User login
Barriers to Mohs Micrographic Surgery in Japanese Patients With Basal Cell Carcinoma
Margin-controlled surgery for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on the lower lip was first performed by Dr. Frederic Mohs on June 30, 1936. Since then, thousands of skin cancer surgeons have refined and adopted the technique. Due to the high cure rate and sparing of normal tissue, Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has become the gold standard treatment for facial and special-site nonmelanoma skin cancer worldwide. Mohs micrographic surgery is performed on more than 876,000 tumors annually in the United States.1 Among 3.5 million Americans diagnosed with nonmelanoma skin cancer in 2006, one-quarter were treated with MMS.2 In Japan, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin malignancy, with an incidence of 3.34 cases per 100,000 individuals; SCC is the second most common, with an incidence of 2.5 cases per 100,000 individuals.3
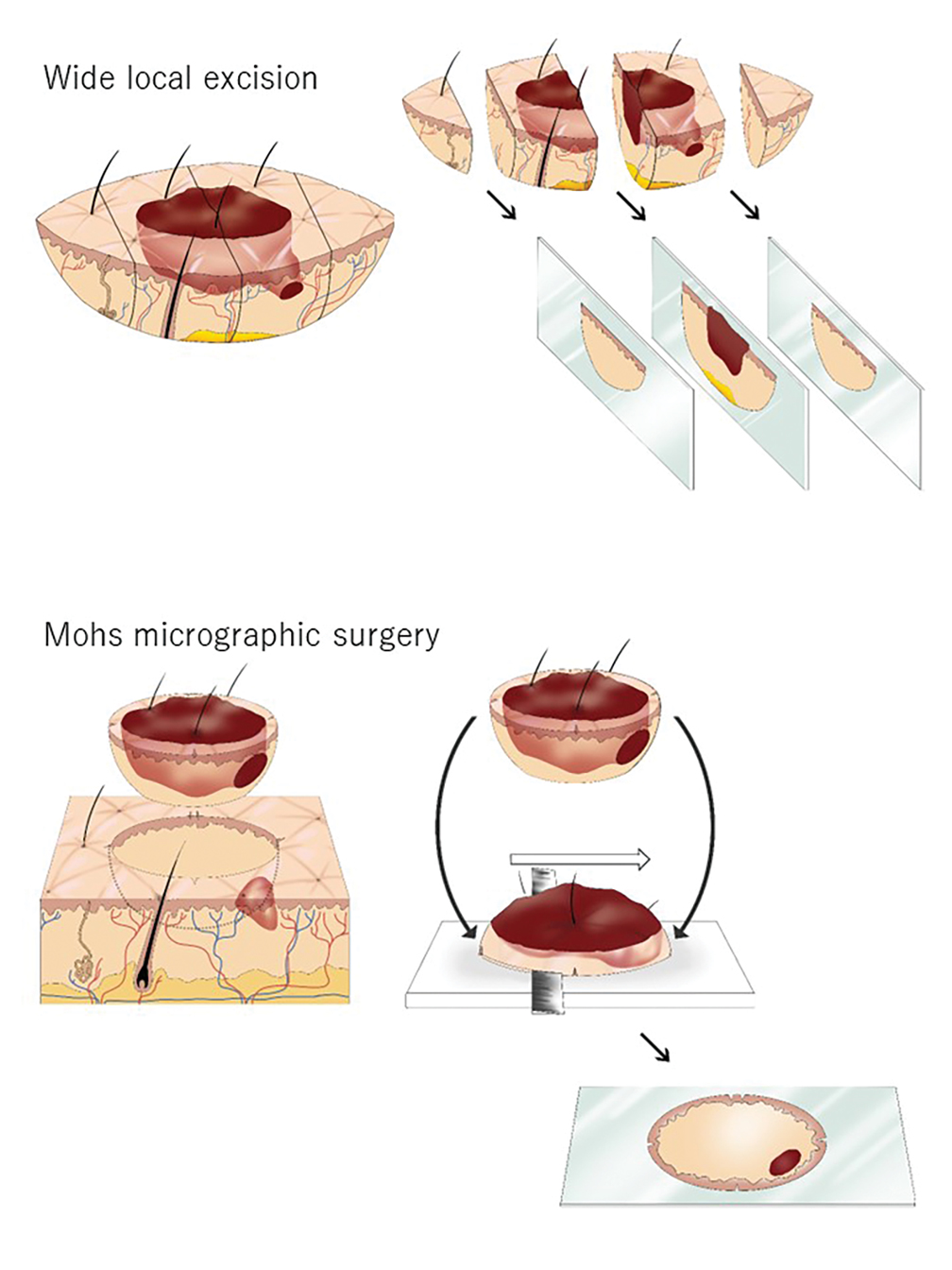
The essential element that makes MMS unique is the careful microscopic examination of the entire margin of the removed specimen. Tissue processing is done with careful en face orientation to ensure that circumferential and deep margins are entirely visible. The surgeon interprets the slides and proceeds to remove the additional tumor as necessary. Because the same physician performs both the surgery and the pathologic assessment throughout the procedure, a precise correlation between the microscopic and surgical findings can be made. The surgeon can begin with smaller margins, removing minimal healthy tissue while removing all the cancer cells, which results in the smallest-possible skin defect and the best prognosis for the malignancy (Figure 1).
At the only facility in Japan offering MMS, the lead author (S.S.) has treated 52 lesions with MMS in 46 patients (2020-2022). Of these patients, 40 were White, 5 were Japanese, and 1 was of African descent. In this case series, we present 5 Japanese patients who had BCC treated with MMS.
Case Series
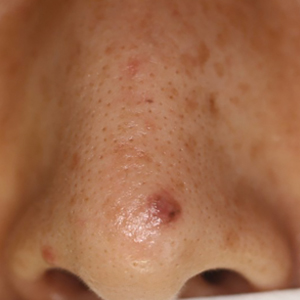
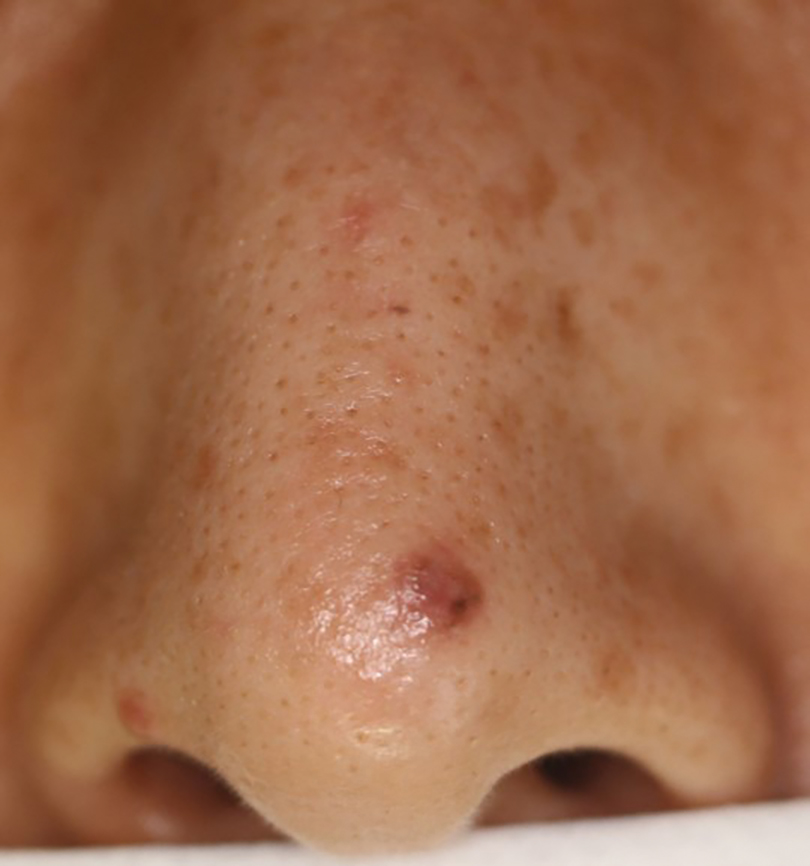
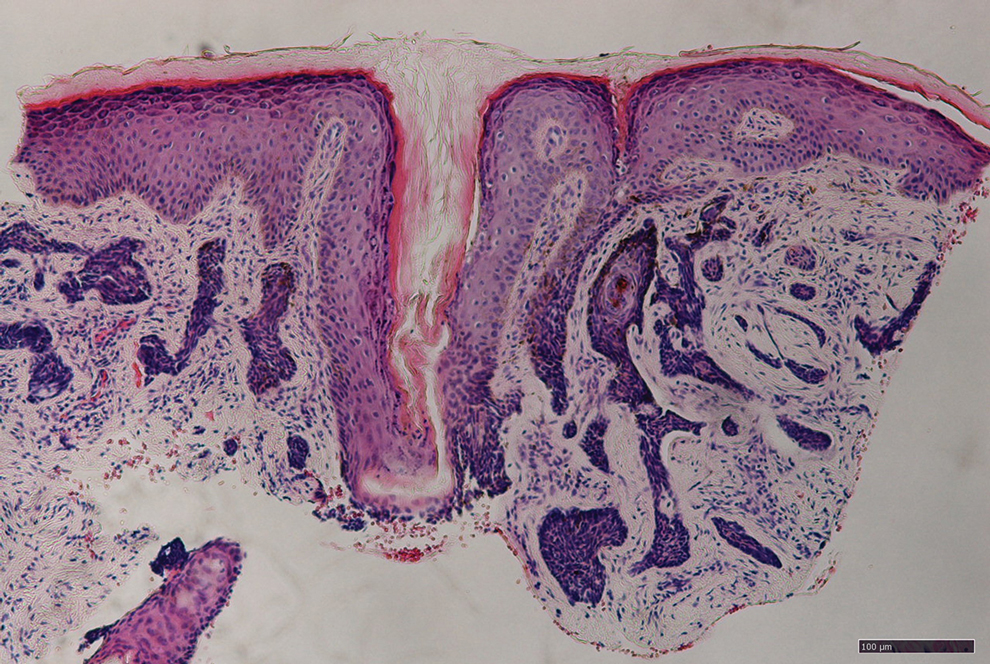
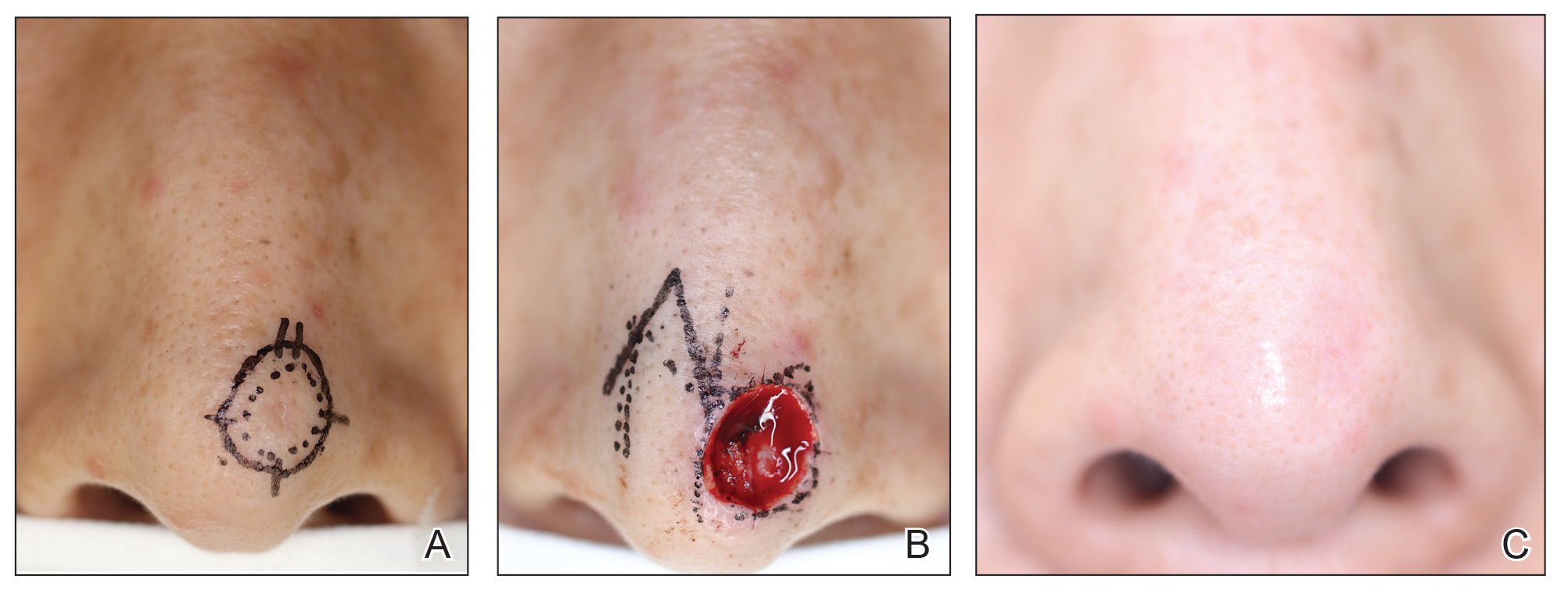
Patient 1—A 50-year-old Japanese woman presented to dermatology with a brown papule on the nasal tip of 1.25 year’s duration (Figure 2). A biopsy revealed infiltrative BCC (Figure 3), and the patient was referred to the dermatology department at a nearby university hospital. Because the BCC was an aggressive variant, wide local excision (WLE) with subsequent flap reconstruction was recommended as well as radiation therapy. The patient learned about MMS through an internet search and refused both options, seeking MMS treatment at our clinic. Although Japanese health insurance does not cover MMS, the patient had supplemental private insurance that did cover the cost. She provided consent to undergo the procedure. Physical examination revealed a 7.5×6-mm, brown-red macule with ill-defined borders on the tip of the nose. We used a 1.5-mm margin for the first stage of MMS (Figure 4A). The frozen section revealed that the tumor had been entirely excised in the first stage, leaving only a 10.5×9-mm skin defect that was reconstructed with a Dufourmentel flap (Figure 4B). No signs of recurrence were noted at 3.5-year follow-up, and the cosmetic outcome was favorable (Figure 4C). National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend a margin greater than 4 mm for infiltrative BCCs4; therefore, our technique reduced the total defect by at least 4 mm in a cosmetically sensitive area. The patient also did not need radiation therapy, which reduced morbidity. She continues to be recurrence free at 3.5-year follow-up.
Patient 2—A 63-year-old Japanese man presented to dermatology with a brown macule on the right lower eyelid of 2 years’ duration. A biopsy of the lesion was positive for nodular BCC. After being advised to undergo WLE and extensive reconstruction with plastic surgery, the patient learned of MMS through an internet search and found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm brown macule on the right lower eyelid. The patient had supplemental private insurance that covered the cost of MMS, and he provided consent for the procedure. A 1.5-mm margin was taken for the first stage, resulting in a 10×8-mm defect superficial to the orbicularis oculi muscle. The frozen section revealed residual tumor exposure in the dermis at the 9- to 10-o’clock position. A second-stage excision was performed to remove an additional 1.5 mm of skin at the 9- to 12-o’clock position with a thin layer of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The subsequent histologic examination revealed no residual BCC, and the final 13×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a rotation flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 2.5-year follow-up with an excellent cosmetic outcome.
Patient 3—A 73-year-old Japanese man presented to a local university dermatology clinic with a new papule on the nose. The dermatologist suggested WLE with 4-mm margins and reconstruction of the skin defect 2 weeks later by a plastic surgeon. The patient was not satisfied with the proposed surgical plan, which led him to learn about MMS on the internet; he subsequently found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 4×3.5-mm brown papule on the tip of the nose. He understood the nature of MMS and chose to pay out-of-pocket because Japanese health insurance did not cover the procedure. We used a 2-mm margin for the first stage, which created a 7.5×7-mm skin defect. The frozen section pathology revealed no residual BCC at the cut surface. The skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 4—A 45-year-old man presented to a dermatology clinic with a papule on the right side of the nose of 1 year’s duration. A biopsy revealed the lesion was a nodular BCC. The dermatologist recommended WLE at a general hospital, but the patient refused after learning about MMS. He subsequently made an appointment with our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×4-mm white papule on the right side of the nose. The patient had private insurance that covered the cost of MMS. The first stage was performed with 1.5-mm margins and was clear of residual tumor. A Limberg rhombic flap from the adjacent cheek was used to repair the final 10×7-mm skin defect. There were no signs of recurrence at 1 year and 9 months’ follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 5—A 76-year-old Japanese woman presented to a university hospital near Tokyo with a black papule on the left cutaneous lip of 5 years’ duration. A biopsy revealed nodular BCC, and WLE with flap reconstruction was recommended. The patient’s son learned about MMS through internet research and referred her to our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm black papule on the left upper lip. The patient’s private insurance covered the cost of MMS, and she consented to the procedure. We used a 2-mm initial margin, and the immediate frozen section revealed no signs of BCC at the cut surface. The 11×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Comment
We presented 5 cases of MMS in Japanese patients with BCC. More than 7000 new cases of nonmelanoma skin cancer occur every year in Japan.3 Only 0.04% of these cases—the 5 cases presented here—were treated with MMS in Japan in 2020 and 2021, in contrast to 25% in the United States in 2006.2
MMS vs Other BCC Treatments—Mohs micrographic surgery offers 2 distinct advantages over conventional excision: an improved cure rate while achieving a smaller final defect size, generally leading to better cosmetic outcomes. Overall 5-year recurrence rates of BCC are 10% for conventional surgical excision vs 1% for MMS, while the recurrence rates for SCC are 8% and 3%, respectively.5 A study of well-demarcated BCCs smaller than 2 cm that were treated with MMS with 2-mm increments revealed that 95% of the cases were free of malignancy within a 4-mm margin of the normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor.6 Several articles have reported a 95% cure rate or higher with conventional excision of localized BCC,7 but 4- to 5-mm excision margins are required, resulting in a greater skin defect and a lower cure rate compared to MMS.
Aggressive subtypes of BCC have a higher recurrence rate. Rowe et al8 reported the following 5-year recurrence rates: 5.6% for MMS, 17.4% for conventional surgical excision, 40.0% for curettage and electrodesiccation, and 9.8% for radiation therapy. Primary BCCs with high-risk histologic subtypes has a 10-year recurrence rate of 4.4% with MMS vs 12.2% with conventional excision.9 These findings reveal that MMS yields a better prognosis compared to traditional treatment methods for recurrent BCCs and BCCs of high-risk histologic subtypes.
The primary reason for the excellent cure rate seen in MMS is the ability to perform complete margin assessment. Peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) is crucial in achieving high cure rates with narrow margins. In WLE (Figure 1), vertical sectioning (also known as bread-loafing) does not achieve direct visualization of the entire surgical margin, as this technique only evaluates random sections and does not achieve PDEMA.10 The bread-loafing method is used almost exclusively in Japan and visualizes only 0.1% of the entire margin compared to 100% with MMS.11 Beyond the superior cure rate, the MMS technique often yields smaller final defects compared to WLE. All 5 of our patients achieved complete tumor removal while sparing more normal tissue compared to conventional WLE, which takes at least a 4-mm margin in all directions.
Barriers to Adopting MMS in Japan—There are many barriers to the broader adoption of MMS in Japan. A guideline of the Japanese Dermatological Association says, MMS “is complicated, requires special training for acquisition, and requires time and labor for implementation of a series of processes, and it has not gained wide acceptance in Japan because of these disadvantages.”3 There currently are no MMS training programs in Japan. We refute this statement from the Japanese Dermatological Association because, in our experience, only 1 surgeon plus a single histotechnician familiar with MMS is sufficient for a facility to offer the procedure (the lead author of this study [S.S.] acts as both the surgeon and the histotechnician). Another misconception among some physicians in Japan is that cancer on ethnically Japanese skin is uniquely suited to excision without microscopic verification of tumor clearance because the borders of the tumors are easily identified, which was based on good cure rates for the excision of well-demarcated pigmented BCCs in a Japanese cohort. This study of a Japanese cohort investigated the specimens with the conventional bread-loafing technique but not with the PDEMA.12
Eighty percent (4/5) of our patients presented with nodular BCC, and only 1 required a second stage. In comparison, we also treated 16 White patients with nodular BCC with MMS during the same period, and 31% (5/16) required more than 1 stage, with 1 patient requiring 3 stages. This cohort, however, is too small to demonstrate a statistically significant difference (S.S., unpublished data, 2020-2022).
A study in Singapore reported the postsurgical complication rate and 5-year recurrence rate for 481 tumors (92% BCC and 7.5% SCC). The median follow-up duration after MMS was 36 months, and the recurrence rate was 0.6%. The postsurgical complications included 11 (2.3%) cases with superficial tip necrosis of surgical flaps/grafts, 2 (0.4%) with mild wound dehiscence, 1 (0.2%) with minor surgical site bleeding, and 1 (0.2%) with minor wound infection.13 This study supports the notion that MMS is equally effective for Asian patients.
Awareness of MMS in Japan is lacking, and most Japanese dermatologists do not know about the technique. All 5 patients in our case series asked their dermatologists about alternative treatment options and were not offered MMS. In each case, the patients learned of the technique through internet research.
The lack of insurance reimbursement for MMS in Japan is another barrier. Because the national health insurance does not reimburse for MMS, the procedure is relatively unavailable to most Japanese citizens who cannot pay out-of-pocket for the treatment and do not have supplemental insurance. Mohs micrographic surgery may seem expensive compared to WLE followed by repair; however, in the authors’ experience, in Japan, excision without MMS may require general sedation and multiple surgeries to reconstruct larger skin defects, leading to greater morbidity and risk for the patient.
Conclusion
Mohs micrographic surgery in Japan is in its infancy, and further studies showing recurrence rates and long-term prognosis are needed. Such data should help increase awareness of MMS among Japanese physicians as an excellent treatment option for their patients. Furthermore, as Japan becomes more heterogenous as a society and the US Military increases its presence in the region, the need for MMS is likely to increase.
Acknowledgments—We appreciate the proofreading support by Mark Bivens, MBA, MSc (Tokyo, Japan), as well as the technical support from Ben Tallon, MBChB, and Robyn Mason (both in Tauranga, New Zealand) to start MMS at our clinic.
- Asgari MM, Olson J, Alam M. Needs assessment for Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.010
- Connolly SM, Baker DR, Baker DR, et al. AAD/ACMS/ASDSA/ASMS 2012 appropriate use criteria for Mohs micrographic surgery: a report of the American Academy of Dermatology, American College of Mohs Surgery, American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association, and the American Society for Mohs Surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:531-550.
- Ansai SI, Umebayashi Y, Katsumata N, et al. Japanese Dermatological Association Guidelines: outlines of guidelines for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma 2020. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E288-E311.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et at. Basal cell skin cancer, version 2.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023;21:1181-1203. doi:10.6004/jncn.2023.0056
- Snow SN, Gunkel J. Mohs surgery. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:2445-2455. doi:10.1016/b978-0-070-94171-3.00041-7
- Wolf DJ, Zitelli JA. Surgical margins for basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:340-344.
- Quazi SJ, Aslam N, Saleem H, et al. Surgical margin of excision in basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of literature. Cureus. 2020;12:E9211.
- Rowe DE, Carroll RJ, Day Jus CL. Mohs surgery is the treatment of choice for recurrent (previously treated) basal cell carcinoma. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989;15:424-431.
- Van Loo, Mosterd K, Krekels GA. Surgical excision versus Mohs’ micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:3011-3020.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, Version 1.2022. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19:1382-1394.
- Hui AM, Jacobson M, Markowitz O, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of melanoma. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:503-515.
- Ito T, Inatomi Y, Nagae K, et al. Narrow-margin excision is a safe, reliable treatment for well-defined, primary pigmented basal cell carcinoma: an analysis of 288 lesions in Japan. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1828-1831.
- Ho WYB, Zhao X, Tan WPM. Mohs micrographic surgery in Singapore: a long-term follow-up review. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2021;50:922-923.
Margin-controlled surgery for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on the lower lip was first performed by Dr. Frederic Mohs on June 30, 1936. Since then, thousands of skin cancer surgeons have refined and adopted the technique. Due to the high cure rate and sparing of normal tissue, Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has become the gold standard treatment for facial and special-site nonmelanoma skin cancer worldwide. Mohs micrographic surgery is performed on more than 876,000 tumors annually in the United States.1 Among 3.5 million Americans diagnosed with nonmelanoma skin cancer in 2006, one-quarter were treated with MMS.2 In Japan, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin malignancy, with an incidence of 3.34 cases per 100,000 individuals; SCC is the second most common, with an incidence of 2.5 cases per 100,000 individuals.3
The essential element that makes MMS unique is the careful microscopic examination of the entire margin of the removed specimen. Tissue processing is done with careful en face orientation to ensure that circumferential and deep margins are entirely visible. The surgeon interprets the slides and proceeds to remove the additional tumor as necessary. Because the same physician performs both the surgery and the pathologic assessment throughout the procedure, a precise correlation between the microscopic and surgical findings can be made. The surgeon can begin with smaller margins, removing minimal healthy tissue while removing all the cancer cells, which results in the smallest-possible skin defect and the best prognosis for the malignancy (Figure 1).
At the only facility in Japan offering MMS, the lead author (S.S.) has treated 52 lesions with MMS in 46 patients (2020-2022). Of these patients, 40 were White, 5 were Japanese, and 1 was of African descent. In this case series, we present 5 Japanese patients who had BCC treated with MMS.
Case Series
Patient 1—A 50-year-old Japanese woman presented to dermatology with a brown papule on the nasal tip of 1.25 year’s duration (Figure 2). A biopsy revealed infiltrative BCC (Figure 3), and the patient was referred to the dermatology department at a nearby university hospital. Because the BCC was an aggressive variant, wide local excision (WLE) with subsequent flap reconstruction was recommended as well as radiation therapy. The patient learned about MMS through an internet search and refused both options, seeking MMS treatment at our clinic. Although Japanese health insurance does not cover MMS, the patient had supplemental private insurance that did cover the cost. She provided consent to undergo the procedure. Physical examination revealed a 7.5×6-mm, brown-red macule with ill-defined borders on the tip of the nose. We used a 1.5-mm margin for the first stage of MMS (Figure 4A). The frozen section revealed that the tumor had been entirely excised in the first stage, leaving only a 10.5×9-mm skin defect that was reconstructed with a Dufourmentel flap (Figure 4B). No signs of recurrence were noted at 3.5-year follow-up, and the cosmetic outcome was favorable (Figure 4C). National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend a margin greater than 4 mm for infiltrative BCCs4; therefore, our technique reduced the total defect by at least 4 mm in a cosmetically sensitive area. The patient also did not need radiation therapy, which reduced morbidity. She continues to be recurrence free at 3.5-year follow-up.




