User login
CDC panel backs mRNA COVID vaccines over J&J because of clot risk
because the Johnson & Johnson shot carries the risk of a rare but potentially fatal side effect that causes blood clots and bleeding in the brain.
In an emergency meeting on December 16, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, or ACIP, voted unanimously (15-0) to state a preference for the mRNA vaccines over the Johnson & Johnson shot. The vote came after the panel heard a safety update on cases of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome, or TTS, a condition that causes large clots that deplete the blood of platelets, resulting in uncontrolled bleeding.
The move brings the United States in line with other wealthy countries. In May, Denmark dropped the Johnson & Johnson shot from its vaccination program because of this risk. Australia and Greece have limited the use of a similar vaccine, made by AstraZeneca, in younger people because of the TTS risk. Both vaccines use the envelope of a different kind of virus, called an adenovirus, to sneak the vaccine instructions into cells. On Dec. 16, health officials said they had determined that TTS was likely due to a class effect, meaning it happens with all adenovirus vector vaccines.
The risk of dying from TTS after a Johnson & Johnson shot is extremely rare. There is an estimated 1 death for every 2 million doses of the vaccine given in the general population. That risk is higher for women ages 30 to 49, rising to about 2 deaths for every 1 million doses given in this age group. There’s no question that the Johnson & Johnson shot has saved many more lives than it has taken, experts said
Still, the committee previously paused the use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in April after the first cases of TTS came to light. That pause was lifted just 10 days later, after a new warning was added to the vaccine’s label to raise awareness of the risk.
In updating the safety information on Johnson & Johnson, the panel noted that the warning label had not sufficiently lowered the risk of death from TTS. Doctors seem to be aware of the condition because none of the patients who had developed TTS had been treated with the blood thinner heparin, which can make the syndrome worse. But patients continued to die even after the label was added, the panel noted, because TTS can progress so quickly that doctors simply don’t have time to treat it.
For that reason, and because there are other, safer vaccines available, the panel decided to make what’s called a preferential statement, saying the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines should be preferred over Johnson & Johnson.
The statement leaves the J&J vaccine on the market and available to patients who are at risk of a severe allergic reaction to the mRNA vaccines. It also means that people can still choose the J&J vaccine if they still want it after being informed about the risks.
About 17 million first doses and 900,000 second doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine have been given in the United States. Through the end of August, 54 cases of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) have occurred after the J&J shots in the United States. Nearly half of those were in women ages 30 to 49. There have been nine deaths from TTS after Johnson & Johnson shots.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
because the Johnson & Johnson shot carries the risk of a rare but potentially fatal side effect that causes blood clots and bleeding in the brain.
In an emergency meeting on December 16, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, or ACIP, voted unanimously (15-0) to state a preference for the mRNA vaccines over the Johnson & Johnson shot. The vote came after the panel heard a safety update on cases of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome, or TTS, a condition that causes large clots that deplete the blood of platelets, resulting in uncontrolled bleeding.
The move brings the United States in line with other wealthy countries. In May, Denmark dropped the Johnson & Johnson shot from its vaccination program because of this risk. Australia and Greece have limited the use of a similar vaccine, made by AstraZeneca, in younger people because of the TTS risk. Both vaccines use the envelope of a different kind of virus, called an adenovirus, to sneak the vaccine instructions into cells. On Dec. 16, health officials said they had determined that TTS was likely due to a class effect, meaning it happens with all adenovirus vector vaccines.
The risk of dying from TTS after a Johnson & Johnson shot is extremely rare. There is an estimated 1 death for every 2 million doses of the vaccine given in the general population. That risk is higher for women ages 30 to 49, rising to about 2 deaths for every 1 million doses given in this age group. There’s no question that the Johnson & Johnson shot has saved many more lives than it has taken, experts said
Still, the committee previously paused the use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in April after the first cases of TTS came to light. That pause was lifted just 10 days later, after a new warning was added to the vaccine’s label to raise awareness of the risk.
In updating the safety information on Johnson & Johnson, the panel noted that the warning label had not sufficiently lowered the risk of death from TTS. Doctors seem to be aware of the condition because none of the patients who had developed TTS had been treated with the blood thinner heparin, which can make the syndrome worse. But patients continued to die even after the label was added, the panel noted, because TTS can progress so quickly that doctors simply don’t have time to treat it.
For that reason, and because there are other, safer vaccines available, the panel decided to make what’s called a preferential statement, saying the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines should be preferred over Johnson & Johnson.
The statement leaves the J&J vaccine on the market and available to patients who are at risk of a severe allergic reaction to the mRNA vaccines. It also means that people can still choose the J&J vaccine if they still want it after being informed about the risks.
About 17 million first doses and 900,000 second doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine have been given in the United States. Through the end of August, 54 cases of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) have occurred after the J&J shots in the United States. Nearly half of those were in women ages 30 to 49. There have been nine deaths from TTS after Johnson & Johnson shots.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
because the Johnson & Johnson shot carries the risk of a rare but potentially fatal side effect that causes blood clots and bleeding in the brain.
In an emergency meeting on December 16, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, or ACIP, voted unanimously (15-0) to state a preference for the mRNA vaccines over the Johnson & Johnson shot. The vote came after the panel heard a safety update on cases of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome, or TTS, a condition that causes large clots that deplete the blood of platelets, resulting in uncontrolled bleeding.
The move brings the United States in line with other wealthy countries. In May, Denmark dropped the Johnson & Johnson shot from its vaccination program because of this risk. Australia and Greece have limited the use of a similar vaccine, made by AstraZeneca, in younger people because of the TTS risk. Both vaccines use the envelope of a different kind of virus, called an adenovirus, to sneak the vaccine instructions into cells. On Dec. 16, health officials said they had determined that TTS was likely due to a class effect, meaning it happens with all adenovirus vector vaccines.
The risk of dying from TTS after a Johnson & Johnson shot is extremely rare. There is an estimated 1 death for every 2 million doses of the vaccine given in the general population. That risk is higher for women ages 30 to 49, rising to about 2 deaths for every 1 million doses given in this age group. There’s no question that the Johnson & Johnson shot has saved many more lives than it has taken, experts said
Still, the committee previously paused the use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in April after the first cases of TTS came to light. That pause was lifted just 10 days later, after a new warning was added to the vaccine’s label to raise awareness of the risk.
In updating the safety information on Johnson & Johnson, the panel noted that the warning label had not sufficiently lowered the risk of death from TTS. Doctors seem to be aware of the condition because none of the patients who had developed TTS had been treated with the blood thinner heparin, which can make the syndrome worse. But patients continued to die even after the label was added, the panel noted, because TTS can progress so quickly that doctors simply don’t have time to treat it.
For that reason, and because there are other, safer vaccines available, the panel decided to make what’s called a preferential statement, saying the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines should be preferred over Johnson & Johnson.
The statement leaves the J&J vaccine on the market and available to patients who are at risk of a severe allergic reaction to the mRNA vaccines. It also means that people can still choose the J&J vaccine if they still want it after being informed about the risks.
About 17 million first doses and 900,000 second doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine have been given in the United States. Through the end of August, 54 cases of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) have occurred after the J&J shots in the United States. Nearly half of those were in women ages 30 to 49. There have been nine deaths from TTS after Johnson & Johnson shots.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA updates risks, cautions for clotting-bleeding disorder on Janssen COVID-19 vaccine
Updated Janssen/Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine fact sheets for health care professionals and the general public now include a contraindication to its use in persons with a history of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after receiving it “or any other adenovirus-vectored COVID-19 vaccine,” the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has announced.
Thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) – thrombocytopenia and increased bleeding risk along with documented thrombosis – after administration of the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccine remains rare. But over all age groups, about one in seven cases have been fatal, said the agency.
the provider fact sheet states.
Although TTS associated with the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine has been reported in men and women aged 18 and older, the highest reported rate has been for women aged 30-49, the agency states. The rate in that group has been about 1 case per 100,000 doses administered.
Symptoms of TTS may occur 1-2 weeks after administration of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, the FDA says, based on data from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS).
Its clinical course shares features with autoimmune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. In individuals with suspected TTS following receipt of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, the agency cautions, the use of heparin “may be harmful and alternative treatments may be needed. Consultation with hematology specialists is strongly recommended.”
The apparent excess risk of TTS remains under investigation, but “the FDA continues to find that the known and potential benefits of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine outweigh its known and potential risks in individuals 18 years of age and older,” the agency states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated Janssen/Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine fact sheets for health care professionals and the general public now include a contraindication to its use in persons with a history of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after receiving it “or any other adenovirus-vectored COVID-19 vaccine,” the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has announced.
Thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) – thrombocytopenia and increased bleeding risk along with documented thrombosis – after administration of the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccine remains rare. But over all age groups, about one in seven cases have been fatal, said the agency.
the provider fact sheet states.
Although TTS associated with the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine has been reported in men and women aged 18 and older, the highest reported rate has been for women aged 30-49, the agency states. The rate in that group has been about 1 case per 100,000 doses administered.
Symptoms of TTS may occur 1-2 weeks after administration of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, the FDA says, based on data from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS).
Its clinical course shares features with autoimmune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. In individuals with suspected TTS following receipt of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, the agency cautions, the use of heparin “may be harmful and alternative treatments may be needed. Consultation with hematology specialists is strongly recommended.”
The apparent excess risk of TTS remains under investigation, but “the FDA continues to find that the known and potential benefits of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine outweigh its known and potential risks in individuals 18 years of age and older,” the agency states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated Janssen/Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine fact sheets for health care professionals and the general public now include a contraindication to its use in persons with a history of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after receiving it “or any other adenovirus-vectored COVID-19 vaccine,” the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has announced.
Thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) – thrombocytopenia and increased bleeding risk along with documented thrombosis – after administration of the Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccine remains rare. But over all age groups, about one in seven cases have been fatal, said the agency.
the provider fact sheet states.
Although TTS associated with the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine has been reported in men and women aged 18 and older, the highest reported rate has been for women aged 30-49, the agency states. The rate in that group has been about 1 case per 100,000 doses administered.
Symptoms of TTS may occur 1-2 weeks after administration of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, the FDA says, based on data from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS).
Its clinical course shares features with autoimmune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. In individuals with suspected TTS following receipt of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine, the agency cautions, the use of heparin “may be harmful and alternative treatments may be needed. Consultation with hematology specialists is strongly recommended.”
The apparent excess risk of TTS remains under investigation, but “the FDA continues to find that the known and potential benefits of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine outweigh its known and potential risks in individuals 18 years of age and older,” the agency states.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A pandemic silver lining? Dramatic drop in teen drug use
Illicit drug use among U.S. teenagers dropped sharply in 2021, likely because of stay-at-home orders and other restrictions on social activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The latest findings, from the Monitoring the Future survey, represent the largest 1-year decrease in overall illicit drug use reported since the survey began in 1975.
“We have never seen such dramatic decreases in drug use among teens in just a 1-year period,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), said in a news release.
“These data are unprecedented and highlight one unexpected potential consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused seismic shifts in the day-to-day lives of adolescents,” said Dr. Volkow.
The annual Monitoring the Future survey is conducted by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and funded by NIDA, to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States.
This year’s self-reported survey included 32,260 students in grades 8, 10, and 12 across 319 public and private schools.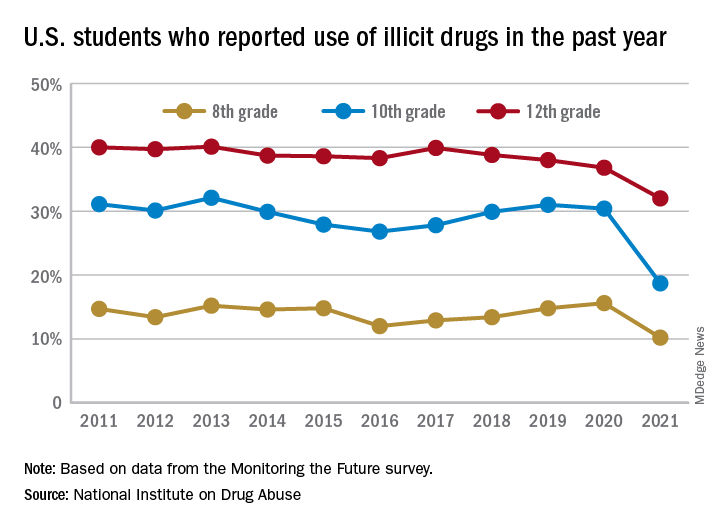
Compared with 2020, the percentage of students reporting any illicit drug use (other than marijuana) in 2021 decreased significantly for 8th graders (down 5.4%), 10th graders (down 11.7%), and 12th graders (down 4.8%).
For alcohol, about 47% of 12th graders and 29% of 10th graders said they drank alcohol in 2021, down significantly from 55% and 41%, respectively, in 2020. The percentage of 8th graders who said they drank alcohol remained stable (17% in 2021 and 20% in 2020).
For teen vaping, about 27% of 12th graders and 20% of 10th graders said they had vaped nicotine in 2021, down significantly from nearly 35% and 31%, respectively, in 2020. Fewer 8th graders also vaped nicotine in 2021 compared with 2020 (12% vs. 17%).
For marijuana, use dropped significantly for all three grades in 2021 compared with 2020. About 31% of 12th graders and 17% of 10th graders said they used marijuana in 2021, down from 35% and 28% in 2020. Among 8th graders, 7% used marijuana in 2021, down from 11% in 2020.
The latest survey also shows significant declines in use of a range of other drugs for many of the age cohorts, including cocaine, hallucinogens, and nonmedical use of amphetamines, tranquilizers, and prescription opioids.
“We knew that this year’s data would illuminate how the COVID-19 pandemic may have impacted substance use among young people, and in the coming years, we will find out whether those impacts are long-lasting as we continue tracking the drug use patterns of these unique cohorts of adolescents,” Richard A. Miech, PhD, who heads the Monitoring the Future study at the University of Michigan, said in the news release.
