User login
The importance of family acceptance for LGBTQ youth
It is well established that LGBTQ individuals experience more health disparities compared with their cisgender, heterosexual counterparts. In general, LGBTQ adolescents and young adults have higher levels of depression, suicide attempts, and substance use than those of their heterosexual peers. However, a key protective factor is family acceptance and support. By encouraging families to modify and change behaviors that are experienced by their LGBTQ children as rejecting and to engage in supportive and affirming behaviors, providers can help families to decrease risk and promote healthy outcomes for LGBTQ youth and young adults. 
We all know that a supportive family can make a difference for any child, but this is especially true for LGBTQ youth and is critical during a pandemic when young people are confined with families and separated from peers and supportive adults outside the home. Several research studies show that family support can improve outcomes related to suicide, depression, homelessness, drug use, and HIV in LGBTQ young people. Family acceptance improves health outcomes, while rejection undermines family relationships and worsens both health and other serious outcomes such as homelessness and placement in custodial care. Pediatricians can help their patients by educating parents and caregivers with LGBTQ children about the critical role of family support – both those who see themselves as accepting and those who believe that being gay or transgender is wrong and are struggling with parenting a child who identifies as LGBTQ or who is gender diverse.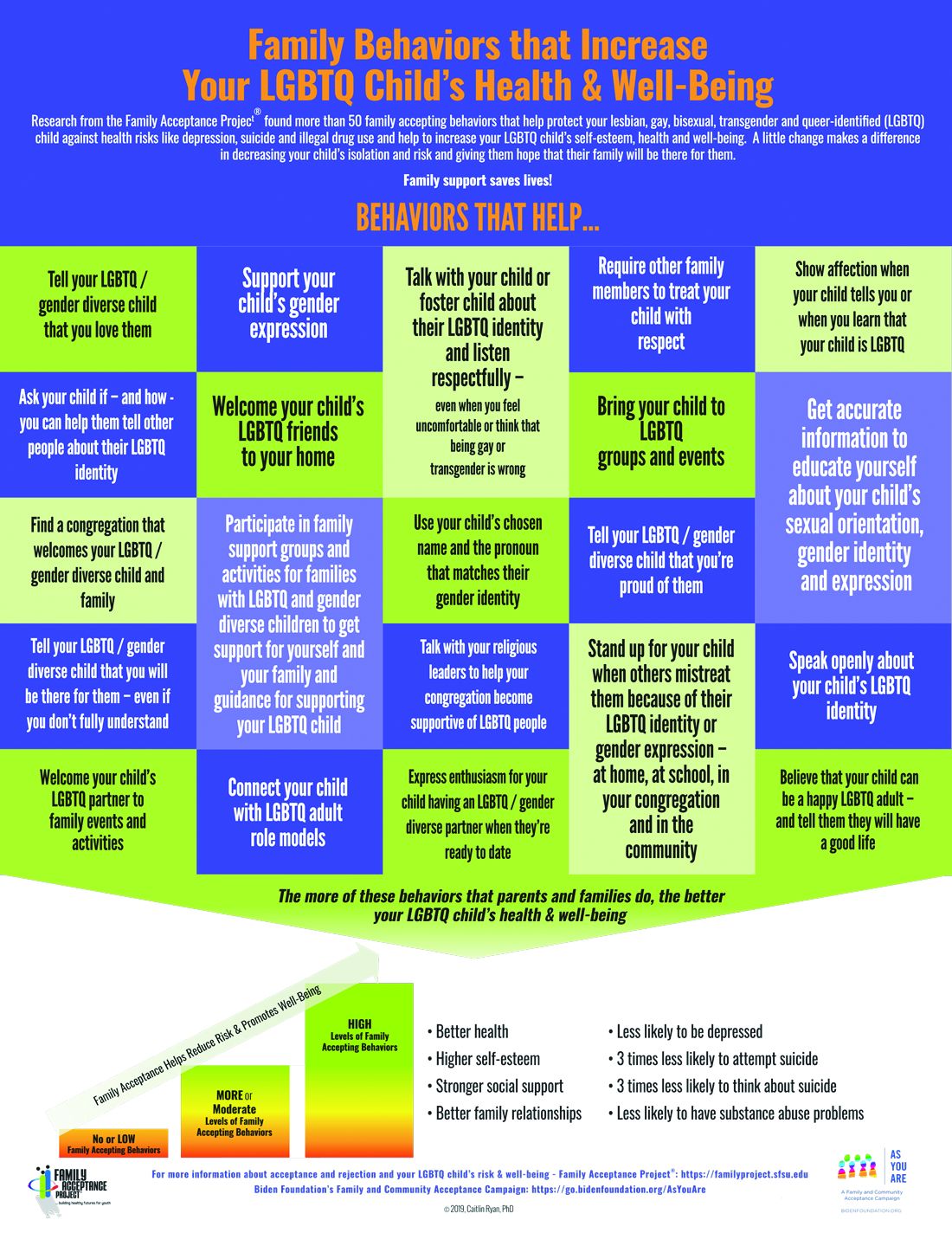
The Family Acceptance Project (FAP) at San Francisco State University conducted the first research on LGBTQ youth and families, developed the first evidence-informed family support model, and has published a range of studies and evidence-based resources that demonstrate the harm caused by family rejection, validate the importance of family acceptance, and provide guidance to increase family support. FAP’s research found that parents and caregivers that engage in rejecting behaviors are typically motivated by care and concern and by trying to protect their children from harm. They believe such behaviors will help their LGBTQ children fit in, have a good life, meet cultural and religious expectations, and be respected by others.1 FAP’s research identified and measured more than 50 rejecting behaviors that parents and caregivers use to respond to their LGBTQ children. Some of these commonly expressed rejecting behaviors include ridiculing and making disparaging comments about their child and other LGBTQ people; excluding them from family activities; blaming their child when others mistreat them because they are LGBTQ; blocking access to LGBTQ resources including friends, support groups, and activities; and trying to change their child’s sexual orientation and gender identity.2 LGBTQ youth experience these and other such behaviors as hurtful, harmful, and traumatic and may feel that they need to hide or repress their identity which can affect their self-esteem, increase isolation, depression, and risky behaviors.3 Providers working with families of LGBTQ youth should focus on shared goals, such as reducing risk and having a happy, healthy child. Most parents love their children and fear for their well-being. However, many are uninformed about their child’s gender identity and sexual orientation and don’t know how to nurture and support them.
In FAP’s initial study, LGB young people who reported higher levels of family rejection had substantially higher rates of attempted suicide, depression, illegal drug use, and unprotected sex.4 These rates were even more significant among Latino gay and bisexual men.4 Those who are rejected by family are less likely to want to have a family or to be parents themselves5 and have lower educational and income levels.6
To reduce risk, pediatricians should ask LGBTQ patients about family rejecting behaviors and help parents and caregivers to identify and understand the effect of such behaviors to reduce health risks and conflict that can lead to running away, expulsion, and removal from the home. Even decreasing rejecting behaviors to moderate levels can significantly improve negative outcomes.5
Caitlin Ryan, PhD, and her team also identified and measured more than 50 family accepting behaviors that help protect against risk and promote well-being. They found that young adults who experience high levels of family acceptance during adolescence report significantly higher levels of self-esteem, social support, and general health with much lower levels of depression, suicidality, and substance abuse.7 Family accepting and supportive behaviors include talking with the child about their LGBTQ identity; advocating for their LGBTQ child when others mistreat them; requiring other family members to treat their LGBTQ child with respect; and supporting their child’s gender identity.5 FAP has developed an evidence-informed family support model and multilingual educational resources for families, providers, youth and religious leaders to decrease rejection and increase family support. These are available in print copies and for download at familyproject.sfsu.edu.
In addition, Dr. Ryan and colleagues1,4,8 recommend the following guidance for providers:
- Ask LGBTQ adolescents about family reactions to their sexual orientation, gender identity, and expression, and refer to LGBTQ community support programs and for supportive counseling, as needed.
- Identify LGBTQ community support programs and online resources to educate parents about how to help their children. Parents need culturally relevant peer support to help decrease rejection and increase family support.
- Advise parents that negative reactions to their adolescent’s LGBTQ identity may negatively impact their child’s health and mental health while supportive and affirming reactions promote well-being.
- Advise parents and caregivers to modify and change family rejecting behaviors that increase their child’s risk for suicide, depression, substance abuse ,and risky sexual behaviors.
- Expand anticipatory guidance to include information on the need for support and the link between family rejection and negative health problems.
- Provide guidance on sexual orientation and gender identity as part of normative child development during well-baby and early childhood care.
- Use FAP’s multilingual family education booklets and Healthy Futures poster series in family and patient education and provide these materials in clinical and community settings. FAP’s Healthy Futures posters include a poster guidance, a version on family acceptance, a version on family rejection and a family acceptance version for conservative families and settings. They are available in camera-ready art in four sizes in English and Spanish and are forthcoming in five Asian languages: familyproject.sfsu.edu/poster.
Dr. Lawlis is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and an adolescent medicine specialist at OU Children’s. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
Resources
• Family Acceptance Project – consultation and training; evidence-based educational materials for families, providers, religious leaders and youth.
• PFLAG – peer support for parents and friends with LGBTQ children in all states and several other countries.
References
1. Ryan C. Generating a revolution in prevention, wellness & care for LGBT children & youth. Temple Political & Civil Rights Law Review. 2014;23(2):331-44.
2. Ryan C. Healthy Futures Poster Series – Family Accepting & Rejecting Behaviors That Impact LGBTQ Children’s Health & Well-Being. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2019.
3. Ryan C. Family Acceptance Project: Culturally grounded framework for supporting LGBTQ children and youth. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatr. 2019;58(10):S58-9.
4. Ryan C et al. Family rejection as a predictor of negative health outcomes in White and Latino lesbian, gay, and bisexual young adults. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):346-52.
5. Ryan C. Supportive families, healthy children: Helping families with lesbian, gay, bisexual & transgender children. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2009.
6. Ryan C et al. Parent-initiated sexual orientation change efforts with LGBT adolescents: Implications for young adult mental health and adjustment. J Homosexuality. 2020;67(2):159-73.
7. Ryan C et al. Family acceptance in adolescence and the health of LGBT young adults. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nursing. 2010;23(4):205-13. 8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. A Practitioner’s Guide: Helping Families to Support Their LGBT Children. In: Administration SAaMhS, ed. Vol PEP14-LGBTKIDS. Rockville, MD: HHS Publication; 2014.
It is well established that LGBTQ individuals experience more health disparities compared with their cisgender, heterosexual counterparts. In general, LGBTQ adolescents and young adults have higher levels of depression, suicide attempts, and substance use than those of their heterosexual peers. However, a key protective factor is family acceptance and support. By encouraging families to modify and change behaviors that are experienced by their LGBTQ children as rejecting and to engage in supportive and affirming behaviors, providers can help families to decrease risk and promote healthy outcomes for LGBTQ youth and young adults. 
We all know that a supportive family can make a difference for any child, but this is especially true for LGBTQ youth and is critical during a pandemic when young people are confined with families and separated from peers and supportive adults outside the home. Several research studies show that family support can improve outcomes related to suicide, depression, homelessness, drug use, and HIV in LGBTQ young people. Family acceptance improves health outcomes, while rejection undermines family relationships and worsens both health and other serious outcomes such as homelessness and placement in custodial care. Pediatricians can help their patients by educating parents and caregivers with LGBTQ children about the critical role of family support – both those who see themselves as accepting and those who believe that being gay or transgender is wrong and are struggling with parenting a child who identifies as LGBTQ or who is gender diverse.
The Family Acceptance Project (FAP) at San Francisco State University conducted the first research on LGBTQ youth and families, developed the first evidence-informed family support model, and has published a range of studies and evidence-based resources that demonstrate the harm caused by family rejection, validate the importance of family acceptance, and provide guidance to increase family support. FAP’s research found that parents and caregivers that engage in rejecting behaviors are typically motivated by care and concern and by trying to protect their children from harm. They believe such behaviors will help their LGBTQ children fit in, have a good life, meet cultural and religious expectations, and be respected by others.1 FAP’s research identified and measured more than 50 rejecting behaviors that parents and caregivers use to respond to their LGBTQ children. Some of these commonly expressed rejecting behaviors include ridiculing and making disparaging comments about their child and other LGBTQ people; excluding them from family activities; blaming their child when others mistreat them because they are LGBTQ; blocking access to LGBTQ resources including friends, support groups, and activities; and trying to change their child’s sexual orientation and gender identity.2 LGBTQ youth experience these and other such behaviors as hurtful, harmful, and traumatic and may feel that they need to hide or repress their identity which can affect their self-esteem, increase isolation, depression, and risky behaviors.3 Providers working with families of LGBTQ youth should focus on shared goals, such as reducing risk and having a happy, healthy child. Most parents love their children and fear for their well-being. However, many are uninformed about their child’s gender identity and sexual orientation and don’t know how to nurture and support them.
In FAP’s initial study, LGB young people who reported higher levels of family rejection had substantially higher rates of attempted suicide, depression, illegal drug use, and unprotected sex.4 These rates were even more significant among Latino gay and bisexual men.4 Those who are rejected by family are less likely to want to have a family or to be parents themselves5 and have lower educational and income levels.6
To reduce risk, pediatricians should ask LGBTQ patients about family rejecting behaviors and help parents and caregivers to identify and understand the effect of such behaviors to reduce health risks and conflict that can lead to running away, expulsion, and removal from the home. Even decreasing rejecting behaviors to moderate levels can significantly improve negative outcomes.5
Caitlin Ryan, PhD, and her team also identified and measured more than 50 family accepting behaviors that help protect against risk and promote well-being. They found that young adults who experience high levels of family acceptance during adolescence report significantly higher levels of self-esteem, social support, and general health with much lower levels of depression, suicidality, and substance abuse.7 Family accepting and supportive behaviors include talking with the child about their LGBTQ identity; advocating for their LGBTQ child when others mistreat them; requiring other family members to treat their LGBTQ child with respect; and supporting their child’s gender identity.5 FAP has developed an evidence-informed family support model and multilingual educational resources for families, providers, youth and religious leaders to decrease rejection and increase family support. These are available in print copies and for download at familyproject.sfsu.edu.
In addition, Dr. Ryan and colleagues1,4,8 recommend the following guidance for providers:
- Ask LGBTQ adolescents about family reactions to their sexual orientation, gender identity, and expression, and refer to LGBTQ community support programs and for supportive counseling, as needed.
- Identify LGBTQ community support programs and online resources to educate parents about how to help their children. Parents need culturally relevant peer support to help decrease rejection and increase family support.
- Advise parents that negative reactions to their adolescent’s LGBTQ identity may negatively impact their child’s health and mental health while supportive and affirming reactions promote well-being.
- Advise parents and caregivers to modify and change family rejecting behaviors that increase their child’s risk for suicide, depression, substance abuse ,and risky sexual behaviors.
- Expand anticipatory guidance to include information on the need for support and the link between family rejection and negative health problems.
- Provide guidance on sexual orientation and gender identity as part of normative child development during well-baby and early childhood care.
- Use FAP’s multilingual family education booklets and Healthy Futures poster series in family and patient education and provide these materials in clinical and community settings. FAP’s Healthy Futures posters include a poster guidance, a version on family acceptance, a version on family rejection and a family acceptance version for conservative families and settings. They are available in camera-ready art in four sizes in English and Spanish and are forthcoming in five Asian languages: familyproject.sfsu.edu/poster.
Dr. Lawlis is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and an adolescent medicine specialist at OU Children’s. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
Resources
• Family Acceptance Project – consultation and training; evidence-based educational materials for families, providers, religious leaders and youth.
• PFLAG – peer support for parents and friends with LGBTQ children in all states and several other countries.
References
1. Ryan C. Generating a revolution in prevention, wellness & care for LGBT children & youth. Temple Political & Civil Rights Law Review. 2014;23(2):331-44.
2. Ryan C. Healthy Futures Poster Series – Family Accepting & Rejecting Behaviors That Impact LGBTQ Children’s Health & Well-Being. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2019.
3. Ryan C. Family Acceptance Project: Culturally grounded framework for supporting LGBTQ children and youth. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatr. 2019;58(10):S58-9.
4. Ryan C et al. Family rejection as a predictor of negative health outcomes in White and Latino lesbian, gay, and bisexual young adults. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):346-52.
5. Ryan C. Supportive families, healthy children: Helping families with lesbian, gay, bisexual & transgender children. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2009.
6. Ryan C et al. Parent-initiated sexual orientation change efforts with LGBT adolescents: Implications for young adult mental health and adjustment. J Homosexuality. 2020;67(2):159-73.
7. Ryan C et al. Family acceptance in adolescence and the health of LGBT young adults. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nursing. 2010;23(4):205-13. 8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. A Practitioner’s Guide: Helping Families to Support Their LGBT Children. In: Administration SAaMhS, ed. Vol PEP14-LGBTKIDS. Rockville, MD: HHS Publication; 2014.
It is well established that LGBTQ individuals experience more health disparities compared with their cisgender, heterosexual counterparts. In general, LGBTQ adolescents and young adults have higher levels of depression, suicide attempts, and substance use than those of their heterosexual peers. However, a key protective factor is family acceptance and support. By encouraging families to modify and change behaviors that are experienced by their LGBTQ children as rejecting and to engage in supportive and affirming behaviors, providers can help families to decrease risk and promote healthy outcomes for LGBTQ youth and young adults. 
We all know that a supportive family can make a difference for any child, but this is especially true for LGBTQ youth and is critical during a pandemic when young people are confined with families and separated from peers and supportive adults outside the home. Several research studies show that family support can improve outcomes related to suicide, depression, homelessness, drug use, and HIV in LGBTQ young people. Family acceptance improves health outcomes, while rejection undermines family relationships and worsens both health and other serious outcomes such as homelessness and placement in custodial care. Pediatricians can help their patients by educating parents and caregivers with LGBTQ children about the critical role of family support – both those who see themselves as accepting and those who believe that being gay or transgender is wrong and are struggling with parenting a child who identifies as LGBTQ or who is gender diverse.
The Family Acceptance Project (FAP) at San Francisco State University conducted the first research on LGBTQ youth and families, developed the first evidence-informed family support model, and has published a range of studies and evidence-based resources that demonstrate the harm caused by family rejection, validate the importance of family acceptance, and provide guidance to increase family support. FAP’s research found that parents and caregivers that engage in rejecting behaviors are typically motivated by care and concern and by trying to protect their children from harm. They believe such behaviors will help their LGBTQ children fit in, have a good life, meet cultural and religious expectations, and be respected by others.1 FAP’s research identified and measured more than 50 rejecting behaviors that parents and caregivers use to respond to their LGBTQ children. Some of these commonly expressed rejecting behaviors include ridiculing and making disparaging comments about their child and other LGBTQ people; excluding them from family activities; blaming their child when others mistreat them because they are LGBTQ; blocking access to LGBTQ resources including friends, support groups, and activities; and trying to change their child’s sexual orientation and gender identity.2 LGBTQ youth experience these and other such behaviors as hurtful, harmful, and traumatic and may feel that they need to hide or repress their identity which can affect their self-esteem, increase isolation, depression, and risky behaviors.3 Providers working with families of LGBTQ youth should focus on shared goals, such as reducing risk and having a happy, healthy child. Most parents love their children and fear for their well-being. However, many are uninformed about their child’s gender identity and sexual orientation and don’t know how to nurture and support them.
In FAP’s initial study, LGB young people who reported higher levels of family rejection had substantially higher rates of attempted suicide, depression, illegal drug use, and unprotected sex.4 These rates were even more significant among Latino gay and bisexual men.4 Those who are rejected by family are less likely to want to have a family or to be parents themselves5 and have lower educational and income levels.6
To reduce risk, pediatricians should ask LGBTQ patients about family rejecting behaviors and help parents and caregivers to identify and understand the effect of such behaviors to reduce health risks and conflict that can lead to running away, expulsion, and removal from the home. Even decreasing rejecting behaviors to moderate levels can significantly improve negative outcomes.5
Caitlin Ryan, PhD, and her team also identified and measured more than 50 family accepting behaviors that help protect against risk and promote well-being. They found that young adults who experience high levels of family acceptance during adolescence report significantly higher levels of self-esteem, social support, and general health with much lower levels of depression, suicidality, and substance abuse.7 Family accepting and supportive behaviors include talking with the child about their LGBTQ identity; advocating for their LGBTQ child when others mistreat them; requiring other family members to treat their LGBTQ child with respect; and supporting their child’s gender identity.5 FAP has developed an evidence-informed family support model and multilingual educational resources for families, providers, youth and religious leaders to decrease rejection and increase family support. These are available in print copies and for download at familyproject.sfsu.edu.
In addition, Dr. Ryan and colleagues1,4,8 recommend the following guidance for providers:
- Ask LGBTQ adolescents about family reactions to their sexual orientation, gender identity, and expression, and refer to LGBTQ community support programs and for supportive counseling, as needed.
- Identify LGBTQ community support programs and online resources to educate parents about how to help their children. Parents need culturally relevant peer support to help decrease rejection and increase family support.
- Advise parents that negative reactions to their adolescent’s LGBTQ identity may negatively impact their child’s health and mental health while supportive and affirming reactions promote well-being.
- Advise parents and caregivers to modify and change family rejecting behaviors that increase their child’s risk for suicide, depression, substance abuse ,and risky sexual behaviors.
- Expand anticipatory guidance to include information on the need for support and the link between family rejection and negative health problems.
- Provide guidance on sexual orientation and gender identity as part of normative child development during well-baby and early childhood care.
- Use FAP’s multilingual family education booklets and Healthy Futures poster series in family and patient education and provide these materials in clinical and community settings. FAP’s Healthy Futures posters include a poster guidance, a version on family acceptance, a version on family rejection and a family acceptance version for conservative families and settings. They are available in camera-ready art in four sizes in English and Spanish and are forthcoming in five Asian languages: familyproject.sfsu.edu/poster.
Dr. Lawlis is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and an adolescent medicine specialist at OU Children’s. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
Resources
• Family Acceptance Project – consultation and training; evidence-based educational materials for families, providers, religious leaders and youth.
• PFLAG – peer support for parents and friends with LGBTQ children in all states and several other countries.
References
1. Ryan C. Generating a revolution in prevention, wellness & care for LGBT children & youth. Temple Political & Civil Rights Law Review. 2014;23(2):331-44.
2. Ryan C. Healthy Futures Poster Series – Family Accepting & Rejecting Behaviors That Impact LGBTQ Children’s Health & Well-Being. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2019.
3. Ryan C. Family Acceptance Project: Culturally grounded framework for supporting LGBTQ children and youth. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatr. 2019;58(10):S58-9.
4. Ryan C et al. Family rejection as a predictor of negative health outcomes in White and Latino lesbian, gay, and bisexual young adults. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):346-52.
5. Ryan C. Supportive families, healthy children: Helping families with lesbian, gay, bisexual & transgender children. In: Family Acceptance Project Marian Wright Edelman Institute SFSU, ed. San Francisco, CA2009.
6. Ryan C et al. Parent-initiated sexual orientation change efforts with LGBT adolescents: Implications for young adult mental health and adjustment. J Homosexuality. 2020;67(2):159-73.
7. Ryan C et al. Family acceptance in adolescence and the health of LGBT young adults. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nursing. 2010;23(4):205-13. 8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. A Practitioner’s Guide: Helping Families to Support Their LGBT Children. In: Administration SAaMhS, ed. Vol PEP14-LGBTKIDS. Rockville, MD: HHS Publication; 2014.
Checkpoint inhibitors’ ‘big picture’ safety shown with preexisting autoimmune diseases
Patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune diseases (AIDs) who were treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) responded well and did not suffer more grade 3 or higher immune-related adverse events than patients without an AID, a new study finds, although some concerns were raised regarding patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to bridge this knowledge gap by presenting ‘real-world’ data on the safety and efficacy of ICI on a national scale,” wrote Monique K. van der Kooij, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and coauthors. The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
To investigate ICI use and response among this specific subset of melanoma patients, the researchers launched a nationwide cohort study set in the Netherlands. Data were gathered via the Dutch Melanoma Treatment Registry (DMTR), in which 4,367 patients with advanced melanoma were enrolled between July 2013 and July 2018.
Within that cohort, 415 (9.5%) had preexisting AIDs. Nearly 55% had rheumatologic AIDs (n = 227) – which included RA, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, sarcoidosis, and vasculitis – with the next most frequent being endocrine AID (n = 143) and IBD (n = 55). Patients with AID were older than patients without (67 vs. 63 years) and were more likely to be female (53% vs. 41%).
The ICIs used in the study included anti-CTLA4 (ipilimumab), anti–programmed death 1 (PD-1) (nivolumab or pembrolizumab), or a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab. Of the patients with AID, 55% (n = 228) were treated with ICI, compared with 58% of patients without AID. A total of 87 AID patients were treated with anti-CTLA4, 187 received anti-PD-1, and 34 received the combination. The combination was not readily available in the Netherlands until 2017, the authors stated, acknowledging that it may be wise to revisit its effects in the coming years.
Incidence of immune-related adverse events
The incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) grade 3 and above for patients with and without AID who were given anti-CTLA4 was 30%. The incidence rate of irAEs was also similar for patients with (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12%-23%) and without (13%; 95% CI, 12%-15%) AID on anti-PD-1. Patients with AIDs who took anti-PD-1 therapy discontinued it more often because of toxicity than did the patients without AIDs.
The combination group had irAE incidence rates of 44% (95% CI, 27%-62%) for patients with AID, compared with 48% (95% CI, 43%-53%) for patients without AIDs. Overall, no patients with AIDs on ICIs died of toxicity, compared with three deaths among patients without AID on anti-CTLA4, five deaths among patients on anti-PD-1, and one patient on the combination.
Patients with IBD had a notably higher risk of anti-PD-1–induced colitis (19%; 95% CI, 7%-37%), compared with patients with other AIDs (3%; 95% CI, 0%-6%) and patients without AIDs (2%; 95% CI, 2%-3%). IBD patients were also more likely than all other groups on ICIs to stop treatment because of toxicity, leading the researchers to note that “close monitoring in patients with IBD is advised.”
Overall survival after diagnosis was similar in patients with AIDs (median, 13 months; 95% CI, 10-16 months) and without (median, 14 months; 95% CI, 13-15 months), as was the objective response rate to anti-CTLA4 treatment (10% vs. 16%), anti-PD-1 treatment (40% vs. 44%), and combination therapy (39% vs. 43%).
Study largely bypasses the effects of checkpoint inhibitors on RA patients
“For detail, you can’t look to this study,” Anne R. Bass, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “But for a big-picture look at ‘how safe are checkpoint inhibitors,’ I think it’s an important one.”
Dr. Bass noted that the investigators lumped certain elements together and bypassed others, including their focus on grade 3 or higher adverse events. That was a decision the authors themselves recognized as a potential limitation of their research.
“Understandably, they were worried about life-threatening adverse events, and that’s fine,” she said. But for patients with arthritis who flare, their events are usually grade 2 or even grade 1 and therefore not captured or analyzed in the study. “This does not really address the risk of flare in an RA patient.”
She also questioned their grouping of AIDs, with a bevy of rheumatic diseases categorized as one cluster and the “other” group being particularly broad in its inclusion of “all AIDs not listed” – though only eight patients were placed into that group.
That said, the researchers relied on an oncology database, not one aimed at AID or adverse events. “The numbers are so much bigger than any other study in this area that’s been done,” she said. “It’s both a strength and a weakness of this kind of database.”
Indeed, the authors considered their use of nationwide, population-based data from the DMTR a benefit, calling it “a strength of our approach.”
The DMTR was funded by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development and sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche Nederland, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pierre Fabre via the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing.
Patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune diseases (AIDs) who were treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) responded well and did not suffer more grade 3 or higher immune-related adverse events than patients without an AID, a new study finds, although some concerns were raised regarding patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to bridge this knowledge gap by presenting ‘real-world’ data on the safety and efficacy of ICI on a national scale,” wrote Monique K. van der Kooij, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and coauthors. The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
To investigate ICI use and response among this specific subset of melanoma patients, the researchers launched a nationwide cohort study set in the Netherlands. Data were gathered via the Dutch Melanoma Treatment Registry (DMTR), in which 4,367 patients with advanced melanoma were enrolled between July 2013 and July 2018.
Within that cohort, 415 (9.5%) had preexisting AIDs. Nearly 55% had rheumatologic AIDs (n = 227) – which included RA, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, sarcoidosis, and vasculitis – with the next most frequent being endocrine AID (n = 143) and IBD (n = 55). Patients with AID were older than patients without (67 vs. 63 years) and were more likely to be female (53% vs. 41%).
The ICIs used in the study included anti-CTLA4 (ipilimumab), anti–programmed death 1 (PD-1) (nivolumab or pembrolizumab), or a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab. Of the patients with AID, 55% (n = 228) were treated with ICI, compared with 58% of patients without AID. A total of 87 AID patients were treated with anti-CTLA4, 187 received anti-PD-1, and 34 received the combination. The combination was not readily available in the Netherlands until 2017, the authors stated, acknowledging that it may be wise to revisit its effects in the coming years.
Incidence of immune-related adverse events
The incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) grade 3 and above for patients with and without AID who were given anti-CTLA4 was 30%. The incidence rate of irAEs was also similar for patients with (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12%-23%) and without (13%; 95% CI, 12%-15%) AID on anti-PD-1. Patients with AIDs who took anti-PD-1 therapy discontinued it more often because of toxicity than did the patients without AIDs.
The combination group had irAE incidence rates of 44% (95% CI, 27%-62%) for patients with AID, compared with 48% (95% CI, 43%-53%) for patients without AIDs. Overall, no patients with AIDs on ICIs died of toxicity, compared with three deaths among patients without AID on anti-CTLA4, five deaths among patients on anti-PD-1, and one patient on the combination.
Patients with IBD had a notably higher risk of anti-PD-1–induced colitis (19%; 95% CI, 7%-37%), compared with patients with other AIDs (3%; 95% CI, 0%-6%) and patients without AIDs (2%; 95% CI, 2%-3%). IBD patients were also more likely than all other groups on ICIs to stop treatment because of toxicity, leading the researchers to note that “close monitoring in patients with IBD is advised.”
Overall survival after diagnosis was similar in patients with AIDs (median, 13 months; 95% CI, 10-16 months) and without (median, 14 months; 95% CI, 13-15 months), as was the objective response rate to anti-CTLA4 treatment (10% vs. 16%), anti-PD-1 treatment (40% vs. 44%), and combination therapy (39% vs. 43%).
Study largely bypasses the effects of checkpoint inhibitors on RA patients
“For detail, you can’t look to this study,” Anne R. Bass, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “But for a big-picture look at ‘how safe are checkpoint inhibitors,’ I think it’s an important one.”
Dr. Bass noted that the investigators lumped certain elements together and bypassed others, including their focus on grade 3 or higher adverse events. That was a decision the authors themselves recognized as a potential limitation of their research.
“Understandably, they were worried about life-threatening adverse events, and that’s fine,” she said. But for patients with arthritis who flare, their events are usually grade 2 or even grade 1 and therefore not captured or analyzed in the study. “This does not really address the risk of flare in an RA patient.”
She also questioned their grouping of AIDs, with a bevy of rheumatic diseases categorized as one cluster and the “other” group being particularly broad in its inclusion of “all AIDs not listed” – though only eight patients were placed into that group.
That said, the researchers relied on an oncology database, not one aimed at AID or adverse events. “The numbers are so much bigger than any other study in this area that’s been done,” she said. “It’s both a strength and a weakness of this kind of database.”
Indeed, the authors considered their use of nationwide, population-based data from the DMTR a benefit, calling it “a strength of our approach.”
The DMTR was funded by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development and sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche Nederland, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pierre Fabre via the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing.
Patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune diseases (AIDs) who were treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) responded well and did not suffer more grade 3 or higher immune-related adverse events than patients without an AID, a new study finds, although some concerns were raised regarding patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to bridge this knowledge gap by presenting ‘real-world’ data on the safety and efficacy of ICI on a national scale,” wrote Monique K. van der Kooij, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and coauthors. The study was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
To investigate ICI use and response among this specific subset of melanoma patients, the researchers launched a nationwide cohort study set in the Netherlands. Data were gathered via the Dutch Melanoma Treatment Registry (DMTR), in which 4,367 patients with advanced melanoma were enrolled between July 2013 and July 2018.
Within that cohort, 415 (9.5%) had preexisting AIDs. Nearly 55% had rheumatologic AIDs (n = 227) – which included RA, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, sarcoidosis, and vasculitis – with the next most frequent being endocrine AID (n = 143) and IBD (n = 55). Patients with AID were older than patients without (67 vs. 63 years) and were more likely to be female (53% vs. 41%).
The ICIs used in the study included anti-CTLA4 (ipilimumab), anti–programmed death 1 (PD-1) (nivolumab or pembrolizumab), or a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab. Of the patients with AID, 55% (n = 228) were treated with ICI, compared with 58% of patients without AID. A total of 87 AID patients were treated with anti-CTLA4, 187 received anti-PD-1, and 34 received the combination. The combination was not readily available in the Netherlands until 2017, the authors stated, acknowledging that it may be wise to revisit its effects in the coming years.
Incidence of immune-related adverse events
The incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) grade 3 and above for patients with and without AID who were given anti-CTLA4 was 30%. The incidence rate of irAEs was also similar for patients with (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12%-23%) and without (13%; 95% CI, 12%-15%) AID on anti-PD-1. Patients with AIDs who took anti-PD-1 therapy discontinued it more often because of toxicity than did the patients without AIDs.
The combination group had irAE incidence rates of 44% (95% CI, 27%-62%) for patients with AID, compared with 48% (95% CI, 43%-53%) for patients without AIDs. Overall, no patients with AIDs on ICIs died of toxicity, compared with three deaths among patients without AID on anti-CTLA4, five deaths among patients on anti-PD-1, and one patient on the combination.
Patients with IBD had a notably higher risk of anti-PD-1–induced colitis (19%; 95% CI, 7%-37%), compared with patients with other AIDs (3%; 95% CI, 0%-6%) and patients without AIDs (2%; 95% CI, 2%-3%). IBD patients were also more likely than all other groups on ICIs to stop treatment because of toxicity, leading the researchers to note that “close monitoring in patients with IBD is advised.”
Overall survival after diagnosis was similar in patients with AIDs (median, 13 months; 95% CI, 10-16 months) and without (median, 14 months; 95% CI, 13-15 months), as was the objective response rate to anti-CTLA4 treatment (10% vs. 16%), anti-PD-1 treatment (40% vs. 44%), and combination therapy (39% vs. 43%).
Study largely bypasses the effects of checkpoint inhibitors on RA patients
“For detail, you can’t look to this study,” Anne R. Bass, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “But for a big-picture look at ‘how safe are checkpoint inhibitors,’ I think it’s an important one.”
Dr. Bass noted that the investigators lumped certain elements together and bypassed others, including their focus on grade 3 or higher adverse events. That was a decision the authors themselves recognized as a potential limitation of their research.
“Understandably, they were worried about life-threatening adverse events, and that’s fine,” she said. But for patients with arthritis who flare, their events are usually grade 2 or even grade 1 and therefore not captured or analyzed in the study. “This does not really address the risk of flare in an RA patient.”
She also questioned their grouping of AIDs, with a bevy of rheumatic diseases categorized as one cluster and the “other” group being particularly broad in its inclusion of “all AIDs not listed” – though only eight patients were placed into that group.
That said, the researchers relied on an oncology database, not one aimed at AID or adverse events. “The numbers are so much bigger than any other study in this area that’s been done,” she said. “It’s both a strength and a weakness of this kind of database.”
Indeed, the authors considered their use of nationwide, population-based data from the DMTR a benefit, calling it “a strength of our approach.”
The DMTR was funded by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development and sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Roche Nederland, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pierre Fabre via the Dutch Institute for Clinical Auditing.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Child ‘Mis’behavior – What’s ‘mis’ing?
“What kind of parent are you? Why don’t you straighten him out!” rants the woman being jostled in the grocery store by your patient. “Easy for you to say,” thinks your patient’s frazzled and now insulted parent.
Blaming the parent for an out-of-control child has historically been a common refrain of neighbors, relatives, and even strangers. But considering child behavior as resulting from both parent and child factors is central to the current transactional model of child development. In this model, mismatch of the parent’s and child’s response patterns is seen as setting them up for chronically rough interactions around parent requests/demands. A parent escalating quickly from a briefly stated request to a tirade may create more tension paired with an anxious child who takes time to act, for example. Once a parent (and ultimately the child) recognize patterns in what leads to conflict, they can become more proactive in predicting and negotiating these situations. Ross Greene, PhD, explains this in his book “The Explosive Child,” calling the method Collaborative Problem Solving (now Collaborative & Proactive Solutions or CPS).
While there are general principles parents can use to modify what they consider “mis”behaviors, these methods often do not account for the “missing” skills of the individual child (and parent) predisposing to those “mis”takes. Thinking of misbehaviors as being because of a kind of “learning disability” in the child rather than willful defiance can help cool off interactions by instead focusing on solving the underlying problem.
What kinds of “gaps in skills” set a child up for defiant or explosive reactions? If you think about what features of children, and parent-child relationships are associated with harmonious interactions this becomes evident. Children over 3 who are patient, easygoing, flexible or adaptable, and good at transitions and problem-solving can delay gratification and tolerate frustration, regulate their emotions, explain their desires, and multitask. They are better at reading the parent’s needs and intent and tend to interpret requests as positive or at least neutral and are more likely to comply with parent requests without a fuss.
What? No kid you know is great at all of these? These skills, at best variable, develop with maturation. Some are part of temperament, considered normal variation in personality. For example, so-called difficult temperament includes low adaptability, high-intensity reactions, low regularity, tendency to withdraw, and negative mood. But in the extreme, weaknesses in these skills are core to or comorbid with diagnosable mental health disorders. Defiance and irritable responses are criteria for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and less severe categories called aggressive/oppositional problem or variation. ODD is often found in children diagnosed with ADHD (65%), Tourette’s (15%-65%), depression (70% if severe), bipolar disorder (85%), OCD, anxiety (45%), autism, and language-processing disorders (55%), or trauma. These conditions variably include lower emotion regulation, poorer executive functioning including poor task shifting and impulsivity, obsessiveness, lower expressive and receptive communication skills, and less social awareness that facilitates harmonious problem solving.
The basic components of the CPS approach to addressing parent-child conflict sound intuitive but defining them clearly is important when families are stuck. There are three levels of plans. If the problem is an emergency or nonnegotiable, e.g., child hurting the cat, it may call for Plan A – parent-imposed solutions, sometimes with consequences or rewards. As children mature, Plan A should be used less frequently. If solving the problem is not a top life priority, Plan C – postponing action, may be appropriate. Plan C highlights that behavior change is a long-term project and “picking your fights” is important.
