User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Why pregnant people were left behind while vaccines moved at ‘warp speed’ to help the masses
Kia Slade was 7 months pregnant, unvaccinated, and fighting for breath, her oxygen levels plummeting, when her son came into the world last May.
A severe case of COVID-19 pneumonia had left Ms. Slade delirious. When the intensive care team tried to place an oxygen mask on her face, she snatched it away, she recalled. Her baby’s heart rate began to drop.
Ms. Slade’s doctor performed an emergency cesarean section at her bedside in the intensive care unit, delivering baby Tristan 10 weeks early. He weighed just 2 pounds, 14 ounces, about half the size of small full-term baby.
But Ms. Slade wouldn’t meet him until July. She was on a ventilator in a medically-induced coma for 8 weeks, and she developed a serious infection and blood clot while unconscious. It was only after a perilous 2½ months in the hospital, during which her heart stopped twice, that Ms. Slade was vaccinated against COVID-19.
“I wish I had gotten the vaccine earlier,” said Ms. Slade, 42, who remains too sick to return to work as a special education teacher in Baltimore. Doctors “kept pushing me to get vaccinated, but there just wasn’t enough information out there for me to do it.”
A year ago, there was little to no vaccine safety data for pregnant people like Ms. Slade, because they had been excluded from clinical trials run by Pfizer, Moderna, and other vaccine makers.
Lacking data, health experts were unsure and divided about how to advise expectant parents. Although U.S. health officials permitted pregnant people to be vaccinated, the World Health Organization in January 2021 actually discouraged them from doing so; it later reversed that recommendation.
The uncertainty led many women to delay vaccination, and only about two-thirds of the pregnant people who have been tracked by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were fully vaccinated as of Feb. 5, 2022, leaving many expectant moms at a high risk of infection and life-threatening complications.
More than 29,000 pregnant people have been hospitalized with COVID-19 and 274 have died, according to the CDC.
“There were surely women who were hospitalized because there wasn’t information available to them,” said Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Vaccine developers say that pregnant people – who have special health needs and risks – were excluded from clinical trials to protect them from potential side effects of novel technologies, including the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines and formulations made with cold viruses, such as the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
But a KHN analysis also shows that pregnant people were left behind because including them in vaccine studies would have complicated and potentially delayed the delivery of COVID-19 vaccines to the broader population.
A growing number of women’s health researchers and advocates say that excluding pregnant people – and the months-long delay in recommending that they be immunized – helped fuel widespread vaccine hesitancy in this vulnerable group.
“Women and their unborn fetuses are dying of COVID infection,” said Jane Van Dis, MD, an ob.gyn. at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center who has treated many patients like Ms. Slade. “Our failure as a society to vaccinate women in pregnancy will be remembered by the children and families who lost their mothers to this disease.”
New technology, uncertain risks
At the time COVID-19 vaccines were being developed, scientists had very little experience using mRNA vaccines in pregnant women, said Jacqueline Miller, MD, a senior vice president involved in vaccine research at Moderna.
“When you study anything in pregnant women, you have two patients, the mom and the unborn child,” Dr. Miller said. “Until we had more safety data on the platform, it wasn’t something we wanted to undertake.”
But Dr. Offit noted that vaccines have a strong record of safety in pregnancy and he sees no reason to have excluded pregnant people. None of the vaccines currently in use – including the chickenpox and rubella vaccines, which contain live viruses – have been shown to harm fetuses, he said. Doctors routinely recommend that pregnant people receive pertussis and flu vaccinations.
Dr. Offit, the coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, said that some concerns about vaccines stem from commercial, not medical, interests. Drug makers don’t want to risk that their product will be blamed for any problems occurring in pregnant people, even if coincidental, he said.
“These companies don’t want bad news,” Dr. Offit said.
In the United States, health officials typically would have told expectant mothers not to take a vaccine that was untested during pregnancy, said Dr. Offit, a member of a committee that advises the Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Due to the urgency of the pandemic, health agencies instead permitted pregnant people to make up their own minds about vaccines without recommending them.
Women’s medical associations were also hampered by the lack of data. Neither the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists nor the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine actively encouraged pregnant people to be vaccinated until July 30, 2021, after the first real-world vaccine studies had been published. The CDC followed suit in August of 2021.
“If we had had this data in the beginning, we would have been able to vaccinate more women,” said Kelli Burroughs, MD, the department chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Memorial Hermann Sugar Land Hospital near Houston.
Yet anti-vaccine groups wasted no time in scaring pregnant people, flooding social media with misinformation about impaired fertility and harm to the fetus.
In the first few months after the COVID-19 vaccines were approved, some doctors were ambivalent about recommending them, and some still advise pregnant patients against vaccination.
An estimated 67% of pregnant people today are fully vaccinated, compared with about 89% of people 65 and older, another high-risk group, and 65% of Americans overall. Vaccination rates are lower among minorities, with 65% of expectant Hispanic mothers and 53% of pregnant African Americans fully vaccinated, according to the CDC.
Vaccination is especially important during pregnancy, because of increased risks of hospitalization, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation, Dr. Burroughs said. A study released in February from the National Institutes of Health found that pregnant people with a moderate to severe COVID-19 infection also were more likely to have a C-section, deliver preterm, or develop a postpartum hemorrhage.
Black moms such as Ms. Slade were already at higher risk of maternal and infant mortality before the pandemic, because of higher underlying risks, unequal access to health care, and other factors. COVID-19 has magnified those risks, said Dr. Burroughs, who has persuaded reluctant patients by revealing that she had a healthy pregnancy and child after being vaccinated.
Ms. Slade said she has never opposed vaccines and had no hesitation about receiving other vaccines while pregnant. But she said she “just wasn’t comfortable” with COVID-19 shots.
“If there had been data out there saying the COVID shot was safe, and that nothing would happen to my baby and there was no risk of birth defects, I would have taken it,” said Ms. Slade, who has had type 2 diabetes for 12 years.
Working at warp speed
Government scientists at the NIH were concerned about the risk of COVID-19 to pregnant people from the very beginning and knew that expectant moms needed vaccines as much or more than anyone else, said Larry Corey, MD, a leader of the COVID-19 Prevention Network, which coordinated COVID-19 vaccine trials for the federal government.
But including pregnant volunteers in the larger vaccine trials could have led to interruptions and delays, Dr. Corey said. Researchers would have had to enroll thousands of pregnant volunteers to achieve statistically robust results that weren’t due to chance, he said.
Pregnancy can bring on a wide range of complications: gestational diabetes, hypertension, anemia, bleeding, blood clots, or problems with the placenta, for example. Up to 20% of people who know they’re pregnant miscarry. Because researchers would have been obliged to investigate any medical problem to make sure it wasn’t caused by one of the COVID-19 vaccines, including pregnant people might have meant having to hit pause on those trials, Dr. Corey said.
With death tolls from the pandemic mounting, “we had a mission to do this as quickly and as thoroughly as possible,” Dr. Corey said. Making COVID-19 vaccines available within a year “saved hundreds of thousands of lives.”
The first data on COVID-19 vaccine safety in pregnancy was published in April of 2021 when the CDC released an analysis of nearly 36,000 vaccinated pregnant people who had enrolled in a registry called V-safe, which allows users to log the dates of their vaccinations and any subsequent symptoms.
Later research showed that COVID-19 vaccines weren’t associated with increased risk of miscarriage or premature delivery.
Brenna Hughes, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and member of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ COVID-19 expert group, agrees that adding pregnant people to large-scale COVID-19 vaccine and drug trials may have been impractical. But researchers could have launched parallel trials of pregnant women, once early studies showed the vaccines were safe in humans, she said.
“Would it have been hard? Everything with COVID is hard,” Dr. Hughes said. “But it would have been feasible.”
The FDA requires that researchers perform additional animal studies – called developmental and reproductive toxicity studies – before testing vaccines in pregnant people. Although these studies are essential, they take 5-6 months, and weren’t completed until late 2020, around the time the first COVID-19 vaccines were authorized for adults, said Emily Erbelding, MD, director of microbiology and infectious diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of the NIH.
Pregnancy studies “were an afterthought,” said Irina Burd, MD, director of Johns Hopkins’ Integrated Research Center for Fetal Medicine and a professor of gynecology and obstetrics. “They should have been done sooner.”
The NIH is conducting a study of pregnant and postpartum people who decided on their own to be vaccinated, Dr. Erbelding said. The study is due to be completed by July 2023.
Janssen and Moderna are also conducting studies in pregnant people, both due to be completed in 2024.
Pfizer scientists encountered problems when they initiated a clinical trial, which would have randomly assigned pregnant people to receive either a vaccine or placebo. Once vaccines were widely available, many patients weren’t willing to take a chance on being unvaccinated until after delivery.
Pfizer has stopped recruiting patients and has not said whether it will publicly report any data from the trial.
Dr. Hughes said vaccine developers need to include pregnant people from the very beginning.
“There is this notion of protecting pregnant people from research,” Dr. Hughes said. “But we should be protecting patients through research, not from research.”
Recovering physically and emotionally
Ms. Slade still regrets being deprived of time with her children while she fought the disease.
Being on a ventilator kept her from spending those early weeks with her newborn, or from seeing her 9-year-old daughter, Zoe.
Even when Ms. Slade was finally able to see her son, she wasn’t able to tell him she loved him or sing a lullaby, or even talk at all, because of a breathing tube in her throat.
Today, Ms. Slade is a strong advocate of COVID-19 vaccinations, urging her friends and family to get their shots to avoid suffering the way she has.
Ms. Slade had to relearn to walk after being bedridden for weeks. Her many weeks on a ventilator may have contributed to her stomach paralysis, which often causes intense pain, nausea, and even vomiting when she eats or drinks. Ms. Slade weighs 50 pounds less today than before she became pregnant and has resorted to going to the emergency department when the pain is unbearable. “Most days, I’m just miserable,” she said.
Her family suffered as well. Like many babies born prematurely, Tristan, now nearly 9 months old and crawling, receives physical therapy to strengthen his muscles. At 15 pounds, Tristan is largely healthy, although his doctor said he has symptoms of asthma.
Ms. Slade said she would like to attend family counseling with Zoe, who rarely complains and tends to keep her feelings to herself. Ms. Slade said she knows her illness must have been terrifying for her little girl.
“The other day she was talking to me,” Ms. Slade said, “and she said, ‘You know, I almost had to bury you.’ ”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Kia Slade was 7 months pregnant, unvaccinated, and fighting for breath, her oxygen levels plummeting, when her son came into the world last May.
A severe case of COVID-19 pneumonia had left Ms. Slade delirious. When the intensive care team tried to place an oxygen mask on her face, she snatched it away, she recalled. Her baby’s heart rate began to drop.
Ms. Slade’s doctor performed an emergency cesarean section at her bedside in the intensive care unit, delivering baby Tristan 10 weeks early. He weighed just 2 pounds, 14 ounces, about half the size of small full-term baby.
But Ms. Slade wouldn’t meet him until July. She was on a ventilator in a medically-induced coma for 8 weeks, and she developed a serious infection and blood clot while unconscious. It was only after a perilous 2½ months in the hospital, during which her heart stopped twice, that Ms. Slade was vaccinated against COVID-19.
“I wish I had gotten the vaccine earlier,” said Ms. Slade, 42, who remains too sick to return to work as a special education teacher in Baltimore. Doctors “kept pushing me to get vaccinated, but there just wasn’t enough information out there for me to do it.”
A year ago, there was little to no vaccine safety data for pregnant people like Ms. Slade, because they had been excluded from clinical trials run by Pfizer, Moderna, and other vaccine makers.
Lacking data, health experts were unsure and divided about how to advise expectant parents. Although U.S. health officials permitted pregnant people to be vaccinated, the World Health Organization in January 2021 actually discouraged them from doing so; it later reversed that recommendation.
The uncertainty led many women to delay vaccination, and only about two-thirds of the pregnant people who have been tracked by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were fully vaccinated as of Feb. 5, 2022, leaving many expectant moms at a high risk of infection and life-threatening complications.
More than 29,000 pregnant people have been hospitalized with COVID-19 and 274 have died, according to the CDC.
“There were surely women who were hospitalized because there wasn’t information available to them,” said Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Vaccine developers say that pregnant people – who have special health needs and risks – were excluded from clinical trials to protect them from potential side effects of novel technologies, including the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines and formulations made with cold viruses, such as the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
But a KHN analysis also shows that pregnant people were left behind because including them in vaccine studies would have complicated and potentially delayed the delivery of COVID-19 vaccines to the broader population.
A growing number of women’s health researchers and advocates say that excluding pregnant people – and the months-long delay in recommending that they be immunized – helped fuel widespread vaccine hesitancy in this vulnerable group.
“Women and their unborn fetuses are dying of COVID infection,” said Jane Van Dis, MD, an ob.gyn. at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center who has treated many patients like Ms. Slade. “Our failure as a society to vaccinate women in pregnancy will be remembered by the children and families who lost their mothers to this disease.”
New technology, uncertain risks
At the time COVID-19 vaccines were being developed, scientists had very little experience using mRNA vaccines in pregnant women, said Jacqueline Miller, MD, a senior vice president involved in vaccine research at Moderna.
“When you study anything in pregnant women, you have two patients, the mom and the unborn child,” Dr. Miller said. “Until we had more safety data on the platform, it wasn’t something we wanted to undertake.”
But Dr. Offit noted that vaccines have a strong record of safety in pregnancy and he sees no reason to have excluded pregnant people. None of the vaccines currently in use – including the chickenpox and rubella vaccines, which contain live viruses – have been shown to harm fetuses, he said. Doctors routinely recommend that pregnant people receive pertussis and flu vaccinations.
Dr. Offit, the coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, said that some concerns about vaccines stem from commercial, not medical, interests. Drug makers don’t want to risk that their product will be blamed for any problems occurring in pregnant people, even if coincidental, he said.
“These companies don’t want bad news,” Dr. Offit said.
In the United States, health officials typically would have told expectant mothers not to take a vaccine that was untested during pregnancy, said Dr. Offit, a member of a committee that advises the Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Due to the urgency of the pandemic, health agencies instead permitted pregnant people to make up their own minds about vaccines without recommending them.
Women’s medical associations were also hampered by the lack of data. Neither the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists nor the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine actively encouraged pregnant people to be vaccinated until July 30, 2021, after the first real-world vaccine studies had been published. The CDC followed suit in August of 2021.
“If we had had this data in the beginning, we would have been able to vaccinate more women,” said Kelli Burroughs, MD, the department chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Memorial Hermann Sugar Land Hospital near Houston.
Yet anti-vaccine groups wasted no time in scaring pregnant people, flooding social media with misinformation about impaired fertility and harm to the fetus.
In the first few months after the COVID-19 vaccines were approved, some doctors were ambivalent about recommending them, and some still advise pregnant patients against vaccination.
An estimated 67% of pregnant people today are fully vaccinated, compared with about 89% of people 65 and older, another high-risk group, and 65% of Americans overall. Vaccination rates are lower among minorities, with 65% of expectant Hispanic mothers and 53% of pregnant African Americans fully vaccinated, according to the CDC.
Vaccination is especially important during pregnancy, because of increased risks of hospitalization, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation, Dr. Burroughs said. A study released in February from the National Institutes of Health found that pregnant people with a moderate to severe COVID-19 infection also were more likely to have a C-section, deliver preterm, or develop a postpartum hemorrhage.
Black moms such as Ms. Slade were already at higher risk of maternal and infant mortality before the pandemic, because of higher underlying risks, unequal access to health care, and other factors. COVID-19 has magnified those risks, said Dr. Burroughs, who has persuaded reluctant patients by revealing that she had a healthy pregnancy and child after being vaccinated.
Ms. Slade said she has never opposed vaccines and had no hesitation about receiving other vaccines while pregnant. But she said she “just wasn’t comfortable” with COVID-19 shots.
“If there had been data out there saying the COVID shot was safe, and that nothing would happen to my baby and there was no risk of birth defects, I would have taken it,” said Ms. Slade, who has had type 2 diabetes for 12 years.
Working at warp speed
Government scientists at the NIH were concerned about the risk of COVID-19 to pregnant people from the very beginning and knew that expectant moms needed vaccines as much or more than anyone else, said Larry Corey, MD, a leader of the COVID-19 Prevention Network, which coordinated COVID-19 vaccine trials for the federal government.
But including pregnant volunteers in the larger vaccine trials could have led to interruptions and delays, Dr. Corey said. Researchers would have had to enroll thousands of pregnant volunteers to achieve statistically robust results that weren’t due to chance, he said.
