User login
Using the tools of positive psychiatry to improve clinical practice
FIRST OF 4 PARTS
What does wellness mean to you? A 2018 survey posed this question to more than 6,000 people living with depression and bipolar disorder. In addition to better treatment and greater understanding of their illnesses, other priorities emerged: a longing for better days, a sense of purpose, and a longing to function well and be happy.1 As one respondent explained, “Wellness means stability; well enough to hold a job, well enough to enjoy activities, well enough to feel joy and hope.” Traditional treatment that focuses on alleviating symptoms may not sufficiently address outcomes patients value. When the focus is primarily deficit-based, clinicians and patients may miss opportunities for optimization and transformation.
Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that seeks to enhance and promote well-being and health through the enhancement of positive psychosocial factors such as resilience, optimism, wisdom, and social support in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as those in the community at large.2 It is based on the principles that there is no health without mental health, and that mental health can improve through preventive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative interventions.3
Positive interventions are defined as “treatment methods or intentional activities that aim to cultivate positive feelings, behaviors, or cognitions.”4 They are evidence-based intentional exercises designed to increase well-being and enhance flourishing. Although positive interventions were originally studied as activities for nonclinical populations and for helping healthy people thrive, they are increasingly being valued for their therapeutic role in treating psychopathology.5 By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, psychiatrists can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients during the treatment process, and bolster positive mental health.
In this article, we provide practical ways to integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into everyday clinical practice. The goal is to broaden how clinicians think about mental health and therapeutic options and, above all, enhance our patients’ everyday well-being. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits are strategies clinicians can apply not only to provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also to enhance the range and richness of their patients’ everyday experience.
Adopt a positive orientation
When a clinician first meets a patient, “What’s wrong?” is a typical conversation starter, and conversations tend to revolve around problems, failures, and negative experiences. Positive psychiatry posits that there is therapeutic benefit to emphasizing and exploring a patient’s positive emotions, experiences, and aspirations. Questions such as “What was your sense of well-being this week? What is your goal for today’s session? What is your goal for the coming week?” can reorient a session towards an individual’s potential and promote exploration of what’s possible.
To promote a positive orientation, clinicians may consider integrating the Savoring and Three Good Things exercises—2 well-studied interventions—into their repertoire to activate and enhance positive emotional states such as gratitude and joy.6 An example of a Savoring activity is taking a 20-minute daily walk while trying to notice as many positive elements as possible. Similarly, the Three Good Things exercise, in which patients are asked to notice and write down 3 positive events and reflect on why they happened, promotes positive reflection and gratitude. A 14-day daily diary study conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic found that higher levels of gratitude were associated with higher levels of positive affect, lower levels of perceived stress related to COVID-19, and better subjective health.7 In addition to coping with life’s negative events, deliberately enhancing the impact of good things is a positive emotion amplifier. As French writer François de La Rochefoucauld argued, “Happiness does not consist in things themselves but in the relish we have of them.”8
Continue to: Harness strengths
Harness strengths
A growing body of evidence suggests that in addition to focusing on a patient’s chief concern, identifying and cultivating an individual’s signature strengths can mitigate stress and enhance well-being. Signature strengths are positive personality qualities that reflect our core identity and are morally valued. The VIA Character Strengths Survey is the most used and validated psychometric instrument to measure and identify signature strengths such as curiosity, self-regulation, honesty, and teamwork.9
To incorporate this tool into clinical practice, ask patients to complete a strengths survey using a validated assessment tool such as the VIA survey (www.viacharacter.org). After a patient identifies their signature strengths, encourage them to explore and apply these strengths in everyday life and in new ways. In addition to becoming aware of and using their signature strengths, encourage patients to “strengths spot” in others. “What strengths did you notice your coworker, family, or friend using today?” is a potential question to explore with patients. A strengths-based approach may be particularly helpful in uncovering motivation and fully engaging patients in treatment. Moreover, integrating strengths into the typically negatively skewed narrative underscores to patients that therapy isn’t only about untwisting distorted thinking, but also about harnessing one’s strengths, talents, and abilities. Strengths expressed through pragmatic actions can boost coping skills as well as enhance well-being.
Mobilize values
Value affirmation exercises have been shown to generate lasting benefits in creating positive feelings and behaviors.10 Encouraging patients to think about what they genuinely value redirects their gaze towards possibility and diverts self-focus. For instance, ask a patient to identify 2 or 3 values and write about why they are important. By reflecting on their values in writing, they affirm their identity and self-worth, thus creating a virtuous cycle of confidence, effort, and achievement. People who put their values front and center are more attuned to the needs of others as well as their own needs, and they make better connections.11 Including a patient’s values in the treatment plan may increase problem-solving skills, boost motivation, and build better stress management skills.
The “life review” is another intervention that facilitates exploration of a patient’s values. This exercise involves asking patients to recount the story of their life and the experiences that were most meaningful to them. This process allows clinicians to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s values, which can help guide treatment. Meta-analytic evidence has demonstrated these reminiscence-based interventions have significant effects on well-being.6 As Mahatma Gandhi famously said, “Happiness is when what you think, what you say, and what you do are in harmony.” Creating more overlap between a patient’s values and their everyday actions and behaviors bolsters resilience, buffers against stress, and can restore a healthier self-concept.
Cultivate social connections
Social connection is recognized as a core psychological need and essential for well-being. The opposite of connection—social isolation—has negative effects on overall health, including increases in inflammatory markers, depression rates, and even all-cause mortality.12 A 2015 meta-analytic review demonstrated that loneliness increased the likelihood of mortality by 26%—a similar increase as seen with smoking 15 cigarettes a day.13
Continue to: As with any vital sign...
As with any vital sign, exploring a patient’s number of social contacts, quantity of social visits per week, and quality of relationships is an important indicator of health. Giving patients tools to cultivate social connection and deepen their relationships can enhance therapeutic outcomes. Asking patients to perform acts of kindness is one example of a “social prescription.” Feeding a stranger’s parking meter, picking up litter, helping a friend with a chore, providing a meal to a person in need, and volunteering are potential ways for patients to engage in kind deeds. After each act, encourage the patient to write down what they did and how it made them feel.
“Prescribing” positive communication is another way to enhance a patient’s social connections. For instance, teaching them about active constructive responding (ACR)—responding with enthusiasm when another person shares information or good news—has been shown to strengthen bonds with friends and family.14 Making eye contact, giving the other person one’s full attention, inquiring about details, and responding with enthusiasm and interest are simple ways patients can apply ACR in their daily lives. Counseling a patient on increasing social connections, prescribing connections, and inquiring about quantity and quality of social interactions can help them not only add years to their life but also add health and well-being to those years.
Optimize healthy habits
Mounting research demonstrates that exercise, sleep, and nutrition are important for well-being. Evidence shows that therapeutic lifestyle changes can reduce depressive symptoms and boost positive feelings. Numerous meta-analyses have demonstrated the benefits of sleep and exercise interventions for reducing depressive symptoms in psychiatric patients.15,16 Longitudinal studies have provided evidence that healthy diets increase happiness, even after controlling for potential confounders such as socioeconomic factors.17 Other lifestyle factors—including financial stability, pet ownership, decreased social media use, and spending time in nature—have been shown to contribute to well-being.18
Despite the substantial evidence that lifestyle factors can improve health outcomes, few clinicians ask about, focus on, or promote positive habits.19 Positive psychiatry seeks to reorient clinicians towards lifestyle factors that enhance well-being. Clinicians can deploy a variety of strategies to support patients in making healthy and sustainable changes. Assessing readiness for change, motivational interviewing, setting SMART (specific, measurable, assignable, realistic, and time-related) goals, and referring patients to relevant community resources are ways to encourage and promote therapeutic lifestyle changes. Inquiring about a patient’s typical day—such as how they spend their free time, what they eat, when they go to bed, and how much time they spend outdoors—opens conversations about general well-being and shows the patient that therapy is about the whole person, and not only symptom management. Helping patients have better days can empower them to lead more satisfied lives.20
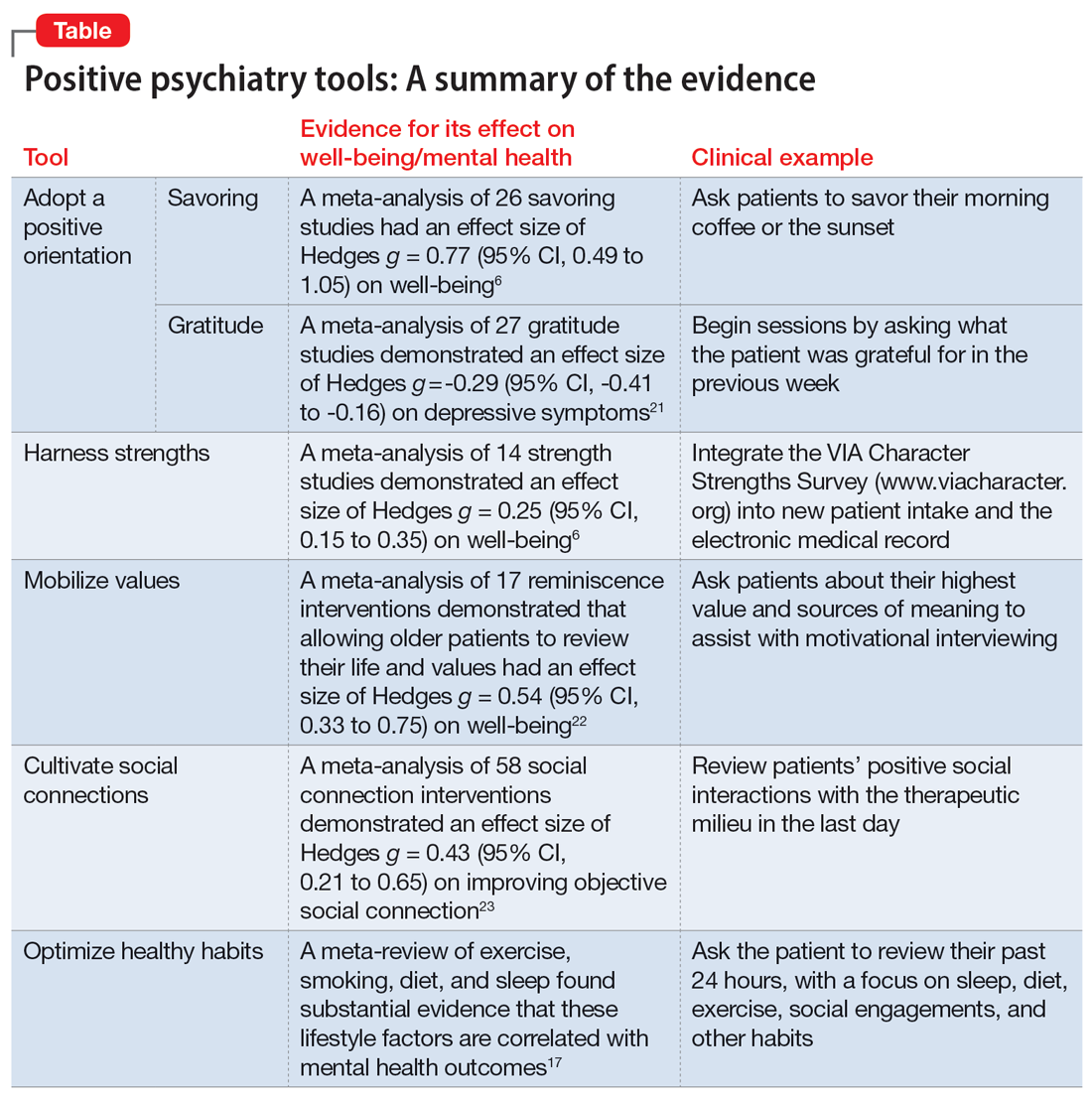
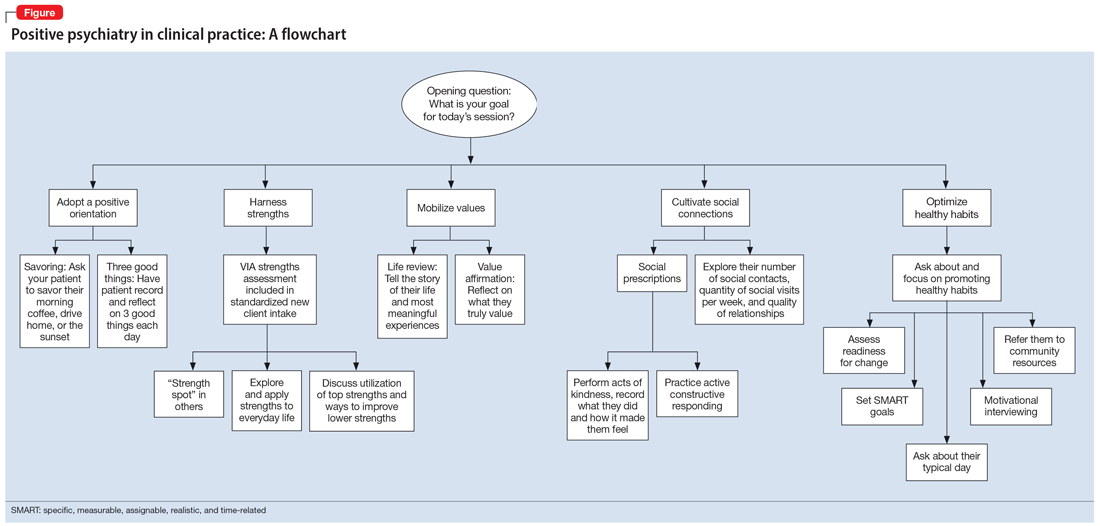
The Table6,17,21-23 summarizes the scientific evidence for the strategies described in this article. The Figure provides a flowchart for using these strategies in clinical practice.
Continue to: Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
By exploring and emphasizing potential and possibility, positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of disease) with salutogenesis (the study and creation of health24). Clinicians are well positioned to manage symptoms and bolster positive states. Rather than an either/or approach to well-being, positive psychiatry strives for a both/and approach to well-being. By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, clinicians can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients in the treatment process, and bolster mental health.
Bottom Line
Clinicians can integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into clinical practice. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits can not only provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also can enhance the range and richness of patients’ everyday experience.
Related Resources
- University of Pennsylvania. Authentic happiness. https://www.authentichappiness.sas.upenn.edu
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW (eds). Positive Psychiatry: A Clinical Handbook. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
1. Morton E, Foxworth P, Dardess P, et al. “Supporting Wellness”: a depression and bipolar support alliance mixed-methods investigation of lived experience perspectives and priorities for mood disorder treatment. J Affect Disord. 2022;299:575-584.
2. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Sin NL, Lyubomirsky S. Enhancing well-being and alleviating depressive symptoms with positive psychology interventions: a practice-friendly meta-analysis. J Clin Psychol. 2009;65(5):467-487.
5. Seligman MEP, Rashid T, Parks AC. Positive psychotherapy. Am Psychol. 2006;61(8):774-788.
6. Carr A, Cullen K, Keeney C, et al. Effectiveness of positive psychology interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Posit Psychol. 2021;16(6):749-769.
7. Jiang D. Feeling gratitude is associated with better well-being across the life span: a daily diary study during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2022;77(4):e36-e45.
8. de La Rochefoucauld F. Maxims and moral reflections (1796). Gale ECCO: 2010.
9. Niemiec RM. VIA character strengths: Research and practice (The first 10 years). In: Knoop HH, Fave AD (eds). Well-being and Cultures. Springer;2013:11-29.
10. Cohen GL, Sherman DK. The psychology of change: self-affirmation and social psychological intervention. Annu Rev Psychol. 2014;65:333-371.
11. Thomaes S, Bushman BJ, de Castro BO, et al. Arousing “gentle passions” in young adolescents: sustained experimental effects of value affirmations on prosocial feelings and behaviors. Dev Psychol. 2012;48(1):103-110.
12. Cacioppo JT, Cacioppo S, Capitanio JP, et al. The neuroendocrinology of social isolation. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66:733-767.
13. Holt-Lunstad J, Smith TB, Baker M, et al. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10(2):227-237.
14. Gable SL, Reis HT, Impett EA, et al. What do you do when things go right? The intrapersonal and interpersonal benefits of sharing positive events. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2004;87(2):228-245.
15. Gee B, Orchard F, Clarke E, et al. The effect of non-pharmacological sleep interventions on depression symptoms: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev. 2019;43:118-128.
16. Krogh J, Hjorthøj C, Speyer H, et al. Exercise for patients with major depression: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e014820. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014820
17. Firth J, Solmi M, Wootton RE, et al. A meta-review of “lifestyle psychiatry”: the role of exercise, smoking, diet and sleep in the prevention and treatment of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):360-380.
18. Piotrowski MC, Lunsford J, Gaynes BN. Lifestyle psychiatry for depression and anxiety: beyond diet and exercise. Lifestyle Med. 2021;2(1):e21. doi:10.1002/lim2.21
19. Janney CA, Brzoznowski KF, Richardson Cret al. Moving towards wellness: physical activity practices, perspectives, and preferences of users of outpatient mental health service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2017;49:63-66.
20. Walsh R. Lifestyle and mental health. Am Psychol. 2011;66(7):579-592.
21. Cregg DR, Cheavens JS. Gratitude interventions: effective self-help? A meta-analysis of the impact on symptoms of depression and anxiety. J Happiness Stud. 2021;22(1):413-445.
22. Bohlmeijer E, Roemer M, Cuijpers P, et al. The effects of reminiscence on psychological well-being in older adults: a meta-analysis. Aging Ment Health. 2007;11(3):291-300.
23. Zagic D, Wuthrich VM, Rapee RM, et al. Interventions to improve social connections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022;57(5):885-906.
24. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
FIRST OF 4 PARTS
What does wellness mean to you? A 2018 survey posed this question to more than 6,000 people living with depression and bipolar disorder. In addition to better treatment and greater understanding of their illnesses, other priorities emerged: a longing for better days, a sense of purpose, and a longing to function well and be happy.1 As one respondent explained, “Wellness means stability; well enough to hold a job, well enough to enjoy activities, well enough to feel joy and hope.” Traditional treatment that focuses on alleviating symptoms may not sufficiently address outcomes patients value. When the focus is primarily deficit-based, clinicians and patients may miss opportunities for optimization and transformation.
Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that seeks to enhance and promote well-being and health through the enhancement of positive psychosocial factors such as resilience, optimism, wisdom, and social support in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as those in the community at large.2 It is based on the principles that there is no health without mental health, and that mental health can improve through preventive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative interventions.3
Positive interventions are defined as “treatment methods or intentional activities that aim to cultivate positive feelings, behaviors, or cognitions.”4 They are evidence-based intentional exercises designed to increase well-being and enhance flourishing. Although positive interventions were originally studied as activities for nonclinical populations and for helping healthy people thrive, they are increasingly being valued for their therapeutic role in treating psychopathology.5 By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, psychiatrists can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients during the treatment process, and bolster positive mental health.
In this article, we provide practical ways to integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into everyday clinical practice. The goal is to broaden how clinicians think about mental health and therapeutic options and, above all, enhance our patients’ everyday well-being. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits are strategies clinicians can apply not only to provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also to enhance the range and richness of their patients’ everyday experience.
Adopt a positive orientation
When a clinician first meets a patient, “What’s wrong?” is a typical conversation starter, and conversations tend to revolve around problems, failures, and negative experiences. Positive psychiatry posits that there is therapeutic benefit to emphasizing and exploring a patient’s positive emotions, experiences, and aspirations. Questions such as “What was your sense of well-being this week? What is your goal for today’s session? What is your goal for the coming week?” can reorient a session towards an individual’s potential and promote exploration of what’s possible.
To promote a positive orientation, clinicians may consider integrating the Savoring and Three Good Things exercises—2 well-studied interventions—into their repertoire to activate and enhance positive emotional states such as gratitude and joy.6 An example of a Savoring activity is taking a 20-minute daily walk while trying to notice as many positive elements as possible. Similarly, the Three Good Things exercise, in which patients are asked to notice and write down 3 positive events and reflect on why they happened, promotes positive reflection and gratitude. A 14-day daily diary study conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic found that higher levels of gratitude were associated with higher levels of positive affect, lower levels of perceived stress related to COVID-19, and better subjective health.7 In addition to coping with life’s negative events, deliberately enhancing the impact of good things is a positive emotion amplifier. As French writer François de La Rochefoucauld argued, “Happiness does not consist in things themselves but in the relish we have of them.”8
Continue to: Harness strengths
Harness strengths
A growing body of evidence suggests that in addition to focusing on a patient’s chief concern, identifying and cultivating an individual’s signature strengths can mitigate stress and enhance well-being. Signature strengths are positive personality qualities that reflect our core identity and are morally valued. The VIA Character Strengths Survey is the most used and validated psychometric instrument to measure and identify signature strengths such as curiosity, self-regulation, honesty, and teamwork.9
To incorporate this tool into clinical practice, ask patients to complete a strengths survey using a validated assessment tool such as the VIA survey (www.viacharacter.org). After a patient identifies their signature strengths, encourage them to explore and apply these strengths in everyday life and in new ways. In addition to becoming aware of and using their signature strengths, encourage patients to “strengths spot” in others. “What strengths did you notice your coworker, family, or friend using today?” is a potential question to explore with patients. A strengths-based approach may be particularly helpful in uncovering motivation and fully engaging patients in treatment. Moreover, integrating strengths into the typically negatively skewed narrative underscores to patients that therapy isn’t only about untwisting distorted thinking, but also about harnessing one’s strengths, talents, and abilities. Strengths expressed through pragmatic actions can boost coping skills as well as enhance well-being.
Mobilize values
Value affirmation exercises have been shown to generate lasting benefits in creating positive feelings and behaviors.10 Encouraging patients to think about what they genuinely value redirects their gaze towards possibility and diverts self-focus. For instance, ask a patient to identify 2 or 3 values and write about why they are important. By reflecting on their values in writing, they affirm their identity and self-worth, thus creating a virtuous cycle of confidence, effort, and achievement. People who put their values front and center are more attuned to the needs of others as well as their own needs, and they make better connections.11 Including a patient’s values in the treatment plan may increase problem-solving skills, boost motivation, and build better stress management skills.
The “life review” is another intervention that facilitates exploration of a patient’s values. This exercise involves asking patients to recount the story of their life and the experiences that were most meaningful to them. This process allows clinicians to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s values, which can help guide treatment. Meta-analytic evidence has demonstrated these reminiscence-based interventions have significant effects on well-being.6 As Mahatma Gandhi famously said, “Happiness is when what you think, what you say, and what you do are in harmony.” Creating more overlap between a patient’s values and their everyday actions and behaviors bolsters resilience, buffers against stress, and can restore a healthier self-concept.
Cultivate social connections
Social connection is recognized as a core psychological need and essential for well-being. The opposite of connection—social isolation—has negative effects on overall health, including increases in inflammatory markers, depression rates, and even all-cause mortality.12 A 2015 meta-analytic review demonstrated that loneliness increased the likelihood of mortality by 26%—a similar increase as seen with smoking 15 cigarettes a day.13
Continue to: As with any vital sign...
As with any vital sign, exploring a patient’s number of social contacts, quantity of social visits per week, and quality of relationships is an important indicator of health. Giving patients tools to cultivate social connection and deepen their relationships can enhance therapeutic outcomes. Asking patients to perform acts of kindness is one example of a “social prescription.” Feeding a stranger’s parking meter, picking up litter, helping a friend with a chore, providing a meal to a person in need, and volunteering are potential ways for patients to engage in kind deeds. After each act, encourage the patient to write down what they did and how it made them feel.
“Prescribing” positive communication is another way to enhance a patient’s social connections. For instance, teaching them about active constructive responding (ACR)—responding with enthusiasm when another person shares information or good news—has been shown to strengthen bonds with friends and family.14 Making eye contact, giving the other person one’s full attention, inquiring about details, and responding with enthusiasm and interest are simple ways patients can apply ACR in their daily lives. Counseling a patient on increasing social connections, prescribing connections, and inquiring about quantity and quality of social interactions can help them not only add years to their life but also add health and well-being to those years.
Optimize healthy habits
Mounting research demonstrates that exercise, sleep, and nutrition are important for well-being. Evidence shows that therapeutic lifestyle changes can reduce depressive symptoms and boost positive feelings. Numerous meta-analyses have demonstrated the benefits of sleep and exercise interventions for reducing depressive symptoms in psychiatric patients.15,16 Longitudinal studies have provided evidence that healthy diets increase happiness, even after controlling for potential confounders such as socioeconomic factors.17 Other lifestyle factors—including financial stability, pet ownership, decreased social media use, and spending time in nature—have been shown to contribute to well-being.18
Despite the substantial evidence that lifestyle factors can improve health outcomes, few clinicians ask about, focus on, or promote positive habits.19 Positive psychiatry seeks to reorient clinicians towards lifestyle factors that enhance well-being. Clinicians can deploy a variety of strategies to support patients in making healthy and sustainable changes. Assessing readiness for change, motivational interviewing, setting SMART (specific, measurable, assignable, realistic, and time-related) goals, and referring patients to relevant community resources are ways to encourage and promote therapeutic lifestyle changes. Inquiring about a patient’s typical day—such as how they spend their free time, what they eat, when they go to bed, and how much time they spend outdoors—opens conversations about general well-being and shows the patient that therapy is about the whole person, and not only symptom management. Helping patients have better days can empower them to lead more satisfied lives.20

The Table6,17,21-23 summarizes the scientific evidence for the strategies described in this article. The Figure provides a flowchart for using these strategies in clinical practice.

Continue to: Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
By exploring and emphasizing potential and possibility, positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of disease) with salutogenesis (the study and creation of health24). Clinicians are well positioned to manage symptoms and bolster positive states. Rather than an either/or approach to well-being, positive psychiatry strives for a both/and approach to well-being. By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, clinicians can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients in the treatment process, and bolster mental health.
Bottom Line
Clinicians can integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into clinical practice. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits can not only provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also can enhance the range and richness of patients’ everyday experience.
Related Resources
- University of Pennsylvania. Authentic happiness. https://www.authentichappiness.sas.upenn.edu
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW (eds). Positive Psychiatry: A Clinical Handbook. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
FIRST OF 4 PARTS
What does wellness mean to you? A 2018 survey posed this question to more than 6,000 people living with depression and bipolar disorder. In addition to better treatment and greater understanding of their illnesses, other priorities emerged: a longing for better days, a sense of purpose, and a longing to function well and be happy.1 As one respondent explained, “Wellness means stability; well enough to hold a job, well enough to enjoy activities, well enough to feel joy and hope.” Traditional treatment that focuses on alleviating symptoms may not sufficiently address outcomes patients value. When the focus is primarily deficit-based, clinicians and patients may miss opportunities for optimization and transformation.
Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that seeks to enhance and promote well-being and health through the enhancement of positive psychosocial factors such as resilience, optimism, wisdom, and social support in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as those in the community at large.2 It is based on the principles that there is no health without mental health, and that mental health can improve through preventive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative interventions.3
Positive interventions are defined as “treatment methods or intentional activities that aim to cultivate positive feelings, behaviors, or cognitions.”4 They are evidence-based intentional exercises designed to increase well-being and enhance flourishing. Although positive interventions were originally studied as activities for nonclinical populations and for helping healthy people thrive, they are increasingly being valued for their therapeutic role in treating psychopathology.5 By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, psychiatrists can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients during the treatment process, and bolster positive mental health.
In this article, we provide practical ways to integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into everyday clinical practice. The goal is to broaden how clinicians think about mental health and therapeutic options and, above all, enhance our patients’ everyday well-being. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits are strategies clinicians can apply not only to provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also to enhance the range and richness of their patients’ everyday experience.
Adopt a positive orientation
When a clinician first meets a patient, “What’s wrong?” is a typical conversation starter, and conversations tend to revolve around problems, failures, and negative experiences. Positive psychiatry posits that there is therapeutic benefit to emphasizing and exploring a patient’s positive emotions, experiences, and aspirations. Questions such as “What was your sense of well-being this week? What is your goal for today’s session? What is your goal for the coming week?” can reorient a session towards an individual’s potential and promote exploration of what’s possible.
To promote a positive orientation, clinicians may consider integrating the Savoring and Three Good Things exercises—2 well-studied interventions—into their repertoire to activate and enhance positive emotional states such as gratitude and joy.6 An example of a Savoring activity is taking a 20-minute daily walk while trying to notice as many positive elements as possible. Similarly, the Three Good Things exercise, in which patients are asked to notice and write down 3 positive events and reflect on why they happened, promotes positive reflection and gratitude. A 14-day daily diary study conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic found that higher levels of gratitude were associated with higher levels of positive affect, lower levels of perceived stress related to COVID-19, and better subjective health.7 In addition to coping with life’s negative events, deliberately enhancing the impact of good things is a positive emotion amplifier. As French writer François de La Rochefoucauld argued, “Happiness does not consist in things themselves but in the relish we have of them.”8
Continue to: Harness strengths
Harness strengths
A growing body of evidence suggests that in addition to focusing on a patient’s chief concern, identifying and cultivating an individual’s signature strengths can mitigate stress and enhance well-being. Signature strengths are positive personality qualities that reflect our core identity and are morally valued. The VIA Character Strengths Survey is the most used and validated psychometric instrument to measure and identify signature strengths such as curiosity, self-regulation, honesty, and teamwork.9
To incorporate this tool into clinical practice, ask patients to complete a strengths survey using a validated assessment tool such as the VIA survey (www.viacharacter.org). After a patient identifies their signature strengths, encourage them to explore and apply these strengths in everyday life and in new ways. In addition to becoming aware of and using their signature strengths, encourage patients to “strengths spot” in others. “What strengths did you notice your coworker, family, or friend using today?” is a potential question to explore with patients. A strengths-based approach may be particularly helpful in uncovering motivation and fully engaging patients in treatment. Moreover, integrating strengths into the typically negatively skewed narrative underscores to patients that therapy isn’t only about untwisting distorted thinking, but also about harnessing one’s strengths, talents, and abilities. Strengths expressed through pragmatic actions can boost coping skills as well as enhance well-being.
Mobilize values
Value affirmation exercises have been shown to generate lasting benefits in creating positive feelings and behaviors.10 Encouraging patients to think about what they genuinely value redirects their gaze towards possibility and diverts self-focus. For instance, ask a patient to identify 2 or 3 values and write about why they are important. By reflecting on their values in writing, they affirm their identity and self-worth, thus creating a virtuous cycle of confidence, effort, and achievement. People who put their values front and center are more attuned to the needs of others as well as their own needs, and they make better connections.11 Including a patient’s values in the treatment plan may increase problem-solving skills, boost motivation, and build better stress management skills.
The “life review” is another intervention that facilitates exploration of a patient’s values. This exercise involves asking patients to recount the story of their life and the experiences that were most meaningful to them. This process allows clinicians to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s values, which can help guide treatment. Meta-analytic evidence has demonstrated these reminiscence-based interventions have significant effects on well-being.6 As Mahatma Gandhi famously said, “Happiness is when what you think, what you say, and what you do are in harmony.” Creating more overlap between a patient’s values and their everyday actions and behaviors bolsters resilience, buffers against stress, and can restore a healthier self-concept.
Cultivate social connections
Social connection is recognized as a core psychological need and essential for well-being. The opposite of connection—social isolation—has negative effects on overall health, including increases in inflammatory markers, depression rates, and even all-cause mortality.12 A 2015 meta-analytic review demonstrated that loneliness increased the likelihood of mortality by 26%—a similar increase as seen with smoking 15 cigarettes a day.13
Continue to: As with any vital sign...
As with any vital sign, exploring a patient’s number of social contacts, quantity of social visits per week, and quality of relationships is an important indicator of health. Giving patients tools to cultivate social connection and deepen their relationships can enhance therapeutic outcomes. Asking patients to perform acts of kindness is one example of a “social prescription.” Feeding a stranger’s parking meter, picking up litter, helping a friend with a chore, providing a meal to a person in need, and volunteering are potential ways for patients to engage in kind deeds. After each act, encourage the patient to write down what they did and how it made them feel.
“Prescribing” positive communication is another way to enhance a patient’s social connections. For instance, teaching them about active constructive responding (ACR)—responding with enthusiasm when another person shares information or good news—has been shown to strengthen bonds with friends and family.14 Making eye contact, giving the other person one’s full attention, inquiring about details, and responding with enthusiasm and interest are simple ways patients can apply ACR in their daily lives. Counseling a patient on increasing social connections, prescribing connections, and inquiring about quantity and quality of social interactions can help them not only add years to their life but also add health and well-being to those years.
Optimize healthy habits
Mounting research demonstrates that exercise, sleep, and nutrition are important for well-being. Evidence shows that therapeutic lifestyle changes can reduce depressive symptoms and boost positive feelings. Numerous meta-analyses have demonstrated the benefits of sleep and exercise interventions for reducing depressive symptoms in psychiatric patients.15,16 Longitudinal studies have provided evidence that healthy diets increase happiness, even after controlling for potential confounders such as socioeconomic factors.17 Other lifestyle factors—including financial stability, pet ownership, decreased social media use, and spending time in nature—have been shown to contribute to well-being.18
Despite the substantial evidence that lifestyle factors can improve health outcomes, few clinicians ask about, focus on, or promote positive habits.19 Positive psychiatry seeks to reorient clinicians towards lifestyle factors that enhance well-being. Clinicians can deploy a variety of strategies to support patients in making healthy and sustainable changes. Assessing readiness for change, motivational interviewing, setting SMART (specific, measurable, assignable, realistic, and time-related) goals, and referring patients to relevant community resources are ways to encourage and promote therapeutic lifestyle changes. Inquiring about a patient’s typical day—such as how they spend their free time, what they eat, when they go to bed, and how much time they spend outdoors—opens conversations about general well-being and shows the patient that therapy is about the whole person, and not only symptom management. Helping patients have better days can empower them to lead more satisfied lives.20

The Table6,17,21-23 summarizes the scientific evidence for the strategies described in this article. The Figure provides a flowchart for using these strategies in clinical practice.

Continue to: Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
By exploring and emphasizing potential and possibility, positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of disease) with salutogenesis (the study and creation of health24). Clinicians are well positioned to manage symptoms and bolster positive states. Rather than an either/or approach to well-being, positive psychiatry strives for a both/and approach to well-being. By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, clinicians can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients in the treatment process, and bolster mental health.
Bottom Line
Clinicians can integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into clinical practice. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits can not only provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also can enhance the range and richness of patients’ everyday experience.