The biggest value of CPS for resolving behavior problems comes from intermediate Plan B. In Plan B the first step of problem solving for parents facing child defiance or upset is to empathically and nonjudgmentally figure out the child’s concern. Questions such as “I’ve noticed that when I remind you that it is trash night you start shouting. What’s up with that?” then patiently asking about the who, what, where, and when of their concern and checking to ensure understanding. Specificity is important as well as noting times when the reaction occurs or not.
Once the child’s concern is clear, e.g., feeling that the demand to take out the trash now interrupts his games during the only time his friends are online, the parents should echo the child’s concern then express their own concern about how the behavior is affecting them and others, potentially including the child; e.g., mother is so upset by the shouting that she can’t sleep, and worry that the child is not learning responsibility, and then checking for child understanding.
Finally, the parent invites brainstorming for a solution that addresses both of their concerns, first asking the child for suggestions, aiming for a strategy that is realistic and specific. Children reluctant to make suggestions may need more time and the parent may be wondering “if there is a way for both of our concerns to be addressed.” Solutions chosen are then tried for several weeks, success tracked, and needed changes negotiated.
For parents, using a collaborative approach to dealing with their child’s behavior takes skills they may not have at the moment, or ever. Especially under the stresses of COVID-19 lockdown, taking a step back from an encounter to consider lack of a skill to turn off the video game promptly when a Zoom meeting starts is challenging. Parents may also genetically share the child’s predisposing ADHD, anxiety, depression, OCD, or weakness in communication or social sensitivity.
Sometimes part of the solution for a conflict is for the parent to reduce expectations. This requires understanding and accepting the child’s cognitive or emotional limitations. Reducing expectations is ideally done before a request rather than by giving in after it, which reinforces protests. For authoritarian adults rigid in their belief that parents are boss, changing expectations can be tough and can feel like losing control or failing as a leader. One benefit of working with a CPS coach (see livesinthebalance.org or ThinkKids.org) is to help parents identify their own limitations.
Predicting the types of demands that tend to create conflict, such as to act immediately or be flexible about options, allows parents to prioritize those requests for calmer moments or when there is more time for discussion. Reviewing a checklist of common gaps in skills and creating a list of expectations and triggers that are difficult for the child helps the family be more proactive in developing solutions. Authors of CPS have validated a checklist of skill deficits, “Thinking Skills Inventory,” to facilitate detection of gaps that is educational plus useful for planning specific solutions.
CPS has been shown in randomized trials with both parent groups and in home counseling to be as effective as Parent Training in reducing oppositional behavior and reducing maternal stress, with effects lasting even longer.
CPS Plan B notably has no reward or punishment components as it assumes the child wants to behave acceptably but can’t; has the “will but not the skill.” When skill deficits are worked around the child is satisfied with complying and pleasing the parents. The idea of a “function” of the misbehavior for the child of gaining attention or reward or avoiding consequences is reinterpreted as serving to communicate the problem the child is having trouble in meeting the parent’s demand. When the parent understands and helps the child solve the problem his/her misbehavior is no longer needed. A benefit of the communication and mutual problem solving used in CPS is on not only improving behavior but empowering parents and children, building parental empathy, and improving child skills.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She has no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication is as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
Greene RW et al. A transactional model of oppositional behavior: Underpinnings of the Collaborative Problem Solving approach. J Psychosom Res. 2003;55(1):67-75.
“What kind of parent are you? Why don’t you straighten him out!” rants the woman being jostled in the grocery store by your patient. “Easy for you to say,” thinks your patient’s frazzled and now insulted parent.
Blaming the parent for an out-of-control child has historically been a common refrain of neighbors, relatives, and even strangers. But considering child behavior as resulting from both parent and child factors is central to the current transactional model of child development. In this model, mismatch of the parent’s and child’s response patterns is seen as setting them up for chronically rough interactions around parent requests/demands. A parent escalating quickly from a briefly stated request to a tirade may create more tension paired with an anxious child who takes time to act, for example. Once a parent (and ultimately the child) recognize patterns in what leads to conflict, they can become more proactive in predicting and negotiating these situations. Ross Greene, PhD, explains this in his book “The Explosive Child,” calling the method Collaborative Problem Solving (now Collaborative & Proactive Solutions or CPS).
While there are general principles parents can use to modify what they consider “mis”behaviors, these methods often do not account for the “missing” skills of the individual child (and parent) predisposing to those “mis”takes. Thinking of misbehaviors as being because of a kind of “learning disability” in the child rather than willful defiance can help cool off interactions by instead focusing on solving the underlying problem.
What kinds of “gaps in skills” set a child up for defiant or explosive reactions? If you think about what features of children, and parent-child relationships are associated with harmonious interactions this becomes evident. Children over 3 who are patient, easygoing, flexible or adaptable, and good at transitions and problem-solving can delay gratification and tolerate frustration, regulate their emotions, explain their desires, and multitask. They are better at reading the parent’s needs and intent and tend to interpret requests as positive or at least neutral and are more likely to comply with parent requests without a fuss.
What? No kid you know is great at all of these? These skills, at best variable, develop with maturation. Some are part of temperament, considered normal variation in personality. For example, so-called difficult temperament includes low adaptability, high-intensity reactions, low regularity, tendency to withdraw, and negative mood. But in the extreme, weaknesses in these skills are core to or comorbid with diagnosable mental health disorders. Defiance and irritable responses are criteria for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and less severe categories called aggressive/oppositional problem or variation. ODD is often found in children diagnosed with ADHD (65%), Tourette’s (15%-65%), depression (70% if severe), bipolar disorder (85%), OCD, anxiety (45%), autism, and language-processing disorders (55%), or trauma. These conditions variably include lower emotion regulation, poorer executive functioning including poor task shifting and impulsivity, obsessiveness, lower expressive and receptive communication skills, and less social awareness that facilitates harmonious problem solving.
The basic components of the CPS approach to addressing parent-child conflict sound intuitive but defining them clearly is important when families are stuck. There are three levels of plans. If the problem is an emergency or nonnegotiable, e.g., child hurting the cat, it may call for Plan A – parent-imposed solutions, sometimes with consequences or rewards. As children mature, Plan A should be used less frequently. If solving the problem is not a top life priority, Plan C – postponing action, may be appropriate. Plan C highlights that behavior change is a long-term project and “picking your fights” is important.
The biggest value of CPS for resolving behavior problems comes from intermediate Plan B. In Plan B the first step of problem solving for parents facing child defiance or upset is to empathically and nonjudgmentally figure out the child’s concern. Questions such as “I’ve noticed that when I remind you that it is trash night you start shouting. What’s up with that?” then patiently asking about the who, what, where, and when of their concern and checking to ensure understanding. Specificity is important as well as noting times when the reaction occurs or not.
Once the child’s concern is clear, e.g., feeling that the demand to take out the trash now interrupts his games during the only time his friends are online, the parents should echo the child’s concern then express their own concern about how the behavior is affecting them and others, potentially including the child; e.g., mother is so upset by the shouting that she can’t sleep, and worry that the child is not learning responsibility, and then checking for child understanding.
Finally, the parent invites brainstorming for a solution that addresses both of their concerns, first asking the child for suggestions, aiming for a strategy that is realistic and specific. Children reluctant to make suggestions may need more time and the parent may be wondering “if there is a way for both of our concerns to be addressed.” Solutions chosen are then tried for several weeks, success tracked, and needed changes negotiated.
For parents, using a collaborative approach to dealing with their child’s behavior takes skills they may not have at the moment, or ever. Especially under the stresses of COVID-19 lockdown, taking a step back from an encounter to consider lack of a skill to turn off the video game promptly when a Zoom meeting starts is challenging. Parents may also genetically share the child’s predisposing ADHD, anxiety, depression, OCD, or weakness in communication or social sensitivity.
Sometimes part of the solution for a conflict is for the parent to reduce expectations. This requires understanding and accepting the child’s cognitive or emotional limitations. Reducing expectations is ideally done before a request rather than by giving in after it, which reinforces protests. For authoritarian adults rigid in their belief that parents are boss, changing expectations can be tough and can feel like losing control or failing as a leader. One benefit of working with a CPS coach (see livesinthebalance.org or ThinkKids.org) is to help parents identify their own limitations.
Predicting the types of demands that tend to create conflict, such as to act immediately or be flexible about options, allows parents to prioritize those requests for calmer moments or when there is more time for discussion. Reviewing a checklist of common gaps in skills and creating a list of expectations and triggers that are difficult for the child helps the family be more proactive in developing solutions. Authors of CPS have validated a checklist of skill deficits, “Thinking Skills Inventory,” to facilitate detection of gaps that is educational plus useful for planning specific solutions.
CPS has been shown in randomized trials with both parent groups and in home counseling to be as effective as Parent Training in reducing oppositional behavior and reducing maternal stress, with effects lasting even longer.
CPS Plan B notably has no reward or punishment components as it assumes the child wants to behave acceptably but can’t; has the “will but not the skill.” When skill deficits are worked around the child is satisfied with complying and pleasing the parents. The idea of a “function” of the misbehavior for the child of gaining attention or reward or avoiding consequences is reinterpreted as serving to communicate the problem the child is having trouble in meeting the parent’s demand. When the parent understands and helps the child solve the problem his/her misbehavior is no longer needed. A benefit of the communication and mutual problem solving used in CPS is on not only improving behavior but empowering parents and children, building parental empathy, and improving child skills.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She has no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication is as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
Greene RW et al. A transactional model of oppositional behavior: Underpinnings of the Collaborative Problem Solving approach. J Psychosom Res. 2003;55(1):67-75.
“What kind of parent are you? Why don’t you straighten him out!” rants the woman being jostled in the grocery store by your patient. “Easy for you to say,” thinks your patient’s frazzled and now insulted parent.
Blaming the parent for an out-of-control child has historically been a common refrain of neighbors, relatives, and even strangers. But considering child behavior as resulting from both parent and child factors is central to the current transactional model of child development. In this model, mismatch of the parent’s and child’s response patterns is seen as setting them up for chronically rough interactions around parent requests/demands. A parent escalating quickly from a briefly stated request to a tirade may create more tension paired with an anxious child who takes time to act, for example. Once a parent (and ultimately the child) recognize patterns in what leads to conflict, they can become more proactive in predicting and negotiating these situations. Ross Greene, PhD, explains this in his book “The Explosive Child,” calling the method Collaborative Problem Solving (now Collaborative & Proactive Solutions or CPS).
While there are general principles parents can use to modify what they consider “mis”behaviors, these methods often do not account for the “missing” skills of the individual child (and parent) predisposing to those “mis”takes. Thinking of misbehaviors as being because of a kind of “learning disability” in the child rather than willful defiance can help cool off interactions by instead focusing on solving the underlying problem.
What kinds of “gaps in skills” set a child up for defiant or explosive reactions? If you think about what features of children, and parent-child relationships are associated with harmonious interactions this becomes evident. Children over 3 who are patient, easygoing, flexible or adaptable, and good at transitions and problem-solving can delay gratification and tolerate frustration, regulate their emotions, explain their desires, and multitask. They are better at reading the parent’s needs and intent and tend to interpret requests as positive or at least neutral and are more likely to comply with parent requests without a fuss.
What? No kid you know is great at all of these? These skills, at best variable, develop with maturation. Some are part of temperament, considered normal variation in personality. For example, so-called difficult temperament includes low adaptability, high-intensity reactions, low regularity, tendency to withdraw, and negative mood. But in the extreme, weaknesses in these skills are core to or comorbid with diagnosable mental health disorders. Defiance and irritable responses are criteria for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and less severe categories called aggressive/oppositional problem or variation. ODD is often found in children diagnosed with ADHD (65%), Tourette’s (15%-65%), depression (70% if severe), bipolar disorder (85%), OCD, anxiety (45%), autism, and language-processing disorders (55%), or trauma. These conditions variably include lower emotion regulation, poorer executive functioning including poor task shifting and impulsivity, obsessiveness, lower expressive and receptive communication skills, and less social awareness that facilitates harmonious problem solving.
The basic components of the CPS approach to addressing parent-child conflict sound intuitive but defining them clearly is important when families are stuck. There are three levels of plans. If the problem is an emergency or nonnegotiable, e.g., child hurting the cat, it may call for Plan A – parent-imposed solutions, sometimes with consequences or rewards. As children mature, Plan A should be used less frequently. If solving the problem is not a top life priority, Plan C – postponing action, may be appropriate. Plan C highlights that behavior change is a long-term project and “picking your fights” is important.
The biggest value of CPS for resolving behavior problems comes from intermediate Plan B. In Plan B the first step of problem solving for parents facing child defiance or upset is to empathically and nonjudgmentally figure out the child’s concern. Questions such as “I’ve noticed that when I remind you that it is trash night you start shouting. What’s up with that?” then patiently asking about the who, what, where, and when of their concern and checking to ensure understanding. Specificity is important as well as noting times when the reaction occurs or not.
Once the child’s concern is clear, e.g., feeling that the demand to take out the trash now interrupts his games during the only time his friends are online, the parents should echo the child’s concern then express their own concern about how the behavior is affecting them and others, potentially including the child; e.g., mother is so upset by the shouting that she can’t sleep, and worry that the child is not learning responsibility, and then checking for child understanding.
Finally, the parent invites brainstorming for a solution that addresses both of their concerns, first asking the child for suggestions, aiming for a strategy that is realistic and specific. Children reluctant to make suggestions may need more time and the parent may be wondering “if there is a way for both of our concerns to be addressed.” Solutions chosen are then tried for several weeks, success tracked, and needed changes negotiated.
For parents, using a collaborative approach to dealing with their child’s behavior takes skills they may not have at the moment, or ever. Especially under the stresses of COVID-19 lockdown, taking a step back from an encounter to consider lack of a skill to turn off the video game promptly when a Zoom meeting starts is challenging. Parents may also genetically share the child’s predisposing ADHD, anxiety, depression, OCD, or weakness in communication or social sensitivity.
Sometimes part of the solution for a conflict is for the parent to reduce expectations. This requires understanding and accepting the child’s cognitive or emotional limitations. Reducing expectations is ideally done before a request rather than by giving in after it, which reinforces protests. For authoritarian adults rigid in their belief that parents are boss, changing expectations can be tough and can feel like losing control or failing as a leader. One benefit of working with a CPS coach (see livesinthebalance.org or ThinkKids.org) is to help parents identify their own limitations.
Predicting the types of demands that tend to create conflict, such as to act immediately or be flexible about options, allows parents to prioritize those requests for calmer moments or when there is more time for discussion. Reviewing a checklist of common gaps in skills and creating a list of expectations and triggers that are difficult for the child helps the family be more proactive in developing solutions. Authors of CPS have validated a checklist of skill deficits, “Thinking Skills Inventory,” to facilitate detection of gaps that is educational plus useful for planning specific solutions.
CPS has been shown in randomized trials with both parent groups and in home counseling to be as effective as Parent Training in reducing oppositional behavior and reducing maternal stress, with effects lasting even longer.
CPS Plan B notably has no reward or punishment components as it assumes the child wants to behave acceptably but can’t; has the “will but not the skill.” When skill deficits are worked around the child is satisfied with complying and pleasing the parents. The idea of a “function” of the misbehavior for the child of gaining attention or reward or avoiding consequences is reinterpreted as serving to communicate the problem the child is having trouble in meeting the parent’s demand. When the parent understands and helps the child solve the problem his/her misbehavior is no longer needed. A benefit of the communication and mutual problem solving used in CPS is on not only improving behavior but empowering parents and children, building parental empathy, and improving child skills.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She has no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication is as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
Greene RW et al. A transactional model of oppositional behavior: Underpinnings of the Collaborative Problem Solving approach. J Psychosom Res. 2003;55(1):67-75.
More Americans hospitalized, readmitted for heart failure
Overall primary HF hospitalization rates per 1,000 adults declined from 4.4 in 2010 to 4.1 in 2013, and then increased from 4.2 in 2014 to 4.9 in 2017.
Rates of unique patient visits for HF were also on the way down – falling from 3.4 in 2010 to 3.2 in 2013 and 2014 – before climbing to 3.8 in 2017.
Similar trends were observed for rates of postdischarge HF readmissions (from 1.0 in 2010 to 0.9 in 2014 to 1.1 in 2017) and all-cause 30-day readmissions (from 0.8 in 2010 to 0.7 in 2014 to 0.9 in 2017).
“We should be emphasizing the things we know work to reduce heart failure hospitalization, which is, No. 1, prevention,” senior author Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Comorbidities that can lead to heart failure crept up over the study period, such that by 2017, hypertension was present in 91.4% of patients, diabetes in 48.9%, and lipid disorders in 53.1%, up from 76.5%, 44.9%, and 40.4%, respectively, in 2010. Half of all patients had coronary artery disease at both time points. Renal disease shot up from 45.9% to 60.6% by 2017.
“If we did a better job of controlling our known risk factors, we would really cut down on the incidence of heart failure being developed and then, among those estimated 6.6 million heart failure patients, we need to get them on our cornerstone therapies,” said Dr. Ziaeian, of the Veterans Affairts Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have shown clear efficacy and safety in trials like DAPA-HF and EMPEROR-Reduced, provide a “huge opportunity” to add on to standard therapies, he noted. Competition for VA contracts has brought the price down to about $50 a month for veterans, compared with a cash price of about $500-$600 a month.
Yet in routine practice, only 8% of veterans with HF at his center are on an SGLT2 inhibitor, compared with 80% on ACE inhibitors or beta blockers, observed Dr. Ziaeian. “This medication has been indicated for the last year and a half and we’re only at 8% in a system where we have pretty easy access to medications.”
As reported online Feb. 10 in JAMA Cardiology, notable sex differences were found in hospitalization, with higher rates per 1,000 persons among men.
In contrast, a 2020 report on HF trends in the VA system showed a 2% decrease in unadjusted 30-day readmissions from 2007 to 2017 and a decline in the adjusted 30-day readmission risk.
The present study did not risk-adjust readmission risk and included a population that was 51% male, compared with about 98% male in the VA, the investigators noted.
“The increasing hospitalization rate in our study may represent an actual increase in HF hospitalizations or shifts in administrative coding practices, increased use of HF biomarkers, or lower thresholds for diagnosis of HF with preserved ejection fraction,” they wrote.
The analysis was based on data from the Nationwide Readmission Database, which included 35,197,725 hospitalizations with a primary or secondary diagnosis of HF and 8,273,270 primary HF hospitalizations from January 2010 to December 2017.
A single primary HF admission occurred in 5,092,626 unique patients and 1,269,109 had two or more HF hospitalizations. The mean age was 72.1 years.
The administrative database did not include clinical data, so it wasn’t possible to differentiate between HF with preserved or reduced ejection fraction, the authors noted. Patient race and ethnicity data also were not available.
“Future studies are needed to verify our findings to better develop and improve individualized strategies for HF prevention, management, and surveillance for men and women,” the investigators concluded.
One coauthor reporting receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall primary HF hospitalization rates per 1,000 adults declined from 4.4 in 2010 to 4.1 in 2013, and then increased from 4.2 in 2014 to 4.9 in 2017.
Rates of unique patient visits for HF were also on the way down – falling from 3.4 in 2010 to 3.2 in 2013 and 2014 – before climbing to 3.8 in 2017.
Similar trends were observed for rates of postdischarge HF readmissions (from 1.0 in 2010 to 0.9 in 2014 to 1.1 in 2017) and all-cause 30-day readmissions (from 0.8 in 2010 to 0.7 in 2014 to 0.9 in 2017).