Pregnancy can bring on a wide range of complications: gestational diabetes, hypertension, anemia, bleeding, blood clots, or problems with the placenta, for example. Up to 20% of people who know they’re pregnant miscarry. Because researchers would have been obliged to investigate any medical problem to make sure it wasn’t caused by one of the COVID-19 vaccines, including pregnant people might have meant having to hit pause on those trials, Dr. Corey said.
With death tolls from the pandemic mounting, “we had a mission to do this as quickly and as thoroughly as possible,” Dr. Corey said. Making COVID-19 vaccines available within a year “saved hundreds of thousands of lives.”
The first data on COVID-19 vaccine safety in pregnancy was published in April of 2021 when the CDC released an analysis of nearly 36,000 vaccinated pregnant people who had enrolled in a registry called V-safe, which allows users to log the dates of their vaccinations and any subsequent symptoms.
Later research showed that COVID-19 vaccines weren’t associated with increased risk of miscarriage or premature delivery.
Brenna Hughes, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and member of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ COVID-19 expert group, agrees that adding pregnant people to large-scale COVID-19 vaccine and drug trials may have been impractical. But researchers could have launched parallel trials of pregnant women, once early studies showed the vaccines were safe in humans, she said.
“Would it have been hard? Everything with COVID is hard,” Dr. Hughes said. “But it would have been feasible.”
The FDA requires that researchers perform additional animal studies – called developmental and reproductive toxicity studies – before testing vaccines in pregnant people. Although these studies are essential, they take 5-6 months, and weren’t completed until late 2020, around the time the first COVID-19 vaccines were authorized for adults, said Emily Erbelding, MD, director of microbiology and infectious diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of the NIH.
Pregnancy studies “were an afterthought,” said Irina Burd, MD, director of Johns Hopkins’ Integrated Research Center for Fetal Medicine and a professor of gynecology and obstetrics. “They should have been done sooner.”
The NIH is conducting a study of pregnant and postpartum people who decided on their own to be vaccinated, Dr. Erbelding said. The study is due to be completed by July 2023.
Janssen and Moderna are also conducting studies in pregnant people, both due to be completed in 2024.
Pfizer scientists encountered problems when they initiated a clinical trial, which would have randomly assigned pregnant people to receive either a vaccine or placebo. Once vaccines were widely available, many patients weren’t willing to take a chance on being unvaccinated until after delivery.
Pfizer has stopped recruiting patients and has not said whether it will publicly report any data from the trial.
Dr. Hughes said vaccine developers need to include pregnant people from the very beginning.
“There is this notion of protecting pregnant people from research,” Dr. Hughes said. “But we should be protecting patients through research, not from research.”
Recovering physically and emotionally
Ms. Slade still regrets being deprived of time with her children while she fought the disease.
Being on a ventilator kept her from spending those early weeks with her newborn, or from seeing her 9-year-old daughter, Zoe.
Even when Ms. Slade was finally able to see her son, she wasn’t able to tell him she loved him or sing a lullaby, or even talk at all, because of a breathing tube in her throat.
Today, Ms. Slade is a strong advocate of COVID-19 vaccinations, urging her friends and family to get their shots to avoid suffering the way she has.
Ms. Slade had to relearn to walk after being bedridden for weeks. Her many weeks on a ventilator may have contributed to her stomach paralysis, which often causes intense pain, nausea, and even vomiting when she eats or drinks. Ms. Slade weighs 50 pounds less today than before she became pregnant and has resorted to going to the emergency department when the pain is unbearable. “Most days, I’m just miserable,” she said.
Her family suffered as well. Like many babies born prematurely, Tristan, now nearly 9 months old and crawling, receives physical therapy to strengthen his muscles. At 15 pounds, Tristan is largely healthy, although his doctor said he has symptoms of asthma.
Ms. Slade said she would like to attend family counseling with Zoe, who rarely complains and tends to keep her feelings to herself. Ms. Slade said she knows her illness must have been terrifying for her little girl.
“The other day she was talking to me,” Ms. Slade said, “and she said, ‘You know, I almost had to bury you.’ ”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Kia Slade was 7 months pregnant, unvaccinated, and fighting for breath, her oxygen levels plummeting, when her son came into the world last May.
A severe case of COVID-19 pneumonia had left Ms. Slade delirious. When the intensive care team tried to place an oxygen mask on her face, she snatched it away, she recalled. Her baby’s heart rate began to drop.
Ms. Slade’s doctor performed an emergency cesarean section at her bedside in the intensive care unit, delivering baby Tristan 10 weeks early. He weighed just 2 pounds, 14 ounces, about half the size of small full-term baby.
But Ms. Slade wouldn’t meet him until July. She was on a ventilator in a medically-induced coma for 8 weeks, and she developed a serious infection and blood clot while unconscious. It was only after a perilous 2½ months in the hospital, during which her heart stopped twice, that Ms. Slade was vaccinated against COVID-19.
“I wish I had gotten the vaccine earlier,” said Ms. Slade, 42, who remains too sick to return to work as a special education teacher in Baltimore. Doctors “kept pushing me to get vaccinated, but there just wasn’t enough information out there for me to do it.”
A year ago, there was little to no vaccine safety data for pregnant people like Ms. Slade, because they had been excluded from clinical trials run by Pfizer, Moderna, and other vaccine makers.
Lacking data, health experts were unsure and divided about how to advise expectant parents. Although U.S. health officials permitted pregnant people to be vaccinated, the World Health Organization in January 2021 actually discouraged them from doing so; it later reversed that recommendation.
The uncertainty led many women to delay vaccination, and only about two-thirds of the pregnant people who have been tracked by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were fully vaccinated as of Feb. 5, 2022, leaving many expectant moms at a high risk of infection and life-threatening complications.
More than 29,000 pregnant people have been hospitalized with COVID-19 and 274 have died, according to the CDC.
“There were surely women who were hospitalized because there wasn’t information available to them,” said Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Vaccine developers say that pregnant people – who have special health needs and risks – were excluded from clinical trials to protect them from potential side effects of novel technologies, including the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines and formulations made with cold viruses, such as the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
But a KHN analysis also shows that pregnant people were left behind because including them in vaccine studies would have complicated and potentially delayed the delivery of COVID-19 vaccines to the broader population.
A growing number of women’s health researchers and advocates say that excluding pregnant people – and the months-long delay in recommending that they be immunized – helped fuel widespread vaccine hesitancy in this vulnerable group.
“Women and their unborn fetuses are dying of COVID infection,” said Jane Van Dis, MD, an ob.gyn. at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center who has treated many patients like Ms. Slade. “Our failure as a society to vaccinate women in pregnancy will be remembered by the children and families who lost their mothers to this disease.”
New technology, uncertain risks
At the time COVID-19 vaccines were being developed, scientists had very little experience using mRNA vaccines in pregnant women, said Jacqueline Miller, MD, a senior vice president involved in vaccine research at Moderna.
“When you study anything in pregnant women, you have two patients, the mom and the unborn child,” Dr. Miller said. “Until we had more safety data on the platform, it wasn’t something we wanted to undertake.”
But Dr. Offit noted that vaccines have a strong record of safety in pregnancy and he sees no reason to have excluded pregnant people. None of the vaccines currently in use – including the chickenpox and rubella vaccines, which contain live viruses – have been shown to harm fetuses, he said. Doctors routinely recommend that pregnant people receive pertussis and flu vaccinations.
Dr. Offit, the coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, said that some concerns about vaccines stem from commercial, not medical, interests. Drug makers don’t want to risk that their product will be blamed for any problems occurring in pregnant people, even if coincidental, he said.
“These companies don’t want bad news,” Dr. Offit said.
In the United States, health officials typically would have told expectant mothers not to take a vaccine that was untested during pregnancy, said Dr. Offit, a member of a committee that advises the Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Due to the urgency of the pandemic, health agencies instead permitted pregnant people to make up their own minds about vaccines without recommending them.
Women’s medical associations were also hampered by the lack of data. Neither the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists nor the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine actively encouraged pregnant people to be vaccinated until July 30, 2021, after the first real-world vaccine studies had been published. The CDC followed suit in August of 2021.
“If we had had this data in the beginning, we would have been able to vaccinate more women,” said Kelli Burroughs, MD, the department chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Memorial Hermann Sugar Land Hospital near Houston.
Yet anti-vaccine groups wasted no time in scaring pregnant people, flooding social media with misinformation about impaired fertility and harm to the fetus.
In the first few months after the COVID-19 vaccines were approved, some doctors were ambivalent about recommending them, and some still advise pregnant patients against vaccination.
An estimated 67% of pregnant people today are fully vaccinated, compared with about 89% of people 65 and older, another high-risk group, and 65% of Americans overall. Vaccination rates are lower among minorities, with 65% of expectant Hispanic mothers and 53% of pregnant African Americans fully vaccinated, according to the CDC.
Vaccination is especially important during pregnancy, because of increased risks of hospitalization, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation, Dr. Burroughs said. A study released in February from the National Institutes of Health found that pregnant people with a moderate to severe COVID-19 infection also were more likely to have a C-section, deliver preterm, or develop a postpartum hemorrhage.
Black moms such as Ms. Slade were already at higher risk of maternal and infant mortality before the pandemic, because of higher underlying risks, unequal access to health care, and other factors. COVID-19 has magnified those risks, said Dr. Burroughs, who has persuaded reluctant patients by revealing that she had a healthy pregnancy and child after being vaccinated.
Ms. Slade said she has never opposed vaccines and had no hesitation about receiving other vaccines while pregnant. But she said she “just wasn’t comfortable” with COVID-19 shots.
“If there had been data out there saying the COVID shot was safe, and that nothing would happen to my baby and there was no risk of birth defects, I would have taken it,” said Ms. Slade, who has had type 2 diabetes for 12 years.
Working at warp speed
Government scientists at the NIH were concerned about the risk of COVID-19 to pregnant people from the very beginning and knew that expectant moms needed vaccines as much or more than anyone else, said Larry Corey, MD, a leader of the COVID-19 Prevention Network, which coordinated COVID-19 vaccine trials for the federal government.
But including pregnant volunteers in the larger vaccine trials could have led to interruptions and delays, Dr. Corey said. Researchers would have had to enroll thousands of pregnant volunteers to achieve statistically robust results that weren’t due to chance, he said.
Pregnancy can bring on a wide range of complications: gestational diabetes, hypertension, anemia, bleeding, blood clots, or problems with the placenta, for example. Up to 20% of people who know they’re pregnant miscarry. Because researchers would have been obliged to investigate any medical problem to make sure it wasn’t caused by one of the COVID-19 vaccines, including pregnant people might have meant having to hit pause on those trials, Dr. Corey said.
With death tolls from the pandemic mounting, “we had a mission to do this as quickly and as thoroughly as possible,” Dr. Corey said. Making COVID-19 vaccines available within a year “saved hundreds of thousands of lives.”
The first data on COVID-19 vaccine safety in pregnancy was published in April of 2021 when the CDC released an analysis of nearly 36,000 vaccinated pregnant people who had enrolled in a registry called V-safe, which allows users to log the dates of their vaccinations and any subsequent symptoms.
Later research showed that COVID-19 vaccines weren’t associated with increased risk of miscarriage or premature delivery.
Brenna Hughes, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and member of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ COVID-19 expert group, agrees that adding pregnant people to large-scale COVID-19 vaccine and drug trials may have been impractical. But researchers could have launched parallel trials of pregnant women, once early studies showed the vaccines were safe in humans, she said.
“Would it have been hard? Everything with COVID is hard,” Dr. Hughes said. “But it would have been feasible.”
The FDA requires that researchers perform additional animal studies – called developmental and reproductive toxicity studies – before testing vaccines in pregnant people. Although these studies are essential, they take 5-6 months, and weren’t completed until late 2020, around the time the first COVID-19 vaccines were authorized for adults, said Emily Erbelding, MD, director of microbiology and infectious diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of the NIH.
Pregnancy studies “were an afterthought,” said Irina Burd, MD, director of Johns Hopkins’ Integrated Research Center for Fetal Medicine and a professor of gynecology and obstetrics. “They should have been done sooner.”
The NIH is conducting a study of pregnant and postpartum people who decided on their own to be vaccinated, Dr. Erbelding said. The study is due to be completed by July 2023.
Janssen and Moderna are also conducting studies in pregnant people, both due to be completed in 2024.
Pfizer scientists encountered problems when they initiated a clinical trial, which would have randomly assigned pregnant people to receive either a vaccine or placebo. Once vaccines were widely available, many patients weren’t willing to take a chance on being unvaccinated until after delivery.
Pfizer has stopped recruiting patients and has not said whether it will publicly report any data from the trial.
Dr. Hughes said vaccine developers need to include pregnant people from the very beginning.
“There is this notion of protecting pregnant people from research,” Dr. Hughes said. “But we should be protecting patients through research, not from research.”
Recovering physically and emotionally
Ms. Slade still regrets being deprived of time with her children while she fought the disease.
Being on a ventilator kept her from spending those early weeks with her newborn, or from seeing her 9-year-old daughter, Zoe.
Even when Ms. Slade was finally able to see her son, she wasn’t able to tell him she loved him or sing a lullaby, or even talk at all, because of a breathing tube in her throat.
Today, Ms. Slade is a strong advocate of COVID-19 vaccinations, urging her friends and family to get their shots to avoid suffering the way she has.
Ms. Slade had to relearn to walk after being bedridden for weeks. Her many weeks on a ventilator may have contributed to her stomach paralysis, which often causes intense pain, nausea, and even vomiting when she eats or drinks. Ms. Slade weighs 50 pounds less today than before she became pregnant and has resorted to going to the emergency department when the pain is unbearable. “Most days, I’m just miserable,” she said.
Her family suffered as well. Like many babies born prematurely, Tristan, now nearly 9 months old and crawling, receives physical therapy to strengthen his muscles. At 15 pounds, Tristan is largely healthy, although his doctor said he has symptoms of asthma.
Ms. Slade said she would like to attend family counseling with Zoe, who rarely complains and tends to keep her feelings to herself. Ms. Slade said she knows her illness must have been terrifying for her little girl.
“The other day she was talking to me,” Ms. Slade said, “and she said, ‘You know, I almost had to bury you.’ ”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Epidural may lower odds of severe maternal birth complications
Use of neuraxial analgesia for vaginal delivery is associated with a 14% decreased risk for severe maternal morbidity, in part from a reduction in postpartum hemorrhage, new research shows.
The findings indicate that increasing the use of epidural or combined spinal-epidural analgesia may improve maternal health outcomes, especially for Hispanic, Black, and uninsured women who are less likely than White women to receive these interventions, according to the researchers, who published their findings online in JAMA Network Open.
About 80% of non-Hispanic White women receive neuraxial analgesia during labor in the United States, compared with 70% of non-Hispanic Black women and 65% of Hispanic women, according to birth certificate data. Among women without health insurance, half receive epidurals.
Programs that inform pregnant women about epidural use, expand Medicaid, and provide in-house obstetric anesthesia teams “may improve patient participation in clinical decision making and access to care,” study author Guohua Li, MD, DrPH, of Columbia University, New York, said in a statement about the research.
Earlier data from France showed that neuraxial analgesia is associated with reduced risk for severe postpartum hemorrhage. To examine the association between labor neuraxial analgesia and severe maternal morbidity in the United States, Dr. Li and colleagues analyzed more than 575,000 vaginal deliveries in New York hospitals between 2010 and 2017; about half (47.4%) of the women received epidurals during labor.
The researchers focused on severe maternal morbidity, including 16 complications, such as heart failure and sepsis, and five procedures, including hysterectomy and ventilation.
They also considered patient characteristics and comorbidities and hospital-related factors to identify patients who were at higher risk for injury or death.
Severe maternal morbidity occurred in 1.3% of the women. Of the 7,712 women with severe morbidity, more than one in three (35.6%) experienced postpartum hemorrhage.
The overall incidence of severe maternal morbidity was 1.3% among women who received an epidural injection and 1.4% among those who did not. In a weighted analysis, the adjusted odds ratio of severe maternal morbidity associated with epidurals was 0.86 (95% confidence interval, 0.82-0.90).
The study is limited by its observational design and does not prove causation, the authors acknowledged.
“Labor neuraxial analgesia may facilitate early evaluation and management of the third stage of labor to avoid escalation of postpartum hemorrhaging into grave complications and death,” study author Jean Guglielminotti, MD, PhD, an anesthesiologist at Columbia University, said in a statement.
