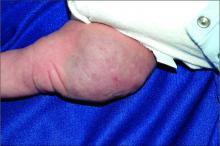
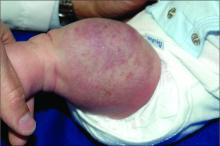
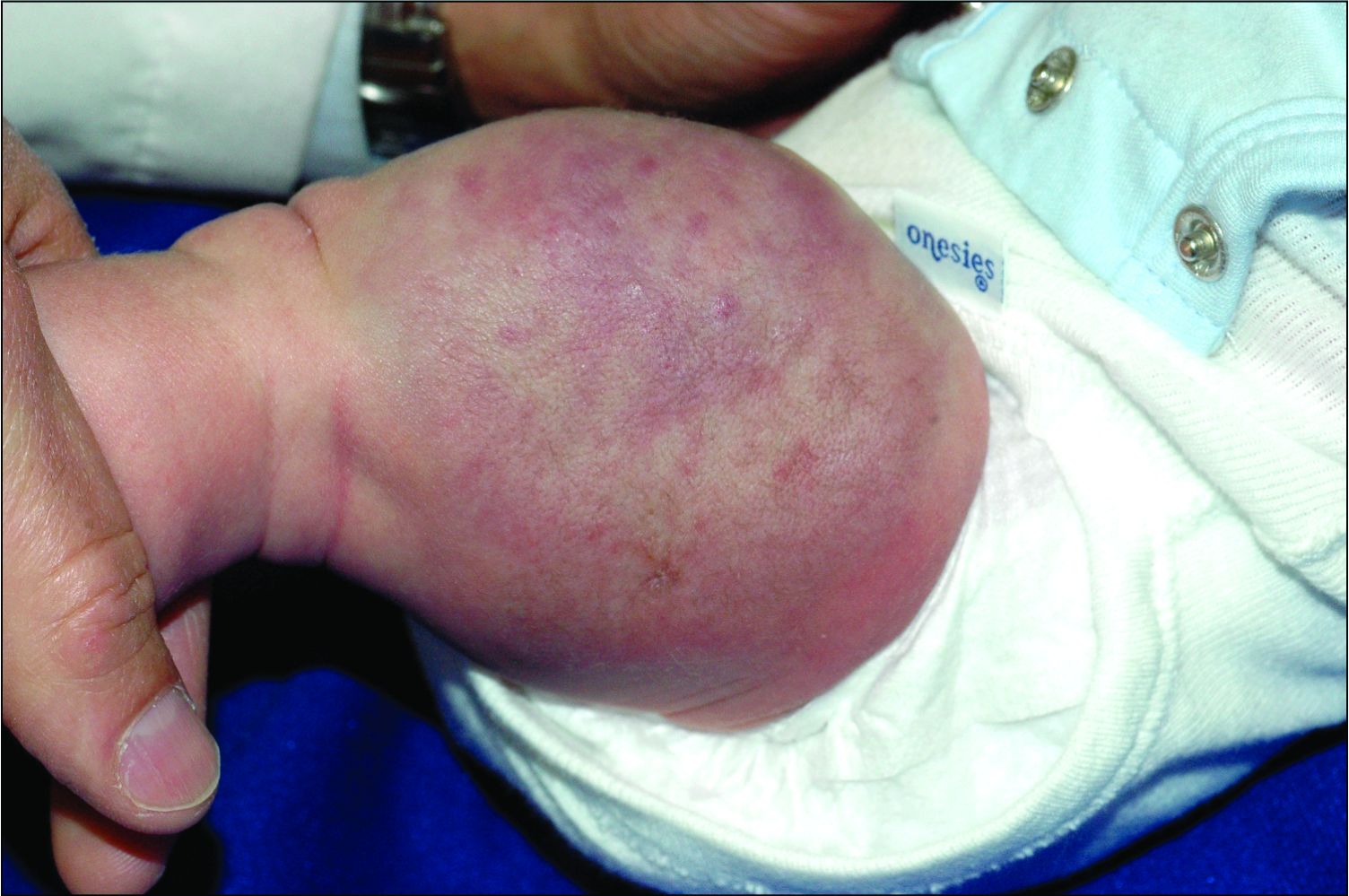
User login
Polycystic ovary syndrome: It’s not just about fertility
Polycystic ovary syndrome, the most common endocrinopathy and most common cause of female infertility, affects 8%-13% of reproductive-aged women. PCOS has a profound impact on a woman’s life yet its diagnosis and management remain confusing despite being first described nearly a century ago by Stein and Leventhal.
To illustrate, in a global survey of 1,385 women with PCOS, one-third or more reported a delay of greater than 2 years and nearly half required evaluation by at least three health professionals before a diagnosis was established (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102[2]:604-12). A vital health problem that urgently requires a gap analysis and needs assessment, PCOS is not “just about fertility” but has extensive gynecologic and metabolic consequences that require a personalized approach to care coordinated among the fields of internal medicine, pediatrics, dermatology, and, of course, gynecology.
Diagnosis in adults and adolescence
Normal menstrual intervals do not always equate with ovulation. Up to 40% of hirsute women with monthly cycles may not ovulate regularly. The Rotterdam criteria are used to confirm PCOS and require two of the following three: 1) ovulation dysfunction (cycle interval > 35 d or < 8 cycles/year); 2) hyperandrogenism (i.e., elevated total or free testosterone, DHEAS, or signs of hirsutism or acne with Ferriman-Gallwey score greater than 6); 3) polycystic ovaries on ultrasound (20 or more 2- to 9-mm follicles on at least one ovary, and/or increased ovarian volume (> 10 mL) – all at the exclusion of other etiologies including hyperprolactinemia, thyroid dysfunction, androgen-secreting tumors including Cushing’s syndrome, and nonclassic adrenal hyperplasia mostly easily screened by obtaining 17-hydroxyprogesterone.
For adolescents, by age 14 most will have adult androgen levels. Ovarian ultrasound should not be used as a criterion in this age group given the frequency of this appearance. Due to frequent menstrual irregularity, it is recommended to wait at least 2 years post menarche before consideration of a diagnosis.
Antimüllerian hormone is two- to threefold higher in women with PCOS but this hormone level has not yet been accepted as a diagnostic criterion.
The metabolic connection
A multisystem disorder whose name misdirects its morbidity, PCOS affects the metabolic, reproductive, and psychological system through vicious cycles of distorted feedback signals. Without a consensus of its origin, there appears to be a hypersensitivity of pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH) to hypothalamic gonadotrophin-releasing hormone. Consequently, elevated LH stimulates ovarian theca cells to increase androgens with resultant hyperandrogenic consequences. Parenthetically, the tonic elevation in LH explains the false-positive surges PCOS women experience when testing their urine during ovulation induction.
Elevations in insulin from unexplained damage to the insulin receptor acts synergistically with LH to increase ovarian androgens and inhibit ovulation. Hyperinsulinemia and abdominal fat deposition contribute to impaired glucose tolerance which is threefold higher with PCOS.
The metabolic syndrome, an association of disorders including hypertension, impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidemia, and obesity, occurs at an increased overall prevalence rate of 43%-47% in women with PCOS, which is twice as high as in women without PCOS. PCOS is associated with low-grade chronic inflammation, which places these women at increased risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dyslipidemia is the most common metabolic disorder in PCOS. These metabolic consequences, including obstructive sleep apnea, are worsened by hyperandrogenemia and an elevated BMI.
A genetic link
Multigenetic in origin, PCOS has a fivefold higher risk of inheritance from mothers with PCOS to daughters influenced by prenatal androgen exposure in utero. Genetic studies suggest a causal relationship between PCOS with body mass index, insulin resistance, onset of menopause, depression, and male-pattern balding (PLoS Genet 2018;14[12]:e10007813).
Fifteen genetic risk areas in the human genome seem to predispose to PCOS. New results suggest that altering the gut microbiome via prebiotic or probiotic therapies may be a potential treatment option.
Reproductive and gynecologic management
Due to chronic anovulation, unopposed estrogen can result in abnormal endometrial bleeding, endometrial hyperplasia, and a fourfold risk of endometrial cancer. This underscores the importance of regular progestin withdrawal, combined oral contraception (COC), or a progestin intrauterine device.
PCOS is a leading cause of infertility and is associated with abnormal bleeding, miscarriage, gestational diabetes, and gestational hypertension, all of which are higher based on a hyperandrogenic phenotype.
The rate of infertility in women with PCOS is 70%-80%, with ovulation dysfunction being the dominant cause. For years, the mainstay for ovulation induction was clomiphene citrate; however, letrozole has shown higher pregnancy success rates, particularly in women who have a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2. (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:119-29). Despite multiple studies demonstrating its efficacy and safety, letrozole remains without Food and Drug Administration approval for ovulation induction.
Metformin has been recommended in women with prediabetes or a BMI above 30, and it may improve menstrual regularity but has not been shown to improve live birth rates nor reduce the pregnancy complications of miscarriage or gestational diabetes. Inositol, the ubiquitous endogenous carbohydrate, has not demonstrated clear improvement in reproduction.
Laparoscopic ovarian diathermy (LOD) is a second-line treatment option, as is the use of gonadotropins, to overcome unsuccessful conservative attempts at ovulation induction. LOD is more invasive but outcomes are equivalent to gonadotropin usage while providing a dramatic reduction in multiple gestation, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, and cost (not including the surgical procedure). Ultimately, in vitro fertilization is an option for continued infertility in women with PCOS.
Metabolic/gynecologic management
Given the multisystem effect of PCOS, health care providers caring for these women should be vigilant and aggressive at ensuring appropriate monitoring and management. For women with PCOS with an elevated BMI, lifestyle modification is the first line of management. Weight loss alone of only 2%-5% may restore ovulation function.
The combination of dyslipidemia, elevated BMI, and impaired glucose tolerance would presumably predict the risk of cardiovascular events, yet the impact is not proven. Despite an increase in carotid intima media thickness, there are data that suggest only an increase in stroke or myocardial infarction (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104[4]:1221-31).
Hyperandrogenism is cosmetically and psychologically disrupting to PCOS patients. The topical application of eflornithine hydrochloride may be of value for mild to moderate facial hair growth. Spironolactone is the preferred first-line agent. (Caution: effective contraception is necessary to avoid feminization of a male fetus). Women with PCOS have a higher risk of disordered eating and body image distress as well as a fivefold higher rate of mental distress such as anxiety and depression.
No specific diet has been determined as part of treatment, yet healthy food selection and caloric intake combined with exercise has been shown to improve metabolic and psychological well-being.
Conclusion
PCOS is a ubiquitous, frustrating, and life-altering disease. Health care providers, particularly those in women’s health, must ensure appropriate counseling and education with evidence-based medicine to empower patients toward improved health.
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE - The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando. He has no conflicts of interest. Please contact him at [email protected].
Polycystic ovary syndrome, the most common endocrinopathy and most common cause of female infertility, affects 8%-13% of reproductive-aged women. PCOS has a profound impact on a woman’s life yet its diagnosis and management remain confusing despite being first described nearly a century ago by Stein and Leventhal.
To illustrate, in a global survey of 1,385 women with PCOS, one-third or more reported a delay of greater than 2 years and nearly half required evaluation by at least three health professionals before a diagnosis was established (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102[2]:604-12). A vital health problem that urgently requires a gap analysis and needs assessment, PCOS is not “just about fertility” but has extensive gynecologic and metabolic consequences that require a personalized approach to care coordinated among the fields of internal medicine, pediatrics, dermatology, and, of course, gynecology.
Diagnosis in adults and adolescence
Normal menstrual intervals do not always equate with ovulation. Up to 40% of hirsute women with monthly cycles may not ovulate regularly. The Rotterdam criteria are used to confirm PCOS and require two of the following three: 1) ovulation dysfunction (cycle interval > 35 d or < 8 cycles/year); 2) hyperandrogenism (i.e., elevated total or free testosterone, DHEAS, or signs of hirsutism or acne with Ferriman-Gallwey score greater than 6); 3) polycystic ovaries on ultrasound (20 or more 2- to 9-mm follicles on at least one ovary, and/or increased ovarian volume (> 10 mL) – all at the exclusion of other etiologies including hyperprolactinemia, thyroid dysfunction, androgen-secreting tumors including Cushing’s syndrome, and nonclassic adrenal hyperplasia mostly easily screened by obtaining 17-hydroxyprogesterone.
For adolescents, by age 14 most will have adult androgen levels. Ovarian ultrasound should not be used as a criterion in this age group given the frequency of this appearance. Due to frequent menstrual irregularity, it is recommended to wait at least 2 years post menarche before consideration of a diagnosis.
Antimüllerian hormone is two- to threefold higher in women with PCOS but this hormone level has not yet been accepted as a diagnostic criterion.
The metabolic connection
A multisystem disorder whose name misdirects its morbidity, PCOS affects the metabolic, reproductive, and psychological system through vicious cycles of distorted feedback signals. Without a consensus of its origin, there appears to be a hypersensitivity of pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH) to hypothalamic gonadotrophin-releasing hormone. Consequently, elevated LH stimulates ovarian theca cells to increase androgens with resultant hyperandrogenic consequences. Parenthetically, the tonic elevation in LH explains the false-positive surges PCOS women experience when testing their urine during ovulation induction.
Elevations in insulin from unexplained damage to the insulin receptor acts synergistically with LH to increase ovarian androgens and inhibit ovulation. Hyperinsulinemia and abdominal fat deposition contribute to impaired glucose tolerance which is threefold higher with PCOS.
The metabolic syndrome, an association of disorders including hypertension, impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidemia, and obesity, occurs at an increased overall prevalence rate of 43%-47% in women with PCOS, which is twice as high as in women without PCOS. PCOS is associated with low-grade chronic inflammation, which places these women at increased risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dyslipidemia is the most common metabolic disorder in PCOS. These metabolic consequences, including obstructive sleep apnea, are worsened by hyperandrogenemia and an elevated BMI.
A genetic link
Multigenetic in origin, PCOS has a fivefold higher risk of inheritance from mothers with PCOS to daughters influenced by prenatal androgen exposure in utero. Genetic studies suggest a causal relationship between PCOS with body mass index, insulin resistance, onset of menopause, depression, and male-pattern balding (PLoS Genet 2018;14[12]:e10007813).
Fifteen genetic risk areas in the human genome seem to predispose to PCOS. New results suggest that altering the gut microbiome via prebiotic or probiotic therapies may be a potential treatment option.
Reproductive and gynecologic management
Due to chronic anovulation, unopposed estrogen can result in abnormal endometrial bleeding, endometrial hyperplasia, and a fourfold risk of endometrial cancer. This underscores the importance of regular progestin withdrawal, combined oral contraception (COC), or a progestin intrauterine device.
PCOS is a leading cause of infertility and is associated with abnormal bleeding, miscarriage, gestational diabetes, and gestational hypertension, all of which are higher based on a hyperandrogenic phenotype.
The rate of infertility in women with PCOS is 70%-80%, with ovulation dysfunction being the dominant cause. For years, the mainstay for ovulation induction was clomiphene citrate; however, letrozole has shown higher pregnancy success rates, particularly in women who have a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2. (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:119-29). Despite multiple studies demonstrating its efficacy and safety, letrozole remains without Food and Drug Administration approval for ovulation induction.
Metformin has been recommended in women with prediabetes or a BMI above 30, and it may improve menstrual regularity but has not been shown to improve live birth rates nor reduce the pregnancy complications of miscarriage or gestational diabetes. Inositol, the ubiquitous endogenous carbohydrate, has not demonstrated clear improvement in reproduction.
Laparoscopic ovarian diathermy (LOD) is a second-line treatment option, as is the use of gonadotropins, to overcome unsuccessful conservative attempts at ovulation induction. LOD is more invasive but outcomes are equivalent to gonadotropin usage while providing a dramatic reduction in multiple gestation, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, and cost (not including the surgical procedure). Ultimately, in vitro fertilization is an option for continued infertility in women with PCOS.
Metabolic/gynecologic management
Given the multisystem effect of PCOS, health care providers caring for these women should be vigilant and aggressive at ensuring appropriate monitoring and management. For women with PCOS with an elevated BMI, lifestyle modification is the first line of management. Weight loss alone of only 2%-5% may restore ovulation function.
The combination of dyslipidemia, elevated BMI, and impaired glucose tolerance would presumably predict the risk of cardiovascular events, yet the impact is not proven. Despite an increase in carotid intima media thickness, there are data that suggest only an increase in stroke or myocardial infarction (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104[4]:1221-31).
Hyperandrogenism is cosmetically and psychologically disrupting to PCOS patients. The topical application of eflornithine hydrochloride may be of value for mild to moderate facial hair growth. Spironolactone is the preferred first-line agent. (Caution: effective contraception is necessary to avoid feminization of a male fetus). Women with PCOS have a higher risk of disordered eating and body image distress as well as a fivefold higher rate of mental distress such as anxiety and depression.
No specific diet has been determined as part of treatment, yet healthy food selection and caloric intake combined with exercise has been shown to improve metabolic and psychological well-being.
Conclusion
PCOS is a ubiquitous, frustrating, and life-altering disease. Health care providers, particularly those in women’s health, must ensure appropriate counseling and education with evidence-based medicine to empower patients toward improved health.
