User login
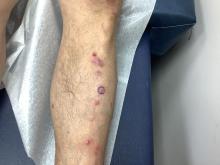
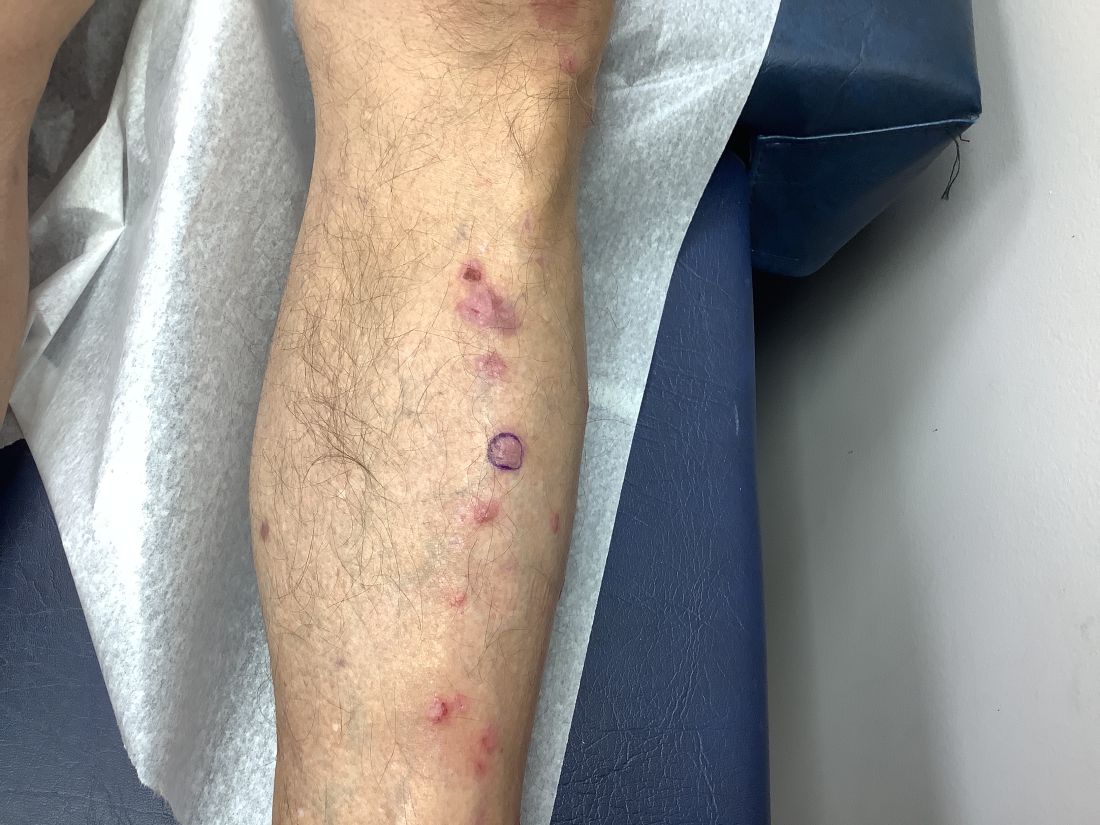
Pruritic, violaceous papules in a patient with renal cell carcinoma
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) is a programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blocking antibody used to treat different malignancies including melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and other advanced solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Lichen planus-like adverse drug reactions, as seen in this patient, are also referred to as lichenoid drug eruption or drug-induced lichen planus. This cutaneous reaction is one of the more rare side effects of pembrolizumab. It should be noted that in lichenoid reactions, keratinocytes expressing PD-L1 are particularly affected, leading to a dense CD4/CD8 positive lymphocytic infiltration in the basal layer, necrosis of keratinocytes, acanthosis, and hypergranulosis. Subsequently, the cutaneous adverse reaction is a target effect of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and not a general hypersensitivity reaction. Clinically, both lichen planus and lichenoid drug eruptions exhibit erythematous papules and plaques. Lichenoid drug eruptions, however, can be scaly, pruritic, and heal with more hyperpigmentation.
A skin biopsy revealed irregular epidermal hyperplasia with jagged rete ridges. Within the dermis, there was a lichenoid inflammatory cell infiltrate obscuring the dermal-epidermal junction. The inflammatory cell infiltrate contained lymphocytes, histiocytes, and eosinophils. A diagnosis of a lichen planus-like adverse drug reaction to pembrolizumab was favored.
If the reaction is mild, topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines can help with the drug-induced lichen planus. For more severe cases, systemic steroids can be given to help ease the reaction. Physicians should be aware of potential adverse drug effects that can mimic other medical conditions.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Berke, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pennsylvania. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Bansal A et al. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2023 Apr 4;14(3):391-4. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_377_22.
Sethi A, Raj M. Cureus. 2021 Mar 8;13(3):e13768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13768.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) is a programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blocking antibody used to treat different malignancies including melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and other advanced solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Lichen planus-like adverse drug reactions, as seen in this patient, are also referred to as lichenoid drug eruption or drug-induced lichen planus. This cutaneous reaction is one of the more rare side effects of pembrolizumab. It should be noted that in lichenoid reactions, keratinocytes expressing PD-L1 are particularly affected, leading to a dense CD4/CD8 positive lymphocytic infiltration in the basal layer, necrosis of keratinocytes, acanthosis, and hypergranulosis. Subsequently, the cutaneous adverse reaction is a target effect of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and not a general hypersensitivity reaction. Clinically, both lichen planus and lichenoid drug eruptions exhibit erythematous papules and plaques. Lichenoid drug eruptions, however, can be scaly, pruritic, and heal with more hyperpigmentation.
A skin biopsy revealed irregular epidermal hyperplasia with jagged rete ridges. Within the dermis, there was a lichenoid inflammatory cell infiltrate obscuring the dermal-epidermal junction. The inflammatory cell infiltrate contained lymphocytes, histiocytes, and eosinophils. A diagnosis of a lichen planus-like adverse drug reaction to pembrolizumab was favored.
If the reaction is mild, topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines can help with the drug-induced lichen planus. For more severe cases, systemic steroids can be given to help ease the reaction. Physicians should be aware of potential adverse drug effects that can mimic other medical conditions.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Berke, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pennsylvania. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Bansal A et al. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2023 Apr 4;14(3):391-4. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_377_22.
Sethi A, Raj M. Cureus. 2021 Mar 8;13(3):e13768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13768.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) is a programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blocking antibody used to treat different malignancies including melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and other advanced solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Lichen planus-like adverse drug reactions, as seen in this patient, are also referred to as lichenoid drug eruption or drug-induced lichen planus. This cutaneous reaction is one of the more rare side effects of pembrolizumab. It should be noted that in lichenoid reactions, keratinocytes expressing PD-L1 are particularly affected, leading to a dense CD4/CD8 positive lymphocytic infiltration in the basal layer, necrosis of keratinocytes, acanthosis, and hypergranulosis. Subsequently, the cutaneous adverse reaction is a target effect of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and not a general hypersensitivity reaction. Clinically, both lichen planus and lichenoid drug eruptions exhibit erythematous papules and plaques. Lichenoid drug eruptions, however, can be scaly, pruritic, and heal with more hyperpigmentation.
A skin biopsy revealed irregular epidermal hyperplasia with jagged rete ridges. Within the dermis, there was a lichenoid inflammatory cell infiltrate obscuring the dermal-epidermal junction. The inflammatory cell infiltrate contained lymphocytes, histiocytes, and eosinophils. A diagnosis of a lichen planus-like adverse drug reaction to pembrolizumab was favored.
If the reaction is mild, topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines can help with the drug-induced lichen planus. For more severe cases, systemic steroids can be given to help ease the reaction. Physicians should be aware of potential adverse drug effects that can mimic other medical conditions.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Berke, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pennsylvania. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Bansal A et al. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2023 Apr 4;14(3):391-4. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_377_22.
Sethi A, Raj M. Cureus. 2021 Mar 8;13(3):e13768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13768.
Shift Needed in Research, Treatment, Care for Aging MS Population
NASHVILLE, TENNESSEE — a phenomenon that’s driving a shift in priorities including the creation of MS aging centers and a push for more clinical trials aimed at this growing patient population.
Given typical patterns of MS onset and its rate of progression, disease duration has long been thought to be the key variable driving disability, but Jennifer Graves, MD, PhD, director of the neuroimmunology research program at the University of California, San Diego, said she now believes that “patient age is actually more important.”
Speaking at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC), Dr. Graves noted that it is well known that key MS symptoms increase over time, particularly during the transition from a relapsing to a progressive phenotype.
However, she maintains that, independent of disease progression, the impact of aging on MS has been underappreciated. She cited research showing that, relative to chronological age, biologic age is more robustly correlated with MS outcomes.
In studies evaluating variables such as telomere length, various markers of senescence, and DNA methylation patterns, Dr. Graves and others have shown that biologic versus chronological aging is more rapid in patients with MS than those without the disease. In addition, within the population with MS, there are also data supporting the premise that disease progression is slower in those with a younger versus older biologic age.
“This raises the question of whether biologic age is a driver of MS and whether we can slow the disease trajectory if we slow [biologic] aging,” Dr. Graves said. While she acknowledged that genetics play an important role in the aging process, she pointed to evidence showing exposure to toxins and other biological stressors, as well as poor lifestyle choices, such as lack of exercise and smoking, are modifiable aging variables.
There are already many avenues of research regarding aging processes and their interaction with MS. Dr. Graves spoke briefly about current research into the relationship between declining ovarian function, declining telomere length, and how this might relate to the transition to progressive MS and advancing disability. To date, her research has revealed a correlation between declining ovarian function and increasing MS disability.
Shifting Priorities
The rapid aging of the population with MS in the United States makes research into slowing biologic aging a priority, said Robert Motl, PhD, professor in the department of physical therapy, University of Alabama at Birmingham Multiple Sclerosis Center. He reported he was able to secure funding from the National MS Society for the Healthy Aging through LifesTyle MS Research Center 10 years ago.
“We are the first and, so far, the only research center devoted to the study of aging in MS,” said Dr. Motl, another participant in the CMSC aging symposium. Dr. Motl said he and a colleague have been evaluating specific strategies to meet the varied needs of aging patients with MS with a key focus on physical therapy and preserving function.
Yinan Zhang, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, recently started a multidisciplinary clinic for the management of older patients with MS and said he hopes these types of clinics will help shed light on the unmet needs of older adults with MS — particularly the need for better therapies to address common types of neurodegeneration in this population.
“We need to move away from immunomodulatory agents [in older patients],” Dr. Zhang said. Older patients are typically excluded from therapeutic MS trials for a number of reasons, not least because trials have been traditionally targeted at relapsing disease, which is less common in older patients with MS. He believes older patients are particularly appropriate candidates for MS therapy trials aimed at progressive neurodegeneration, which is characteristic of late-stage disease. Therapies with the potential to slow, or even reverse, demyelination are among the novel strategies being pursued in progressive MS.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Dr. Zhang acknowledged that his recently established MS clinic is still in the early phases and is largely focused on comprehensive care designed to meet the diverse needs of older individuals who often have advanced disabilities and comorbidities.
Currently, each patient that attends the clinic consults with six different types of providers, including a psychologist, a pharmacist, and a physical therapist — all in a single appointment.
Dr. Zhang said his decision to open a clinic was motivated by the increased volume of older patients with MS and was inspired by similar clinics for other disease states in older individuals.
“The need is already strong and growing,” said Dr. Zhang, who speculated that these types of clinics will become widespread as the need for this care is more broadly recognized and accepted.
As the clinic evolves and matures, Dr. Zhang anticipates there will be a research component to better characterize cell senescence and aging processes that might eventually be modifiable or even reversible. He also speculated that aging in MS might eventually become a subspecialty.
Dr. Graves reported financial relationships with Horizon Therapeutics. Dr. Zhang reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Motl reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NASHVILLE, TENNESSEE — a phenomenon that’s driving a shift in priorities including the creation of MS aging centers and a push for more clinical trials aimed at this growing patient population.
Given typical patterns of MS onset and its rate of progression, disease duration has long been thought to be the key variable driving disability, but Jennifer Graves, MD, PhD, director of the neuroimmunology research program at the University of California, San Diego, said she now believes that “patient age is actually more important.”
Speaking at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC), Dr. Graves noted that it is well known that key MS symptoms increase over time, particularly during the transition from a relapsing to a progressive phenotype.
However, she maintains that, independent of disease progression, the impact of aging on MS has been underappreciated. She cited research showing that, relative to chronological age, biologic age is more robustly correlated with MS outcomes.
In studies evaluating variables such as telomere length, various markers of senescence, and DNA methylation patterns, Dr. Graves and others have shown that biologic versus chronological aging is more rapid in patients with MS than those without the disease. In addition, within the population with MS, there are also data supporting the premise that disease progression is slower in those with a younger versus older biologic age.
“This raises the question of whether biologic age is a driver of MS and whether we can slow the disease trajectory if we slow [biologic] aging,” Dr. Graves said. While she acknowledged that genetics play an important role in the aging process, she pointed to evidence showing exposure to toxins and other biological stressors, as well as poor lifestyle choices, such as lack of exercise and smoking, are modifiable aging variables.
There are already many avenues of research regarding aging processes and their interaction with MS. Dr. Graves spoke briefly about current research into the relationship between declining ovarian function, declining telomere length, and how this might relate to the transition to progressive MS and advancing disability. To date, her research has revealed a correlation between declining ovarian function and increasing MS disability.
Shifting Priorities
The rapid aging of the population with MS in the United States makes research into slowing biologic aging a priority, said Robert Motl, PhD, professor in the department of physical therapy, University of Alabama at Birmingham Multiple Sclerosis Center. He reported he was able to secure funding from the National MS Society for the Healthy Aging through LifesTyle MS Research Center 10 years ago.
“We are the first and, so far, the only research center devoted to the study of aging in MS,” said Dr. Motl, another participant in the CMSC aging symposium. Dr. Motl said he and a colleague have been evaluating specific strategies to meet the varied needs of aging patients with MS with a key focus on physical therapy and preserving function.
Yinan Zhang, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, recently started a multidisciplinary clinic for the management of older patients with MS and said he hopes these types of clinics will help shed light on the unmet needs of older adults with MS — particularly the need for better therapies to address common types of neurodegeneration in this population.
“We need to move away from immunomodulatory agents [in older patients],” Dr. Zhang said. Older patients are typically excluded from therapeutic MS trials for a number of reasons, not least because trials have been traditionally targeted at relapsing disease, which is less common in older patients with MS. He believes older patients are particularly appropriate candidates for MS therapy trials aimed at progressive neurodegeneration, which is characteristic of late-stage disease. Therapies with the potential to slow, or even reverse, demyelination are among the novel strategies being pursued in progressive MS.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Dr. Zhang acknowledged that his recently established MS clinic is still in the early phases and is largely focused on comprehensive care designed to meet the diverse needs of older individuals who often have advanced disabilities and comorbidities.
Currently, each patient that attends the clinic consults with six different types of providers, including a psychologist, a pharmacist, and a physical therapist — all in a single appointment.
Dr. Zhang said his decision to open a clinic was motivated by the increased volume of older patients with MS and was inspired by similar clinics for other disease states in older individuals.
“The need is already strong and growing,” said Dr. Zhang, who speculated that these types of clinics will become widespread as the need for this care is more broadly recognized and accepted.
As the clinic evolves and matures, Dr. Zhang anticipates there will be a research component to better characterize cell senescence and aging processes that might eventually be modifiable or even reversible. He also speculated that aging in MS might eventually become a subspecialty.
Dr. Graves reported financial relationships with Horizon Therapeutics. Dr. Zhang reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Motl reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NASHVILLE, TENNESSEE — a phenomenon that’s driving a shift in priorities including the creation of MS aging centers and a push for more clinical trials aimed at this growing patient population.
Given typical patterns of MS onset and its rate of progression, disease duration has long been thought to be the key variable driving disability, but Jennifer Graves, MD, PhD, director of the neuroimmunology research program at the University of California, San Diego, said she now believes that “patient age is actually more important.”
Speaking at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC), Dr. Graves noted that it is well known that key MS symptoms increase over time, particularly during the transition from a relapsing to a progressive phenotype.
However, she maintains that, independent of disease progression, the impact of aging on MS has been underappreciated. She cited research showing that, relative to chronological age, biologic age is more robustly correlated with MS outcomes.
