User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
FDA OKs first systemic treatment for alopecia areata
.
The disorder with the hallmark signs of patchy baldness affects more than 300,000 people in the United States each year. In patients with the autoimmune disorder, the body attacks its own hair follicles and hair falls out, often in clumps. In February, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA.
Baricitinib (Olumiant) is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which blocks the activity of one or more enzymes, interfering with the pathway that leads to inflammation.
The FDA reports the most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections, headache, acne, hyperlipidemia, increase of creatinine phosphokinase, urinary tract infection, elevated liver enzymes, inflammation of hair follicles, fatigue, lower respiratory tract infections, nausea, Candida infections, anemia, neutropenia, abdominal pain, herpes zoster (shingles), and weight gain. The labeling for baricitinib includes a boxed warning for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Evidence from two trials led to announcement
The decision came after review of the results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE AA-1 and BRAVE AA-2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT score) for more than 6 months.
Patients in these trials got either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36.
In BRAVE AA-1, 22% of the 184 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 35% of the 281 patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 5% of the 189 patients in the placebo group.
In BRAVE AA-2, 17% of the 156 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 32% of the 234 patients who received 4 mg achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 3% of the 156 patients in the placebo group.
The results were reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March.
Baricitinib was originally approved in 2018 as a treatment for adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blockers. It is also approved for treating COVID-19 in certain hospitalized adults.
Two other companies, Pfizer and Concert Pharmaceuticals, have JAK inhibitors in late-stage development for AA. The drugs are already on the market for treating rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. FDA approval is important for insurance coverage of the drugs, which have a list price of nearly $2,500 a month, according to The New York Times.
Until now, the only treatments for moderate to severe AA approved by the FDA have been intralesional steroid injections, contact sensitization, and systemic immunosuppressants, but they have demonstrated limited efficacy, are inconvenient for patients to take, and have been unsuitable for use long term.
“Today’s approval will help fulfill a significant unmet need for patients with severe alopecia areata,” Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release.
As Medscape reported last month, The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval of baricitinib for adults with severe AA.
AA received widespread international attention earlier this year at the Academy Awards ceremony, when actor Will Smith walked from the audience up onto the stage and slapped comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Mr. Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, about her shaved head. Mrs. Pinkett Smith has AA and has been public about her struggles with the disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The disorder with the hallmark signs of patchy baldness affects more than 300,000 people in the United States each year. In patients with the autoimmune disorder, the body attacks its own hair follicles and hair falls out, often in clumps. In February, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA.
Baricitinib (Olumiant) is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which blocks the activity of one or more enzymes, interfering with the pathway that leads to inflammation.
The FDA reports the most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections, headache, acne, hyperlipidemia, increase of creatinine phosphokinase, urinary tract infection, elevated liver enzymes, inflammation of hair follicles, fatigue, lower respiratory tract infections, nausea, Candida infections, anemia, neutropenia, abdominal pain, herpes zoster (shingles), and weight gain. The labeling for baricitinib includes a boxed warning for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Evidence from two trials led to announcement
The decision came after review of the results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE AA-1 and BRAVE AA-2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT score) for more than 6 months.
Patients in these trials got either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36.
In BRAVE AA-1, 22% of the 184 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 35% of the 281 patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 5% of the 189 patients in the placebo group.
In BRAVE AA-2, 17% of the 156 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 32% of the 234 patients who received 4 mg achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 3% of the 156 patients in the placebo group.
The results were reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March.
Baricitinib was originally approved in 2018 as a treatment for adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blockers. It is also approved for treating COVID-19 in certain hospitalized adults.
Two other companies, Pfizer and Concert Pharmaceuticals, have JAK inhibitors in late-stage development for AA. The drugs are already on the market for treating rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. FDA approval is important for insurance coverage of the drugs, which have a list price of nearly $2,500 a month, according to The New York Times.
Until now, the only treatments for moderate to severe AA approved by the FDA have been intralesional steroid injections, contact sensitization, and systemic immunosuppressants, but they have demonstrated limited efficacy, are inconvenient for patients to take, and have been unsuitable for use long term.
“Today’s approval will help fulfill a significant unmet need for patients with severe alopecia areata,” Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release.
As Medscape reported last month, The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval of baricitinib for adults with severe AA.
AA received widespread international attention earlier this year at the Academy Awards ceremony, when actor Will Smith walked from the audience up onto the stage and slapped comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Mr. Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, about her shaved head. Mrs. Pinkett Smith has AA and has been public about her struggles with the disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The disorder with the hallmark signs of patchy baldness affects more than 300,000 people in the United States each year. In patients with the autoimmune disorder, the body attacks its own hair follicles and hair falls out, often in clumps. In February, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA.
Baricitinib (Olumiant) is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which blocks the activity of one or more enzymes, interfering with the pathway that leads to inflammation.
The FDA reports the most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections, headache, acne, hyperlipidemia, increase of creatinine phosphokinase, urinary tract infection, elevated liver enzymes, inflammation of hair follicles, fatigue, lower respiratory tract infections, nausea, Candida infections, anemia, neutropenia, abdominal pain, herpes zoster (shingles), and weight gain. The labeling for baricitinib includes a boxed warning for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Evidence from two trials led to announcement
The decision came after review of the results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE AA-1 and BRAVE AA-2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT score) for more than 6 months.
Patients in these trials got either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36.
In BRAVE AA-1, 22% of the 184 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 35% of the 281 patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 5% of the 189 patients in the placebo group.
In BRAVE AA-2, 17% of the 156 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 32% of the 234 patients who received 4 mg achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 3% of the 156 patients in the placebo group.
The results were reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March.
Baricitinib was originally approved in 2018 as a treatment for adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blockers. It is also approved for treating COVID-19 in certain hospitalized adults.
Two other companies, Pfizer and Concert Pharmaceuticals, have JAK inhibitors in late-stage development for AA. The drugs are already on the market for treating rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. FDA approval is important for insurance coverage of the drugs, which have a list price of nearly $2,500 a month, according to The New York Times.
Until now, the only treatments for moderate to severe AA approved by the FDA have been intralesional steroid injections, contact sensitization, and systemic immunosuppressants, but they have demonstrated limited efficacy, are inconvenient for patients to take, and have been unsuitable for use long term.
“Today’s approval will help fulfill a significant unmet need for patients with severe alopecia areata,” Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release.
As Medscape reported last month, The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval of baricitinib for adults with severe AA.
AA received widespread international attention earlier this year at the Academy Awards ceremony, when actor Will Smith walked from the audience up onto the stage and slapped comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Mr. Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, about her shaved head. Mrs. Pinkett Smith has AA and has been public about her struggles with the disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stimulants may not improve academic learning in children with ADHD
Extended-release methylphenidate (Concerta) had no effect on learning academic material taught in a small group of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a controlled crossover study found.
As in previous studies, however, the stimulant did improve seat work productivity and classroom behavior, but these benefits did not translate into better learning of individual academic learning units, according to William E. Pelham Jr., PhD, of the department of psychology at Florida International University in Miami, and colleagues.
The results were published online in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology.
The authors said the finding raises questions about how stimulant medication leads to improved academic achievement over time. “This is important given that many parents and pediatricians believe that medication will improve academic achievement; parents are more likely to pursue medication (vs. other treatment options) when they identify academic achievement as a primary goal for treatment. The current findings suggest this emphasis may be misguided,” they wrote.
In their view, efforts to improve learning in children with ADHD should focus on delivering effective academic instruction and support such as individualized educational plans rather than stimulant therapy.
The study
The study cohort consisted of 173 children aged 7-12 (77% male, 86% Hispanic) who met Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, criteria for ADHD and were participating in a therapeutic summer camp classroom.
The experimental design was a triple-masked, within-subject, AB/BA crossover trial. Children completed two consecutive phases of daily, 25-minute instruction in both subject-area content (science and social studies) and vocabulary. Each phase was a standard instructional unit lasting for 3 weeks and lessons were given by credentialed teachers via small-group, evidence-based instruction.
Each child was randomized to receive daily osmotic-release oral system methylphenidate (OROS-MPH) during either the first or second instructional phase and to receive placebo during the other.
Seat work referred to the amount of work a pupil completed in a fixed duration of independent work time, and classroom behavior referred to the frequency of violating classroom rules. Learning was measured by tests, and multilevel models were fit separately to the subject and vocabulary test scores, with four observations per child: pretest and posttest in the two academic subject areas.
The results showed that medication had large, salutary, statistically significant effects on children’s academic seat work productivity and classroom behavior on every single day of the instructional period.
Pupils completed 37% more arithmetic problems per minute when taking OROS-MPH and committed 53% fewer rule violations per hour. In terms of learning the material taught during instruction, however, tests showed that children learned the same amount of subject-area and vocabulary content whether they were taking OROS-MPH or placebo during the instructional period.
Consistent with previous studies, medication slightly helped to improve test scores when taken on the day of a test, but not enough to boost most children’s grades. For example, medication helped children increase on average 1.7 percentage points out of 100 on science and social studies tests.
“This finding has relevance for parents deciding whether to medicate their child for occasions such as a psychoeducational evaluation or high-stakes academic testing – while the effect size was small, findings suggest being medicated would improve scores,” the investigators wrote.
Sharing his perspective on the study but not involved in it, Herschel R. Lessin, MD, a pediatrician at The Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., and coauthor of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines on ADHD, said, “If you ignore the sensationalized headlines, this study is an interesting but preliminary first step, and justifies further research on the topic. It also has several potential defects, which the authors in fact address in the supplements.” The cohort size was small, for example, the doses of medication were very low, and the study took place in a controlled therapeutic setting – not the everyday classroom.
Furthermore, Dr. Lessin added, the study’s conclusions “are contrary to my 40 years of experience in treating ADHD. If they had used standard measures of assessment, as in previous studies, they would have found medication did impact learning. More research is clearly needed.”
In other comments, Holly K. Harris, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics-development at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston, said the core symptoms of ADHD are primarily behavioral in nature, not academic learning related.
“Stimulant medications are targeting these core behavioral symptoms of ADHD ... but the goal of treatment is more than just the reduction of symptoms; it is to improve a child’s overall functioning so that they succeed at what is expected of them and avoid developing even more impairments,” Dr. Harris said, adding that symptom improvement can sometimes allow a child to learn better in the classroom and achieve more academically.
Children with ADHD may have diagnosed or undiagnosed comorbid learning disabilities, with one 2013 study suggesting a rate of 31%-45%.
With such learning disabilities being distinct from core behavioral symptoms, stimulant medications would not be expected to address a child’s learning disability. “In fact, best practice is for a child with ADHD who is not responding to stimulant medication (doctors might refer to this as complex ADHD) to undergo full individual evaluations either through the school system or an outside psychological assessment to assess for potential learning disabilities or other comorbid developmental/learning or psychiatric diagnosis,” Dr. Harris said.
Rather than changing prescribing patterns, she continued, pediatricians could consider advising parents to request learning evaluations through the school system if the child continues to struggle academically with no change in learning outcomes despite improvement in some behavioral outcomes.
