liver microsomes with different CYP2C8 genotypes. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;116(6):493-498. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12355
58. Kawahara B, Faull KF, Janzen C, Mascharak PK. Carbon monoxide inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP3A4/2C8 in human breast cancer cells, increasing sensitivity to paclitaxel. J Med Chem. 2021;64(12):8437-8446. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00404
59. Cresteil T, Monsarrat B, Dubois J, Sonnier M, Alvinerie P, Gueritte F. Regioselective metabolism of taxoids by human CYP3A4 and 2C8: structure-activity relationship. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002;30(4):438-445. doi:10.1124/dmd.30.4.438
60. Taniguchi R, Kumai T, Matsumoto N, et al. Utilization of human liver microsomes to explain individual differences in paclitaxel metabolism by CYP2C8 and CYP3A4. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;97(1):83-90. doi:10.1254/jphs.fp0040603
61. Nakayama A, Tsuchiya K, Xu L, Matsumoto T, Makino T. Drug-interaction between paclitaxel and goshajinkigan extract and its constituents. J Nat Med. 2022;76(1):59-67. doi:10.1007/s11418-021-01552-8
62. Monsarrat B, Chatelut E, Royer I, et al. Modification of paclitaxel metabolism in a cancer patient by induction of cytochrome P450 3A4. Drug Metab Dispos. 1998;26(3):229-233.
63. Walle T. Assays of CYP2C8- and CYP3A4-mediated metabolism of taxol in vivo and in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1996;272:145-151. doi:10.1016/s0076-6879(96)72018-9
64. Hanioka N, Matsumoto K, Saito Y, Narimatsu S. Functional characterization of CYP2C8.13 and CYP2C8.14: catalytic activities toward paclitaxel. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;107(1):565-569. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00543.x
65. Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
66. Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with Cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217-224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006
67. Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the military health system. Fed Pract. 2023;40(suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
68. Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
69. World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O) 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
70. Z score calculator for 2 population proportions. Social science statistics. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.socscistatistics.com/tests/ztest/default2.aspx
71. US Food and Drug Administration. Generic drugs: question & answers. FDA.gov. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/frequently-asked-questions-popular-topics/generic-drugs-questions-answers
72. Oura M, Saito H, Nishikawa Y. Shortage of nab-paclitaxel in Japan and around the world: issues in global information sharing. JMA J. 2023;6(2):192-195. doi:10.31662/jmaj.2022-0179
73. Yuan H, Guo H, Luan X, et al. Albumin nanoparticle of paclitaxel (abraxane) decreases while taxol increases breast cancer stem cells in treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(7):2275-2286. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b01221
74. Dranitsaris G, Yu B, Wang L, et al. Abraxane® versus Taxol® for patients with advanced breast cancer: a prospective time and motion analysis from a Chinese health care perspective. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016;22(2):205-211. doi:10.1177/1078155214556008
75. Gradishar WJ, Tjulandin S, Davidson N, et al. Phase III trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with polyethylated castor oil-based paclitaxel in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(31):7794-7803. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.
76. Liu M, Liu S, Yang L, Wang S. Comparison between nab-paclitaxel and solvent-based taxanes as neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):118. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-07831-7
77. Rowinsky EK, Eisenhauer EA, Chaudhry V, Arbuck SG, Donehower RC. Clinical toxicities encountered with paclitaxel (taxol). Semin Oncol. 1993;20(4 Suppl 3):1-15.
78. Banerji A, Lax T, Guyer A, Hurwitz S, Camargo CA Jr, Long AA. Management of hypersensitivity reactions to carboplatin and paclitaxel in an outpatient oncology infusion center: a 5-year review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2(4):428-433. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2014.04.010
79. Staff NP, Fehrenbacher JC, Caillaud M, Damaj MI, Segal RA, Rieger S. Pathogenesis of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: a current review of in vitro and in vivo findings using rodent and human model systems. Exp Neurol. 2020;324:113121. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113121
80. Postma TJ, Vermorken JB, Liefting AJ, Pinedo HM, Heimans JJ. Paclitaxel-induced neuropathy. Ann Oncol. 1995;6(5):489-494. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a059220
81. Liu JM, Chen YM, Chao Y, et al. Paclitaxel-induced severe neuropathy in patients with previous radiotherapy to the head and neck region. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88(14):1000-1002. doi:10.1093/jnci/88.14.1000-a
82. Bayat Mokhtari R, Homayouni TS, Baluch N, et al. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(23):38022-38043. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16723
83. Blagosklonny MV. Analysis of FDA approved anticancer drugs reveals the future of cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 2004;3(8):1035-1042.
84. Yap TA, Omlin A, de Bono JS. Development of therapeutic combinations targeting major cancer signaling pathways. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(12):1592-1605. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.37.6418
85. Gilani B, Cassagnol M. Biochemistry, Cytochrome P450. StatPearls. Updated April 24, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557698/
86. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Carboplatin. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548565/
87. Carboplatin. Prescribing information. Teva Parenteral Medicines; 2012. Accessed June 5, 204. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/077139Orig1s016lbl.pdf
88. Johnson-Arbor K, Dubey R. Doxorubicin. StatPearls. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459232/
89. Doxorubicin hydrochloride injection. Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/050467s078,050629s030lbl.pdf
90. Gor, PP, Su, HI, Gray, RJ, et al. Cyclophosphamide-metabolizing enzyme polymorphisms and survival outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(3):R26. doi:10.1186/bcr2570
91. Cyclophosphamide. Prescribing information. Ingenus Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/212501s000lbl.pdf
92. Gemcitabine. Prescribing information. Hospira; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/200795Orig1s010lbl.pdf
93. Ifex (ifosfamide). Prescribing information. Baxter; 2012. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/019763s017lbl.pdf
94. Cisplatin. Prescribing information. WG Critical Care; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/018057s089lbl.pdf
95. Gerriets V, Kasi A. Bevacizumab. StatPearls. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482126/
96. Avastin (bevacizumab). Prescribing information. Genentech; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata .fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/125085s340lbl.pdf
 97. Keytruda (pembrolizumab). Prescribing information. Merck; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/125514s096lbl.pdf
97. Keytruda (pembrolizumab). Prescribing information. Merck; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/125514s096lbl.pdf
98. Dean L, Kane M. Capecitabine therapy and DPYD genotype. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012. Updated November 2, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK385155/
99. Xeloda (capecitabine). Prescribing information. Roche; 2000. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2000/20896lbl.pdf
100. Pemetrexed injection. Prescribing information. Fareva Unterach; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/214657s000lbl.pdf
101. Topotecan Injection. Prescribing information. Zydus Hospira Oncology; 2014. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/200582s001lbl.pdf
102. Ibrance (palbociclib). Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/207103s008lbl.pdf
103. Navelbine (vinorelbine) injection. Prescribing information. Pierre Fabre Médicament; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020388s037lbl.pdf
104. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Letrozole. Updated July 25, 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548381/
105. Femara (letrozole). Prescribing information. Novartis; 2014. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/020726s027lbl.pdf
106. Soltamox (tamoxifen citrate). Prescribing information. Rosemont Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/021807s005lbl.pdf
107. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Anastrozole. Updated July 25, 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548189/
108. Grimm SW, Dyroff MC. Inhibition of human drug metabolizing cytochromes P450 by anastrozole, a potent and selective inhibitor of aromatase. Drug Metab Dispos. 1997;25(5):598-602.
109. Arimidex (anastrozole). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca; 2010. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020541s026lbl.pdf
110. Megace (megestrol acetate). Prescribing information. Endo Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/021778s024lbl.pdf
111. Imfinzi (durvalumab). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/761069s018lbl.pdf
112. Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, et al. Nortriptyline. StatPearls. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
113. Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Patheon Inc.; 2012. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
114. Wellbutrin (bupropion hydrochloride). Prescribing information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018644s052lbl.pdf
115. Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing information. Apotex Inc.; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
116. Johnson DB, Lopez MJ, Kelley B. Dexamethasone. StatPearls. Updated May 2, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482130/
117. Hemady (dexamethasone). Prescribing information. Dexcel Pharma; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/211379s000lbl.pdf
118. Parker SD, King N, Jacobs TF. Pegfilgrastim. StatPearls. Updated May 9, 2024. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532893/
119. Fylnetra (pegfilgrastim-pbbk). Prescribing information. Kashiv BioSciences; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/761084s000lbl.pdf
120. Emend (aprepitant). Prescribing information. Merck; 2015. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/207865lbl.pdf
121. Lipitor (atorvastatin calcium). Prescribing information. Viatris Specialty; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020702Orig1s079correctedlbl.pdf
122. Cipro (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/019537s090,020780s047lbl.pdf
123. Pino MA, Azer SA. Cimetidine. StatPearls. Updated March 6, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544255/
124. Tagament (Cimetidine). Prescribing information. Mylan; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020238Orig1s024lbl.pdf
125. Neupogen (filgrastim). Prescribing information. Amgen Inc.; 2015. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/103353s5184lbl.pdf
126. Flagyl (metronidazole). Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2013. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/020334s008lbl.pdf
127. Zymaxid (gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution). Prescribing information. Allergan; 2016. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/022548s002lbl.pdf
128. Macrobid (nitrofurantoin monohydrate). Prescribing information. Procter and Gamble Pharmaceutical Inc.; 2009. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/020064s019lbl.pdf
129. Hyzaar (losartan). Prescribing information. Merck; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020387s067lbl.pdf
Background
Paclitaxel was first derived from the bark of the yew tree (Taxus brevifolia). It was discovered as part of a National Cancer Institute program screen of plants and natural products with putative anticancer activity during the 1960s.1-9 Paclitaxel works by suppressing spindle microtube dynamics, which results in the blockage of the metaphase-anaphase transitions, inhibition of mitosis, and induction of apoptosis in a broad spectrum of cancer cells. Paclitaxel also displayed additional anticancer activities, including the suppression of cell proliferation and antiangiogenic effects. However, since the growth of normal body cells may also be affected, other adverse effects (AEs) will also occur.8-18
Two different chemotherapy drugs contain paclitaxel—paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel—and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes them as separate entities.19-21 Taxol (paclitaxel) was approved by the FDA in 1992 for treating advanced ovarian cancer.20 It has since been approved for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma (as an orphan drug), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and cervical cancers (in combination withbevacizumab) in 1994, 1997, 1999, and 2014, respectively.21 Since 2002, a generic version of Taxol, known as paclitaxel injectable, has been FDA-approved from different manufacturers. According to the National Cancer Institute, a combination of carboplatin and Taxol is approved to treat carcinoma of unknown primary, cervical, endometrial, NSCLC, ovarian, and thymoma cancers.19 Abraxane (nab-paclitaxel) was FDA-approved to treat metastatic breast cancer in 2005. It was later approved for first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC and late-stage pancreatic cancer in 2012 and 2013, respectively. In 2018 and 2020, both Taxol and Abraxane were approved for first-line treatment of metastatic squamous cell NSCLC in combination with carboplatin and pembrolizumab and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer in combination with pembrolizumab, respectively.22-26 In 2019, Abraxane was approved with atezolizumab to treat metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, but this approval was withdrawn in 2021. In 2022, a generic version of Abraxane, known as paclitaxel protein-bound, was released in the United States. Furthermore, paclitaxel-containing formulations also are being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.19-32
One of the main limitations of paclitaxel is its low solubility in water, which complicates its drug supply. To distribute this hydrophobic anticancer drug efficiently, paclitaxel is formulated and administered to patients via polyethoxylated castor oil or albumin-bound (nab-paclitaxel). However, polyethoxylated castor oil induces complement activation and is the cause of common hypersensitivity reactions related to paclitaxel use.2,17,33-38 Therefore, many alternatives to polyethoxylated castor oil have been researched.
Since 2000, new paclitaxel formulations have emerged using nanomedicine techniques. The difference between these formulations is the drug vehicle. Different paclitaxel-based nanotechnological vehicles have been developed and approved, such as albumin-based nanoparticles, polymeric lipidic nanoparticles, polymeric micelles, and liposomes, with many others in clinical trial phases.3,37 Albumin-based nanoparticles have a high response rate (33%), whereas the response rate for polyethoxylated castor oil is 25% in patients with metastatic breast cancer.33,39-52 The use of paclitaxel dimer nanoparticles also has been proposed as a method for increasing drug solubility.33,53
Paclitaxel is metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes 2C8 and 3A4. When administering paclitaxel with known inhibitors, inducers, or substrates of CYP2C8 or CYP3A4, caution is required.19-22 Regulations for CYP research were not issued until 2008, so potential interactions between paclitaxel and other drugs have not been extensively evaluated in clinical trials. A study of 12 kinase inhibitors showed strong inhibition of CYP2C8 and/or CYP3A4 pathways by these inhibitors, which could alter the ratio of paclitaxel metabolites in vivo, leading to clinically relevant changes.54 Differential metabolism has been linked to paclitaxel-induced neurotoxicity in patients with cancer.55 Nonetheless, variants in the CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 genes do not account for significant interindividual variability in paclitaxel pharmacokinetics.56 In liver microsomes, losartan inhibited paclitaxel metabolism when used at concentrations > 50 µmol/L.57 Many drug-drug interaction (DDI) studies of CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 have shown similar results for paclitaxel.58-64
The goals of this study are to investigate prescribed drugs used with paclitaxel and determine patient outcomes through several Military Health System (MHS) databases. The investigation focused on (1) the functions of paclitaxel; (2) identifying AEs that patients experienced; (3) evaluating differences when paclitaxel is used alone vs concomitantly and between the completed vs discontinued treatment groups; (4) identifying all drugs used during paclitaxel treatment; and (5) evaluating DDIs with antidepressants (that have an FDA boxed warning and are known to have DDIs confirmed in previous publications) and other drugs.65-67
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, institutionalreview board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and MHS data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and the Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
METHODS
The DoD Cancer Registry Program was established in 1986 and currently contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in the CAPER record represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER includes data from 2003 to 2024.
Each observation in the PDTS record represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary at an MTF through the TRICARE mail-order program or a US retail pharmacy. Missing from this record are prescriptions filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions. The MHS Data Repository PDTS record is available from 2002 to 2024. The legacy Composite Health Care System is being replaced by GENESIS at MTFs.
Data Extraction Design
The study design involved a cross-sectional analysis. We requested data extraction for paclitaxel from 1998 to 2022. Data from the DoD Cancer Registry Program were used to identify patients who received cancer treatment. Once patients were identified, the CAPER database was searched for diagnoses to identify other health conditions, whereas the PDTS database was used to populate a list of prescription medications filled during chemotherapy treatment.
Data collected from the JPC included cancer treatment, cancer information, demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. Collected data from the MHS include diagnosis and filled prescription history from initiation to completion of the therapy period (or 2 years after the diagnosis date). For the analysis of the DoD Cancer Registry Program and CAPER databases, we used all collected data without excluding any. When analyzing PDTS data, we excluded patients with PDTS data but without a record of paclitaxel being filled, or medications filled outside the chemotherapy period (by evaluating the dispensed date and day of supply).
Data Extraction Analysis
The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual 2016 and the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.68,69 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the paclitaxel groups divided by the total number of patients or data variables. The subgroup percentage was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients in that subgroup.
In alone vs concomitant and completed vs discontinued treatment groups, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to statistical significance (P < .05) using a statistics website.70 Concomitant was defined as paclitaxel taken with other antineoplastic agent(s) before, after, or at the same time as cancer therapy. For the retrospective data analysis, physicians’ notes with a period, comma, forward slash, semicolon, or space between medication names were interpreted as concurrent, whereas plus (+), minus/plus (-/+), or “and” between drug names that were dispensed on the same day were interpreted as combined with known common combinations: 2 drugs (DM886 paclitaxel and carboplatin and DM881-TC-1 paclitaxel and cisplatin) or 3 drugs (DM887-ACT doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and paclitaxel). Completed treatment was defined as paclitaxel as the last medication the patient took without recorded AEs; switching or experiencing AEs was defined as discontinued treatment.
RESULTS
The JPC provided 702 entries for 687 patients with a mean age of 56 years (range, 2 months to 88 years) who were treated with paclitaxel from March 1996 to October 2021. Fifteen patients had duplicate entries because they had multiple cancer sites or occurrences. There were 623 patients (89%) who received paclitaxel for FDA-approved indications. The most common types of cancer identified were 344 patients with breast cancer (49%), 91 patients with lung cancer (13%), 79 patients with ovarian cancer (11%), and 75 patients with endometrial cancer (11%) (Table 1). Seventy-nine patients (11%) received paclitaxel for cancers that were not for FDA-approved indications, including 19 for cancers of the fallopian tube (3%) and 17 for esophageal cancer (2%) (Table 2).
There were 477 patients (68%) aged > 50 years. A total of 304 patients (43%) had a stage III or IV cancer diagnosis and 398 (57%) had stage II or lower (combination of data for stages 0, I, and II; not applicable; and unknown) cancer diagnosis. For systemic treatment, 16 patients (2%) were treated with paclitaxel alone and 686 patients (98%) received paclitaxel concomitantly with additional chemotherapy: 59 patients (9%) in the before or after group, 410 patients (58%) had a 2-drug combination, 212 patients (30%) had a 3-drug combination, and 5 patients (1%) had a 4-drug combination. In addition, for doublet therapies, paclitaxel combined with carboplatin, trastuzumab, gemcitabine, or cisplatin had more patients (318, 58, 12, and 11, respectively) than other combinations (≤ 4 patients). For triplet therapies, paclitaxel combined withdoxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide or carboplatin plus bevacizumab had more patients (174 and 20, respectively) than other combinations, including quadruplet therapies (≤ 4 patients) (Table 3).
Patients were more likely to discontinue paclitaxel if they received concomitant treatment. None of the 16 patients receiving paclitaxel monotherapy experienced AEs, whereas 364 of 686 patients (53%) treated concomitantly discontinued (P < .001). Comparisons of 1 drug vs combination (2 to 4 drugs) and use for treating cancers that were FDA-approved indications vs off-label use were significant (P < .001), whereas comparisons of stage II or lower vs stage III and IV cancer and of those aged ≤ 50 years vs aged > 50 years were not significant (P = .50 andP = .30, respectively) (Table 4).
Among the 364 patients who had concomitant treatment and had discontinued their treatment, 332 (91%) switched treatments with no AEs documented and 32 (9%) experienced fatigue with pneumonia, mucositis, neuropathy, neurotoxicity, neutropenia, pneumonitis, allergic or hypersensitivity reaction, or an unknown AE. Patients who discontinued treatment because of unknown AEs had a physician’s note that detailed progressive disease, a significant decline in performance status, and another unknown adverse effect due to a previous sinus tract infection and infectious colitis (Table 5).
Management Analysis and Reporting Tool Database
MHS data analysts provided data on diagnoses for 639 patients among 687 submitteddiagnoses, with 294 patients completing and 345 discontinuing paclitaxel treatment. Patients in the completed treatment group had 3 to 258 unique health conditions documented, while patients in the discontinued treatment group had 4 to 181 unique health conditions documented. The MHS reported 3808 unique diagnosis conditions for the completed group and 3714 for the discontinued group (P = .02).
The mean (SD) number of diagnoses was 51 (31) for the completed and 55 (28) for the discontinued treatment groups (Figure). Among 639 patients who received paclitaxel, the top 5 diagnoses were administrative, including encounters for other administrative examinations; antineoplastic chemotherapy; administrative examination for unspecified; other specified counseling; and adjustment and management of vascular access device. The database does not differentiate between administrative and clinically significant diagnoses.
MHS data analysts provided data for 336 of 687 submitted patients who were prescribed paclitaxel; 46 patients had no PDTS data, and 305 patients had PDTS data without paclitaxel, Taxol, or Abraxane dispensed. Medications that were filled outside the chemotherapy period were removed by evaluating the dispensed date and day of supply. Among these 336 patients, 151 completed the treatment and 185 discontinued, with 14 patients experiencing documented AEs. Patients in the completed treatment group filled 9 to 56 prescriptions while patients in the discontinued treatment group filled 6 to 70 prescriptions.Patients in the discontinued group filled more prescriptions than those who completed treatment: 793 vs 591, respectively (P = .34).
The mean (SD) number of filled prescription drugs was 24 (9) for the completed and 34 (12) for the discontinued treatment group. The 5 most filled prescriptions with paclitaxel from 336 patients with PDTS data were dexamethasone (324 prescriptions with 14 recorded AEs), diphenhydramine (296 prescriptions with 12 recorded AEs), ondansetron (277 prescriptions with 11 recorded AEs), prochlorperazine (265 prescriptions with 12 recorded AEs), and sodium chloride (232 prescriptions with 11 recorded AEs).
DISCUSSION
As a retrospective review, this study is more limited in the strength of its conclusions when compared to randomized control trials. The DoD Cancer Registry Program only contains information about cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes. Therefore, noncancer drugs are based solely on the PDTS database. In most cases, physicians' notes on AEs were not detailed. There was no distinction between initial vs later lines of therapy and dosage reductions. The change in status or appearance of a new medical condition did not indicate whether paclitaxel caused the changes to develop or directly worsen a pre-existing condition. The PDTS records prescriptions filled, but that may not reflect patients taking prescriptions.
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel has a long list of both approved and off-label uses in malignancies as a primary agent and in conjunction with other drugs. The FDA prescribing information for Taxol and Abraxane was last updated in April 2011 and September 2020, respectively.20,21 The National Institutes of Health National Library of Medicine has the current update for paclitaxel on July 2023.19,22 Thus, the prescribed information for paclitaxel referenced in the database may not always be up to date. The combinations of paclitaxel with bevacizumab, carboplatin, or carboplatin and pembrolizumab were not in the Taxol prescribing information. Likewise, a combination of nab-paclitaxel with atezolizumab or carboplatin and pembrolizumab is missing in the Abraxane prescribing information.22-27
The generic name is not the same as a generic drug, which may have slight differences from the brand name product.71 The generic drug versions of Taxol and Abraxane have been approved by the FDA as paclitaxel injectable and paclitaxel-protein bound, respectively. There was a global shortage of nab-paclitaxel from October 2021 to June 2022 because of a manufacturing problem.72 During this shortage, data showed similar comments from physician documents that treatment switched to Taxol due to the Abraxane shortage.
Of 336 patients in the PDTS database with dispensed paclitaxel prescriptions, 276 received paclitaxel (year dispensed, 2013-2022), 27 received Abraxane (year dispensed, 2013-2022), 47 received Taxol (year dispensed, 2004-2015), 8 received both Abraxane and paclitaxel, and 6 received both Taxol and paclitaxel. Based on this information, it appears that the distinction between the drugs was not made in the PDTS until after 2015, 10 years after Abraxane received FDA approval. Abraxane was prescribed in the MHS in 2013, 8 years after FDA approval. There were a few comparison studies of Abraxane and Taxol.73-76
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established for paclitaxel. According to the DoD Cancer Registry Program, the youngest patient was aged 2 months. In 2021, this patient was diagnosed with corpus uteri and treated with carboplatin and Taxol in course 1; in course 2, the patient reacted to Taxol; in course 3, Taxol was replaced with Abraxane; in courses 4 to 7, the patient was treated with carboplatin only.
Discontinued Treatment
Ten patients had prescribed Taxol that was changed due to AEs: 1 was switched to Abraxane and atezolizumab, 3 switched to Abraxane, 2 switched to docetaxel, 1 switched to doxorubicin, and 3 switched to pembrolizumab (based on physician’s comments). Of the 10 patients, 7 had Taxol reaction, 2 experienced disease progression, and 1 experienced high programmed death–ligand 1 expression (this patient with breast cancer was switched to Abraxane and atezolizumab during the accelerated FDA approval phase for atezolizumab, which was later revoked). Five patients were treated with carboplatin and Taxol for cancer of the anal canal (changed to pembrolizumab after disease progression), lung not otherwise specified (changed to carboplatin and pembrolizumab due to Taxol reaction), lower inner quadrant of the breast (changed to doxorubicin due to hypersensitivity reaction), corpus uteri (changed to Abraxane due to Taxol reaction), and ovary (changed to docetaxel due to Taxol reaction). Three patients were treated with doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and Taxol for breast cancer; 2 patients with breast cancer not otherwise specified switched to Abraxane due to cardiopulmonary hypersensitivity and Taxol reaction and 1 patient with cancer of the upper outer quadrant of the breast changed to docetaxel due to allergic reaction. One patient, who was treated with paclitaxel, ifosfamide, and cisplatin for metastasis of the lower lobe of the lung and kidney cancer, experienced complications due to infectious colitis (treated with ciprofloxacin) and then switched to pembrolizumab after the disease progressed. These AEs are known in paclitaxel medical literature on paclitaxel AEs.19-24,77-81
Combining 2 or more treatments to target cancer-inducing or cell-sustaining pathways is a cornerstone of chemotherapy.82-84 Most combinations are given on the same day, but some are not. For 3- or 4-drug combinations, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide were given first, followed by paclitaxel with or withouttrastuzumab, carboplatin, or pembrolizumab. Only 16 patients (2%) were treated with paclitaxel alone; therefore, the completed and discontinued treatment groups are mostly concomitant treatment. As a result, the comparisons of the completed and discontinued treatment groups were almost the same for the diagnosis. The PDTS data have a better result because 2 exclusion criteria were applied before narrowing the analysis down to paclitaxel treatment specifically.
Antidepressants and Other Drugs
Drug response can vary from person to person and can lead to treatment failure related to AEs. One major factor in drug metabolism is CYP.85 CYP2C8 is the major pathway for paclitaxel and CYP3A4 is the minor pathway. When evaluating the noncancer drugs, there were no reports of CYP2C8 inhibition or induction.Over the years, many DDI warnings have been issued for paclitaxel with different drugs in various electronic resources.
Oncologists follow guidelines to prevent DDIs, as paclitaxel is known to have severe, moderate, and minor interactions with other drugs. Among 687 patients, 261 (38%) were prescribed any of 14 antidepressants. Eight of these antidepressants (amitriptyline, citalopram, desipramine, doxepin, venlafaxine, escitalopram, nortriptyline, and trazodone) are metabolized, 3 (mirtazapine, sertraline, and fluoxetine) are metabolized and inhibited, 2 (bupropion and duloxetine) are neither metabolized nor inhibited, and 1 (paroxetine) is inhibited by CYP3A4. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, and trazodone were more commonly dispensed (84, 78, and 42 patients, respectively) than others (≤ 33 patients).
Of 32 patients with documented AEs,14 (44%) had 168 dispensed drugs in the PDTS database. Six patients (19%) were treated with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel for breast cancer; 6 (19%) were treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel for cancer of the lung (n = 3), corpus uteri (n = 2), and ovary (n = 1); 1 patient (3%) was treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel, then switched to carboplatin, bevacizumab, and paclitaxel, and then completed treatment with carboplatin and paclitaxel for an unspecified female genital cancer; and 1 patient (3%) was treated with cisplatin, ifosfamide, and paclitaxel for metastasis of the lower lobe lung and kidney cancer.
The 14 patients with PDTS data had 18 cancer drugs dispensed. Eleven had moderate interaction reports and 7 had no interaction reports. A total of 165 noncancer drugs were dispensed, of which 3 were antidepressants and had no interactions reported, 8 had moderate interactions reported, and 2 had minor interactions with Taxol and Abraxane, respectively (Table 6).86-129
Of 3 patients who were dispensed bupropion, nortriptyline, or paroxetine, 1 patient with breast cancer was treated with doxorubicin andcyclophosphamide, followed by paclitaxel with bupropion, nortriptyline, pegfilgrastim,dexamethasone, and 17 other noncancer drugs that had no interaction report dispensed during paclitaxel treatment. Of 2 patients with lung cancer, 1 patient was treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel with nortriptyline, dexamethasone, and 13 additional medications, and the second patient was treated with paroxetine, cimetidine, dexamethasone, and 12 other medications. Patients were dispensed up to6 noncancer medications on the same day as paclitaxel administration to control the AEs, not including the prodrugs filled before the treatments. Paroxetine and cimetidine have weak inhibition, and dexamethasone has weak induction of CYP3A4. Therefore, while 1:1 DDIs might have little or no effect with weak inhibit/induce CYP3A4 drugs, 1:1:1 or more combinations could have a different outcome (confirmed in previous publications).65-67
Dispensed on the same day may not mean taken at the same time. One patient experienced an AE with dispensed 50 mg losartan, carboplatin plus paclitaxel, dexamethasone, and 6 other noncancer drugs. Losartan inhibits paclitaxel, which can lead to negative AEs.57,66,67 However, there were no blood or plasma samples taken to confirm the losartan was taken at the same time as the paclitaxel given this was not a clinical trial.
Conclusions
This retrospective study discusses the use of paclitaxel in the MHS and the potential DDIs associated with it. The study population consisted mostly of active-duty personnel, who are required to be healthy or have controlled or nonactive medical diagnoses and be physically fit. This group is mixed with dependents and retirees that are more reflective of the average US population. As a result, this patient population is healthier than the general population, with a lower prevalence of common illnesses such as diabetes and obesity. The study aimed to identify drugs used alongside paclitaxel treatment. While further research is needed to identify potential DDIs among patients who experienced AEs, in vitro testing will need to be conducted before confirming causality. The low number of AEs experienced by only 32 of 702 patients (5%), with no deaths during paclitaxel treatment, indicates that the drug is generally well tolerated. Although this study cannot conclude that concomitant use with noncancer drugs led to the discontinuation of paclitaxel, we can conclude that there seems to be no significant DDIsidentified between paclitaxel and antidepressants. This comprehensive overview provides clinicians with a complete picture of paclitaxel use for 27 years (1996-2022), enabling them to make informed decisions about paclitaxel treatment.
Acknowledgments
The Department of Research Program funds at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center supported this protocol. We sincerely appreciate the contribution of data extraction from the Joint Pathology Center teams (Francisco J. Rentas, John D. McGeeney, Beatriz A. Hallo, and Johnny P. Beason) and the MHS database personnel (Maj Ryan Costantino, Brandon E. Jenkins, and Alexander G. Rittel). We gratefully thank you for the protocol support from the Department of Research programs: CDR Martin L. Boese, CDR Wesley R. Campbell, Maj. Abhimanyu Chandel, CDR Ling Ye, Chelsea N. Powers, Yaling Zhou, Elizabeth Schafer, Micah Stretch, Diane Beaner, and Adrienne Woodard.
Background
Paclitaxel was first derived from the bark of the yew tree (Taxus brevifolia). It was discovered as part of a National Cancer Institute program screen of plants and natural products with putative anticancer activity during the 1960s.1-9 Paclitaxel works by suppressing spindle microtube dynamics, which results in the blockage of the metaphase-anaphase transitions, inhibition of mitosis, and induction of apoptosis in a broad spectrum of cancer cells. Paclitaxel also displayed additional anticancer activities, including the suppression of cell proliferation and antiangiogenic effects. However, since the growth of normal body cells may also be affected, other adverse effects (AEs) will also occur.8-18
Two different chemotherapy drugs contain paclitaxel—paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel—and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes them as separate entities.19-21 Taxol (paclitaxel) was approved by the FDA in 1992 for treating advanced ovarian cancer.20 It has since been approved for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma (as an orphan drug), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and cervical cancers (in combination withbevacizumab) in 1994, 1997, 1999, and 2014, respectively.21 Since 2002, a generic version of Taxol, known as paclitaxel injectable, has been FDA-approved from different manufacturers. According to the National Cancer Institute, a combination of carboplatin and Taxol is approved to treat carcinoma of unknown primary, cervical, endometrial, NSCLC, ovarian, and thymoma cancers.19 Abraxane (nab-paclitaxel) was FDA-approved to treat metastatic breast cancer in 2005. It was later approved for first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC and late-stage pancreatic cancer in 2012 and 2013, respectively. In 2018 and 2020, both Taxol and Abraxane were approved for first-line treatment of metastatic squamous cell NSCLC in combination with carboplatin and pembrolizumab and metastatic triple-negative breast cancer in combination with pembrolizumab, respectively.22-26 In 2019, Abraxane was approved with atezolizumab to treat metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, but this approval was withdrawn in 2021. In 2022, a generic version of Abraxane, known as paclitaxel protein-bound, was released in the United States. Furthermore, paclitaxel-containing formulations also are being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.19-32
One of the main limitations of paclitaxel is its low solubility in water, which complicates its drug supply. To distribute this hydrophobic anticancer drug efficiently, paclitaxel is formulated and administered to patients via polyethoxylated castor oil or albumin-bound (nab-paclitaxel). However, polyethoxylated castor oil induces complement activation and is the cause of common hypersensitivity reactions related to paclitaxel use.2,17,33-38 Therefore, many alternatives to polyethoxylated castor oil have been researched.
Since 2000, new paclitaxel formulations have emerged using nanomedicine techniques. The difference between these formulations is the drug vehicle. Different paclitaxel-based nanotechnological vehicles have been developed and approved, such as albumin-based nanoparticles, polymeric lipidic nanoparticles, polymeric micelles, and liposomes, with many others in clinical trial phases.3,37 Albumin-based nanoparticles have a high response rate (33%), whereas the response rate for polyethoxylated castor oil is 25% in patients with metastatic breast cancer.33,39-52 The use of paclitaxel dimer nanoparticles also has been proposed as a method for increasing drug solubility.33,53
Paclitaxel is metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes 2C8 and 3A4. When administering paclitaxel with known inhibitors, inducers, or substrates of CYP2C8 or CYP3A4, caution is required.19-22 Regulations for CYP research were not issued until 2008, so potential interactions between paclitaxel and other drugs have not been extensively evaluated in clinical trials. A study of 12 kinase inhibitors showed strong inhibition of CYP2C8 and/or CYP3A4 pathways by these inhibitors, which could alter the ratio of paclitaxel metabolites in vivo, leading to clinically relevant changes.54 Differential metabolism has been linked to paclitaxel-induced neurotoxicity in patients with cancer.55 Nonetheless, variants in the CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 genes do not account for significant interindividual variability in paclitaxel pharmacokinetics.56 In liver microsomes, losartan inhibited paclitaxel metabolism when used at concentrations > 50 µmol/L.57 Many drug-drug interaction (DDI) studies of CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 have shown similar results for paclitaxel.58-64
The goals of this study are to investigate prescribed drugs used with paclitaxel and determine patient outcomes through several Military Health System (MHS) databases. The investigation focused on (1) the functions of paclitaxel; (2) identifying AEs that patients experienced; (3) evaluating differences when paclitaxel is used alone vs concomitantly and between the completed vs discontinued treatment groups; (4) identifying all drugs used during paclitaxel treatment; and (5) evaluating DDIs with antidepressants (that have an FDA boxed warning and are known to have DDIs confirmed in previous publications) and other drugs.65-67
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, institutionalreview board approved the study protocol and ensured compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act as an exempt protocol. The Joint Pathology Center (JPC) of the US Department of Defense (DoD) Cancer Registry Program and MHS data experts from the Comprehensive Ambulatory/Professional Encounter Record (CAPER) and the Pharmacy Data Transaction Service (PDTS) provided data for the analysis.
METHODS
The DoD Cancer Registry Program was established in 1986 and currently contains data from 1998 to 2024. CAPER and PDTS are part of the MHS Data Repository/Management Analysis and Reporting Tool database. Each observation in the CAPER record represents an ambulatory encounter at a military treatment facility (MTF). CAPER includes data from 2003 to 2024.
Each observation in the PDTS record represents a prescription filled for an MHS beneficiary at an MTF through the TRICARE mail-order program or a US retail pharmacy. Missing from this record are prescriptions filled at international civilian pharmacies and inpatient pharmacy prescriptions. The MHS Data Repository PDTS record is available from 2002 to 2024. The legacy Composite Health Care System is being replaced by GENESIS at MTFs.
Data Extraction Design
The study design involved a cross-sectional analysis. We requested data extraction for paclitaxel from 1998 to 2022. Data from the DoD Cancer Registry Program were used to identify patients who received cancer treatment. Once patients were identified, the CAPER database was searched for diagnoses to identify other health conditions, whereas the PDTS database was used to populate a list of prescription medications filled during chemotherapy treatment.
Data collected from the JPC included cancer treatment, cancer information, demographics, and physicians’ comments on AEs. Collected data from the MHS include diagnosis and filled prescription history from initiation to completion of the therapy period (or 2 years after the diagnosis date). For the analysis of the DoD Cancer Registry Program and CAPER databases, we used all collected data without excluding any. When analyzing PDTS data, we excluded patients with PDTS data but without a record of paclitaxel being filled, or medications filled outside the chemotherapy period (by evaluating the dispensed date and day of supply).
Data Extraction Analysis
The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Coding and Staging Manual 2016 and the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition, 1st revision, were used to decode disease and cancer types.68,69 Data sorting and analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel. The percentage for the total was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the paclitaxel groups divided by the total number of patients or data variables. The subgroup percentage was calculated by using the number of patients or data available within the subgroup divided by the total number of patients in that subgroup.
In alone vs concomitant and completed vs discontinued treatment groups, a 2-tailed, 2-sample z test was used to statistical significance (P < .05) using a statistics website.70 Concomitant was defined as paclitaxel taken with other antineoplastic agent(s) before, after, or at the same time as cancer therapy. For the retrospective data analysis, physicians’ notes with a period, comma, forward slash, semicolon, or space between medication names were interpreted as concurrent, whereas plus (+), minus/plus (-/+), or “and” between drug names that were dispensed on the same day were interpreted as combined with known common combinations: 2 drugs (DM886 paclitaxel and carboplatin and DM881-TC-1 paclitaxel and cisplatin) or 3 drugs (DM887-ACT doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and paclitaxel). Completed treatment was defined as paclitaxel as the last medication the patient took without recorded AEs; switching or experiencing AEs was defined as discontinued treatment.
RESULTS
The JPC provided 702 entries for 687 patients with a mean age of 56 years (range, 2 months to 88 years) who were treated with paclitaxel from March 1996 to October 2021. Fifteen patients had duplicate entries because they had multiple cancer sites or occurrences. There were 623 patients (89%) who received paclitaxel for FDA-approved indications. The most common types of cancer identified were 344 patients with breast cancer (49%), 91 patients with lung cancer (13%), 79 patients with ovarian cancer (11%), and 75 patients with endometrial cancer (11%) (Table 1). Seventy-nine patients (11%) received paclitaxel for cancers that were not for FDA-approved indications, including 19 for cancers of the fallopian tube (3%) and 17 for esophageal cancer (2%) (Table 2).
There were 477 patients (68%) aged > 50 years. A total of 304 patients (43%) had a stage III or IV cancer diagnosis and 398 (57%) had stage II or lower (combination of data for stages 0, I, and II; not applicable; and unknown) cancer diagnosis. For systemic treatment, 16 patients (2%) were treated with paclitaxel alone and 686 patients (98%) received paclitaxel concomitantly with additional chemotherapy: 59 patients (9%) in the before or after group, 410 patients (58%) had a 2-drug combination, 212 patients (30%) had a 3-drug combination, and 5 patients (1%) had a 4-drug combination. In addition, for doublet therapies, paclitaxel combined with carboplatin, trastuzumab, gemcitabine, or cisplatin had more patients (318, 58, 12, and 11, respectively) than other combinations (≤ 4 patients). For triplet therapies, paclitaxel combined withdoxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide or carboplatin plus bevacizumab had more patients (174 and 20, respectively) than other combinations, including quadruplet therapies (≤ 4 patients) (Table 3).
Patients were more likely to discontinue paclitaxel if they received concomitant treatment. None of the 16 patients receiving paclitaxel monotherapy experienced AEs, whereas 364 of 686 patients (53%) treated concomitantly discontinued (P < .001). Comparisons of 1 drug vs combination (2 to 4 drugs) and use for treating cancers that were FDA-approved indications vs off-label use were significant (P < .001), whereas comparisons of stage II or lower vs stage III and IV cancer and of those aged ≤ 50 years vs aged > 50 years were not significant (P = .50 andP = .30, respectively) (Table 4).
Among the 364 patients who had concomitant treatment and had discontinued their treatment, 332 (91%) switched treatments with no AEs documented and 32 (9%) experienced fatigue with pneumonia, mucositis, neuropathy, neurotoxicity, neutropenia, pneumonitis, allergic or hypersensitivity reaction, or an unknown AE. Patients who discontinued treatment because of unknown AEs had a physician’s note that detailed progressive disease, a significant decline in performance status, and another unknown adverse effect due to a previous sinus tract infection and infectious colitis (Table 5).
Management Analysis and Reporting Tool Database
MHS data analysts provided data on diagnoses for 639 patients among 687 submitteddiagnoses, with 294 patients completing and 345 discontinuing paclitaxel treatment. Patients in the completed treatment group had 3 to 258 unique health conditions documented, while patients in the discontinued treatment group had 4 to 181 unique health conditions documented. The MHS reported 3808 unique diagnosis conditions for the completed group and 3714 for the discontinued group (P = .02).
The mean (SD) number of diagnoses was 51 (31) for the completed and 55 (28) for the discontinued treatment groups (Figure). Among 639 patients who received paclitaxel, the top 5 diagnoses were administrative, including encounters for other administrative examinations; antineoplastic chemotherapy; administrative examination for unspecified; other specified counseling; and adjustment and management of vascular access device. The database does not differentiate between administrative and clinically significant diagnoses.
MHS data analysts provided data for 336 of 687 submitted patients who were prescribed paclitaxel; 46 patients had no PDTS data, and 305 patients had PDTS data without paclitaxel, Taxol, or Abraxane dispensed. Medications that were filled outside the chemotherapy period were removed by evaluating the dispensed date and day of supply. Among these 336 patients, 151 completed the treatment and 185 discontinued, with 14 patients experiencing documented AEs. Patients in the completed treatment group filled 9 to 56 prescriptions while patients in the discontinued treatment group filled 6 to 70 prescriptions.Patients in the discontinued group filled more prescriptions than those who completed treatment: 793 vs 591, respectively (P = .34).
The mean (SD) number of filled prescription drugs was 24 (9) for the completed and 34 (12) for the discontinued treatment group. The 5 most filled prescriptions with paclitaxel from 336 patients with PDTS data were dexamethasone (324 prescriptions with 14 recorded AEs), diphenhydramine (296 prescriptions with 12 recorded AEs), ondansetron (277 prescriptions with 11 recorded AEs), prochlorperazine (265 prescriptions with 12 recorded AEs), and sodium chloride (232 prescriptions with 11 recorded AEs).
DISCUSSION
As a retrospective review, this study is more limited in the strength of its conclusions when compared to randomized control trials. The DoD Cancer Registry Program only contains information about cancer types, stages, treatment regimens, and physicians’ notes. Therefore, noncancer drugs are based solely on the PDTS database. In most cases, physicians' notes on AEs were not detailed. There was no distinction between initial vs later lines of therapy and dosage reductions. The change in status or appearance of a new medical condition did not indicate whether paclitaxel caused the changes to develop or directly worsen a pre-existing condition. The PDTS records prescriptions filled, but that may not reflect patients taking prescriptions.
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel has a long list of both approved and off-label uses in malignancies as a primary agent and in conjunction with other drugs. The FDA prescribing information for Taxol and Abraxane was last updated in April 2011 and September 2020, respectively.20,21 The National Institutes of Health National Library of Medicine has the current update for paclitaxel on July 2023.19,22 Thus, the prescribed information for paclitaxel referenced in the database may not always be up to date. The combinations of paclitaxel with bevacizumab, carboplatin, or carboplatin and pembrolizumab were not in the Taxol prescribing information. Likewise, a combination of nab-paclitaxel with atezolizumab or carboplatin and pembrolizumab is missing in the Abraxane prescribing information.22-27
The generic name is not the same as a generic drug, which may have slight differences from the brand name product.71 The generic drug versions of Taxol and Abraxane have been approved by the FDA as paclitaxel injectable and paclitaxel-protein bound, respectively. There was a global shortage of nab-paclitaxel from October 2021 to June 2022 because of a manufacturing problem.72 During this shortage, data showed similar comments from physician documents that treatment switched to Taxol due to the Abraxane shortage.
Of 336 patients in the PDTS database with dispensed paclitaxel prescriptions, 276 received paclitaxel (year dispensed, 2013-2022), 27 received Abraxane (year dispensed, 2013-2022), 47 received Taxol (year dispensed, 2004-2015), 8 received both Abraxane and paclitaxel, and 6 received both Taxol and paclitaxel. Based on this information, it appears that the distinction between the drugs was not made in the PDTS until after 2015, 10 years after Abraxane received FDA approval. Abraxane was prescribed in the MHS in 2013, 8 years after FDA approval. There were a few comparison studies of Abraxane and Taxol.73-76
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established for paclitaxel. According to the DoD Cancer Registry Program, the youngest patient was aged 2 months. In 2021, this patient was diagnosed with corpus uteri and treated with carboplatin and Taxol in course 1; in course 2, the patient reacted to Taxol; in course 3, Taxol was replaced with Abraxane; in courses 4 to 7, the patient was treated with carboplatin only.