“Moving forward, it will be crucial to identify the pivotal elements of this past year that contributed to decreased drug use – whether related to drug availability, family involvement, differences in peer pressure, or other factors – and harness them to inform future prevention efforts,” Dr. Volkow added.
In 2021, students across all age groups reported moderate increases in feelings of boredom, anxiety, depression, loneliness, worry, difficulty sleeping, and other negative mental health indicators since the beginning of the pandemic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Illicit drug use among U.S. teenagers dropped sharply in 2021, likely because of stay-at-home orders and other restrictions on social activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The latest findings, from the Monitoring the Future survey, represent the largest 1-year decrease in overall illicit drug use reported since the survey began in 1975.
“We have never seen such dramatic decreases in drug use among teens in just a 1-year period,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), said in a news release.
“These data are unprecedented and highlight one unexpected potential consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused seismic shifts in the day-to-day lives of adolescents,” said Dr. Volkow.
The annual Monitoring the Future survey is conducted by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and funded by NIDA, to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States.
This year’s self-reported survey included 32,260 students in grades 8, 10, and 12 across 319 public and private schools.
Compared with 2020, the percentage of students reporting any illicit drug use (other than marijuana) in 2021 decreased significantly for 8th graders (down 5.4%), 10th graders (down 11.7%), and 12th graders (down 4.8%).
For alcohol, about 47% of 12th graders and 29% of 10th graders said they drank alcohol in 2021, down significantly from 55% and 41%, respectively, in 2020. The percentage of 8th graders who said they drank alcohol remained stable (17% in 2021 and 20% in 2020).
For teen vaping, about 27% of 12th graders and 20% of 10th graders said they had vaped nicotine in 2021, down significantly from nearly 35% and 31%, respectively, in 2020. Fewer 8th graders also vaped nicotine in 2021 compared with 2020 (12% vs. 17%).
For marijuana, use dropped significantly for all three grades in 2021 compared with 2020. About 31% of 12th graders and 17% of 10th graders said they used marijuana in 2021, down from 35% and 28% in 2020. Among 8th graders, 7% used marijuana in 2021, down from 11% in 2020.
The latest survey also shows significant declines in use of a range of other drugs for many of the age cohorts, including cocaine, hallucinogens, and nonmedical use of amphetamines, tranquilizers, and prescription opioids.
“We knew that this year’s data would illuminate how the COVID-19 pandemic may have impacted substance use among young people, and in the coming years, we will find out whether those impacts are long-lasting as we continue tracking the drug use patterns of these unique cohorts of adolescents,” Richard A. Miech, PhD, who heads the Monitoring the Future study at the University of Michigan, said in the news release.
“Moving forward, it will be crucial to identify the pivotal elements of this past year that contributed to decreased drug use – whether related to drug availability, family involvement, differences in peer pressure, or other factors – and harness them to inform future prevention efforts,” Dr. Volkow added.
In 2021, students across all age groups reported moderate increases in feelings of boredom, anxiety, depression, loneliness, worry, difficulty sleeping, and other negative mental health indicators since the beginning of the pandemic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Illicit drug use among U.S. teenagers dropped sharply in 2021, likely because of stay-at-home orders and other restrictions on social activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The latest findings, from the Monitoring the Future survey, represent the largest 1-year decrease in overall illicit drug use reported since the survey began in 1975.
“We have never seen such dramatic decreases in drug use among teens in just a 1-year period,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), said in a news release.
“These data are unprecedented and highlight one unexpected potential consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused seismic shifts in the day-to-day lives of adolescents,” said Dr. Volkow.
The annual Monitoring the Future survey is conducted by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and funded by NIDA, to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States.
This year’s self-reported survey included 32,260 students in grades 8, 10, and 12 across 319 public and private schools.
Compared with 2020, the percentage of students reporting any illicit drug use (other than marijuana) in 2021 decreased significantly for 8th graders (down 5.4%), 10th graders (down 11.7%), and 12th graders (down 4.8%).
For alcohol, about 47% of 12th graders and 29% of 10th graders said they drank alcohol in 2021, down significantly from 55% and 41%, respectively, in 2020. The percentage of 8th graders who said they drank alcohol remained stable (17% in 2021 and 20% in 2020).
For teen vaping, about 27% of 12th graders and 20% of 10th graders said they had vaped nicotine in 2021, down significantly from nearly 35% and 31%, respectively, in 2020. Fewer 8th graders also vaped nicotine in 2021 compared with 2020 (12% vs. 17%).
For marijuana, use dropped significantly for all three grades in 2021 compared with 2020. About 31% of 12th graders and 17% of 10th graders said they used marijuana in 2021, down from 35% and 28% in 2020. Among 8th graders, 7% used marijuana in 2021, down from 11% in 2020.
The latest survey also shows significant declines in use of a range of other drugs for many of the age cohorts, including cocaine, hallucinogens, and nonmedical use of amphetamines, tranquilizers, and prescription opioids.
“We knew that this year’s data would illuminate how the COVID-19 pandemic may have impacted substance use among young people, and in the coming years, we will find out whether those impacts are long-lasting as we continue tracking the drug use patterns of these unique cohorts of adolescents,” Richard A. Miech, PhD, who heads the Monitoring the Future study at the University of Michigan, said in the news release.
“Moving forward, it will be crucial to identify the pivotal elements of this past year that contributed to decreased drug use – whether related to drug availability, family involvement, differences in peer pressure, or other factors – and harness them to inform future prevention efforts,” Dr. Volkow added.
In 2021, students across all age groups reported moderate increases in feelings of boredom, anxiety, depression, loneliness, worry, difficulty sleeping, and other negative mental health indicators since the beginning of the pandemic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 asymptomatic infection rate remains high
Based on data from a meta-analysis of 95 studies that included nearly 30,000,000 individuals, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections was 0.25% in the tested population and 40.5% among confirmed cases.
, wrote Qiuyue Ma, PhD, and colleagues of Peking University, Beijing.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open the researchers identified 44 cross-sectional studies, 41 cohort studies, seven case series, and three case series on transmission studies. A total of 74 studies were conducted in developed countries, including those in Europe, North America, and Asia. Approximately one-third (37) of the studies were conducted among health care workers or in-hospital patients, 17 among nursing home staff or residents, and 14 among community residents. In addition, 13 studies involved pregnant women, eight involved air or cruise ship travelers, and six involved close contacts of individuals with confirmed infections.
The meta-analysis included 29,776,306 tested individuals; 11,516 of them had asymptomatic infections.
Overall, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the tested population was 0.25%. In an analysis of different study populations, the percentage was higher in nursing home residents or staff (4.52%), air or cruise ship travelers (2.02%), and pregnant women (2.34%), compared against the pooled percentage.
The pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the confirmed population was 40.50%, and this percentage was higher in pregnant women (54.11%), air or cruise ship travelers (52.91%), and nursing home residents or staff (47.53%).
The pooled percentage in the tested population was higher than the overall percentage when the mean age of the study population was 60 years or older (3.69%). By contrast, in the confirmed population, the pooled percentage was higher than the overall percentage when the study population was younger than 20 years (60.2%) or aged 20 to 39 years (49.5%).
The researchers noted in their discussion that the varying percentage of asymptomatic individuals according to community prevalence might impact the heterogeneity of the included studies. They also noted the high number of studies conducted in nursing home populations, groups in which asymptomatic individuals were more likely to be tested.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for missed studies that were not published at the time of the meta-analysis, as well as the exclusion of studies written in Chinese, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of follow-up on presymptomatic and covert infections, and the focus on specific populations, factors that may limit the degree to which the results can be generalized.
However, the results highlight the need to screen for asymptomatic infections, especially in countries where COVID-19 has been better controlled, the researchers said. Management strategies for asymptomatic infections, when identified, should include isolation and contact tracing similar to strategies used with confirmed cases, they added.
More testing needed to catch cases early
“During the initial phase of [the] COVID-19 pandemic, testing was not widely available in the United States or the rest of the world,” Setu Patolia, MD, of Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Missouri, said in an interview. Much of the world still lacks access to COVID-19 testing, and early in the pandemic only severely symptomatic patients were tested, he said. “With new variants, particularly the Omicron variant, which may have mild or minimally symptomatic disease, asymptomatic carriers play an important role in propagation of the pandemic,” he explained. “It is important to know the asymptomatic carrier rate among the general population for the future control of [the] pandemic,” he added.
Dr. Patolia said he was surprised by the study finding that one in 400 people in the general population could be asymptomatic carriers of COVID-19.
“Also, nursing home patients are more at risk of complications of COVID, and I expected that they would have a higher rate of symptomatic disease as compared to [the] general population,” said Dr. Patolia. He was also surprised by the high rate of asymptomatic infections in travelers.
“Physicians should be more aware about the asymptomatic carrier rate, particularly in travelers and nursing home patients,” he noted. “Travelers carry high risk of transferring infection from one region to another region of the world, and physicians should advise them to get tested despite the absence of symptoms,” Dr. Patolia emphasized. “Similarly, once any nursing home patient has been diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians should be more careful with the rest of the nursing home patients and test them despite the absence of the symptoms,” he added.
Dr. Patolia also recommended that pregnant women wear masks to help prevent disease transmission when visiting a doctor’s office or labor unit.
Looking ahead, there is a need for cheaper at-home testing kits so that all vulnerable populations can be tested fast and frequently, Dr. Patolia said.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Patolia has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Based on data from a meta-analysis of 95 studies that included nearly 30,000,000 individuals, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections was 0.25% in the tested population and 40.5% among confirmed cases.
, wrote Qiuyue Ma, PhD, and colleagues of Peking University, Beijing.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open the researchers identified 44 cross-sectional studies, 41 cohort studies, seven case series, and three case series on transmission studies. A total of 74 studies were conducted in developed countries, including those in Europe, North America, and Asia. Approximately one-third (37) of the studies were conducted among health care workers or in-hospital patients, 17 among nursing home staff or residents, and 14 among community residents. In addition, 13 studies involved pregnant women, eight involved air or cruise ship travelers, and six involved close contacts of individuals with confirmed infections.
The meta-analysis included 29,776,306 tested individuals; 11,516 of them had asymptomatic infections.
Overall, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the tested population was 0.25%. In an analysis of different study populations, the percentage was higher in nursing home residents or staff (4.52%), air or cruise ship travelers (2.02%), and pregnant women (2.34%), compared against the pooled percentage.
The pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the confirmed population was 40.50%, and this percentage was higher in pregnant women (54.11%), air or cruise ship travelers (52.91%), and nursing home residents or staff (47.53%).
The pooled percentage in the tested population was higher than the overall percentage when the mean age of the study population was 60 years or older (3.69%). By contrast, in the confirmed population, the pooled percentage was higher than the overall percentage when the study population was younger than 20 years (60.2%) or aged 20 to 39 years (49.5%).
The researchers noted in their discussion that the varying percentage of asymptomatic individuals according to community prevalence might impact the heterogeneity of the included studies. They also noted the high number of studies conducted in nursing home populations, groups in which asymptomatic individuals were more likely to be tested.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for missed studies that were not published at the time of the meta-analysis, as well as the exclusion of studies written in Chinese, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of follow-up on presymptomatic and covert infections, and the focus on specific populations, factors that may limit the degree to which the results can be generalized.
However, the results highlight the need to screen for asymptomatic infections, especially in countries where COVID-19 has been better controlled, the researchers said. Management strategies for asymptomatic infections, when identified, should include isolation and contact tracing similar to strategies used with confirmed cases, they added.
More testing needed to catch cases early
“During the initial phase of [the] COVID-19 pandemic, testing was not widely available in the United States or the rest of the world,” Setu Patolia, MD, of Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Missouri, said in an interview. Much of the world still lacks access to COVID-19 testing, and early in the pandemic only severely symptomatic patients were tested, he said. “With new variants, particularly the Omicron variant, which may have mild or minimally symptomatic disease, asymptomatic carriers play an important role in propagation of the pandemic,” he explained. “It is important to know the asymptomatic carrier rate among the general population for the future control of [the] pandemic,” he added.
Dr. Patolia said he was surprised by the study finding that one in 400 people in the general population could be asymptomatic carriers of COVID-19.
“Also, nursing home patients are more at risk of complications of COVID, and I expected that they would have a higher rate of symptomatic disease as compared to [the] general population,” said Dr. Patolia. He was also surprised by the high rate of asymptomatic infections in travelers.
“Physicians should be more aware about the asymptomatic carrier rate, particularly in travelers and nursing home patients,” he noted. “Travelers carry high risk of transferring infection from one region to another region of the world, and physicians should advise them to get tested despite the absence of symptoms,” Dr. Patolia emphasized. “Similarly, once any nursing home patient has been diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians should be more careful with the rest of the nursing home patients and test them despite the absence of the symptoms,” he added.
Dr. Patolia also recommended that pregnant women wear masks to help prevent disease transmission when visiting a doctor’s office or labor unit.
Looking ahead, there is a need for cheaper at-home testing kits so that all vulnerable populations can be tested fast and frequently, Dr. Patolia said.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Patolia has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Based on data from a meta-analysis of 95 studies that included nearly 30,000,000 individuals, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections was 0.25% in the tested population and 40.5% among confirmed cases.
, wrote Qiuyue Ma, PhD, and colleagues of Peking University, Beijing.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open the researchers identified 44 cross-sectional studies, 41 cohort studies, seven case series, and three case series on transmission studies. A total of 74 studies were conducted in developed countries, including those in Europe, North America, and Asia. Approximately one-third (37) of the studies were conducted among health care workers or in-hospital patients, 17 among nursing home staff or residents, and 14 among community residents. In addition, 13 studies involved pregnant women, eight involved air or cruise ship travelers, and six involved close contacts of individuals with confirmed infections.
The meta-analysis included 29,776,306 tested individuals; 11,516 of them had asymptomatic infections.
Overall, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the tested population was 0.25%. In an analysis of different study populations, the percentage was higher in nursing home residents or staff (4.52%), air or cruise ship travelers (2.02%), and pregnant women (2.34%), compared against the pooled percentage.
The pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the confirmed population was 40.50%, and this percentage was higher in pregnant women (54.11%), air or cruise ship travelers (52.91%), and nursing home residents or staff (47.53%).
The pooled percentage in the tested population was higher than the overall percentage when the mean age of the study population was 60 years or older (3.69%). By contrast, in the confirmed population, the pooled percentage was higher than the overall percentage when the study population was younger than 20 years (60.2%) or aged 20 to 39 years (49.5%).
The researchers noted in their discussion that the varying percentage of asymptomatic individuals according to community prevalence might impact the heterogeneity of the included studies. They also noted the high number of studies conducted in nursing home populations, groups in which asymptomatic individuals were more likely to be tested.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for missed studies that were not published at the time of the meta-analysis, as well as the exclusion of studies written in Chinese, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of follow-up on presymptomatic and covert infections, and the focus on specific populations, factors that may limit the degree to which the results can be generalized.
However, the results highlight the need to screen for asymptomatic infections, especially in countries where COVID-19 has been better controlled, the researchers said. Management strategies for asymptomatic infections, when identified, should include isolation and contact tracing similar to strategies used with confirmed cases, they added.
More testing needed to catch cases early
“During the initial phase of [the] COVID-19 pandemic, testing was not widely available in the United States or the rest of the world,” Setu Patolia, MD, of Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Missouri, said in an interview. Much of the world still lacks access to COVID-19 testing, and early in the pandemic only severely symptomatic patients were tested, he said. “With new variants, particularly the Omicron variant, which may have mild or minimally symptomatic disease, asymptomatic carriers play an important role in propagation of the pandemic,” he explained. “It is important to know the asymptomatic carrier rate among the general population for the future control of [the] pandemic,” he added.
Dr. Patolia said he was surprised by the study finding that one in 400 people in the general population could be asymptomatic carriers of COVID-19.
“Also, nursing home patients are more at risk of complications of COVID, and I expected that they would have a higher rate of symptomatic disease as compared to [the] general population,” said Dr. Patolia. He was also surprised by the high rate of asymptomatic infections in travelers.
“Physicians should be more aware about the asymptomatic carrier rate, particularly in travelers and nursing home patients,” he noted. “Travelers carry high risk of transferring infection from one region to another region of the world, and physicians should advise them to get tested despite the absence of symptoms,” Dr. Patolia emphasized. “Similarly, once any nursing home patient has been diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians should be more careful with the rest of the nursing home patients and test them despite the absence of the symptoms,” he added.
Dr. Patolia also recommended that pregnant women wear masks to help prevent disease transmission when visiting a doctor’s office or labor unit.
Looking ahead, there is a need for cheaper at-home testing kits so that all vulnerable populations can be tested fast and frequently, Dr. Patolia said.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Patolia has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases resume their climb
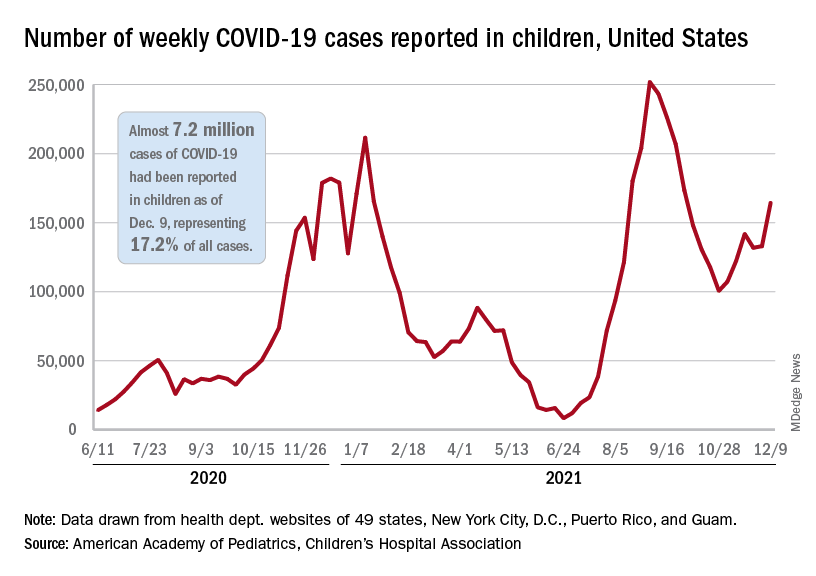
After a brief lull in activity, weekly COVID-19 cases in children returned to the upward trend that began in early November, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New COVID-19 cases were up by 23.5% for the week of Dec. 3-9, after a 2-week period that saw a drop and then just a slight increase, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly COVID report. There were 164,000 new cases from Dec. 3 to Dec. 9 in 46 states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer of 2021 and New York has never reported by age), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The increase occurred across all four regions of the country, but the largest share came in the Midwest, with over 65,000 new cases, followed by the West (just over 35,000), the Northeast (just under 35,000), and the South (close to 28,000), the AAP/CHA data show.
The 7.2 million cumulative cases in children as of Dec. 9 represent 17.2% of all cases reported in the United States since the start of the pandemic, with available state reports showing that proportion ranges from 12.3% in Florida to 26.1% in Vermont. Alaska has the highest incidence of COVID at 19,000 cases per 100,000 children, and Hawaii has the lowest (5,300 per 100,000) among the states currently reporting, the AAP and CHA said.
State reporting on vaccinations shows that 37% of children aged 5-11 years in Massachusetts have received at least one dose, the highest of any state, while West Virginia is lowest at just 4%. The highest vaccination rate for children aged 12-17 goes to Massachusetts at 84%, with Wyoming lowest at 37%, the AAP said in a separate report.
Nationally, new vaccinations fell by a third during the week of Dec. 7-13, compared with the previous week, with the largest decline (34.7%) coming from the 5- to 11-year-olds, who still represented the majority (almost 84%) of the 430,000 new child vaccinations received, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker. Corresponding declines for the last week were 27.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 22.7% for those aged 16-17.
Altogether, 21.2 million children aged 5-17 had received at least one dose and 16.0 million were fully vaccinated as of Dec. 13. By age group, 19.2% of children aged 5-11 years have gotten at least one dose and 9.6% are fully vaccinated, compared with 62.1% and 52.3%, respectively, among children aged 12-17, the CDC said.
After a brief lull in activity, weekly COVID-19 cases in children returned to the upward trend that began in early November, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New COVID-19 cases were up by 23.5% for the week of Dec. 3-9, after a 2-week period that saw a drop and then just a slight increase, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly COVID report. There were 164,000 new cases from Dec. 3 to Dec. 9 in 46 states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer of 2021 and New York has never reported by age), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The increase occurred across all four regions of the country, but the largest share came in the Midwest, with over 65,000 new cases, followed by the West (just over 35,000), the Northeast (just under 35,000), and the South (close to 28,000), the AAP/CHA data show.
The 7.2 million cumulative cases in children as of Dec. 9 represent 17.2% of all cases reported in the United States since the start of the pandemic, with available state reports showing that proportion ranges from 12.3% in Florida to 26.1% in Vermont. Alaska has the highest incidence of COVID at 19,000 cases per 100,000 children, and Hawaii has the lowest (5,300 per 100,000) among the states currently reporting, the AAP and CHA said.
State reporting on vaccinations shows that 37% of children aged 5-11 years in Massachusetts have received at least one dose, the highest of any state, while West Virginia is lowest at just 4%. The highest vaccination rate for children aged 12-17 goes to Massachusetts at 84%, with Wyoming lowest at 37%, the AAP said in a separate report.
Nationally, new vaccinations fell by a third during the week of Dec. 7-13, compared with the previous week, with the largest decline (34.7%) coming from the 5- to 11-year-olds, who still represented the majority (almost 84%) of the 430,000 new child vaccinations received, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker. Corresponding declines for the last week were 27.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 22.7% for those aged 16-17.
Altogether, 21.2 million children aged 5-17 had received at least one dose and 16.0 million were fully vaccinated as of Dec. 13. By age group, 19.2% of children aged 5-11 years have gotten at least one dose and 9.6% are fully vaccinated, compared with 62.1% and 52.3%, respectively, among children aged 12-17, the CDC said.
After a brief lull in activity, weekly COVID-19 cases in children returned to the upward trend that began in early November, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New COVID-19 cases were up by 23.5% for the week of Dec. 3-9, after a 2-week period that saw a drop and then just a slight increase, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly COVID report. There were 164,000 new cases from Dec. 3 to Dec. 9 in 46 states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer of 2021 and New York has never reported by age), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The increase occurred across all four regions of the country, but the largest share came in the Midwest, with over 65,000 new cases, followed by the West (just over 35,000), the Northeast (just under 35,000), and the South (close to 28,000), the AAP/CHA data show.
The 7.2 million cumulative cases in children as of Dec. 9 represent 17.2% of all cases reported in the United States since the start of the pandemic, with available state reports showing that proportion ranges from 12.3% in Florida to 26.1% in Vermont. Alaska has the highest incidence of COVID at 19,000 cases per 100,000 children, and Hawaii has the lowest (5,300 per 100,000) among the states currently reporting, the AAP and CHA said.
State reporting on vaccinations shows that 37% of children aged 5-11 years in Massachusetts have received at least one dose, the highest of any state, while West Virginia is lowest at just 4%. The highest vaccination rate for children aged 12-17 goes to Massachusetts at 84%, with Wyoming lowest at 37%, the AAP said in a separate report.
Nationally, new vaccinations fell by a third during the week of Dec. 7-13, compared with the previous week, with the largest decline (34.7%) coming from the 5- to 11-year-olds, who still represented the majority (almost 84%) of the 430,000 new child vaccinations received, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker. Corresponding declines for the last week were 27.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 22.7% for those aged 16-17.
Altogether, 21.2 million children aged 5-17 had received at least one dose and 16.0 million were fully vaccinated as of Dec. 13. By age group, 19.2% of children aged 5-11 years have gotten at least one dose and 9.6% are fully vaccinated, compared with 62.1% and 52.3%, respectively, among children aged 12-17, the CDC said.
Epilepsy linked to 1.5-fold higher COVID-19 mortality in hospital
according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. While the findings are preliminary and not yet adjusted for various confounders, the authors say they are a warning sign that patients with epilepsy may face higher risks.
“These findings suggest that epilepsy may be a pre-existing condition that places patients at increased risk for death if hospitalized with a COVID-19 infection. It may offer neurologists guidance when counseling patients on critical preventative measures such as masking, social distancing, and most importantly, vaccination,” lead author Claire Ufongene, a student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
According to Ms. Ufongene, there’s sparse data about COVID-19 outcomes in patients with epilepsy, although she highlighted a 2021 meta-analysis of 13 studies that found a higher risk of severity (odds ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-2.59, P = .010) and mortality (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.14-2.56, P = .010).
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked identified 334 patients with epilepsy and COVID-19 and 9,499 other patients with COVID-19 from March 15, 2020, to May 17, 2021. All were treated at hospitals within the New York–based Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The groups of patients with and without epilepsy were similar in some ways: 45% and 46%, respectively, were female (P = .674), and their ages were similar (average, 62 years and 65 years, respectively; P = .02). Racial makeup was also similar (non-Hispanic groups made up 27.8% of those with epilepsy and 24.5% of those without; the difference was not statistically significant).
“In addition, more of those with epilepsy were English speaking [83.2% vs. 77.9%] and had Medicaid insurance [50.9% vs. 38.9%], while fewer of those with epilepsy had private insurance [16.2% vs. 25.5%] or were Spanish speaking [14.0% vs. 9.3%],” study coauthor Nathalie Jette, MD, MSc, a neurologist at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said in an interview.
In terms of outcomes, patients with epilepsy were much more likely to need ventilator support (37.7% vs. 14.3%; P < .001), to be admitted to the ICU (39.2% vs. 17.7%; P < .001), and to die in the hospital (29.6% vs. 19.9%; P < .001).
“Most patients we follow in our practices with epilepsy who experienced COVID-19 in general have had symptoms similar to the general population,” Dr. Jette said. “There are rare instances where COVID-19 can result in an exacerbation of seizures in some with pre-existing epilepsy. This is not surprising as infections in particular can decrease the seizure threshold and result in breakthrough seizures in people living with epilepsy.”
Loss of seizure control
How might epilepsy be related to worse outcomes in COVID-19? Andrew Wilner, MD, a neurologist and internist at University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, who’s familiar with the study findings, said COVID-19 itself may not worsen epilepsy. “Evidence to suggest that COVID-19 directly affects the central nervous system is extremely limited. As such, one would not expect that a COVID-19 infection would cause epilepsy or exacerbate epilepsy,” he said. “However, patients with epilepsy who suffer from infections may be predisposed to decreased seizure control. Consequently, it would not be surprising if patients with epilepsy who also had COVID-19 had loss of seizure control and even status epilepticus, which could adversely affect their hospital course. However, there are no data on this potential phenomenon.”
Dr. Wilner suspected that comorbidities explain the higher mortality in patients with epilepsy. “The findings are probably most useful in that they call attention to the fact that epilepsy patients are more vulnerable to a host of comorbidities and resultant poorer outcomes due to any acute illness.”
As for treatment, Dr. Wilner urged colleagues to make sure that hospitalized patients with epilepsy “continue to receive their antiepileptic medications, which they may no longer be able to take orally. They may need to be switched temporarily to an intravenous formulation.”
In an interview, Selim Benbadis, MD, a neurologist from the University of South Florida, Tampa, suggested that antiseizure medications may play a role in the COVID-19 disease course because they can reduce the efficacy of other medications, although he noted that drug treatments for COVID-19 were limited early on. He recommended that neurologists “avoid old enzyme-inducing seizure medications, as is generally recommended.”
No study funding is reported. The study authors and Dr. Benbadis reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wilner is a medical adviser for the epilepsy disease management program for CVS/Health.
according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. While the findings are preliminary and not yet adjusted for various confounders, the authors say they are a warning sign that patients with epilepsy may face higher risks.
“These findings suggest that epilepsy may be a pre-existing condition that places patients at increased risk for death if hospitalized with a COVID-19 infection. It may offer neurologists guidance when counseling patients on critical preventative measures such as masking, social distancing, and most importantly, vaccination,” lead author Claire Ufongene, a student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
According to Ms. Ufongene, there’s sparse data about COVID-19 outcomes in patients with epilepsy, although she highlighted a 2021 meta-analysis of 13 studies that found a higher risk of severity (odds ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-2.59, P = .010) and mortality (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.14-2.56, P = .010).
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked identified 334 patients with epilepsy and COVID-19 and 9,499 other patients with COVID-19 from March 15, 2020, to May 17, 2021. All were treated at hospitals within the New York–based Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The groups of patients with and without epilepsy were similar in some ways: 45% and 46%, respectively, were female (P = .674), and their ages were similar (average, 62 years and 65 years, respectively; P = .02). Racial makeup was also similar (non-Hispanic groups made up 27.8% of those with epilepsy and 24.5% of those without; the difference was not statistically significant).
“In addition, more of those with epilepsy were English speaking [83.2% vs. 77.9%] and had Medicaid insurance [50.9% vs. 38.9%], while fewer of those with epilepsy had private insurance [16.2% vs. 25.5%] or were Spanish speaking [14.0% vs. 9.3%],” study coauthor Nathalie Jette, MD, MSc, a neurologist at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said in an interview.
In terms of outcomes, patients with epilepsy were much more likely to need ventilator support (37.7% vs. 14.3%; P < .001), to be admitted to the ICU (39.2% vs. 17.7%; P < .001), and to die in the hospital (29.6% vs. 19.9%; P < .001).
“Most patients we follow in our practices with epilepsy who experienced COVID-19 in general have had symptoms similar to the general population,” Dr. Jette said. “There are rare instances where COVID-19 can result in an exacerbation of seizures in some with pre-existing epilepsy. This is not surprising as infections in particular can decrease the seizure threshold and result in breakthrough seizures in people living with epilepsy.”
Loss of seizure control
How might epilepsy be related to worse outcomes in COVID-19? Andrew Wilner, MD, a neurologist and internist at University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, who’s familiar with the study findings, said COVID-19 itself may not worsen epilepsy. “Evidence to suggest that COVID-19 directly affects the central nervous system is extremely limited. As such, one would not expect that a COVID-19 infection would cause epilepsy or exacerbate epilepsy,” he said. “However, patients with epilepsy who suffer from infections may be predisposed to decreased seizure control. Consequently, it would not be surprising if patients with epilepsy who also had COVID-19 had loss of seizure control and even status epilepticus, which could adversely affect their hospital course. However, there are no data on this potential phenomenon.”
Dr. Wilner suspected that comorbidities explain the higher mortality in patients with epilepsy. “The findings are probably most useful in that they call attention to the fact that epilepsy patients are more vulnerable to a host of comorbidities and resultant poorer outcomes due to any acute illness.”
As for treatment, Dr. Wilner urged colleagues to make sure that hospitalized patients with epilepsy “continue to receive their antiepileptic medications, which they may no longer be able to take orally. They may need to be switched temporarily to an intravenous formulation.”
In an interview, Selim Benbadis, MD, a neurologist from the University of South Florida, Tampa, suggested that antiseizure medications may play a role in the COVID-19 disease course because they can reduce the efficacy of other medications, although he noted that drug treatments for COVID-19 were limited early on. He recommended that neurologists “avoid old enzyme-inducing seizure medications, as is generally recommended.”
No study funding is reported. The study authors and Dr. Benbadis reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wilner is a medical adviser for the epilepsy disease management program for CVS/Health.
according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. While the findings are preliminary and not yet adjusted for various confounders, the authors say they are a warning sign that patients with epilepsy may face higher risks.
“These findings suggest that epilepsy may be a pre-existing condition that places patients at increased risk for death if hospitalized with a COVID-19 infection. It may offer neurologists guidance when counseling patients on critical preventative measures such as masking, social distancing, and most importantly, vaccination,” lead author Claire Ufongene, a student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
According to Ms. Ufongene, there’s sparse data about COVID-19 outcomes in patients with epilepsy, although she highlighted a 2021 meta-analysis of 13 studies that found a higher risk of severity (odds ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-2.59, P = .010) and mortality (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.14-2.56, P = .010).
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked identified 334 patients with epilepsy and COVID-19 and 9,499 other patients with COVID-19 from March 15, 2020, to May 17, 2021. All were treated at hospitals within the New York–based Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The groups of patients with and without epilepsy were similar in some ways: 45% and 46%, respectively, were female (P = .674), and their ages were similar (average, 62 years and 65 years, respectively; P = .02). Racial makeup was also similar (non-Hispanic groups made up 27.8% of those with epilepsy and 24.5% of those without; the difference was not statistically significant).
“In addition, more of those with epilepsy were English speaking [83.2% vs. 77.9%] and had Medicaid insurance [50.9% vs. 38.9%], while fewer of those with epilepsy had private insurance [16.2% vs. 25.5%] or were Spanish speaking [14.0% vs. 9.3%],” study coauthor Nathalie Jette, MD, MSc, a neurologist at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said in an interview.
In terms of outcomes, patients with epilepsy were much more likely to need ventilator support (37.7% vs. 14.3%; P < .001), to be admitted to the ICU (39.2% vs. 17.7%; P < .001), and to die in the hospital (29.6% vs. 19.9%; P < .001).
“Most patients we follow in our practices with epilepsy who experienced COVID-19 in general have had symptoms similar to the general population,” Dr. Jette said. “There are rare instances where COVID-19 can result in an exacerbation of seizures in some with pre-existing epilepsy. This is not surprising as infections in particular can decrease the seizure threshold and result in breakthrough seizures in people living with epilepsy.”
Loss of seizure control
How might epilepsy be related to worse outcomes in COVID-19? Andrew Wilner, MD, a neurologist and internist at University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, who’s familiar with the study findings, said COVID-19 itself may not worsen epilepsy. “Evidence to suggest that COVID-19 directly affects the central nervous system is extremely limited. As such, one would not expect that a COVID-19 infection would cause epilepsy or exacerbate epilepsy,” he said. “However, patients with epilepsy who suffer from infections may be predisposed to decreased seizure control. Consequently, it would not be surprising if patients with epilepsy who also had COVID-19 had loss of seizure control and even status epilepticus, which could adversely affect their hospital course. However, there are no data on this potential phenomenon.”
Dr. Wilner suspected that comorbidities explain the higher mortality in patients with epilepsy. “The findings are probably most useful in that they call attention to the fact that epilepsy patients are more vulnerable to a host of comorbidities and resultant poorer outcomes due to any acute illness.”
As for treatment, Dr. Wilner urged colleagues to make sure that hospitalized patients with epilepsy “continue to receive their antiepileptic medications, which they may no longer be able to take orally. They may need to be switched temporarily to an intravenous formulation.”
In an interview, Selim Benbadis, MD, a neurologist from the University of South Florida, Tampa, suggested that antiseizure medications may play a role in the COVID-19 disease course because they can reduce the efficacy of other medications, although he noted that drug treatments for COVID-19 were limited early on. He recommended that neurologists “avoid old enzyme-inducing seizure medications, as is generally recommended.”
No study funding is reported. The study authors and Dr. Benbadis reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wilner is a medical adviser for the epilepsy disease management program for CVS/Health.
FROM AES 2021
Booster recommendations for pregnant women, teens, and other groups explained
These recommendations have been widened because of the continued emergence of new variants of the virus and the wane of protection over time for both vaccinations and previous disease.
The new recommendations take away some of the questions surrounding eligibility for booster vaccinations while potentially leaving some additional questions. All in all, they provide flexibility for individuals to help protect themselves against the COVID-19 virus, as many are considering celebrating the holidays with friends and family.
The first item that has become clear is that all individuals over 18 are now not only eligible for a booster vaccination a certain time after they have completed their series, but have a recommendation for one.1
But what about a fourth dose? There is a possibility that some patients should be receiving one. For those who require a three-dose series due to a condition that makes them immunocompromised, they should receive their booster vaccination six months after completion of the three-dose series. This distinction may cause confusion for some, but is important for those immunocompromised.
Boosters in women who are pregnant
The recommendations also include specific comments about individuals who are pregnant. Although initial studies did not include pregnant individuals, there has been increasing real world data that vaccination against COVID, including booster vaccinations, is safe and recommended. As pregnancy increases the risk of severe disease if infected by COVID-19, both the CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,2 along with other specialty organizations, such as the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, recommend vaccinations for pregnant individuals.
The CDC goes on to describe that there is no evidence of vaccination increasing the risk of infertility. The vaccine protects the pregnant individual and also provides protection to the baby once born. The same is true of breastfeeding individuals.3
I hope that this information allows physicians to feel comfortable recommending vaccinations and boosters to those who are pregnant and breast feeding.
Expanded recommendations for those aged 16-17 years
Recently, the CDC also expanded booster recommendations to include those aged 16-17 years, 6 months after completing their vaccine series.
Those under 18 are currently only able to receive the Pfizer-BioNtech vaccine. This new guidance has left some parents wondering if there will also be approval for booster vaccinations soon for those aged 12-16 who are approaching or have reached six months past the initial vaccine.1
Booster brand for those over 18 years?
Although the recommendation has been simplified for all over age 18 years, there is still a decision to be made about which vaccine to use as the booster.
The recommendations allow individuals to decide which brand of vaccine they would like to have as a booster. They may choose to be vaccinated with the same vaccine they originally received or with a different vaccine. This vaccine flexibility may cause confusion, but ultimately is a good thing as it allows individuals to receive whatever vaccine is available and most convenient. This also allows individuals who have been vaccinated outside of the United States by a different brand of vaccine to also receive a booster vaccination with one of the options available here.
Take home message
Overall, the expansion of booster recommendations will help everyone avoid severe disease from COVID-19 infections. Physicians now have more clarity on who should be receiving these vaccines. Along with testing, masking, and appropriate distancing, these recommendations should help prevent severe disease and death from COVID-19.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, also in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Shots. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Dec 9.
2. COVID-19 Vaccines and Pregnancy: Conversation Guide. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. 2021 November.
3. COVID-19 Vaccines While Pregnant or Breastfeeding. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Dec 6.
These recommendations have been widened because of the continued emergence of new variants of the virus and the wane of protection over time for both vaccinations and previous disease.
The new recommendations take away some of the questions surrounding eligibility for booster vaccinations while potentially leaving some additional questions. All in all, they provide flexibility for individuals to help protect themselves against the COVID-19 virus, as many are considering celebrating the holidays with friends and family.
The first item that has become clear is that all individuals over 18 are now not only eligible for a booster vaccination a certain time after they have completed their series, but have a recommendation for one.1
But what about a fourth dose? There is a possibility that some patients should be receiving one. For those who require a three-dose series due to a condition that makes them immunocompromised, they should receive their booster vaccination six months after completion of the three-dose series. This distinction may cause confusion for some, but is important for those immunocompromised.
Boosters in women who are pregnant
The recommendations also include specific comments about individuals who are pregnant. Although initial studies did not include pregnant individuals, there has been increasing real world data that vaccination against COVID, including booster vaccinations, is safe and recommended. As pregnancy increases the risk of severe disease if infected by COVID-19, both the CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,2 along with other specialty organizations, such as the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, recommend vaccinations for pregnant individuals.
The CDC goes on to describe that there is no evidence of vaccination increasing the risk of infertility. The vaccine protects the pregnant individual and also provides protection to the baby once born. The same is true of breastfeeding individuals.3
I hope that this information allows physicians to feel comfortable recommending vaccinations and boosters to those who are pregnant and breast feeding.
Expanded recommendations for those aged 16-17 years
Recently, the CDC also expanded booster recommendations to include those aged 16-17 years, 6 months after completing their vaccine series.
Those under 18 are currently only able to receive the Pfizer-BioNtech vaccine. This new guidance has left some parents wondering if there will also be approval for booster vaccinations soon for those aged 12-16 who are approaching or have reached six months past the initial vaccine.1
Booster brand for those over 18 years?
Although the recommendation has been simplified for all over age 18 years, there is still a decision to be made about which vaccine to use as the booster.
The recommendations allow individuals to decide which brand of vaccine they would like to have as a booster. They may choose to be vaccinated with the same vaccine they originally received or with a different vaccine. This vaccine flexibility may cause confusion, but ultimately is a good thing as it allows individuals to receive whatever vaccine is available and most convenient. This also allows individuals who have been vaccinated outside of the United States by a different brand of vaccine to also receive a booster vaccination with one of the options available here.
Take home message
Overall, the expansion of booster recommendations will help everyone avoid severe disease from COVID-19 infections. Physicians now have more clarity on who should be receiving these vaccines. Along with testing, masking, and appropriate distancing, these recommendations should help prevent severe disease and death from COVID-19.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, also in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Shots. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Dec 9.
2. COVID-19 Vaccines and Pregnancy: Conversation Guide. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. 2021 November.
3. COVID-19 Vaccines While Pregnant or Breastfeeding. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Dec 6.
These recommendations have been widened because of the continued emergence of new variants of the virus and the wane of protection over time for both vaccinations and previous disease.
The new recommendations take away some of the questions surrounding eligibility for booster vaccinations while potentially leaving some additional questions. All in all, they provide flexibility for individuals to help protect themselves against the COVID-19 virus, as many are considering celebrating the holidays with friends and family.
The first item that has become clear is that all individuals over 18 are now not only eligible for a booster vaccination a certain time after they have completed their series, but have a recommendation for one.1
But what about a fourth dose? There is a possibility that some patients should be receiving one. For those who require a three-dose series due to a condition that makes them immunocompromised, they should receive their booster vaccination six months after completion of the three-dose series. This distinction may cause confusion for some, but is important for those immunocompromised.
