User login
Hair Repigmentation as a Melanoma Warning Sign
To the Editor:
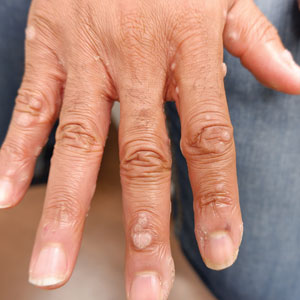
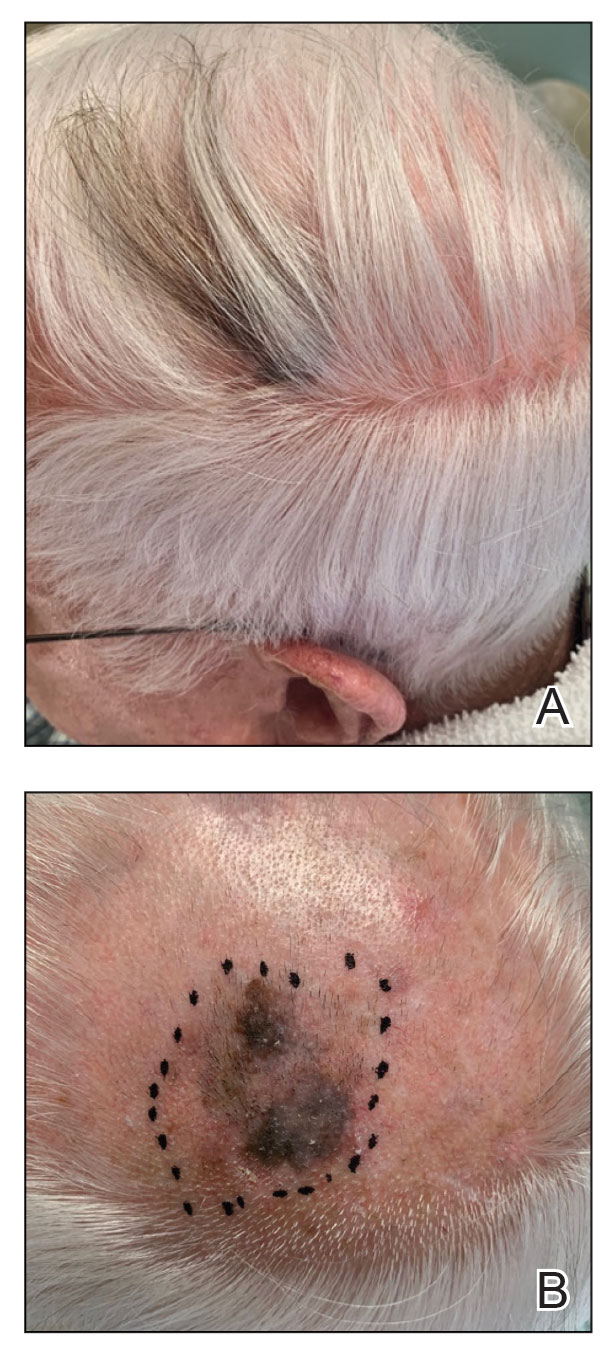
An 85-year-old man with a history of hypertension and chronic kidney disease presented with a localized darkening patch of hair on the left parietal scalp that had progressed over the last 7 years (Figure 1A). He had no prior history of skin cancer. Physical examination revealed the remainder of the hair was gray. There was an irregularly pigmented plaque on the skin underlying the darkened hair measuring 5.0 cm in diameter that was confirmed to be melanoma (Figure 1B). He underwent a staged excision to remove the lesion. The surgical defect was closed via a 5.0×6.0-cm full-thickness skin graft.
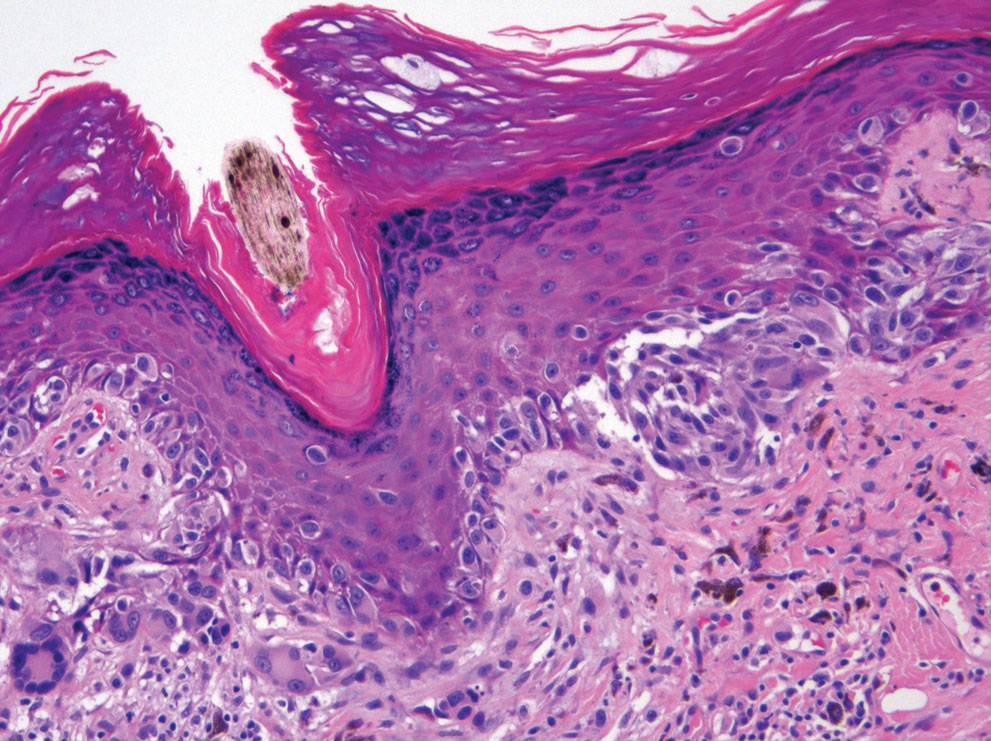
The initial biopsy showed melanoma in situ. However, the final pathology report following the excision revealed an invasive melanoma with a Breslow depth of 1.0 mm (Clark level IV; American Joint Committee on Cancer T1b).1 Histopathology showed pigment deposition with surrounding deep follicular extension of melanoma (Figure 2).
The patient declined a sentinel lymph node biopsy and agreed to a genetic profile assessment.2 The results of the test identified the patient had a low probability of a positive sentinel lymph node and the lowest risk of melanoma recurrence within 5 years. The patient was clear of disease at 12-month follow-up.
Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms hair repigmentation and melanoma, there have been 11 other reported cases of hair repigmentation associated with melanoma (Table).3-13 It initially was suspected that this rare phenomenon primarily existed in the female population, as the first 5 cases were reported solely in females,3-7 possibly due to the prevalence of androgenetic alopecia in males.11 However, 6 cases of repigmentation associated with melanoma were later reported in males8-13; our patient represents an additional reported case in a male. It is unknown if there is a higher prevalence of this phenomenon among males or females.

Most previously reported cases of repigmentation were associated with melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type. Repigmentation also has been reported in malignant melanoma, as documented in our patient, as well as desmoplastic and amelanotic melanoma.5,6 In every case, the color of the repigmentation was darker than the rest of the patient’s hair; however, the repigmentation color can be different from the patient’s original hair color from their youth.4,5,11
The exact mechanism responsible for hair repigmentation in the setting of melanoma is unclear. It has been speculated from prior cases that repigmentation may be caused by paracrine stimulation from melanoma cells activating adjacent benign hair follicle melanocytes to produce melanin.7,14,15 This process likely is due to cytokines or growth factors, such as c-kit ligand.14,15 Several neural and immune networks and mediators activate the receptor tyrosine kinase KIT, which is thought to play a role in activating melanogenesis within the hair bulb.14 These signals also could originate from changes in the microenvironment instead of the melanoma cells themselves.6 Another possible mechanism is that repigmentation was caused by melanin-producing malignant melanocytes.4
Because this phenomenon typically occurs in older patients, the cause of repigmentation also could be related to chronic sun damage, which may result in upregulation of stem cell factor and α-melanocyte–stimulating hormone, as well as other molecules associated with melanogenesis, such as c-KIT receptor and tyrosinase.15,16 Upregulation of these molecules can lead to an increased number of melanocytes within the hair bulb. In addition, UVA and narrowband UVB have been recognized as major players in melanocyte stimulation. Phototherapy with UVA or narrowband UVB has been used for repigmentation in vitiligo patients.17
In cases without invasion of hair follicles by malignant cells, repigmentation more likely results from external signals stimulating benign bulbar melanocytes to produce melanin rather than melanoma cell growth extending into the hair bulb.6 In these cases, there is an increase in the number of hair bulbar melanocytes with a lack of malignant morphology in the hair bulb.8 If the signals are directly from melanoma cells in the hair bulb, it is unknown how the malignant cells upregulated melanogenesis in adjacent benign melanocytes or which specific signals required for normal pigmentation were involved in these repigmentation cases.6
Use of medications was ruled out as an underlying cause of the repigmentation in our patient. Drug-related repigmentation of the hair typically is observed in a diffuse generalized pattern. In our case, the repigmentation was localized to the area of the underlying dark patch, and the patient was not on any medications that could cause hair hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation has been associated with acitretin, lenalidomide, corticosteroids, erlotinib, latanoprost, verapamil, tamoxifen, levodopa, thalidomide, PD-1 inhibitors, and tumor necrosis α inhibitors.18-30 Repigmentation also has been reported after local radiotherapy and herpes zoster infection.31,32
The underlying melanoma in our patient was removed by staged square excision. Excision was the treatment of choice for most similar reported cases. Radiotherapy was utilized in two different cases.3,4 In one case, radiotherapy was successfully used to treat melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type; the patient’s hair grew back to its original color, which suggests that normal hair physiology was restored once melanoma cells were eliminated.3 One reported case demonstrated successful treatment of lentigo maligna type–melanoma with imiquimod cream 5% applied 6 times weekly for 9 months with a positive cosmetic result.9 The exact mechanism of imiquimod is not fully understood. Imiquimod induces cytokines to stimulate the production of IFN-α via activation of toll-like receptor 7.33 There was complete clearing of the lesion as well as the hair pigmentation,9 which suggests that the treatment also eliminated deeper cells influencing pigmentation. A case of malignant amelanotic melanoma was successfully treated with anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), with no recurrence at 12 months. Pembrolizumab acts as an immune checkpoint inhibitor by binding to the PD-1 receptor and allowing the immune system to recognize and attack melanoma cells. After 5 doses of pembrolizumab, the patient was clear of disease and his hair color returned to gray.5
In 2022, melanoma was estimated to be the fifth most commonly diagnosed cancer among men and women in the United States.34 Early melanoma detection is a critical factor in achieving positive patient outcomes. Hair repigmentation is a potentially serious phenomenon that warrants a physician visit. Melanoma lesions under the hair may be overlooked because of limited visibility. Physicians must inspect spontaneous hair repigmentation with high suspicion and interpret the change as a possible indirect result of melanoma. Overall, it is important to increase public awareness of regular skin checks and melanoma warning signs.
- Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA, Hess KR, et al. Melanoma staging: evidence‐based changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:472-492.
- Vetto JT, Hsueh EC, Gastman BR, et al. Guidance of sentinel lymph node biopsy decisions in patients with T1–T2 melanoma using gene expression profiling. Futur Oncol. 2019;15:1207-1217.
- Dummer R. Hair repigmentation in lentigo maligna. Lancet. 2001;357:598.
- Inzinger M, Massone C, Arzberger E, et al. Hair repigmentation in melanoma. Lancet. 2013;382:1224.
- Rahim RR, Husain A, Tobin DJ, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma presenting with localized hair repigmentation. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1371-1373.
- Tiger JB, Habeshian KA, Barton DT, et al. Repigmentation of hair associated with melanoma in situ of scalp. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E144-E145.
- Amann VC, Dummer R. Localized hair repigmentation in a 91-year-old woman. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:81-82.
- Chan C, Magro CM, Pham AK, et al. Spontaneous hair repigmentation in an 80-year-old man: a case of melanoma-associated hair repigmentation and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:671-674.
- Lackey AE, Glassman G, Grichnik J, et al. Repigmentation of gray hairs with lentigo maligna and response to topical imiquimod. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:1015-1017.
- Chew T, Pannell M, Jeeves A. Focal hair re-pigmentation associated with melanoma of the scalp. ANZ J Surg. 2019;90:1175-1176.
- López-Sánchez C, Collgros H. Hair repigmentation as a clue for scalp melanoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;61:179-180.
- Gessler J, Tejasvi T, Bresler SC. Repigmentation of scalp hair: a feature of early melanoma. Am J Med. 2023;136:E7-E8.
- Hasegawa T, Iino S, Kitakaze K, et al. Repigmentation of aging gray hair associated with unrecognized development and progression of amelanotic melanoma of the scalp: a physiological alert underlying hair rejuvenation. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E281-E283. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.15881
- D’Mello SAN, Finlay GJ, Baguley BC, et al. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1144.
- Hachiya A, Kobayashi A, Ohuchi A, et al. The paracrine role of stem cell factor/c-kit signaling in the activation of human melanocytes in ultraviolet-B-induced pigmentation. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:578-586.
- Slominski A, Wortsman J, Plonka PM, et al. Hair follicle pigmentation. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:13-21.
- Falabella R. Vitiligo and the melanocyte reservoir. Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54:313.
- Seckin D, Yildiz A. Repigmentation and curling of hair after acitretin therapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2009;50:214-216.
- Dasanu CA, Mitsis D, Alexandrescu DT. Hair repigmentation associated with the use of lenalidomide: graying may not be an irreversible process! J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2013;19:165-169.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AI, Lowe PM. Hair repigmentation with anti–PD-1 and anti–PD-L1 immunotherapy: a novel hypothesis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:112-113. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4420
- Tintle SJ, Dabade TS, Kalish RA, et al. Repigmentation of hair following adalimumab therapy. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6fn0t1xz.
- Penzi LR, Manatis-Lornell A, Saavedra A, et al. Hair repigmentation associated with the use of brentuximab. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:563-565.
- Khaled A, Trojjets S, Zeglaoui F, et al. Repigmentation of the white hair after systemic corticosteroids for bullous pemphigoid. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2008;22:1018-1020.
- Cheng YP, Chen HJ, Chiu HC. Erlotinib-induced hair repigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E55-E57.
- Bellandi S, Amato L, Cipollini EM, et al. Repigmentation of hair after latanoprost therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2011;25:1485-1487.
- Read GM. Verapamil and hair colour change. Lancet. 1991;338:1520.
- Hampson JP, Donnelly A, Lewis‐Jones MS, et al. Tamoxifen‐induced hair colour change. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:483-484.
- Reynolds NJ, Crossley J, Ferguson I, et al. Darkening of white hair in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1989;14:317-318.
- Lovering S, Miao W, Bailie T, et al. Hair repigmentation associated with thalidomide use for the treatment of multiple myeloma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016215521.
- Rivera N, Boada A, Bielsa MI, et al. Hair repigmentation during immunotherapy treatment with an anti–programmed cell death 1 and anti–programmed cell death ligand 1 agent for lung cancer. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1162-1165.
- Prasad S, Dougheney N, Hong A. Scalp hair repigmentation in the penumbral region of radiotherapy–a case series. Int J Radiol Radiat Ther. 2020;7:151-157.
- Adiga GU, Rehman KL, Wiernik PH. Permanent localized hair repigmentation following herpes zoster infection. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:569-570.
- Hanna E, Abadi R, Abbas O. Imiquimod in dermatology: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:831-844.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7-33.
To the Editor:
An 85-year-old man with a history of hypertension and chronic kidney disease presented with a localized darkening patch of hair on the left parietal scalp that had progressed over the last 7 years (Figure 1A). He had no prior history of skin cancer. Physical examination revealed the remainder of the hair was gray. There was an irregularly pigmented plaque on the skin underlying the darkened hair measuring 5.0 cm in diameter that was confirmed to be melanoma (Figure 1B). He underwent a staged excision to remove the lesion. The surgical defect was closed via a 5.0×6.0-cm full-thickness skin graft.

The initial biopsy showed melanoma in situ. However, the final pathology report following the excision revealed an invasive melanoma with a Breslow depth of 1.0 mm (Clark level IV; American Joint Committee on Cancer T1b).1 Histopathology showed pigment deposition with surrounding deep follicular extension of melanoma (Figure 2).

The patient declined a sentinel lymph node biopsy and agreed to a genetic profile assessment.2 The results of the test identified the patient had a low probability of a positive sentinel lymph node and the lowest risk of melanoma recurrence within 5 years. The patient was clear of disease at 12-month follow-up.
Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms hair repigmentation and melanoma, there have been 11 other reported cases of hair repigmentation associated with melanoma (Table).3-13 It initially was suspected that this rare phenomenon primarily existed in the female population, as the first 5 cases were reported solely in females,3-7 possibly due to the prevalence of androgenetic alopecia in males.11 However, 6 cases of repigmentation associated with melanoma were later reported in males8-13; our patient represents an additional reported case in a male. It is unknown if there is a higher prevalence of this phenomenon among males or females.

Most previously reported cases of repigmentation were associated with melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type. Repigmentation also has been reported in malignant melanoma, as documented in our patient, as well as desmoplastic and amelanotic melanoma.5,6 In every case, the color of the repigmentation was darker than the rest of the patient’s hair; however, the repigmentation color can be different from the patient’s original hair color from their youth.4,5,11
The exact mechanism responsible for hair repigmentation in the setting of melanoma is unclear. It has been speculated from prior cases that repigmentation may be caused by paracrine stimulation from melanoma cells activating adjacent benign hair follicle melanocytes to produce melanin.7,14,15 This process likely is due to cytokines or growth factors, such as c-kit ligand.14,15 Several neural and immune networks and mediators activate the receptor tyrosine kinase KIT, which is thought to play a role in activating melanogenesis within the hair bulb.14 These signals also could originate from changes in the microenvironment instead of the melanoma cells themselves.6 Another possible mechanism is that repigmentation was caused by melanin-producing malignant melanocytes.4
Because this phenomenon typically occurs in older patients, the cause of repigmentation also could be related to chronic sun damage, which may result in upregulation of stem cell factor and α-melanocyte–stimulating hormone, as well as other molecules associated with melanogenesis, such as c-KIT receptor and tyrosinase.15,16 Upregulation of these molecules can lead to an increased number of melanocytes within the hair bulb. In addition, UVA and narrowband UVB have been recognized as major players in melanocyte stimulation. Phototherapy with UVA or narrowband UVB has been used for repigmentation in vitiligo patients.17
In cases without invasion of hair follicles by malignant cells, repigmentation more likely results from external signals stimulating benign bulbar melanocytes to produce melanin rather than melanoma cell growth extending into the hair bulb.6 In these cases, there is an increase in the number of hair bulbar melanocytes with a lack of malignant morphology in the hair bulb.8 If the signals are directly from melanoma cells in the hair bulb, it is unknown how the malignant cells upregulated melanogenesis in adjacent benign melanocytes or which specific signals required for normal pigmentation were involved in these repigmentation cases.6
Use of medications was ruled out as an underlying cause of the repigmentation in our patient. Drug-related repigmentation of the hair typically is observed in a diffuse generalized pattern. In our case, the repigmentation was localized to the area of the underlying dark patch, and the patient was not on any medications that could cause hair hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation has been associated with acitretin, lenalidomide, corticosteroids, erlotinib, latanoprost, verapamil, tamoxifen, levodopa, thalidomide, PD-1 inhibitors, and tumor necrosis α inhibitors.18-30 Repigmentation also has been reported after local radiotherapy and herpes zoster infection.31,32
The underlying melanoma in our patient was removed by staged square excision. Excision was the treatment of choice for most similar reported cases. Radiotherapy was utilized in two different cases.3,4 In one case, radiotherapy was successfully used to treat melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type; the patient’s hair grew back to its original color, which suggests that normal hair physiology was restored once melanoma cells were eliminated.3 One reported case demonstrated successful treatment of lentigo maligna type–melanoma with imiquimod cream 5% applied 6 times weekly for 9 months with a positive cosmetic result.9 The exact mechanism of imiquimod is not fully understood. Imiquimod induces cytokines to stimulate the production of IFN-α via activation of toll-like receptor 7.33 There was complete clearing of the lesion as well as the hair pigmentation,9 which suggests that the treatment also eliminated deeper cells influencing pigmentation. A case of malignant amelanotic melanoma was successfully treated with anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), with no recurrence at 12 months. Pembrolizumab acts as an immune checkpoint inhibitor by binding to the PD-1 receptor and allowing the immune system to recognize and attack melanoma cells. After 5 doses of pembrolizumab, the patient was clear of disease and his hair color returned to gray.5
In 2022, melanoma was estimated to be the fifth most commonly diagnosed cancer among men and women in the United States.34 Early melanoma detection is a critical factor in achieving positive patient outcomes. Hair repigmentation is a potentially serious phenomenon that warrants a physician visit. Melanoma lesions under the hair may be overlooked because of limited visibility. Physicians must inspect spontaneous hair repigmentation with high suspicion and interpret the change as a possible indirect result of melanoma. Overall, it is important to increase public awareness of regular skin checks and melanoma warning signs.
To the Editor:
An 85-year-old man with a history of hypertension and chronic kidney disease presented with a localized darkening patch of hair on the left parietal scalp that had progressed over the last 7 years (Figure 1A). He had no prior history of skin cancer. Physical examination revealed the remainder of the hair was gray. There was an irregularly pigmented plaque on the skin underlying the darkened hair measuring 5.0 cm in diameter that was confirmed to be melanoma (Figure 1B). He underwent a staged excision to remove the lesion. The surgical defect was closed via a 5.0×6.0-cm full-thickness skin graft.

The initial biopsy showed melanoma in situ. However, the final pathology report following the excision revealed an invasive melanoma with a Breslow depth of 1.0 mm (Clark level IV; American Joint Committee on Cancer T1b).1 Histopathology showed pigment deposition with surrounding deep follicular extension of melanoma (Figure 2).

The patient declined a sentinel lymph node biopsy and agreed to a genetic profile assessment.2 The results of the test identified the patient had a low probability of a positive sentinel lymph node and the lowest risk of melanoma recurrence within 5 years. The patient was clear of disease at 12-month follow-up.
Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms hair repigmentation and melanoma, there have been 11 other reported cases of hair repigmentation associated with melanoma (Table).3-13 It initially was suspected that this rare phenomenon primarily existed in the female population, as the first 5 cases were reported solely in females,3-7 possibly due to the prevalence of androgenetic alopecia in males.11 However, 6 cases of repigmentation associated with melanoma were later reported in males8-13; our patient represents an additional reported case in a male. It is unknown if there is a higher prevalence of this phenomenon among males or females.