Related Resources
- University of Pennsylvania. Authentic happiness. https://www.authentichappiness.sas.upenn.edu
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW (eds). Positive Psychiatry: A Clinical Handbook. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
1. Morton E, Foxworth P, Dardess P, et al. “Supporting Wellness”: a depression and bipolar support alliance mixed-methods investigation of lived experience perspectives and priorities for mood disorder treatment. J Affect Disord. 2022;299:575-584.
2. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Sin NL, Lyubomirsky S. Enhancing well-being and alleviating depressive symptoms with positive psychology interventions: a practice-friendly meta-analysis. J Clin Psychol. 2009;65(5):467-487.
5. Seligman MEP, Rashid T, Parks AC. Positive psychotherapy. Am Psychol. 2006;61(8):774-788.
6. Carr A, Cullen K, Keeney C, et al. Effectiveness of positive psychology interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Posit Psychol. 2021;16(6):749-769.
7. Jiang D. Feeling gratitude is associated with better well-being across the life span: a daily diary study during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2022;77(4):e36-e45.
8. de La Rochefoucauld F. Maxims and moral reflections (1796). Gale ECCO: 2010.
9. Niemiec RM. VIA character strengths: Research and practice (The first 10 years). In: Knoop HH, Fave AD (eds). Well-being and Cultures. Springer;2013:11-29.
10. Cohen GL, Sherman DK. The psychology of change: self-affirmation and social psychological intervention. Annu Rev Psychol. 2014;65:333-371.
11. Thomaes S, Bushman BJ, de Castro BO, et al. Arousing “gentle passions” in young adolescents: sustained experimental effects of value affirmations on prosocial feelings and behaviors. Dev Psychol. 2012;48(1):103-110.
12. Cacioppo JT, Cacioppo S, Capitanio JP, et al. The neuroendocrinology of social isolation. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66:733-767.
13. Holt-Lunstad J, Smith TB, Baker M, et al. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10(2):227-237.
14. Gable SL, Reis HT, Impett EA, et al. What do you do when things go right? The intrapersonal and interpersonal benefits of sharing positive events. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2004;87(2):228-245.
15. Gee B, Orchard F, Clarke E, et al. The effect of non-pharmacological sleep interventions on depression symptoms: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev. 2019;43:118-128.
16. Krogh J, Hjorthøj C, Speyer H, et al. Exercise for patients with major depression: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e014820. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014820
17. Firth J, Solmi M, Wootton RE, et al. A meta-review of “lifestyle psychiatry”: the role of exercise, smoking, diet and sleep in the prevention and treatment of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):360-380.
18. Piotrowski MC, Lunsford J, Gaynes BN. Lifestyle psychiatry for depression and anxiety: beyond diet and exercise. Lifestyle Med. 2021;2(1):e21. doi:10.1002/lim2.21
19. Janney CA, Brzoznowski KF, Richardson Cret al. Moving towards wellness: physical activity practices, perspectives, and preferences of users of outpatient mental health service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2017;49:63-66.
20. Walsh R. Lifestyle and mental health. Am Psychol. 2011;66(7):579-592.
21. Cregg DR, Cheavens JS. Gratitude interventions: effective self-help? A meta-analysis of the impact on symptoms of depression and anxiety. J Happiness Stud. 2021;22(1):413-445.
22. Bohlmeijer E, Roemer M, Cuijpers P, et al. The effects of reminiscence on psychological well-being in older adults: a meta-analysis. Aging Ment Health. 2007;11(3):291-300.
23. Zagic D, Wuthrich VM, Rapee RM, et al. Interventions to improve social connections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022;57(5):885-906.
24. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
1. Morton E, Foxworth P, Dardess P, et al. “Supporting Wellness”: a depression and bipolar support alliance mixed-methods investigation of lived experience perspectives and priorities for mood disorder treatment. J Affect Disord. 2022;299:575-584.
2. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Sin NL, Lyubomirsky S. Enhancing well-being and alleviating depressive symptoms with positive psychology interventions: a practice-friendly meta-analysis. J Clin Psychol. 2009;65(5):467-487.
5. Seligman MEP, Rashid T, Parks AC. Positive psychotherapy. Am Psychol. 2006;61(8):774-788.
6. Carr A, Cullen K, Keeney C, et al. Effectiveness of positive psychology interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Posit Psychol. 2021;16(6):749-769.
7. Jiang D. Feeling gratitude is associated with better well-being across the life span: a daily diary study during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2022;77(4):e36-e45.
8. de La Rochefoucauld F. Maxims and moral reflections (1796). Gale ECCO: 2010.
9. Niemiec RM. VIA character strengths: Research and practice (The first 10 years). In: Knoop HH, Fave AD (eds). Well-being and Cultures. Springer;2013:11-29.
10. Cohen GL, Sherman DK. The psychology of change: self-affirmation and social psychological intervention. Annu Rev Psychol. 2014;65:333-371.
11. Thomaes S, Bushman BJ, de Castro BO, et al. Arousing “gentle passions” in young adolescents: sustained experimental effects of value affirmations on prosocial feelings and behaviors. Dev Psychol. 2012;48(1):103-110.
12. Cacioppo JT, Cacioppo S, Capitanio JP, et al. The neuroendocrinology of social isolation. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66:733-767.
13. Holt-Lunstad J, Smith TB, Baker M, et al. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10(2):227-237.
14. Gable SL, Reis HT, Impett EA, et al. What do you do when things go right? The intrapersonal and interpersonal benefits of sharing positive events. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2004;87(2):228-245.
15. Gee B, Orchard F, Clarke E, et al. The effect of non-pharmacological sleep interventions on depression symptoms: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev. 2019;43:118-128.
16. Krogh J, Hjorthøj C, Speyer H, et al. Exercise for patients with major depression: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e014820. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014820
17. Firth J, Solmi M, Wootton RE, et al. A meta-review of “lifestyle psychiatry”: the role of exercise, smoking, diet and sleep in the prevention and treatment of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):360-380.
18. Piotrowski MC, Lunsford J, Gaynes BN. Lifestyle psychiatry for depression and anxiety: beyond diet and exercise. Lifestyle Med. 2021;2(1):e21. doi:10.1002/lim2.21
19. Janney CA, Brzoznowski KF, Richardson Cret al. Moving towards wellness: physical activity practices, perspectives, and preferences of users of outpatient mental health service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2017;49:63-66.
20. Walsh R. Lifestyle and mental health. Am Psychol. 2011;66(7):579-592.
21. Cregg DR, Cheavens JS. Gratitude interventions: effective self-help? A meta-analysis of the impact on symptoms of depression and anxiety. J Happiness Stud. 2021;22(1):413-445.
22. Bohlmeijer E, Roemer M, Cuijpers P, et al. The effects of reminiscence on psychological well-being in older adults: a meta-analysis. Aging Ment Health. 2007;11(3):291-300.
23. Zagic D, Wuthrich VM, Rapee RM, et al. Interventions to improve social connections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022;57(5):885-906.
24. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
The accelerating societal entropy undermines mental health
According to the second law of thermodynamics, it is inevitable that entropy will continue to increase over time.1 Entropy is a measure of disorder, which can eventuate in chaos and lead to profound uncertainty, with serious psychological consequences.
The increase in entropy is usually gradual. It took hundreds of years for powerful empires and civilizations to collapse and disappear. Inanimate objects such as a house, a piece of furniture, or a piece of equipment eventually deteriorate and break down over time. Tidy offices will become messy, cluttered, and dirty unless attended to regularly. Living organisms, including humans, inevitably undergo an aging process with cellular senescence, atrophy, and loss of cerebral, muscle, and bone tissue, ending in death. Even human relationships will eventually fracture, wither, and end. The passage of time ruthlessly increases the entropy of everything in life. Even the 13-billion-year-old universe, which currently looks formidable and permanent to us, is inexorably expanding and hurtling towards a calamitous end a few billion years from now.
To slow down, halt, or reverse entropy, work and energy must be invested. A house requires regular maintenance for all its components to avoid deteriorating and becoming uninhabitable (very high entropy). Humans require massive amounts of work during fetal life, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and throughout old age. This includes work by parents, teachers, friends, physicians, farmers, and manufacturers of food, clothing, and sundry supplies, all targeted to maintain an individual and slow the rate of entropy. But death is inevitable as the final stage of human entropy.
The brain is an entropic organ.2 Psychiatric disorders can be conceptualized as a neurobiologic consequence of a major rise in brain entropy. The chaos created by high brain entropy will lead to a disruption of basic mental functions such as thought, mood, affect, impulses, behavior, and cognition. Brain entropy increases can be due to genetics or the environment, but most often are due an interaction of both (G x E).
Societal entropy and our patients
Psychiatric patients are deeply influenced by the context in which they live (society). The entropy of contemporary society is rising at an alarming rate, which means that order is rapidly degenerating into disorder at an unprecedented pace. When the COVID-19 pandemic abruptly emerged in early 2020, it was a major public health shock that drastically changed the lives of all citizens and dramatically increased societal entropy. The pandemic led to lockdowns, fear of death, gut-wrenching uncertainty (especially for a whole year before vaccines were developed, but even after), loss of socialization and sexual intimacy, loss of employment, financial straits, and an inability to access routine medical or surgical procedures. Everyone in society developed anxiety and acute stress reaction, but those with pre-existing psychiatric disorders suffered the most with an intensification of their symptoms.
The unforeseen, sudden, and traumatically life-altering pandemic triggered various degrees of posttraumatic stress disorder across all age groups, and painful death in medically compromised individuals and older adults. Both physical and psychological entropy skyrocketed and the “order” of life as we knew it rapidly disintegrated into shambles and disorder. The abrupt traumatic jolt triggered various degrees of deleterious impacts on the brains of all who experienced it in real time. The rise in the psychobiological entropy was unprecedented across the structures of society, especially the population, its vulnerable human component.
But even as the worst of the pandemic is in our rearview mirror and life again has a semblance of normality, the rise of entropy continues to accelerate because we continue to be surrounded and engulfed by countless stressful events in contemporary society. Those nagging stresses continue to transmute order to chaos and metamorphose comforting predictability to entrenched uncertainty:
- Toxic political hyperpartisanship, with intense animus and visceral bidirectional hatred
- Racial tensions, with overt bias across groups
- Economic turmoil, with inflation and threats of recession
- Actual wars and threats of war
- Social media that spreads bad news and distorts facts
- An opioid crisis, with hundreds of thousands of deaths
- Skyrocketing crime, with a decline in policing and quick release of criminals without bail
- A ruthless and arbitrary “cancel culture” that doesn’t even spare the previously revered founders of the republic
- Cognitive dissonance of disparaging Abraham Lincoln despite his major achievement of eliminating slavery by waging a civil war
- The social and medical strife regarding access to abortion.
Continue to: I also would include...
(I also would include some “entropy pet peeves” of mine: Torn clothes as a fashion statement, transforming tattoos from an oddity to a fad, nose rings that disfigure pretty faces, and banishing neckties for men.)
Our role in this scenario
As psychiatrists, we must step up to intensify the work needed to slow down and even reverse the dangerously rising brain entropy in our patients. But that is not an easy task given the implosion of societal norms and traditional values, along with the radicalization of beliefs, with utter intolerance of others’ beliefs. We also face the challenge of maintaining a modicum of resilience and wellness in ourselves, which can be antidotes to entropy.
It’s impossible to stop the inevitability of rising entropy, both physical and psychological, but psychiatrists and other mental health professionals must invest their skills and talents now more than ever to at least slow down the pace of entropy among our patients. Otherwise, psychological chaos and disorder will be quite damaging to their lives, and worsen their outcomes.
1. Ben-Naim A. Entropy Demystified. World Scientific; 2007.
2. Carhart-Harris RL. The entropic brain - revisited. Neuropharmacology. 2018;142:167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.010
According to the second law of thermodynamics, it is inevitable that entropy will continue to increase over time.1 Entropy is a measure of disorder, which can eventuate in chaos and lead to profound uncertainty, with serious psychological consequences.
The increase in entropy is usually gradual. It took hundreds of years for powerful empires and civilizations to collapse and disappear. Inanimate objects such as a house, a piece of furniture, or a piece of equipment eventually deteriorate and break down over time. Tidy offices will become messy, cluttered, and dirty unless attended to regularly. Living organisms, including humans, inevitably undergo an aging process with cellular senescence, atrophy, and loss of cerebral, muscle, and bone tissue, ending in death. Even human relationships will eventually fracture, wither, and end. The passage of time ruthlessly increases the entropy of everything in life. Even the 13-billion-year-old universe, which currently looks formidable and permanent to us, is inexorably expanding and hurtling towards a calamitous end a few billion years from now.
To slow down, halt, or reverse entropy, work and energy must be invested. A house requires regular maintenance for all its components to avoid deteriorating and becoming uninhabitable (very high entropy). Humans require massive amounts of work during fetal life, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and throughout old age. This includes work by parents, teachers, friends, physicians, farmers, and manufacturers of food, clothing, and sundry supplies, all targeted to maintain an individual and slow the rate of entropy. But death is inevitable as the final stage of human entropy.
The brain is an entropic organ.2 Psychiatric disorders can be conceptualized as a neurobiologic consequence of a major rise in brain entropy. The chaos created by high brain entropy will lead to a disruption of basic mental functions such as thought, mood, affect, impulses, behavior, and cognition. Brain entropy increases can be due to genetics or the environment, but most often are due an interaction of both (G x E).
Societal entropy and our patients
Psychiatric patients are deeply influenced by the context in which they live (society). The entropy of contemporary society is rising at an alarming rate, which means that order is rapidly degenerating into disorder at an unprecedented pace. When the COVID-19 pandemic abruptly emerged in early 2020, it was a major public health shock that drastically changed the lives of all citizens and dramatically increased societal entropy. The pandemic led to lockdowns, fear of death, gut-wrenching uncertainty (especially for a whole year before vaccines were developed, but even after), loss of socialization and sexual intimacy, loss of employment, financial straits, and an inability to access routine medical or surgical procedures. Everyone in society developed anxiety and acute stress reaction, but those with pre-existing psychiatric disorders suffered the most with an intensification of their symptoms.
The unforeseen, sudden, and traumatically life-altering pandemic triggered various degrees of posttraumatic stress disorder across all age groups, and painful death in medically compromised individuals and older adults. Both physical and psychological entropy skyrocketed and the “order” of life as we knew it rapidly disintegrated into shambles and disorder. The abrupt traumatic jolt triggered various degrees of deleterious impacts on the brains of all who experienced it in real time. The rise in the psychobiological entropy was unprecedented across the structures of society, especially the population, its vulnerable human component.
But even as the worst of the pandemic is in our rearview mirror and life again has a semblance of normality, the rise of entropy continues to accelerate because we continue to be surrounded and engulfed by countless stressful events in contemporary society. Those nagging stresses continue to transmute order to chaos and metamorphose comforting predictability to entrenched uncertainty:
- Toxic political hyperpartisanship, with intense animus and visceral bidirectional hatred
- Racial tensions, with overt bias across groups
- Economic turmoil, with inflation and threats of recession
- Actual wars and threats of war
- Social media that spreads bad news and distorts facts
- An opioid crisis, with hundreds of thousands of deaths
- Skyrocketing crime, with a decline in policing and quick release of criminals without bail
- A ruthless and arbitrary “cancel culture” that doesn’t even spare the previously revered founders of the republic
- Cognitive dissonance of disparaging Abraham Lincoln despite his major achievement of eliminating slavery by waging a civil war
- The social and medical strife regarding access to abortion.
Continue to: I also would include...
(I also would include some “entropy pet peeves” of mine: Torn clothes as a fashion statement, transforming tattoos from an oddity to a fad, nose rings that disfigure pretty faces, and banishing neckties for men.)
Our role in this scenario
As psychiatrists, we must step up to intensify the work needed to slow down and even reverse the dangerously rising brain entropy in our patients. But that is not an easy task given the implosion of societal norms and traditional values, along with the radicalization of beliefs, with utter intolerance of others’ beliefs. We also face the challenge of maintaining a modicum of resilience and wellness in ourselves, which can be antidotes to entropy.
It’s impossible to stop the inevitability of rising entropy, both physical and psychological, but psychiatrists and other mental health professionals must invest their skills and talents now more than ever to at least slow down the pace of entropy among our patients. Otherwise, psychological chaos and disorder will be quite damaging to their lives, and worsen their outcomes.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, it is inevitable that entropy will continue to increase over time.1 Entropy is a measure of disorder, which can eventuate in chaos and lead to profound uncertainty, with serious psychological consequences.
The increase in entropy is usually gradual. It took hundreds of years for powerful empires and civilizations to collapse and disappear. Inanimate objects such as a house, a piece of furniture, or a piece of equipment eventually deteriorate and break down over time. Tidy offices will become messy, cluttered, and dirty unless attended to regularly. Living organisms, including humans, inevitably undergo an aging process with cellular senescence, atrophy, and loss of cerebral, muscle, and bone tissue, ending in death. Even human relationships will eventually fracture, wither, and end. The passage of time ruthlessly increases the entropy of everything in life. Even the 13-billion-year-old universe, which currently looks formidable and permanent to us, is inexorably expanding and hurtling towards a calamitous end a few billion years from now.
To slow down, halt, or reverse entropy, work and energy must be invested. A house requires regular maintenance for all its components to avoid deteriorating and becoming uninhabitable (very high entropy). Humans require massive amounts of work during fetal life, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and throughout old age. This includes work by parents, teachers, friends, physicians, farmers, and manufacturers of food, clothing, and sundry supplies, all targeted to maintain an individual and slow the rate of entropy. But death is inevitable as the final stage of human entropy.
The brain is an entropic organ.2 Psychiatric disorders can be conceptualized as a neurobiologic consequence of a major rise in brain entropy. The chaos created by high brain entropy will lead to a disruption of basic mental functions such as thought, mood, affect, impulses, behavior, and cognition. Brain entropy increases can be due to genetics or the environment, but most often are due an interaction of both (G x E).
Societal entropy and our patients
Psychiatric patients are deeply influenced by the context in which they live (society). The entropy of contemporary society is rising at an alarming rate, which means that order is rapidly degenerating into disorder at an unprecedented pace. When the COVID-19 pandemic abruptly emerged in early 2020, it was a major public health shock that drastically changed the lives of all citizens and dramatically increased societal entropy. The pandemic led to lockdowns, fear of death, gut-wrenching uncertainty (especially for a whole year before vaccines were developed, but even after), loss of socialization and sexual intimacy, loss of employment, financial straits, and an inability to access routine medical or surgical procedures. Everyone in society developed anxiety and acute stress reaction, but those with pre-existing psychiatric disorders suffered the most with an intensification of their symptoms.
The unforeseen, sudden, and traumatically life-altering pandemic triggered various degrees of posttraumatic stress disorder across all age groups, and painful death in medically compromised individuals and older adults. Both physical and psychological entropy skyrocketed and the “order” of life as we knew it rapidly disintegrated into shambles and disorder. The abrupt traumatic jolt triggered various degrees of deleterious impacts on the brains of all who experienced it in real time. The rise in the psychobiological entropy was unprecedented across the structures of society, especially the population, its vulnerable human component.
But even as the worst of the pandemic is in our rearview mirror and life again has a semblance of normality, the rise of entropy continues to accelerate because we continue to be surrounded and engulfed by countless stressful events in contemporary society. Those nagging stresses continue to transmute order to chaos and metamorphose comforting predictability to entrenched uncertainty:
- Toxic political hyperpartisanship, with intense animus and visceral bidirectional hatred
- Racial tensions, with overt bias across groups
- Economic turmoil, with inflation and threats of recession
- Actual wars and threats of war
- Social media that spreads bad news and distorts facts
- An opioid crisis, with hundreds of thousands of deaths
- Skyrocketing crime, with a decline in policing and quick release of criminals without bail
- A ruthless and arbitrary “cancel culture” that doesn’t even spare the previously revered founders of the republic
- Cognitive dissonance of disparaging Abraham Lincoln despite his major achievement of eliminating slavery by waging a civil war
- The social and medical strife regarding access to abortion.
Continue to: I also would include...
(I also would include some “entropy pet peeves” of mine: Torn clothes as a fashion statement, transforming tattoos from an oddity to a fad, nose rings that disfigure pretty faces, and banishing neckties for men.)
Our role in this scenario
As psychiatrists, we must step up to intensify the work needed to slow down and even reverse the dangerously rising brain entropy in our patients. But that is not an easy task given the implosion of societal norms and traditional values, along with the radicalization of beliefs, with utter intolerance of others’ beliefs. We also face the challenge of maintaining a modicum of resilience and wellness in ourselves, which can be antidotes to entropy.
It’s impossible to stop the inevitability of rising entropy, both physical and psychological, but psychiatrists and other mental health professionals must invest their skills and talents now more than ever to at least slow down the pace of entropy among our patients. Otherwise, psychological chaos and disorder will be quite damaging to their lives, and worsen their outcomes.
1. Ben-Naim A. Entropy Demystified. World Scientific; 2007.
2. Carhart-Harris RL. The entropic brain - revisited. Neuropharmacology. 2018;142:167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.010
1. Ben-Naim A. Entropy Demystified. World Scientific; 2007.
2. Carhart-Harris RL. The entropic brain - revisited. Neuropharmacology. 2018;142:167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.010
More on varenicline
Murray et al have written a timely, thoughtful, and useful article (“Smoking cessation: Varenicline and the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse events,”
Just a few caveats regarding Murray et al’s excellent summary:
• The article did not address that nicotine is consumed in multiple ways, such as vaping, snuff, chewing tobacco, and hookah
• The safety of varenicline appears fair when psychiatric illness is well controlled but can be problematic (and even severely detrimental) when mental illness is not well controlled. This should not be glossed over, especially since it was the reason for the original black-box warning (for risks including behavioral impulsivity, suicidality, severe insomnia, and nightmares) that was removed in 2016
• Patients with severe mental illness may not fully understand the risks, benefits, and priorities of the treatment intervention. The importance of psychiatric and internal medicine in addition to pharmacy follow-up is critical and needs to be documented.
Varenicline has been contextualized in its current role as a first-line treatment for smoking cessation. By bypassing a sizeable population of patients who have unstable psychiatric illness (especially bipolar I disorder), the path has been opened for risky “off-label” varenicline prescribing to this population by internists, who should be very cautious and prudent about prescribing for such patients. This alone is probably a good reason to reinstate the black-box warning.
Interestingly, one review found that only 1 of 11 patients receiving varenicline stopped smoking.1 Not dramatically beneficial for a first-line treatment! Decreasing smoking occurs as well and is more robust with combinational use with bupropion, nicotine replacement therapy, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
If we are focusing on patients with unstable mental illness—who are seen primarily by psychiatrists—adherence, urgency of intervention, and context regarding acute safety for this population must be seen as top priorities.
So-called “second-line” treatment options must also be considered. Sandiego et al3 make excellent points regarding the role of alpha-adrenergic agonists such as guanfacine, which have been shown to be helpful in smoking cessation. They work by decreasing cortical dopamine release and their calming effects on the noradrenergic system, which may decrease smoking precipitated by stress. For the particularly challenging subpopulation of unstable smokers, the combination of varenicline plus guanfacine ER may turn out to be a game-changer.
Varenicline has not proven itself to be useful in patients who are severely mentally ill, and due to its low success rate, expectations should remain tempered, pragmatically realistic, and safety-based.4,5 The bottom line is that in an unstable psychiatrically ill patient, interventions other than varenicline should be first-line.
1. Crawford P, Cieslak D. Varenicline for smoking cessation. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(5).
2. Beard E, Jackson SE, Anthenelli RM, et al. Estimation of risk of neuropsychiatric adverse events from varenicline, bupropion and nicotine patch versus placebo: secondary analysis of results from the EAGLES trial using Bayes factors. Addiction. 2021;116(10):2816-2824.
3. Sandiego CM, Matuskey D, Lavery M, et al. The effect of treatment with guanfacine, an alpha2 adrenergic agonist, on dopaminergic tone in tobacco smokers: an [11C]FLB457 PET study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018;43(5):1052-1058.
4. Sharma R, Alla K, Pfeffer D, et al. An appraisal of practice guidelines for smoking cessation in people with severe mental illness. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2017;51(11):1106-1120.
5. Tofler IR. Varenicline for smoking cessation in the bipolar patient. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(5):625.
Murray et al have written a timely, thoughtful, and useful article (“Smoking cessation: Varenicline and the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse events,”
Just a few caveats regarding Murray et al’s excellent summary:
• The article did not address that nicotine is consumed in multiple ways, such as vaping, snuff, chewing tobacco, and hookah
• The safety of varenicline appears fair when psychiatric illness is well controlled but can be problematic (and even severely detrimental) when mental illness is not well controlled. This should not be glossed over, especially since it was the reason for the original black-box warning (for risks including behavioral impulsivity, suicidality, severe insomnia, and nightmares) that was removed in 2016
• Patients with severe mental illness may not fully understand the risks, benefits, and priorities of the treatment intervention. The importance of psychiatric and internal medicine in addition to pharmacy follow-up is critical and needs to be documented.
Varenicline has been contextualized in its current role as a first-line treatment for smoking cessation. By bypassing a sizeable population of patients who have unstable psychiatric illness (especially bipolar I disorder), the path has been opened for risky “off-label” varenicline prescribing to this population by internists, who should be very cautious and prudent about prescribing for such patients. This alone is probably a good reason to reinstate the black-box warning.
Interestingly, one review found that only 1 of 11 patients receiving varenicline stopped smoking.1 Not dramatically beneficial for a first-line treatment! Decreasing smoking occurs as well and is more robust with combinational use with bupropion, nicotine replacement therapy, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
If we are focusing on patients with unstable mental illness—who are seen primarily by psychiatrists—adherence, urgency of intervention, and context regarding acute safety for this population must be seen as top priorities.
So-called “second-line” treatment options must also be considered. Sandiego et al3 make excellent points regarding the role of alpha-adrenergic agonists such as guanfacine, which have been shown to be helpful in smoking cessation. They work by decreasing cortical dopamine release and their calming effects on the noradrenergic system, which may decrease smoking precipitated by stress. For the particularly challenging subpopulation of unstable smokers, the combination of varenicline plus guanfacine ER may turn out to be a game-changer.
Varenicline has not proven itself to be useful in patients who are severely mentally ill, and due to its low success rate, expectations should remain tempered, pragmatically realistic, and safety-based.4,5 The bottom line is that in an unstable psychiatrically ill patient, interventions other than varenicline should be first-line.
Murray et al have written a timely, thoughtful, and useful article (“Smoking cessation: Varenicline and the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse events,”
Just a few caveats regarding Murray et al’s excellent summary:
• The article did not address that nicotine is consumed in multiple ways, such as vaping, snuff, chewing tobacco, and hookah
• The safety of varenicline appears fair when psychiatric illness is well controlled but can be problematic (and even severely detrimental) when mental illness is not well controlled. This should not be glossed over, especially since it was the reason for the original black-box warning (for risks including behavioral impulsivity, suicidality, severe insomnia, and nightmares) that was removed in 2016
• Patients with severe mental illness may not fully understand the risks, benefits, and priorities of the treatment intervention. The importance of psychiatric and internal medicine in addition to pharmacy follow-up is critical and needs to be documented.
Varenicline has been contextualized in its current role as a first-line treatment for smoking cessation. By bypassing a sizeable population of patients who have unstable psychiatric illness (especially bipolar I disorder), the path has been opened for risky “off-label” varenicline prescribing to this population by internists, who should be very cautious and prudent about prescribing for such patients. This alone is probably a good reason to reinstate the black-box warning.
Interestingly, one review found that only 1 of 11 patients receiving varenicline stopped smoking.1 Not dramatically beneficial for a first-line treatment! Decreasing smoking occurs as well and is more robust with combinational use with bupropion, nicotine replacement therapy, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
If we are focusing on patients with unstable mental illness—who are seen primarily by psychiatrists—adherence, urgency of intervention, and context regarding acute safety for this population must be seen as top priorities.
So-called “second-line” treatment options must also be considered. Sandiego et al3 make excellent points regarding the role of alpha-adrenergic agonists such as guanfacine, which have been shown to be helpful in smoking cessation. They work by decreasing cortical dopamine release and their calming effects on the noradrenergic system, which may decrease smoking precipitated by stress. For the particularly challenging subpopulation of unstable smokers, the combination of varenicline plus guanfacine ER may turn out to be a game-changer.
Varenicline has not proven itself to be useful in patients who are severely mentally ill, and due to its low success rate, expectations should remain tempered, pragmatically realistic, and safety-based.4,5 The bottom line is that in an unstable psychiatrically ill patient, interventions other than varenicline should be first-line.
1. Crawford P, Cieslak D. Varenicline for smoking cessation. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(5).
2. Beard E, Jackson SE, Anthenelli RM, et al. Estimation of risk of neuropsychiatric adverse events from varenicline, bupropion and nicotine patch versus placebo: secondary analysis of results from the EAGLES trial using Bayes factors. Addiction. 2021;116(10):2816-2824.
3. Sandiego CM, Matuskey D, Lavery M, et al. The effect of treatment with guanfacine, an alpha2 adrenergic agonist, on dopaminergic tone in tobacco smokers: an [11C]FLB457 PET study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018;43(5):1052-1058.
4. Sharma R, Alla K, Pfeffer D, et al. An appraisal of practice guidelines for smoking cessation in people with severe mental illness. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2017;51(11):1106-1120.
5. Tofler IR. Varenicline for smoking cessation in the bipolar patient. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(5):625.
1. Crawford P, Cieslak D. Varenicline for smoking cessation. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(5).
2. Beard E, Jackson SE, Anthenelli RM, et al. Estimation of risk of neuropsychiatric adverse events from varenicline, bupropion and nicotine patch versus placebo: secondary analysis of results from the EAGLES trial using Bayes factors. Addiction. 2021;116(10):2816-2824.
3. Sandiego CM, Matuskey D, Lavery M, et al. The effect of treatment with guanfacine, an alpha2 adrenergic agonist, on dopaminergic tone in tobacco smokers: an [11C]FLB457 PET study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018;43(5):1052-1058.
4. Sharma R, Alla K, Pfeffer D, et al. An appraisal of practice guidelines for smoking cessation in people with severe mental illness. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2017;51(11):1106-1120.
5. Tofler IR. Varenicline for smoking cessation in the bipolar patient. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(5):625.
Faulty fences: Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in schizophrenia
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an essential barrier of closely spaced cells that regulates entry into the CNS. What passes should be highly regulated to protect the brain from potentially harmful peripheral cells or molecules from the rest of the body. However, research has revealed that the BBB is pathologically permeable in several disease states, including schizophrenia, epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, autism, and DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome, which often presents with symptoms of schizophrenia).1,2 In this article, we discuss potential markers of BBB dysfunction, the consequences of a porous BBB, the effect of BBB permeability on microglial activation, and possible treatment implications.
Detecting a BBB leak
The BBB is composed of microvascular endothelial cell units. Adherens junctions, astrocyte endfeet, and pericytes are all part of these units, but tight junctions have the most significant role in BBB barrier function. Tight junction protein composition varies depending on the location of the endothelium. In the BBB, they are primarily composed of claudin-5, occludin, zonulin, and junction adhesion molecules (JAMs) (Figure). Claudins and occludins are especially important components of the tight junction because they span plasma membranes.3
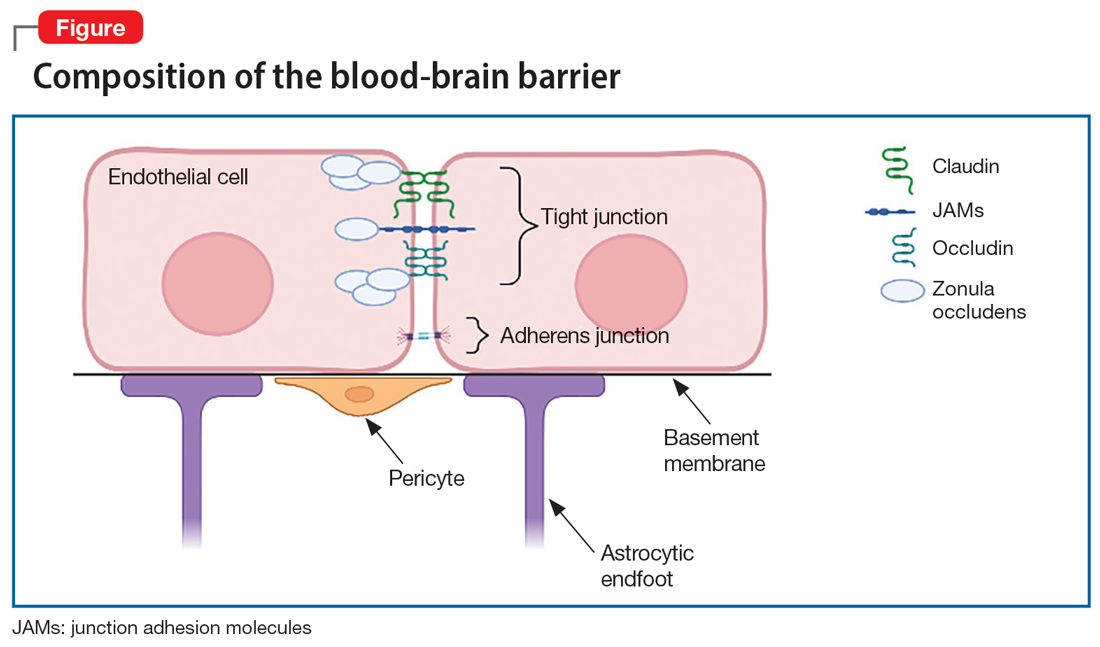
Researchers began to suspect tight junction permeability in schizophrenia while searching for schizophrenia biomarkers. For example, S100B is a marker of astrocytic reactivity to damage. It is increased in schizophrenia, major depressive disorder, and bipolar disorder.4 Studies found elevated S100B specifically in drug-free patients with schizophrenia,5 which prompted research suggesting it could predict the severity of negative symptoms.6 The accuracy of S100B as a biomarker was later complicated by the finding that adipose tissue also secretes S100B. This is problematic due to the high rates of comorbid obesity in psychiatric populations.2
Perhaps a better biomarker is the ratio of albumin in the CSF vs that in peripheral serum. The CSF-to-blood albumin ratio (Q-Alb) is widely considered an acceptable marker of BBB dysfunction because albumin must cross the BBB to alter the ratio. Studies have found a high Q-Alb in neurodegenerative disorders such as multiple sclerosis as well as in schizophrenia, which suggests that some level of BBB dysfunction is occurring. Although the Q-Alb may change slightly when confounded by antipsychotic use or with CSF flow changes,2,4 both S100B and Q-Alb elevation are sufficient for further investigation into tight junction alteration in schizophrenia.
