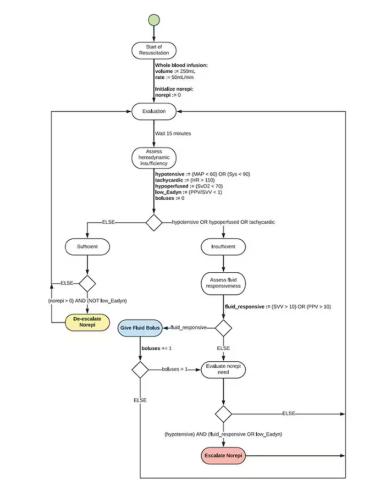
User login
Listen to earn your patients’ trust
Recently, I had an interesting conversation while getting my hair cut. It gave me a great deal of insight into some of the problems we have right now with how medical information is shared and some of the disconnect our patients may feel.
The young woman who was cutting my hair asked me what I did for an occupation. I said that I was a physician. She said, “Can I please ask you an important question?” She asked me what my thoughts were about the COVID vaccine. She prefaced it with “I am so confused on whether I should get the vaccine. I have seen a number of TikTok videos that talk about nano particles in the COVID vaccine that can be very dangerous.”
I discussed with her how the COVID vaccine actually works and shared with her the remarkable success of the vaccine. I asked her what side effects she was worried about from the vaccine and what her fears were. She said that she had heard that a lot of people had died from the vaccine. I told her that severe reactions from the vaccine were very uncommon.
She then made a very telling comment: “I wish I could talk to a doctor about my concerns. I have been going to the same health center for the last 5 years and every time I go I see a different person.” She added, “I rarely have more than 5-10 minutes with the person that I am seeing and I rarely get the opportunity to ask questions.”
She thanked me for the information and said that she would be getting the COVID vaccine in the future. She said it is so hard to know where to get information now and the very different things that she heard confused her. She told me that she thought her generation got most of its information from short sound bites or TikTok and Instagram videos.
Why did she trust me? I still think that the medical profession is respected. We are all pressured to do more with less time. Conversations where we can listen and then respond go a long way. We can always listen and learn what information people need and will appreciate. I was also struck by how alone this person felt in our health care system. She did not have a relationship with any one person whom she could trust and reach out to with questions. Relationships with our patients go a long way to establishing trust.
Pearl
It takes time to listen to and answer our patients’ questions. We need to do that to fight the waves of misinformation our patients face.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
Recently, I had an interesting conversation while getting my hair cut. It gave me a great deal of insight into some of the problems we have right now with how medical information is shared and some of the disconnect our patients may feel.
The young woman who was cutting my hair asked me what I did for an occupation. I said that I was a physician. She said, “Can I please ask you an important question?” She asked me what my thoughts were about the COVID vaccine. She prefaced it with “I am so confused on whether I should get the vaccine. I have seen a number of TikTok videos that talk about nano particles in the COVID vaccine that can be very dangerous.”
I discussed with her how the COVID vaccine actually works and shared with her the remarkable success of the vaccine. I asked her what side effects she was worried about from the vaccine and what her fears were. She said that she had heard that a lot of people had died from the vaccine. I told her that severe reactions from the vaccine were very uncommon.
She then made a very telling comment: “I wish I could talk to a doctor about my concerns. I have been going to the same health center for the last 5 years and every time I go I see a different person.” She added, “I rarely have more than 5-10 minutes with the person that I am seeing and I rarely get the opportunity to ask questions.”
She thanked me for the information and said that she would be getting the COVID vaccine in the future. She said it is so hard to know where to get information now and the very different things that she heard confused her. She told me that she thought her generation got most of its information from short sound bites or TikTok and Instagram videos.
Why did she trust me? I still think that the medical profession is respected. We are all pressured to do more with less time. Conversations where we can listen and then respond go a long way. We can always listen and learn what information people need and will appreciate. I was also struck by how alone this person felt in our health care system. She did not have a relationship with any one person whom she could trust and reach out to with questions. Relationships with our patients go a long way to establishing trust.
Pearl
It takes time to listen to and answer our patients’ questions. We need to do that to fight the waves of misinformation our patients face.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
Recently, I had an interesting conversation while getting my hair cut. It gave me a great deal of insight into some of the problems we have right now with how medical information is shared and some of the disconnect our patients may feel.
The young woman who was cutting my hair asked me what I did for an occupation. I said that I was a physician. She said, “Can I please ask you an important question?” She asked me what my thoughts were about the COVID vaccine. She prefaced it with “I am so confused on whether I should get the vaccine. I have seen a number of TikTok videos that talk about nano particles in the COVID vaccine that can be very dangerous.”
I discussed with her how the COVID vaccine actually works and shared with her the remarkable success of the vaccine. I asked her what side effects she was worried about from the vaccine and what her fears were. She said that she had heard that a lot of people had died from the vaccine. I told her that severe reactions from the vaccine were very uncommon.
She then made a very telling comment: “I wish I could talk to a doctor about my concerns. I have been going to the same health center for the last 5 years and every time I go I see a different person.” She added, “I rarely have more than 5-10 minutes with the person that I am seeing and I rarely get the opportunity to ask questions.”
She thanked me for the information and said that she would be getting the COVID vaccine in the future. She said it is so hard to know where to get information now and the very different things that she heard confused her. She told me that she thought her generation got most of its information from short sound bites or TikTok and Instagram videos.
Why did she trust me? I still think that the medical profession is respected. We are all pressured to do more with less time. Conversations where we can listen and then respond go a long way. We can always listen and learn what information people need and will appreciate. I was also struck by how alone this person felt in our health care system. She did not have a relationship with any one person whom she could trust and reach out to with questions. Relationships with our patients go a long way to establishing trust.
Pearl
It takes time to listen to and answer our patients’ questions. We need to do that to fight the waves of misinformation our patients face.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
The Tyranny of Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are excellent drugs. They’re cheap and effective; feature prominently in hypertension guidelines; and remain a sine qua non for coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and heart failure treatment. They’ve been around forever, and we know they work. Good luck finding an adult medicine patient who isn’t on one.
Beta-blockers act by slowing resting heart rate (and blunting the heart rate response to exercise. The latter is a pernicious cause of activity intolerance that often goes unchecked. Even when the adverse effects of beta-blockers are appreciated, providers are loath to alter dosing, much less stop the drug. After all, beta-blockers are an integral part of guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT), and GDMT saves lives.
Balancing Heart Rate and Stroke Volume Effects
To augment cardiac output and optimize oxygen uptake (VO2) during exercise, we need the heart rate response. In fact, the heart rate response contributes more to cardiac output than augmenting stroke volume (SV) and more to VO2 than the increase in arteriovenous (AV) oxygen difference. An inability to increase the heart rate commensurate with physiologic work is called chronotropic incompetence (CI). That’s what beta-blockers do ─ they cause CI.
Physiology dictates that CI will cause activity intolerance. That said, it’s hard to quantify the impact from beta-blockers at the individual patient level. Data suggest the heart rate effect is profound. A study in patients without heart failure found that 22% of participants on beta-blockers had CI, and the investigators used a conservative CI definition (≤ 62% of heart rate reserve used). A recent report published in JAMA Cardiology found that stopping beta-blockers in patients with heart failure allowed for an extra 30 beats/min at max exercise.
Wasserman and Whipp’s textbook, the last word on all things exercise, presents a sample subject who undergoes two separate cardiopulmonary exercise tests (CPETs). Before the first, he’s given a placebo, and before the second, he gets an intravenous beta-blocker. He’s a 23-year-old otherwise healthy male — the perfect test case for isolating beta-blocker impact without confounding by comorbid diseases, other medications, or deconditioning. His max heart rate dropped by 30 beats/min after the beta-blocker, identical to what we saw in the JAMA Cardiology study (with the heart rate increasing by 30 beats/min following withdrawal). Case closed. Stop the beta-blockers on your patients so they can meet their exercise goals and get healthy!
Such pithy enthusiasm discounts physiology’s complexities. When blunting our patient’s heart rate response with beta-blockers, we also increase diastolic filling time, which increases SV. For the 23-year-old in Wasserman and Whipp’s physiology textbook, the beta-blocker increased O2 pulse (the product of SV and AV difference). Presumably, this is mediated by the increased SV. There was a net reduction in VO2 peak, but it was nominal, suggesting that the drop in heart rate was largely offset by the increase in O2 pulse. For the patients in the JAMA Cardiology study, the entire group had a small increase in VO2 peak with beta-blocker withdrawal, but the effect differed by left ventricular function. Across different studies, the beta-blocker effect on heart rate is consistent but the change in overall exercise capacity is not.
Patient Variability in Beta-Blocker Response
In addition to left ventricular function, there are other factors likely to drive variability at the patient level. We’ve treated the response to beta-blockers as a class effect — an obvious oversimplification. The impact on exercise and the heart will vary by dose and drug (eg, atenolol vs metoprolol vs carvedilol, and so on). Beta-blockers can also affect the lungs, and we’re still debating how cautious to be in the presence of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In a world of infinite time, resources, and expertise, we’d CPET everyone before and after beta-blocker use. Our current reality requires the unthinkable: We’ll have to talk to each other and our patients. For example, heart failure guidelines recommend titrating drugs to match the dose from trials that proved efficacy. These doses are quite high. Simple discussion with the cardiologist and the patient may allow for an adjustment back down with careful monitoring and close attention to activity tolerance. With any luck, you’ll preserve the benefits from GDMT while optimizing your patient›s ability to meet their exercise goals.
Dr. Holley, professor in the department of medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Beta-blockers are excellent drugs. They’re cheap and effective; feature prominently in hypertension guidelines; and remain a sine qua non for coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and heart failure treatment. They’ve been around forever, and we know they work. Good luck finding an adult medicine patient who isn’t on one.
Beta-blockers act by slowing resting heart rate (and blunting the heart rate response to exercise. The latter is a pernicious cause of activity intolerance that often goes unchecked. Even when the adverse effects of beta-blockers are appreciated, providers are loath to alter dosing, much less stop the drug. After all, beta-blockers are an integral part of guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT), and GDMT saves lives.
Balancing Heart Rate and Stroke Volume Effects
To augment cardiac output and optimize oxygen uptake (VO2) during exercise, we need the heart rate response. In fact, the heart rate response contributes more to cardiac output than augmenting stroke volume (SV) and more to VO2 than the increase in arteriovenous (AV) oxygen difference. An inability to increase the heart rate commensurate with physiologic work is called chronotropic incompetence (CI). That’s what beta-blockers do ─ they cause CI.
Physiology dictates that CI will cause activity intolerance. That said, it’s hard to quantify the impact from beta-blockers at the individual patient level. Data suggest the heart rate effect is profound. A study in patients without heart failure found that 22% of participants on beta-blockers had CI, and the investigators used a conservative CI definition (≤ 62% of heart rate reserve used). A recent report published in JAMA Cardiology found that stopping beta-blockers in patients with heart failure allowed for an extra 30 beats/min at max exercise.
Wasserman and Whipp’s textbook, the last word on all things exercise, presents a sample subject who undergoes two separate cardiopulmonary exercise tests (CPETs). Before the first, he’s given a placebo, and before the second, he gets an intravenous beta-blocker. He’s a 23-year-old otherwise healthy male — the perfect test case for isolating beta-blocker impact without confounding by comorbid diseases, other medications, or deconditioning. His max heart rate dropped by 30 beats/min after the beta-blocker, identical to what we saw in the JAMA Cardiology study (with the heart rate increasing by 30 beats/min following withdrawal). Case closed. Stop the beta-blockers on your patients so they can meet their exercise goals and get healthy!
Such pithy enthusiasm discounts physiology’s complexities. When blunting our patient’s heart rate response with beta-blockers, we also increase diastolic filling time, which increases SV. For the 23-year-old in Wasserman and Whipp’s physiology textbook, the beta-blocker increased O2 pulse (the product of SV and AV difference). Presumably, this is mediated by the increased SV. There was a net reduction in VO2 peak, but it was nominal, suggesting that the drop in heart rate was largely offset by the increase in O2 pulse. For the patients in the JAMA Cardiology study, the entire group had a small increase in VO2 peak with beta-blocker withdrawal, but the effect differed by left ventricular function. Across different studies, the beta-blocker effect on heart rate is consistent but the change in overall exercise capacity is not.
Patient Variability in Beta-Blocker Response
In addition to left ventricular function, there are other factors likely to drive variability at the patient level. We’ve treated the response to beta-blockers as a class effect — an obvious oversimplification. The impact on exercise and the heart will vary by dose and drug (eg, atenolol vs metoprolol vs carvedilol, and so on). Beta-blockers can also affect the lungs, and we’re still debating how cautious to be in the presence of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In a world of infinite time, resources, and expertise, we’d CPET everyone before and after beta-blocker use. Our current reality requires the unthinkable: We’ll have to talk to each other and our patients. For example, heart failure guidelines recommend titrating drugs to match the dose from trials that proved efficacy. These doses are quite high. Simple discussion with the cardiologist and the patient may allow for an adjustment back down with careful monitoring and close attention to activity tolerance. With any luck, you’ll preserve the benefits from GDMT while optimizing your patient›s ability to meet their exercise goals.
Dr. Holley, professor in the department of medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Beta-blockers are excellent drugs. They’re cheap and effective; feature prominently in hypertension guidelines; and remain a sine qua non for coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and heart failure treatment. They’ve been around forever, and we know they work. Good luck finding an adult medicine patient who isn’t on one.
Beta-blockers act by slowing resting heart rate (and blunting the heart rate response to exercise. The latter is a pernicious cause of activity intolerance that often goes unchecked. Even when the adverse effects of beta-blockers are appreciated, providers are loath to alter dosing, much less stop the drug. After all, beta-blockers are an integral part of guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT), and GDMT saves lives.
Balancing Heart Rate and Stroke Volume Effects
To augment cardiac output and optimize oxygen uptake (VO2) during exercise, we need the heart rate response. In fact, the heart rate response contributes more to cardiac output than augmenting stroke volume (SV) and more to VO2 than the increase in arteriovenous (AV) oxygen difference. An inability to increase the heart rate commensurate with physiologic work is called chronotropic incompetence (CI). That’s what beta-blockers do ─ they cause CI.
Physiology dictates that CI will cause activity intolerance. That said, it’s hard to quantify the impact from beta-blockers at the individual patient level. Data suggest the heart rate effect is profound. A study in patients without heart failure found that 22% of participants on beta-blockers had CI, and the investigators used a conservative CI definition (≤ 62% of heart rate reserve used). A recent report published in JAMA Cardiology found that stopping beta-blockers in patients with heart failure allowed for an extra 30 beats/min at max exercise.
Wasserman and Whipp’s textbook, the last word on all things exercise, presents a sample subject who undergoes two separate cardiopulmonary exercise tests (CPETs). Before the first, he’s given a placebo, and before the second, he gets an intravenous beta-blocker. He’s a 23-year-old otherwise healthy male — the perfect test case for isolating beta-blocker impact without confounding by comorbid diseases, other medications, or deconditioning. His max heart rate dropped by 30 beats/min after the beta-blocker, identical to what we saw in the JAMA Cardiology study (with the heart rate increasing by 30 beats/min following withdrawal). Case closed. Stop the beta-blockers on your patients so they can meet their exercise goals and get healthy!
Such pithy enthusiasm discounts physiology’s complexities. When blunting our patient’s heart rate response with beta-blockers, we also increase diastolic filling time, which increases SV. For the 23-year-old in Wasserman and Whipp’s physiology textbook, the beta-blocker increased O2 pulse (the product of SV and AV difference). Presumably, this is mediated by the increased SV. There was a net reduction in VO2 peak, but it was nominal, suggesting that the drop in heart rate was largely offset by the increase in O2 pulse. For the patients in the JAMA Cardiology study, the entire group had a small increase in VO2 peak with beta-blocker withdrawal, but the effect differed by left ventricular function. Across different studies, the beta-blocker effect on heart rate is consistent but the change in overall exercise capacity is not.
