User login
Acetophenone Azine: The 2021 American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year
It’s time for the American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS) Allergen of the Year! For 2021, the esteemed award goes to acetophenone azine (AA). If you have never heard of this chemical, you are not alone. Acetophenone azine has been identified in foam materials made of the copolymer ethyl-vinyl acetate (EVA). Contact allergy to AA initially was reported in 2016.1 There are only a few European and Canadian case reports and one case series of AA contact allergy in the literature, all of which are associated with foam shin pads or shin guards, shoe insoles, and/or flip-flops.2-6 Acetophenone azine is an important emerging allergen, and in this column, we will introduce you to AA and the sneaky places it can lurk and cause allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). We also highlight diagnosis, management, and patch testing for AA contact allergy.
AA Contact Allergy in the Literature
The first case of AA contact allergy was reported in Europe in 2016 when a 13-year-old male soccer player developed severe lower leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis associated with wearing foam shin guards.1 Patch testing to standard and supplemental trays was negative or not relevant; however, the patient exhibited strong reactions when patch tested directly to a piece of the shin guard soaked in acetone, water, and ethanol. Additional testing with AA diluted in acetone, water, and petrolatum resulted in positive patch test reactions to acetone dilutions of 1%, 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.001% and aqueous solutions of 1% and 0.1%. Chromatographic analyses with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of shin guard extracts confirmed the culprit allergen to be AA.1
In the following months, the same clinic saw 2 more cases of AA contact allergy.2 An 11-year-old male soccer player developed lower leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis from wearing shin guards. Months later, he also developed dermatitis on the soles of the feet, which was attributed to wearing flip-flops. Patch tests to pieces of the shin guards and flip-flops were positive; AA in acetone 0.1% and 0.01% also was positive. As you might expect, HPLC again confirmed the presence of AA in the shin guards and flip-flops. The third patient was a 12-year-old boy with dermatitis on the soles of both feet; later he also developed a generalized dermatitis. Patch testing to pieces of the insoles of his sneakers and AA in acetone 0.1% and 0.01% was positive. Again, HPLC was positive for the presence of AA in the insoles of his sneakers.2
Several more cases of AA contact allergy have been reported in the literature. A 29-year-old European male hockey player demonstrated contact allergy to the gray foam of his shin pads as well as localized leg dermatitis followed by generalized dermatitis (are you noticing a trend yet?), and later dermatitis on the soles of the feet with positive patch-test reactions to pieces of his shin pads and shoe insoles as well as AA 0.1% and 0.01% in acetone.3 A 6-year-old Canadian male soccer player presented with leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis and dermatitis on the soles of the feet with positive reactions to pieces of his shin pads and shoe insoles as well as to AA 1% and 0.1% in petrolatum.4 A 17-year-old British male (another trend, all males so far!) hockey player developed dermatitis localized to the legs and positive patch tests to the worn foam inner lining of his shin pads as well as to AA 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.001% in acetone.5Finally, Darrigade et al6 published a case series of 6 European children with AA contact allergy associated with shin pads and shoes; all had localized leg dermatitis, and some had generalized dermatitis. Patch testing to pieces of shin pads and shoe parts as well as to AA 0.1% in petrolatum and/or acetone showed with positive reactions to the foam pieces and AA in all 6 patients.
What’s the Deal With AA?
Acetophenone azine (also known as methylphenylketazine or bis[1-phenylethylidene]hydrazine) is composed of 2 acetophenone structures and a hydrazine moiety. It has been identified in EVA foam, which can be found in sports equipment such as shin pads or shin guards, shoes, and flip-flops. Raison-Peyron et al1 confirmed the presence of AA in EVA foam but reported that they did not know the exact reason for its presence. The authors theorized that AA might be a catalyst during EVA polymerization and also noted that it has antimicrobial and antihelminthic activity.1 Several authors noted that AA could be a by-product of EVA synthesis and that sports equipment manufacturers might not be aware of its presence in EVA.2,4-6 Some noted that AA concentration was higher in shin guards than in shoe insoles; they thought this explained why patients reacted first to their shin guards and were perhaps even initially sensitized to the shin guards, as well as why shoe insole contact allergy commonly was reported later or only after allergy to shin guards had already developed.4,6
Differential Diagnosis of Shin Pad or Shin Guard Dermatitis
We would be remiss if we did not mention the appropriate differential diagnosis when shin pad or shin guard dermatitis is identified. In fact, in most cases, shin guard dermatitis results from irritant contact dermatitis from friction, heat, and/or perspiration. Acetophenone azine contact allergy is not the most likely diagnosis when your sports-savvy, shin guard–wearing patient presents with anterior lower leg dermatitis. However, when conservative therapy (eg, barrier between the shin guard and the skin, control or management of perspiration, topical corticosteroid therapy) fails, patch testing to evaluate for ACD is indicated.
Management of AA Contact Allergy
As astute readers of this column are already aware, treatment of ACD requires strict allergen avoidance. You will find that we have the same recommendations for AA contact allergy. Given that there are only a handful of cases in the literature, there are limited recommendations on practical allergen avoidance other than “don’t wear the problem shin guards, shoe insoles, or flip-flops.” However, Darrigade et al6 recommended wearing polyurethane shin guards and leather insoles as alternatives when AA contact allergy is suspected or confirmed. They also made it clear that thick socks worn between shin guards and the skin often are not good enough to avoid ACD because the relevant allergens may achieve skin contact despite the barrier.6
Patch Testing for AA Contact Allergy
Historically, ACD to shin guards or shin pads, insoles of shoes, and even flip-flops has been associated with rubber-related chemicals such as mercapto mix, thiuram mix, N-isopropyl-N’-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine, thioureas, and carbamates, as well as dyes, benzoyl peroxide, and urea formaldehyde or phenol formaldehyde resins.1 Most of these chemicals can be tested with standard screening series or supplemental series. Patients with contact allergy to AA may have negative patch testing to screening series and/or supplemental series and may have strong positive reactions to pieces of suspected foam shin pads or shin guards, shoes, and/or flip-flops. Although Koumaki et al5 recommended patch testing for AA contact allergy with AA 0.1% in acetone, Besner Morin et al4 mentioned that petrolatum may be a more desirable vehicle because it could maintain stability for a longer period of time. In fact, a 2021 article highlighting the American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year recommends testing with either AA 0.1% in acetone or AA 0.1% in petrolatum.7 Unfortunately, AA is not commercially available for purchase at the time of publication. We are hopeful that this will change in the near future.
Final Interpretation
Acetophenone azine is an emerging allergen commonly identified in EVA foam and attributed to contact allergy to shin guards or pads, soles of shoes, and flip-flops. Most cases have been reported in Europe and Canada and have been identified in young male athletes. In addition to standard patch testing, athletes with lower leg dermatitis and/or dermatitis of the soles of the feet should undergo patch testing with AA 0.1% in acetone or petrolatum and pieces of the equipment and/or footwear.
- Raison-Peyron N, Bergendorff O, Bourrain JL, et al. Acetophenone azine: a new allergen responsible for severe contact dermatitis from shin pads. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:106-110.
- Raison-Peyron N, Bergendorff O, Du-Thanh A, et al. Two new cases of severe allergic contact dermatitis caused by acetophenone azine. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:380-381.
- De Fré C, Bergendorff O, Raison-Peyron N, et al. Acetophenone azine: a new shoe allergen causing severe foot dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:416-417.
- Besner Morin C, Stanciu M, Miedzybrodzki B, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from acetophenone azine in a Canadian child. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:41-42.
- Koumaki D, Bergendorff O, Bruze M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to shin pads in a hockey player: acetophenone is an emerging allergen. Dermatitis. 2019;30:162-163.
- Darrigade AS, Raison-Peyron N, Courouge-Dorcier D, et al. The chemical acetophenone azine: an important cause of shin and foot dermatitis in children. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:E61-E62.
- Raison-Peyron N, Sasseville D. Acetophenone azine. Dermatitis. 2021;32:5-9.
It’s time for the American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS) Allergen of the Year! For 2021, the esteemed award goes to acetophenone azine (AA). If you have never heard of this chemical, you are not alone. Acetophenone azine has been identified in foam materials made of the copolymer ethyl-vinyl acetate (EVA). Contact allergy to AA initially was reported in 2016.1 There are only a few European and Canadian case reports and one case series of AA contact allergy in the literature, all of which are associated with foam shin pads or shin guards, shoe insoles, and/or flip-flops.2-6 Acetophenone azine is an important emerging allergen, and in this column, we will introduce you to AA and the sneaky places it can lurk and cause allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). We also highlight diagnosis, management, and patch testing for AA contact allergy.
AA Contact Allergy in the Literature
The first case of AA contact allergy was reported in Europe in 2016 when a 13-year-old male soccer player developed severe lower leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis associated with wearing foam shin guards.1 Patch testing to standard and supplemental trays was negative or not relevant; however, the patient exhibited strong reactions when patch tested directly to a piece of the shin guard soaked in acetone, water, and ethanol. Additional testing with AA diluted in acetone, water, and petrolatum resulted in positive patch test reactions to acetone dilutions of 1%, 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.001% and aqueous solutions of 1% and 0.1%. Chromatographic analyses with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of shin guard extracts confirmed the culprit allergen to be AA.1
In the following months, the same clinic saw 2 more cases of AA contact allergy.2 An 11-year-old male soccer player developed lower leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis from wearing shin guards. Months later, he also developed dermatitis on the soles of the feet, which was attributed to wearing flip-flops. Patch tests to pieces of the shin guards and flip-flops were positive; AA in acetone 0.1% and 0.01% also was positive. As you might expect, HPLC again confirmed the presence of AA in the shin guards and flip-flops. The third patient was a 12-year-old boy with dermatitis on the soles of both feet; later he also developed a generalized dermatitis. Patch testing to pieces of the insoles of his sneakers and AA in acetone 0.1% and 0.01% was positive. Again, HPLC was positive for the presence of AA in the insoles of his sneakers.2
Several more cases of AA contact allergy have been reported in the literature. A 29-year-old European male hockey player demonstrated contact allergy to the gray foam of his shin pads as well as localized leg dermatitis followed by generalized dermatitis (are you noticing a trend yet?), and later dermatitis on the soles of the feet with positive patch-test reactions to pieces of his shin pads and shoe insoles as well as AA 0.1% and 0.01% in acetone.3 A 6-year-old Canadian male soccer player presented with leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis and dermatitis on the soles of the feet with positive reactions to pieces of his shin pads and shoe insoles as well as to AA 1% and 0.1% in petrolatum.4 A 17-year-old British male (another trend, all males so far!) hockey player developed dermatitis localized to the legs and positive patch tests to the worn foam inner lining of his shin pads as well as to AA 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.001% in acetone.5Finally, Darrigade et al6 published a case series of 6 European children with AA contact allergy associated with shin pads and shoes; all had localized leg dermatitis, and some had generalized dermatitis. Patch testing to pieces of shin pads and shoe parts as well as to AA 0.1% in petrolatum and/or acetone showed with positive reactions to the foam pieces and AA in all 6 patients.
What’s the Deal With AA?
Acetophenone azine (also known as methylphenylketazine or bis[1-phenylethylidene]hydrazine) is composed of 2 acetophenone structures and a hydrazine moiety. It has been identified in EVA foam, which can be found in sports equipment such as shin pads or shin guards, shoes, and flip-flops. Raison-Peyron et al1 confirmed the presence of AA in EVA foam but reported that they did not know the exact reason for its presence. The authors theorized that AA might be a catalyst during EVA polymerization and also noted that it has antimicrobial and antihelminthic activity.1 Several authors noted that AA could be a by-product of EVA synthesis and that sports equipment manufacturers might not be aware of its presence in EVA.2,4-6 Some noted that AA concentration was higher in shin guards than in shoe insoles; they thought this explained why patients reacted first to their shin guards and were perhaps even initially sensitized to the shin guards, as well as why shoe insole contact allergy commonly was reported later or only after allergy to shin guards had already developed.4,6
Differential Diagnosis of Shin Pad or Shin Guard Dermatitis
We would be remiss if we did not mention the appropriate differential diagnosis when shin pad or shin guard dermatitis is identified. In fact, in most cases, shin guard dermatitis results from irritant contact dermatitis from friction, heat, and/or perspiration. Acetophenone azine contact allergy is not the most likely diagnosis when your sports-savvy, shin guard–wearing patient presents with anterior lower leg dermatitis. However, when conservative therapy (eg, barrier between the shin guard and the skin, control or management of perspiration, topical corticosteroid therapy) fails, patch testing to evaluate for ACD is indicated.
Management of AA Contact Allergy
As astute readers of this column are already aware, treatment of ACD requires strict allergen avoidance. You will find that we have the same recommendations for AA contact allergy. Given that there are only a handful of cases in the literature, there are limited recommendations on practical allergen avoidance other than “don’t wear the problem shin guards, shoe insoles, or flip-flops.” However, Darrigade et al6 recommended wearing polyurethane shin guards and leather insoles as alternatives when AA contact allergy is suspected or confirmed. They also made it clear that thick socks worn between shin guards and the skin often are not good enough to avoid ACD because the relevant allergens may achieve skin contact despite the barrier.6
Patch Testing for AA Contact Allergy
Historically, ACD to shin guards or shin pads, insoles of shoes, and even flip-flops has been associated with rubber-related chemicals such as mercapto mix, thiuram mix, N-isopropyl-N’-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine, thioureas, and carbamates, as well as dyes, benzoyl peroxide, and urea formaldehyde or phenol formaldehyde resins.1 Most of these chemicals can be tested with standard screening series or supplemental series. Patients with contact allergy to AA may have negative patch testing to screening series and/or supplemental series and may have strong positive reactions to pieces of suspected foam shin pads or shin guards, shoes, and/or flip-flops. Although Koumaki et al5 recommended patch testing for AA contact allergy with AA 0.1% in acetone, Besner Morin et al4 mentioned that petrolatum may be a more desirable vehicle because it could maintain stability for a longer period of time. In fact, a 2021 article highlighting the American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year recommends testing with either AA 0.1% in acetone or AA 0.1% in petrolatum.7 Unfortunately, AA is not commercially available for purchase at the time of publication. We are hopeful that this will change in the near future.
Final Interpretation
Acetophenone azine is an emerging allergen commonly identified in EVA foam and attributed to contact allergy to shin guards or pads, soles of shoes, and flip-flops. Most cases have been reported in Europe and Canada and have been identified in young male athletes. In addition to standard patch testing, athletes with lower leg dermatitis and/or dermatitis of the soles of the feet should undergo patch testing with AA 0.1% in acetone or petrolatum and pieces of the equipment and/or footwear.
It’s time for the American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS) Allergen of the Year! For 2021, the esteemed award goes to acetophenone azine (AA). If you have never heard of this chemical, you are not alone. Acetophenone azine has been identified in foam materials made of the copolymer ethyl-vinyl acetate (EVA). Contact allergy to AA initially was reported in 2016.1 There are only a few European and Canadian case reports and one case series of AA contact allergy in the literature, all of which are associated with foam shin pads or shin guards, shoe insoles, and/or flip-flops.2-6 Acetophenone azine is an important emerging allergen, and in this column, we will introduce you to AA and the sneaky places it can lurk and cause allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). We also highlight diagnosis, management, and patch testing for AA contact allergy.
AA Contact Allergy in the Literature
The first case of AA contact allergy was reported in Europe in 2016 when a 13-year-old male soccer player developed severe lower leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis associated with wearing foam shin guards.1 Patch testing to standard and supplemental trays was negative or not relevant; however, the patient exhibited strong reactions when patch tested directly to a piece of the shin guard soaked in acetone, water, and ethanol. Additional testing with AA diluted in acetone, water, and petrolatum resulted in positive patch test reactions to acetone dilutions of 1%, 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.001% and aqueous solutions of 1% and 0.1%. Chromatographic analyses with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of shin guard extracts confirmed the culprit allergen to be AA.1
In the following months, the same clinic saw 2 more cases of AA contact allergy.2 An 11-year-old male soccer player developed lower leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis from wearing shin guards. Months later, he also developed dermatitis on the soles of the feet, which was attributed to wearing flip-flops. Patch tests to pieces of the shin guards and flip-flops were positive; AA in acetone 0.1% and 0.01% also was positive. As you might expect, HPLC again confirmed the presence of AA in the shin guards and flip-flops. The third patient was a 12-year-old boy with dermatitis on the soles of both feet; later he also developed a generalized dermatitis. Patch testing to pieces of the insoles of his sneakers and AA in acetone 0.1% and 0.01% was positive. Again, HPLC was positive for the presence of AA in the insoles of his sneakers.2
Several more cases of AA contact allergy have been reported in the literature. A 29-year-old European male hockey player demonstrated contact allergy to the gray foam of his shin pads as well as localized leg dermatitis followed by generalized dermatitis (are you noticing a trend yet?), and later dermatitis on the soles of the feet with positive patch-test reactions to pieces of his shin pads and shoe insoles as well as AA 0.1% and 0.01% in acetone.3 A 6-year-old Canadian male soccer player presented with leg dermatitis and later generalized dermatitis and dermatitis on the soles of the feet with positive reactions to pieces of his shin pads and shoe insoles as well as to AA 1% and 0.1% in petrolatum.4 A 17-year-old British male (another trend, all males so far!) hockey player developed dermatitis localized to the legs and positive patch tests to the worn foam inner lining of his shin pads as well as to AA 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.001% in acetone.5Finally, Darrigade et al6 published a case series of 6 European children with AA contact allergy associated with shin pads and shoes; all had localized leg dermatitis, and some had generalized dermatitis. Patch testing to pieces of shin pads and shoe parts as well as to AA 0.1% in petrolatum and/or acetone showed with positive reactions to the foam pieces and AA in all 6 patients.
What’s the Deal With AA?
Acetophenone azine (also known as methylphenylketazine or bis[1-phenylethylidene]hydrazine) is composed of 2 acetophenone structures and a hydrazine moiety. It has been identified in EVA foam, which can be found in sports equipment such as shin pads or shin guards, shoes, and flip-flops. Raison-Peyron et al1 confirmed the presence of AA in EVA foam but reported that they did not know the exact reason for its presence. The authors theorized that AA might be a catalyst during EVA polymerization and also noted that it has antimicrobial and antihelminthic activity.1 Several authors noted that AA could be a by-product of EVA synthesis and that sports equipment manufacturers might not be aware of its presence in EVA.2,4-6 Some noted that AA concentration was higher in shin guards than in shoe insoles; they thought this explained why patients reacted first to their shin guards and were perhaps even initially sensitized to the shin guards, as well as why shoe insole contact allergy commonly was reported later or only after allergy to shin guards had already developed.4,6
Differential Diagnosis of Shin Pad or Shin Guard Dermatitis
We would be remiss if we did not mention the appropriate differential diagnosis when shin pad or shin guard dermatitis is identified. In fact, in most cases, shin guard dermatitis results from irritant contact dermatitis from friction, heat, and/or perspiration. Acetophenone azine contact allergy is not the most likely diagnosis when your sports-savvy, shin guard–wearing patient presents with anterior lower leg dermatitis. However, when conservative therapy (eg, barrier between the shin guard and the skin, control or management of perspiration, topical corticosteroid therapy) fails, patch testing to evaluate for ACD is indicated.
Management of AA Contact Allergy
As astute readers of this column are already aware, treatment of ACD requires strict allergen avoidance. You will find that we have the same recommendations for AA contact allergy. Given that there are only a handful of cases in the literature, there are limited recommendations on practical allergen avoidance other than “don’t wear the problem shin guards, shoe insoles, or flip-flops.” However, Darrigade et al6 recommended wearing polyurethane shin guards and leather insoles as alternatives when AA contact allergy is suspected or confirmed. They also made it clear that thick socks worn between shin guards and the skin often are not good enough to avoid ACD because the relevant allergens may achieve skin contact despite the barrier.6
Patch Testing for AA Contact Allergy
Historically, ACD to shin guards or shin pads, insoles of shoes, and even flip-flops has been associated with rubber-related chemicals such as mercapto mix, thiuram mix, N-isopropyl-N’-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine, thioureas, and carbamates, as well as dyes, benzoyl peroxide, and urea formaldehyde or phenol formaldehyde resins.1 Most of these chemicals can be tested with standard screening series or supplemental series. Patients with contact allergy to AA may have negative patch testing to screening series and/or supplemental series and may have strong positive reactions to pieces of suspected foam shin pads or shin guards, shoes, and/or flip-flops. Although Koumaki et al5 recommended patch testing for AA contact allergy with AA 0.1% in acetone, Besner Morin et al4 mentioned that petrolatum may be a more desirable vehicle because it could maintain stability for a longer period of time. In fact, a 2021 article highlighting the American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year recommends testing with either AA 0.1% in acetone or AA 0.1% in petrolatum.7 Unfortunately, AA is not commercially available for purchase at the time of publication. We are hopeful that this will change in the near future.
Final Interpretation
Acetophenone azine is an emerging allergen commonly identified in EVA foam and attributed to contact allergy to shin guards or pads, soles of shoes, and flip-flops. Most cases have been reported in Europe and Canada and have been identified in young male athletes. In addition to standard patch testing, athletes with lower leg dermatitis and/or dermatitis of the soles of the feet should undergo patch testing with AA 0.1% in acetone or petrolatum and pieces of the equipment and/or footwear.
- Raison-Peyron N, Bergendorff O, Bourrain JL, et al. Acetophenone azine: a new allergen responsible for severe contact dermatitis from shin pads. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:106-110.
- Raison-Peyron N, Bergendorff O, Du-Thanh A, et al. Two new cases of severe allergic contact dermatitis caused by acetophenone azine. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:380-381.
- De Fré C, Bergendorff O, Raison-Peyron N, et al. Acetophenone azine: a new shoe allergen causing severe foot dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:416-417.
- Besner Morin C, Stanciu M, Miedzybrodzki B, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from acetophenone azine in a Canadian child. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:41-42.
- Koumaki D, Bergendorff O, Bruze M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to shin pads in a hockey player: acetophenone is an emerging allergen. Dermatitis. 2019;30:162-163.
- Darrigade AS, Raison-Peyron N, Courouge-Dorcier D, et al. The chemical acetophenone azine: an important cause of shin and foot dermatitis in children. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:E61-E62.
- Raison-Peyron N, Sasseville D. Acetophenone azine. Dermatitis. 2021;32:5-9.
- Raison-Peyron N, Bergendorff O, Bourrain JL, et al. Acetophenone azine: a new allergen responsible for severe contact dermatitis from shin pads. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:106-110.
- Raison-Peyron N, Bergendorff O, Du-Thanh A, et al. Two new cases of severe allergic contact dermatitis caused by acetophenone azine. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:380-381.
- De Fré C, Bergendorff O, Raison-Peyron N, et al. Acetophenone azine: a new shoe allergen causing severe foot dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;77:416-417.
- Besner Morin C, Stanciu M, Miedzybrodzki B, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis from acetophenone azine in a Canadian child. Contact Dermatitis. 2020;83:41-42.
- Koumaki D, Bergendorff O, Bruze M, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis to shin pads in a hockey player: acetophenone is an emerging allergen. Dermatitis. 2019;30:162-163.
- Darrigade AS, Raison-Peyron N, Courouge-Dorcier D, et al. The chemical acetophenone azine: an important cause of shin and foot dermatitis in children. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:E61-E62.
- Raison-Peyron N, Sasseville D. Acetophenone azine. Dermatitis. 2021;32:5-9.
Practice Points
- Acetophenone azine is an emerging allergen identified in ethyl-vinyl acetate foam used in shin guards, shoe soles, and flip-flops.
- Cases have been reported in young male athletes in Europe and Canada.
- Patch testing can be completed with acetophenone azine 0.1% in acetone or petrolatum.
Desmoplastic Melanoma Masquerading as Neurofibroma
Desmoplastic melanoma (DMM) is a rare variant of melanoma that presents major challenges to both clinicians and pathologists.1 Clinically, the lesions may appear as subtle bland papules, nodules, or plaques. They can be easily mistaken for benign growths, leading to a delayed diagnosis. Consequently, most DMMs at the time of diagnosis tend to be thick, with a mean Breslow depth ranging from 2.0 to 6.5 mm.2 Histopathologic evaluation has its difficulties. At scanning magnification, these tumors may show low cellularity, mimicking a benign proliferation. It is well recognized that S-100 and other tumor markers lack specificity for DMM, which can be positive in a range of neural tumors and other cell types.2 In some amelanotic tumors, DMM becomes virtually indistinguishable from benign peripheral sheath tumors such as neurofribroma.3
Desmoplastic melanoma is exceedingly uncommon in the United States, with an estimated annual incidence rate of 2.0 cases per million.2 Typical locations of presentation include sun-exposed skin, with the head and neck regions representing more than half of reported cases.2 Desmoplastic melanoma largely is a disease of fair-skinned patients, with 95.5% of cases in the United States occurring in white non-Hispanic individuals. Advancing age, male gender, and head and neck location are associated with an increased risk for DMM-specific death.2 It is important that new or changing lesions in the correct cohort and location are biopsied promptly. We present this case to highlight the ongoing challenges of diagnosing DMM both clinically and histologically and to review the salient features of this often benign-appearing tumor.