Claudin-5 is a promising factor in detecting BBB permeability. Claudin-5 is deleted in DiGeorge syndrome, which is highly comorbid with schizophrenia and psychosis.1 Mouse knockdown studies show that full suppression of claudin-5 results in psychotic symptoms before fatal seizures,2,7 but a partial absence may enable psychotic symptoms. The same study showed that normally continuous claudin-5 was patchy along blood vessels in the affected sample.7 Follow-up experiments suggest that loss of claudin-5 in schizophrenia is especially prominent in the hippocampus, and there is mixed evidence of a decrease in the prefrontal cortex.8
Outside of claudin-5 alone, JAM-A plays a more regulatory role. It is upstream from an enhancer protein gene that serves as a transcription factor for the claudin-5 promoter, so when JAM-A is deleted, there is less claudin-5.9 However, while this decrease in claudin-5 may be pathological, there could still be various upstream changes that lead to schizophrenia.
What are the consequences of a porous BBB?
Although it is well established that the BBB passes small molecules and solutes, there is significant evidence of inflammatory trafficking in disease states. The BBB moves proinflammatory cytokines, alters transporters, and may even let white blood cells (WBCs) pass through. Immune cell infiltration has different requirements depending on the cell type. T cells rely on integrins, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (vCAM1), and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (iCAM1) for binding, rolling, adhering, crossing, and migration to sites of inflammation.10,11 Both iCAM1 and vCAM1 are elevated in schizophrenia compared to other psychiatric disorders (such as unipolar depression) and correlate with other biomarkers. For example, vCAM1, responsible for recruitment and crossing, is correlated with a high Q-Alb.12 Primarily produced by astrocytes and endothelial cells, iCAM1 plays the largest role in crossing the BBB and migration. Postmortem tissue demonstrates that cytokines upregulate iCAM1 mRNA at the BBB in schizophrenia.13 Increased cytokines are well documented in the inflammatory model of schizophrenia. Interestingly, decreasing claudin-5 also upregulates iCAM1 production.14 Therefore, low baseline claudin-5 may contribute to additional inflammation and symptoms.
Continue to: BBB permeability also results...
BBB permeability also results in a certain pattern of leukocyte and cytokine activity. Interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha can all cross the BBB during neuroimmune inflammation,10 but there are abnormal heightened and sustained responses of these molecules in schizophrenia. IL-6 is a proinflammatory cytokine in both acute and chronic inflammation that is expressed by astrocytes, endothelial cells, and microglia.15 IL-6 and its soluble receptor are both elevated in schizophrenia and are associated with white matter degeneration16,17 and an increase in vCAM1.15 This implies that while neuroinflammation in schizophrenia is occurring, additional leukocytes are being recruited and secreting their own cytokines in a chronic destructive positive feedback loop. Meanwhile, atypical IL-10 levels can no longer maintain balanced levels of inflammatory molecules,16 which leads to reduced control of inflammation.
Genetics and immunohistochemistry suggest that the BBB allows the passage of excess B cells and T cells in schizophrenia. Cytokines from WBCs or the BBB during inflammation recruit these additional infiltrating lymphocytes. In gene-wide association studies, there are several genes in schizophrenia important for B cells and T cells in addition to inflammation that interact in a proinflammatory network.16 These cells are also diffusely found in the white matter18 and hippocampal tissue19 of patients with schizophrenia. Taken together, an increase in adhesion molecules, WBCs, and cytokine crosstalk supports a leaky BBB as an important component of the inflammatory model of schizophrenia.
The role of microglia in BBB dysfunction
The effect of BBB permeability on microglial activation is an important caveat in the current research. Although several reports have linked neuroinflammation to confirmed microglial activation in schizophrenia, there is not enough evidence to claim that the BBB alone is the missing link between these theories. Some research suggests that chronic release of cytokines such as IL-6 from macrophages and T cells could increase migration across the BBB for microglial activation.16,20 However, positron emission tomography has shown mixed results at best. Translocator protein (TSPO) is expressed by microglia that are actively secreting cytokines.21 Researchers tracking TSPO changes in relation to BBB alteration have not seen elevated binding in schizophrenia, change due to stage of disease course, or differentiation from low-grade inflammation.21-24 Moreover, TSPO may be confounded by antipsychotic use25 and microglial expression did not correlate with any changes in adhesion molecules.13 TSPO is not an ideal indicator of microglial activation due to BBB breakdown, but that does not bar the possibility of at least a partial contribution to the development of schizophrenia.
Corsi-Zuelli et al26 created a model that attempts to merge BBB permeability and microglial activation through a different medium—T regulatory cells (TRegs). They write that if TRegs mediate interactions between astrocytes and microglia, their hypofunction would impose a prolonged T cell response. The increased access to a high level of IL-6 and its soluble receptors may keep the TRegs hypofunctional in schizophrenia and promote T cell conversion to inflammatory cell types. Experimentally, TReg induction reversed some psychotic symptoms, and greater TReg expression was associated with fewer negative symptoms.26 In an already insufficient BBB, more access to cytokines and leukocytes would sustain inflammation and microglial secretions.
In addition to the issues described regarding the BBB, the blood-CSF barrier at the choroid plexus may also be insufficient in schizophrenia (Box27-31).
Box
The choroid plexus’ primary role is to make CSF, but it also secretes cytokines and to some extent serves as a barrier. Unlike the blood-brain barrier (BBB), the blood-CSF barrier is composed of endothelial cells with fenestrations as well as tight junctions, which make the blood-CSF barrier overall more permeable.27,28 The most unusual finding regarding the choroid plexus in schizophrenia is size. The choroid plexus is physically larger in patients with schizophrenia, and to a lesser extent, in their first-degree relatives.29 A larger choroid plexus is correlated with more severe cognitive symptoms, increased risk for psychosis via biological stress, and significantly higher interleukin-6 (IL-6).27,29 The increased thickness could be an attempt to compensate for hyperactivity and toxic processes in a permeable environment. More circulating cytokines such as IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha from microglia can trigger an increase in intercellular adhesion molecule 1, resulting in leukocyte attachment and entry.30 Less claudin-5 at the choroid plexus in schizophrenia implicates similar permissive effects as seen at the BBB.31 Although the contribution of blood-CSF barrier dysfunction to schizophrenia requires further study, reduced barrier function outside the BBB is a viable line of inquiry.
Continue to: Caveats about this research
Caveats about this research
There are 3 important points to note about the current research concerning abnormal BBB permeability:
1. BBB dysfunction may exist only in a subset of people diagnosed with schizophrenia. In most human studies, only some patients with schizophrenia demonstrated alterations that suggested pathological BBB permeability. In addition, even when there is BBB dysfunction, it could be a secondary phenomenon, rather than a primary etiologic process.
2. Patient demographics across studies have not always been adequately described. Potential confounds such as obesity, smoking, or antipsychotic use were not consistently recorded or examined as a possible factor.
3. Currently available biomarkers are not perfect. Cytokine elevation, S100B, and Q-Alb are indirect measures of BBB disruption and are found in other disorders. Therefore, they only support the theory of BBB dysfunction in schizophrenia, rather than prove it. They are also not reliable markers for schizophrenia alone. Researchers have pointed out that these markers and proteins work in concert, which necessitates a network analysis approach.16 More research regarding the details of permeability is required to establish more reliable biomarkers and tailored treatment.
Treatment implications
One of the first treatment directions that comes to mind is managing the gaps in the BBB via tight junctions. Presently, there are no FDA-approved medications for altering tight junction proteins, but researchers are exploring potential agents that can induce claudin-5 and reduce inflammation.14 While we wait for such a medication, patients may benefit from existing anti-inflammatory treatments to control immune infiltration and its products. Various anti-inflammatory agents—including cyclooxygenase inhibitors,
Bottom Line
Recent research has revealed that the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is pathologically permeable in several disease states, including schizophrenia. Better characterization of the leaky BBB in schizophrenia has enormous potential in helping us understand how current theories fit together and could serve as a missing puzzle piece in treating schizophrenia.
Related Resources
- Levine A, Strawn JR. The brain’s Twitter system: neuronal extracellular vesicles. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(6):9-11, 17-19,27. doi:10.12788/cp.0257
Drug Brand Names
Minocycline • Dynacin, Minocin
1. Li Y, Xia Y, Zhu H, et al. Investigation of neurodevelopmental deficits of 22 q11.2 deletion syndrome with a patient-iPSC-derived blood-brain barrier model. Cells. 2021;10(10):2576. doi:10.3390/cells10102576
2. Kealy J, Greene C, Campbell M. Blood-brain barrier regulation in psychiatric disorders. Neurosci Lett. 2020;726:133664. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.033
3. Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M. The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis. 2004;16(1):1-13. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2003.12.016
4. Futtrup J, Margolinsky R, Benros ME, et al. Blood-brain barrier pathology in patients with severe mental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of biomarkers in case-control studies. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020;6:100102. doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100102
5. Chen S, Tian L, Chen N, et al. Cognitive dysfunction correlates with elevated serum S100B concentration in drug-free acutely relapsed patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2017;247:6-11. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2016.09.029
6. Wu YF, Sytwu HK, Lung FW. Human aquaporin 4 gene polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with serum S100B level and negative symptoms of schizophrenia in a southern Chinese Han population. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:657. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00657
7. Greene C, Kealy J, Humphries MM, et al. Dose-dependent expression of claudin-5 is a modifying factor in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(11):2156-2166. doi:10.1038/MP.2017.156
8. Greene C, Hanley N, Campbell M. Blood-brain barrier associated tight junction disruption is a hallmark feature of major psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):373. doi:10.1038/s41398-020-01054-3
9. Kakogiannos N, Ferrari L, Giampietro C, et al. JAM-A acts via C/EBP-α to promote claudin-5 expression and enhance endothelial barrier function. Circ Res. 2020:1056-1073. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316742
10. Erickson MA, Dohi K, Banks WA. Neuroinflammation: a common pathway in CNS diseases as mediated at the blood-brain barrier. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2012;19(2):121-130. doi:10.1159/000330247
11. Ao LY, Yan YY, Zhou L, et al. Immune cells after ischemic stroke onset: roles, migration, and target intervention. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;66(3):342-355. doi:10.1007/s12031-018-1173-4
12. Meixensberger S, Kuzior H, Fiebich BL, et al. Upregulation of sICAM-1 and sVCAM-1 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(7):1134. doi:10.3390diagnostics11071134
13. Cai HQ, Catts VS, Webster MJ, et al. Increased macrophages and changed brain endothelial cell gene expression in the frontal cortex of people with schizophrenia displaying inflammation. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(4):761-775. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0235-x
14. Greene C, Hanley N, Reschke CR, et al. Microvascular stabilization via blood-brain barrier regulation prevents seizure activity. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2003. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29657-y
15. García-Juárez M, Camacho-Morales A. Defining the role of anti- and pro-inflammatory outcomes of interleukin-6 in mental health. Neuroscience. 2022;492:32-46. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.03.020
16. Pong S, Karmacharya R, Sofman M, et al. The role of brain microvascular endothelial cell and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in schizophrenia. Complex Psychiatry. 2020;6(1-2):30-46. doi:10.1159/000511552
17. Patel A, Zhu Y, Kuzhikandathil EV, et al. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor induces motor stereotypies and co-localizes with gp130 in regions linked to cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuits. PLoS One. 2012;7(7): e41623. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041623
18. Schlaaff K, Dobrowolny H, Frodl T, et al. Increased densities of T and B lymphocytes indicate neuroinflammation in subgroups of schizophrenia and mood disorder patients. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;88:497-506. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.021
19. Busse S, Busse M, Schiltz K, et al. Different distribution patterns of lymphocytes and microglia in the hippocampus of patients with residual versus paranoid schizophrenia: further evidence for disease course-related immune alterations? Brain Behav Immun. 2012;26(8):1273-1279. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2012.08.005
20. Na KS, Jung HY, Kim YK. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the neuroinflammation and neurogenesis of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014;48:277-286. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.10.022
21. Conen S, Gregory CJ, Hinz R, et al. Neuroinflammation as measured by positron emission tomography in patients with recent onset and established schizophrenia: implications for immune pathogenesis. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(9):5398-5406. doi:10.1038/S41380-020-0829-Y
22. Najjar S, Pahlajani S, De Sanctis V, et al. Neurovascular unit dysfunction and blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability contribute to schizophrenia neurobiology: a theoretical integration of clinical and experimental evidence. Front Psychiatry. 2017;8:83. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00083
23. Pinjari OF, Dasgupta SK, Okusaga OO. Plasma soluble P-selectin, interleukin-6 and S100B protein in patients with schizophrenia: a pilot study. Psychiatr Q. 2022;93(1):335-345. doi:10.1007/s11126-021-09954-3
24. Di Biase MA, Zalesky A, O’keefe G, et al. PET imaging of putative microglial activation in individuals at ultra-high risk for psychosis, recently diagnosed and chronically ill with schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7(8):e1225. doi:10.1038/tp.2017.193
25. Holmes SE, Hinz R, Drake RJ, et al. In vivo imaging of brain microglial activity in antipsychotic-free and medicated schizophrenia: a [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(12):1672-1679. doi:10.1038/mp.2016.180
26. Corsi-Zuelli F, Deakin B, de Lima MHF, et al. T regulatory cells as a potential therapeutic target in psychosis? Current challenges and future perspectives. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021;17:100330. doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100330
27. Bannai D, Lutz O, Lizano P. Neuroimaging considerations when investigating choroid plexus morphology in idiopathic psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2020;224:19-21. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2020.07.013
28. Hladky SB, Barrand MA. Fluid and ion transfer across the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers; a comparative account of mechanisms and roles. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016;13(1):19. doi:10.1186/s12987-016-0040-3
29. Lizano P, Lutz O, Ling G, et al. Association of choroid plexus enlargement with cognitive, inflammatory, and structural phenotypes across the psychosis spectrum. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(7):564-572. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18070825
30. Castellani G, Contarini G, Mereu M, et al. Dopamine-mediated immunomodulation affects choroid plexus function. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;81:138-150. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2019.06.006
31. Bitanihirwe BKY, Lizano P, Woo TW. Deconstructing the functional neuroanatomy of the choroid plexus: an ontogenetic perspective for studying neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;1-10. doi:10.1038/s41380-022-01623-6
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an essential barrier of closely spaced cells that regulates entry into the CNS. What passes should be highly regulated to protect the brain from potentially harmful peripheral cells or molecules from the rest of the body. However, research has revealed that the BBB is pathologically permeable in several disease states, including schizophrenia, epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, autism, and DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome, which often presents with symptoms of schizophrenia).1,2 In this article, we discuss potential markers of BBB dysfunction, the consequences of a porous BBB, the effect of BBB permeability on microglial activation, and possible treatment implications.
Detecting a BBB leak
The BBB is composed of microvascular endothelial cell units. Adherens junctions, astrocyte endfeet, and pericytes are all part of these units, but tight junctions have the most significant role in BBB barrier function. Tight junction protein composition varies depending on the location of the endothelium. In the BBB, they are primarily composed of claudin-5, occludin, zonulin, and junction adhesion molecules (JAMs) (Figure). Claudins and occludins are especially important components of the tight junction because they span plasma membranes.3

Researchers began to suspect tight junction permeability in schizophrenia while searching for schizophrenia biomarkers. For example, S100B is a marker of astrocytic reactivity to damage. It is increased in schizophrenia, major depressive disorder, and bipolar disorder.4 Studies found elevated S100B specifically in drug-free patients with schizophrenia,5 which prompted research suggesting it could predict the severity of negative symptoms.6 The accuracy of S100B as a biomarker was later complicated by the finding that adipose tissue also secretes S100B. This is problematic due to the high rates of comorbid obesity in psychiatric populations.2
Perhaps a better biomarker is the ratio of albumin in the CSF vs that in peripheral serum. The CSF-to-blood albumin ratio (Q-Alb) is widely considered an acceptable marker of BBB dysfunction because albumin must cross the BBB to alter the ratio. Studies have found a high Q-Alb in neurodegenerative disorders such as multiple sclerosis as well as in schizophrenia, which suggests that some level of BBB dysfunction is occurring. Although the Q-Alb may change slightly when confounded by antipsychotic use or with CSF flow changes,2,4 both S100B and Q-Alb elevation are sufficient for further investigation into tight junction alteration in schizophrenia.
Claudin-5 is a promising factor in detecting BBB permeability. Claudin-5 is deleted in DiGeorge syndrome, which is highly comorbid with schizophrenia and psychosis.1 Mouse knockdown studies show that full suppression of claudin-5 results in psychotic symptoms before fatal seizures,2,7 but a partial absence may enable psychotic symptoms. The same study showed that normally continuous claudin-5 was patchy along blood vessels in the affected sample.7 Follow-up experiments suggest that loss of claudin-5 in schizophrenia is especially prominent in the hippocampus, and there is mixed evidence of a decrease in the prefrontal cortex.8
Outside of claudin-5 alone, JAM-A plays a more regulatory role. It is upstream from an enhancer protein gene that serves as a transcription factor for the claudin-5 promoter, so when JAM-A is deleted, there is less claudin-5.9 However, while this decrease in claudin-5 may be pathological, there could still be various upstream changes that lead to schizophrenia.
What are the consequences of a porous BBB?
Although it is well established that the BBB passes small molecules and solutes, there is significant evidence of inflammatory trafficking in disease states. The BBB moves proinflammatory cytokines, alters transporters, and may even let white blood cells (WBCs) pass through. Immune cell infiltration has different requirements depending on the cell type. T cells rely on integrins, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (vCAM1), and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (iCAM1) for binding, rolling, adhering, crossing, and migration to sites of inflammation.10,11 Both iCAM1 and vCAM1 are elevated in schizophrenia compared to other psychiatric disorders (such as unipolar depression) and correlate with other biomarkers. For example, vCAM1, responsible for recruitment and crossing, is correlated with a high Q-Alb.12 Primarily produced by astrocytes and endothelial cells, iCAM1 plays the largest role in crossing the BBB and migration. Postmortem tissue demonstrates that cytokines upregulate iCAM1 mRNA at the BBB in schizophrenia.13 Increased cytokines are well documented in the inflammatory model of schizophrenia. Interestingly, decreasing claudin-5 also upregulates iCAM1 production.14 Therefore, low baseline claudin-5 may contribute to additional inflammation and symptoms.
Continue to: BBB permeability also results...
BBB permeability also results in a certain pattern of leukocyte and cytokine activity. Interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha can all cross the BBB during neuroimmune inflammation,10 but there are abnormal heightened and sustained responses of these molecules in schizophrenia. IL-6 is a proinflammatory cytokine in both acute and chronic inflammation that is expressed by astrocytes, endothelial cells, and microglia.15 IL-6 and its soluble receptor are both elevated in schizophrenia and are associated with white matter degeneration16,17 and an increase in vCAM1.15 This implies that while neuroinflammation in schizophrenia is occurring, additional leukocytes are being recruited and secreting their own cytokines in a chronic destructive positive feedback loop. Meanwhile, atypical IL-10 levels can no longer maintain balanced levels of inflammatory molecules,16 which leads to reduced control of inflammation.
Genetics and immunohistochemistry suggest that the BBB allows the passage of excess B cells and T cells in schizophrenia. Cytokines from WBCs or the BBB during inflammation recruit these additional infiltrating lymphocytes. In gene-wide association studies, there are several genes in schizophrenia important for B cells and T cells in addition to inflammation that interact in a proinflammatory network.16 These cells are also diffusely found in the white matter18 and hippocampal tissue19 of patients with schizophrenia. Taken together, an increase in adhesion molecules, WBCs, and cytokine crosstalk supports a leaky BBB as an important component of the inflammatory model of schizophrenia.
The role of microglia in BBB dysfunction
The effect of BBB permeability on microglial activation is an important caveat in the current research. Although several reports have linked neuroinflammation to confirmed microglial activation in schizophrenia, there is not enough evidence to claim that the BBB alone is the missing link between these theories. Some research suggests that chronic release of cytokines such as IL-6 from macrophages and T cells could increase migration across the BBB for microglial activation.16,20 However, positron emission tomography has shown mixed results at best. Translocator protein (TSPO) is expressed by microglia that are actively secreting cytokines.21 Researchers tracking TSPO changes in relation to BBB alteration have not seen elevated binding in schizophrenia, change due to stage of disease course, or differentiation from low-grade inflammation.21-24 Moreover, TSPO may be confounded by antipsychotic use25 and microglial expression did not correlate with any changes in adhesion molecules.13 TSPO is not an ideal indicator of microglial activation due to BBB breakdown, but that does not bar the possibility of at least a partial contribution to the development of schizophrenia.
Corsi-Zuelli et al26 created a model that attempts to merge BBB permeability and microglial activation through a different medium—T regulatory cells (TRegs). They write that if TRegs mediate interactions between astrocytes and microglia, their hypofunction would impose a prolonged T cell response. The increased access to a high level of IL-6 and its soluble receptors may keep the TRegs hypofunctional in schizophrenia and promote T cell conversion to inflammatory cell types. Experimentally, TReg induction reversed some psychotic symptoms, and greater TReg expression was associated with fewer negative symptoms.26 In an already insufficient BBB, more access to cytokines and leukocytes would sustain inflammation and microglial secretions.
In addition to the issues described regarding the BBB, the blood-CSF barrier at the choroid plexus may also be insufficient in schizophrenia (Box27-31).
Box
The choroid plexus’ primary role is to make CSF, but it also secretes cytokines and to some extent serves as a barrier. Unlike the blood-brain barrier (BBB), the blood-CSF barrier is composed of endothelial cells with fenestrations as well as tight junctions, which make the blood-CSF barrier overall more permeable.27,28 The most unusual finding regarding the choroid plexus in schizophrenia is size. The choroid plexus is physically larger in patients with schizophrenia, and to a lesser extent, in their first-degree relatives.29 A larger choroid plexus is correlated with more severe cognitive symptoms, increased risk for psychosis via biological stress, and significantly higher interleukin-6 (IL-6).27,29 The increased thickness could be an attempt to compensate for hyperactivity and toxic processes in a permeable environment. More circulating cytokines such as IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha from microglia can trigger an increase in intercellular adhesion molecule 1, resulting in leukocyte attachment and entry.30 Less claudin-5 at the choroid plexus in schizophrenia implicates similar permissive effects as seen at the BBB.31 Although the contribution of blood-CSF barrier dysfunction to schizophrenia requires further study, reduced barrier function outside the BBB is a viable line of inquiry.
Continue to: Caveats about this research
Caveats about this research
There are 3 important points to note about the current research concerning abnormal BBB permeability:
1. BBB dysfunction may exist only in a subset of people diagnosed with schizophrenia. In most human studies, only some patients with schizophrenia demonstrated alterations that suggested pathological BBB permeability. In addition, even when there is BBB dysfunction, it could be a secondary phenomenon, rather than a primary etiologic process.
2. Patient demographics across studies have not always been adequately described. Potential confounds such as obesity, smoking, or antipsychotic use were not consistently recorded or examined as a possible factor.
3. Currently available biomarkers are not perfect. Cytokine elevation, S100B, and Q-Alb are indirect measures of BBB disruption and are found in other disorders. Therefore, they only support the theory of BBB dysfunction in schizophrenia, rather than prove it. They are also not reliable markers for schizophrenia alone. Researchers have pointed out that these markers and proteins work in concert, which necessitates a network analysis approach.16 More research regarding the details of permeability is required to establish more reliable biomarkers and tailored treatment.
Treatment implications
One of the first treatment directions that comes to mind is managing the gaps in the BBB via tight junctions. Presently, there are no FDA-approved medications for altering tight junction proteins, but researchers are exploring potential agents that can induce claudin-5 and reduce inflammation.14 While we wait for such a medication, patients may benefit from existing anti-inflammatory treatments to control immune infiltration and its products. Various anti-inflammatory agents—including cyclooxygenase inhibitors,
Bottom Line
Recent research has revealed that the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is pathologically permeable in several disease states, including schizophrenia. Better characterization of the leaky BBB in schizophrenia has enormous potential in helping us understand how current theories fit together and could serve as a missing puzzle piece in treating schizophrenia.
Related Resources
- Levine A, Strawn JR. The brain’s Twitter system: neuronal extracellular vesicles. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(6):9-11, 17-19,27. doi:10.12788/cp.0257
Drug Brand Names
Minocycline • Dynacin, Minocin
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an essential barrier of closely spaced cells that regulates entry into the CNS. What passes should be highly regulated to protect the brain from potentially harmful peripheral cells or molecules from the rest of the body. However, research has revealed that the BBB is pathologically permeable in several disease states, including schizophrenia, epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, autism, and DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome, which often presents with symptoms of schizophrenia).1,2 In this article, we discuss potential markers of BBB dysfunction, the consequences of a porous BBB, the effect of BBB permeability on microglial activation, and possible treatment implications.
Detecting a BBB leak
The BBB is composed of microvascular endothelial cell units. Adherens junctions, astrocyte endfeet, and pericytes are all part of these units, but tight junctions have the most significant role in BBB barrier function. Tight junction protein composition varies depending on the location of the endothelium. In the BBB, they are primarily composed of claudin-5, occludin, zonulin, and junction adhesion molecules (JAMs) (Figure). Claudins and occludins are especially important components of the tight junction because they span plasma membranes.3

Researchers began to suspect tight junction permeability in schizophrenia while searching for schizophrenia biomarkers. For example, S100B is a marker of astrocytic reactivity to damage. It is increased in schizophrenia, major depressive disorder, and bipolar disorder.4 Studies found elevated S100B specifically in drug-free patients with schizophrenia,5 which prompted research suggesting it could predict the severity of negative symptoms.6 The accuracy of S100B as a biomarker was later complicated by the finding that adipose tissue also secretes S100B. This is problematic due to the high rates of comorbid obesity in psychiatric populations.2
Perhaps a better biomarker is the ratio of albumin in the CSF vs that in peripheral serum. The CSF-to-blood albumin ratio (Q-Alb) is widely considered an acceptable marker of BBB dysfunction because albumin must cross the BBB to alter the ratio. Studies have found a high Q-Alb in neurodegenerative disorders such as multiple sclerosis as well as in schizophrenia, which suggests that some level of BBB dysfunction is occurring. Although the Q-Alb may change slightly when confounded by antipsychotic use or with CSF flow changes,2,4 both S100B and Q-Alb elevation are sufficient for further investigation into tight junction alteration in schizophrenia.
Claudin-5 is a promising factor in detecting BBB permeability. Claudin-5 is deleted in DiGeorge syndrome, which is highly comorbid with schizophrenia and psychosis.1 Mouse knockdown studies show that full suppression of claudin-5 results in psychotic symptoms before fatal seizures,2,7 but a partial absence may enable psychotic symptoms. The same study showed that normally continuous claudin-5 was patchy along blood vessels in the affected sample.7 Follow-up experiments suggest that loss of claudin-5 in schizophrenia is especially prominent in the hippocampus, and there is mixed evidence of a decrease in the prefrontal cortex.8
Outside of claudin-5 alone, JAM-A plays a more regulatory role. It is upstream from an enhancer protein gene that serves as a transcription factor for the claudin-5 promoter, so when JAM-A is deleted, there is less claudin-5.9 However, while this decrease in claudin-5 may be pathological, there could still be various upstream changes that lead to schizophrenia.
What are the consequences of a porous BBB?
Although it is well established that the BBB passes small molecules and solutes, there is significant evidence of inflammatory trafficking in disease states. The BBB moves proinflammatory cytokines, alters transporters, and may even let white blood cells (WBCs) pass through. Immune cell infiltration has different requirements depending on the cell type. T cells rely on integrins, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (vCAM1), and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (iCAM1) for binding, rolling, adhering, crossing, and migration to sites of inflammation.10,11 Both iCAM1 and vCAM1 are elevated in schizophrenia compared to other psychiatric disorders (such as unipolar depression) and correlate with other biomarkers. For example, vCAM1, responsible for recruitment and crossing, is correlated with a high Q-Alb.12 Primarily produced by astrocytes and endothelial cells, iCAM1 plays the largest role in crossing the BBB and migration. Postmortem tissue demonstrates that cytokines upregulate iCAM1 mRNA at the BBB in schizophrenia.13 Increased cytokines are well documented in the inflammatory model of schizophrenia. Interestingly, decreasing claudin-5 also upregulates iCAM1 production.14 Therefore, low baseline claudin-5 may contribute to additional inflammation and symptoms.
Continue to: BBB permeability also results...
BBB permeability also results in a certain pattern of leukocyte and cytokine activity. Interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor–alpha can all cross the BBB during neuroimmune inflammation,10 but there are abnormal heightened and sustained responses of these molecules in schizophrenia. IL-6 is a proinflammatory cytokine in both acute and chronic inflammation that is expressed by astrocytes, endothelial cells, and microglia.15 IL-6 and its soluble receptor are both elevated in schizophrenia and are associated with white matter degeneration16,17 and an increase in vCAM1.15 This implies that while neuroinflammation in schizophrenia is occurring, additional leukocytes are being recruited and secreting their own cytokines in a chronic destructive positive feedback loop. Meanwhile, atypical IL-10 levels can no longer maintain balanced levels of inflammatory molecules,16 which leads to reduced control of inflammation.
Genetics and immunohistochemistry suggest that the BBB allows the passage of excess B cells and T cells in schizophrenia. Cytokines from WBCs or the BBB during inflammation recruit these additional infiltrating lymphocytes. In gene-wide association studies, there are several genes in schizophrenia important for B cells and T cells in addition to inflammation that interact in a proinflammatory network.16 These cells are also diffusely found in the white matter18 and hippocampal tissue19 of patients with schizophrenia. Taken together, an increase in adhesion molecules, WBCs, and cytokine crosstalk supports a leaky BBB as an important component of the inflammatory model of schizophrenia.
The role of microglia in BBB dysfunction
The effect of BBB permeability on microglial activation is an important caveat in the current research. Although several reports have linked neuroinflammation to confirmed microglial activation in schizophrenia, there is not enough evidence to claim that the BBB alone is the missing link between these theories. Some research suggests that chronic release of cytokines such as IL-6 from macrophages and T cells could increase migration across the BBB for microglial activation.16,20 However, positron emission tomography has shown mixed results at best. Translocator protein (TSPO) is expressed by microglia that are actively secreting cytokines.21 Researchers tracking TSPO changes in relation to BBB alteration have not seen elevated binding in schizophrenia, change due to stage of disease course, or differentiation from low-grade inflammation.21-24 Moreover, TSPO may be confounded by antipsychotic use25 and microglial expression did not correlate with any changes in adhesion molecules.13 TSPO is not an ideal indicator of microglial activation due to BBB breakdown, but that does not bar the possibility of at least a partial contribution to the development of schizophrenia.
Corsi-Zuelli et al26 created a model that attempts to merge BBB permeability and microglial activation through a different medium—T regulatory cells (TRegs). They write that if TRegs mediate interactions between astrocytes and microglia, their hypofunction would impose a prolonged T cell response. The increased access to a high level of IL-6 and its soluble receptors may keep the TRegs hypofunctional in schizophrenia and promote T cell conversion to inflammatory cell types. Experimentally, TReg induction reversed some psychotic symptoms, and greater TReg expression was associated with fewer negative symptoms.26 In an already insufficient BBB, more access to cytokines and leukocytes would sustain inflammation and microglial secretions.
In addition to the issues described regarding the BBB, the blood-CSF barrier at the choroid plexus may also be insufficient in schizophrenia (Box27-31).
Box
The choroid plexus’ primary role is to make CSF, but it also secretes cytokines and to some extent serves as a barrier. Unlike the blood-brain barrier (BBB), the blood-CSF barrier is composed of endothelial cells with fenestrations as well as tight junctions, which make the blood-CSF barrier overall more permeable.27,28 The most unusual finding regarding the choroid plexus in schizophrenia is size. The choroid plexus is physically larger in patients with schizophrenia, and to a lesser extent, in their first-degree relatives.29 A larger choroid plexus is correlated with more severe cognitive symptoms, increased risk for psychosis via biological stress, and significantly higher interleukin-6 (IL-6).27,29 The increased thickness could be an attempt to compensate for hyperactivity and toxic processes in a permeable environment. More circulating cytokines such as IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha from microglia can trigger an increase in intercellular adhesion molecule 1, resulting in leukocyte attachment and entry.30 Less claudin-5 at the choroid plexus in schizophrenia implicates similar permissive effects as seen at the BBB.31 Although the contribution of blood-CSF barrier dysfunction to schizophrenia requires further study, reduced barrier function outside the BBB is a viable line of inquiry.
Continue to: Caveats about this research
Caveats about this research
There are 3 important points to note about the current research concerning abnormal BBB permeability:
1. BBB dysfunction may exist only in a subset of people diagnosed with schizophrenia. In most human studies, only some patients with schizophrenia demonstrated alterations that suggested pathological BBB permeability. In addition, even when there is BBB dysfunction, it could be a secondary phenomenon, rather than a primary etiologic process.
2. Patient demographics across studies have not always been adequately described. Potential confounds such as obesity, smoking, or antipsychotic use were not consistently recorded or examined as a possible factor.
3. Currently available biomarkers are not perfect. Cytokine elevation, S100B, and Q-Alb are indirect measures of BBB disruption and are found in other disorders. Therefore, they only support the theory of BBB dysfunction in schizophrenia, rather than prove it. They are also not reliable markers for schizophrenia alone. Researchers have pointed out that these markers and proteins work in concert, which necessitates a network analysis approach.16 More research regarding the details of permeability is required to establish more reliable biomarkers and tailored treatment.
Treatment implications
One of the first treatment directions that comes to mind is managing the gaps in the BBB via tight junctions. Presently, there are no FDA-approved medications for altering tight junction proteins, but researchers are exploring potential agents that can induce claudin-5 and reduce inflammation.14 While we wait for such a medication, patients may benefit from existing anti-inflammatory treatments to control immune infiltration and its products. Various anti-inflammatory agents—including cyclooxygenase inhibitors,
Bottom Line
Recent research has revealed that the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is pathologically permeable in several disease states, including schizophrenia. Better characterization of the leaky BBB in schizophrenia has enormous potential in helping us understand how current theories fit together and could serve as a missing puzzle piece in treating schizophrenia.
