User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Pandemic has helped clinicians to gain better insight on pernio, expert says
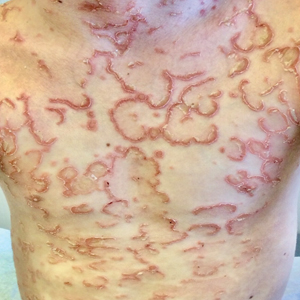
PORTLAND, ORE. – while others are not, according to Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the hospital consultation service at the University of California, San Francisco.
“We’re learning a lot about pernio because of COVID,” Dr. Fox, a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. “Patients with pernio tend to either have bright red or purple individual lesions or an erythromelalgia-like presentation, often waking up in the middle of the night saying ‘my feet hurt. I can’t put sheets over my feet.’ In my experience, the patients with an erythromelalgia-like presentation tend to be a lot harder to treat.”
Establishing terminology to describe pernio-like lesions was a challenge in the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fox added, with clinicians using terms like erythema multiforme-like, coxsackie-like, or even necrotic to describe the lesions. “I don’t think pernio is truly necrotic; I think it’s really inflammatory and purpuric,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, studies suggesting a link with these cases and COVID-19 infection include a case series of 318 patients with pernio-like skin lesions who had confirmed or suspected COVID-19. Most of these patients were generally young and healthy and most had relatively mild COVID-19; 7% were laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 positive, and 6% were close contacts of patients with confirmed COVID-19. Pernio-like lesions were the only symptoms in 55% of the patients.
In another study, researchers in France evaluated the clinical, laboratory, and pathologic characteristics of 40 patients who developed chilblain-like lesions (mostly involving the toes) during the COVID-19 pandemic and were seen as outpatients in April 2020 . All were polymerase chain reaction (PCR) negative, 30% were SARS-CoV-2 serology positive, and 60% had elevated D-dimers. Histology obtained from 19 of the patients revealed lymphocytic inflammation and vascular damage, and 8 had IgA positivity.
In a retrospective analysis of seven pediatric chilblains cases during the pandemic, researchers examined the skin biopsies to evaluate histopathological features and explored the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the tissue. All patients were PCR negative. The authors observed cytoplasmic granular positivity for SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in endothelial cells, a feature that they said showed coronavirus-like particles, consistent with SARS-CoV-2.
Not all studies in the medical literature have demonstrated an association between pernio-like/chilblains-like lesions and COVID-19, though. An analysis of 23 patients, with skin eruptions considered associated with SARS-CoV-2 infections (including 21 cases of chilblains) during the first wave of the pandemic found that the antibody and T-cell response in patients with pandemic chilblains was the same as in negative controls.
“What’s remarkably interesting about this study is that they did autopsies of samples from patients who had died prepandemic, so there was no such thing as COVID-19,” said Dr. Fox, who was not involved with the study. “They stained for viral particles in those patients, and they were positive in a subset of patients. This makes me wonder about what the significance of that staining positivity is.”
Yet another group of investigators looked at what was happening with pernio during the waves of COVID in a study of chilblains cases in children in Spain, and found a stronger association between lockdown and cold temperature, which argues against a direct association between pernio and COVID infection.
In Dr. Fox’s experience, COVID toes can recur, especially upon exposure to cold. “What taught me this in real life is a patient who I saw remotely by video,” she recalled. “It was early on in the pandemic. I could not prove he had COVID no matter how hard I tried, but I do think he had COVID toes at that time.” When he later was confirmed to have COVID, “he got pernio in the same exact location as his original suspected COVID toes.”
According to an analysis of long COVID in the skin, based on cases reported to the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatological Societies registry from April 8 to Oct. 8, 2020, pernio-like lesions lasted a median of 12 days in patients with lab-confirmed COVID-19 and a median of 15 days in those with suspected COVID-19. But almost 7% of the 103 pernio cases were long-haulers, defined as those with dermatologic signs of COVID that lasted beyond 60 days.
“There are some patients who are resistant to treatment,” Dr. Fox said. “In addition, recurrent lesions make me think that maybe all pernio is triggered by some viral cause. This causes an immunologic phenomenon that’s responding to a viral trigger you’re trying to deal with. That may be the better way to think about COVID toes.”
Different variants of COVID also appear to be changing the characteristics of dermatologic manifestations associated with infection. Results from a large retrospective analysis of nearly 350,000 users of a COVID study App in the United Kingdom found that skin lesions were more predictive of a positive test in the Delta wave, compared with the Omicron wave, while pernio-like lesions were predictive of infection in the Delta wave but not in the Omicron wave.
“And, whether you were vaccinated or unvaccinated really did not influence whether or not you were going to have a skin rash as a presenting sign of COVID, except for the burning rash, which was less in vaccinated patients,” said Dr. Fox, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Fox reported having no relevant disclosures.
PORTLAND, ORE. – while others are not, according to Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the hospital consultation service at the University of California, San Francisco.
“We’re learning a lot about pernio because of COVID,” Dr. Fox, a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. “Patients with pernio tend to either have bright red or purple individual lesions or an erythromelalgia-like presentation, often waking up in the middle of the night saying ‘my feet hurt. I can’t put sheets over my feet.’ In my experience, the patients with an erythromelalgia-like presentation tend to be a lot harder to treat.”
Establishing terminology to describe pernio-like lesions was a challenge in the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fox added, with clinicians using terms like erythema multiforme-like, coxsackie-like, or even necrotic to describe the lesions. “I don’t think pernio is truly necrotic; I think it’s really inflammatory and purpuric,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, studies suggesting a link with these cases and COVID-19 infection include a case series of 318 patients with pernio-like skin lesions who had confirmed or suspected COVID-19. Most of these patients were generally young and healthy and most had relatively mild COVID-19; 7% were laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 positive, and 6% were close contacts of patients with confirmed COVID-19. Pernio-like lesions were the only symptoms in 55% of the patients.
In another study, researchers in France evaluated the clinical, laboratory, and pathologic characteristics of 40 patients who developed chilblain-like lesions (mostly involving the toes) during the COVID-19 pandemic and were seen as outpatients in April 2020 . All were polymerase chain reaction (PCR) negative, 30% were SARS-CoV-2 serology positive, and 60% had elevated D-dimers. Histology obtained from 19 of the patients revealed lymphocytic inflammation and vascular damage, and 8 had IgA positivity.
In a retrospective analysis of seven pediatric chilblains cases during the pandemic, researchers examined the skin biopsies to evaluate histopathological features and explored the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the tissue. All patients were PCR negative. The authors observed cytoplasmic granular positivity for SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in endothelial cells, a feature that they said showed coronavirus-like particles, consistent with SARS-CoV-2.
Not all studies in the medical literature have demonstrated an association between pernio-like/chilblains-like lesions and COVID-19, though. An analysis of 23 patients, with skin eruptions considered associated with SARS-CoV-2 infections (including 21 cases of chilblains) during the first wave of the pandemic found that the antibody and T-cell response in patients with pandemic chilblains was the same as in negative controls.
“What’s remarkably interesting about this study is that they did autopsies of samples from patients who had died prepandemic, so there was no such thing as COVID-19,” said Dr. Fox, who was not involved with the study. “They stained for viral particles in those patients, and they were positive in a subset of patients. This makes me wonder about what the significance of that staining positivity is.”
Yet another group of investigators looked at what was happening with pernio during the waves of COVID in a study of chilblains cases in children in Spain, and found a stronger association between lockdown and cold temperature, which argues against a direct association between pernio and COVID infection.
In Dr. Fox’s experience, COVID toes can recur, especially upon exposure to cold. “What taught me this in real life is a patient who I saw remotely by video,” she recalled. “It was early on in the pandemic. I could not prove he had COVID no matter how hard I tried, but I do think he had COVID toes at that time.” When he later was confirmed to have COVID, “he got pernio in the same exact location as his original suspected COVID toes.”
According to an analysis of long COVID in the skin, based on cases reported to the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatological Societies registry from April 8 to Oct. 8, 2020, pernio-like lesions lasted a median of 12 days in patients with lab-confirmed COVID-19 and a median of 15 days in those with suspected COVID-19. But almost 7% of the 103 pernio cases were long-haulers, defined as those with dermatologic signs of COVID that lasted beyond 60 days.
“There are some patients who are resistant to treatment,” Dr. Fox said. “In addition, recurrent lesions make me think that maybe all pernio is triggered by some viral cause. This causes an immunologic phenomenon that’s responding to a viral trigger you’re trying to deal with. That may be the better way to think about COVID toes.”
Different variants of COVID also appear to be changing the characteristics of dermatologic manifestations associated with infection. Results from a large retrospective analysis of nearly 350,000 users of a COVID study App in the United Kingdom found that skin lesions were more predictive of a positive test in the Delta wave, compared with the Omicron wave, while pernio-like lesions were predictive of infection in the Delta wave but not in the Omicron wave.
“And, whether you were vaccinated or unvaccinated really did not influence whether or not you were going to have a skin rash as a presenting sign of COVID, except for the burning rash, which was less in vaccinated patients,” said Dr. Fox, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Fox reported having no relevant disclosures.
PORTLAND, ORE. – while others are not, according to Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the hospital consultation service at the University of California, San Francisco.
“We’re learning a lot about pernio because of COVID,” Dr. Fox, a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force on COVID-19, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. “Patients with pernio tend to either have bright red or purple individual lesions or an erythromelalgia-like presentation, often waking up in the middle of the night saying ‘my feet hurt. I can’t put sheets over my feet.’ In my experience, the patients with an erythromelalgia-like presentation tend to be a lot harder to treat.”
Establishing terminology to describe pernio-like lesions was a challenge in the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fox added, with clinicians using terms like erythema multiforme-like, coxsackie-like, or even necrotic to describe the lesions. “I don’t think pernio is truly necrotic; I think it’s really inflammatory and purpuric,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, studies suggesting a link with these cases and COVID-19 infection include a case series of 318 patients with pernio-like skin lesions who had confirmed or suspected COVID-19. Most of these patients were generally young and healthy and most had relatively mild COVID-19; 7% were laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 positive, and 6% were close contacts of patients with confirmed COVID-19. Pernio-like lesions were the only symptoms in 55% of the patients.
In another study, researchers in France evaluated the clinical, laboratory, and pathologic characteristics of 40 patients who developed chilblain-like lesions (mostly involving the toes) during the COVID-19 pandemic and were seen as outpatients in April 2020 . All were polymerase chain reaction (PCR) negative, 30% were SARS-CoV-2 serology positive, and 60% had elevated D-dimers. Histology obtained from 19 of the patients revealed lymphocytic inflammation and vascular damage, and 8 had IgA positivity.
In a retrospective analysis of seven pediatric chilblains cases during the pandemic, researchers examined the skin biopsies to evaluate histopathological features and explored the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the tissue. All patients were PCR negative. The authors observed cytoplasmic granular positivity for SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in endothelial cells, a feature that they said showed coronavirus-like particles, consistent with SARS-CoV-2.
Not all studies in the medical literature have demonstrated an association between pernio-like/chilblains-like lesions and COVID-19, though. An analysis of 23 patients, with skin eruptions considered associated with SARS-CoV-2 infections (including 21 cases of chilblains) during the first wave of the pandemic found that the antibody and T-cell response in patients with pandemic chilblains was the same as in negative controls.
“What’s remarkably interesting about this study is that they did autopsies of samples from patients who had died prepandemic, so there was no such thing as COVID-19,” said Dr. Fox, who was not involved with the study. “They stained for viral particles in those patients, and they were positive in a subset of patients. This makes me wonder about what the significance of that staining positivity is.”
Yet another group of investigators looked at what was happening with pernio during the waves of COVID in a study of chilblains cases in children in Spain, and found a stronger association between lockdown and cold temperature, which argues against a direct association between pernio and COVID infection.
In Dr. Fox’s experience, COVID toes can recur, especially upon exposure to cold. “What taught me this in real life is a patient who I saw remotely by video,” she recalled. “It was early on in the pandemic. I could not prove he had COVID no matter how hard I tried, but I do think he had COVID toes at that time.” When he later was confirmed to have COVID, “he got pernio in the same exact location as his original suspected COVID toes.”
According to an analysis of long COVID in the skin, based on cases reported to the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatological Societies registry from April 8 to Oct. 8, 2020, pernio-like lesions lasted a median of 12 days in patients with lab-confirmed COVID-19 and a median of 15 days in those with suspected COVID-19. But almost 7% of the 103 pernio cases were long-haulers, defined as those with dermatologic signs of COVID that lasted beyond 60 days.
“There are some patients who are resistant to treatment,” Dr. Fox said. “In addition, recurrent lesions make me think that maybe all pernio is triggered by some viral cause. This causes an immunologic phenomenon that’s responding to a viral trigger you’re trying to deal with. That may be the better way to think about COVID toes.”
Different variants of COVID also appear to be changing the characteristics of dermatologic manifestations associated with infection. Results from a large retrospective analysis of nearly 350,000 users of a COVID study App in the United Kingdom found that skin lesions were more predictive of a positive test in the Delta wave, compared with the Omicron wave, while pernio-like lesions were predictive of infection in the Delta wave but not in the Omicron wave.
“And, whether you were vaccinated or unvaccinated really did not influence whether or not you were going to have a skin rash as a presenting sign of COVID, except for the burning rash, which was less in vaccinated patients,” said Dr. Fox, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Fox reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT PDA 2022
Talking to teens
After 15 years as a high school teacher at urban schools, I realized adults widely misunderstand that teenagers do not want to talk to them. In fact, most crave finding an adult they can trust and have serious conversations about issues like sex, drugs, and death. G was a sophomore who was going blind from a rare degenerative disease and one day sought my guidance about a sexual orgy he accidentally got in involved in. Was it wrong? Would God send him to hell? Why was he now so anxious after?
Because I was an openly gay teacher, students every semester would come out to me, asking what the “gay scene” was like, or how to deal with a homophobic family. Sometimes, students would seek counsel about an unplanned pregnancy, about abortion. In one instance, a student sought counsel about her violent thoughts, and eventually checked herself into a psychiatric ward. Five separate times, students in my class were murdered and I accompanied my classes through mourning.
Unlike many pediatricians, a teacher has a lot of time with these young adults: daily, sometimes over years. Students often admit they spend more time with their teachers than their parents. I can’t give you that time, but here are some general tips.
Attitude promoting trust
My guiding attitude toward teens was that they were my equals. I would “do unto them as I would have them do unto me.” Not less, but also not more – because sometimes “more” can cloak condescension. When I was a student, I trusted teachers who shared their fears and mistakes, not performing under a confessional spotlight, but to establish commonality, to flatten hierarchy. I also trusted those who could set boundaries and wield authority compassionately. Because sometimes I needed a firm hand. And so, as an adult I tried to give this to my students as well.
Although my students and I were equals, our situations are different. That is true with gender, race, and class, and it is also true with adults versus teens. The first step toward treating someone authentically as an equal when in a position of authority is to understand the unique stressors of their life. That means asking questions and listening to what they need.
Stressors in a teen’s life
A typical high school junior or senior goes to work 8-10 hours a day. Unpaid. They sit for hours at a small desk in a small room with sometimes 34 others. Most of the time they cannot eat or use their phone. If they need to pee, they need to ask permission. They have to ask permission to speak. And then when they go home, they sit at a small desk again for homework. They often do not even have their own room. They also have to ask for permission to buy something for themselves, for money, for a ride anywhere. Their values are often compromised so they won’t get kicked out of a house or a class. The life of a teen is not at all “carefree” but largely prescribed and with little control.
When I think about my youth and how little freedom, privacy, and control I had compared with now, it softens my attitude to even the rudest student. (Isn’t rudeness often a sign of resistance against an oppressive system?) But, some may say, these teens do not have to worry about bills. But if I think back honestly to my teen years, would I trade the responsibilities I have now for those supposed carefree years? Carefree is not how most teens describe their lives but a nostalgic rosy retrospection adults assign. Almost all teens I taught would rather work to gain some control over their lives. Which is why so many work 4-5 hours after school on top of homework, giving up their weekends, and binding themselves to a “carefree” 60- to 80-hour work week.
Talking about drugs, sex, and mental health
Drugs
It’s a good idea to first disarm teens of their fear of judgment or punishment, saying things like: “It’s normal to experiment with drugs, even hard ones.” The most successful, respected adults you see now have, so it’s not a reflection of who you are. Tell me what you’re worried about and it’ll be just between us.
After rapport is established, follow-up questions that elicit and affirm their feelings and thoughts can encourage more revelations: Do you think you have a problem? Why? How do you get your drugs and I’m curious only because finding that out can help us understand risks and solutions. What made you start? And keep on using?
Sex
Again, first disarm their fears: You can talk to me freely and confidently about sex: What you do, who you do it with, how you do it, and how often – I know that people are very different in their sexual interests and activities.
