User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
COVID-19 cases dropping in U.S., but variants threaten progress
COVID-19 cases are continuing to fall in the United States, according to the New York Times tracker, though the number of deaths from the disease again neared 4,000 on Feb. 3.
The United States has averaged 141,146 cases a day in the past week, down 30% from the average 2 weeks ago. For the first time since November 2020, the country is averaging fewer than 150,000 cases a day, according to the tracker.
“Although we have seen declines in cases and admissions and a recent slowing of deaths, cases remain extraordinarily high, still twice as high as the peak number of cases over the summer. And the continued proliferation of variants, variants that likely have increased transmissibility, that spread more easily, threatens to reverse these recent trends.
“Based on contact tracing of recent variant cases, not wearing masks and participating in in-person social gatherings have contributed to the variants’ spread,” she said at a White House COVID-19 briefing on Feb. 3, 2021.
The number of cases worldwide neared 104 million on Feb. 3 and the U.S. numbers made up 26.4 million of that total.
As of Feb. 4, COVID-19 had killed at least 454,000 people and infected about 26.6 million in the United States since January 2020, according to the Johns Hopkins University tracker.
The Johns Hopkins tracker found that, per capita, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Rhode Island have reported the most cases while New Jersey and New York have recorded the most deaths.
According to the COVID tracking project, hospitalizations for COVID-19 nationwide were down to 91,440 on Feb. 3.
The tracking report noted, “compared to last week, the number of people currently hospitalized with COVID-19 is down by 10% or more in 38 states.”
Even in hard-hit Los Angeles County, infections and case numbers are on the decline, according to the Los Angeles Times. However, officials, warn the numbers remain well above presurge levels. Over the past week, 201 city residents have died every day.
Reuters also reports that Anthony S. Fauci, MD, the government’s top infectious disease expert, said despite some good news in the numbers, Americans should continue to follow social distancing guidelines. He added that double-masking may add protection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 cases are continuing to fall in the United States, according to the New York Times tracker, though the number of deaths from the disease again neared 4,000 on Feb. 3.
The United States has averaged 141,146 cases a day in the past week, down 30% from the average 2 weeks ago. For the first time since November 2020, the country is averaging fewer than 150,000 cases a day, according to the tracker.
“Although we have seen declines in cases and admissions and a recent slowing of deaths, cases remain extraordinarily high, still twice as high as the peak number of cases over the summer. And the continued proliferation of variants, variants that likely have increased transmissibility, that spread more easily, threatens to reverse these recent trends.
“Based on contact tracing of recent variant cases, not wearing masks and participating in in-person social gatherings have contributed to the variants’ spread,” she said at a White House COVID-19 briefing on Feb. 3, 2021.
The number of cases worldwide neared 104 million on Feb. 3 and the U.S. numbers made up 26.4 million of that total.
As of Feb. 4, COVID-19 had killed at least 454,000 people and infected about 26.6 million in the United States since January 2020, according to the Johns Hopkins University tracker.
The Johns Hopkins tracker found that, per capita, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Rhode Island have reported the most cases while New Jersey and New York have recorded the most deaths.
According to the COVID tracking project, hospitalizations for COVID-19 nationwide were down to 91,440 on Feb. 3.
The tracking report noted, “compared to last week, the number of people currently hospitalized with COVID-19 is down by 10% or more in 38 states.”
Even in hard-hit Los Angeles County, infections and case numbers are on the decline, according to the Los Angeles Times. However, officials, warn the numbers remain well above presurge levels. Over the past week, 201 city residents have died every day.
Reuters also reports that Anthony S. Fauci, MD, the government’s top infectious disease expert, said despite some good news in the numbers, Americans should continue to follow social distancing guidelines. He added that double-masking may add protection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 cases are continuing to fall in the United States, according to the New York Times tracker, though the number of deaths from the disease again neared 4,000 on Feb. 3.
The United States has averaged 141,146 cases a day in the past week, down 30% from the average 2 weeks ago. For the first time since November 2020, the country is averaging fewer than 150,000 cases a day, according to the tracker.
“Although we have seen declines in cases and admissions and a recent slowing of deaths, cases remain extraordinarily high, still twice as high as the peak number of cases over the summer. And the continued proliferation of variants, variants that likely have increased transmissibility, that spread more easily, threatens to reverse these recent trends.
“Based on contact tracing of recent variant cases, not wearing masks and participating in in-person social gatherings have contributed to the variants’ spread,” she said at a White House COVID-19 briefing on Feb. 3, 2021.
The number of cases worldwide neared 104 million on Feb. 3 and the U.S. numbers made up 26.4 million of that total.
As of Feb. 4, COVID-19 had killed at least 454,000 people and infected about 26.6 million in the United States since January 2020, according to the Johns Hopkins University tracker.
The Johns Hopkins tracker found that, per capita, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Rhode Island have reported the most cases while New Jersey and New York have recorded the most deaths.
According to the COVID tracking project, hospitalizations for COVID-19 nationwide were down to 91,440 on Feb. 3.
The tracking report noted, “compared to last week, the number of people currently hospitalized with COVID-19 is down by 10% or more in 38 states.”
Even in hard-hit Los Angeles County, infections and case numbers are on the decline, according to the Los Angeles Times. However, officials, warn the numbers remain well above presurge levels. Over the past week, 201 city residents have died every day.
Reuters also reports that Anthony S. Fauci, MD, the government’s top infectious disease expert, said despite some good news in the numbers, Americans should continue to follow social distancing guidelines. He added that double-masking may add protection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Views on ethical issues shifting in family, internal medicine
according to the Medscape Internal Medicine Ethics Report 2020 and the corresponding report for Family Medicine.
An example comes in an apparent loosening of attitudes about romantic/sexual relationships with former patients. Now, 31% of internists believe such a relationship is acceptable at least 6 months after the medical relationship has ended. That’s up from 22% in 2018. The number of family physicians this year who said 6 months later was acceptable also increased, but by a smaller margin – from 28% in 2018 to 33% in 2020.
“It’s acceptable as long as there is no undue influence,” David Fleming, MD, a member of the American Medical Association Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs, said in an interview. “The important thing is that you don’t mix the two.”
Thoughts on upcoding
Views on billing are also shifting. Ten years ago, 17% of physicians overall thought upcoding was acceptable when submitting claims or getting prior authorization. Today just 8% of physicians overall said it was, as did 8% of family medicine (FM) physicians, according to responses.
The number of internal medicine (IM) physicians clearly opposed to upcoding declined a bit from 79% in 2018 to 75% this year, while the number saying “it depends” increased from 11% to 15%.
Many responders in both specialties said they would upgrade a code in the interest of patient advocacy.
An internist put it this way: “If the system is set up so that the only thing that would work for the patient’s condition can be obtained by an upcode, then I would consider this.”
More than a third say random drug checks needed
More than one-third of physicians in both specialties (34% in IM and 38% in FM) said physicians should be subjected to random alcohol and drug testing.
However, many say testing should only happen if abuse is suspected.
Some said specialty matters when it comes to random checks. An internist responded: “I think this is more important for procedure-based physicians.”
Some family physicians said that, if other health care workers were subjected to the same checks in the same circumstances, they would not object, but said doctors shouldn’t be singled out.
Vast majority would report an impaired peer
Nine out of 10 internists and family physicians say they would report a physician who occasionally seemed impaired but most (60% of IM respondents and 62% of FM respondents) said they would do so only after talking with the physician first.
Some noted their decision would depend on the setting.
“Big difference if they are on vacation and drink too much so they need a ride home versus being impaired at work or when on call,” one FM physician said.
About one-third of family physicians (34%) and internists (33%) now favor physician-assisted dying/suicide for incurable suffering. A substantial number (26%-28%) hesitated to make a clear decision in both specialties, responding “it depends.”
“Patient control over quality of life can be even more important than control over its quantity/duration,” one internist wrote.
The proportion of physicians who agreed physician-assisted dying/suicide should be legalized for the terminally ill was much larger, with 49% of family physicians and 52% of IM physicians saying it should.
Talking politics
Data in this survey were collected in summer months of 2020, before the U.S. presidential election, in a highly polarized climate. Some numbers reflect increasing distaste for such conversations with patients.
For example, the number of family physicians who said talking about politics with patients was ethical dropped from 31% in 2018 to 23% in the latest survey. The numbers remained nearly flat among IM physicians in the past 2 years – at 21% in 2018 and 23% this year.
Should a flu shot be mandatory?
Almost three-fourths of physicians overall – and 76% of IM physicians – say annual flu shots should be required for physicians who have patient contact. Agreement was somewhat lower among family physicians at 68%.
Some family physicians cited “freedom of choice” and that they would want to see a higher effectiveness rate before they were mandatory.
Data for this survey, with 5,130 respondents, were collected before COVID-19 vaccines became available.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the Medscape Internal Medicine Ethics Report 2020 and the corresponding report for Family Medicine.
An example comes in an apparent loosening of attitudes about romantic/sexual relationships with former patients. Now, 31% of internists believe such a relationship is acceptable at least 6 months after the medical relationship has ended. That’s up from 22% in 2018. The number of family physicians this year who said 6 months later was acceptable also increased, but by a smaller margin – from 28% in 2018 to 33% in 2020.
“It’s acceptable as long as there is no undue influence,” David Fleming, MD, a member of the American Medical Association Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs, said in an interview. “The important thing is that you don’t mix the two.”
Thoughts on upcoding
Views on billing are also shifting. Ten years ago, 17% of physicians overall thought upcoding was acceptable when submitting claims or getting prior authorization. Today just 8% of physicians overall said it was, as did 8% of family medicine (FM) physicians, according to responses.
The number of internal medicine (IM) physicians clearly opposed to upcoding declined a bit from 79% in 2018 to 75% this year, while the number saying “it depends” increased from 11% to 15%.
Many responders in both specialties said they would upgrade a code in the interest of patient advocacy.
An internist put it this way: “If the system is set up so that the only thing that would work for the patient’s condition can be obtained by an upcode, then I would consider this.”
More than a third say random drug checks needed
More than one-third of physicians in both specialties (34% in IM and 38% in FM) said physicians should be subjected to random alcohol and drug testing.
However, many say testing should only happen if abuse is suspected.
Some said specialty matters when it comes to random checks. An internist responded: “I think this is more important for procedure-based physicians.”
Some family physicians said that, if other health care workers were subjected to the same checks in the same circumstances, they would not object, but said doctors shouldn’t be singled out.
Vast majority would report an impaired peer
Nine out of 10 internists and family physicians say they would report a physician who occasionally seemed impaired but most (60% of IM respondents and 62% of FM respondents) said they would do so only after talking with the physician first.
Some noted their decision would depend on the setting.
“Big difference if they are on vacation and drink too much so they need a ride home versus being impaired at work or when on call,” one FM physician said.
About one-third of family physicians (34%) and internists (33%) now favor physician-assisted dying/suicide for incurable suffering. A substantial number (26%-28%) hesitated to make a clear decision in both specialties, responding “it depends.”
“Patient control over quality of life can be even more important than control over its quantity/duration,” one internist wrote.
The proportion of physicians who agreed physician-assisted dying/suicide should be legalized for the terminally ill was much larger, with 49% of family physicians and 52% of IM physicians saying it should.
Talking politics
Data in this survey were collected in summer months of 2020, before the U.S. presidential election, in a highly polarized climate. Some numbers reflect increasing distaste for such conversations with patients.
For example, the number of family physicians who said talking about politics with patients was ethical dropped from 31% in 2018 to 23% in the latest survey. The numbers remained nearly flat among IM physicians in the past 2 years – at 21% in 2018 and 23% this year.
Should a flu shot be mandatory?
Almost three-fourths of physicians overall – and 76% of IM physicians – say annual flu shots should be required for physicians who have patient contact. Agreement was somewhat lower among family physicians at 68%.
Some family physicians cited “freedom of choice” and that they would want to see a higher effectiveness rate before they were mandatory.
Data for this survey, with 5,130 respondents, were collected before COVID-19 vaccines became available.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the Medscape Internal Medicine Ethics Report 2020 and the corresponding report for Family Medicine.
An example comes in an apparent loosening of attitudes about romantic/sexual relationships with former patients. Now, 31% of internists believe such a relationship is acceptable at least 6 months after the medical relationship has ended. That’s up from 22% in 2018. The number of family physicians this year who said 6 months later was acceptable also increased, but by a smaller margin – from 28% in 2018 to 33% in 2020.
“It’s acceptable as long as there is no undue influence,” David Fleming, MD, a member of the American Medical Association Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs, said in an interview. “The important thing is that you don’t mix the two.”
Thoughts on upcoding
Views on billing are also shifting. Ten years ago, 17% of physicians overall thought upcoding was acceptable when submitting claims or getting prior authorization. Today just 8% of physicians overall said it was, as did 8% of family medicine (FM) physicians, according to responses.
The number of internal medicine (IM) physicians clearly opposed to upcoding declined a bit from 79% in 2018 to 75% this year, while the number saying “it depends” increased from 11% to 15%.
Many responders in both specialties said they would upgrade a code in the interest of patient advocacy.
An internist put it this way: “If the system is set up so that the only thing that would work for the patient’s condition can be obtained by an upcode, then I would consider this.”
More than a third say random drug checks needed
More than one-third of physicians in both specialties (34% in IM and 38% in FM) said physicians should be subjected to random alcohol and drug testing.
However, many say testing should only happen if abuse is suspected.
