User login
The Official Newspaper of the American Association for Thoracic Surgery
Tobacco-related cancer incidence, mortality drop
Tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality rates dropped from 2004 to 2013, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report published on Nov. 11, 2016.
Overall, tobacco-related invasive cancer incidence decreased from 206 cases per 100,000 during 2004-2008 to 193 cases per 100,000 during 2009-2013.
The announcement of this data marks a continuation of the downward trend that has been observed since the 1990s, lead author S. Jane Henley, MSPH, and her associates at the CDC wrote in the report (MMWR. 2016 Nov 11;65[44]:1212-8).
Despite this continued decline in tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality rates, the tobacco-related cancer burden remains high, and disparities in the rates and decline of tobacco-related cancer persists.
“Tobacco use remains the leading preventable cause of disease and death in the United States,” reported Henley and her associates. For each year between 2009 and 2013, an estimated 660,000 Americans were diagnosed with tobacco-related cancer, and an estimated 343,000 people died from those cancers, according to the investigators’ analysis of data collected by the United States Cancer Statistics working group, which compiles data from multiple nationwide sources including the National Program of Cancer Registries and the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program.
Tobacco-related cancer incidence and deaths were higher among men than women and higher among blacks than any other ethnic group. However, the cancer incidence and mortality rates also declined the fastest among men and blacks, compared with women and other ethnic groups, respectively.
Cancer incidence and death were also highest and decreased the most slowly in counties with lower educational attainment or highest poverty. Conversely, cancer incidence and mortality was the lowest and decreased the most quickly in metropolitan areas with populations greater than 1 million people.
Given that an estimated 40% of cancers diagnosed in the country and 3 in 10 cancer deaths are attributable to cigarette smoking and the use of smokeless tobacco, it is imperative that the CDC implement programs to help the almost 6 million smokers quit, CDC director Tom Frieden, MD, said in an associated telebriefing. Most people who smoke want to quit, and the health care system should do all it can to help them, Dr. Frieden said. At the same time, he echoed a claim from Henley’s paper, which said many tobacco-related cancers could be prevented by reducing tobacco use through implementation of evidence-based tobacco prevention and control interventions, such as increasing tobacco product prices, enforcing smoke-free laws, and promoting anti-tobacco mass media campaigns. These programs should be tailored to local geographic areas and demographics given the continued inconsistent progress and persistent disparities in tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality, Dr. Frieden added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
Tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality rates dropped from 2004 to 2013, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report published on Nov. 11, 2016.
Overall, tobacco-related invasive cancer incidence decreased from 206 cases per 100,000 during 2004-2008 to 193 cases per 100,000 during 2009-2013.
The announcement of this data marks a continuation of the downward trend that has been observed since the 1990s, lead author S. Jane Henley, MSPH, and her associates at the CDC wrote in the report (MMWR. 2016 Nov 11;65[44]:1212-8).
Despite this continued decline in tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality rates, the tobacco-related cancer burden remains high, and disparities in the rates and decline of tobacco-related cancer persists.
“Tobacco use remains the leading preventable cause of disease and death in the United States,” reported Henley and her associates. For each year between 2009 and 2013, an estimated 660,000 Americans were diagnosed with tobacco-related cancer, and an estimated 343,000 people died from those cancers, according to the investigators’ analysis of data collected by the United States Cancer Statistics working group, which compiles data from multiple nationwide sources including the National Program of Cancer Registries and the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program.
Tobacco-related cancer incidence and deaths were higher among men than women and higher among blacks than any other ethnic group. However, the cancer incidence and mortality rates also declined the fastest among men and blacks, compared with women and other ethnic groups, respectively.
Cancer incidence and death were also highest and decreased the most slowly in counties with lower educational attainment or highest poverty. Conversely, cancer incidence and mortality was the lowest and decreased the most quickly in metropolitan areas with populations greater than 1 million people.
Given that an estimated 40% of cancers diagnosed in the country and 3 in 10 cancer deaths are attributable to cigarette smoking and the use of smokeless tobacco, it is imperative that the CDC implement programs to help the almost 6 million smokers quit, CDC director Tom Frieden, MD, said in an associated telebriefing. Most people who smoke want to quit, and the health care system should do all it can to help them, Dr. Frieden said. At the same time, he echoed a claim from Henley’s paper, which said many tobacco-related cancers could be prevented by reducing tobacco use through implementation of evidence-based tobacco prevention and control interventions, such as increasing tobacco product prices, enforcing smoke-free laws, and promoting anti-tobacco mass media campaigns. These programs should be tailored to local geographic areas and demographics given the continued inconsistent progress and persistent disparities in tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality, Dr. Frieden added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
Tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality rates dropped from 2004 to 2013, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report published on Nov. 11, 2016.
Overall, tobacco-related invasive cancer incidence decreased from 206 cases per 100,000 during 2004-2008 to 193 cases per 100,000 during 2009-2013.
The announcement of this data marks a continuation of the downward trend that has been observed since the 1990s, lead author S. Jane Henley, MSPH, and her associates at the CDC wrote in the report (MMWR. 2016 Nov 11;65[44]:1212-8).
Despite this continued decline in tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality rates, the tobacco-related cancer burden remains high, and disparities in the rates and decline of tobacco-related cancer persists.
“Tobacco use remains the leading preventable cause of disease and death in the United States,” reported Henley and her associates. For each year between 2009 and 2013, an estimated 660,000 Americans were diagnosed with tobacco-related cancer, and an estimated 343,000 people died from those cancers, according to the investigators’ analysis of data collected by the United States Cancer Statistics working group, which compiles data from multiple nationwide sources including the National Program of Cancer Registries and the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program.
Tobacco-related cancer incidence and deaths were higher among men than women and higher among blacks than any other ethnic group. However, the cancer incidence and mortality rates also declined the fastest among men and blacks, compared with women and other ethnic groups, respectively.
Cancer incidence and death were also highest and decreased the most slowly in counties with lower educational attainment or highest poverty. Conversely, cancer incidence and mortality was the lowest and decreased the most quickly in metropolitan areas with populations greater than 1 million people.
Given that an estimated 40% of cancers diagnosed in the country and 3 in 10 cancer deaths are attributable to cigarette smoking and the use of smokeless tobacco, it is imperative that the CDC implement programs to help the almost 6 million smokers quit, CDC director Tom Frieden, MD, said in an associated telebriefing. Most people who smoke want to quit, and the health care system should do all it can to help them, Dr. Frieden said. At the same time, he echoed a claim from Henley’s paper, which said many tobacco-related cancers could be prevented by reducing tobacco use through implementation of evidence-based tobacco prevention and control interventions, such as increasing tobacco product prices, enforcing smoke-free laws, and promoting anti-tobacco mass media campaigns. These programs should be tailored to local geographic areas and demographics given the continued inconsistent progress and persistent disparities in tobacco-related cancer incidence and mortality, Dr. Frieden added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
FROM MMWR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Tobacco-related cancer mortality dropped from 108 deaths per 100,000 during 2004-2008 to 100 per 100,000 during 2009-2013.
Data source: Retrospective analysis of United States Cancer Statistics data for 2004 to 2013.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors’ disclosures were not reported.
Home oxygen upped survival in PAH with severely impaired DLCO
LOS ANGELES – Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) patients with severely impaired diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) were much more likely to survive when they received home oxygen therapy, according to a disease registry analysis.
“We all know that supplemental oxygen is widely used with PAH,” said Harrison W. Farber, MD, director of the pulmonary hypertension center at Boston University. But there are practically no data showing that it is successful, and there are even fewer data for patients with PAH who have very low diffusion capacity, he added.
That knowledge gap prompted Dr. Farber and his colleagues to analyze data from the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term PAH Disease Management (REVEAL), the largest disease registry in the world of patients with PAH.
“Patients in that group – the severe DLCO group – who got oxygen had poorer prognostic features but improved overall survival relative to those who didn’t,” Dr. Farber explained during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “Based on this, it makes us think that home oxygen, supplemental oxygen treatment, is associated with improved survival in patients, especially those with severe DLCO and PAH.”
The 3,046 patients analyzed by Dr. Farber and his colleagues had World Health Organization Group 1 PAH with right heart catheterization hemodynamic criteria: a mean pulmonary artery pressure greater than 25 mm Hg, a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure less than or equal to 15 mm Hg, and a pulmonary vascular resistance of at least 3 Wood units (WU). Patients were at least 18 years of age and grouped by oxygen use, which was defined as any use at any time from study enrollment to the end of follow-up, and by DLCO group.
A total of 57% of the patients (1,734) received oxygen, and the remaining 43% of the patients (1,312) did not receive oxygen. Among the patients who received oxygen, 71% (1,227) received the therapy continuously, and 24% (408) received oxygen at night only.
The 424 patients with a DLCO of less than 40% were considered to have a severe DLCO impairment. The other two groups comprised 505 patients with a moderate DLCO impairment (at least 40%, but less than 60%) and 844 patients with a mild to normal DLCO (at least 60%). The DLCOs of 1,273 patients analyzed were unknown.
Among those patients with severe DLCO impairment, the risk of death was significantly lower in those who received oxygen, compared with those who did not receive oxygen (hazard ratio, 0.56; P = .0033). Oxygen use was associated with significant improvements in overall survival in both the newly diagnosed (HR, 0.47; P = .029) and previously diagnosed (HR, 0.59; P = .026) severe DLCO cohorts, Dr. Farber said.
Patients receiving oxygen were more likely to be treated with PAH-specific medications, regardless of their DLCO group.
Among the analysis’s limitations was that the lengths of time patients had been undergoing oxygen treatment were unknown. That prevented adjustments for duration of oxygen treatment, according to Dr. Farber.
Dr. Farber disclosed serving on the steering committees or advisory boards for Actelion, Bayer, Bellerophon, Gilead, and United Therapeutics. He has received research support from Actelion, Gilead, and United Therapeutics, and has been a speaker for Actelion, Bayer, and Gilead.