It is also good to set up clear boundaries. I had instances where students had romantic interest in me and would use these conversations as overtures. If you feel like your patient may be interested in you, then be explicit about boundaries: I’m a doctor who can point you to resources or offer treatments related to any sexual practice and its consequences, but that is all I am. Anything else is illegal and would end our patient-doctor relationship. (I would also immediately document the interaction and tell it to a witness.)
I never escalated incidences like this because I understood that most teens are naturally curious and often not taught about sexual boundaries, so I tried to make these encounters “teachable moments,” not punitive ones. Many teens are more aware of health consequences, like STDs or pregnancy, than psychological ones. So, it’s useful to ask: When you have sex outside your relationship, how does that make you feel? Does sex with multiple partners make you anxious or guilty afterwards? I like to use straightforward language and normalize taboo sexual practices with an even tone to allow teens to speak truthfully.
Suicide/depression
First, disarm and normalize: It is very common for people to have depression or thoughts of suicide. Most of the adults around you probably have and so have I (if that is true). Have you experienced this? Older teens often crave an intelligent open discussion about depression and suicide. If they look particularly distressed, I also tell them that I, and countless others, found strategies to deal with these thoughts. For most older teens, talking about causes of mental health issues and treatments is a breath of fresh air. This is especially true for teens from urban communities who have dealt precociously with death and violence, minority communities where mental health is often stigmatized, and young males whose machismo code can prevent them from acknowledging their feelings.
Some follow-up questions: Where do you think these thoughts come from? And if they don’t know: It’s perfectly normal for there to be no reason. The important thing is that they don’t last too long and that you know that. And if they do, then I can provide you resources and potential treatments.
Summary
Treating teens as equals by understanding their situation allows understanding and compassion for their stressors. This motivates an inquisitive and collaborative patient-centric approach that allows a sharing of sensitive topics like drugs, sex, and mental health.
Dr. Nguyen is a resident in psychiatry at the University of California, San Francisco.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
After 15 years as a high school teacher at urban schools, I realized adults widely misunderstand that teenagers do not want to talk to them. In fact, most crave finding an adult they can trust and have serious conversations about issues like sex, drugs, and death. G was a sophomore who was going blind from a rare degenerative disease and one day sought my guidance about a sexual orgy he accidentally got in involved in. Was it wrong? Would God send him to hell? Why was he now so anxious after?
Because I was an openly gay teacher, students every semester would come out to me, asking what the “gay scene” was like, or how to deal with a homophobic family. Sometimes, students would seek counsel about an unplanned pregnancy, about abortion. In one instance, a student sought counsel about her violent thoughts, and eventually checked herself into a psychiatric ward. Five separate times, students in my class were murdered and I accompanied my classes through mourning.
Unlike many pediatricians, a teacher has a lot of time with these young adults: daily, sometimes over years. Students often admit they spend more time with their teachers than their parents. I can’t give you that time, but here are some general tips.
Attitude promoting trust
My guiding attitude toward teens was that they were my equals. I would “do unto them as I would have them do unto me.” Not less, but also not more – because sometimes “more” can cloak condescension. When I was a student, I trusted teachers who shared their fears and mistakes, not performing under a confessional spotlight, but to establish commonality, to flatten hierarchy. I also trusted those who could set boundaries and wield authority compassionately. Because sometimes I needed a firm hand. And so, as an adult I tried to give this to my students as well.
Although my students and I were equals, our situations are different. That is true with gender, race, and class, and it is also true with adults versus teens. The first step toward treating someone authentically as an equal when in a position of authority is to understand the unique stressors of their life. That means asking questions and listening to what they need.
Stressors in a teen’s life
A typical high school junior or senior goes to work 8-10 hours a day. Unpaid. They sit for hours at a small desk in a small room with sometimes 34 others. Most of the time they cannot eat or use their phone. If they need to pee, they need to ask permission. They have to ask permission to speak. And then when they go home, they sit at a small desk again for homework. They often do not even have their own room. They also have to ask for permission to buy something for themselves, for money, for a ride anywhere. Their values are often compromised so they won’t get kicked out of a house or a class. The life of a teen is not at all “carefree” but largely prescribed and with little control.
When I think about my youth and how little freedom, privacy, and control I had compared with now, it softens my attitude to even the rudest student. (Isn’t rudeness often a sign of resistance against an oppressive system?) But, some may say, these teens do not have to worry about bills. But if I think back honestly to my teen years, would I trade the responsibilities I have now for those supposed carefree years? Carefree is not how most teens describe their lives but a nostalgic rosy retrospection adults assign. Almost all teens I taught would rather work to gain some control over their lives. Which is why so many work 4-5 hours after school on top of homework, giving up their weekends, and binding themselves to a “carefree” 60- to 80-hour work week.
Talking about drugs, sex, and mental health
Drugs
It’s a good idea to first disarm teens of their fear of judgment or punishment, saying things like: “It’s normal to experiment with drugs, even hard ones.” The most successful, respected adults you see now have, so it’s not a reflection of who you are. Tell me what you’re worried about and it’ll be just between us.
After rapport is established, follow-up questions that elicit and affirm their feelings and thoughts can encourage more revelations: Do you think you have a problem? Why? How do you get your drugs and I’m curious only because finding that out can help us understand risks and solutions. What made you start? And keep on using?
Sex
Again, first disarm their fears: You can talk to me freely and confidently about sex: What you do, who you do it with, how you do it, and how often – I know that people are very different in their sexual interests and activities.
It is also good to set up clear boundaries. I had instances where students had romantic interest in me and would use these conversations as overtures. If you feel like your patient may be interested in you, then be explicit about boundaries: I’m a doctor who can point you to resources or offer treatments related to any sexual practice and its consequences, but that is all I am. Anything else is illegal and would end our patient-doctor relationship. (I would also immediately document the interaction and tell it to a witness.)
I never escalated incidences like this because I understood that most teens are naturally curious and often not taught about sexual boundaries, so I tried to make these encounters “teachable moments,” not punitive ones. Many teens are more aware of health consequences, like STDs or pregnancy, than psychological ones. So, it’s useful to ask: When you have sex outside your relationship, how does that make you feel? Does sex with multiple partners make you anxious or guilty afterwards? I like to use straightforward language and normalize taboo sexual practices with an even tone to allow teens to speak truthfully.
Suicide/depression
First, disarm and normalize: It is very common for people to have depression or thoughts of suicide. Most of the adults around you probably have and so have I (if that is true). Have you experienced this? Older teens often crave an intelligent open discussion about depression and suicide. If they look particularly distressed, I also tell them that I, and countless others, found strategies to deal with these thoughts. For most older teens, talking about causes of mental health issues and treatments is a breath of fresh air. This is especially true for teens from urban communities who have dealt precociously with death and violence, minority communities where mental health is often stigmatized, and young males whose machismo code can prevent them from acknowledging their feelings.
Some follow-up questions: Where do you think these thoughts come from? And if they don’t know: It’s perfectly normal for there to be no reason. The important thing is that they don’t last too long and that you know that. And if they do, then I can provide you resources and potential treatments.
Summary
Treating teens as equals by understanding their situation allows understanding and compassion for their stressors. This motivates an inquisitive and collaborative patient-centric approach that allows a sharing of sensitive topics like drugs, sex, and mental health.
Dr. Nguyen is a resident in psychiatry at the University of California, San Francisco.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
After 15 years as a high school teacher at urban schools, I realized adults widely misunderstand that teenagers do not want to talk to them. In fact, most crave finding an adult they can trust and have serious conversations about issues like sex, drugs, and death. G was a sophomore who was going blind from a rare degenerative disease and one day sought my guidance about a sexual orgy he accidentally got in involved in. Was it wrong? Would God send him to hell? Why was he now so anxious after?
Because I was an openly gay teacher, students every semester would come out to me, asking what the “gay scene” was like, or how to deal with a homophobic family. Sometimes, students would seek counsel about an unplanned pregnancy, about abortion. In one instance, a student sought counsel about her violent thoughts, and eventually checked herself into a psychiatric ward. Five separate times, students in my class were murdered and I accompanied my classes through mourning.
Unlike many pediatricians, a teacher has a lot of time with these young adults: daily, sometimes over years. Students often admit they spend more time with their teachers than their parents. I can’t give you that time, but here are some general tips.
Attitude promoting trust
My guiding attitude toward teens was that they were my equals. I would “do unto them as I would have them do unto me.” Not less, but also not more – because sometimes “more” can cloak condescension. When I was a student, I trusted teachers who shared their fears and mistakes, not performing under a confessional spotlight, but to establish commonality, to flatten hierarchy. I also trusted those who could set boundaries and wield authority compassionately. Because sometimes I needed a firm hand. And so, as an adult I tried to give this to my students as well.
Although my students and I were equals, our situations are different. That is true with gender, race, and class, and it is also true with adults versus teens. The first step toward treating someone authentically as an equal when in a position of authority is to understand the unique stressors of their life. That means asking questions and listening to what they need.
Stressors in a teen’s life
A typical high school junior or senior goes to work 8-10 hours a day. Unpaid. They sit for hours at a small desk in a small room with sometimes 34 others. Most of the time they cannot eat or use their phone. If they need to pee, they need to ask permission. They have to ask permission to speak. And then when they go home, they sit at a small desk again for homework. They often do not even have their own room. They also have to ask for permission to buy something for themselves, for money, for a ride anywhere. Their values are often compromised so they won’t get kicked out of a house or a class. The life of a teen is not at all “carefree” but largely prescribed and with little control.
When I think about my youth and how little freedom, privacy, and control I had compared with now, it softens my attitude to even the rudest student. (Isn’t rudeness often a sign of resistance against an oppressive system?) But, some may say, these teens do not have to worry about bills. But if I think back honestly to my teen years, would I trade the responsibilities I have now for those supposed carefree years? Carefree is not how most teens describe their lives but a nostalgic rosy retrospection adults assign. Almost all teens I taught would rather work to gain some control over their lives. Which is why so many work 4-5 hours after school on top of homework, giving up their weekends, and binding themselves to a “carefree” 60- to 80-hour work week.
Talking about drugs, sex, and mental health
Drugs
It’s a good idea to first disarm teens of their fear of judgment or punishment, saying things like: “It’s normal to experiment with drugs, even hard ones.” The most successful, respected adults you see now have, so it’s not a reflection of who you are. Tell me what you’re worried about and it’ll be just between us.
After rapport is established, follow-up questions that elicit and affirm their feelings and thoughts can encourage more revelations: Do you think you have a problem? Why? How do you get your drugs and I’m curious only because finding that out can help us understand risks and solutions. What made you start? And keep on using?
Sex
Again, first disarm their fears: You can talk to me freely and confidently about sex: What you do, who you do it with, how you do it, and how often – I know that people are very different in their sexual interests and activities.
It is also good to set up clear boundaries. I had instances where students had romantic interest in me and would use these conversations as overtures. If you feel like your patient may be interested in you, then be explicit about boundaries: I’m a doctor who can point you to resources or offer treatments related to any sexual practice and its consequences, but that is all I am. Anything else is illegal and would end our patient-doctor relationship. (I would also immediately document the interaction and tell it to a witness.)
I never escalated incidences like this because I understood that most teens are naturally curious and often not taught about sexual boundaries, so I tried to make these encounters “teachable moments,” not punitive ones. Many teens are more aware of health consequences, like STDs or pregnancy, than psychological ones. So, it’s useful to ask: When you have sex outside your relationship, how does that make you feel? Does sex with multiple partners make you anxious or guilty afterwards? I like to use straightforward language and normalize taboo sexual practices with an even tone to allow teens to speak truthfully.
Suicide/depression
First, disarm and normalize: It is very common for people to have depression or thoughts of suicide. Most of the adults around you probably have and so have I (if that is true). Have you experienced this? Older teens often crave an intelligent open discussion about depression and suicide. If they look particularly distressed, I also tell them that I, and countless others, found strategies to deal with these thoughts. For most older teens, talking about causes of mental health issues and treatments is a breath of fresh air. This is especially true for teens from urban communities who have dealt precociously with death and violence, minority communities where mental health is often stigmatized, and young males whose machismo code can prevent them from acknowledging their feelings.
Some follow-up questions: Where do you think these thoughts come from? And if they don’t know: It’s perfectly normal for there to be no reason. The important thing is that they don’t last too long and that you know that. And if they do, then I can provide you resources and potential treatments.
Summary
Treating teens as equals by understanding their situation allows understanding and compassion for their stressors. This motivates an inquisitive and collaborative patient-centric approach that allows a sharing of sensitive topics like drugs, sex, and mental health.
Dr. Nguyen is a resident in psychiatry at the University of California, San Francisco.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
Newborns get routine heel blood tests, but should states keep those samples?
Close to 4 million babies are born in the United States every year, and within their first 48 hours nearly all are pricked in the heel so their blood can be tested for dozens of life-threatening genetic and metabolic problems. The heel-stick test is considered such a crucial public health measure that states typically require it and parents aren’t asked for their permission before it’s done.
But the lab tests for newborn screenings generally don’t use all of the half-dozen or so drops of blood collected on filter paper cards. So states hold on to the leftover “dried blood spots,” as they’re called, often without parents’ knowledge or consent. In recent years, privacy-related concerns have grown about the sometimes decades-long storage and use of the material.
Some states allow the blood spots to be used in research studies, sometimes by third parties for a fee, or provided to law enforcement personnel investigating a crime. Permitting these or other uses without parents’ informed consent that they understand and agree to the use has prompted lawsuits from parents who want to make those decisions themselves and who seek to protect their children’s medical and genetic information.
In May, Michigan officials reportedly agreed to destroy more than 3 million blood spots as a partial settlement in a lawsuit brought by parents who said they didn’t receive enough clear information to provide informed consent for the blood to be used in research the state might conduct. The fate of millions of additional blood spots stored by the state will be determined at trial.
Philip L. Ellison, an attorney in Hemlock, Mich., who is spearheading the suit, said he became aware of the issue when his son was born 5 years ago. Mr. Ellison’s son, Patton, spent his first days in the neonatal intensive care unit after his blood sugar levels dropped precipitously after birth. The next morning, Mr. Ellison said, he was approached by a hospital staffer who asked whether he wanted to sign a consent form allowing the blood from Patton’s heel-stick test to be donated for research.
The unexpected request set off alarm bells for Mr. Ellison.
“We don’t know what the future will bring in terms of information that can be extracted from our blood,” he said. How the rules for using that blood might evolve over time is difficult to know. “A program that first starts out for one purpose, to test for disease, has now crept into medical research and then to law enforcement.”
Michigan is the rare state that asks parents for permission to use leftover newborn blood spots in research. Most do not, experts said. The state screens newborns for more than 50 diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and congenital hypothyroidism, because identifying and treating such illnesses early in a child’s life are crucial.
Afterward, whatever is left over is stored for up to 100 years and, if parents agree to it, may be used in research approved by the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services. Some recent studies have used deidentified blood spots to study the relationship between viral infection at birth and the development of autism later in life, as well as the impact of maternal exposure to manufactured chemicals known as PFAS on health outcomes.
Parents have also asked that their children’s blood spots be sent to researchers to help diagnose a disorder or to try to find a reason for a child’s death, said Chelsea Wuth, a spokesperson for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services.
Michigan parents can request that the state destroy the leftover blood spots if they don’t want the state to hold on to them.
Since the 1960s, states have screened newborn blood for conditions that can lead to devastating physical or mental disabilities or death if they are not diagnosed and treated. The federal government recommends that roughly three dozen screening tests be performed, but some states conduct many more. Every year, an estimated 13,000 infants with serious medical conditions are identified through newborn screening programs, according to data published by the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Many public health experts strongly support mandatory newborn screening as a critical component of infants’ clinical care. But some are receptive to giving parents a say in what happens to the blood after the screening.
“I have always believed that parents should be able to have the opportunity to say ‘yes’ or ‘no’ ” to having their newborns’ leftover blood used in research, said Beth Tarini, MD, a pediatrician and the associate director of the Center for Translational Research at Children’s National Research Institute in Washington, D.C. “Since it is not part of the clinical care, it is a different standard of engagement with the parents.”
In Michigan, 64% of parents consented to participate, according to court documents in Mr. Ellison’s case.
Encouraging people to participate is important, some public health experts say, because the blood spot repositories provide a rare opportunity for population-level research. People of European descent are often overrepresented in genetic databases, which can skew the results of studies. But the newborn screening program includes virtually everyone born in the United States.
“There’s strong evidence that research conducted on samples of white people creates disparities in the benefits of biomedical research for people who are not white,” said Kyle Brothers, MD, PhD, a pediatrician and bioethicist at Norton Children’s Research Institute in Louisville, Ky.
After privacy-related lawsuits were brought in 2009 and 2011 by parents in Texas and Minnesota, respectively, millions of blood spots were destroyed.
Brothers said an unwillingness to participate in research programs reflects larger trends, including more emphasis on the individual and less on contributing to the general good.
