User login
Recommended Use of Anticoagulant Reversal in Bleeding Events
The number of patients treated with anticoagulants has significantly increased over the past decade, largely owing to the introduction of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). Currently, more than 6 million people nationwide are taking anticoagulants; these include patients receiving care through the Veterans Health Administration.
However, the growing use of oral anticoagulants has been accompanied by a rise in anticoagulant-related bleeding incidents. Dr Geoffrey Barnes from the University of Michigan discusses strategies to assess and manage bleeding events, and he reviews the most current recommendations on the appropriate selection and use of anticoagulation reversal agents.
Dr Barnes also underscores the importance of monitoring for thromboembolic complications in patients treated for life-threatening bleeding to prevent post-bleed thromboembolic events.
--
Associate Professor, Frankel Cardiovascular Center, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Pfizer; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Janssen; Bayer; AstraZeneca; Sanofi; Anthos; Abbott Vascular; Boston Scientific
Received research grant from: Boston Scientific
The number of patients treated with anticoagulants has significantly increased over the past decade, largely owing to the introduction of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). Currently, more than 6 million people nationwide are taking anticoagulants; these include patients receiving care through the Veterans Health Administration.
However, the growing use of oral anticoagulants has been accompanied by a rise in anticoagulant-related bleeding incidents. Dr Geoffrey Barnes from the University of Michigan discusses strategies to assess and manage bleeding events, and he reviews the most current recommendations on the appropriate selection and use of anticoagulation reversal agents.
Dr Barnes also underscores the importance of monitoring for thromboembolic complications in patients treated for life-threatening bleeding to prevent post-bleed thromboembolic events.
--
Associate Professor, Frankel Cardiovascular Center, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Pfizer; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Janssen; Bayer; AstraZeneca; Sanofi; Anthos; Abbott Vascular; Boston Scientific
Received research grant from: Boston Scientific
The number of patients treated with anticoagulants has significantly increased over the past decade, largely owing to the introduction of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). Currently, more than 6 million people nationwide are taking anticoagulants; these include patients receiving care through the Veterans Health Administration.
However, the growing use of oral anticoagulants has been accompanied by a rise in anticoagulant-related bleeding incidents. Dr Geoffrey Barnes from the University of Michigan discusses strategies to assess and manage bleeding events, and he reviews the most current recommendations on the appropriate selection and use of anticoagulation reversal agents.
Dr Barnes also underscores the importance of monitoring for thromboembolic complications in patients treated for life-threatening bleeding to prevent post-bleed thromboembolic events.
--
Associate Professor, Frankel Cardiovascular Center, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Pfizer; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Janssen; Bayer; AstraZeneca; Sanofi; Anthos; Abbott Vascular; Boston Scientific
Received research grant from: Boston Scientific

Do You Have Patients With JAKne — JAK Inhibitor–Associated Acne? Here’s What to Know
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
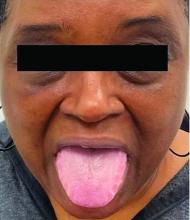
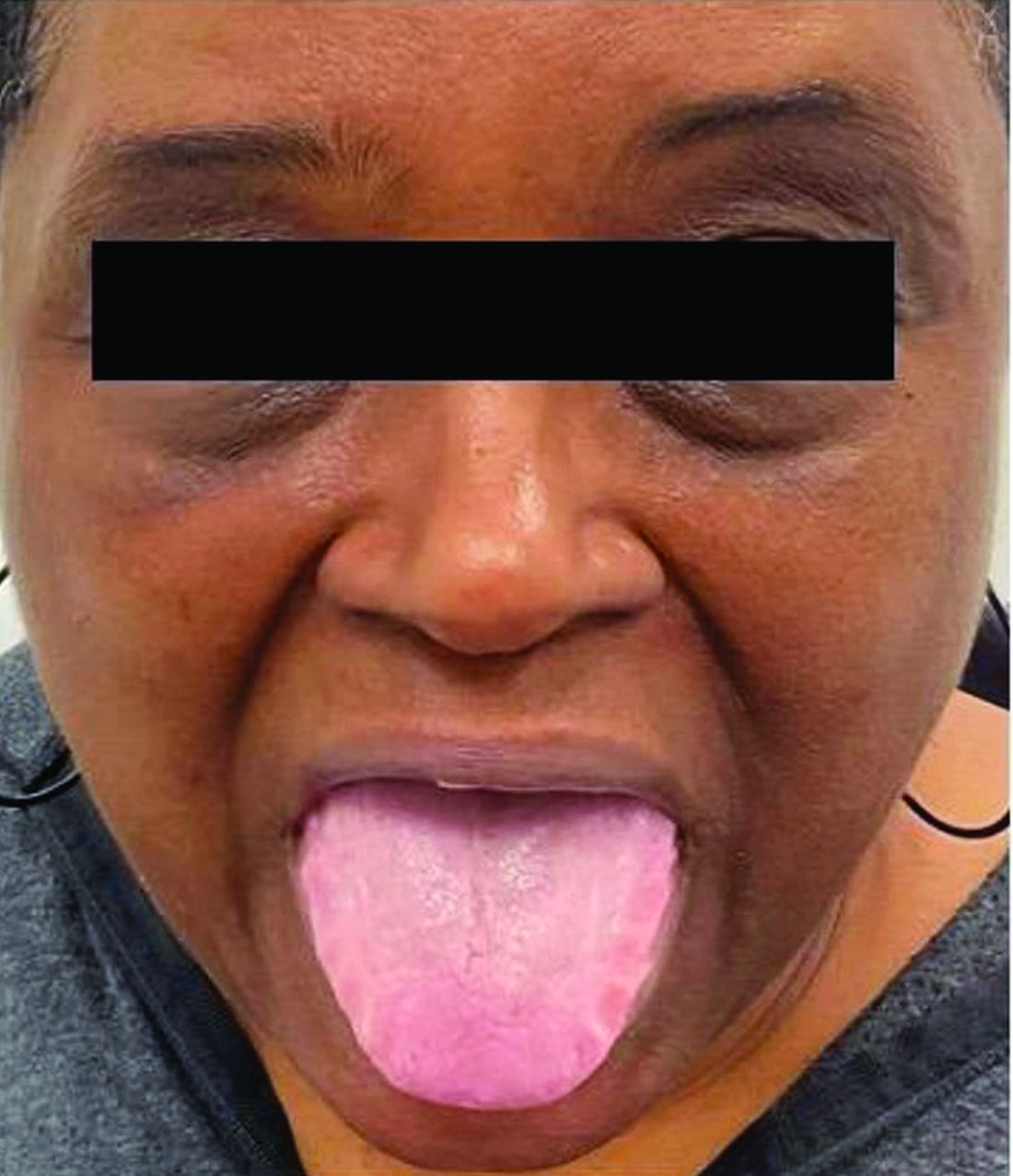
A 62-year-old Black female presented with an epidermal inclusion cyst on her left upper back
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
FDA Issues Complete Response Letter for Myeloma Drug
On August 20, Regeneron announced that it had received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its Biologics License Application for linvoseltamab, citing issues at a third-party manufacturer.