LOS ANGELES – Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) patients with severely impaired diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) were much more likely to survive when they received home oxygen therapy, according to a disease registry analysis.
“We all know that supplemental oxygen is widely used with PAH,” said Harrison W. Farber, MD, director of the pulmonary hypertension center at Boston University. But there are practically no data showing that it is successful, and there are even fewer data for patients with PAH who have very low diffusion capacity, he added.
That knowledge gap prompted Dr. Farber and his colleagues to analyze data from the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term PAH Disease Management (REVEAL), the largest disease registry in the world of patients with PAH.
“Patients in that group – the severe DLCO group – who got oxygen had poorer prognostic features but improved overall survival relative to those who didn’t,” Dr. Farber explained during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “Based on this, it makes us think that home oxygen, supplemental oxygen treatment, is associated with improved survival in patients, especially those with severe DLCO and PAH.”
The 3,046 patients analyzed by Dr. Farber and his colleagues had World Health Organization Group 1 PAH with right heart catheterization hemodynamic criteria: a mean pulmonary artery pressure greater than 25 mm Hg, a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure less than or equal to 15 mm Hg, and a pulmonary vascular resistance of at least 3 Wood units (WU). Patients were at least 18 years of age and grouped by oxygen use, which was defined as any use at any time from study enrollment to the end of follow-up, and by DLCO group.
A total of 57% of the patients (1,734) received oxygen, and the remaining 43% of the patients (1,312) did not receive oxygen. Among the patients who received oxygen, 71% (1,227) received the therapy continuously, and 24% (408) received oxygen at night only.
The 424 patients with a DLCO of less than 40% were considered to have a severe DLCO impairment. The other two groups comprised 505 patients with a moderate DLCO impairment (at least 40%, but less than 60%) and 844 patients with a mild to normal DLCO (at least 60%). The DLCOs of 1,273 patients analyzed were unknown.
Among those patients with severe DLCO impairment, the risk of death was significantly lower in those who received oxygen, compared with those who did not receive oxygen (hazard ratio, 0.56; P = .0033). Oxygen use was associated with significant improvements in overall survival in both the newly diagnosed (HR, 0.47; P = .029) and previously diagnosed (HR, 0.59; P = .026) severe DLCO cohorts, Dr. Farber said.
Patients receiving oxygen were more likely to be treated with PAH-specific medications, regardless of their DLCO group.
Among the analysis’s limitations was that the lengths of time patients had been undergoing oxygen treatment were unknown. That prevented adjustments for duration of oxygen treatment, according to Dr. Farber.
Dr. Farber disclosed serving on the steering committees or advisory boards for Actelion, Bayer, Bellerophon, Gilead, and United Therapeutics. He has received research support from Actelion, Gilead, and United Therapeutics, and has been a speaker for Actelion, Bayer, and Gilead.
LOS ANGELES – Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) patients with severely impaired diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) were much more likely to survive when they received home oxygen therapy, according to a disease registry analysis.
“We all know that supplemental oxygen is widely used with PAH,” said Harrison W. Farber, MD, director of the pulmonary hypertension center at Boston University. But there are practically no data showing that it is successful, and there are even fewer data for patients with PAH who have very low diffusion capacity, he added.
That knowledge gap prompted Dr. Farber and his colleagues to analyze data from the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term PAH Disease Management (REVEAL), the largest disease registry in the world of patients with PAH.
“Patients in that group – the severe DLCO group – who got oxygen had poorer prognostic features but improved overall survival relative to those who didn’t,” Dr. Farber explained during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “Based on this, it makes us think that home oxygen, supplemental oxygen treatment, is associated with improved survival in patients, especially those with severe DLCO and PAH.”
The 3,046 patients analyzed by Dr. Farber and his colleagues had World Health Organization Group 1 PAH with right heart catheterization hemodynamic criteria: a mean pulmonary artery pressure greater than 25 mm Hg, a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure less than or equal to 15 mm Hg, and a pulmonary vascular resistance of at least 3 Wood units (WU). Patients were at least 18 years of age and grouped by oxygen use, which was defined as any use at any time from study enrollment to the end of follow-up, and by DLCO group.
A total of 57% of the patients (1,734) received oxygen, and the remaining 43% of the patients (1,312) did not receive oxygen. Among the patients who received oxygen, 71% (1,227) received the therapy continuously, and 24% (408) received oxygen at night only.
The 424 patients with a DLCO of less than 40% were considered to have a severe DLCO impairment. The other two groups comprised 505 patients with a moderate DLCO impairment (at least 40%, but less than 60%) and 844 patients with a mild to normal DLCO (at least 60%). The DLCOs of 1,273 patients analyzed were unknown.
Among those patients with severe DLCO impairment, the risk of death was significantly lower in those who received oxygen, compared with those who did not receive oxygen (hazard ratio, 0.56; P = .0033). Oxygen use was associated with significant improvements in overall survival in both the newly diagnosed (HR, 0.47; P = .029) and previously diagnosed (HR, 0.59; P = .026) severe DLCO cohorts, Dr. Farber said.
Patients receiving oxygen were more likely to be treated with PAH-specific medications, regardless of their DLCO group.
Among the analysis’s limitations was that the lengths of time patients had been undergoing oxygen treatment were unknown. That prevented adjustments for duration of oxygen treatment, according to Dr. Farber.
Dr. Farber disclosed serving on the steering committees or advisory boards for Actelion, Bayer, Bellerophon, Gilead, and United Therapeutics. He has received research support from Actelion, Gilead, and United Therapeutics, and has been a speaker for Actelion, Bayer, and Gilead.
Key clinical point:
Major finding: PAH patients with severe DLCO impairment who received oxygen had a significantly higher probability of survival than those who didn’t receive oxygen (HR, 0.56; P = .0033).
Data source: An analysis of 3,046 patients in the U.S. multicenter, observational REVEAL disease registry.
Disclosures: Dr. Farber disclosed serving on the steering committees or advisory boards for Actelion, Bayer, Bellerophon, Gilead, and United Therapeutics. He has received research support from Actelion, Gilead, and United Therapeutics, and has been a speaker for Actelion, Bayer, and Gilead.
What will the Trump administration mean for medicine?
The Affordable Care Act is in the crosshairs as the transition to the Trump administration begins Nov. 9.
The primary tenet of Donald J. Trump’s health care platform calls for Congress to repeal the ACA.
In fact, Mr. Trump has called for ACA repeal efforts to begin on his administration’s first day.
The Trump administration is likely to find plentiful allies in Congress as both the House and the Senate were projected at press time to have Republican majorities, albeit slim ones. Since the ACA’s passage in 2010, House Republicans have put forward repeal legislation scores of times.
While many medical specialty societies have supported the ACA and other major health care reforms enacted over the last 8 years – Meaningful Use from the HITECH ACT and value-based payment from MACRA among them – large numbers of physicians have chafed under the myriad reporting requirements and administrative hassles.
A recent survey commissioned by the Physicians Foundation and conducted by Merritt Hawkins found that nearly half (48%) of physicians are considering a change of practice – including leaving medicine – in the next 1-3 years. Reasons cited by survey respondents included the MACRA (Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015) transition to value-based care, the increased coding required by ICD-10, the growth of physician employment, the continued sale of private practices to hospitals and health systems, the increased number of patients in the system because of the ACA coupled with a shortage of physicians, and the “businessification” of heath care.
“If any of these [changes] occurred in a period of time, it would be impactful,” Walker Ray, MD, president of the Physicians Foundation, said in an interview. “But to have all occur simultaneously, we say now that to be a physician is to feel the ground shaking under your feet. This is the landscape in which the survey was taken.”
Mr. Trump supports several free market reforms to replace repealed provisions of the ACA, as well as address other issues in the health care system. The proposals include the following:
• Foster interstate insurance sales.
• Reinstate the tax deductibility of health insurance premiums.
• Promote the more widespread use of health savings accounts.
• Require price transparency so that patients can shop for medical procedures, exams, and tests.
• Block grant Medicaid to the states.
• Allow patients to import drugs from outside of the United States.
The Trump platform also promises to reduce fraud and waste, as well as save approximately $11 billion annually by not providing health care to illegal immigrants.
Speculation has also begun regarding who might lead health care agencies and policy for the Trump administration. Among the names that have been floated for secretary of Health and Human Services are Ben Carson, MD, the former presidential candidate and retired neurosurgeon; former House Speaker Newt Gingrich (who also has been suggested as a potential secretary of State); as well as Florida Gov. Rick Scott, former chief executive of Columbia/HCA, according to Politico.com.
[email protected]
On Twitter @denisefulton
Gregory Twachtman contributed to this story.
The Affordable Care Act is in the crosshairs as the transition to the Trump administration begins Nov. 9.
The primary tenet of Donald J. Trump’s health care platform calls for Congress to repeal the ACA.
In fact, Mr. Trump has called for ACA repeal efforts to begin on his administration’s first day.
The Trump administration is likely to find plentiful allies in Congress as both the House and the Senate were projected at press time to have Republican majorities, albeit slim ones. Since the ACA’s passage in 2010, House Republicans have put forward repeal legislation scores of times.
While many medical specialty societies have supported the ACA and other major health care reforms enacted over the last 8 years – Meaningful Use from the HITECH ACT and value-based payment from MACRA among them – large numbers of physicians have chafed under the myriad reporting requirements and administrative hassles.
A recent survey commissioned by the Physicians Foundation and conducted by Merritt Hawkins found that nearly half (48%) of physicians are considering a change of practice – including leaving medicine – in the next 1-3 years. Reasons cited by survey respondents included the MACRA (Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015) transition to value-based care, the increased coding required by ICD-10, the growth of physician employment, the continued sale of private practices to hospitals and health systems, the increased number of patients in the system because of the ACA coupled with a shortage of physicians, and the “businessification” of heath care.
