User login
Chronic opioid use during pregnancy linked with reduced head circumference in NAS newborns
(HC), reported Craig V. Towers, MD, and his associates at the University of Tennessee Medical Center in Knoxville in Pediatrics.
In the first large prospective cohort study to compare HC in newborns being treated for NAS, a total of 858 neonates, including 429 with NAS and 429 controls, were enrolled and assessed at the University of Tennessee Medical Center, Knoxville, from April 1, 2014, to Dec. 31, 2016.
Dr. Towers and his associates found that mean HC in those neonates with NAS was significantly smaller, by 9.5 mm, than it was in controls. Of the 429 newborns with NAS, 62% had a normal HC, 30% had an HC less than the 10th percentile, and 8% had an HC less than or equal to the third percentile. Of the controls, 12% had an HC less than the 10th percentile.
The authors identified a significant 3% reduction in mean HC as well as a 2% reduction in mean birth weight. “Because newborn HC is an indirect measure of brain volume, further research is necessary to determine if this finding increases the risk for long-term neurodevelopmental delay,” they said.
Even though the newborns with NAS were found to experience greater coexposure to benzodiazepines, stimulants, marijuana, gabapentin, tobacco, and SSRIs, compared with controls, none of these coexposures was determined to be a significant risk factor for smaller head circumference at birth when individual drug exposure relationships within the newborn population alone were assessed, the researchers observed.
Dr. Towers and his associates did consider it noteworthy, however, that the majority of NAS cases included in the study were born to mothers receiving opioid agonist medication–assisted treatment (MAT), which is the recommended treatment in cases where opioid use disorder is addressed during pregnancy. Among the 429 NAS cases, the mothers of 372 (87%) were on opioid agonist MAT (320 buprenorphine and 52 methadone); the remaining 13% were born to mothers who were prescribed other opioid drugs.
There is limited data available to determine whether detoxification during pregnancy for patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) has any effect on lessening the risk of lower HC. In fact, the authors caution that detoxification during pregnancy is not recommended for managing OUD. To date, there are only a few locations in the United States and other countries offering such treatment. If the practice becomes more widespread, they cautioned, further research examining new born HC and long-term outcomes “is of paramount importance.”
Further prospective studies evaluating the effects of opioid exposure in newborns who do not develop NAS also are needed. Such data could provide clues concerning whether there is a crucial period of exposure that leads to reduced HC or whether the effects of opioid exposure are in fact cumulative. In cases where newborns are exposed as a result of maintenance MAT, through illicit use, or as a result of maternal detoxification, such studies also could assist with determining whether it is necessary to reconsider current practices for managing OUD in pregnancy.
The study was partially funded through the Blue Cross Blue Shield Research Foundation. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Towers CV et al. Pediatrics. 2019;143(1):e20180541.
At a time when more people in the United States are dying from opioid overdose than from automobile trauma, the number of newborns with NAS has virtually exploded, rising fivefold since 2000. In some states, more than 30 infants per 1,000 live births develop NAS “effectively transforming some NICUs into NAS wards,” Mark L. Hudak, MD, and Kartikeya Makker, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Among the strengths of the current study, they cited “universal dating of pregnancies by early ultrasound, multiple antenatal maternal urine drug tests for exposures in both cases and controls, and the use of a fairly robust statistical methodology to account for confounding exposures.”
Among the findings of the study were that, “compared with well-matched controls, newborns with NAS demonstrated a highly significant (nearly 1 cm) decrease in the mean head circumference. Another finding was that newborns with NAS showed proportionately greater decreases in head circumference than in birth weight,” the editorialists said.
Dr. Hadak and Dr. Makker noted that, while NAS can be challenging to manage, the acute effects of withdrawal are transient. The more important questions, they propose are: “What are the best methods to prevent NAS?” and “What, if any, are the long-term effects of fetal and neonatal opioid exposure on the developing child?”
Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker question the practicality of closely following maternal opioid usage during pregnancy, but they do foresee value in the anticipated findings of a current study in which Dr. Towers and his associates are observing newborns with reduced fetal exposure to opioids who have not developed NAS.
“Additional evidence revealing that the reduction of maternal opioid use can protect normal fetal head and brain growth should energize discussion about refining the management of the opioid-maintained maternal-fetal dyad, with the goal not solely to prevent NAS but more importantly to optimize the outcome of the child,” they said.
Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker are affiliated with the department of pediatrics at the University of Florida, Jacksonville. These comments are summarized from an editorial commenting on the study by Towers et al. (Pediatrics. 2019;143[1]:e20183376). Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker said they had no relevant financial disclosures.
At a time when more people in the United States are dying from opioid overdose than from automobile trauma, the number of newborns with NAS has virtually exploded, rising fivefold since 2000. In some states, more than 30 infants per 1,000 live births develop NAS “effectively transforming some NICUs into NAS wards,” Mark L. Hudak, MD, and Kartikeya Makker, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Among the strengths of the current study, they cited “universal dating of pregnancies by early ultrasound, multiple antenatal maternal urine drug tests for exposures in both cases and controls, and the use of a fairly robust statistical methodology to account for confounding exposures.”
Among the findings of the study were that, “compared with well-matched controls, newborns with NAS demonstrated a highly significant (nearly 1 cm) decrease in the mean head circumference. Another finding was that newborns with NAS showed proportionately greater decreases in head circumference than in birth weight,” the editorialists said.
Dr. Hadak and Dr. Makker noted that, while NAS can be challenging to manage, the acute effects of withdrawal are transient. The more important questions, they propose are: “What are the best methods to prevent NAS?” and “What, if any, are the long-term effects of fetal and neonatal opioid exposure on the developing child?”
Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker question the practicality of closely following maternal opioid usage during pregnancy, but they do foresee value in the anticipated findings of a current study in which Dr. Towers and his associates are observing newborns with reduced fetal exposure to opioids who have not developed NAS.
“Additional evidence revealing that the reduction of maternal opioid use can protect normal fetal head and brain growth should energize discussion about refining the management of the opioid-maintained maternal-fetal dyad, with the goal not solely to prevent NAS but more importantly to optimize the outcome of the child,” they said.
Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker are affiliated with the department of pediatrics at the University of Florida, Jacksonville. These comments are summarized from an editorial commenting on the study by Towers et al. (Pediatrics. 2019;143[1]:e20183376). Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker said they had no relevant financial disclosures.
At a time when more people in the United States are dying from opioid overdose than from automobile trauma, the number of newborns with NAS has virtually exploded, rising fivefold since 2000. In some states, more than 30 infants per 1,000 live births develop NAS “effectively transforming some NICUs into NAS wards,” Mark L. Hudak, MD, and Kartikeya Makker, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Among the strengths of the current study, they cited “universal dating of pregnancies by early ultrasound, multiple antenatal maternal urine drug tests for exposures in both cases and controls, and the use of a fairly robust statistical methodology to account for confounding exposures.”
Among the findings of the study were that, “compared with well-matched controls, newborns with NAS demonstrated a highly significant (nearly 1 cm) decrease in the mean head circumference. Another finding was that newborns with NAS showed proportionately greater decreases in head circumference than in birth weight,” the editorialists said.
Dr. Hadak and Dr. Makker noted that, while NAS can be challenging to manage, the acute effects of withdrawal are transient. The more important questions, they propose are: “What are the best methods to prevent NAS?” and “What, if any, are the long-term effects of fetal and neonatal opioid exposure on the developing child?”
Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker question the practicality of closely following maternal opioid usage during pregnancy, but they do foresee value in the anticipated findings of a current study in which Dr. Towers and his associates are observing newborns with reduced fetal exposure to opioids who have not developed NAS.
“Additional evidence revealing that the reduction of maternal opioid use can protect normal fetal head and brain growth should energize discussion about refining the management of the opioid-maintained maternal-fetal dyad, with the goal not solely to prevent NAS but more importantly to optimize the outcome of the child,” they said.
Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker are affiliated with the department of pediatrics at the University of Florida, Jacksonville. These comments are summarized from an editorial commenting on the study by Towers et al. (Pediatrics. 2019;143[1]:e20183376). Dr. Hudak and Dr. Makker said they had no relevant financial disclosures.
(HC), reported Craig V. Towers, MD, and his associates at the University of Tennessee Medical Center in Knoxville in Pediatrics.
In the first large prospective cohort study to compare HC in newborns being treated for NAS, a total of 858 neonates, including 429 with NAS and 429 controls, were enrolled and assessed at the University of Tennessee Medical Center, Knoxville, from April 1, 2014, to Dec. 31, 2016.
Dr. Towers and his associates found that mean HC in those neonates with NAS was significantly smaller, by 9.5 mm, than it was in controls. Of the 429 newborns with NAS, 62% had a normal HC, 30% had an HC less than the 10th percentile, and 8% had an HC less than or equal to the third percentile. Of the controls, 12% had an HC less than the 10th percentile.
The authors identified a significant 3% reduction in mean HC as well as a 2% reduction in mean birth weight. “Because newborn HC is an indirect measure of brain volume, further research is necessary to determine if this finding increases the risk for long-term neurodevelopmental delay,” they said.
Even though the newborns with NAS were found to experience greater coexposure to benzodiazepines, stimulants, marijuana, gabapentin, tobacco, and SSRIs, compared with controls, none of these coexposures was determined to be a significant risk factor for smaller head circumference at birth when individual drug exposure relationships within the newborn population alone were assessed, the researchers observed.
Dr. Towers and his associates did consider it noteworthy, however, that the majority of NAS cases included in the study were born to mothers receiving opioid agonist medication–assisted treatment (MAT), which is the recommended treatment in cases where opioid use disorder is addressed during pregnancy. Among the 429 NAS cases, the mothers of 372 (87%) were on opioid agonist MAT (320 buprenorphine and 52 methadone); the remaining 13% were born to mothers who were prescribed other opioid drugs.
There is limited data available to determine whether detoxification during pregnancy for patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) has any effect on lessening the risk of lower HC. In fact, the authors caution that detoxification during pregnancy is not recommended for managing OUD. To date, there are only a few locations in the United States and other countries offering such treatment. If the practice becomes more widespread, they cautioned, further research examining new born HC and long-term outcomes “is of paramount importance.”
Further prospective studies evaluating the effects of opioid exposure in newborns who do not develop NAS also are needed. Such data could provide clues concerning whether there is a crucial period of exposure that leads to reduced HC or whether the effects of opioid exposure are in fact cumulative. In cases where newborns are exposed as a result of maintenance MAT, through illicit use, or as a result of maternal detoxification, such studies also could assist with determining whether it is necessary to reconsider current practices for managing OUD in pregnancy.
The study was partially funded through the Blue Cross Blue Shield Research Foundation. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Towers CV et al. Pediatrics. 2019;143(1):e20180541.
(HC), reported Craig V. Towers, MD, and his associates at the University of Tennessee Medical Center in Knoxville in Pediatrics.
In the first large prospective cohort study to compare HC in newborns being treated for NAS, a total of 858 neonates, including 429 with NAS and 429 controls, were enrolled and assessed at the University of Tennessee Medical Center, Knoxville, from April 1, 2014, to Dec. 31, 2016.
Dr. Towers and his associates found that mean HC in those neonates with NAS was significantly smaller, by 9.5 mm, than it was in controls. Of the 429 newborns with NAS, 62% had a normal HC, 30% had an HC less than the 10th percentile, and 8% had an HC less than or equal to the third percentile. Of the controls, 12% had an HC less than the 10th percentile.
The authors identified a significant 3% reduction in mean HC as well as a 2% reduction in mean birth weight. “Because newborn HC is an indirect measure of brain volume, further research is necessary to determine if this finding increases the risk for long-term neurodevelopmental delay,” they said.
Even though the newborns with NAS were found to experience greater coexposure to benzodiazepines, stimulants, marijuana, gabapentin, tobacco, and SSRIs, compared with controls, none of these coexposures was determined to be a significant risk factor for smaller head circumference at birth when individual drug exposure relationships within the newborn population alone were assessed, the researchers observed.
Dr. Towers and his associates did consider it noteworthy, however, that the majority of NAS cases included in the study were born to mothers receiving opioid agonist medication–assisted treatment (MAT), which is the recommended treatment in cases where opioid use disorder is addressed during pregnancy. Among the 429 NAS cases, the mothers of 372 (87%) were on opioid agonist MAT (320 buprenorphine and 52 methadone); the remaining 13% were born to mothers who were prescribed other opioid drugs.
There is limited data available to determine whether detoxification during pregnancy for patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) has any effect on lessening the risk of lower HC. In fact, the authors caution that detoxification during pregnancy is not recommended for managing OUD. To date, there are only a few locations in the United States and other countries offering such treatment. If the practice becomes more widespread, they cautioned, further research examining new born HC and long-term outcomes “is of paramount importance.”
Further prospective studies evaluating the effects of opioid exposure in newborns who do not develop NAS also are needed. Such data could provide clues concerning whether there is a crucial period of exposure that leads to reduced HC or whether the effects of opioid exposure are in fact cumulative. In cases where newborns are exposed as a result of maintenance MAT, through illicit use, or as a result of maternal detoxification, such studies also could assist with determining whether it is necessary to reconsider current practices for managing OUD in pregnancy.
The study was partially funded through the Blue Cross Blue Shield Research Foundation. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Towers CV et al. Pediatrics. 2019;143(1):e20180541.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point: Detoxification during pregnancy may be ill advised for patients with opioid use disorder.
Major finding: Head circumference was smaller by a mean 9.5 mm.
Study details: Prospective cohort study of 429 NAS neonates and 429 controls.
Disclosures: The study was partially funded through the Blue Cross Blue Shield Research Foundation. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Towers CV et al. Pediatrics. 2019;143(1):e20180541.
HPV-16/-18 dramatically increases risk of high-grade CIN in young women
Young women with HPV-16/-18 are significantly more likely to develop high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), compared with young women who do not have HPV-16/-18, and therefore require close monitoring, according to a 9-year study of more than 500 women.
Specific strain of HPV had less effect on risk in women aged 30 years or older, compared with younger women, reported lead author Maria Fröberg, MD, PhD, of Karolinska University Hospital and Institute in Stockholm and her colleagues.
“With today’s introduction of HPV primary screening into several organized screening programs and with many triage algorithms available, further research is needed to ensure safe follow-up management and prevent the unnecessary treatment of transient positive HPV findings associated with regressive high-grade CIN,” the investigators wrote in Cancer.
To better understand risk associated with HPV, the investigators drew from a database of 9,464 Swedish women who were cytologically negative for cervical intraepithelial lesions or malignancy (NILM) at baseline during 2005-2007. These baseline-negative women were followed for 9 years; during this time, 96 women developed histologically confirmed, high-grade CIN (CIN2, CIN3, cervical cancer, or adenocarcinoma in situ [AIS]). For each case, five age-matched women were selected who did not develop high-grade CIN to make a control cohort of 480 women.
Approximately half of the cases had CIN2 (45.8%), and half had CIN3 or worse histopathology (CIN3+, 54.2%). HPV-16/-18 was more often associated with CIN3+, compared with CIN2 (Pearson x2, 6.12; P less than .02 [2-sided]). Women with high-grade CIN were significantly more likely to have HPV of any strain, compared with controls (odds ratio, 6.78). Women aged younger than 30 years who had HPV-16/-18 at baseline were far more likely to develop high-grade CIN (OR, 9.44) but showed less impact from other strains of HPV (OR, 2.24). In contrast, women aged 30 years or older showed similar increases in high-grade CIN risk when comparing HPV-16/-18 with other strains (OR, 8.16 vs. 9.04).
“These latter findings suggest that genotyping for HPV-16/-18 might be useful for risk stratification among younger women,” the investigators suggested, noting that “further prospective study on this topic is warranted.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Stockholm County Council, the Swedish Research Council, and the King Gustaf V Jubilee Fund, and the Karolinska Institute. During the study, one investigator received grants from VALGENT and the 7th Framework Programme of DG Research and Innovation (European Commission).
SOURCE: Fröberg M et al. Cancer. 2018 Dec 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31788.
Young women with HPV-16/-18 are significantly more likely to develop high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), compared with young women who do not have HPV-16/-18, and therefore require close monitoring, according to a 9-year study of more than 500 women.
Specific strain of HPV had less effect on risk in women aged 30 years or older, compared with younger women, reported lead author Maria Fröberg, MD, PhD, of Karolinska University Hospital and Institute in Stockholm and her colleagues.
“With today’s introduction of HPV primary screening into several organized screening programs and with many triage algorithms available, further research is needed to ensure safe follow-up management and prevent the unnecessary treatment of transient positive HPV findings associated with regressive high-grade CIN,” the investigators wrote in Cancer.
To better understand risk associated with HPV, the investigators drew from a database of 9,464 Swedish women who were cytologically negative for cervical intraepithelial lesions or malignancy (NILM) at baseline during 2005-2007. These baseline-negative women were followed for 9 years; during this time, 96 women developed histologically confirmed, high-grade CIN (CIN2, CIN3, cervical cancer, or adenocarcinoma in situ [AIS]). For each case, five age-matched women were selected who did not develop high-grade CIN to make a control cohort of 480 women.
Approximately half of the cases had CIN2 (45.8%), and half had CIN3 or worse histopathology (CIN3+, 54.2%). HPV-16/-18 was more often associated with CIN3+, compared with CIN2 (Pearson x2, 6.12; P less than .02 [2-sided]). Women with high-grade CIN were significantly more likely to have HPV of any strain, compared with controls (odds ratio, 6.78). Women aged younger than 30 years who had HPV-16/-18 at baseline were far more likely to develop high-grade CIN (OR, 9.44) but showed less impact from other strains of HPV (OR, 2.24). In contrast, women aged 30 years or older showed similar increases in high-grade CIN risk when comparing HPV-16/-18 with other strains (OR, 8.16 vs. 9.04).
“These latter findings suggest that genotyping for HPV-16/-18 might be useful for risk stratification among younger women,” the investigators suggested, noting that “further prospective study on this topic is warranted.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Stockholm County Council, the Swedish Research Council, and the King Gustaf V Jubilee Fund, and the Karolinska Institute. During the study, one investigator received grants from VALGENT and the 7th Framework Programme of DG Research and Innovation (European Commission).
SOURCE: Fröberg M et al. Cancer. 2018 Dec 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31788.
Young women with HPV-16/-18 are significantly more likely to develop high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), compared with young women who do not have HPV-16/-18, and therefore require close monitoring, according to a 9-year study of more than 500 women.
Specific strain of HPV had less effect on risk in women aged 30 years or older, compared with younger women, reported lead author Maria Fröberg, MD, PhD, of Karolinska University Hospital and Institute in Stockholm and her colleagues.
“With today’s introduction of HPV primary screening into several organized screening programs and with many triage algorithms available, further research is needed to ensure safe follow-up management and prevent the unnecessary treatment of transient positive HPV findings associated with regressive high-grade CIN,” the investigators wrote in Cancer.
To better understand risk associated with HPV, the investigators drew from a database of 9,464 Swedish women who were cytologically negative for cervical intraepithelial lesions or malignancy (NILM) at baseline during 2005-2007. These baseline-negative women were followed for 9 years; during this time, 96 women developed histologically confirmed, high-grade CIN (CIN2, CIN3, cervical cancer, or adenocarcinoma in situ [AIS]). For each case, five age-matched women were selected who did not develop high-grade CIN to make a control cohort of 480 women.
Approximately half of the cases had CIN2 (45.8%), and half had CIN3 or worse histopathology (CIN3+, 54.2%). HPV-16/-18 was more often associated with CIN3+, compared with CIN2 (Pearson x2, 6.12; P less than .02 [2-sided]). Women with high-grade CIN were significantly more likely to have HPV of any strain, compared with controls (odds ratio, 6.78). Women aged younger than 30 years who had HPV-16/-18 at baseline were far more likely to develop high-grade CIN (OR, 9.44) but showed less impact from other strains of HPV (OR, 2.24). In contrast, women aged 30 years or older showed similar increases in high-grade CIN risk when comparing HPV-16/-18 with other strains (OR, 8.16 vs. 9.04).
“These latter findings suggest that genotyping for HPV-16/-18 might be useful for risk stratification among younger women,” the investigators suggested, noting that “further prospective study on this topic is warranted.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Stockholm County Council, the Swedish Research Council, and the King Gustaf V Jubilee Fund, and the Karolinska Institute. During the study, one investigator received grants from VALGENT and the 7th Framework Programme of DG Research and Innovation (European Commission).
SOURCE: Fröberg M et al. Cancer. 2018 Dec 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31788.
FROM CANCER
Key clinical point: Women with HPV-16/-18 are at significantly higher risk of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), compared with women without HPV-16/-18, and therefore require close monitoring.
Major finding: Women younger than 30 years who test positive for HPV-16/-18 are almost 10 times as likely to develop high-grade CIN, compared with young women negative for HPV-16/-18 (odds ratio, 9.44).
Study details: A nested case-control study involving 96 women who developed high-grade CIN over the 9-year study period, compared with 480 age-matched controls who did not develop cervical lesions.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Stockholm County Council, the Swedish Research Council, and the King Gustaf V Jubilee Fund, and the Karolinska Institute. During the study, one investigator received grants from VALGENT and the 7th Framework Programme of DG Research and Innovation (European Commission).
Source: Fröberg M et al. Cancer. 2018 Dec 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31788.
Clinical trial: Robotic or open radical cystectomy in treating patients with bladder cancer
Patients who are recruited will undergo either open or robotic radical cystectomy. In open radical cystectomy, the surgeon cuts into the lower abdomen to expose the urinary tract in order to remove the bladder. In robotic radical cystectomy, small cuts are made in the abdomen into which a scope is inserted; with robotic help, the surgeon removes the bladder. It is currently unknown which approach results in fewer complications, better quality of life, and faster recovery time.
Patients are eligible for the study if they are indicated for radical cystectomy, have Tis-T3 urothelial cancer, and meet surgical candidate criteria. Exclusion factors include having a bulky lymphadenopathy, prior pelvic radiation, or uncontrolled coagulopathy.
The primary outcome measure is change in patient-reported quality of life, as reported using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC)-QLQ-C30, 1 month post surgery. The secondary outcome measure is change in erectile dysfunction, as measured by the Sexual Health Inventory For Men score, over a follow-up of up to 12 months.
Recruitment ends on Oct. 12, 2019, and the estimated study completion date is Oct. 12, 2020. About 208 participants are expected to be included.
Find more information on the study page at Clinicaltrials.gov.
Patients who are recruited will undergo either open or robotic radical cystectomy. In open radical cystectomy, the surgeon cuts into the lower abdomen to expose the urinary tract in order to remove the bladder. In robotic radical cystectomy, small cuts are made in the abdomen into which a scope is inserted; with robotic help, the surgeon removes the bladder. It is currently unknown which approach results in fewer complications, better quality of life, and faster recovery time.
Patients are eligible for the study if they are indicated for radical cystectomy, have Tis-T3 urothelial cancer, and meet surgical candidate criteria. Exclusion factors include having a bulky lymphadenopathy, prior pelvic radiation, or uncontrolled coagulopathy.
The primary outcome measure is change in patient-reported quality of life, as reported using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC)-QLQ-C30, 1 month post surgery. The secondary outcome measure is change in erectile dysfunction, as measured by the Sexual Health Inventory For Men score, over a follow-up of up to 12 months.
Recruitment ends on Oct. 12, 2019, and the estimated study completion date is Oct. 12, 2020. About 208 participants are expected to be included.
Find more information on the study page at Clinicaltrials.gov.
Patients who are recruited will undergo either open or robotic radical cystectomy. In open radical cystectomy, the surgeon cuts into the lower abdomen to expose the urinary tract in order to remove the bladder. In robotic radical cystectomy, small cuts are made in the abdomen into which a scope is inserted; with robotic help, the surgeon removes the bladder. It is currently unknown which approach results in fewer complications, better quality of life, and faster recovery time.
Patients are eligible for the study if they are indicated for radical cystectomy, have Tis-T3 urothelial cancer, and meet surgical candidate criteria. Exclusion factors include having a bulky lymphadenopathy, prior pelvic radiation, or uncontrolled coagulopathy.
The primary outcome measure is change in patient-reported quality of life, as reported using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC)-QLQ-C30, 1 month post surgery. The secondary outcome measure is change in erectile dysfunction, as measured by the Sexual Health Inventory For Men score, over a follow-up of up to 12 months.
Recruitment ends on Oct. 12, 2019, and the estimated study completion date is Oct. 12, 2020. About 208 participants are expected to be included.
Find more information on the study page at Clinicaltrials.gov.
CPN welcomes Andrea Murru, MD, PhD, to CPN board
Clinical Psychiatry News is pleased to announce that Andrea Murru, MD, PhD, has joined the Editorial Advisory Board.
Dr. Murru is senior clinician in the bipolar disorder and sleep disorder units of the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona in Spain, and is a postdoctoral researcher of the Spanish Network of Research in Mental Health, which is led by Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD.
In addition, His research focuses on using, long-term treatments, and implementing clinical guidelines in daily practice. He also researches tolerability in patients with bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorder, and sleep-related disorders and biomarkers.
He earned his medical degree from the University of Cagliari (Italy).
Clinical Psychiatry News is pleased to announce that Andrea Murru, MD, PhD, has joined the Editorial Advisory Board.
Dr. Murru is senior clinician in the bipolar disorder and sleep disorder units of the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona in Spain, and is a postdoctoral researcher of the Spanish Network of Research in Mental Health, which is led by Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD.
In addition, His research focuses on using, long-term treatments, and implementing clinical guidelines in daily practice. He also researches tolerability in patients with bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorder, and sleep-related disorders and biomarkers.
He earned his medical degree from the University of Cagliari (Italy).
Clinical Psychiatry News is pleased to announce that Andrea Murru, MD, PhD, has joined the Editorial Advisory Board.
Dr. Murru is senior clinician in the bipolar disorder and sleep disorder units of the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona in Spain, and is a postdoctoral researcher of the Spanish Network of Research in Mental Health, which is led by Eduard Vieta, MD, PhD.
In addition, His research focuses on using, long-term treatments, and implementing clinical guidelines in daily practice. He also researches tolerability in patients with bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorder, and sleep-related disorders and biomarkers.
He earned his medical degree from the University of Cagliari (Italy).
New insight gained into natural history of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
CHICAGO – than are those with idiopathic interstitial lung disease who don’t meet the criteria, Michail Alevizos, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“We think this is a very novel finding. It means that patients with IPAF [interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features] should be followed and evaluated by rheumatologists over time,” said Dr. Alevizos, who was a rheumatology fellow at Columbia University in New York at the time of the study.
Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF) is a term proposed by a joint task force of the American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society in 2015 to describe patients diagnosed with idiopathic interstitial lung disease who possess some features of autoimmunity without meeting formal criteria for a full-blown rheumatic disease. The designation requires the presence of interstitial lung disease by imaging or biopsy, exclusion of all other etiologies, and at least one feature from within at least two of three domains: clinical, serologic, and morphologic.
The clinical domain includes Raynaud’s, palmar telangiectasias, distal digital tip ulceration, and other entities. The serologic criteria include any of a dozen possible autoantibodies. And the morphologic domain encompasses a radiographic or histopathologic pattern suggestive of organizing pneumonia, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, or other specific abnormalities (Eur Respir J. 2015 Oct;46[4]:976-87).
The natural history of IPAF is largely unknown, which was the impetus for Dr. Alevizos’ study. He presented a single-center, retrospective study of 697 patients diagnosed with interstitial lung disease, 174 of whom had idiopathic interstitial lung disease at baseline. Fifty of the 174 met criteria for IPAF, while the other 124 did not.
During a median follow-up of 5.2 years, 8 of the 50 patients with IPAF (16%) were diagnosed with a systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease, as were 2 of the 124 non-IPAF group (1.6%). The average time to diagnosis of a formal rheumatic disease was 3.4 years in the IPAF group and 7.8 years in the comparator arm. The rheumatic diseases that arose in the IPAF group consisted of two cases of rheumatoid arthritis, two of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, three of systemic sclerosis, and one of polymyositis.
In an analysis adjusted for age, sex, smoking status, and immunosuppressive therapy at baseline, patients with IPAF were 14.1 times more likely to progress to an autoimmune rheumatic disease.
In terms of distinguishing features, the IPAF patients were on average 10 years younger at baseline and more commonly female. On high-resolution CT, 82% of them displayed a pattern of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, compared with only 15% of the non-IPAF group. Also, 96% of the IPAF patients were on immunosuppressive therapy at baseline, as were 52% of the non-IPAF group. Usual interstitial pneumonia was evident on high-resolution CT in 18% of the IPAF group, compared with 75% of patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia without IPAF.
Dr. Alevizos said he hopes to validate these findings in a prospective study. He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was conducted free of commercial support.
SOURCE: Alevizos M et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 1305.
CHICAGO – than are those with idiopathic interstitial lung disease who don’t meet the criteria, Michail Alevizos, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“We think this is a very novel finding. It means that patients with IPAF [interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features] should be followed and evaluated by rheumatologists over time,” said Dr. Alevizos, who was a rheumatology fellow at Columbia University in New York at the time of the study.
Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF) is a term proposed by a joint task force of the American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society in 2015 to describe patients diagnosed with idiopathic interstitial lung disease who possess some features of autoimmunity without meeting formal criteria for a full-blown rheumatic disease. The designation requires the presence of interstitial lung disease by imaging or biopsy, exclusion of all other etiologies, and at least one feature from within at least two of three domains: clinical, serologic, and morphologic.
The clinical domain includes Raynaud’s, palmar telangiectasias, distal digital tip ulceration, and other entities. The serologic criteria include any of a dozen possible autoantibodies. And the morphologic domain encompasses a radiographic or histopathologic pattern suggestive of organizing pneumonia, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, or other specific abnormalities (Eur Respir J. 2015 Oct;46[4]:976-87).
The natural history of IPAF is largely unknown, which was the impetus for Dr. Alevizos’ study. He presented a single-center, retrospective study of 697 patients diagnosed with interstitial lung disease, 174 of whom had idiopathic interstitial lung disease at baseline. Fifty of the 174 met criteria for IPAF, while the other 124 did not.
During a median follow-up of 5.2 years, 8 of the 50 patients with IPAF (16%) were diagnosed with a systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease, as were 2 of the 124 non-IPAF group (1.6%). The average time to diagnosis of a formal rheumatic disease was 3.4 years in the IPAF group and 7.8 years in the comparator arm. The rheumatic diseases that arose in the IPAF group consisted of two cases of rheumatoid arthritis, two of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, three of systemic sclerosis, and one of polymyositis.
In an analysis adjusted for age, sex, smoking status, and immunosuppressive therapy at baseline, patients with IPAF were 14.1 times more likely to progress to an autoimmune rheumatic disease.
In terms of distinguishing features, the IPAF patients were on average 10 years younger at baseline and more commonly female. On high-resolution CT, 82% of them displayed a pattern of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, compared with only 15% of the non-IPAF group. Also, 96% of the IPAF patients were on immunosuppressive therapy at baseline, as were 52% of the non-IPAF group. Usual interstitial pneumonia was evident on high-resolution CT in 18% of the IPAF group, compared with 75% of patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia without IPAF.
Dr. Alevizos said he hopes to validate these findings in a prospective study. He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was conducted free of commercial support.
SOURCE: Alevizos M et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 1305.
CHICAGO – than are those with idiopathic interstitial lung disease who don’t meet the criteria, Michail Alevizos, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“We think this is a very novel finding. It means that patients with IPAF [interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features] should be followed and evaluated by rheumatologists over time,” said Dr. Alevizos, who was a rheumatology fellow at Columbia University in New York at the time of the study.
Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF) is a term proposed by a joint task force of the American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society in 2015 to describe patients diagnosed with idiopathic interstitial lung disease who possess some features of autoimmunity without meeting formal criteria for a full-blown rheumatic disease. The designation requires the presence of interstitial lung disease by imaging or biopsy, exclusion of all other etiologies, and at least one feature from within at least two of three domains: clinical, serologic, and morphologic.
The clinical domain includes Raynaud’s, palmar telangiectasias, distal digital tip ulceration, and other entities. The serologic criteria include any of a dozen possible autoantibodies. And the morphologic domain encompasses a radiographic or histopathologic pattern suggestive of organizing pneumonia, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, or other specific abnormalities (Eur Respir J. 2015 Oct;46[4]:976-87).
The natural history of IPAF is largely unknown, which was the impetus for Dr. Alevizos’ study. He presented a single-center, retrospective study of 697 patients diagnosed with interstitial lung disease, 174 of whom had idiopathic interstitial lung disease at baseline. Fifty of the 174 met criteria for IPAF, while the other 124 did not.
During a median follow-up of 5.2 years, 8 of the 50 patients with IPAF (16%) were diagnosed with a systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease, as were 2 of the 124 non-IPAF group (1.6%). The average time to diagnosis of a formal rheumatic disease was 3.4 years in the IPAF group and 7.8 years in the comparator arm. The rheumatic diseases that arose in the IPAF group consisted of two cases of rheumatoid arthritis, two of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, three of systemic sclerosis, and one of polymyositis.
In an analysis adjusted for age, sex, smoking status, and immunosuppressive therapy at baseline, patients with IPAF were 14.1 times more likely to progress to an autoimmune rheumatic disease.
In terms of distinguishing features, the IPAF patients were on average 10 years younger at baseline and more commonly female. On high-resolution CT, 82% of them displayed a pattern of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, compared with only 15% of the non-IPAF group. Also, 96% of the IPAF patients were on immunosuppressive therapy at baseline, as were 52% of the non-IPAF group. Usual interstitial pneumonia was evident on high-resolution CT in 18% of the IPAF group, compared with 75% of patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia without IPAF.
Dr. Alevizos said he hopes to validate these findings in a prospective study. He reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was conducted free of commercial support.
SOURCE: Alevizos M et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 1305.
REPORTING FROM the ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: The adjusted risk of progression to a systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease is 14.1 times greater in interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features than in idiopathic interstitial lung disease without such features.
Major finding: A total of 16% of patients with interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features progressed to a systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease during follow-up, compared with 1.6% of patients with idiopathic interstitial lung disease without such features.
Study details: This retrospective, single-center study included 174 patients with idiopathic interstitial lung disease followed for a median of 5.2 years.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was conducted free of commercial support.
Source: Alevizos M et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 1305.
Drug-drug interactions in rheumatology patients on PPIs: An underappreciated problem?
CHICAGO – posing a distinct danger of unwelcome drug-drug interactions affecting the rate and extent of absorption of selected oral antirheumatic drugs, Nicholas Jones, PharmD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Of particular interest is the fact that the oral Janus kinase inhibitors – a drug class that’s a red hot research topic now in rheumatology – are weak bases whose absorption can be greatly affected by pH-dependent solubility, according to Dr. Jones, a research scientist at Genentech in South San Francisco.
Other commonly prescribed oral antirheumatic drugs whose solubility is affected by the level of stomach acidity include azathioprine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and sulfasalazine. On the other hand, solubility is not pH-dependent for apremilast, chloroquine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, or tacrolimus.
Dr. Jones presented a retrospective analysis of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) utilization patterns during 2012-2015 in 77,034 rheumatoid arthritis and 2,224 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients included in the national Truven Health MarketScan database.
Thirty-five percent of the rheumatoid arthritis patients and 34% of SLE patients were chronic users of PPIs as defined by continuous daily use for more than a month during 2 years of follow-up. Among the SLE cohort, chronic utilization of PPIs increased stepwise with disease severity: The rate was 27% in those with mild SLE, 39% with moderate disease, and 54% among those with severe SLE.
Omeprazole was far and away the most widely used PPI. It was the one used by 53% of the RA patients who were chronic users of PPIs, followed by pantoprazole at 20% and esomeprazole at 15%. The PPI distribution pattern closely followed suit in SLE patients who were chronic users.
Esomeprazole is 60% more potent and pantoprazole 77% less potent than omeprazole, Dr. Jones noted. The pharmacokinetic clearance routes for omeprazole and esomeprazole involve CYP2C19 and CYP3A4. Clearance of pantoprazole is by those two mechanisms as well as by CYP2D6 and CYP2C9.
Dr. Jones recommended that physicians who treat rheumatoid arthritis and SLE patients be sure to ask them about concomitant use of PPIs, including OTC formulations. And clinical trialists need to be attentive to PPI usage in potential study participants.
Genentech sponsored the study.
SOURCE: Keebler D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 228
CHICAGO – posing a distinct danger of unwelcome drug-drug interactions affecting the rate and extent of absorption of selected oral antirheumatic drugs, Nicholas Jones, PharmD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Of particular interest is the fact that the oral Janus kinase inhibitors – a drug class that’s a red hot research topic now in rheumatology – are weak bases whose absorption can be greatly affected by pH-dependent solubility, according to Dr. Jones, a research scientist at Genentech in South San Francisco.
Other commonly prescribed oral antirheumatic drugs whose solubility is affected by the level of stomach acidity include azathioprine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and sulfasalazine. On the other hand, solubility is not pH-dependent for apremilast, chloroquine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, or tacrolimus.
Dr. Jones presented a retrospective analysis of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) utilization patterns during 2012-2015 in 77,034 rheumatoid arthritis and 2,224 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients included in the national Truven Health MarketScan database.
Thirty-five percent of the rheumatoid arthritis patients and 34% of SLE patients were chronic users of PPIs as defined by continuous daily use for more than a month during 2 years of follow-up. Among the SLE cohort, chronic utilization of PPIs increased stepwise with disease severity: The rate was 27% in those with mild SLE, 39% with moderate disease, and 54% among those with severe SLE.
Omeprazole was far and away the most widely used PPI. It was the one used by 53% of the RA patients who were chronic users of PPIs, followed by pantoprazole at 20% and esomeprazole at 15%. The PPI distribution pattern closely followed suit in SLE patients who were chronic users.
Esomeprazole is 60% more potent and pantoprazole 77% less potent than omeprazole, Dr. Jones noted. The pharmacokinetic clearance routes for omeprazole and esomeprazole involve CYP2C19 and CYP3A4. Clearance of pantoprazole is by those two mechanisms as well as by CYP2D6 and CYP2C9.
Dr. Jones recommended that physicians who treat rheumatoid arthritis and SLE patients be sure to ask them about concomitant use of PPIs, including OTC formulations. And clinical trialists need to be attentive to PPI usage in potential study participants.
Genentech sponsored the study.
SOURCE: Keebler D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 228
CHICAGO – posing a distinct danger of unwelcome drug-drug interactions affecting the rate and extent of absorption of selected oral antirheumatic drugs, Nicholas Jones, PharmD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Of particular interest is the fact that the oral Janus kinase inhibitors – a drug class that’s a red hot research topic now in rheumatology – are weak bases whose absorption can be greatly affected by pH-dependent solubility, according to Dr. Jones, a research scientist at Genentech in South San Francisco.
Other commonly prescribed oral antirheumatic drugs whose solubility is affected by the level of stomach acidity include azathioprine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and sulfasalazine. On the other hand, solubility is not pH-dependent for apremilast, chloroquine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, or tacrolimus.
Dr. Jones presented a retrospective analysis of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) utilization patterns during 2012-2015 in 77,034 rheumatoid arthritis and 2,224 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients included in the national Truven Health MarketScan database.
Thirty-five percent of the rheumatoid arthritis patients and 34% of SLE patients were chronic users of PPIs as defined by continuous daily use for more than a month during 2 years of follow-up. Among the SLE cohort, chronic utilization of PPIs increased stepwise with disease severity: The rate was 27% in those with mild SLE, 39% with moderate disease, and 54% among those with severe SLE.
Omeprazole was far and away the most widely used PPI. It was the one used by 53% of the RA patients who were chronic users of PPIs, followed by pantoprazole at 20% and esomeprazole at 15%. The PPI distribution pattern closely followed suit in SLE patients who were chronic users.
Esomeprazole is 60% more potent and pantoprazole 77% less potent than omeprazole, Dr. Jones noted. The pharmacokinetic clearance routes for omeprazole and esomeprazole involve CYP2C19 and CYP3A4. Clearance of pantoprazole is by those two mechanisms as well as by CYP2D6 and CYP2C9.
Dr. Jones recommended that physicians who treat rheumatoid arthritis and SLE patients be sure to ask them about concomitant use of PPIs, including OTC formulations. And clinical trialists need to be attentive to PPI usage in potential study participants.
Genentech sponsored the study.
SOURCE: Keebler D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 228
REPORTING FROM the ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Ask your RA and SLE patients about concomitant chronic use of PPIs to avoid drug-drug interactions.
Major finding: More than one-third of RA and SLE patients are chronic users of PPIs, which raises potential drug-drug interaction issues for many commonly prescribed oral antirheumatic drugs.
Study details: This retrospective study utilized national claims data to examine chronic use of PPIs among more than 77,000 patients with RA and 2,224 with SLE.
Disclosures: The presenter is employed at Genentech, which sponsored the study.
Source: Keebler D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 228
Verrucous Coalescing Dry Papules and Plaques on the Hip and Flank
The Diagnosis: Blaschkitis
A punch biopsy from the right lateral hip was performed. Histopathologic examination revealed orthokeratosis overlying mild psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia associated with a lichenoid infiltrate composed almost entirely of lymphocytes (Figure). The infiltrate did not entirely obscure the dermoepidermal junction and spared the adnexal structures. The clinical presentation along with histopathologic analysis confirmed a diagnosis of blaschkitis. The lesions were treated with triamcinolone ointment twice daily as needed, and the patient reported symptomatic and clinical improvement with this intervention at 4-week follow-up.
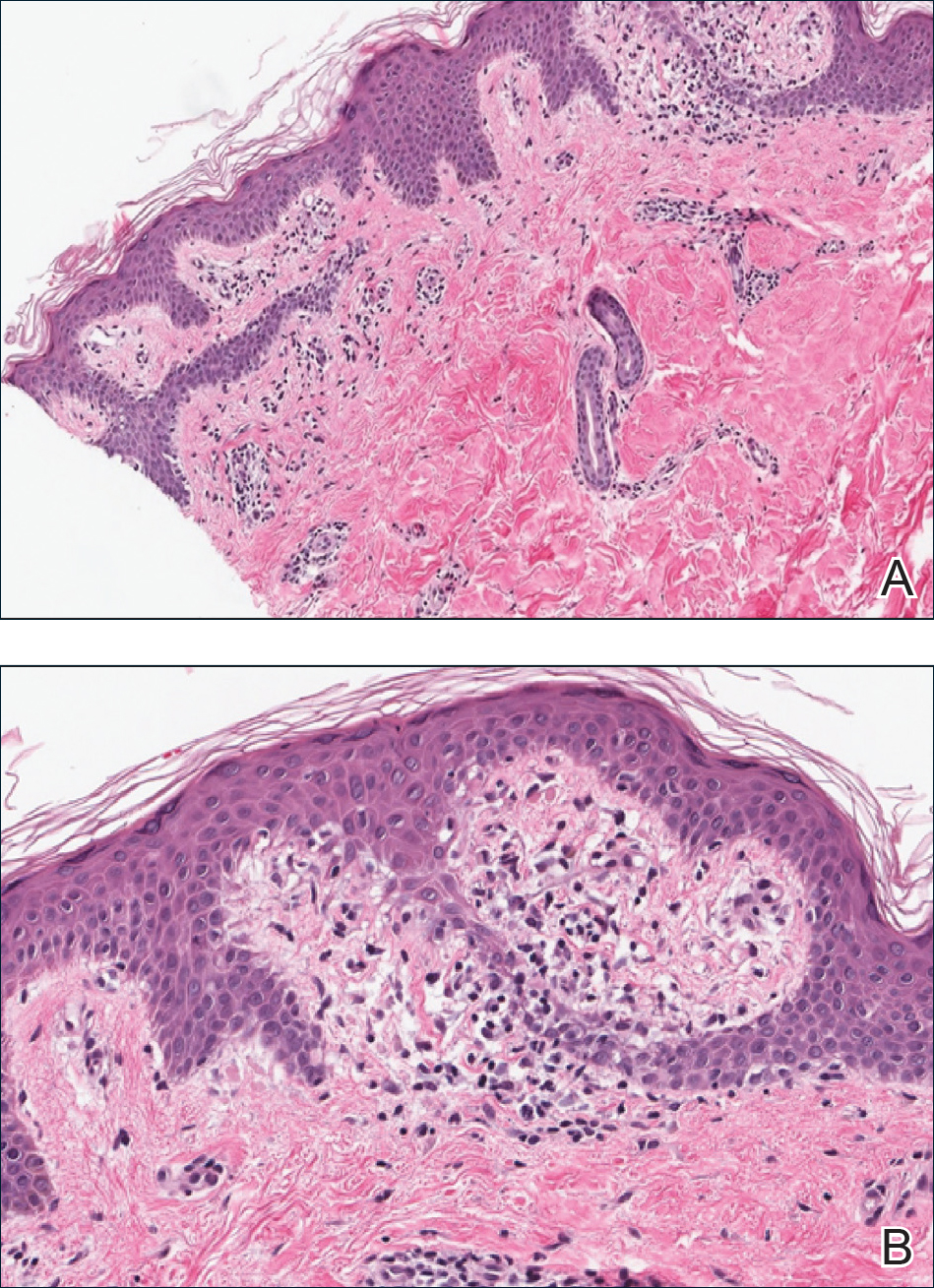
Described by Grosshans and Marot1 in 1990, blaschkitis is an acquired inflammatory dermatosis following the lines of Blaschko. It predominantly is seen on the trunk and typically presents with pruritic papules and vesicles. It frequently has a relapsing course and is more commonly found in adults. Blaschkitis is considered a form of cutaneous mosaicism representing somatic mutations affecting epidermal cell growth and migration during embryogenesis. It has been proposed that these aberrant cells are not clinically apparent at birth; however, viral infection and drug or other environmental triggers can induce antigen presentation of the clone cells activating a T cell–mediated inflammatory response.2-4
The differential diagnosis includes other acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses such as lichen striatus, inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus, unilateral lichen planus, linear lichen sclerosus, linear psoriasis, linear fixed drug reaction, lichen nitidus, and others.1,4 Given the overlap in clinical and histopathological presentations of the entities in the differential, it often is difficult to discern the etiology of the papular and vesicular eruption in question. Discrimination of one etiology from the others is further confounded by the fact that these lesions can all be pruritic and initially are treated with topical corticosteroids. A degree of clinical suspicion for blaschkitis coupled with prior understanding of lesional manifestations is helpful in this circumstance. Although classic lichen planus often affects the arms, legs, flexor surfaces, and occasionally the oral mucosa, blaschkitis generally is limited to the trunk. The lesions of lichen planus generally are violaceous, flattopped, polygonal papules that tend to coalesce. They often have a thin, transparent, and adherent scale overlying the papular lesions, and they occasionally demonstrate Wickham striae, which are faint white reticulated networks typically seen in oral mucosal lesions. In the case of lichen nitidus, lesions often follow a geometric line due to the Köbner response, whereas physical trauma from scratching or injury causes lesions to form along the line of insult. Assessing patients for any newly initiated medications can help eliminate lichenoid drug eruptions. Lichen striatus perhaps has the most overlap with blaschkitis, having been described as also following the lines of Blaschko but occurring in children rather than adults. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevi also can be distinguished from blaschkitis on this premise, as these lesions arise during the first 5 years of life and generally affect the lower extremities.4,5
Histopathology is somewhat variable but generally includes spongiotic dermatitis with concomitant interface
dermatitis characterized by T-cell infiltration. Spongiosis is a feature less commonly seen in lichen striatus. Lesions can progress over time from spongiotic dermatitis to spongiotic psoriasiform dermatitis and later to spongiotic psoriasiform lichenoid dermatitis.4 Treatment of blaschkitis should begin with reassurance of the benign nature of the dermatosis. Pruritic symptoms can be managed with a course of topical steroids.
Blaschkitis is a rare and self-limiting acquired dermatosis that should be incorporated into the differential diagnosis of Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Further investigation is needed to determine if blaschkitis and lichen striatus represent the ends of a disease spectrum or completely distinct entities.
- Grosshans E, Marot L. Blaschkitis in adults. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1990;117:9-15.
- Müller CS, Schmaltz R, Vogt T, et al. Lichen striatus and blaschkitis: reappraisal of the concept of blaschkolinear dermatoses [published online November 29, 2010]. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:257-262.
- Sun BK, Tsao H. X-chromosome inactivation and skin disease. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:2753-2759.
- Keegan BR, Kamino H, Fangman W, et al. “Pediatric blaschkitis”: expanding spectrum of childhood acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:261-267.
- Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012.
The Diagnosis: Blaschkitis
A punch biopsy from the right lateral hip was performed. Histopathologic examination revealed orthokeratosis overlying mild psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia associated with a lichenoid infiltrate composed almost entirely of lymphocytes (Figure). The infiltrate did not entirely obscure the dermoepidermal junction and spared the adnexal structures. The clinical presentation along with histopathologic analysis confirmed a diagnosis of blaschkitis. The lesions were treated with triamcinolone ointment twice daily as needed, and the patient reported symptomatic and clinical improvement with this intervention at 4-week follow-up.

Described by Grosshans and Marot1 in 1990, blaschkitis is an acquired inflammatory dermatosis following the lines of Blaschko. It predominantly is seen on the trunk and typically presents with pruritic papules and vesicles. It frequently has a relapsing course and is more commonly found in adults. Blaschkitis is considered a form of cutaneous mosaicism representing somatic mutations affecting epidermal cell growth and migration during embryogenesis. It has been proposed that these aberrant cells are not clinically apparent at birth; however, viral infection and drug or other environmental triggers can induce antigen presentation of the clone cells activating a T cell–mediated inflammatory response.2-4
The differential diagnosis includes other acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses such as lichen striatus, inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus, unilateral lichen planus, linear lichen sclerosus, linear psoriasis, linear fixed drug reaction, lichen nitidus, and others.1,4 Given the overlap in clinical and histopathological presentations of the entities in the differential, it often is difficult to discern the etiology of the papular and vesicular eruption in question. Discrimination of one etiology from the others is further confounded by the fact that these lesions can all be pruritic and initially are treated with topical corticosteroids. A degree of clinical suspicion for blaschkitis coupled with prior understanding of lesional manifestations is helpful in this circumstance. Although classic lichen planus often affects the arms, legs, flexor surfaces, and occasionally the oral mucosa, blaschkitis generally is limited to the trunk. The lesions of lichen planus generally are violaceous, flattopped, polygonal papules that tend to coalesce. They often have a thin, transparent, and adherent scale overlying the papular lesions, and they occasionally demonstrate Wickham striae, which are faint white reticulated networks typically seen in oral mucosal lesions. In the case of lichen nitidus, lesions often follow a geometric line due to the Köbner response, whereas physical trauma from scratching or injury causes lesions to form along the line of insult. Assessing patients for any newly initiated medications can help eliminate lichenoid drug eruptions. Lichen striatus perhaps has the most overlap with blaschkitis, having been described as also following the lines of Blaschko but occurring in children rather than adults. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevi also can be distinguished from blaschkitis on this premise, as these lesions arise during the first 5 years of life and generally affect the lower extremities.4,5
Histopathology is somewhat variable but generally includes spongiotic dermatitis with concomitant interface
dermatitis characterized by T-cell infiltration. Spongiosis is a feature less commonly seen in lichen striatus. Lesions can progress over time from spongiotic dermatitis to spongiotic psoriasiform dermatitis and later to spongiotic psoriasiform lichenoid dermatitis.4 Treatment of blaschkitis should begin with reassurance of the benign nature of the dermatosis. Pruritic symptoms can be managed with a course of topical steroids.
Blaschkitis is a rare and self-limiting acquired dermatosis that should be incorporated into the differential diagnosis of Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Further investigation is needed to determine if blaschkitis and lichen striatus represent the ends of a disease spectrum or completely distinct entities.
The Diagnosis: Blaschkitis
A punch biopsy from the right lateral hip was performed. Histopathologic examination revealed orthokeratosis overlying mild psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia associated with a lichenoid infiltrate composed almost entirely of lymphocytes (Figure). The infiltrate did not entirely obscure the dermoepidermal junction and spared the adnexal structures. The clinical presentation along with histopathologic analysis confirmed a diagnosis of blaschkitis. The lesions were treated with triamcinolone ointment twice daily as needed, and the patient reported symptomatic and clinical improvement with this intervention at 4-week follow-up.

Described by Grosshans and Marot1 in 1990, blaschkitis is an acquired inflammatory dermatosis following the lines of Blaschko. It predominantly is seen on the trunk and typically presents with pruritic papules and vesicles. It frequently has a relapsing course and is more commonly found in adults. Blaschkitis is considered a form of cutaneous mosaicism representing somatic mutations affecting epidermal cell growth and migration during embryogenesis. It has been proposed that these aberrant cells are not clinically apparent at birth; however, viral infection and drug or other environmental triggers can induce antigen presentation of the clone cells activating a T cell–mediated inflammatory response.2-4
The differential diagnosis includes other acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses such as lichen striatus, inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus, unilateral lichen planus, linear lichen sclerosus, linear psoriasis, linear fixed drug reaction, lichen nitidus, and others.1,4 Given the overlap in clinical and histopathological presentations of the entities in the differential, it often is difficult to discern the etiology of the papular and vesicular eruption in question. Discrimination of one etiology from the others is further confounded by the fact that these lesions can all be pruritic and initially are treated with topical corticosteroids. A degree of clinical suspicion for blaschkitis coupled with prior understanding of lesional manifestations is helpful in this circumstance. Although classic lichen planus often affects the arms, legs, flexor surfaces, and occasionally the oral mucosa, blaschkitis generally is limited to the trunk. The lesions of lichen planus generally are violaceous, flattopped, polygonal papules that tend to coalesce. They often have a thin, transparent, and adherent scale overlying the papular lesions, and they occasionally demonstrate Wickham striae, which are faint white reticulated networks typically seen in oral mucosal lesions. In the case of lichen nitidus, lesions often follow a geometric line due to the Köbner response, whereas physical trauma from scratching or injury causes lesions to form along the line of insult. Assessing patients for any newly initiated medications can help eliminate lichenoid drug eruptions. Lichen striatus perhaps has the most overlap with blaschkitis, having been described as also following the lines of Blaschko but occurring in children rather than adults. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevi also can be distinguished from blaschkitis on this premise, as these lesions arise during the first 5 years of life and generally affect the lower extremities.4,5
Histopathology is somewhat variable but generally includes spongiotic dermatitis with concomitant interface
dermatitis characterized by T-cell infiltration. Spongiosis is a feature less commonly seen in lichen striatus. Lesions can progress over time from spongiotic dermatitis to spongiotic psoriasiform dermatitis and later to spongiotic psoriasiform lichenoid dermatitis.4 Treatment of blaschkitis should begin with reassurance of the benign nature of the dermatosis. Pruritic symptoms can be managed with a course of topical steroids.
Blaschkitis is a rare and self-limiting acquired dermatosis that should be incorporated into the differential diagnosis of Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Further investigation is needed to determine if blaschkitis and lichen striatus represent the ends of a disease spectrum or completely distinct entities.
- Grosshans E, Marot L. Blaschkitis in adults. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1990;117:9-15.
- Müller CS, Schmaltz R, Vogt T, et al. Lichen striatus and blaschkitis: reappraisal of the concept of blaschkolinear dermatoses [published online November 29, 2010]. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:257-262.
- Sun BK, Tsao H. X-chromosome inactivation and skin disease. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:2753-2759.
- Keegan BR, Kamino H, Fangman W, et al. “Pediatric blaschkitis”: expanding spectrum of childhood acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:261-267.
- Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012.
- Grosshans E, Marot L. Blaschkitis in adults. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1990;117:9-15.
- Müller CS, Schmaltz R, Vogt T, et al. Lichen striatus and blaschkitis: reappraisal of the concept of blaschkolinear dermatoses [published online November 29, 2010]. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:257-262.
- Sun BK, Tsao H. X-chromosome inactivation and skin disease. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:2753-2759.
- Keegan BR, Kamino H, Fangman W, et al. “Pediatric blaschkitis”: expanding spectrum of childhood acquired Blaschko-linear dermatoses. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:261-267.
- Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012.
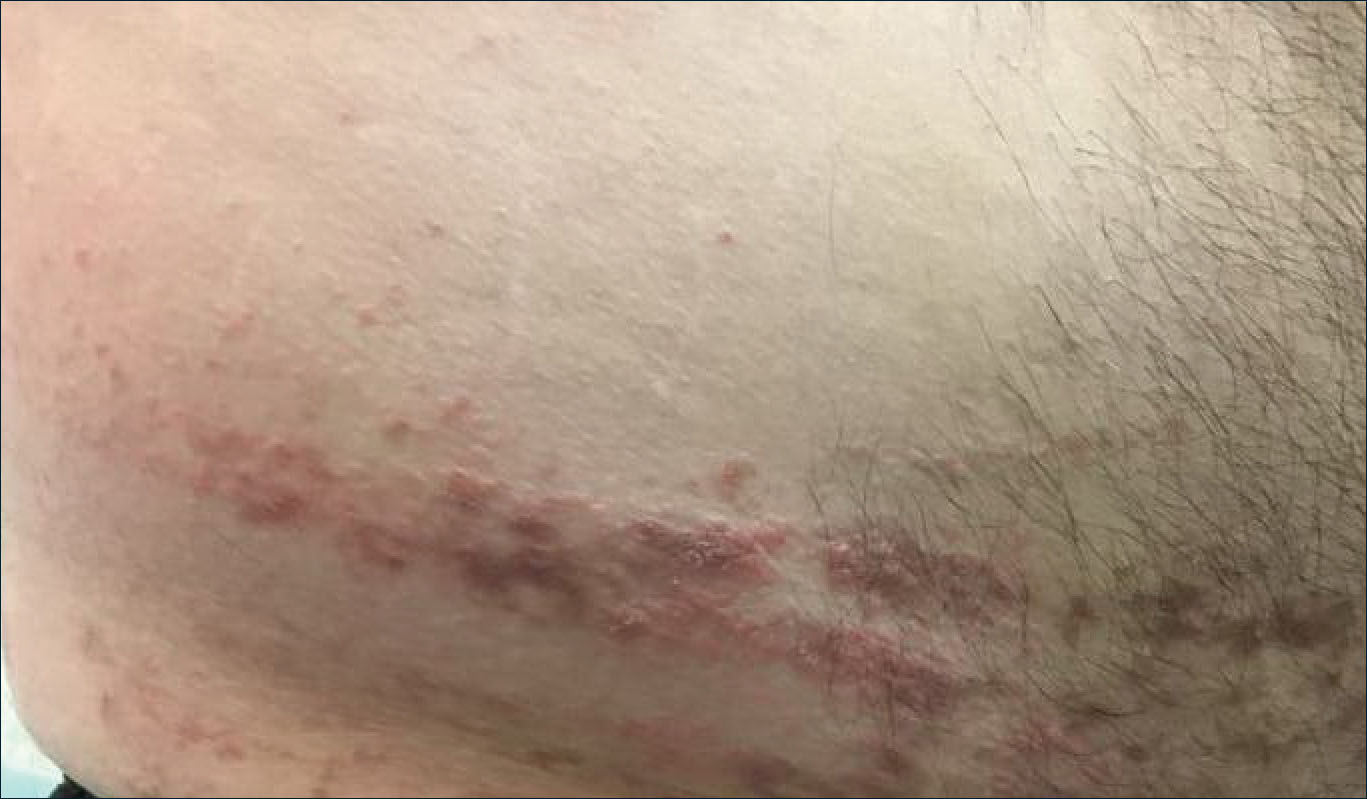
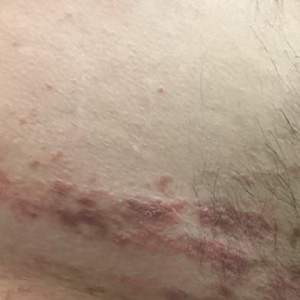
A 31-year-old man presented with a recurring pruritic rash on the right lateral flank and hip of 2 years’ duration. Physical examination revealed erythematous, verrucous, dry papules and plaques coalescing into larger plaques on the right flank and hip in dermatomal distributions involving the T10 and T11 dermatomes. A few papules were scattered in a linear eruption along the right flank and right upper thigh. Some postinflammatory changes were noted. No rash was noted over any other area of the body. Physical examination was otherwise unremarkable.
Data underscore the importance of lifestyle interventions in breast cancer patients
SAN ANTONIO – Data continue to underscore the benefits of lifestyle interventions in women with breast cancer, but questions remain about their effects on recurrence, according to Jennifer Ligibel, MD.
Findings from the EBBA-II trial as presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, for example, showed that exercise improves cardiorespiratory fitness in women with early breast cancer, and findings from the SUCCESS C study showed that breast cancer patients who completed a weight-loss intervention showed some improvements, compared with those who did not, said Dr. Ligibel of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, who was the discussant for those and other lifestyle-intervention studies at the symposium.
SUCCESS C failed to show an overall reduction in breast cancer recurrence or survival, but weight loss among intervention-group participants was modest, and more than half of the participants dropped out of the study, so it’s hard to make any firm conclusions, she said.
Overall, the findings – in the context of what is already known about lifestyle interventions among women with breast cancer – provide “yet another reason to tell women that it’s important to exercise during treatment,” she said.

In this video interview, Dr. Ligibel discussed the studies and the implications of the findings, and also mentioned an ongoing study for which she is an investigator. In that study – the Breast Cancer Weight Loss study (BWEL) – adherence among the approximately 1,700 women enrolled has been high. “So we’re hoping that this study in a few years will give us a bit more information about the power of weight loss to potentially reduce recurrence.”
For now, the available data show that there are “lots of concrete benefits” associated with improving lifestyle in women with breast cancer, she said, noting that she tells all of her patients to live as healthy a lifestyle as possible, and especially to exercise.
SAN ANTONIO – Data continue to underscore the benefits of lifestyle interventions in women with breast cancer, but questions remain about their effects on recurrence, according to Jennifer Ligibel, MD.
Findings from the EBBA-II trial as presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, for example, showed that exercise improves cardiorespiratory fitness in women with early breast cancer, and findings from the SUCCESS C study showed that breast cancer patients who completed a weight-loss intervention showed some improvements, compared with those who did not, said Dr. Ligibel of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, who was the discussant for those and other lifestyle-intervention studies at the symposium.
SUCCESS C failed to show an overall reduction in breast cancer recurrence or survival, but weight loss among intervention-group participants was modest, and more than half of the participants dropped out of the study, so it’s hard to make any firm conclusions, she said.
Overall, the findings – in the context of what is already known about lifestyle interventions among women with breast cancer – provide “yet another reason to tell women that it’s important to exercise during treatment,” she said.

In this video interview, Dr. Ligibel discussed the studies and the implications of the findings, and also mentioned an ongoing study for which she is an investigator. In that study – the Breast Cancer Weight Loss study (BWEL) – adherence among the approximately 1,700 women enrolled has been high. “So we’re hoping that this study in a few years will give us a bit more information about the power of weight loss to potentially reduce recurrence.”
For now, the available data show that there are “lots of concrete benefits” associated with improving lifestyle in women with breast cancer, she said, noting that she tells all of her patients to live as healthy a lifestyle as possible, and especially to exercise.
SAN ANTONIO – Data continue to underscore the benefits of lifestyle interventions in women with breast cancer, but questions remain about their effects on recurrence, according to Jennifer Ligibel, MD.
Findings from the EBBA-II trial as presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, for example, showed that exercise improves cardiorespiratory fitness in women with early breast cancer, and findings from the SUCCESS C study showed that breast cancer patients who completed a weight-loss intervention showed some improvements, compared with those who did not, said Dr. Ligibel of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, who was the discussant for those and other lifestyle-intervention studies at the symposium.
SUCCESS C failed to show an overall reduction in breast cancer recurrence or survival, but weight loss among intervention-group participants was modest, and more than half of the participants dropped out of the study, so it’s hard to make any firm conclusions, she said.
Overall, the findings – in the context of what is already known about lifestyle interventions among women with breast cancer – provide “yet another reason to tell women that it’s important to exercise during treatment,” she said.

In this video interview, Dr. Ligibel discussed the studies and the implications of the findings, and also mentioned an ongoing study for which she is an investigator. In that study – the Breast Cancer Weight Loss study (BWEL) – adherence among the approximately 1,700 women enrolled has been high. “So we’re hoping that this study in a few years will give us a bit more information about the power of weight loss to potentially reduce recurrence.”
For now, the available data show that there are “lots of concrete benefits” associated with improving lifestyle in women with breast cancer, she said, noting that she tells all of her patients to live as healthy a lifestyle as possible, and especially to exercise.
REPORTING FROM SABCS 2018
Return to Play After an Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: Prioritizing Neurological and Psychological Factors of the Decision-Making Algorithm
ABSTRACT
Soccer players recovering from anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries have better options for treatment today than they did 25 years ago. Surgical techniques have improved, and rehabilitation protocols have evolved considerably. Although the rehabilitation community is doing a better job of treating this patient population, the evidence does demonstrate that both re-injury and return- to-play (RTP) rates are still suboptimal. Most protocols focus on normalizing strength and range of motion (ROM) and achieving limb symmetry with soccer-specific movements. While these factors are certainly prerequisites for returning to the field, their inclusion does not provide a complete picture of the athlete’s presentation. An additional factor that should be prioritized with this patient population is the central nervous system (CNS). Advanced imaging has shown that peripheral deafferentation does occur with musculoskeletal injuries; this ultimately results in cortical reorganization, which makes movement planning more difficult for the player, since simpler tasks must now be processed at higher levels in the CNS. The evidence also shows that the CNS demonstrates plasticity in these cases, so that through focused neuromotor rehabilitation techniques, it is possible to bring movement planning back down to a sub-cortical level. Cognitive issues may also be a factor in preventing the player from returning. Fear of re-injury and diminished confidence can influence the way the player moves on the field, and diminish ability to demonstrate protective kinematics with all soccer-specific tasks. We believe that an approach incorporating traditional musculoskeletal rehabilitation, CNS neuro-motor training, and consideration for cognitive factors, may define an improved paradigm for treating the soccer player and assessing readiness for RTP following ACL injury.
Continue to: Although anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)...
Although anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rehabilitation has evolved considerably over the past 2 decades, the basic paradigm has remained consistent: normalize strength and range of motion, reduce swelling and pain, achieve limb symmetry with functional tasks, and return to sport-specific activities gradually over a 6 to 12-month period. There have been some slight additions to this basic premise, such as evaluating knee and hip mechanics in the frontal plane, but the requirements here are vaguely defined and are typically only evaluated within the context of controlled clinical testing.
It is interesting to note that the typical ACL injury pattern occurs during a normal sport-specific movement, yet most rehabilitation protocols fail to recognize the potential causes of the aberrant movement pattern and how to best modify it so that the risk of repeated stress to the ACL can be minimized. It should be understood that movement occurs through the interaction of 3 discrete factors: the individual, the task being performed, and the environment in which it is performed.1 All of these factors will play a role in how the final movement pattern is produced. For example, a soccer player (individual) may backpedal and pivot to the left 60° and accelerate to sprint after a player moving towards the touchline (task) while receiving instructions from teammates and monitoring the movements of opposing players (environment). A small variance in any 1 of these factors could significantly impact the movement pattern as the player completes the task.
In most rehabilitation programs, each of these factors may be treated in a singular, non-specific manner, but if these factors are not coordinated effectively throughout the program to produce the desired sport-specific movement, a faulty pattern may persist, leaving the player at risk for injury. Current rehabilitation programs seem to have a strong focus on creating stability, mobility, and strength, but these are trained in silos, with an internal focus of control, which only solves the biomechanical equation. Often, it is difficult for the player to coordinate good biomechanics into an efficient, protective movement pattern that is specific to the tasks performed on the field during the normal course of play. The missing link here is the central nervous system (CNS).
Limitations to the current ACL protocols may be that they rely heavily on musculoskeletal rehabilitation and that they have limited emphasis on neurological rehabilitation. As will be discussed later, the CNS has a large impact on the final movement selected by the player. In fact, cognition, perception, and action are the three factors that comprise the individual’s part of the movement paradigm,1 yet rarely are these factors addressed in most ACL rehabilitation programs. These elements are a large part of the movement equation, so it is easy to understand how failing to address these features can lead to poor movement quality and subsequent ACL re-injury.
In addition to central neurological factors, cognitive issues may play a role in the player’s ability to return to sport. Determining optimal readiness for return to play is a difficult task for the medical community, with many variables to consider. Previous research studies have assessed the variability in return to play for various sports, including football, rugby, soccer, skiing, running, and tennis, with return-to-play rates ranging from 18% to 100%.2,3,4-10 The risk of secondary injury may cast doubt and fear on athletes as they contemplate their successful return to play.8,11 Although robust functional testing has become commonplace for determining athlete readiness after injury,12-20 the assessment of psychological readiness, persistent fear, and loss of confidence are often neglected and not as commonly integrated into the return-to-play algorithm.21-24 The purpose of this paper is to assess the various cognitive and central neural factors affecting a soccer player’s ability to recover from an ACL injury and offer suggestions for integrating treatments into the protocols to address these issues.
Continue to: CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEUROPLASTICITY...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEUROPLASTICITY
Despite the vast amount of attention and research focused on the ACL, the re-injury rate still remains quite high. It has been reported that rehabilitation programs that employ traditional neuromotor training produce a re-injury rate as high as 30% after the athlete returns to sport.25-28 The overall rate of sustaining a second ACL injury is 15%11 in all patient populations. For the general population <25 years of age, the re-injury rate is 21%, and for athletes <25 years of age, the re-injury rate rises to 23%.11 With re-injury rates at this level, it is certainly fair to consider and be critical of the current rehabilitation methods being used with this population. One opportunity for improvement lies in the general approach used to rehabilitate ACL-injured patients. Therapy for this injury is protocol-driven, and the fact remains that most protocols prioritize restoration of peripheral systems, with minimal thought given to the cortical control necessary to manage those systems.29,30 When neural factors are considered, it is usually within the context of increasing strength, balance, power, and biomechanical control,31-34 which are certainly important but peripheral factors nonetheless. The missing element in many ACL protocols may be how to best manage the central neural components and cognitive factors associated with this injury.
If the CNS were to receive more consideration in ACL protocols, the opportunity for improved outcomes could be substantial because the CNS has been proven to be a very malleable system, as long as it receives the correct input. The CNS demonstrates neuroplasticity,35 which means that it is capable of reorganization, based on the stimuli that it receives, whether internal or external.36
This is an important consideration in ACL rehabilitation because the ACL graft, while restoring the biomechanical properties to the knee, is not fully capable of producing the same neurosensory properties of the original ACL.37-42This is an important concept to understand because an ACL tear does indeed cause deafferentation in the ascending pathways to the brain.37-40,42-46 This can lead to CNS reorganization and subsequent alterations in efferent output to the periphery.37-40,42-46 Therefore, if a protocol with traditional musculoskeletal principles was used, then the mechanical function of the knee may certainly be remediated, but the neurosensory function will remain in a maladaptive state,47-50 potentially leading to aberrant, non-protective movement strategies and a higher risk of re-injury.
The process of CNS reorganization may begin with the initial ACL injury. A peripheral musculoskeletal injury creates an inflammatory response that results in the arrival of chemical mediators such as histamine, substance P, calcitonin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide at the site of injury.51 As edema accumulates in the joint, tension is applied to the capsule, which may adversely affect proprioception from the receptors located within.45 The interruption of consistent input from the peripheral mechanoreceptors may lead to long-term differentiation of the ascending pathways.52 This information is synthesized at 3 different levels of the CNS (spinal cord, brain stem, and motor cortex) to produce motor output.53-56 Differentiation in the ascending circuitry can cause inhibition of motor neurons at the spinal cord.45Animal research has shown that this differentiation can cause a breakdown in the cuneate nucleus of the brainstem,57which provides sensory information from the upper body, while the gracile nucleus does the same for the lower body. These structures transfer proprioceptive input to the ventral posterior lateral nucleus in the thalamus, where it is then sent to the primary somatosensory cortex.57 In general, the somatosensory, visual, and vestibular systems interpret afferent inputs to control movement, balance, and stability.58,59 In a sport like soccer, where the movement tasks are dynamic and unpredictable, it is easy to see why even a slight deficit in somatosensory processing could disrupt a movement. Valeriani and colleagues42,46 showed that somatosensory-evoked potentials were indeed altered in a cohort of ACL reconstruction (ACLR) subjects, indicating reorganization within the CNS. Additionally, the deafferentation could not be changed by other afferent input coming from the knee or by the new ACL graft placed in the knee.42,46The primary motor cortex has been found to have a substantial network of connectivity with the primary somatosensory cortex, which supports the theory that the motor cortex has a very strong linkage with the peripheral receptors in the joint.60 The ligaments in the joint contain Ruffini, Pacinian, and Golgi receptors, all of which react to changes in the collagen fibers and send information regarding tension, length, speed, acceleration, position, and movement back to the CNS.61-64 Unfortunately, the ascending pathway deafferentation can cause reorganization within the CNS, which makes the feedback provided from the periphery less effective in motor planning.
Ward and colleagues65 have reported that reorganization within the motor cortex is the primary cause of chronic neuromuscular movement deficits in peripheral joint injuries. Researchers have used functional magnetic resonance imaging, transcranial magnetic stimulation, and electroencephalography in ACL patients to demonstrate changes in cortical activity and subsequent CNS reorganization.65 Kapreli and colleagues41 reported that subjects with an ACL injury demonstrated higher cortical activation in the pre-supplementary motor area (pre-SMA). This is a region that is responsible for more complex motor planning.66,67 This area becomes active before the primary motor cortex and is responsible for preparing the final movement pattern that the motor cortex executes.41 As the task becomes more complex, activity in the pre-SMA will increase.41 Additionally, they found that the posterior secondary somatosensory area and posterior inferior temporal gyrus showed increased cortical activity compared with controls.41 Visual planning is processed in the posterior inferior temporal gyrus, and so, it appears that the difficulty in processing somatosensory information due to ascending pathway deafferentation places an increased reliance on the visual system for movement planning.68-70 This was observed while ACL-injured subjects performed a simple knee flexion-extension movement encompassing 40°, indicating the need to incorporate higher central levels of planning for a very simple movement pattern.41 Baumeister and colleagues37,38 also showed that subjects with ACLR had higher levels of cortical activation in the areas of the brain that require attention and that process sensory input. They theorized that this occurred because of reduced efficiency of neural processing at lower levels in the CNS. Despite the higher levels of cortical activity observed, they found that subjects with an ACLR demonstrated proprioceptive testing that was deficient compared with that of controls. Heroux and Tremblay71 also demonstrated that subjects with an ACLR had increased resting motor cortex activity. They believed that this occurred as the motor cortex attempted to maintain neuromotor output to the periphery in the face of diminished afferent input.
Continue to: The reorganization that results in movement planning...
The reorganization that results in movement planning, transitioning from subcortical levels to cortical levels, is a phenomenon that researchers believe can lead to deficiencies even as the athlete has returned to sport. Grooms et al72revealed in a case report that a subject with an ACLR showed higher levels of activity in the crus region of the cerebellum. This area contains corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts that transmit neural input to maintain balance and coordination.73 These changes in the cerebellum, combined with increased motor cortex activity, are thought to be indicative of a global neural strategy that uses higher levels of the CNS, as opposed to subcortical processing.72
The current research makes a clear and compelling argument for the importance of CNS reorganization after an ACL injury, placing increased reliance on higher cortical levels of control, as well as the visual system to coordinate balance and movement. It is thought that this reorganized method of neural transmission can then become imprinted within the CNS, if not corrected.35,74 If this is the case, then traditional strength programs may not be sufficient to restore these connections to their pre-injury level. If the CNS has the ability to reorganize based on the aberrant input that it receives from the periphery, then it also certainly has the potential to adapt to more specific structured input via the ascending afferent pathways.41,45 The rehabilitation program, however, needs to be structured specifically to target the reorganized regions of the brain. There needs to be an emphasis on rehabilitating not only the peripheral neuromotor structures but also the CNS.75
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM REHABILITATION PRINCIPLES
For a neurological rehabilitation to be successful, the interventions need to be repetitive and task-specific, involve learning, employ whole and part practice, and transition from using an internal to an external focus of control.76Movements that are repetitive, but which lack structured learning and skill, have been shown to have no effect on inducing neuroplastic changes in the primary motor cortex.77,78 However, using neurological rehabilitation techniques that facilitate the acquisition of new motor skills by the CNS have been shown to cause neuroplastic adaptation in the motor cortex.79-85 This occurs because neuroplasticity is determined by experience and practice.78 The CNS operates on cues received in the ascending tracts by mechanoreceptors in the joint. If a new movement pattern is being learned by the athlete, then this new afferent input received from the periphery will start to initiate reorganization in the higher learning centers. If this occurs with optimal repetition and precision, then a positive reorganization can take place within the CNS that results in a higher percentage of motor planning and control being filtered down to a subcortical level. Essentially, the movements become instinctive, which is crucial in athletics, where attention in higher cortical areas is frequently diverted to external aspects of the competition and not solely used to focus on movement.
This is why shifting neurological rehabilitation from an internal focus of control to an external focus of control is paramount. While using an internal focus of control is required early in rehabilitation to enable the athlete to understand the specific tasks required in a composite movement, a gradual transition to an external focus of control is necessary as the athlete begins to perform tasks that are more soccer-specific. This autonomous stage of motor learning is crucial because it transfers the burden of motor planning from higher to lower levels of the CNS and frees up the pre-SMA and primary motor cortex to handle more complex patterns.58,86-88
Continue to: ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RISK POTENTIAL IN SOCCER PLAYERS...
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RISK POTENTIAL IN SOCCER PLAYERS
If a comprehensive neuromotor rehabilitation program is to be used effectively with soccer athletes, then the first priority is to define how the players should move, so that they can demonstrate protective kinematics with all soccer-specific tasks and minimize stress to the ACL. As the ideal movement pattern becomes autonomous, then it should be trained within the context of a dynamic environment; remembering that environmental changes have a large impact on the final movement pattern selected by the individual. Brophy et al89 evaluated videos of non-contact ACL injuries in male and female soccer players and determined that 45% occurred while cutting, 25% while landing, and 16% during deceleration. These 3 patterns represent 86% of the ACL injuries observed and offer an opportunity for evaluation and treatment with specific central neuromotor rehabilitation techniques.
The foundational movement patterns for the soccer player should focus on producing leverage that minimizes stress to the ACL during the 3 primary tasks outlined above. To achieve this, it is necessary to reduce posterior ground reaction forces at the hip and knee joint during these movements. There is a high correlation between the magnitude of the posterior ground reaction force, and anterior tibial shear, and subsequent displacement.90,91 This stress can be reduced by increasing the hip and knee flexion angles during soccer-specific movements that involve pivoting, decelerating, and landing from a jump in a unipedal stance.92
This phenomenon can be explained by observing changes in the ACL elevation angle, hamstring insertion angle, and patella tendon-tibial tuberosity insertion angle. As the knee moves into flexion, the ACL takes on a more parallel orientation to the tibia, and its fibers are better able to resist elastic deformation accompanied by a posterior ground reaction force.93,94 The quadriceps will produce less anterior translation on the tibia because the patella tendon insertion angle is reduced relative to the longitudinal axis of the tibia, and the mechanical advantage of the quadriceps is decreased.95 Lastly, the hamstrings will be able to provide better leverage posteriorly because the resultant force trends toward a more parallel orientation to the tibial plateau, which enables the player to counter, more effectively, the posterior ground reaction force and the anterior pull directed by the quadriceps.95
This theory is supported by the work of Li and colleagues,96 who showed that there is an inverse relationship between knee flexion angle and ACL loading. In their study, they applied a constant quadriceps force of 200 N at 15°, 30°, and 60° angles. The anterior shear force was obviously the highest at 15° and reduced by 20% at 30° and 60% at 60°. When hamstrings co-contraction was added, there was an additional 30% reduction in anterior shear at 15° and 50% at 30° and 60°. From a more flexed position, the hamstrings can increase joint compression and reduce the anterior translation by allowing the concave medial tibial plateau to limit the anterior drawer effect and absorb the forces that occur with excessive anterior shear, internal rotation, and valgus loads.97 As the knee flexion angle approximates 60°, the hamstring leverage is increased, and the quadriceps leverage is diminished to the point where its ability to produce anterior tibial translation is neutralized.98 Daniel and colleagues98 referred to this as the quadriceps neutral angle.
For soccer-specific movements that are potentially injurious to the ACL, it may then be beneficial to create a default movement pattern at the knee that approximates this value. In keeping with the information presented in this paper, it will be important to have the player reproduce this angle consistently during activities that involve pivoting, decelerating, and landing from a jump within the context of match play. This will certainly require that segments located both proximal and distal to the knee are able to function within specific parameters so that a cohesive protective synergy is produced throughout the lower quarter which minimizes posterior ground reaction forces and is protective of the ACL. This is where structured neuromotor training that is able to modulate networks within the CNS may be beneficial.
Continue to: CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TREATMENT TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOCCER PLAYER...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TREATMENT TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOCCER PLAYER
The ultimate goal is to create a foundational movement pattern that optimizes leverage and is protective of the ACL during decelerating, pivoting, and landing in a unipedal stance from a jump. The composite segments that are necessary to achieve this include local core stability to create lumbopelvic stiffness, and global core activation to enhance posterior chain stability. This should enable the player to feel more balanced when placing the pelvis in a more posterior and inferior position while still maintaining the trunk in a position that is parallel with the tibia, as the knee is flexed to an approximate 60° angle (Figure 1). From a frontal plane perspective, the acetabulum should bisect the malleoli of the stance leg, with a neutral tibiofemoral joint alignment (Figure 1).
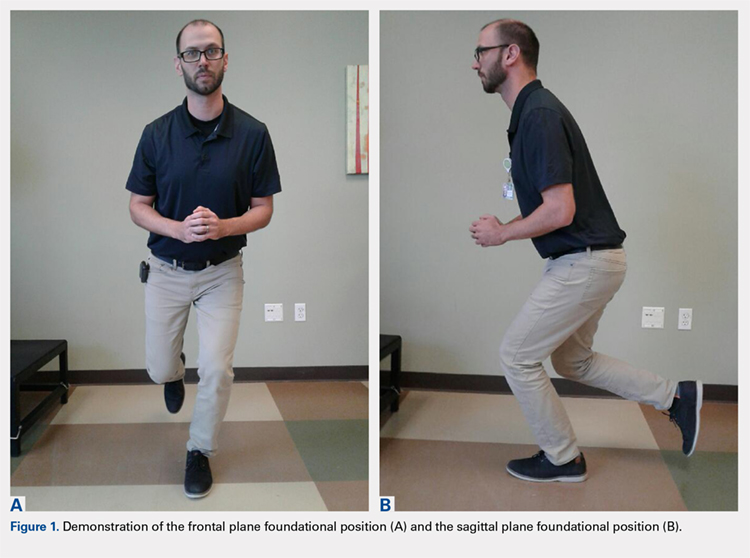
The neuromotor training for the composite segments of this movement can begin in the “acute postoperative phase” (Table 1). Because the surgical repair will limit the player’s capabilities in this stage, this is a good time to break down the foundational movement pattern into its component parts and ensure that the CNS receives a high number of quality repetitions of parts. In this phase, the player may begin an isolated training for the transversus abdominis, multifidus, and pubococcygeus. This can start in a supine position using biofeedback with an isometric contraction, progress to a standing position, and incorporate deep core activation with stance-phase gait training, mini squats, and lunge variations. This phase will require an abundance of visual and verbal feedback with an internal focus of control as the player gets used to activating the deep core and quad/hip synergy during functional lower extremity movements. Even in this early phase, the player should look to minimize anterior and/or posterior pelvic tilting and maintain a stiff thoracolumbar segment that remains parallel with the tibia during all functional movements.
Table 1. Adjunct CNS Treatment Principles for ACL Reconstruction in Soccer Athletes
Phase | Goal | CNS Rehabilitation Techniques |
Acute postoperative | Local core activation with weightbearing exercise. Produce trunk stiffness with lower extremity movements. | High repetitions. Verbal or tactile cues. Internal focus of control. Partial practice. |
Subacute postoperative | Lumbopelvic, foot or ankle, and posterior chain segments learn to participate in movement effectively. | Requires higher levels of cortical planning. Internal focus of control. CIMT. |
Static stability | Able to adopt foundational movement pattern consistently with vision eliminated. | Somatosensory vs visual processing. Partial-to-whole practice. Use internal and/or external focus of control. |
Dynamic stability | Able to perform plyometrics in a single-leg position using foundational movement pattern with subcortical processing. | Increase velocity with movement challenges. Occlude or eliminate vision. Heavy reliance on an external focus of control. Prioritize movement quality. |
Dynamic agility | Pivoting, decelerating, and landing are performed with hip flexion/knee flexion synergy, trunk stiffness, and posterior chain activation. | Unanticipated movement challenges. Whole practice. Ball reaction drills with vision obstructed or occluded. Contact drills with vision obstructed or occluded. Use external focus of control to include soccer-specific tasks. |
Abbreviations: ACL, anterior cruciate ligament; CNS, central nervous system; CIMT, constraint-induced movement therapy.
As the player moves into the “subacute postoperative phase” (Table 1). He or she will continue to use an internal focus of control to activate the local/global core synergy with functional movements progressing from double-leg, to single-leg positions. Partial practice, instead of whole practice, is still the predominant theme of the neural training process. In this phase, the knee and hip flexion angles can increase, and the player’s trunk and pelvic position should be critiqued in a single-leg position so that the trunk remains parallel with the tibia in the sagittal plane with a slight forward hip hinge. The pelvis should remain level throughout single-leg stance to ensure adequate activation of the lateral hip stabilizers. This is the stage where the player can learn to isolate closed kinetic chain hip rotation for pivoting, and so, single-leg hip internal and external rotation drills are useful, both with and without resistance. Skill acquisition is crucial in this phase because the patterns that the CNS adopts will form the foundation for more dynamic patterns that will occur in the later soccer-specific stages. Higher levels of cortical planning are still needed in this phase. For this reason, it is important that poor quality repetitions are recognized by the player and clinician so that he or she can learn to perform them correctly, albeit still with an internal focus of control. This is also a good time to begin to employ constraint-induced movement therapy as the player is able to replicate the desired pattern with more precision. For example, by eliminating the use of the upper extremities as a source of balance, the CNS is forced to program alternate synergies such as the lumbopelvic, and foot and ankle segments to maintain the desired alignment.
The “lower quarter static stability phase” (Table 1) marks a point where it may be useful to use direct strategies that have the capability to change CNS efferent owutput from a primary reliance on the visual processing areas in the posterior-inferior temporal gyrus back to the somatosensory area. It is critical that the player is able to make this transition in cortical reorganization and control, because ACL-injured subjects have been shown to have balance scores similar to healthy controls when they are able to use their vision, but this is reduced when vision is taken away.99-105 Their balance will diminish even further if vision is modulated during more complex landing and pivoting maneuvers.99-105 This may certainly explain why defending is a riskier task for ACL-injured players89 as their visual system is focused more on tracking a player than attending to precision with movement planning.
To enhance this cortical reorganization within the context of soccer-specific movements, it is useful to start from a foundational single-leg position, with the knee approximating 60° of flexion and the trunk parallel to the tibia. In the frontal plane, the pelvis should be level, the trunk vertical, and the acetabulum bisecting the malleoli of the stance leg (Figure 1). The player may initially work on getting into this foundational position with vision either partially obstructed using stroboscopic eyewear or completely obstructed if this equipment is unavailable.106-108 The pattern can be progressed by constraining the upper extremities to force reliance on the lumbopelvic and foot/ankle strategies for balance. Head and/or trunk turns can be added to simulate the external focus of control that is required with movement in soccer. These should progress from slow to fast and anticipated to unanticipated as the player demonstrates competence in maintaining stability at each segment within the foundational stance position. Once this is in play, a ball should be introduced into the drills. As the player maintains the foundational position with vision diminished and upper extremities constrained, they should attempt to reach for or trap a ball from this position. If vision is completely obstructed, then the player can be instructed to open his/her eyes just as the ball arrives to induce a reactive response. Again, quality repetitions are essential for learning to occur, and subsequent skill acquisition to take place in the CNS; thus, close scrutiny should be paid to the qualitative essence of the movement patterns to ensure pristine biomechanics during this phase.
The “lower quarter dynamic stability phase” (Table 1) should continue with the same neuromotor training principles employed in the previous phase, except that the drills will now involve plyometrics. The player should ultimately progress from double-leg, to single-leg jumps and then linear to diagonal. Vision should still be obstructed and upper extremities constrained to channel the lumbopelvic region for force production and balance. Movement quality in the foundational position remains paramount with these drills to ensure that skill acquisition is occurring and injury risk is being mitigated. An external focus of control can be introduced by applying an unanticipated perturbation during a jump. Additional learning opportunities should include unanticipated head and trunk turns while landing in a unipedal stance from a jump. The task can be made more specific by having the player trap a pass while doing linear or diagonal single-leg hop progressions. In this manner, the player’s CNS can become reorganized to program the requisite synergies to maintain a protective foundational position on the stance leg, as the contralateral limb is required to perform work that is far outside the player’s base of support.
Continue to: The final segment of the CNS neuromotor rehabilitation program...
The final segment of the CNS neuromotor rehabilitation program is the “lower quarter dynamic agility phase” (Table 1), when the player will learn to perform an unanticipated directional change in a foundational position for the pivot leg. The player can begin this phase by initiating sprint-deceleration-pivot efforts, progressing at 45°, 90°, 120°, and 180° turns. This should be trained in both a forward and backpedal position. Close attention should be paid to the deceleration phase of the sprint-pivot effort, as this will set the player up to demonstrate protective kinematics during the pivot phase of the task. In this phase, the center of mass should become lower and move posteriorly, so that a deeper knee and hip flexion angle, supported by posterior chain synergies, can occur at the pivot point. This is an important skill for the player to acquire, as Cortes and colleagues92 have reported that female collegiate soccer players tend to perform a pivoting task with a more erect trunk position. In the same cohort, they also measured the mean knee flexion angle at initial contact during pivoting to be 24°.92 Movement patterns that reflect an elevated center of mass, with arms abducted away from the trunk, should be discouraged here. The drills can be progressed to have the player react to a command and perform unanticipated pivots within a 5 × 5-meter box to simulate defending. This should be progressed from eyes open and arms unconstrained, to vision disrupted and arms constrained. From here, an external focus of control can be added by playing a ball to the athlete. Vision should be withheld until the instant that the ball arrives at the player, when he/she is required to play the ball to an unanticipated spot. As is the case in all other phases of the neuromotor training, the quality of movement is the most important parameter to critique with each drill. From a qualitative standpoint, the player should demonstrate stiffness throughout the thoracolumbar region and power and control through the pelvis with each directional change. In addition, he or she should maintain a low and posteriorly oriented center of mass to optimize leverage in the hamstrings/gluteals compared with the quadriceps and reduce posterior ground reaction forces.
PSYCHOLOGICAL READINESS FOR RETURN TO PLAY
After an injury is sustained, an athlete is often subjected to a range of psychological responses in addition to the functional impairment, including stress, hesitancy, alterations in self-esteem, depression, fear of re-injury, and anxiety.43,109-111 The aforementioned responses are often at their height in the time immediately following an injury and generally subside over time during the rehabilitation process.110 The rates at which athletes experience psychological distress following an injury range between 5% and 19%; the levels are comparable with patients receiving treatment for mental health illness.43 However, these elements may persist, or even increase, in the later stages of the rehabilitation process as the topic of return to play is deliberated.112,113 If these fears are left unresolved, then a significant delay can be incurred during the rehabilitation process, which might ultimately jeopardize the successful return to play.114,115
When athletes have been cleared to return to sport, fear tends to be the most common reason for their decision to not return to play.21,116 The persistence of fear has clinical implications and warrants close monitoring to ensure that the athlete feels adequately supported in the decision to return to sport.117,118 Building the athlete’s confidence by addressing hesitation, lack of confidence, heightened awareness of risk or re-injury, and safe reintegration into athletic participation are important themes identified to encourage a safe return to play.43 A variety of validated tools can be integrated into an existing return-to-play decision-making algorithm (Table 2).118-120
Abbreviations: ACL, anterior cruciate ligament; CNS, central nervous system; CIMT, constraint-induced movement therapy.
Table 2. Self-Report Measurement Tools to Integrate into Return-to-Play Decision-Making Algorithm
Self-report Measurement Tools |
13-item Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia |
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Return to Sport after Injury Scale (ACL-RSI) |
Global Rating Scale (GRS) |
International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) Subjective Knee Evaluation Form |
Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) |
Lysholm Knee Scoring Scale |
Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36) |
Subjective Patient Outcome for Return to Sport (SPORTS) |
Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
By integrating the necessary screening of patients for kinesiophobia and assessing patient expectations after enduring an ACL injury, clinicians may be able to identify patients who are at risk for poorer functional outcomes. A consideration of psychosocial elements such as activity avoidance, fear of movement and re-injury, loss of confidence and expectations/assumptions during the continuum of the rehabilitation process, and the decision to return to play may favorably impact the individual’s ability to safely return to sport. It is critical to address both the physical and psychosocial factors during the rehabilitation process to more optimally transition individuals back to their prior level of athleticism.
CONCLUSION
Psychosocial factors may play a role in determining a player’s readiness to return to sport, as well as a potential for re-injury. A number of tests are available for use with this patient population to identify mental deficits that may impact player performance upon return. Additionally, the CNS should be considered as a source of impairment in players with ACL injuries. Current protocols may not fully appreciate the CNS’ impact on the player’s functional outcome. Therefore, an approach that includes CNS neuromotor training with traditional musculoskeletal rehabilitation, which also incorporates cognitive and psychosocial factors, may define an improved paradigm for treating soccer athletes following an ACL injury and assessing return-to-play capability.
- Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott MH Motor control: translating research into clinical practice. 4th ed: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, 2012.
- Ardern CL, Webster KE, Taylor NF, Feller JA. Return to the preinjury level of competitive sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: two-thirds of patients have not returned by 12 months after surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(3):538-543. doi:10.1177/0363546510384798.
- Bauer M, Feeley BT, Wawrzyniak JR, Pinkowsky G, Gallo RA. Factors affecting return to play after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a review of the current literature. Phys Sportsmed. 2014;42(4):71-79. doi:10.3810/psm.2014.11.2093.
- Eisenstein ED, Rawicki NL, Rensing NJ, Kusnezov NA, Lanzi JT. Variables afftecting return to play after anterior cruciate ligament injury in the national football league. Orthop J Sports Med. 2016;4(10):2325967116670117.
- Ellman MB, Sherman SL, Forsythe B, LaPrade RF, Cole BJ, Bach BR. Return to play following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(5):283-296. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-13-00183.
- Fabricant PD, Chin CS, Conte S, Conte S, Coleman SH, Pearle AD, Dines JS. Return to play after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in major league baseball athletes. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(5):896-900. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2014.12.008.
- Morris RC, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming BC, Owens BD, Fadale PD. Return to play following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Clin Sports Med. 2016;35:(4):655-668. doi:10.1016/j.csm.2016.05.009.
- Paterno MV, Rauh MJ, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Incidence of second ACL injuries 2 years after primary ACL reconstruction and return to sport. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(7):1567-1573. doi:10.1177/0363546514530088.
- Sclafani MP, Davis CC. Return to play progression for rugby following injury to the lower extremity. A clinical commentary and review of the literature. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016;11(2):302-320.
- Walden M, Hagglund M, Magnusson H, Ekstrand J. ACL injuries in men’s professional football: a 15-year prospective study on time trends and return-to-play rates reveals only 65% of players still play at the top level 3 years after ACL rupture. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(12):744-750. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2015-095952.
- Wiggins AJ, Grandhi RK, Schneider DK, Stanfield D, Webster KE, Myer GD. Risk of secondary injury in younger athletes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(7):1861-1876. doi:10.1177/0363546515621554.
- Arundale AJ, Cummer K, Capin JJ, Zarzycki R, Snyder-Mackler L. Report of the clinical and functional primary outcomes in men of the ACL-SPORTS trial: similar outcomes in men receiving secondary prevention with and without perturbation training 1 and 2 years after ACL reconstruction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(10):2523-2534. doi:10.1007/s11999-017-5280-2.
- Brumitt J, HB, Manske RC, Niemuth PE, Rauh MJ. Lower extremity functional tests and risk of injury in division III collegiate athletes. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013;8:216-227.
- Cacolice PA, Carcia CR, Scibek JS, Phelps AL. The use of functional tests to predict sagittal plane knee kinematics in ncaa-d1 female athlets. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015;10(4):493-504.
- Goodstadt NM, Hunter-Giordano A, Axe MJ, Snyder-Mackler L. Functonal testing to determine readiness to discontinue brace use one year after acl reconstruction. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013;8(2):91-96.
- Herbst E, Hoser C, Hildebrandt C, Raschner C, Hepperger C, Pointner H, Fink C. Functional assessments for decision-making regarding return to sports following ACL reconstruction. Part ll: clinical application of a new test battery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(5):1283-1291. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3546-3.
- Hoog P, Warren M, Smith CA, Chimera NJ. Functional hop tests and tuck jump assessment scores between female division l collegiate athletes participating in high versus low acl injury prone sports: a cross sectional analysis. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016;11(6):945-953.
- Mohammadi F, Salavati M, Akhbari B, Mazaheri M, Mohsen Mir S, Etemadi Y. Comparison of functional outcome measures after ACL reconstruction in competitive soccer players: a randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg, (Am.). 2013;95(14):1271-1277. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.00724.
- Rambaud A, Samozino P, Edouard P. Functional tests can they help in the decision to return to sports after anterior cruciate ligament? Example with hop tests. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59s:e19-ee20. doi:10.1016/j.rehab.2016.07.047.
- Xergia SA, Pappas E, Zampeli F, Georgiou S, Georgoulis AD. Asymmetries in functional hop tests, lower extremity kinematics, and isokinetic strength persist 6 to 9 months following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2013;43(3):154-162. doi:10.2519/jospt.2013.3967.
- Ardern CL, Taylor NF, Feller JA, Webster KE. A systematic review of the psychological factors associated with returning to sport following injury. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(17):1120-1126. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2012-091203.
- Ardern CL, Taylor NF, Feller JA, Whitehead TS, Webster KE. Psychological responses matter in returning to preinjury level of sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(7):1549-1558. doi:10.1177/0363546513489284.
- Christino MA, Fantry AJ, Vopat BG. Psychological aspects of recovery following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(8):501-509. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00173.
- Naghdi S, Nakhostin Ansari N, Farhadi Y, Ebadi S, Entezary E, Glazer D. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Injury-Psychological Readiness to Return to Sport scale to Persian language. Physiother Theory Pract. 2016;32(7):528-535. doi:10.1080/09593985.2016.1221486.
- Hui C, Salmon LJ, Kok A, Maeno S, Linklater J, Pinczewski LA. Fifteen-year outcome of endoscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with patellar tendon autograft for “isolated” anterior cruciate ligament tear. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:89-98. doi:10.1177/0363546510379975.
- Paterno MV, Rauh MJ, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Incidence of contralateral and ipsilateral anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury after primary ACL reconstruction and return to sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2012;22:116-121. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e318246ef9e.
- Paterno MV, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Rauh MJ, Myer GD, Huang B, Hewett TE. Biomechanical measures during landing and postural stability predict second anterior cruciate ligament injury after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and return to sport. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38:1968-1978. doi:10.1177/0363546510376053.
- Wright RW, Dunn WR, Amendola A, Andrish JT, Bergfeld J, Kaeding CC, Marx RG, McCarty EC, Parker RD, Wolcott M, Wolf BR, Spindler KP. Risk of tearing the intact anterior cruciate ligament in the contralateral knee and rupturing the anterior cruciate ligament graft during the first 2 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective MOON cohort study. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:1131-1134. doi:10.1177/0363546507301318.
- Bystrom MG, Rasmussen-Barr E, Grooten WJ. Motor control exercises reduces pain and disability in chronic and recurrent low back pain: a meta-analysis. Spine. 2013;38(6):E350-E358. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31828435fb.
- Macedo LG, Maher CG, Latimer J, McAuley JH. Motor control exercise for persistent nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2009;89(1):9-25. doi:10.2522/ptj.20080103.
- Grindstaff TL, Hammill RR, Tuzson AE, Hertel J. Neuromuscular control training programs and noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injur rates in female athletes: a numbers-needed-to-treat analysis. J Athl Train. 2006;41:450-456.
- Myer GD, Ford KR, Brent JL, Hewett TE. An integrated approach to change the outcome part II: Targeted neuromuscular training techniques to reduce identified ACL injury risk factors. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26:2272-2292. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31825c2c7d.
- Myer GD, Paterno MV, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Neuromuscular training techniques to target deficits before return to sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22:987-1014. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31816a86cd.
- Yoo JH, Lim BO, Ha M, Lee SW, Oh SJ, Lee YS, Kim JG. A meta-analysis of the effect of neuromuscular training on the prevention of the anterior cruciate ligament injury in female athletes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:824-830. doi:10.1007/s00167-009-0901-2.
- Moseley GL, Flor H. Targeting cortical representations in the treatment of chronic pain; a review. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26(6):646-652. doi:10.1177/1545968311433209.
- Cramer SC. Brain repair after stroke. New Engl J Med 2010;362(19):1827-1829. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1003399.
- Baumeister J, Reinecke K, Weiss M. Changed cortical activity after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a joint position paradigm: an EEG study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008;18:473-484. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2007.00702.x.
- Baumeister J, Reinecke K, Schubert M, Weiss M. Altered electrocortical brain activity after ACL reconstruction during force control. J Orthop Res. 2011;29:1383-1389. doi:10.1002/jor.21380.
- Courtney C, Rine RM. Central somatosensory changes associated with improved dynamic balance in subjects with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Gait Posture. 2006;24:190-195. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2005.08.006.
- Courtney C, Rine RM, Kroll P. Central somatosensory changes and altered muscle synergies in subjects with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Gait Posture. 2005;22:69-74. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2004.07.002.
- Kapreli E, Athanasopoulos S, Gliatis J, Papathanasiou M, Peeters R, Strimpakos N, Van Hecke P, Gouliamos A, Sunaert S. Anterior cruciate ligament deficiency causes brain plasticity: a functional MRI study. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37:2419-2426. doi:10.1177/0363546509343201.
- Valeriani M, Restuccia D, Di Lazaro V, Franceschi F, Fabbriciani C, Tonali P. Clinical and neurophysiological abnormalities before and after reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Acta Neurol Scand. 1999;99:303-307. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.1999.tb00680.x.
- Burland JP, Toonstra J, Werner JL, Mattacola CG, Howell DM, Howard JS. Decision to return to sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, Part 1: A qualitative investigation of psychosocial factors. J Athl Train. 2018;53(5):452-463. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-313-16
- Johansson H, Sjolander P, Sojka P. A sensory role for the cruciate ligaments. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;268:161-178.
- Kaprelli E, Athanasopoulos S. The anterior cruciate ligament deficiency as a model of brain plasticity. Med Hypo. 2006;67:645-650. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.01.063.
- Valeriani M, Restuccia D, Di Lazzaro V, Franceschi F, Fabbriciani C, Tonali P. Central nervous system modifications in patients with lesion of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Brain. 1996;119(Pt 5):1751-1762. doi:10.1093/brain/119.5.1751.
- Nyland J, Fisher B, Brad E, Krupp R, Caborn DN. Osseous deficits after anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction: a systematic review with suggestions to improve osseous homeostasis. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1248-1257. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.03.017.
- Nyland J, Klein S, Caborn DN. Lower extremity compensatory neuromuscular and biomechanical adaptations 2 to 11 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1212-1225. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.01.003.
- Paterno MV, Ford KR, Myer GD, Heyl R, Hewett TE. Limb asymmetries in landing and jumping 2 years following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Clin. J Sports Med. 2007;17:258-262. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e31804c77ea.
- Wojtys EM, Huston LJ. Longitudinal effects of anterior cruciate ligament injury and patellar tendon autograft reconstruction on neuromuscular performance. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28:336-344. doi:10.1177/03635465000280030901.
- Levine JD, Dardick SJ, Basbaum AI, Scipio E. Reflex neurogenic inflammation. I. Contribution of the peripheral nervous system to spatially remote inflammatory responses that follow injury. J Neurosci. 1985;5:1380-1386. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-05-01380.1985.
- McNair PJ, Marshall RN, Maguire K, Brown C. Knee joint effusion and proprioception. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995;76:566-568. doi:10.1016/S0003-9993(95)80512-5.
- Jerosch J, Prymka M. Knee joint proprioception in normal volunteers and patients with anterior cruciate ligament tears, taking special account of the effect of a knee bandage. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1996;115:162-166. doi:10.1007/BF00434546.
- Lattanzio PJ, Petrella RJ. Knee proprioception: a review of mechanisms, measurements, and implications of muscular fatigue. Orthopedics. 1998;21:463-470.
- Lephart SM, Pincivero DM, Giraido JL, Fu FH. The role of proprioception in the management and rehabilitation of athletic injuries. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25:130-137. doi:10.1177/036354659702500126.
- Lephart SM, Riemann BL, Fu FH. Introduction to the sensorimotor system. In: Lephart SM, Fu FH, editors. Proprioception and neuromuscular control in joint stability: Champaign (IL): Human Kinetics Publishers, 2000.
- Pelletier R, Higgins J, Bourbonnais D. Is neuroplasticity in the central nervous system the missing link to our understanding of chronic musculoskeletal disorders? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:25. doi:10.1186/s12891-015-0480-y.
- Magill R Motor learning and control: concepts and applications. Boston, MA: WCB/McGraw-hill. 8th ed, 2007.
- Winter DA Biomechanics and motor control of human movement. 4th ed: Hoboken, NJ:Wiley, 2009.
- Hoffman M, Koceja D. Hoffmann reflex profiles and strength rations in postoperative anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients. Int J Neurosci. 2000;104:17-27. doi:10.3109/00207450009035006.
- Duthon VB, Barea C, Abrassart S, Fasel JH, Fritschy D, Ménétrey J. Anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:204-213. doi:10.1007/s00167-005-0679-9.
- Zimny ML. Mechanoreceptors in articular tissues. Am J Anat. 1988;182:16-32. doi:10.1002/aja.1001820103.
- Zimny ML, Schutte M, Dabezies E. Mechanoreceptors in the human anterior cruciate ligament. Anat Rec. 1986;214:204-209. doi:10.1002/ar.1092140216.
- Zimny ML, Wink CS. Neuroreceptors in the tissues of the knee joint. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 1991;1:148-157. doi:10.1016/1050-6411(91)90031-Y.
- Ward S, Pearce AJ, Pietrosimone B, Bennell K, Clark R, Bryant AL. Neuromuscular deficits after peripheral joint injury: a neurophysiological hypothesis. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51(3):327-332. doi:10.1002/mus.24463.
- Ball T, Schreiber A, Feige B, Wagner M, Lücking CH, Kristeva-Feige R. The role of higher-order motor areas in voluntary movement as revealed by high resolution EEG and fMRI. Neuroimage. 1999;10:682-694. doi:10.1006/nimg.1999.0507.
- Nachev P, Wydell H, O’Neill K, Husain M, Kennard C. The role of the pre-supplementary motor area in the control of action. Neuroimage. 2007;36(suppl. 2):T155-TT163. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.03.034.
- Binder JR, Desai RH. The neurobiology of semantic memory. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011;15:527-536. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2011.10.001.
- Bonner MF, Price AR. Where is the anterior temporal lobe and what does it do? J Neurosci. 2013;33:4213-4215. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0041-13.2013.
- Peuskens H, Vanrie J, Verfaillie K, Orban GA. Specificity of regions processing biological motion. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:2864-2875. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04106.x.
- Heroux ME, Tremblay F. Corticomotor excitability associated with unilateral knee dysfunction secondary to anterior cruciate ligament injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:823-833. doi:10.1007/s00167-006-0063-4.
- Grooms D, Page S, Onate J. Brain activation for knee movement measured days before second anterior cruciate ligament injury: neuroimaging in musculoskeletal medicine. J Athl Train.2015;50(10):1005-1010. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-50.10.02.
- Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD. Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage. 2009;44(2):489-501. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.039.
- Mansour A, Farmer M, Baliki M, Apkarian AV. Chronic pain: the role of learning and brain plasticity. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2014;32:129-139. doi:10.3233/RNN-139003.
- Nyland J, Wera J, Klein S, Caborn DN. Lower extremity neuromuscular compensations during instrumented single leg hop testing 2-10 years following ACL reconstruction. Knee. 2014;21:1191-1197. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2014.07.017.
- Van Vliet PM, Heneghan N. Motor control and the management of musculoskeletal dysfunction. Man Ther. 2006;11(3):208-213. doi:10.1016/j.math.2006.03.009.
- Bayona NA, Bitensky J, Teasell R. Plasticity and reorganization of the uninjured brain. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2005;12:1-10. doi:10.1310/A422-G91U-Q4HB-86XC.
- Remple M, Bruneau R, VandenBerg P, Goertzen C, Kleim JA. Sensitivity of cortical movement representations to motor experience evidence that skilled learning but not strength training induces cortical reorganization. Behav Brain Res. 2001;123:133-141. doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(01)00199-1.
- Jull GA, Falla D, Vicenzino B, Hodges PW. The effect of therapeutic exercise on activation of the deep cervical flexor muscles in people with chronic neck pain. Man Ther. 2009;14:696-701. doi:10.1016/j.math.2009.05.004.
- Karni A, Meyer G, Jezzard P, Adams MM, Turner R, Ungerleider LG. Functional MRI evidence for adult motor cortex plasticity during motor skill learning. Nature. 1995;377:155-158. doi:10.1038/377155a0.
- Koeneke S, Lutz K, Herwig U, Ziemann U, Jäncke L. Extensive training of elementary finger tapping movements changes the pattern of motor cortex excitability. Exp Brain Res. 2006;174:199-209. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0440-8.
- O’Leary S, Falla D, Elliott JM, Jull G. Muscle dysfunction in cervical spine pain: implications for assessment and management. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2009;39:324-333. doi:10.2519/jospt.2009.2872.
- Pascual-Leone A, Nguyet D, Cohen LG, Brasil-Neto JP, Cammarota A, Hallett M. Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new fine motor skills. J Neurophysiol. 1995;74:1037-1045. doi:10.1152/jn.1995.74.3.1037.
- Svensson P, Romaniello A, Wang K, Arendt-Nielsen L, Sessle BJ. One hour of tongue-task training is associated with plasticity in corticomotor control of the human tongue musculature. Exp Brain Res. 2006;173:165-173. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0380-3.
- Tsao H, Druitt TR, Schollum TM, Hodges PW. Motor training of the lumbar paraspinal muscles induces immediate changes in motor coordination in patients with recurrent low back pain. J Pain. 2010;11:1120-1128. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2010.02.004.
- Gokeler A, Banjaminse A, Hewett TE, Paterno MV, Ford KR, Otten E, Myer GD. Feedback techniques to target functional deficits following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: implications for motor control and reduction of second injury risk. Sports. Med. 2013;43:1065-1074. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0095-0.
- Powers CM, Fisher B. Mechanisms underlying ACL injury-prevention training: the brain-behavior relationship. J Athl Train. 2010;45:513-515. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-45.5.513.
- Seidler RD, Noll DC. Neuroanatomical correlates of motor acquisition and motor transfer. J Neurophysiol. 2008;99:1836-1845. doi:10.1152/jn.01187.2007.
- Brophy RH, Stepan JG, Silvers HL, Mandelbaum BR. Defending puts the anterior cruciate ligament at risk during soccer: a gender-based analysis. Sports Health. 2015;7:244-249. doi:10.1177/1941738114535184.
- Sell TC, Ferris CM, Abt JP, Tsai YS, Myers JB, Fu FH, Lephart SM. Predictors of proximal tibia anterior shear force during a vertical stop-jump. J Orthop Sports Res. 2007;25:1589-1597. doi:10.1002/jor.20459.
- Yu B, Lin CF, Garrett WE. Lower extremity biomechanics during the landing of a stop-jump task. Clin Bio. 2006;21:297-305. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2005.11.003.
- Cortes N, Onate J, Van Lunen B. Pivot task increases knee frontal plane loading compared with sidestep and drop-jump. J Sports Sci. 2011;29:83-92. doi:10.1080/02640414.2010.523087.
- Blackburn JT, Padua DA. Influence of trunk flexion on hip and knee joint kinematics during a controlled drop landing. Clin Biomech. 2008;23:313-319. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2007.10.003.
- Li G, Papannagari R, DeFrate LE, Yoo JD, Park SE, Gill TJ. Comparison of the ACL and ACL graft forces before and after ACL reconstruction: an in-vitro robotic investigation. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:267-274. doi:10.1080/17453670610046019.
- Zheng N, Fleisig GS, Escamilla RF, Barrentine SW. An analytical model of the knee for estimation of internal forces during exercise. J Biomech. 1998;31:963-967. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(98)00056-6.
- Li G, Rudy TW, Sakan M, Kanamori A, Ma CB, Woo SL. The importance of quadriceps and hamstring muscle loading on knee kinematics and in situ forces in the ACL. J Biomech. 1999;32:395-400. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(98)00181-X.
- Hewett TE, Myer GD, Ford KR. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries in female athletes, Part l: Mechanisms and risk factors. Am J Sports Med.2006;34:299-311. doi:10.1177/0363546505284183.
- Daniel DM, Stone ML, Barnett P. Use of the quadriceps active test to diagnose to diagnose posterior cruciate ligament disruption and measure posterior laxity of the knee. J Bone Jt SurA, (Am.).1988;70:386-391.
- Hoffman M, Schrader J, Koceja D. An investigation of postural control in postoperative anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients. J Athl Train. 1999;34:130-136.
- Mattacola CG, Perrin DH, Gansneder BM, Gieck JH, Saliba EN, McCue FC. Strength, functional outcome, and postural stability after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Athl Train.2002;37:262-268.
- McLean SG, Lipfert SW, van den Boget AJ. Effect of gender and defensive opponent on the biomechanics of sidestep cutting. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36:1008-1016. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000128180.51443.83.
- McLean SG, Neal RJ, Myers PT, Walters MR. Knee joint kinematics during the sidestep cutting maneuver: potential for injury in women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31:959-968. doi:10.1097/00005768-199907000-00007.
- O’Connell M, George K, Stock D. Postural sway and balane testing: a comparison of normal and anterior cruciate ligament deficient knees. Gait Posture. 1998;8:136-142. doi:10.1016/S0966-6362(98)00023-X.
- Okuda K, Abe N, Katayama Y, Senda M, Kuroda T, Inoue H. Effect of vision on postural sway in anterior cruciate ligament injured knees. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10:277-283. doi:10.1007/s00776-005-0893-9.
- Swanik CB, Lephart SM, Giraldo JL, Demont RG, Fu FH. Reactive muscle firing of anterior cruciate ligament-injured females during functional activities. J Athl Train. 1999;34:121-129.
- Bennett S, Ashford D, Rioja N, Elliott D. Intermittent vision and one-handed catching: the effect of general and specific task experience. J Mot Behav. 2004;36:442-449. doi:10.3200/JMBR.36.4.442-449.
- Bennett SJ, Elliott D, Weeks DJ, Keil D. The effects of intermittent vision on prehension under binocular and monocular viewing. Mot Contr. 2003;7:46-56. doi:10.1123/mcj.7.1.46.
- Grooms D, Appelbaum G, Onate J. Neuroplasticity following anterior cruciate ligament injury: a framework for visual-motor training approaches in rehabilitation. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.2015;45(5):381-393. doi:10.2519/jospt.2015.5549.
- Ardern CL. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction-not exactly a one-way ticket back to the preinjury level: a review of contextual factors affecting return to sport after surgery. Sports Health.2015;7(3):224-230. doi:10.1177/1941738115578131.
- Hsu CJ, Meierbachtol A, George SZ, Chmielewski TL. Fear of reinjury in athletes. Sports Health.2017;9(2):162-167. doi:10.1177/1941738116666813.
- Medvecky MJ, Nelson S. Kinesiophobia and return to sports after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Conn Med. 2015;79(3):155-157.
- Chmielewski TL, ZG, Lentz TA, Tillman SM, Moser MW, Indelicato PA, George SZ. Longitudinal changes in psychosocial factors and their association with knee pain and function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Phys Ther. 2011;91:1355-1366. doi:10.2522/ptj.20100277.
- Clement D, Arvinen-Barrow M, Fetty T. A-BM, Fetty T. Psychosocial responses during different phases of sport-injury rehabilitation: a qualitative study. J Athl Train. 2014;50:95-104. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-49.3.52.
- Te Wierike SC, van der Sluis A, van den Akker-Scheek I, Elferink-Gemser MT, Visscher C. Psychosocial factors influencing the recovery of athletes with anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013;23(5):527-540. doi:10.1111/sms.12010.
- Wiese-Bjornstal DM. Psychology and socioculture affect injury risk, response, and recovery in high-intensity athletes: a consensus statement. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010;20(Suppl. 2):103-111. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01195.x.
- Crossman J, GL, Jamieson J. The emotional responses of injured athletes. NZ J Sports Med. 1995;23:1-2.
- Hambly K. The use of the tegner activity scale for articular cartilage repair of the knee: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(4):604-614. doi:10.1007/s00167-010-1301-3.
- Hambly K, Griva K. IKDC or KOOS: which one captures symptoms and disabilities most important to patients who have undergone initial anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction? Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(7):1395-1404. doi:10.1177/0363546509359678.
- Archer K, Reinke E, Huston LJ, Bird M, Scaramuzza E, Coronado R, Haug C, Vanston S, Spindler KP. Impact of preoperative expectations and fear of movement on return to sport and KOOS scores at 6 months following ACL reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2015;3(7 suppl.2):2325967115S2325900113. doi:10.1177/2325967115S00113.
- Zarzycki R, Failla M, Arundale AJH, Capin JJ, Snyder-Mackler L. Athletes with a positive psychological response to return to sport training have better outcomes one and two years after ACL reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(7 suppl.6):2325967117S2325900324. doi:10.1177/2325967117
ABSTRACT
Soccer players recovering from anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries have better options for treatment today than they did 25 years ago. Surgical techniques have improved, and rehabilitation protocols have evolved considerably. Although the rehabilitation community is doing a better job of treating this patient population, the evidence does demonstrate that both re-injury and return- to-play (RTP) rates are still suboptimal. Most protocols focus on normalizing strength and range of motion (ROM) and achieving limb symmetry with soccer-specific movements. While these factors are certainly prerequisites for returning to the field, their inclusion does not provide a complete picture of the athlete’s presentation. An additional factor that should be prioritized with this patient population is the central nervous system (CNS). Advanced imaging has shown that peripheral deafferentation does occur with musculoskeletal injuries; this ultimately results in cortical reorganization, which makes movement planning more difficult for the player, since simpler tasks must now be processed at higher levels in the CNS. The evidence also shows that the CNS demonstrates plasticity in these cases, so that through focused neuromotor rehabilitation techniques, it is possible to bring movement planning back down to a sub-cortical level. Cognitive issues may also be a factor in preventing the player from returning. Fear of re-injury and diminished confidence can influence the way the player moves on the field, and diminish ability to demonstrate protective kinematics with all soccer-specific tasks. We believe that an approach incorporating traditional musculoskeletal rehabilitation, CNS neuro-motor training, and consideration for cognitive factors, may define an improved paradigm for treating the soccer player and assessing readiness for RTP following ACL injury.
Continue to: Although anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)...
Although anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rehabilitation has evolved considerably over the past 2 decades, the basic paradigm has remained consistent: normalize strength and range of motion, reduce swelling and pain, achieve limb symmetry with functional tasks, and return to sport-specific activities gradually over a 6 to 12-month period. There have been some slight additions to this basic premise, such as evaluating knee and hip mechanics in the frontal plane, but the requirements here are vaguely defined and are typically only evaluated within the context of controlled clinical testing.
It is interesting to note that the typical ACL injury pattern occurs during a normal sport-specific movement, yet most rehabilitation protocols fail to recognize the potential causes of the aberrant movement pattern and how to best modify it so that the risk of repeated stress to the ACL can be minimized. It should be understood that movement occurs through the interaction of 3 discrete factors: the individual, the task being performed, and the environment in which it is performed.1 All of these factors will play a role in how the final movement pattern is produced. For example, a soccer player (individual) may backpedal and pivot to the left 60° and accelerate to sprint after a player moving towards the touchline (task) while receiving instructions from teammates and monitoring the movements of opposing players (environment). A small variance in any 1 of these factors could significantly impact the movement pattern as the player completes the task.
In most rehabilitation programs, each of these factors may be treated in a singular, non-specific manner, but if these factors are not coordinated effectively throughout the program to produce the desired sport-specific movement, a faulty pattern may persist, leaving the player at risk for injury. Current rehabilitation programs seem to have a strong focus on creating stability, mobility, and strength, but these are trained in silos, with an internal focus of control, which only solves the biomechanical equation. Often, it is difficult for the player to coordinate good biomechanics into an efficient, protective movement pattern that is specific to the tasks performed on the field during the normal course of play. The missing link here is the central nervous system (CNS).
Limitations to the current ACL protocols may be that they rely heavily on musculoskeletal rehabilitation and that they have limited emphasis on neurological rehabilitation. As will be discussed later, the CNS has a large impact on the final movement selected by the player. In fact, cognition, perception, and action are the three factors that comprise the individual’s part of the movement paradigm,1 yet rarely are these factors addressed in most ACL rehabilitation programs. These elements are a large part of the movement equation, so it is easy to understand how failing to address these features can lead to poor movement quality and subsequent ACL re-injury.
In addition to central neurological factors, cognitive issues may play a role in the player’s ability to return to sport. Determining optimal readiness for return to play is a difficult task for the medical community, with many variables to consider. Previous research studies have assessed the variability in return to play for various sports, including football, rugby, soccer, skiing, running, and tennis, with return-to-play rates ranging from 18% to 100%.2,3,4-10 The risk of secondary injury may cast doubt and fear on athletes as they contemplate their successful return to play.8,11 Although robust functional testing has become commonplace for determining athlete readiness after injury,12-20 the assessment of psychological readiness, persistent fear, and loss of confidence are often neglected and not as commonly integrated into the return-to-play algorithm.21-24 The purpose of this paper is to assess the various cognitive and central neural factors affecting a soccer player’s ability to recover from an ACL injury and offer suggestions for integrating treatments into the protocols to address these issues.
Continue to: CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEUROPLASTICITY...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEUROPLASTICITY
Despite the vast amount of attention and research focused on the ACL, the re-injury rate still remains quite high. It has been reported that rehabilitation programs that employ traditional neuromotor training produce a re-injury rate as high as 30% after the athlete returns to sport.25-28 The overall rate of sustaining a second ACL injury is 15%11 in all patient populations. For the general population <25 years of age, the re-injury rate is 21%, and for athletes <25 years of age, the re-injury rate rises to 23%.11 With re-injury rates at this level, it is certainly fair to consider and be critical of the current rehabilitation methods being used with this population. One opportunity for improvement lies in the general approach used to rehabilitate ACL-injured patients. Therapy for this injury is protocol-driven, and the fact remains that most protocols prioritize restoration of peripheral systems, with minimal thought given to the cortical control necessary to manage those systems.29,30 When neural factors are considered, it is usually within the context of increasing strength, balance, power, and biomechanical control,31-34 which are certainly important but peripheral factors nonetheless. The missing element in many ACL protocols may be how to best manage the central neural components and cognitive factors associated with this injury.
If the CNS were to receive more consideration in ACL protocols, the opportunity for improved outcomes could be substantial because the CNS has been proven to be a very malleable system, as long as it receives the correct input. The CNS demonstrates neuroplasticity,35 which means that it is capable of reorganization, based on the stimuli that it receives, whether internal or external.36
This is an important consideration in ACL rehabilitation because the ACL graft, while restoring the biomechanical properties to the knee, is not fully capable of producing the same neurosensory properties of the original ACL.37-42This is an important concept to understand because an ACL tear does indeed cause deafferentation in the ascending pathways to the brain.37-40,42-46 This can lead to CNS reorganization and subsequent alterations in efferent output to the periphery.37-40,42-46 Therefore, if a protocol with traditional musculoskeletal principles was used, then the mechanical function of the knee may certainly be remediated, but the neurosensory function will remain in a maladaptive state,47-50 potentially leading to aberrant, non-protective movement strategies and a higher risk of re-injury.
The process of CNS reorganization may begin with the initial ACL injury. A peripheral musculoskeletal injury creates an inflammatory response that results in the arrival of chemical mediators such as histamine, substance P, calcitonin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide at the site of injury.51 As edema accumulates in the joint, tension is applied to the capsule, which may adversely affect proprioception from the receptors located within.45 The interruption of consistent input from the peripheral mechanoreceptors may lead to long-term differentiation of the ascending pathways.52 This information is synthesized at 3 different levels of the CNS (spinal cord, brain stem, and motor cortex) to produce motor output.53-56 Differentiation in the ascending circuitry can cause inhibition of motor neurons at the spinal cord.45Animal research has shown that this differentiation can cause a breakdown in the cuneate nucleus of the brainstem,57which provides sensory information from the upper body, while the gracile nucleus does the same for the lower body. These structures transfer proprioceptive input to the ventral posterior lateral nucleus in the thalamus, where it is then sent to the primary somatosensory cortex.57 In general, the somatosensory, visual, and vestibular systems interpret afferent inputs to control movement, balance, and stability.58,59 In a sport like soccer, where the movement tasks are dynamic and unpredictable, it is easy to see why even a slight deficit in somatosensory processing could disrupt a movement. Valeriani and colleagues42,46 showed that somatosensory-evoked potentials were indeed altered in a cohort of ACL reconstruction (ACLR) subjects, indicating reorganization within the CNS. Additionally, the deafferentation could not be changed by other afferent input coming from the knee or by the new ACL graft placed in the knee.42,46The primary motor cortex has been found to have a substantial network of connectivity with the primary somatosensory cortex, which supports the theory that the motor cortex has a very strong linkage with the peripheral receptors in the joint.60 The ligaments in the joint contain Ruffini, Pacinian, and Golgi receptors, all of which react to changes in the collagen fibers and send information regarding tension, length, speed, acceleration, position, and movement back to the CNS.61-64 Unfortunately, the ascending pathway deafferentation can cause reorganization within the CNS, which makes the feedback provided from the periphery less effective in motor planning.
Ward and colleagues65 have reported that reorganization within the motor cortex is the primary cause of chronic neuromuscular movement deficits in peripheral joint injuries. Researchers have used functional magnetic resonance imaging, transcranial magnetic stimulation, and electroencephalography in ACL patients to demonstrate changes in cortical activity and subsequent CNS reorganization.65 Kapreli and colleagues41 reported that subjects with an ACL injury demonstrated higher cortical activation in the pre-supplementary motor area (pre-SMA). This is a region that is responsible for more complex motor planning.66,67 This area becomes active before the primary motor cortex and is responsible for preparing the final movement pattern that the motor cortex executes.41 As the task becomes more complex, activity in the pre-SMA will increase.41 Additionally, they found that the posterior secondary somatosensory area and posterior inferior temporal gyrus showed increased cortical activity compared with controls.41 Visual planning is processed in the posterior inferior temporal gyrus, and so, it appears that the difficulty in processing somatosensory information due to ascending pathway deafferentation places an increased reliance on the visual system for movement planning.68-70 This was observed while ACL-injured subjects performed a simple knee flexion-extension movement encompassing 40°, indicating the need to incorporate higher central levels of planning for a very simple movement pattern.41 Baumeister and colleagues37,38 also showed that subjects with ACLR had higher levels of cortical activation in the areas of the brain that require attention and that process sensory input. They theorized that this occurred because of reduced efficiency of neural processing at lower levels in the CNS. Despite the higher levels of cortical activity observed, they found that subjects with an ACLR demonstrated proprioceptive testing that was deficient compared with that of controls. Heroux and Tremblay71 also demonstrated that subjects with an ACLR had increased resting motor cortex activity. They believed that this occurred as the motor cortex attempted to maintain neuromotor output to the periphery in the face of diminished afferent input.
Continue to: The reorganization that results in movement planning...
The reorganization that results in movement planning, transitioning from subcortical levels to cortical levels, is a phenomenon that researchers believe can lead to deficiencies even as the athlete has returned to sport. Grooms et al72revealed in a case report that a subject with an ACLR showed higher levels of activity in the crus region of the cerebellum. This area contains corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts that transmit neural input to maintain balance and coordination.73 These changes in the cerebellum, combined with increased motor cortex activity, are thought to be indicative of a global neural strategy that uses higher levels of the CNS, as opposed to subcortical processing.72
The current research makes a clear and compelling argument for the importance of CNS reorganization after an ACL injury, placing increased reliance on higher cortical levels of control, as well as the visual system to coordinate balance and movement. It is thought that this reorganized method of neural transmission can then become imprinted within the CNS, if not corrected.35,74 If this is the case, then traditional strength programs may not be sufficient to restore these connections to their pre-injury level. If the CNS has the ability to reorganize based on the aberrant input that it receives from the periphery, then it also certainly has the potential to adapt to more specific structured input via the ascending afferent pathways.41,45 The rehabilitation program, however, needs to be structured specifically to target the reorganized regions of the brain. There needs to be an emphasis on rehabilitating not only the peripheral neuromotor structures but also the CNS.75
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM REHABILITATION PRINCIPLES
For a neurological rehabilitation to be successful, the interventions need to be repetitive and task-specific, involve learning, employ whole and part practice, and transition from using an internal to an external focus of control.76Movements that are repetitive, but which lack structured learning and skill, have been shown to have no effect on inducing neuroplastic changes in the primary motor cortex.77,78 However, using neurological rehabilitation techniques that facilitate the acquisition of new motor skills by the CNS have been shown to cause neuroplastic adaptation in the motor cortex.79-85 This occurs because neuroplasticity is determined by experience and practice.78 The CNS operates on cues received in the ascending tracts by mechanoreceptors in the joint. If a new movement pattern is being learned by the athlete, then this new afferent input received from the periphery will start to initiate reorganization in the higher learning centers. If this occurs with optimal repetition and precision, then a positive reorganization can take place within the CNS that results in a higher percentage of motor planning and control being filtered down to a subcortical level. Essentially, the movements become instinctive, which is crucial in athletics, where attention in higher cortical areas is frequently diverted to external aspects of the competition and not solely used to focus on movement.
This is why shifting neurological rehabilitation from an internal focus of control to an external focus of control is paramount. While using an internal focus of control is required early in rehabilitation to enable the athlete to understand the specific tasks required in a composite movement, a gradual transition to an external focus of control is necessary as the athlete begins to perform tasks that are more soccer-specific. This autonomous stage of motor learning is crucial because it transfers the burden of motor planning from higher to lower levels of the CNS and frees up the pre-SMA and primary motor cortex to handle more complex patterns.58,86-88
Continue to: ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RISK POTENTIAL IN SOCCER PLAYERS...
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RISK POTENTIAL IN SOCCER PLAYERS
If a comprehensive neuromotor rehabilitation program is to be used effectively with soccer athletes, then the first priority is to define how the players should move, so that they can demonstrate protective kinematics with all soccer-specific tasks and minimize stress to the ACL. As the ideal movement pattern becomes autonomous, then it should be trained within the context of a dynamic environment; remembering that environmental changes have a large impact on the final movement pattern selected by the individual. Brophy et al89 evaluated videos of non-contact ACL injuries in male and female soccer players and determined that 45% occurred while cutting, 25% while landing, and 16% during deceleration. These 3 patterns represent 86% of the ACL injuries observed and offer an opportunity for evaluation and treatment with specific central neuromotor rehabilitation techniques.
The foundational movement patterns for the soccer player should focus on producing leverage that minimizes stress to the ACL during the 3 primary tasks outlined above. To achieve this, it is necessary to reduce posterior ground reaction forces at the hip and knee joint during these movements. There is a high correlation between the magnitude of the posterior ground reaction force, and anterior tibial shear, and subsequent displacement.90,91 This stress can be reduced by increasing the hip and knee flexion angles during soccer-specific movements that involve pivoting, decelerating, and landing from a jump in a unipedal stance.92
This phenomenon can be explained by observing changes in the ACL elevation angle, hamstring insertion angle, and patella tendon-tibial tuberosity insertion angle. As the knee moves into flexion, the ACL takes on a more parallel orientation to the tibia, and its fibers are better able to resist elastic deformation accompanied by a posterior ground reaction force.93,94 The quadriceps will produce less anterior translation on the tibia because the patella tendon insertion angle is reduced relative to the longitudinal axis of the tibia, and the mechanical advantage of the quadriceps is decreased.95 Lastly, the hamstrings will be able to provide better leverage posteriorly because the resultant force trends toward a more parallel orientation to the tibial plateau, which enables the player to counter, more effectively, the posterior ground reaction force and the anterior pull directed by the quadriceps.95
This theory is supported by the work of Li and colleagues,96 who showed that there is an inverse relationship between knee flexion angle and ACL loading. In their study, they applied a constant quadriceps force of 200 N at 15°, 30°, and 60° angles. The anterior shear force was obviously the highest at 15° and reduced by 20% at 30° and 60% at 60°. When hamstrings co-contraction was added, there was an additional 30% reduction in anterior shear at 15° and 50% at 30° and 60°. From a more flexed position, the hamstrings can increase joint compression and reduce the anterior translation by allowing the concave medial tibial plateau to limit the anterior drawer effect and absorb the forces that occur with excessive anterior shear, internal rotation, and valgus loads.97 As the knee flexion angle approximates 60°, the hamstring leverage is increased, and the quadriceps leverage is diminished to the point where its ability to produce anterior tibial translation is neutralized.98 Daniel and colleagues98 referred to this as the quadriceps neutral angle.
For soccer-specific movements that are potentially injurious to the ACL, it may then be beneficial to create a default movement pattern at the knee that approximates this value. In keeping with the information presented in this paper, it will be important to have the player reproduce this angle consistently during activities that involve pivoting, decelerating, and landing from a jump within the context of match play. This will certainly require that segments located both proximal and distal to the knee are able to function within specific parameters so that a cohesive protective synergy is produced throughout the lower quarter which minimizes posterior ground reaction forces and is protective of the ACL. This is where structured neuromotor training that is able to modulate networks within the CNS may be beneficial.
Continue to: CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TREATMENT TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOCCER PLAYER...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TREATMENT TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOCCER PLAYER
The ultimate goal is to create a foundational movement pattern that optimizes leverage and is protective of the ACL during decelerating, pivoting, and landing in a unipedal stance from a jump. The composite segments that are necessary to achieve this include local core stability to create lumbopelvic stiffness, and global core activation to enhance posterior chain stability. This should enable the player to feel more balanced when placing the pelvis in a more posterior and inferior position while still maintaining the trunk in a position that is parallel with the tibia, as the knee is flexed to an approximate 60° angle (Figure 1). From a frontal plane perspective, the acetabulum should bisect the malleoli of the stance leg, with a neutral tibiofemoral joint alignment (Figure 1).

The neuromotor training for the composite segments of this movement can begin in the “acute postoperative phase” (Table 1). Because the surgical repair will limit the player’s capabilities in this stage, this is a good time to break down the foundational movement pattern into its component parts and ensure that the CNS receives a high number of quality repetitions of parts. In this phase, the player may begin an isolated training for the transversus abdominis, multifidus, and pubococcygeus. This can start in a supine position using biofeedback with an isometric contraction, progress to a standing position, and incorporate deep core activation with stance-phase gait training, mini squats, and lunge variations. This phase will require an abundance of visual and verbal feedback with an internal focus of control as the player gets used to activating the deep core and quad/hip synergy during functional lower extremity movements. Even in this early phase, the player should look to minimize anterior and/or posterior pelvic tilting and maintain a stiff thoracolumbar segment that remains parallel with the tibia during all functional movements.
Table 1. Adjunct CNS Treatment Principles for ACL Reconstruction in Soccer Athletes
Phase | Goal | CNS Rehabilitation Techniques |
Acute postoperative | Local core activation with weightbearing exercise. Produce trunk stiffness with lower extremity movements. | High repetitions. Verbal or tactile cues. Internal focus of control. Partial practice. |
Subacute postoperative | Lumbopelvic, foot or ankle, and posterior chain segments learn to participate in movement effectively. | Requires higher levels of cortical planning. Internal focus of control. CIMT. |
Static stability | Able to adopt foundational movement pattern consistently with vision eliminated. | Somatosensory vs visual processing. Partial-to-whole practice. Use internal and/or external focus of control. |
Dynamic stability | Able to perform plyometrics in a single-leg position using foundational movement pattern with subcortical processing. | Increase velocity with movement challenges. Occlude or eliminate vision. Heavy reliance on an external focus of control. Prioritize movement quality. |
Dynamic agility | Pivoting, decelerating, and landing are performed with hip flexion/knee flexion synergy, trunk stiffness, and posterior chain activation. | Unanticipated movement challenges. Whole practice. Ball reaction drills with vision obstructed or occluded. Contact drills with vision obstructed or occluded. Use external focus of control to include soccer-specific tasks. |
Abbreviations: ACL, anterior cruciate ligament; CNS, central nervous system; CIMT, constraint-induced movement therapy.
As the player moves into the “subacute postoperative phase” (Table 1). He or she will continue to use an internal focus of control to activate the local/global core synergy with functional movements progressing from double-leg, to single-leg positions. Partial practice, instead of whole practice, is still the predominant theme of the neural training process. In this phase, the knee and hip flexion angles can increase, and the player’s trunk and pelvic position should be critiqued in a single-leg position so that the trunk remains parallel with the tibia in the sagittal plane with a slight forward hip hinge. The pelvis should remain level throughout single-leg stance to ensure adequate activation of the lateral hip stabilizers. This is the stage where the player can learn to isolate closed kinetic chain hip rotation for pivoting, and so, single-leg hip internal and external rotation drills are useful, both with and without resistance. Skill acquisition is crucial in this phase because the patterns that the CNS adopts will form the foundation for more dynamic patterns that will occur in the later soccer-specific stages. Higher levels of cortical planning are still needed in this phase. For this reason, it is important that poor quality repetitions are recognized by the player and clinician so that he or she can learn to perform them correctly, albeit still with an internal focus of control. This is also a good time to begin to employ constraint-induced movement therapy as the player is able to replicate the desired pattern with more precision. For example, by eliminating the use of the upper extremities as a source of balance, the CNS is forced to program alternate synergies such as the lumbopelvic, and foot and ankle segments to maintain the desired alignment.
The “lower quarter static stability phase” (Table 1) marks a point where it may be useful to use direct strategies that have the capability to change CNS efferent owutput from a primary reliance on the visual processing areas in the posterior-inferior temporal gyrus back to the somatosensory area. It is critical that the player is able to make this transition in cortical reorganization and control, because ACL-injured subjects have been shown to have balance scores similar to healthy controls when they are able to use their vision, but this is reduced when vision is taken away.99-105 Their balance will diminish even further if vision is modulated during more complex landing and pivoting maneuvers.99-105 This may certainly explain why defending is a riskier task for ACL-injured players89 as their visual system is focused more on tracking a player than attending to precision with movement planning.
To enhance this cortical reorganization within the context of soccer-specific movements, it is useful to start from a foundational single-leg position, with the knee approximating 60° of flexion and the trunk parallel to the tibia. In the frontal plane, the pelvis should be level, the trunk vertical, and the acetabulum bisecting the malleoli of the stance leg (Figure 1). The player may initially work on getting into this foundational position with vision either partially obstructed using stroboscopic eyewear or completely obstructed if this equipment is unavailable.106-108 The pattern can be progressed by constraining the upper extremities to force reliance on the lumbopelvic and foot/ankle strategies for balance. Head and/or trunk turns can be added to simulate the external focus of control that is required with movement in soccer. These should progress from slow to fast and anticipated to unanticipated as the player demonstrates competence in maintaining stability at each segment within the foundational stance position. Once this is in play, a ball should be introduced into the drills. As the player maintains the foundational position with vision diminished and upper extremities constrained, they should attempt to reach for or trap a ball from this position. If vision is completely obstructed, then the player can be instructed to open his/her eyes just as the ball arrives to induce a reactive response. Again, quality repetitions are essential for learning to occur, and subsequent skill acquisition to take place in the CNS; thus, close scrutiny should be paid to the qualitative essence of the movement patterns to ensure pristine biomechanics during this phase.
The “lower quarter dynamic stability phase” (Table 1) should continue with the same neuromotor training principles employed in the previous phase, except that the drills will now involve plyometrics. The player should ultimately progress from double-leg, to single-leg jumps and then linear to diagonal. Vision should still be obstructed and upper extremities constrained to channel the lumbopelvic region for force production and balance. Movement quality in the foundational position remains paramount with these drills to ensure that skill acquisition is occurring and injury risk is being mitigated. An external focus of control can be introduced by applying an unanticipated perturbation during a jump. Additional learning opportunities should include unanticipated head and trunk turns while landing in a unipedal stance from a jump. The task can be made more specific by having the player trap a pass while doing linear or diagonal single-leg hop progressions. In this manner, the player’s CNS can become reorganized to program the requisite synergies to maintain a protective foundational position on the stance leg, as the contralateral limb is required to perform work that is far outside the player’s base of support.
Continue to: The final segment of the CNS neuromotor rehabilitation program...
The final segment of the CNS neuromotor rehabilitation program is the “lower quarter dynamic agility phase” (Table 1), when the player will learn to perform an unanticipated directional change in a foundational position for the pivot leg. The player can begin this phase by initiating sprint-deceleration-pivot efforts, progressing at 45°, 90°, 120°, and 180° turns. This should be trained in both a forward and backpedal position. Close attention should be paid to the deceleration phase of the sprint-pivot effort, as this will set the player up to demonstrate protective kinematics during the pivot phase of the task. In this phase, the center of mass should become lower and move posteriorly, so that a deeper knee and hip flexion angle, supported by posterior chain synergies, can occur at the pivot point. This is an important skill for the player to acquire, as Cortes and colleagues92 have reported that female collegiate soccer players tend to perform a pivoting task with a more erect trunk position. In the same cohort, they also measured the mean knee flexion angle at initial contact during pivoting to be 24°.92 Movement patterns that reflect an elevated center of mass, with arms abducted away from the trunk, should be discouraged here. The drills can be progressed to have the player react to a command and perform unanticipated pivots within a 5 × 5-meter box to simulate defending. This should be progressed from eyes open and arms unconstrained, to vision disrupted and arms constrained. From here, an external focus of control can be added by playing a ball to the athlete. Vision should be withheld until the instant that the ball arrives at the player, when he/she is required to play the ball to an unanticipated spot. As is the case in all other phases of the neuromotor training, the quality of movement is the most important parameter to critique with each drill. From a qualitative standpoint, the player should demonstrate stiffness throughout the thoracolumbar region and power and control through the pelvis with each directional change. In addition, he or she should maintain a low and posteriorly oriented center of mass to optimize leverage in the hamstrings/gluteals compared with the quadriceps and reduce posterior ground reaction forces.
PSYCHOLOGICAL READINESS FOR RETURN TO PLAY
After an injury is sustained, an athlete is often subjected to a range of psychological responses in addition to the functional impairment, including stress, hesitancy, alterations in self-esteem, depression, fear of re-injury, and anxiety.43,109-111 The aforementioned responses are often at their height in the time immediately following an injury and generally subside over time during the rehabilitation process.110 The rates at which athletes experience psychological distress following an injury range between 5% and 19%; the levels are comparable with patients receiving treatment for mental health illness.43 However, these elements may persist, or even increase, in the later stages of the rehabilitation process as the topic of return to play is deliberated.112,113 If these fears are left unresolved, then a significant delay can be incurred during the rehabilitation process, which might ultimately jeopardize the successful return to play.114,115
When athletes have been cleared to return to sport, fear tends to be the most common reason for their decision to not return to play.21,116 The persistence of fear has clinical implications and warrants close monitoring to ensure that the athlete feels adequately supported in the decision to return to sport.117,118 Building the athlete’s confidence by addressing hesitation, lack of confidence, heightened awareness of risk or re-injury, and safe reintegration into athletic participation are important themes identified to encourage a safe return to play.43 A variety of validated tools can be integrated into an existing return-to-play decision-making algorithm (Table 2).118-120
Abbreviations: ACL, anterior cruciate ligament; CNS, central nervous system; CIMT, constraint-induced movement therapy.
Table 2. Self-Report Measurement Tools to Integrate into Return-to-Play Decision-Making Algorithm
Self-report Measurement Tools |
13-item Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia |
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Return to Sport after Injury Scale (ACL-RSI) |
Global Rating Scale (GRS) |
International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) Subjective Knee Evaluation Form |
Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) |
Lysholm Knee Scoring Scale |
Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36) |
Subjective Patient Outcome for Return to Sport (SPORTS) |
Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
By integrating the necessary screening of patients for kinesiophobia and assessing patient expectations after enduring an ACL injury, clinicians may be able to identify patients who are at risk for poorer functional outcomes. A consideration of psychosocial elements such as activity avoidance, fear of movement and re-injury, loss of confidence and expectations/assumptions during the continuum of the rehabilitation process, and the decision to return to play may favorably impact the individual’s ability to safely return to sport. It is critical to address both the physical and psychosocial factors during the rehabilitation process to more optimally transition individuals back to their prior level of athleticism.
CONCLUSION
Psychosocial factors may play a role in determining a player’s readiness to return to sport, as well as a potential for re-injury. A number of tests are available for use with this patient population to identify mental deficits that may impact player performance upon return. Additionally, the CNS should be considered as a source of impairment in players with ACL injuries. Current protocols may not fully appreciate the CNS’ impact on the player’s functional outcome. Therefore, an approach that includes CNS neuromotor training with traditional musculoskeletal rehabilitation, which also incorporates cognitive and psychosocial factors, may define an improved paradigm for treating soccer athletes following an ACL injury and assessing return-to-play capability.
ABSTRACT
Soccer players recovering from anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries have better options for treatment today than they did 25 years ago. Surgical techniques have improved, and rehabilitation protocols have evolved considerably. Although the rehabilitation community is doing a better job of treating this patient population, the evidence does demonstrate that both re-injury and return- to-play (RTP) rates are still suboptimal. Most protocols focus on normalizing strength and range of motion (ROM) and achieving limb symmetry with soccer-specific movements. While these factors are certainly prerequisites for returning to the field, their inclusion does not provide a complete picture of the athlete’s presentation. An additional factor that should be prioritized with this patient population is the central nervous system (CNS). Advanced imaging has shown that peripheral deafferentation does occur with musculoskeletal injuries; this ultimately results in cortical reorganization, which makes movement planning more difficult for the player, since simpler tasks must now be processed at higher levels in the CNS. The evidence also shows that the CNS demonstrates plasticity in these cases, so that through focused neuromotor rehabilitation techniques, it is possible to bring movement planning back down to a sub-cortical level. Cognitive issues may also be a factor in preventing the player from returning. Fear of re-injury and diminished confidence can influence the way the player moves on the field, and diminish ability to demonstrate protective kinematics with all soccer-specific tasks. We believe that an approach incorporating traditional musculoskeletal rehabilitation, CNS neuro-motor training, and consideration for cognitive factors, may define an improved paradigm for treating the soccer player and assessing readiness for RTP following ACL injury.
Continue to: Although anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)...
Although anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rehabilitation has evolved considerably over the past 2 decades, the basic paradigm has remained consistent: normalize strength and range of motion, reduce swelling and pain, achieve limb symmetry with functional tasks, and return to sport-specific activities gradually over a 6 to 12-month period. There have been some slight additions to this basic premise, such as evaluating knee and hip mechanics in the frontal plane, but the requirements here are vaguely defined and are typically only evaluated within the context of controlled clinical testing.
It is interesting to note that the typical ACL injury pattern occurs during a normal sport-specific movement, yet most rehabilitation protocols fail to recognize the potential causes of the aberrant movement pattern and how to best modify it so that the risk of repeated stress to the ACL can be minimized. It should be understood that movement occurs through the interaction of 3 discrete factors: the individual, the task being performed, and the environment in which it is performed.1 All of these factors will play a role in how the final movement pattern is produced. For example, a soccer player (individual) may backpedal and pivot to the left 60° and accelerate to sprint after a player moving towards the touchline (task) while receiving instructions from teammates and monitoring the movements of opposing players (environment). A small variance in any 1 of these factors could significantly impact the movement pattern as the player completes the task.
In most rehabilitation programs, each of these factors may be treated in a singular, non-specific manner, but if these factors are not coordinated effectively throughout the program to produce the desired sport-specific movement, a faulty pattern may persist, leaving the player at risk for injury. Current rehabilitation programs seem to have a strong focus on creating stability, mobility, and strength, but these are trained in silos, with an internal focus of control, which only solves the biomechanical equation. Often, it is difficult for the player to coordinate good biomechanics into an efficient, protective movement pattern that is specific to the tasks performed on the field during the normal course of play. The missing link here is the central nervous system (CNS).
Limitations to the current ACL protocols may be that they rely heavily on musculoskeletal rehabilitation and that they have limited emphasis on neurological rehabilitation. As will be discussed later, the CNS has a large impact on the final movement selected by the player. In fact, cognition, perception, and action are the three factors that comprise the individual’s part of the movement paradigm,1 yet rarely are these factors addressed in most ACL rehabilitation programs. These elements are a large part of the movement equation, so it is easy to understand how failing to address these features can lead to poor movement quality and subsequent ACL re-injury.
In addition to central neurological factors, cognitive issues may play a role in the player’s ability to return to sport. Determining optimal readiness for return to play is a difficult task for the medical community, with many variables to consider. Previous research studies have assessed the variability in return to play for various sports, including football, rugby, soccer, skiing, running, and tennis, with return-to-play rates ranging from 18% to 100%.2,3,4-10 The risk of secondary injury may cast doubt and fear on athletes as they contemplate their successful return to play.8,11 Although robust functional testing has become commonplace for determining athlete readiness after injury,12-20 the assessment of psychological readiness, persistent fear, and loss of confidence are often neglected and not as commonly integrated into the return-to-play algorithm.21-24 The purpose of this paper is to assess the various cognitive and central neural factors affecting a soccer player’s ability to recover from an ACL injury and offer suggestions for integrating treatments into the protocols to address these issues.
Continue to: CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEUROPLASTICITY...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEUROPLASTICITY
Despite the vast amount of attention and research focused on the ACL, the re-injury rate still remains quite high. It has been reported that rehabilitation programs that employ traditional neuromotor training produce a re-injury rate as high as 30% after the athlete returns to sport.25-28 The overall rate of sustaining a second ACL injury is 15%11 in all patient populations. For the general population <25 years of age, the re-injury rate is 21%, and for athletes <25 years of age, the re-injury rate rises to 23%.11 With re-injury rates at this level, it is certainly fair to consider and be critical of the current rehabilitation methods being used with this population. One opportunity for improvement lies in the general approach used to rehabilitate ACL-injured patients. Therapy for this injury is protocol-driven, and the fact remains that most protocols prioritize restoration of peripheral systems, with minimal thought given to the cortical control necessary to manage those systems.29,30 When neural factors are considered, it is usually within the context of increasing strength, balance, power, and biomechanical control,31-34 which are certainly important but peripheral factors nonetheless. The missing element in many ACL protocols may be how to best manage the central neural components and cognitive factors associated with this injury.
If the CNS were to receive more consideration in ACL protocols, the opportunity for improved outcomes could be substantial because the CNS has been proven to be a very malleable system, as long as it receives the correct input. The CNS demonstrates neuroplasticity,35 which means that it is capable of reorganization, based on the stimuli that it receives, whether internal or external.36
This is an important consideration in ACL rehabilitation because the ACL graft, while restoring the biomechanical properties to the knee, is not fully capable of producing the same neurosensory properties of the original ACL.37-42This is an important concept to understand because an ACL tear does indeed cause deafferentation in the ascending pathways to the brain.37-40,42-46 This can lead to CNS reorganization and subsequent alterations in efferent output to the periphery.37-40,42-46 Therefore, if a protocol with traditional musculoskeletal principles was used, then the mechanical function of the knee may certainly be remediated, but the neurosensory function will remain in a maladaptive state,47-50 potentially leading to aberrant, non-protective movement strategies and a higher risk of re-injury.
The process of CNS reorganization may begin with the initial ACL injury. A peripheral musculoskeletal injury creates an inflammatory response that results in the arrival of chemical mediators such as histamine, substance P, calcitonin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide at the site of injury.51 As edema accumulates in the joint, tension is applied to the capsule, which may adversely affect proprioception from the receptors located within.45 The interruption of consistent input from the peripheral mechanoreceptors may lead to long-term differentiation of the ascending pathways.52 This information is synthesized at 3 different levels of the CNS (spinal cord, brain stem, and motor cortex) to produce motor output.53-56 Differentiation in the ascending circuitry can cause inhibition of motor neurons at the spinal cord.45Animal research has shown that this differentiation can cause a breakdown in the cuneate nucleus of the brainstem,57which provides sensory information from the upper body, while the gracile nucleus does the same for the lower body. These structures transfer proprioceptive input to the ventral posterior lateral nucleus in the thalamus, where it is then sent to the primary somatosensory cortex.57 In general, the somatosensory, visual, and vestibular systems interpret afferent inputs to control movement, balance, and stability.58,59 In a sport like soccer, where the movement tasks are dynamic and unpredictable, it is easy to see why even a slight deficit in somatosensory processing could disrupt a movement. Valeriani and colleagues42,46 showed that somatosensory-evoked potentials were indeed altered in a cohort of ACL reconstruction (ACLR) subjects, indicating reorganization within the CNS. Additionally, the deafferentation could not be changed by other afferent input coming from the knee or by the new ACL graft placed in the knee.42,46The primary motor cortex has been found to have a substantial network of connectivity with the primary somatosensory cortex, which supports the theory that the motor cortex has a very strong linkage with the peripheral receptors in the joint.60 The ligaments in the joint contain Ruffini, Pacinian, and Golgi receptors, all of which react to changes in the collagen fibers and send information regarding tension, length, speed, acceleration, position, and movement back to the CNS.61-64 Unfortunately, the ascending pathway deafferentation can cause reorganization within the CNS, which makes the feedback provided from the periphery less effective in motor planning.
Ward and colleagues65 have reported that reorganization within the motor cortex is the primary cause of chronic neuromuscular movement deficits in peripheral joint injuries. Researchers have used functional magnetic resonance imaging, transcranial magnetic stimulation, and electroencephalography in ACL patients to demonstrate changes in cortical activity and subsequent CNS reorganization.65 Kapreli and colleagues41 reported that subjects with an ACL injury demonstrated higher cortical activation in the pre-supplementary motor area (pre-SMA). This is a region that is responsible for more complex motor planning.66,67 This area becomes active before the primary motor cortex and is responsible for preparing the final movement pattern that the motor cortex executes.41 As the task becomes more complex, activity in the pre-SMA will increase.41 Additionally, they found that the posterior secondary somatosensory area and posterior inferior temporal gyrus showed increased cortical activity compared with controls.41 Visual planning is processed in the posterior inferior temporal gyrus, and so, it appears that the difficulty in processing somatosensory information due to ascending pathway deafferentation places an increased reliance on the visual system for movement planning.68-70 This was observed while ACL-injured subjects performed a simple knee flexion-extension movement encompassing 40°, indicating the need to incorporate higher central levels of planning for a very simple movement pattern.41 Baumeister and colleagues37,38 also showed that subjects with ACLR had higher levels of cortical activation in the areas of the brain that require attention and that process sensory input. They theorized that this occurred because of reduced efficiency of neural processing at lower levels in the CNS. Despite the higher levels of cortical activity observed, they found that subjects with an ACLR demonstrated proprioceptive testing that was deficient compared with that of controls. Heroux and Tremblay71 also demonstrated that subjects with an ACLR had increased resting motor cortex activity. They believed that this occurred as the motor cortex attempted to maintain neuromotor output to the periphery in the face of diminished afferent input.
Continue to: The reorganization that results in movement planning...
The reorganization that results in movement planning, transitioning from subcortical levels to cortical levels, is a phenomenon that researchers believe can lead to deficiencies even as the athlete has returned to sport. Grooms et al72revealed in a case report that a subject with an ACLR showed higher levels of activity in the crus region of the cerebellum. This area contains corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts that transmit neural input to maintain balance and coordination.73 These changes in the cerebellum, combined with increased motor cortex activity, are thought to be indicative of a global neural strategy that uses higher levels of the CNS, as opposed to subcortical processing.72
The current research makes a clear and compelling argument for the importance of CNS reorganization after an ACL injury, placing increased reliance on higher cortical levels of control, as well as the visual system to coordinate balance and movement. It is thought that this reorganized method of neural transmission can then become imprinted within the CNS, if not corrected.35,74 If this is the case, then traditional strength programs may not be sufficient to restore these connections to their pre-injury level. If the CNS has the ability to reorganize based on the aberrant input that it receives from the periphery, then it also certainly has the potential to adapt to more specific structured input via the ascending afferent pathways.41,45 The rehabilitation program, however, needs to be structured specifically to target the reorganized regions of the brain. There needs to be an emphasis on rehabilitating not only the peripheral neuromotor structures but also the CNS.75
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM REHABILITATION PRINCIPLES
For a neurological rehabilitation to be successful, the interventions need to be repetitive and task-specific, involve learning, employ whole and part practice, and transition from using an internal to an external focus of control.76Movements that are repetitive, but which lack structured learning and skill, have been shown to have no effect on inducing neuroplastic changes in the primary motor cortex.77,78 However, using neurological rehabilitation techniques that facilitate the acquisition of new motor skills by the CNS have been shown to cause neuroplastic adaptation in the motor cortex.79-85 This occurs because neuroplasticity is determined by experience and practice.78 The CNS operates on cues received in the ascending tracts by mechanoreceptors in the joint. If a new movement pattern is being learned by the athlete, then this new afferent input received from the periphery will start to initiate reorganization in the higher learning centers. If this occurs with optimal repetition and precision, then a positive reorganization can take place within the CNS that results in a higher percentage of motor planning and control being filtered down to a subcortical level. Essentially, the movements become instinctive, which is crucial in athletics, where attention in higher cortical areas is frequently diverted to external aspects of the competition and not solely used to focus on movement.
This is why shifting neurological rehabilitation from an internal focus of control to an external focus of control is paramount. While using an internal focus of control is required early in rehabilitation to enable the athlete to understand the specific tasks required in a composite movement, a gradual transition to an external focus of control is necessary as the athlete begins to perform tasks that are more soccer-specific. This autonomous stage of motor learning is crucial because it transfers the burden of motor planning from higher to lower levels of the CNS and frees up the pre-SMA and primary motor cortex to handle more complex patterns.58,86-88
Continue to: ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RISK POTENTIAL IN SOCCER PLAYERS...
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RISK POTENTIAL IN SOCCER PLAYERS
If a comprehensive neuromotor rehabilitation program is to be used effectively with soccer athletes, then the first priority is to define how the players should move, so that they can demonstrate protective kinematics with all soccer-specific tasks and minimize stress to the ACL. As the ideal movement pattern becomes autonomous, then it should be trained within the context of a dynamic environment; remembering that environmental changes have a large impact on the final movement pattern selected by the individual. Brophy et al89 evaluated videos of non-contact ACL injuries in male and female soccer players and determined that 45% occurred while cutting, 25% while landing, and 16% during deceleration. These 3 patterns represent 86% of the ACL injuries observed and offer an opportunity for evaluation and treatment with specific central neuromotor rehabilitation techniques.
The foundational movement patterns for the soccer player should focus on producing leverage that minimizes stress to the ACL during the 3 primary tasks outlined above. To achieve this, it is necessary to reduce posterior ground reaction forces at the hip and knee joint during these movements. There is a high correlation between the magnitude of the posterior ground reaction force, and anterior tibial shear, and subsequent displacement.90,91 This stress can be reduced by increasing the hip and knee flexion angles during soccer-specific movements that involve pivoting, decelerating, and landing from a jump in a unipedal stance.92
This phenomenon can be explained by observing changes in the ACL elevation angle, hamstring insertion angle, and patella tendon-tibial tuberosity insertion angle. As the knee moves into flexion, the ACL takes on a more parallel orientation to the tibia, and its fibers are better able to resist elastic deformation accompanied by a posterior ground reaction force.93,94 The quadriceps will produce less anterior translation on the tibia because the patella tendon insertion angle is reduced relative to the longitudinal axis of the tibia, and the mechanical advantage of the quadriceps is decreased.95 Lastly, the hamstrings will be able to provide better leverage posteriorly because the resultant force trends toward a more parallel orientation to the tibial plateau, which enables the player to counter, more effectively, the posterior ground reaction force and the anterior pull directed by the quadriceps.95
This theory is supported by the work of Li and colleagues,96 who showed that there is an inverse relationship between knee flexion angle and ACL loading. In their study, they applied a constant quadriceps force of 200 N at 15°, 30°, and 60° angles. The anterior shear force was obviously the highest at 15° and reduced by 20% at 30° and 60% at 60°. When hamstrings co-contraction was added, there was an additional 30% reduction in anterior shear at 15° and 50% at 30° and 60°. From a more flexed position, the hamstrings can increase joint compression and reduce the anterior translation by allowing the concave medial tibial plateau to limit the anterior drawer effect and absorb the forces that occur with excessive anterior shear, internal rotation, and valgus loads.97 As the knee flexion angle approximates 60°, the hamstring leverage is increased, and the quadriceps leverage is diminished to the point where its ability to produce anterior tibial translation is neutralized.98 Daniel and colleagues98 referred to this as the quadriceps neutral angle.
For soccer-specific movements that are potentially injurious to the ACL, it may then be beneficial to create a default movement pattern at the knee that approximates this value. In keeping with the information presented in this paper, it will be important to have the player reproduce this angle consistently during activities that involve pivoting, decelerating, and landing from a jump within the context of match play. This will certainly require that segments located both proximal and distal to the knee are able to function within specific parameters so that a cohesive protective synergy is produced throughout the lower quarter which minimizes posterior ground reaction forces and is protective of the ACL. This is where structured neuromotor training that is able to modulate networks within the CNS may be beneficial.
Continue to: CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TREATMENT TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOCCER PLAYER...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TREATMENT TECHNIQUES FOR THE SOCCER PLAYER
The ultimate goal is to create a foundational movement pattern that optimizes leverage and is protective of the ACL during decelerating, pivoting, and landing in a unipedal stance from a jump. The composite segments that are necessary to achieve this include local core stability to create lumbopelvic stiffness, and global core activation to enhance posterior chain stability. This should enable the player to feel more balanced when placing the pelvis in a more posterior and inferior position while still maintaining the trunk in a position that is parallel with the tibia, as the knee is flexed to an approximate 60° angle (Figure 1). From a frontal plane perspective, the acetabulum should bisect the malleoli of the stance leg, with a neutral tibiofemoral joint alignment (Figure 1).

The neuromotor training for the composite segments of this movement can begin in the “acute postoperative phase” (Table 1). Because the surgical repair will limit the player’s capabilities in this stage, this is a good time to break down the foundational movement pattern into its component parts and ensure that the CNS receives a high number of quality repetitions of parts. In this phase, the player may begin an isolated training for the transversus abdominis, multifidus, and pubococcygeus. This can start in a supine position using biofeedback with an isometric contraction, progress to a standing position, and incorporate deep core activation with stance-phase gait training, mini squats, and lunge variations. This phase will require an abundance of visual and verbal feedback with an internal focus of control as the player gets used to activating the deep core and quad/hip synergy during functional lower extremity movements. Even in this early phase, the player should look to minimize anterior and/or posterior pelvic tilting and maintain a stiff thoracolumbar segment that remains parallel with the tibia during all functional movements.
Table 1. Adjunct CNS Treatment Principles for ACL Reconstruction in Soccer Athletes
Phase | Goal | CNS Rehabilitation Techniques |
Acute postoperative | Local core activation with weightbearing exercise. Produce trunk stiffness with lower extremity movements. | High repetitions. Verbal or tactile cues. Internal focus of control. Partial practice. |
Subacute postoperative | Lumbopelvic, foot or ankle, and posterior chain segments learn to participate in movement effectively. | Requires higher levels of cortical planning. Internal focus of control. CIMT. |
Static stability | Able to adopt foundational movement pattern consistently with vision eliminated. | Somatosensory vs visual processing. Partial-to-whole practice. Use internal and/or external focus of control. |
Dynamic stability | Able to perform plyometrics in a single-leg position using foundational movement pattern with subcortical processing. | Increase velocity with movement challenges. Occlude or eliminate vision. Heavy reliance on an external focus of control. Prioritize movement quality. |
Dynamic agility | Pivoting, decelerating, and landing are performed with hip flexion/knee flexion synergy, trunk stiffness, and posterior chain activation. | Unanticipated movement challenges. Whole practice. Ball reaction drills with vision obstructed or occluded. Contact drills with vision obstructed or occluded. Use external focus of control to include soccer-specific tasks. |
Abbreviations: ACL, anterior cruciate ligament; CNS, central nervous system; CIMT, constraint-induced movement therapy.
As the player moves into the “subacute postoperative phase” (Table 1). He or she will continue to use an internal focus of control to activate the local/global core synergy with functional movements progressing from double-leg, to single-leg positions. Partial practice, instead of whole practice, is still the predominant theme of the neural training process. In this phase, the knee and hip flexion angles can increase, and the player’s trunk and pelvic position should be critiqued in a single-leg position so that the trunk remains parallel with the tibia in the sagittal plane with a slight forward hip hinge. The pelvis should remain level throughout single-leg stance to ensure adequate activation of the lateral hip stabilizers. This is the stage where the player can learn to isolate closed kinetic chain hip rotation for pivoting, and so, single-leg hip internal and external rotation drills are useful, both with and without resistance. Skill acquisition is crucial in this phase because the patterns that the CNS adopts will form the foundation for more dynamic patterns that will occur in the later soccer-specific stages. Higher levels of cortical planning are still needed in this phase. For this reason, it is important that poor quality repetitions are recognized by the player and clinician so that he or she can learn to perform them correctly, albeit still with an internal focus of control. This is also a good time to begin to employ constraint-induced movement therapy as the player is able to replicate the desired pattern with more precision. For example, by eliminating the use of the upper extremities as a source of balance, the CNS is forced to program alternate synergies such as the lumbopelvic, and foot and ankle segments to maintain the desired alignment.
The “lower quarter static stability phase” (Table 1) marks a point where it may be useful to use direct strategies that have the capability to change CNS efferent owutput from a primary reliance on the visual processing areas in the posterior-inferior temporal gyrus back to the somatosensory area. It is critical that the player is able to make this transition in cortical reorganization and control, because ACL-injured subjects have been shown to have balance scores similar to healthy controls when they are able to use their vision, but this is reduced when vision is taken away.99-105 Their balance will diminish even further if vision is modulated during more complex landing and pivoting maneuvers.99-105 This may certainly explain why defending is a riskier task for ACL-injured players89 as their visual system is focused more on tracking a player than attending to precision with movement planning.
To enhance this cortical reorganization within the context of soccer-specific movements, it is useful to start from a foundational single-leg position, with the knee approximating 60° of flexion and the trunk parallel to the tibia. In the frontal plane, the pelvis should be level, the trunk vertical, and the acetabulum bisecting the malleoli of the stance leg (Figure 1). The player may initially work on getting into this foundational position with vision either partially obstructed using stroboscopic eyewear or completely obstructed if this equipment is unavailable.106-108 The pattern can be progressed by constraining the upper extremities to force reliance on the lumbopelvic and foot/ankle strategies for balance. Head and/or trunk turns can be added to simulate the external focus of control that is required with movement in soccer. These should progress from slow to fast and anticipated to unanticipated as the player demonstrates competence in maintaining stability at each segment within the foundational stance position. Once this is in play, a ball should be introduced into the drills. As the player maintains the foundational position with vision diminished and upper extremities constrained, they should attempt to reach for or trap a ball from this position. If vision is completely obstructed, then the player can be instructed to open his/her eyes just as the ball arrives to induce a reactive response. Again, quality repetitions are essential for learning to occur, and subsequent skill acquisition to take place in the CNS; thus, close scrutiny should be paid to the qualitative essence of the movement patterns to ensure pristine biomechanics during this phase.
The “lower quarter dynamic stability phase” (Table 1) should continue with the same neuromotor training principles employed in the previous phase, except that the drills will now involve plyometrics. The player should ultimately progress from double-leg, to single-leg jumps and then linear to diagonal. Vision should still be obstructed and upper extremities constrained to channel the lumbopelvic region for force production and balance. Movement quality in the foundational position remains paramount with these drills to ensure that skill acquisition is occurring and injury risk is being mitigated. An external focus of control can be introduced by applying an unanticipated perturbation during a jump. Additional learning opportunities should include unanticipated head and trunk turns while landing in a unipedal stance from a jump. The task can be made more specific by having the player trap a pass while doing linear or diagonal single-leg hop progressions. In this manner, the player’s CNS can become reorganized to program the requisite synergies to maintain a protective foundational position on the stance leg, as the contralateral limb is required to perform work that is far outside the player’s base of support.
Continue to: The final segment of the CNS neuromotor rehabilitation program...
The final segment of the CNS neuromotor rehabilitation program is the “lower quarter dynamic agility phase” (Table 1), when the player will learn to perform an unanticipated directional change in a foundational position for the pivot leg. The player can begin this phase by initiating sprint-deceleration-pivot efforts, progressing at 45°, 90°, 120°, and 180° turns. This should be trained in both a forward and backpedal position. Close attention should be paid to the deceleration phase of the sprint-pivot effort, as this will set the player up to demonstrate protective kinematics during the pivot phase of the task. In this phase, the center of mass should become lower and move posteriorly, so that a deeper knee and hip flexion angle, supported by posterior chain synergies, can occur at the pivot point. This is an important skill for the player to acquire, as Cortes and colleagues92 have reported that female collegiate soccer players tend to perform a pivoting task with a more erect trunk position. In the same cohort, they also measured the mean knee flexion angle at initial contact during pivoting to be 24°.92 Movement patterns that reflect an elevated center of mass, with arms abducted away from the trunk, should be discouraged here. The drills can be progressed to have the player react to a command and perform unanticipated pivots within a 5 × 5-meter box to simulate defending. This should be progressed from eyes open and arms unconstrained, to vision disrupted and arms constrained. From here, an external focus of control can be added by playing a ball to the athlete. Vision should be withheld until the instant that the ball arrives at the player, when he/she is required to play the ball to an unanticipated spot. As is the case in all other phases of the neuromotor training, the quality of movement is the most important parameter to critique with each drill. From a qualitative standpoint, the player should demonstrate stiffness throughout the thoracolumbar region and power and control through the pelvis with each directional change. In addition, he or she should maintain a low and posteriorly oriented center of mass to optimize leverage in the hamstrings/gluteals compared with the quadriceps and reduce posterior ground reaction forces.
PSYCHOLOGICAL READINESS FOR RETURN TO PLAY
After an injury is sustained, an athlete is often subjected to a range of psychological responses in addition to the functional impairment, including stress, hesitancy, alterations in self-esteem, depression, fear of re-injury, and anxiety.43,109-111 The aforementioned responses are often at their height in the time immediately following an injury and generally subside over time during the rehabilitation process.110 The rates at which athletes experience psychological distress following an injury range between 5% and 19%; the levels are comparable with patients receiving treatment for mental health illness.43 However, these elements may persist, or even increase, in the later stages of the rehabilitation process as the topic of return to play is deliberated.112,113 If these fears are left unresolved, then a significant delay can be incurred during the rehabilitation process, which might ultimately jeopardize the successful return to play.114,115
When athletes have been cleared to return to sport, fear tends to be the most common reason for their decision to not return to play.21,116 The persistence of fear has clinical implications and warrants close monitoring to ensure that the athlete feels adequately supported in the decision to return to sport.117,118 Building the athlete’s confidence by addressing hesitation, lack of confidence, heightened awareness of risk or re-injury, and safe reintegration into athletic participation are important themes identified to encourage a safe return to play.43 A variety of validated tools can be integrated into an existing return-to-play decision-making algorithm (Table 2).118-120
Abbreviations: ACL, anterior cruciate ligament; CNS, central nervous system; CIMT, constraint-induced movement therapy.
Table 2. Self-Report Measurement Tools to Integrate into Return-to-Play Decision-Making Algorithm
Self-report Measurement Tools |
13-item Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia |
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Return to Sport after Injury Scale (ACL-RSI) |
Global Rating Scale (GRS) |
International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) Subjective Knee Evaluation Form |
Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) |
Lysholm Knee Scoring Scale |
Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36) |
Subjective Patient Outcome for Return to Sport (SPORTS) |
Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
By integrating the necessary screening of patients for kinesiophobia and assessing patient expectations after enduring an ACL injury, clinicians may be able to identify patients who are at risk for poorer functional outcomes. A consideration of psychosocial elements such as activity avoidance, fear of movement and re-injury, loss of confidence and expectations/assumptions during the continuum of the rehabilitation process, and the decision to return to play may favorably impact the individual’s ability to safely return to sport. It is critical to address both the physical and psychosocial factors during the rehabilitation process to more optimally transition individuals back to their prior level of athleticism.
CONCLUSION
Psychosocial factors may play a role in determining a player’s readiness to return to sport, as well as a potential for re-injury. A number of tests are available for use with this patient population to identify mental deficits that may impact player performance upon return. Additionally, the CNS should be considered as a source of impairment in players with ACL injuries. Current protocols may not fully appreciate the CNS’ impact on the player’s functional outcome. Therefore, an approach that includes CNS neuromotor training with traditional musculoskeletal rehabilitation, which also incorporates cognitive and psychosocial factors, may define an improved paradigm for treating soccer athletes following an ACL injury and assessing return-to-play capability.
- Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott MH Motor control: translating research into clinical practice. 4th ed: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, 2012.
- Ardern CL, Webster KE, Taylor NF, Feller JA. Return to the preinjury level of competitive sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: two-thirds of patients have not returned by 12 months after surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(3):538-543. doi:10.1177/0363546510384798.
- Bauer M, Feeley BT, Wawrzyniak JR, Pinkowsky G, Gallo RA. Factors affecting return to play after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a review of the current literature. Phys Sportsmed. 2014;42(4):71-79. doi:10.3810/psm.2014.11.2093.
- Eisenstein ED, Rawicki NL, Rensing NJ, Kusnezov NA, Lanzi JT. Variables afftecting return to play after anterior cruciate ligament injury in the national football league. Orthop J Sports Med. 2016;4(10):2325967116670117.
- Ellman MB, Sherman SL, Forsythe B, LaPrade RF, Cole BJ, Bach BR. Return to play following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(5):283-296. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-13-00183.
- Fabricant PD, Chin CS, Conte S, Conte S, Coleman SH, Pearle AD, Dines JS. Return to play after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in major league baseball athletes. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(5):896-900. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2014.12.008.
- Morris RC, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming BC, Owens BD, Fadale PD. Return to play following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Clin Sports Med. 2016;35:(4):655-668. doi:10.1016/j.csm.2016.05.009.
- Paterno MV, Rauh MJ, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Incidence of second ACL injuries 2 years after primary ACL reconstruction and return to sport. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(7):1567-1573. doi:10.1177/0363546514530088.
- Sclafani MP, Davis CC. Return to play progression for rugby following injury to the lower extremity. A clinical commentary and review of the literature. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016;11(2):302-320.
- Walden M, Hagglund M, Magnusson H, Ekstrand J. ACL injuries in men’s professional football: a 15-year prospective study on time trends and return-to-play rates reveals only 65% of players still play at the top level 3 years after ACL rupture. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(12):744-750. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2015-095952.
- Wiggins AJ, Grandhi RK, Schneider DK, Stanfield D, Webster KE, Myer GD. Risk of secondary injury in younger athletes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(7):1861-1876. doi:10.1177/0363546515621554.
- Arundale AJ, Cummer K, Capin JJ, Zarzycki R, Snyder-Mackler L. Report of the clinical and functional primary outcomes in men of the ACL-SPORTS trial: similar outcomes in men receiving secondary prevention with and without perturbation training 1 and 2 years after ACL reconstruction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(10):2523-2534. doi:10.1007/s11999-017-5280-2.
- Brumitt J, HB, Manske RC, Niemuth PE, Rauh MJ. Lower extremity functional tests and risk of injury in division III collegiate athletes. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013;8:216-227.
- Cacolice PA, Carcia CR, Scibek JS, Phelps AL. The use of functional tests to predict sagittal plane knee kinematics in ncaa-d1 female athlets. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015;10(4):493-504.
- Goodstadt NM, Hunter-Giordano A, Axe MJ, Snyder-Mackler L. Functonal testing to determine readiness to discontinue brace use one year after acl reconstruction. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013;8(2):91-96.
- Herbst E, Hoser C, Hildebrandt C, Raschner C, Hepperger C, Pointner H, Fink C. Functional assessments for decision-making regarding return to sports following ACL reconstruction. Part ll: clinical application of a new test battery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(5):1283-1291. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3546-3.
- Hoog P, Warren M, Smith CA, Chimera NJ. Functional hop tests and tuck jump assessment scores between female division l collegiate athletes participating in high versus low acl injury prone sports: a cross sectional analysis. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016;11(6):945-953.
- Mohammadi F, Salavati M, Akhbari B, Mazaheri M, Mohsen Mir S, Etemadi Y. Comparison of functional outcome measures after ACL reconstruction in competitive soccer players: a randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg, (Am.). 2013;95(14):1271-1277. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.00724.
- Rambaud A, Samozino P, Edouard P. Functional tests can they help in the decision to return to sports after anterior cruciate ligament? Example with hop tests. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59s:e19-ee20. doi:10.1016/j.rehab.2016.07.047.
- Xergia SA, Pappas E, Zampeli F, Georgiou S, Georgoulis AD. Asymmetries in functional hop tests, lower extremity kinematics, and isokinetic strength persist 6 to 9 months following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2013;43(3):154-162. doi:10.2519/jospt.2013.3967.
- Ardern CL, Taylor NF, Feller JA, Webster KE. A systematic review of the psychological factors associated with returning to sport following injury. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(17):1120-1126. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2012-091203.
- Ardern CL, Taylor NF, Feller JA, Whitehead TS, Webster KE. Psychological responses matter in returning to preinjury level of sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(7):1549-1558. doi:10.1177/0363546513489284.
- Christino MA, Fantry AJ, Vopat BG. Psychological aspects of recovery following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(8):501-509. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00173.
- Naghdi S, Nakhostin Ansari N, Farhadi Y, Ebadi S, Entezary E, Glazer D. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Injury-Psychological Readiness to Return to Sport scale to Persian language. Physiother Theory Pract. 2016;32(7):528-535. doi:10.1080/09593985.2016.1221486.
- Hui C, Salmon LJ, Kok A, Maeno S, Linklater J, Pinczewski LA. Fifteen-year outcome of endoscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with patellar tendon autograft for “isolated” anterior cruciate ligament tear. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:89-98. doi:10.1177/0363546510379975.
- Paterno MV, Rauh MJ, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Incidence of contralateral and ipsilateral anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury after primary ACL reconstruction and return to sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2012;22:116-121. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e318246ef9e.
- Paterno MV, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Rauh MJ, Myer GD, Huang B, Hewett TE. Biomechanical measures during landing and postural stability predict second anterior cruciate ligament injury after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and return to sport. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38:1968-1978. doi:10.1177/0363546510376053.
- Wright RW, Dunn WR, Amendola A, Andrish JT, Bergfeld J, Kaeding CC, Marx RG, McCarty EC, Parker RD, Wolcott M, Wolf BR, Spindler KP. Risk of tearing the intact anterior cruciate ligament in the contralateral knee and rupturing the anterior cruciate ligament graft during the first 2 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective MOON cohort study. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:1131-1134. doi:10.1177/0363546507301318.
- Bystrom MG, Rasmussen-Barr E, Grooten WJ. Motor control exercises reduces pain and disability in chronic and recurrent low back pain: a meta-analysis. Spine. 2013;38(6):E350-E358. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31828435fb.
- Macedo LG, Maher CG, Latimer J, McAuley JH. Motor control exercise for persistent nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2009;89(1):9-25. doi:10.2522/ptj.20080103.
- Grindstaff TL, Hammill RR, Tuzson AE, Hertel J. Neuromuscular control training programs and noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injur rates in female athletes: a numbers-needed-to-treat analysis. J Athl Train. 2006;41:450-456.
- Myer GD, Ford KR, Brent JL, Hewett TE. An integrated approach to change the outcome part II: Targeted neuromuscular training techniques to reduce identified ACL injury risk factors. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26:2272-2292. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31825c2c7d.
- Myer GD, Paterno MV, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Neuromuscular training techniques to target deficits before return to sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22:987-1014. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31816a86cd.
- Yoo JH, Lim BO, Ha M, Lee SW, Oh SJ, Lee YS, Kim JG. A meta-analysis of the effect of neuromuscular training on the prevention of the anterior cruciate ligament injury in female athletes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:824-830. doi:10.1007/s00167-009-0901-2.
- Moseley GL, Flor H. Targeting cortical representations in the treatment of chronic pain; a review. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26(6):646-652. doi:10.1177/1545968311433209.
- Cramer SC. Brain repair after stroke. New Engl J Med 2010;362(19):1827-1829. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1003399.
- Baumeister J, Reinecke K, Weiss M. Changed cortical activity after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a joint position paradigm: an EEG study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008;18:473-484. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2007.00702.x.
- Baumeister J, Reinecke K, Schubert M, Weiss M. Altered electrocortical brain activity after ACL reconstruction during force control. J Orthop Res. 2011;29:1383-1389. doi:10.1002/jor.21380.
- Courtney C, Rine RM. Central somatosensory changes associated with improved dynamic balance in subjects with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Gait Posture. 2006;24:190-195. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2005.08.006.
- Courtney C, Rine RM, Kroll P. Central somatosensory changes and altered muscle synergies in subjects with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Gait Posture. 2005;22:69-74. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2004.07.002.
- Kapreli E, Athanasopoulos S, Gliatis J, Papathanasiou M, Peeters R, Strimpakos N, Van Hecke P, Gouliamos A, Sunaert S. Anterior cruciate ligament deficiency causes brain plasticity: a functional MRI study. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37:2419-2426. doi:10.1177/0363546509343201.
- Valeriani M, Restuccia D, Di Lazaro V, Franceschi F, Fabbriciani C, Tonali P. Clinical and neurophysiological abnormalities before and after reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Acta Neurol Scand. 1999;99:303-307. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.1999.tb00680.x.
- Burland JP, Toonstra J, Werner JL, Mattacola CG, Howell DM, Howard JS. Decision to return to sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, Part 1: A qualitative investigation of psychosocial factors. J Athl Train. 2018;53(5):452-463. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-313-16
- Johansson H, Sjolander P, Sojka P. A sensory role for the cruciate ligaments. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;268:161-178.
- Kaprelli E, Athanasopoulos S. The anterior cruciate ligament deficiency as a model of brain plasticity. Med Hypo. 2006;67:645-650. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.01.063.
- Valeriani M, Restuccia D, Di Lazzaro V, Franceschi F, Fabbriciani C, Tonali P. Central nervous system modifications in patients with lesion of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Brain. 1996;119(Pt 5):1751-1762. doi:10.1093/brain/119.5.1751.
- Nyland J, Fisher B, Brad E, Krupp R, Caborn DN. Osseous deficits after anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction: a systematic review with suggestions to improve osseous homeostasis. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1248-1257. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.03.017.
- Nyland J, Klein S, Caborn DN. Lower extremity compensatory neuromuscular and biomechanical adaptations 2 to 11 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1212-1225. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.01.003.
- Paterno MV, Ford KR, Myer GD, Heyl R, Hewett TE. Limb asymmetries in landing and jumping 2 years following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Clin. J Sports Med. 2007;17:258-262. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e31804c77ea.
- Wojtys EM, Huston LJ. Longitudinal effects of anterior cruciate ligament injury and patellar tendon autograft reconstruction on neuromuscular performance. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28:336-344. doi:10.1177/03635465000280030901.
- Levine JD, Dardick SJ, Basbaum AI, Scipio E. Reflex neurogenic inflammation. I. Contribution of the peripheral nervous system to spatially remote inflammatory responses that follow injury. J Neurosci. 1985;5:1380-1386. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-05-01380.1985.
- McNair PJ, Marshall RN, Maguire K, Brown C. Knee joint effusion and proprioception. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995;76:566-568. doi:10.1016/S0003-9993(95)80512-5.
- Jerosch J, Prymka M. Knee joint proprioception in normal volunteers and patients with anterior cruciate ligament tears, taking special account of the effect of a knee bandage. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1996;115:162-166. doi:10.1007/BF00434546.
- Lattanzio PJ, Petrella RJ. Knee proprioception: a review of mechanisms, measurements, and implications of muscular fatigue. Orthopedics. 1998;21:463-470.
- Lephart SM, Pincivero DM, Giraido JL, Fu FH. The role of proprioception in the management and rehabilitation of athletic injuries. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25:130-137. doi:10.1177/036354659702500126.
- Lephart SM, Riemann BL, Fu FH. Introduction to the sensorimotor system. In: Lephart SM, Fu FH, editors. Proprioception and neuromuscular control in joint stability: Champaign (IL): Human Kinetics Publishers, 2000.
- Pelletier R, Higgins J, Bourbonnais D. Is neuroplasticity in the central nervous system the missing link to our understanding of chronic musculoskeletal disorders? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:25. doi:10.1186/s12891-015-0480-y.
- Magill R Motor learning and control: concepts and applications. Boston, MA: WCB/McGraw-hill. 8th ed, 2007.
- Winter DA Biomechanics and motor control of human movement. 4th ed: Hoboken, NJ:Wiley, 2009.
- Hoffman M, Koceja D. Hoffmann reflex profiles and strength rations in postoperative anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients. Int J Neurosci. 2000;104:17-27. doi:10.3109/00207450009035006.
- Duthon VB, Barea C, Abrassart S, Fasel JH, Fritschy D, Ménétrey J. Anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:204-213. doi:10.1007/s00167-005-0679-9.
- Zimny ML. Mechanoreceptors in articular tissues. Am J Anat. 1988;182:16-32. doi:10.1002/aja.1001820103.
- Zimny ML, Schutte M, Dabezies E. Mechanoreceptors in the human anterior cruciate ligament. Anat Rec. 1986;214:204-209. doi:10.1002/ar.1092140216.
- Zimny ML, Wink CS. Neuroreceptors in the tissues of the knee joint. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 1991;1:148-157. doi:10.1016/1050-6411(91)90031-Y.
- Ward S, Pearce AJ, Pietrosimone B, Bennell K, Clark R, Bryant AL. Neuromuscular deficits after peripheral joint injury: a neurophysiological hypothesis. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51(3):327-332. doi:10.1002/mus.24463.
- Ball T, Schreiber A, Feige B, Wagner M, Lücking CH, Kristeva-Feige R. The role of higher-order motor areas in voluntary movement as revealed by high resolution EEG and fMRI. Neuroimage. 1999;10:682-694. doi:10.1006/nimg.1999.0507.
- Nachev P, Wydell H, O’Neill K, Husain M, Kennard C. The role of the pre-supplementary motor area in the control of action. Neuroimage. 2007;36(suppl. 2):T155-TT163. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.03.034.
- Binder JR, Desai RH. The neurobiology of semantic memory. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011;15:527-536. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2011.10.001.
- Bonner MF, Price AR. Where is the anterior temporal lobe and what does it do? J Neurosci. 2013;33:4213-4215. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0041-13.2013.
- Peuskens H, Vanrie J, Verfaillie K, Orban GA. Specificity of regions processing biological motion. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:2864-2875. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04106.x.
- Heroux ME, Tremblay F. Corticomotor excitability associated with unilateral knee dysfunction secondary to anterior cruciate ligament injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:823-833. doi:10.1007/s00167-006-0063-4.
- Grooms D, Page S, Onate J. Brain activation for knee movement measured days before second anterior cruciate ligament injury: neuroimaging in musculoskeletal medicine. J Athl Train.2015;50(10):1005-1010. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-50.10.02.
- Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD. Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage. 2009;44(2):489-501. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.039.
- Mansour A, Farmer M, Baliki M, Apkarian AV. Chronic pain: the role of learning and brain plasticity. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2014;32:129-139. doi:10.3233/RNN-139003.
- Nyland J, Wera J, Klein S, Caborn DN. Lower extremity neuromuscular compensations during instrumented single leg hop testing 2-10 years following ACL reconstruction. Knee. 2014;21:1191-1197. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2014.07.017.
- Van Vliet PM, Heneghan N. Motor control and the management of musculoskeletal dysfunction. Man Ther. 2006;11(3):208-213. doi:10.1016/j.math.2006.03.009.
- Bayona NA, Bitensky J, Teasell R. Plasticity and reorganization of the uninjured brain. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2005;12:1-10. doi:10.1310/A422-G91U-Q4HB-86XC.
- Remple M, Bruneau R, VandenBerg P, Goertzen C, Kleim JA. Sensitivity of cortical movement representations to motor experience evidence that skilled learning but not strength training induces cortical reorganization. Behav Brain Res. 2001;123:133-141. doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(01)00199-1.
- Jull GA, Falla D, Vicenzino B, Hodges PW. The effect of therapeutic exercise on activation of the deep cervical flexor muscles in people with chronic neck pain. Man Ther. 2009;14:696-701. doi:10.1016/j.math.2009.05.004.
- Karni A, Meyer G, Jezzard P, Adams MM, Turner R, Ungerleider LG. Functional MRI evidence for adult motor cortex plasticity during motor skill learning. Nature. 1995;377:155-158. doi:10.1038/377155a0.
- Koeneke S, Lutz K, Herwig U, Ziemann U, Jäncke L. Extensive training of elementary finger tapping movements changes the pattern of motor cortex excitability. Exp Brain Res. 2006;174:199-209. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0440-8.
- O’Leary S, Falla D, Elliott JM, Jull G. Muscle dysfunction in cervical spine pain: implications for assessment and management. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2009;39:324-333. doi:10.2519/jospt.2009.2872.
- Pascual-Leone A, Nguyet D, Cohen LG, Brasil-Neto JP, Cammarota A, Hallett M. Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new fine motor skills. J Neurophysiol. 1995;74:1037-1045. doi:10.1152/jn.1995.74.3.1037.
- Svensson P, Romaniello A, Wang K, Arendt-Nielsen L, Sessle BJ. One hour of tongue-task training is associated with plasticity in corticomotor control of the human tongue musculature. Exp Brain Res. 2006;173:165-173. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0380-3.
- Tsao H, Druitt TR, Schollum TM, Hodges PW. Motor training of the lumbar paraspinal muscles induces immediate changes in motor coordination in patients with recurrent low back pain. J Pain. 2010;11:1120-1128. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2010.02.004.
- Gokeler A, Banjaminse A, Hewett TE, Paterno MV, Ford KR, Otten E, Myer GD. Feedback techniques to target functional deficits following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: implications for motor control and reduction of second injury risk. Sports. Med. 2013;43:1065-1074. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0095-0.
- Powers CM, Fisher B. Mechanisms underlying ACL injury-prevention training: the brain-behavior relationship. J Athl Train. 2010;45:513-515. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-45.5.513.
- Seidler RD, Noll DC. Neuroanatomical correlates of motor acquisition and motor transfer. J Neurophysiol. 2008;99:1836-1845. doi:10.1152/jn.01187.2007.
- Brophy RH, Stepan JG, Silvers HL, Mandelbaum BR. Defending puts the anterior cruciate ligament at risk during soccer: a gender-based analysis. Sports Health. 2015;7:244-249. doi:10.1177/1941738114535184.
- Sell TC, Ferris CM, Abt JP, Tsai YS, Myers JB, Fu FH, Lephart SM. Predictors of proximal tibia anterior shear force during a vertical stop-jump. J Orthop Sports Res. 2007;25:1589-1597. doi:10.1002/jor.20459.
- Yu B, Lin CF, Garrett WE. Lower extremity biomechanics during the landing of a stop-jump task. Clin Bio. 2006;21:297-305. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2005.11.003.
- Cortes N, Onate J, Van Lunen B. Pivot task increases knee frontal plane loading compared with sidestep and drop-jump. J Sports Sci. 2011;29:83-92. doi:10.1080/02640414.2010.523087.
- Blackburn JT, Padua DA. Influence of trunk flexion on hip and knee joint kinematics during a controlled drop landing. Clin Biomech. 2008;23:313-319. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2007.10.003.
- Li G, Papannagari R, DeFrate LE, Yoo JD, Park SE, Gill TJ. Comparison of the ACL and ACL graft forces before and after ACL reconstruction: an in-vitro robotic investigation. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:267-274. doi:10.1080/17453670610046019.
- Zheng N, Fleisig GS, Escamilla RF, Barrentine SW. An analytical model of the knee for estimation of internal forces during exercise. J Biomech. 1998;31:963-967. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(98)00056-6.
- Li G, Rudy TW, Sakan M, Kanamori A, Ma CB, Woo SL. The importance of quadriceps and hamstring muscle loading on knee kinematics and in situ forces in the ACL. J Biomech. 1999;32:395-400. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(98)00181-X.
- Hewett TE, Myer GD, Ford KR. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries in female athletes, Part l: Mechanisms and risk factors. Am J Sports Med.2006;34:299-311. doi:10.1177/0363546505284183.
- Daniel DM, Stone ML, Barnett P. Use of the quadriceps active test to diagnose to diagnose posterior cruciate ligament disruption and measure posterior laxity of the knee. J Bone Jt SurA, (Am.).1988;70:386-391.
- Hoffman M, Schrader J, Koceja D. An investigation of postural control in postoperative anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients. J Athl Train. 1999;34:130-136.
- Mattacola CG, Perrin DH, Gansneder BM, Gieck JH, Saliba EN, McCue FC. Strength, functional outcome, and postural stability after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Athl Train.2002;37:262-268.
- McLean SG, Lipfert SW, van den Boget AJ. Effect of gender and defensive opponent on the biomechanics of sidestep cutting. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36:1008-1016. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000128180.51443.83.
- McLean SG, Neal RJ, Myers PT, Walters MR. Knee joint kinematics during the sidestep cutting maneuver: potential for injury in women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31:959-968. doi:10.1097/00005768-199907000-00007.
- O’Connell M, George K, Stock D. Postural sway and balane testing: a comparison of normal and anterior cruciate ligament deficient knees. Gait Posture. 1998;8:136-142. doi:10.1016/S0966-6362(98)00023-X.
- Okuda K, Abe N, Katayama Y, Senda M, Kuroda T, Inoue H. Effect of vision on postural sway in anterior cruciate ligament injured knees. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10:277-283. doi:10.1007/s00776-005-0893-9.
- Swanik CB, Lephart SM, Giraldo JL, Demont RG, Fu FH. Reactive muscle firing of anterior cruciate ligament-injured females during functional activities. J Athl Train. 1999;34:121-129.
- Bennett S, Ashford D, Rioja N, Elliott D. Intermittent vision and one-handed catching: the effect of general and specific task experience. J Mot Behav. 2004;36:442-449. doi:10.3200/JMBR.36.4.442-449.
- Bennett SJ, Elliott D, Weeks DJ, Keil D. The effects of intermittent vision on prehension under binocular and monocular viewing. Mot Contr. 2003;7:46-56. doi:10.1123/mcj.7.1.46.
- Grooms D, Appelbaum G, Onate J. Neuroplasticity following anterior cruciate ligament injury: a framework for visual-motor training approaches in rehabilitation. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.2015;45(5):381-393. doi:10.2519/jospt.2015.5549.
- Ardern CL. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction-not exactly a one-way ticket back to the preinjury level: a review of contextual factors affecting return to sport after surgery. Sports Health.2015;7(3):224-230. doi:10.1177/1941738115578131.
- Hsu CJ, Meierbachtol A, George SZ, Chmielewski TL. Fear of reinjury in athletes. Sports Health.2017;9(2):162-167. doi:10.1177/1941738116666813.
- Medvecky MJ, Nelson S. Kinesiophobia and return to sports after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Conn Med. 2015;79(3):155-157.
- Chmielewski TL, ZG, Lentz TA, Tillman SM, Moser MW, Indelicato PA, George SZ. Longitudinal changes in psychosocial factors and their association with knee pain and function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Phys Ther. 2011;91:1355-1366. doi:10.2522/ptj.20100277.
- Clement D, Arvinen-Barrow M, Fetty T. A-BM, Fetty T. Psychosocial responses during different phases of sport-injury rehabilitation: a qualitative study. J Athl Train. 2014;50:95-104. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-49.3.52.
- Te Wierike SC, van der Sluis A, van den Akker-Scheek I, Elferink-Gemser MT, Visscher C. Psychosocial factors influencing the recovery of athletes with anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013;23(5):527-540. doi:10.1111/sms.12010.
- Wiese-Bjornstal DM. Psychology and socioculture affect injury risk, response, and recovery in high-intensity athletes: a consensus statement. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010;20(Suppl. 2):103-111. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01195.x.
- Crossman J, GL, Jamieson J. The emotional responses of injured athletes. NZ J Sports Med. 1995;23:1-2.
- Hambly K. The use of the tegner activity scale for articular cartilage repair of the knee: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(4):604-614. doi:10.1007/s00167-010-1301-3.
- Hambly K, Griva K. IKDC or KOOS: which one captures symptoms and disabilities most important to patients who have undergone initial anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction? Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(7):1395-1404. doi:10.1177/0363546509359678.
- Archer K, Reinke E, Huston LJ, Bird M, Scaramuzza E, Coronado R, Haug C, Vanston S, Spindler KP. Impact of preoperative expectations and fear of movement on return to sport and KOOS scores at 6 months following ACL reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2015;3(7 suppl.2):2325967115S2325900113. doi:10.1177/2325967115S00113.
- Zarzycki R, Failla M, Arundale AJH, Capin JJ, Snyder-Mackler L. Athletes with a positive psychological response to return to sport training have better outcomes one and two years after ACL reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(7 suppl.6):2325967117S2325900324. doi:10.1177/2325967117
- Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott MH Motor control: translating research into clinical practice. 4th ed: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, 2012.
- Ardern CL, Webster KE, Taylor NF, Feller JA. Return to the preinjury level of competitive sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: two-thirds of patients have not returned by 12 months after surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(3):538-543. doi:10.1177/0363546510384798.
- Bauer M, Feeley BT, Wawrzyniak JR, Pinkowsky G, Gallo RA. Factors affecting return to play after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a review of the current literature. Phys Sportsmed. 2014;42(4):71-79. doi:10.3810/psm.2014.11.2093.
- Eisenstein ED, Rawicki NL, Rensing NJ, Kusnezov NA, Lanzi JT. Variables afftecting return to play after anterior cruciate ligament injury in the national football league. Orthop J Sports Med. 2016;4(10):2325967116670117.
- Ellman MB, Sherman SL, Forsythe B, LaPrade RF, Cole BJ, Bach BR. Return to play following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(5):283-296. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-13-00183.
- Fabricant PD, Chin CS, Conte S, Conte S, Coleman SH, Pearle AD, Dines JS. Return to play after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in major league baseball athletes. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(5):896-900. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2014.12.008.
- Morris RC, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming BC, Owens BD, Fadale PD. Return to play following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Clin Sports Med. 2016;35:(4):655-668. doi:10.1016/j.csm.2016.05.009.
- Paterno MV, Rauh MJ, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Incidence of second ACL injuries 2 years after primary ACL reconstruction and return to sport. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(7):1567-1573. doi:10.1177/0363546514530088.
- Sclafani MP, Davis CC. Return to play progression for rugby following injury to the lower extremity. A clinical commentary and review of the literature. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016;11(2):302-320.
- Walden M, Hagglund M, Magnusson H, Ekstrand J. ACL injuries in men’s professional football: a 15-year prospective study on time trends and return-to-play rates reveals only 65% of players still play at the top level 3 years after ACL rupture. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(12):744-750. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2015-095952.
- Wiggins AJ, Grandhi RK, Schneider DK, Stanfield D, Webster KE, Myer GD. Risk of secondary injury in younger athletes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(7):1861-1876. doi:10.1177/0363546515621554.
- Arundale AJ, Cummer K, Capin JJ, Zarzycki R, Snyder-Mackler L. Report of the clinical and functional primary outcomes in men of the ACL-SPORTS trial: similar outcomes in men receiving secondary prevention with and without perturbation training 1 and 2 years after ACL reconstruction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(10):2523-2534. doi:10.1007/s11999-017-5280-2.
- Brumitt J, HB, Manske RC, Niemuth PE, Rauh MJ. Lower extremity functional tests and risk of injury in division III collegiate athletes. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013;8:216-227.
- Cacolice PA, Carcia CR, Scibek JS, Phelps AL. The use of functional tests to predict sagittal plane knee kinematics in ncaa-d1 female athlets. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015;10(4):493-504.
- Goodstadt NM, Hunter-Giordano A, Axe MJ, Snyder-Mackler L. Functonal testing to determine readiness to discontinue brace use one year after acl reconstruction. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013;8(2):91-96.
- Herbst E, Hoser C, Hildebrandt C, Raschner C, Hepperger C, Pointner H, Fink C. Functional assessments for decision-making regarding return to sports following ACL reconstruction. Part ll: clinical application of a new test battery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(5):1283-1291. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3546-3.
- Hoog P, Warren M, Smith CA, Chimera NJ. Functional hop tests and tuck jump assessment scores between female division l collegiate athletes participating in high versus low acl injury prone sports: a cross sectional analysis. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2016;11(6):945-953.
- Mohammadi F, Salavati M, Akhbari B, Mazaheri M, Mohsen Mir S, Etemadi Y. Comparison of functional outcome measures after ACL reconstruction in competitive soccer players: a randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg, (Am.). 2013;95(14):1271-1277. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.00724.
- Rambaud A, Samozino P, Edouard P. Functional tests can they help in the decision to return to sports after anterior cruciate ligament? Example with hop tests. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59s:e19-ee20. doi:10.1016/j.rehab.2016.07.047.
- Xergia SA, Pappas E, Zampeli F, Georgiou S, Georgoulis AD. Asymmetries in functional hop tests, lower extremity kinematics, and isokinetic strength persist 6 to 9 months following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2013;43(3):154-162. doi:10.2519/jospt.2013.3967.
- Ardern CL, Taylor NF, Feller JA, Webster KE. A systematic review of the psychological factors associated with returning to sport following injury. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(17):1120-1126. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2012-091203.
- Ardern CL, Taylor NF, Feller JA, Whitehead TS, Webster KE. Psychological responses matter in returning to preinjury level of sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(7):1549-1558. doi:10.1177/0363546513489284.
- Christino MA, Fantry AJ, Vopat BG. Psychological aspects of recovery following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(8):501-509. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00173.
- Naghdi S, Nakhostin Ansari N, Farhadi Y, Ebadi S, Entezary E, Glazer D. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Injury-Psychological Readiness to Return to Sport scale to Persian language. Physiother Theory Pract. 2016;32(7):528-535. doi:10.1080/09593985.2016.1221486.
- Hui C, Salmon LJ, Kok A, Maeno S, Linklater J, Pinczewski LA. Fifteen-year outcome of endoscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with patellar tendon autograft for “isolated” anterior cruciate ligament tear. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:89-98. doi:10.1177/0363546510379975.
- Paterno MV, Rauh MJ, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Incidence of contralateral and ipsilateral anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury after primary ACL reconstruction and return to sport. Clin J Sport Med. 2012;22:116-121. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e318246ef9e.
- Paterno MV, Schmitt LC, Ford KR, Rauh MJ, Myer GD, Huang B, Hewett TE. Biomechanical measures during landing and postural stability predict second anterior cruciate ligament injury after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and return to sport. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38:1968-1978. doi:10.1177/0363546510376053.
- Wright RW, Dunn WR, Amendola A, Andrish JT, Bergfeld J, Kaeding CC, Marx RG, McCarty EC, Parker RD, Wolcott M, Wolf BR, Spindler KP. Risk of tearing the intact anterior cruciate ligament in the contralateral knee and rupturing the anterior cruciate ligament graft during the first 2 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective MOON cohort study. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:1131-1134. doi:10.1177/0363546507301318.
- Bystrom MG, Rasmussen-Barr E, Grooten WJ. Motor control exercises reduces pain and disability in chronic and recurrent low back pain: a meta-analysis. Spine. 2013;38(6):E350-E358. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31828435fb.
- Macedo LG, Maher CG, Latimer J, McAuley JH. Motor control exercise for persistent nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2009;89(1):9-25. doi:10.2522/ptj.20080103.
- Grindstaff TL, Hammill RR, Tuzson AE, Hertel J. Neuromuscular control training programs and noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injur rates in female athletes: a numbers-needed-to-treat analysis. J Athl Train. 2006;41:450-456.
- Myer GD, Ford KR, Brent JL, Hewett TE. An integrated approach to change the outcome part II: Targeted neuromuscular training techniques to reduce identified ACL injury risk factors. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26:2272-2292. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31825c2c7d.
- Myer GD, Paterno MV, Ford KR, Hewett TE. Neuromuscular training techniques to target deficits before return to sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22:987-1014. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31816a86cd.
- Yoo JH, Lim BO, Ha M, Lee SW, Oh SJ, Lee YS, Kim JG. A meta-analysis of the effect of neuromuscular training on the prevention of the anterior cruciate ligament injury in female athletes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:824-830. doi:10.1007/s00167-009-0901-2.
- Moseley GL, Flor H. Targeting cortical representations in the treatment of chronic pain; a review. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26(6):646-652. doi:10.1177/1545968311433209.
- Cramer SC. Brain repair after stroke. New Engl J Med 2010;362(19):1827-1829. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1003399.
- Baumeister J, Reinecke K, Weiss M. Changed cortical activity after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a joint position paradigm: an EEG study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008;18:473-484. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2007.00702.x.
- Baumeister J, Reinecke K, Schubert M, Weiss M. Altered electrocortical brain activity after ACL reconstruction during force control. J Orthop Res. 2011;29:1383-1389. doi:10.1002/jor.21380.
- Courtney C, Rine RM. Central somatosensory changes associated with improved dynamic balance in subjects with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Gait Posture. 2006;24:190-195. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2005.08.006.
- Courtney C, Rine RM, Kroll P. Central somatosensory changes and altered muscle synergies in subjects with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Gait Posture. 2005;22:69-74. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2004.07.002.
- Kapreli E, Athanasopoulos S, Gliatis J, Papathanasiou M, Peeters R, Strimpakos N, Van Hecke P, Gouliamos A, Sunaert S. Anterior cruciate ligament deficiency causes brain plasticity: a functional MRI study. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37:2419-2426. doi:10.1177/0363546509343201.
- Valeriani M, Restuccia D, Di Lazaro V, Franceschi F, Fabbriciani C, Tonali P. Clinical and neurophysiological abnormalities before and after reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Acta Neurol Scand. 1999;99:303-307. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.1999.tb00680.x.
- Burland JP, Toonstra J, Werner JL, Mattacola CG, Howell DM, Howard JS. Decision to return to sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, Part 1: A qualitative investigation of psychosocial factors. J Athl Train. 2018;53(5):452-463. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-313-16
- Johansson H, Sjolander P, Sojka P. A sensory role for the cruciate ligaments. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;268:161-178.
- Kaprelli E, Athanasopoulos S. The anterior cruciate ligament deficiency as a model of brain plasticity. Med Hypo. 2006;67:645-650. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.01.063.
- Valeriani M, Restuccia D, Di Lazzaro V, Franceschi F, Fabbriciani C, Tonali P. Central nervous system modifications in patients with lesion of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Brain. 1996;119(Pt 5):1751-1762. doi:10.1093/brain/119.5.1751.
- Nyland J, Fisher B, Brad E, Krupp R, Caborn DN. Osseous deficits after anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction: a systematic review with suggestions to improve osseous homeostasis. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1248-1257. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.03.017.
- Nyland J, Klein S, Caborn DN. Lower extremity compensatory neuromuscular and biomechanical adaptations 2 to 11 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1212-1225. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.01.003.
- Paterno MV, Ford KR, Myer GD, Heyl R, Hewett TE. Limb asymmetries in landing and jumping 2 years following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Clin. J Sports Med. 2007;17:258-262. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e31804c77ea.
- Wojtys EM, Huston LJ. Longitudinal effects of anterior cruciate ligament injury and patellar tendon autograft reconstruction on neuromuscular performance. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28:336-344. doi:10.1177/03635465000280030901.
- Levine JD, Dardick SJ, Basbaum AI, Scipio E. Reflex neurogenic inflammation. I. Contribution of the peripheral nervous system to spatially remote inflammatory responses that follow injury. J Neurosci. 1985;5:1380-1386. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-05-01380.1985.
- McNair PJ, Marshall RN, Maguire K, Brown C. Knee joint effusion and proprioception. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995;76:566-568. doi:10.1016/S0003-9993(95)80512-5.
- Jerosch J, Prymka M. Knee joint proprioception in normal volunteers and patients with anterior cruciate ligament tears, taking special account of the effect of a knee bandage. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1996;115:162-166. doi:10.1007/BF00434546.
- Lattanzio PJ, Petrella RJ. Knee proprioception: a review of mechanisms, measurements, and implications of muscular fatigue. Orthopedics. 1998;21:463-470.
- Lephart SM, Pincivero DM, Giraido JL, Fu FH. The role of proprioception in the management and rehabilitation of athletic injuries. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25:130-137. doi:10.1177/036354659702500126.
- Lephart SM, Riemann BL, Fu FH. Introduction to the sensorimotor system. In: Lephart SM, Fu FH, editors. Proprioception and neuromuscular control in joint stability: Champaign (IL): Human Kinetics Publishers, 2000.
- Pelletier R, Higgins J, Bourbonnais D. Is neuroplasticity in the central nervous system the missing link to our understanding of chronic musculoskeletal disorders? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:25. doi:10.1186/s12891-015-0480-y.
- Magill R Motor learning and control: concepts and applications. Boston, MA: WCB/McGraw-hill. 8th ed, 2007.
- Winter DA Biomechanics and motor control of human movement. 4th ed: Hoboken, NJ:Wiley, 2009.
- Hoffman M, Koceja D. Hoffmann reflex profiles and strength rations in postoperative anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients. Int J Neurosci. 2000;104:17-27. doi:10.3109/00207450009035006.
- Duthon VB, Barea C, Abrassart S, Fasel JH, Fritschy D, Ménétrey J. Anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:204-213. doi:10.1007/s00167-005-0679-9.
- Zimny ML. Mechanoreceptors in articular tissues. Am J Anat. 1988;182:16-32. doi:10.1002/aja.1001820103.
- Zimny ML, Schutte M, Dabezies E. Mechanoreceptors in the human anterior cruciate ligament. Anat Rec. 1986;214:204-209. doi:10.1002/ar.1092140216.
- Zimny ML, Wink CS. Neuroreceptors in the tissues of the knee joint. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 1991;1:148-157. doi:10.1016/1050-6411(91)90031-Y.
- Ward S, Pearce AJ, Pietrosimone B, Bennell K, Clark R, Bryant AL. Neuromuscular deficits after peripheral joint injury: a neurophysiological hypothesis. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51(3):327-332. doi:10.1002/mus.24463.
- Ball T, Schreiber A, Feige B, Wagner M, Lücking CH, Kristeva-Feige R. The role of higher-order motor areas in voluntary movement as revealed by high resolution EEG and fMRI. Neuroimage. 1999;10:682-694. doi:10.1006/nimg.1999.0507.
- Nachev P, Wydell H, O’Neill K, Husain M, Kennard C. The role of the pre-supplementary motor area in the control of action. Neuroimage. 2007;36(suppl. 2):T155-TT163. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.03.034.
- Binder JR, Desai RH. The neurobiology of semantic memory. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011;15:527-536. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2011.10.001.
- Bonner MF, Price AR. Where is the anterior temporal lobe and what does it do? J Neurosci. 2013;33:4213-4215. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0041-13.2013.
- Peuskens H, Vanrie J, Verfaillie K, Orban GA. Specificity of regions processing biological motion. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:2864-2875. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04106.x.
- Heroux ME, Tremblay F. Corticomotor excitability associated with unilateral knee dysfunction secondary to anterior cruciate ligament injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:823-833. doi:10.1007/s00167-006-0063-4.
- Grooms D, Page S, Onate J. Brain activation for knee movement measured days before second anterior cruciate ligament injury: neuroimaging in musculoskeletal medicine. J Athl Train.2015;50(10):1005-1010. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-50.10.02.
- Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD. Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage. 2009;44(2):489-501. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.039.
- Mansour A, Farmer M, Baliki M, Apkarian AV. Chronic pain: the role of learning and brain plasticity. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2014;32:129-139. doi:10.3233/RNN-139003.
- Nyland J, Wera J, Klein S, Caborn DN. Lower extremity neuromuscular compensations during instrumented single leg hop testing 2-10 years following ACL reconstruction. Knee. 2014;21:1191-1197. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2014.07.017.
- Van Vliet PM, Heneghan N. Motor control and the management of musculoskeletal dysfunction. Man Ther. 2006;11(3):208-213. doi:10.1016/j.math.2006.03.009.
- Bayona NA, Bitensky J, Teasell R. Plasticity and reorganization of the uninjured brain. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2005;12:1-10. doi:10.1310/A422-G91U-Q4HB-86XC.
- Remple M, Bruneau R, VandenBerg P, Goertzen C, Kleim JA. Sensitivity of cortical movement representations to motor experience evidence that skilled learning but not strength training induces cortical reorganization. Behav Brain Res. 2001;123:133-141. doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(01)00199-1.
- Jull GA, Falla D, Vicenzino B, Hodges PW. The effect of therapeutic exercise on activation of the deep cervical flexor muscles in people with chronic neck pain. Man Ther. 2009;14:696-701. doi:10.1016/j.math.2009.05.004.
- Karni A, Meyer G, Jezzard P, Adams MM, Turner R, Ungerleider LG. Functional MRI evidence for adult motor cortex plasticity during motor skill learning. Nature. 1995;377:155-158. doi:10.1038/377155a0.
- Koeneke S, Lutz K, Herwig U, Ziemann U, Jäncke L. Extensive training of elementary finger tapping movements changes the pattern of motor cortex excitability. Exp Brain Res. 2006;174:199-209. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0440-8.
- O’Leary S, Falla D, Elliott JM, Jull G. Muscle dysfunction in cervical spine pain: implications for assessment and management. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2009;39:324-333. doi:10.2519/jospt.2009.2872.
- Pascual-Leone A, Nguyet D, Cohen LG, Brasil-Neto JP, Cammarota A, Hallett M. Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new fine motor skills. J Neurophysiol. 1995;74:1037-1045. doi:10.1152/jn.1995.74.3.1037.
- Svensson P, Romaniello A, Wang K, Arendt-Nielsen L, Sessle BJ. One hour of tongue-task training is associated with plasticity in corticomotor control of the human tongue musculature. Exp Brain Res. 2006;173:165-173. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0380-3.
- Tsao H, Druitt TR, Schollum TM, Hodges PW. Motor training of the lumbar paraspinal muscles induces immediate changes in motor coordination in patients with recurrent low back pain. J Pain. 2010;11:1120-1128. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2010.02.004.
- Gokeler A, Banjaminse A, Hewett TE, Paterno MV, Ford KR, Otten E, Myer GD. Feedback techniques to target functional deficits following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: implications for motor control and reduction of second injury risk. Sports. Med. 2013;43:1065-1074. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0095-0.
- Powers CM, Fisher B. Mechanisms underlying ACL injury-prevention training: the brain-behavior relationship. J Athl Train. 2010;45:513-515. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-45.5.513.
- Seidler RD, Noll DC. Neuroanatomical correlates of motor acquisition and motor transfer. J Neurophysiol. 2008;99:1836-1845. doi:10.1152/jn.01187.2007.
- Brophy RH, Stepan JG, Silvers HL, Mandelbaum BR. Defending puts the anterior cruciate ligament at risk during soccer: a gender-based analysis. Sports Health. 2015;7:244-249. doi:10.1177/1941738114535184.
- Sell TC, Ferris CM, Abt JP, Tsai YS, Myers JB, Fu FH, Lephart SM. Predictors of proximal tibia anterior shear force during a vertical stop-jump. J Orthop Sports Res. 2007;25:1589-1597. doi:10.1002/jor.20459.
- Yu B, Lin CF, Garrett WE. Lower extremity biomechanics during the landing of a stop-jump task. Clin Bio. 2006;21:297-305. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2005.11.003.
- Cortes N, Onate J, Van Lunen B. Pivot task increases knee frontal plane loading compared with sidestep and drop-jump. J Sports Sci. 2011;29:83-92. doi:10.1080/02640414.2010.523087.
- Blackburn JT, Padua DA. Influence of trunk flexion on hip and knee joint kinematics during a controlled drop landing. Clin Biomech. 2008;23:313-319. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2007.10.003.
- Li G, Papannagari R, DeFrate LE, Yoo JD, Park SE, Gill TJ. Comparison of the ACL and ACL graft forces before and after ACL reconstruction: an in-vitro robotic investigation. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:267-274. doi:10.1080/17453670610046019.
- Zheng N, Fleisig GS, Escamilla RF, Barrentine SW. An analytical model of the knee for estimation of internal forces during exercise. J Biomech. 1998;31:963-967. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(98)00056-6.
- Li G, Rudy TW, Sakan M, Kanamori A, Ma CB, Woo SL. The importance of quadriceps and hamstring muscle loading on knee kinematics and in situ forces in the ACL. J Biomech. 1999;32:395-400. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(98)00181-X.
- Hewett TE, Myer GD, Ford KR. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries in female athletes, Part l: Mechanisms and risk factors. Am J Sports Med.2006;34:299-311. doi:10.1177/0363546505284183.
- Daniel DM, Stone ML, Barnett P. Use of the quadriceps active test to diagnose to diagnose posterior cruciate ligament disruption and measure posterior laxity of the knee. J Bone Jt SurA, (Am.).1988;70:386-391.
- Hoffman M, Schrader J, Koceja D. An investigation of postural control in postoperative anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients. J Athl Train. 1999;34:130-136.
- Mattacola CG, Perrin DH, Gansneder BM, Gieck JH, Saliba EN, McCue FC. Strength, functional outcome, and postural stability after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Athl Train.2002;37:262-268.
- McLean SG, Lipfert SW, van den Boget AJ. Effect of gender and defensive opponent on the biomechanics of sidestep cutting. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36:1008-1016. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000128180.51443.83.
- McLean SG, Neal RJ, Myers PT, Walters MR. Knee joint kinematics during the sidestep cutting maneuver: potential for injury in women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31:959-968. doi:10.1097/00005768-199907000-00007.
- O’Connell M, George K, Stock D. Postural sway and balane testing: a comparison of normal and anterior cruciate ligament deficient knees. Gait Posture. 1998;8:136-142. doi:10.1016/S0966-6362(98)00023-X.
- Okuda K, Abe N, Katayama Y, Senda M, Kuroda T, Inoue H. Effect of vision on postural sway in anterior cruciate ligament injured knees. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10:277-283. doi:10.1007/s00776-005-0893-9.
- Swanik CB, Lephart SM, Giraldo JL, Demont RG, Fu FH. Reactive muscle firing of anterior cruciate ligament-injured females during functional activities. J Athl Train. 1999;34:121-129.
- Bennett S, Ashford D, Rioja N, Elliott D. Intermittent vision and one-handed catching: the effect of general and specific task experience. J Mot Behav. 2004;36:442-449. doi:10.3200/JMBR.36.4.442-449.
- Bennett SJ, Elliott D, Weeks DJ, Keil D. The effects of intermittent vision on prehension under binocular and monocular viewing. Mot Contr. 2003;7:46-56. doi:10.1123/mcj.7.1.46.
- Grooms D, Appelbaum G, Onate J. Neuroplasticity following anterior cruciate ligament injury: a framework for visual-motor training approaches in rehabilitation. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.2015;45(5):381-393. doi:10.2519/jospt.2015.5549.
- Ardern CL. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction-not exactly a one-way ticket back to the preinjury level: a review of contextual factors affecting return to sport after surgery. Sports Health.2015;7(3):224-230. doi:10.1177/1941738115578131.
- Hsu CJ, Meierbachtol A, George SZ, Chmielewski TL. Fear of reinjury in athletes. Sports Health.2017;9(2):162-167. doi:10.1177/1941738116666813.
- Medvecky MJ, Nelson S. Kinesiophobia and return to sports after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Conn Med. 2015;79(3):155-157.
- Chmielewski TL, ZG, Lentz TA, Tillman SM, Moser MW, Indelicato PA, George SZ. Longitudinal changes in psychosocial factors and their association with knee pain and function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Phys Ther. 2011;91:1355-1366. doi:10.2522/ptj.20100277.
- Clement D, Arvinen-Barrow M, Fetty T. A-BM, Fetty T. Psychosocial responses during different phases of sport-injury rehabilitation: a qualitative study. J Athl Train. 2014;50:95-104. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-49.3.52.
- Te Wierike SC, van der Sluis A, van den Akker-Scheek I, Elferink-Gemser MT, Visscher C. Psychosocial factors influencing the recovery of athletes with anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013;23(5):527-540. doi:10.1111/sms.12010.
- Wiese-Bjornstal DM. Psychology and socioculture affect injury risk, response, and recovery in high-intensity athletes: a consensus statement. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010;20(Suppl. 2):103-111. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01195.x.
- Crossman J, GL, Jamieson J. The emotional responses of injured athletes. NZ J Sports Med. 1995;23:1-2.
- Hambly K. The use of the tegner activity scale for articular cartilage repair of the knee: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(4):604-614. doi:10.1007/s00167-010-1301-3.
- Hambly K, Griva K. IKDC or KOOS: which one captures symptoms and disabilities most important to patients who have undergone initial anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction? Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(7):1395-1404. doi:10.1177/0363546509359678.
- Archer K, Reinke E, Huston LJ, Bird M, Scaramuzza E, Coronado R, Haug C, Vanston S, Spindler KP. Impact of preoperative expectations and fear of movement on return to sport and KOOS scores at 6 months following ACL reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2015;3(7 suppl.2):2325967115S2325900113. doi:10.1177/2325967115S00113.
- Zarzycki R, Failla M, Arundale AJH, Capin JJ, Snyder-Mackler L. Athletes with a positive psychological response to return to sport training have better outcomes one and two years after ACL reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(7 suppl.6):2325967117S2325900324. doi:10.1177/2325967117
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- The CNS demonstrates neurophysiological changes during an ACL injury.
- Traditional orthopedic treatment based on principals of musculoskeletal rehabilitation may not be sufficient to address CNS deficits.
- The CNS is neuroplastic and able to change with neuromotor rehabilitation that focuses on the CNS.
- Psychosocial factors may contribute to impairments after an ACL injury, and adversely affect functional outcomes.
- Assessment of RTP criteria should consider psychosocial, and central neural factors to minimize risk, and optimize outcomes.
Vaping soars among American teens in 2018 survey
Teenage use of vaping devices jumped significantly in the past year, with 37% of 12th-grade students reporting any vaping in 2018, compared with 28% in 2017, data announced Dec. 17 from the 2018 Monitoring the Future survey show.
In particular, nicotine vaping use in the 30 days prior to the survey nearly doubled among high school seniors, from approximately 11% in 2017 to 21% in 2018. Nicotine vaping also increased by 7.9% (from 8.2% to 16.1%) among 10th graders and by 2.6% (from 3.5% to 6.1%) among 8th graders, according to the survey results.
Vaping involves using a device such as an e-cigarette to inhale a heated aerosol product that usually contains nicotine but can be used to administer other types of drugs, said Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse at the National Institutes of Health, in a press conference announcing the findings.
The increased prevalence of nicotine vaping in 10th and 12th graders is the largest annual increase in use of any substance recorded by Monitoring the Future, said Richard A. Miech, PhD, MPH, of the Institute for Social Research at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and the principal survey investigator. “Something about this delivery device of vaping seems to really appeal to kids,” he said. The flavorings, concealability of the devices (which can be about the size of a flash drive), and ease of use seem to be contributing to the popularity of vaping, Dr. Miech added.
In addition, marijuana vaping increased significantly across all three grade levels in 2018 from 2017. Within 30 days of the survey, marijuana vaping increased from 4.9% to 7.5% in 12th graders, from 4.3% to 7.0% in 10th graders, and from 1.6% to 2.6% in 8th graders.
A take-home message for clinicians is the need to emphasize to teens that “vaping is not innocuous and not harmless,” said Dr. Miech in a question-and-answer session. Of note, data from multiple studies show that children who vape are about five times more likely to smoke cigarettes, he said.
The vaping devices are manufactured to deliver drugs into the lungs and ultimately high concentrations into the brain – which suggests the use of vaping devices to deliver other types of drugs might increase in the future, Dr. Volkow added.
Use of most other substances, including inhalants, heroin, cocaine, ecstasy, overall marijuana use, alcohol use, and extreme binge drinking remained stable, the researchers said. Cigarette smoking declined slightly among 12th graders but did not change significantly among 8th or 10th graders. Use of prescription opioids and tranquilizers declined in 2018 across all age groups.
“Vaping is reversing hard-fought declines in the number of adolescents who use nicotine,” Dr. Miech said in the news release announcing the results. “These results suggest that vaping is leading youth into nicotine use and nicotine addiction, not away from it.”
The data on vaping and nicotine use among American teens were published in a letter (N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1814130) – with a warning. “These results indicate that the policies in place as of the 2017-2018 school year were not sufficient to stop the spread of nicotine vaping among adolescents,” wrote the authors, led by Dr. Miech. “The rapid entry of new vaping devices on the market ... will require continual updates and modification strategies to keep adolescents from vaping and its associated negative health effects.”
The Monitoring the Future survey tracks annual drug use and drug use attitudes in a nationally representative sample of U.S. students in 8th, 10th, and 12th grades. This year’s survey included 44,482 participants. The survey is funded by a government grant to the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, from the NIH’s NIDA.
Teenage use of vaping devices jumped significantly in the past year, with 37% of 12th-grade students reporting any vaping in 2018, compared with 28% in 2017, data announced Dec. 17 from the 2018 Monitoring the Future survey show.
In particular, nicotine vaping use in the 30 days prior to the survey nearly doubled among high school seniors, from approximately 11% in 2017 to 21% in 2018. Nicotine vaping also increased by 7.9% (from 8.2% to 16.1%) among 10th graders and by 2.6% (from 3.5% to 6.1%) among 8th graders, according to the survey results.
Vaping involves using a device such as an e-cigarette to inhale a heated aerosol product that usually contains nicotine but can be used to administer other types of drugs, said Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse at the National Institutes of Health, in a press conference announcing the findings.
The increased prevalence of nicotine vaping in 10th and 12th graders is the largest annual increase in use of any substance recorded by Monitoring the Future, said Richard A. Miech, PhD, MPH, of the Institute for Social Research at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and the principal survey investigator. “Something about this delivery device of vaping seems to really appeal to kids,” he said. The flavorings, concealability of the devices (which can be about the size of a flash drive), and ease of use seem to be contributing to the popularity of vaping, Dr. Miech added.
In addition, marijuana vaping increased significantly across all three grade levels in 2018 from 2017. Within 30 days of the survey, marijuana vaping increased from 4.9% to 7.5% in 12th graders, from 4.3% to 7.0% in 10th graders, and from 1.6% to 2.6% in 8th graders.
A take-home message for clinicians is the need to emphasize to teens that “vaping is not innocuous and not harmless,” said Dr. Miech in a question-and-answer session. Of note, data from multiple studies show that children who vape are about five times more likely to smoke cigarettes, he said.
The vaping devices are manufactured to deliver drugs into the lungs and ultimately high concentrations into the brain – which suggests the use of vaping devices to deliver other types of drugs might increase in the future, Dr. Volkow added.
Use of most other substances, including inhalants, heroin, cocaine, ecstasy, overall marijuana use, alcohol use, and extreme binge drinking remained stable, the researchers said. Cigarette smoking declined slightly among 12th graders but did not change significantly among 8th or 10th graders. Use of prescription opioids and tranquilizers declined in 2018 across all age groups.
“Vaping is reversing hard-fought declines in the number of adolescents who use nicotine,” Dr. Miech said in the news release announcing the results. “These results suggest that vaping is leading youth into nicotine use and nicotine addiction, not away from it.”
The data on vaping and nicotine use among American teens were published in a letter (N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1814130) – with a warning. “These results indicate that the policies in place as of the 2017-2018 school year were not sufficient to stop the spread of nicotine vaping among adolescents,” wrote the authors, led by Dr. Miech. “The rapid entry of new vaping devices on the market ... will require continual updates and modification strategies to keep adolescents from vaping and its associated negative health effects.”
The Monitoring the Future survey tracks annual drug use and drug use attitudes in a nationally representative sample of U.S. students in 8th, 10th, and 12th grades. This year’s survey included 44,482 participants. The survey is funded by a government grant to the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, from the NIH’s NIDA.
Teenage use of vaping devices jumped significantly in the past year, with 37% of 12th-grade students reporting any vaping in 2018, compared with 28% in 2017, data announced Dec. 17 from the 2018 Monitoring the Future survey show.
In particular, nicotine vaping use in the 30 days prior to the survey nearly doubled among high school seniors, from approximately 11% in 2017 to 21% in 2018. Nicotine vaping also increased by 7.9% (from 8.2% to 16.1%) among 10th graders and by 2.6% (from 3.5% to 6.1%) among 8th graders, according to the survey results.
Vaping involves using a device such as an e-cigarette to inhale a heated aerosol product that usually contains nicotine but can be used to administer other types of drugs, said Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse at the National Institutes of Health, in a press conference announcing the findings.
The increased prevalence of nicotine vaping in 10th and 12th graders is the largest annual increase in use of any substance recorded by Monitoring the Future, said Richard A. Miech, PhD, MPH, of the Institute for Social Research at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and the principal survey investigator. “Something about this delivery device of vaping seems to really appeal to kids,” he said. The flavorings, concealability of the devices (which can be about the size of a flash drive), and ease of use seem to be contributing to the popularity of vaping, Dr. Miech added.
In addition, marijuana vaping increased significantly across all three grade levels in 2018 from 2017. Within 30 days of the survey, marijuana vaping increased from 4.9% to 7.5% in 12th graders, from 4.3% to 7.0% in 10th graders, and from 1.6% to 2.6% in 8th graders.
A take-home message for clinicians is the need to emphasize to teens that “vaping is not innocuous and not harmless,” said Dr. Miech in a question-and-answer session. Of note, data from multiple studies show that children who vape are about five times more likely to smoke cigarettes, he said.
The vaping devices are manufactured to deliver drugs into the lungs and ultimately high concentrations into the brain – which suggests the use of vaping devices to deliver other types of drugs might increase in the future, Dr. Volkow added.
Use of most other substances, including inhalants, heroin, cocaine, ecstasy, overall marijuana use, alcohol use, and extreme binge drinking remained stable, the researchers said. Cigarette smoking declined slightly among 12th graders but did not change significantly among 8th or 10th graders. Use of prescription opioids and tranquilizers declined in 2018 across all age groups.
“Vaping is reversing hard-fought declines in the number of adolescents who use nicotine,” Dr. Miech said in the news release announcing the results. “These results suggest that vaping is leading youth into nicotine use and nicotine addiction, not away from it.”
The data on vaping and nicotine use among American teens were published in a letter (N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1814130) – with a warning. “These results indicate that the policies in place as of the 2017-2018 school year were not sufficient to stop the spread of nicotine vaping among adolescents,” wrote the authors, led by Dr. Miech. “The rapid entry of new vaping devices on the market ... will require continual updates and modification strategies to keep adolescents from vaping and its associated negative health effects.”
The Monitoring the Future survey tracks annual drug use and drug use attitudes in a nationally representative sample of U.S. students in 8th, 10th, and 12th grades. This year’s survey included 44,482 participants. The survey is funded by a government grant to the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, from the NIH’s NIDA.