Discontinued Treatment
Ten patients had prescribed Taxol that was changed due to AEs: 1 was switched to Abraxane and atezolizumab, 3 switched to Abraxane, 2 switched to docetaxel, 1 switched to doxorubicin, and 3 switched to pembrolizumab (based on physician’s comments). Of the 10 patients, 7 had Taxol reaction, 2 experienced disease progression, and 1 experienced high programmed death–ligand 1 expression (this patient with breast cancer was switched to Abraxane and atezolizumab during the accelerated FDA approval phase for atezolizumab, which was later revoked). Five patients were treated with carboplatin and Taxol for cancer of the anal canal (changed to pembrolizumab after disease progression), lung not otherwise specified (changed to carboplatin and pembrolizumab due to Taxol reaction), lower inner quadrant of the breast (changed to doxorubicin due to hypersensitivity reaction), corpus uteri (changed to Abraxane due to Taxol reaction), and ovary (changed to docetaxel due to Taxol reaction). Three patients were treated with doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and Taxol for breast cancer; 2 patients with breast cancer not otherwise specified switched to Abraxane due to cardiopulmonary hypersensitivity and Taxol reaction and 1 patient with cancer of the upper outer quadrant of the breast changed to docetaxel due to allergic reaction. One patient, who was treated with paclitaxel, ifosfamide, and cisplatin for metastasis of the lower lobe of the lung and kidney cancer, experienced complications due to infectious colitis (treated with ciprofloxacin) and then switched to pembrolizumab after the disease progressed. These AEs are known in paclitaxel medical literature on paclitaxel AEs.19-24,77-81
Combining 2 or more treatments to target cancer-inducing or cell-sustaining pathways is a cornerstone of chemotherapy.82-84 Most combinations are given on the same day, but some are not. For 3- or 4-drug combinations, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide were given first, followed by paclitaxel with or withouttrastuzumab, carboplatin, or pembrolizumab. Only 16 patients (2%) were treated with paclitaxel alone; therefore, the completed and discontinued treatment groups are mostly concomitant treatment. As a result, the comparisons of the completed and discontinued treatment groups were almost the same for the diagnosis. The PDTS data have a better result because 2 exclusion criteria were applied before narrowing the analysis down to paclitaxel treatment specifically.
Antidepressants and Other Drugs
Drug response can vary from person to person and can lead to treatment failure related to AEs. One major factor in drug metabolism is CYP.85 CYP2C8 is the major pathway for paclitaxel and CYP3A4 is the minor pathway. When evaluating the noncancer drugs, there were no reports of CYP2C8 inhibition or induction.Over the years, many DDI warnings have been issued for paclitaxel with different drugs in various electronic resources.
Oncologists follow guidelines to prevent DDIs, as paclitaxel is known to have severe, moderate, and minor interactions with other drugs. Among 687 patients, 261 (38%) were prescribed any of 14 antidepressants. Eight of these antidepressants (amitriptyline, citalopram, desipramine, doxepin, venlafaxine, escitalopram, nortriptyline, and trazodone) are metabolized, 3 (mirtazapine, sertraline, and fluoxetine) are metabolized and inhibited, 2 (bupropion and duloxetine) are neither metabolized nor inhibited, and 1 (paroxetine) is inhibited by CYP3A4. Duloxetine, venlafaxine, and trazodone were more commonly dispensed (84, 78, and 42 patients, respectively) than others (≤ 33 patients).
Of 32 patients with documented AEs,14 (44%) had 168 dispensed drugs in the PDTS database. Six patients (19%) were treated with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel for breast cancer; 6 (19%) were treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel for cancer of the lung (n = 3), corpus uteri (n = 2), and ovary (n = 1); 1 patient (3%) was treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel, then switched to carboplatin, bevacizumab, and paclitaxel, and then completed treatment with carboplatin and paclitaxel for an unspecified female genital cancer; and 1 patient (3%) was treated with cisplatin, ifosfamide, and paclitaxel for metastasis of the lower lobe lung and kidney cancer.
The 14 patients with PDTS data had 18 cancer drugs dispensed. Eleven had moderate interaction reports and 7 had no interaction reports. A total of 165 noncancer drugs were dispensed, of which 3 were antidepressants and had no interactions reported, 8 had moderate interactions reported, and 2 had minor interactions with Taxol and Abraxane, respectively (Table 6).86-129
Of 3 patients who were dispensed bupropion, nortriptyline, or paroxetine, 1 patient with breast cancer was treated with doxorubicin andcyclophosphamide, followed by paclitaxel with bupropion, nortriptyline, pegfilgrastim,dexamethasone, and 17 other noncancer drugs that had no interaction report dispensed during paclitaxel treatment. Of 2 patients with lung cancer, 1 patient was treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel with nortriptyline, dexamethasone, and 13 additional medications, and the second patient was treated with paroxetine, cimetidine, dexamethasone, and 12 other medications. Patients were dispensed up to6 noncancer medications on the same day as paclitaxel administration to control the AEs, not including the prodrugs filled before the treatments. Paroxetine and cimetidine have weak inhibition, and dexamethasone has weak induction of CYP3A4. Therefore, while 1:1 DDIs might have little or no effect with weak inhibit/induce CYP3A4 drugs, 1:1:1 or more combinations could have a different outcome (confirmed in previous publications).65-67
Dispensed on the same day may not mean taken at the same time. One patient experienced an AE with dispensed 50 mg losartan, carboplatin plus paclitaxel, dexamethasone, and 6 other noncancer drugs. Losartan inhibits paclitaxel, which can lead to negative AEs.57,66,67 However, there were no blood or plasma samples taken to confirm the losartan was taken at the same time as the paclitaxel given this was not a clinical trial.
Conclusions
This retrospective study discusses the use of paclitaxel in the MHS and the potential DDIs associated with it. The study population consisted mostly of active-duty personnel, who are required to be healthy or have controlled or nonactive medical diagnoses and be physically fit. This group is mixed with dependents and retirees that are more reflective of the average US population. As a result, this patient population is healthier than the general population, with a lower prevalence of common illnesses such as diabetes and obesity. The study aimed to identify drugs used alongside paclitaxel treatment. While further research is needed to identify potential DDIs among patients who experienced AEs, in vitro testing will need to be conducted before confirming causality. The low number of AEs experienced by only 32 of 702 patients (5%), with no deaths during paclitaxel treatment, indicates that the drug is generally well tolerated. Although this study cannot conclude that concomitant use with noncancer drugs led to the discontinuation of paclitaxel, we can conclude that there seems to be no significant DDIsidentified between paclitaxel and antidepressants. This comprehensive overview provides clinicians with a complete picture of paclitaxel use for 27 years (1996-2022), enabling them to make informed decisions about paclitaxel treatment.
Acknowledgments
The Department of Research Program funds at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center supported this protocol. We sincerely appreciate the contribution of data extraction from the Joint Pathology Center teams (Francisco J. Rentas, John D. McGeeney, Beatriz A. Hallo, and Johnny P. Beason) and the MHS database personnel (Maj Ryan Costantino, Brandon E. Jenkins, and Alexander G. Rittel). We gratefully thank you for the protocol support from the Department of Research programs: CDR Martin L. Boese, CDR Wesley R. Campbell, Maj. Abhimanyu Chandel, CDR Ling Ye, Chelsea N. Powers, Yaling Zhou, Elizabeth Schafer, Micah Stretch, Diane Beaner, and Adrienne Woodard.
1. American Chemical Society. Discovery of camptothecin and taxol. acs.org. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.acs.org/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/camptothecintaxol.html
2. Bocci G, Di Paolo A, Danesi R. The pharmacological bases of the antiangiogenic activity of paclitaxel. Angiogenesis. 2013;16(3):481-492. doi:10.1007/s10456-013-9334-0.
3. Meštrovic T. Paclitaxel history. News Medical Life Sciences. Updated March 11, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Paclitaxel-History.aspx
4. Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC. Paclitaxel (taxol). N Engl J Med. 1995;332(15):1004-1014. doi:10.1056/NEJM199504133321507
5. Walsh V, Goodman J. The billion dollar molecule: Taxol in historical and theoretical perspective. Clio Med. 2002;66:245-267. doi:10.1163/9789004333499_013
6. Perdue RE, Jr, Hartwell JL. The search for plant sources of anticancer drugs. Morris Arboretum Bull. 1969;20:35-53.
7. Wall ME, Wani MC. Camptothecin and taxol: discovery to clinic—thirteenth Bruce F. Cain Memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 1995;55:753-760.
8. Wani MC, Taylor HL, Wall ME, Coggon P, McPhail AT. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971;93(9):2325-2327. doi:10.1021/ja00738a045
9. Weaver BA. How taxol/paclitaxel kills cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2014;25(18):2677-2681. doi:10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0916
10. Chen JG, Horwitz SB. Differential mitotic responses to microtubule-stabilizing and-destabilizing drugs. Cancer Res. 2002;62(7):1935-1938.
11. Singh S, Dash AK. Paclitaxel in cancer treatment: perspectives and prospects of its delivery challenges. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2009;26(4):333-372. doi:10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.v26.i4.10
12. Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979;277(5698):665-667. doi:10.1038/277665a0
13. Fuchs DA, Johnson RK. Cytologic evidence that taxol, an antineoplastic agent from taxus brevifolia, acts as a mitotic spindle poison. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978;62(8):1219-1222.
14. Walsh V, Goodman J. From taxol to taxol: the changing identities and ownership of an anti-cancer drug. Med Anthropol. 2002;21(3-4):307-336. doi:10.1080/01459740214074
15. Walsh V, Goodman J. Cancer chemotherapy, biodiversity, public and private property: the case of the anti-cancer drug taxol. Soc Sci Med. 1999;49(9):1215-1225. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00161-6
16. Jordan MA, Wendell K, Gardiner S, Derry WB, Copp H, Wilson L. Mitotic block induced in HeLa cells by low concentrations of paclitaxel (taxol) results in abnormal mitotic exit and apoptotic cell death. Cancer Res. 1996;56(4):816-825.
17. Picard M, Castells MC. Re-visiting hypersensitivity reactions to taxanes: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015;49(2):177-191. doi:10.1007/s12016-014-8416-0
18. Zasadil LM, Andersen KA, Yeum D, et al. Cytotoxicity of paclitaxel in breast cancer is due to chromosome missegregation on multipolar spindles. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:229ra243. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007965
19. National Cancer Institute. Carboplatin-Taxol. Published May 30, 2012. Updated March 22, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/carboplatin-taxol
20. Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb; 2011. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
21. Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2021. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
22. Awosika AO, Farrar MC, Jacobs TF. Paclitaxel. StatPearls. Updated November 18, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536917/
23. Gerriets V, Kasi A. Bevacizumab. StatPearls. Updated September 1, 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482126/
24. American Cancer Society. Chemotherapy for endometrial cancer. Updated March 27, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/endometrial-cancer/treating/chemotherapy.html
25. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy for first-line treatment of metastatic squamous NSCLC. October 30, 2018. Updated December 14, 2018. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-combination-chemotherapy-first-line-treatment-metastatic-squamous-nsclc
26. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for locally recurrent unresectable or metastatic triple negative breast cancer. November 13, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-pembrolizumab-locally-recurrent-unresectable-or-metastatic-triple
27. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves atezolizumab for PD-L1 positive unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast. March 8, 2019. Updated March 18, 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-approves-atezolizumab-pd-l1-positive-unresectable-locally-advanced-or-metastatic-triple-negative
28. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA issues alert about efficacy and potential safety concerns with atezolizumab in combination with paclitaxel for treatment of breast cancer. September 8, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-issues-alert-about-efficacy-and-potential-safety-concerns-atezolizumab-combination-paclitaxel
29. Tan AR. Chemoimmunotherapy: still the standard of care for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. ASCO Daily News. February 23, 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://dailynews.ascopubs.org/do/chemoimmunotherapy-still-standard-care-metastatic-triple-negative-breast-cancer
30. McGuire WP, Rowinsky EK, Rosenshein NB, et al. Taxol: a unique antineoplastic agent with significant activity in advanced ovarian epithelial neoplasms. Ann Intern Med. 1989;111(4):273-279. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-111-4-273
31. Milas L, Hunter NR, Kurdoglu B, et al. Kinetics of mitotic arrest and apoptosis in murine mammary and ovarian tumors treated with taxol. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;35(4):297-303. doi:10.1007/BF00689448
32. Searle J, Collins DJ, Harmon B, Kerr JF. The spontaneous occurrence of apoptosis in squamous carcinomas of the uterine cervix. Pathology. 1973;5(2):163-169. doi:10.3109/00313027309060831
33. Gallego-Jara J, Lozano-Terol G, Sola-Martínez RA, Cánovas-Díaz M, de Diego Puente T. A compressive review about taxol®: history and future challenges. Molecules. 2020;25(24):5986. doi:10.3390/molecules25245986
34. Bernabeu E, Cagel M, Lagomarsino E, Moretton M, Chiappetta DA. Paclitaxel: What has been done and the challenges remain ahead. Int J Pharm. 2017;526(1-2):474-495. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.016
35. Nehate C, Jain S, Saneja A, et al. Paclitaxel formulations: challenges and novel delivery options. Curr Drug Deliv. 2014;11(6):666-686. doi:10.2174/1567201811666140609154949
36. Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Sparreboom A, Cremophor EL. The drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(13):1590-1598. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(01)00171-x
37. Chowdhury MR, Moshikur RM, Wakabayashi R, et al. In vivo biocompatibility, pharmacokinetics, antitumor efficacy, and hypersensitivity evaluation of ionic liquid-mediated paclitaxel formulations. Int J Pharm. 2019;565:219-226. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.05.020
38. Borgå O, Henriksson R, Bjermo H, Lilienberg E, Heldring N, Loman N. Maximum tolerated dose and pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel micellar in patients with recurrent malignant solid tumours: a dose-escalation study. Adv Ther. 2019;36(5):1150-1163. doi:10.1007/s12325-019-00909-6
39. Rouzier R, Rajan R, Wagner P, et al. Microtubule-associated protein tau: a marker of paclitaxel sensitivity in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(23):8315-8320. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408974102
40. Choudhury H, Gorain B, Tekade RK, Pandey M, Karmakar S, Pal TK. Safety against nephrotoxicity in paclitaxel treatment: oral nanocarrier as an effective tool in preclinical evaluation with marked in vivo antitumor activity. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017;91:179-189. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.10.023
41. Barkat MA, Beg S, Pottoo FH, Ahmad FJ. Nanopaclitaxel therapy: an evidence based review on the battle for next-generation formulation challenges. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2019;14(10):1323-1341. doi:10.2217/nnm-2018-0313
42. Sofias AM, Dunne M, Storm G, Allen C. The battle of “nano” paclitaxel. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;122:20-30. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2017.02.003
43. Yang N, Wang C, Wang J, et al. Aurora inase a stabilizes FOXM1 to enhance paclitaxel resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(9):6442-6453. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14538
44. Chowdhury MR, Moshikur RM, Wakabayashi R, et al. Ionic-liquid-based paclitaxel preparation: a new potential formulation for cancer treatment. Mol Pharm. 2018;15(16):2484-2488. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00305
45. Chung HJ, Kim HJ, Hong ST. Tumor-specific delivery of a paclitaxel-loading HSA-haemin nanoparticle for cancer treatment. Nanomedicine. 2020;23:102089. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2019.102089
46. Ye L, He J, Hu Z, et al. Antitumor effect and toxicity of lipusu in rat ovarian cancer xenografts. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;52:200-206. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.11.004
47. Ma WW, Lam ET, Dy GK, et al. A pharmacokinetic and dose-escalating study of paclitaxel injection concentrate for nano-dispersion (PICN) alone and with arboplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2557. doi:10.1200/jco.2013.31.15_suppl.2557
48. Micha JP, Goldstein BH, Birk CL, Rettenmaier MA, Brown JV. Abraxane in the treatment of ovarian cancer: the absence of hypersensitivity reactions. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;100(2):437-438. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.09.012
49. Ingle SG, Pai RV, Monpara JD, Vavia PR. Liposils: an effective strategy for stabilizing paclitaxel loaded liposomes by surface coating with silica. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;122:51-63. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2018.06.025
50. Abriata JP, Turatti RC, Luiz MT, et al. Development, characterization and biological in vitro assays of paclitaxel-loaded PCL polymeric nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:347-355. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.035
51. Hu J, Fu S, Peng Q, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded polymeric nanoparticles combined with chronomodulated chemotherapy on lung cancer: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2017;516(1-2):313-322. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.11.047
52. Dranitsaris G, Yu B, Wang L, et al. Abraxane® vs Taxol® for patients with advanced breast cancer: a prospective time and motion analysis from a chinese health care perspective. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016;22(2):205-211. doi:10.1177/1078155214556008
53. Pei Q, Hu X, Liu S, Li Y, Xie Z, Jing X. Paclitaxel dimers assembling nanomedicines for treatment of cervix carcinoma. J Control Release. 2017;254:23-33. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.03.391
54. Wang Y, Wang M, Qi H, et al. Pathway-dependent inhibition of paclitaxel hydroxylation by kinase inhibitors and assessment of drug-drug interaction potentials. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42(4):782-795. doi:10.1124/dmd.113.053793
55. Shen F, Jiang G, Philips S, et al. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (POR) associated with severe paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients of european ancestry from ECOG-ACRIN E5103. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29(13):2494-2500. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2431
56. Henningsson A, Marsh S, Loos WJ, et al. Association of CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 polymorphisms with the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(22):8097-8104. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1152
57. Mukai Y, Senda A, Toda T, et al. Drug-drug interaction between losartan and paclitaxel in human liver microsomes with different CYP2C8 genotypes. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;116(6):493-498. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12355
58. Kawahara B, Faull KF, Janzen C, Mascharak PK. Carbon monoxide inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP3A4/2C8 in human breast cancer cells, increasing sensitivity to paclitaxel. J Med Chem. 2021;64(12):8437-8446. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00404
59. Cresteil T, Monsarrat B, Dubois J, Sonnier M, Alvinerie P, Gueritte F. Regioselective metabolism of taxoids by human CYP3A4 and 2C8: structure-activity relationship. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002;30(4):438-445. doi:10.1124/dmd.30.4.438
60. Taniguchi R, Kumai T, Matsumoto N, et al. Utilization of human liver microsomes to explain individual differences in paclitaxel metabolism by CYP2C8 and CYP3A4. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;97(1):83-90. doi:10.1254/jphs.fp0040603
61. Nakayama A, Tsuchiya K, Xu L, Matsumoto T, Makino T. Drug-interaction between paclitaxel and goshajinkigan extract and its constituents. J Nat Med. 2022;76(1):59-67. doi:10.1007/s11418-021-01552-8
62. Monsarrat B, Chatelut E, Royer I, et al. Modification of paclitaxel metabolism in a cancer patient by induction of cytochrome P450 3A4. Drug Metab Dispos. 1998;26(3):229-233.