Case Report
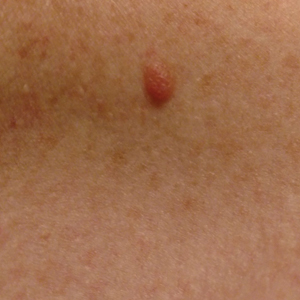
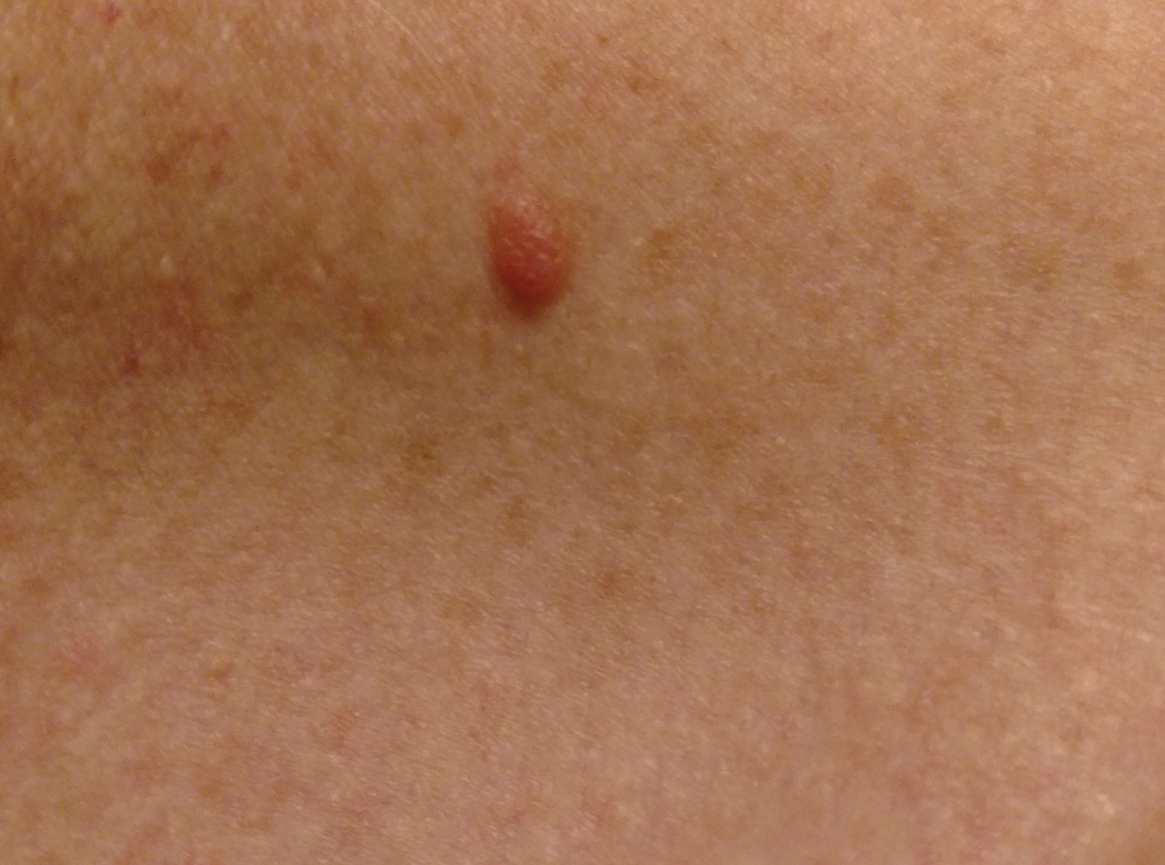
A 51-year-old White man with a history of prostate cancer, a personal and family history of melanoma, and benign neurofibromas presented with a 6-mm, pink, well-demarcated, soft papule on the left lateral neck (Figure 1). The lesion had been stable for many years but began growing more rapidly 1 to 2 years prior to presentation. The lesion was asymptomatic, and he denied changes in color or texture. There also was no bleeding or ulceration. A review of systems was unremarkable. A shave biopsy of the lesion revealed a nodular spindle cell tumor in the dermis resembling a neurofibroma on low power (Figure 2). However, overlying the tumor was a confluent proliferation positive for MART-1 and S-100, which was consistent with a diagnosis of melanoma in situ (Figure 3). Higher-power evaluation of the dermal proliferation showed both bland and hyperchromatic spindled and epithelioid cells (Figure 4), with rare mitotic figures highlighted by PHH3, an uncommon finding in neurofibromas (Figure 5). The dermal spindle cells were positive for S-100 and p75 and negative for Melan-A. Epithelial membrane antigen highlighted a faint sheath surrounding the dermal component. Ki-67 revealed a mildly increased proliferative index in the dermal component. The diagnosis of DMM was made after outside dermatopathology consultation was in agreement. However, the possibility of a melanoma in situ growing in association with an underlying neurofibroma remained a diagnostic consideration histologically. The lesion was widely excised.
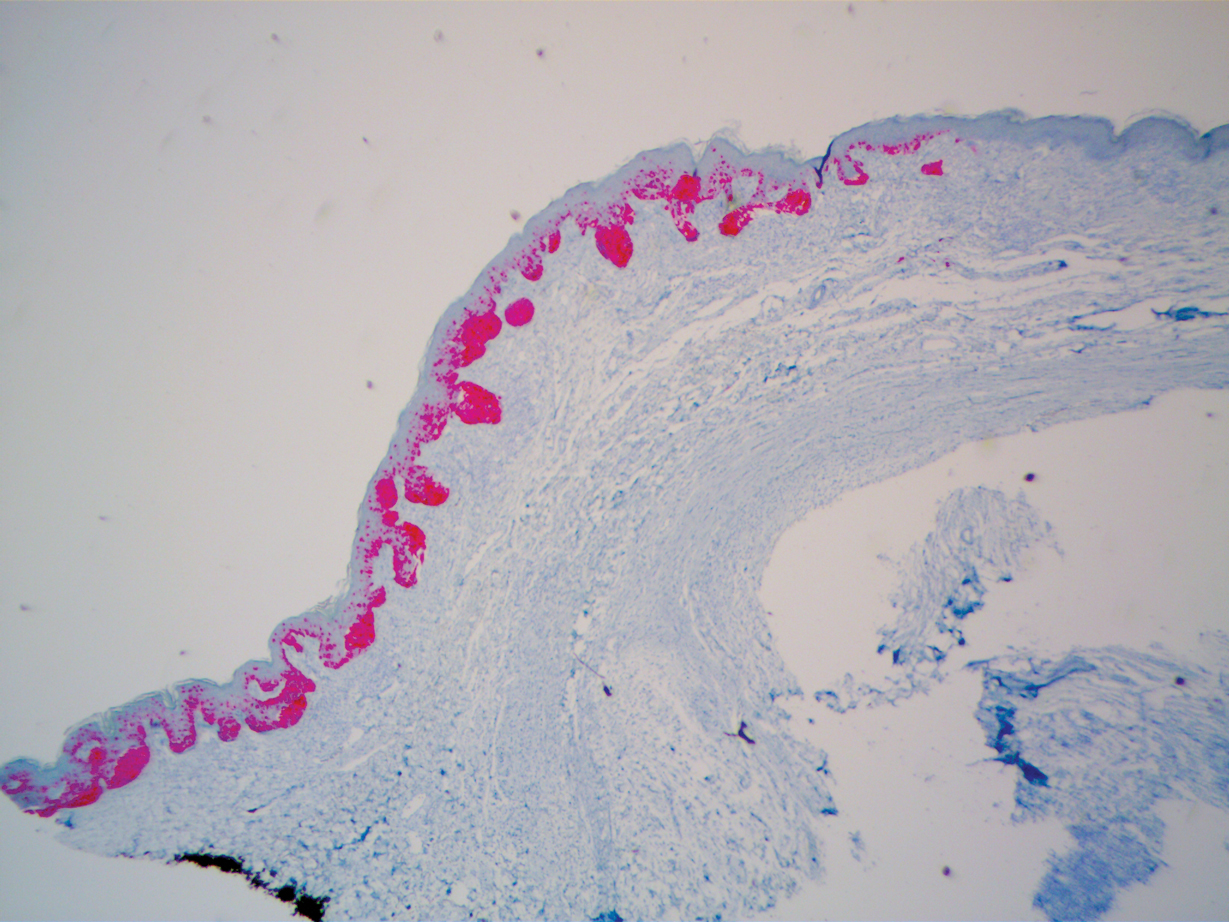
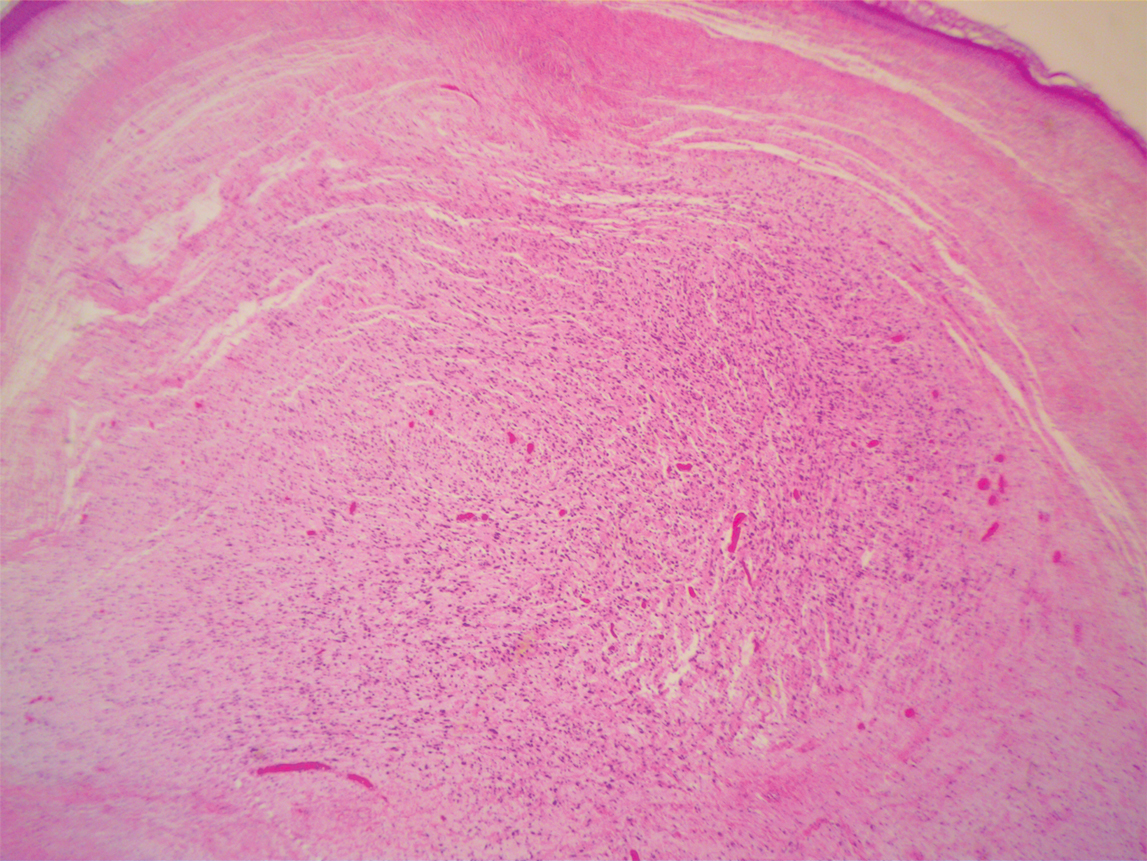
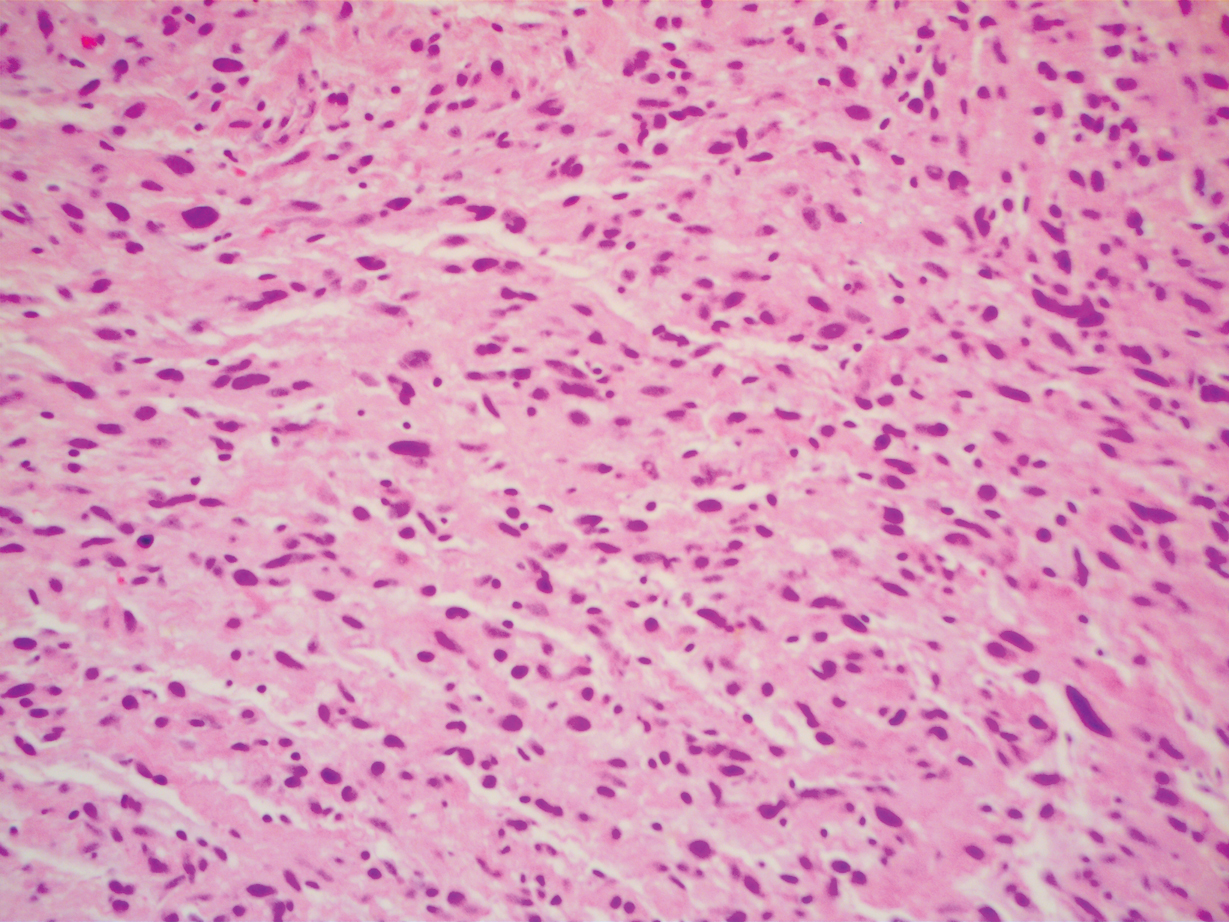
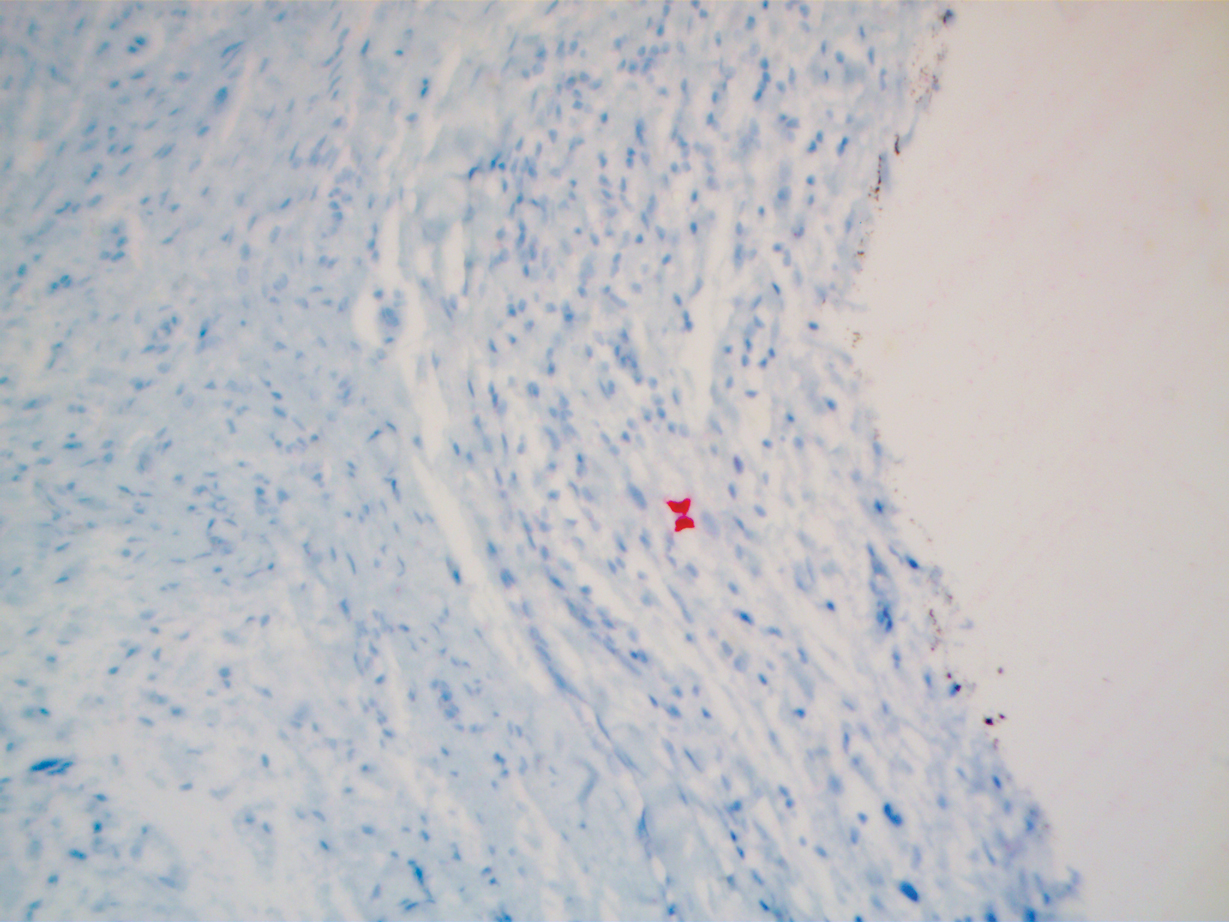
Comment
Differential for DMM
Early DMMs may not show sufficient cytologic atypia to permit obvious distinction from neurofibromas, which becomes problematic when encountering a spindle cell proliferation within severely sun-damaged skin, or even more so when an intraepidermal population of melanocytes is situated above a dermal population of slender, spindled, S-100–positive cells, as seen in our patient.4 For these challenging scenarios, Yeh and McCalmont4 have proposed evaluating for a CD34 “fingerprint” pattern. This pattern typically is widespread in neurofibroma but absent or limited in DMM, and it is a useful adjunct in the differential diagnosis when conventional immunohistochemistry has little contribution.
There are several case reports in the literature of DMM mimicking other benign or malignant proliferations. In 2012, Jou et al5 described a case of a 62-year-old White man who presented with an oral nodule consistent with fibrous inflammatory hyperplasia clinically. Incisional biopsy later confirmed the diagnosis of amelanotic DMM.5 Similar case reports have been described in which the diagnosis of DMM was later found to resemble a sarcoma and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor.6,7
Diagnosis of DMM
The prototypical DMM is an asymmetrical and deeply infiltrative spindle cell lesion in severely sun-damaged skin. By definition, the individual melanocytes are separated by connective tissue components, giving the tumor a paucicellular appearance.1 Although the low cellularity can give a deceptively bland scanning aspect, on high-power examination there usually are identifiable atypical spindled cells with enlarged, elongated, and hyperchromatic nuclei. S-100 typically is diffusely positive in DMM, though occasional cases show more limited staining.8 Other commonly used and more specific markers of melanocytic differentiation, including HMB45 and Melan-A, typically are negative in the paucicellular spindle cell components.9 Desmoplastic melanoma can be further categorized by the degree of fibrosis within a particular tumor. If fibrosis is prominent throughout the entire tumor, it is named pure DMM. On the other hand, fibrosis may only represent a portion of an otherwise nondesmoplastic melanoma, which is known as combined DMM.10
Conclusion
We present this case to highlight the ongoing challenges of diagnosing DMM both clinically and histologically. Although a bland-appearing lesion, key clinical features prompting a biopsy in our patient included recent growth of the lesion, a personal history of melanoma, the patient’s fair skin type, a history of heavy sun exposure, and the location of the lesion. According to Busam,11 an associated melanoma in situ component is identified in 80% to 85% of DMM cases. Detection of a melanoma in situ component associated with a malignant spindle cell tumor can help establish the diagnosis of DMM. In the absence of melanoma in situ, a strong diffuse immunoreactivity for S-100 and lack of epithelial markers support the diagnosis.11 After review of the literature, our case likely represents DMM as opposed to a melanoma in situ developing within a neurofibroma.
- Wood BA. Desmoplastic melanoma: recent advances and persisting challenges. Pathology. 2013;45:453-463.
- Chen LL, Jaimes N, Barker CA, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:825-833.
- Machado I, Llombart B, Cruz J, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma may mimic a cutaneous peripheral nerve sheath tumor: report of 3 challenging cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;4:632-638.
- Yeh I, McCalmont, TH. Distinguishing neurofibroma from desmoplastic melanoma: the value of the CD34 fingerprint. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:625-630.
- Jou A, Miranda FV, Oliveira MG, et al. Oral desmoplastic melanoma mimicking inflammatory hyperplasia. Gerodontology. 2012;29:E1163-E1167.
- Ishikura H, Kojo T, Ichimura H, et al. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma of the uterine cervix: a rare primary malignancy in the uterus mimicking a sarcoma. Histopathology. 1998;33:93-94.
- Barnett SL, Wells MJ, Mickey B, et al. Perineural extension of cutaneous desmoplastic melanoma mimicking an intracranial malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. case report. J Neurosurg. 2011;115:273-277.
- Jain S, Allen PW. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma and its variants. a study of 45 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989;13:358-373.
- Skelton HG, Maceira J, Smith KJ, et al. HMB45 negative spindle cell malignant melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:580-584.
- George E, McClain SE, Slingluff CL, et al. Subclassification of desmoplastic melanoma: pure and mixed variants have significantly different capacities for lymph node metastasis. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:425-432.
- Busam KJ. Desmoplastic melanoma. Clin Lab Med. 2011;31:321-330.
Desmoplastic melanoma (DMM) is a rare variant of melanoma that presents major challenges to both clinicians and pathologists.1 Clinically, the lesions may appear as subtle bland papules, nodules, or plaques. They can be easily mistaken for benign growths, leading to a delayed diagnosis. Consequently, most DMMs at the time of diagnosis tend to be thick, with a mean Breslow depth ranging from 2.0 to 6.5 mm.2 Histopathologic evaluation has its difficulties. At scanning magnification, these tumors may show low cellularity, mimicking a benign proliferation. It is well recognized that S-100 and other tumor markers lack specificity for DMM, which can be positive in a range of neural tumors and other cell types.2 In some amelanotic tumors, DMM becomes virtually indistinguishable from benign peripheral sheath tumors such as neurofribroma.3
Desmoplastic melanoma is exceedingly uncommon in the United States, with an estimated annual incidence rate of 2.0 cases per million.2 Typical locations of presentation include sun-exposed skin, with the head and neck regions representing more than half of reported cases.2 Desmoplastic melanoma largely is a disease of fair-skinned patients, with 95.5% of cases in the United States occurring in white non-Hispanic individuals. Advancing age, male gender, and head and neck location are associated with an increased risk for DMM-specific death.2 It is important that new or changing lesions in the correct cohort and location are biopsied promptly. We present this case to highlight the ongoing challenges of diagnosing DMM both clinically and histologically and to review the salient features of this often benign-appearing tumor.
Case Report
A 51-year-old White man with a history of prostate cancer, a personal and family history of melanoma, and benign neurofibromas presented with a 6-mm, pink, well-demarcated, soft papule on the left lateral neck (Figure 1). The lesion had been stable for many years but began growing more rapidly 1 to 2 years prior to presentation. The lesion was asymptomatic, and he denied changes in color or texture. There also was no bleeding or ulceration. A review of systems was unremarkable. A shave biopsy of the lesion revealed a nodular spindle cell tumor in the dermis resembling a neurofibroma on low power (Figure 2). However, overlying the tumor was a confluent proliferation positive for MART-1 and S-100, which was consistent with a diagnosis of melanoma in situ (Figure 3). Higher-power evaluation of the dermal proliferation showed both bland and hyperchromatic spindled and epithelioid cells (Figure 4), with rare mitotic figures highlighted by PHH3, an uncommon finding in neurofibromas (Figure 5). The dermal spindle cells were positive for S-100 and p75 and negative for Melan-A. Epithelial membrane antigen highlighted a faint sheath surrounding the dermal component. Ki-67 revealed a mildly increased proliferative index in the dermal component. The diagnosis of DMM was made after outside dermatopathology consultation was in agreement. However, the possibility of a melanoma in situ growing in association with an underlying neurofibroma remained a diagnostic consideration histologically. The lesion was widely excised.





Comment
Differential for DMM
Early DMMs may not show sufficient cytologic atypia to permit obvious distinction from neurofibromas, which becomes problematic when encountering a spindle cell proliferation within severely sun-damaged skin, or even more so when an intraepidermal population of melanocytes is situated above a dermal population of slender, spindled, S-100–positive cells, as seen in our patient.4 For these challenging scenarios, Yeh and McCalmont4 have proposed evaluating for a CD34 “fingerprint” pattern. This pattern typically is widespread in neurofibroma but absent or limited in DMM, and it is a useful adjunct in the differential diagnosis when conventional immunohistochemistry has little contribution.
There are several case reports in the literature of DMM mimicking other benign or malignant proliferations. In 2012, Jou et al5 described a case of a 62-year-old White man who presented with an oral nodule consistent with fibrous inflammatory hyperplasia clinically. Incisional biopsy later confirmed the diagnosis of amelanotic DMM.5 Similar case reports have been described in which the diagnosis of DMM was later found to resemble a sarcoma and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor.6,7
Diagnosis of DMM
The prototypical DMM is an asymmetrical and deeply infiltrative spindle cell lesion in severely sun-damaged skin. By definition, the individual melanocytes are separated by connective tissue components, giving the tumor a paucicellular appearance.1 Although the low cellularity can give a deceptively bland scanning aspect, on high-power examination there usually are identifiable atypical spindled cells with enlarged, elongated, and hyperchromatic nuclei. S-100 typically is diffusely positive in DMM, though occasional cases show more limited staining.8 Other commonly used and more specific markers of melanocytic differentiation, including HMB45 and Melan-A, typically are negative in the paucicellular spindle cell components.9 Desmoplastic melanoma can be further categorized by the degree of fibrosis within a particular tumor. If fibrosis is prominent throughout the entire tumor, it is named pure DMM. On the other hand, fibrosis may only represent a portion of an otherwise nondesmoplastic melanoma, which is known as combined DMM.10
Conclusion
We present this case to highlight the ongoing challenges of diagnosing DMM both clinically and histologically. Although a bland-appearing lesion, key clinical features prompting a biopsy in our patient included recent growth of the lesion, a personal history of melanoma, the patient’s fair skin type, a history of heavy sun exposure, and the location of the lesion. According to Busam,11 an associated melanoma in situ component is identified in 80% to 85% of DMM cases. Detection of a melanoma in situ component associated with a malignant spindle cell tumor can help establish the diagnosis of DMM. In the absence of melanoma in situ, a strong diffuse immunoreactivity for S-100 and lack of epithelial markers support the diagnosis.11 After review of the literature, our case likely represents DMM as opposed to a melanoma in situ developing within a neurofibroma.
Desmoplastic melanoma (DMM) is a rare variant of melanoma that presents major challenges to both clinicians and pathologists.1 Clinically, the lesions may appear as subtle bland papules, nodules, or plaques. They can be easily mistaken for benign growths, leading to a delayed diagnosis. Consequently, most DMMs at the time of diagnosis tend to be thick, with a mean Breslow depth ranging from 2.0 to 6.5 mm.2 Histopathologic evaluation has its difficulties. At scanning magnification, these tumors may show low cellularity, mimicking a benign proliferation. It is well recognized that S-100 and other tumor markers lack specificity for DMM, which can be positive in a range of neural tumors and other cell types.2 In some amelanotic tumors, DMM becomes virtually indistinguishable from benign peripheral sheath tumors such as neurofribroma.3
Desmoplastic melanoma is exceedingly uncommon in the United States, with an estimated annual incidence rate of 2.0 cases per million.2 Typical locations of presentation include sun-exposed skin, with the head and neck regions representing more than half of reported cases.2 Desmoplastic melanoma largely is a disease of fair-skinned patients, with 95.5% of cases in the United States occurring in white non-Hispanic individuals. Advancing age, male gender, and head and neck location are associated with an increased risk for DMM-specific death.2 It is important that new or changing lesions in the correct cohort and location are biopsied promptly. We present this case to highlight the ongoing challenges of diagnosing DMM both clinically and histologically and to review the salient features of this often benign-appearing tumor.