In studies evaluating variables such as telomere length, various markers of senescence, and DNA methylation patterns, Dr. Graves and others have shown that biologic versus chronological aging is more rapid in patients with MS than those without the disease. In addition, within the population with MS, there are also data supporting the premise that disease progression is slower in those with a younger versus older biologic age.
“This raises the question of whether biologic age is a driver of MS and whether we can slow the disease trajectory if we slow [biologic] aging,” Dr. Graves said. While she acknowledged that genetics play an important role in the aging process, she pointed to evidence showing exposure to toxins and other biological stressors, as well as poor lifestyle choices, such as lack of exercise and smoking, are modifiable aging variables.
There are already many avenues of research regarding aging processes and their interaction with MS. Dr. Graves spoke briefly about current research into the relationship between declining ovarian function, declining telomere length, and how this might relate to the transition to progressive MS and advancing disability. To date, her research has revealed a correlation between declining ovarian function and increasing MS disability.
Shifting Priorities
The rapid aging of the population with MS in the United States makes research into slowing biologic aging a priority, said Robert Motl, PhD, professor in the department of physical therapy, University of Alabama at Birmingham Multiple Sclerosis Center. He reported he was able to secure funding from the National MS Society for the Healthy Aging through LifesTyle MS Research Center 10 years ago.
“We are the first and, so far, the only research center devoted to the study of aging in MS,” said Dr. Motl, another participant in the CMSC aging symposium. Dr. Motl said he and a colleague have been evaluating specific strategies to meet the varied needs of aging patients with MS with a key focus on physical therapy and preserving function.
Yinan Zhang, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, recently started a multidisciplinary clinic for the management of older patients with MS and said he hopes these types of clinics will help shed light on the unmet needs of older adults with MS — particularly the need for better therapies to address common types of neurodegeneration in this population.
“We need to move away from immunomodulatory agents [in older patients],” Dr. Zhang said. Older patients are typically excluded from therapeutic MS trials for a number of reasons, not least because trials have been traditionally targeted at relapsing disease, which is less common in older patients with MS. He believes older patients are particularly appropriate candidates for MS therapy trials aimed at progressive neurodegeneration, which is characteristic of late-stage disease. Therapies with the potential to slow, or even reverse, demyelination are among the novel strategies being pursued in progressive MS.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Dr. Zhang acknowledged that his recently established MS clinic is still in the early phases and is largely focused on comprehensive care designed to meet the diverse needs of older individuals who often have advanced disabilities and comorbidities.
Currently, each patient that attends the clinic consults with six different types of providers, including a psychologist, a pharmacist, and a physical therapist — all in a single appointment.
Dr. Zhang said his decision to open a clinic was motivated by the increased volume of older patients with MS and was inspired by similar clinics for other disease states in older individuals.
“The need is already strong and growing,” said Dr. Zhang, who speculated that these types of clinics will become widespread as the need for this care is more broadly recognized and accepted.
As the clinic evolves and matures, Dr. Zhang anticipates there will be a research component to better characterize cell senescence and aging processes that might eventually be modifiable or even reversible. He also speculated that aging in MS might eventually become a subspecialty.
Dr. Graves reported financial relationships with Horizon Therapeutics. Dr. Zhang reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Motl reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CMSC 2024
Managing Heart Failure in Women: Key Differences and Clinical Tips
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Dr Eileen Hsich. I’m the medical director for heart transplantation at the Cleveland Clinic, and my specialty is sex differences in heart failure. I’m excited to talk to you about heart failure treatment in women, addressing the differences in managing heart failure in women as well as practical tips for clinicians. You think that I’m going to be starting off by telling you about the differences in how we’re going to manage the patients, but I’m not. The reason I’m not going to do that is because our national guidelines are not sex specific.
What I’m really going to discuss with you today are the data so that you can decide for yourself what we should do and whether there really are differences. As we begin, I always think about the prevalence of the disease. Currently, there are 6.7 million Americans with heart failure, and approximately 45% of them are women. Globally, our best research shows that there are over 56 million people living with heart failure, and half of them are women.
We also know that there are different underlying causes in women and men. For women, the four risk factors are hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation (AFib), and left bundle branch block. I know you knew about hypertension. Diabetes may not have been right up there in your mind. You see many women with AFib, so I know that you were thinking about it. We’re going to come back to left bundle branch block; it really is very interesting.
For men, it is the risk for heart failure development after a myocardial infarction. Men are more likely to have an ischemic cardiomyopathy. It is also important to state that when women have heart failure, it is often with more preserved ejection fraction. We know that heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is more common in women and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is more common in men.
Now we’re going to talk about the four pillars in medical management, and we’re going to start out with the easy medications that show no sex differences in benefit. The mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) show that there are no sex differences in regard to benefit. Women benefit as much as men, based on two of the largest studies, which were the RALES study, which studied heart failure that was ischemic and nonischemic, and then the EPHESUS study, which was specific to patients who had myocardial infarction. There was a mortality benefit in the women.
The next set of drugs that we’re going to mention are the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. The combined endpoint for women and men was a combined endpoint of death and heart failure hospitalization. No matter what the ejection fraction was, women benefited like men for this drug.
The third class of agents that I want to discuss is the beta-blockers, which are really very interesting because they’re so powerful. The studies for these drugs were stopped prematurely. When you take into consideration that women are underenrolled in clinical trials, remember that the studies for these drugs were stopped, so there weren’t that many women. The fact that we showed a mortality benefit is really important.
The first drug that we’re going to refer to is bisoprolol because CIBIS II was the first trial for this drug to demonstrate a mortality benefit in women and men. The second drug that I want to mention is metoprolol XL, which did not demonstrate a mortality benefit in the MERIT-HF study, but did demonstrate a benefit in reduced heart failure hospitalizations, which is also very important.
The third drug is carvedilol, which had been shown to reduce a combined endpoint of mortality and heart failure hospitalizations for patients with moderate symptoms. When I talk about these studies, they have anywhere from 250 to 1000 women enrolled, so these are relatively small studies and they still did demonstrate a benefit.
When we talk about angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI), I think that’s when it gets a little complex. The data are not very clear because ARNI is a combination pill — sacubitril combined with valsartan. When you have an ideal control for a study and you want to know what your magic ingredient is, which is the sacubitril, you really want to compare valsartan with ARNI so that you can find out what your magic little ingredient is doing.
When we had the PARAGON-HF study, which was for HFpEF patients who had an ejection fraction greater than 45%, there was a benefit in the women and not in the men, and that really was in the women with the lower ejection fractions. That’s very interesting because the control was valsartan.
When we had the PARADIGM-HF study, that was more complex. The control was an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, which is not an ideal control for women since, even in a meta-analysis that had over 1000 women, there has not been a proven benefit. The confidence intervals remain wide. Therefore, it’s not quite a fair comparison to randomize women to ARNI versus an ACE inhibitor. Comparing ARNI to valsartan would be better in order to determine the additional benefit of sacubitril since valsartan alone has already been shown, in the Val-HeFT study, to reduce heart failure hospitalizations in women — although not mortality. There was a benefit.
When you look at the PARADIGM-HF study, which was for HFrEF patients, and you see that there is a benefit in the women, where the combined endpoint was heart failure hospitalization and mortality, you then see that there’s a figure that shows what happens when we look at mortality alone. The benefit is not driven by mortality; it’s driven by heart failure hospitalizations for the women, for which valsartan already had been shown to do this. Therefore, I don’t know if sacubitril/valsartan is more powerful because we didn’t have the right control in studies. From my standpoint, the data really are not there. We can all have our own biased opinions.
When we talk about devices, that gets really interesting because it goes back to those risk factors. We’re going to start with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs). We have shown in many ICD trials that women and men had similar survival. There were very few women in these device trials. If you think the medical trials had only a few women, just imagine what the ICD trials had.
Santangeli and colleagues hypothesized that an ICD only saves you from sudden death. It doesn›t really save you from anything else. In heart failure, women do live longer than men. Is this device really saving you? They weren’t interested in all-cause mortality; they were interested in whether the device fired appropriately for ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. They demonstrated in that meta-analysis that it was not very clear that women had the benefit. The rationale behind that comes from the MADIT studies that showed that men were more likely than women to have ventricular arrhythmias.
This is also true based on the Seattle Heart Failure Model. The derivation cohort had very few ICDs at that time, and women were less likely than men to have ventricular arrhythmias as the cause of death. It’s not that we shouldn’t put them in — I very strongly believe that we should — but we don’t have that data.
In fact, in the Santangeli and colleagues study, women were more likely to have inappropriate firing for AFib. Remember that we talked about how one of the risk factors for heart failure was AFib. Women are more likely to have AFib and the ICD firing for AFib and not ventricular arrhythmias. This may be dependent on the type of cardiomyopathy.
Next, we’re going to talk about biventricular pacemakers. Women tend to benefit more so that there is an improvement in symptoms and survival. What is fascinating is that left bundle branch block is a risk factor for the development of heart failure in women, which makes this next statement even more fascinating.
The FDA does their own analysis when they are reviewing devices and everything else, and they published one of them in JAMA Internal Medicine, taking three studies and seeing the benefit in women and men. They found that everybody benefits when the left bundle branch block has a QRS greater than 150 milliseconds. But with a QRS between 130 and 149 milliseconds, only the women benefited. That›s fascinating because that is a risk factor — the development of the left bundle branch block causing heart failure in women. It makes you wonder whether you are correcting something that actually was responsible for their heart failure.
In advanced heart failure, we have left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) and heart transplantation. For years, we couldn’t get LVADs small enough to fit in women. When they were larger, there were complications that were more common in women, such as stroke. With the newer devices — the HeartMate 3 is small, for instance — complications for everyone are very infrequent, and women and men benefit. I’m going to encourage clinicians to use them.
For heart transplantation, as I mentioned before, women tend to get HFpEF. I didn’t mention that they get heart failure when they’re older, for the most part. There are fewer women who are transplanted than men and eligible at younger ages. What we had for decades was that women were dying while they were on the waitlist for heart transplantation at a faster rate than men but living longer after transplantation. As LVADs became more appropriately sized for women, the complication rates went down; and we did see an improvement on the waitlist mortality rate before we changed the allocation system. But it really wasn’t until after we changed the allocation system in 2018 that we saw great success. Now, women have similar survival while on the waitlist. They’re transplanted at a faster rate despite the fact that they’re less likely to receive the temporary mechanical support, and they tend to still do very well.
We have some differences in therapy response. Thank you.
Dr. Hsich disclosed ties with Natera, DEFINE steering committee (no money), and MEDCAC (Medicare/Medicaid) committee. She received research grant from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Dr Eileen Hsich. I’m the medical director for heart transplantation at the Cleveland Clinic, and my specialty is sex differences in heart failure. I’m excited to talk to you about heart failure treatment in women, addressing the differences in managing heart failure in women as well as practical tips for clinicians. You think that I’m going to be starting off by telling you about the differences in how we’re going to manage the patients, but I’m not. The reason I’m not going to do that is because our national guidelines are not sex specific.
What I’m really going to discuss with you today are the data so that you can decide for yourself what we should do and whether there really are differences. As we begin, I always think about the prevalence of the disease. Currently, there are 6.7 million Americans with heart failure, and approximately 45% of them are women. Globally, our best research shows that there are over 56 million people living with heart failure, and half of them are women.
We also know that there are different underlying causes in women and men. For women, the four risk factors are hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation (AFib), and left bundle branch block. I know you knew about hypertension. Diabetes may not have been right up there in your mind. You see many women with AFib, so I know that you were thinking about it. We’re going to come back to left bundle branch block; it really is very interesting.
For men, it is the risk for heart failure development after a myocardial infarction. Men are more likely to have an ischemic cardiomyopathy. It is also important to state that when women have heart failure, it is often with more preserved ejection fraction. We know that heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is more common in women and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is more common in men.
Now we’re going to talk about the four pillars in medical management, and we’re going to start out with the easy medications that show no sex differences in benefit. The mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) show that there are no sex differences in regard to benefit. Women benefit as much as men, based on two of the largest studies, which were the RALES study, which studied heart failure that was ischemic and nonischemic, and then the EPHESUS study, which was specific to patients who had myocardial infarction. There was a mortality benefit in the women.
The next set of drugs that we’re going to mention are the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. The combined endpoint for women and men was a combined endpoint of death and heart failure hospitalization. No matter what the ejection fraction was, women benefited like men for this drug.
The third class of agents that I want to discuss is the beta-blockers, which are really very interesting because they’re so powerful. The studies for these drugs were stopped prematurely. When you take into consideration that women are underenrolled in clinical trials, remember that the studies for these drugs were stopped, so there weren’t that many women. The fact that we showed a mortality benefit is really important.
The first drug that we’re going to refer to is bisoprolol because CIBIS II was the first trial for this drug to demonstrate a mortality benefit in women and men. The second drug that I want to mention is metoprolol XL, which did not demonstrate a mortality benefit in the MERIT-HF study, but did demonstrate a benefit in reduced heart failure hospitalizations, which is also very important.
The third drug is carvedilol, which had been shown to reduce a combined endpoint of mortality and heart failure hospitalizations for patients with moderate symptoms. When I talk about these studies, they have anywhere from 250 to 1000 women enrolled, so these are relatively small studies and they still did demonstrate a benefit.
When we talk about angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI), I think that’s when it gets a little complex. The data are not very clear because ARNI is a combination pill — sacubitril combined with valsartan. When you have an ideal control for a study and you want to know what your magic ingredient is, which is the sacubitril, you really want to compare valsartan with ARNI so that you can find out what your magic little ingredient is doing.
When we had the PARAGON-HF study, which was for HFpEF patients who had an ejection fraction greater than 45%, there was a benefit in the women and not in the men, and that really was in the women with the lower ejection fractions. That’s very interesting because the control was valsartan.
When we had the PARADIGM-HF study, that was more complex. The control was an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, which is not an ideal control for women since, even in a meta-analysis that had over 1000 women, there has not been a proven benefit. The confidence intervals remain wide. Therefore, it’s not quite a fair comparison to randomize women to ARNI versus an ACE inhibitor. Comparing ARNI to valsartan would be better in order to determine the additional benefit of sacubitril since valsartan alone has already been shown, in the Val-HeFT study, to reduce heart failure hospitalizations in women — although not mortality. There was a benefit.
When you look at the PARADIGM-HF study, which was for HFrEF patients, and you see that there is a benefit in the women, where the combined endpoint was heart failure hospitalization and mortality, you then see that there’s a figure that shows what happens when we look at mortality alone. The benefit is not driven by mortality; it’s driven by heart failure hospitalizations for the women, for which valsartan already had been shown to do this. Therefore, I don’t know if sacubitril/valsartan is more powerful because we didn’t have the right control in studies. From my standpoint, the data really are not there. We can all have our own biased opinions.
When we talk about devices, that gets really interesting because it goes back to those risk factors. We’re going to start with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs). We have shown in many ICD trials that women and men had similar survival. There were very few women in these device trials. If you think the medical trials had only a few women, just imagine what the ICD trials had.
Santangeli and colleagues hypothesized that an ICD only saves you from sudden death. It doesn›t really save you from anything else. In heart failure, women do live longer than men. Is this device really saving you? They weren’t interested in all-cause mortality; they were interested in whether the device fired appropriately for ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. They demonstrated in that meta-analysis that it was not very clear that women had the benefit. The rationale behind that comes from the MADIT studies that showed that men were more likely than women to have ventricular arrhythmias.
This is also true based on the Seattle Heart Failure Model. The derivation cohort had very few ICDs at that time, and women were less likely than men to have ventricular arrhythmias as the cause of death. It’s not that we shouldn’t put them in — I very strongly believe that we should — but we don’t have that data.
In fact, in the Santangeli and colleagues study, women were more likely to have inappropriate firing for AFib. Remember that we talked about how one of the risk factors for heart failure was AFib. Women are more likely to have AFib and the ICD firing for AFib and not ventricular arrhythmias. This may be dependent on the type of cardiomyopathy.
Next, we’re going to talk about biventricular pacemakers. Women tend to benefit more so that there is an improvement in symptoms and survival. What is fascinating is that left bundle branch block is a risk factor for the development of heart failure in women, which makes this next statement even more fascinating.
The FDA does their own analysis when they are reviewing devices and everything else, and they published one of them in JAMA Internal Medicine, taking three studies and seeing the benefit in women and men. They found that everybody benefits when the left bundle branch block has a QRS greater than 150 milliseconds. But with a QRS between 130 and 149 milliseconds, only the women benefited. That›s fascinating because that is a risk factor — the development of the left bundle branch block causing heart failure in women. It makes you wonder whether you are correcting something that actually was responsible for their heart failure.
In advanced heart failure, we have left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) and heart transplantation. For years, we couldn’t get LVADs small enough to fit in women. When they were larger, there were complications that were more common in women, such as stroke. With the newer devices — the HeartMate 3 is small, for instance — complications for everyone are very infrequent, and women and men benefit. I’m going to encourage clinicians to use them.
For heart transplantation, as I mentioned before, women tend to get HFpEF. I didn’t mention that they get heart failure when they’re older, for the most part. There are fewer women who are transplanted than men and eligible at younger ages. What we had for decades was that women were dying while they were on the waitlist for heart transplantation at a faster rate than men but living longer after transplantation. As LVADs became more appropriately sized for women, the complication rates went down; and we did see an improvement on the waitlist mortality rate before we changed the allocation system. But it really wasn’t until after we changed the allocation system in 2018 that we saw great success. Now, women have similar survival while on the waitlist. They’re transplanted at a faster rate despite the fact that they’re less likely to receive the temporary mechanical support, and they tend to still do very well.
We have some differences in therapy response. Thank you.
Dr. Hsich disclosed ties with Natera, DEFINE steering committee (no money), and MEDCAC (Medicare/Medicaid) committee. She received research grant from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Dr Eileen Hsich. I’m the medical director for heart transplantation at the Cleveland Clinic, and my specialty is sex differences in heart failure. I’m excited to talk to you about heart failure treatment in women, addressing the differences in managing heart failure in women as well as practical tips for clinicians. You think that I’m going to be starting off by telling you about the differences in how we’re going to manage the patients, but I’m not. The reason I’m not going to do that is because our national guidelines are not sex specific.
What I’m really going to discuss with you today are the data so that you can decide for yourself what we should do and whether there really are differences. As we begin, I always think about the prevalence of the disease. Currently, there are 6.7 million Americans with heart failure, and approximately 45% of them are women. Globally, our best research shows that there are over 56 million people living with heart failure, and half of them are women.
We also know that there are different underlying causes in women and men. For women, the four risk factors are hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation (AFib), and left bundle branch block. I know you knew about hypertension. Diabetes may not have been right up there in your mind. You see many women with AFib, so I know that you were thinking about it. We’re going to come back to left bundle branch block; it really is very interesting.
For men, it is the risk for heart failure development after a myocardial infarction. Men are more likely to have an ischemic cardiomyopathy. It is also important to state that when women have heart failure, it is often with more preserved ejection fraction. We know that heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is more common in women and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is more common in men.
Now we’re going to talk about the four pillars in medical management, and we’re going to start out with the easy medications that show no sex differences in benefit. The mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) show that there are no sex differences in regard to benefit. Women benefit as much as men, based on two of the largest studies, which were the RALES study, which studied heart failure that was ischemic and nonischemic, and then the EPHESUS study, which was specific to patients who had myocardial infarction. There was a mortality benefit in the women.
The next set of drugs that we’re going to mention are the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. The combined endpoint for women and men was a combined endpoint of death and heart failure hospitalization. No matter what the ejection fraction was, women benefited like men for this drug.
The third class of agents that I want to discuss is the beta-blockers, which are really very interesting because they’re so powerful. The studies for these drugs were stopped prematurely. When you take into consideration that women are underenrolled in clinical trials, remember that the studies for these drugs were stopped, so there weren’t that many women. The fact that we showed a mortality benefit is really important.
The first drug that we’re going to refer to is bisoprolol because CIBIS II was the first trial for this drug to demonstrate a mortality benefit in women and men. The second drug that I want to mention is metoprolol XL, which did not demonstrate a mortality benefit in the MERIT-HF study, but did demonstrate a benefit in reduced heart failure hospitalizations, which is also very important.
The third drug is carvedilol, which had been shown to reduce a combined endpoint of mortality and heart failure hospitalizations for patients with moderate symptoms. When I talk about these studies, they have anywhere from 250 to 1000 women enrolled, so these are relatively small studies and they still did demonstrate a benefit.
When we talk about angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI), I think that’s when it gets a little complex. The data are not very clear because ARNI is a combination pill — sacubitril combined with valsartan. When you have an ideal control for a study and you want to know what your magic ingredient is, which is the sacubitril, you really want to compare valsartan with ARNI so that you can find out what your magic little ingredient is doing.
When we had the PARAGON-HF study, which was for HFpEF patients who had an ejection fraction greater than 45%, there was a benefit in the women and not in the men, and that really was in the women with the lower ejection fractions. That’s very interesting because the control was valsartan.
When we had the PARADIGM-HF study, that was more complex. The control was an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, which is not an ideal control for women since, even in a meta-analysis that had over 1000 women, there has not been a proven benefit. The confidence intervals remain wide. Therefore, it’s not quite a fair comparison to randomize women to ARNI versus an ACE inhibitor. Comparing ARNI to valsartan would be better in order to determine the additional benefit of sacubitril since valsartan alone has already been shown, in the Val-HeFT study, to reduce heart failure hospitalizations in women — although not mortality. There was a benefit.
When you look at the PARADIGM-HF study, which was for HFrEF patients, and you see that there is a benefit in the women, where the combined endpoint was heart failure hospitalization and mortality, you then see that there’s a figure that shows what happens when we look at mortality alone. The benefit is not driven by mortality; it’s driven by heart failure hospitalizations for the women, for which valsartan already had been shown to do this. Therefore, I don’t know if sacubitril/valsartan is more powerful because we didn’t have the right control in studies. From my standpoint, the data really are not there. We can all have our own biased opinions.
When we talk about devices, that gets really interesting because it goes back to those risk factors. We’re going to start with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs). We have shown in many ICD trials that women and men had similar survival. There were very few women in these device trials. If you think the medical trials had only a few women, just imagine what the ICD trials had.
Santangeli and colleagues hypothesized that an ICD only saves you from sudden death. It doesn›t really save you from anything else. In heart failure, women do live longer than men. Is this device really saving you? They weren’t interested in all-cause mortality; they were interested in whether the device fired appropriately for ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. They demonstrated in that meta-analysis that it was not very clear that women had the benefit. The rationale behind that comes from the MADIT studies that showed that men were more likely than women to have ventricular arrhythmias.
This is also true based on the Seattle Heart Failure Model. The derivation cohort had very few ICDs at that time, and women were less likely than men to have ventricular arrhythmias as the cause of death. It’s not that we shouldn’t put them in — I very strongly believe that we should — but we don’t have that data.
In fact, in the Santangeli and colleagues study, women were more likely to have inappropriate firing for AFib. Remember that we talked about how one of the risk factors for heart failure was AFib. Women are more likely to have AFib and the ICD firing for AFib and not ventricular arrhythmias. This may be dependent on the type of cardiomyopathy.
Next, we’re going to talk about biventricular pacemakers. Women tend to benefit more so that there is an improvement in symptoms and survival. What is fascinating is that left bundle branch block is a risk factor for the development of heart failure in women, which makes this next statement even more fascinating.
The FDA does their own analysis when they are reviewing devices and everything else, and they published one of them in JAMA Internal Medicine, taking three studies and seeing the benefit in women and men. They found that everybody benefits when the left bundle branch block has a QRS greater than 150 milliseconds. But with a QRS between 130 and 149 milliseconds, only the women benefited. That›s fascinating because that is a risk factor — the development of the left bundle branch block causing heart failure in women. It makes you wonder whether you are correcting something that actually was responsible for their heart failure.
In advanced heart failure, we have left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) and heart transplantation. For years, we couldn’t get LVADs small enough to fit in women. When they were larger, there were complications that were more common in women, such as stroke. With the newer devices — the HeartMate 3 is small, for instance — complications for everyone are very infrequent, and women and men benefit. I’m going to encourage clinicians to use them.
For heart transplantation, as I mentioned before, women tend to get HFpEF. I didn’t mention that they get heart failure when they’re older, for the most part. There are fewer women who are transplanted than men and eligible at younger ages. What we had for decades was that women were dying while they were on the waitlist for heart transplantation at a faster rate than men but living longer after transplantation. As LVADs became more appropriately sized for women, the complication rates went down; and we did see an improvement on the waitlist mortality rate before we changed the allocation system. But it really wasn’t until after we changed the allocation system in 2018 that we saw great success. Now, women have similar survival while on the waitlist. They’re transplanted at a faster rate despite the fact that they’re less likely to receive the temporary mechanical support, and they tend to still do very well.
We have some differences in therapy response. Thank you.
Dr. Hsich disclosed ties with Natera, DEFINE steering committee (no money), and MEDCAC (Medicare/Medicaid) committee. She received research grant from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mediterranean Diet Lowers Tachyarrhythmia in Paroxysmal AF
BOSTON — A Mediterranean diet with extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) significantly reduced the risk for tachyarrhythmia recurrence after atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation in patients with paroxysmal disease, but the diet had less of an impact on patients with persistent AF, a new study showed.
“An intervention with the Mediterranean diet with EVOO produced a nonsignificant reduction in any atrial tachycardia in a selected population after undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation, but this intervention produced a significant reduction in any atrial tachyarrhythmias in patients with paroxysmal AF,” said Maria Teresa Barrio-Lopez, MD, PhD, an electrophysiologist at University Hospital HM Monteprincipe in Madrid, Spain, who presented results from the PREDIMAR trial at the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) 2024 annual meeting.
The PREDIMAR study enrolled 720 patients from the larger PREDIMED study, which showed that patients without AF at enrollment and who followed a Mediterranean diet enriched with EVOO had a 38% lower rate of incidental AF than control individuals.
PREDIMAR evaluated the impact of the diet on arrhythmia recurrence in patients after ablation. The patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either the dietary intervention group or the control group.
PREDIMAR Study Results
However, among the 431 patients with paroxysmal AF, 25.2% in the diet group and 34.7% in the control group had no tachyarrhythmia recurrence, which translates into a 31% lower risk in the diet group.
In this study, the diet was rich in fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables and was complemented with EVOO. Participants were also permitted moderate wine consumption.
The intervention involved dietitians who remotely followed patients and made periodic telephone calls to encourage them to stay on the diet. Participants had weight and body measurements taken at baseline and at 3, 6, 12, and 18 months and underwent an ECG at 6, 12, and 18 months. Labs were obtained at baseline and at 12 months. Participants were also given educational materials throughout the intervention.
Average scores, based on a scale of 0-13, excluding an item for wine intake, were 7.8 in the diet group and 7.2 in the control group.
Daily average alcohol intake was higher in the diet group than in the control group (9.8 vs 8.2 g), but “the weight of the patient during the study didn’t change in any group,” Dr. Barrio-Lopez reported.
Baseline characteristics were similar in the two groups. About 60% were taking antiarrhythmic drugs, and about 84% were taking anticoagulants.
‘A Tour de Force’
PREDIMAR was “really a tour de force,” Christine Albert, MD, MPH, chair of cardiology at the Smidt Heart Institute at the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California, said during a commentary presented at HRS. “We talk about how we’re going to do these dietary interventions and weight loss and all the risk-factor reduction, and they pulled it off with 700 individuals and also did it in a way that was very novel.”
This is the first large-scale dietary intervention trial of patients with AF. However, Dr. Albert noted later in an interview, the Mediterranean diet poses potential challenges for some people with AF.
“The Mediterranean diet recommends that people drink wine, but then there’s clear evidence that abstinence from alcohol actually reduces recurrences of atrial fibrillation, so even though there are a lot of things about the Mediterranean diet that are probably healthy and good for atrial fibrillation, that aspect of it might be working against the patient,” she explained.
The finding that patients in the Mediterranean diet group experienced no significant weight loss could be counterintuitive when it comes to preventing AF. But “you could adapt the diet for AF,” Dr. Albert said. You could “leave out the wine and focus more on weight loss if the patient is obese because those are also the pillars of what we’ve learned for patients with atrial fibrillation.”
Making weight loss a key component of the study could be significant for the American population. “At least in the United States, that’s a huge part of the risk factors for atrial fibrillation after ablation,” she said.
The remote follow-up component of the PREDIMAR study is also intriguing. “I think what’s most exciting about what they did is, they showed they can do all these things remotely,” Dr. Albert added.
Dr. Barrio-Lopez had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Albert disclosed relationships with Abbott, Roche Diagnostics, St. Jude Medical, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Element Science.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — A Mediterranean diet with extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) significantly reduced the risk for tachyarrhythmia recurrence after atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation in patients with paroxysmal disease, but the diet had less of an impact on patients with persistent AF, a new study showed.
“An intervention with the Mediterranean diet with EVOO produced a nonsignificant reduction in any atrial tachycardia in a selected population after undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation, but this intervention produced a significant reduction in any atrial tachyarrhythmias in patients with paroxysmal AF,” said Maria Teresa Barrio-Lopez, MD, PhD, an electrophysiologist at University Hospital HM Monteprincipe in Madrid, Spain, who presented results from the PREDIMAR trial at the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) 2024 annual meeting.
The PREDIMAR study enrolled 720 patients from the larger PREDIMED study, which showed that patients without AF at enrollment and who followed a Mediterranean diet enriched with EVOO had a 38% lower rate of incidental AF than control individuals.
PREDIMAR evaluated the impact of the diet on arrhythmia recurrence in patients after ablation. The patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either the dietary intervention group or the control group.
PREDIMAR Study Results
However, among the 431 patients with paroxysmal AF, 25.2% in the diet group and 34.7% in the control group had no tachyarrhythmia recurrence, which translates into a 31% lower risk in the diet group.
In this study, the diet was rich in fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables and was complemented with EVOO. Participants were also permitted moderate wine consumption.
The intervention involved dietitians who remotely followed patients and made periodic telephone calls to encourage them to stay on the diet. Participants had weight and body measurements taken at baseline and at 3, 6, 12, and 18 months and underwent an ECG at 6, 12, and 18 months. Labs were obtained at baseline and at 12 months. Participants were also given educational materials throughout the intervention.
Average scores, based on a scale of 0-13, excluding an item for wine intake, were 7.8 in the diet group and 7.2 in the control group.
Daily average alcohol intake was higher in the diet group than in the control group (9.8 vs 8.2 g), but “the weight of the patient during the study didn’t change in any group,” Dr. Barrio-Lopez reported.
Baseline characteristics were similar in the two groups. About 60% were taking antiarrhythmic drugs, and about 84% were taking anticoagulants.
‘A Tour de Force’
PREDIMAR was “really a tour de force,” Christine Albert, MD, MPH, chair of cardiology at the Smidt Heart Institute at the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California, said during a commentary presented at HRS. “We talk about how we’re going to do these dietary interventions and weight loss and all the risk-factor reduction, and they pulled it off with 700 individuals and also did it in a way that was very novel.”
This is the first large-scale dietary intervention trial of patients with AF. However, Dr. Albert noted later in an interview, the Mediterranean diet poses potential challenges for some people with AF.
“The Mediterranean diet recommends that people drink wine, but then there’s clear evidence that abstinence from alcohol actually reduces recurrences of atrial fibrillation, so even though there are a lot of things about the Mediterranean diet that are probably healthy and good for atrial fibrillation, that aspect of it might be working against the patient,” she explained.
The finding that patients in the Mediterranean diet group experienced no significant weight loss could be counterintuitive when it comes to preventing AF. But “you could adapt the diet for AF,” Dr. Albert said. You could “leave out the wine and focus more on weight loss if the patient is obese because those are also the pillars of what we’ve learned for patients with atrial fibrillation.”
Making weight loss a key component of the study could be significant for the American population. “At least in the United States, that’s a huge part of the risk factors for atrial fibrillation after ablation,” she said.
The remote follow-up component of the PREDIMAR study is also intriguing. “I think what’s most exciting about what they did is, they showed they can do all these things remotely,” Dr. Albert added.
Dr. Barrio-Lopez had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Albert disclosed relationships with Abbott, Roche Diagnostics, St. Jude Medical, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Element Science.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — A Mediterranean diet with extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) significantly reduced the risk for tachyarrhythmia recurrence after atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation in patients with paroxysmal disease, but the diet had less of an impact on patients with persistent AF, a new study showed.
“An intervention with the Mediterranean diet with EVOO produced a nonsignificant reduction in any atrial tachycardia in a selected population after undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation, but this intervention produced a significant reduction in any atrial tachyarrhythmias in patients with paroxysmal AF,” said Maria Teresa Barrio-Lopez, MD, PhD, an electrophysiologist at University Hospital HM Monteprincipe in Madrid, Spain, who presented results from the PREDIMAR trial at the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) 2024 annual meeting.
The PREDIMAR study enrolled 720 patients from the larger PREDIMED study, which showed that patients without AF at enrollment and who followed a Mediterranean diet enriched with EVOO had a 38% lower rate of incidental AF than control individuals.
PREDIMAR evaluated the impact of the diet on arrhythmia recurrence in patients after ablation. The patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either the dietary intervention group or the control group.
PREDIMAR Study Results
However, among the 431 patients with paroxysmal AF, 25.2% in the diet group and 34.7% in the control group had no tachyarrhythmia recurrence, which translates into a 31% lower risk in the diet group.
In this study, the diet was rich in fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables and was complemented with EVOO. Participants were also permitted moderate wine consumption.
The intervention involved dietitians who remotely followed patients and made periodic telephone calls to encourage them to stay on the diet. Participants had weight and body measurements taken at baseline and at 3, 6, 12, and 18 months and underwent an ECG at 6, 12, and 18 months. Labs were obtained at baseline and at 12 months. Participants were also given educational materials throughout the intervention.
Average scores, based on a scale of 0-13, excluding an item for wine intake, were 7.8 in the diet group and 7.2 in the control group.
Daily average alcohol intake was higher in the diet group than in the control group (9.8 vs 8.2 g), but “the weight of the patient during the study didn’t change in any group,” Dr. Barrio-Lopez reported.
Baseline characteristics were similar in the two groups. About 60% were taking antiarrhythmic drugs, and about 84% were taking anticoagulants.
‘A Tour de Force’
PREDIMAR was “really a tour de force,” Christine Albert, MD, MPH, chair of cardiology at the Smidt Heart Institute at the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, California, said during a commentary presented at HRS. “We talk about how we’re going to do these dietary interventions and weight loss and all the risk-factor reduction, and they pulled it off with 700 individuals and also did it in a way that was very novel.”
This is the first large-scale dietary intervention trial of patients with AF. However, Dr. Albert noted later in an interview, the Mediterranean diet poses potential challenges for some people with AF.
“The Mediterranean diet recommends that people drink wine, but then there’s clear evidence that abstinence from alcohol actually reduces recurrences of atrial fibrillation, so even though there are a lot of things about the Mediterranean diet that are probably healthy and good for atrial fibrillation, that aspect of it might be working against the patient,” she explained.
The finding that patients in the Mediterranean diet group experienced no significant weight loss could be counterintuitive when it comes to preventing AF. But “you could adapt the diet for AF,” Dr. Albert said. You could “leave out the wine and focus more on weight loss if the patient is obese because those are also the pillars of what we’ve learned for patients with atrial fibrillation.”
Making weight loss a key component of the study could be significant for the American population. “At least in the United States, that’s a huge part of the risk factors for atrial fibrillation after ablation,” she said.
The remote follow-up component of the PREDIMAR study is also intriguing. “I think what’s most exciting about what they did is, they showed they can do all these things remotely,” Dr. Albert added.
Dr. Barrio-Lopez had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Albert disclosed relationships with Abbott, Roche Diagnostics, St. Jude Medical, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Element Science.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HRS 2024
Commentary: Predicting Migraine Treatment Outcomes, July 2024
Medications classified as anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibodies (mAb), a relatively new category of migraine therapy, have shown strong evidence of efficacy for migraine treatment and prevention. However, as these medications — which include Aimovig (erenumab), Emgality (galcanezumab), Ajovy (fremanezumab), and Vyepti (eptinezumab) — are new, their long-term outcomes are not known; in addition, they are expensive and they do not work for everyone. Patients who are doing relatively well on other medications might ask about switching to one of the anti-CGRP mAb so that they can experience the better outcomes and low side-effect profile that they've been hearing about. New research is showing some prognostic indicators that can help identify which patients might experience a better response to anti-CGRP mAb.
A prospective real-world study published in the May 2024 issue of Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry included 5818 patients who had been treated with an anti-CGRP mAb for high-frequency episodic or chronic migraine. The researchers assessed responses after 6 months of use, defining a good response as ≥50% reduction in monthly headache days and excellent response as ≥75% reduction in monthly headache days. They found that several pretreatment baseline factors were predictors of a good or excellent 6-month response: older age, the presence of unilateral pain, the absence of depression, fewer monthly migraine days, and lower Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) score. Notably, men and women experienced comparable outcomes. While it's not completely clear why these factors were associated with better responses to anti-CGRP mAb, the results could help in selecting patients who might or might not benefit from this new medication class.
Results of a prospective study published in the May 2024 in The Journal of Headache and Pain demonstrated that patients treated with eptinezumab for 3 months experienced a reduction of monthly headaches, migraines, and the use of acute medication. The patients who had previously had an inadequate response to or were unable to tolerate other anti-CGRP mAb (erenumab, galcanezumab, fremanezumab) were less likely to experience improvement with eptinezumab than patients who had not had previous unsuccessful attempts with anti-CGRP mAb. This suggests that it might not be beneficial for patents to try multiple medications in this category if they have had an inadequate response or intolerability to others in the same drug class.
Lifestyle factors can play a role in migraine outcomes and may reduce the need for medication. A study published in The Journal of Headache and Pain in May 2024 examined the relationship between migraine and the American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health recommended lifestyle factors. The study included 332,895 participants, with a median follow-up of 13.58 years. Researchers found that maintaining targeted or recommended body mass index (BMI), physical activity, sleep duration, sleep pattern, and sedentary time were associated with substantial reductions in migraine risk.
Diet, another lifestyle factor, can also have an effect on migraine. Avoiding dietary triggers is a well-known adjustment that many patients are advised to make. Overall diet quality can play a role in migraine outcomes as well. According to a study published in the May 2024 issue of Nutritional Neuroscience, participants who followed a diet that qualified as having a high Carbohydrate Quality Index (CQI) had lower migraine severity and duration than participants whose diets did not qualify as high CQI. The study included 266 women (age 18-45 years), using a 147-item food frequency questionnaire to assess CQI. The CQI, a relatively new index for measuring carbohydrate quality, includes four components: glycemic index, dietary fiber intake, ratio of whole grain to total grain, ratio of solid carbohydrates to total (solid + liquid) carbohydrates.1 A low glycemic index and higher scores for the other three factors translates to a high CQI.
While the results of the AHA/migraine study and the CQI/migraine study are interesting, the physiologic reasons for the outcomes and validation of the results need further investigation. It's not clear whether the decrease in migraines that's associated with optimal carbohydrate intake is associated with outcomes such as low BMI or better sleep, or whether carbohydrate metabolism could be an independent factor.
Predictive factors can be beneficial in making migraine treatment decisions. While trial and error will always remain part of optimal migraine therapy, customizing treatment on the basis of an individual patient's characteristics can help in reaching an effective treatment and better quality of life sooner.
Additional References
1. Sawicki CM, Lichtenstein AH, Rogers GT, et al. Comparison of indices of carbohydrate quality and food sources of dietary fiber on longitudinal changes in waist circumference in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Nutrients. 2021;13:997. Source
Medications classified as anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibodies (mAb), a relatively new category of migraine therapy, have shown strong evidence of efficacy for migraine treatment and prevention. However, as these medications — which include Aimovig (erenumab), Emgality (galcanezumab), Ajovy (fremanezumab), and Vyepti (eptinezumab) — are new, their long-term outcomes are not known; in addition, they are expensive and they do not work for everyone. Patients who are doing relatively well on other medications might ask about switching to one of the anti-CGRP mAb so that they can experience the better outcomes and low side-effect profile that they've been hearing about. New research is showing some prognostic indicators that can help identify which patients might experience a better response to anti-CGRP mAb.
A prospective real-world study published in the May 2024 issue of Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry included 5818 patients who had been treated with an anti-CGRP mAb for high-frequency episodic or chronic migraine. The researchers assessed responses after 6 months of use, defining a good response as ≥50% reduction in monthly headache days and excellent response as ≥75% reduction in monthly headache days. They found that several pretreatment baseline factors were predictors of a good or excellent 6-month response: older age, the presence of unilateral pain, the absence of depression, fewer monthly migraine days, and lower Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) score. Notably, men and women experienced comparable outcomes. While it's not completely clear why these factors were associated with better responses to anti-CGRP mAb, the results could help in selecting patients who might or might not benefit from this new medication class.
Results of a prospective study published in the May 2024 in The Journal of Headache and Pain demonstrated that patients treated with eptinezumab for 3 months experienced a reduction of monthly headaches, migraines, and the use of acute medication. The patients who had previously had an inadequate response to or were unable to tolerate other anti-CGRP mAb (erenumab, galcanezumab, fremanezumab) were less likely to experience improvement with eptinezumab than patients who had not had previous unsuccessful attempts with anti-CGRP mAb. This suggests that it might not be beneficial for patents to try multiple medications in this category if they have had an inadequate response or intolerability to others in the same drug class.
Lifestyle factors can play a role in migraine outcomes and may reduce the need for medication. A study published in The Journal of Headache and Pain in May 2024 examined the relationship between migraine and the American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health recommended lifestyle factors. The study included 332,895 participants, with a median follow-up of 13.58 years. Researchers found that maintaining targeted or recommended body mass index (BMI), physical activity, sleep duration, sleep pattern, and sedentary time were associated with substantial reductions in migraine risk.
Diet, another lifestyle factor, can also have an effect on migraine. Avoiding dietary triggers is a well-known adjustment that many patients are advised to make. Overall diet quality can play a role in migraine outcomes as well. According to a study published in the May 2024 issue of Nutritional Neuroscience, participants who followed a diet that qualified as having a high Carbohydrate Quality Index (CQI) had lower migraine severity and duration than participants whose diets did not qualify as high CQI. The study included 266 women (age 18-45 years), using a 147-item food frequency questionnaire to assess CQI. The CQI, a relatively new index for measuring carbohydrate quality, includes four components: glycemic index, dietary fiber intake, ratio of whole grain to total grain, ratio of solid carbohydrates to total (solid + liquid) carbohydrates.1 A low glycemic index and higher scores for the other three factors translates to a high CQI.
While the results of the AHA/migraine study and the CQI/migraine study are interesting, the physiologic reasons for the outcomes and validation of the results need further investigation. It's not clear whether the decrease in migraines that's associated with optimal carbohydrate intake is associated with outcomes such as low BMI or better sleep, or whether carbohydrate metabolism could be an independent factor.
Predictive factors can be beneficial in making migraine treatment decisions. While trial and error will always remain part of optimal migraine therapy, customizing treatment on the basis of an individual patient's characteristics can help in reaching an effective treatment and better quality of life sooner.
Additional References
1. Sawicki CM, Lichtenstein AH, Rogers GT, et al. Comparison of indices of carbohydrate quality and food sources of dietary fiber on longitudinal changes in waist circumference in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Nutrients. 2021;13:997. Source
Medications classified as anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibodies (mAb), a relatively new category of migraine therapy, have shown strong evidence of efficacy for migraine treatment and prevention. However, as these medications — which include Aimovig (erenumab), Emgality (galcanezumab), Ajovy (fremanezumab), and Vyepti (eptinezumab) — are new, their long-term outcomes are not known; in addition, they are expensive and they do not work for everyone. Patients who are doing relatively well on other medications might ask about switching to one of the anti-CGRP mAb so that they can experience the better outcomes and low side-effect profile that they've been hearing about. New research is showing some prognostic indicators that can help identify which patients might experience a better response to anti-CGRP mAb.
A prospective real-world study published in the May 2024 issue of Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry included 5818 patients who had been treated with an anti-CGRP mAb for high-frequency episodic or chronic migraine. The researchers assessed responses after 6 months of use, defining a good response as ≥50% reduction in monthly headache days and excellent response as ≥75% reduction in monthly headache days. They found that several pretreatment baseline factors were predictors of a good or excellent 6-month response: older age, the presence of unilateral pain, the absence of depression, fewer monthly migraine days, and lower Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) score. Notably, men and women experienced comparable outcomes. While it's not completely clear why these factors were associated with better responses to anti-CGRP mAb, the results could help in selecting patients who might or might not benefit from this new medication class.
Results of a prospective study published in the May 2024 in The Journal of Headache and Pain demonstrated that patients treated with eptinezumab for 3 months experienced a reduction of monthly headaches, migraines, and the use of acute medication. The patients who had previously had an inadequate response to or were unable to tolerate other anti-CGRP mAb (erenumab, galcanezumab, fremanezumab) were less likely to experience improvement with eptinezumab than patients who had not had previous unsuccessful attempts with anti-CGRP mAb. This suggests that it might not be beneficial for patents to try multiple medications in this category if they have had an inadequate response or intolerability to others in the same drug class.
Lifestyle factors can play a role in migraine outcomes and may reduce the need for medication. A study published in The Journal of Headache and Pain in May 2024 examined the relationship between migraine and the American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health recommended lifestyle factors. The study included 332,895 participants, with a median follow-up of 13.58 years. Researchers found that maintaining targeted or recommended body mass index (BMI), physical activity, sleep duration, sleep pattern, and sedentary time were associated with substantial reductions in migraine risk.
Diet, another lifestyle factor, can also have an effect on migraine. Avoiding dietary triggers is a well-known adjustment that many patients are advised to make. Overall diet quality can play a role in migraine outcomes as well. According to a study published in the May 2024 issue of Nutritional Neuroscience, participants who followed a diet that qualified as having a high Carbohydrate Quality Index (CQI) had lower migraine severity and duration than participants whose diets did not qualify as high CQI. The study included 266 women (age 18-45 years), using a 147-item food frequency questionnaire to assess CQI. The CQI, a relatively new index for measuring carbohydrate quality, includes four components: glycemic index, dietary fiber intake, ratio of whole grain to total grain, ratio of solid carbohydrates to total (solid + liquid) carbohydrates.1 A low glycemic index and higher scores for the other three factors translates to a high CQI.
While the results of the AHA/migraine study and the CQI/migraine study are interesting, the physiologic reasons for the outcomes and validation of the results need further investigation. It's not clear whether the decrease in migraines that's associated with optimal carbohydrate intake is associated with outcomes such as low BMI or better sleep, or whether carbohydrate metabolism could be an independent factor.
Predictive factors can be beneficial in making migraine treatment decisions. While trial and error will always remain part of optimal migraine therapy, customizing treatment on the basis of an individual patient's characteristics can help in reaching an effective treatment and better quality of life sooner.
Additional References
1. Sawicki CM, Lichtenstein AH, Rogers GT, et al. Comparison of indices of carbohydrate quality and food sources of dietary fiber on longitudinal changes in waist circumference in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Nutrients. 2021;13:997. Source
A New Psychotherapeutic ‘Gold Standard’ for Chronic Pain?
, the current psychotherapeutic gold standard, a new study suggested.
Two thirds of the patients who received EAET reported at least a 30% reduction in pain compared with 17% of those who received CBT. The randomized clinical trial also showed that individuals with depression and anxiety responded more favorably to EAET, a novel finding.
The study is one of only a few to directly compare EAET with CBT.
“Most people with chronic pain don’t consider psychotherapy at all,” said study investigator Brandon C. Yarns, MD, a staff psychiatrist at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, and clinical professor of health sciences at the Department of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, UCLA Health.
Although patients were allowed to continue medication for pain and other comorbidities during the study, those who received EAET “had larger improvements in pain, depression, and anxiety,” Dr. Yarns said. “That suggests that the effect was due to the EAET.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
‘Gold Standard’
EAET was first used in the early 2010s. In the therapy, patients are asked to recall a difficult or traumatic memory, engage in experiencing how the related emotions feel in the body, express those feelings in words, and release or let them go. They are taught that the brain’s perception of pain is strongly influenced by the evasion of grief, fear, rage, or guilt, Dr. Yarns said.
This contrasts with CBT — considered the current gold standard for chronic pain — which teaches patients to improve the ability to tolerate pain though guided imagery, muscle relaxation, and other exercises and to adapt their thinking to change how they think about pain.
Although prior studies suggested EAET is effective in reducing pain in fibromyalgia and chronic musculoskeletal, pelvic, and head pain, most included primarily younger, female patients.
The research is the “first full-scale evaluation of EAET, to our knowledge, in a medically or psychiatrically complex, racially and ethnically diverse, older sample comprising predominantly men,” investigators wrote.
The trial enrolled 126 veterans (92% men; 55% Black or African American) aged 60-95 years with at least 3 months of musculoskeletal pain. More than two thirds of patients had a psychiatric diagnosis, with about one third having posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Almost all had back pain, and many had pain in multiple locations.
All services were delivered in-person at the US Department of Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, Los Angeles. Half underwent CBT, while the other half received EAET.
Each patient had one 90-minute individual session and eight additional 90-minute group sessions.
Patients were asked to rate their pain using a 0-10 scale in the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) before starting treatment, at the end of the nine sessions (at week 10), and 6 months after the sessions ended. Baseline BPI score for both groups was a mean of around 6.
Post treatment, people in the EAET versus CBT group had a mean two-point reduction versus 0.60 reduction, respectively, on the BPI scale. A clinically significant reduction in pain — defined as ≥ 30% decrease — was reported in 63% of EAET patients versus 17% of CBT patients (odds ratio [OR], 21.54; P < .001).
At 6 months, the mean reduction was 1.2 for the EAET group compared with 0.25 for the CBT group, and 40% of the EAET group reported a clinically significant reduction in pain.
A little more than a third (35%) of veterans receiving EAET reported at least a 50% reduction in pain at 10 weeks compared with 7% of those receiving CBT. At 6 months, 16% of the EAET arm reported a halving of their pain.
EAET was also superior to CBT in reducing anxiety, depression, and PTSD symptoms at the 10-week mark.
More Work Needed
In an accompanying editorial, Matthias Karst, MD, PhD, a clinician with the Pain Clinic, Hannover Medical School, in Hannover, Germany, noted that EAET’s effects “are significantly superior to those of CBT in almost all dimensions, even after 6 months.”
EAET “assigns a special place to the integration of the body into the emotional experience,” he wrote.
The study demonstrated that “the evocation and expression of emotions is superior to the mere cognitive discussion of these emotions in therapy of patients with chronic pain.”
Commenting on the findings, Traci J. Speed, MD, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and an attending psychiatrist of the Johns Hopkins Pain Treatment Program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, called the study “ground-breaking” because it showed effectiveness in people with high rates of PTSD, anxiety, and depression.
“It is a little bit surprising how impressive the study outcomes are in terms of maintaining the effects at the end of the treatment and sustaining some of the effects on pain sensitivity even at the 6-month follow-up,” said Dr. Speed, who was not part of the study.
However, she continued, “I don’t think it changes the current standard of practice yet. CBT has decades of research and evidence that it is effective for chronic pain and that will I think continue to be the standard of care.”
Although EAET is in its infancy, chronic pain experts are interested in learning more about the therapy, Dr. Speed added.
“It blends well with the current techniques and extends the current gold standard treatment approaches,” she said. “We are starting to really appreciate the role that emotions play in pain sensitivity.”
Both Dr. Karst and Dr. Speed noted that more study is needed to determine the sustainability of treatment effects.
Dr. Yarns agreed. “We need more research on what the appropriate dose is and perhaps how one might go about personalizing that for the patient,” he said.
The study was funded by a career development award to Dr. Yarns from the VA Clinical Science Research and Development Service. Dr. Yarns reported receiving grants from the US Department of Veterans Affairs during the study. Other authors’ disclosures are in the original article. Dr. Speed reported no conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, the current psychotherapeutic gold standard, a new study suggested.
Two thirds of the patients who received EAET reported at least a 30% reduction in pain compared with 17% of those who received CBT. The randomized clinical trial also showed that individuals with depression and anxiety responded more favorably to EAET, a novel finding.
The study is one of only a few to directly compare EAET with CBT.
“Most people with chronic pain don’t consider psychotherapy at all,” said study investigator Brandon C. Yarns, MD, a staff psychiatrist at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, and clinical professor of health sciences at the Department of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, UCLA Health.
Although patients were allowed to continue medication for pain and other comorbidities during the study, those who received EAET “had larger improvements in pain, depression, and anxiety,” Dr. Yarns said. “That suggests that the effect was due to the EAET.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
‘Gold Standard’
EAET was first used in the early 2010s. In the therapy, patients are asked to recall a difficult or traumatic memory, engage in experiencing how the related emotions feel in the body, express those feelings in words, and release or let them go. They are taught that the brain’s perception of pain is strongly influenced by the evasion of grief, fear, rage, or guilt, Dr. Yarns said.
This contrasts with CBT — considered the current gold standard for chronic pain — which teaches patients to improve the ability to tolerate pain though guided imagery, muscle relaxation, and other exercises and to adapt their thinking to change how they think about pain.
Although prior studies suggested EAET is effective in reducing pain in fibromyalgia and chronic musculoskeletal, pelvic, and head pain, most included primarily younger, female patients.
The research is the “first full-scale evaluation of EAET, to our knowledge, in a medically or psychiatrically complex, racially and ethnically diverse, older sample comprising predominantly men,” investigators wrote.
The trial enrolled 126 veterans (92% men; 55% Black or African American) aged 60-95 years with at least 3 months of musculoskeletal pain. More than two thirds of patients had a psychiatric diagnosis, with about one third having posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Almost all had back pain, and many had pain in multiple locations.
All services were delivered in-person at the US Department of Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, Los Angeles. Half underwent CBT, while the other half received EAET.
Each patient had one 90-minute individual session and eight additional 90-minute group sessions.
Patients were asked to rate their pain using a 0-10 scale in the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) before starting treatment, at the end of the nine sessions (at week 10), and 6 months after the sessions ended. Baseline BPI score for both groups was a mean of around 6.
Post treatment, people in the EAET versus CBT group had a mean two-point reduction versus 0.60 reduction, respectively, on the BPI scale. A clinically significant reduction in pain — defined as ≥ 30% decrease — was reported in 63% of EAET patients versus 17% of CBT patients (odds ratio [OR], 21.54; P < .001).
At 6 months, the mean reduction was 1.2 for the EAET group compared with 0.25 for the CBT group, and 40% of the EAET group reported a clinically significant reduction in pain.
A little more than a third (35%) of veterans receiving EAET reported at least a 50% reduction in pain at 10 weeks compared with 7% of those receiving CBT. At 6 months, 16% of the EAET arm reported a halving of their pain.
EAET was also superior to CBT in reducing anxiety, depression, and PTSD symptoms at the 10-week mark.
More Work Needed
In an accompanying editorial, Matthias Karst, MD, PhD, a clinician with the Pain Clinic, Hannover Medical School, in Hannover, Germany, noted that EAET’s effects “are significantly superior to those of CBT in almost all dimensions, even after 6 months.”
EAET “assigns a special place to the integration of the body into the emotional experience,” he wrote.
The study demonstrated that “the evocation and expression of emotions is superior to the mere cognitive discussion of these emotions in therapy of patients with chronic pain.”
Commenting on the findings, Traci J. Speed, MD, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and an attending psychiatrist of the Johns Hopkins Pain Treatment Program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, called the study “ground-breaking” because it showed effectiveness in people with high rates of PTSD, anxiety, and depression.
“It is a little bit surprising how impressive the study outcomes are in terms of maintaining the effects at the end of the treatment and sustaining some of the effects on pain sensitivity even at the 6-month follow-up,” said Dr. Speed, who was not part of the study.
However, she continued, “I don’t think it changes the current standard of practice yet. CBT has decades of research and evidence that it is effective for chronic pain and that will I think continue to be the standard of care.”
Although EAET is in its infancy, chronic pain experts are interested in learning more about the therapy, Dr. Speed added.
“It blends well with the current techniques and extends the current gold standard treatment approaches,” she said. “We are starting to really appreciate the role that emotions play in pain sensitivity.”
Both Dr. Karst and Dr. Speed noted that more study is needed to determine the sustainability of treatment effects.
Dr. Yarns agreed. “We need more research on what the appropriate dose is and perhaps how one might go about personalizing that for the patient,” he said.
The study was funded by a career development award to Dr. Yarns from the VA Clinical Science Research and Development Service. Dr. Yarns reported receiving grants from the US Department of Veterans Affairs during the study. Other authors’ disclosures are in the original article. Dr. Speed reported no conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, the current psychotherapeutic gold standard, a new study suggested.
Two thirds of the patients who received EAET reported at least a 30% reduction in pain compared with 17% of those who received CBT. The randomized clinical trial also showed that individuals with depression and anxiety responded more favorably to EAET, a novel finding.
The study is one of only a few to directly compare EAET with CBT.
“Most people with chronic pain don’t consider psychotherapy at all,” said study investigator Brandon C. Yarns, MD, a staff psychiatrist at the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, and clinical professor of health sciences at the Department of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences, UCLA Health.
Although patients were allowed to continue medication for pain and other comorbidities during the study, those who received EAET “had larger improvements in pain, depression, and anxiety,” Dr. Yarns said. “That suggests that the effect was due to the EAET.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
‘Gold Standard’
EAET was first used in the early 2010s. In the therapy, patients are asked to recall a difficult or traumatic memory, engage in experiencing how the related emotions feel in the body, express those feelings in words, and release or let them go. They are taught that the brain’s perception of pain is strongly influenced by the evasion of grief, fear, rage, or guilt, Dr. Yarns said.
This contrasts with CBT — considered the current gold standard for chronic pain — which teaches patients to improve the ability to tolerate pain though guided imagery, muscle relaxation, and other exercises and to adapt their thinking to change how they think about pain.
Although prior studies suggested EAET is effective in reducing pain in fibromyalgia and chronic musculoskeletal, pelvic, and head pain, most included primarily younger, female patients.
The research is the “first full-scale evaluation of EAET, to our knowledge, in a medically or psychiatrically complex, racially and ethnically diverse, older sample comprising predominantly men,” investigators wrote.
The trial enrolled 126 veterans (92% men; 55% Black or African American) aged 60-95 years with at least 3 months of musculoskeletal pain. More than two thirds of patients had a psychiatric diagnosis, with about one third having posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Almost all had back pain, and many had pain in multiple locations.
All services were delivered in-person at the US Department of Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System, Los Angeles. Half underwent CBT, while the other half received EAET.
Each patient had one 90-minute individual session and eight additional 90-minute group sessions.
Patients were asked to rate their pain using a 0-10 scale in the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) before starting treatment, at the end of the nine sessions (at week 10), and 6 months after the sessions ended. Baseline BPI score for both groups was a mean of around 6.
Post treatment, people in the EAET versus CBT group had a mean two-point reduction versus 0.60 reduction, respectively, on the BPI scale. A clinically significant reduction in pain — defined as ≥ 30% decrease — was reported in 63% of EAET patients versus 17% of CBT patients (odds ratio [OR], 21.54; P < .001).
At 6 months, the mean reduction was 1.2 for the EAET group compared with 0.25 for the CBT group, and 40% of the EAET group reported a clinically significant reduction in pain.
A little more than a third (35%) of veterans receiving EAET reported at least a 50% reduction in pain at 10 weeks compared with 7% of those receiving CBT. At 6 months, 16% of the EAET arm reported a halving of their pain.
EAET was also superior to CBT in reducing anxiety, depression, and PTSD symptoms at the 10-week mark.
More Work Needed
In an accompanying editorial, Matthias Karst, MD, PhD, a clinician with the Pain Clinic, Hannover Medical School, in Hannover, Germany, noted that EAET’s effects “are significantly superior to those of CBT in almost all dimensions, even after 6 months.”
EAET “assigns a special place to the integration of the body into the emotional experience,” he wrote.
The study demonstrated that “the evocation and expression of emotions is superior to the mere cognitive discussion of these emotions in therapy of patients with chronic pain.”
Commenting on the findings, Traci J. Speed, MD, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and an attending psychiatrist of the Johns Hopkins Pain Treatment Program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, called the study “ground-breaking” because it showed effectiveness in people with high rates of PTSD, anxiety, and depression.
“It is a little bit surprising how impressive the study outcomes are in terms of maintaining the effects at the end of the treatment and sustaining some of the effects on pain sensitivity even at the 6-month follow-up,” said Dr. Speed, who was not part of the study.
However, she continued, “I don’t think it changes the current standard of practice yet. CBT has decades of research and evidence that it is effective for chronic pain and that will I think continue to be the standard of care.”
Although EAET is in its infancy, chronic pain experts are interested in learning more about the therapy, Dr. Speed added.
“It blends well with the current techniques and extends the current gold standard treatment approaches,” she said. “We are starting to really appreciate the role that emotions play in pain sensitivity.”
Both Dr. Karst and Dr. Speed noted that more study is needed to determine the sustainability of treatment effects.
Dr. Yarns agreed. “We need more research on what the appropriate dose is and perhaps how one might go about personalizing that for the patient,” he said.
The study was funded by a career development award to Dr. Yarns from the VA Clinical Science Research and Development Service. Dr. Yarns reported receiving grants from the US Department of Veterans Affairs during the study. Other authors’ disclosures are in the original article. Dr. Speed reported no conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Just Be Prepared’: MD Finds Overdose Victim in an Alley
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a Medscape Medical News series telling these stories.
I had worked a normal 7:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. shift in our emergency department. It was a nice day out, so I put my headphones in and started walking home through the Capitol Hill neighborhood in Denver. I passed a couple of buildings and reached an alleyway. At that moment, I glanced over.
Two guys were standing over a third person who was down on the ground. One of the people standing was on the phone. I paused for a second and thought, that doesn’t look right.
The guy on the ground was clearly out. And the other two were looking concerned like they didn’t know what to do.
I walked up the alley and asked, “What’s going on? Can I help?” One of the guys explained that they had just found this man lying here and had already called 911. They sounded a little bit out of their element. They certainly weren’t medically trained.
I leaned down next to the man on the ground. He was probably in his mid-to-late 40s. Unconscious. I always start with, “Hello? Can you hear me?” No response.
I felt for a pulse and he had one, but he didn’t appear to be breathing. I thought, I know what this is. I said, “Sir, I’m going to open your eyes.” I opened his eyes, and his pupils were tiny. It was almost certainly an opioid overdose.
And I had naloxone in my bag.
I got it out and started to assemble it. I didn’t have Narcan, which is the easy one. I had to put this kit together, draw up the medication, and put on the little nasal atomizer.
The two other guys were standing there watching. Then the one on the phone walked down to the end of the alley to where the ambulance was probably going to arrive so he could wave them down.
I gave the man the 4 mg of naloxone, two in each nostril.
He still wasn’t breathing. I did a basic maneuver where you lift his jaw a little bit to help open up the airway.
Suddenly, he started breathing again. I couldn’t do any meaningful measurements of his oxygen saturation or anything like that. I just kind of looked at him and thought, Okay, he has a pulse. He’s breathing now. That’s good.
Luckily, the cavalry arrived soon after that. Our Denver Health paramedics pulled up into the alley, and one of them recognized me from the ER. I explained that I had already given the guy naloxone. They did their assessment, and he still wasn’t breathing well, so they gave him some breaths with a mask and a bag.
We got him onto the gurney and into the back of the ambulance. They started an IV. He seemed to be breathing okay by then, and his numbers looked okay. But he wasn’t awake yet by any means.
I handed off care to them and disposed of my sharp in the ambulance. Then they took him into the ER that I had just left moments ago.
The two other guys had already disappeared. I think they saw the ambulance and thought, our job is done. So, I didn’t end up talking to them at all.
So, just like that ... I started walking home again.
I like to think of myself as a cool, calm, collected person working in the ER. But my heart was definitely going fast at that point. I called my wife to tell her about the crazy thing that just happened, and she could hear in my voice how amped up I was.
In the ER, it’s very common to see patients who need naloxone, have opioid toxicity, or have received Narcan in the community. Luckily, this man was found right away. He had likely overdosed only a few minutes earlier. Those scenarios can go bad very quickly. If there’s no one there, people often die.
That’s why I started carrying naloxone.
Now, I encourage all my friends to have some, and I suggest all medical professionals to keep some with them. Just be prepared. Put it in your backpack, your purse, keep it in the house, in the car, wherever. The nasal autoinjectors are incredibly easy. Like, stick it up the nose, push the big red button. Done.
When we train lay people to administer Narcan, we try to keep it simple. If you see someone, and they’re not responsive, not breathing, just give it. It’s not that there’s no possible harm if you’re wrong. But the benefits so vastly outweigh the risks that we are very aggressive to say, go ahead and give it.
I think we all have a responsibility to care for our communities. Obviously, that can take a lot of different forms. I had the privilege of being in the right place at the right time with the right tool to potentially save a life. That was the form it took for me that day.
Later, I followed up with a friend who took care of the man in the ER. He went through our standard procedure, being monitored to make sure the opioids didn’t outlast the naloxone. We have a lot of resources and next steps for people that have opioid use disorder. He was made aware of those. And then he walked out. I never saw him again.
It’s not the sexy part of our job in emergency medicine, not the super high–intensity adrenaline rush–type work, but a lot of what we do is talk to people like this guy. We counsel them. We think about their longer-term health and not just the overdose. This is an incredibly high-risk population in terms of their mortality risk from the opioid use disorder. It’s astronomical.
I obviously believed in this work before, but that day changed something for me. It added a layer of urgency. Now, when I have a moment in the emergency room to connect with someone, I know the reality — this person sitting in front of me could die in an alley. Maybe not today, but next week or next month.
I have the naloxone in my bag. Just in case.
Patrick Joynt, MD, is an emergency medicine physician with Denver Health in Denver.
Are you a medical professional with a dramatic story outside the clinic? Medscape Medical News would love to consider your story for Is There a Doctor in the House? Please email your contact information and a short summary to [email protected].
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a Medscape Medical News series telling these stories.
I had worked a normal 7:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. shift in our emergency department. It was a nice day out, so I put my headphones in and started walking home through the Capitol Hill neighborhood in Denver. I passed a couple of buildings and reached an alleyway. At that moment, I glanced over.
Two guys were standing over a third person who was down on the ground. One of the people standing was on the phone. I paused for a second and thought, that doesn’t look right.
The guy on the ground was clearly out. And the other two were looking concerned like they didn’t know what to do.
I walked up the alley and asked, “What’s going on? Can I help?” One of the guys explained that they had just found this man lying here and had already called 911. They sounded a little bit out of their element. They certainly weren’t medically trained.
I leaned down next to the man on the ground. He was probably in his mid-to-late 40s. Unconscious. I always start with, “Hello? Can you hear me?” No response.
I felt for a pulse and he had one, but he didn’t appear to be breathing. I thought, I know what this is. I said, “Sir, I’m going to open your eyes.” I opened his eyes, and his pupils were tiny. It was almost certainly an opioid overdose.
And I had naloxone in my bag.
I got it out and started to assemble it. I didn’t have Narcan, which is the easy one. I had to put this kit together, draw up the medication, and put on the little nasal atomizer.
The two other guys were standing there watching. Then the one on the phone walked down to the end of the alley to where the ambulance was probably going to arrive so he could wave them down.
I gave the man the 4 mg of naloxone, two in each nostril.
He still wasn’t breathing. I did a basic maneuver where you lift his jaw a little bit to help open up the airway.
Suddenly, he started breathing again. I couldn’t do any meaningful measurements of his oxygen saturation or anything like that. I just kind of looked at him and thought, Okay, he has a pulse. He’s breathing now. That’s good.
Luckily, the cavalry arrived soon after that. Our Denver Health paramedics pulled up into the alley, and one of them recognized me from the ER. I explained that I had already given the guy naloxone. They did their assessment, and he still wasn’t breathing well, so they gave him some breaths with a mask and a bag.
We got him onto the gurney and into the back of the ambulance. They started an IV. He seemed to be breathing okay by then, and his numbers looked okay. But he wasn’t awake yet by any means.
I handed off care to them and disposed of my sharp in the ambulance. Then they took him into the ER that I had just left moments ago.
The two other guys had already disappeared. I think they saw the ambulance and thought, our job is done. So, I didn’t end up talking to them at all.
So, just like that ... I started walking home again.
I like to think of myself as a cool, calm, collected person working in the ER. But my heart was definitely going fast at that point. I called my wife to tell her about the crazy thing that just happened, and she could hear in my voice how amped up I was.
In the ER, it’s very common to see patients who need naloxone, have opioid toxicity, or have received Narcan in the community. Luckily, this man was found right away. He had likely overdosed only a few minutes earlier. Those scenarios can go bad very quickly. If there’s no one there, people often die.
That’s why I started carrying naloxone.
Now, I encourage all my friends to have some, and I suggest all medical professionals to keep some with them. Just be prepared. Put it in your backpack, your purse, keep it in the house, in the car, wherever. The nasal autoinjectors are incredibly easy. Like, stick it up the nose, push the big red button. Done.
When we train lay people to administer Narcan, we try to keep it simple. If you see someone, and they’re not responsive, not breathing, just give it. It’s not that there’s no possible harm if you’re wrong. But the benefits so vastly outweigh the risks that we are very aggressive to say, go ahead and give it.
I think we all have a responsibility to care for our communities. Obviously, that can take a lot of different forms. I had the privilege of being in the right place at the right time with the right tool to potentially save a life. That was the form it took for me that day.
Later, I followed up with a friend who took care of the man in the ER. He went through our standard procedure, being monitored to make sure the opioids didn’t outlast the naloxone. We have a lot of resources and next steps for people that have opioid use disorder. He was made aware of those. And then he walked out. I never saw him again.
It’s not the sexy part of our job in emergency medicine, not the super high–intensity adrenaline rush–type work, but a lot of what we do is talk to people like this guy. We counsel them. We think about their longer-term health and not just the overdose. This is an incredibly high-risk population in terms of their mortality risk from the opioid use disorder. It’s astronomical.
I obviously believed in this work before, but that day changed something for me. It added a layer of urgency. Now, when I have a moment in the emergency room to connect with someone, I know the reality — this person sitting in front of me could die in an alley. Maybe not today, but next week or next month.
I have the naloxone in my bag. Just in case.
Patrick Joynt, MD, is an emergency medicine physician with Denver Health in Denver.
Are you a medical professional with a dramatic story outside the clinic? Medscape Medical News would love to consider your story for Is There a Doctor in the House? Please email your contact information and a short summary to [email protected].
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime, and sometimes, medical professionals find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. Is There a Doctor in the House? is a Medscape Medical News series telling these stories.
I had worked a normal 7:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. shift in our emergency department. It was a nice day out, so I put my headphones in and started walking home through the Capitol Hill neighborhood in Denver. I passed a couple of buildings and reached an alleyway. At that moment, I glanced over.
Two guys were standing over a third person who was down on the ground. One of the people standing was on the phone. I paused for a second and thought, that doesn’t look right.
The guy on the ground was clearly out. And the other two were looking concerned like they didn’t know what to do.
I walked up the alley and asked, “What’s going on? Can I help?” One of the guys explained that they had just found this man lying here and had already called 911. They sounded a little bit out of their element. They certainly weren’t medically trained.
I leaned down next to the man on the ground. He was probably in his mid-to-late 40s. Unconscious. I always start with, “Hello? Can you hear me?” No response.
I felt for a pulse and he had one, but he didn’t appear to be breathing. I thought, I know what this is. I said, “Sir, I’m going to open your eyes.” I opened his eyes, and his pupils were tiny. It was almost certainly an opioid overdose.
And I had naloxone in my bag.
I got it out and started to assemble it. I didn’t have Narcan, which is the easy one. I had to put this kit together, draw up the medication, and put on the little nasal atomizer.
The two other guys were standing there watching. Then the one on the phone walked down to the end of the alley to where the ambulance was probably going to arrive so he could wave them down.
I gave the man the 4 mg of naloxone, two in each nostril.
He still wasn’t breathing. I did a basic maneuver where you lift his jaw a little bit to help open up the airway.
Suddenly, he started breathing again. I couldn’t do any meaningful measurements of his oxygen saturation or anything like that. I just kind of looked at him and thought, Okay, he has a pulse. He’s breathing now. That’s good.
Luckily, the cavalry arrived soon after that. Our Denver Health paramedics pulled up into the alley, and one of them recognized me from the ER. I explained that I had already given the guy naloxone. They did their assessment, and he still wasn’t breathing well, so they gave him some breaths with a mask and a bag.
We got him onto the gurney and into the back of the ambulance. They started an IV. He seemed to be breathing okay by then, and his numbers looked okay. But he wasn’t awake yet by any means.
I handed off care to them and disposed of my sharp in the ambulance. Then they took him into the ER that I had just left moments ago.
The two other guys had already disappeared. I think they saw the ambulance and thought, our job is done. So, I didn’t end up talking to them at all.
So, just like that ... I started walking home again.
I like to think of myself as a cool, calm, collected person working in the ER. But my heart was definitely going fast at that point. I called my wife to tell her about the crazy thing that just happened, and she could hear in my voice how amped up I was.
In the ER, it’s very common to see patients who need naloxone, have opioid toxicity, or have received Narcan in the community. Luckily, this man was found right away. He had likely overdosed only a few minutes earlier. Those scenarios can go bad very quickly. If there’s no one there, people often die.
That’s why I started carrying naloxone.
Now, I encourage all my friends to have some, and I suggest all medical professionals to keep some with them. Just be prepared. Put it in your backpack, your purse, keep it in the house, in the car, wherever. The nasal autoinjectors are incredibly easy. Like, stick it up the nose, push the big red button. Done.
When we train lay people to administer Narcan, we try to keep it simple. If you see someone, and they’re not responsive, not breathing, just give it. It’s not that there’s no possible harm if you’re wrong. But the benefits so vastly outweigh the risks that we are very aggressive to say, go ahead and give it.
I think we all have a responsibility to care for our communities. Obviously, that can take a lot of different forms. I had the privilege of being in the right place at the right time with the right tool to potentially save a life. That was the form it took for me that day.
Later, I followed up with a friend who took care of the man in the ER. He went through our standard procedure, being monitored to make sure the opioids didn’t outlast the naloxone. We have a lot of resources and next steps for people that have opioid use disorder. He was made aware of those. And then he walked out. I never saw him again.
It’s not the sexy part of our job in emergency medicine, not the super high–intensity adrenaline rush–type work, but a lot of what we do is talk to people like this guy. We counsel them. We think about their longer-term health and not just the overdose. This is an incredibly high-risk population in terms of their mortality risk from the opioid use disorder. It’s astronomical.
I obviously believed in this work before, but that day changed something for me. It added a layer of urgency. Now, when I have a moment in the emergency room to connect with someone, I know the reality — this person sitting in front of me could die in an alley. Maybe not today, but next week or next month.
I have the naloxone in my bag. Just in case.
Patrick Joynt, MD, is an emergency medicine physician with Denver Health in Denver.
Are you a medical professional with a dramatic story outside the clinic? Medscape Medical News would love to consider your story for Is There a Doctor in the House? Please email your contact information and a short summary to [email protected].
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Long COVID Can’t Be Solved Until We Decide What It Is
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I want to help people suffering from long COVID as much as anyone. But we have a real problem. In brief, we are being too inclusive. The first thing you learn, when you start studying the epidemiology of diseases, is that you need a good case definition. And our case definition for long COVID sucks. Just last week, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) issued a definition of long COVID with the aim of “improving consistency, documentation, and treatment.” Good news, right? Here’s the definition: “Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems.”
This is not helpful. The symptoms can be in any organ system, can be continuous or relapsing and remitting. Basically, if you’ve had COVID — and essentially all of us have by now — and you have any symptom, even one that comes and goes, 3 months after that, it’s long COVID. They don’t even specify that it has to be a new symptom.
And I have sort of a case study in this problem today, based on a paper getting a lot of press suggesting that one out of every five people has long COVID.
We are talking about this study, “Epidemiologic Features of Recovery From SARS-CoV-2 Infection,” appearing in JAMA Network Open this week. While I think the idea is important, the study really highlights why it can be so hard to study long COVID.
As part of efforts to understand long COVID, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) leveraged 14 of its ongoing cohort studies. The NIH has multiple longitudinal cohort studies that follow various groups of people over time. You may have heard of the REGARDS study, for example, which focuses on cardiovascular risks to people living in the southern United States. Or the ARIC study, which followed adults in four communities across the United States for the development of heart disease. All 14 of the cohorts in this study are long-running projects with ongoing data collection. So, it was not a huge lift to add some questions to the yearly surveys and studies the participants were already getting.
To wit: “Do you think that you have had COVID-19?” and “Would you say that you are completely recovered now?” Those who said they weren’t fully recovered were asked how long it had been since their infection, and anyone who answered with a duration > 90 days was considered to have long COVID.
So, we have self-report of infection, self-report of duration of symptoms, and self-report of recovery. This is fine, of course; individuals’ perceptions of their own health are meaningful. But the vagaries inherent in those perceptions are going to muddy the waters as we attempt to discover the true nature of the long COVID syndrome.
But let’s look at some results. Out of 4708 individuals studied, 842 (17.9%) had not recovered by 90 days.
This study included not only people hospitalized with COVID, as some prior long COVID studies did, but people self-diagnosed, tested at home, etc. This estimate is as reflective of the broader US population as we can get.
And there are some interesting trends here.
Recovery time was longer in the first waves of COVID than in the Omicron wave.
Recovery times were longer for smokers, those with diabetes, and those who were obese.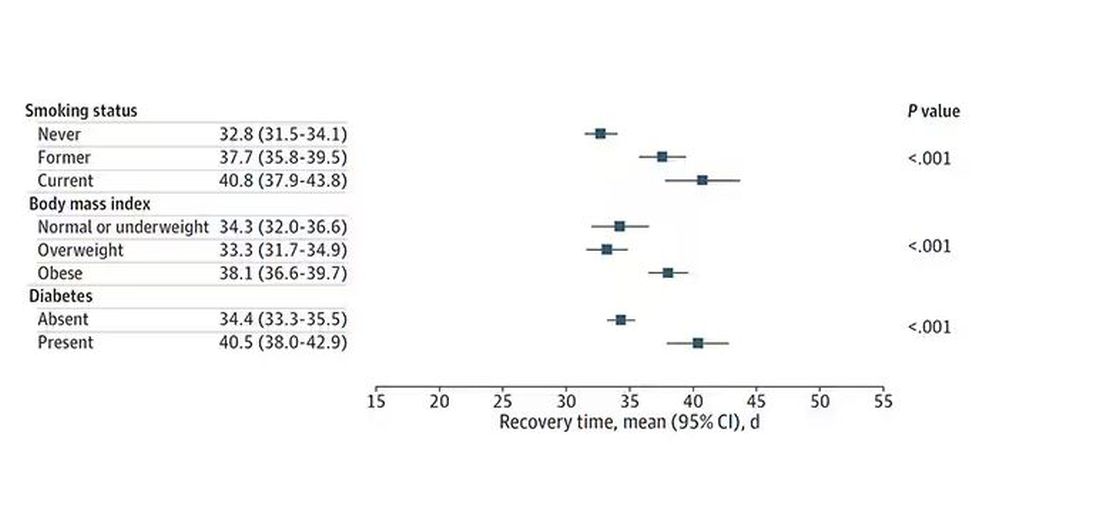
Recovery times were longer if the disease was more severe, in general. Though there is an unusual finding that women had longer recovery times despite their lower average severity of illness.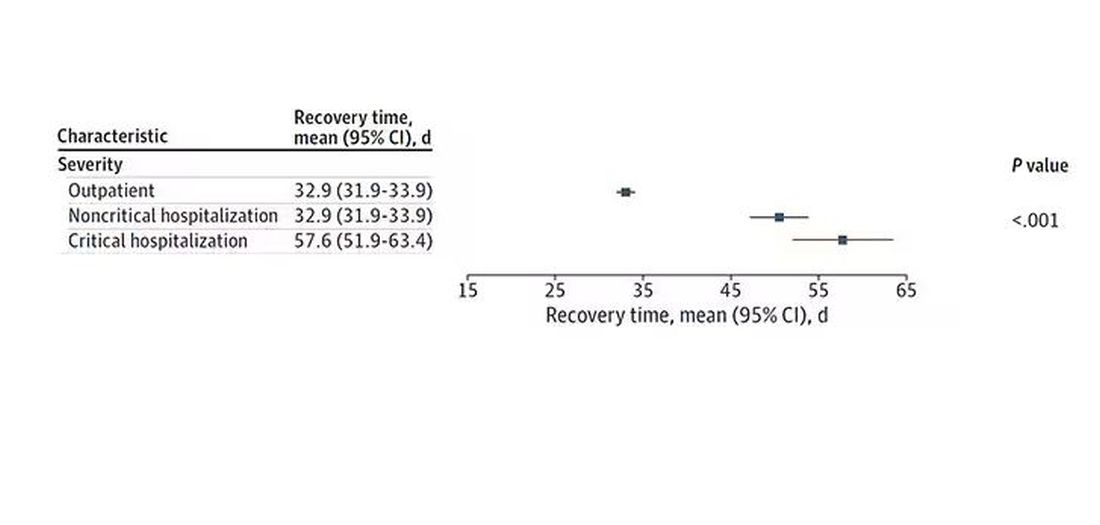
Vaccination was associated with shorter recovery times, as you can see here. 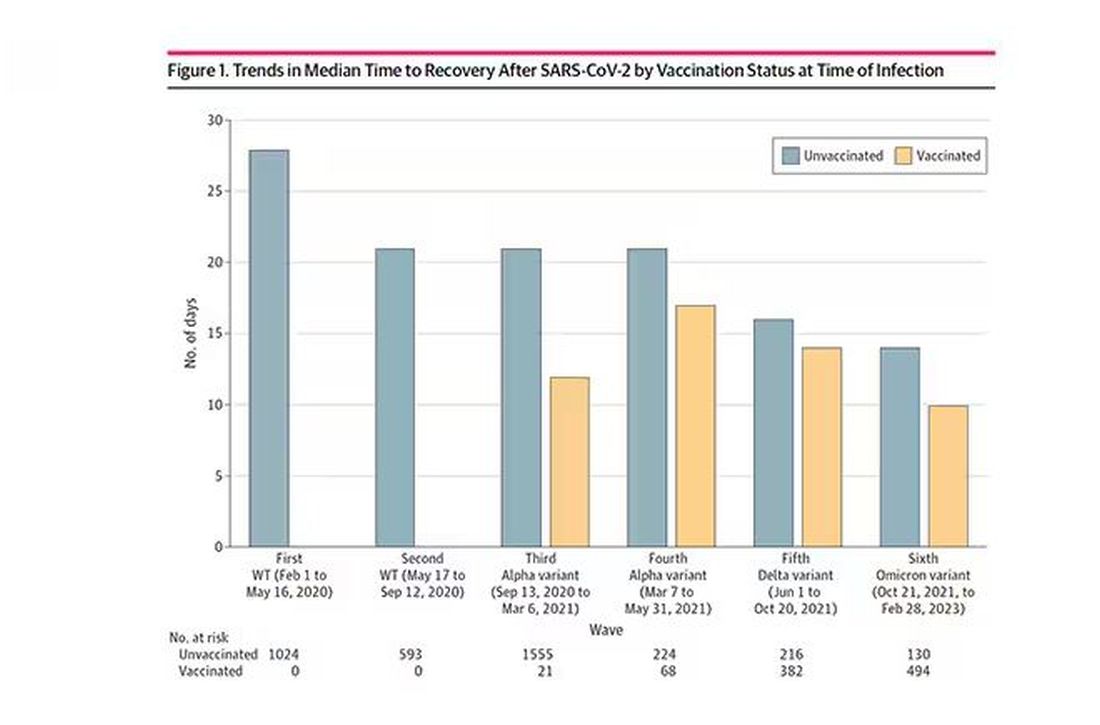
This is all quite interesting. It’s clear that people feel they are sick for a while after COVID. But we need to understand whether these symptoms are due to the lingering effects of a bad infection that knocks you down a peg, or to an ongoing syndrome — this thing we call long COVID — that has a physiologic basis and thus can be treated. And this study doesn’t help us much with that.
Not that this was the authors’ intention. This is a straight-up epidemiology study. But the problem is deeper than that. Let’s imagine that you want to really dig into this long COVID thing and get blood samples from people with it, ideally from controls with some other respiratory virus infection, and do all kinds of genetic and proteomic studies and stuff to really figure out what’s going on. Who do you enroll to be in the long COVID group? Do you enroll anyone who says they had COVID and still has some symptom more than 90 days after? You are going to find an awful lot of eligible people, and I guarantee that if there is a pathognomonic signature of long COVID, not all of them will have it.
And what about other respiratory viruses? This study in The Lancet Infectious Diseases compared long-term outcomes among hospitalized patients with COVID vs influenza. In general, the COVID outcomes are worse, but let’s not knock the concept of “long flu.” Across the board, roughly 50% of people report symptoms across any given organ system.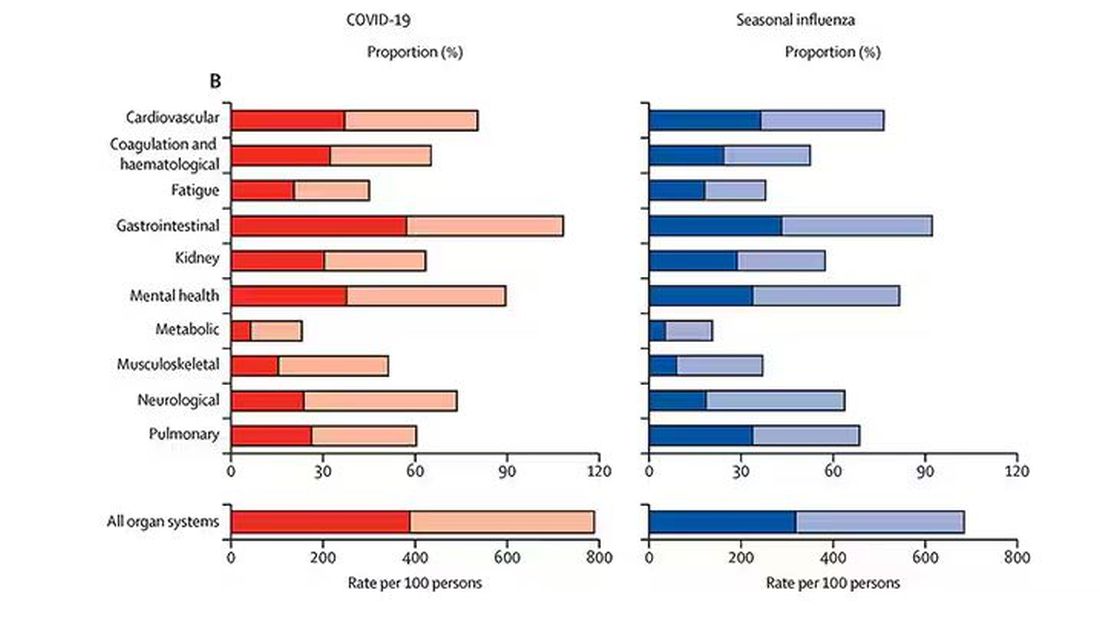
What this is all about is something called misclassification bias, a form of information bias that arises in a study where you label someone as diseased when they are not, or vice versa. If this happens at random, it’s bad; you’ve lost your ability to distinguish characteristics from the diseased and nondiseased population.
When it’s not random, it’s really bad. If we are more likely to misclassify women as having long COVID, for example, then it will appear that long COVID is more likely among women, or more likely among those with higher estrogen levels, or something. And that might simply be wrong.
I’m not saying that’s what happened here; this study does a really great job of what it set out to do, which was to describe the patterns of lingering symptoms after COVID. But we are not going to make progress toward understanding long COVID until we are less inclusive with our case definition. To paraphrase Syndrome from The Incredibles: If everyone has long COVID, then no one does.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I want to help people suffering from long COVID as much as anyone. But we have a real problem. In brief, we are being too inclusive. The first thing you learn, when you start studying the epidemiology of diseases, is that you need a good case definition. And our case definition for long COVID sucks. Just last week, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) issued a definition of long COVID with the aim of “improving consistency, documentation, and treatment.” Good news, right? Here’s the definition: “Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems.”
This is not helpful. The symptoms can be in any organ system, can be continuous or relapsing and remitting. Basically, if you’ve had COVID — and essentially all of us have by now — and you have any symptom, even one that comes and goes, 3 months after that, it’s long COVID. They don’t even specify that it has to be a new symptom.
And I have sort of a case study in this problem today, based on a paper getting a lot of press suggesting that one out of every five people has long COVID.
We are talking about this study, “Epidemiologic Features of Recovery From SARS-CoV-2 Infection,” appearing in JAMA Network Open this week. While I think the idea is important, the study really highlights why it can be so hard to study long COVID.
As part of efforts to understand long COVID, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) leveraged 14 of its ongoing cohort studies. The NIH has multiple longitudinal cohort studies that follow various groups of people over time. You may have heard of the REGARDS study, for example, which focuses on cardiovascular risks to people living in the southern United States. Or the ARIC study, which followed adults in four communities across the United States for the development of heart disease. All 14 of the cohorts in this study are long-running projects with ongoing data collection. So, it was not a huge lift to add some questions to the yearly surveys and studies the participants were already getting.
To wit: “Do you think that you have had COVID-19?” and “Would you say that you are completely recovered now?” Those who said they weren’t fully recovered were asked how long it had been since their infection, and anyone who answered with a duration > 90 days was considered to have long COVID.
So, we have self-report of infection, self-report of duration of symptoms, and self-report of recovery. This is fine, of course; individuals’ perceptions of their own health are meaningful. But the vagaries inherent in those perceptions are going to muddy the waters as we attempt to discover the true nature of the long COVID syndrome.
But let’s look at some results. Out of 4708 individuals studied, 842 (17.9%) had not recovered by 90 days.
This study included not only people hospitalized with COVID, as some prior long COVID studies did, but people self-diagnosed, tested at home, etc. This estimate is as reflective of the broader US population as we can get.
And there are some interesting trends here.
Recovery time was longer in the first waves of COVID than in the Omicron wave.
Recovery times were longer for smokers, those with diabetes, and those who were obese.
Recovery times were longer if the disease was more severe, in general. Though there is an unusual finding that women had longer recovery times despite their lower average severity of illness.
Vaccination was associated with shorter recovery times, as you can see here. 
This is all quite interesting. It’s clear that people feel they are sick for a while after COVID. But we need to understand whether these symptoms are due to the lingering effects of a bad infection that knocks you down a peg, or to an ongoing syndrome — this thing we call long COVID — that has a physiologic basis and thus can be treated. And this study doesn’t help us much with that.
Not that this was the authors’ intention. This is a straight-up epidemiology study. But the problem is deeper than that. Let’s imagine that you want to really dig into this long COVID thing and get blood samples from people with it, ideally from controls with some other respiratory virus infection, and do all kinds of genetic and proteomic studies and stuff to really figure out what’s going on. Who do you enroll to be in the long COVID group? Do you enroll anyone who says they had COVID and still has some symptom more than 90 days after? You are going to find an awful lot of eligible people, and I guarantee that if there is a pathognomonic signature of long COVID, not all of them will have it.
And what about other respiratory viruses? This study in The Lancet Infectious Diseases compared long-term outcomes among hospitalized patients with COVID vs influenza. In general, the COVID outcomes are worse, but let’s not knock the concept of “long flu.” Across the board, roughly 50% of people report symptoms across any given organ system.
What this is all about is something called misclassification bias, a form of information bias that arises in a study where you label someone as diseased when they are not, or vice versa. If this happens at random, it’s bad; you’ve lost your ability to distinguish characteristics from the diseased and nondiseased population.
When it’s not random, it’s really bad. If we are more likely to misclassify women as having long COVID, for example, then it will appear that long COVID is more likely among women, or more likely among those with higher estrogen levels, or something. And that might simply be wrong.
I’m not saying that’s what happened here; this study does a really great job of what it set out to do, which was to describe the patterns of lingering symptoms after COVID. But we are not going to make progress toward understanding long COVID until we are less inclusive with our case definition. To paraphrase Syndrome from The Incredibles: If everyone has long COVID, then no one does.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I want to help people suffering from long COVID as much as anyone. But we have a real problem. In brief, we are being too inclusive. The first thing you learn, when you start studying the epidemiology of diseases, is that you need a good case definition. And our case definition for long COVID sucks. Just last week, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) issued a definition of long COVID with the aim of “improving consistency, documentation, and treatment.” Good news, right? Here’s the definition: “Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems.”
This is not helpful. The symptoms can be in any organ system, can be continuous or relapsing and remitting. Basically, if you’ve had COVID — and essentially all of us have by now — and you have any symptom, even one that comes and goes, 3 months after that, it’s long COVID. They don’t even specify that it has to be a new symptom.
And I have sort of a case study in this problem today, based on a paper getting a lot of press suggesting that one out of every five people has long COVID.
We are talking about this study, “Epidemiologic Features of Recovery From SARS-CoV-2 Infection,” appearing in JAMA Network Open this week. While I think the idea is important, the study really highlights why it can be so hard to study long COVID.
As part of efforts to understand long COVID, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) leveraged 14 of its ongoing cohort studies. The NIH has multiple longitudinal cohort studies that follow various groups of people over time. You may have heard of the REGARDS study, for example, which focuses on cardiovascular risks to people living in the southern United States. Or the ARIC study, which followed adults in four communities across the United States for the development of heart disease. All 14 of the cohorts in this study are long-running projects with ongoing data collection. So, it was not a huge lift to add some questions to the yearly surveys and studies the participants were already getting.
To wit: “Do you think that you have had COVID-19?” and “Would you say that you are completely recovered now?” Those who said they weren’t fully recovered were asked how long it had been since their infection, and anyone who answered with a duration > 90 days was considered to have long COVID.
So, we have self-report of infection, self-report of duration of symptoms, and self-report of recovery. This is fine, of course; individuals’ perceptions of their own health are meaningful. But the vagaries inherent in those perceptions are going to muddy the waters as we attempt to discover the true nature of the long COVID syndrome.
But let’s look at some results. Out of 4708 individuals studied, 842 (17.9%) had not recovered by 90 days.
This study included not only people hospitalized with COVID, as some prior long COVID studies did, but people self-diagnosed, tested at home, etc. This estimate is as reflective of the broader US population as we can get.
And there are some interesting trends here.
Recovery time was longer in the first waves of COVID than in the Omicron wave.
Recovery times were longer for smokers, those with diabetes, and those who were obese.
Recovery times were longer if the disease was more severe, in general. Though there is an unusual finding that women had longer recovery times despite their lower average severity of illness.
Vaccination was associated with shorter recovery times, as you can see here. 
This is all quite interesting. It’s clear that people feel they are sick for a while after COVID. But we need to understand whether these symptoms are due to the lingering effects of a bad infection that knocks you down a peg, or to an ongoing syndrome — this thing we call long COVID — that has a physiologic basis and thus can be treated. And this study doesn’t help us much with that.
Not that this was the authors’ intention. This is a straight-up epidemiology study. But the problem is deeper than that. Let’s imagine that you want to really dig into this long COVID thing and get blood samples from people with it, ideally from controls with some other respiratory virus infection, and do all kinds of genetic and proteomic studies and stuff to really figure out what’s going on. Who do you enroll to be in the long COVID group? Do you enroll anyone who says they had COVID and still has some symptom more than 90 days after? You are going to find an awful lot of eligible people, and I guarantee that if there is a pathognomonic signature of long COVID, not all of them will have it.
And what about other respiratory viruses? This study in The Lancet Infectious Diseases compared long-term outcomes among hospitalized patients with COVID vs influenza. In general, the COVID outcomes are worse, but let’s not knock the concept of “long flu.” Across the board, roughly 50% of people report symptoms across any given organ system.
What this is all about is something called misclassification bias, a form of information bias that arises in a study where you label someone as diseased when they are not, or vice versa. If this happens at random, it’s bad; you’ve lost your ability to distinguish characteristics from the diseased and nondiseased population.
When it’s not random, it’s really bad. If we are more likely to misclassify women as having long COVID, for example, then it will appear that long COVID is more likely among women, or more likely among those with higher estrogen levels, or something. And that might simply be wrong.
I’m not saying that’s what happened here; this study does a really great job of what it set out to do, which was to describe the patterns of lingering symptoms after COVID. But we are not going to make progress toward understanding long COVID until we are less inclusive with our case definition. To paraphrase Syndrome from The Incredibles: If everyone has long COVID, then no one does.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Approves New Pneumococcal Vaccine
A new vaccine to prevent invasive pneumococcal disease and pneumococcal pneumonia in adults has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The injectable drug, Capvaxive (Pneumococcal 21-valent Conjugate Vaccine), protects against 22 serotypes that cause invasive pneumococcal disease in adults, the company said in a news release. These strains account for about 84% of invasive pneumococcal disease cases among adults aged 50 years or older and about 85% of these cases in adults aged 65 years or older.
The drug company said about 150,000 adults in the United States are hospitalized annually because of pneumococcal pneumonia.
“Many cases of adult disease are caused by serotypes not included in other approved pneumococcal conjugate vaccines,” Walter Orenstein, MD, a professor emeritus of medicine, epidemiology, global health, and pediatrics at Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, and a member of Merck’s Scientific Advisory Committee, said in the release.
A draft agenda shows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advisory panel will meet on June 27 to discuss the vaccine. If the committee votes to approve Capvaxive, the CDC director will decide whether to make it available across the country.
Testing showed that Capvaxive was well tolerated by people it was tested on, with the main reports being pain where they got the shot, fatigue, headaches, and muscle aches, Merck said.
The eight unique serotypes included in CAPVAXIVE will protect against invasive pneumococcal disease and pneumococcal pneumonia, not just pneumonia.
According to Reuters, Merck said Capvaxive has a wholesale acquisition price of $287 per dose, but most people will probably have access to it at no cost if the drug receives a routine CDC recommendation. Capvaxive’s main competition is expected to be Pfizer’s shot, Prevnar 20, which was approved in 2021 for use in adults aged 18 years or older, Reuters reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new vaccine to prevent invasive pneumococcal disease and pneumococcal pneumonia in adults has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The injectable drug, Capvaxive (Pneumococcal 21-valent Conjugate Vaccine), protects against 22 serotypes that cause invasive pneumococcal disease in adults, the company said in a news release. These strains account for about 84% of invasive pneumococcal disease cases among adults aged 50 years or older and about 85% of these cases in adults aged 65 years or older.
The drug company said about 150,000 adults in the United States are hospitalized annually because of pneumococcal pneumonia.
“Many cases of adult disease are caused by serotypes not included in other approved pneumococcal conjugate vaccines,” Walter Orenstein, MD, a professor emeritus of medicine, epidemiology, global health, and pediatrics at Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, and a member of Merck’s Scientific Advisory Committee, said in the release.
A draft agenda shows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advisory panel will meet on June 27 to discuss the vaccine. If the committee votes to approve Capvaxive, the CDC director will decide whether to make it available across the country.
Testing showed that Capvaxive was well tolerated by people it was tested on, with the main reports being pain where they got the shot, fatigue, headaches, and muscle aches, Merck said.
The eight unique serotypes included in CAPVAXIVE will protect against invasive pneumococcal disease and pneumococcal pneumonia, not just pneumonia.
According to Reuters, Merck said Capvaxive has a wholesale acquisition price of $287 per dose, but most people will probably have access to it at no cost if the drug receives a routine CDC recommendation. Capvaxive’s main competition is expected to be Pfizer’s shot, Prevnar 20, which was approved in 2021 for use in adults aged 18 years or older, Reuters reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new vaccine to prevent invasive pneumococcal disease and pneumococcal pneumonia in adults has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
The injectable drug, Capvaxive (Pneumococcal 21-valent Conjugate Vaccine), protects against 22 serotypes that cause invasive pneumococcal disease in adults, the company said in a news release. These strains account for about 84% of invasive pneumococcal disease cases among adults aged 50 years or older and about 85% of these cases in adults aged 65 years or older.
The drug company said about 150,000 adults in the United States are hospitalized annually because of pneumococcal pneumonia.
“Many cases of adult disease are caused by serotypes not included in other approved pneumococcal conjugate vaccines,” Walter Orenstein, MD, a professor emeritus of medicine, epidemiology, global health, and pediatrics at Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, and a member of Merck’s Scientific Advisory Committee, said in the release.
A draft agenda shows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advisory panel will meet on June 27 to discuss the vaccine. If the committee votes to approve Capvaxive, the CDC director will decide whether to make it available across the country.
Testing showed that Capvaxive was well tolerated by people it was tested on, with the main reports being pain where they got the shot, fatigue, headaches, and muscle aches, Merck said.
The eight unique serotypes included in CAPVAXIVE will protect against invasive pneumococcal disease and pneumococcal pneumonia, not just pneumonia.
According to Reuters, Merck said Capvaxive has a wholesale acquisition price of $287 per dose, but most people will probably have access to it at no cost if the drug receives a routine CDC recommendation. Capvaxive’s main competition is expected to be Pfizer’s shot, Prevnar 20, which was approved in 2021 for use in adults aged 18 years or older, Reuters reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Why Don’t Migraine Patients Seek Treatment?
SAN DIEGO — results of a recent survey showed.
Participants cited concerns that their complaints would be dismissed, a belief that healthcare providers could offer no additional help, and a prior unsuccessful clinician visit as reasons for not seeking care. Survey respondents saw an average of four clinicians before finally receiving a diagnosis.
“I was shocked that a third of patients were reluctant to seek care,” said study investigator Elizabeth K. Seng, PhD, associate professor, Ferkauf Graduate School of Psychology, Yeshiva University, and research associate professor, department of neurology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, both in New York City. “That just shows a much higher level of medical distress than I expected from this community of people who are obviously suffering from this significant neurologic disease.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
‘Significant Disease’
The study included 500 adults with migraine (mean age, 40 years) who signed up for a patient support group sponsored by Eli Lilly and completed a comprehensive survey. Respondents were mostly female, White, non-Hispanic, and well-educated individuals.
Half of participants had episodic migraines, and half had chronic migraines; 46% reported experiencing anxiety and 33% reported depression.
Almost all respondents had initiated treatment with a first calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibody.
“These are people who have significant enough disease that eventually they needed our top-tier preventive medication,” Dr. Seng said.
Participants answered a variety of questions pertaining to disease factors and treatment seeking. Just over 70% said they suspected they had migraine prior to diagnosis, “which means for almost 30%, it was a surprise when they received the diagnosis,” said Dr. Seng.
Nearly 40% reported that a relative first suggested they may have migraine, and 33% suspected it themselves. Only 17.4% said a healthcare provider suggested they may have the condition.
Almost a third of respondents (30.5%) reported they were reluctant to seek medical help.
“Some said they didn’t think their physician could do anything more than they were already doing for themselves, or that they’d be taken seriously, or they had had talked to doctors before and this wasn’t helpful,” said Dr. Seng.
These responses speak to the need for better public health messaging, she said. “People have this idea that migraine attacks aren’t a big deal when, in fact, these attacks area big deal and certainly deserve treatment.”
Family and friends were participants’ most common source of information on migraine, followed by the Internet. “This highlights the importance of getting migraine-related information out there so that when people talk to their friends and family, they’re receiving accurate information,” said Dr. Seng.
When asked about the path to a diagnosis, respondents reported consulting an average of four providers before receiving an accurate diagnosis. “That’s pretty remarkable,” Dr. Seng said.
An increase in frequency or severity of migraine attacks or attacks that interfered with work or school “pushed people over the threshold to seek care,” Dr. Seng said.
A subset of patients was asked about the factors they believed could help with migraine attacks. Of these, 80% cited diet and 70% stress reduction. Supplements, exercise, and relaxation techniques were cited much less frequently, said Dr. Seng.
The mean age of respondents’ migraine diagnosis was 26 years, so there was about 18 years from the time of diagnosis to participation in the survey, which could introduce recall bias. Other potential limitations included the fact that the survey had no open-ended questions, and men and ethnic minorities were underrepresented.
Useful Data
Commenting on the study findings, Nina Riggins, MD, PhD, president, Brain Performance Center and Research Institute, and director of the Headache Center at The Neuron Clinic, San Diego, California, said the survey findings are “very useful” and highlight “significant opportunities for improvement in migraine education for clinicians and people living with migraine disease.”
The fact that participants reported consulting an average of four healthcare providers before receiving an accurate diagnosis underscores the importance of providing clinicians with tools to identify migraine, she said.
This is especially relevant as new migraine therapies that may improve efficacy and have fewer side effects become available, she added.
“It would be interesting to see in future studies if migraine recognition by non-headache specialists improved after CGRP-blocking medications for migraine management became available,” said Dr. Riggins, who is cochair of the AHS First Contact program which is aimed at improving headache management in primary care.
She added that she and her colleagues will keep these survey results in mind when creating future educational materials for clinicians.
The study was supported by Eli Lily. Dr. Seng is a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Theranica, and Abbvie, and receives research support from the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, Veterans Health Administration, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, and the American Heart Association. Dr. Riggins reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — results of a recent survey showed.
Participants cited concerns that their complaints would be dismissed, a belief that healthcare providers could offer no additional help, and a prior unsuccessful clinician visit as reasons for not seeking care. Survey respondents saw an average of four clinicians before finally receiving a diagnosis.
“I was shocked that a third of patients were reluctant to seek care,” said study investigator Elizabeth K. Seng, PhD, associate professor, Ferkauf Graduate School of Psychology, Yeshiva University, and research associate professor, department of neurology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, both in New York City. “That just shows a much higher level of medical distress than I expected from this community of people who are obviously suffering from this significant neurologic disease.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
‘Significant Disease’
The study included 500 adults with migraine (mean age, 40 years) who signed up for a patient support group sponsored by Eli Lilly and completed a comprehensive survey. Respondents were mostly female, White, non-Hispanic, and well-educated individuals.
Half of participants had episodic migraines, and half had chronic migraines; 46% reported experiencing anxiety and 33% reported depression.
Almost all respondents had initiated treatment with a first calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibody.
“These are people who have significant enough disease that eventually they needed our top-tier preventive medication,” Dr. Seng said.
Participants answered a variety of questions pertaining to disease factors and treatment seeking. Just over 70% said they suspected they had migraine prior to diagnosis, “which means for almost 30%, it was a surprise when they received the diagnosis,” said Dr. Seng.
Nearly 40% reported that a relative first suggested they may have migraine, and 33% suspected it themselves. Only 17.4% said a healthcare provider suggested they may have the condition.
Almost a third of respondents (30.5%) reported they were reluctant to seek medical help.
“Some said they didn’t think their physician could do anything more than they were already doing for themselves, or that they’d be taken seriously, or they had had talked to doctors before and this wasn’t helpful,” said Dr. Seng.
These responses speak to the need for better public health messaging, she said. “People have this idea that migraine attacks aren’t a big deal when, in fact, these attacks area big deal and certainly deserve treatment.”
Family and friends were participants’ most common source of information on migraine, followed by the Internet. “This highlights the importance of getting migraine-related information out there so that when people talk to their friends and family, they’re receiving accurate information,” said Dr. Seng.
When asked about the path to a diagnosis, respondents reported consulting an average of four providers before receiving an accurate diagnosis. “That’s pretty remarkable,” Dr. Seng said.
An increase in frequency or severity of migraine attacks or attacks that interfered with work or school “pushed people over the threshold to seek care,” Dr. Seng said.
A subset of patients was asked about the factors they believed could help with migraine attacks. Of these, 80% cited diet and 70% stress reduction. Supplements, exercise, and relaxation techniques were cited much less frequently, said Dr. Seng.
The mean age of respondents’ migraine diagnosis was 26 years, so there was about 18 years from the time of diagnosis to participation in the survey, which could introduce recall bias. Other potential limitations included the fact that the survey had no open-ended questions, and men and ethnic minorities were underrepresented.
Useful Data
Commenting on the study findings, Nina Riggins, MD, PhD, president, Brain Performance Center and Research Institute, and director of the Headache Center at The Neuron Clinic, San Diego, California, said the survey findings are “very useful” and highlight “significant opportunities for improvement in migraine education for clinicians and people living with migraine disease.”
The fact that participants reported consulting an average of four healthcare providers before receiving an accurate diagnosis underscores the importance of providing clinicians with tools to identify migraine, she said.
This is especially relevant as new migraine therapies that may improve efficacy and have fewer side effects become available, she added.
“It would be interesting to see in future studies if migraine recognition by non-headache specialists improved after CGRP-blocking medications for migraine management became available,” said Dr. Riggins, who is cochair of the AHS First Contact program which is aimed at improving headache management in primary care.
She added that she and her colleagues will keep these survey results in mind when creating future educational materials for clinicians.
The study was supported by Eli Lily. Dr. Seng is a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Theranica, and Abbvie, and receives research support from the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, Veterans Health Administration, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, and the American Heart Association. Dr. Riggins reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — results of a recent survey showed.
Participants cited concerns that their complaints would be dismissed, a belief that healthcare providers could offer no additional help, and a prior unsuccessful clinician visit as reasons for not seeking care. Survey respondents saw an average of four clinicians before finally receiving a diagnosis.
“I was shocked that a third of patients were reluctant to seek care,” said study investigator Elizabeth K. Seng, PhD, associate professor, Ferkauf Graduate School of Psychology, Yeshiva University, and research associate professor, department of neurology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, both in New York City. “That just shows a much higher level of medical distress than I expected from this community of people who are obviously suffering from this significant neurologic disease.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
‘Significant Disease’
The study included 500 adults with migraine (mean age, 40 years) who signed up for a patient support group sponsored by Eli Lilly and completed a comprehensive survey. Respondents were mostly female, White, non-Hispanic, and well-educated individuals.
Half of participants had episodic migraines, and half had chronic migraines; 46% reported experiencing anxiety and 33% reported depression.
Almost all respondents had initiated treatment with a first calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibody.
“These are people who have significant enough disease that eventually they needed our top-tier preventive medication,” Dr. Seng said.
Participants answered a variety of questions pertaining to disease factors and treatment seeking. Just over 70% said they suspected they had migraine prior to diagnosis, “which means for almost 30%, it was a surprise when they received the diagnosis,” said Dr. Seng.
Nearly 40% reported that a relative first suggested they may have migraine, and 33% suspected it themselves. Only 17.4% said a healthcare provider suggested they may have the condition.
Almost a third of respondents (30.5%) reported they were reluctant to seek medical help.
“Some said they didn’t think their physician could do anything more than they were already doing for themselves, or that they’d be taken seriously, or they had had talked to doctors before and this wasn’t helpful,” said Dr. Seng.
These responses speak to the need for better public health messaging, she said. “People have this idea that migraine attacks aren’t a big deal when, in fact, these attacks area big deal and certainly deserve treatment.”
Family and friends were participants’ most common source of information on migraine, followed by the Internet. “This highlights the importance of getting migraine-related information out there so that when people talk to their friends and family, they’re receiving accurate information,” said Dr. Seng.
When asked about the path to a diagnosis, respondents reported consulting an average of four providers before receiving an accurate diagnosis. “That’s pretty remarkable,” Dr. Seng said.
An increase in frequency or severity of migraine attacks or attacks that interfered with work or school “pushed people over the threshold to seek care,” Dr. Seng said.
A subset of patients was asked about the factors they believed could help with migraine attacks. Of these, 80% cited diet and 70% stress reduction. Supplements, exercise, and relaxation techniques were cited much less frequently, said Dr. Seng.
The mean age of respondents’ migraine diagnosis was 26 years, so there was about 18 years from the time of diagnosis to participation in the survey, which could introduce recall bias. Other potential limitations included the fact that the survey had no open-ended questions, and men and ethnic minorities were underrepresented.
Useful Data
Commenting on the study findings, Nina Riggins, MD, PhD, president, Brain Performance Center and Research Institute, and director of the Headache Center at The Neuron Clinic, San Diego, California, said the survey findings are “very useful” and highlight “significant opportunities for improvement in migraine education for clinicians and people living with migraine disease.”
The fact that participants reported consulting an average of four healthcare providers before receiving an accurate diagnosis underscores the importance of providing clinicians with tools to identify migraine, she said.
This is especially relevant as new migraine therapies that may improve efficacy and have fewer side effects become available, she added.
“It would be interesting to see in future studies if migraine recognition by non-headache specialists improved after CGRP-blocking medications for migraine management became available,” said Dr. Riggins, who is cochair of the AHS First Contact program which is aimed at improving headache management in primary care.
She added that she and her colleagues will keep these survey results in mind when creating future educational materials for clinicians.
The study was supported by Eli Lily. Dr. Seng is a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Theranica, and Abbvie, and receives research support from the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, Veterans Health Administration, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, and the American Heart Association. Dr. Riggins reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHS 2024