Some said specialty matters when it comes to random checks. An internist responded: “I think this is more important for procedure-based physicians.”
Some family physicians said that, if other health care workers were subjected to the same checks in the same circumstances, they would not object, but said doctors shouldn’t be singled out.
Vast majority would report an impaired peer
Nine out of 10 internists and family physicians say they would report a physician who occasionally seemed impaired but most (60% of IM respondents and 62% of FM respondents) said they would do so only after talking with the physician first.
Some noted their decision would depend on the setting.
“Big difference if they are on vacation and drink too much so they need a ride home versus being impaired at work or when on call,” one FM physician said.
About one-third of family physicians (34%) and internists (33%) now favor physician-assisted dying/suicide for incurable suffering. A substantial number (26%-28%) hesitated to make a clear decision in both specialties, responding “it depends.”
“Patient control over quality of life can be even more important than control over its quantity/duration,” one internist wrote.
The proportion of physicians who agreed physician-assisted dying/suicide should be legalized for the terminally ill was much larger, with 49% of family physicians and 52% of IM physicians saying it should.
Talking politics
Data in this survey were collected in summer months of 2020, before the U.S. presidential election, in a highly polarized climate. Some numbers reflect increasing distaste for such conversations with patients.
For example, the number of family physicians who said talking about politics with patients was ethical dropped from 31% in 2018 to 23% in the latest survey. The numbers remained nearly flat among IM physicians in the past 2 years – at 21% in 2018 and 23% this year.
Should a flu shot be mandatory?
Almost three-fourths of physicians overall – and 76% of IM physicians – say annual flu shots should be required for physicians who have patient contact. Agreement was somewhat lower among family physicians at 68%.
Some family physicians cited “freedom of choice” and that they would want to see a higher effectiveness rate before they were mandatory.
Data for this survey, with 5,130 respondents, were collected before COVID-19 vaccines became available.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New campaign fights COVID-19 vaccine disinformation
As health care providers work against the clock to administer as many COVID-19 vaccine doses as soon as possible, logistics aren’t the only thing standing in their way.
Misinformation – which has hampered the nation’s coronavirus response – is now hurting vaccination efforts, too.
About one in five Americans say they won’t take a COVID-19 vaccine, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation’s COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor. Even a third of health care workers have voiced their hesitance.
The spread of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation creates “a really powerful parallel pandemic to the real pandemic,” Imran Ahmed, CEO of the Center for Countering Digital Hate, told NPR. The center has tracked the links between vaccine misinformation and vaccine hesitancy during the past year.
The “infodemic” is essentially “working in concert to really undermine our capacity to contain COVID,” Mr. Ahmed said.
To help combat vaccine misinformation and address lingering concerns that people have, corporate, nonprofit, and media leaders, including this news organization, are joining a public service campaign called VaxFacts. Led by HealthGuard, the goal of the campaign is to provide facts and tools to help consumers make informed decisions about vaccines.
Steven Brill, co-CEO of HealthGuard, said credible information that comes from trusted messengers is critical to counter vaccine hesitancy.
“There’s traditionally a lot of skepticism about vaccines. That has really ramped up in the last few years based on campaigns about the measles vaccine. ... And now you have the COVID vaccine, which by everybody’s understanding has been ‘rushed,’ ” Mr. Brill said during an interview on Coronavirus in Context, a video series hosted by John Whyte, MD, chief medical officer for WebMD.
“There may be less understanding of the nature of what rushed really means. It’s still gone through the clinical trials it needs to go through.”
HealthGuard is a browser extension that flags health hoaxes, provides credibility ratings for hundreds of websites, and guides users to sources that offer trusted information. The tool is a new service from NewsGuard, which veteran journalists Mr. Brill and co-CEO Gordon Crovitz created in 2018 to combat misinformation in the news. HealthGuard, which is free for users globally through June, is specifically aimed at informing readers about health myths related to vaccines and COVID-19. It will cost $35 per year after that.
The HealthGuard Coronavirus Tracking Center has flagged nearly 400 websites for publishing misinformation about the coronavirus, including several top myths about COVID-19 vaccines:
- The mRNA vaccines can alter human DNA.
- Vaccines will use microchip surveillance technology.
- COVID-19 vaccines cause infertility.
- The vaccine developed by Oxford University will turn people into monkeys.
- COVID-19 vaccines contain aborted human fetal tissue.
As a partner, this news organization will feature continuing coverage of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation, including articles and videos.
There will be other efforts this year. Google has launched a $3 million fund to back fact-checking organizations to counter vaccine misinformation, and social media platforms are monitoring posts that actively promote disinformation around vaccines.
The United States has distributed nearly 50 million vaccine doses, and states have administered more than 32 million of them, including 5.9 million second doses in the two-shot vaccines, according to the latest CDC update.
To reach herd immunity, about 75%-85% of Americans will need to receive a vaccine, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said in December 2020.
Vaccine skepticism has increased in recent years, which has led to a decline in vaccination rates and the highest annual number of measles cases in the United States in more than 25 years, according to the Pew Research Center. In 2019, the World Health Organization named vaccine hesitancy as 1 of 10 threats to global health.
With the COVID-19 vaccines in particular, people have voiced concerns about their safety and how well they work, given their accelerated development, according to Kaiser’s poll. They’re also worried about potential side effects, the perceived role of politics in the development process, and a lack of trust in government. Others don’t trust vaccines in general or believe they may contract COVID-19 from a vaccine, the Kaiser poll found, “suggesting that messages combating particular types of misinformation may be especially important for increasing vaccine confidence.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As health care providers work against the clock to administer as many COVID-19 vaccine doses as soon as possible, logistics aren’t the only thing standing in their way.
Misinformation – which has hampered the nation’s coronavirus response – is now hurting vaccination efforts, too.
About one in five Americans say they won’t take a COVID-19 vaccine, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation’s COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor. Even a third of health care workers have voiced their hesitance.
The spread of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation creates “a really powerful parallel pandemic to the real pandemic,” Imran Ahmed, CEO of the Center for Countering Digital Hate, told NPR. The center has tracked the links between vaccine misinformation and vaccine hesitancy during the past year.
The “infodemic” is essentially “working in concert to really undermine our capacity to contain COVID,” Mr. Ahmed said.
To help combat vaccine misinformation and address lingering concerns that people have, corporate, nonprofit, and media leaders, including this news organization, are joining a public service campaign called VaxFacts. Led by HealthGuard, the goal of the campaign is to provide facts and tools to help consumers make informed decisions about vaccines.
Steven Brill, co-CEO of HealthGuard, said credible information that comes from trusted messengers is critical to counter vaccine hesitancy.
“There’s traditionally a lot of skepticism about vaccines. That has really ramped up in the last few years based on campaigns about the measles vaccine. ... And now you have the COVID vaccine, which by everybody’s understanding has been ‘rushed,’ ” Mr. Brill said during an interview on Coronavirus in Context, a video series hosted by John Whyte, MD, chief medical officer for WebMD.
“There may be less understanding of the nature of what rushed really means. It’s still gone through the clinical trials it needs to go through.”
HealthGuard is a browser extension that flags health hoaxes, provides credibility ratings for hundreds of websites, and guides users to sources that offer trusted information. The tool is a new service from NewsGuard, which veteran journalists Mr. Brill and co-CEO Gordon Crovitz created in 2018 to combat misinformation in the news. HealthGuard, which is free for users globally through June, is specifically aimed at informing readers about health myths related to vaccines and COVID-19. It will cost $35 per year after that.
The HealthGuard Coronavirus Tracking Center has flagged nearly 400 websites for publishing misinformation about the coronavirus, including several top myths about COVID-19 vaccines:
- The mRNA vaccines can alter human DNA.
- Vaccines will use microchip surveillance technology.
- COVID-19 vaccines cause infertility.
- The vaccine developed by Oxford University will turn people into monkeys.
- COVID-19 vaccines contain aborted human fetal tissue.
As a partner, this news organization will feature continuing coverage of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation, including articles and videos.
There will be other efforts this year. Google has launched a $3 million fund to back fact-checking organizations to counter vaccine misinformation, and social media platforms are monitoring posts that actively promote disinformation around vaccines.
The United States has distributed nearly 50 million vaccine doses, and states have administered more than 32 million of them, including 5.9 million second doses in the two-shot vaccines, according to the latest CDC update.
To reach herd immunity, about 75%-85% of Americans will need to receive a vaccine, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said in December 2020.
Vaccine skepticism has increased in recent years, which has led to a decline in vaccination rates and the highest annual number of measles cases in the United States in more than 25 years, according to the Pew Research Center. In 2019, the World Health Organization named vaccine hesitancy as 1 of 10 threats to global health.
With the COVID-19 vaccines in particular, people have voiced concerns about their safety and how well they work, given their accelerated development, according to Kaiser’s poll. They’re also worried about potential side effects, the perceived role of politics in the development process, and a lack of trust in government. Others don’t trust vaccines in general or believe they may contract COVID-19 from a vaccine, the Kaiser poll found, “suggesting that messages combating particular types of misinformation may be especially important for increasing vaccine confidence.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As health care providers work against the clock to administer as many COVID-19 vaccine doses as soon as possible, logistics aren’t the only thing standing in their way.
Misinformation – which has hampered the nation’s coronavirus response – is now hurting vaccination efforts, too.
About one in five Americans say they won’t take a COVID-19 vaccine, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation’s COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor. Even a third of health care workers have voiced their hesitance.
The spread of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation creates “a really powerful parallel pandemic to the real pandemic,” Imran Ahmed, CEO of the Center for Countering Digital Hate, told NPR. The center has tracked the links between vaccine misinformation and vaccine hesitancy during the past year.
The “infodemic” is essentially “working in concert to really undermine our capacity to contain COVID,” Mr. Ahmed said.
To help combat vaccine misinformation and address lingering concerns that people have, corporate, nonprofit, and media leaders, including this news organization, are joining a public service campaign called VaxFacts. Led by HealthGuard, the goal of the campaign is to provide facts and tools to help consumers make informed decisions about vaccines.
Steven Brill, co-CEO of HealthGuard, said credible information that comes from trusted messengers is critical to counter vaccine hesitancy.
“There’s traditionally a lot of skepticism about vaccines. That has really ramped up in the last few years based on campaigns about the measles vaccine. ... And now you have the COVID vaccine, which by everybody’s understanding has been ‘rushed,’ ” Mr. Brill said during an interview on Coronavirus in Context, a video series hosted by John Whyte, MD, chief medical officer for WebMD.
“There may be less understanding of the nature of what rushed really means. It’s still gone through the clinical trials it needs to go through.”
HealthGuard is a browser extension that flags health hoaxes, provides credibility ratings for hundreds of websites, and guides users to sources that offer trusted information. The tool is a new service from NewsGuard, which veteran journalists Mr. Brill and co-CEO Gordon Crovitz created in 2018 to combat misinformation in the news. HealthGuard, which is free for users globally through June, is specifically aimed at informing readers about health myths related to vaccines and COVID-19. It will cost $35 per year after that.
The HealthGuard Coronavirus Tracking Center has flagged nearly 400 websites for publishing misinformation about the coronavirus, including several top myths about COVID-19 vaccines:
- The mRNA vaccines can alter human DNA.
- Vaccines will use microchip surveillance technology.
- COVID-19 vaccines cause infertility.
- The vaccine developed by Oxford University will turn people into monkeys.
- COVID-19 vaccines contain aborted human fetal tissue.
As a partner, this news organization will feature continuing coverage of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation, including articles and videos.
There will be other efforts this year. Google has launched a $3 million fund to back fact-checking organizations to counter vaccine misinformation, and social media platforms are monitoring posts that actively promote disinformation around vaccines.
The United States has distributed nearly 50 million vaccine doses, and states have administered more than 32 million of them, including 5.9 million second doses in the two-shot vaccines, according to the latest CDC update.
To reach herd immunity, about 75%-85% of Americans will need to receive a vaccine, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said in December 2020.
Vaccine skepticism has increased in recent years, which has led to a decline in vaccination rates and the highest annual number of measles cases in the United States in more than 25 years, according to the Pew Research Center. In 2019, the World Health Organization named vaccine hesitancy as 1 of 10 threats to global health.
With the COVID-19 vaccines in particular, people have voiced concerns about their safety and how well they work, given their accelerated development, according to Kaiser’s poll. They’re also worried about potential side effects, the perceived role of politics in the development process, and a lack of trust in government. Others don’t trust vaccines in general or believe they may contract COVID-19 from a vaccine, the Kaiser poll found, “suggesting that messages combating particular types of misinformation may be especially important for increasing vaccine confidence.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19: Another study links colchicine to better results
The gout drug colchicine appears to lower the severity of COVID-19, a small new Brazilian study finds, adding to evidence that the familiar medication holds promise as a treatment for hospitalized patients.
Patients who received colchicine in this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial presented better evolution in terms of the need for supplemental oxygen and the length of hospitalisation. ... Colchicine was safe and well tolerated,” the study authors wrote in RMD Open. However, deaths were rare in the trial, they added, and it is impossible to “evaluate the capacity of colchicine to avoid admission to ICU and reduce mortality.”
The oral anti-inflammatory colchicine, widely used as treatment in rheumatic disease, was first approved in the United States 60 years ago. Researchers began to explore its potential as a COVID-19 treatment in the early months of the pandemic.
