User login
The Clinical Diversity of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects individuals worldwide.1 Although AD previously was commonly described as a skin-limited disease of childhood characterized by eczema in the flexural folds and pruritus, our current understanding supports a more heterogeneous condition.2 We review the wide range of cutaneous presentations of AD with a focus on clinical and morphological presentations across diverse skin types—commonly referred to as skin of color (SOC).
Defining SOC in Relation to AD
The terms SOC, race, and ethnicity are used interchangeably, but their true meanings are distinct. Traditionally, race has been defined as a biological concept, grouping cohorts of individuals with a large degree of shared ancestry and genetic similarities,3 and ethnicity as a social construct, grouping individuals with common racial, national, tribal, religious, linguistic, or cultural backgrounds.4 In practice, both concepts can broadly be envisioned as mixed social, political, and economic constructs, as no one gene or biologic characteristic distinguishes one racial or ethnic group from another.5
The US Census Bureau recognizes 5 racial groupings: White, Black or African American, American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander.6 Hispanic or Latinx origin is considered an ethnicity. It is important to note the limitations of these labels, as they do not completely encapsulate the heterogeneity of the US population. Overgeneralization of racial and ethnic categories may dull or obscure true differences among populations.7
From an evolutionary perspective, skin pigmentation represents the product of 2 opposing clines produced by natural selection in response to both need for and protection from UV radiation across lattitudes.8 Defining SOC is not quite as simple. Skin of color often is equated with certain racial/ethnic groups, or even binary categories of Black vs non-Black or White vs non-White. Others may use the Fitzpatrick scale to discuss SOC, though this scale was originally created to measure the response of skin to UVA radiation exposure.9 The reality is that SOC is a complex term that cannot simply be defined by a certain group of skin tones, races, ethnicities, and/or Fitzpatrick skin types. With this in mind, SOC in the context of this article will often refer to non-White individuals based on the investigators’ terminology, but this definition is not all-encompassing.
Historically in medicine, racial/ethnic differences in outcomes have been equated to differences in biology/genetics without consideration of many external factors.10 The effects of racism, economic stability, health care access, environment, and education quality rarely are discussed, though they have a major impact on health and may better define associations with race or an SOC population. A discussion of the structural and social determinants of health contributing to disease outcomes should accompany any race-based guidelines to prevent inaccurately pathologizing race or SOC.10
Within the scope of AD, social determinants of health play an important role in contributing to disease morbidity. Environmental factors, including tobacco smoke, climate, pollutants, water hardness, und urban living, are related to AD prevalence and severity.11 Higher socioeconomic status is associated with increased AD rates,12 yet lower socioeconomic status is associated with more severe disease.13 Barriers to health care access and suboptimal care drive worse AD outcomes.14 Underrepresentation in clinical trials prevents the generalizability and safety of AD treatments.15 Disparities in these health determinants associated with AD likely are among the most important drivers of observed differences in disease presentation, severity, burden, and even prevalence—more so than genetics or ancestry alone16—yet this relationship is poorly understood and often presented as a consequence of race. It is critical to redefine the narrative when considering the heterogeneous presentations of AD in patients with SOC and acknowledge the limitations of current terminology when attempting to capture clinical diversity in AD, including in this review, where published findings often are limited by race-based analysis.
Epidemiology
The prevalence of AD has been increasing over the last few decades, and rates vary by region. In the United States, the prevalence of childhood and adult AD is 13% and 7%, respectively.17,18 Globally, higher rates of pediatric AD are seen in Africa, Oceania, Southeast Asia (SEA), and Latin America compared to South Asia, Northern Europe, and Eastern Europe.19 The prevalence of AD varies widely within the same continent and country; for example, throughout Africa, prevalence was found to be anywhere between 4.7% and 23.3%.20
Lesion Morphology
Although AD lesions often are described as pruritic erythematous papules and plaques, other common morphologies in SOC populations include prurigo nodules, lichenoid papules, perifollicular papules, nummular lesions, and psoriasiform lesions (Table). Instead of applying normative terms such as classic vs atypical to AD morphology, we urge clinicians to be familiar with the full spectrum of AD skin signs.
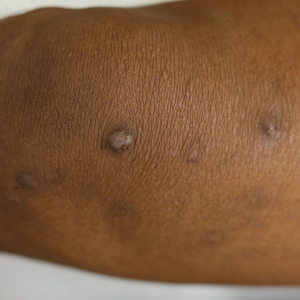
Prurigo Nodules—Prurigo nodules are hyperkeratotic or erosive nodules with severe pruritus, often grouped symmetrically on the extensor surfaces of the arms, legs, and trunk (Figure 1).14,21 The skin between lesions usually is unaffected but can be dry or lichenified or display postinflammatory pigmentary changes.14 Prurigo nodules are common. In a study of a cohort of patients with prurigo nodularis (N=108), nearly half (46.3%) were determined to have either an atopic predisposition or underlying AD as a contributing cause of the lesions.21
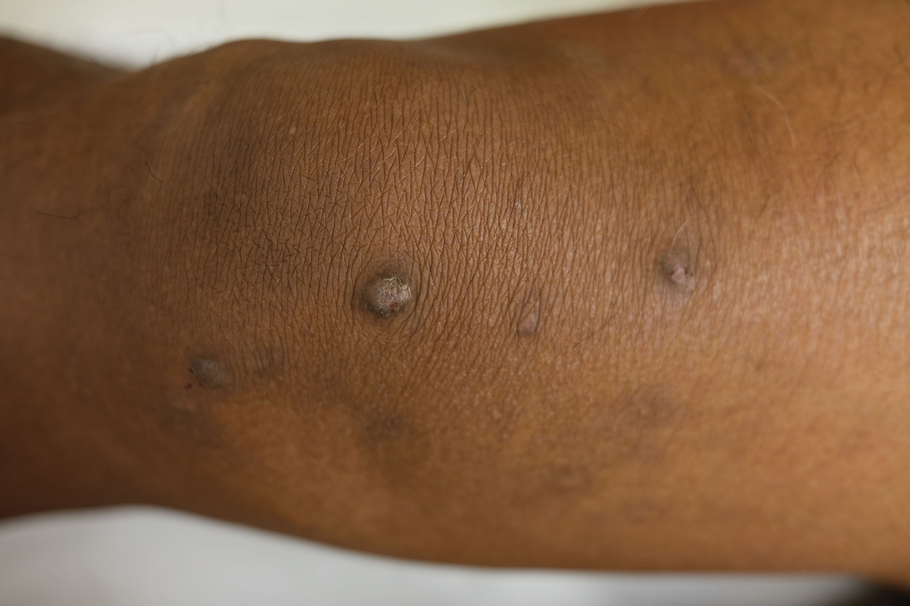
Prurigo nodules as a phenotype of AD may be more common in certain SOC populations. Studies from SEA have reported a higher prevalence of prurigo nodules among patients with AD.28 Although there are limited formal studies assessing the true prevalence of this lesion type in African American AD patients in the United States, clinical evidence supports more frequent appearance of prurigo nodules in non-White patients.29 Contributing factors include suboptimal care for AD in SOC populations and/or barriers to health care access, resulting in more severe disease that increases the risk for this lesion type.14
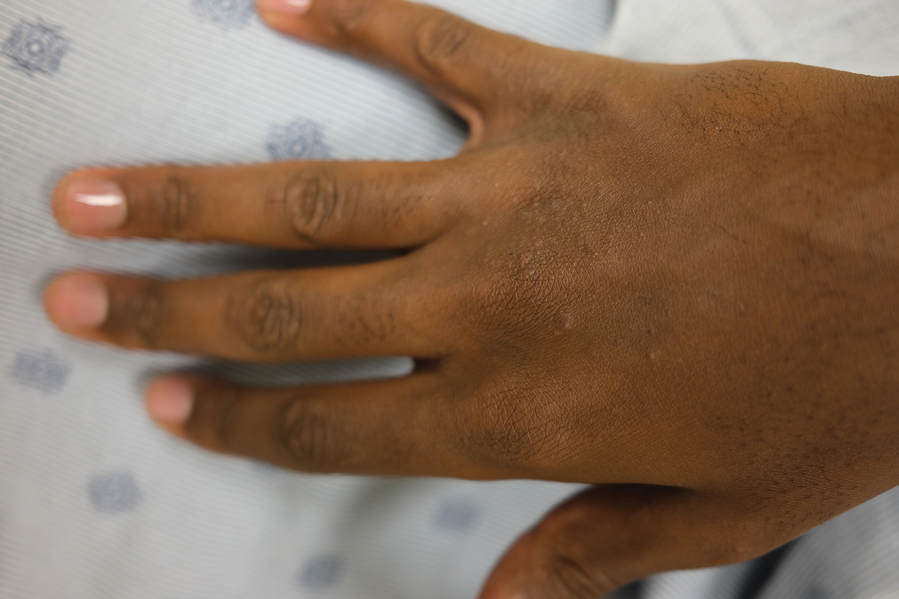
Lichenoid Papules—Papular lichenoid lesions often present on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs in AD (Figure 2).22 In a study of Nigerian patients with AD (N=1019), 54.1% had lichenoid papules.24 A systematic review of AD characteristics by region similarly reported an increased prevalence of this lesion type in African studies.28 Lichenoid variants of AD have been well described in SOC patients in the United States.23 In contrast to the lesions of lichen planus, the lichenoid papules of AD usually are round, rarely display koebnerization, do not have Wickham striae, and predominantly are located on extensor surfaces.
Perifollicular Papules—Perifollicular accentuation—dermatitis enhanced around hair follicles—is a well-described lesional morphology of AD that is noted in all racial/ethnic groups (Figure 3).22 In fact, perifollicular accentuation is included as one of the Hanifin and Rajka minor criteria for AD.30 Studies performed in Nigeria and India showed perifollicular accentuation in up to 70% of AD patients.24,31 In a study of adult Thai patients (N=56), follicular lesions were found more frequently in intrinsic AD (29%) compared with extrinsic AD (12%).32
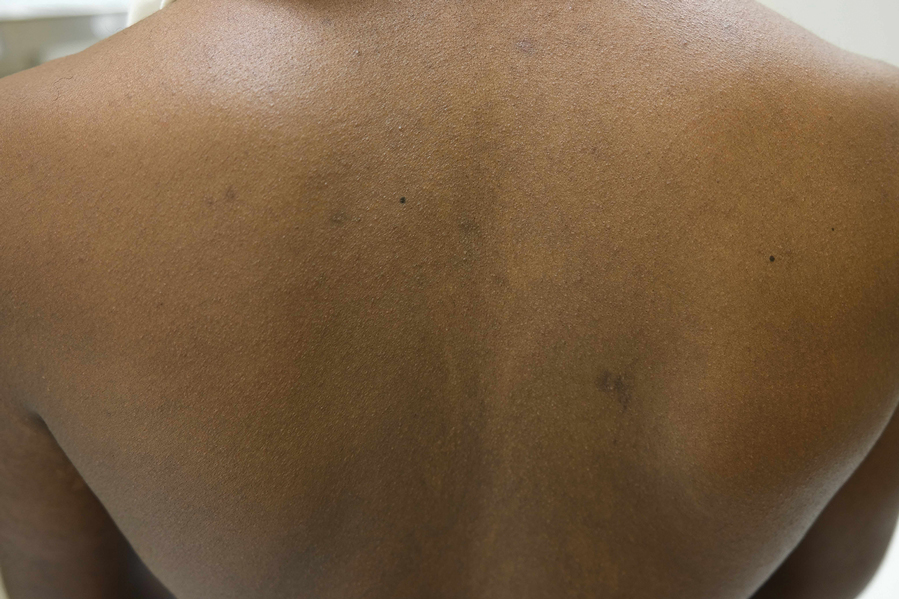
Nummular and Psoriasiform Lesions—Nummular lesions may be red, oozing, excoriated, studded with pustules and/or present on the extensor extremities (Figure 4). In SOC patients, these lesions often occur in areas where hyperpigmentation is noted.22 Studies in the United States and Mexico demonstrated that 15% to 17% of AD patients displayed nummular lesions.23,33 Similar to follicular papules, nummular lesions were linked to intrinsic AD in a study of adult Thai patients.32
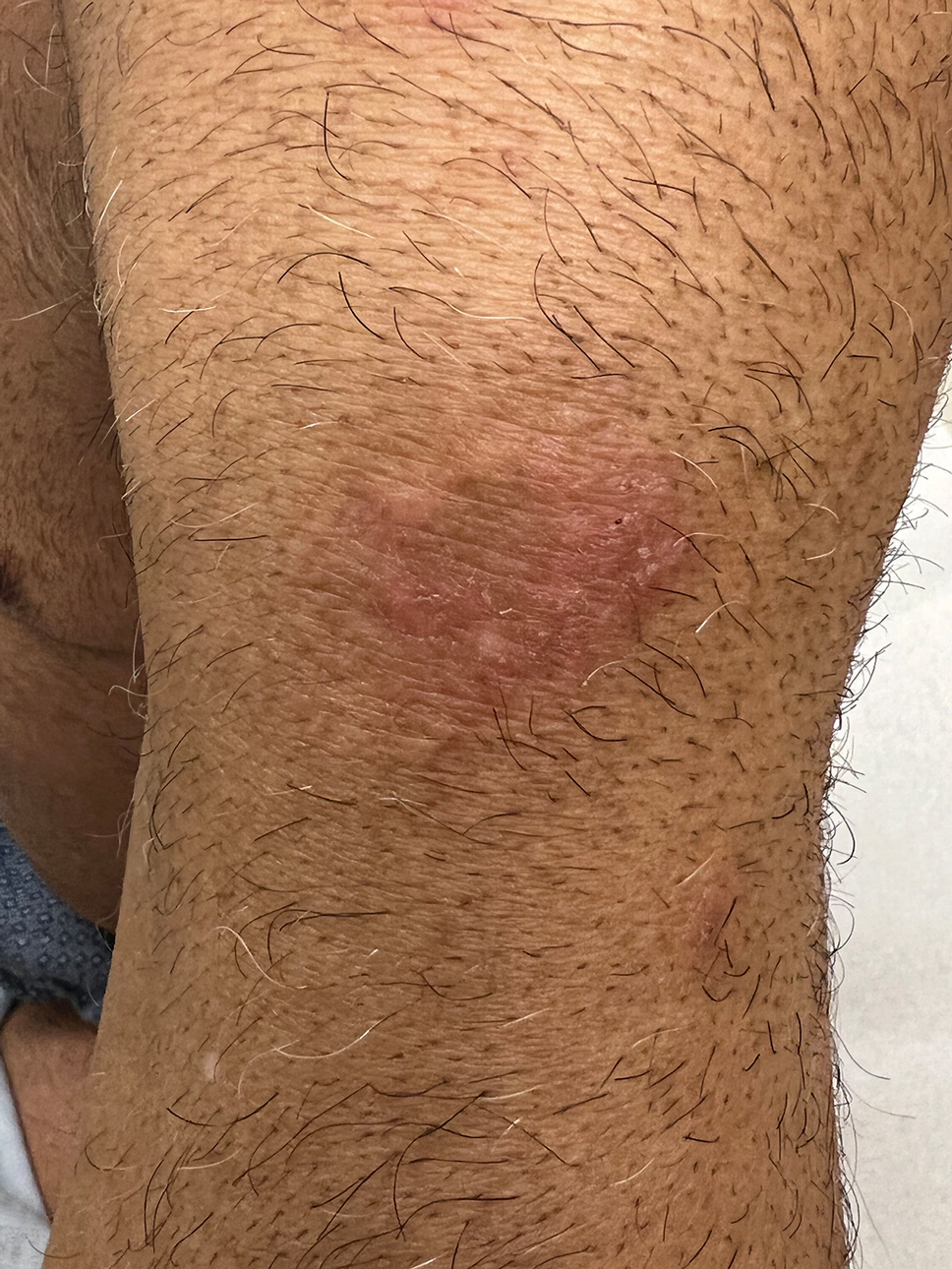
Psoriasiform lesions show prominent scaling, lichenification, and clear demarcation.25 It has been reported that the psoriasiform phenotype of AD is more common in Asian patients,25 though this is likely an oversimplification. The participants in these studies were of Japanese and Korean ancestry, which covers a broad geographic region, and the grouping of individuals under a heterogeneous Asian category is unlikely to convey generalizable biologic or clinical information. Unsurprisingly, a systematic review of AD characteristics by region noted considerable phenotypical differences among patients in SEA, East Asia, Iran, and India.28
Disease Severity
Several factors contribute to AD disease severity,34 including objective assessments of inflammation, such as erythema and lichenification (Table), as well as subjective measures of symptoms, such as itch. The severity of AD is exacerbated by the social determinants of health, and a lower socioeconomic status, lower household income, lower parental education level and health, dilapidated housing, and presence of garbage on the street are among factors linked to worse AD disease severity.13,17 Although non-White individuals with AD often are reported to have more severe disease than their White counterparts,35 these types of health determinants may be the most relevant causes of observed differences.
Erythema—Erythema is a feature of inflammation used in the AD severity assessment. Erythema may appear in shades beyond red, including maroon, violaceous, or brown, in patients with darker pigmented skin, which may contribute to diagnosis of AD at a later disease stage.26 Multiple AD severity scoring tools, such as the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema Area and Severity Index, include erythema as a measure, which can lead to underestimation of AD severity in SOC populations. After adjusting for erythema score, one study found that Black children with AD had a risk for severe disease that was 6-times higher than White children.36 Dermatological training must adequately teach physicians to recognize erythema across all skin tones.37
Erythroderma (also known as exfoliative dermatitis) is rapidly spreading erythema on at least 90% of the total body surface area, often sparing the palms and soles.32 Erythroderma is a potentially life-threatening manifestation of severe AD. Although erythroderma may have many underlying causes, AD has been reported to be the cause in 5% to 24% of cases,38 and compared to studies in Europe, the prevalence of erythroderma was higher in East Asian studies of AD.28
Excoriation and Pruritus—Pruritus is a defining characteristic of AD, and the resulting excoriations often are predominant on physical examination, which is a key part of severity scores. Itch is the most prevalent symptom among patients with AD, and a greater itch severity has been linked to decreased health-related quality of life, increased mental health symptoms, impaired sleep, and decreased daily function.39,40 The burden of itch may be greater in SOC populations. The impact of itch on quality of life among US military veterans was significantly higher in those who identified as non-White (P=.05).41 In another study of US military veterans, African American individuals reported a significantly higher emotional impact from itch (P<.05).42
Lichenification—Lichenification is thickening of the skin due to chronic rubbing and scratching that causes a leathery elevated appearance with exaggerated skin lines.27 Lichenification is included as a factor in common clinical scoring tools, with greater lichenification indicating greater disease severity. Studies from SEA and Africa suggested a higher prevalence of lichenification in AD patients.28 A greater itch burden and thus increased rubbing/scratching in these populations may contribute to some of these findings.42,43
Xerosis—Xerosis (or dry skin) is a common finding in AD that results from increased transepidermal water loss due to a dysfunctional epidermal barrier.44 In a systematic review of AD characteristics by region, xerosis was among the top 5 most reported AD features globally in all regions except SEA.28 Xerosis may be more stigmatizing in SOC populations because of the greater visibility of scaling and dryness on darker skin tones.1
Postinflammatory Dyspigmentation—Postinflammatory pigment alteration may be a consequence of AD lesions, resulting in hyperpigmented and hypopigmented macules and patches. Patients with AD with darker skin tones are more likely to develop postinflammatory dyspigmentation.26 A study of AD patients in Nigeria found that 63% displayed postinflammatory dyspigmentation.45 Dyschromia, including postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, is one of the most common reasons for SOC patients to seek dermatologic care.46 Postinflammatory pigment alteration can cause severe distress in patients, even more so than the cutaneous findings of AD. Although altered skin pigmentation usually returns to normal over weeks to months, skin depigmentation from chronic excoriation may be permanent.26 Appropriately treating hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation in SOC populations can greatly improve quality of life.47
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis is a cutaneous inflammatory disease that presents with many clinical phenotypes. Dermatologists should be trained to recognize the heterogeneous signs of AD present across the diverse skin types in SOC patients. Future research should move away from race-based analyses and focus on the complex interplay of environmental factors, social determinants of health, and skin pigmentation, as well as how these factors drive variations in AD lesional morphology and inflammation.
- Alexis A, Woolery-Lloyd H, Andriessen A, et al. Insights in skin of color patients with atopic dermatitis and the role of skincare in improving outcomes. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:462-470. doi:10.36849/jdd.6609
- Chovatiya R, Silverberg JI. The heterogeneity of atopic dermatitis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:172-176. doi:10.36849/JDD.6408
- Taylor SC, Cook-Bolden F. Defining skin of color. Cutis. 2002;69:435-437.
- Georgetown University Center for Child and Human Development. Bridging the cultural divide in health care settings: the essential role of cultural broker programs. Accessed October 6, 2023. https://nccc.georgetown.edu/culturalbroker/8_Definitions/2_Definitions.html#:~:text=ethnic%3A%20Of%20or%20relating%20to,or%20cultural%20origin%20or%20background
- Shoo BA, Kashani-Sabet M. Melanoma arising in African-, Asian-, Latino- and Native-American populations. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:96-102. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2009.04.005
- US Census Bureau. About the topic of race. Revised March 1, 2022. Accessed October 5, 2023. https://www.census.gov/topics/population/race/about.html
- Williams HC. Have you ever seen an Asian/Pacific Islander? Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:673-674. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.5.673
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Colloquium paper: human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(Suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Fitzpatrick TB. The validity and practicality of sun-reactive skin types I through VI. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:869-871. doi:10.1001/archderm.124.6.869
- Amutah C, Greenidge K, Mante A, et al. Misrepresenting race—the role of medical schools in propagating physician bias. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:872-878. doi:10.1056/NEJMms2025768
- Kantor R, Silverberg JI. Environmental risk factors and their role in the management of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017;13:15-26. doi:10.1080/1744666x.2016.1212660
- Fu T, Keiser E, Linos E, et al. Eczema and sensitization to common allergens in the United States: a multiethnic, population-based study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:21-26. doi:10.1111/pde.12237
- Tackett KJ, Jenkins F, Morrell DS, et al. Structural racism and its influence on the severity of atopic dermatitis in African American children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:142-146. doi:10.1111/pde.14058
- Huang AH, Williams KA, Kwatra SG. Prurigo nodularis: epidemiology and clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1559-1565. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.183
- Hirano SA, Murray SB, Harvey VM. Reporting, representation, and subgroup analysis of race and ethnicity in published clinical trials of atopic dermatitis in the United States between 2000 and 2009. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:749-755. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01797.x
- Polcari I, Becker L, Stein SL, et al. Filaggrin gene mutations in African Americans with both ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:489-492. doi:10.1111/pde.12355
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL. Associations of childhood eczema severity: a US population-based study. Dermatitis. 2014;25:107-114. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000034
- Hua T, Silverberg JI. Atopic dermatitis in US adults: epidemiology, association with marital status, and atopy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:622-624. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2018.07.019
- Odhiambo JA, Williams HC, Clayton TO, et al. Global variations in prevalence of eczema symptoms in children from ISAAC Phase Three. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1251-8.e23. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.009
- Ait-Khaled N, Odhiambo J, Pearce N, et al. Prevalence of symptoms of asthma, rhinitis and eczema in 13- to 14-year-old children in Africa: the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood Phase III. Allergy. 2007;62:247-258. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01325.x
- Iking A, Grundmann S, Chatzigeorgakidis E, et al. Prurigo as a symptom of atopic and non-atopic diseases: aetiological survey in a consecutive cohort of 108 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:550-557. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04481.x
- Silverberg NB. Typical and atypical clinical appearance of atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:354-359. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2017.03.007
- Allen HB, Jones NP, Bowen SE. Lichenoid and other clinical presentations of atopic dermatitis in an inner city practice. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:503-504. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.03.033
- Nnoruka EN. Current epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in south-eastern Nigeria. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:739-744. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02360.x
- Noda S, Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, et al. The Asian atopic dermatitis phenotype combines features of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis with increased TH17 polarization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1254-1264. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.08.015
- Kaufman BP, Guttman-Yassky E, Alexis AF. Atopic dermatitis in diverse racial and ethnic groups-variations in epidemiology, genetics, clinical presentation and treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:340-357. doi:10.1111/exd.13514
- Girolomoni G, de Bruin-Weller M, Aoki V, et al. Nomenclature and clinical phenotypes of atopic dermatitis. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021;12:20406223211002979. doi:10.1177/20406223211002979
- Yew YW, Thyssen JP, Silverberg JI. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the regional and age-related differences in atopic dermatitis clinical characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:390-401. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.035
- Vachiramon V, Tey HL, Thompson AE, et al. Atopic dermatitis in African American children: addressing unmet needs of a common disease. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:395-402. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01740.x
- Hanifin JM. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1980;92:44-47.
- Dutta A, De A, Das S, et al. A cross-sectional evaluation of the usefulness of the minor features of Hanifin and Rajka diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in the pediatric population. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:583-590. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_1046_20
- Kulthanan K, Boochangkool K, Tuchinda P, et al. Clinical features of the extrinsic and intrinsic types of adult-onset atopic dermatitis. Asia Pac Allergy. 2011;1:80-86. doi:10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.2.80
- Julián-Gónzalez RE, Orozco-Covarrubias L, Durán-McKinster C, et al. Less common clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis: prevalence by age. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:580-583. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01739.x
- Chovatiya R, Silverberg JI. Evaluating the longitudinal course of atopic dermatitis: a review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:688-689. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.02.005
- Kim Y, Blomberg M, Rifas-Shiman SL, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in incidence and persistence of childhood atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:827-834. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.029
- Ben-Gashir MA, Hay RJ. Reliance on erythema scores may mask severe atopic dermatitis in black children compared with their white counterparts. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:920-925. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04965.x
- McKenzie S, Brown-Korsah JB, Syder NC, et al. Variations in genetics, biology, and phenotype of cutaneous disorders in skin of color. part II: differences in clinical presentation and disparities in cutaneous disorders in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1261-1270. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.03.067
- Cuellar-Barboza A, Ocampo-Candiani J, Herz-Ruelas ME. A practical approach to the diagnosis and treatment of adult erythroderma [in English, Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2018;109:777-790. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2018.05.011
- Lei DK, Yousaf M, Janmohamed SR, et al. Validation of patient-reported outcomes information system sleep disturbance and sleep-related impairment in adults with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:875-882. doi:10.1111/bjd.18920
- Silverberg JI, Gelfand JM, Margolis DJ, et al. Patient burden and quality of life in atopic dermatitis in US adults: a population-based cross-sectional study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:340-347. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2018.07.006
- Carr CW, Veledar E, Chen SC. Factors mediating the impact of chronic pruritus on quality of life. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:613-620. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.7696
- Shaw FM, Luk KMH, Chen KH, et al. Racial disparities in the impact of chronic pruritus: a cross-sectional study on quality of life and resource utilization in United States veterans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:63-69. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.01.016
- Oh CC, Li H, Lee W, et al. Biopsychosocial factors associated with prurigo nodularis in endogenous eczema. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:525. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.164451
- Vyumvuhore R, Michael-Jubeli R, Verzeaux L, et al. Lipid organization in xerosis: the key of the problem? Int J Cosmet Sci. 2018;40:549-554. doi:10.1111/ics.12496
- George AO. Atopic dermatitis in Nigeria. Int J Dermatol. 1989;28:237-239. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1989.tb04811.x
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Dupilumab improves atopic dermatitis and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in patient with skin of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:776-778. doi:10.36849/jdd.2020.4937
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects individuals worldwide.1 Although AD previously was commonly described as a skin-limited disease of childhood characterized by eczema in the flexural folds and pruritus, our current understanding supports a more heterogeneous condition.2 We review the wide range of cutaneous presentations of AD with a focus on clinical and morphological presentations across diverse skin types—commonly referred to as skin of color (SOC).
Defining SOC in Relation to AD
The terms SOC, race, and ethnicity are used interchangeably, but their true meanings are distinct. Traditionally, race has been defined as a biological concept, grouping cohorts of individuals with a large degree of shared ancestry and genetic similarities,3 and ethnicity as a social construct, grouping individuals with common racial, national, tribal, religious, linguistic, or cultural backgrounds.4 In practice, both concepts can broadly be envisioned as mixed social, political, and economic constructs, as no one gene or biologic characteristic distinguishes one racial or ethnic group from another.5
The US Census Bureau recognizes 5 racial groupings: White, Black or African American, American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander.6 Hispanic or Latinx origin is considered an ethnicity. It is important to note the limitations of these labels, as they do not completely encapsulate the heterogeneity of the US population. Overgeneralization of racial and ethnic categories may dull or obscure true differences among populations.7
From an evolutionary perspective, skin pigmentation represents the product of 2 opposing clines produced by natural selection in response to both need for and protection from UV radiation across lattitudes.8 Defining SOC is not quite as simple. Skin of color often is equated with certain racial/ethnic groups, or even binary categories of Black vs non-Black or White vs non-White. Others may use the Fitzpatrick scale to discuss SOC, though this scale was originally created to measure the response of skin to UVA radiation exposure.9 The reality is that SOC is a complex term that cannot simply be defined by a certain group of skin tones, races, ethnicities, and/or Fitzpatrick skin types. With this in mind, SOC in the context of this article will often refer to non-White individuals based on the investigators’ terminology, but this definition is not all-encompassing.
Historically in medicine, racial/ethnic differences in outcomes have been equated to differences in biology/genetics without consideration of many external factors.10 The effects of racism, economic stability, health care access, environment, and education quality rarely are discussed, though they have a major impact on health and may better define associations with race or an SOC population. A discussion of the structural and social determinants of health contributing to disease outcomes should accompany any race-based guidelines to prevent inaccurately pathologizing race or SOC.10
Within the scope of AD, social determinants of health play an important role in contributing to disease morbidity. Environmental factors, including tobacco smoke, climate, pollutants, water hardness, und urban living, are related to AD prevalence and severity.11 Higher socioeconomic status is associated with increased AD rates,12 yet lower socioeconomic status is associated with more severe disease.13 Barriers to health care access and suboptimal care drive worse AD outcomes.14 Underrepresentation in clinical trials prevents the generalizability and safety of AD treatments.15 Disparities in these health determinants associated with AD likely are among the most important drivers of observed differences in disease presentation, severity, burden, and even prevalence—more so than genetics or ancestry alone16—yet this relationship is poorly understood and often presented as a consequence of race. It is critical to redefine the narrative when considering the heterogeneous presentations of AD in patients with SOC and acknowledge the limitations of current terminology when attempting to capture clinical diversity in AD, including in this review, where published findings often are limited by race-based analysis.
Epidemiology
The prevalence of AD has been increasing over the last few decades, and rates vary by region. In the United States, the prevalence of childhood and adult AD is 13% and 7%, respectively.17,18 Globally, higher rates of pediatric AD are seen in Africa, Oceania, Southeast Asia (SEA), and Latin America compared to South Asia, Northern Europe, and Eastern Europe.19 The prevalence of AD varies widely within the same continent and country; for example, throughout Africa, prevalence was found to be anywhere between 4.7% and 23.3%.20
Lesion Morphology
Although AD lesions often are described as pruritic erythematous papules and plaques, other common morphologies in SOC populations include prurigo nodules, lichenoid papules, perifollicular papules, nummular lesions, and psoriasiform lesions (Table). Instead of applying normative terms such as classic vs atypical to AD morphology, we urge clinicians to be familiar with the full spectrum of AD skin signs.

Prurigo Nodules—Prurigo nodules are hyperkeratotic or erosive nodules with severe pruritus, often grouped symmetrically on the extensor surfaces of the arms, legs, and trunk (Figure 1).14,21 The skin between lesions usually is unaffected but can be dry or lichenified or display postinflammatory pigmentary changes.14 Prurigo nodules are common. In a study of a cohort of patients with prurigo nodularis (N=108), nearly half (46.3%) were determined to have either an atopic predisposition or underlying AD as a contributing cause of the lesions.21

Prurigo nodules as a phenotype of AD may be more common in certain SOC populations. Studies from SEA have reported a higher prevalence of prurigo nodules among patients with AD.28 Although there are limited formal studies assessing the true prevalence of this lesion type in African American AD patients in the United States, clinical evidence supports more frequent appearance of prurigo nodules in non-White patients.29 Contributing factors include suboptimal care for AD in SOC populations and/or barriers to health care access, resulting in more severe disease that increases the risk for this lesion type.14
Lichenoid Papules—Papular lichenoid lesions often present on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs in AD (Figure 2).22 In a study of Nigerian patients with AD (N=1019), 54.1% had lichenoid papules.24 A systematic review of AD characteristics by region similarly reported an increased prevalence of this lesion type in African studies.28 Lichenoid variants of AD have been well described in SOC patients in the United States.23 In contrast to the lesions of lichen planus, the lichenoid papules of AD usually are round, rarely display koebnerization, do not have Wickham striae, and predominantly are located on extensor surfaces.

Perifollicular Papules—Perifollicular accentuation—dermatitis enhanced around hair follicles—is a well-described lesional morphology of AD that is noted in all racial/ethnic groups (Figure 3).22 In fact, perifollicular accentuation is included as one of the Hanifin and Rajka minor criteria for AD.30 Studies performed in Nigeria and India showed perifollicular accentuation in up to 70% of AD patients.24,31 In a study of adult Thai patients (N=56), follicular lesions were found more frequently in intrinsic AD (29%) compared with extrinsic AD (12%).32
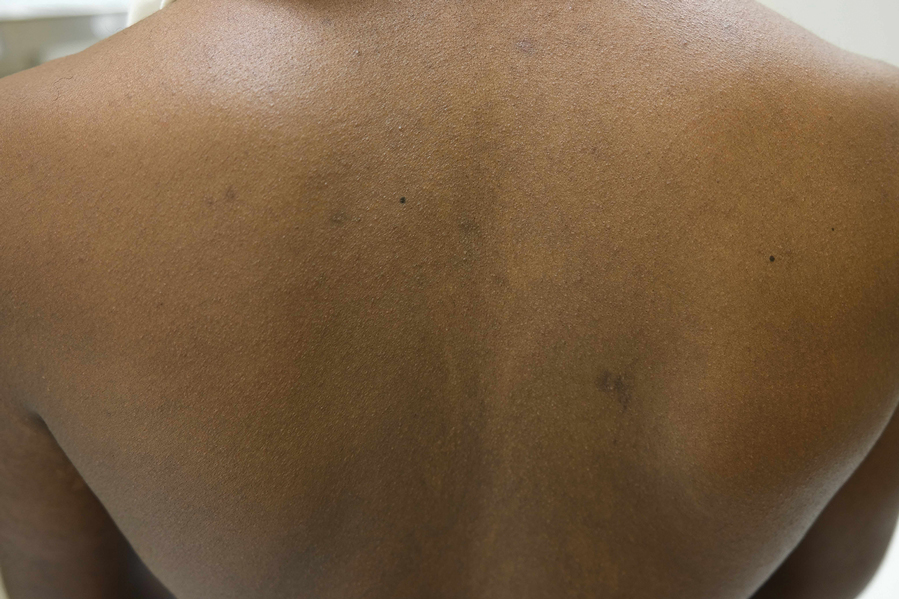
Nummular and Psoriasiform Lesions—Nummular lesions may be red, oozing, excoriated, studded with pustules and/or present on the extensor extremities (Figure 4). In SOC patients, these lesions often occur in areas where hyperpigmentation is noted.22 Studies in the United States and Mexico demonstrated that 15% to 17% of AD patients displayed nummular lesions.23,33 Similar to follicular papules, nummular lesions were linked to intrinsic AD in a study of adult Thai patients.32

Psoriasiform lesions show prominent scaling, lichenification, and clear demarcation.25 It has been reported that the psoriasiform phenotype of AD is more common in Asian patients,25 though this is likely an oversimplification. The participants in these studies were of Japanese and Korean ancestry, which covers a broad geographic region, and the grouping of individuals under a heterogeneous Asian category is unlikely to convey generalizable biologic or clinical information. Unsurprisingly, a systematic review of AD characteristics by region noted considerable phenotypical differences among patients in SEA, East Asia, Iran, and India.28
Disease Severity
Several factors contribute to AD disease severity,34 including objective assessments of inflammation, such as erythema and lichenification (Table), as well as subjective measures of symptoms, such as itch. The severity of AD is exacerbated by the social determinants of health, and a lower socioeconomic status, lower household income, lower parental education level and health, dilapidated housing, and presence of garbage on the street are among factors linked to worse AD disease severity.13,17 Although non-White individuals with AD often are reported to have more severe disease than their White counterparts,35 these types of health determinants may be the most relevant causes of observed differences.
Erythema—Erythema is a feature of inflammation used in the AD severity assessment. Erythema may appear in shades beyond red, including maroon, violaceous, or brown, in patients with darker pigmented skin, which may contribute to diagnosis of AD at a later disease stage.26 Multiple AD severity scoring tools, such as the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema Area and Severity Index, include erythema as a measure, which can lead to underestimation of AD severity in SOC populations. After adjusting for erythema score, one study found that Black children with AD had a risk for severe disease that was 6-times higher than White children.36 Dermatological training must adequately teach physicians to recognize erythema across all skin tones.37
Erythroderma (also known as exfoliative dermatitis) is rapidly spreading erythema on at least 90% of the total body surface area, often sparing the palms and soles.32 Erythroderma is a potentially life-threatening manifestation of severe AD. Although erythroderma may have many underlying causes, AD has been reported to be the cause in 5% to 24% of cases,38 and compared to studies in Europe, the prevalence of erythroderma was higher in East Asian studies of AD.28
Excoriation and Pruritus—Pruritus is a defining characteristic of AD, and the resulting excoriations often are predominant on physical examination, which is a key part of severity scores. Itch is the most prevalent symptom among patients with AD, and a greater itch severity has been linked to decreased health-related quality of life, increased mental health symptoms, impaired sleep, and decreased daily function.39,40 The burden of itch may be greater in SOC populations. The impact of itch on quality of life among US military veterans was significantly higher in those who identified as non-White (P=.05).41 In another study of US military veterans, African American individuals reported a significantly higher emotional impact from itch (P<.05).42
Lichenification—Lichenification is thickening of the skin due to chronic rubbing and scratching that causes a leathery elevated appearance with exaggerated skin lines.27 Lichenification is included as a factor in common clinical scoring tools, with greater lichenification indicating greater disease severity. Studies from SEA and Africa suggested a higher prevalence of lichenification in AD patients.28 A greater itch burden and thus increased rubbing/scratching in these populations may contribute to some of these findings.42,43
Xerosis—Xerosis (or dry skin) is a common finding in AD that results from increased transepidermal water loss due to a dysfunctional epidermal barrier.44 In a systematic review of AD characteristics by region, xerosis was among the top 5 most reported AD features globally in all regions except SEA.28 Xerosis may be more stigmatizing in SOC populations because of the greater visibility of scaling and dryness on darker skin tones.1
Postinflammatory Dyspigmentation—Postinflammatory pigment alteration may be a consequence of AD lesions, resulting in hyperpigmented and hypopigmented macules and patches. Patients with AD with darker skin tones are more likely to develop postinflammatory dyspigmentation.26 A study of AD patients in Nigeria found that 63% displayed postinflammatory dyspigmentation.45 Dyschromia, including postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, is one of the most common reasons for SOC patients to seek dermatologic care.46 Postinflammatory pigment alteration can cause severe distress in patients, even more so than the cutaneous findings of AD. Although altered skin pigmentation usually returns to normal over weeks to months, skin depigmentation from chronic excoriation may be permanent.26 Appropriately treating hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation in SOC populations can greatly improve quality of life.47
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis is a cutaneous inflammatory disease that presents with many clinical phenotypes. Dermatologists should be trained to recognize the heterogeneous signs of AD present across the diverse skin types in SOC patients. Future research should move away from race-based analyses and focus on the complex interplay of environmental factors, social determinants of health, and skin pigmentation, as well as how these factors drive variations in AD lesional morphology and inflammation.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects individuals worldwide.1 Although AD previously was commonly described as a skin-limited disease of childhood characterized by eczema in the flexural folds and pruritus, our current understanding supports a more heterogeneous condition.2 We review the wide range of cutaneous presentations of AD with a focus on clinical and morphological presentations across diverse skin types—commonly referred to as skin of color (SOC).
Defining SOC in Relation to AD
The terms SOC, race, and ethnicity are used interchangeably, but their true meanings are distinct. Traditionally, race has been defined as a biological concept, grouping cohorts of individuals with a large degree of shared ancestry and genetic similarities,3 and ethnicity as a social construct, grouping individuals with common racial, national, tribal, religious, linguistic, or cultural backgrounds.4 In practice, both concepts can broadly be envisioned as mixed social, political, and economic constructs, as no one gene or biologic characteristic distinguishes one racial or ethnic group from another.5
The US Census Bureau recognizes 5 racial groupings: White, Black or African American, American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander.6 Hispanic or Latinx origin is considered an ethnicity. It is important to note the limitations of these labels, as they do not completely encapsulate the heterogeneity of the US population. Overgeneralization of racial and ethnic categories may dull or obscure true differences among populations.7
From an evolutionary perspective, skin pigmentation represents the product of 2 opposing clines produced by natural selection in response to both need for and protection from UV radiation across lattitudes.8 Defining SOC is not quite as simple. Skin of color often is equated with certain racial/ethnic groups, or even binary categories of Black vs non-Black or White vs non-White. Others may use the Fitzpatrick scale to discuss SOC, though this scale was originally created to measure the response of skin to UVA radiation exposure.9 The reality is that SOC is a complex term that cannot simply be defined by a certain group of skin tones, races, ethnicities, and/or Fitzpatrick skin types. With this in mind, SOC in the context of this article will often refer to non-White individuals based on the investigators’ terminology, but this definition is not all-encompassing.
Historically in medicine, racial/ethnic differences in outcomes have been equated to differences in biology/genetics without consideration of many external factors.10 The effects of racism, economic stability, health care access, environment, and education quality rarely are discussed, though they have a major impact on health and may better define associations with race or an SOC population. A discussion of the structural and social determinants of health contributing to disease outcomes should accompany any race-based guidelines to prevent inaccurately pathologizing race or SOC.10
Within the scope of AD, social determinants of health play an important role in contributing to disease morbidity. Environmental factors, including tobacco smoke, climate, pollutants, water hardness, und urban living, are related to AD prevalence and severity.11 Higher socioeconomic status is associated with increased AD rates,12 yet lower socioeconomic status is associated with more severe disease.13 Barriers to health care access and suboptimal care drive worse AD outcomes.14 Underrepresentation in clinical trials prevents the generalizability and safety of AD treatments.15 Disparities in these health determinants associated with AD likely are among the most important drivers of observed differences in disease presentation, severity, burden, and even prevalence—more so than genetics or ancestry alone16—yet this relationship is poorly understood and often presented as a consequence of race. It is critical to redefine the narrative when considering the heterogeneous presentations of AD in patients with SOC and acknowledge the limitations of current terminology when attempting to capture clinical diversity in AD, including in this review, where published findings often are limited by race-based analysis.
Epidemiology
The prevalence of AD has been increasing over the last few decades, and rates vary by region. In the United States, the prevalence of childhood and adult AD is 13% and 7%, respectively.17,18 Globally, higher rates of pediatric AD are seen in Africa, Oceania, Southeast Asia (SEA), and Latin America compared to South Asia, Northern Europe, and Eastern Europe.19 The prevalence of AD varies widely within the same continent and country; for example, throughout Africa, prevalence was found to be anywhere between 4.7% and 23.3%.20
Lesion Morphology
Although AD lesions often are described as pruritic erythematous papules and plaques, other common morphologies in SOC populations include prurigo nodules, lichenoid papules, perifollicular papules, nummular lesions, and psoriasiform lesions (Table). Instead of applying normative terms such as classic vs atypical to AD morphology, we urge clinicians to be familiar with the full spectrum of AD skin signs.

Prurigo Nodules—Prurigo nodules are hyperkeratotic or erosive nodules with severe pruritus, often grouped symmetrically on the extensor surfaces of the arms, legs, and trunk (Figure 1).14,21 The skin between lesions usually is unaffected but can be dry or lichenified or display postinflammatory pigmentary changes.14 Prurigo nodules are common. In a study of a cohort of patients with prurigo nodularis (N=108), nearly half (46.3%) were determined to have either an atopic predisposition or underlying AD as a contributing cause of the lesions.21

Prurigo nodules as a phenotype of AD may be more common in certain SOC populations. Studies from SEA have reported a higher prevalence of prurigo nodules among patients with AD.28 Although there are limited formal studies assessing the true prevalence of this lesion type in African American AD patients in the United States, clinical evidence supports more frequent appearance of prurigo nodules in non-White patients.29 Contributing factors include suboptimal care for AD in SOC populations and/or barriers to health care access, resulting in more severe disease that increases the risk for this lesion type.14
Lichenoid Papules—Papular lichenoid lesions often present on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs in AD (Figure 2).22 In a study of Nigerian patients with AD (N=1019), 54.1% had lichenoid papules.24 A systematic review of AD characteristics by region similarly reported an increased prevalence of this lesion type in African studies.28 Lichenoid variants of AD have been well described in SOC patients in the United States.23 In contrast to the lesions of lichen planus, the lichenoid papules of AD usually are round, rarely display koebnerization, do not have Wickham striae, and predominantly are located on extensor surfaces.

Perifollicular Papules—Perifollicular accentuation—dermatitis enhanced around hair follicles—is a well-described lesional morphology of AD that is noted in all racial/ethnic groups (Figure 3).22 In fact, perifollicular accentuation is included as one of the Hanifin and Rajka minor criteria for AD.30 Studies performed in Nigeria and India showed perifollicular accentuation in up to 70% of AD patients.24,31 In a study of adult Thai patients (N=56), follicular lesions were found more frequently in intrinsic AD (29%) compared with extrinsic AD (12%).32
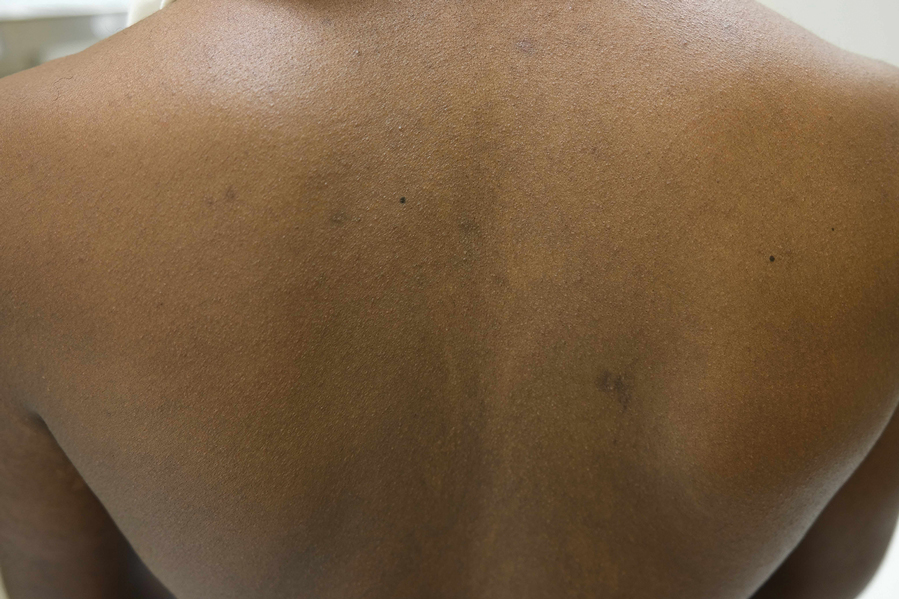
Nummular and Psoriasiform Lesions—Nummular lesions may be red, oozing, excoriated, studded with pustules and/or present on the extensor extremities (Figure 4). In SOC patients, these lesions often occur in areas where hyperpigmentation is noted.22 Studies in the United States and Mexico demonstrated that 15% to 17% of AD patients displayed nummular lesions.23,33 Similar to follicular papules, nummular lesions were linked to intrinsic AD in a study of adult Thai patients.32

Psoriasiform lesions show prominent scaling, lichenification, and clear demarcation.25 It has been reported that the psoriasiform phenotype of AD is more common in Asian patients,25 though this is likely an oversimplification. The participants in these studies were of Japanese and Korean ancestry, which covers a broad geographic region, and the grouping of individuals under a heterogeneous Asian category is unlikely to convey generalizable biologic or clinical information. Unsurprisingly, a systematic review of AD characteristics by region noted considerable phenotypical differences among patients in SEA, East Asia, Iran, and India.28
Disease Severity
Several factors contribute to AD disease severity,34 including objective assessments of inflammation, such as erythema and lichenification (Table), as well as subjective measures of symptoms, such as itch. The severity of AD is exacerbated by the social determinants of health, and a lower socioeconomic status, lower household income, lower parental education level and health, dilapidated housing, and presence of garbage on the street are among factors linked to worse AD disease severity.13,17 Although non-White individuals with AD often are reported to have more severe disease than their White counterparts,35 these types of health determinants may be the most relevant causes of observed differences.
Erythema—Erythema is a feature of inflammation used in the AD severity assessment. Erythema may appear in shades beyond red, including maroon, violaceous, or brown, in patients with darker pigmented skin, which may contribute to diagnosis of AD at a later disease stage.26 Multiple AD severity scoring tools, such as the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema Area and Severity Index, include erythema as a measure, which can lead to underestimation of AD severity in SOC populations. After adjusting for erythema score, one study found that Black children with AD had a risk for severe disease that was 6-times higher than White children.36 Dermatological training must adequately teach physicians to recognize erythema across all skin tones.37
Erythroderma (also known as exfoliative dermatitis) is rapidly spreading erythema on at least 90% of the total body surface area, often sparing the palms and soles.32 Erythroderma is a potentially life-threatening manifestation of severe AD. Although erythroderma may have many underlying causes, AD has been reported to be the cause in 5% to 24% of cases,38 and compared to studies in Europe, the prevalence of erythroderma was higher in East Asian studies of AD.28
Excoriation and Pruritus—Pruritus is a defining characteristic of AD, and the resulting excoriations often are predominant on physical examination, which is a key part of severity scores. Itch is the most prevalent symptom among patients with AD, and a greater itch severity has been linked to decreased health-related quality of life, increased mental health symptoms, impaired sleep, and decreased daily function.39,40 The burden of itch may be greater in SOC populations. The impact of itch on quality of life among US military veterans was significantly higher in those who identified as non-White (P=.05).41 In another study of US military veterans, African American individuals reported a significantly higher emotional impact from itch (P<.05).42
Lichenification—Lichenification is thickening of the skin due to chronic rubbing and scratching that causes a leathery elevated appearance with exaggerated skin lines.27 Lichenification is included as a factor in common clinical scoring tools, with greater lichenification indicating greater disease severity. Studies from SEA and Africa suggested a higher prevalence of lichenification in AD patients.28 A greater itch burden and thus increased rubbing/scratching in these populations may contribute to some of these findings.42,43
Xerosis—Xerosis (or dry skin) is a common finding in AD that results from increased transepidermal water loss due to a dysfunctional epidermal barrier.44 In a systematic review of AD characteristics by region, xerosis was among the top 5 most reported AD features globally in all regions except SEA.28 Xerosis may be more stigmatizing in SOC populations because of the greater visibility of scaling and dryness on darker skin tones.1
Postinflammatory Dyspigmentation—Postinflammatory pigment alteration may be a consequence of AD lesions, resulting in hyperpigmented and hypopigmented macules and patches. Patients with AD with darker skin tones are more likely to develop postinflammatory dyspigmentation.26 A study of AD patients in Nigeria found that 63% displayed postinflammatory dyspigmentation.45 Dyschromia, including postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, is one of the most common reasons for SOC patients to seek dermatologic care.46 Postinflammatory pigment alteration can cause severe distress in patients, even more so than the cutaneous findings of AD. Although altered skin pigmentation usually returns to normal over weeks to months, skin depigmentation from chronic excoriation may be permanent.26 Appropriately treating hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation in SOC populations can greatly improve quality of life.47
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis is a cutaneous inflammatory disease that presents with many clinical phenotypes. Dermatologists should be trained to recognize the heterogeneous signs of AD present across the diverse skin types in SOC patients. Future research should move away from race-based analyses and focus on the complex interplay of environmental factors, social determinants of health, and skin pigmentation, as well as how these factors drive variations in AD lesional morphology and inflammation.
- Alexis A, Woolery-Lloyd H, Andriessen A, et al. Insights in skin of color patients with atopic dermatitis and the role of skincare in improving outcomes. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:462-470. doi:10.36849/jdd.6609
- Chovatiya R, Silverberg JI. The heterogeneity of atopic dermatitis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:172-176. doi:10.36849/JDD.6408
- Taylor SC, Cook-Bolden F. Defining skin of color. Cutis. 2002;69:435-437.
- Georgetown University Center for Child and Human Development. Bridging the cultural divide in health care settings: the essential role of cultural broker programs. Accessed October 6, 2023. https://nccc.georgetown.edu/culturalbroker/8_Definitions/2_Definitions.html#:~:text=ethnic%3A%20Of%20or%20relating%20to,or%20cultural%20origin%20or%20background
- Shoo BA, Kashani-Sabet M. Melanoma arising in African-, Asian-, Latino- and Native-American populations. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:96-102. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2009.04.005
- US Census Bureau. About the topic of race. Revised March 1, 2022. Accessed October 5, 2023. https://www.census.gov/topics/population/race/about.html
- Williams HC. Have you ever seen an Asian/Pacific Islander? Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:673-674. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.5.673
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Colloquium paper: human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(Suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Fitzpatrick TB. The validity and practicality of sun-reactive skin types I through VI. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:869-871. doi:10.1001/archderm.124.6.869
- Amutah C, Greenidge K, Mante A, et al. Misrepresenting race—the role of medical schools in propagating physician bias. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:872-878. doi:10.1056/NEJMms2025768
- Kantor R, Silverberg JI. Environmental risk factors and their role in the management of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017;13:15-26. doi:10.1080/1744666x.2016.1212660
- Fu T, Keiser E, Linos E, et al. Eczema and sensitization to common allergens in the United States: a multiethnic, population-based study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:21-26. doi:10.1111/pde.12237
- Tackett KJ, Jenkins F, Morrell DS, et al. Structural racism and its influence on the severity of atopic dermatitis in African American children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:142-146. doi:10.1111/pde.14058
- Huang AH, Williams KA, Kwatra SG. Prurigo nodularis: epidemiology and clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1559-1565. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.183
- Hirano SA, Murray SB, Harvey VM. Reporting, representation, and subgroup analysis of race and ethnicity in published clinical trials of atopic dermatitis in the United States between 2000 and 2009. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:749-755. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01797.x
- Polcari I, Becker L, Stein SL, et al. Filaggrin gene mutations in African Americans with both ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:489-492. doi:10.1111/pde.12355
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL. Associations of childhood eczema severity: a US population-based study. Dermatitis. 2014;25:107-114. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000034
- Hua T, Silverberg JI. Atopic dermatitis in US adults: epidemiology, association with marital status, and atopy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:622-624. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2018.07.019
- Odhiambo JA, Williams HC, Clayton TO, et al. Global variations in prevalence of eczema symptoms in children from ISAAC Phase Three. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1251-8.e23. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.009
- Ait-Khaled N, Odhiambo J, Pearce N, et al. Prevalence of symptoms of asthma, rhinitis and eczema in 13- to 14-year-old children in Africa: the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood Phase III. Allergy. 2007;62:247-258. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01325.x
- Iking A, Grundmann S, Chatzigeorgakidis E, et al. Prurigo as a symptom of atopic and non-atopic diseases: aetiological survey in a consecutive cohort of 108 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:550-557. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04481.x
- Silverberg NB. Typical and atypical clinical appearance of atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:354-359. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2017.03.007
- Allen HB, Jones NP, Bowen SE. Lichenoid and other clinical presentations of atopic dermatitis in an inner city practice. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:503-504. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.03.033
- Nnoruka EN. Current epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in south-eastern Nigeria. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:739-744. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02360.x
- Noda S, Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, et al. The Asian atopic dermatitis phenotype combines features of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis with increased TH17 polarization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1254-1264. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.08.015
- Kaufman BP, Guttman-Yassky E, Alexis AF. Atopic dermatitis in diverse racial and ethnic groups-variations in epidemiology, genetics, clinical presentation and treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:340-357. doi:10.1111/exd.13514
- Girolomoni G, de Bruin-Weller M, Aoki V, et al. Nomenclature and clinical phenotypes of atopic dermatitis. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021;12:20406223211002979. doi:10.1177/20406223211002979
- Yew YW, Thyssen JP, Silverberg JI. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the regional and age-related differences in atopic dermatitis clinical characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:390-401. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.035
- Vachiramon V, Tey HL, Thompson AE, et al. Atopic dermatitis in African American children: addressing unmet needs of a common disease. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:395-402. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01740.x
- Hanifin JM. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1980;92:44-47.
- Dutta A, De A, Das S, et al. A cross-sectional evaluation of the usefulness of the minor features of Hanifin and Rajka diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in the pediatric population. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:583-590. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_1046_20
- Kulthanan K, Boochangkool K, Tuchinda P, et al. Clinical features of the extrinsic and intrinsic types of adult-onset atopic dermatitis. Asia Pac Allergy. 2011;1:80-86. doi:10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.2.80
- Julián-Gónzalez RE, Orozco-Covarrubias L, Durán-McKinster C, et al. Less common clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis: prevalence by age. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:580-583. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01739.x
- Chovatiya R, Silverberg JI. Evaluating the longitudinal course of atopic dermatitis: a review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:688-689. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.02.005
- Kim Y, Blomberg M, Rifas-Shiman SL, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in incidence and persistence of childhood atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:827-834. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.029
- Ben-Gashir MA, Hay RJ. Reliance on erythema scores may mask severe atopic dermatitis in black children compared with their white counterparts. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:920-925. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04965.x
- McKenzie S, Brown-Korsah JB, Syder NC, et al. Variations in genetics, biology, and phenotype of cutaneous disorders in skin of color. part II: differences in clinical presentation and disparities in cutaneous disorders in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1261-1270. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.03.067
- Cuellar-Barboza A, Ocampo-Candiani J, Herz-Ruelas ME. A practical approach to the diagnosis and treatment of adult erythroderma [in English, Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2018;109:777-790. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2018.05.011
- Lei DK, Yousaf M, Janmohamed SR, et al. Validation of patient-reported outcomes information system sleep disturbance and sleep-related impairment in adults with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:875-882. doi:10.1111/bjd.18920
- Silverberg JI, Gelfand JM, Margolis DJ, et al. Patient burden and quality of life in atopic dermatitis in US adults: a population-based cross-sectional study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:340-347. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2018.07.006
- Carr CW, Veledar E, Chen SC. Factors mediating the impact of chronic pruritus on quality of life. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:613-620. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.7696
- Shaw FM, Luk KMH, Chen KH, et al. Racial disparities in the impact of chronic pruritus: a cross-sectional study on quality of life and resource utilization in United States veterans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:63-69. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.01.016
- Oh CC, Li H, Lee W, et al. Biopsychosocial factors associated with prurigo nodularis in endogenous eczema. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:525. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.164451
- Vyumvuhore R, Michael-Jubeli R, Verzeaux L, et al. Lipid organization in xerosis: the key of the problem? Int J Cosmet Sci. 2018;40:549-554. doi:10.1111/ics.12496
- George AO. Atopic dermatitis in Nigeria. Int J Dermatol. 1989;28:237-239. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1989.tb04811.x
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Dupilumab improves atopic dermatitis and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in patient with skin of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:776-778. doi:10.36849/jdd.2020.4937
- Alexis A, Woolery-Lloyd H, Andriessen A, et al. Insights in skin of color patients with atopic dermatitis and the role of skincare in improving outcomes. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:462-470. doi:10.36849/jdd.6609
- Chovatiya R, Silverberg JI. The heterogeneity of atopic dermatitis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:172-176. doi:10.36849/JDD.6408
- Taylor SC, Cook-Bolden F. Defining skin of color. Cutis. 2002;69:435-437.
- Georgetown University Center for Child and Human Development. Bridging the cultural divide in health care settings: the essential role of cultural broker programs. Accessed October 6, 2023. https://nccc.georgetown.edu/culturalbroker/8_Definitions/2_Definitions.html#:~:text=ethnic%3A%20Of%20or%20relating%20to,or%20cultural%20origin%20or%20background
- Shoo BA, Kashani-Sabet M. Melanoma arising in African-, Asian-, Latino- and Native-American populations. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:96-102. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2009.04.005
- US Census Bureau. About the topic of race. Revised March 1, 2022. Accessed October 5, 2023. https://www.census.gov/topics/population/race/about.html
- Williams HC. Have you ever seen an Asian/Pacific Islander? Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:673-674. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.5.673
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Colloquium paper: human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(Suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Fitzpatrick TB. The validity and practicality of sun-reactive skin types I through VI. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:869-871. doi:10.1001/archderm.124.6.869
- Amutah C, Greenidge K, Mante A, et al. Misrepresenting race—the role of medical schools in propagating physician bias. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:872-878. doi:10.1056/NEJMms2025768
- Kantor R, Silverberg JI. Environmental risk factors and their role in the management of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017;13:15-26. doi:10.1080/1744666x.2016.1212660
- Fu T, Keiser E, Linos E, et al. Eczema and sensitization to common allergens in the United States: a multiethnic, population-based study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:21-26. doi:10.1111/pde.12237
- Tackett KJ, Jenkins F, Morrell DS, et al. Structural racism and its influence on the severity of atopic dermatitis in African American children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37:142-146. doi:10.1111/pde.14058
- Huang AH, Williams KA, Kwatra SG. Prurigo nodularis: epidemiology and clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1559-1565. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.183
- Hirano SA, Murray SB, Harvey VM. Reporting, representation, and subgroup analysis of race and ethnicity in published clinical trials of atopic dermatitis in the United States between 2000 and 2009. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:749-755. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01797.x
- Polcari I, Becker L, Stein SL, et al. Filaggrin gene mutations in African Americans with both ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:489-492. doi:10.1111/pde.12355
- Silverberg JI, Simpson EL. Associations of childhood eczema severity: a US population-based study. Dermatitis. 2014;25:107-114. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000034
- Hua T, Silverberg JI. Atopic dermatitis in US adults: epidemiology, association with marital status, and atopy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:622-624. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2018.07.019
- Odhiambo JA, Williams HC, Clayton TO, et al. Global variations in prevalence of eczema symptoms in children from ISAAC Phase Three. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1251-8.e23. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.009
- Ait-Khaled N, Odhiambo J, Pearce N, et al. Prevalence of symptoms of asthma, rhinitis and eczema in 13- to 14-year-old children in Africa: the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood Phase III. Allergy. 2007;62:247-258. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01325.x
- Iking A, Grundmann S, Chatzigeorgakidis E, et al. Prurigo as a symptom of atopic and non-atopic diseases: aetiological survey in a consecutive cohort of 108 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:550-557. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04481.x
- Silverberg NB. Typical and atypical clinical appearance of atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:354-359. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2017.03.007
- Allen HB, Jones NP, Bowen SE. Lichenoid and other clinical presentations of atopic dermatitis in an inner city practice. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:503-504. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.03.033
- Nnoruka EN. Current epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in south-eastern Nigeria. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:739-744. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02360.x
- Noda S, Suárez-Fariñas M, Ungar B, et al. The Asian atopic dermatitis phenotype combines features of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis with increased TH17 polarization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1254-1264. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.08.015
- Kaufman BP, Guttman-Yassky E, Alexis AF. Atopic dermatitis in diverse racial and ethnic groups-variations in epidemiology, genetics, clinical presentation and treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:340-357. doi:10.1111/exd.13514
- Girolomoni G, de Bruin-Weller M, Aoki V, et al. Nomenclature and clinical phenotypes of atopic dermatitis. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021;12:20406223211002979. doi:10.1177/20406223211002979
- Yew YW, Thyssen JP, Silverberg JI. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the regional and age-related differences in atopic dermatitis clinical characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:390-401. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.035
- Vachiramon V, Tey HL, Thompson AE, et al. Atopic dermatitis in African American children: addressing unmet needs of a common disease. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:395-402. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01740.x
- Hanifin JM. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1980;92:44-47.
- Dutta A, De A, Das S, et al. A cross-sectional evaluation of the usefulness of the minor features of Hanifin and Rajka diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in the pediatric population. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:583-590. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_1046_20
- Kulthanan K, Boochangkool K, Tuchinda P, et al. Clinical features of the extrinsic and intrinsic types of adult-onset atopic dermatitis. Asia Pac Allergy. 2011;1:80-86. doi:10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.2.80
- Julián-Gónzalez RE, Orozco-Covarrubias L, Durán-McKinster C, et al. Less common clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis: prevalence by age. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:580-583. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01739.x
- Chovatiya R, Silverberg JI. Evaluating the longitudinal course of atopic dermatitis: a review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:688-689. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.02.005
- Kim Y, Blomberg M, Rifas-Shiman SL, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in incidence and persistence of childhood atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:827-834. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.029
- Ben-Gashir MA, Hay RJ. Reliance on erythema scores may mask severe atopic dermatitis in black children compared with their white counterparts. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:920-925. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04965.x
- McKenzie S, Brown-Korsah JB, Syder NC, et al. Variations in genetics, biology, and phenotype of cutaneous disorders in skin of color. part II: differences in clinical presentation and disparities in cutaneous disorders in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1261-1270. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.03.067
- Cuellar-Barboza A, Ocampo-Candiani J, Herz-Ruelas ME. A practical approach to the diagnosis and treatment of adult erythroderma [in English, Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2018;109:777-790. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2018.05.011
- Lei DK, Yousaf M, Janmohamed SR, et al. Validation of patient-reported outcomes information system sleep disturbance and sleep-related impairment in adults with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:875-882. doi:10.1111/bjd.18920
- Silverberg JI, Gelfand JM, Margolis DJ, et al. Patient burden and quality of life in atopic dermatitis in US adults: a population-based cross-sectional study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121:340-347. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2018.07.006
- Carr CW, Veledar E, Chen SC. Factors mediating the impact of chronic pruritus on quality of life. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:613-620. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.7696
- Shaw FM, Luk KMH, Chen KH, et al. Racial disparities in the impact of chronic pruritus: a cross-sectional study on quality of life and resource utilization in United States veterans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:63-69. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.01.016
- Oh CC, Li H, Lee W, et al. Biopsychosocial factors associated with prurigo nodularis in endogenous eczema. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:525. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.164451
- Vyumvuhore R, Michael-Jubeli R, Verzeaux L, et al. Lipid organization in xerosis: the key of the problem? Int J Cosmet Sci. 2018;40:549-554. doi:10.1111/ics.12496
- George AO. Atopic dermatitis in Nigeria. Int J Dermatol. 1989;28:237-239. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1989.tb04811.x
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Dupilumab improves atopic dermatitis and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in patient with skin of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:776-778. doi:10.36849/jdd.2020.4937
Practice Points
- Social determinants of health play a central role in observed racial and ethnic differences in studies of atopic dermatitis (AD) in patients with skin of color.
- Prurigo nodules, lichenoid papules, perifollicular papules, nummular lesions, and psoriasiform lesions are among the diverse lesion morphologies seen with AD.
- Key signs of cutaneous inflammation and lesional severity, including erythema, may present differently in darker skin tones and contribute to underestimation of severity.
- Postinflammatory dyspigmentation is common among patients with skin of color, and treatment can substantially improve quality of life.
Predictors of prescription opioid overdose
A Canadian systematic review of 28 observational studies has identified 10 strong predictors of fatal and nonfatal prescription opioid overdose.
Published in CMAJ, the analysis found the risk of fatal and nonfatal opioid overdose was notably tied to such factors as high-dose and fentanyl prescriptions, multiple opioid prescribers or pharmacies, and several mental health issues. High-certainty evidence from 14 studies involving more than a million patients showed a linear dose-response relationship with opioid overdose.
“Our findings suggest that awareness of, and attention to, several patient and prescription characteristics may help reduce the risk of opioid overdose among people living with chronic pain,” wrote a research team led by Li Wang, PhD, a researcher at the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Pain Research and Care and the department of anesthesia at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
Predictors of fatal and nonfatal overdose
Reporting on studies of 103 possible predictors in a pooled cohort of almost 24 million patients, the review found moderate- to high-certainty evidence for large relative associations with the following 10 criteria:
- A history of overdose (odds ratio, 5.85; 95% confidence interval, 3.78-9.04).
- A higher opioid dosage (OR, 2.57; 95% CI, 2.08-3.18 per 90-mg increment).
- Three or more prescribers (OR, 4.68; 95% CI, 3.57-6.12).
- Four or more dispensing pharmacies (OR, 4.92; 95% CI, 4.35-5.57).
- Prescription for fentanyl (OR, 2.80; 95% CI, 2.30-3.41).
- Current substance use disorder (OR, 2.62; 95% CI, 2.09-3.27).
- Any mental health diagnosis (OR, 2.12; 95% CI, 1.73-2.61).
- Depression (OR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.57-314).
- Bipolar disorder (OR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.77-2.41).
- Pancreatitis (OR, 2.00; 95% CI,1.52-2.64).
Absolute risks in patients with the predictor ranged from 2 to 6 per 1,000 for fatal overdose and 4 to 12 per 1,000 for nonfatal overdose.
The authors noted that chronic pain affects 20% of the world’s population worldwide, and a 2021 meta-analysis of 60 observational studies revealed that opioids are prescribed for 27% of adults living with chronic pain, with a higher prevalence of prescribing in North America than in Europe.
International review
A total of 28 observational studies comprising 23,963,716 patients (52% female) with mean age of 52 years were enrolled. All used administrative databases. Twenty-four studies were conducted in the United States, three in Canada, and one in the United Kingdom. Twenty-one studies included only patients with noncancer chronic pain, while seven included patients with either cancer-related or noncancer chronic pain. Twenty-two studies accepted patients with previous or current substance use disorder and three excluded patients with comorbid substance use disorder. Twenty-three studies included patients with comorbid mental illness and five exclusively recruited veterans.
The median sample size was 43,885. As a limitation, 25 studies (89%) were at high risk of bias for at least one criterion, the authors acknowledged. Moderate-certainty evidence showed the pooled prevalence of fatal opioid overdose after prescription for chronic pain was 1.3 per 1,000 (95% CI, 0.6-2.3 per 1,000) for fatal overdose and 3.2 per 1,000 (95% CI, 2.0-4.7 per 1,000) for nonfatal overdose.
“Awareness of these predictors may facilitate shared decision-making regarding prescribing opioids for chronic pain and may inform harm-reduction strategies,” Dr. Wang and associates wrote.
This study was supported by a grant from Health Canada’s Substance Use and Addictions Program. Coauthor Dr. Corey Hayes was supported by Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development and the National Institute on Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network. Dr. Jason Busse is supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. David Juurlink has received travel support for presentations from the CIHR, Stanford University, and Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center.
A Canadian systematic review of 28 observational studies has identified 10 strong predictors of fatal and nonfatal prescription opioid overdose.
Published in CMAJ, the analysis found the risk of fatal and nonfatal opioid overdose was notably tied to such factors as high-dose and fentanyl prescriptions, multiple opioid prescribers or pharmacies, and several mental health issues. High-certainty evidence from 14 studies involving more than a million patients showed a linear dose-response relationship with opioid overdose.
“Our findings suggest that awareness of, and attention to, several patient and prescription characteristics may help reduce the risk of opioid overdose among people living with chronic pain,” wrote a research team led by Li Wang, PhD, a researcher at the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Pain Research and Care and the department of anesthesia at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
Predictors of fatal and nonfatal overdose
Reporting on studies of 103 possible predictors in a pooled cohort of almost 24 million patients, the review found moderate- to high-certainty evidence for large relative associations with the following 10 criteria:
- A history of overdose (odds ratio, 5.85; 95% confidence interval, 3.78-9.04).
- A higher opioid dosage (OR, 2.57; 95% CI, 2.08-3.18 per 90-mg increment).
- Three or more prescribers (OR, 4.68; 95% CI, 3.57-6.12).
- Four or more dispensing pharmacies (OR, 4.92; 95% CI, 4.35-5.57).
- Prescription for fentanyl (OR, 2.80; 95% CI, 2.30-3.41).
- Current substance use disorder (OR, 2.62; 95% CI, 2.09-3.27).
- Any mental health diagnosis (OR, 2.12; 95% CI, 1.73-2.61).
- Depression (OR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.57-314).
- Bipolar disorder (OR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.77-2.41).
- Pancreatitis (OR, 2.00; 95% CI,1.52-2.64).
Absolute risks in patients with the predictor ranged from 2 to 6 per 1,000 for fatal overdose and 4 to 12 per 1,000 for nonfatal overdose.
The authors noted that chronic pain affects 20% of the world’s population worldwide, and a 2021 meta-analysis of 60 observational studies revealed that opioids are prescribed for 27% of adults living with chronic pain, with a higher prevalence of prescribing in North America than in Europe.
International review
A total of 28 observational studies comprising 23,963,716 patients (52% female) with mean age of 52 years were enrolled. All used administrative databases. Twenty-four studies were conducted in the United States, three in Canada, and one in the United Kingdom. Twenty-one studies included only patients with noncancer chronic pain, while seven included patients with either cancer-related or noncancer chronic pain. Twenty-two studies accepted patients with previous or current substance use disorder and three excluded patients with comorbid substance use disorder. Twenty-three studies included patients with comorbid mental illness and five exclusively recruited veterans.
The median sample size was 43,885. As a limitation, 25 studies (89%) were at high risk of bias for at least one criterion, the authors acknowledged. Moderate-certainty evidence showed the pooled prevalence of fatal opioid overdose after prescription for chronic pain was 1.3 per 1,000 (95% CI, 0.6-2.3 per 1,000) for fatal overdose and 3.2 per 1,000 (95% CI, 2.0-4.7 per 1,000) for nonfatal overdose.
“Awareness of these predictors may facilitate shared decision-making regarding prescribing opioids for chronic pain and may inform harm-reduction strategies,” Dr. Wang and associates wrote.
This study was supported by a grant from Health Canada’s Substance Use and Addictions Program. Coauthor Dr. Corey Hayes was supported by Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development and the National Institute on Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network. Dr. Jason Busse is supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. David Juurlink has received travel support for presentations from the CIHR, Stanford University, and Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center.
A Canadian systematic review of 28 observational studies has identified 10 strong predictors of fatal and nonfatal prescription opioid overdose.
Published in CMAJ, the analysis found the risk of fatal and nonfatal opioid overdose was notably tied to such factors as high-dose and fentanyl prescriptions, multiple opioid prescribers or pharmacies, and several mental health issues. High-certainty evidence from 14 studies involving more than a million patients showed a linear dose-response relationship with opioid overdose.
“Our findings suggest that awareness of, and attention to, several patient and prescription characteristics may help reduce the risk of opioid overdose among people living with chronic pain,” wrote a research team led by Li Wang, PhD, a researcher at the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Pain Research and Care and the department of anesthesia at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
Predictors of fatal and nonfatal overdose
Reporting on studies of 103 possible predictors in a pooled cohort of almost 24 million patients, the review found moderate- to high-certainty evidence for large relative associations with the following 10 criteria:
- A history of overdose (odds ratio, 5.85; 95% confidence interval, 3.78-9.04).
- A higher opioid dosage (OR, 2.57; 95% CI, 2.08-3.18 per 90-mg increment).
- Three or more prescribers (OR, 4.68; 95% CI, 3.57-6.12).
- Four or more dispensing pharmacies (OR, 4.92; 95% CI, 4.35-5.57).
- Prescription for fentanyl (OR, 2.80; 95% CI, 2.30-3.41).
- Current substance use disorder (OR, 2.62; 95% CI, 2.09-3.27).
- Any mental health diagnosis (OR, 2.12; 95% CI, 1.73-2.61).
- Depression (OR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.57-314).
- Bipolar disorder (OR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.77-2.41).
- Pancreatitis (OR, 2.00; 95% CI,1.52-2.64).
Absolute risks in patients with the predictor ranged from 2 to 6 per 1,000 for fatal overdose and 4 to 12 per 1,000 for nonfatal overdose.
The authors noted that chronic pain affects 20% of the world’s population worldwide, and a 2021 meta-analysis of 60 observational studies revealed that opioids are prescribed for 27% of adults living with chronic pain, with a higher prevalence of prescribing in North America than in Europe.
International review
A total of 28 observational studies comprising 23,963,716 patients (52% female) with mean age of 52 years were enrolled. All used administrative databases. Twenty-four studies were conducted in the United States, three in Canada, and one in the United Kingdom. Twenty-one studies included only patients with noncancer chronic pain, while seven included patients with either cancer-related or noncancer chronic pain. Twenty-two studies accepted patients with previous or current substance use disorder and three excluded patients with comorbid substance use disorder. Twenty-three studies included patients with comorbid mental illness and five exclusively recruited veterans.
The median sample size was 43,885. As a limitation, 25 studies (89%) were at high risk of bias for at least one criterion, the authors acknowledged. Moderate-certainty evidence showed the pooled prevalence of fatal opioid overdose after prescription for chronic pain was 1.3 per 1,000 (95% CI, 0.6-2.3 per 1,000) for fatal overdose and 3.2 per 1,000 (95% CI, 2.0-4.7 per 1,000) for nonfatal overdose.
“Awareness of these predictors may facilitate shared decision-making regarding prescribing opioids for chronic pain and may inform harm-reduction strategies,” Dr. Wang and associates wrote.
This study was supported by a grant from Health Canada’s Substance Use and Addictions Program. Coauthor Dr. Corey Hayes was supported by Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development and the National Institute on Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network. Dr. Jason Busse is supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. David Juurlink has received travel support for presentations from the CIHR, Stanford University, and Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center.
FROM CMAJ
Frontline myeloma treatments: ASCT vs. CAR T
“In an otherwise healthy treatment-naive patient with multiple myeloma, to ensure the best chances of overall survival, I would always recommend standard of care consolidation therapy of chemotherapy + ASCT,” said Sergio Giralt, MD, of New York’s Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, debating the merits of ASCT versus CAR T as consolidation therapy at the Lymphoma, Leukemia & Myeloma (LLM) Congress 2023 in New York.
Final results from the phase II GRIFFIN trial highlight the benchmarks that CAR T-cell therapy would need to reach to achieve equivalence with ASCT. At a 4-year follow-up, newly diagnosed MM patients who received daratumumab, lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (D-RVd) followed by ASCT + D-RVd consolidation, and daratumumab maintenance, had a progression-free survival (PFS) rate of 87.3%, 92.7% overall survival (OS) rate, and 50% achieved minimal residual disease negativity.
Dr. Adriana Rossi, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, cited a convergence of evidence suggesting that CAR T could achieve impressive results as a consolidation therapy in fit patients with MM, including: CARTITUDE 1 and CARTITUDE 4, which studied CAR T in RR MM patients. However, due to the fact that no head-to-head study of CAR T vs. ASCT as consolidation therapy in otherwise healthy MM patients exists, “There is not enough long-term data to support the equivalence CAR T with ASCT,” Dr. Giralt concluded.
Dr. Rossi further advocated for considering CAR T as a consolidation treatment because of the risks of secondary malignancies associated with ACST maintenance regimens.
Dr. Giralt rebutted this argument by citing data about averse events (AE) in studies of CAR-T therapies in RR MM patients like KarMMa-2, in which grade 3-4 neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia occurred in 94.6%, 45.9%, and 37.8% of patients respectively. Furthermore, 2 of 37 patients in KarMMA died (1 pneumonia, 1 pseudomonal sepsis), while rates of death from AEs related to ASCT occur in less than 1% of patients, according to Dr. Giralt.
Beyond a dearth of evidence thus far about the long term PFS, OS, and safety profile superiority of CAR-T therapies, compared with ASCT in treatment-naive MM patients, Dr. Giralt also noted the facts that CAR T-cell therapies are expensive and require manufacturing infrastructure also demonstrate that they cannot be easily adopted everywhere, even as a third-line therapy.
“In many places like Morocco, where I practice, we do not have access to CAR-T therapies,” said Sadia Zafad, MD, of the Clinique Al Madina Hematology and Oncology Center in Casablanca, Morocco. Dr. Zafad attended the debate.
A lack of access to CAR T is also a problem in the United States, where wait times for the therapy can stretch up to 6 months, getting insurance approval is challenging, and many patients simply don’t live near a center where CAR T-cell therapy is available. Citing all these factors, Dr. Giralt concluded: “Even if CAR T can be shown to have the same results as transplant, it is much more resource-intensive than transplant, and insurers are going to start saying there’s no necessary benefit. We have yet to use value as a primary end point, but as cancer care gets more and more expensive, that’s going to come up more, for CAR T and other novel therapies.”
Dr. Giralt reported relationships with Actinuum, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Crisper, J&J, Jazz, Kite, Miltenyi, Novartis, Sanofi, and Takeda. Dr. Rossi disclosed ties with Adaptive, BMS, Celgene, JNJ, Sanofi & Genzyme. Dr. Zafad reported no disclosures.
“In an otherwise healthy treatment-naive patient with multiple myeloma, to ensure the best chances of overall survival, I would always recommend standard of care consolidation therapy of chemotherapy + ASCT,” said Sergio Giralt, MD, of New York’s Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, debating the merits of ASCT versus CAR T as consolidation therapy at the Lymphoma, Leukemia & Myeloma (LLM) Congress 2023 in New York.
Final results from the phase II GRIFFIN trial highlight the benchmarks that CAR T-cell therapy would need to reach to achieve equivalence with ASCT. At a 4-year follow-up, newly diagnosed MM patients who received daratumumab, lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (D-RVd) followed by ASCT + D-RVd consolidation, and daratumumab maintenance, had a progression-free survival (PFS) rate of 87.3%, 92.7% overall survival (OS) rate, and 50% achieved minimal residual disease negativity.
Dr. Adriana Rossi, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, cited a convergence of evidence suggesting that CAR T could achieve impressive results as a consolidation therapy in fit patients with MM, including: CARTITUDE 1 and CARTITUDE 4, which studied CAR T in RR MM patients. However, due to the fact that no head-to-head study of CAR T vs. ASCT as consolidation therapy in otherwise healthy MM patients exists, “There is not enough long-term data to support the equivalence CAR T with ASCT,” Dr. Giralt concluded.
Dr. Rossi further advocated for considering CAR T as a consolidation treatment because of the risks of secondary malignancies associated with ACST maintenance regimens.
Dr. Giralt rebutted this argument by citing data about averse events (AE) in studies of CAR-T therapies in RR MM patients like KarMMa-2, in which grade 3-4 neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia occurred in 94.6%, 45.9%, and 37.8% of patients respectively. Furthermore, 2 of 37 patients in KarMMA died (1 pneumonia, 1 pseudomonal sepsis), while rates of death from AEs related to ASCT occur in less than 1% of patients, according to Dr. Giralt.
Beyond a dearth of evidence thus far about the long term PFS, OS, and safety profile superiority of CAR-T therapies, compared with ASCT in treatment-naive MM patients, Dr. Giralt also noted the facts that CAR T-cell therapies are expensive and require manufacturing infrastructure also demonstrate that they cannot be easily adopted everywhere, even as a third-line therapy.
“In many places like Morocco, where I practice, we do not have access to CAR-T therapies,” said Sadia Zafad, MD, of the Clinique Al Madina Hematology and Oncology Center in Casablanca, Morocco. Dr. Zafad attended the debate.
A lack of access to CAR T is also a problem in the United States, where wait times for the therapy can stretch up to 6 months, getting insurance approval is challenging, and many patients simply don’t live near a center where CAR T-cell therapy is available. Citing all these factors, Dr. Giralt concluded: “Even if CAR T can be shown to have the same results as transplant, it is much more resource-intensive than transplant, and insurers are going to start saying there’s no necessary benefit. We have yet to use value as a primary end point, but as cancer care gets more and more expensive, that’s going to come up more, for CAR T and other novel therapies.”
Dr. Giralt reported relationships with Actinuum, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Crisper, J&J, Jazz, Kite, Miltenyi, Novartis, Sanofi, and Takeda. Dr. Rossi disclosed ties with Adaptive, BMS, Celgene, JNJ, Sanofi & Genzyme. Dr. Zafad reported no disclosures.
“In an otherwise healthy treatment-naive patient with multiple myeloma, to ensure the best chances of overall survival, I would always recommend standard of care consolidation therapy of chemotherapy + ASCT,” said Sergio Giralt, MD, of New York’s Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, debating the merits of ASCT versus CAR T as consolidation therapy at the Lymphoma, Leukemia & Myeloma (LLM) Congress 2023 in New York.
Final results from the phase II GRIFFIN trial highlight the benchmarks that CAR T-cell therapy would need to reach to achieve equivalence with ASCT. At a 4-year follow-up, newly diagnosed MM patients who received daratumumab, lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (D-RVd) followed by ASCT + D-RVd consolidation, and daratumumab maintenance, had a progression-free survival (PFS) rate of 87.3%, 92.7% overall survival (OS) rate, and 50% achieved minimal residual disease negativity.
Dr. Adriana Rossi, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, cited a convergence of evidence suggesting that CAR T could achieve impressive results as a consolidation therapy in fit patients with MM, including: CARTITUDE 1 and CARTITUDE 4, which studied CAR T in RR MM patients. However, due to the fact that no head-to-head study of CAR T vs. ASCT as consolidation therapy in otherwise healthy MM patients exists, “There is not enough long-term data to support the equivalence CAR T with ASCT,” Dr. Giralt concluded.
Dr. Rossi further advocated for considering CAR T as a consolidation treatment because of the risks of secondary malignancies associated with ACST maintenance regimens.
Dr. Giralt rebutted this argument by citing data about averse events (AE) in studies of CAR-T therapies in RR MM patients like KarMMa-2, in which grade 3-4 neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia occurred in 94.6%, 45.9%, and 37.8% of patients respectively. Furthermore, 2 of 37 patients in KarMMA died (1 pneumonia, 1 pseudomonal sepsis), while rates of death from AEs related to ASCT occur in less than 1% of patients, according to Dr. Giralt.
Beyond a dearth of evidence thus far about the long term PFS, OS, and safety profile superiority of CAR-T therapies, compared with ASCT in treatment-naive MM patients, Dr. Giralt also noted the facts that CAR T-cell therapies are expensive and require manufacturing infrastructure also demonstrate that they cannot be easily adopted everywhere, even as a third-line therapy.
“In many places like Morocco, where I practice, we do not have access to CAR-T therapies,” said Sadia Zafad, MD, of the Clinique Al Madina Hematology and Oncology Center in Casablanca, Morocco. Dr. Zafad attended the debate.
A lack of access to CAR T is also a problem in the United States, where wait times for the therapy can stretch up to 6 months, getting insurance approval is challenging, and many patients simply don’t live near a center where CAR T-cell therapy is available. Citing all these factors, Dr. Giralt concluded: “Even if CAR T can be shown to have the same results as transplant, it is much more resource-intensive than transplant, and insurers are going to start saying there’s no necessary benefit. We have yet to use value as a primary end point, but as cancer care gets more and more expensive, that’s going to come up more, for CAR T and other novel therapies.”
Dr. Giralt reported relationships with Actinuum, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Crisper, J&J, Jazz, Kite, Miltenyi, Novartis, Sanofi, and Takeda. Dr. Rossi disclosed ties with Adaptive, BMS, Celgene, JNJ, Sanofi & Genzyme. Dr. Zafad reported no disclosures.
AT LLM CONGRESS 2023
Q&A: Cancer screening in older patients – who to screen and when to stop
More than 1 in 10 Americans over age 60 years will be diagnosed with cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute, making screening for the disease in older patients imperative. Much of the burden of cancer screening falls on primary care physicians. This news organization spoke recently with William L. Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer of the American Cancer Society, about the particular challenges of screening in older patients.
Question: How much does cancer screening change with age? What are the considerations for clinicians – what risks and comorbidities are important to consider in older populations?
Answer: We at the American Cancer Society are giving a lot of thought to how to help primary care practices keep up with screening, particularly with respect to guidelines, but also best practices where judgment is required, such as cancer screening in their older patients.
We’ve had a lot of conversations recently about cancer risk in the young, largely because data show rates are going up for colorectal and breast cancer in this population. But it’s not one size fits all. Screening for young women who have a BRCA gene, if they have dense breasts, or if they have a strong family history of breast cancer should be different from those who are at average risk of the disease.
But statistically, there are about 15 per 100,000 breast cancer diagnoses in women under the age of 40 while over the age of 65 it’s 443 per 100,000. So, the risk significantly increases with age but we should not have an arbitrary cut-off. The life expectancy of a woman at age 75 is about 13.5 years. If you’re over the age of 70 or 75, then it’s going to be comorbidities that you look at, as well as individual patient decisions. Patients may say, “I don’t want to ever go through a mammogram again, because I don’t want to have a biopsy again, and I’m not going to get treated.” Or they may say, “My mom died of metastatic breast cancer when she was 82 and I want to know.”
Q: How should primary care physicians interpret conflicting guidance from the major medical groups? For example, the American College of Gastroenterology and your own organization recommend colorectal cancer screening start at age 45 now. But the American College of Physicians recently came out and said 50. What is a well-meaning primary care physician supposed to do?
A: We make more of guideline differences than we should. Sometimes guideline differences aren’t a reflection of different judgments, but rather what data were available when the most recent update took place. For colorectal cancer screening, the ACS dropped the age to begin screening to 45 in 2018 based on a very careful consideration of disease burden data and within several years most other guideline developers reached the same conclusion.
However, I think it’s good for family practice and internal medicine doctors to know that significant GI symptoms in a young patient could be colorectal cancer. It’s not as if nobody sees a 34-year-old or 27-year-old with colorectal cancer. They should be aware that if something goes away in a day or two, that’s fine, but persistent GI symptoms need a cancer workup – colonoscopy or referral to a gastroenterologist. So that’s why I think age 45 is the time when folks should begin screening.
Q: What are the medical-legal issues for a physician who is trying to follow guideline-based care when there are different guidelines?
A: Any physician can say, “We follow the guidelines of this particular organization.” I don’t think anyone can say that an organization’s guidelines are malpractice. For individual physicians, following a set of office-based guidelines will hopefully keep them out of legal difficulty.
Q: What are the risks of overscreening, especially in breast cancer where false positives may result in invasive testing?
A: What people think of as overscreening takes a number of different forms. What one guideline would imply is overscreening is recommended screening by another guideline. I think we would all agree that in an average-risk population, beginning screening before it is recommended would be overscreening, and continuing screening when a patient has life-limiting comorbidities would constitute overscreening. Screening too frequently can constitute overscreening.
For example, many women report that their doctors still are advising a baseline mammogram at age 35. Most guideline-developing organizations would regard this as overscreening in an average-risk population.
I think we are also getting better, certainly in prostate cancer, about knowing who needs to be treated and not treated. There are a lot of cancers that would have been treated 20-30 years ago but now are being safely followed with PSA and MRI. We may be able to get to that point with breast cancer over time, too.
Q: Are you saying that there may be breast cancers for which active surveillance is appropriate? Is that already the case?
A: We’re not there yet. I think some of the DCIS breast cancers are part of the discussion on whether hormonal treatment or surgeries are done. I think people do have those discussions in the context of morbidity and life expectancy. Over time, we’re likely to have more cancers for which we won’t need surgical treatments.
Q: Why did the American Cancer Society change the upper limit for lung cancer screening from 75 to 80 years of age?
A: For an individual older than 65, screening will now continue until the patient is 80, assuming the patient is in good health. According to the previous guideline, if a patient was 65 and more than 15 years beyond smoking cessation, then screening would end. This is exactly the time when we see lung cancers increase in the population and so a curable lung cancer would not previously have been detected by a screening CT scan. *
Q: What role do the multicancer blood and DNA tests play in screening now?
A: As you know, the Exact Sciences Cologuard test is already included in major guidelines for colorectal cancer screening and covered by insurance. Our philosophy on multicancer early detection tests is that we’re supportive of Medicare reimbursement when two things occur: 1. When we know there’s clinical benefit, and 2. When the test has been approved by the FDA.
The multicancer early detection tests in development and undergoing prospective research would not now replace screening for the cancers with established screening programs, but if they are shown to have clinical utility for the cancers in their panel, we would be able to reduce deaths from cancers that mostly are diagnosed at late stages and have poor prognoses.
There’s going to be a need for expertise in primary care practices to help interpret the tests. These are new questions, which are well beyond what even the typical oncologist is trained in, much less primary care physicians. We and other organizations are working on providing those answers.
Q: While we’re on the subject of the future, how do you envision AI helping or hindering cancer screening specifically in primary care?
A: I think AI is going to help things for a couple of reasons. The ability of AI is to get through data quickly and get you information that’s personalized and useful. If AI tools could let a patient know their individual risk of a cancer in the near and long term, that would help the primary care doctor screen in an individualized way. I think AI is going to be able to improve both diagnostic radiology and pathology, and could make a very big difference in settings outside of large cancer centers that operate at high volume every day. The data look very promising for AI to contribute to risk estimation by operating like a second reader in imaging and pathology.
Q: Anything else you’d like to say on this subject that clinicians should know?
A: The questions about whether or not patients should be screened is being pushed on family practice doctors and internists and these questions require a relationship with the patient. A hard stopping point at age 70 when lots of people will live 20 years or more doesn’t make sense.
There’s very little data from randomized clinical trials of screening people over the age of 70. We know that cancer risk does obviously increase with age, particularly prostate and breast cancer. And these are the cancers that are going to be the most common in your practices. If someone has a known mutation, I think you’re going to look differently at screening them. And first-degree family members, particularly for the more aggressive cancers, should be considered for screening.
My philosophy on cancer screening in the elderly is that I think the guidelines are guidelines. If patients have very limited life expectancy, then they shouldn’t be screened. There are calculators that estimate life expectancy in the context of current age and current health status, and these can be useful for decision making and counseling. Patients never think their life expectancy is shorter than 10 years. If their life expectancy is longer than 10 years, then I think, all things being equal, they should continue screening, but the question of ongoing screening needs to be periodically revisited.
*This story was updated on Nov. 1, 2023.
More than 1 in 10 Americans over age 60 years will be diagnosed with cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute, making screening for the disease in older patients imperative. Much of the burden of cancer screening falls on primary care physicians. This news organization spoke recently with William L. Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer of the American Cancer Society, about the particular challenges of screening in older patients.
Question: How much does cancer screening change with age? What are the considerations for clinicians – what risks and comorbidities are important to consider in older populations?
Answer: We at the American Cancer Society are giving a lot of thought to how to help primary care practices keep up with screening, particularly with respect to guidelines, but also best practices where judgment is required, such as cancer screening in their older patients.
We’ve had a lot of conversations recently about cancer risk in the young, largely because data show rates are going up for colorectal and breast cancer in this population. But it’s not one size fits all. Screening for young women who have a BRCA gene, if they have dense breasts, or if they have a strong family history of breast cancer should be different from those who are at average risk of the disease.
But statistically, there are about 15 per 100,000 breast cancer diagnoses in women under the age of 40 while over the age of 65 it’s 443 per 100,000. So, the risk significantly increases with age but we should not have an arbitrary cut-off. The life expectancy of a woman at age 75 is about 13.5 years. If you’re over the age of 70 or 75, then it’s going to be comorbidities that you look at, as well as individual patient decisions. Patients may say, “I don’t want to ever go through a mammogram again, because I don’t want to have a biopsy again, and I’m not going to get treated.” Or they may say, “My mom died of metastatic breast cancer when she was 82 and I want to know.”
Q: How should primary care physicians interpret conflicting guidance from the major medical groups? For example, the American College of Gastroenterology and your own organization recommend colorectal cancer screening start at age 45 now. But the American College of Physicians recently came out and said 50. What is a well-meaning primary care physician supposed to do?
A: We make more of guideline differences than we should. Sometimes guideline differences aren’t a reflection of different judgments, but rather what data were available when the most recent update took place. For colorectal cancer screening, the ACS dropped the age to begin screening to 45 in 2018 based on a very careful consideration of disease burden data and within several years most other guideline developers reached the same conclusion.
However, I think it’s good for family practice and internal medicine doctors to know that significant GI symptoms in a young patient could be colorectal cancer. It’s not as if nobody sees a 34-year-old or 27-year-old with colorectal cancer. They should be aware that if something goes away in a day or two, that’s fine, but persistent GI symptoms need a cancer workup – colonoscopy or referral to a gastroenterologist. So that’s why I think age 45 is the time when folks should begin screening.
Q: What are the medical-legal issues for a physician who is trying to follow guideline-based care when there are different guidelines?
A: Any physician can say, “We follow the guidelines of this particular organization.” I don’t think anyone can say that an organization’s guidelines are malpractice. For individual physicians, following a set of office-based guidelines will hopefully keep them out of legal difficulty.
Q: What are the risks of overscreening, especially in breast cancer where false positives may result in invasive testing?
A: What people think of as overscreening takes a number of different forms. What one guideline would imply is overscreening is recommended screening by another guideline. I think we would all agree that in an average-risk population, beginning screening before it is recommended would be overscreening, and continuing screening when a patient has life-limiting comorbidities would constitute overscreening. Screening too frequently can constitute overscreening.
For example, many women report that their doctors still are advising a baseline mammogram at age 35. Most guideline-developing organizations would regard this as overscreening in an average-risk population.
I think we are also getting better, certainly in prostate cancer, about knowing who needs to be treated and not treated. There are a lot of cancers that would have been treated 20-30 years ago but now are being safely followed with PSA and MRI. We may be able to get to that point with breast cancer over time, too.
Q: Are you saying that there may be breast cancers for which active surveillance is appropriate? Is that already the case?
A: We’re not there yet. I think some of the DCIS breast cancers are part of the discussion on whether hormonal treatment or surgeries are done. I think people do have those discussions in the context of morbidity and life expectancy. Over time, we’re likely to have more cancers for which we won’t need surgical treatments.
Q: Why did the American Cancer Society change the upper limit for lung cancer screening from 75 to 80 years of age?
A: For an individual older than 65, screening will now continue until the patient is 80, assuming the patient is in good health. According to the previous guideline, if a patient was 65 and more than 15 years beyond smoking cessation, then screening would end. This is exactly the time when we see lung cancers increase in the population and so a curable lung cancer would not previously have been detected by a screening CT scan. *
Q: What role do the multicancer blood and DNA tests play in screening now?
A: As you know, the Exact Sciences Cologuard test is already included in major guidelines for colorectal cancer screening and covered by insurance. Our philosophy on multicancer early detection tests is that we’re supportive of Medicare reimbursement when two things occur: 1. When we know there’s clinical benefit, and 2. When the test has been approved by the FDA.
The multicancer early detection tests in development and undergoing prospective research would not now replace screening for the cancers with established screening programs, but if they are shown to have clinical utility for the cancers in their panel, we would be able to reduce deaths from cancers that mostly are diagnosed at late stages and have poor prognoses.
There’s going to be a need for expertise in primary care practices to help interpret the tests. These are new questions, which are well beyond what even the typical oncologist is trained in, much less primary care physicians. We and other organizations are working on providing those answers.
Q: While we’re on the subject of the future, how do you envision AI helping or hindering cancer screening specifically in primary care?
A: I think AI is going to help things for a couple of reasons. The ability of AI is to get through data quickly and get you information that’s personalized and useful. If AI tools could let a patient know their individual risk of a cancer in the near and long term, that would help the primary care doctor screen in an individualized way. I think AI is going to be able to improve both diagnostic radiology and pathology, and could make a very big difference in settings outside of large cancer centers that operate at high volume every day. The data look very promising for AI to contribute to risk estimation by operating like a second reader in imaging and pathology.
Q: Anything else you’d like to say on this subject that clinicians should know?
A: The questions about whether or not patients should be screened is being pushed on family practice doctors and internists and these questions require a relationship with the patient. A hard stopping point at age 70 when lots of people will live 20 years or more doesn’t make sense.
There’s very little data from randomized clinical trials of screening people over the age of 70. We know that cancer risk does obviously increase with age, particularly prostate and breast cancer. And these are the cancers that are going to be the most common in your practices. If someone has a known mutation, I think you’re going to look differently at screening them. And first-degree family members, particularly for the more aggressive cancers, should be considered for screening.
My philosophy on cancer screening in the elderly is that I think the guidelines are guidelines. If patients have very limited life expectancy, then they shouldn’t be screened. There are calculators that estimate life expectancy in the context of current age and current health status, and these can be useful for decision making and counseling. Patients never think their life expectancy is shorter than 10 years. If their life expectancy is longer than 10 years, then I think, all things being equal, they should continue screening, but the question of ongoing screening needs to be periodically revisited.
*This story was updated on Nov. 1, 2023.
More than 1 in 10 Americans over age 60 years will be diagnosed with cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute, making screening for the disease in older patients imperative. Much of the burden of cancer screening falls on primary care physicians. This news organization spoke recently with William L. Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer of the American Cancer Society, about the particular challenges of screening in older patients.
Question: How much does cancer screening change with age? What are the considerations for clinicians – what risks and comorbidities are important to consider in older populations?
Answer: We at the American Cancer Society are giving a lot of thought to how to help primary care practices keep up with screening, particularly with respect to guidelines, but also best practices where judgment is required, such as cancer screening in their older patients.
We’ve had a lot of conversations recently about cancer risk in the young, largely because data show rates are going up for colorectal and breast cancer in this population. But it’s not one size fits all. Screening for young women who have a BRCA gene, if they have dense breasts, or if they have a strong family history of breast cancer should be different from those who are at average risk of the disease.
But statistically, there are about 15 per 100,000 breast cancer diagnoses in women under the age of 40 while over the age of 65 it’s 443 per 100,000. So, the risk significantly increases with age but we should not have an arbitrary cut-off. The life expectancy of a woman at age 75 is about 13.5 years. If you’re over the age of 70 or 75, then it’s going to be comorbidities that you look at, as well as individual patient decisions. Patients may say, “I don’t want to ever go through a mammogram again, because I don’t want to have a biopsy again, and I’m not going to get treated.” Or they may say, “My mom died of metastatic breast cancer when she was 82 and I want to know.”
Q: How should primary care physicians interpret conflicting guidance from the major medical groups? For example, the American College of Gastroenterology and your own organization recommend colorectal cancer screening start at age 45 now. But the American College of Physicians recently came out and said 50. What is a well-meaning primary care physician supposed to do?
A: We make more of guideline differences than we should. Sometimes guideline differences aren’t a reflection of different judgments, but rather what data were available when the most recent update took place. For colorectal cancer screening, the ACS dropped the age to begin screening to 45 in 2018 based on a very careful consideration of disease burden data and within several years most other guideline developers reached the same conclusion.
However, I think it’s good for family practice and internal medicine doctors to know that significant GI symptoms in a young patient could be colorectal cancer. It’s not as if nobody sees a 34-year-old or 27-year-old with colorectal cancer. They should be aware that if something goes away in a day or two, that’s fine, but persistent GI symptoms need a cancer workup – colonoscopy or referral to a gastroenterologist. So that’s why I think age 45 is the time when folks should begin screening.
Q: What are the medical-legal issues for a physician who is trying to follow guideline-based care when there are different guidelines?
A: Any physician can say, “We follow the guidelines of this particular organization.” I don’t think anyone can say that an organization’s guidelines are malpractice. For individual physicians, following a set of office-based guidelines will hopefully keep them out of legal difficulty.
Q: What are the risks of overscreening, especially in breast cancer where false positives may result in invasive testing?
A: What people think of as overscreening takes a number of different forms. What one guideline would imply is overscreening is recommended screening by another guideline. I think we would all agree that in an average-risk population, beginning screening before it is recommended would be overscreening, and continuing screening when a patient has life-limiting comorbidities would constitute overscreening. Screening too frequently can constitute overscreening.
For example, many women report that their doctors still are advising a baseline mammogram at age 35. Most guideline-developing organizations would regard this as overscreening in an average-risk population.
I think we are also getting better, certainly in prostate cancer, about knowing who needs to be treated and not treated. There are a lot of cancers that would have been treated 20-30 years ago but now are being safely followed with PSA and MRI. We may be able to get to that point with breast cancer over time, too.
Q: Are you saying that there may be breast cancers for which active surveillance is appropriate? Is that already the case?
A: We’re not there yet. I think some of the DCIS breast cancers are part of the discussion on whether hormonal treatment or surgeries are done. I think people do have those discussions in the context of morbidity and life expectancy. Over time, we’re likely to have more cancers for which we won’t need surgical treatments.
Q: Why did the American Cancer Society change the upper limit for lung cancer screening from 75 to 80 years of age?
A: For an individual older than 65, screening will now continue until the patient is 80, assuming the patient is in good health. According to the previous guideline, if a patient was 65 and more than 15 years beyond smoking cessation, then screening would end. This is exactly the time when we see lung cancers increase in the population and so a curable lung cancer would not previously have been detected by a screening CT scan. *
Q: What role do the multicancer blood and DNA tests play in screening now?
A: As you know, the Exact Sciences Cologuard test is already included in major guidelines for colorectal cancer screening and covered by insurance. Our philosophy on multicancer early detection tests is that we’re supportive of Medicare reimbursement when two things occur: 1. When we know there’s clinical benefit, and 2. When the test has been approved by the FDA.
The multicancer early detection tests in development and undergoing prospective research would not now replace screening for the cancers with established screening programs, but if they are shown to have clinical utility for the cancers in their panel, we would be able to reduce deaths from cancers that mostly are diagnosed at late stages and have poor prognoses.
There’s going to be a need for expertise in primary care practices to help interpret the tests. These are new questions, which are well beyond what even the typical oncologist is trained in, much less primary care physicians. We and other organizations are working on providing those answers.
Q: While we’re on the subject of the future, how do you envision AI helping or hindering cancer screening specifically in primary care?
A: I think AI is going to help things for a couple of reasons. The ability of AI is to get through data quickly and get you information that’s personalized and useful. If AI tools could let a patient know their individual risk of a cancer in the near and long term, that would help the primary care doctor screen in an individualized way. I think AI is going to be able to improve both diagnostic radiology and pathology, and could make a very big difference in settings outside of large cancer centers that operate at high volume every day. The data look very promising for AI to contribute to risk estimation by operating like a second reader in imaging and pathology.
Q: Anything else you’d like to say on this subject that clinicians should know?
A: The questions about whether or not patients should be screened is being pushed on family practice doctors and internists and these questions require a relationship with the patient. A hard stopping point at age 70 when lots of people will live 20 years or more doesn’t make sense.
There’s very little data from randomized clinical trials of screening people over the age of 70. We know that cancer risk does obviously increase with age, particularly prostate and breast cancer. And these are the cancers that are going to be the most common in your practices. If someone has a known mutation, I think you’re going to look differently at screening them. And first-degree family members, particularly for the more aggressive cancers, should be considered for screening.
My philosophy on cancer screening in the elderly is that I think the guidelines are guidelines. If patients have very limited life expectancy, then they shouldn’t be screened. There are calculators that estimate life expectancy in the context of current age and current health status, and these can be useful for decision making and counseling. Patients never think their life expectancy is shorter than 10 years. If their life expectancy is longer than 10 years, then I think, all things being equal, they should continue screening, but the question of ongoing screening needs to be periodically revisited.
*This story was updated on Nov. 1, 2023.
New Canadian guidelines for high-risk drinking, AUD
TOPLINE:
New Canadian guidelines for the management of high-risk drinking and alcohol use disorder (AUD) include 15 recommendations on screening, diagnosis, withdrawal management, and ongoing treatment including psychosocial interventions, drug therapies, and community-based programs.
METHODOLOGY:
- The Canadian Research Initiative in Substance Misuse convened a 36-member committee of clinicians, researchers, people with personal experience of alcohol use, and Indigenous or Métis individuals to develop the guidelines, using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation Instrument.
- Risk assessment was based on Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption scores.
- The definition of AUD was based on patients experiencing “clinically significant impairment or distress” from their alcohol use, with severity being mild, moderate, or severe.
TAKEAWAY:
- All adult and youth patients at moderate or high risk for AUD should be screened annually for alcohol use, and those screening positive should receive a diagnostic interview for AUD and an individualized treatment plan.
- Assessment of severe alcohol withdrawal complications should include clinical parameters such as past seizures or delirium tremens and the Prediction of Alcohol Withdrawal Severity Scale, with treatment including nonbenzodiazepine medications for low-risk patients and a short-term benzodiazepine prescription for high-risk patients, ideally in an inpatient setting.
- All patients with AUD should be referred for psychosocial treatment, and those with moderate to severe AUD should be offered naltrexone, acamprosate, topiramate, or gabapentin, depending on contraindications and effectiveness.
- Antipsychotics or SSRI antidepressants have little benefit and may worsen outcomes and should not be prescribed for AUD.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors noted that more than half of people aged 15 years or older in Canada drink more than the recommended amount, and about 18% meet the definition for AUD. “The aim of this guideline is to support primary care providers and services to offer more effective treatments routinely to patients with AUD as the standard of practice, with resulting improvements in health as well as potential for considerable cost savings in health and social systems,” the investigators write. They also note that policy makers can substantially improve standards of care by promoting adoption of the guideline and its recommendations.
SOURCE:
The article was written by Evan Wood, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues. It was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
LIMITATIONS:
The guideline was published more than 3 years after the initial literature search in September 2020 and did not include comprehensive guidance for AUD with co-occurring substance use disorders or with severe mental health conditions. Certain groups, including immigrant and refugee populations, were not represented.
DISCLOSURES:
Development of the guideline received support from Health Canada’s Substance Use and Addictions Program, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and BC Centre on Substance Use. No committee members disclosed direct monetary or nonmonetary support from alcohol or pharmaceutical industry sources within the past 5 years, or that their clinical revenue would be influenced by the guideline recommendations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New Canadian guidelines for the management of high-risk drinking and alcohol use disorder (AUD) include 15 recommendations on screening, diagnosis, withdrawal management, and ongoing treatment including psychosocial interventions, drug therapies, and community-based programs.
METHODOLOGY:
- The Canadian Research Initiative in Substance Misuse convened a 36-member committee of clinicians, researchers, people with personal experience of alcohol use, and Indigenous or Métis individuals to develop the guidelines, using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation Instrument.
- Risk assessment was based on Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption scores.
- The definition of AUD was based on patients experiencing “clinically significant impairment or distress” from their alcohol use, with severity being mild, moderate, or severe.
TAKEAWAY:
- All adult and youth patients at moderate or high risk for AUD should be screened annually for alcohol use, and those screening positive should receive a diagnostic interview for AUD and an individualized treatment plan.
- Assessment of severe alcohol withdrawal complications should include clinical parameters such as past seizures or delirium tremens and the Prediction of Alcohol Withdrawal Severity Scale, with treatment including nonbenzodiazepine medications for low-risk patients and a short-term benzodiazepine prescription for high-risk patients, ideally in an inpatient setting.
- All patients with AUD should be referred for psychosocial treatment, and those with moderate to severe AUD should be offered naltrexone, acamprosate, topiramate, or gabapentin, depending on contraindications and effectiveness.
- Antipsychotics or SSRI antidepressants have little benefit and may worsen outcomes and should not be prescribed for AUD.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors noted that more than half of people aged 15 years or older in Canada drink more than the recommended amount, and about 18% meet the definition for AUD. “The aim of this guideline is to support primary care providers and services to offer more effective treatments routinely to patients with AUD as the standard of practice, with resulting improvements in health as well as potential for considerable cost savings in health and social systems,” the investigators write. They also note that policy makers can substantially improve standards of care by promoting adoption of the guideline and its recommendations.
SOURCE:
The article was written by Evan Wood, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues. It was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
LIMITATIONS:
The guideline was published more than 3 years after the initial literature search in September 2020 and did not include comprehensive guidance for AUD with co-occurring substance use disorders or with severe mental health conditions. Certain groups, including immigrant and refugee populations, were not represented.
DISCLOSURES:
Development of the guideline received support from Health Canada’s Substance Use and Addictions Program, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and BC Centre on Substance Use. No committee members disclosed direct monetary or nonmonetary support from alcohol or pharmaceutical industry sources within the past 5 years, or that their clinical revenue would be influenced by the guideline recommendations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New Canadian guidelines for the management of high-risk drinking and alcohol use disorder (AUD) include 15 recommendations on screening, diagnosis, withdrawal management, and ongoing treatment including psychosocial interventions, drug therapies, and community-based programs.
METHODOLOGY:
- The Canadian Research Initiative in Substance Misuse convened a 36-member committee of clinicians, researchers, people with personal experience of alcohol use, and Indigenous or Métis individuals to develop the guidelines, using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation Instrument.
- Risk assessment was based on Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption scores.
- The definition of AUD was based on patients experiencing “clinically significant impairment or distress” from their alcohol use, with severity being mild, moderate, or severe.
TAKEAWAY:
- All adult and youth patients at moderate or high risk for AUD should be screened annually for alcohol use, and those screening positive should receive a diagnostic interview for AUD and an individualized treatment plan.
- Assessment of severe alcohol withdrawal complications should include clinical parameters such as past seizures or delirium tremens and the Prediction of Alcohol Withdrawal Severity Scale, with treatment including nonbenzodiazepine medications for low-risk patients and a short-term benzodiazepine prescription for high-risk patients, ideally in an inpatient setting.
- All patients with AUD should be referred for psychosocial treatment, and those with moderate to severe AUD should be offered naltrexone, acamprosate, topiramate, or gabapentin, depending on contraindications and effectiveness.
- Antipsychotics or SSRI antidepressants have little benefit and may worsen outcomes and should not be prescribed for AUD.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors noted that more than half of people aged 15 years or older in Canada drink more than the recommended amount, and about 18% meet the definition for AUD. “The aim of this guideline is to support primary care providers and services to offer more effective treatments routinely to patients with AUD as the standard of practice, with resulting improvements in health as well as potential for considerable cost savings in health and social systems,” the investigators write. They also note that policy makers can substantially improve standards of care by promoting adoption of the guideline and its recommendations.
SOURCE:
The article was written by Evan Wood, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues. It was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
LIMITATIONS:
The guideline was published more than 3 years after the initial literature search in September 2020 and did not include comprehensive guidance for AUD with co-occurring substance use disorders or with severe mental health conditions. Certain groups, including immigrant and refugee populations, were not represented.
DISCLOSURES:
Development of the guideline received support from Health Canada’s Substance Use and Addictions Program, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and BC Centre on Substance Use. No committee members disclosed direct monetary or nonmonetary support from alcohol or pharmaceutical industry sources within the past 5 years, or that their clinical revenue would be influenced by the guideline recommendations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dato-DXd trumps chemo in advanced HR+/HER2– breast cancer
The investigational anti-body drug conjugate (ADC) resistant to endocrine therapy, data from the phase 3 TROPION-Breast01 trial showed.
At a median follow-up of 10.8 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.9 months for patients randomly assigned to receive Dato-DXd, compared with 4.9 months for the investigator’s choice of chemotherapy with either eribulin mesylate, vinorelbine, capecitabine, or gemcitabine. This difference translated into a 37% reduction in risk of disease progression with the ADC, reported Aditya Bardia, MD, MPH, director of the breast cancer research program at the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
Patients who received Dato-DXd had less than half the number of grade 3 or greater toxicities and fewer dose reductions or interruptions than patients who received chemotherapy, he noted in an oral abstract session at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“Overall, results support Dato-DXd as a potential new therapeutic option for patients with metastatic hormone receptor–positive breast cancer,” he said.
Different ADC, same target
Dr. Bardia noted that there is an unmet need for effective therapies for patients with metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer who experience disease progression after endocrine therapy and at least one line of systemic therapy.
Although chemotherapy is widely used in this population, it’s associated with low response rates, poor prognosis, and significant toxicities, including hematologic and neurologic adverse events (AEs).
Dato-DXd is composed of a monoclonal antibody targeting TROP2, a transmembrane glycoprotein overexpressed in cancer cells, linked to the topoisomerase 1 inhibitor deruxtecan as the toxic payload.
Dr. Bardia explained that Dato-DXd has four properties that distinguish it from other TROP2-directed ADCs: an optimized drug to antibody ratio of 4, a stable linker-payload, tumor-selective cleavable linker, both of which reduce off-target toxicities, and a bystander antitumor effect that can target TROP2-expressing cells in the tumor microenvironment.
In the phase I TROPION-PanTumor01 trial, Dato-DXd had promising anti-tumor activity and a manageable safety profile in patients with metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer, paving the way for the TROPION-Breast01 study reported here.
Efficacy results
In the Breast01 trial, 732 patients with inoperable or metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer previously treated with 1 or 2 lines of chemotherapy that had progressed on endocrine therapy were stratified by number of prior chemotherapy lines, geographic region, and prior CDK4/6 inhibitor status, and then randomized to either Dato-DXd 6 mg/kg intravenously on day 1 of each 3-week cycle (365 patients) or to investigator’s choice of chemotherapy (367 patients). According to the protocol, chemotherapy could be eribulin mesylate, vinorelbine, or gemcitabine delivered via IV on days 1 and 8 every 3 weeks, or oral capecitabine on days 1 through 14 of every 3-week cycle.
At the time of data cutoff, 93 patients assigned to the ADC and 39 assigned to chemotherapy were still on treatment.
As noted before, median PFS by blinded independent central review, one of two primary endpoints, was 6.9 months with Dato-DXd, compared with 4.9 months with chemotherapy, translating into a hazard ratio for progression of 0.63 (P < .0001).
The benefit was seen across nearly all subgroups except among patients who had not previously received a CDK4/6 inhibitor, and patients who had received a prior anthracycline but not a taxane.
Objective response rates (ORR) were 36.4% with Dato-DXd (99.5% partial and .5% complete response), compared with 22.9% with chemotherapy (all partial responses; P values not reported).
Overall survival data, the other primary endpoint, were not mature at a median OS follow-up of 9.7 months, and will be reported at a later date.
Safety results
“In terms of safety, the rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs in the Dato-DXd arm was less as compared to investigator choice of chemotherapy. This is a bit different from most of the studies; in general we see that the rate of adverse events is higher in the intervention arm as compared to the control arm,” Dr. Bardia commented.
Rates of dose reductions and dose interruptions due to treatment-related AEs were also lower with the ADC.
There were no patient deaths associated with Dato-DXd. One patient assigned to chemotherapy died from a complication associated with febrile neutropenia.
Most treatment-related AEs occurring in 15% of patients and AEs of special interest were of grade 1 and manageable.
The most common toxicities seen with the ADC were oral mucositis and dry eye. The most common side effects with chemotherapy were neutropenia and anemia, “the usual side effects you would expect with chemotherapy,” Dr. Bardia said, pointing out that the rate of grade 3 neutropenia was 31% with standard chemotherapy, compared with 1% with Dato-DXd.
Good, but we can do better
ESMO invited discussant Sarat Chandarlapaty, MD, PhD, a breast oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, commented that while the trial data showed superior efficacy and safety with Dato-DXd, compared with standard chemotherapy, it’s still unclear how it and other ADCs on the market and in the research pipeline may be used in therapy for this patient population.
“Would I rather prescribe Dato-DXd or more chemo after 1 to 2 lines of chemo in unselected HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer? The answer is Dato-DXd, but it leaves several unanswered questions for us,” he said.
“First, we have two ADCs approved in HR-positive breast cancer: another TROP2 ADC sacituzumab [govitecan] and a HER2 ADC trastuzumab deruxtecan. Would I rather give Dato over one of these? I don’t have an answer,” he added.
In addition, it’s unknown whether these drugs, which have the same topoisomerase-targeted payload, could be given in sequence, and there are as yet no clear answers as to whether patients might do better with Dato-DXd or with a PIK3ca inhibitor.
“I would say that the elephant in the room is really another question, and that is, ‘Is Dato-DXd in this context delivering on the promise of an ADC?’ ” Dr. Chandarlapaty said.
“I think translational research is urgently needed if we’re ultimately to deliver on the promise of these agents in the clinic,” he concluded.
The TROPION-Breast01 study is sponsored AstraZeneca, which is collaborating with Daiichi-Sankyo on global development and commercialization of Dato-DXd. Dr. Bardia disclosed advisory board activities and institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Daiichi-Sankyo and others. Dr. Chandarlapaty disclosed research funding from both companies, and advisory board activities for AstraZeneca and others.
The investigational anti-body drug conjugate (ADC) resistant to endocrine therapy, data from the phase 3 TROPION-Breast01 trial showed.
At a median follow-up of 10.8 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.9 months for patients randomly assigned to receive Dato-DXd, compared with 4.9 months for the investigator’s choice of chemotherapy with either eribulin mesylate, vinorelbine, capecitabine, or gemcitabine. This difference translated into a 37% reduction in risk of disease progression with the ADC, reported Aditya Bardia, MD, MPH, director of the breast cancer research program at the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
Patients who received Dato-DXd had less than half the number of grade 3 or greater toxicities and fewer dose reductions or interruptions than patients who received chemotherapy, he noted in an oral abstract session at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“Overall, results support Dato-DXd as a potential new therapeutic option for patients with metastatic hormone receptor–positive breast cancer,” he said.
Different ADC, same target
Dr. Bardia noted that there is an unmet need for effective therapies for patients with metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer who experience disease progression after endocrine therapy and at least one line of systemic therapy.
Although chemotherapy is widely used in this population, it’s associated with low response rates, poor prognosis, and significant toxicities, including hematologic and neurologic adverse events (AEs).
Dato-DXd is composed of a monoclonal antibody targeting TROP2, a transmembrane glycoprotein overexpressed in cancer cells, linked to the topoisomerase 1 inhibitor deruxtecan as the toxic payload.
Dr. Bardia explained that Dato-DXd has four properties that distinguish it from other TROP2-directed ADCs: an optimized drug to antibody ratio of 4, a stable linker-payload, tumor-selective cleavable linker, both of which reduce off-target toxicities, and a bystander antitumor effect that can target TROP2-expressing cells in the tumor microenvironment.
In the phase I TROPION-PanTumor01 trial, Dato-DXd had promising anti-tumor activity and a manageable safety profile in patients with metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer, paving the way for the TROPION-Breast01 study reported here.
Efficacy results
In the Breast01 trial, 732 patients with inoperable or metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer previously treated with 1 or 2 lines of chemotherapy that had progressed on endocrine therapy were stratified by number of prior chemotherapy lines, geographic region, and prior CDK4/6 inhibitor status, and then randomized to either Dato-DXd 6 mg/kg intravenously on day 1 of each 3-week cycle (365 patients) or to investigator’s choice of chemotherapy (367 patients). According to the protocol, chemotherapy could be eribulin mesylate, vinorelbine, or gemcitabine delivered via IV on days 1 and 8 every 3 weeks, or oral capecitabine on days 1 through 14 of every 3-week cycle.
At the time of data cutoff, 93 patients assigned to the ADC and 39 assigned to chemotherapy were still on treatment.
As noted before, median PFS by blinded independent central review, one of two primary endpoints, was 6.9 months with Dato-DXd, compared with 4.9 months with chemotherapy, translating into a hazard ratio for progression of 0.63 (P < .0001).
The benefit was seen across nearly all subgroups except among patients who had not previously received a CDK4/6 inhibitor, and patients who had received a prior anthracycline but not a taxane.
Objective response rates (ORR) were 36.4% with Dato-DXd (99.5% partial and .5% complete response), compared with 22.9% with chemotherapy (all partial responses; P values not reported).
Overall survival data, the other primary endpoint, were not mature at a median OS follow-up of 9.7 months, and will be reported at a later date.
Safety results
“In terms of safety, the rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs in the Dato-DXd arm was less as compared to investigator choice of chemotherapy. This is a bit different from most of the studies; in general we see that the rate of adverse events is higher in the intervention arm as compared to the control arm,” Dr. Bardia commented.
Rates of dose reductions and dose interruptions due to treatment-related AEs were also lower with the ADC.
There were no patient deaths associated with Dato-DXd. One patient assigned to chemotherapy died from a complication associated with febrile neutropenia.
Most treatment-related AEs occurring in 15% of patients and AEs of special interest were of grade 1 and manageable.
The most common toxicities seen with the ADC were oral mucositis and dry eye. The most common side effects with chemotherapy were neutropenia and anemia, “the usual side effects you would expect with chemotherapy,” Dr. Bardia said, pointing out that the rate of grade 3 neutropenia was 31% with standard chemotherapy, compared with 1% with Dato-DXd.
Good, but we can do better
ESMO invited discussant Sarat Chandarlapaty, MD, PhD, a breast oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, commented that while the trial data showed superior efficacy and safety with Dato-DXd, compared with standard chemotherapy, it’s still unclear how it and other ADCs on the market and in the research pipeline may be used in therapy for this patient population.
“Would I rather prescribe Dato-DXd or more chemo after 1 to 2 lines of chemo in unselected HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer? The answer is Dato-DXd, but it leaves several unanswered questions for us,” he said.
“First, we have two ADCs approved in HR-positive breast cancer: another TROP2 ADC sacituzumab [govitecan] and a HER2 ADC trastuzumab deruxtecan. Would I rather give Dato over one of these? I don’t have an answer,” he added.
In addition, it’s unknown whether these drugs, which have the same topoisomerase-targeted payload, could be given in sequence, and there are as yet no clear answers as to whether patients might do better with Dato-DXd or with a PIK3ca inhibitor.
“I would say that the elephant in the room is really another question, and that is, ‘Is Dato-DXd in this context delivering on the promise of an ADC?’ ” Dr. Chandarlapaty said.
“I think translational research is urgently needed if we’re ultimately to deliver on the promise of these agents in the clinic,” he concluded.
The TROPION-Breast01 study is sponsored AstraZeneca, which is collaborating with Daiichi-Sankyo on global development and commercialization of Dato-DXd. Dr. Bardia disclosed advisory board activities and institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Daiichi-Sankyo and others. Dr. Chandarlapaty disclosed research funding from both companies, and advisory board activities for AstraZeneca and others.
The investigational anti-body drug conjugate (ADC) resistant to endocrine therapy, data from the phase 3 TROPION-Breast01 trial showed.
At a median follow-up of 10.8 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.9 months for patients randomly assigned to receive Dato-DXd, compared with 4.9 months for the investigator’s choice of chemotherapy with either eribulin mesylate, vinorelbine, capecitabine, or gemcitabine. This difference translated into a 37% reduction in risk of disease progression with the ADC, reported Aditya Bardia, MD, MPH, director of the breast cancer research program at the Mass General Cancer Center in Boston.
Patients who received Dato-DXd had less than half the number of grade 3 or greater toxicities and fewer dose reductions or interruptions than patients who received chemotherapy, he noted in an oral abstract session at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
“Overall, results support Dato-DXd as a potential new therapeutic option for patients with metastatic hormone receptor–positive breast cancer,” he said.
Different ADC, same target
Dr. Bardia noted that there is an unmet need for effective therapies for patients with metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer who experience disease progression after endocrine therapy and at least one line of systemic therapy.
Although chemotherapy is widely used in this population, it’s associated with low response rates, poor prognosis, and significant toxicities, including hematologic and neurologic adverse events (AEs).
Dato-DXd is composed of a monoclonal antibody targeting TROP2, a transmembrane glycoprotein overexpressed in cancer cells, linked to the topoisomerase 1 inhibitor deruxtecan as the toxic payload.
Dr. Bardia explained that Dato-DXd has four properties that distinguish it from other TROP2-directed ADCs: an optimized drug to antibody ratio of 4, a stable linker-payload, tumor-selective cleavable linker, both of which reduce off-target toxicities, and a bystander antitumor effect that can target TROP2-expressing cells in the tumor microenvironment.
In the phase I TROPION-PanTumor01 trial, Dato-DXd had promising anti-tumor activity and a manageable safety profile in patients with metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer, paving the way for the TROPION-Breast01 study reported here.
Efficacy results
In the Breast01 trial, 732 patients with inoperable or metastatic HR+/HER2– breast cancer previously treated with 1 or 2 lines of chemotherapy that had progressed on endocrine therapy were stratified by number of prior chemotherapy lines, geographic region, and prior CDK4/6 inhibitor status, and then randomized to either Dato-DXd 6 mg/kg intravenously on day 1 of each 3-week cycle (365 patients) or to investigator’s choice of chemotherapy (367 patients). According to the protocol, chemotherapy could be eribulin mesylate, vinorelbine, or gemcitabine delivered via IV on days 1 and 8 every 3 weeks, or oral capecitabine on days 1 through 14 of every 3-week cycle.
At the time of data cutoff, 93 patients assigned to the ADC and 39 assigned to chemotherapy were still on treatment.
As noted before, median PFS by blinded independent central review, one of two primary endpoints, was 6.9 months with Dato-DXd, compared with 4.9 months with chemotherapy, translating into a hazard ratio for progression of 0.63 (P < .0001).
The benefit was seen across nearly all subgroups except among patients who had not previously received a CDK4/6 inhibitor, and patients who had received a prior anthracycline but not a taxane.
Objective response rates (ORR) were 36.4% with Dato-DXd (99.5% partial and .5% complete response), compared with 22.9% with chemotherapy (all partial responses; P values not reported).
Overall survival data, the other primary endpoint, were not mature at a median OS follow-up of 9.7 months, and will be reported at a later date.
Safety results
“In terms of safety, the rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs in the Dato-DXd arm was less as compared to investigator choice of chemotherapy. This is a bit different from most of the studies; in general we see that the rate of adverse events is higher in the intervention arm as compared to the control arm,” Dr. Bardia commented.
Rates of dose reductions and dose interruptions due to treatment-related AEs were also lower with the ADC.
There were no patient deaths associated with Dato-DXd. One patient assigned to chemotherapy died from a complication associated with febrile neutropenia.
Most treatment-related AEs occurring in 15% of patients and AEs of special interest were of grade 1 and manageable.
The most common toxicities seen with the ADC were oral mucositis and dry eye. The most common side effects with chemotherapy were neutropenia and anemia, “the usual side effects you would expect with chemotherapy,” Dr. Bardia said, pointing out that the rate of grade 3 neutropenia was 31% with standard chemotherapy, compared with 1% with Dato-DXd.
Good, but we can do better
ESMO invited discussant Sarat Chandarlapaty, MD, PhD, a breast oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, commented that while the trial data showed superior efficacy and safety with Dato-DXd, compared with standard chemotherapy, it’s still unclear how it and other ADCs on the market and in the research pipeline may be used in therapy for this patient population.
“Would I rather prescribe Dato-DXd or more chemo after 1 to 2 lines of chemo in unselected HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer? The answer is Dato-DXd, but it leaves several unanswered questions for us,” he said.
“First, we have two ADCs approved in HR-positive breast cancer: another TROP2 ADC sacituzumab [govitecan] and a HER2 ADC trastuzumab deruxtecan. Would I rather give Dato over one of these? I don’t have an answer,” he added.
In addition, it’s unknown whether these drugs, which have the same topoisomerase-targeted payload, could be given in sequence, and there are as yet no clear answers as to whether patients might do better with Dato-DXd or with a PIK3ca inhibitor.
“I would say that the elephant in the room is really another question, and that is, ‘Is Dato-DXd in this context delivering on the promise of an ADC?’ ” Dr. Chandarlapaty said.
“I think translational research is urgently needed if we’re ultimately to deliver on the promise of these agents in the clinic,” he concluded.
The TROPION-Breast01 study is sponsored AstraZeneca, which is collaborating with Daiichi-Sankyo on global development and commercialization of Dato-DXd. Dr. Bardia disclosed advisory board activities and institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Daiichi-Sankyo and others. Dr. Chandarlapaty disclosed research funding from both companies, and advisory board activities for AstraZeneca and others.
FROM ESMO CONGRESS 2023
‘Why did I choose this?’ Tackling burnout in oncology
MADRID – “Why did I choose this?”
That is the core question a Portuguese oncologist posed from the audience during a session at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) that was dedicated to building a sustainable oncology workforce.
“Ten, twenty years ago, being a doctor was a dream,” she said, but right now doctors are underpaid, under strain, and have very few resources.
This oncologist is hardly alone.
A survey from ESMO conducted almost a decade ago found that more than 50% of oncologists across Europe, many of whom were early in their careers, reported being burned out.
This, Dr. Lim said, “was the starting point,” well before the COVID pandemic struck.
More recently, the pandemic has taken its own toll on the well-being of oncologists. A survey presented at ESMO 2020 revealed that 38% of participants, spanning 101 countries, reported experiencing burnout, and 66% said they were not able to perform their job.
Medscape’s 2023 Physician Burnout and Depression Report highlighted similar burnout rates, with 53% of U.S. physicians and 52% of oncologists saying they felt burned out, compared with about 42% in 2018, before the pandemic.
The oncology workforce is in crisis in every country, said Dr. Lim, from the Cancer Dynamics Lab, the Francis Crick Institute, London.
Burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization or feelings of cynicism, and a low sense of personal accomplishment, can result in a poor work-life balance as well as poor mental and physical health. Factors linked to burnout include social isolation, increased workload, reduced quality of work, lack of control over work, and stressful professional experiences.
Together, these factors can affect patient care and further exacerbate staffing issues, Dr. Lim said.
Staffing shortages are common. Oncologists often work long hours or on weekends to cover gaps caused by staffing shortages. Recent data revealed that in high-income countries, there are on average 0.65 medical oncologists and 0.25 radiation oncologists per 100 patients — a situation made worse by professionals taking early retirement or leaving medicine during the pandemic.
“We have seen that the shortage of human resources in many countries as well as the increasing workload related to the increasing number of cancers,” as well as patients surviving longer, have increased pressures on the healthcare system, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, president of ESMO, explained in a press conference.
While tackling these oncology workforce problems requires smaller, local changes to a physician’s daily routine, “the real change,” Dr. Lim said, lies at an infrastructure level.
In response to this chronic and growing problem, ESMO launched its Resilience Task Force in 2020 to evaluate burnout and well-being. The task force plans to publish a position paper in which it will propose a set of recommendations regarding the psychosocial risks of burnout as well as flexible work patterns, well-being resources, and targeted support.
A panel of experts at the meeting touched on some of these solutions.
Dealing with staff shortages is a must, said Jean-Yves Blay, MD, PhD, during the session. “It’s a simple mathematical equation,” Dr. Blay said. “We must increase the number of doctors in medical schools and the number of nurses and healthcare professionals in all schools.” Improving staffing would also help reduce chronic workload issues.
Resilience training should also be incorporated into physician training starting in medical school. Teaching oncologists how to deal with bad news and to cope when patients dies is particularly important.
“I was not taught that,” said the oncologist from Portugal. “I had to learn that at my own cost.”
The good news is that it’s possible to develop resiliency skills over time, said Claire Hardy, PhD, from Lancaster University, United Kingdom, who agreed that training programs could be one approach to improve oncologists’ work life.
However, a person’s needs are determined by their institution and personal responsibilities. “No one knows your job better than you,” Dr. Hardy said. “No one knows better than you where the inefficiencies are, where the bureaucracy is that could be taken away, or it could be done by somebody whose role it is to sort all that out.”
But having this understanding is not enough. Physician also need to feel “psychological safety to be able to speak out and say that something isn’t working right now or is too much,” or, “I’m spending too much time doing this.”
In other words, oncologists need to be able to set boundaries and say no.
Dr. Hardy said this concept “has been around a while, but it’s really gaining momentum,” and being able to discuss these issues in a forum such as the ESMO Congress is a promising start.
Dr. Lim has relationships with Janseen and SEOM. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – “Why did I choose this?”
That is the core question a Portuguese oncologist posed from the audience during a session at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) that was dedicated to building a sustainable oncology workforce.
“Ten, twenty years ago, being a doctor was a dream,” she said, but right now doctors are underpaid, under strain, and have very few resources.
This oncologist is hardly alone.
A survey from ESMO conducted almost a decade ago found that more than 50% of oncologists across Europe, many of whom were early in their careers, reported being burned out.
This, Dr. Lim said, “was the starting point,” well before the COVID pandemic struck.
More recently, the pandemic has taken its own toll on the well-being of oncologists. A survey presented at ESMO 2020 revealed that 38% of participants, spanning 101 countries, reported experiencing burnout, and 66% said they were not able to perform their job.
Medscape’s 2023 Physician Burnout and Depression Report highlighted similar burnout rates, with 53% of U.S. physicians and 52% of oncologists saying they felt burned out, compared with about 42% in 2018, before the pandemic.
The oncology workforce is in crisis in every country, said Dr. Lim, from the Cancer Dynamics Lab, the Francis Crick Institute, London.
Burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization or feelings of cynicism, and a low sense of personal accomplishment, can result in a poor work-life balance as well as poor mental and physical health. Factors linked to burnout include social isolation, increased workload, reduced quality of work, lack of control over work, and stressful professional experiences.
Together, these factors can affect patient care and further exacerbate staffing issues, Dr. Lim said.
Staffing shortages are common. Oncologists often work long hours or on weekends to cover gaps caused by staffing shortages. Recent data revealed that in high-income countries, there are on average 0.65 medical oncologists and 0.25 radiation oncologists per 100 patients — a situation made worse by professionals taking early retirement or leaving medicine during the pandemic.
“We have seen that the shortage of human resources in many countries as well as the increasing workload related to the increasing number of cancers,” as well as patients surviving longer, have increased pressures on the healthcare system, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, president of ESMO, explained in a press conference.
While tackling these oncology workforce problems requires smaller, local changes to a physician’s daily routine, “the real change,” Dr. Lim said, lies at an infrastructure level.
In response to this chronic and growing problem, ESMO launched its Resilience Task Force in 2020 to evaluate burnout and well-being. The task force plans to publish a position paper in which it will propose a set of recommendations regarding the psychosocial risks of burnout as well as flexible work patterns, well-being resources, and targeted support.
A panel of experts at the meeting touched on some of these solutions.
Dealing with staff shortages is a must, said Jean-Yves Blay, MD, PhD, during the session. “It’s a simple mathematical equation,” Dr. Blay said. “We must increase the number of doctors in medical schools and the number of nurses and healthcare professionals in all schools.” Improving staffing would also help reduce chronic workload issues.
Resilience training should also be incorporated into physician training starting in medical school. Teaching oncologists how to deal with bad news and to cope when patients dies is particularly important.
“I was not taught that,” said the oncologist from Portugal. “I had to learn that at my own cost.”
The good news is that it’s possible to develop resiliency skills over time, said Claire Hardy, PhD, from Lancaster University, United Kingdom, who agreed that training programs could be one approach to improve oncologists’ work life.
However, a person’s needs are determined by their institution and personal responsibilities. “No one knows your job better than you,” Dr. Hardy said. “No one knows better than you where the inefficiencies are, where the bureaucracy is that could be taken away, or it could be done by somebody whose role it is to sort all that out.”
But having this understanding is not enough. Physician also need to feel “psychological safety to be able to speak out and say that something isn’t working right now or is too much,” or, “I’m spending too much time doing this.”
In other words, oncologists need to be able to set boundaries and say no.
Dr. Hardy said this concept “has been around a while, but it’s really gaining momentum,” and being able to discuss these issues in a forum such as the ESMO Congress is a promising start.
Dr. Lim has relationships with Janseen and SEOM. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – “Why did I choose this?”
That is the core question a Portuguese oncologist posed from the audience during a session at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) that was dedicated to building a sustainable oncology workforce.
“Ten, twenty years ago, being a doctor was a dream,” she said, but right now doctors are underpaid, under strain, and have very few resources.
This oncologist is hardly alone.
A survey from ESMO conducted almost a decade ago found that more than 50% of oncologists across Europe, many of whom were early in their careers, reported being burned out.
This, Dr. Lim said, “was the starting point,” well before the COVID pandemic struck.
More recently, the pandemic has taken its own toll on the well-being of oncologists. A survey presented at ESMO 2020 revealed that 38% of participants, spanning 101 countries, reported experiencing burnout, and 66% said they were not able to perform their job.
Medscape’s 2023 Physician Burnout and Depression Report highlighted similar burnout rates, with 53% of U.S. physicians and 52% of oncologists saying they felt burned out, compared with about 42% in 2018, before the pandemic.
The oncology workforce is in crisis in every country, said Dr. Lim, from the Cancer Dynamics Lab, the Francis Crick Institute, London.
Burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization or feelings of cynicism, and a low sense of personal accomplishment, can result in a poor work-life balance as well as poor mental and physical health. Factors linked to burnout include social isolation, increased workload, reduced quality of work, lack of control over work, and stressful professional experiences.
Together, these factors can affect patient care and further exacerbate staffing issues, Dr. Lim said.
Staffing shortages are common. Oncologists often work long hours or on weekends to cover gaps caused by staffing shortages. Recent data revealed that in high-income countries, there are on average 0.65 medical oncologists and 0.25 radiation oncologists per 100 patients — a situation made worse by professionals taking early retirement or leaving medicine during the pandemic.
“We have seen that the shortage of human resources in many countries as well as the increasing workload related to the increasing number of cancers,” as well as patients surviving longer, have increased pressures on the healthcare system, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, president of ESMO, explained in a press conference.
While tackling these oncology workforce problems requires smaller, local changes to a physician’s daily routine, “the real change,” Dr. Lim said, lies at an infrastructure level.
In response to this chronic and growing problem, ESMO launched its Resilience Task Force in 2020 to evaluate burnout and well-being. The task force plans to publish a position paper in which it will propose a set of recommendations regarding the psychosocial risks of burnout as well as flexible work patterns, well-being resources, and targeted support.
A panel of experts at the meeting touched on some of these solutions.
Dealing with staff shortages is a must, said Jean-Yves Blay, MD, PhD, during the session. “It’s a simple mathematical equation,” Dr. Blay said. “We must increase the number of doctors in medical schools and the number of nurses and healthcare professionals in all schools.” Improving staffing would also help reduce chronic workload issues.
Resilience training should also be incorporated into physician training starting in medical school. Teaching oncologists how to deal with bad news and to cope when patients dies is particularly important.
“I was not taught that,” said the oncologist from Portugal. “I had to learn that at my own cost.”
The good news is that it’s possible to develop resiliency skills over time, said Claire Hardy, PhD, from Lancaster University, United Kingdom, who agreed that training programs could be one approach to improve oncologists’ work life.
However, a person’s needs are determined by their institution and personal responsibilities. “No one knows your job better than you,” Dr. Hardy said. “No one knows better than you where the inefficiencies are, where the bureaucracy is that could be taken away, or it could be done by somebody whose role it is to sort all that out.”
But having this understanding is not enough. Physician also need to feel “psychological safety to be able to speak out and say that something isn’t working right now or is too much,” or, “I’m spending too much time doing this.”
In other words, oncologists need to be able to set boundaries and say no.
Dr. Hardy said this concept “has been around a while, but it’s really gaining momentum,” and being able to discuss these issues in a forum such as the ESMO Congress is a promising start.
Dr. Lim has relationships with Janseen and SEOM. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESMO 2023
FDA OKs ivosidenib for IDH1-mutated myelodysplastic syndromes
The agency also approved the Abbott RealTime IDH1 Assay to test for the mutation.
Almost 4% of the 16,000 people diagnosed with MDS in the United States each year carry an isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation, which increases their risk for poor outcomes, such as transformation to acute myeloid leukemia, Servier explained in a press announcement.
Ivosidenib is an IDH1 inhibitor that has previously been approved for IDH1-mutated AML and locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. The new approval makes it the only targeted therapy approved for relapsed or refractory MDS with the mutation, Servier said.
The FDA approval was based on a phase 1 study in 18 adults aged 61-82 years with IDH1-mutated relapsed or refractory MDS. Patients started at a dose of 500 mg daily in 28-day cycles until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Median treatment duration was 9.3 months, and one patient went on to receive a transplant.
Overall survival was a median of 35.7 months. Fifteen patients (83.3%) had an objective response and 7 (38.9%) went into complete remission after a median of 1.9 months of treatment. The median duration of remission had not been reached at data cutoff.
Among the 9 patients dependent on RBC or platelet transfusions at baseline, 6 (66.7%) no longer needed them during any 56-day post-baseline period.
Grade 3/4 adverse events in 5% or more of patients included arthralgia, hypertension, fatigue, mucositis, and leukocytosis.
Labeling carries a boxed warning of potentially fatal differentiation syndrome. Ivosidenib can also cause QTc prolongation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The agency also approved the Abbott RealTime IDH1 Assay to test for the mutation.
Almost 4% of the 16,000 people diagnosed with MDS in the United States each year carry an isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation, which increases their risk for poor outcomes, such as transformation to acute myeloid leukemia, Servier explained in a press announcement.
Ivosidenib is an IDH1 inhibitor that has previously been approved for IDH1-mutated AML and locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. The new approval makes it the only targeted therapy approved for relapsed or refractory MDS with the mutation, Servier said.
The FDA approval was based on a phase 1 study in 18 adults aged 61-82 years with IDH1-mutated relapsed or refractory MDS. Patients started at a dose of 500 mg daily in 28-day cycles until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Median treatment duration was 9.3 months, and one patient went on to receive a transplant.
Overall survival was a median of 35.7 months. Fifteen patients (83.3%) had an objective response and 7 (38.9%) went into complete remission after a median of 1.9 months of treatment. The median duration of remission had not been reached at data cutoff.
Among the 9 patients dependent on RBC or platelet transfusions at baseline, 6 (66.7%) no longer needed them during any 56-day post-baseline period.
Grade 3/4 adverse events in 5% or more of patients included arthralgia, hypertension, fatigue, mucositis, and leukocytosis.
Labeling carries a boxed warning of potentially fatal differentiation syndrome. Ivosidenib can also cause QTc prolongation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The agency also approved the Abbott RealTime IDH1 Assay to test for the mutation.
Almost 4% of the 16,000 people diagnosed with MDS in the United States each year carry an isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation, which increases their risk for poor outcomes, such as transformation to acute myeloid leukemia, Servier explained in a press announcement.
Ivosidenib is an IDH1 inhibitor that has previously been approved for IDH1-mutated AML and locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. The new approval makes it the only targeted therapy approved for relapsed or refractory MDS with the mutation, Servier said.
The FDA approval was based on a phase 1 study in 18 adults aged 61-82 years with IDH1-mutated relapsed or refractory MDS. Patients started at a dose of 500 mg daily in 28-day cycles until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Median treatment duration was 9.3 months, and one patient went on to receive a transplant.
Overall survival was a median of 35.7 months. Fifteen patients (83.3%) had an objective response and 7 (38.9%) went into complete remission after a median of 1.9 months of treatment. The median duration of remission had not been reached at data cutoff.
Among the 9 patients dependent on RBC or platelet transfusions at baseline, 6 (66.7%) no longer needed them during any 56-day post-baseline period.
Grade 3/4 adverse events in 5% or more of patients included arthralgia, hypertension, fatigue, mucositis, and leukocytosis.
Labeling carries a boxed warning of potentially fatal differentiation syndrome. Ivosidenib can also cause QTc prolongation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Enfortumab vedotin/pembrolizumab hailed as new standard for upfront mUC
following a phase 3 trial presented at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology annual meeting.
The combination soundly beat the current standard of care – platinum-based chemotherapy – with a median overall survival of 31.5 months among 442 subjects versus 16.1 months among 444 randomized to gemcitabine with cisplatin or carboplatin, an unprecedented 53% drop in the risk of mortality (P < .00001).
The elimination of chemotherapy also meant that there were substantially fewer grade 3 or higher adverse events with the new combination.
“This is the first time we’ve managed to beat chemotherapy in the first-line setting for overall survival despite multiple previous attempts.” The 30% remission rate with enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab “is not something we’ve seen before,” said lead investigator Thomas Powles, MBBS, MD, a urologic oncologist and researcher at the University of London, who presented the findings.
“We welcome a new standard of care in the management of advanced, metastatic urothelial carcinoma, enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab,” said Andrea Apolo, MD, a urologic oncology researcher at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md., and discussant on the trial, dubbed EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39.
The news overshadowed a second trial presented immediately after Dr. Powles’ that also showed improvement in overall survival versus standard platinum-based chemotherapy, CheckMate 901.
Instead of replacing chemotherapy, CheckMate 901 added nivolumab. With 304 patients randomized to each arm, nivolumab add-on led to a median overall survival of 21.7 months versus 18.9 months with stand-alone gemcitabine/cisplatin, a 22% drop in the risk of mortality (P = .0171).
It’s the first time that adding immunotherapy to first-line chemotherapy improved survival in metastatic urothelial carcinoma, said lead investigator Michiel van der Heijden, MD, PhD, a urologic oncologist and researcher at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam.
After decades of stagnation, Dr. Apolo said, it’s “monumental for our field” to have two trials that beat chemotherapy in the first-line setting.
However, she said that the much better survival with enfortumab vedotin/pembrolizumab means that the combination now “takes first place as the best first-line regimen in urothelial carcinoma.”
Major disruptions in the treatment paradigm
The crowning of a new first-line standard for locally advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma means that everything else in the treatment paradigm has to shift, Dr. Apolo said, and there are many new questions that need to be answered.
Among the most pressing, should the previous first-line standard – platinum-based chemotherapy – now move to the second line and be considered the treatment of choice after progression? Also, is there still a role for the previous second-line standards, pembrolizumab and other immunotherapies, if pembrolizumab fails in the first line?
Dr. Apolo said investigators also need to figure out if there is a role for enfortumab vedotin/pembrolizumab in earlier-stage disease, such as muscle-invasive bladder cancer, and if the dose and duration of enfortumab vedotin can be reduced to limit its peculiar ocular and other toxicities.
Finally, “we must discuss cost,” she said. Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab (EV+P) is expensive. “Will payers be able to afford” it?
Dr. Powles, the lead investigator on EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39, said he doesn’t know how negotiations are going with payers, but that he hopes they move quickly. “We’ve seen transformative results” with the combination for even aggressive cancers in very sick people. “I think it’s going to be a challenge with patients not to talk about these data.”
EV-302/KEYNOTE-059 details
Merck, the maker of pembrolizumab, and the makers/marketers of enfortumab vedotin, Astellas and Seagen, said they will use EV-302/KEYNOTE-059 to seek a first-line indication for locally advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and other regulators.
They also said the results serve as the confirmation FDA required when it gave accelerated approval to the combination in April 2023 for cisplatin-ineligible patients based on tumor response rates and response durability, according to press releases from the companies.
Pembrolizumab (P) in the trial was dosed at 200 mg on the first day of 3-week treatment cycles to a maximum of 35 cycles; enfortumab vedotin (EV) was given on the first and eighth day of the cycle with no limit in the number of cycles until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Cisplatin or carboplatin (C) in the control arm was delivered on the first day and gemcitabine (G) on the first and eighth days for up to six 3-week cycles.
Patients in both arms were split about equally between performance statuses of 0 or 1; less than 4% in each group had statuses of 2.
Echoing the overall survival (OS) results, progression-free survival (PFS) was a median of 12.5 months with EV-P versus 6.3 months with GC, a 55% drop in the risk of progression or death (P < .00001).
The results held regardless of PD-L1 expression, cisplatin eligibility, and the presence or absence of visceral metastases.
Follow-up treatments in the trial begin to address Dr. Apolo’s questions: Almost 60% of GC patients went on to a PD-1/L1 for subsequent maintenance or progression, and almost a quarter of EV+P patients went on to subsequent platinum-based chemotherapy.
Grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred in 55.9% of subjects in the EV+P group versus 69.5% in the GC arm.
The most common in the chemotherapy arm were anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, fatigue, and nausea. The most common with EV+P were skin reactions, hyperglycemia, neutropenia, peripheral neuropathy, diarrhea, and anemia,
CheckMate 901 details
In CheckMate 901, gemcitabine and cisplatin were administered on the first day of 3-week treatment cycles for up to 6 cycles; subjects randomized to nivolumab add-on received 360 mg on day 1 of each cycle, followed by 480 mg every 4 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity for up to 2 years.
PFS results again mirrored OS, with a median PFS of 7.9 months in the nivolumab arm versus 7.6 months with stand-alone chemotherapy, a 28% drop in the risk of progression or death (P = .0012).
Although OS and PFS benefits were statistically significant overall, they were not significant in subgroup analyses of patients 65 years and older, women, or in patients with liver metastases.
Trends in OS and PFS actually favored chemotherapy in the 40 U.S. subjects (HR OS, 1.92; 95% confidence interval, 0.95-3.88).
The rate of grade 3 or higher adverse events was 61.8% with nivolumab add-on versus 51.7% with chemotherapy alone. Anemia and neutropenia were the most common in both arms, and higher in the nivolumab group.
EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39 was funded by Seagen, Astellas, and Merck. CheckMate 901 was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb, the maker of nivolumab.
Dr. Powles reported extensive financial ties to pharmaceutical companies, including being an advisor to and receiving research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, SeaGen, and Astellas, as well as travel expenses from Merck. Among other disclosures, Dr. Heijden is an advisor to Seagen and an advisor and researcher for Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Apolo is an unpaid consultant to Merck, Astellas, Seagen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
following a phase 3 trial presented at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology annual meeting.
The combination soundly beat the current standard of care – platinum-based chemotherapy – with a median overall survival of 31.5 months among 442 subjects versus 16.1 months among 444 randomized to gemcitabine with cisplatin or carboplatin, an unprecedented 53% drop in the risk of mortality (P < .00001).
The elimination of chemotherapy also meant that there were substantially fewer grade 3 or higher adverse events with the new combination.
“This is the first time we’ve managed to beat chemotherapy in the first-line setting for overall survival despite multiple previous attempts.” The 30% remission rate with enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab “is not something we’ve seen before,” said lead investigator Thomas Powles, MBBS, MD, a urologic oncologist and researcher at the University of London, who presented the findings.
“We welcome a new standard of care in the management of advanced, metastatic urothelial carcinoma, enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab,” said Andrea Apolo, MD, a urologic oncology researcher at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md., and discussant on the trial, dubbed EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39.
The news overshadowed a second trial presented immediately after Dr. Powles’ that also showed improvement in overall survival versus standard platinum-based chemotherapy, CheckMate 901.
Instead of replacing chemotherapy, CheckMate 901 added nivolumab. With 304 patients randomized to each arm, nivolumab add-on led to a median overall survival of 21.7 months versus 18.9 months with stand-alone gemcitabine/cisplatin, a 22% drop in the risk of mortality (P = .0171).
It’s the first time that adding immunotherapy to first-line chemotherapy improved survival in metastatic urothelial carcinoma, said lead investigator Michiel van der Heijden, MD, PhD, a urologic oncologist and researcher at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam.
After decades of stagnation, Dr. Apolo said, it’s “monumental for our field” to have two trials that beat chemotherapy in the first-line setting.
However, she said that the much better survival with enfortumab vedotin/pembrolizumab means that the combination now “takes first place as the best first-line regimen in urothelial carcinoma.”
Major disruptions in the treatment paradigm
The crowning of a new first-line standard for locally advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma means that everything else in the treatment paradigm has to shift, Dr. Apolo said, and there are many new questions that need to be answered.
Among the most pressing, should the previous first-line standard – platinum-based chemotherapy – now move to the second line and be considered the treatment of choice after progression? Also, is there still a role for the previous second-line standards, pembrolizumab and other immunotherapies, if pembrolizumab fails in the first line?
Dr. Apolo said investigators also need to figure out if there is a role for enfortumab vedotin/pembrolizumab in earlier-stage disease, such as muscle-invasive bladder cancer, and if the dose and duration of enfortumab vedotin can be reduced to limit its peculiar ocular and other toxicities.
Finally, “we must discuss cost,” she said. Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab (EV+P) is expensive. “Will payers be able to afford” it?
Dr. Powles, the lead investigator on EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39, said he doesn’t know how negotiations are going with payers, but that he hopes they move quickly. “We’ve seen transformative results” with the combination for even aggressive cancers in very sick people. “I think it’s going to be a challenge with patients not to talk about these data.”
EV-302/KEYNOTE-059 details
Merck, the maker of pembrolizumab, and the makers/marketers of enfortumab vedotin, Astellas and Seagen, said they will use EV-302/KEYNOTE-059 to seek a first-line indication for locally advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and other regulators.
They also said the results serve as the confirmation FDA required when it gave accelerated approval to the combination in April 2023 for cisplatin-ineligible patients based on tumor response rates and response durability, according to press releases from the companies.
Pembrolizumab (P) in the trial was dosed at 200 mg on the first day of 3-week treatment cycles to a maximum of 35 cycles; enfortumab vedotin (EV) was given on the first and eighth day of the cycle with no limit in the number of cycles until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Cisplatin or carboplatin (C) in the control arm was delivered on the first day and gemcitabine (G) on the first and eighth days for up to six 3-week cycles.
Patients in both arms were split about equally between performance statuses of 0 or 1; less than 4% in each group had statuses of 2.
Echoing the overall survival (OS) results, progression-free survival (PFS) was a median of 12.5 months with EV-P versus 6.3 months with GC, a 55% drop in the risk of progression or death (P < .00001).
The results held regardless of PD-L1 expression, cisplatin eligibility, and the presence or absence of visceral metastases.
Follow-up treatments in the trial begin to address Dr. Apolo’s questions: Almost 60% of GC patients went on to a PD-1/L1 for subsequent maintenance or progression, and almost a quarter of EV+P patients went on to subsequent platinum-based chemotherapy.
Grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred in 55.9% of subjects in the EV+P group versus 69.5% in the GC arm.
The most common in the chemotherapy arm were anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, fatigue, and nausea. The most common with EV+P were skin reactions, hyperglycemia, neutropenia, peripheral neuropathy, diarrhea, and anemia,
CheckMate 901 details
In CheckMate 901, gemcitabine and cisplatin were administered on the first day of 3-week treatment cycles for up to 6 cycles; subjects randomized to nivolumab add-on received 360 mg on day 1 of each cycle, followed by 480 mg every 4 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity for up to 2 years.
PFS results again mirrored OS, with a median PFS of 7.9 months in the nivolumab arm versus 7.6 months with stand-alone chemotherapy, a 28% drop in the risk of progression or death (P = .0012).
Although OS and PFS benefits were statistically significant overall, they were not significant in subgroup analyses of patients 65 years and older, women, or in patients with liver metastases.
Trends in OS and PFS actually favored chemotherapy in the 40 U.S. subjects (HR OS, 1.92; 95% confidence interval, 0.95-3.88).
The rate of grade 3 or higher adverse events was 61.8% with nivolumab add-on versus 51.7% with chemotherapy alone. Anemia and neutropenia were the most common in both arms, and higher in the nivolumab group.
EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39 was funded by Seagen, Astellas, and Merck. CheckMate 901 was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb, the maker of nivolumab.
Dr. Powles reported extensive financial ties to pharmaceutical companies, including being an advisor to and receiving research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, SeaGen, and Astellas, as well as travel expenses from Merck. Among other disclosures, Dr. Heijden is an advisor to Seagen and an advisor and researcher for Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Apolo is an unpaid consultant to Merck, Astellas, Seagen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
following a phase 3 trial presented at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology annual meeting.
The combination soundly beat the current standard of care – platinum-based chemotherapy – with a median overall survival of 31.5 months among 442 subjects versus 16.1 months among 444 randomized to gemcitabine with cisplatin or carboplatin, an unprecedented 53% drop in the risk of mortality (P < .00001).
The elimination of chemotherapy also meant that there were substantially fewer grade 3 or higher adverse events with the new combination.
“This is the first time we’ve managed to beat chemotherapy in the first-line setting for overall survival despite multiple previous attempts.” The 30% remission rate with enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab “is not something we’ve seen before,” said lead investigator Thomas Powles, MBBS, MD, a urologic oncologist and researcher at the University of London, who presented the findings.
“We welcome a new standard of care in the management of advanced, metastatic urothelial carcinoma, enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab,” said Andrea Apolo, MD, a urologic oncology researcher at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md., and discussant on the trial, dubbed EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39.
The news overshadowed a second trial presented immediately after Dr. Powles’ that also showed improvement in overall survival versus standard platinum-based chemotherapy, CheckMate 901.
Instead of replacing chemotherapy, CheckMate 901 added nivolumab. With 304 patients randomized to each arm, nivolumab add-on led to a median overall survival of 21.7 months versus 18.9 months with stand-alone gemcitabine/cisplatin, a 22% drop in the risk of mortality (P = .0171).
It’s the first time that adding immunotherapy to first-line chemotherapy improved survival in metastatic urothelial carcinoma, said lead investigator Michiel van der Heijden, MD, PhD, a urologic oncologist and researcher at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam.
After decades of stagnation, Dr. Apolo said, it’s “monumental for our field” to have two trials that beat chemotherapy in the first-line setting.
However, she said that the much better survival with enfortumab vedotin/pembrolizumab means that the combination now “takes first place as the best first-line regimen in urothelial carcinoma.”
Major disruptions in the treatment paradigm
The crowning of a new first-line standard for locally advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma means that everything else in the treatment paradigm has to shift, Dr. Apolo said, and there are many new questions that need to be answered.
Among the most pressing, should the previous first-line standard – platinum-based chemotherapy – now move to the second line and be considered the treatment of choice after progression? Also, is there still a role for the previous second-line standards, pembrolizumab and other immunotherapies, if pembrolizumab fails in the first line?
Dr. Apolo said investigators also need to figure out if there is a role for enfortumab vedotin/pembrolizumab in earlier-stage disease, such as muscle-invasive bladder cancer, and if the dose and duration of enfortumab vedotin can be reduced to limit its peculiar ocular and other toxicities.
Finally, “we must discuss cost,” she said. Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab (EV+P) is expensive. “Will payers be able to afford” it?
Dr. Powles, the lead investigator on EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39, said he doesn’t know how negotiations are going with payers, but that he hopes they move quickly. “We’ve seen transformative results” with the combination for even aggressive cancers in very sick people. “I think it’s going to be a challenge with patients not to talk about these data.”
EV-302/KEYNOTE-059 details
Merck, the maker of pembrolizumab, and the makers/marketers of enfortumab vedotin, Astellas and Seagen, said they will use EV-302/KEYNOTE-059 to seek a first-line indication for locally advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and other regulators.
They also said the results serve as the confirmation FDA required when it gave accelerated approval to the combination in April 2023 for cisplatin-ineligible patients based on tumor response rates and response durability, according to press releases from the companies.
Pembrolizumab (P) in the trial was dosed at 200 mg on the first day of 3-week treatment cycles to a maximum of 35 cycles; enfortumab vedotin (EV) was given on the first and eighth day of the cycle with no limit in the number of cycles until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Cisplatin or carboplatin (C) in the control arm was delivered on the first day and gemcitabine (G) on the first and eighth days for up to six 3-week cycles.
Patients in both arms were split about equally between performance statuses of 0 or 1; less than 4% in each group had statuses of 2.
Echoing the overall survival (OS) results, progression-free survival (PFS) was a median of 12.5 months with EV-P versus 6.3 months with GC, a 55% drop in the risk of progression or death (P < .00001).
The results held regardless of PD-L1 expression, cisplatin eligibility, and the presence or absence of visceral metastases.
Follow-up treatments in the trial begin to address Dr. Apolo’s questions: Almost 60% of GC patients went on to a PD-1/L1 for subsequent maintenance or progression, and almost a quarter of EV+P patients went on to subsequent platinum-based chemotherapy.
Grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred in 55.9% of subjects in the EV+P group versus 69.5% in the GC arm.
The most common in the chemotherapy arm were anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, fatigue, and nausea. The most common with EV+P were skin reactions, hyperglycemia, neutropenia, peripheral neuropathy, diarrhea, and anemia,
CheckMate 901 details
In CheckMate 901, gemcitabine and cisplatin were administered on the first day of 3-week treatment cycles for up to 6 cycles; subjects randomized to nivolumab add-on received 360 mg on day 1 of each cycle, followed by 480 mg every 4 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity for up to 2 years.
PFS results again mirrored OS, with a median PFS of 7.9 months in the nivolumab arm versus 7.6 months with stand-alone chemotherapy, a 28% drop in the risk of progression or death (P = .0012).
Although OS and PFS benefits were statistically significant overall, they were not significant in subgroup analyses of patients 65 years and older, women, or in patients with liver metastases.
Trends in OS and PFS actually favored chemotherapy in the 40 U.S. subjects (HR OS, 1.92; 95% confidence interval, 0.95-3.88).
The rate of grade 3 or higher adverse events was 61.8% with nivolumab add-on versus 51.7% with chemotherapy alone. Anemia and neutropenia were the most common in both arms, and higher in the nivolumab group.
EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39 was funded by Seagen, Astellas, and Merck. CheckMate 901 was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb, the maker of nivolumab.
Dr. Powles reported extensive financial ties to pharmaceutical companies, including being an advisor to and receiving research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, SeaGen, and Astellas, as well as travel expenses from Merck. Among other disclosures, Dr. Heijden is an advisor to Seagen and an advisor and researcher for Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Apolo is an unpaid consultant to Merck, Astellas, Seagen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and other companies.
FROM ESMO 2023
The sobering facts about alcohol and cancer
There is an urgent need to raise global awareness about the direct link between alcohol consumption and cancer risk.
That message was delivered by Isabelle Soerjomataram, PhD, with the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Lyon, France, at a session devoted to alcohol and cancer at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Dr. Soerjomataram told the audience. “Health professionals – oncologists, nurses, medical doctors, GPs – have an important role in increasing awareness and bringing this knowledge to people, which may lead to reduced consumption.”
Session chair Gilberto Morgan, MD, medical oncologist, Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden, agreed.
Dr. Morgan noted that healthcare professionals tend to downplay their influence over patients’ drinking habits and often don’t address these behaviors.
But that needs to change.
“We have absolutely no problem asking patients if they take supplements or vitamins or if they’re eating [healthy],” Dr. Morgan said. “So, what is the difference? Why not recommend that they cut down their alcohol intake and leave it up to everybody’s personal choice to do it or not?”
In the session, Dr. Soerjomataram highlighted the global statistics on alcohol use. IARC data show, for instance, that nearly half (46%) of the world’s population consumes alcohol, with rates higher in men (54%) than women (38%).
How much are people drinking?
Globally, on average, the amount comes to about six liters of pure ethanol per year per drinker, or about one wine bottle per week. However, consumption patterns vary widely by country. In France, people consume about 12 liters per year or about two wine bottles per week.
Dr. Soerjomataram stressed the link between alcohol consumption and cancer.
According to IARC data, heavy drinking – defined as more than 60 g/day or about six daily drinks – accounts for 47% of the alcohol-attributable cancers. Risky drinking – between 20 and 60 g/day – accounts for 29%, she explained, while moderate drinking – less than 20 g/day or about two daily drinks – accounts for roughly 14% of cases of alcohol-attributable cancers.
Globally, alcohol intake accounted for 4% of all cancers diagnosed in 2020, according to a 2021 analysis by IARC.
In the United Kingdom alone, “alcohol drinking caused nearly 17,000 cases of cancer in 2020,” Dr. Soerjomataram said, and breast cancer made up almost one in four of those new cases.
In addition to breast cancer, six other cancer types – oral cavity, pharyngeal, laryngeal, esophageal, colorectal, and liver cancer – can be attributed to alcohol consumption, and emerging evidence suggests stomach and pancreatic cancer may be as well.
The good news, said Dr. Soerjomataram, is that long-term trends show declines in alcohol drinking in many countries, including the high wine-producing countries of France and Italy, where large reductions in consumption have been noted since the peak of intake in the 1920s.
“If it’s possible in these countries, I can imagine it’s possible elsewhere,” said Dr. Soerjomataram.
Dr. Soerjomataram and Dr. Morgan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is an urgent need to raise global awareness about the direct link between alcohol consumption and cancer risk.
That message was delivered by Isabelle Soerjomataram, PhD, with the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Lyon, France, at a session devoted to alcohol and cancer at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Dr. Soerjomataram told the audience. “Health professionals – oncologists, nurses, medical doctors, GPs – have an important role in increasing awareness and bringing this knowledge to people, which may lead to reduced consumption.”
Session chair Gilberto Morgan, MD, medical oncologist, Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden, agreed.
Dr. Morgan noted that healthcare professionals tend to downplay their influence over patients’ drinking habits and often don’t address these behaviors.
But that needs to change.
“We have absolutely no problem asking patients if they take supplements or vitamins or if they’re eating [healthy],” Dr. Morgan said. “So, what is the difference? Why not recommend that they cut down their alcohol intake and leave it up to everybody’s personal choice to do it or not?”
In the session, Dr. Soerjomataram highlighted the global statistics on alcohol use. IARC data show, for instance, that nearly half (46%) of the world’s population consumes alcohol, with rates higher in men (54%) than women (38%).
How much are people drinking?
Globally, on average, the amount comes to about six liters of pure ethanol per year per drinker, or about one wine bottle per week. However, consumption patterns vary widely by country. In France, people consume about 12 liters per year or about two wine bottles per week.
Dr. Soerjomataram stressed the link between alcohol consumption and cancer.
According to IARC data, heavy drinking – defined as more than 60 g/day or about six daily drinks – accounts for 47% of the alcohol-attributable cancers. Risky drinking – between 20 and 60 g/day – accounts for 29%, she explained, while moderate drinking – less than 20 g/day or about two daily drinks – accounts for roughly 14% of cases of alcohol-attributable cancers.
Globally, alcohol intake accounted for 4% of all cancers diagnosed in 2020, according to a 2021 analysis by IARC.
In the United Kingdom alone, “alcohol drinking caused nearly 17,000 cases of cancer in 2020,” Dr. Soerjomataram said, and breast cancer made up almost one in four of those new cases.
In addition to breast cancer, six other cancer types – oral cavity, pharyngeal, laryngeal, esophageal, colorectal, and liver cancer – can be attributed to alcohol consumption, and emerging evidence suggests stomach and pancreatic cancer may be as well.
The good news, said Dr. Soerjomataram, is that long-term trends show declines in alcohol drinking in many countries, including the high wine-producing countries of France and Italy, where large reductions in consumption have been noted since the peak of intake in the 1920s.
“If it’s possible in these countries, I can imagine it’s possible elsewhere,” said Dr. Soerjomataram.
Dr. Soerjomataram and Dr. Morgan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is an urgent need to raise global awareness about the direct link between alcohol consumption and cancer risk.
That message was delivered by Isabelle Soerjomataram, PhD, with the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Lyon, France, at a session devoted to alcohol and cancer at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Dr. Soerjomataram told the audience. “Health professionals – oncologists, nurses, medical doctors, GPs – have an important role in increasing awareness and bringing this knowledge to people, which may lead to reduced consumption.”
Session chair Gilberto Morgan, MD, medical oncologist, Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden, agreed.
Dr. Morgan noted that healthcare professionals tend to downplay their influence over patients’ drinking habits and often don’t address these behaviors.
But that needs to change.
“We have absolutely no problem asking patients if they take supplements or vitamins or if they’re eating [healthy],” Dr. Morgan said. “So, what is the difference? Why not recommend that they cut down their alcohol intake and leave it up to everybody’s personal choice to do it or not?”
In the session, Dr. Soerjomataram highlighted the global statistics on alcohol use. IARC data show, for instance, that nearly half (46%) of the world’s population consumes alcohol, with rates higher in men (54%) than women (38%).
How much are people drinking?
Globally, on average, the amount comes to about six liters of pure ethanol per year per drinker, or about one wine bottle per week. However, consumption patterns vary widely by country. In France, people consume about 12 liters per year or about two wine bottles per week.
Dr. Soerjomataram stressed the link between alcohol consumption and cancer.
According to IARC data, heavy drinking – defined as more than 60 g/day or about six daily drinks – accounts for 47% of the alcohol-attributable cancers. Risky drinking – between 20 and 60 g/day – accounts for 29%, she explained, while moderate drinking – less than 20 g/day or about two daily drinks – accounts for roughly 14% of cases of alcohol-attributable cancers.
Globally, alcohol intake accounted for 4% of all cancers diagnosed in 2020, according to a 2021 analysis by IARC.
In the United Kingdom alone, “alcohol drinking caused nearly 17,000 cases of cancer in 2020,” Dr. Soerjomataram said, and breast cancer made up almost one in four of those new cases.
In addition to breast cancer, six other cancer types – oral cavity, pharyngeal, laryngeal, esophageal, colorectal, and liver cancer – can be attributed to alcohol consumption, and emerging evidence suggests stomach and pancreatic cancer may be as well.
The good news, said Dr. Soerjomataram, is that long-term trends show declines in alcohol drinking in many countries, including the high wine-producing countries of France and Italy, where large reductions in consumption have been noted since the peak of intake in the 1920s.
“If it’s possible in these countries, I can imagine it’s possible elsewhere,” said Dr. Soerjomataram.
Dr. Soerjomataram and Dr. Morgan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESMO 2023