User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'medstat-accordion-set article-series')]
Psoriatic arthritis management should target both clinical and biochemical inflammation
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), clinical inflammation monitored by swollen joint counts (SJC) and biochemical inflammation monitored by C-reactive protein (CRP) level, have a direct effect on structural progression.
Major finding: Progression was significantly higher in patients with active vs. inactive time-averaged SJC (odds ratio [OR] 1.24; P = .016) and time-averaged CRP (OR 6.08; P = .036). Progression was greatest in presence of both clinical and biochemical inflammation and lowest in absence of both (P = .05).
Study details: Findings are secondary analysis of patient data from the IMPACT 2 trial, including 145 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as associate editor or receiving grants and honoraria from several sources.
Source: Borst C et al. RMD Open. 2021;7:e002038 (Dec 8). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002038.
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), clinical inflammation monitored by swollen joint counts (SJC) and biochemical inflammation monitored by C-reactive protein (CRP) level, have a direct effect on structural progression.
Major finding: Progression was significantly higher in patients with active vs. inactive time-averaged SJC (odds ratio [OR] 1.24; P = .016) and time-averaged CRP (OR 6.08; P = .036). Progression was greatest in presence of both clinical and biochemical inflammation and lowest in absence of both (P = .05).
Study details: Findings are secondary analysis of patient data from the IMPACT 2 trial, including 145 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as associate editor or receiving grants and honoraria from several sources.
Source: Borst C et al. RMD Open. 2021;7:e002038 (Dec 8). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002038.
Key clinical point: In patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), clinical inflammation monitored by swollen joint counts (SJC) and biochemical inflammation monitored by C-reactive protein (CRP) level, have a direct effect on structural progression.
Major finding: Progression was significantly higher in patients with active vs. inactive time-averaged SJC (odds ratio [OR] 1.24; P = .016) and time-averaged CRP (OR 6.08; P = .036). Progression was greatest in presence of both clinical and biochemical inflammation and lowest in absence of both (P = .05).
Study details: Findings are secondary analysis of patient data from the IMPACT 2 trial, including 145 patients with PsA.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared serving as associate editor or receiving grants and honoraria from several sources.
Source: Borst C et al. RMD Open. 2021;7:e002038 (Dec 8). Doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002038.
PsA: Upadacitinib shows similar benefits as monotherapy or in combination with nbDMARDs
Key clinical point: Upadacitinib showed similar efficacy and a consistent safety profile as monotherapy or in combination with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (nbDMARDs) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: At week 12, ≥20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI, 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI, 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI, 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI, 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar with monotherapy and combination therapy.
Study details: This is a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, including 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 nbDMARD/bDMARD who were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks.
Disclosures: This work was supported by AbbVie. Six authors reported being employees and stockholders of AbbVie. The other authors reported ties with several sources including AbbVie.
Source: Nash P et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab905 (Dec 3). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab905.
Key clinical point: Upadacitinib showed similar efficacy and a consistent safety profile as monotherapy or in combination with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (nbDMARDs) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: At week 12, ≥20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI, 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI, 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI, 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI, 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar with monotherapy and combination therapy.
Study details: This is a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, including 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 nbDMARD/bDMARD who were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks.
Disclosures: This work was supported by AbbVie. Six authors reported being employees and stockholders of AbbVie. The other authors reported ties with several sources including AbbVie.
Source: Nash P et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab905 (Dec 3). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab905.
Key clinical point: Upadacitinib showed similar efficacy and a consistent safety profile as monotherapy or in combination with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (nbDMARDs) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: At week 12, ≥20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI, 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI, 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI, 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI, 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar with monotherapy and combination therapy.
Study details: This is a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, including 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 nbDMARD/bDMARD who were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks.
Disclosures: This work was supported by AbbVie. Six authors reported being employees and stockholders of AbbVie. The other authors reported ties with several sources including AbbVie.
Source: Nash P et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab905 (Dec 3). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab905.
Discontinuing TNF inhibitors may not be required in PsA patients receiving BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine
Key clinical point: Continuation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy throughout the vaccination period was safe and did not hamper the immune response elicited by BNT162b2 (BioNTech-Pfizer) mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: There was no change in Clinical Disease Activity Index in patients with PsA before and after vaccination (P = .92). After 2 doses of BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, all patients with PsA showed a positive immune response with mean anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody level not significantly different from matched controls (P = .08).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 40 patients with PsA on TNF inhibitor therapy matched with 40 healthy controls; both groups received 2 shots of the BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Venerito V et al. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001847 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1136/ rmdopen-2021-001847.
Key clinical point: Continuation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy throughout the vaccination period was safe and did not hamper the immune response elicited by BNT162b2 (BioNTech-Pfizer) mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: There was no change in Clinical Disease Activity Index in patients with PsA before and after vaccination (P = .92). After 2 doses of BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, all patients with PsA showed a positive immune response with mean anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody level not significantly different from matched controls (P = .08).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 40 patients with PsA on TNF inhibitor therapy matched with 40 healthy controls; both groups received 2 shots of the BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Venerito V et al. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001847 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1136/ rmdopen-2021-001847.
Key clinical point: Continuation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy throughout the vaccination period was safe and did not hamper the immune response elicited by BNT162b2 (BioNTech-Pfizer) mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: There was no change in Clinical Disease Activity Index in patients with PsA before and after vaccination (P = .92). After 2 doses of BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, all patients with PsA showed a positive immune response with mean anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody level not significantly different from matched controls (P = .08).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 40 patients with PsA on TNF inhibitor therapy matched with 40 healthy controls; both groups received 2 shots of the BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Disclosures: The study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Venerito V et al. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001847 (Jan 5). Doi: 10.1136/ rmdopen-2021-001847.
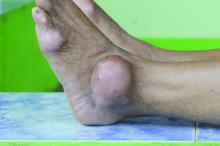
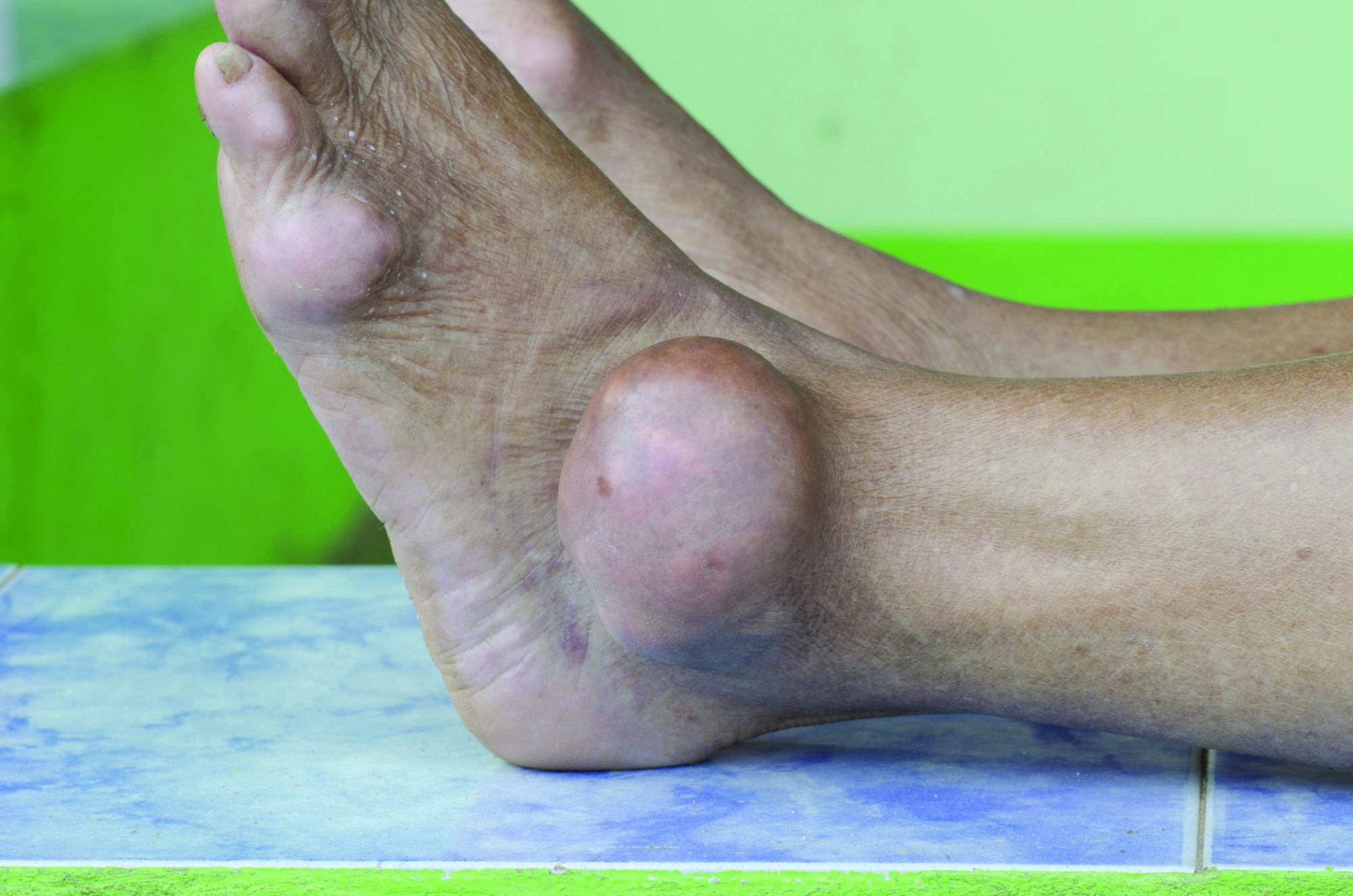
Allopurinol found safe in patients with concomitant gout, CKD
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Allopurinol treatment is not associated with increased mortality in patients with gout and chronic kidney disease even at 5 years after starting treatment, a study has found.
Around one in five patients with gout also have chronic kidney disease, and previous research suggests that hyperuricemia is itself a contributor to renal disease, which is why there has been interest in the use of serum urate–lowering medication in patients with both conditions.
Since the publication of two earlier randomized controlled trials suggested a twofold increase in mortality among patients with renal disease who were treated with allopurinol in an attempt to slow progression, there has been wariness about the drug in patients with compromised renal function.
In a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, Jie Wei, PhD, of Xiangya Hospital at Central South University in Changsha, China, and coauthors report the results of their retrospective, population-based study of 5,277 adults aged 40 and older with gout and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease who were initiated on allopurinol and 5,277 matched individuals not on allopurinol.
At 5 years after the patients started allopurinol, the study found that mortality was a statistically significant 15% lower (hazard ratio, 0.85; 95% confidence interval, 0.77-0.93) among those on allopurinol, compared with those not taking the drug. The rate was 4.9 deaths per 100 person-years among those on allopurinol, compared with 5.8 among those not taking it.
The researchers also created two simulated randomized clinical trials from the data for initiators of allopurinol, replicating each initiator twice. The first trial assigned patient replicates either to achieving a target serum urate level of less than 0.36 mmol/L within a year or not achieving it. The second assigned patient replicates to either an allopurinol dose-escalation group or no dose escalation.
For the target serum urate level study, 1,484 achieved the target, and this was associated with a 13% lower hazard ratio for mortality that just missed statistical significance (HR, 0.87; 95% confidence interval, 0.75-1.01).
In the dose-escalation study, there were 773 participants who increased their dose of allopurinol in the first year after initiation – from a median of 100 mg/day to a median final dose of 300 mg/day – and 2,923 who didn’t. Those who escalated their dose had a nonsignificant 12% lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.73-1.07), compared with those who didn’t.
The authors suggest that this could be the result of confounding, as patients who achieved target serum urate levels may have been of better health generally than those who didn’t, which could also have contributed to lower mortality.
Coauthor of the study Yuqing Zhang, DSc, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said there had previously been a theory that allopurinol could protect against progression of renal disease. However, the two randomized, controlled trials in patients with chronic kidney disease but not gout published in 2020 suggested that allopurinol was instead associated with a doubling of mortality in this group.
“This study really shows convincing evidence that among gout patients with renal disease, allopurinol does not increase mortality,” Dr. Zhang told this news organization. He suggested the reason that the earlier studies had found higher mortality among patients on allopurinol was because those patients did not have gout. Given that gout can increase mortality, treating it effectively with allopurinol may therefore reduce mortality even in patients with concurrent chronic kidney disease.
Commenting on the study, Angelo Gaffo, MD, from the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that, while there had been data suggesting increased mortality, the findings from this “very well-done” study were reassuring and even suggested a possible decrease in mortality associated with allopurinol.
“I wouldn’t scream it out loud because it needs confirmation, but it’s something also that we have a sense that could be true,” he said.
Dr. Gaffo noted that patients treated with allopurinol tended to be those with fewer comorbidities. “Patients who have a lot of comorbidities probably are less likely to have their dose of allopurinol started or increased because of some concerns that practitioners may have about putting them on another medicine or increasing the dose of that medicine,” he said.
He also stressed that the findings still need replication in other large database studies, given that a prospective, randomized clinical trial addressing such a question would be difficult to conduct.
The study was supported by the Project Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Two authors reported consulting fees from the pharmaceutical sector unrelated to the study. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Watch, but don’t worry yet, about new Omicron subvariant
In the meantime, it’s worth watching BA.2, the World Health Organization said. The subvariant has been identified across at least 40 countries, including three cases reported in Houston and several in Washington state.
BA.2 accounts for only a small minority of reported cases so far, including 5% in India, 4% of those in the United Kingdom, and 2% each of cases in Sweden and Singapore.
The one exception is Denmark, a country with robust genetic sequencing abilities, where estimates range from 50% to 81% of cases.
The news throws a little more uncertainty into an already uncertain situation, including how close the world might be to a less life-altering infectious disease.
For example, the world is at an ideal point for a new variant to emerge, WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, said during a Jan. 24 meeting of the WHO executive board. He also said it’s too early to call an “end game” to the pandemic.