On Jan. 25, an international team of researchers reported in a press release – but not yet a published paper – that the drug seemed to reduce hospitalizations, mechanical ventilation, and deaths in the ColCORONA trial. Earlier, a much-smaller, randomized, open-label, Greek trial linked the drug to reduced time to clinical deterioration and hospital stay.
The Brazilian authors of the new study, led by Maria Isabel Lopes of the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Medical School, randomly assigned 75 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 to colchicine or placebo. A total of 72 subjects completed the April-August 2020 trial: 36 received colchicine (typically 0.5 mg three times for 5 days, then 0.5 mg twice daily for 5 days; doses were adjusted in low-weight patients and those with chronic kidney disease). The other 36 received the placebo.
(In the United States, 0.6-mg tablets of generic colchicine cost as little as $1.90 each with free coupons, according to goodrx.com.)
The median age in the groups was similar (55 years); and the placebo group had more women (61% vs. 47% in the colchicine group, P = .34). All 72 patients received the same COVID-19 treatment at the time of the trial: azithromycin, hydroxychloroquine, and unfractionated heparin. Most patients, about two-thirds in both groups, also received methylprednisolone because they needed higher amounts of supplemental oxygen.
Patients in the colchicine group needed supplemental oxygen for less time: Their median time of need was 4.0 days (interquartile range [IQR], 2.0-6.0) vs. 6.5 days (IQR, 4.0-9.0) for the placebo group (P < .001). The median time for hospitalization was also lower at 7.0 days (IQR, 5.0–9.0) for the colchicine group vs. 9.0 (IQR, 7.0–12.0) for the placebo group (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001).
The researchers also reported the percentage of patients who needed supplemental oxygen at day 2 as 67% with colchicine vs. 86% with placebo, and at day 7 as 9% vs. 42% (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001). Two patients in the placebo group died, both from ventilator-associated pneumonia.
As for side effects, new or worsened diarrhea was reported more often in the colchicine group (17% vs. 6% with placebo), but the difference was not statistically significant (P = .26), and diarrhea was controlled via medication.
The researchers reported that limitations include the exclusion criteria and their inability to link colchicine to rates of ICU admissions and death.
The drug appears to help patients with COVID-19, the study authors wrote, by “inhibiting inflammasome, reducing neutrophil migration and activation, or preventing endothelial damage.”
A “well-conceived and well-designed” study
In an interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatologist Michael H. Pillinger, MD – an investigator with the ColCORONA trial – praised the Brazilian study. It “appears well-conceived and well-designed, and was enrolled at a rate that was greater than the sample size that was estimated to be needed based on power analysis,” he said.
The Brazilian study is small, he noted. (In contrast, the ColCORONA trial had 4,488 outpatient participants.) “This study differs from ColCORONA in several ways – the most important being that it is a study of inpatients with moderate to severe COVID (really mostly moderate),” he added. “ColCORONA is looking at a target audience that is much larger – outpatients with mild to moderate COVID with risk factors for hospitalization. Both questions are really important and certainly not mutually exclusive, since our care remains inadequate in both venues. This study also adds value in that several other studies have been conducted in hospital patients with enrollment criteria relatively similar to this one, and all showed benefit, but those were open-label or retrospective, and this is blinded and placebo-controlled.”
Using colchicine in patients with COVID-19
Should physicians turn to colchicine in patients with COVID-19? “I would rather that it still be used in the context of research until formal recommendations can be made by bodies like the NIH and CDC,” Dr. Pillinger said. “But certainly, there may be times when physicians feel compelled to treat patients off label.”
He cautioned, however, that colchicine should never be used with some other drugs. Its interaction with the antibiotic clarithromycin can be fatal, he noted. And, he said, the drug must be monitored in general since it can cause rare, severe problems.
“Overall, colchicine probably works on the overabundant inflammatory response to COVID, and it may be that it can be combined with other drugs that affect viral replication or promote immunity – e.g. vaccines,” Dr. Pillinger said. “So far, it seems as if there is no safety problem with combining colchicine with other approaches, but this has not been studied in a rigorous manner.”
Moving forward, he said, the drug’s very low price outside of the United States “could provide resource-poor countries with a way to help keep patients out of precious hospital beds – or help them go home sooner once admitted.” For now, however, “we need a large-scale inpatient study, and one is currently going on in Great Britain. We also need validation of the outpatient ColCORONA study, and studies to look at whether colchicine can work in conjunction with other strategies.”
The study was funded by grants from the São Paulo Research Foundation, Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, and CAPES Foundation. No disclosures are reported. Dr. Pillinger reports serving as an investigator for the ColCORONA trial and receiving a unrelated investigator-initiated grant from Hikma, a colchicine manufacturer.
The gout drug colchicine appears to lower the severity of COVID-19, a small new Brazilian study finds, adding to evidence that the familiar medication holds promise as a treatment for hospitalized patients.
Patients who received colchicine in this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial presented better evolution in terms of the need for supplemental oxygen and the length of hospitalisation. ... Colchicine was safe and well tolerated,” the study authors wrote in RMD Open. However, deaths were rare in the trial, they added, and it is impossible to “evaluate the capacity of colchicine to avoid admission to ICU and reduce mortality.”
The oral anti-inflammatory colchicine, widely used as treatment in rheumatic disease, was first approved in the United States 60 years ago. Researchers began to explore its potential as a COVID-19 treatment in the early months of the pandemic.
On Jan. 25, an international team of researchers reported in a press release – but not yet a published paper – that the drug seemed to reduce hospitalizations, mechanical ventilation, and deaths in the ColCORONA trial. Earlier, a much-smaller, randomized, open-label, Greek trial linked the drug to reduced time to clinical deterioration and hospital stay.
The Brazilian authors of the new study, led by Maria Isabel Lopes of the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Medical School, randomly assigned 75 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 to colchicine or placebo. A total of 72 subjects completed the April-August 2020 trial: 36 received colchicine (typically 0.5 mg three times for 5 days, then 0.5 mg twice daily for 5 days; doses were adjusted in low-weight patients and those with chronic kidney disease). The other 36 received the placebo.
(In the United States, 0.6-mg tablets of generic colchicine cost as little as $1.90 each with free coupons, according to goodrx.com.)
The median age in the groups was similar (55 years); and the placebo group had more women (61% vs. 47% in the colchicine group, P = .34). All 72 patients received the same COVID-19 treatment at the time of the trial: azithromycin, hydroxychloroquine, and unfractionated heparin. Most patients, about two-thirds in both groups, also received methylprednisolone because they needed higher amounts of supplemental oxygen.
Patients in the colchicine group needed supplemental oxygen for less time: Their median time of need was 4.0 days (interquartile range [IQR], 2.0-6.0) vs. 6.5 days (IQR, 4.0-9.0) for the placebo group (P < .001). The median time for hospitalization was also lower at 7.0 days (IQR, 5.0–9.0) for the colchicine group vs. 9.0 (IQR, 7.0–12.0) for the placebo group (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001).
The researchers also reported the percentage of patients who needed supplemental oxygen at day 2 as 67% with colchicine vs. 86% with placebo, and at day 7 as 9% vs. 42% (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001). Two patients in the placebo group died, both from ventilator-associated pneumonia.
As for side effects, new or worsened diarrhea was reported more often in the colchicine group (17% vs. 6% with placebo), but the difference was not statistically significant (P = .26), and diarrhea was controlled via medication.
The researchers reported that limitations include the exclusion criteria and their inability to link colchicine to rates of ICU admissions and death.
The drug appears to help patients with COVID-19, the study authors wrote, by “inhibiting inflammasome, reducing neutrophil migration and activation, or preventing endothelial damage.”
A “well-conceived and well-designed” study
In an interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatologist Michael H. Pillinger, MD – an investigator with the ColCORONA trial – praised the Brazilian study. It “appears well-conceived and well-designed, and was enrolled at a rate that was greater than the sample size that was estimated to be needed based on power analysis,” he said.
The Brazilian study is small, he noted. (In contrast, the ColCORONA trial had 4,488 outpatient participants.) “This study differs from ColCORONA in several ways – the most important being that it is a study of inpatients with moderate to severe COVID (really mostly moderate),” he added. “ColCORONA is looking at a target audience that is much larger – outpatients with mild to moderate COVID with risk factors for hospitalization. Both questions are really important and certainly not mutually exclusive, since our care remains inadequate in both venues. This study also adds value in that several other studies have been conducted in hospital patients with enrollment criteria relatively similar to this one, and all showed benefit, but those were open-label or retrospective, and this is blinded and placebo-controlled.”
Using colchicine in patients with COVID-19
Should physicians turn to colchicine in patients with COVID-19? “I would rather that it still be used in the context of research until formal recommendations can be made by bodies like the NIH and CDC,” Dr. Pillinger said. “But certainly, there may be times when physicians feel compelled to treat patients off label.”
He cautioned, however, that colchicine should never be used with some other drugs. Its interaction with the antibiotic clarithromycin can be fatal, he noted. And, he said, the drug must be monitored in general since it can cause rare, severe problems.
“Overall, colchicine probably works on the overabundant inflammatory response to COVID, and it may be that it can be combined with other drugs that affect viral replication or promote immunity – e.g. vaccines,” Dr. Pillinger said. “So far, it seems as if there is no safety problem with combining colchicine with other approaches, but this has not been studied in a rigorous manner.”
Moving forward, he said, the drug’s very low price outside of the United States “could provide resource-poor countries with a way to help keep patients out of precious hospital beds – or help them go home sooner once admitted.” For now, however, “we need a large-scale inpatient study, and one is currently going on in Great Britain. We also need validation of the outpatient ColCORONA study, and studies to look at whether colchicine can work in conjunction with other strategies.”
The study was funded by grants from the São Paulo Research Foundation, Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, and CAPES Foundation. No disclosures are reported. Dr. Pillinger reports serving as an investigator for the ColCORONA trial and receiving a unrelated investigator-initiated grant from Hikma, a colchicine manufacturer.
The gout drug colchicine appears to lower the severity of COVID-19, a small new Brazilian study finds, adding to evidence that the familiar medication holds promise as a treatment for hospitalized patients.
Patients who received colchicine in this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial presented better evolution in terms of the need for supplemental oxygen and the length of hospitalisation. ... Colchicine was safe and well tolerated,” the study authors wrote in RMD Open. However, deaths were rare in the trial, they added, and it is impossible to “evaluate the capacity of colchicine to avoid admission to ICU and reduce mortality.”
The oral anti-inflammatory colchicine, widely used as treatment in rheumatic disease, was first approved in the United States 60 years ago. Researchers began to explore its potential as a COVID-19 treatment in the early months of the pandemic.
On Jan. 25, an international team of researchers reported in a press release – but not yet a published paper – that the drug seemed to reduce hospitalizations, mechanical ventilation, and deaths in the ColCORONA trial. Earlier, a much-smaller, randomized, open-label, Greek trial linked the drug to reduced time to clinical deterioration and hospital stay.
The Brazilian authors of the new study, led by Maria Isabel Lopes of the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Medical School, randomly assigned 75 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 to colchicine or placebo. A total of 72 subjects completed the April-August 2020 trial: 36 received colchicine (typically 0.5 mg three times for 5 days, then 0.5 mg twice daily for 5 days; doses were adjusted in low-weight patients and those with chronic kidney disease). The other 36 received the placebo.
(In the United States, 0.6-mg tablets of generic colchicine cost as little as $1.90 each with free coupons, according to goodrx.com.)
The median age in the groups was similar (55 years); and the placebo group had more women (61% vs. 47% in the colchicine group, P = .34). All 72 patients received the same COVID-19 treatment at the time of the trial: azithromycin, hydroxychloroquine, and unfractionated heparin. Most patients, about two-thirds in both groups, also received methylprednisolone because they needed higher amounts of supplemental oxygen.
Patients in the colchicine group needed supplemental oxygen for less time: Their median time of need was 4.0 days (interquartile range [IQR], 2.0-6.0) vs. 6.5 days (IQR, 4.0-9.0) for the placebo group (P < .001). The median time for hospitalization was also lower at 7.0 days (IQR, 5.0–9.0) for the colchicine group vs. 9.0 (IQR, 7.0–12.0) for the placebo group (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001).
The researchers also reported the percentage of patients who needed supplemental oxygen at day 2 as 67% with colchicine vs. 86% with placebo, and at day 7 as 9% vs. 42% (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001). Two patients in the placebo group died, both from ventilator-associated pneumonia.
As for side effects, new or worsened diarrhea was reported more often in the colchicine group (17% vs. 6% with placebo), but the difference was not statistically significant (P = .26), and diarrhea was controlled via medication.
The researchers reported that limitations include the exclusion criteria and their inability to link colchicine to rates of ICU admissions and death.
The drug appears to help patients with COVID-19, the study authors wrote, by “inhibiting inflammasome, reducing neutrophil migration and activation, or preventing endothelial damage.”
A “well-conceived and well-designed” study
In an interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatologist Michael H. Pillinger, MD – an investigator with the ColCORONA trial – praised the Brazilian study. It “appears well-conceived and well-designed, and was enrolled at a rate that was greater than the sample size that was estimated to be needed based on power analysis,” he said.