63. Walle T. Assays of CYP2C8- and CYP3A4-mediated metabolism of taxol in vivo and in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1996;272:145-151. doi:10.1016/s0076-6879(96)72018-9
64. Hanioka N, Matsumoto K, Saito Y, Narimatsu S. Functional characterization of CYP2C8.13 and CYP2C8.14: catalytic activities toward paclitaxel. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;107(1):565-569. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00543.x
65. Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
66. Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with Cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217-224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006
67. Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the military health system. Fed Pract. 2023;40(suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
68. Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
69. World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O) 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
70. Z score calculator for 2 population proportions. Social science statistics. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.socscistatistics.com/tests/ztest/default2.aspx
71. US Food and Drug Administration. Generic drugs: question & answers. FDA.gov. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/frequently-asked-questions-popular-topics/generic-drugs-questions-answers
72. Oura M, Saito H, Nishikawa Y. Shortage of nab-paclitaxel in Japan and around the world: issues in global information sharing. JMA J. 2023;6(2):192-195. doi:10.31662/jmaj.2022-0179
73. Yuan H, Guo H, Luan X, et al. Albumin nanoparticle of paclitaxel (abraxane) decreases while taxol increases breast cancer stem cells in treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(7):2275-2286. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b01221
74. Dranitsaris G, Yu B, Wang L, et al. Abraxane® versus Taxol® for patients with advanced breast cancer: a prospective time and motion analysis from a Chinese health care perspective. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016;22(2):205-211. doi:10.1177/1078155214556008
75. Gradishar WJ, Tjulandin S, Davidson N, et al. Phase III trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with polyethylated castor oil-based paclitaxel in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(31):7794-7803. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.
76. Liu M, Liu S, Yang L, Wang S. Comparison between nab-paclitaxel and solvent-based taxanes as neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):118. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-07831-7
77. Rowinsky EK, Eisenhauer EA, Chaudhry V, Arbuck SG, Donehower RC. Clinical toxicities encountered with paclitaxel (taxol). Semin Oncol. 1993;20(4 Suppl 3):1-15.
78. Banerji A, Lax T, Guyer A, Hurwitz S, Camargo CA Jr, Long AA. Management of hypersensitivity reactions to carboplatin and paclitaxel in an outpatient oncology infusion center: a 5-year review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2(4):428-433. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2014.04.010
79. Staff NP, Fehrenbacher JC, Caillaud M, Damaj MI, Segal RA, Rieger S. Pathogenesis of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: a current review of in vitro and in vivo findings using rodent and human model systems. Exp Neurol. 2020;324:113121. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113121
80. Postma TJ, Vermorken JB, Liefting AJ, Pinedo HM, Heimans JJ. Paclitaxel-induced neuropathy. Ann Oncol. 1995;6(5):489-494. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a059220
81. Liu JM, Chen YM, Chao Y, et al. Paclitaxel-induced severe neuropathy in patients with previous radiotherapy to the head and neck region. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88(14):1000-1002. doi:10.1093/jnci/88.14.1000-a
82. Bayat Mokhtari R, Homayouni TS, Baluch N, et al. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(23):38022-38043. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16723
83. Blagosklonny MV. Analysis of FDA approved anticancer drugs reveals the future of cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 2004;3(8):1035-1042.
84. Yap TA, Omlin A, de Bono JS. Development of therapeutic combinations targeting major cancer signaling pathways. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(12):1592-1605. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.37.6418
85. Gilani B, Cassagnol M. Biochemistry, Cytochrome P450. StatPearls. Updated April 24, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557698/
86. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Carboplatin. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548565/
87. Carboplatin. Prescribing information. Teva Parenteral Medicines; 2012. Accessed June 5, 204. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/077139Orig1s016lbl.pdf
88. Johnson-Arbor K, Dubey R. Doxorubicin. StatPearls. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459232/
89. Doxorubicin hydrochloride injection. Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/050467s078,050629s030lbl.pdf
90. Gor, PP, Su, HI, Gray, RJ, et al. Cyclophosphamide-metabolizing enzyme polymorphisms and survival outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(3):R26. doi:10.1186/bcr2570
91. Cyclophosphamide. Prescribing information. Ingenus Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/212501s000lbl.pdf
92. Gemcitabine. Prescribing information. Hospira; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/200795Orig1s010lbl.pdf
93. Ifex (ifosfamide). Prescribing information. Baxter; 2012. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/019763s017lbl.pdf
94. Cisplatin. Prescribing information. WG Critical Care; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/018057s089lbl.pdf
95. Gerriets V, Kasi A. Bevacizumab. StatPearls. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482126/
96. Avastin (bevacizumab). Prescribing information. Genentech; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata .fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/125085s340lbl.pdf
 97. Keytruda (pembrolizumab). Prescribing information. Merck; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/125514s096lbl.pdf
97. Keytruda (pembrolizumab). Prescribing information. Merck; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/125514s096lbl.pdf
98. Dean L, Kane M. Capecitabine therapy and DPYD genotype. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012. Updated November 2, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK385155/
99. Xeloda (capecitabine). Prescribing information. Roche; 2000. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2000/20896lbl.pdf
100. Pemetrexed injection. Prescribing information. Fareva Unterach; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/214657s000lbl.pdf
101. Topotecan Injection. Prescribing information. Zydus Hospira Oncology; 2014. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/200582s001lbl.pdf
102. Ibrance (palbociclib). Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/207103s008lbl.pdf
103. Navelbine (vinorelbine) injection. Prescribing information. Pierre Fabre Médicament; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020388s037lbl.pdf
104. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Letrozole. Updated July 25, 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548381/
105. Femara (letrozole). Prescribing information. Novartis; 2014. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/020726s027lbl.pdf
106. Soltamox (tamoxifen citrate). Prescribing information. Rosemont Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/021807s005lbl.pdf
107. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Anastrozole. Updated July 25, 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548189/
108. Grimm SW, Dyroff MC. Inhibition of human drug metabolizing cytochromes P450 by anastrozole, a potent and selective inhibitor of aromatase. Drug Metab Dispos. 1997;25(5):598-602.
109. Arimidex (anastrozole). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca; 2010. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020541s026lbl.pdf
110. Megace (megestrol acetate). Prescribing information. Endo Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/021778s024lbl.pdf
111. Imfinzi (durvalumab). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/761069s018lbl.pdf
112. Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, et al. Nortriptyline. StatPearls. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
113. Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Patheon Inc.; 2012. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
114. Wellbutrin (bupropion hydrochloride). Prescribing information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018644s052lbl.pdf
115. Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing information. Apotex Inc.; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
116. Johnson DB, Lopez MJ, Kelley B. Dexamethasone. StatPearls. Updated May 2, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482130/
117. Hemady (dexamethasone). Prescribing information. Dexcel Pharma; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/211379s000lbl.pdf
118. Parker SD, King N, Jacobs TF. Pegfilgrastim. StatPearls. Updated May 9, 2024. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532893/
119. Fylnetra (pegfilgrastim-pbbk). Prescribing information. Kashiv BioSciences; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/761084s000lbl.pdf
120. Emend (aprepitant). Prescribing information. Merck; 2015. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/207865lbl.pdf
121. Lipitor (atorvastatin calcium). Prescribing information. Viatris Specialty; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020702Orig1s079correctedlbl.pdf
122. Cipro (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/019537s090,020780s047lbl.pdf
123. Pino MA, Azer SA. Cimetidine. StatPearls. Updated March 6, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544255/
124. Tagament (Cimetidine). Prescribing information. Mylan; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020238Orig1s024lbl.pdf
125. Neupogen (filgrastim). Prescribing information. Amgen Inc.; 2015. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/103353s5184lbl.pdf
126. Flagyl (metronidazole). Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2013. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/020334s008lbl.pdf
127. Zymaxid (gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution). Prescribing information. Allergan; 2016. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/022548s002lbl.pdf
128. Macrobid (nitrofurantoin monohydrate). Prescribing information. Procter and Gamble Pharmaceutical Inc.; 2009. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/020064s019lbl.pdf
129. Hyzaar (losartan). Prescribing information. Merck; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020387s067lbl.pdf
1. American Chemical Society. Discovery of camptothecin and taxol. acs.org. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.acs.org/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/camptothecintaxol.html
2. Bocci G, Di Paolo A, Danesi R. The pharmacological bases of the antiangiogenic activity of paclitaxel. Angiogenesis. 2013;16(3):481-492. doi:10.1007/s10456-013-9334-0.
3. Meštrovic T. Paclitaxel history. News Medical Life Sciences. Updated March 11, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Paclitaxel-History.aspx
4. Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC. Paclitaxel (taxol). N Engl J Med. 1995;332(15):1004-1014. doi:10.1056/NEJM199504133321507
5. Walsh V, Goodman J. The billion dollar molecule: Taxol in historical and theoretical perspective. Clio Med. 2002;66:245-267. doi:10.1163/9789004333499_013
6. Perdue RE, Jr, Hartwell JL. The search for plant sources of anticancer drugs. Morris Arboretum Bull. 1969;20:35-53.
7. Wall ME, Wani MC. Camptothecin and taxol: discovery to clinic—thirteenth Bruce F. Cain Memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 1995;55:753-760.
8. Wani MC, Taylor HL, Wall ME, Coggon P, McPhail AT. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971;93(9):2325-2327. doi:10.1021/ja00738a045
9. Weaver BA. How taxol/paclitaxel kills cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2014;25(18):2677-2681. doi:10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0916
10. Chen JG, Horwitz SB. Differential mitotic responses to microtubule-stabilizing and-destabilizing drugs. Cancer Res. 2002;62(7):1935-1938.
11. Singh S, Dash AK. Paclitaxel in cancer treatment: perspectives and prospects of its delivery challenges. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2009;26(4):333-372. doi:10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.v26.i4.10
12. Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979;277(5698):665-667. doi:10.1038/277665a0
13. Fuchs DA, Johnson RK. Cytologic evidence that taxol, an antineoplastic agent from taxus brevifolia, acts as a mitotic spindle poison. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978;62(8):1219-1222.
14. Walsh V, Goodman J. From taxol to taxol: the changing identities and ownership of an anti-cancer drug. Med Anthropol. 2002;21(3-4):307-336. doi:10.1080/01459740214074
15. Walsh V, Goodman J. Cancer chemotherapy, biodiversity, public and private property: the case of the anti-cancer drug taxol. Soc Sci Med. 1999;49(9):1215-1225. doi:10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00161-6
16. Jordan MA, Wendell K, Gardiner S, Derry WB, Copp H, Wilson L. Mitotic block induced in HeLa cells by low concentrations of paclitaxel (taxol) results in abnormal mitotic exit and apoptotic cell death. Cancer Res. 1996;56(4):816-825.
17. Picard M, Castells MC. Re-visiting hypersensitivity reactions to taxanes: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015;49(2):177-191. doi:10.1007/s12016-014-8416-0
18. Zasadil LM, Andersen KA, Yeum D, et al. Cytotoxicity of paclitaxel in breast cancer is due to chromosome missegregation on multipolar spindles. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:229ra243. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007965
19. National Cancer Institute. Carboplatin-Taxol. Published May 30, 2012. Updated March 22, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/carboplatin-taxol
20. Taxol (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Bristol-Myers Squibb; 2011. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020262s049lbl.pdf
21. Abraxane (paclitaxel). Prescribing information. Celgene Corporation; 2021. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/021660s047lbl.pdf
22. Awosika AO, Farrar MC, Jacobs TF. Paclitaxel. StatPearls. Updated November 18, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536917/
23. Gerriets V, Kasi A. Bevacizumab. StatPearls. Updated September 1, 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482126/
24. American Cancer Society. Chemotherapy for endometrial cancer. Updated March 27, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/endometrial-cancer/treating/chemotherapy.html
25. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy for first-line treatment of metastatic squamous NSCLC. October 30, 2018. Updated December 14, 2018. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-combination-chemotherapy-first-line-treatment-metastatic-squamous-nsclc
26. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to pembrolizumab for locally recurrent unresectable or metastatic triple negative breast cancer. November 13, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-pembrolizumab-locally-recurrent-unresectable-or-metastatic-triple
27. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves atezolizumab for PD-L1 positive unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast. March 8, 2019. Updated March 18, 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-approves-atezolizumab-pd-l1-positive-unresectable-locally-advanced-or-metastatic-triple-negative
28. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA issues alert about efficacy and potential safety concerns with atezolizumab in combination with paclitaxel for treatment of breast cancer. September 8, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-issues-alert-about-efficacy-and-potential-safety-concerns-atezolizumab-combination-paclitaxel
29. Tan AR. Chemoimmunotherapy: still the standard of care for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. ASCO Daily News. February 23, 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://dailynews.ascopubs.org/do/chemoimmunotherapy-still-standard-care-metastatic-triple-negative-breast-cancer
30. McGuire WP, Rowinsky EK, Rosenshein NB, et al. Taxol: a unique antineoplastic agent with significant activity in advanced ovarian epithelial neoplasms. Ann Intern Med. 1989;111(4):273-279. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-111-4-273
31. Milas L, Hunter NR, Kurdoglu B, et al. Kinetics of mitotic arrest and apoptosis in murine mammary and ovarian tumors treated with taxol. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;35(4):297-303. doi:10.1007/BF00689448
32. Searle J, Collins DJ, Harmon B, Kerr JF. The spontaneous occurrence of apoptosis in squamous carcinomas of the uterine cervix. Pathology. 1973;5(2):163-169. doi:10.3109/00313027309060831
33. Gallego-Jara J, Lozano-Terol G, Sola-Martínez RA, Cánovas-Díaz M, de Diego Puente T. A compressive review about taxol®: history and future challenges. Molecules. 2020;25(24):5986. doi:10.3390/molecules25245986
34. Bernabeu E, Cagel M, Lagomarsino E, Moretton M, Chiappetta DA. Paclitaxel: What has been done and the challenges remain ahead. Int J Pharm. 2017;526(1-2):474-495. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.016
35. Nehate C, Jain S, Saneja A, et al. Paclitaxel formulations: challenges and novel delivery options. Curr Drug Deliv. 2014;11(6):666-686. doi:10.2174/1567201811666140609154949
36. Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Sparreboom A, Cremophor EL. The drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(13):1590-1598. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(01)00171-x
37. Chowdhury MR, Moshikur RM, Wakabayashi R, et al. In vivo biocompatibility, pharmacokinetics, antitumor efficacy, and hypersensitivity evaluation of ionic liquid-mediated paclitaxel formulations. Int J Pharm. 2019;565:219-226. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.05.020
38. Borgå O, Henriksson R, Bjermo H, Lilienberg E, Heldring N, Loman N. Maximum tolerated dose and pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel micellar in patients with recurrent malignant solid tumours: a dose-escalation study. Adv Ther. 2019;36(5):1150-1163. doi:10.1007/s12325-019-00909-6
39. Rouzier R, Rajan R, Wagner P, et al. Microtubule-associated protein tau: a marker of paclitaxel sensitivity in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(23):8315-8320. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408974102
40. Choudhury H, Gorain B, Tekade RK, Pandey M, Karmakar S, Pal TK. Safety against nephrotoxicity in paclitaxel treatment: oral nanocarrier as an effective tool in preclinical evaluation with marked in vivo antitumor activity. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017;91:179-189. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.10.023
41. Barkat MA, Beg S, Pottoo FH, Ahmad FJ. Nanopaclitaxel therapy: an evidence based review on the battle for next-generation formulation challenges. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2019;14(10):1323-1341. doi:10.2217/nnm-2018-0313
42. Sofias AM, Dunne M, Storm G, Allen C. The battle of “nano” paclitaxel. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;122:20-30. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2017.02.003
43. Yang N, Wang C, Wang J, et al. Aurora inase a stabilizes FOXM1 to enhance paclitaxel resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(9):6442-6453. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14538
44. Chowdhury MR, Moshikur RM, Wakabayashi R, et al. Ionic-liquid-based paclitaxel preparation: a new potential formulation for cancer treatment. Mol Pharm. 2018;15(16):2484-2488. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00305
45. Chung HJ, Kim HJ, Hong ST. Tumor-specific delivery of a paclitaxel-loading HSA-haemin nanoparticle for cancer treatment. Nanomedicine. 2020;23:102089. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2019.102089
46. Ye L, He J, Hu Z, et al. Antitumor effect and toxicity of lipusu in rat ovarian cancer xenografts. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;52:200-206. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.11.004
47. Ma WW, Lam ET, Dy GK, et al. A pharmacokinetic and dose-escalating study of paclitaxel injection concentrate for nano-dispersion (PICN) alone and with arboplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2557. doi:10.1200/jco.2013.31.15_suppl.2557
48. Micha JP, Goldstein BH, Birk CL, Rettenmaier MA, Brown JV. Abraxane in the treatment of ovarian cancer: the absence of hypersensitivity reactions. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;100(2):437-438. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.09.012
49. Ingle SG, Pai RV, Monpara JD, Vavia PR. Liposils: an effective strategy for stabilizing paclitaxel loaded liposomes by surface coating with silica. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;122:51-63. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2018.06.025
50. Abriata JP, Turatti RC, Luiz MT, et al. Development, characterization and biological in vitro assays of paclitaxel-loaded PCL polymeric nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:347-355. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.035
51. Hu J, Fu S, Peng Q, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded polymeric nanoparticles combined with chronomodulated chemotherapy on lung cancer: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2017;516(1-2):313-322. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.11.047
52. Dranitsaris G, Yu B, Wang L, et al. Abraxane® vs Taxol® for patients with advanced breast cancer: a prospective time and motion analysis from a chinese health care perspective. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016;22(2):205-211. doi:10.1177/1078155214556008
53. Pei Q, Hu X, Liu S, Li Y, Xie Z, Jing X. Paclitaxel dimers assembling nanomedicines for treatment of cervix carcinoma. J Control Release. 2017;254:23-33. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.03.391
54. Wang Y, Wang M, Qi H, et al. Pathway-dependent inhibition of paclitaxel hydroxylation by kinase inhibitors and assessment of drug-drug interaction potentials. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42(4):782-795. doi:10.1124/dmd.113.053793
55. Shen F, Jiang G, Philips S, et al. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (POR) associated with severe paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients of european ancestry from ECOG-ACRIN E5103. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29(13):2494-2500. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2431
56. Henningsson A, Marsh S, Loos WJ, et al. Association of CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 polymorphisms with the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(22):8097-8104. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1152
57. Mukai Y, Senda A, Toda T, et al. Drug-drug interaction between losartan and paclitaxel in human liver microsomes with different CYP2C8 genotypes. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;116(6):493-498. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12355
58. Kawahara B, Faull KF, Janzen C, Mascharak PK. Carbon monoxide inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP3A4/2C8 in human breast cancer cells, increasing sensitivity to paclitaxel. J Med Chem. 2021;64(12):8437-8446. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00404
59. Cresteil T, Monsarrat B, Dubois J, Sonnier M, Alvinerie P, Gueritte F. Regioselective metabolism of taxoids by human CYP3A4 and 2C8: structure-activity relationship. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002;30(4):438-445. doi:10.1124/dmd.30.4.438
60. Taniguchi R, Kumai T, Matsumoto N, et al. Utilization of human liver microsomes to explain individual differences in paclitaxel metabolism by CYP2C8 and CYP3A4. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;97(1):83-90. doi:10.1254/jphs.fp0040603
61. Nakayama A, Tsuchiya K, Xu L, Matsumoto T, Makino T. Drug-interaction between paclitaxel and goshajinkigan extract and its constituents. J Nat Med. 2022;76(1):59-67. doi:10.1007/s11418-021-01552-8
62. Monsarrat B, Chatelut E, Royer I, et al. Modification of paclitaxel metabolism in a cancer patient by induction of cytochrome P450 3A4. Drug Metab Dispos. 1998;26(3):229-233.
63. Walle T. Assays of CYP2C8- and CYP3A4-mediated metabolism of taxol in vivo and in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1996;272:145-151. doi:10.1016/s0076-6879(96)72018-9
64. Hanioka N, Matsumoto K, Saito Y, Narimatsu S. Functional characterization of CYP2C8.13 and CYP2C8.14: catalytic activities toward paclitaxel. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;107(1):565-569. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00543.x
65. Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interactions (DDIs) of gefitinib with/without losartan and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100112. doi:10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100112
66. Luong TT, McAnulty MJ, Evers DL, Reinhardt BJ, Weina PJ. Pre-clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) of gefitinib or erlotinib with Cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibiting drugs, fluoxetine and/or losartan. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021;2:217-224. doi:10.1016/j.crtox.2021.05.006
67. Luong TT, Powers CN, Reinhardt BJ, et al. Retrospective evaluation of drug-drug interactions with erlotinib and gefitinib use in the military health system. Fed Pract. 2023;40(suppl 3):S24-S34. doi:10.12788/fp.0401
68. Adamo M, Dickie L, Ruhl J. SEER program coding and staging manual 2016. National Cancer Institute. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/manuals/2016/SPCSM_2016_maindoc.pdf
69. World Health Organization. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O) 3rd ed, 1st revision. World Health Organization; 2013. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
70. Z score calculator for 2 population proportions. Social science statistics. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.socscistatistics.com/tests/ztest/default2.aspx
71. US Food and Drug Administration. Generic drugs: question & answers. FDA.gov. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/frequently-asked-questions-popular-topics/generic-drugs-questions-answers
72. Oura M, Saito H, Nishikawa Y. Shortage of nab-paclitaxel in Japan and around the world: issues in global information sharing. JMA J. 2023;6(2):192-195. doi:10.31662/jmaj.2022-0179
73. Yuan H, Guo H, Luan X, et al. Albumin nanoparticle of paclitaxel (abraxane) decreases while taxol increases breast cancer stem cells in treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(7):2275-2286. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b01221
74. Dranitsaris G, Yu B, Wang L, et al. Abraxane® versus Taxol® for patients with advanced breast cancer: a prospective time and motion analysis from a Chinese health care perspective. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016;22(2):205-211. doi:10.1177/1078155214556008
75. Gradishar WJ, Tjulandin S, Davidson N, et al. Phase III trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with polyethylated castor oil-based paclitaxel in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(31):7794-7803. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.
76. Liu M, Liu S, Yang L, Wang S. Comparison between nab-paclitaxel and solvent-based taxanes as neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):118. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-07831-7
77. Rowinsky EK, Eisenhauer EA, Chaudhry V, Arbuck SG, Donehower RC. Clinical toxicities encountered with paclitaxel (taxol). Semin Oncol. 1993;20(4 Suppl 3):1-15.
78. Banerji A, Lax T, Guyer A, Hurwitz S, Camargo CA Jr, Long AA. Management of hypersensitivity reactions to carboplatin and paclitaxel in an outpatient oncology infusion center: a 5-year review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2(4):428-433. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2014.04.010
79. Staff NP, Fehrenbacher JC, Caillaud M, Damaj MI, Segal RA, Rieger S. Pathogenesis of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: a current review of in vitro and in vivo findings using rodent and human model systems. Exp Neurol. 2020;324:113121. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113121
80. Postma TJ, Vermorken JB, Liefting AJ, Pinedo HM, Heimans JJ. Paclitaxel-induced neuropathy. Ann Oncol. 1995;6(5):489-494. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a059220
81. Liu JM, Chen YM, Chao Y, et al. Paclitaxel-induced severe neuropathy in patients with previous radiotherapy to the head and neck region. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88(14):1000-1002. doi:10.1093/jnci/88.14.1000-a
82. Bayat Mokhtari R, Homayouni TS, Baluch N, et al. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(23):38022-38043. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16723
83. Blagosklonny MV. Analysis of FDA approved anticancer drugs reveals the future of cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 2004;3(8):1035-1042.
84. Yap TA, Omlin A, de Bono JS. Development of therapeutic combinations targeting major cancer signaling pathways. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(12):1592-1605. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.37.6418
85. Gilani B, Cassagnol M. Biochemistry, Cytochrome P450. StatPearls. Updated April 24, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557698/
86. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Carboplatin. Updated September 15, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548565/
87. Carboplatin. Prescribing information. Teva Parenteral Medicines; 2012. Accessed June 5, 204. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/077139Orig1s016lbl.pdf
88. Johnson-Arbor K, Dubey R. Doxorubicin. StatPearls. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459232/
89. Doxorubicin hydrochloride injection. Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/050467s078,050629s030lbl.pdf
90. Gor, PP, Su, HI, Gray, RJ, et al. Cyclophosphamide-metabolizing enzyme polymorphisms and survival outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12(3):R26. doi:10.1186/bcr2570
91. Cyclophosphamide. Prescribing information. Ingenus Pharmaceuticals; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/212501s000lbl.pdf
92. Gemcitabine. Prescribing information. Hospira; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/200795Orig1s010lbl.pdf
93. Ifex (ifosfamide). Prescribing information. Baxter; 2012. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/019763s017lbl.pdf
94. Cisplatin. Prescribing information. WG Critical Care; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/018057s089lbl.pdf
95. Gerriets V, Kasi A. Bevacizumab. StatPearls. Updated August 28, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482126/
96. Avastin (bevacizumab). Prescribing information. Genentech; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata .fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/125085s340lbl.pdf
 97. Keytruda (pembrolizumab). Prescribing information. Merck; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/125514s096lbl.pdf
97. Keytruda (pembrolizumab). Prescribing information. Merck; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/125514s096lbl.pdf
98. Dean L, Kane M. Capecitabine therapy and DPYD genotype. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012. Updated November 2, 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK385155/
99. Xeloda (capecitabine). Prescribing information. Roche; 2000. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2000/20896lbl.pdf
100. Pemetrexed injection. Prescribing information. Fareva Unterach; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/214657s000lbl.pdf
101. Topotecan Injection. Prescribing information. Zydus Hospira Oncology; 2014. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/200582s001lbl.pdf
102. Ibrance (palbociclib). Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/207103s008lbl.pdf
103. Navelbine (vinorelbine) injection. Prescribing information. Pierre Fabre Médicament; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020388s037lbl.pdf
104. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Letrozole. Updated July 25, 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548381/
105. Femara (letrozole). Prescribing information. Novartis; 2014. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/020726s027lbl.pdf
106. Soltamox (tamoxifen citrate). Prescribing information. Rosemont Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/021807s005lbl.pdf
107. LiverTox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury; 2012. Anastrozole. Updated July 25, 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548189/
108. Grimm SW, Dyroff MC. Inhibition of human drug metabolizing cytochromes P450 by anastrozole, a potent and selective inhibitor of aromatase. Drug Metab Dispos. 1997;25(5):598-602.