Patient Variability in Beta-Blocker Response
In addition to left ventricular function, there are other factors likely to drive variability at the patient level. We’ve treated the response to beta-blockers as a class effect — an obvious oversimplification. The impact on exercise and the heart will vary by dose and drug (eg, atenolol vs metoprolol vs carvedilol, and so on). Beta-blockers can also affect the lungs, and we’re still debating how cautious to be in the presence of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In a world of infinite time, resources, and expertise, we’d CPET everyone before and after beta-blocker use. Our current reality requires the unthinkable: We’ll have to talk to each other and our patients. For example, heart failure guidelines recommend titrating drugs to match the dose from trials that proved efficacy. These doses are quite high. Simple discussion with the cardiologist and the patient may allow for an adjustment back down with careful monitoring and close attention to activity tolerance. With any luck, you’ll preserve the benefits from GDMT while optimizing your patient›s ability to meet their exercise goals.
Dr. Holley, professor in the department of medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Effects of Immigration on the Parent-Child Relationship
In their native country, they learned throughout their life cultural norms and systems that defined their environment. When these parents immigrate to a new country, their different set of knowledge may not be applicable in many ways to their new environment.
The Disruption of Social Roles
Culturally, language is one of the most important types of knowledge parents pass to their children. Nearly half of adult immigrants in the United States have limited English proficiency. 1
Their children often learn the language faster, often placing these children in the position of interpreters for their parents. These parents can become dependent on their children to negotiate social structures instead of vice versa, potentially undermining the social hierarchy and role of parenting. 2 Both Mr. Contreras and Dr. Nguyen recall that as children of immigrant parents — from Mexico and Vietnam, respectively — they commanded English better than their parents, which often made them take on more “adult roles.” For example, Dr. Nguyen recalls that his mother would solicit his help in grocery shopping because she could neither navigate the aisles effectively nor ask for help. Mr. Contreras commonly found himself acting as an impromptu medical translator for his mother on several occasions. This dependence of immigrant parents on their children for guidance in their host country can be pervasive in other social structures such as legal and academic.
Impact on School
Potentially, an immigrant parent’s lack of knowledge of the language and systems of their host country can make them ineffective advocates for their children at school. Mr. Contreras’s intervention for his patient as a medical student demonstrates this in the arena of school.
Mr. Contreras was rotating at a hospital burn unit in 2023 when R, a young middle school student, and his mother arrived in the emergency department. An incident had occurred at his school. R had been the victim of aggravated battery and assault, sustaining a 3x2 cm burn on his forearm from students placing hot glue onto a piece of cardboard then immediately onto his skin and silencing him by covering his mouth. For months the older students had been bullying R. R’s mother made multiple attempts with both the school’s front desk and counselors to address the issue, but to no avail. R himself, though encouraged to speak up, did not out of fear. As Mr. Contreras realized the situation and the impasse, he used his fluency in Spanish and English to facilitate a joint call with the school district. Within 10 minutes, they were able to connect with a student safety specialist and launch a full investigation. A language barrier and the lack of knowledge of their rights and school system had prevented R’s mother from effectively advocating for her child’s safety.
In Dr. Nguyen’s experience as a teacher, even in classrooms dominated by minority students, the advocacy for students struggling in classes was disproportionate. It favored White parents, but also generally more educated families. This is further supported by a study of 225 schools across six states of kindergarten children showing similar trends, that African American, Latino, and less-educated parents were less involved in their children’s education as reported by teachers.3 It is important to note that in this study teachers were 80% White, 9% Latino, 7% African American, 3% multiracial, and 1% Asian American, suggesting that cultural discrepancy between teachers and parents could be an important factor affecting parent-teacher communication. Dr. Nguyen also recalled trying to discipline several students who were disruptive in his class by telling them he would speak to their parents. Several times, these students would counter defiantly, “Well, good luck, they can’t speak English.” The parents’ dependency on their children to communicate with teachers undermined the abilities of both adults to manage their behaviors and promote learning.
The Mental Health of Immigrant Parents
Migrants often have greater incidence of mental health problems, including depression, PTSD, and anxiety, from a combination of peri-migrational experiences. 4 Immigrant mothers are known to have higher rates of post-natal depression, which cause problems later with child development. 5 Though she warns larger studies are needed, Dr. Fazel’s review of Croatian refugees suggests that displacement from one’s native country is a risk factor for poorer mental health, namely due to difficulty in psychosocial adaptation. 6 The likely mechanism is that lack of access to one’s language and culture, or a language and culture that one can navigate effectively, exacerbates, even engenders mental health sequelae. Because of this, first-generation immigrant children often face harsher and more violent parenting. 7,8 Immigrant parents also may have less access to mental health resources since they often resort to their own cultural practices. Both Mr. Contreras’s and Dr. Nguyen’s following narratives of their mothers’ struggle with mental health illustrate the causes and consequences.
Mr. Contreras, who grew up in a Mexican immigrant household in Los Angeles, saw firsthand how his mother, who faced language barriers and a distrust of Western medicine, turned to traditional healers and herbal remedies for her health needs. Accompanying her to doctor appointments as her translator, he often felt the disconnect between her cultural background and the Western medical system. For her, seeking help from traditional healers was not just about addressing physical ailments but also about finding comfort and familiarity in practices rooted in her cultural beliefs. This preference for cultural or religious methods for mental health support is not uncommon among Mexican immigrant families.
Dr. Nguyen, whose mother was a refugee from Vietnam, recalls her constant depressed mood and suicidal thoughts in the immediate years after she resettled in San Diego. This was caused mostly by the missing of her social supports in Vietnam, her difficulty adjusting to American culture and language, and her difficulty finding work. Often her depression and stress took a darker turn in terms of more violent parenting. Of course, the cause of her poor mental health is hard to parse from the traumas and violence she had faced as a refugee, but in subsequent years, her many brothers and sisters who immigrated through a more orderly process also displayed similar mental health vulnerabilities.
The Mental Health of Children of Immigrant Parents
The relationship between an immigrant parent’s poor mental health and their children is difficult to parse from what we know about native parents and their children. But the primary differences appear to be a great disruption of social roles, the effects of migration itself, and the oftentimes more strict and disciplinarian parenting style as discussed above. Given this, one would expect immigrant children to suffer greater mental health difficulties. However, a recent study of almost 500,000 children in Canada revealed decreased prevalence of conduct disorder, ADHD, and mood and anxiety disorders in immigrant youth, both first- and second-generation, as compared to non-immigrants. 9 This perhaps surprising result highlights how much more we need to understand about the effects of culture on the mental health diagnosis of immigrant youth. It suggests differences in mental health access and use from the cultural factors we mentioned above, to problems with using Western-based mental criteria and symptomatology for diagnosing non-Western children. It can even suggest the underestimation of the protective effects of native culture such as strong ethnic identity and cultural support systems, thereby challenging a purely deficit mental health model of the immigrant experience.
Summary
Dr. Duy Nguyen and Mr. Andrew Contreras are both children of immigrant parents from Vietnam and Mexico, respectively. Dr. Nguyen spent 15 years as an English teacher at San Leandro High School, whose student body was roughly 50% Hispanic and 25% Asian, making immigrant parents a huge swath of his educational partners. Mr. Contreras founded a high school outreach program where he interacted with K-12 children of immigrant youth. In addition, he partners with Fresno’s Economic Opportunity Commission to educate immigrant Hispanic parents and their teens on having difficult conversations with their teenage children on topics such as mental and reproductive health. Dr. Duy Nguyen and Mr. Andrew Contreras will explore the differences in immigrant parent-child relationships, compared with native ones, as they relate to mental health ramifications for the child and parent. They reveal immigrant mental health disruptions regarding culture and language, familial hierarchies, parenting styles, as well as parental mental health sequelae brought about by immigration using research and their own personal experiences.
Dr. Nguyen is a second-year resident at the University of California, San Francisco, Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously. Mr. Contreras is currently a 4th-year medical student at University of California, San Francisco, and applying to Psychiatry for the 2025 match.
References
1. Rao A et al. Five Key Facts About Immigrants With Limited English Proficiency. KFF. 2024 March 14. https://www.kff.org/racial-equity-and-health-policy/issue-brief-five-key-facts-about-immigrants-with-limited-english-proficiency .
2. Raffaetà R. Migration and Parenting: Reviewing the Debate and Calling for Future Research. International Journal of Migration, Health and Social Care. 2016;12(1):38-50. doi: 10.1108/IJMHSC-12-2014-0052/full/html .
3. Nzinga‐Johnson S et al. Teacher‐Parent Relationships and School Involvement Among Racially and Educationally Diverse Parents of Kindergartners. Elementary School Journal. 2009 Sept. doi: 10.1086/598844 .
4. Close C et al. The Mental Health and Wellbeing of First Generation Migrants: A Systematic-Narrative Review of Reviews. Global Health. 2016 Aug 25;12(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12992-016-0187-3.
5. Collins CH et al. Refugee, Asylum Seeker, Immigrant Women and Postnatal Depression: Rates and Risk Factors. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2011 Feb;14(1):3-11. doi: 10.1007/s00737-010-0198-7 .
6. Fazel M, Betancourt TS. Preventive Mental Health Interventions for Refugee Children and Adolescents in High-Income Settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-132. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5 .
7. Pottie K et al. Do First Generation Immigrant Adolescents Face Higher Rates of Bullying, Violence and Suicidal Behaviours Than Do Third Generation and Native Born? J Immigr Minor Health. 2015 Oct;17(5):1557-1566. doi: 10.1007/s10903-014-0108-6.
8. Smokowski PR, Bacallao ML. Acculturation and Aggression in Latino Adolescents: A Structural Model Focusing on Cultural Risk Factors and Assets. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2006 Oct;34(5):659-673. doi: 10.1007/s10802-006-9049-4 .
9. Gadermann AM et al. Prevalence of Mental Health Disorders Among Immigrant, Refugee, and Nonimmigrant Children and Youth in British Columbia, Canada. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e2144934. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44934 .
In their native country, they learned throughout their life cultural norms and systems that defined their environment. When these parents immigrate to a new country, their different set of knowledge may not be applicable in many ways to their new environment.
The Disruption of Social Roles
Culturally, language is one of the most important types of knowledge parents pass to their children. Nearly half of adult immigrants in the United States have limited English proficiency. 1
Their children often learn the language faster, often placing these children in the position of interpreters for their parents. These parents can become dependent on their children to negotiate social structures instead of vice versa, potentially undermining the social hierarchy and role of parenting. 2 Both Mr. Contreras and Dr. Nguyen recall that as children of immigrant parents — from Mexico and Vietnam, respectively — they commanded English better than their parents, which often made them take on more “adult roles.” For example, Dr. Nguyen recalls that his mother would solicit his help in grocery shopping because she could neither navigate the aisles effectively nor ask for help. Mr. Contreras commonly found himself acting as an impromptu medical translator for his mother on several occasions. This dependence of immigrant parents on their children for guidance in their host country can be pervasive in other social structures such as legal and academic.
Impact on School
Potentially, an immigrant parent’s lack of knowledge of the language and systems of their host country can make them ineffective advocates for their children at school. Mr. Contreras’s intervention for his patient as a medical student demonstrates this in the arena of school.
Mr. Contreras was rotating at a hospital burn unit in 2023 when R, a young middle school student, and his mother arrived in the emergency department. An incident had occurred at his school. R had been the victim of aggravated battery and assault, sustaining a 3x2 cm burn on his forearm from students placing hot glue onto a piece of cardboard then immediately onto his skin and silencing him by covering his mouth. For months the older students had been bullying R. R’s mother made multiple attempts with both the school’s front desk and counselors to address the issue, but to no avail. R himself, though encouraged to speak up, did not out of fear. As Mr. Contreras realized the situation and the impasse, he used his fluency in Spanish and English to facilitate a joint call with the school district. Within 10 minutes, they were able to connect with a student safety specialist and launch a full investigation. A language barrier and the lack of knowledge of their rights and school system had prevented R’s mother from effectively advocating for her child’s safety.
In Dr. Nguyen’s experience as a teacher, even in classrooms dominated by minority students, the advocacy for students struggling in classes was disproportionate. It favored White parents, but also generally more educated families. This is further supported by a study of 225 schools across six states of kindergarten children showing similar trends, that African American, Latino, and less-educated parents were less involved in their children’s education as reported by teachers.3 It is important to note that in this study teachers were 80% White, 9% Latino, 7% African American, 3% multiracial, and 1% Asian American, suggesting that cultural discrepancy between teachers and parents could be an important factor affecting parent-teacher communication. Dr. Nguyen also recalled trying to discipline several students who were disruptive in his class by telling them he would speak to their parents. Several times, these students would counter defiantly, “Well, good luck, they can’t speak English.” The parents’ dependency on their children to communicate with teachers undermined the abilities of both adults to manage their behaviors and promote learning.
The Mental Health of Immigrant Parents
Migrants often have greater incidence of mental health problems, including depression, PTSD, and anxiety, from a combination of peri-migrational experiences. 4 Immigrant mothers are known to have higher rates of post-natal depression, which cause problems later with child development. 5 Though she warns larger studies are needed, Dr. Fazel’s review of Croatian refugees suggests that displacement from one’s native country is a risk factor for poorer mental health, namely due to difficulty in psychosocial adaptation. 6 The likely mechanism is that lack of access to one’s language and culture, or a language and culture that one can navigate effectively, exacerbates, even engenders mental health sequelae. Because of this, first-generation immigrant children often face harsher and more violent parenting. 7,8 Immigrant parents also may have less access to mental health resources since they often resort to their own cultural practices. Both Mr. Contreras’s and Dr. Nguyen’s following narratives of their mothers’ struggle with mental health illustrate the causes and consequences.
Mr. Contreras, who grew up in a Mexican immigrant household in Los Angeles, saw firsthand how his mother, who faced language barriers and a distrust of Western medicine, turned to traditional healers and herbal remedies for her health needs. Accompanying her to doctor appointments as her translator, he often felt the disconnect between her cultural background and the Western medical system. For her, seeking help from traditional healers was not just about addressing physical ailments but also about finding comfort and familiarity in practices rooted in her cultural beliefs. This preference for cultural or religious methods for mental health support is not uncommon among Mexican immigrant families.
Dr. Nguyen, whose mother was a refugee from Vietnam, recalls her constant depressed mood and suicidal thoughts in the immediate years after she resettled in San Diego. This was caused mostly by the missing of her social supports in Vietnam, her difficulty adjusting to American culture and language, and her difficulty finding work. Often her depression and stress took a darker turn in terms of more violent parenting. Of course, the cause of her poor mental health is hard to parse from the traumas and violence she had faced as a refugee, but in subsequent years, her many brothers and sisters who immigrated through a more orderly process also displayed similar mental health vulnerabilities.
The Mental Health of Children of Immigrant Parents
The relationship between an immigrant parent’s poor mental health and their children is difficult to parse from what we know about native parents and their children. But the primary differences appear to be a great disruption of social roles, the effects of migration itself, and the oftentimes more strict and disciplinarian parenting style as discussed above. Given this, one would expect immigrant children to suffer greater mental health difficulties. However, a recent study of almost 500,000 children in Canada revealed decreased prevalence of conduct disorder, ADHD, and mood and anxiety disorders in immigrant youth, both first- and second-generation, as compared to non-immigrants. 9 This perhaps surprising result highlights how much more we need to understand about the effects of culture on the mental health diagnosis of immigrant youth. It suggests differences in mental health access and use from the cultural factors we mentioned above, to problems with using Western-based mental criteria and symptomatology for diagnosing non-Western children. It can even suggest the underestimation of the protective effects of native culture such as strong ethnic identity and cultural support systems, thereby challenging a purely deficit mental health model of the immigrant experience.