Related Resources
- Levine A, Strawn JR. The brain’s Twitter system: neuronal extracellular vesicles. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(6):9-11, 17-19,27. doi:10.12788/cp.0257
Drug Brand Names
Minocycline • Dynacin, Minocin
1. Li Y, Xia Y, Zhu H, et al. Investigation of neurodevelopmental deficits of 22 q11.2 deletion syndrome with a patient-iPSC-derived blood-brain barrier model. Cells. 2021;10(10):2576. doi:10.3390/cells10102576
2. Kealy J, Greene C, Campbell M. Blood-brain barrier regulation in psychiatric disorders. Neurosci Lett. 2020;726:133664. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.033
3. Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M. The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis. 2004;16(1):1-13. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2003.12.016
4. Futtrup J, Margolinsky R, Benros ME, et al. Blood-brain barrier pathology in patients with severe mental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of biomarkers in case-control studies. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020;6:100102. doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100102
5. Chen S, Tian L, Chen N, et al. Cognitive dysfunction correlates with elevated serum S100B concentration in drug-free acutely relapsed patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2017;247:6-11. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2016.09.029
6. Wu YF, Sytwu HK, Lung FW. Human aquaporin 4 gene polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with serum S100B level and negative symptoms of schizophrenia in a southern Chinese Han population. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:657. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00657
7. Greene C, Kealy J, Humphries MM, et al. Dose-dependent expression of claudin-5 is a modifying factor in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(11):2156-2166. doi:10.1038/MP.2017.156
8. Greene C, Hanley N, Campbell M. Blood-brain barrier associated tight junction disruption is a hallmark feature of major psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):373. doi:10.1038/s41398-020-01054-3
9. Kakogiannos N, Ferrari L, Giampietro C, et al. JAM-A acts via C/EBP-α to promote claudin-5 expression and enhance endothelial barrier function. Circ Res. 2020:1056-1073. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316742
10. Erickson MA, Dohi K, Banks WA. Neuroinflammation: a common pathway in CNS diseases as mediated at the blood-brain barrier. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2012;19(2):121-130. doi:10.1159/000330247
11. Ao LY, Yan YY, Zhou L, et al. Immune cells after ischemic stroke onset: roles, migration, and target intervention. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;66(3):342-355. doi:10.1007/s12031-018-1173-4
12. Meixensberger S, Kuzior H, Fiebich BL, et al. Upregulation of sICAM-1 and sVCAM-1 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(7):1134. doi:10.3390diagnostics11071134
13. Cai HQ, Catts VS, Webster MJ, et al. Increased macrophages and changed brain endothelial cell gene expression in the frontal cortex of people with schizophrenia displaying inflammation. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(4):761-775. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0235-x
14. Greene C, Hanley N, Reschke CR, et al. Microvascular stabilization via blood-brain barrier regulation prevents seizure activity. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2003. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29657-y
15. García-Juárez M, Camacho-Morales A. Defining the role of anti- and pro-inflammatory outcomes of interleukin-6 in mental health. Neuroscience. 2022;492:32-46. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.03.020
16. Pong S, Karmacharya R, Sofman M, et al. The role of brain microvascular endothelial cell and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in schizophrenia. Complex Psychiatry. 2020;6(1-2):30-46. doi:10.1159/000511552
17. Patel A, Zhu Y, Kuzhikandathil EV, et al. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor induces motor stereotypies and co-localizes with gp130 in regions linked to cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuits. PLoS One. 2012;7(7): e41623. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041623
18. Schlaaff K, Dobrowolny H, Frodl T, et al. Increased densities of T and B lymphocytes indicate neuroinflammation in subgroups of schizophrenia and mood disorder patients. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;88:497-506. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.021
19. Busse S, Busse M, Schiltz K, et al. Different distribution patterns of lymphocytes and microglia in the hippocampus of patients with residual versus paranoid schizophrenia: further evidence for disease course-related immune alterations? Brain Behav Immun. 2012;26(8):1273-1279. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2012.08.005
20. Na KS, Jung HY, Kim YK. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the neuroinflammation and neurogenesis of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014;48:277-286. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.10.022
21. Conen S, Gregory CJ, Hinz R, et al. Neuroinflammation as measured by positron emission tomography in patients with recent onset and established schizophrenia: implications for immune pathogenesis. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(9):5398-5406. doi:10.1038/S41380-020-0829-Y
22. Najjar S, Pahlajani S, De Sanctis V, et al. Neurovascular unit dysfunction and blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability contribute to schizophrenia neurobiology: a theoretical integration of clinical and experimental evidence. Front Psychiatry. 2017;8:83. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00083
23. Pinjari OF, Dasgupta SK, Okusaga OO. Plasma soluble P-selectin, interleukin-6 and S100B protein in patients with schizophrenia: a pilot study. Psychiatr Q. 2022;93(1):335-345. doi:10.1007/s11126-021-09954-3
24. Di Biase MA, Zalesky A, O’keefe G, et al. PET imaging of putative microglial activation in individuals at ultra-high risk for psychosis, recently diagnosed and chronically ill with schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7(8):e1225. doi:10.1038/tp.2017.193
25. Holmes SE, Hinz R, Drake RJ, et al. In vivo imaging of brain microglial activity in antipsychotic-free and medicated schizophrenia: a [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(12):1672-1679. doi:10.1038/mp.2016.180
26. Corsi-Zuelli F, Deakin B, de Lima MHF, et al. T regulatory cells as a potential therapeutic target in psychosis? Current challenges and future perspectives. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021;17:100330. doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100330
27. Bannai D, Lutz O, Lizano P. Neuroimaging considerations when investigating choroid plexus morphology in idiopathic psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2020;224:19-21. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2020.07.013
28. Hladky SB, Barrand MA. Fluid and ion transfer across the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers; a comparative account of mechanisms and roles. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016;13(1):19. doi:10.1186/s12987-016-0040-3
29. Lizano P, Lutz O, Ling G, et al. Association of choroid plexus enlargement with cognitive, inflammatory, and structural phenotypes across the psychosis spectrum. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(7):564-572. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18070825
30. Castellani G, Contarini G, Mereu M, et al. Dopamine-mediated immunomodulation affects choroid plexus function. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;81:138-150. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2019.06.006
31. Bitanihirwe BKY, Lizano P, Woo TW. Deconstructing the functional neuroanatomy of the choroid plexus: an ontogenetic perspective for studying neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;1-10. doi:10.1038/s41380-022-01623-6
1. Li Y, Xia Y, Zhu H, et al. Investigation of neurodevelopmental deficits of 22 q11.2 deletion syndrome with a patient-iPSC-derived blood-brain barrier model. Cells. 2021;10(10):2576. doi:10.3390/cells10102576
2. Kealy J, Greene C, Campbell M. Blood-brain barrier regulation in psychiatric disorders. Neurosci Lett. 2020;726:133664. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.033
3. Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M. The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis. 2004;16(1):1-13. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2003.12.016
4. Futtrup J, Margolinsky R, Benros ME, et al. Blood-brain barrier pathology in patients with severe mental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of biomarkers in case-control studies. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020;6:100102. doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100102
5. Chen S, Tian L, Chen N, et al. Cognitive dysfunction correlates with elevated serum S100B concentration in drug-free acutely relapsed patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2017;247:6-11. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2016.09.029
6. Wu YF, Sytwu HK, Lung FW. Human aquaporin 4 gene polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with serum S100B level and negative symptoms of schizophrenia in a southern Chinese Han population. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:657. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00657
7. Greene C, Kealy J, Humphries MM, et al. Dose-dependent expression of claudin-5 is a modifying factor in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(11):2156-2166. doi:10.1038/MP.2017.156
8. Greene C, Hanley N, Campbell M. Blood-brain barrier associated tight junction disruption is a hallmark feature of major psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):373. doi:10.1038/s41398-020-01054-3
9. Kakogiannos N, Ferrari L, Giampietro C, et al. JAM-A acts via C/EBP-α to promote claudin-5 expression and enhance endothelial barrier function. Circ Res. 2020:1056-1073. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316742
10. Erickson MA, Dohi K, Banks WA. Neuroinflammation: a common pathway in CNS diseases as mediated at the blood-brain barrier. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2012;19(2):121-130. doi:10.1159/000330247
11. Ao LY, Yan YY, Zhou L, et al. Immune cells after ischemic stroke onset: roles, migration, and target intervention. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;66(3):342-355. doi:10.1007/s12031-018-1173-4
12. Meixensberger S, Kuzior H, Fiebich BL, et al. Upregulation of sICAM-1 and sVCAM-1 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(7):1134. doi:10.3390diagnostics11071134
13. Cai HQ, Catts VS, Webster MJ, et al. Increased macrophages and changed brain endothelial cell gene expression in the frontal cortex of people with schizophrenia displaying inflammation. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(4):761-775. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0235-x
14. Greene C, Hanley N, Reschke CR, et al. Microvascular stabilization via blood-brain barrier regulation prevents seizure activity. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2003. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29657-y
15. García-Juárez M, Camacho-Morales A. Defining the role of anti- and pro-inflammatory outcomes of interleukin-6 in mental health. Neuroscience. 2022;492:32-46. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.03.020
16. Pong S, Karmacharya R, Sofman M, et al. The role of brain microvascular endothelial cell and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in schizophrenia. Complex Psychiatry. 2020;6(1-2):30-46. doi:10.1159/000511552
17. Patel A, Zhu Y, Kuzhikandathil EV, et al. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor induces motor stereotypies and co-localizes with gp130 in regions linked to cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuits. PLoS One. 2012;7(7): e41623. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041623
18. Schlaaff K, Dobrowolny H, Frodl T, et al. Increased densities of T and B lymphocytes indicate neuroinflammation in subgroups of schizophrenia and mood disorder patients. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;88:497-506. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.021
19. Busse S, Busse M, Schiltz K, et al. Different distribution patterns of lymphocytes and microglia in the hippocampus of patients with residual versus paranoid schizophrenia: further evidence for disease course-related immune alterations? Brain Behav Immun. 2012;26(8):1273-1279. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2012.08.005
20. Na KS, Jung HY, Kim YK. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the neuroinflammation and neurogenesis of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014;48:277-286. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.10.022
21. Conen S, Gregory CJ, Hinz R, et al. Neuroinflammation as measured by positron emission tomography in patients with recent onset and established schizophrenia: implications for immune pathogenesis. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(9):5398-5406. doi:10.1038/S41380-020-0829-Y
22. Najjar S, Pahlajani S, De Sanctis V, et al. Neurovascular unit dysfunction and blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability contribute to schizophrenia neurobiology: a theoretical integration of clinical and experimental evidence. Front Psychiatry. 2017;8:83. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00083
23. Pinjari OF, Dasgupta SK, Okusaga OO. Plasma soluble P-selectin, interleukin-6 and S100B protein in patients with schizophrenia: a pilot study. Psychiatr Q. 2022;93(1):335-345. doi:10.1007/s11126-021-09954-3
24. Di Biase MA, Zalesky A, O’keefe G, et al. PET imaging of putative microglial activation in individuals at ultra-high risk for psychosis, recently diagnosed and chronically ill with schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7(8):e1225. doi:10.1038/tp.2017.193
25. Holmes SE, Hinz R, Drake RJ, et al. In vivo imaging of brain microglial activity in antipsychotic-free and medicated schizophrenia: a [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(12):1672-1679. doi:10.1038/mp.2016.180
26. Corsi-Zuelli F, Deakin B, de Lima MHF, et al. T regulatory cells as a potential therapeutic target in psychosis? Current challenges and future perspectives. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021;17:100330. doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100330
27. Bannai D, Lutz O, Lizano P. Neuroimaging considerations when investigating choroid plexus morphology in idiopathic psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2020;224:19-21. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2020.07.013
28. Hladky SB, Barrand MA. Fluid and ion transfer across the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers; a comparative account of mechanisms and roles. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016;13(1):19. doi:10.1186/s12987-016-0040-3
29. Lizano P, Lutz O, Ling G, et al. Association of choroid plexus enlargement with cognitive, inflammatory, and structural phenotypes across the psychosis spectrum. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(7):564-572. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18070825
30. Castellani G, Contarini G, Mereu M, et al. Dopamine-mediated immunomodulation affects choroid plexus function. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;81:138-150. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2019.06.006
31. Bitanihirwe BKY, Lizano P, Woo TW. Deconstructing the functional neuroanatomy of the choroid plexus: an ontogenetic perspective for studying neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;1-10. doi:10.1038/s41380-022-01623-6
Generalized anxiety disorder: 8 studies of psychosocial interventions
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
For patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), the intensity, duration, and frequency of an individual’s anxiety and worry are out of proportion to the actual likelihood or impact of an anticipated event, and they often find it difficult to prevent worrisome thoughts from interfering with daily life.1 Successful treatment for GAD is patient-specific and requires clinicians to consider all available psychotherapeutic and pharmacologic options.
In a 2020 meta-analysis of 79 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 11,002 participants diagnosed with GAD, Carl et al2 focused on pooled effect sizes of evidence-based psychotherapies and medications for GAD. Their analysis showed a medium to large effect size (Hedges g = 0.76) for psychotherapy, compared to a small effect size (Hedges g = 0.38) for medication on GAD outcomes. Other meta-analyses have shown that evidence-based psychotherapies have large effect sizes on GAD outcomes.3
However, in most of the studies included in these meta-analyses, the 2 treatment modalities—psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy—use different control types. The pharmacotherapy trials used a placebo, while psychotherapy studies often had a waitlist control. Thus, the findings of these meta-analyses should not lead to the conclusion that psychotherapy is necessarily more effective for GAD symptoms than pharmacotherapy. However, there is clear evidence that psychosocial interventions are at least as effective as medications for treating GAD. Also, patients often prefer psychosocial treatment over medication.
Part 1 (
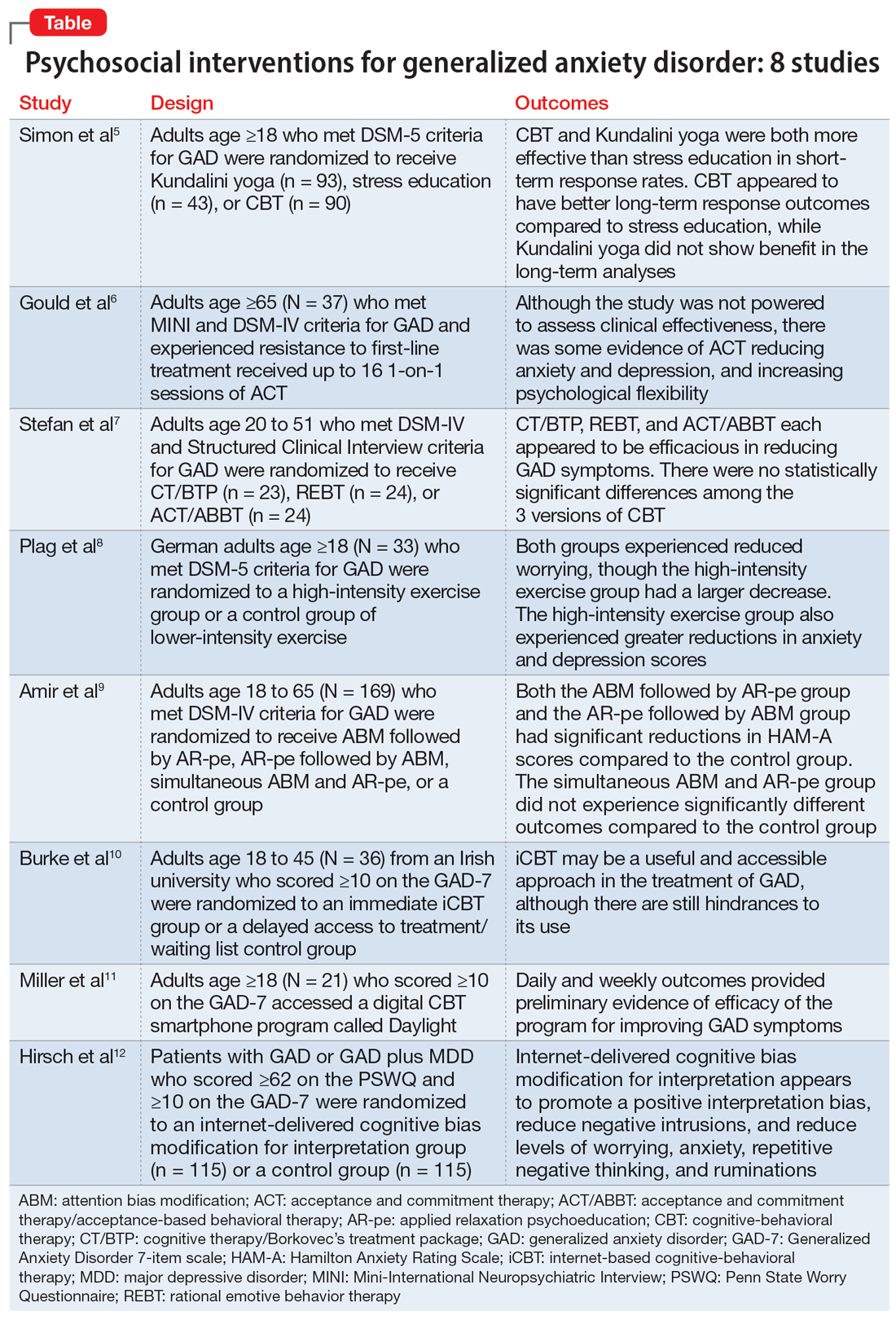
1. Simon NM, Hofmann SG, Rosenfield D, et al. Efficacy of yoga vs cognitive behavioral therapy vs stress education for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(1):13-20. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.2496
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a first-line therapy for GAD.13 However, patients may not pursue CBT due to fiscal and logistical constraints, as well as the stigma associated with it. Yoga is a common complementary health practice used by adults in the United States,14 although evidence has been inconclusive for its use in treating anxiety. Simon et al5 examined the efficacy of Kundalini yoga (KY) vs stress education (SE) and CBT for treating GAD.
Study design
- A prospective, parallel-group, randomized-controlled, single-blind trial in 2 academic centers evaluated 226 adults age ≥18 who met DSM-5 criteria for GAD.
- Participants were randomized into 3 groups: KY (n = 93), SE (n = 43), or CBT (n = 90), and monitored for 12 weeks to determine the efficacy of each therapy.
- Exclusion criteria included current posttraumatic stress disorder, eating disorders, substance use disorders, significant suicidal ideation, mental disorder due to a medical or neurocognitive condition, lifetime psychosis, bipolar disorder (BD), developmental disorders, and having completed more than 5 yoga or CBT sessions in the past 5 years. Additionally, patients were either not taking medication for ≥2 weeks prior to the trial or had a stable regimen for ≥6 weeks.
- Each therapy was guided by 2 instructors during 12 120-minute sessions with 20 minutes of daily assignments and presented in cohorts of 4 to 6 participants.
- The primary outcome was an improvement in score on the Clinical Global Impression–Improvement scale from baseline at Week 12. Secondary measures included scores on the Meta-Cognitions Questionnaire and the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire.
Outcomes
- A total of 155 participants finished the posttreatment assessment, with similar completion rates between the groups, and 123 participants completed the 6-month follow-up assessment.
- The KY group had a significantly higher response rate (54.2%) than the SE group (33%) at posttreatment, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of 4.59. At 6-month follow-up, the response rate in the KY group was not significantly higher than that of the SE group.
- The CBT group had a significantly higher response rate (70.8%) than the SE group (33%) at posttreatment, with a NNT of 2.62. At 6-month follow-up, the CBT response rate (76.7%) was significantly higher than the SE group (48%), with a NNT of 3.51.
- KY was not found to be as effective as CBT on noninferiority testing.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- CBT and KY were both more effective than SE as assessed by short-term response rates.
- The authors did not find KY to be as effective as CBT at posttreatment or the 6-month follow-up. Additionally, CBT appeared to have better long-term response outcomes compared to SE, while KY did not display a benefit in follow-up analyses. Overall, KY appears to have a less robust efficacy compared to CBT in the treatment of GAD.
- These findings may not generalize to how CBT and yoga are approached in the community. Future studies can assess community-based methods.
2. Gould RL, Wetherell JL, Serfaty MA, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for older people with treatment-resistant generalised anxiety disorder: the FACTOID feasibility study. Health Technol Assess. 2021;25(54):1-150. doi:10.3310/hta25540
Older adults with GAD may experience treatment resistance to first-line therapies, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and CBT. Gould et al6 assessed whether acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) could be a cost-effective option for older adults with treatment-resistant GAD (TR-GAD).
Study design
- In Stage 1 (intervention planning), individual interviews were conducted with 15 participants (11 female) with TR-GAD and 31 health care professionals, as well as 5 academic clinicians. The objective was to assess intervention preferences and priorities.
- Stage 2 included 37 participants, 8 clinicians, and 15 therapists, with the goal of assessing intervention design and feedback on the interventions.
- Participants were age ≥65 and met Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) and DSM-IV criteria for GAD. They were living in the community and had not responded to the 3 steps of the stepped-care approach for GAD (ie, 6 weeks of an age-appropriate dose of antidepressant or a course of individual psychotherapy). Patients with dementia were excluded.
- Patients received ≤16 1-on-1 sessions of ACT.
- Self-reported outcomes were assessed at baseline and Week 20.
- The primary outcomes for Stage 2 were acceptability (attendance and satisfaction with ACT) and feasibility (recruitment and retention).
Outcomes
- ACT had high feasibility, with a recruitment rate of 93% and a retention rate of 81%.
- It also had high acceptability, with 70% of participants attending ≥10 sessions and 60% of participants showing satisfaction with therapy by scoring ≥21 points on the Satisfaction with Therapy subscale of the Satisfaction with Therapy and Therapist Scale-Revised. However, 80% of participants had not finished their ACT sessions when scores were collected.
- At Week 20, 13 patients showed reliable improvement on the Geriatric Anxiety Inventory, and 15 showed no reliable change. Seven participants showed reliable improvement in Geriatric Depression Scale-15 scores and 22 showed no reliable change. Seven participants showed improvement in the Action and Acceptance Questionnaire-II and 19 showed no reliable change.
Conclusions/limitations
- ACT had high levels of feasibility and acceptability, and large RCTs warrant further assessment of the benefits of this intervention.
- There was some evidence of reductions in anxiety and depression, as well as improvement with psychological flexibility.
- The study was not powered to assess clinical effectiveness, and recruitment for Stage 2 was limited to London.
Continue to: #3
3. Stefan S, Cristea IA, Szentagotai Tatar A, et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for generalized anxiety disorder: contrasting various CBT approaches in a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Psychol. 2019;75(7):1188-1202. doi:10.1002/jclp.22779
Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of CBT for treating GAD.15,16 However, CBT involves varying approaches, which make it difficult to conclude which model of CBT is more effective. Stefan et al7 aimed to assess the efficacy of 3 versions of CBT for GAD.
Study design
- This RCT investigated 3 versions of CBT: cognitive therapy/Borkovec’s treatment package (CT/BTP), rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT), and acceptance and commitment therapy/acceptance-based behavioral therapy (ACT/ABBT).
- A total of 75 adults (60 women) age 20 to 51 and diagnosed with GAD by the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV were initially randomized to one of the treatment arms for 20 sessions; 4 dropped out before receiving the allocated intervention. Exclusion criteria included panic disorder, severe major depressive disorder (MDD), BD, substance use or dependence, psychotic disorders, suicidal or homicidal ideation, organic brain syndrome, disabling medical conditions, intellectual disability, treatment with a psychotropic drug within the past 3 months, and psychotherapy provided outside the trial.
- The primary outcomes were scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire IV (GAD-Q-IV) and the Penn State Worry Questionnaire (PSWQ). A secondary outcome included assessing negative automatic thoughts by the Automatic Thoughts Questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There were no significant differences among the 3 treatment groups with regards to demographic data.
- Approximately 70% of patients (16 of 23) in the CT/BTP group had scores below the cutoff point for response (9) on the GAD-Q-IV, approximately 71% of patients (17 of 24) in the REBT group scored below the cutoff point, and approximately 79% of patients (19 of 24) in the ACT/ABBT group scored below the cutoff point.
- Approximately 83% of patients in the CT/BTP scored below the cutoff point for response (65) on the PSWQ, approximately 83% of patients in the REBT group scored below the cutoff point, and approximately 80% of patients in the ACT/ABBT group scored below the cutoff point.
- There were positive correlations between pre-post changes in GAD symptoms and dysfunctional automatic thoughts in each group.
- There was no statistically significant difference among the 3 versions of CBT.
Conclusions/limitations
- CT/BTP, REBT, and ACT/ABBT each appear to be efficacious in reducing GAD symptoms, allowing the choice of treatment to be determined by patient and clinician preference.
- The study’s small sample size may have prevented differences between the groups from being detected.
- There was no control group, and only 39 of 75 individuals completed the study in its entirety.
4. Plag J, Schmidt-Hellinger P, Klippstein T, et al. Working out the worries: a randomized controlled trial of high intensity interval training in generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2020;76:102311. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2020.10231
Research has shown the efficacy of aerobic exercise for various anxiety disorders,17-19 but differs regarding the type of exercise and its intensity, frequency, and duration. There is evidence that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) may be beneficial in treating serious mental illness.20 Plag et al8 examined the efficacy and acceptance of HIIT in patients with GAD.
Continue to: Study design
Study design
- A total of 33 German adults (24 women) age ≥18 who met DSM-5 criteria for GAD were enrolled in a parallel-group, assessor-blinded RCT. Participants were blinded to the hypotheses of the trial, but not to the intervention.
- Participants were randomized to a HIIT group (engaged in HIIT on a bicycle ergometer every second day within 12 days, with each session lasting 20 minutes and consisting of alternating sessions of 77% to 95% maximum heart rate and <70% maximum heart rate) or a control group of lower-intensity exercise (LIT; consisted of 6 30-minute sessions within 12 days involving stretching and adapted yoga positions with heart rate <70% maximum heart rate).
- Exclusion criteria included severe depression, schizophrenia, borderline personality disorder (BPD), substance use disorder, suicidality, epilepsy, severe respiratory or cardiovascular diseases, and current psychotherapy. The use of medications was allowed if the patient was stable ≥4 weeks prior to the trial and remained stable during the trial.
- The primary outcome of worrying was assessed by the PSWQ. Other assessment tools included the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Anxiety Control Questionnaire, and Screening for Somatoform Symptoms-7 (SOMS-7).
Outcomes
- Baseline PSWQ scores in both groups were >60, indicating “high worriers.”
- Both groups experienced reductions in worrying as measured by PSWQ scores. However, the HIIT group had a larger decrease in worrying compared to the LIT group (P < .02). Post-hoc analyses showed significant reductions in symptom severity from baseline to poststudy (P < .01; d = 0.68), and at 30-day follow-up (P < .01; d = 0.62) in the HIIT group. There was no significant difference in the LIT group from baseline to poststudy or at follow-up.
- Secondary outcome measures included a greater reduction in anxiety and depression as determined by change in HAM-A and HAM-D scores in the HIIT group compared to the LIT group.
- All measures showed improvement in the HIIT group, whereas the LIT group showed improvement in HAM-A and HAM-D scores poststudy and at follow-up, as well as SOMS-7 scores at follow-up.
Conclusions/limitations
- HIIT demonstrated a large treatment effect for treating GAD, including somatic symptoms and worrying.
- HIIT displayed a fast onset of action and low cancellation rate, which suggests it is tolerable.
- This study had a small sample size consisting of participants from only 1 institution, which limits generalizability, and did not look at the long-term effects of the interventions.
5. Amir N, Taboas W, Montero M. Feasibility and dissemination of a computerized home-based treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Behav Res Ther. 2019;120:103446. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2019.103446
Many patients with anxiety disorders do not receive treatment, and logistical factors such as limited time, expertise, and available resources hinder patients from obtaining quality CBT. Attention bias modification (ABM) is a computer-based approach in which patients complete tasks guiding their attention away from threat-relevant cues.21 Applied relaxation psychoeducation (AR-pe) is another empirically supported treatment that can be administered via computer. Amir et al9 examined the feasibility and effectiveness of a home-based computerized regimen of sequenced or simultaneous ABM and AR-pe in patients with GAD.
Study design
- A total of 169 adults age 18 to 65 who met DSM-IV criteria for GAD were randomized into 4 groups: ABM followed by AR-pe, AR-pe followed by ABM, simultaneous ABM and AR-pe, or a clinical monitoring assessment only control group (CM).
- Participants were expected to complete up to 24 30-minute sessions on their home computer over 12 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included current psychotropic medications/CBT initiated 3 months prior to the study, BD, schizophrenia, or substance use disorder.
- The primary outcome measure was anxiety symptoms as assessed by the HAM-A (remission was defined as a score ≤7 at Week 13). Other measures included the PSWQ, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, Sheehan Disability Scale, and Beck Depression Inventory.
- Participants were assessed at Month 3, Month 6, and Month 12 poststudy.
Continue to: Outcomes
Outcomes
- Baseline characteristics did not significantly differ between groups.
- In the active groups, 41% of participants met remission criteria, compared to 19% in the CM group.
- The ABM followed by AR-pe group and the AR-pe followed by ABM group had significant reductions in HAM-A scores (P = .003 and P = .020) compared to the CM group.
- The simultaneous ABM and AR-pe group did not have a significant difference in outcomes compared to the CM group (P = .081).
- On the PSWQ, the CM group had a larger decrease in worry than all active cohorts combined, with follow-up analysis indicating the CM group surpassed the ABM group (P = .019).
Conclusions/limitations
- Sequential delivery of ABM and AR-pe may be a viable, easy-to-access treatment option for patients with GAD who have limited access to other therapies.
- Individuals assigned to receive simultaneous ABM and AR-pe appeared to complete fewer tasks compared to those in the sequential groups, which suggests that participants were less inclined to complete all tasks despite being allowed more time.
- This study did not examine the effects of ABM only or AR-pe only.
- This study was unable to accurately assess home usage of the program.
6. Burke J, Richards D, Timulak L. Helpful and hindering events in internet-delivered cognitive behavioural treatment for generalized anxiety. Behav Cogn Psychother. 2019;47(3):386-399. doi:10.1017/S1352465818000504
Patients with GAD may not be able to obtain adequate treatment due to financial or logistical constraints. Internet-delivered interventions are easily accessible and provide an opportunity for patients who cannot or do not want to seek traditional therapy options. Burke et al10 aimed to better understand the useful and impeding events of internet-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (iCBT).
Study design
- A total of 36 adults (25 women) age 18 to 45 from an Irish university were randomized to an immediate iCBT treatment group or a delayed access to treatment/waiting list control group. The iCBT program, called Calming Anxiety, involved 6 modules of CBT for GAD.
- Participants initially scored ≥10 on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7).
- The study employed the Helpful and Hindering Aspects of Therapy (HAT) questionnaire to assess the most useful and impeding events in therapy.
- The data were divided into 4 domains: helpful events, helpful impacts, hindering events, and hindering impacts.
Outcomes
- Of the 8 helpful events identified, the top 3 were psychoeducation, supporter interaction, and monitoring.
- Of the 5 helpful impacts identified, the top 3 were support and validation, applying coping strategies/behavioral change, and clarification, awareness, and insight.
- The 2 identified hindering events were treatment content/form and amount of work/technical issues.
- The 3 identified hindering impacts were frustration/irritation, increased anxiety, and isolation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- iCBT may be a useful and accessible approach for treating GAD, although there are still hindrances to its use.
- This study was qualitative and did not comment on the efficacy of the applied intervention.
- The benefits of iCBT may differ depending on the patient’s level of computer literacy.
7. Miller CB, Gu J, Henry AL, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of a digital CBT intervention for symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized multiple-baseline study. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2021;70:101609. doi:10.1016/j.jbtep.2020.101609
Access to CBT is limited due to cost, dearth of trained therapists, scheduling availability, stigma, and transportation. Digital CBT may help overcome these obstacles. Miller et al11 studied the feasibility and efficacy of a new automated, digital CBT intervention named Daylight.
Study design
- This randomized, multiple-baseline, single-case, experimental trial included 21 adults (20 women) age ≥18 who scored ≥10 on the GAD-7 and screened positive for GAD on MINI version 7 for DSM-5.
- Participants were not taking psychotropic medications or had been on a stable medication regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included past or present psychosis, schizophrenia, BD, seizure disorder, substance use disorder, trauma to the head or brain damage, severe cognitive impairment, serious physical health concerns necessitating surgery or with prognosis <6 months, and pregnancy.
- Participants were randomized to 1 of 3 baseline durations: 2 weeks, 4 weeks, or 6 weeks. They then could access the smartphone program Daylight. The trial lasted for 12 to 16 weeks.
- Primary anxiety outcomes were assessed daily and weekly, while secondary outcomes (depressive symptoms, sleep) were measured weekly.
- Postintervention was defined as 6 weeks after the start of the intervention and follow-up was 10 weeks after the start of the intervention.
- Participants were deemed not to have clinically significant anxiety if they scored <10 on GAD-7; not to have significant depressive symptoms if they scored <10 on the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9); and not to have sleep difficulty if they scored >16 on the Sleep Condition Indicator (SCI-8). The change was considered reliable if patients scored below the previously discussed thresholds and showed a difference in score greater than the known unreliability of the questionnaire (GAD-7 reductions ≥5, PHQ-9 reductions ≥6, SCI-8 increases ≥7).
Outcomes
- In terms of feasibility, 76% of participants completed all 4 modules, 81% completed 3 modules, 86% completed 2 modules, and all participants completed at least 1 module.
- No serious adverse events were observed, but 43% of participants reported unwanted symptoms such as agitation, fatigue, low mood, or reduced motivation.
- As evaluated by the Credibility/Expectancy Questionnaire, the program received moderate to high credibility scores. Participants indicated they were mostly satisfied with the program, although some expressed technical difficulties and a lack of specificity to their anxiety symptoms.
- Overall daily anxiety scores significantly decreased from baseline to postintervention (P < .001). Weekly anxiety scores significantly decreased from baseline to postintervention (P = .024), and follow-up (P = .017) as measured by the GAD-7.
- For participants with anxiety, 70% no longer had clinically significant anxiety symptoms postintervention, and 65% had both clinically significant and reliable change at postintervention. Eighty percent had clinically significant and reliable change at follow-up.
- For participants with depressive symptoms, 61% had clinical and reliable change at postintervention and 44% maintained both at follow-up.
- For participants with sleep disturbances, 35% had clinical and reliable improvement at postintervention and 40% had clinical and reliable change at follow-up.
Conclusions/limitations
- Daylight appears to be a feasible program with regards to acceptability, engagement, credibility, satisfaction, and safety.