To those who might argue that parents’ privacy concerns are overblown, a recent lawsuit in New Jersey raises troubling questions.
In a public records lawsuit, the New Jersey Office of the Public Defender and the New Jersey Monitor, a nonprofit news site, charge that the state police used a subpoena to obtain an infant blood spot of a child who is now 9 years old from the state’s newborn screening laboratory. The lawsuit says a DNA analysis was conducted on the blood spot so evidence could be gathered against the child’s father, who was being represented by the public defender’s office, in connection with a sexual assault committed in 1996. The effort allowed police to get the DNA information without having to show a court probable cause, the suit alleges.
The lawsuit seeks to find out how often in the past 5 years New Jersey law enforcement agencies have used the newborn screening lab as a tool in investigations and subjected defendants to “warrantless searches and seizures.”
New Jersey keeps the records on file for 23 years, said CJ Griffin, a lawyer representing the public defender’s office and the New Jersey Monitor in the lawsuit.
Ms. Griffin said her clients aren’t challenging the program to test newborn blood for diseases. “It’s more the lack of transparency, and safeguards, and information about storage, and we don’t have any information about appropriate use.”
The New Jersey Department of Health doesn’t comment on pending litigation, spokesperson Nancy Kearney said. Ms. Kearney didn’t respond to a request for information about the state’s practices and policies related to the newborn screening program.
A recent Texas Law Review article found that more than a quarter of states lack policies on law enforcement access to newborn blood spot samples and related information and that nearly a third may allow access in certain circumstances.
In Michigan, the state gives law enforcement agencies dried blood spots only to identify the victim of a crime, Ms. Wuth said. “Typically, this means someone has been killed or gone missing,” she added.
Many clinicians and bioethicists say that standards for the use of blood spots need to be set.
“It’s nearly impossible for us to monitor the potential uses of our data,” said Andrew Crawford, senior policy counsel for the privacy and data project at the Center for Democracy and Technology. “That’s why need to put limitations on the use.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Close to 4 million babies are born in the United States every year, and within their first 48 hours nearly all are pricked in the heel so their blood can be tested for dozens of life-threatening genetic and metabolic problems. The heel-stick test is considered such a crucial public health measure that states typically require it and parents aren’t asked for their permission before it’s done.
But the lab tests for newborn screenings generally don’t use all of the half-dozen or so drops of blood collected on filter paper cards. So states hold on to the leftover “dried blood spots,” as they’re called, often without parents’ knowledge or consent. In recent years, privacy-related concerns have grown about the sometimes decades-long storage and use of the material.
Some states allow the blood spots to be used in research studies, sometimes by third parties for a fee, or provided to law enforcement personnel investigating a crime. Permitting these or other uses without parents’ informed consent that they understand and agree to the use has prompted lawsuits from parents who want to make those decisions themselves and who seek to protect their children’s medical and genetic information.
In May, Michigan officials reportedly agreed to destroy more than 3 million blood spots as a partial settlement in a lawsuit brought by parents who said they didn’t receive enough clear information to provide informed consent for the blood to be used in research the state might conduct. The fate of millions of additional blood spots stored by the state will be determined at trial.
Philip L. Ellison, an attorney in Hemlock, Mich., who is spearheading the suit, said he became aware of the issue when his son was born 5 years ago. Mr. Ellison’s son, Patton, spent his first days in the neonatal intensive care unit after his blood sugar levels dropped precipitously after birth. The next morning, Mr. Ellison said, he was approached by a hospital staffer who asked whether he wanted to sign a consent form allowing the blood from Patton’s heel-stick test to be donated for research.
The unexpected request set off alarm bells for Mr. Ellison.
“We don’t know what the future will bring in terms of information that can be extracted from our blood,” he said. How the rules for using that blood might evolve over time is difficult to know. “A program that first starts out for one purpose, to test for disease, has now crept into medical research and then to law enforcement.”
Michigan is the rare state that asks parents for permission to use leftover newborn blood spots in research. Most do not, experts said. The state screens newborns for more than 50 diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and congenital hypothyroidism, because identifying and treating such illnesses early in a child’s life are crucial.
Afterward, whatever is left over is stored for up to 100 years and, if parents agree to it, may be used in research approved by the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services. Some recent studies have used deidentified blood spots to study the relationship between viral infection at birth and the development of autism later in life, as well as the impact of maternal exposure to manufactured chemicals known as PFAS on health outcomes.
Parents have also asked that their children’s blood spots be sent to researchers to help diagnose a disorder or to try to find a reason for a child’s death, said Chelsea Wuth, a spokesperson for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services.
Michigan parents can request that the state destroy the leftover blood spots if they don’t want the state to hold on to them.
Since the 1960s, states have screened newborn blood for conditions that can lead to devastating physical or mental disabilities or death if they are not diagnosed and treated. The federal government recommends that roughly three dozen screening tests be performed, but some states conduct many more. Every year, an estimated 13,000 infants with serious medical conditions are identified through newborn screening programs, according to data published by the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Many public health experts strongly support mandatory newborn screening as a critical component of infants’ clinical care. But some are receptive to giving parents a say in what happens to the blood after the screening.
“I have always believed that parents should be able to have the opportunity to say ‘yes’ or ‘no’ ” to having their newborns’ leftover blood used in research, said Beth Tarini, MD, a pediatrician and the associate director of the Center for Translational Research at Children’s National Research Institute in Washington, D.C. “Since it is not part of the clinical care, it is a different standard of engagement with the parents.”
In Michigan, 64% of parents consented to participate, according to court documents in Mr. Ellison’s case.
Encouraging people to participate is important, some public health experts say, because the blood spot repositories provide a rare opportunity for population-level research. People of European descent are often overrepresented in genetic databases, which can skew the results of studies. But the newborn screening program includes virtually everyone born in the United States.
“There’s strong evidence that research conducted on samples of white people creates disparities in the benefits of biomedical research for people who are not white,” said Kyle Brothers, MD, PhD, a pediatrician and bioethicist at Norton Children’s Research Institute in Louisville, Ky.
After privacy-related lawsuits were brought in 2009 and 2011 by parents in Texas and Minnesota, respectively, millions of blood spots were destroyed.
Brothers said an unwillingness to participate in research programs reflects larger trends, including more emphasis on the individual and less on contributing to the general good.
To those who might argue that parents’ privacy concerns are overblown, a recent lawsuit in New Jersey raises troubling questions.
In a public records lawsuit, the New Jersey Office of the Public Defender and the New Jersey Monitor, a nonprofit news site, charge that the state police used a subpoena to obtain an infant blood spot of a child who is now 9 years old from the state’s newborn screening laboratory. The lawsuit says a DNA analysis was conducted on the blood spot so evidence could be gathered against the child’s father, who was being represented by the public defender’s office, in connection with a sexual assault committed in 1996. The effort allowed police to get the DNA information without having to show a court probable cause, the suit alleges.
The lawsuit seeks to find out how often in the past 5 years New Jersey law enforcement agencies have used the newborn screening lab as a tool in investigations and subjected defendants to “warrantless searches and seizures.”
New Jersey keeps the records on file for 23 years, said CJ Griffin, a lawyer representing the public defender’s office and the New Jersey Monitor in the lawsuit.
Ms. Griffin said her clients aren’t challenging the program to test newborn blood for diseases. “It’s more the lack of transparency, and safeguards, and information about storage, and we don’t have any information about appropriate use.”
The New Jersey Department of Health doesn’t comment on pending litigation, spokesperson Nancy Kearney said. Ms. Kearney didn’t respond to a request for information about the state’s practices and policies related to the newborn screening program.
A recent Texas Law Review article found that more than a quarter of states lack policies on law enforcement access to newborn blood spot samples and related information and that nearly a third may allow access in certain circumstances.
In Michigan, the state gives law enforcement agencies dried blood spots only to identify the victim of a crime, Ms. Wuth said. “Typically, this means someone has been killed or gone missing,” she added.
Many clinicians and bioethicists say that standards for the use of blood spots need to be set.
“It’s nearly impossible for us to monitor the potential uses of our data,” said Andrew Crawford, senior policy counsel for the privacy and data project at the Center for Democracy and Technology. “That’s why need to put limitations on the use.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Close to 4 million babies are born in the United States every year, and within their first 48 hours nearly all are pricked in the heel so their blood can be tested for dozens of life-threatening genetic and metabolic problems. The heel-stick test is considered such a crucial public health measure that states typically require it and parents aren’t asked for their permission before it’s done.
But the lab tests for newborn screenings generally don’t use all of the half-dozen or so drops of blood collected on filter paper cards. So states hold on to the leftover “dried blood spots,” as they’re called, often without parents’ knowledge or consent. In recent years, privacy-related concerns have grown about the sometimes decades-long storage and use of the material.
Some states allow the blood spots to be used in research studies, sometimes by third parties for a fee, or provided to law enforcement personnel investigating a crime. Permitting these or other uses without parents’ informed consent that they understand and agree to the use has prompted lawsuits from parents who want to make those decisions themselves and who seek to protect their children’s medical and genetic information.
In May, Michigan officials reportedly agreed to destroy more than 3 million blood spots as a partial settlement in a lawsuit brought by parents who said they didn’t receive enough clear information to provide informed consent for the blood to be used in research the state might conduct. The fate of millions of additional blood spots stored by the state will be determined at trial.
Philip L. Ellison, an attorney in Hemlock, Mich., who is spearheading the suit, said he became aware of the issue when his son was born 5 years ago. Mr. Ellison’s son, Patton, spent his first days in the neonatal intensive care unit after his blood sugar levels dropped precipitously after birth. The next morning, Mr. Ellison said, he was approached by a hospital staffer who asked whether he wanted to sign a consent form allowing the blood from Patton’s heel-stick test to be donated for research.
The unexpected request set off alarm bells for Mr. Ellison.
“We don’t know what the future will bring in terms of information that can be extracted from our blood,” he said. How the rules for using that blood might evolve over time is difficult to know. “A program that first starts out for one purpose, to test for disease, has now crept into medical research and then to law enforcement.”
Michigan is the rare state that asks parents for permission to use leftover newborn blood spots in research. Most do not, experts said. The state screens newborns for more than 50 diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and congenital hypothyroidism, because identifying and treating such illnesses early in a child’s life are crucial.
Afterward, whatever is left over is stored for up to 100 years and, if parents agree to it, may be used in research approved by the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services. Some recent studies have used deidentified blood spots to study the relationship between viral infection at birth and the development of autism later in life, as well as the impact of maternal exposure to manufactured chemicals known as PFAS on health outcomes.
Parents have also asked that their children’s blood spots be sent to researchers to help diagnose a disorder or to try to find a reason for a child’s death, said Chelsea Wuth, a spokesperson for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services.
Michigan parents can request that the state destroy the leftover blood spots if they don’t want the state to hold on to them.
Since the 1960s, states have screened newborn blood for conditions that can lead to devastating physical or mental disabilities or death if they are not diagnosed and treated. The federal government recommends that roughly three dozen screening tests be performed, but some states conduct many more. Every year, an estimated 13,000 infants with serious medical conditions are identified through newborn screening programs, according to data published by the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Many public health experts strongly support mandatory newborn screening as a critical component of infants’ clinical care. But some are receptive to giving parents a say in what happens to the blood after the screening.
“I have always believed that parents should be able to have the opportunity to say ‘yes’ or ‘no’ ” to having their newborns’ leftover blood used in research, said Beth Tarini, MD, a pediatrician and the associate director of the Center for Translational Research at Children’s National Research Institute in Washington, D.C. “Since it is not part of the clinical care, it is a different standard of engagement with the parents.”
In Michigan, 64% of parents consented to participate, according to court documents in Mr. Ellison’s case.
Encouraging people to participate is important, some public health experts say, because the blood spot repositories provide a rare opportunity for population-level research. People of European descent are often overrepresented in genetic databases, which can skew the results of studies. But the newborn screening program includes virtually everyone born in the United States.
“There’s strong evidence that research conducted on samples of white people creates disparities in the benefits of biomedical research for people who are not white,” said Kyle Brothers, MD, PhD, a pediatrician and bioethicist at Norton Children’s Research Institute in Louisville, Ky.
After privacy-related lawsuits were brought in 2009 and 2011 by parents in Texas and Minnesota, respectively, millions of blood spots were destroyed.
Brothers said an unwillingness to participate in research programs reflects larger trends, including more emphasis on the individual and less on contributing to the general good.
To those who might argue that parents’ privacy concerns are overblown, a recent lawsuit in New Jersey raises troubling questions.
In a public records lawsuit, the New Jersey Office of the Public Defender and the New Jersey Monitor, a nonprofit news site, charge that the state police used a subpoena to obtain an infant blood spot of a child who is now 9 years old from the state’s newborn screening laboratory. The lawsuit says a DNA analysis was conducted on the blood spot so evidence could be gathered against the child’s father, who was being represented by the public defender’s office, in connection with a sexual assault committed in 1996. The effort allowed police to get the DNA information without having to show a court probable cause, the suit alleges.
The lawsuit seeks to find out how often in the past 5 years New Jersey law enforcement agencies have used the newborn screening lab as a tool in investigations and subjected defendants to “warrantless searches and seizures.”
New Jersey keeps the records on file for 23 years, said CJ Griffin, a lawyer representing the public defender’s office and the New Jersey Monitor in the lawsuit.
Ms. Griffin said her clients aren’t challenging the program to test newborn blood for diseases. “It’s more the lack of transparency, and safeguards, and information about storage, and we don’t have any information about appropriate use.”
The New Jersey Department of Health doesn’t comment on pending litigation, spokesperson Nancy Kearney said. Ms. Kearney didn’t respond to a request for information about the state’s practices and policies related to the newborn screening program.
A recent Texas Law Review article found that more than a quarter of states lack policies on law enforcement access to newborn blood spot samples and related information and that nearly a third may allow access in certain circumstances.
In Michigan, the state gives law enforcement agencies dried blood spots only to identify the victim of a crime, Ms. Wuth said. “Typically, this means someone has been killed or gone missing,” she added.
Many clinicians and bioethicists say that standards for the use of blood spots need to be set.
“It’s nearly impossible for us to monitor the potential uses of our data,” said Andrew Crawford, senior policy counsel for the privacy and data project at the Center for Democracy and Technology. “That’s why need to put limitations on the use.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Two states aim to curb diet pill sales to minors
California and New York are on the cusp of going further than the Food and Drug Administration in restricting the sale of nonprescription diet pills to minors as pediatricians and public health advocates try to protect kids from extreme weight-loss gimmicks online.
A bill before Gov. Gavin Newsom would bar anyone under 18 in California from buying over-the-counter weight-loss supplements – whether online or in shops – without a prescription. A similar bill passed by New York lawmakers is on Gov. Kathy Hochul’s desk. Neither Democrat has indicated how he or she will act.
If both bills are signed into law, proponents hope the momentum will build to restrict diet pill sales to children in more states. Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Missouri have introduced similar bills and backers plan to continue their push next year.
Nearly 30 million people in the United States will have an eating disorder in their lifetime; 95% of them are aged between 12 and 25, according to Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital. The hospital added that eating disorders pose the highest risk of mortality of any mental health disorder. And it has become easier than ever for minors to get pills that are sold online or on drugstore shelves. All dietary supplements, which include those for weight loss, accounted for nearly 35% of the $63 billion over-the-counter health products industry in 2021, according to Vision Research Reports, a market research firm.
Dietary supplements, which encompass a broad range of vitamins, herbs, and minerals, are classified by the FDA as food and don’t undergo scientific and safety testing as prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines do.
Public health advocates want to keep weight-loss products – with ads that may promise to “Drop 5 pounds a week!” and pill names like Slim Sense – away from young people, particularly girls, since some research has linked some products to eating disorders. A study in the American Journal of Public Health, which followed more than 10,000 women aged 14-36 over 15 years, found that “those who used diet pills had more than 5 times higher adjusted odds of receiving an eating disorder diagnosis from a health care provider within 1-3 years than those who did not.”
Many pills have been found tainted with banned and dangerous ingredients that may cause cancer, heart attacks, strokes, and other ailments. For example, the FDA advised the public to avoid Slim Sense by Dr. Reade because it contains lorcaserin, which has been found to cause psychiatric disturbances and impairments in attention or memory. The FDA ordered it discontinued and the company couldn’t be reached for comment.
“Unscrupulous manufacturers are willing to take risks with consumers’ health – and they are lacing their products with illegal pharmaceuticals, banned pharmaceuticals, steroids, excessive stimulants, even experimental stimulants,” said S. Bryn Austin, ScD, founding director of the Strategic Training Initiative for the Prevention of Eating Disorders, or STRIPED, which supports the restrictions. “Consumers have no idea that this is what’s in these types of products.”
STRIPED is a public health initiative based at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and Boston Children’s Hospital.
An industry trade group, the Natural Products Association, disputes that diet pills cause eating disorders, citing the lack of consumer complaints to the FDA of adverse events from their members’ products. “According to FDA data, there is no association between the two,” said Kyle Turk, the association’s director of government affairs.
The association contends that its members adhere to safe manufacturing processes, random product testing, and appropriate marketing guidelines. Representatives also worry that if minors can’t buy supplements over the counter, they may buy them from “crooks” on the black market and undermine the integrity of the industry. Under the bills, minors purchasing weight-loss products must show identification along with a prescription.
Not all business groups oppose the ban. The American Herbal Products Association, a trade group representing dietary supplement manufacturers and retailers, dropped its opposition to California’s bill once it was amended to remove ingredient categories that are found in non-diet supplements and vitamins, according to Robert Marriott, director of regulatory affairs.
Children’s advocates have found worrisome trends among young people who envision their ideal body type based on what they see on social media. According to a study commissioned by Fairplay, a nonprofit that seeks to stop harmful marketing practices targeting children, kids as young as 9 were found to be following three or more eating disorder accounts on Instagram, while the median age was 19. The authors called it a “pro–eating disorder bubble.”
Meta, which owns Instagram and Facebook, said the report lacks nuance, such as recognizing the human need to share life’s difficult moments. The company argues that blanket censorship isn’t the answer. “Experts and safety organizations have told us it’s important to strike a balance and allow people to share their personal stories while removing any content that encourages or promotes eating disorders,” Liza Crenshaw, a Meta spokesperson, said in an email.
Jason Nagata, MD, a pediatrician who cares for children and young adults with life-threatening eating disorders, believes that easy access to diet pills contributes to his patients’ conditions at UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital in San Francisco. That was the case for one of his patients, an emaciated 11-year-old girl.
“She had basically entered a starvation state because she was not getting enough nutrition,” said Dr. Nagata, who provided supporting testimony for the California bill. “She was taking these pills and using other kinds of extreme behaviors to lose weight.”
Dr. Nagata said the number of patients he sees with eating disorders has tripled since the pandemic began. They are desperate to get diet pills, some with modest results. “We’ve had patients who have been so dependent on these products that they will be hospitalized and they’re still ordering these products on Amazon,” he said.
Public health advocates turned to state legislatures in response to the federal government’s limited authority to regulate diet pills. Under a 1994 federal law known as the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act, the FDA “cannot step in until after there is a clear issue of harm to consumers,” said Dr. Austin.
No match for the supplement industry’s heavy lobbying on Capitol Hill, public health advocates shifted to a state-by-state approach.
There is, however, a push for the FDA to improve oversight of what goes into diet pills. Sen. Dick Durbin (D-Ill.) in April introduced a bill that would require dietary supplement manufacturers to register their products – along with the ingredients – with the regulator.
Proponents say the change is needed because manufacturers have been known to include dangerous ingredients. C. Michael White, PharmD, of the University of Connecticut, Storrs, found 35% of tainted health products came from weight-loss supplements in a review of a health fraud database.
A few ingredients have been banned, including sibutramine, a stimulant. “It was a very commonly used weight-loss supplement that ended up being removed from the U.S. market because of its elevated risk of causing things like heart attacks, strokes, and arrhythmias,” Dr. White said.
Another ingredient was phenolphthalein, which was used in laxatives until it was identified as a suspected carcinogen and banned in 1999. “To think,” he said, “that that product would still be on the U.S. market is just unconscionable.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
California and New York are on the cusp of going further than the Food and Drug Administration in restricting the sale of nonprescription diet pills to minors as pediatricians and public health advocates try to protect kids from extreme weight-loss gimmicks online.
A bill before Gov. Gavin Newsom would bar anyone under 18 in California from buying over-the-counter weight-loss supplements – whether online or in shops – without a prescription. A similar bill passed by New York lawmakers is on Gov. Kathy Hochul’s desk. Neither Democrat has indicated how he or she will act.
If both bills are signed into law, proponents hope the momentum will build to restrict diet pill sales to children in more states. Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Missouri have introduced similar bills and backers plan to continue their push next year.
Nearly 30 million people in the United States will have an eating disorder in their lifetime; 95% of them are aged between 12 and 25, according to Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital. The hospital added that eating disorders pose the highest risk of mortality of any mental health disorder. And it has become easier than ever for minors to get pills that are sold online or on drugstore shelves. All dietary supplements, which include those for weight loss, accounted for nearly 35% of the $63 billion over-the-counter health products industry in 2021, according to Vision Research Reports, a market research firm.
Dietary supplements, which encompass a broad range of vitamins, herbs, and minerals, are classified by the FDA as food and don’t undergo scientific and safety testing as prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines do.
Public health advocates want to keep weight-loss products – with ads that may promise to “Drop 5 pounds a week!” and pill names like Slim Sense – away from young people, particularly girls, since some research has linked some products to eating disorders. A study in the American Journal of Public Health, which followed more than 10,000 women aged 14-36 over 15 years, found that “those who used diet pills had more than 5 times higher adjusted odds of receiving an eating disorder diagnosis from a health care provider within 1-3 years than those who did not.”
Many pills have been found tainted with banned and dangerous ingredients that may cause cancer, heart attacks, strokes, and other ailments. For example, the FDA advised the public to avoid Slim Sense by Dr. Reade because it contains lorcaserin, which has been found to cause psychiatric disturbances and impairments in attention or memory. The FDA ordered it discontinued and the company couldn’t be reached for comment.
“Unscrupulous manufacturers are willing to take risks with consumers’ health – and they are lacing their products with illegal pharmaceuticals, banned pharmaceuticals, steroids, excessive stimulants, even experimental stimulants,” said S. Bryn Austin, ScD, founding director of the Strategic Training Initiative for the Prevention of Eating Disorders, or STRIPED, which supports the restrictions. “Consumers have no idea that this is what’s in these types of products.”
STRIPED is a public health initiative based at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and Boston Children’s Hospital.
An industry trade group, the Natural Products Association, disputes that diet pills cause eating disorders, citing the lack of consumer complaints to the FDA of adverse events from their members’ products. “According to FDA data, there is no association between the two,” said Kyle Turk, the association’s director of government affairs.
The association contends that its members adhere to safe manufacturing processes, random product testing, and appropriate marketing guidelines. Representatives also worry that if minors can’t buy supplements over the counter, they may buy them from “crooks” on the black market and undermine the integrity of the industry. Under the bills, minors purchasing weight-loss products must show identification along with a prescription.
Not all business groups oppose the ban. The American Herbal Products Association, a trade group representing dietary supplement manufacturers and retailers, dropped its opposition to California’s bill once it was amended to remove ingredient categories that are found in non-diet supplements and vitamins, according to Robert Marriott, director of regulatory affairs.
Children’s advocates have found worrisome trends among young people who envision their ideal body type based on what they see on social media. According to a study commissioned by Fairplay, a nonprofit that seeks to stop harmful marketing practices targeting children, kids as young as 9 were found to be following three or more eating disorder accounts on Instagram, while the median age was 19. The authors called it a “pro–eating disorder bubble.”
Meta, which owns Instagram and Facebook, said the report lacks nuance, such as recognizing the human need to share life’s difficult moments. The company argues that blanket censorship isn’t the answer. “Experts and safety organizations have told us it’s important to strike a balance and allow people to share their personal stories while removing any content that encourages or promotes eating disorders,” Liza Crenshaw, a Meta spokesperson, said in an email.
Jason Nagata, MD, a pediatrician who cares for children and young adults with life-threatening eating disorders, believes that easy access to diet pills contributes to his patients’ conditions at UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital in San Francisco. That was the case for one of his patients, an emaciated 11-year-old girl.
“She had basically entered a starvation state because she was not getting enough nutrition,” said Dr. Nagata, who provided supporting testimony for the California bill. “She was taking these pills and using other kinds of extreme behaviors to lose weight.”
Dr. Nagata said the number of patients he sees with eating disorders has tripled since the pandemic began. They are desperate to get diet pills, some with modest results. “We’ve had patients who have been so dependent on these products that they will be hospitalized and they’re still ordering these products on Amazon,” he said.
Public health advocates turned to state legislatures in response to the federal government’s limited authority to regulate diet pills. Under a 1994 federal law known as the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act, the FDA “cannot step in until after there is a clear issue of harm to consumers,” said Dr. Austin.
No match for the supplement industry’s heavy lobbying on Capitol Hill, public health advocates shifted to a state-by-state approach.
There is, however, a push for the FDA to improve oversight of what goes into diet pills. Sen. Dick Durbin (D-Ill.) in April introduced a bill that would require dietary supplement manufacturers to register their products – along with the ingredients – with the regulator.
Proponents say the change is needed because manufacturers have been known to include dangerous ingredients. C. Michael White, PharmD, of the University of Connecticut, Storrs, found 35% of tainted health products came from weight-loss supplements in a review of a health fraud database.
A few ingredients have been banned, including sibutramine, a stimulant. “It was a very commonly used weight-loss supplement that ended up being removed from the U.S. market because of its elevated risk of causing things like heart attacks, strokes, and arrhythmias,” Dr. White said.
Another ingredient was phenolphthalein, which was used in laxatives until it was identified as a suspected carcinogen and banned in 1999. “To think,” he said, “that that product would still be on the U.S. market is just unconscionable.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
California and New York are on the cusp of going further than the Food and Drug Administration in restricting the sale of nonprescription diet pills to minors as pediatricians and public health advocates try to protect kids from extreme weight-loss gimmicks online.
A bill before Gov. Gavin Newsom would bar anyone under 18 in California from buying over-the-counter weight-loss supplements – whether online or in shops – without a prescription. A similar bill passed by New York lawmakers is on Gov. Kathy Hochul’s desk. Neither Democrat has indicated how he or she will act.
If both bills are signed into law, proponents hope the momentum will build to restrict diet pill sales to children in more states. Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Missouri have introduced similar bills and backers plan to continue their push next year.
Nearly 30 million people in the United States will have an eating disorder in their lifetime; 95% of them are aged between 12 and 25, according to Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital. The hospital added that eating disorders pose the highest risk of mortality of any mental health disorder. And it has become easier than ever for minors to get pills that are sold online or on drugstore shelves. All dietary supplements, which include those for weight loss, accounted for nearly 35% of the $63 billion over-the-counter health products industry in 2021, according to Vision Research Reports, a market research firm.
Dietary supplements, which encompass a broad range of vitamins, herbs, and minerals, are classified by the FDA as food and don’t undergo scientific and safety testing as prescription drugs and over-the-counter medicines do.
Public health advocates want to keep weight-loss products – with ads that may promise to “Drop 5 pounds a week!” and pill names like Slim Sense – away from young people, particularly girls, since some research has linked some products to eating disorders. A study in the American Journal of Public Health, which followed more than 10,000 women aged 14-36 over 15 years, found that “those who used diet pills had more than 5 times higher adjusted odds of receiving an eating disorder diagnosis from a health care provider within 1-3 years than those who did not.”
Many pills have been found tainted with banned and dangerous ingredients that may cause cancer, heart attacks, strokes, and other ailments. For example, the FDA advised the public to avoid Slim Sense by Dr. Reade because it contains lorcaserin, which has been found to cause psychiatric disturbances and impairments in attention or memory. The FDA ordered it discontinued and the company couldn’t be reached for comment.
“Unscrupulous manufacturers are willing to take risks with consumers’ health – and they are lacing their products with illegal pharmaceuticals, banned pharmaceuticals, steroids, excessive stimulants, even experimental stimulants,” said S. Bryn Austin, ScD, founding director of the Strategic Training Initiative for the Prevention of Eating Disorders, or STRIPED, which supports the restrictions. “Consumers have no idea that this is what’s in these types of products.”
STRIPED is a public health initiative based at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and Boston Children’s Hospital.
An industry trade group, the Natural Products Association, disputes that diet pills cause eating disorders, citing the lack of consumer complaints to the FDA of adverse events from their members’ products. “According to FDA data, there is no association between the two,” said Kyle Turk, the association’s director of government affairs.
The association contends that its members adhere to safe manufacturing processes, random product testing, and appropriate marketing guidelines. Representatives also worry that if minors can’t buy supplements over the counter, they may buy them from “crooks” on the black market and undermine the integrity of the industry. Under the bills, minors purchasing weight-loss products must show identification along with a prescription.
Not all business groups oppose the ban. The American Herbal Products Association, a trade group representing dietary supplement manufacturers and retailers, dropped its opposition to California’s bill once it was amended to remove ingredient categories that are found in non-diet supplements and vitamins, according to Robert Marriott, director of regulatory affairs.
Children’s advocates have found worrisome trends among young people who envision their ideal body type based on what they see on social media. According to a study commissioned by Fairplay, a nonprofit that seeks to stop harmful marketing practices targeting children, kids as young as 9 were found to be following three or more eating disorder accounts on Instagram, while the median age was 19. The authors called it a “pro–eating disorder bubble.”
Meta, which owns Instagram and Facebook, said the report lacks nuance, such as recognizing the human need to share life’s difficult moments. The company argues that blanket censorship isn’t the answer. “Experts and safety organizations have told us it’s important to strike a balance and allow people to share their personal stories while removing any content that encourages or promotes eating disorders,” Liza Crenshaw, a Meta spokesperson, said in an email.
Jason Nagata, MD, a pediatrician who cares for children and young adults with life-threatening eating disorders, believes that easy access to diet pills contributes to his patients’ conditions at UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital in San Francisco. That was the case for one of his patients, an emaciated 11-year-old girl.
“She had basically entered a starvation state because she was not getting enough nutrition,” said Dr. Nagata, who provided supporting testimony for the California bill. “She was taking these pills and using other kinds of extreme behaviors to lose weight.”
Dr. Nagata said the number of patients he sees with eating disorders has tripled since the pandemic began. They are desperate to get diet pills, some with modest results. “We’ve had patients who have been so dependent on these products that they will be hospitalized and they’re still ordering these products on Amazon,” he said.
Public health advocates turned to state legislatures in response to the federal government’s limited authority to regulate diet pills. Under a 1994 federal law known as the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act, the FDA “cannot step in until after there is a clear issue of harm to consumers,” said Dr. Austin.
No match for the supplement industry’s heavy lobbying on Capitol Hill, public health advocates shifted to a state-by-state approach.
There is, however, a push for the FDA to improve oversight of what goes into diet pills. Sen. Dick Durbin (D-Ill.) in April introduced a bill that would require dietary supplement manufacturers to register their products – along with the ingredients – with the regulator.
Proponents say the change is needed because manufacturers have been known to include dangerous ingredients. C. Michael White, PharmD, of the University of Connecticut, Storrs, found 35% of tainted health products came from weight-loss supplements in a review of a health fraud database.
A few ingredients have been banned, including sibutramine, a stimulant. “It was a very commonly used weight-loss supplement that ended up being removed from the U.S. market because of its elevated risk of causing things like heart attacks, strokes, and arrhythmias,” Dr. White said.
Another ingredient was phenolphthalein, which was used in laxatives until it was identified as a suspected carcinogen and banned in 1999. “To think,” he said, “that that product would still be on the U.S. market is just unconscionable.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Mental health in America: ‘The kids are not alright’
A new report shines a light on the toll the pandemic and other stressors have taken on the mental health of U.S. children and adolescents over the last 6 years.
The report shows a dramatic increase in use of acute care services for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions, especially among teens and preteens.
The report – The Kids Are Not Alright: Pediatric Mental Health Care Utilization from 2016-2021 – is the work of researchers at the Clarify Health Institute, the research arm of Clarify Health.
The results are “deeply concerning” and should “spark a conversation” around the need to improve access, utilization, and quality of pediatric behavioral health services, Niall Brennan, chief analytics and privacy officer for the Clarify Health Institute, told this news organization.
‘Startling’ trends
Leveraging an observational, national sample of insurance claims from more than 20 million children aged 1-19 years annually, the researchers observed several disturbing trends in mental health care.
From 2016 to 2021, inpatient (IP) admissions rose 61% (from 30 to 48 visits annually per 1,000) and emergency department visits rose 20% (from 55 to 66 visits annually per 1,000).
Mental health IP admissions ranged from a low of 27% in the West North Central region to a high of 137% in the Middle Atlantic region.
There were substantial increases from 2016 to 2021 in mental health IP admissions among children of all age groups, but particularly among adolescents 12 to 15 years old, increasing 84% among girls and 83% among boys in this age group.
There was also a sharp increase in mental health ED visits among girls and boys aged 12-15 years, increasing 20% overall during the study period.
Mental health IP use grew faster from 2016 to 2021 among children with commercial insurance than among those with Medicaid (103% vs. 40%).
In contrast, mental health–specific ED visits declined 10% among children with commercial insurance and increased by 20% among those with Medicaid.
ED utilization rates in 2021 were nearly twice as high in the Medicaid population, compared with those for children with commercial insurance.
These are “startling” increases, Mr. Brennan said in an interview.