“We should be emphasizing the things we know work to reduce heart failure hospitalization, which is, No. 1, prevention,” senior author Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Comorbidities that can lead to heart failure crept up over the study period, such that by 2017, hypertension was present in 91.4% of patients, diabetes in 48.9%, and lipid disorders in 53.1%, up from 76.5%, 44.9%, and 40.4%, respectively, in 2010. Half of all patients had coronary artery disease at both time points. Renal disease shot up from 45.9% to 60.6% by 2017.
“If we did a better job of controlling our known risk factors, we would really cut down on the incidence of heart failure being developed and then, among those estimated 6.6 million heart failure patients, we need to get them on our cornerstone therapies,” said Dr. Ziaeian, of the Veterans Affairts Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have shown clear efficacy and safety in trials like DAPA-HF and EMPEROR-Reduced, provide a “huge opportunity” to add on to standard therapies, he noted. Competition for VA contracts has brought the price down to about $50 a month for veterans, compared with a cash price of about $500-$600 a month.
Yet in routine practice, only 8% of veterans with HF at his center are on an SGLT2 inhibitor, compared with 80% on ACE inhibitors or beta blockers, observed Dr. Ziaeian. “This medication has been indicated for the last year and a half and we’re only at 8% in a system where we have pretty easy access to medications.”
As reported online Feb. 10 in JAMA Cardiology, notable sex differences were found in hospitalization, with higher rates per 1,000 persons among men.
In contrast, a 2020 report on HF trends in the VA system showed a 2% decrease in unadjusted 30-day readmissions from 2007 to 2017 and a decline in the adjusted 30-day readmission risk.
The present study did not risk-adjust readmission risk and included a population that was 51% male, compared with about 98% male in the VA, the investigators noted.
“The increasing hospitalization rate in our study may represent an actual increase in HF hospitalizations or shifts in administrative coding practices, increased use of HF biomarkers, or lower thresholds for diagnosis of HF with preserved ejection fraction,” they wrote.
The analysis was based on data from the Nationwide Readmission Database, which included 35,197,725 hospitalizations with a primary or secondary diagnosis of HF and 8,273,270 primary HF hospitalizations from January 2010 to December 2017.
A single primary HF admission occurred in 5,092,626 unique patients and 1,269,109 had two or more HF hospitalizations. The mean age was 72.1 years.
The administrative database did not include clinical data, so it wasn’t possible to differentiate between HF with preserved or reduced ejection fraction, the authors noted. Patient race and ethnicity data also were not available.
“Future studies are needed to verify our findings to better develop and improve individualized strategies for HF prevention, management, and surveillance for men and women,” the investigators concluded.
One coauthor reporting receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall primary HF hospitalization rates per 1,000 adults declined from 4.4 in 2010 to 4.1 in 2013, and then increased from 4.2 in 2014 to 4.9 in 2017.
Rates of unique patient visits for HF were also on the way down – falling from 3.4 in 2010 to 3.2 in 2013 and 2014 – before climbing to 3.8 in 2017.
Similar trends were observed for rates of postdischarge HF readmissions (from 1.0 in 2010 to 0.9 in 2014 to 1.1 in 2017) and all-cause 30-day readmissions (from 0.8 in 2010 to 0.7 in 2014 to 0.9 in 2017).
“We should be emphasizing the things we know work to reduce heart failure hospitalization, which is, No. 1, prevention,” senior author Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Comorbidities that can lead to heart failure crept up over the study period, such that by 2017, hypertension was present in 91.4% of patients, diabetes in 48.9%, and lipid disorders in 53.1%, up from 76.5%, 44.9%, and 40.4%, respectively, in 2010. Half of all patients had coronary artery disease at both time points. Renal disease shot up from 45.9% to 60.6% by 2017.
“If we did a better job of controlling our known risk factors, we would really cut down on the incidence of heart failure being developed and then, among those estimated 6.6 million heart failure patients, we need to get them on our cornerstone therapies,” said Dr. Ziaeian, of the Veterans Affairts Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have shown clear efficacy and safety in trials like DAPA-HF and EMPEROR-Reduced, provide a “huge opportunity” to add on to standard therapies, he noted. Competition for VA contracts has brought the price down to about $50 a month for veterans, compared with a cash price of about $500-$600 a month.
Yet in routine practice, only 8% of veterans with HF at his center are on an SGLT2 inhibitor, compared with 80% on ACE inhibitors or beta blockers, observed Dr. Ziaeian. “This medication has been indicated for the last year and a half and we’re only at 8% in a system where we have pretty easy access to medications.”
As reported online Feb. 10 in JAMA Cardiology, notable sex differences were found in hospitalization, with higher rates per 1,000 persons among men.
In contrast, a 2020 report on HF trends in the VA system showed a 2% decrease in unadjusted 30-day readmissions from 2007 to 2017 and a decline in the adjusted 30-day readmission risk.
The present study did not risk-adjust readmission risk and included a population that was 51% male, compared with about 98% male in the VA, the investigators noted.
“The increasing hospitalization rate in our study may represent an actual increase in HF hospitalizations or shifts in administrative coding practices, increased use of HF biomarkers, or lower thresholds for diagnosis of HF with preserved ejection fraction,” they wrote.
The analysis was based on data from the Nationwide Readmission Database, which included 35,197,725 hospitalizations with a primary or secondary diagnosis of HF and 8,273,270 primary HF hospitalizations from January 2010 to December 2017.
A single primary HF admission occurred in 5,092,626 unique patients and 1,269,109 had two or more HF hospitalizations. The mean age was 72.1 years.
The administrative database did not include clinical data, so it wasn’t possible to differentiate between HF with preserved or reduced ejection fraction, the authors noted. Patient race and ethnicity data also were not available.
“Future studies are needed to verify our findings to better develop and improve individualized strategies for HF prevention, management, and surveillance for men and women,” the investigators concluded.
One coauthor reporting receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Multifocal Annular Pink Plaques With a Central Violaceous Hue
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Erythema Chronicum Migrans
Empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 14 days was initiated for suspected early disseminated Lyme disease manifesting as disseminated multifocal erythema chronicum migrans (Figure). Lyme screening immunoassay and confirmatory IgM Western blot testing subsequently were found to be positive. The clinical history of recent travel to an endemic area and tick bite combined with the recent onset of multifocal erythema migrans lesions, systemic symptoms, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and positive Lyme serology supported the diagnosis of Lyme disease.
The appropriate clinical context and cutaneous morphology are key when considering the differential diagnosis for multifocal annular lesions. Several entities comprised the differential diagnosis considered in our patient. Sweet syndrome is a neutrophilic dermatosis that can present with fever and varying painful cutaneous lesions. It often is associated with certain medications, underlying illnesses, and infections.1 Our patient’s lesions were not painful, and she had no notable medical history, recent infections, or new medication use, making Sweet syndrome unlikely. A fixed drug eruption was low on the differential, as the patient denied starting any new medications within the 3 months prior to presentation. Erythema multiforme is an acute-onset immunemediated condition of the skin and mucous membranes that typically affects young adults and often is associated with infection (eg, herpes simplex virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) or medication use. Cutaneous lesions typically are self-limited, less than 3 cm targets with 3 concentric distinct color zones, often with central bullae or erosions. Although erythema multiforme was higher on the differential, it was less likely, as the patient lacked mucosal lesions and did not have symptoms of underlying herpetic or mycoplasma infection, and the clinical picture was more consistent with Lyme disease. Lastly, the failure for individual skin lesions to resolve within
24 hours excluded the diagnosis of urticaria.
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by 3 species of the Borrelia spirochete: Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia afzelii, and Borrelia garinii.2 In the United States, the disease predominantly is caused by B burgdorferi that is endemic in the upper Midwest and Northeast regions.3 There are 3 stages of Lyme disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated disease. Early localized disease typically presents with a characteristic single erythema migrans (EM) lesion 3 to 30 days following a bite by the tick Ixodes scapularis.2 The EM lesion gradually can enlarge over a period of several days, reaching up to 12 inches in diameter.2 Early disseminated disease can occur weeks to months following a tick bite and may present with systemic symptoms, multiple widespread
EM lesions, neurologic features such as meningitis or facial nerve palsy, and/or cardiac manifestations such as atrioventricular block or myocarditis. Late disseminated disease can present with chronic arthritis or encephalopathy after months to years if the disease is left untreated.4
Early localized Lyme disease can be diagnosed clinically if the characteristic EM lesion is present in a patient who visited an endemic area. Laboratory testing and Lyme serology are neither required nor recommended in these cases, as the lesion often appears before adequate time has lapsed to develop an adaptive immune response to the organism.5 In contrast, Lyme serology should be ordered in any patient who meets all of the following criteria: (1) patient lives in or has recently traveled to an area endemic for Lyme disease, (2) presence of a risk factor for tick exposure, and (3) symptoms consistent with early disseminated or late Lyme disease. Patients with signs of early or late disseminated disease typically are seropositive, as IgM antibodies can be detected within 2 weeks of onset of the EM lesion and IgG antibodies within 2 to 6 weeks.6 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a 2-tiered approach when testing for Lyme disease.7 A screening test with high sensitivity such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or an immunofluorescence assay initially should be performed.7 If results of the screening test are equivocal or positive, secondary confirmatory testing should be performed via IgM, with or without IgG Western immunoblot assay.7 Biopsy with histologic evaluation can reveal nonspecific findings of vascular endothelial injury and increased mucin deposition. Patients with suspected Lyme disease should immediately be started on empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for a minimum of 10 days (14–28 days if there is concern for dissemination) to prevent post-Lyme sequelae.5 Our patient’s cutaneous lesions responded to oral doxycycline.
- Sweet’s syndrome. Mayo Clinic. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sweets-syndrome /symptoms-causes/syc-20351117
- Steere AC. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:115-125.
- Lyme disease maps: most recent year. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated November 22, 2019. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance /maps-recent.html.
- Steere AC, Sikand VK. The present manifestations of Lyme disease and the outcomes of treatment. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2472-2474.
- Sanchez E, Vannier E, Wormser GP, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: a review. JAMA. 2016;315:1767-1777.
- Shapiro ED. Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease). Pediatr Rev. 2014; 35:500-509.
- Mead P, Petersen J, Hinckley A. Updated CDC recommendation for serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:703
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Erythema Chronicum Migrans
Empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 14 days was initiated for suspected early disseminated Lyme disease manifesting as disseminated multifocal erythema chronicum migrans (Figure). Lyme screening immunoassay and confirmatory IgM Western blot testing subsequently were found to be positive. The clinical history of recent travel to an endemic area and tick bite combined with the recent onset of multifocal erythema migrans lesions, systemic symptoms, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and positive Lyme serology supported the diagnosis of Lyme disease.

The appropriate clinical context and cutaneous morphology are key when considering the differential diagnosis for multifocal annular lesions. Several entities comprised the differential diagnosis considered in our patient. Sweet syndrome is a neutrophilic dermatosis that can present with fever and varying painful cutaneous lesions. It often is associated with certain medications, underlying illnesses, and infections.1 Our patient’s lesions were not painful, and she had no notable medical history, recent infections, or new medication use, making Sweet syndrome unlikely. A fixed drug eruption was low on the differential, as the patient denied starting any new medications within the 3 months prior to presentation. Erythema multiforme is an acute-onset immunemediated condition of the skin and mucous membranes that typically affects young adults and often is associated with infection (eg, herpes simplex virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) or medication use. Cutaneous lesions typically are self-limited, less than 3 cm targets with 3 concentric distinct color zones, often with central bullae or erosions. Although erythema multiforme was higher on the differential, it was less likely, as the patient lacked mucosal lesions and did not have symptoms of underlying herpetic or mycoplasma infection, and the clinical picture was more consistent with Lyme disease. Lastly, the failure for individual skin lesions to resolve within
24 hours excluded the diagnosis of urticaria.
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by 3 species of the Borrelia spirochete: Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia afzelii, and Borrelia garinii.2 In the United States, the disease predominantly is caused by B burgdorferi that is endemic in the upper Midwest and Northeast regions.3 There are 3 stages of Lyme disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated disease. Early localized disease typically presents with a characteristic single erythema migrans (EM) lesion 3 to 30 days following a bite by the tick Ixodes scapularis.2 The EM lesion gradually can enlarge over a period of several days, reaching up to 12 inches in diameter.2 Early disseminated disease can occur weeks to months following a tick bite and may present with systemic symptoms, multiple widespread
EM lesions, neurologic features such as meningitis or facial nerve palsy, and/or cardiac manifestations such as atrioventricular block or myocarditis. Late disseminated disease can present with chronic arthritis or encephalopathy after months to years if the disease is left untreated.4
Early localized Lyme disease can be diagnosed clinically if the characteristic EM lesion is present in a patient who visited an endemic area. Laboratory testing and Lyme serology are neither required nor recommended in these cases, as the lesion often appears before adequate time has lapsed to develop an adaptive immune response to the organism.5 In contrast, Lyme serology should be ordered in any patient who meets all of the following criteria: (1) patient lives in or has recently traveled to an area endemic for Lyme disease, (2) presence of a risk factor for tick exposure, and (3) symptoms consistent with early disseminated or late Lyme disease. Patients with signs of early or late disseminated disease typically are seropositive, as IgM antibodies can be detected within 2 weeks of onset of the EM lesion and IgG antibodies within 2 to 6 weeks.6 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a 2-tiered approach when testing for Lyme disease.7 A screening test with high sensitivity such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or an immunofluorescence assay initially should be performed.7 If results of the screening test are equivocal or positive, secondary confirmatory testing should be performed via IgM, with or without IgG Western immunoblot assay.7 Biopsy with histologic evaluation can reveal nonspecific findings of vascular endothelial injury and increased mucin deposition. Patients with suspected Lyme disease should immediately be started on empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for a minimum of 10 days (14–28 days if there is concern for dissemination) to prevent post-Lyme sequelae.5 Our patient’s cutaneous lesions responded to oral doxycycline.
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Erythema Chronicum Migrans
Empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 14 days was initiated for suspected early disseminated Lyme disease manifesting as disseminated multifocal erythema chronicum migrans (Figure). Lyme screening immunoassay and confirmatory IgM Western blot testing subsequently were found to be positive. The clinical history of recent travel to an endemic area and tick bite combined with the recent onset of multifocal erythema migrans lesions, systemic symptoms, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and positive Lyme serology supported the diagnosis of Lyme disease.

The appropriate clinical context and cutaneous morphology are key when considering the differential diagnosis for multifocal annular lesions. Several entities comprised the differential diagnosis considered in our patient. Sweet syndrome is a neutrophilic dermatosis that can present with fever and varying painful cutaneous lesions. It often is associated with certain medications, underlying illnesses, and infections.1 Our patient’s lesions were not painful, and she had no notable medical history, recent infections, or new medication use, making Sweet syndrome unlikely. A fixed drug eruption was low on the differential, as the patient denied starting any new medications within the 3 months prior to presentation. Erythema multiforme is an acute-onset immunemediated condition of the skin and mucous membranes that typically affects young adults and often is associated with infection (eg, herpes simplex virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) or medication use. Cutaneous lesions typically are self-limited, less than 3 cm targets with 3 concentric distinct color zones, often with central bullae or erosions. Although erythema multiforme was higher on the differential, it was less likely, as the patient lacked mucosal lesions and did not have symptoms of underlying herpetic or mycoplasma infection, and the clinical picture was more consistent with Lyme disease. Lastly, the failure for individual skin lesions to resolve within
24 hours excluded the diagnosis of urticaria.
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by 3 species of the Borrelia spirochete: Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia afzelii, and Borrelia garinii.2 In the United States, the disease predominantly is caused by B burgdorferi that is endemic in the upper Midwest and Northeast regions.3 There are 3 stages of Lyme disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated disease. Early localized disease typically presents with a characteristic single erythema migrans (EM) lesion 3 to 30 days following a bite by the tick Ixodes scapularis.2 The EM lesion gradually can enlarge over a period of several days, reaching up to 12 inches in diameter.2 Early disseminated disease can occur weeks to months following a tick bite and may present with systemic symptoms, multiple widespread
EM lesions, neurologic features such as meningitis or facial nerve palsy, and/or cardiac manifestations such as atrioventricular block or myocarditis. Late disseminated disease can present with chronic arthritis or encephalopathy after months to years if the disease is left untreated.4
Early localized Lyme disease can be diagnosed clinically if the characteristic EM lesion is present in a patient who visited an endemic area. Laboratory testing and Lyme serology are neither required nor recommended in these cases, as the lesion often appears before adequate time has lapsed to develop an adaptive immune response to the organism.5 In contrast, Lyme serology should be ordered in any patient who meets all of the following criteria: (1) patient lives in or has recently traveled to an area endemic for Lyme disease, (2) presence of a risk factor for tick exposure, and (3) symptoms consistent with early disseminated or late Lyme disease. Patients with signs of early or late disseminated disease typically are seropositive, as IgM antibodies can be detected within 2 weeks of onset of the EM lesion and IgG antibodies within 2 to 6 weeks.6 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a 2-tiered approach when testing for Lyme disease.7 A screening test with high sensitivity such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or an immunofluorescence assay initially should be performed.7 If results of the screening test are equivocal or positive, secondary confirmatory testing should be performed via IgM, with or without IgG Western immunoblot assay.7 Biopsy with histologic evaluation can reveal nonspecific findings of vascular endothelial injury and increased mucin deposition. Patients with suspected Lyme disease should immediately be started on empiric treatment with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for a minimum of 10 days (14–28 days if there is concern for dissemination) to prevent post-Lyme sequelae.5 Our patient’s cutaneous lesions responded to oral doxycycline.
- Sweet’s syndrome. Mayo Clinic. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sweets-syndrome /symptoms-causes/syc-20351117
- Steere AC. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:115-125.
- Lyme disease maps: most recent year. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated November 22, 2019. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance /maps-recent.html.
- Steere AC, Sikand VK. The present manifestations of Lyme disease and the outcomes of treatment. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2472-2474.
- Sanchez E, Vannier E, Wormser GP, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: a review. JAMA. 2016;315:1767-1777.
- Shapiro ED. Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease). Pediatr Rev. 2014; 35:500-509.
- Mead P, Petersen J, Hinckley A. Updated CDC recommendation for serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:703
- Sweet’s syndrome. Mayo Clinic. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sweets-syndrome /symptoms-causes/syc-20351117
- Steere AC. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:115-125.
- Lyme disease maps: most recent year. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated November 22, 2019. Accessed January 8, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/datasurveillance /maps-recent.html.
- Steere AC, Sikand VK. The present manifestations of Lyme disease and the outcomes of treatment. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2472-2474.
- Sanchez E, Vannier E, Wormser GP, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: a review. JAMA. 2016;315:1767-1777.
- Shapiro ED. Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease). Pediatr Rev. 2014; 35:500-509.
- Mead P, Petersen J, Hinckley A. Updated CDC recommendation for serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:703
An otherwise healthy 78-year-old woman presented with a diffuse, mildly itchy rash of 5 days’ duration with associated fatigue, chills, decreased appetite, and nausea. She reported waking up with her arms “feeling like they weigh a ton.” She denied any pain, bleeding, or oozing and was unsure if new spots were continuing to develop. The patient reported having allergies to numerous medications but denied any new medications or recent illnesses. She had recently spent time on a farm in Minnesota, and upon further questioning she recalled a tick bite 2 months prior to presentation. She stated that she removed the nonengorged tick and that it could not have been attached for more than 24 hours. Her medical and family history were unremarkable. Physical examination showed multiple annular pink plaques with a central violaceous hue in a generalized distribution involving the face, trunk, arms, and legs with mild erythema of the palms. The plantar surfaces were clear, and there was no evidence of lymphadenopathy. The remainder of the physical examination and review of systems was negative. Laboratory screening was notable for an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level with negative antinuclear antibodies.