“If any of these [changes] occurred in a period of time, it would be impactful,” Walker Ray, MD, president of the Physicians Foundation, said in an interview. “But to have all occur simultaneously, we say now that to be a physician is to feel the ground shaking under your feet. This is the landscape in which the survey was taken.”
Mr. Trump supports several free market reforms to replace repealed provisions of the ACA, as well as address other issues in the health care system. The proposals include the following:
• Foster interstate insurance sales.
• Reinstate the tax deductibility of health insurance premiums.
• Promote the more widespread use of health savings accounts.
• Require price transparency so that patients can shop for medical procedures, exams, and tests.
• Block grant Medicaid to the states.
• Allow patients to import drugs from outside of the United States.
The Trump platform also promises to reduce fraud and waste, as well as save approximately $11 billion annually by not providing health care to illegal immigrants.
Speculation has also begun regarding who might lead health care agencies and policy for the Trump administration. Among the names that have been floated for secretary of Health and Human Services are Ben Carson, MD, the former presidential candidate and retired neurosurgeon; former House Speaker Newt Gingrich (who also has been suggested as a potential secretary of State); as well as Florida Gov. Rick Scott, former chief executive of Columbia/HCA, according to Politico.com.
[email protected]
On Twitter @denisefulton
Gregory Twachtman contributed to this story.
The Affordable Care Act is in the crosshairs as the transition to the Trump administration begins Nov. 9.
The primary tenet of Donald J. Trump’s health care platform calls for Congress to repeal the ACA.
In fact, Mr. Trump has called for ACA repeal efforts to begin on his administration’s first day.
The Trump administration is likely to find plentiful allies in Congress as both the House and the Senate were projected at press time to have Republican majorities, albeit slim ones. Since the ACA’s passage in 2010, House Republicans have put forward repeal legislation scores of times.
While many medical specialty societies have supported the ACA and other major health care reforms enacted over the last 8 years – Meaningful Use from the HITECH ACT and value-based payment from MACRA among them – large numbers of physicians have chafed under the myriad reporting requirements and administrative hassles.
A recent survey commissioned by the Physicians Foundation and conducted by Merritt Hawkins found that nearly half (48%) of physicians are considering a change of practice – including leaving medicine – in the next 1-3 years. Reasons cited by survey respondents included the MACRA (Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015) transition to value-based care, the increased coding required by ICD-10, the growth of physician employment, the continued sale of private practices to hospitals and health systems, the increased number of patients in the system because of the ACA coupled with a shortage of physicians, and the “businessification” of heath care.
“If any of these [changes] occurred in a period of time, it would be impactful,” Walker Ray, MD, president of the Physicians Foundation, said in an interview. “But to have all occur simultaneously, we say now that to be a physician is to feel the ground shaking under your feet. This is the landscape in which the survey was taken.”
Mr. Trump supports several free market reforms to replace repealed provisions of the ACA, as well as address other issues in the health care system. The proposals include the following:
• Foster interstate insurance sales.
• Reinstate the tax deductibility of health insurance premiums.
• Promote the more widespread use of health savings accounts.
• Require price transparency so that patients can shop for medical procedures, exams, and tests.
• Block grant Medicaid to the states.
• Allow patients to import drugs from outside of the United States.
The Trump platform also promises to reduce fraud and waste, as well as save approximately $11 billion annually by not providing health care to illegal immigrants.
Speculation has also begun regarding who might lead health care agencies and policy for the Trump administration. Among the names that have been floated for secretary of Health and Human Services are Ben Carson, MD, the former presidential candidate and retired neurosurgeon; former House Speaker Newt Gingrich (who also has been suggested as a potential secretary of State); as well as Florida Gov. Rick Scott, former chief executive of Columbia/HCA, according to Politico.com.
[email protected]
On Twitter @denisefulton
Gregory Twachtman contributed to this story.
Cardiorespiratory fitness improves survival after depression
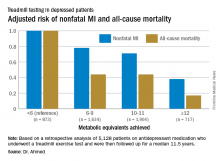
ROME – Cardiorespiratory fitness provided strong and graded protection against all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI in a study of more than 5,000 patients treated for depression, Amjad M. Ahmed, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“These results highlight the importance of assessing fitness to identify risk as well as promoting an active lifestyle in patients with depression,” said Dr. Ahmed of Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
This analysis focused on the 5,128 subjects who were on antidepressant medication at the time of their treadmill test. Their baseline cardiorespiratory fitness, as estimated by achieved peak metabolic equivalents (METs) on the treadmill, varied inversely with their risks of acute MI and all-cause mortality in the years to come. However, the less fit a patient was, the greater the burden of traditional cardiovascular risk factors. For example, the prevalence of hypertension was 86% in patients who achieved fewer than 6 METs, 75% in those who achieved 6-9 METs, 62% in depressed patients who reached 10-11 METs, and 51% in those who achieved 12 METs or more.
For this reason, Dr. Ahmed and coinvestigators performed a Cox multivariate regression analysis adjusted extensively for potential confounders, including age, sex, race, cardiovascular risk factors, known coronary artery disease, the use of cardiovascular medications, and the reason for the referral for stress testing.
When an achieved MET below 6 was used as the reference standard, for every 1 MET above 6 that patients achieved, their adjusted risk of all-cause mortality decreased by 18%, and the risk of nonfatal MI fell by 8%.
Session cochair Martin Halle, MD, pointed out what he viewed as a major limitation of the study.
“You didn’t follow their physical fitness over time, so you can’t say that increasing their METs would bring a better prognosis,” said Dr. Halle, professor and chairman of the department of preventive and rehabilitative sports medicine at the Technical University of Munich.
Dr. Ahmed reported having no financial conflicts of interest related to the Henry Ford FIT Project.
ROME – Cardiorespiratory fitness provided strong and graded protection against all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI in a study of more than 5,000 patients treated for depression, Amjad M. Ahmed, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“These results highlight the importance of assessing fitness to identify risk as well as promoting an active lifestyle in patients with depression,” said Dr. Ahmed of Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
This analysis focused on the 5,128 subjects who were on antidepressant medication at the time of their treadmill test. Their baseline cardiorespiratory fitness, as estimated by achieved peak metabolic equivalents (METs) on the treadmill, varied inversely with their risks of acute MI and all-cause mortality in the years to come. However, the less fit a patient was, the greater the burden of traditional cardiovascular risk factors. For example, the prevalence of hypertension was 86% in patients who achieved fewer than 6 METs, 75% in those who achieved 6-9 METs, 62% in depressed patients who reached 10-11 METs, and 51% in those who achieved 12 METs or more.
For this reason, Dr. Ahmed and coinvestigators performed a Cox multivariate regression analysis adjusted extensively for potential confounders, including age, sex, race, cardiovascular risk factors, known coronary artery disease, the use of cardiovascular medications, and the reason for the referral for stress testing.
When an achieved MET below 6 was used as the reference standard, for every 1 MET above 6 that patients achieved, their adjusted risk of all-cause mortality decreased by 18%, and the risk of nonfatal MI fell by 8%.
Session cochair Martin Halle, MD, pointed out what he viewed as a major limitation of the study.
“You didn’t follow their physical fitness over time, so you can’t say that increasing their METs would bring a better prognosis,” said Dr. Halle, professor and chairman of the department of preventive and rehabilitative sports medicine at the Technical University of Munich.
Dr. Ahmed reported having no financial conflicts of interest related to the Henry Ford FIT Project.
ROME – Cardiorespiratory fitness provided strong and graded protection against all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI in a study of more than 5,000 patients treated for depression, Amjad M. Ahmed, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“These results highlight the importance of assessing fitness to identify risk as well as promoting an active lifestyle in patients with depression,” said Dr. Ahmed of Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
This analysis focused on the 5,128 subjects who were on antidepressant medication at the time of their treadmill test. Their baseline cardiorespiratory fitness, as estimated by achieved peak metabolic equivalents (METs) on the treadmill, varied inversely with their risks of acute MI and all-cause mortality in the years to come. However, the less fit a patient was, the greater the burden of traditional cardiovascular risk factors. For example, the prevalence of hypertension was 86% in patients who achieved fewer than 6 METs, 75% in those who achieved 6-9 METs, 62% in depressed patients who reached 10-11 METs, and 51% in those who achieved 12 METs or more.
For this reason, Dr. Ahmed and coinvestigators performed a Cox multivariate regression analysis adjusted extensively for potential confounders, including age, sex, race, cardiovascular risk factors, known coronary artery disease, the use of cardiovascular medications, and the reason for the referral for stress testing.
When an achieved MET below 6 was used as the reference standard, for every 1 MET above 6 that patients achieved, their adjusted risk of all-cause mortality decreased by 18%, and the risk of nonfatal MI fell by 8%.
Session cochair Martin Halle, MD, pointed out what he viewed as a major limitation of the study.
“You didn’t follow their physical fitness over time, so you can’t say that increasing their METs would bring a better prognosis,” said Dr. Halle, professor and chairman of the department of preventive and rehabilitative sports medicine at the Technical University of Munich.
Dr. Ahmed reported having no financial conflicts of interest related to the Henry Ford FIT Project.
AT THE ESC CONGRESS 2016
Key clinical point:
Major finding: For every 1-MET increase a patient on antidepressant medication achieved above 6 METs during a Bruce protocol treadmill exercise test, the risk of all-cause mortality during the subsequent 11.5 years decreased by an adjusted 18%.
Data source: A retrospective analysis of 5,128 patients on antidepressant medication who underwent a treadmill exercise test as part of the Henry Ford Exercise Testing Project and were then followed up for a median of 11.5 years.
Disclosures: The study presenter reported having no relevant financial conflicts.
Delayed bleeding possible with EBUS-TBNA on antiplatelets
LOS ANGELES – There might be a slight increase in delayed bleeding when patients have endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration within 5 days of taking oral antiplatelets, according to a review of 404 patients at Riverside Methodist Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
This study is unusual in that it looked at the 48 hour mark. Previous studies have tended to focus on immediate bleeding events that require the procedure to be stopped; only some of that research has found an increased bleeding risk with antiplatelet therapy.
In the study at Riverside Methodist, none of the 20 patients on dual antiplatelet therapy – clopidogrel (Plavix) plus aspirin – bled during the procedure, but one (5%) had a hemoglobin drop of more than 2 g within 48 hours and another was readmitted to the hospital within 48 hours for procedure-related hemoptysis. Overall, the delayed bleeding event rate for patients using the dual antiplatelet therapy was 10%. Additionally, one of the 13 patients (7.7%) on clopidogrel alone experienced a greater than 2 g drop in hemoglobin.
Among the 270 patients not exposed to antiplatelets, the overall bleeding event rate was 2.6%, and the event rate for delayed bleeding was 1.1%. Four patients (1.5%) bled during the procedure, two (0.7%) had hemoglobin drops greater than 2 g within 48 hours, and one (0.4%) was readmitted for hemoptysis.
There were no bleeding events in the 101 patients who only took aspirin.
“There was a trend toward delayed bleeding events in patients” on clopidogrel or dual antiplatelets. “It’s worth considering a thoughtful pause in decision making. Maybe with the bleeding events we’re seeing, it would be worthwhile, if possible, to defer” endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration “until after the antiplatelet therapy,” said Kevin Swiatek, DO, a medicine resident at Riverside.
Patients were excluded from the study if they had histories of bleeding or clotting disorders; low platelet counts; or if they were on anticoagulation. Subjects on antiplatelets were about 10 years older, on average, than those who were not (about 68 versus 59 years old), and more likely to have had a heart attack or stroke, and to be hypertensive.
There was no industry funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – There might be a slight increase in delayed bleeding when patients have endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration within 5 days of taking oral antiplatelets, according to a review of 404 patients at Riverside Methodist Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
This study is unusual in that it looked at the 48 hour mark. Previous studies have tended to focus on immediate bleeding events that require the procedure to be stopped; only some of that research has found an increased bleeding risk with antiplatelet therapy.
In the study at Riverside Methodist, none of the 20 patients on dual antiplatelet therapy – clopidogrel (Plavix) plus aspirin – bled during the procedure, but one (5%) had a hemoglobin drop of more than 2 g within 48 hours and another was readmitted to the hospital within 48 hours for procedure-related hemoptysis. Overall, the delayed bleeding event rate for patients using the dual antiplatelet therapy was 10%. Additionally, one of the 13 patients (7.7%) on clopidogrel alone experienced a greater than 2 g drop in hemoglobin.
Among the 270 patients not exposed to antiplatelets, the overall bleeding event rate was 2.6%, and the event rate for delayed bleeding was 1.1%. Four patients (1.5%) bled during the procedure, two (0.7%) had hemoglobin drops greater than 2 g within 48 hours, and one (0.4%) was readmitted for hemoptysis.
There were no bleeding events in the 101 patients who only took aspirin.
“There was a trend toward delayed bleeding events in patients” on clopidogrel or dual antiplatelets. “It’s worth considering a thoughtful pause in decision making. Maybe with the bleeding events we’re seeing, it would be worthwhile, if possible, to defer” endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration “until after the antiplatelet therapy,” said Kevin Swiatek, DO, a medicine resident at Riverside.
Patients were excluded from the study if they had histories of bleeding or clotting disorders; low platelet counts; or if they were on anticoagulation. Subjects on antiplatelets were about 10 years older, on average, than those who were not (about 68 versus 59 years old), and more likely to have had a heart attack or stroke, and to be hypertensive.
There was no industry funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – There might be a slight increase in delayed bleeding when patients have endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration within 5 days of taking oral antiplatelets, according to a review of 404 patients at Riverside Methodist Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
This study is unusual in that it looked at the 48 hour mark. Previous studies have tended to focus on immediate bleeding events that require the procedure to be stopped; only some of that research has found an increased bleeding risk with antiplatelet therapy.
In the study at Riverside Methodist, none of the 20 patients on dual antiplatelet therapy – clopidogrel (Plavix) plus aspirin – bled during the procedure, but one (5%) had a hemoglobin drop of more than 2 g within 48 hours and another was readmitted to the hospital within 48 hours for procedure-related hemoptysis. Overall, the delayed bleeding event rate for patients using the dual antiplatelet therapy was 10%. Additionally, one of the 13 patients (7.7%) on clopidogrel alone experienced a greater than 2 g drop in hemoglobin.
Among the 270 patients not exposed to antiplatelets, the overall bleeding event rate was 2.6%, and the event rate for delayed bleeding was 1.1%. Four patients (1.5%) bled during the procedure, two (0.7%) had hemoglobin drops greater than 2 g within 48 hours, and one (0.4%) was readmitted for hemoptysis.
There were no bleeding events in the 101 patients who only took aspirin.
“There was a trend toward delayed bleeding events in patients” on clopidogrel or dual antiplatelets. “It’s worth considering a thoughtful pause in decision making. Maybe with the bleeding events we’re seeing, it would be worthwhile, if possible, to defer” endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration “until after the antiplatelet therapy,” said Kevin Swiatek, DO, a medicine resident at Riverside.
Patients were excluded from the study if they had histories of bleeding or clotting disorders; low platelet counts; or if they were on anticoagulation. Subjects on antiplatelets were about 10 years older, on average, than those who were not (about 68 versus 59 years old), and more likely to have had a heart attack or stroke, and to be hypertensive.
There was no industry funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
AT CHEST 2016
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Ten percent of patients on dual antiplatelet therapy bled within 48 hours, versus 1.1% of those not on antiplatelet therapy.
Data source: Single-center review of 404 patients.
Disclosures: There was no industry funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
Most infective endocarditis calls for early surgery
CHICAGO - Turning to surgery earlier in infective endocarditis may hold the key to a cure for some patients. Upcoming guidelines for surgical treatment of infective endocarditis lend evidence-based support to early surgical intervention in this high-mortality condition.
“Infective endocarditis is the most severe and potentially devastating complication for heart valve disease,” said Joseph Coselli, MD, in a presentation that reviewed current trends in incidence of infective endocarditis (IE) and laid out a rationale and strategy for early surgical intervention in some patients.
“Untreated infective endocarditis is universally fatal,” said Dr. Coselli. Even with current treatments, however, overall mortality for infective endocarditis is 20%-25%, he said.
Speaking at the joint AATS-ACC Heart Valve Summit, Dr. Coselli, chief of the division of cardiothoracic surgery at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, reviewed the key points in the upcoming guideline and the evidence that backs up the guidelines.
Dr. Coselli served on the writing committee for the 2016 AATS consensus guidelines for the surgical treatment of infective endocarditis; the guidelines are currently in press.
The guidelines propose that “at the time of surgery, the patient should be on an effective antimicrobial regimen to which the causative agent is sensitive,” he said. This is a level I recommendation, as is the recommendation that the surgeon should understand the pathology as well as possible before the procedure. Usually, say the guidelines, this is obtained by means of a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), assigning level I status to this recommendation as well.
According to the guidelines, patients with IE who may be surgical candidates during their hospitalization, regardless of whether their antimicrobial course is complete, include those who present with valve dysfunction that results in symptoms of heart failure. Surgery should also be considered in patients with left-sided IE with S. aureus, fungi, or other highly resistant organisms as the causative pathogen. If heart block, an aortic or annular abscess, or destructive penetrating lesions are present, surgery is also indicated. Finally, the guidelines recommend considering surgery if patients have persistent bacteremia or fevers at 5 to 7 days after initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy. All of these are class I indications in the upcoming guidelines, he said.
The patient who has relapsing infection, defined by the guidelines as recurrent bacteremia “after a complete course of appropriate antibiotics and subsequently negative blood culture,” who has no other identifiable source of infection, may also be a candidate.
Given the dearth of randomized trials in the area, no recommendation for intervention is backed by a level of evidence greater than B, said Dr. Coselli. And knowledge gaps persist in many areas, such as the appropriate timing of surgery in IE when there are neurological complications. Also, he said, “embolism risk needs to be better understood.” Imaging improvements would help guide decision-making, as would better data about contemporary rates of IE relapse and recurrence, said Dr. Coselli.
Though these surgeries should be done at centers that can field a complete team, and by experience valve surgeons, early intervention may be a key to success: “Operate before a devastating complication occurs,” said Dr. Coselli. “Understand what you see; don’t be afraid of radical debridement, and master alternative options to reconstruction” depending on the heart’s appearance in the OR, he said.
Surgeons can run into trouble in IE cases if they wait too long. “A patient who’s already had an embolic stroke may be too sick,” said Dr. Coselli. Insensitive organisms and ineffective antimicrobial therapy set the patient up for recurrent IE or treatment failure as well.
Having guidance for surgical intervention is important because cardiologists and surgeons will be seeing more infective endocarditis patients as heroin and other illicit intravenous drug use continues to rise, said Dr. Coselli. IE in intravenous drug users now accounts for up to 30% of all patients who seek treatment for IE, he said, citing a study that tracked characteristics of endocarditis patients undergoing surgery at a single institution from 2002-2014 (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Sep;152:832-41). Incidence in intravenous drug users can range to 2,000 cases per 100,000 patient-years, he said.
The study, conducted by Joon Bum Kim, MD, PhD, and his colleagues at Massachusetts General and Brigham and Women’s hospitals, both in Boston, followed 436 patients with IE, 78 of whom were intravenous drug users (IVDUs) at the time of diagnosis. Overall, the IVDUs were younger (mean age, 36 plus or minus 10 years) when compared with the non-IVDU group (mean age, 58 plus or minus 14 years; P less than 0.001). The non-IVDU cohort were also significantly more likely to have hypertension and diabetes, but less likely to smoke. However, IVDUs were more likely to have embolic events, and to have right-sided valve involvement.
Though early mortality was better in the IVDU group post-surgically, late complications, including reinfection and reoperation, were significantly more likely to occur in the IVDUs, with reinfection more than four times as frequent in IVDUs (aggregate valve-related complications, 41% in IVDUs vs. 10% in non-IVDUs; P = 0.001).
Despite the additional morbidity seen in IVDU-associated endocarditis, the 10-year survival rate was virtually identical between the two groups.
For many IE patients, said Dr. Coselli, “the arguments against surgery have lost strength.” Active systemic infections are treatable, sicker patients can be operated on earlier, and surgeons will gain experience with this sometimes technically challenging surgery, he said. Finally, Dr. Coselli said, even though the best available data support early surgical intervention in select IE patients, “final cure of IE is always the result of antimicrobial treatment and the patient’s own defense.”
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
CHICAGO - Turning to surgery earlier in infective endocarditis may hold the key to a cure for some patients. Upcoming guidelines for surgical treatment of infective endocarditis lend evidence-based support to early surgical intervention in this high-mortality condition.
“Infective endocarditis is the most severe and potentially devastating complication for heart valve disease,” said Joseph Coselli, MD, in a presentation that reviewed current trends in incidence of infective endocarditis (IE) and laid out a rationale and strategy for early surgical intervention in some patients.
“Untreated infective endocarditis is universally fatal,” said Dr. Coselli. Even with current treatments, however, overall mortality for infective endocarditis is 20%-25%, he said.
Speaking at the joint AATS-ACC Heart Valve Summit, Dr. Coselli, chief of the division of cardiothoracic surgery at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, reviewed the key points in the upcoming guideline and the evidence that backs up the guidelines.
Dr. Coselli served on the writing committee for the 2016 AATS consensus guidelines for the surgical treatment of infective endocarditis; the guidelines are currently in press.
The guidelines propose that “at the time of surgery, the patient should be on an effective antimicrobial regimen to which the causative agent is sensitive,” he said. This is a level I recommendation, as is the recommendation that the surgeon should understand the pathology as well as possible before the procedure. Usually, say the guidelines, this is obtained by means of a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), assigning level I status to this recommendation as well.
According to the guidelines, patients with IE who may be surgical candidates during their hospitalization, regardless of whether their antimicrobial course is complete, include those who present with valve dysfunction that results in symptoms of heart failure. Surgery should also be considered in patients with left-sided IE with S. aureus, fungi, or other highly resistant organisms as the causative pathogen. If heart block, an aortic or annular abscess, or destructive penetrating lesions are present, surgery is also indicated. Finally, the guidelines recommend considering surgery if patients have persistent bacteremia or fevers at 5 to 7 days after initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy. All of these are class I indications in the upcoming guidelines, he said.
The patient who has relapsing infection, defined by the guidelines as recurrent bacteremia “after a complete course of appropriate antibiotics and subsequently negative blood culture,” who has no other identifiable source of infection, may also be a candidate.
Given the dearth of randomized trials in the area, no recommendation for intervention is backed by a level of evidence greater than B, said Dr. Coselli. And knowledge gaps persist in many areas, such as the appropriate timing of surgery in IE when there are neurological complications. Also, he said, “embolism risk needs to be better understood.” Imaging improvements would help guide decision-making, as would better data about contemporary rates of IE relapse and recurrence, said Dr. Coselli.
Though these surgeries should be done at centers that can field a complete team, and by experience valve surgeons, early intervention may be a key to success: “Operate before a devastating complication occurs,” said Dr. Coselli. “Understand what you see; don’t be afraid of radical debridement, and master alternative options to reconstruction” depending on the heart’s appearance in the OR, he said.
Surgeons can run into trouble in IE cases if they wait too long. “A patient who’s already had an embolic stroke may be too sick,” said Dr. Coselli. Insensitive organisms and ineffective antimicrobial therapy set the patient up for recurrent IE or treatment failure as well.
Having guidance for surgical intervention is important because cardiologists and surgeons will be seeing more infective endocarditis patients as heroin and other illicit intravenous drug use continues to rise, said Dr. Coselli. IE in intravenous drug users now accounts for up to 30% of all patients who seek treatment for IE, he said, citing a study that tracked characteristics of endocarditis patients undergoing surgery at a single institution from 2002-2014 (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Sep;152:832-41). Incidence in intravenous drug users can range to 2,000 cases per 100,000 patient-years, he said.
The study, conducted by Joon Bum Kim, MD, PhD, and his colleagues at Massachusetts General and Brigham and Women’s hospitals, both in Boston, followed 436 patients with IE, 78 of whom were intravenous drug users (IVDUs) at the time of diagnosis. Overall, the IVDUs were younger (mean age, 36 plus or minus 10 years) when compared with the non-IVDU group (mean age, 58 plus or minus 14 years; P less than 0.001). The non-IVDU cohort were also significantly more likely to have hypertension and diabetes, but less likely to smoke. However, IVDUs were more likely to have embolic events, and to have right-sided valve involvement.
Though early mortality was better in the IVDU group post-surgically, late complications, including reinfection and reoperation, were significantly more likely to occur in the IVDUs, with reinfection more than four times as frequent in IVDUs (aggregate valve-related complications, 41% in IVDUs vs. 10% in non-IVDUs; P = 0.001).
Despite the additional morbidity seen in IVDU-associated endocarditis, the 10-year survival rate was virtually identical between the two groups.
For many IE patients, said Dr. Coselli, “the arguments against surgery have lost strength.” Active systemic infections are treatable, sicker patients can be operated on earlier, and surgeons will gain experience with this sometimes technically challenging surgery, he said. Finally, Dr. Coselli said, even though the best available data support early surgical intervention in select IE patients, “final cure of IE is always the result of antimicrobial treatment and the patient’s own defense.”
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
CHICAGO - Turning to surgery earlier in infective endocarditis may hold the key to a cure for some patients. Upcoming guidelines for surgical treatment of infective endocarditis lend evidence-based support to early surgical intervention in this high-mortality condition.
“Infective endocarditis is the most severe and potentially devastating complication for heart valve disease,” said Joseph Coselli, MD, in a presentation that reviewed current trends in incidence of infective endocarditis (IE) and laid out a rationale and strategy for early surgical intervention in some patients.
“Untreated infective endocarditis is universally fatal,” said Dr. Coselli. Even with current treatments, however, overall mortality for infective endocarditis is 20%-25%, he said.
Speaking at the joint AATS-ACC Heart Valve Summit, Dr. Coselli, chief of the division of cardiothoracic surgery at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, reviewed the key points in the upcoming guideline and the evidence that backs up the guidelines.
Dr. Coselli served on the writing committee for the 2016 AATS consensus guidelines for the surgical treatment of infective endocarditis; the guidelines are currently in press.
The guidelines propose that “at the time of surgery, the patient should be on an effective antimicrobial regimen to which the causative agent is sensitive,” he said. This is a level I recommendation, as is the recommendation that the surgeon should understand the pathology as well as possible before the procedure. Usually, say the guidelines, this is obtained by means of a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), assigning level I status to this recommendation as well.
According to the guidelines, patients with IE who may be surgical candidates during their hospitalization, regardless of whether their antimicrobial course is complete, include those who present with valve dysfunction that results in symptoms of heart failure. Surgery should also be considered in patients with left-sided IE with S. aureus, fungi, or other highly resistant organisms as the causative pathogen. If heart block, an aortic or annular abscess, or destructive penetrating lesions are present, surgery is also indicated. Finally, the guidelines recommend considering surgery if patients have persistent bacteremia or fevers at 5 to 7 days after initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy. All of these are class I indications in the upcoming guidelines, he said.
The patient who has relapsing infection, defined by the guidelines as recurrent bacteremia “after a complete course of appropriate antibiotics and subsequently negative blood culture,” who has no other identifiable source of infection, may also be a candidate.
Given the dearth of randomized trials in the area, no recommendation for intervention is backed by a level of evidence greater than B, said Dr. Coselli. And knowledge gaps persist in many areas, such as the appropriate timing of surgery in IE when there are neurological complications. Also, he said, “embolism risk needs to be better understood.” Imaging improvements would help guide decision-making, as would better data about contemporary rates of IE relapse and recurrence, said Dr. Coselli.
Though these surgeries should be done at centers that can field a complete team, and by experience valve surgeons, early intervention may be a key to success: “Operate before a devastating complication occurs,” said Dr. Coselli. “Understand what you see; don’t be afraid of radical debridement, and master alternative options to reconstruction” depending on the heart’s appearance in the OR, he said.
Surgeons can run into trouble in IE cases if they wait too long. “A patient who’s already had an embolic stroke may be too sick,” said Dr. Coselli. Insensitive organisms and ineffective antimicrobial therapy set the patient up for recurrent IE or treatment failure as well.
Having guidance for surgical intervention is important because cardiologists and surgeons will be seeing more infective endocarditis patients as heroin and other illicit intravenous drug use continues to rise, said Dr. Coselli. IE in intravenous drug users now accounts for up to 30% of all patients who seek treatment for IE, he said, citing a study that tracked characteristics of endocarditis patients undergoing surgery at a single institution from 2002-2014 (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Sep;152:832-41). Incidence in intravenous drug users can range to 2,000 cases per 100,000 patient-years, he said.
The study, conducted by Joon Bum Kim, MD, PhD, and his colleagues at Massachusetts General and Brigham and Women’s hospitals, both in Boston, followed 436 patients with IE, 78 of whom were intravenous drug users (IVDUs) at the time of diagnosis. Overall, the IVDUs were younger (mean age, 36 plus or minus 10 years) when compared with the non-IVDU group (mean age, 58 plus or minus 14 years; P less than 0.001). The non-IVDU cohort were also significantly more likely to have hypertension and diabetes, but less likely to smoke. However, IVDUs were more likely to have embolic events, and to have right-sided valve involvement.