Most previously reported cases of repigmentation were associated with melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type. Repigmentation also has been reported in malignant melanoma, as documented in our patient, as well as desmoplastic and amelanotic melanoma.5,6 In every case, the color of the repigmentation was darker than the rest of the patient’s hair; however, the repigmentation color can be different from the patient’s original hair color from their youth.4,5,11
The exact mechanism responsible for hair repigmentation in the setting of melanoma is unclear. It has been speculated from prior cases that repigmentation may be caused by paracrine stimulation from melanoma cells activating adjacent benign hair follicle melanocytes to produce melanin.7,14,15 This process likely is due to cytokines or growth factors, such as c-kit ligand.14,15 Several neural and immune networks and mediators activate the receptor tyrosine kinase KIT, which is thought to play a role in activating melanogenesis within the hair bulb.14 These signals also could originate from changes in the microenvironment instead of the melanoma cells themselves.6 Another possible mechanism is that repigmentation was caused by melanin-producing malignant melanocytes.4
Because this phenomenon typically occurs in older patients, the cause of repigmentation also could be related to chronic sun damage, which may result in upregulation of stem cell factor and α-melanocyte–stimulating hormone, as well as other molecules associated with melanogenesis, such as c-KIT receptor and tyrosinase.15,16 Upregulation of these molecules can lead to an increased number of melanocytes within the hair bulb. In addition, UVA and narrowband UVB have been recognized as major players in melanocyte stimulation. Phototherapy with UVA or narrowband UVB has been used for repigmentation in vitiligo patients.17
In cases without invasion of hair follicles by malignant cells, repigmentation more likely results from external signals stimulating benign bulbar melanocytes to produce melanin rather than melanoma cell growth extending into the hair bulb.6 In these cases, there is an increase in the number of hair bulbar melanocytes with a lack of malignant morphology in the hair bulb.8 If the signals are directly from melanoma cells in the hair bulb, it is unknown how the malignant cells upregulated melanogenesis in adjacent benign melanocytes or which specific signals required for normal pigmentation were involved in these repigmentation cases.6
Use of medications was ruled out as an underlying cause of the repigmentation in our patient. Drug-related repigmentation of the hair typically is observed in a diffuse generalized pattern. In our case, the repigmentation was localized to the area of the underlying dark patch, and the patient was not on any medications that could cause hair hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation has been associated with acitretin, lenalidomide, corticosteroids, erlotinib, latanoprost, verapamil, tamoxifen, levodopa, thalidomide, PD-1 inhibitors, and tumor necrosis α inhibitors.18-30 Repigmentation also has been reported after local radiotherapy and herpes zoster infection.31,32
The underlying melanoma in our patient was removed by staged square excision. Excision was the treatment of choice for most similar reported cases. Radiotherapy was utilized in two different cases.3,4 In one case, radiotherapy was successfully used to treat melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type; the patient’s hair grew back to its original color, which suggests that normal hair physiology was restored once melanoma cells were eliminated.3 One reported case demonstrated successful treatment of lentigo maligna type–melanoma with imiquimod cream 5% applied 6 times weekly for 9 months with a positive cosmetic result.9 The exact mechanism of imiquimod is not fully understood. Imiquimod induces cytokines to stimulate the production of IFN-α via activation of toll-like receptor 7.33 There was complete clearing of the lesion as well as the hair pigmentation,9 which suggests that the treatment also eliminated deeper cells influencing pigmentation. A case of malignant amelanotic melanoma was successfully treated with anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), with no recurrence at 12 months. Pembrolizumab acts as an immune checkpoint inhibitor by binding to the PD-1 receptor and allowing the immune system to recognize and attack melanoma cells. After 5 doses of pembrolizumab, the patient was clear of disease and his hair color returned to gray.5
In 2022, melanoma was estimated to be the fifth most commonly diagnosed cancer among men and women in the United States.34 Early melanoma detection is a critical factor in achieving positive patient outcomes. Hair repigmentation is a potentially serious phenomenon that warrants a physician visit. Melanoma lesions under the hair may be overlooked because of limited visibility. Physicians must inspect spontaneous hair repigmentation with high suspicion and interpret the change as a possible indirect result of melanoma. Overall, it is important to increase public awareness of regular skin checks and melanoma warning signs.
- Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA, Hess KR, et al. Melanoma staging: evidence‐based changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:472-492.
- Vetto JT, Hsueh EC, Gastman BR, et al. Guidance of sentinel lymph node biopsy decisions in patients with T1–T2 melanoma using gene expression profiling. Futur Oncol. 2019;15:1207-1217.
- Dummer R. Hair repigmentation in lentigo maligna. Lancet. 2001;357:598.
- Inzinger M, Massone C, Arzberger E, et al. Hair repigmentation in melanoma. Lancet. 2013;382:1224.
- Rahim RR, Husain A, Tobin DJ, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma presenting with localized hair repigmentation. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1371-1373.
- Tiger JB, Habeshian KA, Barton DT, et al. Repigmentation of hair associated with melanoma in situ of scalp. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E144-E145.
- Amann VC, Dummer R. Localized hair repigmentation in a 91-year-old woman. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:81-82.
- Chan C, Magro CM, Pham AK, et al. Spontaneous hair repigmentation in an 80-year-old man: a case of melanoma-associated hair repigmentation and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:671-674.
- Lackey AE, Glassman G, Grichnik J, et al. Repigmentation of gray hairs with lentigo maligna and response to topical imiquimod. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:1015-1017.
- Chew T, Pannell M, Jeeves A. Focal hair re-pigmentation associated with melanoma of the scalp. ANZ J Surg. 2019;90:1175-1176.
- López-Sánchez C, Collgros H. Hair repigmentation as a clue for scalp melanoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;61:179-180.
- Gessler J, Tejasvi T, Bresler SC. Repigmentation of scalp hair: a feature of early melanoma. Am J Med. 2023;136:E7-E8.
- Hasegawa T, Iino S, Kitakaze K, et al. Repigmentation of aging gray hair associated with unrecognized development and progression of amelanotic melanoma of the scalp: a physiological alert underlying hair rejuvenation. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E281-E283. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.15881
- D’Mello SAN, Finlay GJ, Baguley BC, et al. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1144.
- Hachiya A, Kobayashi A, Ohuchi A, et al. The paracrine role of stem cell factor/c-kit signaling in the activation of human melanocytes in ultraviolet-B-induced pigmentation. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:578-586.
- Slominski A, Wortsman J, Plonka PM, et al. Hair follicle pigmentation. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:13-21.
- Falabella R. Vitiligo and the melanocyte reservoir. Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54:313.
- Seckin D, Yildiz A. Repigmentation and curling of hair after acitretin therapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2009;50:214-216.
- Dasanu CA, Mitsis D, Alexandrescu DT. Hair repigmentation associated with the use of lenalidomide: graying may not be an irreversible process! J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2013;19:165-169.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AI, Lowe PM. Hair repigmentation with anti–PD-1 and anti–PD-L1 immunotherapy: a novel hypothesis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:112-113. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4420
- Tintle SJ, Dabade TS, Kalish RA, et al. Repigmentation of hair following adalimumab therapy. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6fn0t1xz.
- Penzi LR, Manatis-Lornell A, Saavedra A, et al. Hair repigmentation associated with the use of brentuximab. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:563-565.
- Khaled A, Trojjets S, Zeglaoui F, et al. Repigmentation of the white hair after systemic corticosteroids for bullous pemphigoid. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2008;22:1018-1020.
- Cheng YP, Chen HJ, Chiu HC. Erlotinib-induced hair repigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E55-E57.
- Bellandi S, Amato L, Cipollini EM, et al. Repigmentation of hair after latanoprost therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2011;25:1485-1487.
- Read GM. Verapamil and hair colour change. Lancet. 1991;338:1520.
- Hampson JP, Donnelly A, Lewis‐Jones MS, et al. Tamoxifen‐induced hair colour change. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:483-484.
- Reynolds NJ, Crossley J, Ferguson I, et al. Darkening of white hair in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1989;14:317-318.
- Lovering S, Miao W, Bailie T, et al. Hair repigmentation associated with thalidomide use for the treatment of multiple myeloma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016215521.
- Rivera N, Boada A, Bielsa MI, et al. Hair repigmentation during immunotherapy treatment with an anti–programmed cell death 1 and anti–programmed cell death ligand 1 agent for lung cancer. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1162-1165.
- Prasad S, Dougheney N, Hong A. Scalp hair repigmentation in the penumbral region of radiotherapy–a case series. Int J Radiol Radiat Ther. 2020;7:151-157.
- Adiga GU, Rehman KL, Wiernik PH. Permanent localized hair repigmentation following herpes zoster infection. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:569-570.
- Hanna E, Abadi R, Abbas O. Imiquimod in dermatology: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:831-844.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7-33.
- Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA, Hess KR, et al. Melanoma staging: evidence‐based changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:472-492.
- Vetto JT, Hsueh EC, Gastman BR, et al. Guidance of sentinel lymph node biopsy decisions in patients with T1–T2 melanoma using gene expression profiling. Futur Oncol. 2019;15:1207-1217.
- Dummer R. Hair repigmentation in lentigo maligna. Lancet. 2001;357:598.
- Inzinger M, Massone C, Arzberger E, et al. Hair repigmentation in melanoma. Lancet. 2013;382:1224.
- Rahim RR, Husain A, Tobin DJ, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma presenting with localized hair repigmentation. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1371-1373.
- Tiger JB, Habeshian KA, Barton DT, et al. Repigmentation of hair associated with melanoma in situ of scalp. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E144-E145.
- Amann VC, Dummer R. Localized hair repigmentation in a 91-year-old woman. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:81-82.
- Chan C, Magro CM, Pham AK, et al. Spontaneous hair repigmentation in an 80-year-old man: a case of melanoma-associated hair repigmentation and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:671-674.
- Lackey AE, Glassman G, Grichnik J, et al. Repigmentation of gray hairs with lentigo maligna and response to topical imiquimod. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:1015-1017.
- Chew T, Pannell M, Jeeves A. Focal hair re-pigmentation associated with melanoma of the scalp. ANZ J Surg. 2019;90:1175-1176.
- López-Sánchez C, Collgros H. Hair repigmentation as a clue for scalp melanoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;61:179-180.
- Gessler J, Tejasvi T, Bresler SC. Repigmentation of scalp hair: a feature of early melanoma. Am J Med. 2023;136:E7-E8.
- Hasegawa T, Iino S, Kitakaze K, et al. Repigmentation of aging gray hair associated with unrecognized development and progression of amelanotic melanoma of the scalp: a physiological alert underlying hair rejuvenation. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E281-E283. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.15881
- D’Mello SAN, Finlay GJ, Baguley BC, et al. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1144.
- Hachiya A, Kobayashi A, Ohuchi A, et al. The paracrine role of stem cell factor/c-kit signaling in the activation of human melanocytes in ultraviolet-B-induced pigmentation. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:578-586.
- Slominski A, Wortsman J, Plonka PM, et al. Hair follicle pigmentation. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:13-21.
- Falabella R. Vitiligo and the melanocyte reservoir. Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54:313.
- Seckin D, Yildiz A. Repigmentation and curling of hair after acitretin therapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2009;50:214-216.
- Dasanu CA, Mitsis D, Alexandrescu DT. Hair repigmentation associated with the use of lenalidomide: graying may not be an irreversible process! J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2013;19:165-169.
- Sebaratnam DF, Rodríguez Bandera AI, Lowe PM. Hair repigmentation with anti–PD-1 and anti–PD-L1 immunotherapy: a novel hypothesis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:112-113. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4420
- Tintle SJ, Dabade TS, Kalish RA, et al. Repigmentation of hair following adalimumab therapy. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6fn0t1xz.
- Penzi LR, Manatis-Lornell A, Saavedra A, et al. Hair repigmentation associated with the use of brentuximab. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:563-565.
- Khaled A, Trojjets S, Zeglaoui F, et al. Repigmentation of the white hair after systemic corticosteroids for bullous pemphigoid. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2008;22:1018-1020.
- Cheng YP, Chen HJ, Chiu HC. Erlotinib-induced hair repigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E55-E57.
- Bellandi S, Amato L, Cipollini EM, et al. Repigmentation of hair after latanoprost therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2011;25:1485-1487.
- Read GM. Verapamil and hair colour change. Lancet. 1991;338:1520.
- Hampson JP, Donnelly A, Lewis‐Jones MS, et al. Tamoxifen‐induced hair colour change. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132:483-484.
- Reynolds NJ, Crossley J, Ferguson I, et al. Darkening of white hair in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1989;14:317-318.
- Lovering S, Miao W, Bailie T, et al. Hair repigmentation associated with thalidomide use for the treatment of multiple myeloma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016215521.
- Rivera N, Boada A, Bielsa MI, et al. Hair repigmentation during immunotherapy treatment with an anti–programmed cell death 1 and anti–programmed cell death ligand 1 agent for lung cancer. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1162-1165.
- Prasad S, Dougheney N, Hong A. Scalp hair repigmentation in the penumbral region of radiotherapy–a case series. Int J Radiol Radiat Ther. 2020;7:151-157.
- Adiga GU, Rehman KL, Wiernik PH. Permanent localized hair repigmentation following herpes zoster infection. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:569-570.
- Hanna E, Abadi R, Abbas O. Imiquimod in dermatology: an overview. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:831-844.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7-33.
Practice Points
- Localized repigmentation of the hair is a rare phenomenon that may indicate underlying melanoma.
- Careful clinicopathologic correlation is necessary to appropriately diagnose and manage this unusual presentation of melanoma.
Generalized Essential Telangiectasia Treated With Pulsed Dye Laser
To the Editor:
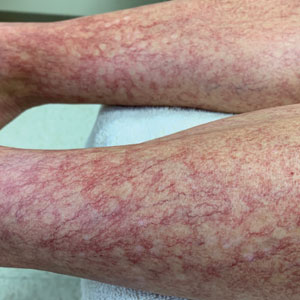
Generalized essential telangiectasia (GET) is a rare, benign, and progressive primary cutaneous disease manifesting as telangiectases of the skin without systemic symptoms. It is unique in that it has widespread distribution on the body. Generalized essential telangiectasia more commonly affects women, usually in the fourth decade of life. The telangiectases most frequently appear on the legs, advancing over time to involve the trunk and arms and presenting in several patterns, including diffuse, macular, plaquelike, discrete, or confluent. Although GET typically is asymptomatic, numbness, tingling, and burning of the involved areas have been reported.1 Treatment modalities for GET vary, though pulsed dye laser (PDL) therapy is most common. We report the case of a 40-year-old woman with a 5-year history of GET who was treated successfully with PDL.
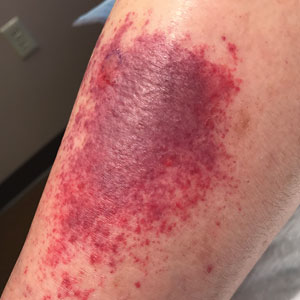
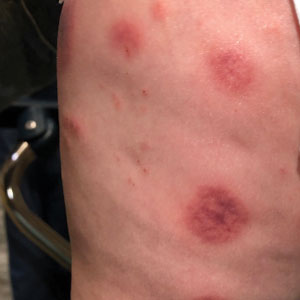
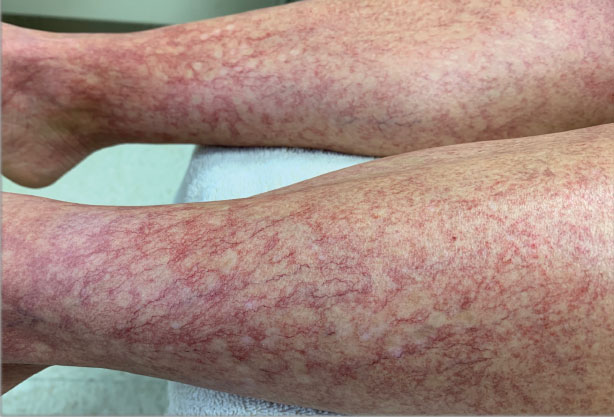
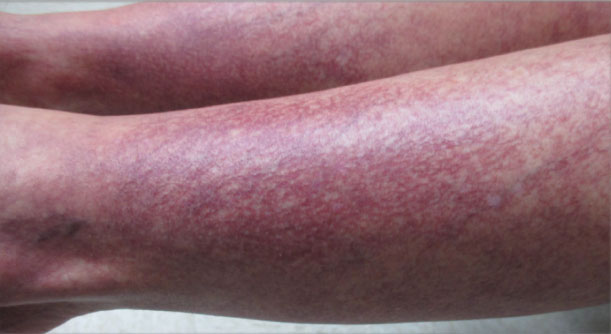
A 40-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with progressive prominence of blood vessels involving the dorsal aspects of the feet of 5 years’ duration. The prominent vessels had spread to involve the legs (Figure 1), buttocks, lower abdomen, forearms, and medial upper arms. The patient denied any personal history of bleeding disorders or family history of inherited conditions associated with visceral vascular malformations, such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Notably, magnetic resonance imaging of the liver approximately 3 weeks prior to initiating treatment with PDL demonstrated multiple hepatic lesions consistent with hemangiomas. The patient reported an occasional tingling sensation in the feet. She was otherwise asymptomatic but did report psychological distress associated with the skin changes.
Punch biopsies from the right lower leg and right buttock demonstrated increased vascularity of the dermis, a mild superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, and mild edema of the upper dermis without evidence of vasculitis. Autoimmune and coagulopathy workups were negative. The clinical and pathological findings were most consistent with GET.
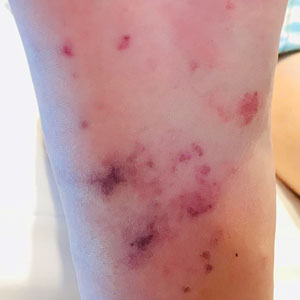
Over the next 2.5 years, the patient underwent treatment with doxycycline and a series of 16 treatments with PDL (fluence, 6–12 J/cm2; pulse width, 10 milliseconds) with a positive cosmetic response. Considerable improvement in the lower legs was noted after 2 years of treatment with PDL (Figure 2).
Recurrence of GET was noted between PDL treatments, which led to progression of the disease process; all treated sites showed slow recurrence of lesions within several months after treatment. After 2 years, doxycycline was discontinued because of a perceived lack of continued benefit and the patient’s desire for alternative therapy. She was started on a 3-month trial of supplementation with ascorbic acid and rutin (or rutoside, a bioflavinoid), without noticeable improvement.
The diffuse distribution of dramatic telangiectases in GET makes treatment difficult. Standard treatments are not well established or studied due to the rarity of the condition. A review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms treatment and generalized essential telangiectasias demonstrated several attempted treatment modalities for GET with varying success. In 4 cases in which PDL was used,2-5 a positive cosmetic response was noted, similar to what was seen in our patient. In 1 of the 4 cases, conservative management with ascorbic acid and compression stockings was unsuccessful; however, 6-mercaptopurine, used to treat that patient’s ulcerative colitis, incidentally resulted in resolution of GET.2 In 2 cases, response was maintained at 1.5-year follow-up.3,5 Two cases noted successful treatment with acyclovir,6,7 and 2 more demonstrated successful treatment with systemic ketoconazole.6,8 Some improvement was reported with oral doxycycline or tetracycline in 2 cases.9,10 Sclerotherapy improved the cosmetic appearance of telangiectases in one patient but was unsustainable because of the pain associated with the procedure.11 Nd:YAG laser therapy was effective in one case12; however, the patient experienced relapse at 6-month follow-up—similar to what we observed in our patient. Three patients treated with intense pulsed light therapy experienced results that were maintained at 2-year follow-up.13
Generalized essential telangiectasia generally is considered a skin-limited disease without systemic manifestations, but 2 reports11,14 described its association with gastric antral vascular ectasia—known as watermelon stomach. Hepatic hemangiomas are the most common benign liver lesions; however, the findings on magnetic resonance imaging in our patient, in combination with the 2 reported cases of watermelon stomach, suggest that the vascular changes of GET might extend below the skin.
Of the cases we reviewed, our patient had the longest reported duration of PDL treatment and follow-up for GET in which a successful, albeit transient, response was demonstrated. Our review of the literature revealed other reports of success with PDL and intense pulsed light therapy; results were maintained in some patients, while disease relapsed in others. Further studies are needed to understand why results are maintained in some but not all patients.
Although the cost of PDL as a cosmetic procedure must be taken into consideration when planning treatment of GET, we conclude that it is a safe option that can be effective until other treatment options are established to control the disease.
- McGrae JD Jr, Winkelmann RK. Generalized essential telangiectasia: report of a clinical and histochemical study of 13 patients with acquired cutaneous lesions. JAMA. 1963;185:909-913. doi:10.1001/jama.1963.03060120019015
- Glazer AM, Sofen BD, Rigel DS, et al. Successful treatment of generalized essential telangiectasia with 6-mercaptopurine. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:280-282.
- B, M, Boixeda P, et al. Progressive ascending telangiectasia treated with the 585 nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser. Lasers Surg Med. 1997;21:413-416. doi:10.1002/(sici)1096-9101(1997)21:5<413::aid-lsm1>3.0.co;2-t
- Buscaglia DA, Conte ET. Successful treatment of generalized essential telangiectasia with the 585-nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser. Cutis. 2001;67:107-108.
- Powell E, Markus R, Malone CH. Generalized essential telangiectasia treated with PDL. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1086-1087. doi:10.1111/jocd.13938
- Ali MM, Teimory M, Sarhan M. Generalized essential telangiectasia with conjunctival involvement. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:781-782. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02217.x
- Shelley WB, Shelley ED. Essential progressive telangiectasia in an autoimmune setting: successful treatment with acyclovir. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(5 pt 2):1094-1096. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70303-0
- Shelley WB, Fierer JA. Focal intravascular coagulation in progressive ascending telangiectasia: ultrastructural studies of ketoconazole-induced involution of vessels. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10(5 pt 2):876-887. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(84)80439-9
- Wiznia LE, Steuer AB, Penn LA, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia [published online December 15, 2018]. Dermatol Online J. doi:https://doi.org/10.5070/D32412042395
- Shelley WB. Essential progressive telangiectasia. successful treatment with tetracycline. JAMA. 1971;216:1343-1344.
- Checketts SR, Burton PS, Bjorkman DJ, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia in the presence of gastrointestinal bleeding. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37(2 pt 2):321-325.
- Gambichler T, Avermaete A, Wilmert M, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia successfully treated with high-energy, long-pulse, frequency-doubled Nd:YAG laser. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:355-357. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00307.x
- -Torres R, del Pozo J, de la Torre C, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia: a report of three cases treated using an intense pulsed light system. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:192-193.
- Tetart F, Lorthioir A, Girszyn N, et al. Watermelon stomach revealing generalized essential telangiectasia. Intern Med J. 2009;39:781-783. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2009.02048.x
To the Editor:
Generalized essential telangiectasia (GET) is a rare, benign, and progressive primary cutaneous disease manifesting as telangiectases of the skin without systemic symptoms. It is unique in that it has widespread distribution on the body. Generalized essential telangiectasia more commonly affects women, usually in the fourth decade of life. The telangiectases most frequently appear on the legs, advancing over time to involve the trunk and arms and presenting in several patterns, including diffuse, macular, plaquelike, discrete, or confluent. Although GET typically is asymptomatic, numbness, tingling, and burning of the involved areas have been reported.1 Treatment modalities for GET vary, though pulsed dye laser (PDL) therapy is most common. We report the case of a 40-year-old woman with a 5-year history of GET who was treated successfully with PDL.
A 40-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with progressive prominence of blood vessels involving the dorsal aspects of the feet of 5 years’ duration. The prominent vessels had spread to involve the legs (Figure 1), buttocks, lower abdomen, forearms, and medial upper arms. The patient denied any personal history of bleeding disorders or family history of inherited conditions associated with visceral vascular malformations, such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Notably, magnetic resonance imaging of the liver approximately 3 weeks prior to initiating treatment with PDL demonstrated multiple hepatic lesions consistent with hemangiomas. The patient reported an occasional tingling sensation in the feet. She was otherwise asymptomatic but did report psychological distress associated with the skin changes.

Punch biopsies from the right lower leg and right buttock demonstrated increased vascularity of the dermis, a mild superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, and mild edema of the upper dermis without evidence of vasculitis. Autoimmune and coagulopathy workups were negative. The clinical and pathological findings were most consistent with GET.
Over the next 2.5 years, the patient underwent treatment with doxycycline and a series of 16 treatments with PDL (fluence, 6–12 J/cm2; pulse width, 10 milliseconds) with a positive cosmetic response. Considerable improvement in the lower legs was noted after 2 years of treatment with PDL (Figure 2).

Recurrence of GET was noted between PDL treatments, which led to progression of the disease process; all treated sites showed slow recurrence of lesions within several months after treatment. After 2 years, doxycycline was discontinued because of a perceived lack of continued benefit and the patient’s desire for alternative therapy. She was started on a 3-month trial of supplementation with ascorbic acid and rutin (or rutoside, a bioflavinoid), without noticeable improvement.
The diffuse distribution of dramatic telangiectases in GET makes treatment difficult. Standard treatments are not well established or studied due to the rarity of the condition. A review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms treatment and generalized essential telangiectasias demonstrated several attempted treatment modalities for GET with varying success. In 4 cases in which PDL was used,2-5 a positive cosmetic response was noted, similar to what was seen in our patient. In 1 of the 4 cases, conservative management with ascorbic acid and compression stockings was unsuccessful; however, 6-mercaptopurine, used to treat that patient’s ulcerative colitis, incidentally resulted in resolution of GET.2 In 2 cases, response was maintained at 1.5-year follow-up.3,5 Two cases noted successful treatment with acyclovir,6,7 and 2 more demonstrated successful treatment with systemic ketoconazole.6,8 Some improvement was reported with oral doxycycline or tetracycline in 2 cases.9,10 Sclerotherapy improved the cosmetic appearance of telangiectases in one patient but was unsustainable because of the pain associated with the procedure.11 Nd:YAG laser therapy was effective in one case12; however, the patient experienced relapse at 6-month follow-up—similar to what we observed in our patient. Three patients treated with intense pulsed light therapy experienced results that were maintained at 2-year follow-up.13
Generalized essential telangiectasia generally is considered a skin-limited disease without systemic manifestations, but 2 reports11,14 described its association with gastric antral vascular ectasia—known as watermelon stomach. Hepatic hemangiomas are the most common benign liver lesions; however, the findings on magnetic resonance imaging in our patient, in combination with the 2 reported cases of watermelon stomach, suggest that the vascular changes of GET might extend below the skin.
Of the cases we reviewed, our patient had the longest reported duration of PDL treatment and follow-up for GET in which a successful, albeit transient, response was demonstrated. Our review of the literature revealed other reports of success with PDL and intense pulsed light therapy; results were maintained in some patients, while disease relapsed in others. Further studies are needed to understand why results are maintained in some but not all patients.
Although the cost of PDL as a cosmetic procedure must be taken into consideration when planning treatment of GET, we conclude that it is a safe option that can be effective until other treatment options are established to control the disease.
To the Editor:
Generalized essential telangiectasia (GET) is a rare, benign, and progressive primary cutaneous disease manifesting as telangiectases of the skin without systemic symptoms. It is unique in that it has widespread distribution on the body. Generalized essential telangiectasia more commonly affects women, usually in the fourth decade of life. The telangiectases most frequently appear on the legs, advancing over time to involve the trunk and arms and presenting in several patterns, including diffuse, macular, plaquelike, discrete, or confluent. Although GET typically is asymptomatic, numbness, tingling, and burning of the involved areas have been reported.1 Treatment modalities for GET vary, though pulsed dye laser (PDL) therapy is most common. We report the case of a 40-year-old woman with a 5-year history of GET who was treated successfully with PDL.
A 40-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with progressive prominence of blood vessels involving the dorsal aspects of the feet of 5 years’ duration. The prominent vessels had spread to involve the legs (Figure 1), buttocks, lower abdomen, forearms, and medial upper arms. The patient denied any personal history of bleeding disorders or family history of inherited conditions associated with visceral vascular malformations, such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Notably, magnetic resonance imaging of the liver approximately 3 weeks prior to initiating treatment with PDL demonstrated multiple hepatic lesions consistent with hemangiomas. The patient reported an occasional tingling sensation in the feet. She was otherwise asymptomatic but did report psychological distress associated with the skin changes.

Punch biopsies from the right lower leg and right buttock demonstrated increased vascularity of the dermis, a mild superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, and mild edema of the upper dermis without evidence of vasculitis. Autoimmune and coagulopathy workups were negative. The clinical and pathological findings were most consistent with GET.
Over the next 2.5 years, the patient underwent treatment with doxycycline and a series of 16 treatments with PDL (fluence, 6–12 J/cm2; pulse width, 10 milliseconds) with a positive cosmetic response. Considerable improvement in the lower legs was noted after 2 years of treatment with PDL (Figure 2).

Recurrence of GET was noted between PDL treatments, which led to progression of the disease process; all treated sites showed slow recurrence of lesions within several months after treatment. After 2 years, doxycycline was discontinued because of a perceived lack of continued benefit and the patient’s desire for alternative therapy. She was started on a 3-month trial of supplementation with ascorbic acid and rutin (or rutoside, a bioflavinoid), without noticeable improvement.
The diffuse distribution of dramatic telangiectases in GET makes treatment difficult. Standard treatments are not well established or studied due to the rarity of the condition. A review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms treatment and generalized essential telangiectasias demonstrated several attempted treatment modalities for GET with varying success. In 4 cases in which PDL was used,2-5 a positive cosmetic response was noted, similar to what was seen in our patient. In 1 of the 4 cases, conservative management with ascorbic acid and compression stockings was unsuccessful; however, 6-mercaptopurine, used to treat that patient’s ulcerative colitis, incidentally resulted in resolution of GET.2 In 2 cases, response was maintained at 1.5-year follow-up.3,5 Two cases noted successful treatment with acyclovir,6,7 and 2 more demonstrated successful treatment with systemic ketoconazole.6,8 Some improvement was reported with oral doxycycline or tetracycline in 2 cases.9,10 Sclerotherapy improved the cosmetic appearance of telangiectases in one patient but was unsustainable because of the pain associated with the procedure.11 Nd:YAG laser therapy was effective in one case12; however, the patient experienced relapse at 6-month follow-up—similar to what we observed in our patient. Three patients treated with intense pulsed light therapy experienced results that were maintained at 2-year follow-up.13
Generalized essential telangiectasia generally is considered a skin-limited disease without systemic manifestations, but 2 reports11,14 described its association with gastric antral vascular ectasia—known as watermelon stomach. Hepatic hemangiomas are the most common benign liver lesions; however, the findings on magnetic resonance imaging in our patient, in combination with the 2 reported cases of watermelon stomach, suggest that the vascular changes of GET might extend below the skin.
Of the cases we reviewed, our patient had the longest reported duration of PDL treatment and follow-up for GET in which a successful, albeit transient, response was demonstrated. Our review of the literature revealed other reports of success with PDL and intense pulsed light therapy; results were maintained in some patients, while disease relapsed in others. Further studies are needed to understand why results are maintained in some but not all patients.
Although the cost of PDL as a cosmetic procedure must be taken into consideration when planning treatment of GET, we conclude that it is a safe option that can be effective until other treatment options are established to control the disease.
- McGrae JD Jr, Winkelmann RK. Generalized essential telangiectasia: report of a clinical and histochemical study of 13 patients with acquired cutaneous lesions. JAMA. 1963;185:909-913. doi:10.1001/jama.1963.03060120019015
- Glazer AM, Sofen BD, Rigel DS, et al. Successful treatment of generalized essential telangiectasia with 6-mercaptopurine. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:280-282.
- B, M, Boixeda P, et al. Progressive ascending telangiectasia treated with the 585 nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser. Lasers Surg Med. 1997;21:413-416. doi:10.1002/(sici)1096-9101(1997)21:5<413::aid-lsm1>3.0.co;2-t
- Buscaglia DA, Conte ET. Successful treatment of generalized essential telangiectasia with the 585-nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser. Cutis. 2001;67:107-108.
- Powell E, Markus R, Malone CH. Generalized essential telangiectasia treated with PDL. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1086-1087. doi:10.1111/jocd.13938
- Ali MM, Teimory M, Sarhan M. Generalized essential telangiectasia with conjunctival involvement. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:781-782. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02217.x
- Shelley WB, Shelley ED. Essential progressive telangiectasia in an autoimmune setting: successful treatment with acyclovir. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(5 pt 2):1094-1096. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70303-0
- Shelley WB, Fierer JA. Focal intravascular coagulation in progressive ascending telangiectasia: ultrastructural studies of ketoconazole-induced involution of vessels. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10(5 pt 2):876-887. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(84)80439-9
- Wiznia LE, Steuer AB, Penn LA, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia [published online December 15, 2018]. Dermatol Online J. doi:https://doi.org/10.5070/D32412042395
- Shelley WB. Essential progressive telangiectasia. successful treatment with tetracycline. JAMA. 1971;216:1343-1344.
- Checketts SR, Burton PS, Bjorkman DJ, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia in the presence of gastrointestinal bleeding. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37(2 pt 2):321-325.
- Gambichler T, Avermaete A, Wilmert M, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia successfully treated with high-energy, long-pulse, frequency-doubled Nd:YAG laser. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:355-357. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00307.x
- -Torres R, del Pozo J, de la Torre C, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia: a report of three cases treated using an intense pulsed light system. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:192-193.
- Tetart F, Lorthioir A, Girszyn N, et al. Watermelon stomach revealing generalized essential telangiectasia. Intern Med J. 2009;39:781-783. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2009.02048.x
- McGrae JD Jr, Winkelmann RK. Generalized essential telangiectasia: report of a clinical and histochemical study of 13 patients with acquired cutaneous lesions. JAMA. 1963;185:909-913. doi:10.1001/jama.1963.03060120019015
- Glazer AM, Sofen BD, Rigel DS, et al. Successful treatment of generalized essential telangiectasia with 6-mercaptopurine. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:280-282.
- B, M, Boixeda P, et al. Progressive ascending telangiectasia treated with the 585 nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser. Lasers Surg Med. 1997;21:413-416. doi:10.1002/(sici)1096-9101(1997)21:5<413::aid-lsm1>3.0.co;2-t
- Buscaglia DA, Conte ET. Successful treatment of generalized essential telangiectasia with the 585-nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser. Cutis. 2001;67:107-108.
- Powell E, Markus R, Malone CH. Generalized essential telangiectasia treated with PDL. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1086-1087. doi:10.1111/jocd.13938
- Ali MM, Teimory M, Sarhan M. Generalized essential telangiectasia with conjunctival involvement. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:781-782. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02217.x
- Shelley WB, Shelley ED. Essential progressive telangiectasia in an autoimmune setting: successful treatment with acyclovir. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(5 pt 2):1094-1096. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70303-0
- Shelley WB, Fierer JA. Focal intravascular coagulation in progressive ascending telangiectasia: ultrastructural studies of ketoconazole-induced involution of vessels. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10(5 pt 2):876-887. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(84)80439-9
- Wiznia LE, Steuer AB, Penn LA, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia [published online December 15, 2018]. Dermatol Online J. doi:https://doi.org/10.5070/D32412042395
- Shelley WB. Essential progressive telangiectasia. successful treatment with tetracycline. JAMA. 1971;216:1343-1344.
- Checketts SR, Burton PS, Bjorkman DJ, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia in the presence of gastrointestinal bleeding. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37(2 pt 2):321-325.
- Gambichler T, Avermaete A, Wilmert M, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia successfully treated with high-energy, long-pulse, frequency-doubled Nd:YAG laser. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:355-357. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00307.x
- -Torres R, del Pozo J, de la Torre C, et al. Generalized essential telangiectasia: a report of three cases treated using an intense pulsed light system. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:192-193.
- Tetart F, Lorthioir A, Girszyn N, et al. Watermelon stomach revealing generalized essential telangiectasia. Intern Med J. 2009;39:781-783. doi:10.1111/j.1445-5994.2009.02048.x
Practice Points
- Generalized essential telangiectasia (GET) is a primary benign skin condition in which there is progressive development of telangiectases but a lack of systemic symptoms.
- Although patients should be assured that GET is a benign disease, its manifestation on the skin may cause negative psychologic impacts that should not be overlooked.
- Pulsed dye laser therapy does lead to improvement of the condition, but it does not prevent progression.
Fat Necrosis of the Breast Mimicking Breast Cancer in a Male Patient Following Wax Hair Removal
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
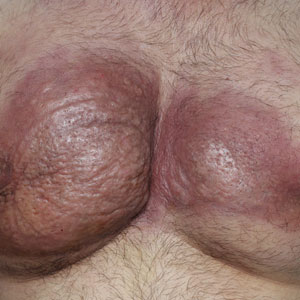
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
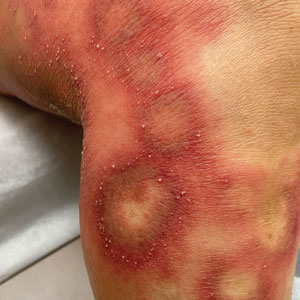
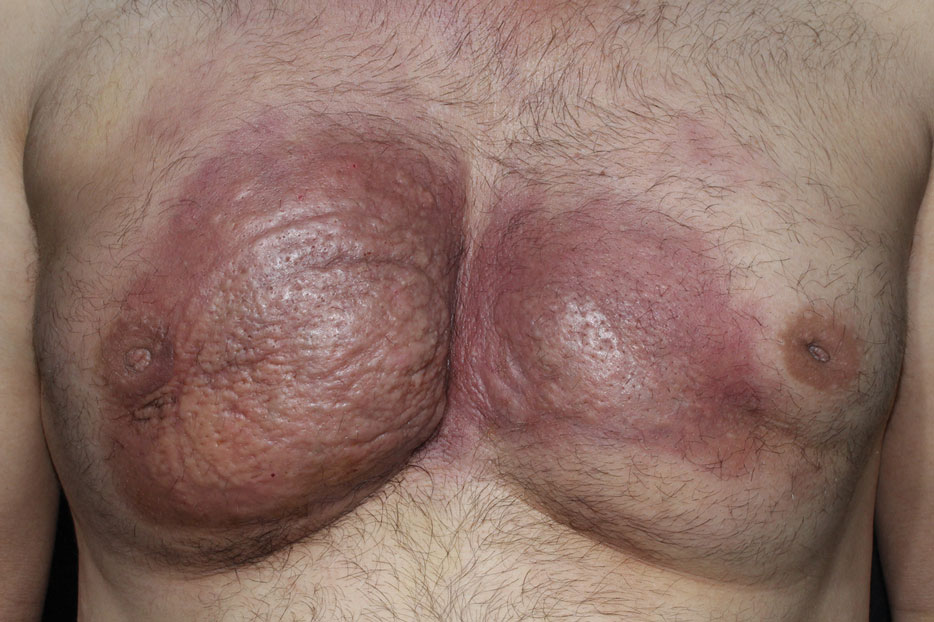
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.
Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
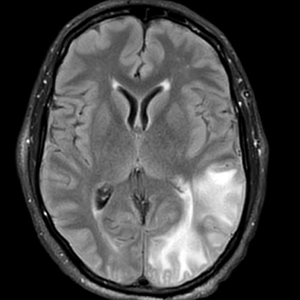
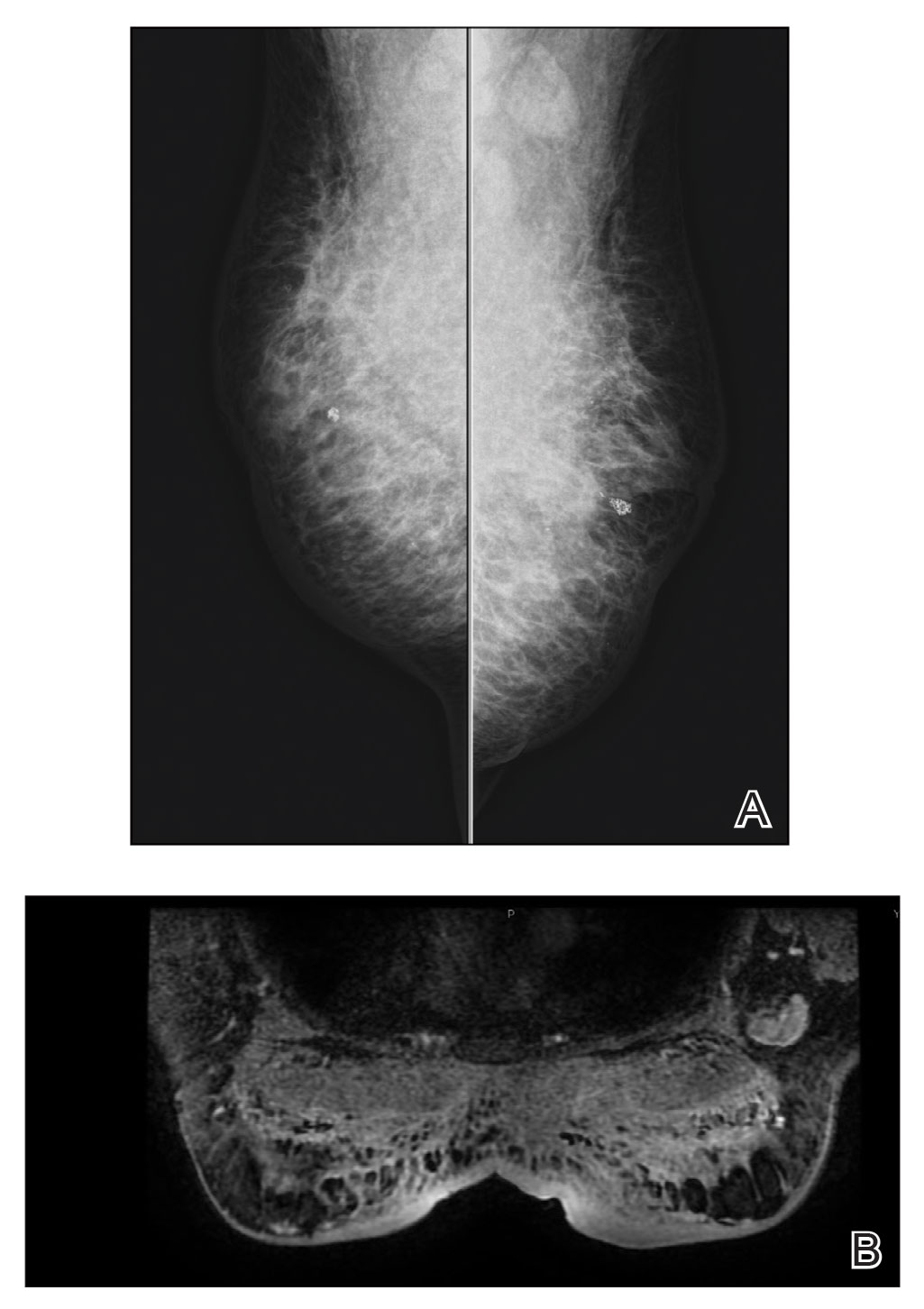
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).
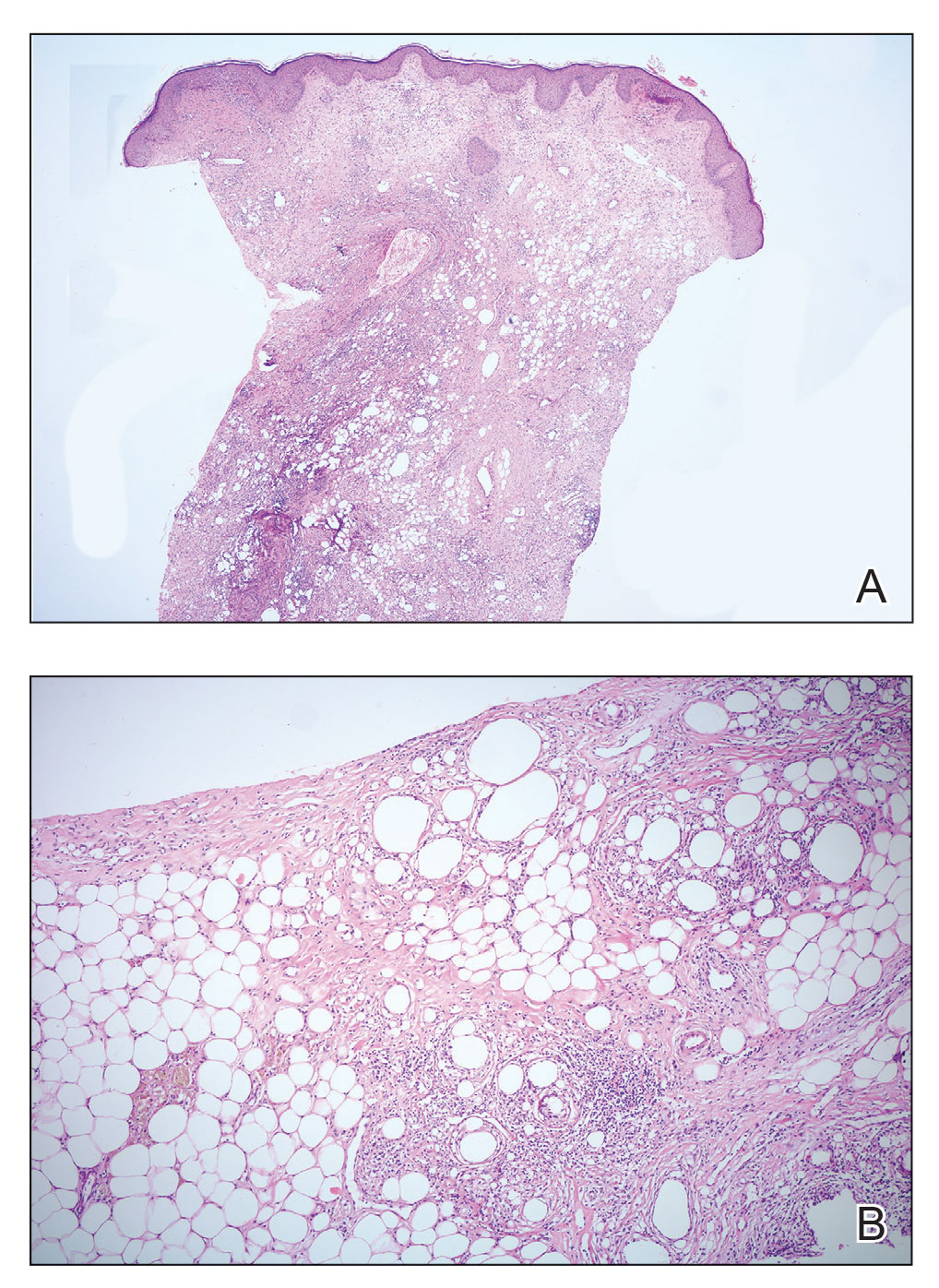
Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.
Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.

Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).

Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.

Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.

Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).

Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.

Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
Practice Points
- Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy; therefore, diagnosis should be confirmed by histopathology in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, and hair removal with wax may be a rare cause of the disease.
Cyclosporine-Induced Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: An Adverse Effect in a Patient With Atopic Dermatitis
To the Editor:
Cyclosporine is an immunomodulatory medication that impacts T-lymphocyte function through calcineurin inhibition and suppression of IL-2 expression. Oral cyclosporine at low doses (1–3 mg/kg/d) is one of the more common systemic treatment options for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. At these doses it has been shown to have therapeutic benefit in several skin conditions, including chronic spontaneous urticaria,1 psoriasis,2 and atopic dermatitis.3 When used at higher doses for conditions such as glomerulonephritis or transplantation, adverse effects may be notable, and close monitoring of drug metabolism as well as end-organ function is required. In contrast, severe adverse effects are uncommon with the lower doses of cyclosporine used for cutaneous conditions, and monitoring serum drug levels is not routinely practiced.4
A 58-year-old man was referred to clinic with severe atopic dermatitis refractory to maximal topical therapy prescribed by an outside physician. He was started on cyclosporine as an anticipated bridge to dupilumab biologic therapy. He had no history of hypertension, renal disease, or hepatic insufficiency prior to starting therapy. He demonstrated notable clinical improvement at a cyclosporine dosage of 300 mg/d (equating to 3.7 mg/kg/d). Three months after initiation of therapy, the patient presented to a local emergency department with new-onset seizurelike activity, confusion, and agitation. He was normotensive with clinical concern for status epilepticus. An initial laboratory assessment included a complete blood cell count, serum electrolyte panel, and urine toxicology screen, which were unremarkable. Computed tomography of the head showed confluent white-matter hypodensities in the left parietal-temporal-occipital lobes. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain showed innumerable peripherally distributed foci of microhemorrhage and vasogenic edema within the left parietal-temporal-occipital lobes (Figure).
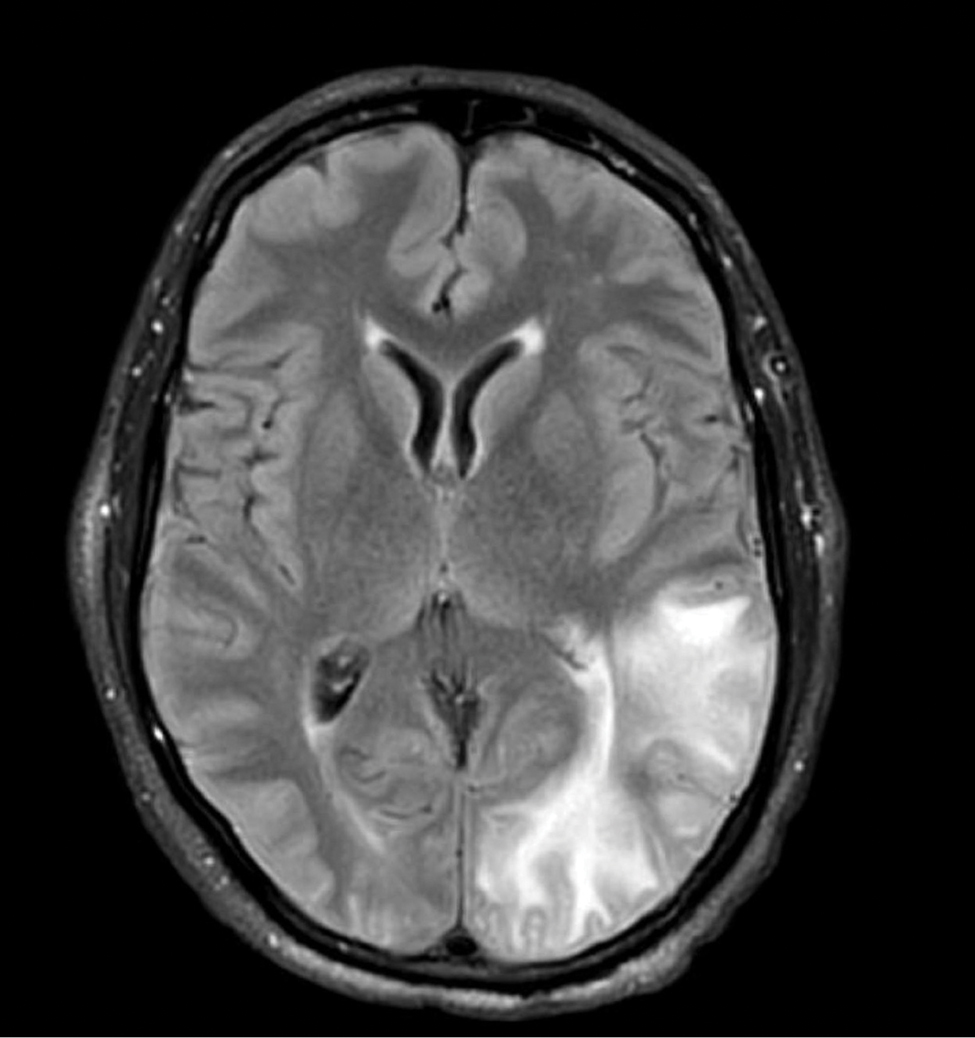
He was intubated and sedated with admission to the medical intensive care unit, where a random cyclosporine level drawn approximately 9 hours after the prior dose was noted to be 263 ng/mL. Although target therapeutic levels for cyclosporine vary based on indication, toxic supratherapeutic levels generally are considered to be greater than 400 ng/mL.5 He had no evidence of acute kidney injury, uremia, or hypertension throughout hospitalization. An electroencephalogram showed left parieto-occipital periodic epileptiform discharges with generalized slowing. Cyclosporine was discontinued, and he was started on levetiracetam. His clinical and neuroimaging findings improved over the course of the 1-week hospitalization without any further intervention. Four weeks after hospitalization, he had full neurologic, electroencephalogram, and imaging recovery. Based on the presenting symptoms, transient neuroimaging findings, and full recovery with discontinuation of cyclosporine, the patient was diagnosed with cyclosporine-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES).
The diagnosis of PRES requires evidence of acute neurologic symptoms and radiographic findings of cortical/subcortical white-matter changes on computed tomography or MRI consistent with edema. The pathophysiology is not fully understood but appears to be related to vasogenic edema, primarily impacting the posterior aspect of the brain. There have been many reported offending agents, and symptoms typically resolve following cessation of these medications. Cases of cyclosporine-induced PRES have been reported, but most occurred at higher doses within weeks of medication initiation. Two cases of cyclosporine-induced PRES treated with cutaneous dosing have been reported; neither patient was taking it for atopic dermatitis.6
Cyclosporine-induced PRES remains a pathophysiologic conundrum. However, there is evidence to support direct endothelial damage causing cellular apoptosis in the brain of mouse models that is medication specific and not necessarily related to the dosages used.7 Our case highlights a rare but important adverse event associated with even low-dose cyclosporine use that should be considered in patients currently taking cyclosporine who present with acute neurologic changes.
- Kulthanan K, Chaweekulrat P, Komoltri C, et al. Cyclosporine for chronic spontaneous urticaria: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6:586-599. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2017.07.017
- Armstrong AW, Read C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review. JAMA. 2020;323:1945-1960. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4006
- Seger EW, Wechter T, Strowd L, et al. Relative efficacy of systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis [published online October 6, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:411-416.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.053
- Blake SC, Murrell DF. Monitoring trough levels in cyclosporine for atopic dermatitis: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:843-853. doi:10.1111/pde.13999
- Tapia C, Nessel TA, Zito PM. Cyclosporine. StatPearls Publishing: 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482450/
- Cosottini M, Lazzarotti G, Ceravolo R, et al. Cyclosporine‐related posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in non‐transplant patient: a case report and literature review. Eur J Neurol. 2003;10:461-462. doi:10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00608_1.x
- Kochi S, Takanaga H, Matsuo H, et al. Induction of apoptosis in mouse brain capillary endothelial cells by cyclosporin A and tacrolimus. Life Sci. 2000;66:2255-2260. doi:10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00554-3
To the Editor:
Cyclosporine is an immunomodulatory medication that impacts T-lymphocyte function through calcineurin inhibition and suppression of IL-2 expression. Oral cyclosporine at low doses (1–3 mg/kg/d) is one of the more common systemic treatment options for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. At these doses it has been shown to have therapeutic benefit in several skin conditions, including chronic spontaneous urticaria,1 psoriasis,2 and atopic dermatitis.3 When used at higher doses for conditions such as glomerulonephritis or transplantation, adverse effects may be notable, and close monitoring of drug metabolism as well as end-organ function is required. In contrast, severe adverse effects are uncommon with the lower doses of cyclosporine used for cutaneous conditions, and monitoring serum drug levels is not routinely practiced.4
A 58-year-old man was referred to clinic with severe atopic dermatitis refractory to maximal topical therapy prescribed by an outside physician. He was started on cyclosporine as an anticipated bridge to dupilumab biologic therapy. He had no history of hypertension, renal disease, or hepatic insufficiency prior to starting therapy. He demonstrated notable clinical improvement at a cyclosporine dosage of 300 mg/d (equating to 3.7 mg/kg/d). Three months after initiation of therapy, the patient presented to a local emergency department with new-onset seizurelike activity, confusion, and agitation. He was normotensive with clinical concern for status epilepticus. An initial laboratory assessment included a complete blood cell count, serum electrolyte panel, and urine toxicology screen, which were unremarkable. Computed tomography of the head showed confluent white-matter hypodensities in the left parietal-temporal-occipital lobes. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain showed innumerable peripherally distributed foci of microhemorrhage and vasogenic edema within the left parietal-temporal-occipital lobes (Figure).

He was intubated and sedated with admission to the medical intensive care unit, where a random cyclosporine level drawn approximately 9 hours after the prior dose was noted to be 263 ng/mL. Although target therapeutic levels for cyclosporine vary based on indication, toxic supratherapeutic levels generally are considered to be greater than 400 ng/mL.5 He had no evidence of acute kidney injury, uremia, or hypertension throughout hospitalization. An electroencephalogram showed left parieto-occipital periodic epileptiform discharges with generalized slowing. Cyclosporine was discontinued, and he was started on levetiracetam. His clinical and neuroimaging findings improved over the course of the 1-week hospitalization without any further intervention. Four weeks after hospitalization, he had full neurologic, electroencephalogram, and imaging recovery. Based on the presenting symptoms, transient neuroimaging findings, and full recovery with discontinuation of cyclosporine, the patient was diagnosed with cyclosporine-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES).
The diagnosis of PRES requires evidence of acute neurologic symptoms and radiographic findings of cortical/subcortical white-matter changes on computed tomography or MRI consistent with edema. The pathophysiology is not fully understood but appears to be related to vasogenic edema, primarily impacting the posterior aspect of the brain. There have been many reported offending agents, and symptoms typically resolve following cessation of these medications. Cases of cyclosporine-induced PRES have been reported, but most occurred at higher doses within weeks of medication initiation. Two cases of cyclosporine-induced PRES treated with cutaneous dosing have been reported; neither patient was taking it for atopic dermatitis.6
Cyclosporine-induced PRES remains a pathophysiologic conundrum. However, there is evidence to support direct endothelial damage causing cellular apoptosis in the brain of mouse models that is medication specific and not necessarily related to the dosages used.7 Our case highlights a rare but important adverse event associated with even low-dose cyclosporine use that should be considered in patients currently taking cyclosporine who present with acute neurologic changes.
To the Editor:
Cyclosporine is an immunomodulatory medication that impacts T-lymphocyte function through calcineurin inhibition and suppression of IL-2 expression. Oral cyclosporine at low doses (1–3 mg/kg/d) is one of the more common systemic treatment options for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. At these doses it has been shown to have therapeutic benefit in several skin conditions, including chronic spontaneous urticaria,1 psoriasis,2 and atopic dermatitis.3 When used at higher doses for conditions such as glomerulonephritis or transplantation, adverse effects may be notable, and close monitoring of drug metabolism as well as end-organ function is required. In contrast, severe adverse effects are uncommon with the lower doses of cyclosporine used for cutaneous conditions, and monitoring serum drug levels is not routinely practiced.4
A 58-year-old man was referred to clinic with severe atopic dermatitis refractory to maximal topical therapy prescribed by an outside physician. He was started on cyclosporine as an anticipated bridge to dupilumab biologic therapy. He had no history of hypertension, renal disease, or hepatic insufficiency prior to starting therapy. He demonstrated notable clinical improvement at a cyclosporine dosage of 300 mg/d (equating to 3.7 mg/kg/d). Three months after initiation of therapy, the patient presented to a local emergency department with new-onset seizurelike activity, confusion, and agitation. He was normotensive with clinical concern for status epilepticus. An initial laboratory assessment included a complete blood cell count, serum electrolyte panel, and urine toxicology screen, which were unremarkable. Computed tomography of the head showed confluent white-matter hypodensities in the left parietal-temporal-occipital lobes. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain showed innumerable peripherally distributed foci of microhemorrhage and vasogenic edema within the left parietal-temporal-occipital lobes (Figure).

He was intubated and sedated with admission to the medical intensive care unit, where a random cyclosporine level drawn approximately 9 hours after the prior dose was noted to be 263 ng/mL. Although target therapeutic levels for cyclosporine vary based on indication, toxic supratherapeutic levels generally are considered to be greater than 400 ng/mL.5 He had no evidence of acute kidney injury, uremia, or hypertension throughout hospitalization. An electroencephalogram showed left parieto-occipital periodic epileptiform discharges with generalized slowing. Cyclosporine was discontinued, and he was started on levetiracetam. His clinical and neuroimaging findings improved over the course of the 1-week hospitalization without any further intervention. Four weeks after hospitalization, he had full neurologic, electroencephalogram, and imaging recovery. Based on the presenting symptoms, transient neuroimaging findings, and full recovery with discontinuation of cyclosporine, the patient was diagnosed with cyclosporine-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES).
The diagnosis of PRES requires evidence of acute neurologic symptoms and radiographic findings of cortical/subcortical white-matter changes on computed tomography or MRI consistent with edema. The pathophysiology is not fully understood but appears to be related to vasogenic edema, primarily impacting the posterior aspect of the brain. There have been many reported offending agents, and symptoms typically resolve following cessation of these medications. Cases of cyclosporine-induced PRES have been reported, but most occurred at higher doses within weeks of medication initiation. Two cases of cyclosporine-induced PRES treated with cutaneous dosing have been reported; neither patient was taking it for atopic dermatitis.6
Cyclosporine-induced PRES remains a pathophysiologic conundrum. However, there is evidence to support direct endothelial damage causing cellular apoptosis in the brain of mouse models that is medication specific and not necessarily related to the dosages used.7 Our case highlights a rare but important adverse event associated with even low-dose cyclosporine use that should be considered in patients currently taking cyclosporine who present with acute neurologic changes.
- Kulthanan K, Chaweekulrat P, Komoltri C, et al. Cyclosporine for chronic spontaneous urticaria: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6:586-599. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2017.07.017
- Armstrong AW, Read C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review. JAMA. 2020;323:1945-1960. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4006
- Seger EW, Wechter T, Strowd L, et al. Relative efficacy of systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis [published online October 6, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:411-416.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.053
- Blake SC, Murrell DF. Monitoring trough levels in cyclosporine for atopic dermatitis: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:843-853. doi:10.1111/pde.13999
- Tapia C, Nessel TA, Zito PM. Cyclosporine. StatPearls Publishing: 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482450/
- Cosottini M, Lazzarotti G, Ceravolo R, et al. Cyclosporine‐related posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in non‐transplant patient: a case report and literature review. Eur J Neurol. 2003;10:461-462. doi:10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00608_1.x
- Kochi S, Takanaga H, Matsuo H, et al. Induction of apoptosis in mouse brain capillary endothelial cells by cyclosporin A and tacrolimus. Life Sci. 2000;66:2255-2260. doi:10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00554-3
- Kulthanan K, Chaweekulrat P, Komoltri C, et al. Cyclosporine for chronic spontaneous urticaria: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6:586-599. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2017.07.017
- Armstrong AW, Read C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review. JAMA. 2020;323:1945-1960. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4006
- Seger EW, Wechter T, Strowd L, et al. Relative efficacy of systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis [published online October 6, 2018]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:411-416.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.053
- Blake SC, Murrell DF. Monitoring trough levels in cyclosporine for atopic dermatitis: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:843-853. doi:10.1111/pde.13999
- Tapia C, Nessel TA, Zito PM. Cyclosporine. StatPearls Publishing: 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482450/
- Cosottini M, Lazzarotti G, Ceravolo R, et al. Cyclosporine‐related posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in non‐transplant patient: a case report and literature review. Eur J Neurol. 2003;10:461-462. doi:10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00608_1.x
- Kochi S, Takanaga H, Matsuo H, et al. Induction of apoptosis in mouse brain capillary endothelial cells by cyclosporin A and tacrolimus. Life Sci. 2000;66:2255-2260. doi:10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00554-3
Practice Points
- Cyclosporine is an immunomodulatory therapeutic utilized for several indications in dermatology practice, most commonly in low doses.
- Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a known but rare adverse effect of cyclosporine presenting with acute encephalopathic changes and radiographic findings on central imaging.
- Knowledge of this association is critical, as symptoms are reversible with prompt recognition, appropriate inpatient supportive care, and discontinuation of offending medications.
Kaposi Varicelliform Eruption of Mpox in a Peeling Sunburn
To the Editor:
The recent global mpox (monkeypox) outbreak that started in May 2022 has distinctive risk factors, clinical features, and patient attributes that can portend dissemination of infection. We report a case of Kaposi varicelliform eruption (KVE) over a peeling sunburn after mpox infection. Dermatologists should recognize cutaneous risk factors for dissemination of mpox.
A 35-year-old man who was otherwise healthy presented with a papulopustular eruption that began on the shoulders in an area that had been sunburned 24 to 48 hours earlier. He experienced fever (temperature, 38.6 °C)[101.5 °F]), chills, malaise, and the appearance of a painful penile ulcer. He reported a recent male sexual partner a week prior to the eruption during travel to eastern Asia and a subsequent male partner in the United States 5 days prior to eruption. Physical examination revealed a peeling sunburn with sharp clothing demarcation. Locations with the most notable desquamation—the superior shoulders, dorsal arms, upper chest, and ventral thighs—positively correlated with the highest density of scattered, discrete, erythematous-based pustules and pink papules, some with crusted umbilication (Figures 1 and 2). Lesions spared sun-protected locations except a punctate painful ulcer on the buccal mucosa and a tender well-demarcated ulcer with elevated borders on the ventral penile shaft. HIV antigen/antibody testing was negative; syphilis antibody testing was positive due to a prior infection 1 year earlier with titers down to 1:1. A penile ulcer swab did not detect herpes simplex virus types 1/2 DNA. Pharyngeal, penile, and rectal swabs were negative for chlamydia or gonorrhea DNA. A polymerase chain reaction assay of a pustule was positive for orthopoxvirus, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed Monkeypox virus. On day 12, a penile ulcer biopsy was nonspecific with dense mixed inflammation; immunohistochemical stains for Treponema pallidum and herpes simplex virus types 1/2 were negative. Consideration was given to starting antiviral treatment with tecovirimat, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for smallpox caused by variola virus, through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expanded access protocol, but the patient’s symptoms and lesions cleared quickly without intervention. The patient’s recent sexual contact in the United States later tested positive for mpox. Given that the density of our patient’s mpox lesions positively correlated with areas of peeling sunburn with rapid spread during the period of desquamation, he was diagnosed with KVE due to mpox in the setting of a peeling sunburn.
The recent mpox outbreak began in May 2022, and within 3 months there were more than 31,000 confirmed mpox cases worldwide, with more than 11,000 of those cases within the United States across 49 states and Puerto Rico.1 Gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men have constituted the majority of cases. Although prior outbreaks have exhibited cases of classic mpox lesions, the current cases are clinically distinctive from classic mpox due to prevalent orogenital involvement and generalized symptoms that often are mild, nonexistent, or can occur after the cutaneous lesions.2
Although most current cases of mpox have been mildly symptomatic, several patients have been ill enough to require hospital admission, including patients with severe anogenital ulcerative lesions or bacterial superinfection.3 Antiviral treatment with tecovirimat may be warranted for patients with severe disease or those at risk of becoming severe due to immunosuppression, pregnancy/breastfeeding, complications (as determined by the provider), younger age (ie, pediatric patients), or skin barrier disruption. Dermatologists play a particularly important role in identifying cutaneous risk factors that may indicate progression of infection (eg, atopic dermatitis, severe acne, intertrigo, Darier disease). Kaposi varicelliform eruption is the phenomenon where a more typically localized vesicular infection is disseminated to areas with a defective skin barrier.2 Eczema herpeticum refers to the most common type of KVE due to herpes simplex virus, but other known etiologies of KVE include coxsackievirus A16, vaccinia virus, varicella-zoster virus, and smallpox.2 Although classic mpox previously had only the theoretical potential to lead to a secondary KVE, we expect the literature to evolve as cases spread, with one recent report of eczema monkeypoxicum in the setting of atopic dermatitis.4
At the time of publication, mpox cases have notably dropped globally due to public health interventions; however, mpox infections are ongoing in areas previously identified as nonendemic. Given the distinctive risk factors and clinical presentations of this most recent outbreak, clinicians will need to be adept at identifying not only infection but also risk for dissemination, including skin barrier disruption.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Mpox: 2022 US map & case count. Updated February 15, 2023. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/response/2022/us-map.html
- Karray M, Kwan E, Souissi A. Kaposi varicelliform eruption. StatPearls. Updated September 12, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482432
- Girometti N, Byrne R, Bracchi M, et al. Demographic and clinical characteristics of confirmed human monkeypox virus cases in individuals attending a sexual health centre in London, UK: an observational analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;S1473-3099(22)00411-X. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00411-X
- Xia J, Huang CL, Chu P, et al. Eczema monkeypoxicum: report of monkeypox transmission in patients with atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Reports. 2022;29:95-99.
To the Editor:
The recent global mpox (monkeypox) outbreak that started in May 2022 has distinctive risk factors, clinical features, and patient attributes that can portend dissemination of infection. We report a case of Kaposi varicelliform eruption (KVE) over a peeling sunburn after mpox infection. Dermatologists should recognize cutaneous risk factors for dissemination of mpox.
A 35-year-old man who was otherwise healthy presented with a papulopustular eruption that began on the shoulders in an area that had been sunburned 24 to 48 hours earlier. He experienced fever (temperature, 38.6 °C)[101.5 °F]), chills, malaise, and the appearance of a painful penile ulcer. He reported a recent male sexual partner a week prior to the eruption during travel to eastern Asia and a subsequent male partner in the United States 5 days prior to eruption. Physical examination revealed a peeling sunburn with sharp clothing demarcation. Locations with the most notable desquamation—the superior shoulders, dorsal arms, upper chest, and ventral thighs—positively correlated with the highest density of scattered, discrete, erythematous-based pustules and pink papules, some with crusted umbilication (Figures 1 and 2). Lesions spared sun-protected locations except a punctate painful ulcer on the buccal mucosa and a tender well-demarcated ulcer with elevated borders on the ventral penile shaft. HIV antigen/antibody testing was negative; syphilis antibody testing was positive due to a prior infection 1 year earlier with titers down to 1:1. A penile ulcer swab did not detect herpes simplex virus types 1/2 DNA. Pharyngeal, penile, and rectal swabs were negative for chlamydia or gonorrhea DNA. A polymerase chain reaction assay of a pustule was positive for orthopoxvirus, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed Monkeypox virus. On day 12, a penile ulcer biopsy was nonspecific with dense mixed inflammation; immunohistochemical stains for Treponema pallidum and herpes simplex virus types 1/2 were negative. Consideration was given to starting antiviral treatment with tecovirimat, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for smallpox caused by variola virus, through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expanded access protocol, but the patient’s symptoms and lesions cleared quickly without intervention. The patient’s recent sexual contact in the United States later tested positive for mpox. Given that the density of our patient’s mpox lesions positively correlated with areas of peeling sunburn with rapid spread during the period of desquamation, he was diagnosed with KVE due to mpox in the setting of a peeling sunburn.