As a reference, Dr. Harris recommended the Society for Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics guidelines for complex ADHD.
This study was funded by the National Institute on Mental Health with additional support from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and the Institute of Education Sciences. Coauthor James Waxmonsky, MD, has received research funding from the National Institutes of Health, Supernus, and Pfizer and served on the advisory board for Iron Shore, NLS Pharma, and Purdue Pharma.
Extended-release methylphenidate (Concerta) had no effect on learning academic material taught in a small group of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a controlled crossover study found.
As in previous studies, however, the stimulant did improve seat work productivity and classroom behavior, but these benefits did not translate into better learning of individual academic learning units, according to William E. Pelham Jr., PhD, of the department of psychology at Florida International University in Miami, and colleagues.
The results were published online in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology.
The authors said the finding raises questions about how stimulant medication leads to improved academic achievement over time. “This is important given that many parents and pediatricians believe that medication will improve academic achievement; parents are more likely to pursue medication (vs. other treatment options) when they identify academic achievement as a primary goal for treatment. The current findings suggest this emphasis may be misguided,” they wrote.
In their view, efforts to improve learning in children with ADHD should focus on delivering effective academic instruction and support such as individualized educational plans rather than stimulant therapy.
The study
The study cohort consisted of 173 children aged 7-12 (77% male, 86% Hispanic) who met Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, criteria for ADHD and were participating in a therapeutic summer camp classroom.
The experimental design was a triple-masked, within-subject, AB/BA crossover trial. Children completed two consecutive phases of daily, 25-minute instruction in both subject-area content (science and social studies) and vocabulary. Each phase was a standard instructional unit lasting for 3 weeks and lessons were given by credentialed teachers via small-group, evidence-based instruction.
Each child was randomized to receive daily osmotic-release oral system methylphenidate (OROS-MPH) during either the first or second instructional phase and to receive placebo during the other.
Seat work referred to the amount of work a pupil completed in a fixed duration of independent work time, and classroom behavior referred to the frequency of violating classroom rules. Learning was measured by tests, and multilevel models were fit separately to the subject and vocabulary test scores, with four observations per child: pretest and posttest in the two academic subject areas.
The results showed that medication had large, salutary, statistically significant effects on children’s academic seat work productivity and classroom behavior on every single day of the instructional period.
Pupils completed 37% more arithmetic problems per minute when taking OROS-MPH and committed 53% fewer rule violations per hour. In terms of learning the material taught during instruction, however, tests showed that children learned the same amount of subject-area and vocabulary content whether they were taking OROS-MPH or placebo during the instructional period.
Consistent with previous studies, medication slightly helped to improve test scores when taken on the day of a test, but not enough to boost most children’s grades. For example, medication helped children increase on average 1.7 percentage points out of 100 on science and social studies tests.
“This finding has relevance for parents deciding whether to medicate their child for occasions such as a psychoeducational evaluation or high-stakes academic testing – while the effect size was small, findings suggest being medicated would improve scores,” the investigators wrote.
Sharing his perspective on the study but not involved in it, Herschel R. Lessin, MD, a pediatrician at The Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., and coauthor of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines on ADHD, said, “If you ignore the sensationalized headlines, this study is an interesting but preliminary first step, and justifies further research on the topic. It also has several potential defects, which the authors in fact address in the supplements.” The cohort size was small, for example, the doses of medication were very low, and the study took place in a controlled therapeutic setting – not the everyday classroom.
Furthermore, Dr. Lessin added, the study’s conclusions “are contrary to my 40 years of experience in treating ADHD. If they had used standard measures of assessment, as in previous studies, they would have found medication did impact learning. More research is clearly needed.”
In other comments, Holly K. Harris, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics-development at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston, said the core symptoms of ADHD are primarily behavioral in nature, not academic learning related.
“Stimulant medications are targeting these core behavioral symptoms of ADHD ... but the goal of treatment is more than just the reduction of symptoms; it is to improve a child’s overall functioning so that they succeed at what is expected of them and avoid developing even more impairments,” Dr. Harris said, adding that symptom improvement can sometimes allow a child to learn better in the classroom and achieve more academically.
Children with ADHD may have diagnosed or undiagnosed comorbid learning disabilities, with one 2013 study suggesting a rate of 31%-45%.
With such learning disabilities being distinct from core behavioral symptoms, stimulant medications would not be expected to address a child’s learning disability. “In fact, best practice is for a child with ADHD who is not responding to stimulant medication (doctors might refer to this as complex ADHD) to undergo full individual evaluations either through the school system or an outside psychological assessment to assess for potential learning disabilities or other comorbid developmental/learning or psychiatric diagnosis,” Dr. Harris said.
Rather than changing prescribing patterns, she continued, pediatricians could consider advising parents to request learning evaluations through the school system if the child continues to struggle academically with no change in learning outcomes despite improvement in some behavioral outcomes.
As a reference, Dr. Harris recommended the Society for Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics guidelines for complex ADHD.
This study was funded by the National Institute on Mental Health with additional support from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and the Institute of Education Sciences. Coauthor James Waxmonsky, MD, has received research funding from the National Institutes of Health, Supernus, and Pfizer and served on the advisory board for Iron Shore, NLS Pharma, and Purdue Pharma.
Extended-release methylphenidate (Concerta) had no effect on learning academic material taught in a small group of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a controlled crossover study found.
As in previous studies, however, the stimulant did improve seat work productivity and classroom behavior, but these benefits did not translate into better learning of individual academic learning units, according to William E. Pelham Jr., PhD, of the department of psychology at Florida International University in Miami, and colleagues.
The results were published online in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology.
The authors said the finding raises questions about how stimulant medication leads to improved academic achievement over time. “This is important given that many parents and pediatricians believe that medication will improve academic achievement; parents are more likely to pursue medication (vs. other treatment options) when they identify academic achievement as a primary goal for treatment. The current findings suggest this emphasis may be misguided,” they wrote.
In their view, efforts to improve learning in children with ADHD should focus on delivering effective academic instruction and support such as individualized educational plans rather than stimulant therapy.
The study
The study cohort consisted of 173 children aged 7-12 (77% male, 86% Hispanic) who met Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, criteria for ADHD and were participating in a therapeutic summer camp classroom.
The experimental design was a triple-masked, within-subject, AB/BA crossover trial. Children completed two consecutive phases of daily, 25-minute instruction in both subject-area content (science and social studies) and vocabulary. Each phase was a standard instructional unit lasting for 3 weeks and lessons were given by credentialed teachers via small-group, evidence-based instruction.
Each child was randomized to receive daily osmotic-release oral system methylphenidate (OROS-MPH) during either the first or second instructional phase and to receive placebo during the other.
Seat work referred to the amount of work a pupil completed in a fixed duration of independent work time, and classroom behavior referred to the frequency of violating classroom rules. Learning was measured by tests, and multilevel models were fit separately to the subject and vocabulary test scores, with four observations per child: pretest and posttest in the two academic subject areas.
The results showed that medication had large, salutary, statistically significant effects on children’s academic seat work productivity and classroom behavior on every single day of the instructional period.
Pupils completed 37% more arithmetic problems per minute when taking OROS-MPH and committed 53% fewer rule violations per hour. In terms of learning the material taught during instruction, however, tests showed that children learned the same amount of subject-area and vocabulary content whether they were taking OROS-MPH or placebo during the instructional period.
Consistent with previous studies, medication slightly helped to improve test scores when taken on the day of a test, but not enough to boost most children’s grades. For example, medication helped children increase on average 1.7 percentage points out of 100 on science and social studies tests.
“This finding has relevance for parents deciding whether to medicate their child for occasions such as a psychoeducational evaluation or high-stakes academic testing – while the effect size was small, findings suggest being medicated would improve scores,” the investigators wrote.
Sharing his perspective on the study but not involved in it, Herschel R. Lessin, MD, a pediatrician at The Children’s Medical Group in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., and coauthor of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines on ADHD, said, “If you ignore the sensationalized headlines, this study is an interesting but preliminary first step, and justifies further research on the topic. It also has several potential defects, which the authors in fact address in the supplements.” The cohort size was small, for example, the doses of medication were very low, and the study took place in a controlled therapeutic setting – not the everyday classroom.
Furthermore, Dr. Lessin added, the study’s conclusions “are contrary to my 40 years of experience in treating ADHD. If they had used standard measures of assessment, as in previous studies, they would have found medication did impact learning. More research is clearly needed.”
In other comments, Holly K. Harris, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics-development at Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston, said the core symptoms of ADHD are primarily behavioral in nature, not academic learning related.
“Stimulant medications are targeting these core behavioral symptoms of ADHD ... but the goal of treatment is more than just the reduction of symptoms; it is to improve a child’s overall functioning so that they succeed at what is expected of them and avoid developing even more impairments,” Dr. Harris said, adding that symptom improvement can sometimes allow a child to learn better in the classroom and achieve more academically.
Children with ADHD may have diagnosed or undiagnosed comorbid learning disabilities, with one 2013 study suggesting a rate of 31%-45%.
With such learning disabilities being distinct from core behavioral symptoms, stimulant medications would not be expected to address a child’s learning disability. “In fact, best practice is for a child with ADHD who is not responding to stimulant medication (doctors might refer to this as complex ADHD) to undergo full individual evaluations either through the school system or an outside psychological assessment to assess for potential learning disabilities or other comorbid developmental/learning or psychiatric diagnosis,” Dr. Harris said.
Rather than changing prescribing patterns, she continued, pediatricians could consider advising parents to request learning evaluations through the school system if the child continues to struggle academically with no change in learning outcomes despite improvement in some behavioral outcomes.
As a reference, Dr. Harris recommended the Society for Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics guidelines for complex ADHD.
This study was funded by the National Institute on Mental Health with additional support from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and the Institute of Education Sciences. Coauthor James Waxmonsky, MD, has received research funding from the National Institutes of Health, Supernus, and Pfizer and served on the advisory board for Iron Shore, NLS Pharma, and Purdue Pharma.
FROM JOURNAL OF CONSULTING AND CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGY
Just 20 minutes of vigorous activity daily benefits teens
Vigorous physical activity for 20 minutes a day was enough to maximize cardiorespiratory benefits in adolescents, based on data from more than 300 individuals.
Current recommendations for physical activity in children and adolescents from the World Health Organization call for moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) for an average of 60 minutes a day for physical and mental health; however, guidance on how much physical activity teens need to maximize cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) has not been determined, Samuel Joseph Burden, BMedSci, of John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford (England), and colleagues wrote.
“Although data in young people are limited, adult studies have shown that regular, brief vigorous physical activity is highly effective at improving health markers, including CRF, which is also an important marker of health in youth,” the researchers wrote.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers examined the associations between physical activity intensity and maximal CRF. The study population included 339 adolescents aged 13-14 years who were evaluated during the 2018-2019 and 2019-2020 school years. Participants wore wrist accelerometers to measure the intensity of physical activity and participated in 20-meter shuttle runs to demonstrate CRF. The researchers used partial multivariable linear regression to assess variables at different intensities including moderate physical activity (MPA), light physical activity (LPA), and sedentary time, as well as vigorous physical activity (VPA).