More specifically, Regeneron said in a company press release that the FDA issued the complete response letter based on findings from “a preapproval inspection at a third-party fill/finish manufacturer for another company’s product candidate.”
The third-party manufacturer told Regeneron it believes that the issues have been resolved, Regeneron said, and that facility is now awaiting a follow-up FDA inspection in the “coming months.”
Regeneron noted that this “anticipated outcome” from the FDA preapproval inspection had been disclosed previously during a company earnings call on August 1.
On that call, Regeneron had discussed the FDA’s concerns about the third-party manufacturer and anticipated that “any potential FDA approval for linvoseltamab is likely to be delayed beyond the August 22 PDUFA date.”
Regeneron had initially filed a Biologics License Application for its bispecific antibody in 2023, based on findings from the phase 1/2 single arm LINKER-MM1 trial.
In the latest published trial findings, investigators reported that, at a median follow-up of about 14 months, 71% of the 117 patients receiving 200 mg of linvoseltamab achieved an overall response, with 50% achieving a complete response. The probability of survival at 12 months was 75.3%.
This would have been the first approval for linvoseltamab, which would have joined two agents already on the US market for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: teclistamab (Tecvayli, Janssen) and elranatamab (Elrexfio, Pfizer).
Pricing information for linvoseltamab is not yet available, but its competitors teclistamab and elranatamab are reported to cost around $40,000 per month.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 20, Regeneron announced that it had received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its Biologics License Application for linvoseltamab, citing issues at a third-party manufacturer.
More specifically, Regeneron said in a company press release that the FDA issued the complete response letter based on findings from “a preapproval inspection at a third-party fill/finish manufacturer for another company’s product candidate.”
The third-party manufacturer told Regeneron it believes that the issues have been resolved, Regeneron said, and that facility is now awaiting a follow-up FDA inspection in the “coming months.”
Regeneron noted that this “anticipated outcome” from the FDA preapproval inspection had been disclosed previously during a company earnings call on August 1.
On that call, Regeneron had discussed the FDA’s concerns about the third-party manufacturer and anticipated that “any potential FDA approval for linvoseltamab is likely to be delayed beyond the August 22 PDUFA date.”
Regeneron had initially filed a Biologics License Application for its bispecific antibody in 2023, based on findings from the phase 1/2 single arm LINKER-MM1 trial.
In the latest published trial findings, investigators reported that, at a median follow-up of about 14 months, 71% of the 117 patients receiving 200 mg of linvoseltamab achieved an overall response, with 50% achieving a complete response. The probability of survival at 12 months was 75.3%.
This would have been the first approval for linvoseltamab, which would have joined two agents already on the US market for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: teclistamab (Tecvayli, Janssen) and elranatamab (Elrexfio, Pfizer).
Pricing information for linvoseltamab is not yet available, but its competitors teclistamab and elranatamab are reported to cost around $40,000 per month.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 20, Regeneron announced that it had received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its Biologics License Application for linvoseltamab, citing issues at a third-party manufacturer.
More specifically, Regeneron said in a company press release that the FDA issued the complete response letter based on findings from “a preapproval inspection at a third-party fill/finish manufacturer for another company’s product candidate.”
The third-party manufacturer told Regeneron it believes that the issues have been resolved, Regeneron said, and that facility is now awaiting a follow-up FDA inspection in the “coming months.”
Regeneron noted that this “anticipated outcome” from the FDA preapproval inspection had been disclosed previously during a company earnings call on August 1.
On that call, Regeneron had discussed the FDA’s concerns about the third-party manufacturer and anticipated that “any potential FDA approval for linvoseltamab is likely to be delayed beyond the August 22 PDUFA date.”
Regeneron had initially filed a Biologics License Application for its bispecific antibody in 2023, based on findings from the phase 1/2 single arm LINKER-MM1 trial.
In the latest published trial findings, investigators reported that, at a median follow-up of about 14 months, 71% of the 117 patients receiving 200 mg of linvoseltamab achieved an overall response, with 50% achieving a complete response. The probability of survival at 12 months was 75.3%.
This would have been the first approval for linvoseltamab, which would have joined two agents already on the US market for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: teclistamab (Tecvayli, Janssen) and elranatamab (Elrexfio, Pfizer).
Pricing information for linvoseltamab is not yet available, but its competitors teclistamab and elranatamab are reported to cost around $40,000 per month.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Do New Blood Tests for Cancer Meet the Right Standards?
Biotech startups worldwide are rushing to market screening tests that they claim can detect various cancers in early stages with just a few drops of blood. The tests allegedly will simplify cancer care by eliminating tedious scans, scopes, and swabs at the doctor’s office.
The promise of these early detection tests is truly “enticing,” Hilary A. Robbins, PhD, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization in Lyon, France, said in an interview.
In an opinion article in The New England Journal of Medicine, she emphasized that the new cancer tests are much less cumbersome than traditional screening strategies for individual cancers. Moreover, they could enable the early detection of dozens of cancer types for which no screening has been available so far.
Meeting the Criteria
The problem is that these tests have not met the strict criteria typically required for traditional cancer screening tests. To be considered for introduction as a screening procedure, a test usually needs to meet the following four minimum requirements:
- The disease that the test screens for must have a presymptomatic form.
- The screening test must be able to identify this presymptomatic disease.
- Treating the disease in the presymptomatic phase improves prognosis (specifically, it affects cancer-specific mortality in a randomized controlled trial).
- The screening test is feasible, and the benefits outweigh potential risks.
“The new blood tests for multiple cancers have so far only met the second criteria, showing they can detect presymptomatic cancer,” Dr. Robbins wrote.
The next step would be to demonstrate that they affect cancer-specific mortality. “But currently, commercial interests seem to be influencing the evidence standards for these cancer tests,” said Dr. Robbins.
Inappropriate Endpoints?
Some proponents of such tests argue that, unlike for previous cancer screening procedures, initial approval should not depend on the endpoint of cancer-specific mortality. It would take too long to gather sufficient outcome data, and in the meantime, people would die, they argue.
Eric A. Klein, MD, from the Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute in Cleveland, Ohio, and colleagues advocate for alternative endpoints such as the incidence of late-stage cancer in an article published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
“The concept would be,” they wrote, “that a negative signal would not indicate a mortality benefit, leading to the study being stopped. A positive signal, on the other hand, could result in provisional approval until mortality data and real-world evidence of effectiveness are available. This would resemble the accelerated approval of new cancer drugs, which often is based on progression-free survival until there postmarketing data on overall survival emerge.”
Dr. Klein is also employed at the US biotech start-up Grail, which developed the Galleri test, which is one of the best-known and most advanced cancer screening tests. The Galleri test uses cell-free DNA and machine learning to detect a common cancer signal in more than 50 cancer types and predict the origin of the cancer signal. Consumers in the United States can already order and perform the test.
An NHS Study
Arguments for different endpoints apparently resonated with the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS). Three years ago, they initiated the Galleri study, a large randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of Grail’s cancer test. The primary endpoint was not cancer-specific mortality, but the incidence of stage III or IV cancer.
The results are expected in 2026. But recruitment was stopped after 140,000 participants were enrolled. The NHS reported that the initial results were not convincing enough to continue the trial. Exact numbers were not disclosed.
The Galleri study deviates from the standard randomized controlled trial design for cancer screening procedures not only in terms of the primary endpoint, but also in blinding. The only participants who were unblinded and informed of their test results are those in the intervention group with a positive cancer test.
False Security
This trial design encourages participants to undergo blood tests once per year. But according to Dr. Robbins, it prevents the exploration of the phenomenon of “false security,” which is a potential drawback of the new cancer tests.
“Women with a negative mammogram can reasonably assume that they probably do not have breast cancer. But individuals with a negative cancer blood test could mistakenly believe they cannot have any cancer at all. As a result, they may not undergo standard early detection screenings or seek medical help early enough for potential cancer symptoms,” said Dr. Robbins.
To assess the actual risk-benefit ratio of the Galleri test, participants must receive their test results, she said. “Under real-world conditions, benefits and risks can come from positive and negative results.”
Upcoming Trial
More illuminating results may come from a large trial planned by the National Cancer Institute in the United States. Several new cancer tests will be evaluated for their ability to reduce cancer-specific mortality. A pilot phase will start later in 2024. “This study may be the only one with sufficient statistical power to determine whether an approach based on these cancer tests can reduce cancer-specific mortality,” said Dr. Robbins.
For the new blood tests for multiple cancers, it is crucial that health authorities “set a high bar for a benefit,” she said. This, according to her, also means that they must show an effect on cancer-specific mortality before being introduced. “This evidence must come from studies in which commercial interests do not influence the design, execution, data management, or data analysis.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Biotech startups worldwide are rushing to market screening tests that they claim can detect various cancers in early stages with just a few drops of blood. The tests allegedly will simplify cancer care by eliminating tedious scans, scopes, and swabs at the doctor’s office.
The promise of these early detection tests is truly “enticing,” Hilary A. Robbins, PhD, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization in Lyon, France, said in an interview.
In an opinion article in The New England Journal of Medicine, she emphasized that the new cancer tests are much less cumbersome than traditional screening strategies for individual cancers. Moreover, they could enable the early detection of dozens of cancer types for which no screening has been available so far.
Meeting the Criteria
The problem is that these tests have not met the strict criteria typically required for traditional cancer screening tests. To be considered for introduction as a screening procedure, a test usually needs to meet the following four minimum requirements:
- The disease that the test screens for must have a presymptomatic form.
- The screening test must be able to identify this presymptomatic disease.
- Treating the disease in the presymptomatic phase improves prognosis (specifically, it affects cancer-specific mortality in a randomized controlled trial).
- The screening test is feasible, and the benefits outweigh potential risks.
“The new blood tests for multiple cancers have so far only met the second criteria, showing they can detect presymptomatic cancer,” Dr. Robbins wrote.
The next step would be to demonstrate that they affect cancer-specific mortality. “But currently, commercial interests seem to be influencing the evidence standards for these cancer tests,” said Dr. Robbins.
Inappropriate Endpoints?
Some proponents of such tests argue that, unlike for previous cancer screening procedures, initial approval should not depend on the endpoint of cancer-specific mortality. It would take too long to gather sufficient outcome data, and in the meantime, people would die, they argue.
Eric A. Klein, MD, from the Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute in Cleveland, Ohio, and colleagues advocate for alternative endpoints such as the incidence of late-stage cancer in an article published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
“The concept would be,” they wrote, “that a negative signal would not indicate a mortality benefit, leading to the study being stopped. A positive signal, on the other hand, could result in provisional approval until mortality data and real-world evidence of effectiveness are available. This would resemble the accelerated approval of new cancer drugs, which often is based on progression-free survival until there postmarketing data on overall survival emerge.”
Dr. Klein is also employed at the US biotech start-up Grail, which developed the Galleri test, which is one of the best-known and most advanced cancer screening tests. The Galleri test uses cell-free DNA and machine learning to detect a common cancer signal in more than 50 cancer types and predict the origin of the cancer signal. Consumers in the United States can already order and perform the test.
An NHS Study
Arguments for different endpoints apparently resonated with the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS). Three years ago, they initiated the Galleri study, a large randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of Grail’s cancer test. The primary endpoint was not cancer-specific mortality, but the incidence of stage III or IV cancer.
The results are expected in 2026. But recruitment was stopped after 140,000 participants were enrolled. The NHS reported that the initial results were not convincing enough to continue the trial. Exact numbers were not disclosed.
The Galleri study deviates from the standard randomized controlled trial design for cancer screening procedures not only in terms of the primary endpoint, but also in blinding. The only participants who were unblinded and informed of their test results are those in the intervention group with a positive cancer test.
False Security
This trial design encourages participants to undergo blood tests once per year. But according to Dr. Robbins, it prevents the exploration of the phenomenon of “false security,” which is a potential drawback of the new cancer tests.
“Women with a negative mammogram can reasonably assume that they probably do not have breast cancer. But individuals with a negative cancer blood test could mistakenly believe they cannot have any cancer at all. As a result, they may not undergo standard early detection screenings or seek medical help early enough for potential cancer symptoms,” said Dr. Robbins.
To assess the actual risk-benefit ratio of the Galleri test, participants must receive their test results, she said. “Under real-world conditions, benefits and risks can come from positive and negative results.”
Upcoming Trial
More illuminating results may come from a large trial planned by the National Cancer Institute in the United States. Several new cancer tests will be evaluated for their ability to reduce cancer-specific mortality. A pilot phase will start later in 2024. “This study may be the only one with sufficient statistical power to determine whether an approach based on these cancer tests can reduce cancer-specific mortality,” said Dr. Robbins.
For the new blood tests for multiple cancers, it is crucial that health authorities “set a high bar for a benefit,” she said. This, according to her, also means that they must show an effect on cancer-specific mortality before being introduced. “This evidence must come from studies in which commercial interests do not influence the design, execution, data management, or data analysis.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Biotech startups worldwide are rushing to market screening tests that they claim can detect various cancers in early stages with just a few drops of blood. The tests allegedly will simplify cancer care by eliminating tedious scans, scopes, and swabs at the doctor’s office.
The promise of these early detection tests is truly “enticing,” Hilary A. Robbins, PhD, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization in Lyon, France, said in an interview.
In an opinion article in The New England Journal of Medicine, she emphasized that the new cancer tests are much less cumbersome than traditional screening strategies for individual cancers. Moreover, they could enable the early detection of dozens of cancer types for which no screening has been available so far.