Similarly, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said on Jan. 19 that it remained “an open question” whether the Omicron variant could hasten endemic COVID-19, a situation where the virus still circulates but is much less disruptive to everyday life.
No Pi for you
This could be the first time a coronavirus subvariant rises to the level of a household name, or – if previous variants of the moment have shown us – it could recede from the spotlight.
For example, a lot of focus on the potential of the Mu variant to wreak havoc fizzled out a few weeks after the WHO listed it as a variant of interest on Aug. 30.
Subvariants can feature mutations and other small differences but are not distinct enough from an existing strain to be called a variant on their own and be named after the next letter in the Greek alphabet. That’s why BA.2 is not called the “Pi variant.”
Predicting what’s next for the coronavirus has puzzled many experts throughout the pandemic. That is why many public health officials wait for the WHO to officially designate a strain as a variant of interest or variant of concern before taking action.
At the moment with BA.2, it seems close monitoring is warranted.
Because it’s too early to call, expert predictions about BA.2 vary widely, from worry to cautious optimism.
For example, early data indicates that BA.2 could be more worrisome than original Omicron, Eric Feigl-Ding, ScD, an epidemiologist and health economist, said on Twitter.
Information from Denmark seems to show BA.2 either has “much faster transmission or it evades immunity even more,” he said.
The same day, Jan. 23, Dr. Feigl-Ding tweeted that other data shows the subvariant can spread twice as fast as Omicron, which was already much more contagious than previous versions of the virus.
At the same time, other experts appear less concerned. Robert Garry, PhD, a virologist at Tulane University, New Orleans, told the Washington Post that there is no reason to think BA.2 will be any worse than the original Omicron strain.
So which expert predictions will come closer to BA.2’s potential? For now, it’s just a watch-and-see situation.
For updated information, the website outbreak.info tracks BA.2’s average daily and cumulative prevalence in the United States and in other locations.
Also, if and when WHO experts decide to elevate BA.2 to a variant of interest or a variant of concern, it will be noted on its coronavirus variant tracking website.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In the meantime, it’s worth watching BA.2, the World Health Organization said. The subvariant has been identified across at least 40 countries, including three cases reported in Houston and several in Washington state.
BA.2 accounts for only a small minority of reported cases so far, including 5% in India, 4% of those in the United Kingdom, and 2% each of cases in Sweden and Singapore.
The one exception is Denmark, a country with robust genetic sequencing abilities, where estimates range from 50% to 81% of cases.
The news throws a little more uncertainty into an already uncertain situation, including how close the world might be to a less life-altering infectious disease.
For example, the world is at an ideal point for a new variant to emerge, WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, said during a Jan. 24 meeting of the WHO executive board. He also said it’s too early to call an “end game” to the pandemic.
Similarly, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said on Jan. 19 that it remained “an open question” whether the Omicron variant could hasten endemic COVID-19, a situation where the virus still circulates but is much less disruptive to everyday life.
No Pi for you
This could be the first time a coronavirus subvariant rises to the level of a household name, or – if previous variants of the moment have shown us – it could recede from the spotlight.
For example, a lot of focus on the potential of the Mu variant to wreak havoc fizzled out a few weeks after the WHO listed it as a variant of interest on Aug. 30.
Subvariants can feature mutations and other small differences but are not distinct enough from an existing strain to be called a variant on their own and be named after the next letter in the Greek alphabet. That’s why BA.2 is not called the “Pi variant.”
Predicting what’s next for the coronavirus has puzzled many experts throughout the pandemic. That is why many public health officials wait for the WHO to officially designate a strain as a variant of interest or variant of concern before taking action.
At the moment with BA.2, it seems close monitoring is warranted.
Because it’s too early to call, expert predictions about BA.2 vary widely, from worry to cautious optimism.
For example, early data indicates that BA.2 could be more worrisome than original Omicron, Eric Feigl-Ding, ScD, an epidemiologist and health economist, said on Twitter.
Information from Denmark seems to show BA.2 either has “much faster transmission or it evades immunity even more,” he said.
The same day, Jan. 23, Dr. Feigl-Ding tweeted that other data shows the subvariant can spread twice as fast as Omicron, which was already much more contagious than previous versions of the virus.
At the same time, other experts appear less concerned. Robert Garry, PhD, a virologist at Tulane University, New Orleans, told the Washington Post that there is no reason to think BA.2 will be any worse than the original Omicron strain.
So which expert predictions will come closer to BA.2’s potential? For now, it’s just a watch-and-see situation.
For updated information, the website outbreak.info tracks BA.2’s average daily and cumulative prevalence in the United States and in other locations.
Also, if and when WHO experts decide to elevate BA.2 to a variant of interest or a variant of concern, it will be noted on its coronavirus variant tracking website.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In the meantime, it’s worth watching BA.2, the World Health Organization said. The subvariant has been identified across at least 40 countries, including three cases reported in Houston and several in Washington state.
BA.2 accounts for only a small minority of reported cases so far, including 5% in India, 4% of those in the United Kingdom, and 2% each of cases in Sweden and Singapore.
The one exception is Denmark, a country with robust genetic sequencing abilities, where estimates range from 50% to 81% of cases.
The news throws a little more uncertainty into an already uncertain situation, including how close the world might be to a less life-altering infectious disease.
For example, the world is at an ideal point for a new variant to emerge, WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, said during a Jan. 24 meeting of the WHO executive board. He also said it’s too early to call an “end game” to the pandemic.
Similarly, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said on Jan. 19 that it remained “an open question” whether the Omicron variant could hasten endemic COVID-19, a situation where the virus still circulates but is much less disruptive to everyday life.
No Pi for you
This could be the first time a coronavirus subvariant rises to the level of a household name, or – if previous variants of the moment have shown us – it could recede from the spotlight.
For example, a lot of focus on the potential of the Mu variant to wreak havoc fizzled out a few weeks after the WHO listed it as a variant of interest on Aug. 30.
Subvariants can feature mutations and other small differences but are not distinct enough from an existing strain to be called a variant on their own and be named after the next letter in the Greek alphabet. That’s why BA.2 is not called the “Pi variant.”
Predicting what’s next for the coronavirus has puzzled many experts throughout the pandemic. That is why many public health officials wait for the WHO to officially designate a strain as a variant of interest or variant of concern before taking action.
At the moment with BA.2, it seems close monitoring is warranted.
Because it’s too early to call, expert predictions about BA.2 vary widely, from worry to cautious optimism.
For example, early data indicates that BA.2 could be more worrisome than original Omicron, Eric Feigl-Ding, ScD, an epidemiologist and health economist, said on Twitter.
Information from Denmark seems to show BA.2 either has “much faster transmission or it evades immunity even more,” he said.
The same day, Jan. 23, Dr. Feigl-Ding tweeted that other data shows the subvariant can spread twice as fast as Omicron, which was already much more contagious than previous versions of the virus.
At the same time, other experts appear less concerned. Robert Garry, PhD, a virologist at Tulane University, New Orleans, told the Washington Post that there is no reason to think BA.2 will be any worse than the original Omicron strain.
So which expert predictions will come closer to BA.2’s potential? For now, it’s just a watch-and-see situation.
For updated information, the website outbreak.info tracks BA.2’s average daily and cumulative prevalence in the United States and in other locations.
Also, if and when WHO experts decide to elevate BA.2 to a variant of interest or a variant of concern, it will be noted on its coronavirus variant tracking website.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
This doc still supports NP/PA-led care ... with caveats
Two years ago, I argued that independent care from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) would not have ill effects on health outcomes. To the surprise of no one, NPs and PAs embraced the argument; physicians clobbered it.
My case had three pegs: One was that medicine isn’t rocket science and clinicians control a lot less than we think we do. The second peg was that technology levels the playing field of clinical care. High-sensitivity troponin assays, for instance, make missing MI a lot less likely. The third peg was empirical: Studies have found little difference in MD versus non–MD-led care. Looking back, I now see empiricism as the weakest part of the argument because the studies had so many limitations.
I update this viewpoint now because health care is increasingly delivered by NPs and PAs. And there are two concerning trends regarding NP education and experience. First is that nurses are turning to advanced practitioner training earlier in their careers – without gathering much bedside experience. And these training programs are increasingly likely to be online, with minimal hands-on clinical tutoring.
Education and experience pop in my head often. Not every day, but many days I think back to my lucky 7 years in Indiana learning under the supervision of master clinicians – at a time when trainees were allowed the leeway to make decisions ... and mistakes. Then, when I joined private practice, I continued to learn from experienced practitioners.
It would be foolish to argue that training and experience aren’t important.
But here’s the thing:
I will make three points: First, I will bolster two of my old arguments as to why we shouldn’t be worried about non-MD clinicians, then I will propose some ideas to increase confidence in NP and PA care.
Health care does not equal health
On the matter of how much clinicians affect outcomes, a recently published randomized controlled trial performed in India found that subsidizing insurance care led to increased utilization of hospital services but had no significant effect on health outcomes. This follows the RAND and Oregon Health Insurance studies in the United States, which largely reported similar results.
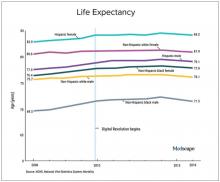
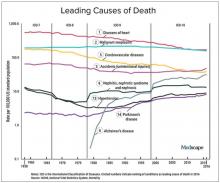
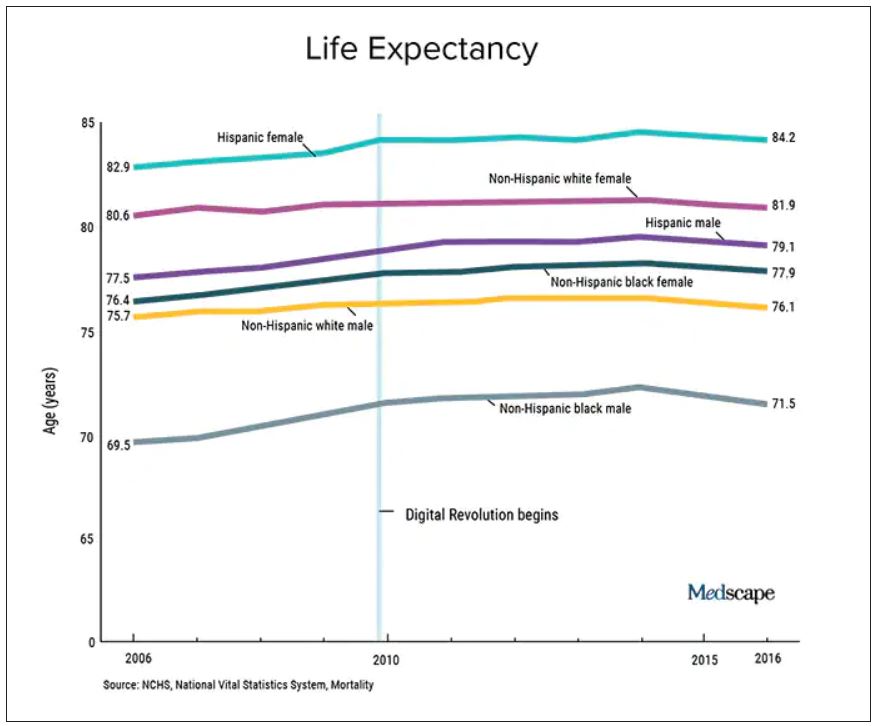
We should also not dismiss the fact that – despite the massive technology gains over the past half-century in digital health and artificial intelligence and increased use of quality measures, new drugs and procedures, and mega-medical centers – the average lifespan of Americans is flat to declining (in most ethnic and racial groups). Worse than no gains in longevity, perhaps, is that death from diseases like dementia and Parkinson’s disease are on the rise.
A neutral Martian would look down and wonder why all this health care hasn’t translated to longer and better lives. The causes of this paradox remain speculative, and are for another column, but the point remains that – on average – more health care is clearly not delivering more health. And if that is true, one may deduce that much of U.S. health care is marginal when it comes to affecting major outcomes.
It’s about the delta
Logos trumps pathos. Sure, my physician colleagues can tell scary anecdotes of bad outcomes caused by an inexperienced NP or PA. I would counter that by saying I have sat on our hospital’s peer review committee for 2 decades, including the era before NPs or PAs were practicing, and I have plenty of stories of physician errors. These include, of course, my own errors.
Logos: We must consider the difference between non–MD-led care and MD-led care.
My arguments from 2020 remain relevant today. Most medical problems are not engineering puzzles. Many, perhaps most, patients fall into an easy protocol – say, chest pain, dyspnea, or atrial fibrillation. With basic training, a motivated serious person quickly gains skill in recognizing and treating everyday problems.
And just 2 years on, technology further levels the playing field. Consider radiology in 2022 – it’s easy to take for granted the speed of the CT scan, the fidelity of the MRI, and the easy access to both in the U.S. hospital system. Less experienced clinicians have never had more tools to assist with diagnostics and therapeutics.
The expansion of team-based care has also mitigated the effects of inexperience. It took Americans longer than Canadians to figure out how helpful pharmacists could be. Pharmacists in my hospital now help us dose complicated medicines and protect us against prescribing errors.
Then there is the immediate access to online information. Gone are the days when you had to memorize long-QT syndromes. Book knowledge – that I spent years acquiring – now comes in seconds. The other day an NP corrected me. I asked, Are you sure? Boom, she took out her phone and showed me the evidence.
In sum, if it were even possible to measure the clinical competence of care from NP and PA versus physicians, there would be two bell-shaped curves with a tremendous amount of overlap. And that overlap would steadily increase as a given NP or PA gathered experience. (The NP in our electrophysiology division has more than 25 years’ experience in heart rhythm care, and it is common for colleagues to call her before one of us docs. Rightly so.)
Three basic proposals regarding NP and PA care
To ensure quality of care, I have three proposals.
It has always seemed strange to me that an NP or PA can flip from one field to another without a period of training. I can’t just change practice from electrophysiology to dermatology without doing a residency. But NPs and PAs can.
My first proposal would be that NPs and PAs spend a substantial period of training in a field before practice – a legit apprenticeship. The duration of this period is a matter of debate, but it ought to be standardized.
My second proposal is that, if physicians are required to pass certification exams, so should NPs. (PAs have an exam every 10 years.) The exam should be the same as (or very similar to) the physician exam, and it should be specific to their field of practice.
While I have argued (and still feel) that the American Board of Internal Medicine brand of certification is dubious, the fact remains that physicians must maintain proficiency in their field. Requiring NPs and PAs to do the same would help foster specialization. And while I can’t cite empirical evidence, specialization seems super-important. We have NPs at my hospital who have been in the same area for years, and they exude clinical competence.
Finally, I have come to believe that the best way for nearly any clinician to practice medicine is as part of a team. (The exception being primary care in rural areas where there are clinician shortages.)
On the matter of team care, I’ve practiced for a long time, but nearly every day I run situations by a colleague; often this person is an NP. The economist Friedrich Hayek proposed that dispersed knowledge always outpaces the wisdom of any individual. That notion pertains well to the increasing complexities and specialization of modern medical practice.
A person who commits to learning one area of medicine, enjoys helping people, asks often for help, and has the support of colleagues is set up to be a successful clinician – whether the letters after their name are APRN, PA, DO, or MD.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. He did not report any relevant financial disclosures. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two years ago, I argued that independent care from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) would not have ill effects on health outcomes. To the surprise of no one, NPs and PAs embraced the argument; physicians clobbered it.
My case had three pegs: One was that medicine isn’t rocket science and clinicians control a lot less than we think we do. The second peg was that technology levels the playing field of clinical care. High-sensitivity troponin assays, for instance, make missing MI a lot less likely. The third peg was empirical: Studies have found little difference in MD versus non–MD-led care. Looking back, I now see empiricism as the weakest part of the argument because the studies had so many limitations.
I update this viewpoint now because health care is increasingly delivered by NPs and PAs. And there are two concerning trends regarding NP education and experience. First is that nurses are turning to advanced practitioner training earlier in their careers – without gathering much bedside experience. And these training programs are increasingly likely to be online, with minimal hands-on clinical tutoring.
Education and experience pop in my head often. Not every day, but many days I think back to my lucky 7 years in Indiana learning under the supervision of master clinicians – at a time when trainees were allowed the leeway to make decisions ... and mistakes. Then, when I joined private practice, I continued to learn from experienced practitioners.
It would be foolish to argue that training and experience aren’t important.
But here’s the thing:
I will make three points: First, I will bolster two of my old arguments as to why we shouldn’t be worried about non-MD clinicians, then I will propose some ideas to increase confidence in NP and PA care.
Health care does not equal health
On the matter of how much clinicians affect outcomes, a recently published randomized controlled trial performed in India found that subsidizing insurance care led to increased utilization of hospital services but had no significant effect on health outcomes. This follows the RAND and Oregon Health Insurance studies in the United States, which largely reported similar results.
We should also not dismiss the fact that – despite the massive technology gains over the past half-century in digital health and artificial intelligence and increased use of quality measures, new drugs and procedures, and mega-medical centers – the average lifespan of Americans is flat to declining (in most ethnic and racial groups). Worse than no gains in longevity, perhaps, is that death from diseases like dementia and Parkinson’s disease are on the rise.
A neutral Martian would look down and wonder why all this health care hasn’t translated to longer and better lives. The causes of this paradox remain speculative, and are for another column, but the point remains that – on average – more health care is clearly not delivering more health. And if that is true, one may deduce that much of U.S. health care is marginal when it comes to affecting major outcomes.
It’s about the delta
Logos trumps pathos. Sure, my physician colleagues can tell scary anecdotes of bad outcomes caused by an inexperienced NP or PA. I would counter that by saying I have sat on our hospital’s peer review committee for 2 decades, including the era before NPs or PAs were practicing, and I have plenty of stories of physician errors. These include, of course, my own errors.
Logos: We must consider the difference between non–MD-led care and MD-led care.
My arguments from 2020 remain relevant today. Most medical problems are not engineering puzzles. Many, perhaps most, patients fall into an easy protocol – say, chest pain, dyspnea, or atrial fibrillation. With basic training, a motivated serious person quickly gains skill in recognizing and treating everyday problems.
And just 2 years on, technology further levels the playing field. Consider radiology in 2022 – it’s easy to take for granted the speed of the CT scan, the fidelity of the MRI, and the easy access to both in the U.S. hospital system. Less experienced clinicians have never had more tools to assist with diagnostics and therapeutics.
The expansion of team-based care has also mitigated the effects of inexperience. It took Americans longer than Canadians to figure out how helpful pharmacists could be. Pharmacists in my hospital now help us dose complicated medicines and protect us against prescribing errors.
Then there is the immediate access to online information. Gone are the days when you had to memorize long-QT syndromes. Book knowledge – that I spent years acquiring – now comes in seconds. The other day an NP corrected me. I asked, Are you sure? Boom, she took out her phone and showed me the evidence.
In sum, if it were even possible to measure the clinical competence of care from NP and PA versus physicians, there would be two bell-shaped curves with a tremendous amount of overlap. And that overlap would steadily increase as a given NP or PA gathered experience. (The NP in our electrophysiology division has more than 25 years’ experience in heart rhythm care, and it is common for colleagues to call her before one of us docs. Rightly so.)
Three basic proposals regarding NP and PA care
To ensure quality of care, I have three proposals.
It has always seemed strange to me that an NP or PA can flip from one field to another without a period of training. I can’t just change practice from electrophysiology to dermatology without doing a residency. But NPs and PAs can.
My first proposal would be that NPs and PAs spend a substantial period of training in a field before practice – a legit apprenticeship. The duration of this period is a matter of debate, but it ought to be standardized.
My second proposal is that, if physicians are required to pass certification exams, so should NPs. (PAs have an exam every 10 years.) The exam should be the same as (or very similar to) the physician exam, and it should be specific to their field of practice.
While I have argued (and still feel) that the American Board of Internal Medicine brand of certification is dubious, the fact remains that physicians must maintain proficiency in their field. Requiring NPs and PAs to do the same would help foster specialization. And while I can’t cite empirical evidence, specialization seems super-important. We have NPs at my hospital who have been in the same area for years, and they exude clinical competence.
Finally, I have come to believe that the best way for nearly any clinician to practice medicine is as part of a team. (The exception being primary care in rural areas where there are clinician shortages.)
On the matter of team care, I’ve practiced for a long time, but nearly every day I run situations by a colleague; often this person is an NP. The economist Friedrich Hayek proposed that dispersed knowledge always outpaces the wisdom of any individual. That notion pertains well to the increasing complexities and specialization of modern medical practice.
A person who commits to learning one area of medicine, enjoys helping people, asks often for help, and has the support of colleagues is set up to be a successful clinician – whether the letters after their name are APRN, PA, DO, or MD.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. He did not report any relevant financial disclosures. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two years ago, I argued that independent care from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) would not have ill effects on health outcomes. To the surprise of no one, NPs and PAs embraced the argument; physicians clobbered it.
My case had three pegs: One was that medicine isn’t rocket science and clinicians control a lot less than we think we do. The second peg was that technology levels the playing field of clinical care. High-sensitivity troponin assays, for instance, make missing MI a lot less likely. The third peg was empirical: Studies have found little difference in MD versus non–MD-led care. Looking back, I now see empiricism as the weakest part of the argument because the studies had so many limitations.
I update this viewpoint now because health care is increasingly delivered by NPs and PAs. And there are two concerning trends regarding NP education and experience. First is that nurses are turning to advanced practitioner training earlier in their careers – without gathering much bedside experience. And these training programs are increasingly likely to be online, with minimal hands-on clinical tutoring.
Education and experience pop in my head often. Not every day, but many days I think back to my lucky 7 years in Indiana learning under the supervision of master clinicians – at a time when trainees were allowed the leeway to make decisions ... and mistakes. Then, when I joined private practice, I continued to learn from experienced practitioners.
It would be foolish to argue that training and experience aren’t important.
But here’s the thing:
I will make three points: First, I will bolster two of my old arguments as to why we shouldn’t be worried about non-MD clinicians, then I will propose some ideas to increase confidence in NP and PA care.
Health care does not equal health
On the matter of how much clinicians affect outcomes, a recently published randomized controlled trial performed in India found that subsidizing insurance care led to increased utilization of hospital services but had no significant effect on health outcomes. This follows the RAND and Oregon Health Insurance studies in the United States, which largely reported similar results.
We should also not dismiss the fact that – despite the massive technology gains over the past half-century in digital health and artificial intelligence and increased use of quality measures, new drugs and procedures, and mega-medical centers – the average lifespan of Americans is flat to declining (in most ethnic and racial groups). Worse than no gains in longevity, perhaps, is that death from diseases like dementia and Parkinson’s disease are on the rise.
A neutral Martian would look down and wonder why all this health care hasn’t translated to longer and better lives. The causes of this paradox remain speculative, and are for another column, but the point remains that – on average – more health care is clearly not delivering more health. And if that is true, one may deduce that much of U.S. health care is marginal when it comes to affecting major outcomes.
It’s about the delta
Logos trumps pathos. Sure, my physician colleagues can tell scary anecdotes of bad outcomes caused by an inexperienced NP or PA. I would counter that by saying I have sat on our hospital’s peer review committee for 2 decades, including the era before NPs or PAs were practicing, and I have plenty of stories of physician errors. These include, of course, my own errors.
Logos: We must consider the difference between non–MD-led care and MD-led care.
My arguments from 2020 remain relevant today. Most medical problems are not engineering puzzles. Many, perhaps most, patients fall into an easy protocol – say, chest pain, dyspnea, or atrial fibrillation. With basic training, a motivated serious person quickly gains skill in recognizing and treating everyday problems.
And just 2 years on, technology further levels the playing field. Consider radiology in 2022 – it’s easy to take for granted the speed of the CT scan, the fidelity of the MRI, and the easy access to both in the U.S. hospital system. Less experienced clinicians have never had more tools to assist with diagnostics and therapeutics.
The expansion of team-based care has also mitigated the effects of inexperience. It took Americans longer than Canadians to figure out how helpful pharmacists could be. Pharmacists in my hospital now help us dose complicated medicines and protect us against prescribing errors.
Then there is the immediate access to online information. Gone are the days when you had to memorize long-QT syndromes. Book knowledge – that I spent years acquiring – now comes in seconds. The other day an NP corrected me. I asked, Are you sure? Boom, she took out her phone and showed me the evidence.
In sum, if it were even possible to measure the clinical competence of care from NP and PA versus physicians, there would be two bell-shaped curves with a tremendous amount of overlap. And that overlap would steadily increase as a given NP or PA gathered experience. (The NP in our electrophysiology division has more than 25 years’ experience in heart rhythm care, and it is common for colleagues to call her before one of us docs. Rightly so.)
Three basic proposals regarding NP and PA care
To ensure quality of care, I have three proposals.
It has always seemed strange to me that an NP or PA can flip from one field to another without a period of training. I can’t just change practice from electrophysiology to dermatology without doing a residency. But NPs and PAs can.
My first proposal would be that NPs and PAs spend a substantial period of training in a field before practice – a legit apprenticeship. The duration of this period is a matter of debate, but it ought to be standardized.
My second proposal is that, if physicians are required to pass certification exams, so should NPs. (PAs have an exam every 10 years.) The exam should be the same as (or very similar to) the physician exam, and it should be specific to their field of practice.
While I have argued (and still feel) that the American Board of Internal Medicine brand of certification is dubious, the fact remains that physicians must maintain proficiency in their field. Requiring NPs and PAs to do the same would help foster specialization. And while I can’t cite empirical evidence, specialization seems super-important. We have NPs at my hospital who have been in the same area for years, and they exude clinical competence.
Finally, I have come to believe that the best way for nearly any clinician to practice medicine is as part of a team. (The exception being primary care in rural areas where there are clinician shortages.)
On the matter of team care, I’ve practiced for a long time, but nearly every day I run situations by a colleague; often this person is an NP. The economist Friedrich Hayek proposed that dispersed knowledge always outpaces the wisdom of any individual. That notion pertains well to the increasing complexities and specialization of modern medical practice.
A person who commits to learning one area of medicine, enjoys helping people, asks often for help, and has the support of colleagues is set up to be a successful clinician – whether the letters after their name are APRN, PA, DO, or MD.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. He did not report any relevant financial disclosures. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seven ways doctors could get better payment from insurers
, say experts in physician-payer contracts.
Many doctors sign long-term agreements and then forget about them, says Marcia Brauchler, president and founder of Physicians’ Ally, Littleton, Colorado, a health care consulting company. “The average doctor is trying to run a practice on 2010 rates because they haven’t touched their insurance contracts for 10 years,” she says.
Payers also make a lot of money by adopting dozens of unilateral policy and procedure changes every year that they know physicians are too busy to read. They are counting on the fact that few doctors will understand what the policy changes are and that even fewer will contest them, says Greg Brodek, JD, chair of the health law practice group and head of the managed care litigation practice at Duane Morris, who represents doctors in disputes with payers.
These experts say doctors can push back on one-sided payer contracts and negotiate changes. Mr. Brodek says some practices have more leverage than others to influence payers – if they are larger, in a specialty that the payer needs in its network, or located in a remote area where the payer has limited options.
Here are seven key areas to pay attention to:
1. Long-term contracts. Most doctors sign multiyear “evergreen” contracts that renew automatically every year. This allows insurers to continue to pay doctors the same rate for years.
To avoid this, doctors should negotiate new rates when their agreements renew or, if they prefer, ask that a cost-of-living adjustment be included in the multiyear contract that applies to subsequent years, says Ms. Brauchler.
2. Fee schedules. Payers will “whitewash” what they’re paying you by saying it’s 100% of the payer fee schedule. When it comes to Medicare, they may be paying you a lot less, says Ms. Brauchler.
“My biggest takeaway is to compare the CPT codes of the payer’s fee schedule against what Medicare allows. For example, for CPT code 99213, a 15-minute established office visit, if Medicare pays you $100 and Aetna pays you $75.00, you’re getting 75% of Medicare,” says Ms. Brauchler. To avoid this, doctors should ask that the contract state that reimbursement be made according to Medicare’s medical policies rather than the payer’s.
3. Audits. Commercial payers will claim they have a contractual right to conduct pre- and post-payment audits of physicians’ claims that can result in reduced payments. The contract only states that if doctors correctly submit claims, they will get paid, not that they will have to go through extra steps, which is a breach of their agreement, says Mr. Brodek.
In his experience, 90% of payers back down when asked to provide the contractual basis to conduct these audits. “Or, they take the position that it’s not in the contract but that they have a policy.”
4. Contract amendments versus policies and procedures. This is a huge area that needs to be clarified in contracts and monitored by providers throughout their relationships with payers. Contracts have three elements: the parties, the services provided, and the payment. Changing any one of those terms requires an amendment and advance written notice that has to be delivered to the other party in a certain way, such as by overnight delivery, says Mr. Brodek.
In addition, both parties have to sign that they agree to an amendment. “But, that’s too cumbersome and complicated for payers who have decided to adopt policies instead. These are unilateral changes made with no advance notice given, since the payer typically posts the change on its website,” says Mr. Brodek.
5. Recoupment efforts. Payers will review claims after they’re paid and contact the doctor saying they found a mistake, such as inappropriate coding. They will claim that the doctor now owes them a large sum of money based on a percentage of claims reviewed. “They typically send the doctor a letter that ends with, ‘If you do not pay this amount within 30 days, we will offset the amount due against future payments that we would otherwise make to you,’” says Mr. Brodek.
He recommends that contracts include the doctors’ right to contest an audit so the “payer doesn’t have the unilateral right to disregard the initial coding that the doctor appropriately assigned to the claim and recoup the money anyway,” says Mr. Brodek.
6. Medical network rentals and products. Most contracts say that payers can rent out their medical networks to other health plans, such as HMOs, and that the clinicians agree to comply with all of their policies and procedures. The agreement may also cover the products of other plans.
“The problem is that physicians are not given information about the other plans, including their terms and conditions for getting paid,” says Mr. Brodek. If a problem with payment arises, they have no written agreement with that plan, which makes it harder to enforce.
“That’s why we recommend that doctors negotiate agreements that only cover the main payer. Most of the time, the payer is amenable to putting that language in the contract,” he says.
7. Payer products. In the past several years, a typical contract has included appendices that list the payer’s products, such as Medicare, workers compensation, auto insurance liability, or health care exchange products. Many clinicians don’t realize they can pick the plans they want to participate in by accepting or opting out, says Mr. Brodek.
“We advise clients to limit the contract to what you want covered and to make informed decisions, because some products have low fees set by the states, such as workers compensation and health care exchanges,” says Mr. Brodek.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, say experts in physician-payer contracts.
Many doctors sign long-term agreements and then forget about them, says Marcia Brauchler, president and founder of Physicians’ Ally, Littleton, Colorado, a health care consulting company. “The average doctor is trying to run a practice on 2010 rates because they haven’t touched their insurance contracts for 10 years,” she says.
Payers also make a lot of money by adopting dozens of unilateral policy and procedure changes every year that they know physicians are too busy to read. They are counting on the fact that few doctors will understand what the policy changes are and that even fewer will contest them, says Greg Brodek, JD, chair of the health law practice group and head of the managed care litigation practice at Duane Morris, who represents doctors in disputes with payers.
These experts say doctors can push back on one-sided payer contracts and negotiate changes. Mr. Brodek says some practices have more leverage than others to influence payers – if they are larger, in a specialty that the payer needs in its network, or located in a remote area where the payer has limited options.
Here are seven key areas to pay attention to:
1. Long-term contracts. Most doctors sign multiyear “evergreen” contracts that renew automatically every year. This allows insurers to continue to pay doctors the same rate for years.
To avoid this, doctors should negotiate new rates when their agreements renew or, if they prefer, ask that a cost-of-living adjustment be included in the multiyear contract that applies to subsequent years, says Ms. Brauchler.
2. Fee schedules. Payers will “whitewash” what they’re paying you by saying it’s 100% of the payer fee schedule. When it comes to Medicare, they may be paying you a lot less, says Ms. Brauchler.
“My biggest takeaway is to compare the CPT codes of the payer’s fee schedule against what Medicare allows. For example, for CPT code 99213, a 15-minute established office visit, if Medicare pays you $100 and Aetna pays you $75.00, you’re getting 75% of Medicare,” says Ms. Brauchler. To avoid this, doctors should ask that the contract state that reimbursement be made according to Medicare’s medical policies rather than the payer’s.
3. Audits. Commercial payers will claim they have a contractual right to conduct pre- and post-payment audits of physicians’ claims that can result in reduced payments. The contract only states that if doctors correctly submit claims, they will get paid, not that they will have to go through extra steps, which is a breach of their agreement, says Mr. Brodek.
In his experience, 90% of payers back down when asked to provide the contractual basis to conduct these audits. “Or, they take the position that it’s not in the contract but that they have a policy.”
4. Contract amendments versus policies and procedures. This is a huge area that needs to be clarified in contracts and monitored by providers throughout their relationships with payers. Contracts have three elements: the parties, the services provided, and the payment. Changing any one of those terms requires an amendment and advance written notice that has to be delivered to the other party in a certain way, such as by overnight delivery, says Mr. Brodek.
In addition, both parties have to sign that they agree to an amendment. “But, that’s too cumbersome and complicated for payers who have decided to adopt policies instead. These are unilateral changes made with no advance notice given, since the payer typically posts the change on its website,” says Mr. Brodek.
5. Recoupment efforts. Payers will review claims after they’re paid and contact the doctor saying they found a mistake, such as inappropriate coding. They will claim that the doctor now owes them a large sum of money based on a percentage of claims reviewed. “They typically send the doctor a letter that ends with, ‘If you do not pay this amount within 30 days, we will offset the amount due against future payments that we would otherwise make to you,’” says Mr. Brodek.
He recommends that contracts include the doctors’ right to contest an audit so the “payer doesn’t have the unilateral right to disregard the initial coding that the doctor appropriately assigned to the claim and recoup the money anyway,” says Mr. Brodek.
6. Medical network rentals and products. Most contracts say that payers can rent out their medical networks to other health plans, such as HMOs, and that the clinicians agree to comply with all of their policies and procedures. The agreement may also cover the products of other plans.
“The problem is that physicians are not given information about the other plans, including their terms and conditions for getting paid,” says Mr. Brodek. If a problem with payment arises, they have no written agreement with that plan, which makes it harder to enforce.
“That’s why we recommend that doctors negotiate agreements that only cover the main payer. Most of the time, the payer is amenable to putting that language in the contract,” he says.
7. Payer products. In the past several years, a typical contract has included appendices that list the payer’s products, such as Medicare, workers compensation, auto insurance liability, or health care exchange products. Many clinicians don’t realize they can pick the plans they want to participate in by accepting or opting out, says Mr. Brodek.
“We advise clients to limit the contract to what you want covered and to make informed decisions, because some products have low fees set by the states, such as workers compensation and health care exchanges,” says Mr. Brodek.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, say experts in physician-payer contracts.
Many doctors sign long-term agreements and then forget about them, says Marcia Brauchler, president and founder of Physicians’ Ally, Littleton, Colorado, a health care consulting company. “The average doctor is trying to run a practice on 2010 rates because they haven’t touched their insurance contracts for 10 years,” she says.
Payers also make a lot of money by adopting dozens of unilateral policy and procedure changes every year that they know physicians are too busy to read. They are counting on the fact that few doctors will understand what the policy changes are and that even fewer will contest them, says Greg Brodek, JD, chair of the health law practice group and head of the managed care litigation practice at Duane Morris, who represents doctors in disputes with payers.
These experts say doctors can push back on one-sided payer contracts and negotiate changes. Mr. Brodek says some practices have more leverage than others to influence payers – if they are larger, in a specialty that the payer needs in its network, or located in a remote area where the payer has limited options.
Here are seven key areas to pay attention to:
1. Long-term contracts. Most doctors sign multiyear “evergreen” contracts that renew automatically every year. This allows insurers to continue to pay doctors the same rate for years.
To avoid this, doctors should negotiate new rates when their agreements renew or, if they prefer, ask that a cost-of-living adjustment be included in the multiyear contract that applies to subsequent years, says Ms. Brauchler.
2. Fee schedules. Payers will “whitewash” what they’re paying you by saying it’s 100% of the payer fee schedule. When it comes to Medicare, they may be paying you a lot less, says Ms. Brauchler.
“My biggest takeaway is to compare the CPT codes of the payer’s fee schedule against what Medicare allows. For example, for CPT code 99213, a 15-minute established office visit, if Medicare pays you $100 and Aetna pays you $75.00, you’re getting 75% of Medicare,” says Ms. Brauchler. To avoid this, doctors should ask that the contract state that reimbursement be made according to Medicare’s medical policies rather than the payer’s.
3. Audits. Commercial payers will claim they have a contractual right to conduct pre- and post-payment audits of physicians’ claims that can result in reduced payments. The contract only states that if doctors correctly submit claims, they will get paid, not that they will have to go through extra steps, which is a breach of their agreement, says Mr. Brodek.
In his experience, 90% of payers back down when asked to provide the contractual basis to conduct these audits. “Or, they take the position that it’s not in the contract but that they have a policy.”
4. Contract amendments versus policies and procedures. This is a huge area that needs to be clarified in contracts and monitored by providers throughout their relationships with payers. Contracts have three elements: the parties, the services provided, and the payment. Changing any one of those terms requires an amendment and advance written notice that has to be delivered to the other party in a certain way, such as by overnight delivery, says Mr. Brodek.
In addition, both parties have to sign that they agree to an amendment. “But, that’s too cumbersome and complicated for payers who have decided to adopt policies instead. These are unilateral changes made with no advance notice given, since the payer typically posts the change on its website,” says Mr. Brodek.
5. Recoupment efforts. Payers will review claims after they’re paid and contact the doctor saying they found a mistake, such as inappropriate coding. They will claim that the doctor now owes them a large sum of money based on a percentage of claims reviewed. “They typically send the doctor a letter that ends with, ‘If you do not pay this amount within 30 days, we will offset the amount due against future payments that we would otherwise make to you,’” says Mr. Brodek.
He recommends that contracts include the doctors’ right to contest an audit so the “payer doesn’t have the unilateral right to disregard the initial coding that the doctor appropriately assigned to the claim and recoup the money anyway,” says Mr. Brodek.
6. Medical network rentals and products. Most contracts say that payers can rent out their medical networks to other health plans, such as HMOs, and that the clinicians agree to comply with all of their policies and procedures. The agreement may also cover the products of other plans.
“The problem is that physicians are not given information about the other plans, including their terms and conditions for getting paid,” says Mr. Brodek. If a problem with payment arises, they have no written agreement with that plan, which makes it harder to enforce.
“That’s why we recommend that doctors negotiate agreements that only cover the main payer. Most of the time, the payer is amenable to putting that language in the contract,” he says.
7. Payer products. In the past several years, a typical contract has included appendices that list the payer’s products, such as Medicare, workers compensation, auto insurance liability, or health care exchange products. Many clinicians don’t realize they can pick the plans they want to participate in by accepting or opting out, says Mr. Brodek.
“We advise clients to limit the contract to what you want covered and to make informed decisions, because some products have low fees set by the states, such as workers compensation and health care exchanges,” says Mr. Brodek.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ways to make sure 2022 doesn’t stink for docs
Depending on the data you’re looking at, 40%-60% of physicians are burned out.
Research studies and the eye test reveal the painfully obvious: Colleagues are tired, winded, spent, and at times way past burned out. People aren’t asking me if they’re burned out. They know they’re burned out; heck, they can even recite the Maslach burnout inventory, forward and backward, in a mask, or while completing a COVID quarantine. A fair share of people know the key steps to prevent burnout and promote recovery.
What I’m starting to see more of is, “Why should I even bother to recover from this? Why pick myself up again just to get another occupational stress injury (burnout, demoralization, moral injury, etc.)?” In other words, it’s not just simply about negating burnout; it’s about supporting and facilitating the motivation to work.
We’ve been through so much with COVID that it might be challenging to remember when you saw a truly engaged work environment. No doubt, we have outstanding professionals across medicine who answer the bell every day. However, if you’ve been looking closely, many teams/units have lost a bit of the zip and pep. The synergy and trust aren’t as smooth, and at noon, everyone counts the hours to the end of the shift.
You may be thinking, Well, of course, they are; we’re still amid a pandemic, and people have been through hell. Your observation would be correct, except I’ve personally seen some teams weather the pandemic storm and still remain engaged (some even more involved).
The No. 1 consult result for the GW Resiliency and Well-Being Center, where I work, has been on lectures for burnout. The R&WC has given so many of these lectures that my dreams take the form of a PowerPoint presentation. Overall the talks have gone very well. We’ve added skills sections on practices of whole-person care. We’ve blitzed the daylights out of restorative sleep, yet I know we are still searching for the correct narrative.
Motivated staff, faculty, and students will genuinely take in the information and follow the recommendations; however, they still struggle to find that drive and zest for work. Yes, moving from burnout to neutral is reasonable but likely won’t move the needle of your professional or personal life. We need to have the emotional energy and the clear desire to utilize that energy for a meaningful purpose.
Talking about burnout in specific ways is straightforward and, in my opinion, much easier than talking about engagement. Part of the challenge when trying to discuss engagement is that people can feel invalidated or that you’re telling them to be stoic. Or worse yet, that the problem of burnout primarily lies with them. It’s essential to recognize the role of an organizational factor in burnout (approximately 80%, depending on the study); still, even if you address burnout, people may not be miserable, but it doesn’t mean they will stay at their current job (please cue intro music for the Great Resignation).
Engagement models have existed for some time and certainly have gained much more attention in health care settings over the past 2 decades. Engagement can be described as having three components: dedication, vigor, and absorption. When a person is filling all three of these components over time, presto – you get the much-sought-after state of the supremely engaged professional.
These models definitely give us excellent starting points to approach engagement from a pre-COVID era. In COVID and beyond, I’m not sure how these models will stand up in a hybrid work environment, where autonomy and flexibility could be more valued than ever. Personally, COVID revealed some things I was missing in my work pre-COVID:
- Time to think and process. This was one of the great things about being a consultation-liaison psychiatrist; it was literally feast or famine.
- Doing what I’m talented at and really enjoy.
- Time is short, and I want to be more present in the life of my family.
The list above isn’t exhaustive, but I’ve found them to be my own personal recipe for being engaged. Over the next series of articles, I’m going to focus on engagement and factors related to key resilience. These articles will be informed by a front-line view from my colleagues, and hopefully start to separate the myth from reality on the subject of health professional engagement and resilience.
Everyone be safe and well!
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depending on the data you’re looking at, 40%-60% of physicians are burned out.
Research studies and the eye test reveal the painfully obvious: Colleagues are tired, winded, spent, and at times way past burned out. People aren’t asking me if they’re burned out. They know they’re burned out; heck, they can even recite the Maslach burnout inventory, forward and backward, in a mask, or while completing a COVID quarantine. A fair share of people know the key steps to prevent burnout and promote recovery.
What I’m starting to see more of is, “Why should I even bother to recover from this? Why pick myself up again just to get another occupational stress injury (burnout, demoralization, moral injury, etc.)?” In other words, it’s not just simply about negating burnout; it’s about supporting and facilitating the motivation to work.
We’ve been through so much with COVID that it might be challenging to remember when you saw a truly engaged work environment. No doubt, we have outstanding professionals across medicine who answer the bell every day. However, if you’ve been looking closely, many teams/units have lost a bit of the zip and pep. The synergy and trust aren’t as smooth, and at noon, everyone counts the hours to the end of the shift.
You may be thinking, Well, of course, they are; we’re still amid a pandemic, and people have been through hell. Your observation would be correct, except I’ve personally seen some teams weather the pandemic storm and still remain engaged (some even more involved).
The No. 1 consult result for the GW Resiliency and Well-Being Center, where I work, has been on lectures for burnout. The R&WC has given so many of these lectures that my dreams take the form of a PowerPoint presentation. Overall the talks have gone very well. We’ve added skills sections on practices of whole-person care. We’ve blitzed the daylights out of restorative sleep, yet I know we are still searching for the correct narrative.
Motivated staff, faculty, and students will genuinely take in the information and follow the recommendations; however, they still struggle to find that drive and zest for work. Yes, moving from burnout to neutral is reasonable but likely won’t move the needle of your professional or personal life. We need to have the emotional energy and the clear desire to utilize that energy for a meaningful purpose.
Talking about burnout in specific ways is straightforward and, in my opinion, much easier than talking about engagement. Part of the challenge when trying to discuss engagement is that people can feel invalidated or that you’re telling them to be stoic. Or worse yet, that the problem of burnout primarily lies with them. It’s essential to recognize the role of an organizational factor in burnout (approximately 80%, depending on the study); still, even if you address burnout, people may not be miserable, but it doesn’t mean they will stay at their current job (please cue intro music for the Great Resignation).
Engagement models have existed for some time and certainly have gained much more attention in health care settings over the past 2 decades. Engagement can be described as having three components: dedication, vigor, and absorption. When a person is filling all three of these components over time, presto – you get the much-sought-after state of the supremely engaged professional.
These models definitely give us excellent starting points to approach engagement from a pre-COVID era. In COVID and beyond, I’m not sure how these models will stand up in a hybrid work environment, where autonomy and flexibility could be more valued than ever. Personally, COVID revealed some things I was missing in my work pre-COVID:
- Time to think and process. This was one of the great things about being a consultation-liaison psychiatrist; it was literally feast or famine.
- Doing what I’m talented at and really enjoy.
- Time is short, and I want to be more present in the life of my family.
The list above isn’t exhaustive, but I’ve found them to be my own personal recipe for being engaged. Over the next series of articles, I’m going to focus on engagement and factors related to key resilience. These articles will be informed by a front-line view from my colleagues, and hopefully start to separate the myth from reality on the subject of health professional engagement and resilience.
Everyone be safe and well!
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depending on the data you’re looking at, 40%-60% of physicians are burned out.
Research studies and the eye test reveal the painfully obvious: Colleagues are tired, winded, spent, and at times way past burned out. People aren’t asking me if they’re burned out. They know they’re burned out; heck, they can even recite the Maslach burnout inventory, forward and backward, in a mask, or while completing a COVID quarantine. A fair share of people know the key steps to prevent burnout and promote recovery.
What I’m starting to see more of is, “Why should I even bother to recover from this? Why pick myself up again just to get another occupational stress injury (burnout, demoralization, moral injury, etc.)?” In other words, it’s not just simply about negating burnout; it’s about supporting and facilitating the motivation to work.
We’ve been through so much with COVID that it might be challenging to remember when you saw a truly engaged work environment. No doubt, we have outstanding professionals across medicine who answer the bell every day. However, if you’ve been looking closely, many teams/units have lost a bit of the zip and pep. The synergy and trust aren’t as smooth, and at noon, everyone counts the hours to the end of the shift.
You may be thinking, Well, of course, they are; we’re still amid a pandemic, and people have been through hell. Your observation would be correct, except I’ve personally seen some teams weather the pandemic storm and still remain engaged (some even more involved).
The No. 1 consult result for the GW Resiliency and Well-Being Center, where I work, has been on lectures for burnout. The R&WC has given so many of these lectures that my dreams take the form of a PowerPoint presentation. Overall the talks have gone very well. We’ve added skills sections on practices of whole-person care. We’ve blitzed the daylights out of restorative sleep, yet I know we are still searching for the correct narrative.
Motivated staff, faculty, and students will genuinely take in the information and follow the recommendations; however, they still struggle to find that drive and zest for work. Yes, moving from burnout to neutral is reasonable but likely won’t move the needle of your professional or personal life. We need to have the emotional energy and the clear desire to utilize that energy for a meaningful purpose.
Talking about burnout in specific ways is straightforward and, in my opinion, much easier than talking about engagement. Part of the challenge when trying to discuss engagement is that people can feel invalidated or that you’re telling them to be stoic. Or worse yet, that the problem of burnout primarily lies with them. It’s essential to recognize the role of an organizational factor in burnout (approximately 80%, depending on the study); still, even if you address burnout, people may not be miserable, but it doesn’t mean they will stay at their current job (please cue intro music for the Great Resignation).
Engagement models have existed for some time and certainly have gained much more attention in health care settings over the past 2 decades. Engagement can be described as having three components: dedication, vigor, and absorption. When a person is filling all three of these components over time, presto – you get the much-sought-after state of the supremely engaged professional.
These models definitely give us excellent starting points to approach engagement from a pre-COVID era. In COVID and beyond, I’m not sure how these models will stand up in a hybrid work environment, where autonomy and flexibility could be more valued than ever. Personally, COVID revealed some things I was missing in my work pre-COVID:
- Time to think and process. This was one of the great things about being a consultation-liaison psychiatrist; it was literally feast or famine.
- Doing what I’m talented at and really enjoy.
- Time is short, and I want to be more present in the life of my family.
The list above isn’t exhaustive, but I’ve found them to be my own personal recipe for being engaged. Over the next series of articles, I’m going to focus on engagement and factors related to key resilience. These articles will be informed by a front-line view from my colleagues, and hopefully start to separate the myth from reality on the subject of health professional engagement and resilience.
Everyone be safe and well!
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gut bacteria linked with long COVID
While links have been found between the gut’s microbiome and COVID-19, as well as other diseases, this is the first published research to show a link specifically to COVID’s long-term effects, the investigators, based at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, wrote in Gut.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that altered gut microbiome composition is strongly associated with persistent symptoms in patients with COVID-19 up to 6 months after clearance of SARS-CoV-2 virus,” said Siew Ng, MBBS, PhD, associate director at the university’s Center for Gut Microbiota Research.
At three hospitals, the researchers enrolled 106 patients with COVID-19 from February to August 2020 with stool samples at admission and at 1 month and 6 months after discharge, and compared them with people who did not have COVID, recruited in 2019. The severity of COVID in the enrolled patients was mostly mild to moderate.
At 3 months, 86 of the patients with COVID had post–acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS) – defined as at least one persistent, otherwise unexplained symptom 4 weeks after clearance of the virus. And 81 patients had PACS at 6 months, most commonly fatigue, poor memory, hair loss, anxiety, and trouble sleeping.
Using stool samples for their analysis, the researchers found that, broadly, the diversity of the types of bacteria, and the abundance of these bacteria, were significantly lower at 6 months for those with PACS, compared with those without PACS and with controls (P < .05 and P < .0001, respectively). Among those with PACS, 28 bacteria species were diminished and 14 were enriched, both at baseline and follow-up. Those patients who had COVID but not PACS showed just 25 alterations of bacteria species at the time of hospital admission, and they all normalized by 6 months.
Having respiratory symptoms at 6 months was linked with higher levels of opportunistic pathogens such as Streptococcus anginosus and S. vestibularis. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and fatigue were associated with nosocomial pathogens that are linked to opportunistic infections, such as Clostridium innocuum and Actinomyces naeslundii (P < .05).
Bacteria known for producing butyrate, a beneficial fatty acid, were significantly depleted in those patients with hair loss. And certain of these bacteria, including Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, had the largest inverse correlations with PACS at 6 months (P < .05), the researchers found.
“Particular gut microbial profiles may indicate heightened susceptibility,” Dr. Ng said.
Although the findings were drawn from patients with earlier strains of the COVID-19 virus, the findings still apply to new variants, including Omicron, since these pose the same problem of persistent disruption of the immune system, Dr. Ng said.
Her group is conducting trials to look at how modulating the microbiome might prevent long COVID and boost antibodies after vaccination in high-risk people, she said.
“Gut microbiota influences the health of the host,” Dr. Ng said. “It provides crucial benefits in the form of immune system development, prevention of infections, nutrient acquisition, and brain and nervous system functionality. Considering the millions of people infected during the ongoing pandemic, our findings are a strong impetus for consideration of microbiota modulation to facilitate timely recovery and reduce the burden of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.”
John Haran, MD, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and physiological systems and emergency medicine at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said the research adds to the evidence base on the gut microbiome’s links to COVID, but there was likely be no clinical impact yet. Still, he said the findings linking specific species to specific symptoms was particularly interesting.
“Very early on during hospitalization, [the researchers] saw these differences and correlated out with people who have longer symptoms, and especially different groups of people that have longer symptoms, too,” said Dr. Haran, who has done research on the topic. “It’s very different if you have different symptoms, for example, you keep coughing for months versus you have brain fog and fatigue, or other debilitating symptoms.”
Dr. Haran noted that the findings didn’t identify bacteria types especially linked to COVID, but rather species that have already been found to be associated with a “bad” microbiome. He also pointed out that the patients enrolled in the study were not vaccinated, because vaccines weren’t available at the time. Still, further study to see whether modulation of gut bacteria can be a therapy seems worthwhile.
“Microbiome modulation is pretty safe, and that’s really the next big step that needs to be taken in this,” he said.
For now, the findings don’t give the clinician much new ammunition for treatment.
“We’re not there yet,” he added. “It’s not as if clinicians are going to tell their COVID patients: ‘Go out and buy some kale.’ ”
Eugene Chang, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who has studied the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal disease, said it’s “too preliminary” to say whether the findings could lead to a clinical impact. The measures used merely identify the microbes present, but not what they are doing.
“These measures are unlikely to perform well enough to be useful for risk assessment or predicting clinical outcomes,” he said. “That being said, advances in technology are being made where next generations of metrics could be developed and useful as stratifiers and predictors of risk.”
Seeing shifting patterns associated with certain symptoms, he said, is “notable because it suggests that the disturbances of the gut microbiota in PACS are significant.”
But he said it’s important to know whether these changes are a cause of PACS in some way or just an effect of it.
“If causative or contributory – this has to be proven – then ‘microbiota modulation’ would make sense and could be a priority for development,” he said. “If merely an effect, these metrics and better ones to come could be useful as predictors or measures of the patient’s general state of health.”
As seen in his group’s work and other work, he said, “the gut microbiota is highly sensitive to changes in their ecosystem, which is influenced by the health state of the patient.”
Dr. Ng, Dr. Haran, and Dr. Chang reported no relevant disclosures.
This article was updated Jan. 27, 2022.
While links have been found between the gut’s microbiome and COVID-19, as well as other diseases, this is the first published research to show a link specifically to COVID’s long-term effects, the investigators, based at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, wrote in Gut.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that altered gut microbiome composition is strongly associated with persistent symptoms in patients with COVID-19 up to 6 months after clearance of SARS-CoV-2 virus,” said Siew Ng, MBBS, PhD, associate director at the university’s Center for Gut Microbiota Research.
At three hospitals, the researchers enrolled 106 patients with COVID-19 from February to August 2020 with stool samples at admission and at 1 month and 6 months after discharge, and compared them with people who did not have COVID, recruited in 2019. The severity of COVID in the enrolled patients was mostly mild to moderate.
At 3 months, 86 of the patients with COVID had post–acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS) – defined as at least one persistent, otherwise unexplained symptom 4 weeks after clearance of the virus. And 81 patients had PACS at 6 months, most commonly fatigue, poor memory, hair loss, anxiety, and trouble sleeping.
Using stool samples for their analysis, the researchers found that, broadly, the diversity of the types of bacteria, and the abundance of these bacteria, were significantly lower at 6 months for those with PACS, compared with those without PACS and with controls (P < .05 and P < .0001, respectively). Among those with PACS, 28 bacteria species were diminished and 14 were enriched, both at baseline and follow-up. Those patients who had COVID but not PACS showed just 25 alterations of bacteria species at the time of hospital admission, and they all normalized by 6 months.
Having respiratory symptoms at 6 months was linked with higher levels of opportunistic pathogens such as Streptococcus anginosus and S. vestibularis. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and fatigue were associated with nosocomial pathogens that are linked to opportunistic infections, such as Clostridium innocuum and Actinomyces naeslundii (P < .05).
Bacteria known for producing butyrate, a beneficial fatty acid, were significantly depleted in those patients with hair loss. And certain of these bacteria, including Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, had the largest inverse correlations with PACS at 6 months (P < .05), the researchers found.
“Particular gut microbial profiles may indicate heightened susceptibility,” Dr. Ng said.
Although the findings were drawn from patients with earlier strains of the COVID-19 virus, the findings still apply to new variants, including Omicron, since these pose the same problem of persistent disruption of the immune system, Dr. Ng said.
Her group is conducting trials to look at how modulating the microbiome might prevent long COVID and boost antibodies after vaccination in high-risk people, she said.
“Gut microbiota influences the health of the host,” Dr. Ng said. “It provides crucial benefits in the form of immune system development, prevention of infections, nutrient acquisition, and brain and nervous system functionality. Considering the millions of people infected during the ongoing pandemic, our findings are a strong impetus for consideration of microbiota modulation to facilitate timely recovery and reduce the burden of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.”
John Haran, MD, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and physiological systems and emergency medicine at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said the research adds to the evidence base on the gut microbiome’s links to COVID, but there was likely be no clinical impact yet. Still, he said the findings linking specific species to specific symptoms was particularly interesting.
“Very early on during hospitalization, [the researchers] saw these differences and correlated out with people who have longer symptoms, and especially different groups of people that have longer symptoms, too,” said Dr. Haran, who has done research on the topic. “It’s very different if you have different symptoms, for example, you keep coughing for months versus you have brain fog and fatigue, or other debilitating symptoms.”
Dr. Haran noted that the findings didn’t identify bacteria types especially linked to COVID, but rather species that have already been found to be associated with a “bad” microbiome. He also pointed out that the patients enrolled in the study were not vaccinated, because vaccines weren’t available at the time. Still, further study to see whether modulation of gut bacteria can be a therapy seems worthwhile.
“Microbiome modulation is pretty safe, and that’s really the next big step that needs to be taken in this,” he said.
For now, the findings don’t give the clinician much new ammunition for treatment.
“We’re not there yet,” he added. “It’s not as if clinicians are going to tell their COVID patients: ‘Go out and buy some kale.’ ”
Eugene Chang, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who has studied the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal disease, said it’s “too preliminary” to say whether the findings could lead to a clinical impact. The measures used merely identify the microbes present, but not what they are doing.
“These measures are unlikely to perform well enough to be useful for risk assessment or predicting clinical outcomes,” he said. “That being said, advances in technology are being made where next generations of metrics could be developed and useful as stratifiers and predictors of risk.”
Seeing shifting patterns associated with certain symptoms, he said, is “notable because it suggests that the disturbances of the gut microbiota in PACS are significant.”
But he said it’s important to know whether these changes are a cause of PACS in some way or just an effect of it.
“If causative or contributory – this has to be proven – then ‘microbiota modulation’ would make sense and could be a priority for development,” he said. “If merely an effect, these metrics and better ones to come could be useful as predictors or measures of the patient’s general state of health.”
As seen in his group’s work and other work, he said, “the gut microbiota is highly sensitive to changes in their ecosystem, which is influenced by the health state of the patient.”
Dr. Ng, Dr. Haran, and Dr. Chang reported no relevant disclosures.
This article was updated Jan. 27, 2022.
While links have been found between the gut’s microbiome and COVID-19, as well as other diseases, this is the first published research to show a link specifically to COVID’s long-term effects, the investigators, based at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, wrote in Gut.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that altered gut microbiome composition is strongly associated with persistent symptoms in patients with COVID-19 up to 6 months after clearance of SARS-CoV-2 virus,” said Siew Ng, MBBS, PhD, associate director at the university’s Center for Gut Microbiota Research.
At three hospitals, the researchers enrolled 106 patients with COVID-19 from February to August 2020 with stool samples at admission and at 1 month and 6 months after discharge, and compared them with people who did not have COVID, recruited in 2019. The severity of COVID in the enrolled patients was mostly mild to moderate.
At 3 months, 86 of the patients with COVID had post–acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS) – defined as at least one persistent, otherwise unexplained symptom 4 weeks after clearance of the virus. And 81 patients had PACS at 6 months, most commonly fatigue, poor memory, hair loss, anxiety, and trouble sleeping.
Using stool samples for their analysis, the researchers found that, broadly, the diversity of the types of bacteria, and the abundance of these bacteria, were significantly lower at 6 months for those with PACS, compared with those without PACS and with controls (P < .05 and P < .0001, respectively). Among those with PACS, 28 bacteria species were diminished and 14 were enriched, both at baseline and follow-up. Those patients who had COVID but not PACS showed just 25 alterations of bacteria species at the time of hospital admission, and they all normalized by 6 months.
Having respiratory symptoms at 6 months was linked with higher levels of opportunistic pathogens such as Streptococcus anginosus and S. vestibularis. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and fatigue were associated with nosocomial pathogens that are linked to opportunistic infections, such as Clostridium innocuum and Actinomyces naeslundii (P < .05).
Bacteria known for producing butyrate, a beneficial fatty acid, were significantly depleted in those patients with hair loss. And certain of these bacteria, including Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, had the largest inverse correlations with PACS at 6 months (P < .05), the researchers found.
“Particular gut microbial profiles may indicate heightened susceptibility,” Dr. Ng said.
Although the findings were drawn from patients with earlier strains of the COVID-19 virus, the findings still apply to new variants, including Omicron, since these pose the same problem of persistent disruption of the immune system, Dr. Ng said.
Her group is conducting trials to look at how modulating the microbiome might prevent long COVID and boost antibodies after vaccination in high-risk people, she said.
“Gut microbiota influences the health of the host,” Dr. Ng said. “It provides crucial benefits in the form of immune system development, prevention of infections, nutrient acquisition, and brain and nervous system functionality. Considering the millions of people infected during the ongoing pandemic, our findings are a strong impetus for consideration of microbiota modulation to facilitate timely recovery and reduce the burden of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.”
John Haran, MD, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and physiological systems and emergency medicine at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said the research adds to the evidence base on the gut microbiome’s links to COVID, but there was likely be no clinical impact yet. Still, he said the findings linking specific species to specific symptoms was particularly interesting.
“Very early on during hospitalization, [the researchers] saw these differences and correlated out with people who have longer symptoms, and especially different groups of people that have longer symptoms, too,” said Dr. Haran, who has done research on the topic. “It’s very different if you have different symptoms, for example, you keep coughing for months versus you have brain fog and fatigue, or other debilitating symptoms.”
Dr. Haran noted that the findings didn’t identify bacteria types especially linked to COVID, but rather species that have already been found to be associated with a “bad” microbiome. He also pointed out that the patients enrolled in the study were not vaccinated, because vaccines weren’t available at the time. Still, further study to see whether modulation of gut bacteria can be a therapy seems worthwhile.
“Microbiome modulation is pretty safe, and that’s really the next big step that needs to be taken in this,” he said.
For now, the findings don’t give the clinician much new ammunition for treatment.
“We’re not there yet,” he added. “It’s not as if clinicians are going to tell their COVID patients: ‘Go out and buy some kale.’ ”
Eugene Chang, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who has studied the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal disease, said it’s “too preliminary” to say whether the findings could lead to a clinical impact. The measures used merely identify the microbes present, but not what they are doing.
“These measures are unlikely to perform well enough to be useful for risk assessment or predicting clinical outcomes,” he said. “That being said, advances in technology are being made where next generations of metrics could be developed and useful as stratifiers and predictors of risk.”
Seeing shifting patterns associated with certain symptoms, he said, is “notable because it suggests that the disturbances of the gut microbiota in PACS are significant.”
But he said it’s important to know whether these changes are a cause of PACS in some way or just an effect of it.
“If causative or contributory – this has to be proven – then ‘microbiota modulation’ would make sense and could be a priority for development,” he said. “If merely an effect, these metrics and better ones to come could be useful as predictors or measures of the patient’s general state of health.”
As seen in his group’s work and other work, he said, “the gut microbiota is highly sensitive to changes in their ecosystem, which is influenced by the health state of the patient.”
Dr. Ng, Dr. Haran, and Dr. Chang reported no relevant disclosures.
This article was updated Jan. 27, 2022.
FROM GUT
‘Post-truth era’ hurts COVID-19 response, trust in science
Can you tell which of the following statements are true and which are false?
COVID-19 is not a threat to younger people, and only those who have other medical conditions are dying from it.
The mRNA vaccines developed to prevent the coronavirus alter your genes, can make your body “magnetic,” and are killing more people than the virus itself.
President Joe Biden’s climate change plan calls for a ban on meat consumption to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
The 2020 presidential election was rigged and stolen.
If you guessed that all of these claims are false, you’re right – take a bow. Not a single one of these statements has any factual support, according to scientific research, legal rulings, and legitimate government authorities.
And yet public opinion surveys show millions of Americans, and others around the world, believe some of these falsehoods are true and can’t be convinced otherwise.
Social media, politicians and partisan websites, TV programs, and commentators have widely circulated these and other unfounded claims so frequently that many people say they simply can’t tell what’s objectively true and not anymore.
So much so,
The new study – The Rise and Fall of Rationality in Language, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – found that facts have become less important in public discourse.
As a result, unsupported beliefs have taken precedent over readily identifiable truths in discussions of health, science, and politics. The upshot: “Feelings trump facts” in social media, news reports, books, and other sources of information.
And here’s the kicker: The trend did not begin with the rise of former President Donald Trump, the COVID-19 pandemic, or the advent of social media; in fact, it has been growing for much longer than you might think.
“While the current ‘post-truth era’ has taken many by surprise, the study shows that over the past 40 years, public interest has undergone an accelerating shift from the collective to the individual, and from rationality towards emotion,” concluded the researchers from Indiana University and Wageningen University & Research in the Netherlands.
“Our work suggests that the societal balance between emotion and reason has shifted back to what it used to be around 150 years ago,” says lead researcher Marten Scheffer, PhD, a professor in the department of environmental sciences at WUR. “This implies that scientists, experts, and policymakers will have to think about the best way to respond to that social change.”
Researchers surprised by findings
The findings are based on a very detailed analysis of language from millions of books, newspaper articles, Google searches, TV reports, social media posts, and other sources dating back to 1850.
The researchers analyzed how often the 5,000 most used words appeared over the past 170 years and found that the use of those having to do with facts and reasoning, such as “determine” and “conclusion,” has fallen dramatically since 1980. Meanwhile, the use of words related to human emotion, such as “feel” and “believe,” have skyrocketed.
Dr. Scheffer notes rapid developments in science and technology from 1850 to 1980 had profound social and economic benefits that helped boost the status of the scientific approach. That shift in public attitudes had ripple effects on culture, society, education, politics, and religion – and “the role of spiritualism dwindled” in the modern world, he says.
But since 1980, that trend has seen a major reversal, with beliefs becoming more important than facts to many people, he says. At the same time, trust in science and scientists has fallen.
Dr. Scheffer says the researchers expected to find some evidence of a swing toward more belief-based sentiments during the Trump era but were surprised to discover how strong it is and that the trend has actually been a long time coming.
“The shift in interest from rational to intuitive/emotional is pretty obvious now in the post-truth political and social media discussion,” he says. “However, our work shows that it already started in the 1980s. For me personally, that went under the radar, except perhaps for the rise of alternative (to religion) forms of spirituality.
“We were especially struck by how strong the patterns are and how universal they appear across languages, nonfiction and fiction, and even in The New York Times.”
In the political world, the implications are significant enough – impacting policies and politicians on both sides of the aisle and across the globe. Just look at the deepening political divisions during the Trump presidency.
But for health and science, the spread of misinformation and falsehoods can be matters of life or death, as we have seen in the politically charged debates over how best to combat COVID-19 and global climate change.
“Our public debate seems increasingly driven by what people want to be true rather than what is actually true. As a scientist, that worries me,” says study co-author Johan Bollen, PhD, a professor of informatics at Indiana University.
“As a society, we are now faced with major collective problems that we need to approach from a pragmatic, rational, and objective perspective to be successful,” he says. “After all, global warming doesn’t care about whether you believe in it or not … but we will all suffer as a society if we fail to take adequate measures.”
For WUR co-researcher Ingrid van de Leemput, the trend isn’t merely academic; she’s seen it play out in her personal life.
“I do speak to people that, for instance, think the vaccines are poison,” she says. “I’m also on Twitter, and there, I’m every day surprised about how easily many people form their opinions, based on feelings, on what others say, or on some unfounded source.”
Public health experts say the embrace of personal beliefs over facts is one reason only 63% of Americans have been vaccinated against COVID-19. The result: millions of preventable infections among those who downplay the risks of the virus and reject the strong scientific evidence of vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“None of this really surprises me,” Johns Hopkins University social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, says of the new study findings. Dr. Limaye coauthored a paper in 2016 in JAMA Pediatrics about how to talk to parents about vaccine hesitancy and the fact that we’re living in what they called “this post-truth era.”
Dr. Limaye says the trend has made it difficult for doctors, scientists, and health authorities to make fact-based arguments for COVID-19 vaccination, mask-wearing, social distancing, and other measures to control the virus.
“It’s been really hard being a scientist to hear people say, ‘Well, that’s not true’ when we say something very basic that I think all of us can agree on – like the grass is green,” she says. “To be honest, I worry that a lot of scientists are going to quit being in science because they’re exhausted.”
What’s driving the trend?
So, what’s behind the embrace of “alternative facts,” as former White House counselor Kellyanne Conway put it so brazenly in 2017, in defending the White House’s false claims that Trump’s inauguration crowd was the largest ever?
Dr. Scheffer and colleagues identified a handful of things that have encouraged the embrace of falsehoods over facts in recent years.
- The Internet: Its rise in the late 1980s, and its growing role as a primary source of news and information, has allowed more belief-based misinformation to flourish and spread like wildfire.
- Social media: The new study found the use of sentiment- and intuition-related words accelerated around 2007, along with a global surge in social media that catapulted Facebook, Twitter, and others into the mainstream, replacing more traditional fact-based media (i.e., newspapers and magazines).
- The 2007 financial crisis: The downturn in the global economy meant more people were dealing with job stress, investment losses, and other problems that fed the interest in belief-based, anti-establishment social media posts.
- Conspiracy theories: Falsehoods involving hidden political agendas, shadow “elites,” and wealthy people with dark motives tend to thrive during times of crisis and societal anxiety. “Conspiracy theories originate particularly in times of uncertainty and crisis and generally depict established institutions as hiding the truth and sustaining an unfair situation,” the researchers noted. “As a result, they may find fertile grounds on social media platforms promulgating a sense of unfairness, subsequently feeding anti-system sentiments.”
Dr. Scheffer says that growing political divisions during the Trump era have widened the fact-vs.-fiction divide. The ex-president voiced many anti-science views on global climate change, for instance, and spread so many falsehoods about COVID-19 and the 2020 election that Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube suspended his accounts.
Yet Trump remains a popular figure among Republicans, with most saying in a December poll they believe his baseless claims that the 2020 election was “rigged” and “stolen,” despite all credible, easily accessible evidence that it was secure, according to a recent poll by the University of Massachusetts at Amherst.
More than 60 courts have rejected Trump’s lawsuits seeking to overturn the election results. All 50 states, the District of Columbia, and both branches of Congress have certified the election results, giving Biden the White House. Even Trump’s own Justice Department confirmed that the 2020 election was free and fair.
Nevertheless, the University of Massachusetts survey found that most Republicans believe one or more conspiracy theories floated by the former president and those pushing his “big lie” that Democrats rigged the election to elect Biden.
Ed Berliner, an Emmy Award-winning broadcast journalist and media consultant, suggests something else is driving the spread of misinformation: the pursuit of ratings by cable TV and media companies to boost ad and subscriber revenues.
As a former executive producer and syndicated cable TV show host, he says he has seen firsthand how facts are often lost in opinion-driven news programs, even on network programs claiming to offer “fair and balanced” journalism.
“Propaganda is the new currency in America, and those who do not fight back against it are doomed to be overrun by the misinformation,” says Mr. Berliner, host of The Man in the Arena and CEO of Entourage Media LLC.
“The broadcast news media has to stop this incessant ‘infotainment’ prattle, stop trying to nuzzle up to a soft side, and bear down on hard facts, exposing the lies and refusing to back down.”
Public health implications
Public health and media experts alike say the PNAS study findings are disheartening but underscore the need for doctors and scientists to do a better job of communicating about COVID-19 and other pressing issues.
Dr. Limaye, from Johns Hopkins, is particularly concerned about the rise in conspiracy theories that has led to COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy.
“When we speak to individuals about getting the COVID vaccine…the types of concerns that come up now are very different than they were 8 years ago,” she says. “The comments we used to hear were much more related to vaccine safety. [People] would say, ‘I’m worried about an ingredient in the vaccine’ or ‘I’m worried that my kiddo has to get three different shots within 6 months to have a series dose completed.’”
But now, a lot of comments they receive are about government and pharma conspiracies.
What that means is doctors and scientists must do more than simply say “here are the facts” and “trust me, I’m a doctor or a scientist,” she says. And these approaches don’t only apply to public health.
“It’s funny, because when we talk to climate change scientists, as vaccine [specialists], we’ll say we can’t believe that people think COVID is a hoax,” she says. “And they’re like, ‘Hold my beer, we’ve been dealing with this for 20 years. Hello, it’s just your guys’ turn to deal with this public denial of science.’”
Dr. Limaye is also concerned about the impacts on funding for scientific research.
“There’s always been a really strong bipartisan effort with regards to funding for science, when you look at Congress and when you look at appropriations,” she says. “But what ended up happening, especially with the Trump administration, was that there was a real shift in that. We’ve never really seen that before in past generations.”
So, what’s the big take-home message?
Dr. Limaye believes doctors and public health experts must show more empathy – and not be combative or arrogant – in communicating science in one-on-one conversations. This month, she’s launching a new course for parents, school administrators, and nurses on how to do precisely that.
“It’s really all about how to have hard conversations with people who might be anti-science,” she says. “It’s being empathetic and not being dismissive. But it’s hard work, and I think a lot of people are just not cut out for it and just don’t have the time for it…You can’t just say, ‘Well, this is science, and I’m a doctor’ – that doesn’t work anymore.”
Brendan Nyhan, PhD, a Dartmouth College political scientist, echoes those sentiments in a separate paper recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In fact, he suggests that providing accurate, fact-based information to counter false claims may actually backfire and reinforce some people’s unfounded beliefs.
“One response to the prevalence of mistaken beliefs is to try to set the record straight by providing accurate information – for instance, by providing evidence of the scientific consensus on climate change,” he writes. “The failures of this approach, which is sometimes referred to as the ‘deficit model’ in science communication, are well-known.”
Dr. Nyhan argues two things make some people more prone to believe falsehoods:
What scientists call “ingrouping,” a kind of tribal mentality that makes some people choose social identity or politics over truth-seeking and demonize others who don’t agree with their views
The rise of high-profile political figures, such as Trump, who encourage their followers to indulge in their desire for “identify-affirming misinformation”
Dr. Scheffer says the most important thing for doctors, health experts, and scientists to recognize is that it’s crucial to gain the trust of someone who may believe fictions over facts to make any persuasive argument on COVID-19 or any other issue.
He also has a standard response to those who present falsehoods to him as facts that he suggests anyone can use: “That is interesting. Would you mind helping me understand how you came to that opinion?”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Can you tell which of the following statements are true and which are false?
COVID-19 is not a threat to younger people, and only those who have other medical conditions are dying from it.
The mRNA vaccines developed to prevent the coronavirus alter your genes, can make your body “magnetic,” and are killing more people than the virus itself.
President Joe Biden’s climate change plan calls for a ban on meat consumption to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
The 2020 presidential election was rigged and stolen.
If you guessed that all of these claims are false, you’re right – take a bow. Not a single one of these statements has any factual support, according to scientific research, legal rulings, and legitimate government authorities.
And yet public opinion surveys show millions of Americans, and others around the world, believe some of these falsehoods are true and can’t be convinced otherwise.
Social media, politicians and partisan websites, TV programs, and commentators have widely circulated these and other unfounded claims so frequently that many people say they simply can’t tell what’s objectively true and not anymore.
So much so,
The new study – The Rise and Fall of Rationality in Language, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – found that facts have become less important in public discourse.
As a result, unsupported beliefs have taken precedent over readily identifiable truths in discussions of health, science, and politics. The upshot: “Feelings trump facts” in social media, news reports, books, and other sources of information.
And here’s the kicker: The trend did not begin with the rise of former President Donald Trump, the COVID-19 pandemic, or the advent of social media; in fact, it has been growing for much longer than you might think.
“While the current ‘post-truth era’ has taken many by surprise, the study shows that over the past 40 years, public interest has undergone an accelerating shift from the collective to the individual, and from rationality towards emotion,” concluded the researchers from Indiana University and Wageningen University & Research in the Netherlands.
“Our work suggests that the societal balance between emotion and reason has shifted back to what it used to be around 150 years ago,” says lead researcher Marten Scheffer, PhD, a professor in the department of environmental sciences at WUR. “This implies that scientists, experts, and policymakers will have to think about the best way to respond to that social change.”
Researchers surprised by findings
The findings are based on a very detailed analysis of language from millions of books, newspaper articles, Google searches, TV reports, social media posts, and other sources dating back to 1850.
The researchers analyzed how often the 5,000 most used words appeared over the past 170 years and found that the use of those having to do with facts and reasoning, such as “determine” and “conclusion,” has fallen dramatically since 1980. Meanwhile, the use of words related to human emotion, such as “feel” and “believe,” have skyrocketed.
Dr. Scheffer notes rapid developments in science and technology from 1850 to 1980 had profound social and economic benefits that helped boost the status of the scientific approach. That shift in public attitudes had ripple effects on culture, society, education, politics, and religion – and “the role of spiritualism dwindled” in the modern world, he says.
But since 1980, that trend has seen a major reversal, with beliefs becoming more important than facts to many people, he says. At the same time, trust in science and scientists has fallen.
Dr. Scheffer says the researchers expected to find some evidence of a swing toward more belief-based sentiments during the Trump era but were surprised to discover how strong it is and that the trend has actually been a long time coming.
“The shift in interest from rational to intuitive/emotional is pretty obvious now in the post-truth political and social media discussion,” he says. “However, our work shows that it already started in the 1980s. For me personally, that went under the radar, except perhaps for the rise of alternative (to religion) forms of spirituality.
“We were especially struck by how strong the patterns are and how universal they appear across languages, nonfiction and fiction, and even in The New York Times.”
In the political world, the implications are significant enough – impacting policies and politicians on both sides of the aisle and across the globe. Just look at the deepening political divisions during the Trump presidency.
But for health and science, the spread of misinformation and falsehoods can be matters of life or death, as we have seen in the politically charged debates over how best to combat COVID-19 and global climate change.
“Our public debate seems increasingly driven by what people want to be true rather than what is actually true. As a scientist, that worries me,” says study co-author Johan Bollen, PhD, a professor of informatics at Indiana University.
“As a society, we are now faced with major collective problems that we need to approach from a pragmatic, rational, and objective perspective to be successful,” he says. “After all, global warming doesn’t care about whether you believe in it or not … but we will all suffer as a society if we fail to take adequate measures.”
For WUR co-researcher Ingrid van de Leemput, the trend isn’t merely academic; she’s seen it play out in her personal life.
“I do speak to people that, for instance, think the vaccines are poison,” she says. “I’m also on Twitter, and there, I’m every day surprised about how easily many people form their opinions, based on feelings, on what others say, or on some unfounded source.”
Public health experts say the embrace of personal beliefs over facts is one reason only 63% of Americans have been vaccinated against COVID-19. The result: millions of preventable infections among those who downplay the risks of the virus and reject the strong scientific evidence of vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“None of this really surprises me,” Johns Hopkins University social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, says of the new study findings. Dr. Limaye coauthored a paper in 2016 in JAMA Pediatrics about how to talk to parents about vaccine hesitancy and the fact that we’re living in what they called “this post-truth era.”
Dr. Limaye says the trend has made it difficult for doctors, scientists, and health authorities to make fact-based arguments for COVID-19 vaccination, mask-wearing, social distancing, and other measures to control the virus.
“It’s been really hard being a scientist to hear people say, ‘Well, that’s not true’ when we say something very basic that I think all of us can agree on – like the grass is green,” she says. “To be honest, I worry that a lot of scientists are going to quit being in science because they’re exhausted.”
What’s driving the trend?
So, what’s behind the embrace of “alternative facts,” as former White House counselor Kellyanne Conway put it so brazenly in 2017, in defending the White House’s false claims that Trump’s inauguration crowd was the largest ever?
Dr. Scheffer and colleagues identified a handful of things that have encouraged the embrace of falsehoods over facts in recent years.
- The Internet: Its rise in the late 1980s, and its growing role as a primary source of news and information, has allowed more belief-based misinformation to flourish and spread like wildfire.
- Social media: The new study found the use of sentiment- and intuition-related words accelerated around 2007, along with a global surge in social media that catapulted Facebook, Twitter, and others into the mainstream, replacing more traditional fact-based media (i.e., newspapers and magazines).
- The 2007 financial crisis: The downturn in the global economy meant more people were dealing with job stress, investment losses, and other problems that fed the interest in belief-based, anti-establishment social media posts.
- Conspiracy theories: Falsehoods involving hidden political agendas, shadow “elites,” and wealthy people with dark motives tend to thrive during times of crisis and societal anxiety. “Conspiracy theories originate particularly in times of uncertainty and crisis and generally depict established institutions as hiding the truth and sustaining an unfair situation,” the researchers noted. “As a result, they may find fertile grounds on social media platforms promulgating a sense of unfairness, subsequently feeding anti-system sentiments.”
Dr. Scheffer says that growing political divisions during the Trump era have widened the fact-vs.-fiction divide. The ex-president voiced many anti-science views on global climate change, for instance, and spread so many falsehoods about COVID-19 and the 2020 election that Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube suspended his accounts.
Yet Trump remains a popular figure among Republicans, with most saying in a December poll they believe his baseless claims that the 2020 election was “rigged” and “stolen,” despite all credible, easily accessible evidence that it was secure, according to a recent poll by the University of Massachusetts at Amherst.
More than 60 courts have rejected Trump’s lawsuits seeking to overturn the election results. All 50 states, the District of Columbia, and both branches of Congress have certified the election results, giving Biden the White House. Even Trump’s own Justice Department confirmed that the 2020 election was free and fair.
Nevertheless, the University of Massachusetts survey found that most Republicans believe one or more conspiracy theories floated by the former president and those pushing his “big lie” that Democrats rigged the election to elect Biden.
Ed Berliner, an Emmy Award-winning broadcast journalist and media consultant, suggests something else is driving the spread of misinformation: the pursuit of ratings by cable TV and media companies to boost ad and subscriber revenues.
As a former executive producer and syndicated cable TV show host, he says he has seen firsthand how facts are often lost in opinion-driven news programs, even on network programs claiming to offer “fair and balanced” journalism.
“Propaganda is the new currency in America, and those who do not fight back against it are doomed to be overrun by the misinformation,” says Mr. Berliner, host of The Man in the Arena and CEO of Entourage Media LLC.
“The broadcast news media has to stop this incessant ‘infotainment’ prattle, stop trying to nuzzle up to a soft side, and bear down on hard facts, exposing the lies and refusing to back down.”
Public health implications
Public health and media experts alike say the PNAS study findings are disheartening but underscore the need for doctors and scientists to do a better job of communicating about COVID-19 and other pressing issues.
Dr. Limaye, from Johns Hopkins, is particularly concerned about the rise in conspiracy theories that has led to COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy.
“When we speak to individuals about getting the COVID vaccine…the types of concerns that come up now are very different than they were 8 years ago,” she says. “The comments we used to hear were much more related to vaccine safety. [People] would say, ‘I’m worried about an ingredient in the vaccine’ or ‘I’m worried that my kiddo has to get three different shots within 6 months to have a series dose completed.’”
But now, a lot of comments they receive are about government and pharma conspiracies.
What that means is doctors and scientists must do more than simply say “here are the facts” and “trust me, I’m a doctor or a scientist,” she says. And these approaches don’t only apply to public health.
“It’s funny, because when we talk to climate change scientists, as vaccine [specialists], we’ll say we can’t believe that people think COVID is a hoax,” she says. “And they’re like, ‘Hold my beer, we’ve been dealing with this for 20 years. Hello, it’s just your guys’ turn to deal with this public denial of science.’”
Dr. Limaye is also concerned about the impacts on funding for scientific research.
“There’s always been a really strong bipartisan effort with regards to funding for science, when you look at Congress and when you look at appropriations,” she says. “But what ended up happening, especially with the Trump administration, was that there was a real shift in that. We’ve never really seen that before in past generations.”
So, what’s the big take-home message?
Dr. Limaye believes doctors and public health experts must show more empathy – and not be combative or arrogant – in communicating science in one-on-one conversations. This month, she’s launching a new course for parents, school administrators, and nurses on how to do precisely that.
“It’s really all about how to have hard conversations with people who might be anti-science,” she says. “It’s being empathetic and not being dismissive. But it’s hard work, and I think a lot of people are just not cut out for it and just don’t have the time for it…You can’t just say, ‘Well, this is science, and I’m a doctor’ – that doesn’t work anymore.”
Brendan Nyhan, PhD, a Dartmouth College political scientist, echoes those sentiments in a separate paper recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In fact, he suggests that providing accurate, fact-based information to counter false claims may actually backfire and reinforce some people’s unfounded beliefs.
“One response to the prevalence of mistaken beliefs is to try to set the record straight by providing accurate information – for instance, by providing evidence of the scientific consensus on climate change,” he writes. “The failures of this approach, which is sometimes referred to as the ‘deficit model’ in science communication, are well-known.”
Dr. Nyhan argues two things make some people more prone to believe falsehoods:
What scientists call “ingrouping,” a kind of tribal mentality that makes some people choose social identity or politics over truth-seeking and demonize others who don’t agree with their views
The rise of high-profile political figures, such as Trump, who encourage their followers to indulge in their desire for “identify-affirming misinformation”
Dr. Scheffer says the most important thing for doctors, health experts, and scientists to recognize is that it’s crucial to gain the trust of someone who may believe fictions over facts to make any persuasive argument on COVID-19 or any other issue.
He also has a standard response to those who present falsehoods to him as facts that he suggests anyone can use: “That is interesting. Would you mind helping me understand how you came to that opinion?”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Can you tell which of the following statements are true and which are false?
COVID-19 is not a threat to younger people, and only those who have other medical conditions are dying from it.
The mRNA vaccines developed to prevent the coronavirus alter your genes, can make your body “magnetic,” and are killing more people than the virus itself.
President Joe Biden’s climate change plan calls for a ban on meat consumption to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
The 2020 presidential election was rigged and stolen.
If you guessed that all of these claims are false, you’re right – take a bow. Not a single one of these statements has any factual support, according to scientific research, legal rulings, and legitimate government authorities.
And yet public opinion surveys show millions of Americans, and others around the world, believe some of these falsehoods are true and can’t be convinced otherwise.
Social media, politicians and partisan websites, TV programs, and commentators have widely circulated these and other unfounded claims so frequently that many people say they simply can’t tell what’s objectively true and not anymore.
So much so,
The new study – The Rise and Fall of Rationality in Language, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – found that facts have become less important in public discourse.
As a result, unsupported beliefs have taken precedent over readily identifiable truths in discussions of health, science, and politics. The upshot: “Feelings trump facts” in social media, news reports, books, and other sources of information.
And here’s the kicker: The trend did not begin with the rise of former President Donald Trump, the COVID-19 pandemic, or the advent of social media; in fact, it has been growing for much longer than you might think.
“While the current ‘post-truth era’ has taken many by surprise, the study shows that over the past 40 years, public interest has undergone an accelerating shift from the collective to the individual, and from rationality towards emotion,” concluded the researchers from Indiana University and Wageningen University & Research in the Netherlands.
“Our work suggests that the societal balance between emotion and reason has shifted back to what it used to be around 150 years ago,” says lead researcher Marten Scheffer, PhD, a professor in the department of environmental sciences at WUR. “This implies that scientists, experts, and policymakers will have to think about the best way to respond to that social change.”
Researchers surprised by findings
The findings are based on a very detailed analysis of language from millions of books, newspaper articles, Google searches, TV reports, social media posts, and other sources dating back to 1850.
The researchers analyzed how often the 5,000 most used words appeared over the past 170 years and found that the use of those having to do with facts and reasoning, such as “determine” and “conclusion,” has fallen dramatically since 1980. Meanwhile, the use of words related to human emotion, such as “feel” and “believe,” have skyrocketed.
Dr. Scheffer notes rapid developments in science and technology from 1850 to 1980 had profound social and economic benefits that helped boost the status of the scientific approach. That shift in public attitudes had ripple effects on culture, society, education, politics, and religion – and “the role of spiritualism dwindled” in the modern world, he says.
But since 1980, that trend has seen a major reversal, with beliefs becoming more important than facts to many people, he says. At the same time, trust in science and scientists has fallen.
Dr. Scheffer says the researchers expected to find some evidence of a swing toward more belief-based sentiments during the Trump era but were surprised to discover how strong it is and that the trend has actually been a long time coming.
“The shift in interest from rational to intuitive/emotional is pretty obvious now in the post-truth political and social media discussion,” he says. “However, our work shows that it already started in the 1980s. For me personally, that went under the radar, except perhaps for the rise of alternative (to religion) forms of spirituality.
“We were especially struck by how strong the patterns are and how universal they appear across languages, nonfiction and fiction, and even in The New York Times.”
In the political world, the implications are significant enough – impacting policies and politicians on both sides of the aisle and across the globe. Just look at the deepening political divisions during the Trump presidency.
But for health and science, the spread of misinformation and falsehoods can be matters of life or death, as we have seen in the politically charged debates over how best to combat COVID-19 and global climate change.
“Our public debate seems increasingly driven by what people want to be true rather than what is actually true. As a scientist, that worries me,” says study co-author Johan Bollen, PhD, a professor of informatics at Indiana University.
“As a society, we are now faced with major collective problems that we need to approach from a pragmatic, rational, and objective perspective to be successful,” he says. “After all, global warming doesn’t care about whether you believe in it or not … but we will all suffer as a society if we fail to take adequate measures.”
For WUR co-researcher Ingrid van de Leemput, the trend isn’t merely academic; she’s seen it play out in her personal life.
“I do speak to people that, for instance, think the vaccines are poison,” she says. “I’m also on Twitter, and there, I’m every day surprised about how easily many people form their opinions, based on feelings, on what others say, or on some unfounded source.”
Public health experts say the embrace of personal beliefs over facts is one reason only 63% of Americans have been vaccinated against COVID-19. The result: millions of preventable infections among those who downplay the risks of the virus and reject the strong scientific evidence of vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“None of this really surprises me,” Johns Hopkins University social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, says of the new study findings. Dr. Limaye coauthored a paper in 2016 in JAMA Pediatrics about how to talk to parents about vaccine hesitancy and the fact that we’re living in what they called “this post-truth era.”
Dr. Limaye says the trend has made it difficult for doctors, scientists, and health authorities to make fact-based arguments for COVID-19 vaccination, mask-wearing, social distancing, and other measures to control the virus.
“It’s been really hard being a scientist to hear people say, ‘Well, that’s not true’ when we say something very basic that I think all of us can agree on – like the grass is green,” she says. “To be honest, I worry that a lot of scientists are going to quit being in science because they’re exhausted.”
What’s driving the trend?
So, what’s behind the embrace of “alternative facts,” as former White House counselor Kellyanne Conway put it so brazenly in 2017, in defending the White House’s false claims that Trump’s inauguration crowd was the largest ever?
Dr. Scheffer and colleagues identified a handful of things that have encouraged the embrace of falsehoods over facts in recent years.
- The Internet: Its rise in the late 1980s, and its growing role as a primary source of news and information, has allowed more belief-based misinformation to flourish and spread like wildfire.
- Social media: The new study found the use of sentiment- and intuition-related words accelerated around 2007, along with a global surge in social media that catapulted Facebook, Twitter, and others into the mainstream, replacing more traditional fact-based media (i.e., newspapers and magazines).
- The 2007 financial crisis: The downturn in the global economy meant more people were dealing with job stress, investment losses, and other problems that fed the interest in belief-based, anti-establishment social media posts.
- Conspiracy theories: Falsehoods involving hidden political agendas, shadow “elites,” and wealthy people with dark motives tend to thrive during times of crisis and societal anxiety. “Conspiracy theories originate particularly in times of uncertainty and crisis and generally depict established institutions as hiding the truth and sustaining an unfair situation,” the researchers noted. “As a result, they may find fertile grounds on social media platforms promulgating a sense of unfairness, subsequently feeding anti-system sentiments.”
Dr. Scheffer says that growing political divisions during the Trump era have widened the fact-vs.-fiction divide. The ex-president voiced many anti-science views on global climate change, for instance, and spread so many falsehoods about COVID-19 and the 2020 election that Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube suspended his accounts.
Yet Trump remains a popular figure among Republicans, with most saying in a December poll they believe his baseless claims that the 2020 election was “rigged” and “stolen,” despite all credible, easily accessible evidence that it was secure, according to a recent poll by the University of Massachusetts at Amherst.
More than 60 courts have rejected Trump’s lawsuits seeking to overturn the election results. All 50 states, the District of Columbia, and both branches of Congress have certified the election results, giving Biden the White House. Even Trump’s own Justice Department confirmed that the 2020 election was free and fair.
Nevertheless, the University of Massachusetts survey found that most Republicans believe one or more conspiracy theories floated by the former president and those pushing his “big lie” that Democrats rigged the election to elect Biden.
Ed Berliner, an Emmy Award-winning broadcast journalist and media consultant, suggests something else is driving the spread of misinformation: the pursuit of ratings by cable TV and media companies to boost ad and subscriber revenues.
As a former executive producer and syndicated cable TV show host, he says he has seen firsthand how facts are often lost in opinion-driven news programs, even on network programs claiming to offer “fair and balanced” journalism.
“Propaganda is the new currency in America, and those who do not fight back against it are doomed to be overrun by the misinformation,” says Mr. Berliner, host of The Man in the Arena and CEO of Entourage Media LLC.
“The broadcast news media has to stop this incessant ‘infotainment’ prattle, stop trying to nuzzle up to a soft side, and bear down on hard facts, exposing the lies and refusing to back down.”
Public health implications
Public health and media experts alike say the PNAS study findings are disheartening but underscore the need for doctors and scientists to do a better job of communicating about COVID-19 and other pressing issues.
Dr. Limaye, from Johns Hopkins, is particularly concerned about the rise in conspiracy theories that has led to COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy.
“When we speak to individuals about getting the COVID vaccine…the types of concerns that come up now are very different than they were 8 years ago,” she says. “The comments we used to hear were much more related to vaccine safety. [People] would say, ‘I’m worried about an ingredient in the vaccine’ or ‘I’m worried that my kiddo has to get three different shots within 6 months to have a series dose completed.’”
But now, a lot of comments they receive are about government and pharma conspiracies.
What that means is doctors and scientists must do more than simply say “here are the facts” and “trust me, I’m a doctor or a scientist,” she says. And these approaches don’t only apply to public health.
“It’s funny, because when we talk to climate change scientists, as vaccine [specialists], we’ll say we can’t believe that people think COVID is a hoax,” she says. “And they’re like, ‘Hold my beer, we’ve been dealing with this for 20 years. Hello, it’s just your guys’ turn to deal with this public denial of science.’”
Dr. Limaye is also concerned about the impacts on funding for scientific research.
“There’s always been a really strong bipartisan effort with regards to funding for science, when you look at Congress and when you look at appropriations,” she says. “But what ended up happening, especially with the Trump administration, was that there was a real shift in that. We’ve never really seen that before in past generations.”
So, what’s the big take-home message?
Dr. Limaye believes doctors and public health experts must show more empathy – and not be combative or arrogant – in communicating science in one-on-one conversations. This month, she’s launching a new course for parents, school administrators, and nurses on how to do precisely that.
“It’s really all about how to have hard conversations with people who might be anti-science,” she says. “It’s being empathetic and not being dismissive. But it’s hard work, and I think a lot of people are just not cut out for it and just don’t have the time for it…You can’t just say, ‘Well, this is science, and I’m a doctor’ – that doesn’t work anymore.”
Brendan Nyhan, PhD, a Dartmouth College political scientist, echoes those sentiments in a separate paper recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In fact, he suggests that providing accurate, fact-based information to counter false claims may actually backfire and reinforce some people’s unfounded beliefs.
“One response to the prevalence of mistaken beliefs is to try to set the record straight by providing accurate information – for instance, by providing evidence of the scientific consensus on climate change,” he writes. “The failures of this approach, which is sometimes referred to as the ‘deficit model’ in science communication, are well-known.”
Dr. Nyhan argues two things make some people more prone to believe falsehoods:
What scientists call “ingrouping,” a kind of tribal mentality that makes some people choose social identity or politics over truth-seeking and demonize others who don’t agree with their views
The rise of high-profile political figures, such as Trump, who encourage their followers to indulge in their desire for “identify-affirming misinformation”
Dr. Scheffer says the most important thing for doctors, health experts, and scientists to recognize is that it’s crucial to gain the trust of someone who may believe fictions over facts to make any persuasive argument on COVID-19 or any other issue.
He also has a standard response to those who present falsehoods to him as facts that he suggests anyone can use: “That is interesting. Would you mind helping me understand how you came to that opinion?”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.