The recent mpox outbreak began in May 2022, and within 3 months there were more than 31,000 confirmed mpox cases worldwide, with more than 11,000 of those cases within the United States across 49 states and Puerto Rico.1 Gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men have constituted the majority of cases. Although prior outbreaks have exhibited cases of classic mpox lesions, the current cases are clinically distinctive from classic mpox due to prevalent orogenital involvement and generalized symptoms that often are mild, nonexistent, or can occur after the cutaneous lesions.2

Although most current cases of mpox have been mildly symptomatic, several patients have been ill enough to require hospital admission, including patients with severe anogenital ulcerative lesions or bacterial superinfection.3 Antiviral treatment with tecovirimat may be warranted for patients with severe disease or those at risk of becoming severe due to immunosuppression, pregnancy/breastfeeding, complications (as determined by the provider), younger age (ie, pediatric patients), or skin barrier disruption. Dermatologists play a particularly important role in identifying cutaneous risk factors that may indicate progression of infection (eg, atopic dermatitis, severe acne, intertrigo, Darier disease). Kaposi varicelliform eruption is the phenomenon where a more typically localized vesicular infection is disseminated to areas with a defective skin barrier.2 Eczema herpeticum refers to the most common type of KVE due to herpes simplex virus, but other known etiologies of KVE include coxsackievirus A16, vaccinia virus, varicella-zoster virus, and smallpox.2 Although classic mpox previously had only the theoretical potential to lead to a secondary KVE, we expect the literature to evolve as cases spread, with one recent report of eczema monkeypoxicum in the setting of atopic dermatitis.4
At the time of publication, mpox cases have notably dropped globally due to public health interventions; however, mpox infections are ongoing in areas previously identified as nonendemic. Given the distinctive risk factors and clinical presentations of this most recent outbreak, clinicians will need to be adept at identifying not only infection but also risk for dissemination, including skin barrier disruption.
To the Editor:
The recent global mpox (monkeypox) outbreak that started in May 2022 has distinctive risk factors, clinical features, and patient attributes that can portend dissemination of infection. We report a case of Kaposi varicelliform eruption (KVE) over a peeling sunburn after mpox infection. Dermatologists should recognize cutaneous risk factors for dissemination of mpox.
A 35-year-old man who was otherwise healthy presented with a papulopustular eruption that began on the shoulders in an area that had been sunburned 24 to 48 hours earlier. He experienced fever (temperature, 38.6 °C)[101.5 °F]), chills, malaise, and the appearance of a painful penile ulcer. He reported a recent male sexual partner a week prior to the eruption during travel to eastern Asia and a subsequent male partner in the United States 5 days prior to eruption. Physical examination revealed a peeling sunburn with sharp clothing demarcation. Locations with the most notable desquamation—the superior shoulders, dorsal arms, upper chest, and ventral thighs—positively correlated with the highest density of scattered, discrete, erythematous-based pustules and pink papules, some with crusted umbilication (Figures 1 and 2). Lesions spared sun-protected locations except a punctate painful ulcer on the buccal mucosa and a tender well-demarcated ulcer with elevated borders on the ventral penile shaft. HIV antigen/antibody testing was negative; syphilis antibody testing was positive due to a prior infection 1 year earlier with titers down to 1:1. A penile ulcer swab did not detect herpes simplex virus types 1/2 DNA. Pharyngeal, penile, and rectal swabs were negative for chlamydia or gonorrhea DNA. A polymerase chain reaction assay of a pustule was positive for orthopoxvirus, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed Monkeypox virus. On day 12, a penile ulcer biopsy was nonspecific with dense mixed inflammation; immunohistochemical stains for Treponema pallidum and herpes simplex virus types 1/2 were negative. Consideration was given to starting antiviral treatment with tecovirimat, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for smallpox caused by variola virus, through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expanded access protocol, but the patient’s symptoms and lesions cleared quickly without intervention. The patient’s recent sexual contact in the United States later tested positive for mpox. Given that the density of our patient’s mpox lesions positively correlated with areas of peeling sunburn with rapid spread during the period of desquamation, he was diagnosed with KVE due to mpox in the setting of a peeling sunburn.

The recent mpox outbreak began in May 2022, and within 3 months there were more than 31,000 confirmed mpox cases worldwide, with more than 11,000 of those cases within the United States across 49 states and Puerto Rico.1 Gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men have constituted the majority of cases. Although prior outbreaks have exhibited cases of classic mpox lesions, the current cases are clinically distinctive from classic mpox due to prevalent orogenital involvement and generalized symptoms that often are mild, nonexistent, or can occur after the cutaneous lesions.2

Although most current cases of mpox have been mildly symptomatic, several patients have been ill enough to require hospital admission, including patients with severe anogenital ulcerative lesions or bacterial superinfection.3 Antiviral treatment with tecovirimat may be warranted for patients with severe disease or those at risk of becoming severe due to immunosuppression, pregnancy/breastfeeding, complications (as determined by the provider), younger age (ie, pediatric patients), or skin barrier disruption. Dermatologists play a particularly important role in identifying cutaneous risk factors that may indicate progression of infection (eg, atopic dermatitis, severe acne, intertrigo, Darier disease). Kaposi varicelliform eruption is the phenomenon where a more typically localized vesicular infection is disseminated to areas with a defective skin barrier.2 Eczema herpeticum refers to the most common type of KVE due to herpes simplex virus, but other known etiologies of KVE include coxsackievirus A16, vaccinia virus, varicella-zoster virus, and smallpox.2 Although classic mpox previously had only the theoretical potential to lead to a secondary KVE, we expect the literature to evolve as cases spread, with one recent report of eczema monkeypoxicum in the setting of atopic dermatitis.4
At the time of publication, mpox cases have notably dropped globally due to public health interventions; however, mpox infections are ongoing in areas previously identified as nonendemic. Given the distinctive risk factors and clinical presentations of this most recent outbreak, clinicians will need to be adept at identifying not only infection but also risk for dissemination, including skin barrier disruption.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Mpox: 2022 US map & case count. Updated February 15, 2023. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/response/2022/us-map.html
- Karray M, Kwan E, Souissi A. Kaposi varicelliform eruption. StatPearls. Updated September 12, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482432
- Girometti N, Byrne R, Bracchi M, et al. Demographic and clinical characteristics of confirmed human monkeypox virus cases in individuals attending a sexual health centre in London, UK: an observational analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;S1473-3099(22)00411-X. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00411-X
- Xia J, Huang CL, Chu P, et al. Eczema monkeypoxicum: report of monkeypox transmission in patients with atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Reports. 2022;29:95-99.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Mpox: 2022 US map & case count. Updated February 15, 2023. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/response/2022/us-map.html
- Karray M, Kwan E, Souissi A. Kaposi varicelliform eruption. StatPearls. Updated September 12, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482432
- Girometti N, Byrne R, Bracchi M, et al. Demographic and clinical characteristics of confirmed human monkeypox virus cases in individuals attending a sexual health centre in London, UK: an observational analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;S1473-3099(22)00411-X. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00411-X
- Xia J, Huang CL, Chu P, et al. Eczema monkeypoxicum: report of monkeypox transmission in patients with atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Reports. 2022;29:95-99.
Practice Points
- Desquamation can be associated with dissemination and higher severity course in the setting of mpox (monkeypox) viral infection.
- Antiviral treatment with tecovirimat is warranted in those with severe mpox infection or those at risk of severe infection including skin barrier disruption.
- Kaposi varicelliform–like eruptions can happen in the setting of barrier disruption from peeling sunburns, atopic dermatitis, severe acne, and other dermatologic conditions.
Multimodal Treatment of Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis in an HIV-Positive Man
To the Editor:
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EDV) is a rare generalized form of epidermal dysplasia that is linked to certain subtypes of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and inherited or acquired states of immunodeficiency.1-3 The inherited form most commonly manifests via autosomal-recessive inactivation of the EVER1 and EVER2 genes that encode integral membrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, though cases of autosomal-dominant and X-linked inheritance have been reported.1-3 Acquired cases have been reported in patients lacking immunocompetency, including transplant recipients and patients living with HIV.4-11 We present the case of a patient with HIV-associated EDV who was treated successfully with intralesional Candida albicans antigen, oral acitretin, and cryotherapy.
A 56-year-old man presented for evaluation of several cutaneous lesions that had developed over several months on the neck and over many years on the hands and feet. He had a 16-year history of HIV, Castleman disease, and primary effusion lymphoma in remission that was treated with rituximab, etoposide phosphate, prednisone, vincristine sulfate, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin hydrochloride 10 or more years ago. The patient denied pruritus or pain associated with the skin lesions. He was intermittently taking immunosuppressants and antiretrovirals including dolutegravir and emtricitabine-tenofovir for 3 years. Prior treatments of the lesions included cryotherapy and over-the-counter 17% salicylic acid. Physical examination revealed the presence of innumerable, clustered, verrucous, scaly papules on the dorsal and palmoplantar regions of the hands (Figure 1), as well as hypopigmented macules clustered on the neck that morphologically resembled tinea versicolor (Figure 2). The physical examination was otherwise unremarkable.
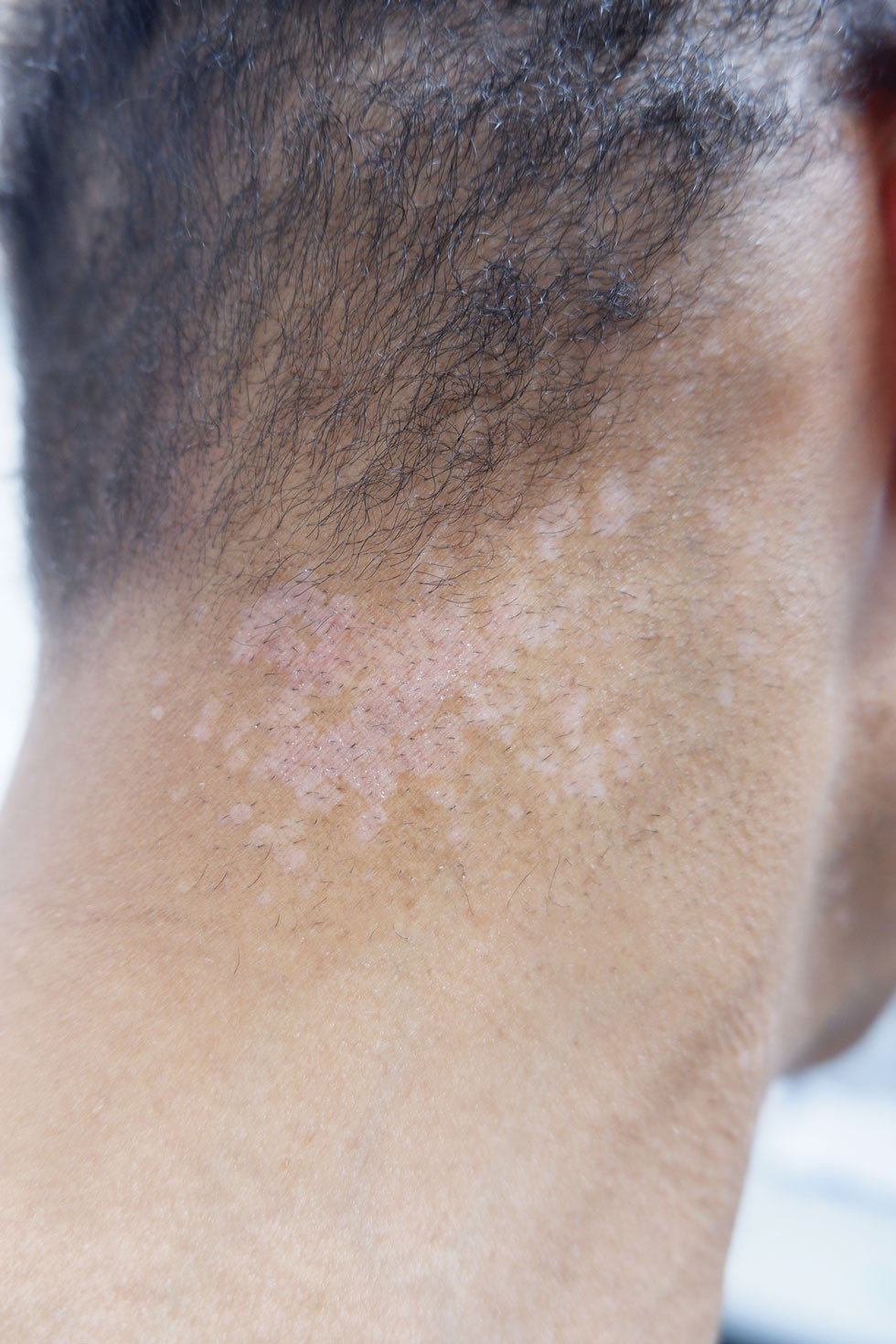
Complete blood cell counts as well as lipid, liver, and renal function panel results were unremarkable. Laboratory examination also revealed a CD4 cell count of 373/µL (reference range, 320–1900/µL) and an undetectable HIV copy number (<40 copies/mL). A punch biopsy of a hypopigmented macule on the left side of the neck revealed epidermal acanthosis, hypergranulosis, and hyperkeratosis, with blue-gray cytoplasm observed in the keratinocytes (Figure 3). Koilocytes with perinuclear clearing associated with keratinocytes in the upper epidermis were noted. Based on the clinical and histopathologic correlation, acquired EDV was diagnosed.
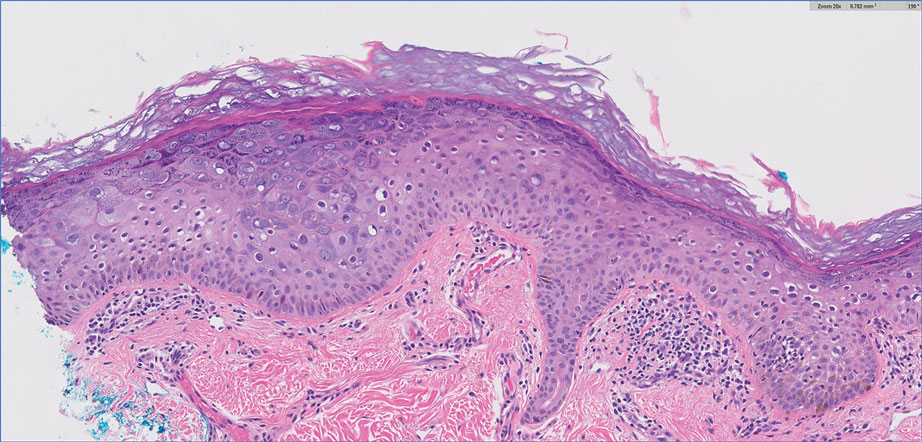
Given that HIV-associated EDV often is recalcitrant and there is a lack of consistent and effective treatment, the patient initially was prescribed oral acitretin 25 mg/d with intralesional C albicans antigen injected once per month into the lesions along with concurrent cryotherapy. At subsequent monthly follow-ups, the involved areas were notably thinner and flat. The patient reported no remarkable side effects from the systemic retinoid treatment such as abdominal pain, photosensitivity, or headaches, though he did experience mild xerosis. Complete resolution of EDV occurred with multimodal therapy—acitretin, cryotherapy, and intralesional Candida antigen. Palmar verrucae were much improved, and he is currently continuing therapy.
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is a rare genodermatosis associated with an abnormal susceptibility to cutaneous HPV and can be acquired in immunocompromised patients. Patients with EDV present with a clinically heterogeneous disease that can manifest as hypopigmented, red-brown macules with scaling on the trunk, neck, and extremities, which are morphologically similar to tinea versicolor, or patients can present with flat wartlike papules that are most commonly found on the face, hands, and feet.2,3 Epidermodysplasia verruciformis can be distinguished from EDV-like eruptions and other generalized verrucoses by its characteristic histologic appearance and by the demonstration of HPV within the lesions, typically subtypes HPV-5 and HPV-8.1-3 Classic EDV histopathologic findings include mild to moderate acanthosis and hyperkeratosis with enlarged keratinocytes featuring blue-gray cytoplasm and perinuclear halos.1
The histologic differential diagnosis of EDV is quite broad and includes common verrucae, which may be distinguished by the absence of blue-gray discoloration of the cytoplasm among the individual keratinocytes.1 Verruca plana and condylomata also may mimic EDV, and patients may present with minimal papillomatosis of the surface epidermis.2 Squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCC-IS) and particularly bowenoid papulosis also may share similar histologic features.2 However, in SCC-IS, there typically is full-thickness dysplasia of the epidermis, which is not present in EDV. Nonetheless, EDV is equivalent to SCC-IS in its clinical behavior. Bowenoid papulosis shares similar findings, but lesions generally are located in the genital areas and linked to HPV-16 and HPV-18.2 Additional histologic features of EDV have been described in the entity of EDV acanthoma, specifically incidental findings present in association with other cutaneous neoplasms including acantholytic acanthomas, condylomas, intradermal nevi, and seborrheic keratoses.12
The pathophysiology of EDV is thought to be specifically associated with patients with immunocompromised conditions. Particular attention has been paid to the association between EDV and HIV. Anselmo et al13 reported a case of HIV-associated acquired EDV with preexisting lesions that were spread along the distribution of the patient’s tattoo, suggesting potential autoinoculation. In individuals living with HIV, the cutaneous features of EDV are not associated with immune status.14
Acquired EDV also may be associated with other conditions including renal transplantation, IgM deficiency, severe combined immunodeficiency, common variable immunodeficiency, systemic lupus erythematosus, and myasthenia gravis.2 Hematologic malignancies such as Hodgkin disease,4 natural killer/T-cell lymphoma,5 cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,6 adult T-cell leukemia,7 intestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma,8,9 transformed acute myelogenous lymphoma,10 and chronic myelogenous leukemia11 also may be associated with EDV. In the inherited form, integral membrane proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum encoded by the genes EVER1 and EVER2 on chromosome 17 are thought to act as restriction factors for certain types of HPV.2,3 Inactivating mutations in EVER1 and EVER2 result in defects in cell-mediated immunity, rendering patients susceptible to both benign and oncogenic verrucous infections.2,3 Currently, it is believed that immunosuppressed states may result in defects in cell-mediated immunity that make patients similarly susceptible to these virulent strains of HPV, resulting in an acquired form of EDV.3 Interestingly, the clinical and histologic presentation is identical for acquired EDV and genetic EDV.
Due to the general resistance of EDV to treatment, a variety of options for acquired EDV have been explored including topical and systemic retinoids, cryotherapy, interferon alfa‐2a, zidovudine, ketoconazole, corticosteroids, podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, cidofovir, electrosurgery, 5‐fluorouracil, glycolic acid, temporized diathermy, and methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy.3 Highly active antiretroviral therapy has been proposed as a potential treatment modality for HIV-associated cases; however, acquired EDV has been reported to develop as an immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after the initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy.15
Combination therapy consisting of a systemic retinoid, immunotherapy, and cryotherapy was initiated for our patient. Human papillomavirus infection is marked by epithelial hyperplasia, and retinoids induce antiproliferation through the control of epithelial cell differentiation.16 The specific mechanism of action of retinoids in EDV treatment is unknown; however, the beneficial effects may result from the modification of terminal differentiation, a direct antiviral action, or the enhancement of killer T cells.17 Immunotherapy with C albicans antigen initiates an inflammatory reaction that leads to an immune response directed against the virus, thus reducing the number of warts.2 Cryotherapy aims to destroy the lesion but not the virus.2 The combination of systemic retinoids, immunotherapy, and destruction may target EDV via multiple potentially synergistic mechanisms. Thus, a multimodal approach can be beneficial in patients with recalcitrant acquired EDV.
The occurrence of EDV is rare, and data on treatment are limited in number resulting in general uncertainty about the efficacy of therapies. Elucidation of the specific mechanism of immunosuppression and its effects on T lymphocytes in acquired EDV may shed light on the most effective treatments. We present this novel case of a patient with HIV-associated acquired EDV who responded favorably to a combination treatment of acitretin, intralesional C albicans antigen, and cryotherapy.
- Nuovo GJ, Ishag M. The histologic spectrum of epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1400-1406.
- Sri JC, Dubina MI, Kao GF, et al. Generalized verrucosis: a review of the associated diseases, evaluation, and treatments. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:292-311.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Gross G, Ellinger K, Roussaki A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in a patient with Hodgkin’s disease: characterization of a new papillomavirus type and interferon treatment. J Invest Dermatol. 1988;91:43-48.
- Boran P, Tokuc G, Ozberk M, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with natural killer/T cell lymphoma. J Pediatr. 2010;156:340-340.e1.
- Cutlan JE, Rashid RM, Torres-Cabala C, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis after cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: periungual presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:12.
- Kawai K, Egawa N, Kiyono T, et al. Epidermodysplasia-verruciformis-like eruption associated with gamma-papillomavirus infection in a patient with adult T-cell leukemia. Dermatology. 2009;219:274-278.
- Slawsky LD, Gilson RT, Hockley AJ, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with severe immunodeficiency, lymphoma, and disseminated molluscum contagiosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:448-450.
- Youssef M, Denguezli M, Ghariani N, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with intestinal lymphoma: a model of viral oncogenicity. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:511-513.
- Kunishige JH, Hymes SR, Madkan V, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in the setting of graft-versus-host disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57(5 suppl):S78-S80.
- Binkley GW. A case for diagnosis (epidermodysplasia verruciformis?) chronic myeloid leukemia. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1947;55:280-282.
- Ko CJ, Iftner T, Barr RJ, et al. Changes of epidermodysplasia verruciformis in benign skin lesions: the EV acanthoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:44-48.
- Anselmo F, Ansari U, Gagnier JM, et al. Verrucous lesions in an HIV-positive man. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;5:825-827.
- Huang S, Wu JH, Lewis DJ, et al. A novel approach to the classification of epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1344-1350.
- Jacobelli S, Laude H, Carlotti A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: a marker of human papillomavirus-related disorders not affected by antiretroviral therapy. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:590-596.
- Limmer AL, Wu JH, Doan HQ, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a 10-year anniversary update. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:790-792.
- Anadolu R, Oskay T, Erdem C, et al. Treatment of epidermodysplasia verruciformis with a combination of acitretin and interferon alfa-2a.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:296-299.
To the Editor:
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EDV) is a rare generalized form of epidermal dysplasia that is linked to certain subtypes of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and inherited or acquired states of immunodeficiency.1-3 The inherited form most commonly manifests via autosomal-recessive inactivation of the EVER1 and EVER2 genes that encode integral membrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, though cases of autosomal-dominant and X-linked inheritance have been reported.1-3 Acquired cases have been reported in patients lacking immunocompetency, including transplant recipients and patients living with HIV.4-11 We present the case of a patient with HIV-associated EDV who was treated successfully with intralesional Candida albicans antigen, oral acitretin, and cryotherapy.

A 56-year-old man presented for evaluation of several cutaneous lesions that had developed over several months on the neck and over many years on the hands and feet. He had a 16-year history of HIV, Castleman disease, and primary effusion lymphoma in remission that was treated with rituximab, etoposide phosphate, prednisone, vincristine sulfate, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin hydrochloride 10 or more years ago. The patient denied pruritus or pain associated with the skin lesions. He was intermittently taking immunosuppressants and antiretrovirals including dolutegravir and emtricitabine-tenofovir for 3 years. Prior treatments of the lesions included cryotherapy and over-the-counter 17% salicylic acid. Physical examination revealed the presence of innumerable, clustered, verrucous, scaly papules on the dorsal and palmoplantar regions of the hands (Figure 1), as well as hypopigmented macules clustered on the neck that morphologically resembled tinea versicolor (Figure 2). The physical examination was otherwise unremarkable.

Complete blood cell counts as well as lipid, liver, and renal function panel results were unremarkable. Laboratory examination also revealed a CD4 cell count of 373/µL (reference range, 320–1900/µL) and an undetectable HIV copy number (<40 copies/mL). A punch biopsy of a hypopigmented macule on the left side of the neck revealed epidermal acanthosis, hypergranulosis, and hyperkeratosis, with blue-gray cytoplasm observed in the keratinocytes (Figure 3). Koilocytes with perinuclear clearing associated with keratinocytes in the upper epidermis were noted. Based on the clinical and histopathologic correlation, acquired EDV was diagnosed.

Given that HIV-associated EDV often is recalcitrant and there is a lack of consistent and effective treatment, the patient initially was prescribed oral acitretin 25 mg/d with intralesional C albicans antigen injected once per month into the lesions along with concurrent cryotherapy. At subsequent monthly follow-ups, the involved areas were notably thinner and flat. The patient reported no remarkable side effects from the systemic retinoid treatment such as abdominal pain, photosensitivity, or headaches, though he did experience mild xerosis. Complete resolution of EDV occurred with multimodal therapy—acitretin, cryotherapy, and intralesional Candida antigen. Palmar verrucae were much improved, and he is currently continuing therapy.
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is a rare genodermatosis associated with an abnormal susceptibility to cutaneous HPV and can be acquired in immunocompromised patients. Patients with EDV present with a clinically heterogeneous disease that can manifest as hypopigmented, red-brown macules with scaling on the trunk, neck, and extremities, which are morphologically similar to tinea versicolor, or patients can present with flat wartlike papules that are most commonly found on the face, hands, and feet.2,3 Epidermodysplasia verruciformis can be distinguished from EDV-like eruptions and other generalized verrucoses by its characteristic histologic appearance and by the demonstration of HPV within the lesions, typically subtypes HPV-5 and HPV-8.1-3 Classic EDV histopathologic findings include mild to moderate acanthosis and hyperkeratosis with enlarged keratinocytes featuring blue-gray cytoplasm and perinuclear halos.1
The histologic differential diagnosis of EDV is quite broad and includes common verrucae, which may be distinguished by the absence of blue-gray discoloration of the cytoplasm among the individual keratinocytes.1 Verruca plana and condylomata also may mimic EDV, and patients may present with minimal papillomatosis of the surface epidermis.2 Squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCC-IS) and particularly bowenoid papulosis also may share similar histologic features.2 However, in SCC-IS, there typically is full-thickness dysplasia of the epidermis, which is not present in EDV. Nonetheless, EDV is equivalent to SCC-IS in its clinical behavior. Bowenoid papulosis shares similar findings, but lesions generally are located in the genital areas and linked to HPV-16 and HPV-18.2 Additional histologic features of EDV have been described in the entity of EDV acanthoma, specifically incidental findings present in association with other cutaneous neoplasms including acantholytic acanthomas, condylomas, intradermal nevi, and seborrheic keratoses.12
The pathophysiology of EDV is thought to be specifically associated with patients with immunocompromised conditions. Particular attention has been paid to the association between EDV and HIV. Anselmo et al13 reported a case of HIV-associated acquired EDV with preexisting lesions that were spread along the distribution of the patient’s tattoo, suggesting potential autoinoculation. In individuals living with HIV, the cutaneous features of EDV are not associated with immune status.14
Acquired EDV also may be associated with other conditions including renal transplantation, IgM deficiency, severe combined immunodeficiency, common variable immunodeficiency, systemic lupus erythematosus, and myasthenia gravis.2 Hematologic malignancies such as Hodgkin disease,4 natural killer/T-cell lymphoma,5 cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,6 adult T-cell leukemia,7 intestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma,8,9 transformed acute myelogenous lymphoma,10 and chronic myelogenous leukemia11 also may be associated with EDV. In the inherited form, integral membrane proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum encoded by the genes EVER1 and EVER2 on chromosome 17 are thought to act as restriction factors for certain types of HPV.2,3 Inactivating mutations in EVER1 and EVER2 result in defects in cell-mediated immunity, rendering patients susceptible to both benign and oncogenic verrucous infections.2,3 Currently, it is believed that immunosuppressed states may result in defects in cell-mediated immunity that make patients similarly susceptible to these virulent strains of HPV, resulting in an acquired form of EDV.3 Interestingly, the clinical and histologic presentation is identical for acquired EDV and genetic EDV.
Due to the general resistance of EDV to treatment, a variety of options for acquired EDV have been explored including topical and systemic retinoids, cryotherapy, interferon alfa‐2a, zidovudine, ketoconazole, corticosteroids, podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, cidofovir, electrosurgery, 5‐fluorouracil, glycolic acid, temporized diathermy, and methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy.3 Highly active antiretroviral therapy has been proposed as a potential treatment modality for HIV-associated cases; however, acquired EDV has been reported to develop as an immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after the initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy.15
Combination therapy consisting of a systemic retinoid, immunotherapy, and cryotherapy was initiated for our patient. Human papillomavirus infection is marked by epithelial hyperplasia, and retinoids induce antiproliferation through the control of epithelial cell differentiation.16 The specific mechanism of action of retinoids in EDV treatment is unknown; however, the beneficial effects may result from the modification of terminal differentiation, a direct antiviral action, or the enhancement of killer T cells.17 Immunotherapy with C albicans antigen initiates an inflammatory reaction that leads to an immune response directed against the virus, thus reducing the number of warts.2 Cryotherapy aims to destroy the lesion but not the virus.2 The combination of systemic retinoids, immunotherapy, and destruction may target EDV via multiple potentially synergistic mechanisms. Thus, a multimodal approach can be beneficial in patients with recalcitrant acquired EDV.
The occurrence of EDV is rare, and data on treatment are limited in number resulting in general uncertainty about the efficacy of therapies. Elucidation of the specific mechanism of immunosuppression and its effects on T lymphocytes in acquired EDV may shed light on the most effective treatments. We present this novel case of a patient with HIV-associated acquired EDV who responded favorably to a combination treatment of acitretin, intralesional C albicans antigen, and cryotherapy.
To the Editor:
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EDV) is a rare generalized form of epidermal dysplasia that is linked to certain subtypes of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and inherited or acquired states of immunodeficiency.1-3 The inherited form most commonly manifests via autosomal-recessive inactivation of the EVER1 and EVER2 genes that encode integral membrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, though cases of autosomal-dominant and X-linked inheritance have been reported.1-3 Acquired cases have been reported in patients lacking immunocompetency, including transplant recipients and patients living with HIV.4-11 We present the case of a patient with HIV-associated EDV who was treated successfully with intralesional Candida albicans antigen, oral acitretin, and cryotherapy.

A 56-year-old man presented for evaluation of several cutaneous lesions that had developed over several months on the neck and over many years on the hands and feet. He had a 16-year history of HIV, Castleman disease, and primary effusion lymphoma in remission that was treated with rituximab, etoposide phosphate, prednisone, vincristine sulfate, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin hydrochloride 10 or more years ago. The patient denied pruritus or pain associated with the skin lesions. He was intermittently taking immunosuppressants and antiretrovirals including dolutegravir and emtricitabine-tenofovir for 3 years. Prior treatments of the lesions included cryotherapy and over-the-counter 17% salicylic acid. Physical examination revealed the presence of innumerable, clustered, verrucous, scaly papules on the dorsal and palmoplantar regions of the hands (Figure 1), as well as hypopigmented macules clustered on the neck that morphologically resembled tinea versicolor (Figure 2). The physical examination was otherwise unremarkable.

Complete blood cell counts as well as lipid, liver, and renal function panel results were unremarkable. Laboratory examination also revealed a CD4 cell count of 373/µL (reference range, 320–1900/µL) and an undetectable HIV copy number (<40 copies/mL). A punch biopsy of a hypopigmented macule on the left side of the neck revealed epidermal acanthosis, hypergranulosis, and hyperkeratosis, with blue-gray cytoplasm observed in the keratinocytes (Figure 3). Koilocytes with perinuclear clearing associated with keratinocytes in the upper epidermis were noted. Based on the clinical and histopathologic correlation, acquired EDV was diagnosed.

Given that HIV-associated EDV often is recalcitrant and there is a lack of consistent and effective treatment, the patient initially was prescribed oral acitretin 25 mg/d with intralesional C albicans antigen injected once per month into the lesions along with concurrent cryotherapy. At subsequent monthly follow-ups, the involved areas were notably thinner and flat. The patient reported no remarkable side effects from the systemic retinoid treatment such as abdominal pain, photosensitivity, or headaches, though he did experience mild xerosis. Complete resolution of EDV occurred with multimodal therapy—acitretin, cryotherapy, and intralesional Candida antigen. Palmar verrucae were much improved, and he is currently continuing therapy.
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is a rare genodermatosis associated with an abnormal susceptibility to cutaneous HPV and can be acquired in immunocompromised patients. Patients with EDV present with a clinically heterogeneous disease that can manifest as hypopigmented, red-brown macules with scaling on the trunk, neck, and extremities, which are morphologically similar to tinea versicolor, or patients can present with flat wartlike papules that are most commonly found on the face, hands, and feet.2,3 Epidermodysplasia verruciformis can be distinguished from EDV-like eruptions and other generalized verrucoses by its characteristic histologic appearance and by the demonstration of HPV within the lesions, typically subtypes HPV-5 and HPV-8.1-3 Classic EDV histopathologic findings include mild to moderate acanthosis and hyperkeratosis with enlarged keratinocytes featuring blue-gray cytoplasm and perinuclear halos.1
The histologic differential diagnosis of EDV is quite broad and includes common verrucae, which may be distinguished by the absence of blue-gray discoloration of the cytoplasm among the individual keratinocytes.1 Verruca plana and condylomata also may mimic EDV, and patients may present with minimal papillomatosis of the surface epidermis.2 Squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCC-IS) and particularly bowenoid papulosis also may share similar histologic features.2 However, in SCC-IS, there typically is full-thickness dysplasia of the epidermis, which is not present in EDV. Nonetheless, EDV is equivalent to SCC-IS in its clinical behavior. Bowenoid papulosis shares similar findings, but lesions generally are located in the genital areas and linked to HPV-16 and HPV-18.2 Additional histologic features of EDV have been described in the entity of EDV acanthoma, specifically incidental findings present in association with other cutaneous neoplasms including acantholytic acanthomas, condylomas, intradermal nevi, and seborrheic keratoses.12
The pathophysiology of EDV is thought to be specifically associated with patients with immunocompromised conditions. Particular attention has been paid to the association between EDV and HIV. Anselmo et al13 reported a case of HIV-associated acquired EDV with preexisting lesions that were spread along the distribution of the patient’s tattoo, suggesting potential autoinoculation. In individuals living with HIV, the cutaneous features of EDV are not associated with immune status.14
Acquired EDV also may be associated with other conditions including renal transplantation, IgM deficiency, severe combined immunodeficiency, common variable immunodeficiency, systemic lupus erythematosus, and myasthenia gravis.2 Hematologic malignancies such as Hodgkin disease,4 natural killer/T-cell lymphoma,5 cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,6 adult T-cell leukemia,7 intestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma,8,9 transformed acute myelogenous lymphoma,10 and chronic myelogenous leukemia11 also may be associated with EDV. In the inherited form, integral membrane proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum encoded by the genes EVER1 and EVER2 on chromosome 17 are thought to act as restriction factors for certain types of HPV.2,3 Inactivating mutations in EVER1 and EVER2 result in defects in cell-mediated immunity, rendering patients susceptible to both benign and oncogenic verrucous infections.2,3 Currently, it is believed that immunosuppressed states may result in defects in cell-mediated immunity that make patients similarly susceptible to these virulent strains of HPV, resulting in an acquired form of EDV.3 Interestingly, the clinical and histologic presentation is identical for acquired EDV and genetic EDV.
Due to the general resistance of EDV to treatment, a variety of options for acquired EDV have been explored including topical and systemic retinoids, cryotherapy, interferon alfa‐2a, zidovudine, ketoconazole, corticosteroids, podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, cidofovir, electrosurgery, 5‐fluorouracil, glycolic acid, temporized diathermy, and methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy.3 Highly active antiretroviral therapy has been proposed as a potential treatment modality for HIV-associated cases; however, acquired EDV has been reported to develop as an immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after the initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy.15
Combination therapy consisting of a systemic retinoid, immunotherapy, and cryotherapy was initiated for our patient. Human papillomavirus infection is marked by epithelial hyperplasia, and retinoids induce antiproliferation through the control of epithelial cell differentiation.16 The specific mechanism of action of retinoids in EDV treatment is unknown; however, the beneficial effects may result from the modification of terminal differentiation, a direct antiviral action, or the enhancement of killer T cells.17 Immunotherapy with C albicans antigen initiates an inflammatory reaction that leads to an immune response directed against the virus, thus reducing the number of warts.2 Cryotherapy aims to destroy the lesion but not the virus.2 The combination of systemic retinoids, immunotherapy, and destruction may target EDV via multiple potentially synergistic mechanisms. Thus, a multimodal approach can be beneficial in patients with recalcitrant acquired EDV.
The occurrence of EDV is rare, and data on treatment are limited in number resulting in general uncertainty about the efficacy of therapies. Elucidation of the specific mechanism of immunosuppression and its effects on T lymphocytes in acquired EDV may shed light on the most effective treatments. We present this novel case of a patient with HIV-associated acquired EDV who responded favorably to a combination treatment of acitretin, intralesional C albicans antigen, and cryotherapy.
- Nuovo GJ, Ishag M. The histologic spectrum of epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1400-1406.
- Sri JC, Dubina MI, Kao GF, et al. Generalized verrucosis: a review of the associated diseases, evaluation, and treatments. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:292-311.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Gross G, Ellinger K, Roussaki A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in a patient with Hodgkin’s disease: characterization of a new papillomavirus type and interferon treatment. J Invest Dermatol. 1988;91:43-48.
- Boran P, Tokuc G, Ozberk M, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with natural killer/T cell lymphoma. J Pediatr. 2010;156:340-340.e1.
- Cutlan JE, Rashid RM, Torres-Cabala C, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis after cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: periungual presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:12.
- Kawai K, Egawa N, Kiyono T, et al. Epidermodysplasia-verruciformis-like eruption associated with gamma-papillomavirus infection in a patient with adult T-cell leukemia. Dermatology. 2009;219:274-278.
- Slawsky LD, Gilson RT, Hockley AJ, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with severe immunodeficiency, lymphoma, and disseminated molluscum contagiosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:448-450.
- Youssef M, Denguezli M, Ghariani N, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with intestinal lymphoma: a model of viral oncogenicity. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:511-513.
- Kunishige JH, Hymes SR, Madkan V, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in the setting of graft-versus-host disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57(5 suppl):S78-S80.
- Binkley GW. A case for diagnosis (epidermodysplasia verruciformis?) chronic myeloid leukemia. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1947;55:280-282.
- Ko CJ, Iftner T, Barr RJ, et al. Changes of epidermodysplasia verruciformis in benign skin lesions: the EV acanthoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:44-48.
- Anselmo F, Ansari U, Gagnier JM, et al. Verrucous lesions in an HIV-positive man. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;5:825-827.
- Huang S, Wu JH, Lewis DJ, et al. A novel approach to the classification of epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1344-1350.
- Jacobelli S, Laude H, Carlotti A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: a marker of human papillomavirus-related disorders not affected by antiretroviral therapy. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:590-596.
- Limmer AL, Wu JH, Doan HQ, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a 10-year anniversary update. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:790-792.
- Anadolu R, Oskay T, Erdem C, et al. Treatment of epidermodysplasia verruciformis with a combination of acitretin and interferon alfa-2a.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:296-299.
- Nuovo GJ, Ishag M. The histologic spectrum of epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1400-1406.
- Sri JC, Dubina MI, Kao GF, et al. Generalized verrucosis: a review of the associated diseases, evaluation, and treatments. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:292-311.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Gross G, Ellinger K, Roussaki A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in a patient with Hodgkin’s disease: characterization of a new papillomavirus type and interferon treatment. J Invest Dermatol. 1988;91:43-48.
- Boran P, Tokuc G, Ozberk M, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with natural killer/T cell lymphoma. J Pediatr. 2010;156:340-340.e1.
- Cutlan JE, Rashid RM, Torres-Cabala C, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis after cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: periungual presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:12.
- Kawai K, Egawa N, Kiyono T, et al. Epidermodysplasia-verruciformis-like eruption associated with gamma-papillomavirus infection in a patient with adult T-cell leukemia. Dermatology. 2009;219:274-278.
- Slawsky LD, Gilson RT, Hockley AJ, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with severe immunodeficiency, lymphoma, and disseminated molluscum contagiosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;27:448-450.
- Youssef M, Denguezli M, Ghariani N, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated with intestinal lymphoma: a model of viral oncogenicity. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:511-513.
- Kunishige JH, Hymes SR, Madkan V, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in the setting of graft-versus-host disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57(5 suppl):S78-S80.
- Binkley GW. A case for diagnosis (epidermodysplasia verruciformis?) chronic myeloid leukemia. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1947;55:280-282.
- Ko CJ, Iftner T, Barr RJ, et al. Changes of epidermodysplasia verruciformis in benign skin lesions: the EV acanthoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:44-48.
- Anselmo F, Ansari U, Gagnier JM, et al. Verrucous lesions in an HIV-positive man. JAAD Case Reports. 2019;5:825-827.
- Huang S, Wu JH, Lewis DJ, et al. A novel approach to the classification of epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1344-1350.
- Jacobelli S, Laude H, Carlotti A, et al. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: a marker of human papillomavirus-related disorders not affected by antiretroviral therapy. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:590-596.
- Limmer AL, Wu JH, Doan HQ, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a 10-year anniversary update. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:790-792.
- Anadolu R, Oskay T, Erdem C, et al. Treatment of epidermodysplasia verruciformis with a combination of acitretin and interferon alfa-2a.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:296-299.
Practice Points
- Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EDV) is associated with immunocompromised patients with conditions such as HIV.
- Multimodal treatment of HIV-associated acquired EDV with acitretin, intralesional Candida albicans antigen, and cryotherapy may be efficacious for patients with recalcitrant disease.
Ticking Time: Spreading Awareness About African Tick-Bite Fever
To the Editor:
One of the more common tick-borne infections seen in travelers returning from sub-Saharan Africa is caused by Rickettsia africae, which is the etiologic agent of African tick-bite fever (ATBF), the most common tick-borne bacterial zoonosis.1 There are 2 known tick vectors of disease: Amblyomma variegatum, found in sub-Saharan Africa and the West Indies, and Amblyomma hebraeum, found specifically in southern Africa.2,3
Unlike other disease-carrying ticks that passively wait on vegetation to be picked up by a host, A hebraeum uniquely attract other nearby ticks to the host. Studies have shown that male ticks feeding on a nonhuman host (usually cattle) can emit an aggression-attachment pheromone that attracts other ticks to the host. The presence of the pheromone allows unfed ticks to actively discriminate between hosts on which these parasites have fed successfully (ie, suitable hosts) and those on which they have not.4
The aggressive hunting nature of A hebraeum explains the clinical presentation of multiple eschars and why large groups of exposed travelers—such as soldiers, leisure safari tourists, game hunters, and foreign-aid workers—are affected.2
Another southern African spotted fever group, Rickettsia conorii is the causative agent of Mediterranean spotted fever (MSF). Ticks carrying R conorii exhibit a much less aggressive hunting stylethan A hebraeum; consequently, infected patients present with a single eschar site.5
Rickettsia africae is estimated to have very high prevalence (95.2%) in Amblyomma ticks and a fairly high prevalence (approximately 4.0% to 8.6%) in travelers coming from rural southern Africa,6,7 with an incubation period of 5 to 10 days after inoculation by an infected tick.8 Signs include fever, a generalized maculopapular or papulovesicular rash, and regional lymphadenopathy; symptoms include fatigue, headache, and myalgia.
The inoculation eschar—single or multiple—commonly presents on the legs and is accompanied by tender lymphadenopathy of draining nodes1,8 More severe findings, such as myocarditis and subacute neuropathy, have been reported in elderly patients.9
A 77-year-old man presented with a pruritic maculopapular and papulovesicular rash distributed over the upper and lower extremities of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient reported having been on a 12-day mission trip to Limpopo, South Africa, where he was constructing and installing safe toilets to replace dangerous toilet pits. He believed he had been bitten by 2 ticks, after which he noted a dark purple and black patch on the left lower leg by the third day of the trip. He developed a sudden persistent pruritic rash, first on the lower extremities and then spreading to the upper extremities. The patient was seen by an American physician in South Africa who gave him a 7-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate 100 mg twice daily. He then returned to the United States.
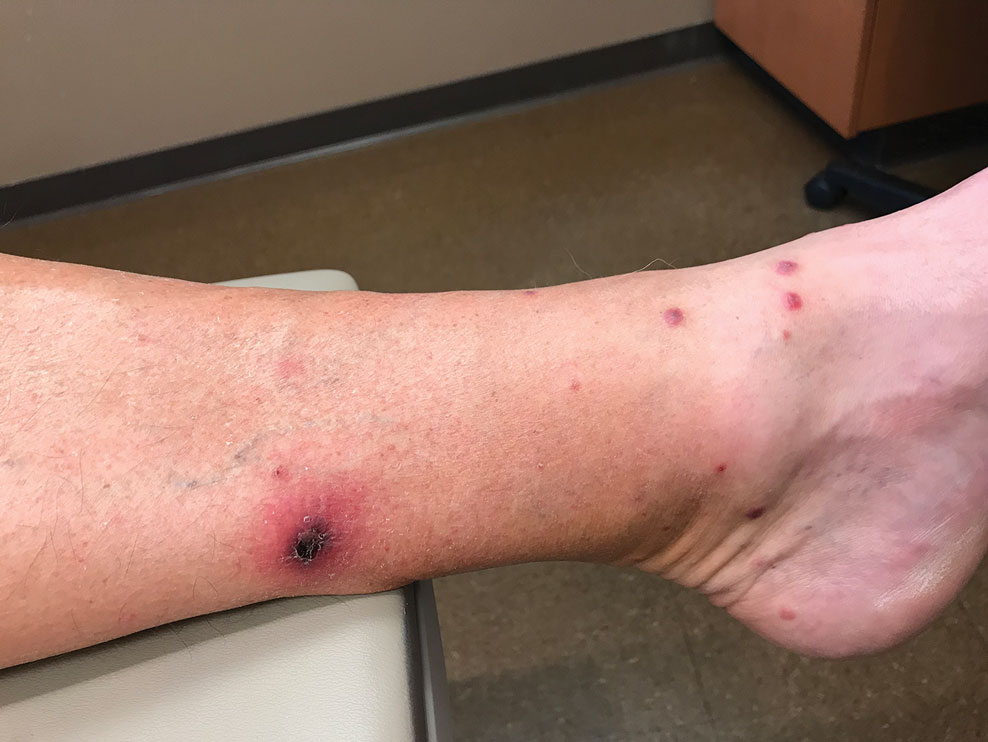
Sixteen days after being bitten by the ticks, the patient was examined in our dermatology office. Physical examination revealed an erythematous plaque with a central eschar over the medial aspect of the left leg (Figure 1) and multiple 3- to 6-mm, erythematous, dome-shaped papules scattered over the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles (Figure 2). The examination was otherwise normal. Blood was drawn the same day for laboratory analysis; no abnormalities of platelets, red blood cells, or white blood cells were found. Results of a chemistry panel and liver enzyme tests were within reference range.
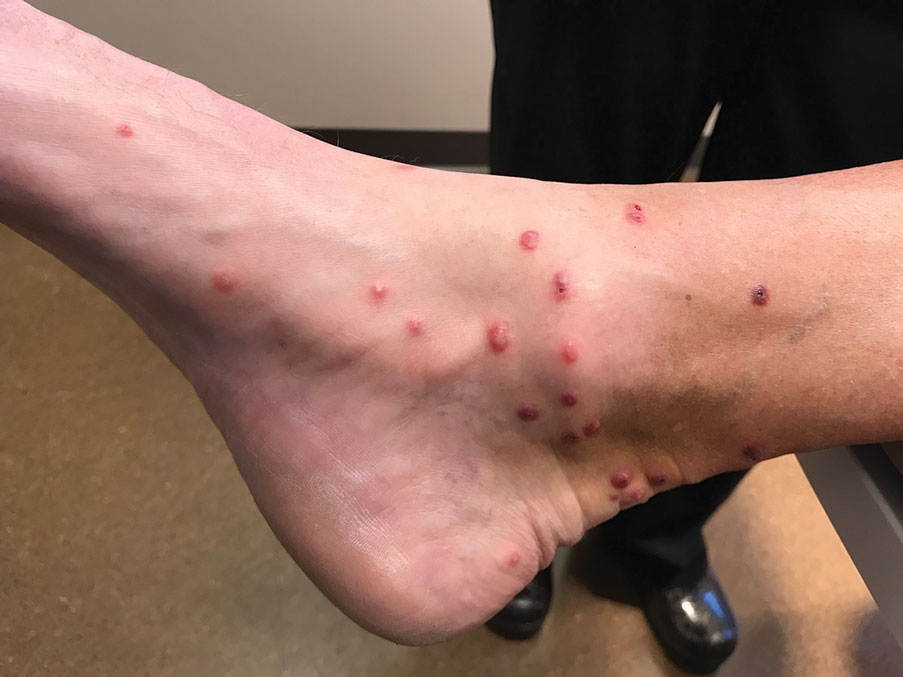
Skin biopsies were taken to elucidate the underlying pathology. Although an arthropod assault was suspected, there also was concern for deep vessel vasculitis because of the presence of considerable petechiae and purpura (Figure 3). Histologically, leukocytoclasia was seen in deep dermal blood vessels. A mild eosinophilic spongiosis with a mixed dermal infiltrate was identified—strengthening our suspicion of an arthropod assault. Bacterial cultures for aerobes and anaerobes using material taken from the right shin showed no growth.
Ten days after the initial biopsies, serum specimens were drawn and swabs of eschar were collected and sent to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for further testing. Serum was tested by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) for spotted fever group IgG to detect Rocky Mountain spotted fever and ATBF antibodies; both tests were negative. Swab material from eschar was tested again by IFA for spotted fever group IgG (Rocky Mountain spotted fever) and antibodies to ATBF and with bacterial culture isolation and nucleic acid amplification; the culture and amplification came back positive for R africae.
Because the specialized tests confirmed infection with R africae, the patient was given triamcinolone cream 0.1% to apply twice daily to the pruritic lesions for as long as 4 weeks; an additional 14-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate (100 mg twice daily) was given. At follow-up, the lesions had fully resolved without evident scarring.
Various diagnostic techniques can detect R africae. Bacterial culture and the polymerase chain reaction are specific and therefore diagnostic. In addition, the diagnosis of rickettsiosis can be made with serology testing, in which disease-specific antibodies are detected by indirect IFA using disease-specific antigens.
Antigens from R rickettsii (the agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever), R conorii (Mediterranean spotted fever), and R africae (ATBF) are commercially available for making the diagnosis of rickettsiosis. However, antigens from R conorii exhibit cross-reactivity with R africae, which can confound the diagnosis.1,10 Serologic IFA tests have been shown to be less sensitive, especially when performed after antibacterial treatment has started.
In a study, 17 of 65 (26%) ATBF-confirmed patients were seronegative (acute and convalescent-phase sera) against R africae; 14 had received doxycycline during the first week of clinical signs. The current hypothesis is that R africae is highly sensitive to doxycycline and that early exposure to the drug prevented development of detectable titers of reactive antibodies, thus producing a negative serology test.11
Furthermore, it has been shown that seroconversion of IgG and IgM antibodies in R africae–infected sera is delayed compared to what is observed with R conorii–infected sera. Typically, seroconversion of R conorii–infected sera can be detected within 2 weeks; seroconversion in R africae–infected sera can take 4 weeks or longer.11
Our patient had a confirmed case of ATBF secondary to R africae infection, which was evident from tissue culture isolation and polymerase chain reaction analysis of swab material obtained from eschar sites, both of which yielded a positive result for R africae. The traveler’s negative serologic status might be due to his early exposure to doxycycline or to the 4-week delay in R africae seroconversion; his serum was collected only 3 weeks after the tick bites.
Clinical signs also aid in making the diagnosis of ATBF and distinguishing R conorii from R africae infection. Because of the aggressive hunting nature of the tick carrying R africae, they are associated with multiple eschars and tend to affect groups of multiple people, especially in rural areas.4,5 In contrast, ticks carrying R conorii yield a single eschar due to their passive style of infecting a host and because they favor a single host within urban areas.5 Both infections exhibit a maculopapular or papulovesicular rash and are accompanied by fatigue, headache, and myalgia, though ATBF tends to present with a milder rash than MSF.
Infection with either R conorii or R africae responds to tetracyclines, quinolones, and macrolides.10,12
African tick-bite fever is becoming more common, which should encourage clinicians to become familiar with the disease. Less than 2 decades ago, ATBF virtually was unknown outside of Zimbabwe, Botswana, Tanzania, Zambia, and Kenya, where it is endemic. However, after the abolition of apartheid in the 1990s, international tourism in southern Africa increased 6-fold.13 African tick-bite fever is now one of the most common rickettsial infections in Africa.7 In addition to diagnosing ATBF and managing infected patients, clinicians can help prevent ATBF in individuals who travel to endemic areas by recommending commercial topical insect repellents containing at least 19.5% N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET).14
- Parola P, Paddock CD, Socolovschi C, et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: a geographic approach. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:657-702. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-13
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Vene S, et al; Norwegian African Tick Bite Fever Study Group. African tick bite fever in travelers to rural sub-equatorial Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:1411-1417. doi:10.1086/375083
- Parola P, Jourdan J, Raoult D. Tick-borne infection caused by Rickettsia africae in the West Indies. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1391-1392. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805073381918
- Norval RA, Andrew HR, Yunker CE. Pheromone-mediation of host-selection in bont ticks (Amblyomma hebraeum Koch). Science. 1989;243:364-365. doi:10.1126/science.2911745
- Parola P, Raoult D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: an emerging infectious threat. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:897-928. doi:10.1086/319347
- Kelly PJ, Mason PR. Transmission of a spotted fever group rickettsia by Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1991;28:598-600. doi:10.1093/jmedent/28.5.598
- Maina AN, Jiang J, Omulo SA, et al. High prevalence of Rickettsia africae variants in Amblyomma variegatum ticks from domestic mammals in rural Western Kenya: implications for human health. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:693-702. doi:10.1089/vbz.2014.1578
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Kelly P, et al. African tick bite fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:557-564. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(03)00739-4
- Roch N, Epaulard O, Pelloux I, et al. African tick bite fever in elderly patients: 8 cases in French tourists returning from South Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:E28-E35. doi:10.1086/589868
- Palau L, Pankey GA. Mediterranean spotted fever in travelers from the United States. J Travel Med. 1997;4:179-182. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.1997.tb00816.x
- Fournier P-E, Jensenius M, Laferl H, et al. Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:324-328. doi:10.1128/cdli.9.2.324-328.2002
- Brouqui P, Bacellar F, Baranton G, et al; ; . Guidelines for the diagnosis of tick-borne bacterial diseases in Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10:1108-1132. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.01019.x
- Rolain JM, Jensenius M, Raoult D. Rickettsial infections—a threat to travelers? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2004;17:433-437. doi:10.1097/00001432-200410000-00008
- Jensenius M, Pretorius AM, Clarke F, et al. Repellent efficacy of four commercial DEET lotions against Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae), the principal vector of Rickettsia africae in southern Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2005;99:708-711. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.01.006
To the Editor:
One of the more common tick-borne infections seen in travelers returning from sub-Saharan Africa is caused by Rickettsia africae, which is the etiologic agent of African tick-bite fever (ATBF), the most common tick-borne bacterial zoonosis.1 There are 2 known tick vectors of disease: Amblyomma variegatum, found in sub-Saharan Africa and the West Indies, and Amblyomma hebraeum, found specifically in southern Africa.2,3
Unlike other disease-carrying ticks that passively wait on vegetation to be picked up by a host, A hebraeum uniquely attract other nearby ticks to the host. Studies have shown that male ticks feeding on a nonhuman host (usually cattle) can emit an aggression-attachment pheromone that attracts other ticks to the host. The presence of the pheromone allows unfed ticks to actively discriminate between hosts on which these parasites have fed successfully (ie, suitable hosts) and those on which they have not.4
The aggressive hunting nature of A hebraeum explains the clinical presentation of multiple eschars and why large groups of exposed travelers—such as soldiers, leisure safari tourists, game hunters, and foreign-aid workers—are affected.2
Another southern African spotted fever group, Rickettsia conorii is the causative agent of Mediterranean spotted fever (MSF). Ticks carrying R conorii exhibit a much less aggressive hunting stylethan A hebraeum; consequently, infected patients present with a single eschar site.5
Rickettsia africae is estimated to have very high prevalence (95.2%) in Amblyomma ticks and a fairly high prevalence (approximately 4.0% to 8.6%) in travelers coming from rural southern Africa,6,7 with an incubation period of 5 to 10 days after inoculation by an infected tick.8 Signs include fever, a generalized maculopapular or papulovesicular rash, and regional lymphadenopathy; symptoms include fatigue, headache, and myalgia.
The inoculation eschar—single or multiple—commonly presents on the legs and is accompanied by tender lymphadenopathy of draining nodes1,8 More severe findings, such as myocarditis and subacute neuropathy, have been reported in elderly patients.9
A 77-year-old man presented with a pruritic maculopapular and papulovesicular rash distributed over the upper and lower extremities of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient reported having been on a 12-day mission trip to Limpopo, South Africa, where he was constructing and installing safe toilets to replace dangerous toilet pits. He believed he had been bitten by 2 ticks, after which he noted a dark purple and black patch on the left lower leg by the third day of the trip. He developed a sudden persistent pruritic rash, first on the lower extremities and then spreading to the upper extremities. The patient was seen by an American physician in South Africa who gave him a 7-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate 100 mg twice daily. He then returned to the United States.

Sixteen days after being bitten by the ticks, the patient was examined in our dermatology office. Physical examination revealed an erythematous plaque with a central eschar over the medial aspect of the left leg (Figure 1) and multiple 3- to 6-mm, erythematous, dome-shaped papules scattered over the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles (Figure 2). The examination was otherwise normal. Blood was drawn the same day for laboratory analysis; no abnormalities of platelets, red blood cells, or white blood cells were found. Results of a chemistry panel and liver enzyme tests were within reference range.

Skin biopsies were taken to elucidate the underlying pathology. Although an arthropod assault was suspected, there also was concern for deep vessel vasculitis because of the presence of considerable petechiae and purpura (Figure 3). Histologically, leukocytoclasia was seen in deep dermal blood vessels. A mild eosinophilic spongiosis with a mixed dermal infiltrate was identified—strengthening our suspicion of an arthropod assault. Bacterial cultures for aerobes and anaerobes using material taken from the right shin showed no growth.