- The daily and weekly outcomes support preliminary evidence of program efficacy in improving GAD symptoms.
- Most participants identified as female and were recruited online, which limits generalizability, and the study had a small sample size.
Continue to: #8
8. Hirsch CR, Krahé C, Whyte J, et al. Internet-delivered interpretation training reduces worry and anxiety in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled experiment. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2021;89(7):575-589. doi:10.1037/ccp0000660
The cognitive model of pathological worry posits that worry in GAD occurs due to various factors, including automatic cognitive bias in which ambiguous events are perceived as threatening to the individual.22 Cognitive bias modification for interpretation (CBM) is an approach that assesses an individual’s interpretation bias and resolves ambiguity through the individual’s reading or listening to multiple ambiguous situations.12 Hirsch et al12 examined if an internet-delivered CBM approach would promote positive interpretations and reduce worry and anxiety in patients with GAD.
Study design
- In this dual-arm, parallel group, single-blind RCT, adult participants were randomized to a CBM group (n = 115) or a control group (n = 115); only 186 participants were included in the analyses.
- Patients with GAD only and those with GAD comorbid with MDD who scored ≥62 on the PSWQ and ≥10 on the GAD-7 were recruited. Patients receiving psychotropic medication had to be stable on their regimen for ≥3 months prior to the trial.
- Exclusion criteria included residing outside the United Kingdom, severe depression as measured by a PHQ-9 score ≥23, self-harm in the past 12 months or suicide attempt in past 2 years, a PHQ-9 suicidal ideation score >1, concurrent psychosis, BD, BPD, substance abuse, and current or recent (within the past 6 months) psychological treatment.
- The groups completed up to 10 online training (CBM) or control (listened to ambiguous scenarios but not asked to resolve the ambiguity) sessions in 1 month.
- Primary outcome measures included the scrambled sentences test (SST) and a recognition test (RT) to assess interpretation bias.
- Secondary outcome measures included a breathing focus task (BFT), PSWQ and PSWQ-past week, Ruminative Response Scale (RRS), Repetitive Thinking Questionnaire-trait (RTQ-T), PHQ-9, and GAD-7.
- Scores were assessed preintervention (T0), postintervention (T1), 1 month postintervention (T2), and 3 months postintervention (T3).
Outcomes
- CBM was associated with a more positive interpretation at T1 than the control sessions (P < .001 on both SST and RT).
- CBM was associated with significantly reduced negative intrusions as per BFTs at T1.
- The CBM group had significant less worry as per PSWQ, and significantly less anxiety as per GAD-7 at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly fewer depressive symptoms as per PHQ-9 at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly lower levels of ruminations as per RRS at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly lower levels of general repetitive negative thinking (RNT) as per RTQ-T at T1 and T2, but not T3.
Conclusions/limitations
- Digital CBM appears to promote a positive interpretation bias.
- CBM appears to reduce negative intrusions after the intervention, as well as reduced levels of worrying, anxiety, RNT, and ruminations, with effects lasting ≤3 months except for the RNT.
- CBM appears to be an efficacious, low-intensity, easily accessible intervention that can help individuals with GAD.
- The study recruited participants via advertisements rather than clinical services, and excluded individuals with severe depression.
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed., text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
2. Carl E, Witcraft SM, Kauffman BY, et al. Psychological and pharmacological treatments for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cogn Behav Ther. 2020;49(1):1-21. doi:10.1080/16506073.2018.1560358
3. Cuijpers P, Cristea IA, Karyotaki E, et al. How effective are cognitive behavior therapies for major depression and anxiety disorders? A meta‐analytic update of the evidence. World Psychiatry. 2016;15(3):245-258. doi:10.1002/wps.20346
4. Saeed SA, Majarwitz DJ. Generalized anxiety disorder: 8 studies of biological interventions. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(7):10-12,20,22-27. doi:10.12788/cp.02645
5. Simon NM, Hofmann SG, Rosenfield D, et al. Efficacy of yoga vs cognitive behavioral therapy vs stress education for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(1):13-20. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.2496
6. Gould RL, Wetherell JL, Serfaty MA, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for older people with treatment-resistant generalised anxiety disorder: the FACTOID feasibility study. Health Technol Assess. 2021;25(54):1-150. doi:10.3310/hta25540
7. Stefan S, Cristea IA, Szentagotai Tatar A, et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for generalized anxiety disorder: contrasting various CBT approaches in a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Psychol. 2019;75(7):1188-1202. doi:10.1002/jclp.22779
8. Plag J, Schmidt-Hellinger P, Klippstein T, et al. Working out the worries: a randomized controlled trial of high intensity interval training in generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2020;76:102311. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2020.102311
9. Amir N, Taboas W, Montero M. Feasibility and dissemination of a computerized home-based treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Behav Res Ther. 2019;120:103446. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2019.103446
10. Burke J, Richards D, Timulak L. Helpful and hindering events in internet-delivered cognitive behavioural treatment for generalized anxiety. Behav Cogn Psychother. 2019;47(3):386-399. doi:10.1017/S1352465818000504
11. Miller CB, Gu J, Henry AL, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of a digital CBT intervention for symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized multiple-baseline study. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2021;70:101609. doi:10.1016/j.jbtep.2020.101609
12. Hirsch CR, Krahé C, Whyte J, et al. Internet-delivered interpretation training reduces worry and anxiety in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled experiment. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2021;89(7):575-589. doi:10.1037/ccp0000660
13. Hofmann SG, Smits JAJ. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for adult anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008;69(4):621-632. doi:10.4088/jcp.v69n0415
14. Clarke TC, Barnes PM, Black LI, et al. Use of yoga, meditation, and chiropractors among U.S. adults aged 18 and over. NCHS Data Brief. 2018;(325):1-8.
15. Carpenter JK, Andrews LA, Witcraft SM, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and related disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Depress Anxiety. 2018;35(6):502-514. doi:10.1002/da.22728
16. Covin R, Ouimet AJ, Seeds PM, et al. A meta-analysis of CBT for pathological worry among clients with GAD. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22(1):108-116. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.01.002
17. Merom D, Phongsavan P, Wagner R, et al. Promoting walking as an adjunct intervention to group cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety disorders--a pilot group randomized trial. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22(6):959-968. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.09.010
18. Herring MP, Jacob ML, Suveg C, et al. Feasibility of exercise training for the short-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Psychother Psychosom. 2012;81(1):21-28. doi:10.1159/000327898
19. Bischoff S, Wieder G, Einsle F, et al. Running for extinction? Aerobic exercise as an augmentation of exposure therapy in panic disorder with agoraphobia. J Psychiatr Res. 2018;101:34-41. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.03.001
20. Korman N, Armour M, Chapman J, et al. High Intensity Interval training (HIIT) for people with severe mental illness: a systematic review & meta-analysis of intervention studies- considering diverse approaches for mental and physical recovery. Psychiatry Res. 2020;284:112601. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112601
21. Amir N, Beard C, Cobb M, et al. Attention modification program in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder. J Abnorm Psychol. 2009;118(1):28-33. doi:10.1037/a0012589
22. Hirsh CR, Mathews A. A cognitive model of pathological worry. Behav Res Ther. 2012;50(10):636-646. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2012.007
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
For patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), the intensity, duration, and frequency of an individual’s anxiety and worry are out of proportion to the actual likelihood or impact of an anticipated event, and they often find it difficult to prevent worrisome thoughts from interfering with daily life.1 Successful treatment for GAD is patient-specific and requires clinicians to consider all available psychotherapeutic and pharmacologic options.
In a 2020 meta-analysis of 79 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 11,002 participants diagnosed with GAD, Carl et al2 focused on pooled effect sizes of evidence-based psychotherapies and medications for GAD. Their analysis showed a medium to large effect size (Hedges g = 0.76) for psychotherapy, compared to a small effect size (Hedges g = 0.38) for medication on GAD outcomes. Other meta-analyses have shown that evidence-based psychotherapies have large effect sizes on GAD outcomes.3
However, in most of the studies included in these meta-analyses, the 2 treatment modalities—psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy—use different control types. The pharmacotherapy trials used a placebo, while psychotherapy studies often had a waitlist control. Thus, the findings of these meta-analyses should not lead to the conclusion that psychotherapy is necessarily more effective for GAD symptoms than pharmacotherapy. However, there is clear evidence that psychosocial interventions are at least as effective as medications for treating GAD. Also, patients often prefer psychosocial treatment over medication.
Part 1 (

1. Simon NM, Hofmann SG, Rosenfield D, et al. Efficacy of yoga vs cognitive behavioral therapy vs stress education for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(1):13-20. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.2496
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a first-line therapy for GAD.13 However, patients may not pursue CBT due to fiscal and logistical constraints, as well as the stigma associated with it. Yoga is a common complementary health practice used by adults in the United States,14 although evidence has been inconclusive for its use in treating anxiety. Simon et al5 examined the efficacy of Kundalini yoga (KY) vs stress education (SE) and CBT for treating GAD.
Study design
- A prospective, parallel-group, randomized-controlled, single-blind trial in 2 academic centers evaluated 226 adults age ≥18 who met DSM-5 criteria for GAD.
- Participants were randomized into 3 groups: KY (n = 93), SE (n = 43), or CBT (n = 90), and monitored for 12 weeks to determine the efficacy of each therapy.
- Exclusion criteria included current posttraumatic stress disorder, eating disorders, substance use disorders, significant suicidal ideation, mental disorder due to a medical or neurocognitive condition, lifetime psychosis, bipolar disorder (BD), developmental disorders, and having completed more than 5 yoga or CBT sessions in the past 5 years. Additionally, patients were either not taking medication for ≥2 weeks prior to the trial or had a stable regimen for ≥6 weeks.
- Each therapy was guided by 2 instructors during 12 120-minute sessions with 20 minutes of daily assignments and presented in cohorts of 4 to 6 participants.
- The primary outcome was an improvement in score on the Clinical Global Impression–Improvement scale from baseline at Week 12. Secondary measures included scores on the Meta-Cognitions Questionnaire and the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire.
Outcomes
- A total of 155 participants finished the posttreatment assessment, with similar completion rates between the groups, and 123 participants completed the 6-month follow-up assessment.
- The KY group had a significantly higher response rate (54.2%) than the SE group (33%) at posttreatment, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of 4.59. At 6-month follow-up, the response rate in the KY group was not significantly higher than that of the SE group.
- The CBT group had a significantly higher response rate (70.8%) than the SE group (33%) at posttreatment, with a NNT of 2.62. At 6-month follow-up, the CBT response rate (76.7%) was significantly higher than the SE group (48%), with a NNT of 3.51.
- KY was not found to be as effective as CBT on noninferiority testing.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- CBT and KY were both more effective than SE as assessed by short-term response rates.
- The authors did not find KY to be as effective as CBT at posttreatment or the 6-month follow-up. Additionally, CBT appeared to have better long-term response outcomes compared to SE, while KY did not display a benefit in follow-up analyses. Overall, KY appears to have a less robust efficacy compared to CBT in the treatment of GAD.
- These findings may not generalize to how CBT and yoga are approached in the community. Future studies can assess community-based methods.
2. Gould RL, Wetherell JL, Serfaty MA, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for older people with treatment-resistant generalised anxiety disorder: the FACTOID feasibility study. Health Technol Assess. 2021;25(54):1-150. doi:10.3310/hta25540
Older adults with GAD may experience treatment resistance to first-line therapies, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and CBT. Gould et al6 assessed whether acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) could be a cost-effective option for older adults with treatment-resistant GAD (TR-GAD).
Study design
- In Stage 1 (intervention planning), individual interviews were conducted with 15 participants (11 female) with TR-GAD and 31 health care professionals, as well as 5 academic clinicians. The objective was to assess intervention preferences and priorities.
- Stage 2 included 37 participants, 8 clinicians, and 15 therapists, with the goal of assessing intervention design and feedback on the interventions.
- Participants were age ≥65 and met Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) and DSM-IV criteria for GAD. They were living in the community and had not responded to the 3 steps of the stepped-care approach for GAD (ie, 6 weeks of an age-appropriate dose of antidepressant or a course of individual psychotherapy). Patients with dementia were excluded.
- Patients received ≤16 1-on-1 sessions of ACT.
- Self-reported outcomes were assessed at baseline and Week 20.
- The primary outcomes for Stage 2 were acceptability (attendance and satisfaction with ACT) and feasibility (recruitment and retention).
Outcomes
- ACT had high feasibility, with a recruitment rate of 93% and a retention rate of 81%.
- It also had high acceptability, with 70% of participants attending ≥10 sessions and 60% of participants showing satisfaction with therapy by scoring ≥21 points on the Satisfaction with Therapy subscale of the Satisfaction with Therapy and Therapist Scale-Revised. However, 80% of participants had not finished their ACT sessions when scores were collected.
- At Week 20, 13 patients showed reliable improvement on the Geriatric Anxiety Inventory, and 15 showed no reliable change. Seven participants showed reliable improvement in Geriatric Depression Scale-15 scores and 22 showed no reliable change. Seven participants showed improvement in the Action and Acceptance Questionnaire-II and 19 showed no reliable change.
Conclusions/limitations
- ACT had high levels of feasibility and acceptability, and large RCTs warrant further assessment of the benefits of this intervention.
- There was some evidence of reductions in anxiety and depression, as well as improvement with psychological flexibility.
- The study was not powered to assess clinical effectiveness, and recruitment for Stage 2 was limited to London.
Continue to: #3
3. Stefan S, Cristea IA, Szentagotai Tatar A, et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for generalized anxiety disorder: contrasting various CBT approaches in a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Psychol. 2019;75(7):1188-1202. doi:10.1002/jclp.22779
Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of CBT for treating GAD.15,16 However, CBT involves varying approaches, which make it difficult to conclude which model of CBT is more effective. Stefan et al7 aimed to assess the efficacy of 3 versions of CBT for GAD.
Study design
- This RCT investigated 3 versions of CBT: cognitive therapy/Borkovec’s treatment package (CT/BTP), rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT), and acceptance and commitment therapy/acceptance-based behavioral therapy (ACT/ABBT).
- A total of 75 adults (60 women) age 20 to 51 and diagnosed with GAD by the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV were initially randomized to one of the treatment arms for 20 sessions; 4 dropped out before receiving the allocated intervention. Exclusion criteria included panic disorder, severe major depressive disorder (MDD), BD, substance use or dependence, psychotic disorders, suicidal or homicidal ideation, organic brain syndrome, disabling medical conditions, intellectual disability, treatment with a psychotropic drug within the past 3 months, and psychotherapy provided outside the trial.
- The primary outcomes were scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire IV (GAD-Q-IV) and the Penn State Worry Questionnaire (PSWQ). A secondary outcome included assessing negative automatic thoughts by the Automatic Thoughts Questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There were no significant differences among the 3 treatment groups with regards to demographic data.
- Approximately 70% of patients (16 of 23) in the CT/BTP group had scores below the cutoff point for response (9) on the GAD-Q-IV, approximately 71% of patients (17 of 24) in the REBT group scored below the cutoff point, and approximately 79% of patients (19 of 24) in the ACT/ABBT group scored below the cutoff point.
- Approximately 83% of patients in the CT/BTP scored below the cutoff point for response (65) on the PSWQ, approximately 83% of patients in the REBT group scored below the cutoff point, and approximately 80% of patients in the ACT/ABBT group scored below the cutoff point.
- There were positive correlations between pre-post changes in GAD symptoms and dysfunctional automatic thoughts in each group.
- There was no statistically significant difference among the 3 versions of CBT.
Conclusions/limitations
- CT/BTP, REBT, and ACT/ABBT each appear to be efficacious in reducing GAD symptoms, allowing the choice of treatment to be determined by patient and clinician preference.
- The study’s small sample size may have prevented differences between the groups from being detected.
- There was no control group, and only 39 of 75 individuals completed the study in its entirety.
4. Plag J, Schmidt-Hellinger P, Klippstein T, et al. Working out the worries: a randomized controlled trial of high intensity interval training in generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2020;76:102311. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2020.10231
Research has shown the efficacy of aerobic exercise for various anxiety disorders,17-19 but differs regarding the type of exercise and its intensity, frequency, and duration. There is evidence that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) may be beneficial in treating serious mental illness.20 Plag et al8 examined the efficacy and acceptance of HIIT in patients with GAD.
Continue to: Study design
Study design
- A total of 33 German adults (24 women) age ≥18 who met DSM-5 criteria for GAD were enrolled in a parallel-group, assessor-blinded RCT. Participants were blinded to the hypotheses of the trial, but not to the intervention.
- Participants were randomized to a HIIT group (engaged in HIIT on a bicycle ergometer every second day within 12 days, with each session lasting 20 minutes and consisting of alternating sessions of 77% to 95% maximum heart rate and <70% maximum heart rate) or a control group of lower-intensity exercise (LIT; consisted of 6 30-minute sessions within 12 days involving stretching and adapted yoga positions with heart rate <70% maximum heart rate).
- Exclusion criteria included severe depression, schizophrenia, borderline personality disorder (BPD), substance use disorder, suicidality, epilepsy, severe respiratory or cardiovascular diseases, and current psychotherapy. The use of medications was allowed if the patient was stable ≥4 weeks prior to the trial and remained stable during the trial.
- The primary outcome of worrying was assessed by the PSWQ. Other assessment tools included the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Anxiety Control Questionnaire, and Screening for Somatoform Symptoms-7 (SOMS-7).
Outcomes
- Baseline PSWQ scores in both groups were >60, indicating “high worriers.”
- Both groups experienced reductions in worrying as measured by PSWQ scores. However, the HIIT group had a larger decrease in worrying compared to the LIT group (P < .02). Post-hoc analyses showed significant reductions in symptom severity from baseline to poststudy (P < .01; d = 0.68), and at 30-day follow-up (P < .01; d = 0.62) in the HIIT group. There was no significant difference in the LIT group from baseline to poststudy or at follow-up.
- Secondary outcome measures included a greater reduction in anxiety and depression as determined by change in HAM-A and HAM-D scores in the HIIT group compared to the LIT group.
- All measures showed improvement in the HIIT group, whereas the LIT group showed improvement in HAM-A and HAM-D scores poststudy and at follow-up, as well as SOMS-7 scores at follow-up.
Conclusions/limitations
- HIIT demonstrated a large treatment effect for treating GAD, including somatic symptoms and worrying.
- HIIT displayed a fast onset of action and low cancellation rate, which suggests it is tolerable.
- This study had a small sample size consisting of participants from only 1 institution, which limits generalizability, and did not look at the long-term effects of the interventions.
5. Amir N, Taboas W, Montero M. Feasibility and dissemination of a computerized home-based treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Behav Res Ther. 2019;120:103446. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2019.103446
Many patients with anxiety disorders do not receive treatment, and logistical factors such as limited time, expertise, and available resources hinder patients from obtaining quality CBT. Attention bias modification (ABM) is a computer-based approach in which patients complete tasks guiding their attention away from threat-relevant cues.21 Applied relaxation psychoeducation (AR-pe) is another empirically supported treatment that can be administered via computer. Amir et al9 examined the feasibility and effectiveness of a home-based computerized regimen of sequenced or simultaneous ABM and AR-pe in patients with GAD.
Study design
- A total of 169 adults age 18 to 65 who met DSM-IV criteria for GAD were randomized into 4 groups: ABM followed by AR-pe, AR-pe followed by ABM, simultaneous ABM and AR-pe, or a clinical monitoring assessment only control group (CM).
- Participants were expected to complete up to 24 30-minute sessions on their home computer over 12 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included current psychotropic medications/CBT initiated 3 months prior to the study, BD, schizophrenia, or substance use disorder.
- The primary outcome measure was anxiety symptoms as assessed by the HAM-A (remission was defined as a score ≤7 at Week 13). Other measures included the PSWQ, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, Sheehan Disability Scale, and Beck Depression Inventory.
- Participants were assessed at Month 3, Month 6, and Month 12 poststudy.
Continue to: Outcomes
Outcomes
- Baseline characteristics did not significantly differ between groups.
- In the active groups, 41% of participants met remission criteria, compared to 19% in the CM group.
- The ABM followed by AR-pe group and the AR-pe followed by ABM group had significant reductions in HAM-A scores (P = .003 and P = .020) compared to the CM group.
- The simultaneous ABM and AR-pe group did not have a significant difference in outcomes compared to the CM group (P = .081).
- On the PSWQ, the CM group had a larger decrease in worry than all active cohorts combined, with follow-up analysis indicating the CM group surpassed the ABM group (P = .019).
Conclusions/limitations
- Sequential delivery of ABM and AR-pe may be a viable, easy-to-access treatment option for patients with GAD who have limited access to other therapies.
- Individuals assigned to receive simultaneous ABM and AR-pe appeared to complete fewer tasks compared to those in the sequential groups, which suggests that participants were less inclined to complete all tasks despite being allowed more time.
- This study did not examine the effects of ABM only or AR-pe only.
- This study was unable to accurately assess home usage of the program.
6. Burke J, Richards D, Timulak L. Helpful and hindering events in internet-delivered cognitive behavioural treatment for generalized anxiety. Behav Cogn Psychother. 2019;47(3):386-399. doi:10.1017/S1352465818000504
Patients with GAD may not be able to obtain adequate treatment due to financial or logistical constraints. Internet-delivered interventions are easily accessible and provide an opportunity for patients who cannot or do not want to seek traditional therapy options. Burke et al10 aimed to better understand the useful and impeding events of internet-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (iCBT).
Study design
- A total of 36 adults (25 women) age 18 to 45 from an Irish university were randomized to an immediate iCBT treatment group or a delayed access to treatment/waiting list control group. The iCBT program, called Calming Anxiety, involved 6 modules of CBT for GAD.
- Participants initially scored ≥10 on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7).
- The study employed the Helpful and Hindering Aspects of Therapy (HAT) questionnaire to assess the most useful and impeding events in therapy.
- The data were divided into 4 domains: helpful events, helpful impacts, hindering events, and hindering impacts.
Outcomes
- Of the 8 helpful events identified, the top 3 were psychoeducation, supporter interaction, and monitoring.
- Of the 5 helpful impacts identified, the top 3 were support and validation, applying coping strategies/behavioral change, and clarification, awareness, and insight.
- The 2 identified hindering events were treatment content/form and amount of work/technical issues.
- The 3 identified hindering impacts were frustration/irritation, increased anxiety, and isolation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- iCBT may be a useful and accessible approach for treating GAD, although there are still hindrances to its use.
- This study was qualitative and did not comment on the efficacy of the applied intervention.
- The benefits of iCBT may differ depending on the patient’s level of computer literacy.
7. Miller CB, Gu J, Henry AL, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of a digital CBT intervention for symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized multiple-baseline study. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2021;70:101609. doi:10.1016/j.jbtep.2020.101609
Access to CBT is limited due to cost, dearth of trained therapists, scheduling availability, stigma, and transportation. Digital CBT may help overcome these obstacles. Miller et al11 studied the feasibility and efficacy of a new automated, digital CBT intervention named Daylight.
Study design
- This randomized, multiple-baseline, single-case, experimental trial included 21 adults (20 women) age ≥18 who scored ≥10 on the GAD-7 and screened positive for GAD on MINI version 7 for DSM-5.
- Participants were not taking psychotropic medications or had been on a stable medication regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included past or present psychosis, schizophrenia, BD, seizure disorder, substance use disorder, trauma to the head or brain damage, severe cognitive impairment, serious physical health concerns necessitating surgery or with prognosis <6 months, and pregnancy.
- Participants were randomized to 1 of 3 baseline durations: 2 weeks, 4 weeks, or 6 weeks. They then could access the smartphone program Daylight. The trial lasted for 12 to 16 weeks.
- Primary anxiety outcomes were assessed daily and weekly, while secondary outcomes (depressive symptoms, sleep) were measured weekly.
- Postintervention was defined as 6 weeks after the start of the intervention and follow-up was 10 weeks after the start of the intervention.
- Participants were deemed not to have clinically significant anxiety if they scored <10 on GAD-7; not to have significant depressive symptoms if they scored <10 on the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9); and not to have sleep difficulty if they scored >16 on the Sleep Condition Indicator (SCI-8). The change was considered reliable if patients scored below the previously discussed thresholds and showed a difference in score greater than the known unreliability of the questionnaire (GAD-7 reductions ≥5, PHQ-9 reductions ≥6, SCI-8 increases ≥7).
Outcomes
- In terms of feasibility, 76% of participants completed all 4 modules, 81% completed 3 modules, 86% completed 2 modules, and all participants completed at least 1 module.
- No serious adverse events were observed, but 43% of participants reported unwanted symptoms such as agitation, fatigue, low mood, or reduced motivation.
- As evaluated by the Credibility/Expectancy Questionnaire, the program received moderate to high credibility scores. Participants indicated they were mostly satisfied with the program, although some expressed technical difficulties and a lack of specificity to their anxiety symptoms.
- Overall daily anxiety scores significantly decreased from baseline to postintervention (P < .001). Weekly anxiety scores significantly decreased from baseline to postintervention (P = .024), and follow-up (P = .017) as measured by the GAD-7.
- For participants with anxiety, 70% no longer had clinically significant anxiety symptoms postintervention, and 65% had both clinically significant and reliable change at postintervention. Eighty percent had clinically significant and reliable change at follow-up.
- For participants with depressive symptoms, 61% had clinical and reliable change at postintervention and 44% maintained both at follow-up.
- For participants with sleep disturbances, 35% had clinical and reliable improvement at postintervention and 40% had clinical and reliable change at follow-up.
Conclusions/limitations
- Daylight appears to be a feasible program with regards to acceptability, engagement, credibility, satisfaction, and safety.
- The daily and weekly outcomes support preliminary evidence of program efficacy in improving GAD symptoms.
- Most participants identified as female and were recruited online, which limits generalizability, and the study had a small sample size.
Continue to: #8
8. Hirsch CR, Krahé C, Whyte J, et al. Internet-delivered interpretation training reduces worry and anxiety in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled experiment. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2021;89(7):575-589. doi:10.1037/ccp0000660
The cognitive model of pathological worry posits that worry in GAD occurs due to various factors, including automatic cognitive bias in which ambiguous events are perceived as threatening to the individual.22 Cognitive bias modification for interpretation (CBM) is an approach that assesses an individual’s interpretation bias and resolves ambiguity through the individual’s reading or listening to multiple ambiguous situations.12 Hirsch et al12 examined if an internet-delivered CBM approach would promote positive interpretations and reduce worry and anxiety in patients with GAD.
Study design
- In this dual-arm, parallel group, single-blind RCT, adult participants were randomized to a CBM group (n = 115) or a control group (n = 115); only 186 participants were included in the analyses.
- Patients with GAD only and those with GAD comorbid with MDD who scored ≥62 on the PSWQ and ≥10 on the GAD-7 were recruited. Patients receiving psychotropic medication had to be stable on their regimen for ≥3 months prior to the trial.
- Exclusion criteria included residing outside the United Kingdom, severe depression as measured by a PHQ-9 score ≥23, self-harm in the past 12 months or suicide attempt in past 2 years, a PHQ-9 suicidal ideation score >1, concurrent psychosis, BD, BPD, substance abuse, and current or recent (within the past 6 months) psychological treatment.
- The groups completed up to 10 online training (CBM) or control (listened to ambiguous scenarios but not asked to resolve the ambiguity) sessions in 1 month.
- Primary outcome measures included the scrambled sentences test (SST) and a recognition test (RT) to assess interpretation bias.
- Secondary outcome measures included a breathing focus task (BFT), PSWQ and PSWQ-past week, Ruminative Response Scale (RRS), Repetitive Thinking Questionnaire-trait (RTQ-T), PHQ-9, and GAD-7.
- Scores were assessed preintervention (T0), postintervention (T1), 1 month postintervention (T2), and 3 months postintervention (T3).
Outcomes
- CBM was associated with a more positive interpretation at T1 than the control sessions (P < .001 on both SST and RT).
- CBM was associated with significantly reduced negative intrusions as per BFTs at T1.
- The CBM group had significant less worry as per PSWQ, and significantly less anxiety as per GAD-7 at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly fewer depressive symptoms as per PHQ-9 at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly lower levels of ruminations as per RRS at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly lower levels of general repetitive negative thinking (RNT) as per RTQ-T at T1 and T2, but not T3.
Conclusions/limitations
- Digital CBM appears to promote a positive interpretation bias.
- CBM appears to reduce negative intrusions after the intervention, as well as reduced levels of worrying, anxiety, RNT, and ruminations, with effects lasting ≤3 months except for the RNT.
- CBM appears to be an efficacious, low-intensity, easily accessible intervention that can help individuals with GAD.
- The study recruited participants via advertisements rather than clinical services, and excluded individuals with severe depression.
SECOND OF 2 PARTS
For patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), the intensity, duration, and frequency of an individual’s anxiety and worry are out of proportion to the actual likelihood or impact of an anticipated event, and they often find it difficult to prevent worrisome thoughts from interfering with daily life.1 Successful treatment for GAD is patient-specific and requires clinicians to consider all available psychotherapeutic and pharmacologic options.
In a 2020 meta-analysis of 79 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 11,002 participants diagnosed with GAD, Carl et al2 focused on pooled effect sizes of evidence-based psychotherapies and medications for GAD. Their analysis showed a medium to large effect size (Hedges g = 0.76) for psychotherapy, compared to a small effect size (Hedges g = 0.38) for medication on GAD outcomes. Other meta-analyses have shown that evidence-based psychotherapies have large effect sizes on GAD outcomes.3
However, in most of the studies included in these meta-analyses, the 2 treatment modalities—psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy—use different control types. The pharmacotherapy trials used a placebo, while psychotherapy studies often had a waitlist control. Thus, the findings of these meta-analyses should not lead to the conclusion that psychotherapy is necessarily more effective for GAD symptoms than pharmacotherapy. However, there is clear evidence that psychosocial interventions are at least as effective as medications for treating GAD. Also, patients often prefer psychosocial treatment over medication.
Part 1 (

1. Simon NM, Hofmann SG, Rosenfield D, et al. Efficacy of yoga vs cognitive behavioral therapy vs stress education for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(1):13-20. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.2496
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a first-line therapy for GAD.13 However, patients may not pursue CBT due to fiscal and logistical constraints, as well as the stigma associated with it. Yoga is a common complementary health practice used by adults in the United States,14 although evidence has been inconclusive for its use in treating anxiety. Simon et al5 examined the efficacy of Kundalini yoga (KY) vs stress education (SE) and CBT for treating GAD.
Study design
- A prospective, parallel-group, randomized-controlled, single-blind trial in 2 academic centers evaluated 226 adults age ≥18 who met DSM-5 criteria for GAD.
- Participants were randomized into 3 groups: KY (n = 93), SE (n = 43), or CBT (n = 90), and monitored for 12 weeks to determine the efficacy of each therapy.
- Exclusion criteria included current posttraumatic stress disorder, eating disorders, substance use disorders, significant suicidal ideation, mental disorder due to a medical or neurocognitive condition, lifetime psychosis, bipolar disorder (BD), developmental disorders, and having completed more than 5 yoga or CBT sessions in the past 5 years. Additionally, patients were either not taking medication for ≥2 weeks prior to the trial or had a stable regimen for ≥6 weeks.
- Each therapy was guided by 2 instructors during 12 120-minute sessions with 20 minutes of daily assignments and presented in cohorts of 4 to 6 participants.
- The primary outcome was an improvement in score on the Clinical Global Impression–Improvement scale from baseline at Week 12. Secondary measures included scores on the Meta-Cognitions Questionnaire and the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire.
Outcomes
- A total of 155 participants finished the posttreatment assessment, with similar completion rates between the groups, and 123 participants completed the 6-month follow-up assessment.
- The KY group had a significantly higher response rate (54.2%) than the SE group (33%) at posttreatment, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of 4.59. At 6-month follow-up, the response rate in the KY group was not significantly higher than that of the SE group.
- The CBT group had a significantly higher response rate (70.8%) than the SE group (33%) at posttreatment, with a NNT of 2.62. At 6-month follow-up, the CBT response rate (76.7%) was significantly higher than the SE group (48%), with a NNT of 3.51.
- KY was not found to be as effective as CBT on noninferiority testing.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- CBT and KY were both more effective than SE as assessed by short-term response rates.
- The authors did not find KY to be as effective as CBT at posttreatment or the 6-month follow-up. Additionally, CBT appeared to have better long-term response outcomes compared to SE, while KY did not display a benefit in follow-up analyses. Overall, KY appears to have a less robust efficacy compared to CBT in the treatment of GAD.
- These findings may not generalize to how CBT and yoga are approached in the community. Future studies can assess community-based methods.
2. Gould RL, Wetherell JL, Serfaty MA, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for older people with treatment-resistant generalised anxiety disorder: the FACTOID feasibility study. Health Technol Assess. 2021;25(54):1-150. doi:10.3310/hta25540
Older adults with GAD may experience treatment resistance to first-line therapies, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and CBT. Gould et al6 assessed whether acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) could be a cost-effective option for older adults with treatment-resistant GAD (TR-GAD).
Study design
- In Stage 1 (intervention planning), individual interviews were conducted with 15 participants (11 female) with TR-GAD and 31 health care professionals, as well as 5 academic clinicians. The objective was to assess intervention preferences and priorities.
- Stage 2 included 37 participants, 8 clinicians, and 15 therapists, with the goal of assessing intervention design and feedback on the interventions.
- Participants were age ≥65 and met Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) and DSM-IV criteria for GAD. They were living in the community and had not responded to the 3 steps of the stepped-care approach for GAD (ie, 6 weeks of an age-appropriate dose of antidepressant or a course of individual psychotherapy). Patients with dementia were excluded.
- Patients received ≤16 1-on-1 sessions of ACT.
- Self-reported outcomes were assessed at baseline and Week 20.
- The primary outcomes for Stage 2 were acceptability (attendance and satisfaction with ACT) and feasibility (recruitment and retention).
Outcomes
- ACT had high feasibility, with a recruitment rate of 93% and a retention rate of 81%.
- It also had high acceptability, with 70% of participants attending ≥10 sessions and 60% of participants showing satisfaction with therapy by scoring ≥21 points on the Satisfaction with Therapy subscale of the Satisfaction with Therapy and Therapist Scale-Revised. However, 80% of participants had not finished their ACT sessions when scores were collected.
- At Week 20, 13 patients showed reliable improvement on the Geriatric Anxiety Inventory, and 15 showed no reliable change. Seven participants showed reliable improvement in Geriatric Depression Scale-15 scores and 22 showed no reliable change. Seven participants showed improvement in the Action and Acceptance Questionnaire-II and 19 showed no reliable change.