Case Report
A 51-year-old White man with a history of prostate cancer, a personal and family history of melanoma, and benign neurofibromas presented with a 6-mm, pink, well-demarcated, soft papule on the left lateral neck (Figure 1). The lesion had been stable for many years but began growing more rapidly 1 to 2 years prior to presentation. The lesion was asymptomatic, and he denied changes in color or texture. There also was no bleeding or ulceration. A review of systems was unremarkable. A shave biopsy of the lesion revealed a nodular spindle cell tumor in the dermis resembling a neurofibroma on low power (Figure 2). However, overlying the tumor was a confluent proliferation positive for MART-1 and S-100, which was consistent with a diagnosis of melanoma in situ (Figure 3). Higher-power evaluation of the dermal proliferation showed both bland and hyperchromatic spindled and epithelioid cells (Figure 4), with rare mitotic figures highlighted by PHH3, an uncommon finding in neurofibromas (Figure 5). The dermal spindle cells were positive for S-100 and p75 and negative for Melan-A. Epithelial membrane antigen highlighted a faint sheath surrounding the dermal component. Ki-67 revealed a mildly increased proliferative index in the dermal component. The diagnosis of DMM was made after outside dermatopathology consultation was in agreement. However, the possibility of a melanoma in situ growing in association with an underlying neurofibroma remained a diagnostic consideration histologically. The lesion was widely excised.





Comment
Differential for DMM
Early DMMs may not show sufficient cytologic atypia to permit obvious distinction from neurofibromas, which becomes problematic when encountering a spindle cell proliferation within severely sun-damaged skin, or even more so when an intraepidermal population of melanocytes is situated above a dermal population of slender, spindled, S-100–positive cells, as seen in our patient.4 For these challenging scenarios, Yeh and McCalmont4 have proposed evaluating for a CD34 “fingerprint” pattern. This pattern typically is widespread in neurofibroma but absent or limited in DMM, and it is a useful adjunct in the differential diagnosis when conventional immunohistochemistry has little contribution.
There are several case reports in the literature of DMM mimicking other benign or malignant proliferations. In 2012, Jou et al5 described a case of a 62-year-old White man who presented with an oral nodule consistent with fibrous inflammatory hyperplasia clinically. Incisional biopsy later confirmed the diagnosis of amelanotic DMM.5 Similar case reports have been described in which the diagnosis of DMM was later found to resemble a sarcoma and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor.6,7
Diagnosis of DMM
The prototypical DMM is an asymmetrical and deeply infiltrative spindle cell lesion in severely sun-damaged skin. By definition, the individual melanocytes are separated by connective tissue components, giving the tumor a paucicellular appearance.1 Although the low cellularity can give a deceptively bland scanning aspect, on high-power examination there usually are identifiable atypical spindled cells with enlarged, elongated, and hyperchromatic nuclei. S-100 typically is diffusely positive in DMM, though occasional cases show more limited staining.8 Other commonly used and more specific markers of melanocytic differentiation, including HMB45 and Melan-A, typically are negative in the paucicellular spindle cell components.9 Desmoplastic melanoma can be further categorized by the degree of fibrosis within a particular tumor. If fibrosis is prominent throughout the entire tumor, it is named pure DMM. On the other hand, fibrosis may only represent a portion of an otherwise nondesmoplastic melanoma, which is known as combined DMM.10
Conclusion
We present this case to highlight the ongoing challenges of diagnosing DMM both clinically and histologically. Although a bland-appearing lesion, key clinical features prompting a biopsy in our patient included recent growth of the lesion, a personal history of melanoma, the patient’s fair skin type, a history of heavy sun exposure, and the location of the lesion. According to Busam,11 an associated melanoma in situ component is identified in 80% to 85% of DMM cases. Detection of a melanoma in situ component associated with a malignant spindle cell tumor can help establish the diagnosis of DMM. In the absence of melanoma in situ, a strong diffuse immunoreactivity for S-100 and lack of epithelial markers support the diagnosis.11 After review of the literature, our case likely represents DMM as opposed to a melanoma in situ developing within a neurofibroma.
- Wood BA. Desmoplastic melanoma: recent advances and persisting challenges. Pathology. 2013;45:453-463.
- Chen LL, Jaimes N, Barker CA, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:825-833.
- Machado I, Llombart B, Cruz J, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma may mimic a cutaneous peripheral nerve sheath tumor: report of 3 challenging cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;4:632-638.
- Yeh I, McCalmont, TH. Distinguishing neurofibroma from desmoplastic melanoma: the value of the CD34 fingerprint. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:625-630.
- Jou A, Miranda FV, Oliveira MG, et al. Oral desmoplastic melanoma mimicking inflammatory hyperplasia. Gerodontology. 2012;29:E1163-E1167.
- Ishikura H, Kojo T, Ichimura H, et al. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma of the uterine cervix: a rare primary malignancy in the uterus mimicking a sarcoma. Histopathology. 1998;33:93-94.
- Barnett SL, Wells MJ, Mickey B, et al. Perineural extension of cutaneous desmoplastic melanoma mimicking an intracranial malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. case report. J Neurosurg. 2011;115:273-277.
- Jain S, Allen PW. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma and its variants. a study of 45 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989;13:358-373.
- Skelton HG, Maceira J, Smith KJ, et al. HMB45 negative spindle cell malignant melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:580-584.
- George E, McClain SE, Slingluff CL, et al. Subclassification of desmoplastic melanoma: pure and mixed variants have significantly different capacities for lymph node metastasis. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:425-432.
- Busam KJ. Desmoplastic melanoma. Clin Lab Med. 2011;31:321-330.
- Wood BA. Desmoplastic melanoma: recent advances and persisting challenges. Pathology. 2013;45:453-463.
- Chen LL, Jaimes N, Barker CA, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:825-833.
- Machado I, Llombart B, Cruz J, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma may mimic a cutaneous peripheral nerve sheath tumor: report of 3 challenging cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;4:632-638.
- Yeh I, McCalmont, TH. Distinguishing neurofibroma from desmoplastic melanoma: the value of the CD34 fingerprint. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:625-630.
- Jou A, Miranda FV, Oliveira MG, et al. Oral desmoplastic melanoma mimicking inflammatory hyperplasia. Gerodontology. 2012;29:E1163-E1167.
- Ishikura H, Kojo T, Ichimura H, et al. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma of the uterine cervix: a rare primary malignancy in the uterus mimicking a sarcoma. Histopathology. 1998;33:93-94.
- Barnett SL, Wells MJ, Mickey B, et al. Perineural extension of cutaneous desmoplastic melanoma mimicking an intracranial malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. case report. J Neurosurg. 2011;115:273-277.
- Jain S, Allen PW. Desmoplastic malignant melanoma and its variants. a study of 45 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989;13:358-373.
- Skelton HG, Maceira J, Smith KJ, et al. HMB45 negative spindle cell malignant melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1997;19:580-584.
- George E, McClain SE, Slingluff CL, et al. Subclassification of desmoplastic melanoma: pure and mixed variants have significantly different capacities for lymph node metastasis. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:425-432.
- Busam KJ. Desmoplastic melanoma. Clin Lab Med. 2011;31:321-330.
Practice Points
- Desmoplastic melanoma remains a diagnostic challenge both clinically and histologically.
- New or changing lesions on sun-exposed sites of elderly patients with fair skin types should have a low threshold for biopsy.
- Consensus between more than one dermatopathologist is sometimes required to make the diagnosis histologically.
What’s Eating You? Culex Mosquitoes and West Nile Virus
What is West Nile virus? How is it contracted, and who can become infected?
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus of the Flaviviridae family and Flavivirus genus, a lineage that also includes the yellow fever, dengue, Zika, Japanese encephalitis, and Saint Louis encephalitis viruses.1 Birds serve as the reservoir hosts of WNV, and mosquitoes acquire the virus during feeding.2 West Nile virus then is transmitted to humans primarily by bites from Culex mosquitoes, which are especially prevalent in wooded areas during peak mosquito season (summer through early fall in North America).1 Mosquitoes also can infect horses; however, humans and horses are dead-end hosts, meaning they do not pass the virus on to other biting mosquitoes.3 There also have been rare reports of transmission of WNV through blood and donation as well as mother-to-baby transmission.2
What is the epidemiology of WNV in the United States?
Since the introduction of WNV to the United States in 1999, it has become an important public health concern, with 48,183 cases and 2163 deaths reported since 1999.2,3 In 2018, Nebraska had the highest number of cases of WNV (n=251), followed by California (n=217), North Dakota (n=204), Illinois (n=176), and South Dakota (n=169).3 West Nile virus is endemic to all 48 contiguous states and Canada, though the Great Plains region is especially affected by WNV due to several factors, such as a greater percentage of rural land, forests, and irrigated areas.4 The Great Plains region also has been thought to be an ecological niche for a more virulent species (Culex tarsalis) compared to other regions in the United States.5
The annual incidence of WNV in the United States peaked in 2003 at 9862 cases (up from 62 cases in 1999), then declined gradually until 2008 to 2011, during which the incidence was stable at 700 to 1100 new cases per year. However, there was a resurgence of cases (n=5674) in 2012 that steadied at around 2200 cases annually in subsequent years.6 Although there likely are several factors affecting WNV incidence trends in the United States, interannual changes in temperature and precipitation have been described. An increased mean annual temperature (from September through October, the end of peak mosquito season) and an increased temperature in winter months (from January through March, prior to peak mosquito season) have both been associated with an increased incidence of WNV.7 An increased temperature is thought to increase population numbers of mosquitoes both by increasing reproductive rates and creating ideal breeding environments via pooled water areas.8 Depending on the region, both above average and below average precipitation levels in the United States can increase WNV incidence the following year.7,9
What are the signs and symptoms of WNV infection?
Up to 80% of those infected with WNV are asymptomatic.3 After an incubation period of roughly 2 to 14 days, the remaining 20% may develop symptoms of West Nile fever (WNF), typically a self-limited illness that consists of 3 to 10 days of nonspecific symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue, muscle pain and/or weakness, eye pain, gastrointestinal tract upset, and a macular rash that usually presents on the trunk or extremities.1,3 Less than 1% of patients affected by WNV develop neuroinvasive disease, including meningitis, encephalitis, and/or acute flaccid paralysis.10 West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease can cause permanent neurologic sequelae such as muscle weakness, confusion, memory loss, and fatigue; it carries a mortality rate of 10% to 30%, which is mainly dependent on older age and immunosuppression status.1,10
What is the reported spectrum of cutaneous findings in WNV?
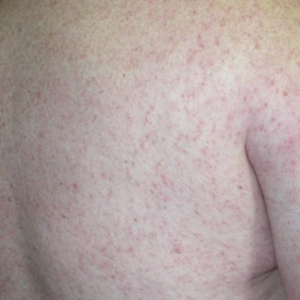
Of the roughly 20% of patients infected with WNV that develop WNF, approximately 25% to 50% will develop an associated rash.1 It most commonly is described as a morbilliform or maculopapular rash located on the chest, back, and arms, usually sparing the palms and soles, though 1 case report noted involvement with these areas (Figure).11,12 It typically appears 5 days after symptom onset, can be associated with defervescence, and lasts less than a week.1,13 Pruritus and dysesthesia are sometimes present.13 Other rare presentations that have been reported include an ill-defined pseudovesicular rash with erythematous papules on the palms and pink, scaly, psoriasiform papules on the feet and thighs, as well as neuroinvasive WNV leading to purpura fulminans.14,15 A diffuse, erythematous, petechial rash on the face, neck, trunk, and extremities was reported in a pediatric patient, but there have been no reports of a petechial rash associated with WNV in adult patients.16 These findings suggest some potential variability in the presentation of the WNV rash.
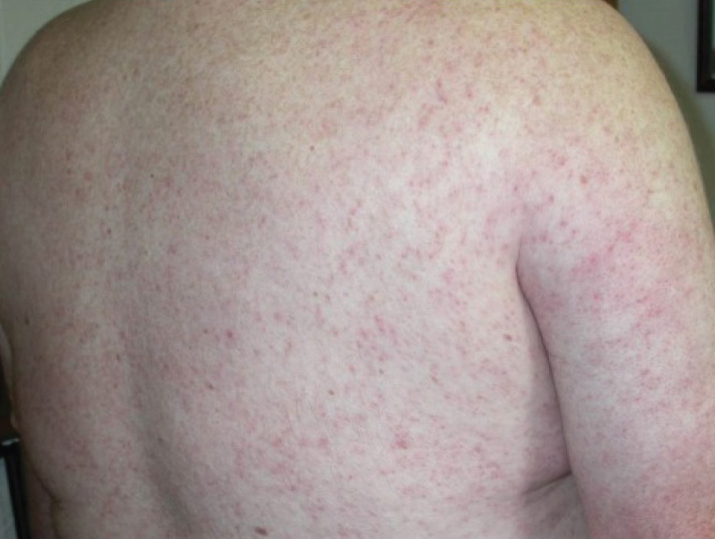
What role does the presence of rash play diagnostically and prognostically?
The rash of WNV has been implicated as a potential prognostic factor in predicting more favorable outcomes.17 Using 2002 data from the Illinois Department of Public Health and 2003 data from the Colorado Department of Public Health, Huhn and Dworkin17 found the age-adjusted risk of encephalitis and death to be decreased in WNV patients with a rash (relative risk, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.21-0.92). The reasons for this are not definitively known, but we hypothesize that the rash may prompt patients to seek earlier medical attention or indicate a more robust immune response. Additionally, a rash in WNV more commonly is seen in younger patients, whereas WNV neuroinvasive disease is more common in older patients, who also tend to have worse outcomes.10 One study found rash to be the only symptom that demonstrated a significant association with seropositivity (overall risk=6.35; P<.05; 95% CI, 3.75-10.80) by multivariate analysis.18
How is WNV diagnosed? What are the downsides to WNV testing?
Given that the presenting symptoms of WNV and WNF are nonspecific, it becomes challenging to arrive at the diagnosis based solely on physical examination. As such, the patient’s clinical and epidemiologic history, such as timing, pattern, and appearance of the rash or recent history of mosquito bites, is key to arriving at the correct diagnosis. With clinical suspicion, possible diagnostic tests include an IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for WNV, a plaque reduction neutralization test (PNRT), and blood polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
An ELISA is a confirmatory test to detect IgM antibodies to WNV in the serum. Because IgM seroconversion typically occurs between days 4 and 10 of symptom onset, there is a high probability of initial false-negative testing within the first 8 days after symptom onset.19,20 Clinical understanding of this fact is imperative, as an initial negative ELISA does not rule out WNV, and a retest is warranted if clinical suspicion is high. In addition to a high initial false-negative rate with ELISA, there are several other limitations to note. IgM antibodies remain elevated for 1 to 3 months or possibly up to a year in immunocompromised patients.1 Due to this, false positives may be present if there was a recent prior infection. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay may not distinguish from different flaviviruses, including the yellow fever, dengue, Zika, Japanese encephalitis, and Saint Louis encephalitis viruses. Seropositivity has been estimated in some states, including 1999 data from New York (2.6%), 2003 data from Nebraska (9.5%), and 2012-2014 data from Connecticut (8.5%).21-23 Regional variance may be expected, as there also were significant differences in WNV seropositivity between different regions in Nebraska (P<.001).23
Because ELISA testing for WNV has readily apparent flaws, other tests have been utilized in its diagnosis. The PNRT is the most specific test, and it works by measuring neutralizing antibody titers for different flaviviruses. It has the ability to determine cross-reactivity with other flaviviruses; however, it does not discriminate between a current infection and a prior infection or prior flavivirus vaccine (ie, yellow fever vaccine). Despite this, a positive PNRT can lend credibility to a positive ELISA test and determine specificity for WNV for those with no prior flavivirus exposure.24 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this test can be performed by the CDC or in reference laboratories designated by the CDC.3 Additionally, some state health laboratories may perform PRNTs.
Viral detection with PCR currently is used to screen blood donations and may be beneficial for immunocompromised patients that lack the ability to form a robust antibody response or if a patient presents early, as PCR works best within the first week of symptom onset.1 Tilley et al25 showed that a combination of PCR and ELISA were able to accurately predict 94.2% of patients (180/191) with documented WNV on a first blood sample compared to 45% and 58.1% for only viral detection or ELISA, respectively. Based on costs from a Midwest academic center, antibody detection tests are around $100 while PCR may range from $500 to $1000 and is only performed in reference laboratories. Although these tests remain in the repertoire for WNV diagnosis, financial stewardship is important.
If there are symptoms of photophobia, phonophobia, nuchal rigidity, loss of consciousness, or marked personality changes, a lumbar puncture for WNV IgM in the cerebrospinal fluid can be performed. As with most viral infections, cerebrospinal fluid findings normally include an elevated protein and lymphocyte count, but neutrophils may be predominantly elevated if the infection is early in its course.26
What are the management options?
To date, there is no curative treatment for WNV, and management is largely supportive. For WNF, over-the-counter pain medications may be helpful to reduce fever and pain. If more severe disease develops, hospitalization for further supportive care may be needed.27 If meningitis or encephalitis is suspected, broad-spectrum antibiotics may need to be started until other common etiologies are ruled out.28
How can you prevent WNV infection?
Disease prevention largely consists of educating the public to avoid heavily wooded areas, especially in areas of high prevalence and during peak months, and to use protective clothing and insect repellant that has been approved by the Environmental Protection Agency.3 Insect repellants approved by the Environmental Protection Agency contain ingredients such as DEET (N, N-diethyl-meta-toluamide), picaridin, IR3535 (ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate), and oil of lemon eucalyptus, which have been proven safe and effective.29 Patients also can protect their homes by using window screens and promptly repairing screens with holes.3
What is the differential diagnosis for WNV?
The differential diagnosis for fever with generalized maculopapular rash broadly ranges from viral etiologies (eg, WNV, Zika, measles), to tick bites (eg, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis), to drug-induced rashes. A detailed patient history inquiring on recent sick contacts, travel (WNV in the Midwest, ehrlichiosis in the Southeast), environmental exposures (ticks, mosquitoes), and new medications (typically 7–10 days after starting) is imperative to narrow the differential.30 In addition, the distribution, timing, and clinical characteristics of the rash may aid in diagnosis, along with an appropriately correlated clinical picture. West Nile virus likely will present in the summer in mid central geographic locations and often develops on the trunk and extremities as a blanching, generalized, maculopapular rash around 5 days after symptom onset or with defervescence.1
- Petersen LR. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of West Nile virus infection. UpToDate website. Updated August 7, 2020. Accessed April 16, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-west-nile-virus-infection?search=clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-west-nile-virusinfection.&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~78&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
- Sampathkumar P. West Nile virus: epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and prevention. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78:1137-1144.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile virus. Updated June 3, 2020. Accessed April 16, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/index.html
- Chuang TW, Hockett CW, Kightlinger L, et al. Landscape-level spatial patterns of West Nile virus risk in the northern Great Plains. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;86:724-731.
- Wimberly MC, Hildreth MB, Boyte SP, et al. Ecological niche of the 2003 West Nile virus epidemic in the northern great plains of the United States. PLoS One. 2008;3:E3744. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003744
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile virus disease cases reported to CDC by state of residence, 1999-2019. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/resources/pdfs/data/West-Nile-virus-disease-cases-by-state_1999-2019-P.pdf
- Hahn MB, Monaghan AJ, Hayden MH, et al. Meteorological conditions associated with increased incidence of West Nile virus disease in the United States, 2004–2012. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;92:1013-1022.
- Brown CM, DeMaria A Jr. The resurgence of West Nile virus. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157:823-824.
- Landesman WJ, Allan BF, Langerhans RB, et al. Inter-annual associations between precipitation and human incidence of West Nile virus in the United States. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007;7:337-343.
- Hart J Jr, Tillman G, Kraut MA, et al. West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease: neurological manifestations and prospective longitudinal outcomes. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:248.
- Wu JJ, Huang DB, Tyring SK. West Nile virus rash on the palms and soles of the feet. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1393-1394.
- Sejvar J. Clinical manifestations and outcomes of West Nile virus infection. Viruses. 2014;6:606-623.
- Ferguson DD, Gershman K, LeBailly A, et al. Characteristics of the rash associated with West Nile virus fever. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1204-1207.
- Marszalek R, Chen A, Gjede J. Psoriasiform eruption in the setting of West Nile virus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:AB4. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.01.017
- Shah S, Fite LP, Lane N, et al. Purpura fulminans associated with acute West Nile virus encephalitis. J Clin Virol. 2016;75:1-4.
- Civen R, Villacorte F, Robles DT, et al. West Nile virus infection in the pediatric population. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:75-78.
- Huhn GD, Dworkin MS. Rash as a prognostic factor in West Nile virus disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:388-389.
- Murphy TD, Grandpre J, Novick SL, et al. West Nile virus infection among health-fair participants, Wyoming 2003: assessment of symptoms and risk factors. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005;5:246-251.
- Prince HE, Tobler LH, Lapé-Nixon M, et al. Development and persistence of West Nile virus–specific immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgA, and IgG in viremic blood donors. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:4316-4320.
- Busch MP, Kleinman SH, Tobler LH, et al. Virus and antibody dynamics in acute West Nile Virus infection. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:984-993.
- Mostashari F, Bunning ML, Kitsutani PT, et al. Epidemic West Nile encephalitis, New York, 1999: results of a household-based seroepidemiological survey. Lancet. 2001;358:261-264.
- Cahill ME, Yao Y, Nock D, et al. West Nile virus seroprevalence, Connecticut, USA, 2000–2014. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:708-710.
- Schweitzer BK, Kramer WL, Sambol AR, et al. Geographic factors contributing to a high seroprevalence of West Nile virus-specific antibodies in humans following an epidemic. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2006;13:314-318.
- Maeda A, Maeda J. Review of diagnostic plaque reduction neutralization tests for flavivirus infection. Vet J. 2013;195:33-40.
- Tilley PA, Fox JD, Jayaraman GC, et al. Nucleic acid testing for west nile virus RNA in plasma enhances rapid diagnosis of acute infection in symptomatic patients. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1361-1364.
- Petersen LR, Brault AC, Nasci RS. West Nile virus: review of the literature. JAMA. 2013;310:308-315.
- Yu A, Ferenczi E, Moussa K, et al. Clinical spectrum of West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease. Neurohospitalist. 2020;10:43-47.
- Michaelis M, Kleinschmidt MC, Doerr HW, et al. Minocycline inhibits West Nile virus replication and apoptosis in human neuronal cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60:981-986.
- United State Environmental Protection Agency. Skin-applied repellent ingredients. https://www.epa.gov/insect-repellents/skin-applied-repellent-ingredients. Accessed April 16, 2021.
- Muzumdar S, Rothe MJ, Grant-Kels JM. The rash with maculopapules and fever in adults. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:109-118.
What is West Nile virus? How is it contracted, and who can become infected?
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus of the Flaviviridae family and Flavivirus genus, a lineage that also includes the yellow fever, dengue, Zika, Japanese encephalitis, and Saint Louis encephalitis viruses.1 Birds serve as the reservoir hosts of WNV, and mosquitoes acquire the virus during feeding.2 West Nile virus then is transmitted to humans primarily by bites from Culex mosquitoes, which are especially prevalent in wooded areas during peak mosquito season (summer through early fall in North America).1 Mosquitoes also can infect horses; however, humans and horses are dead-end hosts, meaning they do not pass the virus on to other biting mosquitoes.3 There also have been rare reports of transmission of WNV through blood and donation as well as mother-to-baby transmission.2
What is the epidemiology of WNV in the United States?
Since the introduction of WNV to the United States in 1999, it has become an important public health concern, with 48,183 cases and 2163 deaths reported since 1999.2,3 In 2018, Nebraska had the highest number of cases of WNV (n=251), followed by California (n=217), North Dakota (n=204), Illinois (n=176), and South Dakota (n=169).3 West Nile virus is endemic to all 48 contiguous states and Canada, though the Great Plains region is especially affected by WNV due to several factors, such as a greater percentage of rural land, forests, and irrigated areas.4 The Great Plains region also has been thought to be an ecological niche for a more virulent species (Culex tarsalis) compared to other regions in the United States.5
The annual incidence of WNV in the United States peaked in 2003 at 9862 cases (up from 62 cases in 1999), then declined gradually until 2008 to 2011, during which the incidence was stable at 700 to 1100 new cases per year. However, there was a resurgence of cases (n=5674) in 2012 that steadied at around 2200 cases annually in subsequent years.6 Although there likely are several factors affecting WNV incidence trends in the United States, interannual changes in temperature and precipitation have been described. An increased mean annual temperature (from September through October, the end of peak mosquito season) and an increased temperature in winter months (from January through March, prior to peak mosquito season) have both been associated with an increased incidence of WNV.7 An increased temperature is thought to increase population numbers of mosquitoes both by increasing reproductive rates and creating ideal breeding environments via pooled water areas.8 Depending on the region, both above average and below average precipitation levels in the United States can increase WNV incidence the following year.7,9
What are the signs and symptoms of WNV infection?
Up to 80% of those infected with WNV are asymptomatic.3 After an incubation period of roughly 2 to 14 days, the remaining 20% may develop symptoms of West Nile fever (WNF), typically a self-limited illness that consists of 3 to 10 days of nonspecific symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue, muscle pain and/or weakness, eye pain, gastrointestinal tract upset, and a macular rash that usually presents on the trunk or extremities.1,3 Less than 1% of patients affected by WNV develop neuroinvasive disease, including meningitis, encephalitis, and/or acute flaccid paralysis.10 West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease can cause permanent neurologic sequelae such as muscle weakness, confusion, memory loss, and fatigue; it carries a mortality rate of 10% to 30%, which is mainly dependent on older age and immunosuppression status.1,10
What is the reported spectrum of cutaneous findings in WNV?
Of the roughly 20% of patients infected with WNV that develop WNF, approximately 25% to 50% will develop an associated rash.1 It most commonly is described as a morbilliform or maculopapular rash located on the chest, back, and arms, usually sparing the palms and soles, though 1 case report noted involvement with these areas (Figure).11,12 It typically appears 5 days after symptom onset, can be associated with defervescence, and lasts less than a week.1,13 Pruritus and dysesthesia are sometimes present.13 Other rare presentations that have been reported include an ill-defined pseudovesicular rash with erythematous papules on the palms and pink, scaly, psoriasiform papules on the feet and thighs, as well as neuroinvasive WNV leading to purpura fulminans.14,15 A diffuse, erythematous, petechial rash on the face, neck, trunk, and extremities was reported in a pediatric patient, but there have been no reports of a petechial rash associated with WNV in adult patients.16 These findings suggest some potential variability in the presentation of the WNV rash.