Meeting the Criteria
The problem is that these tests have not met the strict criteria typically required for traditional cancer screening tests. To be considered for introduction as a screening procedure, a test usually needs to meet the following four minimum requirements:
- The disease that the test screens for must have a presymptomatic form.
- The screening test must be able to identify this presymptomatic disease.
- Treating the disease in the presymptomatic phase improves prognosis (specifically, it affects cancer-specific mortality in a randomized controlled trial).
- The screening test is feasible, and the benefits outweigh potential risks.
“The new blood tests for multiple cancers have so far only met the second criteria, showing they can detect presymptomatic cancer,” Dr. Robbins wrote.
The next step would be to demonstrate that they affect cancer-specific mortality. “But currently, commercial interests seem to be influencing the evidence standards for these cancer tests,” said Dr. Robbins.
Inappropriate Endpoints?
Some proponents of such tests argue that, unlike for previous cancer screening procedures, initial approval should not depend on the endpoint of cancer-specific mortality. It would take too long to gather sufficient outcome data, and in the meantime, people would die, they argue.
Eric A. Klein, MD, from the Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute in Cleveland, Ohio, and colleagues advocate for alternative endpoints such as the incidence of late-stage cancer in an article published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
“The concept would be,” they wrote, “that a negative signal would not indicate a mortality benefit, leading to the study being stopped. A positive signal, on the other hand, could result in provisional approval until mortality data and real-world evidence of effectiveness are available. This would resemble the accelerated approval of new cancer drugs, which often is based on progression-free survival until there postmarketing data on overall survival emerge.”
Dr. Klein is also employed at the US biotech start-up Grail, which developed the Galleri test, which is one of the best-known and most advanced cancer screening tests. The Galleri test uses cell-free DNA and machine learning to detect a common cancer signal in more than 50 cancer types and predict the origin of the cancer signal. Consumers in the United States can already order and perform the test.
An NHS Study
Arguments for different endpoints apparently resonated with the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS). Three years ago, they initiated the Galleri study, a large randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of Grail’s cancer test. The primary endpoint was not cancer-specific mortality, but the incidence of stage III or IV cancer.
The results are expected in 2026. But recruitment was stopped after 140,000 participants were enrolled. The NHS reported that the initial results were not convincing enough to continue the trial. Exact numbers were not disclosed.
The Galleri study deviates from the standard randomized controlled trial design for cancer screening procedures not only in terms of the primary endpoint, but also in blinding. The only participants who were unblinded and informed of their test results are those in the intervention group with a positive cancer test.
False Security
This trial design encourages participants to undergo blood tests once per year. But according to Dr. Robbins, it prevents the exploration of the phenomenon of “false security,” which is a potential drawback of the new cancer tests.
“Women with a negative mammogram can reasonably assume that they probably do not have breast cancer. But individuals with a negative cancer blood test could mistakenly believe they cannot have any cancer at all. As a result, they may not undergo standard early detection screenings or seek medical help early enough for potential cancer symptoms,” said Dr. Robbins.
To assess the actual risk-benefit ratio of the Galleri test, participants must receive their test results, she said. “Under real-world conditions, benefits and risks can come from positive and negative results.”
Upcoming Trial
More illuminating results may come from a large trial planned by the National Cancer Institute in the United States. Several new cancer tests will be evaluated for their ability to reduce cancer-specific mortality. A pilot phase will start later in 2024. “This study may be the only one with sufficient statistical power to determine whether an approach based on these cancer tests can reduce cancer-specific mortality,” said Dr. Robbins.
For the new blood tests for multiple cancers, it is crucial that health authorities “set a high bar for a benefit,” she said. This, according to her, also means that they must show an effect on cancer-specific mortality before being introduced. “This evidence must come from studies in which commercial interests do not influence the design, execution, data management, or data analysis.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnosing, Treating Rashes In Patients on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Liver Transplant Delays Progression in Colorectal Metastasis
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Research has shown promising results for well-selected patients with unresectable colorectal liver metastasis undergoing liver transplant; however, the absence of a suitable comparison group makes it difficult to evaluate the overall effectiveness of this treatment method.
- Researchers evaluated 33 patients with colorectal cancer and unresectable liver metastasis (mean age, 43.5 years; 52% women) who were eligible for liver transplants, according to validated selection criteria.
- Of these, 20 patients (61%) underwent a liver transplant, while 13 (39%) declined transplantation and received alternative therapy.
- Patients who received liver transplants did not undergo regular chemotherapy until recurrence, whereas those in the alternative therapy group continued systemic chemotherapy, with hepatic artery infusion pump placement (n = 5), liver resections (n = 6), and locoregional therapies (n = 6).
- The main outcomes of the study were overall survival and PFS.
TAKEAWAY:
- The median follow-up duration was 986 days in the liver transplant group and 657 days in the alternative therapy group.
- Patients who underwent liver transplant showed higher PFS rates at 1 year (90.0% vs 41.7%), 2 years (72.7% vs 10.4%), and 3 years (36.4% vs 10.4%). The PFS gains were statistically significant (P < .01).
- Overall survival was also higher in the transplant group — 100% vs 83.9% at 1 year, and 90.0% vs 73.4% at both 2 and 3 years. The differences, however, did not reach significance (P = .12).
- Liver transplant was associated with a lower recurrence rate (5% vs 23%), which also did not reach significance (P = .28) possibly because of the small patient population.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study represents the best available data for evaluating alternatives to [liver transplant],” the authors wrote, adding that the patients should be “referred for multidisciplinary evaluation to transplant oncology centers with strict criteria.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Matthew M. Byrne, MD, Department of Surgery, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York, and was published online in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The patient population was small, making it difficult to interpret statistical significance. The inclusion of patients with financial and social support might limit generalizability. The survival was calculated from the date of transplant or dropout. Additionally, the study did not explore sex-based differences in treatment choice.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any funding information. One author reported holding shares with HistoSonics, not related to the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Research has shown promising results for well-selected patients with unresectable colorectal liver metastasis undergoing liver transplant; however, the absence of a suitable comparison group makes it difficult to evaluate the overall effectiveness of this treatment method.
- Researchers evaluated 33 patients with colorectal cancer and unresectable liver metastasis (mean age, 43.5 years; 52% women) who were eligible for liver transplants, according to validated selection criteria.
- Of these, 20 patients (61%) underwent a liver transplant, while 13 (39%) declined transplantation and received alternative therapy.
- Patients who received liver transplants did not undergo regular chemotherapy until recurrence, whereas those in the alternative therapy group continued systemic chemotherapy, with hepatic artery infusion pump placement (n = 5), liver resections (n = 6), and locoregional therapies (n = 6).
- The main outcomes of the study were overall survival and PFS.
TAKEAWAY:
- The median follow-up duration was 986 days in the liver transplant group and 657 days in the alternative therapy group.
