User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Link between PCOS and increased risk of pancreatic cancer?
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be at a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer, say researchers reporting a single-center case-control study.
A diagnosis of PCOS was associated with a 1.9-fold higher risk of pancreatic cancer after adjusting for age, race, ethnicity, estrogen level, and diabetes.
This is the second study to find such an association.
“Our study findings combined with those from the 2019 Swedish Registry study offer compelling evidence that PCOS may be a novel risk factor for pancreatic cancer,” said corresponding author Mengmeng Du, ScD, department of epidemiology and biostatistics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
“These data suggest some individuals may have unknown metabolic derangements that may underlie the development of both conditions,” the team concluded.
The findings were published in JAMA Oncology.
Approached for comment, Srinivas Gaddam, MD, MPH, associate director of pancreatic biliary research medicine, Cedars-Sinai, suggested that the findings may pave the way for a better understanding of the two diseases, but he emphasized that more research is needed.
“I think there’s more research to be done because now we’re seeing more younger women get pancreatic cancer,” Dr. Gaddam said. “So that makes it interesting whether PCOS itself contributes to pancreatic cancer. I still think the jury is out there.”
Dr. Gaddam drew attention to the confidence interval for the finding – the adjusted odds ratio was 1.88 (95% confidence interval, 1.02-3.46). “Because their odds ratio includes 1, I’m left with the question as to whether or not this is truly associated. I’m not certain that we can draw any conclusions based on this,” he commented.
The investigators acknowledge that they did “not observe statistically significant interactions” and comment that “prospective studies are needed to examine underlying biologic mechanisms and confirm our findings.”
For the study, the team used data from the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Pancreatic Tumor Registry. They identified patients with pancreatic cancer who also self-reported a diagnosis of PCOS.
The investigators compared data from 446 women with pathologically or cytologically confirmed pancreatic adenocarcinoma with 209 women who had no history of cancer. The mean age at cancer diagnosis or enrollment was 63.8 years among patients with pancreatic cancer and 57.7 years in the control group.
The study found that having PCOS nearly doubled a person’s risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
When adjusted for type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the odds ratio fell slightly to 1.78 (95% CI, 0.95-3.34).
Dr. Du, along with lead author Noah Peeri, PhD, were surprised that even after adjusting for body mass index and the presence of type 2 diabetes, PCOS remained strongly associated with pancreatic cancer risk.
“We originally thought type 2 diabetes may drive this association, given more than half of those with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age 40, according to the CDC, and type 2 diabetes has also been linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk,” said Dr. Du.
“While the association was slightly weaker and no longer statistically significant after we controlled for type 2 diabetes, the magnitude of the association remained largely unchanged,” he said.
Dr. Peeri believes that some of the factors that have been causally related to PCOS may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.
“PCOS itself does not likely cause pancreatic cancer, but metabolic problems (for example, improper breakdown of insulin) and chronic inflammation can contribute to both PCOS and pancreatic cancer risk,” Dr. Peeri said.
He concluded that the study results “suggest other underlying metabolic dysfunction may increase an individual’s pancreatic cancer risk.”
An important limitation of this study was that women in the study self-reported PCOS and may have incorrectly recalled their diagnosis. However, the authors believe it is unlikely that that had a bearing on the study findings.
The study was supported by National Cancer Institute grants, the Geoffrey Beene Foundation, and the Arnold and Arlene Goldstein Family Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
DTC telemedicine expands access to gender-affirming therapy
Direct-to-consumer telemedicine services that provide gender-affirming hormone therapy appear to follow evidence-based guidelines and charge about the same as brick-and-mortar medical centers, according to researchers who reviewed the platforms’ websites.
The findings suggest that virtual care “may be a good option” for transgender, nonbinary, and intersex people, who often report difficulty finding physicians they trust, Erin Jesse, MD, a fifth-year urology resident at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, who is the first author of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Jesse’s group presented their findings at a joint scientific meeting of the Sexual Medicine Society of North America and the International Society for Sexual Medicine in Miami. The results have not been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
New direct-to-consumer telemedicine companies have emerged with gender-diverse staff and services tailored to the needs of these individuals. They offer “a more inclusive feel” than might be encountered at a physician’s office, Dr. Jesse said.
Confirming that these companies adhere to standards of care and cost-effectiveness “is especially important considering the reduced access to care and potentially increased vulnerability of the gender-diverse population,” she and her colleagues wrote.
From a Google search in March, the team identified six U.S.-based platforms that offer gender-affirming medical therapy: FOLX, True U Clinic, QueerDoc, Queer Med, TransClinique, and Plume.
From information posted on the companies’ websites, the researchers determined that all aligned with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health’s Standards of Care in two areas: use of an informed consent model to ensure that patients have sufficient information and understanding to decide on their own treatment and endorsement of frequent laboratory monitoring of hormone levels in early stages of treatment.
The team also compared the costs listed on the websites for the first year of therapy to the costs of similar care at a tertiary center, as determined using University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center’s online estimator.
The platforms offered various pricing models, including fee-for-service and monthly membership plans ranging from $59 to $139. For individuals without insurance, estimates ranged from $1,022 to $1,428 for oral estradiol and from $1,184 to $1,668 for intramuscular testosterone from the online companies, compared with $1,184 and $1,216, respectively, at the tertiary center.
Although some platforms accept insurance, the researchers were not able to evaluate the cost of using private insurance or Medicaid, Dr. Jesse said. She noted that transgender individuals are more likely to lack insurance than are cisgender patients.
The team also assessed the scope of services. All companies offered legal help with changes to names and gender markers, such as “M” and “F.” Three or more companies offered preexposure prophylaxis to prevent HIV infection, treatment for erectile dysfunction, referrals for surgery, and medical letters of support for surgery.
Two offered puberty blockers, although the researchers were unable to determine the risk of adolescents obtaining treatment without proper assessments, because details of those services are not disclosed on websites, Dr. Jesse said.
An avenue of further research would be to interview patients to learn how platforms operate in practice and whether patients are properly assessed before treatment. “Those sorts of questions we can’t answer just by looking at the websites,” she said.
However, Charlotte Hoffman, JD, senior policy counsel for the National Center for Transgender Equality, an advocacy group, said she does not harbor concerns about patients being treated inappropriately simply because care is virtual. All clinicians who provide gender-affirming care face potential repercussions, such as malpractice lawsuits or state disciplinary action, if they veer from treatment guidelines, she said.
“I don’t necessarily take the premise that telehealth is inherently worse than in-person care as a given,” Ms. Hoffman said.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. Hoffman added, direct-to-consumer telemedicine has expanded access for individuals in rural areas, people with disabilities, and those who live in places where in-person providers of transgender care face public hostility, although individuals without the resources to pay may still be left out.
What might happen to that access if telemedicine restrictions that were loosened during the pandemic are reinstated is unclear, she said.
The researchers and Ms. Hoffman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Direct-to-consumer telemedicine services that provide gender-affirming hormone therapy appear to follow evidence-based guidelines and charge about the same as brick-and-mortar medical centers, according to researchers who reviewed the platforms’ websites.
The findings suggest that virtual care “may be a good option” for transgender, nonbinary, and intersex people, who often report difficulty finding physicians they trust, Erin Jesse, MD, a fifth-year urology resident at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, who is the first author of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Jesse’s group presented their findings at a joint scientific meeting of the Sexual Medicine Society of North America and the International Society for Sexual Medicine in Miami. The results have not been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
New direct-to-consumer telemedicine companies have emerged with gender-diverse staff and services tailored to the needs of these individuals. They offer “a more inclusive feel” than might be encountered at a physician’s office, Dr. Jesse said.
Confirming that these companies adhere to standards of care and cost-effectiveness “is especially important considering the reduced access to care and potentially increased vulnerability of the gender-diverse population,” she and her colleagues wrote.
From a Google search in March, the team identified six U.S.-based platforms that offer gender-affirming medical therapy: FOLX, True U Clinic, QueerDoc, Queer Med, TransClinique, and Plume.
From information posted on the companies’ websites, the researchers determined that all aligned with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health’s Standards of Care in two areas: use of an informed consent model to ensure that patients have sufficient information and understanding to decide on their own treatment and endorsement of frequent laboratory monitoring of hormone levels in early stages of treatment.
The team also compared the costs listed on the websites for the first year of therapy to the costs of similar care at a tertiary center, as determined using University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center’s online estimator.
The platforms offered various pricing models, including fee-for-service and monthly membership plans ranging from $59 to $139. For individuals without insurance, estimates ranged from $1,022 to $1,428 for oral estradiol and from $1,184 to $1,668 for intramuscular testosterone from the online companies, compared with $1,184 and $1,216, respectively, at the tertiary center.
Although some platforms accept insurance, the researchers were not able to evaluate the cost of using private insurance or Medicaid, Dr. Jesse said. She noted that transgender individuals are more likely to lack insurance than are cisgender patients.
The team also assessed the scope of services. All companies offered legal help with changes to names and gender markers, such as “M” and “F.” Three or more companies offered preexposure prophylaxis to prevent HIV infection, treatment for erectile dysfunction, referrals for surgery, and medical letters of support for surgery.
Two offered puberty blockers, although the researchers were unable to determine the risk of adolescents obtaining treatment without proper assessments, because details of those services are not disclosed on websites, Dr. Jesse said.
An avenue of further research would be to interview patients to learn how platforms operate in practice and whether patients are properly assessed before treatment. “Those sorts of questions we can’t answer just by looking at the websites,” she said.
However, Charlotte Hoffman, JD, senior policy counsel for the National Center for Transgender Equality, an advocacy group, said she does not harbor concerns about patients being treated inappropriately simply because care is virtual. All clinicians who provide gender-affirming care face potential repercussions, such as malpractice lawsuits or state disciplinary action, if they veer from treatment guidelines, she said.
“I don’t necessarily take the premise that telehealth is inherently worse than in-person care as a given,” Ms. Hoffman said.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. Hoffman added, direct-to-consumer telemedicine has expanded access for individuals in rural areas, people with disabilities, and those who live in places where in-person providers of transgender care face public hostility, although individuals without the resources to pay may still be left out.
What might happen to that access if telemedicine restrictions that were loosened during the pandemic are reinstated is unclear, she said.
The researchers and Ms. Hoffman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Direct-to-consumer telemedicine services that provide gender-affirming hormone therapy appear to follow evidence-based guidelines and charge about the same as brick-and-mortar medical centers, according to researchers who reviewed the platforms’ websites.
The findings suggest that virtual care “may be a good option” for transgender, nonbinary, and intersex people, who often report difficulty finding physicians they trust, Erin Jesse, MD, a fifth-year urology resident at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, who is the first author of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Jesse’s group presented their findings at a joint scientific meeting of the Sexual Medicine Society of North America and the International Society for Sexual Medicine in Miami. The results have not been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
New direct-to-consumer telemedicine companies have emerged with gender-diverse staff and services tailored to the needs of these individuals. They offer “a more inclusive feel” than might be encountered at a physician’s office, Dr. Jesse said.
Confirming that these companies adhere to standards of care and cost-effectiveness “is especially important considering the reduced access to care and potentially increased vulnerability of the gender-diverse population,” she and her colleagues wrote.
From a Google search in March, the team identified six U.S.-based platforms that offer gender-affirming medical therapy: FOLX, True U Clinic, QueerDoc, Queer Med, TransClinique, and Plume.
From information posted on the companies’ websites, the researchers determined that all aligned with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health’s Standards of Care in two areas: use of an informed consent model to ensure that patients have sufficient information and understanding to decide on their own treatment and endorsement of frequent laboratory monitoring of hormone levels in early stages of treatment.
The team also compared the costs listed on the websites for the first year of therapy to the costs of similar care at a tertiary center, as determined using University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center’s online estimator.
The platforms offered various pricing models, including fee-for-service and monthly membership plans ranging from $59 to $139. For individuals without insurance, estimates ranged from $1,022 to $1,428 for oral estradiol and from $1,184 to $1,668 for intramuscular testosterone from the online companies, compared with $1,184 and $1,216, respectively, at the tertiary center.
Although some platforms accept insurance, the researchers were not able to evaluate the cost of using private insurance or Medicaid, Dr. Jesse said. She noted that transgender individuals are more likely to lack insurance than are cisgender patients.
The team also assessed the scope of services. All companies offered legal help with changes to names and gender markers, such as “M” and “F.” Three or more companies offered preexposure prophylaxis to prevent HIV infection, treatment for erectile dysfunction, referrals for surgery, and medical letters of support for surgery.
Two offered puberty blockers, although the researchers were unable to determine the risk of adolescents obtaining treatment without proper assessments, because details of those services are not disclosed on websites, Dr. Jesse said.
An avenue of further research would be to interview patients to learn how platforms operate in practice and whether patients are properly assessed before treatment. “Those sorts of questions we can’t answer just by looking at the websites,” she said.
However, Charlotte Hoffman, JD, senior policy counsel for the National Center for Transgender Equality, an advocacy group, said she does not harbor concerns about patients being treated inappropriately simply because care is virtual. All clinicians who provide gender-affirming care face potential repercussions, such as malpractice lawsuits or state disciplinary action, if they veer from treatment guidelines, she said.
“I don’t necessarily take the premise that telehealth is inherently worse than in-person care as a given,” Ms. Hoffman said.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Ms. Hoffman added, direct-to-consumer telemedicine has expanded access for individuals in rural areas, people with disabilities, and those who live in places where in-person providers of transgender care face public hostility, although individuals without the resources to pay may still be left out.
What might happen to that access if telemedicine restrictions that were loosened during the pandemic are reinstated is unclear, she said.
The researchers and Ms. Hoffman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Medicare physician fee schedule leaves docs fuming over pay cuts
The rule also seeks to ease financial and administrative burdens on accountable care organizations (ACOs).
But physician groups’ initial reactions centered on what the American Medical Association describes as a “damaging across-the-board reduction” of 4.4% in a base calculation, known as a conversion factor.
The reduction is only one of the current threats to physician’s finances, Jack Resneck Jr, MD, AMA’s president, said in a statement. Medicare payment rates also fail to account for inflation in practice costs and COVID-related challenges. Physician’s Medicare payments could be cut by nearly 8.5% in 2023, factoring in other budget cuts, Dr. Resneck said in the statement.
That “would severely impede patient access to care due to the forced closure of physician practices and put further strain on those that remained open during the pandemic,” he said.
A key driver of these cuts is a law that was intended to resolve budget battles between Congress and physicians, while also transitioning Medicare away from fee-for-service payments and pegging reimbursement to judgments about value of care provided. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services thus had little choice about cuts mandated by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) of 2015.
For AMA and other physician groups, the finalization of the Medicare rule served as a rallying point to build support for pending legislation intended to stave off at least some payment cuts.
Federal officials should act soon to block the expected cuts before this season of Congress ends in January, said Anders Gilberg, senior vice president for government affairs at the Medical Group Management Association, in a statement.
“This cannot wait until next Congress – there are claims-processing implications for retroactively applying these policies,” Mr. Gilberg said.
He said MGMA would work with Congress and CMS “to mitigate these cuts and develop sustainable payment policies to allow physician practices to focus on treating patients instead of scrambling to keep their doors open.”
Chronic budget battles
Once seen as a promising resolution to chronic annual budget battles between physicians and Medicare, MACRA has proven a near-universal disappointment. A federal advisory commission in 2018 recommended that Congress scrap MACRA’s Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) and replace it with a new approach for attempting to tie reimbursement to judgments about the quality of medical care.
MACRA replaced an earlier budgeting approach on Medicare physician pay, known as the sustainable growth rate (SGR). Physician groups successfully lobbied Congress for many years to block threatened Medicare payment cuts. Between 2003 and April 2014, Congress passed 17 laws overriding the cuts to physician pay that the lawmakers earlier mandated through the SGR.
A similar pattern has emerged as Congress now acts on short-term fixes to stave off MACRA-mandated cuts. A law passed last December postponed cuts in physician pay from MACRA and federal budget laws.
And more than 70 members of the House support a bill (HR 8800) intended to block a slated 4.4% MACRA-related cut in physician pay for 2023. Two physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD, (D-CA) and Rep. Larry Bucshon (R-IN) sponsored the bill.
Among the groups backing the bill are the AMA, American Academy of Family Physicians, and American College of Physicians. The lawmakers may try to attach this bill to a large spending measure, known as an omnibus, that Congress will try to clear in December to avoid a partial government shutdown.
In a statement, Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, the president of AAFP, urged Congress to factor in inflation in setting physician reimbursement and to reconsider Medicare’s approach to paying physicians.
“It’s past time to end the untenable physician payment cuts – which have now become an annual threat to the stability of physician practices – caused by Medicare budget neutrality requirements and the ongoing freeze in annual payment updates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
Congress also needs to retool its approach to alternative payment models (APMs) intended to improve the quality of patient care, Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
“Physicians in APMs are better equipped to address unmet social needs and provide other enhanced services that are not supported by fee-for-service payment rates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “However, insufficient Medicare fee-for-service payment rates, inadequate support, and burdensome timelines are undermining the move to value-based care and exacerbating our nation’s underinvestment in primary care.”
Policy changes
But the new rule did have some good news for family physicians, Dr. Iroku-Malize told this news organization in an email.
CMS said it will pay psychologists and social workers to help manage behavioral health needs as part of the primary care team, in addition to their own services. This change will give primary care practices more flexibility to coordinate with behavioral health professionals, Dr. Iroku-Malize noted.
“We know that primary care physicians are the first point of contact for many patients, and behavioral health integration increases critical access to mental health care, decreases stigma for patients, and can prevent more severe medical and behavioral health events,” she wrote.
CMS also eased a supervision requirement for nonphysicians providing behavioral health services.
It intends to allow certain health professionals to provide this care without requiring that a supervising physician or nurse practitioner be physically on site. This shift from direct supervision to what’s called general supervision applies to marriage and family therapists, licensed professional counselors, addiction counselors, certified peer recovery specialists, and behavioral health specialists, CMS said.
Other major policy changes include:
Medicare will pay for telehealth opioid treatment programs allowing patients to initiate treatment with buprenorphine. CMS also clarified that certain programs can bill for opioid use disorder treatment services provided through mobile units, such as vans.
Medicare enrollees may see audiologists for nonacute hearing conditions without an order from a physician or nurse practitioner. The policy is meant to allow audiologists to examine patients to prescribe, fit, or change hearing aids, or to provide hearing tests unrelated to disequilibrium.
CMS created new reimbursement codes for chronic pain management and treatment services to encourage clinicians to see patients with this condition. The codes also are meant to encourage practitioners already treating Medicare patients with chronic pain to spend more time helping them manage their condition “within a trusting, supportive, and ongoing care partnership,” CMS said.
CMS also made changes to the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) intended to reduce administrative burdens and offer more financial support to practices involved in ACOs. These steps include expanding opportunities for certain low-revenue ACOs to share in savings even if they do not meet a target rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The rule also seeks to ease financial and administrative burdens on accountable care organizations (ACOs).
But physician groups’ initial reactions centered on what the American Medical Association describes as a “damaging across-the-board reduction” of 4.4% in a base calculation, known as a conversion factor.
The reduction is only one of the current threats to physician’s finances, Jack Resneck Jr, MD, AMA’s president, said in a statement. Medicare payment rates also fail to account for inflation in practice costs and COVID-related challenges. Physician’s Medicare payments could be cut by nearly 8.5% in 2023, factoring in other budget cuts, Dr. Resneck said in the statement.
That “would severely impede patient access to care due to the forced closure of physician practices and put further strain on those that remained open during the pandemic,” he said.
A key driver of these cuts is a law that was intended to resolve budget battles between Congress and physicians, while also transitioning Medicare away from fee-for-service payments and pegging reimbursement to judgments about value of care provided. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services thus had little choice about cuts mandated by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) of 2015.
For AMA and other physician groups, the finalization of the Medicare rule served as a rallying point to build support for pending legislation intended to stave off at least some payment cuts.
Federal officials should act soon to block the expected cuts before this season of Congress ends in January, said Anders Gilberg, senior vice president for government affairs at the Medical Group Management Association, in a statement.
“This cannot wait until next Congress – there are claims-processing implications for retroactively applying these policies,” Mr. Gilberg said.
He said MGMA would work with Congress and CMS “to mitigate these cuts and develop sustainable payment policies to allow physician practices to focus on treating patients instead of scrambling to keep their doors open.”
Chronic budget battles
Once seen as a promising resolution to chronic annual budget battles between physicians and Medicare, MACRA has proven a near-universal disappointment. A federal advisory commission in 2018 recommended that Congress scrap MACRA’s Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) and replace it with a new approach for attempting to tie reimbursement to judgments about the quality of medical care.
MACRA replaced an earlier budgeting approach on Medicare physician pay, known as the sustainable growth rate (SGR). Physician groups successfully lobbied Congress for many years to block threatened Medicare payment cuts. Between 2003 and April 2014, Congress passed 17 laws overriding the cuts to physician pay that the lawmakers earlier mandated through the SGR.
A similar pattern has emerged as Congress now acts on short-term fixes to stave off MACRA-mandated cuts. A law passed last December postponed cuts in physician pay from MACRA and federal budget laws.
And more than 70 members of the House support a bill (HR 8800) intended to block a slated 4.4% MACRA-related cut in physician pay for 2023. Two physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD, (D-CA) and Rep. Larry Bucshon (R-IN) sponsored the bill.
Among the groups backing the bill are the AMA, American Academy of Family Physicians, and American College of Physicians. The lawmakers may try to attach this bill to a large spending measure, known as an omnibus, that Congress will try to clear in December to avoid a partial government shutdown.
In a statement, Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, the president of AAFP, urged Congress to factor in inflation in setting physician reimbursement and to reconsider Medicare’s approach to paying physicians.
“It’s past time to end the untenable physician payment cuts – which have now become an annual threat to the stability of physician practices – caused by Medicare budget neutrality requirements and the ongoing freeze in annual payment updates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
Congress also needs to retool its approach to alternative payment models (APMs) intended to improve the quality of patient care, Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
“Physicians in APMs are better equipped to address unmet social needs and provide other enhanced services that are not supported by fee-for-service payment rates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “However, insufficient Medicare fee-for-service payment rates, inadequate support, and burdensome timelines are undermining the move to value-based care and exacerbating our nation’s underinvestment in primary care.”
Policy changes
But the new rule did have some good news for family physicians, Dr. Iroku-Malize told this news organization in an email.
CMS said it will pay psychologists and social workers to help manage behavioral health needs as part of the primary care team, in addition to their own services. This change will give primary care practices more flexibility to coordinate with behavioral health professionals, Dr. Iroku-Malize noted.
“We know that primary care physicians are the first point of contact for many patients, and behavioral health integration increases critical access to mental health care, decreases stigma for patients, and can prevent more severe medical and behavioral health events,” she wrote.
CMS also eased a supervision requirement for nonphysicians providing behavioral health services.
It intends to allow certain health professionals to provide this care without requiring that a supervising physician or nurse practitioner be physically on site. This shift from direct supervision to what’s called general supervision applies to marriage and family therapists, licensed professional counselors, addiction counselors, certified peer recovery specialists, and behavioral health specialists, CMS said.
Other major policy changes include:
Medicare will pay for telehealth opioid treatment programs allowing patients to initiate treatment with buprenorphine. CMS also clarified that certain programs can bill for opioid use disorder treatment services provided through mobile units, such as vans.
Medicare enrollees may see audiologists for nonacute hearing conditions without an order from a physician or nurse practitioner. The policy is meant to allow audiologists to examine patients to prescribe, fit, or change hearing aids, or to provide hearing tests unrelated to disequilibrium.
CMS created new reimbursement codes for chronic pain management and treatment services to encourage clinicians to see patients with this condition. The codes also are meant to encourage practitioners already treating Medicare patients with chronic pain to spend more time helping them manage their condition “within a trusting, supportive, and ongoing care partnership,” CMS said.
CMS also made changes to the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) intended to reduce administrative burdens and offer more financial support to practices involved in ACOs. These steps include expanding opportunities for certain low-revenue ACOs to share in savings even if they do not meet a target rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The rule also seeks to ease financial and administrative burdens on accountable care organizations (ACOs).
But physician groups’ initial reactions centered on what the American Medical Association describes as a “damaging across-the-board reduction” of 4.4% in a base calculation, known as a conversion factor.
The reduction is only one of the current threats to physician’s finances, Jack Resneck Jr, MD, AMA’s president, said in a statement. Medicare payment rates also fail to account for inflation in practice costs and COVID-related challenges. Physician’s Medicare payments could be cut by nearly 8.5% in 2023, factoring in other budget cuts, Dr. Resneck said in the statement.
That “would severely impede patient access to care due to the forced closure of physician practices and put further strain on those that remained open during the pandemic,” he said.
A key driver of these cuts is a law that was intended to resolve budget battles between Congress and physicians, while also transitioning Medicare away from fee-for-service payments and pegging reimbursement to judgments about value of care provided. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services thus had little choice about cuts mandated by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) of 2015.
For AMA and other physician groups, the finalization of the Medicare rule served as a rallying point to build support for pending legislation intended to stave off at least some payment cuts.
Federal officials should act soon to block the expected cuts before this season of Congress ends in January, said Anders Gilberg, senior vice president for government affairs at the Medical Group Management Association, in a statement.
“This cannot wait until next Congress – there are claims-processing implications for retroactively applying these policies,” Mr. Gilberg said.
He said MGMA would work with Congress and CMS “to mitigate these cuts and develop sustainable payment policies to allow physician practices to focus on treating patients instead of scrambling to keep their doors open.”
Chronic budget battles
Once seen as a promising resolution to chronic annual budget battles between physicians and Medicare, MACRA has proven a near-universal disappointment. A federal advisory commission in 2018 recommended that Congress scrap MACRA’s Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) and replace it with a new approach for attempting to tie reimbursement to judgments about the quality of medical care.
MACRA replaced an earlier budgeting approach on Medicare physician pay, known as the sustainable growth rate (SGR). Physician groups successfully lobbied Congress for many years to block threatened Medicare payment cuts. Between 2003 and April 2014, Congress passed 17 laws overriding the cuts to physician pay that the lawmakers earlier mandated through the SGR.
A similar pattern has emerged as Congress now acts on short-term fixes to stave off MACRA-mandated cuts. A law passed last December postponed cuts in physician pay from MACRA and federal budget laws.
And more than 70 members of the House support a bill (HR 8800) intended to block a slated 4.4% MACRA-related cut in physician pay for 2023. Two physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD, (D-CA) and Rep. Larry Bucshon (R-IN) sponsored the bill.
Among the groups backing the bill are the AMA, American Academy of Family Physicians, and American College of Physicians. The lawmakers may try to attach this bill to a large spending measure, known as an omnibus, that Congress will try to clear in December to avoid a partial government shutdown.
In a statement, Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, the president of AAFP, urged Congress to factor in inflation in setting physician reimbursement and to reconsider Medicare’s approach to paying physicians.
“It’s past time to end the untenable physician payment cuts – which have now become an annual threat to the stability of physician practices – caused by Medicare budget neutrality requirements and the ongoing freeze in annual payment updates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
Congress also needs to retool its approach to alternative payment models (APMs) intended to improve the quality of patient care, Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
“Physicians in APMs are better equipped to address unmet social needs and provide other enhanced services that are not supported by fee-for-service payment rates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “However, insufficient Medicare fee-for-service payment rates, inadequate support, and burdensome timelines are undermining the move to value-based care and exacerbating our nation’s underinvestment in primary care.”
Policy changes
But the new rule did have some good news for family physicians, Dr. Iroku-Malize told this news organization in an email.
CMS said it will pay psychologists and social workers to help manage behavioral health needs as part of the primary care team, in addition to their own services. This change will give primary care practices more flexibility to coordinate with behavioral health professionals, Dr. Iroku-Malize noted.
“We know that primary care physicians are the first point of contact for many patients, and behavioral health integration increases critical access to mental health care, decreases stigma for patients, and can prevent more severe medical and behavioral health events,” she wrote.
CMS also eased a supervision requirement for nonphysicians providing behavioral health services.
It intends to allow certain health professionals to provide this care without requiring that a supervising physician or nurse practitioner be physically on site. This shift from direct supervision to what’s called general supervision applies to marriage and family therapists, licensed professional counselors, addiction counselors, certified peer recovery specialists, and behavioral health specialists, CMS said.
Other major policy changes include:
Medicare will pay for telehealth opioid treatment programs allowing patients to initiate treatment with buprenorphine. CMS also clarified that certain programs can bill for opioid use disorder treatment services provided through mobile units, such as vans.
Medicare enrollees may see audiologists for nonacute hearing conditions without an order from a physician or nurse practitioner. The policy is meant to allow audiologists to examine patients to prescribe, fit, or change hearing aids, or to provide hearing tests unrelated to disequilibrium.
CMS created new reimbursement codes for chronic pain management and treatment services to encourage clinicians to see patients with this condition. The codes also are meant to encourage practitioners already treating Medicare patients with chronic pain to spend more time helping them manage their condition “within a trusting, supportive, and ongoing care partnership,” CMS said.
CMS also made changes to the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) intended to reduce administrative burdens and offer more financial support to practices involved in ACOs. These steps include expanding opportunities for certain low-revenue ACOs to share in savings even if they do not meet a target rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) pathway?

Cesarean birth is one of the most common major surgical procedures performed in developed countries1 with over 1,170,000 cesarean births in the United States in 2021.2 Many surgeons and anesthesiologists believe that Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) pathways improve surgical outcomes.3,4 Important goals of ERAS include setting patient expectations for the surgical procedure, accelerating patient recovery to full function, and minimizing perioperative complications such as severe nausea, aspiration, surgical site infection, wound complications, and perioperative anemia. The ERAS Society in 20185-7 and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology (SOAP) in 20218 proposed ERAS pathways for cesarean birth. Both societies recommended that obstetric units consider adopting an ERAS pathway compatible with local clinical resources. In addition, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has provided guidance for implementing ERAS pathways for gynecologic surgery.9 The consistent use of standardized protocols to improve surgical care in obstetrics should lead to a reduction in care variation and improve health equity outcomes.
The clinical interventions recommended for ERAS cesarean birth occur sequentially in the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative phases of care. The recommendations associated with each of these phases are reviewed below. It is important to note that each obstetric unit should use a multidisciplinary process to develop an ERAS pathway that best supports local practice given clinician preferences, patient characteristics, and resource availability.
Preoperative components of ERAS
Standardized patient education (SPE). SPE is an important component of ERAS, although evidence to support the recommendation is limited. At a minimum a written handout describing steps in the cesarean birth process, or a patient-education video should be part of patient education. The University of Michigan Medical Center has produced a 3-minute video for patients explaining ERAS cesarean birth.10 The University of Maryland Medical Center has produced a 2.5-minute video in English and Spanish, explaining ERAS cesarean birth for patients.11 Some surgeons place a telephone call to patients the evening before surgery to help orient the patient to ERAS cesarean birth.
Breastfeeding education. An important goal of obstetric care is to optimize the rate of exclusive breastfeeding at birth. Breastfeeding education, including a commitment to support the initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth, may enhance the rate of exclusive breastfeeding. There are numerous videos available for patients about breastfeeding after cesarean birth (as an example, see: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9iOGn85NdTg).
Limit fasting. In the past, surgical guidelines recommended fasting after midnight prior to surgery. The ERAS Society recommends that patients should be encouraged to drink clear fluids up to 2 hours before surgery and may have a light meal up to 6 hours before surgery (Part 1).
Carbohydrate loading. Surgery causes a metabolic stress that is increased by fasting. Carbohydrate loading prior to surgery reduces the magnitude of the catabolic state caused by the combination of surgery and fasting.12 SOAP and the ERAS Society recommend oral carbohydrate fluid supplementation 2 hours before surgery for nondiabetic patients. SOAP suggests 32 oz of Gatorade or 16 oz of clear apple juice as options for carbohydrate loading. For diabetic patients, the carbohydrate load can be omitted. In fasting pregnant patients at term, gastric emptying was near complete 2 hours after consumption of 400 mL of a carbohydrate drink.13 In one study, consumption of 400 mL of a carbohydrate drink 2 hours before cesarean resulted in a 7% increase in the newborn blood glucose level at 20 min after delivery.14
Minimize preoperative anemia. Approximately 50% of pregnant women are iron deficient and approximately 10% are anemic in the third trimester.15,16 Cesarean birth is associated with significant blood loss necessitating the need to optimize red blood cell mass before surgery. Measuring ferritin to identify patients with iron deficiency and aggressive iron replacement, including intravenous iron if necessary, will reduce the prevalence of anemia prior to cesarean birth.17 Another cause of anemia in pregnancy is vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency. Low vitamin B12 is especially common in pregnant patients who have previously had bariatric surgery. One study reported that, of 113 pregnant patients who were, on average, 3 years from a bariatric surgery procedure, 12% had vitamin B12 circulating levels < 130 pg/mL.18 Among pregnant patients who are anemic, and do not have a hemoglobinopathy, measuring ferritin, folic acid, and vitamin B12 will help identify the cause of anemia and guide treatment.19
Optimize preoperative physical condition. Improving healthy behaviors and reducing unhealthy behaviors preoperatively may enhance patient recovery to full function. In the weeks before scheduled cesarean birth, cessation of the use of tobacco products, optimizing activity and improving diet quality, including increasing protein intake, may best prepare patients for the metabolic stress of surgery.
Continue to: Intraoperative components of ERAS...
Intraoperative components of ERAS
Reduce the risk of surgical site infection (SSI) and wound complications. Bundles that include antibiotics, chlorhexidine (or an alternative antibacterial soap) and clippers have been shown to reduce SSI.20 Routine administration of preoperative antibiotics is a consensus recommendation and there is high adherence with this recommendation in the United States. Chlorhexidine-alcohol is the preferred solution for skin preparation. Vaginal preparation with povidine-iodine or chlorhexidine may be considered.6
Surgical technique. Blunt extension of a transverse hysterotomy may reduce blood loss. Closure of the hysterotomy incision in 2 layers is recommended to reduce uterine scar dehiscence in a subsequent pregnancy. If the patient has ≥2 cm of subcutaneous tissue, this layer should be approximated with sutures. Skin closure should be with subcuticular suture.6
Optimize uterotonic administration. Routine use of uterotonics reduces the risk of blood loss, transfusion, and postoperative anemia. There is high adherence with the use of uterotonic administration after birth in the United States.6,8
Ensure normothermia. Many patients become hypothermic during a cesarean birth. Active warming of the patient with an in-line IV fluid warmer and forced air warming over the patient’s body can reduce the risk of hypothermia.8
Initiate multimodal anesthesia. Anesthesiologists often use intrathecal or epidural morphine to enhance analgesia. Ketorolac administration prior to completion of the cesarean procedure and perioperative administration of acetaminophen may reduce postoperative pain.8 The use of preoperative antiemetics will reduce intraoperative and postoperative nausea and vomiting.
Initiate VTE prophylaxis. Pneumatic compression stockings are recommended. Anticoagulation should not be routinely used for VTE prophylaxis.6
Postoperative components of ERAS
Patient education to prepare for discharge home when ready. Patient education focused on home when ready is important in preparing the patient for discharge home.7 Completion of required newborn testing, lactation education, and contraception planning plus coordination of newborn pediatric follow-up is necessary before discharge.
Support early return of bowel function. Early return of bowel function is best supported by a multimodal approach including initiation of clear fluid intake immediately following surgery, encouraging consumption of a regular diet within 27 to 4 hours8 following surgery. Gum chewing for at least 5 minutes 3 times daily accelerates return of bowel function.8 In a meta-analysis of 10 randomized studies examining the effect of gum chewing after cesarean, the investigators reported that gum chewing shortened the time to passage of flatus and defecation.21
Early ambulation.
Sequentially advanced activity, starting with sitting on the edge of the bed, sitting in a chair, and ambulation within 8 hours of surgery, is recommended to facilitate faster recovery, reduce rates of complications, and enable transition to home.8
Early removal of the urinary catheter. It is recommended that the urinary catheter be removed within 12 hours after cesarean birth.8 Early removal of the urinary catheter increases patient mobility and reduces the length of hospitalization. Early removal of the urinary catheter may be associated with postoperative urinary retention and recatheterization in a small number of patients.
Prescribe routinely scheduled acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and ketorolac. A key component of ERAS cesarean birth is the standardized administration of nonopioid pain medicines, alternating doses of acetaminophen and an NSAID. ERAS cesarean birth is likely to result in a reduction in inpatient and postdischarge opioid use.22-24
VTE prophylaxis. Pneumatic compression stockings are recommended. Anticoagulation should not be routinely used for VTE prophylaxis.8
Auditing and reporting adherence with components of ERAS
In clinical practice there may be a gap between a clinician’s subjective perception of their performance and an independent audit of their clinical performance. ERAS pathways should be implemented with a commitment to performing audits and providing quantitative feedback to clinicians. Consistent use of measurement, feedback, and coaching can improve performance and reduce variation among individual clinicians. As an example, in one study of the use of a surgical safety checklist, 99% of the surgeons reported that they routinely used a surgical safety checklist, but the audit showed that the checklist was used in only 60% of cases.25 Gaps between self-reported performance and audited performance are common in clinical practice. Audits with feedback are critical to improving adherence with the components of an ERAS pathway.
Three independent systematic reviews and meta-analyses report that ERAS pathways reduce hospital length of stay without increasing the readmission rate.26-28 One meta-analysis reported that ERAS may also reduce time to first mobilization and result in earlier removal of the urinary catheter.26 ERAS pathways also may reduce postoperative complications, lower pain scores, and decrease opioid use.27 The general consensus among quality and safety experts is that reducing variation through standardization of pathways is generally associated with improved quality and enhanced safety. ERAS pathways have been widely accepted in multiple surgical fields. ERAS pathways should become the standard for performing cesarean procedures.●
1. Molina G, Weiser RG, Lipsitz SR, et al. Relationship between cesarean delivery rate and maternal and neonatal mortality. JAMA. 2015;314:2263-2270.
2. Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Osterman MJK. Births: provisional data for 2021. Vital Statistics Release; No. 20. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. May 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/vsrr/vsrr020.pdf.
3. Berian JR, Ban KA, Liu JB, et al. Adherence to enhanced recovery protocols in NSQIP and association with colectomy outcomes. Ann Surg. 2019;486-493.
4. Ljungqvist O, Scott M, Fearon KC. Enhanced recovery after surgery: a review. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:292-298.
5. Wilson RD, Caughey AB, Wood SL, et al. Guidelines for antenatal and preoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 1). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;219:523.e1-523.e15.
6. Caughey AB, Wood SL, Macones GA, et al Guidelines for intraoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 2). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;219:533-544.
7. Macones GA, Caughey AB, Wood SL, et al. Guidelines for postoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 3). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:247.e1-247.e9.
8. Bollag L, Lim G, Sultan P, et al. Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology: Consensus statement and recommendations for enhanced recovery after cesarean. Anesth Analg. 2021;132:1362-1377.
9. Perioperative pathways: enhanced recovery after surgery. ACOG Committee Opinion No 750. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:e120-130.
10. University of Michigan. ERAS: A patient education video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CoFtgdluBc0. Accessed October 24, 2022.
11. University of Maryland. ERAS. https://www.umms.org/ummc/health-services/womens-health/ostetrics-gynecology/pregnancy-childbirth/labor-delivery/enhanced-recovery-after-cesarean. Accessed October 24, 2022.
12. Bilku DK, Dennison AR, Hall TC, et al. Role of preoperative carbohydrate loading: a systematic review. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2014;96:15-22.
13. Popivanov P, Irwin R, Walsh M, et al. Gastric emptying of carbohydrate drinks in term parturients before elective caesarean surgery: an observational study. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2020;41:29-34.
14. He Y, Liu C, Han Y, et al. The impact of carbohydrate-rich supplement taken two hours before caesarean delivery on maternal and neonatal perioperative outcomes- a randomized clinical trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021;21:682.
15. Auerbach M, Abernathy J, Juul S, et al. Prevalence of iron deficiency in first trimester, nonanemic pregnant women. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021;34:1002-1005.
16. Mei Z, Cogswell ME, Looker AC, et al. Assessment of iron status in US pregnant women from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1996-2006. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93:1312-1320.
17. Nour N, Barbieri RL. Optimize detection and treatment of iron deficiency in pregnancy. OBG Manag. 2022;34:9-11.
18. Mead NC, Sakkatos P, Sakellaropoulos GC, et al. Pregnancy outcomes and nutritional indices after 3 types of bariatric surgery performed at a single institution. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014;10:1166-1173.
19. Achebe MM, Gafter-Gvili A. How I treat anemia in pregnancy: iron, cobalamin and folate. Blood. 2017;129:940-949.
20. Carter EB, Temming LA, Fowler S, et al. Evidence-based bundles and cesarean delivery surgical site infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:735-746.
21. Wen Z, Shen M, Wu C, et al. Chewing gum for intestinal function recovery after caesarean section: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:105.
22. McCoy JA, Gutman S, Hamm RF, et al. The association between implementation of an enhanced recovery after cesarean pathway with standardized discharge prescriptions and opioid use and pain experience after cesarean delivery. Am J Perinatol. 2021;38:1341-1347.
23. Mullman L, Hilden P, Goral J, et al. Improved outcomes with an enhanced recovery approach to cesarean delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;136:685-691.
24. Hedderson M, Lee D, Hunt E, et al. Enhanced recovery after surgery to change process measures and reduce opioid use after cesarean delivery: a quality improvement initiative. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:511-519.
25. Sendlhofer G, Lumenta DB, Leitgeb K, et al. The gap between individual perception and compliance: a quantitative follow-up study of the surgical safety checklist application. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0149212.
26. Sultan P, Sharawi N, Blake L, et al. Impact of enhanced recovery after cesarean delivery on maternal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2021;40:100935.
27. Meng X, Chen K, Yang C, et al. The clinical efficacy and safety of enhanced recovery after surgery for cesarean section: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. Front Med. 2021;8:694385.
28. Corson E, Hind D, Beever D, et al. Enhanced recovery after elective caesarean: a rapid review of clinical protocols and an umbrella review of systematic reviews. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:91.

Cesarean birth is one of the most common major surgical procedures performed in developed countries1 with over 1,170,000 cesarean births in the United States in 2021.2 Many surgeons and anesthesiologists believe that Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) pathways improve surgical outcomes.3,4 Important goals of ERAS include setting patient expectations for the surgical procedure, accelerating patient recovery to full function, and minimizing perioperative complications such as severe nausea, aspiration, surgical site infection, wound complications, and perioperative anemia. The ERAS Society in 20185-7 and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology (SOAP) in 20218 proposed ERAS pathways for cesarean birth. Both societies recommended that obstetric units consider adopting an ERAS pathway compatible with local clinical resources. In addition, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has provided guidance for implementing ERAS pathways for gynecologic surgery.9 The consistent use of standardized protocols to improve surgical care in obstetrics should lead to a reduction in care variation and improve health equity outcomes.
The clinical interventions recommended for ERAS cesarean birth occur sequentially in the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative phases of care. The recommendations associated with each of these phases are reviewed below. It is important to note that each obstetric unit should use a multidisciplinary process to develop an ERAS pathway that best supports local practice given clinician preferences, patient characteristics, and resource availability.
Preoperative components of ERAS
Standardized patient education (SPE). SPE is an important component of ERAS, although evidence to support the recommendation is limited. At a minimum a written handout describing steps in the cesarean birth process, or a patient-education video should be part of patient education. The University of Michigan Medical Center has produced a 3-minute video for patients explaining ERAS cesarean birth.10 The University of Maryland Medical Center has produced a 2.5-minute video in English and Spanish, explaining ERAS cesarean birth for patients.11 Some surgeons place a telephone call to patients the evening before surgery to help orient the patient to ERAS cesarean birth.
Breastfeeding education. An important goal of obstetric care is to optimize the rate of exclusive breastfeeding at birth. Breastfeeding education, including a commitment to support the initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth, may enhance the rate of exclusive breastfeeding. There are numerous videos available for patients about breastfeeding after cesarean birth (as an example, see: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9iOGn85NdTg).
Limit fasting. In the past, surgical guidelines recommended fasting after midnight prior to surgery. The ERAS Society recommends that patients should be encouraged to drink clear fluids up to 2 hours before surgery and may have a light meal up to 6 hours before surgery (Part 1).
Carbohydrate loading. Surgery causes a metabolic stress that is increased by fasting. Carbohydrate loading prior to surgery reduces the magnitude of the catabolic state caused by the combination of surgery and fasting.12 SOAP and the ERAS Society recommend oral carbohydrate fluid supplementation 2 hours before surgery for nondiabetic patients. SOAP suggests 32 oz of Gatorade or 16 oz of clear apple juice as options for carbohydrate loading. For diabetic patients, the carbohydrate load can be omitted. In fasting pregnant patients at term, gastric emptying was near complete 2 hours after consumption of 400 mL of a carbohydrate drink.13 In one study, consumption of 400 mL of a carbohydrate drink 2 hours before cesarean resulted in a 7% increase in the newborn blood glucose level at 20 min after delivery.14
Minimize preoperative anemia. Approximately 50% of pregnant women are iron deficient and approximately 10% are anemic in the third trimester.15,16 Cesarean birth is associated with significant blood loss necessitating the need to optimize red blood cell mass before surgery. Measuring ferritin to identify patients with iron deficiency and aggressive iron replacement, including intravenous iron if necessary, will reduce the prevalence of anemia prior to cesarean birth.17 Another cause of anemia in pregnancy is vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency. Low vitamin B12 is especially common in pregnant patients who have previously had bariatric surgery. One study reported that, of 113 pregnant patients who were, on average, 3 years from a bariatric surgery procedure, 12% had vitamin B12 circulating levels < 130 pg/mL.18 Among pregnant patients who are anemic, and do not have a hemoglobinopathy, measuring ferritin, folic acid, and vitamin B12 will help identify the cause of anemia and guide treatment.19
Optimize preoperative physical condition. Improving healthy behaviors and reducing unhealthy behaviors preoperatively may enhance patient recovery to full function. In the weeks before scheduled cesarean birth, cessation of the use of tobacco products, optimizing activity and improving diet quality, including increasing protein intake, may best prepare patients for the metabolic stress of surgery.
Continue to: Intraoperative components of ERAS...
Intraoperative components of ERAS
Reduce the risk of surgical site infection (SSI) and wound complications. Bundles that include antibiotics, chlorhexidine (or an alternative antibacterial soap) and clippers have been shown to reduce SSI.20 Routine administration of preoperative antibiotics is a consensus recommendation and there is high adherence with this recommendation in the United States. Chlorhexidine-alcohol is the preferred solution for skin preparation. Vaginal preparation with povidine-iodine or chlorhexidine may be considered.6
Surgical technique. Blunt extension of a transverse hysterotomy may reduce blood loss. Closure of the hysterotomy incision in 2 layers is recommended to reduce uterine scar dehiscence in a subsequent pregnancy. If the patient has ≥2 cm of subcutaneous tissue, this layer should be approximated with sutures. Skin closure should be with subcuticular suture.6
Optimize uterotonic administration. Routine use of uterotonics reduces the risk of blood loss, transfusion, and postoperative anemia. There is high adherence with the use of uterotonic administration after birth in the United States.6,8
Ensure normothermia. Many patients become hypothermic during a cesarean birth. Active warming of the patient with an in-line IV fluid warmer and forced air warming over the patient’s body can reduce the risk of hypothermia.8
Initiate multimodal anesthesia. Anesthesiologists often use intrathecal or epidural morphine to enhance analgesia. Ketorolac administration prior to completion of the cesarean procedure and perioperative administration of acetaminophen may reduce postoperative pain.8 The use of preoperative antiemetics will reduce intraoperative and postoperative nausea and vomiting.
Initiate VTE prophylaxis. Pneumatic compression stockings are recommended. Anticoagulation should not be routinely used for VTE prophylaxis.6
Postoperative components of ERAS
Patient education to prepare for discharge home when ready. Patient education focused on home when ready is important in preparing the patient for discharge home.7 Completion of required newborn testing, lactation education, and contraception planning plus coordination of newborn pediatric follow-up is necessary before discharge.
Support early return of bowel function. Early return of bowel function is best supported by a multimodal approach including initiation of clear fluid intake immediately following surgery, encouraging consumption of a regular diet within 27 to 4 hours8 following surgery. Gum chewing for at least 5 minutes 3 times daily accelerates return of bowel function.8 In a meta-analysis of 10 randomized studies examining the effect of gum chewing after cesarean, the investigators reported that gum chewing shortened the time to passage of flatus and defecation.21
Early ambulation.
Sequentially advanced activity, starting with sitting on the edge of the bed, sitting in a chair, and ambulation within 8 hours of surgery, is recommended to facilitate faster recovery, reduce rates of complications, and enable transition to home.8
Early removal of the urinary catheter. It is recommended that the urinary catheter be removed within 12 hours after cesarean birth.8 Early removal of the urinary catheter increases patient mobility and reduces the length of hospitalization. Early removal of the urinary catheter may be associated with postoperative urinary retention and recatheterization in a small number of patients.
Prescribe routinely scheduled acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and ketorolac. A key component of ERAS cesarean birth is the standardized administration of nonopioid pain medicines, alternating doses of acetaminophen and an NSAID. ERAS cesarean birth is likely to result in a reduction in inpatient and postdischarge opioid use.22-24
VTE prophylaxis. Pneumatic compression stockings are recommended. Anticoagulation should not be routinely used for VTE prophylaxis.8
Auditing and reporting adherence with components of ERAS
In clinical practice there may be a gap between a clinician’s subjective perception of their performance and an independent audit of their clinical performance. ERAS pathways should be implemented with a commitment to performing audits and providing quantitative feedback to clinicians. Consistent use of measurement, feedback, and coaching can improve performance and reduce variation among individual clinicians. As an example, in one study of the use of a surgical safety checklist, 99% of the surgeons reported that they routinely used a surgical safety checklist, but the audit showed that the checklist was used in only 60% of cases.25 Gaps between self-reported performance and audited performance are common in clinical practice. Audits with feedback are critical to improving adherence with the components of an ERAS pathway.
Three independent systematic reviews and meta-analyses report that ERAS pathways reduce hospital length of stay without increasing the readmission rate.26-28 One meta-analysis reported that ERAS may also reduce time to first mobilization and result in earlier removal of the urinary catheter.26 ERAS pathways also may reduce postoperative complications, lower pain scores, and decrease opioid use.27 The general consensus among quality and safety experts is that reducing variation through standardization of pathways is generally associated with improved quality and enhanced safety. ERAS pathways have been widely accepted in multiple surgical fields. ERAS pathways should become the standard for performing cesarean procedures.●

Cesarean birth is one of the most common major surgical procedures performed in developed countries1 with over 1,170,000 cesarean births in the United States in 2021.2 Many surgeons and anesthesiologists believe that Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) pathways improve surgical outcomes.3,4 Important goals of ERAS include setting patient expectations for the surgical procedure, accelerating patient recovery to full function, and minimizing perioperative complications such as severe nausea, aspiration, surgical site infection, wound complications, and perioperative anemia. The ERAS Society in 20185-7 and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology (SOAP) in 20218 proposed ERAS pathways for cesarean birth. Both societies recommended that obstetric units consider adopting an ERAS pathway compatible with local clinical resources. In addition, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has provided guidance for implementing ERAS pathways for gynecologic surgery.9 The consistent use of standardized protocols to improve surgical care in obstetrics should lead to a reduction in care variation and improve health equity outcomes.
The clinical interventions recommended for ERAS cesarean birth occur sequentially in the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative phases of care. The recommendations associated with each of these phases are reviewed below. It is important to note that each obstetric unit should use a multidisciplinary process to develop an ERAS pathway that best supports local practice given clinician preferences, patient characteristics, and resource availability.
Preoperative components of ERAS
Standardized patient education (SPE). SPE is an important component of ERAS, although evidence to support the recommendation is limited. At a minimum a written handout describing steps in the cesarean birth process, or a patient-education video should be part of patient education. The University of Michigan Medical Center has produced a 3-minute video for patients explaining ERAS cesarean birth.10 The University of Maryland Medical Center has produced a 2.5-minute video in English and Spanish, explaining ERAS cesarean birth for patients.11 Some surgeons place a telephone call to patients the evening before surgery to help orient the patient to ERAS cesarean birth.
Breastfeeding education. An important goal of obstetric care is to optimize the rate of exclusive breastfeeding at birth. Breastfeeding education, including a commitment to support the initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth, may enhance the rate of exclusive breastfeeding. There are numerous videos available for patients about breastfeeding after cesarean birth (as an example, see: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9iOGn85NdTg).
Limit fasting. In the past, surgical guidelines recommended fasting after midnight prior to surgery. The ERAS Society recommends that patients should be encouraged to drink clear fluids up to 2 hours before surgery and may have a light meal up to 6 hours before surgery (Part 1).
Carbohydrate loading. Surgery causes a metabolic stress that is increased by fasting. Carbohydrate loading prior to surgery reduces the magnitude of the catabolic state caused by the combination of surgery and fasting.12 SOAP and the ERAS Society recommend oral carbohydrate fluid supplementation 2 hours before surgery for nondiabetic patients. SOAP suggests 32 oz of Gatorade or 16 oz of clear apple juice as options for carbohydrate loading. For diabetic patients, the carbohydrate load can be omitted. In fasting pregnant patients at term, gastric emptying was near complete 2 hours after consumption of 400 mL of a carbohydrate drink.13 In one study, consumption of 400 mL of a carbohydrate drink 2 hours before cesarean resulted in a 7% increase in the newborn blood glucose level at 20 min after delivery.14
Minimize preoperative anemia. Approximately 50% of pregnant women are iron deficient and approximately 10% are anemic in the third trimester.15,16 Cesarean birth is associated with significant blood loss necessitating the need to optimize red blood cell mass before surgery. Measuring ferritin to identify patients with iron deficiency and aggressive iron replacement, including intravenous iron if necessary, will reduce the prevalence of anemia prior to cesarean birth.17 Another cause of anemia in pregnancy is vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency. Low vitamin B12 is especially common in pregnant patients who have previously had bariatric surgery. One study reported that, of 113 pregnant patients who were, on average, 3 years from a bariatric surgery procedure, 12% had vitamin B12 circulating levels < 130 pg/mL.18 Among pregnant patients who are anemic, and do not have a hemoglobinopathy, measuring ferritin, folic acid, and vitamin B12 will help identify the cause of anemia and guide treatment.19
Optimize preoperative physical condition. Improving healthy behaviors and reducing unhealthy behaviors preoperatively may enhance patient recovery to full function. In the weeks before scheduled cesarean birth, cessation of the use of tobacco products, optimizing activity and improving diet quality, including increasing protein intake, may best prepare patients for the metabolic stress of surgery.
Continue to: Intraoperative components of ERAS...
Intraoperative components of ERAS
Reduce the risk of surgical site infection (SSI) and wound complications. Bundles that include antibiotics, chlorhexidine (or an alternative antibacterial soap) and clippers have been shown to reduce SSI.20 Routine administration of preoperative antibiotics is a consensus recommendation and there is high adherence with this recommendation in the United States. Chlorhexidine-alcohol is the preferred solution for skin preparation. Vaginal preparation with povidine-iodine or chlorhexidine may be considered.6
Surgical technique. Blunt extension of a transverse hysterotomy may reduce blood loss. Closure of the hysterotomy incision in 2 layers is recommended to reduce uterine scar dehiscence in a subsequent pregnancy. If the patient has ≥2 cm of subcutaneous tissue, this layer should be approximated with sutures. Skin closure should be with subcuticular suture.6
Optimize uterotonic administration. Routine use of uterotonics reduces the risk of blood loss, transfusion, and postoperative anemia. There is high adherence with the use of uterotonic administration after birth in the United States.6,8
Ensure normothermia. Many patients become hypothermic during a cesarean birth. Active warming of the patient with an in-line IV fluid warmer and forced air warming over the patient’s body can reduce the risk of hypothermia.8
Initiate multimodal anesthesia. Anesthesiologists often use intrathecal or epidural morphine to enhance analgesia. Ketorolac administration prior to completion of the cesarean procedure and perioperative administration of acetaminophen may reduce postoperative pain.8 The use of preoperative antiemetics will reduce intraoperative and postoperative nausea and vomiting.
Initiate VTE prophylaxis. Pneumatic compression stockings are recommended. Anticoagulation should not be routinely used for VTE prophylaxis.6
Postoperative components of ERAS
Patient education to prepare for discharge home when ready. Patient education focused on home when ready is important in preparing the patient for discharge home.7 Completion of required newborn testing, lactation education, and contraception planning plus coordination of newborn pediatric follow-up is necessary before discharge.
Support early return of bowel function. Early return of bowel function is best supported by a multimodal approach including initiation of clear fluid intake immediately following surgery, encouraging consumption of a regular diet within 27 to 4 hours8 following surgery. Gum chewing for at least 5 minutes 3 times daily accelerates return of bowel function.8 In a meta-analysis of 10 randomized studies examining the effect of gum chewing after cesarean, the investigators reported that gum chewing shortened the time to passage of flatus and defecation.21
Early ambulation.
Sequentially advanced activity, starting with sitting on the edge of the bed, sitting in a chair, and ambulation within 8 hours of surgery, is recommended to facilitate faster recovery, reduce rates of complications, and enable transition to home.8
Early removal of the urinary catheter. It is recommended that the urinary catheter be removed within 12 hours after cesarean birth.8 Early removal of the urinary catheter increases patient mobility and reduces the length of hospitalization. Early removal of the urinary catheter may be associated with postoperative urinary retention and recatheterization in a small number of patients.
Prescribe routinely scheduled acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and ketorolac. A key component of ERAS cesarean birth is the standardized administration of nonopioid pain medicines, alternating doses of acetaminophen and an NSAID. ERAS cesarean birth is likely to result in a reduction in inpatient and postdischarge opioid use.22-24
VTE prophylaxis. Pneumatic compression stockings are recommended. Anticoagulation should not be routinely used for VTE prophylaxis.8
Auditing and reporting adherence with components of ERAS
In clinical practice there may be a gap between a clinician’s subjective perception of their performance and an independent audit of their clinical performance. ERAS pathways should be implemented with a commitment to performing audits and providing quantitative feedback to clinicians. Consistent use of measurement, feedback, and coaching can improve performance and reduce variation among individual clinicians. As an example, in one study of the use of a surgical safety checklist, 99% of the surgeons reported that they routinely used a surgical safety checklist, but the audit showed that the checklist was used in only 60% of cases.25 Gaps between self-reported performance and audited performance are common in clinical practice. Audits with feedback are critical to improving adherence with the components of an ERAS pathway.
Three independent systematic reviews and meta-analyses report that ERAS pathways reduce hospital length of stay without increasing the readmission rate.26-28 One meta-analysis reported that ERAS may also reduce time to first mobilization and result in earlier removal of the urinary catheter.26 ERAS pathways also may reduce postoperative complications, lower pain scores, and decrease opioid use.27 The general consensus among quality and safety experts is that reducing variation through standardization of pathways is generally associated with improved quality and enhanced safety. ERAS pathways have been widely accepted in multiple surgical fields. ERAS pathways should become the standard for performing cesarean procedures.●
1. Molina G, Weiser RG, Lipsitz SR, et al. Relationship between cesarean delivery rate and maternal and neonatal mortality. JAMA. 2015;314:2263-2270.
2. Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Osterman MJK. Births: provisional data for 2021. Vital Statistics Release; No. 20. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. May 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/vsrr/vsrr020.pdf.
3. Berian JR, Ban KA, Liu JB, et al. Adherence to enhanced recovery protocols in NSQIP and association with colectomy outcomes. Ann Surg. 2019;486-493.
4. Ljungqvist O, Scott M, Fearon KC. Enhanced recovery after surgery: a review. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:292-298.
5. Wilson RD, Caughey AB, Wood SL, et al. Guidelines for antenatal and preoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 1). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;219:523.e1-523.e15.
6. Caughey AB, Wood SL, Macones GA, et al Guidelines for intraoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 2). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;219:533-544.
7. Macones GA, Caughey AB, Wood SL, et al. Guidelines for postoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 3). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:247.e1-247.e9.
8. Bollag L, Lim G, Sultan P, et al. Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology: Consensus statement and recommendations for enhanced recovery after cesarean. Anesth Analg. 2021;132:1362-1377.
9. Perioperative pathways: enhanced recovery after surgery. ACOG Committee Opinion No 750. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:e120-130.
10. University of Michigan. ERAS: A patient education video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CoFtgdluBc0. Accessed October 24, 2022.
11. University of Maryland. ERAS. https://www.umms.org/ummc/health-services/womens-health/ostetrics-gynecology/pregnancy-childbirth/labor-delivery/enhanced-recovery-after-cesarean. Accessed October 24, 2022.
12. Bilku DK, Dennison AR, Hall TC, et al. Role of preoperative carbohydrate loading: a systematic review. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2014;96:15-22.
13. Popivanov P, Irwin R, Walsh M, et al. Gastric emptying of carbohydrate drinks in term parturients before elective caesarean surgery: an observational study. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2020;41:29-34.
14. He Y, Liu C, Han Y, et al. The impact of carbohydrate-rich supplement taken two hours before caesarean delivery on maternal and neonatal perioperative outcomes- a randomized clinical trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021;21:682.
15. Auerbach M, Abernathy J, Juul S, et al. Prevalence of iron deficiency in first trimester, nonanemic pregnant women. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021;34:1002-1005.
16. Mei Z, Cogswell ME, Looker AC, et al. Assessment of iron status in US pregnant women from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1996-2006. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93:1312-1320.
17. Nour N, Barbieri RL. Optimize detection and treatment of iron deficiency in pregnancy. OBG Manag. 2022;34:9-11.
18. Mead NC, Sakkatos P, Sakellaropoulos GC, et al. Pregnancy outcomes and nutritional indices after 3 types of bariatric surgery performed at a single institution. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014;10:1166-1173.
19. Achebe MM, Gafter-Gvili A. How I treat anemia in pregnancy: iron, cobalamin and folate. Blood. 2017;129:940-949.
20. Carter EB, Temming LA, Fowler S, et al. Evidence-based bundles and cesarean delivery surgical site infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:735-746.
21. Wen Z, Shen M, Wu C, et al. Chewing gum for intestinal function recovery after caesarean section: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:105.
22. McCoy JA, Gutman S, Hamm RF, et al. The association between implementation of an enhanced recovery after cesarean pathway with standardized discharge prescriptions and opioid use and pain experience after cesarean delivery. Am J Perinatol. 2021;38:1341-1347.
23. Mullman L, Hilden P, Goral J, et al. Improved outcomes with an enhanced recovery approach to cesarean delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;136:685-691.
24. Hedderson M, Lee D, Hunt E, et al. Enhanced recovery after surgery to change process measures and reduce opioid use after cesarean delivery: a quality improvement initiative. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:511-519.
25. Sendlhofer G, Lumenta DB, Leitgeb K, et al. The gap between individual perception and compliance: a quantitative follow-up study of the surgical safety checklist application. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0149212.
26. Sultan P, Sharawi N, Blake L, et al. Impact of enhanced recovery after cesarean delivery on maternal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2021;40:100935.
27. Meng X, Chen K, Yang C, et al. The clinical efficacy and safety of enhanced recovery after surgery for cesarean section: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. Front Med. 2021;8:694385.
28. Corson E, Hind D, Beever D, et al. Enhanced recovery after elective caesarean: a rapid review of clinical protocols and an umbrella review of systematic reviews. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:91.
1. Molina G, Weiser RG, Lipsitz SR, et al. Relationship between cesarean delivery rate and maternal and neonatal mortality. JAMA. 2015;314:2263-2270.
2. Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Osterman MJK. Births: provisional data for 2021. Vital Statistics Release; No. 20. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. May 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/vsrr/vsrr020.pdf.
3. Berian JR, Ban KA, Liu JB, et al. Adherence to enhanced recovery protocols in NSQIP and association with colectomy outcomes. Ann Surg. 2019;486-493.
4. Ljungqvist O, Scott M, Fearon KC. Enhanced recovery after surgery: a review. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:292-298.
5. Wilson RD, Caughey AB, Wood SL, et al. Guidelines for antenatal and preoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 1). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;219:523.e1-523.e15.
6. Caughey AB, Wood SL, Macones GA, et al Guidelines for intraoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 2). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;219:533-544.
7. Macones GA, Caughey AB, Wood SL, et al. Guidelines for postoperative care in cesarean delivery: Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Society recommendations (Part 3). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:247.e1-247.e9.
8. Bollag L, Lim G, Sultan P, et al. Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology: Consensus statement and recommendations for enhanced recovery after cesarean. Anesth Analg. 2021;132:1362-1377.
9. Perioperative pathways: enhanced recovery after surgery. ACOG Committee Opinion No 750. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:e120-130.
10. University of Michigan. ERAS: A patient education video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CoFtgdluBc0. Accessed October 24, 2022.
11. University of Maryland. ERAS. https://www.umms.org/ummc/health-services/womens-health/ostetrics-gynecology/pregnancy-childbirth/labor-delivery/enhanced-recovery-after-cesarean. Accessed October 24, 2022.
12. Bilku DK, Dennison AR, Hall TC, et al. Role of preoperative carbohydrate loading: a systematic review. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2014;96:15-22.
13. Popivanov P, Irwin R, Walsh M, et al. Gastric emptying of carbohydrate drinks in term parturients before elective caesarean surgery: an observational study. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2020;41:29-34.
14. He Y, Liu C, Han Y, et al. The impact of carbohydrate-rich supplement taken two hours before caesarean delivery on maternal and neonatal perioperative outcomes- a randomized clinical trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021;21:682.
15. Auerbach M, Abernathy J, Juul S, et al. Prevalence of iron deficiency in first trimester, nonanemic pregnant women. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021;34:1002-1005.
16. Mei Z, Cogswell ME, Looker AC, et al. Assessment of iron status in US pregnant women from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1996-2006. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93:1312-1320.
17. Nour N, Barbieri RL. Optimize detection and treatment of iron deficiency in pregnancy. OBG Manag. 2022;34:9-11.
18. Mead NC, Sakkatos P, Sakellaropoulos GC, et al. Pregnancy outcomes and nutritional indices after 3 types of bariatric surgery performed at a single institution. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014;10:1166-1173.
19. Achebe MM, Gafter-Gvili A. How I treat anemia in pregnancy: iron, cobalamin and folate. Blood. 2017;129:940-949.
20. Carter EB, Temming LA, Fowler S, et al. Evidence-based bundles and cesarean delivery surgical site infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:735-746.
21. Wen Z, Shen M, Wu C, et al. Chewing gum for intestinal function recovery after caesarean section: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:105.
22. McCoy JA, Gutman S, Hamm RF, et al. The association between implementation of an enhanced recovery after cesarean pathway with standardized discharge prescriptions and opioid use and pain experience after cesarean delivery. Am J Perinatol. 2021;38:1341-1347.
23. Mullman L, Hilden P, Goral J, et al. Improved outcomes with an enhanced recovery approach to cesarean delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;136:685-691.
24. Hedderson M, Lee D, Hunt E, et al. Enhanced recovery after surgery to change process measures and reduce opioid use after cesarean delivery: a quality improvement initiative. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:511-519.
25. Sendlhofer G, Lumenta DB, Leitgeb K, et al. The gap between individual perception and compliance: a quantitative follow-up study of the surgical safety checklist application. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0149212.
26. Sultan P, Sharawi N, Blake L, et al. Impact of enhanced recovery after cesarean delivery on maternal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2021;40:100935.
27. Meng X, Chen K, Yang C, et al. The clinical efficacy and safety of enhanced recovery after surgery for cesarean section: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. Front Med. 2021;8:694385.
28. Corson E, Hind D, Beever D, et al. Enhanced recovery after elective caesarean: a rapid review of clinical protocols and an umbrella review of systematic reviews. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17:91.
Chagas disease: An unusual and dangerous infection for both mother and baby
CASE Pregnant woman with a suspected parasitic infection
A 20-year-old, previously healthy, primigravid woman at 24 weeks’ gestation immigrated from Bolivia to the United States 3 days ago. On the morning of her international flight, she awoke to discover a small insect bite just below her left eye. She sought medical evaluation because her eyelid is now significantly swollen, and she has a headache, anorexia, fatigue, and a fever of 38.4° C. The examining physician ordered a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for Trypanosoma cruzi, and the test is positive.
- How should this patient be treated during, and after, her delivery?
- Does this infection pose a risk to the newborn baby?
- What type of surveillance and treatment is indicated for the baby?
Chagas disease is common in South America, Central America, and Mexico and is well known to physicians in those countries. Clinicians who practice in the United States are much less familiar with the condition, but it is becoming increasingly common as a result of international travel within the Americas.
In this article, we review the interesting microbiology and epidemiology of Chagas disease, focus on its clinical manifestations, and discuss the most useful diagnostic tests for the illness. We conclude with a summary of preventive and treatment measures, with particular emphasis on managing the disease in pregnancy.
How Chagas disease is transmitted and who is at risk
Chagas disease was named in honor of a Brazilian physician, Carlos Chagas, who first described the condition in 1909. The disease is endemic in South America, Central America, and Mexico, and, recently, its prevalence has increased in the southern United States. Approximately 300,000 people in the United States are infected.1,2
The illness is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, and it is also known as American trypanosomiasis. The parasite is spread primarily by the bite of triatomine insects (“kissing bugs”). Approximately 60% of these insects are infected with the parasite. The insects live and thrive in the interspaces of mud walls (adobe homes) and thatched roofs. At night, the insects leave their darkened spaces and feed on the exposed skin of sleeping persons. They are particularly likely to bite the moist skin surfaces near the eye and mouth, and, as they do, they defecate and excrete the parasite into the blood vessels beneath the skin. Within the blood, the trypomastigotes invade various host cells. Inside the host cells, the organism transforms into an amastigote, which is the replicative form of the parasite. After several rounds of replication, the amastigote transforms back into a trypomastigote, bursts from the cell, and goes on to infect other host cells.1
In addition to transmission by the insect vector, the parasite also can be transmitted by blood transfusion and organ donation. When contaminated blood is transfused, the risk of transmission is approximately 10% to 25% for each unit. Following implementation of effective screening programs by blood banks in Central America, South America, Mexico, and the United States, the risk of transmission from undetected infection is now approximately 1:200,000 per unit.
When a transplant procedure with an infected heart is performed, the risk of transmission is 75% to 100%. For liver transplants, the frequency of transmission is 0% to 29%; for kidney transplants, the risk of transmission is 0% to 19%.
Consumption of contaminated food or drink, particularly nonpasteurized items sold by street vendors, is also an important mechanism of transmission. In addition, transmission can occur as a result of laboratory exposure and by exposure to wild animals (racoons, opossums, marmosets, bats, armadillos) in forested areas. Finally, perinatal transmission now accounts for about 22% of infections. As effective vector control programs have been introduced in endemic areas, the proportion of cases caused by the insect vector has steadily decreased1-3 (FIGURE 1).
Continue to: Clinical manifestations of Chagas disease...
Clinical manifestations of Chagas disease
Chagas disease occurs in 2 stages, acute and chronic.1,2,4 In patients who are infected via an insect vector, the acute stage typically begins 1 to 2 weeks after the insect bite. This phase of the illness usually lasts 4 to 8 weeks and almost always resolves without treatment.
Some infected patients will be completely free of symptoms. Others will have manifestations such as:
- fever
- malaise
- headache
- hepatosplenomegaly
- lymphadenopathy
- swollen nodule at the site of infection
—Romaña’s sign, when the lesion is on the eyelid
—Chagoma, when the lesion is elsewhere on the skin.
Fortunately, less than 5% of patients will have severe illness, manifested by myocarditis, pericarditis, encephalitis, or meningitis.
People infected by ingestion of the parasite in food or drink often become more severely ill within 3 weeks. Their clinical manifestations include fever, vomiting, dyspnea, cough, chest pain, abdominal pain, and myalgias. Individuals infected through organ transplant or blood transfusion present more like those infected by the insect vector, but their illness may not develop until several weeks to 5 months after exposure.
In the absence of effective treatment, approximately 40% of patients with acute infection will develop chronic infection, often several decades later. The most common, and most ominous, feature of chronic illness is cardiac disease, experienced by about 30% of patients. Cardiac disease may be manifested as a serious arrhythmia, chest pain, congestive heart failure, or thromboembolism.
The other organ system that is likely to be adversely affected in patients with chronic disease is the gastrointestinal (GI) system, and approximately 10% of chronically infected patients experience this complication. Patients may develop a dilated esophagus, which leads to odynophagia and dysphagia. Diminished motility in other areas of the GI tract also may result in chronic constipation and even bowel obstruction. Chronically infected patients who are immunosuppressed due to HIV infection may become gravely ill as a result of encephalitis and brain abscesses. Cardiac and GI dysfunction is due to the parasite’s massive destruction of nerve endings.
Continue to: Making the diagnosis...
Making the diagnosis
The diagnosis of Chagas disease begins with screening patients who have epidemiologic risk factors that place them at high risk for contracting the infection and at significantly increased risk for morbidity and mortality as a result of either the acute infection or the later chronic stage of infection. A thorough history is vital in the evaluation because the acute illness can have such vague clinical manifestations, and many patients remain asymptomatic until signs of chronic infection appear.
Risk factors that warrant screening include being born in a country endemic for Chagas disease, living in an endemic country for more than 6 months, living with someone who has a confirmed diagnosis, residing in a house made of natural materials (mud walls, thatched roof) in an endemic area, and a history of discovering the triatomine bug in the household.
Screening options include serology, microscopy, and PCR testing. Screening with a single, highly sensitive immunoglobulin G (IgG) serologic test is recommended for nonendemic clinical or community settings. In patients who were born in or who lived in an endemic area for more than 6 months, special consideration should be given to screening women of reproductive age, patients of all ages who were born to a mother with a confirmed diagnosis, individuals who were exposed to a triatomine insect, and people who are immunocompromised.5
A positive serologic test should be confirmed with a second assay based on a different antigen. Currently, 4 IgG tests have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for diagnosis. If a patient has 2 positive serologic tests, the diagnosis is confirmed, regardless of clinical presentation. Discordant results warrant a third test to differentiate between positive and negative results (FIGURE 2).5 All patients with a confirmed diagnosis should have an electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan to assess for cardiac or GI abnormalities.
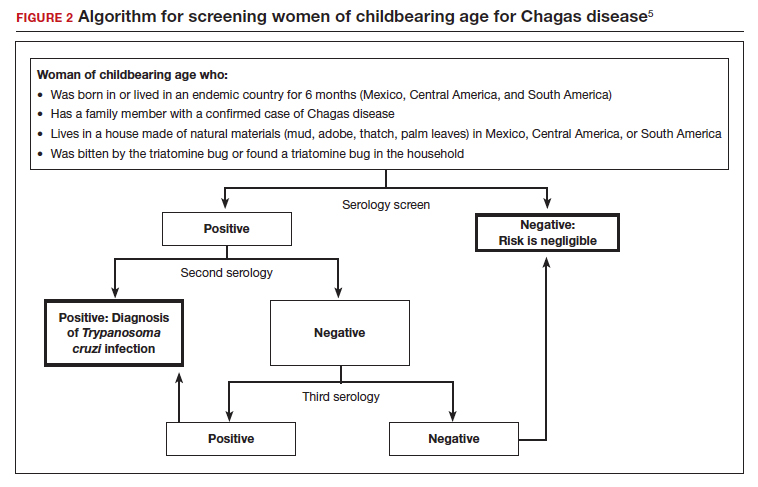
Neonates and infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed infection merit special attention. These children may demonstrate hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pneumonitis, heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, or meningoencephalitis. Newborns delivered to infected mothers will invariably have positive tests for IgG antibody because of transplacental transfer of maternal antibody. Therefore, they should be evaluated by PCR or by direct microscopic examination of the blood for trypomastigotes. In neonates with a negative initial result, repeat testing should be performed by PCR at 4 to 6 weeks of age. Even if the second screening test is negative, the infant should be retested at 9 to 12 months. At this point, maternal IgG no longer should be circulating in the infant’s blood. Three negative tests should effectively rule out T cruzi infection (FIGURE 3).5-7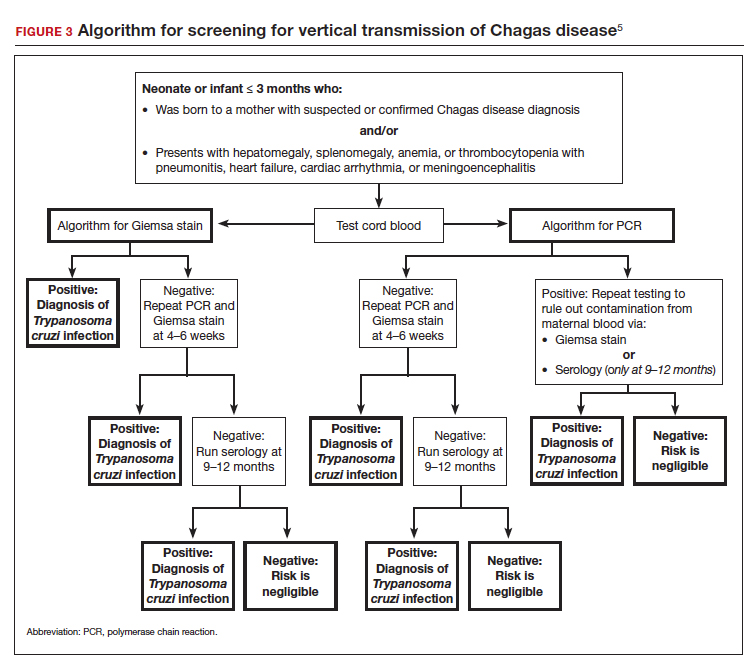
Organ recipients merit special consideration because, in these individuals, the late stages of Chagas disease may be fatal. In these patients, the preferred diagnostic test is PCR. For transplant patients, monitoring should occur every week for 2 months, bimonthly for the third month, and monthly for 6 months after transplantation. Routine monitoring is not recommended in patients with HIV infection who show no clinical signs of Chagas disease and who are not from endemic areas.
Treatment options
No vaccine or hyperimmune globulin can be used to treat Chagas disease. At this time, 2 antiparasitic drugs are available to treat the condition. One is benznidazole, which inhibits DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis within the microorganism. The medication is given in a dose of 5 to 8 mg/kg per day, divided into 2 doses, for 60 days. Benznidazole is FDA approved for the treatment of individuals older than age 2. It has been used off-label in children younger than 2 years of age. The drug is commercially available at http://www.benznidazoletablets.com.
Benznidazole causes multiple minor side effects and several very serious adverse effects. The serious adverse effects include acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, peripheral neuropathy, marrow suppression, and hepatotoxicity. Benznidazole has been teratogenic and carcinogenic in animal studies and should not be used in pregnancy.1,3,6
The second drug is nifurtimox. This drug is FDA approved for the treatment of Chagas disease in adults and for newborns and young children. It is commercially available for pharmacies to purchase from several drug wholesalers. Nifurtimox produces reactive oxygen species and toxic intermediates that induce DNA damage and cause cell death of the microorganism. The appropriate oral dose is 8 to 10 mg/kg per day, divided into 3 to 4 equal doses. The duration of treatment is 60 to 90 days, depending on the patient’s response. Like benznidazole, nifurtimox also is highly toxic. Severe adverse effects include a hypersensitivity reaction, anaphylaxis, angioedema, syncope, seizures, and psychosis. Nifurtimox also is teratogenic and is contraindicated in pregnancy.1,3,6
Clinicians who have questions about the use of either of these medications should contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Division of Parasitic Diseases public inquiries telephone line at (404) 718-4745.
Potential for cure. When either benznidazole or nifurtimox is administered early in the course of a patient’s acute infection, the chance for complete cure is excellent. The same is true for early treatment of the infected neonate. When treatment is delayed, or if it cannot be completed because of intolerable adverse effects, the prognosis for complete cure is diminished.
In adults who have chronic disease, antiparasitic treatment is unlikely to be effective. In such a situation, secondary treatment is directed toward correction of heart failure, control of cardiac rhythm disturbances, and control of GI motility disorders. For both cardiac and GI conditions, medication and surgery may be indicated. Antiparasitic treatment is more effective in children with chronic disease but it is still not uniformly effective.1,3,5,6
Preventing infection
Vector control is the key to preventing infection in areas where Chagas disease is endemic. One important, but often financially unaffordable, measure is construction of homes with building materials that do not support the growth of the triatomine insects that transmit the disease. A second critical preventive measure is the spraying of mud and thatched homes and surrounding areas with long-lasting insecticides. Pyrethroids are the preferred agents today. Alternative agents include fenitrothion and bendiocarb.1
Other important preventive measures include:
- screening the blood supply for T cruzi and eliminating units contaminated with the parasite
- screening for the parasite in organs targeted for transplant
- screening infected women of reproductive age in endemic areas and treating those who are positive before they become pregnant; this measure may be almost 95% effective in preventing congenital infection
- using mosquito netting when housing is insecure and air conditioning is not available
- in endemic areas, avoiding unpasteurized fruit drinks and unwashed fruits and vegetables.
Unique considerations in pregnancy
Chagas disease does not cause specific anatomic birth defects. However, infected women are more likely to experience spontaneous abortion, preterm premature rupture of membranes, preterm labor, and fetal growth restriction. Overall, the risk of perinatal transmission is approximately 5%, but it may be higher in women who have a very high parasite load. Infected neonates who remain untreated are at risk for developing the serious sequelae of chronic infection. At least half of neonates who are infected will initially be asymptomatic. Therefore, screening of at-risk neonates is essential in order to implement effective treatment.3,6
As noted earlier, the usual drugs used for treating Chagas disease should not be used in pregnancy. Nevertheless, it is still important to screen certain individuals for infection and, subsequently, target them and their neonates for treatment immediately following delivery. The following pregnant patients should be screened5,6:
- women with clinical manifestations that suggest acute or chronic infection
- women from areas of the world in which Chagas disease is endemic, namely, from the southern United States to northern Chile and Argentina. Although the disease is endemic in 21 countries, the countries with the highest prevalence are Bolivia, Argentina, and Paraguay.
- newborns delivered to mothers who have been identified as infected.
As mentioned, several tests are available for screening: PCR, antibody assays, and examination of peripheral blood smears. At least 2 test results should be positive to confirm the diagnosis of infection. Neonates should be followed for 9 to 12 months after delivery to determine if perinatal transmission has occurred. Treatment with antiparasitic drugs is indicated for all infected children.5
CASE Continue surveillance during pregnancy, treat after delivery
This patient should not be treated during pregnancy because the 2 major antiparasitic drugs are teratogenic. Antenatally, she should be followed for evidence of preterm labor and fetal growth restriction. She also should have an electrocardiogram and echocardiogram to evaluate for cardiac disease. Immediately after delivery, the patient should be treated with benznidazole for 60 days. Breastfeeding is acceptable. Her neonate should be screened for infection for up to 9 months, following the algorithm outlined earlier (FIGURE 3), and treated if the surveillance tests are positive. ●
- Chagas disease is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, which is spread by the bite of the triatomine insect (the “kissing bug”).
- The condition is widespread among impoverished populations in South America, Central America, and Mexico, but it is rare in the United States except in individuals who immigrated here from endemic areas.
- Chagas disease evolves through 2 phases: acute and chronic. Manifestations of acute infection include fever, malaise, headache, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, and swelling at the site of the insect bite. The chronic phase is manifested by serious cardiac and gastrointestinal dysfunction.
- The diagnosis can be established by identifying the organism in a blood smear and by detecting antibody or antigen in the blood.
- The 2 drugs of choice for treatment of Chagas disease are benznidazole and nifurtimox. These drugs are teratogenic and are contraindicated in pregnancy.
- Women at risk for infection should be screened prior to, or during, pregnancy. Infants of infected mothers should be screened for infection for up to 9 to 12 months after delivery and treated if they test positive. Treatment of the infant is almost 100% effective in preventing chronic illness.
- Bern C. Chagas disease: epidemiology, screening, and prevention. UpToDate. Updated April 8, 2022. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents /chagas-disease-epidemiology-screening-and-prevention
- Chagas disease. Cleveland Clinic. Reviewed October 8, 2021. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org /health/diseases/21876-chagas-disease
- Howard EJ, Xiong X, Carlier Y, et al. Frequency of the congenital transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG. 2014;121:22-33.
- Chagas disease. Mayo Clinic. November 12, 2020. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases -conditions/chagas-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20356212
- Forsyth CJ, Manne-Goehler J, Bern C, et al. Recommendations for screening and diagnosis of Chagas disease in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2022;225:1601-1610.
- Torrico F, Alonso-Vega C, Suarez E. et al. Maternal Trypanosoma cruzi infection, pregnancy outcome, morbidity, and mortality of congenitally infected and non-infected newborns in Bolivia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70:201-209.
- Messenger LA, Bern C. Congenital Chagas disease: current diagnostics, limitations and future perspectives. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018;31:415-421.
CASE Pregnant woman with a suspected parasitic infection
A 20-year-old, previously healthy, primigravid woman at 24 weeks’ gestation immigrated from Bolivia to the United States 3 days ago. On the morning of her international flight, she awoke to discover a small insect bite just below her left eye. She sought medical evaluation because her eyelid is now significantly swollen, and she has a headache, anorexia, fatigue, and a fever of 38.4° C. The examining physician ordered a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for Trypanosoma cruzi, and the test is positive.
- How should this patient be treated during, and after, her delivery?
- Does this infection pose a risk to the newborn baby?
- What type of surveillance and treatment is indicated for the baby?
Chagas disease is common in South America, Central America, and Mexico and is well known to physicians in those countries. Clinicians who practice in the United States are much less familiar with the condition, but it is becoming increasingly common as a result of international travel within the Americas.
In this article, we review the interesting microbiology and epidemiology of Chagas disease, focus on its clinical manifestations, and discuss the most useful diagnostic tests for the illness. We conclude with a summary of preventive and treatment measures, with particular emphasis on managing the disease in pregnancy.
How Chagas disease is transmitted and who is at risk
Chagas disease was named in honor of a Brazilian physician, Carlos Chagas, who first described the condition in 1909. The disease is endemic in South America, Central America, and Mexico, and, recently, its prevalence has increased in the southern United States. Approximately 300,000 people in the United States are infected.1,2
The illness is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, and it is also known as American trypanosomiasis. The parasite is spread primarily by the bite of triatomine insects (“kissing bugs”). Approximately 60% of these insects are infected with the parasite. The insects live and thrive in the interspaces of mud walls (adobe homes) and thatched roofs. At night, the insects leave their darkened spaces and feed on the exposed skin of sleeping persons. They are particularly likely to bite the moist skin surfaces near the eye and mouth, and, as they do, they defecate and excrete the parasite into the blood vessels beneath the skin. Within the blood, the trypomastigotes invade various host cells. Inside the host cells, the organism transforms into an amastigote, which is the replicative form of the parasite. After several rounds of replication, the amastigote transforms back into a trypomastigote, bursts from the cell, and goes on to infect other host cells.1
In addition to transmission by the insect vector, the parasite also can be transmitted by blood transfusion and organ donation. When contaminated blood is transfused, the risk of transmission is approximately 10% to 25% for each unit. Following implementation of effective screening programs by blood banks in Central America, South America, Mexico, and the United States, the risk of transmission from undetected infection is now approximately 1:200,000 per unit.
When a transplant procedure with an infected heart is performed, the risk of transmission is 75% to 100%. For liver transplants, the frequency of transmission is 0% to 29%; for kidney transplants, the risk of transmission is 0% to 19%.
Consumption of contaminated food or drink, particularly nonpasteurized items sold by street vendors, is also an important mechanism of transmission. In addition, transmission can occur as a result of laboratory exposure and by exposure to wild animals (racoons, opossums, marmosets, bats, armadillos) in forested areas. Finally, perinatal transmission now accounts for about 22% of infections. As effective vector control programs have been introduced in endemic areas, the proportion of cases caused by the insect vector has steadily decreased1-3 (FIGURE 1).
Continue to: Clinical manifestations of Chagas disease...
Clinical manifestations of Chagas disease
Chagas disease occurs in 2 stages, acute and chronic.1,2,4 In patients who are infected via an insect vector, the acute stage typically begins 1 to 2 weeks after the insect bite. This phase of the illness usually lasts 4 to 8 weeks and almost always resolves without treatment.
Some infected patients will be completely free of symptoms. Others will have manifestations such as:
- fever
- malaise
- headache
- hepatosplenomegaly
- lymphadenopathy
- swollen nodule at the site of infection
—Romaña’s sign, when the lesion is on the eyelid
—Chagoma, when the lesion is elsewhere on the skin.
Fortunately, less than 5% of patients will have severe illness, manifested by myocarditis, pericarditis, encephalitis, or meningitis.
People infected by ingestion of the parasite in food or drink often become more severely ill within 3 weeks. Their clinical manifestations include fever, vomiting, dyspnea, cough, chest pain, abdominal pain, and myalgias. Individuals infected through organ transplant or blood transfusion present more like those infected by the insect vector, but their illness may not develop until several weeks to 5 months after exposure.
In the absence of effective treatment, approximately 40% of patients with acute infection will develop chronic infection, often several decades later. The most common, and most ominous, feature of chronic illness is cardiac disease, experienced by about 30% of patients. Cardiac disease may be manifested as a serious arrhythmia, chest pain, congestive heart failure, or thromboembolism.
The other organ system that is likely to be adversely affected in patients with chronic disease is the gastrointestinal (GI) system, and approximately 10% of chronically infected patients experience this complication. Patients may develop a dilated esophagus, which leads to odynophagia and dysphagia. Diminished motility in other areas of the GI tract also may result in chronic constipation and even bowel obstruction. Chronically infected patients who are immunosuppressed due to HIV infection may become gravely ill as a result of encephalitis and brain abscesses. Cardiac and GI dysfunction is due to the parasite’s massive destruction of nerve endings.
Continue to: Making the diagnosis...
Making the diagnosis
The diagnosis of Chagas disease begins with screening patients who have epidemiologic risk factors that place them at high risk for contracting the infection and at significantly increased risk for morbidity and mortality as a result of either the acute infection or the later chronic stage of infection. A thorough history is vital in the evaluation because the acute illness can have such vague clinical manifestations, and many patients remain asymptomatic until signs of chronic infection appear.
Risk factors that warrant screening include being born in a country endemic for Chagas disease, living in an endemic country for more than 6 months, living with someone who has a confirmed diagnosis, residing in a house made of natural materials (mud walls, thatched roof) in an endemic area, and a history of discovering the triatomine bug in the household.
Screening options include serology, microscopy, and PCR testing. Screening with a single, highly sensitive immunoglobulin G (IgG) serologic test is recommended for nonendemic clinical or community settings. In patients who were born in or who lived in an endemic area for more than 6 months, special consideration should be given to screening women of reproductive age, patients of all ages who were born to a mother with a confirmed diagnosis, individuals who were exposed to a triatomine insect, and people who are immunocompromised.5
A positive serologic test should be confirmed with a second assay based on a different antigen. Currently, 4 IgG tests have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for diagnosis. If a patient has 2 positive serologic tests, the diagnosis is confirmed, regardless of clinical presentation. Discordant results warrant a third test to differentiate between positive and negative results (FIGURE 2).5 All patients with a confirmed diagnosis should have an electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan to assess for cardiac or GI abnormalities.

Neonates and infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed infection merit special attention. These children may demonstrate hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pneumonitis, heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, or meningoencephalitis. Newborns delivered to infected mothers will invariably have positive tests for IgG antibody because of transplacental transfer of maternal antibody. Therefore, they should be evaluated by PCR or by direct microscopic examination of the blood for trypomastigotes. In neonates with a negative initial result, repeat testing should be performed by PCR at 4 to 6 weeks of age. Even if the second screening test is negative, the infant should be retested at 9 to 12 months. At this point, maternal IgG no longer should be circulating in the infant’s blood. Three negative tests should effectively rule out T cruzi infection (FIGURE 3).5-7
Organ recipients merit special consideration because, in these individuals, the late stages of Chagas disease may be fatal. In these patients, the preferred diagnostic test is PCR. For transplant patients, monitoring should occur every week for 2 months, bimonthly for the third month, and monthly for 6 months after transplantation. Routine monitoring is not recommended in patients with HIV infection who show no clinical signs of Chagas disease and who are not from endemic areas.
Treatment options
No vaccine or hyperimmune globulin can be used to treat Chagas disease. At this time, 2 antiparasitic drugs are available to treat the condition. One is benznidazole, which inhibits DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis within the microorganism. The medication is given in a dose of 5 to 8 mg/kg per day, divided into 2 doses, for 60 days. Benznidazole is FDA approved for the treatment of individuals older than age 2. It has been used off-label in children younger than 2 years of age. The drug is commercially available at http://www.benznidazoletablets.com.
Benznidazole causes multiple minor side effects and several very serious adverse effects. The serious adverse effects include acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, peripheral neuropathy, marrow suppression, and hepatotoxicity. Benznidazole has been teratogenic and carcinogenic in animal studies and should not be used in pregnancy.1,3,6
The second drug is nifurtimox. This drug is FDA approved for the treatment of Chagas disease in adults and for newborns and young children. It is commercially available for pharmacies to purchase from several drug wholesalers. Nifurtimox produces reactive oxygen species and toxic intermediates that induce DNA damage and cause cell death of the microorganism. The appropriate oral dose is 8 to 10 mg/kg per day, divided into 3 to 4 equal doses. The duration of treatment is 60 to 90 days, depending on the patient’s response. Like benznidazole, nifurtimox also is highly toxic. Severe adverse effects include a hypersensitivity reaction, anaphylaxis, angioedema, syncope, seizures, and psychosis. Nifurtimox also is teratogenic and is contraindicated in pregnancy.1,3,6
Clinicians who have questions about the use of either of these medications should contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Division of Parasitic Diseases public inquiries telephone line at (404) 718-4745.
Potential for cure. When either benznidazole or nifurtimox is administered early in the course of a patient’s acute infection, the chance for complete cure is excellent. The same is true for early treatment of the infected neonate. When treatment is delayed, or if it cannot be completed because of intolerable adverse effects, the prognosis for complete cure is diminished.
In adults who have chronic disease, antiparasitic treatment is unlikely to be effective. In such a situation, secondary treatment is directed toward correction of heart failure, control of cardiac rhythm disturbances, and control of GI motility disorders. For both cardiac and GI conditions, medication and surgery may be indicated. Antiparasitic treatment is more effective in children with chronic disease but it is still not uniformly effective.1,3,5,6
Preventing infection
Vector control is the key to preventing infection in areas where Chagas disease is endemic. One important, but often financially unaffordable, measure is construction of homes with building materials that do not support the growth of the triatomine insects that transmit the disease. A second critical preventive measure is the spraying of mud and thatched homes and surrounding areas with long-lasting insecticides. Pyrethroids are the preferred agents today. Alternative agents include fenitrothion and bendiocarb.1
Other important preventive measures include:
- screening the blood supply for T cruzi and eliminating units contaminated with the parasite
- screening for the parasite in organs targeted for transplant
- screening infected women of reproductive age in endemic areas and treating those who are positive before they become pregnant; this measure may be almost 95% effective in preventing congenital infection
- using mosquito netting when housing is insecure and air conditioning is not available
- in endemic areas, avoiding unpasteurized fruit drinks and unwashed fruits and vegetables.
Unique considerations in pregnancy
Chagas disease does not cause specific anatomic birth defects. However, infected women are more likely to experience spontaneous abortion, preterm premature rupture of membranes, preterm labor, and fetal growth restriction. Overall, the risk of perinatal transmission is approximately 5%, but it may be higher in women who have a very high parasite load. Infected neonates who remain untreated are at risk for developing the serious sequelae of chronic infection. At least half of neonates who are infected will initially be asymptomatic. Therefore, screening of at-risk neonates is essential in order to implement effective treatment.3,6
As noted earlier, the usual drugs used for treating Chagas disease should not be used in pregnancy. Nevertheless, it is still important to screen certain individuals for infection and, subsequently, target them and their neonates for treatment immediately following delivery. The following pregnant patients should be screened5,6:
- women with clinical manifestations that suggest acute or chronic infection
- women from areas of the world in which Chagas disease is endemic, namely, from the southern United States to northern Chile and Argentina. Although the disease is endemic in 21 countries, the countries with the highest prevalence are Bolivia, Argentina, and Paraguay.
- newborns delivered to mothers who have been identified as infected.
As mentioned, several tests are available for screening: PCR, antibody assays, and examination of peripheral blood smears. At least 2 test results should be positive to confirm the diagnosis of infection. Neonates should be followed for 9 to 12 months after delivery to determine if perinatal transmission has occurred. Treatment with antiparasitic drugs is indicated for all infected children.5
CASE Continue surveillance during pregnancy, treat after delivery
This patient should not be treated during pregnancy because the 2 major antiparasitic drugs are teratogenic. Antenatally, she should be followed for evidence of preterm labor and fetal growth restriction. She also should have an electrocardiogram and echocardiogram to evaluate for cardiac disease. Immediately after delivery, the patient should be treated with benznidazole for 60 days. Breastfeeding is acceptable. Her neonate should be screened for infection for up to 9 months, following the algorithm outlined earlier (FIGURE 3), and treated if the surveillance tests are positive. ●
- Chagas disease is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, which is spread by the bite of the triatomine insect (the “kissing bug”).
- The condition is widespread among impoverished populations in South America, Central America, and Mexico, but it is rare in the United States except in individuals who immigrated here from endemic areas.
- Chagas disease evolves through 2 phases: acute and chronic. Manifestations of acute infection include fever, malaise, headache, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, and swelling at the site of the insect bite. The chronic phase is manifested by serious cardiac and gastrointestinal dysfunction.
- The diagnosis can be established by identifying the organism in a blood smear and by detecting antibody or antigen in the blood.
- The 2 drugs of choice for treatment of Chagas disease are benznidazole and nifurtimox. These drugs are teratogenic and are contraindicated in pregnancy.
- Women at risk for infection should be screened prior to, or during, pregnancy. Infants of infected mothers should be screened for infection for up to 9 to 12 months after delivery and treated if they test positive. Treatment of the infant is almost 100% effective in preventing chronic illness.
CASE Pregnant woman with a suspected parasitic infection
A 20-year-old, previously healthy, primigravid woman at 24 weeks’ gestation immigrated from Bolivia to the United States 3 days ago. On the morning of her international flight, she awoke to discover a small insect bite just below her left eye. She sought medical evaluation because her eyelid is now significantly swollen, and she has a headache, anorexia, fatigue, and a fever of 38.4° C. The examining physician ordered a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for Trypanosoma cruzi, and the test is positive.
- How should this patient be treated during, and after, her delivery?
- Does this infection pose a risk to the newborn baby?
- What type of surveillance and treatment is indicated for the baby?
Chagas disease is common in South America, Central America, and Mexico and is well known to physicians in those countries. Clinicians who practice in the United States are much less familiar with the condition, but it is becoming increasingly common as a result of international travel within the Americas.
In this article, we review the interesting microbiology and epidemiology of Chagas disease, focus on its clinical manifestations, and discuss the most useful diagnostic tests for the illness. We conclude with a summary of preventive and treatment measures, with particular emphasis on managing the disease in pregnancy.
How Chagas disease is transmitted and who is at risk
Chagas disease was named in honor of a Brazilian physician, Carlos Chagas, who first described the condition in 1909. The disease is endemic in South America, Central America, and Mexico, and, recently, its prevalence has increased in the southern United States. Approximately 300,000 people in the United States are infected.1,2
The illness is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, and it is also known as American trypanosomiasis. The parasite is spread primarily by the bite of triatomine insects (“kissing bugs”). Approximately 60% of these insects are infected with the parasite. The insects live and thrive in the interspaces of mud walls (adobe homes) and thatched roofs. At night, the insects leave their darkened spaces and feed on the exposed skin of sleeping persons. They are particularly likely to bite the moist skin surfaces near the eye and mouth, and, as they do, they defecate and excrete the parasite into the blood vessels beneath the skin. Within the blood, the trypomastigotes invade various host cells. Inside the host cells, the organism transforms into an amastigote, which is the replicative form of the parasite. After several rounds of replication, the amastigote transforms back into a trypomastigote, bursts from the cell, and goes on to infect other host cells.1
In addition to transmission by the insect vector, the parasite also can be transmitted by blood transfusion and organ donation. When contaminated blood is transfused, the risk of transmission is approximately 10% to 25% for each unit. Following implementation of effective screening programs by blood banks in Central America, South America, Mexico, and the United States, the risk of transmission from undetected infection is now approximately 1:200,000 per unit.
When a transplant procedure with an infected heart is performed, the risk of transmission is 75% to 100%. For liver transplants, the frequency of transmission is 0% to 29%; for kidney transplants, the risk of transmission is 0% to 19%.
Consumption of contaminated food or drink, particularly nonpasteurized items sold by street vendors, is also an important mechanism of transmission. In addition, transmission can occur as a result of laboratory exposure and by exposure to wild animals (racoons, opossums, marmosets, bats, armadillos) in forested areas. Finally, perinatal transmission now accounts for about 22% of infections. As effective vector control programs have been introduced in endemic areas, the proportion of cases caused by the insect vector has steadily decreased1-3 (FIGURE 1).
Continue to: Clinical manifestations of Chagas disease...
Clinical manifestations of Chagas disease
Chagas disease occurs in 2 stages, acute and chronic.1,2,4 In patients who are infected via an insect vector, the acute stage typically begins 1 to 2 weeks after the insect bite. This phase of the illness usually lasts 4 to 8 weeks and almost always resolves without treatment.
Some infected patients will be completely free of symptoms. Others will have manifestations such as:
- fever
- malaise
- headache
- hepatosplenomegaly
- lymphadenopathy
- swollen nodule at the site of infection
—Romaña’s sign, when the lesion is on the eyelid
—Chagoma, when the lesion is elsewhere on the skin.
Fortunately, less than 5% of patients will have severe illness, manifested by myocarditis, pericarditis, encephalitis, or meningitis.
People infected by ingestion of the parasite in food or drink often become more severely ill within 3 weeks. Their clinical manifestations include fever, vomiting, dyspnea, cough, chest pain, abdominal pain, and myalgias. Individuals infected through organ transplant or blood transfusion present more like those infected by the insect vector, but their illness may not develop until several weeks to 5 months after exposure.
In the absence of effective treatment, approximately 40% of patients with acute infection will develop chronic infection, often several decades later. The most common, and most ominous, feature of chronic illness is cardiac disease, experienced by about 30% of patients. Cardiac disease may be manifested as a serious arrhythmia, chest pain, congestive heart failure, or thromboembolism.
The other organ system that is likely to be adversely affected in patients with chronic disease is the gastrointestinal (GI) system, and approximately 10% of chronically infected patients experience this complication. Patients may develop a dilated esophagus, which leads to odynophagia and dysphagia. Diminished motility in other areas of the GI tract also may result in chronic constipation and even bowel obstruction. Chronically infected patients who are immunosuppressed due to HIV infection may become gravely ill as a result of encephalitis and brain abscesses. Cardiac and GI dysfunction is due to the parasite’s massive destruction of nerve endings.
Continue to: Making the diagnosis...
Making the diagnosis
The diagnosis of Chagas disease begins with screening patients who have epidemiologic risk factors that place them at high risk for contracting the infection and at significantly increased risk for morbidity and mortality as a result of either the acute infection or the later chronic stage of infection. A thorough history is vital in the evaluation because the acute illness can have such vague clinical manifestations, and many patients remain asymptomatic until signs of chronic infection appear.
Risk factors that warrant screening include being born in a country endemic for Chagas disease, living in an endemic country for more than 6 months, living with someone who has a confirmed diagnosis, residing in a house made of natural materials (mud walls, thatched roof) in an endemic area, and a history of discovering the triatomine bug in the household.
Screening options include serology, microscopy, and PCR testing. Screening with a single, highly sensitive immunoglobulin G (IgG) serologic test is recommended for nonendemic clinical or community settings. In patients who were born in or who lived in an endemic area for more than 6 months, special consideration should be given to screening women of reproductive age, patients of all ages who were born to a mother with a confirmed diagnosis, individuals who were exposed to a triatomine insect, and people who are immunocompromised.5
A positive serologic test should be confirmed with a second assay based on a different antigen. Currently, 4 IgG tests have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for diagnosis. If a patient has 2 positive serologic tests, the diagnosis is confirmed, regardless of clinical presentation. Discordant results warrant a third test to differentiate between positive and negative results (FIGURE 2).5 All patients with a confirmed diagnosis should have an electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan to assess for cardiac or GI abnormalities.

Neonates and infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed infection merit special attention. These children may demonstrate hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pneumonitis, heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, or meningoencephalitis. Newborns delivered to infected mothers will invariably have positive tests for IgG antibody because of transplacental transfer of maternal antibody. Therefore, they should be evaluated by PCR or by direct microscopic examination of the blood for trypomastigotes. In neonates with a negative initial result, repeat testing should be performed by PCR at 4 to 6 weeks of age. Even if the second screening test is negative, the infant should be retested at 9 to 12 months. At this point, maternal IgG no longer should be circulating in the infant’s blood. Three negative tests should effectively rule out T cruzi infection (FIGURE 3).5-7
Organ recipients merit special consideration because, in these individuals, the late stages of Chagas disease may be fatal. In these patients, the preferred diagnostic test is PCR. For transplant patients, monitoring should occur every week for 2 months, bimonthly for the third month, and monthly for 6 months after transplantation. Routine monitoring is not recommended in patients with HIV infection who show no clinical signs of Chagas disease and who are not from endemic areas.
Treatment options
No vaccine or hyperimmune globulin can be used to treat Chagas disease. At this time, 2 antiparasitic drugs are available to treat the condition. One is benznidazole, which inhibits DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis within the microorganism. The medication is given in a dose of 5 to 8 mg/kg per day, divided into 2 doses, for 60 days. Benznidazole is FDA approved for the treatment of individuals older than age 2. It has been used off-label in children younger than 2 years of age. The drug is commercially available at http://www.benznidazoletablets.com.
Benznidazole causes multiple minor side effects and several very serious adverse effects. The serious adverse effects include acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, peripheral neuropathy, marrow suppression, and hepatotoxicity. Benznidazole has been teratogenic and carcinogenic in animal studies and should not be used in pregnancy.1,3,6
The second drug is nifurtimox. This drug is FDA approved for the treatment of Chagas disease in adults and for newborns and young children. It is commercially available for pharmacies to purchase from several drug wholesalers. Nifurtimox produces reactive oxygen species and toxic intermediates that induce DNA damage and cause cell death of the microorganism. The appropriate oral dose is 8 to 10 mg/kg per day, divided into 3 to 4 equal doses. The duration of treatment is 60 to 90 days, depending on the patient’s response. Like benznidazole, nifurtimox also is highly toxic. Severe adverse effects include a hypersensitivity reaction, anaphylaxis, angioedema, syncope, seizures, and psychosis. Nifurtimox also is teratogenic and is contraindicated in pregnancy.1,3,6
Clinicians who have questions about the use of either of these medications should contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Division of Parasitic Diseases public inquiries telephone line at (404) 718-4745.
Potential for cure. When either benznidazole or nifurtimox is administered early in the course of a patient’s acute infection, the chance for complete cure is excellent. The same is true for early treatment of the infected neonate. When treatment is delayed, or if it cannot be completed because of intolerable adverse effects, the prognosis for complete cure is diminished.
In adults who have chronic disease, antiparasitic treatment is unlikely to be effective. In such a situation, secondary treatment is directed toward correction of heart failure, control of cardiac rhythm disturbances, and control of GI motility disorders. For both cardiac and GI conditions, medication and surgery may be indicated. Antiparasitic treatment is more effective in children with chronic disease but it is still not uniformly effective.1,3,5,6
Preventing infection
Vector control is the key to preventing infection in areas where Chagas disease is endemic. One important, but often financially unaffordable, measure is construction of homes with building materials that do not support the growth of the triatomine insects that transmit the disease. A second critical preventive measure is the spraying of mud and thatched homes and surrounding areas with long-lasting insecticides. Pyrethroids are the preferred agents today. Alternative agents include fenitrothion and bendiocarb.1
Other important preventive measures include:
- screening the blood supply for T cruzi and eliminating units contaminated with the parasite
- screening for the parasite in organs targeted for transplant
- screening infected women of reproductive age in endemic areas and treating those who are positive before they become pregnant; this measure may be almost 95% effective in preventing congenital infection
- using mosquito netting when housing is insecure and air conditioning is not available
- in endemic areas, avoiding unpasteurized fruit drinks and unwashed fruits and vegetables.
Unique considerations in pregnancy
Chagas disease does not cause specific anatomic birth defects. However, infected women are more likely to experience spontaneous abortion, preterm premature rupture of membranes, preterm labor, and fetal growth restriction. Overall, the risk of perinatal transmission is approximately 5%, but it may be higher in women who have a very high parasite load. Infected neonates who remain untreated are at risk for developing the serious sequelae of chronic infection. At least half of neonates who are infected will initially be asymptomatic. Therefore, screening of at-risk neonates is essential in order to implement effective treatment.3,6
As noted earlier, the usual drugs used for treating Chagas disease should not be used in pregnancy. Nevertheless, it is still important to screen certain individuals for infection and, subsequently, target them and their neonates for treatment immediately following delivery. The following pregnant patients should be screened5,6:
- women with clinical manifestations that suggest acute or chronic infection
- women from areas of the world in which Chagas disease is endemic, namely, from the southern United States to northern Chile and Argentina. Although the disease is endemic in 21 countries, the countries with the highest prevalence are Bolivia, Argentina, and Paraguay.
- newborns delivered to mothers who have been identified as infected.
As mentioned, several tests are available for screening: PCR, antibody assays, and examination of peripheral blood smears. At least 2 test results should be positive to confirm the diagnosis of infection. Neonates should be followed for 9 to 12 months after delivery to determine if perinatal transmission has occurred. Treatment with antiparasitic drugs is indicated for all infected children.5
CASE Continue surveillance during pregnancy, treat after delivery
This patient should not be treated during pregnancy because the 2 major antiparasitic drugs are teratogenic. Antenatally, she should be followed for evidence of preterm labor and fetal growth restriction. She also should have an electrocardiogram and echocardiogram to evaluate for cardiac disease. Immediately after delivery, the patient should be treated with benznidazole for 60 days. Breastfeeding is acceptable. Her neonate should be screened for infection for up to 9 months, following the algorithm outlined earlier (FIGURE 3), and treated if the surveillance tests are positive. ●
- Chagas disease is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, which is spread by the bite of the triatomine insect (the “kissing bug”).
- The condition is widespread among impoverished populations in South America, Central America, and Mexico, but it is rare in the United States except in individuals who immigrated here from endemic areas.
- Chagas disease evolves through 2 phases: acute and chronic. Manifestations of acute infection include fever, malaise, headache, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, and swelling at the site of the insect bite. The chronic phase is manifested by serious cardiac and gastrointestinal dysfunction.
- The diagnosis can be established by identifying the organism in a blood smear and by detecting antibody or antigen in the blood.
- The 2 drugs of choice for treatment of Chagas disease are benznidazole and nifurtimox. These drugs are teratogenic and are contraindicated in pregnancy.
- Women at risk for infection should be screened prior to, or during, pregnancy. Infants of infected mothers should be screened for infection for up to 9 to 12 months after delivery and treated if they test positive. Treatment of the infant is almost 100% effective in preventing chronic illness.
- Bern C. Chagas disease: epidemiology, screening, and prevention. UpToDate. Updated April 8, 2022. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents /chagas-disease-epidemiology-screening-and-prevention
- Chagas disease. Cleveland Clinic. Reviewed October 8, 2021. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org /health/diseases/21876-chagas-disease
- Howard EJ, Xiong X, Carlier Y, et al. Frequency of the congenital transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG. 2014;121:22-33.
- Chagas disease. Mayo Clinic. November 12, 2020. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases -conditions/chagas-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20356212
- Forsyth CJ, Manne-Goehler J, Bern C, et al. Recommendations for screening and diagnosis of Chagas disease in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2022;225:1601-1610.
- Torrico F, Alonso-Vega C, Suarez E. et al. Maternal Trypanosoma cruzi infection, pregnancy outcome, morbidity, and mortality of congenitally infected and non-infected newborns in Bolivia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70:201-209.
- Messenger LA, Bern C. Congenital Chagas disease: current diagnostics, limitations and future perspectives. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018;31:415-421.
- Bern C. Chagas disease: epidemiology, screening, and prevention. UpToDate. Updated April 8, 2022. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents /chagas-disease-epidemiology-screening-and-prevention
- Chagas disease. Cleveland Clinic. Reviewed October 8, 2021. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org /health/diseases/21876-chagas-disease
- Howard EJ, Xiong X, Carlier Y, et al. Frequency of the congenital transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG. 2014;121:22-33.
- Chagas disease. Mayo Clinic. November 12, 2020. Accessed October 6, 2022. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases -conditions/chagas-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20356212
- Forsyth CJ, Manne-Goehler J, Bern C, et al. Recommendations for screening and diagnosis of Chagas disease in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2022;225:1601-1610.
- Torrico F, Alonso-Vega C, Suarez E. et al. Maternal Trypanosoma cruzi infection, pregnancy outcome, morbidity, and mortality of congenitally infected and non-infected newborns in Bolivia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70:201-209.
- Messenger LA, Bern C. Congenital Chagas disease: current diagnostics, limitations and future perspectives. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018;31:415-421.
Treating recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis

Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC) is a common cause of vaginitis and gynecologic morbidity in the United States and globally.1 RVVC is defined as at least 3 laboratory-confirmed (for example, culture, nucleic acid amplification test [NAAT]) symptomatic episodes in the previous 12 months.2 Common symptoms include vulvar pruritus, erythema, local skin and mucosal irritation, and abnormal discharge that may be thick and white or thin and watery.
The true incidence of RVVC is difficult to determine due to clinical diagnostic inaccuracy that results in over- and underdiagnosis of VVC and the general availability of over-the-counter topical antifungal medications that individuals who self-diagnose use to treat VVC.3
Causative organisms
Vulvovaginal yeast infections are caused by Candida species, a family of ubiquitous fungi that are a part of normal genitourinary and gastrointestinal flora.4 As such, these infections are commonly termed VVC. The presence of Candida species in the vagina without evidence of inflammation is not considered an infection but rather is more consistent with vaginal colonization. Inflammation in the setting of Candida species is what characterizes a true VVC infection.4
Candida albicans is responsible for the vast majority of VVC cases in the United States, with Candida glabrata accounting for most of the remaining infections.5 The majority of RVVC infections that are caused by C albicans are due to azole-sensitive strains (85%–95% of infections).2C glabrata, by contrast, is intrinsically resistant to azoles, which is thought primarily to be due to overexpression of drug efflux pumps that remove active drug from the cell.6,7
Why does VVC reoccur?
The pathogenesis of RVVC is not well understood. Predisposing factors may include frequent or recent antibiotic use, poorly controlled diabetes, immunodeficiency, and other host factors. However, many cases of RVVC are idiopathic and no predisposing or underlying conditions are identified.7
The role of genetic factors in predisposing to or triggering RVVC is unclear and is an area of ongoing investigation.2 Longitudinal DNA-typing studies suggest that recurrent disease is usually due to relapse from a persistent vaginal reservoir of organisms (that is, vaginal colonization) or endogenous reinfection with identical strains of susceptible C albicans.8,9 Symptomatic VVC likely results when the symbiotic balance between yeast and the normal vaginal microbiota is disrupted (by either Candida species overgrowth or changes in host immune factors).2 Less commonly, “recurrent” infections may in fact be due to azole-resistant Candida and non-Candida species.2
Clinical aspects and diagnosis of VVC
Signs and symptoms suggestive of VVC include vulvovaginal erythema, edema, vaginal discharge, vulvovaginal pruritus, and irritation. Given the lack of specificity of individual clinical findings in diagnosing VVC, or for distinguishing between other common causes of vaginitis (such as bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis), laboratory testing (that is, microscopy) should be performed in combination with a clinical exam in order to make a confident diagnosis of VVC.10 Self-diagnosis of VVC is inaccurate and is not recommended, as misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment is cost ineffective, delays accurate diagnoses, and may contribute to growing azole resistance.
In patients with signs and symptoms of VVC, saline and potassium hydroxide microscopy should be performed.7 TABLE 1 summarizes other major diagnostic techniques for VVC.
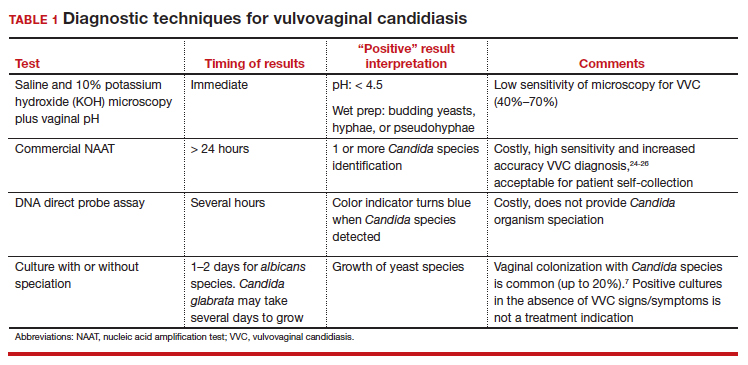
Diagnostic considerations
Non-albicans Candida species, such as C glabrata, may be associated with minimally symptomatic or completely asymptomatic infections and may not be identified easily on wet mount as it does not form pseudohyphae or hyphae.11 Therefore, culture and susceptibility or NAAT testing is highly recommended for patients who remain symptomatic and/or have a nondiagnostic microscopy and a normal vaginal pH.7
Treatment options
Prior to May 2022, there had been no drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat RVVC. The mainstay of treatment is long-term maintenance therapy to achieve mycologic remission (TABLE 2).

In general, recurrent episodes of VVC should be treated with a longer duration of therapy (for example, oral fluconazole 150 mg every 72 hours for a total of 3 doses or topical azole for 7–14 days).7 If recurrent maintenance/suppressive therapy is started, the induction phase should be longer as well, at least 10 to 14 days with a topical or oral azole followed by a 6-month or longer course of weekly oral or topical azole therapy (such as 6–12 months).12,13
Patients with underlying immunodeficiency (such as poorly controlled diabetes, chronic corticosteroid treatment) may need prolonged courses of therapy. Correction of modifiable conditions and optimization of comorbidities should be prioritized—for example, optimized glucose control, weight loss, durable viral suppression, and so on. Of note, symptomatic VVC is more frequent among individuals with HIV and correlates with severity of immunodeficiency. Pharmacologic options for RVVC for individuals with HIV do not differ from standard recommendations.14
Fluconazole
Fluconazole is a safe, affordable, and convenient prescription oral medication that can be used for initial and maintenance/suppressive therapy.2 Fluconazole levels in vaginal secretions remain at therapeutic concentrations for at least 72 hours after a 150-mg dose.15 Induction therapy consists of oral fluconazole 150 mg every 72 hours for a total of 3 doses, followed by a maintenance regimen of a once-weekly dose of oral fluconazole 150 mg for a total of 6 months. Unfortunately, up to 55% of patients will experience a relapse in symptoms.12
Routine liver function test monitoring is not indicated for fluconazole maintenance therapy, but it should be performed if patients are treated with daily or long-term alternative oral azole medications, such as ketoconazole and itraconazole.
During pregnancy, only topical azole therapy is recommended for use, given the potential risk for adverse fetal outcomes, such as spontaneous abortion and congenital malformations, with fetal exposure to oral fluconazole ingested by the pregnant person.16 Fluconazole is present in breast milk, but it is safe to use during lactation when used at recommended doses.17
Continue to: Options for fluconazole-resistant C albicans infection...
Options for fluconazole-resistant C albicans infection
Patients who have RVVC with frequent and/or prolonged use of fluconazole are at risk for developing azole-resistant isolates of C albicans.12 For patients found to have azole-resistant infections, treatment options include increasing the azole dose based on isolate minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) to various antifungals, therapy with a non-fluconazole azole regimen, or switching to a different therapeutic drug class altogether.7
Options for non- albicans Candida species infection
Given the intrinsic resistance to azole therapy in some non-albicans Candida species (specifically C glabrata and Candida krusei), boric acid or nystatin regimens can be used. An induction course of vaginal boric acid is given as 600 mg per vagina daily for up to 14 days and is associated with a 70% rate of mycologic control.7 Boric acid is known to cause local irritation and dermatitis for both the patient and any sexual partners. If ingested orally, boric acid is associated with significant toxicity and even death.7
Vaginal nystatin also may be considered, with an induction course of 100,000 U for 14 days, with a similar regimen recommended for maintenance therapy. However, data are limited on maintenance regimens for RVVC due to non-albicans Candida species.2
Gentian violet
Gentian violet is a topical antiseptic agent that is available over the counter. Use of this agent is uncommon given the availability of highly effective azole-based therapy. Although useful due to its antipruritic properties, gentian violet can be messy to use and tends to stain clothing permanently.
Gentian violet use may be considered in cases of refractory RVVC with or without azole-resistant infections; it is applied as a 1% or 2% solution directly to affected areas for 10 to 14 days.18
Lactobacilli probiotics and dietary changes
Data that support the oral and/or vaginal use of probiotics that contain live lactobacilli are conflicting. In the absence of conclusive evidence to support probiotic use to treat and prevent RVVC, as well as variable quality of available products, use of these agents is not recommended.19
No controlled studies have evaluated the role of various diets in preventing RVVC; thus, no specific dietary changes are recommended.
Behavioral therapy
Available evidence does not support the treatment of sexual partners of patients with RVVC.7
Continue to: What’s new in treatment?...
What’s new in treatment?
Until recently, the main standard of care for RVVC has been oral fluconazole-based therapy. For patients whose symptoms do not respond to oral fluconazole therapy, oteseconazole is now available as a noninferior treatment option to fluconazole for both induction and maintenance therapy. Like other azoles, oteseconazole works by inhibiting a fungal enzyme (CYP51) that is essential in fungal cell membrane integrity and fungal growth.20 Oteseconazole is a more selective inhibitor of the fungal CYP51 enzyme and has demonstrated excellent potency against Candida species in in vitro pharmacologic studies.21
In a phase 3 study that evaluated the safety and efficacy of oteseconazole in the treatment and prevention of RVVC, oteseconazole was found to be both safe and efficacious in both the induction and maintenance phases of treatment for RVVC.20 In this trial, induction and maintenance with oteseconazole was compared with induction with fluconazole and placebo maintenance. Among the 185 participants with culture-verified RVVC, the oteseconazole regimen (n = 123) was associated with fewer recurrences of culture-verified VVC infections than was the fluconazole induction/placebo maintenance regimen (n = 62) during the 48-week maintenance phase of therapy (5% vs 42%).20
Single- and dual-drug dosing regimens of oteseconazole are recommended based on previous trial data that compared safety and efficacy of oteseconazole versus fluconazole induction therapy and oteseconazole versus placebo maintenance therapy.22 However, widespread use of oteseconazole regimens are limited due to its higher costs and limited access to the drug outside of a research setting.20
Single-drug induction therapy with oteseconazole consists of a single 600-mg oral dose on day 1 followed by a second dose of 450 mg orally on day 2. Starting on day 14, maintenance therapy starts with a single oral dose of 150 mg and is continued weekly for 11 weeks.22
Dual-drug induction therapy consists of oral fluconazole 150 mg on days 1, 4, and 7 followed by daily dosing of oral oteseconazole 150 mg on days 14 through 20. Then, starting on day 28, weekly dosing of oral oteseconazole 150 mg is continued for 11 weeks.22
Effects on pregnancy and lactation. Concerns of oteseconazole’s fetal teratogenicity are based on animal reproduction studies that reported ocular abnormalities from in utero exposure. Human data are insufficient to determine if oteseconazole is excreted in breast milk or what its effects are on milk production. Among breastfed infants whose mothers were exposed to oteseconazole during lactation, no adverse outcomes were reported, but follow up of oteseconazole-exposed infants was limited. 22 Therefore, use of oteseconazole among pregnant and/or lactating persons with RVVC is contraindicated at this time. The long-half life (approximately 138 days) of oteseconazole may preclude use among persons attempting pregnancy. 22
Other therapies. The other common classes of antifungal therapy used in the treatment of RVVC include the polyenes (for example, amphotericin B) and echinocandins (such as caspofungin) drug classes. Emerging azole-resistance among Candida species has been recognized as a significant concern from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 7 Echinocandins, which are generally better tolerated and have a lower adverse side effect profile than polyenes, are a promising therapeutic class, but currently they are limited to intravenous options. SCY-078, a novel oral echinocandin in development, has shown in vitro fungicidal activity against multiple albicans and non-albicans Candida species in pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies.23
Continued development of alternative, non-azole-based therapies for Candida species is needed.●
- Sobel JD. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985;152(7 pt 2):924-935. doi:10.1016/S0002-9378(85)80003-x
- Sobel JD. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214:15-21. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2015.06.067
- Rathod SD, Buffler PA. Highly-cited estimates of the cumulative incidence and recurrence of vulvovaginal candidiasis are inadequately documented. BMC Womens Health. 2014;14:43. doi:10.1186/1472-6874-14-43
- Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, et al, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2022:515-542.
- Gonçalves B, Ferreira C, Alves CT, et al. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42:905-927. doi:10.3109/1040841X.2015.1091805
- Sobel JD, Sobel R. Current treatment options for vulvovaginal candidiasis caused by azole-resistant Candida species. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018;19:971-977. doi:10.1080/14656566.2018.1476490
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Vazquez JA, Sobel JD, Demitriou R, et al. Karyotyping of Candida albicans isolates obtained longitudinally in women with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:1566-1569. doi:10.1093/infdis/170.6.1566
- Lockhart SR, Reed BD, Pierson CL, et al. Most frequent scenario for recurrent Candida vaginitis is strain maintenance with “substrain shuffling”: demonstration by sequential DNA fingerprinting with probes Ca3, C1, and CARE2. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:767-777. doi:10.1128/jcm.34.4.767-777.1996
- Anderson MR, Klink K, Cohrssen A. Evaluation of vaginal complaints. JAMA. 2004;291:1368-1379. doi:10.1001/jama.291.11.1368
- Sobel JD. Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet. 2007;369:1961-1971. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60917-9
- Collins LM, Moore R, Sobel JD. Prognosis and long-term outcome of women with idiopathic recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis caused by Candida albicans. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24:48-52. doi:10.1097/LGT.0000000000000496
- Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes DR, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:e1-50. doi:10.1093/cid/civ933
- Duerr A, Heilig CM, Meikle SF, et al; HER Study Group. Incident and persistent vulvovaginal candidiasis among human immunodeficiency virus–infected women: risk factors and severity. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:548-556. doi:10.1016/s0029-7844(02)02729-1
- Houang ET, Chappatte O, Byrne D, et al. Fluconazole levels in plasma and vaginal secretions of patients after a 150-milligram single oral dose and rate of eradication of infection in vaginal candidiasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990;34:909-910. doi:10.1128/AAC.34.5.909
- Bérard A, Sheehy O, Zhao JP, et al. Associations between low- and high-dose oral fluconazole and pregnancy outcomes: 3 nested case-control studies. CMAJ. 2019;191:E179-E187. doi:10.1503/cmaj.180963
- Fluconazole. In: Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed). National Library of Medicine (US); 2006. Revised October 31, 2018. Accessed September 23, 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501223/
- White DJ, Johnson EM, Warnock DW. Management of persistent vulvo vaginal candidosis due to azole-resistant Candida glabrata. Genitourin Med. 1993;69:112-114. doi:10.1136/sti.69.2.112
- Falagas ME, Betsi GI, Athanasiou S. Probiotics for prevention of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: a review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;58:266-272. doi:10.1093/jac/dkl246
- Martens MG, Maximos B, Degenhardt T, et al. Phase 3 study evaluating the safety and efficacy of oteseconazole in the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis and acute vulvovaginal candidiasis infections. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022:S0002-9378(22)005774. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.07.023
- Sobel JD, Nyirjesy P. Oteseconazole: an advance in treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Future Microbiol. 2021;16:1453-1461. doi:10.2217/fmb-2021-0173
- Vivjoa (oteseconazole). Prescribing information. Mycovia Pharmaceuticals, Inc. April 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215888s000lbl.pdf
- Scorneaux B, Angulo D, Borroto-Esoda K, et al. SCY-078 is fungicidal against Candida species in time-kill studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:e01961-16. doi:10.1128/AAC.01961-16
- Schwebke JR, Taylor SN, Ackerman R, et al. Clinical validation of the Aptima bacterial vaginosis and Aptima Candida/Trichomonas vaginitis assays: results from a prospective multicenter clinical study. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58:e01643-19. doi:10.1128/JCM.01643-19
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Nyirjesy P, et al. Diagnostic performance of a molecular test versus clinician assessment of vaginitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56:e00252-18. doi:10.1128/JCM.00252-18
- Broache M, Cammarata CL, Stonebraker E, et al. Performance of a vaginal panel assay compared with the clinical diagnosis of vaginitis. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:853-859. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004592

Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC) is a common cause of vaginitis and gynecologic morbidity in the United States and globally.1 RVVC is defined as at least 3 laboratory-confirmed (for example, culture, nucleic acid amplification test [NAAT]) symptomatic episodes in the previous 12 months.2 Common symptoms include vulvar pruritus, erythema, local skin and mucosal irritation, and abnormal discharge that may be thick and white or thin and watery.
The true incidence of RVVC is difficult to determine due to clinical diagnostic inaccuracy that results in over- and underdiagnosis of VVC and the general availability of over-the-counter topical antifungal medications that individuals who self-diagnose use to treat VVC.3
Causative organisms
Vulvovaginal yeast infections are caused by Candida species, a family of ubiquitous fungi that are a part of normal genitourinary and gastrointestinal flora.4 As such, these infections are commonly termed VVC. The presence of Candida species in the vagina without evidence of inflammation is not considered an infection but rather is more consistent with vaginal colonization. Inflammation in the setting of Candida species is what characterizes a true VVC infection.4
Candida albicans is responsible for the vast majority of VVC cases in the United States, with Candida glabrata accounting for most of the remaining infections.5 The majority of RVVC infections that are caused by C albicans are due to azole-sensitive strains (85%–95% of infections).2C glabrata, by contrast, is intrinsically resistant to azoles, which is thought primarily to be due to overexpression of drug efflux pumps that remove active drug from the cell.6,7
Why does VVC reoccur?
The pathogenesis of RVVC is not well understood. Predisposing factors may include frequent or recent antibiotic use, poorly controlled diabetes, immunodeficiency, and other host factors. However, many cases of RVVC are idiopathic and no predisposing or underlying conditions are identified.7
The role of genetic factors in predisposing to or triggering RVVC is unclear and is an area of ongoing investigation.2 Longitudinal DNA-typing studies suggest that recurrent disease is usually due to relapse from a persistent vaginal reservoir of organisms (that is, vaginal colonization) or endogenous reinfection with identical strains of susceptible C albicans.8,9 Symptomatic VVC likely results when the symbiotic balance between yeast and the normal vaginal microbiota is disrupted (by either Candida species overgrowth or changes in host immune factors).2 Less commonly, “recurrent” infections may in fact be due to azole-resistant Candida and non-Candida species.2
Clinical aspects and diagnosis of VVC
Signs and symptoms suggestive of VVC include vulvovaginal erythema, edema, vaginal discharge, vulvovaginal pruritus, and irritation. Given the lack of specificity of individual clinical findings in diagnosing VVC, or for distinguishing between other common causes of vaginitis (such as bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis), laboratory testing (that is, microscopy) should be performed in combination with a clinical exam in order to make a confident diagnosis of VVC.10 Self-diagnosis of VVC is inaccurate and is not recommended, as misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment is cost ineffective, delays accurate diagnoses, and may contribute to growing azole resistance.
In patients with signs and symptoms of VVC, saline and potassium hydroxide microscopy should be performed.7 TABLE 1 summarizes other major diagnostic techniques for VVC.

Diagnostic considerations
Non-albicans Candida species, such as C glabrata, may be associated with minimally symptomatic or completely asymptomatic infections and may not be identified easily on wet mount as it does not form pseudohyphae or hyphae.11 Therefore, culture and susceptibility or NAAT testing is highly recommended for patients who remain symptomatic and/or have a nondiagnostic microscopy and a normal vaginal pH.7
Treatment options
Prior to May 2022, there had been no drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat RVVC. The mainstay of treatment is long-term maintenance therapy to achieve mycologic remission (TABLE 2).

In general, recurrent episodes of VVC should be treated with a longer duration of therapy (for example, oral fluconazole 150 mg every 72 hours for a total of 3 doses or topical azole for 7–14 days).7 If recurrent maintenance/suppressive therapy is started, the induction phase should be longer as well, at least 10 to 14 days with a topical or oral azole followed by a 6-month or longer course of weekly oral or topical azole therapy (such as 6–12 months).12,13
Patients with underlying immunodeficiency (such as poorly controlled diabetes, chronic corticosteroid treatment) may need prolonged courses of therapy. Correction of modifiable conditions and optimization of comorbidities should be prioritized—for example, optimized glucose control, weight loss, durable viral suppression, and so on. Of note, symptomatic VVC is more frequent among individuals with HIV and correlates with severity of immunodeficiency. Pharmacologic options for RVVC for individuals with HIV do not differ from standard recommendations.14
Fluconazole
Fluconazole is a safe, affordable, and convenient prescription oral medication that can be used for initial and maintenance/suppressive therapy.2 Fluconazole levels in vaginal secretions remain at therapeutic concentrations for at least 72 hours after a 150-mg dose.15 Induction therapy consists of oral fluconazole 150 mg every 72 hours for a total of 3 doses, followed by a maintenance regimen of a once-weekly dose of oral fluconazole 150 mg for a total of 6 months. Unfortunately, up to 55% of patients will experience a relapse in symptoms.12
Routine liver function test monitoring is not indicated for fluconazole maintenance therapy, but it should be performed if patients are treated with daily or long-term alternative oral azole medications, such as ketoconazole and itraconazole.
During pregnancy, only topical azole therapy is recommended for use, given the potential risk for adverse fetal outcomes, such as spontaneous abortion and congenital malformations, with fetal exposure to oral fluconazole ingested by the pregnant person.16 Fluconazole is present in breast milk, but it is safe to use during lactation when used at recommended doses.17
Continue to: Options for fluconazole-resistant C albicans infection...
Options for fluconazole-resistant C albicans infection
Patients who have RVVC with frequent and/or prolonged use of fluconazole are at risk for developing azole-resistant isolates of C albicans.12 For patients found to have azole-resistant infections, treatment options include increasing the azole dose based on isolate minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) to various antifungals, therapy with a non-fluconazole azole regimen, or switching to a different therapeutic drug class altogether.7
Options for non- albicans Candida species infection
Given the intrinsic resistance to azole therapy in some non-albicans Candida species (specifically C glabrata and Candida krusei), boric acid or nystatin regimens can be used. An induction course of vaginal boric acid is given as 600 mg per vagina daily for up to 14 days and is associated with a 70% rate of mycologic control.7 Boric acid is known to cause local irritation and dermatitis for both the patient and any sexual partners. If ingested orally, boric acid is associated with significant toxicity and even death.7
Vaginal nystatin also may be considered, with an induction course of 100,000 U for 14 days, with a similar regimen recommended for maintenance therapy. However, data are limited on maintenance regimens for RVVC due to non-albicans Candida species.2
Gentian violet
Gentian violet is a topical antiseptic agent that is available over the counter. Use of this agent is uncommon given the availability of highly effective azole-based therapy. Although useful due to its antipruritic properties, gentian violet can be messy to use and tends to stain clothing permanently.
Gentian violet use may be considered in cases of refractory RVVC with or without azole-resistant infections; it is applied as a 1% or 2% solution directly to affected areas for 10 to 14 days.18
Lactobacilli probiotics and dietary changes
Data that support the oral and/or vaginal use of probiotics that contain live lactobacilli are conflicting. In the absence of conclusive evidence to support probiotic use to treat and prevent RVVC, as well as variable quality of available products, use of these agents is not recommended.19
No controlled studies have evaluated the role of various diets in preventing RVVC; thus, no specific dietary changes are recommended.
Behavioral therapy
Available evidence does not support the treatment of sexual partners of patients with RVVC.7
Continue to: What’s new in treatment?...
What’s new in treatment?
Until recently, the main standard of care for RVVC has been oral fluconazole-based therapy. For patients whose symptoms do not respond to oral fluconazole therapy, oteseconazole is now available as a noninferior treatment option to fluconazole for both induction and maintenance therapy. Like other azoles, oteseconazole works by inhibiting a fungal enzyme (CYP51) that is essential in fungal cell membrane integrity and fungal growth.20 Oteseconazole is a more selective inhibitor of the fungal CYP51 enzyme and has demonstrated excellent potency against Candida species in in vitro pharmacologic studies.21
In a phase 3 study that evaluated the safety and efficacy of oteseconazole in the treatment and prevention of RVVC, oteseconazole was found to be both safe and efficacious in both the induction and maintenance phases of treatment for RVVC.20 In this trial, induction and maintenance with oteseconazole was compared with induction with fluconazole and placebo maintenance. Among the 185 participants with culture-verified RVVC, the oteseconazole regimen (n = 123) was associated with fewer recurrences of culture-verified VVC infections than was the fluconazole induction/placebo maintenance regimen (n = 62) during the 48-week maintenance phase of therapy (5% vs 42%).20
Single- and dual-drug dosing regimens of oteseconazole are recommended based on previous trial data that compared safety and efficacy of oteseconazole versus fluconazole induction therapy and oteseconazole versus placebo maintenance therapy.22 However, widespread use of oteseconazole regimens are limited due to its higher costs and limited access to the drug outside of a research setting.20
Single-drug induction therapy with oteseconazole consists of a single 600-mg oral dose on day 1 followed by a second dose of 450 mg orally on day 2. Starting on day 14, maintenance therapy starts with a single oral dose of 150 mg and is continued weekly for 11 weeks.22
Dual-drug induction therapy consists of oral fluconazole 150 mg on days 1, 4, and 7 followed by daily dosing of oral oteseconazole 150 mg on days 14 through 20. Then, starting on day 28, weekly dosing of oral oteseconazole 150 mg is continued for 11 weeks.22
Effects on pregnancy and lactation. Concerns of oteseconazole’s fetal teratogenicity are based on animal reproduction studies that reported ocular abnormalities from in utero exposure. Human data are insufficient to determine if oteseconazole is excreted in breast milk or what its effects are on milk production. Among breastfed infants whose mothers were exposed to oteseconazole during lactation, no adverse outcomes were reported, but follow up of oteseconazole-exposed infants was limited. 22 Therefore, use of oteseconazole among pregnant and/or lactating persons with RVVC is contraindicated at this time. The long-half life (approximately 138 days) of oteseconazole may preclude use among persons attempting pregnancy. 22
Other therapies. The other common classes of antifungal therapy used in the treatment of RVVC include the polyenes (for example, amphotericin B) and echinocandins (such as caspofungin) drug classes. Emerging azole-resistance among Candida species has been recognized as a significant concern from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 7 Echinocandins, which are generally better tolerated and have a lower adverse side effect profile than polyenes, are a promising therapeutic class, but currently they are limited to intravenous options. SCY-078, a novel oral echinocandin in development, has shown in vitro fungicidal activity against multiple albicans and non-albicans Candida species in pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies.23
Continued development of alternative, non-azole-based therapies for Candida species is needed.●

Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC) is a common cause of vaginitis and gynecologic morbidity in the United States and globally.1 RVVC is defined as at least 3 laboratory-confirmed (for example, culture, nucleic acid amplification test [NAAT]) symptomatic episodes in the previous 12 months.2 Common symptoms include vulvar pruritus, erythema, local skin and mucosal irritation, and abnormal discharge that may be thick and white or thin and watery.
The true incidence of RVVC is difficult to determine due to clinical diagnostic inaccuracy that results in over- and underdiagnosis of VVC and the general availability of over-the-counter topical antifungal medications that individuals who self-diagnose use to treat VVC.3
Causative organisms
Vulvovaginal yeast infections are caused by Candida species, a family of ubiquitous fungi that are a part of normal genitourinary and gastrointestinal flora.4 As such, these infections are commonly termed VVC. The presence of Candida species in the vagina without evidence of inflammation is not considered an infection but rather is more consistent with vaginal colonization. Inflammation in the setting of Candida species is what characterizes a true VVC infection.4
Candida albicans is responsible for the vast majority of VVC cases in the United States, with Candida glabrata accounting for most of the remaining infections.5 The majority of RVVC infections that are caused by C albicans are due to azole-sensitive strains (85%–95% of infections).2C glabrata, by contrast, is intrinsically resistant to azoles, which is thought primarily to be due to overexpression of drug efflux pumps that remove active drug from the cell.6,7
Why does VVC reoccur?
The pathogenesis of RVVC is not well understood. Predisposing factors may include frequent or recent antibiotic use, poorly controlled diabetes, immunodeficiency, and other host factors. However, many cases of RVVC are idiopathic and no predisposing or underlying conditions are identified.7
The role of genetic factors in predisposing to or triggering RVVC is unclear and is an area of ongoing investigation.2 Longitudinal DNA-typing studies suggest that recurrent disease is usually due to relapse from a persistent vaginal reservoir of organisms (that is, vaginal colonization) or endogenous reinfection with identical strains of susceptible C albicans.8,9 Symptomatic VVC likely results when the symbiotic balance between yeast and the normal vaginal microbiota is disrupted (by either Candida species overgrowth or changes in host immune factors).2 Less commonly, “recurrent” infections may in fact be due to azole-resistant Candida and non-Candida species.2
Clinical aspects and diagnosis of VVC
Signs and symptoms suggestive of VVC include vulvovaginal erythema, edema, vaginal discharge, vulvovaginal pruritus, and irritation. Given the lack of specificity of individual clinical findings in diagnosing VVC, or for distinguishing between other common causes of vaginitis (such as bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis), laboratory testing (that is, microscopy) should be performed in combination with a clinical exam in order to make a confident diagnosis of VVC.10 Self-diagnosis of VVC is inaccurate and is not recommended, as misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment is cost ineffective, delays accurate diagnoses, and may contribute to growing azole resistance.
In patients with signs and symptoms of VVC, saline and potassium hydroxide microscopy should be performed.7 TABLE 1 summarizes other major diagnostic techniques for VVC.

Diagnostic considerations
Non-albicans Candida species, such as C glabrata, may be associated with minimally symptomatic or completely asymptomatic infections and may not be identified easily on wet mount as it does not form pseudohyphae or hyphae.11 Therefore, culture and susceptibility or NAAT testing is highly recommended for patients who remain symptomatic and/or have a nondiagnostic microscopy and a normal vaginal pH.7
Treatment options
Prior to May 2022, there had been no drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat RVVC. The mainstay of treatment is long-term maintenance therapy to achieve mycologic remission (TABLE 2).

In general, recurrent episodes of VVC should be treated with a longer duration of therapy (for example, oral fluconazole 150 mg every 72 hours for a total of 3 doses or topical azole for 7–14 days).7 If recurrent maintenance/suppressive therapy is started, the induction phase should be longer as well, at least 10 to 14 days with a topical or oral azole followed by a 6-month or longer course of weekly oral or topical azole therapy (such as 6–12 months).12,13
Patients with underlying immunodeficiency (such as poorly controlled diabetes, chronic corticosteroid treatment) may need prolonged courses of therapy. Correction of modifiable conditions and optimization of comorbidities should be prioritized—for example, optimized glucose control, weight loss, durable viral suppression, and so on. Of note, symptomatic VVC is more frequent among individuals with HIV and correlates with severity of immunodeficiency. Pharmacologic options for RVVC for individuals with HIV do not differ from standard recommendations.14
Fluconazole
Fluconazole is a safe, affordable, and convenient prescription oral medication that can be used for initial and maintenance/suppressive therapy.2 Fluconazole levels in vaginal secretions remain at therapeutic concentrations for at least 72 hours after a 150-mg dose.15 Induction therapy consists of oral fluconazole 150 mg every 72 hours for a total of 3 doses, followed by a maintenance regimen of a once-weekly dose of oral fluconazole 150 mg for a total of 6 months. Unfortunately, up to 55% of patients will experience a relapse in symptoms.12
Routine liver function test monitoring is not indicated for fluconazole maintenance therapy, but it should be performed if patients are treated with daily or long-term alternative oral azole medications, such as ketoconazole and itraconazole.
During pregnancy, only topical azole therapy is recommended for use, given the potential risk for adverse fetal outcomes, such as spontaneous abortion and congenital malformations, with fetal exposure to oral fluconazole ingested by the pregnant person.16 Fluconazole is present in breast milk, but it is safe to use during lactation when used at recommended doses.17
Continue to: Options for fluconazole-resistant C albicans infection...
Options for fluconazole-resistant C albicans infection
Patients who have RVVC with frequent and/or prolonged use of fluconazole are at risk for developing azole-resistant isolates of C albicans.12 For patients found to have azole-resistant infections, treatment options include increasing the azole dose based on isolate minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) to various antifungals, therapy with a non-fluconazole azole regimen, or switching to a different therapeutic drug class altogether.7
Options for non- albicans Candida species infection
Given the intrinsic resistance to azole therapy in some non-albicans Candida species (specifically C glabrata and Candida krusei), boric acid or nystatin regimens can be used. An induction course of vaginal boric acid is given as 600 mg per vagina daily for up to 14 days and is associated with a 70% rate of mycologic control.7 Boric acid is known to cause local irritation and dermatitis for both the patient and any sexual partners. If ingested orally, boric acid is associated with significant toxicity and even death.7
Vaginal nystatin also may be considered, with an induction course of 100,000 U for 14 days, with a similar regimen recommended for maintenance therapy. However, data are limited on maintenance regimens for RVVC due to non-albicans Candida species.2
Gentian violet
Gentian violet is a topical antiseptic agent that is available over the counter. Use of this agent is uncommon given the availability of highly effective azole-based therapy. Although useful due to its antipruritic properties, gentian violet can be messy to use and tends to stain clothing permanently.
Gentian violet use may be considered in cases of refractory RVVC with or without azole-resistant infections; it is applied as a 1% or 2% solution directly to affected areas for 10 to 14 days.18
Lactobacilli probiotics and dietary changes
Data that support the oral and/or vaginal use of probiotics that contain live lactobacilli are conflicting. In the absence of conclusive evidence to support probiotic use to treat and prevent RVVC, as well as variable quality of available products, use of these agents is not recommended.19
No controlled studies have evaluated the role of various diets in preventing RVVC; thus, no specific dietary changes are recommended.
Behavioral therapy
Available evidence does not support the treatment of sexual partners of patients with RVVC.7
Continue to: What’s new in treatment?...
What’s new in treatment?
Until recently, the main standard of care for RVVC has been oral fluconazole-based therapy. For patients whose symptoms do not respond to oral fluconazole therapy, oteseconazole is now available as a noninferior treatment option to fluconazole for both induction and maintenance therapy. Like other azoles, oteseconazole works by inhibiting a fungal enzyme (CYP51) that is essential in fungal cell membrane integrity and fungal growth.20 Oteseconazole is a more selective inhibitor of the fungal CYP51 enzyme and has demonstrated excellent potency against Candida species in in vitro pharmacologic studies.21
In a phase 3 study that evaluated the safety and efficacy of oteseconazole in the treatment and prevention of RVVC, oteseconazole was found to be both safe and efficacious in both the induction and maintenance phases of treatment for RVVC.20 In this trial, induction and maintenance with oteseconazole was compared with induction with fluconazole and placebo maintenance. Among the 185 participants with culture-verified RVVC, the oteseconazole regimen (n = 123) was associated with fewer recurrences of culture-verified VVC infections than was the fluconazole induction/placebo maintenance regimen (n = 62) during the 48-week maintenance phase of therapy (5% vs 42%).20
Single- and dual-drug dosing regimens of oteseconazole are recommended based on previous trial data that compared safety and efficacy of oteseconazole versus fluconazole induction therapy and oteseconazole versus placebo maintenance therapy.22 However, widespread use of oteseconazole regimens are limited due to its higher costs and limited access to the drug outside of a research setting.20
Single-drug induction therapy with oteseconazole consists of a single 600-mg oral dose on day 1 followed by a second dose of 450 mg orally on day 2. Starting on day 14, maintenance therapy starts with a single oral dose of 150 mg and is continued weekly for 11 weeks.22
Dual-drug induction therapy consists of oral fluconazole 150 mg on days 1, 4, and 7 followed by daily dosing of oral oteseconazole 150 mg on days 14 through 20. Then, starting on day 28, weekly dosing of oral oteseconazole 150 mg is continued for 11 weeks.22
Effects on pregnancy and lactation. Concerns of oteseconazole’s fetal teratogenicity are based on animal reproduction studies that reported ocular abnormalities from in utero exposure. Human data are insufficient to determine if oteseconazole is excreted in breast milk or what its effects are on milk production. Among breastfed infants whose mothers were exposed to oteseconazole during lactation, no adverse outcomes were reported, but follow up of oteseconazole-exposed infants was limited. 22 Therefore, use of oteseconazole among pregnant and/or lactating persons with RVVC is contraindicated at this time. The long-half life (approximately 138 days) of oteseconazole may preclude use among persons attempting pregnancy. 22
Other therapies. The other common classes of antifungal therapy used in the treatment of RVVC include the polyenes (for example, amphotericin B) and echinocandins (such as caspofungin) drug classes. Emerging azole-resistance among Candida species has been recognized as a significant concern from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 7 Echinocandins, which are generally better tolerated and have a lower adverse side effect profile than polyenes, are a promising therapeutic class, but currently they are limited to intravenous options. SCY-078, a novel oral echinocandin in development, has shown in vitro fungicidal activity against multiple albicans and non-albicans Candida species in pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies.23
Continued development of alternative, non-azole-based therapies for Candida species is needed.●
- Sobel JD. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985;152(7 pt 2):924-935. doi:10.1016/S0002-9378(85)80003-x
- Sobel JD. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214:15-21. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2015.06.067
- Rathod SD, Buffler PA. Highly-cited estimates of the cumulative incidence and recurrence of vulvovaginal candidiasis are inadequately documented. BMC Womens Health. 2014;14:43. doi:10.1186/1472-6874-14-43
- Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, et al, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2022:515-542.
- Gonçalves B, Ferreira C, Alves CT, et al. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42:905-927. doi:10.3109/1040841X.2015.1091805
- Sobel JD, Sobel R. Current treatment options for vulvovaginal candidiasis caused by azole-resistant Candida species. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018;19:971-977. doi:10.1080/14656566.2018.1476490
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Vazquez JA, Sobel JD, Demitriou R, et al. Karyotyping of Candida albicans isolates obtained longitudinally in women with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:1566-1569. doi:10.1093/infdis/170.6.1566
- Lockhart SR, Reed BD, Pierson CL, et al. Most frequent scenario for recurrent Candida vaginitis is strain maintenance with “substrain shuffling”: demonstration by sequential DNA fingerprinting with probes Ca3, C1, and CARE2. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:767-777. doi:10.1128/jcm.34.4.767-777.1996
- Anderson MR, Klink K, Cohrssen A. Evaluation of vaginal complaints. JAMA. 2004;291:1368-1379. doi:10.1001/jama.291.11.1368
- Sobel JD. Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet. 2007;369:1961-1971. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60917-9
- Collins LM, Moore R, Sobel JD. Prognosis and long-term outcome of women with idiopathic recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis caused by Candida albicans. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24:48-52. doi:10.1097/LGT.0000000000000496
- Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes DR, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:e1-50. doi:10.1093/cid/civ933
- Duerr A, Heilig CM, Meikle SF, et al; HER Study Group. Incident and persistent vulvovaginal candidiasis among human immunodeficiency virus–infected women: risk factors and severity. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:548-556. doi:10.1016/s0029-7844(02)02729-1
- Houang ET, Chappatte O, Byrne D, et al. Fluconazole levels in plasma and vaginal secretions of patients after a 150-milligram single oral dose and rate of eradication of infection in vaginal candidiasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990;34:909-910. doi:10.1128/AAC.34.5.909
- Bérard A, Sheehy O, Zhao JP, et al. Associations between low- and high-dose oral fluconazole and pregnancy outcomes: 3 nested case-control studies. CMAJ. 2019;191:E179-E187. doi:10.1503/cmaj.180963
- Fluconazole. In: Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed). National Library of Medicine (US); 2006. Revised October 31, 2018. Accessed September 23, 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501223/
- White DJ, Johnson EM, Warnock DW. Management of persistent vulvo vaginal candidosis due to azole-resistant Candida glabrata. Genitourin Med. 1993;69:112-114. doi:10.1136/sti.69.2.112
- Falagas ME, Betsi GI, Athanasiou S. Probiotics for prevention of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: a review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;58:266-272. doi:10.1093/jac/dkl246
- Martens MG, Maximos B, Degenhardt T, et al. Phase 3 study evaluating the safety and efficacy of oteseconazole in the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis and acute vulvovaginal candidiasis infections. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022:S0002-9378(22)005774. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.07.023
- Sobel JD, Nyirjesy P. Oteseconazole: an advance in treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Future Microbiol. 2021;16:1453-1461. doi:10.2217/fmb-2021-0173
- Vivjoa (oteseconazole). Prescribing information. Mycovia Pharmaceuticals, Inc. April 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215888s000lbl.pdf
- Scorneaux B, Angulo D, Borroto-Esoda K, et al. SCY-078 is fungicidal against Candida species in time-kill studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:e01961-16. doi:10.1128/AAC.01961-16
- Schwebke JR, Taylor SN, Ackerman R, et al. Clinical validation of the Aptima bacterial vaginosis and Aptima Candida/Trichomonas vaginitis assays: results from a prospective multicenter clinical study. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58:e01643-19. doi:10.1128/JCM.01643-19
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Nyirjesy P, et al. Diagnostic performance of a molecular test versus clinician assessment of vaginitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56:e00252-18. doi:10.1128/JCM.00252-18
- Broache M, Cammarata CL, Stonebraker E, et al. Performance of a vaginal panel assay compared with the clinical diagnosis of vaginitis. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:853-859. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004592
- Sobel JD. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985;152(7 pt 2):924-935. doi:10.1016/S0002-9378(85)80003-x
- Sobel JD. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214:15-21. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2015.06.067
- Rathod SD, Buffler PA. Highly-cited estimates of the cumulative incidence and recurrence of vulvovaginal candidiasis are inadequately documented. BMC Womens Health. 2014;14:43. doi:10.1186/1472-6874-14-43
- Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, et al, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2022:515-542.
- Gonçalves B, Ferreira C, Alves CT, et al. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42:905-927. doi:10.3109/1040841X.2015.1091805
- Sobel JD, Sobel R. Current treatment options for vulvovaginal candidiasis caused by azole-resistant Candida species. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018;19:971-977. doi:10.1080/14656566.2018.1476490
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Vazquez JA, Sobel JD, Demitriou R, et al. Karyotyping of Candida albicans isolates obtained longitudinally in women with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:1566-1569. doi:10.1093/infdis/170.6.1566
- Lockhart SR, Reed BD, Pierson CL, et al. Most frequent scenario for recurrent Candida vaginitis is strain maintenance with “substrain shuffling”: demonstration by sequential DNA fingerprinting with probes Ca3, C1, and CARE2. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:767-777. doi:10.1128/jcm.34.4.767-777.1996
- Anderson MR, Klink K, Cohrssen A. Evaluation of vaginal complaints. JAMA. 2004;291:1368-1379. doi:10.1001/jama.291.11.1368
- Sobel JD. Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet. 2007;369:1961-1971. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60917-9
- Collins LM, Moore R, Sobel JD. Prognosis and long-term outcome of women with idiopathic recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis caused by Candida albicans. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24:48-52. doi:10.1097/LGT.0000000000000496
- Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes DR, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:e1-50. doi:10.1093/cid/civ933
- Duerr A, Heilig CM, Meikle SF, et al; HER Study Group. Incident and persistent vulvovaginal candidiasis among human immunodeficiency virus–infected women: risk factors and severity. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:548-556. doi:10.1016/s0029-7844(02)02729-1
- Houang ET, Chappatte O, Byrne D, et al. Fluconazole levels in plasma and vaginal secretions of patients after a 150-milligram single oral dose and rate of eradication of infection in vaginal candidiasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990;34:909-910. doi:10.1128/AAC.34.5.909
- Bérard A, Sheehy O, Zhao JP, et al. Associations between low- and high-dose oral fluconazole and pregnancy outcomes: 3 nested case-control studies. CMAJ. 2019;191:E179-E187. doi:10.1503/cmaj.180963
- Fluconazole. In: Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed). National Library of Medicine (US); 2006. Revised October 31, 2018. Accessed September 23, 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501223/
- White DJ, Johnson EM, Warnock DW. Management of persistent vulvo vaginal candidosis due to azole-resistant Candida glabrata. Genitourin Med. 1993;69:112-114. doi:10.1136/sti.69.2.112
- Falagas ME, Betsi GI, Athanasiou S. Probiotics for prevention of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: a review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;58:266-272. doi:10.1093/jac/dkl246
- Martens MG, Maximos B, Degenhardt T, et al. Phase 3 study evaluating the safety and efficacy of oteseconazole in the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis and acute vulvovaginal candidiasis infections. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022:S0002-9378(22)005774. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.07.023
- Sobel JD, Nyirjesy P. Oteseconazole: an advance in treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Future Microbiol. 2021;16:1453-1461. doi:10.2217/fmb-2021-0173
- Vivjoa (oteseconazole). Prescribing information. Mycovia Pharmaceuticals, Inc. April 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215888s000lbl.pdf
- Scorneaux B, Angulo D, Borroto-Esoda K, et al. SCY-078 is fungicidal against Candida species in time-kill studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:e01961-16. doi:10.1128/AAC.01961-16
- Schwebke JR, Taylor SN, Ackerman R, et al. Clinical validation of the Aptima bacterial vaginosis and Aptima Candida/Trichomonas vaginitis assays: results from a prospective multicenter clinical study. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58:e01643-19. doi:10.1128/JCM.01643-19
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Nyirjesy P, et al. Diagnostic performance of a molecular test versus clinician assessment of vaginitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56:e00252-18. doi:10.1128/JCM.00252-18
- Broache M, Cammarata CL, Stonebraker E, et al. Performance of a vaginal panel assay compared with the clinical diagnosis of vaginitis. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:853-859. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004592
“Blind” endometrial sampling: A call to end the practice
Linda Bradley, MD: The standard in ObGyn for many years has been our reliance on the blind dilation and curettage (D&C)—it has been the mainstay for evaluation of the endometrial cavity. We know that it has risks, but most importantly, the procedure has low sensitivity for detecting focal pathology. This basic lack of confirmation of lesions makes a diagnosis impossible and patients are challenged in getting adequate treatment, and will not, since they may not know what options they have for the treatment of intrauterine pathology.
Because it is a “blind procedure,” done without looking, we don’t know the endpoints, such as when is the procedure completed, how do we know we removed all of the lesions? Let’s look at our colleagues, like GI and colorectal physicians. If a patient presents with rectal bleeding, we would perform an exam, followed by either a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. If a patient were vomiting up blood, a gastroenterologist would perform an upper endoscopy, look with a tube to see if there is an ulcer or something else as a source of the bleeding. If a patient were bleeding from the bladder, a urologist would use a cystoscope for direct inspection.
Unfortunately for gynecologists, only about 15% to 25% of us will use hysteroscopy as a diagnostic method2—a method that has excellent sensitivity in detecting endocervical disease, intrauterine disease, and proximal tubal pathology. Compared with blind curettage, we can visualize the cavity; we can sample the cavity directly; we can determine what the patient has and determine the proper surgical procedure, medical therapy, or reassurance that a patient may be offered. We often are looking at focal lesions, lesions in the uterine cavity that could be cancer, so we can make a diagnosis. Or we may be looking at small things, like endometrial hyperplasia, endocervical or endometrial polyps, retained products of conception, or fibroids. We can look at uterine pathology as well as anatomic issues and malformations—such as bicornuate or septate uterus.
I actually say, “My hysteroscope is my stethoscope” because it allows us to evaluate for many things. The beauty of the new office hysteroscopes is that they are miniaturized. Doctors now have the ability to use reusable devices that are as small as 3 millimeters. There are disposable ones that are up to 3.5 to 4 millimeters in size. Gynecologists have the options to choose from reusuable rigid or flexible hysteroscopes or completely disposable devices. So, truly, we now should not have an excuse for evaluating a woman’s anatomy, especially for bleeding. We should no longer rely, as we have for the last century or more, just on blind sampling, because we miss focal lesions.
OBG Management: When was the hysteroscope first introduced into the field?
Dr. Bradley: The technology employed in hysteroscopy has been around really since the last 150+ years, introduced by Dr. Pantaleoni. We just have not embraced its usefulness in our clinical practice for many years. Today, about 15% to 25% of gynecologists practicing in the United States are performing hysteroscopy in the office.1
OBG Management: How does using hysteroscopy contribute to better patient outcomes?
Dr. Bradley: We can get a more accurate diagnosis—fewer false-negatives and a high degree of sensitivity in detecting focal lesions. With D&C, much focal pathology can be left behind. In a 2001 study, 105 symptomatic postmenopausal women with bleeding and thickened lining of the uterus greater than 5 mm on ultrasound underwent blind D&C. They found that 80% of the women had intracavitary lesions and 90% had focal lesions. In fact, 87% of the patients with focal lesions still had residual pathology after the blind D&C.3 The D&C procedure missed 58% of polyps, 50% of endometrial hyperplasia, 60% of cases of complex atypical hyperplasia, and even 11% of endometrial cancers. So these numbers are just not very good. Direct inspection of the uterus, with uninterrupted visualization through hysteroscopy, with removal of lesions under direct visualization, should be our goal.
Blind sampling also poses greater risk for things like perforation. In addition, you not only can miss lesions by just scraping the endometrium, D&C also can leave lesions just floating around in the uterine cavity, with those lesions never retrieved. With office hysteroscopy, the physician can be more successful in treating a condition because once you see what is going on in the uterine cavity, you can say, “Okay, I can fix this with a surgical procedure. What instruments do I need? How much time is it going to take? Is this a straightforward case? Is it more complicated? Do I let an intern do the case? Is this for a more senior resident or fellow?” So I think it helps to direct the next steps for surgical management and even medical management, which also could be what we call “one-stop shopping.” For instance, for directed biopsies for removal of small polyps, for patients that can tolerate the procedure a little longer, the diagnostic hysteroscopy then becomes a management, an operative procedure, that really, for myself, can be done in the office. Removal of larger fibroids, because of fluid management and other concerns, would not be done in the office. Most patients tolerate office procedures, but it also depends on a patient’s weight, and her ability to relax during the procedure.
The ultimate goal for hysteroscopy is a minimum of diagnosis, meaning in less than 2, 3 minutes, you can look inside the uterus. Our devices are 3 millimeters in size; I tell my patients, it’s the size of “a piece of spaghetti or pasta,” and we will just take a look. If we see a polyp, okay, if your office is not equipped, because then you need a different type of equipment for removal, then take her to the operating room. The patient would be under brief anesthesia and go home an hour or 2 later. So really, for physicians, we just need to embrace the technology to make a diagnosis, just look, and then from there decide what is next.
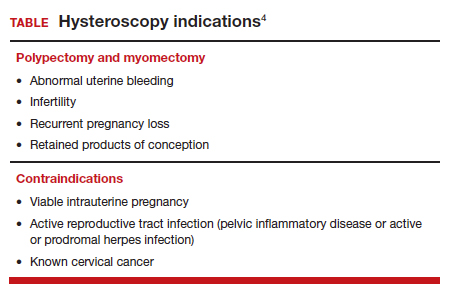
OBG Management: What techniques do you use to minimize or eliminate patient discomfort during hysteroscopy?...
OBG Management: What techniques do you use to minimize or eliminate patient discomfort during hysteroscopy?
Dr. Bradley: I think first is always be patient-centric. Let patients be prepared for the procedure. We have reading materials; our nurses explain the procedure. In the office, I try to prepare the patient for success. I let her know what is going on. A friend, family member can be with her. We have a nurse that understands the procedure; she explains it well. We have a type of bed that allows the patients’ legs to rest more comfortably in the stirrups—a leg rest kind of stirrup. We use a heating pad. Some patients like to hear music. Some patients like to have aromatherapy. We are quick and efficient, and typically just talk to the patient throughout the procedure. Although some patients don’t like this explanatory, “talkative” approach—they say, “Dr. Bradley, just do the procedure. I don’t want to know you are touching the cervix. I don’t want to know that you’re prepping. Just do it.”
But I like what we called it when I was growing up: vocal-local (talk to your patient and explain as you proceed). It’s like local anesthesia. For these procedures in the office you usually do not have to use numbing medicine or a paracervical block. Look at the patient’s age, number of years in menopause, whether or not she has delivered vaginally, and what her cervix looks like. Does she have a sexually transmitted infection or pelvic inflammatory disease? Sometimes we will use misoprostol, my personal preference is oral, but there are data to suggest that vaginal can be of help.4 We suggest Motrin, Tylenol an hour or 2 before, and we always want patients to not come in on an empty stomach. There is also the option of primrose oil, a supplement, that patients buy at the drug store in the vitamin section. It’s used for cervical softening. It is taken orally.5-7
If they want, patients can watch a video—similar to watching childbirth videos when I used to deliver babies. At some point we started putting mirrors where women could see their efforts of pushing a baby out, as it might give them more willpower to push harder. Some people don’t want to look. But the majority of women will do well in this setting. I do have a small number of women that just say, “I can’t do this in the office,” and so in those cases, they can go to the operating room. But the main idea is, even in an operating room, you are not just doing a D&C. You are still going to look inside with a hysteroscope and have a great panoramic view of what is going on, and remove a lesion with an instrument while you watch. Not a process of looking with the hysteroscope, scraping with a curettage, and thinking that you are complete. Targeted removal of focal lesions under continuous visualization is the goal.
OBG Management: Can you describe the goals of the consensus document on ending blind sampling co-created by the European Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy, AAGL, and the Global Community on Hysteroscopy?
Dr. Bradley: Our goal for this year is to get a systematic review and guidelines paper written that speaks to what we have just talked about. We want to have as many articles about why blind sampling is not beneficial, with too many misses, and now we have new technology available. We want to speak to physicians to solve the conundrum of bleeding, with equivocal ultrasounds, equivocal saline infusion, sonograms, equivocal MRIs—be able to take a look. Let’s come up to speed like our other colleagues in other specialties that “look.” A systematic review guideline document will provide the evidence that blind D&C is fraught with problems and how often we miss disease and its inherent risk.
We need to, by itself, for most of our patients, abandon D&C because we have too many missed diagnoses. As doctors we have to be lifelong learners. There was no robot back in the day. We were not able to do laparoscopic hysterectomies, there were no MRIs. I remember in our city, there was one CT scan. We just did not have a lot of technology. The half-life of medical knowledge used to be decades—you graduated in the ‘60s, you could be a great gynecologist for the next 30 years because there was not that much going on. When I finished in the mid to late ‘80s, there was no hysteroscopy training. But I have come to see its value, the science behind it.
So what I say to doctors is, “We learn so many new things, we shouldn’t get stuck in just saying, ‘I didn’t do this when I was in training.’” And if your thought is, “Oh, in my practice, I don’t have that many cases,” you still need to be able to know who in your community can be a resource to your patients. As Maya Angelou says, “When you know better, you should do better.” And that’s where I am now—to be a lifelong learner, and just do it.
Lastly, patient influence is very important. If patients ask, “How are you going to do the procedure?” it’s a driver for change. By utilizing hysteroscopy in the evaluation of the intrauterine cavity, we have the opportunity to change the face of evaluation and treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding.●
To maximize visualization and procedure ease, schedule office hysteroscopy shortly after menstruation for reproductive-age women with regular menstrual cycles, which corresponds to timing of the thinnest endometrial lining.1 By contrast, the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle may be associated with the presence of secretory endometrium, which may mimic endometrial polyps or obscure intrauterine pathology, including FIGO type 1 and 2 submucous leiomyomas.
The following patients can have their procedures scheduled at any time, as they do not regularly cycle:
- those receiving continuous hormonal contraception
- women taking menopausal hormonal therapy
- women on progestin therapy (including those using intrauterine devices).
For patients with irregular cycles, timing is crucial as the topography of the endometrium can be variable. To increase successful visualization and diagnostic accuracy, a short course of combined hormonal contraceptives2 or progestin therapy3,4 can be considered for 10-14 days, followed by a withdrawal menses, and immediate procedure scheduling after bleeding subsides, as this will produce a thin endometrium. This approach may be especially beneficial for operative procedures such as polypectomy in order to promote complete specimen extraction.
Pharmacologic endometrial preparation also is an option and has been associated with decreased procedure time and improved patient and clinician satisfaction during operative hysteroscopy.2,3 We discourage the use of hormonal pre-treatment for diagnostic hysteroscopy alone, as this may alter endometrial histology and provide misleading results. Overall, data related to pharmacologic endometrial preparation are limited to small studies with varying treatment protocols, and an optimal regimen has yet to be determined.
References
1. The use of hysteroscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology: ACOG Committee Opinion, number 800. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e138-e148. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000003712.
2. Cicinelli E, Pinto V, Quattromini P, et al. Endometrial preparation with estradiol plus dienogest (Qlaira) for office hysteroscopic polypectomy: randomized pilot study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:356-359. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2011.12.020.
3. Laganà AS, Vitale SG, Muscia V, et al. Endometrial preparation with dienogest before hysteroscopic surgery: a systematic review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:661-667. doi:10.1007/s00404-016-4244-1.
4. Ciebiera M, Zgliczyńska M, Zgliczyński S, et al. Oral desogestrel as endometrial preparation before operative hysteroscopy: a systematic review. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2021;86:209-217. doi:10.1159/000514584.
- Orlando MS, Bradley LD. Implementation of office hysteroscopy for the evaluation and treatment of intrauterine pathology. Obstet Gynecol. August 3, 2022. doi: 10.1097/ AOG.0000000000004898.
- Salazar CA, Isaacson KB. Office operative hysteroscopy: an update. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:199-208.
- Epstein E, Ramirez A, Skoog L, et al. Dilatation and curettage fails to detect most focal lesions in the uterine cavity in women with postmenopausal bleeding. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2001;80:1131-1136. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0412.2001.801210.x.
- The use of hysteroscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology: ACOG Committee Opinion, number 800. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e138-e148. doi:10.1097/ AOG.0000000000003712.
- Vahdat M, Tahermanesh K, Mehdizadeh Kashi A, et al. Evening Primrose Oil effect on the ease of cervical ripening and dilatation before operative hysteroscopy. Thrita. 2015;4:7-10. doi:10.5812/thrita.29876
- Nouri B, Baghestani A, Pooransari P. Evening primrose versus misoprostol for cervical dilatation before gynecologic surgeries: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Obstet Gynecol Cancer Res. 2021;6:87-94. doi:10.30699/jogcr.6.2.87
- Verano RMA, Veloso-borromeo MG. The efficacy of evening primrose oil as a cervical ripening agent for gynecologic procedures: a single-blinded, randomized controlled trial. PJOG. 2015;39:24-28.

Linda Bradley, MD: The standard in ObGyn for many years has been our reliance on the blind dilation and curettage (D&C)—it has been the mainstay for evaluation of the endometrial cavity. We know that it has risks, but most importantly, the procedure has low sensitivity for detecting focal pathology. This basic lack of confirmation of lesions makes a diagnosis impossible and patients are challenged in getting adequate treatment, and will not, since they may not know what options they have for the treatment of intrauterine pathology.
Because it is a “blind procedure,” done without looking, we don’t know the endpoints, such as when is the procedure completed, how do we know we removed all of the lesions? Let’s look at our colleagues, like GI and colorectal physicians. If a patient presents with rectal bleeding, we would perform an exam, followed by either a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. If a patient were vomiting up blood, a gastroenterologist would perform an upper endoscopy, look with a tube to see if there is an ulcer or something else as a source of the bleeding. If a patient were bleeding from the bladder, a urologist would use a cystoscope for direct inspection.
Unfortunately for gynecologists, only about 15% to 25% of us will use hysteroscopy as a diagnostic method2—a method that has excellent sensitivity in detecting endocervical disease, intrauterine disease, and proximal tubal pathology. Compared with blind curettage, we can visualize the cavity; we can sample the cavity directly; we can determine what the patient has and determine the proper surgical procedure, medical therapy, or reassurance that a patient may be offered. We often are looking at focal lesions, lesions in the uterine cavity that could be cancer, so we can make a diagnosis. Or we may be looking at small things, like endometrial hyperplasia, endocervical or endometrial polyps, retained products of conception, or fibroids. We can look at uterine pathology as well as anatomic issues and malformations—such as bicornuate or septate uterus.
I actually say, “My hysteroscope is my stethoscope” because it allows us to evaluate for many things. The beauty of the new office hysteroscopes is that they are miniaturized. Doctors now have the ability to use reusable devices that are as small as 3 millimeters. There are disposable ones that are up to 3.5 to 4 millimeters in size. Gynecologists have the options to choose from reusuable rigid or flexible hysteroscopes or completely disposable devices. So, truly, we now should not have an excuse for evaluating a woman’s anatomy, especially for bleeding. We should no longer rely, as we have for the last century or more, just on blind sampling, because we miss focal lesions.
OBG Management: When was the hysteroscope first introduced into the field?
Dr. Bradley: The technology employed in hysteroscopy has been around really since the last 150+ years, introduced by Dr. Pantaleoni. We just have not embraced its usefulness in our clinical practice for many years. Today, about 15% to 25% of gynecologists practicing in the United States are performing hysteroscopy in the office.1
OBG Management: How does using hysteroscopy contribute to better patient outcomes?
Dr. Bradley: We can get a more accurate diagnosis—fewer false-negatives and a high degree of sensitivity in detecting focal lesions. With D&C, much focal pathology can be left behind. In a 2001 study, 105 symptomatic postmenopausal women with bleeding and thickened lining of the uterus greater than 5 mm on ultrasound underwent blind D&C. They found that 80% of the women had intracavitary lesions and 90% had focal lesions. In fact, 87% of the patients with focal lesions still had residual pathology after the blind D&C.3 The D&C procedure missed 58% of polyps, 50% of endometrial hyperplasia, 60% of cases of complex atypical hyperplasia, and even 11% of endometrial cancers. So these numbers are just not very good. Direct inspection of the uterus, with uninterrupted visualization through hysteroscopy, with removal of lesions under direct visualization, should be our goal.
Blind sampling also poses greater risk for things like perforation. In addition, you not only can miss lesions by just scraping the endometrium, D&C also can leave lesions just floating around in the uterine cavity, with those lesions never retrieved. With office hysteroscopy, the physician can be more successful in treating a condition because once you see what is going on in the uterine cavity, you can say, “Okay, I can fix this with a surgical procedure. What instruments do I need? How much time is it going to take? Is this a straightforward case? Is it more complicated? Do I let an intern do the case? Is this for a more senior resident or fellow?” So I think it helps to direct the next steps for surgical management and even medical management, which also could be what we call “one-stop shopping.” For instance, for directed biopsies for removal of small polyps, for patients that can tolerate the procedure a little longer, the diagnostic hysteroscopy then becomes a management, an operative procedure, that really, for myself, can be done in the office. Removal of larger fibroids, because of fluid management and other concerns, would not be done in the office. Most patients tolerate office procedures, but it also depends on a patient’s weight, and her ability to relax during the procedure.
The ultimate goal for hysteroscopy is a minimum of diagnosis, meaning in less than 2, 3 minutes, you can look inside the uterus. Our devices are 3 millimeters in size; I tell my patients, it’s the size of “a piece of spaghetti or pasta,” and we will just take a look. If we see a polyp, okay, if your office is not equipped, because then you need a different type of equipment for removal, then take her to the operating room. The patient would be under brief anesthesia and go home an hour or 2 later. So really, for physicians, we just need to embrace the technology to make a diagnosis, just look, and then from there decide what is next.

OBG Management: What techniques do you use to minimize or eliminate patient discomfort during hysteroscopy?...
OBG Management: What techniques do you use to minimize or eliminate patient discomfort during hysteroscopy?
Dr. Bradley: I think first is always be patient-centric. Let patients be prepared for the procedure. We have reading materials; our nurses explain the procedure. In the office, I try to prepare the patient for success. I let her know what is going on. A friend, family member can be with her. We have a nurse that understands the procedure; she explains it well. We have a type of bed that allows the patients’ legs to rest more comfortably in the stirrups—a leg rest kind of stirrup. We use a heating pad. Some patients like to hear music. Some patients like to have aromatherapy. We are quick and efficient, and typically just talk to the patient throughout the procedure. Although some patients don’t like this explanatory, “talkative” approach—they say, “Dr. Bradley, just do the procedure. I don’t want to know you are touching the cervix. I don’t want to know that you’re prepping. Just do it.”
But I like what we called it when I was growing up: vocal-local (talk to your patient and explain as you proceed). It’s like local anesthesia. For these procedures in the office you usually do not have to use numbing medicine or a paracervical block. Look at the patient’s age, number of years in menopause, whether or not she has delivered vaginally, and what her cervix looks like. Does she have a sexually transmitted infection or pelvic inflammatory disease? Sometimes we will use misoprostol, my personal preference is oral, but there are data to suggest that vaginal can be of help.4 We suggest Motrin, Tylenol an hour or 2 before, and we always want patients to not come in on an empty stomach. There is also the option of primrose oil, a supplement, that patients buy at the drug store in the vitamin section. It’s used for cervical softening. It is taken orally.5-7
If they want, patients can watch a video—similar to watching childbirth videos when I used to deliver babies. At some point we started putting mirrors where women could see their efforts of pushing a baby out, as it might give them more willpower to push harder. Some people don’t want to look. But the majority of women will do well in this setting. I do have a small number of women that just say, “I can’t do this in the office,” and so in those cases, they can go to the operating room. But the main idea is, even in an operating room, you are not just doing a D&C. You are still going to look inside with a hysteroscope and have a great panoramic view of what is going on, and remove a lesion with an instrument while you watch. Not a process of looking with the hysteroscope, scraping with a curettage, and thinking that you are complete. Targeted removal of focal lesions under continuous visualization is the goal.
OBG Management: Can you describe the goals of the consensus document on ending blind sampling co-created by the European Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy, AAGL, and the Global Community on Hysteroscopy?
Dr. Bradley: Our goal for this year is to get a systematic review and guidelines paper written that speaks to what we have just talked about. We want to have as many articles about why blind sampling is not beneficial, with too many misses, and now we have new technology available. We want to speak to physicians to solve the conundrum of bleeding, with equivocal ultrasounds, equivocal saline infusion, sonograms, equivocal MRIs—be able to take a look. Let’s come up to speed like our other colleagues in other specialties that “look.” A systematic review guideline document will provide the evidence that blind D&C is fraught with problems and how often we miss disease and its inherent risk.
We need to, by itself, for most of our patients, abandon D&C because we have too many missed diagnoses. As doctors we have to be lifelong learners. There was no robot back in the day. We were not able to do laparoscopic hysterectomies, there were no MRIs. I remember in our city, there was one CT scan. We just did not have a lot of technology. The half-life of medical knowledge used to be decades—you graduated in the ‘60s, you could be a great gynecologist for the next 30 years because there was not that much going on. When I finished in the mid to late ‘80s, there was no hysteroscopy training. But I have come to see its value, the science behind it.
So what I say to doctors is, “We learn so many new things, we shouldn’t get stuck in just saying, ‘I didn’t do this when I was in training.’” And if your thought is, “Oh, in my practice, I don’t have that many cases,” you still need to be able to know who in your community can be a resource to your patients. As Maya Angelou says, “When you know better, you should do better.” And that’s where I am now—to be a lifelong learner, and just do it.
Lastly, patient influence is very important. If patients ask, “How are you going to do the procedure?” it’s a driver for change. By utilizing hysteroscopy in the evaluation of the intrauterine cavity, we have the opportunity to change the face of evaluation and treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding.●
To maximize visualization and procedure ease, schedule office hysteroscopy shortly after menstruation for reproductive-age women with regular menstrual cycles, which corresponds to timing of the thinnest endometrial lining.1 By contrast, the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle may be associated with the presence of secretory endometrium, which may mimic endometrial polyps or obscure intrauterine pathology, including FIGO type 1 and 2 submucous leiomyomas.
The following patients can have their procedures scheduled at any time, as they do not regularly cycle:
- those receiving continuous hormonal contraception
- women taking menopausal hormonal therapy
- women on progestin therapy (including those using intrauterine devices).
For patients with irregular cycles, timing is crucial as the topography of the endometrium can be variable. To increase successful visualization and diagnostic accuracy, a short course of combined hormonal contraceptives2 or progestin therapy3,4 can be considered for 10-14 days, followed by a withdrawal menses, and immediate procedure scheduling after bleeding subsides, as this will produce a thin endometrium. This approach may be especially beneficial for operative procedures such as polypectomy in order to promote complete specimen extraction.
Pharmacologic endometrial preparation also is an option and has been associated with decreased procedure time and improved patient and clinician satisfaction during operative hysteroscopy.2,3 We discourage the use of hormonal pre-treatment for diagnostic hysteroscopy alone, as this may alter endometrial histology and provide misleading results. Overall, data related to pharmacologic endometrial preparation are limited to small studies with varying treatment protocols, and an optimal regimen has yet to be determined.
References
1. The use of hysteroscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology: ACOG Committee Opinion, number 800. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e138-e148. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000003712.
2. Cicinelli E, Pinto V, Quattromini P, et al. Endometrial preparation with estradiol plus dienogest (Qlaira) for office hysteroscopic polypectomy: randomized pilot study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:356-359. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2011.12.020.
3. Laganà AS, Vitale SG, Muscia V, et al. Endometrial preparation with dienogest before hysteroscopic surgery: a systematic review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:661-667. doi:10.1007/s00404-016-4244-1.
4. Ciebiera M, Zgliczyńska M, Zgliczyński S, et al. Oral desogestrel as endometrial preparation before operative hysteroscopy: a systematic review. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2021;86:209-217. doi:10.1159/000514584.

Linda Bradley, MD: The standard in ObGyn for many years has been our reliance on the blind dilation and curettage (D&C)—it has been the mainstay for evaluation of the endometrial cavity. We know that it has risks, but most importantly, the procedure has low sensitivity for detecting focal pathology. This basic lack of confirmation of lesions makes a diagnosis impossible and patients are challenged in getting adequate treatment, and will not, since they may not know what options they have for the treatment of intrauterine pathology.
Because it is a “blind procedure,” done without looking, we don’t know the endpoints, such as when is the procedure completed, how do we know we removed all of the lesions? Let’s look at our colleagues, like GI and colorectal physicians. If a patient presents with rectal bleeding, we would perform an exam, followed by either a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. If a patient were vomiting up blood, a gastroenterologist would perform an upper endoscopy, look with a tube to see if there is an ulcer or something else as a source of the bleeding. If a patient were bleeding from the bladder, a urologist would use a cystoscope for direct inspection.
Unfortunately for gynecologists, only about 15% to 25% of us will use hysteroscopy as a diagnostic method2—a method that has excellent sensitivity in detecting endocervical disease, intrauterine disease, and proximal tubal pathology. Compared with blind curettage, we can visualize the cavity; we can sample the cavity directly; we can determine what the patient has and determine the proper surgical procedure, medical therapy, or reassurance that a patient may be offered. We often are looking at focal lesions, lesions in the uterine cavity that could be cancer, so we can make a diagnosis. Or we may be looking at small things, like endometrial hyperplasia, endocervical or endometrial polyps, retained products of conception, or fibroids. We can look at uterine pathology as well as anatomic issues and malformations—such as bicornuate or septate uterus.
I actually say, “My hysteroscope is my stethoscope” because it allows us to evaluate for many things. The beauty of the new office hysteroscopes is that they are miniaturized. Doctors now have the ability to use reusable devices that are as small as 3 millimeters. There are disposable ones that are up to 3.5 to 4 millimeters in size. Gynecologists have the options to choose from reusuable rigid or flexible hysteroscopes or completely disposable devices. So, truly, we now should not have an excuse for evaluating a woman’s anatomy, especially for bleeding. We should no longer rely, as we have for the last century or more, just on blind sampling, because we miss focal lesions.
OBG Management: When was the hysteroscope first introduced into the field?
Dr. Bradley: The technology employed in hysteroscopy has been around really since the last 150+ years, introduced by Dr. Pantaleoni. We just have not embraced its usefulness in our clinical practice for many years. Today, about 15% to 25% of gynecologists practicing in the United States are performing hysteroscopy in the office.1
OBG Management: How does using hysteroscopy contribute to better patient outcomes?
Dr. Bradley: We can get a more accurate diagnosis—fewer false-negatives and a high degree of sensitivity in detecting focal lesions. With D&C, much focal pathology can be left behind. In a 2001 study, 105 symptomatic postmenopausal women with bleeding and thickened lining of the uterus greater than 5 mm on ultrasound underwent blind D&C. They found that 80% of the women had intracavitary lesions and 90% had focal lesions. In fact, 87% of the patients with focal lesions still had residual pathology after the blind D&C.3 The D&C procedure missed 58% of polyps, 50% of endometrial hyperplasia, 60% of cases of complex atypical hyperplasia, and even 11% of endometrial cancers. So these numbers are just not very good. Direct inspection of the uterus, with uninterrupted visualization through hysteroscopy, with removal of lesions under direct visualization, should be our goal.
Blind sampling also poses greater risk for things like perforation. In addition, you not only can miss lesions by just scraping the endometrium, D&C also can leave lesions just floating around in the uterine cavity, with those lesions never retrieved. With office hysteroscopy, the physician can be more successful in treating a condition because once you see what is going on in the uterine cavity, you can say, “Okay, I can fix this with a surgical procedure. What instruments do I need? How much time is it going to take? Is this a straightforward case? Is it more complicated? Do I let an intern do the case? Is this for a more senior resident or fellow?” So I think it helps to direct the next steps for surgical management and even medical management, which also could be what we call “one-stop shopping.” For instance, for directed biopsies for removal of small polyps, for patients that can tolerate the procedure a little longer, the diagnostic hysteroscopy then becomes a management, an operative procedure, that really, for myself, can be done in the office. Removal of larger fibroids, because of fluid management and other concerns, would not be done in the office. Most patients tolerate office procedures, but it also depends on a patient’s weight, and her ability to relax during the procedure.
The ultimate goal for hysteroscopy is a minimum of diagnosis, meaning in less than 2, 3 minutes, you can look inside the uterus. Our devices are 3 millimeters in size; I tell my patients, it’s the size of “a piece of spaghetti or pasta,” and we will just take a look. If we see a polyp, okay, if your office is not equipped, because then you need a different type of equipment for removal, then take her to the operating room. The patient would be under brief anesthesia and go home an hour or 2 later. So really, for physicians, we just need to embrace the technology to make a diagnosis, just look, and then from there decide what is next.

OBG Management: What techniques do you use to minimize or eliminate patient discomfort during hysteroscopy?...
OBG Management: What techniques do you use to minimize or eliminate patient discomfort during hysteroscopy?
Dr. Bradley: I think first is always be patient-centric. Let patients be prepared for the procedure. We have reading materials; our nurses explain the procedure. In the office, I try to prepare the patient for success. I let her know what is going on. A friend, family member can be with her. We have a nurse that understands the procedure; she explains it well. We have a type of bed that allows the patients’ legs to rest more comfortably in the stirrups—a leg rest kind of stirrup. We use a heating pad. Some patients like to hear music. Some patients like to have aromatherapy. We are quick and efficient, and typically just talk to the patient throughout the procedure. Although some patients don’t like this explanatory, “talkative” approach—they say, “Dr. Bradley, just do the procedure. I don’t want to know you are touching the cervix. I don’t want to know that you’re prepping. Just do it.”
But I like what we called it when I was growing up: vocal-local (talk to your patient and explain as you proceed). It’s like local anesthesia. For these procedures in the office you usually do not have to use numbing medicine or a paracervical block. Look at the patient’s age, number of years in menopause, whether or not she has delivered vaginally, and what her cervix looks like. Does she have a sexually transmitted infection or pelvic inflammatory disease? Sometimes we will use misoprostol, my personal preference is oral, but there are data to suggest that vaginal can be of help.4 We suggest Motrin, Tylenol an hour or 2 before, and we always want patients to not come in on an empty stomach. There is also the option of primrose oil, a supplement, that patients buy at the drug store in the vitamin section. It’s used for cervical softening. It is taken orally.5-7
If they want, patients can watch a video—similar to watching childbirth videos when I used to deliver babies. At some point we started putting mirrors where women could see their efforts of pushing a baby out, as it might give them more willpower to push harder. Some people don’t want to look. But the majority of women will do well in this setting. I do have a small number of women that just say, “I can’t do this in the office,” and so in those cases, they can go to the operating room. But the main idea is, even in an operating room, you are not just doing a D&C. You are still going to look inside with a hysteroscope and have a great panoramic view of what is going on, and remove a lesion with an instrument while you watch. Not a process of looking with the hysteroscope, scraping with a curettage, and thinking that you are complete. Targeted removal of focal lesions under continuous visualization is the goal.
OBG Management: Can you describe the goals of the consensus document on ending blind sampling co-created by the European Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy, AAGL, and the Global Community on Hysteroscopy?
Dr. Bradley: Our goal for this year is to get a systematic review and guidelines paper written that speaks to what we have just talked about. We want to have as many articles about why blind sampling is not beneficial, with too many misses, and now we have new technology available. We want to speak to physicians to solve the conundrum of bleeding, with equivocal ultrasounds, equivocal saline infusion, sonograms, equivocal MRIs—be able to take a look. Let’s come up to speed like our other colleagues in other specialties that “look.” A systematic review guideline document will provide the evidence that blind D&C is fraught with problems and how often we miss disease and its inherent risk.
We need to, by itself, for most of our patients, abandon D&C because we have too many missed diagnoses. As doctors we have to be lifelong learners. There was no robot back in the day. We were not able to do laparoscopic hysterectomies, there were no MRIs. I remember in our city, there was one CT scan. We just did not have a lot of technology. The half-life of medical knowledge used to be decades—you graduated in the ‘60s, you could be a great gynecologist for the next 30 years because there was not that much going on. When I finished in the mid to late ‘80s, there was no hysteroscopy training. But I have come to see its value, the science behind it.
So what I say to doctors is, “We learn so many new things, we shouldn’t get stuck in just saying, ‘I didn’t do this when I was in training.’” And if your thought is, “Oh, in my practice, I don’t have that many cases,” you still need to be able to know who in your community can be a resource to your patients. As Maya Angelou says, “When you know better, you should do better.” And that’s where I am now—to be a lifelong learner, and just do it.
Lastly, patient influence is very important. If patients ask, “How are you going to do the procedure?” it’s a driver for change. By utilizing hysteroscopy in the evaluation of the intrauterine cavity, we have the opportunity to change the face of evaluation and treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding.●
To maximize visualization and procedure ease, schedule office hysteroscopy shortly after menstruation for reproductive-age women with regular menstrual cycles, which corresponds to timing of the thinnest endometrial lining.1 By contrast, the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle may be associated with the presence of secretory endometrium, which may mimic endometrial polyps or obscure intrauterine pathology, including FIGO type 1 and 2 submucous leiomyomas.
The following patients can have their procedures scheduled at any time, as they do not regularly cycle:
- those receiving continuous hormonal contraception
- women taking menopausal hormonal therapy
- women on progestin therapy (including those using intrauterine devices).
For patients with irregular cycles, timing is crucial as the topography of the endometrium can be variable. To increase successful visualization and diagnostic accuracy, a short course of combined hormonal contraceptives2 or progestin therapy3,4 can be considered for 10-14 days, followed by a withdrawal menses, and immediate procedure scheduling after bleeding subsides, as this will produce a thin endometrium. This approach may be especially beneficial for operative procedures such as polypectomy in order to promote complete specimen extraction.
Pharmacologic endometrial preparation also is an option and has been associated with decreased procedure time and improved patient and clinician satisfaction during operative hysteroscopy.2,3 We discourage the use of hormonal pre-treatment for diagnostic hysteroscopy alone, as this may alter endometrial histology and provide misleading results. Overall, data related to pharmacologic endometrial preparation are limited to small studies with varying treatment protocols, and an optimal regimen has yet to be determined.
References
1. The use of hysteroscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology: ACOG Committee Opinion, number 800. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e138-e148. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000003712.
2. Cicinelli E, Pinto V, Quattromini P, et al. Endometrial preparation with estradiol plus dienogest (Qlaira) for office hysteroscopic polypectomy: randomized pilot study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:356-359. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2011.12.020.
3. Laganà AS, Vitale SG, Muscia V, et al. Endometrial preparation with dienogest before hysteroscopic surgery: a systematic review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:661-667. doi:10.1007/s00404-016-4244-1.
4. Ciebiera M, Zgliczyńska M, Zgliczyński S, et al. Oral desogestrel as endometrial preparation before operative hysteroscopy: a systematic review. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2021;86:209-217. doi:10.1159/000514584.
- Orlando MS, Bradley LD. Implementation of office hysteroscopy for the evaluation and treatment of intrauterine pathology. Obstet Gynecol. August 3, 2022. doi: 10.1097/ AOG.0000000000004898.
- Salazar CA, Isaacson KB. Office operative hysteroscopy: an update. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:199-208.
- Epstein E, Ramirez A, Skoog L, et al. Dilatation and curettage fails to detect most focal lesions in the uterine cavity in women with postmenopausal bleeding. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2001;80:1131-1136. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0412.2001.801210.x.
- The use of hysteroscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology: ACOG Committee Opinion, number 800. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e138-e148. doi:10.1097/ AOG.0000000000003712.
- Vahdat M, Tahermanesh K, Mehdizadeh Kashi A, et al. Evening Primrose Oil effect on the ease of cervical ripening and dilatation before operative hysteroscopy. Thrita. 2015;4:7-10. doi:10.5812/thrita.29876
- Nouri B, Baghestani A, Pooransari P. Evening primrose versus misoprostol for cervical dilatation before gynecologic surgeries: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Obstet Gynecol Cancer Res. 2021;6:87-94. doi:10.30699/jogcr.6.2.87
- Verano RMA, Veloso-borromeo MG. The efficacy of evening primrose oil as a cervical ripening agent for gynecologic procedures: a single-blinded, randomized controlled trial. PJOG. 2015;39:24-28.
- Orlando MS, Bradley LD. Implementation of office hysteroscopy for the evaluation and treatment of intrauterine pathology. Obstet Gynecol. August 3, 2022. doi: 10.1097/ AOG.0000000000004898.
- Salazar CA, Isaacson KB. Office operative hysteroscopy: an update. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:199-208.
- Epstein E, Ramirez A, Skoog L, et al. Dilatation and curettage fails to detect most focal lesions in the uterine cavity in women with postmenopausal bleeding. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2001;80:1131-1136. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0412.2001.801210.x.
- The use of hysteroscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology: ACOG Committee Opinion, number 800. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e138-e148. doi:10.1097/ AOG.0000000000003712.
- Vahdat M, Tahermanesh K, Mehdizadeh Kashi A, et al. Evening Primrose Oil effect on the ease of cervical ripening and dilatation before operative hysteroscopy. Thrita. 2015;4:7-10. doi:10.5812/thrita.29876
- Nouri B, Baghestani A, Pooransari P. Evening primrose versus misoprostol for cervical dilatation before gynecologic surgeries: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Obstet Gynecol Cancer Res. 2021;6:87-94. doi:10.30699/jogcr.6.2.87
- Verano RMA, Veloso-borromeo MG. The efficacy of evening primrose oil as a cervical ripening agent for gynecologic procedures: a single-blinded, randomized controlled trial. PJOG. 2015;39:24-28.
Working while sick: Why doctors don’t stay home when ill
The reasons are likely as varied as, “you weren’t feeling bad enough to miss work,” “you couldn’t afford to miss pay,” “you had too many patients to see,” or “too much work to do.”
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy, 61% of physicians reported that they sometimes or often come to work sick. Only 2% of respondents said they never come to work unwell.
Medscape wanted to know more about how often you call in sick, how often you come to work feeling unwell, what symptoms you have, and the dogma of your workplace culture regarding sick days. Not to mention the brutal ethos that starts in medical school, in which calling in sick shows weakness or is unacceptable.
So, we polled 2,347 physicians in the United States and abroad and asked them about their sniffling, sneezing, cold, flu, and fever symptoms, and, of course, COVID. Results were split about 50-50 among male and female physicians. The poll ran from Sept. 28 through Oct. 11.
Coming to work sick
It’s no surprise that the majority of physicians who were polled (85%) have come to work sick in 2022. In the last prepandemic year (2019), about 70% came to work feeling sick one to five times, and 13% worked while sick six to ten times.
When asked about the symptoms that they’ve previously come to work with, 48% of U.S. physicians said multiple symptoms. They gave high marks for runny nose, cough, congestion, and sore throat. Only 27% have worked with a fever, 22% have worked with other symptoms, and 7% have worked with both strep throat and COVID.
“My workplace, especially in the COVID years, accommodates persons who honestly do not feel well enough to report. Sooner or later, everyone covers for someone else who has to be out,” says Kenneth Abbott, MD, an oncologist in Maryland.
The culture of working while sick
Why doctors come to work when they’re sick is complicated. The overwhelming majority of U.S. respondents cited professional obligations; 73% noted that they feel a professional obligation to their patients, and 72% feel a professional obligation to their co-workers. Half of the polled U.S. physicians said they didn’t feel bad enough to stay home, while 48% said they had too much work to do to stay home.
Some 45% said the expectation at their workplace is to come to work unless seriously ill; 43% had too many patients to see; and 18% didn’t think they were contagious when they headed to work sick. Unfortunately, 15% chose to work while sick because otherwise they would lose pay.
In light of these responses, it’s not surprising that 93% reported they’d seen other medical professionals working when sick.
“My schedule is almost always booked weeks in advance. If someone misses or has to cancel their appointment, they typically have 2-4 weeks to wait to get back in. If I was sick and a full day of patients (or God forbid more than a day) had to be canceled because I called in, it’s so much more work when I return,” says Caitlin Briggs, MD, a psychiatrist in Lexington, Ky.
Doctors’ workplace sick day policy
Most employees’ benefits allow at least a few sick days, but doctors who treat society’s ill patients don’t seem to stay home from work when they’re suffering. So, we asked physicians, official policy aside, whether they thought going to work sick was expected in their workplace. The majority (76%) said yes, while 24% said no.
“Unless I’m dying or extremely contagious, I usually work. At least now, I have the telehealth option. Not saying any of this is right, but it’s the reality we deal with and the choice we must make,” says Dr. Briggs.
Additionally, 58% of polled physicians said their workplace did not have a clearly defined policy against coming to work sick, while 20% said theirs did, and 22% weren’t sure.
“The first thing I heard on the subject as a medical student was that sick people come to the hospital, so if you’re sick, then you come to the hospital too ... to work. If you can’t work, then you will be admitted. Another aphorism was from Churchill, that ‘most of the world’s work is done by people who don’t feel very well,’ ” says Paul Andreason, MD, a psychiatrist in Bethesda, Md.
Working in the time of COVID
Working while ill during ordinary times is one thing, but what about working in the time of COVID? Has the pandemic changed the culture of coming to work sick because medical facilities, such as doctor’s offices and hospitals, don’t want their staff coming in when they have COVID?
Surprisingly, when we asked physicians whether the pandemic has made it more or less acceptable to come to work sick, only 61% thought COVID has made it less acceptable to work while sick, while 16% thought it made it more acceptable, and 23% said there’s no change.
“I draw the line at fevers/chills, feeling like you’ve just been run over, or significant enteritis,” says Dr. Abbott. “Also, if I have to take palliative meds that interfere with alertness, I’m not doing my patients any favors.”
While a minority of physicians may call in sick, most still suffer through their sneezing, coughing, chills, and fever while seeing patients as usual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The reasons are likely as varied as, “you weren’t feeling bad enough to miss work,” “you couldn’t afford to miss pay,” “you had too many patients to see,” or “too much work to do.”
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy, 61% of physicians reported that they sometimes or often come to work sick. Only 2% of respondents said they never come to work unwell.
Medscape wanted to know more about how often you call in sick, how often you come to work feeling unwell, what symptoms you have, and the dogma of your workplace culture regarding sick days. Not to mention the brutal ethos that starts in medical school, in which calling in sick shows weakness or is unacceptable.
So, we polled 2,347 physicians in the United States and abroad and asked them about their sniffling, sneezing, cold, flu, and fever symptoms, and, of course, COVID. Results were split about 50-50 among male and female physicians. The poll ran from Sept. 28 through Oct. 11.
Coming to work sick
It’s no surprise that the majority of physicians who were polled (85%) have come to work sick in 2022. In the last prepandemic year (2019), about 70% came to work feeling sick one to five times, and 13% worked while sick six to ten times.
When asked about the symptoms that they’ve previously come to work with, 48% of U.S. physicians said multiple symptoms. They gave high marks for runny nose, cough, congestion, and sore throat. Only 27% have worked with a fever, 22% have worked with other symptoms, and 7% have worked with both strep throat and COVID.
“My workplace, especially in the COVID years, accommodates persons who honestly do not feel well enough to report. Sooner or later, everyone covers for someone else who has to be out,” says Kenneth Abbott, MD, an oncologist in Maryland.
The culture of working while sick
Why doctors come to work when they’re sick is complicated. The overwhelming majority of U.S. respondents cited professional obligations; 73% noted that they feel a professional obligation to their patients, and 72% feel a professional obligation to their co-workers. Half of the polled U.S. physicians said they didn’t feel bad enough to stay home, while 48% said they had too much work to do to stay home.
Some 45% said the expectation at their workplace is to come to work unless seriously ill; 43% had too many patients to see; and 18% didn’t think they were contagious when they headed to work sick. Unfortunately, 15% chose to work while sick because otherwise they would lose pay.
In light of these responses, it’s not surprising that 93% reported they’d seen other medical professionals working when sick.
“My schedule is almost always booked weeks in advance. If someone misses or has to cancel their appointment, they typically have 2-4 weeks to wait to get back in. If I was sick and a full day of patients (or God forbid more than a day) had to be canceled because I called in, it’s so much more work when I return,” says Caitlin Briggs, MD, a psychiatrist in Lexington, Ky.
Doctors’ workplace sick day policy
Most employees’ benefits allow at least a few sick days, but doctors who treat society’s ill patients don’t seem to stay home from work when they’re suffering. So, we asked physicians, official policy aside, whether they thought going to work sick was expected in their workplace. The majority (76%) said yes, while 24% said no.
“Unless I’m dying or extremely contagious, I usually work. At least now, I have the telehealth option. Not saying any of this is right, but it’s the reality we deal with and the choice we must make,” says Dr. Briggs.
Additionally, 58% of polled physicians said their workplace did not have a clearly defined policy against coming to work sick, while 20% said theirs did, and 22% weren’t sure.
“The first thing I heard on the subject as a medical student was that sick people come to the hospital, so if you’re sick, then you come to the hospital too ... to work. If you can’t work, then you will be admitted. Another aphorism was from Churchill, that ‘most of the world’s work is done by people who don’t feel very well,’ ” says Paul Andreason, MD, a psychiatrist in Bethesda, Md.
Working in the time of COVID
Working while ill during ordinary times is one thing, but what about working in the time of COVID? Has the pandemic changed the culture of coming to work sick because medical facilities, such as doctor’s offices and hospitals, don’t want their staff coming in when they have COVID?
Surprisingly, when we asked physicians whether the pandemic has made it more or less acceptable to come to work sick, only 61% thought COVID has made it less acceptable to work while sick, while 16% thought it made it more acceptable, and 23% said there’s no change.
“I draw the line at fevers/chills, feeling like you’ve just been run over, or significant enteritis,” says Dr. Abbott. “Also, if I have to take palliative meds that interfere with alertness, I’m not doing my patients any favors.”
While a minority of physicians may call in sick, most still suffer through their sneezing, coughing, chills, and fever while seeing patients as usual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The reasons are likely as varied as, “you weren’t feeling bad enough to miss work,” “you couldn’t afford to miss pay,” “you had too many patients to see,” or “too much work to do.”
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy, 61% of physicians reported that they sometimes or often come to work sick. Only 2% of respondents said they never come to work unwell.
Medscape wanted to know more about how often you call in sick, how often you come to work feeling unwell, what symptoms you have, and the dogma of your workplace culture regarding sick days. Not to mention the brutal ethos that starts in medical school, in which calling in sick shows weakness or is unacceptable.
So, we polled 2,347 physicians in the United States and abroad and asked them about their sniffling, sneezing, cold, flu, and fever symptoms, and, of course, COVID. Results were split about 50-50 among male and female physicians. The poll ran from Sept. 28 through Oct. 11.
Coming to work sick
It’s no surprise that the majority of physicians who were polled (85%) have come to work sick in 2022. In the last prepandemic year (2019), about 70% came to work feeling sick one to five times, and 13% worked while sick six to ten times.
When asked about the symptoms that they’ve previously come to work with, 48% of U.S. physicians said multiple symptoms. They gave high marks for runny nose, cough, congestion, and sore throat. Only 27% have worked with a fever, 22% have worked with other symptoms, and 7% have worked with both strep throat and COVID.
“My workplace, especially in the COVID years, accommodates persons who honestly do not feel well enough to report. Sooner or later, everyone covers for someone else who has to be out,” says Kenneth Abbott, MD, an oncologist in Maryland.
The culture of working while sick
Why doctors come to work when they’re sick is complicated. The overwhelming majority of U.S. respondents cited professional obligations; 73% noted that they feel a professional obligation to their patients, and 72% feel a professional obligation to their co-workers. Half of the polled U.S. physicians said they didn’t feel bad enough to stay home, while 48% said they had too much work to do to stay home.
Some 45% said the expectation at their workplace is to come to work unless seriously ill; 43% had too many patients to see; and 18% didn’t think they were contagious when they headed to work sick. Unfortunately, 15% chose to work while sick because otherwise they would lose pay.
In light of these responses, it’s not surprising that 93% reported they’d seen other medical professionals working when sick.
“My schedule is almost always booked weeks in advance. If someone misses or has to cancel their appointment, they typically have 2-4 weeks to wait to get back in. If I was sick and a full day of patients (or God forbid more than a day) had to be canceled because I called in, it’s so much more work when I return,” says Caitlin Briggs, MD, a psychiatrist in Lexington, Ky.
Doctors’ workplace sick day policy
Most employees’ benefits allow at least a few sick days, but doctors who treat society’s ill patients don’t seem to stay home from work when they’re suffering. So, we asked physicians, official policy aside, whether they thought going to work sick was expected in their workplace. The majority (76%) said yes, while 24% said no.
“Unless I’m dying or extremely contagious, I usually work. At least now, I have the telehealth option. Not saying any of this is right, but it’s the reality we deal with and the choice we must make,” says Dr. Briggs.
Additionally, 58% of polled physicians said their workplace did not have a clearly defined policy against coming to work sick, while 20% said theirs did, and 22% weren’t sure.
“The first thing I heard on the subject as a medical student was that sick people come to the hospital, so if you’re sick, then you come to the hospital too ... to work. If you can’t work, then you will be admitted. Another aphorism was from Churchill, that ‘most of the world’s work is done by people who don’t feel very well,’ ” says Paul Andreason, MD, a psychiatrist in Bethesda, Md.
Working in the time of COVID
Working while ill during ordinary times is one thing, but what about working in the time of COVID? Has the pandemic changed the culture of coming to work sick because medical facilities, such as doctor’s offices and hospitals, don’t want their staff coming in when they have COVID?
Surprisingly, when we asked physicians whether the pandemic has made it more or less acceptable to come to work sick, only 61% thought COVID has made it less acceptable to work while sick, while 16% thought it made it more acceptable, and 23% said there’s no change.
“I draw the line at fevers/chills, feeling like you’ve just been run over, or significant enteritis,” says Dr. Abbott. “Also, if I have to take palliative meds that interfere with alertness, I’m not doing my patients any favors.”
While a minority of physicians may call in sick, most still suffer through their sneezing, coughing, chills, and fever while seeing patients as usual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sexual activities in seniors: Experts advise on what to ask
Sexual activity in older adults is something of a taboo, rarely discussed and largely ignored by researchers.
But failing to address human sexuality in old age can lead doctors to ask seniors the wrong questions about sex – if they ask at all.
When researchers do look at the issue, they find surprises, as Janie Steckenrider, PhD, has learned. In a new study presented at the annual scientific meeting of the Gerontological Society of America, Dr. Steckenrider, a professor of political science at Loyola Marymount University, Los Angeles, found that previous attempts to qualify the sexual activities of seniors appear to be limited largely to partnered sex – despite the fact that many older people tend to practice “solo sex,” another term for masturbation.
“Maybe they don’t have a partner, or their partner has sexual dysfunction, or has died. There could be pain involved,” Dr. Steckenrider said. “In the hierarchy of sexual activity, penetrative sex is the cultural norm. As people get older, penetrative sex becomes less important. The hierarchy shifts to include more emotional intimacy like touching and fondling.”
Of the 17 survey questionnaires Dr. Steckenrider analyzed, 11 had questions that focused exclusively on sex with a partner. Nine defined sexual activity and just five included questions about masturbation.
Take, for example, a 2018 poll by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who found that 40% of people ages 65-80 said they were sexually active. Meanwhile, nearly two thirds of older adults said they were interested in sex, and more than half said sex was important to their quality of life.
But Dr. Steckenrider said this poll, like others, left the term “sexually active” undefined – raising questions about the meaning of the findings.
Sheryl A. Kingsberg, PhD, chief of behavioral medicine in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, said she was surprised so few of the studies analyzed by Dr. Steckenrider included masturbation in their definition of sex.
“Clinical trials of potential treatments for female sexual problems, like hypoactive sexual desire disorder or painful sex, include both definitions of sexual activity and questions about masturbation, she said. “Definitions also should not assume partnered sex is male or female,” she added.
Dr. Steckenrider and Dr. Kingsberg encouraged healthcare providers to address the sexual health of their patients by asking questions about their sexual health and concerns.
“Health care professionals cannot address sexual concerns if they don’t acknowledge their patients as sexual beings and inquire about sexual problems,” Dr. Kingsberg said.
The key, according to Dr. Steckenrider, is for clinicians to ask the right questions. But which ones?
Detail is crucial.
“I think that’s far better than asking whether they are sexually active, yes or no,” she said. “Ask: ‘How often have you engaged in these types of sexual activities?’ If you are looking for frequency, and be specific about the types of sex: kissing, fondling, or masturbation.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sexual activity in older adults is something of a taboo, rarely discussed and largely ignored by researchers.
But failing to address human sexuality in old age can lead doctors to ask seniors the wrong questions about sex – if they ask at all.
When researchers do look at the issue, they find surprises, as Janie Steckenrider, PhD, has learned. In a new study presented at the annual scientific meeting of the Gerontological Society of America, Dr. Steckenrider, a professor of political science at Loyola Marymount University, Los Angeles, found that previous attempts to qualify the sexual activities of seniors appear to be limited largely to partnered sex – despite the fact that many older people tend to practice “solo sex,” another term for masturbation.
“Maybe they don’t have a partner, or their partner has sexual dysfunction, or has died. There could be pain involved,” Dr. Steckenrider said. “In the hierarchy of sexual activity, penetrative sex is the cultural norm. As people get older, penetrative sex becomes less important. The hierarchy shifts to include more emotional intimacy like touching and fondling.”
Of the 17 survey questionnaires Dr. Steckenrider analyzed, 11 had questions that focused exclusively on sex with a partner. Nine defined sexual activity and just five included questions about masturbation.
Take, for example, a 2018 poll by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who found that 40% of people ages 65-80 said they were sexually active. Meanwhile, nearly two thirds of older adults said they were interested in sex, and more than half said sex was important to their quality of life.
But Dr. Steckenrider said this poll, like others, left the term “sexually active” undefined – raising questions about the meaning of the findings.
Sheryl A. Kingsberg, PhD, chief of behavioral medicine in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, said she was surprised so few of the studies analyzed by Dr. Steckenrider included masturbation in their definition of sex.
“Clinical trials of potential treatments for female sexual problems, like hypoactive sexual desire disorder or painful sex, include both definitions of sexual activity and questions about masturbation, she said. “Definitions also should not assume partnered sex is male or female,” she added.
Dr. Steckenrider and Dr. Kingsberg encouraged healthcare providers to address the sexual health of their patients by asking questions about their sexual health and concerns.
“Health care professionals cannot address sexual concerns if they don’t acknowledge their patients as sexual beings and inquire about sexual problems,” Dr. Kingsberg said.
The key, according to Dr. Steckenrider, is for clinicians to ask the right questions. But which ones?
Detail is crucial.
“I think that’s far better than asking whether they are sexually active, yes or no,” she said. “Ask: ‘How often have you engaged in these types of sexual activities?’ If you are looking for frequency, and be specific about the types of sex: kissing, fondling, or masturbation.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sexual activity in older adults is something of a taboo, rarely discussed and largely ignored by researchers.
But failing to address human sexuality in old age can lead doctors to ask seniors the wrong questions about sex – if they ask at all.
When researchers do look at the issue, they find surprises, as Janie Steckenrider, PhD, has learned. In a new study presented at the annual scientific meeting of the Gerontological Society of America, Dr. Steckenrider, a professor of political science at Loyola Marymount University, Los Angeles, found that previous attempts to qualify the sexual activities of seniors appear to be limited largely to partnered sex – despite the fact that many older people tend to practice “solo sex,” another term for masturbation.
“Maybe they don’t have a partner, or their partner has sexual dysfunction, or has died. There could be pain involved,” Dr. Steckenrider said. “In the hierarchy of sexual activity, penetrative sex is the cultural norm. As people get older, penetrative sex becomes less important. The hierarchy shifts to include more emotional intimacy like touching and fondling.”
Of the 17 survey questionnaires Dr. Steckenrider analyzed, 11 had questions that focused exclusively on sex with a partner. Nine defined sexual activity and just five included questions about masturbation.
Take, for example, a 2018 poll by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who found that 40% of people ages 65-80 said they were sexually active. Meanwhile, nearly two thirds of older adults said they were interested in sex, and more than half said sex was important to their quality of life.
But Dr. Steckenrider said this poll, like others, left the term “sexually active” undefined – raising questions about the meaning of the findings.
Sheryl A. Kingsberg, PhD, chief of behavioral medicine in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, said she was surprised so few of the studies analyzed by Dr. Steckenrider included masturbation in their definition of sex.
“Clinical trials of potential treatments for female sexual problems, like hypoactive sexual desire disorder or painful sex, include both definitions of sexual activity and questions about masturbation, she said. “Definitions also should not assume partnered sex is male or female,” she added.
Dr. Steckenrider and Dr. Kingsberg encouraged healthcare providers to address the sexual health of their patients by asking questions about their sexual health and concerns.
“Health care professionals cannot address sexual concerns if they don’t acknowledge their patients as sexual beings and inquire about sexual problems,” Dr. Kingsberg said.
The key, according to Dr. Steckenrider, is for clinicians to ask the right questions. But which ones?
Detail is crucial.
“I think that’s far better than asking whether they are sexually active, yes or no,” she said. “Ask: ‘How often have you engaged in these types of sexual activities?’ If you are looking for frequency, and be specific about the types of sex: kissing, fondling, or masturbation.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
RSV vaccine given during pregnancy protects newborns: Pfizer
New trial data from drugmaker Pfizer shows promising results of a vaccine given to mothers during pregnancy that later protects infants in their first months from the worst effects of respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV.
Pfizer will apply for FDA approval by the end of the year, the company said in a statement Nov. 1.
Trial results are so promising that – after talking with government regulators – the company will stop enrolling new people in the study.
Specifically, the company reported that the vaccine prevented severe illness particularly well during the first 90 days of life, with measurable protection against severe illness continuing through 6 months of age. (That period is when infants are the most fragile if they get sick with RSV.)
RSV is a respiratory illness than can affect anyone, usually resulting in no symptoms or those similar to the common cold. But it can be particularly dangerous – and even deadly – for babies and for people over the age of 65. Pfizer and another drug company, GSK, are developing promising vaccines for older adults, the Washington Post reported.
RSV is the leading cause of hospitalization for infants, the Post noted.
The Pfizer study, called MATISSE, enrolled 7,400 pregnant women in 18 countries worldwide. Those who received the vaccine were given it during the late second to third trimester of pregnancy. Women in the study were monitored for safety through the rest of their pregnancy and 6 months after their children were born. Infants were monitored for at least 1 year for safety and effectiveness; more than half of them were monitored for 2 years.
The Pfizer vaccine works by passing maternal antibodies to the infant during pregnancy, the Post reported, noting that other vaccines transmitted via maternal immunization include those for influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
Annually, RSV has a devastating impact on young children, hospitalizing tens of thousands and causing up to 300 deaths, data show.
For every 100 children who get RSV under 6 months of age, one or two of them may need to be hospitalized, according to the CDC. Those hospitalized infants may need oxygen, intubation, or even mechanical ventilation to help with breathing.
“Most improve with this type of supportive care and are discharged in a few days,” the CDC said.
“I think this is a big step for protecting babies against RSV and improving overall lung health,” vaccine researcher Barney Graham, PhD, told the Post. “Overall, it’s an exciting time for RSV. It’s also a troubling time, because you see how the patterns of infection have been changed by COVID, and we’re having an earlier, bigger season this year than we have for a couple of years – and it’s causing a lot of hospitalization and misery for people.”
As many as four RSV vaccines may have applications submitted to the FDA in 2022, according to CNN. Also in development is an antibody shot given to infants just after they are born, the news outlet reported.
Pfizer’s data, announced Tuesday, has not yet been published or peer-reviewed, but the company said it is seeking peer-reviewed publication.
“We are thrilled by these data, as this is the first-ever investigational vaccine shown to help protect newborns against severe RSV-related respiratory illness immediately at birth,” Annaliesa Anderson, PhD, Pfizer chief scientific officer for vaccine research & development, said in a statement. “We look forward to working with the FDA and other regulatory agencies to bring this vaccine candidate to expectant mothers to help protect their infants against severe RSV during their most vulnerable first six months of life, which has the highest burden of RSV illness in infants.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
New trial data from drugmaker Pfizer shows promising results of a vaccine given to mothers during pregnancy that later protects infants in their first months from the worst effects of respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV.
Pfizer will apply for FDA approval by the end of the year, the company said in a statement Nov. 1.
Trial results are so promising that – after talking with government regulators – the company will stop enrolling new people in the study.
Specifically, the company reported that the vaccine prevented severe illness particularly well during the first 90 days of life, with measurable protection against severe illness continuing through 6 months of age. (That period is when infants are the most fragile if they get sick with RSV.)
RSV is a respiratory illness than can affect anyone, usually resulting in no symptoms or those similar to the common cold. But it can be particularly dangerous – and even deadly – for babies and for people over the age of 65. Pfizer and another drug company, GSK, are developing promising vaccines for older adults, the Washington Post reported.
RSV is the leading cause of hospitalization for infants, the Post noted.
The Pfizer study, called MATISSE, enrolled 7,400 pregnant women in 18 countries worldwide. Those who received the vaccine were given it during the late second to third trimester of pregnancy. Women in the study were monitored for safety through the rest of their pregnancy and 6 months after their children were born. Infants were monitored for at least 1 year for safety and effectiveness; more than half of them were monitored for 2 years.
The Pfizer vaccine works by passing maternal antibodies to the infant during pregnancy, the Post reported, noting that other vaccines transmitted via maternal immunization include those for influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
Annually, RSV has a devastating impact on young children, hospitalizing tens of thousands and causing up to 300 deaths, data show.
For every 100 children who get RSV under 6 months of age, one or two of them may need to be hospitalized, according to the CDC. Those hospitalized infants may need oxygen, intubation, or even mechanical ventilation to help with breathing.
“Most improve with this type of supportive care and are discharged in a few days,” the CDC said.
“I think this is a big step for protecting babies against RSV and improving overall lung health,” vaccine researcher Barney Graham, PhD, told the Post. “Overall, it’s an exciting time for RSV. It’s also a troubling time, because you see how the patterns of infection have been changed by COVID, and we’re having an earlier, bigger season this year than we have for a couple of years – and it’s causing a lot of hospitalization and misery for people.”
As many as four RSV vaccines may have applications submitted to the FDA in 2022, according to CNN. Also in development is an antibody shot given to infants just after they are born, the news outlet reported.
Pfizer’s data, announced Tuesday, has not yet been published or peer-reviewed, but the company said it is seeking peer-reviewed publication.
“We are thrilled by these data, as this is the first-ever investigational vaccine shown to help protect newborns against severe RSV-related respiratory illness immediately at birth,” Annaliesa Anderson, PhD, Pfizer chief scientific officer for vaccine research & development, said in a statement. “We look forward to working with the FDA and other regulatory agencies to bring this vaccine candidate to expectant mothers to help protect their infants against severe RSV during their most vulnerable first six months of life, which has the highest burden of RSV illness in infants.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
New trial data from drugmaker Pfizer shows promising results of a vaccine given to mothers during pregnancy that later protects infants in their first months from the worst effects of respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV.
Pfizer will apply for FDA approval by the end of the year, the company said in a statement Nov. 1.
Trial results are so promising that – after talking with government regulators – the company will stop enrolling new people in the study.
Specifically, the company reported that the vaccine prevented severe illness particularly well during the first 90 days of life, with measurable protection against severe illness continuing through 6 months of age. (That period is when infants are the most fragile if they get sick with RSV.)
RSV is a respiratory illness than can affect anyone, usually resulting in no symptoms or those similar to the common cold. But it can be particularly dangerous – and even deadly – for babies and for people over the age of 65. Pfizer and another drug company, GSK, are developing promising vaccines for older adults, the Washington Post reported.
RSV is the leading cause of hospitalization for infants, the Post noted.
The Pfizer study, called MATISSE, enrolled 7,400 pregnant women in 18 countries worldwide. Those who received the vaccine were given it during the late second to third trimester of pregnancy. Women in the study were monitored for safety through the rest of their pregnancy and 6 months after their children were born. Infants were monitored for at least 1 year for safety and effectiveness; more than half of them were monitored for 2 years.
The Pfizer vaccine works by passing maternal antibodies to the infant during pregnancy, the Post reported, noting that other vaccines transmitted via maternal immunization include those for influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
Annually, RSV has a devastating impact on young children, hospitalizing tens of thousands and causing up to 300 deaths, data show.
For every 100 children who get RSV under 6 months of age, one or two of them may need to be hospitalized, according to the CDC. Those hospitalized infants may need oxygen, intubation, or even mechanical ventilation to help with breathing.
“Most improve with this type of supportive care and are discharged in a few days,” the CDC said.
“I think this is a big step for protecting babies against RSV and improving overall lung health,” vaccine researcher Barney Graham, PhD, told the Post. “Overall, it’s an exciting time for RSV. It’s also a troubling time, because you see how the patterns of infection have been changed by COVID, and we’re having an earlier, bigger season this year than we have for a couple of years – and it’s causing a lot of hospitalization and misery for people.”
As many as four RSV vaccines may have applications submitted to the FDA in 2022, according to CNN. Also in development is an antibody shot given to infants just after they are born, the news outlet reported.
Pfizer’s data, announced Tuesday, has not yet been published or peer-reviewed, but the company said it is seeking peer-reviewed publication.
“We are thrilled by these data, as this is the first-ever investigational vaccine shown to help protect newborns against severe RSV-related respiratory illness immediately at birth,” Annaliesa Anderson, PhD, Pfizer chief scientific officer for vaccine research & development, said in a statement. “We look forward to working with the FDA and other regulatory agencies to bring this vaccine candidate to expectant mothers to help protect their infants against severe RSV during their most vulnerable first six months of life, which has the highest burden of RSV illness in infants.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.