The Brazilian study is small, he noted. (In contrast, the ColCORONA trial had 4,488 outpatient participants.) “This study differs from ColCORONA in several ways – the most important being that it is a study of inpatients with moderate to severe COVID (really mostly moderate),” he added. “ColCORONA is looking at a target audience that is much larger – outpatients with mild to moderate COVID with risk factors for hospitalization. Both questions are really important and certainly not mutually exclusive, since our care remains inadequate in both venues. This study also adds value in that several other studies have been conducted in hospital patients with enrollment criteria relatively similar to this one, and all showed benefit, but those were open-label or retrospective, and this is blinded and placebo-controlled.”
Using colchicine in patients with COVID-19
Should physicians turn to colchicine in patients with COVID-19? “I would rather that it still be used in the context of research until formal recommendations can be made by bodies like the NIH and CDC,” Dr. Pillinger said. “But certainly, there may be times when physicians feel compelled to treat patients off label.”
He cautioned, however, that colchicine should never be used with some other drugs. Its interaction with the antibiotic clarithromycin can be fatal, he noted. And, he said, the drug must be monitored in general since it can cause rare, severe problems.
“Overall, colchicine probably works on the overabundant inflammatory response to COVID, and it may be that it can be combined with other drugs that affect viral replication or promote immunity – e.g. vaccines,” Dr. Pillinger said. “So far, it seems as if there is no safety problem with combining colchicine with other approaches, but this has not been studied in a rigorous manner.”
Moving forward, he said, the drug’s very low price outside of the United States “could provide resource-poor countries with a way to help keep patients out of precious hospital beds – or help them go home sooner once admitted.” For now, however, “we need a large-scale inpatient study, and one is currently going on in Great Britain. We also need validation of the outpatient ColCORONA study, and studies to look at whether colchicine can work in conjunction with other strategies.”
The study was funded by grants from the São Paulo Research Foundation, Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, and CAPES Foundation. No disclosures are reported. Dr. Pillinger reports serving as an investigator for the ColCORONA trial and receiving a unrelated investigator-initiated grant from Hikma, a colchicine manufacturer.
FROM RMD OPEN
U.S. COVID-19 death toll passes 450,000
The United States has now reported more than 450,000 COVID-19 deaths during the pandemic, adding 3,912 more on Wednesday, according to data from Johns Hopkins University.
Daily COVID-19 deaths still remain high in the United States, though they’ve decreased slightly from the peak of 4,466 deaths on Jan. 12.
The United States also reported more than 121,000 new COVID-19 cases on Wednesday, which is down from a peak of more than 300,000 new cases on Tuesday. In total, more than 26.5 million people in the United States have been diagnosed with COVID-19, making up a quarter of the 104.5 million cases reported worldwide.
The 7-day average for COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths continues to decline, according to the COVID Tracking Project. The 7-day average for hospitalizations is around 96,500, and the 7-day average for deaths is about 3,000. With the exception of Vermont, all states and territories have reported declines or no changes in their hospitalizations and deaths.
“We have seen the 7-day average for new deaths decrease for over a week. At the same time, states are reporting an average of 3,000 people dying per day,” the COVID Tracking Project wrote in a post on Twitter. “The data is hopeful and devastating.”
More than 2.2 million COVID-19 deaths have been reported worldwide. The United States continues to report the most deaths, followed by Brazil with 227,500, Mexico with 161,200, and India with 154,700 deaths.
The U.S. COVID-19 death toll could reach 496,000-534,000 by the end of February, according to a new forecast by the CDC, which includes models from 36 national groups. Deaths will likely decrease during the next 4 weeks, with about 11,300-22,600 deaths possibly reported during the last week of February.
The 534,000 total would equal about 1 death for every minute of the pandemic, according to CNN, given that the first U.S. death was reported on Feb. 29 last year.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States has now reported more than 450,000 COVID-19 deaths during the pandemic, adding 3,912 more on Wednesday, according to data from Johns Hopkins University.
Daily COVID-19 deaths still remain high in the United States, though they’ve decreased slightly from the peak of 4,466 deaths on Jan. 12.
The United States also reported more than 121,000 new COVID-19 cases on Wednesday, which is down from a peak of more than 300,000 new cases on Tuesday. In total, more than 26.5 million people in the United States have been diagnosed with COVID-19, making up a quarter of the 104.5 million cases reported worldwide.
The 7-day average for COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths continues to decline, according to the COVID Tracking Project. The 7-day average for hospitalizations is around 96,500, and the 7-day average for deaths is about 3,000. With the exception of Vermont, all states and territories have reported declines or no changes in their hospitalizations and deaths.
“We have seen the 7-day average for new deaths decrease for over a week. At the same time, states are reporting an average of 3,000 people dying per day,” the COVID Tracking Project wrote in a post on Twitter. “The data is hopeful and devastating.”
More than 2.2 million COVID-19 deaths have been reported worldwide. The United States continues to report the most deaths, followed by Brazil with 227,500, Mexico with 161,200, and India with 154,700 deaths.
The U.S. COVID-19 death toll could reach 496,000-534,000 by the end of February, according to a new forecast by the CDC, which includes models from 36 national groups. Deaths will likely decrease during the next 4 weeks, with about 11,300-22,600 deaths possibly reported during the last week of February.
The 534,000 total would equal about 1 death for every minute of the pandemic, according to CNN, given that the first U.S. death was reported on Feb. 29 last year.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States has now reported more than 450,000 COVID-19 deaths during the pandemic, adding 3,912 more on Wednesday, according to data from Johns Hopkins University.
Daily COVID-19 deaths still remain high in the United States, though they’ve decreased slightly from the peak of 4,466 deaths on Jan. 12.
The United States also reported more than 121,000 new COVID-19 cases on Wednesday, which is down from a peak of more than 300,000 new cases on Tuesday. In total, more than 26.5 million people in the United States have been diagnosed with COVID-19, making up a quarter of the 104.5 million cases reported worldwide.
The 7-day average for COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths continues to decline, according to the COVID Tracking Project. The 7-day average for hospitalizations is around 96,500, and the 7-day average for deaths is about 3,000. With the exception of Vermont, all states and territories have reported declines or no changes in their hospitalizations and deaths.
“We have seen the 7-day average for new deaths decrease for over a week. At the same time, states are reporting an average of 3,000 people dying per day,” the COVID Tracking Project wrote in a post on Twitter. “The data is hopeful and devastating.”
More than 2.2 million COVID-19 deaths have been reported worldwide. The United States continues to report the most deaths, followed by Brazil with 227,500, Mexico with 161,200, and India with 154,700 deaths.
The U.S. COVID-19 death toll could reach 496,000-534,000 by the end of February, according to a new forecast by the CDC, which includes models from 36 national groups. Deaths will likely decrease during the next 4 weeks, with about 11,300-22,600 deaths possibly reported during the last week of February.
The 534,000 total would equal about 1 death for every minute of the pandemic, according to CNN, given that the first U.S. death was reported on Feb. 29 last year.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Cannabis tied to self-harm, death in youth with mood disorders
Adolescents and young adults with mood disorders and cannabis use disorder (CUD) are at significantly increased risk for self-harm, all-cause mortality, homicide, and death by unintentional overdose, new research suggests.
Investigators found the risk for self-harm was three times higher, all-cause mortality was 59% higher, unintentional overdose was 2.5 times higher, and homicide was more than three times higher in those with versus without CUD.
“The take-home message of these findings is that we need to be aware of the perception that cannabis use is harmless, when it’s actually not,” lead author Cynthia Fontanella, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
“We need to educate parents and clinicians that there are risks associated with cannabis, including increased risk for self-harm and death, and we need to effectively treat both cannabis use disorder and mood disorders,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 19, 2021, in JAMA Pediatrics.
Little research in youth
“There has been very little research conducted on CUD in the adolescent population, and most studies have been conducted with adults,” Dr. Fontanella said.
Research on adults has shown that, even in people without mood disorders, cannabis use is associated with the early onset of mood disorders, psychosis, and anxiety disorders and has also been linked with suicidal behavior and increased risk for motor vehicle accidents, Dr. Fontanella said.
“We were motivated to conduct this study because we treat kids with depression and bipolar disorder and we noticed a high prevalence of CUD in this population, so we were curious about what its negative effects might be,” Dr. Fontanella recounted.
The researchers analyzed 7-year data drawn from Ohio Medicaid claims and linked to data from death certificates in 204,780 youths between the ages of 10 and 24 years (mean age was 17.2 years at the time of mood disorder diagnosis). Most were female, non-Hispanic White, enrolled in Medicaid because of poverty, and living in a metropolitan area (65.0%, 66.9%, 87.6%, and 77.1%, respectively).
Participants were followed up to 1 year from diagnosis until the end of enrollment, a self-harm event, or death.
Researchers included demographic, clinical, and treatment factors as covariates.
Close to three-quarters (72.7%) of the cohort had a depressive disorder, followed by unspecified/persistent mood disorder and bipolar disorder (14.9% and 12.4%, respectively). Comorbidities included ADHD (12.4%), anxiety disorder (12.3%), and other mental disorders (13.1%).
One -tenth of the cohort (10.3%) were diagnosed with CUD.
CUD treatment referrals
“Although CUD was associated with suicide in the unadjusted model, it was not significantly associated in adjusted models,” the authors reported.
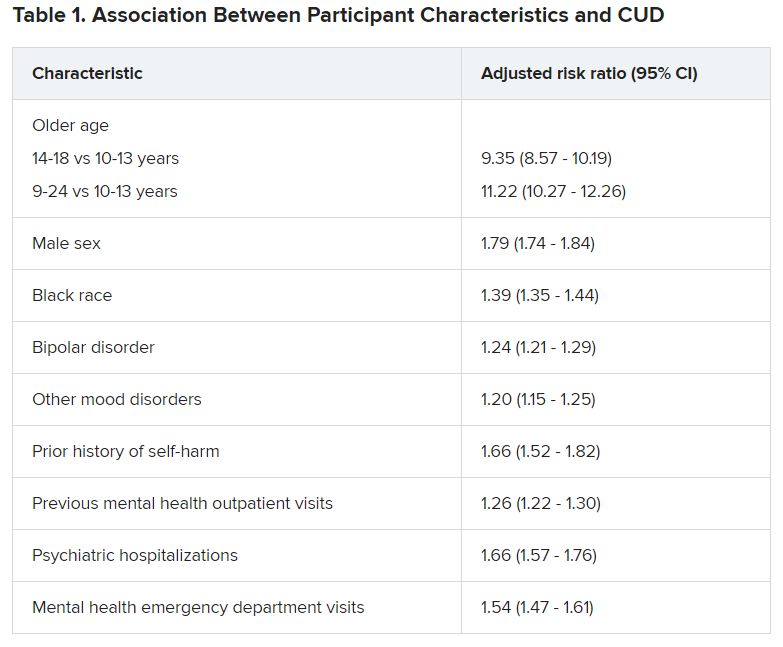
Dr. Fontanella noted that the risk for these adverse outcomes is greater among those who engage in heavy, frequent use or who use cannabis that has higher-potency tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content.
Reasons why CUD might be associated with these adverse outcomes are that it can increase impulsivity, poor judgment, and clouded thinking, which may in turn increase the risk for self-harm behaviors, she said.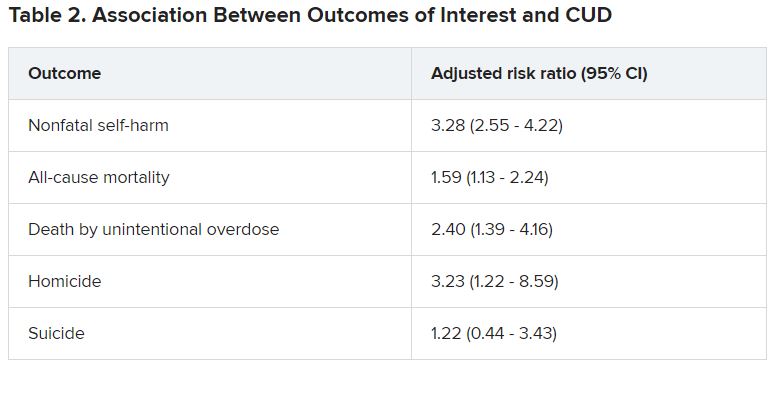
She recommended that clinicians refer youth with CUD for “effective treatments,” including family-based models and individual approaches, such as cognitive behavioral therapy and motivational enhancement therapy.
Open dialogue
In a comment, Wilfrid Noel Raby, MD, PhD, adjunct clinical professor, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, noted that psychosis can occur in patients with CUD and mood disorders – especially bipolar disorder – but was not included as a study outcome. “I would have liked to see more data about that,” he said.
However, “The trend is that cannabis use is starting at younger and younger ages, which has all kinds of ramifications in terms of cerebral development.”
Christopher Hammond, MD, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said: “Three major strengths of the study are the size of the sample, its longitudinal analysis, and that the authors controlled for a number of potential confounding variables.”
In light of the findings, Dr. Hammond recommended clinicians and other health professionals who work with young people “should screen for cannabis-related problems in youth with mood disorders.”
Dr. Hammond, who is the director of the Co-occurring Disorders in Adolescents and Young Adults Clinical and Research Program, Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, Baltimore, and was not involved with the study, recommended counseling youth with mood disorders and their parents and families “regarding the potential adverse health effects related to cannabis use.”
He also recommended “open dialogue with youth with and without mental health conditions about misleading reports in the national media and advertising about cannabis’ health benefits.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. Dr. Fontanella reported receiving grants from the National Institute of Mental Health during the conduct of the study. Dr. Raby reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hammond reported receiving research grant funding from the National Institutes of Health, the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration, the National Network of Depression Centers, and the Armstrong Institute at Johns Hopkins Bayview and serves as a scientific adviser for the National Courts and Science Institute and as a subject matter expert for SAMHSA related to co-occurring substance use disorders and severe emotional disturbance in youth.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents and young adults with mood disorders and cannabis use disorder (CUD) are at significantly increased risk for self-harm, all-cause mortality, homicide, and death by unintentional overdose, new research suggests.
Investigators found the risk for self-harm was three times higher, all-cause mortality was 59% higher, unintentional overdose was 2.5 times higher, and homicide was more than three times higher in those with versus without CUD.
“The take-home message of these findings is that we need to be aware of the perception that cannabis use is harmless, when it’s actually not,” lead author Cynthia Fontanella, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
“We need to educate parents and clinicians that there are risks associated with cannabis, including increased risk for self-harm and death, and we need to effectively treat both cannabis use disorder and mood disorders,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 19, 2021, in JAMA Pediatrics.
Little research in youth
“There has been very little research conducted on CUD in the adolescent population, and most studies have been conducted with adults,” Dr. Fontanella said.
Research on adults has shown that, even in people without mood disorders, cannabis use is associated with the early onset of mood disorders, psychosis, and anxiety disorders and has also been linked with suicidal behavior and increased risk for motor vehicle accidents, Dr. Fontanella said.
“We were motivated to conduct this study because we treat kids with depression and bipolar disorder and we noticed a high prevalence of CUD in this population, so we were curious about what its negative effects might be,” Dr. Fontanella recounted.
The researchers analyzed 7-year data drawn from Ohio Medicaid claims and linked to data from death certificates in 204,780 youths between the ages of 10 and 24 years (mean age was 17.2 years at the time of mood disorder diagnosis). Most were female, non-Hispanic White, enrolled in Medicaid because of poverty, and living in a metropolitan area (65.0%, 66.9%, 87.6%, and 77.1%, respectively).
Participants were followed up to 1 year from diagnosis until the end of enrollment, a self-harm event, or death.
Researchers included demographic, clinical, and treatment factors as covariates.
Close to three-quarters (72.7%) of the cohort had a depressive disorder, followed by unspecified/persistent mood disorder and bipolar disorder (14.9% and 12.4%, respectively). Comorbidities included ADHD (12.4%), anxiety disorder (12.3%), and other mental disorders (13.1%).
One -tenth of the cohort (10.3%) were diagnosed with CUD.
CUD treatment referrals
“Although CUD was associated with suicide in the unadjusted model, it was not significantly associated in adjusted models,” the authors reported.

Dr. Fontanella noted that the risk for these adverse outcomes is greater among those who engage in heavy, frequent use or who use cannabis that has higher-potency tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content.
Reasons why CUD might be associated with these adverse outcomes are that it can increase impulsivity, poor judgment, and clouded thinking, which may in turn increase the risk for self-harm behaviors, she said.
She recommended that clinicians refer youth with CUD for “effective treatments,” including family-based models and individual approaches, such as cognitive behavioral therapy and motivational enhancement therapy.
Open dialogue
In a comment, Wilfrid Noel Raby, MD, PhD, adjunct clinical professor, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, noted that psychosis can occur in patients with CUD and mood disorders – especially bipolar disorder – but was not included as a study outcome. “I would have liked to see more data about that,” he said.
However, “The trend is that cannabis use is starting at younger and younger ages, which has all kinds of ramifications in terms of cerebral development.”
Christopher Hammond, MD, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said: “Three major strengths of the study are the size of the sample, its longitudinal analysis, and that the authors controlled for a number of potential confounding variables.”
In light of the findings, Dr. Hammond recommended clinicians and other health professionals who work with young people “should screen for cannabis-related problems in youth with mood disorders.”
Dr. Hammond, who is the director of the Co-occurring Disorders in Adolescents and Young Adults Clinical and Research Program, Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, Baltimore, and was not involved with the study, recommended counseling youth with mood disorders and their parents and families “regarding the potential adverse health effects related to cannabis use.”
He also recommended “open dialogue with youth with and without mental health conditions about misleading reports in the national media and advertising about cannabis’ health benefits.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. Dr. Fontanella reported receiving grants from the National Institute of Mental Health during the conduct of the study. Dr. Raby reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hammond reported receiving research grant funding from the National Institutes of Health, the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration, the National Network of Depression Centers, and the Armstrong Institute at Johns Hopkins Bayview and serves as a scientific adviser for the National Courts and Science Institute and as a subject matter expert for SAMHSA related to co-occurring substance use disorders and severe emotional disturbance in youth.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents and young adults with mood disorders and cannabis use disorder (CUD) are at significantly increased risk for self-harm, all-cause mortality, homicide, and death by unintentional overdose, new research suggests.
Investigators found the risk for self-harm was three times higher, all-cause mortality was 59% higher, unintentional overdose was 2.5 times higher, and homicide was more than three times higher in those with versus without CUD.
“The take-home message of these findings is that we need to be aware of the perception that cannabis use is harmless, when it’s actually not,” lead author Cynthia Fontanella, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
“We need to educate parents and clinicians that there are risks associated with cannabis, including increased risk for self-harm and death, and we need to effectively treat both cannabis use disorder and mood disorders,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 19, 2021, in JAMA Pediatrics.
Little research in youth
“There has been very little research conducted on CUD in the adolescent population, and most studies have been conducted with adults,” Dr. Fontanella said.
Research on adults has shown that, even in people without mood disorders, cannabis use is associated with the early onset of mood disorders, psychosis, and anxiety disorders and has also been linked with suicidal behavior and increased risk for motor vehicle accidents, Dr. Fontanella said.
“We were motivated to conduct this study because we treat kids with depression and bipolar disorder and we noticed a high prevalence of CUD in this population, so we were curious about what its negative effects might be,” Dr. Fontanella recounted.
The researchers analyzed 7-year data drawn from Ohio Medicaid claims and linked to data from death certificates in 204,780 youths between the ages of 10 and 24 years (mean age was 17.2 years at the time of mood disorder diagnosis). Most were female, non-Hispanic White, enrolled in Medicaid because of poverty, and living in a metropolitan area (65.0%, 66.9%, 87.6%, and 77.1%, respectively).
Participants were followed up to 1 year from diagnosis until the end of enrollment, a self-harm event, or death.
Researchers included demographic, clinical, and treatment factors as covariates.
Close to three-quarters (72.7%) of the cohort had a depressive disorder, followed by unspecified/persistent mood disorder and bipolar disorder (14.9% and 12.4%, respectively). Comorbidities included ADHD (12.4%), anxiety disorder (12.3%), and other mental disorders (13.1%).
One -tenth of the cohort (10.3%) were diagnosed with CUD.
CUD treatment referrals
“Although CUD was associated with suicide in the unadjusted model, it was not significantly associated in adjusted models,” the authors reported.

Dr. Fontanella noted that the risk for these adverse outcomes is greater among those who engage in heavy, frequent use or who use cannabis that has higher-potency tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content.
Reasons why CUD might be associated with these adverse outcomes are that it can increase impulsivity, poor judgment, and clouded thinking, which may in turn increase the risk for self-harm behaviors, she said.
She recommended that clinicians refer youth with CUD for “effective treatments,” including family-based models and individual approaches, such as cognitive behavioral therapy and motivational enhancement therapy.
Open dialogue
In a comment, Wilfrid Noel Raby, MD, PhD, adjunct clinical professor, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, noted that psychosis can occur in patients with CUD and mood disorders – especially bipolar disorder – but was not included as a study outcome. “I would have liked to see more data about that,” he said.
However, “The trend is that cannabis use is starting at younger and younger ages, which has all kinds of ramifications in terms of cerebral development.”
Christopher Hammond, MD, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said: “Three major strengths of the study are the size of the sample, its longitudinal analysis, and that the authors controlled for a number of potential confounding variables.”
In light of the findings, Dr. Hammond recommended clinicians and other health professionals who work with young people “should screen for cannabis-related problems in youth with mood disorders.”
Dr. Hammond, who is the director of the Co-occurring Disorders in Adolescents and Young Adults Clinical and Research Program, Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, Baltimore, and was not involved with the study, recommended counseling youth with mood disorders and their parents and families “regarding the potential adverse health effects related to cannabis use.”
He also recommended “open dialogue with youth with and without mental health conditions about misleading reports in the national media and advertising about cannabis’ health benefits.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. Dr. Fontanella reported receiving grants from the National Institute of Mental Health during the conduct of the study. Dr. Raby reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hammond reported receiving research grant funding from the National Institutes of Health, the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration, the National Network of Depression Centers, and the Armstrong Institute at Johns Hopkins Bayview and serves as a scientific adviser for the National Courts and Science Institute and as a subject matter expert for SAMHSA related to co-occurring substance use disorders and severe emotional disturbance in youth.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TBI beats chemoconditioning for ALL transplants in children
The investigators sought to answer a question many physicians have raised: With improvements in human leukocyte antigen typing, better graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, and other advances, can myeloablative chemotherapy conditioning replace TBI, which is more toxic?
The downstream effects of TBI can include secondary malignancies and cataracts, as well as impaired growth and impaired gonadal and cognitive function.
But the answer to that question is no, or at least, not yet.
The phase 3 trial included individuals with ALL who were aged 4-21 years at time of transplant. They were randomly assigned to receive either fractionated TBI at 12 Gy plus etoposide or chemotherapy based on a myeloablative regimen: fludarabine, thiotepa, and either busulfan or treosulfan.
The trial was stopped after 413 patients had undergone randomization – quite a bit short of the 1,000-patient goal. The trial was terminated because TBI proved clearly superior on an interim analysis at a median follow-up of 2.1 years.
The results showed that 72% of the TBI group – but only 51% of the chemotherapy arm – were relapse free at 2 years with no graft-versus-host disease (P = .0003).
The 2-year treatment-related mortality rate was 2% in the TBI group but 9% with chemotherapy conditioning (P = .03).
The study was published Feb. 1, 2020, in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“We recommend TBI plus etoposide conditioning for patients [aged over] 4 years old with high-risk ALL undergoing allogeneic HSCT [hematopoietic stem cell transplant],” they concluded. The investigators were led by Christina Peters, MD, a pediatrics professor at the St. Anna Children’s Cancer Research Institute, Vienna.
The benefits of TBI held on multivariate analysis and across subgroups, including children in their first and second remissions and among those with high-risk cytogenetics. Relapse risk factors, such as age at transplant, leukemic phenotype, and molecular aberrations, did not significantly affect outcomes, the authors reported.
Given that relapses plateaued with TBI at 2.5 years but were still on the upswing for patients who underwent chemoconditioning, “it is unlikely that secondary malignancies after TBI could jeopardize the survival advantage,” they wrote.
“So does this mean that the HCT community is forever chained to TBI as a standard of care? Certainly, it means that without very sound rationale to deviate, a TBI-based preparative regimen is the preferred therapy at present,” Michael Pulsipher, MD, head of blood and marrow transplantation at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, commented in an accompanying editorial.
However, “there are approaches under study currently that may define patients who do not need TBI for high rates of cure,” he suggested. Those approaches include selecting patients with the deepest remissions and using KIR-favorable haplotype to harness natural killer cell activity.
“In our new world of chimeric antigen receptor T-cells and immunotherapies, surely we can find safer paths to success,” Dr. Pulsipher wrote.
With regard to patient selection, the investigators noted that a recent review that included more than 3,000 children with ALL found no overall survival benefit with TBI versus chemoconditioning for patients in first complete remission but worse outcomes with chemoconditioning among patients in second complete remission. “A similar trend was observed in our subgroup analyses; however, our study was not powered to assess statistical significance in a sample size of 413 patients,” they wrote.
Minimal residual disease did not influence survival outcomes, probably because the investigators were aggressive in inducing deep remission in their patients before transplant, so for most patients, MRD was undetectable or very low beforehand.
The study was funded by Amgen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Neovii, Medac, and others. Dr. Peters and coauthors, as well as Dr. Pulsipher have disclosed numerous ties with those and/or other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigators sought to answer a question many physicians have raised: With improvements in human leukocyte antigen typing, better graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, and other advances, can myeloablative chemotherapy conditioning replace TBI, which is more toxic?
The downstream effects of TBI can include secondary malignancies and cataracts, as well as impaired growth and impaired gonadal and cognitive function.
But the answer to that question is no, or at least, not yet.
The phase 3 trial included individuals with ALL who were aged 4-21 years at time of transplant. They were randomly assigned to receive either fractionated TBI at 12 Gy plus etoposide or chemotherapy based on a myeloablative regimen: fludarabine, thiotepa, and either busulfan or treosulfan.
The trial was stopped after 413 patients had undergone randomization – quite a bit short of the 1,000-patient goal. The trial was terminated because TBI proved clearly superior on an interim analysis at a median follow-up of 2.1 years.
The results showed that 72% of the TBI group – but only 51% of the chemotherapy arm – were relapse free at 2 years with no graft-versus-host disease (P = .0003).
The 2-year treatment-related mortality rate was 2% in the TBI group but 9% with chemotherapy conditioning (P = .03).
The study was published Feb. 1, 2020, in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“We recommend TBI plus etoposide conditioning for patients [aged over] 4 years old with high-risk ALL undergoing allogeneic HSCT [hematopoietic stem cell transplant],” they concluded. The investigators were led by Christina Peters, MD, a pediatrics professor at the St. Anna Children’s Cancer Research Institute, Vienna.
The benefits of TBI held on multivariate analysis and across subgroups, including children in their first and second remissions and among those with high-risk cytogenetics. Relapse risk factors, such as age at transplant, leukemic phenotype, and molecular aberrations, did not significantly affect outcomes, the authors reported.
Given that relapses plateaued with TBI at 2.5 years but were still on the upswing for patients who underwent chemoconditioning, “it is unlikely that secondary malignancies after TBI could jeopardize the survival advantage,” they wrote.
“So does this mean that the HCT community is forever chained to TBI as a standard of care? Certainly, it means that without very sound rationale to deviate, a TBI-based preparative regimen is the preferred therapy at present,” Michael Pulsipher, MD, head of blood and marrow transplantation at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, commented in an accompanying editorial.
However, “there are approaches under study currently that may define patients who do not need TBI for high rates of cure,” he suggested. Those approaches include selecting patients with the deepest remissions and using KIR-favorable haplotype to harness natural killer cell activity.
“In our new world of chimeric antigen receptor T-cells and immunotherapies, surely we can find safer paths to success,” Dr. Pulsipher wrote.
With regard to patient selection, the investigators noted that a recent review that included more than 3,000 children with ALL found no overall survival benefit with TBI versus chemoconditioning for patients in first complete remission but worse outcomes with chemoconditioning among patients in second complete remission. “A similar trend was observed in our subgroup analyses; however, our study was not powered to assess statistical significance in a sample size of 413 patients,” they wrote.
Minimal residual disease did not influence survival outcomes, probably because the investigators were aggressive in inducing deep remission in their patients before transplant, so for most patients, MRD was undetectable or very low beforehand.
The study was funded by Amgen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Neovii, Medac, and others. Dr. Peters and coauthors, as well as Dr. Pulsipher have disclosed numerous ties with those and/or other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigators sought to answer a question many physicians have raised: With improvements in human leukocyte antigen typing, better graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, and other advances, can myeloablative chemotherapy conditioning replace TBI, which is more toxic?
The downstream effects of TBI can include secondary malignancies and cataracts, as well as impaired growth and impaired gonadal and cognitive function.
But the answer to that question is no, or at least, not yet.
The phase 3 trial included individuals with ALL who were aged 4-21 years at time of transplant. They were randomly assigned to receive either fractionated TBI at 12 Gy plus etoposide or chemotherapy based on a myeloablative regimen: fludarabine, thiotepa, and either busulfan or treosulfan.
The trial was stopped after 413 patients had undergone randomization – quite a bit short of the 1,000-patient goal. The trial was terminated because TBI proved clearly superior on an interim analysis at a median follow-up of 2.1 years.
The results showed that 72% of the TBI group – but only 51% of the chemotherapy arm – were relapse free at 2 years with no graft-versus-host disease (P = .0003).
The 2-year treatment-related mortality rate was 2% in the TBI group but 9% with chemotherapy conditioning (P = .03).
The study was published Feb. 1, 2020, in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“We recommend TBI plus etoposide conditioning for patients [aged over] 4 years old with high-risk ALL undergoing allogeneic HSCT [hematopoietic stem cell transplant],” they concluded. The investigators were led by Christina Peters, MD, a pediatrics professor at the St. Anna Children’s Cancer Research Institute, Vienna.
The benefits of TBI held on multivariate analysis and across subgroups, including children in their first and second remissions and among those with high-risk cytogenetics. Relapse risk factors, such as age at transplant, leukemic phenotype, and molecular aberrations, did not significantly affect outcomes, the authors reported.
Given that relapses plateaued with TBI at 2.5 years but were still on the upswing for patients who underwent chemoconditioning, “it is unlikely that secondary malignancies after TBI could jeopardize the survival advantage,” they wrote.
“So does this mean that the HCT community is forever chained to TBI as a standard of care? Certainly, it means that without very sound rationale to deviate, a TBI-based preparative regimen is the preferred therapy at present,” Michael Pulsipher, MD, head of blood and marrow transplantation at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, commented in an accompanying editorial.
However, “there are approaches under study currently that may define patients who do not need TBI for high rates of cure,” he suggested. Those approaches include selecting patients with the deepest remissions and using KIR-favorable haplotype to harness natural killer cell activity.
“In our new world of chimeric antigen receptor T-cells and immunotherapies, surely we can find safer paths to success,” Dr. Pulsipher wrote.
With regard to patient selection, the investigators noted that a recent review that included more than 3,000 children with ALL found no overall survival benefit with TBI versus chemoconditioning for patients in first complete remission but worse outcomes with chemoconditioning among patients in second complete remission. “A similar trend was observed in our subgroup analyses; however, our study was not powered to assess statistical significance in a sample size of 413 patients,” they wrote.
Minimal residual disease did not influence survival outcomes, probably because the investigators were aggressive in inducing deep remission in their patients before transplant, so for most patients, MRD was undetectable or very low beforehand.
The study was funded by Amgen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Neovii, Medac, and others. Dr. Peters and coauthors, as well as Dr. Pulsipher have disclosed numerous ties with those and/or other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Match and COVID-19: Stolen interviews, swag bags, and stress
The final numbers won’t look much different, but the 2021 Match results will be unlike any before. As of mid-January, only 16 more institutions were confirmed to be participating in Match Day this year, resulting in about 800 more positions, said Donna Lamb, president and CEO of the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP). The Electronic Residency Application Service reported about 50,000 individual applicant submissions, a slight increase from prior years.
The stats may be similar, but the current residency application cycle may lead to wildly different results after the pandemic forced interviews to be conducted virtually and caused the cancellation of most away clinical rotations. Troy Amen, a fifth-year MD-MBA student at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and copresident of his student class, says the lack of on-campus, in-person experiences means students feel more in the dark than ever. The same is true for institutions. “The programs are also suffering because now they don’t know which students are a good ‘cultural fit’ for them,” he said.
Standing out has always been a concern for prospective residents, but Mr. Amen says fears are even higher this year. “[Institutions are] struggling to vet out 850 applicants, and they have no connection to us.”
Organizations have scrambled to keep the process as fair and informative as possible. “Everyone is trying to do the right thing here,” said Alison J. Whelan, MD, chief academic officer of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). She says that although the process has significantly changed, the heart of it remains the same. “The bottom line is directors really want to fill their intern class, and schools and students really want to match.”
Since the NRMP was established in 1952, it has never had to contend with a pandemic of this scale. The unprecedented circumstances have led to some much-feared and some unexpected changes, like top candidates “stealing” interview slots, “swag bags” sent to entice residents, beefed-up online profiles, as well as “Zoom fatigue,” a spike in home-field advantage for institutions, and massive anxiety for those students staking their future to a city they may have never seen in person.
What was lost and what was gained
“It’s really hard to get a real feel for the program when you’ve not been there in person,” said Christopher Smith, MD, director of the internal medicine residency program at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. Dr. Smith recalled interviewing for residencies 25 years ago. His wife, a teacher, took time off to travel with him.
“She would ‘interview the town’ while I interviewed the program, and we compared notes at night,” he said. Because of COVID-19-related travel restrictions, just physically seeing the city in which they may live for years wasn’t an option for many. “I have a lot of sympathy for students applying right now,” Dr. Smith said.
For the residency class of 2021, the first shoe really dropped last March, when the AAMC issued guidance strongly recommending that programs pause clinical rotations away from their home schools. As established doctors know well, and as graduating medical students confirmed, these rotations are crucial to understanding a program’s culture and gaining experience that can boost candidacy. “I’m applying to orthopedic surgery, where away rotations are the gold standard for impressing attendees and residents at institutions away from home,” said Mr. Amen.
The pandemic completely cut off that key source of information to determine the right fit. It also meant applicants couldn’t have as diverse a portfolio of recommendation letters, something many worry may be detrimental to their soon-to-be-released Match rankings.
Unlike the loss of away rotations, the forced shift from in-person to virtual interviews had some meaningful benefits. Students no longer incurred expenses for airline flights, hotel rooms, and rental cars. Many organizations and programs have been trying for years to figure out how to lower the financial burden of interviews to make the process more equitable for those at economic or other disadvantage.
“The equity piece of this is huge – decreasing barriers and leveling the field a little bit is a really huge advantage,” said Kate Shaw, MD, residency program director and associate chair of education for the obstetrics and gynecology program at Stanford (Calif.) University. In some ways, this latest change is an extension of a strategy Dr. Shaw and others had already begun implementing.
“Over the last 5 to 10 years, we’ve been working to address the implicit bias in the application process, so we’ve gone to a holistic review of applicants, where we don’t have score cutoffs. We look at the whole person,” she said. “And we did that in an effort to increase diversity and equity.” Dr. Shaw and others hope that the accidental positive changes from COVID restrictions may be intentionally preserved long after the pandemic ends.
Home-field advantage vs. swag bags
Many medical students applying to residencies this year say they have given greater weight to their home programs than they might have without the pandemic. “I didn’t get a sense of anyone’s culture other than my home institution,” said Alex Skidmore, a fourth-year medical student at Washington University in St. Louis. “I definitely am ranking Wash-U higher.”
The desire to emphasize the known quality of a student’s home institution isn’t surprising to program directors. Dr. Shaw said she thinks this year’s Match could well end with a higher percentage of students matching either in their home programs or in programs close to loved ones. “The value of being close to family has come up in our conversations, where students are considering the right program for them but also the other life factors,” she said.
To overcome this home-field advantage, many programs have beefed up their websites, including providing video tours of their facilities. They also “upped their social media game” and encouraged residents to create online groups for prospective residents to share information about programs and life outside of work. Some residents even offered video tours of their personal apartments to applicants.
Without in-person access to facilities and staff, a program’s online presence became a deciding factor, applicants said. “If you have a bad website, it’s like having a dirty building to interview applicants in,” Mr. Skidmore said. For many prospective residents, an institution’s Internet presence was a “make or break” factor. “It’s the only thing I saw for many programs, and when we are doing the amount of research we are doing remotely, when I saw a program with a bad website, it made me not like the program as much,” he said.
Some programs, hoping to woo candidates as well as to provide them with more insight into what they and their cities have to offer, sent “swag bags” to candidates. These included things like gift cards for food delivery and offerings from local businesses. Washington University’s pediatrics residency program sent gooey butter cakes – a St. Louis staple – along with other treats from small businesses and copies of magazines that showcased the city’s dining and entertainment scene.
Other programs, even those at the same medical institution, felt quite strongly that those types of packages shouldn’t be sent. “We interviewed almost 500 applicants, so there was no way we could have afforded that,” said Dominique Cosco, MD, director of Washington University’s internal medicine residency program. “Our normal recruitment budget is almost $100,000 in a normal year, and that got cut because of COVID. For us, it was thinking about allocations of resources.”
Interview slot theft and zoom fatigue
Remote interviewing also meant that applicants could accept more interviews, something that raised a big concern. Without expenses or travel time, would top-tier candidates take more interviews than normal and thus take limited interview spots from other qualified candidates? Maybe so, says the AAMC’s Dr. Whelan.
“We didn’t have systematic data, but we heard from enough schools and programs ... that students who were maybe not the top-top ranked students in the class but in every way solid were receiving fewer interviews than previous years,” Dr. Whelan said. This is despite guidance that recommended programs add interview slots to serve as a counterbalance.
Some students say they accepted more interview slots in the beginning of the interview season, partly because they could, and partly because some thought of early interviews as “practice” for later interviews. However, as video interviews piled up, some of them described feeling “Zoom fatigue” and said they later canceled interviews with programs they didn’t anticipate joining.
More SOAP, less clarity
As for what comes next, the NRMP is preparing for a longer-than-normal Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) than in years past. SOAP usually offers three rounds of matches after the initial Match Day; Ms. Lamb said things are different this year.
“SOAP will be the same number of days, but we’ve added an additional round on Thursday afternoon,” she said. Will it be unnecessary or not enough? Nobody knows. “How big SOAP actually is going to be is one of the things that we really don’t have a sense of right now and probably aren’t going to have a sense of until the Match.”
Uncertainty is the name of the game. More than any other Match before, programs and applicants won’t know how results from this pandemic year stack up for a few months at the very least. “I really want to see what this looks like on the other side,” Dr. Smith said. “Are applicants happy with the way it looks when they come here? Do they feel like they matched with the right place?”
Whether this unprecedented year will be remembered more for positive changes moving forward, including more flexibility on remote interviews, or for less-informed decisions that result in dissatisfied participants is also unclear.
“I think after the Match is over, we’ll be talking to everyone to get more perspective on what people who are applying now would tell the next class, and how programs can adjust,” said Kathy Diemer, MD, assistant dean for career counseling at Washington University. At the very least, those who are involved in this year after year can start thinking about what the future should look like.
“We’re going to need to do some kind of debriefing after this is over, both program directors and our students as well, so we can determine how to move forward next year and beyond.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The final numbers won’t look much different, but the 2021 Match results will be unlike any before. As of mid-January, only 16 more institutions were confirmed to be participating in Match Day this year, resulting in about 800 more positions, said Donna Lamb, president and CEO of the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP). The Electronic Residency Application Service reported about 50,000 individual applicant submissions, a slight increase from prior years.