Concerning trends
The Department of Health & Human Services has labeled severe maternal morbidity a public health priority. Recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show an increase in maternal mortality rates and worsening disparities by race and ethnicity.
According to the CDC, 861 women died of maternal causes in 2020, up from 754 in 2019. The rate of maternal mortality increased from 20.1 to 23.8 deaths per 100,000 live births.
For Black women, however, the maternal mortality rate was far higher: 55.3 deaths per 100,000 live births – nearly triple the figure of 19.1 per 100,000 for White women. Between 2019 and 2020, the mortality rate increased significantly for Black and Hispanic women, but not White mothers.
Researchers affiliated with University of Toronto and the Hospital for Sick Children agreed in an accompanying editorial that more access to neuraxial labor analgesia for vaginal delivery might improve maternal health outcomes and “may be a strategy well worth pursuing in public health policy.”
The intervention is relatively safe and can “alleviate discomfort and distress,” they wrote.
Neuraxial anesthesia in surgical procedures has been shown to decrease the risk for complications like deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolus, transfusion requirements, and kidney failure, said editorialists Evelina Pankiv, MD; Alan Yang, MSc; and Kazuyoshi Aoyama, MD, PhD.
Benefits potentially could stem from improving blood flow, mitigating hypercoagulation, or reducing surgical stress response. But there are rare risks to consider as well, including hemorrhage, infection, and neurologic injury, they added.
Guglielminotti disclosed grants from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. Dr. Aoyama reported receiving grants from the Perioperative Services Facilitator Grant Program and Hospital for Sick Children. The other authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of neuraxial analgesia for vaginal delivery is associated with a 14% decreased risk for severe maternal morbidity, in part from a reduction in postpartum hemorrhage, new research shows.
The findings indicate that increasing the use of epidural or combined spinal-epidural analgesia may improve maternal health outcomes, especially for Hispanic, Black, and uninsured women who are less likely than White women to receive these interventions, according to the researchers, who published their findings online in JAMA Network Open.
About 80% of non-Hispanic White women receive neuraxial analgesia during labor in the United States, compared with 70% of non-Hispanic Black women and 65% of Hispanic women, according to birth certificate data. Among women without health insurance, half receive epidurals.
Programs that inform pregnant women about epidural use, expand Medicaid, and provide in-house obstetric anesthesia teams “may improve patient participation in clinical decision making and access to care,” study author Guohua Li, MD, DrPH, of Columbia University, New York, said in a statement about the research.
Earlier data from France showed that neuraxial analgesia is associated with reduced risk for severe postpartum hemorrhage. To examine the association between labor neuraxial analgesia and severe maternal morbidity in the United States, Dr. Li and colleagues analyzed more than 575,000 vaginal deliveries in New York hospitals between 2010 and 2017; about half (47.4%) of the women received epidurals during labor.
The researchers focused on severe maternal morbidity, including 16 complications, such as heart failure and sepsis, and five procedures, including hysterectomy and ventilation.
They also considered patient characteristics and comorbidities and hospital-related factors to identify patients who were at higher risk for injury or death.
Severe maternal morbidity occurred in 1.3% of the women. Of the 7,712 women with severe morbidity, more than one in three (35.6%) experienced postpartum hemorrhage.
The overall incidence of severe maternal morbidity was 1.3% among women who received an epidural injection and 1.4% among those who did not. In a weighted analysis, the adjusted odds ratio of severe maternal morbidity associated with epidurals was 0.86 (95% confidence interval, 0.82-0.90).
The study is limited by its observational design and does not prove causation, the authors acknowledged.
“Labor neuraxial analgesia may facilitate early evaluation and management of the third stage of labor to avoid escalation of postpartum hemorrhaging into grave complications and death,” study author Jean Guglielminotti, MD, PhD, an anesthesiologist at Columbia University, said in a statement.
Concerning trends
The Department of Health & Human Services has labeled severe maternal morbidity a public health priority. Recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show an increase in maternal mortality rates and worsening disparities by race and ethnicity.
According to the CDC, 861 women died of maternal causes in 2020, up from 754 in 2019. The rate of maternal mortality increased from 20.1 to 23.8 deaths per 100,000 live births.
For Black women, however, the maternal mortality rate was far higher: 55.3 deaths per 100,000 live births – nearly triple the figure of 19.1 per 100,000 for White women. Between 2019 and 2020, the mortality rate increased significantly for Black and Hispanic women, but not White mothers.
Researchers affiliated with University of Toronto and the Hospital for Sick Children agreed in an accompanying editorial that more access to neuraxial labor analgesia for vaginal delivery might improve maternal health outcomes and “may be a strategy well worth pursuing in public health policy.”
The intervention is relatively safe and can “alleviate discomfort and distress,” they wrote.
Neuraxial anesthesia in surgical procedures has been shown to decrease the risk for complications like deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolus, transfusion requirements, and kidney failure, said editorialists Evelina Pankiv, MD; Alan Yang, MSc; and Kazuyoshi Aoyama, MD, PhD.
Benefits potentially could stem from improving blood flow, mitigating hypercoagulation, or reducing surgical stress response. But there are rare risks to consider as well, including hemorrhage, infection, and neurologic injury, they added.
Guglielminotti disclosed grants from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. Dr. Aoyama reported receiving grants from the Perioperative Services Facilitator Grant Program and Hospital for Sick Children. The other authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of neuraxial analgesia for vaginal delivery is associated with a 14% decreased risk for severe maternal morbidity, in part from a reduction in postpartum hemorrhage, new research shows.
The findings indicate that increasing the use of epidural or combined spinal-epidural analgesia may improve maternal health outcomes, especially for Hispanic, Black, and uninsured women who are less likely than White women to receive these interventions, according to the researchers, who published their findings online in JAMA Network Open.
About 80% of non-Hispanic White women receive neuraxial analgesia during labor in the United States, compared with 70% of non-Hispanic Black women and 65% of Hispanic women, according to birth certificate data. Among women without health insurance, half receive epidurals.
Programs that inform pregnant women about epidural use, expand Medicaid, and provide in-house obstetric anesthesia teams “may improve patient participation in clinical decision making and access to care,” study author Guohua Li, MD, DrPH, of Columbia University, New York, said in a statement about the research.
Earlier data from France showed that neuraxial analgesia is associated with reduced risk for severe postpartum hemorrhage. To examine the association between labor neuraxial analgesia and severe maternal morbidity in the United States, Dr. Li and colleagues analyzed more than 575,000 vaginal deliveries in New York hospitals between 2010 and 2017; about half (47.4%) of the women received epidurals during labor.
The researchers focused on severe maternal morbidity, including 16 complications, such as heart failure and sepsis, and five procedures, including hysterectomy and ventilation.
They also considered patient characteristics and comorbidities and hospital-related factors to identify patients who were at higher risk for injury or death.
Severe maternal morbidity occurred in 1.3% of the women. Of the 7,712 women with severe morbidity, more than one in three (35.6%) experienced postpartum hemorrhage.
The overall incidence of severe maternal morbidity was 1.3% among women who received an epidural injection and 1.4% among those who did not. In a weighted analysis, the adjusted odds ratio of severe maternal morbidity associated with epidurals was 0.86 (95% confidence interval, 0.82-0.90).
The study is limited by its observational design and does not prove causation, the authors acknowledged.
“Labor neuraxial analgesia may facilitate early evaluation and management of the third stage of labor to avoid escalation of postpartum hemorrhaging into grave complications and death,” study author Jean Guglielminotti, MD, PhD, an anesthesiologist at Columbia University, said in a statement.
Concerning trends
The Department of Health & Human Services has labeled severe maternal morbidity a public health priority. Recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show an increase in maternal mortality rates and worsening disparities by race and ethnicity.
According to the CDC, 861 women died of maternal causes in 2020, up from 754 in 2019. The rate of maternal mortality increased from 20.1 to 23.8 deaths per 100,000 live births.
For Black women, however, the maternal mortality rate was far higher: 55.3 deaths per 100,000 live births – nearly triple the figure of 19.1 per 100,000 for White women. Between 2019 and 2020, the mortality rate increased significantly for Black and Hispanic women, but not White mothers.
Researchers affiliated with University of Toronto and the Hospital for Sick Children agreed in an accompanying editorial that more access to neuraxial labor analgesia for vaginal delivery might improve maternal health outcomes and “may be a strategy well worth pursuing in public health policy.”
The intervention is relatively safe and can “alleviate discomfort and distress,” they wrote.
Neuraxial anesthesia in surgical procedures has been shown to decrease the risk for complications like deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolus, transfusion requirements, and kidney failure, said editorialists Evelina Pankiv, MD; Alan Yang, MSc; and Kazuyoshi Aoyama, MD, PhD.
Benefits potentially could stem from improving blood flow, mitigating hypercoagulation, or reducing surgical stress response. But there are rare risks to consider as well, including hemorrhage, infection, and neurologic injury, they added.
Guglielminotti disclosed grants from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. Dr. Aoyama reported receiving grants from the Perioperative Services Facilitator Grant Program and Hospital for Sick Children. The other authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Stress and infertility – is it a proven cause and effect?
“Just relax, stop thinking about it and, more than likely, it will happen.” If ever there was a controversial subject in medicine, especially in reproduction, the relationship between stress and infertility would be high on the list. Who among us has not overheard or even personally shared with an infertility patient that they should try and reduce their stress to improve fertility? The theory is certainly not new. Hippocrates, back in the 5th century B.C., was one of the first to associate a woman’s psychological state with her reproductive potential. His contention was that a physical sign of psychological stress in women (which scholars later dubbed “hysteria”) could result in sterility. In medieval times, a German abbess and mystic named Hildegard of Bingen posited women suffering from melancholy – a condition that we today might call depression – were infertile as a result.
The deeper meaning behind the flippant advice to relax is implicit blame; that is, a woman interprets the link of stress and infertility as a declaration that she is sabotaging reproduction. Not only is this assumption flawed, but it does further damage to a woman’s emotional fragility. To provide the presumption of stress affecting reproduction, a recent survey of over 5,000 infertility patients found, remarkably, 98% considered emotional stress as either a cause or a contributor to infertility, and 31% believed stress was a cause of miscarriage, although racial differences existed (J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 Apr;38[4]:877-87). This relationship was mostly seen in women who used complementary and alternative medicine, Black women, and those who frequented Internet search engines. Whereas women who had a professional degree, had more infertility insurance coverage, and were nonreligious were less likely to attribute stress to infertility. Intriguingly, the more engaged the physicians, the less patients linked stress with infertility, while the contrary also applied.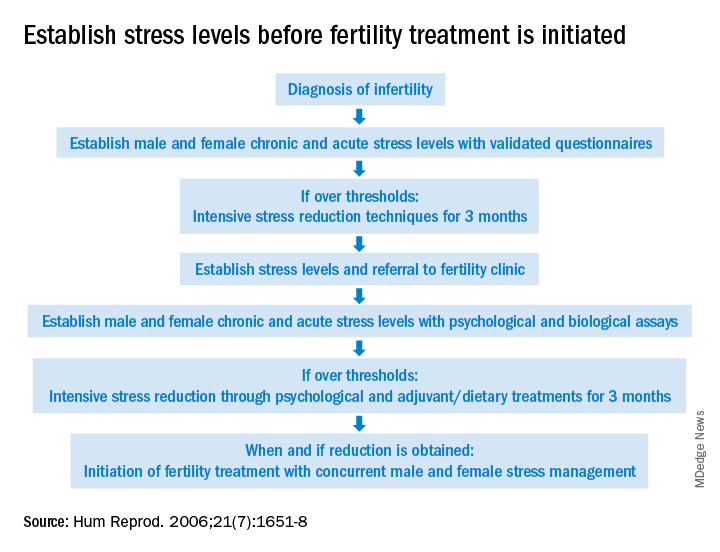
The power of stress can be exemplified by the pathophysiology of amenorrhea. Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea is the most common cause of the female athlete triad of secondary amenorrhea in women of childbearing age. It is a reversible disorder caused by stress related to weight loss, excessive exercise and/or traumatic mental experiences (Endocrines. 2021;2:203-11). Stress of infertility has also been demonstrated to be equivalent to a diagnosis of cancer and other major medical morbidities (J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 1993;14[Suppl]:45-52).
A definitive link between stress and infertility is evasive because of the lack of controlled, prospective longitudinal studies and the challenge of reducing variables in the analysis. The question remains which developed initially – the stress or the infertility? Infertility treatment is a physical, emotional, and financial investment. Stress and the duration of infertility are correlative. The additive factor is that poor insurance coverage for costly fertility treatment can not only heighten stress but, concurrently, subject the patient to the risk of exploitation driven by desperation whereby they accept unproven “add-ons” offered with assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Both acute and chronic stress affect the number of oocytes retrieved and fertilized with ART as well as live birth delivery and birth weights (Fertil Steril. 2001;76:675-87). Men are also affected by stress, which is manifested by decreased libido and impaired semen, further compromised as the duration of infertility continues. The gut-derived hormone ghrelin appears to play a role with stress and reproduction (Endocr Rev. 2017;38:432-67).
As the relationship between stress and infertility is far from proven, there are conflicting study results. Two meta-analyses failed to show any association between stress and the outcomes of ART cycles (Hum Reprod. 2011;26:2763-76; BMJ. 2011;342:d223). In contrast, a recent study suggested stress during infertility treatment was contributed by the variables of low spousal support, financial constraints, and social coercion in the early years of marriage (J Hum Reprod Sci. 2018;11:172-9). Emotional distress was found to be three times greater in women whose families had unrealistic expectations from treatments.
Fortunately, psychotherapy during the ART cycle has demonstrated a benefit in outcomes. Domar revealed psychological support and cognitive behavior therapy resulted in higher pregnancy rates than in the control group (Fertil Steril. 2000;73:805-12). Another recent study appears to support stress reduction improving reproductive potential (Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20[1]:41-7).
Given the evidence provided in this article, it behooves infertility clinics to address baseline (chronic) stress and acute stress (because of infertility) prior to initiating treatment (see Figure). While the definitive answer addressing the impact of stress on reproduction remains unknown, we may share with our patients a definition in which they may find enlightenment, “Stress is trying to control an event in which one is incapable.”
Dr. Mark P Trolice is director of Fertility CARE: The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
“Just relax, stop thinking about it and, more than likely, it will happen.” If ever there was a controversial subject in medicine, especially in reproduction, the relationship between stress and infertility would be high on the list. Who among us has not overheard or even personally shared with an infertility patient that they should try and reduce their stress to improve fertility? The theory is certainly not new. Hippocrates, back in the 5th century B.C., was one of the first to associate a woman’s psychological state with her reproductive potential. His contention was that a physical sign of psychological stress in women (which scholars later dubbed “hysteria”) could result in sterility. In medieval times, a German abbess and mystic named Hildegard of Bingen posited women suffering from melancholy – a condition that we today might call depression – were infertile as a result.
The deeper meaning behind the flippant advice to relax is implicit blame; that is, a woman interprets the link of stress and infertility as a declaration that she is sabotaging reproduction. Not only is this assumption flawed, but it does further damage to a woman’s emotional fragility. To provide the presumption of stress affecting reproduction, a recent survey of over 5,000 infertility patients found, remarkably, 98% considered emotional stress as either a cause or a contributor to infertility, and 31% believed stress was a cause of miscarriage, although racial differences existed (J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 Apr;38[4]:877-87). This relationship was mostly seen in women who used complementary and alternative medicine, Black women, and those who frequented Internet search engines. Whereas women who had a professional degree, had more infertility insurance coverage, and were nonreligious were less likely to attribute stress to infertility. Intriguingly, the more engaged the physicians, the less patients linked stress with infertility, while the contrary also applied.
The power of stress can be exemplified by the pathophysiology of amenorrhea. Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea is the most common cause of the female athlete triad of secondary amenorrhea in women of childbearing age. It is a reversible disorder caused by stress related to weight loss, excessive exercise and/or traumatic mental experiences (Endocrines. 2021;2:203-11). Stress of infertility has also been demonstrated to be equivalent to a diagnosis of cancer and other major medical morbidities (J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 1993;14[Suppl]:45-52).
A definitive link between stress and infertility is evasive because of the lack of controlled, prospective longitudinal studies and the challenge of reducing variables in the analysis. The question remains which developed initially – the stress or the infertility? Infertility treatment is a physical, emotional, and financial investment. Stress and the duration of infertility are correlative. The additive factor is that poor insurance coverage for costly fertility treatment can not only heighten stress but, concurrently, subject the patient to the risk of exploitation driven by desperation whereby they accept unproven “add-ons” offered with assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Both acute and chronic stress affect the number of oocytes retrieved and fertilized with ART as well as live birth delivery and birth weights (Fertil Steril. 2001;76:675-87). Men are also affected by stress, which is manifested by decreased libido and impaired semen, further compromised as the duration of infertility continues. The gut-derived hormone ghrelin appears to play a role with stress and reproduction (Endocr Rev. 2017;38:432-67).