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE - The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando. He has no conflicts of interest. Please contact him at [email protected].
Polycystic ovary syndrome, the most common endocrinopathy and most common cause of female infertility, affects 8%-13% of reproductive-aged women. PCOS has a profound impact on a woman’s life yet its diagnosis and management remain confusing despite being first described nearly a century ago by Stein and Leventhal.
To illustrate, in a global survey of 1,385 women with PCOS, one-third or more reported a delay of greater than 2 years and nearly half required evaluation by at least three health professionals before a diagnosis was established (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102[2]:604-12). A vital health problem that urgently requires a gap analysis and needs assessment, PCOS is not “just about fertility” but has extensive gynecologic and metabolic consequences that require a personalized approach to care coordinated among the fields of internal medicine, pediatrics, dermatology, and, of course, gynecology.
Diagnosis in adults and adolescence
Normal menstrual intervals do not always equate with ovulation. Up to 40% of hirsute women with monthly cycles may not ovulate regularly. The Rotterdam criteria are used to confirm PCOS and require two of the following three: 1) ovulation dysfunction (cycle interval > 35 d or < 8 cycles/year); 2) hyperandrogenism (i.e., elevated total or free testosterone, DHEAS, or signs of hirsutism or acne with Ferriman-Gallwey score greater than 6); 3) polycystic ovaries on ultrasound (20 or more 2- to 9-mm follicles on at least one ovary, and/or increased ovarian volume (> 10 mL) – all at the exclusion of other etiologies including hyperprolactinemia, thyroid dysfunction, androgen-secreting tumors including Cushing’s syndrome, and nonclassic adrenal hyperplasia mostly easily screened by obtaining 17-hydroxyprogesterone.
For adolescents, by age 14 most will have adult androgen levels. Ovarian ultrasound should not be used as a criterion in this age group given the frequency of this appearance. Due to frequent menstrual irregularity, it is recommended to wait at least 2 years post menarche before consideration of a diagnosis.
Antimüllerian hormone is two- to threefold higher in women with PCOS but this hormone level has not yet been accepted as a diagnostic criterion.
The metabolic connection
A multisystem disorder whose name misdirects its morbidity, PCOS affects the metabolic, reproductive, and psychological system through vicious cycles of distorted feedback signals. Without a consensus of its origin, there appears to be a hypersensitivity of pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH) to hypothalamic gonadotrophin-releasing hormone. Consequently, elevated LH stimulates ovarian theca cells to increase androgens with resultant hyperandrogenic consequences. Parenthetically, the tonic elevation in LH explains the false-positive surges PCOS women experience when testing their urine during ovulation induction.
Elevations in insulin from unexplained damage to the insulin receptor acts synergistically with LH to increase ovarian androgens and inhibit ovulation. Hyperinsulinemia and abdominal fat deposition contribute to impaired glucose tolerance which is threefold higher with PCOS.
The metabolic syndrome, an association of disorders including hypertension, impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidemia, and obesity, occurs at an increased overall prevalence rate of 43%-47% in women with PCOS, which is twice as high as in women without PCOS. PCOS is associated with low-grade chronic inflammation, which places these women at increased risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dyslipidemia is the most common metabolic disorder in PCOS. These metabolic consequences, including obstructive sleep apnea, are worsened by hyperandrogenemia and an elevated BMI.
A genetic link
Multigenetic in origin, PCOS has a fivefold higher risk of inheritance from mothers with PCOS to daughters influenced by prenatal androgen exposure in utero. Genetic studies suggest a causal relationship between PCOS with body mass index, insulin resistance, onset of menopause, depression, and male-pattern balding (PLoS Genet 2018;14[12]:e10007813).
Fifteen genetic risk areas in the human genome seem to predispose to PCOS. New results suggest that altering the gut microbiome via prebiotic or probiotic therapies may be a potential treatment option.
Reproductive and gynecologic management
Due to chronic anovulation, unopposed estrogen can result in abnormal endometrial bleeding, endometrial hyperplasia, and a fourfold risk of endometrial cancer. This underscores the importance of regular progestin withdrawal, combined oral contraception (COC), or a progestin intrauterine device.
PCOS is a leading cause of infertility and is associated with abnormal bleeding, miscarriage, gestational diabetes, and gestational hypertension, all of which are higher based on a hyperandrogenic phenotype.
The rate of infertility in women with PCOS is 70%-80%, with ovulation dysfunction being the dominant cause. For years, the mainstay for ovulation induction was clomiphene citrate; however, letrozole has shown higher pregnancy success rates, particularly in women who have a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2. (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:119-29). Despite multiple studies demonstrating its efficacy and safety, letrozole remains without Food and Drug Administration approval for ovulation induction.
Metformin has been recommended in women with prediabetes or a BMI above 30, and it may improve menstrual regularity but has not been shown to improve live birth rates nor reduce the pregnancy complications of miscarriage or gestational diabetes. Inositol, the ubiquitous endogenous carbohydrate, has not demonstrated clear improvement in reproduction.
Laparoscopic ovarian diathermy (LOD) is a second-line treatment option, as is the use of gonadotropins, to overcome unsuccessful conservative attempts at ovulation induction. LOD is more invasive but outcomes are equivalent to gonadotropin usage while providing a dramatic reduction in multiple gestation, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, and cost (not including the surgical procedure). Ultimately, in vitro fertilization is an option for continued infertility in women with PCOS.
Metabolic/gynecologic management
Given the multisystem effect of PCOS, health care providers caring for these women should be vigilant and aggressive at ensuring appropriate monitoring and management. For women with PCOS with an elevated BMI, lifestyle modification is the first line of management. Weight loss alone of only 2%-5% may restore ovulation function.
The combination of dyslipidemia, elevated BMI, and impaired glucose tolerance would presumably predict the risk of cardiovascular events, yet the impact is not proven. Despite an increase in carotid intima media thickness, there are data that suggest only an increase in stroke or myocardial infarction (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104[4]:1221-31).
Hyperandrogenism is cosmetically and psychologically disrupting to PCOS patients. The topical application of eflornithine hydrochloride may be of value for mild to moderate facial hair growth. Spironolactone is the preferred first-line agent. (Caution: effective contraception is necessary to avoid feminization of a male fetus). Women with PCOS have a higher risk of disordered eating and body image distress as well as a fivefold higher rate of mental distress such as anxiety and depression.
No specific diet has been determined as part of treatment, yet healthy food selection and caloric intake combined with exercise has been shown to improve metabolic and psychological well-being.
Conclusion
PCOS is a ubiquitous, frustrating, and life-altering disease. Health care providers, particularly those in women’s health, must ensure appropriate counseling and education with evidence-based medicine to empower patients toward improved health.
Dr. Trolice is director of Fertility CARE - The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando. He has no conflicts of interest. Please contact him at [email protected].
Coping with postpandemic school hesitancy
As the protective effect of the vaccines becomes increasingly apparent, a large number of school systems are beginning to return to prepandemic in-school learning. But anecdotal reports from around the country are making it clear that some children or their families are hesitant to return to the old norm of face to face learning (Goldstein D. “Schools Are Open, but Many Families Remain Hesitant to Return.” New York Times. 2021 May 9). The possible explanations for this hesitancy include a broad list that goes well beyond the obvious concern about the child contracting COVID-19.
I hear from my grandchildren that remote learning has for the most part been unpleasant and lacked the rigor of their in-class experiences. But, they admit that they have found that, in some situations, they prefer the environment at home because it is less distracting. They also acknowledge that, while they miss seeing their friends, at times the isolation has allowed them to be more efficient. Of course, their observations must be viewed in light of their personalities and the support provided by their parents. For these motivated teenagers, the bottom line is that they would prefer to be in school.
However, for the children who have always been a bit ambivalent about school either because they were anxious in social situations or because they found the academics too challenging, one can easily understand why they might prefer to remain in a less-intimidating home environment. For them, missing their friends may have little draw because they may not have had any friends. And, the negative feedback and bullying they have received at school is too overwhelming. A teenager for whom the pandemic has offered the out-of-school free time to explore her independence, feel more like an adult, and enjoy the benefits of having a job may be hesitant to return to the restrictions imposed by what she sees as the childishness of in-school learning.
Compounding the problem is the risk avoidance posture of some school systems and the hesitancy of some teachers to return to an environment that they continue to view as unsafe despite the evidence of the effectiveness of the vaccines and the minimal threat of in-school spread. It is going to be interesting to see how school administrators and politicians deal with this level of institutional hesitancy. Some schools may take what might be considered a hard-line approach and eliminate remote learning completely.
Regardless of how swiftly and thoughtfully schools return to in-class learning, a large number of children will eventually be faced with the stark reality of returning to a place in which they had felt painfully uncomfortable in the past. Pediatricians must be prepared to see this current wave of school hesitancy morph into a full-fledged tsunami of school refusals.
Successful management of a family whose child finds school too challenging emotionally has always required a combination of careful attention to the possible medical causes of the child’s complaints, consultation with a mental health practitioner, and thoughtful coordination with educators sensitive to the child’s school-generated distress.
It has never been easy to reassure the family of a child with frequent headaches or belly pain that his symptoms have no physical basis and then gently point out that the stress of school attendance may be a contributing factor. Some families who buy into the association may be fortunate enough to be able to offer their child home schooling as a solution to school refusal. But this strategy often requires that one parent remain home and has the temperament and the skills to teach.
Now that we have all seen that remote learning has the potential to work in a crisis, will some parents begin to demand it for their children with school refusal? Who will pay for it? I think you and I would prefer to see a solution that targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at getting the child back in school. But you and I also know those strategies don’t always work.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
As the protective effect of the vaccines becomes increasingly apparent, a large number of school systems are beginning to return to prepandemic in-school learning. But anecdotal reports from around the country are making it clear that some children or their families are hesitant to return to the old norm of face to face learning (Goldstein D. “Schools Are Open, but Many Families Remain Hesitant to Return.” New York Times. 2021 May 9). The possible explanations for this hesitancy include a broad list that goes well beyond the obvious concern about the child contracting COVID-19.
I hear from my grandchildren that remote learning has for the most part been unpleasant and lacked the rigor of their in-class experiences. But, they admit that they have found that, in some situations, they prefer the environment at home because it is less distracting. They also acknowledge that, while they miss seeing their friends, at times the isolation has allowed them to be more efficient. Of course, their observations must be viewed in light of their personalities and the support provided by their parents. For these motivated teenagers, the bottom line is that they would prefer to be in school.
However, for the children who have always been a bit ambivalent about school either because they were anxious in social situations or because they found the academics too challenging, one can easily understand why they might prefer to remain in a less-intimidating home environment. For them, missing their friends may have little draw because they may not have had any friends. And, the negative feedback and bullying they have received at school is too overwhelming. A teenager for whom the pandemic has offered the out-of-school free time to explore her independence, feel more like an adult, and enjoy the benefits of having a job may be hesitant to return to the restrictions imposed by what she sees as the childishness of in-school learning.
Compounding the problem is the risk avoidance posture of some school systems and the hesitancy of some teachers to return to an environment that they continue to view as unsafe despite the evidence of the effectiveness of the vaccines and the minimal threat of in-school spread. It is going to be interesting to see how school administrators and politicians deal with this level of institutional hesitancy. Some schools may take what might be considered a hard-line approach and eliminate remote learning completely.
Regardless of how swiftly and thoughtfully schools return to in-class learning, a large number of children will eventually be faced with the stark reality of returning to a place in which they had felt painfully uncomfortable in the past. Pediatricians must be prepared to see this current wave of school hesitancy morph into a full-fledged tsunami of school refusals.
Successful management of a family whose child finds school too challenging emotionally has always required a combination of careful attention to the possible medical causes of the child’s complaints, consultation with a mental health practitioner, and thoughtful coordination with educators sensitive to the child’s school-generated distress.
It has never been easy to reassure the family of a child with frequent headaches or belly pain that his symptoms have no physical basis and then gently point out that the stress of school attendance may be a contributing factor. Some families who buy into the association may be fortunate enough to be able to offer their child home schooling as a solution to school refusal. But this strategy often requires that one parent remain home and has the temperament and the skills to teach.
Now that we have all seen that remote learning has the potential to work in a crisis, will some parents begin to demand it for their children with school refusal? Who will pay for it? I think you and I would prefer to see a solution that targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at getting the child back in school. But you and I also know those strategies don’t always work.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
As the protective effect of the vaccines becomes increasingly apparent, a large number of school systems are beginning to return to prepandemic in-school learning. But anecdotal reports from around the country are making it clear that some children or their families are hesitant to return to the old norm of face to face learning (Goldstein D. “Schools Are Open, but Many Families Remain Hesitant to Return.” New York Times. 2021 May 9). The possible explanations for this hesitancy include a broad list that goes well beyond the obvious concern about the child contracting COVID-19.
I hear from my grandchildren that remote learning has for the most part been unpleasant and lacked the rigor of their in-class experiences. But, they admit that they have found that, in some situations, they prefer the environment at home because it is less distracting. They also acknowledge that, while they miss seeing their friends, at times the isolation has allowed them to be more efficient. Of course, their observations must be viewed in light of their personalities and the support provided by their parents. For these motivated teenagers, the bottom line is that they would prefer to be in school.
However, for the children who have always been a bit ambivalent about school either because they were anxious in social situations or because they found the academics too challenging, one can easily understand why they might prefer to remain in a less-intimidating home environment. For them, missing their friends may have little draw because they may not have had any friends. And, the negative feedback and bullying they have received at school is too overwhelming. A teenager for whom the pandemic has offered the out-of-school free time to explore her independence, feel more like an adult, and enjoy the benefits of having a job may be hesitant to return to the restrictions imposed by what she sees as the childishness of in-school learning.
Compounding the problem is the risk avoidance posture of some school systems and the hesitancy of some teachers to return to an environment that they continue to view as unsafe despite the evidence of the effectiveness of the vaccines and the minimal threat of in-school spread. It is going to be interesting to see how school administrators and politicians deal with this level of institutional hesitancy. Some schools may take what might be considered a hard-line approach and eliminate remote learning completely.
Regardless of how swiftly and thoughtfully schools return to in-class learning, a large number of children will eventually be faced with the stark reality of returning to a place in which they had felt painfully uncomfortable in the past. Pediatricians must be prepared to see this current wave of school hesitancy morph into a full-fledged tsunami of school refusals.
Successful management of a family whose child finds school too challenging emotionally has always required a combination of careful attention to the possible medical causes of the child’s complaints, consultation with a mental health practitioner, and thoughtful coordination with educators sensitive to the child’s school-generated distress.
It has never been easy to reassure the family of a child with frequent headaches or belly pain that his symptoms have no physical basis and then gently point out that the stress of school attendance may be a contributing factor. Some families who buy into the association may be fortunate enough to be able to offer their child home schooling as a solution to school refusal. But this strategy often requires that one parent remain home and has the temperament and the skills to teach.
Now that we have all seen that remote learning has the potential to work in a crisis, will some parents begin to demand it for their children with school refusal? Who will pay for it? I think you and I would prefer to see a solution that targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at getting the child back in school. But you and I also know those strategies don’t always work.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Fall prevention advice for patients with Parkinson’s
A 75-year-old man with Parkinson’s disease has had three falls over the past 4 weeks. He has been compliant with his Parkinson’s treatment. Which of the following options would most help decrease his fall risk?
A. Vitamin D supplementation
B. Vitamin B12 supplementation
C. Calcium supplementation
D. Tai chi
There has been recent evidence that vitamin D supplementation is not helpful in preventing falls in most community-dwelling older adults. Bolland and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 81 randomized, controlled trials and found that vitamin D supplementation does not prevent fractures or falls.1 They found no difference or benefit in high-dose versus low-dose vitamin D supplementation.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends against vitamin D supplementation for the purpose of preventing falls in community-dwelling adults over the age of 65.2 The same USPSTF report recommends exercise intervention, as having the strongest evidence for fall prevention in community-dwelling adults age 65 or older who are at risk for falls.
The benefits of tai chi
Tai chi with it’s emphasis on balance, strength training as well as stress reduction is an excellent option for older adults.
Lui and colleagues performed a meta-analyses of five randomized, controlled trials (355 patients) of tai chi in patients with Parkinson disease.3 Tai chi significantly decreased fall rates (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.74; P = .001) and significantly improved balance and functional mobility (P < .001) in people with Parkinson disease, compared with no training.
Tai chi can also help prevent falls in a more general population of elderly patients. Lomas-Vega and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 10 high-quality studies that met inclusion criteria evaluating tai chi for fall prevention.4 Fall risk was reduced over short-term follow-up (incident rate ratio, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.46-0.70) and a small protective effect was seen over long-term follow-up (IRR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.98).
Pearl: Consider tai chi in your elderly patients with fall risk to increase their balance and reduce risks of falls.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Bolland MJ et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(11):847.
2. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018;319(16):1696.
3. Liu HH et al. Parkinsons Dis. 2019 Feb 21;2019:9626934
4. Lomas-Vega R et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(9):2037.
A 75-year-old man with Parkinson’s disease has had three falls over the past 4 weeks. He has been compliant with his Parkinson’s treatment. Which of the following options would most help decrease his fall risk?