Patient 2—A 63-year-old Japanese man presented to dermatology with a brown macule on the right lower eyelid of 2 years’ duration. A biopsy of the lesion was positive for nodular BCC. After being advised to undergo WLE and extensive reconstruction with plastic surgery, the patient learned of MMS through an internet search and found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm brown macule on the right lower eyelid. The patient had supplemental private insurance that covered the cost of MMS, and he provided consent for the procedure. A 1.5-mm margin was taken for the first stage, resulting in a 10×8-mm defect superficial to the orbicularis oculi muscle. The frozen section revealed residual tumor exposure in the dermis at the 9- to 10-o’clock position. A second-stage excision was performed to remove an additional 1.5 mm of skin at the 9- to 12-o’clock position with a thin layer of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The subsequent histologic examination revealed no residual BCC, and the final 13×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a rotation flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 2.5-year follow-up with an excellent cosmetic outcome.
Patient 3—A 73-year-old Japanese man presented to a local university dermatology clinic with a new papule on the nose. The dermatologist suggested WLE with 4-mm margins and reconstruction of the skin defect 2 weeks later by a plastic surgeon. The patient was not satisfied with the proposed surgical plan, which led him to learn about MMS on the internet; he subsequently found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 4×3.5-mm brown papule on the tip of the nose. He understood the nature of MMS and chose to pay out-of-pocket because Japanese health insurance did not cover the procedure. We used a 2-mm margin for the first stage, which created a 7.5×7-mm skin defect. The frozen section pathology revealed no residual BCC at the cut surface. The skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 4—A 45-year-old man presented to a dermatology clinic with a papule on the right side of the nose of 1 year’s duration. A biopsy revealed the lesion was a nodular BCC. The dermatologist recommended WLE at a general hospital, but the patient refused after learning about MMS. He subsequently made an appointment with our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×4-mm white papule on the right side of the nose. The patient had private insurance that covered the cost of MMS. The first stage was performed with 1.5-mm margins and was clear of residual tumor. A Limberg rhombic flap from the adjacent cheek was used to repair the final 10×7-mm skin defect. There were no signs of recurrence at 1 year and 9 months’ follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 5—A 76-year-old Japanese woman presented to a university hospital near Tokyo with a black papule on the left cutaneous lip of 5 years’ duration. A biopsy revealed nodular BCC, and WLE with flap reconstruction was recommended. The patient’s son learned about MMS through internet research and referred her to our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm black papule on the left upper lip. The patient’s private insurance covered the cost of MMS, and she consented to the procedure. We used a 2-mm initial margin, and the immediate frozen section revealed no signs of BCC at the cut surface. The 11×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Comment
We presented 5 cases of MMS in Japanese patients with BCC. More than 7000 new cases of nonmelanoma skin cancer occur every year in Japan.3 Only 0.04% of these cases—the 5 cases presented here—were treated with MMS in Japan in 2020 and 2021, in contrast to 25% in the United States in 2006.2
MMS vs Other BCC Treatments—Mohs micrographic surgery offers 2 distinct advantages over conventional excision: an improved cure rate while achieving a smaller final defect size, generally leading to better cosmetic outcomes. Overall 5-year recurrence rates of BCC are 10% for conventional surgical excision vs 1% for MMS, while the recurrence rates for SCC are 8% and 3%, respectively.5 A study of well-demarcated BCCs smaller than 2 cm that were treated with MMS with 2-mm increments revealed that 95% of the cases were free of malignancy within a 4-mm margin of the normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor.6 Several articles have reported a 95% cure rate or higher with conventional excision of localized BCC,7 but 4- to 5-mm excision margins are required, resulting in a greater skin defect and a lower cure rate compared to MMS.
Aggressive subtypes of BCC have a higher recurrence rate. Rowe et al8 reported the following 5-year recurrence rates: 5.6% for MMS, 17.4% for conventional surgical excision, 40.0% for curettage and electrodesiccation, and 9.8% for radiation therapy. Primary BCCs with high-risk histologic subtypes has a 10-year recurrence rate of 4.4% with MMS vs 12.2% with conventional excision.9 These findings reveal that MMS yields a better prognosis compared to traditional treatment methods for recurrent BCCs and BCCs of high-risk histologic subtypes.
The primary reason for the excellent cure rate seen in MMS is the ability to perform complete margin assessment. Peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) is crucial in achieving high cure rates with narrow margins. In WLE (Figure 1), vertical sectioning (also known as bread-loafing) does not achieve direct visualization of the entire surgical margin, as this technique only evaluates random sections and does not achieve PDEMA.10 The bread-loafing method is used almost exclusively in Japan and visualizes only 0.1% of the entire margin compared to 100% with MMS.11 Beyond the superior cure rate, the MMS technique often yields smaller final defects compared to WLE. All 5 of our patients achieved complete tumor removal while sparing more normal tissue compared to conventional WLE, which takes at least a 4-mm margin in all directions.
Barriers to Adopting MMS in Japan—There are many barriers to the broader adoption of MMS in Japan. A guideline of the Japanese Dermatological Association says, MMS “is complicated, requires special training for acquisition, and requires time and labor for implementation of a series of processes, and it has not gained wide acceptance in Japan because of these disadvantages.”3 There currently are no MMS training programs in Japan. We refute this statement from the Japanese Dermatological Association because, in our experience, only 1 surgeon plus a single histotechnician familiar with MMS is sufficient for a facility to offer the procedure (the lead author of this study [S.S.] acts as both the surgeon and the histotechnician). Another misconception among some physicians in Japan is that cancer on ethnically Japanese skin is uniquely suited to excision without microscopic verification of tumor clearance because the borders of the tumors are easily identified, which was based on good cure rates for the excision of well-demarcated pigmented BCCs in a Japanese cohort. This study of a Japanese cohort investigated the specimens with the conventional bread-loafing technique but not with the PDEMA.12
Eighty percent (4/5) of our patients presented with nodular BCC, and only 1 required a second stage. In comparison, we also treated 16 White patients with nodular BCC with MMS during the same period, and 31% (5/16) required more than 1 stage, with 1 patient requiring 3 stages. This cohort, however, is too small to demonstrate a statistically significant difference (S.S., unpublished data, 2020-2022).
A study in Singapore reported the postsurgical complication rate and 5-year recurrence rate for 481 tumors (92% BCC and 7.5% SCC). The median follow-up duration after MMS was 36 months, and the recurrence rate was 0.6%. The postsurgical complications included 11 (2.3%) cases with superficial tip necrosis of surgical flaps/grafts, 2 (0.4%) with mild wound dehiscence, 1 (0.2%) with minor surgical site bleeding, and 1 (0.2%) with minor wound infection.13 This study supports the notion that MMS is equally effective for Asian patients.
Awareness of MMS in Japan is lacking, and most Japanese dermatologists do not know about the technique. All 5 patients in our case series asked their dermatologists about alternative treatment options and were not offered MMS. In each case, the patients learned of the technique through internet research.
The lack of insurance reimbursement for MMS in Japan is another barrier. Because the national health insurance does not reimburse for MMS, the procedure is relatively unavailable to most Japanese citizens who cannot pay out-of-pocket for the treatment and do not have supplemental insurance. Mohs micrographic surgery may seem expensive compared to WLE followed by repair; however, in the authors’ experience, in Japan, excision without MMS may require general sedation and multiple surgeries to reconstruct larger skin defects, leading to greater morbidity and risk for the patient.
Conclusion
Mohs micrographic surgery in Japan is in its infancy, and further studies showing recurrence rates and long-term prognosis are needed. Such data should help increase awareness of MMS among Japanese physicians as an excellent treatment option for their patients. Furthermore, as Japan becomes more heterogenous as a society and the US Military increases its presence in the region, the need for MMS is likely to increase.
Acknowledgments—We appreciate the proofreading support by Mark Bivens, MBA, MSc (Tokyo, Japan), as well as the technical support from Ben Tallon, MBChB, and Robyn Mason (both in Tauranga, New Zealand) to start MMS at our clinic.
Margin-controlled surgery for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on the lower lip was first performed by Dr. Frederic Mohs on June 30, 1936. Since then, thousands of skin cancer surgeons have refined and adopted the technique. Due to the high cure rate and sparing of normal tissue, Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has become the gold standard treatment for facial and special-site nonmelanoma skin cancer worldwide. Mohs micrographic surgery is performed on more than 876,000 tumors annually in the United States.1 Among 3.5 million Americans diagnosed with nonmelanoma skin cancer in 2006, one-quarter were treated with MMS.2 In Japan, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin malignancy, with an incidence of 3.34 cases per 100,000 individuals; SCC is the second most common, with an incidence of 2.5 cases per 100,000 individuals.3
The essential element that makes MMS unique is the careful microscopic examination of the entire margin of the removed specimen. Tissue processing is done with careful en face orientation to ensure that circumferential and deep margins are entirely visible. The surgeon interprets the slides and proceeds to remove the additional tumor as necessary. Because the same physician performs both the surgery and the pathologic assessment throughout the procedure, a precise correlation between the microscopic and surgical findings can be made. The surgeon can begin with smaller margins, removing minimal healthy tissue while removing all the cancer cells, which results in the smallest-possible skin defect and the best prognosis for the malignancy (Figure 1).
At the only facility in Japan offering MMS, the lead author (S.S.) has treated 52 lesions with MMS in 46 patients (2020-2022). Of these patients, 40 were White, 5 were Japanese, and 1 was of African descent. In this case series, we present 5 Japanese patients who had BCC treated with MMS.
Case Series
Patient 1—A 50-year-old Japanese woman presented to dermatology with a brown papule on the nasal tip of 1.25 year’s duration (Figure 2). A biopsy revealed infiltrative BCC (Figure 3), and the patient was referred to the dermatology department at a nearby university hospital. Because the BCC was an aggressive variant, wide local excision (WLE) with subsequent flap reconstruction was recommended as well as radiation therapy. The patient learned about MMS through an internet search and refused both options, seeking MMS treatment at our clinic. Although Japanese health insurance does not cover MMS, the patient had supplemental private insurance that did cover the cost. She provided consent to undergo the procedure. Physical examination revealed a 7.5×6-mm, brown-red macule with ill-defined borders on the tip of the nose. We used a 1.5-mm margin for the first stage of MMS (Figure 4A). The frozen section revealed that the tumor had been entirely excised in the first stage, leaving only a 10.5×9-mm skin defect that was reconstructed with a Dufourmentel flap (Figure 4B). No signs of recurrence were noted at 3.5-year follow-up, and the cosmetic outcome was favorable (Figure 4C). National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend a margin greater than 4 mm for infiltrative BCCs4; therefore, our technique reduced the total defect by at least 4 mm in a cosmetically sensitive area. The patient also did not need radiation therapy, which reduced morbidity. She continues to be recurrence free at 3.5-year follow-up.




Patient 2—A 63-year-old Japanese man presented to dermatology with a brown macule on the right lower eyelid of 2 years’ duration. A biopsy of the lesion was positive for nodular BCC. After being advised to undergo WLE and extensive reconstruction with plastic surgery, the patient learned of MMS through an internet search and found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm brown macule on the right lower eyelid. The patient had supplemental private insurance that covered the cost of MMS, and he provided consent for the procedure. A 1.5-mm margin was taken for the first stage, resulting in a 10×8-mm defect superficial to the orbicularis oculi muscle. The frozen section revealed residual tumor exposure in the dermis at the 9- to 10-o’clock position. A second-stage excision was performed to remove an additional 1.5 mm of skin at the 9- to 12-o’clock position with a thin layer of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The subsequent histologic examination revealed no residual BCC, and the final 13×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a rotation flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 2.5-year follow-up with an excellent cosmetic outcome.
Patient 3—A 73-year-old Japanese man presented to a local university dermatology clinic with a new papule on the nose. The dermatologist suggested WLE with 4-mm margins and reconstruction of the skin defect 2 weeks later by a plastic surgeon. The patient was not satisfied with the proposed surgical plan, which led him to learn about MMS on the internet; he subsequently found our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 4×3.5-mm brown papule on the tip of the nose. He understood the nature of MMS and chose to pay out-of-pocket because Japanese health insurance did not cover the procedure. We used a 2-mm margin for the first stage, which created a 7.5×7-mm skin defect. The frozen section pathology revealed no residual BCC at the cut surface. The skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 4—A 45-year-old man presented to a dermatology clinic with a papule on the right side of the nose of 1 year’s duration. A biopsy revealed the lesion was a nodular BCC. The dermatologist recommended WLE at a general hospital, but the patient refused after learning about MMS. He subsequently made an appointment with our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×4-mm white papule on the right side of the nose. The patient had private insurance that covered the cost of MMS. The first stage was performed with 1.5-mm margins and was clear of residual tumor. A Limberg rhombic flap from the adjacent cheek was used to repair the final 10×7-mm skin defect. There were no signs of recurrence at 1 year and 9 months’ follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Patient 5—A 76-year-old Japanese woman presented to a university hospital near Tokyo with a black papule on the left cutaneous lip of 5 years’ duration. A biopsy revealed nodular BCC, and WLE with flap reconstruction was recommended. The patient’s son learned about MMS through internet research and referred her to our clinic. Physical examination revealed a 7×5-mm black papule on the left upper lip. The patient’s private insurance covered the cost of MMS, and she consented to the procedure. We used a 2-mm initial margin, and the immediate frozen section revealed no signs of BCC at the cut surface. The 11×9-mm skin defect was reconstructed with a Limberg rhombic flap. There were no signs of recurrence at 1.5-year follow-up with a favorable cosmetic outcome.
Comment
We presented 5 cases of MMS in Japanese patients with BCC. More than 7000 new cases of nonmelanoma skin cancer occur every year in Japan.3 Only 0.04% of these cases—the 5 cases presented here—were treated with MMS in Japan in 2020 and 2021, in contrast to 25% in the United States in 2006.2
MMS vs Other BCC Treatments—Mohs micrographic surgery offers 2 distinct advantages over conventional excision: an improved cure rate while achieving a smaller final defect size, generally leading to better cosmetic outcomes. Overall 5-year recurrence rates of BCC are 10% for conventional surgical excision vs 1% for MMS, while the recurrence rates for SCC are 8% and 3%, respectively.5 A study of well-demarcated BCCs smaller than 2 cm that were treated with MMS with 2-mm increments revealed that 95% of the cases were free of malignancy within a 4-mm margin of the normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor.6 Several articles have reported a 95% cure rate or higher with conventional excision of localized BCC,7 but 4- to 5-mm excision margins are required, resulting in a greater skin defect and a lower cure rate compared to MMS.
Aggressive subtypes of BCC have a higher recurrence rate. Rowe et al8 reported the following 5-year recurrence rates: 5.6% for MMS, 17.4% for conventional surgical excision, 40.0% for curettage and electrodesiccation, and 9.8% for radiation therapy. Primary BCCs with high-risk histologic subtypes has a 10-year recurrence rate of 4.4% with MMS vs 12.2% with conventional excision.9 These findings reveal that MMS yields a better prognosis compared to traditional treatment methods for recurrent BCCs and BCCs of high-risk histologic subtypes.
The primary reason for the excellent cure rate seen in MMS is the ability to perform complete margin assessment. Peripheral and deep en face margin assessment (PDEMA) is crucial in achieving high cure rates with narrow margins. In WLE (Figure 1), vertical sectioning (also known as bread-loafing) does not achieve direct visualization of the entire surgical margin, as this technique only evaluates random sections and does not achieve PDEMA.10 The bread-loafing method is used almost exclusively in Japan and visualizes only 0.1% of the entire margin compared to 100% with MMS.11 Beyond the superior cure rate, the MMS technique often yields smaller final defects compared to WLE. All 5 of our patients achieved complete tumor removal while sparing more normal tissue compared to conventional WLE, which takes at least a 4-mm margin in all directions.
Barriers to Adopting MMS in Japan—There are many barriers to the broader adoption of MMS in Japan. A guideline of the Japanese Dermatological Association says, MMS “is complicated, requires special training for acquisition, and requires time and labor for implementation of a series of processes, and it has not gained wide acceptance in Japan because of these disadvantages.”3 There currently are no MMS training programs in Japan. We refute this statement from the Japanese Dermatological Association because, in our experience, only 1 surgeon plus a single histotechnician familiar with MMS is sufficient for a facility to offer the procedure (the lead author of this study [S.S.] acts as both the surgeon and the histotechnician). Another misconception among some physicians in Japan is that cancer on ethnically Japanese skin is uniquely suited to excision without microscopic verification of tumor clearance because the borders of the tumors are easily identified, which was based on good cure rates for the excision of well-demarcated pigmented BCCs in a Japanese cohort. This study of a Japanese cohort investigated the specimens with the conventional bread-loafing technique but not with the PDEMA.12
Eighty percent (4/5) of our patients presented with nodular BCC, and only 1 required a second stage. In comparison, we also treated 16 White patients with nodular BCC with MMS during the same period, and 31% (5/16) required more than 1 stage, with 1 patient requiring 3 stages. This cohort, however, is too small to demonstrate a statistically significant difference (S.S., unpublished data, 2020-2022).
A study in Singapore reported the postsurgical complication rate and 5-year recurrence rate for 481 tumors (92% BCC and 7.5% SCC). The median follow-up duration after MMS was 36 months, and the recurrence rate was 0.6%. The postsurgical complications included 11 (2.3%) cases with superficial tip necrosis of surgical flaps/grafts, 2 (0.4%) with mild wound dehiscence, 1 (0.2%) with minor surgical site bleeding, and 1 (0.2%) with minor wound infection.13 This study supports the notion that MMS is equally effective for Asian patients.
Awareness of MMS in Japan is lacking, and most Japanese dermatologists do not know about the technique. All 5 patients in our case series asked their dermatologists about alternative treatment options and were not offered MMS. In each case, the patients learned of the technique through internet research.
The lack of insurance reimbursement for MMS in Japan is another barrier. Because the national health insurance does not reimburse for MMS, the procedure is relatively unavailable to most Japanese citizens who cannot pay out-of-pocket for the treatment and do not have supplemental insurance. Mohs micrographic surgery may seem expensive compared to WLE followed by repair; however, in the authors’ experience, in Japan, excision without MMS may require general sedation and multiple surgeries to reconstruct larger skin defects, leading to greater morbidity and risk for the patient.
Conclusion
Mohs micrographic surgery in Japan is in its infancy, and further studies showing recurrence rates and long-term prognosis are needed. Such data should help increase awareness of MMS among Japanese physicians as an excellent treatment option for their patients. Furthermore, as Japan becomes more heterogenous as a society and the US Military increases its presence in the region, the need for MMS is likely to increase.
Acknowledgments—We appreciate the proofreading support by Mark Bivens, MBA, MSc (Tokyo, Japan), as well as the technical support from Ben Tallon, MBChB, and Robyn Mason (both in Tauranga, New Zealand) to start MMS at our clinic.
- Asgari MM, Olson J, Alam M. Needs assessment for Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.010
- Connolly SM, Baker DR, Baker DR, et al. AAD/ACMS/ASDSA/ASMS 2012 appropriate use criteria for Mohs micrographic surgery: a report of the American Academy of Dermatology, American College of Mohs Surgery, American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association, and the American Society for Mohs Surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:531-550.
- Ansai SI, Umebayashi Y, Katsumata N, et al. Japanese Dermatological Association Guidelines: outlines of guidelines for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma 2020. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E288-E311.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et at. Basal cell skin cancer, version 2.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023;21:1181-1203. doi:10.6004/jncn.2023.0056
- Snow SN, Gunkel J. Mohs surgery. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:2445-2455. doi:10.1016/b978-0-070-94171-3.00041-7
- Wolf DJ, Zitelli JA. Surgical margins for basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:340-344.
- Quazi SJ, Aslam N, Saleem H, et al. Surgical margin of excision in basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of literature. Cureus. 2020;12:E9211.
- Rowe DE, Carroll RJ, Day Jus CL. Mohs surgery is the treatment of choice for recurrent (previously treated) basal cell carcinoma. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989;15:424-431.
- Van Loo, Mosterd K, Krekels GA. Surgical excision versus Mohs’ micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:3011-3020.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, Version 1.2022. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19:1382-1394.
- Hui AM, Jacobson M, Markowitz O, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of melanoma. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:503-515.
- Ito T, Inatomi Y, Nagae K, et al. Narrow-margin excision is a safe, reliable treatment for well-defined, primary pigmented basal cell carcinoma: an analysis of 288 lesions in Japan. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1828-1831.
- Ho WYB, Zhao X, Tan WPM. Mohs micrographic surgery in Singapore: a long-term follow-up review. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2021;50:922-923.
- Asgari MM, Olson J, Alam M. Needs assessment for Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.010
- Connolly SM, Baker DR, Baker DR, et al. AAD/ACMS/ASDSA/ASMS 2012 appropriate use criteria for Mohs micrographic surgery: a report of the American Academy of Dermatology, American College of Mohs Surgery, American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association, and the American Society for Mohs Surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:531-550.
- Ansai SI, Umebayashi Y, Katsumata N, et al. Japanese Dermatological Association Guidelines: outlines of guidelines for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma 2020. J Dermatol. 2021;48:E288-E311.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et at. Basal cell skin cancer, version 2.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023;21:1181-1203. doi:10.6004/jncn.2023.0056
- Snow SN, Gunkel J. Mohs surgery. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017:2445-2455. doi:10.1016/b978-0-070-94171-3.00041-7
- Wolf DJ, Zitelli JA. Surgical margins for basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:340-344.
- Quazi SJ, Aslam N, Saleem H, et al. Surgical margin of excision in basal cell carcinoma: a systematic review of literature. Cureus. 2020;12:E9211.
- Rowe DE, Carroll RJ, Day Jus CL. Mohs surgery is the treatment of choice for recurrent (previously treated) basal cell carcinoma. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989;15:424-431.
- Van Loo, Mosterd K, Krekels GA. Surgical excision versus Mohs’ micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma of the face. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:3011-3020.
- Schmults CD, Blitzblau R, Aasi SZ, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Squamous Cell Skin Cancer, Version 1.2022. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19:1382-1394.
- Hui AM, Jacobson M, Markowitz O, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of melanoma. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:503-515.
- Ito T, Inatomi Y, Nagae K, et al. Narrow-margin excision is a safe, reliable treatment for well-defined, primary pigmented basal cell carcinoma: an analysis of 288 lesions in Japan. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1828-1831.
- Ho WYB, Zhao X, Tan WPM. Mohs micrographic surgery in Singapore: a long-term follow-up review. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2021;50:922-923.
Practice Points
- Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is a safe and effective treatment method for nonmelanoma skin cancer. In some cases, this procedure is superior to standard wide local excision and repair.
- For the broader adaptation of this vital technique in Japan—where MMS is not well established—increased awareness of treatment outcomes among Japanese physicians is needed.
Uproar Over Vitamin D Disease-Prevention Guideline
A recent report by this news organization of a vitamin D clinical practice guideline released by the Endocrine Society in June triggered an outpouring of objections in the comments section from doctors and other readers.
A society press release listed the key new recommendations on the use of vitamin D supplementation and screening to reduce disease risks in individuals without established indications for such treatment or testing:
- For healthy adults younger than 75, no supplementation at doses above the recommended dietary intakes.
- Populations that may benefit from higher doses include: children and adolescents 18 and younger to prevent rickets and to reduce risk for respiratory infection, individuals 75 and older to possibly lower mortality risk, “pregnant people” to potentially reduce various risks, and people with prediabetes to potentially reduce risk of progression.
- No routine testing for 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels because outcome-specific benefits based on those levels have not been identified (including screening in people with dark complexion or obesity).
- Based on insufficient evidence, the panel could not determine specific blood-level thresholds for 25-hydroxyvitamin D for adequacy or for target levels for disease prevention.
This news organization covered the guideline release and simultaneous presentation at the Endocrine Society annual meeting. In response to the coverage, more than 200 doctors and other readers expressed concerns about the guideline, and some said outright that they would not follow it (readers quoted below are identified by the usernames they registered with on the website).
One reader who posted as Dr. Joseph Destefano went so far as to call the guideline “dangerous” and “almost ... evil.” Ironically, some readers attacked this news organization, thinking that the coverage implied an endorsement, rather than a news report.
Ignores Potential Benefits
“They address issues dealing only with endocrinology and bone health for the most part,” Dr. Emilio Gonzalez wrote. “However, vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency are not rare, and they impact the treatment of autoimmune disorders, chronic pain control, immunosuppression, cancer prevention, cardiovascular health, etc. There is plenty of literature in this regard.”
“They make these claims as if quality studies contradicting their guidelines have not been out there for years,” Dr. Brian Batcheldor said. “What about the huge demographic with diseases that impact intestinal absorption, eg, Crohn’s and celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, and ulcerative colitis? What about the one in nine that now have autoimmune diseases still awaiting diagnosis? What about night workers or anyone with more restricted access to sun exposure? How about those whose cultural or religious dress code limit skin exposure?”
The latter group was also mentioned in a post from Dr. Eve Finkelstein who said, “They don’t take into account women who are totally covered for religious reasons. They have no skin other than part of their face exposed. It does not make sense not to supplement them. Ignoring women’s health needs seems to be the norm.”
“I don’t think they considered the oral health effects of vitamin D deficiency,” pointed out commenter Corie Lewis. “Excess dental calculus (tartar) from excess calcium/phosphate in saliva significantly increases an individual’s periodontal disease risks (gum disease), and low saliva calcium/phosphate increases dental caries (cavities) risks, which generally indicates an imbalance of the oral microbiome. Vitamin D can help create balance and reduce those oral health risks.”
Noted Kimberley Morris-Windisch, “Having worked in rheumatology and pain for most of my career, I have seen too many people benefit from correcting deficiency of vitamin D. To ignore this is to miss opportunities to improve patient health.” Furthermore, “I find it unlikely that it would only improve mortality after age 75. That makes no sense.”
“Also,” she added, “what is the number [needed] to harm? In my 25 years, I have seen vitamin D toxicity once and an excessively high level without symptoms one other time.”
“WHY? Just WHY?” lamented Anne Kinchen. “Low levels in pregnant women have long-term effects on the developing fetus — higher and earlier rates of osteopenia in female children, weaker immune systems overall. There are just SO many reasons to test. These guidelines for no testing are absurd!”
No Screening, No Need for Decision-Making?
Several readers questioned the society’s rationale for not screening, as expressed by session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it,” Dr. Rosen said. “That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen. ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life. ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Among the reader comments in this regard:
“So misguided. Don’t look because we don’t know what do to with data. That’s the message this article exposes. The recommendation is do nothing. But, doing nothing IS an action — not a default.” (Lisa Tracy)
“So now, you will not screen for vitamin D because you do not know what to do next? See a naturopathic doctor — we know what to do next!” (Dr. Joyce Roberson)
“Gee, how do we treat it? ... What to do? Sounds incompetent at minimum. I suspect it’s vital, easy, and inexpensive ... so hide it.” (Holly Kohley)
“Just because we do not know is not a rationale for not testing. The opposite should be done.” (Dr. JJ Gold)
Caters to Industry?
Many commentators intimated that pharma and/or insurance company considerations played a role in the recommendations. Their comments included the following:
“I have been under the impression people do routine checkups to verify there are no hidden problems. If only some testing is done, the probability of not finding a problem is huge. ... Preventive healthcare should be looking for something to prevent instead of waiting until they can cure it. Of course, it might come back to ‘follow the money.’ It is much more profitable to diagnose and treat than it is to prevent.” (Grace Kyser)
“The current irrational ‘recommendation’ gives insurance companies an excuse to deny ALL tests of vitamin D — even if the proper code is supplied. The result is — people suffer. This recommendation does harm!” (Dr JJ Gold)
“Essentially, they are saying let’s not screen ‘healthy’ individuals and ignore it altogether. Better to wait till they’re old, pregnant, or already sick and diagnosed with a disease. This is the problem with the healthcare in this country.” (Brittney Lesher)
“Until allopathic medicine stops waiting for severe symptoms to develop before even screening for potential health problems, the most expensive healthcare (aka, sick care) system in the world will continue to be content to focus on medical emergencies and ignore prevention. ...” (Dean Raffelock)
“Don’t test? Are you kidding me? Especially when people are supplementing? That is akin to taking a blood pressure medication without measuring blood pressures! ... Don’t test? Don’t supplement? ... I have only one explanation for such nonsense: Pharma lives off sick people, not healthy ones.” (Georg Schlomka)
On a somewhat conciliatory and pointed note, Dr Francesca Luna-Rudin commented, “I would like to remind all of my fellow physicians that recommendations should be regarded as just that, a ‘recommendation.’ As doctors, we can use guidelines and recommendations in our practice, but if a new one is presented that does not make sense or would lead to harm based on our education and training, then we are not bound to follow it!”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent report by this news organization of a vitamin D clinical practice guideline released by the Endocrine Society in June triggered an outpouring of objections in the comments section from doctors and other readers.
A society press release listed the key new recommendations on the use of vitamin D supplementation and screening to reduce disease risks in individuals without established indications for such treatment or testing:
- For healthy adults younger than 75, no supplementation at doses above the recommended dietary intakes.
- Populations that may benefit from higher doses include: children and adolescents 18 and younger to prevent rickets and to reduce risk for respiratory infection, individuals 75 and older to possibly lower mortality risk, “pregnant people” to potentially reduce various risks, and people with prediabetes to potentially reduce risk of progression.
- No routine testing for 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels because outcome-specific benefits based on those levels have not been identified (including screening in people with dark complexion or obesity).
- Based on insufficient evidence, the panel could not determine specific blood-level thresholds for 25-hydroxyvitamin D for adequacy or for target levels for disease prevention.
This news organization covered the guideline release and simultaneous presentation at the Endocrine Society annual meeting. In response to the coverage, more than 200 doctors and other readers expressed concerns about the guideline, and some said outright that they would not follow it (readers quoted below are identified by the usernames they registered with on the website).
One reader who posted as Dr. Joseph Destefano went so far as to call the guideline “dangerous” and “almost ... evil.” Ironically, some readers attacked this news organization, thinking that the coverage implied an endorsement, rather than a news report.
Ignores Potential Benefits
“They address issues dealing only with endocrinology and bone health for the most part,” Dr. Emilio Gonzalez wrote. “However, vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency are not rare, and they impact the treatment of autoimmune disorders, chronic pain control, immunosuppression, cancer prevention, cardiovascular health, etc. There is plenty of literature in this regard.”
“They make these claims as if quality studies contradicting their guidelines have not been out there for years,” Dr. Brian Batcheldor said. “What about the huge demographic with diseases that impact intestinal absorption, eg, Crohn’s and celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, and ulcerative colitis? What about the one in nine that now have autoimmune diseases still awaiting diagnosis? What about night workers or anyone with more restricted access to sun exposure? How about those whose cultural or religious dress code limit skin exposure?”
The latter group was also mentioned in a post from Dr. Eve Finkelstein who said, “They don’t take into account women who are totally covered for religious reasons. They have no skin other than part of their face exposed. It does not make sense not to supplement them. Ignoring women’s health needs seems to be the norm.”
“I don’t think they considered the oral health effects of vitamin D deficiency,” pointed out commenter Corie Lewis. “Excess dental calculus (tartar) from excess calcium/phosphate in saliva significantly increases an individual’s periodontal disease risks (gum disease), and low saliva calcium/phosphate increases dental caries (cavities) risks, which generally indicates an imbalance of the oral microbiome. Vitamin D can help create balance and reduce those oral health risks.”
Noted Kimberley Morris-Windisch, “Having worked in rheumatology and pain for most of my career, I have seen too many people benefit from correcting deficiency of vitamin D. To ignore this is to miss opportunities to improve patient health.” Furthermore, “I find it unlikely that it would only improve mortality after age 75. That makes no sense.”
“Also,” she added, “what is the number [needed] to harm? In my 25 years, I have seen vitamin D toxicity once and an excessively high level without symptoms one other time.”
“WHY? Just WHY?” lamented Anne Kinchen. “Low levels in pregnant women have long-term effects on the developing fetus — higher and earlier rates of osteopenia in female children, weaker immune systems overall. There are just SO many reasons to test. These guidelines for no testing are absurd!”
No Screening, No Need for Decision-Making?
Several readers questioned the society’s rationale for not screening, as expressed by session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it,” Dr. Rosen said. “That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen. ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life. ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Among the reader comments in this regard:
“So misguided. Don’t look because we don’t know what do to with data. That’s the message this article exposes. The recommendation is do nothing. But, doing nothing IS an action — not a default.” (Lisa Tracy)
“So now, you will not screen for vitamin D because you do not know what to do next? See a naturopathic doctor — we know what to do next!” (Dr. Joyce Roberson)
“Gee, how do we treat it? ... What to do? Sounds incompetent at minimum. I suspect it’s vital, easy, and inexpensive ... so hide it.” (Holly Kohley)
“Just because we do not know is not a rationale for not testing. The opposite should be done.” (Dr. JJ Gold)
Caters to Industry?
Many commentators intimated that pharma and/or insurance company considerations played a role in the recommendations. Their comments included the following:
“I have been under the impression people do routine checkups to verify there are no hidden problems. If only some testing is done, the probability of not finding a problem is huge. ... Preventive healthcare should be looking for something to prevent instead of waiting until they can cure it. Of course, it might come back to ‘follow the money.’ It is much more profitable to diagnose and treat than it is to prevent.” (Grace Kyser)
“The current irrational ‘recommendation’ gives insurance companies an excuse to deny ALL tests of vitamin D — even if the proper code is supplied. The result is — people suffer. This recommendation does harm!” (Dr JJ Gold)
“Essentially, they are saying let’s not screen ‘healthy’ individuals and ignore it altogether. Better to wait till they’re old, pregnant, or already sick and diagnosed with a disease. This is the problem with the healthcare in this country.” (Brittney Lesher)
“Until allopathic medicine stops waiting for severe symptoms to develop before even screening for potential health problems, the most expensive healthcare (aka, sick care) system in the world will continue to be content to focus on medical emergencies and ignore prevention. ...” (Dean Raffelock)
“Don’t test? Are you kidding me? Especially when people are supplementing? That is akin to taking a blood pressure medication without measuring blood pressures! ... Don’t test? Don’t supplement? ... I have only one explanation for such nonsense: Pharma lives off sick people, not healthy ones.” (Georg Schlomka)
On a somewhat conciliatory and pointed note, Dr Francesca Luna-Rudin commented, “I would like to remind all of my fellow physicians that recommendations should be regarded as just that, a ‘recommendation.’ As doctors, we can use guidelines and recommendations in our practice, but if a new one is presented that does not make sense or would lead to harm based on our education and training, then we are not bound to follow it!”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent report by this news organization of a vitamin D clinical practice guideline released by the Endocrine Society in June triggered an outpouring of objections in the comments section from doctors and other readers.
A society press release listed the key new recommendations on the use of vitamin D supplementation and screening to reduce disease risks in individuals without established indications for such treatment or testing:
- For healthy adults younger than 75, no supplementation at doses above the recommended dietary intakes.
- Populations that may benefit from higher doses include: children and adolescents 18 and younger to prevent rickets and to reduce risk for respiratory infection, individuals 75 and older to possibly lower mortality risk, “pregnant people” to potentially reduce various risks, and people with prediabetes to potentially reduce risk of progression.
- No routine testing for 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels because outcome-specific benefits based on those levels have not been identified (including screening in people with dark complexion or obesity).
- Based on insufficient evidence, the panel could not determine specific blood-level thresholds for 25-hydroxyvitamin D for adequacy or for target levels for disease prevention.
This news organization covered the guideline release and simultaneous presentation at the Endocrine Society annual meeting. In response to the coverage, more than 200 doctors and other readers expressed concerns about the guideline, and some said outright that they would not follow it (readers quoted below are identified by the usernames they registered with on the website).
One reader who posted as Dr. Joseph Destefano went so far as to call the guideline “dangerous” and “almost ... evil.” Ironically, some readers attacked this news organization, thinking that the coverage implied an endorsement, rather than a news report.
Ignores Potential Benefits
“They address issues dealing only with endocrinology and bone health for the most part,” Dr. Emilio Gonzalez wrote. “However, vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency are not rare, and they impact the treatment of autoimmune disorders, chronic pain control, immunosuppression, cancer prevention, cardiovascular health, etc. There is plenty of literature in this regard.”
“They make these claims as if quality studies contradicting their guidelines have not been out there for years,” Dr. Brian Batcheldor said. “What about the huge demographic with diseases that impact intestinal absorption, eg, Crohn’s and celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, and ulcerative colitis? What about the one in nine that now have autoimmune diseases still awaiting diagnosis? What about night workers or anyone with more restricted access to sun exposure? How about those whose cultural or religious dress code limit skin exposure?”
The latter group was also mentioned in a post from Dr. Eve Finkelstein who said, “They don’t take into account women who are totally covered for religious reasons. They have no skin other than part of their face exposed. It does not make sense not to supplement them. Ignoring women’s health needs seems to be the norm.”
“I don’t think they considered the oral health effects of vitamin D deficiency,” pointed out commenter Corie Lewis. “Excess dental calculus (tartar) from excess calcium/phosphate in saliva significantly increases an individual’s periodontal disease risks (gum disease), and low saliva calcium/phosphate increases dental caries (cavities) risks, which generally indicates an imbalance of the oral microbiome. Vitamin D can help create balance and reduce those oral health risks.”
Noted Kimberley Morris-Windisch, “Having worked in rheumatology and pain for most of my career, I have seen too many people benefit from correcting deficiency of vitamin D. To ignore this is to miss opportunities to improve patient health.” Furthermore, “I find it unlikely that it would only improve mortality after age 75. That makes no sense.”
“Also,” she added, “what is the number [needed] to harm? In my 25 years, I have seen vitamin D toxicity once and an excessively high level without symptoms one other time.”
“WHY? Just WHY?” lamented Anne Kinchen. “Low levels in pregnant women have long-term effects on the developing fetus — higher and earlier rates of osteopenia in female children, weaker immune systems overall. There are just SO many reasons to test. These guidelines for no testing are absurd!”
No Screening, No Need for Decision-Making?
Several readers questioned the society’s rationale for not screening, as expressed by session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it,” Dr. Rosen said. “That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen. ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life. ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Among the reader comments in this regard:
“So misguided. Don’t look because we don’t know what do to with data. That’s the message this article exposes. The recommendation is do nothing. But, doing nothing IS an action — not a default.” (Lisa Tracy)
“So now, you will not screen for vitamin D because you do not know what to do next? See a naturopathic doctor — we know what to do next!” (Dr. Joyce Roberson)
“Gee, how do we treat it? ... What to do? Sounds incompetent at minimum. I suspect it’s vital, easy, and inexpensive ... so hide it.” (Holly Kohley)
“Just because we do not know is not a rationale for not testing. The opposite should be done.” (Dr. JJ Gold)
Caters to Industry?
Many commentators intimated that pharma and/or insurance company considerations played a role in the recommendations. Their comments included the following:
“I have been under the impression people do routine checkups to verify there are no hidden problems. If only some testing is done, the probability of not finding a problem is huge. ... Preventive healthcare should be looking for something to prevent instead of waiting until they can cure it. Of course, it might come back to ‘follow the money.’ It is much more profitable to diagnose and treat than it is to prevent.” (Grace Kyser)
“The current irrational ‘recommendation’ gives insurance companies an excuse to deny ALL tests of vitamin D — even if the proper code is supplied. The result is — people suffer. This recommendation does harm!” (Dr JJ Gold)
“Essentially, they are saying let’s not screen ‘healthy’ individuals and ignore it altogether. Better to wait till they’re old, pregnant, or already sick and diagnosed with a disease. This is the problem with the healthcare in this country.” (Brittney Lesher)
“Until allopathic medicine stops waiting for severe symptoms to develop before even screening for potential health problems, the most expensive healthcare (aka, sick care) system in the world will continue to be content to focus on medical emergencies and ignore prevention. ...” (Dean Raffelock)
“Don’t test? Are you kidding me? Especially when people are supplementing? That is akin to taking a blood pressure medication without measuring blood pressures! ... Don’t test? Don’t supplement? ... I have only one explanation for such nonsense: Pharma lives off sick people, not healthy ones.” (Georg Schlomka)
On a somewhat conciliatory and pointed note, Dr Francesca Luna-Rudin commented, “I would like to remind all of my fellow physicians that recommendations should be regarded as just that, a ‘recommendation.’ As doctors, we can use guidelines and recommendations in our practice, but if a new one is presented that does not make sense or would lead to harm based on our education and training, then we are not bound to follow it!”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Change in Clinical Definition of Parkinson’s Triggers Debate
Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy bodies are currently defined by clinical features, which can be heterogeneous and do not capture the presymptomatic phase of neurodegeneration.
Recent advances have enabled the detection of misfolded and aggregated alpha-synuclein protein (synucleinopathy) — a key pathologic feature of these diseases — allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnosis. This has led two international research groups to propose a major shift from a clinical to a biological definition of the disease.
Both groups emphasized the detection of alpha-synuclein through recently developed seed amplification assays as a key diagnostic and staging tool, although they differ in their approaches and criteria.
NSD-ISS
NSD is defined by the presence during life of pathologic neuronal alpha-synuclein (S, the first biological anchor) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), regardless of the presence of any specific clinical syndrome. Individuals with pathologic neuronal alpha-synuclein aggregates are at a high risk for dopaminergic neuronal dysfunction (D, the second key biological anchor).
Dr. Simuni and colleagues also proposed the NSD integrated staging system (NSD-ISS) rooted in the S and D biological anchors coupled with the degree of functional impairment caused by clinical signs or symptoms.
Stages 0-1 occur without signs or symptoms and are defined by the presence of pathogenic variants in the SNCA gene (stage 0), S alone (stage 1A), or S and D (stage 1B).
The presence of clinical manifestations marks the transition to stage 2 and beyond, with stage 2 characterized by subtle signs or symptoms but without functional impairment. Stages 2B-6 require both S and D and stage-specific increases in functional impairment.
“An advantage of the NSD-ISS will be to reduce heterogeneity in clinical trials by requiring biological consistency within the study cohort rather than identifying study participants on the basis of clinical criteria for Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies,” Dr. Simuni and colleagues pointed out in a position paper describing the NSD-ISS published online earlier this year in The Lancet Neurology.
The NSD-ISS will “evolve to include the incorporation of data-driven definitions of stage-specific functional anchors and additional biomarkers as they emerge and are validated.”
For now, the NSD-ISS is intended for research use only and not in the clinic.
The SynNeurGe Research Diagnostic Criteria
Separately, a team led by Anthony Lang, MD, with the Krembil Brain Institute at Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, proposed the SynNeurGe biological classification of PD.
Described in a companion paper published online in The Lancet Neurology, their “S-N-G” classification emphasizes the important interactions between three biological factors that contribute to disease: The presence or absence of pathologic alpha-synuclein (S) in tissues or CSF, an evidence of underlying neurodegeneration (N) defined by neuroimaging procedures, and the documentation of pathogenic gene variants (G) that cause or strongly predispose to PD.
These three components link to a clinical component, defined either by a single high-specificity clinical feature or by multiple lower-specificity clinical features.
As with the NSD-ISS, the SynNeurGe model is intended for research purposes only and is not ready for immediate application in the clinic.
Both groups acknowledged the need for studies to test and validate the proposed classification systems.
Caveats, Cautionary Notes
Adopting a biological definition of PD would represent a shift as the field has prompted considerable discussion and healthy debate.
Commenting for this news organization, James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, said the principle behind the proposed classifications is where “the field needs to go.”
“Right now, people with Parkinson’s take too long to get a confirmed diagnosis of their disease, and despite best efforts, clinicians can get it wrong, not diagnosing people or maybe misdiagnosing people,” Dr. Beck said. “Moving to a biological basis, where we have better certainty, is going to be really important.”
Beck noted that the NSD-ISS “goes all in on alpha-synuclein,” which does play a big role in PD, but added, “I don’t know if I want to declare a winner after the first heat. There are other biomarkers that are coming to fruition but still need validation, and alpha-synuclein may be just one of many to help determine whether someone has Parkinson’s disease or not.”
Un Kang, MD, director of translational research at the Fresco Institute for Parkinson’s & Movement Disorders at NYU Langone Health, New York City, told this news organization that alpha-synuclein has “very high diagnostic accuracy” but cautioned that the adoption of a biological definition for PD would not usurp a clinical diagnosis.
“We need both,” Dr. Kang said. “But knowing the underlying pathology is important for earlier diagnosis and testing of potential therapies to treat the molecular pathology. If a patient doesn’t have abnormal synuclein, you may be treating the wrong disease.”
The coauthors of recent JAMA Neurology perspective said the biological definitions are “exciting, but there is “wisdom” in tapping the brakes when attempting to establish a biological definition and classification system for PD.
“Although these two proposals represent significant steps forward, a sprint toward the finish line may not be wise,” wrote Njideka U. Okubadejo, MD, with University of Lagos, Nigeria; Joseph Jankovic, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston; and Michael S. Okun, MD, with University of Florida Health, Gainesville, Florida.
“A process that embraces inclusivity and weaves in evolving technological advancements will be important. Who benefits if implementation of a biologically based staging system for PD is hurried?” they continued.
The proposals rely heavily on alpha-synuclein assays, they noted, which currently require subjective interpretation and lack extensive validation. They also worry that the need for expensive and, in some regions, unattainable biological fluids (CSF) or imaging studies (dopamine transporter scan) may limit global access to both PD trials and future therapeutics.
They also worry about retiring the name Parkinson’s disease.
“Beyond the historical importance of the term Parkinson disease, any classification that proposes abandoning the two words in either clinical or research descriptions could have unintended global repercussions,” Dr. Okubadejo, Dr. Jankovic, and Dr. Okun cautioned.
Dr. Beck told this news organization he’s spoken to clinicians at meetings about this and “no one really likes the idea” of retiring the term Parkinson’s disease.
Frederick Ketchum, MD, and Nathaniel Chin, MD, with University of Wisconsin–Madison, worry about the “lived” experience of the asymptomatic patient after receiving a biological diagnosis.
“Biological diagnosis might enable effective prognostication and treatment in the future but will substantially change the experience of illness for patients now as new frameworks are slowly adopted and knowledge is gained,” they said in a correspondence in The Lancet Neurology.
“Understanding and addressing this lived experience remains a core task for health professionals and must be made central as we begin an era in which neurological diseases are redefined on a biological basis,” Dr. Ketchum and Dr. Chin advised.
A complete list of agencies that supported this work and author disclosures are available with the original articles. Dr. Beck and Dr. Kang had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy bodies are currently defined by clinical features, which can be heterogeneous and do not capture the presymptomatic phase of neurodegeneration.
Recent advances have enabled the detection of misfolded and aggregated alpha-synuclein protein (synucleinopathy) — a key pathologic feature of these diseases — allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnosis. This has led two international research groups to propose a major shift from a clinical to a biological definition of the disease.
Both groups emphasized the detection of alpha-synuclein through recently developed seed amplification assays as a key diagnostic and staging tool, although they differ in their approaches and criteria.
NSD-ISS
NSD is defined by the presence during life of pathologic neuronal alpha-synuclein (S, the first biological anchor) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), regardless of the presence of any specific clinical syndrome. Individuals with pathologic neuronal alpha-synuclein aggregates are at a high risk for dopaminergic neuronal dysfunction (D, the second key biological anchor).
Dr. Simuni and colleagues also proposed the NSD integrated staging system (NSD-ISS) rooted in the S and D biological anchors coupled with the degree of functional impairment caused by clinical signs or symptoms.
Stages 0-1 occur without signs or symptoms and are defined by the presence of pathogenic variants in the SNCA gene (stage 0), S alone (stage 1A), or S and D (stage 1B).
The presence of clinical manifestations marks the transition to stage 2 and beyond, with stage 2 characterized by subtle signs or symptoms but without functional impairment. Stages 2B-6 require both S and D and stage-specific increases in functional impairment.
“An advantage of the NSD-ISS will be to reduce heterogeneity in clinical trials by requiring biological consistency within the study cohort rather than identifying study participants on the basis of clinical criteria for Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies,” Dr. Simuni and colleagues pointed out in a position paper describing the NSD-ISS published online earlier this year in The Lancet Neurology.
The NSD-ISS will “evolve to include the incorporation of data-driven definitions of stage-specific functional anchors and additional biomarkers as they emerge and are validated.”
For now, the NSD-ISS is intended for research use only and not in the clinic.
The SynNeurGe Research Diagnostic Criteria
Separately, a team led by Anthony Lang, MD, with the Krembil Brain Institute at Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, proposed the SynNeurGe biological classification of PD.
Described in a companion paper published online in The Lancet Neurology, their “S-N-G” classification emphasizes the important interactions between three biological factors that contribute to disease: The presence or absence of pathologic alpha-synuclein (S) in tissues or CSF, an evidence of underlying neurodegeneration (N) defined by neuroimaging procedures, and the documentation of pathogenic gene variants (G) that cause or strongly predispose to PD.
These three components link to a clinical component, defined either by a single high-specificity clinical feature or by multiple lower-specificity clinical features.
As with the NSD-ISS, the SynNeurGe model is intended for research purposes only and is not ready for immediate application in the clinic.
Both groups acknowledged the need for studies to test and validate the proposed classification systems.
Caveats, Cautionary Notes
Adopting a biological definition of PD would represent a shift as the field has prompted considerable discussion and healthy debate.
Commenting for this news organization, James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, said the principle behind the proposed classifications is where “the field needs to go.”
“Right now, people with Parkinson’s take too long to get a confirmed diagnosis of their disease, and despite best efforts, clinicians can get it wrong, not diagnosing people or maybe misdiagnosing people,” Dr. Beck said. “Moving to a biological basis, where we have better certainty, is going to be really important.”
Beck noted that the NSD-ISS “goes all in on alpha-synuclein,” which does play a big role in PD, but added, “I don’t know if I want to declare a winner after the first heat. There are other biomarkers that are coming to fruition but still need validation, and alpha-synuclein may be just one of many to help determine whether someone has Parkinson’s disease or not.”
Un Kang, MD, director of translational research at the Fresco Institute for Parkinson’s & Movement Disorders at NYU Langone Health, New York City, told this news organization that alpha-synuclein has “very high diagnostic accuracy” but cautioned that the adoption of a biological definition for PD would not usurp a clinical diagnosis.
“We need both,” Dr. Kang said. “But knowing the underlying pathology is important for earlier diagnosis and testing of potential therapies to treat the molecular pathology. If a patient doesn’t have abnormal synuclein, you may be treating the wrong disease.”
The coauthors of recent JAMA Neurology perspective said the biological definitions are “exciting, but there is “wisdom” in tapping the brakes when attempting to establish a biological definition and classification system for PD.
“Although these two proposals represent significant steps forward, a sprint toward the finish line may not be wise,” wrote Njideka U. Okubadejo, MD, with University of Lagos, Nigeria; Joseph Jankovic, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston; and Michael S. Okun, MD, with University of Florida Health, Gainesville, Florida.
“A process that embraces inclusivity and weaves in evolving technological advancements will be important. Who benefits if implementation of a biologically based staging system for PD is hurried?” they continued.
The proposals rely heavily on alpha-synuclein assays, they noted, which currently require subjective interpretation and lack extensive validation. They also worry that the need for expensive and, in some regions, unattainable biological fluids (CSF) or imaging studies (dopamine transporter scan) may limit global access to both PD trials and future therapeutics.
They also worry about retiring the name Parkinson’s disease.
“Beyond the historical importance of the term Parkinson disease, any classification that proposes abandoning the two words in either clinical or research descriptions could have unintended global repercussions,” Dr. Okubadejo, Dr. Jankovic, and Dr. Okun cautioned.
Dr. Beck told this news organization he’s spoken to clinicians at meetings about this and “no one really likes the idea” of retiring the term Parkinson’s disease.
Frederick Ketchum, MD, and Nathaniel Chin, MD, with University of Wisconsin–Madison, worry about the “lived” experience of the asymptomatic patient after receiving a biological diagnosis.
“Biological diagnosis might enable effective prognostication and treatment in the future but will substantially change the experience of illness for patients now as new frameworks are slowly adopted and knowledge is gained,” they said in a correspondence in The Lancet Neurology.
“Understanding and addressing this lived experience remains a core task for health professionals and must be made central as we begin an era in which neurological diseases are redefined on a biological basis,” Dr. Ketchum and Dr. Chin advised.
A complete list of agencies that supported this work and author disclosures are available with the original articles. Dr. Beck and Dr. Kang had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy bodies are currently defined by clinical features, which can be heterogeneous and do not capture the presymptomatic phase of neurodegeneration.
Recent advances have enabled the detection of misfolded and aggregated alpha-synuclein protein (synucleinopathy) — a key pathologic feature of these diseases — allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnosis. This has led two international research groups to propose a major shift from a clinical to a biological definition of the disease.
Both groups emphasized the detection of alpha-synuclein through recently developed seed amplification assays as a key diagnostic and staging tool, although they differ in their approaches and criteria.
NSD-ISS
NSD is defined by the presence during life of pathologic neuronal alpha-synuclein (S, the first biological anchor) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), regardless of the presence of any specific clinical syndrome. Individuals with pathologic neuronal alpha-synuclein aggregates are at a high risk for dopaminergic neuronal dysfunction (D, the second key biological anchor).
Dr. Simuni and colleagues also proposed the NSD integrated staging system (NSD-ISS) rooted in the S and D biological anchors coupled with the degree of functional impairment caused by clinical signs or symptoms.
Stages 0-1 occur without signs or symptoms and are defined by the presence of pathogenic variants in the SNCA gene (stage 0), S alone (stage 1A), or S and D (stage 1B).
The presence of clinical manifestations marks the transition to stage 2 and beyond, with stage 2 characterized by subtle signs or symptoms but without functional impairment. Stages 2B-6 require both S and D and stage-specific increases in functional impairment.
“An advantage of the NSD-ISS will be to reduce heterogeneity in clinical trials by requiring biological consistency within the study cohort rather than identifying study participants on the basis of clinical criteria for Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies,” Dr. Simuni and colleagues pointed out in a position paper describing the NSD-ISS published online earlier this year in The Lancet Neurology.
The NSD-ISS will “evolve to include the incorporation of data-driven definitions of stage-specific functional anchors and additional biomarkers as they emerge and are validated.”
For now, the NSD-ISS is intended for research use only and not in the clinic.
The SynNeurGe Research Diagnostic Criteria
Separately, a team led by Anthony Lang, MD, with the Krembil Brain Institute at Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, proposed the SynNeurGe biological classification of PD.
Described in a companion paper published online in The Lancet Neurology, their “S-N-G” classification emphasizes the important interactions between three biological factors that contribute to disease: The presence or absence of pathologic alpha-synuclein (S) in tissues or CSF, an evidence of underlying neurodegeneration (N) defined by neuroimaging procedures, and the documentation of pathogenic gene variants (G) that cause or strongly predispose to PD.
These three components link to a clinical component, defined either by a single high-specificity clinical feature or by multiple lower-specificity clinical features.
As with the NSD-ISS, the SynNeurGe model is intended for research purposes only and is not ready for immediate application in the clinic.
Both groups acknowledged the need for studies to test and validate the proposed classification systems.
Caveats, Cautionary Notes
Adopting a biological definition of PD would represent a shift as the field has prompted considerable discussion and healthy debate.
Commenting for this news organization, James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer at the Parkinson’s Foundation, said the principle behind the proposed classifications is where “the field needs to go.”
“Right now, people with Parkinson’s take too long to get a confirmed diagnosis of their disease, and despite best efforts, clinicians can get it wrong, not diagnosing people or maybe misdiagnosing people,” Dr. Beck said. “Moving to a biological basis, where we have better certainty, is going to be really important.”
Beck noted that the NSD-ISS “goes all in on alpha-synuclein,” which does play a big role in PD, but added, “I don’t know if I want to declare a winner after the first heat. There are other biomarkers that are coming to fruition but still need validation, and alpha-synuclein may be just one of many to help determine whether someone has Parkinson’s disease or not.”
Un Kang, MD, director of translational research at the Fresco Institute for Parkinson’s & Movement Disorders at NYU Langone Health, New York City, told this news organization that alpha-synuclein has “very high diagnostic accuracy” but cautioned that the adoption of a biological definition for PD would not usurp a clinical diagnosis.
“We need both,” Dr. Kang said. “But knowing the underlying pathology is important for earlier diagnosis and testing of potential therapies to treat the molecular pathology. If a patient doesn’t have abnormal synuclein, you may be treating the wrong disease.”
The coauthors of recent JAMA Neurology perspective said the biological definitions are “exciting, but there is “wisdom” in tapping the brakes when attempting to establish a biological definition and classification system for PD.
“Although these two proposals represent significant steps forward, a sprint toward the finish line may not be wise,” wrote Njideka U. Okubadejo, MD, with University of Lagos, Nigeria; Joseph Jankovic, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston; and Michael S. Okun, MD, with University of Florida Health, Gainesville, Florida.
“A process that embraces inclusivity and weaves in evolving technological advancements will be important. Who benefits if implementation of a biologically based staging system for PD is hurried?” they continued.
The proposals rely heavily on alpha-synuclein assays, they noted, which currently require subjective interpretation and lack extensive validation. They also worry that the need for expensive and, in some regions, unattainable biological fluids (CSF) or imaging studies (dopamine transporter scan) may limit global access to both PD trials and future therapeutics.
They also worry about retiring the name Parkinson’s disease.
“Beyond the historical importance of the term Parkinson disease, any classification that proposes abandoning the two words in either clinical or research descriptions could have unintended global repercussions,” Dr. Okubadejo, Dr. Jankovic, and Dr. Okun cautioned.
Dr. Beck told this news organization he’s spoken to clinicians at meetings about this and “no one really likes the idea” of retiring the term Parkinson’s disease.
Frederick Ketchum, MD, and Nathaniel Chin, MD, with University of Wisconsin–Madison, worry about the “lived” experience of the asymptomatic patient after receiving a biological diagnosis.
“Biological diagnosis might enable effective prognostication and treatment in the future but will substantially change the experience of illness for patients now as new frameworks are slowly adopted and knowledge is gained,” they said in a correspondence in The Lancet Neurology.
“Understanding and addressing this lived experience remains a core task for health professionals and must be made central as we begin an era in which neurological diseases are redefined on a biological basis,” Dr. Ketchum and Dr. Chin advised.
A complete list of agencies that supported this work and author disclosures are available with the original articles. Dr. Beck and Dr. Kang had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study: AFib May Be Linked to Dementia in T2D
TOPLINE:
New-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a substantially higher risk for all-cause dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies suggest a potential link between AF and dementia in the broader population, but evidence is scarce in people with diabetes, who are at increased risk for both conditions.
- This longitudinal observational study assessed the association between new-onset AF and dementia in 22,989 patients with T2D (median age at enrollment, 61.0 years; 62.3% men; 86.3% White individuals).
- New-onset AF was identified through hospital admission records using the International Classification of Diseases – 9th Revision (ICD-9) and ICD-10 codes, and dementia cases were identified using an algorithm developed by the UK Biobank.
- Time-varying Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to determine the association between incident dementia and new-onset AF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up duration of about 12 years, 844 patients developed all-cause dementia, 342 were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, and 246 had vascular dementia.
- Patients with incident AF had a higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 2.15; 95% CI, 1.80-2.57), Alzheimer’s disease (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.06-1.96), and vascular dementia (HR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.32-4.17) than those without incident AF.
- The results are independent of common dementia risk factors, such as sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle factors.
- The mean time intervals from the onset of AF to all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia were 2.95, 2.81, and 3.37 years, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“AF is a significant risk factor for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes, suggesting the importance of timely and effective treatment of AF, such as early rhythm control strategies and anticoagulant use, in preventing dementia among this demographic,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ying Zhou, PhD, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study could not explore the link between different AF subtypes and dementia owing to its small sample size. The effects of AF treatment on the risk for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes were not considered because of lack of information. The mostly White study population limits the generalizability of the findings to other races and ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a substantially higher risk for all-cause dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies suggest a potential link between AF and dementia in the broader population, but evidence is scarce in people with diabetes, who are at increased risk for both conditions.
- This longitudinal observational study assessed the association between new-onset AF and dementia in 22,989 patients with T2D (median age at enrollment, 61.0 years; 62.3% men; 86.3% White individuals).
- New-onset AF was identified through hospital admission records using the International Classification of Diseases – 9th Revision (ICD-9) and ICD-10 codes, and dementia cases were identified using an algorithm developed by the UK Biobank.
- Time-varying Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to determine the association between incident dementia and new-onset AF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up duration of about 12 years, 844 patients developed all-cause dementia, 342 were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, and 246 had vascular dementia.
- Patients with incident AF had a higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 2.15; 95% CI, 1.80-2.57), Alzheimer’s disease (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.06-1.96), and vascular dementia (HR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.32-4.17) than those without incident AF.
- The results are independent of common dementia risk factors, such as sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle factors.
- The mean time intervals from the onset of AF to all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia were 2.95, 2.81, and 3.37 years, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“AF is a significant risk factor for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes, suggesting the importance of timely and effective treatment of AF, such as early rhythm control strategies and anticoagulant use, in preventing dementia among this demographic,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ying Zhou, PhD, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study could not explore the link between different AF subtypes and dementia owing to its small sample size. The effects of AF treatment on the risk for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes were not considered because of lack of information. The mostly White study population limits the generalizability of the findings to other races and ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a substantially higher risk for all-cause dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies suggest a potential link between AF and dementia in the broader population, but evidence is scarce in people with diabetes, who are at increased risk for both conditions.
- This longitudinal observational study assessed the association between new-onset AF and dementia in 22,989 patients with T2D (median age at enrollment, 61.0 years; 62.3% men; 86.3% White individuals).
- New-onset AF was identified through hospital admission records using the International Classification of Diseases – 9th Revision (ICD-9) and ICD-10 codes, and dementia cases were identified using an algorithm developed by the UK Biobank.
- Time-varying Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to determine the association between incident dementia and new-onset AF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up duration of about 12 years, 844 patients developed all-cause dementia, 342 were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, and 246 had vascular dementia.
- Patients with incident AF had a higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 2.15; 95% CI, 1.80-2.57), Alzheimer’s disease (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.06-1.96), and vascular dementia (HR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.32-4.17) than those without incident AF.
- The results are independent of common dementia risk factors, such as sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle factors.
- The mean time intervals from the onset of AF to all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia were 2.95, 2.81, and 3.37 years, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“AF is a significant risk factor for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes, suggesting the importance of timely and effective treatment of AF, such as early rhythm control strategies and anticoagulant use, in preventing dementia among this demographic,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ying Zhou, PhD, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study could not explore the link between different AF subtypes and dementia owing to its small sample size. The effects of AF treatment on the risk for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes were not considered because of lack of information. The mostly White study population limits the generalizability of the findings to other races and ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Trial of Impella Heart Pump Stopped
An international trial of the Impella heart pump in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and cardiogenic shock has been stopped by the sponsor, Abiomed Inc. The termination followed news that another international trial, DanGer Shock, found that the pump improved survival in these patients.
“I was convinced that the study could not continue,” one of the principal investigators William O’Neill, MD, an interventional cardiologist with the Henry Ford Health in Detroit, said in an interview. After 3.5 years of work and thousands of person-hours, he added, “It’s not a decision that people took lightly.”
The trial already had three sites in Europe and one in the United States up and running, with two more US sites slated to join the trial. It had started enrolling patients, although few to date.
DanGer Shock trial results were expected to have a serious effect on how RECOVER IV would unfold. It was previously uncertain whether the Impella heart pump would save lives vs existing approaches, said O’Neill and co-principal investigator Navin Kapur, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Tufts Medical Center in Boston. Once the DanGer Shock trial showed the benefits of using the heart pump, that equipoise vanished.
Loss of Clinical Equipoise
“The clinicians were challenged in getting consent from patients where they had to say, ‘If you are randomized to the control arm, we are not able to use an Impella,’ ” said Dr. Kapur. He pointed out that patients would be unlikely to agree to participate in a trial where they might not get the treatment already shown to improve survival.
Dr. Kapur and Dr. O’Neill said the clinicians participating in the trial expressed discomfort at continuing. The RECOVER IV trial was expected to take many years to enroll the targeted number of patients. To participate, hospitals had to have the equipment and expertise to use the Impella heart pump, as well as the control treatments — balloon-pump support and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), Dr. Kapur explained. He said most patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock would present to their nearest community hospitals, many of which would not have these treatments and would be unable to participate in the study.
Patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock are uncommon. About 80,000 patients in the United States each year present with cardiogenic shock, of whom about 40% are not experiencing a STEMI, said Dr. O’Neill.
But those who do fit into the population of both STEMI and cardiogenic shock are at very high risk, said Dr. Kapur. “One in three or one in two patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock will die in hospital.”
Getting Hearts Pumping
The Impella heart pump was originally developed by Impella Cardiosystems in Aachen, Germany, which was acquired by Abiomed in 2005, according to the Abiomed website. And Abiomed was acquired by Johnson & Johnson MedTech in 2022. The company has developed a series of models over the years and said that Impella CP — the model used in DanGer Shock and RECOVER IV trials — is the world’s smallest heart pump.
“Impella is the only heart pump that can be introduced percutaneously through the leg,” said Dr. O’Neill, whereas other pumps available are used only in open-heart surgery. While Impella is the first pump to be used this way, he said it won’t be the last. Other, more powerful pumps are being developed.
DanGer Shock: A Leap Forward
Despite leading to the halt of another trial, the DanGer Shock results are a good news story, said the RECOVER IV investigators.
“The DanGer trial is a huge advance,” said Dr. O’Neill. “It’s the first study this century that shows something that improves survival in cardiogenic shock. You treat eight patients, and you save one life.” Dr. O’Neill said this is one of the best outcomes he has seen during his long career.
Dr. Kapur said the DanGer trial is also a leap forward in designing trials for cardiogenic shock. He said previous trials of mechanical support in cardiogenic shock had neutral results, probably due to broad inclusion criteria for patients.
“The DanGer trial was selective in its inclusion and exclusion criteria. That made it more difficult to enroll the population, so it took a lot longer. But it used the right device at the right time in the right patient, and it was successful,” he said.
“The DanGer investigators need to be applauded,” he added. “The lesson is, we have to design the right trials.”
New Cardiogenic Shock Trials
Dr. O’Neill and Dr. Kapur said the groundwork they laid for RECOVER IV can be used for new trials.
“We have 50 sites in the US, Germany, and Denmark. They’re interested, and they’re waiting,” said Dr. O’Neill. The researchers are poised to begin new trials once protocols are developed.
What will the next trials investigate?
DanGer Shock results showed higher rates of adverse events following Impella use than after standard care. “We need to come up with strategies to decrease bleeding problems and renal failure,” said Dr. O’Neill, and these could be tested in trials.
Other questions he would like to see investigated are using the Impella heart pump before or after angioplasty, and multi-vessel vs culprit-vessel percutaneous coronary intervention in cardiogenic shock with Impella support.
Dr. Kapur mentioned studying patients excluded from the DanGer Shock trial — such as those needing right ventricular support — because DanGer Shock covered only left ventricular support and those suffering cardiac arrest outside hospital. He said trials could compare differences between models of Impella and investigate the role of ECMO.
“I’m optimistic that we can design more randomized controlled trials with the right patient population and right treatment algorithm,” Dr. Kapur said. This is a critical step toward better outcomes for patients, he added. Another step is optimizing the design of heart pumps, which should decrease the rates of adverse events, he said. “I have a lot of optimism for the future of device design.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An international trial of the Impella heart pump in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and cardiogenic shock has been stopped by the sponsor, Abiomed Inc. The termination followed news that another international trial, DanGer Shock, found that the pump improved survival in these patients.
“I was convinced that the study could not continue,” one of the principal investigators William O’Neill, MD, an interventional cardiologist with the Henry Ford Health in Detroit, said in an interview. After 3.5 years of work and thousands of person-hours, he added, “It’s not a decision that people took lightly.”
The trial already had three sites in Europe and one in the United States up and running, with two more US sites slated to join the trial. It had started enrolling patients, although few to date.
DanGer Shock trial results were expected to have a serious effect on how RECOVER IV would unfold. It was previously uncertain whether the Impella heart pump would save lives vs existing approaches, said O’Neill and co-principal investigator Navin Kapur, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Tufts Medical Center in Boston. Once the DanGer Shock trial showed the benefits of using the heart pump, that equipoise vanished.
Loss of Clinical Equipoise
“The clinicians were challenged in getting consent from patients where they had to say, ‘If you are randomized to the control arm, we are not able to use an Impella,’ ” said Dr. Kapur. He pointed out that patients would be unlikely to agree to participate in a trial where they might not get the treatment already shown to improve survival.
Dr. Kapur and Dr. O’Neill said the clinicians participating in the trial expressed discomfort at continuing. The RECOVER IV trial was expected to take many years to enroll the targeted number of patients. To participate, hospitals had to have the equipment and expertise to use the Impella heart pump, as well as the control treatments — balloon-pump support and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), Dr. Kapur explained. He said most patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock would present to their nearest community hospitals, many of which would not have these treatments and would be unable to participate in the study.
Patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock are uncommon. About 80,000 patients in the United States each year present with cardiogenic shock, of whom about 40% are not experiencing a STEMI, said Dr. O’Neill.
But those who do fit into the population of both STEMI and cardiogenic shock are at very high risk, said Dr. Kapur. “One in three or one in two patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock will die in hospital.”
Getting Hearts Pumping
The Impella heart pump was originally developed by Impella Cardiosystems in Aachen, Germany, which was acquired by Abiomed in 2005, according to the Abiomed website. And Abiomed was acquired by Johnson & Johnson MedTech in 2022. The company has developed a series of models over the years and said that Impella CP — the model used in DanGer Shock and RECOVER IV trials — is the world’s smallest heart pump.
“Impella is the only heart pump that can be introduced percutaneously through the leg,” said Dr. O’Neill, whereas other pumps available are used only in open-heart surgery. While Impella is the first pump to be used this way, he said it won’t be the last. Other, more powerful pumps are being developed.
DanGer Shock: A Leap Forward
Despite leading to the halt of another trial, the DanGer Shock results are a good news story, said the RECOVER IV investigators.
“The DanGer trial is a huge advance,” said Dr. O’Neill. “It’s the first study this century that shows something that improves survival in cardiogenic shock. You treat eight patients, and you save one life.” Dr. O’Neill said this is one of the best outcomes he has seen during his long career.
Dr. Kapur said the DanGer trial is also a leap forward in designing trials for cardiogenic shock. He said previous trials of mechanical support in cardiogenic shock had neutral results, probably due to broad inclusion criteria for patients.
“The DanGer trial was selective in its inclusion and exclusion criteria. That made it more difficult to enroll the population, so it took a lot longer. But it used the right device at the right time in the right patient, and it was successful,” he said.
“The DanGer investigators need to be applauded,” he added. “The lesson is, we have to design the right trials.”
New Cardiogenic Shock Trials
Dr. O’Neill and Dr. Kapur said the groundwork they laid for RECOVER IV can be used for new trials.
“We have 50 sites in the US, Germany, and Denmark. They’re interested, and they’re waiting,” said Dr. O’Neill. The researchers are poised to begin new trials once protocols are developed.
What will the next trials investigate?
DanGer Shock results showed higher rates of adverse events following Impella use than after standard care. “We need to come up with strategies to decrease bleeding problems and renal failure,” said Dr. O’Neill, and these could be tested in trials.
Other questions he would like to see investigated are using the Impella heart pump before or after angioplasty, and multi-vessel vs culprit-vessel percutaneous coronary intervention in cardiogenic shock with Impella support.
Dr. Kapur mentioned studying patients excluded from the DanGer Shock trial — such as those needing right ventricular support — because DanGer Shock covered only left ventricular support and those suffering cardiac arrest outside hospital. He said trials could compare differences between models of Impella and investigate the role of ECMO.
“I’m optimistic that we can design more randomized controlled trials with the right patient population and right treatment algorithm,” Dr. Kapur said. This is a critical step toward better outcomes for patients, he added. Another step is optimizing the design of heart pumps, which should decrease the rates of adverse events, he said. “I have a lot of optimism for the future of device design.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An international trial of the Impella heart pump in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and cardiogenic shock has been stopped by the sponsor, Abiomed Inc. The termination followed news that another international trial, DanGer Shock, found that the pump improved survival in these patients.
“I was convinced that the study could not continue,” one of the principal investigators William O’Neill, MD, an interventional cardiologist with the Henry Ford Health in Detroit, said in an interview. After 3.5 years of work and thousands of person-hours, he added, “It’s not a decision that people took lightly.”
The trial already had three sites in Europe and one in the United States up and running, with two more US sites slated to join the trial. It had started enrolling patients, although few to date.
DanGer Shock trial results were expected to have a serious effect on how RECOVER IV would unfold. It was previously uncertain whether the Impella heart pump would save lives vs existing approaches, said O’Neill and co-principal investigator Navin Kapur, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Tufts Medical Center in Boston. Once the DanGer Shock trial showed the benefits of using the heart pump, that equipoise vanished.
Loss of Clinical Equipoise
“The clinicians were challenged in getting consent from patients where they had to say, ‘If you are randomized to the control arm, we are not able to use an Impella,’ ” said Dr. Kapur. He pointed out that patients would be unlikely to agree to participate in a trial where they might not get the treatment already shown to improve survival.
Dr. Kapur and Dr. O’Neill said the clinicians participating in the trial expressed discomfort at continuing. The RECOVER IV trial was expected to take many years to enroll the targeted number of patients. To participate, hospitals had to have the equipment and expertise to use the Impella heart pump, as well as the control treatments — balloon-pump support and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), Dr. Kapur explained. He said most patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock would present to their nearest community hospitals, many of which would not have these treatments and would be unable to participate in the study.
Patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock are uncommon. About 80,000 patients in the United States each year present with cardiogenic shock, of whom about 40% are not experiencing a STEMI, said Dr. O’Neill.
But those who do fit into the population of both STEMI and cardiogenic shock are at very high risk, said Dr. Kapur. “One in three or one in two patients with STEMI and cardiogenic shock will die in hospital.”
Getting Hearts Pumping
The Impella heart pump was originally developed by Impella Cardiosystems in Aachen, Germany, which was acquired by Abiomed in 2005, according to the Abiomed website. And Abiomed was acquired by Johnson & Johnson MedTech in 2022. The company has developed a series of models over the years and said that Impella CP — the model used in DanGer Shock and RECOVER IV trials — is the world’s smallest heart pump.
“Impella is the only heart pump that can be introduced percutaneously through the leg,” said Dr. O’Neill, whereas other pumps available are used only in open-heart surgery. While Impella is the first pump to be used this way, he said it won’t be the last. Other, more powerful pumps are being developed.
DanGer Shock: A Leap Forward
Despite leading to the halt of another trial, the DanGer Shock results are a good news story, said the RECOVER IV investigators.
“The DanGer trial is a huge advance,” said Dr. O’Neill. “It’s the first study this century that shows something that improves survival in cardiogenic shock. You treat eight patients, and you save one life.” Dr. O’Neill said this is one of the best outcomes he has seen during his long career.
Dr. Kapur said the DanGer trial is also a leap forward in designing trials for cardiogenic shock. He said previous trials of mechanical support in cardiogenic shock had neutral results, probably due to broad inclusion criteria for patients.
“The DanGer trial was selective in its inclusion and exclusion criteria. That made it more difficult to enroll the population, so it took a lot longer. But it used the right device at the right time in the right patient, and it was successful,” he said.
“The DanGer investigators need to be applauded,” he added. “The lesson is, we have to design the right trials.”
New Cardiogenic Shock Trials
Dr. O’Neill and Dr. Kapur said the groundwork they laid for RECOVER IV can be used for new trials.
“We have 50 sites in the US, Germany, and Denmark. They’re interested, and they’re waiting,” said Dr. O’Neill. The researchers are poised to begin new trials once protocols are developed.
What will the next trials investigate?
DanGer Shock results showed higher rates of adverse events following Impella use than after standard care. “We need to come up with strategies to decrease bleeding problems and renal failure,” said Dr. O’Neill, and these could be tested in trials.
Other questions he would like to see investigated are using the Impella heart pump before or after angioplasty, and multi-vessel vs culprit-vessel percutaneous coronary intervention in cardiogenic shock with Impella support.
Dr. Kapur mentioned studying patients excluded from the DanGer Shock trial — such as those needing right ventricular support — because DanGer Shock covered only left ventricular support and those suffering cardiac arrest outside hospital. He said trials could compare differences between models of Impella and investigate the role of ECMO.
“I’m optimistic that we can design more randomized controlled trials with the right patient population and right treatment algorithm,” Dr. Kapur said. This is a critical step toward better outcomes for patients, he added. Another step is optimizing the design of heart pumps, which should decrease the rates of adverse events, he said. “I have a lot of optimism for the future of device design.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mounjaro Beats Ozempic, So Why Isn’t It More Popular?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.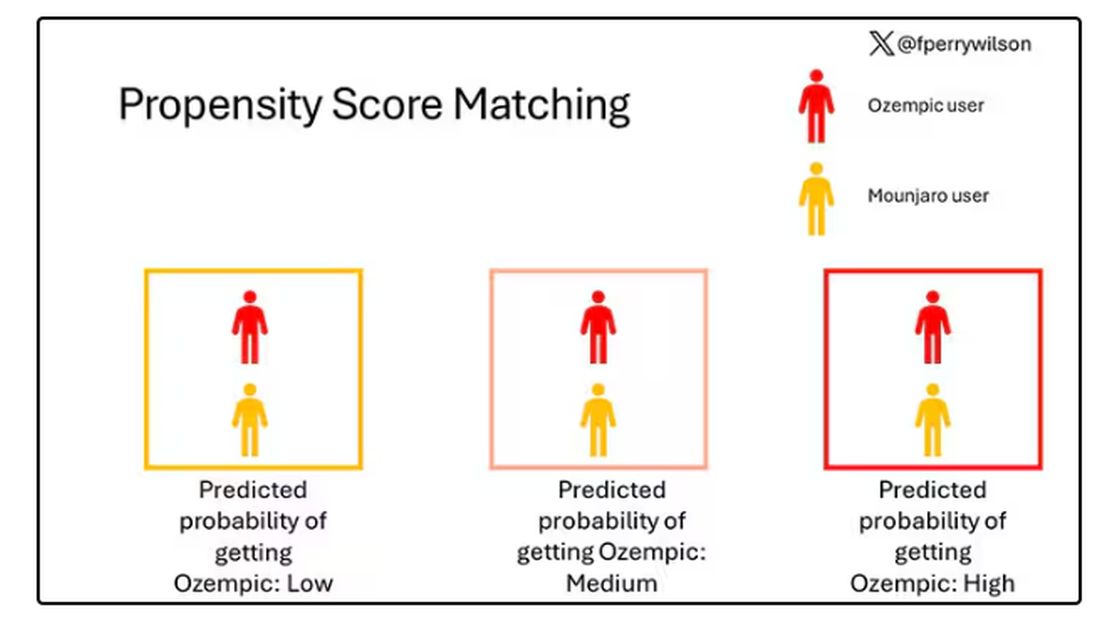
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.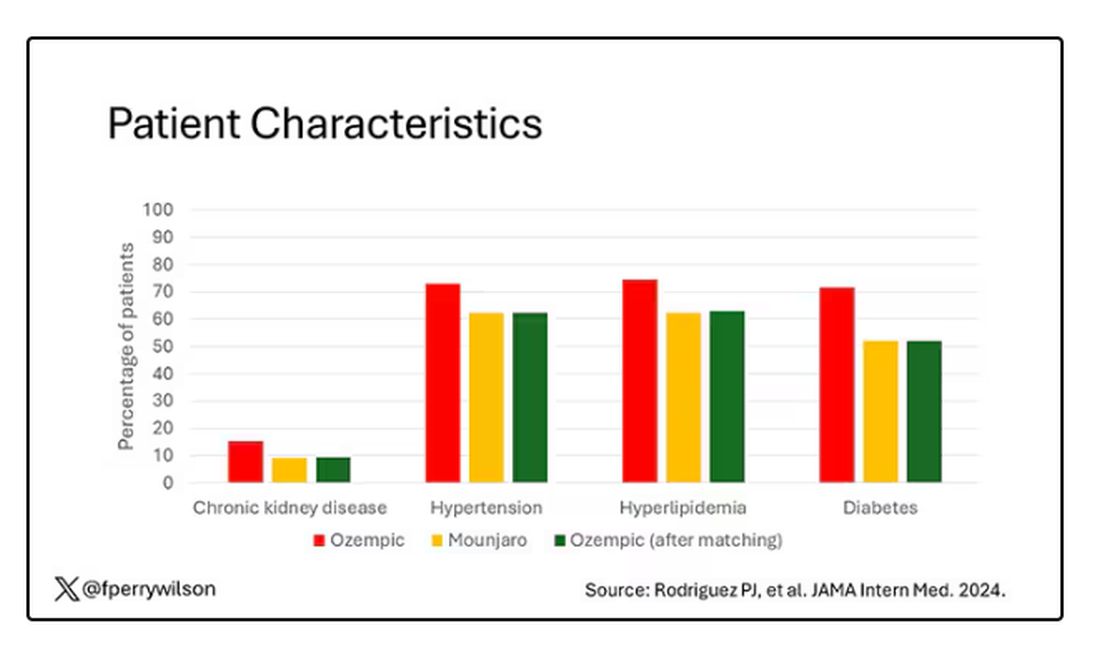
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 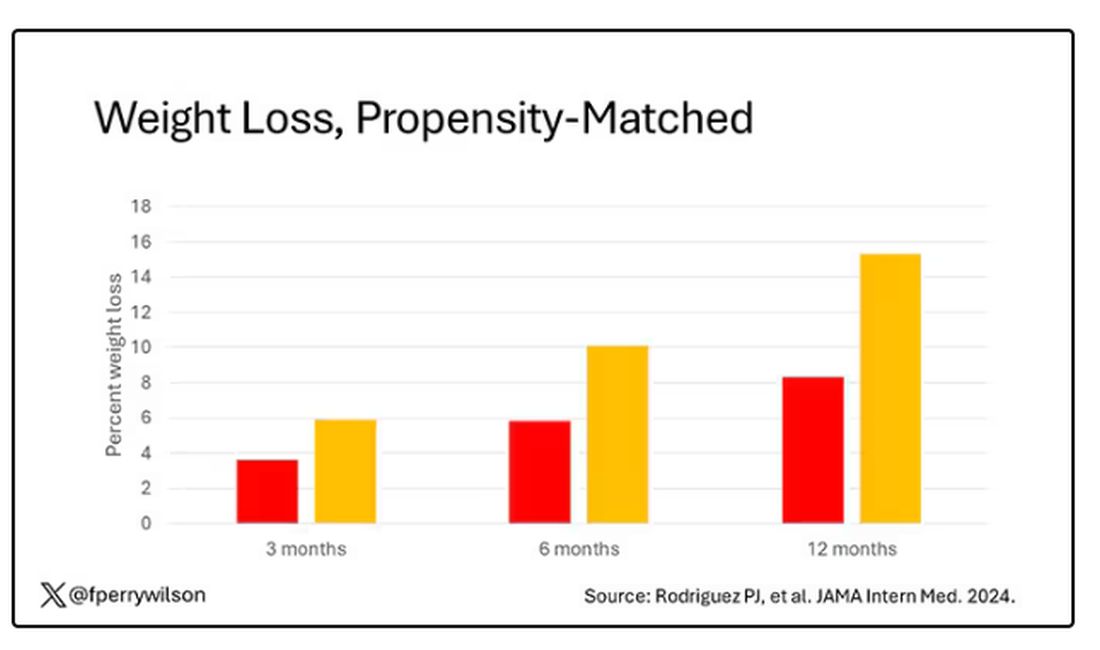
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.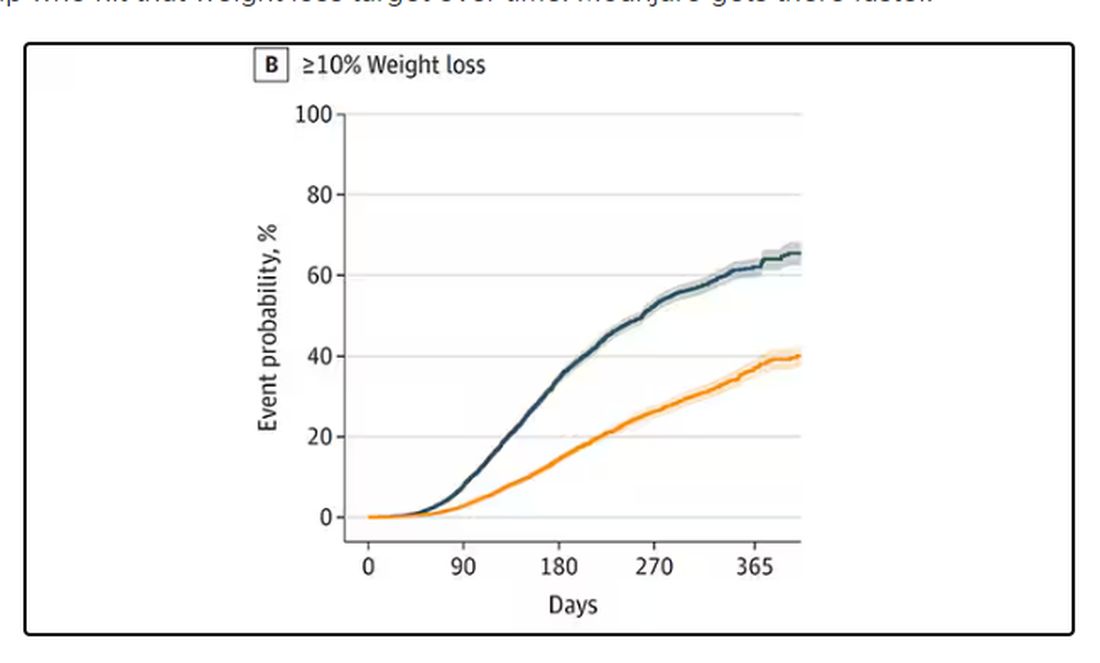
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic Neck Pain: A Primary Care Approach
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Medicare Enrollment Raise Diabetes Medication Costs?
TOPLINE:
Reaching age 65 years and enrolling in Medicare is associated with a $23 increase in quarterly out-of-pocket costs for type 2 diabetes (T2D) medications. Medication usage decreased by 5.3%, with a notable shift toward more expensive insulin use.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using 2012-2020 prescription drug claims data from the TriNetX Diamond Network.
- A total of 129,997 individuals diagnosed with T2D were included, with claims observed both before and after age 65 years.
- The primary outcome was patient out-of-pocket costs for T2D drugs per quarter, adjusted to 2020 dollars.
- Drugs measured included biguanides (metformin), sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, insulin, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2 inhibitors), and amylin analogs, among others.
- Regression discontinuity design was used to examine the outcomes, adjusting for differential linear quarterly time trends, year fixed effects, and utilization composition and intensity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Reaching age 65 years was associated with an increase of $23.04 in mean quarterly out-of-pocket costs for T2D drugs (95% confidence interval [CI], $19.86-$26.22).
- The 95th percentile of out-of-pocket spending increased by $56.36 (95% CI, $51.48-$61.23) after utilization adjustment.
- T2D medication usage decreased by 5.3% at age 65 years, from 3.40 claims per quarter to 3.22 claims per quarter.
- Higher out-of-pockets were associated with insulin use, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1s, and SGLT2 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results have important implications for the provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act, many of which aim to reduce these costs. Reduced patient cost burden will improve adherence and the management of type 2 diabetes, likely leading to reductions in T2D complications,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Douglas Barthold, PhD, Jing Li, MA, PhD, and Anirban Basu, MS, PhD, at the Comparative Health Outcomes, Policy, and Economics Institute, School of Pharmacy, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations include the possibility that not all claims of an individual were observed, as TriNetX claims data may not capture individuals who leave the healthcare system or have inaccurate or changing diagnoses. Additionally, the data lack individual-level insurance characteristics. The assumption that individuals transition to Medicare at age 65 years may not be true for all participants. The study also lacks clinical information regarding the severity of T2D, which could influence medication usage and out-of-pocket costs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) and the University of Washington’s Population Health Initiative, Student Technology Fee program, and Provost’s office. Dr. Barthold and Dr. Li received grants from the NIA. Dr. Basu reported receiving personal fees from Salutis Consulting LLC outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Reaching age 65 years and enrolling in Medicare is associated with a $23 increase in quarterly out-of-pocket costs for type 2 diabetes (T2D) medications. Medication usage decreased by 5.3%, with a notable shift toward more expensive insulin use.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using 2012-2020 prescription drug claims data from the TriNetX Diamond Network.
- A total of 129,997 individuals diagnosed with T2D were included, with claims observed both before and after age 65 years.
- The primary outcome was patient out-of-pocket costs for T2D drugs per quarter, adjusted to 2020 dollars.
- Drugs measured included biguanides (metformin), sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, insulin, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2 inhibitors), and amylin analogs, among others.
- Regression discontinuity design was used to examine the outcomes, adjusting for differential linear quarterly time trends, year fixed effects, and utilization composition and intensity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Reaching age 65 years was associated with an increase of $23.04 in mean quarterly out-of-pocket costs for T2D drugs (95% confidence interval [CI], $19.86-$26.22).
- The 95th percentile of out-of-pocket spending increased by $56.36 (95% CI, $51.48-$61.23) after utilization adjustment.
- T2D medication usage decreased by 5.3% at age 65 years, from 3.40 claims per quarter to 3.22 claims per quarter.
- Higher out-of-pockets were associated with insulin use, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1s, and SGLT2 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results have important implications for the provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act, many of which aim to reduce these costs. Reduced patient cost burden will improve adherence and the management of type 2 diabetes, likely leading to reductions in T2D complications,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Douglas Barthold, PhD, Jing Li, MA, PhD, and Anirban Basu, MS, PhD, at the Comparative Health Outcomes, Policy, and Economics Institute, School of Pharmacy, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations include the possibility that not all claims of an individual were observed, as TriNetX claims data may not capture individuals who leave the healthcare system or have inaccurate or changing diagnoses. Additionally, the data lack individual-level insurance characteristics. The assumption that individuals transition to Medicare at age 65 years may not be true for all participants. The study also lacks clinical information regarding the severity of T2D, which could influence medication usage and out-of-pocket costs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) and the University of Washington’s Population Health Initiative, Student Technology Fee program, and Provost’s office. Dr. Barthold and Dr. Li received grants from the NIA. Dr. Basu reported receiving personal fees from Salutis Consulting LLC outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Reaching age 65 years and enrolling in Medicare is associated with a $23 increase in quarterly out-of-pocket costs for type 2 diabetes (T2D) medications. Medication usage decreased by 5.3%, with a notable shift toward more expensive insulin use.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using 2012-2020 prescription drug claims data from the TriNetX Diamond Network.
- A total of 129,997 individuals diagnosed with T2D were included, with claims observed both before and after age 65 years.
- The primary outcome was patient out-of-pocket costs for T2D drugs per quarter, adjusted to 2020 dollars.
- Drugs measured included biguanides (metformin), sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, insulin, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2 inhibitors), and amylin analogs, among others.
- Regression discontinuity design was used to examine the outcomes, adjusting for differential linear quarterly time trends, year fixed effects, and utilization composition and intensity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Reaching age 65 years was associated with an increase of $23.04 in mean quarterly out-of-pocket costs for T2D drugs (95% confidence interval [CI], $19.86-$26.22).
- The 95th percentile of out-of-pocket spending increased by $56.36 (95% CI, $51.48-$61.23) after utilization adjustment.
- T2D medication usage decreased by 5.3% at age 65 years, from 3.40 claims per quarter to 3.22 claims per quarter.
- Higher out-of-pockets were associated with insulin use, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1s, and SGLT2 inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results have important implications for the provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act, many of which aim to reduce these costs. Reduced patient cost burden will improve adherence and the management of type 2 diabetes, likely leading to reductions in T2D complications,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Douglas Barthold, PhD, Jing Li, MA, PhD, and Anirban Basu, MS, PhD, at the Comparative Health Outcomes, Policy, and Economics Institute, School of Pharmacy, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations include the possibility that not all claims of an individual were observed, as TriNetX claims data may not capture individuals who leave the healthcare system or have inaccurate or changing diagnoses. Additionally, the data lack individual-level insurance characteristics. The assumption that individuals transition to Medicare at age 65 years may not be true for all participants. The study also lacks clinical information regarding the severity of T2D, which could influence medication usage and out-of-pocket costs.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) and the University of Washington’s Population Health Initiative, Student Technology Fee program, and Provost’s office. Dr. Barthold and Dr. Li received grants from the NIA. Dr. Basu reported receiving personal fees from Salutis Consulting LLC outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tackling Inflammatory and Infectious Nail Disorders in Children
Nail disorders are common among pediatric patients but often are underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed because of their unique disease manifestations. These conditions may severely impact quality of life. There are few nail disease clinical trials that include children. Consequently, most treatment recommendations are based on case series and expert consensus recommendations. We review inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in pediatric patients. By describing characteristics, clinical manifestations, and management approaches for these conditions, we aim to provide guidance to dermatologists in their diagnosis and treatment.
INFLAMMATORY NAIL DISORDERS
Nail Psoriasis
Nail involvement in children with psoriasis is common, with prevalence estimates ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail matrix psoriasis may manifest with pitting (large irregular pits) and leukonychia as well as chromonychia and nail plate crumbling. Onycholysis, oil drop spots (salmon patches), and subungual hyperkeratosis can be seen in nail bed psoriasis. Nail pitting is the most frequently observed clinical finding (Figure 1).2,3 In a cross-sectional multicenter study of 313 children with cutaneous psoriasis in France, nail findings were present in 101 patients (32.3%). There were associations between nail findings and presence of psoriatic arthritis (P=.03), palmoplantar psoriasis (P<.001), and severity of psoriatic disease, defined as use of systemic treatment with phototherapy (psoralen plus UVA, UVB), traditional systemic treatment (acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporine), or a biologic (P=.003).4
Topical steroids and vitamin D analogues may be used with or without occlusion and may be efficacious.5 Several case reports describe systemic treatments for psoriasis in children, including methotrexate, acitretin, and apremilast (approved for children 6 years and older for plaque psoriasis by the US Food and Drug Administration [FDA]).2 There are 5 biologic drugs currently approved for the treatment of pediatric psoriasis—adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab—and 6 drugs currently undergoing phase 3 studies—brodalumab, guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, certolizumab pegol, and deucravacitinib (Table 1).6-15 Adalimumab is specifically approved for moderate to severe nail psoriasis in adults 18 years and older.
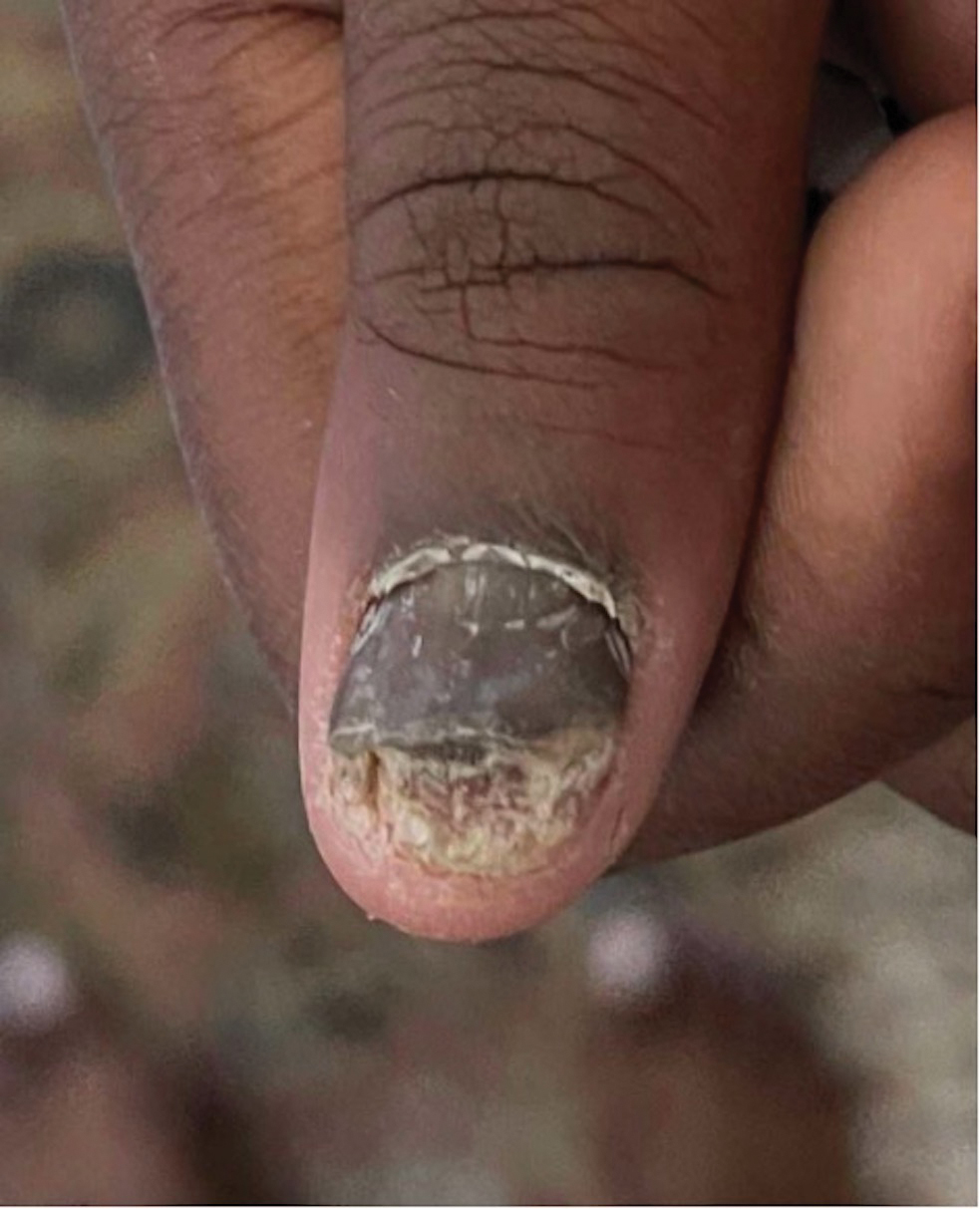
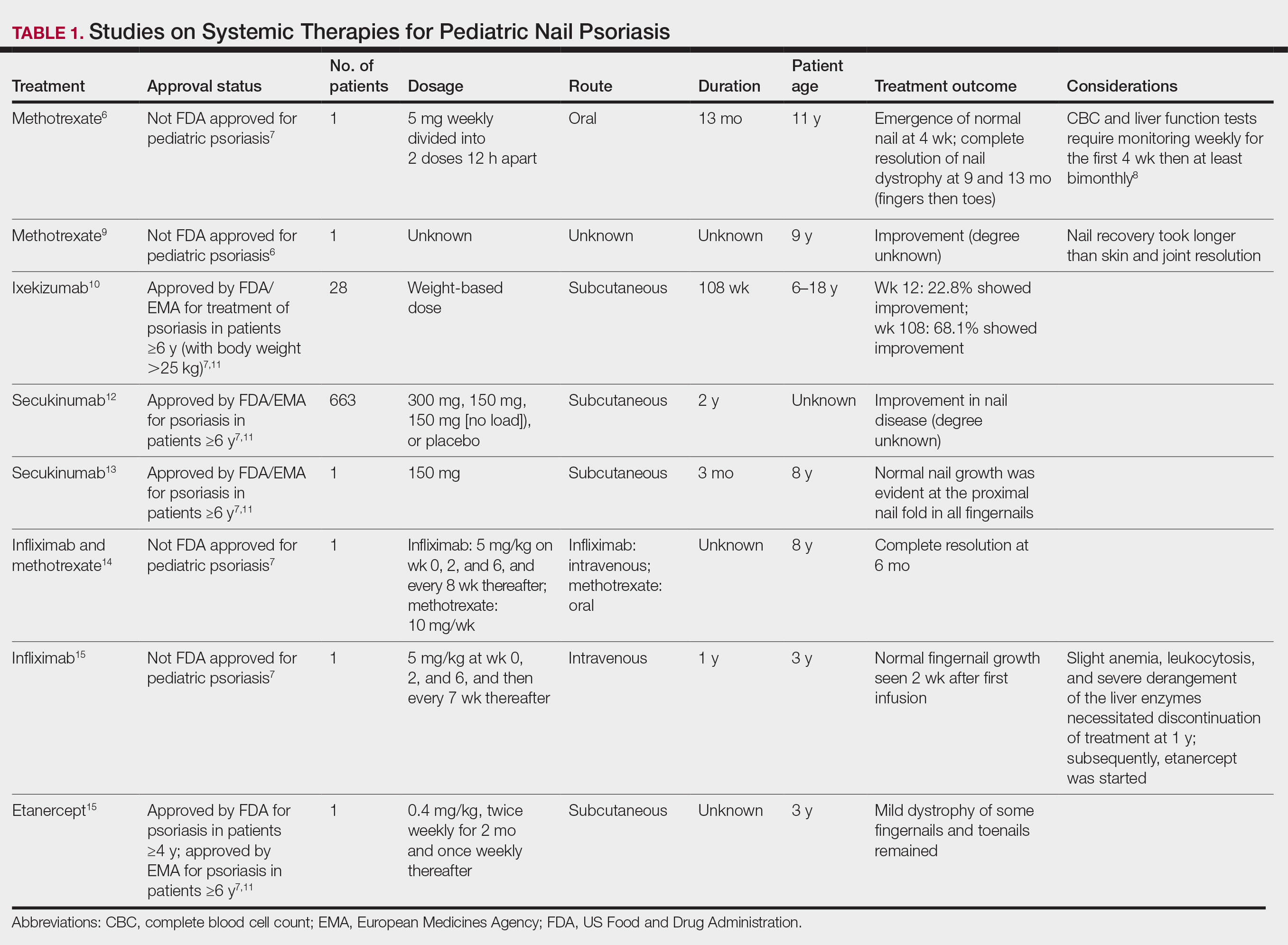
Intralesional steroid injections are sometimes useful in the management of nail matrix psoriasis; however, appropriate patient selection is critical due to the pain associated with the procedure. In a prospective study of 16 children (age range, 9–17 years) with nail psoriasis treated with intralesional triamcinolone (ILTAC) 2.5 to 5 mg/mL every 4 to 8 weeks for a minimum of 3 to 6 months, 9 patients achieved resolution and 6 had improvement of clinical findings.16 Local adverse events were mild, including injection-site pain (66%), subungual hematoma (n=1), Beau lines (n=1), proximal nail fold hypopigmentation (n=2), and proximal nail fold atrophy (n=2). Because the proximal nail fold in children is thinner than in adults, there may be an increased risk for nail fold hypopigmentation and atrophy in children. Therefore, a maximum ILTAC concentration of 2.5 mg/mL with 0.2 mL maximum volume per nail per session is recommended for children younger than 15 years.16
Nail Lichen Planus
Nail lichen planus (NLP) is uncommon in children, with few biopsy-proven cases documented in the literature.17 Common clinical findings are onychorrhexis, nail plate thinning, fissuring, splitting, and atrophy with koilonychia.5 Although pterygium development (irreversible nail matrix scarring) is uncommon in pediatric patients, NLP can be progressive and may cause irreversible destruction of the nail matrix and subsequent nail loss, warranting therapeutic intervention.18
Treatment of NLP may be difficult, as there are no options that work in all patients. Current literature supports the use of systemic corticosteroids or ILTAC for the treatment of NLP; however, recurrence rates can be high. According to an expert consensus paper on NLP treatment, ILTAC may be injected in a concentration of 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/mL according to disease severity.19 In severe or resistant cases, intramuscular (IM) triamcinolone may be considered, especially if more than 3 nails are affected. A dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/mo for at least 3 to 6 months is recommended for both children and adults, with 1 mg/kg/mo recommended in the active treatment phase (first 2–3 months).19 In a retrospective review of 5 pediatric patients with NLP treated with IM triamcinolone 0.5 mg/kg/mo, 3 patients had resolution and 2 improved with treatment.20 In a prospective study of 10 children with NLP, IM triamcinolone at a dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg every 30 days for 3 to 6 months resulted in resolution of nail findings in 9 patients.17 In a prospective study of 14 pediatric patients with NLP treated with 2.5 to 5 mg/mL of ILTAC, 10 achieved resolution and 3 improved.16
Intralesional triamcinolone injections may be better suited for teenagers compared to younger children who may be more apprehensive of needles. To minimize pain, it is recommended to inject ILTAC slowly at room temperature, with use of “talkesthesia” and vibration devices, 1% lidocaine, or ethyl chloride spray.18
Trachyonychia
Trachyonychia is characterized by the presence of sandpaperlike nails. It manifests with brittle thin nails with longitudinal ridging, onychoschizia, and thickened hyperkeratotic cuticles. Trachyonychia typically involves multiple nails, with a peak age of onset between 3 and 12 years.21,22 There are 2 variants: the opaque type with rough longitudinal ridging, and the shiny variant with opalescent nails and pits that reflect light. The opaque variant is more common and is associated with psoriasis, whereas the shiny variant is less common and is associated with alopecia areata.23 Although most cases are idiopathic, some are associated with psoriasis and alopecia areata, as previously noted, as well as atopic dermatitis (AD) and lichen planus.22,24
Fortunately, trachyonychia does not lead to permanent nail damage or pterygium, making treatment primarily focused on addressing functional and cosmetic concerns.24 Spontaneous resolution occurs in approximately 50% of patients. In a prospective study of 11 patients with idiopathic trachyonychia, there was partial improvement in 5 of 9 patients treated with topical steroids, 1 with only petrolatum, and 1 with vitamin supplements. Complete resolution was reported in 1 patient treated with topical steroids.25 Because trachyonychia often is self-resolving, no treatment is required and a conservative approach is strongly recommended.26 Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and 5-fluorouracil. Intralesional triamcinolone, systemic cyclosporine, retinoids, systemic corticosteroids, and tofacitinib have been described in case reports, though none of these have been shown to be 100% efficacious.24
Nail Lichen Striatus
Lichen striatus involving the nail is uncommon and is characterized by onycholysis, longitudinal ridging, splitting, and fraying, as well as what appears to be a subungual tumor. It can encompass the entire nail or may be isolated to a portion of the nail (Figure 2). Usually, a Blaschko-linear array of flesh-colored papules on the more proximal digit directly adjacent to the nail dystrophy will be seen, though nail findings can occur in isolation.27-29 The underlying pathophysiology is not clear; however, one hypothesis is that a triggering event, such as trauma, induces the expression of antigens that elicit a self-limiting immune-mediated response by CD8 T lymphocytes.30
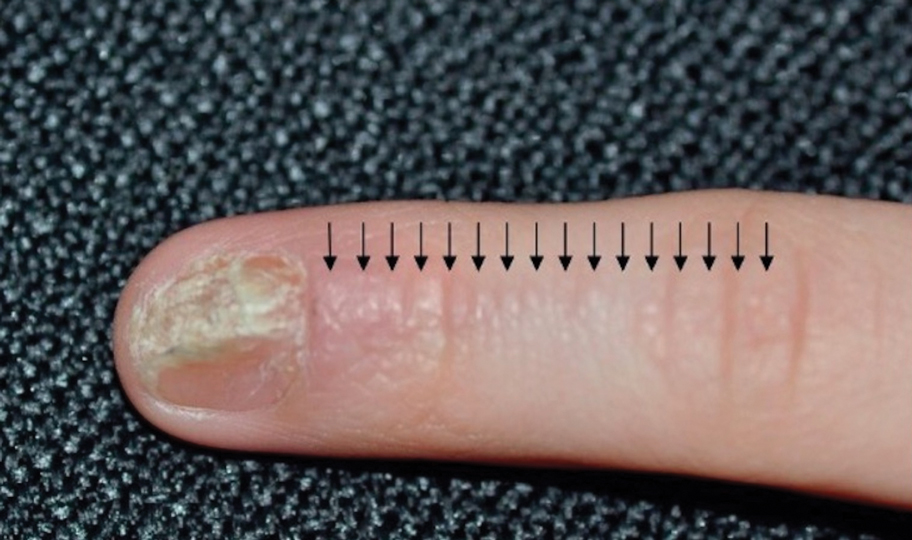
Generally, nail lichen striatus spontaneously resolves in 1 to 2 years without treatment. In a prospective study of 5 patients with nail lichen striatus, the median time to resolution was 22.6 months (range, 10–30 months).31 Topical steroids may be used for pruritus. In one case report, a 3-year-old boy with nail lichen striatus of 4 months’ duration was treated with tacrolimus ointment 0.03% daily for 3 months.28
Nail AD
Nail changes with AD may be more common in adults than children or are underreported. In a study of 777 adults with AD, nail dystrophy was present in 124 patients (16%), whereas in a study of 250 pediatric patients with AD (aged 0-2 years), nail dystrophy was present in only 4 patients.32,33
Periungual inflammation from AD causes the nail changes.34 In a cross-sectional study of 24 pediatric patients with nail dystrophy due to AD, transverse grooves (Beau lines) were present in 25% (6/24), nail pitting in 16.7% (4/24), koilonychia in 16.7% (4/24), trachyonychia in 12.5% (3/24), leukonychia in 12.5% (3/24), brachyonychia in 8.3% (2/24), melanonychia in 8.3% (2/24), onychomadesis in 8.3% (2/24), onychoschizia in 8.3% (2/24), and onycholysis in 8.3% (2/24). There was an association between disease severity and presence of toenail dystrophy (P=.03).35
Topical steroids with or without occlusion can be used to treat nail changes. Although there is limited literature describing the treatment of nail AD in children, a 61-year-old man with nail changes associated with AD achieved resolution with 3 months of treatment with dupilumab.36 Anecdotally, most patients will improve with usual cutaneous AD management.
INFECTIOUS NAIL DISORDERS
Viral Infections
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease—Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood viral infection caused by various enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16, with the A6 variant causing more severe disease. Fever and painful vesicles involving the oral mucosa as well as palms and soles give the disease its name. Nail changes are common. In a prospective study involving 130 patients with laboratory-confirmed coxsackievirus CA6 serotype infection, 37% developed onychomadesis vs only 5% of 145 cases with non-CA6 enterovirus infection who developed nail findings. There was an association between CA6 infection and presence of nail changes (P<.001).37
Findings ranging from transverse grooves (Beau lines) to complete nail shedding (onychomadesis)(Figure 3) may be seen.38,39 Nail findings in HFMD are due to transient inhibition of nail growth and present approximately 3 to 6 weeks after infection.40 Onychomadesis is seen in 30% to 68% of patients with HFMD.37,41,42 Nail findings in HFMD spontaneously resolve with nail growth (2–3 mm per month for fingernails and 1 mm per month for toenails) and do not require specific treatment. Although the appearance of nail changes associated with HFMD can be disturbing, dermatologists can reassure children and their parents that the nails will resolve with the next cycle of growth.
Kawasaki Disease—Kawasaki disease (KD) is a vasculitis primarily affecting children and infants. Although the specific pathogen and pathophysiology is not entirely clear, clinical observations have suggested an infectious cause, most likely a virus.43 In Japan, more than 15,000 cases of KD are documented annually, while approximately 4200 cases are seen in the United States.44 In a prospective study from 1984 to 1990, 4 of 26 (15.4%) patients with KD presented with nail manifestations during the late acute phase or early convalescent phase of disease. There were no significant associations between nail dystrophy and severity of KD, such as coronary artery aneurysm.45
Nail changes reported in children with KD include onychomadesis, onycholysis, orange-brown chromonychia, splinter hemorrhages, Beau lines, and pincer nails. In a review of nail changes associated with KD from 1980 to 2021, orange-brown transverse chromonychia, which may evolve into transverse leukonychia, was the most common nail finding reported, occurring in 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients.44 It has been hypothesized that nail changes may result from blood flow disturbance due to the underlying vasculitis.46 Nail changes appear several weeks after the onset of fever and are self-limited. Resolution occurs with nail growth, with no treatment required.
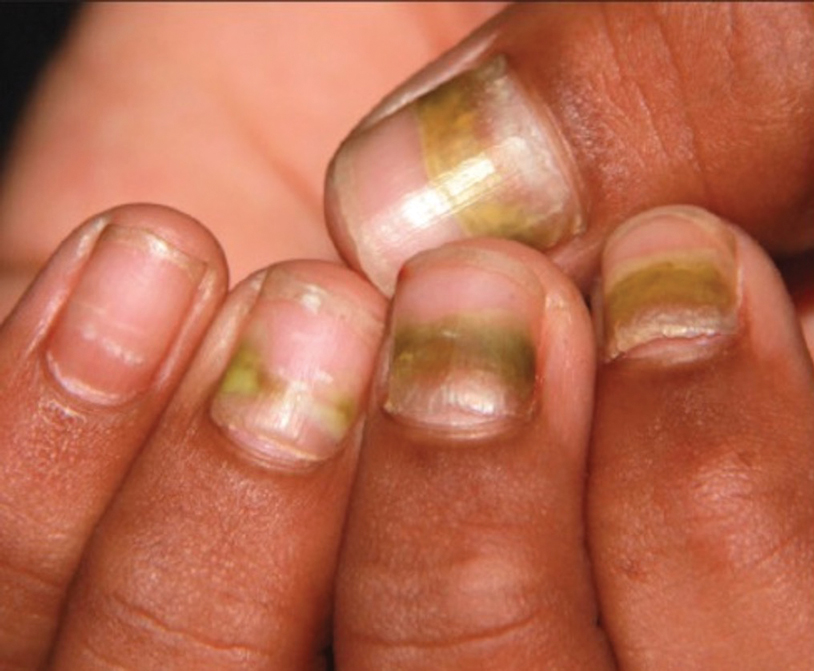
FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails that occurs in 0.2% to 5.5% of pediatric patients, and its prevalence may be increasing, which may be due to environmental factors or increased rates of diabetes mellitus and obesity in the pediatric population.47 Onychomycosis represents 15.5% of nail dystrophies in pediatric patients.48 Some dermatologists treat presumptive onychomycosis without confirmation; however, we do not recommend that approach. Because the differential is broad and the duration of treatment is long, mycologic examination (potassium hydroxide preparation, fungal culture, polymerase chain reaction, and/or histopathology) should be obtained to confirm onychomycosis prior to initiation of antifungal management. Family members of affected individuals should be evaluated and treated, if indicated, for onychomycosis and tinea pedis, as household transmission is common.
Currently, there are 2 topical FDA-approved treatments for pediatric onychomycosis in children 6 years and older (Table 2).49,50 There is a discussion of the need for confirmatory testing for onychomycosis in children, particularly when systemic treatment is prescribed. In a retrospective review of 269 pediatric patients with onychomycosis prescribed terbinafine, 53.5% (n=144) underwent laboratory monitoring of liver function and complete blood cell counts, and 12.5% had grade 1 laboratory abnormalities either prior to (12/144 [8.3%]) or during (6/144 [4.2%]) therapy.51 Baseline transaminase monitoring is recommended, though subsequent routine laboratory monitoring in healthy children may have limited utility with associated increased costs, incidental findings, and patient discomfort and likely is not needed.51
Pediatric onychomycosis responds better to topical therapy than adult disease, and pediatric patients do not always require systemic treatment.52 Ciclopirox is not FDA approved for the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis, but in a 32-week clinical trial of ciclopirox lacquer 8% use in 40 patients, 77% (27/35) of treated patients achieved mycologic cure. Overall, 71% of treated patients (25/35) vs 22% (2/9) of controls achieved efficacy (defined as investigator global assessment score of 2 or lower).52 In an open-label, single-arm clinical trial assessing tavaborole solution 5% applied once daily for 48 weeks for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients (aged 6–17 years), 36.2% (20/55) of patients achieved mycologic cure, and 8.5% (5/55) achieved complete cure at week 52 with mild or minimal adverse effects.53 In an open-label, phase 4 study of the safety and efficacy of efinaconazole solution 10% applied once daily for 48 weeks in pediatric patients (aged 6 to 16 years) (n=60), 65% (35/60) achieved mycologic cure, 42% (25/60) achieved clinical cure, and 40% (24/60) achieved complete cure at 52 weeks. The most common adverse effects of efinaconazole were local and included ingrown toenail (1/60), application-site dermatitis (1/60), application-site vesicles (1/60), and application-site pain (1/60).54
In a systematic review of systemic antifungals for onychomycosis in 151 pediatric patients, itraconazole, fluconazole, griseofulvin, and terbinafine resulted in complete cure rates similar to those of the adult population, with excellent safety profiles.55 Depending on the situation, initiation of treatment with topical medications followed by addition of systemic antifungal agents only if needed may be an appropriate course of action.
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
Acute Paronychia
Acute paronychia is a nail-fold infection that develops after the protective nail barrier has been compromised.56 In children, thumb-sucking, nail-biting, frequent oral manipulation of the digits, and poor skin hygiene are risk factors. Acute paronychia also may develop in association with congenital malalignment of the great toenails.57
Clinical manifestations include localized pain, erythema, and nail fold edema (Figure 4). Purulent material and abscess formation may ensue. Staphylococcus aureus as well as methicillin-resistant S aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are classically the most common causes of acute paronychia. Treatment of paronychia is based on severity. In mild cases, warm soaks with topical antibiotics are indicated. Oral antibiotics should be prescribed for more severe presentations. If there is no improvement after 48 hours, surgical drainage is required to facilitate healing.56
FINAL THOUGHTS
Inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in children are relatively common and may impact the physical and emotional well-being of young patients. By understanding the distinctive features of these nail disorders in pediatric patients, dermatologists can provide anticipatory guidance and informed treatment options to children and their parents. Further research is needed to expand our understanding of pediatric nail disorders and create targeted therapeutic interventions, particularly for NLP and psoriasis.
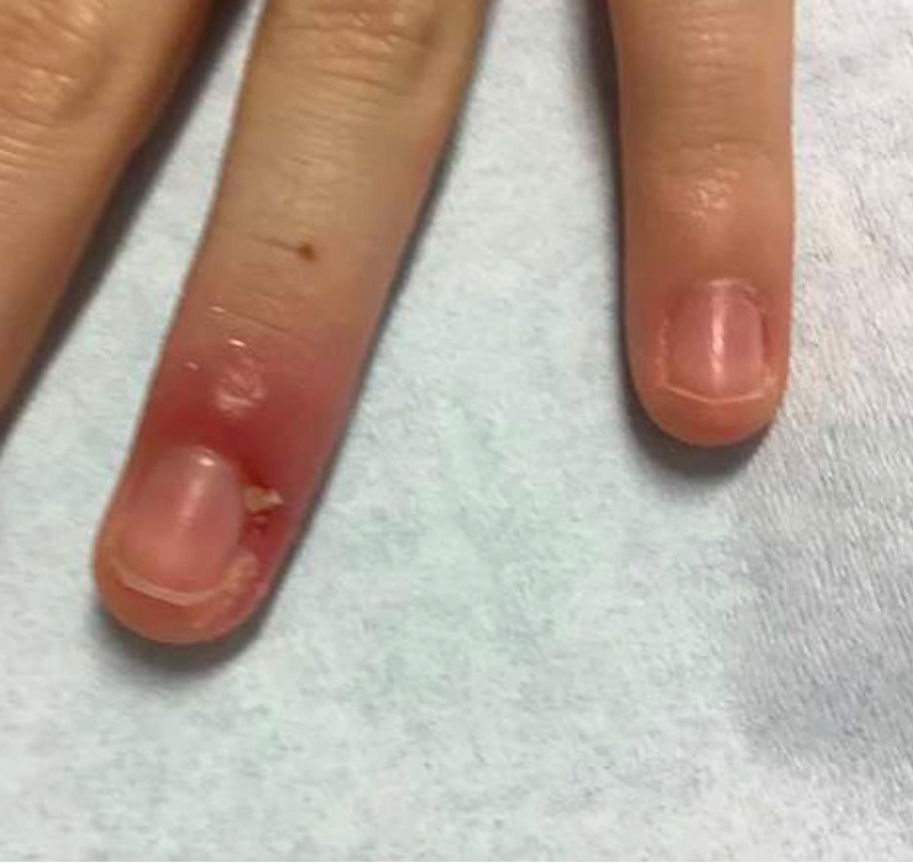
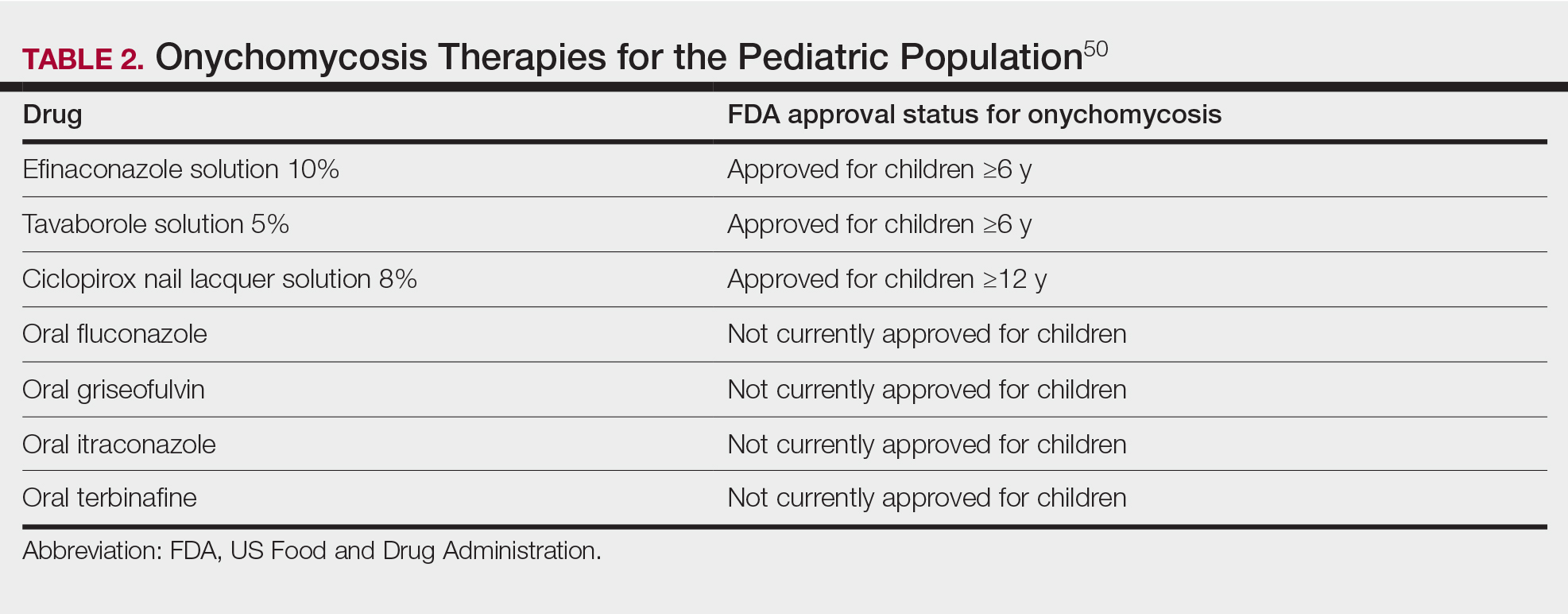
- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207. doi:10.1111/pde.13402
- Plachouri KM, Mulita F, Georgiou S. Management of pediatric nail psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:292-294. doi:10.12788/cutis.0386
- Smith RJ, Rubin AI. Pediatric nail disorders: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:506-515. doi:10.1097/mop.0000000000000921
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63. doi:10.1111/pde.13028
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112. doi:10.2165/11537110-000000000-00000
- Lee JYY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Nogueira M, Paller AS, Torres T. Targeted therapy for pediatric psoriasis. Paediatr Drugs. May 2021;23:203-212. doi:10.1007/s40272-021-00443-5
- Hanoodi M, Mittal M. Methotrexate. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556114/
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-179
- Paller AS, Seyger MMB, Magariños GA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of up to 108 weeks of ixekizumab in pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: the IXORA-PEDS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:533-541. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0655
- Diotallevi F, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Biological treatments for pediatric psoriasis: state of the art and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11128. doi:10.3390/ijms231911128
- Nash P, Mease PJ, Kirkham B, et al. Secukinumab provides sustained improvement in nail psoriasis, signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis and low rate of radiographic progression in patients with concomitant nail involvement: 2-year results from the Phase III FUTURE 5 study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40:952-959. doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3nuz51
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385. doi:10.1111/pde.13767
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriaticonycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2616
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352. doi:10.1159/000096202
- Iorizzo M, Gioia Di Chiacchio N, Di Chiacchio N, et al. Intralesional steroid injections for inflammatory nail dystrophies in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023;40:759-761. doi:10.1111/pde.15295
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Cambiaghi S, et al. Nail lichen planus in children: clinical features, response to treatment, and long-term follow-up. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1027-1032.
- Lipner SR. Nail lichen planus: a true nail emergency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:e177-e178. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.065
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Piraccini BM, Saccani E, Starace M, et al. Nail lichen planus: response to treatment and long term follow-up. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:489-496. doi:10.1684/ejd.2010.0952
- Mahajan R, Kaushik A, De D, et al. Pediatric trachyonychia- a retrospective study of 17 cases. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:689-690. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_42_21
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Trachyonychia. J Pediatr. 2020;216:239-239.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.08.034
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
- Jacobsen AA, Tosti A. Trachyonychia and twenty-nail dystrophy: a comprehensive review and discussion of diagnostic accuracy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2016;2:7-13. doi:10.1159/000445544
- Kumar MG, Ciliberto H, Bayliss SJ. Long-term follow-up of pediatric trachyonychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:198-200. doi:10.1111/pde.12427
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Iorizzo M. Trachyonychia and related disorders: evaluation and treatment plans. Dermatolog Ther. 2002;15:121-125. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8019.2002.01511.x
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Lichen striatus with nail involvement in a 6-year-old boy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2020;2020:1494760. doi:10.1155/2020/1494760
- Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00720.x
- Iorizzo M, Rubin AI, Starace M. Nail lichen striatus: is dermoscopy useful for the diagnosis? Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:859-863. doi:10.1111/pde.13916
- Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1993.tb00399.x
- Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(6, pt 1):908-913. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80270-8
- Simpson EL, Thompson MM, Hanifin JM. Prevalence and morphology of hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2006;17:123-127. doi:10.2310/6620.2006.06005
- Sarifakioglu E, Yilmaz AE, Gorpelioglu C. Nail alterations in 250 infant patients: a clinical study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:741-744. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02592.x
- Milanesi N, D’Erme AM, Gola M. Nail improvement during alitretinoin treatment: three case reports and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:533-536. doi:10.1111/ced.12584
- Chung BY, Choi YW, Kim HO, et al. Nail dystrophy in patients with atopic dermatitis and its association with disease severity. Ann Dermatol. 2019;31:121-126. doi:10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.121
- Navarro-Triviño FJ, Vega-Castillo JJ, Ruiz-Villaverde R. Nail changes successfully treated with dupilumab in a patient with severe atopic dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2021;62:e468-e469. doi:10.1111/ajd.13633
- Wei SH, Huang YP, Liu MC, et al. An outbreak of coxsackievirus A6 hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with onychomadesis in Taiwan, 2010. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:346. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-11-346
- Shin JY, Cho BK, Park HJ. A clinical study of nail changes occurring secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: onychomadesis and Beau’s lines. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:280-283. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.280
- Verma S, Singal A. Nail changes in hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD). Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021;12:656-657. doi:10.4103 /idoj.IDOJ_271_20
- Giordano LMC, de la Fuente LA, Lorca JMB, et al. Onychomadesis secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: a frequent manifestation and cause of concern for parents. Article in Spanish. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018;89:380-383. doi:10.4067/s0370-41062018005000203
- Justino MCA, da SMD, Souza MF, et al. Atypical hand-foot-mouth disease in Belém, Amazon region, northern Brazil, with detection of coxsackievirus A6. J Clin Virol. 2020;126:104307. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104307
- Cheng FF, Zhang BB, Cao ML, et al. Clinical characteristics of 68 children with atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6: a single-center retrospective analysis. Transl Pediatr. 2022;11:1502-1509. doi:10.21037/tp-22-352
- Nagata S. Causes of Kawasaki disease-from past to present. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:18. doi:10.3389/fped.2019.00018
- Mitsuishi T, Miyata K, Ando A, et al. Characteristic nail lesions in Kawasaki disease: case series and literature review. J Dermatol. 2022;49:232-238. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16276
- Lindsley CB. Nail-bed lines in Kawasaki disease. Am J Dis Child. 1992;146:659-660. doi:10.1001/archpedi.1992.02160180017005
- Matsumura O, Nakagishi Y. Pincer nails upon convalescence from Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2022;246:279. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2022.03.002
- Solís-Arias MP, García-Romero MT. Onychomycosis in children. a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:123-130. doi:10.1111/ijd.13392
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Onychomycosis in children: safety and efficacy of antifungal agents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:552-559. doi:10.1111/pde.13561
- 49. Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Shear NH, et al. Labeled use of efinaconazole topical solution 10% in treating onychomycosis in children and a review of the management of pediatric onychomycosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13613. doi:10.1111/dth.13613
- Falotico JM, Lipner SR. Updated perspectives on the diagnosis and management of onychomycosis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:1933-1957. doi:10.2147/ccid.S362635
- Patel D, Castelo-Soccio LA, Rubin AI, et al. Laboratory monitoring during systemic terbinafine therapy for pediatric onychomycosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1326-1327. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4483
- Friedlander SF, Chan YC, Chan YH, et al. Onychomycosis does not always require systemic treatment for cure: a trial using topical therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:316-322. doi:10.1111/pde.12064
- Rich P, Spellman M, Purohit V, et al. Tavaborole 5% topical solution for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients: results from a phase 4 open-label study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:190-195.
- Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Abramovits W, et al. JUBLIA (efinaconazole 10% solution) in the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis. Skinmed. 2021;19:206-210.
- Gupta AK, Paquet M. Systemic antifungals to treat onychomycosis in children: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:294-302. doi:10.1111/pde.12048
- Leggit JC. Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96:44-51.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Congenital malalignment of the great toenails with acute paronychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e288-e289.doi:10.1111/pde.12924
Nail disorders are common among pediatric patients but often are underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed because of their unique disease manifestations. These conditions may severely impact quality of life. There are few nail disease clinical trials that include children. Consequently, most treatment recommendations are based on case series and expert consensus recommendations. We review inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in pediatric patients. By describing characteristics, clinical manifestations, and management approaches for these conditions, we aim to provide guidance to dermatologists in their diagnosis and treatment.
INFLAMMATORY NAIL DISORDERS
Nail Psoriasis
Nail involvement in children with psoriasis is common, with prevalence estimates ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail matrix psoriasis may manifest with pitting (large irregular pits) and leukonychia as well as chromonychia and nail plate crumbling. Onycholysis, oil drop spots (salmon patches), and subungual hyperkeratosis can be seen in nail bed psoriasis. Nail pitting is the most frequently observed clinical finding (Figure 1).2,3 In a cross-sectional multicenter study of 313 children with cutaneous psoriasis in France, nail findings were present in 101 patients (32.3%). There were associations between nail findings and presence of psoriatic arthritis (P=.03), palmoplantar psoriasis (P<.001), and severity of psoriatic disease, defined as use of systemic treatment with phototherapy (psoralen plus UVA, UVB), traditional systemic treatment (acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporine), or a biologic (P=.003).4
Topical steroids and vitamin D analogues may be used with or without occlusion and may be efficacious.5 Several case reports describe systemic treatments for psoriasis in children, including methotrexate, acitretin, and apremilast (approved for children 6 years and older for plaque psoriasis by the US Food and Drug Administration [FDA]).2 There are 5 biologic drugs currently approved for the treatment of pediatric psoriasis—adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab—and 6 drugs currently undergoing phase 3 studies—brodalumab, guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, certolizumab pegol, and deucravacitinib (Table 1).6-15 Adalimumab is specifically approved for moderate to severe nail psoriasis in adults 18 years and older.


Intralesional steroid injections are sometimes useful in the management of nail matrix psoriasis; however, appropriate patient selection is critical due to the pain associated with the procedure. In a prospective study of 16 children (age range, 9–17 years) with nail psoriasis treated with intralesional triamcinolone (ILTAC) 2.5 to 5 mg/mL every 4 to 8 weeks for a minimum of 3 to 6 months, 9 patients achieved resolution and 6 had improvement of clinical findings.16 Local adverse events were mild, including injection-site pain (66%), subungual hematoma (n=1), Beau lines (n=1), proximal nail fold hypopigmentation (n=2), and proximal nail fold atrophy (n=2). Because the proximal nail fold in children is thinner than in adults, there may be an increased risk for nail fold hypopigmentation and atrophy in children. Therefore, a maximum ILTAC concentration of 2.5 mg/mL with 0.2 mL maximum volume per nail per session is recommended for children younger than 15 years.16
Nail Lichen Planus
Nail lichen planus (NLP) is uncommon in children, with few biopsy-proven cases documented in the literature.17 Common clinical findings are onychorrhexis, nail plate thinning, fissuring, splitting, and atrophy with koilonychia.5 Although pterygium development (irreversible nail matrix scarring) is uncommon in pediatric patients, NLP can be progressive and may cause irreversible destruction of the nail matrix and subsequent nail loss, warranting therapeutic intervention.18
Treatment of NLP may be difficult, as there are no options that work in all patients. Current literature supports the use of systemic corticosteroids or ILTAC for the treatment of NLP; however, recurrence rates can be high. According to an expert consensus paper on NLP treatment, ILTAC may be injected in a concentration of 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/mL according to disease severity.19 In severe or resistant cases, intramuscular (IM) triamcinolone may be considered, especially if more than 3 nails are affected. A dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/mo for at least 3 to 6 months is recommended for both children and adults, with 1 mg/kg/mo recommended in the active treatment phase (first 2–3 months).19 In a retrospective review of 5 pediatric patients with NLP treated with IM triamcinolone 0.5 mg/kg/mo, 3 patients had resolution and 2 improved with treatment.20 In a prospective study of 10 children with NLP, IM triamcinolone at a dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg every 30 days for 3 to 6 months resulted in resolution of nail findings in 9 patients.17 In a prospective study of 14 pediatric patients with NLP treated with 2.5 to 5 mg/mL of ILTAC, 10 achieved resolution and 3 improved.16
Intralesional triamcinolone injections may be better suited for teenagers compared to younger children who may be more apprehensive of needles. To minimize pain, it is recommended to inject ILTAC slowly at room temperature, with use of “talkesthesia” and vibration devices, 1% lidocaine, or ethyl chloride spray.18
Trachyonychia
Trachyonychia is characterized by the presence of sandpaperlike nails. It manifests with brittle thin nails with longitudinal ridging, onychoschizia, and thickened hyperkeratotic cuticles. Trachyonychia typically involves multiple nails, with a peak age of onset between 3 and 12 years.21,22 There are 2 variants: the opaque type with rough longitudinal ridging, and the shiny variant with opalescent nails and pits that reflect light. The opaque variant is more common and is associated with psoriasis, whereas the shiny variant is less common and is associated with alopecia areata.23 Although most cases are idiopathic, some are associated with psoriasis and alopecia areata, as previously noted, as well as atopic dermatitis (AD) and lichen planus.22,24
Fortunately, trachyonychia does not lead to permanent nail damage or pterygium, making treatment primarily focused on addressing functional and cosmetic concerns.24 Spontaneous resolution occurs in approximately 50% of patients. In a prospective study of 11 patients with idiopathic trachyonychia, there was partial improvement in 5 of 9 patients treated with topical steroids, 1 with only petrolatum, and 1 with vitamin supplements. Complete resolution was reported in 1 patient treated with topical steroids.25 Because trachyonychia often is self-resolving, no treatment is required and a conservative approach is strongly recommended.26 Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and 5-fluorouracil. Intralesional triamcinolone, systemic cyclosporine, retinoids, systemic corticosteroids, and tofacitinib have been described in case reports, though none of these have been shown to be 100% efficacious.24
Nail Lichen Striatus
Lichen striatus involving the nail is uncommon and is characterized by onycholysis, longitudinal ridging, splitting, and fraying, as well as what appears to be a subungual tumor. It can encompass the entire nail or may be isolated to a portion of the nail (Figure 2). Usually, a Blaschko-linear array of flesh-colored papules on the more proximal digit directly adjacent to the nail dystrophy will be seen, though nail findings can occur in isolation.27-29 The underlying pathophysiology is not clear; however, one hypothesis is that a triggering event, such as trauma, induces the expression of antigens that elicit a self-limiting immune-mediated response by CD8 T lymphocytes.30

Generally, nail lichen striatus spontaneously resolves in 1 to 2 years without treatment. In a prospective study of 5 patients with nail lichen striatus, the median time to resolution was 22.6 months (range, 10–30 months).31 Topical steroids may be used for pruritus. In one case report, a 3-year-old boy with nail lichen striatus of 4 months’ duration was treated with tacrolimus ointment 0.03% daily for 3 months.28
Nail AD
Nail changes with AD may be more common in adults than children or are underreported. In a study of 777 adults with AD, nail dystrophy was present in 124 patients (16%), whereas in a study of 250 pediatric patients with AD (aged 0-2 years), nail dystrophy was present in only 4 patients.32,33
Periungual inflammation from AD causes the nail changes.34 In a cross-sectional study of 24 pediatric patients with nail dystrophy due to AD, transverse grooves (Beau lines) were present in 25% (6/24), nail pitting in 16.7% (4/24), koilonychia in 16.7% (4/24), trachyonychia in 12.5% (3/24), leukonychia in 12.5% (3/24), brachyonychia in 8.3% (2/24), melanonychia in 8.3% (2/24), onychomadesis in 8.3% (2/24), onychoschizia in 8.3% (2/24), and onycholysis in 8.3% (2/24). There was an association between disease severity and presence of toenail dystrophy (P=.03).35
Topical steroids with or without occlusion can be used to treat nail changes. Although there is limited literature describing the treatment of nail AD in children, a 61-year-old man with nail changes associated with AD achieved resolution with 3 months of treatment with dupilumab.36 Anecdotally, most patients will improve with usual cutaneous AD management.
INFECTIOUS NAIL DISORDERS
Viral Infections
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease—Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood viral infection caused by various enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16, with the A6 variant causing more severe disease. Fever and painful vesicles involving the oral mucosa as well as palms and soles give the disease its name. Nail changes are common. In a prospective study involving 130 patients with laboratory-confirmed coxsackievirus CA6 serotype infection, 37% developed onychomadesis vs only 5% of 145 cases with non-CA6 enterovirus infection who developed nail findings. There was an association between CA6 infection and presence of nail changes (P<.001).37
Findings ranging from transverse grooves (Beau lines) to complete nail shedding (onychomadesis)(Figure 3) may be seen.38,39 Nail findings in HFMD are due to transient inhibition of nail growth and present approximately 3 to 6 weeks after infection.40 Onychomadesis is seen in 30% to 68% of patients with HFMD.37,41,42 Nail findings in HFMD spontaneously resolve with nail growth (2–3 mm per month for fingernails and 1 mm per month for toenails) and do not require specific treatment. Although the appearance of nail changes associated with HFMD can be disturbing, dermatologists can reassure children and their parents that the nails will resolve with the next cycle of growth.
Kawasaki Disease—Kawasaki disease (KD) is a vasculitis primarily affecting children and infants. Although the specific pathogen and pathophysiology is not entirely clear, clinical observations have suggested an infectious cause, most likely a virus.43 In Japan, more than 15,000 cases of KD are documented annually, while approximately 4200 cases are seen in the United States.44 In a prospective study from 1984 to 1990, 4 of 26 (15.4%) patients with KD presented with nail manifestations during the late acute phase or early convalescent phase of disease. There were no significant associations between nail dystrophy and severity of KD, such as coronary artery aneurysm.45
Nail changes reported in children with KD include onychomadesis, onycholysis, orange-brown chromonychia, splinter hemorrhages, Beau lines, and pincer nails. In a review of nail changes associated with KD from 1980 to 2021, orange-brown transverse chromonychia, which may evolve into transverse leukonychia, was the most common nail finding reported, occurring in 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients.44 It has been hypothesized that nail changes may result from blood flow disturbance due to the underlying vasculitis.46 Nail changes appear several weeks after the onset of fever and are self-limited. Resolution occurs with nail growth, with no treatment required.

FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails that occurs in 0.2% to 5.5% of pediatric patients, and its prevalence may be increasing, which may be due to environmental factors or increased rates of diabetes mellitus and obesity in the pediatric population.47 Onychomycosis represents 15.5% of nail dystrophies in pediatric patients.48 Some dermatologists treat presumptive onychomycosis without confirmation; however, we do not recommend that approach. Because the differential is broad and the duration of treatment is long, mycologic examination (potassium hydroxide preparation, fungal culture, polymerase chain reaction, and/or histopathology) should be obtained to confirm onychomycosis prior to initiation of antifungal management. Family members of affected individuals should be evaluated and treated, if indicated, for onychomycosis and tinea pedis, as household transmission is common.
Currently, there are 2 topical FDA-approved treatments for pediatric onychomycosis in children 6 years and older (Table 2).49,50 There is a discussion of the need for confirmatory testing for onychomycosis in children, particularly when systemic treatment is prescribed. In a retrospective review of 269 pediatric patients with onychomycosis prescribed terbinafine, 53.5% (n=144) underwent laboratory monitoring of liver function and complete blood cell counts, and 12.5% had grade 1 laboratory abnormalities either prior to (12/144 [8.3%]) or during (6/144 [4.2%]) therapy.51 Baseline transaminase monitoring is recommended, though subsequent routine laboratory monitoring in healthy children may have limited utility with associated increased costs, incidental findings, and patient discomfort and likely is not needed.51
Pediatric onychomycosis responds better to topical therapy than adult disease, and pediatric patients do not always require systemic treatment.52 Ciclopirox is not FDA approved for the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis, but in a 32-week clinical trial of ciclopirox lacquer 8% use in 40 patients, 77% (27/35) of treated patients achieved mycologic cure. Overall, 71% of treated patients (25/35) vs 22% (2/9) of controls achieved efficacy (defined as investigator global assessment score of 2 or lower).52 In an open-label, single-arm clinical trial assessing tavaborole solution 5% applied once daily for 48 weeks for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients (aged 6–17 years), 36.2% (20/55) of patients achieved mycologic cure, and 8.5% (5/55) achieved complete cure at week 52 with mild or minimal adverse effects.53 In an open-label, phase 4 study of the safety and efficacy of efinaconazole solution 10% applied once daily for 48 weeks in pediatric patients (aged 6 to 16 years) (n=60), 65% (35/60) achieved mycologic cure, 42% (25/60) achieved clinical cure, and 40% (24/60) achieved complete cure at 52 weeks. The most common adverse effects of efinaconazole were local and included ingrown toenail (1/60), application-site dermatitis (1/60), application-site vesicles (1/60), and application-site pain (1/60).54
In a systematic review of systemic antifungals for onychomycosis in 151 pediatric patients, itraconazole, fluconazole, griseofulvin, and terbinafine resulted in complete cure rates similar to those of the adult population, with excellent safety profiles.55 Depending on the situation, initiation of treatment with topical medications followed by addition of systemic antifungal agents only if needed may be an appropriate course of action.
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
Acute Paronychia
Acute paronychia is a nail-fold infection that develops after the protective nail barrier has been compromised.56 In children, thumb-sucking, nail-biting, frequent oral manipulation of the digits, and poor skin hygiene are risk factors. Acute paronychia also may develop in association with congenital malalignment of the great toenails.57
Clinical manifestations include localized pain, erythema, and nail fold edema (Figure 4). Purulent material and abscess formation may ensue. Staphylococcus aureus as well as methicillin-resistant S aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are classically the most common causes of acute paronychia. Treatment of paronychia is based on severity. In mild cases, warm soaks with topical antibiotics are indicated. Oral antibiotics should be prescribed for more severe presentations. If there is no improvement after 48 hours, surgical drainage is required to facilitate healing.56
FINAL THOUGHTS
Inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in children are relatively common and may impact the physical and emotional well-being of young patients. By understanding the distinctive features of these nail disorders in pediatric patients, dermatologists can provide anticipatory guidance and informed treatment options to children and their parents. Further research is needed to expand our understanding of pediatric nail disorders and create targeted therapeutic interventions, particularly for NLP and psoriasis.


Nail disorders are common among pediatric patients but often are underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed because of their unique disease manifestations. These conditions may severely impact quality of life. There are few nail disease clinical trials that include children. Consequently, most treatment recommendations are based on case series and expert consensus recommendations. We review inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in pediatric patients. By describing characteristics, clinical manifestations, and management approaches for these conditions, we aim to provide guidance to dermatologists in their diagnosis and treatment.
INFLAMMATORY NAIL DISORDERS
Nail Psoriasis
Nail involvement in children with psoriasis is common, with prevalence estimates ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail matrix psoriasis may manifest with pitting (large irregular pits) and leukonychia as well as chromonychia and nail plate crumbling. Onycholysis, oil drop spots (salmon patches), and subungual hyperkeratosis can be seen in nail bed psoriasis. Nail pitting is the most frequently observed clinical finding (Figure 1).2,3 In a cross-sectional multicenter study of 313 children with cutaneous psoriasis in France, nail findings were present in 101 patients (32.3%). There were associations between nail findings and presence of psoriatic arthritis (P=.03), palmoplantar psoriasis (P<.001), and severity of psoriatic disease, defined as use of systemic treatment with phototherapy (psoralen plus UVA, UVB), traditional systemic treatment (acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporine), or a biologic (P=.003).4
Topical steroids and vitamin D analogues may be used with or without occlusion and may be efficacious.5 Several case reports describe systemic treatments for psoriasis in children, including methotrexate, acitretin, and apremilast (approved for children 6 years and older for plaque psoriasis by the US Food and Drug Administration [FDA]).2 There are 5 biologic drugs currently approved for the treatment of pediatric psoriasis—adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab—and 6 drugs currently undergoing phase 3 studies—brodalumab, guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, certolizumab pegol, and deucravacitinib (Table 1).6-15 Adalimumab is specifically approved for moderate to severe nail psoriasis in adults 18 years and older.


Intralesional steroid injections are sometimes useful in the management of nail matrix psoriasis; however, appropriate patient selection is critical due to the pain associated with the procedure. In a prospective study of 16 children (age range, 9–17 years) with nail psoriasis treated with intralesional triamcinolone (ILTAC) 2.5 to 5 mg/mL every 4 to 8 weeks for a minimum of 3 to 6 months, 9 patients achieved resolution and 6 had improvement of clinical findings.16 Local adverse events were mild, including injection-site pain (66%), subungual hematoma (n=1), Beau lines (n=1), proximal nail fold hypopigmentation (n=2), and proximal nail fold atrophy (n=2). Because the proximal nail fold in children is thinner than in adults, there may be an increased risk for nail fold hypopigmentation and atrophy in children. Therefore, a maximum ILTAC concentration of 2.5 mg/mL with 0.2 mL maximum volume per nail per session is recommended for children younger than 15 years.16
Nail Lichen Planus
Nail lichen planus (NLP) is uncommon in children, with few biopsy-proven cases documented in the literature.17 Common clinical findings are onychorrhexis, nail plate thinning, fissuring, splitting, and atrophy with koilonychia.5 Although pterygium development (irreversible nail matrix scarring) is uncommon in pediatric patients, NLP can be progressive and may cause irreversible destruction of the nail matrix and subsequent nail loss, warranting therapeutic intervention.18
Treatment of NLP may be difficult, as there are no options that work in all patients. Current literature supports the use of systemic corticosteroids or ILTAC for the treatment of NLP; however, recurrence rates can be high. According to an expert consensus paper on NLP treatment, ILTAC may be injected in a concentration of 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/mL according to disease severity.19 In severe or resistant cases, intramuscular (IM) triamcinolone may be considered, especially if more than 3 nails are affected. A dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/mo for at least 3 to 6 months is recommended for both children and adults, with 1 mg/kg/mo recommended in the active treatment phase (first 2–3 months).19 In a retrospective review of 5 pediatric patients with NLP treated with IM triamcinolone 0.5 mg/kg/mo, 3 patients had resolution and 2 improved with treatment.20 In a prospective study of 10 children with NLP, IM triamcinolone at a dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg every 30 days for 3 to 6 months resulted in resolution of nail findings in 9 patients.17 In a prospective study of 14 pediatric patients with NLP treated with 2.5 to 5 mg/mL of ILTAC, 10 achieved resolution and 3 improved.16
Intralesional triamcinolone injections may be better suited for teenagers compared to younger children who may be more apprehensive of needles. To minimize pain, it is recommended to inject ILTAC slowly at room temperature, with use of “talkesthesia” and vibration devices, 1% lidocaine, or ethyl chloride spray.18
Trachyonychia
Trachyonychia is characterized by the presence of sandpaperlike nails. It manifests with brittle thin nails with longitudinal ridging, onychoschizia, and thickened hyperkeratotic cuticles. Trachyonychia typically involves multiple nails, with a peak age of onset between 3 and 12 years.21,22 There are 2 variants: the opaque type with rough longitudinal ridging, and the shiny variant with opalescent nails and pits that reflect light. The opaque variant is more common and is associated with psoriasis, whereas the shiny variant is less common and is associated with alopecia areata.23 Although most cases are idiopathic, some are associated with psoriasis and alopecia areata, as previously noted, as well as atopic dermatitis (AD) and lichen planus.22,24
Fortunately, trachyonychia does not lead to permanent nail damage or pterygium, making treatment primarily focused on addressing functional and cosmetic concerns.24 Spontaneous resolution occurs in approximately 50% of patients. In a prospective study of 11 patients with idiopathic trachyonychia, there was partial improvement in 5 of 9 patients treated with topical steroids, 1 with only petrolatum, and 1 with vitamin supplements. Complete resolution was reported in 1 patient treated with topical steroids.25 Because trachyonychia often is self-resolving, no treatment is required and a conservative approach is strongly recommended.26 Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and 5-fluorouracil. Intralesional triamcinolone, systemic cyclosporine, retinoids, systemic corticosteroids, and tofacitinib have been described in case reports, though none of these have been shown to be 100% efficacious.24
Nail Lichen Striatus
Lichen striatus involving the nail is uncommon and is characterized by onycholysis, longitudinal ridging, splitting, and fraying, as well as what appears to be a subungual tumor. It can encompass the entire nail or may be isolated to a portion of the nail (Figure 2). Usually, a Blaschko-linear array of flesh-colored papules on the more proximal digit directly adjacent to the nail dystrophy will be seen, though nail findings can occur in isolation.27-29 The underlying pathophysiology is not clear; however, one hypothesis is that a triggering event, such as trauma, induces the expression of antigens that elicit a self-limiting immune-mediated response by CD8 T lymphocytes.30

Generally, nail lichen striatus spontaneously resolves in 1 to 2 years without treatment. In a prospective study of 5 patients with nail lichen striatus, the median time to resolution was 22.6 months (range, 10–30 months).31 Topical steroids may be used for pruritus. In one case report, a 3-year-old boy with nail lichen striatus of 4 months’ duration was treated with tacrolimus ointment 0.03% daily for 3 months.28
Nail AD
Nail changes with AD may be more common in adults than children or are underreported. In a study of 777 adults with AD, nail dystrophy was present in 124 patients (16%), whereas in a study of 250 pediatric patients with AD (aged 0-2 years), nail dystrophy was present in only 4 patients.32,33
Periungual inflammation from AD causes the nail changes.34 In a cross-sectional study of 24 pediatric patients with nail dystrophy due to AD, transverse grooves (Beau lines) were present in 25% (6/24), nail pitting in 16.7% (4/24), koilonychia in 16.7% (4/24), trachyonychia in 12.5% (3/24), leukonychia in 12.5% (3/24), brachyonychia in 8.3% (2/24), melanonychia in 8.3% (2/24), onychomadesis in 8.3% (2/24), onychoschizia in 8.3% (2/24), and onycholysis in 8.3% (2/24). There was an association between disease severity and presence of toenail dystrophy (P=.03).35
Topical steroids with or without occlusion can be used to treat nail changes. Although there is limited literature describing the treatment of nail AD in children, a 61-year-old man with nail changes associated with AD achieved resolution with 3 months of treatment with dupilumab.36 Anecdotally, most patients will improve with usual cutaneous AD management.
INFECTIOUS NAIL DISORDERS
Viral Infections
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease—Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood viral infection caused by various enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16, with the A6 variant causing more severe disease. Fever and painful vesicles involving the oral mucosa as well as palms and soles give the disease its name. Nail changes are common. In a prospective study involving 130 patients with laboratory-confirmed coxsackievirus CA6 serotype infection, 37% developed onychomadesis vs only 5% of 145 cases with non-CA6 enterovirus infection who developed nail findings. There was an association between CA6 infection and presence of nail changes (P<.001).37
Findings ranging from transverse grooves (Beau lines) to complete nail shedding (onychomadesis)(Figure 3) may be seen.38,39 Nail findings in HFMD are due to transient inhibition of nail growth and present approximately 3 to 6 weeks after infection.40 Onychomadesis is seen in 30% to 68% of patients with HFMD.37,41,42 Nail findings in HFMD spontaneously resolve with nail growth (2–3 mm per month for fingernails and 1 mm per month for toenails) and do not require specific treatment. Although the appearance of nail changes associated with HFMD can be disturbing, dermatologists can reassure children and their parents that the nails will resolve with the next cycle of growth.
Kawasaki Disease—Kawasaki disease (KD) is a vasculitis primarily affecting children and infants. Although the specific pathogen and pathophysiology is not entirely clear, clinical observations have suggested an infectious cause, most likely a virus.43 In Japan, more than 15,000 cases of KD are documented annually, while approximately 4200 cases are seen in the United States.44 In a prospective study from 1984 to 1990, 4 of 26 (15.4%) patients with KD presented with nail manifestations during the late acute phase or early convalescent phase of disease. There were no significant associations between nail dystrophy and severity of KD, such as coronary artery aneurysm.45
Nail changes reported in children with KD include onychomadesis, onycholysis, orange-brown chromonychia, splinter hemorrhages, Beau lines, and pincer nails. In a review of nail changes associated with KD from 1980 to 2021, orange-brown transverse chromonychia, which may evolve into transverse leukonychia, was the most common nail finding reported, occurring in 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients.44 It has been hypothesized that nail changes may result from blood flow disturbance due to the underlying vasculitis.46 Nail changes appear several weeks after the onset of fever and are self-limited. Resolution occurs with nail growth, with no treatment required.

FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails that occurs in 0.2% to 5.5% of pediatric patients, and its prevalence may be increasing, which may be due to environmental factors or increased rates of diabetes mellitus and obesity in the pediatric population.47 Onychomycosis represents 15.5% of nail dystrophies in pediatric patients.48 Some dermatologists treat presumptive onychomycosis without confirmation; however, we do not recommend that approach. Because the differential is broad and the duration of treatment is long, mycologic examination (potassium hydroxide preparation, fungal culture, polymerase chain reaction, and/or histopathology) should be obtained to confirm onychomycosis prior to initiation of antifungal management. Family members of affected individuals should be evaluated and treated, if indicated, for onychomycosis and tinea pedis, as household transmission is common.
Currently, there are 2 topical FDA-approved treatments for pediatric onychomycosis in children 6 years and older (Table 2).49,50 There is a discussion of the need for confirmatory testing for onychomycosis in children, particularly when systemic treatment is prescribed. In a retrospective review of 269 pediatric patients with onychomycosis prescribed terbinafine, 53.5% (n=144) underwent laboratory monitoring of liver function and complete blood cell counts, and 12.5% had grade 1 laboratory abnormalities either prior to (12/144 [8.3%]) or during (6/144 [4.2%]) therapy.51 Baseline transaminase monitoring is recommended, though subsequent routine laboratory monitoring in healthy children may have limited utility with associated increased costs, incidental findings, and patient discomfort and likely is not needed.51
Pediatric onychomycosis responds better to topical therapy than adult disease, and pediatric patients do not always require systemic treatment.52 Ciclopirox is not FDA approved for the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis, but in a 32-week clinical trial of ciclopirox lacquer 8% use in 40 patients, 77% (27/35) of treated patients achieved mycologic cure. Overall, 71% of treated patients (25/35) vs 22% (2/9) of controls achieved efficacy (defined as investigator global assessment score of 2 or lower).52 In an open-label, single-arm clinical trial assessing tavaborole solution 5% applied once daily for 48 weeks for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients (aged 6–17 years), 36.2% (20/55) of patients achieved mycologic cure, and 8.5% (5/55) achieved complete cure at week 52 with mild or minimal adverse effects.53 In an open-label, phase 4 study of the safety and efficacy of efinaconazole solution 10% applied once daily for 48 weeks in pediatric patients (aged 6 to 16 years) (n=60), 65% (35/60) achieved mycologic cure, 42% (25/60) achieved clinical cure, and 40% (24/60) achieved complete cure at 52 weeks. The most common adverse effects of efinaconazole were local and included ingrown toenail (1/60), application-site dermatitis (1/60), application-site vesicles (1/60), and application-site pain (1/60).54
In a systematic review of systemic antifungals for onychomycosis in 151 pediatric patients, itraconazole, fluconazole, griseofulvin, and terbinafine resulted in complete cure rates similar to those of the adult population, with excellent safety profiles.55 Depending on the situation, initiation of treatment with topical medications followed by addition of systemic antifungal agents only if needed may be an appropriate course of action.
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
Acute Paronychia
Acute paronychia is a nail-fold infection that develops after the protective nail barrier has been compromised.56 In children, thumb-sucking, nail-biting, frequent oral manipulation of the digits, and poor skin hygiene are risk factors. Acute paronychia also may develop in association with congenital malalignment of the great toenails.57
Clinical manifestations include localized pain, erythema, and nail fold edema (Figure 4). Purulent material and abscess formation may ensue. Staphylococcus aureus as well as methicillin-resistant S aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are classically the most common causes of acute paronychia. Treatment of paronychia is based on severity. In mild cases, warm soaks with topical antibiotics are indicated. Oral antibiotics should be prescribed for more severe presentations. If there is no improvement after 48 hours, surgical drainage is required to facilitate healing.56
FINAL THOUGHTS
Inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in children are relatively common and may impact the physical and emotional well-being of young patients. By understanding the distinctive features of these nail disorders in pediatric patients, dermatologists can provide anticipatory guidance and informed treatment options to children and their parents. Further research is needed to expand our understanding of pediatric nail disorders and create targeted therapeutic interventions, particularly for NLP and psoriasis.


- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207. doi:10.1111/pde.13402
- Plachouri KM, Mulita F, Georgiou S. Management of pediatric nail psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:292-294. doi:10.12788/cutis.0386
- Smith RJ, Rubin AI. Pediatric nail disorders: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:506-515. doi:10.1097/mop.0000000000000921
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63. doi:10.1111/pde.13028
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112. doi:10.2165/11537110-000000000-00000
- Lee JYY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Nogueira M, Paller AS, Torres T. Targeted therapy for pediatric psoriasis. Paediatr Drugs. May 2021;23:203-212. doi:10.1007/s40272-021-00443-5
- Hanoodi M, Mittal M. Methotrexate. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556114/
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-179
- Paller AS, Seyger MMB, Magariños GA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of up to 108 weeks of ixekizumab in pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: the IXORA-PEDS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:533-541. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0655
- Diotallevi F, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Biological treatments for pediatric psoriasis: state of the art and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11128. doi:10.3390/ijms231911128
- Nash P, Mease PJ, Kirkham B, et al. Secukinumab provides sustained improvement in nail psoriasis, signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis and low rate of radiographic progression in patients with concomitant nail involvement: 2-year results from the Phase III FUTURE 5 study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40:952-959. doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3nuz51
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385. doi:10.1111/pde.13767
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriaticonycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2616
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352. doi:10.1159/000096202
- Iorizzo M, Gioia Di Chiacchio N, Di Chiacchio N, et al. Intralesional steroid injections for inflammatory nail dystrophies in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023;40:759-761. doi:10.1111/pde.15295
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Cambiaghi S, et al. Nail lichen planus in children: clinical features, response to treatment, and long-term follow-up. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1027-1032.
- Lipner SR. Nail lichen planus: a true nail emergency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:e177-e178. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.065
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Piraccini BM, Saccani E, Starace M, et al. Nail lichen planus: response to treatment and long term follow-up. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:489-496. doi:10.1684/ejd.2010.0952
- Mahajan R, Kaushik A, De D, et al. Pediatric trachyonychia- a retrospective study of 17 cases. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:689-690. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_42_21
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Trachyonychia. J Pediatr. 2020;216:239-239.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.08.034
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
- Jacobsen AA, Tosti A. Trachyonychia and twenty-nail dystrophy: a comprehensive review and discussion of diagnostic accuracy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2016;2:7-13. doi:10.1159/000445544
- Kumar MG, Ciliberto H, Bayliss SJ. Long-term follow-up of pediatric trachyonychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:198-200. doi:10.1111/pde.12427
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Iorizzo M. Trachyonychia and related disorders: evaluation and treatment plans. Dermatolog Ther. 2002;15:121-125. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8019.2002.01511.x
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Lichen striatus with nail involvement in a 6-year-old boy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2020;2020:1494760. doi:10.1155/2020/1494760
- Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00720.x
- Iorizzo M, Rubin AI, Starace M. Nail lichen striatus: is dermoscopy useful for the diagnosis? Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:859-863. doi:10.1111/pde.13916
- Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1993.tb00399.x
- Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(6, pt 1):908-913. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80270-8
- Simpson EL, Thompson MM, Hanifin JM. Prevalence and morphology of hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2006;17:123-127. doi:10.2310/6620.2006.06005
- Sarifakioglu E, Yilmaz AE, Gorpelioglu C. Nail alterations in 250 infant patients: a clinical study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:741-744. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02592.x
- Milanesi N, D’Erme AM, Gola M. Nail improvement during alitretinoin treatment: three case reports and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:533-536. doi:10.1111/ced.12584
- Chung BY, Choi YW, Kim HO, et al. Nail dystrophy in patients with atopic dermatitis and its association with disease severity. Ann Dermatol. 2019;31:121-126. doi:10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.121
- Navarro-Triviño FJ, Vega-Castillo JJ, Ruiz-Villaverde R. Nail changes successfully treated with dupilumab in a patient with severe atopic dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2021;62:e468-e469. doi:10.1111/ajd.13633
- Wei SH, Huang YP, Liu MC, et al. An outbreak of coxsackievirus A6 hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with onychomadesis in Taiwan, 2010. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:346. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-11-346
- Shin JY, Cho BK, Park HJ. A clinical study of nail changes occurring secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: onychomadesis and Beau’s lines. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:280-283. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.280
- Verma S, Singal A. Nail changes in hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD). Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021;12:656-657. doi:10.4103 /idoj.IDOJ_271_20
- Giordano LMC, de la Fuente LA, Lorca JMB, et al. Onychomadesis secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: a frequent manifestation and cause of concern for parents. Article in Spanish. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018;89:380-383. doi:10.4067/s0370-41062018005000203
- Justino MCA, da SMD, Souza MF, et al. Atypical hand-foot-mouth disease in Belém, Amazon region, northern Brazil, with detection of coxsackievirus A6. J Clin Virol. 2020;126:104307. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104307
- Cheng FF, Zhang BB, Cao ML, et al. Clinical characteristics of 68 children with atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6: a single-center retrospective analysis. Transl Pediatr. 2022;11:1502-1509. doi:10.21037/tp-22-352
- Nagata S. Causes of Kawasaki disease-from past to present. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:18. doi:10.3389/fped.2019.00018
- Mitsuishi T, Miyata K, Ando A, et al. Characteristic nail lesions in Kawasaki disease: case series and literature review. J Dermatol. 2022;49:232-238. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16276
- Lindsley CB. Nail-bed lines in Kawasaki disease. Am J Dis Child. 1992;146:659-660. doi:10.1001/archpedi.1992.02160180017005
- Matsumura O, Nakagishi Y. Pincer nails upon convalescence from Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2022;246:279. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2022.03.002
- Solís-Arias MP, García-Romero MT. Onychomycosis in children. a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:123-130. doi:10.1111/ijd.13392
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Onychomycosis in children: safety and efficacy of antifungal agents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:552-559. doi:10.1111/pde.13561
- 49. Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Shear NH, et al. Labeled use of efinaconazole topical solution 10% in treating onychomycosis in children and a review of the management of pediatric onychomycosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13613. doi:10.1111/dth.13613
- Falotico JM, Lipner SR. Updated perspectives on the diagnosis and management of onychomycosis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:1933-1957. doi:10.2147/ccid.S362635
- Patel D, Castelo-Soccio LA, Rubin AI, et al. Laboratory monitoring during systemic terbinafine therapy for pediatric onychomycosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1326-1327. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4483
- Friedlander SF, Chan YC, Chan YH, et al. Onychomycosis does not always require systemic treatment for cure: a trial using topical therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:316-322. doi:10.1111/pde.12064
- Rich P, Spellman M, Purohit V, et al. Tavaborole 5% topical solution for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients: results from a phase 4 open-label study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:190-195.
- Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Abramovits W, et al. JUBLIA (efinaconazole 10% solution) in the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis. Skinmed. 2021;19:206-210.
- Gupta AK, Paquet M. Systemic antifungals to treat onychomycosis in children: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:294-302. doi:10.1111/pde.12048
- Leggit JC. Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96:44-51.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Congenital malalignment of the great toenails with acute paronychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e288-e289.doi:10.1111/pde.12924
- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207. doi:10.1111/pde.13402
- Plachouri KM, Mulita F, Georgiou S. Management of pediatric nail psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:292-294. doi:10.12788/cutis.0386
- Smith RJ, Rubin AI. Pediatric nail disorders: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:506-515. doi:10.1097/mop.0000000000000921
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63. doi:10.1111/pde.13028
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112. doi:10.2165/11537110-000000000-00000
- Lee JYY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Nogueira M, Paller AS, Torres T. Targeted therapy for pediatric psoriasis. Paediatr Drugs. May 2021;23:203-212. doi:10.1007/s40272-021-00443-5
- Hanoodi M, Mittal M. Methotrexate. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556114/
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-179
- Paller AS, Seyger MMB, Magariños GA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of up to 108 weeks of ixekizumab in pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: the IXORA-PEDS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:533-541. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0655
- Diotallevi F, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Biological treatments for pediatric psoriasis: state of the art and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11128. doi:10.3390/ijms231911128
- Nash P, Mease PJ, Kirkham B, et al. Secukinumab provides sustained improvement in nail psoriasis, signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis and low rate of radiographic progression in patients with concomitant nail involvement: 2-year results from the Phase III FUTURE 5 study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40:952-959. doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3nuz51
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385. doi:10.1111/pde.13767
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriaticonycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2616
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352. doi:10.1159/000096202
- Iorizzo M, Gioia Di Chiacchio N, Di Chiacchio N, et al. Intralesional steroid injections for inflammatory nail dystrophies in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023;40:759-761. doi:10.1111/pde.15295
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Cambiaghi S, et al. Nail lichen planus in children: clinical features, response to treatment, and long-term follow-up. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1027-1032.
- Lipner SR. Nail lichen planus: a true nail emergency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:e177-e178. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.065
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Piraccini BM, Saccani E, Starace M, et al. Nail lichen planus: response to treatment and long term follow-up. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:489-496. doi:10.1684/ejd.2010.0952
- Mahajan R, Kaushik A, De D, et al. Pediatric trachyonychia- a retrospective study of 17 cases. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:689-690. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_42_21
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Trachyonychia. J Pediatr. 2020;216:239-239.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.08.034
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
- Jacobsen AA, Tosti A. Trachyonychia and twenty-nail dystrophy: a comprehensive review and discussion of diagnostic accuracy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2016;2:7-13. doi:10.1159/000445544
- Kumar MG, Ciliberto H, Bayliss SJ. Long-term follow-up of pediatric trachyonychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:198-200. doi:10.1111/pde.12427
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Iorizzo M. Trachyonychia and related disorders: evaluation and treatment plans. Dermatolog Ther. 2002;15:121-125. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8019.2002.01511.x
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Lichen striatus with nail involvement in a 6-year-old boy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2020;2020:1494760. doi:10.1155/2020/1494760
- Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00720.x
- Iorizzo M, Rubin AI, Starace M. Nail lichen striatus: is dermoscopy useful for the diagnosis? Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:859-863. doi:10.1111/pde.13916
- Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1993.tb00399.x
- Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(6, pt 1):908-913. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80270-8
- Simpson EL, Thompson MM, Hanifin JM. Prevalence and morphology of hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2006;17:123-127. doi:10.2310/6620.2006.06005
- Sarifakioglu E, Yilmaz AE, Gorpelioglu C. Nail alterations in 250 infant patients: a clinical study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:741-744. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02592.x
- Milanesi N, D’Erme AM, Gola M. Nail improvement during alitretinoin treatment: three case reports and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:533-536. doi:10.1111/ced.12584
- Chung BY, Choi YW, Kim HO, et al. Nail dystrophy in patients with atopic dermatitis and its association with disease severity. Ann Dermatol. 2019;31:121-126. doi:10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.121
- Navarro-Triviño FJ, Vega-Castillo JJ, Ruiz-Villaverde R. Nail changes successfully treated with dupilumab in a patient with severe atopic dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2021;62:e468-e469. doi:10.1111/ajd.13633
- Wei SH, Huang YP, Liu MC, et al. An outbreak of coxsackievirus A6 hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with onychomadesis in Taiwan, 2010. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:346. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-11-346
- Shin JY, Cho BK, Park HJ. A clinical study of nail changes occurring secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: onychomadesis and Beau’s lines. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:280-283. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.280
- Verma S, Singal A. Nail changes in hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD). Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021;12:656-657. doi:10.4103 /idoj.IDOJ_271_20
- Giordano LMC, de la Fuente LA, Lorca JMB, et al. Onychomadesis secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: a frequent manifestation and cause of concern for parents. Article in Spanish. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018;89:380-383. doi:10.4067/s0370-41062018005000203
- Justino MCA, da SMD, Souza MF, et al. Atypical hand-foot-mouth disease in Belém, Amazon region, northern Brazil, with detection of coxsackievirus A6. J Clin Virol. 2020;126:104307. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104307
- Cheng FF, Zhang BB, Cao ML, et al. Clinical characteristics of 68 children with atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6: a single-center retrospective analysis. Transl Pediatr. 2022;11:1502-1509. doi:10.21037/tp-22-352
- Nagata S. Causes of Kawasaki disease-from past to present. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:18. doi:10.3389/fped.2019.00018
- Mitsuishi T, Miyata K, Ando A, et al. Characteristic nail lesions in Kawasaki disease: case series and literature review. J Dermatol. 2022;49:232-238. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16276
- Lindsley CB. Nail-bed lines in Kawasaki disease. Am J Dis Child. 1992;146:659-660. doi:10.1001/archpedi.1992.02160180017005
- Matsumura O, Nakagishi Y. Pincer nails upon convalescence from Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2022;246:279. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2022.03.002
- Solís-Arias MP, García-Romero MT. Onychomycosis in children. a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:123-130. doi:10.1111/ijd.13392
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Onychomycosis in children: safety and efficacy of antifungal agents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:552-559. doi:10.1111/pde.13561
- 49. Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Shear NH, et al. Labeled use of efinaconazole topical solution 10% in treating onychomycosis in children and a review of the management of pediatric onychomycosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13613. doi:10.1111/dth.13613
- Falotico JM, Lipner SR. Updated perspectives on the diagnosis and management of onychomycosis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:1933-1957. doi:10.2147/ccid.S362635
- Patel D, Castelo-Soccio LA, Rubin AI, et al. Laboratory monitoring during systemic terbinafine therapy for pediatric onychomycosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1326-1327. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4483
- Friedlander SF, Chan YC, Chan YH, et al. Onychomycosis does not always require systemic treatment for cure: a trial using topical therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:316-322. doi:10.1111/pde.12064
- Rich P, Spellman M, Purohit V, et al. Tavaborole 5% topical solution for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients: results from a phase 4 open-label study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:190-195.
- Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Abramovits W, et al. JUBLIA (efinaconazole 10% solution) in the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis. Skinmed. 2021;19:206-210.
- Gupta AK, Paquet M. Systemic antifungals to treat onychomycosis in children: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:294-302. doi:10.1111/pde.12048
- Leggit JC. Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96:44-51.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Congenital malalignment of the great toenails with acute paronychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e288-e289.doi:10.1111/pde.12924
Practice Points
- Nail plate pitting is the most common clinical sign of nail psoriasis in children.
- Nail changes are common in hand, foot, and mouth disease, with the most frequent being onychomadesis.
- Because onychomycosis may resemble other nail disorders, mycologic confirmation is recommended to avoid misdiagnosis.
- Many nail conditions in children self-resolve but recognizing these manifestations is important in providing anticipatory guidance to patients and caregivers.
Combination Therapy Looks Promising for Hepatitis D
, a multinational phase 2b open-label study in Europe found.
The combination resulted in higher rates of HDV RNA suppression levels at 24 weeks after end of treatment, especially at a higher, 10-mg dose of bulevirtide, according to researchers led by Tarik Asselah, MD. PhD, a professor of medicine and hepatology at Hôpital Beaujon, APHP, Clichy, France, and the University of Paris.
“This response appeared to be maintained from 24-48 weeks after the end of treatment — a finding that supports the concept that sustained undetectable HDV RNA for at least 1 year after treatment is possible in patients with chronic hepatitis D who have been treated with a finite duration of therapy of at least 96 weeks, including 48 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy,” the investigators wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“As of today, there is no approved treatment for chronic HDV infection in the United States. Pegylated interferon alfa-2a, which is not approved for treatment of HDV, is the only option recommended by US treatment guidelines,” said study corresponding author Fabien Zoulim, MD, PhD, a hepatologist at the Lyon Hepatology Institute and a professor of medicine at the University of Lyon in France, in comments to GI & Hepatology News. “Bulevirtide 2 mg is approved for treating chronic HDV and compensated liver disease, and both bulevirtide and peginterferon are recommended options by the European treatment guidelines.”
The study found that most patients with undetectable HDV RNA levels during treatment-free follow-up showed no reduction in HepB surface antigen (HBsAg), suggesting an undetectable HDV RNA level can be achieved and sustained without HBsAg loss, the authors wrote.
While very small numbers in the combo groups and the higher-dose bulevirtide arm cleared HBsAg, “the study was not powered to evaluate the HBsAg response,” Dr. Zoulim said.
HDV is a defective virus that requires HBsAg for assembly and propagation, the authors noted. It affects as many as 20 million persons worldwide, and as the most severe form of chronic viral hepatitis, is associated with 2-6 times the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and 2-3 times the risk of death associated with HBV monoinfection.
Though not common in the United States, it affects an estimated 10 to 20 million people worldwide (J Hepatol. 2020 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.008). One US database study found HepD in 4.6% of patients with HepB infection.
Commenting on the study but not a participant in it, Ahmet O. Gurakar, MD, AGAF, a professor of medicine in the sections of gastroenterology and hepatology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, said the study findings look promising for the future treatment of HepD, but cautioned that it will be “a slow process to get approval for combination therapy with bulevirtide since the FDA has previously said it needs to see more studies. The findings need to be confirmed in larger groups, but it’s difficult to recruit enough patients in the United States for a trial since hepatitis D is not common in this country — it’s more common in the Mediterranean basin Eastern European populations.”
The Trial
The investigators randomly assigned 174, largely male, patients ages 18-65 (mean, about 41) years to receive one of four treatments:
- Pegylated interferon alfa-2a alone at 180 μg per week) for 48 weeks (n = 24).
- Bulevirtide at a daily dose of 2 mg plus peginterferon alfa-2a at 180 μg per week for 48 weeks, followed by the same daily dose of bulevirtide for 48 weeks (n = 50).
- Bulevirtide at 10 mg plus peginterferon alfa-2a at 180 μg per week for 48 weeks, followed by the same daily dose of bulevirtide for 48 weeks (n = 50).
- Bulevirtide at a daily dose of 10 mg alone for 96 weeks (n = 50).
All were followed for 48 weeks after treatment. The primary comparison was between the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group and the 10-mg bulevirtide monotherapy group.
At 24 weeks post-treatment, HDV RNA was undetectable in 17% of patients in the peginterferon alfa-2a group. In the other arms, HDV RNA was undetectable in 32% in the 2-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, in 46% of the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, and in 12% of the 10-mg bulevirtide group.
For the primary comparison, the between-group difference was 34 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 15-50; P < .001).
At 48 weeks after the end of treatment, HDV RNA was undetectable in 25% in the peginterferon alfa-2a group, 26% in the 2-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, 46% in the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, and 12% in the 10-mg bulevirtide group.
Also calling the findings promising, Anna Lok, MBBS, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said that, “Given that the European Medicines Agency’s approval is for bulevirtide alone at 2 mg, results of this study should prompt reassessment whether bulevirtide should be used in combination with pegylated interferon in patients with no contraindications, and if 10 mg is more appropriate than a 2-mg dose.”
As to safety, the most frequent adverse events were leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia, with the majority of adverse events being grade 1 or 2.
In comparison with other research, the current trial found that 70% in the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group had an undetectable HDV RNA level at the end of treatment versus results of the Hep-Net International Delta Hepatitis Interventional Trial II (HIDIT-II), in which 33%-48% had undetectable levels after 96 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy, with or without tenofovir disoproxil. And in the phase 3 MYR301 trial, HDV RNA was undetectable in 20%-36% after 96 weeks of bulevirtide monotherapy.
The authors acknowledged that in addition to the lack of blinding, the trial was not designed to compare the two doses of bulevirtide and therefore lacked an adequate sample size to allow for formal comparisons. And although it included a peginterferon alfa-2a monotherapy group, it was not sufficiently powered to allow for comparison. They are currently considering plans for further studies in this area.
This study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Asselah disclosed consulting, safety/data monitoring, or travel for Gilead Sciences, AbbVie, Antio Therapeutics, Eiger Biopharmaceutical, Enyo Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson Healthcare Systems, and Vir Biotechnology. Dr. Zoulim reported consulting or research for multiple pharmaceutical/biotech companies, including Gilead Sciences. Numerous study coauthors declared financial relationships such as consulting, research, or employment with multiple private-sector companies, including Gilead Sciences. Dr. Lok and Dr. Gurakar disclosed no competing interests relevant to their comments.
, a multinational phase 2b open-label study in Europe found.
The combination resulted in higher rates of HDV RNA suppression levels at 24 weeks after end of treatment, especially at a higher, 10-mg dose of bulevirtide, according to researchers led by Tarik Asselah, MD. PhD, a professor of medicine and hepatology at Hôpital Beaujon, APHP, Clichy, France, and the University of Paris.
“This response appeared to be maintained from 24-48 weeks after the end of treatment — a finding that supports the concept that sustained undetectable HDV RNA for at least 1 year after treatment is possible in patients with chronic hepatitis D who have been treated with a finite duration of therapy of at least 96 weeks, including 48 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy,” the investigators wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“As of today, there is no approved treatment for chronic HDV infection in the United States. Pegylated interferon alfa-2a, which is not approved for treatment of HDV, is the only option recommended by US treatment guidelines,” said study corresponding author Fabien Zoulim, MD, PhD, a hepatologist at the Lyon Hepatology Institute and a professor of medicine at the University of Lyon in France, in comments to GI & Hepatology News. “Bulevirtide 2 mg is approved for treating chronic HDV and compensated liver disease, and both bulevirtide and peginterferon are recommended options by the European treatment guidelines.”
The study found that most patients with undetectable HDV RNA levels during treatment-free follow-up showed no reduction in HepB surface antigen (HBsAg), suggesting an undetectable HDV RNA level can be achieved and sustained without HBsAg loss, the authors wrote.
While very small numbers in the combo groups and the higher-dose bulevirtide arm cleared HBsAg, “the study was not powered to evaluate the HBsAg response,” Dr. Zoulim said.
HDV is a defective virus that requires HBsAg for assembly and propagation, the authors noted. It affects as many as 20 million persons worldwide, and as the most severe form of chronic viral hepatitis, is associated with 2-6 times the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and 2-3 times the risk of death associated with HBV monoinfection.
Though not common in the United States, it affects an estimated 10 to 20 million people worldwide (J Hepatol. 2020 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.008). One US database study found HepD in 4.6% of patients with HepB infection.
Commenting on the study but not a participant in it, Ahmet O. Gurakar, MD, AGAF, a professor of medicine in the sections of gastroenterology and hepatology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, said the study findings look promising for the future treatment of HepD, but cautioned that it will be “a slow process to get approval for combination therapy with bulevirtide since the FDA has previously said it needs to see more studies. The findings need to be confirmed in larger groups, but it’s difficult to recruit enough patients in the United States for a trial since hepatitis D is not common in this country — it’s more common in the Mediterranean basin Eastern European populations.”
The Trial
The investigators randomly assigned 174, largely male, patients ages 18-65 (mean, about 41) years to receive one of four treatments:
- Pegylated interferon alfa-2a alone at 180 μg per week) for 48 weeks (n = 24).
- Bulevirtide at a daily dose of 2 mg plus peginterferon alfa-2a at 180 μg per week for 48 weeks, followed by the same daily dose of bulevirtide for 48 weeks (n = 50).
- Bulevirtide at 10 mg plus peginterferon alfa-2a at 180 μg per week for 48 weeks, followed by the same daily dose of bulevirtide for 48 weeks (n = 50).
- Bulevirtide at a daily dose of 10 mg alone for 96 weeks (n = 50).
All were followed for 48 weeks after treatment. The primary comparison was between the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group and the 10-mg bulevirtide monotherapy group.
At 24 weeks post-treatment, HDV RNA was undetectable in 17% of patients in the peginterferon alfa-2a group. In the other arms, HDV RNA was undetectable in 32% in the 2-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, in 46% of the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, and in 12% of the 10-mg bulevirtide group.
For the primary comparison, the between-group difference was 34 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 15-50; P < .001).
At 48 weeks after the end of treatment, HDV RNA was undetectable in 25% in the peginterferon alfa-2a group, 26% in the 2-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, 46% in the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, and 12% in the 10-mg bulevirtide group.
Also calling the findings promising, Anna Lok, MBBS, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said that, “Given that the European Medicines Agency’s approval is for bulevirtide alone at 2 mg, results of this study should prompt reassessment whether bulevirtide should be used in combination with pegylated interferon in patients with no contraindications, and if 10 mg is more appropriate than a 2-mg dose.”
As to safety, the most frequent adverse events were leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia, with the majority of adverse events being grade 1 or 2.
In comparison with other research, the current trial found that 70% in the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group had an undetectable HDV RNA level at the end of treatment versus results of the Hep-Net International Delta Hepatitis Interventional Trial II (HIDIT-II), in which 33%-48% had undetectable levels after 96 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy, with or without tenofovir disoproxil. And in the phase 3 MYR301 trial, HDV RNA was undetectable in 20%-36% after 96 weeks of bulevirtide monotherapy.
The authors acknowledged that in addition to the lack of blinding, the trial was not designed to compare the two doses of bulevirtide and therefore lacked an adequate sample size to allow for formal comparisons. And although it included a peginterferon alfa-2a monotherapy group, it was not sufficiently powered to allow for comparison. They are currently considering plans for further studies in this area.
This study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Asselah disclosed consulting, safety/data monitoring, or travel for Gilead Sciences, AbbVie, Antio Therapeutics, Eiger Biopharmaceutical, Enyo Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson Healthcare Systems, and Vir Biotechnology. Dr. Zoulim reported consulting or research for multiple pharmaceutical/biotech companies, including Gilead Sciences. Numerous study coauthors declared financial relationships such as consulting, research, or employment with multiple private-sector companies, including Gilead Sciences. Dr. Lok and Dr. Gurakar disclosed no competing interests relevant to their comments.
, a multinational phase 2b open-label study in Europe found.
The combination resulted in higher rates of HDV RNA suppression levels at 24 weeks after end of treatment, especially at a higher, 10-mg dose of bulevirtide, according to researchers led by Tarik Asselah, MD. PhD, a professor of medicine and hepatology at Hôpital Beaujon, APHP, Clichy, France, and the University of Paris.
“This response appeared to be maintained from 24-48 weeks after the end of treatment — a finding that supports the concept that sustained undetectable HDV RNA for at least 1 year after treatment is possible in patients with chronic hepatitis D who have been treated with a finite duration of therapy of at least 96 weeks, including 48 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy,” the investigators wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“As of today, there is no approved treatment for chronic HDV infection in the United States. Pegylated interferon alfa-2a, which is not approved for treatment of HDV, is the only option recommended by US treatment guidelines,” said study corresponding author Fabien Zoulim, MD, PhD, a hepatologist at the Lyon Hepatology Institute and a professor of medicine at the University of Lyon in France, in comments to GI & Hepatology News. “Bulevirtide 2 mg is approved for treating chronic HDV and compensated liver disease, and both bulevirtide and peginterferon are recommended options by the European treatment guidelines.”
The study found that most patients with undetectable HDV RNA levels during treatment-free follow-up showed no reduction in HepB surface antigen (HBsAg), suggesting an undetectable HDV RNA level can be achieved and sustained without HBsAg loss, the authors wrote.
While very small numbers in the combo groups and the higher-dose bulevirtide arm cleared HBsAg, “the study was not powered to evaluate the HBsAg response,” Dr. Zoulim said.
HDV is a defective virus that requires HBsAg for assembly and propagation, the authors noted. It affects as many as 20 million persons worldwide, and as the most severe form of chronic viral hepatitis, is associated with 2-6 times the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and 2-3 times the risk of death associated with HBV monoinfection.
Though not common in the United States, it affects an estimated 10 to 20 million people worldwide (J Hepatol. 2020 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.008). One US database study found HepD in 4.6% of patients with HepB infection.
Commenting on the study but not a participant in it, Ahmet O. Gurakar, MD, AGAF, a professor of medicine in the sections of gastroenterology and hepatology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, said the study findings look promising for the future treatment of HepD, but cautioned that it will be “a slow process to get approval for combination therapy with bulevirtide since the FDA has previously said it needs to see more studies. The findings need to be confirmed in larger groups, but it’s difficult to recruit enough patients in the United States for a trial since hepatitis D is not common in this country — it’s more common in the Mediterranean basin Eastern European populations.”
The Trial
The investigators randomly assigned 174, largely male, patients ages 18-65 (mean, about 41) years to receive one of four treatments:
- Pegylated interferon alfa-2a alone at 180 μg per week) for 48 weeks (n = 24).
- Bulevirtide at a daily dose of 2 mg plus peginterferon alfa-2a at 180 μg per week for 48 weeks, followed by the same daily dose of bulevirtide for 48 weeks (n = 50).
- Bulevirtide at 10 mg plus peginterferon alfa-2a at 180 μg per week for 48 weeks, followed by the same daily dose of bulevirtide for 48 weeks (n = 50).
- Bulevirtide at a daily dose of 10 mg alone for 96 weeks (n = 50).
All were followed for 48 weeks after treatment. The primary comparison was between the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group and the 10-mg bulevirtide monotherapy group.
At 24 weeks post-treatment, HDV RNA was undetectable in 17% of patients in the peginterferon alfa-2a group. In the other arms, HDV RNA was undetectable in 32% in the 2-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, in 46% of the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, and in 12% of the 10-mg bulevirtide group.
For the primary comparison, the between-group difference was 34 percentage points (95% confidence interval, 15-50; P < .001).
At 48 weeks after the end of treatment, HDV RNA was undetectable in 25% in the peginterferon alfa-2a group, 26% in the 2-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, 46% in the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group, and 12% in the 10-mg bulevirtide group.
Also calling the findings promising, Anna Lok, MBBS, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said that, “Given that the European Medicines Agency’s approval is for bulevirtide alone at 2 mg, results of this study should prompt reassessment whether bulevirtide should be used in combination with pegylated interferon in patients with no contraindications, and if 10 mg is more appropriate than a 2-mg dose.”
As to safety, the most frequent adverse events were leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia, with the majority of adverse events being grade 1 or 2.
In comparison with other research, the current trial found that 70% in the 10-mg bulevirtide plus peginterferon alfa-2a group had an undetectable HDV RNA level at the end of treatment versus results of the Hep-Net International Delta Hepatitis Interventional Trial II (HIDIT-II), in which 33%-48% had undetectable levels after 96 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy, with or without tenofovir disoproxil. And in the phase 3 MYR301 trial, HDV RNA was undetectable in 20%-36% after 96 weeks of bulevirtide monotherapy.
The authors acknowledged that in addition to the lack of blinding, the trial was not designed to compare the two doses of bulevirtide and therefore lacked an adequate sample size to allow for formal comparisons. And although it included a peginterferon alfa-2a monotherapy group, it was not sufficiently powered to allow for comparison. They are currently considering plans for further studies in this area.
This study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Asselah disclosed consulting, safety/data monitoring, or travel for Gilead Sciences, AbbVie, Antio Therapeutics, Eiger Biopharmaceutical, Enyo Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson Healthcare Systems, and Vir Biotechnology. Dr. Zoulim reported consulting or research for multiple pharmaceutical/biotech companies, including Gilead Sciences. Numerous study coauthors declared financial relationships such as consulting, research, or employment with multiple private-sector companies, including Gilead Sciences. Dr. Lok and Dr. Gurakar disclosed no competing interests relevant to their comments.
FROM NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE