User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
Johnson & Johnson requests FDA approval for vaccine booster doses
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The company said it filed a request for people ages 18 and older who have received the one-shot vaccine. Johnson & Johnson submitted data for several different booster intervals -- ranging from 2 months to 6 months -- but didn’t formally recommend one to the FDA, The Associated Press reported.
“We’re describing the data to them,” Mathai Mammen, MD, head of global research and development for Janssen, the company’s vaccine division, told CNN.
“The process is not that we asked for a very specific interval -- we’re providing them data and we’re going to be presenting to the committee,” he said. “They’ll take all that into consideration when they ultimately decide on an appropriate interval.”
The FDA’s independent vaccine advisory committee meets next week to review data on booster shots from both Johnson & Johnson and Moderna. It’s the first step in the review process, which then requires approval from leaders at the FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. If both agencies authorize the extra shots, Americans could receive boosters from Johnson & Johnson and Moderna later this month, the AP reported.
Johnson & Johnson previously released data that showed the vaccine remains highly effective against COVID-19 at least 5 months after vaccination, with 81% efficacy against hospitalizations in the United States.
Two weeks ago, the company reported that a booster dose at 2 months or 6 months further lifted immunity, with a booster at 2 months providing 94% protection against moderate and severe COVID-19. The company said the 6-month booster raised antibodies by 12 times but didn’t release additional data at that time.
In September, the FDA authorized booster shots of the Pfizer vaccine for ages 65 and older, those who live in long-term care facilities, and those with higher risks for contracting COVID-19. The Biden administration is supporting a booster campaign to address potential waning vaccine immunity and remaining surges of the more contagious Delta variant, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Ruxolitinib cream meets primary endpoints in phase 3 vitiligo trial
presented together at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
On the primary endpoint of F-VASI 75 (75% improvement in the Facial and Vitiligo Scoring Index), rates were nearly four times higher at 24 weeks in one trial (29.9% vs. 7.5%; P < .0001) and more than twice as great in the other (29.9% vs. 12.9%; P < .01).
“The larger phase 3 trials confirm the previous phase 2 findings,” reported David Rosmarin, MD, vice chairman for research and education, department of dermatology, Tufts Medical Center, Boston. These findings not only include substantial clinical efficacy but good tolerability with “no serious treatment-related adverse events,” he noted.
600 patients randomized
In one of the trials, called TRuE-V1, 330 patients with vitiligo were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to 1.5% ruxolitinib or vehicle applied twice daily. In the other trial, called TRuE-V2, 344 patients were randomly assigned. The participating centers were in Europe and North America.
Patients aged 12 years or older with nonsegmental vitiligo and depigmentation covering no more than 10% of the total body surface area were eligible. The mean baseline F-VASI values were 1.0. The mean total VASI (T-FASI) values were 6.5. On those enrolled, half were female, 11% were adolescents, and 73% had Fitzpatrick skin phototypes III-VI.
Ruxolitinib cream provided near-complete vitiligo clearance (F-VASI 90) on the face at 24 weeks in only about 15% of patients, but this was several times higher than the 2% achieved on vehicle in the TRuE-V1 (P < .01) and the TRuE-V2 trials (P < .05), respectively.
F-VASI 50 response rates greater than 50%
For F-VASI 50, the response rate with ruxolitinib in both studies was approximately 51%. Relative to the 17.2% response on vehicle in TRuE-v1 and 23.4% in TRuE-V2 (both P < .0001 vs. active therapy), the advantage of the topical JAK inhibitor was considered to be a clinically meaningful, not just significant from a statistical standpoint.
In fact, improvement on the 5-point Vitiligo Noticeability Scale “also supported a clinically meaningful benefit,” Dr. Rosmarin reported. When those achieving a score of 4 (much less noticeable) or 5 (no longer noticeable), the response rates at 24 weeks were 24.5% and 21.6% in the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 trials, respectively. Again, these response rates were several times greater than the 3.3% (P < .001) and 6.6% (P < .01) observed in the vehicle arms of TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 (P < .01), respectively.
Treatment-related adverse events were infrequent. The most common were acne at the application site, which occurred in about 5% of patients receiving ruxolitinib (vs. 2% or fewer of those receiving vehicle) and pruritus, which also occurred in about 5% of patients. However, the rates of pruritus among those on placebo reached 4% in TRuE-V1 and 2% in TRuE-V2 trials.
In vitiligo, where there has been recent progress in understanding the pathophysiology, loss of melanocytes in immune dysregulation has been linked to activation of the JAK signaling pathway, according to Dr. Rosmarin. In the 52-week phase 2 trial with 205 patients, ruxolitinib was associated with a sustained response and no serious treatment-related adverse events.
52-week data might show more benefit
Patients are continuing to be followed in the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V-2 trials. Based on the phase 2 data and on the progressive improvement still being observed at the end of 24 weeks in the phase 3 trials, Dr. Rosmarin expects 52-week results be valuable in understanding the clinical role of ruxolitinib.
“We will be looking for further improvement in response as we follow these patients out to 1 year,” he said.
This further follow-up is important, agreed Iltefat Hamzavi, MD, senior staff physician, department of dermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit.
Despite the promise of perhaps other JAK inhibitors, “we still need to understand how long it will take for the drug to offer optimal results. We already know that is more than 24 weeks,” said Dr. Hamzavi, who has been involved in the clinical trials with this drug but was not involved with the TRuE-V1 or -V2 trials.
He also said more follow-up is needed to understand the duration of effect. He is, however, optimistic about the clinical role of this mechanism for treatment of vitiligo.
“I do think that JAK inhibitors show a lot of promise [in vitiligo] for certain locations of the body,” he said.
Given the limited treatment options for effective and prolonged improvement in vitiligo, both Dr. Hamzavi and Dr. Rosmarin indicated an effective topical cream is likely to be considered by physicians and patients to be a substantial advance.
On Sept. 21, ruxolitinib (Opzelura) 1.5% cream was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adults ages 12 years and older – the first FDA approval of this product.
Dr. Rosmarin reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte, which provided funding for the TRuE-V1 and -V2 trials. Dr. Hamzavi reported financial relationships with more than 15 companies with pharmaceutical or cosmetic products, including Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
presented together at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
On the primary endpoint of F-VASI 75 (75% improvement in the Facial and Vitiligo Scoring Index), rates were nearly four times higher at 24 weeks in one trial (29.9% vs. 7.5%; P < .0001) and more than twice as great in the other (29.9% vs. 12.9%; P < .01).
“The larger phase 3 trials confirm the previous phase 2 findings,” reported David Rosmarin, MD, vice chairman for research and education, department of dermatology, Tufts Medical Center, Boston. These findings not only include substantial clinical efficacy but good tolerability with “no serious treatment-related adverse events,” he noted.
600 patients randomized
In one of the trials, called TRuE-V1, 330 patients with vitiligo were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to 1.5% ruxolitinib or vehicle applied twice daily. In the other trial, called TRuE-V2, 344 patients were randomly assigned. The participating centers were in Europe and North America.
Patients aged 12 years or older with nonsegmental vitiligo and depigmentation covering no more than 10% of the total body surface area were eligible. The mean baseline F-VASI values were 1.0. The mean total VASI (T-FASI) values were 6.5. On those enrolled, half were female, 11% were adolescents, and 73% had Fitzpatrick skin phototypes III-VI.
Ruxolitinib cream provided near-complete vitiligo clearance (F-VASI 90) on the face at 24 weeks in only about 15% of patients, but this was several times higher than the 2% achieved on vehicle in the TRuE-V1 (P < .01) and the TRuE-V2 trials (P < .05), respectively.
F-VASI 50 response rates greater than 50%
For F-VASI 50, the response rate with ruxolitinib in both studies was approximately 51%. Relative to the 17.2% response on vehicle in TRuE-v1 and 23.4% in TRuE-V2 (both P < .0001 vs. active therapy), the advantage of the topical JAK inhibitor was considered to be a clinically meaningful, not just significant from a statistical standpoint.
In fact, improvement on the 5-point Vitiligo Noticeability Scale “also supported a clinically meaningful benefit,” Dr. Rosmarin reported. When those achieving a score of 4 (much less noticeable) or 5 (no longer noticeable), the response rates at 24 weeks were 24.5% and 21.6% in the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 trials, respectively. Again, these response rates were several times greater than the 3.3% (P < .001) and 6.6% (P < .01) observed in the vehicle arms of TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 (P < .01), respectively.
Treatment-related adverse events were infrequent. The most common were acne at the application site, which occurred in about 5% of patients receiving ruxolitinib (vs. 2% or fewer of those receiving vehicle) and pruritus, which also occurred in about 5% of patients. However, the rates of pruritus among those on placebo reached 4% in TRuE-V1 and 2% in TRuE-V2 trials.
In vitiligo, where there has been recent progress in understanding the pathophysiology, loss of melanocytes in immune dysregulation has been linked to activation of the JAK signaling pathway, according to Dr. Rosmarin. In the 52-week phase 2 trial with 205 patients, ruxolitinib was associated with a sustained response and no serious treatment-related adverse events.
52-week data might show more benefit
Patients are continuing to be followed in the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V-2 trials. Based on the phase 2 data and on the progressive improvement still being observed at the end of 24 weeks in the phase 3 trials, Dr. Rosmarin expects 52-week results be valuable in understanding the clinical role of ruxolitinib.
“We will be looking for further improvement in response as we follow these patients out to 1 year,” he said.
This further follow-up is important, agreed Iltefat Hamzavi, MD, senior staff physician, department of dermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit.
Despite the promise of perhaps other JAK inhibitors, “we still need to understand how long it will take for the drug to offer optimal results. We already know that is more than 24 weeks,” said Dr. Hamzavi, who has been involved in the clinical trials with this drug but was not involved with the TRuE-V1 or -V2 trials.
He also said more follow-up is needed to understand the duration of effect. He is, however, optimistic about the clinical role of this mechanism for treatment of vitiligo.
“I do think that JAK inhibitors show a lot of promise [in vitiligo] for certain locations of the body,” he said.
Given the limited treatment options for effective and prolonged improvement in vitiligo, both Dr. Hamzavi and Dr. Rosmarin indicated an effective topical cream is likely to be considered by physicians and patients to be a substantial advance.
On Sept. 21, ruxolitinib (Opzelura) 1.5% cream was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adults ages 12 years and older – the first FDA approval of this product.
Dr. Rosmarin reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte, which provided funding for the TRuE-V1 and -V2 trials. Dr. Hamzavi reported financial relationships with more than 15 companies with pharmaceutical or cosmetic products, including Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
presented together at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
On the primary endpoint of F-VASI 75 (75% improvement in the Facial and Vitiligo Scoring Index), rates were nearly four times higher at 24 weeks in one trial (29.9% vs. 7.5%; P < .0001) and more than twice as great in the other (29.9% vs. 12.9%; P < .01).
“The larger phase 3 trials confirm the previous phase 2 findings,” reported David Rosmarin, MD, vice chairman for research and education, department of dermatology, Tufts Medical Center, Boston. These findings not only include substantial clinical efficacy but good tolerability with “no serious treatment-related adverse events,” he noted.
600 patients randomized
In one of the trials, called TRuE-V1, 330 patients with vitiligo were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to 1.5% ruxolitinib or vehicle applied twice daily. In the other trial, called TRuE-V2, 344 patients were randomly assigned. The participating centers were in Europe and North America.
Patients aged 12 years or older with nonsegmental vitiligo and depigmentation covering no more than 10% of the total body surface area were eligible. The mean baseline F-VASI values were 1.0. The mean total VASI (T-FASI) values were 6.5. On those enrolled, half were female, 11% were adolescents, and 73% had Fitzpatrick skin phototypes III-VI.
Ruxolitinib cream provided near-complete vitiligo clearance (F-VASI 90) on the face at 24 weeks in only about 15% of patients, but this was several times higher than the 2% achieved on vehicle in the TRuE-V1 (P < .01) and the TRuE-V2 trials (P < .05), respectively.
F-VASI 50 response rates greater than 50%
For F-VASI 50, the response rate with ruxolitinib in both studies was approximately 51%. Relative to the 17.2% response on vehicle in TRuE-v1 and 23.4% in TRuE-V2 (both P < .0001 vs. active therapy), the advantage of the topical JAK inhibitor was considered to be a clinically meaningful, not just significant from a statistical standpoint.
In fact, improvement on the 5-point Vitiligo Noticeability Scale “also supported a clinically meaningful benefit,” Dr. Rosmarin reported. When those achieving a score of 4 (much less noticeable) or 5 (no longer noticeable), the response rates at 24 weeks were 24.5% and 21.6% in the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 trials, respectively. Again, these response rates were several times greater than the 3.3% (P < .001) and 6.6% (P < .01) observed in the vehicle arms of TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 (P < .01), respectively.
Treatment-related adverse events were infrequent. The most common were acne at the application site, which occurred in about 5% of patients receiving ruxolitinib (vs. 2% or fewer of those receiving vehicle) and pruritus, which also occurred in about 5% of patients. However, the rates of pruritus among those on placebo reached 4% in TRuE-V1 and 2% in TRuE-V2 trials.
In vitiligo, where there has been recent progress in understanding the pathophysiology, loss of melanocytes in immune dysregulation has been linked to activation of the JAK signaling pathway, according to Dr. Rosmarin. In the 52-week phase 2 trial with 205 patients, ruxolitinib was associated with a sustained response and no serious treatment-related adverse events.
52-week data might show more benefit
Patients are continuing to be followed in the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V-2 trials. Based on the phase 2 data and on the progressive improvement still being observed at the end of 24 weeks in the phase 3 trials, Dr. Rosmarin expects 52-week results be valuable in understanding the clinical role of ruxolitinib.
“We will be looking for further improvement in response as we follow these patients out to 1 year,” he said.
This further follow-up is important, agreed Iltefat Hamzavi, MD, senior staff physician, department of dermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit.
Despite the promise of perhaps other JAK inhibitors, “we still need to understand how long it will take for the drug to offer optimal results. We already know that is more than 24 weeks,” said Dr. Hamzavi, who has been involved in the clinical trials with this drug but was not involved with the TRuE-V1 or -V2 trials.
He also said more follow-up is needed to understand the duration of effect. He is, however, optimistic about the clinical role of this mechanism for treatment of vitiligo.
“I do think that JAK inhibitors show a lot of promise [in vitiligo] for certain locations of the body,” he said.
Given the limited treatment options for effective and prolonged improvement in vitiligo, both Dr. Hamzavi and Dr. Rosmarin indicated an effective topical cream is likely to be considered by physicians and patients to be a substantial advance.
On Sept. 21, ruxolitinib (Opzelura) 1.5% cream was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adults ages 12 years and older – the first FDA approval of this product.
Dr. Rosmarin reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Incyte, which provided funding for the TRuE-V1 and -V2 trials. Dr. Hamzavi reported financial relationships with more than 15 companies with pharmaceutical or cosmetic products, including Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
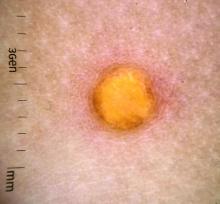
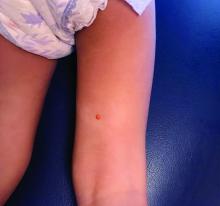
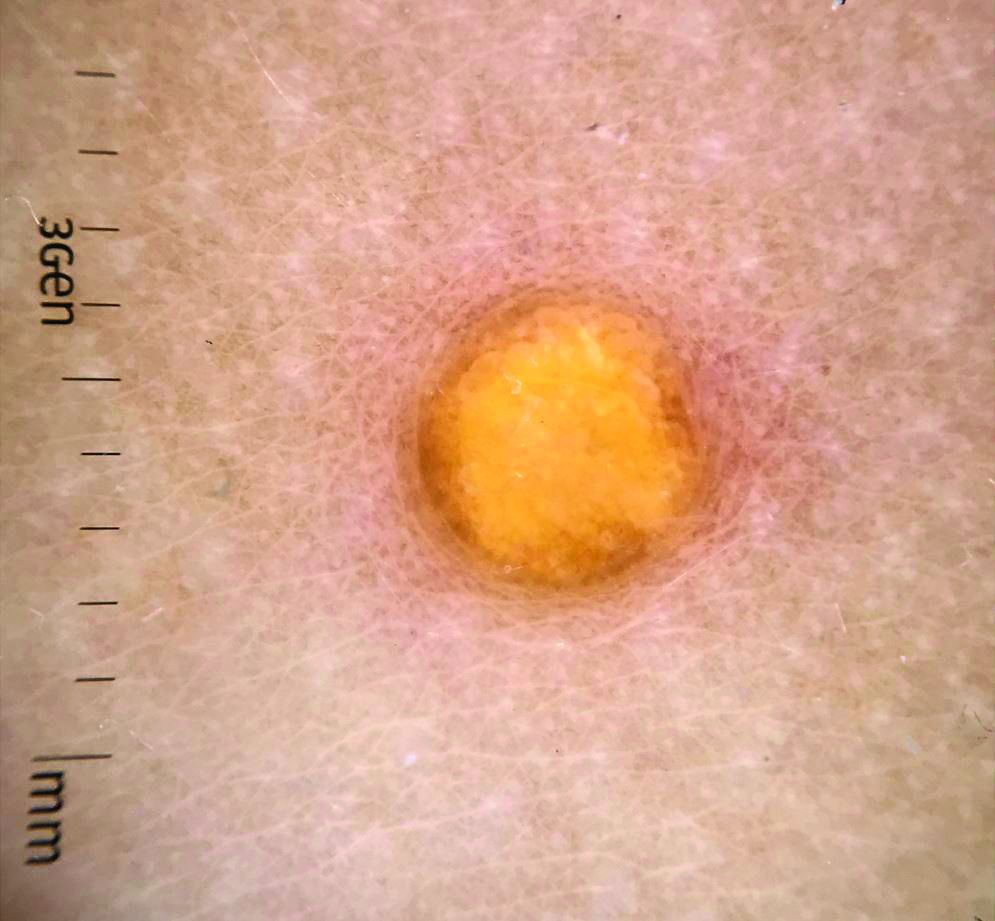
COVID-19: Two more cases of mucosal skin ulcers reported in male teens
Irish A similar case in an adolescent, also with ulcers affecting the mouth and penis, was reported earlier in 2021 in the United States.
“Our cases show that a swab for COVID-19 can be added to the list of investigations for mucosal and cutaneous rashes in children and probably adults,” said dermatologist Stephanie Bowe, MD, of South Infirmary-Victoria University Hospital in Cork, Ireland, in an interview. “Our patients seemed to improve with IV steroids, but there is not enough data to recommend them to all patients or for use in the different cutaneous presentations associated with COVID-19.”
The new case reports were presented at the 2021 meeting of the World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology and published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Researchers have noted that skin disorders linked to COVID-19 infection are different than those in adults. In children, the conditions include morbilliform rash, pernio-like acral lesions, urticaria, macular erythema, vesicular eruption, papulosquamous eruption, and retiform purpura. “The pathogenesis of each is not fully understood but likely related to the inflammatory response to COVID-19 and the various pathways within the body, which become activated,” Dr. Bowe said.
The first patient, a 17-year-old boy, presented at clinic 6 days after he’d been confirmed to be infected with COVID-19 and 8 days after developing fever and cough. “He had a 2-day history of conjunctivitis and ulceration of his oral mucosa, erythematous circumferential erosions of the glans penis with no other cutaneous findings,” the authors write in the report.
The boy “was distressed and embarrassed about his genital ulceration and also found eating very painful due to his oral ulceration,” Dr. Bowe said.
The second patient, a 14-year-old boy, was hospitalized 7 days after a positive COVID-19 test and 9 days after developing cough and fever. “He had a 5-day history of ulceration of the oral mucosa with mild conjunctivitis,” the authors wrote. “Ulceration of the glans penis developed on day 2 of admission.”
The 14-year-old was sicker than the 17-year-old boy, Dr. Bowe said. “He was unable to tolerate an oral diet for several days and had exquisite pain and vomiting with his coughing fits.”
This patient had a history of recurrent herpes labialis, but it’s unclear whether herpes simplex virus (HSV) played a role in the COVID-19–related case. “There is a possibility that the patient was more susceptible to viral cutaneous reactions during COVID-19 infection, but we didn’t have any definite history of HSV infection at the time of mucositis,” Dr. Bowe said. “We also didn’t have any swabs positive for HSV even though several were done at the time.”
Both patients received IV steroids – hydrocortisone at 100 mg 3 times daily for 3 days. This treatment was used “because of deterioration in symptoms and COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Bowe said. “IV steroids were used for respiratory symptoms of COVID-19, so we felt these cutaneous symptoms may have also been caused by an inflammatory response and might benefit from steroids. There was very little literature about this specific situation, though.”
She added that intravenous steroids wouldn’t be appropriate for most pediatric patients, and noted that “their use is controversial in the literature for erythema multiforme and RIME.”
In addition, the patients received betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment once daily, hydrocortisone 2.5 mg buccal tablets 4 times daily, analgesia with acetaminophen and ibuprofen, and intravenous hydration. The first patient also received prednisolone 1% eye drops, while the second patient was given lidocaine hydrochloride mouthwash and total parenteral nutrition for 5 days.
The patients were discharged after 4 and 14 days, respectively.
Dermatologists in Massachusetts reported a similar case earlier in 2021 in a 17-year-old boy who was positive for COVID-19 and presented with “shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities.”
The patient received betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment for the lips and penis, intraoral dexamethasone solution, viscous lidocaine, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen. He also received oral prednisone at approximately 1 mg/kg daily for 4 consecutive days after worsening oral pain. A recurrence of oral pain 3 months later was resolved with a higher and longer treatment with oral prednisone.
Dermatologists have also reported cases of erythema multiforme lesions of the mucosa in adults with COVID-19. One case was reported in Iran, and the other in France.
The authors report no study funding and disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Irish A similar case in an adolescent, also with ulcers affecting the mouth and penis, was reported earlier in 2021 in the United States.
“Our cases show that a swab for COVID-19 can be added to the list of investigations for mucosal and cutaneous rashes in children and probably adults,” said dermatologist Stephanie Bowe, MD, of South Infirmary-Victoria University Hospital in Cork, Ireland, in an interview. “Our patients seemed to improve with IV steroids, but there is not enough data to recommend them to all patients or for use in the different cutaneous presentations associated with COVID-19.”
The new case reports were presented at the 2021 meeting of the World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology and published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Researchers have noted that skin disorders linked to COVID-19 infection are different than those in adults. In children, the conditions include morbilliform rash, pernio-like acral lesions, urticaria, macular erythema, vesicular eruption, papulosquamous eruption, and retiform purpura. “The pathogenesis of each is not fully understood but likely related to the inflammatory response to COVID-19 and the various pathways within the body, which become activated,” Dr. Bowe said.
The first patient, a 17-year-old boy, presented at clinic 6 days after he’d been confirmed to be infected with COVID-19 and 8 days after developing fever and cough. “He had a 2-day history of conjunctivitis and ulceration of his oral mucosa, erythematous circumferential erosions of the glans penis with no other cutaneous findings,” the authors write in the report.
The boy “was distressed and embarrassed about his genital ulceration and also found eating very painful due to his oral ulceration,” Dr. Bowe said.
The second patient, a 14-year-old boy, was hospitalized 7 days after a positive COVID-19 test and 9 days after developing cough and fever. “He had a 5-day history of ulceration of the oral mucosa with mild conjunctivitis,” the authors wrote. “Ulceration of the glans penis developed on day 2 of admission.”
The 14-year-old was sicker than the 17-year-old boy, Dr. Bowe said. “He was unable to tolerate an oral diet for several days and had exquisite pain and vomiting with his coughing fits.”
This patient had a history of recurrent herpes labialis, but it’s unclear whether herpes simplex virus (HSV) played a role in the COVID-19–related case. “There is a possibility that the patient was more susceptible to viral cutaneous reactions during COVID-19 infection, but we didn’t have any definite history of HSV infection at the time of mucositis,” Dr. Bowe said. “We also didn’t have any swabs positive for HSV even though several were done at the time.”
Both patients received IV steroids – hydrocortisone at 100 mg 3 times daily for 3 days. This treatment was used “because of deterioration in symptoms and COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Bowe said. “IV steroids were used for respiratory symptoms of COVID-19, so we felt these cutaneous symptoms may have also been caused by an inflammatory response and might benefit from steroids. There was very little literature about this specific situation, though.”
She added that intravenous steroids wouldn’t be appropriate for most pediatric patients, and noted that “their use is controversial in the literature for erythema multiforme and RIME.”
In addition, the patients received betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment once daily, hydrocortisone 2.5 mg buccal tablets 4 times daily, analgesia with acetaminophen and ibuprofen, and intravenous hydration. The first patient also received prednisolone 1% eye drops, while the second patient was given lidocaine hydrochloride mouthwash and total parenteral nutrition for 5 days.
The patients were discharged after 4 and 14 days, respectively.
Dermatologists in Massachusetts reported a similar case earlier in 2021 in a 17-year-old boy who was positive for COVID-19 and presented with “shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities.”
The patient received betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment for the lips and penis, intraoral dexamethasone solution, viscous lidocaine, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen. He also received oral prednisone at approximately 1 mg/kg daily for 4 consecutive days after worsening oral pain. A recurrence of oral pain 3 months later was resolved with a higher and longer treatment with oral prednisone.
Dermatologists have also reported cases of erythema multiforme lesions of the mucosa in adults with COVID-19. One case was reported in Iran, and the other in France.
The authors report no study funding and disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Irish A similar case in an adolescent, also with ulcers affecting the mouth and penis, was reported earlier in 2021 in the United States.