109. Arimidex (anastrozole). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca; 2010. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020541s026lbl.pdf
110. Megace (megestrol acetate). Prescribing information. Endo Pharmaceuticals; 2018. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/021778s024lbl.pdf
111. Imfinzi (durvalumab). Prescribing information. AstraZeneca; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/761069s018lbl.pdf
112. Merwar G, Gibbons JR, Hosseini SA, et al. Nortriptyline. StatPearls. Updated June 5, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482214/
113. Pamelor (nortriptyline HCl). Prescribing information. Patheon Inc.; 2012. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/018012s029,018013s061lbl.pdf
114. Wellbutrin (bupropion hydrochloride). Prescribing information. GlaxoSmithKline; 2017. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018644s052lbl.pdf
115. Paxil (paroxetine). Prescribing information. Apotex Inc.; 2021. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/020031s077lbl.pdf
116. Johnson DB, Lopez MJ, Kelley B. Dexamethasone. StatPearls. Updated May 2, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482130/
117. Hemady (dexamethasone). Prescribing information. Dexcel Pharma; 2019. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/211379s000lbl.pdf
118. Parker SD, King N, Jacobs TF. Pegfilgrastim. StatPearls. Updated May 9, 2024. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532893/
119. Fylnetra (pegfilgrastim-pbbk). Prescribing information. Kashiv BioSciences; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/761084s000lbl.pdf
120. Emend (aprepitant). Prescribing information. Merck; 2015. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/207865lbl.pdf
121. Lipitor (atorvastatin calcium). Prescribing information. Viatris Specialty; 2022. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/020702Orig1s079correctedlbl.pdf
122. Cipro (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride). Prescribing information. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/019537s090,020780s047lbl.pdf
123. Pino MA, Azer SA. Cimetidine. StatPearls. Updated March 6, 2023. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544255/
124. Tagament (Cimetidine). Prescribing information. Mylan; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020238Orig1s024lbl.pdf
125. Neupogen (filgrastim). Prescribing information. Amgen Inc.; 2015. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/103353s5184lbl.pdf
126. Flagyl (metronidazole). Prescribing information. Pfizer; 2013. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/020334s008lbl.pdf
127. Zymaxid (gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution). Prescribing information. Allergan; 2016. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/022548s002lbl.pdf
128. Macrobid (nitrofurantoin monohydrate). Prescribing information. Procter and Gamble Pharmaceutical Inc.; 2009. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/020064s019lbl.pdf
129. Hyzaar (losartan). Prescribing information. Merck; 2020. Accessed June 5, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020387s067lbl.pdf
Circulating Tumor DNA Hints at BC Recurrence Risk
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
CHICAGO — Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can predict relapse risk in some cases of early, high-risk breast cancer, but it’s too soon to use it to guide adjuvant therapy decisions, according to a study presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting.
Detectable ctDNA is “highly prognostic of worse outcomes, particularly in patients who [remain] persistently positive,” but the correlation isn’t perfect, said lead investigator Sherene Loi, MMBS, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne, Australia.
Although less likely, relapses also occurred in the study among women without ctDNA elevation. Conversely, there were women with elevated ctDNA who did not relapse, she said. The study was a subanalysis of the monarchE trial of adjuvant abemaciclib, a CDK 4/6 inhibitor.
Eventually, “we would like to use” ctDNA to guide adjuvant treatment decisions, but the research isn’t there yet, Dr. Loi said. It’s possible, for instance, that persistently detectable ctDNA indicates early treatment failure and the need for treatment intensification. Future research should tackle the issue.
Study discussant Francois-Clement Bidard, MD, PhD, a breast cancer specialist at Institut Curie, Paris, agreed that ctDNA isn’t ready for primetime in adjuvant early, high-risk breast cancer.
“There is no clinical evidence to suggest that there is clinical utility in this setting. There are several trials that are ongoing,” he said, but for now “you shouldn’t,” for example, “use ctDNA to de-escalate adjuvant CDK4/6 [inhibitors]. It could be in the future that we could have data on this, but at the moment, [the] clear clinical message [is] no way.”
At 5-year follow-up, the monarchE trial found a 7.6% invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) improvement when abemaciclib was added to the first 2 years of endocrine therapy in women with HR+, HER2-, node positive, high-risk early breast cancer. The combination is now a standard adjuvant option for the disease.
The ctDNA study focused on a subset of 910 subjects with adequate ctDNA testing to run the analysis. The study population was also selected to be enriched for overall IDFS events (27% versus 18% across the trial’s 5,637 subjects). An IDFS event was defined as a local, regional, contralateral or distant invasive recurrence; a new primary tumor; or death from any cause.
Testing was performed using the Signatera ctDNA assay. Baseline samples were taken after completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, then again at 3, 6, or 24 months.
Overall, ctDNA detection was infrequent. Just 8% of patients were positive at baseline and 17% were positive at any point during the trial. Even so, ctDNA detection at any point was adversely prognostic.
Patients who were ctDNA positive at baseline were more likely to experience an IDFS event, compared with those who were ctDNA negative at baseline (80% at 4 years follow-up versus 23%).
Similarly, those who remained positive or became positive during testing were more likely to experience an IDFS event compared with those who became negative or remained negative throughout testing.
For instance, all 34 patients who were positive at baseline and remained positive had an IDFS event by year 4, versus just 40% who started positive but then cleared their ctDNA.
Among women who were negative at baseline and remained negative, 13% had an IDFS event versus 89% who started negative but then turned positive. Subjects who turned positive also had the shortest time to an IDFS event, a median of 7 months.
Among women who recurred, those who were ctDNA negative tended to have local, regional, or contralateral recurrences, while ctDNA positive patients tended to have distant recurrences.
The finding “really highlights that ctDNA antedates the metastatic clinical relapse. What the ctDNA is telling you is that the metastatic process has been completed, and metastases are about to grow,” Dr. Bidard said.
The work was funded by Eli Lilly, maker of abemaciclib, with collaboration from Natera, maker of the Signatera assay. Dr. Loi is an adviser and researcher for Lilly, among other industry ties. Dr. Bidard is a speaker and consultant for Lilly, among other ties.
FROM ASCO 2024
Greater Transparency of Oncologists’ Pharma Relationships Needed
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
FROM ASCO 2024
Could an EHR Nudge Reduce Unnecessary Biopsies?
Participating surgeons noted that the reminder system added minimal friction to their workflow, as it did not require additional clicks or actions on the day of the patient visit, reported lead author Neil Carleton, PhD, of UPMC Hillman Cancer Center, Pittsburgh, and colleagues in JAMA Surgery (JAMA Surg. 2024 Jul 17. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.2407).
This effort to reduce the rate of SLNB stems from the Choosing Wisely campaign, which recommends against axillary staging in women 70 years and older with early-stage, clinically node-negative (cN0), hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer, the investigators said.
“These recommendations were developed because axillary staging did not impact survival, and rates of SLN positivity were low because of the tumor’s biological phenotype,” they wrote. “Even in older patients with tumors that exhibit concerning clinicopathologic features, limited nodal involvement does not often alter receipt of chemotherapy independently from genomic testing. Despite these recommendations, most women still receive axillary surgery.”
How Did the Nudge System Aim to Reduce the Rate of SLNB?
The nudge intervention involved adding a new column to the Epic schedule view, which flagged eligible patients during their first outpatient surgical consultation. The flag appeared as a caution sign or red clipboard icon. When surgeons hovered over the icon, a text box appeared, reminding them to consider omitting SLNB after a detailed review of core biopsy pathology and ultrasonographic imaging.
The intervention was evaluated at eight outpatient clinics within an integrated healthcare system that included seven breast surgical oncologists.
The study began with a 12-month preintervention period to serve as a control, during which time SLNB rate was determined via 194 patients in the target demographic. SLNB rate was again collected during the 12-month intervention period, which involved 193 patients meeting enrollment criteria. Between these periods, the investigators conducted a brief session lasting less than 30 minutes to introduce the surgeons to the rationale and design of the nudge column.
How Effective Was the Nudge System?
The intervention reduced the SLNB rate from 46.9% to 23.8%, representing a 49.3% decrease in use of SLNB. Efficacy was further supported by a significant reduction in SLNB according to an interrupted time series model (adjusted odds ratio, 0.26; 95% confidence interval, 0.07 to 0.90; P = .03). Extended follow-up showed that this effect was durable beyond the intervention period, with a 6-month mean reduction in SLNB of 15.6%.
Omission of SLNB led to higher rates of pathological node positivity during the intervention period (15.2% vs 8.8%), with all positive cases staged as pN1. Adjuvant therapy recommendations were similar between groups and driven by genomic testing, not nodal status. The intervention period also saw a decrease in referrals for lymphedema evaluation (3.6% vs. 6.2%).
How Might the Nudge System Be Implemented in Other Practices?
Although the SLNB nudge system was effective in the present study, likelihood of uptake among practices could vary widely, according to Anne M. Wallace, MD, professor of clinical surgery at UC San Diego Health and director of the Moores Comprehensive Breast Health Program.
On a fundamental level, not all centers use Epic software, which could present issues with compatibility, Dr. Wallace said in an interview. More importantly, she added, many institutions already have EHR-based alerts and reminders in place, so it is not always feasible to add a new nudge for every possible clinical scenario.
“Already there are so many little icons that we have to go through now when we close a note,” she said. “That’s why electronic medical records are becoming one of the leading stressors in medicine.”
This presents a more complex challenge, Dr. Wallace said, particularly as potentially practice-changing data are becoming available, and physicians may not have time to learn about them and integrate them into routine practice. She suggested that the present system may be most appropriate for oncologists in solo practice, or in small group practices where it is more challenging to have routine conversations about changing standards of care.
What Are the Risks of Using the Nudge System?
One of those conversations may surround the validity of the recommendation implemented in the present study.
Although the Society of Surgical Oncology recommends against SLNB in the described demographic, other experts, including Dr. Wallace, take a more nuanced view of the decision.
She noted that some patients with a chronological age of 70 may have a lower biological age, casting doubt on the legitimacy of the age threshold, and those near the threshold may wish to make the decision about staging for themselves.
Beyond these concerns, Dr. Wallace described two potential risks involved in forgoing SLNB.
First, there’s the potential for underestimating the tumor’s severity, she said, as this could mean a trip back to the operating room. A tumor initially thought to be low-grade might later be found to be high-grade, necessitating further surgery. Some patients might refuse additional surgery, leaving the more aggressive tumor untreated.
Second, the nudge system could complicate radiation treatment decisions, Dr. Wallace said. Without full nodal status, some radiation oncologists might push for additional radiation therapy, which incurs a greater treatment burden than SNLB.
What Are Some Alternatives to the Nudge System?
After discussing the strengths and weaknesses of the present EHR-based nudge system, and others like it, Dr. Wallace returned to the importance of ongoing communication among colleagues managing complex cases.
At UC San Diego Health, where oncologists meet weekly for a 2-hour breast cancer conference, “we nudge each other,” she said.
This study was supported by the Shear Family Foundation, UPMC eRecord Ambulatory Decision Support and Analytics, UPMC Hillman Cancer Center Biostatistics Facility, and National Institutes of Health. The investigators disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Amgen, the Lewin Group, and Milestone Pennsylvania, and others.
Participating surgeons noted that the reminder system added minimal friction to their workflow, as it did not require additional clicks or actions on the day of the patient visit, reported lead author Neil Carleton, PhD, of UPMC Hillman Cancer Center, Pittsburgh, and colleagues in JAMA Surgery (JAMA Surg. 2024 Jul 17. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.2407).
This effort to reduce the rate of SLNB stems from the Choosing Wisely campaign, which recommends against axillary staging in women 70 years and older with early-stage, clinically node-negative (cN0), hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer, the investigators said.
“These recommendations were developed because axillary staging did not impact survival, and rates of SLN positivity were low because of the tumor’s biological phenotype,” they wrote. “Even in older patients with tumors that exhibit concerning clinicopathologic features, limited nodal involvement does not often alter receipt of chemotherapy independently from genomic testing. Despite these recommendations, most women still receive axillary surgery.”
How Did the Nudge System Aim to Reduce the Rate of SLNB?
The nudge intervention involved adding a new column to the Epic schedule view, which flagged eligible patients during their first outpatient surgical consultation. The flag appeared as a caution sign or red clipboard icon. When surgeons hovered over the icon, a text box appeared, reminding them to consider omitting SLNB after a detailed review of core biopsy pathology and ultrasonographic imaging.
The intervention was evaluated at eight outpatient clinics within an integrated healthcare system that included seven breast surgical oncologists.
The study began with a 12-month preintervention period to serve as a control, during which time SLNB rate was determined via 194 patients in the target demographic. SLNB rate was again collected during the 12-month intervention period, which involved 193 patients meeting enrollment criteria. Between these periods, the investigators conducted a brief session lasting less than 30 minutes to introduce the surgeons to the rationale and design of the nudge column.
How Effective Was the Nudge System?
The intervention reduced the SLNB rate from 46.9% to 23.8%, representing a 49.3% decrease in use of SLNB. Efficacy was further supported by a significant reduction in SLNB according to an interrupted time series model (adjusted odds ratio, 0.26; 95% confidence interval, 0.07 to 0.90; P = .03). Extended follow-up showed that this effect was durable beyond the intervention period, with a 6-month mean reduction in SLNB of 15.6%.
Omission of SLNB led to higher rates of pathological node positivity during the intervention period (15.2% vs 8.8%), with all positive cases staged as pN1. Adjuvant therapy recommendations were similar between groups and driven by genomic testing, not nodal status. The intervention period also saw a decrease in referrals for lymphedema evaluation (3.6% vs. 6.2%).
How Might the Nudge System Be Implemented in Other Practices?
Although the SLNB nudge system was effective in the present study, likelihood of uptake among practices could vary widely, according to Anne M. Wallace, MD, professor of clinical surgery at UC San Diego Health and director of the Moores Comprehensive Breast Health Program.
On a fundamental level, not all centers use Epic software, which could present issues with compatibility, Dr. Wallace said in an interview. More importantly, she added, many institutions already have EHR-based alerts and reminders in place, so it is not always feasible to add a new nudge for every possible clinical scenario.
“Already there are so many little icons that we have to go through now when we close a note,” she said. “That’s why electronic medical records are becoming one of the leading stressors in medicine.”
This presents a more complex challenge, Dr. Wallace said, particularly as potentially practice-changing data are becoming available, and physicians may not have time to learn about them and integrate them into routine practice. She suggested that the present system may be most appropriate for oncologists in solo practice, or in small group practices where it is more challenging to have routine conversations about changing standards of care.
What Are the Risks of Using the Nudge System?
One of those conversations may surround the validity of the recommendation implemented in the present study.
Although the Society of Surgical Oncology recommends against SLNB in the described demographic, other experts, including Dr. Wallace, take a more nuanced view of the decision.
She noted that some patients with a chronological age of 70 may have a lower biological age, casting doubt on the legitimacy of the age threshold, and those near the threshold may wish to make the decision about staging for themselves.
Beyond these concerns, Dr. Wallace described two potential risks involved in forgoing SLNB.
First, there’s the potential for underestimating the tumor’s severity, she said, as this could mean a trip back to the operating room. A tumor initially thought to be low-grade might later be found to be high-grade, necessitating further surgery. Some patients might refuse additional surgery, leaving the more aggressive tumor untreated.
Second, the nudge system could complicate radiation treatment decisions, Dr. Wallace said. Without full nodal status, some radiation oncologists might push for additional radiation therapy, which incurs a greater treatment burden than SNLB.
What Are Some Alternatives to the Nudge System?
After discussing the strengths and weaknesses of the present EHR-based nudge system, and others like it, Dr. Wallace returned to the importance of ongoing communication among colleagues managing complex cases.
At UC San Diego Health, where oncologists meet weekly for a 2-hour breast cancer conference, “we nudge each other,” she said.