As the relationship between stress and infertility is far from proven, there are conflicting study results. Two meta-analyses failed to show any association between stress and the outcomes of ART cycles (Hum Reprod. 2011;26:2763-76; BMJ. 2011;342:d223). In contrast, a recent study suggested stress during infertility treatment was contributed by the variables of low spousal support, financial constraints, and social coercion in the early years of marriage (J Hum Reprod Sci. 2018;11:172-9). Emotional distress was found to be three times greater in women whose families had unrealistic expectations from treatments.
Fortunately, psychotherapy during the ART cycle has demonstrated a benefit in outcomes. Domar revealed psychological support and cognitive behavior therapy resulted in higher pregnancy rates than in the control group (Fertil Steril. 2000;73:805-12). Another recent study appears to support stress reduction improving reproductive potential (Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20[1]:41-7).
Given the evidence provided in this article, it behooves infertility clinics to address baseline (chronic) stress and acute stress (because of infertility) prior to initiating treatment (see Figure). While the definitive answer addressing the impact of stress on reproduction remains unknown, we may share with our patients a definition in which they may find enlightenment, “Stress is trying to control an event in which one is incapable.”
Dr. Mark P Trolice is director of Fertility CARE: The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
“Just relax, stop thinking about it and, more than likely, it will happen.” If ever there was a controversial subject in medicine, especially in reproduction, the relationship between stress and infertility would be high on the list. Who among us has not overheard or even personally shared with an infertility patient that they should try and reduce their stress to improve fertility? The theory is certainly not new. Hippocrates, back in the 5th century B.C., was one of the first to associate a woman’s psychological state with her reproductive potential. His contention was that a physical sign of psychological stress in women (which scholars later dubbed “hysteria”) could result in sterility. In medieval times, a German abbess and mystic named Hildegard of Bingen posited women suffering from melancholy – a condition that we today might call depression – were infertile as a result.
The deeper meaning behind the flippant advice to relax is implicit blame; that is, a woman interprets the link of stress and infertility as a declaration that she is sabotaging reproduction. Not only is this assumption flawed, but it does further damage to a woman’s emotional fragility. To provide the presumption of stress affecting reproduction, a recent survey of over 5,000 infertility patients found, remarkably, 98% considered emotional stress as either a cause or a contributor to infertility, and 31% believed stress was a cause of miscarriage, although racial differences existed (J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 Apr;38[4]:877-87). This relationship was mostly seen in women who used complementary and alternative medicine, Black women, and those who frequented Internet search engines. Whereas women who had a professional degree, had more infertility insurance coverage, and were nonreligious were less likely to attribute stress to infertility. Intriguingly, the more engaged the physicians, the less patients linked stress with infertility, while the contrary also applied.
The power of stress can be exemplified by the pathophysiology of amenorrhea. Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea is the most common cause of the female athlete triad of secondary amenorrhea in women of childbearing age. It is a reversible disorder caused by stress related to weight loss, excessive exercise and/or traumatic mental experiences (Endocrines. 2021;2:203-11). Stress of infertility has also been demonstrated to be equivalent to a diagnosis of cancer and other major medical morbidities (J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 1993;14[Suppl]:45-52).
A definitive link between stress and infertility is evasive because of the lack of controlled, prospective longitudinal studies and the challenge of reducing variables in the analysis. The question remains which developed initially – the stress or the infertility? Infertility treatment is a physical, emotional, and financial investment. Stress and the duration of infertility are correlative. The additive factor is that poor insurance coverage for costly fertility treatment can not only heighten stress but, concurrently, subject the patient to the risk of exploitation driven by desperation whereby they accept unproven “add-ons” offered with assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Both acute and chronic stress affect the number of oocytes retrieved and fertilized with ART as well as live birth delivery and birth weights (Fertil Steril. 2001;76:675-87). Men are also affected by stress, which is manifested by decreased libido and impaired semen, further compromised as the duration of infertility continues. The gut-derived hormone ghrelin appears to play a role with stress and reproduction (Endocr Rev. 2017;38:432-67).
As the relationship between stress and infertility is far from proven, there are conflicting study results. Two meta-analyses failed to show any association between stress and the outcomes of ART cycles (Hum Reprod. 2011;26:2763-76; BMJ. 2011;342:d223). In contrast, a recent study suggested stress during infertility treatment was contributed by the variables of low spousal support, financial constraints, and social coercion in the early years of marriage (J Hum Reprod Sci. 2018;11:172-9). Emotional distress was found to be three times greater in women whose families had unrealistic expectations from treatments.
Fortunately, psychotherapy during the ART cycle has demonstrated a benefit in outcomes. Domar revealed psychological support and cognitive behavior therapy resulted in higher pregnancy rates than in the control group (Fertil Steril. 2000;73:805-12). Another recent study appears to support stress reduction improving reproductive potential (Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20[1]:41-7).
Given the evidence provided in this article, it behooves infertility clinics to address baseline (chronic) stress and acute stress (because of infertility) prior to initiating treatment (see Figure). While the definitive answer addressing the impact of stress on reproduction remains unknown, we may share with our patients a definition in which they may find enlightenment, “Stress is trying to control an event in which one is incapable.”
Dr. Mark P Trolice is director of Fertility CARE: The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
More than half of U.S. women enter pregnancy at higher CVD risk
Less than half of women in the United States enter pregnancy in favorable cardiovascular health, new research suggests.
In 2019, among women aged 20 to 44 years with live births in the United States, only 40.2% were in favorable cardiovascular health prior to pregnancy, defined as normal weight, no diabetes, and no hypertension.
Although all regions and states showed a decline in prepregnancy favorable cardiometabolic health, there were significant differences among geographic regions in the country, the authors report. “These data reveal critical deficiencies and geographic disparities in prepregnancy cardiometabolic health,” they conclude.
“One of the things that we know in the U.S. is that the maternal mortality rate has been increasing, and there are significant differences at the state level in both adverse maternal outcomes, such as maternal mortality, as well as adverse pregnancy outcomes,” corresponding author Sadiya S. Khan, MD, MS, FACC, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization.
“These outcomes are often related to health factors that predate pregnancy,” Dr. Khan explained, “and the processes that begin at the very, very beginning of conception are informed by health factors prior to pregnancy, in particular cardiometabolic factors like body mass index or obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.”
The results were published online on Feb. 14 in a special “Go Red for Women” spotlight issue of Circulation.
Cardiometabolic health factors
Using maternal birth records from live births in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Natality Database between 2016 and 2019, the authors analyzed data on 14,174,625 women with live births aged 20 to 44 years. The majority (81.4%) were 20 to 34 years of age, 22.7% were Hispanic or Latina, and 52.7% were non-Hispanic White.
Favorable cardiometabolic health was defined as a BMI of 18 to 24.9 kg/m2, absence of diabetes, and absence of hypertension.
Although all regions and states experienced a decline in favorable cardiometabolic health during the study period of 2016 to 2019, with a drop overall of 3.2% – from 43.5 to 40.2 per 100 live births – it was especially true of the South and Midwest regions.
In 2019, favorable prepregnancy cardiometabolic health was lowest in the South (38.1%) and Midwest (38.8%) and highest in the West (42.2%) and Northeast (43.6%).
State by state, the lowest prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health was found in Mississippi, at 31.2%, and highest in Utah, at 47.2%.
They also found a correlation between favorable cardiometabolic health and state-level percentages of high-school education or less and enrollment in Medicaid in 2019.
Similar to what has been seen with cardiovascular disease, “we observe that the states with the lowest prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health were in the Southeast United States,” said Dr. Khan, “and similar geographic variation was observed with some more patterns in education and Medicaid coverage for birth, and these were used as proxies for socioeconomic status in those areas.”
Although Dr. Khan notes that the relationships cannot be determined to be causal from this analysis, she said that “it does suggest that upstream social determinants of health are important determinants of cardiometabolic health.”
Socioeconomic intervention
Dr. Khan noted that policies at the federal and state level can identify ways to “ensure that individuals who are thinking about pregnancy have access to health care and have access to resources, too, from a broad range of health determinants, including housing stability, food security, as well as access to health care be optimized prior to pregnancy.”
The authors note that this analysis may actually overestimate the prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health, and data on cholesterol, diet, a distinction between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and physical activity were not available.
Only individuals with live births were included, which could result in the elimination of a potentially high-risk group; however, late pregnancy losses represent less than 0.3% of all pregnancies, they say.
The authors conclude that “future research is needed to equitably improve health prior to pregnancy and quantify the potential benefits in cardiovascular disease outcomes for birthing individuals and their offspring.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and American Heart Association Transformational Project Award awarded to Sadiya S. Khan.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Less than half of women in the United States enter pregnancy in favorable cardiovascular health, new research suggests.
In 2019, among women aged 20 to 44 years with live births in the United States, only 40.2% were in favorable cardiovascular health prior to pregnancy, defined as normal weight, no diabetes, and no hypertension.
Although all regions and states showed a decline in prepregnancy favorable cardiometabolic health, there were significant differences among geographic regions in the country, the authors report. “These data reveal critical deficiencies and geographic disparities in prepregnancy cardiometabolic health,” they conclude.
“One of the things that we know in the U.S. is that the maternal mortality rate has been increasing, and there are significant differences at the state level in both adverse maternal outcomes, such as maternal mortality, as well as adverse pregnancy outcomes,” corresponding author Sadiya S. Khan, MD, MS, FACC, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization.
“These outcomes are often related to health factors that predate pregnancy,” Dr. Khan explained, “and the processes that begin at the very, very beginning of conception are informed by health factors prior to pregnancy, in particular cardiometabolic factors like body mass index or obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.”
The results were published online on Feb. 14 in a special “Go Red for Women” spotlight issue of Circulation.
Cardiometabolic health factors
Using maternal birth records from live births in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Natality Database between 2016 and 2019, the authors analyzed data on 14,174,625 women with live births aged 20 to 44 years. The majority (81.4%) were 20 to 34 years of age, 22.7% were Hispanic or Latina, and 52.7% were non-Hispanic White.
Favorable cardiometabolic health was defined as a BMI of 18 to 24.9 kg/m2, absence of diabetes, and absence of hypertension.
Although all regions and states experienced a decline in favorable cardiometabolic health during the study period of 2016 to 2019, with a drop overall of 3.2% – from 43.5 to 40.2 per 100 live births – it was especially true of the South and Midwest regions.
In 2019, favorable prepregnancy cardiometabolic health was lowest in the South (38.1%) and Midwest (38.8%) and highest in the West (42.2%) and Northeast (43.6%).
State by state, the lowest prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health was found in Mississippi, at 31.2%, and highest in Utah, at 47.2%.
They also found a correlation between favorable cardiometabolic health and state-level percentages of high-school education or less and enrollment in Medicaid in 2019.
Similar to what has been seen with cardiovascular disease, “we observe that the states with the lowest prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health were in the Southeast United States,” said Dr. Khan, “and similar geographic variation was observed with some more patterns in education and Medicaid coverage for birth, and these were used as proxies for socioeconomic status in those areas.”
Although Dr. Khan notes that the relationships cannot be determined to be causal from this analysis, she said that “it does suggest that upstream social determinants of health are important determinants of cardiometabolic health.”
Socioeconomic intervention
Dr. Khan noted that policies at the federal and state level can identify ways to “ensure that individuals who are thinking about pregnancy have access to health care and have access to resources, too, from a broad range of health determinants, including housing stability, food security, as well as access to health care be optimized prior to pregnancy.”
The authors note that this analysis may actually overestimate the prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health, and data on cholesterol, diet, a distinction between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and physical activity were not available.
Only individuals with live births were included, which could result in the elimination of a potentially high-risk group; however, late pregnancy losses represent less than 0.3% of all pregnancies, they say.
The authors conclude that “future research is needed to equitably improve health prior to pregnancy and quantify the potential benefits in cardiovascular disease outcomes for birthing individuals and their offspring.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and American Heart Association Transformational Project Award awarded to Sadiya S. Khan.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Less than half of women in the United States enter pregnancy in favorable cardiovascular health, new research suggests.
In 2019, among women aged 20 to 44 years with live births in the United States, only 40.2% were in favorable cardiovascular health prior to pregnancy, defined as normal weight, no diabetes, and no hypertension.
Although all regions and states showed a decline in prepregnancy favorable cardiometabolic health, there were significant differences among geographic regions in the country, the authors report. “These data reveal critical deficiencies and geographic disparities in prepregnancy cardiometabolic health,” they conclude.
“One of the things that we know in the U.S. is that the maternal mortality rate has been increasing, and there are significant differences at the state level in both adverse maternal outcomes, such as maternal mortality, as well as adverse pregnancy outcomes,” corresponding author Sadiya S. Khan, MD, MS, FACC, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, told this news organization.
“These outcomes are often related to health factors that predate pregnancy,” Dr. Khan explained, “and the processes that begin at the very, very beginning of conception are informed by health factors prior to pregnancy, in particular cardiometabolic factors like body mass index or obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.”
The results were published online on Feb. 14 in a special “Go Red for Women” spotlight issue of Circulation.
Cardiometabolic health factors
Using maternal birth records from live births in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Natality Database between 2016 and 2019, the authors analyzed data on 14,174,625 women with live births aged 20 to 44 years. The majority (81.4%) were 20 to 34 years of age, 22.7% were Hispanic or Latina, and 52.7% were non-Hispanic White.
Favorable cardiometabolic health was defined as a BMI of 18 to 24.9 kg/m2, absence of diabetes, and absence of hypertension.
Although all regions and states experienced a decline in favorable cardiometabolic health during the study period of 2016 to 2019, with a drop overall of 3.2% – from 43.5 to 40.2 per 100 live births – it was especially true of the South and Midwest regions.
In 2019, favorable prepregnancy cardiometabolic health was lowest in the South (38.1%) and Midwest (38.8%) and highest in the West (42.2%) and Northeast (43.6%).
State by state, the lowest prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health was found in Mississippi, at 31.2%, and highest in Utah, at 47.2%.
They also found a correlation between favorable cardiometabolic health and state-level percentages of high-school education or less and enrollment in Medicaid in 2019.
Similar to what has been seen with cardiovascular disease, “we observe that the states with the lowest prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health were in the Southeast United States,” said Dr. Khan, “and similar geographic variation was observed with some more patterns in education and Medicaid coverage for birth, and these were used as proxies for socioeconomic status in those areas.”
Although Dr. Khan notes that the relationships cannot be determined to be causal from this analysis, she said that “it does suggest that upstream social determinants of health are important determinants of cardiometabolic health.”
Socioeconomic intervention
Dr. Khan noted that policies at the federal and state level can identify ways to “ensure that individuals who are thinking about pregnancy have access to health care and have access to resources, too, from a broad range of health determinants, including housing stability, food security, as well as access to health care be optimized prior to pregnancy.”
The authors note that this analysis may actually overestimate the prevalence of favorable cardiometabolic health, and data on cholesterol, diet, a distinction between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and physical activity were not available.
Only individuals with live births were included, which could result in the elimination of a potentially high-risk group; however, late pregnancy losses represent less than 0.3% of all pregnancies, they say.
The authors conclude that “future research is needed to equitably improve health prior to pregnancy and quantify the potential benefits in cardiovascular disease outcomes for birthing individuals and their offspring.”
This work was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and American Heart Association Transformational Project Award awarded to Sadiya S. Khan.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than half of U.S. abortions now done with pills: Report
according to a report from the Guttmacher Institute, a research group that supports abortion rights.
A survey of abortion providers showed that 54% of all U.S. abortions were done with medication in 2020, marking the first time the proportion of medication abortions topped 50%, Guttmacher said.
In 2017, the last time such a survey was done, 39% of abortions were performed by medication, Guttmacher said. The organization said 24% of abortions were done with medication in 2011 and 6% in 2001, the year after the FDA approved the pills.
The 54% estimate is based on early findings, Guttmacher said in a news release. It said that “final estimates will be released in late 2022 and the proportion for medication abortion use is not expected to fall below 50%.”