- Patients who underwent liver transplant showed higher PFS rates at 1 year (90.0% vs 41.7%), 2 years (72.7% vs 10.4%), and 3 years (36.4% vs 10.4%). The PFS gains were statistically significant (P < .01).
- Overall survival was also higher in the transplant group — 100% vs 83.9% at 1 year, and 90.0% vs 73.4% at both 2 and 3 years. The differences, however, did not reach significance (P = .12).
- Liver transplant was associated with a lower recurrence rate (5% vs 23%), which also did not reach significance (P = .28) possibly because of the small patient population.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study represents the best available data for evaluating alternatives to [liver transplant],” the authors wrote, adding that the patients should be “referred for multidisciplinary evaluation to transplant oncology centers with strict criteria.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Matthew M. Byrne, MD, Department of Surgery, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York, and was published online in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The patient population was small, making it difficult to interpret statistical significance. The inclusion of patients with financial and social support might limit generalizability. The survival was calculated from the date of transplant or dropout. Additionally, the study did not explore sex-based differences in treatment choice.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any funding information. One author reported holding shares with HistoSonics, not related to the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Research has shown promising results for well-selected patients with unresectable colorectal liver metastasis undergoing liver transplant; however, the absence of a suitable comparison group makes it difficult to evaluate the overall effectiveness of this treatment method.
- Researchers evaluated 33 patients with colorectal cancer and unresectable liver metastasis (mean age, 43.5 years; 52% women) who were eligible for liver transplants, according to validated selection criteria.
- Of these, 20 patients (61%) underwent a liver transplant, while 13 (39%) declined transplantation and received alternative therapy.
- Patients who received liver transplants did not undergo regular chemotherapy until recurrence, whereas those in the alternative therapy group continued systemic chemotherapy, with hepatic artery infusion pump placement (n = 5), liver resections (n = 6), and locoregional therapies (n = 6).
- The main outcomes of the study were overall survival and PFS.
TAKEAWAY:
- The median follow-up duration was 986 days in the liver transplant group and 657 days in the alternative therapy group.
- Patients who underwent liver transplant showed higher PFS rates at 1 year (90.0% vs 41.7%), 2 years (72.7% vs 10.4%), and 3 years (36.4% vs 10.4%). The PFS gains were statistically significant (P < .01).
- Overall survival was also higher in the transplant group — 100% vs 83.9% at 1 year, and 90.0% vs 73.4% at both 2 and 3 years. The differences, however, did not reach significance (P = .12).
- Liver transplant was associated with a lower recurrence rate (5% vs 23%), which also did not reach significance (P = .28) possibly because of the small patient population.
IN PRACTICE:
“This study represents the best available data for evaluating alternatives to [liver transplant],” the authors wrote, adding that the patients should be “referred for multidisciplinary evaluation to transplant oncology centers with strict criteria.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Matthew M. Byrne, MD, Department of Surgery, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York, and was published online in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The patient population was small, making it difficult to interpret statistical significance. The inclusion of patients with financial and social support might limit generalizability. The survival was calculated from the date of transplant or dropout. Additionally, the study did not explore sex-based differences in treatment choice.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any funding information. One author reported holding shares with HistoSonics, not related to the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD, Giant of Cancer Care, Dies
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To Live Longer, Get to Know Your Toes
The more flexible you are as you age, the longer you’re likely to live. That’s the conclusion of a new study that associated increased flexibility in middle age with lower odds of mortality over the next dozen or so years.
Claudio Gil Araújo, MD, PhD, the research director of the Exercise Medicine Clinic-CLINIMEX in Rio de Janeiro, who led the study, said his group was not surprised by the results. “We found what we expected. Reduced flexibility was related to poor survival,” he said.
The findings, published in the Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, used data from 2087 men and 1052 women who underwent a medical-functional evaluation at CLINIMEX. They received a body flexibility score, called the Flexindex, based on range of motion in 20 movements in seven joints, with a minimum score of 0 and a maximum score of 80.
Among the 3139 participants, there were 302 deaths (9.6%) during a mean follow-up of 12.9 years, with cardiovascular diseases and cancer the most common underlying causes in men and women, respectively.
“The probability of death during nearly 13 years of follow-up was close to 1% when Flexindex scores exceed 49 for men and 56 for women,” Dr. Araújo told this news organization. “On the other hand, for men and women placed in the lower 10 percent of Flexindex scores, death rates were, respectively, 26.9% and 18.2%.”
Barry Franklin, PhD, director of preventive cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in Royal Oak, Michigan, and a co-author of the new study, said men with the poorest flexibility were nearly twice as likely to die over the follow-up period than men with high flexibility. Women with the poorest flexibility were almost five times more likely to die than those with high flexibility.
Flexibility Assessment and Training
Dr. Araújo opened CLINIMEX in 1994, and since then, its staff of five physicians have evaluated more than 10,000 individuals using the Flexitest. Dr. Araújo has published two previous studies on flexibility. The first showed that the ability to rise from a sitting position on the floor is a strong predictor of longevity, and the second demonstrated that the inability to stand on one leg for at least 10 seconds is linked to an increased risk for death over 7 years.
Dr. Araújo and his colleagues believe the current study is the first to assess the association between levels of body flexibility and mortality. But the observational analysis was unable to establish causality, and therefore, they could not show a definitive mechanism to explain the association between low levels of flexibility and premature mortality.
The authors noted several limitations of their study. The participants were primarily affluent White people, and the researchers did not control for the time of day flexibility was measured or for variables such as diet and physical activity. They also acknowledged reduced flexibility may be a consequence of poor lifestyle habits rather than a causal risk factor for mortality.
Jonathan Bonnet, MD, MPH, an exercise expert at the Stanford Center on Longevity Lifestyle Medicine in California, said the researchers used a more robust evaluation of flexibility than a traditional sit-and-reach test. However, he expressed concern that the primary comparisons were of the upper and lower 10% of performers and that the average differences in Flexindex scores between people who died and those who survived were only a handful of points in an 80-point test.
“People who are not flexible probably have other health-related issues that limit their mobility and those who are very flexible are either genetically different from inflexible individuals or are doing something to maintain or increase their flexibility to a high level,” Dr. Bonnet said. “Not knowing how active or inactive people are at baseline when flexibility was assessed or over the duration of the study limits how confident we can be that flexibility is the cause of mortality.”
Dr. Bonnet, a member of the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, noted that the latest guidelines on physical activity from the US Department of Health and Human Services do not include recommendations on stretching, given the lack of data demonstrating its specific health benefits. While maintaining mobility and range of motion in joints is important for long-term health, he said the new study does not provide sufficient evidence to recommend stretching as a way to reduce mortality.
“Until there are more data that can show a cause-and-effect relationship with stretching and health outcomes, time is better spent doing aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities,” Dr. Bonnet said.
Dr. Franklin said future studies could better account for missing potential confounders like physical activity and whether individuals were taking protective medications, such as aspirin, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or beta-blockers. Studies also are needed to assess whether training-induced gains in flexibility are specifically related to increases in survival and whether their findings apply to people over the age of 65, he said.
The current findings “give us some additional ammo to say, ‘Wow, being more flexible may, in fact, improve long-term survival or outcomes’,” Dr. Franklin said. Regardless, flexibility still “improves quality of life, it improves balance and reduces the potential for falls, and all those things make it worthy of better recognition or appreciation by the general public and clinicians,” he added.
Dr. Araújo said he would like his research to influence people’s health. “While to exercise regularly is advisable, what really matters is to be physically fit and not only in aerobic or strength fitness but also in flexibility,” he said. “The study is adding a new and, I believe, important ‘relevant for survival’ label on flexibility assessment and training.”
Recommended Stretches for Increased Mobility and Flexibility
By Matthew Accetta, MS, exercise physiologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City
Hip Hug Stretch
This stretch effectively targets the gluteal muscles, piriformis, and other deep hip rotators, which can become tight from prolonged sitting or lack of movement. Tight hips can contribute to lower back pain. By stretching the hip muscles, you can reduce tension and pressure on the lower back. Regularly performing this stretch helps to improve hip joint mobility, which is essential for maintaining functional movement and preventing stiffness as you age.
- Start by sitting and crossing one leg over the other.
- Hug your knee to your chest.
- Focus on keeping your chest up to feel the stretch in the glute.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Half Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch
As people age, they often spend more time sitting, which can lead to tight hip flexors. This stretch specifically targets these muscles, helping to alleviate tightness and improve mobility. Tight hip flexors can contribute to poor posture by pulling the pelvis into an anterior tilt, which can lead to lower back pain and other postural issues. Stretching these muscles helps to counteract this effect and promote better posture.
- Kneel on a pad (the side you kneel on is the side being stretched); position the front leg far enough away so the front knee stays behind the toes.
- With a tall posture, engage your abdominals and tuck your tailbone by engaging your glutes until a stretch is felt in the front of the thigh on the kneeling leg.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Calf Stretch at a Wall
Tight calf muscles can lead to discomfort and limit the range of motion in the ankles. Stretching the calves helps to maintain and improve flexibility in these muscles. Flexible calf muscles contribute to better mobility in the ankles and feet, making daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, and running more comfortable. Tight calves can increase the risk for strains, Achilles tendinitis, and other injuries. Stand facing a wall with your hands on the wall at about eye level. Put the leg you want to stretch about a step behind your other leg.
- Stand in a staggered stance in front of a wall with your arms stretched out.
- Keeping your back heel on the floor, bend your front knee until you feel a stretch in the back leg.
- Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Standing Quad Stretch
Regularly stretching the quadriceps helps maintain and improve flexibility in these muscles, which is crucial for overall lower body mobility. Flexible quadriceps are less prone to strains and injuries. Tight quadriceps can contribute to knee pain and discomfort by exerting excessive pressure on the knee joint. Stretching these muscles helps alleviate this pressure and reduce knee pain.
- While standing, hold onto a countertop or chair back to assist in balance.
- Bend your knee by grasping your ankle with one hand and moving your foot toward your buttocks.
- Gently pull on your ankle to bend your knee as far as possible.
- Maintain the position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Seated Hamstring Stretch
Regularly stretching the hamstrings helps maintain and improve their flexibility, which is crucial for the overall mobility of the lower body. Tight hamstrings can contribute to lower back pain by pulling on the pelvis and causing an anterior pelvic tilt. Stretching these muscles can help alleviate tension and reduce back pain. Hamstring flexibility helps to contribute to a better range of motion in the hip and knee joints, making daily activities such as walking, bending, and reaching easier.
- Sit on the front half of a firm chair with your back straight.
- Extend one leg out in front of you with your heel on the floor and your toes pointed up.
- Bend the opposite knee so that your foot is flat on the floor.
- Center your chest over your straight leg.
- Slowly lean forward at the hips until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh.
- Hold the stretch for 30 seconds.
- Slowly return to your original position and repeat on the opposite side.
The sources in this story reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The more flexible you are as you age, the longer you’re likely to live. That’s the conclusion of a new study that associated increased flexibility in middle age with lower odds of mortality over the next dozen or so years.
Claudio Gil Araújo, MD, PhD, the research director of the Exercise Medicine Clinic-CLINIMEX in Rio de Janeiro, who led the study, said his group was not surprised by the results. “We found what we expected. Reduced flexibility was related to poor survival,” he said.
The findings, published in the Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, used data from 2087 men and 1052 women who underwent a medical-functional evaluation at CLINIMEX. They received a body flexibility score, called the Flexindex, based on range of motion in 20 movements in seven joints, with a minimum score of 0 and a maximum score of 80.
Among the 3139 participants, there were 302 deaths (9.6%) during a mean follow-up of 12.9 years, with cardiovascular diseases and cancer the most common underlying causes in men and women, respectively.
“The probability of death during nearly 13 years of follow-up was close to 1% when Flexindex scores exceed 49 for men and 56 for women,” Dr. Araújo told this news organization. “On the other hand, for men and women placed in the lower 10 percent of Flexindex scores, death rates were, respectively, 26.9% and 18.2%.”
Barry Franklin, PhD, director of preventive cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in Royal Oak, Michigan, and a co-author of the new study, said men with the poorest flexibility were nearly twice as likely to die over the follow-up period than men with high flexibility. Women with the poorest flexibility were almost five times more likely to die than those with high flexibility.
Flexibility Assessment and Training
Dr. Araújo opened CLINIMEX in 1994, and since then, its staff of five physicians have evaluated more than 10,000 individuals using the Flexitest. Dr. Araújo has published two previous studies on flexibility. The first showed that the ability to rise from a sitting position on the floor is a strong predictor of longevity, and the second demonstrated that the inability to stand on one leg for at least 10 seconds is linked to an increased risk for death over 7 years.
Dr. Araújo and his colleagues believe the current study is the first to assess the association between levels of body flexibility and mortality. But the observational analysis was unable to establish causality, and therefore, they could not show a definitive mechanism to explain the association between low levels of flexibility and premature mortality.
The authors noted several limitations of their study. The participants were primarily affluent White people, and the researchers did not control for the time of day flexibility was measured or for variables such as diet and physical activity. They also acknowledged reduced flexibility may be a consequence of poor lifestyle habits rather than a causal risk factor for mortality.
Jonathan Bonnet, MD, MPH, an exercise expert at the Stanford Center on Longevity Lifestyle Medicine in California, said the researchers used a more robust evaluation of flexibility than a traditional sit-and-reach test. However, he expressed concern that the primary comparisons were of the upper and lower 10% of performers and that the average differences in Flexindex scores between people who died and those who survived were only a handful of points in an 80-point test.
“People who are not flexible probably have other health-related issues that limit their mobility and those who are very flexible are either genetically different from inflexible individuals or are doing something to maintain or increase their flexibility to a high level,” Dr. Bonnet said. “Not knowing how active or inactive people are at baseline when flexibility was assessed or over the duration of the study limits how confident we can be that flexibility is the cause of mortality.”
Dr. Bonnet, a member of the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, noted that the latest guidelines on physical activity from the US Department of Health and Human Services do not include recommendations on stretching, given the lack of data demonstrating its specific health benefits. While maintaining mobility and range of motion in joints is important for long-term health, he said the new study does not provide sufficient evidence to recommend stretching as a way to reduce mortality.
“Until there are more data that can show a cause-and-effect relationship with stretching and health outcomes, time is better spent doing aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities,” Dr. Bonnet said.
Dr. Franklin said future studies could better account for missing potential confounders like physical activity and whether individuals were taking protective medications, such as aspirin, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or beta-blockers. Studies also are needed to assess whether training-induced gains in flexibility are specifically related to increases in survival and whether their findings apply to people over the age of 65, he said.
The current findings “give us some additional ammo to say, ‘Wow, being more flexible may, in fact, improve long-term survival or outcomes’,” Dr. Franklin said. Regardless, flexibility still “improves quality of life, it improves balance and reduces the potential for falls, and all those things make it worthy of better recognition or appreciation by the general public and clinicians,” he added.
Dr. Araújo said he would like his research to influence people’s health. “While to exercise regularly is advisable, what really matters is to be physically fit and not only in aerobic or strength fitness but also in flexibility,” he said. “The study is adding a new and, I believe, important ‘relevant for survival’ label on flexibility assessment and training.”
Recommended Stretches for Increased Mobility and Flexibility
By Matthew Accetta, MS, exercise physiologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City
Hip Hug Stretch
This stretch effectively targets the gluteal muscles, piriformis, and other deep hip rotators, which can become tight from prolonged sitting or lack of movement. Tight hips can contribute to lower back pain. By stretching the hip muscles, you can reduce tension and pressure on the lower back. Regularly performing this stretch helps to improve hip joint mobility, which is essential for maintaining functional movement and preventing stiffness as you age.
- Start by sitting and crossing one leg over the other.
- Hug your knee to your chest.
- Focus on keeping your chest up to feel the stretch in the glute.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Half Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch
As people age, they often spend more time sitting, which can lead to tight hip flexors. This stretch specifically targets these muscles, helping to alleviate tightness and improve mobility. Tight hip flexors can contribute to poor posture by pulling the pelvis into an anterior tilt, which can lead to lower back pain and other postural issues. Stretching these muscles helps to counteract this effect and promote better posture.
- Kneel on a pad (the side you kneel on is the side being stretched); position the front leg far enough away so the front knee stays behind the toes.
- With a tall posture, engage your abdominals and tuck your tailbone by engaging your glutes until a stretch is felt in the front of the thigh on the kneeling leg.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Calf Stretch at a Wall
Tight calf muscles can lead to discomfort and limit the range of motion in the ankles. Stretching the calves helps to maintain and improve flexibility in these muscles. Flexible calf muscles contribute to better mobility in the ankles and feet, making daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, and running more comfortable. Tight calves can increase the risk for strains, Achilles tendinitis, and other injuries. Stand facing a wall with your hands on the wall at about eye level. Put the leg you want to stretch about a step behind your other leg.
- Stand in a staggered stance in front of a wall with your arms stretched out.
- Keeping your back heel on the floor, bend your front knee until you feel a stretch in the back leg.
- Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Standing Quad Stretch
Regularly stretching the quadriceps helps maintain and improve flexibility in these muscles, which is crucial for overall lower body mobility. Flexible quadriceps are less prone to strains and injuries. Tight quadriceps can contribute to knee pain and discomfort by exerting excessive pressure on the knee joint. Stretching these muscles helps alleviate this pressure and reduce knee pain.
- While standing, hold onto a countertop or chair back to assist in balance.
- Bend your knee by grasping your ankle with one hand and moving your foot toward your buttocks.
- Gently pull on your ankle to bend your knee as far as possible.
- Maintain the position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Seated Hamstring Stretch
Regularly stretching the hamstrings helps maintain and improve their flexibility, which is crucial for the overall mobility of the lower body. Tight hamstrings can contribute to lower back pain by pulling on the pelvis and causing an anterior pelvic tilt. Stretching these muscles can help alleviate tension and reduce back pain. Hamstring flexibility helps to contribute to a better range of motion in the hip and knee joints, making daily activities such as walking, bending, and reaching easier.
- Sit on the front half of a firm chair with your back straight.
- Extend one leg out in front of you with your heel on the floor and your toes pointed up.
- Bend the opposite knee so that your foot is flat on the floor.
- Center your chest over your straight leg.
- Slowly lean forward at the hips until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh.
- Hold the stretch for 30 seconds.
- Slowly return to your original position and repeat on the opposite side.
The sources in this story reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The more flexible you are as you age, the longer you’re likely to live. That’s the conclusion of a new study that associated increased flexibility in middle age with lower odds of mortality over the next dozen or so years.
Claudio Gil Araújo, MD, PhD, the research director of the Exercise Medicine Clinic-CLINIMEX in Rio de Janeiro, who led the study, said his group was not surprised by the results. “We found what we expected. Reduced flexibility was related to poor survival,” he said.
The findings, published in the Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, used data from 2087 men and 1052 women who underwent a medical-functional evaluation at CLINIMEX. They received a body flexibility score, called the Flexindex, based on range of motion in 20 movements in seven joints, with a minimum score of 0 and a maximum score of 80.
Among the 3139 participants, there were 302 deaths (9.6%) during a mean follow-up of 12.9 years, with cardiovascular diseases and cancer the most common underlying causes in men and women, respectively.
“The probability of death during nearly 13 years of follow-up was close to 1% when Flexindex scores exceed 49 for men and 56 for women,” Dr. Araújo told this news organization. “On the other hand, for men and women placed in the lower 10 percent of Flexindex scores, death rates were, respectively, 26.9% and 18.2%.”
Barry Franklin, PhD, director of preventive cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in Royal Oak, Michigan, and a co-author of the new study, said men with the poorest flexibility were nearly twice as likely to die over the follow-up period than men with high flexibility. Women with the poorest flexibility were almost five times more likely to die than those with high flexibility.
Flexibility Assessment and Training
Dr. Araújo opened CLINIMEX in 1994, and since then, its staff of five physicians have evaluated more than 10,000 individuals using the Flexitest. Dr. Araújo has published two previous studies on flexibility. The first showed that the ability to rise from a sitting position on the floor is a strong predictor of longevity, and the second demonstrated that the inability to stand on one leg for at least 10 seconds is linked to an increased risk for death over 7 years.
Dr. Araújo and his colleagues believe the current study is the first to assess the association between levels of body flexibility and mortality. But the observational analysis was unable to establish causality, and therefore, they could not show a definitive mechanism to explain the association between low levels of flexibility and premature mortality.
The authors noted several limitations of their study. The participants were primarily affluent White people, and the researchers did not control for the time of day flexibility was measured or for variables such as diet and physical activity. They also acknowledged reduced flexibility may be a consequence of poor lifestyle habits rather than a causal risk factor for mortality.
Jonathan Bonnet, MD, MPH, an exercise expert at the Stanford Center on Longevity Lifestyle Medicine in California, said the researchers used a more robust evaluation of flexibility than a traditional sit-and-reach test. However, he expressed concern that the primary comparisons were of the upper and lower 10% of performers and that the average differences in Flexindex scores between people who died and those who survived were only a handful of points in an 80-point test.
“People who are not flexible probably have other health-related issues that limit their mobility and those who are very flexible are either genetically different from inflexible individuals or are doing something to maintain or increase their flexibility to a high level,” Dr. Bonnet said. “Not knowing how active or inactive people are at baseline when flexibility was assessed or over the duration of the study limits how confident we can be that flexibility is the cause of mortality.”
Dr. Bonnet, a member of the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, noted that the latest guidelines on physical activity from the US Department of Health and Human Services do not include recommendations on stretching, given the lack of data demonstrating its specific health benefits. While maintaining mobility and range of motion in joints is important for long-term health, he said the new study does not provide sufficient evidence to recommend stretching as a way to reduce mortality.
“Until there are more data that can show a cause-and-effect relationship with stretching and health outcomes, time is better spent doing aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities,” Dr. Bonnet said.
Dr. Franklin said future studies could better account for missing potential confounders like physical activity and whether individuals were taking protective medications, such as aspirin, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or beta-blockers. Studies also are needed to assess whether training-induced gains in flexibility are specifically related to increases in survival and whether their findings apply to people over the age of 65, he said.
The current findings “give us some additional ammo to say, ‘Wow, being more flexible may, in fact, improve long-term survival or outcomes’,” Dr. Franklin said. Regardless, flexibility still “improves quality of life, it improves balance and reduces the potential for falls, and all those things make it worthy of better recognition or appreciation by the general public and clinicians,” he added.
Dr. Araújo said he would like his research to influence people’s health. “While to exercise regularly is advisable, what really matters is to be physically fit and not only in aerobic or strength fitness but also in flexibility,” he said. “The study is adding a new and, I believe, important ‘relevant for survival’ label on flexibility assessment and training.”
Recommended Stretches for Increased Mobility and Flexibility
By Matthew Accetta, MS, exercise physiologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York City
Hip Hug Stretch
This stretch effectively targets the gluteal muscles, piriformis, and other deep hip rotators, which can become tight from prolonged sitting or lack of movement. Tight hips can contribute to lower back pain. By stretching the hip muscles, you can reduce tension and pressure on the lower back. Regularly performing this stretch helps to improve hip joint mobility, which is essential for maintaining functional movement and preventing stiffness as you age.
- Start by sitting and crossing one leg over the other.
- Hug your knee to your chest.
- Focus on keeping your chest up to feel the stretch in the glute.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Half Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch
As people age, they often spend more time sitting, which can lead to tight hip flexors. This stretch specifically targets these muscles, helping to alleviate tightness and improve mobility. Tight hip flexors can contribute to poor posture by pulling the pelvis into an anterior tilt, which can lead to lower back pain and other postural issues. Stretching these muscles helps to counteract this effect and promote better posture.
- Kneel on a pad (the side you kneel on is the side being stretched); position the front leg far enough away so the front knee stays behind the toes.
- With a tall posture, engage your abdominals and tuck your tailbone by engaging your glutes until a stretch is felt in the front of the thigh on the kneeling leg.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Calf Stretch at a Wall
Tight calf muscles can lead to discomfort and limit the range of motion in the ankles. Stretching the calves helps to maintain and improve flexibility in these muscles. Flexible calf muscles contribute to better mobility in the ankles and feet, making daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, and running more comfortable. Tight calves can increase the risk for strains, Achilles tendinitis, and other injuries. Stand facing a wall with your hands on the wall at about eye level. Put the leg you want to stretch about a step behind your other leg.
- Stand in a staggered stance in front of a wall with your arms stretched out.
- Keeping your back heel on the floor, bend your front knee until you feel a stretch in the back leg.
- Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Standing Quad Stretch
Regularly stretching the quadriceps helps maintain and improve flexibility in these muscles, which is crucial for overall lower body mobility. Flexible quadriceps are less prone to strains and injuries. Tight quadriceps can contribute to knee pain and discomfort by exerting excessive pressure on the knee joint. Stretching these muscles helps alleviate this pressure and reduce knee pain.
- While standing, hold onto a countertop or chair back to assist in balance.
- Bend your knee by grasping your ankle with one hand and moving your foot toward your buttocks.
- Gently pull on your ankle to bend your knee as far as possible.
- Maintain the position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Seated Hamstring Stretch
Regularly stretching the hamstrings helps maintain and improve their flexibility, which is crucial for the overall mobility of the lower body. Tight hamstrings can contribute to lower back pain by pulling on the pelvis and causing an anterior pelvic tilt. Stretching these muscles can help alleviate tension and reduce back pain. Hamstring flexibility helps to contribute to a better range of motion in the hip and knee joints, making daily activities such as walking, bending, and reaching easier.
- Sit on the front half of a firm chair with your back straight.
- Extend one leg out in front of you with your heel on the floor and your toes pointed up.
- Bend the opposite knee so that your foot is flat on the floor.
- Center your chest over your straight leg.
- Slowly lean forward at the hips until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh.
- Hold the stretch for 30 seconds.
- Slowly return to your original position and repeat on the opposite side.
The sources in this story reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Second Treatment for Prurigo Nodularis Approved by FDA
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 13, 2024, the
A first-in-class monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL)–31 signaling, nemolizumab, will be available in a prefilled pen for subcutaneous injection and will be marketed as Nemluvio. It is currently under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis in adolescents and adults.
Approval for PN is based on data from the phase 3 OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in 560 patients with PN, according to a press release from Galderma, the manufacturer.
According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and OLYMPIA 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a 4-point reduction in itch intensity at week 16 as measured by the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale, compared with 16% in both placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the Investigator Global Assessment score at week 16, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
According to the company press release, the most common side effects of nemolizumab are headache and rashes in the form of eczema, atopic dermatitis, and nummular eczema.
“By inhibiting the signaling of IL-31, Nemluvio addresses a key driver of prurigo nodularis, safely and effectively improving itch as well as skin nodules,” Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, PhD, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and lead investigator of the OLYMPIA program, stated in the press release.
The regulatory submission of nemolizumab in atopic dermatitis is based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. A decision on approval for this indication from the FDA is expected in December 2024.
In September 2022, dupilumab became the first FDA-approved treatment for PN in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.