User login
NIAID trial to test asthma drug in disadvantaged urban children
The Prevention of Asthma Exacerbations Using Dupilumab in Urban Children and Adolescents (PANDA) trial was launched in order to examine the effects of treatment on children with poorly controlled allergic asthma who live in low-income urban environments in the United States, according to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Black and Hispanic children who live in these environments are at particularly high risk for asthma and are prone to attacks. These children and adolescents often have many allergies and are exposed to both high levels of indoor allergens and traffic-related pollution, which can make their asthma even more difficult to control, according to a June 2 NIAID press release.
PANDA is a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of dupilumab adjunctive therapy for the reduction of asthma exacerbations in urban children and adolescents 6-17 years with T2-high exacerbation-prone asthma. Approximately 240 participants will be randomized 2:1 to one of two study arms: 1) guidelines-based asthma treatment plus dupilumab, or 2) guidelines-based asthma treatment plus placebo. The planned study treatment will continue for 1 year with an additional 3 months of follow-up following completion of study treatment, according to the study details.
In an earlier study, NIAID-supported investigators identified numerous networks of genes that are activated together and are associated with asthma attacks in minority children and adolescents living in low-income urban settings
“We need to find out how well approved asthma drugs work for disadvantaged children of color living in urban areas, and whether biological markers can help predict how the drugs affect their asthma,” NIAID director Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said in the release. “The PANDA trial is an important step toward these goals.”
Participant criteria for the study include children of either sex, ages 6-17 years, who live in prespecified urban areas. Participants must have a diagnosis of asthma and must have had at least two asthma exacerbations in the prior year (defined as a requirement for systemic corticosteroids and/or hospitalization). At the screening visit, participants must have the following requirements for asthma controller medication: For children ages 6-11 years: treatments with at least fluticasone 250 mcg dry powder inhaler (DPI) one puff twice daily or its equivalent; for children ages 12 years and older, treatment with at least fluticasone 250 mcg plus long-acting beta agonist (LABA) DPI one puff twice daily or its equivalent.
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05347771Location: The NIAID-funded Childhood Asthma in Urban Settings (CAUSE) Network is conducting the study at seven medical centers located in Aurora, Colo.; Boston; Chicago; Cincinnati; New York, and Washington, D.C.
Sponsor: NIAID, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi are cofunding the phase 2 trial.
Study start date: April 2022
Expected completion Date: March 31, 2025
The Prevention of Asthma Exacerbations Using Dupilumab in Urban Children and Adolescents (PANDA) trial was launched in order to examine the effects of treatment on children with poorly controlled allergic asthma who live in low-income urban environments in the United States, according to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Black and Hispanic children who live in these environments are at particularly high risk for asthma and are prone to attacks. These children and adolescents often have many allergies and are exposed to both high levels of indoor allergens and traffic-related pollution, which can make their asthma even more difficult to control, according to a June 2 NIAID press release.
PANDA is a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of dupilumab adjunctive therapy for the reduction of asthma exacerbations in urban children and adolescents 6-17 years with T2-high exacerbation-prone asthma. Approximately 240 participants will be randomized 2:1 to one of two study arms: 1) guidelines-based asthma treatment plus dupilumab, or 2) guidelines-based asthma treatment plus placebo. The planned study treatment will continue for 1 year with an additional 3 months of follow-up following completion of study treatment, according to the study details.
In an earlier study, NIAID-supported investigators identified numerous networks of genes that are activated together and are associated with asthma attacks in minority children and adolescents living in low-income urban settings
“We need to find out how well approved asthma drugs work for disadvantaged children of color living in urban areas, and whether biological markers can help predict how the drugs affect their asthma,” NIAID director Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said in the release. “The PANDA trial is an important step toward these goals.”
Participant criteria for the study include children of either sex, ages 6-17 years, who live in prespecified urban areas. Participants must have a diagnosis of asthma and must have had at least two asthma exacerbations in the prior year (defined as a requirement for systemic corticosteroids and/or hospitalization). At the screening visit, participants must have the following requirements for asthma controller medication: For children ages 6-11 years: treatments with at least fluticasone 250 mcg dry powder inhaler (DPI) one puff twice daily or its equivalent; for children ages 12 years and older, treatment with at least fluticasone 250 mcg plus long-acting beta agonist (LABA) DPI one puff twice daily or its equivalent.
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05347771Location: The NIAID-funded Childhood Asthma in Urban Settings (CAUSE) Network is conducting the study at seven medical centers located in Aurora, Colo.; Boston; Chicago; Cincinnati; New York, and Washington, D.C.
Sponsor: NIAID, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi are cofunding the phase 2 trial.
Study start date: April 2022
Expected completion Date: March 31, 2025
The Prevention of Asthma Exacerbations Using Dupilumab in Urban Children and Adolescents (PANDA) trial was launched in order to examine the effects of treatment on children with poorly controlled allergic asthma who live in low-income urban environments in the United States, according to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Black and Hispanic children who live in these environments are at particularly high risk for asthma and are prone to attacks. These children and adolescents often have many allergies and are exposed to both high levels of indoor allergens and traffic-related pollution, which can make their asthma even more difficult to control, according to a June 2 NIAID press release.
PANDA is a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of dupilumab adjunctive therapy for the reduction of asthma exacerbations in urban children and adolescents 6-17 years with T2-high exacerbation-prone asthma. Approximately 240 participants will be randomized 2:1 to one of two study arms: 1) guidelines-based asthma treatment plus dupilumab, or 2) guidelines-based asthma treatment plus placebo. The planned study treatment will continue for 1 year with an additional 3 months of follow-up following completion of study treatment, according to the study details.
In an earlier study, NIAID-supported investigators identified numerous networks of genes that are activated together and are associated with asthma attacks in minority children and adolescents living in low-income urban settings
“We need to find out how well approved asthma drugs work for disadvantaged children of color living in urban areas, and whether biological markers can help predict how the drugs affect their asthma,” NIAID director Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said in the release. “The PANDA trial is an important step toward these goals.”
Participant criteria for the study include children of either sex, ages 6-17 years, who live in prespecified urban areas. Participants must have a diagnosis of asthma and must have had at least two asthma exacerbations in the prior year (defined as a requirement for systemic corticosteroids and/or hospitalization). At the screening visit, participants must have the following requirements for asthma controller medication: For children ages 6-11 years: treatments with at least fluticasone 250 mcg dry powder inhaler (DPI) one puff twice daily or its equivalent; for children ages 12 years and older, treatment with at least fluticasone 250 mcg plus long-acting beta agonist (LABA) DPI one puff twice daily or its equivalent.
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05347771Location: The NIAID-funded Childhood Asthma in Urban Settings (CAUSE) Network is conducting the study at seven medical centers located in Aurora, Colo.; Boston; Chicago; Cincinnati; New York, and Washington, D.C.
Sponsor: NIAID, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi are cofunding the phase 2 trial.
Study start date: April 2022
Expected completion Date: March 31, 2025
‘Smart inhalers’ may help diagnose and treat asthma – if used
After years going on and off medications for occasional asthma symptoms, things went downhill for Brian Blome in November 2020. The retired carpenter started feeling short of breath and wheezing during bike rides. At home, he struggled with chores.
“I was having a hard time climbing a flight of stairs, just doing laundry,” said Mr. Blome, who lives in the Chicago suburb of Palatine.
To get things under control, he saw an allergist and started regular medications – two tablets, two nasal sprays, and inhaled corticosteroids each day, plus an albuterol inhaler for flare-ups.
The inhalers have an extra feature: an electronic monitor that attaches to the device and automatically tracks where and when the medication is used. Bluetooth sends this information to an app on the patient’s mobile phone and to a dashboard where the medical team can see, at a glance, when symptoms are popping up and how regularly medications are taken – leading to the devices often being called “smart inhalers.”
At the 2022 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology conference in Phoenix, researchers explained how digital monitoring devices can help diagnose and treat hard-to-control asthma, potentially reducing the need for oral steroids or biologic therapies.
Even though electric monitors have been on the market for years, their use has been slow to catch on because of uncertainties around insurance coverage, liability, and how to manage and best use the data. One recent study said these devices cost $100-$500, but that price depends on many things, such as insurance.
About 17% of adult asthma patients have “difficult-to-control” asthma, meaning they limit their activity because of breathing symptoms and use reliever medications multiple times a week.
But research suggests that correcting inhaling technique and sticking to the use of the medications can cut that 17% down to just 3.7%, said Mr. Blome’s allergist, Giselle Mosnaim, MD, of NorthShore University HealthSystem in Glenview, Ill. Dr. Mosnaim spoke about digital monitoring at a conference session on digital technologies for asthma management.
A study of more than 5,000 asthma patients “showed that, if you have critical errors in inhaler technique, this leads to worse asthma outcomes and increased asthma exacerbations,” she said. It also shows that, despite new devices and new technologies, “we still have poor inhaler technique.”
Yet adherence is poorly gauged by doctors and patient self-reporting. “The ideal measure of adherence should be objective, accurate, and unobtrusive to minimize impact on patient behavior and allow reliable data collection in real-world settings,” Dr. Mosnaim said. “So electronic medication monitors are the gold standard.”
Improving use
Patients not following instructions or guidelines “is something we saw nonstop with kids,” said Caroline Moassessi, founder of the allergy and asthma blog Gratefulfoodie.com who formerly served on a regional board of the American Lung Association. She’s also the mother of two asthmatic children, now in college, who years ago used electronic medication monitors as part of a research trial.
They were “unimpressed – mostly since I think they thought their asthma was controlled,” she said. “When patients are not in crisis, they don’t manage their asthma well.”
Even in research studies such as the one Rachelle Ramsey, PhD, presented at the conference, it’s not only hard to determine if better adherence leads to improved health, but when.
“For example, does your adherence this week impact your asthma control this week, or does it impact your asthma control next week? Or is it even further out? Do you need to have some level of adherence over the course of a month in order to have better outcomes at the end of that month?” said Dr. Ramsey, a pediatric research psychologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I think it’s a little complicated.”
That said, results from several small studies do show a connection between remote monitoring and better clinical outcomes. One study enrolled asthma patients in the United Kingdom, and another was done by Dr. Mosnaim with Chicago-area patients.
In the U.K. quality improvement project, nurses asked patients with difficult-to-control asthma if they knew how to use their inhalers and were following treatment guidelines.
Those who said “yes” were invited to swap their steroid/inhalers for a controller fitted with a device that tracks use and measures acoustics to test inhaler technique. After 28 days of monitoring, many people in the study had better clinical outcomes.
And after 3 months of digital monitoring, patients didn’t use their rescue medication quite as often.
Mr. Blome has seen a marked improvement in his asthma since starting regular appointments and getting back on daily medications a year and a half ago. He says that now and then, he has wheezing and shortness of breath, usually while biking or exercising. But those symptoms aren’t as severe or frequent as before.
From a doctor’s perspective, “digital inhaler systems allow me to discern patterns in order to determine what triggers his asthma symptoms and to adjust medications at different times of the year,” Dr. Mosnaim said.
Electronic systems can monitor pollen counts and air quality as well as how often a patient uses a quick reliever medication. Thus, she said, tracking these measures year-round could raise attention to impending asthma attacks and suggest when to increase the dose of controller medications or add other treatments.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
After years going on and off medications for occasional asthma symptoms, things went downhill for Brian Blome in November 2020. The retired carpenter started feeling short of breath and wheezing during bike rides. At home, he struggled with chores.
“I was having a hard time climbing a flight of stairs, just doing laundry,” said Mr. Blome, who lives in the Chicago suburb of Palatine.
To get things under control, he saw an allergist and started regular medications – two tablets, two nasal sprays, and inhaled corticosteroids each day, plus an albuterol inhaler for flare-ups.
The inhalers have an extra feature: an electronic monitor that attaches to the device and automatically tracks where and when the medication is used. Bluetooth sends this information to an app on the patient’s mobile phone and to a dashboard where the medical team can see, at a glance, when symptoms are popping up and how regularly medications are taken – leading to the devices often being called “smart inhalers.”
At the 2022 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology conference in Phoenix, researchers explained how digital monitoring devices can help diagnose and treat hard-to-control asthma, potentially reducing the need for oral steroids or biologic therapies.
Even though electric monitors have been on the market for years, their use has been slow to catch on because of uncertainties around insurance coverage, liability, and how to manage and best use the data. One recent study said these devices cost $100-$500, but that price depends on many things, such as insurance.
About 17% of adult asthma patients have “difficult-to-control” asthma, meaning they limit their activity because of breathing symptoms and use reliever medications multiple times a week.
But research suggests that correcting inhaling technique and sticking to the use of the medications can cut that 17% down to just 3.7%, said Mr. Blome’s allergist, Giselle Mosnaim, MD, of NorthShore University HealthSystem in Glenview, Ill. Dr. Mosnaim spoke about digital monitoring at a conference session on digital technologies for asthma management.
A study of more than 5,000 asthma patients “showed that, if you have critical errors in inhaler technique, this leads to worse asthma outcomes and increased asthma exacerbations,” she said. It also shows that, despite new devices and new technologies, “we still have poor inhaler technique.”
Yet adherence is poorly gauged by doctors and patient self-reporting. “The ideal measure of adherence should be objective, accurate, and unobtrusive to minimize impact on patient behavior and allow reliable data collection in real-world settings,” Dr. Mosnaim said. “So electronic medication monitors are the gold standard.”
Improving use
Patients not following instructions or guidelines “is something we saw nonstop with kids,” said Caroline Moassessi, founder of the allergy and asthma blog Gratefulfoodie.com who formerly served on a regional board of the American Lung Association. She’s also the mother of two asthmatic children, now in college, who years ago used electronic medication monitors as part of a research trial.
They were “unimpressed – mostly since I think they thought their asthma was controlled,” she said. “When patients are not in crisis, they don’t manage their asthma well.”
Even in research studies such as the one Rachelle Ramsey, PhD, presented at the conference, it’s not only hard to determine if better adherence leads to improved health, but when.
“For example, does your adherence this week impact your asthma control this week, or does it impact your asthma control next week? Or is it even further out? Do you need to have some level of adherence over the course of a month in order to have better outcomes at the end of that month?” said Dr. Ramsey, a pediatric research psychologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I think it’s a little complicated.”
That said, results from several small studies do show a connection between remote monitoring and better clinical outcomes. One study enrolled asthma patients in the United Kingdom, and another was done by Dr. Mosnaim with Chicago-area patients.
In the U.K. quality improvement project, nurses asked patients with difficult-to-control asthma if they knew how to use their inhalers and were following treatment guidelines.
Those who said “yes” were invited to swap their steroid/inhalers for a controller fitted with a device that tracks use and measures acoustics to test inhaler technique. After 28 days of monitoring, many people in the study had better clinical outcomes.
And after 3 months of digital monitoring, patients didn’t use their rescue medication quite as often.
Mr. Blome has seen a marked improvement in his asthma since starting regular appointments and getting back on daily medications a year and a half ago. He says that now and then, he has wheezing and shortness of breath, usually while biking or exercising. But those symptoms aren’t as severe or frequent as before.
From a doctor’s perspective, “digital inhaler systems allow me to discern patterns in order to determine what triggers his asthma symptoms and to adjust medications at different times of the year,” Dr. Mosnaim said.
Electronic systems can monitor pollen counts and air quality as well as how often a patient uses a quick reliever medication. Thus, she said, tracking these measures year-round could raise attention to impending asthma attacks and suggest when to increase the dose of controller medications or add other treatments.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
After years going on and off medications for occasional asthma symptoms, things went downhill for Brian Blome in November 2020. The retired carpenter started feeling short of breath and wheezing during bike rides. At home, he struggled with chores.
“I was having a hard time climbing a flight of stairs, just doing laundry,” said Mr. Blome, who lives in the Chicago suburb of Palatine.
To get things under control, he saw an allergist and started regular medications – two tablets, two nasal sprays, and inhaled corticosteroids each day, plus an albuterol inhaler for flare-ups.
The inhalers have an extra feature: an electronic monitor that attaches to the device and automatically tracks where and when the medication is used. Bluetooth sends this information to an app on the patient’s mobile phone and to a dashboard where the medical team can see, at a glance, when symptoms are popping up and how regularly medications are taken – leading to the devices often being called “smart inhalers.”
At the 2022 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology conference in Phoenix, researchers explained how digital monitoring devices can help diagnose and treat hard-to-control asthma, potentially reducing the need for oral steroids or biologic therapies.
Even though electric monitors have been on the market for years, their use has been slow to catch on because of uncertainties around insurance coverage, liability, and how to manage and best use the data. One recent study said these devices cost $100-$500, but that price depends on many things, such as insurance.
About 17% of adult asthma patients have “difficult-to-control” asthma, meaning they limit their activity because of breathing symptoms and use reliever medications multiple times a week.
But research suggests that correcting inhaling technique and sticking to the use of the medications can cut that 17% down to just 3.7%, said Mr. Blome’s allergist, Giselle Mosnaim, MD, of NorthShore University HealthSystem in Glenview, Ill. Dr. Mosnaim spoke about digital monitoring at a conference session on digital technologies for asthma management.
A study of more than 5,000 asthma patients “showed that, if you have critical errors in inhaler technique, this leads to worse asthma outcomes and increased asthma exacerbations,” she said. It also shows that, despite new devices and new technologies, “we still have poor inhaler technique.”
Yet adherence is poorly gauged by doctors and patient self-reporting. “The ideal measure of adherence should be objective, accurate, and unobtrusive to minimize impact on patient behavior and allow reliable data collection in real-world settings,” Dr. Mosnaim said. “So electronic medication monitors are the gold standard.”
Improving use
Patients not following instructions or guidelines “is something we saw nonstop with kids,” said Caroline Moassessi, founder of the allergy and asthma blog Gratefulfoodie.com who formerly served on a regional board of the American Lung Association. She’s also the mother of two asthmatic children, now in college, who years ago used electronic medication monitors as part of a research trial.
They were “unimpressed – mostly since I think they thought their asthma was controlled,” she said. “When patients are not in crisis, they don’t manage their asthma well.”
Even in research studies such as the one Rachelle Ramsey, PhD, presented at the conference, it’s not only hard to determine if better adherence leads to improved health, but when.
“For example, does your adherence this week impact your asthma control this week, or does it impact your asthma control next week? Or is it even further out? Do you need to have some level of adherence over the course of a month in order to have better outcomes at the end of that month?” said Dr. Ramsey, a pediatric research psychologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I think it’s a little complicated.”
That said, results from several small studies do show a connection between remote monitoring and better clinical outcomes. One study enrolled asthma patients in the United Kingdom, and another was done by Dr. Mosnaim with Chicago-area patients.
In the U.K. quality improvement project, nurses asked patients with difficult-to-control asthma if they knew how to use their inhalers and were following treatment guidelines.
Those who said “yes” were invited to swap their steroid/inhalers for a controller fitted with a device that tracks use and measures acoustics to test inhaler technique. After 28 days of monitoring, many people in the study had better clinical outcomes.
And after 3 months of digital monitoring, patients didn’t use their rescue medication quite as often.
Mr. Blome has seen a marked improvement in his asthma since starting regular appointments and getting back on daily medications a year and a half ago. He says that now and then, he has wheezing and shortness of breath, usually while biking or exercising. But those symptoms aren’t as severe or frequent as before.
From a doctor’s perspective, “digital inhaler systems allow me to discern patterns in order to determine what triggers his asthma symptoms and to adjust medications at different times of the year,” Dr. Mosnaim said.
Electronic systems can monitor pollen counts and air quality as well as how often a patient uses a quick reliever medication. Thus, she said, tracking these measures year-round could raise attention to impending asthma attacks and suggest when to increase the dose of controller medications or add other treatments.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Food allergy risk not greater in C-section infants
Cesarean births are not likely linked to an elevated risk of food allergy during the first year of life, an Australian study found.
Published online in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, the findings may help assess the risks and benefits of cesarean delivery and reassure women who require it that their babies are not more likely to develop food allergy, according to Rachel L. Peters, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Murdoch Child Research Institute (MCRI) in Melbourne, and colleagues.
Dr. Peters’ group undertook the analysis to clarify a possible association between mode of delivery and food allergy risk, which has remained unclear owing to the absence of studies with both challenge-proven food allergy outcomes and detailed information on the type and timing of cesarean delivery.
“The infant immune system undergoes rapid development during the neonatal period,” Dr. Peters said in an MCRI press release, and the mode of delivery may interfere with the normal development of the immune system. “Babies born by cesarean have less exposure to the bacteria from the mother’s gut and vagina, which influence the composition of the baby’s microbiome and immune system development. However, this doesn’t appear to play a major role in the development of food allergy,” she said.
The HealthNuts study
In the period 2007-2011, the longitudinal population-based HealthNuts cohort study enrolled 5,276 12-month-olds who underwent skin prick testing and oral food challenge for sensitization to egg, peanut, sesame, and either shellfish or cow’s milk. It linked the resulting data to additional birth statistics from the Victorian Perinatal Data Collection when children turned 6.
Birth data were obtained on 2,045 babies, and in this subgroup with linked data, 30% were born by cesarean – similar to the 31.7% of U.S. cesarean births in 2019 – and 12.7% of these had food allergy versus 13.2% of those delivered vaginally.
Compared with vaginal birth, C-section was not associated with the risk of food allergy (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.95, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.70-0.30).
Nor did the timing of the C-section have an effect. Cesarean delivery either before labor or after onset of labor was not associated with the risk of food allergy (aOR, 0.83, 95% CI, 0.55-1.23) and aOR, 1.13, 95% CI, 0.75-1.72), respectively.
Compared with vaginal delivery, elective or emergency cesarean was not associated with food allergy risk (aOR, 1.05, 95% CI, 0.71-1.55, and aOR, 0.86, 95% CI, 0.56-1.31).
Similarly, no evidence emerged of an effect modification by breastfeeding, older siblings, pet dog ownership, or maternal allergy.
“This study is helpful because in addition to blood and skin tests, it also used food challenge, which is the gold standard,” Terri Brown-Whitehorn, MD, an attending physician in the division of allergy and immunology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview. “If no actual food is given, the other tests could lead to false positives.”
Dr. Brown-Whitehorn, who was not involved in the MCRI research, said the findings are not likely to affect most decisions about C-sections because most are not voluntary. “But if a mother had a first baby by emergency cesarean section, she might be given the option of having the next one by the same method.”
She said the current advice is to introduce even high-risk foods to a child’s diet early on to ward off the development of food allergies.
According to the microbial exposure hypothesis, it was previously thought that a potential link between cesarean birth and allergy might reflect differences in early exposure to maternal flora beneficial to the immune system in the vagina during delivery. A C-section might bypass the opportunity for neonatal gut colonization with maternal gut and vaginal flora, thereby raising allergy risk. A 2018 meta-analysis, for example, suggested cesarean birth could raise the risk for food allergies by 21%.
In other research from HealthNuts, 30% of child peanut allergy and 90% of egg allergy appear to resolve naturally by age 6. These numbers are somewhat higher than what Dr. Brown-Whitehorn sees. “We find that about 20% of peanut allergies and about 70% or 80% – maybe a bit less – of egg allergies resolve by age 6.”
This research was supported by the National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia, the Ilhan Food Allergy Foundation, AnaphylaxiStop, the Charles and Sylvia Viertel Medical Research Foundation, the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program, and the Melbourne Children’s Clinician-Scientist Fellowship.
Dr. Peters disclosed no competing interests. Several coauthors reported research support or employment with private companies and one is the inventor of an MCRI-held patent. Dr. Brown-Whitehorn had no competing interests to disclose.
Cesarean births are not likely linked to an elevated risk of food allergy during the first year of life, an Australian study found.
Published online in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, the findings may help assess the risks and benefits of cesarean delivery and reassure women who require it that their babies are not more likely to develop food allergy, according to Rachel L. Peters, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Murdoch Child Research Institute (MCRI) in Melbourne, and colleagues.
Dr. Peters’ group undertook the analysis to clarify a possible association between mode of delivery and food allergy risk, which has remained unclear owing to the absence of studies with both challenge-proven food allergy outcomes and detailed information on the type and timing of cesarean delivery.
“The infant immune system undergoes rapid development during the neonatal period,” Dr. Peters said in an MCRI press release, and the mode of delivery may interfere with the normal development of the immune system. “Babies born by cesarean have less exposure to the bacteria from the mother’s gut and vagina, which influence the composition of the baby’s microbiome and immune system development. However, this doesn’t appear to play a major role in the development of food allergy,” she said.
The HealthNuts study
In the period 2007-2011, the longitudinal population-based HealthNuts cohort study enrolled 5,276 12-month-olds who underwent skin prick testing and oral food challenge for sensitization to egg, peanut, sesame, and either shellfish or cow’s milk. It linked the resulting data to additional birth statistics from the Victorian Perinatal Data Collection when children turned 6.
Birth data were obtained on 2,045 babies, and in this subgroup with linked data, 30% were born by cesarean – similar to the 31.7% of U.S. cesarean births in 2019 – and 12.7% of these had food allergy versus 13.2% of those delivered vaginally.
Compared with vaginal birth, C-section was not associated with the risk of food allergy (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.95, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.70-0.30).
Nor did the timing of the C-section have an effect. Cesarean delivery either before labor or after onset of labor was not associated with the risk of food allergy (aOR, 0.83, 95% CI, 0.55-1.23) and aOR, 1.13, 95% CI, 0.75-1.72), respectively.
Compared with vaginal delivery, elective or emergency cesarean was not associated with food allergy risk (aOR, 1.05, 95% CI, 0.71-1.55, and aOR, 0.86, 95% CI, 0.56-1.31).
Similarly, no evidence emerged of an effect modification by breastfeeding, older siblings, pet dog ownership, or maternal allergy.
“This study is helpful because in addition to blood and skin tests, it also used food challenge, which is the gold standard,” Terri Brown-Whitehorn, MD, an attending physician in the division of allergy and immunology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview. “If no actual food is given, the other tests could lead to false positives.”
Dr. Brown-Whitehorn, who was not involved in the MCRI research, said the findings are not likely to affect most decisions about C-sections because most are not voluntary. “But if a mother had a first baby by emergency cesarean section, she might be given the option of having the next one by the same method.”
She said the current advice is to introduce even high-risk foods to a child’s diet early on to ward off the development of food allergies.
According to the microbial exposure hypothesis, it was previously thought that a potential link between cesarean birth and allergy might reflect differences in early exposure to maternal flora beneficial to the immune system in the vagina during delivery. A C-section might bypass the opportunity for neonatal gut colonization with maternal gut and vaginal flora, thereby raising allergy risk. A 2018 meta-analysis, for example, suggested cesarean birth could raise the risk for food allergies by 21%.
In other research from HealthNuts, 30% of child peanut allergy and 90% of egg allergy appear to resolve naturally by age 6. These numbers are somewhat higher than what Dr. Brown-Whitehorn sees. “We find that about 20% of peanut allergies and about 70% or 80% – maybe a bit less – of egg allergies resolve by age 6.”
This research was supported by the National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia, the Ilhan Food Allergy Foundation, AnaphylaxiStop, the Charles and Sylvia Viertel Medical Research Foundation, the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program, and the Melbourne Children’s Clinician-Scientist Fellowship.
Dr. Peters disclosed no competing interests. Several coauthors reported research support or employment with private companies and one is the inventor of an MCRI-held patent. Dr. Brown-Whitehorn had no competing interests to disclose.
Cesarean births are not likely linked to an elevated risk of food allergy during the first year of life, an Australian study found.
Published online in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, the findings may help assess the risks and benefits of cesarean delivery and reassure women who require it that their babies are not more likely to develop food allergy, according to Rachel L. Peters, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Murdoch Child Research Institute (MCRI) in Melbourne, and colleagues.
Dr. Peters’ group undertook the analysis to clarify a possible association between mode of delivery and food allergy risk, which has remained unclear owing to the absence of studies with both challenge-proven food allergy outcomes and detailed information on the type and timing of cesarean delivery.
“The infant immune system undergoes rapid development during the neonatal period,” Dr. Peters said in an MCRI press release, and the mode of delivery may interfere with the normal development of the immune system. “Babies born by cesarean have less exposure to the bacteria from the mother’s gut and vagina, which influence the composition of the baby’s microbiome and immune system development. However, this doesn’t appear to play a major role in the development of food allergy,” she said.
The HealthNuts study
In the period 2007-2011, the longitudinal population-based HealthNuts cohort study enrolled 5,276 12-month-olds who underwent skin prick testing and oral food challenge for sensitization to egg, peanut, sesame, and either shellfish or cow’s milk. It linked the resulting data to additional birth statistics from the Victorian Perinatal Data Collection when children turned 6.
Birth data were obtained on 2,045 babies, and in this subgroup with linked data, 30% were born by cesarean – similar to the 31.7% of U.S. cesarean births in 2019 – and 12.7% of these had food allergy versus 13.2% of those delivered vaginally.
Compared with vaginal birth, C-section was not associated with the risk of food allergy (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.95, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.70-0.30).
Nor did the timing of the C-section have an effect. Cesarean delivery either before labor or after onset of labor was not associated with the risk of food allergy (aOR, 0.83, 95% CI, 0.55-1.23) and aOR, 1.13, 95% CI, 0.75-1.72), respectively.
Compared with vaginal delivery, elective or emergency cesarean was not associated with food allergy risk (aOR, 1.05, 95% CI, 0.71-1.55, and aOR, 0.86, 95% CI, 0.56-1.31).
Similarly, no evidence emerged of an effect modification by breastfeeding, older siblings, pet dog ownership, or maternal allergy.
“This study is helpful because in addition to blood and skin tests, it also used food challenge, which is the gold standard,” Terri Brown-Whitehorn, MD, an attending physician in the division of allergy and immunology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview. “If no actual food is given, the other tests could lead to false positives.”
Dr. Brown-Whitehorn, who was not involved in the MCRI research, said the findings are not likely to affect most decisions about C-sections because most are not voluntary. “But if a mother had a first baby by emergency cesarean section, she might be given the option of having the next one by the same method.”
She said the current advice is to introduce even high-risk foods to a child’s diet early on to ward off the development of food allergies.
According to the microbial exposure hypothesis, it was previously thought that a potential link between cesarean birth and allergy might reflect differences in early exposure to maternal flora beneficial to the immune system in the vagina during delivery. A C-section might bypass the opportunity for neonatal gut colonization with maternal gut and vaginal flora, thereby raising allergy risk. A 2018 meta-analysis, for example, suggested cesarean birth could raise the risk for food allergies by 21%.
In other research from HealthNuts, 30% of child peanut allergy and 90% of egg allergy appear to resolve naturally by age 6. These numbers are somewhat higher than what Dr. Brown-Whitehorn sees. “We find that about 20% of peanut allergies and about 70% or 80% – maybe a bit less – of egg allergies resolve by age 6.”
This research was supported by the National Health & Medical Research Council of Australia, the Ilhan Food Allergy Foundation, AnaphylaxiStop, the Charles and Sylvia Viertel Medical Research Foundation, the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program, and the Melbourne Children’s Clinician-Scientist Fellowship.
Dr. Peters disclosed no competing interests. Several coauthors reported research support or employment with private companies and one is the inventor of an MCRI-held patent. Dr. Brown-Whitehorn had no competing interests to disclose.
FROM JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
NAVIGATOR steers uncontrolled asthma toward calmer seas
SAN FRANCISCO – Nearly half of all patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma who received a full course of the biologic agent tezepelumab (Tezspire) in the NAVIGATOR trial had a complete response to treatment at 1 year, results of a prespecified exploratory analysis indicated.
Among 471 patients assigned to tezepelumab who completed the on-treatment period of the phase 3 randomized trial, 46% had a complete response at 52 weeks, compared with 24% of patients assigned to placebo.
Complete response was defined as reduction in exacerbations of at least 50% over the previous year, improvement from baseline in Asthma Control Questionnaire 6 (ACQ-6) total score of at least 0.5 points, improvement in prebronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (pre-BD FEV1), and physician-assessed Clinical Global Impression measure of clinical change (CGI-C) score.
“These data further support the efficacy of tezepelumab in a broad population of patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma,” said Njira Lugogo, MD, of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Dr. Lugogo presented results of the exploratory analysis at the American Thoracic Society’s international conference.
Exacerbations reduced, lung function improved
Primary results from NAVIGATOR, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, showed that patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma randomly assigned to tezepelumab had fewer exacerbations and better lung function, asthma control, and health-related quality of life compared with patients assigned to placebo.
The investigators noted that approximately 10% of patients with asthma have symptoms and exacerbations despite maximal standard-of-care controller therapy.
Tezepelumab is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits action of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), an epithelial cytokine that is released in response to airborne triggers of asthma. TSLP is a major contributor to initiation and persistence of airway inflammation, Dr. Lugogo said.
The on-treatment analysis looked at all patients in the trial who completed 52 weeks of treatment and had complete data for all criteria studied.
The odds ratios (OR) for patients on tezepelumab achieving each of the response criteria are shown in the table.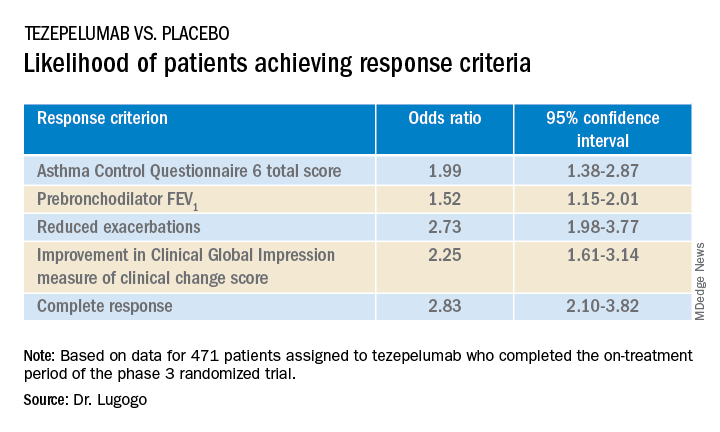
Exacerbations explored
In a separate presentation, Christopher S. Ambrose, MD, MBA, of AstraZeneca in Gaithersburg, Md., presented information from investigator-narrative descriptions of all hospitalization events related to asthma exacerbations (mild, moderate, or severe) that occurred while the investigator was blinded to each patient’s treatment assignment in NAVIGATOR.
In all, 39 of 531 patients (7.3%) assigned to placebo had a total of 78 exacerbations requiring hospitalization, compared with 13 of 528 patients (2.5%) assigned to tezepelumab. The latter group had a total of 14 exacerbations requiring hospitalization during the study.
Among hospitalized patients, 32 of the 39 assigned to placebo had severe, incapacitating exacerbations, compared with 5 of 13 assigned to tezepelumab.
Reported symptoms were generally similar between hospitalized patients in the two treatment groups, although there appeared to be trends toward lower incidence of dyspnea, fever, and tachycardia with tezepelumab.
Health care resource utilization, a surrogate marker for disease burden, was substantially lower for patients assigned to tezepelumab.
Infections were the most common triggers of exacerbations in both groups.
“These data provide further evidence that tezepelumab can reduce the burden of disease of severe uncontrolled asthma, both to patients and to health care systems,” Dr. Ambrose said.
Head-to-head studies needed
Although there have been no head-to-head comparisons of biologic agents for asthma to date, results of these studies suggest that tezepelumab has efficacy similar to that of other agents for reducing exacerbation, said Fernando Holguin, MD, MPH, from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who comoderated the oral session where the data were presented but was not involved in the study.
Biologic agents appear to be slightly more effective against type 2 inflammation in asthma, “but in general I think we give it to a broader severe population, so that’s exciting,” he told this news organization.
Comoderator Amisha Barochia, MBBS, MHS, of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., told this news organization that head-to-head trials of biologic agents would provide important clinical information going forward.
“Should we switch to a different biologic or add a second biologic? Those are questions we need answers for,” she said.
The NAVIGATOR trial is funded by AstraZeneca and Amgen. Dr. Lugogo disclosed financial relationships with both companies. Dr. Holguin and Dr. Barochia have disclosed no financial relationships relevant to the studies presented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – Nearly half of all patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma who received a full course of the biologic agent tezepelumab (Tezspire) in the NAVIGATOR trial had a complete response to treatment at 1 year, results of a prespecified exploratory analysis indicated.
Among 471 patients assigned to tezepelumab who completed the on-treatment period of the phase 3 randomized trial, 46% had a complete response at 52 weeks, compared with 24% of patients assigned to placebo.
Complete response was defined as reduction in exacerbations of at least 50% over the previous year, improvement from baseline in Asthma Control Questionnaire 6 (ACQ-6) total score of at least 0.5 points, improvement in prebronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (pre-BD FEV1), and physician-assessed Clinical Global Impression measure of clinical change (CGI-C) score.
“These data further support the efficacy of tezepelumab in a broad population of patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma,” said Njira Lugogo, MD, of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Dr. Lugogo presented results of the exploratory analysis at the American Thoracic Society’s international conference.
Exacerbations reduced, lung function improved
Primary results from NAVIGATOR, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, showed that patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma randomly assigned to tezepelumab had fewer exacerbations and better lung function, asthma control, and health-related quality of life compared with patients assigned to placebo.
The investigators noted that approximately 10% of patients with asthma have symptoms and exacerbations despite maximal standard-of-care controller therapy.
Tezepelumab is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits action of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), an epithelial cytokine that is released in response to airborne triggers of asthma. TSLP is a major contributor to initiation and persistence of airway inflammation, Dr. Lugogo said.
The on-treatment analysis looked at all patients in the trial who completed 52 weeks of treatment and had complete data for all criteria studied.
The odds ratios (OR) for patients on tezepelumab achieving each of the response criteria are shown in the table.
Exacerbations explored
In a separate presentation, Christopher S. Ambrose, MD, MBA, of AstraZeneca in Gaithersburg, Md., presented information from investigator-narrative descriptions of all hospitalization events related to asthma exacerbations (mild, moderate, or severe) that occurred while the investigator was blinded to each patient’s treatment assignment in NAVIGATOR.
In all, 39 of 531 patients (7.3%) assigned to placebo had a total of 78 exacerbations requiring hospitalization, compared with 13 of 528 patients (2.5%) assigned to tezepelumab. The latter group had a total of 14 exacerbations requiring hospitalization during the study.
Among hospitalized patients, 32 of the 39 assigned to placebo had severe, incapacitating exacerbations, compared with 5 of 13 assigned to tezepelumab.
Reported symptoms were generally similar between hospitalized patients in the two treatment groups, although there appeared to be trends toward lower incidence of dyspnea, fever, and tachycardia with tezepelumab.
Health care resource utilization, a surrogate marker for disease burden, was substantially lower for patients assigned to tezepelumab.
Infections were the most common triggers of exacerbations in both groups.
“These data provide further evidence that tezepelumab can reduce the burden of disease of severe uncontrolled asthma, both to patients and to health care systems,” Dr. Ambrose said.
Head-to-head studies needed
Although there have been no head-to-head comparisons of biologic agents for asthma to date, results of these studies suggest that tezepelumab has efficacy similar to that of other agents for reducing exacerbation, said Fernando Holguin, MD, MPH, from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who comoderated the oral session where the data were presented but was not involved in the study.
Biologic agents appear to be slightly more effective against type 2 inflammation in asthma, “but in general I think we give it to a broader severe population, so that’s exciting,” he told this news organization.
Comoderator Amisha Barochia, MBBS, MHS, of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., told this news organization that head-to-head trials of biologic agents would provide important clinical information going forward.
“Should we switch to a different biologic or add a second biologic? Those are questions we need answers for,” she said.
The NAVIGATOR trial is funded by AstraZeneca and Amgen. Dr. Lugogo disclosed financial relationships with both companies. Dr. Holguin and Dr. Barochia have disclosed no financial relationships relevant to the studies presented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – Nearly half of all patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma who received a full course of the biologic agent tezepelumab (Tezspire) in the NAVIGATOR trial had a complete response to treatment at 1 year, results of a prespecified exploratory analysis indicated.
Among 471 patients assigned to tezepelumab who completed the on-treatment period of the phase 3 randomized trial, 46% had a complete response at 52 weeks, compared with 24% of patients assigned to placebo.
Complete response was defined as reduction in exacerbations of at least 50% over the previous year, improvement from baseline in Asthma Control Questionnaire 6 (ACQ-6) total score of at least 0.5 points, improvement in prebronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (pre-BD FEV1), and physician-assessed Clinical Global Impression measure of clinical change (CGI-C) score.
“These data further support the efficacy of tezepelumab in a broad population of patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma,” said Njira Lugogo, MD, of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Dr. Lugogo presented results of the exploratory analysis at the American Thoracic Society’s international conference.
Exacerbations reduced, lung function improved
Primary results from NAVIGATOR, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, showed that patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma randomly assigned to tezepelumab had fewer exacerbations and better lung function, asthma control, and health-related quality of life compared with patients assigned to placebo.
The investigators noted that approximately 10% of patients with asthma have symptoms and exacerbations despite maximal standard-of-care controller therapy.
Tezepelumab is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits action of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), an epithelial cytokine that is released in response to airborne triggers of asthma. TSLP is a major contributor to initiation and persistence of airway inflammation, Dr. Lugogo said.
The on-treatment analysis looked at all patients in the trial who completed 52 weeks of treatment and had complete data for all criteria studied.
The odds ratios (OR) for patients on tezepelumab achieving each of the response criteria are shown in the table.
Exacerbations explored
In a separate presentation, Christopher S. Ambrose, MD, MBA, of AstraZeneca in Gaithersburg, Md., presented information from investigator-narrative descriptions of all hospitalization events related to asthma exacerbations (mild, moderate, or severe) that occurred while the investigator was blinded to each patient’s treatment assignment in NAVIGATOR.
In all, 39 of 531 patients (7.3%) assigned to placebo had a total of 78 exacerbations requiring hospitalization, compared with 13 of 528 patients (2.5%) assigned to tezepelumab. The latter group had a total of 14 exacerbations requiring hospitalization during the study.
Among hospitalized patients, 32 of the 39 assigned to placebo had severe, incapacitating exacerbations, compared with 5 of 13 assigned to tezepelumab.
Reported symptoms were generally similar between hospitalized patients in the two treatment groups, although there appeared to be trends toward lower incidence of dyspnea, fever, and tachycardia with tezepelumab.
Health care resource utilization, a surrogate marker for disease burden, was substantially lower for patients assigned to tezepelumab.
Infections were the most common triggers of exacerbations in both groups.
“These data provide further evidence that tezepelumab can reduce the burden of disease of severe uncontrolled asthma, both to patients and to health care systems,” Dr. Ambrose said.
Head-to-head studies needed
Although there have been no head-to-head comparisons of biologic agents for asthma to date, results of these studies suggest that tezepelumab has efficacy similar to that of other agents for reducing exacerbation, said Fernando Holguin, MD, MPH, from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who comoderated the oral session where the data were presented but was not involved in the study.
Biologic agents appear to be slightly more effective against type 2 inflammation in asthma, “but in general I think we give it to a broader severe population, so that’s exciting,” he told this news organization.
Comoderator Amisha Barochia, MBBS, MHS, of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., told this news organization that head-to-head trials of biologic agents would provide important clinical information going forward.
“Should we switch to a different biologic or add a second biologic? Those are questions we need answers for,” she said.
The NAVIGATOR trial is funded by AstraZeneca and Amgen. Dr. Lugogo disclosed financial relationships with both companies. Dr. Holguin and Dr. Barochia have disclosed no financial relationships relevant to the studies presented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ATS 2022
More evidence links asthma severity to age of onset
A recently published multinational cohort study may be the largest to date that’s found the age of asthma onset is an integral factor in defining the severity of disease and the frequency of comorbidities.
“It’s very simple to ask your patient: ‘Did you have asthma as a child? When did your asthma start?’ ” coauthor Guy Brusselle, MD, a professor at the University of Ghent (Belgium), said in an interview. “You do not need expensive investigations, CT scans or proteomics or genomics; just two simple questions.”
The retrospective cohort study, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, combined national electronic health records databases from five different countries – the United Kingdom, Spain, Italy, the Netherlands, and Denmark – that included 586,436 adult asthma patients. The study divided the patients into three subtypes: childhood-onset asthma, meaning a diagnosis before age 18 (n = 81,691); adult-onset disease, defined as a diagnosis between ages 18 and 40 (n = 218,184); and late onset, defined as a diagnosis made after age 40 (n = 286,561).
Dr. Brusselle said the study found stark differences in characteristics between the three subtypes, including an increasing risk for women with later age of onset. Across the five databases, females comprised approximately 45% of those with childhood-onset asthma, but about 60% of those with later-onset disease, Dr. Brusselle said.
As for characteristics of asthma, 7.2% of the cohort (n = 42,611) had severe asthma, but the proportion was highest in late-onset asthma, 10% versus 5% in adult onset and 3% in childhood onset. The percentage of uncontrolled asthma followed a similar trend: 8%, 6%, and 0.4% in the respective treatment groups.
The most common comorbidities were atopic disorders (31%) and overweight/obesity (50%). The prevalence of atopic disorders was highest in the childhood-onset group, 45% versus 35%, and 25% in the adult-onset and late-onset patients. However, the trend for overweight/obesity was reversed: 30%, 43%, and 61%, respectively.
“The larger differences were when late-onset asthma was compared to adult-onset asthma with respect to comorbidities,” Dr. Brusselle said. “The late-onset asthma patients more frequently had nasal polyposis.” These patients typically lose their sense of smell, as in COVID-19. However, in nasal polyposis the loss is chronic rather than transient.
Pulmonologists should be attuned to the prevalence of overweight/obesity in the late-onset group, Dr. Brusselle said. “We know that obesity is an important risk factor for diabetes, and then obesity is also associated with gastroesophageal reflux – and we know that gastroesophageal reflux is a risk factor for asthma exacerbations.”
Smaller studies have arrived at the same conclusions regarding the relationships between asthma severity and age of onset, Dr. Brusselle said. What’s notable about this study is its size and the consistency of findings across different national databases.
“In childhood onset you need to watch for different allergies – atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis – but in late-onset asthma look for obesity, diabetes and reflux disease, and nasal polyposis,” he said.
Sally E. Wenzel, MD, professor at the University of Pittsburgh and director of the Asthma and Environmental Lung Health Institute at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, concurred that the size of this study makes it noteworthy.
“It’s certainly far and away the largest study of its kind that’s ever been done, and it’s multinational,” she said in an interview. “Just doing a study like this with thousands and thousands of patients is a step in the right direction. That’s probably what’s very unique about it, to bring all of these clinical cohorts as it were together and to look at what is the relationship of the age of onset.”
She also said the study is unique in how it delineates the groups by age of onset.
“In addition to this concept that there’s a difference in asthma by the age that you got diagnosed with it, I think it’s also important to just remember that when any physician, be they a specialist or nonspecialist, sees a patient with asthma, they should ask them when did their symptoms develop,” she said. “These are really simple questions that don’t take any sophisticated training and don’t take any sophisticated instruments to measure, but they can be really helpful.”
GlaxoSmithKline supplied a grant for the study. Dr. Brusselle disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Novartis, Sanofi, and Teva. A study coauthor is an employee of GSK. Dr. Wenzel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recently published multinational cohort study may be the largest to date that’s found the age of asthma onset is an integral factor in defining the severity of disease and the frequency of comorbidities.
“It’s very simple to ask your patient: ‘Did you have asthma as a child? When did your asthma start?’ ” coauthor Guy Brusselle, MD, a professor at the University of Ghent (Belgium), said in an interview. “You do not need expensive investigations, CT scans or proteomics or genomics; just two simple questions.”
The retrospective cohort study, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, combined national electronic health records databases from five different countries – the United Kingdom, Spain, Italy, the Netherlands, and Denmark – that included 586,436 adult asthma patients. The study divided the patients into three subtypes: childhood-onset asthma, meaning a diagnosis before age 18 (n = 81,691); adult-onset disease, defined as a diagnosis between ages 18 and 40 (n = 218,184); and late onset, defined as a diagnosis made after age 40 (n = 286,561).
Dr. Brusselle said the study found stark differences in characteristics between the three subtypes, including an increasing risk for women with later age of onset. Across the five databases, females comprised approximately 45% of those with childhood-onset asthma, but about 60% of those with later-onset disease, Dr. Brusselle said.
As for characteristics of asthma, 7.2% of the cohort (n = 42,611) had severe asthma, but the proportion was highest in late-onset asthma, 10% versus 5% in adult onset and 3% in childhood onset. The percentage of uncontrolled asthma followed a similar trend: 8%, 6%, and 0.4% in the respective treatment groups.
The most common comorbidities were atopic disorders (31%) and overweight/obesity (50%). The prevalence of atopic disorders was highest in the childhood-onset group, 45% versus 35%, and 25% in the adult-onset and late-onset patients. However, the trend for overweight/obesity was reversed: 30%, 43%, and 61%, respectively.
“The larger differences were when late-onset asthma was compared to adult-onset asthma with respect to comorbidities,” Dr. Brusselle said. “The late-onset asthma patients more frequently had nasal polyposis.” These patients typically lose their sense of smell, as in COVID-19. However, in nasal polyposis the loss is chronic rather than transient.
Pulmonologists should be attuned to the prevalence of overweight/obesity in the late-onset group, Dr. Brusselle said. “We know that obesity is an important risk factor for diabetes, and then obesity is also associated with gastroesophageal reflux – and we know that gastroesophageal reflux is a risk factor for asthma exacerbations.”
Smaller studies have arrived at the same conclusions regarding the relationships between asthma severity and age of onset, Dr. Brusselle said. What’s notable about this study is its size and the consistency of findings across different national databases.
“In childhood onset you need to watch for different allergies – atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis – but in late-onset asthma look for obesity, diabetes and reflux disease, and nasal polyposis,” he said.
Sally E. Wenzel, MD, professor at the University of Pittsburgh and director of the Asthma and Environmental Lung Health Institute at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, concurred that the size of this study makes it noteworthy.
“It’s certainly far and away the largest study of its kind that’s ever been done, and it’s multinational,” she said in an interview. “Just doing a study like this with thousands and thousands of patients is a step in the right direction. That’s probably what’s very unique about it, to bring all of these clinical cohorts as it were together and to look at what is the relationship of the age of onset.”
She also said the study is unique in how it delineates the groups by age of onset.
“In addition to this concept that there’s a difference in asthma by the age that you got diagnosed with it, I think it’s also important to just remember that when any physician, be they a specialist or nonspecialist, sees a patient with asthma, they should ask them when did their symptoms develop,” she said. “These are really simple questions that don’t take any sophisticated training and don’t take any sophisticated instruments to measure, but they can be really helpful.”
GlaxoSmithKline supplied a grant for the study. Dr. Brusselle disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Novartis, Sanofi, and Teva. A study coauthor is an employee of GSK. Dr. Wenzel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recently published multinational cohort study may be the largest to date that’s found the age of asthma onset is an integral factor in defining the severity of disease and the frequency of comorbidities.
“It’s very simple to ask your patient: ‘Did you have asthma as a child? When did your asthma start?’ ” coauthor Guy Brusselle, MD, a professor at the University of Ghent (Belgium), said in an interview. “You do not need expensive investigations, CT scans or proteomics or genomics; just two simple questions.”
The retrospective cohort study, published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, combined national electronic health records databases from five different countries – the United Kingdom, Spain, Italy, the Netherlands, and Denmark – that included 586,436 adult asthma patients. The study divided the patients into three subtypes: childhood-onset asthma, meaning a diagnosis before age 18 (n = 81,691); adult-onset disease, defined as a diagnosis between ages 18 and 40 (n = 218,184); and late onset, defined as a diagnosis made after age 40 (n = 286,561).
Dr. Brusselle said the study found stark differences in characteristics between the three subtypes, including an increasing risk for women with later age of onset. Across the five databases, females comprised approximately 45% of those with childhood-onset asthma, but about 60% of those with later-onset disease, Dr. Brusselle said.
As for characteristics of asthma, 7.2% of the cohort (n = 42,611) had severe asthma, but the proportion was highest in late-onset asthma, 10% versus 5% in adult onset and 3% in childhood onset. The percentage of uncontrolled asthma followed a similar trend: 8%, 6%, and 0.4% in the respective treatment groups.
The most common comorbidities were atopic disorders (31%) and overweight/obesity (50%). The prevalence of atopic disorders was highest in the childhood-onset group, 45% versus 35%, and 25% in the adult-onset and late-onset patients. However, the trend for overweight/obesity was reversed: 30%, 43%, and 61%, respectively.
“The larger differences were when late-onset asthma was compared to adult-onset asthma with respect to comorbidities,” Dr. Brusselle said. “The late-onset asthma patients more frequently had nasal polyposis.” These patients typically lose their sense of smell, as in COVID-19. However, in nasal polyposis the loss is chronic rather than transient.
Pulmonologists should be attuned to the prevalence of overweight/obesity in the late-onset group, Dr. Brusselle said. “We know that obesity is an important risk factor for diabetes, and then obesity is also associated with gastroesophageal reflux – and we know that gastroesophageal reflux is a risk factor for asthma exacerbations.”
Smaller studies have arrived at the same conclusions regarding the relationships between asthma severity and age of onset, Dr. Brusselle said. What’s notable about this study is its size and the consistency of findings across different national databases.
“In childhood onset you need to watch for different allergies – atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis – but in late-onset asthma look for obesity, diabetes and reflux disease, and nasal polyposis,” he said.
Sally E. Wenzel, MD, professor at the University of Pittsburgh and director of the Asthma and Environmental Lung Health Institute at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, concurred that the size of this study makes it noteworthy.
“It’s certainly far and away the largest study of its kind that’s ever been done, and it’s multinational,” she said in an interview. “Just doing a study like this with thousands and thousands of patients is a step in the right direction. That’s probably what’s very unique about it, to bring all of these clinical cohorts as it were together and to look at what is the relationship of the age of onset.”
She also said the study is unique in how it delineates the groups by age of onset.
“In addition to this concept that there’s a difference in asthma by the age that you got diagnosed with it, I think it’s also important to just remember that when any physician, be they a specialist or nonspecialist, sees a patient with asthma, they should ask them when did their symptoms develop,” she said. “These are really simple questions that don’t take any sophisticated training and don’t take any sophisticated instruments to measure, but they can be really helpful.”
GlaxoSmithKline supplied a grant for the study. Dr. Brusselle disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Novartis, Sanofi, and Teva. A study coauthor is an employee of GSK. Dr. Wenzel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY: IN PRACTICE
Probiotic LGG doesn’t lessen eczema, asthma, or rhinitis risk by age 7
Giving the probiotic supplement Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) to high-risk infants in the first 6 months of life is not effective in lessening incidence of eczema, asthma, or rhinitis in later childhood, researchers have found.
The researchers, led by Michael D. Cabana, MD, MPH, with the Children’s Hospital of Montefiore, New York, said they cannot support its use in this population of children at high risk for allergic disease. Findings were published in Pediatrics.
Jonathan Spergel, MD, PhD, chief of the allergy program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, who was not part of the study, said the “small, but very interesting study adds to the literature indicating that allergy prevention needs to be a multifactorial approach and simply adding LGG in a select population makes no difference.”
He noted that the study of probiotics for allergic conditions is complex as it depends on many factors, such as the child’s environment, including exposure to pets and pollution, and whether the child was delivered vaginally or by cesarean section.
Study builds on previous work
The new study builds on the same researchers’ randomized, double-masked, parallel-arm, controlled Trial of Infant Probiotic Supplementation (TIPS). That study investigated whether daily administration of LGG in the first 6 months to children at high risk for allergic disease because of asthma in a parent, could decrease their cumulative incidence of eczema. Investigators found LGG had no effect.
These additional results included participants at least 7 years old and also included physician-diagnosed asthma and physician-diagnosed rhinitis as secondary outcomes.
Retention rate over the 7-year follow-up was 56%; 49 (53%) of 92 in the intervention group and 54 (59%) of 92 in the control group.
The researchers performed modified intention-to-treat analyses with all children who received treatment in the study arm to which they had been randomized.
Eczema was diagnosed in 78 participants, asthma in 32, and rhinitis in 15. Incidence of eczema was high in infancy, but low thereafter. Incidence rates for asthma and rhinitis were constant throughout childhood.
The researchers used modeling to compare the incidence of each outcome between the intervention and control groups, adjusting for mode of delivery and how long a child was breastfed.
Cesarean delivery was linked to a greater incidence of rhinitis, with a hazard ratio of 3.33 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-9.21).
Finding the right strain
Heather Cassell, MD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that many researchers, including those at her institution, are trying to find which strain of probiotic might be beneficial in lowering risk for allergic disease.
Though it appears LGG doesn’t have an effect, she said, another strain might be successful and this helps zero in on the right one.
The TIPS trial showed that there were no significant side effects from giving LGG early, which is good information to have as the search resumes for the right strain, she said.
“We know that there’s probably some immune dysregulation in kids with asthma, eczema, other allergies, but we don’t fully know the extent of it,” she said, adding that it may be that skin flora or respiratory flora and microbiomes in other parts of the body play a role.
“We don’t have bacteria just in our guts,” she noted. “It may be a combination of strains or a combination of bacteria.”
The authors, Dr. Spergel, and Dr. Cassell reported no relevant financial relationships.
Giving the probiotic supplement Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) to high-risk infants in the first 6 months of life is not effective in lessening incidence of eczema, asthma, or rhinitis in later childhood, researchers have found.
The researchers, led by Michael D. Cabana, MD, MPH, with the Children’s Hospital of Montefiore, New York, said they cannot support its use in this population of children at high risk for allergic disease. Findings were published in Pediatrics.
Jonathan Spergel, MD, PhD, chief of the allergy program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, who was not part of the study, said the “small, but very interesting study adds to the literature indicating that allergy prevention needs to be a multifactorial approach and simply adding LGG in a select population makes no difference.”
He noted that the study of probiotics for allergic conditions is complex as it depends on many factors, such as the child’s environment, including exposure to pets and pollution, and whether the child was delivered vaginally or by cesarean section.
Study builds on previous work
The new study builds on the same researchers’ randomized, double-masked, parallel-arm, controlled Trial of Infant Probiotic Supplementation (TIPS). That study investigated whether daily administration of LGG in the first 6 months to children at high risk for allergic disease because of asthma in a parent, could decrease their cumulative incidence of eczema. Investigators found LGG had no effect.
These additional results included participants at least 7 years old and also included physician-diagnosed asthma and physician-diagnosed rhinitis as secondary outcomes.
Retention rate over the 7-year follow-up was 56%; 49 (53%) of 92 in the intervention group and 54 (59%) of 92 in the control group.
The researchers performed modified intention-to-treat analyses with all children who received treatment in the study arm to which they had been randomized.
Eczema was diagnosed in 78 participants, asthma in 32, and rhinitis in 15. Incidence of eczema was high in infancy, but low thereafter. Incidence rates for asthma and rhinitis were constant throughout childhood.
The researchers used modeling to compare the incidence of each outcome between the intervention and control groups, adjusting for mode of delivery and how long a child was breastfed.
Cesarean delivery was linked to a greater incidence of rhinitis, with a hazard ratio of 3.33 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-9.21).
Finding the right strain
Heather Cassell, MD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that many researchers, including those at her institution, are trying to find which strain of probiotic might be beneficial in lowering risk for allergic disease.
Though it appears LGG doesn’t have an effect, she said, another strain might be successful and this helps zero in on the right one.
The TIPS trial showed that there were no significant side effects from giving LGG early, which is good information to have as the search resumes for the right strain, she said.
“We know that there’s probably some immune dysregulation in kids with asthma, eczema, other allergies, but we don’t fully know the extent of it,” she said, adding that it may be that skin flora or respiratory flora and microbiomes in other parts of the body play a role.
“We don’t have bacteria just in our guts,” she noted. “It may be a combination of strains or a combination of bacteria.”
The authors, Dr. Spergel, and Dr. Cassell reported no relevant financial relationships.
Giving the probiotic supplement Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) to high-risk infants in the first 6 months of life is not effective in lessening incidence of eczema, asthma, or rhinitis in later childhood, researchers have found.
The researchers, led by Michael D. Cabana, MD, MPH, with the Children’s Hospital of Montefiore, New York, said they cannot support its use in this population of children at high risk for allergic disease. Findings were published in Pediatrics.
Jonathan Spergel, MD, PhD, chief of the allergy program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, who was not part of the study, said the “small, but very interesting study adds to the literature indicating that allergy prevention needs to be a multifactorial approach and simply adding LGG in a select population makes no difference.”
He noted that the study of probiotics for allergic conditions is complex as it depends on many factors, such as the child’s environment, including exposure to pets and pollution, and whether the child was delivered vaginally or by cesarean section.
Study builds on previous work
The new study builds on the same researchers’ randomized, double-masked, parallel-arm, controlled Trial of Infant Probiotic Supplementation (TIPS). That study investigated whether daily administration of LGG in the first 6 months to children at high risk for allergic disease because of asthma in a parent, could decrease their cumulative incidence of eczema. Investigators found LGG had no effect.
These additional results included participants at least 7 years old and also included physician-diagnosed asthma and physician-diagnosed rhinitis as secondary outcomes.
Retention rate over the 7-year follow-up was 56%; 49 (53%) of 92 in the intervention group and 54 (59%) of 92 in the control group.
The researchers performed modified intention-to-treat analyses with all children who received treatment in the study arm to which they had been randomized.
Eczema was diagnosed in 78 participants, asthma in 32, and rhinitis in 15. Incidence of eczema was high in infancy, but low thereafter. Incidence rates for asthma and rhinitis were constant throughout childhood.
The researchers used modeling to compare the incidence of each outcome between the intervention and control groups, adjusting for mode of delivery and how long a child was breastfed.
Cesarean delivery was linked to a greater incidence of rhinitis, with a hazard ratio of 3.33 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-9.21).
Finding the right strain
Heather Cassell, MD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist at University of Arizona, Tucson, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that many researchers, including those at her institution, are trying to find which strain of probiotic might be beneficial in lowering risk for allergic disease.
Though it appears LGG doesn’t have an effect, she said, another strain might be successful and this helps zero in on the right one.
The TIPS trial showed that there were no significant side effects from giving LGG early, which is good information to have as the search resumes for the right strain, she said.
“We know that there’s probably some immune dysregulation in kids with asthma, eczema, other allergies, but we don’t fully know the extent of it,” she said, adding that it may be that skin flora or respiratory flora and microbiomes in other parts of the body play a role.
“We don’t have bacteria just in our guts,” she noted. “It may be a combination of strains or a combination of bacteria.”
The authors, Dr. Spergel, and Dr. Cassell reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Treat or refer? New primary care flow diagrams for allergy patients
Most patients with allergy problems first see PCPs, not allergists, the authors write in Allergy. The new flow diagrams help PCPs treat anaphylaxis, asthma, drug allergy, food allergy, and urticaria.
“The European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology established the Logogram Task Force to create a set of simple flow diagrams to assist allergy nonspecialist, generalist, and primary care teams in the diagnosis of five common allergic diseases encountered in primary care,” lead author Dermot Ryan, MB BCh, BAO, FRGCP, of the University of Edinburgh told this news organization.
“The source documents were mainstream guidelines coupled with ancillary literature,” he added in an email. “A multi-disciplinary taskforce ... distilled these guidelines into accessible, comprehensible, usable, and context-specific flow diagrams.”
The flow diagrams developed in Europe can be used by providers in the United States and elsewhere
“These diagrams are consistent with practices in the U.S.,” Christina E. Ciaccio, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and the section chief of pediatric allergy and immunology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said in an email. “They will prove helpful to PCPs in the U.S. and elsewhere, particularly to young physicians new to practice.
“Treating allergies is part of the ‘bread-and-butter’ practice of primary care physicians in the U.S.,” Dr. Ciaccio, who was not involved in developing the flow diagrams, explained. “Up to 30% of Americans are atopic, and the vast majority seek treatment advice from their PCP first.”
The flow diagrams can help providers in developing countries, where allergic diseases are common, provide the best patient care possible, she said.
At some point, a PCP may need to think beyond flow diagrams and refer the patient to an allergist
“If the treatment plan for a patient falls outside first- or second-line medications, or if a diagnosis is unclear with preliminary testing, a PCP may reach out to an allergy/immunology specialist to assist in providing care,” Dr. Ciaccio advised. “Allergists may provide treatment options, such as immunotherapy, that the PCP does not offer. PCPs also often reach out to allergy team members for help with patients whose allergies are not ‘run-of-the-mill.’
“The flow diagrams are complex and may not be practical in the middle of a busy clinic,” she cautioned. “However, when a patient comes into a primary care clinic with an atypical presentation of an allergic disease, the diagrams are likely to help a physician feel confident that an allergist is the right physician for consultation.”
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, an associate professor of medicine in pulmonary, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C., noted that providers in the U.S. can use the flow diagrams because the definitions, differential diagnosis, and treatments for the conditions they cover are similar.
“The flow diagrams are comprehensive, and they attempt to condense a great deal of information into summary points. They are very useful in the U.S., and not just for generalists,” Dr. Lugar, who also was not involved in the project, said. “Even emergency rooms would benefit from these flow diagrams, especially regarding the recognition of symptoms and differential diagnosis.”
Asthma and seasonal and environmental allergies are often managed by PCPs, and the flow diagrams would help them decide when to refer their patients to an allergist, she added in an email.
Dr. Lugar advises PCPs to “recognize the symptoms of an allergic condition, offer treatment based on confidence the diagnosis is correct, and offer a referral for testing to confirm the allergy.
“Because 50% or more of asthmatics are allergic, all asthmatics should be offered an allergy evaluation to determine their allergies and avoid exacerbating the asthma,” she added. “I do not see the flow diagrams as comprehensive enough to manage chronic urticaria, asthma, venom allergy, and drug allergy.”
With food allergy, environmental allergy, venom allergy, or anaphylaxis, “allergists are experts at considering the differential diagnosis and providing the next steps in the diagnostic workup,” Dr. Lugar said. “Allergists can also provide special treatments, such as allergen-specific immunotherapy or desensitization.”
The flow diagrams guide nonspecialists in diagnosis and treatment of their patients with allergy, with supplementary information as needed. The diagrams recommend referral to a specialist when appropriate, as in cases of anaphylaxis, or chronic urticaria.
The task force was funded by EAACI. Dr. Ryan and several other authors report financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ciaccio and Dr. Lugar report no such relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most patients with allergy problems first see PCPs, not allergists, the authors write in Allergy. The new flow diagrams help PCPs treat anaphylaxis, asthma, drug allergy, food allergy, and urticaria.
“The European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology established the Logogram Task Force to create a set of simple flow diagrams to assist allergy nonspecialist, generalist, and primary care teams in the diagnosis of five common allergic diseases encountered in primary care,” lead author Dermot Ryan, MB BCh, BAO, FRGCP, of the University of Edinburgh told this news organization.
“The source documents were mainstream guidelines coupled with ancillary literature,” he added in an email. “A multi-disciplinary taskforce ... distilled these guidelines into accessible, comprehensible, usable, and context-specific flow diagrams.”
The flow diagrams developed in Europe can be used by providers in the United States and elsewhere
“These diagrams are consistent with practices in the U.S.,” Christina E. Ciaccio, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and the section chief of pediatric allergy and immunology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said in an email. “They will prove helpful to PCPs in the U.S. and elsewhere, particularly to young physicians new to practice.
“Treating allergies is part of the ‘bread-and-butter’ practice of primary care physicians in the U.S.,” Dr. Ciaccio, who was not involved in developing the flow diagrams, explained. “Up to 30% of Americans are atopic, and the vast majority seek treatment advice from their PCP first.”
The flow diagrams can help providers in developing countries, where allergic diseases are common, provide the best patient care possible, she said.
At some point, a PCP may need to think beyond flow diagrams and refer the patient to an allergist
“If the treatment plan for a patient falls outside first- or second-line medications, or if a diagnosis is unclear with preliminary testing, a PCP may reach out to an allergy/immunology specialist to assist in providing care,” Dr. Ciaccio advised. “Allergists may provide treatment options, such as immunotherapy, that the PCP does not offer. PCPs also often reach out to allergy team members for help with patients whose allergies are not ‘run-of-the-mill.’
“The flow diagrams are complex and may not be practical in the middle of a busy clinic,” she cautioned. “However, when a patient comes into a primary care clinic with an atypical presentation of an allergic disease, the diagrams are likely to help a physician feel confident that an allergist is the right physician for consultation.”
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, an associate professor of medicine in pulmonary, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C., noted that providers in the U.S. can use the flow diagrams because the definitions, differential diagnosis, and treatments for the conditions they cover are similar.
“The flow diagrams are comprehensive, and they attempt to condense a great deal of information into summary points. They are very useful in the U.S., and not just for generalists,” Dr. Lugar, who also was not involved in the project, said. “Even emergency rooms would benefit from these flow diagrams, especially regarding the recognition of symptoms and differential diagnosis.”
Asthma and seasonal and environmental allergies are often managed by PCPs, and the flow diagrams would help them decide when to refer their patients to an allergist, she added in an email.
Dr. Lugar advises PCPs to “recognize the symptoms of an allergic condition, offer treatment based on confidence the diagnosis is correct, and offer a referral for testing to confirm the allergy.
“Because 50% or more of asthmatics are allergic, all asthmatics should be offered an allergy evaluation to determine their allergies and avoid exacerbating the asthma,” she added. “I do not see the flow diagrams as comprehensive enough to manage chronic urticaria, asthma, venom allergy, and drug allergy.”
With food allergy, environmental allergy, venom allergy, or anaphylaxis, “allergists are experts at considering the differential diagnosis and providing the next steps in the diagnostic workup,” Dr. Lugar said. “Allergists can also provide special treatments, such as allergen-specific immunotherapy or desensitization.”
The flow diagrams guide nonspecialists in diagnosis and treatment of their patients with allergy, with supplementary information as needed. The diagrams recommend referral to a specialist when appropriate, as in cases of anaphylaxis, or chronic urticaria.
The task force was funded by EAACI. Dr. Ryan and several other authors report financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ciaccio and Dr. Lugar report no such relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most patients with allergy problems first see PCPs, not allergists, the authors write in Allergy. The new flow diagrams help PCPs treat anaphylaxis, asthma, drug allergy, food allergy, and urticaria.
“The European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology established the Logogram Task Force to create a set of simple flow diagrams to assist allergy nonspecialist, generalist, and primary care teams in the diagnosis of five common allergic diseases encountered in primary care,” lead author Dermot Ryan, MB BCh, BAO, FRGCP, of the University of Edinburgh told this news organization.
“The source documents were mainstream guidelines coupled with ancillary literature,” he added in an email. “A multi-disciplinary taskforce ... distilled these guidelines into accessible, comprehensible, usable, and context-specific flow diagrams.”
The flow diagrams developed in Europe can be used by providers in the United States and elsewhere
“These diagrams are consistent with practices in the U.S.,” Christina E. Ciaccio, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and the section chief of pediatric allergy and immunology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said in an email. “They will prove helpful to PCPs in the U.S. and elsewhere, particularly to young physicians new to practice.
“Treating allergies is part of the ‘bread-and-butter’ practice of primary care physicians in the U.S.,” Dr. Ciaccio, who was not involved in developing the flow diagrams, explained. “Up to 30% of Americans are atopic, and the vast majority seek treatment advice from their PCP first.”
The flow diagrams can help providers in developing countries, where allergic diseases are common, provide the best patient care possible, she said.
At some point, a PCP may need to think beyond flow diagrams and refer the patient to an allergist
“If the treatment plan for a patient falls outside first- or second-line medications, or if a diagnosis is unclear with preliminary testing, a PCP may reach out to an allergy/immunology specialist to assist in providing care,” Dr. Ciaccio advised. “Allergists may provide treatment options, such as immunotherapy, that the PCP does not offer. PCPs also often reach out to allergy team members for help with patients whose allergies are not ‘run-of-the-mill.’
“The flow diagrams are complex and may not be practical in the middle of a busy clinic,” she cautioned. “However, when a patient comes into a primary care clinic with an atypical presentation of an allergic disease, the diagrams are likely to help a physician feel confident that an allergist is the right physician for consultation.”
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, an associate professor of medicine in pulmonary, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C., noted that providers in the U.S. can use the flow diagrams because the definitions, differential diagnosis, and treatments for the conditions they cover are similar.
“The flow diagrams are comprehensive, and they attempt to condense a great deal of information into summary points. They are very useful in the U.S., and not just for generalists,” Dr. Lugar, who also was not involved in the project, said. “Even emergency rooms would benefit from these flow diagrams, especially regarding the recognition of symptoms and differential diagnosis.”
Asthma and seasonal and environmental allergies are often managed by PCPs, and the flow diagrams would help them decide when to refer their patients to an allergist, she added in an email.
Dr. Lugar advises PCPs to “recognize the symptoms of an allergic condition, offer treatment based on confidence the diagnosis is correct, and offer a referral for testing to confirm the allergy.
“Because 50% or more of asthmatics are allergic, all asthmatics should be offered an allergy evaluation to determine their allergies and avoid exacerbating the asthma,” she added. “I do not see the flow diagrams as comprehensive enough to manage chronic urticaria, asthma, venom allergy, and drug allergy.”
With food allergy, environmental allergy, venom allergy, or anaphylaxis, “allergists are experts at considering the differential diagnosis and providing the next steps in the diagnostic workup,” Dr. Lugar said. “Allergists can also provide special treatments, such as allergen-specific immunotherapy or desensitization.”
The flow diagrams guide nonspecialists in diagnosis and treatment of their patients with allergy, with supplementary information as needed. The diagrams recommend referral to a specialist when appropriate, as in cases of anaphylaxis, or chronic urticaria.
The task force was funded by EAACI. Dr. Ryan and several other authors report financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Ciaccio and Dr. Lugar report no such relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ALLERGY
Gaps in follow-up care put kids with asthma at risk of severe recurrence
Jo Ward’s twin boys have been to the emergency department for respiratory problems about as many times as the dozen years they’ve been alive. Both have asthma and bronchopulmonary dysplasia, a form of chronic airway damage that can occur in children born premature, as the twins were. But each time Ms. Ward took them in for treatment during an acute bout of breathing distress, the staff told her to schedule a follow-up visit for the children with their physician only if they didn’t get better, not regardless of the outcome – as medical guidelines recommend.
“They asked questions, they did the exams, but they really didn’t give you a lot of information to help you at home,” Ms. Ward told this news organization. If they had, she doesn’t think she’d have needed to take them in for emergency care so often.
A new study, published in Academic Pediatrics, suggests she’s right.
Current clinical guidelines for asthma recommend that patients who visit the ED for an asthma-related problem should have a follow-up appointment within a month after the visit, independent of how well they have recovered once home, according to Naomi S. Bardach, MD, a professor of pediatrics and health policy at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the new study.
Her research found that children who have a follow-up appointment within 2 weeks of such a visit are less likely to come back again the next year. Yet the study also found that only about one in five youth had a follow-up visit within that 2-week window.
“The emergency department visit is probably a sign that they need some additional attention for their asthma,” Dr. Bardach said. “We know we can prevent emergency department visits if they get the right kind of medication or if they figure out how to avoid the things that are going to cause an asthma exacerbation or flare.”
For the study, Dr. Bardach and colleagues analyzed data from California, Vermont, and Massachusetts for all asthma-related emergency visits for patients aged 3-21 years between 2013 and 2016.
Out of the 90,267 such visits they identified, 22.6% of patients had a follow-up within 2 weeks, more often by patients who were younger, had commercial insurance, had evidence of prior asthma, or had complex chronic conditions.
Whereas 5.7% of patients who had follow-up visits returned to the ED within 60 days, 6.4% of those who didn’t came back – a 12% difference (P < .001). The gap was larger a year out, with 25% of those with follow-ups returning to the ED, compared with 28.3% of those without follow-ups returning (P < .001), according to the researchers.
Overall, Dr. Bardach’s group estimates that for every 30 children who have follow-up visits with a physician, one would avoid a return trip to the emergency department for asthma within a year.
But given the sheer number of asthma-related trips to the ED each year – 164,145 for kids age 1-17 years in the United States in 2016 alone – that translates into big numbers of kids not going back to the hospital: approximately 72,000 such trips avoided at a savings to the health care system of at least $8.6 million annually.
Missed opportunities
Had Ms. Ward’s boys been among the one in five to receive follow-up care earlier in their lives, she might have saved a significant amount of time, money, anxiety, and heartache. When the twins were 9 years old, she took them to a new pediatric pulmonologist. That changed everything. In that first visit, “they gave me way more information than I ever had in the first 9 years,” she said.
The doctor told Ms. Ward to keep steroids on hand, gave her a prescription for extra doses of the powerful medication, and explained that they needed to be used within 24 hours of the first sign of a breathing problem.
“She said if you give them the steroids right away, it keeps them out of the emergency room, and that’s actually worked,” Ms. Ward said. “She made sure we had care plans every visit and asked me each time if I still had it or we needed to rewrite it. They gave me signs to look for, for when to go to hospital visits. I think that when you go to the doctor, they should be telling you stuff like that.”
Dr. Bardach said visits with a primary care doctor or asthma specialist offer families a chance to receive information to keep the condition from becoming critical.
“Going to that follow-up visit, they can get access to education from the provider about how to avoid things that trigger asthma, and there’s medication that kids can take that keeps the lungs calm and less likely to have a big asthma reaction, so getting access to that medication can be really helpful,” she said.
That was the case for Amy Davenport, of Chapel Hill, N.C., whose 6-year-old son has been to the ED twice for his asthma.
The first time, when he was 3, he was having trouble breathing with a respiratory tract infection and received nebulizer treatment – although he received it in the ED since no beds were available in the ICU. The staff did tell Ms. Davenport to follow up with her primary care provider, but her son’s pediatrician was reluctant to diagnose him with asthma at such a young age and didn’t prescribe any maintenance medications.
A few months later, Ms. Davenport and her son found themselves back in the hospital, and an ICU bed was open this time. The critical care staff referred Davenport to a pediatric pulmonary specialist, and they haven’t been back to the hospital since. Ms. Davenport said she believes if they’d received a maintenance medication after the first visit, it likely would have prevented the second one.
“I’ve definitely seen now that, after the second admission, we got an asthma action plan and it said exactly what to do,” she said. “I felt like we had really good follow-up. We had that action plan on our refrigerator for a long time, and it helped us as parents with three small children to manage.”
Of course, follow-up care takes time – time away from work and school that not all families can spare, the researchers acknowledged. Telehealth may be an option, especially after its use expanded during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We know that health systems have a hard time being flexible enough to actually have a kid be able to make an appointment within a short period of time, and we also know it’s hard for families sometimes to go back into a clinical setting within a certain period of time,” Dr. Bardach said. The urgency for the appointment may wane for those whose children seem to be doing better.
When the researchers adjusted their calculations for socioeconomic status, the results didn’t change much. But the study did find that patients with private insurance were about twice as likely to have follow-up visits as those on Medicaid (43.7% vs. 21.7%). And “the content and conduct” of the follow-up visit makes a difference as well.
Ms. Ward, whose boys are insured through Medicaid, recalled several visits to the ED where she had to push the staff to get the care her children needed. In one case, when one of her boys was a year old and struggling to breathe, the emergency doctor handed her a prescription and recommended she fill it at a neighborhood drugstore that would be cheaper than the hospital’s pharmacy. Then a nurse came in to begin the discharge process.
“I said no, ‘we’re not ready yet. Look at him,’” Ms. Ward said. The nurse took a pulse oximeter reading that showed the boy’s oxygen levels were at 84%, dangerously low. “If I wasn’t so knowledgeable and paid attention when they were born, since they were preemies, if it would have been somebody else, they probably would’ve went home and he’d have died.”
With the pediatric pulmonologist the boys have now, Ms. Ward said she feels more capable of managing their asthma and knowing how to reduce the likelihood that they’ll need to visit the ED.
“Part of what we’re seeing here is that having an existing and trusting relationship with a clinician can be helpful to kids with asthma,” Dr. Bardach said. “If we help establish and maintain those connections, and explain how important that connection can be, that can also help somebody with asthma overall.”
The research was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jo Ward’s twin boys have been to the emergency department for respiratory problems about as many times as the dozen years they’ve been alive. Both have asthma and bronchopulmonary dysplasia, a form of chronic airway damage that can occur in children born premature, as the twins were. But each time Ms. Ward took them in for treatment during an acute bout of breathing distress, the staff told her to schedule a follow-up visit for the children with their physician only if they didn’t get better, not regardless of the outcome – as medical guidelines recommend.
“They asked questions, they did the exams, but they really didn’t give you a lot of information to help you at home,” Ms. Ward told this news organization. If they had, she doesn’t think she’d have needed to take them in for emergency care so often.
A new study, published in Academic Pediatrics, suggests she’s right.
Current clinical guidelines for asthma recommend that patients who visit the ED for an asthma-related problem should have a follow-up appointment within a month after the visit, independent of how well they have recovered once home, according to Naomi S. Bardach, MD, a professor of pediatrics and health policy at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the new study.
Her research found that children who have a follow-up appointment within 2 weeks of such a visit are less likely to come back again the next year. Yet the study also found that only about one in five youth had a follow-up visit within that 2-week window.
“The emergency department visit is probably a sign that they need some additional attention for their asthma,” Dr. Bardach said. “We know we can prevent emergency department visits if they get the right kind of medication or if they figure out how to avoid the things that are going to cause an asthma exacerbation or flare.”
For the study, Dr. Bardach and colleagues analyzed data from California, Vermont, and Massachusetts for all asthma-related emergency visits for patients aged 3-21 years between 2013 and 2016.
Out of the 90,267 such visits they identified, 22.6% of patients had a follow-up within 2 weeks, more often by patients who were younger, had commercial insurance, had evidence of prior asthma, or had complex chronic conditions.
Whereas 5.7% of patients who had follow-up visits returned to the ED within 60 days, 6.4% of those who didn’t came back – a 12% difference (P < .001). The gap was larger a year out, with 25% of those with follow-ups returning to the ED, compared with 28.3% of those without follow-ups returning (P < .001), according to the researchers.
Overall, Dr. Bardach’s group estimates that for every 30 children who have follow-up visits with a physician, one would avoid a return trip to the emergency department for asthma within a year.
But given the sheer number of asthma-related trips to the ED each year – 164,145 for kids age 1-17 years in the United States in 2016 alone – that translates into big numbers of kids not going back to the hospital: approximately 72,000 such trips avoided at a savings to the health care system of at least $8.6 million annually.
Missed opportunities
Had Ms. Ward’s boys been among the one in five to receive follow-up care earlier in their lives, she might have saved a significant amount of time, money, anxiety, and heartache. When the twins were 9 years old, she took them to a new pediatric pulmonologist. That changed everything. In that first visit, “they gave me way more information than I ever had in the first 9 years,” she said.
The doctor told Ms. Ward to keep steroids on hand, gave her a prescription for extra doses of the powerful medication, and explained that they needed to be used within 24 hours of the first sign of a breathing problem.
“She said if you give them the steroids right away, it keeps them out of the emergency room, and that’s actually worked,” Ms. Ward said. “She made sure we had care plans every visit and asked me each time if I still had it or we needed to rewrite it. They gave me signs to look for, for when to go to hospital visits. I think that when you go to the doctor, they should be telling you stuff like that.”
Dr. Bardach said visits with a primary care doctor or asthma specialist offer families a chance to receive information to keep the condition from becoming critical.
“Going to that follow-up visit, they can get access to education from the provider about how to avoid things that trigger asthma, and there’s medication that kids can take that keeps the lungs calm and less likely to have a big asthma reaction, so getting access to that medication can be really helpful,” she said.
That was the case for Amy Davenport, of Chapel Hill, N.C., whose 6-year-old son has been to the ED twice for his asthma.
The first time, when he was 3, he was having trouble breathing with a respiratory tract infection and received nebulizer treatment – although he received it in the ED since no beds were available in the ICU. The staff did tell Ms. Davenport to follow up with her primary care provider, but her son’s pediatrician was reluctant to diagnose him with asthma at such a young age and didn’t prescribe any maintenance medications.
A few months later, Ms. Davenport and her son found themselves back in the hospital, and an ICU bed was open this time. The critical care staff referred Davenport to a pediatric pulmonary specialist, and they haven’t been back to the hospital since. Ms. Davenport said she believes if they’d received a maintenance medication after the first visit, it likely would have prevented the second one.
“I’ve definitely seen now that, after the second admission, we got an asthma action plan and it said exactly what to do,” she said. “I felt like we had really good follow-up. We had that action plan on our refrigerator for a long time, and it helped us as parents with three small children to manage.”
Of course, follow-up care takes time – time away from work and school that not all families can spare, the researchers acknowledged. Telehealth may be an option, especially after its use expanded during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We know that health systems have a hard time being flexible enough to actually have a kid be able to make an appointment within a short period of time, and we also know it’s hard for families sometimes to go back into a clinical setting within a certain period of time,” Dr. Bardach said. The urgency for the appointment may wane for those whose children seem to be doing better.
When the researchers adjusted their calculations for socioeconomic status, the results didn’t change much. But the study did find that patients with private insurance were about twice as likely to have follow-up visits as those on Medicaid (43.7% vs. 21.7%). And “the content and conduct” of the follow-up visit makes a difference as well.
Ms. Ward, whose boys are insured through Medicaid, recalled several visits to the ED where she had to push the staff to get the care her children needed. In one case, when one of her boys was a year old and struggling to breathe, the emergency doctor handed her a prescription and recommended she fill it at a neighborhood drugstore that would be cheaper than the hospital’s pharmacy. Then a nurse came in to begin the discharge process.
“I said no, ‘we’re not ready yet. Look at him,’” Ms. Ward said. The nurse took a pulse oximeter reading that showed the boy’s oxygen levels were at 84%, dangerously low. “If I wasn’t so knowledgeable and paid attention when they were born, since they were preemies, if it would have been somebody else, they probably would’ve went home and he’d have died.”
With the pediatric pulmonologist the boys have now, Ms. Ward said she feels more capable of managing their asthma and knowing how to reduce the likelihood that they’ll need to visit the ED.
“Part of what we’re seeing here is that having an existing and trusting relationship with a clinician can be helpful to kids with asthma,” Dr. Bardach said. “If we help establish and maintain those connections, and explain how important that connection can be, that can also help somebody with asthma overall.”
The research was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jo Ward’s twin boys have been to the emergency department for respiratory problems about as many times as the dozen years they’ve been alive. Both have asthma and bronchopulmonary dysplasia, a form of chronic airway damage that can occur in children born premature, as the twins were. But each time Ms. Ward took them in for treatment during an acute bout of breathing distress, the staff told her to schedule a follow-up visit for the children with their physician only if they didn’t get better, not regardless of the outcome – as medical guidelines recommend.
“They asked questions, they did the exams, but they really didn’t give you a lot of information to help you at home,” Ms. Ward told this news organization. If they had, she doesn’t think she’d have needed to take them in for emergency care so often.
A new study, published in Academic Pediatrics, suggests she’s right.
Current clinical guidelines for asthma recommend that patients who visit the ED for an asthma-related problem should have a follow-up appointment within a month after the visit, independent of how well they have recovered once home, according to Naomi S. Bardach, MD, a professor of pediatrics and health policy at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the new study.
Her research found that children who have a follow-up appointment within 2 weeks of such a visit are less likely to come back again the next year. Yet the study also found that only about one in five youth had a follow-up visit within that 2-week window.
“The emergency department visit is probably a sign that they need some additional attention for their asthma,” Dr. Bardach said. “We know we can prevent emergency department visits if they get the right kind of medication or if they figure out how to avoid the things that are going to cause an asthma exacerbation or flare.”
For the study, Dr. Bardach and colleagues analyzed data from California, Vermont, and Massachusetts for all asthma-related emergency visits for patients aged 3-21 years between 2013 and 2016.
Out of the 90,267 such visits they identified, 22.6% of patients had a follow-up within 2 weeks, more often by patients who were younger, had commercial insurance, had evidence of prior asthma, or had complex chronic conditions.
Whereas 5.7% of patients who had follow-up visits returned to the ED within 60 days, 6.4% of those who didn’t came back – a 12% difference (P < .001). The gap was larger a year out, with 25% of those with follow-ups returning to the ED, compared with 28.3% of those without follow-ups returning (P < .001), according to the researchers.
Overall, Dr. Bardach’s group estimates that for every 30 children who have follow-up visits with a physician, one would avoid a return trip to the emergency department for asthma within a year.
But given the sheer number of asthma-related trips to the ED each year – 164,145 for kids age 1-17 years in the United States in 2016 alone – that translates into big numbers of kids not going back to the hospital: approximately 72,000 such trips avoided at a savings to the health care system of at least $8.6 million annually.
Missed opportunities
Had Ms. Ward’s boys been among the one in five to receive follow-up care earlier in their lives, she might have saved a significant amount of time, money, anxiety, and heartache. When the twins were 9 years old, she took them to a new pediatric pulmonologist. That changed everything. In that first visit, “they gave me way more information than I ever had in the first 9 years,” she said.
The doctor told Ms. Ward to keep steroids on hand, gave her a prescription for extra doses of the powerful medication, and explained that they needed to be used within 24 hours of the first sign of a breathing problem.
“She said if you give them the steroids right away, it keeps them out of the emergency room, and that’s actually worked,” Ms. Ward said. “She made sure we had care plans every visit and asked me each time if I still had it or we needed to rewrite it. They gave me signs to look for, for when to go to hospital visits. I think that when you go to the doctor, they should be telling you stuff like that.”
Dr. Bardach said visits with a primary care doctor or asthma specialist offer families a chance to receive information to keep the condition from becoming critical.
“Going to that follow-up visit, they can get access to education from the provider about how to avoid things that trigger asthma, and there’s medication that kids can take that keeps the lungs calm and less likely to have a big asthma reaction, so getting access to that medication can be really helpful,” she said.
That was the case for Amy Davenport, of Chapel Hill, N.C., whose 6-year-old son has been to the ED twice for his asthma.
The first time, when he was 3, he was having trouble breathing with a respiratory tract infection and received nebulizer treatment – although he received it in the ED since no beds were available in the ICU. The staff did tell Ms. Davenport to follow up with her primary care provider, but her son’s pediatrician was reluctant to diagnose him with asthma at such a young age and didn’t prescribe any maintenance medications.
A few months later, Ms. Davenport and her son found themselves back in the hospital, and an ICU bed was open this time. The critical care staff referred Davenport to a pediatric pulmonary specialist, and they haven’t been back to the hospital since. Ms. Davenport said she believes if they’d received a maintenance medication after the first visit, it likely would have prevented the second one.
“I’ve definitely seen now that, after the second admission, we got an asthma action plan and it said exactly what to do,” she said. “I felt like we had really good follow-up. We had that action plan on our refrigerator for a long time, and it helped us as parents with three small children to manage.”
Of course, follow-up care takes time – time away from work and school that not all families can spare, the researchers acknowledged. Telehealth may be an option, especially after its use expanded during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We know that health systems have a hard time being flexible enough to actually have a kid be able to make an appointment within a short period of time, and we also know it’s hard for families sometimes to go back into a clinical setting within a certain period of time,” Dr. Bardach said. The urgency for the appointment may wane for those whose children seem to be doing better.
When the researchers adjusted their calculations for socioeconomic status, the results didn’t change much. But the study did find that patients with private insurance were about twice as likely to have follow-up visits as those on Medicaid (43.7% vs. 21.7%). And “the content and conduct” of the follow-up visit makes a difference as well.
Ms. Ward, whose boys are insured through Medicaid, recalled several visits to the ED where she had to push the staff to get the care her children needed. In one case, when one of her boys was a year old and struggling to breathe, the emergency doctor handed her a prescription and recommended she fill it at a neighborhood drugstore that would be cheaper than the hospital’s pharmacy. Then a nurse came in to begin the discharge process.
“I said no, ‘we’re not ready yet. Look at him,’” Ms. Ward said. The nurse took a pulse oximeter reading that showed the boy’s oxygen levels were at 84%, dangerously low. “If I wasn’t so knowledgeable and paid attention when they were born, since they were preemies, if it would have been somebody else, they probably would’ve went home and he’d have died.”
With the pediatric pulmonologist the boys have now, Ms. Ward said she feels more capable of managing their asthma and knowing how to reduce the likelihood that they’ll need to visit the ED.
“Part of what we’re seeing here is that having an existing and trusting relationship with a clinician can be helpful to kids with asthma,” Dr. Bardach said. “If we help establish and maintain those connections, and explain how important that connection can be, that can also help somebody with asthma overall.”
The research was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACADEMIC PEDIATRICS
Denosumab boosts bone strength in glucocorticoid users
Bone strength and microarchitecture remained stronger at 24 months after treatment with denosumab compared to risedronate, in a study of 110 adults using glucocorticoids.
Patients using glucocorticoids are at increased risk for vertebral and nonvertebral fractures at both the start of treatment or as treatment continues, wrote Piet Geusens, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
Imaging data collected via high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) allow for the assessment of bone microarchitecture and strength, but specific data comparing the impact of bone treatment in patients using glucocorticoids are lacking, they said.
In a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, the researchers identified a subset of 56 patients randomized to denosumab and 54 to risedronate patients out of a total of 590 patients who were enrolled in a phase 3 randomized, controlled trial of denosumab vs. risedronate for bone mineral density. The main results of the larger trial – presented at EULAR 2018 – showed greater increases in bone strength with denosumab over risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoids.
In the current study, the researchers reviewed HR-pQCT scans of the distal radius and tibia at baseline, 12 months, and 24 months. Bone strength and microarchitecture were defined in terms of failure load (FL) as a primary outcome. Patients also were divided into subpopulations of those initiating glucocorticoid treatment (GC-I) and continuing treatment (GC-C).
Baseline characteristics were mainly balanced among the treatment groups within the GC-I and GC-C categories.
Among the GC-I patients, in the denosumab group, FL increased significantly from baseline to 12 months at the radius at tibia (1.8% and 1.7%, respectively) but did not change significantly in the risedronate group, which translated to a significant treatment difference between the drugs of 3.3% for radius and 2.5% for tibia.
At 24 months, the radius measure of FL was unchanged from baseline in denosumab patients but significantly decreased in risedronate patients, with a difference of –4.1%, which translated to a significant between-treatment difference at the radius of 5.6% (P < .001). Changes at the tibia were not significantly different between the groups at 24 months.
Among the GC-C patients, FL was unchanged from baseline to 12 months for both the denosumab and risedronate groups. However, FL significantly increased with denosumab (4.3%) and remained unchanged in the risedronate group.
The researchers also found significant differences between denosumab and risedronate in percentage changes in cortical bone mineral density, and less prominent changes and differences in trabecular bone mineral density.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of the HR-pQCT scanner, which limits the measurement of trabecular microarchitecture, and the use of only standard HR-pQCT parameters, which do not allow insight into endosteal changes, and the inability to correct for multiplicity of data, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the superiority of denosumab over risedronate for preventing FL and total bone mineral density loss at the radius and tibia in new glucocorticoid users, and for increasing FL and total bone mineral density at the radius in long-term glucocorticoid users, they said.
Denosumab therefore could be a useful therapeutic option and could inform decision-making in patients initiating GC-therapy or on long-term GC-therapy, they concluded.
The study was supported by Amgen. Dr. Geusens disclosed grants from Amgen, Celgene, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Fresenius, Mylan, and Sandoz, and grants and other funding from AbbVie, outside the current study.
Bone strength and microarchitecture remained stronger at 24 months after treatment with denosumab compared to risedronate, in a study of 110 adults using glucocorticoids.