Boosters in women who are pregnant
The recommendations also include specific comments about individuals who are pregnant. Although initial studies did not include pregnant individuals, there has been increasing real world data that vaccination against COVID, including booster vaccinations, is safe and recommended. As pregnancy increases the risk of severe disease if infected by COVID-19, both the CDC and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,2 along with other specialty organizations, such as the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, recommend vaccinations for pregnant individuals.
The CDC goes on to describe that there is no evidence of vaccination increasing the risk of infertility. The vaccine protects the pregnant individual and also provides protection to the baby once born. The same is true of breastfeeding individuals.3
I hope that this information allows physicians to feel comfortable recommending vaccinations and boosters to those who are pregnant and breast feeding.
Expanded recommendations for those aged 16-17 years
Recently, the CDC also expanded booster recommendations to include those aged 16-17 years, 6 months after completing their vaccine series.
Those under 18 are currently only able to receive the Pfizer-BioNtech vaccine. This new guidance has left some parents wondering if there will also be approval for booster vaccinations soon for those aged 12-16 who are approaching or have reached six months past the initial vaccine.1
Booster brand for those over 18 years?
Although the recommendation has been simplified for all over age 18 years, there is still a decision to be made about which vaccine to use as the booster.
The recommendations allow individuals to decide which brand of vaccine they would like to have as a booster. They may choose to be vaccinated with the same vaccine they originally received or with a different vaccine. This vaccine flexibility may cause confusion, but ultimately is a good thing as it allows individuals to receive whatever vaccine is available and most convenient. This also allows individuals who have been vaccinated outside of the United States by a different brand of vaccine to also receive a booster vaccination with one of the options available here.
Take home message
Overall, the expansion of booster recommendations will help everyone avoid severe disease from COVID-19 infections. Physicians now have more clarity on who should be receiving these vaccines. Along with testing, masking, and appropriate distancing, these recommendations should help prevent severe disease and death from COVID-19.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, also in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Shots. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Dec 9.
2. COVID-19 Vaccines and Pregnancy: Conversation Guide. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. 2021 November.
3. COVID-19 Vaccines While Pregnant or Breastfeeding. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Dec 6.
12 state boards have disciplined docs for COVID misinformation
, according to a new survey from the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB).
The FSMB reports that in its 2021 annual survey two-thirds of its 71 member boards (which includes the United States, its territories, and Washington, DC) reported an increase in complaints about doctors spreading false or misleading information.
“The staggering number of state medical boards that have seen an increase in COVID-19 disinformation complaints is a sign of how widespread the issue has become,” said Humayun J. Chaudhry, DO, MACP, president and CEO of the FSMB, in a statement.
The FSMB board of directors warned physicians in July that they risked disciplinary action if they spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation or disinformation.
The organization said 15 state boards have now adopted similar statements.
Dr. Chaudhry said the FSMB was “encouraged by the number of boards that have already taken action to combat COVID-19 disinformation by disciplining physicians who engage in that behavior and by reminding all physicians that their words and actions matter, and they should think twice before spreading disinformation that may harm patients.”
This news organization asked the FSMB for further comment on why more physicians have not been disciplined, but did not receive a response before publication.
Misinformation policies a new battleground
The FSMB and member board policies on COVID-19 around the country have become a new front in the war against mandates and restrictions.
The Tennessee Board of Medical Examiners voted just recently to remove its statement of policy against the spread of misinformation from its website after a Republican lawmaker allegedly threatened to dissolve the board.
The vote came just a few months after the board had approved the policy. The board did not rescind the policy, however, according to a report by the Associated Press.
In California, the president of the state’s medical board tweeted on December 8 about what she said was an incident of harassment by a group that has promoted “fake COVID-19 treatments.”Ms. Kristina Lawson said she observed four men sitting in front of her house in a truck. They flew a drone over her residence, and then followed her to work, parking nose-to-nose with her vehicle.
Ms. Lawson claimed that when she went to drive home the four men ambushed her in what was by then a dark parking garage. She said her “concern turned to terror” as they jumped out, cameras and recording equipment in hand.
The men told law enforcement called to the scene that they were just trying to interview her, according to a statement emailed by Ms. Lawson.
They had not made such a request to the California Medical Board.
Ms. Lawson tweeted that she would continue to volunteer for the board. “That means protecting Californians from bad doctors, and ensuring disinformation and misinformation do not detract from our work to protect patients and consumers,” she wrote.
The men who ambushed Ms. Larson allegedly identified themselves and were wearing clothing emblazoned with the logo of “America’s Frontline Doctors,” an organization that has trafficked in COVID-19 conspiracy theories and promoted unproven treatments like hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin, according to Time. It is led by Simone Gold, MD, who was arrested for breaching the U.S. Capitol on January 6.
Despite her activities, on November 30, the California Medical Board renewed Ms. Gold’s 2-year license to practice.
Who’s being disciplined, who’s not
Dr. Gold is not alone. An investigation by NPRin September found that 15 of 16 physicians who have spread false information in a high-profile manner have medical licenses in good standing.
Sherri Tenpenny, DO, who has claimed that COVID-19 vaccines magnetize people and “interface” with 5G cell phone towers, was able to renew her license with the Ohio State Medical Board on October 1, according to the Cincinnati Enquirer.
Some boards have acted. The Oregon Medical Board revoked the license of Steven LaTulippe, MD, and fined him $10,000 for spreading misinformation about masks and overprescribing opioids.
In August, Rhode Island’s Board of Medical Licensure suspended Mark Brody’s license for 5 years after finding that the doctor spread falsehoods about COVID-19 vaccines, according to board documents.
Maine physician Paul Gosselin, DO, is on temporary suspension until a February hearing, while the osteopathic board investigates his issuance of vaccine exemption letters and the promotion of unproven COVID-19 therapies.
The board found that Gosselin had “engaged in conduct that constitutes fraud or deceit,” according to official documents.
The Washington State Medical Board has opened an investigation into Ryan N. Cole, MD, a physician who has claimed that COVID vaccines are “fake,” and was appointed to a regional health board in Idaho in September, according to the Washington Post.
The Idaho Capital Sun reported that Dr. Cole claims he is licensed in 11 states, including Washington. The Idaho Medical Association has also filed a complaint about Dr. Cole with the Idaho Board of Medicine, according to the paper.
New FSMB guidance coming
The FSMB said it expects more disciplinary actions as investigations continue to unfold.
The organization is drafting a new policy document that will include further guidelines and recommendations for state medical boards “to help address the spread of disinformation,” it said. The final document would be released in April 2022.
In the meantime, some states, like Tennessee and others, are trying to find ways to counter the current policy — a development the FSMB called “troubling.”
“The FSMB strongly opposes any effort to restrict a board’s authority to evaluate the standard of care and assess risk for patient harm,” the organization said in its statement.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
, according to a new survey from the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB).
The FSMB reports that in its 2021 annual survey two-thirds of its 71 member boards (which includes the United States, its territories, and Washington, DC) reported an increase in complaints about doctors spreading false or misleading information.
“The staggering number of state medical boards that have seen an increase in COVID-19 disinformation complaints is a sign of how widespread the issue has become,” said Humayun J. Chaudhry, DO, MACP, president and CEO of the FSMB, in a statement.
The FSMB board of directors warned physicians in July that they risked disciplinary action if they spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation or disinformation.
The organization said 15 state boards have now adopted similar statements.
Dr. Chaudhry said the FSMB was “encouraged by the number of boards that have already taken action to combat COVID-19 disinformation by disciplining physicians who engage in that behavior and by reminding all physicians that their words and actions matter, and they should think twice before spreading disinformation that may harm patients.”
This news organization asked the FSMB for further comment on why more physicians have not been disciplined, but did not receive a response before publication.
Misinformation policies a new battleground
The FSMB and member board policies on COVID-19 around the country have become a new front in the war against mandates and restrictions.
The Tennessee Board of Medical Examiners voted just recently to remove its statement of policy against the spread of misinformation from its website after a Republican lawmaker allegedly threatened to dissolve the board.
The vote came just a few months after the board had approved the policy. The board did not rescind the policy, however, according to a report by the Associated Press.
In California, the president of the state’s medical board tweeted on December 8 about what she said was an incident of harassment by a group that has promoted “fake COVID-19 treatments.”Ms. Kristina Lawson said she observed four men sitting in front of her house in a truck. They flew a drone over her residence, and then followed her to work, parking nose-to-nose with her vehicle.
Ms. Lawson claimed that when she went to drive home the four men ambushed her in what was by then a dark parking garage. She said her “concern turned to terror” as they jumped out, cameras and recording equipment in hand.
The men told law enforcement called to the scene that they were just trying to interview her, according to a statement emailed by Ms. Lawson.
They had not made such a request to the California Medical Board.
Ms. Lawson tweeted that she would continue to volunteer for the board. “That means protecting Californians from bad doctors, and ensuring disinformation and misinformation do not detract from our work to protect patients and consumers,” she wrote.
The men who ambushed Ms. Larson allegedly identified themselves and were wearing clothing emblazoned with the logo of “America’s Frontline Doctors,” an organization that has trafficked in COVID-19 conspiracy theories and promoted unproven treatments like hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin, according to Time. It is led by Simone Gold, MD, who was arrested for breaching the U.S. Capitol on January 6.
Despite her activities, on November 30, the California Medical Board renewed Ms. Gold’s 2-year license to practice.
Who’s being disciplined, who’s not
Dr. Gold is not alone. An investigation by NPRin September found that 15 of 16 physicians who have spread false information in a high-profile manner have medical licenses in good standing.
Sherri Tenpenny, DO, who has claimed that COVID-19 vaccines magnetize people and “interface” with 5G cell phone towers, was able to renew her license with the Ohio State Medical Board on October 1, according to the Cincinnati Enquirer.
Some boards have acted. The Oregon Medical Board revoked the license of Steven LaTulippe, MD, and fined him $10,000 for spreading misinformation about masks and overprescribing opioids.
In August, Rhode Island’s Board of Medical Licensure suspended Mark Brody’s license for 5 years after finding that the doctor spread falsehoods about COVID-19 vaccines, according to board documents.
Maine physician Paul Gosselin, DO, is on temporary suspension until a February hearing, while the osteopathic board investigates his issuance of vaccine exemption letters and the promotion of unproven COVID-19 therapies.
The board found that Gosselin had “engaged in conduct that constitutes fraud or deceit,” according to official documents.
The Washington State Medical Board has opened an investigation into Ryan N. Cole, MD, a physician who has claimed that COVID vaccines are “fake,” and was appointed to a regional health board in Idaho in September, according to the Washington Post.
The Idaho Capital Sun reported that Dr. Cole claims he is licensed in 11 states, including Washington. The Idaho Medical Association has also filed a complaint about Dr. Cole with the Idaho Board of Medicine, according to the paper.
New FSMB guidance coming
The FSMB said it expects more disciplinary actions as investigations continue to unfold.
The organization is drafting a new policy document that will include further guidelines and recommendations for state medical boards “to help address the spread of disinformation,” it said. The final document would be released in April 2022.
In the meantime, some states, like Tennessee and others, are trying to find ways to counter the current policy — a development the FSMB called “troubling.”
“The FSMB strongly opposes any effort to restrict a board’s authority to evaluate the standard of care and assess risk for patient harm,” the organization said in its statement.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
, according to a new survey from the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB).
The FSMB reports that in its 2021 annual survey two-thirds of its 71 member boards (which includes the United States, its territories, and Washington, DC) reported an increase in complaints about doctors spreading false or misleading information.
“The staggering number of state medical boards that have seen an increase in COVID-19 disinformation complaints is a sign of how widespread the issue has become,” said Humayun J. Chaudhry, DO, MACP, president and CEO of the FSMB, in a statement.
The FSMB board of directors warned physicians in July that they risked disciplinary action if they spread COVID-19 vaccine misinformation or disinformation.
The organization said 15 state boards have now adopted similar statements.
Dr. Chaudhry said the FSMB was “encouraged by the number of boards that have already taken action to combat COVID-19 disinformation by disciplining physicians who engage in that behavior and by reminding all physicians that their words and actions matter, and they should think twice before spreading disinformation that may harm patients.”
This news organization asked the FSMB for further comment on why more physicians have not been disciplined, but did not receive a response before publication.
Misinformation policies a new battleground
The FSMB and member board policies on COVID-19 around the country have become a new front in the war against mandates and restrictions.
The Tennessee Board of Medical Examiners voted just recently to remove its statement of policy against the spread of misinformation from its website after a Republican lawmaker allegedly threatened to dissolve the board.
The vote came just a few months after the board had approved the policy. The board did not rescind the policy, however, according to a report by the Associated Press.
In California, the president of the state’s medical board tweeted on December 8 about what she said was an incident of harassment by a group that has promoted “fake COVID-19 treatments.”Ms. Kristina Lawson said she observed four men sitting in front of her house in a truck. They flew a drone over her residence, and then followed her to work, parking nose-to-nose with her vehicle.
Ms. Lawson claimed that when she went to drive home the four men ambushed her in what was by then a dark parking garage. She said her “concern turned to terror” as they jumped out, cameras and recording equipment in hand.
The men told law enforcement called to the scene that they were just trying to interview her, according to a statement emailed by Ms. Lawson.
They had not made such a request to the California Medical Board.
Ms. Lawson tweeted that she would continue to volunteer for the board. “That means protecting Californians from bad doctors, and ensuring disinformation and misinformation do not detract from our work to protect patients and consumers,” she wrote.
The men who ambushed Ms. Larson allegedly identified themselves and were wearing clothing emblazoned with the logo of “America’s Frontline Doctors,” an organization that has trafficked in COVID-19 conspiracy theories and promoted unproven treatments like hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin, according to Time. It is led by Simone Gold, MD, who was arrested for breaching the U.S. Capitol on January 6.
Despite her activities, on November 30, the California Medical Board renewed Ms. Gold’s 2-year license to practice.
Who’s being disciplined, who’s not
Dr. Gold is not alone. An investigation by NPRin September found that 15 of 16 physicians who have spread false information in a high-profile manner have medical licenses in good standing.
Sherri Tenpenny, DO, who has claimed that COVID-19 vaccines magnetize people and “interface” with 5G cell phone towers, was able to renew her license with the Ohio State Medical Board on October 1, according to the Cincinnati Enquirer.
Some boards have acted. The Oregon Medical Board revoked the license of Steven LaTulippe, MD, and fined him $10,000 for spreading misinformation about masks and overprescribing opioids.
In August, Rhode Island’s Board of Medical Licensure suspended Mark Brody’s license for 5 years after finding that the doctor spread falsehoods about COVID-19 vaccines, according to board documents.
Maine physician Paul Gosselin, DO, is on temporary suspension until a February hearing, while the osteopathic board investigates his issuance of vaccine exemption letters and the promotion of unproven COVID-19 therapies.
The board found that Gosselin had “engaged in conduct that constitutes fraud or deceit,” according to official documents.
The Washington State Medical Board has opened an investigation into Ryan N. Cole, MD, a physician who has claimed that COVID vaccines are “fake,” and was appointed to a regional health board in Idaho in September, according to the Washington Post.
The Idaho Capital Sun reported that Dr. Cole claims he is licensed in 11 states, including Washington. The Idaho Medical Association has also filed a complaint about Dr. Cole with the Idaho Board of Medicine, according to the paper.
New FSMB guidance coming
The FSMB said it expects more disciplinary actions as investigations continue to unfold.
The organization is drafting a new policy document that will include further guidelines and recommendations for state medical boards “to help address the spread of disinformation,” it said. The final document would be released in April 2022.
In the meantime, some states, like Tennessee and others, are trying to find ways to counter the current policy — a development the FSMB called “troubling.”
“The FSMB strongly opposes any effort to restrict a board’s authority to evaluate the standard of care and assess risk for patient harm,” the organization said in its statement.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
Lung transplantation in the era of COVID-19: New issues and paradigms
Data is sparse thus far, but there is concern in lung transplant medicine about the long-term risk of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) and a potentially shortened longevity of transplanted lungs in recipients who become ill with COVID-19.
“My fear is that we’re potentially sitting on this iceberg worth of people who, come 6 months or a year from [the acute phase of] their COVID illness, will in fact have earlier and progressive, chronic rejection,” said Cameron R. Wolfe, MBBS, MPH, associate professor of medicine in transplant infectious disease at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Lower respiratory viral infections have long been concerning for lung transplant recipients given their propensity to cause scarring, a decline in lung function, and a heightened risk of allograft rejection. Time will tell whether lung transplant recipients who survive COVID-19 follow a similar path, or one that is worse, he said.
Short-term data
Outcomes beyond hospitalization and acute illness for lung transplant recipients affected by COVID-19 have been reported in the literature by only a few lung transplant programs. These reports – as well as anecdotal experiences being informally shared among transplant programs – have raised the specter of more severe dysfunction following the acute phase and more early CLAD, said Tathagat Narula, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and a consultant in lung transplantation at the Mayo Clinic’s Jacksonville program.
“The available data cover only 3-6 months out. We don’t know what will happen in the next 6 months and beyond,” Dr. Narula said in an interview.
The risks of COVID-19 in already-transplanted patients and issues relating to the inadequate antibody responses to vaccination are just some of the challenges of lung transplant medicine in the era of SARS-CoV-2. “COVID-19,” said Dr. Narula, “has completely changed the way we practice lung transplant medicine – the way we’re looking both at our recipients and our donors.”
Potential donors are being evaluated with lower respiratory SARS-CoV-2 testing and an abundance of caution. And patients with severe COVID-19 affecting their own lungs are roundly expected to drive up lung transplant volume in the near future. “The whole paradigm has changed,” Dr. Narula said.
Post-acute trajectories
A chart review study published in October by the lung transplant team at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, covered 44 consecutive survivors at a median follow-up of 4.5 months from hospital discharge or acute illness (the survival rate was 83.3%). Patients had significantly impaired functional status, and 18 of the 44 (40.9%) had a significant and persistent loss of forced vital capacity or forced expiratory volume in 1 second (>10% from pre–COVID-19 baseline).
Three patients met the criteria for new CLAD after COVID-19 infection, with all three classified as restrictive allograft syndrome (RAS) phenotype.
Moreover, the majority of COVID-19 survivors who had CT chest scans (22 of 28) showed persistent parenchymal opacities – a finding that, regardless of symptomatology, suggests persistent allograft injury, said Amit Banga, MD, associate professor of medicine and medical director of the ex vivo lung perfusion program in UT Southwestern’s lung transplant program.
“The implication is that there may be long-term consequences of COVID-19, perhaps related to some degree of ongoing inflammation and damage,” said Dr. Banga, a coauthor of the postinfection outcomes paper.
The UT Southwestern lung transplant program, which normally performs 60-80 transplants a year, began routine CT scanning 4-5 months into the pandemic, after “stumbling into a few patients who had no symptoms indicative of COVID pneumonia and no changes on an x-ray but significant involvement on a CT,” he said.
Without routine scanning in the general population of COVID-19 patients, Dr. Banga noted, “we’re limited in convincingly saying that COVID is uniquely doing this to lung transplant recipients.” Nor can they conclude that SARS-CoV-2 is unique from other respiratory viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in this regard. (The program has added CT scanning to its protocol for lung transplant recipients afflicted with other respiratory viruses to learn more.)
However, in the big picture, COVID-19 has proven to be far worse for lung transplant recipients than illness with other respiratory viruses, including RSV. “Patients have more frequent and greater loss of lung function, and worse debility from the acute illness,” Dr. Banga said.
“The cornerstones of treatment of both these viruses are very similar, but both the in-hospital course and the postdischarge outcomes are significantly different.”
In an initial paper published in September 2021, Dr. Banga and colleagues compared their first 25 lung transplant patients testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 with a historical cohort of 36 patients with RSV treated during 2016-2018.
Patients with COVID-19 had significantly worse morbidity and mortality, including worse postinfection lung function loss, functional decline, and 3-month survival.
More time, he said, will shed light on the risks of CLAD and the long-term potential for recovery of lung function. Currently, at UT Southwestern, it appears that patients who survive acute illness and the “first 3-6 months after COVID-19, when we’re seeing all the postinfection morbidity, may [enter] a period of stability,” Dr. Banga said.
Overall, he said, patients in their initial cohort are “holding steady” without unusual morbidity, readmissions, or “other setbacks to their allografts.”
At the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, which normally performs 40-50 lung transplants a year, transplant physicians have similarly observed significant declines in lung function beyond the acute phase of COVID-19. “Anecdotally, we’re seeing that some patients are beginning to recover some of their lung function, while others have not,” said Dr. Narula. “And we don’t have predictors as to who will progress to CLAD. It’s a big knowledge gap.”
Dr. Narula noted that patients with restrictive allograft syndrome, such as those reported by the UT Southwestern team, “have scarring of the lung and a much worse prognosis than the obstructive type of chronic rejection.” Whether there’s a role for antifibrotic therapy is a question worthy of research.
In UT Southwestern’s analysis, persistently lower absolute lymphocyte counts (< 600/dL) and higher ferritin levels (>150 ng/mL) at the time of hospital discharge were independently associated with significant lung function loss. This finding, reported in their October paper, has helped guide their management practices, Dr. Banga said.
“Persistently elevated ferritin may indicate ongoing inflammation at the allograft level,” he said. “We now send [such patients] home on a longer course of oral corticosteroids.”
At the front end of care for infected lung transplant recipients, Dr. Banga said that his team and physicians at other lung transplant programs are holding the cell-cycle inhibitor component of patients’ maintenance immunosuppression therapy (commonly mycophenolate or azathioprine) once infection is diagnosed to maximize chances of a better outcome.
“There may be variation on how long [the regimens are adjusted],” he said. “We changed our duration from 4 weeks to 2 due to patients developing a rebound worsening in the third and fourth week of acute illness.”
There is significant variation from institution to institution in how viral infections are managed in lung transplant recipients, he and Dr. Narula said. “Our numbers are so small in lung transplant, and we don’t have standardized protocols – it’s one of the biggest challenges in our field,” said Dr. Narula.
Vaccination issues, evaluation of donors
Whether or not immunosuppression regimens should be adjusted prior to vaccination is a controversial question, but is “an absolutely valid one” and is currently being studied in at least one National Institutes of Health–funded trial involving solid organ transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe.
“Some have jumped to the conclusion [based on some earlier data] that they should reduce immunosuppression regimens for everyone at the time of vaccination ... but I don’t know the answer yet,” he said. “Balancing staying rejection free with potentially gaining more immune response is complicated ... and it may depend on where the pandemic is going in your area and other factors.”
Reductions aside, Dr. Wolfe tells lung transplant recipients that, based on his approximation of a number of different studies in solid organ transplant recipients, approximately 40%-50% of patients who are immunized with two doses of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines will develop meaningful antibody levels – and that this rises to 50%-60% after a third dose.
It is difficult to glean from available studies the level of vaccine response for lung transplant recipients specifically. But given that their level of maintenance immunosuppression is higher than for recipients of other donor organs, “as a broad sweep, lung transplant recipients tend to be lower in the pecking order of response,” he said.
Still, “there’s a lot to gain,” he said, pointing to a recent study from the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (2021 Nov 5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7044e3) showing that effectiveness of mRNA vaccination against COVID-19–associated hospitalization was 77% among immunocompromised adults (compared with 90% in immunocompetent adults).
“This is good vindication to keep vaccinating,” he said, “and perhaps speaks to how difficult it is to assess the vaccine response [through measurement of antibody only].”
Neither Duke University’s transplant program, which performed 100-120 lung transplants a year pre-COVID, nor the programs at UT Southwestern or the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville require that solid organ transplant candidates be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 in order to receive transplants, as some other transplant programs have done. (When asked about the issue, Dr. Banga and Dr. Narula each said that they have had no or little trouble convincing patients awaiting lung transplants of the need for COVID-19 vaccination.)
In an August statement, the American Society of Transplantation recommended vaccination for all solid organ transplant recipients, preferably prior to transplantation, and said that it “support[s] the development of institutional policies regarding pretransplant vaccination.”
The Society is not tracking centers’ vaccination policies. But Kaiser Health News reported in October that a growing number of transplant programs, such as UCHealth in Denver and UW Medicine in Seattle, have decided to either bar patients who refuse to be vaccinated from receiving transplants or give them lower priority on waitlists.
Potential lung donors, meanwhile, must be evaluated with lower respiratory COVID-19 testing, with results available prior to transplantation, according to policy developed by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network and effective in May 2021. The policy followed three published cases of donor-derived COVID-19 in lung transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe, who wrote about use of COVID-positive donors in an editorial published in October.
In each case, the donor had a negative COVID-19 nasopharyngeal swab at the time of organ procurement but was later found to have the virus on bronchoalveolar lavage, he said.
(The use of other organs from COVID-positive donors is appearing thus far to be safe, Dr. Wolfe noted. In the editorial, he references 13 cases of solid organ transplantation from SARS-CoV-2–infected donors into noninfected recipients; none of the 13 transplant recipients developed COVID-19).
Some questions remain, such as how many lower respiratory tests should be run, and how donors should be evaluated in cases of discordant results. Dr. Banga shared the case of a donor with one positive lower respiratory test result followed by two negative results. After internal debate, and consideration of potential false positives and other issues, the team at UT Southwestern decided to decline the donor, Dr. Banga said.
Other programs are likely making similar, appropriately cautious decisions, said Dr. Wolfe. “There’s no way in real-time donor evaluation to know whether the positive test is active virus that could infect the recipient and replicate ... or whether it’s [picking up] inactive or dead fragments of virus that was there several weeks ago. Our tests don’t differentiate that.”
Transplants in COVID-19 patients
Decision-making about lung transplant candidacy among patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome is complex and in need of a new paradigm.
“Some of these patients have the potential to recover, and they’re going to recover way later than what we’re used to,” said Dr. Banga. “We can’t extrapolate for COVID ARDS what we’ve learned for any other virus-related ARDS.”
Dr. Narula also has recently seen at least one COVID-19 patient on ECMO and under evaluation for transplantation recover. “We do not want to transplant too early,” he said, noting that there is consensus that lung transplant should be pursued only when the damage is deemed irreversible clinically and radiologically in the best judgment of the team. Still, “for many of these patients the only exit route will be lung transplants. For the next 12-24 months, a significant proportion of our lung transplant patients will have had post-COVID–related lung damage.”
As of October 2021, 233 lung transplants had been performed in the United States in recipients whose primary diagnosis was reported as COVID related, said Anne Paschke, media relations specialist with the United Network for Organ Sharing.
Dr. Banga, Dr. Wolfe, and Dr. Narula reported that they have no relevant disclosures.
Data is sparse thus far, but there is concern in lung transplant medicine about the long-term risk of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) and a potentially shortened longevity of transplanted lungs in recipients who become ill with COVID-19.
“My fear is that we’re potentially sitting on this iceberg worth of people who, come 6 months or a year from [the acute phase of] their COVID illness, will in fact have earlier and progressive, chronic rejection,” said Cameron R. Wolfe, MBBS, MPH, associate professor of medicine in transplant infectious disease at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Lower respiratory viral infections have long been concerning for lung transplant recipients given their propensity to cause scarring, a decline in lung function, and a heightened risk of allograft rejection. Time will tell whether lung transplant recipients who survive COVID-19 follow a similar path, or one that is worse, he said.
Short-term data
Outcomes beyond hospitalization and acute illness for lung transplant recipients affected by COVID-19 have been reported in the literature by only a few lung transplant programs. These reports – as well as anecdotal experiences being informally shared among transplant programs – have raised the specter of more severe dysfunction following the acute phase and more early CLAD, said Tathagat Narula, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and a consultant in lung transplantation at the Mayo Clinic’s Jacksonville program.
“The available data cover only 3-6 months out. We don’t know what will happen in the next 6 months and beyond,” Dr. Narula said in an interview.
The risks of COVID-19 in already-transplanted patients and issues relating to the inadequate antibody responses to vaccination are just some of the challenges of lung transplant medicine in the era of SARS-CoV-2. “COVID-19,” said Dr. Narula, “has completely changed the way we practice lung transplant medicine – the way we’re looking both at our recipients and our donors.”
Potential donors are being evaluated with lower respiratory SARS-CoV-2 testing and an abundance of caution. And patients with severe COVID-19 affecting their own lungs are roundly expected to drive up lung transplant volume in the near future. “The whole paradigm has changed,” Dr. Narula said.
Post-acute trajectories
A chart review study published in October by the lung transplant team at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, covered 44 consecutive survivors at a median follow-up of 4.5 months from hospital discharge or acute illness (the survival rate was 83.3%). Patients had significantly impaired functional status, and 18 of the 44 (40.9%) had a significant and persistent loss of forced vital capacity or forced expiratory volume in 1 second (>10% from pre–COVID-19 baseline).
Three patients met the criteria for new CLAD after COVID-19 infection, with all three classified as restrictive allograft syndrome (RAS) phenotype.
Moreover, the majority of COVID-19 survivors who had CT chest scans (22 of 28) showed persistent parenchymal opacities – a finding that, regardless of symptomatology, suggests persistent allograft injury, said Amit Banga, MD, associate professor of medicine and medical director of the ex vivo lung perfusion program in UT Southwestern’s lung transplant program.
“The implication is that there may be long-term consequences of COVID-19, perhaps related to some degree of ongoing inflammation and damage,” said Dr. Banga, a coauthor of the postinfection outcomes paper.
The UT Southwestern lung transplant program, which normally performs 60-80 transplants a year, began routine CT scanning 4-5 months into the pandemic, after “stumbling into a few patients who had no symptoms indicative of COVID pneumonia and no changes on an x-ray but significant involvement on a CT,” he said.
Without routine scanning in the general population of COVID-19 patients, Dr. Banga noted, “we’re limited in convincingly saying that COVID is uniquely doing this to lung transplant recipients.” Nor can they conclude that SARS-CoV-2 is unique from other respiratory viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in this regard. (The program has added CT scanning to its protocol for lung transplant recipients afflicted with other respiratory viruses to learn more.)
However, in the big picture, COVID-19 has proven to be far worse for lung transplant recipients than illness with other respiratory viruses, including RSV. “Patients have more frequent and greater loss of lung function, and worse debility from the acute illness,” Dr. Banga said.
“The cornerstones of treatment of both these viruses are very similar, but both the in-hospital course and the postdischarge outcomes are significantly different.”
In an initial paper published in September 2021, Dr. Banga and colleagues compared their first 25 lung transplant patients testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 with a historical cohort of 36 patients with RSV treated during 2016-2018.
Patients with COVID-19 had significantly worse morbidity and mortality, including worse postinfection lung function loss, functional decline, and 3-month survival.
More time, he said, will shed light on the risks of CLAD and the long-term potential for recovery of lung function. Currently, at UT Southwestern, it appears that patients who survive acute illness and the “first 3-6 months after COVID-19, when we’re seeing all the postinfection morbidity, may [enter] a period of stability,” Dr. Banga said.
Overall, he said, patients in their initial cohort are “holding steady” without unusual morbidity, readmissions, or “other setbacks to their allografts.”
At the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, which normally performs 40-50 lung transplants a year, transplant physicians have similarly observed significant declines in lung function beyond the acute phase of COVID-19. “Anecdotally, we’re seeing that some patients are beginning to recover some of their lung function, while others have not,” said Dr. Narula. “And we don’t have predictors as to who will progress to CLAD. It’s a big knowledge gap.”
Dr. Narula noted that patients with restrictive allograft syndrome, such as those reported by the UT Southwestern team, “have scarring of the lung and a much worse prognosis than the obstructive type of chronic rejection.” Whether there’s a role for antifibrotic therapy is a question worthy of research.
In UT Southwestern’s analysis, persistently lower absolute lymphocyte counts (< 600/dL) and higher ferritin levels (>150 ng/mL) at the time of hospital discharge were independently associated with significant lung function loss. This finding, reported in their October paper, has helped guide their management practices, Dr. Banga said.
“Persistently elevated ferritin may indicate ongoing inflammation at the allograft level,” he said. “We now send [such patients] home on a longer course of oral corticosteroids.”
At the front end of care for infected lung transplant recipients, Dr. Banga said that his team and physicians at other lung transplant programs are holding the cell-cycle inhibitor component of patients’ maintenance immunosuppression therapy (commonly mycophenolate or azathioprine) once infection is diagnosed to maximize chances of a better outcome.
“There may be variation on how long [the regimens are adjusted],” he said. “We changed our duration from 4 weeks to 2 due to patients developing a rebound worsening in the third and fourth week of acute illness.”
There is significant variation from institution to institution in how viral infections are managed in lung transplant recipients, he and Dr. Narula said. “Our numbers are so small in lung transplant, and we don’t have standardized protocols – it’s one of the biggest challenges in our field,” said Dr. Narula.
Vaccination issues, evaluation of donors
Whether or not immunosuppression regimens should be adjusted prior to vaccination is a controversial question, but is “an absolutely valid one” and is currently being studied in at least one National Institutes of Health–funded trial involving solid organ transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe.
“Some have jumped to the conclusion [based on some earlier data] that they should reduce immunosuppression regimens for everyone at the time of vaccination ... but I don’t know the answer yet,” he said. “Balancing staying rejection free with potentially gaining more immune response is complicated ... and it may depend on where the pandemic is going in your area and other factors.”
Reductions aside, Dr. Wolfe tells lung transplant recipients that, based on his approximation of a number of different studies in solid organ transplant recipients, approximately 40%-50% of patients who are immunized with two doses of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines will develop meaningful antibody levels – and that this rises to 50%-60% after a third dose.
It is difficult to glean from available studies the level of vaccine response for lung transplant recipients specifically. But given that their level of maintenance immunosuppression is higher than for recipients of other donor organs, “as a broad sweep, lung transplant recipients tend to be lower in the pecking order of response,” he said.
Still, “there’s a lot to gain,” he said, pointing to a recent study from the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (2021 Nov 5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7044e3) showing that effectiveness of mRNA vaccination against COVID-19–associated hospitalization was 77% among immunocompromised adults (compared with 90% in immunocompetent adults).
“This is good vindication to keep vaccinating,” he said, “and perhaps speaks to how difficult it is to assess the vaccine response [through measurement of antibody only].”
Neither Duke University’s transplant program, which performed 100-120 lung transplants a year pre-COVID, nor the programs at UT Southwestern or the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville require that solid organ transplant candidates be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 in order to receive transplants, as some other transplant programs have done. (When asked about the issue, Dr. Banga and Dr. Narula each said that they have had no or little trouble convincing patients awaiting lung transplants of the need for COVID-19 vaccination.)
In an August statement, the American Society of Transplantation recommended vaccination for all solid organ transplant recipients, preferably prior to transplantation, and said that it “support[s] the development of institutional policies regarding pretransplant vaccination.”
The Society is not tracking centers’ vaccination policies. But Kaiser Health News reported in October that a growing number of transplant programs, such as UCHealth in Denver and UW Medicine in Seattle, have decided to either bar patients who refuse to be vaccinated from receiving transplants or give them lower priority on waitlists.
Potential lung donors, meanwhile, must be evaluated with lower respiratory COVID-19 testing, with results available prior to transplantation, according to policy developed by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network and effective in May 2021. The policy followed three published cases of donor-derived COVID-19 in lung transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe, who wrote about use of COVID-positive donors in an editorial published in October.
In each case, the donor had a negative COVID-19 nasopharyngeal swab at the time of organ procurement but was later found to have the virus on bronchoalveolar lavage, he said.
(The use of other organs from COVID-positive donors is appearing thus far to be safe, Dr. Wolfe noted. In the editorial, he references 13 cases of solid organ transplantation from SARS-CoV-2–infected donors into noninfected recipients; none of the 13 transplant recipients developed COVID-19).
Some questions remain, such as how many lower respiratory tests should be run, and how donors should be evaluated in cases of discordant results. Dr. Banga shared the case of a donor with one positive lower respiratory test result followed by two negative results. After internal debate, and consideration of potential false positives and other issues, the team at UT Southwestern decided to decline the donor, Dr. Banga said.
Other programs are likely making similar, appropriately cautious decisions, said Dr. Wolfe. “There’s no way in real-time donor evaluation to know whether the positive test is active virus that could infect the recipient and replicate ... or whether it’s [picking up] inactive or dead fragments of virus that was there several weeks ago. Our tests don’t differentiate that.”
Transplants in COVID-19 patients
Decision-making about lung transplant candidacy among patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome is complex and in need of a new paradigm.
“Some of these patients have the potential to recover, and they’re going to recover way later than what we’re used to,” said Dr. Banga. “We can’t extrapolate for COVID ARDS what we’ve learned for any other virus-related ARDS.”
Dr. Narula also has recently seen at least one COVID-19 patient on ECMO and under evaluation for transplantation recover. “We do not want to transplant too early,” he said, noting that there is consensus that lung transplant should be pursued only when the damage is deemed irreversible clinically and radiologically in the best judgment of the team. Still, “for many of these patients the only exit route will be lung transplants. For the next 12-24 months, a significant proportion of our lung transplant patients will have had post-COVID–related lung damage.”
As of October 2021, 233 lung transplants had been performed in the United States in recipients whose primary diagnosis was reported as COVID related, said Anne Paschke, media relations specialist with the United Network for Organ Sharing.
Dr. Banga, Dr. Wolfe, and Dr. Narula reported that they have no relevant disclosures.
Data is sparse thus far, but there is concern in lung transplant medicine about the long-term risk of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) and a potentially shortened longevity of transplanted lungs in recipients who become ill with COVID-19.
“My fear is that we’re potentially sitting on this iceberg worth of people who, come 6 months or a year from [the acute phase of] their COVID illness, will in fact have earlier and progressive, chronic rejection,” said Cameron R. Wolfe, MBBS, MPH, associate professor of medicine in transplant infectious disease at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Lower respiratory viral infections have long been concerning for lung transplant recipients given their propensity to cause scarring, a decline in lung function, and a heightened risk of allograft rejection. Time will tell whether lung transplant recipients who survive COVID-19 follow a similar path, or one that is worse, he said.
Short-term data
Outcomes beyond hospitalization and acute illness for lung transplant recipients affected by COVID-19 have been reported in the literature by only a few lung transplant programs. These reports – as well as anecdotal experiences being informally shared among transplant programs – have raised the specter of more severe dysfunction following the acute phase and more early CLAD, said Tathagat Narula, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and a consultant in lung transplantation at the Mayo Clinic’s Jacksonville program.
“The available data cover only 3-6 months out. We don’t know what will happen in the next 6 months and beyond,” Dr. Narula said in an interview.
The risks of COVID-19 in already-transplanted patients and issues relating to the inadequate antibody responses to vaccination are just some of the challenges of lung transplant medicine in the era of SARS-CoV-2. “COVID-19,” said Dr. Narula, “has completely changed the way we practice lung transplant medicine – the way we’re looking both at our recipients and our donors.”
Potential donors are being evaluated with lower respiratory SARS-CoV-2 testing and an abundance of caution. And patients with severe COVID-19 affecting their own lungs are roundly expected to drive up lung transplant volume in the near future. “The whole paradigm has changed,” Dr. Narula said.
Post-acute trajectories
A chart review study published in October by the lung transplant team at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, covered 44 consecutive survivors at a median follow-up of 4.5 months from hospital discharge or acute illness (the survival rate was 83.3%). Patients had significantly impaired functional status, and 18 of the 44 (40.9%) had a significant and persistent loss of forced vital capacity or forced expiratory volume in 1 second (>10% from pre–COVID-19 baseline).
Three patients met the criteria for new CLAD after COVID-19 infection, with all three classified as restrictive allograft syndrome (RAS) phenotype.
Moreover, the majority of COVID-19 survivors who had CT chest scans (22 of 28) showed persistent parenchymal opacities – a finding that, regardless of symptomatology, suggests persistent allograft injury, said Amit Banga, MD, associate professor of medicine and medical director of the ex vivo lung perfusion program in UT Southwestern’s lung transplant program.
“The implication is that there may be long-term consequences of COVID-19, perhaps related to some degree of ongoing inflammation and damage,” said Dr. Banga, a coauthor of the postinfection outcomes paper.
The UT Southwestern lung transplant program, which normally performs 60-80 transplants a year, began routine CT scanning 4-5 months into the pandemic, after “stumbling into a few patients who had no symptoms indicative of COVID pneumonia and no changes on an x-ray but significant involvement on a CT,” he said.
Without routine scanning in the general population of COVID-19 patients, Dr. Banga noted, “we’re limited in convincingly saying that COVID is uniquely doing this to lung transplant recipients.” Nor can they conclude that SARS-CoV-2 is unique from other respiratory viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in this regard. (The program has added CT scanning to its protocol for lung transplant recipients afflicted with other respiratory viruses to learn more.)
However, in the big picture, COVID-19 has proven to be far worse for lung transplant recipients than illness with other respiratory viruses, including RSV. “Patients have more frequent and greater loss of lung function, and worse debility from the acute illness,” Dr. Banga said.
“The cornerstones of treatment of both these viruses are very similar, but both the in-hospital course and the postdischarge outcomes are significantly different.”
In an initial paper published in September 2021, Dr. Banga and colleagues compared their first 25 lung transplant patients testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 with a historical cohort of 36 patients with RSV treated during 2016-2018.
Patients with COVID-19 had significantly worse morbidity and mortality, including worse postinfection lung function loss, functional decline, and 3-month survival.
More time, he said, will shed light on the risks of CLAD and the long-term potential for recovery of lung function. Currently, at UT Southwestern, it appears that patients who survive acute illness and the “first 3-6 months after COVID-19, when we’re seeing all the postinfection morbidity, may [enter] a period of stability,” Dr. Banga said.
Overall, he said, patients in their initial cohort are “holding steady” without unusual morbidity, readmissions, or “other setbacks to their allografts.”
At the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, which normally performs 40-50 lung transplants a year, transplant physicians have similarly observed significant declines in lung function beyond the acute phase of COVID-19. “Anecdotally, we’re seeing that some patients are beginning to recover some of their lung function, while others have not,” said Dr. Narula. “And we don’t have predictors as to who will progress to CLAD. It’s a big knowledge gap.”
Dr. Narula noted that patients with restrictive allograft syndrome, such as those reported by the UT Southwestern team, “have scarring of the lung and a much worse prognosis than the obstructive type of chronic rejection.” Whether there’s a role for antifibrotic therapy is a question worthy of research.
In UT Southwestern’s analysis, persistently lower absolute lymphocyte counts (< 600/dL) and higher ferritin levels (>150 ng/mL) at the time of hospital discharge were independently associated with significant lung function loss. This finding, reported in their October paper, has helped guide their management practices, Dr. Banga said.
“Persistently elevated ferritin may indicate ongoing inflammation at the allograft level,” he said. “We now send [such patients] home on a longer course of oral corticosteroids.”
At the front end of care for infected lung transplant recipients, Dr. Banga said that his team and physicians at other lung transplant programs are holding the cell-cycle inhibitor component of patients’ maintenance immunosuppression therapy (commonly mycophenolate or azathioprine) once infection is diagnosed to maximize chances of a better outcome.
“There may be variation on how long [the regimens are adjusted],” he said. “We changed our duration from 4 weeks to 2 due to patients developing a rebound worsening in the third and fourth week of acute illness.”
There is significant variation from institution to institution in how viral infections are managed in lung transplant recipients, he and Dr. Narula said. “Our numbers are so small in lung transplant, and we don’t have standardized protocols – it’s one of the biggest challenges in our field,” said Dr. Narula.
Vaccination issues, evaluation of donors
Whether or not immunosuppression regimens should be adjusted prior to vaccination is a controversial question, but is “an absolutely valid one” and is currently being studied in at least one National Institutes of Health–funded trial involving solid organ transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe.
“Some have jumped to the conclusion [based on some earlier data] that they should reduce immunosuppression regimens for everyone at the time of vaccination ... but I don’t know the answer yet,” he said. “Balancing staying rejection free with potentially gaining more immune response is complicated ... and it may depend on where the pandemic is going in your area and other factors.”
Reductions aside, Dr. Wolfe tells lung transplant recipients that, based on his approximation of a number of different studies in solid organ transplant recipients, approximately 40%-50% of patients who are immunized with two doses of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines will develop meaningful antibody levels – and that this rises to 50%-60% after a third dose.
It is difficult to glean from available studies the level of vaccine response for lung transplant recipients specifically. But given that their level of maintenance immunosuppression is higher than for recipients of other donor organs, “as a broad sweep, lung transplant recipients tend to be lower in the pecking order of response,” he said.
Still, “there’s a lot to gain,” he said, pointing to a recent study from the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (2021 Nov 5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7044e3) showing that effectiveness of mRNA vaccination against COVID-19–associated hospitalization was 77% among immunocompromised adults (compared with 90% in immunocompetent adults).
“This is good vindication to keep vaccinating,” he said, “and perhaps speaks to how difficult it is to assess the vaccine response [through measurement of antibody only].”
Neither Duke University’s transplant program, which performed 100-120 lung transplants a year pre-COVID, nor the programs at UT Southwestern or the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville require that solid organ transplant candidates be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 in order to receive transplants, as some other transplant programs have done. (When asked about the issue, Dr. Banga and Dr. Narula each said that they have had no or little trouble convincing patients awaiting lung transplants of the need for COVID-19 vaccination.)
In an August statement, the American Society of Transplantation recommended vaccination for all solid organ transplant recipients, preferably prior to transplantation, and said that it “support[s] the development of institutional policies regarding pretransplant vaccination.”
The Society is not tracking centers’ vaccination policies. But Kaiser Health News reported in October that a growing number of transplant programs, such as UCHealth in Denver and UW Medicine in Seattle, have decided to either bar patients who refuse to be vaccinated from receiving transplants or give them lower priority on waitlists.
Potential lung donors, meanwhile, must be evaluated with lower respiratory COVID-19 testing, with results available prior to transplantation, according to policy developed by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network and effective in May 2021. The policy followed three published cases of donor-derived COVID-19 in lung transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe, who wrote about use of COVID-positive donors in an editorial published in October.
In each case, the donor had a negative COVID-19 nasopharyngeal swab at the time of organ procurement but was later found to have the virus on bronchoalveolar lavage, he said.
(The use of other organs from COVID-positive donors is appearing thus far to be safe, Dr. Wolfe noted. In the editorial, he references 13 cases of solid organ transplantation from SARS-CoV-2–infected donors into noninfected recipients; none of the 13 transplant recipients developed COVID-19).
Some questions remain, such as how many lower respiratory tests should be run, and how donors should be evaluated in cases of discordant results. Dr. Banga shared the case of a donor with one positive lower respiratory test result followed by two negative results. After internal debate, and consideration of potential false positives and other issues, the team at UT Southwestern decided to decline the donor, Dr. Banga said.
Other programs are likely making similar, appropriately cautious decisions, said Dr. Wolfe. “There’s no way in real-time donor evaluation to know whether the positive test is active virus that could infect the recipient and replicate ... or whether it’s [picking up] inactive or dead fragments of virus that was there several weeks ago. Our tests don’t differentiate that.”
Transplants in COVID-19 patients
Decision-making about lung transplant candidacy among patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome is complex and in need of a new paradigm.
“Some of these patients have the potential to recover, and they’re going to recover way later than what we’re used to,” said Dr. Banga. “We can’t extrapolate for COVID ARDS what we’ve learned for any other virus-related ARDS.”
Dr. Narula also has recently seen at least one COVID-19 patient on ECMO and under evaluation for transplantation recover. “We do not want to transplant too early,” he said, noting that there is consensus that lung transplant should be pursued only when the damage is deemed irreversible clinically and radiologically in the best judgment of the team. Still, “for many of these patients the only exit route will be lung transplants. For the next 12-24 months, a significant proportion of our lung transplant patients will have had post-COVID–related lung damage.”
As of October 2021, 233 lung transplants had been performed in the United States in recipients whose primary diagnosis was reported as COVID related, said Anne Paschke, media relations specialist with the United Network for Organ Sharing.
Dr. Banga, Dr. Wolfe, and Dr. Narula reported that they have no relevant disclosures.
Major COVID-19 case growth expected in coming weeks
by the PolicyLab at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Large metropolitan areas, especially those in the Northeast, are already seeing a major increase in cases following Thanksgiving, and that trend is expected to continue.
“Why? Simply stated, the large amount of Thanksgiving travel and gatherings undermined the nation’s pandemic footing and has elevated disease burden in areas of the country that were fortunate to have lower case rates before the holidays,” the forecasters wrote.
Case numbers in New York City are expected to double throughout December, the forecasters said. Similar growth could happen across Boston, Philadelphia, and Baltimore.
Overall, COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths are rising across the United States but remain below levels seen during the summer and last winter’s surges, according to the New York Times. The increase is still being driven by the Delta variant, though it remains unclear how the Omicron variant, which has been detected in 27 states, could affect the trends in the coming weeks.
During the past week, the United States has reported an average of more than 120,000 new cases each day, the newspaper reported, which is an increase of 38% from two weeks ago.
The daily average of COVID-19 hospitalizations is around 64,000, which marks an increase of 22% from two weeks ago. More than 1,300 deaths are being reported each day, which is up 26%.
Numerous states are reporting double the cases from two weeks ago, stretching across the country from states in the Northeast such as Connecticut and Rhode Island to southern states such as North Carolina and Texas and western states such as California.
The Great Lakes region and the Northeast are seeing some of the most severe increases, the newspaper reported. New Hampshire leads the United States in recent cases per capita, and Maine has reported more cases in the past week than in any other seven-day period during the pandemic.
Michigan has the country’s highest hospitalization rate, and federal medical teams have been sent to the state to help with the surge in patients, according to The Detroit News. Michigan’s top public health officials described the surge as a “critical” and “deeply concerning” situation on Dec. 10, and they requested 200 more ventilators from the Strategic National Stockpile.
Indiana, Maine, and New York have also requested aid from the National Guard, according to USA Today. Health officials in those states urged residents to get vaccines or booster shots and wear masks in indoor public settings.
The Omicron variant can evade some vaccine protection, but booster shots can increase efficacy and offer more coverage, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said Dec. 12.
“If you want to be optimally protected, absolutely get a booster,” he said on ABC’s “This Week.”
In addition, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul has announced a statewide mask mandate, which will take effect Dec. 13. Masks will be required in all indoor public spaces and businesses, unless the location implements a vaccine requirement instead, the news outlet reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
by the PolicyLab at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Large metropolitan areas, especially those in the Northeast, are already seeing a major increase in cases following Thanksgiving, and that trend is expected to continue.
“Why? Simply stated, the large amount of Thanksgiving travel and gatherings undermined the nation’s pandemic footing and has elevated disease burden in areas of the country that were fortunate to have lower case rates before the holidays,” the forecasters wrote.
Case numbers in New York City are expected to double throughout December, the forecasters said. Similar growth could happen across Boston, Philadelphia, and Baltimore.
Overall, COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths are rising across the United States but remain below levels seen during the summer and last winter’s surges, according to the New York Times. The increase is still being driven by the Delta variant, though it remains unclear how the Omicron variant, which has been detected in 27 states, could affect the trends in the coming weeks.
During the past week, the United States has reported an average of more than 120,000 new cases each day, the newspaper reported, which is an increase of 38% from two weeks ago.
The daily average of COVID-19 hospitalizations is around 64,000, which marks an increase of 22% from two weeks ago. More than 1,300 deaths are being reported each day, which is up 26%.
Numerous states are reporting double the cases from two weeks ago, stretching across the country from states in the Northeast such as Connecticut and Rhode Island to southern states such as North Carolina and Texas and western states such as California.
The Great Lakes region and the Northeast are seeing some of the most severe increases, the newspaper reported. New Hampshire leads the United States in recent cases per capita, and Maine has reported more cases in the past week than in any other seven-day period during the pandemic.
Michigan has the country’s highest hospitalization rate, and federal medical teams have been sent to the state to help with the surge in patients, according to The Detroit News. Michigan’s top public health officials described the surge as a “critical” and “deeply concerning” situation on Dec. 10, and they requested 200 more ventilators from the Strategic National Stockpile.
Indiana, Maine, and New York have also requested aid from the National Guard, according to USA Today. Health officials in those states urged residents to get vaccines or booster shots and wear masks in indoor public settings.
The Omicron variant can evade some vaccine protection, but booster shots can increase efficacy and offer more coverage, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said Dec. 12.
“If you want to be optimally protected, absolutely get a booster,” he said on ABC’s “This Week.”
In addition, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul has announced a statewide mask mandate, which will take effect Dec. 13. Masks will be required in all indoor public spaces and businesses, unless the location implements a vaccine requirement instead, the news outlet reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
by the PolicyLab at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Large metropolitan areas, especially those in the Northeast, are already seeing a major increase in cases following Thanksgiving, and that trend is expected to continue.
“Why? Simply stated, the large amount of Thanksgiving travel and gatherings undermined the nation’s pandemic footing and has elevated disease burden in areas of the country that were fortunate to have lower case rates before the holidays,” the forecasters wrote.
Case numbers in New York City are expected to double throughout December, the forecasters said. Similar growth could happen across Boston, Philadelphia, and Baltimore.
Overall, COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths are rising across the United States but remain below levels seen during the summer and last winter’s surges, according to the New York Times. The increase is still being driven by the Delta variant, though it remains unclear how the Omicron variant, which has been detected in 27 states, could affect the trends in the coming weeks.
During the past week, the United States has reported an average of more than 120,000 new cases each day, the newspaper reported, which is an increase of 38% from two weeks ago.
The daily average of COVID-19 hospitalizations is around 64,000, which marks an increase of 22% from two weeks ago. More than 1,300 deaths are being reported each day, which is up 26%.
Numerous states are reporting double the cases from two weeks ago, stretching across the country from states in the Northeast such as Connecticut and Rhode Island to southern states such as North Carolina and Texas and western states such as California.
The Great Lakes region and the Northeast are seeing some of the most severe increases, the newspaper reported. New Hampshire leads the United States in recent cases per capita, and Maine has reported more cases in the past week than in any other seven-day period during the pandemic.
Michigan has the country’s highest hospitalization rate, and federal medical teams have been sent to the state to help with the surge in patients, according to The Detroit News. Michigan’s top public health officials described the surge as a “critical” and “deeply concerning” situation on Dec. 10, and they requested 200 more ventilators from the Strategic National Stockpile.
Indiana, Maine, and New York have also requested aid from the National Guard, according to USA Today. Health officials in those states urged residents to get vaccines or booster shots and wear masks in indoor public settings.
The Omicron variant can evade some vaccine protection, but booster shots can increase efficacy and offer more coverage, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said Dec. 12.
“If you want to be optimally protected, absolutely get a booster,” he said on ABC’s “This Week.”
In addition, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul has announced a statewide mask mandate, which will take effect Dec. 13. Masks will be required in all indoor public spaces and businesses, unless the location implements a vaccine requirement instead, the news outlet reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.