Summary
Dr. Duy Nguyen and Mr. Andrew Contreras are both children of immigrant parents from Vietnam and Mexico, respectively. Dr. Nguyen spent 15 years as an English teacher at San Leandro High School, whose student body was roughly 50% Hispanic and 25% Asian, making immigrant parents a huge swath of his educational partners. Mr. Contreras founded a high school outreach program where he interacted with K-12 children of immigrant youth. In addition, he partners with Fresno’s Economic Opportunity Commission to educate immigrant Hispanic parents and their teens on having difficult conversations with their teenage children on topics such as mental and reproductive health. Dr. Duy Nguyen and Mr. Andrew Contreras will explore the differences in immigrant parent-child relationships, compared with native ones, as they relate to mental health ramifications for the child and parent. They reveal immigrant mental health disruptions regarding culture and language, familial hierarchies, parenting styles, as well as parental mental health sequelae brought about by immigration using research and their own personal experiences.
Dr. Nguyen is a second-year resident at the University of California, San Francisco, Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously. Mr. Contreras is currently a 4th-year medical student at University of California, San Francisco, and applying to Psychiatry for the 2025 match.
References
1. Rao A et al. Five Key Facts About Immigrants With Limited English Proficiency. KFF. 2024 March 14. https://www.kff.org/racial-equity-and-health-policy/issue-brief-five-key-facts-about-immigrants-with-limited-english-proficiency .
2. Raffaetà R. Migration and Parenting: Reviewing the Debate and Calling for Future Research. International Journal of Migration, Health and Social Care. 2016;12(1):38-50. doi: 10.1108/IJMHSC-12-2014-0052/full/html .
3. Nzinga‐Johnson S et al. Teacher‐Parent Relationships and School Involvement Among Racially and Educationally Diverse Parents of Kindergartners. Elementary School Journal. 2009 Sept. doi: 10.1086/598844 .
4. Close C et al. The Mental Health and Wellbeing of First Generation Migrants: A Systematic-Narrative Review of Reviews. Global Health. 2016 Aug 25;12(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12992-016-0187-3.
5. Collins CH et al. Refugee, Asylum Seeker, Immigrant Women and Postnatal Depression: Rates and Risk Factors. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2011 Feb;14(1):3-11. doi: 10.1007/s00737-010-0198-7 .
6. Fazel M, Betancourt TS. Preventive Mental Health Interventions for Refugee Children and Adolescents in High-Income Settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-132. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5 .
7. Pottie K et al. Do First Generation Immigrant Adolescents Face Higher Rates of Bullying, Violence and Suicidal Behaviours Than Do Third Generation and Native Born? J Immigr Minor Health. 2015 Oct;17(5):1557-1566. doi: 10.1007/s10903-014-0108-6.
8. Smokowski PR, Bacallao ML. Acculturation and Aggression in Latino Adolescents: A Structural Model Focusing on Cultural Risk Factors and Assets. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2006 Oct;34(5):659-673. doi: 10.1007/s10802-006-9049-4 .
9. Gadermann AM et al. Prevalence of Mental Health Disorders Among Immigrant, Refugee, and Nonimmigrant Children and Youth in British Columbia, Canada. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e2144934. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44934 .
In their native country, they learned throughout their life cultural norms and systems that defined their environment. When these parents immigrate to a new country, their different set of knowledge may not be applicable in many ways to their new environment.
The Disruption of Social Roles
Culturally, language is one of the most important types of knowledge parents pass to their children. Nearly half of adult immigrants in the United States have limited English proficiency. 1
Their children often learn the language faster, often placing these children in the position of interpreters for their parents. These parents can become dependent on their children to negotiate social structures instead of vice versa, potentially undermining the social hierarchy and role of parenting. 2 Both Mr. Contreras and Dr. Nguyen recall that as children of immigrant parents — from Mexico and Vietnam, respectively — they commanded English better than their parents, which often made them take on more “adult roles.” For example, Dr. Nguyen recalls that his mother would solicit his help in grocery shopping because she could neither navigate the aisles effectively nor ask for help. Mr. Contreras commonly found himself acting as an impromptu medical translator for his mother on several occasions. This dependence of immigrant parents on their children for guidance in their host country can be pervasive in other social structures such as legal and academic.
Impact on School
Potentially, an immigrant parent’s lack of knowledge of the language and systems of their host country can make them ineffective advocates for their children at school. Mr. Contreras’s intervention for his patient as a medical student demonstrates this in the arena of school.
Mr. Contreras was rotating at a hospital burn unit in 2023 when R, a young middle school student, and his mother arrived in the emergency department. An incident had occurred at his school. R had been the victim of aggravated battery and assault, sustaining a 3x2 cm burn on his forearm from students placing hot glue onto a piece of cardboard then immediately onto his skin and silencing him by covering his mouth. For months the older students had been bullying R. R’s mother made multiple attempts with both the school’s front desk and counselors to address the issue, but to no avail. R himself, though encouraged to speak up, did not out of fear. As Mr. Contreras realized the situation and the impasse, he used his fluency in Spanish and English to facilitate a joint call with the school district. Within 10 minutes, they were able to connect with a student safety specialist and launch a full investigation. A language barrier and the lack of knowledge of their rights and school system had prevented R’s mother from effectively advocating for her child’s safety.
In Dr. Nguyen’s experience as a teacher, even in classrooms dominated by minority students, the advocacy for students struggling in classes was disproportionate. It favored White parents, but also generally more educated families. This is further supported by a study of 225 schools across six states of kindergarten children showing similar trends, that African American, Latino, and less-educated parents were less involved in their children’s education as reported by teachers.3 It is important to note that in this study teachers were 80% White, 9% Latino, 7% African American, 3% multiracial, and 1% Asian American, suggesting that cultural discrepancy between teachers and parents could be an important factor affecting parent-teacher communication. Dr. Nguyen also recalled trying to discipline several students who were disruptive in his class by telling them he would speak to their parents. Several times, these students would counter defiantly, “Well, good luck, they can’t speak English.” The parents’ dependency on their children to communicate with teachers undermined the abilities of both adults to manage their behaviors and promote learning.
The Mental Health of Immigrant Parents
Migrants often have greater incidence of mental health problems, including depression, PTSD, and anxiety, from a combination of peri-migrational experiences. 4 Immigrant mothers are known to have higher rates of post-natal depression, which cause problems later with child development. 5 Though she warns larger studies are needed, Dr. Fazel’s review of Croatian refugees suggests that displacement from one’s native country is a risk factor for poorer mental health, namely due to difficulty in psychosocial adaptation. 6 The likely mechanism is that lack of access to one’s language and culture, or a language and culture that one can navigate effectively, exacerbates, even engenders mental health sequelae. Because of this, first-generation immigrant children often face harsher and more violent parenting. 7,8 Immigrant parents also may have less access to mental health resources since they often resort to their own cultural practices. Both Mr. Contreras’s and Dr. Nguyen’s following narratives of their mothers’ struggle with mental health illustrate the causes and consequences.
Mr. Contreras, who grew up in a Mexican immigrant household in Los Angeles, saw firsthand how his mother, who faced language barriers and a distrust of Western medicine, turned to traditional healers and herbal remedies for her health needs. Accompanying her to doctor appointments as her translator, he often felt the disconnect between her cultural background and the Western medical system. For her, seeking help from traditional healers was not just about addressing physical ailments but also about finding comfort and familiarity in practices rooted in her cultural beliefs. This preference for cultural or religious methods for mental health support is not uncommon among Mexican immigrant families.
Dr. Nguyen, whose mother was a refugee from Vietnam, recalls her constant depressed mood and suicidal thoughts in the immediate years after she resettled in San Diego. This was caused mostly by the missing of her social supports in Vietnam, her difficulty adjusting to American culture and language, and her difficulty finding work. Often her depression and stress took a darker turn in terms of more violent parenting. Of course, the cause of her poor mental health is hard to parse from the traumas and violence she had faced as a refugee, but in subsequent years, her many brothers and sisters who immigrated through a more orderly process also displayed similar mental health vulnerabilities.
The Mental Health of Children of Immigrant Parents
The relationship between an immigrant parent’s poor mental health and their children is difficult to parse from what we know about native parents and their children. But the primary differences appear to be a great disruption of social roles, the effects of migration itself, and the oftentimes more strict and disciplinarian parenting style as discussed above. Given this, one would expect immigrant children to suffer greater mental health difficulties. However, a recent study of almost 500,000 children in Canada revealed decreased prevalence of conduct disorder, ADHD, and mood and anxiety disorders in immigrant youth, both first- and second-generation, as compared to non-immigrants. 9 This perhaps surprising result highlights how much more we need to understand about the effects of culture on the mental health diagnosis of immigrant youth. It suggests differences in mental health access and use from the cultural factors we mentioned above, to problems with using Western-based mental criteria and symptomatology for diagnosing non-Western children. It can even suggest the underestimation of the protective effects of native culture such as strong ethnic identity and cultural support systems, thereby challenging a purely deficit mental health model of the immigrant experience.
Summary
Dr. Duy Nguyen and Mr. Andrew Contreras are both children of immigrant parents from Vietnam and Mexico, respectively. Dr. Nguyen spent 15 years as an English teacher at San Leandro High School, whose student body was roughly 50% Hispanic and 25% Asian, making immigrant parents a huge swath of his educational partners. Mr. Contreras founded a high school outreach program where he interacted with K-12 children of immigrant youth. In addition, he partners with Fresno’s Economic Opportunity Commission to educate immigrant Hispanic parents and their teens on having difficult conversations with their teenage children on topics such as mental and reproductive health. Dr. Duy Nguyen and Mr. Andrew Contreras will explore the differences in immigrant parent-child relationships, compared with native ones, as they relate to mental health ramifications for the child and parent. They reveal immigrant mental health disruptions regarding culture and language, familial hierarchies, parenting styles, as well as parental mental health sequelae brought about by immigration using research and their own personal experiences.
Dr. Nguyen is a second-year resident at the University of California, San Francisco, Fresno Psychiatry Residency. He was a public high school English teacher for 15 years previously. Mr. Contreras is currently a 4th-year medical student at University of California, San Francisco, and applying to Psychiatry for the 2025 match.
References
1. Rao A et al. Five Key Facts About Immigrants With Limited English Proficiency. KFF. 2024 March 14. https://www.kff.org/racial-equity-and-health-policy/issue-brief-five-key-facts-about-immigrants-with-limited-english-proficiency .
2. Raffaetà R. Migration and Parenting: Reviewing the Debate and Calling for Future Research. International Journal of Migration, Health and Social Care. 2016;12(1):38-50. doi: 10.1108/IJMHSC-12-2014-0052/full/html .
3. Nzinga‐Johnson S et al. Teacher‐Parent Relationships and School Involvement Among Racially and Educationally Diverse Parents of Kindergartners. Elementary School Journal. 2009 Sept. doi: 10.1086/598844 .
4. Close C et al. The Mental Health and Wellbeing of First Generation Migrants: A Systematic-Narrative Review of Reviews. Global Health. 2016 Aug 25;12(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12992-016-0187-3.
5. Collins CH et al. Refugee, Asylum Seeker, Immigrant Women and Postnatal Depression: Rates and Risk Factors. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2011 Feb;14(1):3-11. doi: 10.1007/s00737-010-0198-7 .
6. Fazel M, Betancourt TS. Preventive Mental Health Interventions for Refugee Children and Adolescents in High-Income Settings. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Feb;2(2):121-132. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30147-5 .
7. Pottie K et al. Do First Generation Immigrant Adolescents Face Higher Rates of Bullying, Violence and Suicidal Behaviours Than Do Third Generation and Native Born? J Immigr Minor Health. 2015 Oct;17(5):1557-1566. doi: 10.1007/s10903-014-0108-6.
8. Smokowski PR, Bacallao ML. Acculturation and Aggression in Latino Adolescents: A Structural Model Focusing on Cultural Risk Factors and Assets. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2006 Oct;34(5):659-673. doi: 10.1007/s10802-006-9049-4 .
9. Gadermann AM et al. Prevalence of Mental Health Disorders Among Immigrant, Refugee, and Nonimmigrant Children and Youth in British Columbia, Canada. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e2144934. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44934 .
Helping Patients Cut Down on Sodium: Useful Substitutes and Strategies
Humans have used salt for centuries, to preserve or cure food before refrigeration was readily available, and even as currency in some cultures. Though modern food preservation efforts have decreased our reliance on salt, we still heavily incorporate it as a flavor enhancer.
It’s only relatively recently that we’ve begun limiting salt in our diets, as research has linked high sodium intake with chronic, preventable conditions like hypertension, heart disease, and kidney disease.
How to Recommend Restriction in a Helpful Way
The US Department of Agriculture’s Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends intake of no more than 2300 mg of sodium daily for adults and children aged 14 years or older. This echoes similar recommendations for people at risk for heart disease, kidney disease, and hypertension. However, the sodium intake of the average American still sits at a whopping 3400 mg daily.
High sodium intake is primarily the result of modern commercial food processing. Food prepared outside the home accounts for up to 70% of sodium intake in the United States, whereas only about 10% comes from salt that is added to food either during or after cooking. For this reason, I hesitate to recommend withholding salt as a primary focus when counseling on a low-sodium diet.
To many people, certain foods just taste better with salt. Many of my patients in the southern United States simply will not eat foods like eggs and tomatoes if they cannot salt them. We can spend every moment of patient interaction time explaining why excess sodium is unhealthy, but the fact remains that humans prefer food that tastes good. This is why I try to avoid counseling a “no-added-salt” diet; instead, I recommend a low-sodium diet with a focus on fresh, whole foods and limiting salt to only a few food items.
Patients should be counseled to slowly restrict their salt intake and be made aware that doing so may increase the time it takes for their sensitivity to the taste of less salty foods to return. But it is also important for them to know that it will return. The surest way to kill progress is for an unprepared patient to believe that their food will taste bland forever. A prepared patient understands that their food may taste different for a couple of weeks, but that the change will not last forever.
Types of Salt
I have often worked with patients who insist that their sodium intake is acceptable because they are using sea salt instead of table salt. This is the result of exceptional marketing and misinformation.
Specialty salts like sea salt and Himalayan pink salt contain about 560 mg and 590 mg of sodium, respectively, per quarter teaspoon. These products do have a slightly different mineral content, with sea salt typically having a negligible amount of calcium, magnesium, or potassium. The very small amount of these minerals offers no obvious health benefits compared with more affordable table salt.
The sodium content of iodized table salt is comparable to these products, with about 590 mg of sodium per quarter teaspoon. Though its high sodium content will put some practitioners off, it is also an excellent source of iodine, at about 75 mg per serving. It has been estimated that upward of 35% of the US population has iodine deficiency, most commonly due to pregnancy, avoidance of dairy products, increasing rates of vegetarianism, intake of highly processed foods, and avoidance of added salt. For this reason, and its relative affordability, I find table salt to be far more appropriate for the average American than specialty salts.
Salt Substitutes
Monosodium glutamate (MSG). MSG was previously at the center of public health concern owing to reports of “Chinese restaurant syndrome” that have since been debunked. I often recommend MSG to people trying to decrease sodium intake because the US Food and Drug Administration has designated it as GRAS (“generally recognized as safe”), and it has about one quarter of the sodium content of table salt at 125 mg per quarter teaspoon. Its crystalline structure makes it a lower-sodium salt substitute in savory applications like soups, stews, and gravies.
Hot sauce. These sauces are generally composed of peppers, vinegar, salt, and sugar. There may be some variation and occasionally added ingredients depending upon the brand. However, I find most hot sauces to be a low-sodium seasoning option that works especially well on proteins like eggs, chicken, and pork.
Potassium-based substitutes. Salt alternatives such as Nu-Salt and Morton Salt Substitute are sodium-free options with a significant amount of potassium, at 525 mg per quarter-teaspoon serving. These alternatives may not be ideal for patients with kidney problems, but they can be very helpful for those with potassium deficiency.
Herb-based seasonings. Garlic and onion powder are both sodium-free seasonings that many of my patients have found help to increase palatability while decreasing salt use. Black pepper; lemon and lime juice; salt-free herb mixes like Mrs. Dash; and spices like cumin, paprika, dill, chili powder, and ginger are also sodium-free or low-sodium alternatives that can help to alleviate blandness for someone new to a low-sodium diet. I recommend them often and use them in my own cooking at home.
Plant-based diet. If the goal of care is to improve cardiovascular or kidney health, then I find that working with patients to increase intake of plant foods to be a helpful option. This way of eating encourages replacing highly processed foods that may be high in sodium and sugar with plants that tend to be higher in potassium and calcium. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), Mediterranean, and other plant-based diets have been shown to increase cardiovascular and metabolic health by significantly decreasing serum lipids, blood pressure, and hemoglobin A1c and promoting weight loss. They have also been shown to increase the gut microbiome and promote increased cognitive function.
I rarely encourage the use of added salt. However, research shows that putting down the salt shaker is probably not the most effective option to restrict sodium intake. For those who can cut back, these options can help keep food flavorful and patients compliant.
Ms. Winfree is a renal dietitian in private practice in Mary Esther, Florida. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Humans have used salt for centuries, to preserve or cure food before refrigeration was readily available, and even as currency in some cultures. Though modern food preservation efforts have decreased our reliance on salt, we still heavily incorporate it as a flavor enhancer.
It’s only relatively recently that we’ve begun limiting salt in our diets, as research has linked high sodium intake with chronic, preventable conditions like hypertension, heart disease, and kidney disease.
How to Recommend Restriction in a Helpful Way
The US Department of Agriculture’s Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends intake of no more than 2300 mg of sodium daily for adults and children aged 14 years or older. This echoes similar recommendations for people at risk for heart disease, kidney disease, and hypertension. However, the sodium intake of the average American still sits at a whopping 3400 mg daily.
High sodium intake is primarily the result of modern commercial food processing. Food prepared outside the home accounts for up to 70% of sodium intake in the United States, whereas only about 10% comes from salt that is added to food either during or after cooking. For this reason, I hesitate to recommend withholding salt as a primary focus when counseling on a low-sodium diet.
To many people, certain foods just taste better with salt. Many of my patients in the southern United States simply will not eat foods like eggs and tomatoes if they cannot salt them. We can spend every moment of patient interaction time explaining why excess sodium is unhealthy, but the fact remains that humans prefer food that tastes good. This is why I try to avoid counseling a “no-added-salt” diet; instead, I recommend a low-sodium diet with a focus on fresh, whole foods and limiting salt to only a few food items.
Patients should be counseled to slowly restrict their salt intake and be made aware that doing so may increase the time it takes for their sensitivity to the taste of less salty foods to return. But it is also important for them to know that it will return. The surest way to kill progress is for an unprepared patient to believe that their food will taste bland forever. A prepared patient understands that their food may taste different for a couple of weeks, but that the change will not last forever.
Types of Salt
I have often worked with patients who insist that their sodium intake is acceptable because they are using sea salt instead of table salt. This is the result of exceptional marketing and misinformation.
Specialty salts like sea salt and Himalayan pink salt contain about 560 mg and 590 mg of sodium, respectively, per quarter teaspoon. These products do have a slightly different mineral content, with sea salt typically having a negligible amount of calcium, magnesium, or potassium. The very small amount of these minerals offers no obvious health benefits compared with more affordable table salt.
The sodium content of iodized table salt is comparable to these products, with about 590 mg of sodium per quarter teaspoon. Though its high sodium content will put some practitioners off, it is also an excellent source of iodine, at about 75 mg per serving. It has been estimated that upward of 35% of the US population has iodine deficiency, most commonly due to pregnancy, avoidance of dairy products, increasing rates of vegetarianism, intake of highly processed foods, and avoidance of added salt. For this reason, and its relative affordability, I find table salt to be far more appropriate for the average American than specialty salts.
Salt Substitutes
Monosodium glutamate (MSG). MSG was previously at the center of public health concern owing to reports of “Chinese restaurant syndrome” that have since been debunked. I often recommend MSG to people trying to decrease sodium intake because the US Food and Drug Administration has designated it as GRAS (“generally recognized as safe”), and it has about one quarter of the sodium content of table salt at 125 mg per quarter teaspoon. Its crystalline structure makes it a lower-sodium salt substitute in savory applications like soups, stews, and gravies.
Hot sauce. These sauces are generally composed of peppers, vinegar, salt, and sugar. There may be some variation and occasionally added ingredients depending upon the brand. However, I find most hot sauces to be a low-sodium seasoning option that works especially well on proteins like eggs, chicken, and pork.
Potassium-based substitutes. Salt alternatives such as Nu-Salt and Morton Salt Substitute are sodium-free options with a significant amount of potassium, at 525 mg per quarter-teaspoon serving. These alternatives may not be ideal for patients with kidney problems, but they can be very helpful for those with potassium deficiency.
Herb-based seasonings. Garlic and onion powder are both sodium-free seasonings that many of my patients have found help to increase palatability while decreasing salt use. Black pepper; lemon and lime juice; salt-free herb mixes like Mrs. Dash; and spices like cumin, paprika, dill, chili powder, and ginger are also sodium-free or low-sodium alternatives that can help to alleviate blandness for someone new to a low-sodium diet. I recommend them often and use them in my own cooking at home.
Plant-based diet. If the goal of care is to improve cardiovascular or kidney health, then I find that working with patients to increase intake of plant foods to be a helpful option. This way of eating encourages replacing highly processed foods that may be high in sodium and sugar with plants that tend to be higher in potassium and calcium. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), Mediterranean, and other plant-based diets have been shown to increase cardiovascular and metabolic health by significantly decreasing serum lipids, blood pressure, and hemoglobin A1c and promoting weight loss. They have also been shown to increase the gut microbiome and promote increased cognitive function.
I rarely encourage the use of added salt. However, research shows that putting down the salt shaker is probably not the most effective option to restrict sodium intake. For those who can cut back, these options can help keep food flavorful and patients compliant.
Ms. Winfree is a renal dietitian in private practice in Mary Esther, Florida. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Humans have used salt for centuries, to preserve or cure food before refrigeration was readily available, and even as currency in some cultures. Though modern food preservation efforts have decreased our reliance on salt, we still heavily incorporate it as a flavor enhancer.
It’s only relatively recently that we’ve begun limiting salt in our diets, as research has linked high sodium intake with chronic, preventable conditions like hypertension, heart disease, and kidney disease.
How to Recommend Restriction in a Helpful Way
The US Department of Agriculture’s Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends intake of no more than 2300 mg of sodium daily for adults and children aged 14 years or older. This echoes similar recommendations for people at risk for heart disease, kidney disease, and hypertension. However, the sodium intake of the average American still sits at a whopping 3400 mg daily.
High sodium intake is primarily the result of modern commercial food processing. Food prepared outside the home accounts for up to 70% of sodium intake in the United States, whereas only about 10% comes from salt that is added to food either during or after cooking. For this reason, I hesitate to recommend withholding salt as a primary focus when counseling on a low-sodium diet.
To many people, certain foods just taste better with salt. Many of my patients in the southern United States simply will not eat foods like eggs and tomatoes if they cannot salt them. We can spend every moment of patient interaction time explaining why excess sodium is unhealthy, but the fact remains that humans prefer food that tastes good. This is why I try to avoid counseling a “no-added-salt” diet; instead, I recommend a low-sodium diet with a focus on fresh, whole foods and limiting salt to only a few food items.
Patients should be counseled to slowly restrict their salt intake and be made aware that doing so may increase the time it takes for their sensitivity to the taste of less salty foods to return. But it is also important for them to know that it will return. The surest way to kill progress is for an unprepared patient to believe that their food will taste bland forever. A prepared patient understands that their food may taste different for a couple of weeks, but that the change will not last forever.
Types of Salt
I have often worked with patients who insist that their sodium intake is acceptable because they are using sea salt instead of table salt. This is the result of exceptional marketing and misinformation.
Specialty salts like sea salt and Himalayan pink salt contain about 560 mg and 590 mg of sodium, respectively, per quarter teaspoon. These products do have a slightly different mineral content, with sea salt typically having a negligible amount of calcium, magnesium, or potassium. The very small amount of these minerals offers no obvious health benefits compared with more affordable table salt.
The sodium content of iodized table salt is comparable to these products, with about 590 mg of sodium per quarter teaspoon. Though its high sodium content will put some practitioners off, it is also an excellent source of iodine, at about 75 mg per serving. It has been estimated that upward of 35% of the US population has iodine deficiency, most commonly due to pregnancy, avoidance of dairy products, increasing rates of vegetarianism, intake of highly processed foods, and avoidance of added salt. For this reason, and its relative affordability, I find table salt to be far more appropriate for the average American than specialty salts.
Salt Substitutes
Monosodium glutamate (MSG). MSG was previously at the center of public health concern owing to reports of “Chinese restaurant syndrome” that have since been debunked. I often recommend MSG to people trying to decrease sodium intake because the US Food and Drug Administration has designated it as GRAS (“generally recognized as safe”), and it has about one quarter of the sodium content of table salt at 125 mg per quarter teaspoon. Its crystalline structure makes it a lower-sodium salt substitute in savory applications like soups, stews, and gravies.
Hot sauce. These sauces are generally composed of peppers, vinegar, salt, and sugar. There may be some variation and occasionally added ingredients depending upon the brand. However, I find most hot sauces to be a low-sodium seasoning option that works especially well on proteins like eggs, chicken, and pork.
Potassium-based substitutes. Salt alternatives such as Nu-Salt and Morton Salt Substitute are sodium-free options with a significant amount of potassium, at 525 mg per quarter-teaspoon serving. These alternatives may not be ideal for patients with kidney problems, but they can be very helpful for those with potassium deficiency.
Herb-based seasonings. Garlic and onion powder are both sodium-free seasonings that many of my patients have found help to increase palatability while decreasing salt use. Black pepper; lemon and lime juice; salt-free herb mixes like Mrs. Dash; and spices like cumin, paprika, dill, chili powder, and ginger are also sodium-free or low-sodium alternatives that can help to alleviate blandness for someone new to a low-sodium diet. I recommend them often and use them in my own cooking at home.
Plant-based diet. If the goal of care is to improve cardiovascular or kidney health, then I find that working with patients to increase intake of plant foods to be a helpful option. This way of eating encourages replacing highly processed foods that may be high in sodium and sugar with plants that tend to be higher in potassium and calcium. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), Mediterranean, and other plant-based diets have been shown to increase cardiovascular and metabolic health by significantly decreasing serum lipids, blood pressure, and hemoglobin A1c and promoting weight loss. They have also been shown to increase the gut microbiome and promote increased cognitive function.
I rarely encourage the use of added salt. However, research shows that putting down the salt shaker is probably not the most effective option to restrict sodium intake. For those who can cut back, these options can help keep food flavorful and patients compliant.
Ms. Winfree is a renal dietitian in private practice in Mary Esther, Florida. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Knowing My Limits
The records came in by fax. A patient who’d recently moved here and needed to connect with a local neurologist.
When I had time, I flipped through the records. He needed ongoing treatment for a rare neurological disease that I’d heard of, but wasn’t otherwise familiar with. It didn’t even exist in the textbooks or conferences when I was in residency. I’d never seen a case of it, just read about it here and there in journals.
I looked it up, reviewed current treatment options, monitoring, and other knowledge about it, then stared at the notes for a minute. Finally, after thinking it over, I attached a sticky note for my secretary that, if the person called, to redirect them to one of the local subspecialty neurology centers.
I have nothing against this patient, but realistically he would be better served seeing someone with time to keep up on advancements in esoteric disorders, not a general neurologist like myself.
Isn’t that why we have subspecialty centers?
Some of it is also me. There was a time in my career when keeping up on newly discovered disorders and their treatments was, well, cool. But after 25 years in practice, that changes.
It’s important to be at least somewhat aware of new developments (such as in this case) as you may encounter them, and need to know when it’s something you can handle and when to send it elsewhere.
Driving home that afternoon I thought, “I’m an old dog. I don’t want to learn new tricks.” Maybe that’s all it is. There are other neurologists my age and older who thrive on the challenge of learning about and treating new and rare disorders that were unknown when they started out. There’s nothing wrong with that.
But I’ve never pretended to be an academic or sub-sub-specialist. My patients depend on me to stay up to date on the large number of commonly seen neurological disorders, and I do my best to do that.
It ain’t easy being an old dog.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
The records came in by fax. A patient who’d recently moved here and needed to connect with a local neurologist.
When I had time, I flipped through the records. He needed ongoing treatment for a rare neurological disease that I’d heard of, but wasn’t otherwise familiar with. It didn’t even exist in the textbooks or conferences when I was in residency. I’d never seen a case of it, just read about it here and there in journals.
I looked it up, reviewed current treatment options, monitoring, and other knowledge about it, then stared at the notes for a minute. Finally, after thinking it over, I attached a sticky note for my secretary that, if the person called, to redirect them to one of the local subspecialty neurology centers.
I have nothing against this patient, but realistically he would be better served seeing someone with time to keep up on advancements in esoteric disorders, not a general neurologist like myself.
Isn’t that why we have subspecialty centers?
Some of it is also me. There was a time in my career when keeping up on newly discovered disorders and their treatments was, well, cool. But after 25 years in practice, that changes.
It’s important to be at least somewhat aware of new developments (such as in this case) as you may encounter them, and need to know when it’s something you can handle and when to send it elsewhere.
Driving home that afternoon I thought, “I’m an old dog. I don’t want to learn new tricks.” Maybe that’s all it is. There are other neurologists my age and older who thrive on the challenge of learning about and treating new and rare disorders that were unknown when they started out. There’s nothing wrong with that.
But I’ve never pretended to be an academic or sub-sub-specialist. My patients depend on me to stay up to date on the large number of commonly seen neurological disorders, and I do my best to do that.
It ain’t easy being an old dog.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
The records came in by fax. A patient who’d recently moved here and needed to connect with a local neurologist.
When I had time, I flipped through the records. He needed ongoing treatment for a rare neurological disease that I’d heard of, but wasn’t otherwise familiar with. It didn’t even exist in the textbooks or conferences when I was in residency. I’d never seen a case of it, just read about it here and there in journals.
I looked it up, reviewed current treatment options, monitoring, and other knowledge about it, then stared at the notes for a minute. Finally, after thinking it over, I attached a sticky note for my secretary that, if the person called, to redirect them to one of the local subspecialty neurology centers.
I have nothing against this patient, but realistically he would be better served seeing someone with time to keep up on advancements in esoteric disorders, not a general neurologist like myself.
Isn’t that why we have subspecialty centers?
Some of it is also me. There was a time in my career when keeping up on newly discovered disorders and their treatments was, well, cool. But after 25 years in practice, that changes.
It’s important to be at least somewhat aware of new developments (such as in this case) as you may encounter them, and need to know when it’s something you can handle and when to send it elsewhere.
Driving home that afternoon I thought, “I’m an old dog. I don’t want to learn new tricks.” Maybe that’s all it is. There are other neurologists my age and older who thrive on the challenge of learning about and treating new and rare disorders that were unknown when they started out. There’s nothing wrong with that.
But I’ve never pretended to be an academic or sub-sub-specialist. My patients depend on me to stay up to date on the large number of commonly seen neurological disorders, and I do my best to do that.
It ain’t easy being an old dog.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
The Value of Early Education
Early education is right up there with motherhood and apple pie as unarguable positive concepts. How could exposing young children to a school-like atmosphere not be a benefit, particularly in communities dominated by socioeconomic challenges? While there are some questions about the value of playing Mozart to infants, early education in the traditional sense continues to be viewed as a key strategy for providing young children a preschool foundation on which a successful academic career can be built. Several oft-cited randomized controlled trials have fueled both private and public interest and funding.
However, a recent commentary published in Science suggests that all programs are “not unequivocally positive and much more research is needed.” “Worrisome results in Tennessee,” “Success in Boston,” and “Largely null results for Headstart” are just a few of the article’s section titles and convey a sense of the inconsistency the investigators found as they reviewed early education systems around the country.
While there may be some politicians who may attempt to use the results of this investigation as a reason to cancel public funding of underperforming early education programs, the authors avoid this baby-and-the-bathwater conclusion. Instead, they urge more rigorous research “to understand how effective programs can be designed and implemented.”
The kind of re-thinking and brainstorming these investigators suggest takes time. While we’re waiting for this process to gain traction, this might be a good time to consider some of the benefits of early education that we don’t usually consider when our focus is on academic metrics.
A recent paper in Children’s Health Care by investigators at the Boston University Medical Center and School of Medicine considered the diet of children attending preschool. Looking at the dietary records of more than 300 children attending 30 childcare centers, the researchers found that the children’s diets before arrival at daycare was less healthy than while they were in daycare. “The hour after pickup appeared to be the least healthful” of any of the time periods surveyed. Of course, we will all conjure up images of what this chaotic post-daycare pickup may look like and cut the harried parents and grandparents some slack when it comes to nutritional choices. However, the bottom line is that for the group of children surveyed being in preschool or daycare protected them from a less healthy diet they were being provided outside of school hours.
Our recent experience with pandemic-related school closures provides more evidence that being in school was superior to any remote experience academically. School-age children and adolescents gained weight when school closures were the norm. Play patterns for children shifted from outdoor play to indoor play — often dominated by more sedentary video games. Both fatal and non-fatal gun-related injuries surged during the pandemic and, by far, the majority of these occur in the home and not at school.
Stepping back to look at this broader picture that includes diet, physical activity, and safety — not to mention the benefits of socialization — leads one to arrive at the unfortunate conclusion that Of course there will be those who point to the belief that schools are petri dishes putting children at greater risk for respiratory infections. On the other hand, we must accept that schools haven’t proved to be a major factor in the spread of COVID that many had feared.
The authors of the study in Science are certainly correct in recommending a more thorough investigation into the academic benefits of preschool education. However, we must keep in mind that preschool offers an environment that can be a positive influence on young children.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Early education is right up there with motherhood and apple pie as unarguable positive concepts. How could exposing young children to a school-like atmosphere not be a benefit, particularly in communities dominated by socioeconomic challenges? While there are some questions about the value of playing Mozart to infants, early education in the traditional sense continues to be viewed as a key strategy for providing young children a preschool foundation on which a successful academic career can be built. Several oft-cited randomized controlled trials have fueled both private and public interest and funding.
However, a recent commentary published in Science suggests that all programs are “not unequivocally positive and much more research is needed.” “Worrisome results in Tennessee,” “Success in Boston,” and “Largely null results for Headstart” are just a few of the article’s section titles and convey a sense of the inconsistency the investigators found as they reviewed early education systems around the country.
While there may be some politicians who may attempt to use the results of this investigation as a reason to cancel public funding of underperforming early education programs, the authors avoid this baby-and-the-bathwater conclusion. Instead, they urge more rigorous research “to understand how effective programs can be designed and implemented.”
The kind of re-thinking and brainstorming these investigators suggest takes time. While we’re waiting for this process to gain traction, this might be a good time to consider some of the benefits of early education that we don’t usually consider when our focus is on academic metrics.
A recent paper in Children’s Health Care by investigators at the Boston University Medical Center and School of Medicine considered the diet of children attending preschool. Looking at the dietary records of more than 300 children attending 30 childcare centers, the researchers found that the children’s diets before arrival at daycare was less healthy than while they were in daycare. “The hour after pickup appeared to be the least healthful” of any of the time periods surveyed. Of course, we will all conjure up images of what this chaotic post-daycare pickup may look like and cut the harried parents and grandparents some slack when it comes to nutritional choices. However, the bottom line is that for the group of children surveyed being in preschool or daycare protected them from a less healthy diet they were being provided outside of school hours.
Our recent experience with pandemic-related school closures provides more evidence that being in school was superior to any remote experience academically. School-age children and adolescents gained weight when school closures were the norm. Play patterns for children shifted from outdoor play to indoor play — often dominated by more sedentary video games. Both fatal and non-fatal gun-related injuries surged during the pandemic and, by far, the majority of these occur in the home and not at school.
Stepping back to look at this broader picture that includes diet, physical activity, and safety — not to mention the benefits of socialization — leads one to arrive at the unfortunate conclusion that Of course there will be those who point to the belief that schools are petri dishes putting children at greater risk for respiratory infections. On the other hand, we must accept that schools haven’t proved to be a major factor in the spread of COVID that many had feared.
The authors of the study in Science are certainly correct in recommending a more thorough investigation into the academic benefits of preschool education. However, we must keep in mind that preschool offers an environment that can be a positive influence on young children.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Early education is right up there with motherhood and apple pie as unarguable positive concepts. How could exposing young children to a school-like atmosphere not be a benefit, particularly in communities dominated by socioeconomic challenges? While there are some questions about the value of playing Mozart to infants, early education in the traditional sense continues to be viewed as a key strategy for providing young children a preschool foundation on which a successful academic career can be built. Several oft-cited randomized controlled trials have fueled both private and public interest and funding.
However, a recent commentary published in Science suggests that all programs are “not unequivocally positive and much more research is needed.” “Worrisome results in Tennessee,” “Success in Boston,” and “Largely null results for Headstart” are just a few of the article’s section titles and convey a sense of the inconsistency the investigators found as they reviewed early education systems around the country.
While there may be some politicians who may attempt to use the results of this investigation as a reason to cancel public funding of underperforming early education programs, the authors avoid this baby-and-the-bathwater conclusion. Instead, they urge more rigorous research “to understand how effective programs can be designed and implemented.”
The kind of re-thinking and brainstorming these investigators suggest takes time. While we’re waiting for this process to gain traction, this might be a good time to consider some of the benefits of early education that we don’t usually consider when our focus is on academic metrics.
A recent paper in Children’s Health Care by investigators at the Boston University Medical Center and School of Medicine considered the diet of children attending preschool. Looking at the dietary records of more than 300 children attending 30 childcare centers, the researchers found that the children’s diets before arrival at daycare was less healthy than while they were in daycare. “The hour after pickup appeared to be the least healthful” of any of the time periods surveyed. Of course, we will all conjure up images of what this chaotic post-daycare pickup may look like and cut the harried parents and grandparents some slack when it comes to nutritional choices. However, the bottom line is that for the group of children surveyed being in preschool or daycare protected them from a less healthy diet they were being provided outside of school hours.
Our recent experience with pandemic-related school closures provides more evidence that being in school was superior to any remote experience academically. School-age children and adolescents gained weight when school closures were the norm. Play patterns for children shifted from outdoor play to indoor play — often dominated by more sedentary video games. Both fatal and non-fatal gun-related injuries surged during the pandemic and, by far, the majority of these occur in the home and not at school.
Stepping back to look at this broader picture that includes diet, physical activity, and safety — not to mention the benefits of socialization — leads one to arrive at the unfortunate conclusion that Of course there will be those who point to the belief that schools are petri dishes putting children at greater risk for respiratory infections. On the other hand, we must accept that schools haven’t proved to be a major factor in the spread of COVID that many had feared.
The authors of the study in Science are certainly correct in recommending a more thorough investigation into the academic benefits of preschool education. However, we must keep in mind that preschool offers an environment that can be a positive influence on young children.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Calcium and CV Risk: Are Supplements and Vitamin D to Blame?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Tricia Ward: Hi. I’m Tricia Ward, from theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology. I’m joined today by Dr Matthew Budoff. He is professor of medicine at UCLA and the endowed chair of preventive cardiology at the Lundquist Institute. Welcome, Dr Budoff.
Matthew J. Budoff, MD: Thank you.
Dietary Calcium vs Coronary Calcium
Ms. Ward: The reason I wanted to talk to you today is because there have been some recent studies linking calcium supplements to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease. I’m old enough to remember when we used to tell people that dietary calcium and coronary calcium weren’t connected and weren’t the same. Were we wrong?
Dr. Budoff: I think there’s a large amount of mixed data out there still. The US Preventive Services Task Force looked into this a number of years ago and said there’s no association between calcium supplementation and increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
As you mentioned, there are a couple of newer studies that point us toward a relationship. I think that we still have a little bit of a mixed bag, but we need to dive a little deeper into that to figure out what’s going on.
Ms. Ward: Does it appear to be connected to calcium in the form of supplements vs calcium from foods?
Dr. Budoff: We looked very carefully at dietary calcium in the MESA study, the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis. There is no relationship between dietary calcium intake and coronary calcium or cardiovascular events. We’re talking mostly about supplements now when we talk about this increased risk that we’re seeing.
Does Vitamin D Exacerbate Risk?
Ms. Ward: Because it’s seen with supplements, is that likely because that’s a much higher concentration of calcium coming in or do you think it’s something inherent in its being in the form of a supplement?
Dr. Budoff: I think there are two things. One, it’s definitely a higher concentration all at once. You get many more milligrams at a time when you take a supplement than if you had a high-calcium food or drink.
Also, most supplements have vitamin D as well. I think vitamin D and calcium work synergistically. When you give them both together simultaneously, I think that may have more of a potentiating effect that might exacerbate any potential risk.
Ms. Ward: Is there any reason to think there might be a difference in type of calcium supplement? I always think of the chalky tablet form vs calcium chews.
Dr. Budoff: I’m not aware of a difference in the supplement type. I think the vitamin D issue is a big problem because we all have patients who take thousands of units of vitamin D — just crazy numbers. People advocate really high numbers and that stays in the system.
Personally, I think part of the explanation is that with very high levels of vitamin D on top of calcium supplementation, you now absorb it better. You now get it into the bone, but maybe also into the coronary arteries. If you’re very high in vitamin D and then are taking a large calcium supplement, it might be the calcium/vitamin D combination that’s giving us some trouble. I think people on vitamin D supplements really need to watch their levels and not get supratherapeutic.
Ms. Ward: With the vitamin D?
Dr. Budoff: With the vitamin D.
Diabetes and Renal Function
Ms. Ward: In some of the studies, there seems to be a higher risk in patients with diabetes. Is there any reason why that would be?
Dr. Budoff: I can’t think of a reason exactly why with diabetes per se, except for renal disease. Patients with diabetes have more intrinsic renal disease, proteinuria, and even a reduced eGFR. We’ve seen that the kidney is very strongly tied to this. We have a very strong relationship, in work I’ve done a decade ago now, showing that calcium supplementation (in the form of phosphate binders) in patients on dialysis or with advanced renal disease is linked to much higher coronary calcium progression.
We did prospective, randomized trials showing that calcium intake as binders to reduce phosphorus led to more coronary calcium. We always thought that was just relegated to the renal population, and there might be an overlap here with the diabetes and more renal disease. I have a feeling that it has to do with more of that. It might be regulation of parathyroid hormone as well, which might be more abnormal in patients with diabetes.
Avoid Supratherapeutic Vitamin D Levels
Ms. Ward:: What are you telling your patients?
Dr. Budoff: I tell patients with normal kidney function that the bone will modulate 99.9% of the calcium uptake. If they have osteopenia or osteoporosis, regardless of their calcium score, I’m very comfortable putting them on supplements.
I’m a little more cautious with the vitamin D levels, and I keep an eye on that and regulate how much vitamin D they get based on their levels. I get them into the normal range, but I don’t want them supratherapeutic. You can even follow their calcium score. Again, we’ve shown that if you’re taking too much calcium, your calcium score will go up. I can just check it again in a couple of years to make sure that it’s safe.
Ms. Ward:: In terms of vitamin D levels, when you’re saying “supratherapeutic,” what levels do you consider a safe amount to take?
Dr. Budoff: I’d like them under 100 ng/mL as far as their upper level. Normal is around 70 ng/mL at most labs. I try to keep them in the normal range. I don’t even want them to be high-normal if I’m going to be concomitantly giving them calcium supplements. Of course, if they have renal insufficiency, then I’m much more cautious. We’ve even seen calcium supplements raise the serum calcium, which you never see with dietary calcium. That’s another potential proof that it might be too much too fast.
For renal patients, even in mild renal insufficiency, maybe even in diabetes where we’ve seen a signal, maybe aim lower in the amount of calcium supplementation if diet is insufficient, and aim a little lower in vitamin D targets, and I think you’ll be in a safer place.
Ms. Ward: Is there anything else you want to add?
Dr. Budoff: The evidence is still evolving. I’d say that it’s interesting and maybe a little frustrating that we don’t have a final answer on all of this. I would stay tuned for more data because we’re looking at many of the epidemiologic studies to try to see what happens in the real world, with both dietary intake of calcium and calcium supplementation.
Ms. Ward: Thank you very much for joining me today.
Dr. Budoff: It’s a pleasure. Thanks for having me.
Dr. Budoff disclosed being a speaker for Amarin Pharma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Tricia Ward: Hi. I’m Tricia Ward, from theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology. I’m joined today by Dr Matthew Budoff. He is professor of medicine at UCLA and the endowed chair of preventive cardiology at the Lundquist Institute. Welcome, Dr Budoff.
Matthew J. Budoff, MD: Thank you.
Dietary Calcium vs Coronary Calcium
Ms. Ward: The reason I wanted to talk to you today is because there have been some recent studies linking calcium supplements to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease. I’m old enough to remember when we used to tell people that dietary calcium and coronary calcium weren’t connected and weren’t the same. Were we wrong?
Dr. Budoff: I think there’s a large amount of mixed data out there still. The US Preventive Services Task Force looked into this a number of years ago and said there’s no association between calcium supplementation and increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
As you mentioned, there are a couple of newer studies that point us toward a relationship. I think that we still have a little bit of a mixed bag, but we need to dive a little deeper into that to figure out what’s going on.
Ms. Ward: Does it appear to be connected to calcium in the form of supplements vs calcium from foods?
Dr. Budoff: We looked very carefully at dietary calcium in the MESA study, the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis. There is no relationship between dietary calcium intake and coronary calcium or cardiovascular events. We’re talking mostly about supplements now when we talk about this increased risk that we’re seeing.
Does Vitamin D Exacerbate Risk?
Ms. Ward: Because it’s seen with supplements, is that likely because that’s a much higher concentration of calcium coming in or do you think it’s something inherent in its being in the form of a supplement?
Dr. Budoff: I think there are two things. One, it’s definitely a higher concentration all at once. You get many more milligrams at a time when you take a supplement than if you had a high-calcium food or drink.
Also, most supplements have vitamin D as well. I think vitamin D and calcium work synergistically. When you give them both together simultaneously, I think that may have more of a potentiating effect that might exacerbate any potential risk.
Ms. Ward: Is there any reason to think there might be a difference in type of calcium supplement? I always think of the chalky tablet form vs calcium chews.
Dr. Budoff: I’m not aware of a difference in the supplement type. I think the vitamin D issue is a big problem because we all have patients who take thousands of units of vitamin D — just crazy numbers. People advocate really high numbers and that stays in the system.
Personally, I think part of the explanation is that with very high levels of vitamin D on top of calcium supplementation, you now absorb it better. You now get it into the bone, but maybe also into the coronary arteries. If you’re very high in vitamin D and then are taking a large calcium supplement, it might be the calcium/vitamin D combination that’s giving us some trouble. I think people on vitamin D supplements really need to watch their levels and not get supratherapeutic.
Ms. Ward: With the vitamin D?
Dr. Budoff: With the vitamin D.
Diabetes and Renal Function
Ms. Ward: In some of the studies, there seems to be a higher risk in patients with diabetes. Is there any reason why that would be?
Dr. Budoff: I can’t think of a reason exactly why with diabetes per se, except for renal disease. Patients with diabetes have more intrinsic renal disease, proteinuria, and even a reduced eGFR. We’ve seen that the kidney is very strongly tied to this. We have a very strong relationship, in work I’ve done a decade ago now, showing that calcium supplementation (in the form of phosphate binders) in patients on dialysis or with advanced renal disease is linked to much higher coronary calcium progression.
We did prospective, randomized trials showing that calcium intake as binders to reduce phosphorus led to more coronary calcium. We always thought that was just relegated to the renal population, and there might be an overlap here with the diabetes and more renal disease. I have a feeling that it has to do with more of that. It might be regulation of parathyroid hormone as well, which might be more abnormal in patients with diabetes.
Avoid Supratherapeutic Vitamin D Levels
Ms. Ward:: What are you telling your patients?
Dr. Budoff: I tell patients with normal kidney function that the bone will modulate 99.9% of the calcium uptake. If they have osteopenia or osteoporosis, regardless of their calcium score, I’m very comfortable putting them on supplements.
I’m a little more cautious with the vitamin D levels, and I keep an eye on that and regulate how much vitamin D they get based on their levels. I get them into the normal range, but I don’t want them supratherapeutic. You can even follow their calcium score. Again, we’ve shown that if you’re taking too much calcium, your calcium score will go up. I can just check it again in a couple of years to make sure that it’s safe.
Ms. Ward:: In terms of vitamin D levels, when you’re saying “supratherapeutic,” what levels do you consider a safe amount to take?
Dr. Budoff: I’d like them under 100 ng/mL as far as their upper level. Normal is around 70 ng/mL at most labs. I try to keep them in the normal range. I don’t even want them to be high-normal if I’m going to be concomitantly giving them calcium supplements. Of course, if they have renal insufficiency, then I’m much more cautious. We’ve even seen calcium supplements raise the serum calcium, which you never see with dietary calcium. That’s another potential proof that it might be too much too fast.
For renal patients, even in mild renal insufficiency, maybe even in diabetes where we’ve seen a signal, maybe aim lower in the amount of calcium supplementation if diet is insufficient, and aim a little lower in vitamin D targets, and I think you’ll be in a safer place.
Ms. Ward: Is there anything else you want to add?
Dr. Budoff: The evidence is still evolving. I’d say that it’s interesting and maybe a little frustrating that we don’t have a final answer on all of this. I would stay tuned for more data because we’re looking at many of the epidemiologic studies to try to see what happens in the real world, with both dietary intake of calcium and calcium supplementation.
Ms. Ward: Thank you very much for joining me today.
Dr. Budoff: It’s a pleasure. Thanks for having me.
Dr. Budoff disclosed being a speaker for Amarin Pharma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Tricia Ward: Hi. I’m Tricia Ward, from theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology. I’m joined today by Dr Matthew Budoff. He is professor of medicine at UCLA and the endowed chair of preventive cardiology at the Lundquist Institute. Welcome, Dr Budoff.
Matthew J. Budoff, MD: Thank you.
Dietary Calcium vs Coronary Calcium
Ms. Ward: The reason I wanted to talk to you today is because there have been some recent studies linking calcium supplements to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease. I’m old enough to remember when we used to tell people that dietary calcium and coronary calcium weren’t connected and weren’t the same. Were we wrong?
Dr. Budoff: I think there’s a large amount of mixed data out there still. The US Preventive Services Task Force looked into this a number of years ago and said there’s no association between calcium supplementation and increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
As you mentioned, there are a couple of newer studies that point us toward a relationship. I think that we still have a little bit of a mixed bag, but we need to dive a little deeper into that to figure out what’s going on.
Ms. Ward: Does it appear to be connected to calcium in the form of supplements vs calcium from foods?
Dr. Budoff: We looked very carefully at dietary calcium in the MESA study, the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis. There is no relationship between dietary calcium intake and coronary calcium or cardiovascular events. We’re talking mostly about supplements now when we talk about this increased risk that we’re seeing.
Does Vitamin D Exacerbate Risk?
Ms. Ward: Because it’s seen with supplements, is that likely because that’s a much higher concentration of calcium coming in or do you think it’s something inherent in its being in the form of a supplement?
Dr. Budoff: I think there are two things. One, it’s definitely a higher concentration all at once. You get many more milligrams at a time when you take a supplement than if you had a high-calcium food or drink.
Also, most supplements have vitamin D as well. I think vitamin D and calcium work synergistically. When you give them both together simultaneously, I think that may have more of a potentiating effect that might exacerbate any potential risk.
Ms. Ward: Is there any reason to think there might be a difference in type of calcium supplement? I always think of the chalky tablet form vs calcium chews.
Dr. Budoff: I’m not aware of a difference in the supplement type. I think the vitamin D issue is a big problem because we all have patients who take thousands of units of vitamin D — just crazy numbers. People advocate really high numbers and that stays in the system.
Personally, I think part of the explanation is that with very high levels of vitamin D on top of calcium supplementation, you now absorb it better. You now get it into the bone, but maybe also into the coronary arteries. If you’re very high in vitamin D and then are taking a large calcium supplement, it might be the calcium/vitamin D combination that’s giving us some trouble. I think people on vitamin D supplements really need to watch their levels and not get supratherapeutic.
Ms. Ward: With the vitamin D?
Dr. Budoff: With the vitamin D.
Diabetes and Renal Function
Ms. Ward: In some of the studies, there seems to be a higher risk in patients with diabetes. Is there any reason why that would be?
Dr. Budoff: I can’t think of a reason exactly why with diabetes per se, except for renal disease. Patients with diabetes have more intrinsic renal disease, proteinuria, and even a reduced eGFR. We’ve seen that the kidney is very strongly tied to this. We have a very strong relationship, in work I’ve done a decade ago now, showing that calcium supplementation (in the form of phosphate binders) in patients on dialysis or with advanced renal disease is linked to much higher coronary calcium progression.
We did prospective, randomized trials showing that calcium intake as binders to reduce phosphorus led to more coronary calcium. We always thought that was just relegated to the renal population, and there might be an overlap here with the diabetes and more renal disease. I have a feeling that it has to do with more of that. It might be regulation of parathyroid hormone as well, which might be more abnormal in patients with diabetes.
Avoid Supratherapeutic Vitamin D Levels
Ms. Ward:: What are you telling your patients?
Dr. Budoff: I tell patients with normal kidney function that the bone will modulate 99.9% of the calcium uptake. If they have osteopenia or osteoporosis, regardless of their calcium score, I’m very comfortable putting them on supplements.
I’m a little more cautious with the vitamin D levels, and I keep an eye on that and regulate how much vitamin D they get based on their levels. I get them into the normal range, but I don’t want them supratherapeutic. You can even follow their calcium score. Again, we’ve shown that if you’re taking too much calcium, your calcium score will go up. I can just check it again in a couple of years to make sure that it’s safe.
Ms. Ward:: In terms of vitamin D levels, when you’re saying “supratherapeutic,” what levels do you consider a safe amount to take?
Dr. Budoff: I’d like them under 100 ng/mL as far as their upper level. Normal is around 70 ng/mL at most labs. I try to keep them in the normal range. I don’t even want them to be high-normal if I’m going to be concomitantly giving them calcium supplements. Of course, if they have renal insufficiency, then I’m much more cautious. We’ve even seen calcium supplements raise the serum calcium, which you never see with dietary calcium. That’s another potential proof that it might be too much too fast.
For renal patients, even in mild renal insufficiency, maybe even in diabetes where we’ve seen a signal, maybe aim lower in the amount of calcium supplementation if diet is insufficient, and aim a little lower in vitamin D targets, and I think you’ll be in a safer place.
Ms. Ward: Is there anything else you want to add?
Dr. Budoff: The evidence is still evolving. I’d say that it’s interesting and maybe a little frustrating that we don’t have a final answer on all of this. I would stay tuned for more data because we’re looking at many of the epidemiologic studies to try to see what happens in the real world, with both dietary intake of calcium and calcium supplementation.
Ms. Ward: Thank you very much for joining me today.
Dr. Budoff: It’s a pleasure. Thanks for having me.
Dr. Budoff disclosed being a speaker for Amarin Pharma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In the Future, a Robot Intensivist May Save Your Life
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.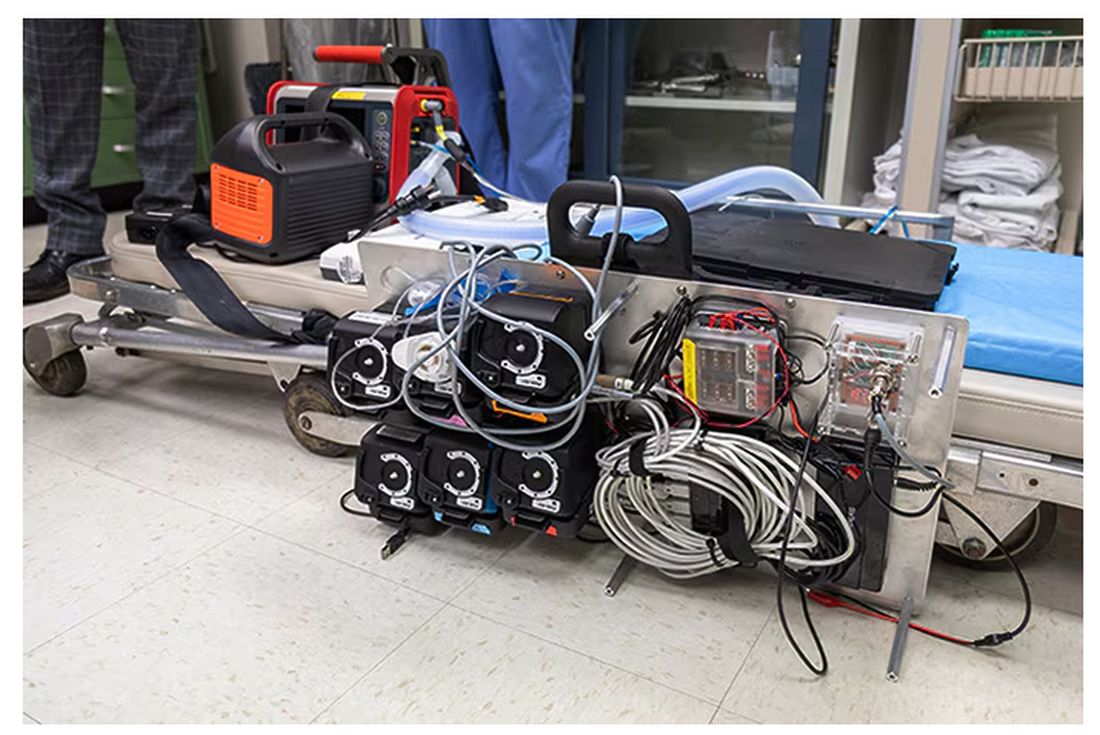
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.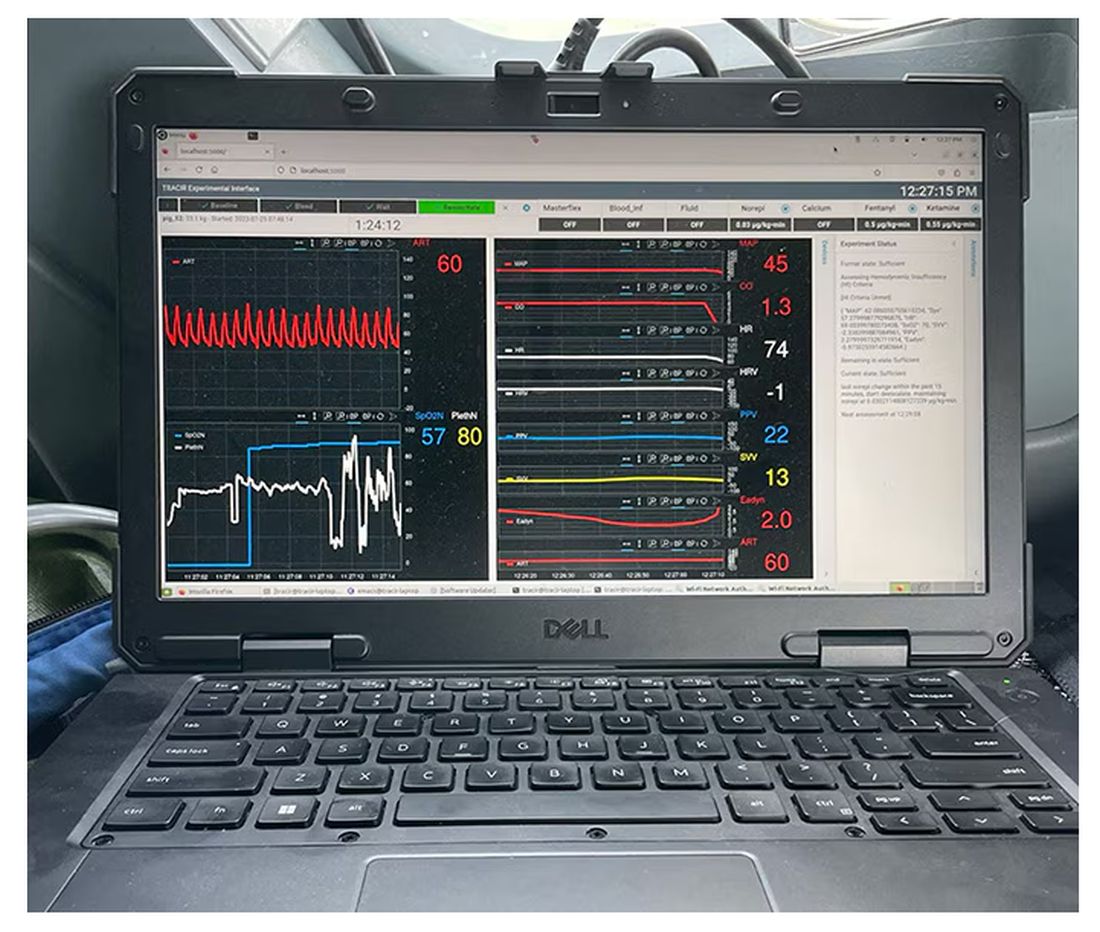
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.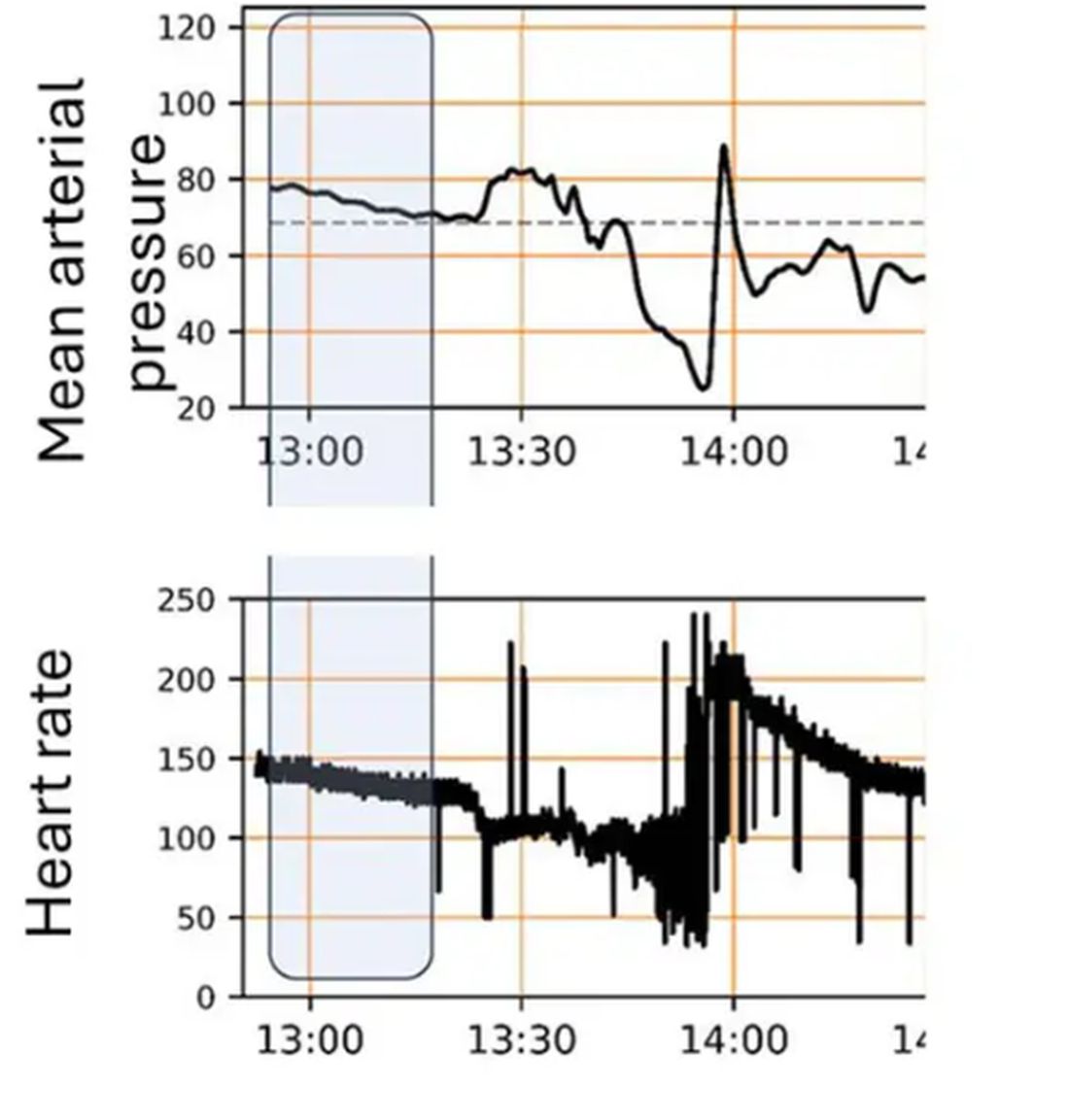
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 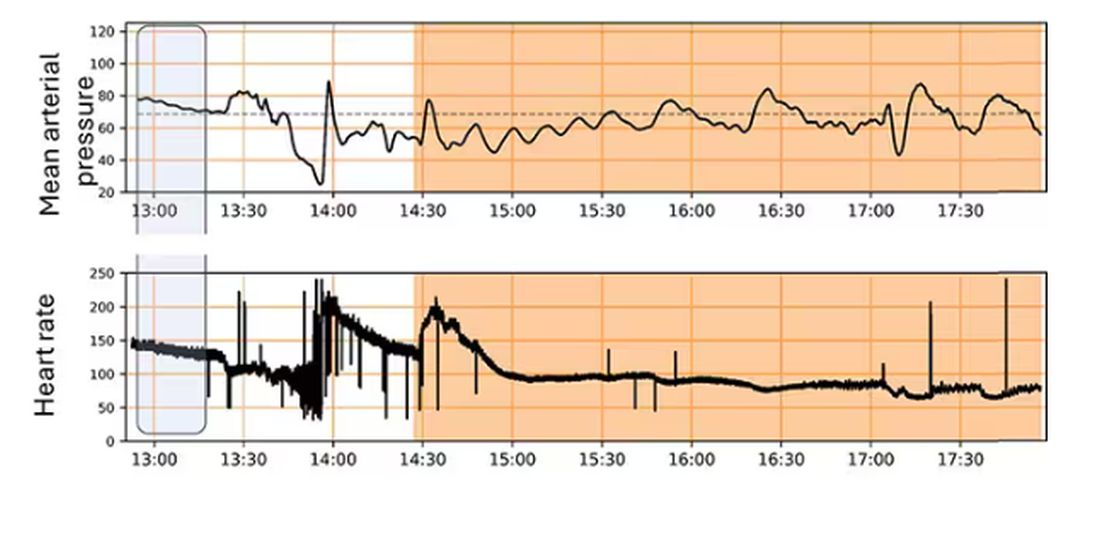
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
They call it the “golden hour”: 60 minutes, give or take, when the chance to save the life of a trauma victim is at its greatest. If the patient can be resuscitated and stabilized in that time window, they stand a good chance of surviving. If not, well, they don’t.
But resuscitation is complicated. It requires blood products, fluids, vasopressors — all given in precise doses in response to rapidly changing hemodynamics. To do it right takes specialized training, advanced life support (ALS). If the patient is in a remote area or an area without ALS-certified emergency medical services, or is far from the nearest trauma center, that golden hour is lost. And the patient may be as well.
But we live in the future. We have robots in factories, self-driving cars, autonomous drones. Why not an autonomous trauma doctor? If you are in a life-threatening accident, would you want to be treated ... by a robot?
Enter “resuscitation based on functional hemodynamic monitoring,” or “ReFit,” introduced in this article appearing in the journal Intensive Care Medicine Experimental.
The idea behind ReFit is straightforward. Resuscitation after trauma should be based on hitting key hemodynamic targets using the tools we have available in the field: blood, fluids, pressors. The researchers wanted to develop a closed-loop system, something that could be used by minimally trained personnel. The input to the system? Hemodynamic data, provided through a single measurement device, an arterial catheter. The output: blood, fluids, and pressors, delivered intravenously.
The body (a prototype) of the system looks like this. You can see various pumps labeled with various fluids, electronic controllers, and so forth.
If that’s the body, then this is the brain – a ruggedized laptop interpreting a readout of that arterial catheter.
If that’s the brain, then the ReFit algorithm is the mind. The algorithm does its best to leverage all the data it can, so I want to walk through it in a bit of detail.
First, check to see whether the patient is stable, defined as a heart rate < 110 beats/min and a mean arterial pressure > 60 mm Hg. If not, you’re off to the races, starting with a bolus of whole blood.
Next, the algorithm gets really interesting. If the patient is still unstable, the computer assesses fluid responsiveness by giving a test dose of fluid and measuring the pulse pressure variation. Greater pulse pressure variation means more fluid responsiveness and the algorithm gives more fluid. Less pulse pressure variation leads the algorithm to uptitrate pressors — in this case, norepinephrine.
This cycle of evaluation and response keeps repeating. The computer titrates fluids and pressors up and down entirely on its own, in theory freeing the human team members to do other things, like getting the patient to a trauma center for definitive care.
So, how do you test whether something like this works? Clearly, you don’t want the trial run of a system like this to be used on a real human suffering from a real traumatic injury.
Once again, we have animals to thank for research advances — in this case, pigs. Fifteen pigs are described in the study. To simulate a severe, hemorrhagic trauma, they were anesthetized and the liver was lacerated. They were then observed passively until the mean arterial pressure had dropped to below 40 mm Hg.
This is a pretty severe injury. Three unfortunate animals served as controls, two of which died within the 3-hour time window of the study. Eight animals were plugged into the ReFit system.
For a window into what happens during this process, let’s take a look at the mean arterial pressure and heart rate readouts for one of the animals. You see that the blood pressure starts to fall precipitously after the liver laceration. The heart rate quickly picks up to compensate, raising the mean arterial pressure a bit, but this would be unsustainable with ongoing bleeding.
Here, the ReFit system takes over. Autonomously, the system administers two units of blood, followed by fluids, and then norepinephrine or further fluids per the protocol I described earlier. 
The practical upshot of all of this is stabilization, despite an as-yet untreated liver laceration.
Could an experienced ALS provider do this? Of course. But, as I mentioned before, you aren’t always near an experienced ALS provider.
This is all well and good in the lab, but in the real world, you actually need to transport a trauma patient. The researchers tried this also. To prove feasibility, four pigs were taken from the lab to the top of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, flown to Allegheny County Airport and back. Total time before liver laceration repair? Three hours. And all four survived.
It won’t surprise you to hear that this work was funded by the Department of Defense. You can see how a system like this, made a bit more rugged, a bit smaller, and a bit more self-contained could have real uses in the battlefield. But trauma is not unique to war, and something that can extend the time you have to safely transport a patient to definitive care — well, that’s worth its weight in golden hours.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Beyond the Prescription Pad
The envelope was a small one, with a handwritten address. Of course, there were other things in the mail to sort through: insurance payments, bills, correspondence. So I attended to those while I made coffee and started my computer.
After a few minutes I came back to the small envelope.
Inside was a card from a recently widowed lady, thanking me for my care of her husband and telling me I was very kind.
I’d only seem him once, about a year ago, and then had a follow-up phone call to go over the results.
In medicine you develop, as I’ve previously written, “Spidey Sense.” Things alert you that something bad is going on, even when you can’t quite put your finger on it yet. His story set off several of my alarms, and I sent him off for tests.
A few days later the electromyography and nerve conduction velocity (EMG/NCV) specialist I’d referred him to called to confirm the gentleman had ALS. He’d given him the diagnosis and started him on riluzole.
I called the patient and his wife that night to discuss things in more detail. My colleague, since neuromuscular disease is his field, had already started the process (this isn’t patient poaching, he and I have worked together long enough that he knows I’d rather he take over the case). I explained things further. They didn’t have any questions.
I didn’t hear from them again until the card came. On the flip side was a picture of them and their extended family. I have no idea how they vote, or what their religion is, or how much money they have. None of that matters.
They’re nice people, and a patient, who came to me for help. I was touched by her appreciation for the little I could do, and that she took time to express that to me.
None of us cures anyone in the long run. We can put off the inevitable, do our best to relieve suffering, and try to bring comfort — even when the last is all we can do.
Here in 2024, with all of our medications and computers and tests it’s hard to believe that we still come up short — very short – against so many diseases. Yet we do.
All of us can only do our best, even when the best we can do is to be kind.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
The envelope was a small one, with a handwritten address. Of course, there were other things in the mail to sort through: insurance payments, bills, correspondence. So I attended to those while I made coffee and started my computer.
After a few minutes I came back to the small envelope.
Inside was a card from a recently widowed lady, thanking me for my care of her husband and telling me I was very kind.
I’d only seem him once, about a year ago, and then had a follow-up phone call to go over the results.
In medicine you develop, as I’ve previously written, “Spidey Sense.” Things alert you that something bad is going on, even when you can’t quite put your finger on it yet. His story set off several of my alarms, and I sent him off for tests.
A few days later the electromyography and nerve conduction velocity (EMG/NCV) specialist I’d referred him to called to confirm the gentleman had ALS. He’d given him the diagnosis and started him on riluzole.
I called the patient and his wife that night to discuss things in more detail. My colleague, since neuromuscular disease is his field, had already started the process (this isn’t patient poaching, he and I have worked together long enough that he knows I’d rather he take over the case). I explained things further. They didn’t have any questions.
I didn’t hear from them again until the card came. On the flip side was a picture of them and their extended family. I have no idea how they vote, or what their religion is, or how much money they have. None of that matters.
They’re nice people, and a patient, who came to me for help. I was touched by her appreciation for the little I could do, and that she took time to express that to me.
None of us cures anyone in the long run. We can put off the inevitable, do our best to relieve suffering, and try to bring comfort — even when the last is all we can do.
Here in 2024, with all of our medications and computers and tests it’s hard to believe that we still come up short — very short – against so many diseases. Yet we do.
All of us can only do our best, even when the best we can do is to be kind.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
The envelope was a small one, with a handwritten address. Of course, there were other things in the mail to sort through: insurance payments, bills, correspondence. So I attended to those while I made coffee and started my computer.
After a few minutes I came back to the small envelope.
Inside was a card from a recently widowed lady, thanking me for my care of her husband and telling me I was very kind.
I’d only seem him once, about a year ago, and then had a follow-up phone call to go over the results.
In medicine you develop, as I’ve previously written, “Spidey Sense.” Things alert you that something bad is going on, even when you can’t quite put your finger on it yet. His story set off several of my alarms, and I sent him off for tests.
A few days later the electromyography and nerve conduction velocity (EMG/NCV) specialist I’d referred him to called to confirm the gentleman had ALS. He’d given him the diagnosis and started him on riluzole.
I called the patient and his wife that night to discuss things in more detail. My colleague, since neuromuscular disease is his field, had already started the process (this isn’t patient poaching, he and I have worked together long enough that he knows I’d rather he take over the case). I explained things further. They didn’t have any questions.
I didn’t hear from them again until the card came. On the flip side was a picture of them and their extended family. I have no idea how they vote, or what their religion is, or how much money they have. None of that matters.
They’re nice people, and a patient, who came to me for help. I was touched by her appreciation for the little I could do, and that she took time to express that to me.
None of us cures anyone in the long run. We can put off the inevitable, do our best to relieve suffering, and try to bring comfort — even when the last is all we can do.
Here in 2024, with all of our medications and computers and tests it’s hard to believe that we still come up short — very short – against so many diseases. Yet we do.
All of us can only do our best, even when the best we can do is to be kind.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Fluoride, Water, and Kids’ Brains: It’s Complicated
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently looked back at my folder full of these medical study commentaries, this weekly video series we call Impact Factor, and realized that I’ve been doing this for a long time. More than 400 articles, believe it or not.
I’ve learned a lot in that time — about medicine, of course — but also about how people react to certain topics. If you’ve been with me this whole time, or even for just a chunk of it, you’ll know that I tend to take a measured approach to most topics. No one study is ever truly definitive, after all. But regardless of how even-keeled I may be, there are some topics that I just know in advance are going to be a bit divisive: studies about gun control; studies about vitamin D; and, of course, studies about fluoride.
Shall We Shake This Hornet’s Nest?
The fluoridation of the US water system began in 1945 with the goal of reducing cavities in the population. The CDC named water fluoridation one of the 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century, along with such inarguable achievements as the recognition of tobacco as a health hazard.
But fluoridation has never been without its detractors. One problem is that the spectrum of beliefs about the potential harm of fluoridation is huge. On one end, you have science-based concerns such as the recognition that excessive fluoride intake can cause fluorosis and stain tooth enamel. I’ll note that the EPA regulates fluoride levels — there is a fair amount of naturally occurring fluoride in water tables around the world — to prevent this. And, of course, on the other end of the spectrum, you have beliefs that are essentially conspiracy theories: “They” add fluoride to the water supply to control us.
The challenge for me is that when one “side” of a scientific debate includes the crazy theories, it can be hard to discuss that whole spectrum, since there are those who will see evidence of any adverse fluoride effect as confirmation that the conspiracy theory is true.
I can’t help this. So I’ll just say this up front: I am about to tell you about a study that shows some potential risk from fluoride exposure. I will tell you up front that there are some significant caveats to the study that call the results into question. And I will tell you up front that no one is controlling your mind, or my mind, with fluoride; they do it with social media.
Let’s Dive Into These Shark-Infested, Fluoridated Waters
We’re talking about the study, “Maternal Urinary Fluoride and Child Neurobehavior at Age 36 Months,” which appears in JAMA Network Open.
It’s a study of 229 mother-child pairs from the Los Angeles area. The moms had their urinary fluoride level measured once before 30 weeks of gestation. A neurobehavioral battery called the Preschool Child Behavior Checklist was administered to the children at age 36 months.
The main thing you’ll hear about this study — in headlines, Facebook posts, and manifestos locked in drawers somewhere — is the primary result: A 0.68-mg/L increase in urinary fluoride in the mothers, about 25 percentile points, was associated with a doubling of the risk for neurobehavioral problems in their kids when they were 3 years old.
Yikes.
But this is not a randomized trial. Researchers didn’t randomly assign some women to have high fluoride intake and some women to have low fluoride intake. They knew that other factors that might lead to neurobehavioral problems could also lead to higher fluoride intake. They represent these factors in what’s known as a directed acyclic graph, as seen here, and account for them statistically using a regression equation.
Not represented here are neighborhood characteristics. Los Angeles does not have uniformly fluoridated water, and neurobehavioral problems in kids are strongly linked to stressors in their environments. Fluoride level could be an innocent bystander.
I’m really just describing the classic issue of correlation versus causation here, the bane of all observational research and — let’s be honest — a bit of a crutch that allows us to disregard the results of studies we don’t like, provided the study wasn’t a randomized trial.
But I have a deeper issue with this study than the old “failure to adjust for relevant confounders” thing, as important as that is.
The exposure of interest in this study is maternal urinary fluoride, as measured in a spot sample. It’s not often that I get to go deep on nephrology in this space, but let’s think about that for a second. Let’s assume for a moment that fluoride is toxic to the developing fetal brain, the main concern raised by the results of the study. How would that work? Presumably, mom would be ingesting fluoride from various sources (like the water supply), and that fluoride would get into her blood, and from her blood across the placenta to the baby’s blood, and into the baby’s brain.
Is Urinary Fluoride a Good Measure of Blood Fluoride?
It’s not great. Empirically, we have data that tell us that levels of urine fluoride are not all that similar to levels of serum fluoride. In 2014, a study investigated the correlation between urine and serum fluoride in a cohort of 60 schoolchildren and found a correlation coefficient of around 0.5.
Why isn’t urine fluoride a great proxy for serum fluoride? The most obvious reason is the urine concentration. Human urine concentration can range from about 50 mmol to 1200 mmol (a 24-fold difference) depending on hydration status. Over the course of 24 hours, for example, the amount of fluoride you put out in your urine may be fairly stable in relation to intake, but for a spot urine sample it would be wildly variable. The authors know this, of course, and so they divide the measured urine fluoride by the specific gravity of the urine to give a sort of “dilution adjusted” value. That’s what is actually used in this study. But specific gravity is, itself, an imperfect measure of how dilute the urine is.
This is something that comes up a lot in urinary biomarker research and it’s not that hard to get around. The best thing would be to just measure blood levels of fluoride. The second best option is 24-hour fluoride excretion. After that, the next best thing would be to adjust the spot concentration by other markers of urinary dilution — creatinine or osmolality — as sensitivity analyses. Any of these approaches would lend credence to the results of the study.
Urinary fluoride excretion is pH dependent. The more acidic the urine, the less fluoride is excreted. Many things — including, importantly, diet — affect urine pH. And it is not a stretch to think that diet may also affect the developing fetus. Neither urine pH nor dietary habits were accounted for in this study.
So, here we are. We have an observational study suggesting a harm that may be associated with fluoride. There may be a causal link here, in which case we need further studies to weigh the harm against the more well-established public health benefit. Or, this is all correlation — an illusion created by the limitations of observational data, and the unique challenges of estimating intake from a single urine sample. In other words, this study has something for everyone, fluoride boosters and skeptics alike. Let the arguments begin. But, if possible, leave me out of it.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently looked back at my folder full of these medical study commentaries, this weekly video series we call Impact Factor, and realized that I’ve been doing this for a long time. More than 400 articles, believe it or not.
I’ve learned a lot in that time — about medicine, of course — but also about how people react to certain topics. If you’ve been with me this whole time, or even for just a chunk of it, you’ll know that I tend to take a measured approach to most topics. No one study is ever truly definitive, after all. But regardless of how even-keeled I may be, there are some topics that I just know in advance are going to be a bit divisive: studies about gun control; studies about vitamin D; and, of course, studies about fluoride.
Shall We Shake This Hornet’s Nest?
The fluoridation of the US water system began in 1945 with the goal of reducing cavities in the population. The CDC named water fluoridation one of the 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century, along with such inarguable achievements as the recognition of tobacco as a health hazard.
But fluoridation has never been without its detractors. One problem is that the spectrum of beliefs about the potential harm of fluoridation is huge. On one end, you have science-based concerns such as the recognition that excessive fluoride intake can cause fluorosis and stain tooth enamel. I’ll note that the EPA regulates fluoride levels — there is a fair amount of naturally occurring fluoride in water tables around the world — to prevent this. And, of course, on the other end of the spectrum, you have beliefs that are essentially conspiracy theories: “They” add fluoride to the water supply to control us.
The challenge for me is that when one “side” of a scientific debate includes the crazy theories, it can be hard to discuss that whole spectrum, since there are those who will see evidence of any adverse fluoride effect as confirmation that the conspiracy theory is true.
I can’t help this. So I’ll just say this up front: I am about to tell you about a study that shows some potential risk from fluoride exposure. I will tell you up front that there are some significant caveats to the study that call the results into question. And I will tell you up front that no one is controlling your mind, or my mind, with fluoride; they do it with social media.
Let’s Dive Into These Shark-Infested, Fluoridated Waters
We’re talking about the study, “Maternal Urinary Fluoride and Child Neurobehavior at Age 36 Months,” which appears in JAMA Network Open.
It’s a study of 229 mother-child pairs from the Los Angeles area. The moms had their urinary fluoride level measured once before 30 weeks of gestation. A neurobehavioral battery called the Preschool Child Behavior Checklist was administered to the children at age 36 months.
The main thing you’ll hear about this study — in headlines, Facebook posts, and manifestos locked in drawers somewhere — is the primary result: A 0.68-mg/L increase in urinary fluoride in the mothers, about 25 percentile points, was associated with a doubling of the risk for neurobehavioral problems in their kids when they were 3 years old.
Yikes.
But this is not a randomized trial. Researchers didn’t randomly assign some women to have high fluoride intake and some women to have low fluoride intake. They knew that other factors that might lead to neurobehavioral problems could also lead to higher fluoride intake. They represent these factors in what’s known as a directed acyclic graph, as seen here, and account for them statistically using a regression equation.
Not represented here are neighborhood characteristics. Los Angeles does not have uniformly fluoridated water, and neurobehavioral problems in kids are strongly linked to stressors in their environments. Fluoride level could be an innocent bystander.
I’m really just describing the classic issue of correlation versus causation here, the bane of all observational research and — let’s be honest — a bit of a crutch that allows us to disregard the results of studies we don’t like, provided the study wasn’t a randomized trial.
But I have a deeper issue with this study than the old “failure to adjust for relevant confounders” thing, as important as that is.
The exposure of interest in this study is maternal urinary fluoride, as measured in a spot sample. It’s not often that I get to go deep on nephrology in this space, but let’s think about that for a second. Let’s assume for a moment that fluoride is toxic to the developing fetal brain, the main concern raised by the results of the study. How would that work? Presumably, mom would be ingesting fluoride from various sources (like the water supply), and that fluoride would get into her blood, and from her blood across the placenta to the baby’s blood, and into the baby’s brain.
Is Urinary Fluoride a Good Measure of Blood Fluoride?
It’s not great. Empirically, we have data that tell us that levels of urine fluoride are not all that similar to levels of serum fluoride. In 2014, a study investigated the correlation between urine and serum fluoride in a cohort of 60 schoolchildren and found a correlation coefficient of around 0.5.
Why isn’t urine fluoride a great proxy for serum fluoride? The most obvious reason is the urine concentration. Human urine concentration can range from about 50 mmol to 1200 mmol (a 24-fold difference) depending on hydration status. Over the course of 24 hours, for example, the amount of fluoride you put out in your urine may be fairly stable in relation to intake, but for a spot urine sample it would be wildly variable. The authors know this, of course, and so they divide the measured urine fluoride by the specific gravity of the urine to give a sort of “dilution adjusted” value. That’s what is actually used in this study. But specific gravity is, itself, an imperfect measure of how dilute the urine is.
This is something that comes up a lot in urinary biomarker research and it’s not that hard to get around. The best thing would be to just measure blood levels of fluoride. The second best option is 24-hour fluoride excretion. After that, the next best thing would be to adjust the spot concentration by other markers of urinary dilution — creatinine or osmolality — as sensitivity analyses. Any of these approaches would lend credence to the results of the study.
Urinary fluoride excretion is pH dependent. The more acidic the urine, the less fluoride is excreted. Many things — including, importantly, diet — affect urine pH. And it is not a stretch to think that diet may also affect the developing fetus. Neither urine pH nor dietary habits were accounted for in this study.
So, here we are. We have an observational study suggesting a harm that may be associated with fluoride. There may be a causal link here, in which case we need further studies to weigh the harm against the more well-established public health benefit. Or, this is all correlation — an illusion created by the limitations of observational data, and the unique challenges of estimating intake from a single urine sample. In other words, this study has something for everyone, fluoride boosters and skeptics alike. Let the arguments begin. But, if possible, leave me out of it.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently looked back at my folder full of these medical study commentaries, this weekly video series we call Impact Factor, and realized that I’ve been doing this for a long time. More than 400 articles, believe it or not.
I’ve learned a lot in that time — about medicine, of course — but also about how people react to certain topics. If you’ve been with me this whole time, or even for just a chunk of it, you’ll know that I tend to take a measured approach to most topics. No one study is ever truly definitive, after all. But regardless of how even-keeled I may be, there are some topics that I just know in advance are going to be a bit divisive: studies about gun control; studies about vitamin D; and, of course, studies about fluoride.
Shall We Shake This Hornet’s Nest?
The fluoridation of the US water system began in 1945 with the goal of reducing cavities in the population. The CDC named water fluoridation one of the 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century, along with such inarguable achievements as the recognition of tobacco as a health hazard.
But fluoridation has never been without its detractors. One problem is that the spectrum of beliefs about the potential harm of fluoridation is huge. On one end, you have science-based concerns such as the recognition that excessive fluoride intake can cause fluorosis and stain tooth enamel. I’ll note that the EPA regulates fluoride levels — there is a fair amount of naturally occurring fluoride in water tables around the world — to prevent this. And, of course, on the other end of the spectrum, you have beliefs that are essentially conspiracy theories: “They” add fluoride to the water supply to control us.
The challenge for me is that when one “side” of a scientific debate includes the crazy theories, it can be hard to discuss that whole spectrum, since there are those who will see evidence of any adverse fluoride effect as confirmation that the conspiracy theory is true.
I can’t help this. So I’ll just say this up front: I am about to tell you about a study that shows some potential risk from fluoride exposure. I will tell you up front that there are some significant caveats to the study that call the results into question. And I will tell you up front that no one is controlling your mind, or my mind, with fluoride; they do it with social media.
Let’s Dive Into These Shark-Infested, Fluoridated Waters
We’re talking about the study, “Maternal Urinary Fluoride and Child Neurobehavior at Age 36 Months,” which appears in JAMA Network Open.
It’s a study of 229 mother-child pairs from the Los Angeles area. The moms had their urinary fluoride level measured once before 30 weeks of gestation. A neurobehavioral battery called the Preschool Child Behavior Checklist was administered to the children at age 36 months.
The main thing you’ll hear about this study — in headlines, Facebook posts, and manifestos locked in drawers somewhere — is the primary result: A 0.68-mg/L increase in urinary fluoride in the mothers, about 25 percentile points, was associated with a doubling of the risk for neurobehavioral problems in their kids when they were 3 years old.
Yikes.
But this is not a randomized trial. Researchers didn’t randomly assign some women to have high fluoride intake and some women to have low fluoride intake. They knew that other factors that might lead to neurobehavioral problems could also lead to higher fluoride intake. They represent these factors in what’s known as a directed acyclic graph, as seen here, and account for them statistically using a regression equation.
Not represented here are neighborhood characteristics. Los Angeles does not have uniformly fluoridated water, and neurobehavioral problems in kids are strongly linked to stressors in their environments. Fluoride level could be an innocent bystander.
I’m really just describing the classic issue of correlation versus causation here, the bane of all observational research and — let’s be honest — a bit of a crutch that allows us to disregard the results of studies we don’t like, provided the study wasn’t a randomized trial.
But I have a deeper issue with this study than the old “failure to adjust for relevant confounders” thing, as important as that is.
The exposure of interest in this study is maternal urinary fluoride, as measured in a spot sample. It’s not often that I get to go deep on nephrology in this space, but let’s think about that for a second. Let’s assume for a moment that fluoride is toxic to the developing fetal brain, the main concern raised by the results of the study. How would that work? Presumably, mom would be ingesting fluoride from various sources (like the water supply), and that fluoride would get into her blood, and from her blood across the placenta to the baby’s blood, and into the baby’s brain.
Is Urinary Fluoride a Good Measure of Blood Fluoride?
It’s not great. Empirically, we have data that tell us that levels of urine fluoride are not all that similar to levels of serum fluoride. In 2014, a study investigated the correlation between urine and serum fluoride in a cohort of 60 schoolchildren and found a correlation coefficient of around 0.5.
Why isn’t urine fluoride a great proxy for serum fluoride? The most obvious reason is the urine concentration. Human urine concentration can range from about 50 mmol to 1200 mmol (a 24-fold difference) depending on hydration status. Over the course of 24 hours, for example, the amount of fluoride you put out in your urine may be fairly stable in relation to intake, but for a spot urine sample it would be wildly variable. The authors know this, of course, and so they divide the measured urine fluoride by the specific gravity of the urine to give a sort of “dilution adjusted” value. That’s what is actually used in this study. But specific gravity is, itself, an imperfect measure of how dilute the urine is.
This is something that comes up a lot in urinary biomarker research and it’s not that hard to get around. The best thing would be to just measure blood levels of fluoride. The second best option is 24-hour fluoride excretion. After that, the next best thing would be to adjust the spot concentration by other markers of urinary dilution — creatinine or osmolality — as sensitivity analyses. Any of these approaches would lend credence to the results of the study.
Urinary fluoride excretion is pH dependent. The more acidic the urine, the less fluoride is excreted. Many things — including, importantly, diet — affect urine pH. And it is not a stretch to think that diet may also affect the developing fetus. Neither urine pH nor dietary habits were accounted for in this study.
So, here we are. We have an observational study suggesting a harm that may be associated with fluoride. There may be a causal link here, in which case we need further studies to weigh the harm against the more well-established public health benefit. Or, this is all correlation — an illusion created by the limitations of observational data, and the unique challenges of estimating intake from a single urine sample. In other words, this study has something for everyone, fluoride boosters and skeptics alike. Let the arguments begin. But, if possible, leave me out of it.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.