The lost year – even for common respiratory viruses
In this column in September 2020, you read how common respiratory viruses’ seasons are usually so predictable, each virus arising, peaking, and then dying out in a predictable virus parade (Figure 1).1 Well, the predictable virus seasonal pattern was lost in 2020. Since March of 2020, it is striking how little activity was detected for the usual seasonal viruses in Kansas City after mid-March 2020 (Figure 2).2 So, my concern in September 2020 for possible rampant coinfections of common viruses with or in tandem with SARS-CoV-2 did not pan out. That said, the seasons for non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses did change; I just didn’t expect they would nearly disappear.
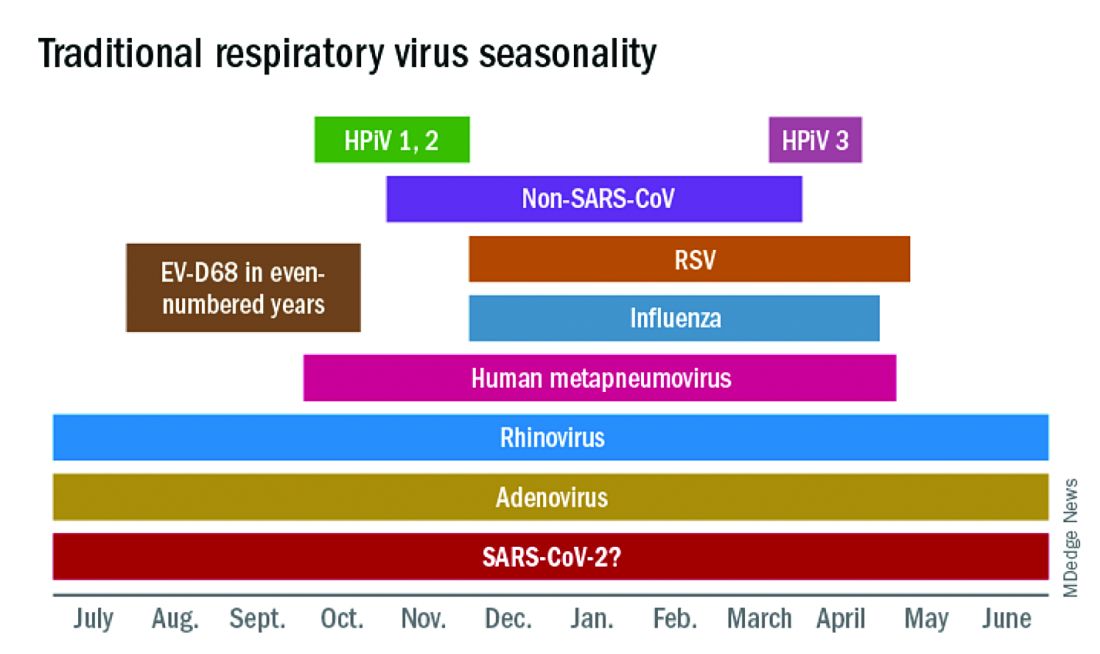
The 2020 winter-spring. In the first quarter (the last part of the overall 2019-2020 respiratory viral season), viral detections were chugging along as usual up to mid-March (Figure 2); influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinovirus were the big players.
Influenza. In most years, influenza type B leads off and is quickly replaced by type A only to see B reemerge to end influenza season in March-April. In early 2020, both influenza type A and influenza type B cocirculated nearly equally, but both dropped like a rock in mid-March (Figure 2).2 Neither type has been seen since with the exception of sporadic detections – perhaps being false positives.
RSV. In the usual year in temperate mid-latitudes of the northern hemisphere, RSV season usually starts in early December, peaks in January-March, and declines gradually until the end of RSV season in April (Figure 1). In southern latitudes, RSV is less seasonal, being present most of the year, but peaking in “winter” months.3 But in 2020, RSV also disappeared in mid-March and has yet to reappear.
Other viruses. Small bumps in detection of parainfluenza of varying types usually frame influenza season, one B bump in early autumn and another in April-May. In most years, human metapneumovirus is detected on and off, with worse years at 2- to 3-year intervals. Adenovirus occurs year-round with bumps as children get back to school in autumn. Yet in 2020, almost no parainfluenza, adenovirus, common coronaviruses, or human metapneumovirus were detected in either spring or autumn. This was supposed to be a banner summer-autumn for EV-D68 – but almost none was detected. Interestingly, the cockroach of viruses, rhinovirus, has its usual year (Figure 2).
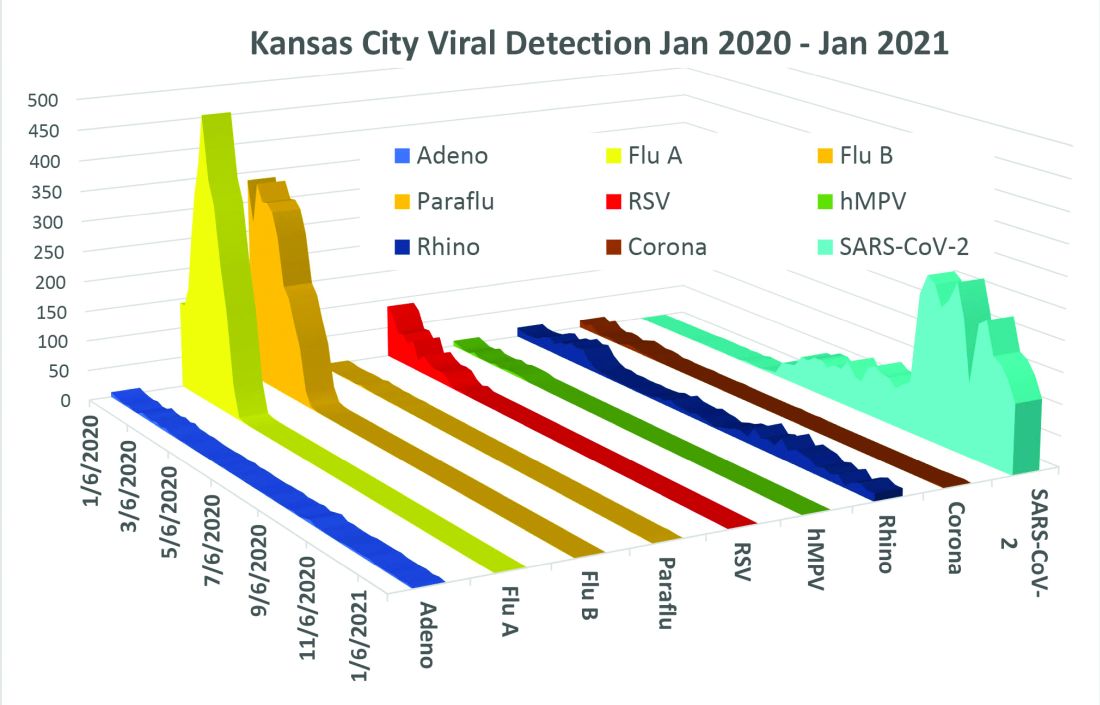
What happened? Intense social mitigation interventions, including social distancing and closing daycares and schools, were likely major factors.4 For influenza, vaccine may have helped but uptake was not remarkably better than most prior years. There may have been “viral competition,”where a new or highly transmissible virus outcompetes less-transmissible viruses with lower affinity for respiratory receptors.5,6 Note that SARS-CoV-2 has very high affinity for the ACE2 receptor and has been highly prevalent. So, SARS-CoV-2 could fit the theoretical mold for a virus that outcompetes others.
Does it matter for the future? Blunted 2019-2020 and nearly absent 2020-2021 respiratory virus season may have set the stage for intense 2021-2022 rebounds for the non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses. We now have two whole and one partial birth cohort with no experience with seasonal respiratory viruses, including EV-D68 (and nonrespiratory viruses too – like norovirus, parechovirus, and other enteroviruses). Most viruses have particularly bad seasons every 2-3 years, thought to be caused by increasing accumulation of susceptible individuals in consecutive birth cohorts until a critical mass of susceptible individuals is achieved. The excess in susceptible individuals means that each contagious case is likely to expose one or more susceptible individuals, enhancing transmission and infection numbers in an ever-extending ripple effect. We have never had this many children aged under 3 years with no immunity to influenza, RSV, etc. So unless mother nature is kind (when has that happened lately?), expect rebound years for seasonal viruses as children return to daycare/schools and as social mitigation becomes less necessary in the waning pandemic.
Options? If you ramped up telehealth visits for the pandemic, that may be a saving grace, i.e., more efficiency so more “visits” can be completed per day, and less potential contact in reception rooms between well and ill children. And if there was ever a time to really intensify efforts to immunize all our pediatric patients, the next two seasons are just that. Adding a bit of a warning to families with young children also seems warranted. If they understand that, while 2021-2022 will be better for SARS-CoV-2, it is likely going to be worse for the other viruses.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Harrison CJ. 2020-2021 respiratory viral season: Onset, presentations, and testing likely to differ in pandemic, Pediatric News: September 17, 2020.
2. Olsen SJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1305-9.
3. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Surveillance. http://www.floridahealth.gov/diseases-and-conditions/respiratory-syncytial-virus/_documents/2021-w4-rsv-summary.pdf
4. Baker RE et al. PNAS. Dec 2020 117;(48):30547-53.
5. Sema Nickbakhsh et al. PNAS. Dec 2019 116;(52):27142-50.
6. Kirsten M et al. PNAS. Mar 2020 117;(13):6987.
In this column in September 2020, you read how common respiratory viruses’ seasons are usually so predictable, each virus arising, peaking, and then dying out in a predictable virus parade (Figure 1).1 Well, the predictable virus seasonal pattern was lost in 2020. Since March of 2020, it is striking how little activity was detected for the usual seasonal viruses in Kansas City after mid-March 2020 (Figure 2).2 So, my concern in September 2020 for possible rampant coinfections of common viruses with or in tandem with SARS-CoV-2 did not pan out. That said, the seasons for non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses did change; I just didn’t expect they would nearly disappear.

The 2020 winter-spring. In the first quarter (the last part of the overall 2019-2020 respiratory viral season), viral detections were chugging along as usual up to mid-March (Figure 2); influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinovirus were the big players.
Influenza. In most years, influenza type B leads off and is quickly replaced by type A only to see B reemerge to end influenza season in March-April. In early 2020, both influenza type A and influenza type B cocirculated nearly equally, but both dropped like a rock in mid-March (Figure 2).2 Neither type has been seen since with the exception of sporadic detections – perhaps being false positives.
RSV. In the usual year in temperate mid-latitudes of the northern hemisphere, RSV season usually starts in early December, peaks in January-March, and declines gradually until the end of RSV season in April (Figure 1). In southern latitudes, RSV is less seasonal, being present most of the year, but peaking in “winter” months.3 But in 2020, RSV also disappeared in mid-March and has yet to reappear.
Other viruses. Small bumps in detection of parainfluenza of varying types usually frame influenza season, one B bump in early autumn and another in April-May. In most years, human metapneumovirus is detected on and off, with worse years at 2- to 3-year intervals. Adenovirus occurs year-round with bumps as children get back to school in autumn. Yet in 2020, almost no parainfluenza, adenovirus, common coronaviruses, or human metapneumovirus were detected in either spring or autumn. This was supposed to be a banner summer-autumn for EV-D68 – but almost none was detected. Interestingly, the cockroach of viruses, rhinovirus, has its usual year (Figure 2).

What happened? Intense social mitigation interventions, including social distancing and closing daycares and schools, were likely major factors.4 For influenza, vaccine may have helped but uptake was not remarkably better than most prior years. There may have been “viral competition,”where a new or highly transmissible virus outcompetes less-transmissible viruses with lower affinity for respiratory receptors.5,6 Note that SARS-CoV-2 has very high affinity for the ACE2 receptor and has been highly prevalent. So, SARS-CoV-2 could fit the theoretical mold for a virus that outcompetes others.
Does it matter for the future? Blunted 2019-2020 and nearly absent 2020-2021 respiratory virus season may have set the stage for intense 2021-2022 rebounds for the non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses. We now have two whole and one partial birth cohort with no experience with seasonal respiratory viruses, including EV-D68 (and nonrespiratory viruses too – like norovirus, parechovirus, and other enteroviruses). Most viruses have particularly bad seasons every 2-3 years, thought to be caused by increasing accumulation of susceptible individuals in consecutive birth cohorts until a critical mass of susceptible individuals is achieved. The excess in susceptible individuals means that each contagious case is likely to expose one or more susceptible individuals, enhancing transmission and infection numbers in an ever-extending ripple effect. We have never had this many children aged under 3 years with no immunity to influenza, RSV, etc. So unless mother nature is kind (when has that happened lately?), expect rebound years for seasonal viruses as children return to daycare/schools and as social mitigation becomes less necessary in the waning pandemic.
Options? If you ramped up telehealth visits for the pandemic, that may be a saving grace, i.e., more efficiency so more “visits” can be completed per day, and less potential contact in reception rooms between well and ill children. And if there was ever a time to really intensify efforts to immunize all our pediatric patients, the next two seasons are just that. Adding a bit of a warning to families with young children also seems warranted. If they understand that, while 2021-2022 will be better for SARS-CoV-2, it is likely going to be worse for the other viruses.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Harrison CJ. 2020-2021 respiratory viral season: Onset, presentations, and testing likely to differ in pandemic, Pediatric News: September 17, 2020.
2. Olsen SJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1305-9.
3. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Surveillance. http://www.floridahealth.gov/diseases-and-conditions/respiratory-syncytial-virus/_documents/2021-w4-rsv-summary.pdf
4. Baker RE et al. PNAS. Dec 2020 117;(48):30547-53.
5. Sema Nickbakhsh et al. PNAS. Dec 2019 116;(52):27142-50.
6. Kirsten M et al. PNAS. Mar 2020 117;(13):6987.
In this column in September 2020, you read how common respiratory viruses’ seasons are usually so predictable, each virus arising, peaking, and then dying out in a predictable virus parade (Figure 1).1 Well, the predictable virus seasonal pattern was lost in 2020. Since March of 2020, it is striking how little activity was detected for the usual seasonal viruses in Kansas City after mid-March 2020 (Figure 2).2 So, my concern in September 2020 for possible rampant coinfections of common viruses with or in tandem with SARS-CoV-2 did not pan out. That said, the seasons for non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses did change; I just didn’t expect they would nearly disappear.

The 2020 winter-spring. In the first quarter (the last part of the overall 2019-2020 respiratory viral season), viral detections were chugging along as usual up to mid-March (Figure 2); influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinovirus were the big players.
Influenza. In most years, influenza type B leads off and is quickly replaced by type A only to see B reemerge to end influenza season in March-April. In early 2020, both influenza type A and influenza type B cocirculated nearly equally, but both dropped like a rock in mid-March (Figure 2).2 Neither type has been seen since with the exception of sporadic detections – perhaps being false positives.
RSV. In the usual year in temperate mid-latitudes of the northern hemisphere, RSV season usually starts in early December, peaks in January-March, and declines gradually until the end of RSV season in April (Figure 1). In southern latitudes, RSV is less seasonal, being present most of the year, but peaking in “winter” months.3 But in 2020, RSV also disappeared in mid-March and has yet to reappear.
Other viruses. Small bumps in detection of parainfluenza of varying types usually frame influenza season, one B bump in early autumn and another in April-May. In most years, human metapneumovirus is detected on and off, with worse years at 2- to 3-year intervals. Adenovirus occurs year-round with bumps as children get back to school in autumn. Yet in 2020, almost no parainfluenza, adenovirus, common coronaviruses, or human metapneumovirus were detected in either spring or autumn. This was supposed to be a banner summer-autumn for EV-D68 – but almost none was detected. Interestingly, the cockroach of viruses, rhinovirus, has its usual year (Figure 2).

What happened? Intense social mitigation interventions, including social distancing and closing daycares and schools, were likely major factors.4 For influenza, vaccine may have helped but uptake was not remarkably better than most prior years. There may have been “viral competition,”where a new or highly transmissible virus outcompetes less-transmissible viruses with lower affinity for respiratory receptors.5,6 Note that SARS-CoV-2 has very high affinity for the ACE2 receptor and has been highly prevalent. So, SARS-CoV-2 could fit the theoretical mold for a virus that outcompetes others.
Does it matter for the future? Blunted 2019-2020 and nearly absent 2020-2021 respiratory virus season may have set the stage for intense 2021-2022 rebounds for the non–SARS-CoV-2 viruses. We now have two whole and one partial birth cohort with no experience with seasonal respiratory viruses, including EV-D68 (and nonrespiratory viruses too – like norovirus, parechovirus, and other enteroviruses). Most viruses have particularly bad seasons every 2-3 years, thought to be caused by increasing accumulation of susceptible individuals in consecutive birth cohorts until a critical mass of susceptible individuals is achieved. The excess in susceptible individuals means that each contagious case is likely to expose one or more susceptible individuals, enhancing transmission and infection numbers in an ever-extending ripple effect. We have never had this many children aged under 3 years with no immunity to influenza, RSV, etc. So unless mother nature is kind (when has that happened lately?), expect rebound years for seasonal viruses as children return to daycare/schools and as social mitigation becomes less necessary in the waning pandemic.
Options? If you ramped up telehealth visits for the pandemic, that may be a saving grace, i.e., more efficiency so more “visits” can be completed per day, and less potential contact in reception rooms between well and ill children. And if there was ever a time to really intensify efforts to immunize all our pediatric patients, the next two seasons are just that. Adding a bit of a warning to families with young children also seems warranted. If they understand that, while 2021-2022 will be better for SARS-CoV-2, it is likely going to be worse for the other viruses.
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Harrison CJ. 2020-2021 respiratory viral season: Onset, presentations, and testing likely to differ in pandemic, Pediatric News: September 17, 2020.
2. Olsen SJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1305-9.
3. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Surveillance. http://www.floridahealth.gov/diseases-and-conditions/respiratory-syncytial-virus/_documents/2021-w4-rsv-summary.pdf
4. Baker RE et al. PNAS. Dec 2020 117;(48):30547-53.
5. Sema Nickbakhsh et al. PNAS. Dec 2019 116;(52):27142-50.
6. Kirsten M et al. PNAS. Mar 2020 117;(13):6987.
Cumulative exposure to high-potency topical steroid doses drives osteoporosis fractures
In support of previously published case reports, in a dose-response relationship.
In a stepwise manner, the hazard ratios for major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) were found to start climbing incrementally for those with a cumulative topical steroid dose equivalent of more than 500 g of mometasone furoate when compared with exposure of 200-499 g, according to the team of investigators from the University of Copenhagen.
“Use of these drugs is very common, and we found an estimated population-attributable risk of as much as 4.3%,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
The retrospective cohort study drew data from the Danish National Patient Registry, which covers 99% of the country’s population. It was linked to the Danish National Prescription Registry, which captures data on pharmacy-dispensed medications. Data collected from the beginning of 2003 to the end of 2017 were evaluated.
Exposures to potent or very potent topical corticosteroids were converted into a single standard with potency equivalent to 1 mg/g of mometasone furoate. Four strata of exposure were compared to a reference exposure of 200-499 g. These were 500-999 g, 1,000-1,999 g, 2,000-9,999 g, and 10,000 g or greater.
For the first strata, the small increased risk for MOF did not reach significance (HR, 1.01; 95% confidence interval, 0.99-1.03), but each of the others did. These climbed from a 5% greater risk (HR 1.05 95% CI 1.02-1.08) for a cumulative exposure of 1,000 to 1,999 g, to a 10% greater risk (HR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.07-1.13) for a cumulative exposure of 2,000-9,999 g, and finally to a 27% greater risk (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.19-1.35) for a cumulative exposure of 10,000 g or higher.
The study included more than 700,000 individuals exposed to topical mometasone at a potency equivalent of 200 g or more over the study period. The reference group (200-499 g) was the largest (317,907 individuals). The first strata (500-999 g) included 186,359 patients; the second (1,000-1,999 g), 111,203 patients; the third (2,000-9,999 g), 94,334 patients; and the fifth (10,000 g or more), 13,448 patients.
“A 3% increase in the relative risk of osteoporosis and MOF was observed per doubling of the TCS dose,” according to the investigators.
Patients exposed to doses of high-potency topical steroids that put them at risk of MOF is limited but substantial, according to the senior author, Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology and allergy at Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Copenhagen.
“It is true that the risk is modest for the average user of topical steroids,” Dr. Egeberg said in an interview. However, despite the fact that topical steroids are intended for short-term use, “2% of all our users had been exposed to the equivalent of 10,000 g of mometasone, which mean 100 tubes of 100 g.”
If the other two strata at significantly increased risk of MOF (greater than 1,000 g) are included, an additional 28% of all users are facing the potential for clinically significant osteoporosis, according to the Danish data.
The adverse effect of steroids on bone metabolism has been established previously, and several studies have linked systemic corticosteroid exposure, including inhaled corticosteroids, with increased risk of osteoporotic fracture. For example, one study showed that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease on daily inhaled doses of the equivalent of fluticasone at or above 1,000 mcg for more than 4 years had about a 10% increased risk of MOF relative to those not exposed.
The data associate topical steroids with increased risk of osteoporotic fracture, but Dr. Egeberg said osteoporosis is not the only reason to use topical steroids prudently.
“It is important to keep in mind that osteoporosis and fractures are at the extreme end of the side-effect profile and that other side effects, such as striae formation, skin thinning, and dysregulated diabetes, can occur with much lower quantities of topical steroids,” Dr. Egeberg said
For avoiding this risk, “there are no specific cutoffs” recommended for topical steroids in current guidelines, but dermatologists should be aware that many of the indications for topical steroids, such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, involve skin with an impaired barrier function, exposing patients to an increased likelihood of absorption, according to Dr. Egeberg.
“A general rule of thumb that we use is that, if a patient with persistent disease activity requires a new prescription of the equivalent of 100 g mometasone every 1-2 months, it might be worth considering if there is a suitable alternative,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In an accompanying editorial, Rebecca D. Jackson, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism in the department of internal medicine at Ohio State University, Columbus, agreed that no guidelines specific to avoiding the risks of topical corticosteroids are currently available, but she advised clinicians to be considering these risks nonetheless. In general, she suggested that topical steroids, like oral steroids, should be used at “the lowest dose for the shortest duration necessary to manage the underlying medical condition.”
The correlation between topical corticosteroids and increased risk of osteoporotic fracture, although not established previously in a large study, is not surprising, according to Victoria Werth, MD, chief of dermatology at the Philadelphia Veterans Affairs Hospital and professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia.
“Systemic absorption of potent topical steroids has previously been demonstrated with a rapid decrease in serum cortisol levels,” Dr. Werth said in an interview. She indicated that concern about the risk of osteoporosis imposed by use of potent steroids over large body surface areas is appropriate.
To minimize this risk, “it is reasonable to use the lowest dose of steroid possible and to try to substitute other medications when possible,” she said.
Dr. Egeberg reported financial relationships with Abbvie, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant Sciences, Galderma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung, Bioepis, and UCB. Five authors had disclosures related to some of those pharmaceutical companies and/or others. Dr. Jackson had no disclosures.
In support of previously published case reports, in a dose-response relationship.
In a stepwise manner, the hazard ratios for major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) were found to start climbing incrementally for those with a cumulative topical steroid dose equivalent of more than 500 g of mometasone furoate when compared with exposure of 200-499 g, according to the team of investigators from the University of Copenhagen.
“Use of these drugs is very common, and we found an estimated population-attributable risk of as much as 4.3%,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
The retrospective cohort study drew data from the Danish National Patient Registry, which covers 99% of the country’s population. It was linked to the Danish National Prescription Registry, which captures data on pharmacy-dispensed medications. Data collected from the beginning of 2003 to the end of 2017 were evaluated.
Exposures to potent or very potent topical corticosteroids were converted into a single standard with potency equivalent to 1 mg/g of mometasone furoate. Four strata of exposure were compared to a reference exposure of 200-499 g. These were 500-999 g, 1,000-1,999 g, 2,000-9,999 g, and 10,000 g or greater.
For the first strata, the small increased risk for MOF did not reach significance (HR, 1.01; 95% confidence interval, 0.99-1.03), but each of the others did. These climbed from a 5% greater risk (HR 1.05 95% CI 1.02-1.08) for a cumulative exposure of 1,000 to 1,999 g, to a 10% greater risk (HR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.07-1.13) for a cumulative exposure of 2,000-9,999 g, and finally to a 27% greater risk (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.19-1.35) for a cumulative exposure of 10,000 g or higher.
The study included more than 700,000 individuals exposed to topical mometasone at a potency equivalent of 200 g or more over the study period. The reference group (200-499 g) was the largest (317,907 individuals). The first strata (500-999 g) included 186,359 patients; the second (1,000-1,999 g), 111,203 patients; the third (2,000-9,999 g), 94,334 patients; and the fifth (10,000 g or more), 13,448 patients.
“A 3% increase in the relative risk of osteoporosis and MOF was observed per doubling of the TCS dose,” according to the investigators.
Patients exposed to doses of high-potency topical steroids that put them at risk of MOF is limited but substantial, according to the senior author, Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology and allergy at Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Copenhagen.
“It is true that the risk is modest for the average user of topical steroids,” Dr. Egeberg said in an interview. However, despite the fact that topical steroids are intended for short-term use, “2% of all our users had been exposed to the equivalent of 10,000 g of mometasone, which mean 100 tubes of 100 g.”
If the other two strata at significantly increased risk of MOF (greater than 1,000 g) are included, an additional 28% of all users are facing the potential for clinically significant osteoporosis, according to the Danish data.
The adverse effect of steroids on bone metabolism has been established previously, and several studies have linked systemic corticosteroid exposure, including inhaled corticosteroids, with increased risk of osteoporotic fracture. For example, one study showed that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease on daily inhaled doses of the equivalent of fluticasone at or above 1,000 mcg for more than 4 years had about a 10% increased risk of MOF relative to those not exposed.
The data associate topical steroids with increased risk of osteoporotic fracture, but Dr. Egeberg said osteoporosis is not the only reason to use topical steroids prudently.
“It is important to keep in mind that osteoporosis and fractures are at the extreme end of the side-effect profile and that other side effects, such as striae formation, skin thinning, and dysregulated diabetes, can occur with much lower quantities of topical steroids,” Dr. Egeberg said
For avoiding this risk, “there are no specific cutoffs” recommended for topical steroids in current guidelines, but dermatologists should be aware that many of the indications for topical steroids, such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, involve skin with an impaired barrier function, exposing patients to an increased likelihood of absorption, according to Dr. Egeberg.
“A general rule of thumb that we use is that, if a patient with persistent disease activity requires a new prescription of the equivalent of 100 g mometasone every 1-2 months, it might be worth considering if there is a suitable alternative,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In an accompanying editorial, Rebecca D. Jackson, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism in the department of internal medicine at Ohio State University, Columbus, agreed that no guidelines specific to avoiding the risks of topical corticosteroids are currently available, but she advised clinicians to be considering these risks nonetheless. In general, she suggested that topical steroids, like oral steroids, should be used at “the lowest dose for the shortest duration necessary to manage the underlying medical condition.”
The correlation between topical corticosteroids and increased risk of osteoporotic fracture, although not established previously in a large study, is not surprising, according to Victoria Werth, MD, chief of dermatology at the Philadelphia Veterans Affairs Hospital and professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia.
“Systemic absorption of potent topical steroids has previously been demonstrated with a rapid decrease in serum cortisol levels,” Dr. Werth said in an interview. She indicated that concern about the risk of osteoporosis imposed by use of potent steroids over large body surface areas is appropriate.
To minimize this risk, “it is reasonable to use the lowest dose of steroid possible and to try to substitute other medications when possible,” she said.
Dr. Egeberg reported financial relationships with Abbvie, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant Sciences, Galderma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung, Bioepis, and UCB. Five authors had disclosures related to some of those pharmaceutical companies and/or others. Dr. Jackson had no disclosures.
In support of previously published case reports, in a dose-response relationship.
In a stepwise manner, the hazard ratios for major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) were found to start climbing incrementally for those with a cumulative topical steroid dose equivalent of more than 500 g of mometasone furoate when compared with exposure of 200-499 g, according to the team of investigators from the University of Copenhagen.
“Use of these drugs is very common, and we found an estimated population-attributable risk of as much as 4.3%,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
The retrospective cohort study drew data from the Danish National Patient Registry, which covers 99% of the country’s population. It was linked to the Danish National Prescription Registry, which captures data on pharmacy-dispensed medications. Data collected from the beginning of 2003 to the end of 2017 were evaluated.
Exposures to potent or very potent topical corticosteroids were converted into a single standard with potency equivalent to 1 mg/g of mometasone furoate. Four strata of exposure were compared to a reference exposure of 200-499 g. These were 500-999 g, 1,000-1,999 g, 2,000-9,999 g, and 10,000 g or greater.
For the first strata, the small increased risk for MOF did not reach significance (HR, 1.01; 95% confidence interval, 0.99-1.03), but each of the others did. These climbed from a 5% greater risk (HR 1.05 95% CI 1.02-1.08) for a cumulative exposure of 1,000 to 1,999 g, to a 10% greater risk (HR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.07-1.13) for a cumulative exposure of 2,000-9,999 g, and finally to a 27% greater risk (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.19-1.35) for a cumulative exposure of 10,000 g or higher.
The study included more than 700,000 individuals exposed to topical mometasone at a potency equivalent of 200 g or more over the study period. The reference group (200-499 g) was the largest (317,907 individuals). The first strata (500-999 g) included 186,359 patients; the second (1,000-1,999 g), 111,203 patients; the third (2,000-9,999 g), 94,334 patients; and the fifth (10,000 g or more), 13,448 patients.
“A 3% increase in the relative risk of osteoporosis and MOF was observed per doubling of the TCS dose,” according to the investigators.
Patients exposed to doses of high-potency topical steroids that put them at risk of MOF is limited but substantial, according to the senior author, Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology and allergy at Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Copenhagen.
“It is true that the risk is modest for the average user of topical steroids,” Dr. Egeberg said in an interview. However, despite the fact that topical steroids are intended for short-term use, “2% of all our users had been exposed to the equivalent of 10,000 g of mometasone, which mean 100 tubes of 100 g.”
If the other two strata at significantly increased risk of MOF (greater than 1,000 g) are included, an additional 28% of all users are facing the potential for clinically significant osteoporosis, according to the Danish data.
The adverse effect of steroids on bone metabolism has been established previously, and several studies have linked systemic corticosteroid exposure, including inhaled corticosteroids, with increased risk of osteoporotic fracture. For example, one study showed that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease on daily inhaled doses of the equivalent of fluticasone at or above 1,000 mcg for more than 4 years had about a 10% increased risk of MOF relative to those not exposed.
The data associate topical steroids with increased risk of osteoporotic fracture, but Dr. Egeberg said osteoporosis is not the only reason to use topical steroids prudently.
“It is important to keep in mind that osteoporosis and fractures are at the extreme end of the side-effect profile and that other side effects, such as striae formation, skin thinning, and dysregulated diabetes, can occur with much lower quantities of topical steroids,” Dr. Egeberg said
For avoiding this risk, “there are no specific cutoffs” recommended for topical steroids in current guidelines, but dermatologists should be aware that many of the indications for topical steroids, such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, involve skin with an impaired barrier function, exposing patients to an increased likelihood of absorption, according to Dr. Egeberg.
“A general rule of thumb that we use is that, if a patient with persistent disease activity requires a new prescription of the equivalent of 100 g mometasone every 1-2 months, it might be worth considering if there is a suitable alternative,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In an accompanying editorial, Rebecca D. Jackson, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism in the department of internal medicine at Ohio State University, Columbus, agreed that no guidelines specific to avoiding the risks of topical corticosteroids are currently available, but she advised clinicians to be considering these risks nonetheless. In general, she suggested that topical steroids, like oral steroids, should be used at “the lowest dose for the shortest duration necessary to manage the underlying medical condition.”
The correlation between topical corticosteroids and increased risk of osteoporotic fracture, although not established previously in a large study, is not surprising, according to Victoria Werth, MD, chief of dermatology at the Philadelphia Veterans Affairs Hospital and professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia.
“Systemic absorption of potent topical steroids has previously been demonstrated with a rapid decrease in serum cortisol levels,” Dr. Werth said in an interview. She indicated that concern about the risk of osteoporosis imposed by use of potent steroids over large body surface areas is appropriate.
To minimize this risk, “it is reasonable to use the lowest dose of steroid possible and to try to substitute other medications when possible,” she said.
Dr. Egeberg reported financial relationships with Abbvie, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dermavant Sciences, Galderma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung, Bioepis, and UCB. Five authors had disclosures related to some of those pharmaceutical companies and/or others. Dr. Jackson had no disclosures.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Back in session
Before the pandemic, the biggest parent-related challenge for Charlie Wray, DO, MS, a hospitalist and assistant clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, was “figuring out what I was going to pack in my kids’ lunches. Like most people, we were very much in our groove – we knew when my wife was going to leave work, and which day I’d pick up the kids,” Dr. Wray said. “I reflect back on that and think how easy it was.”
The old life – the one that seems so comparatively effortless – has been gone for close to a year now. And with the reopening of schools in the fall of 2020, hospitalists with school-age kids felt – and are still feeling – the strain in a variety of ways.
‘Podding up’
“The largest struggles that we have had involve dealing with the daily logistics of doing at-home learning,” said Dr. Wray, father to a 6-year-old and a 3-year-old. Dr. Wray and his wife are both physicians and have been juggling full work schedules with virtual school for their older child, who is not old enough to be autonomous. “For parents who have younger children who require one-on-one attention for the vast majority of their learning, that certainly takes more of a toll on your time, energy, and resources.”
Uncertainty has created anxiety about the future. “We have no idea what’s going to be happening next month. How do we plan for that? How do we allocate our time for that? That has been a real struggle for us, especially for a two-physician household where we are both considered front line and are both needing to be at the hospital or the clinic on a fairly regular basis,” he said.
Then there is the never-ending stress. Dr. Wray observed that physicians are used to operating under stress, especially at work. “What I think is gnawing at me, and probably a lot of other physicians out there, is you go home and that stress is still there. It’s really hard to escape it. And you wake up in the morning and it’s there, whereas in the past, you could have a nice day. There’s little separation between work and domestic life right now.”
Having to work later into the evening has eaten into time for himself and time with his wife too. “That’s another side effect of the pandemic – it not only takes your time during the day, it takes the time you used to have at night to relax.”
To manage these challenges, Dr. Wray said he and his wife regularly double check their schedules. The family has also created a pod – “I think ‘podded up’ is a verb now,” he laughed – with another family and hired a recent college graduate to help the kids with their virtual learning. “Is it as good as being at school and amongst friends and having an actual teacher there? Of course not. But I think it’s the best that we can do.”
Dr. Wray said his employers have been flexible and understanding regarding scheduling conflicts that parents can have. “It’s really difficult for us, so oftentimes I struggle to see how other people are pulling this off. We recognize how fortunate we are, so that’s something I never want to overlook.”
Dividing and conquering
The biggest prepandemic issue for Sridevi Alla, MD, a hospitalist at Baptist Memorial Health in Jackson, Miss., and mother to four children – a 10-year-old, 6-year-old, 2-year-old, and a 9-month-old – was finding a babysitter on the weekend to take her kids out somewhere to burn off energy.
That’s a noticeable departure from the current demand to be not just a parent, but a teacher and a counselor too, thanks to virtual school, noted Dr. Alla. “You are their everything now,” she said. “They don’t have friends. They don’t have any other atmosphere or learning environment to let out their energy, their emotions. You have become their world.”
The beginning of the pandemic was particularly stressful for Dr. Alla, who is in the United States on an H-1B visa. “It was totally worrisome because you’re putting yourself at risk with patients who have the coronavirus, despite not knowing what your future itself is going to be like or what your family’s future is going to be like if anything happens to you,” she said. “We are fortunate we have our jobs. A lot of my immigrant friends lost theirs in the middle of this and they’re still trying to find jobs.”
Dr. Alla’s first challenge was whether to send her older two children to school or keep them at home to do virtual learning. The lack of information from the schools at first did not help that process, but she and her husband ended up choosing virtual school, a decision they still occasionally question.
Next, they had to find child care, and not just someone who could look after the younger two kids – they needed someone with the ability to also help the older ones with their homework.
Though initially the family had help, their first nanny had to quit because her roommate contracted COVID. “After that, we didn’t have help and my husband decided to work from home,” said Dr. Alla. “As of now, we’re still looking for child care. And the main issues are the late hours and the hospitalist week-on, week-off schedule.”
“It’s extremely hard,” she reflected. “At home, there’s no line. A 2-year-old doesn’t understand office time or personal time.” Still, Dr. Alla and her husband are maintaining by dividing up responsibilities and making sure they are always planning ahead.
Maintaining a routine
The greatest challenge for Heather Nye, MD, PhD, a hospitalist and professor of clinical medicine at UCSF, has been “maintaining normalcy for the kids.” She mourns the loss of a normal childhood for her kids, however temporary. “Living with abandon, feeling like you’re invincible, going out there and breaking your arm, meeting people, not fearing the world – those are not things we can instill in them right now,” she said.
The mother of an eighth grader and a second grader, Dr. Nye said their school district did not communicate well about how school would proceed. The district ended up offering only virtual school, with no plans for even hybrid learning in the future, leaving parents scrambling to plan.
Dr. Nye lucked out when her youngest child was accepted for a slot at a day camp offered through a partnership between the YMCA and UCSF. However, her eighth grader did not do well with distance learning in the spring, so having that virtual school as the only option has been difficult.
“Neither of the kids are doing really well in school,” she said. Her older one is overwhelmed by all the disparate online platforms and her youngest is having a hard time adjusting to differences like using a virtual pen. “The learning itself without question has suffered. You wonder about evaluation and this whole cohort of children in what will probably be more or less a lost year.”
Routines are the backbone of the family’s survival. “I think one of the most important things for kids in any stage of development is having a routine and being comfortable with that routine because that creates a sense of wellbeing in this time of uncertainty,” Dr. Nye said.
Neither Dr. Nye nor her husband, a geriatrician, have cut back on their work, so they are balancing a full plate of activities with parenting. Though their family is managing, “there are streaks of days where we’re like: ‘Are we failing our children?’ I’m sure every parent out there is asking themselves: ‘Am I doing enough?’” But she said, “We’re very, very lucky. We got that [camp] slot, we have the money to pay for it, and we both have flexible jobs.”
Rallying resources
Avital O’Glasser, MD, a hospitalist and associate professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, fervently wished she could clone herself when the pandemic first started. Not only were her kids suddenly thrown into online classes, but she was pulled in to create a new service line for the COVID response at her clinic.
“The number of times that I said I think I need a time turner from Harry Potter. ... I felt that nothing was getting done even close to adequately because we were cutting corners left and right,” she said.
Thankfully, things have simmered down and Dr. O’Glasser is now working from home 5 or 6 days a week while her husband, a lawyer, goes to his job. “I think stress is lower now, but that’s in large part because, by the end of June, I really had to just stop and acknowledge how stressed I was and do a dramatic realignment of what I was doing for myself in terms of mental health support and bandwidth,” she said. Part of that involved realizing that the family needed a homeschool nanny for their 10-year-old and 7-year-old. “It’s been a lifesaver,” said Dr. O’Glasser.
Though life is on more of an even keel now, stress pops up in unexpected ways. “My youngest has pretty intense separation anxiety from me. Even with getting attention all day from our homeschool nanny, the day after I’m out of the house at the hospital, he really clings to me,” Dr. O’Glasser said. There’s sibling rivalry too, in an attempt to get parental attention.
Setting boundaries between work and home was her biggest challenge prepandemic, and that has not changed. “You’re trying to find that happy balance between professional development and family,” Dr. O’Glasser said. “Where do I cut corners? Do I try to multitask but spread myself thin? How do I say no to things? When am I going to find time to do laundry? When am I disconnecting? I think that now it’s facets of the same conundrum, but just manifested in different ways.”
She emphasized that parents should go easy on themselves right now. “A lot of parenting rules went out the window. My kids have had more screen time…and the amount of junk food they eat right now? Celebrate the wins.” Dr. O’Glasser chuckled about how her definition of a “win” has changed. “The bar now is something that I may never have considered a win before. Just seize those small moments. If my 7-year-old needs to do reading at my feet while I’m finishing notes from the day before, that’s okay,” she said.
How hospitalist groups can help
All four hospitalists had ideas about how hospitalist groups can help parents with school-age kids during the pandemic.
Providing child care at health care systems gives employees additional support, said Dr. Alla. Some of her friends have been unable to find child care because they are physicians who care for COVID patients and people do not want the extra risk. “I think any institution should think about this option because it’s very beneficial for an employee, especially for the long hours.”
Dr. Wray said he saw a program that matches up a hospitalist who has kids with one who does not in a type of buddy system, and they check in with each other. Then, if the parent has something come up, the other hospitalist can fill in and the parent can “pay it back” at another time. “This doesn’t put all the impetus on the schedule or on a single individual but spreads the risk out a little more and gives parents a bit of a parachute to make them feel like the system is supporting them,” he said.
“I would encourage groups to reach appropriate accommodations that are equitable and that don’t create discord because they’re perceived as unfair,” said Dr. O’Glasser. For instance, giving child care stipends, but limiting them to care at a licensed facility when some people might need to pay for a homeschool tutor. “Some of the policies that I saw seem to leave out the elementary school lot. You can’t just lump all kids together.”
Dr. Nye thought group leaders should take unseen pressures into account when evaluating employee performance. “I think we’re going to need to shift our yardstick because we can’t do everything now,” she said. “I’m talking about the extra things that people do that they’re evaluated on at the end of the year like volunteering for more shifts, sitting on committees, the things that likely aren’t in their job description. We’re going to have times when people are filling every last minute for their families. Face it with kindness and understanding and know that, in future years, things are going to go back to normal.”
Before the pandemic, the biggest parent-related challenge for Charlie Wray, DO, MS, a hospitalist and assistant clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, was “figuring out what I was going to pack in my kids’ lunches. Like most people, we were very much in our groove – we knew when my wife was going to leave work, and which day I’d pick up the kids,” Dr. Wray said. “I reflect back on that and think how easy it was.”
The old life – the one that seems so comparatively effortless – has been gone for close to a year now. And with the reopening of schools in the fall of 2020, hospitalists with school-age kids felt – and are still feeling – the strain in a variety of ways.
‘Podding up’
“The largest struggles that we have had involve dealing with the daily logistics of doing at-home learning,” said Dr. Wray, father to a 6-year-old and a 3-year-old. Dr. Wray and his wife are both physicians and have been juggling full work schedules with virtual school for their older child, who is not old enough to be autonomous. “For parents who have younger children who require one-on-one attention for the vast majority of their learning, that certainly takes more of a toll on your time, energy, and resources.”
Uncertainty has created anxiety about the future. “We have no idea what’s going to be happening next month. How do we plan for that? How do we allocate our time for that? That has been a real struggle for us, especially for a two-physician household where we are both considered front line and are both needing to be at the hospital or the clinic on a fairly regular basis,” he said.
Then there is the never-ending stress. Dr. Wray observed that physicians are used to operating under stress, especially at work. “What I think is gnawing at me, and probably a lot of other physicians out there, is you go home and that stress is still there. It’s really hard to escape it. And you wake up in the morning and it’s there, whereas in the past, you could have a nice day. There’s little separation between work and domestic life right now.”
Having to work later into the evening has eaten into time for himself and time with his wife too. “That’s another side effect of the pandemic – it not only takes your time during the day, it takes the time you used to have at night to relax.”
To manage these challenges, Dr. Wray said he and his wife regularly double check their schedules. The family has also created a pod – “I think ‘podded up’ is a verb now,” he laughed – with another family and hired a recent college graduate to help the kids with their virtual learning. “Is it as good as being at school and amongst friends and having an actual teacher there? Of course not. But I think it’s the best that we can do.”
Dr. Wray said his employers have been flexible and understanding regarding scheduling conflicts that parents can have. “It’s really difficult for us, so oftentimes I struggle to see how other people are pulling this off. We recognize how fortunate we are, so that’s something I never want to overlook.”
Dividing and conquering
The biggest prepandemic issue for Sridevi Alla, MD, a hospitalist at Baptist Memorial Health in Jackson, Miss., and mother to four children – a 10-year-old, 6-year-old, 2-year-old, and a 9-month-old – was finding a babysitter on the weekend to take her kids out somewhere to burn off energy.
That’s a noticeable departure from the current demand to be not just a parent, but a teacher and a counselor too, thanks to virtual school, noted Dr. Alla. “You are their everything now,” she said. “They don’t have friends. They don’t have any other atmosphere or learning environment to let out their energy, their emotions. You have become their world.”
The beginning of the pandemic was particularly stressful for Dr. Alla, who is in the United States on an H-1B visa. “It was totally worrisome because you’re putting yourself at risk with patients who have the coronavirus, despite not knowing what your future itself is going to be like or what your family’s future is going to be like if anything happens to you,” she said. “We are fortunate we have our jobs. A lot of my immigrant friends lost theirs in the middle of this and they’re still trying to find jobs.”
Dr. Alla’s first challenge was whether to send her older two children to school or keep them at home to do virtual learning. The lack of information from the schools at first did not help that process, but she and her husband ended up choosing virtual school, a decision they still occasionally question.
Next, they had to find child care, and not just someone who could look after the younger two kids – they needed someone with the ability to also help the older ones with their homework.
Though initially the family had help, their first nanny had to quit because her roommate contracted COVID. “After that, we didn’t have help and my husband decided to work from home,” said Dr. Alla. “As of now, we’re still looking for child care. And the main issues are the late hours and the hospitalist week-on, week-off schedule.”
“It’s extremely hard,” she reflected. “At home, there’s no line. A 2-year-old doesn’t understand office time or personal time.” Still, Dr. Alla and her husband are maintaining by dividing up responsibilities and making sure they are always planning ahead.
Maintaining a routine
The greatest challenge for Heather Nye, MD, PhD, a hospitalist and professor of clinical medicine at UCSF, has been “maintaining normalcy for the kids.” She mourns the loss of a normal childhood for her kids, however temporary. “Living with abandon, feeling like you’re invincible, going out there and breaking your arm, meeting people, not fearing the world – those are not things we can instill in them right now,” she said.
The mother of an eighth grader and a second grader, Dr. Nye said their school district did not communicate well about how school would proceed. The district ended up offering only virtual school, with no plans for even hybrid learning in the future, leaving parents scrambling to plan.
Dr. Nye lucked out when her youngest child was accepted for a slot at a day camp offered through a partnership between the YMCA and UCSF. However, her eighth grader did not do well with distance learning in the spring, so having that virtual school as the only option has been difficult.
“Neither of the kids are doing really well in school,” she said. Her older one is overwhelmed by all the disparate online platforms and her youngest is having a hard time adjusting to differences like using a virtual pen. “The learning itself without question has suffered. You wonder about evaluation and this whole cohort of children in what will probably be more or less a lost year.”
Routines are the backbone of the family’s survival. “I think one of the most important things for kids in any stage of development is having a routine and being comfortable with that routine because that creates a sense of wellbeing in this time of uncertainty,” Dr. Nye said.
Neither Dr. Nye nor her husband, a geriatrician, have cut back on their work, so they are balancing a full plate of activities with parenting. Though their family is managing, “there are streaks of days where we’re like: ‘Are we failing our children?’ I’m sure every parent out there is asking themselves: ‘Am I doing enough?’” But she said, “We’re very, very lucky. We got that [camp] slot, we have the money to pay for it, and we both have flexible jobs.”
Rallying resources
Avital O’Glasser, MD, a hospitalist and associate professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, fervently wished she could clone herself when the pandemic first started. Not only were her kids suddenly thrown into online classes, but she was pulled in to create a new service line for the COVID response at her clinic.
“The number of times that I said I think I need a time turner from Harry Potter. ... I felt that nothing was getting done even close to adequately because we were cutting corners left and right,” she said.
Thankfully, things have simmered down and Dr. O’Glasser is now working from home 5 or 6 days a week while her husband, a lawyer, goes to his job. “I think stress is lower now, but that’s in large part because, by the end of June, I really had to just stop and acknowledge how stressed I was and do a dramatic realignment of what I was doing for myself in terms of mental health support and bandwidth,” she said. Part of that involved realizing that the family needed a homeschool nanny for their 10-year-old and 7-year-old. “It’s been a lifesaver,” said Dr. O’Glasser.
Though life is on more of an even keel now, stress pops up in unexpected ways. “My youngest has pretty intense separation anxiety from me. Even with getting attention all day from our homeschool nanny, the day after I’m out of the house at the hospital, he really clings to me,” Dr. O’Glasser said. There’s sibling rivalry too, in an attempt to get parental attention.
Setting boundaries between work and home was her biggest challenge prepandemic, and that has not changed. “You’re trying to find that happy balance between professional development and family,” Dr. O’Glasser said. “Where do I cut corners? Do I try to multitask but spread myself thin? How do I say no to things? When am I going to find time to do laundry? When am I disconnecting? I think that now it’s facets of the same conundrum, but just manifested in different ways.”
She emphasized that parents should go easy on themselves right now. “A lot of parenting rules went out the window. My kids have had more screen time…and the amount of junk food they eat right now? Celebrate the wins.” Dr. O’Glasser chuckled about how her definition of a “win” has changed. “The bar now is something that I may never have considered a win before. Just seize those small moments. If my 7-year-old needs to do reading at my feet while I’m finishing notes from the day before, that’s okay,” she said.
How hospitalist groups can help
All four hospitalists had ideas about how hospitalist groups can help parents with school-age kids during the pandemic.
Providing child care at health care systems gives employees additional support, said Dr. Alla. Some of her friends have been unable to find child care because they are physicians who care for COVID patients and people do not want the extra risk. “I think any institution should think about this option because it’s very beneficial for an employee, especially for the long hours.”
Dr. Wray said he saw a program that matches up a hospitalist who has kids with one who does not in a type of buddy system, and they check in with each other. Then, if the parent has something come up, the other hospitalist can fill in and the parent can “pay it back” at another time. “This doesn’t put all the impetus on the schedule or on a single individual but spreads the risk out a little more and gives parents a bit of a parachute to make them feel like the system is supporting them,” he said.
“I would encourage groups to reach appropriate accommodations that are equitable and that don’t create discord because they’re perceived as unfair,” said Dr. O’Glasser. For instance, giving child care stipends, but limiting them to care at a licensed facility when some people might need to pay for a homeschool tutor. “Some of the policies that I saw seem to leave out the elementary school lot. You can’t just lump all kids together.”
Dr. Nye thought group leaders should take unseen pressures into account when evaluating employee performance. “I think we’re going to need to shift our yardstick because we can’t do everything now,” she said. “I’m talking about the extra things that people do that they’re evaluated on at the end of the year like volunteering for more shifts, sitting on committees, the things that likely aren’t in their job description. We’re going to have times when people are filling every last minute for their families. Face it with kindness and understanding and know that, in future years, things are going to go back to normal.”
Before the pandemic, the biggest parent-related challenge for Charlie Wray, DO, MS, a hospitalist and assistant clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, was “figuring out what I was going to pack in my kids’ lunches. Like most people, we were very much in our groove – we knew when my wife was going to leave work, and which day I’d pick up the kids,” Dr. Wray said. “I reflect back on that and think how easy it was.”
The old life – the one that seems so comparatively effortless – has been gone for close to a year now. And with the reopening of schools in the fall of 2020, hospitalists with school-age kids felt – and are still feeling – the strain in a variety of ways.
‘Podding up’
“The largest struggles that we have had involve dealing with the daily logistics of doing at-home learning,” said Dr. Wray, father to a 6-year-old and a 3-year-old. Dr. Wray and his wife are both physicians and have been juggling full work schedules with virtual school for their older child, who is not old enough to be autonomous. “For parents who have younger children who require one-on-one attention for the vast majority of their learning, that certainly takes more of a toll on your time, energy, and resources.”
Uncertainty has created anxiety about the future. “We have no idea what’s going to be happening next month. How do we plan for that? How do we allocate our time for that? That has been a real struggle for us, especially for a two-physician household where we are both considered front line and are both needing to be at the hospital or the clinic on a fairly regular basis,” he said.
Then there is the never-ending stress. Dr. Wray observed that physicians are used to operating under stress, especially at work. “What I think is gnawing at me, and probably a lot of other physicians out there, is you go home and that stress is still there. It’s really hard to escape it. And you wake up in the morning and it’s there, whereas in the past, you could have a nice day. There’s little separation between work and domestic life right now.”
Having to work later into the evening has eaten into time for himself and time with his wife too. “That’s another side effect of the pandemic – it not only takes your time during the day, it takes the time you used to have at night to relax.”
To manage these challenges, Dr. Wray said he and his wife regularly double check their schedules. The family has also created a pod – “I think ‘podded up’ is a verb now,” he laughed – with another family and hired a recent college graduate to help the kids with their virtual learning. “Is it as good as being at school and amongst friends and having an actual teacher there? Of course not. But I think it’s the best that we can do.”
Dr. Wray said his employers have been flexible and understanding regarding scheduling conflicts that parents can have. “It’s really difficult for us, so oftentimes I struggle to see how other people are pulling this off. We recognize how fortunate we are, so that’s something I never want to overlook.”
Dividing and conquering
The biggest prepandemic issue for Sridevi Alla, MD, a hospitalist at Baptist Memorial Health in Jackson, Miss., and mother to four children – a 10-year-old, 6-year-old, 2-year-old, and a 9-month-old – was finding a babysitter on the weekend to take her kids out somewhere to burn off energy.
That’s a noticeable departure from the current demand to be not just a parent, but a teacher and a counselor too, thanks to virtual school, noted Dr. Alla. “You are their everything now,” she said. “They don’t have friends. They don’t have any other atmosphere or learning environment to let out their energy, their emotions. You have become their world.”
The beginning of the pandemic was particularly stressful for Dr. Alla, who is in the United States on an H-1B visa. “It was totally worrisome because you’re putting yourself at risk with patients who have the coronavirus, despite not knowing what your future itself is going to be like or what your family’s future is going to be like if anything happens to you,” she said. “We are fortunate we have our jobs. A lot of my immigrant friends lost theirs in the middle of this and they’re still trying to find jobs.”
Dr. Alla’s first challenge was whether to send her older two children to school or keep them at home to do virtual learning. The lack of information from the schools at first did not help that process, but she and her husband ended up choosing virtual school, a decision they still occasionally question.
Next, they had to find child care, and not just someone who could look after the younger two kids – they needed someone with the ability to also help the older ones with their homework.
Though initially the family had help, their first nanny had to quit because her roommate contracted COVID. “After that, we didn’t have help and my husband decided to work from home,” said Dr. Alla. “As of now, we’re still looking for child care. And the main issues are the late hours and the hospitalist week-on, week-off schedule.”
“It’s extremely hard,” she reflected. “At home, there’s no line. A 2-year-old doesn’t understand office time or personal time.” Still, Dr. Alla and her husband are maintaining by dividing up responsibilities and making sure they are always planning ahead.
Maintaining a routine
The greatest challenge for Heather Nye, MD, PhD, a hospitalist and professor of clinical medicine at UCSF, has been “maintaining normalcy for the kids.” She mourns the loss of a normal childhood for her kids, however temporary. “Living with abandon, feeling like you’re invincible, going out there and breaking your arm, meeting people, not fearing the world – those are not things we can instill in them right now,” she said.
The mother of an eighth grader and a second grader, Dr. Nye said their school district did not communicate well about how school would proceed. The district ended up offering only virtual school, with no plans for even hybrid learning in the future, leaving parents scrambling to plan.
Dr. Nye lucked out when her youngest child was accepted for a slot at a day camp offered through a partnership between the YMCA and UCSF. However, her eighth grader did not do well with distance learning in the spring, so having that virtual school as the only option has been difficult.
“Neither of the kids are doing really well in school,” she said. Her older one is overwhelmed by all the disparate online platforms and her youngest is having a hard time adjusting to differences like using a virtual pen. “The learning itself without question has suffered. You wonder about evaluation and this whole cohort of children in what will probably be more or less a lost year.”
Routines are the backbone of the family’s survival. “I think one of the most important things for kids in any stage of development is having a routine and being comfortable with that routine because that creates a sense of wellbeing in this time of uncertainty,” Dr. Nye said.
Neither Dr. Nye nor her husband, a geriatrician, have cut back on their work, so they are balancing a full plate of activities with parenting. Though their family is managing, “there are streaks of days where we’re like: ‘Are we failing our children?’ I’m sure every parent out there is asking themselves: ‘Am I doing enough?’” But she said, “We’re very, very lucky. We got that [camp] slot, we have the money to pay for it, and we both have flexible jobs.”
Rallying resources
Avital O’Glasser, MD, a hospitalist and associate professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, fervently wished she could clone herself when the pandemic first started. Not only were her kids suddenly thrown into online classes, but she was pulled in to create a new service line for the COVID response at her clinic.
“The number of times that I said I think I need a time turner from Harry Potter. ... I felt that nothing was getting done even close to adequately because we were cutting corners left and right,” she said.
Thankfully, things have simmered down and Dr. O’Glasser is now working from home 5 or 6 days a week while her husband, a lawyer, goes to his job. “I think stress is lower now, but that’s in large part because, by the end of June, I really had to just stop and acknowledge how stressed I was and do a dramatic realignment of what I was doing for myself in terms of mental health support and bandwidth,” she said. Part of that involved realizing that the family needed a homeschool nanny for their 10-year-old and 7-year-old. “It’s been a lifesaver,” said Dr. O’Glasser.
Though life is on more of an even keel now, stress pops up in unexpected ways. “My youngest has pretty intense separation anxiety from me. Even with getting attention all day from our homeschool nanny, the day after I’m out of the house at the hospital, he really clings to me,” Dr. O’Glasser said. There’s sibling rivalry too, in an attempt to get parental attention.
Setting boundaries between work and home was her biggest challenge prepandemic, and that has not changed. “You’re trying to find that happy balance between professional development and family,” Dr. O’Glasser said. “Where do I cut corners? Do I try to multitask but spread myself thin? How do I say no to things? When am I going to find time to do laundry? When am I disconnecting? I think that now it’s facets of the same conundrum, but just manifested in different ways.”
She emphasized that parents should go easy on themselves right now. “A lot of parenting rules went out the window. My kids have had more screen time…and the amount of junk food they eat right now? Celebrate the wins.” Dr. O’Glasser chuckled about how her definition of a “win” has changed. “The bar now is something that I may never have considered a win before. Just seize those small moments. If my 7-year-old needs to do reading at my feet while I’m finishing notes from the day before, that’s okay,” she said.
How hospitalist groups can help
All four hospitalists had ideas about how hospitalist groups can help parents with school-age kids during the pandemic.
Providing child care at health care systems gives employees additional support, said Dr. Alla. Some of her friends have been unable to find child care because they are physicians who care for COVID patients and people do not want the extra risk. “I think any institution should think about this option because it’s very beneficial for an employee, especially for the long hours.”
Dr. Wray said he saw a program that matches up a hospitalist who has kids with one who does not in a type of buddy system, and they check in with each other. Then, if the parent has something come up, the other hospitalist can fill in and the parent can “pay it back” at another time. “This doesn’t put all the impetus on the schedule or on a single individual but spreads the risk out a little more and gives parents a bit of a parachute to make them feel like the system is supporting them,” he said.
“I would encourage groups to reach appropriate accommodations that are equitable and that don’t create discord because they’re perceived as unfair,” said Dr. O’Glasser. For instance, giving child care stipends, but limiting them to care at a licensed facility when some people might need to pay for a homeschool tutor. “Some of the policies that I saw seem to leave out the elementary school lot. You can’t just lump all kids together.”
Dr. Nye thought group leaders should take unseen pressures into account when evaluating employee performance. “I think we’re going to need to shift our yardstick because we can’t do everything now,” she said. “I’m talking about the extra things that people do that they’re evaluated on at the end of the year like volunteering for more shifts, sitting on committees, the things that likely aren’t in their job description. We’re going to have times when people are filling every last minute for their families. Face it with kindness and understanding and know that, in future years, things are going to go back to normal.”
RPLND deemed ‘attractive’ option for early metastatic seminoma
The trial enrolled 55 men with early-stage seminoma and isolated retroperitoneal disease, and all of them underwent retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND). At 2 years, the recurrence rate was 18%, the recurrence-free survival rate was 84%, and the overall survival rate was 100%. Surgical complications occurred in 13% of patients.
“The SEMS trial establishes RPLND as a first-line treatment alternative for testicular seminoma with isolated retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy up to 3 cm ... It’s an attractive option given the favorable long-term morbidity of RPLND,” said co-principal investigator Siamak Daneshmand, MD, of the University of Southern California (USC), Los Angeles.
“The whole point is to offer an alternative treatment that will avoid long-term toxicity ... It makes no sense treating isolated retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy with strong chemotherapy that’s meant for more widely disseminated disease,” Dr. Daneshmand said.
He presented results from the SEMS trial at the 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium (Abstract 375).
Practice-changing?
Dr. Daneshmand called the trial results “practice-changing” and noted that surgery “makes sense” to patients and providers, especially because RPLND is already an established option for early-stage non-seminoma testicular cancer. In fact, USC has continued to offer RPLND for early-stage seminoma since this trial ended 2 years ago, Dr. Daneshmand said.
Study discussant Pilar Laguna, MD, PhD, of Istanbul Medipol University in Turkey, offered a different viewpoint. She said the SEMS trial had an “excellent” design, but, due to the relatively short follow-up, she would recommend caution.
“We in Europe do not recommend primary retroperitoneal lymph node dissection in seminoma outside a trial or institutional study,” Dr. Laguna said.
Still, she said the SEMS trial “establishes a solid base” for ongoing prospective trials of primary RPLND in early-stage seminoma.
Trial details
The SEMS trial enrolled 55 patients with pure testicular seminoma. They had stage I disease with 1-3 cm relapse (25%) or stage IIA/B disease with no more than two lymph nodes in any dimension (75%). Imaging was done within 6 weeks of surgery to avoid under staging, and serum tumor markers could be no more than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal.
The majority of subjects were White, and the median age was 34 years (range, 21-64 years). Including USC, the trial was conducted at 12 North American sites.
Patients had open modified-template surgeries by surgeons who had performed at least eight open RPLNDs in 1 year or more than 24 in 3 years. Surgeries at USC used a midline approach, with a typical hospital stay of 1 day.
The median follow-up was 2 years. The overall recurrence rate was 18% (10/55), with a median time to recurrence of 8 months.
All 10 cases of recurrence were salvageable – 8 with chemotherapy and 2 with surgical resection. All of the recurrences were retroperitoneal.
“If you can cure 80% [of men] without radiation or chemotherapy, that’s very significant. These are young patients, and chemotherapy and radiation have long-term side effects. The important thing to remember is if men do recur, they are salvageable,” Dr. Daneshmand said.
Seven patients (13%) had surgical complications that were largely minor. The exceptions were one case of pulmonary embolism and one case of chylous ascites that required drainage. There were no long-term complications, including retrograde ejaculation.
The SEMS study was funded by the Think Different Foundation. Dr. Daneshmand and Dr. Laguna said they have no relevant disclosures.
The trial enrolled 55 men with early-stage seminoma and isolated retroperitoneal disease, and all of them underwent retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND). At 2 years, the recurrence rate was 18%, the recurrence-free survival rate was 84%, and the overall survival rate was 100%. Surgical complications occurred in 13% of patients.
“The SEMS trial establishes RPLND as a first-line treatment alternative for testicular seminoma with isolated retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy up to 3 cm ... It’s an attractive option given the favorable long-term morbidity of RPLND,” said co-principal investigator Siamak Daneshmand, MD, of the University of Southern California (USC), Los Angeles.
“The whole point is to offer an alternative treatment that will avoid long-term toxicity ... It makes no sense treating isolated retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy with strong chemotherapy that’s meant for more widely disseminated disease,” Dr. Daneshmand said.
He presented results from the SEMS trial at the 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium (Abstract 375).
Practice-changing?
Dr. Daneshmand called the trial results “practice-changing” and noted that surgery “makes sense” to patients and providers, especially because RPLND is already an established option for early-stage non-seminoma testicular cancer. In fact, USC has continued to offer RPLND for early-stage seminoma since this trial ended 2 years ago, Dr. Daneshmand said.
Study discussant Pilar Laguna, MD, PhD, of Istanbul Medipol University in Turkey, offered a different viewpoint. She said the SEMS trial had an “excellent” design, but, due to the relatively short follow-up, she would recommend caution.
“We in Europe do not recommend primary retroperitoneal lymph node dissection in seminoma outside a trial or institutional study,” Dr. Laguna said.
Still, she said the SEMS trial “establishes a solid base” for ongoing prospective trials of primary RPLND in early-stage seminoma.
Trial details
The SEMS trial enrolled 55 patients with pure testicular seminoma. They had stage I disease with 1-3 cm relapse (25%) or stage IIA/B disease with no more than two lymph nodes in any dimension (75%). Imaging was done within 6 weeks of surgery to avoid under staging, and serum tumor markers could be no more than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal.
The majority of subjects were White, and the median age was 34 years (range, 21-64 years). Including USC, the trial was conducted at 12 North American sites.
Patients had open modified-template surgeries by surgeons who had performed at least eight open RPLNDs in 1 year or more than 24 in 3 years. Surgeries at USC used a midline approach, with a typical hospital stay of 1 day.
The median follow-up was 2 years. The overall recurrence rate was 18% (10/55), with a median time to recurrence of 8 months.
All 10 cases of recurrence were salvageable – 8 with chemotherapy and 2 with surgical resection. All of the recurrences were retroperitoneal.
“If you can cure 80% [of men] without radiation or chemotherapy, that’s very significant. These are young patients, and chemotherapy and radiation have long-term side effects. The important thing to remember is if men do recur, they are salvageable,” Dr. Daneshmand said.
Seven patients (13%) had surgical complications that were largely minor. The exceptions were one case of pulmonary embolism and one case of chylous ascites that required drainage. There were no long-term complications, including retrograde ejaculation.
The SEMS study was funded by the Think Different Foundation. Dr. Daneshmand and Dr. Laguna said they have no relevant disclosures.
The trial enrolled 55 men with early-stage seminoma and isolated retroperitoneal disease, and all of them underwent retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND). At 2 years, the recurrence rate was 18%, the recurrence-free survival rate was 84%, and the overall survival rate was 100%. Surgical complications occurred in 13% of patients.
“The SEMS trial establishes RPLND as a first-line treatment alternative for testicular seminoma with isolated retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy up to 3 cm ... It’s an attractive option given the favorable long-term morbidity of RPLND,” said co-principal investigator Siamak Daneshmand, MD, of the University of Southern California (USC), Los Angeles.
“The whole point is to offer an alternative treatment that will avoid long-term toxicity ... It makes no sense treating isolated retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy with strong chemotherapy that’s meant for more widely disseminated disease,” Dr. Daneshmand said.
He presented results from the SEMS trial at the 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium (Abstract 375).
Practice-changing?
Dr. Daneshmand called the trial results “practice-changing” and noted that surgery “makes sense” to patients and providers, especially because RPLND is already an established option for early-stage non-seminoma testicular cancer. In fact, USC has continued to offer RPLND for early-stage seminoma since this trial ended 2 years ago, Dr. Daneshmand said.
Study discussant Pilar Laguna, MD, PhD, of Istanbul Medipol University in Turkey, offered a different viewpoint. She said the SEMS trial had an “excellent” design, but, due to the relatively short follow-up, she would recommend caution.
“We in Europe do not recommend primary retroperitoneal lymph node dissection in seminoma outside a trial or institutional study,” Dr. Laguna said.
Still, she said the SEMS trial “establishes a solid base” for ongoing prospective trials of primary RPLND in early-stage seminoma.
Trial details
The SEMS trial enrolled 55 patients with pure testicular seminoma. They had stage I disease with 1-3 cm relapse (25%) or stage IIA/B disease with no more than two lymph nodes in any dimension (75%). Imaging was done within 6 weeks of surgery to avoid under staging, and serum tumor markers could be no more than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal.
The majority of subjects were White, and the median age was 34 years (range, 21-64 years). Including USC, the trial was conducted at 12 North American sites.
Patients had open modified-template surgeries by surgeons who had performed at least eight open RPLNDs in 1 year or more than 24 in 3 years. Surgeries at USC used a midline approach, with a typical hospital stay of 1 day.
The median follow-up was 2 years. The overall recurrence rate was 18% (10/55), with a median time to recurrence of 8 months.
All 10 cases of recurrence were salvageable – 8 with chemotherapy and 2 with surgical resection. All of the recurrences were retroperitoneal.
“If you can cure 80% [of men] without radiation or chemotherapy, that’s very significant. These are young patients, and chemotherapy and radiation have long-term side effects. The important thing to remember is if men do recur, they are salvageable,” Dr. Daneshmand said.
Seven patients (13%) had surgical complications that were largely minor. The exceptions were one case of pulmonary embolism and one case of chylous ascites that required drainage. There were no long-term complications, including retrograde ejaculation.
The SEMS study was funded by the Think Different Foundation. Dr. Daneshmand and Dr. Laguna said they have no relevant disclosures.
FROM GUCS 2021
FDA approves first drug that protects against chemo-induced myelosuppression
A novel drug that offers multilineage protection from chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The drug, trilaciclib (Cosela, G1 Therapeutics) is administered intravenously as a 30-minute infusion within 4 hours prior to the start of chemotherapy. It is indicated specifically for use in adults with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) who are receiving chemotherapy.
Trilaciclib is a CDK4/6 inhibitor, and this action appears to protect normal bone marrow cells from the harmful effects of chemotherapy.
“For patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer, protecting bone marrow function may help make their chemotherapy safer and allow them to complete their course of treatment on time and according to plan,” Albert Deisseroth, MD, PhD, of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in an FDA press release.
First drug of its type
Trilaciclib “is the first and only therapy designed to help protect bone marrow (myeloprotection) when administered prior to treatment with chemotherapy,” according to the drug’s manufacturer.
Myelosuppression is one of the most severe adverse effects of chemotherapy, and it can be life-threatening. It can increase the risk of infection and lead to severe anemia and/or bleeding.
“These complications impact patients’ quality of life and may also result in chemotherapy dose reductions and delays,” Jeffrey Crawford, MD, of Duke Cancer Institute, Durham, N.C., said in a company press release.
“To date, approaches have included the use of growth factor agents to accelerate blood cell recovery after the bone marrow injury has occurred, along with antibiotics and transfusions as needed. By contrast, trilaciclib provides the first proactive approach to myelosuppression through a unique mechanism of action that helps protect the bone marrow from damage by chemotherapy.”
Approval based on randomized, placebo-controlled trials
The approval of trilaciclib is based on data from three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, involving a total of 245 patients with ES-SCLC.
These patients were being treated with chemotherapy regimens that were based on the combination of carboplatin and etoposide (with or without the immunotherapy atezolizumab) or regimens that were based on topotecan.
Before receiving the chemotherapy, patients were randomly assigned to receive trilaciclib or placebo.
Results showed that patients who had received an infusion of trilaciclib before receiving chemotherapy had a lower chance of developing severe neutropenia compared with patients who received a placebo, the FDA noted. In addition, among the patients who did develop severe neutropenia, this had a shorter duration among patients who received trilaciclib than among those who received placebo.
The most common side effects of trilaciclib were fatigue; low levels of calcium, potassium, and phosphate in the blood; increased levels of aspartate aminotransferase; headache; and pneumonia.
The FDA noted that patients should also be advised about injection site reactions, acute drug hypersensitivity, interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, and embryo-fetal toxicity.
The approval received a priority review, based on the drug’s breakthrough therapy designation. As is common for such products, the company plans postmarketing activities that will assess the effects of trilaciclib on disease progression or survival with at least a 2-year follow up. This clinical trial is scheduled to start in 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel drug that offers multilineage protection from chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The drug, trilaciclib (Cosela, G1 Therapeutics) is administered intravenously as a 30-minute infusion within 4 hours prior to the start of chemotherapy. It is indicated specifically for use in adults with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) who are receiving chemotherapy.
Trilaciclib is a CDK4/6 inhibitor, and this action appears to protect normal bone marrow cells from the harmful effects of chemotherapy.
“For patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer, protecting bone marrow function may help make their chemotherapy safer and allow them to complete their course of treatment on time and according to plan,” Albert Deisseroth, MD, PhD, of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in an FDA press release.
First drug of its type
Trilaciclib “is the first and only therapy designed to help protect bone marrow (myeloprotection) when administered prior to treatment with chemotherapy,” according to the drug’s manufacturer.
Myelosuppression is one of the most severe adverse effects of chemotherapy, and it can be life-threatening. It can increase the risk of infection and lead to severe anemia and/or bleeding.
“These complications impact patients’ quality of life and may also result in chemotherapy dose reductions and delays,” Jeffrey Crawford, MD, of Duke Cancer Institute, Durham, N.C., said in a company press release.
“To date, approaches have included the use of growth factor agents to accelerate blood cell recovery after the bone marrow injury has occurred, along with antibiotics and transfusions as needed. By contrast, trilaciclib provides the first proactive approach to myelosuppression through a unique mechanism of action that helps protect the bone marrow from damage by chemotherapy.”
Approval based on randomized, placebo-controlled trials
The approval of trilaciclib is based on data from three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, involving a total of 245 patients with ES-SCLC.
These patients were being treated with chemotherapy regimens that were based on the combination of carboplatin and etoposide (with or without the immunotherapy atezolizumab) or regimens that were based on topotecan.
Before receiving the chemotherapy, patients were randomly assigned to receive trilaciclib or placebo.
Results showed that patients who had received an infusion of trilaciclib before receiving chemotherapy had a lower chance of developing severe neutropenia compared with patients who received a placebo, the FDA noted. In addition, among the patients who did develop severe neutropenia, this had a shorter duration among patients who received trilaciclib than among those who received placebo.
The most common side effects of trilaciclib were fatigue; low levels of calcium, potassium, and phosphate in the blood; increased levels of aspartate aminotransferase; headache; and pneumonia.
The FDA noted that patients should also be advised about injection site reactions, acute drug hypersensitivity, interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, and embryo-fetal toxicity.
The approval received a priority review, based on the drug’s breakthrough therapy designation. As is common for such products, the company plans postmarketing activities that will assess the effects of trilaciclib on disease progression or survival with at least a 2-year follow up. This clinical trial is scheduled to start in 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel drug that offers multilineage protection from chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The drug, trilaciclib (Cosela, G1 Therapeutics) is administered intravenously as a 30-minute infusion within 4 hours prior to the start of chemotherapy. It is indicated specifically for use in adults with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) who are receiving chemotherapy.
Trilaciclib is a CDK4/6 inhibitor, and this action appears to protect normal bone marrow cells from the harmful effects of chemotherapy.
“For patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer, protecting bone marrow function may help make their chemotherapy safer and allow them to complete their course of treatment on time and according to plan,” Albert Deisseroth, MD, PhD, of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in an FDA press release.
First drug of its type
Trilaciclib “is the first and only therapy designed to help protect bone marrow (myeloprotection) when administered prior to treatment with chemotherapy,” according to the drug’s manufacturer.
Myelosuppression is one of the most severe adverse effects of chemotherapy, and it can be life-threatening. It can increase the risk of infection and lead to severe anemia and/or bleeding.
“These complications impact patients’ quality of life and may also result in chemotherapy dose reductions and delays,” Jeffrey Crawford, MD, of Duke Cancer Institute, Durham, N.C., said in a company press release.
“To date, approaches have included the use of growth factor agents to accelerate blood cell recovery after the bone marrow injury has occurred, along with antibiotics and transfusions as needed. By contrast, trilaciclib provides the first proactive approach to myelosuppression through a unique mechanism of action that helps protect the bone marrow from damage by chemotherapy.”
Approval based on randomized, placebo-controlled trials
The approval of trilaciclib is based on data from three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, involving a total of 245 patients with ES-SCLC.
These patients were being treated with chemotherapy regimens that were based on the combination of carboplatin and etoposide (with or without the immunotherapy atezolizumab) or regimens that were based on topotecan.
Before receiving the chemotherapy, patients were randomly assigned to receive trilaciclib or placebo.
Results showed that patients who had received an infusion of trilaciclib before receiving chemotherapy had a lower chance of developing severe neutropenia compared with patients who received a placebo, the FDA noted. In addition, among the patients who did develop severe neutropenia, this had a shorter duration among patients who received trilaciclib than among those who received placebo.
The most common side effects of trilaciclib were fatigue; low levels of calcium, potassium, and phosphate in the blood; increased levels of aspartate aminotransferase; headache; and pneumonia.
The FDA noted that patients should also be advised about injection site reactions, acute drug hypersensitivity, interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, and embryo-fetal toxicity.
The approval received a priority review, based on the drug’s breakthrough therapy designation. As is common for such products, the company plans postmarketing activities that will assess the effects of trilaciclib on disease progression or survival with at least a 2-year follow up. This clinical trial is scheduled to start in 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.