“Our cases show that a swab for COVID-19 can be added to the list of investigations for mucosal and cutaneous rashes in children and probably adults,” said dermatologist Stephanie Bowe, MD, of South Infirmary-Victoria University Hospital in Cork, Ireland, in an interview. “Our patients seemed to improve with IV steroids, but there is not enough data to recommend them to all patients or for use in the different cutaneous presentations associated with COVID-19.”
The new case reports were presented at the 2021 meeting of the World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology and published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Researchers have noted that skin disorders linked to COVID-19 infection are different than those in adults. In children, the conditions include morbilliform rash, pernio-like acral lesions, urticaria, macular erythema, vesicular eruption, papulosquamous eruption, and retiform purpura. “The pathogenesis of each is not fully understood but likely related to the inflammatory response to COVID-19 and the various pathways within the body, which become activated,” Dr. Bowe said.
The first patient, a 17-year-old boy, presented at clinic 6 days after he’d been confirmed to be infected with COVID-19 and 8 days after developing fever and cough. “He had a 2-day history of conjunctivitis and ulceration of his oral mucosa, erythematous circumferential erosions of the glans penis with no other cutaneous findings,” the authors write in the report.
The boy “was distressed and embarrassed about his genital ulceration and also found eating very painful due to his oral ulceration,” Dr. Bowe said.
The second patient, a 14-year-old boy, was hospitalized 7 days after a positive COVID-19 test and 9 days after developing cough and fever. “He had a 5-day history of ulceration of the oral mucosa with mild conjunctivitis,” the authors wrote. “Ulceration of the glans penis developed on day 2 of admission.”
The 14-year-old was sicker than the 17-year-old boy, Dr. Bowe said. “He was unable to tolerate an oral diet for several days and had exquisite pain and vomiting with his coughing fits.”
This patient had a history of recurrent herpes labialis, but it’s unclear whether herpes simplex virus (HSV) played a role in the COVID-19–related case. “There is a possibility that the patient was more susceptible to viral cutaneous reactions during COVID-19 infection, but we didn’t have any definite history of HSV infection at the time of mucositis,” Dr. Bowe said. “We also didn’t have any swabs positive for HSV even though several were done at the time.”
Both patients received IV steroids – hydrocortisone at 100 mg 3 times daily for 3 days. This treatment was used “because of deterioration in symptoms and COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Bowe said. “IV steroids were used for respiratory symptoms of COVID-19, so we felt these cutaneous symptoms may have also been caused by an inflammatory response and might benefit from steroids. There was very little literature about this specific situation, though.”
She added that intravenous steroids wouldn’t be appropriate for most pediatric patients, and noted that “their use is controversial in the literature for erythema multiforme and RIME.”
In addition, the patients received betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment once daily, hydrocortisone 2.5 mg buccal tablets 4 times daily, analgesia with acetaminophen and ibuprofen, and intravenous hydration. The first patient also received prednisolone 1% eye drops, while the second patient was given lidocaine hydrochloride mouthwash and total parenteral nutrition for 5 days.
The patients were discharged after 4 and 14 days, respectively.
Dermatologists in Massachusetts reported a similar case earlier in 2021 in a 17-year-old boy who was positive for COVID-19 and presented with “shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities.”
The patient received betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment for the lips and penis, intraoral dexamethasone solution, viscous lidocaine, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen. He also received oral prednisone at approximately 1 mg/kg daily for 4 consecutive days after worsening oral pain. A recurrence of oral pain 3 months later was resolved with a higher and longer treatment with oral prednisone.
Dermatologists have also reported cases of erythema multiforme lesions of the mucosa in adults with COVID-19. One case was reported in Iran, and the other in France.
The authors report no study funding and disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer COVID vaccine antibodies may disappear in 7 months, study says
, according to a new study published on the bioRxiv preprint server.
In the study, which hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or formally published in a medical journal, researchers analyzed blood samples from 46 healthy young or middle-aged adults after receiving two doses, and then 6 months after the second dose.
“Our study shows vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine induces high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the original vaccine strain, but these levels drop by nearly 10-fold by 7 months,” the researchers told Reuters.
In about half of the adults, neutralizing antibodies were undetectable at 6 months after the second dose, particularly against coronavirus variants such as Delta, Beta, and Mu.
Neutralizing antibodies only make up part of the body’s immune defense against the virus, Reuters noted, but they are still “critically important” in protecting against coronavirus infections.
“These findings suggest that administering a booster dose at around 6 to 7 months following the initial immunization will likely enhance protection,” the study authors wrote.
BioNTech said a new vaccine formula will likely be needed by mid-2022 to protect against future mutations of the virus, according to the Financial Times.
“This year, [a different vaccine] is completely unneeded, but by mid-next year, it could be a different situation,” Ugur Sahin, MD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, told the news outlet.
Current variants, namely the Delta variant, are more contagious than the original coronavirus strain but not different enough to evade current vaccines, he said. But new strains may be able to evade boosters.
“This virus will stay, and the virus will further adapt,” Dr. Sahin said. “This is a continuous evolution, and that evolution has just started.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published on the bioRxiv preprint server.
In the study, which hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or formally published in a medical journal, researchers analyzed blood samples from 46 healthy young or middle-aged adults after receiving two doses, and then 6 months after the second dose.
“Our study shows vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine induces high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the original vaccine strain, but these levels drop by nearly 10-fold by 7 months,” the researchers told Reuters.
In about half of the adults, neutralizing antibodies were undetectable at 6 months after the second dose, particularly against coronavirus variants such as Delta, Beta, and Mu.
Neutralizing antibodies only make up part of the body’s immune defense against the virus, Reuters noted, but they are still “critically important” in protecting against coronavirus infections.
“These findings suggest that administering a booster dose at around 6 to 7 months following the initial immunization will likely enhance protection,” the study authors wrote.
BioNTech said a new vaccine formula will likely be needed by mid-2022 to protect against future mutations of the virus, according to the Financial Times.
“This year, [a different vaccine] is completely unneeded, but by mid-next year, it could be a different situation,” Ugur Sahin, MD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, told the news outlet.
Current variants, namely the Delta variant, are more contagious than the original coronavirus strain but not different enough to evade current vaccines, he said. But new strains may be able to evade boosters.
“This virus will stay, and the virus will further adapt,” Dr. Sahin said. “This is a continuous evolution, and that evolution has just started.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published on the bioRxiv preprint server.
In the study, which hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or formally published in a medical journal, researchers analyzed blood samples from 46 healthy young or middle-aged adults after receiving two doses, and then 6 months after the second dose.
“Our study shows vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine induces high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the original vaccine strain, but these levels drop by nearly 10-fold by 7 months,” the researchers told Reuters.
In about half of the adults, neutralizing antibodies were undetectable at 6 months after the second dose, particularly against coronavirus variants such as Delta, Beta, and Mu.
Neutralizing antibodies only make up part of the body’s immune defense against the virus, Reuters noted, but they are still “critically important” in protecting against coronavirus infections.
“These findings suggest that administering a booster dose at around 6 to 7 months following the initial immunization will likely enhance protection,” the study authors wrote.
BioNTech said a new vaccine formula will likely be needed by mid-2022 to protect against future mutations of the virus, according to the Financial Times.
“This year, [a different vaccine] is completely unneeded, but by mid-next year, it could be a different situation,” Ugur Sahin, MD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, told the news outlet.
Current variants, namely the Delta variant, are more contagious than the original coronavirus strain but not different enough to evade current vaccines, he said. But new strains may be able to evade boosters.
“This virus will stay, and the virus will further adapt,” Dr. Sahin said. “This is a continuous evolution, and that evolution has just started.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Extension study finds dupilumab effective for up to 1 year in teens with AD
in a phase 3, open-label extension trial, researchers reported.
At 1 year, 86% of 50 remaining patients with weights under 60 kg (132 lb) had achieved 75% improvement on the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75, and 77% of 51 remaining patients with weights over 60 kg reached that level of clearance. Only 5 (1.7%) of 294 patients had serious treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).
The findings back up a perception that patients can stay on dupilumab for some time instead of having to switch from one biologic to another after a few years, study coauthor Eric Simpson, MD, professor of dermatology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview. He added that the drug’s long-term safety profile is “very reassuring.”
The industry-funded findings of the study were released in a poster at the 2021 meeting of the World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology.
The FDA approved dupilumab (Dupixent), an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist, for treating AD in adults in 2017; it is now approved for treating patients ages 6 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with topicals.
The new study tracked patients who received at least 300 mg dupilumab subcutaneously every 4 weeks. The dose could be increased if needed to improve clinical response to once every 2 weeks (200 mg if baseline weight was <60 kg; 300 mg if ≥60 kg).
At 52 weeks, 37% of 52 patients with weights under 60 kg reached an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) of 0/1, a level that had been fairly steady since week 16 (n = 146). Among 51 heavier patients, 49% reached an IGA of 0/1 at 52 weeks; this percentage grew steadily since baseline.
The mean percentage change in EASI was –87% in the lower-weight group (n = 50) at 52 weeks and –80.1% in the larger-weight group (n = 51). The majority of the reduction in EASI occurred in the first 4 weeks of treatment.
At 52 weeks, the mean Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index level, which judges the effect of AD on life, was judged as “small” (low) in 71 patients. At baseline, the mean level among 189 patients was “moderate.” The levels dipped below “moderate” at week 4 and never rose above “small” after that.
“Treatment-emergent adverse events reported in ≥5% of patients were nasopharyngitis (21.1%), AD (19.4%), upper respiratory tract infection (12.4%), headache (9.4%), and oropharyngeal pain (5.7%),” the investigators wrote in the poster. They add that 6.7% of patients experienced injection-site reactions, and 8.7% of patients experienced treatment-emergent “narrow conjunctivitis,” which includes conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis, bacterial conjunctivitis, viral conjunctivitis, and atopic keratoconjunctivitis.
Dr. Simpson noted that cases of conjunctivitis fell over time. It’s not clear why this adverse effect appears, he said.
He said that the findings reflect his own experience in clinic. Many of his adolescent patients took part in early dupilumab trials, he said, and dozens have been taking the drug for more than 5 years. “They just seem to get better and better,” he said.
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, dermatologist Sheilagh Maguiness, MD, who wasn’t involved with the study, said in an interview that dupilumab remains “the safest, most effective and evidence-based therapy we had for children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.”
The new study’s findings are “very reassuring,” she said, and similar to those in a 2021 report that tracked long-term use of the drug in children aged 6-11.
Like Dr. Simpson, Dr. Maguiness said many pediatric patients at her clinic have stayed on the drug for more than 5 years. They still have “sustained improvement in skin disease and in their quality of life as well”
There are, however, still questions about dupilumab treatment. “For children who have responded well, when could we consider dose reduction or discontinuation? I have done this successfully just a handful of times, but I would love to see data about what percentage of pediatric patients experience rebound disease after coming off the drug and after what duration of treatment,” she said. “Another mystery that will be very interesting to unravel is the question as to whether or not early treatment with dupilumab may attenuate other atopic diseases.”
Dr. Maguiness added that “another issue specific to pediatric use of dupilumab is the recommendation surrounding vaccinations. This is an issue that should be studied in terms of antibody response and safety surrounding vaccinations, particularly as we are eagerly awaiting a pediatric FDA approval for the COVID-19 vaccine in children.”
She also urged colleagues to push back against insurers who resist paying for dupilumab. “Whether prescribing this medication on or off label, insurance companies are often requiring patients to try and fail other traditional immunosuppressive medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or to pursue phototherapy,” she said. “Oftentimes, these are not practical or even safe options for children for a multitude of reasons. Don’t be shy about advocating for your patients by second- or even third-level appeals to try and gain approval for children who are in need of treatment.”
The study was funded by Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. The study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Simpson reported investigator and consultant fee relationships from various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Maguiness was an investigator for one of the initial pediatric dupilumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a phase 3, open-label extension trial, researchers reported.
At 1 year, 86% of 50 remaining patients with weights under 60 kg (132 lb) had achieved 75% improvement on the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75, and 77% of 51 remaining patients with weights over 60 kg reached that level of clearance. Only 5 (1.7%) of 294 patients had serious treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).
The findings back up a perception that patients can stay on dupilumab for some time instead of having to switch from one biologic to another after a few years, study coauthor Eric Simpson, MD, professor of dermatology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview. He added that the drug’s long-term safety profile is “very reassuring.”
The industry-funded findings of the study were released in a poster at the 2021 meeting of the World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology.
The FDA approved dupilumab (Dupixent), an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist, for treating AD in adults in 2017; it is now approved for treating patients ages 6 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with topicals.
The new study tracked patients who received at least 300 mg dupilumab subcutaneously every 4 weeks. The dose could be increased if needed to improve clinical response to once every 2 weeks (200 mg if baseline weight was <60 kg; 300 mg if ≥60 kg).