Rachel Jones, PhD, a Guttmacher researcher, said the higher use of abortion pills may be linked to increases in telemedicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic and the FDA’s decision last year to allow the mailing of abortion pills to patients, the Associated Press reported. Those changes mean women can now consult with a doctor online, receive the pills by mail, and complete the abortion at home.
Abortion pills are recommended for the first 10 weeks of pregnancy, though research shows they can be safe in some cases after 10 weeks, Guttmacher said. Patients take the pill mifepristone, which blocks a hormone needed for pregnancy to continue, and a few days later take the pill misoprostol, which causes cramping that empties the womb.
“The introduction and availability of medication abortion has proven to be a game changer in expanding abortion care in the United States, and it will likely be an even more important option for people to obtain an abortion as many states continue to pass legislation to bar or restrict abortion access,” Guttmacher said in the news release.
Arizona, Arkansas, and Texas have banned the mailing of abortion pills. Similar bans were approved in Montana, Oklahoma, and South Dakota but were blocked in the courts, Guttmacher said.
Sixteen state legislatures have proposed bans or restrictions on medication-induced abortion this year, while 32 states require this type of abortion to be prescribed by doctors.
In Texas, orders for abortion pills increased sharply after the state legislature approved a highly restrictive abortion law, Politico reported, citing a study in The Journal of the American Medical Association.
Orders went up 1,180% in the first week after the Texas law took effect in September, researchers said. Orders dipped somewhat in later weeks but remained 175% higher than before the Texas law took effect.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to a report from the Guttmacher Institute, a research group that supports abortion rights.
A survey of abortion providers showed that 54% of all U.S. abortions were done with medication in 2020, marking the first time the proportion of medication abortions topped 50%, Guttmacher said.
In 2017, the last time such a survey was done, 39% of abortions were performed by medication, Guttmacher said. The organization said 24% of abortions were done with medication in 2011 and 6% in 2001, the year after the FDA approved the pills.
The 54% estimate is based on early findings, Guttmacher said in a news release. It said that “final estimates will be released in late 2022 and the proportion for medication abortion use is not expected to fall below 50%.”
Rachel Jones, PhD, a Guttmacher researcher, said the higher use of abortion pills may be linked to increases in telemedicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic and the FDA’s decision last year to allow the mailing of abortion pills to patients, the Associated Press reported. Those changes mean women can now consult with a doctor online, receive the pills by mail, and complete the abortion at home.
Abortion pills are recommended for the first 10 weeks of pregnancy, though research shows they can be safe in some cases after 10 weeks, Guttmacher said. Patients take the pill mifepristone, which blocks a hormone needed for pregnancy to continue, and a few days later take the pill misoprostol, which causes cramping that empties the womb.
“The introduction and availability of medication abortion has proven to be a game changer in expanding abortion care in the United States, and it will likely be an even more important option for people to obtain an abortion as many states continue to pass legislation to bar or restrict abortion access,” Guttmacher said in the news release.
Arizona, Arkansas, and Texas have banned the mailing of abortion pills. Similar bans were approved in Montana, Oklahoma, and South Dakota but were blocked in the courts, Guttmacher said.
Sixteen state legislatures have proposed bans or restrictions on medication-induced abortion this year, while 32 states require this type of abortion to be prescribed by doctors.
In Texas, orders for abortion pills increased sharply after the state legislature approved a highly restrictive abortion law, Politico reported, citing a study in The Journal of the American Medical Association.
Orders went up 1,180% in the first week after the Texas law took effect in September, researchers said. Orders dipped somewhat in later weeks but remained 175% higher than before the Texas law took effect.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to a report from the Guttmacher Institute, a research group that supports abortion rights.
A survey of abortion providers showed that 54% of all U.S. abortions were done with medication in 2020, marking the first time the proportion of medication abortions topped 50%, Guttmacher said.
In 2017, the last time such a survey was done, 39% of abortions were performed by medication, Guttmacher said. The organization said 24% of abortions were done with medication in 2011 and 6% in 2001, the year after the FDA approved the pills.
The 54% estimate is based on early findings, Guttmacher said in a news release. It said that “final estimates will be released in late 2022 and the proportion for medication abortion use is not expected to fall below 50%.”
Rachel Jones, PhD, a Guttmacher researcher, said the higher use of abortion pills may be linked to increases in telemedicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic and the FDA’s decision last year to allow the mailing of abortion pills to patients, the Associated Press reported. Those changes mean women can now consult with a doctor online, receive the pills by mail, and complete the abortion at home.
Abortion pills are recommended for the first 10 weeks of pregnancy, though research shows they can be safe in some cases after 10 weeks, Guttmacher said. Patients take the pill mifepristone, which blocks a hormone needed for pregnancy to continue, and a few days later take the pill misoprostol, which causes cramping that empties the womb.
“The introduction and availability of medication abortion has proven to be a game changer in expanding abortion care in the United States, and it will likely be an even more important option for people to obtain an abortion as many states continue to pass legislation to bar or restrict abortion access,” Guttmacher said in the news release.
Arizona, Arkansas, and Texas have banned the mailing of abortion pills. Similar bans were approved in Montana, Oklahoma, and South Dakota but were blocked in the courts, Guttmacher said.
Sixteen state legislatures have proposed bans or restrictions on medication-induced abortion this year, while 32 states require this type of abortion to be prescribed by doctors.
In Texas, orders for abortion pills increased sharply after the state legislature approved a highly restrictive abortion law, Politico reported, citing a study in The Journal of the American Medical Association.
Orders went up 1,180% in the first week after the Texas law took effect in September, researchers said. Orders dipped somewhat in later weeks but remained 175% higher than before the Texas law took effect.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When physicians are the plaintiffs
Have you experienced malpractice?
No, I’m not asking whether you have experienced litigation. I’m asking whether you, as a physician, have actually experienced substandard care from a colleague. I have heard many such experiences over the years, and mistreatment doesn’t seem to be getting any less frequent.
The first is that, unlike the Pope, who has a dedicated confessor trained to minister to his spiritual needs, no one formally trains physicians to treat physicians. As a result, most of us feel slightly uneasy at treating other physicians. We naturally wish to keep our colleagues well, but at the same time realize that our clinical skills are being very closely scrutinized. What if they are found to be wanting? This discomfiture can make a physician treating a physician overly compulsive, or worse, overtly dismissive.
Second, we physicians are famously poor patients. We pretend we don’t need the advice we give others, to monitor our health and promptly seek care when something feels amiss. And, for the period during which we delay a medical encounter, we often attempt to diagnose and treat ourselves.
Sometimes we are successful, which reinforces this approach. Other times, we fail at being our own caregiver and present to someone else either too late, or with avoidable complications. In the former instance, we congratulate ourselves and learn nothing from the experience. In the latter, we may heap shame upon ourselves for our folly, and we may learn; but it could be a lethal lesson. In the worst scenario, our colleague gives in to frustration (or angst), and heaps even more shame onto their late-presenting physician patient.
Third, when we do submit to being a patient, we often demand VIP treatment. This is probably in response to our anxiety that some of the worst things we have seen happen to patients might happen to us if we are not vigilant to ensure we receive a higher level of care. But of course, such hypervigilance can lead to excessive care and testing, with all the attendant hazards, or alternatively to dilution of care if our caregivers decide we are just too much trouble.
Fourth, as a fifth-generation physician myself, I am convinced that physicians and physician family members are either prone to unusual manifestations of common diseases or unusual diseases, or that rare disease entities and complications are actually more common than literature suggests, and they simply aren’t pursued or diagnosed in nonphysician families.
No matter how we may have arrived in a position to need medical care, how often is such care substandard? And how do we respond when we suspect, or know, this to be the case? Are physicians more, or less, likely to take legal action in the face of it?
I certainly don’t know any statistics. Physicians are in an excellent position to take such action, because judges and juries will likely believe that a doctor can recognize negligence when we fall victim to it. But we may also be reluctant to publicly admit the way (or ways) in which we may have contributed to substandard care or outcome.
Based on decades of working with physician clients who have been sued, and having been sued myself (thus witnessing and also experiencing the effects of litigation), I am probably more reluctant than normal patients or physicians to consider taking legal action. This, despite the fact that I am also a lawyer and (through organized medicine) know many colleagues in all specialties who might serve as expert witnesses.
I have experienced serial substandard care, which has left me highly conflicted about the efficacy of my chosen profession. As a resident, I had my first odd pain condition and consulted an “elder statesperson” from my institution, whom I assumed to be a “doctor’s doctor” because he was a superb teacher (wrong!)
He completely missed the diagnosis and further belittled (indeed, libeled) me in the medical record. (Some years later, I learned that, during that period, he was increasingly demented and tended to view all female patients as having “wandering uterus” equivalents.) Fortunately, I found a better diagnostician, or at least one more willing to lend credence to my complaints, who successfully removed the first of several “zebra” lesions I have experienced.
As a young faculty member, I had an odd presentation of a recurring gynecologic condition, which was treated surgically, successfully, except that my fertility was cut in half – a possibility about which I had not been informed when giving operative consent. Would I have sued this fellow faculty member for that? Never, because she invariably treated me with respect as a colleague.
Later in my career after leaving academia, the same condition recurred in a new location. My old-school gynecologist desired to do an extensive procedure, to which I demurred unless specific pathology was found intraoperatively. Affronted, he subjected me to laparoscopy, did nothing but look, and then left the hospital leaving me and the PACU nurse to try to decipher his instructions (which said, basically, “I didn’t find anything; don’t bother me again.”). Several years of pain later, a younger gynecologist performed the correct procedure to address my problem, which has never recurred. Would I have sued him? No, because I believe he had a disability.
At age 59, I developed a new mole. My beloved general practitioner, in the waning years of his practice, forgot to consult a colleague to remove it for several months. When I forced the issue, the mole was removed and turned out to be a rare pediatric condition considered a precursor to melanoma. The same general practitioner had told me I needn’t worry about my “mild hypercalcemia.”
Ten years later I diagnosed my own parathyroid adenoma, in the interim losing 10% of my bone density. Would I have sued him? No, for he always showed he cared. (Though maybe, if I had fractured my spine or hip.)
If you have been the victim of physician malpractice, how did you respond?
Do we serve our profession well by how we handle substandard care – upon ourselves (or our loved ones)?
Dr. Andrew is a former assistant professor in the department of emergency medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and founder and principal of MDMentor, Victoria, B.C.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Have you experienced malpractice?
No, I’m not asking whether you have experienced litigation. I’m asking whether you, as a physician, have actually experienced substandard care from a colleague. I have heard many such experiences over the years, and mistreatment doesn’t seem to be getting any less frequent.
The first is that, unlike the Pope, who has a dedicated confessor trained to minister to his spiritual needs, no one formally trains physicians to treat physicians. As a result, most of us feel slightly uneasy at treating other physicians. We naturally wish to keep our colleagues well, but at the same time realize that our clinical skills are being very closely scrutinized. What if they are found to be wanting? This discomfiture can make a physician treating a physician overly compulsive, or worse, overtly dismissive.
Second, we physicians are famously poor patients. We pretend we don’t need the advice we give others, to monitor our health and promptly seek care when something feels amiss. And, for the period during which we delay a medical encounter, we often attempt to diagnose and treat ourselves.
Sometimes we are successful, which reinforces this approach. Other times, we fail at being our own caregiver and present to someone else either too late, or with avoidable complications. In the former instance, we congratulate ourselves and learn nothing from the experience. In the latter, we may heap shame upon ourselves for our folly, and we may learn; but it could be a lethal lesson. In the worst scenario, our colleague gives in to frustration (or angst), and heaps even more shame onto their late-presenting physician patient.
Third, when we do submit to being a patient, we often demand VIP treatment. This is probably in response to our anxiety that some of the worst things we have seen happen to patients might happen to us if we are not vigilant to ensure we receive a higher level of care. But of course, such hypervigilance can lead to excessive care and testing, with all the attendant hazards, or alternatively to dilution of care if our caregivers decide we are just too much trouble.
Fourth, as a fifth-generation physician myself, I am convinced that physicians and physician family members are either prone to unusual manifestations of common diseases or unusual diseases, or that rare disease entities and complications are actually more common than literature suggests, and they simply aren’t pursued or diagnosed in nonphysician families.
No matter how we may have arrived in a position to need medical care, how often is such care substandard? And how do we respond when we suspect, or know, this to be the case? Are physicians more, or less, likely to take legal action in the face of it?
I certainly don’t know any statistics. Physicians are in an excellent position to take such action, because judges and juries will likely believe that a doctor can recognize negligence when we fall victim to it. But we may also be reluctant to publicly admit the way (or ways) in which we may have contributed to substandard care or outcome.
Based on decades of working with physician clients who have been sued, and having been sued myself (thus witnessing and also experiencing the effects of litigation), I am probably more reluctant than normal patients or physicians to consider taking legal action. This, despite the fact that I am also a lawyer and (through organized medicine) know many colleagues in all specialties who might serve as expert witnesses.
I have experienced serial substandard care, which has left me highly conflicted about the efficacy of my chosen profession. As a resident, I had my first odd pain condition and consulted an “elder statesperson” from my institution, whom I assumed to be a “doctor’s doctor” because he was a superb teacher (wrong!)
He completely missed the diagnosis and further belittled (indeed, libeled) me in the medical record. (Some years later, I learned that, during that period, he was increasingly demented and tended to view all female patients as having “wandering uterus” equivalents.) Fortunately, I found a better diagnostician, or at least one more willing to lend credence to my complaints, who successfully removed the first of several “zebra” lesions I have experienced.
As a young faculty member, I had an odd presentation of a recurring gynecologic condition, which was treated surgically, successfully, except that my fertility was cut in half – a possibility about which I had not been informed when giving operative consent. Would I have sued this fellow faculty member for that? Never, because she invariably treated me with respect as a colleague.
Later in my career after leaving academia, the same condition recurred in a new location. My old-school gynecologist desired to do an extensive procedure, to which I demurred unless specific pathology was found intraoperatively. Affronted, he subjected me to laparoscopy, did nothing but look, and then left the hospital leaving me and the PACU nurse to try to decipher his instructions (which said, basically, “I didn’t find anything; don’t bother me again.”). Several years of pain later, a younger gynecologist performed the correct procedure to address my problem, which has never recurred. Would I have sued him? No, because I believe he had a disability.
At age 59, I developed a new mole. My beloved general practitioner, in the waning years of his practice, forgot to consult a colleague to remove it for several months. When I forced the issue, the mole was removed and turned out to be a rare pediatric condition considered a precursor to melanoma. The same general practitioner had told me I needn’t worry about my “mild hypercalcemia.”
Ten years later I diagnosed my own parathyroid adenoma, in the interim losing 10% of my bone density. Would I have sued him? No, for he always showed he cared. (Though maybe, if I had fractured my spine or hip.)
If you have been the victim of physician malpractice, how did you respond?
Do we serve our profession well by how we handle substandard care – upon ourselves (or our loved ones)?
Dr. Andrew is a former assistant professor in the department of emergency medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and founder and principal of MDMentor, Victoria, B.C.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Have you experienced malpractice?
No, I’m not asking whether you have experienced litigation. I’m asking whether you, as a physician, have actually experienced substandard care from a colleague. I have heard many such experiences over the years, and mistreatment doesn’t seem to be getting any less frequent.
The first is that, unlike the Pope, who has a dedicated confessor trained to minister to his spiritual needs, no one formally trains physicians to treat physicians. As a result, most of us feel slightly uneasy at treating other physicians. We naturally wish to keep our colleagues well, but at the same time realize that our clinical skills are being very closely scrutinized. What if they are found to be wanting? This discomfiture can make a physician treating a physician overly compulsive, or worse, overtly dismissive.
Second, we physicians are famously poor patients. We pretend we don’t need the advice we give others, to monitor our health and promptly seek care when something feels amiss. And, for the period during which we delay a medical encounter, we often attempt to diagnose and treat ourselves.
Sometimes we are successful, which reinforces this approach. Other times, we fail at being our own caregiver and present to someone else either too late, or with avoidable complications. In the former instance, we congratulate ourselves and learn nothing from the experience. In the latter, we may heap shame upon ourselves for our folly, and we may learn; but it could be a lethal lesson. In the worst scenario, our colleague gives in to frustration (or angst), and heaps even more shame onto their late-presenting physician patient.
Third, when we do submit to being a patient, we often demand VIP treatment. This is probably in response to our anxiety that some of the worst things we have seen happen to patients might happen to us if we are not vigilant to ensure we receive a higher level of care. But of course, such hypervigilance can lead to excessive care and testing, with all the attendant hazards, or alternatively to dilution of care if our caregivers decide we are just too much trouble.
Fourth, as a fifth-generation physician myself, I am convinced that physicians and physician family members are either prone to unusual manifestations of common diseases or unusual diseases, or that rare disease entities and complications are actually more common than literature suggests, and they simply aren’t pursued or diagnosed in nonphysician families.
No matter how we may have arrived in a position to need medical care, how often is such care substandard? And how do we respond when we suspect, or know, this to be the case? Are physicians more, or less, likely to take legal action in the face of it?
I certainly don’t know any statistics. Physicians are in an excellent position to take such action, because judges and juries will likely believe that a doctor can recognize negligence when we fall victim to it. But we may also be reluctant to publicly admit the way (or ways) in which we may have contributed to substandard care or outcome.
Based on decades of working with physician clients who have been sued, and having been sued myself (thus witnessing and also experiencing the effects of litigation), I am probably more reluctant than normal patients or physicians to consider taking legal action. This, despite the fact that I am also a lawyer and (through organized medicine) know many colleagues in all specialties who might serve as expert witnesses.
I have experienced serial substandard care, which has left me highly conflicted about the efficacy of my chosen profession. As a resident, I had my first odd pain condition and consulted an “elder statesperson” from my institution, whom I assumed to be a “doctor’s doctor” because he was a superb teacher (wrong!)
He completely missed the diagnosis and further belittled (indeed, libeled) me in the medical record. (Some years later, I learned that, during that period, he was increasingly demented and tended to view all female patients as having “wandering uterus” equivalents.) Fortunately, I found a better diagnostician, or at least one more willing to lend credence to my complaints, who successfully removed the first of several “zebra” lesions I have experienced.
As a young faculty member, I had an odd presentation of a recurring gynecologic condition, which was treated surgically, successfully, except that my fertility was cut in half – a possibility about which I had not been informed when giving operative consent. Would I have sued this fellow faculty member for that? Never, because she invariably treated me with respect as a colleague.
Later in my career after leaving academia, the same condition recurred in a new location. My old-school gynecologist desired to do an extensive procedure, to which I demurred unless specific pathology was found intraoperatively. Affronted, he subjected me to laparoscopy, did nothing but look, and then left the hospital leaving me and the PACU nurse to try to decipher his instructions (which said, basically, “I didn’t find anything; don’t bother me again.”). Several years of pain later, a younger gynecologist performed the correct procedure to address my problem, which has never recurred. Would I have sued him? No, because I believe he had a disability.
At age 59, I developed a new mole. My beloved general practitioner, in the waning years of his practice, forgot to consult a colleague to remove it for several months. When I forced the issue, the mole was removed and turned out to be a rare pediatric condition considered a precursor to melanoma. The same general practitioner had told me I needn’t worry about my “mild hypercalcemia.”
Ten years later I diagnosed my own parathyroid adenoma, in the interim losing 10% of my bone density. Would I have sued him? No, for he always showed he cared. (Though maybe, if I had fractured my spine or hip.)
If you have been the victim of physician malpractice, how did you respond?
Do we serve our profession well by how we handle substandard care – upon ourselves (or our loved ones)?
Dr. Andrew is a former assistant professor in the department of emergency medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and founder and principal of MDMentor, Victoria, B.C.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs first condom for anal sex
specifically designed for use during anal sex has gained Food and Drug Administration approval.
Anal intercourse is considered to be much riskier than vaginal sex for the transmission of infections such as HIV and HPV, a risk factor for anal cancer, agency officials said in a statement Feb. 23 announcing the decision. And though the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has long encouraged the use of a condom during anal intercourse, the FDA had not until now deemed this practice safe.
The latex ONE Male Condom, from prophylactic maker Global Protection Corp. of Boston, has already been available for vaginal sex. The FDA action now allows the company to market the product for anal intercourse.
“This authorization helps us accomplish our priority to advance health equity through the development of safe and effective products that meet the needs of diverse populations,” Courtney Lias, PhD, the director of the FDA’s Office of GastroRenal, ObGyn, General Hospital, and Urology Devices, said in a statement.
The FDA said it relied on an Emory University clinical study of condom safety of more than 500 men. Those who took part in the study were evenly divided between men who have sex with men and men who have sex with women. The condom failure rate, meaning that a condom either broke or slipped, was less than 1% during anal sex. The failure rate was 3 times higher during vaginal intercourse.
The Emory researchers also found that roughly 70% of men who have sex with men would be more likely to use condoms marked as safe for anal sex, according to a survey of 10,000 people.
ONE Male Condoms sell for between $3.48 for a three-pack and $14.48 for a 24-pack, according to Milla Impola, Global Protection’s director of marketing and communications. The FDA said the condom should be used with a condom-compatible lubricant when used during anal sex.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
specifically designed for use during anal sex has gained Food and Drug Administration approval.
Anal intercourse is considered to be much riskier than vaginal sex for the transmission of infections such as HIV and HPV, a risk factor for anal cancer, agency officials said in a statement Feb. 23 announcing the decision. And though the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has long encouraged the use of a condom during anal intercourse, the FDA had not until now deemed this practice safe.
The latex ONE Male Condom, from prophylactic maker Global Protection Corp. of Boston, has already been available for vaginal sex. The FDA action now allows the company to market the product for anal intercourse.
“This authorization helps us accomplish our priority to advance health equity through the development of safe and effective products that meet the needs of diverse populations,” Courtney Lias, PhD, the director of the FDA’s Office of GastroRenal, ObGyn, General Hospital, and Urology Devices, said in a statement.
The FDA said it relied on an Emory University clinical study of condom safety of more than 500 men. Those who took part in the study were evenly divided between men who have sex with men and men who have sex with women. The condom failure rate, meaning that a condom either broke or slipped, was less than 1% during anal sex. The failure rate was 3 times higher during vaginal intercourse.
The Emory researchers also found that roughly 70% of men who have sex with men would be more likely to use condoms marked as safe for anal sex, according to a survey of 10,000 people.
ONE Male Condoms sell for between $3.48 for a three-pack and $14.48 for a 24-pack, according to Milla Impola, Global Protection’s director of marketing and communications. The FDA said the condom should be used with a condom-compatible lubricant when used during anal sex.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
specifically designed for use during anal sex has gained Food and Drug Administration approval.
Anal intercourse is considered to be much riskier than vaginal sex for the transmission of infections such as HIV and HPV, a risk factor for anal cancer, agency officials said in a statement Feb. 23 announcing the decision. And though the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has long encouraged the use of a condom during anal intercourse, the FDA had not until now deemed this practice safe.
The latex ONE Male Condom, from prophylactic maker Global Protection Corp. of Boston, has already been available for vaginal sex. The FDA action now allows the company to market the product for anal intercourse.
“This authorization helps us accomplish our priority to advance health equity through the development of safe and effective products that meet the needs of diverse populations,” Courtney Lias, PhD, the director of the FDA’s Office of GastroRenal, ObGyn, General Hospital, and Urology Devices, said in a statement.
The FDA said it relied on an Emory University clinical study of condom safety of more than 500 men. Those who took part in the study were evenly divided between men who have sex with men and men who have sex with women. The condom failure rate, meaning that a condom either broke or slipped, was less than 1% during anal sex. The failure rate was 3 times higher during vaginal intercourse.
The Emory researchers also found that roughly 70% of men who have sex with men would be more likely to use condoms marked as safe for anal sex, according to a survey of 10,000 people.
ONE Male Condoms sell for between $3.48 for a three-pack and $14.48 for a 24-pack, according to Milla Impola, Global Protection’s director of marketing and communications. The FDA said the condom should be used with a condom-compatible lubricant when used during anal sex.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Genetic mutation tied to moms’ perception of inadequate milk supply
The perception of an inadequate milk supply can contribute to a new mother’s decision to cease breastfeeding prematurely, but identifying at-risk women is difficult. Now a new study suggests that, for some women, this impression, known as perceived inadequacy of milk supply (PIMS) appears to have a basis in genetics.
Steven D. Hicks, MD, PhD, associate professor of pediatrics at Penn State University, Hershey, and colleagues found that variations in the MFGE8 gene was associated with perceived breast milk supply.
“Genotyping one lactogenic gene aided identification of mothers at risk for PIMS. If validated in a larger cohort, such an approach could be used to identify mothers who may benefit from increased lactation support.” Dr. Hicks’ group wrote in Breastfeeding Medicine.
A simple 24-hour polymerase chain reaction test around the time of delivery could identify vulnerable mothers, who could receive targeted lactation support including galactagogue supplementation and early scheduling of “nurse and pump” routines.
“Also, if a woman is found to have PIMS, she would definitely want to avoid going on oral contraceptives after delivery as these can affect milk supply,” Dr. Hicks said in an interview. “That would be like a double hit in a woman already at risk.“
In other measures, she would meet once a week with a lactation consultant for the first 6 months to make sure good breastfeeding practices as to frequency and duration of placing the baby on the breast are being maintained, Dr. Hicks continued. “She needs to make sure her supply isn’t going backwards because once it starts to dry up, it’s really hard to turn the ship around.”
Dietary interventions to promote lactation may also help.
The study
In the context of a larger study on breast milk factors protecting children from developing allergies, the prospective observational analysis collected data on 221 breastfeeding mothers aged 19-42 years (mean age, 29 years) for 12 months.
All mothers had initially planned to nurse their babies for at least 6 months but some stopped well short of their goal.
“At least a third told us they gave up because they felt their milk supply had run out,” Dr. Hicks said in an interview.
Using salivas swabs, the investigators assessed 18 genes secreted from mammary tissue and previously linked in cows to secretory function for single-nucleotide polymorphisms in 88 age-, race-, and parity-matched women. Of these, 45 had PIMS and 43 had perceived adequate milk supply (PAMS).
Among differences between the two groups:
- PIMS mothers breastfed exclusively for a shorter period than PAMS mothers: 7 ± 12 weeks versus 22 ± 19 weeks(P = .001)
- At 1 month after delivery, their reported milk production was lower: 17.6 ± 13.3 oz/day versus 27.0 ± 12.2 oz/day (P = .0001). This shortfall persisted at 4 months: 16.0 ± 14.1 oz/day versus 27.3 ± 14.9 oz/day (P < .0010.
- Between birth and 1 month, infants of PIMS mothers also showed a smaller average increase in weight-for-length z score between birth and 1 month: 0.74 ± 1.4 versus 1.4 ± 1.5 (P = .038).
Furthermore, maternal genotype for the rs2271714 variant within MFGE8 was associated with PIMS status (P = .009; adjusted P = .09; likelihood ratio, 9.33), and duration of exclusive breastfeeding (P = .009; adjusted P = .09; chi square, 9.39).
Adding the MFGE8 genotype to a model including maternal age, parity, previous breastfeeding duration, body mass index, education, and depression status significantly increased predictive accuracy for PIMS status, the authors noted.
“This is a very exciting observation made by Dr. Hicks and his team, and the first study to identify a genetic variant associated with perceived insufficient milk supply,” said Shannon L. Kelleher, PhD, professor of biological and nutritional sciences at University of Massachusetts, Lowell.
“It provides compelling evidence that insufficient milk supply is very common and supports the urgent need to identify the risk factors and develop interventions to improve breastfeeding success,” added Dr. Kelleher, who was not involved in the study.
“If genetic variants such as the one identified in MFGE8 are confirmed to be common in mothers with insufficient milk supply, the development of lactation-focused genetic tests to identify women at risk for low milk supply would revolutionize our ability to support breastfeeding mothers and help them achieve their breastfeeding goals.”
Although 83% of new mothers initiate breastfeeding, only 57% are still breastfeeding at 6 months and only 35% breastfeed until 12 months, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Breastfeeding Report Card.
This study was funded by grants to Dr. Hicks from the Gerber Foundation and the Center for Research on Women and Newborns Foundation. The authors disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Kelleher reported no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments.
The perception of an inadequate milk supply can contribute to a new mother’s decision to cease breastfeeding prematurely, but identifying at-risk women is difficult. Now a new study suggests that, for some women, this impression, known as perceived inadequacy of milk supply (PIMS) appears to have a basis in genetics.
Steven D. Hicks, MD, PhD, associate professor of pediatrics at Penn State University, Hershey, and colleagues found that variations in the MFGE8 gene was associated with perceived breast milk supply.
“Genotyping one lactogenic gene aided identification of mothers at risk for PIMS. If validated in a larger cohort, such an approach could be used to identify mothers who may benefit from increased lactation support.” Dr. Hicks’ group wrote in Breastfeeding Medicine.
A simple 24-hour polymerase chain reaction test around the time of delivery could identify vulnerable mothers, who could receive targeted lactation support including galactagogue supplementation and early scheduling of “nurse and pump” routines.
“Also, if a woman is found to have PIMS, she would definitely want to avoid going on oral contraceptives after delivery as these can affect milk supply,” Dr. Hicks said in an interview. “That would be like a double hit in a woman already at risk.“
In other measures, she would meet once a week with a lactation consultant for the first 6 months to make sure good breastfeeding practices as to frequency and duration of placing the baby on the breast are being maintained, Dr. Hicks continued. “She needs to make sure her supply isn’t going backwards because once it starts to dry up, it’s really hard to turn the ship around.”
Dietary interventions to promote lactation may also help.
The study
In the context of a larger study on breast milk factors protecting children from developing allergies, the prospective observational analysis collected data on 221 breastfeeding mothers aged 19-42 years (mean age, 29 years) for 12 months.
All mothers had initially planned to nurse their babies for at least 6 months but some stopped well short of their goal.
“At least a third told us they gave up because they felt their milk supply had run out,” Dr. Hicks said in an interview.
Using salivas swabs, the investigators assessed 18 genes secreted from mammary tissue and previously linked in cows to secretory function for single-nucleotide polymorphisms in 88 age-, race-, and parity-matched women. Of these, 45 had PIMS and 43 had perceived adequate milk supply (PAMS).
Among differences between the two groups:
- PIMS mothers breastfed exclusively for a shorter period than PAMS mothers: 7 ± 12 weeks versus 22 ± 19 weeks(P = .001)
- At 1 month after delivery, their reported milk production was lower: 17.6 ± 13.3 oz/day versus 27.0 ± 12.2 oz/day (P = .0001). This shortfall persisted at 4 months: 16.0 ± 14.1 oz/day versus 27.3 ± 14.9 oz/day (P < .0010.
- Between birth and 1 month, infants of PIMS mothers also showed a smaller average increase in weight-for-length z score between birth and 1 month: 0.74 ± 1.4 versus 1.4 ± 1.5 (P = .038).
Furthermore, maternal genotype for the rs2271714 variant within MFGE8 was associated with PIMS status (P = .009; adjusted P = .09; likelihood ratio, 9.33), and duration of exclusive breastfeeding (P = .009; adjusted P = .09; chi square, 9.39).
Adding the MFGE8 genotype to a model including maternal age, parity, previous breastfeeding duration, body mass index, education, and depression status significantly increased predictive accuracy for PIMS status, the authors noted.
“This is a very exciting observation made by Dr. Hicks and his team, and the first study to identify a genetic variant associated with perceived insufficient milk supply,” said Shannon L. Kelleher, PhD, professor of biological and nutritional sciences at University of Massachusetts, Lowell.
“It provides compelling evidence that insufficient milk supply is very common and supports the urgent need to identify the risk factors and develop interventions to improve breastfeeding success,” added Dr. Kelleher, who was not involved in the study.
“If genetic variants such as the one identified in MFGE8 are confirmed to be common in mothers with insufficient milk supply, the development of lactation-focused genetic tests to identify women at risk for low milk supply would revolutionize our ability to support breastfeeding mothers and help them achieve their breastfeeding goals.”
Although 83% of new mothers initiate breastfeeding, only 57% are still breastfeeding at 6 months and only 35% breastfeed until 12 months, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Breastfeeding Report Card.
This study was funded by grants to Dr. Hicks from the Gerber Foundation and the Center for Research on Women and Newborns Foundation. The authors disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Kelleher reported no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments.
The perception of an inadequate milk supply can contribute to a new mother’s decision to cease breastfeeding prematurely, but identifying at-risk women is difficult. Now a new study suggests that, for some women, this impression, known as perceived inadequacy of milk supply (PIMS) appears to have a basis in genetics.
Steven D. Hicks, MD, PhD, associate professor of pediatrics at Penn State University, Hershey, and colleagues found that variations in the MFGE8 gene was associated with perceived breast milk supply.
“Genotyping one lactogenic gene aided identification of mothers at risk for PIMS. If validated in a larger cohort, such an approach could be used to identify mothers who may benefit from increased lactation support.” Dr. Hicks’ group wrote in Breastfeeding Medicine.
A simple 24-hour polymerase chain reaction test around the time of delivery could identify vulnerable mothers, who could receive targeted lactation support including galactagogue supplementation and early scheduling of “nurse and pump” routines.
“Also, if a woman is found to have PIMS, she would definitely want to avoid going on oral contraceptives after delivery as these can affect milk supply,” Dr. Hicks said in an interview. “That would be like a double hit in a woman already at risk.“
In other measures, she would meet once a week with a lactation consultant for the first 6 months to make sure good breastfeeding practices as to frequency and duration of placing the baby on the breast are being maintained, Dr. Hicks continued. “She needs to make sure her supply isn’t going backwards because once it starts to dry up, it’s really hard to turn the ship around.”
Dietary interventions to promote lactation may also help.
The study
In the context of a larger study on breast milk factors protecting children from developing allergies, the prospective observational analysis collected data on 221 breastfeeding mothers aged 19-42 years (mean age, 29 years) for 12 months.
All mothers had initially planned to nurse their babies for at least 6 months but some stopped well short of their goal.
“At least a third told us they gave up because they felt their milk supply had run out,” Dr. Hicks said in an interview.
Using salivas swabs, the investigators assessed 18 genes secreted from mammary tissue and previously linked in cows to secretory function for single-nucleotide polymorphisms in 88 age-, race-, and parity-matched women. Of these, 45 had PIMS and 43 had perceived adequate milk supply (PAMS).
Among differences between the two groups:
- PIMS mothers breastfed exclusively for a shorter period than PAMS mothers: 7 ± 12 weeks versus 22 ± 19 weeks(P = .001)
- At 1 month after delivery, their reported milk production was lower: 17.6 ± 13.3 oz/day versus 27.0 ± 12.2 oz/day (P = .0001). This shortfall persisted at 4 months: 16.0 ± 14.1 oz/day versus 27.3 ± 14.9 oz/day (P < .0010.
- Between birth and 1 month, infants of PIMS mothers also showed a smaller average increase in weight-for-length z score between birth and 1 month: 0.74 ± 1.4 versus 1.4 ± 1.5 (P = .038).
Furthermore, maternal genotype for the rs2271714 variant within MFGE8 was associated with PIMS status (P = .009; adjusted P = .09; likelihood ratio, 9.33), and duration of exclusive breastfeeding (P = .009; adjusted P = .09; chi square, 9.39).
Adding the MFGE8 genotype to a model including maternal age, parity, previous breastfeeding duration, body mass index, education, and depression status significantly increased predictive accuracy for PIMS status, the authors noted.
“This is a very exciting observation made by Dr. Hicks and his team, and the first study to identify a genetic variant associated with perceived insufficient milk supply,” said Shannon L. Kelleher, PhD, professor of biological and nutritional sciences at University of Massachusetts, Lowell.
“It provides compelling evidence that insufficient milk supply is very common and supports the urgent need to identify the risk factors and develop interventions to improve breastfeeding success,” added Dr. Kelleher, who was not involved in the study.
“If genetic variants such as the one identified in MFGE8 are confirmed to be common in mothers with insufficient milk supply, the development of lactation-focused genetic tests to identify women at risk for low milk supply would revolutionize our ability to support breastfeeding mothers and help them achieve their breastfeeding goals.”
Although 83% of new mothers initiate breastfeeding, only 57% are still breastfeeding at 6 months and only 35% breastfeed until 12 months, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Breastfeeding Report Card.
This study was funded by grants to Dr. Hicks from the Gerber Foundation and the Center for Research on Women and Newborns Foundation. The authors disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Kelleher reported no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments.
FROM BREASTFEEDING MEDICINE
Variants of nine breast cancer genes associated with severe disease
Breast cancer risk genes are generally associated with triple-negative and high-grade disease, but differ substantially in their associated pathology, a large case-control analysis shows.
The findings have potential implications for genetic testing, risk prediction, variant classification, and screening, the authors noted.
To assess links between pathogenic germline variants in nine major breast cancer (BC) susceptibility genes and pathological features of nonmetastasized breast tumors, investigators from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium compared 42,680 women with breast cancer and 42,387 population-matched controls from the BRIDGES large-scale sequencing study.
They looked specifically at features relevant to prognosis and distinct therapeutic options, including tumor subtype, morphology, size, stage, and lymph node involvement, and found substantial differences in tumor subtype distribution by gene.
“Pathogenic [protein-truncating variants and pathogenic missense variants] in these ... they wrote, noting that carriers of rare genetic variants in the nine genes comprised more than 27% of women diagnosed at age 40 or younger with triple-negative disease (driven mainly by BRCA1) and about 16% of those diagnosed with hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative high-grade disease.
All together, the nine genes were associated with 14.4% of tumors in women aged 40 years and younger, but less than 4% in women over age 60 years, and among younger women, the prevalence of variants combined was higher in those with triple-negative and HR-positive, HER2-negative disease versus other subtypes, they said.
The findings were published online on Jan. 27, 2022, in JAMA Oncology.
Study subjects were women aged 18-79 years who were sampled, independently of family history, from 38 international population- or hospital-based studies conducted between 1991 and 2016.
The genes assessed included ATM, BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, PALB2, RAD51C, RAD51D, and TP53.
Substantial heterogeneity was observed in the distribution of intrinsic subtypes by gene. For example, RAD51C, RAD51D, and BARD1 variants were associated mainly with triple-negative disease (odds ratios, 6.19, 6.19, and 10.05 respectively), and CHEK2 variants were associated with all subtypes (with ORs ranging from 2.21-3.17) except for triple-negative disease, the authors found.
“For ATM variants, the association was strongest for [HR-positive, HER2-negative]high-grade subtype (OR, 4.99). BRCA1 was associated with increased risk of all subtypes, but the ORs varied widely, being highest for triple-negative disease (OR, 55.32),” they wrote.
BRCA2 and PALB2 variants were also associated with triple-negative disease, TP53 variants were most strongly associated with HR-positive, HER2-negative and HR-negative, HER2-positive subtypes, and tumors occurring in pathogenic variant carriers were of higher grade, they added, noting that for most genes and subtypes, a decline in ORs was observed with increasing age.
All genes except CHEK2 were more strongly associated with high-grade disease.
These and other findings from the study can “inform guidelines for eligibility for gene panel sequencing and breast cancer surveillance in the general population,” the authors explained, adding that tumor characteristics can also be used to determine whether variants of uncertain significance are likely to be pathogenic.
The data should therefore “improve the precision of variant classification algorithms and extend them to a larger set of genes,” they noted.
“This case-control study suggests that rare variants in BC susceptibility genes display marked heterogeneity with respect to tumor phenotype, but also similarities between genes that are consistent with known biological functions. This present study provides detailed quantification of subtype-specific breast cancer risks; these can potentially improve risk prediction models and breast cancer prevention strategies,” they concluded.
More specifically, women found to be carrying variants in these genes may be offered enhanced screening, including by MRI, risk-reducing surgery, chemoprevention, and genetic counseling, corresponding author Nasim Mavaddat, MBBS, PhD, explained in an interview.
“Understanding tumor pathology associated with the genes can inform breast cancer risk prediction models, and management and treatment of women harboring pathogenic variants,” she noted.
The findings “enhance our understanding of breast cancer biology and aid efforts to classify whether genetic variants of uncertain significance are also likely to be pathogenic,” added Dr. Mavaddat, a senior research associate at the University of Cambridge (England).
She also said the investigators are taking steps to include the results in “CanRisk,” a cancer risk prediction model used by genetic counselors and other clinicians, and are “exploring whether variants in these genes are associated with contralateral breast cancer risk and survival after a breast cancer.”
As most participants were European, analyses should be extended to women of other racial and ethnic groups, she added.
The BRIDGES panel sequencing was supported by the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program BRIDGES and the Wellcome Trust. The Breast Cancer Association Consortium is also funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, the PERSPECTIVE I&I project, which is funded by the Government of Canada, and the Confluence project, which is funded with intramural funds from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Mavaddat reported grants from the University of Cambridge, European Union Horizon 2020, Wellcome Trust, Genome Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study.
Breast cancer risk genes are generally associated with triple-negative and high-grade disease, but differ substantially in their associated pathology, a large case-control analysis shows.
The findings have potential implications for genetic testing, risk prediction, variant classification, and screening, the authors noted.
To assess links between pathogenic germline variants in nine major breast cancer (BC) susceptibility genes and pathological features of nonmetastasized breast tumors, investigators from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium compared 42,680 women with breast cancer and 42,387 population-matched controls from the BRIDGES large-scale sequencing study.
They looked specifically at features relevant to prognosis and distinct therapeutic options, including tumor subtype, morphology, size, stage, and lymph node involvement, and found substantial differences in tumor subtype distribution by gene.
“Pathogenic [protein-truncating variants and pathogenic missense variants] in these ... they wrote, noting that carriers of rare genetic variants in the nine genes comprised more than 27% of women diagnosed at age 40 or younger with triple-negative disease (driven mainly by BRCA1) and about 16% of those diagnosed with hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative high-grade disease.
All together, the nine genes were associated with 14.4% of tumors in women aged 40 years and younger, but less than 4% in women over age 60 years, and among younger women, the prevalence of variants combined was higher in those with triple-negative and HR-positive, HER2-negative disease versus other subtypes, they said.
The findings were published online on Jan. 27, 2022, in JAMA Oncology.
Study subjects were women aged 18-79 years who were sampled, independently of family history, from 38 international population- or hospital-based studies conducted between 1991 and 2016.
The genes assessed included ATM, BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, PALB2, RAD51C, RAD51D, and TP53.
Substantial heterogeneity was observed in the distribution of intrinsic subtypes by gene. For example, RAD51C, RAD51D, and BARD1 variants were associated mainly with triple-negative disease (odds ratios, 6.19, 6.19, and 10.05 respectively), and CHEK2 variants were associated with all subtypes (with ORs ranging from 2.21-3.17) except for triple-negative disease, the authors found.
“For ATM variants, the association was strongest for [HR-positive, HER2-negative]high-grade subtype (OR, 4.99). BRCA1 was associated with increased risk of all subtypes, but the ORs varied widely, being highest for triple-negative disease (OR, 55.32),” they wrote.
BRCA2 and PALB2 variants were also associated with triple-negative disease, TP53 variants were most strongly associated with HR-positive, HER2-negative and HR-negative, HER2-positive subtypes, and tumors occurring in pathogenic variant carriers were of higher grade, they added, noting that for most genes and subtypes, a decline in ORs was observed with increasing age.
All genes except CHEK2 were more strongly associated with high-grade disease.
These and other findings from the study can “inform guidelines for eligibility for gene panel sequencing and breast cancer surveillance in the general population,” the authors explained, adding that tumor characteristics can also be used to determine whether variants of uncertain significance are likely to be pathogenic.
The data should therefore “improve the precision of variant classification algorithms and extend them to a larger set of genes,” they noted.
“This case-control study suggests that rare variants in BC susceptibility genes display marked heterogeneity with respect to tumor phenotype, but also similarities between genes that are consistent with known biological functions. This present study provides detailed quantification of subtype-specific breast cancer risks; these can potentially improve risk prediction models and breast cancer prevention strategies,” they concluded.
More specifically, women found to be carrying variants in these genes may be offered enhanced screening, including by MRI, risk-reducing surgery, chemoprevention, and genetic counseling, corresponding author Nasim Mavaddat, MBBS, PhD, explained in an interview.
“Understanding tumor pathology associated with the genes can inform breast cancer risk prediction models, and management and treatment of women harboring pathogenic variants,” she noted.
The findings “enhance our understanding of breast cancer biology and aid efforts to classify whether genetic variants of uncertain significance are also likely to be pathogenic,” added Dr. Mavaddat, a senior research associate at the University of Cambridge (England).
She also said the investigators are taking steps to include the results in “CanRisk,” a cancer risk prediction model used by genetic counselors and other clinicians, and are “exploring whether variants in these genes are associated with contralateral breast cancer risk and survival after a breast cancer.”
As most participants were European, analyses should be extended to women of other racial and ethnic groups, she added.
The BRIDGES panel sequencing was supported by the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program BRIDGES and the Wellcome Trust. The Breast Cancer Association Consortium is also funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, the PERSPECTIVE I&I project, which is funded by the Government of Canada, and the Confluence project, which is funded with intramural funds from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Mavaddat reported grants from the University of Cambridge, European Union Horizon 2020, Wellcome Trust, Genome Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study.
Breast cancer risk genes are generally associated with triple-negative and high-grade disease, but differ substantially in their associated pathology, a large case-control analysis shows.
The findings have potential implications for genetic testing, risk prediction, variant classification, and screening, the authors noted.
To assess links between pathogenic germline variants in nine major breast cancer (BC) susceptibility genes and pathological features of nonmetastasized breast tumors, investigators from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium compared 42,680 women with breast cancer and 42,387 population-matched controls from the BRIDGES large-scale sequencing study.
They looked specifically at features relevant to prognosis and distinct therapeutic options, including tumor subtype, morphology, size, stage, and lymph node involvement, and found substantial differences in tumor subtype distribution by gene.
“Pathogenic [protein-truncating variants and pathogenic missense variants] in these ... they wrote, noting that carriers of rare genetic variants in the nine genes comprised more than 27% of women diagnosed at age 40 or younger with triple-negative disease (driven mainly by BRCA1) and about 16% of those diagnosed with hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative high-grade disease.
All together, the nine genes were associated with 14.4% of tumors in women aged 40 years and younger, but less than 4% in women over age 60 years, and among younger women, the prevalence of variants combined was higher in those with triple-negative and HR-positive, HER2-negative disease versus other subtypes, they said.
The findings were published online on Jan. 27, 2022, in JAMA Oncology.
Study subjects were women aged 18-79 years who were sampled, independently of family history, from 38 international population- or hospital-based studies conducted between 1991 and 2016.
The genes assessed included ATM, BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, PALB2, RAD51C, RAD51D, and TP53.
Substantial heterogeneity was observed in the distribution of intrinsic subtypes by gene. For example, RAD51C, RAD51D, and BARD1 variants were associated mainly with triple-negative disease (odds ratios, 6.19, 6.19, and 10.05 respectively), and CHEK2 variants were associated with all subtypes (with ORs ranging from 2.21-3.17) except for triple-negative disease, the authors found.
“For ATM variants, the association was strongest for [HR-positive, HER2-negative]high-grade subtype (OR, 4.99). BRCA1 was associated with increased risk of all subtypes, but the ORs varied widely, being highest for triple-negative disease (OR, 55.32),” they wrote.
BRCA2 and PALB2 variants were also associated with triple-negative disease, TP53 variants were most strongly associated with HR-positive, HER2-negative and HR-negative, HER2-positive subtypes, and tumors occurring in pathogenic variant carriers were of higher grade, they added, noting that for most genes and subtypes, a decline in ORs was observed with increasing age.
All genes except CHEK2 were more strongly associated with high-grade disease.
These and other findings from the study can “inform guidelines for eligibility for gene panel sequencing and breast cancer surveillance in the general population,” the authors explained, adding that tumor characteristics can also be used to determine whether variants of uncertain significance are likely to be pathogenic.
The data should therefore “improve the precision of variant classification algorithms and extend them to a larger set of genes,” they noted.
“This case-control study suggests that rare variants in BC susceptibility genes display marked heterogeneity with respect to tumor phenotype, but also similarities between genes that are consistent with known biological functions. This present study provides detailed quantification of subtype-specific breast cancer risks; these can potentially improve risk prediction models and breast cancer prevention strategies,” they concluded.
More specifically, women found to be carrying variants in these genes may be offered enhanced screening, including by MRI, risk-reducing surgery, chemoprevention, and genetic counseling, corresponding author Nasim Mavaddat, MBBS, PhD, explained in an interview.
“Understanding tumor pathology associated with the genes can inform breast cancer risk prediction models, and management and treatment of women harboring pathogenic variants,” she noted.
The findings “enhance our understanding of breast cancer biology and aid efforts to classify whether genetic variants of uncertain significance are also likely to be pathogenic,” added Dr. Mavaddat, a senior research associate at the University of Cambridge (England).
She also said the investigators are taking steps to include the results in “CanRisk,” a cancer risk prediction model used by genetic counselors and other clinicians, and are “exploring whether variants in these genes are associated with contralateral breast cancer risk and survival after a breast cancer.”
As most participants were European, analyses should be extended to women of other racial and ethnic groups, she added.
The BRIDGES panel sequencing was supported by the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program BRIDGES and the Wellcome Trust. The Breast Cancer Association Consortium is also funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, the PERSPECTIVE I&I project, which is funded by the Government of Canada, and the Confluence project, which is funded with intramural funds from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Mavaddat reported grants from the University of Cambridge, European Union Horizon 2020, Wellcome Trust, Genome Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Doc says sobbing attorney and crying medical expert led to unfair million-dollar verdict
Jurors found obstetrician-gynecologist Charles H. Marks, DO, negligent for failing to follow up on a patient’s complex cyst and hyperechoic nodule, which resulted in a delayed ovarian cancer diagnosis. But during the doctor’s 4-day trial, several parties had emotional outbursts in front of the jury, including the plaintiff’s’ attorney, a physician expert witness, the patient, and a family member.
According to trial transcripts, a gynecologic oncologist expert began crying on the stand after providing a clinical description of the symptoms that plaintiff, Chasidy Plunkard, would probably experience leading up to her death. When asked how long the patient had to live, the oncologist said “months” and later added, “I think she is living for this trial.”
After these comments, Ms. Plunkard’s attorney, Kila Baldwin, also began crying and requested a break to regain her composure, according to district court documents. During the 3 minutes the attorney was gone, the courtroom was silent other than the sound of Ms. Plunkard and her cousin sobbing.
The following day, U.S. District Judge Jennifer P. Wilson warned Ms. Baldwin that she would consider declaring a mistrial if the outburst happened again, according to trial transcripts.
“I expect counsel to maintain a professional demeanor even when eliciting emotionally laden testimony,” Judge Wilson said. “…I will not allow another recess. Further, if we have another incident like we had yesterday, I would have to entertain, if a motion for mistrial is made, I would have to seriously consider that, because I am concerned that this jury already has had a demonstration of a level of emotion that may make it difficult for them to set that aside and render a verdict that’s based only on a dispassionate consideration of what I perceive to be a legitimate dispute regarding liability.”
Judge Wilson later instructed jurors to disregard certain testimony at the request of Dr. Marks’ attorneys and reminded them not to be influenced by sympathy. After jurors rendered their $1.3 million verdict against Dr. Marks, he requested a new trial, claiming the witness’s testimony and the emotional displays of the witness and the attorney unfairly influenced the jury.
The expert witness “and plaintiff’s counsel undoubtedly affected the jury’s ability to decide this case in a dispassionate and impartial way and denied Dr. Marks his right to a fair trial,” attorney Matthew Rappleye wrote in Dr. Marks’ motion for a retrial. “Just as the court feared, as a result of these events, the jury was ‘tainted’ and could no longer decide this case divorced of sympathy for Ms. Plunkard.”
In response, an attorney for Ms. Plunkard emphasized that Dr. Marks did not request a retrial during the trial and that he was granted objections to the relevant testimony that he sought.
“In any event, the jury had the benefit of substantial evidence concerning Dr. Marks’ negligence, and the jury was entitled to construe that evidence in Plaintiff’s favor” attorney Charles Becker wrote. “…Indeed, the jury’s economic damages award of $585,000 not only fell well below the projection of plaintiff’s expert, but also ran at the low-end of the projection provided by Defendant’s economist. As to the non-economic damages, the jury’s award of $750,000 could have been far higher…. Nothing about either verdict or the damages award suggests a jury that was influenced by impermissible displays of emotion by the trial participants.”
In a December 13, 2021, decision, the U.S. District Court for the Middle District Court of Pennsylvania denied Dr. Marks’ request for a retrial. In her decision, Judge Wilson wrote that nothing in the jury’s verdict appeared to indicate that jurors were swayed by sympathy and that the verdict appeared to be conservative in light of the testimony presented.
Attorneys for Dr. Marks did not respond to a request for comment. In a statement, Ms. Baldwin said that the judge’s decision was correct.
“The district court got it exactly right, and we look forward to Ms. Plunkard receiving the compensation awarded by the jury in this tragic case,” she said.
Why did the patient sue?
Ms. Plunkard’s lawsuit against Dr. Marks stemmed from a January 2016 visit for complaints of bloating, pelvic pain, irregular periods, and an abnormal pelvic ultrasound. The ultrasound, ordered by her primary care physician, showed a thickened endometrial lining; a normal left ovary; and an enlarged, abnormal right ovary containing a complicated cyst, according to Ms. Plunkard’s complaint. Dr. Marks performed an endometrial biopsy and advised Ms. Plunkard that she would not need to take further measures if the result was benign, according to her lawsuit.
The result was benign, so Ms. Plunkard said she sought no further treatment for the cyst and none of her treating physicians followed up on the cyst. In February 2017, Ms. Plunkard presented to an emergency department with severe right upper quadrant abdominal pain and an ultrasound showed possible gallstones and pleural effusion, according to court documents.
After laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it was discovered that Ms. Plunkard had an inflamed pelvis and an omental lymph node was removed and biopsied. Surgeons reported that the lymph node showed metastatic cancer of probable gynecologic origin.
The patient underwent exploratory laparotomy, resulting in a radical abdominal hysterectomy, appendectomy, resection of the rectosigmoid with end-to-end anastomosis, and removal of cancerous implants. She was ultimately diagnosed with stage IVB low-grade metastatic ovarian cancer and went through six chemotherapy courses.
The patent’s cancer briefly went into remission but returned. In her complaint, Ms. Plunkard said Dr. Marks’ negligence allowed the cancer to spread from stage I to stage IVB, increasing her risk for harm and untimely death.
Dr. Marks argued that a follow-up ultrasound was not required, that the cyst on the patient’s right ovary was benign and resolved itself, that Ms. Plunkard’s cancer originated on the left, and that a follow-up ultrasound would not have detected primary cancer on the left ovary, according to legal documents.
On January 7, 2022, Dr. Marks appealed the jury’s verdict and the order denying his request for a retrial to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jurors found obstetrician-gynecologist Charles H. Marks, DO, negligent for failing to follow up on a patient’s complex cyst and hyperechoic nodule, which resulted in a delayed ovarian cancer diagnosis. But during the doctor’s 4-day trial, several parties had emotional outbursts in front of the jury, including the plaintiff’s’ attorney, a physician expert witness, the patient, and a family member.
According to trial transcripts, a gynecologic oncologist expert began crying on the stand after providing a clinical description of the symptoms that plaintiff, Chasidy Plunkard, would probably experience leading up to her death. When asked how long the patient had to live, the oncologist said “months” and later added, “I think she is living for this trial.”
After these comments, Ms. Plunkard’s attorney, Kila Baldwin, also began crying and requested a break to regain her composure, according to district court documents. During the 3 minutes the attorney was gone, the courtroom was silent other than the sound of Ms. Plunkard and her cousin sobbing.
The following day, U.S. District Judge Jennifer P. Wilson warned Ms. Baldwin that she would consider declaring a mistrial if the outburst happened again, according to trial transcripts.
“I expect counsel to maintain a professional demeanor even when eliciting emotionally laden testimony,” Judge Wilson said. “…I will not allow another recess. Further, if we have another incident like we had yesterday, I would have to entertain, if a motion for mistrial is made, I would have to seriously consider that, because I am concerned that this jury already has had a demonstration of a level of emotion that may make it difficult for them to set that aside and render a verdict that’s based only on a dispassionate consideration of what I perceive to be a legitimate dispute regarding liability.”
Judge Wilson later instructed jurors to disregard certain testimony at the request of Dr. Marks’ attorneys and reminded them not to be influenced by sympathy. After jurors rendered their $1.3 million verdict against Dr. Marks, he requested a new trial, claiming the witness’s testimony and the emotional displays of the witness and the attorney unfairly influenced the jury.
The expert witness “and plaintiff’s counsel undoubtedly affected the jury’s ability to decide this case in a dispassionate and impartial way and denied Dr. Marks his right to a fair trial,” attorney Matthew Rappleye wrote in Dr. Marks’ motion for a retrial. “Just as the court feared, as a result of these events, the jury was ‘tainted’ and could no longer decide this case divorced of sympathy for Ms. Plunkard.”
In response, an attorney for Ms. Plunkard emphasized that Dr. Marks did not request a retrial during the trial and that he was granted objections to the relevant testimony that he sought.
“In any event, the jury had the benefit of substantial evidence concerning Dr. Marks’ negligence, and the jury was entitled to construe that evidence in Plaintiff’s favor” attorney Charles Becker wrote. “…Indeed, the jury’s economic damages award of $585,000 not only fell well below the projection of plaintiff’s expert, but also ran at the low-end of the projection provided by Defendant’s economist. As to the non-economic damages, the jury’s award of $750,000 could have been far higher…. Nothing about either verdict or the damages award suggests a jury that was influenced by impermissible displays of emotion by the trial participants.”
In a December 13, 2021, decision, the U.S. District Court for the Middle District Court of Pennsylvania denied Dr. Marks’ request for a retrial. In her decision, Judge Wilson wrote that nothing in the jury’s verdict appeared to indicate that jurors were swayed by sympathy and that the verdict appeared to be conservative in light of the testimony presented.
Attorneys for Dr. Marks did not respond to a request for comment. In a statement, Ms. Baldwin said that the judge’s decision was correct.
“The district court got it exactly right, and we look forward to Ms. Plunkard receiving the compensation awarded by the jury in this tragic case,” she said.
Why did the patient sue?
Ms. Plunkard’s lawsuit against Dr. Marks stemmed from a January 2016 visit for complaints of bloating, pelvic pain, irregular periods, and an abnormal pelvic ultrasound. The ultrasound, ordered by her primary care physician, showed a thickened endometrial lining; a normal left ovary; and an enlarged, abnormal right ovary containing a complicated cyst, according to Ms. Plunkard’s complaint. Dr. Marks performed an endometrial biopsy and advised Ms. Plunkard that she would not need to take further measures if the result was benign, according to her lawsuit.
The result was benign, so Ms. Plunkard said she sought no further treatment for the cyst and none of her treating physicians followed up on the cyst. In February 2017, Ms. Plunkard presented to an emergency department with severe right upper quadrant abdominal pain and an ultrasound showed possible gallstones and pleural effusion, according to court documents.
After laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it was discovered that Ms. Plunkard had an inflamed pelvis and an omental lymph node was removed and biopsied. Surgeons reported that the lymph node showed metastatic cancer of probable gynecologic origin.
The patient underwent exploratory laparotomy, resulting in a radical abdominal hysterectomy, appendectomy, resection of the rectosigmoid with end-to-end anastomosis, and removal of cancerous implants. She was ultimately diagnosed with stage IVB low-grade metastatic ovarian cancer and went through six chemotherapy courses.
The patent’s cancer briefly went into remission but returned. In her complaint, Ms. Plunkard said Dr. Marks’ negligence allowed the cancer to spread from stage I to stage IVB, increasing her risk for harm and untimely death.
Dr. Marks argued that a follow-up ultrasound was not required, that the cyst on the patient’s right ovary was benign and resolved itself, that Ms. Plunkard’s cancer originated on the left, and that a follow-up ultrasound would not have detected primary cancer on the left ovary, according to legal documents.
On January 7, 2022, Dr. Marks appealed the jury’s verdict and the order denying his request for a retrial to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jurors found obstetrician-gynecologist Charles H. Marks, DO, negligent for failing to follow up on a patient’s complex cyst and hyperechoic nodule, which resulted in a delayed ovarian cancer diagnosis. But during the doctor’s 4-day trial, several parties had emotional outbursts in front of the jury, including the plaintiff’s’ attorney, a physician expert witness, the patient, and a family member.
According to trial transcripts, a gynecologic oncologist expert began crying on the stand after providing a clinical description of the symptoms that plaintiff, Chasidy Plunkard, would probably experience leading up to her death. When asked how long the patient had to live, the oncologist said “months” and later added, “I think she is living for this trial.”
After these comments, Ms. Plunkard’s attorney, Kila Baldwin, also began crying and requested a break to regain her composure, according to district court documents. During the 3 minutes the attorney was gone, the courtroom was silent other than the sound of Ms. Plunkard and her cousin sobbing.
The following day, U.S. District Judge Jennifer P. Wilson warned Ms. Baldwin that she would consider declaring a mistrial if the outburst happened again, according to trial transcripts.
“I expect counsel to maintain a professional demeanor even when eliciting emotionally laden testimony,” Judge Wilson said. “…I will not allow another recess. Further, if we have another incident like we had yesterday, I would have to entertain, if a motion for mistrial is made, I would have to seriously consider that, because I am concerned that this jury already has had a demonstration of a level of emotion that may make it difficult for them to set that aside and render a verdict that’s based only on a dispassionate consideration of what I perceive to be a legitimate dispute regarding liability.”
Judge Wilson later instructed jurors to disregard certain testimony at the request of Dr. Marks’ attorneys and reminded them not to be influenced by sympathy. After jurors rendered their $1.3 million verdict against Dr. Marks, he requested a new trial, claiming the witness’s testimony and the emotional displays of the witness and the attorney unfairly influenced the jury.
The expert witness “and plaintiff’s counsel undoubtedly affected the jury’s ability to decide this case in a dispassionate and impartial way and denied Dr. Marks his right to a fair trial,” attorney Matthew Rappleye wrote in Dr. Marks’ motion for a retrial. “Just as the court feared, as a result of these events, the jury was ‘tainted’ and could no longer decide this case divorced of sympathy for Ms. Plunkard.”
In response, an attorney for Ms. Plunkard emphasized that Dr. Marks did not request a retrial during the trial and that he was granted objections to the relevant testimony that he sought.
“In any event, the jury had the benefit of substantial evidence concerning Dr. Marks’ negligence, and the jury was entitled to construe that evidence in Plaintiff’s favor” attorney Charles Becker wrote. “…Indeed, the jury’s economic damages award of $585,000 not only fell well below the projection of plaintiff’s expert, but also ran at the low-end of the projection provided by Defendant’s economist. As to the non-economic damages, the jury’s award of $750,000 could have been far higher…. Nothing about either verdict or the damages award suggests a jury that was influenced by impermissible displays of emotion by the trial participants.”
In a December 13, 2021, decision, the U.S. District Court for the Middle District Court of Pennsylvania denied Dr. Marks’ request for a retrial. In her decision, Judge Wilson wrote that nothing in the jury’s verdict appeared to indicate that jurors were swayed by sympathy and that the verdict appeared to be conservative in light of the testimony presented.
Attorneys for Dr. Marks did not respond to a request for comment. In a statement, Ms. Baldwin said that the judge’s decision was correct.
“The district court got it exactly right, and we look forward to Ms. Plunkard receiving the compensation awarded by the jury in this tragic case,” she said.
Why did the patient sue?
Ms. Plunkard’s lawsuit against Dr. Marks stemmed from a January 2016 visit for complaints of bloating, pelvic pain, irregular periods, and an abnormal pelvic ultrasound. The ultrasound, ordered by her primary care physician, showed a thickened endometrial lining; a normal left ovary; and an enlarged, abnormal right ovary containing a complicated cyst, according to Ms. Plunkard’s complaint. Dr. Marks performed an endometrial biopsy and advised Ms. Plunkard that she would not need to take further measures if the result was benign, according to her lawsuit.
The result was benign, so Ms. Plunkard said she sought no further treatment for the cyst and none of her treating physicians followed up on the cyst. In February 2017, Ms. Plunkard presented to an emergency department with severe right upper quadrant abdominal pain and an ultrasound showed possible gallstones and pleural effusion, according to court documents.
After laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it was discovered that Ms. Plunkard had an inflamed pelvis and an omental lymph node was removed and biopsied. Surgeons reported that the lymph node showed metastatic cancer of probable gynecologic origin.
The patient underwent exploratory laparotomy, resulting in a radical abdominal hysterectomy, appendectomy, resection of the rectosigmoid with end-to-end anastomosis, and removal of cancerous implants. She was ultimately diagnosed with stage IVB low-grade metastatic ovarian cancer and went through six chemotherapy courses.
The patent’s cancer briefly went into remission but returned. In her complaint, Ms. Plunkard said Dr. Marks’ negligence allowed the cancer to spread from stage I to stage IVB, increasing her risk for harm and untimely death.
Dr. Marks argued that a follow-up ultrasound was not required, that the cyst on the patient’s right ovary was benign and resolved itself, that Ms. Plunkard’s cancer originated on the left, and that a follow-up ultrasound would not have detected primary cancer on the left ovary, according to legal documents.
On January 7, 2022, Dr. Marks appealed the jury’s verdict and the order denying his request for a retrial to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.