Conclusions/limitations
- ACT had high levels of feasibility and acceptability, and large RCTs warrant further assessment of the benefits of this intervention.
- There was some evidence of reductions in anxiety and depression, as well as improvement with psychological flexibility.
- The study was not powered to assess clinical effectiveness, and recruitment for Stage 2 was limited to London.
Continue to: #3
3. Stefan S, Cristea IA, Szentagotai Tatar A, et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for generalized anxiety disorder: contrasting various CBT approaches in a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Psychol. 2019;75(7):1188-1202. doi:10.1002/jclp.22779
Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of CBT for treating GAD.15,16 However, CBT involves varying approaches, which make it difficult to conclude which model of CBT is more effective. Stefan et al7 aimed to assess the efficacy of 3 versions of CBT for GAD.
Study design
- This RCT investigated 3 versions of CBT: cognitive therapy/Borkovec’s treatment package (CT/BTP), rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT), and acceptance and commitment therapy/acceptance-based behavioral therapy (ACT/ABBT).
- A total of 75 adults (60 women) age 20 to 51 and diagnosed with GAD by the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV were initially randomized to one of the treatment arms for 20 sessions; 4 dropped out before receiving the allocated intervention. Exclusion criteria included panic disorder, severe major depressive disorder (MDD), BD, substance use or dependence, psychotic disorders, suicidal or homicidal ideation, organic brain syndrome, disabling medical conditions, intellectual disability, treatment with a psychotropic drug within the past 3 months, and psychotherapy provided outside the trial.
- The primary outcomes were scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire IV (GAD-Q-IV) and the Penn State Worry Questionnaire (PSWQ). A secondary outcome included assessing negative automatic thoughts by the Automatic Thoughts Questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There were no significant differences among the 3 treatment groups with regards to demographic data.
- Approximately 70% of patients (16 of 23) in the CT/BTP group had scores below the cutoff point for response (9) on the GAD-Q-IV, approximately 71% of patients (17 of 24) in the REBT group scored below the cutoff point, and approximately 79% of patients (19 of 24) in the ACT/ABBT group scored below the cutoff point.
- Approximately 83% of patients in the CT/BTP scored below the cutoff point for response (65) on the PSWQ, approximately 83% of patients in the REBT group scored below the cutoff point, and approximately 80% of patients in the ACT/ABBT group scored below the cutoff point.
- There were positive correlations between pre-post changes in GAD symptoms and dysfunctional automatic thoughts in each group.
- There was no statistically significant difference among the 3 versions of CBT.
Conclusions/limitations
- CT/BTP, REBT, and ACT/ABBT each appear to be efficacious in reducing GAD symptoms, allowing the choice of treatment to be determined by patient and clinician preference.
- The study’s small sample size may have prevented differences between the groups from being detected.
- There was no control group, and only 39 of 75 individuals completed the study in its entirety.
4. Plag J, Schmidt-Hellinger P, Klippstein T, et al. Working out the worries: a randomized controlled trial of high intensity interval training in generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2020;76:102311. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2020.10231
Research has shown the efficacy of aerobic exercise for various anxiety disorders,17-19 but differs regarding the type of exercise and its intensity, frequency, and duration. There is evidence that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) may be beneficial in treating serious mental illness.20 Plag et al8 examined the efficacy and acceptance of HIIT in patients with GAD.
Continue to: Study design
Study design
- A total of 33 German adults (24 women) age ≥18 who met DSM-5 criteria for GAD were enrolled in a parallel-group, assessor-blinded RCT. Participants were blinded to the hypotheses of the trial, but not to the intervention.
- Participants were randomized to a HIIT group (engaged in HIIT on a bicycle ergometer every second day within 12 days, with each session lasting 20 minutes and consisting of alternating sessions of 77% to 95% maximum heart rate and <70% maximum heart rate) or a control group of lower-intensity exercise (LIT; consisted of 6 30-minute sessions within 12 days involving stretching and adapted yoga positions with heart rate <70% maximum heart rate).
- Exclusion criteria included severe depression, schizophrenia, borderline personality disorder (BPD), substance use disorder, suicidality, epilepsy, severe respiratory or cardiovascular diseases, and current psychotherapy. The use of medications was allowed if the patient was stable ≥4 weeks prior to the trial and remained stable during the trial.
- The primary outcome of worrying was assessed by the PSWQ. Other assessment tools included the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Anxiety Control Questionnaire, and Screening for Somatoform Symptoms-7 (SOMS-7).
Outcomes
- Baseline PSWQ scores in both groups were >60, indicating “high worriers.”
- Both groups experienced reductions in worrying as measured by PSWQ scores. However, the HIIT group had a larger decrease in worrying compared to the LIT group (P < .02). Post-hoc analyses showed significant reductions in symptom severity from baseline to poststudy (P < .01; d = 0.68), and at 30-day follow-up (P < .01; d = 0.62) in the HIIT group. There was no significant difference in the LIT group from baseline to poststudy or at follow-up.
- Secondary outcome measures included a greater reduction in anxiety and depression as determined by change in HAM-A and HAM-D scores in the HIIT group compared to the LIT group.
- All measures showed improvement in the HIIT group, whereas the LIT group showed improvement in HAM-A and HAM-D scores poststudy and at follow-up, as well as SOMS-7 scores at follow-up.
Conclusions/limitations
- HIIT demonstrated a large treatment effect for treating GAD, including somatic symptoms and worrying.
- HIIT displayed a fast onset of action and low cancellation rate, which suggests it is tolerable.
- This study had a small sample size consisting of participants from only 1 institution, which limits generalizability, and did not look at the long-term effects of the interventions.
5. Amir N, Taboas W, Montero M. Feasibility and dissemination of a computerized home-based treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Behav Res Ther. 2019;120:103446. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2019.103446
Many patients with anxiety disorders do not receive treatment, and logistical factors such as limited time, expertise, and available resources hinder patients from obtaining quality CBT. Attention bias modification (ABM) is a computer-based approach in which patients complete tasks guiding their attention away from threat-relevant cues.21 Applied relaxation psychoeducation (AR-pe) is another empirically supported treatment that can be administered via computer. Amir et al9 examined the feasibility and effectiveness of a home-based computerized regimen of sequenced or simultaneous ABM and AR-pe in patients with GAD.
Study design
- A total of 169 adults age 18 to 65 who met DSM-IV criteria for GAD were randomized into 4 groups: ABM followed by AR-pe, AR-pe followed by ABM, simultaneous ABM and AR-pe, or a clinical monitoring assessment only control group (CM).
- Participants were expected to complete up to 24 30-minute sessions on their home computer over 12 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included current psychotropic medications/CBT initiated 3 months prior to the study, BD, schizophrenia, or substance use disorder.
- The primary outcome measure was anxiety symptoms as assessed by the HAM-A (remission was defined as a score ≤7 at Week 13). Other measures included the PSWQ, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, Sheehan Disability Scale, and Beck Depression Inventory.
- Participants were assessed at Month 3, Month 6, and Month 12 poststudy.
Continue to: Outcomes
Outcomes
- Baseline characteristics did not significantly differ between groups.
- In the active groups, 41% of participants met remission criteria, compared to 19% in the CM group.
- The ABM followed by AR-pe group and the AR-pe followed by ABM group had significant reductions in HAM-A scores (P = .003 and P = .020) compared to the CM group.
- The simultaneous ABM and AR-pe group did not have a significant difference in outcomes compared to the CM group (P = .081).
- On the PSWQ, the CM group had a larger decrease in worry than all active cohorts combined, with follow-up analysis indicating the CM group surpassed the ABM group (P = .019).
Conclusions/limitations
- Sequential delivery of ABM and AR-pe may be a viable, easy-to-access treatment option for patients with GAD who have limited access to other therapies.
- Individuals assigned to receive simultaneous ABM and AR-pe appeared to complete fewer tasks compared to those in the sequential groups, which suggests that participants were less inclined to complete all tasks despite being allowed more time.
- This study did not examine the effects of ABM only or AR-pe only.
- This study was unable to accurately assess home usage of the program.
6. Burke J, Richards D, Timulak L. Helpful and hindering events in internet-delivered cognitive behavioural treatment for generalized anxiety. Behav Cogn Psychother. 2019;47(3):386-399. doi:10.1017/S1352465818000504
Patients with GAD may not be able to obtain adequate treatment due to financial or logistical constraints. Internet-delivered interventions are easily accessible and provide an opportunity for patients who cannot or do not want to seek traditional therapy options. Burke et al10 aimed to better understand the useful and impeding events of internet-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (iCBT).
Study design
- A total of 36 adults (25 women) age 18 to 45 from an Irish university were randomized to an immediate iCBT treatment group or a delayed access to treatment/waiting list control group. The iCBT program, called Calming Anxiety, involved 6 modules of CBT for GAD.
- Participants initially scored ≥10 on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7).
- The study employed the Helpful and Hindering Aspects of Therapy (HAT) questionnaire to assess the most useful and impeding events in therapy.
- The data were divided into 4 domains: helpful events, helpful impacts, hindering events, and hindering impacts.
Outcomes
- Of the 8 helpful events identified, the top 3 were psychoeducation, supporter interaction, and monitoring.
- Of the 5 helpful impacts identified, the top 3 were support and validation, applying coping strategies/behavioral change, and clarification, awareness, and insight.
- The 2 identified hindering events were treatment content/form and amount of work/technical issues.
- The 3 identified hindering impacts were frustration/irritation, increased anxiety, and isolation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- iCBT may be a useful and accessible approach for treating GAD, although there are still hindrances to its use.
- This study was qualitative and did not comment on the efficacy of the applied intervention.
- The benefits of iCBT may differ depending on the patient’s level of computer literacy.
7. Miller CB, Gu J, Henry AL, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of a digital CBT intervention for symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized multiple-baseline study. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2021;70:101609. doi:10.1016/j.jbtep.2020.101609
Access to CBT is limited due to cost, dearth of trained therapists, scheduling availability, stigma, and transportation. Digital CBT may help overcome these obstacles. Miller et al11 studied the feasibility and efficacy of a new automated, digital CBT intervention named Daylight.
Study design
- This randomized, multiple-baseline, single-case, experimental trial included 21 adults (20 women) age ≥18 who scored ≥10 on the GAD-7 and screened positive for GAD on MINI version 7 for DSM-5.
- Participants were not taking psychotropic medications or had been on a stable medication regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included past or present psychosis, schizophrenia, BD, seizure disorder, substance use disorder, trauma to the head or brain damage, severe cognitive impairment, serious physical health concerns necessitating surgery or with prognosis <6 months, and pregnancy.
- Participants were randomized to 1 of 3 baseline durations: 2 weeks, 4 weeks, or 6 weeks. They then could access the smartphone program Daylight. The trial lasted for 12 to 16 weeks.
- Primary anxiety outcomes were assessed daily and weekly, while secondary outcomes (depressive symptoms, sleep) were measured weekly.
- Postintervention was defined as 6 weeks after the start of the intervention and follow-up was 10 weeks after the start of the intervention.
- Participants were deemed not to have clinically significant anxiety if they scored <10 on GAD-7; not to have significant depressive symptoms if they scored <10 on the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9); and not to have sleep difficulty if they scored >16 on the Sleep Condition Indicator (SCI-8). The change was considered reliable if patients scored below the previously discussed thresholds and showed a difference in score greater than the known unreliability of the questionnaire (GAD-7 reductions ≥5, PHQ-9 reductions ≥6, SCI-8 increases ≥7).
Outcomes
- In terms of feasibility, 76% of participants completed all 4 modules, 81% completed 3 modules, 86% completed 2 modules, and all participants completed at least 1 module.
- No serious adverse events were observed, but 43% of participants reported unwanted symptoms such as agitation, fatigue, low mood, or reduced motivation.
- As evaluated by the Credibility/Expectancy Questionnaire, the program received moderate to high credibility scores. Participants indicated they were mostly satisfied with the program, although some expressed technical difficulties and a lack of specificity to their anxiety symptoms.
- Overall daily anxiety scores significantly decreased from baseline to postintervention (P < .001). Weekly anxiety scores significantly decreased from baseline to postintervention (P = .024), and follow-up (P = .017) as measured by the GAD-7.
- For participants with anxiety, 70% no longer had clinically significant anxiety symptoms postintervention, and 65% had both clinically significant and reliable change at postintervention. Eighty percent had clinically significant and reliable change at follow-up.
- For participants with depressive symptoms, 61% had clinical and reliable change at postintervention and 44% maintained both at follow-up.
- For participants with sleep disturbances, 35% had clinical and reliable improvement at postintervention and 40% had clinical and reliable change at follow-up.
Conclusions/limitations
- Daylight appears to be a feasible program with regards to acceptability, engagement, credibility, satisfaction, and safety.
- The daily and weekly outcomes support preliminary evidence of program efficacy in improving GAD symptoms.
- Most participants identified as female and were recruited online, which limits generalizability, and the study had a small sample size.
Continue to: #8
8. Hirsch CR, Krahé C, Whyte J, et al. Internet-delivered interpretation training reduces worry and anxiety in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled experiment. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2021;89(7):575-589. doi:10.1037/ccp0000660
The cognitive model of pathological worry posits that worry in GAD occurs due to various factors, including automatic cognitive bias in which ambiguous events are perceived as threatening to the individual.22 Cognitive bias modification for interpretation (CBM) is an approach that assesses an individual’s interpretation bias and resolves ambiguity through the individual’s reading or listening to multiple ambiguous situations.12 Hirsch et al12 examined if an internet-delivered CBM approach would promote positive interpretations and reduce worry and anxiety in patients with GAD.
Study design
- In this dual-arm, parallel group, single-blind RCT, adult participants were randomized to a CBM group (n = 115) or a control group (n = 115); only 186 participants were included in the analyses.
- Patients with GAD only and those with GAD comorbid with MDD who scored ≥62 on the PSWQ and ≥10 on the GAD-7 were recruited. Patients receiving psychotropic medication had to be stable on their regimen for ≥3 months prior to the trial.
- Exclusion criteria included residing outside the United Kingdom, severe depression as measured by a PHQ-9 score ≥23, self-harm in the past 12 months or suicide attempt in past 2 years, a PHQ-9 suicidal ideation score >1, concurrent psychosis, BD, BPD, substance abuse, and current or recent (within the past 6 months) psychological treatment.
- The groups completed up to 10 online training (CBM) or control (listened to ambiguous scenarios but not asked to resolve the ambiguity) sessions in 1 month.
- Primary outcome measures included the scrambled sentences test (SST) and a recognition test (RT) to assess interpretation bias.
- Secondary outcome measures included a breathing focus task (BFT), PSWQ and PSWQ-past week, Ruminative Response Scale (RRS), Repetitive Thinking Questionnaire-trait (RTQ-T), PHQ-9, and GAD-7.
- Scores were assessed preintervention (T0), postintervention (T1), 1 month postintervention (T2), and 3 months postintervention (T3).
Outcomes
- CBM was associated with a more positive interpretation at T1 than the control sessions (P < .001 on both SST and RT).
- CBM was associated with significantly reduced negative intrusions as per BFTs at T1.
- The CBM group had significant less worry as per PSWQ, and significantly less anxiety as per GAD-7 at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly fewer depressive symptoms as per PHQ-9 at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly lower levels of ruminations as per RRS at T1, T2, and T3.
- The CBM group had significantly lower levels of general repetitive negative thinking (RNT) as per RTQ-T at T1 and T2, but not T3.
Conclusions/limitations
- Digital CBM appears to promote a positive interpretation bias.
- CBM appears to reduce negative intrusions after the intervention, as well as reduced levels of worrying, anxiety, RNT, and ruminations, with effects lasting ≤3 months except for the RNT.
- CBM appears to be an efficacious, low-intensity, easily accessible intervention that can help individuals with GAD.
- The study recruited participants via advertisements rather than clinical services, and excluded individuals with severe depression.
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed., text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
2. Carl E, Witcraft SM, Kauffman BY, et al. Psychological and pharmacological treatments for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cogn Behav Ther. 2020;49(1):1-21. doi:10.1080/16506073.2018.1560358
3. Cuijpers P, Cristea IA, Karyotaki E, et al. How effective are cognitive behavior therapies for major depression and anxiety disorders? A meta‐analytic update of the evidence. World Psychiatry. 2016;15(3):245-258. doi:10.1002/wps.20346
4. Saeed SA, Majarwitz DJ. Generalized anxiety disorder: 8 studies of biological interventions. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(7):10-12,20,22-27. doi:10.12788/cp.02645
5. Simon NM, Hofmann SG, Rosenfield D, et al. Efficacy of yoga vs cognitive behavioral therapy vs stress education for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(1):13-20. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.2496
6. Gould RL, Wetherell JL, Serfaty MA, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for older people with treatment-resistant generalised anxiety disorder: the FACTOID feasibility study. Health Technol Assess. 2021;25(54):1-150. doi:10.3310/hta25540
7. Stefan S, Cristea IA, Szentagotai Tatar A, et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for generalized anxiety disorder: contrasting various CBT approaches in a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Psychol. 2019;75(7):1188-1202. doi:10.1002/jclp.22779
8. Plag J, Schmidt-Hellinger P, Klippstein T, et al. Working out the worries: a randomized controlled trial of high intensity interval training in generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2020;76:102311. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2020.102311
9. Amir N, Taboas W, Montero M. Feasibility and dissemination of a computerized home-based treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Behav Res Ther. 2019;120:103446. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2019.103446
10. Burke J, Richards D, Timulak L. Helpful and hindering events in internet-delivered cognitive behavioural treatment for generalized anxiety. Behav Cogn Psychother. 2019;47(3):386-399. doi:10.1017/S1352465818000504
11. Miller CB, Gu J, Henry AL, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of a digital CBT intervention for symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized multiple-baseline study. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2021;70:101609. doi:10.1016/j.jbtep.2020.101609
12. Hirsch CR, Krahé C, Whyte J, et al. Internet-delivered interpretation training reduces worry and anxiety in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled experiment. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2021;89(7):575-589. doi:10.1037/ccp0000660
13. Hofmann SG, Smits JAJ. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for adult anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008;69(4):621-632. doi:10.4088/jcp.v69n0415
14. Clarke TC, Barnes PM, Black LI, et al. Use of yoga, meditation, and chiropractors among U.S. adults aged 18 and over. NCHS Data Brief. 2018;(325):1-8.
15. Carpenter JK, Andrews LA, Witcraft SM, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and related disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Depress Anxiety. 2018;35(6):502-514. doi:10.1002/da.22728
16. Covin R, Ouimet AJ, Seeds PM, et al. A meta-analysis of CBT for pathological worry among clients with GAD. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22(1):108-116. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.01.002
17. Merom D, Phongsavan P, Wagner R, et al. Promoting walking as an adjunct intervention to group cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety disorders--a pilot group randomized trial. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22(6):959-968. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.09.010
18. Herring MP, Jacob ML, Suveg C, et al. Feasibility of exercise training for the short-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Psychother Psychosom. 2012;81(1):21-28. doi:10.1159/000327898
19. Bischoff S, Wieder G, Einsle F, et al. Running for extinction? Aerobic exercise as an augmentation of exposure therapy in panic disorder with agoraphobia. J Psychiatr Res. 2018;101:34-41. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.03.001
20. Korman N, Armour M, Chapman J, et al. High Intensity Interval training (HIIT) for people with severe mental illness: a systematic review & meta-analysis of intervention studies- considering diverse approaches for mental and physical recovery. Psychiatry Res. 2020;284:112601. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112601
21. Amir N, Beard C, Cobb M, et al. Attention modification program in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder. J Abnorm Psychol. 2009;118(1):28-33. doi:10.1037/a0012589
22. Hirsh CR, Mathews A. A cognitive model of pathological worry. Behav Res Ther. 2012;50(10):636-646. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2012.007
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed., text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
2. Carl E, Witcraft SM, Kauffman BY, et al. Psychological and pharmacological treatments for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cogn Behav Ther. 2020;49(1):1-21. doi:10.1080/16506073.2018.1560358
3. Cuijpers P, Cristea IA, Karyotaki E, et al. How effective are cognitive behavior therapies for major depression and anxiety disorders? A meta‐analytic update of the evidence. World Psychiatry. 2016;15(3):245-258. doi:10.1002/wps.20346
4. Saeed SA, Majarwitz DJ. Generalized anxiety disorder: 8 studies of biological interventions. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(7):10-12,20,22-27. doi:10.12788/cp.02645
5. Simon NM, Hofmann SG, Rosenfield D, et al. Efficacy of yoga vs cognitive behavioral therapy vs stress education for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(1):13-20. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.2496
6. Gould RL, Wetherell JL, Serfaty MA, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for older people with treatment-resistant generalised anxiety disorder: the FACTOID feasibility study. Health Technol Assess. 2021;25(54):1-150. doi:10.3310/hta25540
7. Stefan S, Cristea IA, Szentagotai Tatar A, et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for generalized anxiety disorder: contrasting various CBT approaches in a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Psychol. 2019;75(7):1188-1202. doi:10.1002/jclp.22779
8. Plag J, Schmidt-Hellinger P, Klippstein T, et al. Working out the worries: a randomized controlled trial of high intensity interval training in generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2020;76:102311. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2020.102311
9. Amir N, Taboas W, Montero M. Feasibility and dissemination of a computerized home-based treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized clinical trial. Behav Res Ther. 2019;120:103446. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2019.103446
10. Burke J, Richards D, Timulak L. Helpful and hindering events in internet-delivered cognitive behavioural treatment for generalized anxiety. Behav Cogn Psychother. 2019;47(3):386-399. doi:10.1017/S1352465818000504
11. Miller CB, Gu J, Henry AL, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of a digital CBT intervention for symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized multiple-baseline study. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2021;70:101609. doi:10.1016/j.jbtep.2020.101609
12. Hirsch CR, Krahé C, Whyte J, et al. Internet-delivered interpretation training reduces worry and anxiety in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled experiment. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2021;89(7):575-589. doi:10.1037/ccp0000660
13. Hofmann SG, Smits JAJ. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for adult anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008;69(4):621-632. doi:10.4088/jcp.v69n0415
14. Clarke TC, Barnes PM, Black LI, et al. Use of yoga, meditation, and chiropractors among U.S. adults aged 18 and over. NCHS Data Brief. 2018;(325):1-8.
15. Carpenter JK, Andrews LA, Witcraft SM, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and related disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Depress Anxiety. 2018;35(6):502-514. doi:10.1002/da.22728
16. Covin R, Ouimet AJ, Seeds PM, et al. A meta-analysis of CBT for pathological worry among clients with GAD. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22(1):108-116. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.01.002
17. Merom D, Phongsavan P, Wagner R, et al. Promoting walking as an adjunct intervention to group cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety disorders--a pilot group randomized trial. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22(6):959-968. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.09.010
18. Herring MP, Jacob ML, Suveg C, et al. Feasibility of exercise training for the short-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Psychother Psychosom. 2012;81(1):21-28. doi:10.1159/000327898
19. Bischoff S, Wieder G, Einsle F, et al. Running for extinction? Aerobic exercise as an augmentation of exposure therapy in panic disorder with agoraphobia. J Psychiatr Res. 2018;101:34-41. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.03.001
20. Korman N, Armour M, Chapman J, et al. High Intensity Interval training (HIIT) for people with severe mental illness: a systematic review & meta-analysis of intervention studies- considering diverse approaches for mental and physical recovery. Psychiatry Res. 2020;284:112601. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112601
21. Amir N, Beard C, Cobb M, et al. Attention modification program in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder. J Abnorm Psychol. 2009;118(1):28-33. doi:10.1037/a0012589
22. Hirsh CR, Mathews A. A cognitive model of pathological worry. Behav Res Ther. 2012;50(10):636-646. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2012.007
Using SNRIs to prevent migraines in patients with depression
Ms. D, age 45, has major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), migraines, and hypertension. At a follow-up visit, she says she has been under a lot of stress at work in the past several months and feels her antidepressant is not working well for her depression or anxiety. Ms. D notes that lately she has had more frequent migraines, occurring approximately 4 times per month during the past 3 months. She describes a severe throbbing frontal pain that occurs primarily on the left side of her head, but sometimes on the right side. Ms. D says she experiences nausea, vomiting, and photophobia during these migraine episodes. The migraines last up to 12 hours, but often resolve with sumatriptan 50 mg as needed.
Ms. D takes fluoxetine 60 mg/d for depression and anxiety, lisinopril 20 mg/d for hypertension, as well as a women’s multivitamin and vitamin D3 daily. She has not tried other antidepressants and misses doses of her medications about once every other week. Her blood pressure is 125/80 mm Hg; heart rate is 80 beats per minute; and temperature is 37° C. Ms. D’s treatment team is considering switching her to a medication that can act as preventative therapy for migraines while also treating her depression and anxiety.
Migraine is a chronic, disabling neurovascular disorder that affects approximately 15% of the United States population.1 It is the second-leading disabling condition worldwide and may negatively affect social, family, personal, academic, and occupational domains.2 Migraine is often characterized by throbbing pain, is frequently unilateral, and may last 24 to 72 hours.3 It may occur with or without aura and can be associated with nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light.3 Episodic migraines occur <15 days a month, while chronic migraines occur ≥15 days a month.4
Many psychiatric, neurologic, vascular, and cardiac comorbidities are more prevalent in individuals who experience migraine headaches compared to the general population. Common psychiatric comorbidities found in patients with migraines are depression, bipolar disorder, GAD, panic disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder5; MDD is the most common.4 A person who experiences migraine headaches is 2 to 4 times more likely to develop MDD than one who does not experience migraine headaches.4
First-line treatments for preventing migraine including divalproex, topiramate, metoprolol, propranolol, and timolol.6 However, for some patients with migraines and comorbid depression or anxiety, an antidepressant may be an option. This article briefly reviews the evidence for using antidepressants that have been studied for their ability to decrease migraine frequency.
Antidepressants that can prevent migraine
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are second- or third-line options for migraine prevention.6 While TCAs have proven to be effective for preventing migraines, many patients are unable to tolerate their adverse effects (ie, anticholinergic effects, sedation).7 TCAs may be more appealing for younger patients, who may be less bothered by anticholinergic burden, or those who have difficulty sleeping.
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). There has been growing interest in understanding the potential utility of SNRIs as a preventative treatment for migraines. Research has found that SNRIs are as effective as TCAs for preventing migraines and also more tolerable in terms of adverse effects.7 SNRIs such as venlafaxine and duloxetine are currently prescribed off-label to prevent migraines despite a lack of FDA approval for this indication.8
Continue to: Understanding the safety and efficacy...
Understanding the safety and efficacy of SNRIs as preventative treatment for episodic migraines is useful, particularly for patients with comorbid depression. The Table8-17 details clinical information related to SNRI use.
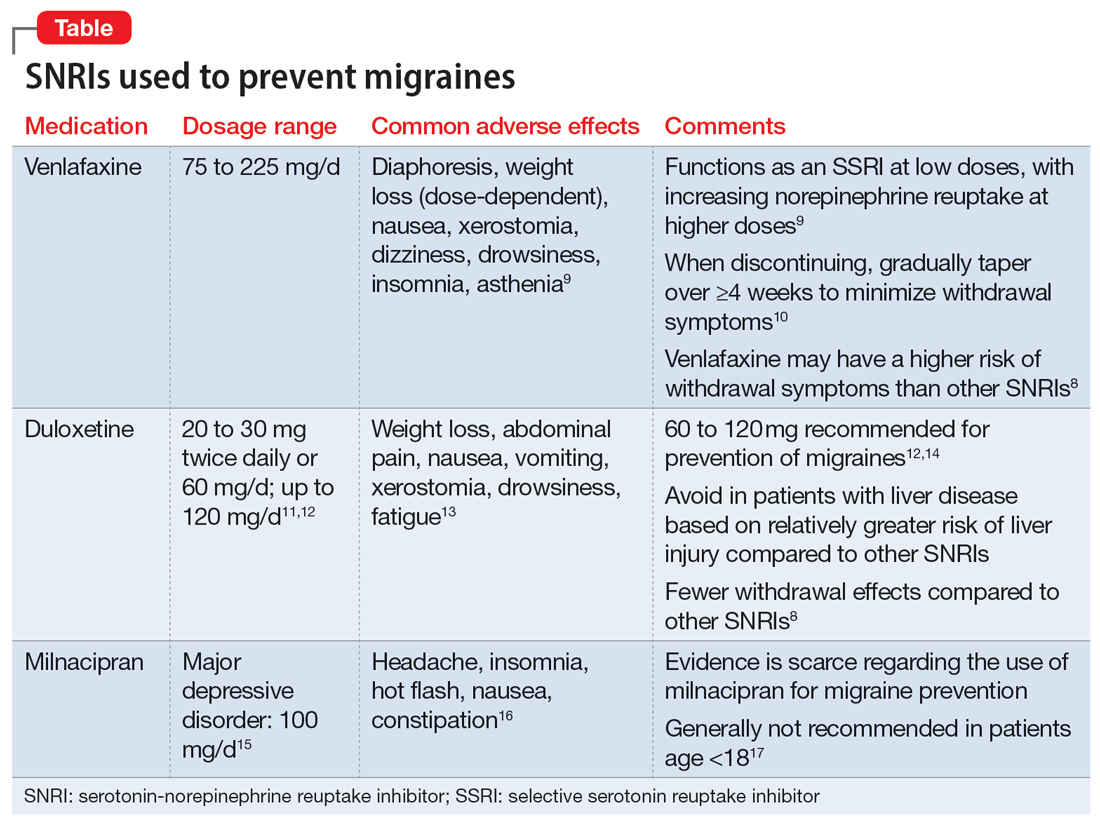
Duloxetine has demonstrated efficacy in preventing migraines in patients with comorbid depression.8 In a 2019 study, Kisler et al14 found that duloxetine 60 mg/d for 7 weeks was more effective for migraine prophylaxis than placebo as measured by the percentage of self-estimated migraine improvement by each patient compared to pretreatment levels (duloxetine: 52.3% ± 30.4%; placebo: 26.0% ± 27.3%; P = .001).
Venlafaxine has also demonstrated efficacy for preventing migraines in patients with comorbid depression.8 One study demonstrated a significant decrease in headaches per month with the use of venlafaxine 150 mg/d compared to placebo.18 Adelman et al19 found a reduction in migraine headaches per month (16.1 to 11.1, P < .0001) in patients who took venlafaxine for an average of 6 months with a mean dose of 150 mg/d. In a study of patients who did not have a mood disorder, Tarlaci20 found that venlafaxine reduced migraine headache independent of its antidepressant action.
Though milnacipran has not been studied as extensively as other SNRIs, evidence suggests it reduces the incidence of headaches and migraines, especially among episodic migraine patients. Although it has an equipotent effect on both serotonin and norepinephrine (NE) reuptake, milnacipran has a greater NE effect compared to other SNRIs approved for treating mood disorders. A prospective, single-arm study by Engel et al21 found a significant (P < .005) reduction from baseline in all headache and migraine days per month with the use of milnacipran 100 mg/d over the course of 3 months. The number of headache days per month was reduced by 4.2 compared to baseline. This same study reported improved functionality and reduced use of acute and symptomatic medications overall due to the decrease in headaches and migraines.21
In addition to demonstrating that certain SNRIs can effectively prevent migraine, some evidence suggests certain patients may benefit from the opportunity to decrease pill burden by using a single medication to treat both depression and migraine.22 Duloxetine may be preferred for patients who struggle with adherence (such as Ms. D) due to its relatively lower incidence of withdrawal symptoms compared to venlafaxine.8
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. D’s psychiatrist concludes she would be an appropriate candidate for treatment with an SNRI due to her history of MDD and chronic migraines. Because Ms. D expresses some difficulty remembering to take her medications, the psychiatrist recommends duloxetine because it is less likely to produce withdrawal symptoms compared to venlafaxine. To decrease pill burden, fluoxetine 60 mg is stopped with no taper due to its long half-life, and duloxetine is started at 30 mg/d, with a planned increase to 60 mg/d after 1 to 2 weeks as tolerated to target both mood and migraine prophylaxis. Duloxetine will not interact with Ms. D’s current medication regimen, including lisinopril, women’s multivitamin, or vitamin D3. The psychiatrist discusses the importance of medication adherence to improve her conditions effectively and safely. Ms. D’s heart rate and blood pressure will continue to be monitored.
Related Resources
- Leo RJ, Khalid K. Antidepressants for chronic pain. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):8-16,21-22.
- Williams AM, Knox ED. When to prescribe antidepressants to treat comorbid depression and pain disorders. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):55-58.
Drug Brand Names
Divalproex • Depakote
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Lisinopril • Zestril, Prinivil
Milnacipran • Savella
Sumatriptan • Imitrex
Topiramate • Topamax
Venlafaxine • Effexor
1. Burch R, Rizzoli P, Loder E. The prevalence and impact of migraine and severe headache in the United States: figures and trends from government health studies. Headache. 2018;58(4):496-505. doi:10.1111/head.13281
2. GBD 2016 Headache Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(11):954-976. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30322-3
3. Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD. Migraine--current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):257-270. doi:10.1056/NEJMra010917
4. Amoozegar F. Depression comorbidity in migraine. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2017;29(5):504-515. doi:10.1080/09540261.2017.1326882
5. Burch RC, Buse DC, Lipton RB. Migraine: epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol Clin. 2019;37(4):631-649. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2019.06.001
6. Ha H, Gonzalez A. Migraine headache prophylaxis. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(1):17-24.
7. Xu XM, Liu Y, Dong MX, et al. Tricyclic antidepressants for preventing migraine in adults. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(22):e6989. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000006989
8. Burch R. Antidepressants for preventive treatment of migraine. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019;21(4):18. doi:10.1007/s11940-019-0557-2
9. Venlafaxine. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
10. Ogle NR, Akkerman SR. Guidance for the discontinuation or switching of antidepressant therapies in adults. J Pharm Pract. 2013;26(4):389-396. doi:10.1177/0897190012467210
11. Duloxetine [package insert]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company; 2004.
12. Young WB, Bradley KC, Anjum MW, et al. Duloxetine prophylaxis for episodic migraine in persons without depression: a prospective study. Headache. 2013;53(9):1430-1437.
13. Duloxetine. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
14. Kisler LB, Weissman-Fogel I, Coghill RC, et al. Individualization of migraine prevention: a randomized controlled trial of psychophysical-based prediction of duloxetine efficacy. Clin J Pain. 2019;35(9):753-765.
15. Mansuy L. Antidepressant therapy with milnacipran and venlafaxine. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2010;6 (Suppl I):17-22.
16. Milnacipran. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
17. Milnacipran. MedlinePlus. Updated January 22, 2022. Accessed August 19, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a609016.html
18. Ozyalcin SN, Talu GK, Kiziltan E, et al. The efficacy and safety of venlafaxine in the prophylaxis of migraine. Headache. 2005;45(2):144-152. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05029.x
19. Adelman LC, Adelman JU, Von Seggern R, et al. Venlafaxine extended release (XR) for the prophylaxis of migraine and tension-type headache: a retrospective study in a clinical setting. Headache. 2000;40(7):572-580. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.00089.x
20. Tarlaci S. Escitalopram and venlafaxine for the prophylaxis of migraine headache without mood disorders. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2009;32(5):254-258. doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181a8c84f
21. Engel ER, Kudrow D, Rapoport AM. A prospective, open-label study of milnacipran in the prevention of headache in patients with episodic or chronic migraine. Neurol Sci. 2014;35(3):429-435. doi:10.1007/s10072-013-1536-0
22. Baumgartner A, Drame K, Geutjens S, et al. Does the polypill improve patient adherence compared to its individual formulations? A systematic review. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(2):190.
Ms. D, age 45, has major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), migraines, and hypertension. At a follow-up visit, she says she has been under a lot of stress at work in the past several months and feels her antidepressant is not working well for her depression or anxiety. Ms. D notes that lately she has had more frequent migraines, occurring approximately 4 times per month during the past 3 months. She describes a severe throbbing frontal pain that occurs primarily on the left side of her head, but sometimes on the right side. Ms. D says she experiences nausea, vomiting, and photophobia during these migraine episodes. The migraines last up to 12 hours, but often resolve with sumatriptan 50 mg as needed.
Ms. D takes fluoxetine 60 mg/d for depression and anxiety, lisinopril 20 mg/d for hypertension, as well as a women’s multivitamin and vitamin D3 daily. She has not tried other antidepressants and misses doses of her medications about once every other week. Her blood pressure is 125/80 mm Hg; heart rate is 80 beats per minute; and temperature is 37° C. Ms. D’s treatment team is considering switching her to a medication that can act as preventative therapy for migraines while also treating her depression and anxiety.
Migraine is a chronic, disabling neurovascular disorder that affects approximately 15% of the United States population.1 It is the second-leading disabling condition worldwide and may negatively affect social, family, personal, academic, and occupational domains.2 Migraine is often characterized by throbbing pain, is frequently unilateral, and may last 24 to 72 hours.3 It may occur with or without aura and can be associated with nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light.3 Episodic migraines occur <15 days a month, while chronic migraines occur ≥15 days a month.4
Many psychiatric, neurologic, vascular, and cardiac comorbidities are more prevalent in individuals who experience migraine headaches compared to the general population. Common psychiatric comorbidities found in patients with migraines are depression, bipolar disorder, GAD, panic disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder5; MDD is the most common.4 A person who experiences migraine headaches is 2 to 4 times more likely to develop MDD than one who does not experience migraine headaches.4
First-line treatments for preventing migraine including divalproex, topiramate, metoprolol, propranolol, and timolol.6 However, for some patients with migraines and comorbid depression or anxiety, an antidepressant may be an option. This article briefly reviews the evidence for using antidepressants that have been studied for their ability to decrease migraine frequency.
Antidepressants that can prevent migraine
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are second- or third-line options for migraine prevention.6 While TCAs have proven to be effective for preventing migraines, many patients are unable to tolerate their adverse effects (ie, anticholinergic effects, sedation).7 TCAs may be more appealing for younger patients, who may be less bothered by anticholinergic burden, or those who have difficulty sleeping.
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). There has been growing interest in understanding the potential utility of SNRIs as a preventative treatment for migraines. Research has found that SNRIs are as effective as TCAs for preventing migraines and also more tolerable in terms of adverse effects.7 SNRIs such as venlafaxine and duloxetine are currently prescribed off-label to prevent migraines despite a lack of FDA approval for this indication.8
Continue to: Understanding the safety and efficacy...
Understanding the safety and efficacy of SNRIs as preventative treatment for episodic migraines is useful, particularly for patients with comorbid depression. The Table8-17 details clinical information related to SNRI use.

Duloxetine has demonstrated efficacy in preventing migraines in patients with comorbid depression.8 In a 2019 study, Kisler et al14 found that duloxetine 60 mg/d for 7 weeks was more effective for migraine prophylaxis than placebo as measured by the percentage of self-estimated migraine improvement by each patient compared to pretreatment levels (duloxetine: 52.3% ± 30.4%; placebo: 26.0% ± 27.3%; P = .001).
Venlafaxine has also demonstrated efficacy for preventing migraines in patients with comorbid depression.8 One study demonstrated a significant decrease in headaches per month with the use of venlafaxine 150 mg/d compared to placebo.18 Adelman et al19 found a reduction in migraine headaches per month (16.1 to 11.1, P < .0001) in patients who took venlafaxine for an average of 6 months with a mean dose of 150 mg/d. In a study of patients who did not have a mood disorder, Tarlaci20 found that venlafaxine reduced migraine headache independent of its antidepressant action.
Though milnacipran has not been studied as extensively as other SNRIs, evidence suggests it reduces the incidence of headaches and migraines, especially among episodic migraine patients. Although it has an equipotent effect on both serotonin and norepinephrine (NE) reuptake, milnacipran has a greater NE effect compared to other SNRIs approved for treating mood disorders. A prospective, single-arm study by Engel et al21 found a significant (P < .005) reduction from baseline in all headache and migraine days per month with the use of milnacipran 100 mg/d over the course of 3 months. The number of headache days per month was reduced by 4.2 compared to baseline. This same study reported improved functionality and reduced use of acute and symptomatic medications overall due to the decrease in headaches and migraines.21
In addition to demonstrating that certain SNRIs can effectively prevent migraine, some evidence suggests certain patients may benefit from the opportunity to decrease pill burden by using a single medication to treat both depression and migraine.22 Duloxetine may be preferred for patients who struggle with adherence (such as Ms. D) due to its relatively lower incidence of withdrawal symptoms compared to venlafaxine.8
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. D’s psychiatrist concludes she would be an appropriate candidate for treatment with an SNRI due to her history of MDD and chronic migraines. Because Ms. D expresses some difficulty remembering to take her medications, the psychiatrist recommends duloxetine because it is less likely to produce withdrawal symptoms compared to venlafaxine. To decrease pill burden, fluoxetine 60 mg is stopped with no taper due to its long half-life, and duloxetine is started at 30 mg/d, with a planned increase to 60 mg/d after 1 to 2 weeks as tolerated to target both mood and migraine prophylaxis. Duloxetine will not interact with Ms. D’s current medication regimen, including lisinopril, women’s multivitamin, or vitamin D3. The psychiatrist discusses the importance of medication adherence to improve her conditions effectively and safely. Ms. D’s heart rate and blood pressure will continue to be monitored.
Related Resources
- Leo RJ, Khalid K. Antidepressants for chronic pain. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):8-16,21-22.
- Williams AM, Knox ED. When to prescribe antidepressants to treat comorbid depression and pain disorders. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):55-58.
Drug Brand Names
Divalproex • Depakote
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Lisinopril • Zestril, Prinivil
Milnacipran • Savella
Sumatriptan • Imitrex
Topiramate • Topamax
Venlafaxine • Effexor
Ms. D, age 45, has major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), migraines, and hypertension. At a follow-up visit, she says she has been under a lot of stress at work in the past several months and feels her antidepressant is not working well for her depression or anxiety. Ms. D notes that lately she has had more frequent migraines, occurring approximately 4 times per month during the past 3 months. She describes a severe throbbing frontal pain that occurs primarily on the left side of her head, but sometimes on the right side. Ms. D says she experiences nausea, vomiting, and photophobia during these migraine episodes. The migraines last up to 12 hours, but often resolve with sumatriptan 50 mg as needed.
Ms. D takes fluoxetine 60 mg/d for depression and anxiety, lisinopril 20 mg/d for hypertension, as well as a women’s multivitamin and vitamin D3 daily. She has not tried other antidepressants and misses doses of her medications about once every other week. Her blood pressure is 125/80 mm Hg; heart rate is 80 beats per minute; and temperature is 37° C. Ms. D’s treatment team is considering switching her to a medication that can act as preventative therapy for migraines while also treating her depression and anxiety.
Migraine is a chronic, disabling neurovascular disorder that affects approximately 15% of the United States population.1 It is the second-leading disabling condition worldwide and may negatively affect social, family, personal, academic, and occupational domains.2 Migraine is often characterized by throbbing pain, is frequently unilateral, and may last 24 to 72 hours.3 It may occur with or without aura and can be associated with nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light.3 Episodic migraines occur <15 days a month, while chronic migraines occur ≥15 days a month.4
Many psychiatric, neurologic, vascular, and cardiac comorbidities are more prevalent in individuals who experience migraine headaches compared to the general population. Common psychiatric comorbidities found in patients with migraines are depression, bipolar disorder, GAD, panic disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder5; MDD is the most common.4 A person who experiences migraine headaches is 2 to 4 times more likely to develop MDD than one who does not experience migraine headaches.4
First-line treatments for preventing migraine including divalproex, topiramate, metoprolol, propranolol, and timolol.6 However, for some patients with migraines and comorbid depression or anxiety, an antidepressant may be an option. This article briefly reviews the evidence for using antidepressants that have been studied for their ability to decrease migraine frequency.
Antidepressants that can prevent migraine
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are second- or third-line options for migraine prevention.6 While TCAs have proven to be effective for preventing migraines, many patients are unable to tolerate their adverse effects (ie, anticholinergic effects, sedation).7 TCAs may be more appealing for younger patients, who may be less bothered by anticholinergic burden, or those who have difficulty sleeping.
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). There has been growing interest in understanding the potential utility of SNRIs as a preventative treatment for migraines. Research has found that SNRIs are as effective as TCAs for preventing migraines and also more tolerable in terms of adverse effects.7 SNRIs such as venlafaxine and duloxetine are currently prescribed off-label to prevent migraines despite a lack of FDA approval for this indication.8
Continue to: Understanding the safety and efficacy...
Understanding the safety and efficacy of SNRIs as preventative treatment for episodic migraines is useful, particularly for patients with comorbid depression. The Table8-17 details clinical information related to SNRI use.

Duloxetine has demonstrated efficacy in preventing migraines in patients with comorbid depression.8 In a 2019 study, Kisler et al14 found that duloxetine 60 mg/d for 7 weeks was more effective for migraine prophylaxis than placebo as measured by the percentage of self-estimated migraine improvement by each patient compared to pretreatment levels (duloxetine: 52.3% ± 30.4%; placebo: 26.0% ± 27.3%; P = .001).
Venlafaxine has also demonstrated efficacy for preventing migraines in patients with comorbid depression.8 One study demonstrated a significant decrease in headaches per month with the use of venlafaxine 150 mg/d compared to placebo.18 Adelman et al19 found a reduction in migraine headaches per month (16.1 to 11.1, P < .0001) in patients who took venlafaxine for an average of 6 months with a mean dose of 150 mg/d. In a study of patients who did not have a mood disorder, Tarlaci20 found that venlafaxine reduced migraine headache independent of its antidepressant action.
Though milnacipran has not been studied as extensively as other SNRIs, evidence suggests it reduces the incidence of headaches and migraines, especially among episodic migraine patients. Although it has an equipotent effect on both serotonin and norepinephrine (NE) reuptake, milnacipran has a greater NE effect compared to other SNRIs approved for treating mood disorders. A prospective, single-arm study by Engel et al21 found a significant (P < .005) reduction from baseline in all headache and migraine days per month with the use of milnacipran 100 mg/d over the course of 3 months. The number of headache days per month was reduced by 4.2 compared to baseline. This same study reported improved functionality and reduced use of acute and symptomatic medications overall due to the decrease in headaches and migraines.21
In addition to demonstrating that certain SNRIs can effectively prevent migraine, some evidence suggests certain patients may benefit from the opportunity to decrease pill burden by using a single medication to treat both depression and migraine.22 Duloxetine may be preferred for patients who struggle with adherence (such as Ms. D) due to its relatively lower incidence of withdrawal symptoms compared to venlafaxine.8
CASE CONTINUED
Ms. D’s psychiatrist concludes she would be an appropriate candidate for treatment with an SNRI due to her history of MDD and chronic migraines. Because Ms. D expresses some difficulty remembering to take her medications, the psychiatrist recommends duloxetine because it is less likely to produce withdrawal symptoms compared to venlafaxine. To decrease pill burden, fluoxetine 60 mg is stopped with no taper due to its long half-life, and duloxetine is started at 30 mg/d, with a planned increase to 60 mg/d after 1 to 2 weeks as tolerated to target both mood and migraine prophylaxis. Duloxetine will not interact with Ms. D’s current medication regimen, including lisinopril, women’s multivitamin, or vitamin D3. The psychiatrist discusses the importance of medication adherence to improve her conditions effectively and safely. Ms. D’s heart rate and blood pressure will continue to be monitored.
Related Resources
- Leo RJ, Khalid K. Antidepressants for chronic pain. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):8-16,21-22.
- Williams AM, Knox ED. When to prescribe antidepressants to treat comorbid depression and pain disorders. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(1):55-58.
Drug Brand Names
Divalproex • Depakote
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Lisinopril • Zestril, Prinivil
Milnacipran • Savella
Sumatriptan • Imitrex
Topiramate • Topamax
Venlafaxine • Effexor
1. Burch R, Rizzoli P, Loder E. The prevalence and impact of migraine and severe headache in the United States: figures and trends from government health studies. Headache. 2018;58(4):496-505. doi:10.1111/head.13281
2. GBD 2016 Headache Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(11):954-976. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30322-3
3. Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD. Migraine--current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):257-270. doi:10.1056/NEJMra010917
4. Amoozegar F. Depression comorbidity in migraine. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2017;29(5):504-515. doi:10.1080/09540261.2017.1326882
5. Burch RC, Buse DC, Lipton RB. Migraine: epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol Clin. 2019;37(4):631-649. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2019.06.001
6. Ha H, Gonzalez A. Migraine headache prophylaxis. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(1):17-24.
7. Xu XM, Liu Y, Dong MX, et al. Tricyclic antidepressants for preventing migraine in adults. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(22):e6989. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000006989
8. Burch R. Antidepressants for preventive treatment of migraine. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019;21(4):18. doi:10.1007/s11940-019-0557-2
9. Venlafaxine. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
10. Ogle NR, Akkerman SR. Guidance for the discontinuation or switching of antidepressant therapies in adults. J Pharm Pract. 2013;26(4):389-396. doi:10.1177/0897190012467210
11. Duloxetine [package insert]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company; 2004.
12. Young WB, Bradley KC, Anjum MW, et al. Duloxetine prophylaxis for episodic migraine in persons without depression: a prospective study. Headache. 2013;53(9):1430-1437.
13. Duloxetine. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
14. Kisler LB, Weissman-Fogel I, Coghill RC, et al. Individualization of migraine prevention: a randomized controlled trial of psychophysical-based prediction of duloxetine efficacy. Clin J Pain. 2019;35(9):753-765.
15. Mansuy L. Antidepressant therapy with milnacipran and venlafaxine. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2010;6 (Suppl I):17-22.
16. Milnacipran. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
17. Milnacipran. MedlinePlus. Updated January 22, 2022. Accessed August 19, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a609016.html
18. Ozyalcin SN, Talu GK, Kiziltan E, et al. The efficacy and safety of venlafaxine in the prophylaxis of migraine. Headache. 2005;45(2):144-152. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05029.x
19. Adelman LC, Adelman JU, Von Seggern R, et al. Venlafaxine extended release (XR) for the prophylaxis of migraine and tension-type headache: a retrospective study in a clinical setting. Headache. 2000;40(7):572-580. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.00089.x
20. Tarlaci S. Escitalopram and venlafaxine for the prophylaxis of migraine headache without mood disorders. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2009;32(5):254-258. doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181a8c84f
21. Engel ER, Kudrow D, Rapoport AM. A prospective, open-label study of milnacipran in the prevention of headache in patients with episodic or chronic migraine. Neurol Sci. 2014;35(3):429-435. doi:10.1007/s10072-013-1536-0
22. Baumgartner A, Drame K, Geutjens S, et al. Does the polypill improve patient adherence compared to its individual formulations? A systematic review. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(2):190.
1. Burch R, Rizzoli P, Loder E. The prevalence and impact of migraine and severe headache in the United States: figures and trends from government health studies. Headache. 2018;58(4):496-505. doi:10.1111/head.13281
2. GBD 2016 Headache Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(11):954-976. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30322-3
3. Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD. Migraine--current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):257-270. doi:10.1056/NEJMra010917
4. Amoozegar F. Depression comorbidity in migraine. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2017;29(5):504-515. doi:10.1080/09540261.2017.1326882
5. Burch RC, Buse DC, Lipton RB. Migraine: epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol Clin. 2019;37(4):631-649. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2019.06.001
6. Ha H, Gonzalez A. Migraine headache prophylaxis. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(1):17-24.
7. Xu XM, Liu Y, Dong MX, et al. Tricyclic antidepressants for preventing migraine in adults. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(22):e6989. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000006989
8. Burch R. Antidepressants for preventive treatment of migraine. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019;21(4):18. doi:10.1007/s11940-019-0557-2
9. Venlafaxine. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
10. Ogle NR, Akkerman SR. Guidance for the discontinuation or switching of antidepressant therapies in adults. J Pharm Pract. 2013;26(4):389-396. doi:10.1177/0897190012467210
11. Duloxetine [package insert]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company; 2004.
12. Young WB, Bradley KC, Anjum MW, et al. Duloxetine prophylaxis for episodic migraine in persons without depression: a prospective study. Headache. 2013;53(9):1430-1437.
13. Duloxetine. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
14. Kisler LB, Weissman-Fogel I, Coghill RC, et al. Individualization of migraine prevention: a randomized controlled trial of psychophysical-based prediction of duloxetine efficacy. Clin J Pain. 2019;35(9):753-765.
15. Mansuy L. Antidepressant therapy with milnacipran and venlafaxine. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2010;6 (Suppl I):17-22.
16. Milnacipran. Lexicomp. 2021. http://online.lexi.com/
17. Milnacipran. MedlinePlus. Updated January 22, 2022. Accessed August 19, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a609016.html
18. Ozyalcin SN, Talu GK, Kiziltan E, et al. The efficacy and safety of venlafaxine in the prophylaxis of migraine. Headache. 2005;45(2):144-152. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05029.x
19. Adelman LC, Adelman JU, Von Seggern R, et al. Venlafaxine extended release (XR) for the prophylaxis of migraine and tension-type headache: a retrospective study in a clinical setting. Headache. 2000;40(7):572-580. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.00089.x
20. Tarlaci S. Escitalopram and venlafaxine for the prophylaxis of migraine headache without mood disorders. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2009;32(5):254-258. doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181a8c84f
21. Engel ER, Kudrow D, Rapoport AM. A prospective, open-label study of milnacipran in the prevention of headache in patients with episodic or chronic migraine. Neurol Sci. 2014;35(3):429-435. doi:10.1007/s10072-013-1536-0
22. Baumgartner A, Drame K, Geutjens S, et al. Does the polypill improve patient adherence compared to its individual formulations? A systematic review. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(2):190.
Medical record documentation: What to do, and what to avoid
Medical record documentation serves as a reminder of previous discussions with patients and what happened during their visits, a reimbursement justification for services, a communication tool to coordinate care with current and future clinicians, and a basis for defense in legal or regulatory matters.1,2 Documentation should be thorough, accurate, timely, and objective, with the ultimate goal of communicating our thoughts in an easily understood manner to other clinicians or attorneys.2 If we fail to achieve this goal, we may inadvertently give the impression that our care was hurried, incomplete, or thoughtless.2
Although not an exhaustive list, this article outlines strategies to employ and practices to avoid in our documentation efforts so we may enhance our defense in case of litigation and ensure the smooth transition of care for our patients.
Strategies to employ
Proper and accurate documentation details the course of patient care, and we should describe our thoughts in a clear and logical manner. Doing so minimizes the risk of misinterpretation by other clinicians or attorneys. Make sure the documentation of each appointment details the reason(s) for the patient’s visit, the effectiveness of treatment, possible treatment nonadherence, our clinical assessment, treatment consent, changes to the patient’s treatment plan, follow-up plans, reasons for not pursuing certain actions (eg, hospitalization), and a suicide risk assessment (and/or a violence risk assessment, if clinically indicated).2 Document missed or rescheduled appointments, and telephone and electronic contact with patients. Also be sure to use only commonly approved abbreviations.2 Document these items sooner rather than later because doing so improves the credibility of your charting.1 If you are handwriting notes, add the date and time to each encounter and make sure your handwriting is legible. Describe the behaviors of patients in objective and nonjudgmental terms.3 Documenting quotes from patients can convey crucial information about what was considered when making clinical decisions.1
Practices to avoid
If there is a need to make changes to previous entries, ensure these corrections are not mistaken for alterations. Each health care institution has its own policy for making corrections and addenda to medical records. Corrections to a patient’s medical record are acceptable, provided they are done appropriately, as I outlined in a previous Pearls article.4 Minimize or eliminate the copying and pasting of information; doing so can improve the efficiency of our documentation, but the practice can undermine the quality of the medical record, increase the risk of outdated and repetitive information being included, lead to clinical errors, and lead to overbilling of services.5 Finally, be sure to avoid speculation, personal commentary about patients and their family members, and language with negative connotations (unless such language is a direct quote from the patient).2,3
1. Mossman D. Tips to make documentation easier, faster, and more satisfying. Current Psychiatry. 2008;7(2):80,84-86.
2. Staus C. Documentation: your very best defense. Psychiatric News. 2022;57(4):7,19.
3. Nelson KJ. How to use patient-centered language in documentation. Current Psychiatry. 2011;10(10):70.
4. Joshi KG. Metadata, malpractice claims, and making changes to the EHR. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(3):e1-e3. doi:10.12788/cp.0106
5. Neal D. Do’s and don’ts of electronic documentation. Psychiatric News. 2021;56(8):7.
Medical record documentation serves as a reminder of previous discussions with patients and what happened during their visits, a reimbursement justification for services, a communication tool to coordinate care with current and future clinicians, and a basis for defense in legal or regulatory matters.1,2 Documentation should be thorough, accurate, timely, and objective, with the ultimate goal of communicating our thoughts in an easily understood manner to other clinicians or attorneys.2 If we fail to achieve this goal, we may inadvertently give the impression that our care was hurried, incomplete, or thoughtless.2
Although not an exhaustive list, this article outlines strategies to employ and practices to avoid in our documentation efforts so we may enhance our defense in case of litigation and ensure the smooth transition of care for our patients.
Strategies to employ
Proper and accurate documentation details the course of patient care, and we should describe our thoughts in a clear and logical manner. Doing so minimizes the risk of misinterpretation by other clinicians or attorneys. Make sure the documentation of each appointment details the reason(s) for the patient’s visit, the effectiveness of treatment, possible treatment nonadherence, our clinical assessment, treatment consent, changes to the patient’s treatment plan, follow-up plans, reasons for not pursuing certain actions (eg, hospitalization), and a suicide risk assessment (and/or a violence risk assessment, if clinically indicated).2 Document missed or rescheduled appointments, and telephone and electronic contact with patients. Also be sure to use only commonly approved abbreviations.2 Document these items sooner rather than later because doing so improves the credibility of your charting.1 If you are handwriting notes, add the date and time to each encounter and make sure your handwriting is legible. Describe the behaviors of patients in objective and nonjudgmental terms.3 Documenting quotes from patients can convey crucial information about what was considered when making clinical decisions.1
Practices to avoid
If there is a need to make changes to previous entries, ensure these corrections are not mistaken for alterations. Each health care institution has its own policy for making corrections and addenda to medical records. Corrections to a patient’s medical record are acceptable, provided they are done appropriately, as I outlined in a previous Pearls article.4 Minimize or eliminate the copying and pasting of information; doing so can improve the efficiency of our documentation, but the practice can undermine the quality of the medical record, increase the risk of outdated and repetitive information being included, lead to clinical errors, and lead to overbilling of services.5 Finally, be sure to avoid speculation, personal commentary about patients and their family members, and language with negative connotations (unless such language is a direct quote from the patient).2,3
Medical record documentation serves as a reminder of previous discussions with patients and what happened during their visits, a reimbursement justification for services, a communication tool to coordinate care with current and future clinicians, and a basis for defense in legal or regulatory matters.1,2 Documentation should be thorough, accurate, timely, and objective, with the ultimate goal of communicating our thoughts in an easily understood manner to other clinicians or attorneys.2 If we fail to achieve this goal, we may inadvertently give the impression that our care was hurried, incomplete, or thoughtless.2
Although not an exhaustive list, this article outlines strategies to employ and practices to avoid in our documentation efforts so we may enhance our defense in case of litigation and ensure the smooth transition of care for our patients.
Strategies to employ
Proper and accurate documentation details the course of patient care, and we should describe our thoughts in a clear and logical manner. Doing so minimizes the risk of misinterpretation by other clinicians or attorneys. Make sure the documentation of each appointment details the reason(s) for the patient’s visit, the effectiveness of treatment, possible treatment nonadherence, our clinical assessment, treatment consent, changes to the patient’s treatment plan, follow-up plans, reasons for not pursuing certain actions (eg, hospitalization), and a suicide risk assessment (and/or a violence risk assessment, if clinically indicated).2 Document missed or rescheduled appointments, and telephone and electronic contact with patients. Also be sure to use only commonly approved abbreviations.2 Document these items sooner rather than later because doing so improves the credibility of your charting.1 If you are handwriting notes, add the date and time to each encounter and make sure your handwriting is legible. Describe the behaviors of patients in objective and nonjudgmental terms.3 Documenting quotes from patients can convey crucial information about what was considered when making clinical decisions.1
Practices to avoid
If there is a need to make changes to previous entries, ensure these corrections are not mistaken for alterations. Each health care institution has its own policy for making corrections and addenda to medical records. Corrections to a patient’s medical record are acceptable, provided they are done appropriately, as I outlined in a previous Pearls article.4 Minimize or eliminate the copying and pasting of information; doing so can improve the efficiency of our documentation, but the practice can undermine the quality of the medical record, increase the risk of outdated and repetitive information being included, lead to clinical errors, and lead to overbilling of services.5 Finally, be sure to avoid speculation, personal commentary about patients and their family members, and language with negative connotations (unless such language is a direct quote from the patient).2,3
1. Mossman D. Tips to make documentation easier, faster, and more satisfying. Current Psychiatry. 2008;7(2):80,84-86.
2. Staus C. Documentation: your very best defense. Psychiatric News. 2022;57(4):7,19.
3. Nelson KJ. How to use patient-centered language in documentation. Current Psychiatry. 2011;10(10):70.
4. Joshi KG. Metadata, malpractice claims, and making changes to the EHR. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(3):e1-e3. doi:10.12788/cp.0106
5. Neal D. Do’s and don’ts of electronic documentation. Psychiatric News. 2021;56(8):7.
1. Mossman D. Tips to make documentation easier, faster, and more satisfying. Current Psychiatry. 2008;7(2):80,84-86.
2. Staus C. Documentation: your very best defense. Psychiatric News. 2022;57(4):7,19.
3. Nelson KJ. How to use patient-centered language in documentation. Current Psychiatry. 2011;10(10):70.
4. Joshi KG. Metadata, malpractice claims, and making changes to the EHR. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(3):e1-e3. doi:10.12788/cp.0106
5. Neal D. Do’s and don’ts of electronic documentation. Psychiatric News. 2021;56(8):7.
Lithium, valproate, and suicide risk: Analysis of 98,831 cases
The current academic psychiatry paradigm reinforces that lithium reduces suicide risk, more so than other medications, including valproate. However, data from multiple sources contradict this “evidence-based” belief.
Data do not support lithium’s supposed advantage
An 8-year prospective study in Sweden by Song et al1 tracked 51,535 patients with bipolar disorder from 2005 to 2013. In their conclusions, the authors of this study omitted some surprising numbers that contradict the dominant paradigm. There were 230 (1.089%) completed suicides in the lithium group (N = 21,129), 99 (1.177%) in the valproate group (N = 8,411), and 308 (1.195%) in the “other medication” group (N = 25,780). This difference of .088% is too small (95% CI, -.180% to .358%) to substantiate the purported advantage of lithium over valproate. More important is that in terms of suicide-related events, the medication group excluding lithium and valproate had 2,018 (7.8%) events vs lithium 2,142 (10.1%) and valproate 1,105 (13.1%). The difference of 2.3% is statistically significant (95% CI, 1.8% to 2.8%). These numbers reflect fewer suicide-related events with psychiatric medications other than lithium and valproate. Compounding the problem is a design flaw in which 3,785 patients were counted twice in the lithium and valproate groups (21,129 + 8,411 + 25,780 = 55,320, which is more than the 51,535 patients in the study). By falsely inflating the denominator (N) for the lithium and valproate groups, the respective published rates are deceptively lower than the actual rates. Song et al1 did not provide an adequate explanation for these findings and omitted them from their conclusions.
In Schatzberg’s Manual of Clinical Psychopharmacology, the authors cited Song et al1 but omitted these findings as well, and stated “lithium is clearly effective in preventing suicide attempts and completions in bipolar patients.”2 In Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology, the author wrote “lithium actually reduces suicide in patients with bipolar disorder.”3 In a review article,
In an overlapping period, National Poison Data System (NPDS) data of single substance exposures painted a different picture in the United States.6 During 2006-2013, the lithium group (N = 26,144) had 32 deaths (all causes) (.122%), and the valproate group (N = 25,630) had 16 deaths (.062%). During 2006-2020, the lithium group (N = 52,262) had 55 deaths (.105%), and the valproate group (N = 46,569) had 31 deaths (.067%). Clearly there is a major disconnect between lithium’s advertised ability to reduce suicide risk and the actual mortality rate, as evidenced by 98,831 cases reported to NPDS during 2006-2020. One would expect a lower rate in the lithium group, but data show it is higher than in the valproate group. This underscores the common fallacy of most lithium studies: each is based on a very small sample (N < 100), and the statistical inference about the entire population is tenuous. If lithium truly reduces suicide risk 5-fold, it would be seen in a sample of 98,831. The law of large numbers and central limit theorem state that as N increases, the variability of the rate progressively decreases. This can be easily demonstrated with computer simulation models and simple Python code, or on the average fuel economy display of most cars.
What about the relative lethality?
The APA Textbook of Suicide Risk Assessment and Management stated that it is important to consider the relative lethality (RL) of prescription medications.7 The RL equation (RL = 310x / LD50) represents the ratio of a 30-day supply of medication to the human equivalent LD50 for a 60-kg person (x is the daily dose and LD50 is the rat oral lethal dose 50).8 Time series analysis shows that the lithium relative morbidity (RM) is consistently double that of valproate (Figure6). Regression models have shown high correlation and causality between RL and RM.9-11 It is surprising that valproate (RL = 1,666%) has a lower RM than lithium (RL = 1,063%). This paradox can be easily explained with clinical insight. The RL equation compares medications at the maximum daily dose, but in routine practice valproate is commonly prescribed at 1,000 mg/d (28% of the maximum 3,600 mg/d). Lithium is commonly prescribed at 1,200 mg/d (67% of the maximum 1,800 mg/d). Within these dosing parameters, the effective RL is valproate 463% and lithium 709%. The 2020 RM is valproate 22% and lithium 43%.12 The COVID-19 pandemic did not affect the predicted RM. Confirming these numbers, Song et al1 acknowledged “greater safety in case of overdose for valproate in clinical practice.” Baldessarini et al4 asserted “the fatality risk of lithium overdose is only moderate, and very similar to modern antidepressants and second-generation antipsychotics.”4 This claim is contradicted by the RL equation and regression models.7-11 Lithium’s RL is 19 times higher than that of fluoxetine, and 30 times higher than that of olanzapine.8 Lithium’s RM is nearly identical to amitriptyline (42%), vs fluoxetine (12%).12
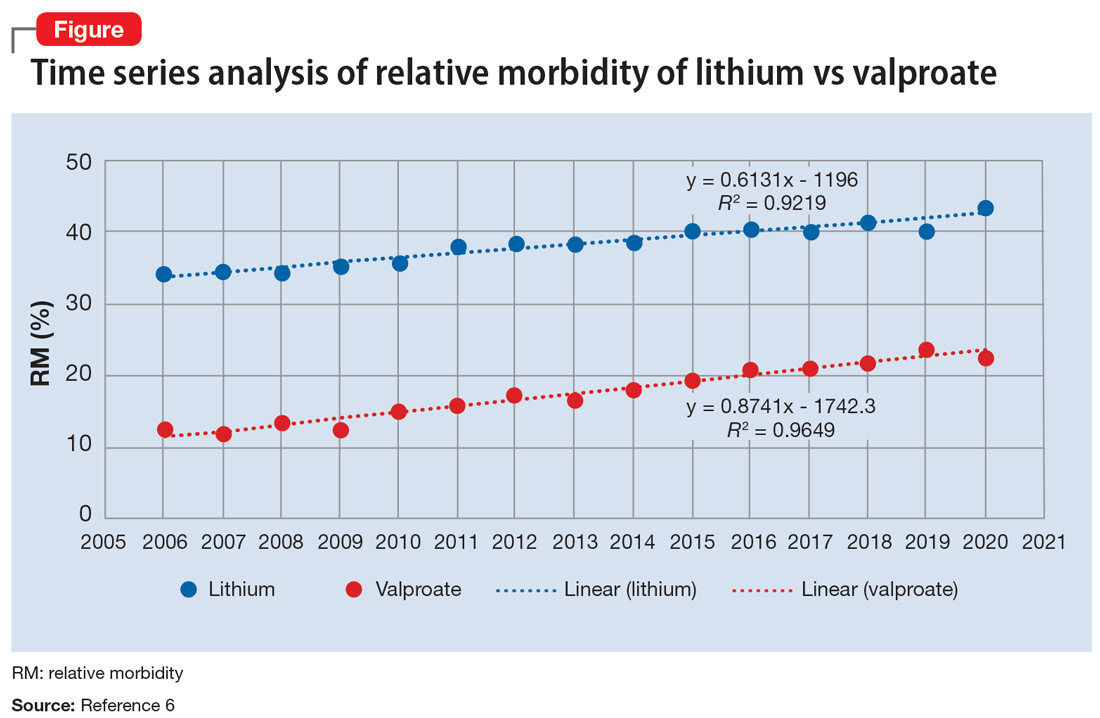
Data-driven analysis shows that lithium has higher rates of morbidity and mortality than valproate, as evidenced by 98,831 NPDS cases during 2006-2020. These hard numbers speak for themselves and contradict the dominant paradigm, which proclaims lithium’s superiority in reducing suicide risk.
1. Song J, Sjölander A, Joas E, et al. Suicidal behavior during lithium and valproate treatment: a within-individual 8-year prospective study of 50,000 patients with bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174(8):795-802.
2. Schatzberg AF, DeBattista C. Schatzberg’s Manual of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 9th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:335.
3. Stahl SM. Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. Cambridge University Press; 2013:372.
4. Baldessarini RJ, Tondo L, Davis P, et al. Decreased risk of suicides and attempts during long-term lithium treatment: a meta-analytic review. Bipolar Disord. 2006;8(5 Pt 2):625-639.
5. Oquendo MA, Galfalvy HC, Currier D, et al. Treatment of suicide attempters with bipolar disorder: a randomized clinical trial comparing lithium and valproate in the prevention of suicidal behavior. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168(10):1050-1056.
6. American Association of Poison Control Centers. Annual reports. Accessed August 25, 2022. https://aapcc.org/annual-reports
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL (eds). The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Risk Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020:17-19.
8. Giurca D. Decreasing suicide risk with math. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):57-59,A,B.
9. Giurca D. Data-driven prescribing. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(10):e6-e8.
10. Giurca D. Time series analysis of poison control data. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(6):e5-e9.
11. Giurca D, Hodgman MJ. Relative lethality of hypertension drugs. J Med Toxicol. 2022;18(2):81. 2022 American College of Medical Toxicology Annual Scientific Meeting abstract 020.
12. Gummin DD, Mowry JB, Beuhler MD, et al. 2020 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 38th Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021;59(12):1282-1501.
The current academic psychiatry paradigm reinforces that lithium reduces suicide risk, more so than other medications, including valproate. However, data from multiple sources contradict this “evidence-based” belief.
Data do not support lithium’s supposed advantage
An 8-year prospective study in Sweden by Song et al1 tracked 51,535 patients with bipolar disorder from 2005 to 2013. In their conclusions, the authors of this study omitted some surprising numbers that contradict the dominant paradigm. There were 230 (1.089%) completed suicides in the lithium group (N = 21,129), 99 (1.177%) in the valproate group (N = 8,411), and 308 (1.195%) in the “other medication” group (N = 25,780). This difference of .088% is too small (95% CI, -.180% to .358%) to substantiate the purported advantage of lithium over valproate. More important is that in terms of suicide-related events, the medication group excluding lithium and valproate had 2,018 (7.8%) events vs lithium 2,142 (10.1%) and valproate 1,105 (13.1%). The difference of 2.3% is statistically significant (95% CI, 1.8% to 2.8%). These numbers reflect fewer suicide-related events with psychiatric medications other than lithium and valproate. Compounding the problem is a design flaw in which 3,785 patients were counted twice in the lithium and valproate groups (21,129 + 8,411 + 25,780 = 55,320, which is more than the 51,535 patients in the study). By falsely inflating the denominator (N) for the lithium and valproate groups, the respective published rates are deceptively lower than the actual rates. Song et al1 did not provide an adequate explanation for these findings and omitted them from their conclusions.
In Schatzberg’s Manual of Clinical Psychopharmacology, the authors cited Song et al1 but omitted these findings as well, and stated “lithium is clearly effective in preventing suicide attempts and completions in bipolar patients.”2 In Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology, the author wrote “lithium actually reduces suicide in patients with bipolar disorder.”3 In a review article,
In an overlapping period, National Poison Data System (NPDS) data of single substance exposures painted a different picture in the United States.6 During 2006-2013, the lithium group (N = 26,144) had 32 deaths (all causes) (.122%), and the valproate group (N = 25,630) had 16 deaths (.062%). During 2006-2020, the lithium group (N = 52,262) had 55 deaths (.105%), and the valproate group (N = 46,569) had 31 deaths (.067%). Clearly there is a major disconnect between lithium’s advertised ability to reduce suicide risk and the actual mortality rate, as evidenced by 98,831 cases reported to NPDS during 2006-2020. One would expect a lower rate in the lithium group, but data show it is higher than in the valproate group. This underscores the common fallacy of most lithium studies: each is based on a very small sample (N < 100), and the statistical inference about the entire population is tenuous. If lithium truly reduces suicide risk 5-fold, it would be seen in a sample of 98,831. The law of large numbers and central limit theorem state that as N increases, the variability of the rate progressively decreases. This can be easily demonstrated with computer simulation models and simple Python code, or on the average fuel economy display of most cars.
What about the relative lethality?
The APA Textbook of Suicide Risk Assessment and Management stated that it is important to consider the relative lethality (RL) of prescription medications.7 The RL equation (RL = 310x / LD50) represents the ratio of a 30-day supply of medication to the human equivalent LD50 for a 60-kg person (x is the daily dose and LD50 is the rat oral lethal dose 50).8 Time series analysis shows that the lithium relative morbidity (RM) is consistently double that of valproate (Figure6). Regression models have shown high correlation and causality between RL and RM.9-11 It is surprising that valproate (RL = 1,666%) has a lower RM than lithium (RL = 1,063%). This paradox can be easily explained with clinical insight. The RL equation compares medications at the maximum daily dose, but in routine practice valproate is commonly prescribed at 1,000 mg/d (28% of the maximum 3,600 mg/d). Lithium is commonly prescribed at 1,200 mg/d (67% of the maximum 1,800 mg/d). Within these dosing parameters, the effective RL is valproate 463% and lithium 709%. The 2020 RM is valproate 22% and lithium 43%.12 The COVID-19 pandemic did not affect the predicted RM. Confirming these numbers, Song et al1 acknowledged “greater safety in case of overdose for valproate in clinical practice.” Baldessarini et al4 asserted “the fatality risk of lithium overdose is only moderate, and very similar to modern antidepressants and second-generation antipsychotics.”4 This claim is contradicted by the RL equation and regression models.7-11 Lithium’s RL is 19 times higher than that of fluoxetine, and 30 times higher than that of olanzapine.8 Lithium’s RM is nearly identical to amitriptyline (42%), vs fluoxetine (12%).12

Data-driven analysis shows that lithium has higher rates of morbidity and mortality than valproate, as evidenced by 98,831 NPDS cases during 2006-2020. These hard numbers speak for themselves and contradict the dominant paradigm, which proclaims lithium’s superiority in reducing suicide risk.
The current academic psychiatry paradigm reinforces that lithium reduces suicide risk, more so than other medications, including valproate. However, data from multiple sources contradict this “evidence-based” belief.
Data do not support lithium’s supposed advantage
An 8-year prospective study in Sweden by Song et al1 tracked 51,535 patients with bipolar disorder from 2005 to 2013. In their conclusions, the authors of this study omitted some surprising numbers that contradict the dominant paradigm. There were 230 (1.089%) completed suicides in the lithium group (N = 21,129), 99 (1.177%) in the valproate group (N = 8,411), and 308 (1.195%) in the “other medication” group (N = 25,780). This difference of .088% is too small (95% CI, -.180% to .358%) to substantiate the purported advantage of lithium over valproate. More important is that in terms of suicide-related events, the medication group excluding lithium and valproate had 2,018 (7.8%) events vs lithium 2,142 (10.1%) and valproate 1,105 (13.1%). The difference of 2.3% is statistically significant (95% CI, 1.8% to 2.8%). These numbers reflect fewer suicide-related events with psychiatric medications other than lithium and valproate. Compounding the problem is a design flaw in which 3,785 patients were counted twice in the lithium and valproate groups (21,129 + 8,411 + 25,780 = 55,320, which is more than the 51,535 patients in the study). By falsely inflating the denominator (N) for the lithium and valproate groups, the respective published rates are deceptively lower than the actual rates. Song et al1 did not provide an adequate explanation for these findings and omitted them from their conclusions.
In Schatzberg’s Manual of Clinical Psychopharmacology, the authors cited Song et al1 but omitted these findings as well, and stated “lithium is clearly effective in preventing suicide attempts and completions in bipolar patients.”2 In Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology, the author wrote “lithium actually reduces suicide in patients with bipolar disorder.”3 In a review article,
In an overlapping period, National Poison Data System (NPDS) data of single substance exposures painted a different picture in the United States.6 During 2006-2013, the lithium group (N = 26,144) had 32 deaths (all causes) (.122%), and the valproate group (N = 25,630) had 16 deaths (.062%). During 2006-2020, the lithium group (N = 52,262) had 55 deaths (.105%), and the valproate group (N = 46,569) had 31 deaths (.067%). Clearly there is a major disconnect between lithium’s advertised ability to reduce suicide risk and the actual mortality rate, as evidenced by 98,831 cases reported to NPDS during 2006-2020. One would expect a lower rate in the lithium group, but data show it is higher than in the valproate group. This underscores the common fallacy of most lithium studies: each is based on a very small sample (N < 100), and the statistical inference about the entire population is tenuous. If lithium truly reduces suicide risk 5-fold, it would be seen in a sample of 98,831. The law of large numbers and central limit theorem state that as N increases, the variability of the rate progressively decreases. This can be easily demonstrated with computer simulation models and simple Python code, or on the average fuel economy display of most cars.
What about the relative lethality?
The APA Textbook of Suicide Risk Assessment and Management stated that it is important to consider the relative lethality (RL) of prescription medications.7 The RL equation (RL = 310x / LD50) represents the ratio of a 30-day supply of medication to the human equivalent LD50 for a 60-kg person (x is the daily dose and LD50 is the rat oral lethal dose 50).8 Time series analysis shows that the lithium relative morbidity (RM) is consistently double that of valproate (Figure6). Regression models have shown high correlation and causality between RL and RM.9-11 It is surprising that valproate (RL = 1,666%) has a lower RM than lithium (RL = 1,063%). This paradox can be easily explained with clinical insight. The RL equation compares medications at the maximum daily dose, but in routine practice valproate is commonly prescribed at 1,000 mg/d (28% of the maximum 3,600 mg/d). Lithium is commonly prescribed at 1,200 mg/d (67% of the maximum 1,800 mg/d). Within these dosing parameters, the effective RL is valproate 463% and lithium 709%. The 2020 RM is valproate 22% and lithium 43%.12 The COVID-19 pandemic did not affect the predicted RM. Confirming these numbers, Song et al1 acknowledged “greater safety in case of overdose for valproate in clinical practice.” Baldessarini et al4 asserted “the fatality risk of lithium overdose is only moderate, and very similar to modern antidepressants and second-generation antipsychotics.”4 This claim is contradicted by the RL equation and regression models.7-11 Lithium’s RL is 19 times higher than that of fluoxetine, and 30 times higher than that of olanzapine.8 Lithium’s RM is nearly identical to amitriptyline (42%), vs fluoxetine (12%).12

Data-driven analysis shows that lithium has higher rates of morbidity and mortality than valproate, as evidenced by 98,831 NPDS cases during 2006-2020. These hard numbers speak for themselves and contradict the dominant paradigm, which proclaims lithium’s superiority in reducing suicide risk.
1. Song J, Sjölander A, Joas E, et al. Suicidal behavior during lithium and valproate treatment: a within-individual 8-year prospective study of 50,000 patients with bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174(8):795-802.
2. Schatzberg AF, DeBattista C. Schatzberg’s Manual of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 9th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:335.
3. Stahl SM. Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. Cambridge University Press; 2013:372.
4. Baldessarini RJ, Tondo L, Davis P, et al. Decreased risk of suicides and attempts during long-term lithium treatment: a meta-analytic review. Bipolar Disord. 2006;8(5 Pt 2):625-639.
5. Oquendo MA, Galfalvy HC, Currier D, et al. Treatment of suicide attempters with bipolar disorder: a randomized clinical trial comparing lithium and valproate in the prevention of suicidal behavior. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168(10):1050-1056.
6. American Association of Poison Control Centers. Annual reports. Accessed August 25, 2022. https://aapcc.org/annual-reports
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL (eds). The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Risk Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020:17-19.
8. Giurca D. Decreasing suicide risk with math. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):57-59,A,B.
9. Giurca D. Data-driven prescribing. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(10):e6-e8.
10. Giurca D. Time series analysis of poison control data. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(6):e5-e9.
11. Giurca D, Hodgman MJ. Relative lethality of hypertension drugs. J Med Toxicol. 2022;18(2):81. 2022 American College of Medical Toxicology Annual Scientific Meeting abstract 020.
12. Gummin DD, Mowry JB, Beuhler MD, et al. 2020 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 38th Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021;59(12):1282-1501.
1. Song J, Sjölander A, Joas E, et al. Suicidal behavior during lithium and valproate treatment: a within-individual 8-year prospective study of 50,000 patients with bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174(8):795-802.
2. Schatzberg AF, DeBattista C. Schatzberg’s Manual of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 9th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:335.
3. Stahl SM. Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology. 4th ed. Cambridge University Press; 2013:372.
4. Baldessarini RJ, Tondo L, Davis P, et al. Decreased risk of suicides and attempts during long-term lithium treatment: a meta-analytic review. Bipolar Disord. 2006;8(5 Pt 2):625-639.
5. Oquendo MA, Galfalvy HC, Currier D, et al. Treatment of suicide attempters with bipolar disorder: a randomized clinical trial comparing lithium and valproate in the prevention of suicidal behavior. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168(10):1050-1056.
6. American Association of Poison Control Centers. Annual reports. Accessed August 25, 2022. https://aapcc.org/annual-reports
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL (eds). The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Risk Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020:17-19.
8. Giurca D. Decreasing suicide risk with math. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(2):57-59,A,B.
9. Giurca D. Data-driven prescribing. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(10):e6-e8.
10. Giurca D. Time series analysis of poison control data. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(6):e5-e9.
11. Giurca D, Hodgman MJ. Relative lethality of hypertension drugs. J Med Toxicol. 2022;18(2):81. 2022 American College of Medical Toxicology Annual Scientific Meeting abstract 020.
12. Gummin DD, Mowry JB, Beuhler MD, et al. 2020 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 38th Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021;59(12):1282-1501.
Postop analgesia in Saudi Arabia and the United States: A resident’s perspective
I had the opportunity to experience first-hand acute postoperative pain management in both the United States and Saudi Arabia. In this article, I discuss some of the differences in how postop pain is managed in each location, potential reasons for these differences, how they may impact patients over time, and the psychiatrist’s role in raising awareness about the hazards of overprescribing analgesic medications.
Vast differences in postop opioid prescribing
From personal observation and literature review, I was appalled by the amount of oxycodone tablets patients are typically discharged home with after a surgical procedure in the United States. Depending on the extent of the surgical procedure, opioid-naïve patients were routinely discharged with 40 to 120 tablets of oxycodone 5 mg. A ventral hernia repair or laparotomy was on the high end of how much oxycodone was provided, and a laparoscopic cholecystectomy or inguinal hernia repair was on the low end. At least one study has supported this observation, finding a wide variation and excessive doses of opioids prescribed postop.1 Notably, among opioids obtained by postsurgical patients, 42% to 71% of all tablets went unused.2 Nevertheless, prescribing in this manner became the standard for postop pain management—possibly in an effort to maximize patient satisfaction on surveys. Additionally, marketing and promotion by the pharmaceutical industry appears to have considerably amplified the prescription, sales, and availability of opioids.3
Signing those prescriptions always left a bad taste in my mouth out of concern for the potential for initiating chronic opioid use.4 Personally, I would prescribe the lowest reasonable number of narcotic tablets for my patients, along with acetaminophen and ibuprofen, knowing that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are sufficient for treating postop pain and will decrease opioid requirements, therefore minimizing opiate-induced adverse events.5 Overtreatment of pain with narcotics as first-line therapy is particularly problematic when treating postop pain in children after minor procedures, such as an umbilical hernia repair.Allowing children to resort to a narcotic analgesic agent as a first-line therapy had the potential to develop into an opioid use disorder (OUD) later in life if environmental factors tipped the scales.6
In the hospital in Saudi Arabia where I initially trained, surgery residents were not permitted to prescribe narcotics. The standard of care was to discharge patients with acetaminophen and ibuprofen. In cases where there was an indication for pain treatment with narcotics, stringent regulations were in place. For example, in my experience, which is corroborated by one study,6 special “narcotic forms” are required in the Middle East. In most of these countries, access to these forms is restricted.7 Moreover, pharmacists would only accept this special form when attested to by the surgery consultant (the equivalent of an attending physician in the United States). These consultants would typically write a prescription for 9 to 15 oxycodone 5 mg tablets. Patients receiving such medications were closely watched and followed up in the surgery clinic 3 to 5 days after discharge. Patients were also required to fill out a form detailing their contact information, including their home address and national ID number, to be able to pick up their prescription. Furthermore, apart from 2 Middle East countries, opioids were only available from hospital pharmacies, which were independent of the general hospital pharmacy in location and staff training.8
The psychiatrist’s role
Adapting similar stringent practices for prescribing narcotics in the United States might reduce 1 risk factor for OUD in postop patients. Surgeons attempt to provide the best care by maximizing analgesia, but psychiatrists see firsthand the consequences of overprescribing, and play a direct role in managing patients’ OUDs. As psychiatrists, we have a duty to continue to raise awareness and alert other clinicians about the hazards of overprescribing narcotic analgesic agents.
1. Hill MV, McMahon ML, Stucke RS, et al. Wide variation and excessive dosage of opioid prescriptions for common general surgical procedures. Ann Surg. 2017;265(4):709-714.
2. Bicket MC, Long JJ, Pronovost PJ, et al. Prescription opioid analgesics commonly unused after surgery: a systematic review. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(11):1066-1071.
3. Van Zee A. The promotion and marketing of oxycontin: commercial triumph, public health tragedy. Am J Public Health. 2009;99(2):221-227.
4. Sun EC, Darnall BD, Baker LC, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for chronic opioid use among opioid-naive patients in the postoperative period. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(9):1286-1293.
5. Gupta A, Bah M. NSAIDs in the treatment of postoperative pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016;20(11):62. doi: 10.1007/s11916-016-0591-7
6. Pollini RA, Banta-Green CJ, Cuevas-Mota J, et al. Problematic use of prescription-type opioids prior to heroin use among young heroin injectors. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2011;2(1):173-180.
7. Cleary J, Silbermann M, Scholten W, et al. Formulary availability and regulatory barriers to accessibility of opioids for cancer pain in the Middle East: a report from the Global Opioid Policy Initiative (GOPI). Ann Oncol. 2013;24 Suppl 11:xi51-xi59. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt503
8. Lankenau SE, Teti M, Silva K, et al. Initiation into prescription opioid misuse amongst young injection drug users. Int J Drug Policy. 2012;23(1):37-44.
I had the opportunity to experience first-hand acute postoperative pain management in both the United States and Saudi Arabia. In this article, I discuss some of the differences in how postop pain is managed in each location, potential reasons for these differences, how they may impact patients over time, and the psychiatrist’s role in raising awareness about the hazards of overprescribing analgesic medications.
Vast differences in postop opioid prescribing
From personal observation and literature review, I was appalled by the amount of oxycodone tablets patients are typically discharged home with after a surgical procedure in the United States. Depending on the extent of the surgical procedure, opioid-naïve patients were routinely discharged with 40 to 120 tablets of oxycodone 5 mg. A ventral hernia repair or laparotomy was on the high end of how much oxycodone was provided, and a laparoscopic cholecystectomy or inguinal hernia repair was on the low end. At least one study has supported this observation, finding a wide variation and excessive doses of opioids prescribed postop.1 Notably, among opioids obtained by postsurgical patients, 42% to 71% of all tablets went unused.2 Nevertheless, prescribing in this manner became the standard for postop pain management—possibly in an effort to maximize patient satisfaction on surveys. Additionally, marketing and promotion by the pharmaceutical industry appears to have considerably amplified the prescription, sales, and availability of opioids.3
Signing those prescriptions always left a bad taste in my mouth out of concern for the potential for initiating chronic opioid use.4 Personally, I would prescribe the lowest reasonable number of narcotic tablets for my patients, along with acetaminophen and ibuprofen, knowing that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are sufficient for treating postop pain and will decrease opioid requirements, therefore minimizing opiate-induced adverse events.5 Overtreatment of pain with narcotics as first-line therapy is particularly problematic when treating postop pain in children after minor procedures, such as an umbilical hernia repair.Allowing children to resort to a narcotic analgesic agent as a first-line therapy had the potential to develop into an opioid use disorder (OUD) later in life if environmental factors tipped the scales.6
In the hospital in Saudi Arabia where I initially trained, surgery residents were not permitted to prescribe narcotics. The standard of care was to discharge patients with acetaminophen and ibuprofen. In cases where there was an indication for pain treatment with narcotics, stringent regulations were in place. For example, in my experience, which is corroborated by one study,6 special “narcotic forms” are required in the Middle East. In most of these countries, access to these forms is restricted.7 Moreover, pharmacists would only accept this special form when attested to by the surgery consultant (the equivalent of an attending physician in the United States). These consultants would typically write a prescription for 9 to 15 oxycodone 5 mg tablets. Patients receiving such medications were closely watched and followed up in the surgery clinic 3 to 5 days after discharge. Patients were also required to fill out a form detailing their contact information, including their home address and national ID number, to be able to pick up their prescription. Furthermore, apart from 2 Middle East countries, opioids were only available from hospital pharmacies, which were independent of the general hospital pharmacy in location and staff training.8
The psychiatrist’s role
Adapting similar stringent practices for prescribing narcotics in the United States might reduce 1 risk factor for OUD in postop patients. Surgeons attempt to provide the best care by maximizing analgesia, but psychiatrists see firsthand the consequences of overprescribing, and play a direct role in managing patients’ OUDs. As psychiatrists, we have a duty to continue to raise awareness and alert other clinicians about the hazards of overprescribing narcotic analgesic agents.
I had the opportunity to experience first-hand acute postoperative pain management in both the United States and Saudi Arabia. In this article, I discuss some of the differences in how postop pain is managed in each location, potential reasons for these differences, how they may impact patients over time, and the psychiatrist’s role in raising awareness about the hazards of overprescribing analgesic medications.
Vast differences in postop opioid prescribing
From personal observation and literature review, I was appalled by the amount of oxycodone tablets patients are typically discharged home with after a surgical procedure in the United States. Depending on the extent of the surgical procedure, opioid-naïve patients were routinely discharged with 40 to 120 tablets of oxycodone 5 mg. A ventral hernia repair or laparotomy was on the high end of how much oxycodone was provided, and a laparoscopic cholecystectomy or inguinal hernia repair was on the low end. At least one study has supported this observation, finding a wide variation and excessive doses of opioids prescribed postop.1 Notably, among opioids obtained by postsurgical patients, 42% to 71% of all tablets went unused.2 Nevertheless, prescribing in this manner became the standard for postop pain management—possibly in an effort to maximize patient satisfaction on surveys. Additionally, marketing and promotion by the pharmaceutical industry appears to have considerably amplified the prescription, sales, and availability of opioids.3
Signing those prescriptions always left a bad taste in my mouth out of concern for the potential for initiating chronic opioid use.4 Personally, I would prescribe the lowest reasonable number of narcotic tablets for my patients, along with acetaminophen and ibuprofen, knowing that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are sufficient for treating postop pain and will decrease opioid requirements, therefore minimizing opiate-induced adverse events.5 Overtreatment of pain with narcotics as first-line therapy is particularly problematic when treating postop pain in children after minor procedures, such as an umbilical hernia repair.Allowing children to resort to a narcotic analgesic agent as a first-line therapy had the potential to develop into an opioid use disorder (OUD) later in life if environmental factors tipped the scales.6
In the hospital in Saudi Arabia where I initially trained, surgery residents were not permitted to prescribe narcotics. The standard of care was to discharge patients with acetaminophen and ibuprofen. In cases where there was an indication for pain treatment with narcotics, stringent regulations were in place. For example, in my experience, which is corroborated by one study,6 special “narcotic forms” are required in the Middle East. In most of these countries, access to these forms is restricted.7 Moreover, pharmacists would only accept this special form when attested to by the surgery consultant (the equivalent of an attending physician in the United States). These consultants would typically write a prescription for 9 to 15 oxycodone 5 mg tablets. Patients receiving such medications were closely watched and followed up in the surgery clinic 3 to 5 days after discharge. Patients were also required to fill out a form detailing their contact information, including their home address and national ID number, to be able to pick up their prescription. Furthermore, apart from 2 Middle East countries, opioids were only available from hospital pharmacies, which were independent of the general hospital pharmacy in location and staff training.8
The psychiatrist’s role
Adapting similar stringent practices for prescribing narcotics in the United States might reduce 1 risk factor for OUD in postop patients. Surgeons attempt to provide the best care by maximizing analgesia, but psychiatrists see firsthand the consequences of overprescribing, and play a direct role in managing patients’ OUDs. As psychiatrists, we have a duty to continue to raise awareness and alert other clinicians about the hazards of overprescribing narcotic analgesic agents.
1. Hill MV, McMahon ML, Stucke RS, et al. Wide variation and excessive dosage of opioid prescriptions for common general surgical procedures. Ann Surg. 2017;265(4):709-714.
2. Bicket MC, Long JJ, Pronovost PJ, et al. Prescription opioid analgesics commonly unused after surgery: a systematic review. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(11):1066-1071.
3. Van Zee A. The promotion and marketing of oxycontin: commercial triumph, public health tragedy. Am J Public Health. 2009;99(2):221-227.
4. Sun EC, Darnall BD, Baker LC, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for chronic opioid use among opioid-naive patients in the postoperative period. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(9):1286-1293.
5. Gupta A, Bah M. NSAIDs in the treatment of postoperative pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016;20(11):62. doi: 10.1007/s11916-016-0591-7
6. Pollini RA, Banta-Green CJ, Cuevas-Mota J, et al. Problematic use of prescription-type opioids prior to heroin use among young heroin injectors. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2011;2(1):173-180.
7. Cleary J, Silbermann M, Scholten W, et al. Formulary availability and regulatory barriers to accessibility of opioids for cancer pain in the Middle East: a report from the Global Opioid Policy Initiative (GOPI). Ann Oncol. 2013;24 Suppl 11:xi51-xi59. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt503
8. Lankenau SE, Teti M, Silva K, et al. Initiation into prescription opioid misuse amongst young injection drug users. Int J Drug Policy. 2012;23(1):37-44.
1. Hill MV, McMahon ML, Stucke RS, et al. Wide variation and excessive dosage of opioid prescriptions for common general surgical procedures. Ann Surg. 2017;265(4):709-714.
2. Bicket MC, Long JJ, Pronovost PJ, et al. Prescription opioid analgesics commonly unused after surgery: a systematic review. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(11):1066-1071.
3. Van Zee A. The promotion and marketing of oxycontin: commercial triumph, public health tragedy. Am J Public Health. 2009;99(2):221-227.
4. Sun EC, Darnall BD, Baker LC, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for chronic opioid use among opioid-naive patients in the postoperative period. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(9):1286-1293.
5. Gupta A, Bah M. NSAIDs in the treatment of postoperative pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016;20(11):62. doi: 10.1007/s11916-016-0591-7
6. Pollini RA, Banta-Green CJ, Cuevas-Mota J, et al. Problematic use of prescription-type opioids prior to heroin use among young heroin injectors. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2011;2(1):173-180.
7. Cleary J, Silbermann M, Scholten W, et al. Formulary availability and regulatory barriers to accessibility of opioids for cancer pain in the Middle East: a report from the Global Opioid Policy Initiative (GOPI). Ann Oncol. 2013;24 Suppl 11:xi51-xi59. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt503
8. Lankenau SE, Teti M, Silva K, et al. Initiation into prescription opioid misuse amongst young injection drug users. Int J Drug Policy. 2012;23(1):37-44.
Top pregnancy apps for your patients
Pregnancy apps are more popular as patients use the internet to seek information about pregnancy and childbirth.1 Research has shown that over 50% of pregnant patients download apps focused on pregnancy, with an average of 3 being tried.2 This is especially true during the COVID-19 pandemic, when patients seek information but may want to minimize clinical exposures. Other research has shown that women primarily use apps to monitor fetal development and to obtain information on nutrition and antenatal care.3
We identified apps and rated their contents and features.4 To identify the apps, we performed a Google search to mimic what a patient may do. We scored the identified apps based on what has been shown to make apps successful, as well as desired functions of the most commonly used apps. The quality of the applications was relatively varied, with many of the apps (60%) not having comprehensive information for every stage of pregnancy and no app attaining a perfect score. However, the top 3 apps had near perfect scores of 15/16 and 14/16, missing points only for having advertisements and requiring an internet connection.
The table details these top 3 recommended pregnancy apps, along with a detailed shortened version of the APPLICATIONS scoring system, APPLI (App comprehensiveness, Price, Platform, Literature Used, Other special features). We hope this column will help you feel comfortable in helping patients use pregnancy apps, should they ask for recommendations.
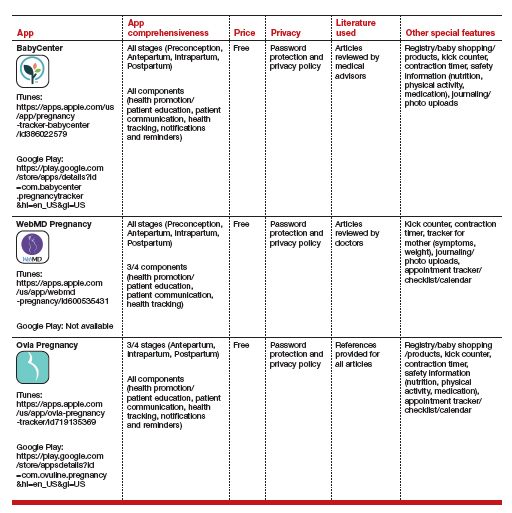
1. Romano AM. A changing landscape: implications of pregnant women’s internet use for childbirth educators. J Perinat Educ. 2007;16:18-24. doi: 10.1624/105812407X244903.
2. Jayaseelan R, Pichandy C, Rushandramani D. Usage of smartphone apps by women on their maternal life. J Mass Communicat Journalism. 2015;29:05:158-164. doi: 10.4172/2165-7912.1000267.
3. Wang N, Deng Z, Wen LM, et al. Understanding the use of smartphone apps for health information among pregnant Chinese women: mixed methods study. JMIR mHealth uHealth. 2019;18:7:e12631. doi: 10.2196/12631.
4. Frid G, Bogaert K, Chen KT. Mobile health apps for pregnant women: systematic search, evaluation, and analysis of features. J Med Internet Res. 2021;18:23:e25667. doi: 10.2196/25667.
Pregnancy apps are more popular as patients use the internet to seek information about pregnancy and childbirth.1 Research has shown that over 50% of pregnant patients download apps focused on pregnancy, with an average of 3 being tried.2 This is especially true during the COVID-19 pandemic, when patients seek information but may want to minimize clinical exposures. Other research has shown that women primarily use apps to monitor fetal development and to obtain information on nutrition and antenatal care.3
We identified apps and rated their contents and features.4 To identify the apps, we performed a Google search to mimic what a patient may do. We scored the identified apps based on what has been shown to make apps successful, as well as desired functions of the most commonly used apps. The quality of the applications was relatively varied, with many of the apps (60%) not having comprehensive information for every stage of pregnancy and no app attaining a perfect score. However, the top 3 apps had near perfect scores of 15/16 and 14/16, missing points only for having advertisements and requiring an internet connection.
The table details these top 3 recommended pregnancy apps, along with a detailed shortened version of the APPLICATIONS scoring system, APPLI (App comprehensiveness, Price, Platform, Literature Used, Other special features). We hope this column will help you feel comfortable in helping patients use pregnancy apps, should they ask for recommendations.

Pregnancy apps are more popular as patients use the internet to seek information about pregnancy and childbirth.1 Research has shown that over 50% of pregnant patients download apps focused on pregnancy, with an average of 3 being tried.2 This is especially true during the COVID-19 pandemic, when patients seek information but may want to minimize clinical exposures. Other research has shown that women primarily use apps to monitor fetal development and to obtain information on nutrition and antenatal care.3
We identified apps and rated their contents and features.4 To identify the apps, we performed a Google search to mimic what a patient may do. We scored the identified apps based on what has been shown to make apps successful, as well as desired functions of the most commonly used apps. The quality of the applications was relatively varied, with many of the apps (60%) not having comprehensive information for every stage of pregnancy and no app attaining a perfect score. However, the top 3 apps had near perfect scores of 15/16 and 14/16, missing points only for having advertisements and requiring an internet connection.
The table details these top 3 recommended pregnancy apps, along with a detailed shortened version of the APPLICATIONS scoring system, APPLI (App comprehensiveness, Price, Platform, Literature Used, Other special features). We hope this column will help you feel comfortable in helping patients use pregnancy apps, should they ask for recommendations.

1. Romano AM. A changing landscape: implications of pregnant women’s internet use for childbirth educators. J Perinat Educ. 2007;16:18-24. doi: 10.1624/105812407X244903.
2. Jayaseelan R, Pichandy C, Rushandramani D. Usage of smartphone apps by women on their maternal life. J Mass Communicat Journalism. 2015;29:05:158-164. doi: 10.4172/2165-7912.1000267.
3. Wang N, Deng Z, Wen LM, et al. Understanding the use of smartphone apps for health information among pregnant Chinese women: mixed methods study. JMIR mHealth uHealth. 2019;18:7:e12631. doi: 10.2196/12631.
4. Frid G, Bogaert K, Chen KT. Mobile health apps for pregnant women: systematic search, evaluation, and analysis of features. J Med Internet Res. 2021;18:23:e25667. doi: 10.2196/25667.
1. Romano AM. A changing landscape: implications of pregnant women’s internet use for childbirth educators. J Perinat Educ. 2007;16:18-24. doi: 10.1624/105812407X244903.
2. Jayaseelan R, Pichandy C, Rushandramani D. Usage of smartphone apps by women on their maternal life. J Mass Communicat Journalism. 2015;29:05:158-164. doi: 10.4172/2165-7912.1000267.
3. Wang N, Deng Z, Wen LM, et al. Understanding the use of smartphone apps for health information among pregnant Chinese women: mixed methods study. JMIR mHealth uHealth. 2019;18:7:e12631. doi: 10.2196/12631.
4. Frid G, Bogaert K, Chen KT. Mobile health apps for pregnant women: systematic search, evaluation, and analysis of features. J Med Internet Res. 2021;18:23:e25667. doi: 10.2196/25667.