User login
Calorie counting and exercise ‘of limited value’ for obesity weight loss
Counting calories, joining a gym, and taking part in exercise programs are popular methods used by people in the United Kingdom who want to shed some pounds, but they seem to be fairly ineffective strategies, according to an investigation.
A survey of adults with obesity from six countries in western Europe found that most who set out to reduce a meaningful amount of weight failed in their attempt.
The preliminary results, presented in two posters at the European Congress on Obesity, underlined the need for better support and solutions for weight management, the authors suggested.
Marc Evans, MB, BCh, a consultant physician in diabetes and endocrinology, from University Hospital, Cardiff, Wales, who led the analysis, said that, “while obesity’s impact on health is well known, our finding that a sizable proportion of adults with obesity appear at elevated risk of hospitalization or surgery due to multiple underlying illnesses, undoubtedly adds a sense of urgency to tackling Europe’s growing obesity epidemic.”
The study, which also involved analytics consultancy firm Lane Clark & Peacock, conducted a cross-sectional survey of 1,850 adults. Of those 500 were from the UK, and the remainder from France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Sweden.
All participants had a body mass index of 30 kg/m2, or higher. More specifically, 56.3%; were classified as obesity class I, 26.8% obesity class II, and 16.9% obesity class III.
Obesity-related conditions
In total, 25.7% of participants reported no obesity-related health conditions, 28.4% had one condition, 19.6% had two, and 26.3% had three or more. The most common comorbidities were hypertension, dyslipidemia, and type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 78.6% of respondents reported having tried to lose weight in the previous year. Asked in a questionnaire about how they had tried to achieve this, the responses indicated that the most common strategies were:
- Calorie-controlled/restricted diet (71.9%)
- Exercise program course (21.9%)
- Pharmaceutical treatment/medication (12.3%)
- Joined a gym (12%)
- Digital health app (9.7%)
Among other participants, 8.1% said they had used alternative treatments, 7.6% a weight loss service, and 2.1% cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Analysis of the survey results showed that 78% of the individuals who attempted to lose weight did not achieve a clinically meaningful loss of 5% or more of their body weight, while some actually weighed more afterward.
Exercise and restricted diet
Notably, while exercise and calorie-controlled or restricted diets were among the most popular weight-loss methods in U.K. participants, they were amongst the least successful strategies. For instance, while 26.5% of adults who controlled their diet said they had lost weight, 17.1% reported their weight had increased. For those who took part in an exercise program, 33.3% said they lost weight, but 15.5% said they gained weight.
Signing up for gym membership also scored poorly, with 27% shedding weight, compared with 32.4% who put weight on.
“Our survey results indicate that, while the majority of adults with obesity are actively trying to reduce their weight, using a variety of strategies, most are unsuccessful,” said Dr. Evans.
Further studies were needed to assess whether people who lose weight succeed in maintaining their weight loss, the authors said.
The conference posters have yet to be published in a journal but were peer reviewed by the ECO selection committee.
The studies were sponsored by Novo Nordisk, a researcher into and manufacturer of diabetes and obesity medications, and employer of several of the coauthors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK/Univadis.
Counting calories, joining a gym, and taking part in exercise programs are popular methods used by people in the United Kingdom who want to shed some pounds, but they seem to be fairly ineffective strategies, according to an investigation.
A survey of adults with obesity from six countries in western Europe found that most who set out to reduce a meaningful amount of weight failed in their attempt.
The preliminary results, presented in two posters at the European Congress on Obesity, underlined the need for better support and solutions for weight management, the authors suggested.
Marc Evans, MB, BCh, a consultant physician in diabetes and endocrinology, from University Hospital, Cardiff, Wales, who led the analysis, said that, “while obesity’s impact on health is well known, our finding that a sizable proportion of adults with obesity appear at elevated risk of hospitalization or surgery due to multiple underlying illnesses, undoubtedly adds a sense of urgency to tackling Europe’s growing obesity epidemic.”
The study, which also involved analytics consultancy firm Lane Clark & Peacock, conducted a cross-sectional survey of 1,850 adults. Of those 500 were from the UK, and the remainder from France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Sweden.
All participants had a body mass index of 30 kg/m2, or higher. More specifically, 56.3%; were classified as obesity class I, 26.8% obesity class II, and 16.9% obesity class III.
Obesity-related conditions
In total, 25.7% of participants reported no obesity-related health conditions, 28.4% had one condition, 19.6% had two, and 26.3% had three or more. The most common comorbidities were hypertension, dyslipidemia, and type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 78.6% of respondents reported having tried to lose weight in the previous year. Asked in a questionnaire about how they had tried to achieve this, the responses indicated that the most common strategies were:
- Calorie-controlled/restricted diet (71.9%)
- Exercise program course (21.9%)
- Pharmaceutical treatment/medication (12.3%)
- Joined a gym (12%)
- Digital health app (9.7%)
Among other participants, 8.1% said they had used alternative treatments, 7.6% a weight loss service, and 2.1% cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Analysis of the survey results showed that 78% of the individuals who attempted to lose weight did not achieve a clinically meaningful loss of 5% or more of their body weight, while some actually weighed more afterward.
Exercise and restricted diet
Notably, while exercise and calorie-controlled or restricted diets were among the most popular weight-loss methods in U.K. participants, they were amongst the least successful strategies. For instance, while 26.5% of adults who controlled their diet said they had lost weight, 17.1% reported their weight had increased. For those who took part in an exercise program, 33.3% said they lost weight, but 15.5% said they gained weight.
Signing up for gym membership also scored poorly, with 27% shedding weight, compared with 32.4% who put weight on.
“Our survey results indicate that, while the majority of adults with obesity are actively trying to reduce their weight, using a variety of strategies, most are unsuccessful,” said Dr. Evans.
Further studies were needed to assess whether people who lose weight succeed in maintaining their weight loss, the authors said.
The conference posters have yet to be published in a journal but were peer reviewed by the ECO selection committee.
The studies were sponsored by Novo Nordisk, a researcher into and manufacturer of diabetes and obesity medications, and employer of several of the coauthors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK/Univadis.
Counting calories, joining a gym, and taking part in exercise programs are popular methods used by people in the United Kingdom who want to shed some pounds, but they seem to be fairly ineffective strategies, according to an investigation.
A survey of adults with obesity from six countries in western Europe found that most who set out to reduce a meaningful amount of weight failed in their attempt.
The preliminary results, presented in two posters at the European Congress on Obesity, underlined the need for better support and solutions for weight management, the authors suggested.
Marc Evans, MB, BCh, a consultant physician in diabetes and endocrinology, from University Hospital, Cardiff, Wales, who led the analysis, said that, “while obesity’s impact on health is well known, our finding that a sizable proportion of adults with obesity appear at elevated risk of hospitalization or surgery due to multiple underlying illnesses, undoubtedly adds a sense of urgency to tackling Europe’s growing obesity epidemic.”
The study, which also involved analytics consultancy firm Lane Clark & Peacock, conducted a cross-sectional survey of 1,850 adults. Of those 500 were from the UK, and the remainder from France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Sweden.
All participants had a body mass index of 30 kg/m2, or higher. More specifically, 56.3%; were classified as obesity class I, 26.8% obesity class II, and 16.9% obesity class III.
Obesity-related conditions
In total, 25.7% of participants reported no obesity-related health conditions, 28.4% had one condition, 19.6% had two, and 26.3% had three or more. The most common comorbidities were hypertension, dyslipidemia, and type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 78.6% of respondents reported having tried to lose weight in the previous year. Asked in a questionnaire about how they had tried to achieve this, the responses indicated that the most common strategies were:
- Calorie-controlled/restricted diet (71.9%)
- Exercise program course (21.9%)
- Pharmaceutical treatment/medication (12.3%)
- Joined a gym (12%)
- Digital health app (9.7%)
Among other participants, 8.1% said they had used alternative treatments, 7.6% a weight loss service, and 2.1% cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Analysis of the survey results showed that 78% of the individuals who attempted to lose weight did not achieve a clinically meaningful loss of 5% or more of their body weight, while some actually weighed more afterward.
Exercise and restricted diet
Notably, while exercise and calorie-controlled or restricted diets were among the most popular weight-loss methods in U.K. participants, they were amongst the least successful strategies. For instance, while 26.5% of adults who controlled their diet said they had lost weight, 17.1% reported their weight had increased. For those who took part in an exercise program, 33.3% said they lost weight, but 15.5% said they gained weight.
Signing up for gym membership also scored poorly, with 27% shedding weight, compared with 32.4% who put weight on.
“Our survey results indicate that, while the majority of adults with obesity are actively trying to reduce their weight, using a variety of strategies, most are unsuccessful,” said Dr. Evans.
Further studies were needed to assess whether people who lose weight succeed in maintaining their weight loss, the authors said.
The conference posters have yet to be published in a journal but were peer reviewed by the ECO selection committee.
The studies were sponsored by Novo Nordisk, a researcher into and manufacturer of diabetes and obesity medications, and employer of several of the coauthors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK/Univadis.
FROM ECO 2022
Three-parent IVF now legal in two countries
: the United Kingdom and Australia.
Australia’s senate passed a bill on March 30 amending pre-existing laws to allow the procedure in certain circumstances.
The goal of this procedure is to prevent genetic disorders caused by defective mitochondria, the power plants inside our cells that provide energy for normal growth and development. When mitochondria don’t produce any energy at all, the resulting genetic disorders are quickly fatal. When mitochondria make only a little energy, children can have severe illnesses and disabilities.
“The outcomes from this problem are really severe, and it’s highly likely that the baby will be very sick or die,” says Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the division of medical ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Mitochondria have a little bit of DNA, and children inherit them from their mother. To avoid children inheriting this damaged genetic material, mitochondrial donation, also known as three-parent in vitro fertilization (IVF), takes the nucleus, which contains most of the DNA that makes us who we are, from an egg of the mother and puts it into a donated egg from a woman with healthy mitochondria.
The egg is then fertilized with sperm through IVF, and the resulting embryo has genetic material from two women and one man.
One ethical conundrum about mitochondrial donation is that any child conceived this way would inherit modified DNA and pass that along to their own children.
“I think it’s likely that we are going to go down this road to repair disease,” Dr. Caplan says. “I don’t think all genetic engineering of embryos is wrong, but we have to draw the line between enhancement versus treating disease.”
For couples who want a child that shares at least some of their own DNA, there are other ways to have a child without damaged mitochondria. One option would be genetic screening of their embryos to find healthy embryos without this defect, which would work for some women who have relatively few mitochondrial mutations. Another alternative is using a donor egg from a woman with healthy mitochondria.
Mitochondrial donation may appeal to couples who want their children to have a genetic connection to both parents, Dr. Caplan says. But prospective parents also need to be aware that this procedure is relatively new and, unlike egg donation, doesn’t have a long track record of success.
“It looks promising, but we don’t have the full safety picture yet, and we’re not going to start to get it for another decade or so,” Dr. Caplan cautions. “I do think it’s worth offering as one option, but you also have to get people to think about how important it is to have a biological child together and make sure that they understand that even if we try this technique, we don’t know the long-term outcomes for children yet.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
: the United Kingdom and Australia.
Australia’s senate passed a bill on March 30 amending pre-existing laws to allow the procedure in certain circumstances.
The goal of this procedure is to prevent genetic disorders caused by defective mitochondria, the power plants inside our cells that provide energy for normal growth and development. When mitochondria don’t produce any energy at all, the resulting genetic disorders are quickly fatal. When mitochondria make only a little energy, children can have severe illnesses and disabilities.
“The outcomes from this problem are really severe, and it’s highly likely that the baby will be very sick or die,” says Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the division of medical ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Mitochondria have a little bit of DNA, and children inherit them from their mother. To avoid children inheriting this damaged genetic material, mitochondrial donation, also known as three-parent in vitro fertilization (IVF), takes the nucleus, which contains most of the DNA that makes us who we are, from an egg of the mother and puts it into a donated egg from a woman with healthy mitochondria.
The egg is then fertilized with sperm through IVF, and the resulting embryo has genetic material from two women and one man.
One ethical conundrum about mitochondrial donation is that any child conceived this way would inherit modified DNA and pass that along to their own children.
“I think it’s likely that we are going to go down this road to repair disease,” Dr. Caplan says. “I don’t think all genetic engineering of embryos is wrong, but we have to draw the line between enhancement versus treating disease.”
For couples who want a child that shares at least some of their own DNA, there are other ways to have a child without damaged mitochondria. One option would be genetic screening of their embryos to find healthy embryos without this defect, which would work for some women who have relatively few mitochondrial mutations. Another alternative is using a donor egg from a woman with healthy mitochondria.
Mitochondrial donation may appeal to couples who want their children to have a genetic connection to both parents, Dr. Caplan says. But prospective parents also need to be aware that this procedure is relatively new and, unlike egg donation, doesn’t have a long track record of success.
“It looks promising, but we don’t have the full safety picture yet, and we’re not going to start to get it for another decade or so,” Dr. Caplan cautions. “I do think it’s worth offering as one option, but you also have to get people to think about how important it is to have a biological child together and make sure that they understand that even if we try this technique, we don’t know the long-term outcomes for children yet.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
: the United Kingdom and Australia.
Australia’s senate passed a bill on March 30 amending pre-existing laws to allow the procedure in certain circumstances.
The goal of this procedure is to prevent genetic disorders caused by defective mitochondria, the power plants inside our cells that provide energy for normal growth and development. When mitochondria don’t produce any energy at all, the resulting genetic disorders are quickly fatal. When mitochondria make only a little energy, children can have severe illnesses and disabilities.
“The outcomes from this problem are really severe, and it’s highly likely that the baby will be very sick or die,” says Arthur Caplan, PhD, head of the division of medical ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Mitochondria have a little bit of DNA, and children inherit them from their mother. To avoid children inheriting this damaged genetic material, mitochondrial donation, also known as three-parent in vitro fertilization (IVF), takes the nucleus, which contains most of the DNA that makes us who we are, from an egg of the mother and puts it into a donated egg from a woman with healthy mitochondria.
The egg is then fertilized with sperm through IVF, and the resulting embryo has genetic material from two women and one man.
One ethical conundrum about mitochondrial donation is that any child conceived this way would inherit modified DNA and pass that along to their own children.
“I think it’s likely that we are going to go down this road to repair disease,” Dr. Caplan says. “I don’t think all genetic engineering of embryos is wrong, but we have to draw the line between enhancement versus treating disease.”
For couples who want a child that shares at least some of their own DNA, there are other ways to have a child without damaged mitochondria. One option would be genetic screening of their embryos to find healthy embryos without this defect, which would work for some women who have relatively few mitochondrial mutations. Another alternative is using a donor egg from a woman with healthy mitochondria.
Mitochondrial donation may appeal to couples who want their children to have a genetic connection to both parents, Dr. Caplan says. But prospective parents also need to be aware that this procedure is relatively new and, unlike egg donation, doesn’t have a long track record of success.
“It looks promising, but we don’t have the full safety picture yet, and we’re not going to start to get it for another decade or so,” Dr. Caplan cautions. “I do think it’s worth offering as one option, but you also have to get people to think about how important it is to have a biological child together and make sure that they understand that even if we try this technique, we don’t know the long-term outcomes for children yet.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Natriuretic Peptide Screening for Primary Prevention or Early Detection of Heart Failure: A Pharmacist-Driven Team-Based Approach
Heart failure (HF) is one of the leading causes of hospitalizations and the most expensive Medicare diagnosis. Its prevalence continues to rise with a projected increase of 46% from 2012 to 2030 resulting in > 8 million people aged ≥ 18 years with HF in the United States. Despite improvements in therapy, mortality remains unacceptably high with a 50% mortality rate within 5 years. Early detection strategies are needed to identify patients at risk of developing HF to delay the disease course and improve survival.1,2
Emerging data indicates that natriuretic peptide biomarker-based screening using B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and early intervention for patients at risk of HF could prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction or new-onset HF.3-5 The 2013 St. Vincent’s Screening to Prevent Heart Failure (STOP-HF) trial is the largest study to date to evaluate BNP as a screening tool for patients at risk for HF.4 Patients at risk of HF who did not have established left ventricular systolic dysfunction or symptomatic HF were assigned randomly to usual primary care or BNP screening. Patients with BNP levels ≥ 50 pg/mL underwent echocardiogram and were referred to a cardiovascular specialty service for management. The cardiovascular specialty clinic included a team of registered nurses, nurse practitioners, pharmacists, dieticians, palliative care specialists, and cardiologists. Individuals in the intervention group showed increased renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor use at follow-up (control, 49.6%; intervention, 59.6%; P = .01). All patients received coaching by a nurse who emphasized individual risk, importance of medication adherence, and healthy lifestyle behaviors. After a mean follow-up of 4.2 years, 59 of 677 participants (8.7%) in the control group and 37 of 697 (5.3%) in the intervention group (odds ratio [OR], 0.55; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.82; P = .003) met the primary end point of left ventricular dysfunction with or without HF. BNP-based screening in conjunction with collaborative care reduced rates of left ventricular dysfunction and HF.
In the 2013 PONTIAC trial, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) without cardiac disease but with NT-proBNP levels > 125 pg/mL were randomized to usual diabetes care or intensified care at a cardiac outpatient clinic for initiation and increase of RAS inhibitors and β blockers.5 After 2 years, patients randomized to the intensified care group showed a 65% risk reduction of the primary endpoint of hospitalization or death from cardiac disease (P = .04).
Based on this evidence, the 2017 focused update of the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA) guideline for managing HF added a IIa recommendation for natriuretic peptide biomarker screening in those at risk of developing HF.6 The guideline recommends biomarker screening in conjunction with team-based care, including a cardiovascular specialist, and guideline-directed management and therapy to prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction or new-onset HF.
Although ordering a natriuretic peptide biomarker laboratory test is straightforward, the variability of team-based care across institutions and health systems makes it difficult to standardize screening and interventions for patients at risk for HF. We developed and piloted a process using clinical pharmacists in primary care for natriuretic peptide biomarker screening and risk factor reduction within the established patient aligned care team (PACT) framework at a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center. In this paper, we describe our implementation process including descriptive preliminary outcomes.
Methods
The PACT team-based approach in primary care clinics is similar to the patient-centered medical home framework. A PACT includes the veteran patient and an interdisciplinary team of health professionals composed of their primary care practitioner (PCP), registered nurse care manager, clinical pharmacist, and other clinical and administrative staff. The PACT clinical pharmacist has prescriptive authority within a scope of practice to provide postdiagnostic chronic disease state management including management of T2DM, hypertension, HF, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, anticoagulation, tobacco cessation, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk reduction. Clinical pharmacists can prescribe and adjust medications and order laboratory tests.
Our institution, Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, has a specialty HF clinic that primarily manages ACC/AHA Stage C HF patients. The HF clinic uses a team-based approach to collaborate and coordinate care for the veteran. The HF team is comprised of cardiology specialists, registered nurses, clinical pharmacists, dietitians, and administrative staff. Two PACT clinical pharmacists also staff the HF clinic at CJZVAMC and work collaboratively to initiate, adjust, and optimize veterans’ HF medication regimens.
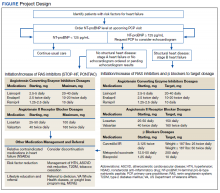
Two primary care PACT panels were selected for this project. Before implementation, a pharmacy resident and 3 PACT clinical pharmacists (2 of whom also staff the HF clinic) met with a HF cardiology specialist and 2 PACT PCPs to finalize the team-based process and workflow. PCPs were presented with the evidence-based background, purpose, and project design, which included patient identification, NT-proBNP laboratory test ordering, medication adjustment schedules, and protocol for ordering echocardiograms (Figure). Templated notes were created to allow for consistent documentation in patients’ electronic health record. A telephone script also was written for the initial telephone call to patients to explain in patient-friendly terms the implications of an elevated NT-proBNP level, the echocardiogram procedure, and recommendations for risk reduction.
Patient Selection
Patients aged ≥ 18 years with hypertension, taking antihypertensive medication for ≥ 1 month, or diagnosed with T2DM for ≥ 6 months were included. Using the parameters provided in the STOP-HF trial, patients with evidence or history of left ventricular dysfunction, defined as a left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) < 50% or an E/e’ ratio > 15 in the setting of normal EF, or symptomatic HF were excluded. Patients with a diagnosis causing life expectancy < 1 year were excluded, which was determined based on review of the patient’s chart or discussion with the PCP.
A clinical pharmacist screened patients with an upcoming PCP appointment between September 2019 and January 2020 for eligibility. For patients who met criteria, the clinical pharmacist ordered a NT-proBNP laboratory test to their already scheduled tests and entered a templated note into the patient’s chart to alert the PCP of the test. NT-proBNP was used rather than BNP because it was the natriuretic peptide laboratory test available at CJZVAMC during this time. Patients with NT-proBNP < 125 pg/mL received usual care from their PCPs. Patients with NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/mL received a follow-up phone call from a clinical pharmacist to discuss the laboratory test result with recommendations for initiation or increase of RAS inhibitors and an echocardiogram. If the patient agreed to an echocardiogram, the PCP was notified to order the test. For patients aged > 80 years with elevated NT-proBNP, risk vs benefit and patient-specific goals of care were discussed with the PCP. For patients whose echocardiograms revealed left ventricular dysfunction, initiation or adjustment of β blockers was considered. During RAS inhibitor increase, the clinical pharmacists provided a review of the patient’s risk factors and optimized management of hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) reduction, and tobacco cessation.
Outcome Measures
Outcome measures included the percentage of patients who met inclusion/exclusion criteria and had an elevated NT-proBNP level, percent change in RAS inhibitor prescriptions and optimized dosing after intervention, frequency of left ventricular dysfunction visualized with echocardiograms, and quantification of pharmacist interventions in disease state management. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze demographic data, RAS inhibitors prescriptions before and after intervention, echocardiogram results, pharmacist recommendations, and acceptance rates of disease state management.
Results
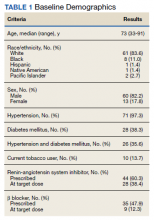
Between September 2019 and January 2020, 570 patients from 2 PACT teams were screened. Of the 570 patients, 246 met inclusion criteria with upcoming appointments. Of these, 24 were excluded, 10 for EF < 50%, 13 for E/e’ > 15 in setting of normal EF, and 1 for hypertension diagnosis without an antihypertensive regimen or elevated blood pressure. The remaining 222 patients had an NT-proBNP level ordered and drawn and 73 (32.9%) patients had an NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/mL. Baseline characteristics are described in Table 1.
Data was collected through March 2020 (due to COVID-19) found that among the 73 patients with elevated NT-proBNP: 14 had an echocardiogram within the past year without evidence of left ventricular dysfunction; 39 had echocardiograms ordered; and 19 had echocardiograms completed by March 2020. Among the 19 echocardiograms, 16 (84%) showed no evidence of left ventricular dysfunction, 2 (11%) revealed mildly reduced EF (40% to 50%), and 1 (5%) revealed a reduced EF (< 40%). These patients were identified early in the disease course before symptom onset and received intervention with RAS inhibitors and disease state management.
Patients prescribed RAS inhibitors increased from 44 to 50. The number of patients who were able to have their RAS inhibitor dosage adjusted increased from 28 to 31. For the 3 patients with mildly reduced or reduced EF, management with β blockers was based on RAS inhibitor adjustment toleration. One patient with mildly reduced EF was switched from metoprolol tartrate to metoprolol succinate.
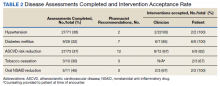
Clinical pharmacists completed disease state assessments to optimize management of hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, oral NSAID reduction, and tobacco cessation (Table 2). Interventions clinical pharmacists recommended for hypertension, in addition to RAS inhibitor management, included initiation and adjustment of amlodipine. For T2DM, interventions included initiation of metformin and initiation or adjustment of empagliflozin. For ASCVD risk reduction, interventions included starting a statin or adjusting statin therapies to appropriate intensities based on clinical ASCVD 10-year risk. Tobacco cessation interventions included pharmacotherapies, counseling, and education with written materials. Pharmacists counseled patients to minimize or eliminate NSAID use and, when appropriate, discontinued active oral NSAID prescriptions.
Discussion
We included patients diagnosed with T2DM and hypertension for several reasons. Most patients (62%) studied in the STOP-HF trial were diagnosed with hypertension. Also, T2DM represented the patient population enrolled in the PONTIAC trial. Guidance from the European Society of Cardiology recommends use of natriuretic peptides in high-risk populations, such as patients with DM and hypertension, to help target initiation of preventive measures.7 Lastly, T2DM and hypertension patients were easily identified using population management software available at the VA.
The percentage of patients in this project with risk factors for HF and an elevated NT-proBNP were similar to the elevated levels described in the STOP-HF trial. In our project, 32.9% of patients had elevated NT-proBNP levels, similar to the 41.6% of patients in STOP-HF. Among the completed echocardiograms, 16% revealed mildly reduced or reduced EF. These patients were identified early in the disease course before symptom onset and received intervention with RAS inhibitors and disease state management.
In addition to early identification of reduced EF, this project allowed a targeted approach to identifying patients for risk factor reduction. Between the 2 PACT teams, 246 patients with T2DM and/or hypertension were seen from September 2019 to January 2020. By using natriuretic peptide screening, the clinical pharmacists were able to prioritize and focus risk factor management on patients at higher risk. Pharmacists were then able to intervene for all risk factors assessed: hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, NSAID use reduction, and tobacco cessation.
During the implementation period, VA criteria of use of the angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan, was restricted to VA cardiology. For patients with reduced EF, it was up to the PCP’s discretion to consult cardiology for further follow-up. In November 2020, the VA removed the restriction to cardiology and PCPs were able to order sacubitril/valsartan. Although not included in the Figure at the time of project implementation, the clinical pharmacist could now transition a patient with reduced EF from a RAS inhibitor to sacubitril/valsartan and adjust to target dosages.
Clinical pharmacists involved in this project had established working relationships with each of the PACT members before project initiation. The PACT employed the clinical pharmacists regularly for chronic disease state management. This facilitated adoption of the natriuretic peptide screening process and PCP buy-in and support. The PCPs agreed to discuss adding a NT-proBNP laboratory test with the patient, when possible, during their in-person appointment and informed the patient that a pharmacist would call if the result was elevated. This warm hand-off facilitated the patient’s reception to the clinical pharmacists’ recommendations after an elevated NT-proBNP result. We also reported PCPs’ high acceptance rate of pharmacist recommendations and interventions for disease state management. These high acceptance rates reflect the established working relationships between clinical pharmacists and the PACT.
Development of templated notes, medication adjustment schedules, and telephone script allowed for consistent implementation into the PACT panels. This process could be duplicated and adopted into other PACTs who want to use a clinical pharmacist to facilitate natriuretic peptide screening and risk factor reduction. The findings from this project can be extrapolated to other team-based care such as the patient-centered medical home model because these programs exhibit many similarities. Both health care models centralize patient care and use interdisciplinary care teams to promote continuity, care coordination, and access to achieve optimized patient outcomes.
Cost was an important factor to consider when implementing this project. With an increase in prescriptions and elective, outpatient echocardiograms, higher outpatient cost is expected. A cost-effectiveness analysis in the STOP-HF trial found an overall cost benefit by reducing the number of patients diagnosed with left ventricular dysfunction or HF and emergency hospitalizations for cardiac events in those who received collaborative care after natriuretic peptide testing.8 These cost savings offset increased outpatient costs.
Limitations
Participants were identified initially through a computer-generated list of patients with hypertension or T2DM without a HF diagnosis documented in their problem list. This problem list is manually updated by PCPs. Although we reviewed records for exclusion criteria, eligible patients might have been excluded. The use and interpretation of an NT-proBNP level is not specific to cardiac disease. Elevations can be seen with increased age, kidney dysfunction, and pulmonary disease. Additionally, an NT-proBNP level might be falsely low in patients who are overweight or obese. Because of the relatively short period of time, we could not analyze associations with HF diagnosis or progression, hospitalizations due to HF, or mortality. Regarding external validity, because of the pre-established interdisciplinary clinic settings and VA pharmacists’ scope of practice with prescriptive authority, implementing this project might have been better received by PCPs and allowed for higher acceptance rates of pharmacist interventions at the VA compared with a community setting.
Conclusions
The ACC/AHA/HFSA guidelines recommended use of natriuretic peptide biomarker screening in conjunction with team-based care for those at risk of developing HF. We describe our process for implementing team-based care using clinical pharmacists in primary care. Our process provides a targeted approach to identifying patients for risk factor reduction through comprehensive medication management and could be replicated by other primary care clinics using a patient-centered medical home model.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Sara Hariman, Dr. Payal Sanghani, and Dr. Cecilia Scholcoff for their support and collaboration with the project.
1. Braunwald E. Heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol HF. 2013;1(1):1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2012.10.002
2. Heidenreich PA, Albert NM, Allen LA, et al; American Heart Association Advocacy Coordinating Committee; Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Stroke Council. Forecasting the impact of heart failure in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6(3):606-619. doi:10.1161/HHF.0b013e318291329a
3. Doust J, Lehman R, Glasziou P. The role of BNP testing in heart failure. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74(11):1893-1900.
4. Ledwidge M, Gallagher J, Conlon C, et al. Natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care for heart failure: the STOP-HF randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;310(1):66-74. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.7588
5. Huelsmann M, Neuhold S, Resl M, et al. PONTIAC (NT-proBNP selected prevention of cardiac events in a population of diabetic patients without a history of cardiac disease): a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(15):1365-1372. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.069
6. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(6):776-803. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.025
7. Mueller C, McDonald K, de Boer RA, et al. Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology practical guidance on the use of natriuretic peptide concentrations. Eu J Heart Fail. 2019;21:715-731. doi:10.1002/ejhf.1494
8. Ledwidge MT, O’Connell E, Gallagher J, et al; Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Cost-effectiveness of natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care: a report from the STOP-HF (St. Vincent’s Screening to Prevent Heart Failure) study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015;17(7):672-679.
Heart failure (HF) is one of the leading causes of hospitalizations and the most expensive Medicare diagnosis. Its prevalence continues to rise with a projected increase of 46% from 2012 to 2030 resulting in > 8 million people aged ≥ 18 years with HF in the United States. Despite improvements in therapy, mortality remains unacceptably high with a 50% mortality rate within 5 years. Early detection strategies are needed to identify patients at risk of developing HF to delay the disease course and improve survival.1,2
Emerging data indicates that natriuretic peptide biomarker-based screening using B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and early intervention for patients at risk of HF could prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction or new-onset HF.3-5 The 2013 St. Vincent’s Screening to Prevent Heart Failure (STOP-HF) trial is the largest study to date to evaluate BNP as a screening tool for patients at risk for HF.4 Patients at risk of HF who did not have established left ventricular systolic dysfunction or symptomatic HF were assigned randomly to usual primary care or BNP screening. Patients with BNP levels ≥ 50 pg/mL underwent echocardiogram and were referred to a cardiovascular specialty service for management. The cardiovascular specialty clinic included a team of registered nurses, nurse practitioners, pharmacists, dieticians, palliative care specialists, and cardiologists. Individuals in the intervention group showed increased renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor use at follow-up (control, 49.6%; intervention, 59.6%; P = .01). All patients received coaching by a nurse who emphasized individual risk, importance of medication adherence, and healthy lifestyle behaviors. After a mean follow-up of 4.2 years, 59 of 677 participants (8.7%) in the control group and 37 of 697 (5.3%) in the intervention group (odds ratio [OR], 0.55; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.82; P = .003) met the primary end point of left ventricular dysfunction with or without HF. BNP-based screening in conjunction with collaborative care reduced rates of left ventricular dysfunction and HF.
In the 2013 PONTIAC trial, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) without cardiac disease but with NT-proBNP levels > 125 pg/mL were randomized to usual diabetes care or intensified care at a cardiac outpatient clinic for initiation and increase of RAS inhibitors and β blockers.5 After 2 years, patients randomized to the intensified care group showed a 65% risk reduction of the primary endpoint of hospitalization or death from cardiac disease (P = .04).
Based on this evidence, the 2017 focused update of the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA) guideline for managing HF added a IIa recommendation for natriuretic peptide biomarker screening in those at risk of developing HF.6 The guideline recommends biomarker screening in conjunction with team-based care, including a cardiovascular specialist, and guideline-directed management and therapy to prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction or new-onset HF.
Although ordering a natriuretic peptide biomarker laboratory test is straightforward, the variability of team-based care across institutions and health systems makes it difficult to standardize screening and interventions for patients at risk for HF. We developed and piloted a process using clinical pharmacists in primary care for natriuretic peptide biomarker screening and risk factor reduction within the established patient aligned care team (PACT) framework at a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center. In this paper, we describe our implementation process including descriptive preliminary outcomes.
Methods
The PACT team-based approach in primary care clinics is similar to the patient-centered medical home framework. A PACT includes the veteran patient and an interdisciplinary team of health professionals composed of their primary care practitioner (PCP), registered nurse care manager, clinical pharmacist, and other clinical and administrative staff. The PACT clinical pharmacist has prescriptive authority within a scope of practice to provide postdiagnostic chronic disease state management including management of T2DM, hypertension, HF, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, anticoagulation, tobacco cessation, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk reduction. Clinical pharmacists can prescribe and adjust medications and order laboratory tests.
Our institution, Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, has a specialty HF clinic that primarily manages ACC/AHA Stage C HF patients. The HF clinic uses a team-based approach to collaborate and coordinate care for the veteran. The HF team is comprised of cardiology specialists, registered nurses, clinical pharmacists, dietitians, and administrative staff. Two PACT clinical pharmacists also staff the HF clinic at CJZVAMC and work collaboratively to initiate, adjust, and optimize veterans’ HF medication regimens.
Two primary care PACT panels were selected for this project. Before implementation, a pharmacy resident and 3 PACT clinical pharmacists (2 of whom also staff the HF clinic) met with a HF cardiology specialist and 2 PACT PCPs to finalize the team-based process and workflow. PCPs were presented with the evidence-based background, purpose, and project design, which included patient identification, NT-proBNP laboratory test ordering, medication adjustment schedules, and protocol for ordering echocardiograms (Figure). Templated notes were created to allow for consistent documentation in patients’ electronic health record. A telephone script also was written for the initial telephone call to patients to explain in patient-friendly terms the implications of an elevated NT-proBNP level, the echocardiogram procedure, and recommendations for risk reduction.
Patient Selection
Patients aged ≥ 18 years with hypertension, taking antihypertensive medication for ≥ 1 month, or diagnosed with T2DM for ≥ 6 months were included. Using the parameters provided in the STOP-HF trial, patients with evidence or history of left ventricular dysfunction, defined as a left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) < 50% or an E/e’ ratio > 15 in the setting of normal EF, or symptomatic HF were excluded. Patients with a diagnosis causing life expectancy < 1 year were excluded, which was determined based on review of the patient’s chart or discussion with the PCP.
A clinical pharmacist screened patients with an upcoming PCP appointment between September 2019 and January 2020 for eligibility. For patients who met criteria, the clinical pharmacist ordered a NT-proBNP laboratory test to their already scheduled tests and entered a templated note into the patient’s chart to alert the PCP of the test. NT-proBNP was used rather than BNP because it was the natriuretic peptide laboratory test available at CJZVAMC during this time. Patients with NT-proBNP < 125 pg/mL received usual care from their PCPs. Patients with NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/mL received a follow-up phone call from a clinical pharmacist to discuss the laboratory test result with recommendations for initiation or increase of RAS inhibitors and an echocardiogram. If the patient agreed to an echocardiogram, the PCP was notified to order the test. For patients aged > 80 years with elevated NT-proBNP, risk vs benefit and patient-specific goals of care were discussed with the PCP. For patients whose echocardiograms revealed left ventricular dysfunction, initiation or adjustment of β blockers was considered. During RAS inhibitor increase, the clinical pharmacists provided a review of the patient’s risk factors and optimized management of hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) reduction, and tobacco cessation.
Outcome Measures
Outcome measures included the percentage of patients who met inclusion/exclusion criteria and had an elevated NT-proBNP level, percent change in RAS inhibitor prescriptions and optimized dosing after intervention, frequency of left ventricular dysfunction visualized with echocardiograms, and quantification of pharmacist interventions in disease state management. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze demographic data, RAS inhibitors prescriptions before and after intervention, echocardiogram results, pharmacist recommendations, and acceptance rates of disease state management.
Results
Between September 2019 and January 2020, 570 patients from 2 PACT teams were screened. Of the 570 patients, 246 met inclusion criteria with upcoming appointments. Of these, 24 were excluded, 10 for EF < 50%, 13 for E/e’ > 15 in setting of normal EF, and 1 for hypertension diagnosis without an antihypertensive regimen or elevated blood pressure. The remaining 222 patients had an NT-proBNP level ordered and drawn and 73 (32.9%) patients had an NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/mL. Baseline characteristics are described in Table 1.
Data was collected through March 2020 (due to COVID-19) found that among the 73 patients with elevated NT-proBNP: 14 had an echocardiogram within the past year without evidence of left ventricular dysfunction; 39 had echocardiograms ordered; and 19 had echocardiograms completed by March 2020. Among the 19 echocardiograms, 16 (84%) showed no evidence of left ventricular dysfunction, 2 (11%) revealed mildly reduced EF (40% to 50%), and 1 (5%) revealed a reduced EF (< 40%). These patients were identified early in the disease course before symptom onset and received intervention with RAS inhibitors and disease state management.
Patients prescribed RAS inhibitors increased from 44 to 50. The number of patients who were able to have their RAS inhibitor dosage adjusted increased from 28 to 31. For the 3 patients with mildly reduced or reduced EF, management with β blockers was based on RAS inhibitor adjustment toleration. One patient with mildly reduced EF was switched from metoprolol tartrate to metoprolol succinate.
Clinical pharmacists completed disease state assessments to optimize management of hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, oral NSAID reduction, and tobacco cessation (Table 2). Interventions clinical pharmacists recommended for hypertension, in addition to RAS inhibitor management, included initiation and adjustment of amlodipine. For T2DM, interventions included initiation of metformin and initiation or adjustment of empagliflozin. For ASCVD risk reduction, interventions included starting a statin or adjusting statin therapies to appropriate intensities based on clinical ASCVD 10-year risk. Tobacco cessation interventions included pharmacotherapies, counseling, and education with written materials. Pharmacists counseled patients to minimize or eliminate NSAID use and, when appropriate, discontinued active oral NSAID prescriptions.
Discussion
We included patients diagnosed with T2DM and hypertension for several reasons. Most patients (62%) studied in the STOP-HF trial were diagnosed with hypertension. Also, T2DM represented the patient population enrolled in the PONTIAC trial. Guidance from the European Society of Cardiology recommends use of natriuretic peptides in high-risk populations, such as patients with DM and hypertension, to help target initiation of preventive measures.7 Lastly, T2DM and hypertension patients were easily identified using population management software available at the VA.
The percentage of patients in this project with risk factors for HF and an elevated NT-proBNP were similar to the elevated levels described in the STOP-HF trial. In our project, 32.9% of patients had elevated NT-proBNP levels, similar to the 41.6% of patients in STOP-HF. Among the completed echocardiograms, 16% revealed mildly reduced or reduced EF. These patients were identified early in the disease course before symptom onset and received intervention with RAS inhibitors and disease state management.
In addition to early identification of reduced EF, this project allowed a targeted approach to identifying patients for risk factor reduction. Between the 2 PACT teams, 246 patients with T2DM and/or hypertension were seen from September 2019 to January 2020. By using natriuretic peptide screening, the clinical pharmacists were able to prioritize and focus risk factor management on patients at higher risk. Pharmacists were then able to intervene for all risk factors assessed: hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, NSAID use reduction, and tobacco cessation.
During the implementation period, VA criteria of use of the angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan, was restricted to VA cardiology. For patients with reduced EF, it was up to the PCP’s discretion to consult cardiology for further follow-up. In November 2020, the VA removed the restriction to cardiology and PCPs were able to order sacubitril/valsartan. Although not included in the Figure at the time of project implementation, the clinical pharmacist could now transition a patient with reduced EF from a RAS inhibitor to sacubitril/valsartan and adjust to target dosages.
Clinical pharmacists involved in this project had established working relationships with each of the PACT members before project initiation. The PACT employed the clinical pharmacists regularly for chronic disease state management. This facilitated adoption of the natriuretic peptide screening process and PCP buy-in and support. The PCPs agreed to discuss adding a NT-proBNP laboratory test with the patient, when possible, during their in-person appointment and informed the patient that a pharmacist would call if the result was elevated. This warm hand-off facilitated the patient’s reception to the clinical pharmacists’ recommendations after an elevated NT-proBNP result. We also reported PCPs’ high acceptance rate of pharmacist recommendations and interventions for disease state management. These high acceptance rates reflect the established working relationships between clinical pharmacists and the PACT.
Development of templated notes, medication adjustment schedules, and telephone script allowed for consistent implementation into the PACT panels. This process could be duplicated and adopted into other PACTs who want to use a clinical pharmacist to facilitate natriuretic peptide screening and risk factor reduction. The findings from this project can be extrapolated to other team-based care such as the patient-centered medical home model because these programs exhibit many similarities. Both health care models centralize patient care and use interdisciplinary care teams to promote continuity, care coordination, and access to achieve optimized patient outcomes.
Cost was an important factor to consider when implementing this project. With an increase in prescriptions and elective, outpatient echocardiograms, higher outpatient cost is expected. A cost-effectiveness analysis in the STOP-HF trial found an overall cost benefit by reducing the number of patients diagnosed with left ventricular dysfunction or HF and emergency hospitalizations for cardiac events in those who received collaborative care after natriuretic peptide testing.8 These cost savings offset increased outpatient costs.
Limitations
Participants were identified initially through a computer-generated list of patients with hypertension or T2DM without a HF diagnosis documented in their problem list. This problem list is manually updated by PCPs. Although we reviewed records for exclusion criteria, eligible patients might have been excluded. The use and interpretation of an NT-proBNP level is not specific to cardiac disease. Elevations can be seen with increased age, kidney dysfunction, and pulmonary disease. Additionally, an NT-proBNP level might be falsely low in patients who are overweight or obese. Because of the relatively short period of time, we could not analyze associations with HF diagnosis or progression, hospitalizations due to HF, or mortality. Regarding external validity, because of the pre-established interdisciplinary clinic settings and VA pharmacists’ scope of practice with prescriptive authority, implementing this project might have been better received by PCPs and allowed for higher acceptance rates of pharmacist interventions at the VA compared with a community setting.
Conclusions
The ACC/AHA/HFSA guidelines recommended use of natriuretic peptide biomarker screening in conjunction with team-based care for those at risk of developing HF. We describe our process for implementing team-based care using clinical pharmacists in primary care. Our process provides a targeted approach to identifying patients for risk factor reduction through comprehensive medication management and could be replicated by other primary care clinics using a patient-centered medical home model.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Sara Hariman, Dr. Payal Sanghani, and Dr. Cecilia Scholcoff for their support and collaboration with the project.
Heart failure (HF) is one of the leading causes of hospitalizations and the most expensive Medicare diagnosis. Its prevalence continues to rise with a projected increase of 46% from 2012 to 2030 resulting in > 8 million people aged ≥ 18 years with HF in the United States. Despite improvements in therapy, mortality remains unacceptably high with a 50% mortality rate within 5 years. Early detection strategies are needed to identify patients at risk of developing HF to delay the disease course and improve survival.1,2
Emerging data indicates that natriuretic peptide biomarker-based screening using B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and early intervention for patients at risk of HF could prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction or new-onset HF.3-5 The 2013 St. Vincent’s Screening to Prevent Heart Failure (STOP-HF) trial is the largest study to date to evaluate BNP as a screening tool for patients at risk for HF.4 Patients at risk of HF who did not have established left ventricular systolic dysfunction or symptomatic HF were assigned randomly to usual primary care or BNP screening. Patients with BNP levels ≥ 50 pg/mL underwent echocardiogram and were referred to a cardiovascular specialty service for management. The cardiovascular specialty clinic included a team of registered nurses, nurse practitioners, pharmacists, dieticians, palliative care specialists, and cardiologists. Individuals in the intervention group showed increased renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor use at follow-up (control, 49.6%; intervention, 59.6%; P = .01). All patients received coaching by a nurse who emphasized individual risk, importance of medication adherence, and healthy lifestyle behaviors. After a mean follow-up of 4.2 years, 59 of 677 participants (8.7%) in the control group and 37 of 697 (5.3%) in the intervention group (odds ratio [OR], 0.55; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.82; P = .003) met the primary end point of left ventricular dysfunction with or without HF. BNP-based screening in conjunction with collaborative care reduced rates of left ventricular dysfunction and HF.
In the 2013 PONTIAC trial, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) without cardiac disease but with NT-proBNP levels > 125 pg/mL were randomized to usual diabetes care or intensified care at a cardiac outpatient clinic for initiation and increase of RAS inhibitors and β blockers.5 After 2 years, patients randomized to the intensified care group showed a 65% risk reduction of the primary endpoint of hospitalization or death from cardiac disease (P = .04).
Based on this evidence, the 2017 focused update of the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA) guideline for managing HF added a IIa recommendation for natriuretic peptide biomarker screening in those at risk of developing HF.6 The guideline recommends biomarker screening in conjunction with team-based care, including a cardiovascular specialist, and guideline-directed management and therapy to prevent development of left ventricular dysfunction or new-onset HF.
Although ordering a natriuretic peptide biomarker laboratory test is straightforward, the variability of team-based care across institutions and health systems makes it difficult to standardize screening and interventions for patients at risk for HF. We developed and piloted a process using clinical pharmacists in primary care for natriuretic peptide biomarker screening and risk factor reduction within the established patient aligned care team (PACT) framework at a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center. In this paper, we describe our implementation process including descriptive preliminary outcomes.
Methods
The PACT team-based approach in primary care clinics is similar to the patient-centered medical home framework. A PACT includes the veteran patient and an interdisciplinary team of health professionals composed of their primary care practitioner (PCP), registered nurse care manager, clinical pharmacist, and other clinical and administrative staff. The PACT clinical pharmacist has prescriptive authority within a scope of practice to provide postdiagnostic chronic disease state management including management of T2DM, hypertension, HF, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, anticoagulation, tobacco cessation, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk reduction. Clinical pharmacists can prescribe and adjust medications and order laboratory tests.
Our institution, Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, has a specialty HF clinic that primarily manages ACC/AHA Stage C HF patients. The HF clinic uses a team-based approach to collaborate and coordinate care for the veteran. The HF team is comprised of cardiology specialists, registered nurses, clinical pharmacists, dietitians, and administrative staff. Two PACT clinical pharmacists also staff the HF clinic at CJZVAMC and work collaboratively to initiate, adjust, and optimize veterans’ HF medication regimens.
Two primary care PACT panels were selected for this project. Before implementation, a pharmacy resident and 3 PACT clinical pharmacists (2 of whom also staff the HF clinic) met with a HF cardiology specialist and 2 PACT PCPs to finalize the team-based process and workflow. PCPs were presented with the evidence-based background, purpose, and project design, which included patient identification, NT-proBNP laboratory test ordering, medication adjustment schedules, and protocol for ordering echocardiograms (Figure). Templated notes were created to allow for consistent documentation in patients’ electronic health record. A telephone script also was written for the initial telephone call to patients to explain in patient-friendly terms the implications of an elevated NT-proBNP level, the echocardiogram procedure, and recommendations for risk reduction.
Patient Selection
Patients aged ≥ 18 years with hypertension, taking antihypertensive medication for ≥ 1 month, or diagnosed with T2DM for ≥ 6 months were included. Using the parameters provided in the STOP-HF trial, patients with evidence or history of left ventricular dysfunction, defined as a left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) < 50% or an E/e’ ratio > 15 in the setting of normal EF, or symptomatic HF were excluded. Patients with a diagnosis causing life expectancy < 1 year were excluded, which was determined based on review of the patient’s chart or discussion with the PCP.
A clinical pharmacist screened patients with an upcoming PCP appointment between September 2019 and January 2020 for eligibility. For patients who met criteria, the clinical pharmacist ordered a NT-proBNP laboratory test to their already scheduled tests and entered a templated note into the patient’s chart to alert the PCP of the test. NT-proBNP was used rather than BNP because it was the natriuretic peptide laboratory test available at CJZVAMC during this time. Patients with NT-proBNP < 125 pg/mL received usual care from their PCPs. Patients with NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/mL received a follow-up phone call from a clinical pharmacist to discuss the laboratory test result with recommendations for initiation or increase of RAS inhibitors and an echocardiogram. If the patient agreed to an echocardiogram, the PCP was notified to order the test. For patients aged > 80 years with elevated NT-proBNP, risk vs benefit and patient-specific goals of care were discussed with the PCP. For patients whose echocardiograms revealed left ventricular dysfunction, initiation or adjustment of β blockers was considered. During RAS inhibitor increase, the clinical pharmacists provided a review of the patient’s risk factors and optimized management of hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) reduction, and tobacco cessation.
Outcome Measures
Outcome measures included the percentage of patients who met inclusion/exclusion criteria and had an elevated NT-proBNP level, percent change in RAS inhibitor prescriptions and optimized dosing after intervention, frequency of left ventricular dysfunction visualized with echocardiograms, and quantification of pharmacist interventions in disease state management. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze demographic data, RAS inhibitors prescriptions before and after intervention, echocardiogram results, pharmacist recommendations, and acceptance rates of disease state management.
Results
Between September 2019 and January 2020, 570 patients from 2 PACT teams were screened. Of the 570 patients, 246 met inclusion criteria with upcoming appointments. Of these, 24 were excluded, 10 for EF < 50%, 13 for E/e’ > 15 in setting of normal EF, and 1 for hypertension diagnosis without an antihypertensive regimen or elevated blood pressure. The remaining 222 patients had an NT-proBNP level ordered and drawn and 73 (32.9%) patients had an NT-proBNP ≥ 125 pg/mL. Baseline characteristics are described in Table 1.
Data was collected through March 2020 (due to COVID-19) found that among the 73 patients with elevated NT-proBNP: 14 had an echocardiogram within the past year without evidence of left ventricular dysfunction; 39 had echocardiograms ordered; and 19 had echocardiograms completed by March 2020. Among the 19 echocardiograms, 16 (84%) showed no evidence of left ventricular dysfunction, 2 (11%) revealed mildly reduced EF (40% to 50%), and 1 (5%) revealed a reduced EF (< 40%). These patients were identified early in the disease course before symptom onset and received intervention with RAS inhibitors and disease state management.
Patients prescribed RAS inhibitors increased from 44 to 50. The number of patients who were able to have their RAS inhibitor dosage adjusted increased from 28 to 31. For the 3 patients with mildly reduced or reduced EF, management with β blockers was based on RAS inhibitor adjustment toleration. One patient with mildly reduced EF was switched from metoprolol tartrate to metoprolol succinate.
Clinical pharmacists completed disease state assessments to optimize management of hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, oral NSAID reduction, and tobacco cessation (Table 2). Interventions clinical pharmacists recommended for hypertension, in addition to RAS inhibitor management, included initiation and adjustment of amlodipine. For T2DM, interventions included initiation of metformin and initiation or adjustment of empagliflozin. For ASCVD risk reduction, interventions included starting a statin or adjusting statin therapies to appropriate intensities based on clinical ASCVD 10-year risk. Tobacco cessation interventions included pharmacotherapies, counseling, and education with written materials. Pharmacists counseled patients to minimize or eliminate NSAID use and, when appropriate, discontinued active oral NSAID prescriptions.
Discussion
We included patients diagnosed with T2DM and hypertension for several reasons. Most patients (62%) studied in the STOP-HF trial were diagnosed with hypertension. Also, T2DM represented the patient population enrolled in the PONTIAC trial. Guidance from the European Society of Cardiology recommends use of natriuretic peptides in high-risk populations, such as patients with DM and hypertension, to help target initiation of preventive measures.7 Lastly, T2DM and hypertension patients were easily identified using population management software available at the VA.
The percentage of patients in this project with risk factors for HF and an elevated NT-proBNP were similar to the elevated levels described in the STOP-HF trial. In our project, 32.9% of patients had elevated NT-proBNP levels, similar to the 41.6% of patients in STOP-HF. Among the completed echocardiograms, 16% revealed mildly reduced or reduced EF. These patients were identified early in the disease course before symptom onset and received intervention with RAS inhibitors and disease state management.
In addition to early identification of reduced EF, this project allowed a targeted approach to identifying patients for risk factor reduction. Between the 2 PACT teams, 246 patients with T2DM and/or hypertension were seen from September 2019 to January 2020. By using natriuretic peptide screening, the clinical pharmacists were able to prioritize and focus risk factor management on patients at higher risk. Pharmacists were then able to intervene for all risk factors assessed: hypertension, T2DM, ASCVD risk reduction, NSAID use reduction, and tobacco cessation.
During the implementation period, VA criteria of use of the angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan, was restricted to VA cardiology. For patients with reduced EF, it was up to the PCP’s discretion to consult cardiology for further follow-up. In November 2020, the VA removed the restriction to cardiology and PCPs were able to order sacubitril/valsartan. Although not included in the Figure at the time of project implementation, the clinical pharmacist could now transition a patient with reduced EF from a RAS inhibitor to sacubitril/valsartan and adjust to target dosages.
Clinical pharmacists involved in this project had established working relationships with each of the PACT members before project initiation. The PACT employed the clinical pharmacists regularly for chronic disease state management. This facilitated adoption of the natriuretic peptide screening process and PCP buy-in and support. The PCPs agreed to discuss adding a NT-proBNP laboratory test with the patient, when possible, during their in-person appointment and informed the patient that a pharmacist would call if the result was elevated. This warm hand-off facilitated the patient’s reception to the clinical pharmacists’ recommendations after an elevated NT-proBNP result. We also reported PCPs’ high acceptance rate of pharmacist recommendations and interventions for disease state management. These high acceptance rates reflect the established working relationships between clinical pharmacists and the PACT.
Development of templated notes, medication adjustment schedules, and telephone script allowed for consistent implementation into the PACT panels. This process could be duplicated and adopted into other PACTs who want to use a clinical pharmacist to facilitate natriuretic peptide screening and risk factor reduction. The findings from this project can be extrapolated to other team-based care such as the patient-centered medical home model because these programs exhibit many similarities. Both health care models centralize patient care and use interdisciplinary care teams to promote continuity, care coordination, and access to achieve optimized patient outcomes.
Cost was an important factor to consider when implementing this project. With an increase in prescriptions and elective, outpatient echocardiograms, higher outpatient cost is expected. A cost-effectiveness analysis in the STOP-HF trial found an overall cost benefit by reducing the number of patients diagnosed with left ventricular dysfunction or HF and emergency hospitalizations for cardiac events in those who received collaborative care after natriuretic peptide testing.8 These cost savings offset increased outpatient costs.
Limitations
Participants were identified initially through a computer-generated list of patients with hypertension or T2DM without a HF diagnosis documented in their problem list. This problem list is manually updated by PCPs. Although we reviewed records for exclusion criteria, eligible patients might have been excluded. The use and interpretation of an NT-proBNP level is not specific to cardiac disease. Elevations can be seen with increased age, kidney dysfunction, and pulmonary disease. Additionally, an NT-proBNP level might be falsely low in patients who are overweight or obese. Because of the relatively short period of time, we could not analyze associations with HF diagnosis or progression, hospitalizations due to HF, or mortality. Regarding external validity, because of the pre-established interdisciplinary clinic settings and VA pharmacists’ scope of practice with prescriptive authority, implementing this project might have been better received by PCPs and allowed for higher acceptance rates of pharmacist interventions at the VA compared with a community setting.
Conclusions
The ACC/AHA/HFSA guidelines recommended use of natriuretic peptide biomarker screening in conjunction with team-based care for those at risk of developing HF. We describe our process for implementing team-based care using clinical pharmacists in primary care. Our process provides a targeted approach to identifying patients for risk factor reduction through comprehensive medication management and could be replicated by other primary care clinics using a patient-centered medical home model.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Sara Hariman, Dr. Payal Sanghani, and Dr. Cecilia Scholcoff for their support and collaboration with the project.
1. Braunwald E. Heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol HF. 2013;1(1):1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2012.10.002
2. Heidenreich PA, Albert NM, Allen LA, et al; American Heart Association Advocacy Coordinating Committee; Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Stroke Council. Forecasting the impact of heart failure in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6(3):606-619. doi:10.1161/HHF.0b013e318291329a
3. Doust J, Lehman R, Glasziou P. The role of BNP testing in heart failure. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74(11):1893-1900.
4. Ledwidge M, Gallagher J, Conlon C, et al. Natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care for heart failure: the STOP-HF randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;310(1):66-74. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.7588
5. Huelsmann M, Neuhold S, Resl M, et al. PONTIAC (NT-proBNP selected prevention of cardiac events in a population of diabetic patients without a history of cardiac disease): a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(15):1365-1372. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.069
6. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(6):776-803. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.025
7. Mueller C, McDonald K, de Boer RA, et al. Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology practical guidance on the use of natriuretic peptide concentrations. Eu J Heart Fail. 2019;21:715-731. doi:10.1002/ejhf.1494
8. Ledwidge MT, O’Connell E, Gallagher J, et al; Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Cost-effectiveness of natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care: a report from the STOP-HF (St. Vincent’s Screening to Prevent Heart Failure) study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015;17(7):672-679.
1. Braunwald E. Heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol HF. 2013;1(1):1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2012.10.002
2. Heidenreich PA, Albert NM, Allen LA, et al; American Heart Association Advocacy Coordinating Committee; Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Stroke Council. Forecasting the impact of heart failure in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6(3):606-619. doi:10.1161/HHF.0b013e318291329a
3. Doust J, Lehman R, Glasziou P. The role of BNP testing in heart failure. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74(11):1893-1900.
4. Ledwidge M, Gallagher J, Conlon C, et al. Natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care for heart failure: the STOP-HF randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;310(1):66-74. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.7588
5. Huelsmann M, Neuhold S, Resl M, et al. PONTIAC (NT-proBNP selected prevention of cardiac events in a population of diabetic patients without a history of cardiac disease): a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(15):1365-1372. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.069
6. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(6):776-803. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.025
7. Mueller C, McDonald K, de Boer RA, et al. Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology practical guidance on the use of natriuretic peptide concentrations. Eu J Heart Fail. 2019;21:715-731. doi:10.1002/ejhf.1494
8. Ledwidge MT, O’Connell E, Gallagher J, et al; Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Cost-effectiveness of natriuretic peptide-based screening and collaborative care: a report from the STOP-HF (St. Vincent’s Screening to Prevent Heart Failure) study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015;17(7):672-679.
New toolkit offers help for climate change anxiety
These strategies include volunteering, building a community, discussing emotions with others, practicing mindfulness, and seeking therapy.
The toolkit, which was developed by nursing experts at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, also offers reflection questions and a film with diverse voices for people to examine their values, emotions, and behaviors in relation to the environment.
“Many people have a hard time understanding the relationship between climate change and mental health and are experiencing high levels of stress about climate change,” Natania Abebe, MSN/MPH, RN, a registered nurse and graduate student at UBC who developed the toolkit, told this news organization.
“Youth, in particular, appear to have higher levels of consciousness regarding climate change because they’re the ones who are going to inherit the planet,” she said. “A big part of why they have mental health issues is that they feel trapped in sociopolitical structures that they didn’t agree to and didn’t necessarily create.”
The toolkit was published online on April 20.
Empowering agents for change
Ms. Abebe was inspired to create the toolkit after giving guest lectures on climate change and mental health as part of UBC’s Nursing 290 course. Her faculty advisor, Raluca Radu, MSN, a lecturer in the School of Nursing at UBC, developed the course in 2020 to teach students about the broad impacts of climate change on communities.
As the course has grown during the past 2 years, Ms. Abebe wanted to create a coping framework and engaging film for health educators to use with students, as well as for everyday people.
The toolkit includes contributions from three Canadian climate change experts, as well as six students from different backgrounds who have taken the course.
“I wanted to center the voices of youth and empower them to think they can be agents for change,” Ms. Abebe said. “I also wanted to highlight diverse voices and take a collaborative approach because climate change is such a big problem that we have to come together to address it.”
Ms. Abebe and Ms. Radu also noticed an increase in climate anxiety in recent years because of the pandemic, worldwide food and energy shortages, and extreme weather events that hit close to home, such as wildfires and floods in British Columbia.
“With the pandemic, people have been spending more time online and thinking about our world at large,” Ms. Abebe said. “At the same time that they’re thinking about it, climate change events are happening simultaneously – not in the future, but right now.”
Economic, social, and political shifts during the past 2 years have also prompted people to question standard practices and institutions, which has created an opportunity to discuss change, Ms. Radu told this news organization.
“It’s a pivotal time to question our values and highly consumerist society,” she said. “We’re at a point in time where, if we don’t take action, the planetary health will be in an irreversible state, and we won’t be able to turn back time and make changes.”
Our psyches and nature
The toolkit includes three main sections that feature video clips and reflective questions around eco-anxiety, eco-paralysis, and ecological grief.
In the first section, eco-anxiety is defined as a “chronic fear of environmental doom,” which could include anxiousness around the likelihood of a severe weather event because of ongoing news coverage and social media. The reflective questions prompt readers to discuss eco-anxiety in their life, work through their emotions, understand their beliefs and values, and determine how to use them to address climate change anxiety.
The second section defines eco-paralysis as the powerlessness that people may feel when they don’t believe they can do anything meaningful on an individual level to address climate change. Paralysis can look like apathy, complacency, or disengagement. The questions prompt readers to observe how paralysis may show up in their lives, explore the tension between individual versus collective responsibility, and consider ways to address their sense of helplessness about climate change.
In the third section, ecological grief centers around “experienced or anticipated ecological losses,” which could include the loss of species, ecosystems, and landscapes because of short- or long-term environmental change. The questions prompt readers to explore their feelings, beliefs, and values and feel empowered to address their ecological grief over climate change.
The toolkit also includes recommendations for books, journal articles, websites, podcasts, and meditations around mental health and climate change, as well as ways to get involved with others. For instance, health care practitioners can register with PaRx, a program in British Columbia that allows providers to prescribe time in nature to improve a client’s health. The program is being adopted across Canada, and people with a prescription can visit local and national parks, historic sites, and marine conservation areas for free.
“This is about recognizing that there is a connection between our psyches and nature, and by talking about it, we can name what we’re feeling,” Ms. Abebe said. “We can take action not only to handle our emotions, but also to live kinder and more sustainable lifestyles.”
Future work will need to focus on population-level approaches to climate change and mental health as well, including policy and financial support to address environmental changes directly.
“We need to start thinking beyond individualized approaches and focus on how to create supportive and resilient communities to respond to climate change,” Kiffer Card, PhD, executive director of the Mental Health and Climate Change Alliance and an assistant professor of health sciences at Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, B.C., told this news organization.
Dr. Card, who wasn’t involved in developing the toolkit, has researched recent trends around climate change anxiety in Canada and fielded questions from health care practitioners and mental health professionals who are looking for ways to help their patients.
“Communities need to be ready to stand up and respond to acute emergency disasters, and government leaders need to take this seriously,” he said. “Those who are experiencing climate anxiety now are the canaries in the coal mine for the severe weather events and consequences to come.”
The toolkit was developed with funding from the Alma Mater Society of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Ms. Abebe, Ms. Radu, and Dr. Card reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
These strategies include volunteering, building a community, discussing emotions with others, practicing mindfulness, and seeking therapy.
The toolkit, which was developed by nursing experts at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, also offers reflection questions and a film with diverse voices for people to examine their values, emotions, and behaviors in relation to the environment.
“Many people have a hard time understanding the relationship between climate change and mental health and are experiencing high levels of stress about climate change,” Natania Abebe, MSN/MPH, RN, a registered nurse and graduate student at UBC who developed the toolkit, told this news organization.
“Youth, in particular, appear to have higher levels of consciousness regarding climate change because they’re the ones who are going to inherit the planet,” she said. “A big part of why they have mental health issues is that they feel trapped in sociopolitical structures that they didn’t agree to and didn’t necessarily create.”
The toolkit was published online on April 20.
Empowering agents for change
Ms. Abebe was inspired to create the toolkit after giving guest lectures on climate change and mental health as part of UBC’s Nursing 290 course. Her faculty advisor, Raluca Radu, MSN, a lecturer in the School of Nursing at UBC, developed the course in 2020 to teach students about the broad impacts of climate change on communities.
As the course has grown during the past 2 years, Ms. Abebe wanted to create a coping framework and engaging film for health educators to use with students, as well as for everyday people.
The toolkit includes contributions from three Canadian climate change experts, as well as six students from different backgrounds who have taken the course.
“I wanted to center the voices of youth and empower them to think they can be agents for change,” Ms. Abebe said. “I also wanted to highlight diverse voices and take a collaborative approach because climate change is such a big problem that we have to come together to address it.”
Ms. Abebe and Ms. Radu also noticed an increase in climate anxiety in recent years because of the pandemic, worldwide food and energy shortages, and extreme weather events that hit close to home, such as wildfires and floods in British Columbia.
“With the pandemic, people have been spending more time online and thinking about our world at large,” Ms. Abebe said. “At the same time that they’re thinking about it, climate change events are happening simultaneously – not in the future, but right now.”
Economic, social, and political shifts during the past 2 years have also prompted people to question standard practices and institutions, which has created an opportunity to discuss change, Ms. Radu told this news organization.
“It’s a pivotal time to question our values and highly consumerist society,” she said. “We’re at a point in time where, if we don’t take action, the planetary health will be in an irreversible state, and we won’t be able to turn back time and make changes.”
Our psyches and nature
The toolkit includes three main sections that feature video clips and reflective questions around eco-anxiety, eco-paralysis, and ecological grief.
In the first section, eco-anxiety is defined as a “chronic fear of environmental doom,” which could include anxiousness around the likelihood of a severe weather event because of ongoing news coverage and social media. The reflective questions prompt readers to discuss eco-anxiety in their life, work through their emotions, understand their beliefs and values, and determine how to use them to address climate change anxiety.
The second section defines eco-paralysis as the powerlessness that people may feel when they don’t believe they can do anything meaningful on an individual level to address climate change. Paralysis can look like apathy, complacency, or disengagement. The questions prompt readers to observe how paralysis may show up in their lives, explore the tension between individual versus collective responsibility, and consider ways to address their sense of helplessness about climate change.
In the third section, ecological grief centers around “experienced or anticipated ecological losses,” which could include the loss of species, ecosystems, and landscapes because of short- or long-term environmental change. The questions prompt readers to explore their feelings, beliefs, and values and feel empowered to address their ecological grief over climate change.
The toolkit also includes recommendations for books, journal articles, websites, podcasts, and meditations around mental health and climate change, as well as ways to get involved with others. For instance, health care practitioners can register with PaRx, a program in British Columbia that allows providers to prescribe time in nature to improve a client’s health. The program is being adopted across Canada, and people with a prescription can visit local and national parks, historic sites, and marine conservation areas for free.
“This is about recognizing that there is a connection between our psyches and nature, and by talking about it, we can name what we’re feeling,” Ms. Abebe said. “We can take action not only to handle our emotions, but also to live kinder and more sustainable lifestyles.”
Future work will need to focus on population-level approaches to climate change and mental health as well, including policy and financial support to address environmental changes directly.
“We need to start thinking beyond individualized approaches and focus on how to create supportive and resilient communities to respond to climate change,” Kiffer Card, PhD, executive director of the Mental Health and Climate Change Alliance and an assistant professor of health sciences at Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, B.C., told this news organization.
Dr. Card, who wasn’t involved in developing the toolkit, has researched recent trends around climate change anxiety in Canada and fielded questions from health care practitioners and mental health professionals who are looking for ways to help their patients.
“Communities need to be ready to stand up and respond to acute emergency disasters, and government leaders need to take this seriously,” he said. “Those who are experiencing climate anxiety now are the canaries in the coal mine for the severe weather events and consequences to come.”
The toolkit was developed with funding from the Alma Mater Society of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Ms. Abebe, Ms. Radu, and Dr. Card reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
These strategies include volunteering, building a community, discussing emotions with others, practicing mindfulness, and seeking therapy.
The toolkit, which was developed by nursing experts at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, also offers reflection questions and a film with diverse voices for people to examine their values, emotions, and behaviors in relation to the environment.
“Many people have a hard time understanding the relationship between climate change and mental health and are experiencing high levels of stress about climate change,” Natania Abebe, MSN/MPH, RN, a registered nurse and graduate student at UBC who developed the toolkit, told this news organization.
“Youth, in particular, appear to have higher levels of consciousness regarding climate change because they’re the ones who are going to inherit the planet,” she said. “A big part of why they have mental health issues is that they feel trapped in sociopolitical structures that they didn’t agree to and didn’t necessarily create.”
The toolkit was published online on April 20.
Empowering agents for change
Ms. Abebe was inspired to create the toolkit after giving guest lectures on climate change and mental health as part of UBC’s Nursing 290 course. Her faculty advisor, Raluca Radu, MSN, a lecturer in the School of Nursing at UBC, developed the course in 2020 to teach students about the broad impacts of climate change on communities.
As the course has grown during the past 2 years, Ms. Abebe wanted to create a coping framework and engaging film for health educators to use with students, as well as for everyday people.
The toolkit includes contributions from three Canadian climate change experts, as well as six students from different backgrounds who have taken the course.
“I wanted to center the voices of youth and empower them to think they can be agents for change,” Ms. Abebe said. “I also wanted to highlight diverse voices and take a collaborative approach because climate change is such a big problem that we have to come together to address it.”
Ms. Abebe and Ms. Radu also noticed an increase in climate anxiety in recent years because of the pandemic, worldwide food and energy shortages, and extreme weather events that hit close to home, such as wildfires and floods in British Columbia.
“With the pandemic, people have been spending more time online and thinking about our world at large,” Ms. Abebe said. “At the same time that they’re thinking about it, climate change events are happening simultaneously – not in the future, but right now.”
Economic, social, and political shifts during the past 2 years have also prompted people to question standard practices and institutions, which has created an opportunity to discuss change, Ms. Radu told this news organization.
“It’s a pivotal time to question our values and highly consumerist society,” she said. “We’re at a point in time where, if we don’t take action, the planetary health will be in an irreversible state, and we won’t be able to turn back time and make changes.”
Our psyches and nature
The toolkit includes three main sections that feature video clips and reflective questions around eco-anxiety, eco-paralysis, and ecological grief.
In the first section, eco-anxiety is defined as a “chronic fear of environmental doom,” which could include anxiousness around the likelihood of a severe weather event because of ongoing news coverage and social media. The reflective questions prompt readers to discuss eco-anxiety in their life, work through their emotions, understand their beliefs and values, and determine how to use them to address climate change anxiety.
The second section defines eco-paralysis as the powerlessness that people may feel when they don’t believe they can do anything meaningful on an individual level to address climate change. Paralysis can look like apathy, complacency, or disengagement. The questions prompt readers to observe how paralysis may show up in their lives, explore the tension between individual versus collective responsibility, and consider ways to address their sense of helplessness about climate change.
In the third section, ecological grief centers around “experienced or anticipated ecological losses,” which could include the loss of species, ecosystems, and landscapes because of short- or long-term environmental change. The questions prompt readers to explore their feelings, beliefs, and values and feel empowered to address their ecological grief over climate change.
The toolkit also includes recommendations for books, journal articles, websites, podcasts, and meditations around mental health and climate change, as well as ways to get involved with others. For instance, health care practitioners can register with PaRx, a program in British Columbia that allows providers to prescribe time in nature to improve a client’s health. The program is being adopted across Canada, and people with a prescription can visit local and national parks, historic sites, and marine conservation areas for free.
“This is about recognizing that there is a connection between our psyches and nature, and by talking about it, we can name what we’re feeling,” Ms. Abebe said. “We can take action not only to handle our emotions, but also to live kinder and more sustainable lifestyles.”
Future work will need to focus on population-level approaches to climate change and mental health as well, including policy and financial support to address environmental changes directly.
“We need to start thinking beyond individualized approaches and focus on how to create supportive and resilient communities to respond to climate change,” Kiffer Card, PhD, executive director of the Mental Health and Climate Change Alliance and an assistant professor of health sciences at Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, B.C., told this news organization.
Dr. Card, who wasn’t involved in developing the toolkit, has researched recent trends around climate change anxiety in Canada and fielded questions from health care practitioners and mental health professionals who are looking for ways to help their patients.
“Communities need to be ready to stand up and respond to acute emergency disasters, and government leaders need to take this seriously,” he said. “Those who are experiencing climate anxiety now are the canaries in the coal mine for the severe weather events and consequences to come.”
The toolkit was developed with funding from the Alma Mater Society of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Ms. Abebe, Ms. Radu, and Dr. Card reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves two vonoprazan therapies for H. pylori eradication
: Voquezna Triple Pak (vonoprazan, amoxicillin, clarithromycin) and Voquezna Dual Pak (vonoprazan, amoxicillin), both from Phathom Pharmaceuticals.
Vonoprazan is an oral potassium-competitive acid blocker and “the first innovative acid suppressant from a new drug class approved in the United States in over 30 years,” the company said in a news release announcing the approval.
“The approval of Voquezna treatment regimens offers physicians and patients two therapeutic options that showed superior eradication rates compared to proton pump inhibitor-based (PPI) lansoprazole triple therapy in the overall patient population in a pivotal trial,” Terrie Curran, president and CEO of Phathom Pharmaceuticals, said in the release.
“H. pylori eradication rates continue to decline in part due to antibiotic resistance, inadequate acid suppression, and complex treatment regimens, resulting in treatment failures and complications for patients,” Ms. Curran noted.
“New therapies that have the potential to address the limitations of current treatments are needed, and we look forward to bringing these innovative vonoprazan-based treatment options to the millions of H pylori sufferers in the United States,” Ms. Curran said.
FDA approval of vonoprazan triple and dual therapy was based on safety and efficacy data from the phase 3 PHALCON-HP trial involving 1,046 patients.
As earlier reported, both treatment regimens were noninferior to PPI-based triple therapy (lansoprazole with amoxicillin and clarithromycin) in patients with H. pylori strains that were not resistant to clarithromycin or amoxicillin at baseline.
In this analysis, the eradication rate was 78.8% with PPI-based triple therapy, compared with 84.7% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 78.5% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Vonoprazan triple and dual therapy were both superior to PPI-based triple therapy among all patients, including patients with clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori.
Among patients with clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori, 31.9% achieved eradication with PPI triple therapy, compared with 65.8% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 69.6% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Among all patients, 68.5% achieved eradication with PPI triple therapy, 80.8% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 77.2% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Adverse event rates for the vonoprazan-based regimens were comparable to lansoprazole triple therapy. Full prescribing information is available online.
“As a practicing physician, I am excited about the potential of two novel, first-line H. pylori treatment options,” William D. Chey, MD, chief of gastroenterology & hepatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in the news release.
“I believe the added flexibility of having two additional effective therapies, including a dual therapy option that does not contain clarithromycin, offers the potential to improve clinical outcomes in patients with H. pylori infection,” Dr. Chey added.
The company expects to launch both products in the third quarter of 2022. Both treatment regimens will be supplied in convenient blister packs to help promote compliance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
: Voquezna Triple Pak (vonoprazan, amoxicillin, clarithromycin) and Voquezna Dual Pak (vonoprazan, amoxicillin), both from Phathom Pharmaceuticals.
Vonoprazan is an oral potassium-competitive acid blocker and “the first innovative acid suppressant from a new drug class approved in the United States in over 30 years,” the company said in a news release announcing the approval.
“The approval of Voquezna treatment regimens offers physicians and patients two therapeutic options that showed superior eradication rates compared to proton pump inhibitor-based (PPI) lansoprazole triple therapy in the overall patient population in a pivotal trial,” Terrie Curran, president and CEO of Phathom Pharmaceuticals, said in the release.
“H. pylori eradication rates continue to decline in part due to antibiotic resistance, inadequate acid suppression, and complex treatment regimens, resulting in treatment failures and complications for patients,” Ms. Curran noted.
“New therapies that have the potential to address the limitations of current treatments are needed, and we look forward to bringing these innovative vonoprazan-based treatment options to the millions of H pylori sufferers in the United States,” Ms. Curran said.
FDA approval of vonoprazan triple and dual therapy was based on safety and efficacy data from the phase 3 PHALCON-HP trial involving 1,046 patients.
As earlier reported, both treatment regimens were noninferior to PPI-based triple therapy (lansoprazole with amoxicillin and clarithromycin) in patients with H. pylori strains that were not resistant to clarithromycin or amoxicillin at baseline.
In this analysis, the eradication rate was 78.8% with PPI-based triple therapy, compared with 84.7% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 78.5% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Vonoprazan triple and dual therapy were both superior to PPI-based triple therapy among all patients, including patients with clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori.
Among patients with clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori, 31.9% achieved eradication with PPI triple therapy, compared with 65.8% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 69.6% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Among all patients, 68.5% achieved eradication with PPI triple therapy, 80.8% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 77.2% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Adverse event rates for the vonoprazan-based regimens were comparable to lansoprazole triple therapy. Full prescribing information is available online.
“As a practicing physician, I am excited about the potential of two novel, first-line H. pylori treatment options,” William D. Chey, MD, chief of gastroenterology & hepatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in the news release.
“I believe the added flexibility of having two additional effective therapies, including a dual therapy option that does not contain clarithromycin, offers the potential to improve clinical outcomes in patients with H. pylori infection,” Dr. Chey added.
The company expects to launch both products in the third quarter of 2022. Both treatment regimens will be supplied in convenient blister packs to help promote compliance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
: Voquezna Triple Pak (vonoprazan, amoxicillin, clarithromycin) and Voquezna Dual Pak (vonoprazan, amoxicillin), both from Phathom Pharmaceuticals.
Vonoprazan is an oral potassium-competitive acid blocker and “the first innovative acid suppressant from a new drug class approved in the United States in over 30 years,” the company said in a news release announcing the approval.
“The approval of Voquezna treatment regimens offers physicians and patients two therapeutic options that showed superior eradication rates compared to proton pump inhibitor-based (PPI) lansoprazole triple therapy in the overall patient population in a pivotal trial,” Terrie Curran, president and CEO of Phathom Pharmaceuticals, said in the release.
“H. pylori eradication rates continue to decline in part due to antibiotic resistance, inadequate acid suppression, and complex treatment regimens, resulting in treatment failures and complications for patients,” Ms. Curran noted.
“New therapies that have the potential to address the limitations of current treatments are needed, and we look forward to bringing these innovative vonoprazan-based treatment options to the millions of H pylori sufferers in the United States,” Ms. Curran said.
FDA approval of vonoprazan triple and dual therapy was based on safety and efficacy data from the phase 3 PHALCON-HP trial involving 1,046 patients.
As earlier reported, both treatment regimens were noninferior to PPI-based triple therapy (lansoprazole with amoxicillin and clarithromycin) in patients with H. pylori strains that were not resistant to clarithromycin or amoxicillin at baseline.
In this analysis, the eradication rate was 78.8% with PPI-based triple therapy, compared with 84.7% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 78.5% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Vonoprazan triple and dual therapy were both superior to PPI-based triple therapy among all patients, including patients with clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori.
Among patients with clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori, 31.9% achieved eradication with PPI triple therapy, compared with 65.8% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 69.6% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Among all patients, 68.5% achieved eradication with PPI triple therapy, 80.8% with vonoprazan triple therapy and 77.2% with vonoprazan dual therapy.
Adverse event rates for the vonoprazan-based regimens were comparable to lansoprazole triple therapy. Full prescribing information is available online.
“As a practicing physician, I am excited about the potential of two novel, first-line H. pylori treatment options,” William D. Chey, MD, chief of gastroenterology & hepatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in the news release.
“I believe the added flexibility of having two additional effective therapies, including a dual therapy option that does not contain clarithromycin, offers the potential to improve clinical outcomes in patients with H. pylori infection,” Dr. Chey added.
The company expects to launch both products in the third quarter of 2022. Both treatment regimens will be supplied in convenient blister packs to help promote compliance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Worst TB outbreak in 20 years reported in Washington state
Tuberculosis cases are increasing in Washington, which has put public health officials on “heightened alert,” according to a recent announcement from the Washington State Department of Health.
Widespread disruptions in health care and missed tuberculosis diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic have likely added to the increase – both locally and globally.
“It’s been 20 years since we saw a cluster of TB cases like this,” Tao Sheng Kwan-Gett, MD, the state’s chief science officer, said in the announcement.
“The pandemic has likely contributed to the rise in cases and the outbreak in at least one correctional facility,” he said. “Increased access to TB testing and treatment in the community is going to be key to getting TB under control.”
Case numbers appeared to fall in Washington during the first year of the pandemic, possibly because of less reporting and missed diagnoses. But in 2021, cases rose quickly. The state reported 199 cases, marking a 22% increase from 2020.
So far this year, 70 cases have been reported, including 17 new cases that all have connections with each other and several state prisons.
The state’s Department of Corrections, Department of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are working together on testing and decreasing spread, MaryAnn Curl, MD, the chief medical officer for the Department of Corrections, said in the statement.
Tuberculosis cases are increasing worldwide. For the first time in more than a decade, TB deaths increased to about 1.5 million, according to the World Health Organization’s 2021 Global Tuberculosis Report.
Across the U.S., the number of reported TB cases significantly declined at the beginning of the pandemic in 2020 but increased again in 2021, according to a recent CDC study.
The Kansas Department of Health also reported an outbreak of TB cases in March, according to USA Today.
At the beginning of the pandemic, some people with TB may have been diagnosed with COVID-19 because both are infectious diseases that attack the lungs and have similar symptoms, the Washington Health Department said.
Like COVID-19, tuberculosis can spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. But unlike COVID-19, TB typically requires that you have prolonged exposure to become infected.
Symptoms of tuberculosis can include chest pain and coughing, with or without blood, as well as fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue.
Tuberculosis is preventable, treatable, and curable, the Washington Health Department said. Those who travel to countries where TB is more common face higher risks for exposure, as well as those who live or work in settings where TB may spread, such as homeless shelters, prisons, jails, and nursing homes.
People can develop inactive TB, also called latent TB, which doesn’t have any symptoms and isn’t contagious. If people with inactive TB don’t get quick diagnosis or treatment, the infection can become active TB and cause symptoms. State health officials estimated that about 200,000 people in Washington have inactive TB.
Tuberculosis treatment can take a minimum of 6 months, and if it’s not followed carefully, symptoms can become more severe, the Health Department said. Incomplete treatment can also contribute to the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains of tuberculosis.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Tuberculosis cases are increasing in Washington, which has put public health officials on “heightened alert,” according to a recent announcement from the Washington State Department of Health.
Widespread disruptions in health care and missed tuberculosis diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic have likely added to the increase – both locally and globally.
“It’s been 20 years since we saw a cluster of TB cases like this,” Tao Sheng Kwan-Gett, MD, the state’s chief science officer, said in the announcement.
“The pandemic has likely contributed to the rise in cases and the outbreak in at least one correctional facility,” he said. “Increased access to TB testing and treatment in the community is going to be key to getting TB under control.”
Case numbers appeared to fall in Washington during the first year of the pandemic, possibly because of less reporting and missed diagnoses. But in 2021, cases rose quickly. The state reported 199 cases, marking a 22% increase from 2020.
So far this year, 70 cases have been reported, including 17 new cases that all have connections with each other and several state prisons.
The state’s Department of Corrections, Department of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are working together on testing and decreasing spread, MaryAnn Curl, MD, the chief medical officer for the Department of Corrections, said in the statement.
Tuberculosis cases are increasing worldwide. For the first time in more than a decade, TB deaths increased to about 1.5 million, according to the World Health Organization’s 2021 Global Tuberculosis Report.
Across the U.S., the number of reported TB cases significantly declined at the beginning of the pandemic in 2020 but increased again in 2021, according to a recent CDC study.
The Kansas Department of Health also reported an outbreak of TB cases in March, according to USA Today.
At the beginning of the pandemic, some people with TB may have been diagnosed with COVID-19 because both are infectious diseases that attack the lungs and have similar symptoms, the Washington Health Department said.
Like COVID-19, tuberculosis can spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. But unlike COVID-19, TB typically requires that you have prolonged exposure to become infected.
Symptoms of tuberculosis can include chest pain and coughing, with or without blood, as well as fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue.
Tuberculosis is preventable, treatable, and curable, the Washington Health Department said. Those who travel to countries where TB is more common face higher risks for exposure, as well as those who live or work in settings where TB may spread, such as homeless shelters, prisons, jails, and nursing homes.
People can develop inactive TB, also called latent TB, which doesn’t have any symptoms and isn’t contagious. If people with inactive TB don’t get quick diagnosis or treatment, the infection can become active TB and cause symptoms. State health officials estimated that about 200,000 people in Washington have inactive TB.
Tuberculosis treatment can take a minimum of 6 months, and if it’s not followed carefully, symptoms can become more severe, the Health Department said. Incomplete treatment can also contribute to the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains of tuberculosis.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Tuberculosis cases are increasing in Washington, which has put public health officials on “heightened alert,” according to a recent announcement from the Washington State Department of Health.
Widespread disruptions in health care and missed tuberculosis diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic have likely added to the increase – both locally and globally.
“It’s been 20 years since we saw a cluster of TB cases like this,” Tao Sheng Kwan-Gett, MD, the state’s chief science officer, said in the announcement.
“The pandemic has likely contributed to the rise in cases and the outbreak in at least one correctional facility,” he said. “Increased access to TB testing and treatment in the community is going to be key to getting TB under control.”
Case numbers appeared to fall in Washington during the first year of the pandemic, possibly because of less reporting and missed diagnoses. But in 2021, cases rose quickly. The state reported 199 cases, marking a 22% increase from 2020.
So far this year, 70 cases have been reported, including 17 new cases that all have connections with each other and several state prisons.
The state’s Department of Corrections, Department of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are working together on testing and decreasing spread, MaryAnn Curl, MD, the chief medical officer for the Department of Corrections, said in the statement.
Tuberculosis cases are increasing worldwide. For the first time in more than a decade, TB deaths increased to about 1.5 million, according to the World Health Organization’s 2021 Global Tuberculosis Report.
Across the U.S., the number of reported TB cases significantly declined at the beginning of the pandemic in 2020 but increased again in 2021, according to a recent CDC study.
The Kansas Department of Health also reported an outbreak of TB cases in March, according to USA Today.
At the beginning of the pandemic, some people with TB may have been diagnosed with COVID-19 because both are infectious diseases that attack the lungs and have similar symptoms, the Washington Health Department said.
Like COVID-19, tuberculosis can spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. But unlike COVID-19, TB typically requires that you have prolonged exposure to become infected.
Symptoms of tuberculosis can include chest pain and coughing, with or without blood, as well as fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue.
Tuberculosis is preventable, treatable, and curable, the Washington Health Department said. Those who travel to countries where TB is more common face higher risks for exposure, as well as those who live or work in settings where TB may spread, such as homeless shelters, prisons, jails, and nursing homes.
People can develop inactive TB, also called latent TB, which doesn’t have any symptoms and isn’t contagious. If people with inactive TB don’t get quick diagnosis or treatment, the infection can become active TB and cause symptoms. State health officials estimated that about 200,000 people in Washington have inactive TB.
Tuberculosis treatment can take a minimum of 6 months, and if it’s not followed carefully, symptoms can become more severe, the Health Department said. Incomplete treatment can also contribute to the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains of tuberculosis.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Antibiotic treatment alone less effective in children with more appendicitis pain
Children who have greater acute appendicitis pain may be less likely to improve if they’re treated with antibiotics alone, according to a secondary analysis of a nonrandomized clinical trial.
“While approximately 35% of families chose nonoperative management, a high pain score between 7-10 on a 10-point scale nearly doubled in-hospital treatment failure,” Rebecca M. Rentea, MD, a pediatric surgeon and the director of the Comprehensive Colorectal Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City, Mo., told this news organization in an email.
“Even if nonoperative management of pediatric appendicitis did not work – resulting in the need to remove the appendix in 34% of cases – families were happy with their decisions 1 year later,” added Dr. Rentea, who coauthored an invited commentary about the study.
Lead study author Peter C. Minneci, MD, MHSc, a pediatric surgeon at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and colleagues analyzed a subgroup of patients from a larger study in 10 tertiary children’s hospitals in the Midwest Pediatric Surgery Consortium.
As they reported in JAMA Network Open, the larger prospective, nonrandomized clinical trial enrolled 1,068 children between 2015 and 2018. The children ranged in age from 7 to 17 years, and they had imaging-confirmed appendicitis with an appendix diameter of 1.1 cm or less, no abscess, no appendicolith, and no phlegmon. White blood cell count was between 5,000 and 18,000 cells/μL, and abdominal pain began less than 48 hours before they received antibiotic therapy.
Caregivers chose either surgery or nonoperative antibiotic management. Patients who were treated first with antibiotics alone and who did not undergo appendectomy within 1 year were considered to have successfully completed nonoperative treatment.
The secondary analysis included the 370 children enrolled in the nonoperative group. Of these, 229 were boys, and the median age was 12.3 years. In this subgroup, the researchers compared outcomes after nonoperative, antibiotic management vs. surgery.
At 1 year, treatment failure had occurred in 125 patients, with 53 having undergone appendectomy during their first hospitalization, and 72 having experienced delayed treatment failure after being discharged.
- Higher patient-reported pain at presentation was linked to higher risk for in-hospital treatment failure (relative risk, 2.1; 95% confidence interval, 1.0-4.4) but not for delayed treatment failure (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 0.7-2.3) or overall treatment failure at 1 year (RR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.0-2.2).
- Pain lasting longer than 24 hours was linked to lower risk for delayed treatment failure (RR, 0.3; 95% CI, 0.1-1.0) but not for in-hospital treatment failure (RR, 1.2; 95% CI, 0.5-2.7) or treatment failure at 1 year (RR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.4-1.2).
- Satisfaction with the decision was higher with successful nonoperative management at 30 days (28.0 vs. 27.0; difference, 1.0; 95% CI, 0.01-2.0) and at 1 year (28.1 vs 27.0; difference, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.2-2.0).
The researchers found no increased risk for treatment failure based on age, sex, race, ethnicity, white blood cell count, primary language, insurance status, transfer status, presentation symptoms, or imaging results.
Antibiotics-only is a safe option for children
“This study suggests that pediatric patients with uncomplicated acute appendicitis should be offered treatment options, including nonoperative management,” the authors write. “Treatment with antibiotics alone is a safe and equitable option for children, with no increased risk of treatment failure based on sociodemographic or objective clinical characteristics at presentation.”
But, the authors advise: “Families need to be made aware that treatment failure is not uncommon, and they should be provided with anticipatory guidance on how to proceed should symptoms recur.”
The investigators acknowledged limitations to the study, including the nonrandomized design that may have introduced bias, the loss to follow-up, and the study population being U.S. Midwest children, who may differ from children elsewhere in the country.
Shawn D. St Peter, MD, a pediatric surgeon, medical chair, and a senior vice president at Children’s Mercy Kansas City told this news organization in an email that having a nonoperative alternative to surgical appendectomy is important.
“Antibiotics are the initial treatment for appendicitis and can be the definitive treatment,” he said.
“Surprisingly, no sociodemographic or clinical characteristics were associated with an increased risk of nonoperative appendicitis treatment failure,” added Dr. St Peter, who coauthored the commentary with Dr. Rentea.
Howard C. Jen, MD, a pediatric surgeon at University of California, Los Angeles, Mattel Children’s Hospital, was not surprised by the findings.
“Nonoperative management for acute noncomplicated appendicitis in children continues to be safe and effective in highly selected patients,” he said in an email. “This alternative to surgery should be offered routinely to patients with early acute appendicitis.”
Dr. Jen, who was not involved with the current study, noted that it did not address the impact and costs to families of nonoperative management vs. surgery.
“For the most vulnerable children who had difficulties accessing medical care, what is the best treatment option? What factors are important to the families when making this decision?” he asked.
All study and editorial authors report no relevant financial relationships. The study was funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children who have greater acute appendicitis pain may be less likely to improve if they’re treated with antibiotics alone, according to a secondary analysis of a nonrandomized clinical trial.
“While approximately 35% of families chose nonoperative management, a high pain score between 7-10 on a 10-point scale nearly doubled in-hospital treatment failure,” Rebecca M. Rentea, MD, a pediatric surgeon and the director of the Comprehensive Colorectal Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City, Mo., told this news organization in an email.
“Even if nonoperative management of pediatric appendicitis did not work – resulting in the need to remove the appendix in 34% of cases – families were happy with their decisions 1 year later,” added Dr. Rentea, who coauthored an invited commentary about the study.
Lead study author Peter C. Minneci, MD, MHSc, a pediatric surgeon at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and colleagues analyzed a subgroup of patients from a larger study in 10 tertiary children’s hospitals in the Midwest Pediatric Surgery Consortium.
As they reported in JAMA Network Open, the larger prospective, nonrandomized clinical trial enrolled 1,068 children between 2015 and 2018. The children ranged in age from 7 to 17 years, and they had imaging-confirmed appendicitis with an appendix diameter of 1.1 cm or less, no abscess, no appendicolith, and no phlegmon. White blood cell count was between 5,000 and 18,000 cells/μL, and abdominal pain began less than 48 hours before they received antibiotic therapy.
Caregivers chose either surgery or nonoperative antibiotic management. Patients who were treated first with antibiotics alone and who did not undergo appendectomy within 1 year were considered to have successfully completed nonoperative treatment.
The secondary analysis included the 370 children enrolled in the nonoperative group. Of these, 229 were boys, and the median age was 12.3 years. In this subgroup, the researchers compared outcomes after nonoperative, antibiotic management vs. surgery.
At 1 year, treatment failure had occurred in 125 patients, with 53 having undergone appendectomy during their first hospitalization, and 72 having experienced delayed treatment failure after being discharged.
- Higher patient-reported pain at presentation was linked to higher risk for in-hospital treatment failure (relative risk, 2.1; 95% confidence interval, 1.0-4.4) but not for delayed treatment failure (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 0.7-2.3) or overall treatment failure at 1 year (RR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.0-2.2).
- Pain lasting longer than 24 hours was linked to lower risk for delayed treatment failure (RR, 0.3; 95% CI, 0.1-1.0) but not for in-hospital treatment failure (RR, 1.2; 95% CI, 0.5-2.7) or treatment failure at 1 year (RR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.4-1.2).
- Satisfaction with the decision was higher with successful nonoperative management at 30 days (28.0 vs. 27.0; difference, 1.0; 95% CI, 0.01-2.0) and at 1 year (28.1 vs 27.0; difference, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.2-2.0).
The researchers found no increased risk for treatment failure based on age, sex, race, ethnicity, white blood cell count, primary language, insurance status, transfer status, presentation symptoms, or imaging results.
Antibiotics-only is a safe option for children
“This study suggests that pediatric patients with uncomplicated acute appendicitis should be offered treatment options, including nonoperative management,” the authors write. “Treatment with antibiotics alone is a safe and equitable option for children, with no increased risk of treatment failure based on sociodemographic or objective clinical characteristics at presentation.”
But, the authors advise: “Families need to be made aware that treatment failure is not uncommon, and they should be provided with anticipatory guidance on how to proceed should symptoms recur.”
The investigators acknowledged limitations to the study, including the nonrandomized design that may have introduced bias, the loss to follow-up, and the study population being U.S. Midwest children, who may differ from children elsewhere in the country.
Shawn D. St Peter, MD, a pediatric surgeon, medical chair, and a senior vice president at Children’s Mercy Kansas City told this news organization in an email that having a nonoperative alternative to surgical appendectomy is important.
“Antibiotics are the initial treatment for appendicitis and can be the definitive treatment,” he said.
“Surprisingly, no sociodemographic or clinical characteristics were associated with an increased risk of nonoperative appendicitis treatment failure,” added Dr. St Peter, who coauthored the commentary with Dr. Rentea.
Howard C. Jen, MD, a pediatric surgeon at University of California, Los Angeles, Mattel Children’s Hospital, was not surprised by the findings.
“Nonoperative management for acute noncomplicated appendicitis in children continues to be safe and effective in highly selected patients,” he said in an email. “This alternative to surgery should be offered routinely to patients with early acute appendicitis.”
Dr. Jen, who was not involved with the current study, noted that it did not address the impact and costs to families of nonoperative management vs. surgery.
“For the most vulnerable children who had difficulties accessing medical care, what is the best treatment option? What factors are important to the families when making this decision?” he asked.
All study and editorial authors report no relevant financial relationships. The study was funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children who have greater acute appendicitis pain may be less likely to improve if they’re treated with antibiotics alone, according to a secondary analysis of a nonrandomized clinical trial.
“While approximately 35% of families chose nonoperative management, a high pain score between 7-10 on a 10-point scale nearly doubled in-hospital treatment failure,” Rebecca M. Rentea, MD, a pediatric surgeon and the director of the Comprehensive Colorectal Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City, Mo., told this news organization in an email.
“Even if nonoperative management of pediatric appendicitis did not work – resulting in the need to remove the appendix in 34% of cases – families were happy with their decisions 1 year later,” added Dr. Rentea, who coauthored an invited commentary about the study.
Lead study author Peter C. Minneci, MD, MHSc, a pediatric surgeon at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and colleagues analyzed a subgroup of patients from a larger study in 10 tertiary children’s hospitals in the Midwest Pediatric Surgery Consortium.
As they reported in JAMA Network Open, the larger prospective, nonrandomized clinical trial enrolled 1,068 children between 2015 and 2018. The children ranged in age from 7 to 17 years, and they had imaging-confirmed appendicitis with an appendix diameter of 1.1 cm or less, no abscess, no appendicolith, and no phlegmon. White blood cell count was between 5,000 and 18,000 cells/μL, and abdominal pain began less than 48 hours before they received antibiotic therapy.
Caregivers chose either surgery or nonoperative antibiotic management. Patients who were treated first with antibiotics alone and who did not undergo appendectomy within 1 year were considered to have successfully completed nonoperative treatment.
The secondary analysis included the 370 children enrolled in the nonoperative group. Of these, 229 were boys, and the median age was 12.3 years. In this subgroup, the researchers compared outcomes after nonoperative, antibiotic management vs. surgery.
At 1 year, treatment failure had occurred in 125 patients, with 53 having undergone appendectomy during their first hospitalization, and 72 having experienced delayed treatment failure after being discharged.
- Higher patient-reported pain at presentation was linked to higher risk for in-hospital treatment failure (relative risk, 2.1; 95% confidence interval, 1.0-4.4) but not for delayed treatment failure (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 0.7-2.3) or overall treatment failure at 1 year (RR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.0-2.2).
- Pain lasting longer than 24 hours was linked to lower risk for delayed treatment failure (RR, 0.3; 95% CI, 0.1-1.0) but not for in-hospital treatment failure (RR, 1.2; 95% CI, 0.5-2.7) or treatment failure at 1 year (RR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.4-1.2).
- Satisfaction with the decision was higher with successful nonoperative management at 30 days (28.0 vs. 27.0; difference, 1.0; 95% CI, 0.01-2.0) and at 1 year (28.1 vs 27.0; difference, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.2-2.0).
The researchers found no increased risk for treatment failure based on age, sex, race, ethnicity, white blood cell count, primary language, insurance status, transfer status, presentation symptoms, or imaging results.
Antibiotics-only is a safe option for children
“This study suggests that pediatric patients with uncomplicated acute appendicitis should be offered treatment options, including nonoperative management,” the authors write. “Treatment with antibiotics alone is a safe and equitable option for children, with no increased risk of treatment failure based on sociodemographic or objective clinical characteristics at presentation.”
But, the authors advise: “Families need to be made aware that treatment failure is not uncommon, and they should be provided with anticipatory guidance on how to proceed should symptoms recur.”
The investigators acknowledged limitations to the study, including the nonrandomized design that may have introduced bias, the loss to follow-up, and the study population being U.S. Midwest children, who may differ from children elsewhere in the country.
Shawn D. St Peter, MD, a pediatric surgeon, medical chair, and a senior vice president at Children’s Mercy Kansas City told this news organization in an email that having a nonoperative alternative to surgical appendectomy is important.
“Antibiotics are the initial treatment for appendicitis and can be the definitive treatment,” he said.
“Surprisingly, no sociodemographic or clinical characteristics were associated with an increased risk of nonoperative appendicitis treatment failure,” added Dr. St Peter, who coauthored the commentary with Dr. Rentea.
Howard C. Jen, MD, a pediatric surgeon at University of California, Los Angeles, Mattel Children’s Hospital, was not surprised by the findings.
“Nonoperative management for acute noncomplicated appendicitis in children continues to be safe and effective in highly selected patients,” he said in an email. “This alternative to surgery should be offered routinely to patients with early acute appendicitis.”
Dr. Jen, who was not involved with the current study, noted that it did not address the impact and costs to families of nonoperative management vs. surgery.
“For the most vulnerable children who had difficulties accessing medical care, what is the best treatment option? What factors are important to the families when making this decision?” he asked.
All study and editorial authors report no relevant financial relationships. The study was funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
New HIV care guidelines from the European AIDS Clinical Society
Version 11.0 of the 2021 revised European AIDS Clinical Society (EACS) Guidelines updates all aspects of HIV care and adds recommendations on COVID-19 and antiretroviral treatment (ART) in children and adolescents, the guidelines authors reported in HIV Medicine.
“Conducting a systematic and timely annual revision of all guidelines recommendations is an EACS cornerstone,” EACS Guidelines coordinator Lene Ryom, MD, PhD, DMSc, a researcher at the University of Copenhagen, said in an interview. “These revisions ensure that the EACS Guidelines remain clinically relevant, are updated with the latest scientific evidence, and that they cover all key aspects related to HIV management.”
Key revisions in this update include:
Antiretroviral therapy (ART)
- Six recommended treatment options for first-line regimens for ART-naive adults include triple-drug regimens consisting of tenofovir (either tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or tenofovir alafenamide) with either lamivudine or emtricitabine plus dolutegravir, raltegravir, bictegravir, or doravirine; abacavir/lamivudine plus dolutegravir; or dual therapy with emtricitabine plus dolutegravir. These drug combinations are recommended in single-tablet form if available.
- Alternatives consisting of triple-drug tenofovir-based regimens along with efavirenz, rilpivirine, or boosted darunavir, are advised when no recommended regimens are feasible.
- Bimonthly injections with long-acting cabotegravir plus rilpivirine are now advised as a switch option for people who are virologically suppressed.
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis on demand is advised for cisgender men, and PrEP may be continued during pregnancy and breastfeeding for people at risk of acquiring HIV.
Drug-drug interactions (DDIs) and other prescribing issues
- Four new DDI tables cover antituberculosis drugs, anxiolytics, hormone therapy, and COVID-19 therapies.
Comorbidities
- This update acknowledged the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on routine health care, provides recommendations, and highlights the role of shared care and consultation for anxiety and other mental health disorders.
- Treatments involving diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, cancer, and sexual health have been updated, with new information about elderly and frail patients, women’s sexual health, and special considerations for transgender people.
Viral hepatitis coinfection
Immediate treatment of recently acquired hepatitis C is recommended for people living with HIV and ongoing risk behavior. Bulevirtide is added as a treatment option for hepatitis Delta virus.
Opportunistic infections and COVID-19
- The revision adds new guidance on management of HIV and COVID-19, covering epidemiology, risk factors for severe COVID-19, COVID-19 management, HIV care during a pandemic, HIV management during COVID-19 treatment, and management of long-term COVID-19 symptoms and prophylaxis.
- It includes guidance on management of tuberculosis meningitis, cryptococcosis, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, and drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Pediatric HIV infection treatments
- This new section, developed with the European pediatric research organization Penta, updates guidance for the use of preferred and alternative first-line drugs from birth to adolescence. Combinations include new child-friendly formulations of dolutegravir as early as 4 weeks of age and 3 kg (6.6 lb) of weight as well as an increased emphasis on dolutegravir as first-line preferred agent for all children except newborns. Abacavir is recommended for children younger than 3 months.
- ART regimens for children with infectious hepatitis or tuberculosis are also provided.
Laura Jane Waters, MD, a genitourinary consultant and HIV and hepatitis lead at Central and North West London National Health Service Mortimer Market Centre, and chair of the British HIV Association (BHIVA), shared her perspective on the revision. She was not involved with the EACS Guidelines revision.
“The addition of a section on COVID-19 in people with HIV, including management, drug interactions, and vaccination, is welcomed, as is the inclusion of key references and, for selected references, the key findings,” Dr. Waters said in an interview.
“Finally, for the first time, EACS covers pediatric HIV treatment by integrating with the Penta guidelines,” she added. “This is an important evolution, considering there are still cases of vertical HIV transmission in Europe, not to mention children living with HIV who have immigrated. Ensuring high and equitable standards of HIV treatment for young people is crucial.”
“This update to the always-pragmatic EACS guidelines further diverges from the United States Department of Health & Human Services guidelines,” Dr. Waters explained. “For 6 months, both guidelines preferred the same ... regimens for first-line therapy, but since DHSS removed raltegravir-based ART in June 2021 and EACS added doravirine-based regimens in October 2021, we’re back in the more familiar territory of EACS offering a broader range of preferred choices.”
Dr. Ryom noted that modern HIV care needs to consider managing coinfections, opportunistic diseases, comorbidities, aging, addictions, and mental health.
“Ensuring an integrated and personalized approach to HIV management is becoming increasingly important in an aging population living with HIV with the potential for complex needs,” she said.
The guidelines are available in several formats: as a free smartphone app, an interactive web version, and an online PDF.
Funding information was not provided. Dr. Ryom and several coauthors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Most of the guideline coauthors declared financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies “outside the submitted work.” Dr. Waters provided no information on conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Version 11.0 of the 2021 revised European AIDS Clinical Society (EACS) Guidelines updates all aspects of HIV care and adds recommendations on COVID-19 and antiretroviral treatment (ART) in children and adolescents, the guidelines authors reported in HIV Medicine.
“Conducting a systematic and timely annual revision of all guidelines recommendations is an EACS cornerstone,” EACS Guidelines coordinator Lene Ryom, MD, PhD, DMSc, a researcher at the University of Copenhagen, said in an interview. “These revisions ensure that the EACS Guidelines remain clinically relevant, are updated with the latest scientific evidence, and that they cover all key aspects related to HIV management.”
Key revisions in this update include:
Antiretroviral therapy (ART)
- Six recommended treatment options for first-line regimens for ART-naive adults include triple-drug regimens consisting of tenofovir (either tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or tenofovir alafenamide) with either lamivudine or emtricitabine plus dolutegravir, raltegravir, bictegravir, or doravirine; abacavir/lamivudine plus dolutegravir; or dual therapy with emtricitabine plus dolutegravir. These drug combinations are recommended in single-tablet form if available.
- Alternatives consisting of triple-drug tenofovir-based regimens along with efavirenz, rilpivirine, or boosted darunavir, are advised when no recommended regimens are feasible.
- Bimonthly injections with long-acting cabotegravir plus rilpivirine are now advised as a switch option for people who are virologically suppressed.
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis on demand is advised for cisgender men, and PrEP may be continued during pregnancy and breastfeeding for people at risk of acquiring HIV.
Drug-drug interactions (DDIs) and other prescribing issues
- Four new DDI tables cover antituberculosis drugs, anxiolytics, hormone therapy, and COVID-19 therapies.
Comorbidities
- This update acknowledged the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on routine health care, provides recommendations, and highlights the role of shared care and consultation for anxiety and other mental health disorders.
- Treatments involving diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, cancer, and sexual health have been updated, with new information about elderly and frail patients, women’s sexual health, and special considerations for transgender people.
Viral hepatitis coinfection
Immediate treatment of recently acquired hepatitis C is recommended for people living with HIV and ongoing risk behavior. Bulevirtide is added as a treatment option for hepatitis Delta virus.
Opportunistic infections and COVID-19
- The revision adds new guidance on management of HIV and COVID-19, covering epidemiology, risk factors for severe COVID-19, COVID-19 management, HIV care during a pandemic, HIV management during COVID-19 treatment, and management of long-term COVID-19 symptoms and prophylaxis.
- It includes guidance on management of tuberculosis meningitis, cryptococcosis, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, and drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Pediatric HIV infection treatments
- This new section, developed with the European pediatric research organization Penta, updates guidance for the use of preferred and alternative first-line drugs from birth to adolescence. Combinations include new child-friendly formulations of dolutegravir as early as 4 weeks of age and 3 kg (6.6 lb) of weight as well as an increased emphasis on dolutegravir as first-line preferred agent for all children except newborns. Abacavir is recommended for children younger than 3 months.
- ART regimens for children with infectious hepatitis or tuberculosis are also provided.
Laura Jane Waters, MD, a genitourinary consultant and HIV and hepatitis lead at Central and North West London National Health Service Mortimer Market Centre, and chair of the British HIV Association (BHIVA), shared her perspective on the revision. She was not involved with the EACS Guidelines revision.
“The addition of a section on COVID-19 in people with HIV, including management, drug interactions, and vaccination, is welcomed, as is the inclusion of key references and, for selected references, the key findings,” Dr. Waters said in an interview.
“Finally, for the first time, EACS covers pediatric HIV treatment by integrating with the Penta guidelines,” she added. “This is an important evolution, considering there are still cases of vertical HIV transmission in Europe, not to mention children living with HIV who have immigrated. Ensuring high and equitable standards of HIV treatment for young people is crucial.”
“This update to the always-pragmatic EACS guidelines further diverges from the United States Department of Health & Human Services guidelines,” Dr. Waters explained. “For 6 months, both guidelines preferred the same ... regimens for first-line therapy, but since DHSS removed raltegravir-based ART in June 2021 and EACS added doravirine-based regimens in October 2021, we’re back in the more familiar territory of EACS offering a broader range of preferred choices.”
Dr. Ryom noted that modern HIV care needs to consider managing coinfections, opportunistic diseases, comorbidities, aging, addictions, and mental health.
“Ensuring an integrated and personalized approach to HIV management is becoming increasingly important in an aging population living with HIV with the potential for complex needs,” she said.
The guidelines are available in several formats: as a free smartphone app, an interactive web version, and an online PDF.
Funding information was not provided. Dr. Ryom and several coauthors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Most of the guideline coauthors declared financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies “outside the submitted work.” Dr. Waters provided no information on conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Version 11.0 of the 2021 revised European AIDS Clinical Society (EACS) Guidelines updates all aspects of HIV care and adds recommendations on COVID-19 and antiretroviral treatment (ART) in children and adolescents, the guidelines authors reported in HIV Medicine.
“Conducting a systematic and timely annual revision of all guidelines recommendations is an EACS cornerstone,” EACS Guidelines coordinator Lene Ryom, MD, PhD, DMSc, a researcher at the University of Copenhagen, said in an interview. “These revisions ensure that the EACS Guidelines remain clinically relevant, are updated with the latest scientific evidence, and that they cover all key aspects related to HIV management.”
Key revisions in this update include:
Antiretroviral therapy (ART)
- Six recommended treatment options for first-line regimens for ART-naive adults include triple-drug regimens consisting of tenofovir (either tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or tenofovir alafenamide) with either lamivudine or emtricitabine plus dolutegravir, raltegravir, bictegravir, or doravirine; abacavir/lamivudine plus dolutegravir; or dual therapy with emtricitabine plus dolutegravir. These drug combinations are recommended in single-tablet form if available.
- Alternatives consisting of triple-drug tenofovir-based regimens along with efavirenz, rilpivirine, or boosted darunavir, are advised when no recommended regimens are feasible.
- Bimonthly injections with long-acting cabotegravir plus rilpivirine are now advised as a switch option for people who are virologically suppressed.
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis on demand is advised for cisgender men, and PrEP may be continued during pregnancy and breastfeeding for people at risk of acquiring HIV.
Drug-drug interactions (DDIs) and other prescribing issues
- Four new DDI tables cover antituberculosis drugs, anxiolytics, hormone therapy, and COVID-19 therapies.
Comorbidities
- This update acknowledged the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on routine health care, provides recommendations, and highlights the role of shared care and consultation for anxiety and other mental health disorders.
- Treatments involving diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, cancer, and sexual health have been updated, with new information about elderly and frail patients, women’s sexual health, and special considerations for transgender people.
Viral hepatitis coinfection
Immediate treatment of recently acquired hepatitis C is recommended for people living with HIV and ongoing risk behavior. Bulevirtide is added as a treatment option for hepatitis Delta virus.
Opportunistic infections and COVID-19
- The revision adds new guidance on management of HIV and COVID-19, covering epidemiology, risk factors for severe COVID-19, COVID-19 management, HIV care during a pandemic, HIV management during COVID-19 treatment, and management of long-term COVID-19 symptoms and prophylaxis.
- It includes guidance on management of tuberculosis meningitis, cryptococcosis, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, and drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Pediatric HIV infection treatments
- This new section, developed with the European pediatric research organization Penta, updates guidance for the use of preferred and alternative first-line drugs from birth to adolescence. Combinations include new child-friendly formulations of dolutegravir as early as 4 weeks of age and 3 kg (6.6 lb) of weight as well as an increased emphasis on dolutegravir as first-line preferred agent for all children except newborns. Abacavir is recommended for children younger than 3 months.
- ART regimens for children with infectious hepatitis or tuberculosis are also provided.
Laura Jane Waters, MD, a genitourinary consultant and HIV and hepatitis lead at Central and North West London National Health Service Mortimer Market Centre, and chair of the British HIV Association (BHIVA), shared her perspective on the revision. She was not involved with the EACS Guidelines revision.
“The addition of a section on COVID-19 in people with HIV, including management, drug interactions, and vaccination, is welcomed, as is the inclusion of key references and, for selected references, the key findings,” Dr. Waters said in an interview.
“Finally, for the first time, EACS covers pediatric HIV treatment by integrating with the Penta guidelines,” she added. “This is an important evolution, considering there are still cases of vertical HIV transmission in Europe, not to mention children living with HIV who have immigrated. Ensuring high and equitable standards of HIV treatment for young people is crucial.”
“This update to the always-pragmatic EACS guidelines further diverges from the United States Department of Health & Human Services guidelines,” Dr. Waters explained. “For 6 months, both guidelines preferred the same ... regimens for first-line therapy, but since DHSS removed raltegravir-based ART in June 2021 and EACS added doravirine-based regimens in October 2021, we’re back in the more familiar territory of EACS offering a broader range of preferred choices.”
Dr. Ryom noted that modern HIV care needs to consider managing coinfections, opportunistic diseases, comorbidities, aging, addictions, and mental health.
“Ensuring an integrated and personalized approach to HIV management is becoming increasingly important in an aging population living with HIV with the potential for complex needs,” she said.
The guidelines are available in several formats: as a free smartphone app, an interactive web version, and an online PDF.
Funding information was not provided. Dr. Ryom and several coauthors disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Most of the guideline coauthors declared financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies “outside the submitted work.” Dr. Waters provided no information on conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HIV MEDICINE
Best antioxidants to prevent age-related dementia identified?
Investigators found that individuals with the highest serum levels of lutein + zeaxanthin and beta-cryptoxanthin at baseline were less likely to have dementia decades later than were their peers with lower levels of these antioxidants.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are found in green leafy vegetables such as kale, spinach, broccoli, and peas. Beta-cryptoxanthin is found in fruits such as oranges, papaya, tangerines, and persimmons.
“Antioxidants may help protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can cause cell damage,” first author May A. Beydoun, PhD, with the National Institute on Aging (NIA), said in a news release.
“This is the first nationally representative study to analyze blood levels of antioxidants in relation to dementia risk,” NIA scientific director Luigi Ferrucci, MD, said in an interview.
“Blood test results may be more representative of the actual antioxidant level than a person’s report of what kind of foods they regularly consume,” Dr. Ferrucci added.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Reduced dementia risk
The researchers tested associations and interactions of serum vitamins A, C and E, and total and individual serum carotenoids and interactions with incident Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and all-cause dementia.
They analyzed data from 7,283 participants in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) who were at least 45 years old at baseline and followed for an average of 16-17 years.
They found serum levels of lutein + zeaxanthin were associated with reduced risk of all-cause dementia among people aged 65 and older in models adjusted for lifestyle.
For lutein + zeaxanthin, every standard deviation (SD) increase (roughly 15.4 µmol/liter) was associated with a 7% decrease in risk for dementia (hazard ratio [HR] 0.93; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-0.99, P = .037). This association was attenuated somewhat after adjustment for socioeconomic status.
Serum levels of beta-cryptoxanthin showed a “strong” inverse relationship with all-cause dementia in age- and sex-adjusted models.
For beta-cryptoxanthin, every SD increase (roughly 8.6 µmol/liter) was associated with a 14% reduced risk for dementia in people aged 45 and older (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.80-0.93, P < .001) and 65 and older (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.80-0.93, P = .001).
This relationship remained strong in models adjusted for sociodemographic and socioeconomic factors but attenuated in subsequent models.
No associations were found for lycopene, alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, or vitamins A, C, or E in the fully adjusted models.
Antagonistic interactions were observed for vitamin A and alpha-carotene, vitamin A and beta-carotene, vitamin E and lycopene, and lycopene and beta-carotene, suggesting putative protective effects of one antioxidant at lower levels of the other, the researchers noted.
“This analysis of an observational study found that the most important carotenoids in potentially protecting the brain may be lutein + zeaxanthin and beta-cryptoxanthin. However, randomized controlled trials are needed to prove causality,” said Dr. Ferrucci.
“Experts do not yet know the daily level of antioxidant intake to promote healthy aging of the brain. More research is needed to establish the necessary level of antioxidant intake – through the diet and/or supplements – to promote brain health and healthy aging,” he added.
An important step forward
In an accompanying editorial, Babak Hooshmand, MD, PhD, and Miia Kivipelto, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, noted that while nutrition and dietary components are “potential targets” for dementia risk reduction, observational studies to date have reported “inconsistent findings.”
This study is “an important step towards exploring the complex relationship between antioxidants and dementia because it accounts for factors that could possibly influence the associations and considers interactions between different components,” they wrote.
The findings are “challenging,” they added, because they may lead to the hypothesis that inhibition of oxidative damage by antioxidants might have beneficial effects on preventing dementia.
However, clinical trials of antioxidant supplementation have been mainly “disappointing” and a recent Cochrane review found a lack of evidence for supplement use to preserve cognitive function or prevent dementia, Dr. Hooshmand and Dr. Kivipelto noted.
They added that the study contributes to the belief that antioxidants don’t act independently of each other or other factors, including socioeconomic status and lifestyle, in the mediation of dementia risk.
“A careful examination of the evidence is required to learn how antioxidants influence the complex pathology of dementia, because it appears to be more to it than meets the eye,”they concluded.
The research was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Beydoun, Dr. Ferrucci, and Dr. Hooshmand report no relevant disclosures. Dr. Kivipelto has supported advisory boards for Combinostics, Roche, and Biogen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that individuals with the highest serum levels of lutein + zeaxanthin and beta-cryptoxanthin at baseline were less likely to have dementia decades later than were their peers with lower levels of these antioxidants.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are found in green leafy vegetables such as kale, spinach, broccoli, and peas. Beta-cryptoxanthin is found in fruits such as oranges, papaya, tangerines, and persimmons.
“Antioxidants may help protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can cause cell damage,” first author May A. Beydoun, PhD, with the National Institute on Aging (NIA), said in a news release.
“This is the first nationally representative study to analyze blood levels of antioxidants in relation to dementia risk,” NIA scientific director Luigi Ferrucci, MD, said in an interview.
“Blood test results may be more representative of the actual antioxidant level than a person’s report of what kind of foods they regularly consume,” Dr. Ferrucci added.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Reduced dementia risk
The researchers tested associations and interactions of serum vitamins A, C and E, and total and individual serum carotenoids and interactions with incident Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and all-cause dementia.
They analyzed data from 7,283 participants in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) who were at least 45 years old at baseline and followed for an average of 16-17 years.
They found serum levels of lutein + zeaxanthin were associated with reduced risk of all-cause dementia among people aged 65 and older in models adjusted for lifestyle.
For lutein + zeaxanthin, every standard deviation (SD) increase (roughly 15.4 µmol/liter) was associated with a 7% decrease in risk for dementia (hazard ratio [HR] 0.93; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-0.99, P = .037). This association was attenuated somewhat after adjustment for socioeconomic status.
Serum levels of beta-cryptoxanthin showed a “strong” inverse relationship with all-cause dementia in age- and sex-adjusted models.
For beta-cryptoxanthin, every SD increase (roughly 8.6 µmol/liter) was associated with a 14% reduced risk for dementia in people aged 45 and older (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.80-0.93, P < .001) and 65 and older (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.80-0.93, P = .001).
This relationship remained strong in models adjusted for sociodemographic and socioeconomic factors but attenuated in subsequent models.
No associations were found for lycopene, alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, or vitamins A, C, or E in the fully adjusted models.
Antagonistic interactions were observed for vitamin A and alpha-carotene, vitamin A and beta-carotene, vitamin E and lycopene, and lycopene and beta-carotene, suggesting putative protective effects of one antioxidant at lower levels of the other, the researchers noted.
“This analysis of an observational study found that the most important carotenoids in potentially protecting the brain may be lutein + zeaxanthin and beta-cryptoxanthin. However, randomized controlled trials are needed to prove causality,” said Dr. Ferrucci.
“Experts do not yet know the daily level of antioxidant intake to promote healthy aging of the brain. More research is needed to establish the necessary level of antioxidant intake – through the diet and/or supplements – to promote brain health and healthy aging,” he added.
An important step forward
In an accompanying editorial, Babak Hooshmand, MD, PhD, and Miia Kivipelto, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, noted that while nutrition and dietary components are “potential targets” for dementia risk reduction, observational studies to date have reported “inconsistent findings.”
This study is “an important step towards exploring the complex relationship between antioxidants and dementia because it accounts for factors that could possibly influence the associations and considers interactions between different components,” they wrote.
The findings are “challenging,” they added, because they may lead to the hypothesis that inhibition of oxidative damage by antioxidants might have beneficial effects on preventing dementia.
However, clinical trials of antioxidant supplementation have been mainly “disappointing” and a recent Cochrane review found a lack of evidence for supplement use to preserve cognitive function or prevent dementia, Dr. Hooshmand and Dr. Kivipelto noted.
They added that the study contributes to the belief that antioxidants don’t act independently of each other or other factors, including socioeconomic status and lifestyle, in the mediation of dementia risk.
“A careful examination of the evidence is required to learn how antioxidants influence the complex pathology of dementia, because it appears to be more to it than meets the eye,”they concluded.
The research was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Beydoun, Dr. Ferrucci, and Dr. Hooshmand report no relevant disclosures. Dr. Kivipelto has supported advisory boards for Combinostics, Roche, and Biogen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that individuals with the highest serum levels of lutein + zeaxanthin and beta-cryptoxanthin at baseline were less likely to have dementia decades later than were their peers with lower levels of these antioxidants.
Lutein and zeaxanthin are found in green leafy vegetables such as kale, spinach, broccoli, and peas. Beta-cryptoxanthin is found in fruits such as oranges, papaya, tangerines, and persimmons.
“Antioxidants may help protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can cause cell damage,” first author May A. Beydoun, PhD, with the National Institute on Aging (NIA), said in a news release.
“This is the first nationally representative study to analyze blood levels of antioxidants in relation to dementia risk,” NIA scientific director Luigi Ferrucci, MD, said in an interview.
“Blood test results may be more representative of the actual antioxidant level than a person’s report of what kind of foods they regularly consume,” Dr. Ferrucci added.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Reduced dementia risk
The researchers tested associations and interactions of serum vitamins A, C and E, and total and individual serum carotenoids and interactions with incident Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and all-cause dementia.
They analyzed data from 7,283 participants in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) who were at least 45 years old at baseline and followed for an average of 16-17 years.
They found serum levels of lutein + zeaxanthin were associated with reduced risk of all-cause dementia among people aged 65 and older in models adjusted for lifestyle.
For lutein + zeaxanthin, every standard deviation (SD) increase (roughly 15.4 µmol/liter) was associated with a 7% decrease in risk for dementia (hazard ratio [HR] 0.93; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-0.99, P = .037). This association was attenuated somewhat after adjustment for socioeconomic status.
Serum levels of beta-cryptoxanthin showed a “strong” inverse relationship with all-cause dementia in age- and sex-adjusted models.
For beta-cryptoxanthin, every SD increase (roughly 8.6 µmol/liter) was associated with a 14% reduced risk for dementia in people aged 45 and older (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.80-0.93, P < .001) and 65 and older (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.80-0.93, P = .001).
This relationship remained strong in models adjusted for sociodemographic and socioeconomic factors but attenuated in subsequent models.
No associations were found for lycopene, alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, or vitamins A, C, or E in the fully adjusted models.
Antagonistic interactions were observed for vitamin A and alpha-carotene, vitamin A and beta-carotene, vitamin E and lycopene, and lycopene and beta-carotene, suggesting putative protective effects of one antioxidant at lower levels of the other, the researchers noted.
“This analysis of an observational study found that the most important carotenoids in potentially protecting the brain may be lutein + zeaxanthin and beta-cryptoxanthin. However, randomized controlled trials are needed to prove causality,” said Dr. Ferrucci.
“Experts do not yet know the daily level of antioxidant intake to promote healthy aging of the brain. More research is needed to establish the necessary level of antioxidant intake – through the diet and/or supplements – to promote brain health and healthy aging,” he added.
An important step forward
In an accompanying editorial, Babak Hooshmand, MD, PhD, and Miia Kivipelto, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, noted that while nutrition and dietary components are “potential targets” for dementia risk reduction, observational studies to date have reported “inconsistent findings.”
This study is “an important step towards exploring the complex relationship between antioxidants and dementia because it accounts for factors that could possibly influence the associations and considers interactions between different components,” they wrote.
The findings are “challenging,” they added, because they may lead to the hypothesis that inhibition of oxidative damage by antioxidants might have beneficial effects on preventing dementia.
However, clinical trials of antioxidant supplementation have been mainly “disappointing” and a recent Cochrane review found a lack of evidence for supplement use to preserve cognitive function or prevent dementia, Dr. Hooshmand and Dr. Kivipelto noted.
They added that the study contributes to the belief that antioxidants don’t act independently of each other or other factors, including socioeconomic status and lifestyle, in the mediation of dementia risk.
“A careful examination of the evidence is required to learn how antioxidants influence the complex pathology of dementia, because it appears to be more to it than meets the eye,”they concluded.
The research was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Beydoun, Dr. Ferrucci, and Dr. Hooshmand report no relevant disclosures. Dr. Kivipelto has supported advisory boards for Combinostics, Roche, and Biogen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Misconceptions remain on gene signature use in breast cancer
BERLIN – , a European survey suggests.
The authors found, for instance, that while most specialists agreed that molecular intrinsic subtypes had clinical utility for understanding prognosis in early-stage hormone receptor (HR)–positive disease and for identifying patients for whom chemotherapy could be safely avoided, about 1 in 4 experts either disagreed or felt neutral about the use of signatures in these settings.
Similarly, almost 75% of respondents felt that these signatures were not useful in the triple-negative or metastatic setting, but a small percentage believed they were, and about 10% were neutral.
“Considering that breast cancer multigene signatures were developed in the post menopausal HR+/HER2- early breast cancer setting, the fact that some experts consider [them] useful in triple-negative, HER2+ breast cancer or in the metastatic setting corroborates a misunderstanding on how to interpret the results,” study author Giuseppe Curigliano, MD, PhD, associate professor of medical oncology at the University of Milan, and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Curigliano, who is also head of the Division of Early Drug Development at the European Institute of Oncology, presented the survey findings on May 4 at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO BCC) Breast Cancer Congress.
Although several breast cancer multigene signatures are available to profile early breast cancer, little information exists on how these signatures should be used in clinical practice.
To investigate, Dr. Curigliano and colleagues convened a scientific committee of eight breast cancer experts to develop a Delphi questionnaire to examine respondents’ opinions and uses of these signatures.
The questionnaire asked about the clinical utility of multigene signatures in breast cancer and recommendations for their use in clinical practice.
In all, 133 breast cancer specialists from 11 European countries completed the questionnaire. Respondents were about 49 years old on average, and most (86.5%) worked in a teaching hospital. More than 72% were medical oncologists; 12% were pathologists.
Consensus was considered to be reached when 70% or more of the respondents were in agreement on a topic.
Participants had “extensive experience in the management of breast cancer patients and have been using breast cancer multigene signatures in clinical practice,” Dr. Curigliano said.
Almost all respondents (93.6%) reported using breast cancer multigene signatures routinely or in selected patients, and 73.4% had more than 5 years of experience with them.
Overall, more than 70% of respondents agreed that identifying tumor intrinsic subtype via gene expression profiling was important in making prognostic and treatment decisions; however, a consensus was not reached on the use of immunohistochemistry.
In addition, most respondents (76%) agreed that identifying breast cancer molecular intrinsic subtypes had clinical utility for prognosis in early-stage HR-positive disease and for identifying patients for whom chemotherapy can be safely avoided (75%). However, in both cases, about one-quarter of respondents either disagreed or felt neutral.
No consensus was reached on the clinical utility of these subtypes for selecting the most appropriate chemotherapy treatment – two-thirds disagreed, while 13% agreed and 17% felt neutral.
When deciding on the use of chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting in early node-negative breast cancer, 88% of respondents felt that breast cancer multigene signatures were important. Moreover, 75% considered such signatures important when deciding whether to use chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting for patients with one to three positive lymph nodes. However, no consensus was reached on the utility of signatures for deciding whether to extend endocrine therapy in either setting.
When examining the usefulness of signatures in more special settings, the authors found that the vast majority (90%) of respondents believed that multigene signatures had clinical utility for postmenopausal early breast cancer patients, and 82% did not consider signatures clinically useful in the early-stage HER2-overexpressed setting.
In addition, 74% thought that breast cancer multigene signatures were not useful in triple-negative disease or in the metastatic setting.
Respondents did not reach a consensus on the clinical utility of multigene signatures in the neoadjuvant setting – only 27% considered them useful, and almost half did not.
The “low percentage” of respondents using the signatures in the neoadjuvant setting and the “misconception regarding the predictive value of these tests on chemotherapy benefits suggest there is still room for training on results interpretation [for breast cancer multigene signatures],” the authors write.
The study was sponsored by Veracyte. Dr. Curigliano has relationships with Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, Roche, Seattle Genetics, Celltrion, and Veracyte. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 5/9/22.
BERLIN – , a European survey suggests.
The authors found, for instance, that while most specialists agreed that molecular intrinsic subtypes had clinical utility for understanding prognosis in early-stage hormone receptor (HR)–positive disease and for identifying patients for whom chemotherapy could be safely avoided, about 1 in 4 experts either disagreed or felt neutral about the use of signatures in these settings.
Similarly, almost 75% of respondents felt that these signatures were not useful in the triple-negative or metastatic setting, but a small percentage believed they were, and about 10% were neutral.
“Considering that breast cancer multigene signatures were developed in the post menopausal HR+/HER2- early breast cancer setting, the fact that some experts consider [them] useful in triple-negative, HER2+ breast cancer or in the metastatic setting corroborates a misunderstanding on how to interpret the results,” study author Giuseppe Curigliano, MD, PhD, associate professor of medical oncology at the University of Milan, and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Curigliano, who is also head of the Division of Early Drug Development at the European Institute of Oncology, presented the survey findings on May 4 at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO BCC) Breast Cancer Congress.
Although several breast cancer multigene signatures are available to profile early breast cancer, little information exists on how these signatures should be used in clinical practice.
To investigate, Dr. Curigliano and colleagues convened a scientific committee of eight breast cancer experts to develop a Delphi questionnaire to examine respondents’ opinions and uses of these signatures.
The questionnaire asked about the clinical utility of multigene signatures in breast cancer and recommendations for their use in clinical practice.
In all, 133 breast cancer specialists from 11 European countries completed the questionnaire. Respondents were about 49 years old on average, and most (86.5%) worked in a teaching hospital. More than 72% were medical oncologists; 12% were pathologists.
Consensus was considered to be reached when 70% or more of the respondents were in agreement on a topic.
Participants had “extensive experience in the management of breast cancer patients and have been using breast cancer multigene signatures in clinical practice,” Dr. Curigliano said.
Almost all respondents (93.6%) reported using breast cancer multigene signatures routinely or in selected patients, and 73.4% had more than 5 years of experience with them.
Overall, more than 70% of respondents agreed that identifying tumor intrinsic subtype via gene expression profiling was important in making prognostic and treatment decisions; however, a consensus was not reached on the use of immunohistochemistry.
In addition, most respondents (76%) agreed that identifying breast cancer molecular intrinsic subtypes had clinical utility for prognosis in early-stage HR-positive disease and for identifying patients for whom chemotherapy can be safely avoided (75%). However, in both cases, about one-quarter of respondents either disagreed or felt neutral.
No consensus was reached on the clinical utility of these subtypes for selecting the most appropriate chemotherapy treatment – two-thirds disagreed, while 13% agreed and 17% felt neutral.
When deciding on the use of chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting in early node-negative breast cancer, 88% of respondents felt that breast cancer multigene signatures were important. Moreover, 75% considered such signatures important when deciding whether to use chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting for patients with one to three positive lymph nodes. However, no consensus was reached on the utility of signatures for deciding whether to extend endocrine therapy in either setting.
When examining the usefulness of signatures in more special settings, the authors found that the vast majority (90%) of respondents believed that multigene signatures had clinical utility for postmenopausal early breast cancer patients, and 82% did not consider signatures clinically useful in the early-stage HER2-overexpressed setting.
In addition, 74% thought that breast cancer multigene signatures were not useful in triple-negative disease or in the metastatic setting.
Respondents did not reach a consensus on the clinical utility of multigene signatures in the neoadjuvant setting – only 27% considered them useful, and almost half did not.
The “low percentage” of respondents using the signatures in the neoadjuvant setting and the “misconception regarding the predictive value of these tests on chemotherapy benefits suggest there is still room for training on results interpretation [for breast cancer multigene signatures],” the authors write.
The study was sponsored by Veracyte. Dr. Curigliano has relationships with Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, Roche, Seattle Genetics, Celltrion, and Veracyte. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 5/9/22.
BERLIN – , a European survey suggests.
The authors found, for instance, that while most specialists agreed that molecular intrinsic subtypes had clinical utility for understanding prognosis in early-stage hormone receptor (HR)–positive disease and for identifying patients for whom chemotherapy could be safely avoided, about 1 in 4 experts either disagreed or felt neutral about the use of signatures in these settings.
Similarly, almost 75% of respondents felt that these signatures were not useful in the triple-negative or metastatic setting, but a small percentage believed they were, and about 10% were neutral.
“Considering that breast cancer multigene signatures were developed in the post menopausal HR+/HER2- early breast cancer setting, the fact that some experts consider [them] useful in triple-negative, HER2+ breast cancer or in the metastatic setting corroborates a misunderstanding on how to interpret the results,” study author Giuseppe Curigliano, MD, PhD, associate professor of medical oncology at the University of Milan, and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Curigliano, who is also head of the Division of Early Drug Development at the European Institute of Oncology, presented the survey findings on May 4 at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO BCC) Breast Cancer Congress.
Although several breast cancer multigene signatures are available to profile early breast cancer, little information exists on how these signatures should be used in clinical practice.
To investigate, Dr. Curigliano and colleagues convened a scientific committee of eight breast cancer experts to develop a Delphi questionnaire to examine respondents’ opinions and uses of these signatures.
The questionnaire asked about the clinical utility of multigene signatures in breast cancer and recommendations for their use in clinical practice.
In all, 133 breast cancer specialists from 11 European countries completed the questionnaire. Respondents were about 49 years old on average, and most (86.5%) worked in a teaching hospital. More than 72% were medical oncologists; 12% were pathologists.
Consensus was considered to be reached when 70% or more of the respondents were in agreement on a topic.
Participants had “extensive experience in the management of breast cancer patients and have been using breast cancer multigene signatures in clinical practice,” Dr. Curigliano said.
Almost all respondents (93.6%) reported using breast cancer multigene signatures routinely or in selected patients, and 73.4% had more than 5 years of experience with them.
Overall, more than 70% of respondents agreed that identifying tumor intrinsic subtype via gene expression profiling was important in making prognostic and treatment decisions; however, a consensus was not reached on the use of immunohistochemistry.
In addition, most respondents (76%) agreed that identifying breast cancer molecular intrinsic subtypes had clinical utility for prognosis in early-stage HR-positive disease and for identifying patients for whom chemotherapy can be safely avoided (75%). However, in both cases, about one-quarter of respondents either disagreed or felt neutral.
No consensus was reached on the clinical utility of these subtypes for selecting the most appropriate chemotherapy treatment – two-thirds disagreed, while 13% agreed and 17% felt neutral.
When deciding on the use of chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting in early node-negative breast cancer, 88% of respondents felt that breast cancer multigene signatures were important. Moreover, 75% considered such signatures important when deciding whether to use chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting for patients with one to three positive lymph nodes. However, no consensus was reached on the utility of signatures for deciding whether to extend endocrine therapy in either setting.
When examining the usefulness of signatures in more special settings, the authors found that the vast majority (90%) of respondents believed that multigene signatures had clinical utility for postmenopausal early breast cancer patients, and 82% did not consider signatures clinically useful in the early-stage HER2-overexpressed setting.
In addition, 74% thought that breast cancer multigene signatures were not useful in triple-negative disease or in the metastatic setting.
Respondents did not reach a consensus on the clinical utility of multigene signatures in the neoadjuvant setting – only 27% considered them useful, and almost half did not.
The “low percentage” of respondents using the signatures in the neoadjuvant setting and the “misconception regarding the predictive value of these tests on chemotherapy benefits suggest there is still room for training on results interpretation [for breast cancer multigene signatures],” the authors write.
The study was sponsored by Veracyte. Dr. Curigliano has relationships with Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, Roche, Seattle Genetics, Celltrion, and Veracyte. No other relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 5/9/22.
AT ESMO BCC 2022