What role does the presence of rash play diagnostically and prognostically?
The rash of WNV has been implicated as a potential prognostic factor in predicting more favorable outcomes.17 Using 2002 data from the Illinois Department of Public Health and 2003 data from the Colorado Department of Public Health, Huhn and Dworkin17 found the age-adjusted risk of encephalitis and death to be decreased in WNV patients with a rash (relative risk, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.21-0.92). The reasons for this are not definitively known, but we hypothesize that the rash may prompt patients to seek earlier medical attention or indicate a more robust immune response. Additionally, a rash in WNV more commonly is seen in younger patients, whereas WNV neuroinvasive disease is more common in older patients, who also tend to have worse outcomes.10 One study found rash to be the only symptom that demonstrated a significant association with seropositivity (overall risk=6.35; P<.05; 95% CI, 3.75-10.80) by multivariate analysis.18
How is WNV diagnosed? What are the downsides to WNV testing?
Given that the presenting symptoms of WNV and WNF are nonspecific, it becomes challenging to arrive at the diagnosis based solely on physical examination. As such, the patient’s clinical and epidemiologic history, such as timing, pattern, and appearance of the rash or recent history of mosquito bites, is key to arriving at the correct diagnosis. With clinical suspicion, possible diagnostic tests include an IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for WNV, a plaque reduction neutralization test (PNRT), and blood polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
An ELISA is a confirmatory test to detect IgM antibodies to WNV in the serum. Because IgM seroconversion typically occurs between days 4 and 10 of symptom onset, there is a high probability of initial false-negative testing within the first 8 days after symptom onset.19,20 Clinical understanding of this fact is imperative, as an initial negative ELISA does not rule out WNV, and a retest is warranted if clinical suspicion is high. In addition to a high initial false-negative rate with ELISA, there are several other limitations to note. IgM antibodies remain elevated for 1 to 3 months or possibly up to a year in immunocompromised patients.1 Due to this, false positives may be present if there was a recent prior infection. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay may not distinguish from different flaviviruses, including the yellow fever, dengue, Zika, Japanese encephalitis, and Saint Louis encephalitis viruses. Seropositivity has been estimated in some states, including 1999 data from New York (2.6%), 2003 data from Nebraska (9.5%), and 2012-2014 data from Connecticut (8.5%).21-23 Regional variance may be expected, as there also were significant differences in WNV seropositivity between different regions in Nebraska (P<.001).23
Because ELISA testing for WNV has readily apparent flaws, other tests have been utilized in its diagnosis. The PNRT is the most specific test, and it works by measuring neutralizing antibody titers for different flaviviruses. It has the ability to determine cross-reactivity with other flaviviruses; however, it does not discriminate between a current infection and a prior infection or prior flavivirus vaccine (ie, yellow fever vaccine). Despite this, a positive PNRT can lend credibility to a positive ELISA test and determine specificity for WNV for those with no prior flavivirus exposure.24 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this test can be performed by the CDC or in reference laboratories designated by the CDC.3 Additionally, some state health laboratories may perform PRNTs.
Viral detection with PCR currently is used to screen blood donations and may be beneficial for immunocompromised patients that lack the ability to form a robust antibody response or if a patient presents early, as PCR works best within the first week of symptom onset.1 Tilley et al25 showed that a combination of PCR and ELISA were able to accurately predict 94.2% of patients (180/191) with documented WNV on a first blood sample compared to 45% and 58.1% for only viral detection or ELISA, respectively. Based on costs from a Midwest academic center, antibody detection tests are around $100 while PCR may range from $500 to $1000 and is only performed in reference laboratories. Although these tests remain in the repertoire for WNV diagnosis, financial stewardship is important.
If there are symptoms of photophobia, phonophobia, nuchal rigidity, loss of consciousness, or marked personality changes, a lumbar puncture for WNV IgM in the cerebrospinal fluid can be performed. As with most viral infections, cerebrospinal fluid findings normally include an elevated protein and lymphocyte count, but neutrophils may be predominantly elevated if the infection is early in its course.26
What are the management options?
To date, there is no curative treatment for WNV, and management is largely supportive. For WNF, over-the-counter pain medications may be helpful to reduce fever and pain. If more severe disease develops, hospitalization for further supportive care may be needed.27 If meningitis or encephalitis is suspected, broad-spectrum antibiotics may need to be started until other common etiologies are ruled out.28
How can you prevent WNV infection?
Disease prevention largely consists of educating the public to avoid heavily wooded areas, especially in areas of high prevalence and during peak months, and to use protective clothing and insect repellant that has been approved by the Environmental Protection Agency.3 Insect repellants approved by the Environmental Protection Agency contain ingredients such as DEET (N, N-diethyl-meta-toluamide), picaridin, IR3535 (ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate), and oil of lemon eucalyptus, which have been proven safe and effective.29 Patients also can protect their homes by using window screens and promptly repairing screens with holes.3
What is the differential diagnosis for WNV?
The differential diagnosis for fever with generalized maculopapular rash broadly ranges from viral etiologies (eg, WNV, Zika, measles), to tick bites (eg, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis), to drug-induced rashes. A detailed patient history inquiring on recent sick contacts, travel (WNV in the Midwest, ehrlichiosis in the Southeast), environmental exposures (ticks, mosquitoes), and new medications (typically 7–10 days after starting) is imperative to narrow the differential.30 In addition, the distribution, timing, and clinical characteristics of the rash may aid in diagnosis, along with an appropriately correlated clinical picture. West Nile virus likely will present in the summer in mid central geographic locations and often develops on the trunk and extremities as a blanching, generalized, maculopapular rash around 5 days after symptom onset or with defervescence.1
What is West Nile virus? How is it contracted, and who can become infected?
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus of the Flaviviridae family and Flavivirus genus, a lineage that also includes the yellow fever, dengue, Zika, Japanese encephalitis, and Saint Louis encephalitis viruses.1 Birds serve as the reservoir hosts of WNV, and mosquitoes acquire the virus during feeding.2 West Nile virus then is transmitted to humans primarily by bites from Culex mosquitoes, which are especially prevalent in wooded areas during peak mosquito season (summer through early fall in North America).1 Mosquitoes also can infect horses; however, humans and horses are dead-end hosts, meaning they do not pass the virus on to other biting mosquitoes.3 There also have been rare reports of transmission of WNV through blood and donation as well as mother-to-baby transmission.2
What is the epidemiology of WNV in the United States?
Since the introduction of WNV to the United States in 1999, it has become an important public health concern, with 48,183 cases and 2163 deaths reported since 1999.2,3 In 2018, Nebraska had the highest number of cases of WNV (n=251), followed by California (n=217), North Dakota (n=204), Illinois (n=176), and South Dakota (n=169).3 West Nile virus is endemic to all 48 contiguous states and Canada, though the Great Plains region is especially affected by WNV due to several factors, such as a greater percentage of rural land, forests, and irrigated areas.4 The Great Plains region also has been thought to be an ecological niche for a more virulent species (Culex tarsalis) compared to other regions in the United States.5
The annual incidence of WNV in the United States peaked in 2003 at 9862 cases (up from 62 cases in 1999), then declined gradually until 2008 to 2011, during which the incidence was stable at 700 to 1100 new cases per year. However, there was a resurgence of cases (n=5674) in 2012 that steadied at around 2200 cases annually in subsequent years.6 Although there likely are several factors affecting WNV incidence trends in the United States, interannual changes in temperature and precipitation have been described. An increased mean annual temperature (from September through October, the end of peak mosquito season) and an increased temperature in winter months (from January through March, prior to peak mosquito season) have both been associated with an increased incidence of WNV.7 An increased temperature is thought to increase population numbers of mosquitoes both by increasing reproductive rates and creating ideal breeding environments via pooled water areas.8 Depending on the region, both above average and below average precipitation levels in the United States can increase WNV incidence the following year.7,9
What are the signs and symptoms of WNV infection?
Up to 80% of those infected with WNV are asymptomatic.3 After an incubation period of roughly 2 to 14 days, the remaining 20% may develop symptoms of West Nile fever (WNF), typically a self-limited illness that consists of 3 to 10 days of nonspecific symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue, muscle pain and/or weakness, eye pain, gastrointestinal tract upset, and a macular rash that usually presents on the trunk or extremities.1,3 Less than 1% of patients affected by WNV develop neuroinvasive disease, including meningitis, encephalitis, and/or acute flaccid paralysis.10 West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease can cause permanent neurologic sequelae such as muscle weakness, confusion, memory loss, and fatigue; it carries a mortality rate of 10% to 30%, which is mainly dependent on older age and immunosuppression status.1,10
What is the reported spectrum of cutaneous findings in WNV?
Of the roughly 20% of patients infected with WNV that develop WNF, approximately 25% to 50% will develop an associated rash.1 It most commonly is described as a morbilliform or maculopapular rash located on the chest, back, and arms, usually sparing the palms and soles, though 1 case report noted involvement with these areas (Figure).11,12 It typically appears 5 days after symptom onset, can be associated with defervescence, and lasts less than a week.1,13 Pruritus and dysesthesia are sometimes present.13 Other rare presentations that have been reported include an ill-defined pseudovesicular rash with erythematous papules on the palms and pink, scaly, psoriasiform papules on the feet and thighs, as well as neuroinvasive WNV leading to purpura fulminans.14,15 A diffuse, erythematous, petechial rash on the face, neck, trunk, and extremities was reported in a pediatric patient, but there have been no reports of a petechial rash associated with WNV in adult patients.16 These findings suggest some potential variability in the presentation of the WNV rash.

What role does the presence of rash play diagnostically and prognostically?
The rash of WNV has been implicated as a potential prognostic factor in predicting more favorable outcomes.17 Using 2002 data from the Illinois Department of Public Health and 2003 data from the Colorado Department of Public Health, Huhn and Dworkin17 found the age-adjusted risk of encephalitis and death to be decreased in WNV patients with a rash (relative risk, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.21-0.92). The reasons for this are not definitively known, but we hypothesize that the rash may prompt patients to seek earlier medical attention or indicate a more robust immune response. Additionally, a rash in WNV more commonly is seen in younger patients, whereas WNV neuroinvasive disease is more common in older patients, who also tend to have worse outcomes.10 One study found rash to be the only symptom that demonstrated a significant association with seropositivity (overall risk=6.35; P<.05; 95% CI, 3.75-10.80) by multivariate analysis.18
How is WNV diagnosed? What are the downsides to WNV testing?
Given that the presenting symptoms of WNV and WNF are nonspecific, it becomes challenging to arrive at the diagnosis based solely on physical examination. As such, the patient’s clinical and epidemiologic history, such as timing, pattern, and appearance of the rash or recent history of mosquito bites, is key to arriving at the correct diagnosis. With clinical suspicion, possible diagnostic tests include an IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for WNV, a plaque reduction neutralization test (PNRT), and blood polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
An ELISA is a confirmatory test to detect IgM antibodies to WNV in the serum. Because IgM seroconversion typically occurs between days 4 and 10 of symptom onset, there is a high probability of initial false-negative testing within the first 8 days after symptom onset.19,20 Clinical understanding of this fact is imperative, as an initial negative ELISA does not rule out WNV, and a retest is warranted if clinical suspicion is high. In addition to a high initial false-negative rate with ELISA, there are several other limitations to note. IgM antibodies remain elevated for 1 to 3 months or possibly up to a year in immunocompromised patients.1 Due to this, false positives may be present if there was a recent prior infection. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay may not distinguish from different flaviviruses, including the yellow fever, dengue, Zika, Japanese encephalitis, and Saint Louis encephalitis viruses. Seropositivity has been estimated in some states, including 1999 data from New York (2.6%), 2003 data from Nebraska (9.5%), and 2012-2014 data from Connecticut (8.5%).21-23 Regional variance may be expected, as there also were significant differences in WNV seropositivity between different regions in Nebraska (P<.001).23
Because ELISA testing for WNV has readily apparent flaws, other tests have been utilized in its diagnosis. The PNRT is the most specific test, and it works by measuring neutralizing antibody titers for different flaviviruses. It has the ability to determine cross-reactivity with other flaviviruses; however, it does not discriminate between a current infection and a prior infection or prior flavivirus vaccine (ie, yellow fever vaccine). Despite this, a positive PNRT can lend credibility to a positive ELISA test and determine specificity for WNV for those with no prior flavivirus exposure.24 According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this test can be performed by the CDC or in reference laboratories designated by the CDC.3 Additionally, some state health laboratories may perform PRNTs.
Viral detection with PCR currently is used to screen blood donations and may be beneficial for immunocompromised patients that lack the ability to form a robust antibody response or if a patient presents early, as PCR works best within the first week of symptom onset.1 Tilley et al25 showed that a combination of PCR and ELISA were able to accurately predict 94.2% of patients (180/191) with documented WNV on a first blood sample compared to 45% and 58.1% for only viral detection or ELISA, respectively. Based on costs from a Midwest academic center, antibody detection tests are around $100 while PCR may range from $500 to $1000 and is only performed in reference laboratories. Although these tests remain in the repertoire for WNV diagnosis, financial stewardship is important.
If there are symptoms of photophobia, phonophobia, nuchal rigidity, loss of consciousness, or marked personality changes, a lumbar puncture for WNV IgM in the cerebrospinal fluid can be performed. As with most viral infections, cerebrospinal fluid findings normally include an elevated protein and lymphocyte count, but neutrophils may be predominantly elevated if the infection is early in its course.26
What are the management options?
To date, there is no curative treatment for WNV, and management is largely supportive. For WNF, over-the-counter pain medications may be helpful to reduce fever and pain. If more severe disease develops, hospitalization for further supportive care may be needed.27 If meningitis or encephalitis is suspected, broad-spectrum antibiotics may need to be started until other common etiologies are ruled out.28
How can you prevent WNV infection?
Disease prevention largely consists of educating the public to avoid heavily wooded areas, especially in areas of high prevalence and during peak months, and to use protective clothing and insect repellant that has been approved by the Environmental Protection Agency.3 Insect repellants approved by the Environmental Protection Agency contain ingredients such as DEET (N, N-diethyl-meta-toluamide), picaridin, IR3535 (ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate), and oil of lemon eucalyptus, which have been proven safe and effective.29 Patients also can protect their homes by using window screens and promptly repairing screens with holes.3
What is the differential diagnosis for WNV?
The differential diagnosis for fever with generalized maculopapular rash broadly ranges from viral etiologies (eg, WNV, Zika, measles), to tick bites (eg, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis), to drug-induced rashes. A detailed patient history inquiring on recent sick contacts, travel (WNV in the Midwest, ehrlichiosis in the Southeast), environmental exposures (ticks, mosquitoes), and new medications (typically 7–10 days after starting) is imperative to narrow the differential.30 In addition, the distribution, timing, and clinical characteristics of the rash may aid in diagnosis, along with an appropriately correlated clinical picture. West Nile virus likely will present in the summer in mid central geographic locations and often develops on the trunk and extremities as a blanching, generalized, maculopapular rash around 5 days after symptom onset or with defervescence.1
- Petersen LR. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of West Nile virus infection. UpToDate website. Updated August 7, 2020. Accessed April 16, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-west-nile-virus-infection?search=clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-west-nile-virusinfection.&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~78&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
- Sampathkumar P. West Nile virus: epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and prevention. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78:1137-1144.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile virus. Updated June 3, 2020. Accessed April 16, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/index.html
- Chuang TW, Hockett CW, Kightlinger L, et al. Landscape-level spatial patterns of West Nile virus risk in the northern Great Plains. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;86:724-731.
- Wimberly MC, Hildreth MB, Boyte SP, et al. Ecological niche of the 2003 West Nile virus epidemic in the northern great plains of the United States. PLoS One. 2008;3:E3744. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003744
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile virus disease cases reported to CDC by state of residence, 1999-2019. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/resources/pdfs/data/West-Nile-virus-disease-cases-by-state_1999-2019-P.pdf
- Hahn MB, Monaghan AJ, Hayden MH, et al. Meteorological conditions associated with increased incidence of West Nile virus disease in the United States, 2004–2012. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;92:1013-1022.
- Brown CM, DeMaria A Jr. The resurgence of West Nile virus. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157:823-824.
- Landesman WJ, Allan BF, Langerhans RB, et al. Inter-annual associations between precipitation and human incidence of West Nile virus in the United States. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007;7:337-343.
- Hart J Jr, Tillman G, Kraut MA, et al. West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease: neurological manifestations and prospective longitudinal outcomes. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:248.
- Wu JJ, Huang DB, Tyring SK. West Nile virus rash on the palms and soles of the feet. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1393-1394.
- Sejvar J. Clinical manifestations and outcomes of West Nile virus infection. Viruses. 2014;6:606-623.
- Ferguson DD, Gershman K, LeBailly A, et al. Characteristics of the rash associated with West Nile virus fever. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1204-1207.
- Marszalek R, Chen A, Gjede J. Psoriasiform eruption in the setting of West Nile virus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:AB4. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.01.017
- Shah S, Fite LP, Lane N, et al. Purpura fulminans associated with acute West Nile virus encephalitis. J Clin Virol. 2016;75:1-4.
- Civen R, Villacorte F, Robles DT, et al. West Nile virus infection in the pediatric population. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:75-78.
- Huhn GD, Dworkin MS. Rash as a prognostic factor in West Nile virus disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:388-389.
- Murphy TD, Grandpre J, Novick SL, et al. West Nile virus infection among health-fair participants, Wyoming 2003: assessment of symptoms and risk factors. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005;5:246-251.
- Prince HE, Tobler LH, Lapé-Nixon M, et al. Development and persistence of West Nile virus–specific immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgA, and IgG in viremic blood donors. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:4316-4320.
- Busch MP, Kleinman SH, Tobler LH, et al. Virus and antibody dynamics in acute West Nile Virus infection. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:984-993.
- Mostashari F, Bunning ML, Kitsutani PT, et al. Epidemic West Nile encephalitis, New York, 1999: results of a household-based seroepidemiological survey. Lancet. 2001;358:261-264.
- Cahill ME, Yao Y, Nock D, et al. West Nile virus seroprevalence, Connecticut, USA, 2000–2014. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:708-710.
- Schweitzer BK, Kramer WL, Sambol AR, et al. Geographic factors contributing to a high seroprevalence of West Nile virus-specific antibodies in humans following an epidemic. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2006;13:314-318.
- Maeda A, Maeda J. Review of diagnostic plaque reduction neutralization tests for flavivirus infection. Vet J. 2013;195:33-40.
- Tilley PA, Fox JD, Jayaraman GC, et al. Nucleic acid testing for west nile virus RNA in plasma enhances rapid diagnosis of acute infection in symptomatic patients. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1361-1364.
- Petersen LR, Brault AC, Nasci RS. West Nile virus: review of the literature. JAMA. 2013;310:308-315.
- Yu A, Ferenczi E, Moussa K, et al. Clinical spectrum of West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease. Neurohospitalist. 2020;10:43-47.
- Michaelis M, Kleinschmidt MC, Doerr HW, et al. Minocycline inhibits West Nile virus replication and apoptosis in human neuronal cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60:981-986.
- United State Environmental Protection Agency. Skin-applied repellent ingredients. https://www.epa.gov/insect-repellents/skin-applied-repellent-ingredients. Accessed April 16, 2021.
- Muzumdar S, Rothe MJ, Grant-Kels JM. The rash with maculopapules and fever in adults. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:109-118.
- Petersen LR. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of West Nile virus infection. UpToDate website. Updated August 7, 2020. Accessed April 16, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-west-nile-virus-infection?search=clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-west-nile-virusinfection.&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~78&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
- Sampathkumar P. West Nile virus: epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and prevention. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78:1137-1144.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile virus. Updated June 3, 2020. Accessed April 16, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/index.html
- Chuang TW, Hockett CW, Kightlinger L, et al. Landscape-level spatial patterns of West Nile virus risk in the northern Great Plains. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;86:724-731.
- Wimberly MC, Hildreth MB, Boyte SP, et al. Ecological niche of the 2003 West Nile virus epidemic in the northern great plains of the United States. PLoS One. 2008;3:E3744. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003744
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile virus disease cases reported to CDC by state of residence, 1999-2019. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/westnile/resources/pdfs/data/West-Nile-virus-disease-cases-by-state_1999-2019-P.pdf
- Hahn MB, Monaghan AJ, Hayden MH, et al. Meteorological conditions associated with increased incidence of West Nile virus disease in the United States, 2004–2012. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;92:1013-1022.
- Brown CM, DeMaria A Jr. The resurgence of West Nile virus. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157:823-824.
- Landesman WJ, Allan BF, Langerhans RB, et al. Inter-annual associations between precipitation and human incidence of West Nile virus in the United States. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007;7:337-343.
- Hart J Jr, Tillman G, Kraut MA, et al. West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease: neurological manifestations and prospective longitudinal outcomes. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:248.
- Wu JJ, Huang DB, Tyring SK. West Nile virus rash on the palms and soles of the feet. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1393-1394.
- Sejvar J. Clinical manifestations and outcomes of West Nile virus infection. Viruses. 2014;6:606-623.
- Ferguson DD, Gershman K, LeBailly A, et al. Characteristics of the rash associated with West Nile virus fever. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1204-1207.
- Marszalek R, Chen A, Gjede J. Psoriasiform eruption in the setting of West Nile virus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:AB4. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.01.017
- Shah S, Fite LP, Lane N, et al. Purpura fulminans associated with acute West Nile virus encephalitis. J Clin Virol. 2016;75:1-4.
- Civen R, Villacorte F, Robles DT, et al. West Nile virus infection in the pediatric population. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:75-78.
- Huhn GD, Dworkin MS. Rash as a prognostic factor in West Nile virus disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:388-389.
- Murphy TD, Grandpre J, Novick SL, et al. West Nile virus infection among health-fair participants, Wyoming 2003: assessment of symptoms and risk factors. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005;5:246-251.
- Prince HE, Tobler LH, Lapé-Nixon M, et al. Development and persistence of West Nile virus–specific immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgA, and IgG in viremic blood donors. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:4316-4320.
- Busch MP, Kleinman SH, Tobler LH, et al. Virus and antibody dynamics in acute West Nile Virus infection. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:984-993.
- Mostashari F, Bunning ML, Kitsutani PT, et al. Epidemic West Nile encephalitis, New York, 1999: results of a household-based seroepidemiological survey. Lancet. 2001;358:261-264.
- Cahill ME, Yao Y, Nock D, et al. West Nile virus seroprevalence, Connecticut, USA, 2000–2014. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:708-710.
- Schweitzer BK, Kramer WL, Sambol AR, et al. Geographic factors contributing to a high seroprevalence of West Nile virus-specific antibodies in humans following an epidemic. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2006;13:314-318.
- Maeda A, Maeda J. Review of diagnostic plaque reduction neutralization tests for flavivirus infection. Vet J. 2013;195:33-40.
- Tilley PA, Fox JD, Jayaraman GC, et al. Nucleic acid testing for west nile virus RNA in plasma enhances rapid diagnosis of acute infection in symptomatic patients. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1361-1364.
- Petersen LR, Brault AC, Nasci RS. West Nile virus: review of the literature. JAMA. 2013;310:308-315.
- Yu A, Ferenczi E, Moussa K, et al. Clinical spectrum of West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease. Neurohospitalist. 2020;10:43-47.
- Michaelis M, Kleinschmidt MC, Doerr HW, et al. Minocycline inhibits West Nile virus replication and apoptosis in human neuronal cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60:981-986.
- United State Environmental Protection Agency. Skin-applied repellent ingredients. https://www.epa.gov/insect-repellents/skin-applied-repellent-ingredients. Accessed April 16, 2021.
- Muzumdar S, Rothe MJ, Grant-Kels JM. The rash with maculopapules and fever in adults. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:109-118.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should be aware of the most common rash associated with West Nile virus (WNV), which is a nonspecific maculopapular rash appearing on the trunk and extremities around 5 days after the onset of fever, fatigue, and other nonspecific symptoms.
- Rash may serve as a prognostic indicator for improved outcomes in WNV due to its association with decreased risk of encephalitis and death.
- An IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for WNV initially may yield false-negative results, as the development of detectable antibodies against the virus may take up to 8 days after symptom onset.
Insoles or braces show best pain relief for knee OA
The use of braces or insoles in combination with nonbiomechanical treatments appear to deliver the greatest pain relief for patients with medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis, although the evidence supporting these interventions has a high degree of uncertainty, according findings from a large meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials presented at the OARSI 2021 World Congress.
“It’s been highlighted for several years now that due to the high rate of joint replacement, we need to promote more effective nonsurgical treatments,” Ans van Ginckel, PhD, of Ghent (Belgium) University, told the conference.
However, guidelines on the use of biomechanical treatments for knee OA pain vary widely, and there are few studies that compare the effectiveness of different interventions.
To address this, Dr. van Ginckel and colleagues conducted a network meta-analysis of 27 randomized, controlled trials – involving a total of 2,413 participants – of biomechanical treatments for knee OA pain. The treatments included were valgus braces, combined brace treatment (with added nonbiomechanical treatment), lateral or medial wedged insoles, combined insole treatment (with added nonbiomechanical treatment), contralateral cane use, gait retraining, and modified shoes.
“These treatments are mainly based on the premise that people with knee osteoarthritis likely experience a higher external knee adduction moment during walking, compared to healthy people,” Dr. van Ginckel told the conference, which is sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International. “This has been associated to some extent with disease onset, severity, and progression.”
When compared to nonbiomechanical controls, walking sticks and canes were the only intervention that showed a benefit in reducing pain, although the authors described the data supporting this as “high risk.”
When all the treatments were ranked according to the degree of pain relief seen in studies, combined insole and/or combined brace treatments showed the greatest degree of benefit.
However, Dr. van Ginckel said the evidence supporting even these treatments was of low to very low certainty, there was significant variation in the control treatments used in the studies, and the confidence intervals were wide. This also reflected the multifactorial nature of pain in knee OA, she said.
“A plausible explanation is the partial role in the biomechanics of the pathogenesis of pain and the multifactorial nature of pain,” she said.
Commenting on the study, Rik Lories, MD, PhD, head of the division of rheumatology at University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) and of the department of development and regeneration at Catholic University Leuven, said the findings of the analysis show how difficult it is to study biomechanical interventions for knee OA.
“It was a smart approach to try to get some more information about a wide array of studies that have been performed, being selective with regards to what to include,” Dr. Lories said. “It’s still a big challenge in terms of how do you control for confounders.”
Dr. Lories said that he took a positive view of the findings, suggesting that these interventions are unlikely to cause harm, and are therefore “not a road to avoid” in helping to reduce knee OA pain. But he also argued that the analysis pointed to a clear need for better studies of biomechanical interventions for knee OA. “I think that’s an important message that somehow the field has to improve the quality of their trials,” he said in an interview, although he acknowledged that such trials may be difficult to run and get funding for.
Dr. van Ginckel was supported by an EU Horizon 2020 fellowship, and a coauthor was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
The use of braces or insoles in combination with nonbiomechanical treatments appear to deliver the greatest pain relief for patients with medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis, although the evidence supporting these interventions has a high degree of uncertainty, according findings from a large meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials presented at the OARSI 2021 World Congress.
“It’s been highlighted for several years now that due to the high rate of joint replacement, we need to promote more effective nonsurgical treatments,” Ans van Ginckel, PhD, of Ghent (Belgium) University, told the conference.
However, guidelines on the use of biomechanical treatments for knee OA pain vary widely, and there are few studies that compare the effectiveness of different interventions.
To address this, Dr. van Ginckel and colleagues conducted a network meta-analysis of 27 randomized, controlled trials – involving a total of 2,413 participants – of biomechanical treatments for knee OA pain. The treatments included were valgus braces, combined brace treatment (with added nonbiomechanical treatment), lateral or medial wedged insoles, combined insole treatment (with added nonbiomechanical treatment), contralateral cane use, gait retraining, and modified shoes.
“These treatments are mainly based on the premise that people with knee osteoarthritis likely experience a higher external knee adduction moment during walking, compared to healthy people,” Dr. van Ginckel told the conference, which is sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International. “This has been associated to some extent with disease onset, severity, and progression.”
When compared to nonbiomechanical controls, walking sticks and canes were the only intervention that showed a benefit in reducing pain, although the authors described the data supporting this as “high risk.”
When all the treatments were ranked according to the degree of pain relief seen in studies, combined insole and/or combined brace treatments showed the greatest degree of benefit.
However, Dr. van Ginckel said the evidence supporting even these treatments was of low to very low certainty, there was significant variation in the control treatments used in the studies, and the confidence intervals were wide. This also reflected the multifactorial nature of pain in knee OA, she said.
“A plausible explanation is the partial role in the biomechanics of the pathogenesis of pain and the multifactorial nature of pain,” she said.
Commenting on the study, Rik Lories, MD, PhD, head of the division of rheumatology at University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) and of the department of development and regeneration at Catholic University Leuven, said the findings of the analysis show how difficult it is to study biomechanical interventions for knee OA.
“It was a smart approach to try to get some more information about a wide array of studies that have been performed, being selective with regards to what to include,” Dr. Lories said. “It’s still a big challenge in terms of how do you control for confounders.”
Dr. Lories said that he took a positive view of the findings, suggesting that these interventions are unlikely to cause harm, and are therefore “not a road to avoid” in helping to reduce knee OA pain. But he also argued that the analysis pointed to a clear need for better studies of biomechanical interventions for knee OA. “I think that’s an important message that somehow the field has to improve the quality of their trials,” he said in an interview, although he acknowledged that such trials may be difficult to run and get funding for.
Dr. van Ginckel was supported by an EU Horizon 2020 fellowship, and a coauthor was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
The use of braces or insoles in combination with nonbiomechanical treatments appear to deliver the greatest pain relief for patients with medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis, although the evidence supporting these interventions has a high degree of uncertainty, according findings from a large meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials presented at the OARSI 2021 World Congress.
“It’s been highlighted for several years now that due to the high rate of joint replacement, we need to promote more effective nonsurgical treatments,” Ans van Ginckel, PhD, of Ghent (Belgium) University, told the conference.
However, guidelines on the use of biomechanical treatments for knee OA pain vary widely, and there are few studies that compare the effectiveness of different interventions.
To address this, Dr. van Ginckel and colleagues conducted a network meta-analysis of 27 randomized, controlled trials – involving a total of 2,413 participants – of biomechanical treatments for knee OA pain. The treatments included were valgus braces, combined brace treatment (with added nonbiomechanical treatment), lateral or medial wedged insoles, combined insole treatment (with added nonbiomechanical treatment), contralateral cane use, gait retraining, and modified shoes.
“These treatments are mainly based on the premise that people with knee osteoarthritis likely experience a higher external knee adduction moment during walking, compared to healthy people,” Dr. van Ginckel told the conference, which is sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International. “This has been associated to some extent with disease onset, severity, and progression.”
When compared to nonbiomechanical controls, walking sticks and canes were the only intervention that showed a benefit in reducing pain, although the authors described the data supporting this as “high risk.”
When all the treatments were ranked according to the degree of pain relief seen in studies, combined insole and/or combined brace treatments showed the greatest degree of benefit.
However, Dr. van Ginckel said the evidence supporting even these treatments was of low to very low certainty, there was significant variation in the control treatments used in the studies, and the confidence intervals were wide. This also reflected the multifactorial nature of pain in knee OA, she said.
“A plausible explanation is the partial role in the biomechanics of the pathogenesis of pain and the multifactorial nature of pain,” she said.
Commenting on the study, Rik Lories, MD, PhD, head of the division of rheumatology at University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) and of the department of development and regeneration at Catholic University Leuven, said the findings of the analysis show how difficult it is to study biomechanical interventions for knee OA.
“It was a smart approach to try to get some more information about a wide array of studies that have been performed, being selective with regards to what to include,” Dr. Lories said. “It’s still a big challenge in terms of how do you control for confounders.”
Dr. Lories said that he took a positive view of the findings, suggesting that these interventions are unlikely to cause harm, and are therefore “not a road to avoid” in helping to reduce knee OA pain. But he also argued that the analysis pointed to a clear need for better studies of biomechanical interventions for knee OA. “I think that’s an important message that somehow the field has to improve the quality of their trials,” he said in an interview, although he acknowledged that such trials may be difficult to run and get funding for.
Dr. van Ginckel was supported by an EU Horizon 2020 fellowship, and a coauthor was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM OARSI 2021
Nodule on the Neck
The Diagnosis: Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Microscopic analysis showed a dense proliferation of mononuclear cells filling and expanding the dermis with focal epidermotropism (Figure 1). Immunohistochemistry demonstrated strong and diffuse staining for CD3, CD4, and CD30 (Figure 2) and lack of staining for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). Workup to exclude systemic disease was initiated and included unremarkable computed tomography (CT) of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis along with no abnormal cells on bone marrow biopsy. Complete blood cell count, basic metabolic panel, and lactate dehydrogenase were within reference range. Given the lack of evidence for systemic involvement, a diagnosis of primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (PC-ALCL) was made. The treatment plan for our patient with a solitary lesion was localized radiation therapy.
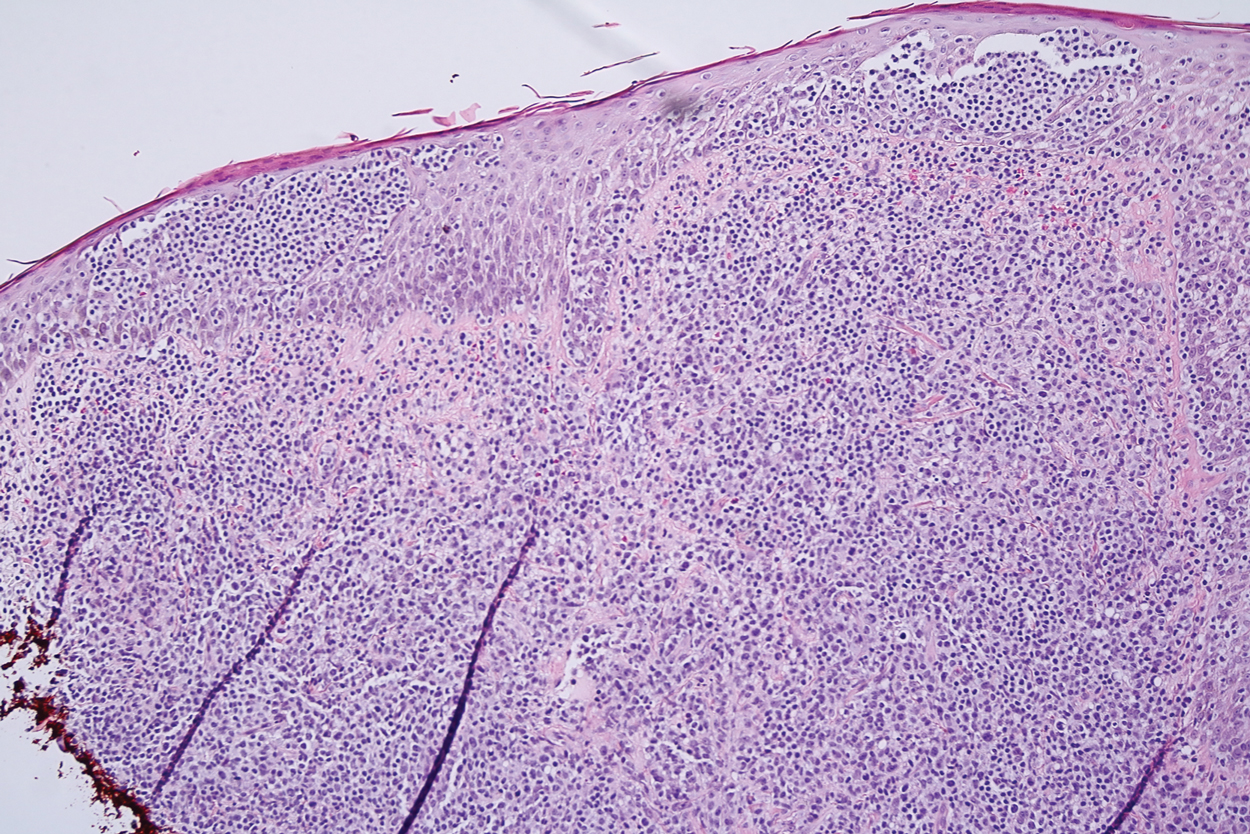
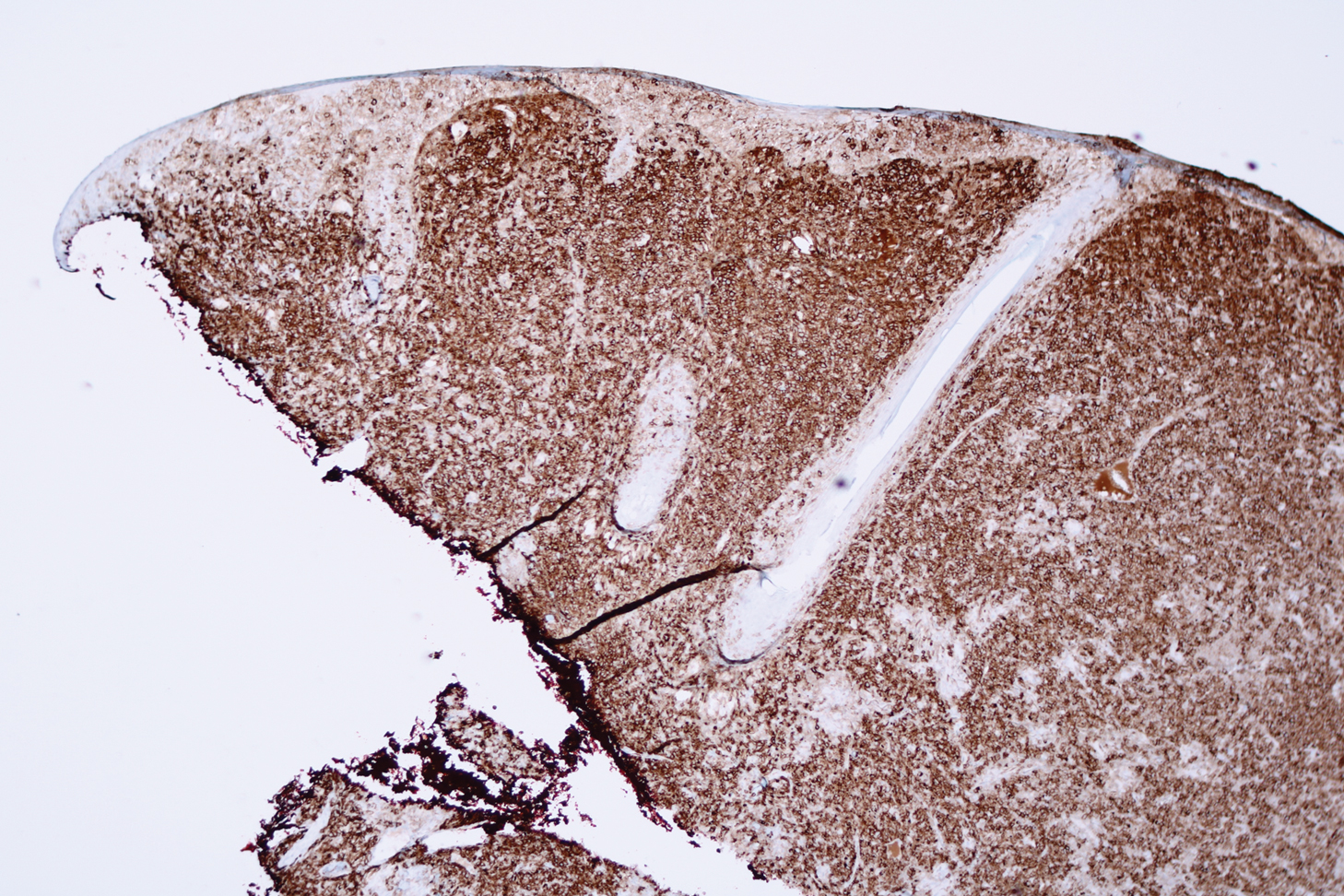
Primary cutaneous CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders encompass a spectrum of conditions, with premalignant lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) at one extreme and the malignant PC-ALCL on the other.1 The diagnosis of PC-ALCL is made by clinicopathologic correlation, and lesions typically present abruptly as solitary or grouped nodules with a tendency to ulcerate over time. Spontaneous regression has been reported, but relapse in the skin is frequent.2
A representative, typically excisional, biopsy should be performed if the clinician suspects PC-ALCL. Histologic criteria include a dense dermal infiltrate of large pleomorphic cells and the expression of CD30 in at least 75% of tumor cells.3 Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma typically lacks the ALK gene translocation with the nucleophosmin gene, NPM, that is common in systemic disease; however, a small subset of PC-ALCL may be ALK positive and indicate a higher chance of transformation into systemic disease.2
The extent of the lymphoma should be staged to exclude the possibility of systemic disease. This assessment includes a complete physical examination; laboratory investigation, including complete blood cell count with differential and blood chemistries; and radiography. A positron emission tomography-CT scan of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis, or a whole-body integrated positron emission tomography-CT are sufficient for the radiographic examination.3
The initial choice of treatment for solitary or localized PC-ALCL is localized radiation therapy or low-dose methotrexate. Targeted therapy such as brentuximab has been shown to be effective for those with multifocal systemic involvement or refractory disease.2 Cure rates from radiation therapy alone approach 95%.3 It is important to highlight radiation therapy as the initial management plan to increase awareness and to avoid inappropriate treatment of PC-ALCL with traditional chemotherapy.
Large lesions of LyP may appear similar to PC-ALCL on histopathology, making the two entities difficult to distinguish. However, in contrast to PC-ALCL, LyP classically has a different clinical course characterized by waxing and waning crops of lesions that typically are smaller (<1 cm) than those of PC-ALCL.2 Large cell transformation of mycosis fungoides is another entity to consider, but these patients usually have a known history of mycosis fungoides.4
Keratoacanthomas, considered to be a variant of a well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, present as rapidly enlarging crateriform nodules with a keratotic core. They usually are found on the head and neck or sun-exposed areas of the extremities and may regress spontaneously.5 Histology will show atypical, highly differentiated squamous epithelia. Merkel cell carcinoma also has a predilection for the head and neck in older patients and may present as a rapidly growing nodule. However, histology will show an aggressive tumor with small round blue cells, and immunohistochemistry will show the characteristic paranuclear dot staining for CK20 along with staining for various neuroendocrine markers. Similarly, atypical fibroxanthoma is a low-grade sarcoma that also presents on the head and neck of elderly sun-damaged patients.5 Histology will show dermal proliferation of spindle cells that often extend up against the epidermis along with pleomorphism and atypical mitoses. Basal cell carcinoma is a common tumor that can present on the head and neck in sun-damaged patients. Nodular basal cell carcinomas can enlarge and ulcerate, but growth is seen over years rather than weeks.5 Histology characteristically will show tumor islands composed of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading and clefting between the tumor islands and the stroma.
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127:2375-2390.
- Brown RA, Fernandez-Pol S, Kim J. Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:570-577.
- Kempf W, Pfaltz K, Vermeer MH, et al. EORTC, ISCL, and USCLC consensus recommendations for the treatment of primary cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders: lymphomatoid papulosis and primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2011;118:4024-4035.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part II. prognosis, management, and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:223.e1-17.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Saunders Elsevier; 2015:475-489.
The Diagnosis: Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Microscopic analysis showed a dense proliferation of mononuclear cells filling and expanding the dermis with focal epidermotropism (Figure 1). Immunohistochemistry demonstrated strong and diffuse staining for CD3, CD4, and CD30 (Figure 2) and lack of staining for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). Workup to exclude systemic disease was initiated and included unremarkable computed tomography (CT) of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis along with no abnormal cells on bone marrow biopsy. Complete blood cell count, basic metabolic panel, and lactate dehydrogenase were within reference range. Given the lack of evidence for systemic involvement, a diagnosis of primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (PC-ALCL) was made. The treatment plan for our patient with a solitary lesion was localized radiation therapy.


Primary cutaneous CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders encompass a spectrum of conditions, with premalignant lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) at one extreme and the malignant PC-ALCL on the other.1 The diagnosis of PC-ALCL is made by clinicopathologic correlation, and lesions typically present abruptly as solitary or grouped nodules with a tendency to ulcerate over time. Spontaneous regression has been reported, but relapse in the skin is frequent.2
A representative, typically excisional, biopsy should be performed if the clinician suspects PC-ALCL. Histologic criteria include a dense dermal infiltrate of large pleomorphic cells and the expression of CD30 in at least 75% of tumor cells.3 Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma typically lacks the ALK gene translocation with the nucleophosmin gene, NPM, that is common in systemic disease; however, a small subset of PC-ALCL may be ALK positive and indicate a higher chance of transformation into systemic disease.2
The extent of the lymphoma should be staged to exclude the possibility of systemic disease. This assessment includes a complete physical examination; laboratory investigation, including complete blood cell count with differential and blood chemistries; and radiography. A positron emission tomography-CT scan of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis, or a whole-body integrated positron emission tomography-CT are sufficient for the radiographic examination.3
The initial choice of treatment for solitary or localized PC-ALCL is localized radiation therapy or low-dose methotrexate. Targeted therapy such as brentuximab has been shown to be effective for those with multifocal systemic involvement or refractory disease.2 Cure rates from radiation therapy alone approach 95%.3 It is important to highlight radiation therapy as the initial management plan to increase awareness and to avoid inappropriate treatment of PC-ALCL with traditional chemotherapy.
Large lesions of LyP may appear similar to PC-ALCL on histopathology, making the two entities difficult to distinguish. However, in contrast to PC-ALCL, LyP classically has a different clinical course characterized by waxing and waning crops of lesions that typically are smaller (<1 cm) than those of PC-ALCL.2 Large cell transformation of mycosis fungoides is another entity to consider, but these patients usually have a known history of mycosis fungoides.4
Keratoacanthomas, considered to be a variant of a well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, present as rapidly enlarging crateriform nodules with a keratotic core. They usually are found on the head and neck or sun-exposed areas of the extremities and may regress spontaneously.5 Histology will show atypical, highly differentiated squamous epithelia. Merkel cell carcinoma also has a predilection for the head and neck in older patients and may present as a rapidly growing nodule. However, histology will show an aggressive tumor with small round blue cells, and immunohistochemistry will show the characteristic paranuclear dot staining for CK20 along with staining for various neuroendocrine markers. Similarly, atypical fibroxanthoma is a low-grade sarcoma that also presents on the head and neck of elderly sun-damaged patients.5 Histology will show dermal proliferation of spindle cells that often extend up against the epidermis along with pleomorphism and atypical mitoses. Basal cell carcinoma is a common tumor that can present on the head and neck in sun-damaged patients. Nodular basal cell carcinomas can enlarge and ulcerate, but growth is seen over years rather than weeks.5 Histology characteristically will show tumor islands composed of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading and clefting between the tumor islands and the stroma.
The Diagnosis: Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Microscopic analysis showed a dense proliferation of mononuclear cells filling and expanding the dermis with focal epidermotropism (Figure 1). Immunohistochemistry demonstrated strong and diffuse staining for CD3, CD4, and CD30 (Figure 2) and lack of staining for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). Workup to exclude systemic disease was initiated and included unremarkable computed tomography (CT) of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis along with no abnormal cells on bone marrow biopsy. Complete blood cell count, basic metabolic panel, and lactate dehydrogenase were within reference range. Given the lack of evidence for systemic involvement, a diagnosis of primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (PC-ALCL) was made. The treatment plan for our patient with a solitary lesion was localized radiation therapy.


Primary cutaneous CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders encompass a spectrum of conditions, with premalignant lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) at one extreme and the malignant PC-ALCL on the other.1 The diagnosis of PC-ALCL is made by clinicopathologic correlation, and lesions typically present abruptly as solitary or grouped nodules with a tendency to ulcerate over time. Spontaneous regression has been reported, but relapse in the skin is frequent.2
A representative, typically excisional, biopsy should be performed if the clinician suspects PC-ALCL. Histologic criteria include a dense dermal infiltrate of large pleomorphic cells and the expression of CD30 in at least 75% of tumor cells.3 Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma typically lacks the ALK gene translocation with the nucleophosmin gene, NPM, that is common in systemic disease; however, a small subset of PC-ALCL may be ALK positive and indicate a higher chance of transformation into systemic disease.2
The extent of the lymphoma should be staged to exclude the possibility of systemic disease. This assessment includes a complete physical examination; laboratory investigation, including complete blood cell count with differential and blood chemistries; and radiography. A positron emission tomography-CT scan of the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis, or a whole-body integrated positron emission tomography-CT are sufficient for the radiographic examination.3
The initial choice of treatment for solitary or localized PC-ALCL is localized radiation therapy or low-dose methotrexate. Targeted therapy such as brentuximab has been shown to be effective for those with multifocal systemic involvement or refractory disease.2 Cure rates from radiation therapy alone approach 95%.3 It is important to highlight radiation therapy as the initial management plan to increase awareness and to avoid inappropriate treatment of PC-ALCL with traditional chemotherapy.
Large lesions of LyP may appear similar to PC-ALCL on histopathology, making the two entities difficult to distinguish. However, in contrast to PC-ALCL, LyP classically has a different clinical course characterized by waxing and waning crops of lesions that typically are smaller (<1 cm) than those of PC-ALCL.2 Large cell transformation of mycosis fungoides is another entity to consider, but these patients usually have a known history of mycosis fungoides.4
Keratoacanthomas, considered to be a variant of a well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, present as rapidly enlarging crateriform nodules with a keratotic core. They usually are found on the head and neck or sun-exposed areas of the extremities and may regress spontaneously.5 Histology will show atypical, highly differentiated squamous epithelia. Merkel cell carcinoma also has a predilection for the head and neck in older patients and may present as a rapidly growing nodule. However, histology will show an aggressive tumor with small round blue cells, and immunohistochemistry will show the characteristic paranuclear dot staining for CK20 along with staining for various neuroendocrine markers. Similarly, atypical fibroxanthoma is a low-grade sarcoma that also presents on the head and neck of elderly sun-damaged patients.5 Histology will show dermal proliferation of spindle cells that often extend up against the epidermis along with pleomorphism and atypical mitoses. Basal cell carcinoma is a common tumor that can present on the head and neck in sun-damaged patients. Nodular basal cell carcinomas can enlarge and ulcerate, but growth is seen over years rather than weeks.5 Histology characteristically will show tumor islands composed of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading and clefting between the tumor islands and the stroma.
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127:2375-2390.
- Brown RA, Fernandez-Pol S, Kim J. Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:570-577.
- Kempf W, Pfaltz K, Vermeer MH, et al. EORTC, ISCL, and USCLC consensus recommendations for the treatment of primary cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders: lymphomatoid papulosis and primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2011;118:4024-4035.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part II. prognosis, management, and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:223.e1-17.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Saunders Elsevier; 2015:475-489.
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127:2375-2390.
- Brown RA, Fernandez-Pol S, Kim J. Primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:570-577.
- Kempf W, Pfaltz K, Vermeer MH, et al. EORTC, ISCL, and USCLC consensus recommendations for the treatment of primary cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders: lymphomatoid papulosis and primary cutaneous anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2011;118:4024-4035.
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part II. prognosis, management, and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:223.e1-17.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Saunders Elsevier; 2015:475-489.
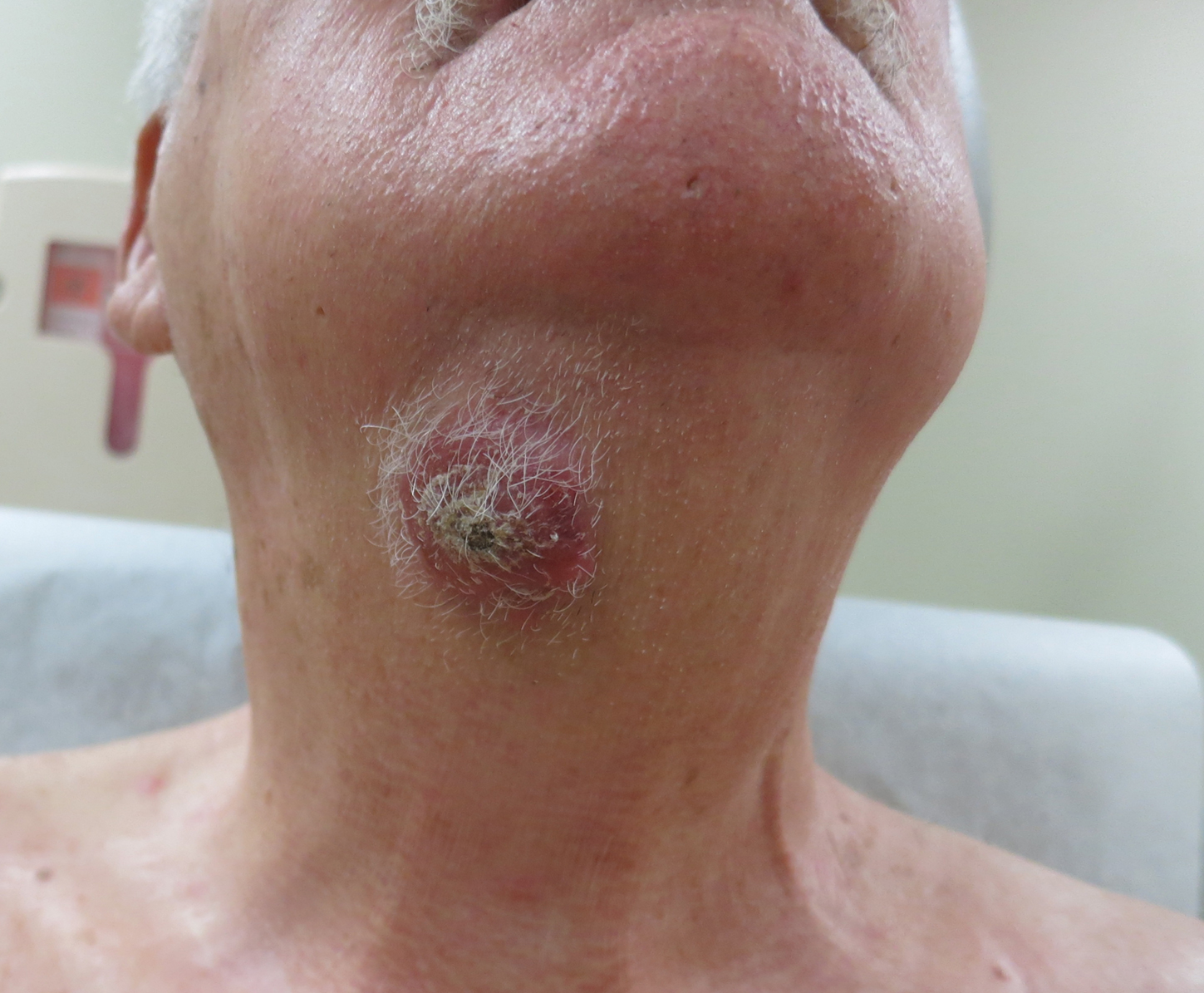
An 80-year-old man presented to our clinic with a large lesion on the right upper neck of approximately 4 weeks’ duration. He reported that it was rapidly increasing in size and had bled on several occasions. No treatments were attempted prior to the initial visit. He denied any constitutional symptoms. The patient had a history of nonmelanoma skin cancers but no other chronic medical problems. Physical examination revealed a large, 35×40-mm, erythematous nodule with central ulceration and overlying hyperkeratosis on the right upper neck. No palpable cervical, supraclavicular, or axillary lymphadenopathy was observed. An excisional biopsy of the lesion was obtained.
A tumultuous and unforgettable year
SHM president bids farewell
As my SHM presidency wraps up, it is a good time to reflect on the past year in hospital medicine. Dominated by COVID-19 preparedness, mitigation, and (now) recovery efforts, the impacts of COVID-19 throughout the medical industry have been profound. For hospital medicine, although we have endured work and home stress unlike anything in recent memory, fortunately a few notably good changes have come about as a result of COVID-19.
Hospitalists have proven that we are extremely capable of adapting to rapidly changing evidence-based practice. The old adage of evidence taking 7 years to become mainstream clinical practice certainly has not been the paradigm during COVID-19. In many cases, clinical care pathways were changing by the week, or even by the day. Usage of SHM’s website, HMX, and educational platforms rose exponentially to keep pace with the changing landscape. Information exchange between and among hospital medicine groups was efficient and effective. This is exactly how it should be, with SHM serving as the catalyst for such information exchange.
Hospitalists were able to shift to telehealth care as the need arose. The use of telehealth is now becoming a core competency for hospitalists around the country, and we are leading the way for other specialists in adoption. COVID-19 enabled not only rapid transformation, but also better payer coverage for the use of all types of telehealth services. SHM will remain a source of training and education in telehealth best practices going forward.
Related, hospitalists also found their programs were being asked to become purveyors for remote monitoring and hospital-at-home programs. Because CMS has allowed some reimbursement for these programs, at least during the public health emergency, hospital medicine programs can more feasibly pursue building and sustaining such programs, and SHM can serve as the hub for best practice exchanges in the field.
The pandemic also created a sizable shift in the mindset of the need and enthusiasm for mainstream maintenance of certification. Although there were already questions about the value of high-stakes exams before the pandemic, both within and outside the medical industry, the pandemic created an immediate need to shift away from such exams. Now, the entire pipeline is questioning the value of these high-stakes exams, such as SATs and ACTs for college admissions, Step 1 exams for medical students, and certification exams for physicians. The pandemic has made us question these milestone exams with more scrutiny and has created a sense of urgency for a change to more adult-learner–focused alternatives. SHM will continue to be at the centerpiece of the discussion, as well as the leader in cultivating educational venues for continuous learning.
So where do we go from here?
I am confident that SHM will continue to pay deep attention to the activities that bring value to hospitalists and support changing practice patterns such as telehealth and hospital-at-home work. Not only will SHM serve as a center for best practices and a conduit for networking and information sharing at the national level – there will be significantly more focus on the support and growth of local chapters. SHM realizes that local chapters are a vital source of networking, education, and pipeline development and will continue to increase the resources to make the chapter programs dynamic and inviting for everyone interested in hospital medicine.
While this presidency year was far different than expected, I have continuously been amazed and delighted with the resiliency and endurance of our hospitalists around the country. We stood out at the front lines of the pandemic, with a mission toward service and a relentless commitment to our patients. Although we still have a long way to go before the pandemic is behind us, I firmly believe we are emerging from the haze stronger and more agile than ever. Thank you for allowing me to serve this incredible organization during such a tumultuous and unforgettable year.
Yours in service.
Dr. Scheurer is a hospitalist and chief quality officer, MUSC Health System, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She is the outgoing president of SHM.
SHM president bids farewell
SHM president bids farewell
As my SHM presidency wraps up, it is a good time to reflect on the past year in hospital medicine. Dominated by COVID-19 preparedness, mitigation, and (now) recovery efforts, the impacts of COVID-19 throughout the medical industry have been profound. For hospital medicine, although we have endured work and home stress unlike anything in recent memory, fortunately a few notably good changes have come about as a result of COVID-19.
Hospitalists have proven that we are extremely capable of adapting to rapidly changing evidence-based practice. The old adage of evidence taking 7 years to become mainstream clinical practice certainly has not been the paradigm during COVID-19. In many cases, clinical care pathways were changing by the week, or even by the day. Usage of SHM’s website, HMX, and educational platforms rose exponentially to keep pace with the changing landscape. Information exchange between and among hospital medicine groups was efficient and effective. This is exactly how it should be, with SHM serving as the catalyst for such information exchange.
Hospitalists were able to shift to telehealth care as the need arose. The use of telehealth is now becoming a core competency for hospitalists around the country, and we are leading the way for other specialists in adoption. COVID-19 enabled not only rapid transformation, but also better payer coverage for the use of all types of telehealth services. SHM will remain a source of training and education in telehealth best practices going forward.
Related, hospitalists also found their programs were being asked to become purveyors for remote monitoring and hospital-at-home programs. Because CMS has allowed some reimbursement for these programs, at least during the public health emergency, hospital medicine programs can more feasibly pursue building and sustaining such programs, and SHM can serve as the hub for best practice exchanges in the field.
The pandemic also created a sizable shift in the mindset of the need and enthusiasm for mainstream maintenance of certification. Although there were already questions about the value of high-stakes exams before the pandemic, both within and outside the medical industry, the pandemic created an immediate need to shift away from such exams. Now, the entire pipeline is questioning the value of these high-stakes exams, such as SATs and ACTs for college admissions, Step 1 exams for medical students, and certification exams for physicians. The pandemic has made us question these milestone exams with more scrutiny and has created a sense of urgency for a change to more adult-learner–focused alternatives. SHM will continue to be at the centerpiece of the discussion, as well as the leader in cultivating educational venues for continuous learning.
So where do we go from here?
I am confident that SHM will continue to pay deep attention to the activities that bring value to hospitalists and support changing practice patterns such as telehealth and hospital-at-home work. Not only will SHM serve as a center for best practices and a conduit for networking and information sharing at the national level – there will be significantly more focus on the support and growth of local chapters. SHM realizes that local chapters are a vital source of networking, education, and pipeline development and will continue to increase the resources to make the chapter programs dynamic and inviting for everyone interested in hospital medicine.
While this presidency year was far different than expected, I have continuously been amazed and delighted with the resiliency and endurance of our hospitalists around the country. We stood out at the front lines of the pandemic, with a mission toward service and a relentless commitment to our patients. Although we still have a long way to go before the pandemic is behind us, I firmly believe we are emerging from the haze stronger and more agile than ever. Thank you for allowing me to serve this incredible organization during such a tumultuous and unforgettable year.
Yours in service.
Dr. Scheurer is a hospitalist and chief quality officer, MUSC Health System, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She is the outgoing president of SHM.
As my SHM presidency wraps up, it is a good time to reflect on the past year in hospital medicine. Dominated by COVID-19 preparedness, mitigation, and (now) recovery efforts, the impacts of COVID-19 throughout the medical industry have been profound. For hospital medicine, although we have endured work and home stress unlike anything in recent memory, fortunately a few notably good changes have come about as a result of COVID-19.
Hospitalists have proven that we are extremely capable of adapting to rapidly changing evidence-based practice. The old adage of evidence taking 7 years to become mainstream clinical practice certainly has not been the paradigm during COVID-19. In many cases, clinical care pathways were changing by the week, or even by the day. Usage of SHM’s website, HMX, and educational platforms rose exponentially to keep pace with the changing landscape. Information exchange between and among hospital medicine groups was efficient and effective. This is exactly how it should be, with SHM serving as the catalyst for such information exchange.
Hospitalists were able to shift to telehealth care as the need arose. The use of telehealth is now becoming a core competency for hospitalists around the country, and we are leading the way for other specialists in adoption. COVID-19 enabled not only rapid transformation, but also better payer coverage for the use of all types of telehealth services. SHM will remain a source of training and education in telehealth best practices going forward.
Related, hospitalists also found their programs were being asked to become purveyors for remote monitoring and hospital-at-home programs. Because CMS has allowed some reimbursement for these programs, at least during the public health emergency, hospital medicine programs can more feasibly pursue building and sustaining such programs, and SHM can serve as the hub for best practice exchanges in the field.
The pandemic also created a sizable shift in the mindset of the need and enthusiasm for mainstream maintenance of certification. Although there were already questions about the value of high-stakes exams before the pandemic, both within and outside the medical industry, the pandemic created an immediate need to shift away from such exams. Now, the entire pipeline is questioning the value of these high-stakes exams, such as SATs and ACTs for college admissions, Step 1 exams for medical students, and certification exams for physicians. The pandemic has made us question these milestone exams with more scrutiny and has created a sense of urgency for a change to more adult-learner–focused alternatives. SHM will continue to be at the centerpiece of the discussion, as well as the leader in cultivating educational venues for continuous learning.
So where do we go from here?
I am confident that SHM will continue to pay deep attention to the activities that bring value to hospitalists and support changing practice patterns such as telehealth and hospital-at-home work. Not only will SHM serve as a center for best practices and a conduit for networking and information sharing at the national level – there will be significantly more focus on the support and growth of local chapters. SHM realizes that local chapters are a vital source of networking, education, and pipeline development and will continue to increase the resources to make the chapter programs dynamic and inviting for everyone interested in hospital medicine.
While this presidency year was far different than expected, I have continuously been amazed and delighted with the resiliency and endurance of our hospitalists around the country. We stood out at the front lines of the pandemic, with a mission toward service and a relentless commitment to our patients. Although we still have a long way to go before the pandemic is behind us, I firmly believe we are emerging from the haze stronger and more agile than ever. Thank you for allowing me to serve this incredible organization during such a tumultuous and unforgettable year.
Yours in service.
Dr. Scheurer is a hospitalist and chief quality officer, MUSC Health System, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She is the outgoing president of SHM.
A ‘mess’ of a diagnosis: Is it type 2 MI or a nonischemic imposter?
Survival gains in the management of acute myocardial infarction in recent decades don’t apply to one increasingly common category of MI.
Type 2 MI, triggered by a surge in myocardial oxygen demand or a drop in its supply, is on the rise and might be more prognostically serious than the “classic” atherothrombotic type 1 form, for which there have been such impressive strides in therapy.
Strategies for assessing and treating type 2 MI and another condition it can resemble clinically – nonischemic myocardial injury – have been less rigorously explored and are far less settled.
That could be partly because recent iterations of the consensus-based universal definition of MI define type 1 MI primarily by the atherothrombotic process, whereas “demand” type 2 MI is characterized as secondary to other disorders. The list of potential primary conditions, cardiac and noncardiac, is long.
As a result, patients with type 1 MI are clinically well defined, but those with type 2 MI have so far defied efforts to be clinically characterized in a consistent way. However, recent efforts might change that, given growing appreciation that all-cause and cardiovascular (CV) mortality outcomes are actually worse for patients with type 2 MI.
“That’s because we have lots of treatments for type 1 MI. Type 2 and myocardial injury? We don’t know how to treat them,” David E. Newby, MD, PhD, University of Edinburgh, said in an interview.
Dr. Newby pointed to a widely cited 2018 publication, of which he is a coauthor, documenting 5-year outcomes of 2,122 patients with type 1 MI, type 2 MI, or nonischemic myocardial injury per the newly minted fourth universal definition.
Risk-factor profiles for patients with the latter two conditions contrasted with those of patients with type 1 MI, he observed. They were “a lot older,” were less likely to be smokers, had more hypertension and previous stroke, and a less prominent CV family history.
“So they’re a different beast,” Dr. Newby said. And their prognosis tended to be worse: all-cause mortality was about 62% for patients with type 2 MI and 72% with nonischemic myocardial injury, but only 37% for patients with type 1 MI. The difference between the two types of infarction was driven by an excess of noncardiovascular death after type 2 MI.
Mortality in patients with type 2 MI is “quite high, but it may well be a marker of the fact that you’ve got other serious diseases on board that are associated with poorer outcome,” he said.
Risk varies
The degree of risk in type 2 MI seems to vary with the underlying condition, a recent cohort study suggests. In about 3,800 patients with cardiac troponin (cTn) elevations qualifying as MI – a younger group; most were in their 30s and 40s – mortality at 10 years was 12% for those with type 1 MI, but 34% for those with type 2 MI and 46% for the remainder with nonischemic myocardial injury.
Underlying precipitating conditions varied widely among the patients with type 2 MI or nonischemic myocardial injury, and there was broad variation in mortality by etiology among those with type 2 MI. Sepsis and anemia entailed some of the highest risk, and hypertension and arrhythmias some of the lowest.
A prospective, community-based study of 5,460 patients with type 1 MI or type 2 MI reached a similar conclusion, but with a twist. Five-year all-cause mortality contrasted significantly between types of MI at 31% and 52%, respectively, but CV mortality rates were similar in this study.
Mortality in type 2 MI again varied by the precipitating etiology, suggesting that patients can be risk stratified according to pathophysiological mechanism behind their demand infarction, the authors concluded, “underscoring that type 2 MI is not a single entity, rather a group of phenotypic clusters.”
The usually high comorbidity burden and CV risk in patients with type 2 MI, one of those authors said in an interview, suggest there are “opportunities to see whether we can reduce that risk.”
Formal recommendations consistently say that, in patients with type 2 MI, “your first and foremost target should be to treat the underlying trigger and cause,” said Yader Sandoval, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. That means such opportunities for further CV risk reduction tend to be “underappreciated.”
“In principle, treating the inciting cause of type 2 MI or the injury is important,” said James L. Januzzi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, in an interview, “but I feel quite strongly that there must be more that we can do for these folks.”
Dr. Januzzi is senior author on a recent analysis based on more than 200,000 admissions across the United States that saw a 43% lower risk for in-hospital death and 54% lower risk for 30-day MI readmission for patients with type 2 MI than those with type 1, adjusted for risk factors and comorbidities.
But, “it is important to emphasize that type 2 MI patients had a substantial risk for adverse outcome, nonetheless, and lack a clear management approach,” Dr. Januzzi and colleagues stated in their publication, as reported by this news organization.
“Due to the high rates of long-term cardiovascular events experienced by the frequently encountered type 2 MI patients,” they wrote, “identifying evidence-based therapies represents a major unmet need.”
That such patients tend to be sick with multiple comorbidities and have not yet been clinically well characterized, Dr. Januzzi said, “has stymied our ability to develop a treatment strategy.”
Role of the universal definitions
That challenge might in some ways be complicated by the universal definition, especially version 4, in which the definitions for type 1 MI, type 2 MI, and nonischemic myocardial injury are unified biochemically.
This version, published in 2018 in the European Heart Journal and Circulation, introduced a formal definition of myocardial injury, which was hailed as an innovation: cTn elevation to the 99th percentile of the upper limit of normal in a reference population.
It differentiates type 1 MI from type 2 MI by the separate pathophysiology of the ischemia – plaque rupture with intracoronary thrombosis and myocardial oxygen supply–demand mismatch, respectively. In both cases, however, there must be symptoms or objective evidence of ischemia. Absent signs of ischemia, the determination would be nonischemic myocardial injury.
Yet clinically and prognostically, type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury in some ways are more similar to each other than either is to type 1 MI. Both occur secondary to other conditions across diverse clinical settings and can be a challenge to tell apart.
The universal definition’s perspective of the three events – so heavily dependent on cTn levels and myocardial ischemia – fails to account for the myriad complexities of individual patients in practice, some say, and so can muddle the process of risk assessment and therapy.
“Abnormal troponin identifies injury, but it doesn’t identify mechanism. Type 2 MI is highly prevalent, but there are other things that cause abnormal troponins,” Dr. Januzzi said. That’s why it’s important to explore and map out the clinical variables associated with the two conditions, to “understand who has a type 2 MI and who has cardiac injury. And believe it or not, it’s actually harder than it sounds to sort that out.”
“Practically speaking, the differentiation between these events is clinical,” Dr. Sandoval agreed. “There’s not always perfect agreement on what we’re calling what.”
Consequently, the universal definitions might categorize some events in ways that seem inconsistent from a management perspective. For example, they make a sharp distinction between coronary atherothrombotic and coronary nonatherothrombotic MI etiologies. Some clinicians would group MI caused by coronary spasm, coronary embolism, or spontaneous coronary artery dissection along with MI from coronary plaque rupture and thrombosis. But, Dr. Sandoval said, “even though these are coronary issues, they would fall into the type 2 bin.”
Also, about half of cases identified as type 2 MI are caused by tachyarrhythmias, which can elevate troponin and cause ECG changes and possibly symptoms resembling angina, Dr. Newby observed. “But that is completely different from other types of myocardial infarction, which are much more serious.”
So, “it’s a real mess of a diagnosis – acute myocardial injury, type 2 and type 1 MI – and it can be quite difficult to disentangle,” he said. “I think that the definition certainly has let us down.”
The diversity of type 2 MI clinical settings might also be a challenge. Myocardial injury according to cTn, with or without ischemia, occurs widely during critical illnesses and acute conditions, including respiratory distress, sepsis, internal bleeding, stroke, and pulmonary embolism.
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, much was made of elevated troponin levels and myocarditis as an apparently frequent complication among hospitalized patients. “I raised my hand and said, we’ve been seeing abnormal troponins in people with influenza for 20 years,” Dr. Januzzi said. “Critical illness, infection, toxicity from drugs, from chemotherapy, from alcohol – there are all sorts of potential triggers of myocardial injury.”
Troponin ‘overdependence’
With many clinical settings in common and the presence or absence of myocardial ischemia to primarily distinguish them, type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury both can be mistaken for the other. That can send management decisions in inappropriate directions.
A 2019 study looked at 633 cases that had been coded as type 2 MI at a major center and readjudicated them according to the fourth universal definition. Only 57% met all the type 2 criteria, 42% were reclassified as nonischemic myocardial injury, and a few were determined to have unstable angina.
“There’s overdependence on the easiest tool in the universal definition,” said Dr. Januzzi, a coauthor on that study. “Frequently people get seduced by the rise in a troponin value and immediately call it a myocardial infarction, lacking the other components of the universal definition that require evidence for coronary ischemia. That happens every day, where someone with an abnormal troponin is incorrectly branded as having an MI.”
It may not help that the current ICD-10-CM system features a diagnostic code for type 2 MI but not for myocardial injury.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” wrote Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, in a recent editorial. They caution against “using this code for myocardial injury because it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading,” thereby worsening the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
That potential suggests there could be a growing population of patients who have been told they had an MI, which then becomes part of their medical record, when, actually, they experienced nonischemic myocardial injury.
“Having seen this occur,” Dr. Januzzi explained, “it affects people emotionally to think they’ve had an MI. Precision in diagnosis is important, which is why the universal definition is so valuable. If people would adhere to it more assiduously, we could reduce the frequency of people getting a misdiagnosis of MI when in fact they had injury.”
Still, he added, “if someone has an illness severe enough to cause myocardial injury, they’re at risk for a bad outcome regardless of whether they did or didn’t have an MI.”
The uncertain role of angiography
Angiography isn’t ordered nearly as often for patients ultimately diagnosed with type 2 MI or myocardial injury as for those with type 1 MI. Type 2 MI can hit some patients who have remained symptom free despite possibly unrecognized obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) when myocardial demand is pushed past supply by a critical illness, tachyarrhythmia, or other acute conditions.
In such cases, “it’s reasonable to hypothesize that revascularization, something that really is not done in the vast majority of patients with type 2 MI, might actually be of benefit,” Dr. Januzzi said.
Whether these patients should routinely have angiography remains an open question. Without intervention, any newly identified obstructive CAD would continue to lurk in the background as a potential threat.
In efforts to differentiate type 2 MI from nonischemic injury, it can be “incredibly hard to know whether or not there’s actual ischemia in the mix. And that’s the only thing that defines the difference before taking an angiogram,” Derek P. Chew, MBBS, MPH, Flinders Medical Centre, Bedford Park, Australia, said in an interview.
Dr. Chew is principal investigator for the ongoing ACT-2 trial that is enrolling hospitalized, hemodynamically stable patients with cTn elevations but no suspicion of type 1 MI and “an unequivocal acute intercurrent diagnosis.” Qualifying diagnoses are prespecified on a list that includes sepsis, pneumonia, septicemia, a systemic inflammatory response, anemia, atrial tachycardia, acute kidney injury, and recent noncardiac surgery.
The patients are randomly assigned to a strategy of routine, usually invasive coronary angiography with discretionary revascularization, or to conservative care with noninvasive functional testing as appropriate. The sicker the patient, the greater the competing risk from other conditions and the less revascularization is likely to improve outcomes, Dr. Chew observed. Importantly, therefore, outcomes in the trial will be stratified by patient risk from comorbidities, measured with baseline GRACE and APACHE III scores.
Dr. Chew said the study aims to determine whether routine angiography is of benefit in patients at some identifiable level of risk, if not the whole range. One possible result, he said, is that there could be a risk-profile “sweet spot” associated with better outcomes in those assigned to angiography.
Enrollment in the trial started about 3 years ago, but “the process has been slow,” he said, because many potentially referring clinicians have a “bias on one side or another,” with about half of them preferring the angiography approach and the other half conservative management.
The unsettled role of drug therapy
With their often-complicated clinical profile, patients with type 2 MI or nonischemic myocardial injury tend to be medically undertreated, yet there is observational evidence they can benefit from familiar drug therapies.
In the previously noted cohort study of 3,800 younger patients with one of the three forms of myocardial injury, less than half of patients with type 2 MI received any form of CAD secondary prevention therapy at discharge, the researchers, with first author Avinainder Singh, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn, wrote.
The finding, consistent with Dr. Newby’s study from 2018, suggests that “categorizing the type of MI in young subjects might inform long-term cardiovascular prognosis,” and “emphasizes the need to identify and implement secondary prevention strategies to mitigate the high rate of cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 MI,” they concluded.
Further, outcomes varied with the number of discharge CV meds in an older cohort of patients with myocardial injury. Those with type 2 MI or acute or chronic nonischemic myocardial injury were far less likely than patients with type 1 MI to be prescribed guideline-based drugs. Survival was greater for those on two or three classes of CV medications, compared with one or none, in patients with acute or chronic nonischemic injury.
The investigators urged that patients with nonischemic myocardial injury or type 2 MI “be treated with cardiovascular medication to a larger degree than what is done today.”
When there is documented CAD in patients with type 2 MI, “it would be reasonable to suggest that preventative secondary prevention approaches, such as such lipid-reduction therapy or aspirin, would be beneficial,” Dr. Sandoval said. “But the reality is, there are no randomized trials, there are no prospective studies. ACT-2 is one of the few and early studies that’s really trying to address this.”
“The great majority of these people are not going to the cath lab, but when they do, there seems to be a signal of potential benefit,” Dr. Januzzi said. “For someone with a type 2 MI, it’s quite possible revascularization might help. Then more long-term treatment with medications that are proven in randomized trials to reduce risk would be a very plausible intervention.”
“We’ve actually proposed a number of potential therapeutic interventions to explore, both in people with type 2 MI and in people with injury without MI,” he said. “They might include sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. They might include antithrombotic therapy or more aggressive lipid lowering, possibly for the pleiotropic effects rather than the effects on atherosclerosis.”
Any such therapies that prove successful in well-designed trials could well earn both type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury, neglected as disorders in their own right, the kind of respect in clinical care pathways that they likely deserve.
Dr. Newby has disclosed receiving consulting fees or honoraria from Eli Lilly, Roche, Toshiba, Jansen, Reckitt Benckiser Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, CellProthera, and Oncoarendi; and conducting research or receiving grants from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Inositec. Sandoval reports serving on an advisory board and as a speaker for Abbott Diagnostics and on an advisory board for Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Januzzi has disclosed receiving grant support from Novartis, Applied Therapeutics, and Innolife; consulting for Abbott Diagnostics, Janssen, Novartis, Quidel, and Roche Diagnostics; and serving on endpoint committees or data safety monitoring boards for trials supported by Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, CVRx, Janssen, MyoKardia, and Takeda. Dr. Chew has reported receiving grants from AstraZeneca and Edwards Life Sciences. ACT-2 is sponsored by the National Medical and Health Research Council of Australia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Survival gains in the management of acute myocardial infarction in recent decades don’t apply to one increasingly common category of MI.
Type 2 MI, triggered by a surge in myocardial oxygen demand or a drop in its supply, is on the rise and might be more prognostically serious than the “classic” atherothrombotic type 1 form, for which there have been such impressive strides in therapy.
Strategies for assessing and treating type 2 MI and another condition it can resemble clinically – nonischemic myocardial injury – have been less rigorously explored and are far less settled.
That could be partly because recent iterations of the consensus-based universal definition of MI define type 1 MI primarily by the atherothrombotic process, whereas “demand” type 2 MI is characterized as secondary to other disorders. The list of potential primary conditions, cardiac and noncardiac, is long.
As a result, patients with type 1 MI are clinically well defined, but those with type 2 MI have so far defied efforts to be clinically characterized in a consistent way. However, recent efforts might change that, given growing appreciation that all-cause and cardiovascular (CV) mortality outcomes are actually worse for patients with type 2 MI.
“That’s because we have lots of treatments for type 1 MI. Type 2 and myocardial injury? We don’t know how to treat them,” David E. Newby, MD, PhD, University of Edinburgh, said in an interview.
Dr. Newby pointed to a widely cited 2018 publication, of which he is a coauthor, documenting 5-year outcomes of 2,122 patients with type 1 MI, type 2 MI, or nonischemic myocardial injury per the newly minted fourth universal definition.
Risk-factor profiles for patients with the latter two conditions contrasted with those of patients with type 1 MI, he observed. They were “a lot older,” were less likely to be smokers, had more hypertension and previous stroke, and a less prominent CV family history.
“So they’re a different beast,” Dr. Newby said. And their prognosis tended to be worse: all-cause mortality was about 62% for patients with type 2 MI and 72% with nonischemic myocardial injury, but only 37% for patients with type 1 MI. The difference between the two types of infarction was driven by an excess of noncardiovascular death after type 2 MI.
Mortality in patients with type 2 MI is “quite high, but it may well be a marker of the fact that you’ve got other serious diseases on board that are associated with poorer outcome,” he said.
Risk varies
The degree of risk in type 2 MI seems to vary with the underlying condition, a recent cohort study suggests. In about 3,800 patients with cardiac troponin (cTn) elevations qualifying as MI – a younger group; most were in their 30s and 40s – mortality at 10 years was 12% for those with type 1 MI, but 34% for those with type 2 MI and 46% for the remainder with nonischemic myocardial injury.
Underlying precipitating conditions varied widely among the patients with type 2 MI or nonischemic myocardial injury, and there was broad variation in mortality by etiology among those with type 2 MI. Sepsis and anemia entailed some of the highest risk, and hypertension and arrhythmias some of the lowest.
A prospective, community-based study of 5,460 patients with type 1 MI or type 2 MI reached a similar conclusion, but with a twist. Five-year all-cause mortality contrasted significantly between types of MI at 31% and 52%, respectively, but CV mortality rates were similar in this study.
Mortality in type 2 MI again varied by the precipitating etiology, suggesting that patients can be risk stratified according to pathophysiological mechanism behind their demand infarction, the authors concluded, “underscoring that type 2 MI is not a single entity, rather a group of phenotypic clusters.”
The usually high comorbidity burden and CV risk in patients with type 2 MI, one of those authors said in an interview, suggest there are “opportunities to see whether we can reduce that risk.”
Formal recommendations consistently say that, in patients with type 2 MI, “your first and foremost target should be to treat the underlying trigger and cause,” said Yader Sandoval, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. That means such opportunities for further CV risk reduction tend to be “underappreciated.”
“In principle, treating the inciting cause of type 2 MI or the injury is important,” said James L. Januzzi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, in an interview, “but I feel quite strongly that there must be more that we can do for these folks.”
Dr. Januzzi is senior author on a recent analysis based on more than 200,000 admissions across the United States that saw a 43% lower risk for in-hospital death and 54% lower risk for 30-day MI readmission for patients with type 2 MI than those with type 1, adjusted for risk factors and comorbidities.
But, “it is important to emphasize that type 2 MI patients had a substantial risk for adverse outcome, nonetheless, and lack a clear management approach,” Dr. Januzzi and colleagues stated in their publication, as reported by this news organization.
“Due to the high rates of long-term cardiovascular events experienced by the frequently encountered type 2 MI patients,” they wrote, “identifying evidence-based therapies represents a major unmet need.”
That such patients tend to be sick with multiple comorbidities and have not yet been clinically well characterized, Dr. Januzzi said, “has stymied our ability to develop a treatment strategy.”
Role of the universal definitions
That challenge might in some ways be complicated by the universal definition, especially version 4, in which the definitions for type 1 MI, type 2 MI, and nonischemic myocardial injury are unified biochemically.
This version, published in 2018 in the European Heart Journal and Circulation, introduced a formal definition of myocardial injury, which was hailed as an innovation: cTn elevation to the 99th percentile of the upper limit of normal in a reference population.
It differentiates type 1 MI from type 2 MI by the separate pathophysiology of the ischemia – plaque rupture with intracoronary thrombosis and myocardial oxygen supply–demand mismatch, respectively. In both cases, however, there must be symptoms or objective evidence of ischemia. Absent signs of ischemia, the determination would be nonischemic myocardial injury.
Yet clinically and prognostically, type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury in some ways are more similar to each other than either is to type 1 MI. Both occur secondary to other conditions across diverse clinical settings and can be a challenge to tell apart.
The universal definition’s perspective of the three events – so heavily dependent on cTn levels and myocardial ischemia – fails to account for the myriad complexities of individual patients in practice, some say, and so can muddle the process of risk assessment and therapy.
“Abnormal troponin identifies injury, but it doesn’t identify mechanism. Type 2 MI is highly prevalent, but there are other things that cause abnormal troponins,” Dr. Januzzi said. That’s why it’s important to explore and map out the clinical variables associated with the two conditions, to “understand who has a type 2 MI and who has cardiac injury. And believe it or not, it’s actually harder than it sounds to sort that out.”
“Practically speaking, the differentiation between these events is clinical,” Dr. Sandoval agreed. “There’s not always perfect agreement on what we’re calling what.”
Consequently, the universal definitions might categorize some events in ways that seem inconsistent from a management perspective. For example, they make a sharp distinction between coronary atherothrombotic and coronary nonatherothrombotic MI etiologies. Some clinicians would group MI caused by coronary spasm, coronary embolism, or spontaneous coronary artery dissection along with MI from coronary plaque rupture and thrombosis. But, Dr. Sandoval said, “even though these are coronary issues, they would fall into the type 2 bin.”
Also, about half of cases identified as type 2 MI are caused by tachyarrhythmias, which can elevate troponin and cause ECG changes and possibly symptoms resembling angina, Dr. Newby observed. “But that is completely different from other types of myocardial infarction, which are much more serious.”
So, “it’s a real mess of a diagnosis – acute myocardial injury, type 2 and type 1 MI – and it can be quite difficult to disentangle,” he said. “I think that the definition certainly has let us down.”
The diversity of type 2 MI clinical settings might also be a challenge. Myocardial injury according to cTn, with or without ischemia, occurs widely during critical illnesses and acute conditions, including respiratory distress, sepsis, internal bleeding, stroke, and pulmonary embolism.
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, much was made of elevated troponin levels and myocarditis as an apparently frequent complication among hospitalized patients. “I raised my hand and said, we’ve been seeing abnormal troponins in people with influenza for 20 years,” Dr. Januzzi said. “Critical illness, infection, toxicity from drugs, from chemotherapy, from alcohol – there are all sorts of potential triggers of myocardial injury.”
Troponin ‘overdependence’
With many clinical settings in common and the presence or absence of myocardial ischemia to primarily distinguish them, type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury both can be mistaken for the other. That can send management decisions in inappropriate directions.
A 2019 study looked at 633 cases that had been coded as type 2 MI at a major center and readjudicated them according to the fourth universal definition. Only 57% met all the type 2 criteria, 42% were reclassified as nonischemic myocardial injury, and a few were determined to have unstable angina.
“There’s overdependence on the easiest tool in the universal definition,” said Dr. Januzzi, a coauthor on that study. “Frequently people get seduced by the rise in a troponin value and immediately call it a myocardial infarction, lacking the other components of the universal definition that require evidence for coronary ischemia. That happens every day, where someone with an abnormal troponin is incorrectly branded as having an MI.”
It may not help that the current ICD-10-CM system features a diagnostic code for type 2 MI but not for myocardial injury.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” wrote Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, in a recent editorial. They caution against “using this code for myocardial injury because it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading,” thereby worsening the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
That potential suggests there could be a growing population of patients who have been told they had an MI, which then becomes part of their medical record, when, actually, they experienced nonischemic myocardial injury.
“Having seen this occur,” Dr. Januzzi explained, “it affects people emotionally to think they’ve had an MI. Precision in diagnosis is important, which is why the universal definition is so valuable. If people would adhere to it more assiduously, we could reduce the frequency of people getting a misdiagnosis of MI when in fact they had injury.”
Still, he added, “if someone has an illness severe enough to cause myocardial injury, they’re at risk for a bad outcome regardless of whether they did or didn’t have an MI.”
The uncertain role of angiography
Angiography isn’t ordered nearly as often for patients ultimately diagnosed with type 2 MI or myocardial injury as for those with type 1 MI. Type 2 MI can hit some patients who have remained symptom free despite possibly unrecognized obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) when myocardial demand is pushed past supply by a critical illness, tachyarrhythmia, or other acute conditions.
In such cases, “it’s reasonable to hypothesize that revascularization, something that really is not done in the vast majority of patients with type 2 MI, might actually be of benefit,” Dr. Januzzi said.
Whether these patients should routinely have angiography remains an open question. Without intervention, any newly identified obstructive CAD would continue to lurk in the background as a potential threat.
In efforts to differentiate type 2 MI from nonischemic injury, it can be “incredibly hard to know whether or not there’s actual ischemia in the mix. And that’s the only thing that defines the difference before taking an angiogram,” Derek P. Chew, MBBS, MPH, Flinders Medical Centre, Bedford Park, Australia, said in an interview.
Dr. Chew is principal investigator for the ongoing ACT-2 trial that is enrolling hospitalized, hemodynamically stable patients with cTn elevations but no suspicion of type 1 MI and “an unequivocal acute intercurrent diagnosis.” Qualifying diagnoses are prespecified on a list that includes sepsis, pneumonia, septicemia, a systemic inflammatory response, anemia, atrial tachycardia, acute kidney injury, and recent noncardiac surgery.
The patients are randomly assigned to a strategy of routine, usually invasive coronary angiography with discretionary revascularization, or to conservative care with noninvasive functional testing as appropriate. The sicker the patient, the greater the competing risk from other conditions and the less revascularization is likely to improve outcomes, Dr. Chew observed. Importantly, therefore, outcomes in the trial will be stratified by patient risk from comorbidities, measured with baseline GRACE and APACHE III scores.
Dr. Chew said the study aims to determine whether routine angiography is of benefit in patients at some identifiable level of risk, if not the whole range. One possible result, he said, is that there could be a risk-profile “sweet spot” associated with better outcomes in those assigned to angiography.
Enrollment in the trial started about 3 years ago, but “the process has been slow,” he said, because many potentially referring clinicians have a “bias on one side or another,” with about half of them preferring the angiography approach and the other half conservative management.
The unsettled role of drug therapy
With their often-complicated clinical profile, patients with type 2 MI or nonischemic myocardial injury tend to be medically undertreated, yet there is observational evidence they can benefit from familiar drug therapies.
In the previously noted cohort study of 3,800 younger patients with one of the three forms of myocardial injury, less than half of patients with type 2 MI received any form of CAD secondary prevention therapy at discharge, the researchers, with first author Avinainder Singh, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn, wrote.
The finding, consistent with Dr. Newby’s study from 2018, suggests that “categorizing the type of MI in young subjects might inform long-term cardiovascular prognosis,” and “emphasizes the need to identify and implement secondary prevention strategies to mitigate the high rate of cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 MI,” they concluded.
Further, outcomes varied with the number of discharge CV meds in an older cohort of patients with myocardial injury. Those with type 2 MI or acute or chronic nonischemic myocardial injury were far less likely than patients with type 1 MI to be prescribed guideline-based drugs. Survival was greater for those on two or three classes of CV medications, compared with one or none, in patients with acute or chronic nonischemic injury.
The investigators urged that patients with nonischemic myocardial injury or type 2 MI “be treated with cardiovascular medication to a larger degree than what is done today.”
When there is documented CAD in patients with type 2 MI, “it would be reasonable to suggest that preventative secondary prevention approaches, such as such lipid-reduction therapy or aspirin, would be beneficial,” Dr. Sandoval said. “But the reality is, there are no randomized trials, there are no prospective studies. ACT-2 is one of the few and early studies that’s really trying to address this.”
“The great majority of these people are not going to the cath lab, but when they do, there seems to be a signal of potential benefit,” Dr. Januzzi said. “For someone with a type 2 MI, it’s quite possible revascularization might help. Then more long-term treatment with medications that are proven in randomized trials to reduce risk would be a very plausible intervention.”
“We’ve actually proposed a number of potential therapeutic interventions to explore, both in people with type 2 MI and in people with injury without MI,” he said. “They might include sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. They might include antithrombotic therapy or more aggressive lipid lowering, possibly for the pleiotropic effects rather than the effects on atherosclerosis.”
Any such therapies that prove successful in well-designed trials could well earn both type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury, neglected as disorders in their own right, the kind of respect in clinical care pathways that they likely deserve.
Dr. Newby has disclosed receiving consulting fees or honoraria from Eli Lilly, Roche, Toshiba, Jansen, Reckitt Benckiser Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, CellProthera, and Oncoarendi; and conducting research or receiving grants from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Inositec. Sandoval reports serving on an advisory board and as a speaker for Abbott Diagnostics and on an advisory board for Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Januzzi has disclosed receiving grant support from Novartis, Applied Therapeutics, and Innolife; consulting for Abbott Diagnostics, Janssen, Novartis, Quidel, and Roche Diagnostics; and serving on endpoint committees or data safety monitoring boards for trials supported by Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, CVRx, Janssen, MyoKardia, and Takeda. Dr. Chew has reported receiving grants from AstraZeneca and Edwards Life Sciences. ACT-2 is sponsored by the National Medical and Health Research Council of Australia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Survival gains in the management of acute myocardial infarction in recent decades don’t apply to one increasingly common category of MI.
Type 2 MI, triggered by a surge in myocardial oxygen demand or a drop in its supply, is on the rise and might be more prognostically serious than the “classic” atherothrombotic type 1 form, for which there have been such impressive strides in therapy.
Strategies for assessing and treating type 2 MI and another condition it can resemble clinically – nonischemic myocardial injury – have been less rigorously explored and are far less settled.
That could be partly because recent iterations of the consensus-based universal definition of MI define type 1 MI primarily by the atherothrombotic process, whereas “demand” type 2 MI is characterized as secondary to other disorders. The list of potential primary conditions, cardiac and noncardiac, is long.
As a result, patients with type 1 MI are clinically well defined, but those with type 2 MI have so far defied efforts to be clinically characterized in a consistent way. However, recent efforts might change that, given growing appreciation that all-cause and cardiovascular (CV) mortality outcomes are actually worse for patients with type 2 MI.
“That’s because we have lots of treatments for type 1 MI. Type 2 and myocardial injury? We don’t know how to treat them,” David E. Newby, MD, PhD, University of Edinburgh, said in an interview.
Dr. Newby pointed to a widely cited 2018 publication, of which he is a coauthor, documenting 5-year outcomes of 2,122 patients with type 1 MI, type 2 MI, or nonischemic myocardial injury per the newly minted fourth universal definition.
Risk-factor profiles for patients with the latter two conditions contrasted with those of patients with type 1 MI, he observed. They were “a lot older,” were less likely to be smokers, had more hypertension and previous stroke, and a less prominent CV family history.
“So they’re a different beast,” Dr. Newby said. And their prognosis tended to be worse: all-cause mortality was about 62% for patients with type 2 MI and 72% with nonischemic myocardial injury, but only 37% for patients with type 1 MI. The difference between the two types of infarction was driven by an excess of noncardiovascular death after type 2 MI.
Mortality in patients with type 2 MI is “quite high, but it may well be a marker of the fact that you’ve got other serious diseases on board that are associated with poorer outcome,” he said.
Risk varies
The degree of risk in type 2 MI seems to vary with the underlying condition, a recent cohort study suggests. In about 3,800 patients with cardiac troponin (cTn) elevations qualifying as MI – a younger group; most were in their 30s and 40s – mortality at 10 years was 12% for those with type 1 MI, but 34% for those with type 2 MI and 46% for the remainder with nonischemic myocardial injury.
Underlying precipitating conditions varied widely among the patients with type 2 MI or nonischemic myocardial injury, and there was broad variation in mortality by etiology among those with type 2 MI. Sepsis and anemia entailed some of the highest risk, and hypertension and arrhythmias some of the lowest.
A prospective, community-based study of 5,460 patients with type 1 MI or type 2 MI reached a similar conclusion, but with a twist. Five-year all-cause mortality contrasted significantly between types of MI at 31% and 52%, respectively, but CV mortality rates were similar in this study.
Mortality in type 2 MI again varied by the precipitating etiology, suggesting that patients can be risk stratified according to pathophysiological mechanism behind their demand infarction, the authors concluded, “underscoring that type 2 MI is not a single entity, rather a group of phenotypic clusters.”
The usually high comorbidity burden and CV risk in patients with type 2 MI, one of those authors said in an interview, suggest there are “opportunities to see whether we can reduce that risk.”
Formal recommendations consistently say that, in patients with type 2 MI, “your first and foremost target should be to treat the underlying trigger and cause,” said Yader Sandoval, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. That means such opportunities for further CV risk reduction tend to be “underappreciated.”
“In principle, treating the inciting cause of type 2 MI or the injury is important,” said James L. Januzzi, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, in an interview, “but I feel quite strongly that there must be more that we can do for these folks.”
Dr. Januzzi is senior author on a recent analysis based on more than 200,000 admissions across the United States that saw a 43% lower risk for in-hospital death and 54% lower risk for 30-day MI readmission for patients with type 2 MI than those with type 1, adjusted for risk factors and comorbidities.
But, “it is important to emphasize that type 2 MI patients had a substantial risk for adverse outcome, nonetheless, and lack a clear management approach,” Dr. Januzzi and colleagues stated in their publication, as reported by this news organization.
“Due to the high rates of long-term cardiovascular events experienced by the frequently encountered type 2 MI patients,” they wrote, “identifying evidence-based therapies represents a major unmet need.”
That such patients tend to be sick with multiple comorbidities and have not yet been clinically well characterized, Dr. Januzzi said, “has stymied our ability to develop a treatment strategy.”
Role of the universal definitions
That challenge might in some ways be complicated by the universal definition, especially version 4, in which the definitions for type 1 MI, type 2 MI, and nonischemic myocardial injury are unified biochemically.
This version, published in 2018 in the European Heart Journal and Circulation, introduced a formal definition of myocardial injury, which was hailed as an innovation: cTn elevation to the 99th percentile of the upper limit of normal in a reference population.
It differentiates type 1 MI from type 2 MI by the separate pathophysiology of the ischemia – plaque rupture with intracoronary thrombosis and myocardial oxygen supply–demand mismatch, respectively. In both cases, however, there must be symptoms or objective evidence of ischemia. Absent signs of ischemia, the determination would be nonischemic myocardial injury.
Yet clinically and prognostically, type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury in some ways are more similar to each other than either is to type 1 MI. Both occur secondary to other conditions across diverse clinical settings and can be a challenge to tell apart.
The universal definition’s perspective of the three events – so heavily dependent on cTn levels and myocardial ischemia – fails to account for the myriad complexities of individual patients in practice, some say, and so can muddle the process of risk assessment and therapy.
“Abnormal troponin identifies injury, but it doesn’t identify mechanism. Type 2 MI is highly prevalent, but there are other things that cause abnormal troponins,” Dr. Januzzi said. That’s why it’s important to explore and map out the clinical variables associated with the two conditions, to “understand who has a type 2 MI and who has cardiac injury. And believe it or not, it’s actually harder than it sounds to sort that out.”
“Practically speaking, the differentiation between these events is clinical,” Dr. Sandoval agreed. “There’s not always perfect agreement on what we’re calling what.”
Consequently, the universal definitions might categorize some events in ways that seem inconsistent from a management perspective. For example, they make a sharp distinction between coronary atherothrombotic and coronary nonatherothrombotic MI etiologies. Some clinicians would group MI caused by coronary spasm, coronary embolism, or spontaneous coronary artery dissection along with MI from coronary plaque rupture and thrombosis. But, Dr. Sandoval said, “even though these are coronary issues, they would fall into the type 2 bin.”
Also, about half of cases identified as type 2 MI are caused by tachyarrhythmias, which can elevate troponin and cause ECG changes and possibly symptoms resembling angina, Dr. Newby observed. “But that is completely different from other types of myocardial infarction, which are much more serious.”
So, “it’s a real mess of a diagnosis – acute myocardial injury, type 2 and type 1 MI – and it can be quite difficult to disentangle,” he said. “I think that the definition certainly has let us down.”
The diversity of type 2 MI clinical settings might also be a challenge. Myocardial injury according to cTn, with or without ischemia, occurs widely during critical illnesses and acute conditions, including respiratory distress, sepsis, internal bleeding, stroke, and pulmonary embolism.
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, much was made of elevated troponin levels and myocarditis as an apparently frequent complication among hospitalized patients. “I raised my hand and said, we’ve been seeing abnormal troponins in people with influenza for 20 years,” Dr. Januzzi said. “Critical illness, infection, toxicity from drugs, from chemotherapy, from alcohol – there are all sorts of potential triggers of myocardial injury.”
Troponin ‘overdependence’
With many clinical settings in common and the presence or absence of myocardial ischemia to primarily distinguish them, type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury both can be mistaken for the other. That can send management decisions in inappropriate directions.
A 2019 study looked at 633 cases that had been coded as type 2 MI at a major center and readjudicated them according to the fourth universal definition. Only 57% met all the type 2 criteria, 42% were reclassified as nonischemic myocardial injury, and a few were determined to have unstable angina.
“There’s overdependence on the easiest tool in the universal definition,” said Dr. Januzzi, a coauthor on that study. “Frequently people get seduced by the rise in a troponin value and immediately call it a myocardial infarction, lacking the other components of the universal definition that require evidence for coronary ischemia. That happens every day, where someone with an abnormal troponin is incorrectly branded as having an MI.”
It may not help that the current ICD-10-CM system features a diagnostic code for type 2 MI but not for myocardial injury.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” wrote Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, in a recent editorial. They caution against “using this code for myocardial injury because it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading,” thereby worsening the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
That potential suggests there could be a growing population of patients who have been told they had an MI, which then becomes part of their medical record, when, actually, they experienced nonischemic myocardial injury.
“Having seen this occur,” Dr. Januzzi explained, “it affects people emotionally to think they’ve had an MI. Precision in diagnosis is important, which is why the universal definition is so valuable. If people would adhere to it more assiduously, we could reduce the frequency of people getting a misdiagnosis of MI when in fact they had injury.”
Still, he added, “if someone has an illness severe enough to cause myocardial injury, they’re at risk for a bad outcome regardless of whether they did or didn’t have an MI.”
The uncertain role of angiography
Angiography isn’t ordered nearly as often for patients ultimately diagnosed with type 2 MI or myocardial injury as for those with type 1 MI. Type 2 MI can hit some patients who have remained symptom free despite possibly unrecognized obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) when myocardial demand is pushed past supply by a critical illness, tachyarrhythmia, or other acute conditions.
In such cases, “it’s reasonable to hypothesize that revascularization, something that really is not done in the vast majority of patients with type 2 MI, might actually be of benefit,” Dr. Januzzi said.
Whether these patients should routinely have angiography remains an open question. Without intervention, any newly identified obstructive CAD would continue to lurk in the background as a potential threat.
In efforts to differentiate type 2 MI from nonischemic injury, it can be “incredibly hard to know whether or not there’s actual ischemia in the mix. And that’s the only thing that defines the difference before taking an angiogram,” Derek P. Chew, MBBS, MPH, Flinders Medical Centre, Bedford Park, Australia, said in an interview.
Dr. Chew is principal investigator for the ongoing ACT-2 trial that is enrolling hospitalized, hemodynamically stable patients with cTn elevations but no suspicion of type 1 MI and “an unequivocal acute intercurrent diagnosis.” Qualifying diagnoses are prespecified on a list that includes sepsis, pneumonia, septicemia, a systemic inflammatory response, anemia, atrial tachycardia, acute kidney injury, and recent noncardiac surgery.
The patients are randomly assigned to a strategy of routine, usually invasive coronary angiography with discretionary revascularization, or to conservative care with noninvasive functional testing as appropriate. The sicker the patient, the greater the competing risk from other conditions and the less revascularization is likely to improve outcomes, Dr. Chew observed. Importantly, therefore, outcomes in the trial will be stratified by patient risk from comorbidities, measured with baseline GRACE and APACHE III scores.
Dr. Chew said the study aims to determine whether routine angiography is of benefit in patients at some identifiable level of risk, if not the whole range. One possible result, he said, is that there could be a risk-profile “sweet spot” associated with better outcomes in those assigned to angiography.
Enrollment in the trial started about 3 years ago, but “the process has been slow,” he said, because many potentially referring clinicians have a “bias on one side or another,” with about half of them preferring the angiography approach and the other half conservative management.
The unsettled role of drug therapy
With their often-complicated clinical profile, patients with type 2 MI or nonischemic myocardial injury tend to be medically undertreated, yet there is observational evidence they can benefit from familiar drug therapies.
In the previously noted cohort study of 3,800 younger patients with one of the three forms of myocardial injury, less than half of patients with type 2 MI received any form of CAD secondary prevention therapy at discharge, the researchers, with first author Avinainder Singh, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn, wrote.
The finding, consistent with Dr. Newby’s study from 2018, suggests that “categorizing the type of MI in young subjects might inform long-term cardiovascular prognosis,” and “emphasizes the need to identify and implement secondary prevention strategies to mitigate the high rate of cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 MI,” they concluded.
Further, outcomes varied with the number of discharge CV meds in an older cohort of patients with myocardial injury. Those with type 2 MI or acute or chronic nonischemic myocardial injury were far less likely than patients with type 1 MI to be prescribed guideline-based drugs. Survival was greater for those on two or three classes of CV medications, compared with one or none, in patients with acute or chronic nonischemic injury.
The investigators urged that patients with nonischemic myocardial injury or type 2 MI “be treated with cardiovascular medication to a larger degree than what is done today.”
When there is documented CAD in patients with type 2 MI, “it would be reasonable to suggest that preventative secondary prevention approaches, such as such lipid-reduction therapy or aspirin, would be beneficial,” Dr. Sandoval said. “But the reality is, there are no randomized trials, there are no prospective studies. ACT-2 is one of the few and early studies that’s really trying to address this.”
“The great majority of these people are not going to the cath lab, but when they do, there seems to be a signal of potential benefit,” Dr. Januzzi said. “For someone with a type 2 MI, it’s quite possible revascularization might help. Then more long-term treatment with medications that are proven in randomized trials to reduce risk would be a very plausible intervention.”
“We’ve actually proposed a number of potential therapeutic interventions to explore, both in people with type 2 MI and in people with injury without MI,” he said. “They might include sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. They might include antithrombotic therapy or more aggressive lipid lowering, possibly for the pleiotropic effects rather than the effects on atherosclerosis.”
Any such therapies that prove successful in well-designed trials could well earn both type 2 MI and nonischemic myocardial injury, neglected as disorders in their own right, the kind of respect in clinical care pathways that they likely deserve.
Dr. Newby has disclosed receiving consulting fees or honoraria from Eli Lilly, Roche, Toshiba, Jansen, Reckitt Benckiser Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, CellProthera, and Oncoarendi; and conducting research or receiving grants from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Inositec. Sandoval reports serving on an advisory board and as a speaker for Abbott Diagnostics and on an advisory board for Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Januzzi has disclosed receiving grant support from Novartis, Applied Therapeutics, and Innolife; consulting for Abbott Diagnostics, Janssen, Novartis, Quidel, and Roche Diagnostics; and serving on endpoint committees or data safety monitoring boards for trials supported by Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, CVRx, Janssen, MyoKardia, and Takeda. Dr. Chew has reported receiving grants from AstraZeneca and Edwards Life Sciences. ACT-2 is sponsored by the National Medical and Health Research Council of Australia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Quinolones and tendon health: Third-generation drugs may be safer
the findings of a new study suggest.
If confirmed, this will be good news for patients who are allergic to beta-lactam antibiotics and others in whom fluoroquinolones are the antibiotics of choice because of their favorable pharmacokinetic properties and broad-spectrum activity, according to Dr. Takashi Chinen of Jichi Medical University in Tochigi, Japan, lead investigator of the new study, published in Annals of Family Medicine.
“This is especially notable for patients who are at increased risk for tendon disorders, such as athletes,” Dr. Chinen said in an interview.
To investigate the association between third-generation fluoroquinolones and tendinopathy, Dr. Chinen and colleagues conducted a self-controlled case series analysis using administrative claims data for a single prefecture in Japan, focusing specifically on the risk of Achilles tendon rupture.
From a database of 780,000 residents in the Kumamoto Prefecture enrolled in the country’s National Health Insurance and Elderly Health Insurance from April 2012 to March 2017, the investigators identified 504 patients who experienced Achilles tendon rupture during the 5-year period and were prescribed an antibiotic at some time during that period. They divided the observation period into antibiotic exposure (30 days from prescription) and nonexposure periods based on previous research linking this fluoroquinolone exposure window to an elevated risk of tendon injury. They classified antibiotics into fluoroquinolones and nonfluoroquinolones and further classified the fluoroquinolones by first, second, and third generation, including the following agents:
- First generation: Norfloxacin, nalidixic acid, pipemidic acid
- Second generation: Levofloxacin, tosufloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, lomefloxacin
- Third generation: Garenoxacin, sitafloxacin, prulifloxacin, moxifloxacin, pazufloxacin.
Tendon rupture risk varied based on fluoroquinolone class
Comparing the incidence of Achilles tendon rupture in the exposure period relative to the nonexposure period, the risk of rupture was not elevated during exposure to third-generation fluoroquinolones (incidence rate ratio, 1.05; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-3.37) and nonfluoroquinolones (IRR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.80- 1.47). Contrasting with those findings, the researchers found that the risk of tendon rupture was significantly elevated during exposure to first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones (IRR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.90-4.54). Similar findings were observed in subgroup analyses by gender and recent corticosteroid use, the authors wrote.
The increased risk associated with exposure to first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones is consistent with the elevated risk observed in previous studies, the majority of which focused on first- and second-generation agents, the authors noted.
“Our study is the first to investigate the risk of Achilles tendon rupture associated with third-generation fluoroquinolones by self-controlled case series analysis and using a large administrative claims database,” they said.
Because the study is based on administrative claims data, it does not support conclusions about differential risks.
“Some preclinical studies suggest that structural differences [in the drugs] may affect the risks,” Dr. Chinen said. In particular, one preclinical study linked methylpiperazinyl substituent with increased risk of tendon injury, and this substituent is more common in first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones.
Outside experts were unable to draw conclusions
The accuracy of the current study is “extremely limited” by its design, according to Dr. Karsten Knobloch, a sports medicine physician in private practice in Hanover, Germany, who has reported on the risk of drug-induced tendon disorders.
“This is a case series only, which is a very strict limitation; therefore, the ability to generalize the data is also very limited,” he said in an interview. “In my view, the study does not add substantial data to support that third-generation [fluoroquinolones] are safer than the prior ones.”
Thomas Lodise, PharmD, PhD, who is a professor at the Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences in New York, pointed out another barrier to determining the value of the new research .
“Without knowing how many received moxifloxacin and descriptors of patients at baseline by each drug, it is hard to draw any definitive results from the paper,” Dr. Lodise noted.
Study design and execution had limitations
The authors acknowledged the limitations in the study design and execution. In particular, reliance on an administrative claims database means that the accuracy of diagnoses cannot be validated. Further, the study sample size may not have been sufficient to estimate the rupture risk for individual fluoroquinolones, they wrote.
Despite these and additional limitations, the findings have merit, according to the authors, who noted that the information may be useful in personalizing antibiotic therapy for individual patients.
“Fluoroquinolone-induced tendon injury is a rare event, and managing risk for even rare adverse events depends on each case,” Dr. Chinen explained. The findings of this study together with previous studies indicate that third-generation fluoroquinolones may be a safer option with respect to risk of Achilles tendon rupture for some patients who can’t be prescribed beta-lactam antibiotics and for some conditions, such as Legionella pneumophila, he said.
To increase internal and external validity of the results, further research including prospective cohort studies in broader populations are necessary, Dr. Chinen stressed.
The authors, Dr. Lodise, and Dr. Knobloch, who is owner of SportPraxis in Hanover, Germany, reported no conflicts.
the findings of a new study suggest.
If confirmed, this will be good news for patients who are allergic to beta-lactam antibiotics and others in whom fluoroquinolones are the antibiotics of choice because of their favorable pharmacokinetic properties and broad-spectrum activity, according to Dr. Takashi Chinen of Jichi Medical University in Tochigi, Japan, lead investigator of the new study, published in Annals of Family Medicine.
“This is especially notable for patients who are at increased risk for tendon disorders, such as athletes,” Dr. Chinen said in an interview.
To investigate the association between third-generation fluoroquinolones and tendinopathy, Dr. Chinen and colleagues conducted a self-controlled case series analysis using administrative claims data for a single prefecture in Japan, focusing specifically on the risk of Achilles tendon rupture.
From a database of 780,000 residents in the Kumamoto Prefecture enrolled in the country’s National Health Insurance and Elderly Health Insurance from April 2012 to March 2017, the investigators identified 504 patients who experienced Achilles tendon rupture during the 5-year period and were prescribed an antibiotic at some time during that period. They divided the observation period into antibiotic exposure (30 days from prescription) and nonexposure periods based on previous research linking this fluoroquinolone exposure window to an elevated risk of tendon injury. They classified antibiotics into fluoroquinolones and nonfluoroquinolones and further classified the fluoroquinolones by first, second, and third generation, including the following agents:
- First generation: Norfloxacin, nalidixic acid, pipemidic acid
- Second generation: Levofloxacin, tosufloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, lomefloxacin
- Third generation: Garenoxacin, sitafloxacin, prulifloxacin, moxifloxacin, pazufloxacin.
Tendon rupture risk varied based on fluoroquinolone class
Comparing the incidence of Achilles tendon rupture in the exposure period relative to the nonexposure period, the risk of rupture was not elevated during exposure to third-generation fluoroquinolones (incidence rate ratio, 1.05; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-3.37) and nonfluoroquinolones (IRR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.80- 1.47). Contrasting with those findings, the researchers found that the risk of tendon rupture was significantly elevated during exposure to first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones (IRR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.90-4.54). Similar findings were observed in subgroup analyses by gender and recent corticosteroid use, the authors wrote.
The increased risk associated with exposure to first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones is consistent with the elevated risk observed in previous studies, the majority of which focused on first- and second-generation agents, the authors noted.
“Our study is the first to investigate the risk of Achilles tendon rupture associated with third-generation fluoroquinolones by self-controlled case series analysis and using a large administrative claims database,” they said.
Because the study is based on administrative claims data, it does not support conclusions about differential risks.
“Some preclinical studies suggest that structural differences [in the drugs] may affect the risks,” Dr. Chinen said. In particular, one preclinical study linked methylpiperazinyl substituent with increased risk of tendon injury, and this substituent is more common in first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones.
Outside experts were unable to draw conclusions
The accuracy of the current study is “extremely limited” by its design, according to Dr. Karsten Knobloch, a sports medicine physician in private practice in Hanover, Germany, who has reported on the risk of drug-induced tendon disorders.
“This is a case series only, which is a very strict limitation; therefore, the ability to generalize the data is also very limited,” he said in an interview. “In my view, the study does not add substantial data to support that third-generation [fluoroquinolones] are safer than the prior ones.”
Thomas Lodise, PharmD, PhD, who is a professor at the Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences in New York, pointed out another barrier to determining the value of the new research .
“Without knowing how many received moxifloxacin and descriptors of patients at baseline by each drug, it is hard to draw any definitive results from the paper,” Dr. Lodise noted.
Study design and execution had limitations
The authors acknowledged the limitations in the study design and execution. In particular, reliance on an administrative claims database means that the accuracy of diagnoses cannot be validated. Further, the study sample size may not have been sufficient to estimate the rupture risk for individual fluoroquinolones, they wrote.
Despite these and additional limitations, the findings have merit, according to the authors, who noted that the information may be useful in personalizing antibiotic therapy for individual patients.
“Fluoroquinolone-induced tendon injury is a rare event, and managing risk for even rare adverse events depends on each case,” Dr. Chinen explained. The findings of this study together with previous studies indicate that third-generation fluoroquinolones may be a safer option with respect to risk of Achilles tendon rupture for some patients who can’t be prescribed beta-lactam antibiotics and for some conditions, such as Legionella pneumophila, he said.
To increase internal and external validity of the results, further research including prospective cohort studies in broader populations are necessary, Dr. Chinen stressed.
The authors, Dr. Lodise, and Dr. Knobloch, who is owner of SportPraxis in Hanover, Germany, reported no conflicts.
the findings of a new study suggest.
If confirmed, this will be good news for patients who are allergic to beta-lactam antibiotics and others in whom fluoroquinolones are the antibiotics of choice because of their favorable pharmacokinetic properties and broad-spectrum activity, according to Dr. Takashi Chinen of Jichi Medical University in Tochigi, Japan, lead investigator of the new study, published in Annals of Family Medicine.
“This is especially notable for patients who are at increased risk for tendon disorders, such as athletes,” Dr. Chinen said in an interview.
To investigate the association between third-generation fluoroquinolones and tendinopathy, Dr. Chinen and colleagues conducted a self-controlled case series analysis using administrative claims data for a single prefecture in Japan, focusing specifically on the risk of Achilles tendon rupture.
From a database of 780,000 residents in the Kumamoto Prefecture enrolled in the country’s National Health Insurance and Elderly Health Insurance from April 2012 to March 2017, the investigators identified 504 patients who experienced Achilles tendon rupture during the 5-year period and were prescribed an antibiotic at some time during that period. They divided the observation period into antibiotic exposure (30 days from prescription) and nonexposure periods based on previous research linking this fluoroquinolone exposure window to an elevated risk of tendon injury. They classified antibiotics into fluoroquinolones and nonfluoroquinolones and further classified the fluoroquinolones by first, second, and third generation, including the following agents:
- First generation: Norfloxacin, nalidixic acid, pipemidic acid
- Second generation: Levofloxacin, tosufloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, lomefloxacin
- Third generation: Garenoxacin, sitafloxacin, prulifloxacin, moxifloxacin, pazufloxacin.
Tendon rupture risk varied based on fluoroquinolone class
Comparing the incidence of Achilles tendon rupture in the exposure period relative to the nonexposure period, the risk of rupture was not elevated during exposure to third-generation fluoroquinolones (incidence rate ratio, 1.05; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-3.37) and nonfluoroquinolones (IRR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.80- 1.47). Contrasting with those findings, the researchers found that the risk of tendon rupture was significantly elevated during exposure to first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones (IRR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.90-4.54). Similar findings were observed in subgroup analyses by gender and recent corticosteroid use, the authors wrote.
The increased risk associated with exposure to first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones is consistent with the elevated risk observed in previous studies, the majority of which focused on first- and second-generation agents, the authors noted.
“Our study is the first to investigate the risk of Achilles tendon rupture associated with third-generation fluoroquinolones by self-controlled case series analysis and using a large administrative claims database,” they said.
Because the study is based on administrative claims data, it does not support conclusions about differential risks.
“Some preclinical studies suggest that structural differences [in the drugs] may affect the risks,” Dr. Chinen said. In particular, one preclinical study linked methylpiperazinyl substituent with increased risk of tendon injury, and this substituent is more common in first- and second-generation fluoroquinolones.
Outside experts were unable to draw conclusions
The accuracy of the current study is “extremely limited” by its design, according to Dr. Karsten Knobloch, a sports medicine physician in private practice in Hanover, Germany, who has reported on the risk of drug-induced tendon disorders.
“This is a case series only, which is a very strict limitation; therefore, the ability to generalize the data is also very limited,” he said in an interview. “In my view, the study does not add substantial data to support that third-generation [fluoroquinolones] are safer than the prior ones.”
Thomas Lodise, PharmD, PhD, who is a professor at the Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences in New York, pointed out another barrier to determining the value of the new research .
“Without knowing how many received moxifloxacin and descriptors of patients at baseline by each drug, it is hard to draw any definitive results from the paper,” Dr. Lodise noted.
Study design and execution had limitations
The authors acknowledged the limitations in the study design and execution. In particular, reliance on an administrative claims database means that the accuracy of diagnoses cannot be validated. Further, the study sample size may not have been sufficient to estimate the rupture risk for individual fluoroquinolones, they wrote.
Despite these and additional limitations, the findings have merit, according to the authors, who noted that the information may be useful in personalizing antibiotic therapy for individual patients.
“Fluoroquinolone-induced tendon injury is a rare event, and managing risk for even rare adverse events depends on each case,” Dr. Chinen explained. The findings of this study together with previous studies indicate that third-generation fluoroquinolones may be a safer option with respect to risk of Achilles tendon rupture for some patients who can’t be prescribed beta-lactam antibiotics and for some conditions, such as Legionella pneumophila, he said.
To increase internal and external validity of the results, further research including prospective cohort studies in broader populations are necessary, Dr. Chinen stressed.
The authors, Dr. Lodise, and Dr. Knobloch, who is owner of SportPraxis in Hanover, Germany, reported no conflicts.
FROM ANNALS OF FAMILY MEDICINE
Finerenone scores second pivotal-trial success in patients with diabetic kidney disease
Finerenone, an investigational agent from a new drug class, just scored a second pivotal trial win after showing significant benefit for slowing progression of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes in the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial with more than 5,700 patients.
Top-line results from FIGARO-DKD showed significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death and nonfatal cardiovascular disease endpoints in a placebo-controlled trial with about 7,400 patients with type 2 diabetes, reported Bayer, the company developing finerenone in statement released on May 10, 2021.
Based on the FIDELIO-DKD results, finerenone is currently under review by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for marketing approval as a treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. FIDELIO-DKD, in addition to the primary endpoint that focused on slowing progression of diabetic kidney disease, had a secondary endpoint that assessed the combined incidence on treatment of cardiovascular death, or nonfatal episodes of stroke, MI, or hospitalization for heart failure. Results from the study published in 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that finerenone was safe and effective for both endpoints.
In the current study, FIGARO-DKD, run at more than 1,000 sites in 47 countries, these endpoints flipped. The primary outcome was a composite of cardiovascular death or nonfatal cardiovascular disease events, and the secondary outcome was prevention of DKD progression.
Other than stating the results significantly fulfilled FIGARO-DKD’s primary endpoint of reducing the incidence of combined cardiovascular disease endpoints, the release gave no further outcome details. The release noted that the enrolled patient cohort in FIGARO-DKD included more patients with earlier-stage chronic kidney disease, compared with FIDELIO-DKD.
Finerenone is a first-in-class investigational nonsteroidal, selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA). As an MRA it shares certain activities with the steroidal MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. But the absence of a steroidal structure means that finerenone does not cause steroidal adverse effects such as gynecomastia. Results in FIDELIO-DKD showed that finerenone caused more hyperkalemia than placebo, but the level of hyperkalemia that it causes relative to spironolactone or eplerenone remains uncertain.
Finerenone, an investigational agent from a new drug class, just scored a second pivotal trial win after showing significant benefit for slowing progression of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes in the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial with more than 5,700 patients.
Top-line results from FIGARO-DKD showed significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death and nonfatal cardiovascular disease endpoints in a placebo-controlled trial with about 7,400 patients with type 2 diabetes, reported Bayer, the company developing finerenone in statement released on May 10, 2021.
Based on the FIDELIO-DKD results, finerenone is currently under review by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for marketing approval as a treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. FIDELIO-DKD, in addition to the primary endpoint that focused on slowing progression of diabetic kidney disease, had a secondary endpoint that assessed the combined incidence on treatment of cardiovascular death, or nonfatal episodes of stroke, MI, or hospitalization for heart failure. Results from the study published in 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that finerenone was safe and effective for both endpoints.
In the current study, FIGARO-DKD, run at more than 1,000 sites in 47 countries, these endpoints flipped. The primary outcome was a composite of cardiovascular death or nonfatal cardiovascular disease events, and the secondary outcome was prevention of DKD progression.
Other than stating the results significantly fulfilled FIGARO-DKD’s primary endpoint of reducing the incidence of combined cardiovascular disease endpoints, the release gave no further outcome details. The release noted that the enrolled patient cohort in FIGARO-DKD included more patients with earlier-stage chronic kidney disease, compared with FIDELIO-DKD.
Finerenone is a first-in-class investigational nonsteroidal, selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA). As an MRA it shares certain activities with the steroidal MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. But the absence of a steroidal structure means that finerenone does not cause steroidal adverse effects such as gynecomastia. Results in FIDELIO-DKD showed that finerenone caused more hyperkalemia than placebo, but the level of hyperkalemia that it causes relative to spironolactone or eplerenone remains uncertain.
Finerenone, an investigational agent from a new drug class, just scored a second pivotal trial win after showing significant benefit for slowing progression of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes in the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial with more than 5,700 patients.
Top-line results from FIGARO-DKD showed significant benefit for the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death and nonfatal cardiovascular disease endpoints in a placebo-controlled trial with about 7,400 patients with type 2 diabetes, reported Bayer, the company developing finerenone in statement released on May 10, 2021.
Based on the FIDELIO-DKD results, finerenone is currently under review by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for marketing approval as a treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. FIDELIO-DKD, in addition to the primary endpoint that focused on slowing progression of diabetic kidney disease, had a secondary endpoint that assessed the combined incidence on treatment of cardiovascular death, or nonfatal episodes of stroke, MI, or hospitalization for heart failure. Results from the study published in 2020 in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that finerenone was safe and effective for both endpoints.
In the current study, FIGARO-DKD, run at more than 1,000 sites in 47 countries, these endpoints flipped. The primary outcome was a composite of cardiovascular death or nonfatal cardiovascular disease events, and the secondary outcome was prevention of DKD progression.
Other than stating the results significantly fulfilled FIGARO-DKD’s primary endpoint of reducing the incidence of combined cardiovascular disease endpoints, the release gave no further outcome details. The release noted that the enrolled patient cohort in FIGARO-DKD included more patients with earlier-stage chronic kidney disease, compared with FIDELIO-DKD.
Finerenone is a first-in-class investigational nonsteroidal, selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA). As an MRA it shares certain activities with the steroidal MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. But the absence of a steroidal structure means that finerenone does not cause steroidal adverse effects such as gynecomastia. Results in FIDELIO-DKD showed that finerenone caused more hyperkalemia than placebo, but the level of hyperkalemia that it causes relative to spironolactone or eplerenone remains uncertain.
Low-fat diet upped quality of life in ulcerative colitis
For patients with mild or remitted ulcerative colitis, a catered, low-fat, high-fiber diet improved quality of life and stool markers of dysbiosis and inflammation, according to the findings of a small crossover trial.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease often ask what they should eat, but few studies have addressed that question, Julia Fritsch, of the University of Miami and her associates wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Building on previous findings that a high-fat diet may contribute to inflammatory bowel disease, they randomly assigned 38 adults whose ulcerative colitis was in remission or mild (with a flare within the past 18 months) to receive either a low-fat diet (with 10% of daily calories from fat and high amounts of fruit and vegetables) or an “improved American standard diet” (with 35%-40% of daily calories from fat but more fruit and vegetables than Americans typically eat). Each diet was catered, delivered to patients’ homes, and lasted 4 weeks, followed by a 2-week washout period, after which each participant switched to the other diet.
Of the 38 patients, 17 completed the study. Food recall surveys over 24 hours showed that both diets were healthier than what participants ate at baseline, and daily web-based food diaries (such as www.nutrihand.com/Static/index.html) confirmed that more than 94% of patients adhered to the amount of fat in each diet. Even though participants in both groups ate only about half of the provided fruits and vegetables, the primary outcome of quality of life based on the short inflammatory bowel disease questionnaire (SIBDQ) significantly improved from a median of 4.98 (interquartile range, 4.1-6.0) at baseline to 5.77 (IQR, 5-6.4) with the low-fat diet and 5.55 (IQR, 4.75-6.25) with the improved American standard diet. Both diets also produced significant improvements in quality of life as measured by the 36-Item Short Form Survey and in disease activity as measured by the partial Mayo score.
Notably, however, only the low-fat diet significantly reduced serum amyloid A, which is a marker of mucosal inflammation, and intestinal dysbiosis, which was quantified by 16S RNA ribosomal sequencing. “Of note, there were several variables that were associated with changes in the microbiota composition,” the researchers wrote. These included the SIBDQ, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, interleukin-1 beta, and 32 dietary components such as protein, potassium, iron, and zinc.
“These data suggest that even patients in remission [from ulcerative colitis] could benefit from a healthier diet,” the investigators concluded. “Just as importantly, neither diet exacerbated symptoms, which is notable given the higher fiber in both catered diets.” They called catering “a feasible way to perform a diet intervention study with high adherence,” noting that “catering a diet for a patient with IBD for a year costs between $19,000 and $21,000 per patient. The cost of a patient on a biologic such as ustekinumab is approximately $130,752 to $261,504.”
The study was supported by the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Broad Medical Research Program, Micky and Madeleine Arison Family Foundation Crohn’s and Colitis Discovery Laboratory, and the Martin Kalser Chair. The senior author disclosed ties to Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, AbbVie, Seres Therapeutics, Shire, Landos, Pfizer, and several other pharmaceutical companies. The other researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
For patients with mild or remitted ulcerative colitis, a catered, low-fat, high-fiber diet improved quality of life and stool markers of dysbiosis and inflammation, according to the findings of a small crossover trial.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease often ask what they should eat, but few studies have addressed that question, Julia Fritsch, of the University of Miami and her associates wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Building on previous findings that a high-fat diet may contribute to inflammatory bowel disease, they randomly assigned 38 adults whose ulcerative colitis was in remission or mild (with a flare within the past 18 months) to receive either a low-fat diet (with 10% of daily calories from fat and high amounts of fruit and vegetables) or an “improved American standard diet” (with 35%-40% of daily calories from fat but more fruit and vegetables than Americans typically eat). Each diet was catered, delivered to patients’ homes, and lasted 4 weeks, followed by a 2-week washout period, after which each participant switched to the other diet.
Of the 38 patients, 17 completed the study. Food recall surveys over 24 hours showed that both diets were healthier than what participants ate at baseline, and daily web-based food diaries (such as www.nutrihand.com/Static/index.html) confirmed that more than 94% of patients adhered to the amount of fat in each diet. Even though participants in both groups ate only about half of the provided fruits and vegetables, the primary outcome of quality of life based on the short inflammatory bowel disease questionnaire (SIBDQ) significantly improved from a median of 4.98 (interquartile range, 4.1-6.0) at baseline to 5.77 (IQR, 5-6.4) with the low-fat diet and 5.55 (IQR, 4.75-6.25) with the improved American standard diet. Both diets also produced significant improvements in quality of life as measured by the 36-Item Short Form Survey and in disease activity as measured by the partial Mayo score.
Notably, however, only the low-fat diet significantly reduced serum amyloid A, which is a marker of mucosal inflammation, and intestinal dysbiosis, which was quantified by 16S RNA ribosomal sequencing. “Of note, there were several variables that were associated with changes in the microbiota composition,” the researchers wrote. These included the SIBDQ, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, interleukin-1 beta, and 32 dietary components such as protein, potassium, iron, and zinc.
“These data suggest that even patients in remission [from ulcerative colitis] could benefit from a healthier diet,” the investigators concluded. “Just as importantly, neither diet exacerbated symptoms, which is notable given the higher fiber in both catered diets.” They called catering “a feasible way to perform a diet intervention study with high adherence,” noting that “catering a diet for a patient with IBD for a year costs between $19,000 and $21,000 per patient. The cost of a patient on a biologic such as ustekinumab is approximately $130,752 to $261,504.”
The study was supported by the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Broad Medical Research Program, Micky and Madeleine Arison Family Foundation Crohn’s and Colitis Discovery Laboratory, and the Martin Kalser Chair. The senior author disclosed ties to Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, AbbVie, Seres Therapeutics, Shire, Landos, Pfizer, and several other pharmaceutical companies. The other researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
For patients with mild or remitted ulcerative colitis, a catered, low-fat, high-fiber diet improved quality of life and stool markers of dysbiosis and inflammation, according to the findings of a small crossover trial.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease often ask what they should eat, but few studies have addressed that question, Julia Fritsch, of the University of Miami and her associates wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Building on previous findings that a high-fat diet may contribute to inflammatory bowel disease, they randomly assigned 38 adults whose ulcerative colitis was in remission or mild (with a flare within the past 18 months) to receive either a low-fat diet (with 10% of daily calories from fat and high amounts of fruit and vegetables) or an “improved American standard diet” (with 35%-40% of daily calories from fat but more fruit and vegetables than Americans typically eat). Each diet was catered, delivered to patients’ homes, and lasted 4 weeks, followed by a 2-week washout period, after which each participant switched to the other diet.
Of the 38 patients, 17 completed the study. Food recall surveys over 24 hours showed that both diets were healthier than what participants ate at baseline, and daily web-based food diaries (such as www.nutrihand.com/Static/index.html) confirmed that more than 94% of patients adhered to the amount of fat in each diet. Even though participants in both groups ate only about half of the provided fruits and vegetables, the primary outcome of quality of life based on the short inflammatory bowel disease questionnaire (SIBDQ) significantly improved from a median of 4.98 (interquartile range, 4.1-6.0) at baseline to 5.77 (IQR, 5-6.4) with the low-fat diet and 5.55 (IQR, 4.75-6.25) with the improved American standard diet. Both diets also produced significant improvements in quality of life as measured by the 36-Item Short Form Survey and in disease activity as measured by the partial Mayo score.
Notably, however, only the low-fat diet significantly reduced serum amyloid A, which is a marker of mucosal inflammation, and intestinal dysbiosis, which was quantified by 16S RNA ribosomal sequencing. “Of note, there were several variables that were associated with changes in the microbiota composition,” the researchers wrote. These included the SIBDQ, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, interleukin-1 beta, and 32 dietary components such as protein, potassium, iron, and zinc.
“These data suggest that even patients in remission [from ulcerative colitis] could benefit from a healthier diet,” the investigators concluded. “Just as importantly, neither diet exacerbated symptoms, which is notable given the higher fiber in both catered diets.” They called catering “a feasible way to perform a diet intervention study with high adherence,” noting that “catering a diet for a patient with IBD for a year costs between $19,000 and $21,000 per patient. The cost of a patient on a biologic such as ustekinumab is approximately $130,752 to $261,504.”
The study was supported by the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Broad Medical Research Program, Micky and Madeleine Arison Family Foundation Crohn’s and Colitis Discovery Laboratory, and the Martin Kalser Chair. The senior author disclosed ties to Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, AbbVie, Seres Therapeutics, Shire, Landos, Pfizer, and several other pharmaceutical companies. The other researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY