User login
My palliative care rotation: Lessons of gratitude, mindfulness, and kindness
As a psychiatry resident and as a part of consultation-liaison service, I have visited many palliative care patients to assist other physicians in managing psychiatric issues such as depression, anxiety, or delirium. But recently, as the first resident from our Department of Psychiatry who was sent to a palliative care rotation, I followed these patients as a part of a primary palliative care team. Doing so allowed me to see patients from the other side of the bridge.
Palliative care focuses on providing relief from the suffering and stress of a patient’s illness, with the primary goal of improving the quality of life of the patient and their families. The palliative care team works in collaboration with the patient’s other clinicians to provide an extra layer of support. They provide biopsychosociocultural interventions that are in harmony with the needs of the patient rather than the prognosis of the illness. To do so, they first must evaluate the needs of the patient and their family. This is a time-consuming, energy-consuming, emotionally draining job.
During my palliative care rotation, I attended table rounds, bedside rounds, family meetings, long counseling sessions, and disposition planning meetings. This rotation also gave me the opportunity to place my feet in the shoes of a palliative care team and to reflect on how it feels to be the physician of a patient who is dying, which as a psychiatric resident I had seldom experienced. I learned that although working with patients who are dying can cause stress, burnout, and compassion fatigue, it also helps physicians appreciate the little things in life. To appreciate all the blessings we have that we usually take for granted. To practice gratitude. To be kind.
Upon reflection, I learned that the rounds of palliative care are actually mindfulness-based discussions that provide cushions of supportive work, facilitate feelings of being in control, tend to alleviate physical as well as mental suffering, foster clear-sighted hope, and assist in establishing small, subjectively significant, realistic goals for the patient’s immediate future, and to help the patient achieve these goals.
A valuable lesson from a patient
I want to highlight a case of a 65-year-old woman I first visited while I was shadowing my attending, who had been providing palliative care to the patient and her family for several months. The patient was admitted to a tertiary care hospital because cancer had invaded her small bowel and caused mechanical obstruction, resulting in intractable vomiting, abdominal distension, and anorexia. She underwent open laparotomy and ileostomy for symptomatic relief. A nasogastric tube was placed, and she was put on total parenteral nutrition. The day I met her was her third postoperative day. She had been improving significantly, and she wanted to eat. She was missing food. Most of the discussion in the round among my attending, the patient, and her family was centered around how to get to the point where she would be able to eat again and appreciate the taste of biryani.
What my attending did was incredible. After assessing the patient’s needs, he instilled a realistic hope: the hope of tasting food again. The attending, while acknowledging the patient’s apprehensions, respectfully and supportively kept her from wandering into the future, made every possible attempt to bring her attention back to the present moment, and helped her establish goals for the present and her immediate future. My attending was not toxic-positive, forcing his patient to uselessly revisit her current trauma. Instead, he was kind, empathic, and considerate. His primary focus was to understand rather than to be understood, to help her find meaning, and to improve her quality of life—a quality she defined for herself, which was to taste the food of her choice.
That day, when I returned to my working station in the psychiatry ward and had lunch in the break room, I thought, “When I eat, how often do I think about eating?” Mostly I either think about work, tasks, and presentations, or I scroll on social media.
Our taste buds indeed get adapted to repetitive stimulation, but the experience of eating our favorite dish is the naked truth of being alive, and is something that I have been taking for granted for a long time. These are little things in life that I need to appreciate, and learn to cultivate their power.
As a psychiatry resident and as a part of consultation-liaison service, I have visited many palliative care patients to assist other physicians in managing psychiatric issues such as depression, anxiety, or delirium. But recently, as the first resident from our Department of Psychiatry who was sent to a palliative care rotation, I followed these patients as a part of a primary palliative care team. Doing so allowed me to see patients from the other side of the bridge.
Palliative care focuses on providing relief from the suffering and stress of a patient’s illness, with the primary goal of improving the quality of life of the patient and their families. The palliative care team works in collaboration with the patient’s other clinicians to provide an extra layer of support. They provide biopsychosociocultural interventions that are in harmony with the needs of the patient rather than the prognosis of the illness. To do so, they first must evaluate the needs of the patient and their family. This is a time-consuming, energy-consuming, emotionally draining job.
During my palliative care rotation, I attended table rounds, bedside rounds, family meetings, long counseling sessions, and disposition planning meetings. This rotation also gave me the opportunity to place my feet in the shoes of a palliative care team and to reflect on how it feels to be the physician of a patient who is dying, which as a psychiatric resident I had seldom experienced. I learned that although working with patients who are dying can cause stress, burnout, and compassion fatigue, it also helps physicians appreciate the little things in life. To appreciate all the blessings we have that we usually take for granted. To practice gratitude. To be kind.
Upon reflection, I learned that the rounds of palliative care are actually mindfulness-based discussions that provide cushions of supportive work, facilitate feelings of being in control, tend to alleviate physical as well as mental suffering, foster clear-sighted hope, and assist in establishing small, subjectively significant, realistic goals for the patient’s immediate future, and to help the patient achieve these goals.
A valuable lesson from a patient
I want to highlight a case of a 65-year-old woman I first visited while I was shadowing my attending, who had been providing palliative care to the patient and her family for several months. The patient was admitted to a tertiary care hospital because cancer had invaded her small bowel and caused mechanical obstruction, resulting in intractable vomiting, abdominal distension, and anorexia. She underwent open laparotomy and ileostomy for symptomatic relief. A nasogastric tube was placed, and she was put on total parenteral nutrition. The day I met her was her third postoperative day. She had been improving significantly, and she wanted to eat. She was missing food. Most of the discussion in the round among my attending, the patient, and her family was centered around how to get to the point where she would be able to eat again and appreciate the taste of biryani.
What my attending did was incredible. After assessing the patient’s needs, he instilled a realistic hope: the hope of tasting food again. The attending, while acknowledging the patient’s apprehensions, respectfully and supportively kept her from wandering into the future, made every possible attempt to bring her attention back to the present moment, and helped her establish goals for the present and her immediate future. My attending was not toxic-positive, forcing his patient to uselessly revisit her current trauma. Instead, he was kind, empathic, and considerate. His primary focus was to understand rather than to be understood, to help her find meaning, and to improve her quality of life—a quality she defined for herself, which was to taste the food of her choice.
That day, when I returned to my working station in the psychiatry ward and had lunch in the break room, I thought, “When I eat, how often do I think about eating?” Mostly I either think about work, tasks, and presentations, or I scroll on social media.
Our taste buds indeed get adapted to repetitive stimulation, but the experience of eating our favorite dish is the naked truth of being alive, and is something that I have been taking for granted for a long time. These are little things in life that I need to appreciate, and learn to cultivate their power.
As a psychiatry resident and as a part of consultation-liaison service, I have visited many palliative care patients to assist other physicians in managing psychiatric issues such as depression, anxiety, or delirium. But recently, as the first resident from our Department of Psychiatry who was sent to a palliative care rotation, I followed these patients as a part of a primary palliative care team. Doing so allowed me to see patients from the other side of the bridge.
Palliative care focuses on providing relief from the suffering and stress of a patient’s illness, with the primary goal of improving the quality of life of the patient and their families. The palliative care team works in collaboration with the patient’s other clinicians to provide an extra layer of support. They provide biopsychosociocultural interventions that are in harmony with the needs of the patient rather than the prognosis of the illness. To do so, they first must evaluate the needs of the patient and their family. This is a time-consuming, energy-consuming, emotionally draining job.
During my palliative care rotation, I attended table rounds, bedside rounds, family meetings, long counseling sessions, and disposition planning meetings. This rotation also gave me the opportunity to place my feet in the shoes of a palliative care team and to reflect on how it feels to be the physician of a patient who is dying, which as a psychiatric resident I had seldom experienced. I learned that although working with patients who are dying can cause stress, burnout, and compassion fatigue, it also helps physicians appreciate the little things in life. To appreciate all the blessings we have that we usually take for granted. To practice gratitude. To be kind.
Upon reflection, I learned that the rounds of palliative care are actually mindfulness-based discussions that provide cushions of supportive work, facilitate feelings of being in control, tend to alleviate physical as well as mental suffering, foster clear-sighted hope, and assist in establishing small, subjectively significant, realistic goals for the patient’s immediate future, and to help the patient achieve these goals.
A valuable lesson from a patient
I want to highlight a case of a 65-year-old woman I first visited while I was shadowing my attending, who had been providing palliative care to the patient and her family for several months. The patient was admitted to a tertiary care hospital because cancer had invaded her small bowel and caused mechanical obstruction, resulting in intractable vomiting, abdominal distension, and anorexia. She underwent open laparotomy and ileostomy for symptomatic relief. A nasogastric tube was placed, and she was put on total parenteral nutrition. The day I met her was her third postoperative day. She had been improving significantly, and she wanted to eat. She was missing food. Most of the discussion in the round among my attending, the patient, and her family was centered around how to get to the point where she would be able to eat again and appreciate the taste of biryani.
What my attending did was incredible. After assessing the patient’s needs, he instilled a realistic hope: the hope of tasting food again. The attending, while acknowledging the patient’s apprehensions, respectfully and supportively kept her from wandering into the future, made every possible attempt to bring her attention back to the present moment, and helped her establish goals for the present and her immediate future. My attending was not toxic-positive, forcing his patient to uselessly revisit her current trauma. Instead, he was kind, empathic, and considerate. His primary focus was to understand rather than to be understood, to help her find meaning, and to improve her quality of life—a quality she defined for herself, which was to taste the food of her choice.
That day, when I returned to my working station in the psychiatry ward and had lunch in the break room, I thought, “When I eat, how often do I think about eating?” Mostly I either think about work, tasks, and presentations, or I scroll on social media.
Our taste buds indeed get adapted to repetitive stimulation, but the experience of eating our favorite dish is the naked truth of being alive, and is something that I have been taking for granted for a long time. These are little things in life that I need to appreciate, and learn to cultivate their power.
Becoming vaccine ambassadors: A new role for psychiatrists
After more than 600,000 deaths in the United States from the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), several safe and effective vaccines against the virus have become available. Vaccines are the most effective preventive measure against COVID-19 and the most promising way to achieve herd immunity to end the current pandemic. However, obstacles to reaching this goal include vaccine skepticism, structural barriers, or simple inertia to get vaccinated. These challenges provide opportunities for psychiatrists to use their medical knowledge and expertise, applying behavior management techniques such as motivational interviewing and nudging to encourage their patients to get vaccinated. In particular, marginalized patients with serious mental illness (SMI), who are subject to disproportionately high rates of COVID-19 infection and more severe outcomes,1 have much to gain if psychiatrists become involved in the COVID-19 vaccination campaign.
In this article, we define vaccine hesitancy and highlight what makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors, given their unique skill set and longitudinal, trust-based connection with their patients. We expand on the particular vulnerabilities of patients with SMI, including structural barriers to vaccination that lead to health disparities and inequity. Finally, building on “The ABCs of successful vaccinations” framework published in
What is vaccine hesitancy?
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines vaccine hesitancy as a “delay in acceptance or refusal of vaccines despite availability of vaccine services.”3,4 Vaccine hesitancy occurs on a continuum ranging from uncertainty about accepting a vaccine to absolute refusal.4,5 It involves a complex decision-making process driven by contextual, individual, and social influences, and vaccine-specific issues.4 In the “3C” model developed by the WHO Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) Working Group, vaccine hesitancy is influenced by confidence (trust in vaccines, in the health care system, and in policy makers), complacency (lower perceived risk), and convenience (availability, affordability, accessibility, language and health literacy, appeal of vaccination program).4
In 2019, the WHO named vaccine hesitancy as one of the top 10 global health threats.3 Hesitancy to receive COVID-19 vaccines may be particularly high because of their rapid development. In addition, the tumultuous political environment that often featured inconsistent messaging about the virus, its dangers, and its transmission since the early days of the pandemic created widespread public confusion and doubt as scientific understandings evolved. “Anti-vaxxer” movements that completely rejected vaccine efficacy disseminated misinformation online. Followers of these movements may have such extreme overvalued ideas that any effort to persuade them otherwise with scientific evidence will accomplish very little.6,7 Therefore, focusing on individuals who are “sitting on the fence” about getting vaccinated can be more productive because they represent a much larger group than those who adamantly refuse vaccines, and they may be more amenable to changing beliefs and behaviors.8
The US Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey asked, “How likely are you to accept the vaccine?”9 As of late June 2021, 11.4% of US adults reported they would “definitely not get a vaccine” or “probably not get a vaccine,” and that number increases to 16.9% when including those who are “unsure,” although there is wide geographical variability.10
A recent study in Denmark showed that willingness to receive the COVID-19 vaccine was slightly lower among patients with mental illness (84.8%) compared with the general population (89.5%).11 Given the small difference, vaccine hesitancy was not considered to be a major barrier for vaccination among patients with mental illness in Denmark. This is similar to the findings of a pre-pandemic study at a community mental health clinic in the United States involving other vaccinations, which suggested that 84% of patients with SMI perceived vaccinations as safe, effective, and important.12 In this clinic, identified barriers to vaccinations in general among patients with SMI included lack of awareness and knowledge (42.2%), accessibility (16.3%), personal cost (13.3%), fears about immunization (10.4%), and lack of recommendations by primary care providers (PCPs) (1.5%).12
It is critical to distinguish attitude-driven vaccine hesitancy from a lack of education and opportunity to receive a vaccine. Particularly disadvantaged communities may be mislabeled as “vaccine hesitant” when in fact they may not have the ability to be as proactive as other population groups (eg, difficulty scheduling appointments over the Internet).
Continue to: What makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors?
What makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors?
There are several reasons psychiatrists can be well-positioned to contribute to the success of vaccination campaigns (Table 1). These include their frequent contact with patients and their care teams, the high trust those patients have in them, and their medical expertise and skills in applied behavioral and social science techniques, including motivational interviewing and nudging. Vaccination efforts and outreach are more effective when led by the clinician with whom the patient has the most contact because resolving vaccine hesitancy is not a one-time discussion but requires ongoing communication, persistence, and consistency.13 Patients may contact their psychiatrists more frequently than their other clinicians, including PCPs. For this reason, psychiatrists can serve as the gateway to health care, particularly for patients with SMI.14 In addition, interruptions in nonemergency services caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may affect vaccine delivery because patients may have been unable to see their PCPs regularly during the pandemic.15

Psychiatrists’ medical expertise and their ability to develop rapport with their patients promote trust-building. Receiving credible information from a trusted source such as a patient’s psychiatrist can be impactful. A recent poll suggested that individual health care clinicians have been consistently identified as the most trusted sources for vaccine information, including for the COVID-19 vaccines.16 There is also higher trust when there is greater continuity of care both in terms of length of time the patient has known the clinician and the number of consultations,17 an inherent part of psychiatric practice. In addition, research has shown that patients trust their psychiatrists as much as they trust their general practitioners.18
Psychiatrists are experts in behavior change, promoting healthy behaviors through motivational interviewing and nudging. They also have experience with managing patients who hold overvalued ideas as well as dealing with uncertainty, given their scientific and medical training.
Motivational interviewing is a patient-centered, collaborative approach widely used by psychiatrists to treat unhealthy behaviors such as substance use. Clinicians elicit and strengthen the patient’s desire and motivation for change while respecting their autonomy. Instead of presenting persuasive facts, the clinician creates a welcoming, nonthreatening, safe environment by engaging patients in open dialogue, reflecting back the patients’ concerns with empathy, helping them realize contradictions in behavior, and supporting self-sufficiency.19 In a nonpsychiatric setting, studies have shown the effectiveness of motivational interviewing in increasing uptake of human papillomavirus vaccines and of pediatric vaccines.20
Nudging, which comes from behavioral economics and psychology, underscores the importance of structuring a choice architecture in changing the way people make their everyday decisions.21 Nudging still gives people a choice and respects autonomy, but it leads patients to more efficient and productive decision-making. Many nudges are based around giving good “default options” because people often do not make efforts to deviate from default options. In addition, social nudges are powerful, giving people a social reference point and normalizing certain behaviors.21 Psychiatrists have become skilled in nudging from working with patients with varying levels of insight and cognitive capabilities. That is, they give simple choices, prompts, and frequent feedback to reinforce “good” decisions and to discourage “bad” decisions.
Continue to: Managing overvalued ideas
Managing overvalued ideas. Psychiatrists are also well-versed in having discussions with patients who hold irrational beliefs (psychosis) or overvalued ideas. For example, psychiatrists frequently manage anorexia nervosa and hypochondria, which are rooted in overvalued ideas.7 While psychiatrists may not be able to directly confront the overvalued ideas, they can work around such ideas while waiting for more flexible moments. Similarly, managing patients with intense emotional commitment7 to commonly held anti-vaccination ideas may not be much different. Psychiatrists can work around resistance until patients may be less strongly attached to those overvalued ideas in instances when other techniques, such as motivational interviewing and nudging, may be more effective.
Managing uncertainty. Psychiatrists are experts in managing “not knowing” and uncertainty. Due to their medical scientific training, they are familiar with the process of science, and how understanding changes through trial and error. In contrast, most patients usually only see the end product (ie, a drug comes to market). Discussions with patients that acknowledge uncertainty and emphasize that changes in what is known are expected and appropriate as scientific knowledge evolves could help preempt skepticism when messages are updated.
Why do patients with SMI need more help?
SMI as a high-risk group. Patients with SMI are part of a “tragic” epidemiologic triad of agent-host-environment15 that places them at remarkably elevated risk for COVID-19 infection and more serious complications and death when infected.1 After age, a diagnosis of a schizophrenia spectrum disorder is the second largest predictor of mortality from COVID-19, with a 2.7-fold increase in mortality.22 This is how the elements of the triad come together: SARS-Cov-2 is a highly infectious agent affecting individuals who are vulnerable hosts because of their high frequency of medical comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and respiratory tract diseases, which are all risk factors for worse outcomes due to COVID-19.23 In addition, SMI is associated with socioeconomic risk factors for SARS-Cov-2 infection, including poverty, homelessness, and crowded settings such as jails, group homes, hospitals, and shelters, which constitute ideal environments for high transmission of the virus.
Structural barriers to vaccination. Studies have suggested lower rates of vaccination among people with SMI for various other infectious diseases compared with the general population.12 For example, in 1 outpatient mental health setting, influenza vaccination rates were 24% to 28%, which was lower than the national vaccination rate of 40.9% for the same influenza season (2010 to 2011).24 More recently, a study in Israel examining the COVID-19 vaccination rate among >25,000 patients with schizophrenia suggested under-vaccination of this cohort. The results showed that the odds of getting the COVID-19 vaccination were significantly lower in the schizophrenia group compared with the general population (odds ratio = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.77 to 0.83).25
Patients with SMI encounter considerable system-level barriers to vaccinations in general, such as reduced access to health care due to cost and a lack of transportation,12 the digital divide given their reduced access to the internet and computers for information and scheduling,26 and lack of vaccination recommendations from their PCPs.12 Studies have also shown that patients with SMI often receive suboptimal medical care because of stigmatization and discrimination.27 They also have lower rates of preventive care utilization, seeking medical services only in times of crisis and seeking mental health services more often than physical health care.28-30
Continue to: Patients with SMI face...
Patients with SMI face additional individual challenges that impede vaccine uptake, such as lack of knowledge and awareness about the virus and vaccinations, general cognitive impairment, low digital literacy skills,31 low language literacy and educational attainment, baseline delusions, and negative symptoms such as apathy, avolition, and anhedonia.1 Thus, even if they overcome the external barriers and obtain vaccine-related information, these patients may experience difficulty in understanding the content and applying this information to their personal circumstances as a result of low health literacy.
How psychiatrists can help
The concept of using mental health care sites and trained clinicians to increase medical disease prevention is not new. The rigorously tested intervention model STIRR (Screen, Test, Immunize, Reduce risk, and Refer) uses co-located nurse practitioners in community mental health centers to provide risk assessment, counseling, and blood testing for hepatitis and HIV, as well as on-site vaccinations for hepatitis to patients dually diagnosed with SMI and substance use disorders.32
Prioritization of patients with SMI for vaccine eligibility does not directly lead to vaccine uptake. Patients with SMI need extra support from their primary point of health care contact, namely their psychiatrists. Psychiatrists may bring a set of specialized skills uniquely suited to this moment to address vaccine hesitancy and overall lack of vaccine resources and awareness. Freudenreich et al2 recently proposed “The ABCs of Successful Vaccinations” framework that psychiatrists can use in their interactions with patients to encourage vaccination by focusing on:
- attitudes towards vaccination
- barriers to vaccination
- completed vaccination series.
Understand attitudes toward vaccination. Decision-making may be an emotional and psychological experience that is informed by thoughts and feelings,34 and psychiatrists are uniquely positioned to tailor messages to individual patients by using motivational interviewing and applying nudging techniques.8 Given the large role of the pandemic in everyday life, it would be natural to address vaccine-related concerns in the course of routine rapport-building. Table 219,34-38 shows example phrases of COVID-19 vaccine messages that are based on communication strategies that have demonstrated success in health behavior domains (including vaccinations).39

Continue to: First, a strong recommendation...
First, a strong recommendation should be made using the presumptive approach.40 If vaccine hesitancy is detected, psychiatrists should next attempt to understand patients’ reasoning with open-ended questions to probe vaccine-related concerns. Motivational interviewing can then be used to target the fence sitters (rather than anti-vaxxers).6 Psychiatrists can also communicate with therapists about the need for further follow up on patients’ hesitancies.
When assuring patients of vaccine safety and efficacy, it is helpful to explain the vaccine development process, including FDA approval, extensive clinical trials, monitoring, and the distribution process. Providing clear, transparent, accurate information about the risks and benefits of the vaccines is important, as well as monitoring misinformation and developing convincing counter messages that elicit positive emotions toward the vaccines.41 Examples of messages to counter common vaccine-related concerns and misinformation are shown in Table 3.42-44

Know the barriers to vaccination. The role of the psychiatrist is to help patients, particularly those with SMIs, overcome logistical barriers and address hesitancy, which are both essential for vaccine uptake. Psychiatrists can help identify actual barriers (eg, transportation, digital access for information and scheduling) and perceived barriers, improve information access, and help patients obtain self-efficacy to take the actions needed to get vaccinated, particularly by collaborating with and communicating these concerns to other social services (Table 4).41
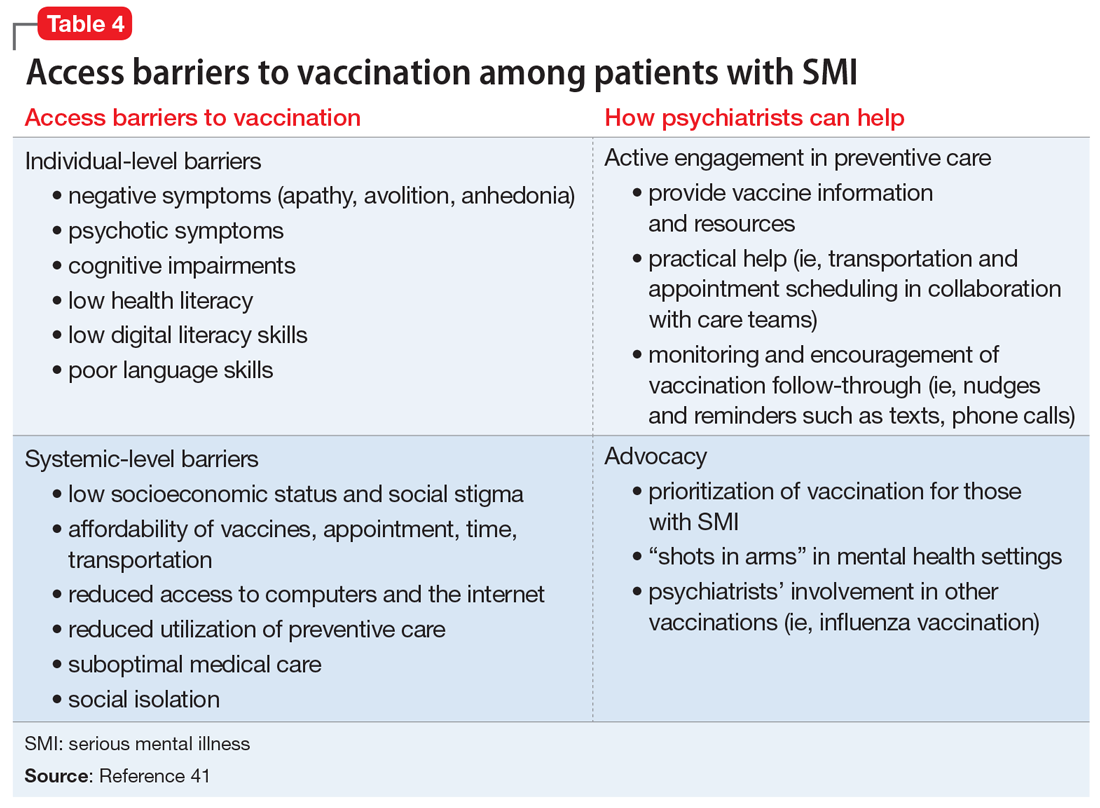
Monitor for vaccination series completion. Especially for vaccines that require more than a single dose over time, patients need more reminders, nudges, practical support, and encouragement to complete vaccination. A surprising degree of confusion regarding the timing of protection and benefit from the second COVID-19 injection (for the 2-injection vaccines) was uncovered in a recent survey of >1,000 US adults who had received their vaccinations in February 2021.45 Attentive monitoring of vaccination series completion by psychiatrists can thus increase the likelihood that a patient will follow through (Table 4).41 This can be as simple as asking about completion of the series during appointments, but further aided by communicating to the larger care team (social workers, care managers, care coordinators) when identifying that the patient may need further assistance.
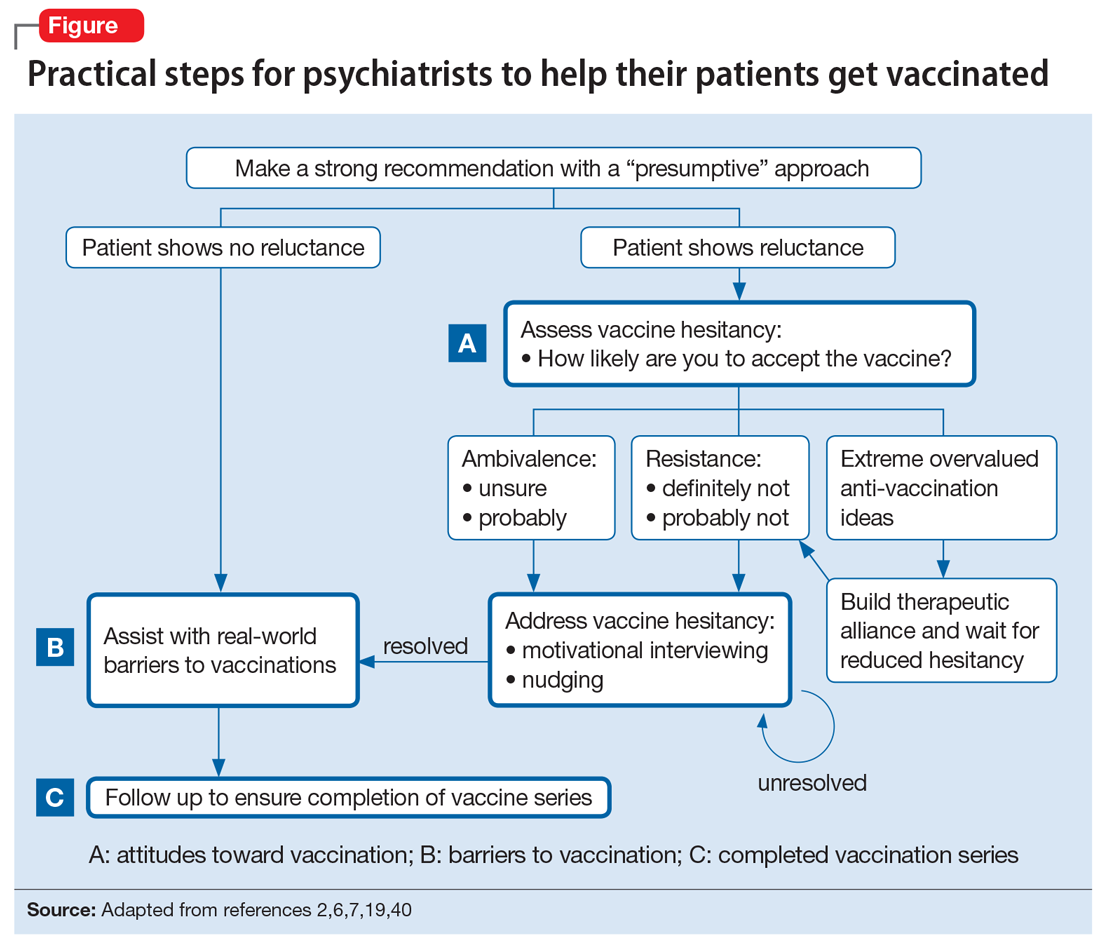
The Figure2,6,7,19,40 summarizes the steps that psychiatrists can take to help patients get vaccinated by assessing attitudes towards vaccination (vaccine hesitancy), helping to remove barriers to vaccination, and ensuring via patient follow-up that a vaccine series is completed.
Continue to: Active involvement is key
Active involvement is key
The active involvement of psychiatrists in COVID-19 vaccination efforts can protect patients from the virus, reduce health disparities among patients with SMI, and promote herd immunity, helping to end the pandemic. Psychiatry practices can serve as ideal platforms to deliver evidence-based COVID-19 vaccine information and encourage vaccine uptake, particularly for marginalized populations.
Vaccination programs in mental health practices can even be conceptualized as a moral mandate in the spirit of addressing distributive injustice. The population management challenges of individual-level barriers and follow-through could be dramatically reduced—if not nearly eliminated—through policy-level changes that allow vaccinations to be administered in places where patients with SMI are already engaged: that is, “shots in arms” in mental health settings. As noted, some studies have shown that mental health settings can play a key role in other preventive care campaigns, such as the annual influenza and hepatitis vaccinations, and thus the incorporation of preventive care need not be limited to just COVID-19 vaccination efforts.
The COVID-19 pandemic is an opportunity to rethink the role of psychiatrists and psychiatric offices and clinics in preventive health care. The health risks and disparities of patients with SMI require the proactive involvement of psychiatrists at both the level of their individual patients and at the federal and state levels to advocate for policy changes that can benefit these populations. Overall, psychiatrists occupy a special role within the medical establishment that enables them to uniquely advocate for patients with SMI and ensure they are not forgotten during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists could apply behavior management techniques such as motivational interviewing and nudging to address vaccine hesitancy in their patients and move them to accepting the COVID-19 vaccination. This could be particularly valuable for patients with serious mental illness, who face increased risks from COVID-19 and additional barriers to getting vaccinated.
Related Resources
- American Psychiatric Association. APA coronavirus resources. https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/covid-19-Coronavirus
- Baddeley M. Behavioural economics: a very short introduction. Oxford University Press; 2017.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccines for COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/index.html
- Chou W, Burgdorf C, Gaysynsky A, et al. COVID-19 vaccination communication: applying behavioral and social science to address vaccine hesitancy and foster vaccine confidence. National Institutes of Health. Published 2020. https://obssr.od.nih.gov/sites/obssr/files/inline-files/OBSSR_VaccineWhitePaper_FINAL_508.pdf
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational interviewing: helping people change. Guilford Press; 2012.
1. Mazereel V, Van Assche K, Detraux J, et al. COVID-19 vaccination for people with severe mental illness: why, what, and how? Lancet Psychiatry. 2021;8(5):444-450.
2. Freudenreich O, Van Alphen MU, Lim C. The ABCs of successful vaccinations: a role for psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(3):48-50.
3. World Health Organization (WHO). Ten threats to global health in 2019. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019
4. MacDonald NE. Vaccine hesitancy: definition, scope and determinants. Vaccine. 2015;33(34):4161-4164.
5. McClure CC, Cataldi JR, O’Leary ST. Vaccine hesitancy: where we are and where we are going. Clin Ther. 2017;39(8):1550-1562.
6. Betsch C, Korn L, Holtmann C. Don’t try to convert the antivaccinators, instead target the fence-sitters. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112(49):E6725-E6726.
7. Rahman T, Hartz SM, Xiong W, et al. Extreme overvalued beliefs. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2020;48(3):319-326.
8. Leask J. Target the fence-sitters. Nature. 2011;473(7348):443-445.
9. United States Census Bureau. Household Pulse Survey COVID-19 Vaccination Tracker. Updated June 30, 2021. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/household-pulse-survey-covid-19-vaccination-tracker.html
10. United States Census Bureau. Measuring household experiences during the coronavirus pandemic. Updated May 5, 2021. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.census.gov/data/experimental-data-products/household-pulse-survey.html
11. Jefsen OH, Kølbæk P, Gil Y, et al. COVID-19 vaccine willingness among patients with mental illness compared with the general population. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2021:1-24. doi:10.1017/neu.2021.15
12. Miles LW, Williams N, Luthy KE, et al. Adult vaccination rates in the mentally ill population: an outpatient improvement project. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2020;26(2):172-180.
13. Lewandowsky S, Ecker UK, Seifert CM, et al. Misinformation and its correction: continued influence and successful debiasing. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2012;13(3):106-131.
14. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Locus of mental health treatment in an integrated service system. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51(7):890-892.
15. Freudenreich O, Kontos N, Querques J. COVID-19 and patients with serious mental illness. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(9):24-35.
16. Hamel L, Kirzinger A, Muñana C, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: December 2020. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/report/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-december-2020/
17. Kai J, Crosland A. Perspectives of people with enduring mental ill health from a community-based qualitative study. Br J Gen Pract. 2001;51(470):730-736.
18. Mather G, Baker D, Laugharne R. Patient trust in psychiatrists. Psychosis. 2012;4(2):161-167.
19. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational interviewing: helping people change. Guilford Press; 2012.
20. Reno JE, O’Leary S, Garrett K, et al. Improving provider communication about HPV vaccines for vaccine-hesitant parents through the use of motivational interviewing. J Health Commun. 2018;23(4):313-320.
21. Baddeley M. Behavioural economics: a very short introduction. Volume 505. Oxford University Press; 2017.
22. Nemani K, Li C, Olfson M, et al. Association of psychiatric disorders with mortality among patients with COVID-19. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(4):380-386.
23. De Hert M, Correll CU, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. I. Prevalence, impact of medications and disparities in health care. World Psychiatry. 2011;10(1):52.
24. Lorenz RA, Norris MM, Norton LC, et al. Factors associated with influenza vaccination decisions among patients with mental illness. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2013;46(1):1-13.
25. Bitan DT. Patients with schizophrenia are under‐vaccinated for COVID‐19: a report from Israel. World Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):300.
26. Robotham D, Satkunanathan S, Doughty L, et al. Do we still have a digital divide in mental health? A five-year survey follow-up. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(11):e309.
27. De Hert M, Cohen D, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. II. Barriers to care, monitoring and treatment guidelines, plus recommendations at the system and individual level. World Psychiatry. 2011;10(2):138.
28. Carrà G, Bartoli F, Carretta D, et al. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in people with severe mental illness: a mediation analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2014;49(11):1739-1746.
29. Lin MT, Burgess JF, Carey K. The association between serious psychological distress and emergency department utilization among young adults in the USA. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2012;47(6):939-947.
30. DeCoux M. Acute versus primary care: the health care decision making process for individuals with severe mental illness. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2005;26(9):935-951.
31. Hoffman L, Wisniewski H, Hays R, et al. Digital opportunities for outcomes in recovery services (DOORS): a pragmatic hands-on group approach toward increasing digital health and smartphone competencies, autonomy, relatedness, and alliance for those with serious mental illness. J Psychiatr Pract. 2020;26(2):80-88.
32. Rosenberg SD, Goldberg RW, Dixon LB, et al. Assessing the STIRR model of best practices for blood-borne infections of clients with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2010;61(9):885-891.
33. Slade EP, Rosenberg S, Dixon LB, et al. Costs of a public health model to increase receipt of hepatitis-related services for persons with mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2013;64(2):127-133.
34. Brewer NT, Chapman GB, Rothman AJ, et al. Increasing vaccination: putting psychological science into action. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2017;18(3):149-207.
35. Nabet B, Gable J, Eder J, et al. PolicyLab evidence to action brief: addressing vaccine hesitancy to protect children & communities against preventable diseases. Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Published Spring 2017. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://policylab.chop.edu/sites/default/files/pdf/publications/Addressing_Vaccine_Hesitancy.pdf
36. Opel DJ, Heritage J, Taylor JA, et al. The architecture of provider-parent vaccine discussions at health supervision visits. Pediatrics. 2013;132(6):1037-1046.
37. Betsch C, Böhm R, Korn L, et al. On the benefits of explaining herd immunity in vaccine advocacy. Nat Hum Behav. 2017;1(3):1-6.
38. Shen F, Sheer VC, Li R. Impact of narratives on persuasion in health communication: a meta-analysis. J Advert. 2015;44(2):105-113.
39. Parkerson N, Leader A. Vaccine hesitancy in the era of COVID. Population Health Leadership Series: PopTalk webinars. Paper 26. Published February 10, 2021. https://jdc.jefferson.edu/phlspoptalk/26/
40. Dempsey AF, O’Leary ST. Human papillomavirus vaccination: narrative review of studies on how providers’ vaccine communication affects attitudes and uptake. Acad Pediatr. 2018;18(2):S23-S27.
41. Chou W, Burgdorf C, Gaysynsky A, et al. COVID-19 vaccination communication: applying behavioral and social science to address vaccine hesitancy and foster vaccine confidence. National Institutes of Health. Published 2020. https://obssr.od.nih.gov/sites/obssr/files/inline-files/OBSSR_VaccineWhitePaper_FINAL_508.pdf
42. International Society for Vaccines and the MJH Life Sciences COVID-19 coalition. Building confidence in COVID-19 vaccination: a toolbox of talks from leaders in the field. March 9, 2021. https://globalmeet.webcasts.com/starthere.jsp?ei=1435659&tp_key=59ed660099
43. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Frequently asked questions about COVID-19 vaccination. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/faq.html
44. Singh BR, Gandharava S, Gandharva R. Covid-19 vaccines and community immunity. Infectious Diseases Research. 2021;2(1):5.
45. Goldfarb JL, Kreps S, Brownstein JS, et al. Beyond the first dose - Covid-19 vaccine follow-through and continued protective measures. N Engl J Med. 2021;85(2):101-103.
After more than 600,000 deaths in the United States from the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), several safe and effective vaccines against the virus have become available. Vaccines are the most effective preventive measure against COVID-19 and the most promising way to achieve herd immunity to end the current pandemic. However, obstacles to reaching this goal include vaccine skepticism, structural barriers, or simple inertia to get vaccinated. These challenges provide opportunities for psychiatrists to use their medical knowledge and expertise, applying behavior management techniques such as motivational interviewing and nudging to encourage their patients to get vaccinated. In particular, marginalized patients with serious mental illness (SMI), who are subject to disproportionately high rates of COVID-19 infection and more severe outcomes,1 have much to gain if psychiatrists become involved in the COVID-19 vaccination campaign.
In this article, we define vaccine hesitancy and highlight what makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors, given their unique skill set and longitudinal, trust-based connection with their patients. We expand on the particular vulnerabilities of patients with SMI, including structural barriers to vaccination that lead to health disparities and inequity. Finally, building on “The ABCs of successful vaccinations” framework published in
What is vaccine hesitancy?
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines vaccine hesitancy as a “delay in acceptance or refusal of vaccines despite availability of vaccine services.”3,4 Vaccine hesitancy occurs on a continuum ranging from uncertainty about accepting a vaccine to absolute refusal.4,5 It involves a complex decision-making process driven by contextual, individual, and social influences, and vaccine-specific issues.4 In the “3C” model developed by the WHO Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) Working Group, vaccine hesitancy is influenced by confidence (trust in vaccines, in the health care system, and in policy makers), complacency (lower perceived risk), and convenience (availability, affordability, accessibility, language and health literacy, appeal of vaccination program).4
In 2019, the WHO named vaccine hesitancy as one of the top 10 global health threats.3 Hesitancy to receive COVID-19 vaccines may be particularly high because of their rapid development. In addition, the tumultuous political environment that often featured inconsistent messaging about the virus, its dangers, and its transmission since the early days of the pandemic created widespread public confusion and doubt as scientific understandings evolved. “Anti-vaxxer” movements that completely rejected vaccine efficacy disseminated misinformation online. Followers of these movements may have such extreme overvalued ideas that any effort to persuade them otherwise with scientific evidence will accomplish very little.6,7 Therefore, focusing on individuals who are “sitting on the fence” about getting vaccinated can be more productive because they represent a much larger group than those who adamantly refuse vaccines, and they may be more amenable to changing beliefs and behaviors.8
The US Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey asked, “How likely are you to accept the vaccine?”9 As of late June 2021, 11.4% of US adults reported they would “definitely not get a vaccine” or “probably not get a vaccine,” and that number increases to 16.9% when including those who are “unsure,” although there is wide geographical variability.10
A recent study in Denmark showed that willingness to receive the COVID-19 vaccine was slightly lower among patients with mental illness (84.8%) compared with the general population (89.5%).11 Given the small difference, vaccine hesitancy was not considered to be a major barrier for vaccination among patients with mental illness in Denmark. This is similar to the findings of a pre-pandemic study at a community mental health clinic in the United States involving other vaccinations, which suggested that 84% of patients with SMI perceived vaccinations as safe, effective, and important.12 In this clinic, identified barriers to vaccinations in general among patients with SMI included lack of awareness and knowledge (42.2%), accessibility (16.3%), personal cost (13.3%), fears about immunization (10.4%), and lack of recommendations by primary care providers (PCPs) (1.5%).12
It is critical to distinguish attitude-driven vaccine hesitancy from a lack of education and opportunity to receive a vaccine. Particularly disadvantaged communities may be mislabeled as “vaccine hesitant” when in fact they may not have the ability to be as proactive as other population groups (eg, difficulty scheduling appointments over the Internet).
Continue to: What makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors?
What makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors?
There are several reasons psychiatrists can be well-positioned to contribute to the success of vaccination campaigns (Table 1). These include their frequent contact with patients and their care teams, the high trust those patients have in them, and their medical expertise and skills in applied behavioral and social science techniques, including motivational interviewing and nudging. Vaccination efforts and outreach are more effective when led by the clinician with whom the patient has the most contact because resolving vaccine hesitancy is not a one-time discussion but requires ongoing communication, persistence, and consistency.13 Patients may contact their psychiatrists more frequently than their other clinicians, including PCPs. For this reason, psychiatrists can serve as the gateway to health care, particularly for patients with SMI.14 In addition, interruptions in nonemergency services caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may affect vaccine delivery because patients may have been unable to see their PCPs regularly during the pandemic.15

Psychiatrists’ medical expertise and their ability to develop rapport with their patients promote trust-building. Receiving credible information from a trusted source such as a patient’s psychiatrist can be impactful. A recent poll suggested that individual health care clinicians have been consistently identified as the most trusted sources for vaccine information, including for the COVID-19 vaccines.16 There is also higher trust when there is greater continuity of care both in terms of length of time the patient has known the clinician and the number of consultations,17 an inherent part of psychiatric practice. In addition, research has shown that patients trust their psychiatrists as much as they trust their general practitioners.18
Psychiatrists are experts in behavior change, promoting healthy behaviors through motivational interviewing and nudging. They also have experience with managing patients who hold overvalued ideas as well as dealing with uncertainty, given their scientific and medical training.
Motivational interviewing is a patient-centered, collaborative approach widely used by psychiatrists to treat unhealthy behaviors such as substance use. Clinicians elicit and strengthen the patient’s desire and motivation for change while respecting their autonomy. Instead of presenting persuasive facts, the clinician creates a welcoming, nonthreatening, safe environment by engaging patients in open dialogue, reflecting back the patients’ concerns with empathy, helping them realize contradictions in behavior, and supporting self-sufficiency.19 In a nonpsychiatric setting, studies have shown the effectiveness of motivational interviewing in increasing uptake of human papillomavirus vaccines and of pediatric vaccines.20
Nudging, which comes from behavioral economics and psychology, underscores the importance of structuring a choice architecture in changing the way people make their everyday decisions.21 Nudging still gives people a choice and respects autonomy, but it leads patients to more efficient and productive decision-making. Many nudges are based around giving good “default options” because people often do not make efforts to deviate from default options. In addition, social nudges are powerful, giving people a social reference point and normalizing certain behaviors.21 Psychiatrists have become skilled in nudging from working with patients with varying levels of insight and cognitive capabilities. That is, they give simple choices, prompts, and frequent feedback to reinforce “good” decisions and to discourage “bad” decisions.
Continue to: Managing overvalued ideas
Managing overvalued ideas. Psychiatrists are also well-versed in having discussions with patients who hold irrational beliefs (psychosis) or overvalued ideas. For example, psychiatrists frequently manage anorexia nervosa and hypochondria, which are rooted in overvalued ideas.7 While psychiatrists may not be able to directly confront the overvalued ideas, they can work around such ideas while waiting for more flexible moments. Similarly, managing patients with intense emotional commitment7 to commonly held anti-vaccination ideas may not be much different. Psychiatrists can work around resistance until patients may be less strongly attached to those overvalued ideas in instances when other techniques, such as motivational interviewing and nudging, may be more effective.
Managing uncertainty. Psychiatrists are experts in managing “not knowing” and uncertainty. Due to their medical scientific training, they are familiar with the process of science, and how understanding changes through trial and error. In contrast, most patients usually only see the end product (ie, a drug comes to market). Discussions with patients that acknowledge uncertainty and emphasize that changes in what is known are expected and appropriate as scientific knowledge evolves could help preempt skepticism when messages are updated.
Why do patients with SMI need more help?
SMI as a high-risk group. Patients with SMI are part of a “tragic” epidemiologic triad of agent-host-environment15 that places them at remarkably elevated risk for COVID-19 infection and more serious complications and death when infected.1 After age, a diagnosis of a schizophrenia spectrum disorder is the second largest predictor of mortality from COVID-19, with a 2.7-fold increase in mortality.22 This is how the elements of the triad come together: SARS-Cov-2 is a highly infectious agent affecting individuals who are vulnerable hosts because of their high frequency of medical comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and respiratory tract diseases, which are all risk factors for worse outcomes due to COVID-19.23 In addition, SMI is associated with socioeconomic risk factors for SARS-Cov-2 infection, including poverty, homelessness, and crowded settings such as jails, group homes, hospitals, and shelters, which constitute ideal environments for high transmission of the virus.
Structural barriers to vaccination. Studies have suggested lower rates of vaccination among people with SMI for various other infectious diseases compared with the general population.12 For example, in 1 outpatient mental health setting, influenza vaccination rates were 24% to 28%, which was lower than the national vaccination rate of 40.9% for the same influenza season (2010 to 2011).24 More recently, a study in Israel examining the COVID-19 vaccination rate among >25,000 patients with schizophrenia suggested under-vaccination of this cohort. The results showed that the odds of getting the COVID-19 vaccination were significantly lower in the schizophrenia group compared with the general population (odds ratio = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.77 to 0.83).25
Patients with SMI encounter considerable system-level barriers to vaccinations in general, such as reduced access to health care due to cost and a lack of transportation,12 the digital divide given their reduced access to the internet and computers for information and scheduling,26 and lack of vaccination recommendations from their PCPs.12 Studies have also shown that patients with SMI often receive suboptimal medical care because of stigmatization and discrimination.27 They also have lower rates of preventive care utilization, seeking medical services only in times of crisis and seeking mental health services more often than physical health care.28-30
Continue to: Patients with SMI face...
Patients with SMI face additional individual challenges that impede vaccine uptake, such as lack of knowledge and awareness about the virus and vaccinations, general cognitive impairment, low digital literacy skills,31 low language literacy and educational attainment, baseline delusions, and negative symptoms such as apathy, avolition, and anhedonia.1 Thus, even if they overcome the external barriers and obtain vaccine-related information, these patients may experience difficulty in understanding the content and applying this information to their personal circumstances as a result of low health literacy.
How psychiatrists can help
The concept of using mental health care sites and trained clinicians to increase medical disease prevention is not new. The rigorously tested intervention model STIRR (Screen, Test, Immunize, Reduce risk, and Refer) uses co-located nurse practitioners in community mental health centers to provide risk assessment, counseling, and blood testing for hepatitis and HIV, as well as on-site vaccinations for hepatitis to patients dually diagnosed with SMI and substance use disorders.32
Prioritization of patients with SMI for vaccine eligibility does not directly lead to vaccine uptake. Patients with SMI need extra support from their primary point of health care contact, namely their psychiatrists. Psychiatrists may bring a set of specialized skills uniquely suited to this moment to address vaccine hesitancy and overall lack of vaccine resources and awareness. Freudenreich et al2 recently proposed “The ABCs of Successful Vaccinations” framework that psychiatrists can use in their interactions with patients to encourage vaccination by focusing on:
- attitudes towards vaccination
- barriers to vaccination
- completed vaccination series.
Understand attitudes toward vaccination. Decision-making may be an emotional and psychological experience that is informed by thoughts and feelings,34 and psychiatrists are uniquely positioned to tailor messages to individual patients by using motivational interviewing and applying nudging techniques.8 Given the large role of the pandemic in everyday life, it would be natural to address vaccine-related concerns in the course of routine rapport-building. Table 219,34-38 shows example phrases of COVID-19 vaccine messages that are based on communication strategies that have demonstrated success in health behavior domains (including vaccinations).39

Continue to: First, a strong recommendation...
First, a strong recommendation should be made using the presumptive approach.40 If vaccine hesitancy is detected, psychiatrists should next attempt to understand patients’ reasoning with open-ended questions to probe vaccine-related concerns. Motivational interviewing can then be used to target the fence sitters (rather than anti-vaxxers).6 Psychiatrists can also communicate with therapists about the need for further follow up on patients’ hesitancies.
When assuring patients of vaccine safety and efficacy, it is helpful to explain the vaccine development process, including FDA approval, extensive clinical trials, monitoring, and the distribution process. Providing clear, transparent, accurate information about the risks and benefits of the vaccines is important, as well as monitoring misinformation and developing convincing counter messages that elicit positive emotions toward the vaccines.41 Examples of messages to counter common vaccine-related concerns and misinformation are shown in Table 3.42-44

Know the barriers to vaccination. The role of the psychiatrist is to help patients, particularly those with SMIs, overcome logistical barriers and address hesitancy, which are both essential for vaccine uptake. Psychiatrists can help identify actual barriers (eg, transportation, digital access for information and scheduling) and perceived barriers, improve information access, and help patients obtain self-efficacy to take the actions needed to get vaccinated, particularly by collaborating with and communicating these concerns to other social services (Table 4).41

Monitor for vaccination series completion. Especially for vaccines that require more than a single dose over time, patients need more reminders, nudges, practical support, and encouragement to complete vaccination. A surprising degree of confusion regarding the timing of protection and benefit from the second COVID-19 injection (for the 2-injection vaccines) was uncovered in a recent survey of >1,000 US adults who had received their vaccinations in February 2021.45 Attentive monitoring of vaccination series completion by psychiatrists can thus increase the likelihood that a patient will follow through (Table 4).41 This can be as simple as asking about completion of the series during appointments, but further aided by communicating to the larger care team (social workers, care managers, care coordinators) when identifying that the patient may need further assistance.
The Figure2,6,7,19,40 summarizes the steps that psychiatrists can take to help patients get vaccinated by assessing attitudes towards vaccination (vaccine hesitancy), helping to remove barriers to vaccination, and ensuring via patient follow-up that a vaccine series is completed.

Continue to: Active involvement is key
Active involvement is key
The active involvement of psychiatrists in COVID-19 vaccination efforts can protect patients from the virus, reduce health disparities among patients with SMI, and promote herd immunity, helping to end the pandemic. Psychiatry practices can serve as ideal platforms to deliver evidence-based COVID-19 vaccine information and encourage vaccine uptake, particularly for marginalized populations.
Vaccination programs in mental health practices can even be conceptualized as a moral mandate in the spirit of addressing distributive injustice. The population management challenges of individual-level barriers and follow-through could be dramatically reduced—if not nearly eliminated—through policy-level changes that allow vaccinations to be administered in places where patients with SMI are already engaged: that is, “shots in arms” in mental health settings. As noted, some studies have shown that mental health settings can play a key role in other preventive care campaigns, such as the annual influenza and hepatitis vaccinations, and thus the incorporation of preventive care need not be limited to just COVID-19 vaccination efforts.
The COVID-19 pandemic is an opportunity to rethink the role of psychiatrists and psychiatric offices and clinics in preventive health care. The health risks and disparities of patients with SMI require the proactive involvement of psychiatrists at both the level of their individual patients and at the federal and state levels to advocate for policy changes that can benefit these populations. Overall, psychiatrists occupy a special role within the medical establishment that enables them to uniquely advocate for patients with SMI and ensure they are not forgotten during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists could apply behavior management techniques such as motivational interviewing and nudging to address vaccine hesitancy in their patients and move them to accepting the COVID-19 vaccination. This could be particularly valuable for patients with serious mental illness, who face increased risks from COVID-19 and additional barriers to getting vaccinated.
Related Resources
- American Psychiatric Association. APA coronavirus resources. https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/covid-19-Coronavirus
- Baddeley M. Behavioural economics: a very short introduction. Oxford University Press; 2017.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccines for COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/index.html
- Chou W, Burgdorf C, Gaysynsky A, et al. COVID-19 vaccination communication: applying behavioral and social science to address vaccine hesitancy and foster vaccine confidence. National Institutes of Health. Published 2020. https://obssr.od.nih.gov/sites/obssr/files/inline-files/OBSSR_VaccineWhitePaper_FINAL_508.pdf
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational interviewing: helping people change. Guilford Press; 2012.
After more than 600,000 deaths in the United States from the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), several safe and effective vaccines against the virus have become available. Vaccines are the most effective preventive measure against COVID-19 and the most promising way to achieve herd immunity to end the current pandemic. However, obstacles to reaching this goal include vaccine skepticism, structural barriers, or simple inertia to get vaccinated. These challenges provide opportunities for psychiatrists to use their medical knowledge and expertise, applying behavior management techniques such as motivational interviewing and nudging to encourage their patients to get vaccinated. In particular, marginalized patients with serious mental illness (SMI), who are subject to disproportionately high rates of COVID-19 infection and more severe outcomes,1 have much to gain if psychiatrists become involved in the COVID-19 vaccination campaign.
In this article, we define vaccine hesitancy and highlight what makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors, given their unique skill set and longitudinal, trust-based connection with their patients. We expand on the particular vulnerabilities of patients with SMI, including structural barriers to vaccination that lead to health disparities and inequity. Finally, building on “The ABCs of successful vaccinations” framework published in
What is vaccine hesitancy?
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines vaccine hesitancy as a “delay in acceptance or refusal of vaccines despite availability of vaccine services.”3,4 Vaccine hesitancy occurs on a continuum ranging from uncertainty about accepting a vaccine to absolute refusal.4,5 It involves a complex decision-making process driven by contextual, individual, and social influences, and vaccine-specific issues.4 In the “3C” model developed by the WHO Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) Working Group, vaccine hesitancy is influenced by confidence (trust in vaccines, in the health care system, and in policy makers), complacency (lower perceived risk), and convenience (availability, affordability, accessibility, language and health literacy, appeal of vaccination program).4
In 2019, the WHO named vaccine hesitancy as one of the top 10 global health threats.3 Hesitancy to receive COVID-19 vaccines may be particularly high because of their rapid development. In addition, the tumultuous political environment that often featured inconsistent messaging about the virus, its dangers, and its transmission since the early days of the pandemic created widespread public confusion and doubt as scientific understandings evolved. “Anti-vaxxer” movements that completely rejected vaccine efficacy disseminated misinformation online. Followers of these movements may have such extreme overvalued ideas that any effort to persuade them otherwise with scientific evidence will accomplish very little.6,7 Therefore, focusing on individuals who are “sitting on the fence” about getting vaccinated can be more productive because they represent a much larger group than those who adamantly refuse vaccines, and they may be more amenable to changing beliefs and behaviors.8
The US Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey asked, “How likely are you to accept the vaccine?”9 As of late June 2021, 11.4% of US adults reported they would “definitely not get a vaccine” or “probably not get a vaccine,” and that number increases to 16.9% when including those who are “unsure,” although there is wide geographical variability.10
A recent study in Denmark showed that willingness to receive the COVID-19 vaccine was slightly lower among patients with mental illness (84.8%) compared with the general population (89.5%).11 Given the small difference, vaccine hesitancy was not considered to be a major barrier for vaccination among patients with mental illness in Denmark. This is similar to the findings of a pre-pandemic study at a community mental health clinic in the United States involving other vaccinations, which suggested that 84% of patients with SMI perceived vaccinations as safe, effective, and important.12 In this clinic, identified barriers to vaccinations in general among patients with SMI included lack of awareness and knowledge (42.2%), accessibility (16.3%), personal cost (13.3%), fears about immunization (10.4%), and lack of recommendations by primary care providers (PCPs) (1.5%).12
It is critical to distinguish attitude-driven vaccine hesitancy from a lack of education and opportunity to receive a vaccine. Particularly disadvantaged communities may be mislabeled as “vaccine hesitant” when in fact they may not have the ability to be as proactive as other population groups (eg, difficulty scheduling appointments over the Internet).
Continue to: What makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors?
What makes psychiatrists ideal vaccine ambassadors?
There are several reasons psychiatrists can be well-positioned to contribute to the success of vaccination campaigns (Table 1). These include their frequent contact with patients and their care teams, the high trust those patients have in them, and their medical expertise and skills in applied behavioral and social science techniques, including motivational interviewing and nudging. Vaccination efforts and outreach are more effective when led by the clinician with whom the patient has the most contact because resolving vaccine hesitancy is not a one-time discussion but requires ongoing communication, persistence, and consistency.13 Patients may contact their psychiatrists more frequently than their other clinicians, including PCPs. For this reason, psychiatrists can serve as the gateway to health care, particularly for patients with SMI.14 In addition, interruptions in nonemergency services caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may affect vaccine delivery because patients may have been unable to see their PCPs regularly during the pandemic.15

Psychiatrists’ medical expertise and their ability to develop rapport with their patients promote trust-building. Receiving credible information from a trusted source such as a patient’s psychiatrist can be impactful. A recent poll suggested that individual health care clinicians have been consistently identified as the most trusted sources for vaccine information, including for the COVID-19 vaccines.16 There is also higher trust when there is greater continuity of care both in terms of length of time the patient has known the clinician and the number of consultations,17 an inherent part of psychiatric practice. In addition, research has shown that patients trust their psychiatrists as much as they trust their general practitioners.18
Psychiatrists are experts in behavior change, promoting healthy behaviors through motivational interviewing and nudging. They also have experience with managing patients who hold overvalued ideas as well as dealing with uncertainty, given their scientific and medical training.
Motivational interviewing is a patient-centered, collaborative approach widely used by psychiatrists to treat unhealthy behaviors such as substance use. Clinicians elicit and strengthen the patient’s desire and motivation for change while respecting their autonomy. Instead of presenting persuasive facts, the clinician creates a welcoming, nonthreatening, safe environment by engaging patients in open dialogue, reflecting back the patients’ concerns with empathy, helping them realize contradictions in behavior, and supporting self-sufficiency.19 In a nonpsychiatric setting, studies have shown the effectiveness of motivational interviewing in increasing uptake of human papillomavirus vaccines and of pediatric vaccines.20
Nudging, which comes from behavioral economics and psychology, underscores the importance of structuring a choice architecture in changing the way people make their everyday decisions.21 Nudging still gives people a choice and respects autonomy, but it leads patients to more efficient and productive decision-making. Many nudges are based around giving good “default options” because people often do not make efforts to deviate from default options. In addition, social nudges are powerful, giving people a social reference point and normalizing certain behaviors.21 Psychiatrists have become skilled in nudging from working with patients with varying levels of insight and cognitive capabilities. That is, they give simple choices, prompts, and frequent feedback to reinforce “good” decisions and to discourage “bad” decisions.
Continue to: Managing overvalued ideas
Managing overvalued ideas. Psychiatrists are also well-versed in having discussions with patients who hold irrational beliefs (psychosis) or overvalued ideas. For example, psychiatrists frequently manage anorexia nervosa and hypochondria, which are rooted in overvalued ideas.7 While psychiatrists may not be able to directly confront the overvalued ideas, they can work around such ideas while waiting for more flexible moments. Similarly, managing patients with intense emotional commitment7 to commonly held anti-vaccination ideas may not be much different. Psychiatrists can work around resistance until patients may be less strongly attached to those overvalued ideas in instances when other techniques, such as motivational interviewing and nudging, may be more effective.
Managing uncertainty. Psychiatrists are experts in managing “not knowing” and uncertainty. Due to their medical scientific training, they are familiar with the process of science, and how understanding changes through trial and error. In contrast, most patients usually only see the end product (ie, a drug comes to market). Discussions with patients that acknowledge uncertainty and emphasize that changes in what is known are expected and appropriate as scientific knowledge evolves could help preempt skepticism when messages are updated.
Why do patients with SMI need more help?
SMI as a high-risk group. Patients with SMI are part of a “tragic” epidemiologic triad of agent-host-environment15 that places them at remarkably elevated risk for COVID-19 infection and more serious complications and death when infected.1 After age, a diagnosis of a schizophrenia spectrum disorder is the second largest predictor of mortality from COVID-19, with a 2.7-fold increase in mortality.22 This is how the elements of the triad come together: SARS-Cov-2 is a highly infectious agent affecting individuals who are vulnerable hosts because of their high frequency of medical comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and respiratory tract diseases, which are all risk factors for worse outcomes due to COVID-19.23 In addition, SMI is associated with socioeconomic risk factors for SARS-Cov-2 infection, including poverty, homelessness, and crowded settings such as jails, group homes, hospitals, and shelters, which constitute ideal environments for high transmission of the virus.
Structural barriers to vaccination. Studies have suggested lower rates of vaccination among people with SMI for various other infectious diseases compared with the general population.12 For example, in 1 outpatient mental health setting, influenza vaccination rates were 24% to 28%, which was lower than the national vaccination rate of 40.9% for the same influenza season (2010 to 2011).24 More recently, a study in Israel examining the COVID-19 vaccination rate among >25,000 patients with schizophrenia suggested under-vaccination of this cohort. The results showed that the odds of getting the COVID-19 vaccination were significantly lower in the schizophrenia group compared with the general population (odds ratio = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.77 to 0.83).25
Patients with SMI encounter considerable system-level barriers to vaccinations in general, such as reduced access to health care due to cost and a lack of transportation,12 the digital divide given their reduced access to the internet and computers for information and scheduling,26 and lack of vaccination recommendations from their PCPs.12 Studies have also shown that patients with SMI often receive suboptimal medical care because of stigmatization and discrimination.27 They also have lower rates of preventive care utilization, seeking medical services only in times of crisis and seeking mental health services more often than physical health care.28-30
Continue to: Patients with SMI face...
Patients with SMI face additional individual challenges that impede vaccine uptake, such as lack of knowledge and awareness about the virus and vaccinations, general cognitive impairment, low digital literacy skills,31 low language literacy and educational attainment, baseline delusions, and negative symptoms such as apathy, avolition, and anhedonia.1 Thus, even if they overcome the external barriers and obtain vaccine-related information, these patients may experience difficulty in understanding the content and applying this information to their personal circumstances as a result of low health literacy.
How psychiatrists can help
The concept of using mental health care sites and trained clinicians to increase medical disease prevention is not new. The rigorously tested intervention model STIRR (Screen, Test, Immunize, Reduce risk, and Refer) uses co-located nurse practitioners in community mental health centers to provide risk assessment, counseling, and blood testing for hepatitis and HIV, as well as on-site vaccinations for hepatitis to patients dually diagnosed with SMI and substance use disorders.32
Prioritization of patients with SMI for vaccine eligibility does not directly lead to vaccine uptake. Patients with SMI need extra support from their primary point of health care contact, namely their psychiatrists. Psychiatrists may bring a set of specialized skills uniquely suited to this moment to address vaccine hesitancy and overall lack of vaccine resources and awareness. Freudenreich et al2 recently proposed “The ABCs of Successful Vaccinations” framework that psychiatrists can use in their interactions with patients to encourage vaccination by focusing on:
- attitudes towards vaccination
- barriers to vaccination
- completed vaccination series.
Understand attitudes toward vaccination. Decision-making may be an emotional and psychological experience that is informed by thoughts and feelings,34 and psychiatrists are uniquely positioned to tailor messages to individual patients by using motivational interviewing and applying nudging techniques.8 Given the large role of the pandemic in everyday life, it would be natural to address vaccine-related concerns in the course of routine rapport-building. Table 219,34-38 shows example phrases of COVID-19 vaccine messages that are based on communication strategies that have demonstrated success in health behavior domains (including vaccinations).39

Continue to: First, a strong recommendation...
First, a strong recommendation should be made using the presumptive approach.40 If vaccine hesitancy is detected, psychiatrists should next attempt to understand patients’ reasoning with open-ended questions to probe vaccine-related concerns. Motivational interviewing can then be used to target the fence sitters (rather than anti-vaxxers).6 Psychiatrists can also communicate with therapists about the need for further follow up on patients’ hesitancies.
When assuring patients of vaccine safety and efficacy, it is helpful to explain the vaccine development process, including FDA approval, extensive clinical trials, monitoring, and the distribution process. Providing clear, transparent, accurate information about the risks and benefits of the vaccines is important, as well as monitoring misinformation and developing convincing counter messages that elicit positive emotions toward the vaccines.41 Examples of messages to counter common vaccine-related concerns and misinformation are shown in Table 3.42-44

Know the barriers to vaccination. The role of the psychiatrist is to help patients, particularly those with SMIs, overcome logistical barriers and address hesitancy, which are both essential for vaccine uptake. Psychiatrists can help identify actual barriers (eg, transportation, digital access for information and scheduling) and perceived barriers, improve information access, and help patients obtain self-efficacy to take the actions needed to get vaccinated, particularly by collaborating with and communicating these concerns to other social services (Table 4).41

Monitor for vaccination series completion. Especially for vaccines that require more than a single dose over time, patients need more reminders, nudges, practical support, and encouragement to complete vaccination. A surprising degree of confusion regarding the timing of protection and benefit from the second COVID-19 injection (for the 2-injection vaccines) was uncovered in a recent survey of >1,000 US adults who had received their vaccinations in February 2021.45 Attentive monitoring of vaccination series completion by psychiatrists can thus increase the likelihood that a patient will follow through (Table 4).41 This can be as simple as asking about completion of the series during appointments, but further aided by communicating to the larger care team (social workers, care managers, care coordinators) when identifying that the patient may need further assistance.
The Figure2,6,7,19,40 summarizes the steps that psychiatrists can take to help patients get vaccinated by assessing attitudes towards vaccination (vaccine hesitancy), helping to remove barriers to vaccination, and ensuring via patient follow-up that a vaccine series is completed.

Continue to: Active involvement is key
Active involvement is key
The active involvement of psychiatrists in COVID-19 vaccination efforts can protect patients from the virus, reduce health disparities among patients with SMI, and promote herd immunity, helping to end the pandemic. Psychiatry practices can serve as ideal platforms to deliver evidence-based COVID-19 vaccine information and encourage vaccine uptake, particularly for marginalized populations.
Vaccination programs in mental health practices can even be conceptualized as a moral mandate in the spirit of addressing distributive injustice. The population management challenges of individual-level barriers and follow-through could be dramatically reduced—if not nearly eliminated—through policy-level changes that allow vaccinations to be administered in places where patients with SMI are already engaged: that is, “shots in arms” in mental health settings. As noted, some studies have shown that mental health settings can play a key role in other preventive care campaigns, such as the annual influenza and hepatitis vaccinations, and thus the incorporation of preventive care need not be limited to just COVID-19 vaccination efforts.
The COVID-19 pandemic is an opportunity to rethink the role of psychiatrists and psychiatric offices and clinics in preventive health care. The health risks and disparities of patients with SMI require the proactive involvement of psychiatrists at both the level of their individual patients and at the federal and state levels to advocate for policy changes that can benefit these populations. Overall, psychiatrists occupy a special role within the medical establishment that enables them to uniquely advocate for patients with SMI and ensure they are not forgotten during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists could apply behavior management techniques such as motivational interviewing and nudging to address vaccine hesitancy in their patients and move them to accepting the COVID-19 vaccination. This could be particularly valuable for patients with serious mental illness, who face increased risks from COVID-19 and additional barriers to getting vaccinated.
Related Resources
- American Psychiatric Association. APA coronavirus resources. https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/covid-19-Coronavirus
- Baddeley M. Behavioural economics: a very short introduction. Oxford University Press; 2017.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccines for COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/index.html
- Chou W, Burgdorf C, Gaysynsky A, et al. COVID-19 vaccination communication: applying behavioral and social science to address vaccine hesitancy and foster vaccine confidence. National Institutes of Health. Published 2020. https://obssr.od.nih.gov/sites/obssr/files/inline-files/OBSSR_VaccineWhitePaper_FINAL_508.pdf
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational interviewing: helping people change. Guilford Press; 2012.
1. Mazereel V, Van Assche K, Detraux J, et al. COVID-19 vaccination for people with severe mental illness: why, what, and how? Lancet Psychiatry. 2021;8(5):444-450.
2. Freudenreich O, Van Alphen MU, Lim C. The ABCs of successful vaccinations: a role for psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(3):48-50.
3. World Health Organization (WHO). Ten threats to global health in 2019. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019
4. MacDonald NE. Vaccine hesitancy: definition, scope and determinants. Vaccine. 2015;33(34):4161-4164.
5. McClure CC, Cataldi JR, O’Leary ST. Vaccine hesitancy: where we are and where we are going. Clin Ther. 2017;39(8):1550-1562.
6. Betsch C, Korn L, Holtmann C. Don’t try to convert the antivaccinators, instead target the fence-sitters. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112(49):E6725-E6726.
7. Rahman T, Hartz SM, Xiong W, et al. Extreme overvalued beliefs. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2020;48(3):319-326.
8. Leask J. Target the fence-sitters. Nature. 2011;473(7348):443-445.
9. United States Census Bureau. Household Pulse Survey COVID-19 Vaccination Tracker. Updated June 30, 2021. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/household-pulse-survey-covid-19-vaccination-tracker.html
10. United States Census Bureau. Measuring household experiences during the coronavirus pandemic. Updated May 5, 2021. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.census.gov/data/experimental-data-products/household-pulse-survey.html
11. Jefsen OH, Kølbæk P, Gil Y, et al. COVID-19 vaccine willingness among patients with mental illness compared with the general population. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2021:1-24. doi:10.1017/neu.2021.15
12. Miles LW, Williams N, Luthy KE, et al. Adult vaccination rates in the mentally ill population: an outpatient improvement project. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2020;26(2):172-180.
13. Lewandowsky S, Ecker UK, Seifert CM, et al. Misinformation and its correction: continued influence and successful debiasing. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2012;13(3):106-131.
14. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Locus of mental health treatment in an integrated service system. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51(7):890-892.
15. Freudenreich O, Kontos N, Querques J. COVID-19 and patients with serious mental illness. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(9):24-35.
16. Hamel L, Kirzinger A, Muñana C, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: December 2020. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/report/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-december-2020/
17. Kai J, Crosland A. Perspectives of people with enduring mental ill health from a community-based qualitative study. Br J Gen Pract. 2001;51(470):730-736.
18. Mather G, Baker D, Laugharne R. Patient trust in psychiatrists. Psychosis. 2012;4(2):161-167.
19. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational interviewing: helping people change. Guilford Press; 2012.
20. Reno JE, O’Leary S, Garrett K, et al. Improving provider communication about HPV vaccines for vaccine-hesitant parents through the use of motivational interviewing. J Health Commun. 2018;23(4):313-320.
21. Baddeley M. Behavioural economics: a very short introduction. Volume 505. Oxford University Press; 2017.
22. Nemani K, Li C, Olfson M, et al. Association of psychiatric disorders with mortality among patients with COVID-19. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(4):380-386.
23. De Hert M, Correll CU, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. I. Prevalence, impact of medications and disparities in health care. World Psychiatry. 2011;10(1):52.
24. Lorenz RA, Norris MM, Norton LC, et al. Factors associated with influenza vaccination decisions among patients with mental illness. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2013;46(1):1-13.
25. Bitan DT. Patients with schizophrenia are under‐vaccinated for COVID‐19: a report from Israel. World Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):300.
26. Robotham D, Satkunanathan S, Doughty L, et al. Do we still have a digital divide in mental health? A five-year survey follow-up. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(11):e309.
27. De Hert M, Cohen D, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. II. Barriers to care, monitoring and treatment guidelines, plus recommendations at the system and individual level. World Psychiatry. 2011;10(2):138.
28. Carrà G, Bartoli F, Carretta D, et al. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in people with severe mental illness: a mediation analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2014;49(11):1739-1746.
29. Lin MT, Burgess JF, Carey K. The association between serious psychological distress and emergency department utilization among young adults in the USA. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2012;47(6):939-947.
30. DeCoux M. Acute versus primary care: the health care decision making process for individuals with severe mental illness. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2005;26(9):935-951.
31. Hoffman L, Wisniewski H, Hays R, et al. Digital opportunities for outcomes in recovery services (DOORS): a pragmatic hands-on group approach toward increasing digital health and smartphone competencies, autonomy, relatedness, and alliance for those with serious mental illness. J Psychiatr Pract. 2020;26(2):80-88.
32. Rosenberg SD, Goldberg RW, Dixon LB, et al. Assessing the STIRR model of best practices for blood-borne infections of clients with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2010;61(9):885-891.
33. Slade EP, Rosenberg S, Dixon LB, et al. Costs of a public health model to increase receipt of hepatitis-related services for persons with mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2013;64(2):127-133.
34. Brewer NT, Chapman GB, Rothman AJ, et al. Increasing vaccination: putting psychological science into action. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2017;18(3):149-207.
35. Nabet B, Gable J, Eder J, et al. PolicyLab evidence to action brief: addressing vaccine hesitancy to protect children & communities against preventable diseases. Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Published Spring 2017. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://policylab.chop.edu/sites/default/files/pdf/publications/Addressing_Vaccine_Hesitancy.pdf
36. Opel DJ, Heritage J, Taylor JA, et al. The architecture of provider-parent vaccine discussions at health supervision visits. Pediatrics. 2013;132(6):1037-1046.
37. Betsch C, Böhm R, Korn L, et al. On the benefits of explaining herd immunity in vaccine advocacy. Nat Hum Behav. 2017;1(3):1-6.
38. Shen F, Sheer VC, Li R. Impact of narratives on persuasion in health communication: a meta-analysis. J Advert. 2015;44(2):105-113.
39. Parkerson N, Leader A. Vaccine hesitancy in the era of COVID. Population Health Leadership Series: PopTalk webinars. Paper 26. Published February 10, 2021. https://jdc.jefferson.edu/phlspoptalk/26/
40. Dempsey AF, O’Leary ST. Human papillomavirus vaccination: narrative review of studies on how providers’ vaccine communication affects attitudes and uptake. Acad Pediatr. 2018;18(2):S23-S27.
41. Chou W, Burgdorf C, Gaysynsky A, et al. COVID-19 vaccination communication: applying behavioral and social science to address vaccine hesitancy and foster vaccine confidence. National Institutes of Health. Published 2020. https://obssr.od.nih.gov/sites/obssr/files/inline-files/OBSSR_VaccineWhitePaper_FINAL_508.pdf
42. International Society for Vaccines and the MJH Life Sciences COVID-19 coalition. Building confidence in COVID-19 vaccination: a toolbox of talks from leaders in the field. March 9, 2021. https://globalmeet.webcasts.com/starthere.jsp?ei=1435659&tp_key=59ed660099
43. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Frequently asked questions about COVID-19 vaccination. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/faq.html
44. Singh BR, Gandharava S, Gandharva R. Covid-19 vaccines and community immunity. Infectious Diseases Research. 2021;2(1):5.
45. Goldfarb JL, Kreps S, Brownstein JS, et al. Beyond the first dose - Covid-19 vaccine follow-through and continued protective measures. N Engl J Med. 2021;85(2):101-103.
1. Mazereel V, Van Assche K, Detraux J, et al. COVID-19 vaccination for people with severe mental illness: why, what, and how? Lancet Psychiatry. 2021;8(5):444-450.
2. Freudenreich O, Van Alphen MU, Lim C. The ABCs of successful vaccinations: a role for psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(3):48-50.
3. World Health Organization (WHO). Ten threats to global health in 2019. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019
4. MacDonald NE. Vaccine hesitancy: definition, scope and determinants. Vaccine. 2015;33(34):4161-4164.
5. McClure CC, Cataldi JR, O’Leary ST. Vaccine hesitancy: where we are and where we are going. Clin Ther. 2017;39(8):1550-1562.
6. Betsch C, Korn L, Holtmann C. Don’t try to convert the antivaccinators, instead target the fence-sitters. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112(49):E6725-E6726.
7. Rahman T, Hartz SM, Xiong W, et al. Extreme overvalued beliefs. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2020;48(3):319-326.
8. Leask J. Target the fence-sitters. Nature. 2011;473(7348):443-445.
9. United States Census Bureau. Household Pulse Survey COVID-19 Vaccination Tracker. Updated June 30, 2021. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/household-pulse-survey-covid-19-vaccination-tracker.html
10. United States Census Bureau. Measuring household experiences during the coronavirus pandemic. Updated May 5, 2021. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.census.gov/data/experimental-data-products/household-pulse-survey.html
11. Jefsen OH, Kølbæk P, Gil Y, et al. COVID-19 vaccine willingness among patients with mental illness compared with the general population. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2021:1-24. doi:10.1017/neu.2021.15
12. Miles LW, Williams N, Luthy KE, et al. Adult vaccination rates in the mentally ill population: an outpatient improvement project. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2020;26(2):172-180.
13. Lewandowsky S, Ecker UK, Seifert CM, et al. Misinformation and its correction: continued influence and successful debiasing. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2012;13(3):106-131.
14. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Locus of mental health treatment in an integrated service system. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51(7):890-892.
15. Freudenreich O, Kontos N, Querques J. COVID-19 and patients with serious mental illness. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(9):24-35.
16. Hamel L, Kirzinger A, Muñana C, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: December 2020. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/report/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-december-2020/
17. Kai J, Crosland A. Perspectives of people with enduring mental ill health from a community-based qualitative study. Br J Gen Pract. 2001;51(470):730-736.
18. Mather G, Baker D, Laugharne R. Patient trust in psychiatrists. Psychosis. 2012;4(2):161-167.
19. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational interviewing: helping people change. Guilford Press; 2012.
20. Reno JE, O’Leary S, Garrett K, et al. Improving provider communication about HPV vaccines for vaccine-hesitant parents through the use of motivational interviewing. J Health Commun. 2018;23(4):313-320.
21. Baddeley M. Behavioural economics: a very short introduction. Volume 505. Oxford University Press; 2017.
22. Nemani K, Li C, Olfson M, et al. Association of psychiatric disorders with mortality among patients with COVID-19. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(4):380-386.
23. De Hert M, Correll CU, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. I. Prevalence, impact of medications and disparities in health care. World Psychiatry. 2011;10(1):52.
24. Lorenz RA, Norris MM, Norton LC, et al. Factors associated with influenza vaccination decisions among patients with mental illness. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2013;46(1):1-13.
25. Bitan DT. Patients with schizophrenia are under‐vaccinated for COVID‐19: a report from Israel. World Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):300.
26. Robotham D, Satkunanathan S, Doughty L, et al. Do we still have a digital divide in mental health? A five-year survey follow-up. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(11):e309.
27. De Hert M, Cohen D, Bobes J, et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. II. Barriers to care, monitoring and treatment guidelines, plus recommendations at the system and individual level. World Psychiatry. 2011;10(2):138.
28. Carrà G, Bartoli F, Carretta D, et al. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in people with severe mental illness: a mediation analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2014;49(11):1739-1746.
29. Lin MT, Burgess JF, Carey K. The association between serious psychological distress and emergency department utilization among young adults in the USA. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2012;47(6):939-947.
30. DeCoux M. Acute versus primary care: the health care decision making process for individuals with severe mental illness. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2005;26(9):935-951.
31. Hoffman L, Wisniewski H, Hays R, et al. Digital opportunities for outcomes in recovery services (DOORS): a pragmatic hands-on group approach toward increasing digital health and smartphone competencies, autonomy, relatedness, and alliance for those with serious mental illness. J Psychiatr Pract. 2020;26(2):80-88.
32. Rosenberg SD, Goldberg RW, Dixon LB, et al. Assessing the STIRR model of best practices for blood-borne infections of clients with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2010;61(9):885-891.
33. Slade EP, Rosenberg S, Dixon LB, et al. Costs of a public health model to increase receipt of hepatitis-related services for persons with mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2013;64(2):127-133.
34. Brewer NT, Chapman GB, Rothman AJ, et al. Increasing vaccination: putting psychological science into action. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2017;18(3):149-207.
35. Nabet B, Gable J, Eder J, et al. PolicyLab evidence to action brief: addressing vaccine hesitancy to protect children & communities against preventable diseases. Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. Published Spring 2017. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://policylab.chop.edu/sites/default/files/pdf/publications/Addressing_Vaccine_Hesitancy.pdf
36. Opel DJ, Heritage J, Taylor JA, et al. The architecture of provider-parent vaccine discussions at health supervision visits. Pediatrics. 2013;132(6):1037-1046.
37. Betsch C, Böhm R, Korn L, et al. On the benefits of explaining herd immunity in vaccine advocacy. Nat Hum Behav. 2017;1(3):1-6.
38. Shen F, Sheer VC, Li R. Impact of narratives on persuasion in health communication: a meta-analysis. J Advert. 2015;44(2):105-113.
39. Parkerson N, Leader A. Vaccine hesitancy in the era of COVID. Population Health Leadership Series: PopTalk webinars. Paper 26. Published February 10, 2021. https://jdc.jefferson.edu/phlspoptalk/26/
40. Dempsey AF, O’Leary ST. Human papillomavirus vaccination: narrative review of studies on how providers’ vaccine communication affects attitudes and uptake. Acad Pediatr. 2018;18(2):S23-S27.
41. Chou W, Burgdorf C, Gaysynsky A, et al. COVID-19 vaccination communication: applying behavioral and social science to address vaccine hesitancy and foster vaccine confidence. National Institutes of Health. Published 2020. https://obssr.od.nih.gov/sites/obssr/files/inline-files/OBSSR_VaccineWhitePaper_FINAL_508.pdf
42. International Society for Vaccines and the MJH Life Sciences COVID-19 coalition. Building confidence in COVID-19 vaccination: a toolbox of talks from leaders in the field. March 9, 2021. https://globalmeet.webcasts.com/starthere.jsp?ei=1435659&tp_key=59ed660099
43. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Frequently asked questions about COVID-19 vaccination. Accessed July 2, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/faq.html
44. Singh BR, Gandharava S, Gandharva R. Covid-19 vaccines and community immunity. Infectious Diseases Research. 2021;2(1):5.
45. Goldfarb JL, Kreps S, Brownstein JS, et al. Beyond the first dose - Covid-19 vaccine follow-through and continued protective measures. N Engl J Med. 2021;85(2):101-103.
Doctors’ offices may be hot spot for transmission of respiratory infections
Prior research has examined the issue of hospital-acquired infections. A 2014 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, for example, found that 4% of hospitalized patients acquired a health care–associated infection during their stay. Furthermore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that, on any given day, one in 31 hospital patients has at least one health care–associated infection. However, researchers for the new study, published in Health Affairs, said evidence about the risk of acquiring respiratory viral infections in medical office settings is limited.
“Hospital-acquired infections has been a problem for a while,” study author Hannah Neprash, PhD, of the department of health policy and management at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health, Minneapolis, said in an interview. “However, there’s never been a similar study of whether a similar phenomenon happens in physician offices. This is especially relevant now when we’re dealing with respiratory infections.”
Methods and results
For the new study, Dr. Neprash and her colleagues analyzed deidentified billing and scheduling data from 2016-2017 for 105,462,600 outpatient visits that occurred at 6,709 office-based primary care practices. They used the World Health Organization case definition for influenzalike illness “to capture cases in which the physician may suspect this illness even if a specific diagnosis code was not present.” Their control conditions included exposure to urinary tract infections and back pain.
Doctor visits were considered unexposed if they were scheduled to start at least 90 minutes before the first influenzalike illness visit of the day. They were considered exposed if they were scheduled to start at the same time or after the first influenzalike illness visit of the day at that practice.
Researchers quantified whether exposed patients were more likely to return with a similar illness in the next 2 weeks, compared with nonexposed patients seen earlier in the day
They found that 2.7 patients per 1,000 returned within 2 weeks with an influenzalike illness.
Patients were more likely to return with influenzalike illness if their visit occurred after an influenzalike illness visit versus before, the researchers said.
The authors of the paper said their new research highlights the importance of infection control in health care settings, including outpatient offices.
Where did the exposure occur?
Diego Hijano, MD, MSc, pediatric infectious disease specialist at St. Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn., said he was not surprised by the findings, but noted that it’s hard to say if the exposure to influenzalike illnesses happened in the office or in the community.
“If you start to see individuals with influenza in your office it’s because [there’s influenza] in the community,” Dr. Hijano explained. “So that means that you will have more patients coming in with influenza.”
To reduce the transmission of infections, Dr. Neprash suggested that doctors’ offices follow the CDC guidelines for indoor conduct, which include masking, washing hands, and “taking appropriate infection control measures.”
So potentially masking within offices is a way to minimize transmission between whatever people are there to be seen when it’s contagious, Dr. Neprash said.
“Telehealth really took off in 2020 and it’s unclear what the state of telehealth will be going forward. [These findings] suggest that there’s a patient safety argument for continuing to enable primary care physicians to provide visits either by phone or by video,” he added.
Dr. Hijano thinks it would be helpful for doctors to separate patients with respiratory illnesses from those without respiratory illnesses.
Driver of transmissions
Dr. Neprash suggested that another driver of these transmissions could be doctors not washing their hands, which is a “notorious issue,” and Dr. Hijano agreed with that statement.
“We did know that the hands of physicians and nurses and care providers are the main driver of infections in the health care setting,” Dr. Hijano explained. “I mean, washing your hands properly between encounters is the single best way that any given health care provider can prevent the spread of infections.”
“We have a unique opportunity with COVID-19 to change how these clinics are operating now,” Dr. Hijano said. “Many clinics are actually asking patients to call ahead of time if you have symptoms of a respiratory illness that could be contagious, and those who are not are still mandating the use of mask and physical distance in the waiting areas and limiting the amount of number of patients in any given hour. So I think that those are really big practices that would kind of make an impact in respiratory illness in terms of decreasing transmission in clinics.”
The authors, who had no conflicts of interest said their hope is that their study will help inform policy for reopening outpatient care settings. Dr. Hijano, who was not involved in the study also had no conflicts.
Prior research has examined the issue of hospital-acquired infections. A 2014 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, for example, found that 4% of hospitalized patients acquired a health care–associated infection during their stay. Furthermore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that, on any given day, one in 31 hospital patients has at least one health care–associated infection. However, researchers for the new study, published in Health Affairs, said evidence about the risk of acquiring respiratory viral infections in medical office settings is limited.
“Hospital-acquired infections has been a problem for a while,” study author Hannah Neprash, PhD, of the department of health policy and management at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health, Minneapolis, said in an interview. “However, there’s never been a similar study of whether a similar phenomenon happens in physician offices. This is especially relevant now when we’re dealing with respiratory infections.”
Methods and results
For the new study, Dr. Neprash and her colleagues analyzed deidentified billing and scheduling data from 2016-2017 for 105,462,600 outpatient visits that occurred at 6,709 office-based primary care practices. They used the World Health Organization case definition for influenzalike illness “to capture cases in which the physician may suspect this illness even if a specific diagnosis code was not present.” Their control conditions included exposure to urinary tract infections and back pain.
Doctor visits were considered unexposed if they were scheduled to start at least 90 minutes before the first influenzalike illness visit of the day. They were considered exposed if they were scheduled to start at the same time or after the first influenzalike illness visit of the day at that practice.
Researchers quantified whether exposed patients were more likely to return with a similar illness in the next 2 weeks, compared with nonexposed patients seen earlier in the day
They found that 2.7 patients per 1,000 returned within 2 weeks with an influenzalike illness.
Patients were more likely to return with influenzalike illness if their visit occurred after an influenzalike illness visit versus before, the researchers said.
The authors of the paper said their new research highlights the importance of infection control in health care settings, including outpatient offices.
Where did the exposure occur?
Diego Hijano, MD, MSc, pediatric infectious disease specialist at St. Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn., said he was not surprised by the findings, but noted that it’s hard to say if the exposure to influenzalike illnesses happened in the office or in the community.
“If you start to see individuals with influenza in your office it’s because [there’s influenza] in the community,” Dr. Hijano explained. “So that means that you will have more patients coming in with influenza.”
To reduce the transmission of infections, Dr. Neprash suggested that doctors’ offices follow the CDC guidelines for indoor conduct, which include masking, washing hands, and “taking appropriate infection control measures.”
So potentially masking within offices is a way to minimize transmission between whatever people are there to be seen when it’s contagious, Dr. Neprash said.
“Telehealth really took off in 2020 and it’s unclear what the state of telehealth will be going forward. [These findings] suggest that there’s a patient safety argument for continuing to enable primary care physicians to provide visits either by phone or by video,” he added.
Dr. Hijano thinks it would be helpful for doctors to separate patients with respiratory illnesses from those without respiratory illnesses.
Driver of transmissions
Dr. Neprash suggested that another driver of these transmissions could be doctors not washing their hands, which is a “notorious issue,” and Dr. Hijano agreed with that statement.
“We did know that the hands of physicians and nurses and care providers are the main driver of infections in the health care setting,” Dr. Hijano explained. “I mean, washing your hands properly between encounters is the single best way that any given health care provider can prevent the spread of infections.”
“We have a unique opportunity with COVID-19 to change how these clinics are operating now,” Dr. Hijano said. “Many clinics are actually asking patients to call ahead of time if you have symptoms of a respiratory illness that could be contagious, and those who are not are still mandating the use of mask and physical distance in the waiting areas and limiting the amount of number of patients in any given hour. So I think that those are really big practices that would kind of make an impact in respiratory illness in terms of decreasing transmission in clinics.”
The authors, who had no conflicts of interest said their hope is that their study will help inform policy for reopening outpatient care settings. Dr. Hijano, who was not involved in the study also had no conflicts.
Prior research has examined the issue of hospital-acquired infections. A 2014 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, for example, found that 4% of hospitalized patients acquired a health care–associated infection during their stay. Furthermore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that, on any given day, one in 31 hospital patients has at least one health care–associated infection. However, researchers for the new study, published in Health Affairs, said evidence about the risk of acquiring respiratory viral infections in medical office settings is limited.
“Hospital-acquired infections has been a problem for a while,” study author Hannah Neprash, PhD, of the department of health policy and management at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health, Minneapolis, said in an interview. “However, there’s never been a similar study of whether a similar phenomenon happens in physician offices. This is especially relevant now when we’re dealing with respiratory infections.”
Methods and results
For the new study, Dr. Neprash and her colleagues analyzed deidentified billing and scheduling data from 2016-2017 for 105,462,600 outpatient visits that occurred at 6,709 office-based primary care practices. They used the World Health Organization case definition for influenzalike illness “to capture cases in which the physician may suspect this illness even if a specific diagnosis code was not present.” Their control conditions included exposure to urinary tract infections and back pain.
Doctor visits were considered unexposed if they were scheduled to start at least 90 minutes before the first influenzalike illness visit of the day. They were considered exposed if they were scheduled to start at the same time or after the first influenzalike illness visit of the day at that practice.
Researchers quantified whether exposed patients were more likely to return with a similar illness in the next 2 weeks, compared with nonexposed patients seen earlier in the day
They found that 2.7 patients per 1,000 returned within 2 weeks with an influenzalike illness.
Patients were more likely to return with influenzalike illness if their visit occurred after an influenzalike illness visit versus before, the researchers said.
The authors of the paper said their new research highlights the importance of infection control in health care settings, including outpatient offices.
Where did the exposure occur?
Diego Hijano, MD, MSc, pediatric infectious disease specialist at St. Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn., said he was not surprised by the findings, but noted that it’s hard to say if the exposure to influenzalike illnesses happened in the office or in the community.
“If you start to see individuals with influenza in your office it’s because [there’s influenza] in the community,” Dr. Hijano explained. “So that means that you will have more patients coming in with influenza.”
To reduce the transmission of infections, Dr. Neprash suggested that doctors’ offices follow the CDC guidelines for indoor conduct, which include masking, washing hands, and “taking appropriate infection control measures.”
So potentially masking within offices is a way to minimize transmission between whatever people are there to be seen when it’s contagious, Dr. Neprash said.
“Telehealth really took off in 2020 and it’s unclear what the state of telehealth will be going forward. [These findings] suggest that there’s a patient safety argument for continuing to enable primary care physicians to provide visits either by phone or by video,” he added.
Dr. Hijano thinks it would be helpful for doctors to separate patients with respiratory illnesses from those without respiratory illnesses.
Driver of transmissions
Dr. Neprash suggested that another driver of these transmissions could be doctors not washing their hands, which is a “notorious issue,” and Dr. Hijano agreed with that statement.
“We did know that the hands of physicians and nurses and care providers are the main driver of infections in the health care setting,” Dr. Hijano explained. “I mean, washing your hands properly between encounters is the single best way that any given health care provider can prevent the spread of infections.”
“We have a unique opportunity with COVID-19 to change how these clinics are operating now,” Dr. Hijano said. “Many clinics are actually asking patients to call ahead of time if you have symptoms of a respiratory illness that could be contagious, and those who are not are still mandating the use of mask and physical distance in the waiting areas and limiting the amount of number of patients in any given hour. So I think that those are really big practices that would kind of make an impact in respiratory illness in terms of decreasing transmission in clinics.”
The authors, who had no conflicts of interest said their hope is that their study will help inform policy for reopening outpatient care settings. Dr. Hijano, who was not involved in the study also had no conflicts.
FROM HEALTH AFFAIRS
Mental illness admissions: 18-44 is the age of prevalence
More mental and/or substance use disorders are ranked among the top-five diagnoses for hospitalized men and women aged 18-44 years than for any other age group, according to a recent report from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
aged 18-44, while depressive disorders were the third-most common (195.0 stays per 100,000) and alcohol-related disorders were fifth at 153.2 per 100,000, Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Prevalence was somewhat lower in women aged 18-44 years, with two mental illnesses appearing among the top five nonmaternal diagnoses: Depressive disorders were second at 222.5 stays per 100,000 and bipolar and related disorders were fourth at 142.0 per 100,000. The leading primary diagnosis in women in 2018 was septicemia, which was the most common cause overall in the age group at a rate of 279.3 per 100,000, the investigators reported.
There were no mental and/or substance use disorders in the top five primary diagnoses for any of the other adult age groups – 45-64, 65-74, and ≥75 – included in the report. Septicemia was the leading diagnosis for men in all three groups and for women in two of three (45-64 and ≥75), with osteoarthritis first among women aged 65-74 years, they said.
There was one mental illness among the top-five diagnoses for children under age 18 years, as depressive disorders were the most common reason for stays in girls (176.6 per 100,000 population) and the fifth most common for boys (74.0 per 100,000), said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of AHRQ.
Septicemia was the leading nonmaternal, nonneonatal diagnosis for all inpatient stays and all ages in 2018 with a rate of 679.5 per 100,000, followed by heart failure (347.9), osteoarthritis (345.5), pneumonia not related to tuberculosis (226.8), and diabetes mellitus (207.8), based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
Depressive disorders were most common mental health diagnosis in those admitted to hospitals and the 12th most common diagnosis overall; schizophrenia, in 16th place overall, was the only other mental illness among the top 20, the investigators said.
“This information can help establish national health priorities, initiatives, and action plans,” Dr. McDermott and Mr. Roemer wrote, and “at the hospital level, administrators can use diagnosis-related information to inform planning and resource allocation, such as optimizing subspecialty services or units for the care of high-priority conditions.”
More mental and/or substance use disorders are ranked among the top-five diagnoses for hospitalized men and women aged 18-44 years than for any other age group, according to a recent report from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