These trends “reinforce health care leaders’ responsibility to address children’s mental health, especially when considering that half of all mental health conditions onset during adolescence and carry into adulthood,” Jean Drouin, MD, Clarify Health’s chief executive office and cofounder, adds in a news release.
“With a growing consensus that mental, behavioral, and physical health intersect, this research report aims to spark a conversation about the overall wellbeing of America’s next generation,” Dr. Drouin says.
Concern for the future
Commenting on the new report, Anish Dube, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Children, Adolescents, and their Families, said the findings are “concerning, though unsurprising.”
“They confirm what those of us in clinical practice have experienced in the last several years. The need for mental health services continues to rise every year, while access to adequate help remains lacking,” Dr. Dube said.
“With the recent COVID-19 pandemic, concerns about the effects of climate change, global political uncertainty, and a rapidly changing employment landscape, young people in particular are vulnerable to worries about their future and feelings of helplessness and hopelessness,” he added.
Dr. Dube said there is no one right solution, and addressing this problem must consider individual and local factors.
However, some of the broader interventions needed to tackle the problem include increasing access to care by enforcing mental health parity and increasing the number of trained and qualified mental health professionals, such as child and adolescent psychiatrists, who can assess and treat these conditions in young people before they become major crises and lead to acute interventions like inpatient hospitalization.
“Public health interventions aimed at schools and families in raising awareness of mental health and well-being, and simple, cost-effective interventions to practice mental wellness will also help reduce the burden of mental illness in young people,” Dr. Dube added.
“The APA continues to fight for mental health parity enforcement and for meaningful access to mental health care for children, adolescents, and their families,” Dr. Dube said.
This research was conducted by the Clarify Health Institute. Mr. Brennan and Dr. Dube report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report shines a light on the toll the pandemic and other stressors have taken on the mental health of U.S. children and adolescents over the last 6 years.
The report shows a dramatic increase in use of acute care services for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions, especially among teens and preteens.
The report – The Kids Are Not Alright: Pediatric Mental Health Care Utilization from 2016-2021 – is the work of researchers at the Clarify Health Institute, the research arm of Clarify Health.
The results are “deeply concerning” and should “spark a conversation” around the need to improve access, utilization, and quality of pediatric behavioral health services, Niall Brennan, chief analytics and privacy officer for the Clarify Health Institute, told this news organization.
‘Startling’ trends
Leveraging an observational, national sample of insurance claims from more than 20 million children aged 1-19 years annually, the researchers observed several disturbing trends in mental health care.
From 2016 to 2021, inpatient (IP) admissions rose 61% (from 30 to 48 visits annually per 1,000) and emergency department visits rose 20% (from 55 to 66 visits annually per 1,000).
Mental health IP admissions ranged from a low of 27% in the West North Central region to a high of 137% in the Middle Atlantic region.
There were substantial increases from 2016 to 2021 in mental health IP admissions among children of all age groups, but particularly among adolescents 12 to 15 years old, increasing 84% among girls and 83% among boys in this age group.
There was also a sharp increase in mental health ED visits among girls and boys aged 12-15 years, increasing 20% overall during the study period.
Mental health IP use grew faster from 2016 to 2021 among children with commercial insurance than among those with Medicaid (103% vs. 40%).
In contrast, mental health–specific ED visits declined 10% among children with commercial insurance and increased by 20% among those with Medicaid.
ED utilization rates in 2021 were nearly twice as high in the Medicaid population, compared with those for children with commercial insurance.
These are “startling” increases, Mr. Brennan said in an interview.
These trends “reinforce health care leaders’ responsibility to address children’s mental health, especially when considering that half of all mental health conditions onset during adolescence and carry into adulthood,” Jean Drouin, MD, Clarify Health’s chief executive office and cofounder, adds in a news release.
“With a growing consensus that mental, behavioral, and physical health intersect, this research report aims to spark a conversation about the overall wellbeing of America’s next generation,” Dr. Drouin says.
Concern for the future
Commenting on the new report, Anish Dube, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Children, Adolescents, and their Families, said the findings are “concerning, though unsurprising.”
“They confirm what those of us in clinical practice have experienced in the last several years. The need for mental health services continues to rise every year, while access to adequate help remains lacking,” Dr. Dube said.
“With the recent COVID-19 pandemic, concerns about the effects of climate change, global political uncertainty, and a rapidly changing employment landscape, young people in particular are vulnerable to worries about their future and feelings of helplessness and hopelessness,” he added.
Dr. Dube said there is no one right solution, and addressing this problem must consider individual and local factors.
However, some of the broader interventions needed to tackle the problem include increasing access to care by enforcing mental health parity and increasing the number of trained and qualified mental health professionals, such as child and adolescent psychiatrists, who can assess and treat these conditions in young people before they become major crises and lead to acute interventions like inpatient hospitalization.
“Public health interventions aimed at schools and families in raising awareness of mental health and well-being, and simple, cost-effective interventions to practice mental wellness will also help reduce the burden of mental illness in young people,” Dr. Dube added.
“The APA continues to fight for mental health parity enforcement and for meaningful access to mental health care for children, adolescents, and their families,” Dr. Dube said.
This research was conducted by the Clarify Health Institute. Mr. Brennan and Dr. Dube report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report shines a light on the toll the pandemic and other stressors have taken on the mental health of U.S. children and adolescents over the last 6 years.
The report shows a dramatic increase in use of acute care services for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions, especially among teens and preteens.
The report – The Kids Are Not Alright: Pediatric Mental Health Care Utilization from 2016-2021 – is the work of researchers at the Clarify Health Institute, the research arm of Clarify Health.
The results are “deeply concerning” and should “spark a conversation” around the need to improve access, utilization, and quality of pediatric behavioral health services, Niall Brennan, chief analytics and privacy officer for the Clarify Health Institute, told this news organization.
‘Startling’ trends
Leveraging an observational, national sample of insurance claims from more than 20 million children aged 1-19 years annually, the researchers observed several disturbing trends in mental health care.
From 2016 to 2021, inpatient (IP) admissions rose 61% (from 30 to 48 visits annually per 1,000) and emergency department visits rose 20% (from 55 to 66 visits annually per 1,000).
Mental health IP admissions ranged from a low of 27% in the West North Central region to a high of 137% in the Middle Atlantic region.
There were substantial increases from 2016 to 2021 in mental health IP admissions among children of all age groups, but particularly among adolescents 12 to 15 years old, increasing 84% among girls and 83% among boys in this age group.
There was also a sharp increase in mental health ED visits among girls and boys aged 12-15 years, increasing 20% overall during the study period.
Mental health IP use grew faster from 2016 to 2021 among children with commercial insurance than among those with Medicaid (103% vs. 40%).
In contrast, mental health–specific ED visits declined 10% among children with commercial insurance and increased by 20% among those with Medicaid.
ED utilization rates in 2021 were nearly twice as high in the Medicaid population, compared with those for children with commercial insurance.
These are “startling” increases, Mr. Brennan said in an interview.
These trends “reinforce health care leaders’ responsibility to address children’s mental health, especially when considering that half of all mental health conditions onset during adolescence and carry into adulthood,” Jean Drouin, MD, Clarify Health’s chief executive office and cofounder, adds in a news release.
“With a growing consensus that mental, behavioral, and physical health intersect, this research report aims to spark a conversation about the overall wellbeing of America’s next generation,” Dr. Drouin says.
Concern for the future
Commenting on the new report, Anish Dube, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Children, Adolescents, and their Families, said the findings are “concerning, though unsurprising.”
“They confirm what those of us in clinical practice have experienced in the last several years. The need for mental health services continues to rise every year, while access to adequate help remains lacking,” Dr. Dube said.
“With the recent COVID-19 pandemic, concerns about the effects of climate change, global political uncertainty, and a rapidly changing employment landscape, young people in particular are vulnerable to worries about their future and feelings of helplessness and hopelessness,” he added.
Dr. Dube said there is no one right solution, and addressing this problem must consider individual and local factors.
However, some of the broader interventions needed to tackle the problem include increasing access to care by enforcing mental health parity and increasing the number of trained and qualified mental health professionals, such as child and adolescent psychiatrists, who can assess and treat these conditions in young people before they become major crises and lead to acute interventions like inpatient hospitalization.
“Public health interventions aimed at schools and families in raising awareness of mental health and well-being, and simple, cost-effective interventions to practice mental wellness will also help reduce the burden of mental illness in young people,” Dr. Dube added.
“The APA continues to fight for mental health parity enforcement and for meaningful access to mental health care for children, adolescents, and their families,” Dr. Dube said.
This research was conducted by the Clarify Health Institute. Mr. Brennan and Dr. Dube report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Dr. Caveman’ had a leg up on amputation
Monkey see, monkey do (advanced medical procedures)
We don’t tend to think too kindly of our prehistoric ancestors. We throw around the word “caveman” – hardly a term of endearment – and depictions of Paleolithic humans rarely flatter their subjects. In many ways, though, our conceptions are correct. Humans of the Stone Age lived short, often brutish lives, but civilization had to start somewhere, and our prehistoric ancestors were often far more capable than we give them credit for.
Case in point is a recent discovery from an archaeological dig in Borneo: A young adult who lived 31,000 years ago was discovered with the lower third of their left leg amputated. Save the clever retort about the person’s untimely death, because this individual did not die from the surgery. The amputation occurred when the individual was a child and the subject lived for several years after the operation.
Amputation is usually unnecessary given our current level of medical technology, but it’s actually quite an advanced procedure, and this example predates the previous first case of amputation by nearly 25,000 years. Not only did the surgeon need to cut at an appropriate place, they needed to understand blood loss, the risk of infection, and the need to preserve skin in order to seal the wound back up. That’s quite a lot for our Paleolithic doctor to know, and it’s even more impressive considering the, shall we say, limited tools they would have had available to perform the operation.
Rocks. They cut off the leg with a rock. And it worked.
This discovery also gives insight into the amputee’s society. Someone knew that amputation was the right move for this person, indicating that it had been done before. In addition, the individual would not have been able to spring back into action hunting mammoths right away, they would require care for the rest of their lives. And clearly the community provided, given the individual’s continued life post operation and their burial in a place of honor.
If only the American health care system was capable of such feats of compassion, but that would require the majority of politicians to be as clever as cavemen. We’re not hopeful on those odds.
The first step is admitting you have a crying baby. The second step is … a step
Knock, knock.
Who’s there?
Crying baby.
Crying baby who?
Crying baby who … umm … doesn’t have a punchline. Let’s try this again.
A priest, a rabbi, and a crying baby walk into a bar and … nope, that’s not going to work.
Why did the crying baby cross the road? Ugh, never mind.
Clearly, crying babies are no laughing matter. What crying babies need is science. And the latest innovation – it’s fresh from a study conducted at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science in Saitama, Japan – in the science of crying babies is … walking. Researchers observed 21 unhappy infants and compared their responses to four strategies: being held by their walking mothers, held by their sitting mothers, lying in a motionless crib, or lying in a rocking cot.
The best strategy is for the mother – the experiment only involved mothers, but the results should apply to any caregiver – to pick up the crying baby, walk around for 5 minutes, sit for another 5-8 minutes, and then put the infant back to bed, the researchers said in a written statement.
The walking strategy, however, isn’t perfect. “Walking for 5 minutes promoted sleep, but only for crying infants. Surprisingly, this effect was absent when babies were already calm beforehand,” lead author Kumi O. Kuroda, MD, PhD, explained in a separate statement from the center.
It also doesn’t work on adults. We could not get a crying LOTME writer to fall asleep no matter how long his mother carried him around the office.
New way to detect Parkinson’s has already passed the sniff test
We humans aren’t generally known for our superpowers, but a woman from Scotland may just be the Smelling Superhero. Not only was she able to literally smell Parkinson’s disease (PD) on her husband 12 years before his diagnosis; she is also the reason that scientists have found a new way to test for PD.
Joy Milne, a retired nurse, told the BBC that her husband “had this musty rather unpleasant smell especially round his shoulders and the back of his neck and his skin had definitely changed.” She put two and two together after he had been diagnosed with PD and she came in contact with others with the same scent at a support group.
Researchers at the University of Manchester, working with Ms. Milne, have now created a skin test that uses mass spectroscopy to analyze a sample of the patient’s sebum in just 3 minutes and is 95% accurate. They tested 79 people with Parkinson’s and 71 without using this method and found “specific compounds unique to PD sebum samples when compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, we have identified two classes of lipids, namely, triacylglycerides and diglycerides, as components of human sebum that are significantly differentially expressed in PD,” they said in JACS Au.
This test could be available to general physicians within 2 years, which would provide new opportunities to the people who are waiting in line for neurologic consults. Ms. Milne’s husband passed away in 2015, but her courageous help and amazing nasal abilities may help millions down the line.
The power of flirting
It’s a common office stereotype: Women flirt with the boss to get ahead in the workplace, while men in power sexually harass women in subordinate positions. Nobody ever suspects the guys in the cubicles. A recent study takes a different look and paints a different picture.
The investigators conducted multiple online and lab experiments in how social sexual identity drives behavior in a workplace setting in relation to job placement. They found that it was most often men in lower-power positions who are insecure about their roles who initiate social sexual behavior, even though they know it’s offensive. Why? Power.
They randomly paired over 200 undergraduate students in a male/female fashion, placed them in subordinate and boss-like roles, and asked them to choose from a series of social sexual questions they wanted to ask their teammate. Male participants who were placed in subordinate positions to a female boss chose social sexual questions more often than did male bosses, female subordinates, and female bosses.
So what does this say about the threat of workplace harassment? The researchers found that men and women differ in their strategy for flirtation. For men, it’s a way to gain more power. But problems arise when they rationalize their behavior with a character trait like being a “big flirt.”
“When we take on that identity, it leads to certain behavioral patterns that reinforce the identity. And then, people use that identity as an excuse,” lead author Laura Kray of the University of California, Berkeley, said in a statement from the school.
The researchers make a point to note that the study isn’t about whether flirting is good or bad, nor are they suggesting that people in powerful positions don’t sexually harass underlings. It’s meant to provide insight to improve corporate sexual harassment training. A comment or conversation held in jest could potentially be a warning sign for future behavior.
Monkey see, monkey do (advanced medical procedures)
We don’t tend to think too kindly of our prehistoric ancestors. We throw around the word “caveman” – hardly a term of endearment – and depictions of Paleolithic humans rarely flatter their subjects. In many ways, though, our conceptions are correct. Humans of the Stone Age lived short, often brutish lives, but civilization had to start somewhere, and our prehistoric ancestors were often far more capable than we give them credit for.
Case in point is a recent discovery from an archaeological dig in Borneo: A young adult who lived 31,000 years ago was discovered with the lower third of their left leg amputated. Save the clever retort about the person’s untimely death, because this individual did not die from the surgery. The amputation occurred when the individual was a child and the subject lived for several years after the operation.
Amputation is usually unnecessary given our current level of medical technology, but it’s actually quite an advanced procedure, and this example predates the previous first case of amputation by nearly 25,000 years. Not only did the surgeon need to cut at an appropriate place, they needed to understand blood loss, the risk of infection, and the need to preserve skin in order to seal the wound back up. That’s quite a lot for our Paleolithic doctor to know, and it’s even more impressive considering the, shall we say, limited tools they would have had available to perform the operation.
Rocks. They cut off the leg with a rock. And it worked.
This discovery also gives insight into the amputee’s society. Someone knew that amputation was the right move for this person, indicating that it had been done before. In addition, the individual would not have been able to spring back into action hunting mammoths right away, they would require care for the rest of their lives. And clearly the community provided, given the individual’s continued life post operation and their burial in a place of honor.
If only the American health care system was capable of such feats of compassion, but that would require the majority of politicians to be as clever as cavemen. We’re not hopeful on those odds.
The first step is admitting you have a crying baby. The second step is … a step
Knock, knock.
Who’s there?
Crying baby.
Crying baby who?
Crying baby who … umm … doesn’t have a punchline. Let’s try this again.
A priest, a rabbi, and a crying baby walk into a bar and … nope, that’s not going to work.
Why did the crying baby cross the road? Ugh, never mind.
Clearly, crying babies are no laughing matter. What crying babies need is science. And the latest innovation – it’s fresh from a study conducted at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science in Saitama, Japan – in the science of crying babies is … walking. Researchers observed 21 unhappy infants and compared their responses to four strategies: being held by their walking mothers, held by their sitting mothers, lying in a motionless crib, or lying in a rocking cot.
The best strategy is for the mother – the experiment only involved mothers, but the results should apply to any caregiver – to pick up the crying baby, walk around for 5 minutes, sit for another 5-8 minutes, and then put the infant back to bed, the researchers said in a written statement.
The walking strategy, however, isn’t perfect. “Walking for 5 minutes promoted sleep, but only for crying infants. Surprisingly, this effect was absent when babies were already calm beforehand,” lead author Kumi O. Kuroda, MD, PhD, explained in a separate statement from the center.
It also doesn’t work on adults. We could not get a crying LOTME writer to fall asleep no matter how long his mother carried him around the office.
New way to detect Parkinson’s has already passed the sniff test
We humans aren’t generally known for our superpowers, but a woman from Scotland may just be the Smelling Superhero. Not only was she able to literally smell Parkinson’s disease (PD) on her husband 12 years before his diagnosis; she is also the reason that scientists have found a new way to test for PD.
Joy Milne, a retired nurse, told the BBC that her husband “had this musty rather unpleasant smell especially round his shoulders and the back of his neck and his skin had definitely changed.” She put two and two together after he had been diagnosed with PD and she came in contact with others with the same scent at a support group.
Researchers at the University of Manchester, working with Ms. Milne, have now created a skin test that uses mass spectroscopy to analyze a sample of the patient’s sebum in just 3 minutes and is 95% accurate. They tested 79 people with Parkinson’s and 71 without using this method and found “specific compounds unique to PD sebum samples when compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, we have identified two classes of lipids, namely, triacylglycerides and diglycerides, as components of human sebum that are significantly differentially expressed in PD,” they said in JACS Au.
This test could be available to general physicians within 2 years, which would provide new opportunities to the people who are waiting in line for neurologic consults. Ms. Milne’s husband passed away in 2015, but her courageous help and amazing nasal abilities may help millions down the line.
The power of flirting
It’s a common office stereotype: Women flirt with the boss to get ahead in the workplace, while men in power sexually harass women in subordinate positions. Nobody ever suspects the guys in the cubicles. A recent study takes a different look and paints a different picture.
The investigators conducted multiple online and lab experiments in how social sexual identity drives behavior in a workplace setting in relation to job placement. They found that it was most often men in lower-power positions who are insecure about their roles who initiate social sexual behavior, even though they know it’s offensive. Why? Power.
They randomly paired over 200 undergraduate students in a male/female fashion, placed them in subordinate and boss-like roles, and asked them to choose from a series of social sexual questions they wanted to ask their teammate. Male participants who were placed in subordinate positions to a female boss chose social sexual questions more often than did male bosses, female subordinates, and female bosses.
So what does this say about the threat of workplace harassment? The researchers found that men and women differ in their strategy for flirtation. For men, it’s a way to gain more power. But problems arise when they rationalize their behavior with a character trait like being a “big flirt.”
“When we take on that identity, it leads to certain behavioral patterns that reinforce the identity. And then, people use that identity as an excuse,” lead author Laura Kray of the University of California, Berkeley, said in a statement from the school.
The researchers make a point to note that the study isn’t about whether flirting is good or bad, nor are they suggesting that people in powerful positions don’t sexually harass underlings. It’s meant to provide insight to improve corporate sexual harassment training. A comment or conversation held in jest could potentially be a warning sign for future behavior.
Monkey see, monkey do (advanced medical procedures)
We don’t tend to think too kindly of our prehistoric ancestors. We throw around the word “caveman” – hardly a term of endearment – and depictions of Paleolithic humans rarely flatter their subjects. In many ways, though, our conceptions are correct. Humans of the Stone Age lived short, often brutish lives, but civilization had to start somewhere, and our prehistoric ancestors were often far more capable than we give them credit for.
Case in point is a recent discovery from an archaeological dig in Borneo: A young adult who lived 31,000 years ago was discovered with the lower third of their left leg amputated. Save the clever retort about the person’s untimely death, because this individual did not die from the surgery. The amputation occurred when the individual was a child and the subject lived for several years after the operation.
Amputation is usually unnecessary given our current level of medical technology, but it’s actually quite an advanced procedure, and this example predates the previous first case of amputation by nearly 25,000 years. Not only did the surgeon need to cut at an appropriate place, they needed to understand blood loss, the risk of infection, and the need to preserve skin in order to seal the wound back up. That’s quite a lot for our Paleolithic doctor to know, and it’s even more impressive considering the, shall we say, limited tools they would have had available to perform the operation.
Rocks. They cut off the leg with a rock. And it worked.
This discovery also gives insight into the amputee’s society. Someone knew that amputation was the right move for this person, indicating that it had been done before. In addition, the individual would not have been able to spring back into action hunting mammoths right away, they would require care for the rest of their lives. And clearly the community provided, given the individual’s continued life post operation and their burial in a place of honor.
If only the American health care system was capable of such feats of compassion, but that would require the majority of politicians to be as clever as cavemen. We’re not hopeful on those odds.
The first step is admitting you have a crying baby. The second step is … a step
Knock, knock.
Who’s there?
Crying baby.
Crying baby who?
Crying baby who … umm … doesn’t have a punchline. Let’s try this again.
A priest, a rabbi, and a crying baby walk into a bar and … nope, that’s not going to work.
Why did the crying baby cross the road? Ugh, never mind.
Clearly, crying babies are no laughing matter. What crying babies need is science. And the latest innovation – it’s fresh from a study conducted at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science in Saitama, Japan – in the science of crying babies is … walking. Researchers observed 21 unhappy infants and compared their responses to four strategies: being held by their walking mothers, held by their sitting mothers, lying in a motionless crib, or lying in a rocking cot.
The best strategy is for the mother – the experiment only involved mothers, but the results should apply to any caregiver – to pick up the crying baby, walk around for 5 minutes, sit for another 5-8 minutes, and then put the infant back to bed, the researchers said in a written statement.
The walking strategy, however, isn’t perfect. “Walking for 5 minutes promoted sleep, but only for crying infants. Surprisingly, this effect was absent when babies were already calm beforehand,” lead author Kumi O. Kuroda, MD, PhD, explained in a separate statement from the center.
It also doesn’t work on adults. We could not get a crying LOTME writer to fall asleep no matter how long his mother carried him around the office.
New way to detect Parkinson’s has already passed the sniff test
We humans aren’t generally known for our superpowers, but a woman from Scotland may just be the Smelling Superhero. Not only was she able to literally smell Parkinson’s disease (PD) on her husband 12 years before his diagnosis; she is also the reason that scientists have found a new way to test for PD.
Joy Milne, a retired nurse, told the BBC that her husband “had this musty rather unpleasant smell especially round his shoulders and the back of his neck and his skin had definitely changed.” She put two and two together after he had been diagnosed with PD and she came in contact with others with the same scent at a support group.
Researchers at the University of Manchester, working with Ms. Milne, have now created a skin test that uses mass spectroscopy to analyze a sample of the patient’s sebum in just 3 minutes and is 95% accurate. They tested 79 people with Parkinson’s and 71 without using this method and found “specific compounds unique to PD sebum samples when compared to healthy controls. Furthermore, we have identified two classes of lipids, namely, triacylglycerides and diglycerides, as components of human sebum that are significantly differentially expressed in PD,” they said in JACS Au.
This test could be available to general physicians within 2 years, which would provide new opportunities to the people who are waiting in line for neurologic consults. Ms. Milne’s husband passed away in 2015, but her courageous help and amazing nasal abilities may help millions down the line.
The power of flirting
It’s a common office stereotype: Women flirt with the boss to get ahead in the workplace, while men in power sexually harass women in subordinate positions. Nobody ever suspects the guys in the cubicles. A recent study takes a different look and paints a different picture.
The investigators conducted multiple online and lab experiments in how social sexual identity drives behavior in a workplace setting in relation to job placement. They found that it was most often men in lower-power positions who are insecure about their roles who initiate social sexual behavior, even though they know it’s offensive. Why? Power.
They randomly paired over 200 undergraduate students in a male/female fashion, placed them in subordinate and boss-like roles, and asked them to choose from a series of social sexual questions they wanted to ask their teammate. Male participants who were placed in subordinate positions to a female boss chose social sexual questions more often than did male bosses, female subordinates, and female bosses.
So what does this say about the threat of workplace harassment? The researchers found that men and women differ in their strategy for flirtation. For men, it’s a way to gain more power. But problems arise when they rationalize their behavior with a character trait like being a “big flirt.”
“When we take on that identity, it leads to certain behavioral patterns that reinforce the identity. And then, people use that identity as an excuse,” lead author Laura Kray of the University of California, Berkeley, said in a statement from the school.
The researchers make a point to note that the study isn’t about whether flirting is good or bad, nor are they suggesting that people in powerful positions don’t sexually harass underlings. It’s meant to provide insight to improve corporate sexual harassment training. A comment or conversation held in jest could potentially be a warning sign for future behavior.
Demystifying psychotherapy
Managing psychiatric illnesses is rapidly becoming routine practice for primary care pediatricians, whether screening for symptoms of anxiety and depression, starting medication, or providing psychoeducation to youth and parents. Pediatricians can provide strategies to address the impairments of sleep, energy, motivation and appetite that can accompany these illnesses. Psychotherapy, a relationship based on understanding and providing support, should be a core element of treatment for emotional disorders, but there is a great deal of uncertainty around what therapies are supported by evidence. This month, we offer a primer on the evidence-based psychotherapies for youth and we also recognize that research defining the effectiveness of psychotherapy is limited and complex.
Cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy (CBT)
Mention psychotherapy and most people think of a patient reclining on a couch free-associating about their childhood while a therapist sits behind them taking notes. This potent image stems from psychoanalytic psychotherapy, developed in the 19th century by Sigmund Freud, and was based on his theory that unconscious conflicts drove most of the puzzling behaviors and emotional distress associated with “neurosis.” Psychoanalysis became popular in 20th century America, even for use with children. Evidence is hard to develop since psychoanalytic therapy often lasts years, there are a limited number of patients, and the method is hard to standardize.
A focus on how to shape behaviors directly also emerged in the early 20th century (in the work of John Watson and Ivan Pavlov). Aaron Beck, MD, the father of CBT, observed in his psychoanalytic treatments that many patients appeared to be experiencing emotional distress around thoughts that were not unconscious. Instead, his patients were experiencing “automatic thoughts,” or rapid, often-distorted thoughts that have the force of truth in the thinker. These thoughts create emotional distress and behaviors that may reinforce the thoughts and emotional distress. For example, a depressed patient who is uncomfortable in social situations may think “nobody ever likes me.” This may cause them to appear uncomfortable or unfriendly in a new social situation and prevent them from making connections, perpetuating a cycle of isolation, insecurity, and loneliness. Identifying these automatic thoughts, and their connection to painful feelings and perpetuating behaviors is at the core of CBT.
In CBT the therapist is much more active than in psychoanalysis. They engage patients in identifying thought distortions together, challenging them on the truth of these thoughts and recognizing the connection to emotional distress. They also identify maladaptive behaviors and focus on strategies to build new more effective behavioral responses to thoughts, feelings, and situations. This is often done with gradual “exposures” to new behaviors, which are naturally reinforced by better outcomes or lowered distress. When performed with high fidelity, CBT is a very structured treatment that is closer to an emotionally supportive form of coaching and skill building. CBT is at the core of most evidence-based psychotherapies that have emerged in the past 60 years.
CBT is the first-line treatment for anxiety disorders in children, adolescents, and adults. A variant called “exposure and response prevention” is the first-line treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder, and is predominantly behavioral. It is focused on preventing patients with anxiety disorders from engaging in the maladaptive behaviors that lower their anxiety in the short term but cause worsened anxiety and impairment over time (such as avoiding social situations when they are worried that others won’t like them).
CBT is also a first-line treatment for major depressive episodes in teenagers and adults, although those for whom the symptoms are severe often need medication to be able to fully participate in therapy. There are variants of CBT that have demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder, bulimia, and even psychosis. It makes developmental sense that therapies with a problem-focused coaching approach might be more effective in children and adolescents than open-ended exploratory psychotherapies.
Traditional CBT was not very effective for patients with a variant of depression that is marked by stormy relationships, irritability, chronic suicidality, and impulsive attempts to regulate discomfort (including bingeing, purging, sexual acting-out, drug use, and self-injury or cutting), a symptom pattern called “borderline personality disorder.” These patients often ended up on multiple medications with only modest improvements in their function and well-being.
But in the 1990s, a research psychologist named Marsha Linnehan developed a modified version of CBT to use with these patients called dialectical-behavioral therapy (DBT). The “dialectic” emphasizes the role of two things being true at once, in this case the need for acceptance and change. DBT helps patients develop distress tolerance and emotional regulation skills alongside adaptive social and communication skills. DBT has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of these patients as well as in the treatment of other disorders marked by poor distress tolerance and self-regulation (such as substance use disorders, binge-eating disorder, and PTSD).
DBT was adapted for use in adolescents given the prevalence of these problems in this age group, and it is the first-line treatment for adolescents with these specific mood and behavioral symptoms. High-fidelity DBT has an individual, group, and family component that are all essential for the treatment to be effective.
Instruction about the principles of CBT and DBT is a part of graduate school in psychology, but not every postgraduate training program includes thorough training in their practice. Completion of this specialized training leads to certification. It is very important that families understand that anyone may call themselves a psychotherapist. Those therapists who have master’s degrees (MSW, MFT, PCC, and others) may not have had exposure to these evidence-based treatments in their shorter graduate programs. Even doctoral-level training programs often do not include complete training in the high-fidelity delivery of these therapies.
It is critical that you help families be educated consumers and ask therapists if they have training and certification in the recommended therapy. The Psychology Today website has a therapist referral resource that includes this information. Training programs can provide access to therapists who are learning these therapies; with skilled supervision, they can provide excellent treatment.
We should note that there are several other evidence-based therapies, including family-based treatment for anorexia nervosa, motivational interviewing for substance use disorders, and interpersonal psychotherapy for depression associated with high family conflict in adolescents.
There is good evidence that the quality of the alliance between therapist and patient is a critical predictor of whether a therapy will be effective. It is appropriate for your patient to look for a therapist that they can trust and talk to and that their therapist be trained in the recommended psychotherapy. Otherwise, your patient is spending valuable time and money on an enterprise that may not be effective. This can leave them and their parents feeling discouraged or even hopeless about the prospects for recovery and promote an overreliance on medications. In addition to providing your patients with effective screening, initiating medication treatment, and psychoeducation, you can enhance their ability to find an optimal therapist to relieve their suffering.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
Managing psychiatric illnesses is rapidly becoming routine practice for primary care pediatricians, whether screening for symptoms of anxiety and depression, starting medication, or providing psychoeducation to youth and parents. Pediatricians can provide strategies to address the impairments of sleep, energy, motivation and appetite that can accompany these illnesses. Psychotherapy, a relationship based on understanding and providing support, should be a core element of treatment for emotional disorders, but there is a great deal of uncertainty around what therapies are supported by evidence. This month, we offer a primer on the evidence-based psychotherapies for youth and we also recognize that research defining the effectiveness of psychotherapy is limited and complex.
Cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy (CBT)
Mention psychotherapy and most people think of a patient reclining on a couch free-associating about their childhood while a therapist sits behind them taking notes. This potent image stems from psychoanalytic psychotherapy, developed in the 19th century by Sigmund Freud, and was based on his theory that unconscious conflicts drove most of the puzzling behaviors and emotional distress associated with “neurosis.” Psychoanalysis became popular in 20th century America, even for use with children. Evidence is hard to develop since psychoanalytic therapy often lasts years, there are a limited number of patients, and the method is hard to standardize.
A focus on how to shape behaviors directly also emerged in the early 20th century (in the work of John Watson and Ivan Pavlov). Aaron Beck, MD, the father of CBT, observed in his psychoanalytic treatments that many patients appeared to be experiencing emotional distress around thoughts that were not unconscious. Instead, his patients were experiencing “automatic thoughts,” or rapid, often-distorted thoughts that have the force of truth in the thinker. These thoughts create emotional distress and behaviors that may reinforce the thoughts and emotional distress. For example, a depressed patient who is uncomfortable in social situations may think “nobody ever likes me.” This may cause them to appear uncomfortable or unfriendly in a new social situation and prevent them from making connections, perpetuating a cycle of isolation, insecurity, and loneliness. Identifying these automatic thoughts, and their connection to painful feelings and perpetuating behaviors is at the core of CBT.
In CBT the therapist is much more active than in psychoanalysis. They engage patients in identifying thought distortions together, challenging them on the truth of these thoughts and recognizing the connection to emotional distress. They also identify maladaptive behaviors and focus on strategies to build new more effective behavioral responses to thoughts, feelings, and situations. This is often done with gradual “exposures” to new behaviors, which are naturally reinforced by better outcomes or lowered distress. When performed with high fidelity, CBT is a very structured treatment that is closer to an emotionally supportive form of coaching and skill building. CBT is at the core of most evidence-based psychotherapies that have emerged in the past 60 years.
CBT is the first-line treatment for anxiety disorders in children, adolescents, and adults. A variant called “exposure and response prevention” is the first-line treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder, and is predominantly behavioral. It is focused on preventing patients with anxiety disorders from engaging in the maladaptive behaviors that lower their anxiety in the short term but cause worsened anxiety and impairment over time (such as avoiding social situations when they are worried that others won’t like them).
CBT is also a first-line treatment for major depressive episodes in teenagers and adults, although those for whom the symptoms are severe often need medication to be able to fully participate in therapy. There are variants of CBT that have demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder, bulimia, and even psychosis. It makes developmental sense that therapies with a problem-focused coaching approach might be more effective in children and adolescents than open-ended exploratory psychotherapies.
Traditional CBT was not very effective for patients with a variant of depression that is marked by stormy relationships, irritability, chronic suicidality, and impulsive attempts to regulate discomfort (including bingeing, purging, sexual acting-out, drug use, and self-injury or cutting), a symptom pattern called “borderline personality disorder.” These patients often ended up on multiple medications with only modest improvements in their function and well-being.
But in the 1990s, a research psychologist named Marsha Linnehan developed a modified version of CBT to use with these patients called dialectical-behavioral therapy (DBT). The “dialectic” emphasizes the role of two things being true at once, in this case the need for acceptance and change. DBT helps patients develop distress tolerance and emotional regulation skills alongside adaptive social and communication skills. DBT has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of these patients as well as in the treatment of other disorders marked by poor distress tolerance and self-regulation (such as substance use disorders, binge-eating disorder, and PTSD).
DBT was adapted for use in adolescents given the prevalence of these problems in this age group, and it is the first-line treatment for adolescents with these specific mood and behavioral symptoms. High-fidelity DBT has an individual, group, and family component that are all essential for the treatment to be effective.
Instruction about the principles of CBT and DBT is a part of graduate school in psychology, but not every postgraduate training program includes thorough training in their practice. Completion of this specialized training leads to certification. It is very important that families understand that anyone may call themselves a psychotherapist. Those therapists who have master’s degrees (MSW, MFT, PCC, and others) may not have had exposure to these evidence-based treatments in their shorter graduate programs. Even doctoral-level training programs often do not include complete training in the high-fidelity delivery of these therapies.
It is critical that you help families be educated consumers and ask therapists if they have training and certification in the recommended therapy. The Psychology Today website has a therapist referral resource that includes this information. Training programs can provide access to therapists who are learning these therapies; with skilled supervision, they can provide excellent treatment.
We should note that there are several other evidence-based therapies, including family-based treatment for anorexia nervosa, motivational interviewing for substance use disorders, and interpersonal psychotherapy for depression associated with high family conflict in adolescents.
There is good evidence that the quality of the alliance between therapist and patient is a critical predictor of whether a therapy will be effective. It is appropriate for your patient to look for a therapist that they can trust and talk to and that their therapist be trained in the recommended psychotherapy. Otherwise, your patient is spending valuable time and money on an enterprise that may not be effective. This can leave them and their parents feeling discouraged or even hopeless about the prospects for recovery and promote an overreliance on medications. In addition to providing your patients with effective screening, initiating medication treatment, and psychoeducation, you can enhance their ability to find an optimal therapist to relieve their suffering.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
Managing psychiatric illnesses is rapidly becoming routine practice for primary care pediatricians, whether screening for symptoms of anxiety and depression, starting medication, or providing psychoeducation to youth and parents. Pediatricians can provide strategies to address the impairments of sleep, energy, motivation and appetite that can accompany these illnesses. Psychotherapy, a relationship based on understanding and providing support, should be a core element of treatment for emotional disorders, but there is a great deal of uncertainty around what therapies are supported by evidence. This month, we offer a primer on the evidence-based psychotherapies for youth and we also recognize that research defining the effectiveness of psychotherapy is limited and complex.
Cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy (CBT)
Mention psychotherapy and most people think of a patient reclining on a couch free-associating about their childhood while a therapist sits behind them taking notes. This potent image stems from psychoanalytic psychotherapy, developed in the 19th century by Sigmund Freud, and was based on his theory that unconscious conflicts drove most of the puzzling behaviors and emotional distress associated with “neurosis.” Psychoanalysis became popular in 20th century America, even for use with children. Evidence is hard to develop since psychoanalytic therapy often lasts years, there are a limited number of patients, and the method is hard to standardize.
A focus on how to shape behaviors directly also emerged in the early 20th century (in the work of John Watson and Ivan Pavlov). Aaron Beck, MD, the father of CBT, observed in his psychoanalytic treatments that many patients appeared to be experiencing emotional distress around thoughts that were not unconscious. Instead, his patients were experiencing “automatic thoughts,” or rapid, often-distorted thoughts that have the force of truth in the thinker. These thoughts create emotional distress and behaviors that may reinforce the thoughts and emotional distress. For example, a depressed patient who is uncomfortable in social situations may think “nobody ever likes me.” This may cause them to appear uncomfortable or unfriendly in a new social situation and prevent them from making connections, perpetuating a cycle of isolation, insecurity, and loneliness. Identifying these automatic thoughts, and their connection to painful feelings and perpetuating behaviors is at the core of CBT.
In CBT the therapist is much more active than in psychoanalysis. They engage patients in identifying thought distortions together, challenging them on the truth of these thoughts and recognizing the connection to emotional distress. They also identify maladaptive behaviors and focus on strategies to build new more effective behavioral responses to thoughts, feelings, and situations. This is often done with gradual “exposures” to new behaviors, which are naturally reinforced by better outcomes or lowered distress. When performed with high fidelity, CBT is a very structured treatment that is closer to an emotionally supportive form of coaching and skill building. CBT is at the core of most evidence-based psychotherapies that have emerged in the past 60 years.
CBT is the first-line treatment for anxiety disorders in children, adolescents, and adults. A variant called “exposure and response prevention” is the first-line treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder, and is predominantly behavioral. It is focused on preventing patients with anxiety disorders from engaging in the maladaptive behaviors that lower their anxiety in the short term but cause worsened anxiety and impairment over time (such as avoiding social situations when they are worried that others won’t like them).
CBT is also a first-line treatment for major depressive episodes in teenagers and adults, although those for whom the symptoms are severe often need medication to be able to fully participate in therapy. There are variants of CBT that have demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder, bulimia, and even psychosis. It makes developmental sense that therapies with a problem-focused coaching approach might be more effective in children and adolescents than open-ended exploratory psychotherapies.
Traditional CBT was not very effective for patients with a variant of depression that is marked by stormy relationships, irritability, chronic suicidality, and impulsive attempts to regulate discomfort (including bingeing, purging, sexual acting-out, drug use, and self-injury or cutting), a symptom pattern called “borderline personality disorder.” These patients often ended up on multiple medications with only modest improvements in their function and well-being.
But in the 1990s, a research psychologist named Marsha Linnehan developed a modified version of CBT to use with these patients called dialectical-behavioral therapy (DBT). The “dialectic” emphasizes the role of two things being true at once, in this case the need for acceptance and change. DBT helps patients develop distress tolerance and emotional regulation skills alongside adaptive social and communication skills. DBT has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of these patients as well as in the treatment of other disorders marked by poor distress tolerance and self-regulation (such as substance use disorders, binge-eating disorder, and PTSD).
DBT was adapted for use in adolescents given the prevalence of these problems in this age group, and it is the first-line treatment for adolescents with these specific mood and behavioral symptoms. High-fidelity DBT has an individual, group, and family component that are all essential for the treatment to be effective.
Instruction about the principles of CBT and DBT is a part of graduate school in psychology, but not every postgraduate training program includes thorough training in their practice. Completion of this specialized training leads to certification. It is very important that families understand that anyone may call themselves a psychotherapist. Those therapists who have master’s degrees (MSW, MFT, PCC, and others) may not have had exposure to these evidence-based treatments in their shorter graduate programs. Even doctoral-level training programs often do not include complete training in the high-fidelity delivery of these therapies.
It is critical that you help families be educated consumers and ask therapists if they have training and certification in the recommended therapy. The Psychology Today website has a therapist referral resource that includes this information. Training programs can provide access to therapists who are learning these therapies; with skilled supervision, they can provide excellent treatment.
We should note that there are several other evidence-based therapies, including family-based treatment for anorexia nervosa, motivational interviewing for substance use disorders, and interpersonal psychotherapy for depression associated with high family conflict in adolescents.
There is good evidence that the quality of the alliance between therapist and patient is a critical predictor of whether a therapy will be effective. It is appropriate for your patient to look for a therapist that they can trust and talk to and that their therapist be trained in the recommended psychotherapy. Otherwise, your patient is spending valuable time and money on an enterprise that may not be effective. This can leave them and their parents feeling discouraged or even hopeless about the prospects for recovery and promote an overreliance on medications. In addition to providing your patients with effective screening, initiating medication treatment, and psychoeducation, you can enhance their ability to find an optimal therapist to relieve their suffering.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
Ages and Stages Questionnaire a first step to find developmental delays
The commonly used but sometimes debated Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ), has modest utility for identifying developmental delays in young children, an Australian review and meta-analysis found.
On this easily administered parent-completed screening tool, scores of more than 2 standard deviations below the mean in more than one of five domains had moderate sensitivity and specificity to predict any delay, severe delay, motor delay, and cognitive delay, according to neonatologist Shripada Rao, PhD, a clinical associate professor in the neonatal intensive care unit at Perth Hospital and the University of Western Australia, also in Perth, and colleagues.
If a child of 12-60 months passes all ASQ domains, there is a moderate probability that child does not have severe developmental delay, the researchers concluded. If a child in that age range fails the motor or cognitive domain, there is a moderate probability that some motor or cognitive delay is present. The authors say the tool may work best as a screening test to identify children in need of more formal assessment.
“Our meta-analysis found that ASQ was somewhat more predictive in older children (older than 24 months), compared with younger age groups of 12-24 months,” Dr. Rao said in an interview. “However, the sample size for these comparisons was too small to reach definite conclusions, and we have called for future studies to evaluate ASQ separately for different age groups.”
Early identification of developmental delay in children is essential to enable timely intervention,” Dr. Rao and associates wrote in JAMA Pediatrics.
While formal assessments such as the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development are the gold standard, they are time-consuming and expensive, need the physical attendance of both the child and caregivers, and “thus may not be feasible in resource-limited settings or in pandemic conditions.”
According to Barbara J. Howard, MD, commenting on a recent update to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s developmental milestones guide, Learn the Signs. Act Early, fewer than 25% of children with delays or disabilities receive intervention before age 3 and most with emotional, behavioral, and developmental condition, other than autism spectrum disorder receive no intervention before age 5.
The ASQ
As an accessible alternative, the ASQ consists of questions on communication (language), gross-motor, fine-motor, problem-solving (cognitive), and personal-adaptive skills. The survey requires only 10-15 minutes, is relatively inexpensive, and also establishes a sense of parental involvement, the authors noted.
“Based on the generally accepted interpretation of LR [likelihood ratio] values, if a child passes ASQ-2SD, there is a moderate probability that the child does not have severe delay,” the investigators concluded.
The analysis
The final meta-analysis reviewed 36 eligible ASQ studies published from 1997 to 2022. Looking at the four indicators of pooled sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative likelihood ratios, the following respective predictive values emerged for scores of more than 2 SDs below the mean across several domains: sensitivity of 0.77 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.86), specificity of 0.81 (95% CI 0.75-0.86), positive likelihood ratio of 4.10 (95% CI 3.17-5.30), and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.28 (95% CI, 0.18-0.44)
They cautioned, however, that the certainty of evidence from the reviewed studies was low or very low and given the small sample sizes for comparing domains, clinicians should be circumspect in interpreting the results.
An initial step
Commenting on the paper but not involved in it, David G. Fagan, MD, vice chairman of pediatric ambulatory administration in the department of pediatrics at Cohen Children’s Medical Center, New York, agreed that screening tools such as the ASQ have a place in clinical practice. “However, the purpose of a screening tool is not to make the diagnosis but to identify children at risk for developmental delays,” he said in an interview. “The meta-analysis highlights the fact that no screening is 100% accurate and that results need to be interpreted in context.
“Before screening tools were widely used, pediatricians trusted their gut,” Dr. Fagan continued. “‘I know it when I see it,’ which obviously resulted in tremendous variability based on experience.”
He added that, even if a child passes this validated questionnaire, any concern on the part of a parent or pediatrician about developmental delay should be addressed with further assessment.
The future
According to Dr. Rao, clinicians should continue to screen for developmental delays in young children using the ASQ. “Given the long wait times to see a developmental pediatrician or a clinical psychologist, a screening tool such as ASQ will enable appropriate triaging.”
Going forward, however, studies should evaluate this questionnaire separately for different age groups such as less than 12 months, 12-23 months, and at least 24 months. They should also be prospective in design and entail a low risk of bias, as well as report raw numbers for true and false positives and negatives. “Even if they use their own cutoff ASQ scores, they should also give results for the conventional cutoff scores to enable comparison with other studies,” the authors wrote.
The authors disclosed no specific funding for this study and no competing interests. Dr. Fagan disclosed no competing interests with regard to his comments.
The commonly used but sometimes debated Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ), has modest utility for identifying developmental delays in young children, an Australian review and meta-analysis found.
On this easily administered parent-completed screening tool, scores of more than 2 standard deviations below the mean in more than one of five domains had moderate sensitivity and specificity to predict any delay, severe delay, motor delay, and cognitive delay, according to neonatologist Shripada Rao, PhD, a clinical associate professor in the neonatal intensive care unit at Perth Hospital and the University of Western Australia, also in Perth, and colleagues.
If a child of 12-60 months passes all ASQ domains, there is a moderate probability that child does not have severe developmental delay, the researchers concluded. If a child in that age range fails the motor or cognitive domain, there is a moderate probability that some motor or cognitive delay is present. The authors say the tool may work best as a screening test to identify children in need of more formal assessment.
“Our meta-analysis found that ASQ was somewhat more predictive in older children (older than 24 months), compared with younger age groups of 12-24 months,” Dr. Rao said in an interview. “However, the sample size for these comparisons was too small to reach definite conclusions, and we have called for future studies to evaluate ASQ separately for different age groups.”
Early identification of developmental delay in children is essential to enable timely intervention,” Dr. Rao and associates wrote in JAMA Pediatrics.
While formal assessments such as the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development are the gold standard, they are time-consuming and expensive, need the physical attendance of both the child and caregivers, and “thus may not be feasible in resource-limited settings or in pandemic conditions.”
According to Barbara J. Howard, MD, commenting on a recent update to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s developmental milestones guide, Learn the Signs. Act Early, fewer than 25% of children with delays or disabilities receive intervention before age 3 and most with emotional, behavioral, and developmental condition, other than autism spectrum disorder receive no intervention before age 5.
The ASQ
As an accessible alternative, the ASQ consists of questions on communication (language), gross-motor, fine-motor, problem-solving (cognitive), and personal-adaptive skills. The survey requires only 10-15 minutes, is relatively inexpensive, and also establishes a sense of parental involvement, the authors noted.
“Based on the generally accepted interpretation of LR [likelihood ratio] values, if a child passes ASQ-2SD, there is a moderate probability that the child does not have severe delay,” the investigators concluded.
The analysis
The final meta-analysis reviewed 36 eligible ASQ studies published from 1997 to 2022. Looking at the four indicators of pooled sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative likelihood ratios, the following respective predictive values emerged for scores of more than 2 SDs below the mean across several domains: sensitivity of 0.77 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.86), specificity of 0.81 (95% CI 0.75-0.86), positive likelihood ratio of 4.10 (95% CI 3.17-5.30), and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.28 (95% CI, 0.18-0.44)
They cautioned, however, that the certainty of evidence from the reviewed studies was low or very low and given the small sample sizes for comparing domains, clinicians should be circumspect in interpreting the results.
An initial step
Commenting on the paper but not involved in it, David G. Fagan, MD, vice chairman of pediatric ambulatory administration in the department of pediatrics at Cohen Children’s Medical Center, New York, agreed that screening tools such as the ASQ have a place in clinical practice. “However, the purpose of a screening tool is not to make the diagnosis but to identify children at risk for developmental delays,” he said in an interview. “The meta-analysis highlights the fact that no screening is 100% accurate and that results need to be interpreted in context.
“Before screening tools were widely used, pediatricians trusted their gut,” Dr. Fagan continued. “‘I know it when I see it,’ which obviously resulted in tremendous variability based on experience.”
He added that, even if a child passes this validated questionnaire, any concern on the part of a parent or pediatrician about developmental delay should be addressed with further assessment.
The future
According to Dr. Rao, clinicians should continue to screen for developmental delays in young children using the ASQ. “Given the long wait times to see a developmental pediatrician or a clinical psychologist, a screening tool such as ASQ will enable appropriate triaging.”
Going forward, however, studies should evaluate this questionnaire separately for different age groups such as less than 12 months, 12-23 months, and at least 24 months. They should also be prospective in design and entail a low risk of bias, as well as report raw numbers for true and false positives and negatives. “Even if they use their own cutoff ASQ scores, they should also give results for the conventional cutoff scores to enable comparison with other studies,” the authors wrote.