At 52 weeks, 37% of 52 patients with weights under 60 kg reached an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) of 0/1, a level that had been fairly steady since week 16 (n = 146). Among 51 heavier patients, 49% reached an IGA of 0/1 at 52 weeks; this percentage grew steadily since baseline.
The mean percentage change in EASI was –87% in the lower-weight group (n = 50) at 52 weeks and –80.1% in the larger-weight group (n = 51). The majority of the reduction in EASI occurred in the first 4 weeks of treatment.
At 52 weeks, the mean Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index level, which judges the effect of AD on life, was judged as “small” (low) in 71 patients. At baseline, the mean level among 189 patients was “moderate.” The levels dipped below “moderate” at week 4 and never rose above “small” after that.
“Treatment-emergent adverse events reported in ≥5% of patients were nasopharyngitis (21.1%), AD (19.4%), upper respiratory tract infection (12.4%), headache (9.4%), and oropharyngeal pain (5.7%),” the investigators wrote in the poster. They add that 6.7% of patients experienced injection-site reactions, and 8.7% of patients experienced treatment-emergent “narrow conjunctivitis,” which includes conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis, bacterial conjunctivitis, viral conjunctivitis, and atopic keratoconjunctivitis.
Dr. Simpson noted that cases of conjunctivitis fell over time. It’s not clear why this adverse effect appears, he said.
He said that the findings reflect his own experience in clinic. Many of his adolescent patients took part in early dupilumab trials, he said, and dozens have been taking the drug for more than 5 years. “They just seem to get better and better,” he said.
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, dermatologist Sheilagh Maguiness, MD, who wasn’t involved with the study, said in an interview that dupilumab remains “the safest, most effective and evidence-based therapy we had for children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.”
The new study’s findings are “very reassuring,” she said, and similar to those in a 2021 report that tracked long-term use of the drug in children aged 6-11.
Like Dr. Simpson, Dr. Maguiness said many pediatric patients at her clinic have stayed on the drug for more than 5 years. They still have “sustained improvement in skin disease and in their quality of life as well”
There are, however, still questions about dupilumab treatment. “For children who have responded well, when could we consider dose reduction or discontinuation? I have done this successfully just a handful of times, but I would love to see data about what percentage of pediatric patients experience rebound disease after coming off the drug and after what duration of treatment,” she said. “Another mystery that will be very interesting to unravel is the question as to whether or not early treatment with dupilumab may attenuate other atopic diseases.”
Dr. Maguiness added that “another issue specific to pediatric use of dupilumab is the recommendation surrounding vaccinations. This is an issue that should be studied in terms of antibody response and safety surrounding vaccinations, particularly as we are eagerly awaiting a pediatric FDA approval for the COVID-19 vaccine in children.”
She also urged colleagues to push back against insurers who resist paying for dupilumab. “Whether prescribing this medication on or off label, insurance companies are often requiring patients to try and fail other traditional immunosuppressive medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or to pursue phototherapy,” she said. “Oftentimes, these are not practical or even safe options for children for a multitude of reasons. Don’t be shy about advocating for your patients by second- or even third-level appeals to try and gain approval for children who are in need of treatment.”
The study was funded by Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. The study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Simpson reported investigator and consultant fee relationships from various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Maguiness was an investigator for one of the initial pediatric dupilumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a phase 3, open-label extension trial, researchers reported.
At 1 year, 86% of 50 remaining patients with weights under 60 kg (132 lb) had achieved 75% improvement on the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75, and 77% of 51 remaining patients with weights over 60 kg reached that level of clearance. Only 5 (1.7%) of 294 patients had serious treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).
The findings back up a perception that patients can stay on dupilumab for some time instead of having to switch from one biologic to another after a few years, study coauthor Eric Simpson, MD, professor of dermatology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said in an interview. He added that the drug’s long-term safety profile is “very reassuring.”
The industry-funded findings of the study were released in a poster at the 2021 meeting of the World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology.
The FDA approved dupilumab (Dupixent), an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist, for treating AD in adults in 2017; it is now approved for treating patients ages 6 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with topicals.
The new study tracked patients who received at least 300 mg dupilumab subcutaneously every 4 weeks. The dose could be increased if needed to improve clinical response to once every 2 weeks (200 mg if baseline weight was <60 kg; 300 mg if ≥60 kg).
At 52 weeks, 37% of 52 patients with weights under 60 kg reached an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) of 0/1, a level that had been fairly steady since week 16 (n = 146). Among 51 heavier patients, 49% reached an IGA of 0/1 at 52 weeks; this percentage grew steadily since baseline.
The mean percentage change in EASI was –87% in the lower-weight group (n = 50) at 52 weeks and –80.1% in the larger-weight group (n = 51). The majority of the reduction in EASI occurred in the first 4 weeks of treatment.
At 52 weeks, the mean Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index level, which judges the effect of AD on life, was judged as “small” (low) in 71 patients. At baseline, the mean level among 189 patients was “moderate.” The levels dipped below “moderate” at week 4 and never rose above “small” after that.
“Treatment-emergent adverse events reported in ≥5% of patients were nasopharyngitis (21.1%), AD (19.4%), upper respiratory tract infection (12.4%), headache (9.4%), and oropharyngeal pain (5.7%),” the investigators wrote in the poster. They add that 6.7% of patients experienced injection-site reactions, and 8.7% of patients experienced treatment-emergent “narrow conjunctivitis,” which includes conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis, bacterial conjunctivitis, viral conjunctivitis, and atopic keratoconjunctivitis.
Dr. Simpson noted that cases of conjunctivitis fell over time. It’s not clear why this adverse effect appears, he said.
He said that the findings reflect his own experience in clinic. Many of his adolescent patients took part in early dupilumab trials, he said, and dozens have been taking the drug for more than 5 years. “They just seem to get better and better,” he said.
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, dermatologist Sheilagh Maguiness, MD, who wasn’t involved with the study, said in an interview that dupilumab remains “the safest, most effective and evidence-based therapy we had for children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.”
The new study’s findings are “very reassuring,” she said, and similar to those in a 2021 report that tracked long-term use of the drug in children aged 6-11.
Like Dr. Simpson, Dr. Maguiness said many pediatric patients at her clinic have stayed on the drug for more than 5 years. They still have “sustained improvement in skin disease and in their quality of life as well”
There are, however, still questions about dupilumab treatment. “For children who have responded well, when could we consider dose reduction or discontinuation? I have done this successfully just a handful of times, but I would love to see data about what percentage of pediatric patients experience rebound disease after coming off the drug and after what duration of treatment,” she said. “Another mystery that will be very interesting to unravel is the question as to whether or not early treatment with dupilumab may attenuate other atopic diseases.”
Dr. Maguiness added that “another issue specific to pediatric use of dupilumab is the recommendation surrounding vaccinations. This is an issue that should be studied in terms of antibody response and safety surrounding vaccinations, particularly as we are eagerly awaiting a pediatric FDA approval for the COVID-19 vaccine in children.”
She also urged colleagues to push back against insurers who resist paying for dupilumab. “Whether prescribing this medication on or off label, insurance companies are often requiring patients to try and fail other traditional immunosuppressive medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or to pursue phototherapy,” she said. “Oftentimes, these are not practical or even safe options for children for a multitude of reasons. Don’t be shy about advocating for your patients by second- or even third-level appeals to try and gain approval for children who are in need of treatment.”
The study was funded by Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. The study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Simpson reported investigator and consultant fee relationships from various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Maguiness was an investigator for one of the initial pediatric dupilumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than half of U.S. children under 6 years show detectable blood lead levels
Lead poisoning remains a significant threat to the health of young children in the United States, based on data from blood tests of more than 1 million children.
Any level of lead is potentially harmful, although blood lead levels have decreased over the past several decades in part because of the elimination of lead from many consumer products, as well as from gas, paint, and plumbing fixtures, wrote Marissa Hauptman, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and colleagues.
However, “numerous environmental sources of legacy lead still exist,” and children living in poverty and in older housing in particular remain at increased risk for lead exposure, they noted.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers analyzed deidentified results from blood lead tests performed at a single clinical laboratory for 1,141,441 children younger than 6 years between Oct. 1, 2018, and Feb. 29, 2020. The mean age of the children was 2.3 years; approximately half were boys.
Overall, 50.5% of the children tested (576,092 children) had detectable blood lead levels (BLLs), defined as 1.0 mcg/dL or higher, and 1.9% (21,172 children) had elevated BLLs, defined as 5.0 mcg/dL or higher.
In multivariate analysis, both detectable BLLs and elevated BLLs were significantly more common among children with public insurance (adjusted odds ratios, 2.01 and 1.08, respectively).
Children in the highest vs. lowest quintile of pre-1950s housing had significantly greater odds of both detectable and elevated BLLs (aOR, 1.65 and aOR, 3.06); those in the highest vs. lowest quintiles of poverty showed similarly increased risk of detectable and elevated BLLs (aOR, 1.89 and aOR, 1.99, respectively; P < .001 for all).
When the data were broken out by ZIP code, children in predominantly Black non-Hispanic and non-Latino neighborhoods were more likely than those living in other ZIP codes to have detectable BLLs (aOR, 1.13), but less likely to have elevated BLLs (aOR, 0.83). States with the highest overall proportions of children with detectable BLLs were Nebraska (83%), Missouri (82%), and Michigan (78%).
The study findings were limited by several factors, especially the potential for selection bias because of the use of a single reference laboratory (Quest Diagnostics), that does not perform all lead testing in the United States, the researchers noted. Other limitations included variability in testing at the state level, and the use of ZIP code–level data to estimate race, ethnicity, housing, and poverty, they said.
However, the results suggest that lead exposure remains a problem in young children, with significant disparities at the individual and community level, and national efforts must focus on further reductions of lead exposure in areas of highest risk, they concluded.
Step up lead elimination efforts
“The removal of lead from gasoline and new paint produced a precipitous decrease in blood lead levels from a population mean of 17 mcg/dL (all ages) in 1976 to 4 mcg/dL in the early 1990s to less than 2 mcg/dL today,” wrote Philip J. Landrigan, MD, of Boston College and David Bellinger, PhD, of Harvard University, Boston, in an accompanying editorial. However, “The findings from this study underscore the urgent need to eliminate all sources of lead exposure from U.S. children’s environments,” and highlight the persistent disparities in children’s lead exposure, they said.
The authors emphasized the need to remove existing lead paint from U.S. homes, as not only the paint itself, but the dust that enters the environment as the pain wears over time, continue to account for most detectable and elevated BLLs in children. A comprehensive lead paint removal effort would be an investment that would protect children now and would protect future generations, they emphasized. They proposed “creating a lead paint removal workforce through federally supported partnerships between city governments and major unions,” that would not only protect children from disease and disability, but could potentially provide jobs and vocational programs that would have a significant impact on communities.
Elevated lead levels may be underreported
In fact, the situation of children’s lead exposure in the United States may be more severe than indicated by the study findings, given the variation in testing at the state and local levels, said Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn.
“There are no available lead test kits in our offices, so I do worry that many elevated lead levels will be missed,” she said.
“The recent case of elevated lead levels in drinking water in Flint, Michigan, was largely detected through pediatric clinic screening and showed that elevated lead levels may remain a major issue in some communities,” said Tim Joos, MD, a clinician in combined internal medicine/pediatrics in Seattle, Wash., in an interview.
“It is important to highlight to what extent baseline and point-source lead contamination still exists, monitor progress towards lowering levels, and identify communities at high risk,” Dr. Joos emphasized. “The exact prevalence of elevated lead levels among the general pediatric populations is hard to estimate from this study because of the methodology, which looked at demographic characteristics of the subset of the pediatric population that had venous samples sent to Quest Lab,” he noted.
“As the authors pointed out, it is hard to know what biases went into deciding whether to screen or not, and whether these were confirmatory tests for elevated point of care testing done earlier in the clinic,” said Dr. Joos. “Nonetheless, it does point to the role of poverty and pre-1950s housing in elevated blood lead levels,” he added. “The study also highlights that, as the CDC considers lowering the level for what is considered an ‘elevated blood lead level’ from 5.0 to perhaps 3.5 mcg/dL, we still have a lot more work to do,” he said.
The study was funded by Quest Diagnostics and the company provided salaries to several coauthors during the study. Dr. Hauptmann disclosed support from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences during the current study and support from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency unrelated to the current study. Dr. Landrigan had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Bellinger disclosed fees from attorneys for testimony in cases unrelated to the editorial. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Lead poisoning remains a significant threat to the health of young children in the United States, based on data from blood tests of more than 1 million children.
Any level of lead is potentially harmful, although blood lead levels have decreased over the past several decades in part because of the elimination of lead from many consumer products, as well as from gas, paint, and plumbing fixtures, wrote Marissa Hauptman, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and colleagues.
However, “numerous environmental sources of legacy lead still exist,” and children living in poverty and in older housing in particular remain at increased risk for lead exposure, they noted.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers analyzed deidentified results from blood lead tests performed at a single clinical laboratory for 1,141,441 children younger than 6 years between Oct. 1, 2018, and Feb. 29, 2020. The mean age of the children was 2.3 years; approximately half were boys.
Overall, 50.5% of the children tested (576,092 children) had detectable blood lead levels (BLLs), defined as 1.0 mcg/dL or higher, and 1.9% (21,172 children) had elevated BLLs, defined as 5.0 mcg/dL or higher.
In multivariate analysis, both detectable BLLs and elevated BLLs were significantly more common among children with public insurance (adjusted odds ratios, 2.01 and 1.08, respectively).
Children in the highest vs. lowest quintile of pre-1950s housing had significantly greater odds of both detectable and elevated BLLs (aOR, 1.65 and aOR, 3.06); those in the highest vs. lowest quintiles of poverty showed similarly increased risk of detectable and elevated BLLs (aOR, 1.89 and aOR, 1.99, respectively; P < .001 for all).
When the data were broken out by ZIP code, children in predominantly Black non-Hispanic and non-Latino neighborhoods were more likely than those living in other ZIP codes to have detectable BLLs (aOR, 1.13), but less likely to have elevated BLLs (aOR, 0.83). States with the highest overall proportions of children with detectable BLLs were Nebraska (83%), Missouri (82%), and Michigan (78%).
The study findings were limited by several factors, especially the potential for selection bias because of the use of a single reference laboratory (Quest Diagnostics), that does not perform all lead testing in the United States, the researchers noted. Other limitations included variability in testing at the state level, and the use of ZIP code–level data to estimate race, ethnicity, housing, and poverty, they said.
However, the results suggest that lead exposure remains a problem in young children, with significant disparities at the individual and community level, and national efforts must focus on further reductions of lead exposure in areas of highest risk, they concluded.
Step up lead elimination efforts
“The removal of lead from gasoline and new paint produced a precipitous decrease in blood lead levels from a population mean of 17 mcg/dL (all ages) in 1976 to 4 mcg/dL in the early 1990s to less than 2 mcg/dL today,” wrote Philip J. Landrigan, MD, of Boston College and David Bellinger, PhD, of Harvard University, Boston, in an accompanying editorial. However, “The findings from this study underscore the urgent need to eliminate all sources of lead exposure from U.S. children’s environments,” and highlight the persistent disparities in children’s lead exposure, they said.
The authors emphasized the need to remove existing lead paint from U.S. homes, as not only the paint itself, but the dust that enters the environment as the pain wears over time, continue to account for most detectable and elevated BLLs in children. A comprehensive lead paint removal effort would be an investment that would protect children now and would protect future generations, they emphasized. They proposed “creating a lead paint removal workforce through federally supported partnerships between city governments and major unions,” that would not only protect children from disease and disability, but could potentially provide jobs and vocational programs that would have a significant impact on communities.
Elevated lead levels may be underreported
In fact, the situation of children’s lead exposure in the United States may be more severe than indicated by the study findings, given the variation in testing at the state and local levels, said Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn.
“There are no available lead test kits in our offices, so I do worry that many elevated lead levels will be missed,” she said.
“The recent case of elevated lead levels in drinking water in Flint, Michigan, was largely detected through pediatric clinic screening and showed that elevated lead levels may remain a major issue in some communities,” said Tim Joos, MD, a clinician in combined internal medicine/pediatrics in Seattle, Wash., in an interview.
“It is important to highlight to what extent baseline and point-source lead contamination still exists, monitor progress towards lowering levels, and identify communities at high risk,” Dr. Joos emphasized. “The exact prevalence of elevated lead levels among the general pediatric populations is hard to estimate from this study because of the methodology, which looked at demographic characteristics of the subset of the pediatric population that had venous samples sent to Quest Lab,” he noted.
“As the authors pointed out, it is hard to know what biases went into deciding whether to screen or not, and whether these were confirmatory tests for elevated point of care testing done earlier in the clinic,” said Dr. Joos. “Nonetheless, it does point to the role of poverty and pre-1950s housing in elevated blood lead levels,” he added. “The study also highlights that, as the CDC considers lowering the level for what is considered an ‘elevated blood lead level’ from 5.0 to perhaps 3.5 mcg/dL, we still have a lot more work to do,” he said.
The study was funded by Quest Diagnostics and the company provided salaries to several coauthors during the study. Dr. Hauptmann disclosed support from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences during the current study and support from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency unrelated to the current study. Dr. Landrigan had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Bellinger disclosed fees from attorneys for testimony in cases unrelated to the editorial. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Lead poisoning remains a significant threat to the health of young children in the United States, based on data from blood tests of more than 1 million children.
Any level of lead is potentially harmful, although blood lead levels have decreased over the past several decades in part because of the elimination of lead from many consumer products, as well as from gas, paint, and plumbing fixtures, wrote Marissa Hauptman, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and colleagues.
However, “numerous environmental sources of legacy lead still exist,” and children living in poverty and in older housing in particular remain at increased risk for lead exposure, they noted.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers analyzed deidentified results from blood lead tests performed at a single clinical laboratory for 1,141,441 children younger than 6 years between Oct. 1, 2018, and Feb. 29, 2020. The mean age of the children was 2.3 years; approximately half were boys.
Overall, 50.5% of the children tested (576,092 children) had detectable blood lead levels (BLLs), defined as 1.0 mcg/dL or higher, and 1.9% (21,172 children) had elevated BLLs, defined as 5.0 mcg/dL or higher.
In multivariate analysis, both detectable BLLs and elevated BLLs were significantly more common among children with public insurance (adjusted odds ratios, 2.01 and 1.08, respectively).
Children in the highest vs. lowest quintile of pre-1950s housing had significantly greater odds of both detectable and elevated BLLs (aOR, 1.65 and aOR, 3.06); those in the highest vs. lowest quintiles of poverty showed similarly increased risk of detectable and elevated BLLs (aOR, 1.89 and aOR, 1.99, respectively; P < .001 for all).
When the data were broken out by ZIP code, children in predominantly Black non-Hispanic and non-Latino neighborhoods were more likely than those living in other ZIP codes to have detectable BLLs (aOR, 1.13), but less likely to have elevated BLLs (aOR, 0.83). States with the highest overall proportions of children with detectable BLLs were Nebraska (83%), Missouri (82%), and Michigan (78%).
The study findings were limited by several factors, especially the potential for selection bias because of the use of a single reference laboratory (Quest Diagnostics), that does not perform all lead testing in the United States, the researchers noted. Other limitations included variability in testing at the state level, and the use of ZIP code–level data to estimate race, ethnicity, housing, and poverty, they said.
However, the results suggest that lead exposure remains a problem in young children, with significant disparities at the individual and community level, and national efforts must focus on further reductions of lead exposure in areas of highest risk, they concluded.
Step up lead elimination efforts
“The removal of lead from gasoline and new paint produced a precipitous decrease in blood lead levels from a population mean of 17 mcg/dL (all ages) in 1976 to 4 mcg/dL in the early 1990s to less than 2 mcg/dL today,” wrote Philip J. Landrigan, MD, of Boston College and David Bellinger, PhD, of Harvard University, Boston, in an accompanying editorial. However, “The findings from this study underscore the urgent need to eliminate all sources of lead exposure from U.S. children’s environments,” and highlight the persistent disparities in children’s lead exposure, they said.
The authors emphasized the need to remove existing lead paint from U.S. homes, as not only the paint itself, but the dust that enters the environment as the pain wears over time, continue to account for most detectable and elevated BLLs in children. A comprehensive lead paint removal effort would be an investment that would protect children now and would protect future generations, they emphasized. They proposed “creating a lead paint removal workforce through federally supported partnerships between city governments and major unions,” that would not only protect children from disease and disability, but could potentially provide jobs and vocational programs that would have a significant impact on communities.
Elevated lead levels may be underreported
In fact, the situation of children’s lead exposure in the United States may be more severe than indicated by the study findings, given the variation in testing at the state and local levels, said Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in Cheshire, Conn.
“There are no available lead test kits in our offices, so I do worry that many elevated lead levels will be missed,” she said.
“The recent case of elevated lead levels in drinking water in Flint, Michigan, was largely detected through pediatric clinic screening and showed that elevated lead levels may remain a major issue in some communities,” said Tim Joos, MD, a clinician in combined internal medicine/pediatrics in Seattle, Wash., in an interview.
“It is important to highlight to what extent baseline and point-source lead contamination still exists, monitor progress towards lowering levels, and identify communities at high risk,” Dr. Joos emphasized. “The exact prevalence of elevated lead levels among the general pediatric populations is hard to estimate from this study because of the methodology, which looked at demographic characteristics of the subset of the pediatric population that had venous samples sent to Quest Lab,” he noted.
“As the authors pointed out, it is hard to know what biases went into deciding whether to screen or not, and whether these were confirmatory tests for elevated point of care testing done earlier in the clinic,” said Dr. Joos. “Nonetheless, it does point to the role of poverty and pre-1950s housing in elevated blood lead levels,” he added. “The study also highlights that, as the CDC considers lowering the level for what is considered an ‘elevated blood lead level’ from 5.0 to perhaps 3.5 mcg/dL, we still have a lot more work to do,” he said.
The study was funded by Quest Diagnostics and the company provided salaries to several coauthors during the study. Dr. Hauptmann disclosed support from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences during the current study and support from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency unrelated to the current study. Dr. Landrigan had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Bellinger disclosed fees from attorneys for testimony in cases unrelated to the editorial. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
A female toddler presents with an itchy yellow nodule
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a benign disorder presenting as firm, yellow-red skin papules or nodules, usually in infancy or early childhood. It derives its name based on its yellowish color and the histologic finding of lipid-filled histiocytes. In fact, it is a form of non-Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. It most commonly presents on the head, neck, and trunk, but can arise anywhere on the body as demonstrated by this case. While often pink to reddish early on, the characteristic yellow or orange, brown appearance over time is common, occasionally with overlying telangiectasia, and ranging in size from 1 mm to 2 cm. While typically asymptomatic, it is possible for lesions to itch. JXG is usually self-limiting, and spontaneously resolves over several years. On dermoscopy (with polarized light), it has a characteristic “setting sun” appearance because of its central yellow area surrounded by a reddish periphery.
JXGs have been associated with neurofibromatosis-1 and a “triple association” of NF-1, JXG, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) has been debated. Many cases are diagnosed on clinical grounds without histologic confirmation, so while the absolute incidence is unknown, they are not uncommon.
What is on the differential?
Spitz nevus is a melanocytic lesion which typically presents as a sharply circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papule or nodule, and is composed of large epithelioid and/or spindled cells. These nevi can present with a spectrum of morphology and biologic activity; commonly with benign melanocytic proliferations and a symmetric appearance or, rarely, with atypical tumors or lesions, characterized as Spitzoid melanomas. The yellowish color of JXG is distinct from the appearance of Spitz tumors.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common pox viral infection seen in children that presents with round, flat-topped firm papules on the skin and distinctive whitish centers with or without umbilication. Like JXG, molluscum contagiosum papules may grow over time and cause pruritus. However, this diagnosis is less likely given the absence of other lesions on the skin, lack of known contacts with similar lesions, and yellowish color without a more typical appearance of molluscum.
Dermatofibromas occur in people of all ages, although more commonly between the ages of 20 and 40 and in those with a history of trauma at the lesion. Like JXGs, dermatofibromas tend to be firm, solitary papules or nodules. They usually are hyperpigmented, and classically “dimple when pinched” as they are fixed to the subcutaneous tissue. However, this patient’s age, lack of trauma, and the lesion morphology are not consistent with dermatofibromas.
Like XJGs, mastocytomas commonly present in the first 2 years of life with maculopapular or nodular lesions that itch. However, the history of new-onset itch in recent months as the lesion grew larger and the yellow color on dermoscopy are more consistent with JXG.
Eruptive xanthomas typically appear suddenly as multiple erythematous yellow, dome-shaped papules on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, buttocks, and hands. They are usually present with hypertriglyceridemia and are very rare in young children. The presence of a solitary lesion in a 6-month-old patient without a history of lipid abnormalities favors the diagnosis of XJG.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Kleinman have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
Hernandez-Martin A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Mar;36(3 Pt 1):355-67.
Prendiville J. Lumps, bumps and hamartomas in “Neonatal and Infant Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2015).
Püttgen KB. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. UpToDate, 2021.
Schaffer JV. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021 Mar;22(2):205-20.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a benign disorder presenting as firm, yellow-red skin papules or nodules, usually in infancy or early childhood. It derives its name based on its yellowish color and the histologic finding of lipid-filled histiocytes. In fact, it is a form of non-Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. It most commonly presents on the head, neck, and trunk, but can arise anywhere on the body as demonstrated by this case. While often pink to reddish early on, the characteristic yellow or orange, brown appearance over time is common, occasionally with overlying telangiectasia, and ranging in size from 1 mm to 2 cm. While typically asymptomatic, it is possible for lesions to itch. JXG is usually self-limiting, and spontaneously resolves over several years. On dermoscopy (with polarized light), it has a characteristic “setting sun” appearance because of its central yellow area surrounded by a reddish periphery.
JXGs have been associated with neurofibromatosis-1 and a “triple association” of NF-1, JXG, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) has been debated. Many cases are diagnosed on clinical grounds without histologic confirmation, so while the absolute incidence is unknown, they are not uncommon.
What is on the differential?
Spitz nevus is a melanocytic lesion which typically presents as a sharply circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papule or nodule, and is composed of large epithelioid and/or spindled cells. These nevi can present with a spectrum of morphology and biologic activity; commonly with benign melanocytic proliferations and a symmetric appearance or, rarely, with atypical tumors or lesions, characterized as Spitzoid melanomas. The yellowish color of JXG is distinct from the appearance of Spitz tumors.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common pox viral infection seen in children that presents with round, flat-topped firm papules on the skin and distinctive whitish centers with or without umbilication. Like JXG, molluscum contagiosum papules may grow over time and cause pruritus. However, this diagnosis is less likely given the absence of other lesions on the skin, lack of known contacts with similar lesions, and yellowish color without a more typical appearance of molluscum.
Dermatofibromas occur in people of all ages, although more commonly between the ages of 20 and 40 and in those with a history of trauma at the lesion. Like JXGs, dermatofibromas tend to be firm, solitary papules or nodules. They usually are hyperpigmented, and classically “dimple when pinched” as they are fixed to the subcutaneous tissue. However, this patient’s age, lack of trauma, and the lesion morphology are not consistent with dermatofibromas.
Like XJGs, mastocytomas commonly present in the first 2 years of life with maculopapular or nodular lesions that itch. However, the history of new-onset itch in recent months as the lesion grew larger and the yellow color on dermoscopy are more consistent with JXG.
Eruptive xanthomas typically appear suddenly as multiple erythematous yellow, dome-shaped papules on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, buttocks, and hands. They are usually present with hypertriglyceridemia and are very rare in young children. The presence of a solitary lesion in a 6-month-old patient without a history of lipid abnormalities favors the diagnosis of XJG.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Kleinman have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
Hernandez-Martin A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Mar;36(3 Pt 1):355-67.
Prendiville J. Lumps, bumps and hamartomas in “Neonatal and Infant Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2015).
Püttgen KB. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. UpToDate, 2021.
Schaffer JV. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021 Mar;22(2):205-20.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a benign disorder presenting as firm, yellow-red skin papules or nodules, usually in infancy or early childhood. It derives its name based on its yellowish color and the histologic finding of lipid-filled histiocytes. In fact, it is a form of non-Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. It most commonly presents on the head, neck, and trunk, but can arise anywhere on the body as demonstrated by this case. While often pink to reddish early on, the characteristic yellow or orange, brown appearance over time is common, occasionally with overlying telangiectasia, and ranging in size from 1 mm to 2 cm. While typically asymptomatic, it is possible for lesions to itch. JXG is usually self-limiting, and spontaneously resolves over several years. On dermoscopy (with polarized light), it has a characteristic “setting sun” appearance because of its central yellow area surrounded by a reddish periphery.
JXGs have been associated with neurofibromatosis-1 and a “triple association” of NF-1, JXG, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) has been debated. Many cases are diagnosed on clinical grounds without histologic confirmation, so while the absolute incidence is unknown, they are not uncommon.
What is on the differential?
Spitz nevus is a melanocytic lesion which typically presents as a sharply circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papule or nodule, and is composed of large epithelioid and/or spindled cells. These nevi can present with a spectrum of morphology and biologic activity; commonly with benign melanocytic proliferations and a symmetric appearance or, rarely, with atypical tumors or lesions, characterized as Spitzoid melanomas. The yellowish color of JXG is distinct from the appearance of Spitz tumors.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common pox viral infection seen in children that presents with round, flat-topped firm papules on the skin and distinctive whitish centers with or without umbilication. Like JXG, molluscum contagiosum papules may grow over time and cause pruritus. However, this diagnosis is less likely given the absence of other lesions on the skin, lack of known contacts with similar lesions, and yellowish color without a more typical appearance of molluscum.
Dermatofibromas occur in people of all ages, although more commonly between the ages of 20 and 40 and in those with a history of trauma at the lesion. Like JXGs, dermatofibromas tend to be firm, solitary papules or nodules. They usually are hyperpigmented, and classically “dimple when pinched” as they are fixed to the subcutaneous tissue. However, this patient’s age, lack of trauma, and the lesion morphology are not consistent with dermatofibromas.
Like XJGs, mastocytomas commonly present in the first 2 years of life with maculopapular or nodular lesions that itch. However, the history of new-onset itch in recent months as the lesion grew larger and the yellow color on dermoscopy are more consistent with JXG.
Eruptive xanthomas typically appear suddenly as multiple erythematous yellow, dome-shaped papules on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, buttocks, and hands. They are usually present with hypertriglyceridemia and are very rare in young children. The presence of a solitary lesion in a 6-month-old patient without a history of lipid abnormalities favors the diagnosis of XJG.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Kleinman have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
Hernandez-Martin A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Mar;36(3 Pt 1):355-67.
Prendiville J. Lumps, bumps and hamartomas in “Neonatal and Infant Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2015).
Püttgen KB. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. UpToDate, 2021.
Schaffer JV. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021 Mar;22(2):205-20.
Drug cocktail significantly reduced severe COVID, death in outpatients
A monoclonal antibody combination of casirivimab and imdevimab (REGEN-COV) significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19–related hospitalizations and death from any cause in the phase 3 portion of an adaptive trial of outpatients.
Researchers, led by David Weinreich, MD, MBA, executive vice president of the drug cocktail’s manufacturer Regeneron, found in the randomized trial that the combination also resolved symptoms and reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load more quickly, compared with placebo.
Findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
COVID-related hospitalization or death from any cause occurred in 18 of 1,355 patients (1.3%) in the group getting 2,400 mg infusions of the study drug, compared with 62 (4.6%) of 1,341 in the matching placebo group, indicating a relative risk reduction of 71.3%; P < .001.
Sunil Joshi, MD, president of the Duval County Medical Society Foundation and an immunologist in Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview that these findings confirm benefits of REGEN-COV and are very good news for a patient group that includes those age 65 and older with high blood pressure, diabetes, or obesity; and for people not vaccinated, who are all at high risk of hospitalization or death if they get COVID-19.
“Vaccines are critically important,” he said, “but if you were to be infected and know that there’s a way to keep yourself out of the hospital, this is very good news.”
Researchers seek lowest doses
This trial found that the effect was similar when researchers cut the doses in half. These outcomes occurred in 7 of 736 (1%) of patients given 1,200 mg of REGEN-COV and in 24 (3.2%) of 748 in the matching placebo group (relative risk reduction, 70.4%; P = .002).
Symptoms were resolved on average 4 days earlier with each REGEN-COV dose than with placebo (10 days vs. 14 days; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Dr. Weinreich said in an interview that trials will continue to find the lowest effective doses that can stand up to all evolving variants.
“This is one of those settings where you don’t want to underdose. You’ve got one shot at this,” he said. “We’d love to do lower doses. It would be more convenient and we could treat more patients, but if it generates more clinical failures or doesn’t work with certain variants, then you’ve done a huge disservice to the world.”
Also new in this study is that researchers tested not only seronegative patients, but patients at high risk regardless of blood antibody status, he said.
“It’s the first suggestion of data that if you’re breaking through a vaccine and you’re at high risk, the use of the cocktail is something to strongly consider because treatment early is better than treatment later,” Dr. Weinreich said.
In addition to efficacy, the phase 3 trial demonstrated the cocktail had a good safety profile. Serious adverse events occurred more often in the placebo group (4%) than in the 1,200-mg group (1.1%) and the 2,400-mg group (1.3%). Infusion reactions (grade 2 or higher) occurred in less than 0.3% of patients in all groups.
William Fales, MD, state medical director for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, said the results confirm the promise of REGEN-COV for reducing hospitalizations and death in a peer-reviewed publication.
COVID-19 a moving target
However, Dr. Fales noted that COVID-19 is a moving target with emerging variants. The criteria for populations at high risk have also broadened since the start of the study, he said.
“A great example is pregnancy is now included as high risk, and that would have likely been a specific contraindication of patients in this clinical trial,” he said.
Dr. Fales said Michigan has been using both REGEN-COV and the Eli Lilly combination of bamlanivimab and etesevimab, which also has an emergency use authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration, with positive results.
REGEN-COV has an EUA to treat people who are at high risk of serious consequences from COVID-19, including those who are already infected (nonhospitalized) or those in certain postexposure prophylaxis settings.
“We’re seeing very low hospitalization rates and few deaths in a state that is predominately Delta,” Dr. Fales said. “So, this makes us feel that we’re doing the right thing and supports the current efforts around the country to make monoclonal antibody therapy available to high-risk patients.”
Dr. Joshi noted that trial results have been emerging from other monoclonal antibody cocktails with different COVID-19 patient groups.
However, he said in an interview, “how much more effective they would be than this is something we’d have to look at, as 71% effectiveness in keeping people out of the hospital is pretty good for any treatment.”
“These are great numbers, but vaccination itself keeps you from getting the disease in the first place and not just for a short time period. This treatment is just that – a treatment. It gets you through that episode but it doesn’t mean you won’t get sick again. You don’t develop an immune response as you do with the vaccine,” he said.
Dr. Weinreich agreed: “This is not a substitute for a vaccine except for the small group who get the vaccine and their bodies can’t respond to it because they’re significantly immunocompromised.”
The results from this paper “are one piece of a large, multistudy, phase 3 program that basically spans from prophylaxis all the way to hospitalization and pretty much the gamut – all of them – have worked. All of these studies have shown dramatic improvement in whatever the definitive regulatory endpoint is,” Dr. Weinreich said.
He said discussions are ongoing for full regulatory approval in the United States and for expanding the EUA for other populations, including pre-exposure prophylaxis, “which the [United Kingdom’s] authority has already granted us but the FDA has not.”
The study is funded by Regeneron and the Department of Health & Human Services. Dr. Weinreich is a vice president of Regeneron. Dr. Joshi reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fales holds stock in Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A monoclonal antibody combination of casirivimab and imdevimab (REGEN-COV) significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19–related hospitalizations and death from any cause in the phase 3 portion of an adaptive trial of outpatients.
Researchers, led by David Weinreich, MD, MBA, executive vice president of the drug cocktail’s manufacturer Regeneron, found in the randomized trial that the combination also resolved symptoms and reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load more quickly, compared with placebo.
Findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
COVID-related hospitalization or death from any cause occurred in 18 of 1,355 patients (1.3%) in the group getting 2,400 mg infusions of the study drug, compared with 62 (4.6%) of 1,341 in the matching placebo group, indicating a relative risk reduction of 71.3%; P < .001.
Sunil Joshi, MD, president of the Duval County Medical Society Foundation and an immunologist in Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview that these findings confirm benefits of REGEN-COV and are very good news for a patient group that includes those age 65 and older with high blood pressure, diabetes, or obesity; and for people not vaccinated, who are all at high risk of hospitalization or death if they get COVID-19.
“Vaccines are critically important,” he said, “but if you were to be infected and know that there’s a way to keep yourself out of the hospital, this is very good news.”
Researchers seek lowest doses
This trial found that the effect was similar when researchers cut the doses in half. These outcomes occurred in 7 of 736 (1%) of patients given 1,200 mg of REGEN-COV and in 24 (3.2%) of 748 in the matching placebo group (relative risk reduction, 70.4%; P = .002).
Symptoms were resolved on average 4 days earlier with each REGEN-COV dose than with placebo (10 days vs. 14 days; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Dr. Weinreich said in an interview that trials will continue to find the lowest effective doses that can stand up to all evolving variants.
“This is one of those settings where you don’t want to underdose. You’ve got one shot at this,” he said. “We’d love to do lower doses. It would be more convenient and we could treat more patients, but if it generates more clinical failures or doesn’t work with certain variants, then you’ve done a huge disservice to the world.”
Also new in this study is that researchers tested not only seronegative patients, but patients at high risk regardless of blood antibody status, he said.
“It’s the first suggestion of data that if you’re breaking through a vaccine and you’re at high risk, the use of the cocktail is something to strongly consider because treatment early is better than treatment later,” Dr. Weinreich said.
In addition to efficacy, the phase 3 trial demonstrated the cocktail had a good safety profile. Serious adverse events occurred more often in the placebo group (4%) than in the 1,200-mg group (1.1%) and the 2,400-mg group (1.3%). Infusion reactions (grade 2 or higher) occurred in less than 0.3% of patients in all groups.
William Fales, MD, state medical director for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, said the results confirm the promise of REGEN-COV for reducing hospitalizations and death in a peer-reviewed publication.
COVID-19 a moving target
However, Dr. Fales noted that COVID-19 is a moving target with emerging variants. The criteria for populations at high risk have also broadened since the start of the study, he said.
“A great example is pregnancy is now included as high risk, and that would have likely been a specific contraindication of patients in this clinical trial,” he said.
Dr. Fales said Michigan has been using both REGEN-COV and the Eli Lilly combination of bamlanivimab and etesevimab, which also has an emergency use authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration, with positive results.
REGEN-COV has an EUA to treat people who are at high risk of serious consequences from COVID-19, including those who are already infected (nonhospitalized) or those in certain postexposure prophylaxis settings.
“We’re seeing very low hospitalization rates and few deaths in a state that is predominately Delta,” Dr. Fales said. “So, this makes us feel that we’re doing the right thing and supports the current efforts around the country to make monoclonal antibody therapy available to high-risk patients.”
Dr. Joshi noted that trial results have been emerging from other monoclonal antibody cocktails with different COVID-19 patient groups.
However, he said in an interview, “how much more effective they would be than this is something we’d have to look at, as 71% effectiveness in keeping people out of the hospital is pretty good for any treatment.”
“These are great numbers, but vaccination itself keeps you from getting the disease in the first place and not just for a short time period. This treatment is just that – a treatment. It gets you through that episode but it doesn’t mean you won’t get sick again. You don’t develop an immune response as you do with the vaccine,” he said.
Dr. Weinreich agreed: “This is not a substitute for a vaccine except for the small group who get the vaccine and their bodies can’t respond to it because they’re significantly immunocompromised.”
The results from this paper “are one piece of a large, multistudy, phase 3 program that basically spans from prophylaxis all the way to hospitalization and pretty much the gamut – all of them – have worked. All of these studies have shown dramatic improvement in whatever the definitive regulatory endpoint is,” Dr. Weinreich said.
He said discussions are ongoing for full regulatory approval in the United States and for expanding the EUA for other populations, including pre-exposure prophylaxis, “which the [United Kingdom’s] authority has already granted us but the FDA has not.”
The study is funded by Regeneron and the Department of Health & Human Services. Dr. Weinreich is a vice president of Regeneron. Dr. Joshi reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fales holds stock in Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A monoclonal antibody combination of casirivimab and imdevimab (REGEN-COV) significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19–related hospitalizations and death from any cause in the phase 3 portion of an adaptive trial of outpatients.
Researchers, led by David Weinreich, MD, MBA, executive vice president of the drug cocktail’s manufacturer Regeneron, found in the randomized trial that the combination also resolved symptoms and reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load more quickly, compared with placebo.
Findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
COVID-related hospitalization or death from any cause occurred in 18 of 1,355 patients (1.3%) in the group getting 2,400 mg infusions of the study drug, compared with 62 (4.6%) of 1,341 in the matching placebo group, indicating a relative risk reduction of 71.3%; P < .001.
Sunil Joshi, MD, president of the Duval County Medical Society Foundation and an immunologist in Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview that these findings confirm benefits of REGEN-COV and are very good news for a patient group that includes those age 65 and older with high blood pressure, diabetes, or obesity; and for people not vaccinated, who are all at high risk of hospitalization or death if they get COVID-19.
“Vaccines are critically important,” he said, “but if you were to be infected and know that there’s a way to keep yourself out of the hospital, this is very good news.”
Researchers seek lowest doses
This trial found that the effect was similar when researchers cut the doses in half. These outcomes occurred in 7 of 736 (1%) of patients given 1,200 mg of REGEN-COV and in 24 (3.2%) of 748 in the matching placebo group (relative risk reduction, 70.4%; P = .002).
Symptoms were resolved on average 4 days earlier with each REGEN-COV dose than with placebo (10 days vs. 14 days; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Dr. Weinreich said in an interview that trials will continue to find the lowest effective doses that can stand up to all evolving variants.
“This is one of those settings where you don’t want to underdose. You’ve got one shot at this,” he said. “We’d love to do lower doses. It would be more convenient and we could treat more patients, but if it generates more clinical failures or doesn’t work with certain variants, then you’ve done a huge disservice to the world.”
Also new in this study is that researchers tested not only seronegative patients, but patients at high risk regardless of blood antibody status, he said.
“It’s the first suggestion of data that if you’re breaking through a vaccine and you’re at high risk, the use of the cocktail is something to strongly consider because treatment early is better than treatment later,” Dr. Weinreich said.
In addition to efficacy, the phase 3 trial demonstrated the cocktail had a good safety profile. Serious adverse events occurred more often in the placebo group (4%) than in the 1,200-mg group (1.1%) and the 2,400-mg group (1.3%). Infusion reactions (grade 2 or higher) occurred in less than 0.3% of patients in all groups.
William Fales, MD, state medical director for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, said the results confirm the promise of REGEN-COV for reducing hospitalizations and death in a peer-reviewed publication.
COVID-19 a moving target
However, Dr. Fales noted that COVID-19 is a moving target with emerging variants. The criteria for populations at high risk have also broadened since the start of the study, he said.
“A great example is pregnancy is now included as high risk, and that would have likely been a specific contraindication of patients in this clinical trial,” he said.
Dr. Fales said Michigan has been using both REGEN-COV and the Eli Lilly combination of bamlanivimab and etesevimab, which also has an emergency use authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration, with positive results.
REGEN-COV has an EUA to treat people who are at high risk of serious consequences from COVID-19, including those who are already infected (nonhospitalized) or those in certain postexposure prophylaxis settings.
“We’re seeing very low hospitalization rates and few deaths in a state that is predominately Delta,” Dr. Fales said. “So, this makes us feel that we’re doing the right thing and supports the current efforts around the country to make monoclonal antibody therapy available to high-risk patients.”
Dr. Joshi noted that trial results have been emerging from other monoclonal antibody cocktails with different COVID-19 patient groups.
However, he said in an interview, “how much more effective they would be than this is something we’d have to look at, as 71% effectiveness in keeping people out of the hospital is pretty good for any treatment.”
“These are great numbers, but vaccination itself keeps you from getting the disease in the first place and not just for a short time period. This treatment is just that – a treatment. It gets you through that episode but it doesn’t mean you won’t get sick again. You don’t develop an immune response as you do with the vaccine,” he said.
Dr. Weinreich agreed: “This is not a substitute for a vaccine except for the small group who get the vaccine and their bodies can’t respond to it because they’re significantly immunocompromised.”
The results from this paper “are one piece of a large, multistudy, phase 3 program that basically spans from prophylaxis all the way to hospitalization and pretty much the gamut – all of them – have worked. All of these studies have shown dramatic improvement in whatever the definitive regulatory endpoint is,” Dr. Weinreich said.
He said discussions are ongoing for full regulatory approval in the United States and for expanding the EUA for other populations, including pre-exposure prophylaxis, “which the [United Kingdom’s] authority has already granted us but the FDA has not.”
The study is funded by Regeneron and the Department of Health & Human Services. Dr. Weinreich is a vice president of Regeneron. Dr. Joshi reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fales holds stock in Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flu shot highly recommended this year
With the Delta variant of COVID-19 still raging in the United States and ICUs in parts of the country filled with patients with the coronavirus, experts are voicing concern about the added risk of a difficult flu season.
Two mathematical models are predicting a big rebound in the number and severity of flu cases in the 2021-22 season after 2020-2021’s flu season failed to show up when public health measures brought in to control COVID-19 seemed to have the added benefit of stopping the flu.
But both analyses, posted to the medRxiv preprint server and not yet peer reviewed by other experts, have come to the same conclusion: The flu could make a comeback this year.
In the worst-case scenario, the United States could see an extra 300,000-400,000 hospitalizations from the flu – almost double the usual number – according to senior study author Mark Roberts, MD, director of the Public Health Dynamics Laboratory at the University of Pittsburgh. These numbers could be a disaster in areas where hospitals are already filled with COVID-19 patients.
Waning natural immunity in the public because of 2020-2021’s missing flu season could make people, especially young children, more likely to get the virus.
“Usually, a combination of natural immunity and vaccination helps tamp down seasonal influenza,” said Dr. Roberts. “If we don’t have the first part, we’ll have to rely more on the vaccine.”
In a typical year, about half of Americans get the flu shot. The new mathematical models predict that the vaccination rate would need to rise to about 75% to avoid the extra hospitalizations. But even a 10% increase in vaccination rates could reduce hospitalizations by 6%-46%, depending on what strains are dominant.
Usually, the Southern Hemisphere flu season, from February to August, helps show what the Northern Hemisphere can expect over the coming winter. But with strict COVID-19 measures and limits on international travel still in place in countries like Australia and New Zealand and much of South America, it has been another record-low year for flu infections, said Ian Barr, PhD, deputy director of the World Health Organization’s Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Influenza in Melbourne.
Australia detected only around 500 cases in 2021, compared with about 300,000 in a normal year, and recorded no hospitalizations or deaths from the flu. New Zealand recorded just two cases.
“I’ve never seen anything like this,” Dr. Barr said.
In Australia, the mild flu season led to fewer people getting their flu shot than usual. The rate fell from around 50% to just 33%, said Dr. Barr. “If that happens in the U.S., the population will be even more vulnerable because there has been almost no flu for more than 12 months,” he said.
Both Dr. Roberts and Dr. Barr say it is vital that as many people as possible get vaccinated during the upcoming flu season, especially children who will have almost no natural immunity to the virus.
“The vaccine is our best weapon against the flu, especially for the most at-risk groups,” said Dr. Barr.
Other parts of the world had mixed results. India saw a high number of flu cases, while neighboring Sri Lanka had very few. West Africa also saw quite a high level of circulating virus. Overall, the flu was detected in 45 countries during the Southern Hemisphere season, less than half of what might be expected in a normal year, said Dr. Barr.
Despite the overall low numbers, the WHO saw enough in the data to make two changes to 2022’s Southern Hemisphere vaccine formulation at its meeting on Sept. 24, after changing just one of the strains for the Northern Hemisphere vaccine at its meeting in February.
The CDC recommends that everyone 6 months or older get the flu shot, with few exceptions.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
With the Delta variant of COVID-19 still raging in the United States and ICUs in parts of the country filled with patients with the coronavirus, experts are voicing concern about the added risk of a difficult flu season.
Two mathematical models are predicting a big rebound in the number and severity of flu cases in the 2021-22 season after 2020-2021’s flu season failed to show up when public health measures brought in to control COVID-19 seemed to have the added benefit of stopping the flu.
But both analyses, posted to the medRxiv preprint server and not yet peer reviewed by other experts, have come to the same conclusion: The flu could make a comeback this year.
In the worst-case scenario, the United States could see an extra 300,000-400,000 hospitalizations from the flu – almost double the usual number – according to senior study author Mark Roberts, MD, director of the Public Health Dynamics Laboratory at the University of Pittsburgh. These numbers could be a disaster in areas where hospitals are already filled with COVID-19 patients.
Waning natural immunity in the public because of 2020-2021’s missing flu season could make people, especially young children, more likely to get the virus.
“Usually, a combination of natural immunity and vaccination helps tamp down seasonal influenza,” said Dr. Roberts. “If we don’t have the first part, we’ll have to rely more on the vaccine.”
In a typical year, about half of Americans get the flu shot. The new mathematical models predict that the vaccination rate would need to rise to about 75% to avoid the extra hospitalizations. But even a 10% increase in vaccination rates could reduce hospitalizations by 6%-46%, depending on what strains are dominant.
Usually, the Southern Hemisphere flu season, from February to August, helps show what the Northern Hemisphere can expect over the coming winter. But with strict COVID-19 measures and limits on international travel still in place in countries like Australia and New Zealand and much of South America, it has been another record-low year for flu infections, said Ian Barr, PhD, deputy director of the World Health Organization’s Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Influenza in Melbourne.
Australia detected only around 500 cases in 2021, compared with about 300,000 in a normal year, and recorded no hospitalizations or deaths from the flu. New Zealand recorded just two cases.
“I’ve never seen anything like this,” Dr. Barr said.
In Australia, the mild flu season led to fewer people getting their flu shot than usual. The rate fell from around 50% to just 33%, said Dr. Barr. “If that happens in the U.S., the population will be even more vulnerable because there has been almost no flu for more than 12 months,” he said.
Both Dr. Roberts and Dr. Barr say it is vital that as many people as possible get vaccinated during the upcoming flu season, especially children who will have almost no natural immunity to the virus.
“The vaccine is our best weapon against the flu, especially for the most at-risk groups,” said Dr. Barr.
Other parts of the world had mixed results. India saw a high number of flu cases, while neighboring Sri Lanka had very few. West Africa also saw quite a high level of circulating virus. Overall, the flu was detected in 45 countries during the Southern Hemisphere season, less than half of what might be expected in a normal year, said Dr. Barr.
Despite the overall low numbers, the WHO saw enough in the data to make two changes to 2022’s Southern Hemisphere vaccine formulation at its meeting on Sept. 24, after changing just one of the strains for the Northern Hemisphere vaccine at its meeting in February.
The CDC recommends that everyone 6 months or older get the flu shot, with few exceptions.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
With the Delta variant of COVID-19 still raging in the United States and ICUs in parts of the country filled with patients with the coronavirus, experts are voicing concern about the added risk of a difficult flu season.
Two mathematical models are predicting a big rebound in the number and severity of flu cases in the 2021-22 season after 2020-2021’s flu season failed to show up when public health measures brought in to control COVID-19 seemed to have the added benefit of stopping the flu.
But both analyses, posted to the medRxiv preprint server and not yet peer reviewed by other experts, have come to the same conclusion: The flu could make a comeback this year.
In the worst-case scenario, the United States could see an extra 300,000-400,000 hospitalizations from the flu – almost double the usual number – according to senior study author Mark Roberts, MD, director of the Public Health Dynamics Laboratory at the University of Pittsburgh. These numbers could be a disaster in areas where hospitals are already filled with COVID-19 patients.
Waning natural immunity in the public because of 2020-2021’s missing flu season could make people, especially young children, more likely to get the virus.
“Usually, a combination of natural immunity and vaccination helps tamp down seasonal influenza,” said Dr. Roberts. “If we don’t have the first part, we’ll have to rely more on the vaccine.”
In a typical year, about half of Americans get the flu shot. The new mathematical models predict that the vaccination rate would need to rise to about 75% to avoid the extra hospitalizations. But even a 10% increase in vaccination rates could reduce hospitalizations by 6%-46%, depending on what strains are dominant.
Usually, the Southern Hemisphere flu season, from February to August, helps show what the Northern Hemisphere can expect over the coming winter. But with strict COVID-19 measures and limits on international travel still in place in countries like Australia and New Zealand and much of South America, it has been another record-low year for flu infections, said Ian Barr, PhD, deputy director of the World Health Organization’s Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Influenza in Melbourne.
Australia detected only around 500 cases in 2021, compared with about 300,000 in a normal year, and recorded no hospitalizations or deaths from the flu. New Zealand recorded just two cases.
“I’ve never seen anything like this,” Dr. Barr said.
In Australia, the mild flu season led to fewer people getting their flu shot than usual. The rate fell from around 50% to just 33%, said Dr. Barr. “If that happens in the U.S., the population will be even more vulnerable because there has been almost no flu for more than 12 months,” he said.
Both Dr. Roberts and Dr. Barr say it is vital that as many people as possible get vaccinated during the upcoming flu season, especially children who will have almost no natural immunity to the virus.
“The vaccine is our best weapon against the flu, especially for the most at-risk groups,” said Dr. Barr.
Other parts of the world had mixed results. India saw a high number of flu cases, while neighboring Sri Lanka had very few. West Africa also saw quite a high level of circulating virus. Overall, the flu was detected in 45 countries during the Southern Hemisphere season, less than half of what might be expected in a normal year, said Dr. Barr.
Despite the overall low numbers, the WHO saw enough in the data to make two changes to 2022’s Southern Hemisphere vaccine formulation at its meeting on Sept. 24, after changing just one of the strains for the Northern Hemisphere vaccine at its meeting in February.
The CDC recommends that everyone 6 months or older get the flu shot, with few exceptions.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Management of pediatric food allergies evolving
The treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) is undergoing a revolution thanks to biologics. Now, an allergist and a dietitian told pediatric dermatologists that the treatment of a related condition – food allergy – is also undergoing a dramatic transformation as the management approach evolves away from blanket avoidance of allergens.
“Over the past 15 years, we’ve seen a shift from a very passive approach where generally we just advised patients to avoid the things they’re allergic to,” said U.K. pediatric allergist Adam Fox, MBBS, MD, in a presentation at The World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology (WCPD) 2021 Annual Meeting. “Now, we have a much better understanding of how allergy develops and strategies to minimize the risk of allergy happening in the first place,” he said.
According to Carina Venter, PhD, RD, associate professor of pediatrics-allergy/immunology at the University of Colorado, Denver, who also spoke at the conference, an estimated 20% to 30% of patients with AD also have food allergies, and up to 90% of infants with cow’s milk allergy develop skin symptoms.
It may not be necessary for a breastfeeding mother to avoid food allergens if a child is allergic, said Dr. Fox, of Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London. “A lot of parents will automatically assume that if their child has an egg or milk allergy, then it’s a good idea to completely eliminate that from their diet if they’re breastfeeding,” but it is “surprisingly uncommon” that this approach makes a difference, he said. “Less goes through the breast milk than people imagine,” he said.
He noted that eliminating foods from the breastfeeding mother’s diet may have negative consequences. “There’s always that risk that if you make life harder for the breastfeeding mom because they’re going to have to avoid all sorts of foods, they’ll be more likely to discontinue breastfeeding. You really need a compelling reason to stop the food.”
As for children themselves, Dr. Fox suggested that there’s often no connection between AD and food allergies. “What will commonly happen when you see and diagnose these kids is that their eczema has been quite significantly undertreated,” he said. “Once you just get them on the right [regimen], they don’t need to be cutting the food out of their diet. It’s just making their life unnecessarily harder.”
Dr. Venter said there may be little choice but to avoid a trigger food if a child develops AD with exposure. However, she noted, it’s important to understand that avoidance of certain foods could make the allergy – and AD – worse. “If you have a child or an adult with atopic dermatitis that’s not controlled by an optimal topical treatment, and you do consider avoidance, we need to be aware that development of more severe IgA-mediated symptoms can happen in a short period of time,” she said.
In a slide that Dr. Venter presented, the dilemma for physicians was expressed this way: “The potential benefit of food avoidance as a management strategy for some patients with AD must now be weighed against the strong evidence that unnecessarily avoiding a food in kids with AD increases the risk of developing anaphylaxis to that food.”
What should pediatric dermatologists do to balance the risks of allergen exposure to the risks that children will develop permanent allergies? Dr. Venter pointed to guidelines about AD that were developed by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. She also highlighted the International Milk Allergy in Primary Care recommendations.
She suggested considering creative ways to bypass complete avoidance and boost a child’s tolerance of allergens if possible. “If we’re going to keep a child with eczema on a mold-free diet for a longer period of time, is there perhaps a role for regularly introducing small amounts of yogurt or even small amounts of milk in the child’s diet to at least keep immune tolerance without necessarily aggravating eczema symptoms?”
Dr. Fox has consulted for DBV and Aimmune through his employer, NHS Trust. He serves as president of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology and as chair of the Allergy UK Health Advisory Board, both of which receive funding from drug companies. Dr. Venter has received support for allergy-related research from the National Peanut Board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) is undergoing a revolution thanks to biologics. Now, an allergist and a dietitian told pediatric dermatologists that the treatment of a related condition – food allergy – is also undergoing a dramatic transformation as the management approach evolves away from blanket avoidance of allergens.
“Over the past 15 years, we’ve seen a shift from a very passive approach where generally we just advised patients to avoid the things they’re allergic to,” said U.K. pediatric allergist Adam Fox, MBBS, MD, in a presentation at The World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology (WCPD) 2021 Annual Meeting. “Now, we have a much better understanding of how allergy develops and strategies to minimize the risk of allergy happening in the first place,” he said.
According to Carina Venter, PhD, RD, associate professor of pediatrics-allergy/immunology at the University of Colorado, Denver, who also spoke at the conference, an estimated 20% to 30% of patients with AD also have food allergies, and up to 90% of infants with cow’s milk allergy develop skin symptoms.
It may not be necessary for a breastfeeding mother to avoid food allergens if a child is allergic, said Dr. Fox, of Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London. “A lot of parents will automatically assume that if their child has an egg or milk allergy, then it’s a good idea to completely eliminate that from their diet if they’re breastfeeding,” but it is “surprisingly uncommon” that this approach makes a difference, he said. “Less goes through the breast milk than people imagine,” he said.
He noted that eliminating foods from the breastfeeding mother’s diet may have negative consequences. “There’s always that risk that if you make life harder for the breastfeeding mom because they’re going to have to avoid all sorts of foods, they’ll be more likely to discontinue breastfeeding. You really need a compelling reason to stop the food.”
As for children themselves, Dr. Fox suggested that there’s often no connection between AD and food allergies. “What will commonly happen when you see and diagnose these kids is that their eczema has been quite significantly undertreated,” he said. “Once you just get them on the right [regimen], they don’t need to be cutting the food out of their diet. It’s just making their life unnecessarily harder.”
Dr. Venter said there may be little choice but to avoid a trigger food if a child develops AD with exposure. However, she noted, it’s important to understand that avoidance of certain foods could make the allergy – and AD – worse. “If you have a child or an adult with atopic dermatitis that’s not controlled by an optimal topical treatment, and you do consider avoidance, we need to be aware that development of more severe IgA-mediated symptoms can happen in a short period of time,” she said.
In a slide that Dr. Venter presented, the dilemma for physicians was expressed this way: “The potential benefit of food avoidance as a management strategy for some patients with AD must now be weighed against the strong evidence that unnecessarily avoiding a food in kids with AD increases the risk of developing anaphylaxis to that food.”
What should pediatric dermatologists do to balance the risks of allergen exposure to the risks that children will develop permanent allergies? Dr. Venter pointed to guidelines about AD that were developed by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. She also highlighted the International Milk Allergy in Primary Care recommendations.
She suggested considering creative ways to bypass complete avoidance and boost a child’s tolerance of allergens if possible. “If we’re going to keep a child with eczema on a mold-free diet for a longer period of time, is there perhaps a role for regularly introducing small amounts of yogurt or even small amounts of milk in the child’s diet to at least keep immune tolerance without necessarily aggravating eczema symptoms?”
Dr. Fox has consulted for DBV and Aimmune through his employer, NHS Trust. He serves as president of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology and as chair of the Allergy UK Health Advisory Board, both of which receive funding from drug companies. Dr. Venter has received support for allergy-related research from the National Peanut Board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) is undergoing a revolution thanks to biologics. Now, an allergist and a dietitian told pediatric dermatologists that the treatment of a related condition – food allergy – is also undergoing a dramatic transformation as the management approach evolves away from blanket avoidance of allergens.
“Over the past 15 years, we’ve seen a shift from a very passive approach where generally we just advised patients to avoid the things they’re allergic to,” said U.K. pediatric allergist Adam Fox, MBBS, MD, in a presentation at The World Congress of Pediatric Dermatology (WCPD) 2021 Annual Meeting. “Now, we have a much better understanding of how allergy develops and strategies to minimize the risk of allergy happening in the first place,” he said.
According to Carina Venter, PhD, RD, associate professor of pediatrics-allergy/immunology at the University of Colorado, Denver, who also spoke at the conference, an estimated 20% to 30% of patients with AD also have food allergies, and up to 90% of infants with cow’s milk allergy develop skin symptoms.
It may not be necessary for a breastfeeding mother to avoid food allergens if a child is allergic, said Dr. Fox, of Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London. “A lot of parents will automatically assume that if their child has an egg or milk allergy, then it’s a good idea to completely eliminate that from their diet if they’re breastfeeding,” but it is “surprisingly uncommon” that this approach makes a difference, he said. “Less goes through the breast milk than people imagine,” he said.
He noted that eliminating foods from the breastfeeding mother’s diet may have negative consequences. “There’s always that risk that if you make life harder for the breastfeeding mom because they’re going to have to avoid all sorts of foods, they’ll be more likely to discontinue breastfeeding. You really need a compelling reason to stop the food.”
As for children themselves, Dr. Fox suggested that there’s often no connection between AD and food allergies. “What will commonly happen when you see and diagnose these kids is that their eczema has been quite significantly undertreated,” he said. “Once you just get them on the right [regimen], they don’t need to be cutting the food out of their diet. It’s just making their life unnecessarily harder.”
Dr. Venter said there may be little choice but to avoid a trigger food if a child develops AD with exposure. However, she noted, it’s important to understand that avoidance of certain foods could make the allergy – and AD – worse. “If you have a child or an adult with atopic dermatitis that’s not controlled by an optimal topical treatment, and you do consider avoidance, we need to be aware that development of more severe IgA-mediated symptoms can happen in a short period of time,” she said.
In a slide that Dr. Venter presented, the dilemma for physicians was expressed this way: “The potential benefit of food avoidance as a management strategy for some patients with AD must now be weighed against the strong evidence that unnecessarily avoiding a food in kids with AD increases the risk of developing anaphylaxis to that food.”
What should pediatric dermatologists do to balance the risks of allergen exposure to the risks that children will develop permanent allergies? Dr. Venter pointed to guidelines about AD that were developed by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. She also highlighted the International Milk Allergy in Primary Care recommendations.
She suggested considering creative ways to bypass complete avoidance and boost a child’s tolerance of allergens if possible. “If we’re going to keep a child with eczema on a mold-free diet for a longer period of time, is there perhaps a role for regularly introducing small amounts of yogurt or even small amounts of milk in the child’s diet to at least keep immune tolerance without necessarily aggravating eczema symptoms?”
Dr. Fox has consulted for DBV and Aimmune through his employer, NHS Trust. He serves as president of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology and as chair of the Allergy UK Health Advisory Board, both of which receive funding from drug companies. Dr. Venter has received support for allergy-related research from the National Peanut Board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.