aged 18-44, while depressive disorders were the third-most common (195.0 stays per 100,000) and alcohol-related disorders were fifth at 153.2 per 100,000, Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Prevalence was somewhat lower in women aged 18-44 years, with two mental illnesses appearing among the top five nonmaternal diagnoses: Depressive disorders were second at 222.5 stays per 100,000 and bipolar and related disorders were fourth at 142.0 per 100,000. The leading primary diagnosis in women in 2018 was septicemia, which was the most common cause overall in the age group at a rate of 279.3 per 100,000, the investigators reported.
There were no mental and/or substance use disorders in the top five primary diagnoses for any of the other adult age groups – 45-64, 65-74, and ≥75 – included in the report. Septicemia was the leading diagnosis for men in all three groups and for women in two of three (45-64 and ≥75), with osteoarthritis first among women aged 65-74 years, they said.
There was one mental illness among the top-five diagnoses for children under age 18 years, as depressive disorders were the most common reason for stays in girls (176.6 per 100,000 population) and the fifth most common for boys (74.0 per 100,000), said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of AHRQ.
Septicemia was the leading nonmaternal, nonneonatal diagnosis for all inpatient stays and all ages in 2018 with a rate of 679.5 per 100,000, followed by heart failure (347.9), osteoarthritis (345.5), pneumonia not related to tuberculosis (226.8), and diabetes mellitus (207.8), based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
Depressive disorders were most common mental health diagnosis in those admitted to hospitals and the 12th most common diagnosis overall; schizophrenia, in 16th place overall, was the only other mental illness among the top 20, the investigators said.
“This information can help establish national health priorities, initiatives, and action plans,” Dr. McDermott and Mr. Roemer wrote, and “at the hospital level, administrators can use diagnosis-related information to inform planning and resource allocation, such as optimizing subspecialty services or units for the care of high-priority conditions.”
More mental and/or substance use disorders are ranked among the top-five diagnoses for hospitalized men and women aged 18-44 years than for any other age group, according to a recent report from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