The authors disclosed no specific funding for this study and no competing interests. Dr. Fagan disclosed no competing interests with regard to his comments.
The commonly used but sometimes debated Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ), has modest utility for identifying developmental delays in young children, an Australian review and meta-analysis found.
On this easily administered parent-completed screening tool, scores of more than 2 standard deviations below the mean in more than one of five domains had moderate sensitivity and specificity to predict any delay, severe delay, motor delay, and cognitive delay, according to neonatologist Shripada Rao, PhD, a clinical associate professor in the neonatal intensive care unit at Perth Hospital and the University of Western Australia, also in Perth, and colleagues.
If a child of 12-60 months passes all ASQ domains, there is a moderate probability that child does not have severe developmental delay, the researchers concluded. If a child in that age range fails the motor or cognitive domain, there is a moderate probability that some motor or cognitive delay is present. The authors say the tool may work best as a screening test to identify children in need of more formal assessment.
“Our meta-analysis found that ASQ was somewhat more predictive in older children (older than 24 months), compared with younger age groups of 12-24 months,” Dr. Rao said in an interview. “However, the sample size for these comparisons was too small to reach definite conclusions, and we have called for future studies to evaluate ASQ separately for different age groups.”
Early identification of developmental delay in children is essential to enable timely intervention,” Dr. Rao and associates wrote in JAMA Pediatrics.
While formal assessments such as the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development are the gold standard, they are time-consuming and expensive, need the physical attendance of both the child and caregivers, and “thus may not be feasible in resource-limited settings or in pandemic conditions.”
According to Barbara J. Howard, MD, commenting on a recent update to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s developmental milestones guide, Learn the Signs. Act Early, fewer than 25% of children with delays or disabilities receive intervention before age 3 and most with emotional, behavioral, and developmental condition, other than autism spectrum disorder receive no intervention before age 5.
The ASQ
As an accessible alternative, the ASQ consists of questions on communication (language), gross-motor, fine-motor, problem-solving (cognitive), and personal-adaptive skills. The survey requires only 10-15 minutes, is relatively inexpensive, and also establishes a sense of parental involvement, the authors noted.
“Based on the generally accepted interpretation of LR [likelihood ratio] values, if a child passes ASQ-2SD, there is a moderate probability that the child does not have severe delay,” the investigators concluded.
The analysis
The final meta-analysis reviewed 36 eligible ASQ studies published from 1997 to 2022. Looking at the four indicators of pooled sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative likelihood ratios, the following respective predictive values emerged for scores of more than 2 SDs below the mean across several domains: sensitivity of 0.77 (95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.86), specificity of 0.81 (95% CI 0.75-0.86), positive likelihood ratio of 4.10 (95% CI 3.17-5.30), and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.28 (95% CI, 0.18-0.44)
They cautioned, however, that the certainty of evidence from the reviewed studies was low or very low and given the small sample sizes for comparing domains, clinicians should be circumspect in interpreting the results.
An initial step
Commenting on the paper but not involved in it, David G. Fagan, MD, vice chairman of pediatric ambulatory administration in the department of pediatrics at Cohen Children’s Medical Center, New York, agreed that screening tools such as the ASQ have a place in clinical practice. “However, the purpose of a screening tool is not to make the diagnosis but to identify children at risk for developmental delays,” he said in an interview. “The meta-analysis highlights the fact that no screening is 100% accurate and that results need to be interpreted in context.
“Before screening tools were widely used, pediatricians trusted their gut,” Dr. Fagan continued. “‘I know it when I see it,’ which obviously resulted in tremendous variability based on experience.”
He added that, even if a child passes this validated questionnaire, any concern on the part of a parent or pediatrician about developmental delay should be addressed with further assessment.
The future
According to Dr. Rao, clinicians should continue to screen for developmental delays in young children using the ASQ. “Given the long wait times to see a developmental pediatrician or a clinical psychologist, a screening tool such as ASQ will enable appropriate triaging.”
Going forward, however, studies should evaluate this questionnaire separately for different age groups such as less than 12 months, 12-23 months, and at least 24 months. They should also be prospective in design and entail a low risk of bias, as well as report raw numbers for true and false positives and negatives. “Even if they use their own cutoff ASQ scores, they should also give results for the conventional cutoff scores to enable comparison with other studies,” the authors wrote.
The authors disclosed no specific funding for this study and no competing interests. Dr. Fagan disclosed no competing interests with regard to his comments.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Polycyclic Scaly Eruption
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
A 9-year-old boy presented to the dermatology clinic with a scaly eruption distributed throughout the body that had been present since birth. He had been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis by multiple dermatologists prior to the current presentation and had been treated with various topical steroids with minimal improvement. He had no family history of similar eruptions and no personal history of asthma or allergies. Physical examination revealed erythematous, serpiginous, polycyclic plaques with peripheral, double-edged scaling. Decreased hair density of the lateral eyebrows also was observed.
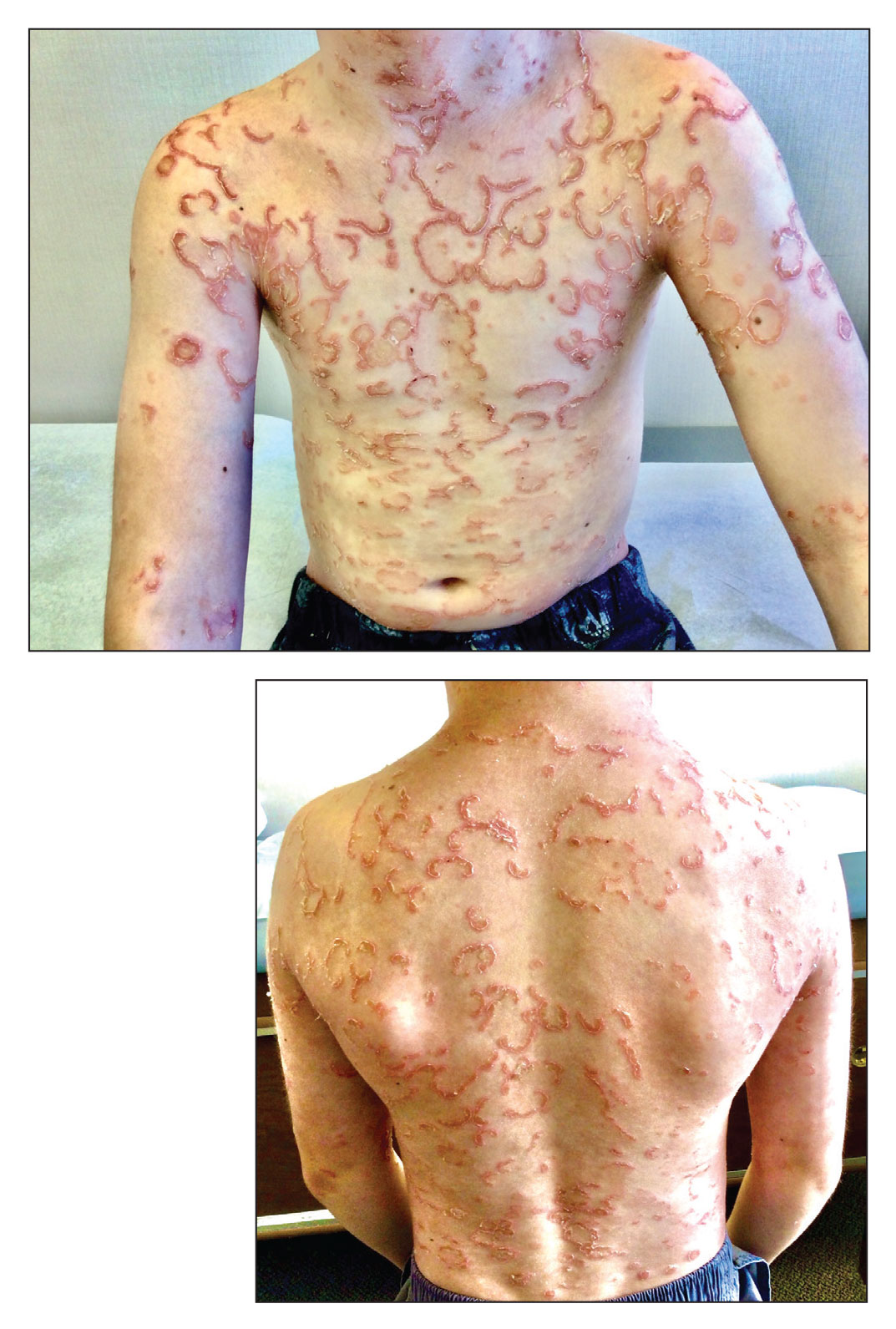
Ketamine promising for rare condition linked to autism
Also known as Helsmoortel–Van Der Aa syndrome, ADNP syndrome is caused by mutations in the ADNP gene. Studies in animal models suggest that low-dose ketamine increases expression of ADNP and is neuroprotective.
Intrigued by the preclinical evidence, Alexander Kolevzon, MD, clinical director of the Seaver Autism Center at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues treated 10 children with ADNP syndrome with a single low dose of ketamine (0.5mg/kg) infused intravenously over 40 minutes. The children ranged in ages 6-12 years.
Using parent-report instruments to assess treatment effects, ketamine was associated with “nominally significant” improvement in a variety of domains, including social behavior, attention-deficit and hyperactivity, restricted and repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities.
Parent reports of improvement in these domains aligned with clinician-rated assessments based on the Clinical Global Impressions–Improvement scale.
The results also highlight the potential utility of electrophysiological measurement of auditory steady-state response and eye-tracking to track change with ketamine treatment, the researchers say.
The study was published online in Human Genetics and Genomic (HGG) Advances.
Hypothesis-generating
Ketamine was generally well tolerated. There were no clinically significant abnormalities in laboratory or cardiac monitoring, and there were no serious adverse events (AEs).
Treatment emergent AEs were all mild to moderate and no child required any interventions.
The most common AEs were elation/silliness in five children (50%), all of whom had a history of similar symptoms. Drowsiness and fatigue occurred in four children (40%) and two of them had a history of drowsiness. Aggression was likewise relatively common, reported in four children (40%), all of whom had aggression at baseline.
Decreased appetite emerged as a new AE in three children (30%), increased anxiety occurred in three children (30%), and irritability, nausea/vomiting, and restlessness each occurred in two children (20%).
The researchers caution that the findings are intended to be “hypothesis generating.”
“We are encouraged by these findings, which provide preliminary support for ketamine to help reduce negative effects of this devastating syndrome,” Dr. Kolevzon said in a news release from Mount Sinai.
Ketamine might help ease symptoms of ADNP syndrome “by increasing expression of the ADNP gene or by promoting synaptic plasticity through glutamatergic pathways,” Dr. Kolevzon told this news organization.
The next step, he said, is to get “a larger, placebo-controlled study approved for funding using repeated dosing over a longer duration of time. We are working with the FDA to get the design approved for an investigational new drug application.”
Support for the study was provided by the ADNP Kids Foundation and the Foundation for Mood Disorders. Support for mediKanren was provided by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and National Institutes of Health through the Biomedical Data Translator Program. Dr. Kolevzon is on the scientific advisory board of Ovid Therapeutics, Ritrova Therapeutics, and Jaguar Therapeutics and consults to Acadia, Alkermes, GW Pharmaceuticals, Neuren Pharmaceuticals, Clinilabs Drug Development Corporation, and Scioto Biosciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Also known as Helsmoortel–Van Der Aa syndrome, ADNP syndrome is caused by mutations in the ADNP gene. Studies in animal models suggest that low-dose ketamine increases expression of ADNP and is neuroprotective.
Intrigued by the preclinical evidence, Alexander Kolevzon, MD, clinical director of the Seaver Autism Center at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues treated 10 children with ADNP syndrome with a single low dose of ketamine (0.5mg/kg) infused intravenously over 40 minutes. The children ranged in ages 6-12 years.
Using parent-report instruments to assess treatment effects, ketamine was associated with “nominally significant” improvement in a variety of domains, including social behavior, attention-deficit and hyperactivity, restricted and repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities.
Parent reports of improvement in these domains aligned with clinician-rated assessments based on the Clinical Global Impressions–Improvement scale.
The results also highlight the potential utility of electrophysiological measurement of auditory steady-state response and eye-tracking to track change with ketamine treatment, the researchers say.
The study was published online in Human Genetics and Genomic (HGG) Advances.
Hypothesis-generating
Ketamine was generally well tolerated. There were no clinically significant abnormalities in laboratory or cardiac monitoring, and there were no serious adverse events (AEs).
Treatment emergent AEs were all mild to moderate and no child required any interventions.
The most common AEs were elation/silliness in five children (50%), all of whom had a history of similar symptoms. Drowsiness and fatigue occurred in four children (40%) and two of them had a history of drowsiness. Aggression was likewise relatively common, reported in four children (40%), all of whom had aggression at baseline.
Decreased appetite emerged as a new AE in three children (30%), increased anxiety occurred in three children (30%), and irritability, nausea/vomiting, and restlessness each occurred in two children (20%).
The researchers caution that the findings are intended to be “hypothesis generating.”
“We are encouraged by these findings, which provide preliminary support for ketamine to help reduce negative effects of this devastating syndrome,” Dr. Kolevzon said in a news release from Mount Sinai.
Ketamine might help ease symptoms of ADNP syndrome “by increasing expression of the ADNP gene or by promoting synaptic plasticity through glutamatergic pathways,” Dr. Kolevzon told this news organization.
The next step, he said, is to get “a larger, placebo-controlled study approved for funding using repeated dosing over a longer duration of time. We are working with the FDA to get the design approved for an investigational new drug application.”
Support for the study was provided by the ADNP Kids Foundation and the Foundation for Mood Disorders. Support for mediKanren was provided by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and National Institutes of Health through the Biomedical Data Translator Program. Dr. Kolevzon is on the scientific advisory board of Ovid Therapeutics, Ritrova Therapeutics, and Jaguar Therapeutics and consults to Acadia, Alkermes, GW Pharmaceuticals, Neuren Pharmaceuticals, Clinilabs Drug Development Corporation, and Scioto Biosciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Also known as Helsmoortel–Van Der Aa syndrome, ADNP syndrome is caused by mutations in the ADNP gene. Studies in animal models suggest that low-dose ketamine increases expression of ADNP and is neuroprotective.
Intrigued by the preclinical evidence, Alexander Kolevzon, MD, clinical director of the Seaver Autism Center at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues treated 10 children with ADNP syndrome with a single low dose of ketamine (0.5mg/kg) infused intravenously over 40 minutes. The children ranged in ages 6-12 years.
Using parent-report instruments to assess treatment effects, ketamine was associated with “nominally significant” improvement in a variety of domains, including social behavior, attention-deficit and hyperactivity, restricted and repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities.
Parent reports of improvement in these domains aligned with clinician-rated assessments based on the Clinical Global Impressions–Improvement scale.
The results also highlight the potential utility of electrophysiological measurement of auditory steady-state response and eye-tracking to track change with ketamine treatment, the researchers say.
The study was published online in Human Genetics and Genomic (HGG) Advances.
Hypothesis-generating
Ketamine was generally well tolerated. There were no clinically significant abnormalities in laboratory or cardiac monitoring, and there were no serious adverse events (AEs).
Treatment emergent AEs were all mild to moderate and no child required any interventions.
The most common AEs were elation/silliness in five children (50%), all of whom had a history of similar symptoms. Drowsiness and fatigue occurred in four children (40%) and two of them had a history of drowsiness. Aggression was likewise relatively common, reported in four children (40%), all of whom had aggression at baseline.
Decreased appetite emerged as a new AE in three children (30%), increased anxiety occurred in three children (30%), and irritability, nausea/vomiting, and restlessness each occurred in two children (20%).
The researchers caution that the findings are intended to be “hypothesis generating.”
“We are encouraged by these findings, which provide preliminary support for ketamine to help reduce negative effects of this devastating syndrome,” Dr. Kolevzon said in a news release from Mount Sinai.
Ketamine might help ease symptoms of ADNP syndrome “by increasing expression of the ADNP gene or by promoting synaptic plasticity through glutamatergic pathways,” Dr. Kolevzon told this news organization.
The next step, he said, is to get “a larger, placebo-controlled study approved for funding using repeated dosing over a longer duration of time. We are working with the FDA to get the design approved for an investigational new drug application.”
Support for the study was provided by the ADNP Kids Foundation and the Foundation for Mood Disorders. Support for mediKanren was provided by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and National Institutes of Health through the Biomedical Data Translator Program. Dr. Kolevzon is on the scientific advisory board of Ovid Therapeutics, Ritrova Therapeutics, and Jaguar Therapeutics and consults to Acadia, Alkermes, GW Pharmaceuticals, Neuren Pharmaceuticals, Clinilabs Drug Development Corporation, and Scioto Biosciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From Human Genetics and Genomic Advances