A. Vitamin D supplementation
B. Vitamin B12 supplementation
C. Calcium supplementation
D. Tai chi
There has been recent evidence that vitamin D supplementation is not helpful in preventing falls in most community-dwelling older adults. Bolland and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 81 randomized, controlled trials and found that vitamin D supplementation does not prevent fractures or falls.1 They found no difference or benefit in high-dose versus low-dose vitamin D supplementation.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends against vitamin D supplementation for the purpose of preventing falls in community-dwelling adults over the age of 65.2 The same USPSTF report recommends exercise intervention, as having the strongest evidence for fall prevention in community-dwelling adults age 65 or older who are at risk for falls.
The benefits of tai chi
Tai chi with it’s emphasis on balance, strength training as well as stress reduction is an excellent option for older adults.
Lui and colleagues performed a meta-analyses of five randomized, controlled trials (355 patients) of tai chi in patients with Parkinson disease.3 Tai chi significantly decreased fall rates (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.74; P = .001) and significantly improved balance and functional mobility (P < .001) in people with Parkinson disease, compared with no training.
Tai chi can also help prevent falls in a more general population of elderly patients. Lomas-Vega and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 10 high-quality studies that met inclusion criteria evaluating tai chi for fall prevention.4 Fall risk was reduced over short-term follow-up (incident rate ratio, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.46-0.70) and a small protective effect was seen over long-term follow-up (IRR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.98).
Pearl: Consider tai chi in your elderly patients with fall risk to increase their balance and reduce risks of falls.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Bolland MJ et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(11):847.
2. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018;319(16):1696.
3. Liu HH et al. Parkinsons Dis. 2019 Feb 21;2019:9626934
4. Lomas-Vega R et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(9):2037.
A 75-year-old man with Parkinson’s disease has had three falls over the past 4 weeks. He has been compliant with his Parkinson’s treatment. Which of the following options would most help decrease his fall risk?
A. Vitamin D supplementation
B. Vitamin B12 supplementation
C. Calcium supplementation
D. Tai chi
There has been recent evidence that vitamin D supplementation is not helpful in preventing falls in most community-dwelling older adults. Bolland and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 81 randomized, controlled trials and found that vitamin D supplementation does not prevent fractures or falls.1 They found no difference or benefit in high-dose versus low-dose vitamin D supplementation.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends against vitamin D supplementation for the purpose of preventing falls in community-dwelling adults over the age of 65.2 The same USPSTF report recommends exercise intervention, as having the strongest evidence for fall prevention in community-dwelling adults age 65 or older who are at risk for falls.
The benefits of tai chi
Tai chi with it’s emphasis on balance, strength training as well as stress reduction is an excellent option for older adults.
Lui and colleagues performed a meta-analyses of five randomized, controlled trials (355 patients) of tai chi in patients with Parkinson disease.3 Tai chi significantly decreased fall rates (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.74; P = .001) and significantly improved balance and functional mobility (P < .001) in people with Parkinson disease, compared with no training.
Tai chi can also help prevent falls in a more general population of elderly patients. Lomas-Vega and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 10 high-quality studies that met inclusion criteria evaluating tai chi for fall prevention.4 Fall risk was reduced over short-term follow-up (incident rate ratio, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.46-0.70) and a small protective effect was seen over long-term follow-up (IRR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.98).
Pearl: Consider tai chi in your elderly patients with fall risk to increase their balance and reduce risks of falls.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Bolland MJ et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(11):847.
2. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018;319(16):1696.
3. Liu HH et al. Parkinsons Dis. 2019 Feb 21;2019:9626934
4. Lomas-Vega R et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(9):2037.
New guidance for those fully vaccinated against COVID-19
As has been dominating the headlines, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released updated public health guidance for those who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
This new guidance applies to those who are fully vaccinated as indicated by 2 weeks after the second dose in a 2-dose series or 2 weeks after a single-dose vaccine. Those who meet these criteria no longer need to wear a mask or physically distance themselves from others in both indoor and outdoor settings. For those not fully vaccinated, masking and social distancing should continue to be practiced.
The new guidance indicates that quarantine after a known exposure is no longer necessary.
Unless required by local, state, or territorial health authorities, testing is no longer required following domestic travel for fully vaccinated individuals. A negative test is still required prior to boarding an international flight to the United States and testing 3-5 days after arrival is still recommended. Self-quarantine is no longer required after international travel for fully vaccinated individuals.
The new guidance recommends that individuals who are fully vaccinated not participate in routine screening programs when feasible. Finally, if an individual has tested positive for COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, that person should isolate and not visit public or private settings for a minimum of ten days.1
Updated guidance for health care facilities
In addition to changes for the general public in all settings, the CDC updated guidance for health care facilities on April 27, 2021. These updated guidelines allow for communal dining and visitation for fully vaccinated patients and their visitors. The guidelines indicate that fully vaccinated health care personnel (HCP) do not require quarantine after exposure to patients who have tested positive for COVID-19 as long as the HCP remains asymptomatic. They should, however, continue to utilize personal protective equipment as previously recommended. HCPs are able to be in break and meeting rooms unmasked if all HCPs are vaccinated.2
There are some important caveats to these updated guidelines. They do not apply to those who have immunocompromising conditions, including those using immunosuppressant agents. They also do not apply to locations subject to federal, state, local, tribal, or territorial laws, rules, and regulations, including local business and workplace guidance.
Those who work or reside in correction or detention facilities and homeless shelters are also still required to test after known exposures. Masking is still required by all travelers on all forms of public transportation into and within the United States.
Most importantly, the guidelines apply only to those who are fully vaccinated. Finally, no vaccine is perfect. As such, anyone who experiences symptoms indicative of COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, should obtain viral testing and isolate themselves from others.1,2
Pros and cons to new guidance
Both sets of updated guidelines are a great example of public health guidance that is changing as the evidence is gathered and changes. This guidance is also a welcome encouragement that the vaccines are effective at decreasing transmission of this virus that has upended our world.
These guidelines leave room for change as evidence is gathered on emerging novel variants. There are, however, a few remaining concerns.
My first concern is for those who are not yet able to be vaccinated, including children under the age of 12. For families with members who are not fully vaccinated, they may have first heard the headlines of “you do not have to mask” to then read the fine print that remains. When truly following these guidelines, many social situations in both the public and private setting should still include both masking and social distancing.
There is no clarity on how these guidelines are enforced. Within the guidance, it is clear that individuals’ privacy is of utmost importance. In the absence of knowledge, that means that the assumption should be that all are not yet vaccinated. Unless there is a way to reliably demonstrate vaccination status, it would likely still be safer to assume that there are individuals who are not fully vaccinated within the setting.
Finally, although this is great news surrounding the efficacy of the vaccine, some are concerned that local mask mandates that have already started to be lifted will be completely removed. As there is still a large portion of the population not yet fully vaccinated, it seems premature for local, state, and territorial authorities to lift these mandates.
How to continue exercising caution
With the outstanding concerns, I will continue to mask in settings, particularly indoors, where I do not definitely know that everyone is vaccinated. I will continue to do this to protect my children and my patients who are not yet vaccinated, and my patients who are immunosuppressed for whom we do not yet have enough information.
I will continue to advise my patients to be thoughtful about the risk for themselves and their families as well.
There has been more benefit to these public health measures then just decreased transmission of COVID-19. I hope that this year has reinforced within us the benefits of masking and self-isolation in the cases of any contagious illnesses.
Although I am looking forward to the opportunities to interact in person with more colleagues and friends, I think we should continue to do this with caution and thoughtfulness. We must be prepared for the possibility of vaccines having decreased efficacy against novel variants as well as eventually the possibility of waning immunity. If these should occur, we need to be prepared for additional recommendation changes and tightening of restrictions.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program at Humboldt Park, Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, May 13, 2021.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated Healthcare Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations in Response to COVID-19 Vaccination. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, April 27, 2021.
As has been dominating the headlines, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released updated public health guidance for those who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
This new guidance applies to those who are fully vaccinated as indicated by 2 weeks after the second dose in a 2-dose series or 2 weeks after a single-dose vaccine. Those who meet these criteria no longer need to wear a mask or physically distance themselves from others in both indoor and outdoor settings. For those not fully vaccinated, masking and social distancing should continue to be practiced.
The new guidance indicates that quarantine after a known exposure is no longer necessary.
Unless required by local, state, or territorial health authorities, testing is no longer required following domestic travel for fully vaccinated individuals. A negative test is still required prior to boarding an international flight to the United States and testing 3-5 days after arrival is still recommended. Self-quarantine is no longer required after international travel for fully vaccinated individuals.
The new guidance recommends that individuals who are fully vaccinated not participate in routine screening programs when feasible. Finally, if an individual has tested positive for COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, that person should isolate and not visit public or private settings for a minimum of ten days.1
Updated guidance for health care facilities
In addition to changes for the general public in all settings, the CDC updated guidance for health care facilities on April 27, 2021. These updated guidelines allow for communal dining and visitation for fully vaccinated patients and their visitors. The guidelines indicate that fully vaccinated health care personnel (HCP) do not require quarantine after exposure to patients who have tested positive for COVID-19 as long as the HCP remains asymptomatic. They should, however, continue to utilize personal protective equipment as previously recommended. HCPs are able to be in break and meeting rooms unmasked if all HCPs are vaccinated.2
There are some important caveats to these updated guidelines. They do not apply to those who have immunocompromising conditions, including those using immunosuppressant agents. They also do not apply to locations subject to federal, state, local, tribal, or territorial laws, rules, and regulations, including local business and workplace guidance.
Those who work or reside in correction or detention facilities and homeless shelters are also still required to test after known exposures. Masking is still required by all travelers on all forms of public transportation into and within the United States.
Most importantly, the guidelines apply only to those who are fully vaccinated. Finally, no vaccine is perfect. As such, anyone who experiences symptoms indicative of COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, should obtain viral testing and isolate themselves from others.1,2
Pros and cons to new guidance
Both sets of updated guidelines are a great example of public health guidance that is changing as the evidence is gathered and changes. This guidance is also a welcome encouragement that the vaccines are effective at decreasing transmission of this virus that has upended our world.
These guidelines leave room for change as evidence is gathered on emerging novel variants. There are, however, a few remaining concerns.
My first concern is for those who are not yet able to be vaccinated, including children under the age of 12. For families with members who are not fully vaccinated, they may have first heard the headlines of “you do not have to mask” to then read the fine print that remains. When truly following these guidelines, many social situations in both the public and private setting should still include both masking and social distancing.
There is no clarity on how these guidelines are enforced. Within the guidance, it is clear that individuals’ privacy is of utmost importance. In the absence of knowledge, that means that the assumption should be that all are not yet vaccinated. Unless there is a way to reliably demonstrate vaccination status, it would likely still be safer to assume that there are individuals who are not fully vaccinated within the setting.
Finally, although this is great news surrounding the efficacy of the vaccine, some are concerned that local mask mandates that have already started to be lifted will be completely removed. As there is still a large portion of the population not yet fully vaccinated, it seems premature for local, state, and territorial authorities to lift these mandates.
How to continue exercising caution
With the outstanding concerns, I will continue to mask in settings, particularly indoors, where I do not definitely know that everyone is vaccinated. I will continue to do this to protect my children and my patients who are not yet vaccinated, and my patients who are immunosuppressed for whom we do not yet have enough information.
I will continue to advise my patients to be thoughtful about the risk for themselves and their families as well.
There has been more benefit to these public health measures then just decreased transmission of COVID-19. I hope that this year has reinforced within us the benefits of masking and self-isolation in the cases of any contagious illnesses.
Although I am looking forward to the opportunities to interact in person with more colleagues and friends, I think we should continue to do this with caution and thoughtfulness. We must be prepared for the possibility of vaccines having decreased efficacy against novel variants as well as eventually the possibility of waning immunity. If these should occur, we need to be prepared for additional recommendation changes and tightening of restrictions.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program at Humboldt Park, Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, May 13, 2021.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated Healthcare Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations in Response to COVID-19 Vaccination. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, April 27, 2021.
As has been dominating the headlines, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released updated public health guidance for those who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
This new guidance applies to those who are fully vaccinated as indicated by 2 weeks after the second dose in a 2-dose series or 2 weeks after a single-dose vaccine. Those who meet these criteria no longer need to wear a mask or physically distance themselves from others in both indoor and outdoor settings. For those not fully vaccinated, masking and social distancing should continue to be practiced.
The new guidance indicates that quarantine after a known exposure is no longer necessary.
Unless required by local, state, or territorial health authorities, testing is no longer required following domestic travel for fully vaccinated individuals. A negative test is still required prior to boarding an international flight to the United States and testing 3-5 days after arrival is still recommended. Self-quarantine is no longer required after international travel for fully vaccinated individuals.
The new guidance recommends that individuals who are fully vaccinated not participate in routine screening programs when feasible. Finally, if an individual has tested positive for COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, that person should isolate and not visit public or private settings for a minimum of ten days.1
Updated guidance for health care facilities
In addition to changes for the general public in all settings, the CDC updated guidance for health care facilities on April 27, 2021. These updated guidelines allow for communal dining and visitation for fully vaccinated patients and their visitors. The guidelines indicate that fully vaccinated health care personnel (HCP) do not require quarantine after exposure to patients who have tested positive for COVID-19 as long as the HCP remains asymptomatic. They should, however, continue to utilize personal protective equipment as previously recommended. HCPs are able to be in break and meeting rooms unmasked if all HCPs are vaccinated.2
There are some important caveats to these updated guidelines. They do not apply to those who have immunocompromising conditions, including those using immunosuppressant agents. They also do not apply to locations subject to federal, state, local, tribal, or territorial laws, rules, and regulations, including local business and workplace guidance.
Those who work or reside in correction or detention facilities and homeless shelters are also still required to test after known exposures. Masking is still required by all travelers on all forms of public transportation into and within the United States.
Most importantly, the guidelines apply only to those who are fully vaccinated. Finally, no vaccine is perfect. As such, anyone who experiences symptoms indicative of COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, should obtain viral testing and isolate themselves from others.1,2
Pros and cons to new guidance
Both sets of updated guidelines are a great example of public health guidance that is changing as the evidence is gathered and changes. This guidance is also a welcome encouragement that the vaccines are effective at decreasing transmission of this virus that has upended our world.
These guidelines leave room for change as evidence is gathered on emerging novel variants. There are, however, a few remaining concerns.
My first concern is for those who are not yet able to be vaccinated, including children under the age of 12. For families with members who are not fully vaccinated, they may have first heard the headlines of “you do not have to mask” to then read the fine print that remains. When truly following these guidelines, many social situations in both the public and private setting should still include both masking and social distancing.
There is no clarity on how these guidelines are enforced. Within the guidance, it is clear that individuals’ privacy is of utmost importance. In the absence of knowledge, that means that the assumption should be that all are not yet vaccinated. Unless there is a way to reliably demonstrate vaccination status, it would likely still be safer to assume that there are individuals who are not fully vaccinated within the setting.
Finally, although this is great news surrounding the efficacy of the vaccine, some are concerned that local mask mandates that have already started to be lifted will be completely removed. As there is still a large portion of the population not yet fully vaccinated, it seems premature for local, state, and territorial authorities to lift these mandates.
How to continue exercising caution
With the outstanding concerns, I will continue to mask in settings, particularly indoors, where I do not definitely know that everyone is vaccinated. I will continue to do this to protect my children and my patients who are not yet vaccinated, and my patients who are immunosuppressed for whom we do not yet have enough information.
I will continue to advise my patients to be thoughtful about the risk for themselves and their families as well.
There has been more benefit to these public health measures then just decreased transmission of COVID-19. I hope that this year has reinforced within us the benefits of masking and self-isolation in the cases of any contagious illnesses.
Although I am looking forward to the opportunities to interact in person with more colleagues and friends, I think we should continue to do this with caution and thoughtfulness. We must be prepared for the possibility of vaccines having decreased efficacy against novel variants as well as eventually the possibility of waning immunity. If these should occur, we need to be prepared for additional recommendation changes and tightening of restrictions.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program at Humboldt Park, Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, May 13, 2021.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated Healthcare Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations in Response to COVID-19 Vaccination. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, April 27, 2021.
Who is my neighbor? The ethics of sharing medical resources in the world
India is in a crisis as the burden of COVID-19 has collapsed parts of the health care system. There are not enough beds, not enough oxygen, and not enough crematoria to handle the pandemic. India is also a major supplier of vaccines for itself and many other countries. That production capacity has also been affected by the local events, further worsening the response to the pandemic over the next few months.
This collapse is the specter that, in April 2020, placed a hospital ship next to Manhattan and rows of beds in its convention center. Fortunately, the lockdown in March 2020 sufficiently flattened the curve. The city avoided utilizing that disaster capacity, though many New Yorkers died out of sight in nursing homes. When the third and largest wave of cases in the United States peaked in January 2021, hospitals throughout California reached capacity but avoided bursting. In April 2021, localized outbreaks in Michigan, Arizona, and Ontario again tested the maximum capacity for providing modern medical treatments. Great Britain used a second lockdown in October 2020 and a third in January 2021 to control the pandemic, with Prime Minister Boris Johnson emphasizing that it was these social interventions, and not vaccines, which provided the mitigating effects. Other European Union nations adopted similar strategies. Prudent choices by government guided by science, combined with the cooperation of the public, have been and still are crucial to mollify the pandemic.
There is hope that soon vaccines will return daily life to a new normal. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has loosened restrictions on social gathering. An increase in daily new cases of COVID-19 in April 2021 has turned into just a blip before continuing to recede. Perhaps that is the first sign of vaccination working at the level of public health. However, the May 2021 lockdown in highly vaccinated Seychelles is a warning that the danger remains. A single match can start a huge forest fire. The first 150 million cases of COVID-19 worldwide have, through natural rates of mutation, produced several variants that might partially evade current vaccines. The danger of newer variants persists with the next 150 million cases as the pandemic continues to rage in many nations which are just one airplane ride away. All human inhabitants of this blue-covered third rock from the sun are interconnected.
The benefits of scientific advancement have been extolled for centuries. This includes both individual discoveries as well as a mindset that favors rationalism over fatalism. On the whole, the benefits of scientific progress outweigh the negatives. Negative environmental impacts include pollution and climate change. Economic impacts include raising the mean economic standard of living but with greater inequity. Historically, governmental and social institutions have attempted to mitigate these negative consequences. Those efforts have attempted to provide guidance and a moral compass to direct the progress of scientific advancement, particularly in fields like gene therapy. Those efforts have called upon developed nations to share the bounties of progress with other nations.
Modern medicine has provided the fruit of these scientific advancements to a limited fraction of the world’s population during the 20th century. The improvements in life expectancy and infant mortality have come primarily from civil engineers getting running water into cities and sewage out. A smaller portion of the benefits are from public health measures that reduced tuberculosis, smallpox, polio, and measles. Agriculture became more reliable, productive, and nutritious. In the 21st century, medical care (control of hypertension, diabetes, and clotting) aimed at reducing heart disease and strokes have added another 2-3 years to the life expectancy in the United States, with much of that benefit erased by the epidemics of obesity and opioid abuse.
Modern medical technology has created treatments that cost $10,000 a month to add a few extra months of life to geriatric patients with terminal cancer. Meanwhile, in more mundane care, efforts like Choosing Wisely seek to save money wasted on low-value, useless, and even harmful tests and therapies. There is no single person or agency managing this chaotic process of inventing expensive new technologies while inadequately addressing the widespread shortages of mental health care, disparities in education, and other social determinants of health. The pandemic has highlighted these preexisting weaknesses in the social fabric.
The cries from India have been accompanied by voices of anger from India and other nations accusing the United States of hoarding vaccines and the raw materials needed to produce them. This has been called vaccine apartheid. The United States is not alone in its political decision to prioritize domestic interests over international ones; India’s recent government is similarly nationalistic. Scientists warn that no one is safe locally as long as the pandemic rages in other countries. The Biden administration, in a delayed response to the crisis in India, finally announced plans to share some unused vaccines (of a brand not yet Food and Drug Administration approved) as well as some vaccine raw materials whose export was forbidden by a regulation under the Defense Production Act. Reading below the headlines, the promised response won’t be implemented for weeks or months. We must do better.
The logistics of sharing the benefits of advanced science are complicated. The ethics are not. Who is my neighbor? If you didn’t learn the answer to that in Sunday school, there isn’t much more I can say.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no financial disclosures, Email him at [email protected]
India is in a crisis as the burden of COVID-19 has collapsed parts of the health care system. There are not enough beds, not enough oxygen, and not enough crematoria to handle the pandemic. India is also a major supplier of vaccines for itself and many other countries. That production capacity has also been affected by the local events, further worsening the response to the pandemic over the next few months.
This collapse is the specter that, in April 2020, placed a hospital ship next to Manhattan and rows of beds in its convention center. Fortunately, the lockdown in March 2020 sufficiently flattened the curve. The city avoided utilizing that disaster capacity, though many New Yorkers died out of sight in nursing homes. When the third and largest wave of cases in the United States peaked in January 2021, hospitals throughout California reached capacity but avoided bursting. In April 2021, localized outbreaks in Michigan, Arizona, and Ontario again tested the maximum capacity for providing modern medical treatments. Great Britain used a second lockdown in October 2020 and a third in January 2021 to control the pandemic, with Prime Minister Boris Johnson emphasizing that it was these social interventions, and not vaccines, which provided the mitigating effects. Other European Union nations adopted similar strategies. Prudent choices by government guided by science, combined with the cooperation of the public, have been and still are crucial to mollify the pandemic.
There is hope that soon vaccines will return daily life to a new normal. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has loosened restrictions on social gathering. An increase in daily new cases of COVID-19 in April 2021 has turned into just a blip before continuing to recede. Perhaps that is the first sign of vaccination working at the level of public health. However, the May 2021 lockdown in highly vaccinated Seychelles is a warning that the danger remains. A single match can start a huge forest fire. The first 150 million cases of COVID-19 worldwide have, through natural rates of mutation, produced several variants that might partially evade current vaccines. The danger of newer variants persists with the next 150 million cases as the pandemic continues to rage in many nations which are just one airplane ride away. All human inhabitants of this blue-covered third rock from the sun are interconnected.
The benefits of scientific advancement have been extolled for centuries. This includes both individual discoveries as well as a mindset that favors rationalism over fatalism. On the whole, the benefits of scientific progress outweigh the negatives. Negative environmental impacts include pollution and climate change. Economic impacts include raising the mean economic standard of living but with greater inequity. Historically, governmental and social institutions have attempted to mitigate these negative consequences. Those efforts have attempted to provide guidance and a moral compass to direct the progress of scientific advancement, particularly in fields like gene therapy. Those efforts have called upon developed nations to share the bounties of progress with other nations.
Modern medicine has provided the fruit of these scientific advancements to a limited fraction of the world’s population during the 20th century. The improvements in life expectancy and infant mortality have come primarily from civil engineers getting running water into cities and sewage out. A smaller portion of the benefits are from public health measures that reduced tuberculosis, smallpox, polio, and measles. Agriculture became more reliable, productive, and nutritious. In the 21st century, medical care (control of hypertension, diabetes, and clotting) aimed at reducing heart disease and strokes have added another 2-3 years to the life expectancy in the United States, with much of that benefit erased by the epidemics of obesity and opioid abuse.
Modern medical technology has created treatments that cost $10,000 a month to add a few extra months of life to geriatric patients with terminal cancer. Meanwhile, in more mundane care, efforts like Choosing Wisely seek to save money wasted on low-value, useless, and even harmful tests and therapies. There is no single person or agency managing this chaotic process of inventing expensive new technologies while inadequately addressing the widespread shortages of mental health care, disparities in education, and other social determinants of health. The pandemic has highlighted these preexisting weaknesses in the social fabric.
The cries from India have been accompanied by voices of anger from India and other nations accusing the United States of hoarding vaccines and the raw materials needed to produce them. This has been called vaccine apartheid. The United States is not alone in its political decision to prioritize domestic interests over international ones; India’s recent government is similarly nationalistic. Scientists warn that no one is safe locally as long as the pandemic rages in other countries. The Biden administration, in a delayed response to the crisis in India, finally announced plans to share some unused vaccines (of a brand not yet Food and Drug Administration approved) as well as some vaccine raw materials whose export was forbidden by a regulation under the Defense Production Act. Reading below the headlines, the promised response won’t be implemented for weeks or months. We must do better.
The logistics of sharing the benefits of advanced science are complicated. The ethics are not. Who is my neighbor? If you didn’t learn the answer to that in Sunday school, there isn’t much more I can say.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no financial disclosures, Email him at [email protected]
India is in a crisis as the burden of COVID-19 has collapsed parts of the health care system. There are not enough beds, not enough oxygen, and not enough crematoria to handle the pandemic. India is also a major supplier of vaccines for itself and many other countries. That production capacity has also been affected by the local events, further worsening the response to the pandemic over the next few months.
This collapse is the specter that, in April 2020, placed a hospital ship next to Manhattan and rows of beds in its convention center. Fortunately, the lockdown in March 2020 sufficiently flattened the curve. The city avoided utilizing that disaster capacity, though many New Yorkers died out of sight in nursing homes. When the third and largest wave of cases in the United States peaked in January 2021, hospitals throughout California reached capacity but avoided bursting. In April 2021, localized outbreaks in Michigan, Arizona, and Ontario again tested the maximum capacity for providing modern medical treatments. Great Britain used a second lockdown in October 2020 and a third in January 2021 to control the pandemic, with Prime Minister Boris Johnson emphasizing that it was these social interventions, and not vaccines, which provided the mitigating effects. Other European Union nations adopted similar strategies. Prudent choices by government guided by science, combined with the cooperation of the public, have been and still are crucial to mollify the pandemic.
There is hope that soon vaccines will return daily life to a new normal. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has loosened restrictions on social gathering. An increase in daily new cases of COVID-19 in April 2021 has turned into just a blip before continuing to recede. Perhaps that is the first sign of vaccination working at the level of public health. However, the May 2021 lockdown in highly vaccinated Seychelles is a warning that the danger remains. A single match can start a huge forest fire. The first 150 million cases of COVID-19 worldwide have, through natural rates of mutation, produced several variants that might partially evade current vaccines. The danger of newer variants persists with the next 150 million cases as the pandemic continues to rage in many nations which are just one airplane ride away. All human inhabitants of this blue-covered third rock from the sun are interconnected.
The benefits of scientific advancement have been extolled for centuries. This includes both individual discoveries as well as a mindset that favors rationalism over fatalism. On the whole, the benefits of scientific progress outweigh the negatives. Negative environmental impacts include pollution and climate change. Economic impacts include raising the mean economic standard of living but with greater inequity. Historically, governmental and social institutions have attempted to mitigate these negative consequences. Those efforts have attempted to provide guidance and a moral compass to direct the progress of scientific advancement, particularly in fields like gene therapy. Those efforts have called upon developed nations to share the bounties of progress with other nations.
Modern medicine has provided the fruit of these scientific advancements to a limited fraction of the world’s population during the 20th century. The improvements in life expectancy and infant mortality have come primarily from civil engineers getting running water into cities and sewage out. A smaller portion of the benefits are from public health measures that reduced tuberculosis, smallpox, polio, and measles. Agriculture became more reliable, productive, and nutritious. In the 21st century, medical care (control of hypertension, diabetes, and clotting) aimed at reducing heart disease and strokes have added another 2-3 years to the life expectancy in the United States, with much of that benefit erased by the epidemics of obesity and opioid abuse.
Modern medical technology has created treatments that cost $10,000 a month to add a few extra months of life to geriatric patients with terminal cancer. Meanwhile, in more mundane care, efforts like Choosing Wisely seek to save money wasted on low-value, useless, and even harmful tests and therapies. There is no single person or agency managing this chaotic process of inventing expensive new technologies while inadequately addressing the widespread shortages of mental health care, disparities in education, and other social determinants of health. The pandemic has highlighted these preexisting weaknesses in the social fabric.
The cries from India have been accompanied by voices of anger from India and other nations accusing the United States of hoarding vaccines and the raw materials needed to produce them. This has been called vaccine apartheid. The United States is not alone in its political decision to prioritize domestic interests over international ones; India’s recent government is similarly nationalistic. Scientists warn that no one is safe locally as long as the pandemic rages in other countries. The Biden administration, in a delayed response to the crisis in India, finally announced plans to share some unused vaccines (of a brand not yet Food and Drug Administration approved) as well as some vaccine raw materials whose export was forbidden by a regulation under the Defense Production Act. Reading below the headlines, the promised response won’t be implemented for weeks or months. We must do better.
The logistics of sharing the benefits of advanced science are complicated. The ethics are not. Who is my neighbor? If you didn’t learn the answer to that in Sunday school, there isn’t much more I can say.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no financial disclosures, Email him at [email protected]
Perinatal depression and the pediatrician’s role
Postpartum depression (PPD) is a common and treatable problem affecting over 10% of all pregnant women. Without routine use of a screening questionnaire, many women go undiagnosed and without treatment. The risks of untreated PPD in a new mother are the risks of depression tripled: to her health and to the health of her new infant and their whole family. Although pediatricians treat children, they take care of the whole family. They appreciate their role in offering support and guidance to new parents, and in the case of PPD, they are in a unique position. The American Academy of Pediatrics recognized this when they issued their policy statement, “Incorporating Recognition and Management of Perinatal Depression into Pediatric Practice,” in January 2019. By screening, tracking, and connecting affected mothers to care and services, you can truly provide “two-generational care” for your youngest patients.
PPD affects an estimated one in seven women (13%) globally. In one large retrospective study that looked at the 39 weeks before and after delivery, 15.4% of mothers received a diagnosis of PPD and a second study indicated that 22% of new mothers had depressive symptoms that were persistent for 6 months.1 The pathways to PPD include prior personal or family history of depression, stressors in the family (connected to social determinants of health), previous miscarriage or serious complications in a previous pregnancy, and sensitivity to hormonal changes. Indeed, PPD is the most common complication of childbirth.2 Although as many as half of all women eventually diagnosed with PPD had symptoms during their pregnancy, the misperception that PPD is only post partum leads to it being mistaken for the normal process of adjustment to parenthood. PPD is particularly insidious as new mothers are likely to be silent if they feel shame for not enjoying what they have been told will be a special and happy time, and those around them may mistake symptoms for the normal “baby blues” that will resolve quickly and with routine supports.
Untreated PPD, creates risks for mother, infant, and family as she manages needless suffering during a critical period for her new baby. While depression may remit over months without treatment, suicide is a real risk, and accounts for 20% of postpartum deaths.3 Infants face serious developmental consequences when their mothers are withdrawn and disconnected from them during the first months of life, including impaired social development, physical growth, and cognitive development. This impairment persists. Exposure to maternal depression during infancy is associated with lower IQ, attentional problems, and special educational needs by elementary school,4 and is a risk factor for psychiatric illnesses in childhood and adolescence.5,6 PPD has a broad range of severity, including psychosis that may include paranoia with the rare risk of infanticide. And maternal depression can add to the strains in a vulnerable caregiver relationship that can raise the risk for neglect or abuse of the mother, children, or both.
It is important to note that anxiety is often the presenting problem in perinatal mood disorders, with mothers experiencing intense morbid worries about their infant’s safety and health, and fear of inadequacy, criticism, and even infant removal. These fears may reinforce silence and isolation. But pediatricians are one group that these mothers are most likely to share their anxieties with as they look for reassurance. It can be challenging to distinguish PPD from obsessive-compulsive disorder or PTSD. The critical work of the pediatrician is not specific diagnosis and treatment. Instead, your task is to provide screening and support, to create a safe place to overcome silence and shame.
There are many reliable and valid screening instruments available for depression, but the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EDPS) has been specially developed for and tested in this population. It is a 10-item scale that is easy to complete and to score. Scores range from 0 to 30 and a score of 10 is considered a cutoff for depression. It can be used to track symptoms and is free and widely available online and in multiple languages. Ideally, this scale can be administered as part of a previsit, automatically entered into an electronic medical record and given at regular intervals during the infant’s first year of primary care. Some new mothers, especially if they are suffering from depression, may feel anxious about filling this out. It is important that your staff tell them that you screen all new mothers in your practice, and that PPD is common and treatable and the pediatrician’s office is committed to the health of the whole family.
If a new mother screens positive, you might consider yourself to have three tasks: Reassure her that she is a wonderful mother and this is a treatable illness, not a cause for guilt, shame, or alarm; expand her support and decrease her isolation by helping her to communicate with her family; and identify treatment resources for her. Start by being curious about some of her specific worries or feelings, her energy level, feelings of isolation or trouble with sleep. Offer compassion and validation around the pain of these experiences in the midst of so much transition. Only after hearing a little detail about her experience, then you may offer that such feelings are common, but when they are persistent or severe, they often indicate PPD, and that her screening test suggests they do for her. Offer that this form of depression is very treatable, with both pharmacologic and psychotherapy interventions. And if she is resistant, gently offer that treatment will be very protective of her new infant’s physical, social, and cognitive growth and development. Hearing this from a pediatrician is powerful for a new mother, even if depressed. Finally, ask if you might help her bring other important adults in her family into an understanding of this. Could she tell her spouse? Her sister? Her best friend? Perhaps she could bring one of them to the next weekly visit, so you can all speak together. This intervention greatly improves the likelihood of her engaging in treatment, and strong interpersonal connections are therapeutic in and of themselves.
For treatment, the easier your office can make it, the more likely she is to follow up. Identify local resources, perhaps through connected community organizations such as Jewish Family and Children’s Services or through a public program like California’s First Five. Connect with the local obstetric practice, which may already have a referral process in place. If you can connect with her primary care provider, they may take on the referral process or may even have integrated capacity for treatment. Identify strategies that may support her restful sleep, including realistic daily exercise, sharing infant care, and being cautious with caffeine and screen time. Identify ways for her to meet other new mothers or reconnect with friends. Reassure her that easy attachment activities, such as reading a book or singing to her baby can be good for both of them without requiring much energy. This may sound like a daunting task, but the conversation will only take a few minutes. Helping an isolated new parent recognize that their feelings of fear, inadequacy, and guilt are not facts, offering some simple immediate strategies and facilitating a referral can be lifesaving.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected]
References
1. Dietz PM et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(10):1515-20.
2. Hanusa BH et al. J Women’s Health (Larchmt) 2008;17(4):585-96.
3. Lindahl V et al. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2005;8(2):77-87.
4. Hay DF et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001;42(7):871-89.
5. Tully EC et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2008:165(9):1148-54.
6. Maternal depression and child development. Paediatr. Child Health 2004;9(8):575-98.
Postpartum depression (PPD) is a common and treatable problem affecting over 10% of all pregnant women. Without routine use of a screening questionnaire, many women go undiagnosed and without treatment. The risks of untreated PPD in a new mother are the risks of depression tripled: to her health and to the health of her new infant and their whole family. Although pediatricians treat children, they take care of the whole family. They appreciate their role in offering support and guidance to new parents, and in the case of PPD, they are in a unique position. The American Academy of Pediatrics recognized this when they issued their policy statement, “Incorporating Recognition and Management of Perinatal Depression into Pediatric Practice,” in January 2019. By screening, tracking, and connecting affected mothers to care and services, you can truly provide “two-generational care” for your youngest patients.
PPD affects an estimated one in seven women (13%) globally. In one large retrospective study that looked at the 39 weeks before and after delivery, 15.4% of mothers received a diagnosis of PPD and a second study indicated that 22% of new mothers had depressive symptoms that were persistent for 6 months.1 The pathways to PPD include prior personal or family history of depression, stressors in the family (connected to social determinants of health), previous miscarriage or serious complications in a previous pregnancy, and sensitivity to hormonal changes. Indeed, PPD is the most common complication of childbirth.2 Although as many as half of all women eventually diagnosed with PPD had symptoms during their pregnancy, the misperception that PPD is only post partum leads to it being mistaken for the normal process of adjustment to parenthood. PPD is particularly insidious as new mothers are likely to be silent if they feel shame for not enjoying what they have been told will be a special and happy time, and those around them may mistake symptoms for the normal “baby blues” that will resolve quickly and with routine supports.
Untreated PPD, creates risks for mother, infant, and family as she manages needless suffering during a critical period for her new baby. While depression may remit over months without treatment, suicide is a real risk, and accounts for 20% of postpartum deaths.3 Infants face serious developmental consequences when their mothers are withdrawn and disconnected from them during the first months of life, including impaired social development, physical growth, and cognitive development. This impairment persists. Exposure to maternal depression during infancy is associated with lower IQ, attentional problems, and special educational needs by elementary school,4 and is a risk factor for psychiatric illnesses in childhood and adolescence.5,6 PPD has a broad range of severity, including psychosis that may include paranoia with the rare risk of infanticide. And maternal depression can add to the strains in a vulnerable caregiver relationship that can raise the risk for neglect or abuse of the mother, children, or both.
It is important to note that anxiety is often the presenting problem in perinatal mood disorders, with mothers experiencing intense morbid worries about their infant’s safety and health, and fear of inadequacy, criticism, and even infant removal. These fears may reinforce silence and isolation. But pediatricians are one group that these mothers are most likely to share their anxieties with as they look for reassurance. It can be challenging to distinguish PPD from obsessive-compulsive disorder or PTSD. The critical work of the pediatrician is not specific diagnosis and treatment. Instead, your task is to provide screening and support, to create a safe place to overcome silence and shame.
There are many reliable and valid screening instruments available for depression, but the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EDPS) has been specially developed for and tested in this population. It is a 10-item scale that is easy to complete and to score. Scores range from 0 to 30 and a score of 10 is considered a cutoff for depression. It can be used to track symptoms and is free and widely available online and in multiple languages. Ideally, this scale can be administered as part of a previsit, automatically entered into an electronic medical record and given at regular intervals during the infant’s first year of primary care. Some new mothers, especially if they are suffering from depression, may feel anxious about filling this out. It is important that your staff tell them that you screen all new mothers in your practice, and that PPD is common and treatable and the pediatrician’s office is committed to the health of the whole family.
If a new mother screens positive, you might consider yourself to have three tasks: Reassure her that she is a wonderful mother and this is a treatable illness, not a cause for guilt, shame, or alarm; expand her support and decrease her isolation by helping her to communicate with her family; and identify treatment resources for her. Start by being curious about some of her specific worries or feelings, her energy level, feelings of isolation or trouble with sleep. Offer compassion and validation around the pain of these experiences in the midst of so much transition. Only after hearing a little detail about her experience, then you may offer that such feelings are common, but when they are persistent or severe, they often indicate PPD, and that her screening test suggests they do for her. Offer that this form of depression is very treatable, with both pharmacologic and psychotherapy interventions. And if she is resistant, gently offer that treatment will be very protective of her new infant’s physical, social, and cognitive growth and development. Hearing this from a pediatrician is powerful for a new mother, even if depressed. Finally, ask if you might help her bring other important adults in her family into an understanding of this. Could she tell her spouse? Her sister? Her best friend? Perhaps she could bring one of them to the next weekly visit, so you can all speak together. This intervention greatly improves the likelihood of her engaging in treatment, and strong interpersonal connections are therapeutic in and of themselves.
For treatment, the easier your office can make it, the more likely she is to follow up. Identify local resources, perhaps through connected community organizations such as Jewish Family and Children’s Services or through a public program like California’s First Five. Connect with the local obstetric practice, which may already have a referral process in place. If you can connect with her primary care provider, they may take on the referral process or may even have integrated capacity for treatment. Identify strategies that may support her restful sleep, including realistic daily exercise, sharing infant care, and being cautious with caffeine and screen time. Identify ways for her to meet other new mothers or reconnect with friends. Reassure her that easy attachment activities, such as reading a book or singing to her baby can be good for both of them without requiring much energy. This may sound like a daunting task, but the conversation will only take a few minutes. Helping an isolated new parent recognize that their feelings of fear, inadequacy, and guilt are not facts, offering some simple immediate strategies and facilitating a referral can be lifesaving.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected]
References
1. Dietz PM et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(10):1515-20.
2. Hanusa BH et al. J Women’s Health (Larchmt) 2008;17(4):585-96.
3. Lindahl V et al. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2005;8(2):77-87.
4. Hay DF et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001;42(7):871-89.
5. Tully EC et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2008:165(9):1148-54.
6. Maternal depression and child development. Paediatr. Child Health 2004;9(8):575-98.
Postpartum depression (PPD) is a common and treatable problem affecting over 10% of all pregnant women. Without routine use of a screening questionnaire, many women go undiagnosed and without treatment. The risks of untreated PPD in a new mother are the risks of depression tripled: to her health and to the health of her new infant and their whole family. Although pediatricians treat children, they take care of the whole family. They appreciate their role in offering support and guidance to new parents, and in the case of PPD, they are in a unique position. The American Academy of Pediatrics recognized this when they issued their policy statement, “Incorporating Recognition and Management of Perinatal Depression into Pediatric Practice,” in January 2019. By screening, tracking, and connecting affected mothers to care and services, you can truly provide “two-generational care” for your youngest patients.
PPD affects an estimated one in seven women (13%) globally. In one large retrospective study that looked at the 39 weeks before and after delivery, 15.4% of mothers received a diagnosis of PPD and a second study indicated that 22% of new mothers had depressive symptoms that were persistent for 6 months.1 The pathways to PPD include prior personal or family history of depression, stressors in the family (connected to social determinants of health), previous miscarriage or serious complications in a previous pregnancy, and sensitivity to hormonal changes. Indeed, PPD is the most common complication of childbirth.2 Although as many as half of all women eventually diagnosed with PPD had symptoms during their pregnancy, the misperception that PPD is only post partum leads to it being mistaken for the normal process of adjustment to parenthood. PPD is particularly insidious as new mothers are likely to be silent if they feel shame for not enjoying what they have been told will be a special and happy time, and those around them may mistake symptoms for the normal “baby blues” that will resolve quickly and with routine supports.
Untreated PPD, creates risks for mother, infant, and family as she manages needless suffering during a critical period for her new baby. While depression may remit over months without treatment, suicide is a real risk, and accounts for 20% of postpartum deaths.3 Infants face serious developmental consequences when their mothers are withdrawn and disconnected from them during the first months of life, including impaired social development, physical growth, and cognitive development. This impairment persists. Exposure to maternal depression during infancy is associated with lower IQ, attentional problems, and special educational needs by elementary school,4 and is a risk factor for psychiatric illnesses in childhood and adolescence.5,6 PPD has a broad range of severity, including psychosis that may include paranoia with the rare risk of infanticide. And maternal depression can add to the strains in a vulnerable caregiver relationship that can raise the risk for neglect or abuse of the mother, children, or both.
It is important to note that anxiety is often the presenting problem in perinatal mood disorders, with mothers experiencing intense morbid worries about their infant’s safety and health, and fear of inadequacy, criticism, and even infant removal. These fears may reinforce silence and isolation. But pediatricians are one group that these mothers are most likely to share their anxieties with as they look for reassurance. It can be challenging to distinguish PPD from obsessive-compulsive disorder or PTSD. The critical work of the pediatrician is not specific diagnosis and treatment. Instead, your task is to provide screening and support, to create a safe place to overcome silence and shame.
There are many reliable and valid screening instruments available for depression, but the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EDPS) has been specially developed for and tested in this population. It is a 10-item scale that is easy to complete and to score. Scores range from 0 to 30 and a score of 10 is considered a cutoff for depression. It can be used to track symptoms and is free and widely available online and in multiple languages. Ideally, this scale can be administered as part of a previsit, automatically entered into an electronic medical record and given at regular intervals during the infant’s first year of primary care. Some new mothers, especially if they are suffering from depression, may feel anxious about filling this out. It is important that your staff tell them that you screen all new mothers in your practice, and that PPD is common and treatable and the pediatrician’s office is committed to the health of the whole family.
If a new mother screens positive, you might consider yourself to have three tasks: Reassure her that she is a wonderful mother and this is a treatable illness, not a cause for guilt, shame, or alarm; expand her support and decrease her isolation by helping her to communicate with her family; and identify treatment resources for her. Start by being curious about some of her specific worries or feelings, her energy level, feelings of isolation or trouble with sleep. Offer compassion and validation around the pain of these experiences in the midst of so much transition. Only after hearing a little detail about her experience, then you may offer that such feelings are common, but when they are persistent or severe, they often indicate PPD, and that her screening test suggests they do for her. Offer that this form of depression is very treatable, with both pharmacologic and psychotherapy interventions. And if she is resistant, gently offer that treatment will be very protective of her new infant’s physical, social, and cognitive growth and development. Hearing this from a pediatrician is powerful for a new mother, even if depressed. Finally, ask if you might help her bring other important adults in her family into an understanding of this. Could she tell her spouse? Her sister? Her best friend? Perhaps she could bring one of them to the next weekly visit, so you can all speak together. This intervention greatly improves the likelihood of her engaging in treatment, and strong interpersonal connections are therapeutic in and of themselves.
For treatment, the easier your office can make it, the more likely she is to follow up. Identify local resources, perhaps through connected community organizations such as Jewish Family and Children’s Services or through a public program like California’s First Five. Connect with the local obstetric practice, which may already have a referral process in place. If you can connect with her primary care provider, they may take on the referral process or may even have integrated capacity for treatment. Identify strategies that may support her restful sleep, including realistic daily exercise, sharing infant care, and being cautious with caffeine and screen time. Identify ways for her to meet other new mothers or reconnect with friends. Reassure her that easy attachment activities, such as reading a book or singing to her baby can be good for both of them without requiring much energy. This may sound like a daunting task, but the conversation will only take a few minutes. Helping an isolated new parent recognize that their feelings of fear, inadequacy, and guilt are not facts, offering some simple immediate strategies and facilitating a referral can be lifesaving.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected]
References
1. Dietz PM et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(10):1515-20.
2. Hanusa BH et al. J Women’s Health (Larchmt) 2008;17(4):585-96.
3. Lindahl V et al. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2005;8(2):77-87.
4. Hay DF et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001;42(7):871-89.
5. Tully EC et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2008:165(9):1148-54.
6. Maternal depression and child development. Paediatr. Child Health 2004;9(8):575-98.
COVID-19 in children and adolescents: Disease burden and severity
My first thought on this column was maybe Pediatric News has written sufficiently about SARS-CoV-2 infection, and it is time to move on. However, the agenda for the May 12th Advisory Committee on Immunization Practice includes a review of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine safety and immunogenicity data for the 12- to 15-year-old age cohort that suggests the potential for vaccine availability and roll out for early adolescents in the near future and the need for up-to-date knowledge about the incidence, severity, and long-term outcome of COVID-19 in the pediatric population.
Updating and summarizing the pediatric experience for the pediatric community on what children and adolescents have experienced because of SARS-CoV-2 infection is critical to address the myriad of questions that will come from colleagues, parents, and adolescents themselves. A great resource, published weekly, is the joint report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.1 As of April 29, 2021, 3,782,724 total child COVID-19 cases have been reported from 49 states, New York City (NYC), the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico. Children represent approximately 14% of cases in the United States and not surprisingly are an increasing proportion of total cases as vaccine impact reduces cases among older age groups. Nearly 5% of the pediatric population has already been infected with SARS-CoV-2. Fortunately, compared with adults, hospitalization, severe disease, and mortality remain far lower both in number and proportion than in the adult population. Cumulative hospitalizations from 24 states and NYC total 15,456 (0.8%) among those infected, with 303 deaths reported (from 43 states, NYC, Guam, and Puerto Rico). Case fatality rate approximates 0.01% in the most recent summary of state reports. One of the limitations of this report is that each state decides how to report the age distribution of COVID-19 cases resulting in variation in age range; another is the data are limited to those details individual states chose to make publicly available.
Although children do not commonly develop severe disease, and the case fatality is low, there are still insights to be learned from understanding risk features for severe disease. Preston et al. reviewed discharge data from 869 medical facilities to describe patients 18 years or younger who had an inpatient or emergency department encounter with a primary or secondary COVID-19 discharge diagnosis from March 1 through October 31, 2020.2 They reported that approximately 2,430 (11.7%) children were hospitalized and 746, nearly 31% of those hospitalized, had severe COVID disease. Those at greatest risk for severe disease were children with comorbid conditions and those less than 12 years, compared with the 12- to 18-year age group. They did not identify race as a risk for severe disease in this study. Moreira et al. described risk factors for morbidity and death from COVID in children less than 18 years of age3 using CDC COVID-NET, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19–associated hospitalization surveillance network. They reported a hospitalization rate of 4.7% among 27,045 cases. They identified three risk factors for hospitalization – age, race/ethnicity, and comorbid conditions. Thirty-nine children (0.19%) died; children who were black, non-Hispanic, and those with an underlying medical condition had a significantly increased risk of death. Thirty-three (85%) children who died had a comorbidity, and 27 (69%) were African American or Hispanic/Latino. The U.S. experience in children is also consistent with reports from the United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Germany, France, and South Korea.4 Deaths from COVID-19 were uncommon but relatively more frequent in older children, compared with younger age groups among children less than 18 years of age in these countries.
Acute COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) do not predominantly target the neurologic systems; however, neurologic complications have been reported, some of which appear to result in long-lasting disability. LaRovere et al. identified 354 (22%) of 1,695 patients less than 21 years of age with acute COVID or MIS-C who had neurologic signs or symptoms during their illness. Among those with neurologic involvement, most children had prior neurologic deficits, mild symptoms, that resolved by the time of discharge. Forty-three (12%) were considered life threatening and included severe encephalopathy, stroke, central nervous system infection/demyelination, Guillain-Barre syndrome or variant, or acute cerebral edema. Several children, including some who were previously healthy prior to COVID, had persistent neurologic deficits at discharge. In addition to neurologic morbidity, long COVID – a syndrome of persistent symptoms following acute COVID that lasts for more than 12 weeks without alternative diagnosis – has also been described in children. Buonsenso et al. assessed 129 children diagnosed with COVID-19 between March and November 2020 in Rome, Italy.5 Persisting symptoms after 120 days were reported by more than 50%. Symptoms like fatigue, muscle and joint pain, headache, insomnia, respiratory problems, and palpitations were most common. Clearly, further follow-up of the long-term outcomes is necessary to understand the full spectrum of morbidity resulting from COVID-19 disease in children and its natural history.
The current picture of COVID infection in children younger than 18 reinforces that children are part of the pandemic. Although deaths in children have now exceeded 300 cases, severe disease remains uncommon in both the United States and western Europe. Risk factors for severe disease include comorbid illness and race/ethnicity with a disproportionate number of severe cases in children with underlying comorbidity and in African American and Hispanic/Latino children. Ongoing surveillance is critical as changes are likely to be observed over time as viral evolution affects disease burden and characteristics.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University schools of medicine and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases, Boston Medical Center. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Children and COVID-19: State-Level Data Report. Services AAP.org.
2. Preston LE et al. JAMA Network Open. 2021;4(4):e215298. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5298
3. Moreira A et al. Eur J Pediatr. 2021;180:1659-63.
4. SS Bhopal et al. Lancet 2021. doi: 10.1016/ S2352-4642(21)00066-3.
5. Buonsenso D et al. medRxiv preprint. doi: 10.1101/2021.01.23.21250375.
My first thought on this column was maybe Pediatric News has written sufficiently about SARS-CoV-2 infection, and it is time to move on. However, the agenda for the May 12th Advisory Committee on Immunization Practice includes a review of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine safety and immunogenicity data for the 12- to 15-year-old age cohort that suggests the potential for vaccine availability and roll out for early adolescents in the near future and the need for up-to-date knowledge about the incidence, severity, and long-term outcome of COVID-19 in the pediatric population.
Updating and summarizing the pediatric experience for the pediatric community on what children and adolescents have experienced because of SARS-CoV-2 infection is critical to address the myriad of questions that will come from colleagues, parents, and adolescents themselves. A great resource, published weekly, is the joint report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.1 As of April 29, 2021, 3,782,724 total child COVID-19 cases have been reported from 49 states, New York City (NYC), the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico. Children represent approximately 14% of cases in the United States and not surprisingly are an increasing proportion of total cases as vaccine impact reduces cases among older age groups. Nearly 5% of the pediatric population has already been infected with SARS-CoV-2. Fortunately, compared with adults, hospitalization, severe disease, and mortality remain far lower both in number and proportion than in the adult population. Cumulative hospitalizations from 24 states and NYC total 15,456 (0.8%) among those infected, with 303 deaths reported (from 43 states, NYC, Guam, and Puerto Rico). Case fatality rate approximates 0.01% in the most recent summary of state reports. One of the limitations of this report is that each state decides how to report the age distribution of COVID-19 cases resulting in variation in age range; another is the data are limited to those details individual states chose to make publicly available.
Although children do not commonly develop severe disease, and the case fatality is low, there are still insights to be learned from understanding risk features for severe disease. Preston et al. reviewed discharge data from 869 medical facilities to describe patients 18 years or younger who had an inpatient or emergency department encounter with a primary or secondary COVID-19 discharge diagnosis from March 1 through October 31, 2020.2 They reported that approximately 2,430 (11.7%) children were hospitalized and 746, nearly 31% of those hospitalized, had severe COVID disease. Those at greatest risk for severe disease were children with comorbid conditions and those less than 12 years, compared with the 12- to 18-year age group. They did not identify race as a risk for severe disease in this study. Moreira et al. described risk factors for morbidity and death from COVID in children less than 18 years of age3 using CDC COVID-NET, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19–associated hospitalization surveillance network. They reported a hospitalization rate of 4.7% among 27,045 cases. They identified three risk factors for hospitalization – age, race/ethnicity, and comorbid conditions. Thirty-nine children (0.19%) died; children who were black, non-Hispanic, and those with an underlying medical condition had a significantly increased risk of death. Thirty-three (85%) children who died had a comorbidity, and 27 (69%) were African American or Hispanic/Latino. The U.S. experience in children is also consistent with reports from the United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Germany, France, and South Korea.4 Deaths from COVID-19 were uncommon but relatively more frequent in older children, compared with younger age groups among children less than 18 years of age in these countries.
Acute COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) do not predominantly target the neurologic systems; however, neurologic complications have been reported, some of which appear to result in long-lasting disability. LaRovere et al. identified 354 (22%) of 1,695 patients less than 21 years of age with acute COVID or MIS-C who had neurologic signs or symptoms during their illness. Among those with neurologic involvement, most children had prior neurologic deficits, mild symptoms, that resolved by the time of discharge. Forty-three (12%) were considered life threatening and included severe encephalopathy, stroke, central nervous system infection/demyelination, Guillain-Barre syndrome or variant, or acute cerebral edema. Several children, including some who were previously healthy prior to COVID, had persistent neurologic deficits at discharge. In addition to neurologic morbidity, long COVID – a syndrome of persistent symptoms following acute COVID that lasts for more than 12 weeks without alternative diagnosis – has also been described in children. Buonsenso et al. assessed 129 children diagnosed with COVID-19 between March and November 2020 in Rome, Italy.5 Persisting symptoms after 120 days were reported by more than 50%. Symptoms like fatigue, muscle and joint pain, headache, insomnia, respiratory problems, and palpitations were most common. Clearly, further follow-up of the long-term outcomes is necessary to understand the full spectrum of morbidity resulting from COVID-19 disease in children and its natural history.
The current picture of COVID infection in children younger than 18 reinforces that children are part of the pandemic. Although deaths in children have now exceeded 300 cases, severe disease remains uncommon in both the United States and western Europe. Risk factors for severe disease include comorbid illness and race/ethnicity with a disproportionate number of severe cases in children with underlying comorbidity and in African American and Hispanic/Latino children. Ongoing surveillance is critical as changes are likely to be observed over time as viral evolution affects disease burden and characteristics.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University schools of medicine and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases, Boston Medical Center. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Children and COVID-19: State-Level Data Report. Services AAP.org.
2. Preston LE et al. JAMA Network Open. 2021;4(4):e215298. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5298
3. Moreira A et al. Eur J Pediatr. 2021;180:1659-63.
4. SS Bhopal et al. Lancet 2021. doi: 10.1016/ S2352-4642(21)00066-3.
5. Buonsenso D et al. medRxiv preprint. doi: 10.1101/2021.01.23.21250375.
My first thought on this column was maybe Pediatric News has written sufficiently about SARS-CoV-2 infection, and it is time to move on. However, the agenda for the May 12th Advisory Committee on Immunization Practice includes a review of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine safety and immunogenicity data for the 12- to 15-year-old age cohort that suggests the potential for vaccine availability and roll out for early adolescents in the near future and the need for up-to-date knowledge about the incidence, severity, and long-term outcome of COVID-19 in the pediatric population.
Updating and summarizing the pediatric experience for the pediatric community on what children and adolescents have experienced because of SARS-CoV-2 infection is critical to address the myriad of questions that will come from colleagues, parents, and adolescents themselves. A great resource, published weekly, is the joint report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.1 As of April 29, 2021, 3,782,724 total child COVID-19 cases have been reported from 49 states, New York City (NYC), the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico. Children represent approximately 14% of cases in the United States and not surprisingly are an increasing proportion of total cases as vaccine impact reduces cases among older age groups. Nearly 5% of the pediatric population has already been infected with SARS-CoV-2. Fortunately, compared with adults, hospitalization, severe disease, and mortality remain far lower both in number and proportion than in the adult population. Cumulative hospitalizations from 24 states and NYC total 15,456 (0.8%) among those infected, with 303 deaths reported (from 43 states, NYC, Guam, and Puerto Rico). Case fatality rate approximates 0.01% in the most recent summary of state reports. One of the limitations of this report is that each state decides how to report the age distribution of COVID-19 cases resulting in variation in age range; another is the data are limited to those details individual states chose to make publicly available.
Although children do not commonly develop severe disease, and the case fatality is low, there are still insights to be learned from understanding risk features for severe disease. Preston et al. reviewed discharge data from 869 medical facilities to describe patients 18 years or younger who had an inpatient or emergency department encounter with a primary or secondary COVID-19 discharge diagnosis from March 1 through October 31, 2020.2 They reported that approximately 2,430 (11.7%) children were hospitalized and 746, nearly 31% of those hospitalized, had severe COVID disease. Those at greatest risk for severe disease were children with comorbid conditions and those less than 12 years, compared with the 12- to 18-year age group. They did not identify race as a risk for severe disease in this study. Moreira et al. described risk factors for morbidity and death from COVID in children less than 18 years of age3 using CDC COVID-NET, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19–associated hospitalization surveillance network. They reported a hospitalization rate of 4.7% among 27,045 cases. They identified three risk factors for hospitalization – age, race/ethnicity, and comorbid conditions. Thirty-nine children (0.19%) died; children who were black, non-Hispanic, and those with an underlying medical condition had a significantly increased risk of death. Thirty-three (85%) children who died had a comorbidity, and 27 (69%) were African American or Hispanic/Latino. The U.S. experience in children is also consistent with reports from the United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Germany, France, and South Korea.4 Deaths from COVID-19 were uncommon but relatively more frequent in older children, compared with younger age groups among children less than 18 years of age in these countries.
Acute COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) do not predominantly target the neurologic systems; however, neurologic complications have been reported, some of which appear to result in long-lasting disability. LaRovere et al. identified 354 (22%) of 1,695 patients less than 21 years of age with acute COVID or MIS-C who had neurologic signs or symptoms during their illness. Among those with neurologic involvement, most children had prior neurologic deficits, mild symptoms, that resolved by the time of discharge. Forty-three (12%) were considered life threatening and included severe encephalopathy, stroke, central nervous system infection/demyelination, Guillain-Barre syndrome or variant, or acute cerebral edema. Several children, including some who were previously healthy prior to COVID, had persistent neurologic deficits at discharge. In addition to neurologic morbidity, long COVID – a syndrome of persistent symptoms following acute COVID that lasts for more than 12 weeks without alternative diagnosis – has also been described in children. Buonsenso et al. assessed 129 children diagnosed with COVID-19 between March and November 2020 in Rome, Italy.5 Persisting symptoms after 120 days were reported by more than 50%. Symptoms like fatigue, muscle and joint pain, headache, insomnia, respiratory problems, and palpitations were most common. Clearly, further follow-up of the long-term outcomes is necessary to understand the full spectrum of morbidity resulting from COVID-19 disease in children and its natural history.
The current picture of COVID infection in children younger than 18 reinforces that children are part of the pandemic. Although deaths in children have now exceeded 300 cases, severe disease remains uncommon in both the United States and western Europe. Risk factors for severe disease include comorbid illness and race/ethnicity with a disproportionate number of severe cases in children with underlying comorbidity and in African American and Hispanic/Latino children. Ongoing surveillance is critical as changes are likely to be observed over time as viral evolution affects disease burden and characteristics.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University schools of medicine and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases, Boston Medical Center. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Children and COVID-19: State-Level Data Report. Services AAP.org.
2. Preston LE et al. JAMA Network Open. 2021;4(4):e215298. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5298
3. Moreira A et al. Eur J Pediatr. 2021;180:1659-63.
4. SS Bhopal et al. Lancet 2021. doi: 10.1016/ S2352-4642(21)00066-3.
5. Buonsenso D et al. medRxiv preprint. doi: 10.1101/2021.01.23.21250375.
An infant girl presents with a growing pink-red leg nodule
The history of a brownish to pink patch with color change and rapid growth within the first year combined with the exam findings, are suggestive of a tufted angioma, though the findings presented may be nonspecific.
A tufted angioma is a rare vascular tumor of infancy or early childhood, that is present at birth in approximately half of cases. It may initially present as a faint pink to brown plaque, but develops as a firm, red to violaceous nodule or plaque, usually with “lumpiness” or nodularity.1-3 Lesions usually are infiltrative with indistinct borders. They are named for their histologic appearance, with lobules of capillaries which appear as “tufts” in the dermis and subdermis with “cannonball” appearance, and are considered to be on a spectrum with another vascular tumor called kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE).4 These vascular tumors can trigger Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, a disease process in which vascular tumors trap platelets and clotting factors, resulting in a life-threatening thrombocytopenia and consumptive coagulopathy with a high risk of bleeding and high-output heart failure.5
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of tufted angioma includes other potentially large vascular lesions including infantile hemangioma, congenital hemangioma, port-wine birth marks (capillary malformations), hemangioendotheliomas, and rhabdomyosarcomas.
Infantile hemangiomas (IH) are common vascular tumors of infancy seen in 4%-5% of infants that are characterized by a growth and involution phase. Classically, lesions can be absent or minimally evident at birth, becoming noticeable within the first months of life with a rapid growth phase and typical progression to bright red papules, nodules, or plaques. Deeper hemangiomas may appear more skin colored on the surface with a bluish coloration underneath. They are usually more discreet, with relatively defined borders. Diagnosis is typically clinical and many IHs self-resolve, albeit with residual findings including skin atrophy, scarring, and telangiectasia. Observation or topical timolol are first-line treatment options for more superficial lesions while systemic propranolol is the treatment of choice for deeper IHs or those resulting in possible airway or vision compromise.
Congenital hemangiomas (CH) are another type of vascular growth characterized by a solitary erythematous to violaceous plaque or nodule present at birth with overlying telangiectasia. CHs can be subdivided into categories including rapidly involuting (RICH), partially involuting (PICH), and noninvoluting (NICH). Diagnosis is usually clinical and, depending on the subtype, treatment can involve watchful waiting (for RICHs) or more active intervention such as pulse dye laser or surgical resection (for PICHs or NICHs). The growing nature of this patient’s mass makes a diagnosis of CH unlikely.
Port-wine birth mark, also known as nevus flammeus, is a vascular malformation that appears at birth as a nonpalpable irregular erythematous to violaceous macular plaque. Port-wine stains may be isolated birthmarks, or associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome, complex vascular malformations, or soft-tissue overgrowth. Klippel-Trenauny syndrome (KTS) describes capillary-venous malformations with limb overgrowth, with or without lymphatic malformations, and many are associated with somatic mutations in the PIK3CA gene. While KTS could be considered in this patient, the nodular appearance with lumpy texture and rapid growth makes a vascular tumor more likely.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a malignancy of skeletal muscle lineage and the most common soft tissue tumor in pediatrics. Cutaneous rhabdomyosarcomas present as erythematous nodules, markedly firm, often “fixed” to deep tissue. A rapidly growing atypical, firm tumor of infancy should raise the consideration of rhabdomyosarcoma and imaging and biopsy are appropriate for evaluation.
What should the evaluation and management of this patient be?
Initial workup should include a complete blood count with platelet count as well as coagulation studies including D-dimer, fibrinogen, prothrombin time, and activated partial thromboplastin time, to assess for any thrombocytopenia or coagulopathy.6 Ultrasound and/or MRI may also be performed to determine lesion extent. While typical MRI findings might be suggestive of a tufted angioma or hemangioendothelioma, biopsy for histologic examination is usually the approach to diagnosis, which will demonstrate stereotypic round lobules of capillaries in a “tufted” distribution.2,7 Biopsy may be performed by a surgeon or dermatologist but bleeding at time of biopsy needs to be considered before moving forward with the procedure.
Tufted angiomas of early life may regress spontaneously, though lesions with symptoms, with functional significance, or associated with KHE may require therapy. Surgical excision is one option, but it may be difficult to execute given that these lesions often have poorly defined margins.1 Other treatment choices include but are not limited to aspirin, systemic corticosteroids, vincristine, interferon-alpha, embolization, and sirolimus.8 No specific expert-directed consensus guidelines exist for these lesions, and suspicion of this lesion should prompt urgent referral to a pediatric dermatologist. Concern for Kasabach-Merritt syndrome should trigger immediate referral for rapid evaluation and management.
Complete blood count with platelet count and coagulation studies were normal in our patient. This infant underwent biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of tufted angioma and MRI to determine lesion extent. The lesion slowly involuted spontaneously without recurrence.
Mr. Haft is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. He is MS4 at the University of Rochester, N.Y. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Mr. Haft nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Herron MD et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19(5):394-401.
2. Jones EW and Orkin M. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2 Pt 1):214-25.
3. Wong SN and Tay YK. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19(5):388-93.
4. Croteau SE and Gupta D. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35(3):147-52.
5. Kelly M. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010;57(5):1085-9.
6. Osio A et al. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146(7):758-63.
7. Padilla RS et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9(4):292-300.
8. Liu XH et al. Int J Cancer. 2016;139(7):1658-66.
The history of a brownish to pink patch with color change and rapid growth within the first year combined with the exam findings, are suggestive of a tufted angioma, though the findings presented may be nonspecific.
A tufted angioma is a rare vascular tumor of infancy or early childhood, that is present at birth in approximately half of cases. It may initially present as a faint pink to brown plaque, but develops as a firm, red to violaceous nodule or plaque, usually with “lumpiness” or nodularity.1-3 Lesions usually are infiltrative with indistinct borders. They are named for their histologic appearance, with lobules of capillaries which appear as “tufts” in the dermis and subdermis with “cannonball” appearance, and are considered to be on a spectrum with another vascular tumor called kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE).4 These vascular tumors can trigger Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, a disease process in which vascular tumors trap platelets and clotting factors, resulting in a life-threatening thrombocytopenia and consumptive coagulopathy with a high risk of bleeding and high-output heart failure.5
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of tufted angioma includes other potentially large vascular lesions including infantile hemangioma, congenital hemangioma, port-wine birth marks (capillary malformations), hemangioendotheliomas, and rhabdomyosarcomas.
Infantile hemangiomas (IH) are common vascular tumors of infancy seen in 4%-5% of infants that are characterized by a growth and involution phase. Classically, lesions can be absent or minimally evident at birth, becoming noticeable within the first months of life with a rapid growth phase and typical progression to bright red papules, nodules, or plaques. Deeper hemangiomas may appear more skin colored on the surface with a bluish coloration underneath. They are usually more discreet, with relatively defined borders. Diagnosis is typically clinical and many IHs self-resolve, albeit with residual findings including skin atrophy, scarring, and telangiectasia. Observation or topical timolol are first-line treatment options for more superficial lesions while systemic propranolol is the treatment of choice for deeper IHs or those resulting in possible airway or vision compromise.
Congenital hemangiomas (CH) are another type of vascular growth characterized by a solitary erythematous to violaceous plaque or nodule present at birth with overlying telangiectasia. CHs can be subdivided into categories including rapidly involuting (RICH), partially involuting (PICH), and noninvoluting (NICH). Diagnosis is usually clinical and, depending on the subtype, treatment can involve watchful waiting (for RICHs) or more active intervention such as pulse dye laser or surgical resection (for PICHs or NICHs). The growing nature of this patient’s mass makes a diagnosis of CH unlikely.
Port-wine birth mark, also known as nevus flammeus, is a vascular malformation that appears at birth as a nonpalpable irregular erythematous to violaceous macular plaque. Port-wine stains may be isolated birthmarks, or associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome, complex vascular malformations, or soft-tissue overgrowth. Klippel-Trenauny syndrome (KTS) describes capillary-venous malformations with limb overgrowth, with or without lymphatic malformations, and many are associated with somatic mutations in the PIK3CA gene. While KTS could be considered in this patient, the nodular appearance with lumpy texture and rapid growth makes a vascular tumor more likely.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a malignancy of skeletal muscle lineage and the most common soft tissue tumor in pediatrics. Cutaneous rhabdomyosarcomas present as erythematous nodules, markedly firm, often “fixed” to deep tissue. A rapidly growing atypical, firm tumor of infancy should raise the consideration of rhabdomyosarcoma and imaging and biopsy are appropriate for evaluation.
What should the evaluation and management of this patient be?
Initial workup should include a complete blood count with platelet count as well as coagulation studies including D-dimer, fibrinogen, prothrombin time, and activated partial thromboplastin time, to assess for any thrombocytopenia or coagulopathy.6 Ultrasound and/or MRI may also be performed to determine lesion extent. While typical MRI findings might be suggestive of a tufted angioma or hemangioendothelioma, biopsy for histologic examination is usually the approach to diagnosis, which will demonstrate stereotypic round lobules of capillaries in a “tufted” distribution.2,7 Biopsy may be performed by a surgeon or dermatologist but bleeding at time of biopsy needs to be considered before moving forward with the procedure.
Tufted angiomas of early life may regress spontaneously, though lesions with symptoms, with functional significance, or associated with KHE may require therapy. Surgical excision is one option, but it may be difficult to execute given that these lesions often have poorly defined margins.1 Other treatment choices include but are not limited to aspirin, systemic corticosteroids, vincristine, interferon-alpha, embolization, and sirolimus.8 No specific expert-directed consensus guidelines exist for these lesions, and suspicion of this lesion should prompt urgent referral to a pediatric dermatologist. Concern for Kasabach-Merritt syndrome should trigger immediate referral for rapid evaluation and management.
Complete blood count with platelet count and coagulation studies were normal in our patient. This infant underwent biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of tufted angioma and MRI to determine lesion extent. The lesion slowly involuted spontaneously without recurrence.
Mr. Haft is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. He is MS4 at the University of Rochester, N.Y. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Mr. Haft nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Herron MD et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19(5):394-401.
2. Jones EW and Orkin M. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2 Pt 1):214-25.
3. Wong SN and Tay YK. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19(5):388-93.
4. Croteau SE and Gupta D. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35(3):147-52.
5. Kelly M. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010;57(5):1085-9.
6. Osio A et al. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146(7):758-63.
7. Padilla RS et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9(4):292-300.
8. Liu XH et al. Int J Cancer. 2016;139(7):1658-66.
The history of a brownish to pink patch with color change and rapid growth within the first year combined with the exam findings, are suggestive of a tufted angioma, though the findings presented may be nonspecific.
A tufted angioma is a rare vascular tumor of infancy or early childhood, that is present at birth in approximately half of cases. It may initially present as a faint pink to brown plaque, but develops as a firm, red to violaceous nodule or plaque, usually with “lumpiness” or nodularity.1-3 Lesions usually are infiltrative with indistinct borders. They are named for their histologic appearance, with lobules of capillaries which appear as “tufts” in the dermis and subdermis with “cannonball” appearance, and are considered to be on a spectrum with another vascular tumor called kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE).4 These vascular tumors can trigger Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, a disease process in which vascular tumors trap platelets and clotting factors, resulting in a life-threatening thrombocytopenia and consumptive coagulopathy with a high risk of bleeding and high-output heart failure.5
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of tufted angioma includes other potentially large vascular lesions including infantile hemangioma, congenital hemangioma, port-wine birth marks (capillary malformations), hemangioendotheliomas, and rhabdomyosarcomas.
Infantile hemangiomas (IH) are common vascular tumors of infancy seen in 4%-5% of infants that are characterized by a growth and involution phase. Classically, lesions can be absent or minimally evident at birth, becoming noticeable within the first months of life with a rapid growth phase and typical progression to bright red papules, nodules, or plaques. Deeper hemangiomas may appear more skin colored on the surface with a bluish coloration underneath. They are usually more discreet, with relatively defined borders. Diagnosis is typically clinical and many IHs self-resolve, albeit with residual findings including skin atrophy, scarring, and telangiectasia. Observation or topical timolol are first-line treatment options for more superficial lesions while systemic propranolol is the treatment of choice for deeper IHs or those resulting in possible airway or vision compromise.
Congenital hemangiomas (CH) are another type of vascular growth characterized by a solitary erythematous to violaceous plaque or nodule present at birth with overlying telangiectasia. CHs can be subdivided into categories including rapidly involuting (RICH), partially involuting (PICH), and noninvoluting (NICH). Diagnosis is usually clinical and, depending on the subtype, treatment can involve watchful waiting (for RICHs) or more active intervention such as pulse dye laser or surgical resection (for PICHs or NICHs). The growing nature of this patient’s mass makes a diagnosis of CH unlikely.
Port-wine birth mark, also known as nevus flammeus, is a vascular malformation that appears at birth as a nonpalpable irregular erythematous to violaceous macular plaque. Port-wine stains may be isolated birthmarks, or associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome, complex vascular malformations, or soft-tissue overgrowth. Klippel-Trenauny syndrome (KTS) describes capillary-venous malformations with limb overgrowth, with or without lymphatic malformations, and many are associated with somatic mutations in the PIK3CA gene. While KTS could be considered in this patient, the nodular appearance with lumpy texture and rapid growth makes a vascular tumor more likely.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a malignancy of skeletal muscle lineage and the most common soft tissue tumor in pediatrics. Cutaneous rhabdomyosarcomas present as erythematous nodules, markedly firm, often “fixed” to deep tissue. A rapidly growing atypical, firm tumor of infancy should raise the consideration of rhabdomyosarcoma and imaging and biopsy are appropriate for evaluation.
What should the evaluation and management of this patient be?
Initial workup should include a complete blood count with platelet count as well as coagulation studies including D-dimer, fibrinogen, prothrombin time, and activated partial thromboplastin time, to assess for any thrombocytopenia or coagulopathy.6 Ultrasound and/or MRI may also be performed to determine lesion extent. While typical MRI findings might be suggestive of a tufted angioma or hemangioendothelioma, biopsy for histologic examination is usually the approach to diagnosis, which will demonstrate stereotypic round lobules of capillaries in a “tufted” distribution.2,7 Biopsy may be performed by a surgeon or dermatologist but bleeding at time of biopsy needs to be considered before moving forward with the procedure.
Tufted angiomas of early life may regress spontaneously, though lesions with symptoms, with functional significance, or associated with KHE may require therapy. Surgical excision is one option, but it may be difficult to execute given that these lesions often have poorly defined margins.1 Other treatment choices include but are not limited to aspirin, systemic corticosteroids, vincristine, interferon-alpha, embolization, and sirolimus.8 No specific expert-directed consensus guidelines exist for these lesions, and suspicion of this lesion should prompt urgent referral to a pediatric dermatologist. Concern for Kasabach-Merritt syndrome should trigger immediate referral for rapid evaluation and management.
Complete blood count with platelet count and coagulation studies were normal in our patient. This infant underwent biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of tufted angioma and MRI to determine lesion extent. The lesion slowly involuted spontaneously without recurrence.
Mr. Haft is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. He is MS4 at the University of Rochester, N.Y. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Neither Mr. Haft nor Dr. Eichenfield have any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Herron MD et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19(5):394-401.
2. Jones EW and Orkin M. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2 Pt 1):214-25.
3. Wong SN and Tay YK. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19(5):388-93.
4. Croteau SE and Gupta D. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2016;35(3):147-52.
5. Kelly M. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2010;57(5):1085-9.
6. Osio A et al. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146(7):758-63.
7. Padilla RS et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9(4):292-300.
8. Liu XH et al. Int J Cancer. 2016;139(7):1658-66.
On physical exam, you see an infant with a mass of the left lower extremity. Close examination reveals an approximately 7 cm x 8 cm poorly defined mass with overlying central erythematous to violaceous color of the left anterior upper leg with a lumpy texture. The lesion is moderately firm and mildly tender on palpation.
Trends in hospital medicine program operations during COVID-19
Staffing was a challenge for most groups
What a year it has been in the world of hospital medicine with all the changes, challenges, and uncertainties surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic. Some hospitalist programs were hit hard early on with an early surge, when little was known about COVID-19, and other programs have had more time to plan and adapt to later surges.
As many readers of The Hospitalist know, the Society of Hospital Medicine publishes a biennial State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report – last published in September 2020 using data from 2019. The SoHM Report contains a wealth of information that many groups find useful in evaluating their programs, with topics ranging from compensation to staffing to scheduling. As some prior months’ Survey Insights columns have alluded to, with the rapid pace of change in 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Society of Hospital Medicine made the decision to publish an addendum highlighting the myriad of adjustments and adaptations that have occurred in such a short period of time. The COVID-19 Addendum is available to all purchasers of the SoHM Report and contains data from survey responses submitted in September 2020.
Let’s take a look at what transpired in 2020, starting with staffing – no doubt a challenge for many groups. During some periods of time, patient volumes may have fallen below historical averages with stay-at-home orders, canceled procedures, and a reluctance by patients to seek medical care. In contrast, for many groups, other parts of the year were all-hands-on-deck scenarios to care for extraordinary surges in patient volume. To compound this, many hospitalist groups had physicians and staff facing quarantine or isolation requirements because of exposures or contracting COVID-19, and locums positions may have been difficult to fill because of travel restrictions and extreme demand.
What operational changes were made in response to these staffing challenges? Perhaps one notable finding from the COVID-19 Addendum was the need for contingency planning and backup systems. From the 2020 SoHM, prior to the pandemic, 47.4% of adult hospital medicine groups had backup systems in place. In our recently published addendum, we found that 61.9% of groups instituted a backup system where none previously existed. In addition, 54.2% of groups modified their existing backup system. Some 39.6% of hospital medicine groups also utilized clinicians from other service lines to help cover service needs.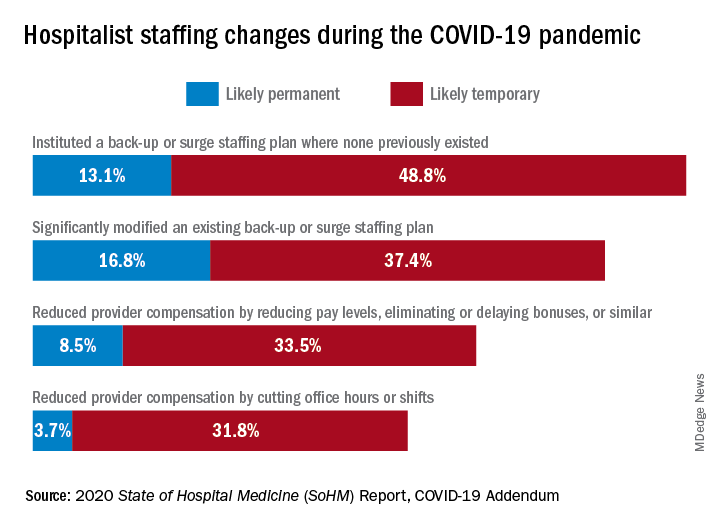
Aside from staffing, hospitals faced unprecedented financial challenges, and these effects rippled through to hospitalists. Our addendum found that 42.0% of hospitalist groups faced reductions in salary or bonuses, and 35.5% of hospital medicine groups reduced provider compensation by a reduction of work hours or shifts. I’ve personally been struck by these findings – that many hospitalists at the front-lines of COVID-19 received salary reductions, albeit temporary for many groups, during one of the most challenging years of their professional careers. Our addendum, interestingly, also found that a smaller 10.7% of groups instituted hazard pay for clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients.
So, are the changes and challenges your group faced similar to what was experienced by other hospital medicine programs? These findings and many more interesting and useful pieces of data are available in the full COVID-19 Addendum. Perhaps my biggest takeaway is that hospitalists have been perhaps the most uniquely positioned specialty to tackle the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic. We have always been a dynamic, changing field, ready to lead and tackle change – and while change may have happened more quickly and in ways that were unforeseen just a year ago, hospitalists have undoubtedly demonstrated their strengths as leaders ready to adapt and rise to the occasion.
I am optimistic that, as we move beyond the pandemic in the coming months and years, the value that hospitalists have proven yet again will yield long-term recognition and benefits to our programs and our specialty.
Dr. Huang is a physician adviser and clinical professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
Staffing was a challenge for most groups
Staffing was a challenge for most groups
What a year it has been in the world of hospital medicine with all the changes, challenges, and uncertainties surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic. Some hospitalist programs were hit hard early on with an early surge, when little was known about COVID-19, and other programs have had more time to plan and adapt to later surges.
As many readers of The Hospitalist know, the Society of Hospital Medicine publishes a biennial State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report – last published in September 2020 using data from 2019. The SoHM Report contains a wealth of information that many groups find useful in evaluating their programs, with topics ranging from compensation to staffing to scheduling. As some prior months’ Survey Insights columns have alluded to, with the rapid pace of change in 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Society of Hospital Medicine made the decision to publish an addendum highlighting the myriad of adjustments and adaptations that have occurred in such a short period of time. The COVID-19 Addendum is available to all purchasers of the SoHM Report and contains data from survey responses submitted in September 2020.
Let’s take a look at what transpired in 2020, starting with staffing – no doubt a challenge for many groups. During some periods of time, patient volumes may have fallen below historical averages with stay-at-home orders, canceled procedures, and a reluctance by patients to seek medical care. In contrast, for many groups, other parts of the year were all-hands-on-deck scenarios to care for extraordinary surges in patient volume. To compound this, many hospitalist groups had physicians and staff facing quarantine or isolation requirements because of exposures or contracting COVID-19, and locums positions may have been difficult to fill because of travel restrictions and extreme demand.
What operational changes were made in response to these staffing challenges? Perhaps one notable finding from the COVID-19 Addendum was the need for contingency planning and backup systems. From the 2020 SoHM, prior to the pandemic, 47.4% of adult hospital medicine groups had backup systems in place. In our recently published addendum, we found that 61.9% of groups instituted a backup system where none previously existed. In addition, 54.2% of groups modified their existing backup system. Some 39.6% of hospital medicine groups also utilized clinicians from other service lines to help cover service needs.
Aside from staffing, hospitals faced unprecedented financial challenges, and these effects rippled through to hospitalists. Our addendum found that 42.0% of hospitalist groups faced reductions in salary or bonuses, and 35.5% of hospital medicine groups reduced provider compensation by a reduction of work hours or shifts. I’ve personally been struck by these findings – that many hospitalists at the front-lines of COVID-19 received salary reductions, albeit temporary for many groups, during one of the most challenging years of their professional careers. Our addendum, interestingly, also found that a smaller 10.7% of groups instituted hazard pay for clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients.
So, are the changes and challenges your group faced similar to what was experienced by other hospital medicine programs? These findings and many more interesting and useful pieces of data are available in the full COVID-19 Addendum. Perhaps my biggest takeaway is that hospitalists have been perhaps the most uniquely positioned specialty to tackle the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic. We have always been a dynamic, changing field, ready to lead and tackle change – and while change may have happened more quickly and in ways that were unforeseen just a year ago, hospitalists have undoubtedly demonstrated their strengths as leaders ready to adapt and rise to the occasion.
I am optimistic that, as we move beyond the pandemic in the coming months and years, the value that hospitalists have proven yet again will yield long-term recognition and benefits to our programs and our specialty.
Dr. Huang is a physician adviser and clinical professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
What a year it has been in the world of hospital medicine with all the changes, challenges, and uncertainties surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic. Some hospitalist programs were hit hard early on with an early surge, when little was known about COVID-19, and other programs have had more time to plan and adapt to later surges.
As many readers of The Hospitalist know, the Society of Hospital Medicine publishes a biennial State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report – last published in September 2020 using data from 2019. The SoHM Report contains a wealth of information that many groups find useful in evaluating their programs, with topics ranging from compensation to staffing to scheduling. As some prior months’ Survey Insights columns have alluded to, with the rapid pace of change in 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Society of Hospital Medicine made the decision to publish an addendum highlighting the myriad of adjustments and adaptations that have occurred in such a short period of time. The COVID-19 Addendum is available to all purchasers of the SoHM Report and contains data from survey responses submitted in September 2020.
Let’s take a look at what transpired in 2020, starting with staffing – no doubt a challenge for many groups. During some periods of time, patient volumes may have fallen below historical averages with stay-at-home orders, canceled procedures, and a reluctance by patients to seek medical care. In contrast, for many groups, other parts of the year were all-hands-on-deck scenarios to care for extraordinary surges in patient volume. To compound this, many hospitalist groups had physicians and staff facing quarantine or isolation requirements because of exposures or contracting COVID-19, and locums positions may have been difficult to fill because of travel restrictions and extreme demand.
What operational changes were made in response to these staffing challenges? Perhaps one notable finding from the COVID-19 Addendum was the need for contingency planning and backup systems. From the 2020 SoHM, prior to the pandemic, 47.4% of adult hospital medicine groups had backup systems in place. In our recently published addendum, we found that 61.9% of groups instituted a backup system where none previously existed. In addition, 54.2% of groups modified their existing backup system. Some 39.6% of hospital medicine groups also utilized clinicians from other service lines to help cover service needs.
Aside from staffing, hospitals faced unprecedented financial challenges, and these effects rippled through to hospitalists. Our addendum found that 42.0% of hospitalist groups faced reductions in salary or bonuses, and 35.5% of hospital medicine groups reduced provider compensation by a reduction of work hours or shifts. I’ve personally been struck by these findings – that many hospitalists at the front-lines of COVID-19 received salary reductions, albeit temporary for many groups, during one of the most challenging years of their professional careers. Our addendum, interestingly, also found that a smaller 10.7% of groups instituted hazard pay for clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients.
So, are the changes and challenges your group faced similar to what was experienced by other hospital medicine programs? These findings and many more interesting and useful pieces of data are available in the full COVID-19 Addendum. Perhaps my biggest takeaway is that hospitalists have been perhaps the most uniquely positioned specialty to tackle the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic. We have always been a dynamic, changing field, ready to lead and tackle change – and while change may have happened more quickly and in ways that were unforeseen just a year ago, hospitalists have undoubtedly demonstrated their strengths as leaders ready to adapt and rise to the occasion.
I am optimistic that, as we move beyond the pandemic in the coming months and years, the value that hospitalists have proven yet again will yield long-term recognition and benefits to our programs and our specialty.
Dr. Huang is a physician adviser and clinical professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
How I got started in advocacy
Rheumatology News and the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations have partnered together to keep rheumatologists regularly informed on the advocacy issues of the day and perhaps inspire those who may be on the fence about finding “room” in their lives for action. This inaugural piece tells how CSRO President Dr. Madelaine (Mattie) A. Feldman views advocacy and how she found her way to action.
As a rheumatologist in private practice for 30 years, with husband and kids (and now grandkids), an active social life, and an exercise regimen, I realized if I were to become active in advocacy I would have to make room for it in my busy schedule. We all come up against the question of where will we find the time for a new hobby, exercise, joining a new organization, or even just eating right? Next comes the priority list discussion. How important is advocacy for my patients, my specialty, and my profession? Ultimately, how important is it for me? Where did that desire to get involved even come from? Why have I become so passionate about the issues?
For me, the answer to these questions goes back to the 1960s when I was growing up in New Orleans. My mom participated in civil rights protests, which did not make our family popular in the neighborhood, back when the KKK put flyers on everyone’s screen door. My mother didn’t care and told me that, no matter what people said, it was our duty to stand up for what was right. That was a long time ago and sadly my mom passed away just a year after I was old enough to vote. Her words have stayed with me and are more important now than ever.
Striving for justice despite how formidable the foe is requires an inner knowing that what you are doing is meaningful and will make a difference maybe not now, maybe not next year. At some point you must believe that your efforts will create a change for the better, small as it may be. My “saying” on Twitter (@MattieRheumMD) is “I’ll keep doing what I’m doing until my cynicism catches up to my passion.”
The story about my mom is just one of the many stories in my life taking me to where I am today. We all have them. I think the reason many of us go into rheumatology may be similar to the reasoning that leads one to advocacy efforts. At this point in time we can’t yet offer a cure, but we can point to a path that leads to improvements in the lives of our patients. I have to remind myself of that, every time there is an advocacy battle ahead, whether with insurance companies or the government ... increments are important.
The four Ps of advocacy
Living with compromise is hard, particularly when working within a system that needs a complete overhaul. Still, compromise is the key to getting anything done. Compromise is one of the four Ps of advocacy. I realize that compromise doesn’t start with a P, but it is such an integral part of advocacy, I am making allowances for it. The other Ps include patience, persistence/perseverance, and passion. I’m sure there are many others that could be part of the P family, like planning and performance, but let’s stick with these.
You don’t need to have all of these qualities when you start on the road to action in advocacy. For example, my passion came first. It developed when my patients could not get access to the treatments they needed. For many reasons, the medications were either unavailable (i.e., not on formulary, tiered very high) or unaffordable (i.e., copay too high, deductible too high). My passion deepened when I saw the hypocrisy within the drug-supply channel and the mistruths being told by those who profit from this channel. It wasn’t the “profit” part that bothered me, as I’m a believer in the free market. But this was not free market, and the companies were actually profiteering on the backs of my patients and justifying it by claiming they were saving the health care system billions of dollars. The fallacy of that claim and the players in this broken system are stories for another day.
Persistence came next for me. If you let up on the message, things might not only stay the same but could get worse. Perseverance is part of persistence because you need it to keep knocking on the same door even after that door is metaphorically (hopefully not literally) slammed in your face. Often, I will feel like a broken record and think that everyone has already heard the issues, not only from me but also from my fellow advocates. But never underestimate how many times a message, particularly on a difficult issue to understand, needs to be heard before it is fully comprehended.
Patience is one of the more difficult attributes to practice when you want action. I want things to happen yesterday – not tomorrow and definitely not next year. I have learned that the wheels of change turn quite slowly in this arena, sometimes pausing for inordinately long periods of time. I realize now that during the long wait, new facts can arise, allowing me to shape a different advocacy approach, one that ultimately bolsters my case. It still is very difficult to hear that a piece of legislation that seemed to be moving forward suddenly died and won’t be heard again until the next session. With patience you move forward with a smile, maybe a half-hearted one, but a smile nonetheless. This just makes life better.
Then there is compromise. This took me the longest to understand, particularly on the issues where my passion ran the deepest. Here is where passion could potentially get in the way of action. Feeling very strongly about an issue makes it difficult to let any piece of your ideal end result fall by the wayside. Here is where the saying “the perfect is the enemy of the good” comes into play. Just because you can’t have it all, doesn’t mean you can’t do good by achieving just part of what you have been striving for. Remember if you seek perfection, without compromise, you may lose the entire battle. Is there such a thing as compromising too much? I think so, but that may just be my passion speaking.
Rheumatology News and the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations started this column to keep you informed about current advocacy issues in rheumatology and perhaps inspire those who may be on the fence about finding “room” in their lives for action.
Advocacy doesn’t have to take up much room in your life. It can be as simple as clicking on CSRO.info/map, finding your state, and taking action by writing a letter to your representative on an important piece of legislation, like an accumulator adjustment ban (lots more on that in future columns). Or maybe just finding the time to read this column is all the action you have room for. We all have different amounts of space for any particular activity in our busy lives. It seems one of my stories from childhood created that space for advocacy in my life. I guess you could say it created a “Rheum” for Action.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is President of the CSRO, chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines, and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
Rheumatology News and the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations have partnered together to keep rheumatologists regularly informed on the advocacy issues of the day and perhaps inspire those who may be on the fence about finding “room” in their lives for action. This inaugural piece tells how CSRO President Dr. Madelaine (Mattie) A. Feldman views advocacy and how she found her way to action.
As a rheumatologist in private practice for 30 years, with husband and kids (and now grandkids), an active social life, and an exercise regimen, I realized if I were to become active in advocacy I would have to make room for it in my busy schedule. We all come up against the question of where will we find the time for a new hobby, exercise, joining a new organization, or even just eating right? Next comes the priority list discussion. How important is advocacy for my patients, my specialty, and my profession? Ultimately, how important is it for me? Where did that desire to get involved even come from? Why have I become so passionate about the issues?
For me, the answer to these questions goes back to the 1960s when I was growing up in New Orleans. My mom participated in civil rights protests, which did not make our family popular in the neighborhood, back when the KKK put flyers on everyone’s screen door. My mother didn’t care and told me that, no matter what people said, it was our duty to stand up for what was right. That was a long time ago and sadly my mom passed away just a year after I was old enough to vote. Her words have stayed with me and are more important now than ever.
Striving for justice despite how formidable the foe is requires an inner knowing that what you are doing is meaningful and will make a difference maybe not now, maybe not next year. At some point you must believe that your efforts will create a change for the better, small as it may be. My “saying” on Twitter (@MattieRheumMD) is “I’ll keep doing what I’m doing until my cynicism catches up to my passion.”
The story about my mom is just one of the many stories in my life taking me to where I am today. We all have them. I think the reason many of us go into rheumatology may be similar to the reasoning that leads one to advocacy efforts. At this point in time we can’t yet offer a cure, but we can point to a path that leads to improvements in the lives of our patients. I have to remind myself of that, every time there is an advocacy battle ahead, whether with insurance companies or the government ... increments are important.
The four Ps of advocacy
Living with compromise is hard, particularly when working within a system that needs a complete overhaul. Still, compromise is the key to getting anything done. Compromise is one of the four Ps of advocacy. I realize that compromise doesn’t start with a P, but it is such an integral part of advocacy, I am making allowances for it. The other Ps include patience, persistence/perseverance, and passion. I’m sure there are many others that could be part of the P family, like planning and performance, but let’s stick with these.
You don’t need to have all of these qualities when you start on the road to action in advocacy. For example, my passion came first. It developed when my patients could not get access to the treatments they needed. For many reasons, the medications were either unavailable (i.e., not on formulary, tiered very high) or unaffordable (i.e., copay too high, deductible too high). My passion deepened when I saw the hypocrisy within the drug-supply channel and the mistruths being told by those who profit from this channel. It wasn’t the “profit” part that bothered me, as I’m a believer in the free market. But this was not free market, and the companies were actually profiteering on the backs of my patients and justifying it by claiming they were saving the health care system billions of dollars. The fallacy of that claim and the players in this broken system are stories for another day.
Persistence came next for me. If you let up on the message, things might not only stay the same but could get worse. Perseverance is part of persistence because you need it to keep knocking on the same door even after that door is metaphorically (hopefully not literally) slammed in your face. Often, I will feel like a broken record and think that everyone has already heard the issues, not only from me but also from my fellow advocates. But never underestimate how many times a message, particularly on a difficult issue to understand, needs to be heard before it is fully comprehended.
Patience is one of the more difficult attributes to practice when you want action. I want things to happen yesterday – not tomorrow and definitely not next year. I have learned that the wheels of change turn quite slowly in this arena, sometimes pausing for inordinately long periods of time. I realize now that during the long wait, new facts can arise, allowing me to shape a different advocacy approach, one that ultimately bolsters my case. It still is very difficult to hear that a piece of legislation that seemed to be moving forward suddenly died and won’t be heard again until the next session. With patience you move forward with a smile, maybe a half-hearted one, but a smile nonetheless. This just makes life better.
Then there is compromise. This took me the longest to understand, particularly on the issues where my passion ran the deepest. Here is where passion could potentially get in the way of action. Feeling very strongly about an issue makes it difficult to let any piece of your ideal end result fall by the wayside. Here is where the saying “the perfect is the enemy of the good” comes into play. Just because you can’t have it all, doesn’t mean you can’t do good by achieving just part of what you have been striving for. Remember if you seek perfection, without compromise, you may lose the entire battle. Is there such a thing as compromising too much? I think so, but that may just be my passion speaking.
Rheumatology News and the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations started this column to keep you informed about current advocacy issues in rheumatology and perhaps inspire those who may be on the fence about finding “room” in their lives for action.
Advocacy doesn’t have to take up much room in your life. It can be as simple as clicking on CSRO.info/map, finding your state, and taking action by writing a letter to your representative on an important piece of legislation, like an accumulator adjustment ban (lots more on that in future columns). Or maybe just finding the time to read this column is all the action you have room for. We all have different amounts of space for any particular activity in our busy lives. It seems one of my stories from childhood created that space for advocacy in my life. I guess you could say it created a “Rheum” for Action.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is President of the CSRO, chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines, and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
Rheumatology News and the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations have partnered together to keep rheumatologists regularly informed on the advocacy issues of the day and perhaps inspire those who may be on the fence about finding “room” in their lives for action. This inaugural piece tells how CSRO President Dr. Madelaine (Mattie) A. Feldman views advocacy and how she found her way to action.
As a rheumatologist in private practice for 30 years, with husband and kids (and now grandkids), an active social life, and an exercise regimen, I realized if I were to become active in advocacy I would have to make room for it in my busy schedule. We all come up against the question of where will we find the time for a new hobby, exercise, joining a new organization, or even just eating right? Next comes the priority list discussion. How important is advocacy for my patients, my specialty, and my profession? Ultimately, how important is it for me? Where did that desire to get involved even come from? Why have I become so passionate about the issues?
For me, the answer to these questions goes back to the 1960s when I was growing up in New Orleans. My mom participated in civil rights protests, which did not make our family popular in the neighborhood, back when the KKK put flyers on everyone’s screen door. My mother didn’t care and told me that, no matter what people said, it was our duty to stand up for what was right. That was a long time ago and sadly my mom passed away just a year after I was old enough to vote. Her words have stayed with me and are more important now than ever.
Striving for justice despite how formidable the foe is requires an inner knowing that what you are doing is meaningful and will make a difference maybe not now, maybe not next year. At some point you must believe that your efforts will create a change for the better, small as it may be. My “saying” on Twitter (@MattieRheumMD) is “I’ll keep doing what I’m doing until my cynicism catches up to my passion.”
The story about my mom is just one of the many stories in my life taking me to where I am today. We all have them. I think the reason many of us go into rheumatology may be similar to the reasoning that leads one to advocacy efforts. At this point in time we can’t yet offer a cure, but we can point to a path that leads to improvements in the lives of our patients. I have to remind myself of that, every time there is an advocacy battle ahead, whether with insurance companies or the government ... increments are important.
The four Ps of advocacy
Living with compromise is hard, particularly when working within a system that needs a complete overhaul. Still, compromise is the key to getting anything done. Compromise is one of the four Ps of advocacy. I realize that compromise doesn’t start with a P, but it is such an integral part of advocacy, I am making allowances for it. The other Ps include patience, persistence/perseverance, and passion. I’m sure there are many others that could be part of the P family, like planning and performance, but let’s stick with these.
You don’t need to have all of these qualities when you start on the road to action in advocacy. For example, my passion came first. It developed when my patients could not get access to the treatments they needed. For many reasons, the medications were either unavailable (i.e., not on formulary, tiered very high) or unaffordable (i.e., copay too high, deductible too high). My passion deepened when I saw the hypocrisy within the drug-supply channel and the mistruths being told by those who profit from this channel. It wasn’t the “profit” part that bothered me, as I’m a believer in the free market. But this was not free market, and the companies were actually profiteering on the backs of my patients and justifying it by claiming they were saving the health care system billions of dollars. The fallacy of that claim and the players in this broken system are stories for another day.
Persistence came next for me. If you let up on the message, things might not only stay the same but could get worse. Perseverance is part of persistence because you need it to keep knocking on the same door even after that door is metaphorically (hopefully not literally) slammed in your face. Often, I will feel like a broken record and think that everyone has already heard the issues, not only from me but also from my fellow advocates. But never underestimate how many times a message, particularly on a difficult issue to understand, needs to be heard before it is fully comprehended.
Patience is one of the more difficult attributes to practice when you want action. I want things to happen yesterday – not tomorrow and definitely not next year. I have learned that the wheels of change turn quite slowly in this arena, sometimes pausing for inordinately long periods of time. I realize now that during the long wait, new facts can arise, allowing me to shape a different advocacy approach, one that ultimately bolsters my case. It still is very difficult to hear that a piece of legislation that seemed to be moving forward suddenly died and won’t be heard again until the next session. With patience you move forward with a smile, maybe a half-hearted one, but a smile nonetheless. This just makes life better.
Then there is compromise. This took me the longest to understand, particularly on the issues where my passion ran the deepest. Here is where passion could potentially get in the way of action. Feeling very strongly about an issue makes it difficult to let any piece of your ideal end result fall by the wayside. Here is where the saying “the perfect is the enemy of the good” comes into play. Just because you can’t have it all, doesn’t mean you can’t do good by achieving just part of what you have been striving for. Remember if you seek perfection, without compromise, you may lose the entire battle. Is there such a thing as compromising too much? I think so, but that may just be my passion speaking.
Rheumatology News and the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations started this column to keep you informed about current advocacy issues in rheumatology and perhaps inspire those who may be on the fence about finding “room” in their lives for action.
Advocacy doesn’t have to take up much room in your life. It can be as simple as clicking on CSRO.info/map, finding your state, and taking action by writing a letter to your representative on an important piece of legislation, like an accumulator adjustment ban (lots more on that in future columns). Or maybe just finding the time to read this column is all the action you have room for. We all have different amounts of space for any particular activity in our busy lives. It seems one of my stories from childhood created that space for advocacy in my life. I guess you could say it created a “Rheum” for Action.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is President of the CSRO, chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines, and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].