aged 18-44, while depressive disorders were the third-most common (195.0 stays per 100,000) and alcohol-related disorders were fifth at 153.2 per 100,000, Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Prevalence was somewhat lower in women aged 18-44 years, with two mental illnesses appearing among the top five nonmaternal diagnoses: Depressive disorders were second at 222.5 stays per 100,000 and bipolar and related disorders were fourth at 142.0 per 100,000. The leading primary diagnosis in women in 2018 was septicemia, which was the most common cause overall in the age group at a rate of 279.3 per 100,000, the investigators reported.
There were no mental and/or substance use disorders in the top five primary diagnoses for any of the other adult age groups – 45-64, 65-74, and ≥75 – included in the report. Septicemia was the leading diagnosis for men in all three groups and for women in two of three (45-64 and ≥75), with osteoarthritis first among women aged 65-74 years, they said.
There was one mental illness among the top-five diagnoses for children under age 18 years, as depressive disorders were the most common reason for stays in girls (176.6 per 100,000 population) and the fifth most common for boys (74.0 per 100,000), said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of AHRQ.
Septicemia was the leading nonmaternal, nonneonatal diagnosis for all inpatient stays and all ages in 2018 with a rate of 679.5 per 100,000, followed by heart failure (347.9), osteoarthritis (345.5), pneumonia not related to tuberculosis (226.8), and diabetes mellitus (207.8), based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
Depressive disorders were most common mental health diagnosis in those admitted to hospitals and the 12th most common diagnosis overall; schizophrenia, in 16th place overall, was the only other mental illness among the top 20, the investigators said.
“This information can help establish national health priorities, initiatives, and action plans,” Dr. McDermott and Mr. Roemer wrote, and “at the hospital level, administrators can use diagnosis-related information to inform planning and resource allocation, such as optimizing subspecialty services or units for the care of high-priority conditions.”
IBD: COVID-19 vaccination still effective in immunosuppressed
In a real-world setting, full vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 was more than 80% effective at reducing infection in people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who were taking immunosuppressive medications.
The study, which examined postvaccine infection rates in a Veterans Affairs cohort, further validates the benefit of COVID-19 vaccines, particularly in a subgroup most at risk for having compromised immune systems. Furthermore, the findings “may serve to increase patient and provider willingness to pursue vaccination in these settings,” wrote study authors Nabeel Khan, MD, of the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center and Nadim Mahmud, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, both in Philadelphia. The report was published in Gastroenterology. In addition, the researchers said the findings “should provide positive reinforcement to IBD patients taking immunosuppressive agents who may otherwise be reluctant to receive vaccination.”
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, concerns have been raised regarding the possible heightened risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with IBD and other diseases associated with immune system dysregulation. Despite these fears, patients with IBD appear to have comparable rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection to that of the general population.
Pfizer’s BNT162b2 and Moderna’s RNA-1273 vaccines are the most widely used COVID-19 vaccines in the United States. These vaccines have demonstrated over 90% efficacy for preventing infection and severe disease in late-stage trials; however, few trials have examined their pooled effectiveness in immunocompromised patients and those taking immunosuppressive therapies.
To address this gap, researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study that included 14,697 patients (median age, 68 years) from the Veterans Health Administration database who had been diagnosed with IBD before the start date of the administration’s vaccination program. A total of 7,321 patients in the cohort had received at least 1 dose of either the Pfizer (45.2%) or Moderna (54.8%) vaccines.
Approximately 61.8% of patients had ulcerative colitis, while the remaining patients had Crohn’s disease. In terms of medications, vaccinated versus unvaccinated patients in the study were exposed to mesalamine alone (54.9% vs. 54.6%), thiopurines (10.8% vs. 10.5%), anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) biologic monotherapy (18.8% vs. 20.9%), vedolizumab (7.2% vs. 6.0%), ustekinumab (1.0% vs. 1.1%), tofacitinib (0.7% vs. 0.8%), methotrexate (2.3% vs. 2.0%%), and/or corticosteroids (6.8% vs. 5.6%).
A total of 3,561 patients who received the Moderna vaccine and 3,017 patients who received the Pfizer vaccine received both doses. The median time between each dose was 21 days for Pfizer and 28 days for Moderna.
Patients who were unvaccinated had significantly fewer comorbidities (P < .001). The majority of patients in the overall cohort were men (92.2%), a group identified as having a much greater risk of worse COVID-19–related outcomes.
Unvaccinated patients in the study had a higher rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared with the fully vaccinated group (1.34% vs. 0.11%, respectively) in follow-up data reported through April 20, 2021. Over a median follow-up duration of 20 days, researchers found 14 infections with SARS-CoV-2 (0.28%) in partially vaccinated individuals. Seven infections (0.11%) were reported in fully vaccinated individuals over a median 38-day follow-up period.
Compared with unvaccinated patients, full vaccination status was associated with a 69% reduction in the hazard ratio of infection (HR, 0.31; 95% confidence interval, 0.17-0.56; P < .001). Corresponding vaccine efficacy rates were 25.1% for partial vaccination and 80.4% for full vaccination.
There were no significant interactions between vaccination status and exposure to steroids (P =.64), mesalamine versus immunosuppressive agents (P =.46), or anti-TNFs with immunomodulators or steroids versus other therapies (P =.34). In addition, no difference was found in the association between vaccination status and infection for patients who received the Moderna versus the Pfizer vaccines (P =.09).
Unvaccinated individuals had the highest raw proportions of severe infection with the novel coronavirus (0.32%) and all-cause mortality (0.66%), compared with people who were partially vaccinated or fully vaccinated. In adjusted Cox regression analyses, there was no significant association between vaccination status and severe SARS-CoV-2 infection (fully vaccinated vs. unvaccinated, P = .18) or all-cause mortality (fully vaccinated vs. unvaccinated, P =.11). The researchers wrote that, “future studies with larger sample size and/or longer follow-up are needed to evaluate this further.”
An important limitation of this study was the inclusion of mostly older men who were also predominantly White (80.4%). Ultimately, this population may limit the generalizability of the findings for women and patients of other races/ethnicities.
While the study received no financial support, Dr. Khan has received research grants from several pharmaceutical companies, but Dr. Mahmud disclosed no conflicts.
In a real-world setting, full vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 was more than 80% effective at reducing infection in people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who were taking immunosuppressive medications.
The study, which examined postvaccine infection rates in a Veterans Affairs cohort, further validates the benefit of COVID-19 vaccines, particularly in a subgroup most at risk for having compromised immune systems. Furthermore, the findings “may serve to increase patient and provider willingness to pursue vaccination in these settings,” wrote study authors Nabeel Khan, MD, of the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center and Nadim Mahmud, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, both in Philadelphia. The report was published in Gastroenterology. In addition, the researchers said the findings “should provide positive reinforcement to IBD patients taking immunosuppressive agents who may otherwise be reluctant to receive vaccination.”
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, concerns have been raised regarding the possible heightened risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with IBD and other diseases associated with immune system dysregulation. Despite these fears, patients with IBD appear to have comparable rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection to that of the general population.
Pfizer’s BNT162b2 and Moderna’s RNA-1273 vaccines are the most widely used COVID-19 vaccines in the United States. These vaccines have demonstrated over 90% efficacy for preventing infection and severe disease in late-stage trials; however, few trials have examined their pooled effectiveness in immunocompromised patients and those taking immunosuppressive therapies.
To address this gap, researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study that included 14,697 patients (median age, 68 years) from the Veterans Health Administration database who had been diagnosed with IBD before the start date of the administration’s vaccination program. A total of 7,321 patients in the cohort had received at least 1 dose of either the Pfizer (45.2%) or Moderna (54.8%) vaccines.
Approximately 61.8% of patients had ulcerative colitis, while the remaining patients had Crohn’s disease. In terms of medications, vaccinated versus unvaccinated patients in the study were exposed to mesalamine alone (54.9% vs. 54.6%), thiopurines (10.8% vs. 10.5%), anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) biologic monotherapy (18.8% vs. 20.9%), vedolizumab (7.2% vs. 6.0%), ustekinumab (1.0% vs. 1.1%), tofacitinib (0.7% vs. 0.8%), methotrexate (2.3% vs. 2.0%%), and/or corticosteroids (6.8% vs. 5.6%).
A total of 3,561 patients who received the Moderna vaccine and 3,017 patients who received the Pfizer vaccine received both doses. The median time between each dose was 21 days for Pfizer and 28 days for Moderna.
Patients who were unvaccinated had significantly fewer comorbidities (P < .001). The majority of patients in the overall cohort were men (92.2%), a group identified as having a much greater risk of worse COVID-19–related outcomes.
Unvaccinated patients in the study had a higher rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared with the fully vaccinated group (1.34% vs. 0.11%, respectively) in follow-up data reported through April 20, 2021. Over a median follow-up duration of 20 days, researchers found 14 infections with SARS-CoV-2 (0.28%) in partially vaccinated individuals. Seven infections (0.11%) were reported in fully vaccinated individuals over a median 38-day follow-up period.
Compared with unvaccinated patients, full vaccination status was associated with a 69% reduction in the hazard ratio of infection (HR, 0.31; 95% confidence interval, 0.17-0.56; P < .001). Corresponding vaccine efficacy rates were 25.1% for partial vaccination and 80.4% for full vaccination.
There were no significant interactions between vaccination status and exposure to steroids (P =.64), mesalamine versus immunosuppressive agents (P =.46), or anti-TNFs with immunomodulators or steroids versus other therapies (P =.34). In addition, no difference was found in the association between vaccination status and infection for patients who received the Moderna versus the Pfizer vaccines (P =.09).
Unvaccinated individuals had the highest raw proportions of severe infection with the novel coronavirus (0.32%) and all-cause mortality (0.66%), compared with people who were partially vaccinated or fully vaccinated. In adjusted Cox regression analyses, there was no significant association between vaccination status and severe SARS-CoV-2 infection (fully vaccinated vs. unvaccinated, P = .18) or all-cause mortality (fully vaccinated vs. unvaccinated, P =.11). The researchers wrote that, “future studies with larger sample size and/or longer follow-up are needed to evaluate this further.”
An important limitation of this study was the inclusion of mostly older men who were also predominantly White (80.4%). Ultimately, this population may limit the generalizability of the findings for women and patients of other races/ethnicities.
While the study received no financial support, Dr. Khan has received research grants from several pharmaceutical companies, but Dr. Mahmud disclosed no conflicts.
In a real-world setting, full vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 was more than 80% effective at reducing infection in people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who were taking immunosuppressive medications.
The study, which examined postvaccine infection rates in a Veterans Affairs cohort, further validates the benefit of COVID-19 vaccines, particularly in a subgroup most at risk for having compromised immune systems. Furthermore, the findings “may serve to increase patient and provider willingness to pursue vaccination in these settings,” wrote study authors Nabeel Khan, MD, of the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center and Nadim Mahmud, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, both in Philadelphia. The report was published in Gastroenterology. In addition, the researchers said the findings “should provide positive reinforcement to IBD patients taking immunosuppressive agents who may otherwise be reluctant to receive vaccination.”
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, concerns have been raised regarding the possible heightened risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with IBD and other diseases associated with immune system dysregulation. Despite these fears, patients with IBD appear to have comparable rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection to that of the general population.
Pfizer’s BNT162b2 and Moderna’s RNA-1273 vaccines are the most widely used COVID-19 vaccines in the United States. These vaccines have demonstrated over 90% efficacy for preventing infection and severe disease in late-stage trials; however, few trials have examined their pooled effectiveness in immunocompromised patients and those taking immunosuppressive therapies.
To address this gap, researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study that included 14,697 patients (median age, 68 years) from the Veterans Health Administration database who had been diagnosed with IBD before the start date of the administration’s vaccination program. A total of 7,321 patients in the cohort had received at least 1 dose of either the Pfizer (45.2%) or Moderna (54.8%) vaccines.
Approximately 61.8% of patients had ulcerative colitis, while the remaining patients had Crohn’s disease. In terms of medications, vaccinated versus unvaccinated patients in the study were exposed to mesalamine alone (54.9% vs. 54.6%), thiopurines (10.8% vs. 10.5%), anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) biologic monotherapy (18.8% vs. 20.9%), vedolizumab (7.2% vs. 6.0%), ustekinumab (1.0% vs. 1.1%), tofacitinib (0.7% vs. 0.8%), methotrexate (2.3% vs. 2.0%%), and/or corticosteroids (6.8% vs. 5.6%).
A total of 3,561 patients who received the Moderna vaccine and 3,017 patients who received the Pfizer vaccine received both doses. The median time between each dose was 21 days for Pfizer and 28 days for Moderna.
Patients who were unvaccinated had significantly fewer comorbidities (P < .001). The majority of patients in the overall cohort were men (92.2%), a group identified as having a much greater risk of worse COVID-19–related outcomes.
Unvaccinated patients in the study had a higher rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared with the fully vaccinated group (1.34% vs. 0.11%, respectively) in follow-up data reported through April 20, 2021. Over a median follow-up duration of 20 days, researchers found 14 infections with SARS-CoV-2 (0.28%) in partially vaccinated individuals. Seven infections (0.11%) were reported in fully vaccinated individuals over a median 38-day follow-up period.
Compared with unvaccinated patients, full vaccination status was associated with a 69% reduction in the hazard ratio of infection (HR, 0.31; 95% confidence interval, 0.17-0.56; P < .001). Corresponding vaccine efficacy rates were 25.1% for partial vaccination and 80.4% for full vaccination.
There were no significant interactions between vaccination status and exposure to steroids (P =.64), mesalamine versus immunosuppressive agents (P =.46), or anti-TNFs with immunomodulators or steroids versus other therapies (P =.34). In addition, no difference was found in the association between vaccination status and infection for patients who received the Moderna versus the Pfizer vaccines (P =.09).
Unvaccinated individuals had the highest raw proportions of severe infection with the novel coronavirus (0.32%) and all-cause mortality (0.66%), compared with people who were partially vaccinated or fully vaccinated. In adjusted Cox regression analyses, there was no significant association between vaccination status and severe SARS-CoV-2 infection (fully vaccinated vs. unvaccinated, P = .18) or all-cause mortality (fully vaccinated vs. unvaccinated, P =.11). The researchers wrote that, “future studies with larger sample size and/or longer follow-up are needed to evaluate this further.”
An important limitation of this study was the inclusion of mostly older men who were also predominantly White (80.4%). Ultimately, this population may limit the generalizability of the findings for women and patients of other races/ethnicities.
While the study received no financial support, Dr. Khan has received research grants from several pharmaceutical companies, but Dr. Mahmud disclosed no conflicts.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Hospital disaster preparation confronts COVID
Hospitalist groups should have disaster response plans
Jason Persoff, MD, SFHM, now a hospitalist at University of Colorado Hospital in Aurora and an amateur storm chaser, got a close look at how natural disasters can impact hospital care when a tornado destroyed St. John’s Regional Medical Center in Joplin, Mo., on May 22, 2011.
He and a colleague who had been following the storm responded to injuries on the highway before reporting for a long day’s service at the other hospital in Joplin, Freeman Hospital West, caring for patients transferred from St. John’s on an impromptu unit without access to their medical records.
“During my medical training, I had done emergency medicine as an EMT, so I was interested in how the system responds to emergencies,” he explained. “At Joplin I learned how it feels when the boots on the ground in a crisis are not connected to an incident command structure.” Another thing he learned was the essential role for hospitalists in a hospital’s response to a crisis – and thus the need to involve them well in advance in the hospital’s planning for future emergencies.
“Disaster preparation – when done right – helps you ‘herd cats’ in a crisis situation,” he said. “The tornado and its wake served as defining moments for me. I used them as the impetus to improve health care’s response to disasters.” Part of that commitment was to help hospitalists understand their part in emergency preparation.1
Dr. Persoff is now the assistant medical director of emergency preparedness at University of Colorado Hospital. He also helped to create a position called physician support supervisor, which is filled by physicians who have held leadership positions in a hospital to help coordinate the disparate needs of all clinicians in a crisis and facilitate rapid response.2
But then along came the COVID pandemic – which in many locales around the world was unprecedented in scope. Dr. Persoff said his hospital was fairly well prepared, after a decade of engagement with emergency planning. It drew on experience with H1N1, also known as swine flu, and the Ebola virus, which killed 11,323 people, primarily in West Africa, from 2013 to 2016, as models. In a matter of days, the CU division of hospital medicine was able to modify and deploy its existing disaster plans to quickly respond to an influx of COVID patients.3
“Basically, what we set out to do was to treat COVID patients as if they were Ebola patients, cordoning them off in a small area of the hospital. That was naive of us,” he said. “We weren’t able to grasp the scale at the outset. It does defy the imagination – how the hospital could fill up with just one type of patient.”
What is disaster planning?
Emergency preparation for hospitals emerged as a recognized medical specialization in the 1970s. Initially it was largely considered the realm of emergency physicians, trauma services, or critical care doctors. Resources such as the World Health Organization, the Federal Emergency Management Agency, and similar groups recommend an all-hazards approach, a broad and flexible strategy for managing emergencies that could include natural disasters – earthquakes, storms, tornadoes, or wildfires – or human-caused events, such as mass shootings or terrorist attacks. The Joint Commission requires accredited hospitals to conduct several disaster drills annually.
The U.S. Hospital Preparedness Program was created in 2002 to enhance the ability of hospitals and health systems to prepare for and respond to bioterrorism attacks on civilians and other public health emergencies, including natural disasters and pandemics. It offers a foundation for national preparedness and a primary source of federal funding for health care system preparedness. The hospital, at the heart of the health care system, is expected to receive the injured and infected, because patients know they can obtain care there.
One of the fundamental tools for crisis response is the incident command system (ICS), which spells out how to quickly establish a command structure and assign responsibility for key tasks as well as overall leadership. The National Incident Management System organizes emergency management across all government levels and the private sector to ensure that the most pressing needs are met and precious resources are used without duplication. ICS is a standardized approach to command, control, and coordination of emergency response using a common hierarchy recognized across organizations, with advance training in how it should be deployed.
A crisis like never before
Nearly every hospital or health system goes through drills for an emergency, said Hassan Khouli, MD, chair of the department of critical care medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, and coauthor of an article in the journal Chest last year outlining 10 principles of emergency preparedness derived from its experience with the COVID pandemic.4 Some of these include: don’t wait; engage a variety of stakeholders; identify sources of truth; and prioritize hospital employees’ safety and well-being.
Part of the preparation is doing table-top exercises, with case scenarios or actual situations presented, working with clinicians on brainstorming and identifying opportunities for improvement, Dr. Khouli said. “These drills are so important, regardless of what the disaster turns out to be. We’ve done that over the years. We are a large health system, very process and detail oriented. Our emergency incident command structure was activated before we saw our first COVID patient,” he said.
“This was a crisis like never before, with huge amounts of uncertainty,” he noted. “But I believe the Cleveland Clinic system did very well, measured by outcomes such as surveys of health care teams across the system, which gave us reassuring results, and clinical outcomes with lower ICU and hospital mortality rates.”
Christopher Whinney, MD, SFHM, department chair of hospital medicine at Cleveland Clinic, said hospitalists worked hand in hand with the health system’s incident command structure and took responsibility for managing non-ICU COVID patients at six hospitals in the system.
“Hospitalists had a place at the table, and we collaborated well with incident command, enterprise redeployment committees, and emergency and critical care colleagues,” he noted. Hospitalists were on the leadership team for a number of planning meetings, and key stakeholders for bringing information back to their groups.
“First thing we did was to look at our workforce. The challenge was how to respond to up to a hundred COVID admissions per day – how to mobilize providers and build surge teams that incorporated primary care providers and medical trainees. We onboarded 200 providers to do hospital care within 60 days,” he said.
“We realized that communication with patients and families was a big part of the challenge, so we assigned people with good communication skills to fill this role. While we were fortunate not to get the terrible surges they had in other places, we felt we were prepared for the worst.”
Challenges of surge capacity
Every disaster is different, said Srikant Polepalli, MD, associate hospitalist medical director for Staten Island University Hospital in New York, part of the Northwell Health system. He brought the experience of being part of the response to Superstorm Sandy in October 2012 to the COVID pandemic.
“Specifically for hospitalists, the biggest challenge is working on surge capacity for a sudden influx of patients,” he said. “But with Northwell as our umbrella, we can triage and load-balance to move patients from hospital to hospital as needed. With the pandemic, we started with one COVID unit and then expanded to fill the entire hospital.”
Dr. Polepalli was appointed medical director for a temporary field hospital installed at South Beach Psychiatric Center, also in Staten Island. “We were able to acquire help and bring in people ranging from hospitalists to ER physicians, travel nurses, operation managers and the National Guard. Our command center did a phenomenal job of allocating and obtaining resources. It helped to have a structure that was already established and to rely on the resources of the health system,” Dr. Polepalli said. Not every hospital has a structure like Northwell’s.
“We’re not out of the pandemic yet, but we’ll continue with disaster drills and planning,” he said. “We must continue to adapt and have converted our temporary facilities to COVID testing centers, antibody infusion centers, and vaccination centers.”
For Alfred Burger, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist at Mount Sinai’s Beth Israel campus in New York, hospital medicine, now in its maturing phase, is still feeling its way through hospital and health care system transformation.
“My group is an academic, multicampus hospitalist group employed by the hospital system. When I meet other hospitalists at SHM conferences, whether they come from privately owned, corporately owned, or contracted models, they vary widely in terms of how involved the hospitalists are in crisis planning and their ability to respond to crises. At large academic medical centers like ours, one or more doctors is tasked with being involved in preparing for the next disaster,” he said.
“I think we responded the best we could, although it was difficult as we lost many patients to COVID. We were trying to save lives using the tools we knew from treating pneumonias and other forms of acute inflammatory lung injuries. We used every bit of our training in situations where no one had the right answers. But disasters teach us how to be flexible and pivot on the fly, and what to do when things don’t go our way.”
What is disaster response?
Medical response to a disaster essentially boils down to three main things: stuff, staff, and space, Dr. Persoff said. Those are the cornerstones of an emergency plan.
“There is not a hazard that exists that you can’t take an all-hazards approach to dealing with fundamental realities on the ground. No plan can be comprehensive enough to deal with all the intricacies of an emergency. But many plans can have the bones of a response that will allow you to face adverse circumstances,” he said.
“We actually became quite efficient early on in the pandemic, able to adapt in the moment. We were able to build an effective bridge between workers on the ground and our incident command structure, which seemed to reduce a lot of stress and create situational awareness. We implemented ICS as soon as we heard that China was building a COVID hospital, back in February of 2020.”
When one thinks about mass trauma, such as a 747 crash, Dr. Persoff said, the need is to treat burn victims and trauma victims in large numbers. At that point, the ED downstairs is filled with medical patients. Hospital medicine can rapidly admit those patients to clear out room in the ED. Surgeons are also dedicated to rapidly treating those patients, but what about patients who are on the floor following their surgeries? Hospitalists can offer consultations or primary management so the surgeons can stay in the OR, and the same in the ICU, while safely discharging hospitalized patients in a timely manner to make room for incoming patients.
“The lessons of COVID have been hard-taught and hard-earned. No good plan survives contact with the enemy,” he said. “But I think we’ll be better prepared for the next pandemic.”
Maria Frank, MD, FACP, SFHM, a hospitalist at Denver Health who chairs SHM’s Disaster Management Special Interest Group, says she got the bug for disaster preparation during postresidency training as an internist in emergency medicine. “I’m also the medical director for our biocontainment unit, created for infections like Ebola.” SHM’s SIG, which has 150 members, is now writing a review article on disaster planning for the field.
“I got a call on Dec. 27, 2019, about this new pneumonia, and they said, ‘We don’t know what it is, but it’s a coronavirus,’” she recalled. “When I got off the phone, I said, ‘Let’s make sure our response plan works and we have enough of everything on hand.’” Dr. Frank said she was expecting something more like SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome). “When they called the public health emergency of international concern for COVID, I was at a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention meeting in Atlanta. It really wasn’t a surprise for us.”
All hospitals plan for disasters, although they use different names and have different levels of commitment, Dr. Frank said. What’s not consistent is the participation of hospitalists. “Even when a disaster is 100% trauma related, consider a hospital like mine that has at least four times as many hospitalists as surgeons at any given time. The hospitalists need to take overall management for the patients who aren’t actually in the operating room.”
Time to debrief
Dr. Frank recommends debriefing on the hospital’s and the hospitalist group’s experience with COVID. “Look at the biggest challenges your group faced. Was it staffing, or time off, or the need for day care? Was it burnout, lack of knowledge, lack of [personal protective equipment]?” Each hospital could use its own COVID experience to work on identifying the challenges and the problems, she said. “I’d encourage each department and division to do this exercise individually. Then come together to find common ground with other departments in the hospital.”
This debriefing exercise isn’t just for doctors – it’s also for nurses, environmental services, security, and many other departments, she said. “COVID showed us how crisis response is a group effort. What will bring us together is to learn the challenges each of us faced. It was amazing to see hospitalists doing what they do best.” Post pandemic, hospitalists should also consider getting involved in research and publications, in order to share their lessons.
“One of the things we learned is that hospitalists are very versatile,” Dr. Frank added. But it’s also good for the group to have members specialize, for example, in biocontainment. “We are experts in discharging patients, in patient flow and operations, in coordinating complex medical care. So we would naturally take the lead in, for example, opening a geographic unit or collaborating with other specialists to create innovative models. That’s our job. It’s essential that we’re involved well in advance.”
COVID may be a once-in-a-lifetime experience, but there will be other disasters to come, she said. “If your hospital doesn’t have a disaster plan for hospitalists, get involved in establishing one. Each hospitalist group should have its own response plan. Talk to your peers at other hospitals, and get involved at the institutional level. I’m happy to share our plan; just contact me.” Readers can contact Dr. Frank at [email protected].
References
1. Persoff J et al. The role of hospital medicine in emergency preparedness: A framework for hospitalist leadership in disaster preparedness, response and recovery. J Hosp Med. 2018 Oct;13(10):713-7. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3073.
2. Persoff J et al. Expanding the hospital incident command system with a physician-centric role during a pandemic: The role of the physician clinical support supervisor. J Hosp Adm. 2020;9(3):7-10. doi: 10.5430/jha.v9n3p7.
3. Bowden K et al. Harnessing the power of hospitalists in operational disaster planning: COVID-19. J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Sep;35(9):273-7. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-05952-6.
4. Orsini E et al. Lessons on outbreak preparedness from the Cleveland Clinic. Chest. 2020;158(5):2090-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.009.
Hospitalist groups should have disaster response plans
Hospitalist groups should have disaster response plans
Jason Persoff, MD, SFHM, now a hospitalist at University of Colorado Hospital in Aurora and an amateur storm chaser, got a close look at how natural disasters can impact hospital care when a tornado destroyed St. John’s Regional Medical Center in Joplin, Mo., on May 22, 2011.
He and a colleague who had been following the storm responded to injuries on the highway before reporting for a long day’s service at the other hospital in Joplin, Freeman Hospital West, caring for patients transferred from St. John’s on an impromptu unit without access to their medical records.
“During my medical training, I had done emergency medicine as an EMT, so I was interested in how the system responds to emergencies,” he explained. “At Joplin I learned how it feels when the boots on the ground in a crisis are not connected to an incident command structure.” Another thing he learned was the essential role for hospitalists in a hospital’s response to a crisis – and thus the need to involve them well in advance in the hospital’s planning for future emergencies.
“Disaster preparation – when done right – helps you ‘herd cats’ in a crisis situation,” he said. “The tornado and its wake served as defining moments for me. I used them as the impetus to improve health care’s response to disasters.” Part of that commitment was to help hospitalists understand their part in emergency preparation.1
Dr. Persoff is now the assistant medical director of emergency preparedness at University of Colorado Hospital. He also helped to create a position called physician support supervisor, which is filled by physicians who have held leadership positions in a hospital to help coordinate the disparate needs of all clinicians in a crisis and facilitate rapid response.2
But then along came the COVID pandemic – which in many locales around the world was unprecedented in scope. Dr. Persoff said his hospital was fairly well prepared, after a decade of engagement with emergency planning. It drew on experience with H1N1, also known as swine flu, and the Ebola virus, which killed 11,323 people, primarily in West Africa, from 2013 to 2016, as models. In a matter of days, the CU division of hospital medicine was able to modify and deploy its existing disaster plans to quickly respond to an influx of COVID patients.3
“Basically, what we set out to do was to treat COVID patients as if they were Ebola patients, cordoning them off in a small area of the hospital. That was naive of us,” he said. “We weren’t able to grasp the scale at the outset. It does defy the imagination – how the hospital could fill up with just one type of patient.”
What is disaster planning?
Emergency preparation for hospitals emerged as a recognized medical specialization in the 1970s. Initially it was largely considered the realm of emergency physicians, trauma services, or critical care doctors. Resources such as the World Health Organization, the Federal Emergency Management Agency, and similar groups recommend an all-hazards approach, a broad and flexible strategy for managing emergencies that could include natural disasters – earthquakes, storms, tornadoes, or wildfires – or human-caused events, such as mass shootings or terrorist attacks. The Joint Commission requires accredited hospitals to conduct several disaster drills annually.
The U.S. Hospital Preparedness Program was created in 2002 to enhance the ability of hospitals and health systems to prepare for and respond to bioterrorism attacks on civilians and other public health emergencies, including natural disasters and pandemics. It offers a foundation for national preparedness and a primary source of federal funding for health care system preparedness. The hospital, at the heart of the health care system, is expected to receive the injured and infected, because patients know they can obtain care there.
One of the fundamental tools for crisis response is the incident command system (ICS), which spells out how to quickly establish a command structure and assign responsibility for key tasks as well as overall leadership. The National Incident Management System organizes emergency management across all government levels and the private sector to ensure that the most pressing needs are met and precious resources are used without duplication. ICS is a standardized approach to command, control, and coordination of emergency response using a common hierarchy recognized across organizations, with advance training in how it should be deployed.
A crisis like never before
Nearly every hospital or health system goes through drills for an emergency, said Hassan Khouli, MD, chair of the department of critical care medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, and coauthor of an article in the journal Chest last year outlining 10 principles of emergency preparedness derived from its experience with the COVID pandemic.4 Some of these include: don’t wait; engage a variety of stakeholders; identify sources of truth; and prioritize hospital employees’ safety and well-being.
Part of the preparation is doing table-top exercises, with case scenarios or actual situations presented, working with clinicians on brainstorming and identifying opportunities for improvement, Dr. Khouli said. “These drills are so important, regardless of what the disaster turns out to be. We’ve done that over the years. We are a large health system, very process and detail oriented. Our emergency incident command structure was activated before we saw our first COVID patient,” he said.
“This was a crisis like never before, with huge amounts of uncertainty,” he noted. “But I believe the Cleveland Clinic system did very well, measured by outcomes such as surveys of health care teams across the system, which gave us reassuring results, and clinical outcomes with lower ICU and hospital mortality rates.”
Christopher Whinney, MD, SFHM, department chair of hospital medicine at Cleveland Clinic, said hospitalists worked hand in hand with the health system’s incident command structure and took responsibility for managing non-ICU COVID patients at six hospitals in the system.
“Hospitalists had a place at the table, and we collaborated well with incident command, enterprise redeployment committees, and emergency and critical care colleagues,” he noted. Hospitalists were on the leadership team for a number of planning meetings, and key stakeholders for bringing information back to their groups.
“First thing we did was to look at our workforce. The challenge was how to respond to up to a hundred COVID admissions per day – how to mobilize providers and build surge teams that incorporated primary care providers and medical trainees. We onboarded 200 providers to do hospital care within 60 days,” he said.
“We realized that communication with patients and families was a big part of the challenge, so we assigned people with good communication skills to fill this role. While we were fortunate not to get the terrible surges they had in other places, we felt we were prepared for the worst.”
Challenges of surge capacity
Every disaster is different, said Srikant Polepalli, MD, associate hospitalist medical director for Staten Island University Hospital in New York, part of the Northwell Health system. He brought the experience of being part of the response to Superstorm Sandy in October 2012 to the COVID pandemic.
“Specifically for hospitalists, the biggest challenge is working on surge capacity for a sudden influx of patients,” he said. “But with Northwell as our umbrella, we can triage and load-balance to move patients from hospital to hospital as needed. With the pandemic, we started with one COVID unit and then expanded to fill the entire hospital.”
Dr. Polepalli was appointed medical director for a temporary field hospital installed at South Beach Psychiatric Center, also in Staten Island. “We were able to acquire help and bring in people ranging from hospitalists to ER physicians, travel nurses, operation managers and the National Guard. Our command center did a phenomenal job of allocating and obtaining resources. It helped to have a structure that was already established and to rely on the resources of the health system,” Dr. Polepalli said. Not every hospital has a structure like Northwell’s.
“We’re not out of the pandemic yet, but we’ll continue with disaster drills and planning,” he said. “We must continue to adapt and have converted our temporary facilities to COVID testing centers, antibody infusion centers, and vaccination centers.”
For Alfred Burger, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist at Mount Sinai’s Beth Israel campus in New York, hospital medicine, now in its maturing phase, is still feeling its way through hospital and health care system transformation.
“My group is an academic, multicampus hospitalist group employed by the hospital system. When I meet other hospitalists at SHM conferences, whether they come from privately owned, corporately owned, or contracted models, they vary widely in terms of how involved the hospitalists are in crisis planning and their ability to respond to crises. At large academic medical centers like ours, one or more doctors is tasked with being involved in preparing for the next disaster,” he said.
“I think we responded the best we could, although it was difficult as we lost many patients to COVID. We were trying to save lives using the tools we knew from treating pneumonias and other forms of acute inflammatory lung injuries. We used every bit of our training in situations where no one had the right answers. But disasters teach us how to be flexible and pivot on the fly, and what to do when things don’t go our way.”
What is disaster response?
Medical response to a disaster essentially boils down to three main things: stuff, staff, and space, Dr. Persoff said. Those are the cornerstones of an emergency plan.
“There is not a hazard that exists that you can’t take an all-hazards approach to dealing with fundamental realities on the ground. No plan can be comprehensive enough to deal with all the intricacies of an emergency. But many plans can have the bones of a response that will allow you to face adverse circumstances,” he said.
“We actually became quite efficient early on in the pandemic, able to adapt in the moment. We were able to build an effective bridge between workers on the ground and our incident command structure, which seemed to reduce a lot of stress and create situational awareness. We implemented ICS as soon as we heard that China was building a COVID hospital, back in February of 2020.”
When one thinks about mass trauma, such as a 747 crash, Dr. Persoff said, the need is to treat burn victims and trauma victims in large numbers. At that point, the ED downstairs is filled with medical patients. Hospital medicine can rapidly admit those patients to clear out room in the ED. Surgeons are also dedicated to rapidly treating those patients, but what about patients who are on the floor following their surgeries? Hospitalists can offer consultations or primary management so the surgeons can stay in the OR, and the same in the ICU, while safely discharging hospitalized patients in a timely manner to make room for incoming patients.
“The lessons of COVID have been hard-taught and hard-earned. No good plan survives contact with the enemy,” he said. “But I think we’ll be better prepared for the next pandemic.”
Maria Frank, MD, FACP, SFHM, a hospitalist at Denver Health who chairs SHM’s Disaster Management Special Interest Group, says she got the bug for disaster preparation during postresidency training as an internist in emergency medicine. “I’m also the medical director for our biocontainment unit, created for infections like Ebola.” SHM’s SIG, which has 150 members, is now writing a review article on disaster planning for the field.
“I got a call on Dec. 27, 2019, about this new pneumonia, and they said, ‘We don’t know what it is, but it’s a coronavirus,’” she recalled. “When I got off the phone, I said, ‘Let’s make sure our response plan works and we have enough of everything on hand.’” Dr. Frank said she was expecting something more like SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome). “When they called the public health emergency of international concern for COVID, I was at a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention meeting in Atlanta. It really wasn’t a surprise for us.”
All hospitals plan for disasters, although they use different names and have different levels of commitment, Dr. Frank said. What’s not consistent is the participation of hospitalists. “Even when a disaster is 100% trauma related, consider a hospital like mine that has at least four times as many hospitalists as surgeons at any given time. The hospitalists need to take overall management for the patients who aren’t actually in the operating room.”
Time to debrief
Dr. Frank recommends debriefing on the hospital’s and the hospitalist group’s experience with COVID. “Look at the biggest challenges your group faced. Was it staffing, or time off, or the need for day care? Was it burnout, lack of knowledge, lack of [personal protective equipment]?” Each hospital could use its own COVID experience to work on identifying the challenges and the problems, she said. “I’d encourage each department and division to do this exercise individually. Then come together to find common ground with other departments in the hospital.”
This debriefing exercise isn’t just for doctors – it’s also for nurses, environmental services, security, and many other departments, she said. “COVID showed us how crisis response is a group effort. What will bring us together is to learn the challenges each of us faced. It was amazing to see hospitalists doing what they do best.” Post pandemic, hospitalists should also consider getting involved in research and publications, in order to share their lessons.
“One of the things we learned is that hospitalists are very versatile,” Dr. Frank added. But it’s also good for the group to have members specialize, for example, in biocontainment. “We are experts in discharging patients, in patient flow and operations, in coordinating complex medical care. So we would naturally take the lead in, for example, opening a geographic unit or collaborating with other specialists to create innovative models. That’s our job. It’s essential that we’re involved well in advance.”
COVID may be a once-in-a-lifetime experience, but there will be other disasters to come, she said. “If your hospital doesn’t have a disaster plan for hospitalists, get involved in establishing one. Each hospitalist group should have its own response plan. Talk to your peers at other hospitals, and get involved at the institutional level. I’m happy to share our plan; just contact me.” Readers can contact Dr. Frank at [email protected].
References
1. Persoff J et al. The role of hospital medicine in emergency preparedness: A framework for hospitalist leadership in disaster preparedness, response and recovery. J Hosp Med. 2018 Oct;13(10):713-7. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3073.
2. Persoff J et al. Expanding the hospital incident command system with a physician-centric role during a pandemic: The role of the physician clinical support supervisor. J Hosp Adm. 2020;9(3):7-10. doi: 10.5430/jha.v9n3p7.
3. Bowden K et al. Harnessing the power of hospitalists in operational disaster planning: COVID-19. J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Sep;35(9):273-7. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-05952-6.
4. Orsini E et al. Lessons on outbreak preparedness from the Cleveland Clinic. Chest. 2020;158(5):2090-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.009.
Jason Persoff, MD, SFHM, now a hospitalist at University of Colorado Hospital in Aurora and an amateur storm chaser, got a close look at how natural disasters can impact hospital care when a tornado destroyed St. John’s Regional Medical Center in Joplin, Mo., on May 22, 2011.
He and a colleague who had been following the storm responded to injuries on the highway before reporting for a long day’s service at the other hospital in Joplin, Freeman Hospital West, caring for patients transferred from St. John’s on an impromptu unit without access to their medical records.
“During my medical training, I had done emergency medicine as an EMT, so I was interested in how the system responds to emergencies,” he explained. “At Joplin I learned how it feels when the boots on the ground in a crisis are not connected to an incident command structure.” Another thing he learned was the essential role for hospitalists in a hospital’s response to a crisis – and thus the need to involve them well in advance in the hospital’s planning for future emergencies.
“Disaster preparation – when done right – helps you ‘herd cats’ in a crisis situation,” he said. “The tornado and its wake served as defining moments for me. I used them as the impetus to improve health care’s response to disasters.” Part of that commitment was to help hospitalists understand their part in emergency preparation.1
Dr. Persoff is now the assistant medical director of emergency preparedness at University of Colorado Hospital. He also helped to create a position called physician support supervisor, which is filled by physicians who have held leadership positions in a hospital to help coordinate the disparate needs of all clinicians in a crisis and facilitate rapid response.2
But then along came the COVID pandemic – which in many locales around the world was unprecedented in scope. Dr. Persoff said his hospital was fairly well prepared, after a decade of engagement with emergency planning. It drew on experience with H1N1, also known as swine flu, and the Ebola virus, which killed 11,323 people, primarily in West Africa, from 2013 to 2016, as models. In a matter of days, the CU division of hospital medicine was able to modify and deploy its existing disaster plans to quickly respond to an influx of COVID patients.3
“Basically, what we set out to do was to treat COVID patients as if they were Ebola patients, cordoning them off in a small area of the hospital. That was naive of us,” he said. “We weren’t able to grasp the scale at the outset. It does defy the imagination – how the hospital could fill up with just one type of patient.”
What is disaster planning?
Emergency preparation for hospitals emerged as a recognized medical specialization in the 1970s. Initially it was largely considered the realm of emergency physicians, trauma services, or critical care doctors. Resources such as the World Health Organization, the Federal Emergency Management Agency, and similar groups recommend an all-hazards approach, a broad and flexible strategy for managing emergencies that could include natural disasters – earthquakes, storms, tornadoes, or wildfires – or human-caused events, such as mass shootings or terrorist attacks. The Joint Commission requires accredited hospitals to conduct several disaster drills annually.
The U.S. Hospital Preparedness Program was created in 2002 to enhance the ability of hospitals and health systems to prepare for and respond to bioterrorism attacks on civilians and other public health emergencies, including natural disasters and pandemics. It offers a foundation for national preparedness and a primary source of federal funding for health care system preparedness. The hospital, at the heart of the health care system, is expected to receive the injured and infected, because patients know they can obtain care there.
One of the fundamental tools for crisis response is the incident command system (ICS), which spells out how to quickly establish a command structure and assign responsibility for key tasks as well as overall leadership. The National Incident Management System organizes emergency management across all government levels and the private sector to ensure that the most pressing needs are met and precious resources are used without duplication. ICS is a standardized approach to command, control, and coordination of emergency response using a common hierarchy recognized across organizations, with advance training in how it should be deployed.
A crisis like never before
Nearly every hospital or health system goes through drills for an emergency, said Hassan Khouli, MD, chair of the department of critical care medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, and coauthor of an article in the journal Chest last year outlining 10 principles of emergency preparedness derived from its experience with the COVID pandemic.4 Some of these include: don’t wait; engage a variety of stakeholders; identify sources of truth; and prioritize hospital employees’ safety and well-being.
Part of the preparation is doing table-top exercises, with case scenarios or actual situations presented, working with clinicians on brainstorming and identifying opportunities for improvement, Dr. Khouli said. “These drills are so important, regardless of what the disaster turns out to be. We’ve done that over the years. We are a large health system, very process and detail oriented. Our emergency incident command structure was activated before we saw our first COVID patient,” he said.
“This was a crisis like never before, with huge amounts of uncertainty,” he noted. “But I believe the Cleveland Clinic system did very well, measured by outcomes such as surveys of health care teams across the system, which gave us reassuring results, and clinical outcomes with lower ICU and hospital mortality rates.”
Christopher Whinney, MD, SFHM, department chair of hospital medicine at Cleveland Clinic, said hospitalists worked hand in hand with the health system’s incident command structure and took responsibility for managing non-ICU COVID patients at six hospitals in the system.
“Hospitalists had a place at the table, and we collaborated well with incident command, enterprise redeployment committees, and emergency and critical care colleagues,” he noted. Hospitalists were on the leadership team for a number of planning meetings, and key stakeholders for bringing information back to their groups.
“First thing we did was to look at our workforce. The challenge was how to respond to up to a hundred COVID admissions per day – how to mobilize providers and build surge teams that incorporated primary care providers and medical trainees. We onboarded 200 providers to do hospital care within 60 days,” he said.
“We realized that communication with patients and families was a big part of the challenge, so we assigned people with good communication skills to fill this role. While we were fortunate not to get the terrible surges they had in other places, we felt we were prepared for the worst.”
Challenges of surge capacity
Every disaster is different, said Srikant Polepalli, MD, associate hospitalist medical director for Staten Island University Hospital in New York, part of the Northwell Health system. He brought the experience of being part of the response to Superstorm Sandy in October 2012 to the COVID pandemic.
“Specifically for hospitalists, the biggest challenge is working on surge capacity for a sudden influx of patients,” he said. “But with Northwell as our umbrella, we can triage and load-balance to move patients from hospital to hospital as needed. With the pandemic, we started with one COVID unit and then expanded to fill the entire hospital.”
Dr. Polepalli was appointed medical director for a temporary field hospital installed at South Beach Psychiatric Center, also in Staten Island. “We were able to acquire help and bring in people ranging from hospitalists to ER physicians, travel nurses, operation managers and the National Guard. Our command center did a phenomenal job of allocating and obtaining resources. It helped to have a structure that was already established and to rely on the resources of the health system,” Dr. Polepalli said. Not every hospital has a structure like Northwell’s.
“We’re not out of the pandemic yet, but we’ll continue with disaster drills and planning,” he said. “We must continue to adapt and have converted our temporary facilities to COVID testing centers, antibody infusion centers, and vaccination centers.”
For Alfred Burger, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist at Mount Sinai’s Beth Israel campus in New York, hospital medicine, now in its maturing phase, is still feeling its way through hospital and health care system transformation.
“My group is an academic, multicampus hospitalist group employed by the hospital system. When I meet other hospitalists at SHM conferences, whether they come from privately owned, corporately owned, or contracted models, they vary widely in terms of how involved the hospitalists are in crisis planning and their ability to respond to crises. At large academic medical centers like ours, one or more doctors is tasked with being involved in preparing for the next disaster,” he said.
“I think we responded the best we could, although it was difficult as we lost many patients to COVID. We were trying to save lives using the tools we knew from treating pneumonias and other forms of acute inflammatory lung injuries. We used every bit of our training in situations where no one had the right answers. But disasters teach us how to be flexible and pivot on the fly, and what to do when things don’t go our way.”
What is disaster response?
Medical response to a disaster essentially boils down to three main things: stuff, staff, and space, Dr. Persoff said. Those are the cornerstones of an emergency plan.
“There is not a hazard that exists that you can’t take an all-hazards approach to dealing with fundamental realities on the ground. No plan can be comprehensive enough to deal with all the intricacies of an emergency. But many plans can have the bones of a response that will allow you to face adverse circumstances,” he said.
“We actually became quite efficient early on in the pandemic, able to adapt in the moment. We were able to build an effective bridge between workers on the ground and our incident command structure, which seemed to reduce a lot of stress and create situational awareness. We implemented ICS as soon as we heard that China was building a COVID hospital, back in February of 2020.”
When one thinks about mass trauma, such as a 747 crash, Dr. Persoff said, the need is to treat burn victims and trauma victims in large numbers. At that point, the ED downstairs is filled with medical patients. Hospital medicine can rapidly admit those patients to clear out room in the ED. Surgeons are also dedicated to rapidly treating those patients, but what about patients who are on the floor following their surgeries? Hospitalists can offer consultations or primary management so the surgeons can stay in the OR, and the same in the ICU, while safely discharging hospitalized patients in a timely manner to make room for incoming patients.
“The lessons of COVID have been hard-taught and hard-earned. No good plan survives contact with the enemy,” he said. “But I think we’ll be better prepared for the next pandemic.”
Maria Frank, MD, FACP, SFHM, a hospitalist at Denver Health who chairs SHM’s Disaster Management Special Interest Group, says she got the bug for disaster preparation during postresidency training as an internist in emergency medicine. “I’m also the medical director for our biocontainment unit, created for infections like Ebola.” SHM’s SIG, which has 150 members, is now writing a review article on disaster planning for the field.
“I got a call on Dec. 27, 2019, about this new pneumonia, and they said, ‘We don’t know what it is, but it’s a coronavirus,’” she recalled. “When I got off the phone, I said, ‘Let’s make sure our response plan works and we have enough of everything on hand.’” Dr. Frank said she was expecting something more like SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome). “When they called the public health emergency of international concern for COVID, I was at a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention meeting in Atlanta. It really wasn’t a surprise for us.”
All hospitals plan for disasters, although they use different names and have different levels of commitment, Dr. Frank said. What’s not consistent is the participation of hospitalists. “Even when a disaster is 100% trauma related, consider a hospital like mine that has at least four times as many hospitalists as surgeons at any given time. The hospitalists need to take overall management for the patients who aren’t actually in the operating room.”
Time to debrief
Dr. Frank recommends debriefing on the hospital’s and the hospitalist group’s experience with COVID. “Look at the biggest challenges your group faced. Was it staffing, or time off, or the need for day care? Was it burnout, lack of knowledge, lack of [personal protective equipment]?” Each hospital could use its own COVID experience to work on identifying the challenges and the problems, she said. “I’d encourage each department and division to do this exercise individually. Then come together to find common ground with other departments in the hospital.”
This debriefing exercise isn’t just for doctors – it’s also for nurses, environmental services, security, and many other departments, she said. “COVID showed us how crisis response is a group effort. What will bring us together is to learn the challenges each of us faced. It was amazing to see hospitalists doing what they do best.” Post pandemic, hospitalists should also consider getting involved in research and publications, in order to share their lessons.
“One of the things we learned is that hospitalists are very versatile,” Dr. Frank added. But it’s also good for the group to have members specialize, for example, in biocontainment. “We are experts in discharging patients, in patient flow and operations, in coordinating complex medical care. So we would naturally take the lead in, for example, opening a geographic unit or collaborating with other specialists to create innovative models. That’s our job. It’s essential that we’re involved well in advance.”
COVID may be a once-in-a-lifetime experience, but there will be other disasters to come, she said. “If your hospital doesn’t have a disaster plan for hospitalists, get involved in establishing one. Each hospitalist group should have its own response plan. Talk to your peers at other hospitals, and get involved at the institutional level. I’m happy to share our plan; just contact me.” Readers can contact Dr. Frank at [email protected].
References
1. Persoff J et al. The role of hospital medicine in emergency preparedness: A framework for hospitalist leadership in disaster preparedness, response and recovery. J Hosp Med. 2018 Oct;13(10):713-7. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3073.
2. Persoff J et al. Expanding the hospital incident command system with a physician-centric role during a pandemic: The role of the physician clinical support supervisor. J Hosp Adm. 2020;9(3):7-10. doi: 10.5430/jha.v9n3p7.
3. Bowden K et al. Harnessing the power of hospitalists in operational disaster planning: COVID-19. J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Sep;35(9):273-7. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-05952-6.
4. Orsini E et al. Lessons on outbreak preparedness from the Cleveland Clinic. Chest. 2020;158(5):2090-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.009.
CDC to show vaccinated people infected with Delta remain contagious
and infect others, the New York Times reported on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the New York Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data shows people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on Jul 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak on Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and infect others, the New York Times reported on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the New York Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data shows people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on Jul 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak on Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and infect others, the New York Times reported on July 29.
The revelation is one reason the agency reversed course this week and said fully vaccinated people should go back to wearing masks in many cases.
The new findings also are a reversal from what scientists had believed to be true about other variants of the virus, the New York Times said. The bottom line is that the CDC data shows people with so-called breakthrough cases of the Delta variant may be just as contagious as unvaccinated people, even if they do not show symptoms.
ABC News reported earlier on Jul 29 that the CDC’s updated mask guidance followed an outbreak on Cape Cod, where crowds gathered for the Fourth of July.
As of July 29, 882 people were tied to the outbreak centered in Provincetown, Mass. Of those who live in Massachusetts, 74% were unvaccinated. ABC said the majority were showing symptoms of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves anifrolumab (Saphnelo) as first new lupus treatment in more than 10 years
Anifrolumab, an inhibitor of type 1 interferons, received approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who are receiving standard therapy, according to a statement released Aug. 2 from its manufacturer, AstraZeneca.
Anifrolumab will be marketed as Saphnelo. It is a fully human monoclonal antibody against subunit 1 of the type 1 interferon receptor, and its approval represents the only new treatment approved for patients with SLE in a decade. The recommended dosage is 300 mg as an intravenous infusion over a 30-minute period every 4 weeks, according to its prescribing information, and it will be sold in a single-dose vial containing 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL).
Increased type I interferon (IFN) signaling is associated with increased disease activity in patients with SLE, and the option of a type I IFN receptor antagonist may allow physicians to treat patients with fewer corticosteroids, according to the statement.
The approval was based on data from three trials. The TULIP (Treatment of Uncontrolled Lupus via the Interferon Pathway) phase 3 research included two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, TULIP-1 and TULIP-2. The TULIP trials each enrolled seropositive patients with moderate to severe active disease despite standard-of-care therapy (SOC), which included oral corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants (methotrexate, azathioprine, or mycophenolate mofetil). All patients met American College of Rheumatology criteria and had an SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)-2K of 6 or greater, as well as British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) index scoring showing one or more organ systems with grade A involvement or two or more with grade B. Both trials required stable SOC therapy throughout the study except for mandatory attempts at oral corticosteroid tapering for patients who were receiving 10 mg/day or more of prednisone or its equivalent at study entry.
TULIP-1 failed to meet its primary endpoint of SLE Responder Index (SRI) at 52 weeks, but investigators determined after the trial that some patients taking anifrolumab had been inappropriately labeled as nonresponders because the trial automatically required any patient who used a restricted drug, including NSAIDs, to be classified as a nonresponder even if they used the medication for something unrelated to SLE. When these rules were amended in a post hoc analysis, differences between the groups treated with anifrolumab and placebo widened in secondary endpoints for oral corticosteroid dose reduction, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Severity Index response, and BILAG-Based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response.
The TULIP-2 trial included 362 patients who received a fixed dose of 300 mg anifrolumab or a placebo intravenously every 4 weeks for 48 weeks. In this study, anifrolumab patients showed significant improvement in disease activity on the BICLA scale, compared with placebo patients. The BICLA response was 47.8% in patients taking anifrolumab and 31.5% in placebo-treated patients (P = .001).
In the MUSE phase 2 trial, 305 adults with SLE were randomized to a fixed-dose intravenous infusion of 300 mg or 1,000 mg of anifrolumab or a placebo every 4 weeks, plus SOC, for 48 weeks. Patients in this study showed significant improvement on either dose, compared with placebo.
The results from the MUSE trial were published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology Nov. 7, 2016, followed by the TULIP-1 trial in The Lancet Rheumatology Nov. 11, 2019, and the TULIP-2 trial in the New England Journal of Medicine Jan. 16, 2020.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in all three studies were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, infusion-related reactions, herpes zoster, and cough. Infusion-related reactions in the trials were similar in anifrolumab and placebo patients, and included headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and dizziness.
Anifrolumab has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus and is not recommended for these patients, according to the statement.
AstraZeneca said in its statement that anifrolumab is also under regulatory review in Japan and the European Union, and it continues to evaluate anifrolumab in patients with SLE in a long-term extension phase 3 trial and a phase 3 trial assessing subcutaneous delivery. The company said it “is exploring the potential of Saphnelo in a variety of diseases where type I IFN plays a key role, including lupus nephritis, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and myositis.”
Anifrolumab, an inhibitor of type 1 interferons, received approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who are receiving standard therapy, according to a statement released Aug. 2 from its manufacturer, AstraZeneca.
Anifrolumab will be marketed as Saphnelo. It is a fully human monoclonal antibody against subunit 1 of the type 1 interferon receptor, and its approval represents the only new treatment approved for patients with SLE in a decade. The recommended dosage is 300 mg as an intravenous infusion over a 30-minute period every 4 weeks, according to its prescribing information, and it will be sold in a single-dose vial containing 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL).
Increased type I interferon (IFN) signaling is associated with increased disease activity in patients with SLE, and the option of a type I IFN receptor antagonist may allow physicians to treat patients with fewer corticosteroids, according to the statement.
The approval was based on data from three trials. The TULIP (Treatment of Uncontrolled Lupus via the Interferon Pathway) phase 3 research included two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, TULIP-1 and TULIP-2. The TULIP trials each enrolled seropositive patients with moderate to severe active disease despite standard-of-care therapy (SOC), which included oral corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants (methotrexate, azathioprine, or mycophenolate mofetil). All patients met American College of Rheumatology criteria and had an SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)-2K of 6 or greater, as well as British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) index scoring showing one or more organ systems with grade A involvement or two or more with grade B. Both trials required stable SOC therapy throughout the study except for mandatory attempts at oral corticosteroid tapering for patients who were receiving 10 mg/day or more of prednisone or its equivalent at study entry.
TULIP-1 failed to meet its primary endpoint of SLE Responder Index (SRI) at 52 weeks, but investigators determined after the trial that some patients taking anifrolumab had been inappropriately labeled as nonresponders because the trial automatically required any patient who used a restricted drug, including NSAIDs, to be classified as a nonresponder even if they used the medication for something unrelated to SLE. When these rules were amended in a post hoc analysis, differences between the groups treated with anifrolumab and placebo widened in secondary endpoints for oral corticosteroid dose reduction, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Severity Index response, and BILAG-Based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response.
The TULIP-2 trial included 362 patients who received a fixed dose of 300 mg anifrolumab or a placebo intravenously every 4 weeks for 48 weeks. In this study, anifrolumab patients showed significant improvement in disease activity on the BICLA scale, compared with placebo patients. The BICLA response was 47.8% in patients taking anifrolumab and 31.5% in placebo-treated patients (P = .001).
In the MUSE phase 2 trial, 305 adults with SLE were randomized to a fixed-dose intravenous infusion of 300 mg or 1,000 mg of anifrolumab or a placebo every 4 weeks, plus SOC, for 48 weeks. Patients in this study showed significant improvement on either dose, compared with placebo.
The results from the MUSE trial were published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology Nov. 7, 2016, followed by the TULIP-1 trial in The Lancet Rheumatology Nov. 11, 2019, and the TULIP-2 trial in the New England Journal of Medicine Jan. 16, 2020.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in all three studies were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, infusion-related reactions, herpes zoster, and cough. Infusion-related reactions in the trials were similar in anifrolumab and placebo patients, and included headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and dizziness.
Anifrolumab has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus and is not recommended for these patients, according to the statement.
AstraZeneca said in its statement that anifrolumab is also under regulatory review in Japan and the European Union, and it continues to evaluate anifrolumab in patients with SLE in a long-term extension phase 3 trial and a phase 3 trial assessing subcutaneous delivery. The company said it “is exploring the potential of Saphnelo in a variety of diseases where type I IFN plays a key role, including lupus nephritis, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and myositis.”
Anifrolumab, an inhibitor of type 1 interferons, received approval from the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who are receiving standard therapy, according to a statement released Aug. 2 from its manufacturer, AstraZeneca.
Anifrolumab will be marketed as Saphnelo. It is a fully human monoclonal antibody against subunit 1 of the type 1 interferon receptor, and its approval represents the only new treatment approved for patients with SLE in a decade. The recommended dosage is 300 mg as an intravenous infusion over a 30-minute period every 4 weeks, according to its prescribing information, and it will be sold in a single-dose vial containing 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL).
Increased type I interferon (IFN) signaling is associated with increased disease activity in patients with SLE, and the option of a type I IFN receptor antagonist may allow physicians to treat patients with fewer corticosteroids, according to the statement.
The approval was based on data from three trials. The TULIP (Treatment of Uncontrolled Lupus via the Interferon Pathway) phase 3 research included two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, TULIP-1 and TULIP-2. The TULIP trials each enrolled seropositive patients with moderate to severe active disease despite standard-of-care therapy (SOC), which included oral corticosteroids, antimalarials, and immunosuppressants (methotrexate, azathioprine, or mycophenolate mofetil). All patients met American College of Rheumatology criteria and had an SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)-2K of 6 or greater, as well as British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) index scoring showing one or more organ systems with grade A involvement or two or more with grade B. Both trials required stable SOC therapy throughout the study except for mandatory attempts at oral corticosteroid tapering for patients who were receiving 10 mg/day or more of prednisone or its equivalent at study entry.
TULIP-1 failed to meet its primary endpoint of SLE Responder Index (SRI) at 52 weeks, but investigators determined after the trial that some patients taking anifrolumab had been inappropriately labeled as nonresponders because the trial automatically required any patient who used a restricted drug, including NSAIDs, to be classified as a nonresponder even if they used the medication for something unrelated to SLE. When these rules were amended in a post hoc analysis, differences between the groups treated with anifrolumab and placebo widened in secondary endpoints for oral corticosteroid dose reduction, Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Severity Index response, and BILAG-Based Composite Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response.
The TULIP-2 trial included 362 patients who received a fixed dose of 300 mg anifrolumab or a placebo intravenously every 4 weeks for 48 weeks. In this study, anifrolumab patients showed significant improvement in disease activity on the BICLA scale, compared with placebo patients. The BICLA response was 47.8% in patients taking anifrolumab and 31.5% in placebo-treated patients (P = .001).
In the MUSE phase 2 trial, 305 adults with SLE were randomized to a fixed-dose intravenous infusion of 300 mg or 1,000 mg of anifrolumab or a placebo every 4 weeks, plus SOC, for 48 weeks. Patients in this study showed significant improvement on either dose, compared with placebo.
The results from the MUSE trial were published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology Nov. 7, 2016, followed by the TULIP-1 trial in The Lancet Rheumatology Nov. 11, 2019, and the TULIP-2 trial in the New England Journal of Medicine Jan. 16, 2020.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in all three studies were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, infusion-related reactions, herpes zoster, and cough. Infusion-related reactions in the trials were similar in anifrolumab and placebo patients, and included headache, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and dizziness.
Anifrolumab has not been evaluated in patients with severe active lupus nephritis or severe active central nervous system lupus and is not recommended for these patients, according to the statement.
AstraZeneca said in its statement that anifrolumab is also under regulatory review in Japan and the European Union, and it continues to evaluate anifrolumab in patients with SLE in a long-term extension phase 3 trial and a phase 3 trial assessing subcutaneous delivery. The company said it “is exploring the potential of Saphnelo in a variety of diseases where type I IFN plays a key role, including lupus nephritis, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and myositis.”
Feasibility of Risk Stratification of Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Chest Pain Using HEART Score
From the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY (Dr. Gandhi), and the School of Medicine, Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College, and King Edward Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, India (Drs. Gandhi and Tiwari).
Objective: Calculation of HEART score to (1) stratify patients as low-risk, intermediate-risk, high-risk, and to predict the short-term incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and (2) demonstrate feasibility of HEART score in our local settings.
Design: A prospective cohort study of patients with a chief complaint of chest pain concerning for acute coronary syndrome.
Setting: Participants were recruited from the emergency department (ED) of King Edward Memorial Hospital, a tertiary care academic medical center and a resource-limited setting in Mumbai, India.
Participants: We evaluated 141 patients aged 18 years and older presenting to the ED and stratified them using the HEART score. To assess patients’ progress, a follow-up phone call was made within 6 weeks after presentation to the ED.
Measurements: The primary outcomes were a risk stratification, 6-week occurrence of MACE, and performance of unscheduled revascularization or stress testing. The secondary outcomes were discharge or death.
Results: The 141 participants were stratified into low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk groups: 67 (47.52%), 44 (31.21%), and 30 (21.28%), respectively. The 6-week incidence of MACE in each category was 1.49%, 18.18%, and 90%, respectively. An acute myocardial infarction was diagnosed in 24 patients (17.02%), 15 patients (10.64%) underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and 4 patients (2.84%) underwent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). Overall, 98.5% of low-risk patients and 93.33% of high-risk patients had an uneventful recovery following discharge; therefore, extrapolation based on results demonstrated reduced health care utilization. All the survey respondents found the HEART score to be feasible. The patient characteristics and risk profile of the patients with and without MACE demonstrated that: patients with MACE were older and had a higher proportion of males, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, prior history of PCI/CABG, and history of stroke.
Conclusion: The HEART score seems to be a useful tool for risk stratification and a reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients and can therefore be used for triage.
Keywords: chest pain; emergency department; HEART score; acute coronary syndrome; major adverse cardiac events; myocardial infarction; revascularization.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), especially coronary heart disease (CHD), have epidemic proportions worldwide. Globally, in 2012, CVD led to 17.5 million deaths,1,2 with more than 75% of them occurring in developing countries. In contrast to developed countries, where mortality from CHD is rapidly declining, it is increasing in developing countries.1,3 Current estimates from epidemiologic studies from various parts of India indicate the prevalence of CHD in India to be between 7% and 13% in urban populations and 2% and 7% in rural populations.4
Premature mortality in terms of years of life lost because of CVD in India increased by 59% over a 20-year span, from 23.2 million in 1990 to 37 million in 2010.5 Studies conducted in Mumbai (Mumbai Cohort Study) reported very high CVD mortality rates, approaching 500 per 100 000 for men and 250 per 100 000 for women.6,7 However, to the best of our knowledge, in the Indian population, there are minimal data on utilization of a triage score, such as the HEART score, in chest pain patients in the emergency department (ED) in a resource-limited setting.
The most common reason for admitting patients to the ED is chest pain.8 There are various cardiac and noncardiac etiologies of chest pain presentation. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) needs to be ruled out first in every patient presenting with chest pain. However, 80% of patients with ACS have no clear diagnostic features on presentation.9 The timely diagnosis and treatment of patients with ACS improves their prognosis. Therefore, clinicians tend to start each patient on ACS treatment to reduce the risk, which often leads to increased costs due to unnecessary, time-consuming diagnostic procedures that may place burdens on both the health care system and the patient.10
Several risk-stratifying tools have been developed in the last few years. Both the GRACE and TIMI risk scores have been designed for risk stratification of patients with proven ACS and not for the chest pain population at the ED.11 Some of these tools are applicable to patients with all types of chest pain presenting to the ED, such as the Manchester Triage System. Other, more selective systems are devoted to the risk stratification of suspected ACS in the ED. One is the HEART score.12
The first study on the HEART score—an acronym that stands for History, Electrocardiogram, Age, Risk factors, and Troponin—was done by Backus et al, who proved that the HEART score is an easy, quick, and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients.10 The HEART score predicts the short-term incidence of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), which allows clinicians to stratify patients as low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk and to guide their clinical decision-making accordingly. It was developed to provide clinicians with a simple, reliable predictor of cardiac risk on the basis of the lowest score of 0 (very low-risk) up to a score of 10 (very high-risk).
We studied the clinical performance of the HEART score in patients with chest pain, focusing on the efficacy and safety of rapidly identifying patients at risk of MACE. We aimed to determine (1) whether the HEART score is a reliable predictor of outcomes of chest pain patients presenting to the ED; (2) whether the score is feasible in our local settings; and (3) whether it describes the risk profile of patients with and without MACE.
Methods
Setting
Participants were recruited from the ED of King Edward Memorial Hospital, a municipal teaching hospital in Mumbai. The study institute is a tertiary care academic medical center located in Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra, and is a resource-limited setting serving urban, suburban, and rural populations. Participants requiring urgent attention are first seen by a casualty officer and then referred to the emergency ward. Here, the physician on duty evaluates them and decides on admission to the various wards, like the general ward, medical intensive care unit (ICU), coronary care unit (CCU), etc. The specialist’s opinion may also be obtained before admission. Critically ill patients are initially admitted to the emergency ward and stabilized before being shifted to other areas of the hospital.
Participants
Patients aged 18 years and older presenting with symptoms of acute chest pain or suspected ACS were stratified by priority using the chest pain scoring system—the HEART score. Only patients presenting to the ED were eligible for the study. Informed consent from the patient or next of kin was mandatory for participation in the study.
Patients were determined ineligible for the following reasons: a clear cause for chest pain other than ACS (eg, trauma, diagnosed aortic dissection), persisting or recurrent chest pain caused by rheumatic diseases or cancer (a terminal illness), pregnancy, unable or unwilling to provide informed consent, or incomplete data.
Study design
We conducted a
We conducted our study to determine the importance of calculating the HEART score in each patient, which will help to correctly place them into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups for clinically important, irreversible adverse cardiac events and guide the clinical decision-making. Patients with low risk will avoid costly tests and hospital admissions, thus decreasing the cost of treatment and ensuring timely discharge from the ED. Patients with high risk will be treated immediately, to possibly prevent a life-threatening, ACS-related incident. Thus, the HEART score will serve as a quick and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients and help clinicians to make accurate diagnostic and therapeutic choices in uncertain situations.
HEART score
The total number of points for History, Electrocardiogram (ECG), Age, Risk factors, and Troponin was noted as the HEART score (Table 1).
For this study, the patient’s history and ECGs were interpreted by internal medicine attending physicians in the ED. The ECG taken in the emergency room was reviewed and classified, and a copy of the admission ECG was added to the file. The recommendation for patients with a HEART score in a particular range was evaluated. Notably, those with a score of 3 or lower led to a recommendation of reassurance and early discharge. Those with a HEART score in the intermediate range (4-6) were admitted to the hospital for further clinical observation and testing, whereas a high HEART score (7-10) led to admission for intensive monitoring and early intervention. In the analysis of HEART score data, we only used those patients having records for all 5 parameters, excluding patients without an ECG or troponin test.
Results
Myocardial infarction (MI) was defined based on Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction.13 Coronary revascularization was defined as angioplasty with or without stent placement or coronary artery bypass surgery.14 Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was defined as any therapeutic catheter intervention in the coronary arteries. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery was defined as any cardiac surgery in which coronary arteries were operated on.
The primary outcomes in this study were the (1) risk stratification of chest pain patients into low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk categories; (2) incidence of a MACE within 6 weeks of initial presentation. MACE consists of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), PCI, CABG, coronary angiography revealing procedurally correctable stenosis managed conservatively, and death due to any cause.
Our secondary outcomes were discharge or death due to any cause within 6 weeks after presentation.
Follow-up
Within 6 weeks after presentation to the ED, a follow-up phone call was placed to assess the patient’s progress. The follow-up focused on the endpoint of MACE, comprising all-cause death, MI, and revascularization. No patient was lost to follow-up.
Statistical analysis
We aimed to find a difference in the 6-week MACE between low-, intermediate-, and high-risk categories of the HEART score. The prevalence of CHD in India is 10%,4 and assuming an α of 0.05, we needed a sample of 141 patients from the ED patient population. Continuous variables were presented by mean (SD), and categorical variables as percentages. We used t test and the Mann-Whitney U test for comparison of means for continuous variables, χ2 for categorical variables, and Fisher’s exact test for comparison of the categorical variables. Results with P < .05 were considered statistically significant.
We evaluated 141 patients presenting to the ED with chest pain concerning for ACS during the study period, from July 2019 to October 2019.
Primary outcomes
The risk stratification of the HEART score in chest pain patients and the incidence of 6-week MACE are outlined in Table 3
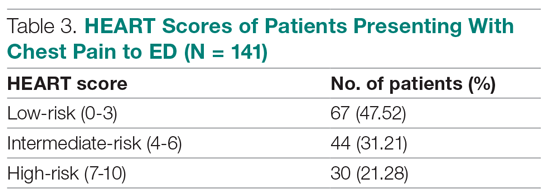
The distribution of the HEART score’s 5 elements in the groups with or without MACE endpoints is shown in Table 5. Notice the significant differences between the groups. A follow-up phone call was made within 6 weeks after the presentation to the ED to assess the patient’s progress. The 6-week follow-up call data are included in Table 6.
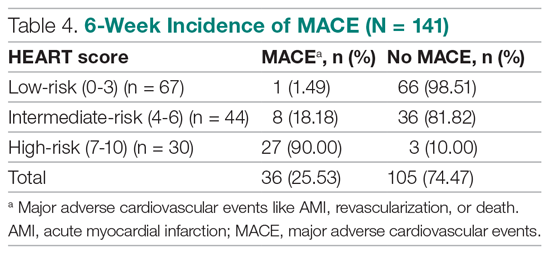
Of 141 patients, 36 patients (25.53%) were diagnosed with MACE within 6 weeks of presentation.
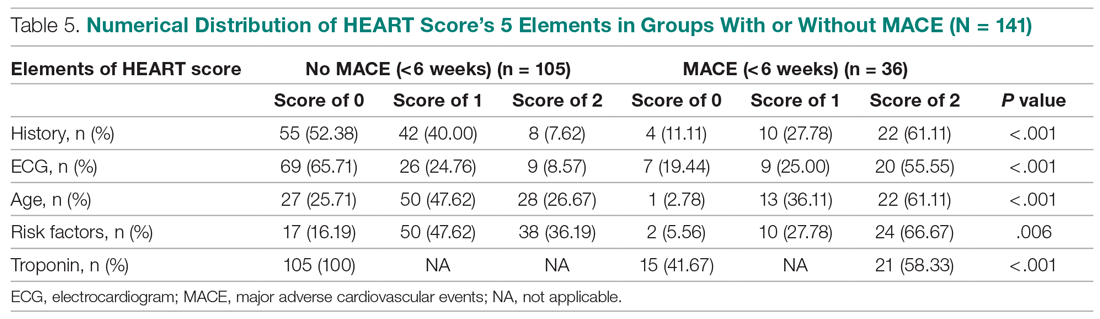
Myocardial infarction—An AMI was diagnosed in 24 of the 141 patients (17.02%). Twenty-one of those already had positive markers on admission (apparently, these AMI had started before their arrival to the emergency room). One AMI occurred 2 days after admission in a 66-year-old male, and another occurred 10 days after discharge. A further AMI occurred 2 weeks after discharge. All 3 patients belonged to the intermediate-risk group.
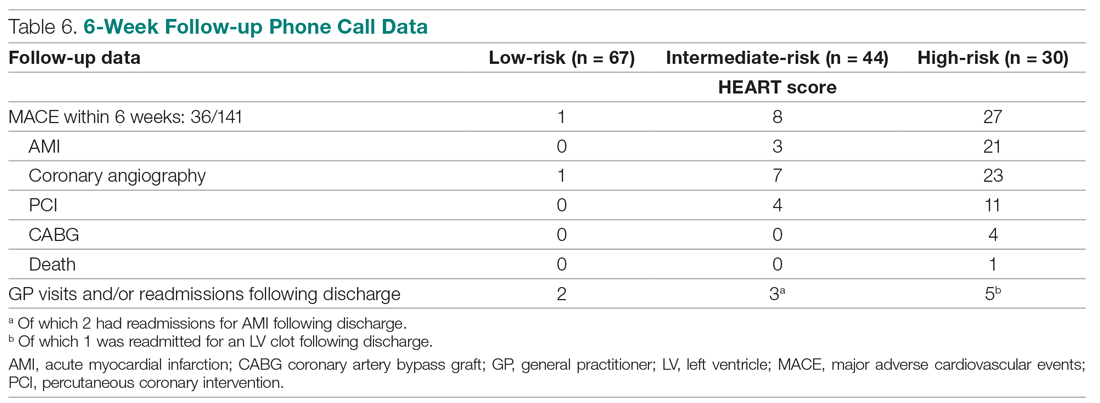
Revascularization—Coronary angiography was performed in 31 of 141 patients (21.99%). Revascularization was performed in 19 patients (13.48%), of which 15 were PCIs (10.64%) and 4 were CABGs (2.84%).
Mortality—One patient died from the study population. He was a 72-year-old male who died 14 days after admission. He had a HEART score of 8.
Among the 67 low-risk patients:
- MACE: Coronary angiography was performed in 1 patient (1.49%). Among the 67 patients in the low-risk category, there was no cases of AMI or deaths. The remaining 66 patients (98.51%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge.
- General practitioner (GP) visits/readmissions following discharge: Two of 67 patients (2.99%) had GP visits following discharge, of which 1 was uneventful. The other patient, a 64-year-old male, was readmitted due to a recurrent history of chest pain and underwent coronary angiography.
Among the 44 intermediate-risk patients:
- MACE: Of the 7 of 44 patients (15.91%) who had coronary angiography, 3 patients (6.82%) had AMI, of which 1 occurred 2 days after admission in a 66-year-old male. Two patients had AMI following discharge. There were no deaths. Overall, 42 of 44 patients (95.55%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge.
- GP visits/readmissions following discharge: Three of 44 patients (6.82%) had repeated visits following discharge. One was a GP visit that was uneventful. The remaining 2 patients were diagnosed with AMI and readmitted following discharge. One AMI occurred 10 days after discharge in a patient with a HEART score of 6; another occurred 2 weeks after discharge in a patient with a HEART score of 5.
Among the 30 high-risk patients:
- MACE: Twenty-three of 30 patients (76.67%) underwent coronary angiography. One patient died 5 days after discharge. The patient had a HEART score of 8. Most patients however, had an uneventful recovery following discharge (28, 93.33%).
- GP visits/readmissions following discharge: Five of 30 patients (16.67%) had repeated visits following discharge. Two were uneventful. Two patients had a history of recurrent chest pain that resolved on Sorbitrate. One patient was readmitted 2 weeks following discharge due to a complication: a left ventricular clot was found. The patient had a HEART score of 10.
Secondary outcome—Overall, 140 of 141 patients were discharged. One patient died: a 72-year-old male with a HEART score of 8.
Feasibility—To determine the ease and feasibility of performing a HEART score in chest pain patients presenting to the ED, a survey was distributed to the internal medicine physicians in the ED. In the survey, the Likert scale was used to rate the ease of utilizing the HEART score and whether the physicians found it feasible to use it for risk stratification of their chest pain patients. A total of 12 of 15 respondents (80%) found it “easy” to use. Of the remaining 3 respondents, 2 (13.33%) rated the HEART score “very easy” to use, while 1 (6.66%) considered it “difficult” to work with. None of the respondents said that it was not feasible to perform a HEART score in the ED.
Risk factors for reaching an endpoint:
We compared risk profiles between the patient groups with and without an endpoint. The group of patients with MACE were older and had a higher proportion of males than the group of patients without MACE. Moreover, they also had a higher prevalence of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, prior history of PCI/CABG, and history of stroke. These also showed a significant association with MACE. Obesity was not included in our risk factors as we did not have data collected to measure body mass index. Results are represented in Table 7.
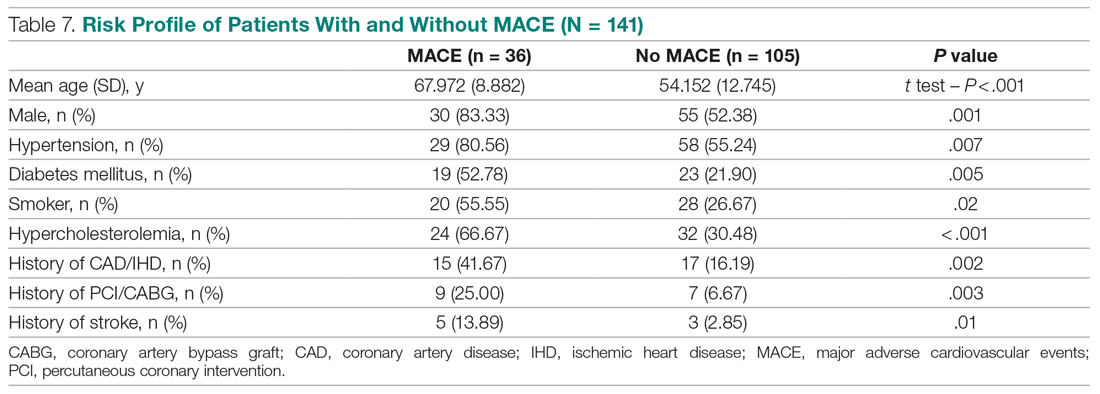
Discussion
Our study described a patient population presenting to an ED with chest pain as their primary complaint. The results of this prospective study confirm that the HEART score is an excellent system to triage chest pain patients. It provides the clinician with a reliable predictor of the outcome (MACE) after the patient’s arrival, based on available clinical data and in a resource-limited setting like ours.
Cardiovascular epidemiology studies indicate that this has become a significant public health problem in India.1 Several risk scores for ACS have been published in European and American guidelines. However, in the Indian population, minimal data are available on utilization of such a triage score (HEART score) in chest pain patients in the ED in a resource-limited setting, to the best of our knowledge. In India, only 1 such study is reported,15 at the Sundaram Medical Foundation, a 170-bed community hospital in Chennai. In this study, 13 of 14 patients (92.86%) with a high HEART score had MACE, indicating a sensitivity of 92.86%; in the 44 patients with a low HEART score, 1 patient (2.22%) had MACE, indicating a specificity of 97.78%; and in the 28 patients with a moderate HEART score, 12 patients (42.86%) had MACE.
In looking for the optimal risk-stratifying system for chest pain patients, we analyzed the HEART score. The first study on the HEART score was done Backus et al, proving that the HEART score is an easy, quick, and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients.10 The HEART score had good discriminatory power, too. The C statistic for the HEART score for ACS occurrence shows a value of 0.83. This signifies a good-to-excellent ability to stratify all-cause chest pain patients in the ED for their risk of MACE. The application of the HEART score to our patient population demonstrated that the majority of the patients belonged to the low-risk category, as reported in the first cohort study that applied the HEART score.8 The relationship between the HEART score category and occurrence of MACE within 6 weeks showed a curve with 3 different patterns, corresponding to the 3 risk categories defined in the literature.11,12 The risk stratification of chest pain patients using the 3 categories (0-3, 4-6, 7-10) identified MACE with an incidence similar to the multicenter study of Backus et al,10,11 but with a greater risk of MACE in the high-risk category (Figure).
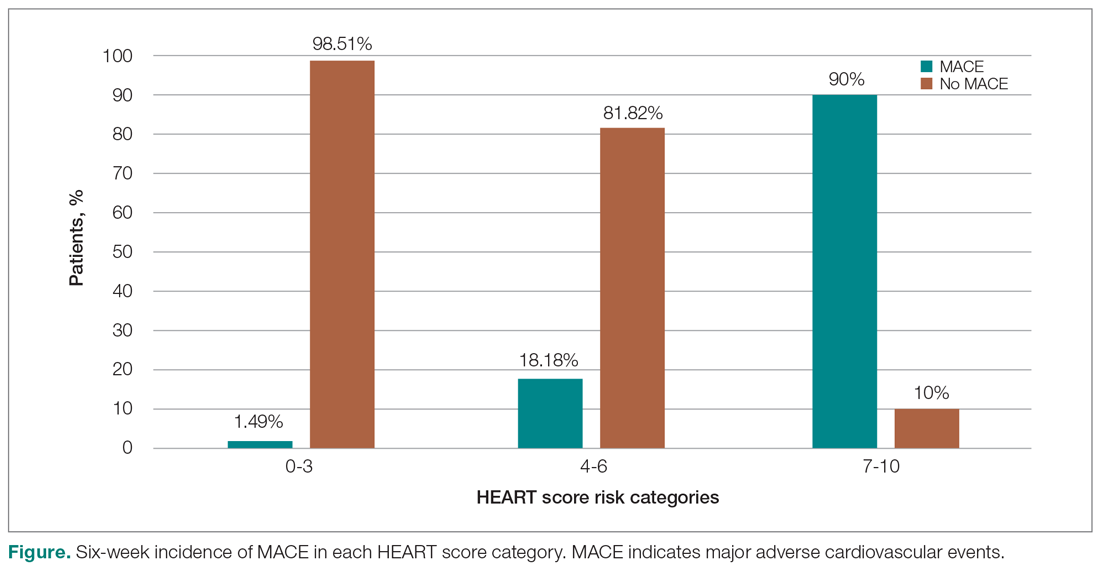
Thus, our study confirmed the utility of the HEART score categories to predict the 6-week incidence of MACE. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for the established cut-off scores of 4 and 7 are shown in Table 8. The patients in the low-risk category, corresponding to a score < 4, had a very high negative predictive value, thus identifying a small-risk population. The patients in the high-risk category (score ≥ 7) showed a high positive predictive value, allowing the identification of a high-risk population, even in patients with more atypical presentations. Therefore, the HEART score may help clinicians to make accurate management choices by being a strong predictor of both event-free survival and potentially life-threatening cardiac events.11,12
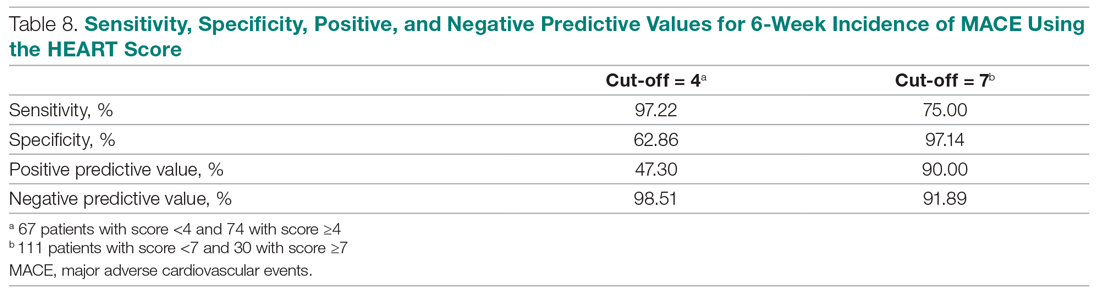
Our study tested the efficacy of the HEART score pathway in helping clinicians make smart diagnostic and therapeutic choices. It confirmed that the HEART score was accurate in predicting the short-term incidence of MACE, thus stratifying patients according to their risk severity. In our study, 67 of 141 patients (47.52%) had low-risk HEART scores, and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 1.49%. We omitted the diagnostic and treatment evaluation for patients in the low-risk category and moved onto discharge. Overall, 66 of 67 patients (98.51%) in the low-risk category had an uneventful recovery following discharge. Only 2 of 67 these patients (2.99%) of patients had health care utilization following discharge. Therefore, extrapolation based on results demonstrates reduced health care utilization. Previous studies have shown similar results.9,12,14,16 For instance, in a prospective study conducted in the Netherlands, low-risk patients representing 36.4% of the total were found to have a low MACE rate (1.7%).9 These low-risk patients were categorized as appropriate and safe for ED discharge without additional cardiac evaluation or inpatient admission.9 Another retrospective study in Portugal,12 and one in Chennai, India,15 found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 2.00% and 2.22%, respectively. The results of the first HEART Pathway Randomized Control Trial14 showed that the HEART score pathway reduces health care utilization (cardiac testing, hospitalization, and hospital length of stay). The study also showed that these gains occurred without any of the patients that were identified for early discharge, suffering from MACE at 30 days, or secondary increase in cardiac-related hospitalizations. Similar results were obtained by a randomized trial conducted in North Carolina17 that also demonstrated a reduction in objective cardiac testing, a doubling of the rate of early discharge from the ED, and a reduced length of stay by half a day. Another study using a modified HEART score also demonstrated that when low-risk patients are evaluated with cardiac testing, the likelihood for false positives is high.16 Hoffman et al also reported that patients randomized to coronary computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) received > 2.5 times more radiation exposure.16 Thus, low-risk patients may be safely discharged without the need for stress testing or CCTA.
In our study, 30 out of 141 patients (21.28%) had high-risk HEART scores (7-10), and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 90%. Based on the pathway leading to inpatient admission and intensive treatment, 23 of 30 patients (76.67%) patients in our study underwent coronary angiography and further therapeutic treatment. In the high-risk category, 28 of 30 patients (93.33%) patients had an uneventful recovery following discharge. Previous studies have shown similar results. A retrospective study in Portugal showed that 76.9% of the high-risk patients had a 6-week incidence of MACE.12 In a study in the Netherlands,9 72.7% of high-risk patients had a 6-week incidence of MACE. Therefore, a HEART score of ≥ 7 in patients implies early aggressive treatment, including invasive strategies, when necessary, without noninvasive treatment preceding it.8
In terms of intermediate risk, in our study 44 of 141 patients (31.21%) patients had an intermediate-risk HEART score (4-6), and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 18.18%. Based on the pathway, they were kept in the observation ward on admission. In our study, 7 of 44 patients (15.91%) underwent coronary angiography and further treatment; 42 of 44 patients (95.55%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge. In a prospective study in the Netherlands, 46.1% of patients with an intermediate score had a 6-week MACE incidence of 16.6%.10 Similarly, in another retrospective study in Portugal, the incidence of 6-week MACE in intermediate-risk patients (36.7%) was found to be 15.6%.12 Therefore, in patients with a HEART score of 4-6 points, immediate discharge is not an option, as this figure indicates a risk of 18.18% for an adverse outcome. These patients should be admitted for clinical observation, treated as an ACS awaiting final diagnosis, and subjected to noninvasive investigations, such as repeated troponin. Using the HEART score as guidance in the treatment of chest pain patients will benefit patients on both sides of the spectrum.11,12
Our sample presented a male predominance, a wide range of age, and a mean age similar to that of previous studies.12.16 Some risk factors, we found, can increase significantly the odds of chest pain being of cardiovascular origin, such as male gender, smoking, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia. Other studies also reported similar findings.8,12,16 Risk factors for premature CHD have been quantified in the case-control INTERHEART study.1 In the INTERHEART study, 8 common risk factors explained > 90% of AMIs in South Asian and Indian patients. The risk factors include dyslipidemia, smoking or tobacco use, known hypertension, known diabetes, abdominal obesity, physical inactivity, low fruit and vegetable intake, and psychosocial stress.1 Regarding the feasibility of treating physicians using the HEART score in the ED, we observed that, based on the Likert scale, 80% of survey respondents found it easy to use, and 100% found it feasible in the ED.
However, there were certain limitations to our study. It involved a single academic medical center and a small sample size, which limit generalizability of the findings. In addition, troponin levels are not calculated at our institution, as it is a resource-limited setting; therefore, we used a positive and negative as +2 and 0, respectively.
Conclusion
The HEART score provides the clinician with a quick and reliable predictor of outcome of patients with chest pain after arrival to the ED and can be used for triage. For patients with low HEART scores (0-3), short-term MACE can be excluded with greater than 98% certainty. In these patients, one may consider reserved treatment and discharge policies that may also reduce health care utilization. In patients with high HEART scores (7-10), the high risk of MACE (90%) may indicate early aggressive treatment, including invasive strategies, when necessary. Therefore, the HEART score may help clinicians make accurate management choices by being a strong predictor of both event-free survival and potentially life-threatening cardiac events. Age, gender, and cardiovascular risk factors may also be considered in the assessment of patients. This study confirmed the utility of the HEART score categories to predict the 6-week incidence of MACE.
Corresponding author: Smrati Bajpai Tiwari, MD, DNB, FAIMER, Department of Medicine, Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College and King Edward Memorial Hospital, Acharya Donde Marg, Parel, Mumbai 400 012, Maharashtra, India; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Gupta R, Mohan I, Narula J. Trends in coronary heart disease epidemiology in India. Ann Glob Health. 2016;82:307-315.
2. World Health Organization. Global status report on non-communicable diseases 2014. Accessed June 22, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/148114/9789241564854_eng.pdf
3. Fuster V, Kelly BB, eds. Promoting Cardiovascular Health in the Developing World: A Critical Challenge to Achieve Global Health. Institutes of Medicine; 2010.
4. Krishnan MN. Coronary heart disease and risk factors in India—on the brink of an epidemic. Indian Heart J. 2012;64:364-367.
5. Prabhakaran D, Jeemon P, Roy A. Cardiovascular diseases in India: current epidemiology and future directions. Circulation. 2016;133:1605-1620.
6. Aeri B, Chauhan S. The rising incidence of cardiovascular diseases in India: assessing its economic impact. J Prev Cardiol. 2015;4:735-740.
7. Pednekar M, Gupta R, Gupta PC. Illiteracy, low educational status and cardiovascular mortality in India. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:567.
8. Six AJ, Backus BE, Kelder JC. Chest pain in the emergency room: value of the HEART score. Neth Heart J. 2008;16:191-196.
9. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JC, et al. A prospective validation of the HEART score for chest pain patients at the emergency department. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168;2153-2158.
10. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JC, et al. Chest pain in the emergency room: a multicenter validation of the HEART score. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2010;9:164-169.
11. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JH, et al. Risk scores for patients with chest pain: evaluation in the emergency department. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2011;7:2-8.
12. Leite L, Baptista R, Leitão J, et al. Chest pain in the emergency department: risk stratification with Manchester triage system and HEART score. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015;15:48.
13. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation. 2018;138:e618-e651.
14. Mahler SA, Riley RF, Hiestand BC, et al. The HEART Pathway randomized trial: identifying emergency department patients with acute chest pain for early discharge. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2015;8:195-203.
15. Natarajan B, Mallick P, Thangalvadi TA, Rajavelu P. Validation of the HEART score in Indian population. Int J Emerg Med. 2015,8(suppl 1):P5.
16. McCord J, Cabrera R, Lindahl B, et al. Prognostic utility of a modified HEART score in chest pain patients in the emergency department. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2017;10:e003101.
17. Mahler SA, Miller CD, Hollander JE, et al. Identifying patients for early discharge: performance of decision rules among patients with acute chest pain. Int J Cardiol. 2012;168:795-802.
From the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY (Dr. Gandhi), and the School of Medicine, Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College, and King Edward Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, India (Drs. Gandhi and Tiwari).
Objective: Calculation of HEART score to (1) stratify patients as low-risk, intermediate-risk, high-risk, and to predict the short-term incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and (2) demonstrate feasibility of HEART score in our local settings.
Design: A prospective cohort study of patients with a chief complaint of chest pain concerning for acute coronary syndrome.
Setting: Participants were recruited from the emergency department (ED) of King Edward Memorial Hospital, a tertiary care academic medical center and a resource-limited setting in Mumbai, India.
Participants: We evaluated 141 patients aged 18 years and older presenting to the ED and stratified them using the HEART score. To assess patients’ progress, a follow-up phone call was made within 6 weeks after presentation to the ED.
Measurements: The primary outcomes were a risk stratification, 6-week occurrence of MACE, and performance of unscheduled revascularization or stress testing. The secondary outcomes were discharge or death.
Results: The 141 participants were stratified into low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk groups: 67 (47.52%), 44 (31.21%), and 30 (21.28%), respectively. The 6-week incidence of MACE in each category was 1.49%, 18.18%, and 90%, respectively. An acute myocardial infarction was diagnosed in 24 patients (17.02%), 15 patients (10.64%) underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and 4 patients (2.84%) underwent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). Overall, 98.5% of low-risk patients and 93.33% of high-risk patients had an uneventful recovery following discharge; therefore, extrapolation based on results demonstrated reduced health care utilization. All the survey respondents found the HEART score to be feasible. The patient characteristics and risk profile of the patients with and without MACE demonstrated that: patients with MACE were older and had a higher proportion of males, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, prior history of PCI/CABG, and history of stroke.
Conclusion: The HEART score seems to be a useful tool for risk stratification and a reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients and can therefore be used for triage.
Keywords: chest pain; emergency department; HEART score; acute coronary syndrome; major adverse cardiac events; myocardial infarction; revascularization.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), especially coronary heart disease (CHD), have epidemic proportions worldwide. Globally, in 2012, CVD led to 17.5 million deaths,1,2 with more than 75% of them occurring in developing countries. In contrast to developed countries, where mortality from CHD is rapidly declining, it is increasing in developing countries.1,3 Current estimates from epidemiologic studies from various parts of India indicate the prevalence of CHD in India to be between 7% and 13% in urban populations and 2% and 7% in rural populations.4
Premature mortality in terms of years of life lost because of CVD in India increased by 59% over a 20-year span, from 23.2 million in 1990 to 37 million in 2010.5 Studies conducted in Mumbai (Mumbai Cohort Study) reported very high CVD mortality rates, approaching 500 per 100 000 for men and 250 per 100 000 for women.6,7 However, to the best of our knowledge, in the Indian population, there are minimal data on utilization of a triage score, such as the HEART score, in chest pain patients in the emergency department (ED) in a resource-limited setting.
The most common reason for admitting patients to the ED is chest pain.8 There are various cardiac and noncardiac etiologies of chest pain presentation. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) needs to be ruled out first in every patient presenting with chest pain. However, 80% of patients with ACS have no clear diagnostic features on presentation.9 The timely diagnosis and treatment of patients with ACS improves their prognosis. Therefore, clinicians tend to start each patient on ACS treatment to reduce the risk, which often leads to increased costs due to unnecessary, time-consuming diagnostic procedures that may place burdens on both the health care system and the patient.10
Several risk-stratifying tools have been developed in the last few years. Both the GRACE and TIMI risk scores have been designed for risk stratification of patients with proven ACS and not for the chest pain population at the ED.11 Some of these tools are applicable to patients with all types of chest pain presenting to the ED, such as the Manchester Triage System. Other, more selective systems are devoted to the risk stratification of suspected ACS in the ED. One is the HEART score.12
The first study on the HEART score—an acronym that stands for History, Electrocardiogram, Age, Risk factors, and Troponin—was done by Backus et al, who proved that the HEART score is an easy, quick, and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients.10 The HEART score predicts the short-term incidence of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), which allows clinicians to stratify patients as low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk and to guide their clinical decision-making accordingly. It was developed to provide clinicians with a simple, reliable predictor of cardiac risk on the basis of the lowest score of 0 (very low-risk) up to a score of 10 (very high-risk).
We studied the clinical performance of the HEART score in patients with chest pain, focusing on the efficacy and safety of rapidly identifying patients at risk of MACE. We aimed to determine (1) whether the HEART score is a reliable predictor of outcomes of chest pain patients presenting to the ED; (2) whether the score is feasible in our local settings; and (3) whether it describes the risk profile of patients with and without MACE.
Methods
Setting
Participants were recruited from the ED of King Edward Memorial Hospital, a municipal teaching hospital in Mumbai. The study institute is a tertiary care academic medical center located in Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra, and is a resource-limited setting serving urban, suburban, and rural populations. Participants requiring urgent attention are first seen by a casualty officer and then referred to the emergency ward. Here, the physician on duty evaluates them and decides on admission to the various wards, like the general ward, medical intensive care unit (ICU), coronary care unit (CCU), etc. The specialist’s opinion may also be obtained before admission. Critically ill patients are initially admitted to the emergency ward and stabilized before being shifted to other areas of the hospital.
Participants
Patients aged 18 years and older presenting with symptoms of acute chest pain or suspected ACS were stratified by priority using the chest pain scoring system—the HEART score. Only patients presenting to the ED were eligible for the study. Informed consent from the patient or next of kin was mandatory for participation in the study.
Patients were determined ineligible for the following reasons: a clear cause for chest pain other than ACS (eg, trauma, diagnosed aortic dissection), persisting or recurrent chest pain caused by rheumatic diseases or cancer (a terminal illness), pregnancy, unable or unwilling to provide informed consent, or incomplete data.
Study design
We conducted a
We conducted our study to determine the importance of calculating the HEART score in each patient, which will help to correctly place them into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups for clinically important, irreversible adverse cardiac events and guide the clinical decision-making. Patients with low risk will avoid costly tests and hospital admissions, thus decreasing the cost of treatment and ensuring timely discharge from the ED. Patients with high risk will be treated immediately, to possibly prevent a life-threatening, ACS-related incident. Thus, the HEART score will serve as a quick and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients and help clinicians to make accurate diagnostic and therapeutic choices in uncertain situations.
HEART score
The total number of points for History, Electrocardiogram (ECG), Age, Risk factors, and Troponin was noted as the HEART score (Table 1).

For this study, the patient’s history and ECGs were interpreted by internal medicine attending physicians in the ED. The ECG taken in the emergency room was reviewed and classified, and a copy of the admission ECG was added to the file. The recommendation for patients with a HEART score in a particular range was evaluated. Notably, those with a score of 3 or lower led to a recommendation of reassurance and early discharge. Those with a HEART score in the intermediate range (4-6) were admitted to the hospital for further clinical observation and testing, whereas a high HEART score (7-10) led to admission for intensive monitoring and early intervention. In the analysis of HEART score data, we only used those patients having records for all 5 parameters, excluding patients without an ECG or troponin test.
Results
Myocardial infarction (MI) was defined based on Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction.13 Coronary revascularization was defined as angioplasty with or without stent placement or coronary artery bypass surgery.14 Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was defined as any therapeutic catheter intervention in the coronary arteries. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery was defined as any cardiac surgery in which coronary arteries were operated on.
The primary outcomes in this study were the (1) risk stratification of chest pain patients into low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk categories; (2) incidence of a MACE within 6 weeks of initial presentation. MACE consists of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), PCI, CABG, coronary angiography revealing procedurally correctable stenosis managed conservatively, and death due to any cause.
Our secondary outcomes were discharge or death due to any cause within 6 weeks after presentation.
Follow-up
Within 6 weeks after presentation to the ED, a follow-up phone call was placed to assess the patient’s progress. The follow-up focused on the endpoint of MACE, comprising all-cause death, MI, and revascularization. No patient was lost to follow-up.
Statistical analysis
We aimed to find a difference in the 6-week MACE between low-, intermediate-, and high-risk categories of the HEART score. The prevalence of CHD in India is 10%,4 and assuming an α of 0.05, we needed a sample of 141 patients from the ED patient population. Continuous variables were presented by mean (SD), and categorical variables as percentages. We used t test and the Mann-Whitney U test for comparison of means for continuous variables, χ2 for categorical variables, and Fisher’s exact test for comparison of the categorical variables. Results with P < .05 were considered statistically significant.
We evaluated 141 patients presenting to the ED with chest pain concerning for ACS during the study period, from July 2019 to October 2019.