The wrist monitors measured the intensities of physical activity based on the bandpass-filtered followed by Euclidean norm metric (BFEN), a validated metric. “Previously validated thresholds for BFEN were used to determine the average duration of daily physical activity at each intensity: 0.1 g for LPA, 0.314 g for MPA, and 0.998 g for VPA,” the researchers wrote. Physical activity below the threshold for LPA was categorized as sedentary time.
Participants wore the accelerometers for 1 week; value recording included at least 3 weekdays and 1 weekend day, and each valid day required more than 6 hours of awake time.
Overall, VPA for up to 20 minutes was significantly associated with improved CRF. However, the benefits on CRF plateaued after that time, and longer duration of VPA was not associated with significantly greater improvements in CRF. Neither MPA nor LPA were associated with any improvements in CRF.
Participants who engaged in an average of 14 minutes (range, 12-17 minutes) of VPA per day met the median CRF.
The researchers also conducted independent t tests to assess differences in VPA at different CRF thresholds.
Those in the highest quartile of VPA had CRF z scores 1.03 higher, compared with those in the lower quartiles.
Given that current PA guidelines involve a combination of moderate and vigorous PA that could be met by MPA with no VPA, the current findings have public health implications for improving CRF in adolescents, the researchers wrote.
Even with MPA as an option, most adolescents fail to meet the recommendations of at least 60 minutes of MVPA, they said. “One possible reason is that this duration is quite long, requiring a daily time commitment that some may find difficult to maintain. A shorter target of 20 minutes might be easier to schedule daily and a focus on VPA would simplify messages about the intensity of activity that is likely to improve CRF.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from only two schools in the United Kingdom, which may limit generalizability, and future research would ideally include a more direct assessment of VO2 max, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, including teens with a wide range of body mass index as well as CRF.
Future research is needed to test whether interventions based on a target of 20 minutes of VPA creates significant improvements in adolescent cardiometabolic health, the researchers concluded.
Any activity has value for sedentary teens
The current study suggests that counseling teens about physical activity may be less challenging for clinicians if optimal cardiorespiratory benefits can be reached with shorter bouts of activity, Michele LaBotz, MD, of Intermed Sports Medicine, South Portland, Maine, and Sarah Hoffman, DO, of Tufts University, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The results have two key implications for pediatricians, the authors said. First, “optimal CRF can be achieved with much shorter periods of activity than previously recommended.” Second, “current ‘moderate to vigorous’ PA recommendations may not be sufficient to improve CRF in adolescents, if achieved through moderate activity only.”
However, the editorialists emphasized that, although shorter periods of higher-intensity exercise reduce the time burden for teens and families, specific education is needed to explain the extra effort involved in exercising vigorously enough for cardiorespiratory benefits.
Patients can be counseled that activity is vigorous when they start to sweat, their face gets red, and they feel short of breath and unable to talk during activity,” they explained. These sensations may be new and uncomfortable for children and teens who have been quite sedentary or used to low-intensity activity. Dr. LaBotz and Dr. Hoffman advised pediatricians to counsel patients to build intensity gradually, with “exercise snacks,” that involve several minutes of activity that become more challenging over time.
“Exercise snacks can include anything that elevates the heart rate for a minute or more, such as running up and down the stairs a few times; chasing the dog around the backyard; or just putting on some music and dancing hard,” the editorialists wrote.
“Some exercise is better than none, and extrapolating from adult data, the biggest benefit likely occurs when we can help our most sedentary and least fit patients become a bit more active, even if it falls short of currently recommended levels,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants to various researchers from the British Heart Foundation, the Elizabeth Casson Trust, the U.K. National Institute of Health Research, the Professor Nigel Groome Studentship scheme (Oxford Brookes University), and the U.K. Department of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Vigorous physical activity for 20 minutes a day was enough to maximize cardiorespiratory benefits in adolescents, based on data from more than 300 individuals.
Current recommendations for physical activity in children and adolescents from the World Health Organization call for moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) for an average of 60 minutes a day for physical and mental health; however, guidance on how much physical activity teens need to maximize cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) has not been determined, Samuel Joseph Burden, BMedSci, of John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford (England), and colleagues wrote.
“Although data in young people are limited, adult studies have shown that regular, brief vigorous physical activity is highly effective at improving health markers, including CRF, which is also an important marker of health in youth,” the researchers wrote.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers examined the associations between physical activity intensity and maximal CRF. The study population included 339 adolescents aged 13-14 years who were evaluated during the 2018-2019 and 2019-2020 school years. Participants wore wrist accelerometers to measure the intensity of physical activity and participated in 20-meter shuttle runs to demonstrate CRF. The researchers used partial multivariable linear regression to assess variables at different intensities including moderate physical activity (MPA), light physical activity (LPA), and sedentary time, as well as vigorous physical activity (VPA).
The wrist monitors measured the intensities of physical activity based on the bandpass-filtered followed by Euclidean norm metric (BFEN), a validated metric. “Previously validated thresholds for BFEN were used to determine the average duration of daily physical activity at each intensity: 0.1 g for LPA, 0.314 g for MPA, and 0.998 g for VPA,” the researchers wrote. Physical activity below the threshold for LPA was categorized as sedentary time.
Participants wore the accelerometers for 1 week; value recording included at least 3 weekdays and 1 weekend day, and each valid day required more than 6 hours of awake time.
Overall, VPA for up to 20 minutes was significantly associated with improved CRF. However, the benefits on CRF plateaued after that time, and longer duration of VPA was not associated with significantly greater improvements in CRF. Neither MPA nor LPA were associated with any improvements in CRF.
Participants who engaged in an average of 14 minutes (range, 12-17 minutes) of VPA per day met the median CRF.
The researchers also conducted independent t tests to assess differences in VPA at different CRF thresholds.
Those in the highest quartile of VPA had CRF z scores 1.03 higher, compared with those in the lower quartiles.
Given that current PA guidelines involve a combination of moderate and vigorous PA that could be met by MPA with no VPA, the current findings have public health implications for improving CRF in adolescents, the researchers wrote.
Even with MPA as an option, most adolescents fail to meet the recommendations of at least 60 minutes of MVPA, they said. “One possible reason is that this duration is quite long, requiring a daily time commitment that some may find difficult to maintain. A shorter target of 20 minutes might be easier to schedule daily and a focus on VPA would simplify messages about the intensity of activity that is likely to improve CRF.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from only two schools in the United Kingdom, which may limit generalizability, and future research would ideally include a more direct assessment of VO2 max, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, including teens with a wide range of body mass index as well as CRF.
Future research is needed to test whether interventions based on a target of 20 minutes of VPA creates significant improvements in adolescent cardiometabolic health, the researchers concluded.
Any activity has value for sedentary teens
The current study suggests that counseling teens about physical activity may be less challenging for clinicians if optimal cardiorespiratory benefits can be reached with shorter bouts of activity, Michele LaBotz, MD, of Intermed Sports Medicine, South Portland, Maine, and Sarah Hoffman, DO, of Tufts University, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The results have two key implications for pediatricians, the authors said. First, “optimal CRF can be achieved with much shorter periods of activity than previously recommended.” Second, “current ‘moderate to vigorous’ PA recommendations may not be sufficient to improve CRF in adolescents, if achieved through moderate activity only.”
However, the editorialists emphasized that, although shorter periods of higher-intensity exercise reduce the time burden for teens and families, specific education is needed to explain the extra effort involved in exercising vigorously enough for cardiorespiratory benefits.
Patients can be counseled that activity is vigorous when they start to sweat, their face gets red, and they feel short of breath and unable to talk during activity,” they explained. These sensations may be new and uncomfortable for children and teens who have been quite sedentary or used to low-intensity activity. Dr. LaBotz and Dr. Hoffman advised pediatricians to counsel patients to build intensity gradually, with “exercise snacks,” that involve several minutes of activity that become more challenging over time.
“Exercise snacks can include anything that elevates the heart rate for a minute or more, such as running up and down the stairs a few times; chasing the dog around the backyard; or just putting on some music and dancing hard,” the editorialists wrote.
“Some exercise is better than none, and extrapolating from adult data, the biggest benefit likely occurs when we can help our most sedentary and least fit patients become a bit more active, even if it falls short of currently recommended levels,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants to various researchers from the British Heart Foundation, the Elizabeth Casson Trust, the U.K. National Institute of Health Research, the Professor Nigel Groome Studentship scheme (Oxford Brookes University), and the U.K. Department of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Vigorous physical activity for 20 minutes a day was enough to maximize cardiorespiratory benefits in adolescents, based on data from more than 300 individuals.
Current recommendations for physical activity in children and adolescents from the World Health Organization call for moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) for an average of 60 minutes a day for physical and mental health; however, guidance on how much physical activity teens need to maximize cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) has not been determined, Samuel Joseph Burden, BMedSci, of John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford (England), and colleagues wrote.
“Although data in young people are limited, adult studies have shown that regular, brief vigorous physical activity is highly effective at improving health markers, including CRF, which is also an important marker of health in youth,” the researchers wrote.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers examined the associations between physical activity intensity and maximal CRF. The study population included 339 adolescents aged 13-14 years who were evaluated during the 2018-2019 and 2019-2020 school years. Participants wore wrist accelerometers to measure the intensity of physical activity and participated in 20-meter shuttle runs to demonstrate CRF. The researchers used partial multivariable linear regression to assess variables at different intensities including moderate physical activity (MPA), light physical activity (LPA), and sedentary time, as well as vigorous physical activity (VPA).
The wrist monitors measured the intensities of physical activity based on the bandpass-filtered followed by Euclidean norm metric (BFEN), a validated metric. “Previously validated thresholds for BFEN were used to determine the average duration of daily physical activity at each intensity: 0.1 g for LPA, 0.314 g for MPA, and 0.998 g for VPA,” the researchers wrote. Physical activity below the threshold for LPA was categorized as sedentary time.
Participants wore the accelerometers for 1 week; value recording included at least 3 weekdays and 1 weekend day, and each valid day required more than 6 hours of awake time.
Overall, VPA for up to 20 minutes was significantly associated with improved CRF. However, the benefits on CRF plateaued after that time, and longer duration of VPA was not associated with significantly greater improvements in CRF. Neither MPA nor LPA were associated with any improvements in CRF.
Participants who engaged in an average of 14 minutes (range, 12-17 minutes) of VPA per day met the median CRF.
The researchers also conducted independent t tests to assess differences in VPA at different CRF thresholds.
Those in the highest quartile of VPA had CRF z scores 1.03 higher, compared with those in the lower quartiles.
Given that current PA guidelines involve a combination of moderate and vigorous PA that could be met by MPA with no VPA, the current findings have public health implications for improving CRF in adolescents, the researchers wrote.
Even with MPA as an option, most adolescents fail to meet the recommendations of at least 60 minutes of MVPA, they said. “One possible reason is that this duration is quite long, requiring a daily time commitment that some may find difficult to maintain. A shorter target of 20 minutes might be easier to schedule daily and a focus on VPA would simplify messages about the intensity of activity that is likely to improve CRF.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from only two schools in the United Kingdom, which may limit generalizability, and future research would ideally include a more direct assessment of VO2 max, the researchers wrote. However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, including teens with a wide range of body mass index as well as CRF.
Future research is needed to test whether interventions based on a target of 20 minutes of VPA creates significant improvements in adolescent cardiometabolic health, the researchers concluded.
Any activity has value for sedentary teens
The current study suggests that counseling teens about physical activity may be less challenging for clinicians if optimal cardiorespiratory benefits can be reached with shorter bouts of activity, Michele LaBotz, MD, of Intermed Sports Medicine, South Portland, Maine, and Sarah Hoffman, DO, of Tufts University, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The results have two key implications for pediatricians, the authors said. First, “optimal CRF can be achieved with much shorter periods of activity than previously recommended.” Second, “current ‘moderate to vigorous’ PA recommendations may not be sufficient to improve CRF in adolescents, if achieved through moderate activity only.”
However, the editorialists emphasized that, although shorter periods of higher-intensity exercise reduce the time burden for teens and families, specific education is needed to explain the extra effort involved in exercising vigorously enough for cardiorespiratory benefits.
Patients can be counseled that activity is vigorous when they start to sweat, their face gets red, and they feel short of breath and unable to talk during activity,” they explained. These sensations may be new and uncomfortable for children and teens who have been quite sedentary or used to low-intensity activity. Dr. LaBotz and Dr. Hoffman advised pediatricians to counsel patients to build intensity gradually, with “exercise snacks,” that involve several minutes of activity that become more challenging over time.
“Exercise snacks can include anything that elevates the heart rate for a minute or more, such as running up and down the stairs a few times; chasing the dog around the backyard; or just putting on some music and dancing hard,” the editorialists wrote.
“Some exercise is better than none, and extrapolating from adult data, the biggest benefit likely occurs when we can help our most sedentary and least fit patients become a bit more active, even if it falls short of currently recommended levels,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants to various researchers from the British Heart Foundation, the Elizabeth Casson Trust, the U.K. National Institute of Health Research, the Professor Nigel Groome Studentship scheme (Oxford Brookes University), and the U.K. Department of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Surprising link between herpes zoster and dementia
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Current monkeypox outbreak marked by unconventional spread, clinical features
When Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, thinks back on what she learned about monkeypox during her training as a dermatologist and an infectious disease epidemiologist, it was widely considered a viral disease with rare outbreaks limited primarily to Central and Western Africa.
“Monkeypox is something we have traditionally only seen very rarely in the U.S.,” Dr. Freeman, director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “In the past, outbreaks in the U.S. have been related to international travel or import of exotic pets, which is very different than what we’re seeing as a global community now.”

Monkeypox virus belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, symptoms develop 5-21 days after infection and may include fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. Typically, within 1-3 days of the fever, a rash develops, followed by the formation of monkeypox lesions. These lesions progress from macules to papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs, before falling off. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
What makes the 2022 monkeypox outbreak different from others is clear evidence of community transmission. According to worldwide data from the CDC, as of June 9, 2022, there were 1,356 confirmed cases in 31 countries, including 44 cases in the United States. This means that person-to-person spread of the monkeypox virus is occurring among individuals who have not traveled outside of their own country.
“This is likely an underestimate, especially when we think about the U.S., which only has 44 confirmed cases at this time,” Dr. Freeman said. “However, at present, monkeypox cases have to be confirmed by the CDC, so there are a lot more suspected cases that are likely to be confirmed in the coming days. As with any outbreak, it’s a rapidly changing situation.”
A different clinical presentation
The clinical presentation of monkeypox cases in the current outbreak also differs from that of previous outbreaks. In the past, monkeypox rashes often morphed from a macule to a pustule and commonly affected the face, hands, feet, and trunk, with some patients harboring as many as 200 lesions at once. That pattern still occurs, but increasingly, the presentation is characterized by a more localized spread, especially in the genital region, which Dr. Freeman described as “unusual and not an area we traditionally thought of in the past as a focus for monkeypox.”
Also, affected individuals in the current outbreak may develop fewer lesions, sometimes between 1 and 5 instead of up to 200. “This doesn’t apply to everybody, but it is a bit of a different picture than what we’ve seen in case descriptions and photographs in the past from places like Central Africa,” she said. “What’s being reported out of case clusters from the United Kingdom and Spain is a mix, where some people are having more generalized involvement while others have more localized involvement.” Visual examples of the monkey pox rash can be found in photos from the United Kingdom, the country with the highest number of confirmed cases, on the CDC’s website, and in a report from Spain.
Clusters of monkeypox cases have been reported worldwide in men who have sex with men, “but this is not limited to a particular subgroup of people,” emphasizes Dr. Freeman, who is also a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force to Develop Monkeypox Content, which created an online resource for clinicians. “There are several mechanisms of spread, but direct contact with lesions or infected fluids is one,” she notes.
Moreover, If you have a patient with a new genital lesion and you’re not sure what it is, testing for monkeypox in addition to classic sexually transmitted infections like HSV or syphilis would be reasonable during the current outbreak situation.”
The 2022 monkeypox outbreak may pale in comparison to the spread of COVID-19 in terms of case numbers and societal impact, but dermatologists may be the first point of contact for a person infected with the monkeypox virus. “It’s important for dermatologists to be able to recognize monkeypox, because by recognizing cases, we can stop the outbreak,” Dr. Freeman said. “In theory, an infected person could show up in your clinic, regardless of where you practice in the U.S. But at the same time, it’s important not to panic. This is not COVID-19 all over again; this is different. Yes, it is an outbreak, but we already have a vaccine that works against monkeypox, and while one of the possible modes of transmission for monkeypox is respiratory, it’s much harder to transmit that way than SARS-CoV-2 – it requires closer and longer contact.”
Confirmation of a monkeypox virus infection is based on results of a PCR test based on swabs of a lesion. The AAD task force recommends contacting the local hospital epidemiologist, infection control personnel, and/or state health department about suspected cases, “as different locations will have different regulations on where to send the [PCR] test. If appropriate, the state health department will contact the CDC.”
According to the CDC, current recommendations for personal protective equipment for possible and confirmed monkeypox cases include gown, gloves, a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health-approved N-95 mask, and eye protection.
Topical antiviral an option
If the lesions in a patient with suspected monkeypox have turned into pustules while waiting for the PCR test results, one option is to prescribe 3%-5% topical cidofovir, according to Stephen K. Tyring, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology, microbiology & molecular genetics, and internal medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. “That’s the effective antiviral that is most available,” he said. Generic cidofovir is also now available.
Dr. Tyring recommends rapid referral of immunocompromised patients with suspected monkeypox to an infectious disease expert and/or consulting with the CDC. “The pediatric population also seems to be at somewhat more risk, as has been seen in sub-Saharan Africa,” said Dr. Tyring, who is one of the editors of the textbook Tropical Dermatology. “Also, by definition, pregnant women are at more risk because their immune systems aren’t up to par. You also want to make sure that if monkeypox is on a person’s skin that they don’t get it in their eyes, because they could lose their vision.” He added that sub-Saharan Africa has a monkeypox mortality of up to 10%, “which is something we don’t see in the U.S. or Europe. Those of us who grew up in the 20th century got routine smallpox vaccines, and we therefore probably have a degree of immunity to monkeypox. But for the past 40 years or so, unless you are in the military, you are not going to get a routine vaccine to prevent smallpox.”
Incubation period, appearance of lesions
Monkeypox has a long incubation period. According to Dr. Freeman, from the point of exposure to the development of symptomatic lesions is typically 7-14 days but can vary from 5-21 days. “It’s important for people to be aware that their exposure may have been in the more distant past, not just a few days ago” she said. “Identifying cases as quickly as possible gives us a window where we can vaccinate close contacts.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Tyring reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CDC guidance on vaccination before and after exposure to monkeypox can be found here . A general Q&A for health care professionals from the CDC can be found here.
When Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, thinks back on what she learned about monkeypox during her training as a dermatologist and an infectious disease epidemiologist, it was widely considered a viral disease with rare outbreaks limited primarily to Central and Western Africa.
“Monkeypox is something we have traditionally only seen very rarely in the U.S.,” Dr. Freeman, director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “In the past, outbreaks in the U.S. have been related to international travel or import of exotic pets, which is very different than what we’re seeing as a global community now.”

Monkeypox virus belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, symptoms develop 5-21 days after infection and may include fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. Typically, within 1-3 days of the fever, a rash develops, followed by the formation of monkeypox lesions. These lesions progress from macules to papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs, before falling off. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
What makes the 2022 monkeypox outbreak different from others is clear evidence of community transmission. According to worldwide data from the CDC, as of June 9, 2022, there were 1,356 confirmed cases in 31 countries, including 44 cases in the United States. This means that person-to-person spread of the monkeypox virus is occurring among individuals who have not traveled outside of their own country.
“This is likely an underestimate, especially when we think about the U.S., which only has 44 confirmed cases at this time,” Dr. Freeman said. “However, at present, monkeypox cases have to be confirmed by the CDC, so there are a lot more suspected cases that are likely to be confirmed in the coming days. As with any outbreak, it’s a rapidly changing situation.”
A different clinical presentation
The clinical presentation of monkeypox cases in the current outbreak also differs from that of previous outbreaks. In the past, monkeypox rashes often morphed from a macule to a pustule and commonly affected the face, hands, feet, and trunk, with some patients harboring as many as 200 lesions at once. That pattern still occurs, but increasingly, the presentation is characterized by a more localized spread, especially in the genital region, which Dr. Freeman described as “unusual and not an area we traditionally thought of in the past as a focus for monkeypox.”
Also, affected individuals in the current outbreak may develop fewer lesions, sometimes between 1 and 5 instead of up to 200. “This doesn’t apply to everybody, but it is a bit of a different picture than what we’ve seen in case descriptions and photographs in the past from places like Central Africa,” she said. “What’s being reported out of case clusters from the United Kingdom and Spain is a mix, where some people are having more generalized involvement while others have more localized involvement.” Visual examples of the monkey pox rash can be found in photos from the United Kingdom, the country with the highest number of confirmed cases, on the CDC’s website, and in a report from Spain.
Clusters of monkeypox cases have been reported worldwide in men who have sex with men, “but this is not limited to a particular subgroup of people,” emphasizes Dr. Freeman, who is also a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force to Develop Monkeypox Content, which created an online resource for clinicians. “There are several mechanisms of spread, but direct contact with lesions or infected fluids is one,” she notes.
Moreover, If you have a patient with a new genital lesion and you’re not sure what it is, testing for monkeypox in addition to classic sexually transmitted infections like HSV or syphilis would be reasonable during the current outbreak situation.”
The 2022 monkeypox outbreak may pale in comparison to the spread of COVID-19 in terms of case numbers and societal impact, but dermatologists may be the first point of contact for a person infected with the monkeypox virus. “It’s important for dermatologists to be able to recognize monkeypox, because by recognizing cases, we can stop the outbreak,” Dr. Freeman said. “In theory, an infected person could show up in your clinic, regardless of where you practice in the U.S. But at the same time, it’s important not to panic. This is not COVID-19 all over again; this is different. Yes, it is an outbreak, but we already have a vaccine that works against monkeypox, and while one of the possible modes of transmission for monkeypox is respiratory, it’s much harder to transmit that way than SARS-CoV-2 – it requires closer and longer contact.”
Confirmation of a monkeypox virus infection is based on results of a PCR test based on swabs of a lesion. The AAD task force recommends contacting the local hospital epidemiologist, infection control personnel, and/or state health department about suspected cases, “as different locations will have different regulations on where to send the [PCR] test. If appropriate, the state health department will contact the CDC.”
According to the CDC, current recommendations for personal protective equipment for possible and confirmed monkeypox cases include gown, gloves, a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health-approved N-95 mask, and eye protection.
Topical antiviral an option
If the lesions in a patient with suspected monkeypox have turned into pustules while waiting for the PCR test results, one option is to prescribe 3%-5% topical cidofovir, according to Stephen K. Tyring, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology, microbiology & molecular genetics, and internal medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. “That’s the effective antiviral that is most available,” he said. Generic cidofovir is also now available.
Dr. Tyring recommends rapid referral of immunocompromised patients with suspected monkeypox to an infectious disease expert and/or consulting with the CDC. “The pediatric population also seems to be at somewhat more risk, as has been seen in sub-Saharan Africa,” said Dr. Tyring, who is one of the editors of the textbook Tropical Dermatology. “Also, by definition, pregnant women are at more risk because their immune systems aren’t up to par. You also want to make sure that if monkeypox is on a person’s skin that they don’t get it in their eyes, because they could lose their vision.” He added that sub-Saharan Africa has a monkeypox mortality of up to 10%, “which is something we don’t see in the U.S. or Europe. Those of us who grew up in the 20th century got routine smallpox vaccines, and we therefore probably have a degree of immunity to monkeypox. But for the past 40 years or so, unless you are in the military, you are not going to get a routine vaccine to prevent smallpox.”
Incubation period, appearance of lesions
Monkeypox has a long incubation period. According to Dr. Freeman, from the point of exposure to the development of symptomatic lesions is typically 7-14 days but can vary from 5-21 days. “It’s important for people to be aware that their exposure may have been in the more distant past, not just a few days ago” she said. “Identifying cases as quickly as possible gives us a window where we can vaccinate close contacts.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Tyring reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CDC guidance on vaccination before and after exposure to monkeypox can be found here . A general Q&A for health care professionals from the CDC can be found here.
When Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, thinks back on what she learned about monkeypox during her training as a dermatologist and an infectious disease epidemiologist, it was widely considered a viral disease with rare outbreaks limited primarily to Central and Western Africa.
“Monkeypox is something we have traditionally only seen very rarely in the U.S.,” Dr. Freeman, director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “In the past, outbreaks in the U.S. have been related to international travel or import of exotic pets, which is very different than what we’re seeing as a global community now.”

Monkeypox virus belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, symptoms develop 5-21 days after infection and may include fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. Typically, within 1-3 days of the fever, a rash develops, followed by the formation of monkeypox lesions. These lesions progress from macules to papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs, before falling off. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
What makes the 2022 monkeypox outbreak different from others is clear evidence of community transmission. According to worldwide data from the CDC, as of June 9, 2022, there were 1,356 confirmed cases in 31 countries, including 44 cases in the United States. This means that person-to-person spread of the monkeypox virus is occurring among individuals who have not traveled outside of their own country.
“This is likely an underestimate, especially when we think about the U.S., which only has 44 confirmed cases at this time,” Dr. Freeman said. “However, at present, monkeypox cases have to be confirmed by the CDC, so there are a lot more suspected cases that are likely to be confirmed in the coming days. As with any outbreak, it’s a rapidly changing situation.”
A different clinical presentation
The clinical presentation of monkeypox cases in the current outbreak also differs from that of previous outbreaks. In the past, monkeypox rashes often morphed from a macule to a pustule and commonly affected the face, hands, feet, and trunk, with some patients harboring as many as 200 lesions at once. That pattern still occurs, but increasingly, the presentation is characterized by a more localized spread, especially in the genital region, which Dr. Freeman described as “unusual and not an area we traditionally thought of in the past as a focus for monkeypox.”
Also, affected individuals in the current outbreak may develop fewer lesions, sometimes between 1 and 5 instead of up to 200. “This doesn’t apply to everybody, but it is a bit of a different picture than what we’ve seen in case descriptions and photographs in the past from places like Central Africa,” she said. “What’s being reported out of case clusters from the United Kingdom and Spain is a mix, where some people are having more generalized involvement while others have more localized involvement.” Visual examples of the monkey pox rash can be found in photos from the United Kingdom, the country with the highest number of confirmed cases, on the CDC’s website, and in a report from Spain.
Clusters of monkeypox cases have been reported worldwide in men who have sex with men, “but this is not limited to a particular subgroup of people,” emphasizes Dr. Freeman, who is also a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force to Develop Monkeypox Content, which created an online resource for clinicians. “There are several mechanisms of spread, but direct contact with lesions or infected fluids is one,” she notes.
Moreover, If you have a patient with a new genital lesion and you’re not sure what it is, testing for monkeypox in addition to classic sexually transmitted infections like HSV or syphilis would be reasonable during the current outbreak situation.”
The 2022 monkeypox outbreak may pale in comparison to the spread of COVID-19 in terms of case numbers and societal impact, but dermatologists may be the first point of contact for a person infected with the monkeypox virus. “It’s important for dermatologists to be able to recognize monkeypox, because by recognizing cases, we can stop the outbreak,” Dr. Freeman said. “In theory, an infected person could show up in your clinic, regardless of where you practice in the U.S. But at the same time, it’s important not to panic. This is not COVID-19 all over again; this is different. Yes, it is an outbreak, but we already have a vaccine that works against monkeypox, and while one of the possible modes of transmission for monkeypox is respiratory, it’s much harder to transmit that way than SARS-CoV-2 – it requires closer and longer contact.”
Confirmation of a monkeypox virus infection is based on results of a PCR test based on swabs of a lesion. The AAD task force recommends contacting the local hospital epidemiologist, infection control personnel, and/or state health department about suspected cases, “as different locations will have different regulations on where to send the [PCR] test. If appropriate, the state health department will contact the CDC.”
According to the CDC, current recommendations for personal protective equipment for possible and confirmed monkeypox cases include gown, gloves, a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health-approved N-95 mask, and eye protection.
Topical antiviral an option
If the lesions in a patient with suspected monkeypox have turned into pustules while waiting for the PCR test results, one option is to prescribe 3%-5% topical cidofovir, according to Stephen K. Tyring, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology, microbiology & molecular genetics, and internal medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. “That’s the effective antiviral that is most available,” he said. Generic cidofovir is also now available.
Dr. Tyring recommends rapid referral of immunocompromised patients with suspected monkeypox to an infectious disease expert and/or consulting with the CDC. “The pediatric population also seems to be at somewhat more risk, as has been seen in sub-Saharan Africa,” said Dr. Tyring, who is one of the editors of the textbook Tropical Dermatology. “Also, by definition, pregnant women are at more risk because their immune systems aren’t up to par. You also want to make sure that if monkeypox is on a person’s skin that they don’t get it in their eyes, because they could lose their vision.” He added that sub-Saharan Africa has a monkeypox mortality of up to 10%, “which is something we don’t see in the U.S. or Europe. Those of us who grew up in the 20th century got routine smallpox vaccines, and we therefore probably have a degree of immunity to monkeypox. But for the past 40 years or so, unless you are in the military, you are not going to get a routine vaccine to prevent smallpox.”
Incubation period, appearance of lesions
Monkeypox has a long incubation period. According to Dr. Freeman, from the point of exposure to the development of symptomatic lesions is typically 7-14 days but can vary from 5-21 days. “It’s important for people to be aware that their exposure may have been in the more distant past, not just a few days ago” she said. “Identifying cases as quickly as possible gives us a window where we can vaccinate close contacts.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Tyring reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CDC guidance on vaccination before and after exposure to monkeypox can be found here . A general Q&A for health care professionals from the CDC can be found here.
‘My malpractice insurance doubled!’ Why, when fewer patients are suing?
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Atopic dermatitis: Options abound, and more are coming
, said at MedscapeLive’s Women’s & Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
More and more treatment options are available and even more are in the pipeline, said Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and vice chair of dermatology at the University of California, San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital. As he put it: “We got pills, injections, things to smear on the skin.”
Those options are welcome and needed, as AD affects up to 20% of children and up to 10% of adults. The course is variable, as is severity, and quality of life is impacted.
Besides new treatment options, there is a new understanding about comorbidities, environmental effects, and triggers, Dr. Eichenfield said. Among the potential comorbidities health care providers should be aware of are allergies, such as food allergies; asthma; rhinitis; mental health issues (depression, anxiety, ADHD, learning disabilities, or in adults, substance abuse); bone health; skin infections; immune disorders such as alopecia areata or urticaria; and cardiovascular issues that could affect adults.
Environmental effects can play a role in aggravating AD, as providers learned after visits for AD increased after Northern California wildfires and also in other areas with high air pollution, Dr. Eichenfield said. “I actually discuss this with my families,” when making them aware of factors that may affect AD, he noted.
Dr. Eichenfield provided an overview of available treatment options, and what treatments may be coming next. Among the highlights:
Topical ruxolitinib: A JAK1,2 inhibitor in a cream formulation, it is now approved for patients with mild to moderate AD aged 12 years and older in the United States. Of the two strengths studied, the higher strength, 1.5%, was approved, Dr. Eichenfield said. How well did it work? In two phase 3 studies in patients aged 12 and older, of those on 1.5%, 53% were clear or almost clear at 8 weeks, versus 11% in the control group given the vehicle; 52% had at least a 4-point reduction in itch from baseline, versus 15.4% on vehicle. Quality of life improved in up to 73.2% of those given the medication versus 19.7% of those on the vehicle. There was a marked and quick improvement in itch, as early as 12 hours, and safety measures also look good, he said.
Topical tapinarof: Approved in May 2022, for adults with plaque psoriasis, phase 3 trials began in September, 2021, for adults and children with AD, according to the manufacturer. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates its anti-inflammatory properties.
Topical roflumilast: A potent PDE-4 inhibitor, phase 3 AD studies are underway. It appears to be well tolerated, Dr. Eichenfield said.
Dupilumab: An IL-4/13 blocker, this biologic produced an itch reduction of 50% and EASI of 80%, improved quality of life, and reduced anxiety and depression. The drug “led the revolution in systemic therapy for atopic dermatitis,” he said. First approved for treating AD in patients aged 18 years and up in 2017, approval for patients 12 years and up followed in March 2019, then for age 6 years and up May 2020.
At the meeting on June 3, Dr. Eichenfield said that approval in children 5 years and under was imminent, and on June 7, the FDA approved dupilumab for use in children aged 6 months to 5 years. In a phase 3, 16-week trial, 28% of children treated with dupilumab added on to low-potency topical corticosteroids met the endpoint of clear or nearly clear skin, compared with 4% of those on the corticosteroids alone (P < .0001).
Tralokinumab: There is no approved indication yet for adolescents, but the injected biologic, an interleukin-13 antagonist, is approved for adults with moderate to severe AD who are not well-controlled with topicals, or who cannot use topicals.
Oral JAK inhibitors: These include abrocitinib and upadacitinib, both approved by the FDA in January 2022 for treating moderate to severe AD, and baricitinib (the latter not in the United States). “For AD, you probably won’t see it in the U.S.,” Dr. Eichenfield said, referring to baricitinib. However, it might get approved for alopecia areata, he noted.
Upadacitinib is approved for adolescents 12 and older with AD. Abrocitinib is approved for adults 18 and older with AD.
Regarding safety and tolerance concerns with oral JAK inhibitors, Dr. Eichenfield cites headache, acne, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infections as relatively common, while herpes zoster, venous thromboembolism, and lab anomalies (neutropenia, elevated CPK) are uncommon.
As the options for AD treatments increase, and expectations by families and clinicians change, Dr. Eichenfield said he often focuses on “bucket duty” – whether a specific patient should be in the topical bucket or the systemic one. It’s a decision that will continue to be crucial, he said.
When presented with treatment options, patients – and parents – often worry about side effects, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas Medical Center, Little Rock, who also spoke at the meeting. She gently tells them: “The worst side effect you can have is probably not treating the disease itself.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Eichenfield is a consultant or investigator for numerous companies that manufacture treatments for AD, but based his discussion on evidence-based recommendations and public presentations or publications.
, said at MedscapeLive’s Women’s & Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
More and more treatment options are available and even more are in the pipeline, said Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and vice chair of dermatology at the University of California, San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital. As he put it: “We got pills, injections, things to smear on the skin.”
Those options are welcome and needed, as AD affects up to 20% of children and up to 10% of adults. The course is variable, as is severity, and quality of life is impacted.
Besides new treatment options, there is a new understanding about comorbidities, environmental effects, and triggers, Dr. Eichenfield said. Among the potential comorbidities health care providers should be aware of are allergies, such as food allergies; asthma; rhinitis; mental health issues (depression, anxiety, ADHD, learning disabilities, or in adults, substance abuse); bone health; skin infections; immune disorders such as alopecia areata or urticaria; and cardiovascular issues that could affect adults.
Environmental effects can play a role in aggravating AD, as providers learned after visits for AD increased after Northern California wildfires and also in other areas with high air pollution, Dr. Eichenfield said. “I actually discuss this with my families,” when making them aware of factors that may affect AD, he noted.
Dr. Eichenfield provided an overview of available treatment options, and what treatments may be coming next. Among the highlights:
Topical ruxolitinib: A JAK1,2 inhibitor in a cream formulation, it is now approved for patients with mild to moderate AD aged 12 years and older in the United States. Of the two strengths studied, the higher strength, 1.5%, was approved, Dr. Eichenfield said. How well did it work? In two phase 3 studies in patients aged 12 and older, of those on 1.5%, 53% were clear or almost clear at 8 weeks, versus 11% in the control group given the vehicle; 52% had at least a 4-point reduction in itch from baseline, versus 15.4% on vehicle. Quality of life improved in up to 73.2% of those given the medication versus 19.7% of those on the vehicle. There was a marked and quick improvement in itch, as early as 12 hours, and safety measures also look good, he said.
Topical tapinarof: Approved in May 2022, for adults with plaque psoriasis, phase 3 trials began in September, 2021, for adults and children with AD, according to the manufacturer. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates its anti-inflammatory properties.
Topical roflumilast: A potent PDE-4 inhibitor, phase 3 AD studies are underway. It appears to be well tolerated, Dr. Eichenfield said.
Dupilumab: An IL-4/13 blocker, this biologic produced an itch reduction of 50% and EASI of 80%, improved quality of life, and reduced anxiety and depression. The drug “led the revolution in systemic therapy for atopic dermatitis,” he said. First approved for treating AD in patients aged 18 years and up in 2017, approval for patients 12 years and up followed in March 2019, then for age 6 years and up May 2020.
At the meeting on June 3, Dr. Eichenfield said that approval in children 5 years and under was imminent, and on June 7, the FDA approved dupilumab for use in children aged 6 months to 5 years. In a phase 3, 16-week trial, 28% of children treated with dupilumab added on to low-potency topical corticosteroids met the endpoint of clear or nearly clear skin, compared with 4% of those on the corticosteroids alone (P < .0001).
Tralokinumab: There is no approved indication yet for adolescents, but the injected biologic, an interleukin-13 antagonist, is approved for adults with moderate to severe AD who are not well-controlled with topicals, or who cannot use topicals.
Oral JAK inhibitors: These include abrocitinib and upadacitinib, both approved by the FDA in January 2022 for treating moderate to severe AD, and baricitinib (the latter not in the United States). “For AD, you probably won’t see it in the U.S.,” Dr. Eichenfield said, referring to baricitinib. However, it might get approved for alopecia areata, he noted.
Upadacitinib is approved for adolescents 12 and older with AD. Abrocitinib is approved for adults 18 and older with AD.
Regarding safety and tolerance concerns with oral JAK inhibitors, Dr. Eichenfield cites headache, acne, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infections as relatively common, while herpes zoster, venous thromboembolism, and lab anomalies (neutropenia, elevated CPK) are uncommon.
As the options for AD treatments increase, and expectations by families and clinicians change, Dr. Eichenfield said he often focuses on “bucket duty” – whether a specific patient should be in the topical bucket or the systemic one. It’s a decision that will continue to be crucial, he said.
When presented with treatment options, patients – and parents – often worry about side effects, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas Medical Center, Little Rock, who also spoke at the meeting. She gently tells them: “The worst side effect you can have is probably not treating the disease itself.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Eichenfield is a consultant or investigator for numerous companies that manufacture treatments for AD, but based his discussion on evidence-based recommendations and public presentations or publications.
, said at MedscapeLive’s Women’s & Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
More and more treatment options are available and even more are in the pipeline, said Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics and vice chair of dermatology at the University of California, San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital. As he put it: “We got pills, injections, things to smear on the skin.”
Those options are welcome and needed, as AD affects up to 20% of children and up to 10% of adults. The course is variable, as is severity, and quality of life is impacted.
Besides new treatment options, there is a new understanding about comorbidities, environmental effects, and triggers, Dr. Eichenfield said. Among the potential comorbidities health care providers should be aware of are allergies, such as food allergies; asthma; rhinitis; mental health issues (depression, anxiety, ADHD, learning disabilities, or in adults, substance abuse); bone health; skin infections; immune disorders such as alopecia areata or urticaria; and cardiovascular issues that could affect adults.
Environmental effects can play a role in aggravating AD, as providers learned after visits for AD increased after Northern California wildfires and also in other areas with high air pollution, Dr. Eichenfield said. “I actually discuss this with my families,” when making them aware of factors that may affect AD, he noted.
Dr. Eichenfield provided an overview of available treatment options, and what treatments may be coming next. Among the highlights:
Topical ruxolitinib: A JAK1,2 inhibitor in a cream formulation, it is now approved for patients with mild to moderate AD aged 12 years and older in the United States. Of the two strengths studied, the higher strength, 1.5%, was approved, Dr. Eichenfield said. How well did it work? In two phase 3 studies in patients aged 12 and older, of those on 1.5%, 53% were clear or almost clear at 8 weeks, versus 11% in the control group given the vehicle; 52% had at least a 4-point reduction in itch from baseline, versus 15.4% on vehicle. Quality of life improved in up to 73.2% of those given the medication versus 19.7% of those on the vehicle. There was a marked and quick improvement in itch, as early as 12 hours, and safety measures also look good, he said.
Topical tapinarof: Approved in May 2022, for adults with plaque psoriasis, phase 3 trials began in September, 2021, for adults and children with AD, according to the manufacturer. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates its anti-inflammatory properties.
Topical roflumilast: A potent PDE-4 inhibitor, phase 3 AD studies are underway. It appears to be well tolerated, Dr. Eichenfield said.
Dupilumab: An IL-4/13 blocker, this biologic produced an itch reduction of 50% and EASI of 80%, improved quality of life, and reduced anxiety and depression. The drug “led the revolution in systemic therapy for atopic dermatitis,” he said. First approved for treating AD in patients aged 18 years and up in 2017, approval for patients 12 years and up followed in March 2019, then for age 6 years and up May 2020.
At the meeting on June 3, Dr. Eichenfield said that approval in children 5 years and under was imminent, and on June 7, the FDA approved dupilumab for use in children aged 6 months to 5 years. In a phase 3, 16-week trial, 28% of children treated with dupilumab added on to low-potency topical corticosteroids met the endpoint of clear or nearly clear skin, compared with 4% of those on the corticosteroids alone (P < .0001).
Tralokinumab: There is no approved indication yet for adolescents, but the injected biologic, an interleukin-13 antagonist, is approved for adults with moderate to severe AD who are not well-controlled with topicals, or who cannot use topicals.
Oral JAK inhibitors: These include abrocitinib and upadacitinib, both approved by the FDA in January 2022 for treating moderate to severe AD, and baricitinib (the latter not in the United States). “For AD, you probably won’t see it in the U.S.,” Dr. Eichenfield said, referring to baricitinib. However, it might get approved for alopecia areata, he noted.
Upadacitinib is approved for adolescents 12 and older with AD. Abrocitinib is approved for adults 18 and older with AD.
Regarding safety and tolerance concerns with oral JAK inhibitors, Dr. Eichenfield cites headache, acne, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infections as relatively common, while herpes zoster, venous thromboembolism, and lab anomalies (neutropenia, elevated CPK) are uncommon.
As the options for AD treatments increase, and expectations by families and clinicians change, Dr. Eichenfield said he often focuses on “bucket duty” – whether a specific patient should be in the topical bucket or the systemic one. It’s a decision that will continue to be crucial, he said.
When presented with treatment options, patients – and parents – often worry about side effects, said Vivian Shi, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas Medical Center, Little Rock, who also spoke at the meeting. She gently tells them: “The worst side effect you can have is probably not treating the disease itself.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Eichenfield is a consultant or investigator for numerous companies that manufacture treatments for AD, but based his discussion on evidence-based recommendations and public presentations or publications.
FROM MEDSCAPELIVE WOMEN’S & PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Asian American teens have highest rate of suicidal ideation
NEW ORLEANS – In an unexpected finding, researchers discovered that According to a weighted analysis, 24% of Asian Americans reported thinking about or planning suicide vs. 22% of Whites and Blacks and 20% of Hispanics (P < .01).
“We were shocked,” said study lead author Esha Hansoti, MD, who conducted the research at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and is now a psychiatry resident at Zucker Hillside Hospital Northwell/Hofstra in Glen Oaks, NY. The findings were released at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Hansoti and colleagues launched the analysis in light of sparse research into Asian American mental health, she said. Even within this population, she said, mental illness “tends to be overlooked” and discussion of the topic may be considered taboo.
For the new study, researchers analyzed the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, conducted biennially by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which had more than 13,000 participants in grades 9-12.
A weighted bivariate analysis of 618 Asian American adolescents – adjusted for age, sex, and depressive symptoms – found no statistically significant impact on suicidal ideation by gender, age, substance use, sexual/physical dating violence, or fluency in English.
However, several groups had a statistically significant higher risk, including victims of forced sexual intercourse and those who were threatened or bullied at school.
Those who didn’t get mostly A grades were also at high risk: Adolescents with mostly Ds and Fs were more likely to have acknowledged suicidal ideation than those with mostly As (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 3.2).
Gays and lesbians (AOR = 7.9 vs. heterosexuals), and bisexuals (AOR = 5.2 vs. heterosexuals) also showed sharply higher rates of suicidal ideation.
It’s not clear why Asian American adolescents may be at higher risk of suicidal ideation. The survey was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which spawned bigotry against people of Asian descent and an ongoing outbreak of high-profile violence against Asian Americans across the country.
Dr. Hansoti noted that Asian Americans face the pressures to live up to the standards of being a “model minority.” In addition, “very few Asian American adolescents are taken to a therapist, and few mental health providers are Asian Americans.”
She urged fellow psychiatrists “to remember that our perceptions of Asian Americans might hinder some of the diagnoses we could be making. Be thoughtful about how their ethnicity and race affects their presentation and their own perception of their illness.”
She added that Asian Americans may experience mental illness and anxiety “more somatically and physically than emotionally.”
In an interview, Anne Saw, PhD, associate professor of clinical-community psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, said the findings are “helpful for corroborating other studies identifying risk factors of suicidal ideation among Asian American adolescents. Since this research utilizes the Youth Risk Behavior Survey, these findings can be compared with risk factors of suicidal ideation among adolescents from other racial/ethnic backgrounds to pinpoint general as well as specific risk factors, thus informing how we can tailor interventions for specific groups.”
According to Dr. Saw, while it’s clear that suicide is a leading cause of death among Asian American adolescents, it’s still unknown which specific subgroups other than girls and LGBTIA+ individuals are especially vulnerable and which culturally tailored interventions are most effective for decreasing suicide risk.
“Psychiatrists should understand that risk and protective factors for suicidal behavior in Asian American adolescents are multifaceted and require careful attention and intervention across different environments,” she said.
No funding and no disclosures were reported.
NEW ORLEANS – In an unexpected finding, researchers discovered that According to a weighted analysis, 24% of Asian Americans reported thinking about or planning suicide vs. 22% of Whites and Blacks and 20% of Hispanics (P < .01).
“We were shocked,” said study lead author Esha Hansoti, MD, who conducted the research at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and is now a psychiatry resident at Zucker Hillside Hospital Northwell/Hofstra in Glen Oaks, NY. The findings were released at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Hansoti and colleagues launched the analysis in light of sparse research into Asian American mental health, she said. Even within this population, she said, mental illness “tends to be overlooked” and discussion of the topic may be considered taboo.
For the new study, researchers analyzed the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, conducted biennially by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which had more than 13,000 participants in grades 9-12.
A weighted bivariate analysis of 618 Asian American adolescents – adjusted for age, sex, and depressive symptoms – found no statistically significant impact on suicidal ideation by gender, age, substance use, sexual/physical dating violence, or fluency in English.
However, several groups had a statistically significant higher risk, including victims of forced sexual intercourse and those who were threatened or bullied at school.
Those who didn’t get mostly A grades were also at high risk: Adolescents with mostly Ds and Fs were more likely to have acknowledged suicidal ideation than those with mostly As (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 3.2).
Gays and lesbians (AOR = 7.9 vs. heterosexuals), and bisexuals (AOR = 5.2 vs. heterosexuals) also showed sharply higher rates of suicidal ideation.
It’s not clear why Asian American adolescents may be at higher risk of suicidal ideation. The survey was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which spawned bigotry against people of Asian descent and an ongoing outbreak of high-profile violence against Asian Americans across the country.
Dr. Hansoti noted that Asian Americans face the pressures to live up to the standards of being a “model minority.” In addition, “very few Asian American adolescents are taken to a therapist, and few mental health providers are Asian Americans.”
She urged fellow psychiatrists “to remember that our perceptions of Asian Americans might hinder some of the diagnoses we could be making. Be thoughtful about how their ethnicity and race affects their presentation and their own perception of their illness.”
She added that Asian Americans may experience mental illness and anxiety “more somatically and physically than emotionally.”
In an interview, Anne Saw, PhD, associate professor of clinical-community psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, said the findings are “helpful for corroborating other studies identifying risk factors of suicidal ideation among Asian American adolescents. Since this research utilizes the Youth Risk Behavior Survey, these findings can be compared with risk factors of suicidal ideation among adolescents from other racial/ethnic backgrounds to pinpoint general as well as specific risk factors, thus informing how we can tailor interventions for specific groups.”
According to Dr. Saw, while it’s clear that suicide is a leading cause of death among Asian American adolescents, it’s still unknown which specific subgroups other than girls and LGBTIA+ individuals are especially vulnerable and which culturally tailored interventions are most effective for decreasing suicide risk.
“Psychiatrists should understand that risk and protective factors for suicidal behavior in Asian American adolescents are multifaceted and require careful attention and intervention across different environments,” she said.
No funding and no disclosures were reported.
NEW ORLEANS – In an unexpected finding, researchers discovered that According to a weighted analysis, 24% of Asian Americans reported thinking about or planning suicide vs. 22% of Whites and Blacks and 20% of Hispanics (P < .01).
“We were shocked,” said study lead author Esha Hansoti, MD, who conducted the research at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and is now a psychiatry resident at Zucker Hillside Hospital Northwell/Hofstra in Glen Oaks, NY. The findings were released at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Hansoti and colleagues launched the analysis in light of sparse research into Asian American mental health, she said. Even within this population, she said, mental illness “tends to be overlooked” and discussion of the topic may be considered taboo.
For the new study, researchers analyzed the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, conducted biennially by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which had more than 13,000 participants in grades 9-12.
A weighted bivariate analysis of 618 Asian American adolescents – adjusted for age, sex, and depressive symptoms – found no statistically significant impact on suicidal ideation by gender, age, substance use, sexual/physical dating violence, or fluency in English.
However, several groups had a statistically significant higher risk, including victims of forced sexual intercourse and those who were threatened or bullied at school.
Those who didn’t get mostly A grades were also at high risk: Adolescents with mostly Ds and Fs were more likely to have acknowledged suicidal ideation than those with mostly As (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 3.2).
Gays and lesbians (AOR = 7.9 vs. heterosexuals), and bisexuals (AOR = 5.2 vs. heterosexuals) also showed sharply higher rates of suicidal ideation.
It’s not clear why Asian American adolescents may be at higher risk of suicidal ideation. The survey was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which spawned bigotry against people of Asian descent and an ongoing outbreak of high-profile violence against Asian Americans across the country.
Dr. Hansoti noted that Asian Americans face the pressures to live up to the standards of being a “model minority.” In addition, “very few Asian American adolescents are taken to a therapist, and few mental health providers are Asian Americans.”
She urged fellow psychiatrists “to remember that our perceptions of Asian Americans might hinder some of the diagnoses we could be making. Be thoughtful about how their ethnicity and race affects their presentation and their own perception of their illness.”
She added that Asian Americans may experience mental illness and anxiety “more somatically and physically than emotionally.”
In an interview, Anne Saw, PhD, associate professor of clinical-community psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, said the findings are “helpful for corroborating other studies identifying risk factors of suicidal ideation among Asian American adolescents. Since this research utilizes the Youth Risk Behavior Survey, these findings can be compared with risk factors of suicidal ideation among adolescents from other racial/ethnic backgrounds to pinpoint general as well as specific risk factors, thus informing how we can tailor interventions for specific groups.”
According to Dr. Saw, while it’s clear that suicide is a leading cause of death among Asian American adolescents, it’s still unknown which specific subgroups other than girls and LGBTIA+ individuals are especially vulnerable and which culturally tailored interventions are most effective for decreasing suicide risk.
“Psychiatrists should understand that risk and protective factors for suicidal behavior in Asian American adolescents are multifaceted and require careful attention and intervention across different environments,” she said.
No funding and no disclosures were reported.
AT APA 2022
Youth with bipolar disorder at high risk of eating disorders
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.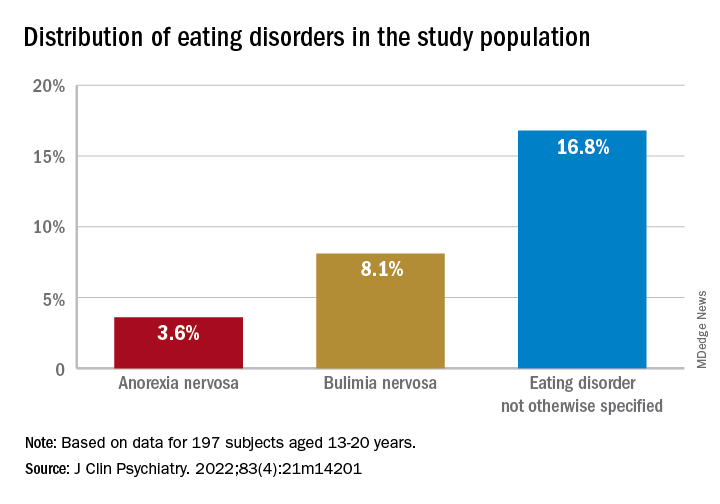
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.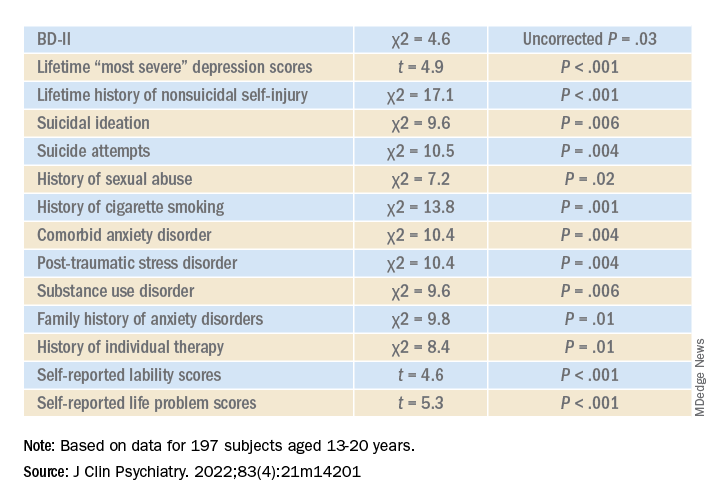
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”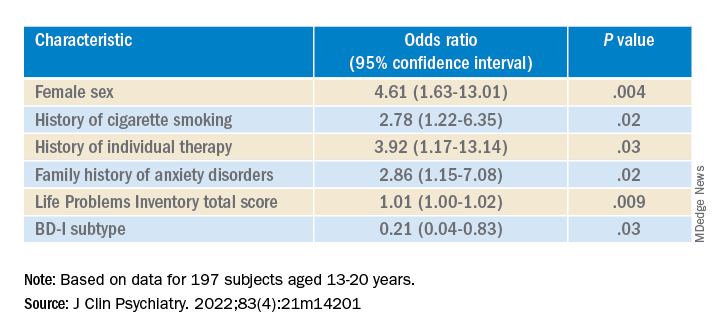
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Alcohol, degraded sleep related in young adults
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Sleep and alcohol consumption in young adults seems to follow a “vicious cycle,” as one observer called it. and those who went to bed earlier and slept longer tended to drink less the next day, a study of drinking and sleeping habits in 21- to 29-year-olds found.
“Sleep is a potential factor that we could intervene on to really identify how to improve drinking behaviors among young adults,” David Reichenberger, a graduate student at Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview after he presented his findings at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
This is one of the few studies of alcohol consumption and sleep patterns that used an objective measure of alcohol consumption, Mr. Reichenberger said. The study evaluated sleep and alcohol consumption patterns in 222 regularly drinking young adults over 6 consecutive days. Study participants completed morning smartphone-based questionnaires, reporting their previous night’s bedtime, sleep duration, sleep quality, and number of drinks consumed. They also wore an alcohol monitor that continuously measured their transdermal alcohol consumption (TAC).
The study analyzed the data using two sets of multilevel models: A linear model that looked at how each drinking predictor was associated with each sleep variable and a Poisson model to determine how sleep predicted next-day alcohol use.
“We found that higher average peak TAC – that is, how intoxicated they got – was associated with a 19-minute later bedtime among young adults,” Mr. Reichenberger said. “Later bedtimes were then associated with a 26% greater TAC among those adults” (P < .02).
Patterns of alcohol consumption and sleep
On days when participants recorded a higher peak TAC, bedtime was delayed, sleep duration was shorter, and subjective sleep quality was worse, he said. However, none of the sleep variables predicted next-day peak TAC.
“We found an association between the duration of the drinking episode and later bedtimes among young adults,” he added. “And on days when the drinking episodes were longer, subsequent sleep was delayed and sleep quality was worse. But we also found that after nights when they had a later bedtime, next-day drinking episodes were about 7% longer.”
Conversely, young adults who had earlier bedtimes and longer sleep durations tended to consume fewer drinks and they achieved lower intoxication levels the next day, Mr. Reichenberger said.
Between-person results showed that young adults who tended to go to bed later drank on average 24% more the next day (P < .01). Also, each extra hour of sleep was associated with a 14% decrease in drinking the next day (P < .03).
Participants who drank more went to bed on average 12-19 minutes later (P < .01) and slept 5 fewer minutes (P < .01). Within-person results showed that on nights when participants drank more than usual they went to bed 8-13 minutes later (P < .01), slept 2-4 fewer minutes (P < .03), and had worse sleep quality (P < .01).
Mr. Reichenberger acknowledged one limitation of the study: Measuring sleep and alcohol consumption patterns over 6 days might not be long enough. Future studies should address that.
A ‘vicious cycle’
Hans P.A. Van Dongen, PhD, director of the Sleep and Performance Research Center at Washington State University, Spokane, said in an interview that the findings imply a “vicious cycle” between sleep and alcohol consumption. “You create a problem and then it perpetuates itself or reinforces itself.”
In older adults, alcohol tends to act as a “sleep aid,” Dr. Van Dongen noted. “Then it disrupts their sleep later on and then the next night they need to use the sleep aid again because they had a really poor night and they’re tired and they want to fall asleep.”
He added: “I think what is new here is that’s not very likely the mechanism that they’re using alcohol as a sleep aid in younger adults that we see in older adults, so I think there is a new element to it. Now does anybody know how that works exactly? No, that’s the next thing.”
The Penn State study identifies “a signal there that needs to be followed up on,” Dr. Van Dongen said. “There’s something nature’s trying to tell us but it’s not exactly clear what it’s trying to tell us.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse provided funding for the study. Mr. Reichenberger has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Van Dongen has no disclosures to report.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Sleep and alcohol consumption in young adults seems to follow a “vicious cycle,” as one observer called it. and those who went to bed earlier and slept longer tended to drink less the next day, a study of drinking and sleeping habits in 21- to 29-year-olds found.
“Sleep is a potential factor that we could intervene on to really identify how to improve drinking behaviors among young adults,” David Reichenberger, a graduate student at Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview after he presented his findings at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
This is one of the few studies of alcohol consumption and sleep patterns that used an objective measure of alcohol consumption, Mr. Reichenberger said. The study evaluated sleep and alcohol consumption patterns in 222 regularly drinking young adults over 6 consecutive days. Study participants completed morning smartphone-based questionnaires, reporting their previous night’s bedtime, sleep duration, sleep quality, and number of drinks consumed. They also wore an alcohol monitor that continuously measured their transdermal alcohol consumption (TAC).
The study analyzed the data using two sets of multilevel models: A linear model that looked at how each drinking predictor was associated with each sleep variable and a Poisson model to determine how sleep predicted next-day alcohol use.
“We found that higher average peak TAC – that is, how intoxicated they got – was associated with a 19-minute later bedtime among young adults,” Mr. Reichenberger said. “Later bedtimes were then associated with a 26% greater TAC among those adults” (P < .02).
Patterns of alcohol consumption and sleep
On days when participants recorded a higher peak TAC, bedtime was delayed, sleep duration was shorter, and subjective sleep quality was worse, he said. However, none of the sleep variables predicted next-day peak TAC.
“We found an association between the duration of the drinking episode and later bedtimes among young adults,” he added. “And on days when the drinking episodes were longer, subsequent sleep was delayed and sleep quality was worse. But we also found that after nights when they had a later bedtime, next-day drinking episodes were about 7% longer.”
Conversely, young adults who had earlier bedtimes and longer sleep durations tended to consume fewer drinks and they achieved lower intoxication levels the next day, Mr. Reichenberger said.
Between-person results showed that young adults who tended to go to bed later drank on average 24% more the next day (P < .01). Also, each extra hour of sleep was associated with a 14% decrease in drinking the next day (P < .03).
Participants who drank more went to bed on average 12-19 minutes later (P < .01) and slept 5 fewer minutes (P < .01). Within-person results showed that on nights when participants drank more than usual they went to bed 8-13 minutes later (P < .01), slept 2-4 fewer minutes (P < .03), and had worse sleep quality (P < .01).
Mr. Reichenberger acknowledged one limitation of the study: Measuring sleep and alcohol consumption patterns over 6 days might not be long enough. Future studies should address that.
A ‘vicious cycle’
Hans P.A. Van Dongen, PhD, director of the Sleep and Performance Research Center at Washington State University, Spokane, said in an interview that the findings imply a “vicious cycle” between sleep and alcohol consumption. “You create a problem and then it perpetuates itself or reinforces itself.”
In older adults, alcohol tends to act as a “sleep aid,” Dr. Van Dongen noted. “Then it disrupts their sleep later on and then the next night they need to use the sleep aid again because they had a really poor night and they’re tired and they want to fall asleep.”
He added: “I think what is new here is that’s not very likely the mechanism that they’re using alcohol as a sleep aid in younger adults that we see in older adults, so I think there is a new element to it. Now does anybody know how that works exactly? No, that’s the next thing.”
The Penn State study identifies “a signal there that needs to be followed up on,” Dr. Van Dongen said. “There’s something nature’s trying to tell us but it’s not exactly clear what it’s trying to tell us.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse provided funding for the study. Mr. Reichenberger has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Van Dongen has no disclosures to report.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Sleep and alcohol consumption in young adults seems to follow a “vicious cycle,” as one observer called it. and those who went to bed earlier and slept longer tended to drink less the next day, a study of drinking and sleeping habits in 21- to 29-year-olds found.
“Sleep is a potential factor that we could intervene on to really identify how to improve drinking behaviors among young adults,” David Reichenberger, a graduate student at Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview after he presented his findings at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
This is one of the few studies of alcohol consumption and sleep patterns that used an objective measure of alcohol consumption, Mr. Reichenberger said. The study evaluated sleep and alcohol consumption patterns in 222 regularly drinking young adults over 6 consecutive days. Study participants completed morning smartphone-based questionnaires, reporting their previous night’s bedtime, sleep duration, sleep quality, and number of drinks consumed. They also wore an alcohol monitor that continuously measured their transdermal alcohol consumption (TAC).
The study analyzed the data using two sets of multilevel models: A linear model that looked at how each drinking predictor was associated with each sleep variable and a Poisson model to determine how sleep predicted next-day alcohol use.
“We found that higher average peak TAC – that is, how intoxicated they got – was associated with a 19-minute later bedtime among young adults,” Mr. Reichenberger said. “Later bedtimes were then associated with a 26% greater TAC among those adults” (P < .02).
Patterns of alcohol consumption and sleep
On days when participants recorded a higher peak TAC, bedtime was delayed, sleep duration was shorter, and subjective sleep quality was worse, he said. However, none of the sleep variables predicted next-day peak TAC.
“We found an association between the duration of the drinking episode and later bedtimes among young adults,” he added. “And on days when the drinking episodes were longer, subsequent sleep was delayed and sleep quality was worse. But we also found that after nights when they had a later bedtime, next-day drinking episodes were about 7% longer.”
Conversely, young adults who had earlier bedtimes and longer sleep durations tended to consume fewer drinks and they achieved lower intoxication levels the next day, Mr. Reichenberger said.
Between-person results showed that young adults who tended to go to bed later drank on average 24% more the next day (P < .01). Also, each extra hour of sleep was associated with a 14% decrease in drinking the next day (P < .03).
Participants who drank more went to bed on average 12-19 minutes later (P < .01) and slept 5 fewer minutes (P < .01). Within-person results showed that on nights when participants drank more than usual they went to bed 8-13 minutes later (P < .01), slept 2-4 fewer minutes (P < .03), and had worse sleep quality (P < .01).
Mr. Reichenberger acknowledged one limitation of the study: Measuring sleep and alcohol consumption patterns over 6 days might not be long enough. Future studies should address that.
A ‘vicious cycle’
Hans P.A. Van Dongen, PhD, director of the Sleep and Performance Research Center at Washington State University, Spokane, said in an interview that the findings imply a “vicious cycle” between sleep and alcohol consumption. “You create a problem and then it perpetuates itself or reinforces itself.”
In older adults, alcohol tends to act as a “sleep aid,” Dr. Van Dongen noted. “Then it disrupts their sleep later on and then the next night they need to use the sleep aid again because they had a really poor night and they’re tired and they want to fall asleep.”
He added: “I think what is new here is that’s not very likely the mechanism that they’re using alcohol as a sleep aid in younger adults that we see in older adults, so I think there is a new element to it. Now does anybody know how that works exactly? No, that’s the next thing.”
The Penn State study identifies “a signal there that needs to be followed up on,” Dr. Van Dongen said. “There’s something nature’s trying to tell us but it’s not exactly clear what it’s trying to tell us.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse provided funding for the study. Mr. Reichenberger has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Van Dongen has no disclosures to report.
At SLEEP 2022