Ten days after the initial biopsies, serum specimens were drawn and swabs of eschar were collected and sent to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for further testing. Serum was tested by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) for spotted fever group IgG to detect Rocky Mountain spotted fever and ATBF antibodies; both tests were negative. Swab material from eschar was tested again by IFA for spotted fever group IgG (Rocky Mountain spotted fever) and antibodies to ATBF and with bacterial culture isolation and nucleic acid amplification; the culture and amplification came back positive for R africae.
Because the specialized tests confirmed infection with R africae, the patient was given triamcinolone cream 0.1% to apply twice daily to the pruritic lesions for as long as 4 weeks; an additional 14-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate (100 mg twice daily) was given. At follow-up, the lesions had fully resolved without evident scarring.
Various diagnostic techniques can detect R africae. Bacterial culture and the polymerase chain reaction are specific and therefore diagnostic. In addition, the diagnosis of rickettsiosis can be made with serology testing, in which disease-specific antibodies are detected by indirect IFA using disease-specific antigens.
Antigens from R rickettsii (the agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever), R conorii (Mediterranean spotted fever), and R africae (ATBF) are commercially available for making the diagnosis of rickettsiosis. However, antigens from R conorii exhibit cross-reactivity with R africae, which can confound the diagnosis.1,10 Serologic IFA tests have been shown to be less sensitive, especially when performed after antibacterial treatment has started.
In a study, 17 of 65 (26%) ATBF-confirmed patients were seronegative (acute and convalescent-phase sera) against R africae; 14 had received doxycycline during the first week of clinical signs. The current hypothesis is that R africae is highly sensitive to doxycycline and that early exposure to the drug prevented development of detectable titers of reactive antibodies, thus producing a negative serology test.11
Furthermore, it has been shown that seroconversion of IgG and IgM antibodies in R africae–infected sera is delayed compared to what is observed with R conorii–infected sera. Typically, seroconversion of R conorii–infected sera can be detected within 2 weeks; seroconversion in R africae–infected sera can take 4 weeks or longer.11
Our patient had a confirmed case of ATBF secondary to R africae infection, which was evident from tissue culture isolation and polymerase chain reaction analysis of swab material obtained from eschar sites, both of which yielded a positive result for R africae. The traveler’s negative serologic status might be due to his early exposure to doxycycline or to the 4-week delay in R africae seroconversion; his serum was collected only 3 weeks after the tick bites.
Clinical signs also aid in making the diagnosis of ATBF and distinguishing R conorii from R africae infection. Because of the aggressive hunting nature of the tick carrying R africae, they are associated with multiple eschars and tend to affect groups of multiple people, especially in rural areas.4,5 In contrast, ticks carrying R conorii yield a single eschar due to their passive style of infecting a host and because they favor a single host within urban areas.5 Both infections exhibit a maculopapular or papulovesicular rash and are accompanied by fatigue, headache, and myalgia, though ATBF tends to present with a milder rash than MSF.
Infection with either R conorii or R africae responds to tetracyclines, quinolones, and macrolides.10,12
African tick-bite fever is becoming more common, which should encourage clinicians to become familiar with the disease. Less than 2 decades ago, ATBF virtually was unknown outside of Zimbabwe, Botswana, Tanzania, Zambia, and Kenya, where it is endemic. However, after the abolition of apartheid in the 1990s, international tourism in southern Africa increased 6-fold.13 African tick-bite fever is now one of the most common rickettsial infections in Africa.7 In addition to diagnosing ATBF and managing infected patients, clinicians can help prevent ATBF in individuals who travel to endemic areas by recommending commercial topical insect repellents containing at least 19.5% N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET).14
To the Editor:
One of the more common tick-borne infections seen in travelers returning from sub-Saharan Africa is caused by Rickettsia africae, which is the etiologic agent of African tick-bite fever (ATBF), the most common tick-borne bacterial zoonosis.1 There are 2 known tick vectors of disease: Amblyomma variegatum, found in sub-Saharan Africa and the West Indies, and Amblyomma hebraeum, found specifically in southern Africa.2,3
Unlike other disease-carrying ticks that passively wait on vegetation to be picked up by a host, A hebraeum uniquely attract other nearby ticks to the host. Studies have shown that male ticks feeding on a nonhuman host (usually cattle) can emit an aggression-attachment pheromone that attracts other ticks to the host. The presence of the pheromone allows unfed ticks to actively discriminate between hosts on which these parasites have fed successfully (ie, suitable hosts) and those on which they have not.4
The aggressive hunting nature of A hebraeum explains the clinical presentation of multiple eschars and why large groups of exposed travelers—such as soldiers, leisure safari tourists, game hunters, and foreign-aid workers—are affected.2
Another southern African spotted fever group, Rickettsia conorii is the causative agent of Mediterranean spotted fever (MSF). Ticks carrying R conorii exhibit a much less aggressive hunting stylethan A hebraeum; consequently, infected patients present with a single eschar site.5
Rickettsia africae is estimated to have very high prevalence (95.2%) in Amblyomma ticks and a fairly high prevalence (approximately 4.0% to 8.6%) in travelers coming from rural southern Africa,6,7 with an incubation period of 5 to 10 days after inoculation by an infected tick.8 Signs include fever, a generalized maculopapular or papulovesicular rash, and regional lymphadenopathy; symptoms include fatigue, headache, and myalgia.
The inoculation eschar—single or multiple—commonly presents on the legs and is accompanied by tender lymphadenopathy of draining nodes1,8 More severe findings, such as myocarditis and subacute neuropathy, have been reported in elderly patients.9
A 77-year-old man presented with a pruritic maculopapular and papulovesicular rash distributed over the upper and lower extremities of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient reported having been on a 12-day mission trip to Limpopo, South Africa, where he was constructing and installing safe toilets to replace dangerous toilet pits. He believed he had been bitten by 2 ticks, after which he noted a dark purple and black patch on the left lower leg by the third day of the trip. He developed a sudden persistent pruritic rash, first on the lower extremities and then spreading to the upper extremities. The patient was seen by an American physician in South Africa who gave him a 7-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate 100 mg twice daily. He then returned to the United States.

Sixteen days after being bitten by the ticks, the patient was examined in our dermatology office. Physical examination revealed an erythematous plaque with a central eschar over the medial aspect of the left leg (Figure 1) and multiple 3- to 6-mm, erythematous, dome-shaped papules scattered over the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles (Figure 2). The examination was otherwise normal. Blood was drawn the same day for laboratory analysis; no abnormalities of platelets, red blood cells, or white blood cells were found. Results of a chemistry panel and liver enzyme tests were within reference range.

Skin biopsies were taken to elucidate the underlying pathology. Although an arthropod assault was suspected, there also was concern for deep vessel vasculitis because of the presence of considerable petechiae and purpura (Figure 3). Histologically, leukocytoclasia was seen in deep dermal blood vessels. A mild eosinophilic spongiosis with a mixed dermal infiltrate was identified—strengthening our suspicion of an arthropod assault. Bacterial cultures for aerobes and anaerobes using material taken from the right shin showed no growth.

Ten days after the initial biopsies, serum specimens were drawn and swabs of eschar were collected and sent to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for further testing. Serum was tested by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) for spotted fever group IgG to detect Rocky Mountain spotted fever and ATBF antibodies; both tests were negative. Swab material from eschar was tested again by IFA for spotted fever group IgG (Rocky Mountain spotted fever) and antibodies to ATBF and with bacterial culture isolation and nucleic acid amplification; the culture and amplification came back positive for R africae.
Because the specialized tests confirmed infection with R africae, the patient was given triamcinolone cream 0.1% to apply twice daily to the pruritic lesions for as long as 4 weeks; an additional 14-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate (100 mg twice daily) was given. At follow-up, the lesions had fully resolved without evident scarring.
Various diagnostic techniques can detect R africae. Bacterial culture and the polymerase chain reaction are specific and therefore diagnostic. In addition, the diagnosis of rickettsiosis can be made with serology testing, in which disease-specific antibodies are detected by indirect IFA using disease-specific antigens.
Antigens from R rickettsii (the agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever), R conorii (Mediterranean spotted fever), and R africae (ATBF) are commercially available for making the diagnosis of rickettsiosis. However, antigens from R conorii exhibit cross-reactivity with R africae, which can confound the diagnosis.1,10 Serologic IFA tests have been shown to be less sensitive, especially when performed after antibacterial treatment has started.
In a study, 17 of 65 (26%) ATBF-confirmed patients were seronegative (acute and convalescent-phase sera) against R africae; 14 had received doxycycline during the first week of clinical signs. The current hypothesis is that R africae is highly sensitive to doxycycline and that early exposure to the drug prevented development of detectable titers of reactive antibodies, thus producing a negative serology test.11
Furthermore, it has been shown that seroconversion of IgG and IgM antibodies in R africae–infected sera is delayed compared to what is observed with R conorii–infected sera. Typically, seroconversion of R conorii–infected sera can be detected within 2 weeks; seroconversion in R africae–infected sera can take 4 weeks or longer.11
Our patient had a confirmed case of ATBF secondary to R africae infection, which was evident from tissue culture isolation and polymerase chain reaction analysis of swab material obtained from eschar sites, both of which yielded a positive result for R africae. The traveler’s negative serologic status might be due to his early exposure to doxycycline or to the 4-week delay in R africae seroconversion; his serum was collected only 3 weeks after the tick bites.
Clinical signs also aid in making the diagnosis of ATBF and distinguishing R conorii from R africae infection. Because of the aggressive hunting nature of the tick carrying R africae, they are associated with multiple eschars and tend to affect groups of multiple people, especially in rural areas.4,5 In contrast, ticks carrying R conorii yield a single eschar due to their passive style of infecting a host and because they favor a single host within urban areas.5 Both infections exhibit a maculopapular or papulovesicular rash and are accompanied by fatigue, headache, and myalgia, though ATBF tends to present with a milder rash than MSF.
Infection with either R conorii or R africae responds to tetracyclines, quinolones, and macrolides.10,12
African tick-bite fever is becoming more common, which should encourage clinicians to become familiar with the disease. Less than 2 decades ago, ATBF virtually was unknown outside of Zimbabwe, Botswana, Tanzania, Zambia, and Kenya, where it is endemic. However, after the abolition of apartheid in the 1990s, international tourism in southern Africa increased 6-fold.13 African tick-bite fever is now one of the most common rickettsial infections in Africa.7 In addition to diagnosing ATBF and managing infected patients, clinicians can help prevent ATBF in individuals who travel to endemic areas by recommending commercial topical insect repellents containing at least 19.5% N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET).14
- Parola P, Paddock CD, Socolovschi C, et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: a geographic approach. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:657-702. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-13
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Vene S, et al; Norwegian African Tick Bite Fever Study Group. African tick bite fever in travelers to rural sub-equatorial Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:1411-1417. doi:10.1086/375083
- Parola P, Jourdan J, Raoult D. Tick-borne infection caused by Rickettsia africae in the West Indies. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1391-1392. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805073381918
- Norval RA, Andrew HR, Yunker CE. Pheromone-mediation of host-selection in bont ticks (Amblyomma hebraeum Koch). Science. 1989;243:364-365. doi:10.1126/science.2911745
- Parola P, Raoult D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: an emerging infectious threat. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:897-928. doi:10.1086/319347
- Kelly PJ, Mason PR. Transmission of a spotted fever group rickettsia by Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1991;28:598-600. doi:10.1093/jmedent/28.5.598
- Maina AN, Jiang J, Omulo SA, et al. High prevalence of Rickettsia africae variants in Amblyomma variegatum ticks from domestic mammals in rural Western Kenya: implications for human health. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:693-702. doi:10.1089/vbz.2014.1578
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Kelly P, et al. African tick bite fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:557-564. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(03)00739-4
- Roch N, Epaulard O, Pelloux I, et al. African tick bite fever in elderly patients: 8 cases in French tourists returning from South Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:E28-E35. doi:10.1086/589868
- Palau L, Pankey GA. Mediterranean spotted fever in travelers from the United States. J Travel Med. 1997;4:179-182. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.1997.tb00816.x
- Fournier P-E, Jensenius M, Laferl H, et al. Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:324-328. doi:10.1128/cdli.9.2.324-328.2002
- Brouqui P, Bacellar F, Baranton G, et al; ; . Guidelines for the diagnosis of tick-borne bacterial diseases in Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10:1108-1132. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.01019.x
- Rolain JM, Jensenius M, Raoult D. Rickettsial infections—a threat to travelers? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2004;17:433-437. doi:10.1097/00001432-200410000-00008
- Jensenius M, Pretorius AM, Clarke F, et al. Repellent efficacy of four commercial DEET lotions against Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae), the principal vector of Rickettsia africae in southern Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2005;99:708-711. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.01.006
- Parola P, Paddock CD, Socolovschi C, et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: a geographic approach. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:657-702. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-13
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Vene S, et al; Norwegian African Tick Bite Fever Study Group. African tick bite fever in travelers to rural sub-equatorial Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:1411-1417. doi:10.1086/375083
- Parola P, Jourdan J, Raoult D. Tick-borne infection caused by Rickettsia africae in the West Indies. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1391-1392. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805073381918
- Norval RA, Andrew HR, Yunker CE. Pheromone-mediation of host-selection in bont ticks (Amblyomma hebraeum Koch). Science. 1989;243:364-365. doi:10.1126/science.2911745
- Parola P, Raoult D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: an emerging infectious threat. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:897-928. doi:10.1086/319347
- Kelly PJ, Mason PR. Transmission of a spotted fever group rickettsia by Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1991;28:598-600. doi:10.1093/jmedent/28.5.598
- Maina AN, Jiang J, Omulo SA, et al. High prevalence of Rickettsia africae variants in Amblyomma variegatum ticks from domestic mammals in rural Western Kenya: implications for human health. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:693-702. doi:10.1089/vbz.2014.1578
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Kelly P, et al. African tick bite fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:557-564. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(03)00739-4
- Roch N, Epaulard O, Pelloux I, et al. African tick bite fever in elderly patients: 8 cases in French tourists returning from South Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:E28-E35. doi:10.1086/589868
- Palau L, Pankey GA. Mediterranean spotted fever in travelers from the United States. J Travel Med. 1997;4:179-182. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.1997.tb00816.x
- Fournier P-E, Jensenius M, Laferl H, et al. Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:324-328. doi:10.1128/cdli.9.2.324-328.2002
- Brouqui P, Bacellar F, Baranton G, et al; ; . Guidelines for the diagnosis of tick-borne bacterial diseases in Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10:1108-1132. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.01019.x
- Rolain JM, Jensenius M, Raoult D. Rickettsial infections—a threat to travelers? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2004;17:433-437. doi:10.1097/00001432-200410000-00008
- Jensenius M, Pretorius AM, Clarke F, et al. Repellent efficacy of four commercial DEET lotions against Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae), the principal vector of Rickettsia africae in southern Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2005;99:708-711. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.01.006
PRACTICE POINTS
- African tick-bite fever (ATBF) is one of the more common tick-borne bacterial zoonoses and should be considered in patients presenting with multiple eschar sites who have had exposure to rural areas of southern Africa in the preceding 2 weeks.
- Ticks carrying Rickettsia africae are unique, given their ability to actively be attracted to and hunt their nonhuman hosts via an aggression-attachment pheromone.
- Laboratory diagnosis of ATBF can be challenging due to the high cross-reactivity of Helvetica Neue LT StdR africae with Helvetica Neue LT StdRickettsia conorii in serologic testing and the delay in seroconversion in Helvetica Neue LT StdR africae infection.
Hemorrhagic Lacrimation and Epistaxis: Rare Findings in Acute Hemorrhagic Edema of Infancy
To the Editor:
Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis are dramatic presentations with a narrow differential diagnosis. It rarely has been reported to present alongside the more typical features of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), which is a benign self-limited leukocytoclastic vasculitis most often seen in children aged 4 months to 2 years. Extracutaneous involvement rarely is seen in AHEI, though joint, gastrointestinal tract, and renal involvement have been reported.1 Most patients present with edematous, annular, or cockade purpuric vasculitic lesions classically involving the face and distal extremities with relative sparing of the trunk. We present a case of a well-appearing, 10-month-old infant boy with hemorrhagic vasculitic lesions, acral edema, and an associated episode of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis.
A 10-month-old infant boy who was otherwise healthy presented to the emergency department (ED) with an acute-onset, progressively worsening cutaneous eruption of 2 days’ duration. A thorough history revealed that the eruption initially had presented as several small, bright-red papules on the thighs. The eruption subsequently spread to involve the buttocks, legs, and arms (Figures 1 and 2). The parents also noted that the patient had experienced an episode of bloody tears and epistaxis that lasted a few minutes at the pediatrician’s office earlier that morning, a finding that prompted the urgent referral to the ED.
Dermatology was then consulted. A review of systems was notable for rhinorrhea and diarrhea during the week leading to the eruption. The patient’s parents denied fevers, decreased oral intake, or a recent course of antibiotics. The patient’s medical history was notable only for atopic dermatitis treated with emollients and occasional topical steroids. The parents denied recent travel or vaccinations. Physical examination showed an afebrile, well-appearing infant with multiple nontender, slightly edematous, circular, purpuric papules and plaques scattered on the buttocks and extremities with edema on the dorsal feet. The remainder of the patient’s workup in the ED was notable for mild elevations in C-reactive protein levels (1.4 mg/dL [reference range, 0–1.2 mg/dL]) and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (22 mm/h [reference range, 2–12 mm/h]). A complete blood cell count; liver function tests; urinalysis; and coagulation studies, including prothrombin, partial thromboplastin time, and international normalized ratio, were unremarkable. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy was diagnosed based on the clinical manifestations.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (also known as Finkelstein disease, medallionlike purpura, Seidemayer syndrome, infantile postinfectious irislike purpura and edema, and purpura en cocarde avec oedeme) is believed to result from an immune complex–related reaction, often in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection; medications, especially antibiotics; or vaccinations. The condition previously was considered a benign form of Henoch-Schönlein purpura; however, it is now recognized as its own clinical entity. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy commonly affects children between the ages of 4 months and 2 years. The incidence peaks in the winter months, and males tend to be more affected than females.1
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is clinically characterized by a triad of large purpuric lesions, low-grade fever, and peripheral acral edema. Edema can develop on the hands, feet, and genitalia. Importantly, facial edema has been noted to precede skin lesions.2 Coin-shaped or targetoid hemorrhagic and purpuric lesions in a cockade or rosette pattern with scalloped margins typically begin on the distal extremities and tend to spread proximally. The lesions are variable in size but have been reported to be as large as 5 cm in diameter. Although joint pain, bloody diarrhea, hematuria, and proteinuria can accompany AHEI, most cases are devoid of systemic symptoms.3 Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—both present in our patient—are rare findings with AHEI. It is likely that most providers, including dermatologists, may be unfamiliar with these striking clinical findings. Although the pathophysiology of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis has not been formally investigated, we postulate that it likely is related to the formation of immune complexes that lead to small vessel vasculitis, underpinning the characteristic findings in AHEI.4,5 This reasoning is supported by the complete resolution of symptoms corresponding with clinical clearance of the cutaneous vasculitis in 2 prior cases4,5 as well as in our patient who did not have a relapse of symptoms following cessation of the cutaneous eruption at a pediatric follow-up appointment 2 weeks later.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a clinical diagnosis; however, a skin biopsy can be performed to confirm the clinical suspicion and rule out more serious conditions. Histopathologic examination reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis involving the capillaries and postcapillary venules of the upper and mid dermis. Laboratory test results usually are nonspecific but can help distinguish AHEI from more serious diseases. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level may be slightly elevated in infants with AHEI. Urinalysis and stool guaiac tests also can be performed to evaluate for any renal or gastrointestinal involvement.6
The differential diagnosis includes IgA vasculitis, erythema multiforme, acute meningococcemia, urticarial vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, and child abuse. IgA vasculitis often presents with more systemic involvement, with abdominal pain, vomiting, hematemesis, diarrhea, and hematochezia occurring in up to 50% of patients. The cutaneous findings of erythema multiforme classically are confined to the limbs and face, and edema of the extremities typically is not seen. Patients with acute meningococcemia appear toxic with high fevers, malaise, and possible septic shock.5
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a self-limited condition typically lasting 1 to 3 weeks and requires only supportive care.7 Antibiotics should be given to treat concurrent bacterial infections, and antihistamines and steroids may be useful for symptomatic relief. Importantly, however, systemic corticosteroids do not appear to conclusively alter the disease course.8
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a rare benign leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a striking presentation often seen following an upper respiratory tract infection or course of antibiotics. Our case demonstrates that on rare occasions, AHEI may be accompanied by hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—findings that can be quite alarming to both parents and medical providers. Nonetheless, patients and their caretakers should be assured that the condition is self-limited and resolves without permanent sequalae.
- Emerich PS, Prebianchi PA, Motta LL, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: report of three cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:1181-1184.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani H. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:356-357.
- Krause I, Lazarov A, Rachmel A, et al. Acute haemorrhagic oedema of infancy, a benign variant of leucocytoclastic vasculitis. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85:114-117.
- Sneller H, Vega C, Zemel L, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy with associated hemorrhagic lacrimation. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2021;37:E70-E72. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001542
- Mreish S, Al-Tatari H. Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis in acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2016;2016:9762185. doi:10.1155/2016/9762185
- Savino F, Lupica MM, Tarasco V, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: a troubling cutaneous presentation with a self-limiting course. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:E149-E152.
- Fiore E, Rizzi M, Ragazzi M, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children (cockade purpura and edema): a case series and systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:684-695.
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children: a concise narrative review. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:1507-1511.
To the Editor:
Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis are dramatic presentations with a narrow differential diagnosis. It rarely has been reported to present alongside the more typical features of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), which is a benign self-limited leukocytoclastic vasculitis most often seen in children aged 4 months to 2 years. Extracutaneous involvement rarely is seen in AHEI, though joint, gastrointestinal tract, and renal involvement have been reported.1 Most patients present with edematous, annular, or cockade purpuric vasculitic lesions classically involving the face and distal extremities with relative sparing of the trunk. We present a case of a well-appearing, 10-month-old infant boy with hemorrhagic vasculitic lesions, acral edema, and an associated episode of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis.

A 10-month-old infant boy who was otherwise healthy presented to the emergency department (ED) with an acute-onset, progressively worsening cutaneous eruption of 2 days’ duration. A thorough history revealed that the eruption initially had presented as several small, bright-red papules on the thighs. The eruption subsequently spread to involve the buttocks, legs, and arms (Figures 1 and 2). The parents also noted that the patient had experienced an episode of bloody tears and epistaxis that lasted a few minutes at the pediatrician’s office earlier that morning, a finding that prompted the urgent referral to the ED.

Dermatology was then consulted. A review of systems was notable for rhinorrhea and diarrhea during the week leading to the eruption. The patient’s parents denied fevers, decreased oral intake, or a recent course of antibiotics. The patient’s medical history was notable only for atopic dermatitis treated with emollients and occasional topical steroids. The parents denied recent travel or vaccinations. Physical examination showed an afebrile, well-appearing infant with multiple nontender, slightly edematous, circular, purpuric papules and plaques scattered on the buttocks and extremities with edema on the dorsal feet. The remainder of the patient’s workup in the ED was notable for mild elevations in C-reactive protein levels (1.4 mg/dL [reference range, 0–1.2 mg/dL]) and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (22 mm/h [reference range, 2–12 mm/h]). A complete blood cell count; liver function tests; urinalysis; and coagulation studies, including prothrombin, partial thromboplastin time, and international normalized ratio, were unremarkable. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy was diagnosed based on the clinical manifestations.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (also known as Finkelstein disease, medallionlike purpura, Seidemayer syndrome, infantile postinfectious irislike purpura and edema, and purpura en cocarde avec oedeme) is believed to result from an immune complex–related reaction, often in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection; medications, especially antibiotics; or vaccinations. The condition previously was considered a benign form of Henoch-Schönlein purpura; however, it is now recognized as its own clinical entity. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy commonly affects children between the ages of 4 months and 2 years. The incidence peaks in the winter months, and males tend to be more affected than females.1
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is clinically characterized by a triad of large purpuric lesions, low-grade fever, and peripheral acral edema. Edema can develop on the hands, feet, and genitalia. Importantly, facial edema has been noted to precede skin lesions.2 Coin-shaped or targetoid hemorrhagic and purpuric lesions in a cockade or rosette pattern with scalloped margins typically begin on the distal extremities and tend to spread proximally. The lesions are variable in size but have been reported to be as large as 5 cm in diameter. Although joint pain, bloody diarrhea, hematuria, and proteinuria can accompany AHEI, most cases are devoid of systemic symptoms.3 Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—both present in our patient—are rare findings with AHEI. It is likely that most providers, including dermatologists, may be unfamiliar with these striking clinical findings. Although the pathophysiology of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis has not been formally investigated, we postulate that it likely is related to the formation of immune complexes that lead to small vessel vasculitis, underpinning the characteristic findings in AHEI.4,5 This reasoning is supported by the complete resolution of symptoms corresponding with clinical clearance of the cutaneous vasculitis in 2 prior cases4,5 as well as in our patient who did not have a relapse of symptoms following cessation of the cutaneous eruption at a pediatric follow-up appointment 2 weeks later.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a clinical diagnosis; however, a skin biopsy can be performed to confirm the clinical suspicion and rule out more serious conditions. Histopathologic examination reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis involving the capillaries and postcapillary venules of the upper and mid dermis. Laboratory test results usually are nonspecific but can help distinguish AHEI from more serious diseases. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level may be slightly elevated in infants with AHEI. Urinalysis and stool guaiac tests also can be performed to evaluate for any renal or gastrointestinal involvement.6
The differential diagnosis includes IgA vasculitis, erythema multiforme, acute meningococcemia, urticarial vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, and child abuse. IgA vasculitis often presents with more systemic involvement, with abdominal pain, vomiting, hematemesis, diarrhea, and hematochezia occurring in up to 50% of patients. The cutaneous findings of erythema multiforme classically are confined to the limbs and face, and edema of the extremities typically is not seen. Patients with acute meningococcemia appear toxic with high fevers, malaise, and possible septic shock.5
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a self-limited condition typically lasting 1 to 3 weeks and requires only supportive care.7 Antibiotics should be given to treat concurrent bacterial infections, and antihistamines and steroids may be useful for symptomatic relief. Importantly, however, systemic corticosteroids do not appear to conclusively alter the disease course.8
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a rare benign leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a striking presentation often seen following an upper respiratory tract infection or course of antibiotics. Our case demonstrates that on rare occasions, AHEI may be accompanied by hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—findings that can be quite alarming to both parents and medical providers. Nonetheless, patients and their caretakers should be assured that the condition is self-limited and resolves without permanent sequalae.
To the Editor:
Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis are dramatic presentations with a narrow differential diagnosis. It rarely has been reported to present alongside the more typical features of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), which is a benign self-limited leukocytoclastic vasculitis most often seen in children aged 4 months to 2 years. Extracutaneous involvement rarely is seen in AHEI, though joint, gastrointestinal tract, and renal involvement have been reported.1 Most patients present with edematous, annular, or cockade purpuric vasculitic lesions classically involving the face and distal extremities with relative sparing of the trunk. We present a case of a well-appearing, 10-month-old infant boy with hemorrhagic vasculitic lesions, acral edema, and an associated episode of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis.

A 10-month-old infant boy who was otherwise healthy presented to the emergency department (ED) with an acute-onset, progressively worsening cutaneous eruption of 2 days’ duration. A thorough history revealed that the eruption initially had presented as several small, bright-red papules on the thighs. The eruption subsequently spread to involve the buttocks, legs, and arms (Figures 1 and 2). The parents also noted that the patient had experienced an episode of bloody tears and epistaxis that lasted a few minutes at the pediatrician’s office earlier that morning, a finding that prompted the urgent referral to the ED.

Dermatology was then consulted. A review of systems was notable for rhinorrhea and diarrhea during the week leading to the eruption. The patient’s parents denied fevers, decreased oral intake, or a recent course of antibiotics. The patient’s medical history was notable only for atopic dermatitis treated with emollients and occasional topical steroids. The parents denied recent travel or vaccinations. Physical examination showed an afebrile, well-appearing infant with multiple nontender, slightly edematous, circular, purpuric papules and plaques scattered on the buttocks and extremities with edema on the dorsal feet. The remainder of the patient’s workup in the ED was notable for mild elevations in C-reactive protein levels (1.4 mg/dL [reference range, 0–1.2 mg/dL]) and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (22 mm/h [reference range, 2–12 mm/h]). A complete blood cell count; liver function tests; urinalysis; and coagulation studies, including prothrombin, partial thromboplastin time, and international normalized ratio, were unremarkable. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy was diagnosed based on the clinical manifestations.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (also known as Finkelstein disease, medallionlike purpura, Seidemayer syndrome, infantile postinfectious irislike purpura and edema, and purpura en cocarde avec oedeme) is believed to result from an immune complex–related reaction, often in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection; medications, especially antibiotics; or vaccinations. The condition previously was considered a benign form of Henoch-Schönlein purpura; however, it is now recognized as its own clinical entity. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy commonly affects children between the ages of 4 months and 2 years. The incidence peaks in the winter months, and males tend to be more affected than females.1
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is clinically characterized by a triad of large purpuric lesions, low-grade fever, and peripheral acral edema. Edema can develop on the hands, feet, and genitalia. Importantly, facial edema has been noted to precede skin lesions.2 Coin-shaped or targetoid hemorrhagic and purpuric lesions in a cockade or rosette pattern with scalloped margins typically begin on the distal extremities and tend to spread proximally. The lesions are variable in size but have been reported to be as large as 5 cm in diameter. Although joint pain, bloody diarrhea, hematuria, and proteinuria can accompany AHEI, most cases are devoid of systemic symptoms.3 Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—both present in our patient—are rare findings with AHEI. It is likely that most providers, including dermatologists, may be unfamiliar with these striking clinical findings. Although the pathophysiology of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis has not been formally investigated, we postulate that it likely is related to the formation of immune complexes that lead to small vessel vasculitis, underpinning the characteristic findings in AHEI.4,5 This reasoning is supported by the complete resolution of symptoms corresponding with clinical clearance of the cutaneous vasculitis in 2 prior cases4,5 as well as in our patient who did not have a relapse of symptoms following cessation of the cutaneous eruption at a pediatric follow-up appointment 2 weeks later.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a clinical diagnosis; however, a skin biopsy can be performed to confirm the clinical suspicion and rule out more serious conditions. Histopathologic examination reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis involving the capillaries and postcapillary venules of the upper and mid dermis. Laboratory test results usually are nonspecific but can help distinguish AHEI from more serious diseases. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level may be slightly elevated in infants with AHEI. Urinalysis and stool guaiac tests also can be performed to evaluate for any renal or gastrointestinal involvement.6
The differential diagnosis includes IgA vasculitis, erythema multiforme, acute meningococcemia, urticarial vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, and child abuse. IgA vasculitis often presents with more systemic involvement, with abdominal pain, vomiting, hematemesis, diarrhea, and hematochezia occurring in up to 50% of patients. The cutaneous findings of erythema multiforme classically are confined to the limbs and face, and edema of the extremities typically is not seen. Patients with acute meningococcemia appear toxic with high fevers, malaise, and possible septic shock.5
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a self-limited condition typically lasting 1 to 3 weeks and requires only supportive care.7 Antibiotics should be given to treat concurrent bacterial infections, and antihistamines and steroids may be useful for symptomatic relief. Importantly, however, systemic corticosteroids do not appear to conclusively alter the disease course.8
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a rare benign leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a striking presentation often seen following an upper respiratory tract infection or course of antibiotics. Our case demonstrates that on rare occasions, AHEI may be accompanied by hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—findings that can be quite alarming to both parents and medical providers. Nonetheless, patients and their caretakers should be assured that the condition is self-limited and resolves without permanent sequalae.
- Emerich PS, Prebianchi PA, Motta LL, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: report of three cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:1181-1184.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani H. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:356-357.
- Krause I, Lazarov A, Rachmel A, et al. Acute haemorrhagic oedema of infancy, a benign variant of leucocytoclastic vasculitis. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85:114-117.
- Sneller H, Vega C, Zemel L, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy with associated hemorrhagic lacrimation. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2021;37:E70-E72. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001542
- Mreish S, Al-Tatari H. Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis in acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2016;2016:9762185. doi:10.1155/2016/9762185
- Savino F, Lupica MM, Tarasco V, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: a troubling cutaneous presentation with a self-limiting course. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:E149-E152.
- Fiore E, Rizzi M, Ragazzi M, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children (cockade purpura and edema): a case series and systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:684-695.
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children: a concise narrative review. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:1507-1511.
- Emerich PS, Prebianchi PA, Motta LL, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: report of three cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:1181-1184.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani H. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:356-357.
- Krause I, Lazarov A, Rachmel A, et al. Acute haemorrhagic oedema of infancy, a benign variant of leucocytoclastic vasculitis. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85:114-117.
- Sneller H, Vega C, Zemel L, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy with associated hemorrhagic lacrimation. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2021;37:E70-E72. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001542
- Mreish S, Al-Tatari H. Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis in acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2016;2016:9762185. doi:10.1155/2016/9762185
- Savino F, Lupica MM, Tarasco V, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: a troubling cutaneous presentation with a self-limiting course. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:E149-E152.
- Fiore E, Rizzi M, Ragazzi M, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children (cockade purpura and edema): a case series and systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:684-695.
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children: a concise narrative review. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:1507-1511.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI) is clinically characterized by a triad of large purpuric lesions, low-grade fever, and peripheral acral edema. Although joint pain, bloody diarrhea, hematuria, and proteinuria can accompany AHEI, most cases are devoid of systemic symptoms.
- It is a self-limited condition typically lasting 1 to 3 weeks and requires only supportive care.
- On rare occasions, AHEI may be accompanied by hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis. Patients should be assured that the condition is self-limited and resolves without permanent sequalae.
Fungal Osler Nodes Indicate Candidal Infective Endocarditis
To the Editor:
A 44-year-old woman presented with a low-grade fever (temperature, 38.0 °C) and painful acral lesions of 1 week’s duration. She had a history of hepatitis C viral infection and intravenous (IV) drug use, as well as polymicrobial infective endocarditis that involved the tricuspid and aortic valves; pathogenic organisms were identified via blood culture as Enterococcus faecalis, Serratia species, Streptococcus viridans, and Candida albicans. The patient had received a mechanical aortic valve and bioprosthetic tricuspid valve replacement 5 months prior with warfarin therapy and had completed a postsurgical 6-week course of high-dose micafungin. She reported that she had developed painful, violaceous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the left foot 2 weeks prior to presentation. Her symptoms improved with a short systemic steroid taper; however, within a week she developed new tender, erythematous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the right foot and the palmar surface of the left hand with associated lower extremity swelling. She denied other symptoms, including fever, chills, neurologic symptoms, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, hematuria, and hematochezia. Due to worsening cutaneous findings, the patient presented to the emergency department, prompting hospital admission for empiric antibacterial therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam for suspected infectious endocarditis. Dermatology was consulted after 1 day of antibacterial therapy without improvement to determine the etiology of the patient’s skin findings.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile with partially blanching violaceous to purpuric, tender, edematous papules on the left fourth and fifth finger pads, as well as scattered, painful, purpuric patches with stellate borders on the right plantar foot (Figure 1). Laboratory test results revealed mild anemia (hemoglobin, 11.9 g/dL [reference range, 12.0–15.0 g/dL], mild neutrophilia (neutrophils, 8.4×109/L [reference range, 1.9–7.9×109/L], elevated acute-phase reactants (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 71 mm/h [reference range, 0–20 mm/h]; C-reactive protein, 5.7 mg/dL [reference range, 0.0–0.5 mg/dL]), and positive hepatitis C virus antibody with an undetectable viral load. At the time of dermatologic evaluation, admission blood cultures and transthoracic echocardiogram were negative. Additionally, a transesophageal echocardiogram, limited by artifact from the mechanical aortic valve, was equivocal for valvular pathology. Subsequent ophthalmologic evaluation was negative for lesions associated with endocarditis, such as retinal hemorrhages.
Punch biopsies of the left fourth finger pad were submitted for histopathologic analysis and tissue cultures. Histopathology demonstrated deep dermal perivascular neutrophilic inflammation with multiple intravascular thrombi, perivascular fibrin, and karyorrhectic debris (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stains revealed fungal spores with rare pseudohyphae within the thrombosed vascular spaces and the perivascular dermis, consistent with fungal septic emboli (Figure 3).
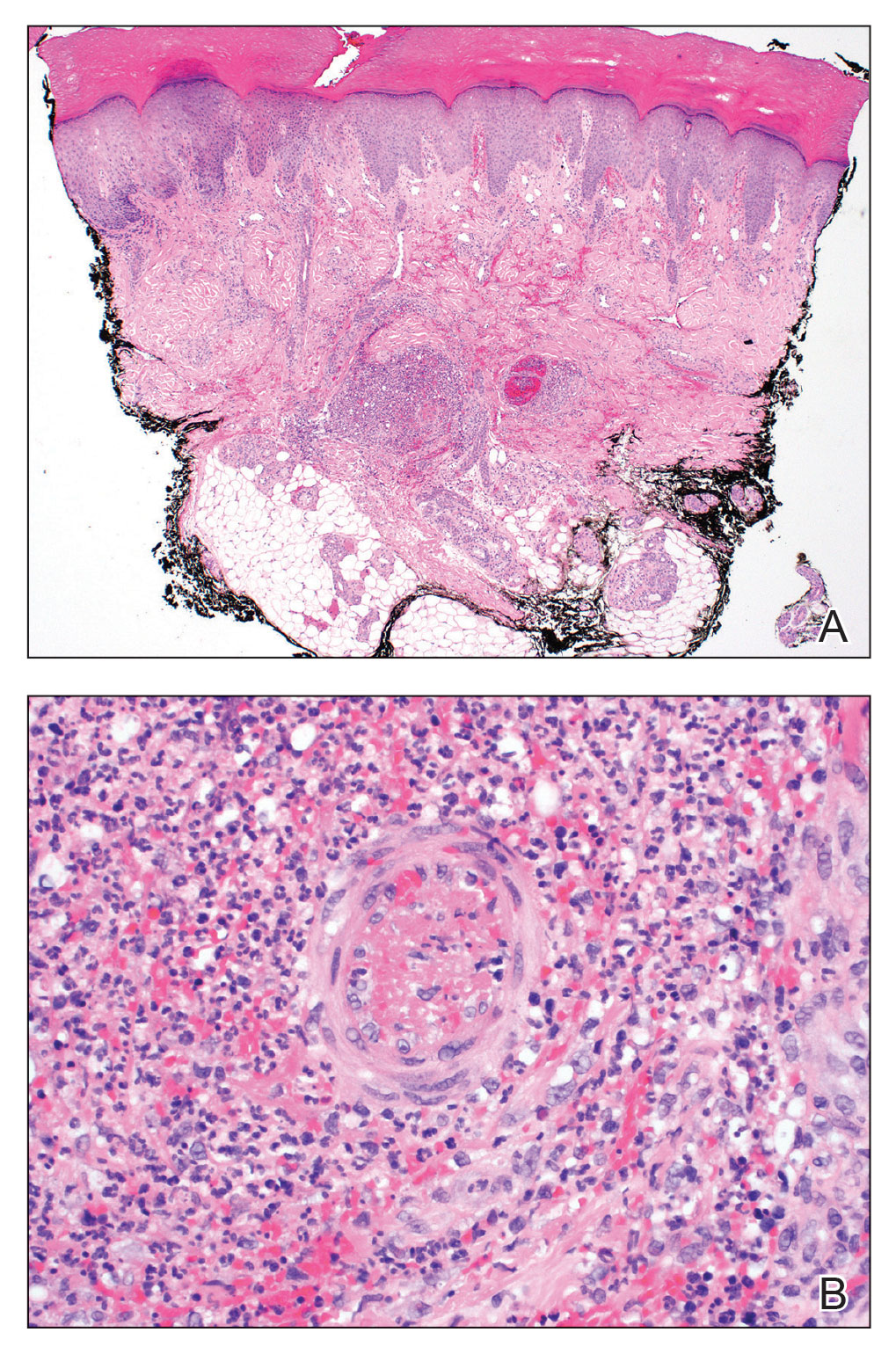
Empiric systemic antifungal coverage composed of IV liposomal amphotericin B and oral flucytosine was initiated, and the patient’s tender acral papules rapidly improved. Within 48 hours of biopsy, skin tissue culture confirmed the presence of C albicans. Four days after the preliminary dermatopathology report, confirmatory blood cultures resulted with pansensitive C albicans. Final tissue and blood cultures were negative for bacteria including mycobacteria. In addition to a 6-week course of IV amphotericin B and flucytosine, repeat surgical intervention was considered, and lifelong suppressive antifungal oral therapy was recommended. Unfortunately, the patient did not present for follow-up. Three months later, she presented to the emergency department with peritonitis; in the operating room, she was found to have ischemia of the entirety of the small and large intestines and died shortly thereafter.
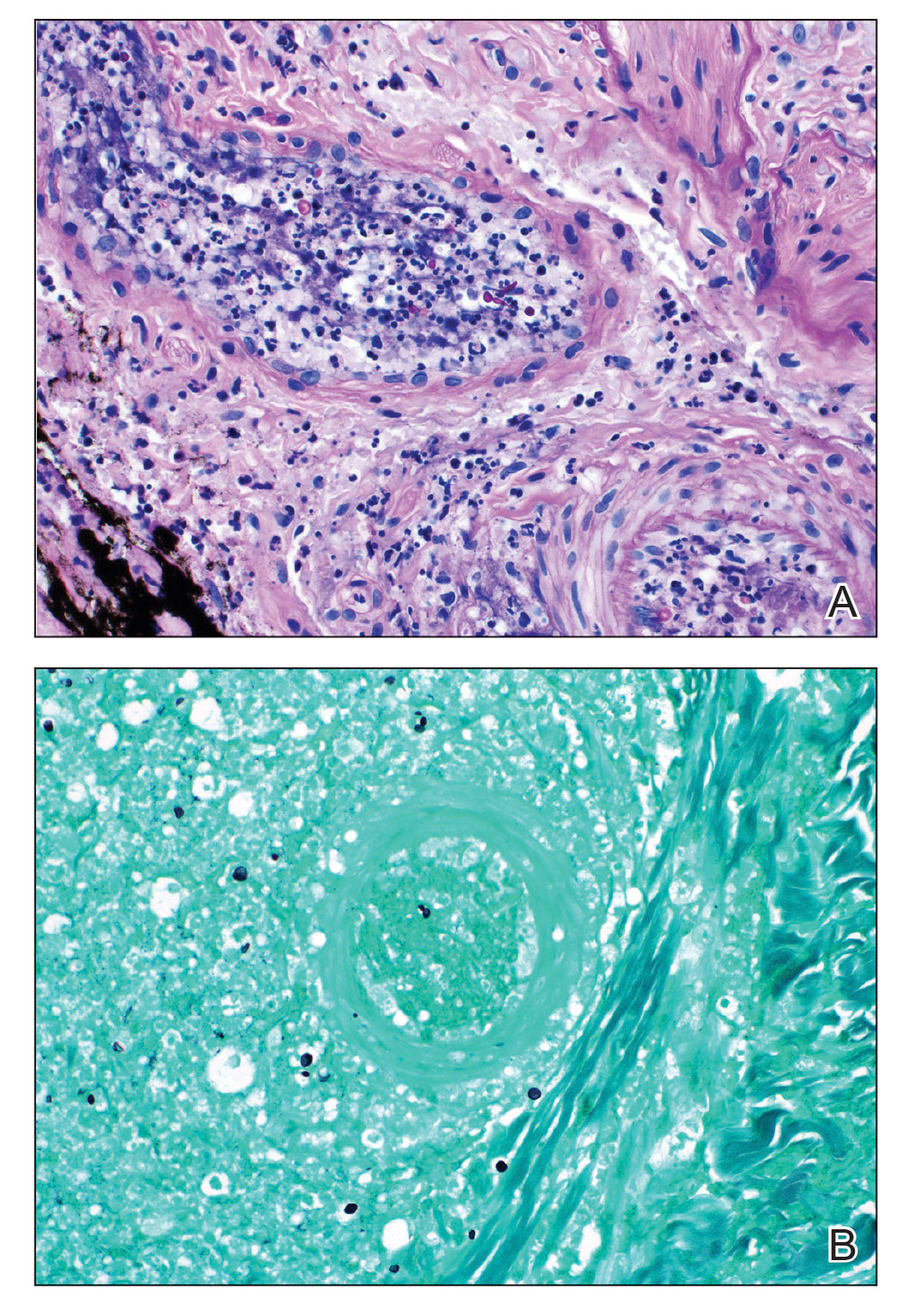
Fungal endocarditis is rare, tending to develop in patient populations with particular risk factors such as immune compromise, structural heart defects or prosthetic valves, and IV drug use. Candida infective endocarditis (CIE) represents less than 2% of infective endocarditis cases and carries a high mortality rate (30%–80%).1-3 Diagnosis may be challenging, as the clinical presentation varies widely. Although some patients may present with classic features of infective endocarditis, including fever, cardiac murmurs, and positive blood cultures, many cases of infective endocarditis present with nonspecific symptoms, raising a broad clinical differential diagnosis. Delay in diagnosis, which is seen in 82% of patients with fungal endocarditis, may be attributed to the slow progression of symptoms, inconclusive cardiac imaging, or negative blood cultures seen in almost one-third of cases.2,3 The feared complication of systemic embolization via infective endocarditis may occur in up to one-half of cases, with the highest rates associated with staphylococcal or fungal pathogens.2 The risk for embolization in fungal endocarditis is independent of the size of the cardiac valve vegetations; accordingly, sequelae of embolic complications may arise despite negative cardiac imaging.4 Embolic complications, which typically are seen within the first 2 to 4 weeks of treatment, may serve as the presenting feature of endocarditis and may even occur after completion of antimicrobial therapy.
Detection of cutaneous manifestations of infective endocarditis, including Janeway lesions, Osler nodes, and splinter hemorrhages, may allow for earlier diagnosis. Despite eponymous recognition, Janeway lesions and Osler nodes are relatively uncommon manifestations of infective endocarditis and may be found in only 5% to 15% of cases.5 Biopsies of suspected Janeway lesions and Osler nodes may allow for recognition of relevant vascular pathology, identification of the causative pathogen, and strong support for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis.4-7
The initial photomicrograph of corresponding Janeway lesion histopathology was published by Kerr in 1955 and revealed dermal microabscesses posited to be secondary to bacterial emboli.8,9 Additional cases through the years have reported overlapping histopathologic features of Janeway lesions and Osler nodes, with the latter often defined by the presence of vasculitis.4 Although there appears to be ongoing debate and overlap between the 2 integumentary findings, a general consensus on differentiation takes into account both the clinical signs and symptoms as well as the histopathologic findings.10,11
Osler nodes present as tender, violaceous, subcutaneous nodules on the acral surfaces, usually on the pads of the fingers and toes.5 The pathogenesis involves the deposition of immune complexes as a sequela of vascular occlusion by microthrombi classically seen in the late phase of subacute endocarditis. Janeway lesions present as nontender erythematous macules on the acral surfaces and are thought to represent microthrombi with dermal microabscesses, more common in acute endocarditis. Our patient demonstrated features of both Osler nodes and Janeway lesions. Despite the presence of fungal thrombi—a pathophysiology closer to that of Janeway lesions—the clinical presentation of painful acral nodules affecting finger pads and histologic features of vasculitis may be better characterized as Osler nodes. Regardless of pathogenesis, these cutaneous findings serve as a minor clinical criterion in the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis when present.12
Candida infective endocarditis should be suspected in a patient with a history of valvular disease or prior infective endocarditis with fungemia, unexplained neurologic signs, or manifestations of peripheral embolization despite negative blood cultures.3 Particularly in the setting of negative cardiac imaging, recognition of CIE requires heightened diagnostic acumen and clinicopathologic correlation. Although culture and pathologic examination of valvular vegetations represents the gold standard for diagnosis of CIE, aspiration and culture of easily accessible septic emboli may provide rapid identification of the etiologic pathogen. In 1976, Alpert et al13 identified C albicans from an aspirated Osler node. Postmortem examination revealed extensive involvement of the homograft valve and aortic root with C albicans.13 Many other examples exist in the literature demonstrating matching pathogenic isolates from microbiologic cultures of skin and blood.4,9,14,15 Thadepalli and Francis7 investigated 26 cases of endocarditis in heroin users in which the admitting diagnosis was endocarditis in only 4 cases. The etiologic pathogen was aspirated from secondary sites of localized infections secondary to emboli, including cutaneous lesions in 10 of the cases. Gram stain and culture revealed the causative organism leading to the ultimate diagnosis and management in 17 of 26 patients with endocarditis.7
The incidence of fungal endocarditis is increasing, with a reported 67% of cases caused by nosocomial infection.1 Given the rising incidence of fungal endocarditis and its accompanying diagnostic difficulties, including frequently negative blood cultures and cardiac imaging, clinicians must perform careful skin examinations, employ judicious use of skin biopsy, and carefully correlate clinical and pathologic findings to improve recognition of this disease and guide patient care.
- Arnold CJ, Johnson M, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis: an observational cohort study with a focus on therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:2365. doi:10.1128/AAC.04867-14
- Chaudhary SC, Sawlani KK, Arora R, et al. Native aortic valve fungal endocarditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2012007144. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007144
- Ellis ME, Al-Abdely H, Sandridge A, et al. Fungal endocarditis: evidence in the world literature, 1965–1995. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:50-62. doi:10.1086/317550
- Gil MP, Velasco M, Botella R, et al. Janeway lesions: differential diagnosis with Osler’s nodes. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:673-674. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1993.tb04025.x
- Gomes RT, Tiberto LR, Bello VNM, et al. Dermatologic manifestations of infective endocarditis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:92-94.
- Yee JM. Osler’s nodes and the recognition of infective endocarditis: a lesion of diagnostic importance. South Med J. 1987;80:753-757.
- Thadepalli H, Francis C. Diagnostic clues in metastatic lesions of endocarditia in addicts. West J Med. 1978;128:1-5.
- Kerr A Jr. Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis. Charles C. Thomas; 1955.
- Kerr A Jr, Tan JS. Biopsies of the Janeway lesion of infective endocarditis. J Cutan Pathol. 1979;6:124-129. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1979.tb01113.x
- Marrie TJ. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Am J Med. 2008;121:105-106. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.035
- Gunson TH, Oliver GF. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Australas J Dermatol. 2007;48:251-255. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2007.00397.x
- Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK, et al. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am J Med. 1994;96:200-209.
- Alpert JS, Krous HF, Dalen JE, et al. Pathogenesis of Osler’s nodes. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85:471-473. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-471
- Cardullo AC, Silvers DN, Grossman ME. Janeway lesions and Osler’s nodes: a review of histopathologic findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1088-1090. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(90)70157-D
- Vinson RP, Chung A, Elston DM, et al. Septic microemboli in a Janeway lesion of bacterial endocarditis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:984-985. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(96)90125-5
To the Editor:
A 44-year-old woman presented with a low-grade fever (temperature, 38.0 °C) and painful acral lesions of 1 week’s duration. She had a history of hepatitis C viral infection and intravenous (IV) drug use, as well as polymicrobial infective endocarditis that involved the tricuspid and aortic valves; pathogenic organisms were identified via blood culture as Enterococcus faecalis, Serratia species, Streptococcus viridans, and Candida albicans. The patient had received a mechanical aortic valve and bioprosthetic tricuspid valve replacement 5 months prior with warfarin therapy and had completed a postsurgical 6-week course of high-dose micafungin. She reported that she had developed painful, violaceous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the left foot 2 weeks prior to presentation. Her symptoms improved with a short systemic steroid taper; however, within a week she developed new tender, erythematous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the right foot and the palmar surface of the left hand with associated lower extremity swelling. She denied other symptoms, including fever, chills, neurologic symptoms, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, hematuria, and hematochezia. Due to worsening cutaneous findings, the patient presented to the emergency department, prompting hospital admission for empiric antibacterial therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam for suspected infectious endocarditis. Dermatology was consulted after 1 day of antibacterial therapy without improvement to determine the etiology of the patient’s skin findings.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile with partially blanching violaceous to purpuric, tender, edematous papules on the left fourth and fifth finger pads, as well as scattered, painful, purpuric patches with stellate borders on the right plantar foot (Figure 1). Laboratory test results revealed mild anemia (hemoglobin, 11.9 g/dL [reference range, 12.0–15.0 g/dL], mild neutrophilia (neutrophils, 8.4×109/L [reference range, 1.9–7.9×109/L], elevated acute-phase reactants (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 71 mm/h [reference range, 0–20 mm/h]; C-reactive protein, 5.7 mg/dL [reference range, 0.0–0.5 mg/dL]), and positive hepatitis C virus antibody with an undetectable viral load. At the time of dermatologic evaluation, admission blood cultures and transthoracic echocardiogram were negative. Additionally, a transesophageal echocardiogram, limited by artifact from the mechanical aortic valve, was equivocal for valvular pathology. Subsequent ophthalmologic evaluation was negative for lesions associated with endocarditis, such as retinal hemorrhages.

Punch biopsies of the left fourth finger pad were submitted for histopathologic analysis and tissue cultures. Histopathology demonstrated deep dermal perivascular neutrophilic inflammation with multiple intravascular thrombi, perivascular fibrin, and karyorrhectic debris (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stains revealed fungal spores with rare pseudohyphae within the thrombosed vascular spaces and the perivascular dermis, consistent with fungal septic emboli (Figure 3).

Empiric systemic antifungal coverage composed of IV liposomal amphotericin B and oral flucytosine was initiated, and the patient’s tender acral papules rapidly improved. Within 48 hours of biopsy, skin tissue culture confirmed the presence of C albicans. Four days after the preliminary dermatopathology report, confirmatory blood cultures resulted with pansensitive C albicans. Final tissue and blood cultures were negative for bacteria including mycobacteria. In addition to a 6-week course of IV amphotericin B and flucytosine, repeat surgical intervention was considered, and lifelong suppressive antifungal oral therapy was recommended. Unfortunately, the patient did not present for follow-up. Three months later, she presented to the emergency department with peritonitis; in the operating room, she was found to have ischemia of the entirety of the small and large intestines and died shortly thereafter.

Fungal endocarditis is rare, tending to develop in patient populations with particular risk factors such as immune compromise, structural heart defects or prosthetic valves, and IV drug use. Candida infective endocarditis (CIE) represents less than 2% of infective endocarditis cases and carries a high mortality rate (30%–80%).1-3 Diagnosis may be challenging, as the clinical presentation varies widely. Although some patients may present with classic features of infective endocarditis, including fever, cardiac murmurs, and positive blood cultures, many cases of infective endocarditis present with nonspecific symptoms, raising a broad clinical differential diagnosis. Delay in diagnosis, which is seen in 82% of patients with fungal endocarditis, may be attributed to the slow progression of symptoms, inconclusive cardiac imaging, or negative blood cultures seen in almost one-third of cases.2,3 The feared complication of systemic embolization via infective endocarditis may occur in up to one-half of cases, with the highest rates associated with staphylococcal or fungal pathogens.2 The risk for embolization in fungal endocarditis is independent of the size of the cardiac valve vegetations; accordingly, sequelae of embolic complications may arise despite negative cardiac imaging.4 Embolic complications, which typically are seen within the first 2 to 4 weeks of treatment, may serve as the presenting feature of endocarditis and may even occur after completion of antimicrobial therapy.
Detection of cutaneous manifestations of infective endocarditis, including Janeway lesions, Osler nodes, and splinter hemorrhages, may allow for earlier diagnosis. Despite eponymous recognition, Janeway lesions and Osler nodes are relatively uncommon manifestations of infective endocarditis and may be found in only 5% to 15% of cases.5 Biopsies of suspected Janeway lesions and Osler nodes may allow for recognition of relevant vascular pathology, identification of the causative pathogen, and strong support for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis.4-7
The initial photomicrograph of corresponding Janeway lesion histopathology was published by Kerr in 1955 and revealed dermal microabscesses posited to be secondary to bacterial emboli.8,9 Additional cases through the years have reported overlapping histopathologic features of Janeway lesions and Osler nodes, with the latter often defined by the presence of vasculitis.4 Although there appears to be ongoing debate and overlap between the 2 integumentary findings, a general consensus on differentiation takes into account both the clinical signs and symptoms as well as the histopathologic findings.10,11
Osler nodes present as tender, violaceous, subcutaneous nodules on the acral surfaces, usually on the pads of the fingers and toes.5 The pathogenesis involves the deposition of immune complexes as a sequela of vascular occlusion by microthrombi classically seen in the late phase of subacute endocarditis. Janeway lesions present as nontender erythematous macules on the acral surfaces and are thought to represent microthrombi with dermal microabscesses, more common in acute endocarditis. Our patient demonstrated features of both Osler nodes and Janeway lesions. Despite the presence of fungal thrombi—a pathophysiology closer to that of Janeway lesions—the clinical presentation of painful acral nodules affecting finger pads and histologic features of vasculitis may be better characterized as Osler nodes. Regardless of pathogenesis, these cutaneous findings serve as a minor clinical criterion in the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis when present.12
Candida infective endocarditis should be suspected in a patient with a history of valvular disease or prior infective endocarditis with fungemia, unexplained neurologic signs, or manifestations of peripheral embolization despite negative blood cultures.3 Particularly in the setting of negative cardiac imaging, recognition of CIE requires heightened diagnostic acumen and clinicopathologic correlation. Although culture and pathologic examination of valvular vegetations represents the gold standard for diagnosis of CIE, aspiration and culture of easily accessible septic emboli may provide rapid identification of the etiologic pathogen. In 1976, Alpert et al13 identified C albicans from an aspirated Osler node. Postmortem examination revealed extensive involvement of the homograft valve and aortic root with C albicans.13 Many other examples exist in the literature demonstrating matching pathogenic isolates from microbiologic cultures of skin and blood.4,9,14,15 Thadepalli and Francis7 investigated 26 cases of endocarditis in heroin users in which the admitting diagnosis was endocarditis in only 4 cases. The etiologic pathogen was aspirated from secondary sites of localized infections secondary to emboli, including cutaneous lesions in 10 of the cases. Gram stain and culture revealed the causative organism leading to the ultimate diagnosis and management in 17 of 26 patients with endocarditis.7
The incidence of fungal endocarditis is increasing, with a reported 67% of cases caused by nosocomial infection.1 Given the rising incidence of fungal endocarditis and its accompanying diagnostic difficulties, including frequently negative blood cultures and cardiac imaging, clinicians must perform careful skin examinations, employ judicious use of skin biopsy, and carefully correlate clinical and pathologic findings to improve recognition of this disease and guide patient care.
To the Editor:
A 44-year-old woman presented with a low-grade fever (temperature, 38.0 °C) and painful acral lesions of 1 week’s duration. She had a history of hepatitis C viral infection and intravenous (IV) drug use, as well as polymicrobial infective endocarditis that involved the tricuspid and aortic valves; pathogenic organisms were identified via blood culture as Enterococcus faecalis, Serratia species, Streptococcus viridans, and Candida albicans. The patient had received a mechanical aortic valve and bioprosthetic tricuspid valve replacement 5 months prior with warfarin therapy and had completed a postsurgical 6-week course of high-dose micafungin. She reported that she had developed painful, violaceous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the left foot 2 weeks prior to presentation. Her symptoms improved with a short systemic steroid taper; however, within a week she developed new tender, erythematous, thin papules on the plantar surface of the right foot and the palmar surface of the left hand with associated lower extremity swelling. She denied other symptoms, including fever, chills, neurologic symptoms, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, hematuria, and hematochezia. Due to worsening cutaneous findings, the patient presented to the emergency department, prompting hospital admission for empiric antibacterial therapy with vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam for suspected infectious endocarditis. Dermatology was consulted after 1 day of antibacterial therapy without improvement to determine the etiology of the patient’s skin findings.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile with partially blanching violaceous to purpuric, tender, edematous papules on the left fourth and fifth finger pads, as well as scattered, painful, purpuric patches with stellate borders on the right plantar foot (Figure 1). Laboratory test results revealed mild anemia (hemoglobin, 11.9 g/dL [reference range, 12.0–15.0 g/dL], mild neutrophilia (neutrophils, 8.4×109/L [reference range, 1.9–7.9×109/L], elevated acute-phase reactants (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 71 mm/h [reference range, 0–20 mm/h]; C-reactive protein, 5.7 mg/dL [reference range, 0.0–0.5 mg/dL]), and positive hepatitis C virus antibody with an undetectable viral load. At the time of dermatologic evaluation, admission blood cultures and transthoracic echocardiogram were negative. Additionally, a transesophageal echocardiogram, limited by artifact from the mechanical aortic valve, was equivocal for valvular pathology. Subsequent ophthalmologic evaluation was negative for lesions associated with endocarditis, such as retinal hemorrhages.

Punch biopsies of the left fourth finger pad were submitted for histopathologic analysis and tissue cultures. Histopathology demonstrated deep dermal perivascular neutrophilic inflammation with multiple intravascular thrombi, perivascular fibrin, and karyorrhectic debris (Figure 2). Periodic acid–Schiff and Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stains revealed fungal spores with rare pseudohyphae within the thrombosed vascular spaces and the perivascular dermis, consistent with fungal septic emboli (Figure 3).

Empiric systemic antifungal coverage composed of IV liposomal amphotericin B and oral flucytosine was initiated, and the patient’s tender acral papules rapidly improved. Within 48 hours of biopsy, skin tissue culture confirmed the presence of C albicans. Four days after the preliminary dermatopathology report, confirmatory blood cultures resulted with pansensitive C albicans. Final tissue and blood cultures were negative for bacteria including mycobacteria. In addition to a 6-week course of IV amphotericin B and flucytosine, repeat surgical intervention was considered, and lifelong suppressive antifungal oral therapy was recommended. Unfortunately, the patient did not present for follow-up. Three months later, she presented to the emergency department with peritonitis; in the operating room, she was found to have ischemia of the entirety of the small and large intestines and died shortly thereafter.

Fungal endocarditis is rare, tending to develop in patient populations with particular risk factors such as immune compromise, structural heart defects or prosthetic valves, and IV drug use. Candida infective endocarditis (CIE) represents less than 2% of infective endocarditis cases and carries a high mortality rate (30%–80%).1-3 Diagnosis may be challenging, as the clinical presentation varies widely. Although some patients may present with classic features of infective endocarditis, including fever, cardiac murmurs, and positive blood cultures, many cases of infective endocarditis present with nonspecific symptoms, raising a broad clinical differential diagnosis. Delay in diagnosis, which is seen in 82% of patients with fungal endocarditis, may be attributed to the slow progression of symptoms, inconclusive cardiac imaging, or negative blood cultures seen in almost one-third of cases.2,3 The feared complication of systemic embolization via infective endocarditis may occur in up to one-half of cases, with the highest rates associated with staphylococcal or fungal pathogens.2 The risk for embolization in fungal endocarditis is independent of the size of the cardiac valve vegetations; accordingly, sequelae of embolic complications may arise despite negative cardiac imaging.4 Embolic complications, which typically are seen within the first 2 to 4 weeks of treatment, may serve as the presenting feature of endocarditis and may even occur after completion of antimicrobial therapy.
Detection of cutaneous manifestations of infective endocarditis, including Janeway lesions, Osler nodes, and splinter hemorrhages, may allow for earlier diagnosis. Despite eponymous recognition, Janeway lesions and Osler nodes are relatively uncommon manifestations of infective endocarditis and may be found in only 5% to 15% of cases.5 Biopsies of suspected Janeway lesions and Osler nodes may allow for recognition of relevant vascular pathology, identification of the causative pathogen, and strong support for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis.4-7
The initial photomicrograph of corresponding Janeway lesion histopathology was published by Kerr in 1955 and revealed dermal microabscesses posited to be secondary to bacterial emboli.8,9 Additional cases through the years have reported overlapping histopathologic features of Janeway lesions and Osler nodes, with the latter often defined by the presence of vasculitis.4 Although there appears to be ongoing debate and overlap between the 2 integumentary findings, a general consensus on differentiation takes into account both the clinical signs and symptoms as well as the histopathologic findings.10,11
Osler nodes present as tender, violaceous, subcutaneous nodules on the acral surfaces, usually on the pads of the fingers and toes.5 The pathogenesis involves the deposition of immune complexes as a sequela of vascular occlusion by microthrombi classically seen in the late phase of subacute endocarditis. Janeway lesions present as nontender erythematous macules on the acral surfaces and are thought to represent microthrombi with dermal microabscesses, more common in acute endocarditis. Our patient demonstrated features of both Osler nodes and Janeway lesions. Despite the presence of fungal thrombi—a pathophysiology closer to that of Janeway lesions—the clinical presentation of painful acral nodules affecting finger pads and histologic features of vasculitis may be better characterized as Osler nodes. Regardless of pathogenesis, these cutaneous findings serve as a minor clinical criterion in the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis when present.12
Candida infective endocarditis should be suspected in a patient with a history of valvular disease or prior infective endocarditis with fungemia, unexplained neurologic signs, or manifestations of peripheral embolization despite negative blood cultures.3 Particularly in the setting of negative cardiac imaging, recognition of CIE requires heightened diagnostic acumen and clinicopathologic correlation. Although culture and pathologic examination of valvular vegetations represents the gold standard for diagnosis of CIE, aspiration and culture of easily accessible septic emboli may provide rapid identification of the etiologic pathogen. In 1976, Alpert et al13 identified C albicans from an aspirated Osler node. Postmortem examination revealed extensive involvement of the homograft valve and aortic root with C albicans.13 Many other examples exist in the literature demonstrating matching pathogenic isolates from microbiologic cultures of skin and blood.4,9,14,15 Thadepalli and Francis7 investigated 26 cases of endocarditis in heroin users in which the admitting diagnosis was endocarditis in only 4 cases. The etiologic pathogen was aspirated from secondary sites of localized infections secondary to emboli, including cutaneous lesions in 10 of the cases. Gram stain and culture revealed the causative organism leading to the ultimate diagnosis and management in 17 of 26 patients with endocarditis.7
The incidence of fungal endocarditis is increasing, with a reported 67% of cases caused by nosocomial infection.1 Given the rising incidence of fungal endocarditis and its accompanying diagnostic difficulties, including frequently negative blood cultures and cardiac imaging, clinicians must perform careful skin examinations, employ judicious use of skin biopsy, and carefully correlate clinical and pathologic findings to improve recognition of this disease and guide patient care.
- Arnold CJ, Johnson M, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis: an observational cohort study with a focus on therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:2365. doi:10.1128/AAC.04867-14
- Chaudhary SC, Sawlani KK, Arora R, et al. Native aortic valve fungal endocarditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2012007144. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007144
- Ellis ME, Al-Abdely H, Sandridge A, et al. Fungal endocarditis: evidence in the world literature, 1965–1995. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:50-62. doi:10.1086/317550
- Gil MP, Velasco M, Botella R, et al. Janeway lesions: differential diagnosis with Osler’s nodes. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:673-674. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1993.tb04025.x
- Gomes RT, Tiberto LR, Bello VNM, et al. Dermatologic manifestations of infective endocarditis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:92-94.
- Yee JM. Osler’s nodes and the recognition of infective endocarditis: a lesion of diagnostic importance. South Med J. 1987;80:753-757.
- Thadepalli H, Francis C. Diagnostic clues in metastatic lesions of endocarditia in addicts. West J Med. 1978;128:1-5.
- Kerr A Jr. Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis. Charles C. Thomas; 1955.
- Kerr A Jr, Tan JS. Biopsies of the Janeway lesion of infective endocarditis. J Cutan Pathol. 1979;6:124-129. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1979.tb01113.x
- Marrie TJ. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Am J Med. 2008;121:105-106. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.035
- Gunson TH, Oliver GF. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Australas J Dermatol. 2007;48:251-255. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2007.00397.x
- Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK, et al. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am J Med. 1994;96:200-209.
- Alpert JS, Krous HF, Dalen JE, et al. Pathogenesis of Osler’s nodes. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85:471-473. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-471
- Cardullo AC, Silvers DN, Grossman ME. Janeway lesions and Osler’s nodes: a review of histopathologic findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1088-1090. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(90)70157-D
- Vinson RP, Chung A, Elston DM, et al. Septic microemboli in a Janeway lesion of bacterial endocarditis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:984-985. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(96)90125-5
- Arnold CJ, Johnson M, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis: an observational cohort study with a focus on therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:2365. doi:10.1128/AAC.04867-14
- Chaudhary SC, Sawlani KK, Arora R, et al. Native aortic valve fungal endocarditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2012007144. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007144
- Ellis ME, Al-Abdely H, Sandridge A, et al. Fungal endocarditis: evidence in the world literature, 1965–1995. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:50-62. doi:10.1086/317550
- Gil MP, Velasco M, Botella R, et al. Janeway lesions: differential diagnosis with Osler’s nodes. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:673-674. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1993.tb04025.x
- Gomes RT, Tiberto LR, Bello VNM, et al. Dermatologic manifestations of infective endocarditis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:92-94.
- Yee JM. Osler’s nodes and the recognition of infective endocarditis: a lesion of diagnostic importance. South Med J. 1987;80:753-757.
- Thadepalli H, Francis C. Diagnostic clues in metastatic lesions of endocarditia in addicts. West J Med. 1978;128:1-5.
- Kerr A Jr. Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis. Charles C. Thomas; 1955.
- Kerr A Jr, Tan JS. Biopsies of the Janeway lesion of infective endocarditis. J Cutan Pathol. 1979;6:124-129. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1979.tb01113.x
- Marrie TJ. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Am J Med. 2008;121:105-106. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.035
- Gunson TH, Oliver GF. Osler’s nodes and Janeway lesions. Australas J Dermatol. 2007;48:251-255. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2007.00397.x
- Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK, et al. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Am J Med. 1994;96:200-209.
- Alpert JS, Krous HF, Dalen JE, et al. Pathogenesis of Osler’s nodes. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85:471-473. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-471
- Cardullo AC, Silvers DN, Grossman ME. Janeway lesions and Osler’s nodes: a review of histopathologic findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:1088-1090. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(90)70157-D
- Vinson RP, Chung A, Elston DM, et al. Septic microemboli in a Janeway lesion of bacterial endocarditis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:984-985. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(96)90125-5
PRACTICE POINTS
- Fungal infective endocarditis is rare, and diagnostic tests such as blood cultures and echocardiography may not detect the disease.
- The mortality rate of fungal endocarditis is high, with improved clinical outcomes if diagnosed and treated early.
- Clinicopathologic correlation between integumentary examination and skin biopsy findings may provide timely diagnosis, thereby guiding appropriate therapy.
Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Treated With Risankizumab
To the Editor:
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare but severe subtype of psoriasis that can present with systemic symptoms and organ failure, sometimes leading to hospitalization and even death.1,2 Due to the rarity of this subtype and GPP being excluded from clinical trials for plaque psoriasis, there is limited information on the optimal treatment of this disease.
More than 20 systemic medications have been described in the literature for treating GPP, including systemic steroids, traditional immunosuppressants, retinoids, and biologics, which often are used in combination; none have been consistently effective.3 Among biologic therapies, the use of tumor necrosis factor α as well as IL-12/23 and IL-17 inhibitors has been reported, with the least amount of experience with IL-17 inhibitors.4
A 53-year-old Korean woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of a widespread painful rash involving the face, neck, torso, arms, and legs that had been treated intermittently with systemic steroids by her primary care physician for several months before presentation. She had no relevant medical or dermatologic history. She denied taking prescription or over-the-counter medications.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile, but she reported general malaise and chills. She had widespread erythematous, annular, scaly plaques that coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the forehead, frontal hairline, neck, chest, abdomen, back, arms, and legs (Figure 1).
![Initial presentation (day 0 [prior to treatment with risankizumab]). A and B, Scaly plaques coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the leg and neck, respectively. Initial presentation (day 0 [prior to treatment with risankizumab]). A and B, Scaly plaques coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the leg and neck, respectively.](https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/CT111002096_Fig1_AB.jpg)
Two 4-mm punch biopsies were performed for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence. Histopathologic analysis showed prominent subcorneal neutrophilic pustules and spongiform collections of neutrophils in the spinous layer without notable eosinophils (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence was negative.
Based on the clinical history, physical examination, histopathology, and unremarkable drug history, a diagnosis of GPP was made. Initially, acitretin 25 mg/d was prescribed, but the patient was unable to start treatment because the cost of the drug was prohibitive. Her condition worsened, and she returned to the clinic 2 days later. Based on knowledge of an ongoing phase 3, open-label study for risankizumab in GPP, a sample of risankizumab 150 mg was administered subcutaneously in this patient. Three days later, most of the pustules on the upper half of the patient’s body had dried up and she began to desquamate from head to toe (Figure 3).The patient developed notable edema of the lower extremities, which required furosemide 20 mg/d andibuprofen 600 mg every 6 hours for symptom relief.
Ten days after the initial dose of risankizumab, the patient continued to steadily improve. All the pustules had dried up and she was already showing signs of re-epithelialization. Edema and pain also had notably improved. She received 2 additional samples of risankizumab 150 mg at weeks 4 and 16, at which point she was able to receive compassionate care through the drug manufacturer’s program. At follow-up 151 days after the initial dose of risankizumab, the patient’s skin was completely clear.
Generalized pustular psoriasis remains a difficult disease to study, given its rarity and unpredictable course. Spesolimab, a humanized anti–IL-36 receptor monoclonal antibody, was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of GPP.5 In the pivotal trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT03782792),5 an astonishingly high 54% of patients (19/35) given a single dose of intravenous spesolimab reached the primary end point of no pustules at day 7. However, safety concerns, such as serious infections and severe cutaneous adverse reactions, as well as logistical challenges that come with intravenous administration for an acute disease, may prevent widespread adoption by community dermatologists.
Tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23 inhibitors currently are approved for the treatment of GPP in Japan, Thailand, and Taiwan based on small, nonrandomized, open-label studies.6-10 More recently, results from a phase 3, randomized, open-label study to assess the efficacy and safety of 2 different dosing regimens of risankizumab with 8 Japanese patients with GPP were published.11 However, there currently is only a single approved medication for GPP in Europe and the United States. Therefore, additional therapies, particularly those that have already been established in dermatology, would be welcome in treating this disease.
A number of questions still need to be answered regarding treating GPP with risankizumab:
• What is the optimal dose and schedule of this drug? Our patient received the standard 150-mg dose that is FDA approved for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis; would a higher dose, such as the FDA-approved 600-mg dosing used to treat Crohn disease, have led to a more rapid and durable response?12
• For how long should these patients be treated? Will their disease follow the same course as psoriasis vulgaris, requiring long-term, continuous treatment?
• An ongoing 5-year, open-label extension study of spesolimab might eventually answer that question and currently is recruiting participants (NCT03886246).
• Is there a way to predict a priori which patients will be responders? Biomarkers—especially through the use of tape stripping—are promising, but validation studies are still needed.13
• Because 69% (24/35) of enrolled patients in the treatment group of the spesolimab trial did not harbor a mutation of the IL36RN gene, how reliable is mutation status in predicting treatment response?5
Of note, some of these questions also apply to guttate psoriasis, a far more common subtype of psoriasis that also is worth exploring.
Nevertheless, these are exciting times for patients with GPP. What was once considered an obscure orphan disease is the focus of major recent publications3 and phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled studies.5 We can be cautiously optimistic that in the next few years we will be in a better position to care for patients with GPP.
- Shah M, Aboud DM Al, Crane JS, et al. Pustular psoriasis. In. Zeichner J, ed. Acneiform Eruptions in Dermatology: A Differential Diagnosis. 2021:295-307. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8344-1_42
- Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:496-509. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804595
- Noe MH, Wan MT, Mostaghimi A, et al. Evaluation of a case series of patients with generalized pustular psoriasis in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:73-78. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.4640
- Miyachi H, Konishi T, Kumazawa R, et al. Treatments and outcomes of generalized pustular psoriasis: a cohort of 1516 patients in a nationwide inpatient database in Japan. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1266-1274. doi:10.1016/J.JAAD.2021.06.008
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al; . Trial of spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2431-2440. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
- Robinson A, Van Voorhees AS, Hsu S, et al. Treatment of pustular psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:279-288. doi:10.1016/J.JAAD.2011.01.032
- Torii H, Nakagawa H; . Long-term study of infliximab in Japanese patients with plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, pustular psoriasis and psoriatic erythroderma. J Dermatol. 2011;38:321-334. doi:10.1111/J.1346-8138.2010.00971.X
- Saeki H, Nakagawa H, Ishii T, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label ixekizumab treatment in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and generalized pustular psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1148-1155. doi:10.1111/JDV.12773
- Imafuku S, Honma M, Okubo Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis: a 52-week analysis from phase III open-label multicenter Japanese study. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1011-1017. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13306
- Torii H, Terui T, Matsukawa M, et al. Safety profiles and efficacy of infliximab therapy in Japanese patients with plaque psoriasis with or without psoriatic arthritis, pustular psoriasis or psoriatic erythroderma: results from the prospective post-marketing surveillance. J Dermatol. 2016;43:767-778. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13214
- Yamanaka K, Okubo Y, Yasuda I, et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab in Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis or erythrodermic psoriasis: primary analysis and 180-week follow-up results from the phase 3, multicenter IMMspire study [published online December 13, 2022]. J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16667
- D’Haens G, Panaccione R, Baert F, et al. Risankizumab as induction therapy for Crohn’s disease: results from the phase 3 ADVANCE and MOTIVATE induction trials. Lancet. 2022;399:2015-2030. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00467-6
- Hughes AJ, Tawfik SS, Baruah KP, et al. Tape strips in dermatology research. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:26-35. doi:10.1111/BJD.19760
To the Editor:
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare but severe subtype of psoriasis that can present with systemic symptoms and organ failure, sometimes leading to hospitalization and even death.1,2 Due to the rarity of this subtype and GPP being excluded from clinical trials for plaque psoriasis, there is limited information on the optimal treatment of this disease.
More than 20 systemic medications have been described in the literature for treating GPP, including systemic steroids, traditional immunosuppressants, retinoids, and biologics, which often are used in combination; none have been consistently effective.3 Among biologic therapies, the use of tumor necrosis factor α as well as IL-12/23 and IL-17 inhibitors has been reported, with the least amount of experience with IL-17 inhibitors.4
A 53-year-old Korean woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of a widespread painful rash involving the face, neck, torso, arms, and legs that had been treated intermittently with systemic steroids by her primary care physician for several months before presentation. She had no relevant medical or dermatologic history. She denied taking prescription or over-the-counter medications.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile, but she reported general malaise and chills. She had widespread erythematous, annular, scaly plaques that coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the forehead, frontal hairline, neck, chest, abdomen, back, arms, and legs (Figure 1).
![Initial presentation (day 0 [prior to treatment with risankizumab]). A and B, Scaly plaques coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the leg and neck, respectively. Initial presentation (day 0 [prior to treatment with risankizumab]). A and B, Scaly plaques coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the leg and neck, respectively.](https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/CT111002096_Fig1_AB.jpg)
Two 4-mm punch biopsies were performed for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence. Histopathologic analysis showed prominent subcorneal neutrophilic pustules and spongiform collections of neutrophils in the spinous layer without notable eosinophils (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence was negative.

Based on the clinical history, physical examination, histopathology, and unremarkable drug history, a diagnosis of GPP was made. Initially, acitretin 25 mg/d was prescribed, but the patient was unable to start treatment because the cost of the drug was prohibitive. Her condition worsened, and she returned to the clinic 2 days later. Based on knowledge of an ongoing phase 3, open-label study for risankizumab in GPP, a sample of risankizumab 150 mg was administered subcutaneously in this patient. Three days later, most of the pustules on the upper half of the patient’s body had dried up and she began to desquamate from head to toe (Figure 3).The patient developed notable edema of the lower extremities, which required furosemide 20 mg/d andibuprofen 600 mg every 6 hours for symptom relief.

Ten days after the initial dose of risankizumab, the patient continued to steadily improve. All the pustules had dried up and she was already showing signs of re-epithelialization. Edema and pain also had notably improved. She received 2 additional samples of risankizumab 150 mg at weeks 4 and 16, at which point she was able to receive compassionate care through the drug manufacturer’s program. At follow-up 151 days after the initial dose of risankizumab, the patient’s skin was completely clear.
Generalized pustular psoriasis remains a difficult disease to study, given its rarity and unpredictable course. Spesolimab, a humanized anti–IL-36 receptor monoclonal antibody, was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of GPP.5 In the pivotal trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT03782792),5 an astonishingly high 54% of patients (19/35) given a single dose of intravenous spesolimab reached the primary end point of no pustules at day 7. However, safety concerns, such as serious infections and severe cutaneous adverse reactions, as well as logistical challenges that come with intravenous administration for an acute disease, may prevent widespread adoption by community dermatologists.
Tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23 inhibitors currently are approved for the treatment of GPP in Japan, Thailand, and Taiwan based on small, nonrandomized, open-label studies.6-10 More recently, results from a phase 3, randomized, open-label study to assess the efficacy and safety of 2 different dosing regimens of risankizumab with 8 Japanese patients with GPP were published.11 However, there currently is only a single approved medication for GPP in Europe and the United States. Therefore, additional therapies, particularly those that have already been established in dermatology, would be welcome in treating this disease.
A number of questions still need to be answered regarding treating GPP with risankizumab:
• What is the optimal dose and schedule of this drug? Our patient received the standard 150-mg dose that is FDA approved for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis; would a higher dose, such as the FDA-approved 600-mg dosing used to treat Crohn disease, have led to a more rapid and durable response?12
• For how long should these patients be treated? Will their disease follow the same course as psoriasis vulgaris, requiring long-term, continuous treatment?
• An ongoing 5-year, open-label extension study of spesolimab might eventually answer that question and currently is recruiting participants (NCT03886246).
• Is there a way to predict a priori which patients will be responders? Biomarkers—especially through the use of tape stripping—are promising, but validation studies are still needed.13
• Because 69% (24/35) of enrolled patients in the treatment group of the spesolimab trial did not harbor a mutation of the IL36RN gene, how reliable is mutation status in predicting treatment response?5
Of note, some of these questions also apply to guttate psoriasis, a far more common subtype of psoriasis that also is worth exploring.
Nevertheless, these are exciting times for patients with GPP. What was once considered an obscure orphan disease is the focus of major recent publications3 and phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled studies.5 We can be cautiously optimistic that in the next few years we will be in a better position to care for patients with GPP.
To the Editor:
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare but severe subtype of psoriasis that can present with systemic symptoms and organ failure, sometimes leading to hospitalization and even death.1,2 Due to the rarity of this subtype and GPP being excluded from clinical trials for plaque psoriasis, there is limited information on the optimal treatment of this disease.
More than 20 systemic medications have been described in the literature for treating GPP, including systemic steroids, traditional immunosuppressants, retinoids, and biologics, which often are used in combination; none have been consistently effective.3 Among biologic therapies, the use of tumor necrosis factor α as well as IL-12/23 and IL-17 inhibitors has been reported, with the least amount of experience with IL-17 inhibitors.4
A 53-year-old Korean woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of a widespread painful rash involving the face, neck, torso, arms, and legs that had been treated intermittently with systemic steroids by her primary care physician for several months before presentation. She had no relevant medical or dermatologic history. She denied taking prescription or over-the-counter medications.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile, but she reported general malaise and chills. She had widespread erythematous, annular, scaly plaques that coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the forehead, frontal hairline, neck, chest, abdomen, back, arms, and legs (Figure 1).
![Initial presentation (day 0 [prior to treatment with risankizumab]). A and B, Scaly plaques coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the leg and neck, respectively. Initial presentation (day 0 [prior to treatment with risankizumab]). A and B, Scaly plaques coalesced into polycyclic plaques studded with nonfollicular-based pustules on the leg and neck, respectively.](https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/CT111002096_Fig1_AB.jpg)
Two 4-mm punch biopsies were performed for hematoxylin and eosin staining and direct immunofluorescence. Histopathologic analysis showed prominent subcorneal neutrophilic pustules and spongiform collections of neutrophils in the spinous layer without notable eosinophils (Figure 2). Direct immunofluorescence was negative.

Based on the clinical history, physical examination, histopathology, and unremarkable drug history, a diagnosis of GPP was made. Initially, acitretin 25 mg/d was prescribed, but the patient was unable to start treatment because the cost of the drug was prohibitive. Her condition worsened, and she returned to the clinic 2 days later. Based on knowledge of an ongoing phase 3, open-label study for risankizumab in GPP, a sample of risankizumab 150 mg was administered subcutaneously in this patient. Three days later, most of the pustules on the upper half of the patient’s body had dried up and she began to desquamate from head to toe (Figure 3).The patient developed notable edema of the lower extremities, which required furosemide 20 mg/d andibuprofen 600 mg every 6 hours for symptom relief.

Ten days after the initial dose of risankizumab, the patient continued to steadily improve. All the pustules had dried up and she was already showing signs of re-epithelialization. Edema and pain also had notably improved. She received 2 additional samples of risankizumab 150 mg at weeks 4 and 16, at which point she was able to receive compassionate care through the drug manufacturer’s program. At follow-up 151 days after the initial dose of risankizumab, the patient’s skin was completely clear.
Generalized pustular psoriasis remains a difficult disease to study, given its rarity and unpredictable course. Spesolimab, a humanized anti–IL-36 receptor monoclonal antibody, was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of GPP.5 In the pivotal trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT03782792),5 an astonishingly high 54% of patients (19/35) given a single dose of intravenous spesolimab reached the primary end point of no pustules at day 7. However, safety concerns, such as serious infections and severe cutaneous adverse reactions, as well as logistical challenges that come with intravenous administration for an acute disease, may prevent widespread adoption by community dermatologists.
Tumor necrosis factor α, IL-17, and IL-23 inhibitors currently are approved for the treatment of GPP in Japan, Thailand, and Taiwan based on small, nonrandomized, open-label studies.6-10 More recently, results from a phase 3, randomized, open-label study to assess the efficacy and safety of 2 different dosing regimens of risankizumab with 8 Japanese patients with GPP were published.11 However, there currently is only a single approved medication for GPP in Europe and the United States. Therefore, additional therapies, particularly those that have already been established in dermatology, would be welcome in treating this disease.
A number of questions still need to be answered regarding treating GPP with risankizumab:
• What is the optimal dose and schedule of this drug? Our patient received the standard 150-mg dose that is FDA approved for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis; would a higher dose, such as the FDA-approved 600-mg dosing used to treat Crohn disease, have led to a more rapid and durable response?12
• For how long should these patients be treated? Will their disease follow the same course as psoriasis vulgaris, requiring long-term, continuous treatment?
• An ongoing 5-year, open-label extension study of spesolimab might eventually answer that question and currently is recruiting participants (NCT03886246).
• Is there a way to predict a priori which patients will be responders? Biomarkers—especially through the use of tape stripping—are promising, but validation studies are still needed.13
• Because 69% (24/35) of enrolled patients in the treatment group of the spesolimab trial did not harbor a mutation of the IL36RN gene, how reliable is mutation status in predicting treatment response?5
Of note, some of these questions also apply to guttate psoriasis, a far more common subtype of psoriasis that also is worth exploring.
Nevertheless, these are exciting times for patients with GPP. What was once considered an obscure orphan disease is the focus of major recent publications3 and phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled studies.5 We can be cautiously optimistic that in the next few years we will be in a better position to care for patients with GPP.
- Shah M, Aboud DM Al, Crane JS, et al. Pustular psoriasis. In. Zeichner J, ed. Acneiform Eruptions in Dermatology: A Differential Diagnosis. 2021:295-307. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8344-1_42
- Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:496-509. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804595
- Noe MH, Wan MT, Mostaghimi A, et al. Evaluation of a case series of patients with generalized pustular psoriasis in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:73-78. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.4640
- Miyachi H, Konishi T, Kumazawa R, et al. Treatments and outcomes of generalized pustular psoriasis: a cohort of 1516 patients in a nationwide inpatient database in Japan. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1266-1274. doi:10.1016/J.JAAD.2021.06.008
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al; . Trial of spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2431-2440. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
- Robinson A, Van Voorhees AS, Hsu S, et al. Treatment of pustular psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:279-288. doi:10.1016/J.JAAD.2011.01.032
- Torii H, Nakagawa H; . Long-term study of infliximab in Japanese patients with plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, pustular psoriasis and psoriatic erythroderma. J Dermatol. 2011;38:321-334. doi:10.1111/J.1346-8138.2010.00971.X
- Saeki H, Nakagawa H, Ishii T, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label ixekizumab treatment in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and generalized pustular psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1148-1155. doi:10.1111/JDV.12773
- Imafuku S, Honma M, Okubo Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis: a 52-week analysis from phase III open-label multicenter Japanese study. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1011-1017. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13306
- Torii H, Terui T, Matsukawa M, et al. Safety profiles and efficacy of infliximab therapy in Japanese patients with plaque psoriasis with or without psoriatic arthritis, pustular psoriasis or psoriatic erythroderma: results from the prospective post-marketing surveillance. J Dermatol. 2016;43:767-778. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13214
- Yamanaka K, Okubo Y, Yasuda I, et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab in Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis or erythrodermic psoriasis: primary analysis and 180-week follow-up results from the phase 3, multicenter IMMspire study [published online December 13, 2022]. J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16667
- D’Haens G, Panaccione R, Baert F, et al. Risankizumab as induction therapy for Crohn’s disease: results from the phase 3 ADVANCE and MOTIVATE induction trials. Lancet. 2022;399:2015-2030. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00467-6
- Hughes AJ, Tawfik SS, Baruah KP, et al. Tape strips in dermatology research. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:26-35. doi:10.1111/BJD.19760
- Shah M, Aboud DM Al, Crane JS, et al. Pustular psoriasis. In. Zeichner J, ed. Acneiform Eruptions in Dermatology: A Differential Diagnosis. 2021:295-307. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8344-1_42
- Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:496-509. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804595
- Noe MH, Wan MT, Mostaghimi A, et al. Evaluation of a case series of patients with generalized pustular psoriasis in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:73-78. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.4640
- Miyachi H, Konishi T, Kumazawa R, et al. Treatments and outcomes of generalized pustular psoriasis: a cohort of 1516 patients in a nationwide inpatient database in Japan. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1266-1274. doi:10.1016/J.JAAD.2021.06.008
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al; . Trial of spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2431-2440. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
- Robinson A, Van Voorhees AS, Hsu S, et al. Treatment of pustular psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:279-288. doi:10.1016/J.JAAD.2011.01.032
- Torii H, Nakagawa H; . Long-term study of infliximab in Japanese patients with plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, pustular psoriasis and psoriatic erythroderma. J Dermatol. 2011;38:321-334. doi:10.1111/J.1346-8138.2010.00971.X
- Saeki H, Nakagawa H, Ishii T, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label ixekizumab treatment in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and generalized pustular psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1148-1155. doi:10.1111/JDV.12773
- Imafuku S, Honma M, Okubo Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis: a 52-week analysis from phase III open-label multicenter Japanese study. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1011-1017. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13306
- Torii H, Terui T, Matsukawa M, et al. Safety profiles and efficacy of infliximab therapy in Japanese patients with plaque psoriasis with or without psoriatic arthritis, pustular psoriasis or psoriatic erythroderma: results from the prospective post-marketing surveillance. J Dermatol. 2016;43:767-778. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13214
- Yamanaka K, Okubo Y, Yasuda I, et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab in Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis or erythrodermic psoriasis: primary analysis and 180-week follow-up results from the phase 3, multicenter IMMspire study [published online December 13, 2022]. J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16667
- D’Haens G, Panaccione R, Baert F, et al. Risankizumab as induction therapy for Crohn’s disease: results from the phase 3 ADVANCE and MOTIVATE induction trials. Lancet. 2022;399:2015-2030. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00467-6
- Hughes AJ, Tawfik SS, Baruah KP, et al. Tape strips in dermatology research. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:26-35. doi:10.1111/BJD.19760
PRACTICE POINTS
- Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a potentially life-threatening condition that can be precipitated by systemic steroids.
- Although more than 20 systemic medications have been tried with varying success, there has not been a single US Food and Drug Administration–approved medication for GPP until recently with the approval of spesolimab, an IL-36 receptor inhibitor.
- Risankizumab, a high-affinity humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the p19 subunit of the IL-23 cytokine, also has shown promise in a recent phase 3, open-label study for GPP.