Though early mortality was better in the IVDU group post-surgically, late complications, including reinfection and reoperation, were significantly more likely to occur in the IVDUs, with reinfection more than four times as frequent in IVDUs (aggregate valve-related complications, 41% in IVDUs vs. 10% in non-IVDUs; P = 0.001).
Despite the additional morbidity seen in IVDU-associated endocarditis, the 10-year survival rate was virtually identical between the two groups.
For many IE patients, said Dr. Coselli, “the arguments against surgery have lost strength.” Active systemic infections are treatable, sicker patients can be operated on earlier, and surgeons will gain experience with this sometimes technically challenging surgery, he said. Finally, Dr. Coselli said, even though the best available data support early surgical intervention in select IE patients, “final cure of IE is always the result of antimicrobial treatment and the patient’s own defense.”
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE HEART VALVE SUMMIT 2016
Cancer type, age at time of diagnosis implicated in risk of CVD-related deaths
Survivorship data derived from a U.K. cancer registry make it possible to more closely pinpoint the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients treated for cancer as adolescents and young adults.
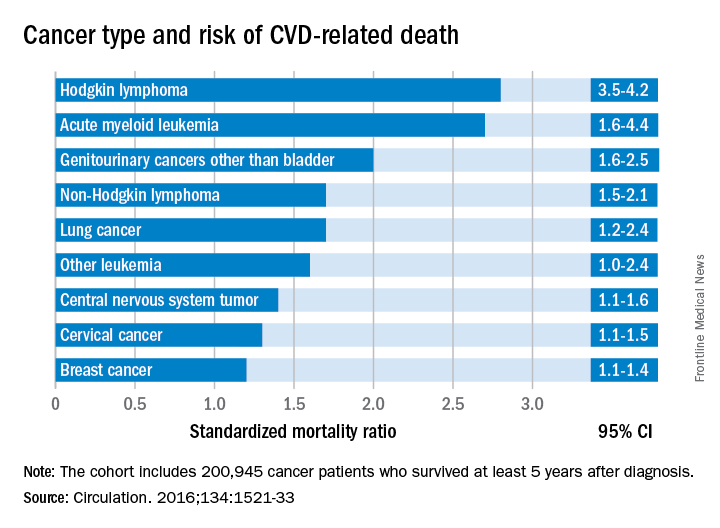
Researchers report that 6% of the 2,016 deaths occurring in 200,945 cancer survivors diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 39 years were directly related to cardiovascular disease. A multivariable Poisson regression analysis of data from the Teenage and Young Adult Cancer Survivor Study also showed that survivors who were diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 19 years had 4.2 times the risk (95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.2) of death from cardiovascular disease, compared with their peers in the general population. But for survivors who were aged 35-39 years when diagnosed, that risk decreased to 1.2 times (95% CI, 1.1-1.3) that of their general population peers (P less than .0001). The standardized mortality ratios and absolute excess risks for ischemic heart disease, valvular heart disease, and cardiomyopathy were similar (Circulation. 2016;134:1521-33).
The findings should help clinicians craft more effective after-cancer care, according to Mike Hawkins, DPhil. “It helps them focus the most intensive follow-up care on those most at risk,” Dr. Hawkins, an epidemiology professor and director of the Centre for Childhood Cancer Survivor Studies at the University of Birmingham (England), said in a statement. “It is important for survivors because it empowers them by providing them with their long-term chances of a specific side effect of cancer treatment.”
The most significant relationship between cardiovascular disease and cancer occurred in those diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma, and at an earlier age. Overall, Hodgkin lymphoma survivors had a 3.8 times higher risk of cardiovascular disease–related death than their peers not diagnosed with any cancer. In those diagnosed at age 15-19 years, 6.9% had died from cardiovascular disease by age 55 years, compared with 2% of those who’d been diagnosed at age 35-39 years. Among these two age groups in the general population, fewer than 1% typically die from cardiovascular disease–related deaths. In Hodgkin lymphoma survivors aged 60 years or older, 27.5% of excess deaths were from cardiovascular disease.
Although not stratified by treatment, the study includes risk estimates for other cancers diagnosed in the teen and young adult years, stratified by the age at diagnosis, something the authors of the study noted is “a considerable advance on previous knowledge.”
Survivors of all age groups in the cohort diagnosed with a variety of cancers experienced a greater risk of death from heart disease, compared with their peers in the general population.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
Survivorship data derived from a U.K. cancer registry make it possible to more closely pinpoint the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients treated for cancer as adolescents and young adults.
Researchers report that 6% of the 2,016 deaths occurring in 200,945 cancer survivors diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 39 years were directly related to cardiovascular disease. A multivariable Poisson regression analysis of data from the Teenage and Young Adult Cancer Survivor Study also showed that survivors who were diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 19 years had 4.2 times the risk (95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.2) of death from cardiovascular disease, compared with their peers in the general population. But for survivors who were aged 35-39 years when diagnosed, that risk decreased to 1.2 times (95% CI, 1.1-1.3) that of their general population peers (P less than .0001). The standardized mortality ratios and absolute excess risks for ischemic heart disease, valvular heart disease, and cardiomyopathy were similar (Circulation. 2016;134:1521-33).
The findings should help clinicians craft more effective after-cancer care, according to Mike Hawkins, DPhil. “It helps them focus the most intensive follow-up care on those most at risk,” Dr. Hawkins, an epidemiology professor and director of the Centre for Childhood Cancer Survivor Studies at the University of Birmingham (England), said in a statement. “It is important for survivors because it empowers them by providing them with their long-term chances of a specific side effect of cancer treatment.”
The most significant relationship between cardiovascular disease and cancer occurred in those diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma, and at an earlier age. Overall, Hodgkin lymphoma survivors had a 3.8 times higher risk of cardiovascular disease–related death than their peers not diagnosed with any cancer. In those diagnosed at age 15-19 years, 6.9% had died from cardiovascular disease by age 55 years, compared with 2% of those who’d been diagnosed at age 35-39 years. Among these two age groups in the general population, fewer than 1% typically die from cardiovascular disease–related deaths. In Hodgkin lymphoma survivors aged 60 years or older, 27.5% of excess deaths were from cardiovascular disease.
Although not stratified by treatment, the study includes risk estimates for other cancers diagnosed in the teen and young adult years, stratified by the age at diagnosis, something the authors of the study noted is “a considerable advance on previous knowledge.”
Survivors of all age groups in the cohort diagnosed with a variety of cancers experienced a greater risk of death from heart disease, compared with their peers in the general population.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
Survivorship data derived from a U.K. cancer registry make it possible to more closely pinpoint the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients treated for cancer as adolescents and young adults.
Researchers report that 6% of the 2,016 deaths occurring in 200,945 cancer survivors diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 39 years were directly related to cardiovascular disease. A multivariable Poisson regression analysis of data from the Teenage and Young Adult Cancer Survivor Study also showed that survivors who were diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 19 years had 4.2 times the risk (95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.2) of death from cardiovascular disease, compared with their peers in the general population. But for survivors who were aged 35-39 years when diagnosed, that risk decreased to 1.2 times (95% CI, 1.1-1.3) that of their general population peers (P less than .0001). The standardized mortality ratios and absolute excess risks for ischemic heart disease, valvular heart disease, and cardiomyopathy were similar (Circulation. 2016;134:1521-33).
The findings should help clinicians craft more effective after-cancer care, according to Mike Hawkins, DPhil. “It helps them focus the most intensive follow-up care on those most at risk,” Dr. Hawkins, an epidemiology professor and director of the Centre for Childhood Cancer Survivor Studies at the University of Birmingham (England), said in a statement. “It is important for survivors because it empowers them by providing them with their long-term chances of a specific side effect of cancer treatment.”
The most significant relationship between cardiovascular disease and cancer occurred in those diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma, and at an earlier age. Overall, Hodgkin lymphoma survivors had a 3.8 times higher risk of cardiovascular disease–related death than their peers not diagnosed with any cancer. In those diagnosed at age 15-19 years, 6.9% had died from cardiovascular disease by age 55 years, compared with 2% of those who’d been diagnosed at age 35-39 years. Among these two age groups in the general population, fewer than 1% typically die from cardiovascular disease–related deaths. In Hodgkin lymphoma survivors aged 60 years or older, 27.5% of excess deaths were from cardiovascular disease.
Although not stratified by treatment, the study includes risk estimates for other cancers diagnosed in the teen and young adult years, stratified by the age at diagnosis, something the authors of the study noted is “a considerable advance on previous knowledge.”
Survivors of all age groups in the cohort diagnosed with a variety of cancers experienced a greater risk of death from heart disease, compared with their peers in the general population.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
FROM CIRCULATION
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Cancer survivors who were diagnosed at age 15-19 years had 4.2 times the risk of death from cardiovascular disease than did their peers in the general population.
Data source: A U.K. cancer registry of 200,945 persons between 15 and 39 years at time of diagnosis.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research in the United Kingdom. The authors had no relevant disclosures.
Indacaterol/glycopyrronium OK as preferred COPD treatment
AT CHEST 2016
LOS ANGELES – Indacaterol/glycopyrronium was superior to salmeterol/fluticasone at reducing the risk and rate of moderate to severe exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients with more than one or zero to one exacerbations in the previous year, results from an indirect comparison showed.
“Acute exacerbations of COPD are associated with accelerated decline in lung function and increased mortality,” Kenneth R. Chapman, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “Current GOLD [Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease] strategy recommends LABA/ICS [long-acting beta-agonist/inhaled corticosteroid] combination, and/or LAMA [long-acting muscarinic antagonist] as the first-line treatment, and LABA/LAMA as an alternative treatment for COPD patients at a high risk of exacerbations.”
In an effort to examine the reduction in moderate or severe exacerbations in COPD patients taking indacaterol/glycopyrronium (a combination of a LABA bronchodilator and a LAMA bronchodilator) or salmeterol/fluticasone (a LABA and inhaled glucocorticoid combination), researchers compared results from the FLAME and LANTERN trials. The FLAME study evaluated the rate and risk of exacerbations with indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus salmeterol/fluticasone in 3,362 moderate to very severe COPD patients with at least one exacerbation in the previous year (N Engl J Med. 2016;374[23]:2222-34).The LANTERN study compared the efficacy and safety of indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus salmeterol/fluticasone in 744 moderate to very severe COPD patients with 0-1 exacerbation in the previous year (Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1015-26).
Dr. Chapman, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, reported that in the FLAME study, which was 52 weeks long, indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly reduced the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations in patients who had one or more exacerbation in the previous year (a rate ratio of 0.83; P less than 0.001), which translated in to a clinically meaningful 17% reduction, compared with their counterparts taking salmeterol/fluticasone. In the LANTERN study, which was 26 weeks long, indacaterol/glycopyrronium also significantly reduced the annualized rate of patients who had 0-1 exacerbation in the previous year, compared with those taking salmeterol/fluticasone (RR, 0.69; P = .048).
In FLAME, indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly delayed the time to first moderate or severe exacerbation, with a clinically meaningful 22% risk reduction, compared with salmeterol/fluticasone (hazard ratio, 0.78; P less than .001). Similar findings were observed in LANTERN; indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly delayed the time to first moderate or severe exacerbation, with a clinically meaningful 35% risk reduction, compared with salmeterol/fluticasone (HR, 0.65; P less than .028).
“These results suggest that LABA/LAMA combinations such as indacaterol/glycopyrronium can be considered as a preferred treatment option in the management of COPD patients, irrespective of exacerbation history,” Dr. Chapman said.He went on to note that in FLAME, the incidence of pneumonia was 3.2% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 4.8% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group P = .02). In LANTERN, the incidence of pneumonia was 0.8% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 2.7% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group. Finally, in FLAME, the incidence of oral candidiasis was 1.2% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 4.2% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group (P less than .001). In LANTERN, the respective values were 0% and 0.3%.
Dr. Chapman reported having numerous financial disclosures, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from Novartis.
[email protected]
AT CHEST 2016
LOS ANGELES – Indacaterol/glycopyrronium was superior to salmeterol/fluticasone at reducing the risk and rate of moderate to severe exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients with more than one or zero to one exacerbations in the previous year, results from an indirect comparison showed.
“Acute exacerbations of COPD are associated with accelerated decline in lung function and increased mortality,” Kenneth R. Chapman, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “Current GOLD [Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease] strategy recommends LABA/ICS [long-acting beta-agonist/inhaled corticosteroid] combination, and/or LAMA [long-acting muscarinic antagonist] as the first-line treatment, and LABA/LAMA as an alternative treatment for COPD patients at a high risk of exacerbations.”
In an effort to examine the reduction in moderate or severe exacerbations in COPD patients taking indacaterol/glycopyrronium (a combination of a LABA bronchodilator and a LAMA bronchodilator) or salmeterol/fluticasone (a LABA and inhaled glucocorticoid combination), researchers compared results from the FLAME and LANTERN trials. The FLAME study evaluated the rate and risk of exacerbations with indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus salmeterol/fluticasone in 3,362 moderate to very severe COPD patients with at least one exacerbation in the previous year (N Engl J Med. 2016;374[23]:2222-34).The LANTERN study compared the efficacy and safety of indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus salmeterol/fluticasone in 744 moderate to very severe COPD patients with 0-1 exacerbation in the previous year (Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1015-26).
Dr. Chapman, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, reported that in the FLAME study, which was 52 weeks long, indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly reduced the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations in patients who had one or more exacerbation in the previous year (a rate ratio of 0.83; P less than 0.001), which translated in to a clinically meaningful 17% reduction, compared with their counterparts taking salmeterol/fluticasone. In the LANTERN study, which was 26 weeks long, indacaterol/glycopyrronium also significantly reduced the annualized rate of patients who had 0-1 exacerbation in the previous year, compared with those taking salmeterol/fluticasone (RR, 0.69; P = .048).
In FLAME, indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly delayed the time to first moderate or severe exacerbation, with a clinically meaningful 22% risk reduction, compared with salmeterol/fluticasone (hazard ratio, 0.78; P less than .001). Similar findings were observed in LANTERN; indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly delayed the time to first moderate or severe exacerbation, with a clinically meaningful 35% risk reduction, compared with salmeterol/fluticasone (HR, 0.65; P less than .028).
“These results suggest that LABA/LAMA combinations such as indacaterol/glycopyrronium can be considered as a preferred treatment option in the management of COPD patients, irrespective of exacerbation history,” Dr. Chapman said.He went on to note that in FLAME, the incidence of pneumonia was 3.2% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 4.8% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group P = .02). In LANTERN, the incidence of pneumonia was 0.8% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 2.7% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group. Finally, in FLAME, the incidence of oral candidiasis was 1.2% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 4.2% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group (P less than .001). In LANTERN, the respective values were 0% and 0.3%.
Dr. Chapman reported having numerous financial disclosures, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from Novartis.
[email protected]
AT CHEST 2016
LOS ANGELES – Indacaterol/glycopyrronium was superior to salmeterol/fluticasone at reducing the risk and rate of moderate to severe exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients with more than one or zero to one exacerbations in the previous year, results from an indirect comparison showed.
“Acute exacerbations of COPD are associated with accelerated decline in lung function and increased mortality,” Kenneth R. Chapman, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “Current GOLD [Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease] strategy recommends LABA/ICS [long-acting beta-agonist/inhaled corticosteroid] combination, and/or LAMA [long-acting muscarinic antagonist] as the first-line treatment, and LABA/LAMA as an alternative treatment for COPD patients at a high risk of exacerbations.”
In an effort to examine the reduction in moderate or severe exacerbations in COPD patients taking indacaterol/glycopyrronium (a combination of a LABA bronchodilator and a LAMA bronchodilator) or salmeterol/fluticasone (a LABA and inhaled glucocorticoid combination), researchers compared results from the FLAME and LANTERN trials. The FLAME study evaluated the rate and risk of exacerbations with indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus salmeterol/fluticasone in 3,362 moderate to very severe COPD patients with at least one exacerbation in the previous year (N Engl J Med. 2016;374[23]:2222-34).The LANTERN study compared the efficacy and safety of indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus salmeterol/fluticasone in 744 moderate to very severe COPD patients with 0-1 exacerbation in the previous year (Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1015-26).
Dr. Chapman, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, reported that in the FLAME study, which was 52 weeks long, indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly reduced the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations in patients who had one or more exacerbation in the previous year (a rate ratio of 0.83; P less than 0.001), which translated in to a clinically meaningful 17% reduction, compared with their counterparts taking salmeterol/fluticasone. In the LANTERN study, which was 26 weeks long, indacaterol/glycopyrronium also significantly reduced the annualized rate of patients who had 0-1 exacerbation in the previous year, compared with those taking salmeterol/fluticasone (RR, 0.69; P = .048).
In FLAME, indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly delayed the time to first moderate or severe exacerbation, with a clinically meaningful 22% risk reduction, compared with salmeterol/fluticasone (hazard ratio, 0.78; P less than .001). Similar findings were observed in LANTERN; indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly delayed the time to first moderate or severe exacerbation, with a clinically meaningful 35% risk reduction, compared with salmeterol/fluticasone (HR, 0.65; P less than .028).
“These results suggest that LABA/LAMA combinations such as indacaterol/glycopyrronium can be considered as a preferred treatment option in the management of COPD patients, irrespective of exacerbation history,” Dr. Chapman said.He went on to note that in FLAME, the incidence of pneumonia was 3.2% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 4.8% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group P = .02). In LANTERN, the incidence of pneumonia was 0.8% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 2.7% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group. Finally, in FLAME, the incidence of oral candidiasis was 1.2% in the indacaterol/glycopyrronium group, compared with 4.2% in the salmeterol/fluticasone group (P less than .001). In LANTERN, the respective values were 0% and 0.3%.
Dr. Chapman reported having numerous financial disclosures, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from Novartis.
[email protected]
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Indacaterol/glycopyrronium significantly reduced the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations in patients who had one or more exacerbation in the previous year (a rate ratio of 0.83; P less than 0.001), which translated into a clinically meaningful 17% reduction, compared with their counterparts taking salmeterol/fluticasone.
Data source: An indirect comparison of 3,362 patients in the FLAME study and 744 patients in the LANTERN study.
Disclosures: Dr. Chapman reported having numerous financial disclosures, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from Novartis.
Meaningful use: CMS extends 90-day reporting period to 2016, 2017
Physicians who already participate in the EHR incentive program for meaningful use will have to demonstrate they are meaningful users for only 90 days in 2016 and 2017.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services finalized the 90-day reporting period in its annual update to the hospital outpatient prospective payment system, scheduled for publication in the Federal Register on Nov. 14.
The CMS was preparing to require a full year of reporting in 2017 to be eligible for bonuses under the EHR Incentive Program; but instead extended the 90-day reporting requirement to address concerns about technical functionalities and to help ease the transition to the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) created by the 2015 MACRA law, according to an agency fact sheet.
The Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) final rule also eliminated clinical decision support and computerized order entry objectives and measures for eligible hospitals and critical access hospitals.
Instead of requiring that eligible professionals and hospitals new to the EHR Incentive Program in 2017 to meet Stage 3 requirements, the CMS has provided modified Stage 2 requirements.
Physicians who are new to the EHR Incentive Program in 2017 but are transitioning their practice to MIPS next year can apply for a significant hardship exemption to avoid any penalties to their 2018 Medicare payments.
Physicians who already participate in the EHR incentive program for meaningful use will have to demonstrate they are meaningful users for only 90 days in 2016 and 2017.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services finalized the 90-day reporting period in its annual update to the hospital outpatient prospective payment system, scheduled for publication in the Federal Register on Nov. 14.
The CMS was preparing to require a full year of reporting in 2017 to be eligible for bonuses under the EHR Incentive Program; but instead extended the 90-day reporting requirement to address concerns about technical functionalities and to help ease the transition to the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) created by the 2015 MACRA law, according to an agency fact sheet.
The Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) final rule also eliminated clinical decision support and computerized order entry objectives and measures for eligible hospitals and critical access hospitals.
Instead of requiring that eligible professionals and hospitals new to the EHR Incentive Program in 2017 to meet Stage 3 requirements, the CMS has provided modified Stage 2 requirements.
Physicians who are new to the EHR Incentive Program in 2017 but are transitioning their practice to MIPS next year can apply for a significant hardship exemption to avoid any penalties to their 2018 Medicare payments.
Physicians who already participate in the EHR incentive program for meaningful use will have to demonstrate they are meaningful users for only 90 days in 2016 and 2017.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services finalized the 90-day reporting period in its annual update to the hospital outpatient prospective payment system, scheduled for publication in the Federal Register on Nov. 14.
The CMS was preparing to require a full year of reporting in 2017 to be eligible for bonuses under the EHR Incentive Program; but instead extended the 90-day reporting requirement to address concerns about technical functionalities and to help ease the transition to the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) created by the 2015 MACRA law, according to an agency fact sheet.
The Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) final rule also eliminated clinical decision support and computerized order entry objectives and measures for eligible hospitals and critical access hospitals.
Instead of requiring that eligible professionals and hospitals new to the EHR Incentive Program in 2017 to meet Stage 3 requirements, the CMS has provided modified Stage 2 requirements.
Physicians who are new to the EHR Incentive Program in 2017 but are transitioning their practice to MIPS next year can apply for a significant hardship exemption to avoid any penalties to their 2018 Medicare payments.
Optimal MPE management requires early pulmonology referral
LOS ANGELES – About half of patients with symptomatic malignant pleural effusions at McGill University Health Centre in Montreal had unnecessary procedures and hospital admissions before definitive treatment with chemical pleurodesis or indwelling pleural catheters, according to researchers.
Instead of chest taps to relieve symptoms followed by referrals for definitive treatment, some patients got chest tubes – without pleurodesis – after presenting to the emergency department and being referred to radiology; they were then admitted to the hospital for a few days while the tubes were in place. In short, cancer patients were wasting what time they had left on medical care they didn’t need, and incurring unnecessary costs, said lead investigator Benjamin Shieh, MD, formerly at McGill but now an interventional pulmonology fellow at the University of Calgary.
McGill is a tertiary care center able to perform both definitive procedures, so “we should be a center of excellence. I imagine there are similar situations” at other hospitals, especially those without the resources of McGill, Dr. Shieh said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
McGill has taken several steps to address the problem, including early ED referral to the pulmonology service and discouraging radiology from placing chest tubes for malignant pleural effusions (MPE). “I think we can avoid a big proportion of hospitalizations for MPE, and certainly a proportion of repeat [ED] visits,” said senior author Anne Gonzalez, MD, an attending pulmonologist at McGill.
The investigators looked into the issue after noting that a lot of their MPE cases had been hospitalized with chest tubes. They reviewed 72 symptomatic MPE cases in 69 patients treated in 2014 and 2015. Management was ideal in 36 cases (50%), meaning that, prior to definitive treatment, patients had no more than two pleural taps for symptom relief, no more than one ED visit, no chest tubes without pleurodesis, and no hospitalizations. “We thought this would be reasonable to try to achieve for MPE,” since there’s no definition of ideal management, Dr. Shieh said.
Nonideal patients had a mean of 2.5 pleural procedures – almost twice the number in the ideal group – before definitive palliation, with no respiratory consult beforehand. Chest tubes were placed in 27 cases (38%) for an average of 3.7 days; 28 cases (39%) were hospitalized. Nonideal patients were far more likely to present first to the ED, and ED presentations were more likely to get chest tubes and be admitted. All the cases were eventually treated definitively, 68 with indwelling pleural catheters and 4 by thoracoscopic talc insufflation. Time from initial presentation to definitive palliation was about 1 month in both groups. The investigators didn’t consider rate of effusion recurrence, which might help explain why the ideal group wasn’t treated sooner; they might not have needed it. The higher number of ED visits in the nonideal group suggests that they may have had quicker recurrences, and should have been treated sooner, Dr. Gonzalez said.
The patients were 70 years old, on average, and about 60% were women. Lung and breast were the most common cancers.
There was no industry funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – About half of patients with symptomatic malignant pleural effusions at McGill University Health Centre in Montreal had unnecessary procedures and hospital admissions before definitive treatment with chemical pleurodesis or indwelling pleural catheters, according to researchers.
Instead of chest taps to relieve symptoms followed by referrals for definitive treatment, some patients got chest tubes – without pleurodesis – after presenting to the emergency department and being referred to radiology; they were then admitted to the hospital for a few days while the tubes were in place. In short, cancer patients were wasting what time they had left on medical care they didn’t need, and incurring unnecessary costs, said lead investigator Benjamin Shieh, MD, formerly at McGill but now an interventional pulmonology fellow at the University of Calgary.
McGill is a tertiary care center able to perform both definitive procedures, so “we should be a center of excellence. I imagine there are similar situations” at other hospitals, especially those without the resources of McGill, Dr. Shieh said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
McGill has taken several steps to address the problem, including early ED referral to the pulmonology service and discouraging radiology from placing chest tubes for malignant pleural effusions (MPE). “I think we can avoid a big proportion of hospitalizations for MPE, and certainly a proportion of repeat [ED] visits,” said senior author Anne Gonzalez, MD, an attending pulmonologist at McGill.
The investigators looked into the issue after noting that a lot of their MPE cases had been hospitalized with chest tubes. They reviewed 72 symptomatic MPE cases in 69 patients treated in 2014 and 2015. Management was ideal in 36 cases (50%), meaning that, prior to definitive treatment, patients had no more than two pleural taps for symptom relief, no more than one ED visit, no chest tubes without pleurodesis, and no hospitalizations. “We thought this would be reasonable to try to achieve for MPE,” since there’s no definition of ideal management, Dr. Shieh said.
Nonideal patients had a mean of 2.5 pleural procedures – almost twice the number in the ideal group – before definitive palliation, with no respiratory consult beforehand. Chest tubes were placed in 27 cases (38%) for an average of 3.7 days; 28 cases (39%) were hospitalized. Nonideal patients were far more likely to present first to the ED, and ED presentations were more likely to get chest tubes and be admitted. All the cases were eventually treated definitively, 68 with indwelling pleural catheters and 4 by thoracoscopic talc insufflation. Time from initial presentation to definitive palliation was about 1 month in both groups. The investigators didn’t consider rate of effusion recurrence, which might help explain why the ideal group wasn’t treated sooner; they might not have needed it. The higher number of ED visits in the nonideal group suggests that they may have had quicker recurrences, and should have been treated sooner, Dr. Gonzalez said.
The patients were 70 years old, on average, and about 60% were women. Lung and breast were the most common cancers.
There was no industry funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – About half of patients with symptomatic malignant pleural effusions at McGill University Health Centre in Montreal had unnecessary procedures and hospital admissions before definitive treatment with chemical pleurodesis or indwelling pleural catheters, according to researchers.
Instead of chest taps to relieve symptoms followed by referrals for definitive treatment, some patients got chest tubes – without pleurodesis – after presenting to the emergency department and being referred to radiology; they were then admitted to the hospital for a few days while the tubes were in place. In short, cancer patients were wasting what time they had left on medical care they didn’t need, and incurring unnecessary costs, said lead investigator Benjamin Shieh, MD, formerly at McGill but now an interventional pulmonology fellow at the University of Calgary.
McGill is a tertiary care center able to perform both definitive procedures, so “we should be a center of excellence. I imagine there are similar situations” at other hospitals, especially those without the resources of McGill, Dr. Shieh said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
McGill has taken several steps to address the problem, including early ED referral to the pulmonology service and discouraging radiology from placing chest tubes for malignant pleural effusions (MPE). “I think we can avoid a big proportion of hospitalizations for MPE, and certainly a proportion of repeat [ED] visits,” said senior author Anne Gonzalez, MD, an attending pulmonologist at McGill.
The investigators looked into the issue after noting that a lot of their MPE cases had been hospitalized with chest tubes. They reviewed 72 symptomatic MPE cases in 69 patients treated in 2014 and 2015. Management was ideal in 36 cases (50%), meaning that, prior to definitive treatment, patients had no more than two pleural taps for symptom relief, no more than one ED visit, no chest tubes without pleurodesis, and no hospitalizations. “We thought this would be reasonable to try to achieve for MPE,” since there’s no definition of ideal management, Dr. Shieh said.
Nonideal patients had a mean of 2.5 pleural procedures – almost twice the number in the ideal group – before definitive palliation, with no respiratory consult beforehand. Chest tubes were placed in 27 cases (38%) for an average of 3.7 days; 28 cases (39%) were hospitalized. Nonideal patients were far more likely to present first to the ED, and ED presentations were more likely to get chest tubes and be admitted. All the cases were eventually treated definitively, 68 with indwelling pleural catheters and 4 by thoracoscopic talc insufflation. Time from initial presentation to definitive palliation was about 1 month in both groups. The investigators didn’t consider rate of effusion recurrence, which might help explain why the ideal group wasn’t treated sooner; they might not have needed it. The higher number of ED visits in the nonideal group suggests that they may have had quicker recurrences, and should have been treated sooner, Dr. Gonzalez said.
The patients were 70 years old, on average, and about 60% were women. Lung and breast were the most common cancers.
There was no industry funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.
AT CHEST 2016
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Those patients had a mean of 2.5 pleural procedures before definitive palliation, with no respiratory consult beforehand. Chest tubes were placed for an average of 3.7 days.
Data source: Review of 72 MPE cases in 69 patients.
Disclosures: There was no industry funding for the work, and the investigators had no disclosures.