Patients using glucocorticoids are at increased risk for vertebral and nonvertebral fractures at both the start of treatment or as treatment continues, wrote Piet Geusens, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
Imaging data collected via high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) allow for the assessment of bone microarchitecture and strength, but specific data comparing the impact of bone treatment in patients using glucocorticoids are lacking, they said.
In a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, the researchers identified a subset of 56 patients randomized to denosumab and 54 to risedronate patients out of a total of 590 patients who were enrolled in a phase 3 randomized, controlled trial of denosumab vs. risedronate for bone mineral density. The main results of the larger trial – presented at EULAR 2018 – showed greater increases in bone strength with denosumab over risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoids.
In the current study, the researchers reviewed HR-pQCT scans of the distal radius and tibia at baseline, 12 months, and 24 months. Bone strength and microarchitecture were defined in terms of failure load (FL) as a primary outcome. Patients also were divided into subpopulations of those initiating glucocorticoid treatment (GC-I) and continuing treatment (GC-C).
Baseline characteristics were mainly balanced among the treatment groups within the GC-I and GC-C categories.
Among the GC-I patients, in the denosumab group, FL increased significantly from baseline to 12 months at the radius at tibia (1.8% and 1.7%, respectively) but did not change significantly in the risedronate group, which translated to a significant treatment difference between the drugs of 3.3% for radius and 2.5% for tibia.
At 24 months, the radius measure of FL was unchanged from baseline in denosumab patients but significantly decreased in risedronate patients, with a difference of –4.1%, which translated to a significant between-treatment difference at the radius of 5.6% (P < .001). Changes at the tibia were not significantly different between the groups at 24 months.
Among the GC-C patients, FL was unchanged from baseline to 12 months for both the denosumab and risedronate groups. However, FL significantly increased with denosumab (4.3%) and remained unchanged in the risedronate group.
The researchers also found significant differences between denosumab and risedronate in percentage changes in cortical bone mineral density, and less prominent changes and differences in trabecular bone mineral density.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of the HR-pQCT scanner, which limits the measurement of trabecular microarchitecture, and the use of only standard HR-pQCT parameters, which do not allow insight into endosteal changes, and the inability to correct for multiplicity of data, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the superiority of denosumab over risedronate for preventing FL and total bone mineral density loss at the radius and tibia in new glucocorticoid users, and for increasing FL and total bone mineral density at the radius in long-term glucocorticoid users, they said.
Denosumab therefore could be a useful therapeutic option and could inform decision-making in patients initiating GC-therapy or on long-term GC-therapy, they concluded.
The study was supported by Amgen. Dr. Geusens disclosed grants from Amgen, Celgene, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Fresenius, Mylan, and Sandoz, and grants and other funding from AbbVie, outside the current study.
Bone strength and microarchitecture remained stronger at 24 months after treatment with denosumab compared to risedronate, in a study of 110 adults using glucocorticoids.
Patients using glucocorticoids are at increased risk for vertebral and nonvertebral fractures at both the start of treatment or as treatment continues, wrote Piet Geusens, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
Imaging data collected via high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) allow for the assessment of bone microarchitecture and strength, but specific data comparing the impact of bone treatment in patients using glucocorticoids are lacking, they said.
In a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, the researchers identified a subset of 56 patients randomized to denosumab and 54 to risedronate patients out of a total of 590 patients who were enrolled in a phase 3 randomized, controlled trial of denosumab vs. risedronate for bone mineral density. The main results of the larger trial – presented at EULAR 2018 – showed greater increases in bone strength with denosumab over risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoids.
In the current study, the researchers reviewed HR-pQCT scans of the distal radius and tibia at baseline, 12 months, and 24 months. Bone strength and microarchitecture were defined in terms of failure load (FL) as a primary outcome. Patients also were divided into subpopulations of those initiating glucocorticoid treatment (GC-I) and continuing treatment (GC-C).
Baseline characteristics were mainly balanced among the treatment groups within the GC-I and GC-C categories.
Among the GC-I patients, in the denosumab group, FL increased significantly from baseline to 12 months at the radius at tibia (1.8% and 1.7%, respectively) but did not change significantly in the risedronate group, which translated to a significant treatment difference between the drugs of 3.3% for radius and 2.5% for tibia.
At 24 months, the radius measure of FL was unchanged from baseline in denosumab patients but significantly decreased in risedronate patients, with a difference of –4.1%, which translated to a significant between-treatment difference at the radius of 5.6% (P < .001). Changes at the tibia were not significantly different between the groups at 24 months.
Among the GC-C patients, FL was unchanged from baseline to 12 months for both the denosumab and risedronate groups. However, FL significantly increased with denosumab (4.3%) and remained unchanged in the risedronate group.
The researchers also found significant differences between denosumab and risedronate in percentage changes in cortical bone mineral density, and less prominent changes and differences in trabecular bone mineral density.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of the HR-pQCT scanner, which limits the measurement of trabecular microarchitecture, and the use of only standard HR-pQCT parameters, which do not allow insight into endosteal changes, and the inability to correct for multiplicity of data, the researchers noted.
However, the results support the superiority of denosumab over risedronate for preventing FL and total bone mineral density loss at the radius and tibia in new glucocorticoid users, and for increasing FL and total bone mineral density at the radius in long-term glucocorticoid users, they said.
Denosumab therefore could be a useful therapeutic option and could inform decision-making in patients initiating GC-therapy or on long-term GC-therapy, they concluded.
The study was supported by Amgen. Dr. Geusens disclosed grants from Amgen, Celgene, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Fresenius, Mylan, and Sandoz, and grants and other funding from AbbVie, outside the current study.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH
Step test signals exercise capacity in asthma patients
The incremental step test is a highly reliable measure of exercise capacity in patients with moderate to severe asthma, based on data from 50 individuals.
Asthma patients often limit their physical exercise to avoid respiratory symptoms, which creates a downward spiral of reduced exercise capacity and ability to perform activities of daily living, wrote Renata Cléia Claudino Barbosa of the University of Sao Paulo and colleagues. “However, exercise training has been shown to be an important adjunctive therapy for asthma treatment that improves exercise capacity and health-related quality of life,” they wrote.
Step tests have been identified as a simpler, less costly alternative to cardiopulmonary exercise tests to measure exercise capacity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but their effectiveness for asthma patients has not investigated, the researchers said.
In a study published in Pulmonology, the researchers recruited 50 adults with moderate or severe asthma during routine care at a university hospital. The participants had been clinically stable for at least 6 months, with no hospitalizations, emergency care, or medication changes in the past 30 days. All participants received short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids. The patients ranged in age from 18 to 60 years, with body mass index measures from 20 kg/m2 to 40 kg/m2.
Participants were randomized to tests on 2 nonconsecutive days at least 48 hours apart. On the first day, patients completed asthma control questionnaires and lung function tests, then performed either a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) or two incremental step tests (IST-1 and IST-2). On the second day, they performed the other test. Participants were instructed to use bronchodilators 15 minutes before each test.
The step test involved stepping up and down on a 20-cm high wooden bench.
Overall, the peak oxygen uptakes were 27.6 mL/kg per minute for the CPET, 22.3 mL/kg per minute for the first IST, and 23.3 mL/kg per minute for the second IST.
“The IST with better performance regarding the peak VO2 value was called the best IST (b-IST),” and these values were used for validity and interpretability analyses, the researchers wrote.
In a reliability analysis, the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was 0.93, the measurement error was 2.5%, and the construct validity for peak VO2 was significantly more reliable than the CPET (P < 0.001), the researchers said. The ICC for total number of steps was 0.88.
Notably, “the present study also demonstrated that IST is not interchangeable with the CPET since the subjects with moderate to severe asthma did not reach the maximal exercise capacity,” the researchers said. However, “we believe that the IST is superior to walking tests in subjects with asthma because it is an activity that requires greater ventilation in a subject’s daily life,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small study population and the small number of male patients, which may limit generalizability to males with asthma or other asthma endotypes, the researchers said. However, the results were strengthened by the randomized design, and support the value of the IST as a cost-effective option for assessing exercise capacity, preferably with two step tests to minimize the learning effect, they said. Additional research is needed to determine whether IST can assess responsiveness to pharmacological and nonpharmalogical treatments in asthma patients, they noted.
The study was supported by the Sao Paulo Research Foundation, Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa, and Coordination of Improvement of Higher Level Personnel--Brazil. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The incremental step test is a highly reliable measure of exercise capacity in patients with moderate to severe asthma, based on data from 50 individuals.
Asthma patients often limit their physical exercise to avoid respiratory symptoms, which creates a downward spiral of reduced exercise capacity and ability to perform activities of daily living, wrote Renata Cléia Claudino Barbosa of the University of Sao Paulo and colleagues. “However, exercise training has been shown to be an important adjunctive therapy for asthma treatment that improves exercise capacity and health-related quality of life,” they wrote.
Step tests have been identified as a simpler, less costly alternative to cardiopulmonary exercise tests to measure exercise capacity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but their effectiveness for asthma patients has not investigated, the researchers said.
In a study published in Pulmonology, the researchers recruited 50 adults with moderate or severe asthma during routine care at a university hospital. The participants had been clinically stable for at least 6 months, with no hospitalizations, emergency care, or medication changes in the past 30 days. All participants received short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids. The patients ranged in age from 18 to 60 years, with body mass index measures from 20 kg/m2 to 40 kg/m2.
Participants were randomized to tests on 2 nonconsecutive days at least 48 hours apart. On the first day, patients completed asthma control questionnaires and lung function tests, then performed either a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) or two incremental step tests (IST-1 and IST-2). On the second day, they performed the other test. Participants were instructed to use bronchodilators 15 minutes before each test.
The step test involved stepping up and down on a 20-cm high wooden bench.
Overall, the peak oxygen uptakes were 27.6 mL/kg per minute for the CPET, 22.3 mL/kg per minute for the first IST, and 23.3 mL/kg per minute for the second IST.
“The IST with better performance regarding the peak VO2 value was called the best IST (b-IST),” and these values were used for validity and interpretability analyses, the researchers wrote.
In a reliability analysis, the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was 0.93, the measurement error was 2.5%, and the construct validity for peak VO2 was significantly more reliable than the CPET (P < 0.001), the researchers said. The ICC for total number of steps was 0.88.
Notably, “the present study also demonstrated that IST is not interchangeable with the CPET since the subjects with moderate to severe asthma did not reach the maximal exercise capacity,” the researchers said. However, “we believe that the IST is superior to walking tests in subjects with asthma because it is an activity that requires greater ventilation in a subject’s daily life,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small study population and the small number of male patients, which may limit generalizability to males with asthma or other asthma endotypes, the researchers said. However, the results were strengthened by the randomized design, and support the value of the IST as a cost-effective option for assessing exercise capacity, preferably with two step tests to minimize the learning effect, they said. Additional research is needed to determine whether IST can assess responsiveness to pharmacological and nonpharmalogical treatments in asthma patients, they noted.
The study was supported by the Sao Paulo Research Foundation, Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa, and Coordination of Improvement of Higher Level Personnel--Brazil. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The incremental step test is a highly reliable measure of exercise capacity in patients with moderate to severe asthma, based on data from 50 individuals.
Asthma patients often limit their physical exercise to avoid respiratory symptoms, which creates a downward spiral of reduced exercise capacity and ability to perform activities of daily living, wrote Renata Cléia Claudino Barbosa of the University of Sao Paulo and colleagues. “However, exercise training has been shown to be an important adjunctive therapy for asthma treatment that improves exercise capacity and health-related quality of life,” they wrote.
Step tests have been identified as a simpler, less costly alternative to cardiopulmonary exercise tests to measure exercise capacity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but their effectiveness for asthma patients has not investigated, the researchers said.
In a study published in Pulmonology, the researchers recruited 50 adults with moderate or severe asthma during routine care at a university hospital. The participants had been clinically stable for at least 6 months, with no hospitalizations, emergency care, or medication changes in the past 30 days. All participants received short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids. The patients ranged in age from 18 to 60 years, with body mass index measures from 20 kg/m2 to 40 kg/m2.
Participants were randomized to tests on 2 nonconsecutive days at least 48 hours apart. On the first day, patients completed asthma control questionnaires and lung function tests, then performed either a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) or two incremental step tests (IST-1 and IST-2). On the second day, they performed the other test. Participants were instructed to use bronchodilators 15 minutes before each test.
The step test involved stepping up and down on a 20-cm high wooden bench.
Overall, the peak oxygen uptakes were 27.6 mL/kg per minute for the CPET, 22.3 mL/kg per minute for the first IST, and 23.3 mL/kg per minute for the second IST.
“The IST with better performance regarding the peak VO2 value was called the best IST (b-IST),” and these values were used for validity and interpretability analyses, the researchers wrote.
In a reliability analysis, the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was 0.93, the measurement error was 2.5%, and the construct validity for peak VO2 was significantly more reliable than the CPET (P < 0.001), the researchers said. The ICC for total number of steps was 0.88.
Notably, “the present study also demonstrated that IST is not interchangeable with the CPET since the subjects with moderate to severe asthma did not reach the maximal exercise capacity,” the researchers said. However, “we believe that the IST is superior to walking tests in subjects with asthma because it is an activity that requires greater ventilation in a subject’s daily life,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small study population and the small number of male patients, which may limit generalizability to males with asthma or other asthma endotypes, the researchers said. However, the results were strengthened by the randomized design, and support the value of the IST as a cost-effective option for assessing exercise capacity, preferably with two step tests to minimize the learning effect, they said. Additional research is needed to determine whether IST can assess responsiveness to pharmacological and nonpharmalogical treatments in asthma patients, they noted.
The study was supported by the Sao Paulo Research Foundation, Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa, and Coordination of Improvement of Higher Level Personnel--Brazil. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PULMONOLOGY