This study was supported by the Shear Family Foundation, UPMC eRecord Ambulatory Decision Support and Analytics, UPMC Hillman Cancer Center Biostatistics Facility, and National Institutes of Health. The investigators disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Amgen, the Lewin Group, and Milestone Pennsylvania, and others.
Participating surgeons noted that the reminder system added minimal friction to their workflow, as it did not require additional clicks or actions on the day of the patient visit, reported lead author Neil Carleton, PhD, of UPMC Hillman Cancer Center, Pittsburgh, and colleagues in JAMA Surgery (JAMA Surg. 2024 Jul 17. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.2407).
This effort to reduce the rate of SLNB stems from the Choosing Wisely campaign, which recommends against axillary staging in women 70 years and older with early-stage, clinically node-negative (cN0), hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer, the investigators said.
“These recommendations were developed because axillary staging did not impact survival, and rates of SLN positivity were low because of the tumor’s biological phenotype,” they wrote. “Even in older patients with tumors that exhibit concerning clinicopathologic features, limited nodal involvement does not often alter receipt of chemotherapy independently from genomic testing. Despite these recommendations, most women still receive axillary surgery.”
How Did the Nudge System Aim to Reduce the Rate of SLNB?
The nudge intervention involved adding a new column to the Epic schedule view, which flagged eligible patients during their first outpatient surgical consultation. The flag appeared as a caution sign or red clipboard icon. When surgeons hovered over the icon, a text box appeared, reminding them to consider omitting SLNB after a detailed review of core biopsy pathology and ultrasonographic imaging.
The intervention was evaluated at eight outpatient clinics within an integrated healthcare system that included seven breast surgical oncologists.
The study began with a 12-month preintervention period to serve as a control, during which time SLNB rate was determined via 194 patients in the target demographic. SLNB rate was again collected during the 12-month intervention period, which involved 193 patients meeting enrollment criteria. Between these periods, the investigators conducted a brief session lasting less than 30 minutes to introduce the surgeons to the rationale and design of the nudge column.
How Effective Was the Nudge System?
The intervention reduced the SLNB rate from 46.9% to 23.8%, representing a 49.3% decrease in use of SLNB. Efficacy was further supported by a significant reduction in SLNB according to an interrupted time series model (adjusted odds ratio, 0.26; 95% confidence interval, 0.07 to 0.90; P = .03). Extended follow-up showed that this effect was durable beyond the intervention period, with a 6-month mean reduction in SLNB of 15.6%.
Omission of SLNB led to higher rates of pathological node positivity during the intervention period (15.2% vs 8.8%), with all positive cases staged as pN1. Adjuvant therapy recommendations were similar between groups and driven by genomic testing, not nodal status. The intervention period also saw a decrease in referrals for lymphedema evaluation (3.6% vs. 6.2%).
How Might the Nudge System Be Implemented in Other Practices?
Although the SLNB nudge system was effective in the present study, likelihood of uptake among practices could vary widely, according to Anne M. Wallace, MD, professor of clinical surgery at UC San Diego Health and director of the Moores Comprehensive Breast Health Program.
On a fundamental level, not all centers use Epic software, which could present issues with compatibility, Dr. Wallace said in an interview. More importantly, she added, many institutions already have EHR-based alerts and reminders in place, so it is not always feasible to add a new nudge for every possible clinical scenario.
“Already there are so many little icons that we have to go through now when we close a note,” she said. “That’s why electronic medical records are becoming one of the leading stressors in medicine.”
This presents a more complex challenge, Dr. Wallace said, particularly as potentially practice-changing data are becoming available, and physicians may not have time to learn about them and integrate them into routine practice. She suggested that the present system may be most appropriate for oncologists in solo practice, or in small group practices where it is more challenging to have routine conversations about changing standards of care.
What Are the Risks of Using the Nudge System?
One of those conversations may surround the validity of the recommendation implemented in the present study.
Although the Society of Surgical Oncology recommends against SLNB in the described demographic, other experts, including Dr. Wallace, take a more nuanced view of the decision.
She noted that some patients with a chronological age of 70 may have a lower biological age, casting doubt on the legitimacy of the age threshold, and those near the threshold may wish to make the decision about staging for themselves.
Beyond these concerns, Dr. Wallace described two potential risks involved in forgoing SLNB.
First, there’s the potential for underestimating the tumor’s severity, she said, as this could mean a trip back to the operating room. A tumor initially thought to be low-grade might later be found to be high-grade, necessitating further surgery. Some patients might refuse additional surgery, leaving the more aggressive tumor untreated.
Second, the nudge system could complicate radiation treatment decisions, Dr. Wallace said. Without full nodal status, some radiation oncologists might push for additional radiation therapy, which incurs a greater treatment burden than SNLB.
What Are Some Alternatives to the Nudge System?
After discussing the strengths and weaknesses of the present EHR-based nudge system, and others like it, Dr. Wallace returned to the importance of ongoing communication among colleagues managing complex cases.
At UC San Diego Health, where oncologists meet weekly for a 2-hour breast cancer conference, “we nudge each other,” she said.
This study was supported by the Shear Family Foundation, UPMC eRecord Ambulatory Decision Support and Analytics, UPMC Hillman Cancer Center Biostatistics Facility, and National Institutes of Health. The investigators disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Amgen, the Lewin Group, and Milestone Pennsylvania, and others.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Cognitive Decline Minimal After Endocrine + CDK4/6 Inhibition in BC
“Patients who are diagnosed with advanced breast cancer and start their first-line treatment already show cognitive impairments due to their previous treatments. And luckily, our results show that during first-line treatment for advanced breast cancer with endocrine therapy, with or without a CDK4/6 inhibitor, further cognitive decline is minimal,” lead investigator Maryse Luijendijk, said during her presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
“It is well known that cancer patients can experience cognitive problems, such as memory loss, problems with concentration or with planning, during or following their treatment,” explained Ms. Luijendijk, a PhD candidate in the department of Psychosocial Research and Epidemiology at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, in Amsterdam. “Much is known about the effects of chemotherapy or irradiation to the brain, but evidence into endocrine therapy is scarce, which is surprising because cognitive effects are biologically plausible.
“We know that estrogen plays an important role in neuronal functioning and that certain types of endocrine therapies are able to cross the blood-brain barrier, where they may interact with estrogen receptors distributed widely throughout the brain … We know that CDK4/6 inhibitors may either negatively affect cognitive function by increased fatigue due to cytokine release or by interrupting the cell cycle of healthy cells, or positively, as they have been associated with reduced inflammation and remyelination.”
Initial results of the SONIA trial, reported at ASCO last year, examined overall and progression-free survival in patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer and no prior treatment for advanced disease. Findings for those who were randomized to treatment with nonsteroidal aromatase inhibition either with or without the addition of CDK4/6 inhibitors showed no between-group differences, explained Ms. Luijendijk.
The new results, described as being from the SONIA-EfFECT (Evaluation of cognitive functioning in patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with endocrine or combined therapy) trial, were based on the authors investigating cognitive functioning in the same cohort used in the SONIA trial plus a control group.
In SONIA-EfFECT, patients who participated in SONIA were asked to identify a female relative or friend without cancer to serve as a cancer-free control. Members of the 130-patient control group were matched for age, education, and computer use.
Participants in the SONIA trial and control group were asked to complete the Amsterdam Cognition Scan, an online neuropsychological test battery at baseline and again after 9 months of treatment. Of those patients from SONIA, 130 had received first-line treatment with aromatase inhibitors with CDK4/6 inhibition (Arm A) and 130 had received aromatase inhibitors without CDK4/6 inhibition (Arm B).
Baseline assessments for SONIA-EfFECT were completed for 260 patients from SONIA and the full 130-person control group. Follow-up assessments were completed for 119 members of the control group and 199 patients from the original SONIA trial (108 from Arm A, and 91 from Arm B). Patients from SONIA who switched to second-line treatment within 9 months were not retested.
Patients in both SONIA arms performed significantly worse than the controls on the domains of verbal memory, working memory, processing speed, executive function, and motor function. In both patient arms and the controls, standardized regression-based change scores showed limited decline in cognitive function over the 9-month interval. Minimal differences in cognitive change were observed between the patients treated with and without CDK4/6 inhibitors, and between patients and the controls, according to the abstract for SONIA-EfFECT, published in the program for the annual meeting of ASCO.
“At baseline, patients show worse cognitive function across all domains compared to the controls. And as expected, there were no differences between the two treatment arms,” Ms. Luijendijk explained. After 9 months of treatment, the testing showed limited further decline among patients, “and even some improvement on some tests,” with minimal differences between treatment arms “implying that cognitive function does not need to be an aspect when deciding on treatment.”
Ms. Luijendijk reported no relevant disclosures.
“Patients who are diagnosed with advanced breast cancer and start their first-line treatment already show cognitive impairments due to their previous treatments. And luckily, our results show that during first-line treatment for advanced breast cancer with endocrine therapy, with or without a CDK4/6 inhibitor, further cognitive decline is minimal,” lead investigator Maryse Luijendijk, said during her presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
“It is well known that cancer patients can experience cognitive problems, such as memory loss, problems with concentration or with planning, during or following their treatment,” explained Ms. Luijendijk, a PhD candidate in the department of Psychosocial Research and Epidemiology at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, in Amsterdam. “Much is known about the effects of chemotherapy or irradiation to the brain, but evidence into endocrine therapy is scarce, which is surprising because cognitive effects are biologically plausible.
“We know that estrogen plays an important role in neuronal functioning and that certain types of endocrine therapies are able to cross the blood-brain barrier, where they may interact with estrogen receptors distributed widely throughout the brain … We know that CDK4/6 inhibitors may either negatively affect cognitive function by increased fatigue due to cytokine release or by interrupting the cell cycle of healthy cells, or positively, as they have been associated with reduced inflammation and remyelination.”
Initial results of the SONIA trial, reported at ASCO last year, examined overall and progression-free survival in patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer and no prior treatment for advanced disease. Findings for those who were randomized to treatment with nonsteroidal aromatase inhibition either with or without the addition of CDK4/6 inhibitors showed no between-group differences, explained Ms. Luijendijk.
The new results, described as being from the SONIA-EfFECT (Evaluation of cognitive functioning in patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with endocrine or combined therapy) trial, were based on the authors investigating cognitive functioning in the same cohort used in the SONIA trial plus a control group.
In SONIA-EfFECT, patients who participated in SONIA were asked to identify a female relative or friend without cancer to serve as a cancer-free control. Members of the 130-patient control group were matched for age, education, and computer use.
Participants in the SONIA trial and control group were asked to complete the Amsterdam Cognition Scan, an online neuropsychological test battery at baseline and again after 9 months of treatment. Of those patients from SONIA, 130 had received first-line treatment with aromatase inhibitors with CDK4/6 inhibition (Arm A) and 130 had received aromatase inhibitors without CDK4/6 inhibition (Arm B).
Baseline assessments for SONIA-EfFECT were completed for 260 patients from SONIA and the full 130-person control group. Follow-up assessments were completed for 119 members of the control group and 199 patients from the original SONIA trial (108 from Arm A, and 91 from Arm B). Patients from SONIA who switched to second-line treatment within 9 months were not retested.
Patients in both SONIA arms performed significantly worse than the controls on the domains of verbal memory, working memory, processing speed, executive function, and motor function. In both patient arms and the controls, standardized regression-based change scores showed limited decline in cognitive function over the 9-month interval. Minimal differences in cognitive change were observed between the patients treated with and without CDK4/6 inhibitors, and between patients and the controls, according to the abstract for SONIA-EfFECT, published in the program for the annual meeting of ASCO.
“At baseline, patients show worse cognitive function across all domains compared to the controls. And as expected, there were no differences between the two treatment arms,” Ms. Luijendijk explained. After 9 months of treatment, the testing showed limited further decline among patients, “and even some improvement on some tests,” with minimal differences between treatment arms “implying that cognitive function does not need to be an aspect when deciding on treatment.”
Ms. Luijendijk reported no relevant disclosures.
“Patients who are diagnosed with advanced breast cancer and start their first-line treatment already show cognitive impairments due to their previous treatments. And luckily, our results show that during first-line treatment for advanced breast cancer with endocrine therapy, with or without a CDK4/6 inhibitor, further cognitive decline is minimal,” lead investigator Maryse Luijendijk, said during her presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
“It is well known that cancer patients can experience cognitive problems, such as memory loss, problems with concentration or with planning, during or following their treatment,” explained Ms. Luijendijk, a PhD candidate in the department of Psychosocial Research and Epidemiology at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, in Amsterdam. “Much is known about the effects of chemotherapy or irradiation to the brain, but evidence into endocrine therapy is scarce, which is surprising because cognitive effects are biologically plausible.
“We know that estrogen plays an important role in neuronal functioning and that certain types of endocrine therapies are able to cross the blood-brain barrier, where they may interact with estrogen receptors distributed widely throughout the brain … We know that CDK4/6 inhibitors may either negatively affect cognitive function by increased fatigue due to cytokine release or by interrupting the cell cycle of healthy cells, or positively, as they have been associated with reduced inflammation and remyelination.”
Initial results of the SONIA trial, reported at ASCO last year, examined overall and progression-free survival in patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer and no prior treatment for advanced disease. Findings for those who were randomized to treatment with nonsteroidal aromatase inhibition either with or without the addition of CDK4/6 inhibitors showed no between-group differences, explained Ms. Luijendijk.
The new results, described as being from the SONIA-EfFECT (Evaluation of cognitive functioning in patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with endocrine or combined therapy) trial, were based on the authors investigating cognitive functioning in the same cohort used in the SONIA trial plus a control group.
In SONIA-EfFECT, patients who participated in SONIA were asked to identify a female relative or friend without cancer to serve as a cancer-free control. Members of the 130-patient control group were matched for age, education, and computer use.
Participants in the SONIA trial and control group were asked to complete the Amsterdam Cognition Scan, an online neuropsychological test battery at baseline and again after 9 months of treatment. Of those patients from SONIA, 130 had received first-line treatment with aromatase inhibitors with CDK4/6 inhibition (Arm A) and 130 had received aromatase inhibitors without CDK4/6 inhibition (Arm B).
Baseline assessments for SONIA-EfFECT were completed for 260 patients from SONIA and the full 130-person control group. Follow-up assessments were completed for 119 members of the control group and 199 patients from the original SONIA trial (108 from Arm A, and 91 from Arm B). Patients from SONIA who switched to second-line treatment within 9 months were not retested.
Patients in both SONIA arms performed significantly worse than the controls on the domains of verbal memory, working memory, processing speed, executive function, and motor function. In both patient arms and the controls, standardized regression-based change scores showed limited decline in cognitive function over the 9-month interval. Minimal differences in cognitive change were observed between the patients treated with and without CDK4/6 inhibitors, and between patients and the controls, according to the abstract for SONIA-EfFECT, published in the program for the annual meeting of ASCO.
“At baseline, patients show worse cognitive function across all domains compared to the controls. And as expected, there were no differences between the two treatment arms,” Ms. Luijendijk explained. After 9 months of treatment, the testing showed limited further decline among patients, “and even some improvement on some tests,” with minimal differences between treatment arms “implying that cognitive function does not need to be an aspect when deciding on treatment.”
Ms. Luijendijk reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM ASCO 2024