The stats may be similar, but the current residency application cycle may lead to wildly different results after the pandemic forced interviews to be conducted virtually and caused the cancellation of most away clinical rotations. Troy Amen, a fifth-year MD-MBA student at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and copresident of his student class, says the lack of on-campus, in-person experiences means students feel more in the dark than ever. The same is true for institutions. “The programs are also suffering because now they don’t know which students are a good ‘cultural fit’ for them,” he said.
Standing out has always been a concern for prospective residents, but Mr. Amen says fears are even higher this year. “[Institutions are] struggling to vet out 850 applicants, and they have no connection to us.”
Organizations have scrambled to keep the process as fair and informative as possible. “Everyone is trying to do the right thing here,” said Alison J. Whelan, MD, chief academic officer of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). She says that although the process has significantly changed, the heart of it remains the same. “The bottom line is directors really want to fill their intern class, and schools and students really want to match.”
Since the NRMP was established in 1952, it has never had to contend with a pandemic of this scale. The unprecedented circumstances have led to some much-feared and some unexpected changes, like top candidates “stealing” interview slots, “swag bags” sent to entice residents, beefed-up online profiles, as well as “Zoom fatigue,” a spike in home-field advantage for institutions, and massive anxiety for those students staking their future to a city they may have never seen in person.
What was lost and what was gained
“It’s really hard to get a real feel for the program when you’ve not been there in person,” said Christopher Smith, MD, director of the internal medicine residency program at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. Dr. Smith recalled interviewing for residencies 25 years ago. His wife, a teacher, took time off to travel with him.
“She would ‘interview the town’ while I interviewed the program, and we compared notes at night,” he said. Because of COVID-19-related travel restrictions, just physically seeing the city in which they may live for years wasn’t an option for many. “I have a lot of sympathy for students applying right now,” Dr. Smith said.
For the residency class of 2021, the first shoe really dropped last March, when the AAMC issued guidance strongly recommending that programs pause clinical rotations away from their home schools. As established doctors know well, and as graduating medical students confirmed, these rotations are crucial to understanding a program’s culture and gaining experience that can boost candidacy. “I’m applying to orthopedic surgery, where away rotations are the gold standard for impressing attendees and residents at institutions away from home,” said Mr. Amen.
The pandemic completely cut off that key source of information to determine the right fit. It also meant applicants couldn’t have as diverse a portfolio of recommendation letters, something many worry may be detrimental to their soon-to-be-released Match rankings.
Unlike the loss of away rotations, the forced shift from in-person to virtual interviews had some meaningful benefits. Students no longer incurred expenses for airline flights, hotel rooms, and rental cars. Many organizations and programs have been trying for years to figure out how to lower the financial burden of interviews to make the process more equitable for those at economic or other disadvantage.
“The equity piece of this is huge – decreasing barriers and leveling the field a little bit is a really huge advantage,” said Kate Shaw, MD, residency program director and associate chair of education for the obstetrics and gynecology program at Stanford (Calif.) University. In some ways, this latest change is an extension of a strategy Dr. Shaw and others had already begun implementing.
“Over the last 5 to 10 years, we’ve been working to address the implicit bias in the application process, so we’ve gone to a holistic review of applicants, where we don’t have score cutoffs. We look at the whole person,” she said. “And we did that in an effort to increase diversity and equity.” Dr. Shaw and others hope that the accidental positive changes from COVID restrictions may be intentionally preserved long after the pandemic ends.
Home-field advantage vs. swag bags
Many medical students applying to residencies this year say they have given greater weight to their home programs than they might have without the pandemic. “I didn’t get a sense of anyone’s culture other than my home institution,” said Alex Skidmore, a fourth-year medical student at Washington University in St. Louis. “I definitely am ranking Wash-U higher.”
The desire to emphasize the known quality of a student’s home institution isn’t surprising to program directors. Dr. Shaw said she thinks this year’s Match could well end with a higher percentage of students matching either in their home programs or in programs close to loved ones. “The value of being close to family has come up in our conversations, where students are considering the right program for them but also the other life factors,” she said.
To overcome this home-field advantage, many programs have beefed up their websites, including providing video tours of their facilities. They also “upped their social media game” and encouraged residents to create online groups for prospective residents to share information about programs and life outside of work. Some residents even offered video tours of their personal apartments to applicants.
Without in-person access to facilities and staff, a program’s online presence became a deciding factor, applicants said. “If you have a bad website, it’s like having a dirty building to interview applicants in,” Mr. Skidmore said. For many prospective residents, an institution’s Internet presence was a “make or break” factor. “It’s the only thing I saw for many programs, and when we are doing the amount of research we are doing remotely, when I saw a program with a bad website, it made me not like the program as much,” he said.
Some programs, hoping to woo candidates as well as to provide them with more insight into what they and their cities have to offer, sent “swag bags” to candidates. These included things like gift cards for food delivery and offerings from local businesses. Washington University’s pediatrics residency program sent gooey butter cakes – a St. Louis staple – along with other treats from small businesses and copies of magazines that showcased the city’s dining and entertainment scene.
Other programs, even those at the same medical institution, felt quite strongly that those types of packages shouldn’t be sent. “We interviewed almost 500 applicants, so there was no way we could have afforded that,” said Dominique Cosco, MD, director of Washington University’s internal medicine residency program. “Our normal recruitment budget is almost $100,000 in a normal year, and that got cut because of COVID. For us, it was thinking about allocations of resources.”
Interview slot theft and zoom fatigue
Remote interviewing also meant that applicants could accept more interviews, something that raised a big concern. Without expenses or travel time, would top-tier candidates take more interviews than normal and thus take limited interview spots from other qualified candidates? Maybe so, says the AAMC’s Dr. Whelan.
“We didn’t have systematic data, but we heard from enough schools and programs ... that students who were maybe not the top-top ranked students in the class but in every way solid were receiving fewer interviews than previous years,” Dr. Whelan said. This is despite guidance that recommended programs add interview slots to serve as a counterbalance.
Some students say they accepted more interview slots in the beginning of the interview season, partly because they could, and partly because some thought of early interviews as “practice” for later interviews. However, as video interviews piled up, some of them described feeling “Zoom fatigue” and said they later canceled interviews with programs they didn’t anticipate joining.
More SOAP, less clarity
As for what comes next, the NRMP is preparing for a longer-than-normal Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) than in years past. SOAP usually offers three rounds of matches after the initial Match Day; Ms. Lamb said things are different this year.
“SOAP will be the same number of days, but we’ve added an additional round on Thursday afternoon,” she said. Will it be unnecessary or not enough? Nobody knows. “How big SOAP actually is going to be is one of the things that we really don’t have a sense of right now and probably aren’t going to have a sense of until the Match.”
Uncertainty is the name of the game. More than any other Match before, programs and applicants won’t know how results from this pandemic year stack up for a few months at the very least. “I really want to see what this looks like on the other side,” Dr. Smith said. “Are applicants happy with the way it looks when they come here? Do they feel like they matched with the right place?”
Whether this unprecedented year will be remembered more for positive changes moving forward, including more flexibility on remote interviews, or for less-informed decisions that result in dissatisfied participants is also unclear.
“I think after the Match is over, we’ll be talking to everyone to get more perspective on what people who are applying now would tell the next class, and how programs can adjust,” said Kathy Diemer, MD, assistant dean for career counseling at Washington University. At the very least, those who are involved in this year after year can start thinking about what the future should look like.
“We’re going to need to do some kind of debriefing after this is over, both program directors and our students as well, so we can determine how to move forward next year and beyond.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The final numbers won’t look much different, but the 2021 Match results will be unlike any before. As of mid-January, only 16 more institutions were confirmed to be participating in Match Day this year, resulting in about 800 more positions, said Donna Lamb, president and CEO of the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP). The Electronic Residency Application Service reported about 50,000 individual applicant submissions, a slight increase from prior years.
The stats may be similar, but the current residency application cycle may lead to wildly different results after the pandemic forced interviews to be conducted virtually and caused the cancellation of most away clinical rotations. Troy Amen, a fifth-year MD-MBA student at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and copresident of his student class, says the lack of on-campus, in-person experiences means students feel more in the dark than ever. The same is true for institutions. “The programs are also suffering because now they don’t know which students are a good ‘cultural fit’ for them,” he said.
Standing out has always been a concern for prospective residents, but Mr. Amen says fears are even higher this year. “[Institutions are] struggling to vet out 850 applicants, and they have no connection to us.”
Organizations have scrambled to keep the process as fair and informative as possible. “Everyone is trying to do the right thing here,” said Alison J. Whelan, MD, chief academic officer of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). She says that although the process has significantly changed, the heart of it remains the same. “The bottom line is directors really want to fill their intern class, and schools and students really want to match.”
Since the NRMP was established in 1952, it has never had to contend with a pandemic of this scale. The unprecedented circumstances have led to some much-feared and some unexpected changes, like top candidates “stealing” interview slots, “swag bags” sent to entice residents, beefed-up online profiles, as well as “Zoom fatigue,” a spike in home-field advantage for institutions, and massive anxiety for those students staking their future to a city they may have never seen in person.
What was lost and what was gained
“It’s really hard to get a real feel for the program when you’ve not been there in person,” said Christopher Smith, MD, director of the internal medicine residency program at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. Dr. Smith recalled interviewing for residencies 25 years ago. His wife, a teacher, took time off to travel with him.
“She would ‘interview the town’ while I interviewed the program, and we compared notes at night,” he said. Because of COVID-19-related travel restrictions, just physically seeing the city in which they may live for years wasn’t an option for many. “I have a lot of sympathy for students applying right now,” Dr. Smith said.
For the residency class of 2021, the first shoe really dropped last March, when the AAMC issued guidance strongly recommending that programs pause clinical rotations away from their home schools. As established doctors know well, and as graduating medical students confirmed, these rotations are crucial to understanding a program’s culture and gaining experience that can boost candidacy. “I’m applying to orthopedic surgery, where away rotations are the gold standard for impressing attendees and residents at institutions away from home,” said Mr. Amen.
The pandemic completely cut off that key source of information to determine the right fit. It also meant applicants couldn’t have as diverse a portfolio of recommendation letters, something many worry may be detrimental to their soon-to-be-released Match rankings.
Unlike the loss of away rotations, the forced shift from in-person to virtual interviews had some meaningful benefits. Students no longer incurred expenses for airline flights, hotel rooms, and rental cars. Many organizations and programs have been trying for years to figure out how to lower the financial burden of interviews to make the process more equitable for those at economic or other disadvantage.
“The equity piece of this is huge – decreasing barriers and leveling the field a little bit is a really huge advantage,” said Kate Shaw, MD, residency program director and associate chair of education for the obstetrics and gynecology program at Stanford (Calif.) University. In some ways, this latest change is an extension of a strategy Dr. Shaw and others had already begun implementing.
“Over the last 5 to 10 years, we’ve been working to address the implicit bias in the application process, so we’ve gone to a holistic review of applicants, where we don’t have score cutoffs. We look at the whole person,” she said. “And we did that in an effort to increase diversity and equity.” Dr. Shaw and others hope that the accidental positive changes from COVID restrictions may be intentionally preserved long after the pandemic ends.
Home-field advantage vs. swag bags
Many medical students applying to residencies this year say they have given greater weight to their home programs than they might have without the pandemic. “I didn’t get a sense of anyone’s culture other than my home institution,” said Alex Skidmore, a fourth-year medical student at Washington University in St. Louis. “I definitely am ranking Wash-U higher.”
The desire to emphasize the known quality of a student’s home institution isn’t surprising to program directors. Dr. Shaw said she thinks this year’s Match could well end with a higher percentage of students matching either in their home programs or in programs close to loved ones. “The value of being close to family has come up in our conversations, where students are considering the right program for them but also the other life factors,” she said.
To overcome this home-field advantage, many programs have beefed up their websites, including providing video tours of their facilities. They also “upped their social media game” and encouraged residents to create online groups for prospective residents to share information about programs and life outside of work. Some residents even offered video tours of their personal apartments to applicants.
Without in-person access to facilities and staff, a program’s online presence became a deciding factor, applicants said. “If you have a bad website, it’s like having a dirty building to interview applicants in,” Mr. Skidmore said. For many prospective residents, an institution’s Internet presence was a “make or break” factor. “It’s the only thing I saw for many programs, and when we are doing the amount of research we are doing remotely, when I saw a program with a bad website, it made me not like the program as much,” he said.
Some programs, hoping to woo candidates as well as to provide them with more insight into what they and their cities have to offer, sent “swag bags” to candidates. These included things like gift cards for food delivery and offerings from local businesses. Washington University’s pediatrics residency program sent gooey butter cakes – a St. Louis staple – along with other treats from small businesses and copies of magazines that showcased the city’s dining and entertainment scene.
Other programs, even those at the same medical institution, felt quite strongly that those types of packages shouldn’t be sent. “We interviewed almost 500 applicants, so there was no way we could have afforded that,” said Dominique Cosco, MD, director of Washington University’s internal medicine residency program. “Our normal recruitment budget is almost $100,000 in a normal year, and that got cut because of COVID. For us, it was thinking about allocations of resources.”
Interview slot theft and zoom fatigue
Remote interviewing also meant that applicants could accept more interviews, something that raised a big concern. Without expenses or travel time, would top-tier candidates take more interviews than normal and thus take limited interview spots from other qualified candidates? Maybe so, says the AAMC’s Dr. Whelan.
“We didn’t have systematic data, but we heard from enough schools and programs ... that students who were maybe not the top-top ranked students in the class but in every way solid were receiving fewer interviews than previous years,” Dr. Whelan said. This is despite guidance that recommended programs add interview slots to serve as a counterbalance.
Some students say they accepted more interview slots in the beginning of the interview season, partly because they could, and partly because some thought of early interviews as “practice” for later interviews. However, as video interviews piled up, some of them described feeling “Zoom fatigue” and said they later canceled interviews with programs they didn’t anticipate joining.
More SOAP, less clarity
As for what comes next, the NRMP is preparing for a longer-than-normal Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) than in years past. SOAP usually offers three rounds of matches after the initial Match Day; Ms. Lamb said things are different this year.
“SOAP will be the same number of days, but we’ve added an additional round on Thursday afternoon,” she said. Will it be unnecessary or not enough? Nobody knows. “How big SOAP actually is going to be is one of the things that we really don’t have a sense of right now and probably aren’t going to have a sense of until the Match.”
Uncertainty is the name of the game. More than any other Match before, programs and applicants won’t know how results from this pandemic year stack up for a few months at the very least. “I really want to see what this looks like on the other side,” Dr. Smith said. “Are applicants happy with the way it looks when they come here? Do they feel like they matched with the right place?”
Whether this unprecedented year will be remembered more for positive changes moving forward, including more flexibility on remote interviews, or for less-informed decisions that result in dissatisfied participants is also unclear.
“I think after the Match is over, we’ll be talking to everyone to get more perspective on what people who are applying now would tell the next class, and how programs can adjust,” said Kathy Diemer, MD, assistant dean for career counseling at Washington University. At the very least, those who are involved in this year after year can start thinking about what the future should look like.
“We’re going to need to do some kind of debriefing after this is over, both program directors and our students as well, so we can determine how to move forward next year and beyond.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nature or nurture in primary care?
Does the name Bruce Lipton sound familiar to you? Until a few years ago the only bell that it rang with me was that I had a high school classmate named Bruce Lipton. I recall that his father owned the local grocery store and he was one of the most prolific pranksters in a class with a long history of prank playing. If the name dredges up any associations for you it may because you have heard of a PhD biologist who has written and lectured extensively on epigenetics. You may have even read his most widely published book, “The Biology of Belief.” It turns out the Epigenetics Guy and my high school prankster classmate are one and the same.
After decades of separation – he is in California and I’m here in Maine – we have reconnected via Zoom mini reunions that our class has organized to combat the isolation that has descended on us with the pandemic. While I haven’t read his books, I have watched and listened to some of his podcasts and lectures. The devilish twinkle in his eye in the 1950s and 1960s has provided the scaffolding on which he has built a charismatic and persuasive presentation style.
Bruce was no dummy in school but his early career as a cell biologist doing research in stem-cell function was a surprise to all of us. But then high school reunions are often full of surprises and should serve as good reminders of the danger of profiling and pigeon-holing adolescents.
Professor Lipton’s take on epigenetics boils down to the notion that our genome should merely be considered a blueprint and not the final determinant of who we are and what illnesses befall us. His research and observations suggest to him that there are an uncountable number extragenomic factors, including environmental conditions and our belief systems, that can influence how that blueprint is read and the resulting expression of the genes we have inherited.
At face value, Bruce’s basic premise falls very close to some of the conclusions I have toyed with in an attempt to explain what I have observed doing primary care pediatrics. For example, I have trouble blaming the meteoric rise of the ADHD phenomenon on a genetic mutation. I suspect there are likely to be extragenomic forces coming into play, such as sleep deprivation and changing child-rearing practices. In my Oct. 9, 2020, Letters from Maine column I referred to a Swedish twins study that suggested children from a family with a strong history of depression were more likely to develop depression when raised in an adopted family that experienced domestic turmoil. His philosophy also fits with my sense that I have more control over my own health outcomes than many other people.
However, Professor Lipton and I part company (just philosophically that is) when he slips into hyperbole and applies what he terms as the New Biology too broadly. He may be correct that the revolutionary changes which came in the wake of Watson and Crick’s double helix discovery have resulted in a view of pathophysiology that is overly focused on what we are learning about our genome. On the other hand it is refreshing to hear someone with his charismatic and persuasive skills question the status quo.
If you haven’t listened to what he has to say I urge you to browse the Internet and sample some of his talks. I am sure you will find what he has to say stimulating. I doubt you will buy his whole package but I suspect you may find some bits you can agree with.
It still boils down to the old nature versus nurture argument. He’s all in for nurture. I’m still more comfortable straddling the fence.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Does the name Bruce Lipton sound familiar to you? Until a few years ago the only bell that it rang with me was that I had a high school classmate named Bruce Lipton. I recall that his father owned the local grocery store and he was one of the most prolific pranksters in a class with a long history of prank playing. If the name dredges up any associations for you it may because you have heard of a PhD biologist who has written and lectured extensively on epigenetics. You may have even read his most widely published book, “The Biology of Belief.” It turns out the Epigenetics Guy and my high school prankster classmate are one and the same.
After decades of separation – he is in California and I’m here in Maine – we have reconnected via Zoom mini reunions that our class has organized to combat the isolation that has descended on us with the pandemic. While I haven’t read his books, I have watched and listened to some of his podcasts and lectures. The devilish twinkle in his eye in the 1950s and 1960s has provided the scaffolding on which he has built a charismatic and persuasive presentation style.
Bruce was no dummy in school but his early career as a cell biologist doing research in stem-cell function was a surprise to all of us. But then high school reunions are often full of surprises and should serve as good reminders of the danger of profiling and pigeon-holing adolescents.
Professor Lipton’s take on epigenetics boils down to the notion that our genome should merely be considered a blueprint and not the final determinant of who we are and what illnesses befall us. His research and observations suggest to him that there are an uncountable number extragenomic factors, including environmental conditions and our belief systems, that can influence how that blueprint is read and the resulting expression of the genes we have inherited.
At face value, Bruce’s basic premise falls very close to some of the conclusions I have toyed with in an attempt to explain what I have observed doing primary care pediatrics. For example, I have trouble blaming the meteoric rise of the ADHD phenomenon on a genetic mutation. I suspect there are likely to be extragenomic forces coming into play, such as sleep deprivation and changing child-rearing practices. In my Oct. 9, 2020, Letters from Maine column I referred to a Swedish twins study that suggested children from a family with a strong history of depression were more likely to develop depression when raised in an adopted family that experienced domestic turmoil. His philosophy also fits with my sense that I have more control over my own health outcomes than many other people.
However, Professor Lipton and I part company (just philosophically that is) when he slips into hyperbole and applies what he terms as the New Biology too broadly. He may be correct that the revolutionary changes which came in the wake of Watson and Crick’s double helix discovery have resulted in a view of pathophysiology that is overly focused on what we are learning about our genome. On the other hand it is refreshing to hear someone with his charismatic and persuasive skills question the status quo.
If you haven’t listened to what he has to say I urge you to browse the Internet and sample some of his talks. I am sure you will find what he has to say stimulating. I doubt you will buy his whole package but I suspect you may find some bits you can agree with.
It still boils down to the old nature versus nurture argument. He’s all in for nurture. I’m still more comfortable straddling the fence.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Does the name Bruce Lipton sound familiar to you? Until a few years ago the only bell that it rang with me was that I had a high school classmate named Bruce Lipton. I recall that his father owned the local grocery store and he was one of the most prolific pranksters in a class with a long history of prank playing. If the name dredges up any associations for you it may because you have heard of a PhD biologist who has written and lectured extensively on epigenetics. You may have even read his most widely published book, “The Biology of Belief.” It turns out the Epigenetics Guy and my high school prankster classmate are one and the same.
After decades of separation – he is in California and I’m here in Maine – we have reconnected via Zoom mini reunions that our class has organized to combat the isolation that has descended on us with the pandemic. While I haven’t read his books, I have watched and listened to some of his podcasts and lectures. The devilish twinkle in his eye in the 1950s and 1960s has provided the scaffolding on which he has built a charismatic and persuasive presentation style.
Bruce was no dummy in school but his early career as a cell biologist doing research in stem-cell function was a surprise to all of us. But then high school reunions are often full of surprises and should serve as good reminders of the danger of profiling and pigeon-holing adolescents.
Professor Lipton’s take on epigenetics boils down to the notion that our genome should merely be considered a blueprint and not the final determinant of who we are and what illnesses befall us. His research and observations suggest to him that there are an uncountable number extragenomic factors, including environmental conditions and our belief systems, that can influence how that blueprint is read and the resulting expression of the genes we have inherited.
At face value, Bruce’s basic premise falls very close to some of the conclusions I have toyed with in an attempt to explain what I have observed doing primary care pediatrics. For example, I have trouble blaming the meteoric rise of the ADHD phenomenon on a genetic mutation. I suspect there are likely to be extragenomic forces coming into play, such as sleep deprivation and changing child-rearing practices. In my Oct. 9, 2020, Letters from Maine column I referred to a Swedish twins study that suggested children from a family with a strong history of depression were more likely to develop depression when raised in an adopted family that experienced domestic turmoil. His philosophy also fits with my sense that I have more control over my own health outcomes than many other people.
However, Professor Lipton and I part company (just philosophically that is) when he slips into hyperbole and applies what he terms as the New Biology too broadly. He may be correct that the revolutionary changes which came in the wake of Watson and Crick’s double helix discovery have resulted in a view of pathophysiology that is overly focused on what we are learning about our genome. On the other hand it is refreshing to hear someone with his charismatic and persuasive skills question the status quo.
If you haven’t listened to what he has to say I urge you to browse the Internet and sample some of his talks. I am sure you will find what he has to say stimulating. I doubt you will buy his whole package but I suspect you may find some bits you can agree with.
It still boils down to the old nature versus nurture argument. He’s all in for nurture. I’m still more comfortable straddling the fence.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children continue to drop
Despite a drop in the number of weekly COVID-19 cases, children made up a larger share of cases for the fourth consecutive week, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Just over 140,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children were reported for the week of Jan. 22-28, down from 165,000 the week before and down from the record high of 211,000 2 weeks earlier, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Since the beginning of January, however, the proportion of weekly cases occurring in children has risen from 12.9% to 15.1%, based on data collected by the AAP/CHA from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, 2.81 million children have been infected by the coronavirus, representing 12.8% of the total for all ages, which is almost 22 million. The cumulative rate since the start of the pandemic passed 3,700 cases per 100,000 children after increasing by 5.2% over the previous week, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Cumulative hospitalizations in children just passed 11,000 in the 24 states (and New York City) that are reporting data for children, which represents 1.8% of COVID-19–related admissions for all ages, a proportion that has not changed since mid-November. Ten more deaths in children were reported during Jan. 22-28, bringing the total to 215 in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are tracking mortality.
In the 10 states that are reporting data on testing, rates of positive results in children range from 7.1% in Indiana, in which children make up the largest proportion of total tests performed (18.1%) to 28.4% in Iowa, where children make up the smallest proportion of tests (6.0%), the AAP and CHA said.
Despite a drop in the number of weekly COVID-19 cases, children made up a larger share of cases for the fourth consecutive week, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Just over 140,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children were reported for the week of Jan. 22-28, down from 165,000 the week before and down from the record high of 211,000 2 weeks earlier, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Since the beginning of January, however, the proportion of weekly cases occurring in children has risen from 12.9% to 15.1%, based on data collected by the AAP/CHA from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, 2.81 million children have been infected by the coronavirus, representing 12.8% of the total for all ages, which is almost 22 million. The cumulative rate since the start of the pandemic passed 3,700 cases per 100,000 children after increasing by 5.2% over the previous week, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Cumulative hospitalizations in children just passed 11,000 in the 24 states (and New York City) that are reporting data for children, which represents 1.8% of COVID-19–related admissions for all ages, a proportion that has not changed since mid-November. Ten more deaths in children were reported during Jan. 22-28, bringing the total to 215 in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are tracking mortality.
In the 10 states that are reporting data on testing, rates of positive results in children range from 7.1% in Indiana, in which children make up the largest proportion of total tests performed (18.1%) to 28.4% in Iowa, where children make up the smallest proportion of tests (6.0%), the AAP and CHA said.
Despite a drop in the number of weekly COVID-19 cases, children made up a larger share of cases for the fourth consecutive week, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Just over 140,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children were reported for the week of Jan. 22-28, down from 165,000 the week before and down from the record high of 211,000 2 weeks earlier, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Since the beginning of January, however, the proportion of weekly cases occurring in children has risen from 12.9% to 15.1%, based on data collected by the AAP/CHA from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, 2.81 million children have been infected by the coronavirus, representing 12.8% of the total for all ages, which is almost 22 million. The cumulative rate since the start of the pandemic passed 3,700 cases per 100,000 children after increasing by 5.2% over the previous week, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Cumulative hospitalizations in children just passed 11,000 in the 24 states (and New York City) that are reporting data for children, which represents 1.8% of COVID-19–related admissions for all ages, a proportion that has not changed since mid-November. Ten more deaths in children were reported during Jan. 22-28, bringing the total to 215 in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are tracking mortality.
In the 10 states that are reporting data on testing, rates of positive results in children range from 7.1% in Indiana, in which children make up the largest proportion of total tests performed (18.1%) to 28.4% in Iowa, where children make up the smallest proportion of tests (6.0%), the AAP and CHA said.