Primary outcomes
The risk stratification of the HEART score in chest pain patients and the incidence of 6-week MACE are outlined in Table 3

The distribution of the HEART score’s 5 elements in the groups with or without MACE endpoints is shown in Table 5. Notice the significant differences between the groups. A follow-up phone call was made within 6 weeks after the presentation to the ED to assess the patient’s progress. The 6-week follow-up call data are included in Table 6.

Of 141 patients, 36 patients (25.53%) were diagnosed with MACE within 6 weeks of presentation.

Myocardial infarction—An AMI was diagnosed in 24 of the 141 patients (17.02%). Twenty-one of those already had positive markers on admission (apparently, these AMI had started before their arrival to the emergency room). One AMI occurred 2 days after admission in a 66-year-old male, and another occurred 10 days after discharge. A further AMI occurred 2 weeks after discharge. All 3 patients belonged to the intermediate-risk group.

Revascularization—Coronary angiography was performed in 31 of 141 patients (21.99%). Revascularization was performed in 19 patients (13.48%), of which 15 were PCIs (10.64%) and 4 were CABGs (2.84%).
Mortality—One patient died from the study population. He was a 72-year-old male who died 14 days after admission. He had a HEART score of 8.
Among the 67 low-risk patients:
- MACE: Coronary angiography was performed in 1 patient (1.49%). Among the 67 patients in the low-risk category, there was no cases of AMI or deaths. The remaining 66 patients (98.51%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge.
- General practitioner (GP) visits/readmissions following discharge: Two of 67 patients (2.99%) had GP visits following discharge, of which 1 was uneventful. The other patient, a 64-year-old male, was readmitted due to a recurrent history of chest pain and underwent coronary angiography.
Among the 44 intermediate-risk patients:
- MACE: Of the 7 of 44 patients (15.91%) who had coronary angiography, 3 patients (6.82%) had AMI, of which 1 occurred 2 days after admission in a 66-year-old male. Two patients had AMI following discharge. There were no deaths. Overall, 42 of 44 patients (95.55%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge.
- GP visits/readmissions following discharge: Three of 44 patients (6.82%) had repeated visits following discharge. One was a GP visit that was uneventful. The remaining 2 patients were diagnosed with AMI and readmitted following discharge. One AMI occurred 10 days after discharge in a patient with a HEART score of 6; another occurred 2 weeks after discharge in a patient with a HEART score of 5.
Among the 30 high-risk patients:
- MACE: Twenty-three of 30 patients (76.67%) underwent coronary angiography. One patient died 5 days after discharge. The patient had a HEART score of 8. Most patients however, had an uneventful recovery following discharge (28, 93.33%).
- GP visits/readmissions following discharge: Five of 30 patients (16.67%) had repeated visits following discharge. Two were uneventful. Two patients had a history of recurrent chest pain that resolved on Sorbitrate. One patient was readmitted 2 weeks following discharge due to a complication: a left ventricular clot was found. The patient had a HEART score of 10.
Secondary outcome—Overall, 140 of 141 patients were discharged. One patient died: a 72-year-old male with a HEART score of 8.
Feasibility—To determine the ease and feasibility of performing a HEART score in chest pain patients presenting to the ED, a survey was distributed to the internal medicine physicians in the ED. In the survey, the Likert scale was used to rate the ease of utilizing the HEART score and whether the physicians found it feasible to use it for risk stratification of their chest pain patients. A total of 12 of 15 respondents (80%) found it “easy” to use. Of the remaining 3 respondents, 2 (13.33%) rated the HEART score “very easy” to use, while 1 (6.66%) considered it “difficult” to work with. None of the respondents said that it was not feasible to perform a HEART score in the ED.
Risk factors for reaching an endpoint:
We compared risk profiles between the patient groups with and without an endpoint. The group of patients with MACE were older and had a higher proportion of males than the group of patients without MACE. Moreover, they also had a higher prevalence of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, prior history of PCI/CABG, and history of stroke. These also showed a significant association with MACE. Obesity was not included in our risk factors as we did not have data collected to measure body mass index. Results are represented in Table 7.

Discussion
Our study described a patient population presenting to an ED with chest pain as their primary complaint. The results of this prospective study confirm that the HEART score is an excellent system to triage chest pain patients. It provides the clinician with a reliable predictor of the outcome (MACE) after the patient’s arrival, based on available clinical data and in a resource-limited setting like ours.
Cardiovascular epidemiology studies indicate that this has become a significant public health problem in India.1 Several risk scores for ACS have been published in European and American guidelines. However, in the Indian population, minimal data are available on utilization of such a triage score (HEART score) in chest pain patients in the ED in a resource-limited setting, to the best of our knowledge. In India, only 1 such study is reported,15 at the Sundaram Medical Foundation, a 170-bed community hospital in Chennai. In this study, 13 of 14 patients (92.86%) with a high HEART score had MACE, indicating a sensitivity of 92.86%; in the 44 patients with a low HEART score, 1 patient (2.22%) had MACE, indicating a specificity of 97.78%; and in the 28 patients with a moderate HEART score, 12 patients (42.86%) had MACE.
In looking for the optimal risk-stratifying system for chest pain patients, we analyzed the HEART score. The first study on the HEART score was done Backus et al, proving that the HEART score is an easy, quick, and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients.10 The HEART score had good discriminatory power, too. The C statistic for the HEART score for ACS occurrence shows a value of 0.83. This signifies a good-to-excellent ability to stratify all-cause chest pain patients in the ED for their risk of MACE. The application of the HEART score to our patient population demonstrated that the majority of the patients belonged to the low-risk category, as reported in the first cohort study that applied the HEART score.8 The relationship between the HEART score category and occurrence of MACE within 6 weeks showed a curve with 3 different patterns, corresponding to the 3 risk categories defined in the literature.11,12 The risk stratification of chest pain patients using the 3 categories (0-3, 4-6, 7-10) identified MACE with an incidence similar to the multicenter study of Backus et al,10,11 but with a greater risk of MACE in the high-risk category (Figure).

Thus, our study confirmed the utility of the HEART score categories to predict the 6-week incidence of MACE. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for the established cut-off scores of 4 and 7 are shown in Table 8. The patients in the low-risk category, corresponding to a score < 4, had a very high negative predictive value, thus identifying a small-risk population. The patients in the high-risk category (score ≥ 7) showed a high positive predictive value, allowing the identification of a high-risk population, even in patients with more atypical presentations. Therefore, the HEART score may help clinicians to make accurate management choices by being a strong predictor of both event-free survival and potentially life-threatening cardiac events.11,12

Our study tested the efficacy of the HEART score pathway in helping clinicians make smart diagnostic and therapeutic choices. It confirmed that the HEART score was accurate in predicting the short-term incidence of MACE, thus stratifying patients according to their risk severity. In our study, 67 of 141 patients (47.52%) had low-risk HEART scores, and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 1.49%. We omitted the diagnostic and treatment evaluation for patients in the low-risk category and moved onto discharge. Overall, 66 of 67 patients (98.51%) in the low-risk category had an uneventful recovery following discharge. Only 2 of 67 these patients (2.99%) of patients had health care utilization following discharge. Therefore, extrapolation based on results demonstrates reduced health care utilization. Previous studies have shown similar results.9,12,14,16 For instance, in a prospective study conducted in the Netherlands, low-risk patients representing 36.4% of the total were found to have a low MACE rate (1.7%).9 These low-risk patients were categorized as appropriate and safe for ED discharge without additional cardiac evaluation or inpatient admission.9 Another retrospective study in Portugal,12 and one in Chennai, India,15 found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 2.00% and 2.22%, respectively. The results of the first HEART Pathway Randomized Control Trial14 showed that the HEART score pathway reduces health care utilization (cardiac testing, hospitalization, and hospital length of stay). The study also showed that these gains occurred without any of the patients that were identified for early discharge, suffering from MACE at 30 days, or secondary increase in cardiac-related hospitalizations. Similar results were obtained by a randomized trial conducted in North Carolina17 that also demonstrated a reduction in objective cardiac testing, a doubling of the rate of early discharge from the ED, and a reduced length of stay by half a day. Another study using a modified HEART score also demonstrated that when low-risk patients are evaluated with cardiac testing, the likelihood for false positives is high.16 Hoffman et al also reported that patients randomized to coronary computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) received > 2.5 times more radiation exposure.16 Thus, low-risk patients may be safely discharged without the need for stress testing or CCTA.
In our study, 30 out of 141 patients (21.28%) had high-risk HEART scores (7-10), and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 90%. Based on the pathway leading to inpatient admission and intensive treatment, 23 of 30 patients (76.67%) patients in our study underwent coronary angiography and further therapeutic treatment. In the high-risk category, 28 of 30 patients (93.33%) patients had an uneventful recovery following discharge. Previous studies have shown similar results. A retrospective study in Portugal showed that 76.9% of the high-risk patients had a 6-week incidence of MACE.12 In a study in the Netherlands,9 72.7% of high-risk patients had a 6-week incidence of MACE. Therefore, a HEART score of ≥ 7 in patients implies early aggressive treatment, including invasive strategies, when necessary, without noninvasive treatment preceding it.8
In terms of intermediate risk, in our study 44 of 141 patients (31.21%) patients had an intermediate-risk HEART score (4-6), and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 18.18%. Based on the pathway, they were kept in the observation ward on admission. In our study, 7 of 44 patients (15.91%) underwent coronary angiography and further treatment; 42 of 44 patients (95.55%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge. In a prospective study in the Netherlands, 46.1% of patients with an intermediate score had a 6-week MACE incidence of 16.6%.10 Similarly, in another retrospective study in Portugal, the incidence of 6-week MACE in intermediate-risk patients (36.7%) was found to be 15.6%.12 Therefore, in patients with a HEART score of 4-6 points, immediate discharge is not an option, as this figure indicates a risk of 18.18% for an adverse outcome. These patients should be admitted for clinical observation, treated as an ACS awaiting final diagnosis, and subjected to noninvasive investigations, such as repeated troponin. Using the HEART score as guidance in the treatment of chest pain patients will benefit patients on both sides of the spectrum.11,12
Our sample presented a male predominance, a wide range of age, and a mean age similar to that of previous studies.12.16 Some risk factors, we found, can increase significantly the odds of chest pain being of cardiovascular origin, such as male gender, smoking, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia. Other studies also reported similar findings.8,12,16 Risk factors for premature CHD have been quantified in the case-control INTERHEART study.1 In the INTERHEART study, 8 common risk factors explained > 90% of AMIs in South Asian and Indian patients. The risk factors include dyslipidemia, smoking or tobacco use, known hypertension, known diabetes, abdominal obesity, physical inactivity, low fruit and vegetable intake, and psychosocial stress.1 Regarding the feasibility of treating physicians using the HEART score in the ED, we observed that, based on the Likert scale, 80% of survey respondents found it easy to use, and 100% found it feasible in the ED.
However, there were certain limitations to our study. It involved a single academic medical center and a small sample size, which limit generalizability of the findings. In addition, troponin levels are not calculated at our institution, as it is a resource-limited setting; therefore, we used a positive and negative as +2 and 0, respectively.
Conclusion
The HEART score provides the clinician with a quick and reliable predictor of outcome of patients with chest pain after arrival to the ED and can be used for triage. For patients with low HEART scores (0-3), short-term MACE can be excluded with greater than 98% certainty. In these patients, one may consider reserved treatment and discharge policies that may also reduce health care utilization. In patients with high HEART scores (7-10), the high risk of MACE (90%) may indicate early aggressive treatment, including invasive strategies, when necessary. Therefore, the HEART score may help clinicians make accurate management choices by being a strong predictor of both event-free survival and potentially life-threatening cardiac events. Age, gender, and cardiovascular risk factors may also be considered in the assessment of patients. This study confirmed the utility of the HEART score categories to predict the 6-week incidence of MACE.
Corresponding author: Smrati Bajpai Tiwari, MD, DNB, FAIMER, Department of Medicine, Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College and King Edward Memorial Hospital, Acharya Donde Marg, Parel, Mumbai 400 012, Maharashtra, India; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
From the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY (Dr. Gandhi), and the School of Medicine, Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College, and King Edward Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, India (Drs. Gandhi and Tiwari).
Objective: Calculation of HEART score to (1) stratify patients as low-risk, intermediate-risk, high-risk, and to predict the short-term incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and (2) demonstrate feasibility of HEART score in our local settings.
Design: A prospective cohort study of patients with a chief complaint of chest pain concerning for acute coronary syndrome.
Setting: Participants were recruited from the emergency department (ED) of King Edward Memorial Hospital, a tertiary care academic medical center and a resource-limited setting in Mumbai, India.
Participants: We evaluated 141 patients aged 18 years and older presenting to the ED and stratified them using the HEART score. To assess patients’ progress, a follow-up phone call was made within 6 weeks after presentation to the ED.
Measurements: The primary outcomes were a risk stratification, 6-week occurrence of MACE, and performance of unscheduled revascularization or stress testing. The secondary outcomes were discharge or death.
Results: The 141 participants were stratified into low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk groups: 67 (47.52%), 44 (31.21%), and 30 (21.28%), respectively. The 6-week incidence of MACE in each category was 1.49%, 18.18%, and 90%, respectively. An acute myocardial infarction was diagnosed in 24 patients (17.02%), 15 patients (10.64%) underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and 4 patients (2.84%) underwent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). Overall, 98.5% of low-risk patients and 93.33% of high-risk patients had an uneventful recovery following discharge; therefore, extrapolation based on results demonstrated reduced health care utilization. All the survey respondents found the HEART score to be feasible. The patient characteristics and risk profile of the patients with and without MACE demonstrated that: patients with MACE were older and had a higher proportion of males, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, prior history of PCI/CABG, and history of stroke.
Conclusion: The HEART score seems to be a useful tool for risk stratification and a reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients and can therefore be used for triage.
Keywords: chest pain; emergency department; HEART score; acute coronary syndrome; major adverse cardiac events; myocardial infarction; revascularization.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), especially coronary heart disease (CHD), have epidemic proportions worldwide. Globally, in 2012, CVD led to 17.5 million deaths,1,2 with more than 75% of them occurring in developing countries. In contrast to developed countries, where mortality from CHD is rapidly declining, it is increasing in developing countries.1,3 Current estimates from epidemiologic studies from various parts of India indicate the prevalence of CHD in India to be between 7% and 13% in urban populations and 2% and 7% in rural populations.4
Premature mortality in terms of years of life lost because of CVD in India increased by 59% over a 20-year span, from 23.2 million in 1990 to 37 million in 2010.5 Studies conducted in Mumbai (Mumbai Cohort Study) reported very high CVD mortality rates, approaching 500 per 100 000 for men and 250 per 100 000 for women.6,7 However, to the best of our knowledge, in the Indian population, there are minimal data on utilization of a triage score, such as the HEART score, in chest pain patients in the emergency department (ED) in a resource-limited setting.
The most common reason for admitting patients to the ED is chest pain.8 There are various cardiac and noncardiac etiologies of chest pain presentation. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) needs to be ruled out first in every patient presenting with chest pain. However, 80% of patients with ACS have no clear diagnostic features on presentation.9 The timely diagnosis and treatment of patients with ACS improves their prognosis. Therefore, clinicians tend to start each patient on ACS treatment to reduce the risk, which often leads to increased costs due to unnecessary, time-consuming diagnostic procedures that may place burdens on both the health care system and the patient.10
Several risk-stratifying tools have been developed in the last few years. Both the GRACE and TIMI risk scores have been designed for risk stratification of patients with proven ACS and not for the chest pain population at the ED.11 Some of these tools are applicable to patients with all types of chest pain presenting to the ED, such as the Manchester Triage System. Other, more selective systems are devoted to the risk stratification of suspected ACS in the ED. One is the HEART score.12
The first study on the HEART score—an acronym that stands for History, Electrocardiogram, Age, Risk factors, and Troponin—was done by Backus et al, who proved that the HEART score is an easy, quick, and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients.10 The HEART score predicts the short-term incidence of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), which allows clinicians to stratify patients as low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk and to guide their clinical decision-making accordingly. It was developed to provide clinicians with a simple, reliable predictor of cardiac risk on the basis of the lowest score of 0 (very low-risk) up to a score of 10 (very high-risk).
We studied the clinical performance of the HEART score in patients with chest pain, focusing on the efficacy and safety of rapidly identifying patients at risk of MACE. We aimed to determine (1) whether the HEART score is a reliable predictor of outcomes of chest pain patients presenting to the ED; (2) whether the score is feasible in our local settings; and (3) whether it describes the risk profile of patients with and without MACE.
Methods
Setting
Participants were recruited from the ED of King Edward Memorial Hospital, a municipal teaching hospital in Mumbai. The study institute is a tertiary care academic medical center located in Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra, and is a resource-limited setting serving urban, suburban, and rural populations. Participants requiring urgent attention are first seen by a casualty officer and then referred to the emergency ward. Here, the physician on duty evaluates them and decides on admission to the various wards, like the general ward, medical intensive care unit (ICU), coronary care unit (CCU), etc. The specialist’s opinion may also be obtained before admission. Critically ill patients are initially admitted to the emergency ward and stabilized before being shifted to other areas of the hospital.
Participants
Patients aged 18 years and older presenting with symptoms of acute chest pain or suspected ACS were stratified by priority using the chest pain scoring system—the HEART score. Only patients presenting to the ED were eligible for the study. Informed consent from the patient or next of kin was mandatory for participation in the study.
Patients were determined ineligible for the following reasons: a clear cause for chest pain other than ACS (eg, trauma, diagnosed aortic dissection), persisting or recurrent chest pain caused by rheumatic diseases or cancer (a terminal illness), pregnancy, unable or unwilling to provide informed consent, or incomplete data.
Study design
We conducted a
We conducted our study to determine the importance of calculating the HEART score in each patient, which will help to correctly place them into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups for clinically important, irreversible adverse cardiac events and guide the clinical decision-making. Patients with low risk will avoid costly tests and hospital admissions, thus decreasing the cost of treatment and ensuring timely discharge from the ED. Patients with high risk will be treated immediately, to possibly prevent a life-threatening, ACS-related incident. Thus, the HEART score will serve as a quick and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients and help clinicians to make accurate diagnostic and therapeutic choices in uncertain situations.
HEART score
The total number of points for History, Electrocardiogram (ECG), Age, Risk factors, and Troponin was noted as the HEART score (Table 1).

For this study, the patient’s history and ECGs were interpreted by internal medicine attending physicians in the ED. The ECG taken in the emergency room was reviewed and classified, and a copy of the admission ECG was added to the file. The recommendation for patients with a HEART score in a particular range was evaluated. Notably, those with a score of 3 or lower led to a recommendation of reassurance and early discharge. Those with a HEART score in the intermediate range (4-6) were admitted to the hospital for further clinical observation and testing, whereas a high HEART score (7-10) led to admission for intensive monitoring and early intervention. In the analysis of HEART score data, we only used those patients having records for all 5 parameters, excluding patients without an ECG or troponin test.
Results
Myocardial infarction (MI) was defined based on Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction.13 Coronary revascularization was defined as angioplasty with or without stent placement or coronary artery bypass surgery.14 Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was defined as any therapeutic catheter intervention in the coronary arteries. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery was defined as any cardiac surgery in which coronary arteries were operated on.
The primary outcomes in this study were the (1) risk stratification of chest pain patients into low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk categories; (2) incidence of a MACE within 6 weeks of initial presentation. MACE consists of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), PCI, CABG, coronary angiography revealing procedurally correctable stenosis managed conservatively, and death due to any cause.
Our secondary outcomes were discharge or death due to any cause within 6 weeks after presentation.
Follow-up
Within 6 weeks after presentation to the ED, a follow-up phone call was placed to assess the patient’s progress. The follow-up focused on the endpoint of MACE, comprising all-cause death, MI, and revascularization. No patient was lost to follow-up.
Statistical analysis
We aimed to find a difference in the 6-week MACE between low-, intermediate-, and high-risk categories of the HEART score. The prevalence of CHD in India is 10%,4 and assuming an α of 0.05, we needed a sample of 141 patients from the ED patient population. Continuous variables were presented by mean (SD), and categorical variables as percentages. We used t test and the Mann-Whitney U test for comparison of means for continuous variables, χ2 for categorical variables, and Fisher’s exact test for comparison of the categorical variables. Results with P < .05 were considered statistically significant.
We evaluated 141 patients presenting to the ED with chest pain concerning for ACS during the study period, from July 2019 to October 2019.

Primary outcomes
The risk stratification of the HEART score in chest pain patients and the incidence of 6-week MACE are outlined in Table 3

The distribution of the HEART score’s 5 elements in the groups with or without MACE endpoints is shown in Table 5. Notice the significant differences between the groups. A follow-up phone call was made within 6 weeks after the presentation to the ED to assess the patient’s progress. The 6-week follow-up call data are included in Table 6.

Of 141 patients, 36 patients (25.53%) were diagnosed with MACE within 6 weeks of presentation.

Myocardial infarction—An AMI was diagnosed in 24 of the 141 patients (17.02%). Twenty-one of those already had positive markers on admission (apparently, these AMI had started before their arrival to the emergency room). One AMI occurred 2 days after admission in a 66-year-old male, and another occurred 10 days after discharge. A further AMI occurred 2 weeks after discharge. All 3 patients belonged to the intermediate-risk group.

Revascularization—Coronary angiography was performed in 31 of 141 patients (21.99%). Revascularization was performed in 19 patients (13.48%), of which 15 were PCIs (10.64%) and 4 were CABGs (2.84%).
Mortality—One patient died from the study population. He was a 72-year-old male who died 14 days after admission. He had a HEART score of 8.
Among the 67 low-risk patients:
- MACE: Coronary angiography was performed in 1 patient (1.49%). Among the 67 patients in the low-risk category, there was no cases of AMI or deaths. The remaining 66 patients (98.51%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge.
- General practitioner (GP) visits/readmissions following discharge: Two of 67 patients (2.99%) had GP visits following discharge, of which 1 was uneventful. The other patient, a 64-year-old male, was readmitted due to a recurrent history of chest pain and underwent coronary angiography.
Among the 44 intermediate-risk patients:
- MACE: Of the 7 of 44 patients (15.91%) who had coronary angiography, 3 patients (6.82%) had AMI, of which 1 occurred 2 days after admission in a 66-year-old male. Two patients had AMI following discharge. There were no deaths. Overall, 42 of 44 patients (95.55%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge.
- GP visits/readmissions following discharge: Three of 44 patients (6.82%) had repeated visits following discharge. One was a GP visit that was uneventful. The remaining 2 patients were diagnosed with AMI and readmitted following discharge. One AMI occurred 10 days after discharge in a patient with a HEART score of 6; another occurred 2 weeks after discharge in a patient with a HEART score of 5.
Among the 30 high-risk patients:
- MACE: Twenty-three of 30 patients (76.67%) underwent coronary angiography. One patient died 5 days after discharge. The patient had a HEART score of 8. Most patients however, had an uneventful recovery following discharge (28, 93.33%).
- GP visits/readmissions following discharge: Five of 30 patients (16.67%) had repeated visits following discharge. Two were uneventful. Two patients had a history of recurrent chest pain that resolved on Sorbitrate. One patient was readmitted 2 weeks following discharge due to a complication: a left ventricular clot was found. The patient had a HEART score of 10.
Secondary outcome—Overall, 140 of 141 patients were discharged. One patient died: a 72-year-old male with a HEART score of 8.
Feasibility—To determine the ease and feasibility of performing a HEART score in chest pain patients presenting to the ED, a survey was distributed to the internal medicine physicians in the ED. In the survey, the Likert scale was used to rate the ease of utilizing the HEART score and whether the physicians found it feasible to use it for risk stratification of their chest pain patients. A total of 12 of 15 respondents (80%) found it “easy” to use. Of the remaining 3 respondents, 2 (13.33%) rated the HEART score “very easy” to use, while 1 (6.66%) considered it “difficult” to work with. None of the respondents said that it was not feasible to perform a HEART score in the ED.
Risk factors for reaching an endpoint:
We compared risk profiles between the patient groups with and without an endpoint. The group of patients with MACE were older and had a higher proportion of males than the group of patients without MACE. Moreover, they also had a higher prevalence of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, prior history of PCI/CABG, and history of stroke. These also showed a significant association with MACE. Obesity was not included in our risk factors as we did not have data collected to measure body mass index. Results are represented in Table 7.

Discussion
Our study described a patient population presenting to an ED with chest pain as their primary complaint. The results of this prospective study confirm that the HEART score is an excellent system to triage chest pain patients. It provides the clinician with a reliable predictor of the outcome (MACE) after the patient’s arrival, based on available clinical data and in a resource-limited setting like ours.
Cardiovascular epidemiology studies indicate that this has become a significant public health problem in India.1 Several risk scores for ACS have been published in European and American guidelines. However, in the Indian population, minimal data are available on utilization of such a triage score (HEART score) in chest pain patients in the ED in a resource-limited setting, to the best of our knowledge. In India, only 1 such study is reported,15 at the Sundaram Medical Foundation, a 170-bed community hospital in Chennai. In this study, 13 of 14 patients (92.86%) with a high HEART score had MACE, indicating a sensitivity of 92.86%; in the 44 patients with a low HEART score, 1 patient (2.22%) had MACE, indicating a specificity of 97.78%; and in the 28 patients with a moderate HEART score, 12 patients (42.86%) had MACE.
In looking for the optimal risk-stratifying system for chest pain patients, we analyzed the HEART score. The first study on the HEART score was done Backus et al, proving that the HEART score is an easy, quick, and reliable predictor of outcomes in chest pain patients.10 The HEART score had good discriminatory power, too. The C statistic for the HEART score for ACS occurrence shows a value of 0.83. This signifies a good-to-excellent ability to stratify all-cause chest pain patients in the ED for their risk of MACE. The application of the HEART score to our patient population demonstrated that the majority of the patients belonged to the low-risk category, as reported in the first cohort study that applied the HEART score.8 The relationship between the HEART score category and occurrence of MACE within 6 weeks showed a curve with 3 different patterns, corresponding to the 3 risk categories defined in the literature.11,12 The risk stratification of chest pain patients using the 3 categories (0-3, 4-6, 7-10) identified MACE with an incidence similar to the multicenter study of Backus et al,10,11 but with a greater risk of MACE in the high-risk category (Figure).

Thus, our study confirmed the utility of the HEART score categories to predict the 6-week incidence of MACE. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for the established cut-off scores of 4 and 7 are shown in Table 8. The patients in the low-risk category, corresponding to a score < 4, had a very high negative predictive value, thus identifying a small-risk population. The patients in the high-risk category (score ≥ 7) showed a high positive predictive value, allowing the identification of a high-risk population, even in patients with more atypical presentations. Therefore, the HEART score may help clinicians to make accurate management choices by being a strong predictor of both event-free survival and potentially life-threatening cardiac events.11,12

Our study tested the efficacy of the HEART score pathway in helping clinicians make smart diagnostic and therapeutic choices. It confirmed that the HEART score was accurate in predicting the short-term incidence of MACE, thus stratifying patients according to their risk severity. In our study, 67 of 141 patients (47.52%) had low-risk HEART scores, and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 1.49%. We omitted the diagnostic and treatment evaluation for patients in the low-risk category and moved onto discharge. Overall, 66 of 67 patients (98.51%) in the low-risk category had an uneventful recovery following discharge. Only 2 of 67 these patients (2.99%) of patients had health care utilization following discharge. Therefore, extrapolation based on results demonstrates reduced health care utilization. Previous studies have shown similar results.9,12,14,16 For instance, in a prospective study conducted in the Netherlands, low-risk patients representing 36.4% of the total were found to have a low MACE rate (1.7%).9 These low-risk patients were categorized as appropriate and safe for ED discharge without additional cardiac evaluation or inpatient admission.9 Another retrospective study in Portugal,12 and one in Chennai, India,15 found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 2.00% and 2.22%, respectively. The results of the first HEART Pathway Randomized Control Trial14 showed that the HEART score pathway reduces health care utilization (cardiac testing, hospitalization, and hospital length of stay). The study also showed that these gains occurred without any of the patients that were identified for early discharge, suffering from MACE at 30 days, or secondary increase in cardiac-related hospitalizations. Similar results were obtained by a randomized trial conducted in North Carolina17 that also demonstrated a reduction in objective cardiac testing, a doubling of the rate of early discharge from the ED, and a reduced length of stay by half a day. Another study using a modified HEART score also demonstrated that when low-risk patients are evaluated with cardiac testing, the likelihood for false positives is high.16 Hoffman et al also reported that patients randomized to coronary computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) received > 2.5 times more radiation exposure.16 Thus, low-risk patients may be safely discharged without the need for stress testing or CCTA.
In our study, 30 out of 141 patients (21.28%) had high-risk HEART scores (7-10), and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 90%. Based on the pathway leading to inpatient admission and intensive treatment, 23 of 30 patients (76.67%) patients in our study underwent coronary angiography and further therapeutic treatment. In the high-risk category, 28 of 30 patients (93.33%) patients had an uneventful recovery following discharge. Previous studies have shown similar results. A retrospective study in Portugal showed that 76.9% of the high-risk patients had a 6-week incidence of MACE.12 In a study in the Netherlands,9 72.7% of high-risk patients had a 6-week incidence of MACE. Therefore, a HEART score of ≥ 7 in patients implies early aggressive treatment, including invasive strategies, when necessary, without noninvasive treatment preceding it.8
In terms of intermediate risk, in our study 44 of 141 patients (31.21%) patients had an intermediate-risk HEART score (4-6), and we found the 6-week incidence of MACE to be 18.18%. Based on the pathway, they were kept in the observation ward on admission. In our study, 7 of 44 patients (15.91%) underwent coronary angiography and further treatment; 42 of 44 patients (95.55%) had an uneventful recovery following discharge. In a prospective study in the Netherlands, 46.1% of patients with an intermediate score had a 6-week MACE incidence of 16.6%.10 Similarly, in another retrospective study in Portugal, the incidence of 6-week MACE in intermediate-risk patients (36.7%) was found to be 15.6%.12 Therefore, in patients with a HEART score of 4-6 points, immediate discharge is not an option, as this figure indicates a risk of 18.18% for an adverse outcome. These patients should be admitted for clinical observation, treated as an ACS awaiting final diagnosis, and subjected to noninvasive investigations, such as repeated troponin. Using the HEART score as guidance in the treatment of chest pain patients will benefit patients on both sides of the spectrum.11,12
Our sample presented a male predominance, a wide range of age, and a mean age similar to that of previous studies.12.16 Some risk factors, we found, can increase significantly the odds of chest pain being of cardiovascular origin, such as male gender, smoking, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia. Other studies also reported similar findings.8,12,16 Risk factors for premature CHD have been quantified in the case-control INTERHEART study.1 In the INTERHEART study, 8 common risk factors explained > 90% of AMIs in South Asian and Indian patients. The risk factors include dyslipidemia, smoking or tobacco use, known hypertension, known diabetes, abdominal obesity, physical inactivity, low fruit and vegetable intake, and psychosocial stress.1 Regarding the feasibility of treating physicians using the HEART score in the ED, we observed that, based on the Likert scale, 80% of survey respondents found it easy to use, and 100% found it feasible in the ED.
However, there were certain limitations to our study. It involved a single academic medical center and a small sample size, which limit generalizability of the findings. In addition, troponin levels are not calculated at our institution, as it is a resource-limited setting; therefore, we used a positive and negative as +2 and 0, respectively.
Conclusion
The HEART score provides the clinician with a quick and reliable predictor of outcome of patients with chest pain after arrival to the ED and can be used for triage. For patients with low HEART scores (0-3), short-term MACE can be excluded with greater than 98% certainty. In these patients, one may consider reserved treatment and discharge policies that may also reduce health care utilization. In patients with high HEART scores (7-10), the high risk of MACE (90%) may indicate early aggressive treatment, including invasive strategies, when necessary. Therefore, the HEART score may help clinicians make accurate management choices by being a strong predictor of both event-free survival and potentially life-threatening cardiac events. Age, gender, and cardiovascular risk factors may also be considered in the assessment of patients. This study confirmed the utility of the HEART score categories to predict the 6-week incidence of MACE.
Corresponding author: Smrati Bajpai Tiwari, MD, DNB, FAIMER, Department of Medicine, Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College and King Edward Memorial Hospital, Acharya Donde Marg, Parel, Mumbai 400 012, Maharashtra, India; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Gupta R, Mohan I, Narula J. Trends in coronary heart disease epidemiology in India. Ann Glob Health. 2016;82:307-315.
2. World Health Organization. Global status report on non-communicable diseases 2014. Accessed June 22, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/148114/9789241564854_eng.pdf
3. Fuster V, Kelly BB, eds. Promoting Cardiovascular Health in the Developing World: A Critical Challenge to Achieve Global Health. Institutes of Medicine; 2010.
4. Krishnan MN. Coronary heart disease and risk factors in India—on the brink of an epidemic. Indian Heart J. 2012;64:364-367.
5. Prabhakaran D, Jeemon P, Roy A. Cardiovascular diseases in India: current epidemiology and future directions. Circulation. 2016;133:1605-1620.
6. Aeri B, Chauhan S. The rising incidence of cardiovascular diseases in India: assessing its economic impact. J Prev Cardiol. 2015;4:735-740.
7. Pednekar M, Gupta R, Gupta PC. Illiteracy, low educational status and cardiovascular mortality in India. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:567.
8. Six AJ, Backus BE, Kelder JC. Chest pain in the emergency room: value of the HEART score. Neth Heart J. 2008;16:191-196.
9. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JC, et al. A prospective validation of the HEART score for chest pain patients at the emergency department. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168;2153-2158.
10. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JC, et al. Chest pain in the emergency room: a multicenter validation of the HEART score. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2010;9:164-169.
11. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JH, et al. Risk scores for patients with chest pain: evaluation in the emergency department. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2011;7:2-8.
12. Leite L, Baptista R, Leitão J, et al. Chest pain in the emergency department: risk stratification with Manchester triage system and HEART score. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015;15:48.
13. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation. 2018;138:e618-e651.
14. Mahler SA, Riley RF, Hiestand BC, et al. The HEART Pathway randomized trial: identifying emergency department patients with acute chest pain for early discharge. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2015;8:195-203.
15. Natarajan B, Mallick P, Thangalvadi TA, Rajavelu P. Validation of the HEART score in Indian population. Int J Emerg Med. 2015,8(suppl 1):P5.
16. McCord J, Cabrera R, Lindahl B, et al. Prognostic utility of a modified HEART score in chest pain patients in the emergency department. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2017;10:e003101.
17. Mahler SA, Miller CD, Hollander JE, et al. Identifying patients for early discharge: performance of decision rules among patients with acute chest pain. Int J Cardiol. 2012;168:795-802.
1. Gupta R, Mohan I, Narula J. Trends in coronary heart disease epidemiology in India. Ann Glob Health. 2016;82:307-315.
2. World Health Organization. Global status report on non-communicable diseases 2014. Accessed June 22, 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/148114/9789241564854_eng.pdf
3. Fuster V, Kelly BB, eds. Promoting Cardiovascular Health in the Developing World: A Critical Challenge to Achieve Global Health. Institutes of Medicine; 2010.
4. Krishnan MN. Coronary heart disease and risk factors in India—on the brink of an epidemic. Indian Heart J. 2012;64:364-367.
5. Prabhakaran D, Jeemon P, Roy A. Cardiovascular diseases in India: current epidemiology and future directions. Circulation. 2016;133:1605-1620.
6. Aeri B, Chauhan S. The rising incidence of cardiovascular diseases in India: assessing its economic impact. J Prev Cardiol. 2015;4:735-740.
7. Pednekar M, Gupta R, Gupta PC. Illiteracy, low educational status and cardiovascular mortality in India. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:567.
8. Six AJ, Backus BE, Kelder JC. Chest pain in the emergency room: value of the HEART score. Neth Heart J. 2008;16:191-196.
9. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JC, et al. A prospective validation of the HEART score for chest pain patients at the emergency department. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168;2153-2158.
10. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JC, et al. Chest pain in the emergency room: a multicenter validation of the HEART score. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2010;9:164-169.
11. Backus BE, Six AJ, Kelder JH, et al. Risk scores for patients with chest pain: evaluation in the emergency department. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2011;7:2-8.
12. Leite L, Baptista R, Leitão J, et al. Chest pain in the emergency department: risk stratification with Manchester triage system and HEART score. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015;15:48.
13. Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation. 2018;138:e618-e651.
14. Mahler SA, Riley RF, Hiestand BC, et al. The HEART Pathway randomized trial: identifying emergency department patients with acute chest pain for early discharge. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2015;8:195-203.
15. Natarajan B, Mallick P, Thangalvadi TA, Rajavelu P. Validation of the HEART score in Indian population. Int J Emerg Med. 2015,8(suppl 1):P5.
16. McCord J, Cabrera R, Lindahl B, et al. Prognostic utility of a modified HEART score in chest pain patients in the emergency department. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2017;10:e003101.
17. Mahler SA, Miller CD, Hollander JE, et al. Identifying patients for early discharge: performance of decision rules among patients with acute chest pain. Int J Cardiol. 2012;168:795-802.
Intracranial atherosclerosis finding on MRA linked to stroke
An incidental diagnosis of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in stroke-free individuals should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, according to the authors of a study identifying risk factors and vascular event risk in asymptomatic ICAS.
That conclusion emerged from data collected on more than 1,000 stroke-free participants in NOMAS (Northern Manhattan Study), a trial that prospectively followed participants who underwent a brain magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) during 2003-2008.
In ICAS patients with stenosis of at least 70%, even with aggressive medical therapy, the annual stroke recurrence rate is 10%-20% in those with occlusions and at least three or more vascular risk factors. This high rate of recurrent vascular events in patients with stroke caused by ICAS warrants greater focus on primary prevention and targeted interventions for stroke-free individuals at highest risk for ICAS-related events, the investigators concluded.
Identify high-risk ICAS
Using NOMAS data, the investigators, led by Jose Gutierrez, MD, MPH, tested the hypothesis that stroke-free subjects at high risk of stroke and vascular events could be identified through the presence of asymptomatic ICAS. NOMAS is an ongoing, population-based epidemiologic study among randomly selected people with home telephones living in northern Manhattan.
During 2003-2008, investigators invited participants who were at least 50 years old, stroke free, and without contraindications to undergo brain MRA. The 1,211 study members were followed annually via telephone and in-person adjudication of events. A control group of 79 patients with no MRA was also identified with similar rates of hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and current smoking.
Mean age was about 71 years (59% female, 65% Hispanic, 45% any stenosis). At the time of MRA, 78% had hypertension, 25% had diabetes, 81% had hypercholesterolemia, and 11% were current smokers.
Researchers rated stenoses in 11 brain arteries as 0, with no stenosis; 1, with less than 50% stenosis or luminal irregularities; 2, 50%-69% stenosis; and 3, at least 70% stenosis or flow gap. Outcomes included vascular death, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, cardioembolic stroke, intracranial artery disease stroke (which combined intracranial small and large artery disease strokes), and any vascular events (defined as a composite of vascular death, any stroke, or MI).
Greater stenosis denotes higher risk
Analysis found ICAS to be associated with older age (odds ratio, 1.02 per year; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.04), hypertension duration (OR, 1.01 per year; 95% CI, 1.00-1.02), higher number of glucose-lowering drugs (OR, 1.64 per each medication; 95% CI, 1.24-2.15), and HDL cholesterol(OR, 0.96 per mg/dL; 95% CI, 0.92-0.99). Event risk was greater among participants with ICAS of at least 70% (5.5% annual risk of vascular events; HR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.4-3.2; compared with those with no ICAS), the investigators reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, 80% of incident strokes initially classified as small artery disease occurred among individuals with evidence of any degree of ICAS at their baseline MRI, the investigators noted. They found also that individuals with ICAS who had a primary care physician at the time of their initial MRI had a lower risk of events. Frequent primary care visits, they observed, might imply greater control of risk factors and other unmeasured confounders, such as health literacy, health care trust, access, and availability.
Incidental ICAS should trigger vascular assessment
An incidental diagnosis of ICAS in stroke-free subjects should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, the investigators concluded. They commented also that prophylaxis of first-ever stroke at this asymptomatic stage “may magnify the societal benefits of vascular prevention and decrease stroke-related disability and vascular death in our communities.”
“The big gap in our knowledge,” Tanya N. Turan, MD, professor of neurology at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, wrote in an accompanying editorial “is understanding the pathophysiological triggers for an asymptomatic stenosis to become a high-risk symptomatic stenosis. Until that question is answered, screening for asymptomatic ICAS is unlikely to change management among patients with known vascular risk factors.” In an interview, she observed further that “MRI plaque imaging could be a useful research tool to see if certain plaque features in an asymptomatic lesion are high risk for causing stroke. If that were proven, then it would make more sense to screen for ICAS and develop specific therapeutic strategies targeting high-risk asymptomatic plaque.”
Focus on recurrent stroke misplaced
Dr. Gutierrez said in an interview: “In the stroke world, most of what we do focuses on preventing recurrent stroke. Nonetheless, three-fourths of strokes in this country are new strokes, so to me it doesn’t make much sense to spend most of our efforts and attention to prevent the smallest fractions of strokes that occur in our society.”
He stressed that “the first immediate application of our results is that if people having a brain MRA for other reasons are found to have incidental, and therefore asymptomatic, ICAS, then they should be aggressively treated for vascular risk factors.” Secondly, “we hope to identify the patients at the highest risk of prevalent ICAS before they have a stroke. Among them, a brain MRI/MRA evaluating the phenotype would determine how aggressively to treat LDL.”
Dr. Gutierrez, professor of neurology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, noted that educating patients of their underlying high risk of events may have the effect of engaging them more in their own care. “There is evidence that actually showing people scans increases compliance and health literacy. It’s not yet standard of care, but we hope our future projects will help advance the field in the primary prevention direction,” he said.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported that they had no relevant financial disclosures.
An incidental diagnosis of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in stroke-free individuals should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, according to the authors of a study identifying risk factors and vascular event risk in asymptomatic ICAS.
That conclusion emerged from data collected on more than 1,000 stroke-free participants in NOMAS (Northern Manhattan Study), a trial that prospectively followed participants who underwent a brain magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) during 2003-2008.
In ICAS patients with stenosis of at least 70%, even with aggressive medical therapy, the annual stroke recurrence rate is 10%-20% in those with occlusions and at least three or more vascular risk factors. This high rate of recurrent vascular events in patients with stroke caused by ICAS warrants greater focus on primary prevention and targeted interventions for stroke-free individuals at highest risk for ICAS-related events, the investigators concluded.
Identify high-risk ICAS
Using NOMAS data, the investigators, led by Jose Gutierrez, MD, MPH, tested the hypothesis that stroke-free subjects at high risk of stroke and vascular events could be identified through the presence of asymptomatic ICAS. NOMAS is an ongoing, population-based epidemiologic study among randomly selected people with home telephones living in northern Manhattan.
During 2003-2008, investigators invited participants who were at least 50 years old, stroke free, and without contraindications to undergo brain MRA. The 1,211 study members were followed annually via telephone and in-person adjudication of events. A control group of 79 patients with no MRA was also identified with similar rates of hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and current smoking.
Mean age was about 71 years (59% female, 65% Hispanic, 45% any stenosis). At the time of MRA, 78% had hypertension, 25% had diabetes, 81% had hypercholesterolemia, and 11% were current smokers.
Researchers rated stenoses in 11 brain arteries as 0, with no stenosis; 1, with less than 50% stenosis or luminal irregularities; 2, 50%-69% stenosis; and 3, at least 70% stenosis or flow gap. Outcomes included vascular death, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, cardioembolic stroke, intracranial artery disease stroke (which combined intracranial small and large artery disease strokes), and any vascular events (defined as a composite of vascular death, any stroke, or MI).
Greater stenosis denotes higher risk
Analysis found ICAS to be associated with older age (odds ratio, 1.02 per year; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.04), hypertension duration (OR, 1.01 per year; 95% CI, 1.00-1.02), higher number of glucose-lowering drugs (OR, 1.64 per each medication; 95% CI, 1.24-2.15), and HDL cholesterol(OR, 0.96 per mg/dL; 95% CI, 0.92-0.99). Event risk was greater among participants with ICAS of at least 70% (5.5% annual risk of vascular events; HR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.4-3.2; compared with those with no ICAS), the investigators reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, 80% of incident strokes initially classified as small artery disease occurred among individuals with evidence of any degree of ICAS at their baseline MRI, the investigators noted. They found also that individuals with ICAS who had a primary care physician at the time of their initial MRI had a lower risk of events. Frequent primary care visits, they observed, might imply greater control of risk factors and other unmeasured confounders, such as health literacy, health care trust, access, and availability.
Incidental ICAS should trigger vascular assessment
An incidental diagnosis of ICAS in stroke-free subjects should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, the investigators concluded. They commented also that prophylaxis of first-ever stroke at this asymptomatic stage “may magnify the societal benefits of vascular prevention and decrease stroke-related disability and vascular death in our communities.”
“The big gap in our knowledge,” Tanya N. Turan, MD, professor of neurology at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, wrote in an accompanying editorial “is understanding the pathophysiological triggers for an asymptomatic stenosis to become a high-risk symptomatic stenosis. Until that question is answered, screening for asymptomatic ICAS is unlikely to change management among patients with known vascular risk factors.” In an interview, she observed further that “MRI plaque imaging could be a useful research tool to see if certain plaque features in an asymptomatic lesion are high risk for causing stroke. If that were proven, then it would make more sense to screen for ICAS and develop specific therapeutic strategies targeting high-risk asymptomatic plaque.”
Focus on recurrent stroke misplaced
Dr. Gutierrez said in an interview: “In the stroke world, most of what we do focuses on preventing recurrent stroke. Nonetheless, three-fourths of strokes in this country are new strokes, so to me it doesn’t make much sense to spend most of our efforts and attention to prevent the smallest fractions of strokes that occur in our society.”
He stressed that “the first immediate application of our results is that if people having a brain MRA for other reasons are found to have incidental, and therefore asymptomatic, ICAS, then they should be aggressively treated for vascular risk factors.” Secondly, “we hope to identify the patients at the highest risk of prevalent ICAS before they have a stroke. Among them, a brain MRI/MRA evaluating the phenotype would determine how aggressively to treat LDL.”
Dr. Gutierrez, professor of neurology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, noted that educating patients of their underlying high risk of events may have the effect of engaging them more in their own care. “There is evidence that actually showing people scans increases compliance and health literacy. It’s not yet standard of care, but we hope our future projects will help advance the field in the primary prevention direction,” he said.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported that they had no relevant financial disclosures.
An incidental diagnosis of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in stroke-free individuals should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, according to the authors of a study identifying risk factors and vascular event risk in asymptomatic ICAS.
That conclusion emerged from data collected on more than 1,000 stroke-free participants in NOMAS (Northern Manhattan Study), a trial that prospectively followed participants who underwent a brain magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) during 2003-2008.
In ICAS patients with stenosis of at least 70%, even with aggressive medical therapy, the annual stroke recurrence rate is 10%-20% in those with occlusions and at least three or more vascular risk factors. This high rate of recurrent vascular events in patients with stroke caused by ICAS warrants greater focus on primary prevention and targeted interventions for stroke-free individuals at highest risk for ICAS-related events, the investigators concluded.
Identify high-risk ICAS
Using NOMAS data, the investigators, led by Jose Gutierrez, MD, MPH, tested the hypothesis that stroke-free subjects at high risk of stroke and vascular events could be identified through the presence of asymptomatic ICAS. NOMAS is an ongoing, population-based epidemiologic study among randomly selected people with home telephones living in northern Manhattan.
During 2003-2008, investigators invited participants who were at least 50 years old, stroke free, and without contraindications to undergo brain MRA. The 1,211 study members were followed annually via telephone and in-person adjudication of events. A control group of 79 patients with no MRA was also identified with similar rates of hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and current smoking.
Mean age was about 71 years (59% female, 65% Hispanic, 45% any stenosis). At the time of MRA, 78% had hypertension, 25% had diabetes, 81% had hypercholesterolemia, and 11% were current smokers.
Researchers rated stenoses in 11 brain arteries as 0, with no stenosis; 1, with less than 50% stenosis or luminal irregularities; 2, 50%-69% stenosis; and 3, at least 70% stenosis or flow gap. Outcomes included vascular death, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, cardioembolic stroke, intracranial artery disease stroke (which combined intracranial small and large artery disease strokes), and any vascular events (defined as a composite of vascular death, any stroke, or MI).
Greater stenosis denotes higher risk
Analysis found ICAS to be associated with older age (odds ratio, 1.02 per year; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.04), hypertension duration (OR, 1.01 per year; 95% CI, 1.00-1.02), higher number of glucose-lowering drugs (OR, 1.64 per each medication; 95% CI, 1.24-2.15), and HDL cholesterol(OR, 0.96 per mg/dL; 95% CI, 0.92-0.99). Event risk was greater among participants with ICAS of at least 70% (5.5% annual risk of vascular events; HR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.4-3.2; compared with those with no ICAS), the investigators reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, 80% of incident strokes initially classified as small artery disease occurred among individuals with evidence of any degree of ICAS at their baseline MRI, the investigators noted. They found also that individuals with ICAS who had a primary care physician at the time of their initial MRI had a lower risk of events. Frequent primary care visits, they observed, might imply greater control of risk factors and other unmeasured confounders, such as health literacy, health care trust, access, and availability.
Incidental ICAS should trigger vascular assessment
An incidental diagnosis of ICAS in stroke-free subjects should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, the investigators concluded. They commented also that prophylaxis of first-ever stroke at this asymptomatic stage “may magnify the societal benefits of vascular prevention and decrease stroke-related disability and vascular death in our communities.”
“The big gap in our knowledge,” Tanya N. Turan, MD, professor of neurology at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, wrote in an accompanying editorial “is understanding the pathophysiological triggers for an asymptomatic stenosis to become a high-risk symptomatic stenosis. Until that question is answered, screening for asymptomatic ICAS is unlikely to change management among patients with known vascular risk factors.” In an interview, she observed further that “MRI plaque imaging could be a useful research tool to see if certain plaque features in an asymptomatic lesion are high risk for causing stroke. If that were proven, then it would make more sense to screen for ICAS and develop specific therapeutic strategies targeting high-risk asymptomatic plaque.”
Focus on recurrent stroke misplaced
Dr. Gutierrez said in an interview: “In the stroke world, most of what we do focuses on preventing recurrent stroke. Nonetheless, three-fourths of strokes in this country are new strokes, so to me it doesn’t make much sense to spend most of our efforts and attention to prevent the smallest fractions of strokes that occur in our society.”
He stressed that “the first immediate application of our results is that if people having a brain MRA for other reasons are found to have incidental, and therefore asymptomatic, ICAS, then they should be aggressively treated for vascular risk factors.” Secondly, “we hope to identify the patients at the highest risk of prevalent ICAS before they have a stroke. Among them, a brain MRI/MRA evaluating the phenotype would determine how aggressively to treat LDL.”
Dr. Gutierrez, professor of neurology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, noted that educating patients of their underlying high risk of events may have the effect of engaging them more in their own care. “There is evidence that actually showing people scans increases compliance and health literacy. It’s not yet standard of care, but we hope our future projects will help advance the field in the primary prevention direction,” he said.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported that they had no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY