User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
New First-Line Therapies for Migraine Prevention
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 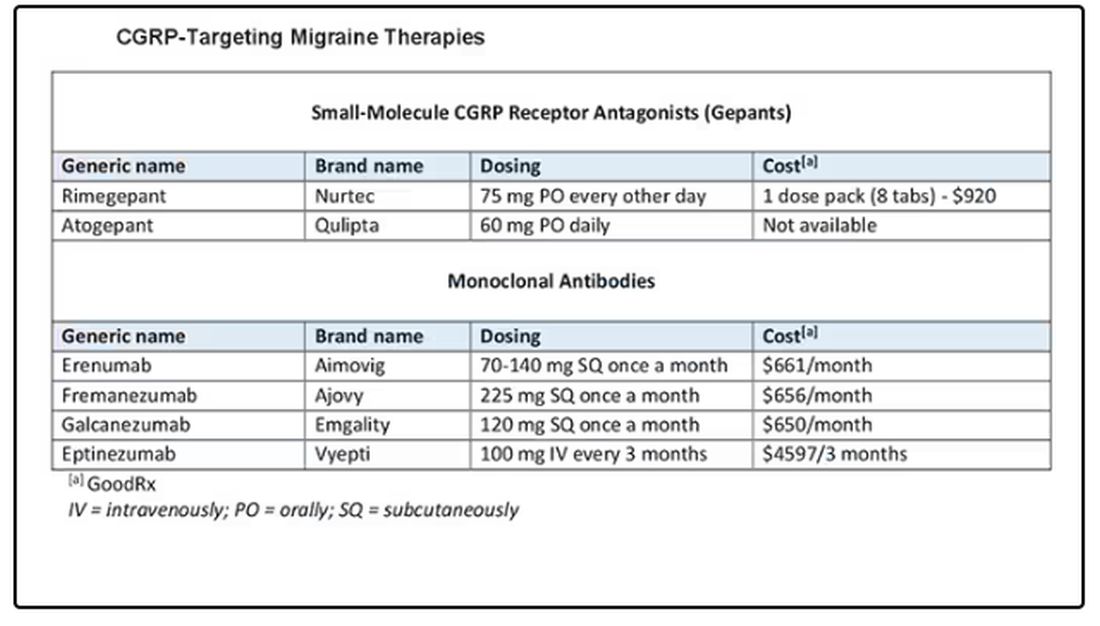
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy May Be Overused in Dying Patients With Cancer
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How Clinicians Can Help Patients Navigate Psychedelics/Microdosing
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Anxiety Linked to a Threefold Increased Risk for Dementia
TOPLINE:
, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 2132 participants aged 55-85 years (mean age, 76 years) were recruited from the Hunter Community Study. Of these, 53% were women.
- Participants were assessed over three different waves, 5 years apart. Demographic and health-related data were captured at wave 1.
- Researchers used the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale (K10) to measure anxiety at two points: Baseline (wave 1) and first follow-up (wave 2), with a 5-year interval between them. Anxiety was classified as chronic if present during both waves, resolved if only present at wave 1, and new if only appearing at wave 2.
- The primary outcome, incident all-cause dementia, during the follow-up period (maximum 13 years after baseline) was identified using the International Classification of Disease-10 codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out of 2132 cognitively healthy participants, 64 developed dementia, with an average time to diagnosis of 10 years. Chronic anxiety was linked to a 2.8-fold increased risk for dementia, while new-onset anxiety was associated with a 3.2-fold increased risk (P = .01).
- Participants younger than 70 years with chronic anxiety had a 4.6-fold increased risk for dementia (P = .03), and those with new-onset anxiety had a 7.2 times higher risk for dementia (P = .004).
- There was no significant risk for dementia in participants with anxiety that had resolved.
- Investigators speculated that individuals with anxiety were more likely to engage in unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, such as poor diet and smoking, which can lead to cardiovascular disease — a condition strongly associated with dementia.
IN PRACTICE:
“This prospective cohort study used causal inference methods to explore the role of anxiety in promoting the development of dementia,” lead author Kay Khaing, MMed, The University of Newcastle, Australia, wrote in a press release. “The findings suggest that anxiety may be a new risk factor to target in the prevention of dementia and also indicate that treating anxiety may reduce this risk.”
SOURCE:
Kay Khaing, MMed, of The University of Newcastle, Australia, led the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
LIMITATIONS:
Anxiety was measured using K10, which assessed symptoms experienced in the most recent 4 weeks, raising concerns about its accuracy over the entire observation period. The authors acknowledged that despite using a combination of the total K10 score and the anxiety subscale, the overlap of anxiety and depression might not be fully disentangled, leading to residual confounding by depression. Additionally, 33% of participants were lost to follow-up, and those lost had higher anxiety rates at baseline, potentially leading to missing cases of dementia and affecting the effect estimate.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not report any funding or conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 2132 participants aged 55-85 years (mean age, 76 years) were recruited from the Hunter Community Study. Of these, 53% were women.
- Participants were assessed over three different waves, 5 years apart. Demographic and health-related data were captured at wave 1.
- Researchers used the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale (K10) to measure anxiety at two points: Baseline (wave 1) and first follow-up (wave 2), with a 5-year interval between them. Anxiety was classified as chronic if present during both waves, resolved if only present at wave 1, and new if only appearing at wave 2.
- The primary outcome, incident all-cause dementia, during the follow-up period (maximum 13 years after baseline) was identified using the International Classification of Disease-10 codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out of 2132 cognitively healthy participants, 64 developed dementia, with an average time to diagnosis of 10 years. Chronic anxiety was linked to a 2.8-fold increased risk for dementia, while new-onset anxiety was associated with a 3.2-fold increased risk (P = .01).
- Participants younger than 70 years with chronic anxiety had a 4.6-fold increased risk for dementia (P = .03), and those with new-onset anxiety had a 7.2 times higher risk for dementia (P = .004).
- There was no significant risk for dementia in participants with anxiety that had resolved.
- Investigators speculated that individuals with anxiety were more likely to engage in unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, such as poor diet and smoking, which can lead to cardiovascular disease — a condition strongly associated with dementia.
IN PRACTICE:
“This prospective cohort study used causal inference methods to explore the role of anxiety in promoting the development of dementia,” lead author Kay Khaing, MMed, The University of Newcastle, Australia, wrote in a press release. “The findings suggest that anxiety may be a new risk factor to target in the prevention of dementia and also indicate that treating anxiety may reduce this risk.”
SOURCE:
Kay Khaing, MMed, of The University of Newcastle, Australia, led the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
LIMITATIONS:
Anxiety was measured using K10, which assessed symptoms experienced in the most recent 4 weeks, raising concerns about its accuracy over the entire observation period. The authors acknowledged that despite using a combination of the total K10 score and the anxiety subscale, the overlap of anxiety and depression might not be fully disentangled, leading to residual confounding by depression. Additionally, 33% of participants were lost to follow-up, and those lost had higher anxiety rates at baseline, potentially leading to missing cases of dementia and affecting the effect estimate.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not report any funding or conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 2132 participants aged 55-85 years (mean age, 76 years) were recruited from the Hunter Community Study. Of these, 53% were women.
- Participants were assessed over three different waves, 5 years apart. Demographic and health-related data were captured at wave 1.
- Researchers used the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale (K10) to measure anxiety at two points: Baseline (wave 1) and first follow-up (wave 2), with a 5-year interval between them. Anxiety was classified as chronic if present during both waves, resolved if only present at wave 1, and new if only appearing at wave 2.
- The primary outcome, incident all-cause dementia, during the follow-up period (maximum 13 years after baseline) was identified using the International Classification of Disease-10 codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Out of 2132 cognitively healthy participants, 64 developed dementia, with an average time to diagnosis of 10 years. Chronic anxiety was linked to a 2.8-fold increased risk for dementia, while new-onset anxiety was associated with a 3.2-fold increased risk (P = .01).
- Participants younger than 70 years with chronic anxiety had a 4.6-fold increased risk for dementia (P = .03), and those with new-onset anxiety had a 7.2 times higher risk for dementia (P = .004).
- There was no significant risk for dementia in participants with anxiety that had resolved.
- Investigators speculated that individuals with anxiety were more likely to engage in unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, such as poor diet and smoking, which can lead to cardiovascular disease — a condition strongly associated with dementia.
IN PRACTICE:
“This prospective cohort study used causal inference methods to explore the role of anxiety in promoting the development of dementia,” lead author Kay Khaing, MMed, The University of Newcastle, Australia, wrote in a press release. “The findings suggest that anxiety may be a new risk factor to target in the prevention of dementia and also indicate that treating anxiety may reduce this risk.”
SOURCE:
Kay Khaing, MMed, of The University of Newcastle, Australia, led the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
LIMITATIONS:
Anxiety was measured using K10, which assessed symptoms experienced in the most recent 4 weeks, raising concerns about its accuracy over the entire observation period. The authors acknowledged that despite using a combination of the total K10 score and the anxiety subscale, the overlap of anxiety and depression might not be fully disentangled, leading to residual confounding by depression. Additionally, 33% of participants were lost to follow-up, and those lost had higher anxiety rates at baseline, potentially leading to missing cases of dementia and affecting the effect estimate.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not report any funding or conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Addressing Depression Reduce Chemo Toxicity in Older Adults?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Headache Surgery Really Work? Neurologists Remain Unconvinced
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cognitive Breakdown: The New Memory Condition Primary Care Needs to Know
Patients experiencing memory problems often come to neurologist David Jones, MD, for second opinions. They repeat questions and sometimes misplace items. Their primary care clinician has suggested they may have Alzheimer’s disease or something else.
In many cases, Dr. Jones, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, performs a series of investigations and finds the patient instead has a different type of neurodegenerative syndrome, one that progresses slowly, seems limited chiefly to loss of memory, and which tests show affects only the limbic system.
The news of diagnosis can be reassuring to patients.
“Memory problems are not always Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Jones said. “It’s important to broaden the differential diagnosis and seek diagnostic clarity and precision for patients who experience problems with brain functioning later in life.”
Dr. Jones and colleagues recently published clinical criteria for what they call limbic-predominant amnestic neurodegenerative syndrome (LANS).
Various underlying etiologies are known to cause degeneration of the limbic system, the most frequent being a buildup of deposits of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) protein referred to as limbic-predominant, age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC). LATE-NC first involves the amygdala, followed by the hippocampus, and then the middle frontal gyrus, and is found in about 40% of autopsied brains in people over age of 85 years.
By contrast, amnestic syndromes originating from neocortical degeneration are largely caused by neuropathological changes from Alzheimer’s disease and often present with non-memory features.
Criteria for LANS
Broken down into core, standard, and advanced features
Core clinical features:
The patient must present with a slow, amnestic, predominant neurodegenerative syndrome — an insidious onset with gradual progression over 2 or more years — without another condition that better accounts for the clinical deficits.
Standard supportive features:
1. Older age at evaluation.
- Most patients are at least the age of 75 years. Older age increases the likelihood that the amnestic syndrome is caused by degeneration of the limbic system.
2. Mild clinical syndrome.
- A diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or mild amnestic dementia (ie, a score of ≤ 4 on the Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes [CDR-SB]) at the first visit.
3. Hippocampal atrophy out of proportion to syndrome severity.
- Hippocampal volume was smaller than expected on MRI, compared with the CDR-SB score.
4. Mildly impaired semantic memory.
Advanced supportive features:
1.Limbic hypometabolism and absence of neocortical degenerative pattern on fludeoxyglucose-18-PET imaging.
2. Low likelihood of significant neocortical tau pathology.
Dr. Jones and colleagues also classified a degree of certainty for LANS to use when making a diagnosis. Those with the highest likelihood meet all core, standard, and advanced features.
Patients with a high likelihood of having LANS meet core features, at least three standard features and one advanced feature; or meet core features, at least two standard features as well as two advanced features. Those with a moderate likelihood meet core features and at least three standard features or meet core features and at least two standard features and one advanced feature. Those with a low likelihood of LANS meet core features and two or fewer standard features.
To develop these criteria, the group screened 218 autopsied patients participating in databases for the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging and the multicenter Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. They conducted neuropathological assessments, reviewed MRI and PET scans of the brains, and studied fluid biomarkers from samples of cerebrospinal fluid.
In LANS, the neocortex exhibits normal function, Dr. Jones said. High-level language functions, visual spatial functions, and executive function are preserved, and the disease stays mild for many years. LANS is highly associated with LATE, for which no biomarkers are yet available.
The National Institute on Aging in May 2023 held a workshop on LATE, and a consensus group was formed to publish criteria to help with the diagnosis. Many LANS criteria likely will be in that publication as well, Dr. Jones said.
Several steps lay ahead to improve the definition of LANS, the authors wrote, including conducting prospective studies and developing clinical tools that are sensitive and specific to its cognitive features. The development of in vivo diagnostic markers of TDP-43 pathology is needed to embed LANS into a disease state driven by LATE-NC, according to Dr. Jones’ group. Because LANS is newly defined, clinical trials are needed to determine the best treatments.
Heterogeneous Dementia
“We are increasingly recognizing that the syndrome of dementia in older adults is heterogeneous,” said Sudha Seshadri, MD, DM, a behavioral neurologist and founding director of the Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative Diseases at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
LANS “is something that needs to be diagnosed early but also needs to be worked up in a nuanced manner, with assessment of the pattern of cognitive deficits, the pattern of brain shrinkage on MRI, and also how the disease progresses over, say, a year,” said Dr. Seshadri. “We need to have both some primary care physicians and geriatricians who are comfortable doing this kind of nuanced advising and others who may refer patients to behavioral neurologists, geriatricians, or psychiatrists who have that kind of expertise.”
About 10% of people presenting to dementia clinics potentially could fit the LANS definition, Dr. Seshadri said. Dr. Seshadri was not a coauthor of the classification article but sees patients in the clinic who fit this description.
“It may be that as we start more freely giving the diagnosis of a possible LANS, the proportion of people will go up,” Dr. Seshadri said.
Primary care physicians can use a variety of assessments to help diagnose dementias, she said. These include the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which takes about 10 minutes to administer, or an MRI to determine the level of hippocampal atrophy. Blood tests for p-tau 217 and other plasma tests can stratify risk and guide referrals to a neurologist. Clinicians also should look for reversible causes of memory complaints, such as deficiencies in vitamin B12, folate, or the thyroid hormone.
“There aren’t enough behavioral neurologists around to work up every single person who has memory problems,” Dr. Seshadri said. “We really need to partner on educating and learning from our primary care partners as to what challenges they face, advocating for them to be able to address that, and then sharing what we know, because what we know is an evolving thing.”
Other tools primary care clinicians can use in the initial evaluation of dementia include the General Practitioner Assessment of Cognition and the Mini-Cog, as part of annual Medicare wellness visits or in response to patient or caregiver concerns about memory, said Allison Kaplan, MD, a family physician at Desert Grove Family Medical in Gilbert, Arizona, who coauthored a point-of-care guide for the American Academy of Family Physicians. Each of these tests takes just 3-4 minutes to administer.
If a patient has a positive result on the Mini-Cog or similar test, they should return for further dementia evaluation using the MoCA, Mini-Mental State Examination, or Saint Louis University Mental Status examination, she said. Physicians also can order brain imaging and lab work, as Dr. Seshadri noted. Dementias often accompany some type of cardiovascular disease, which should be managed.
Even if a patient or family member doesn’t express concern about memory, physicians can look for certain signs during medical visits.
“Patients will keep asking the same question, or you notice they’re having difficulty taking care of themselves, especially independent activities of daily living, which could clue you in to a dementia diagnosis,” she said.
Dr. Jones ,Dr. Seshadri, and Dr. Kaplan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients experiencing memory problems often come to neurologist David Jones, MD, for second opinions. They repeat questions and sometimes misplace items. Their primary care clinician has suggested they may have Alzheimer’s disease or something else.
In many cases, Dr. Jones, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, performs a series of investigations and finds the patient instead has a different type of neurodegenerative syndrome, one that progresses slowly, seems limited chiefly to loss of memory, and which tests show affects only the limbic system.
The news of diagnosis can be reassuring to patients.
“Memory problems are not always Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Jones said. “It’s important to broaden the differential diagnosis and seek diagnostic clarity and precision for patients who experience problems with brain functioning later in life.”
Dr. Jones and colleagues recently published clinical criteria for what they call limbic-predominant amnestic neurodegenerative syndrome (LANS).
Various underlying etiologies are known to cause degeneration of the limbic system, the most frequent being a buildup of deposits of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) protein referred to as limbic-predominant, age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC). LATE-NC first involves the amygdala, followed by the hippocampus, and then the middle frontal gyrus, and is found in about 40% of autopsied brains in people over age of 85 years.
By contrast, amnestic syndromes originating from neocortical degeneration are largely caused by neuropathological changes from Alzheimer’s disease and often present with non-memory features.
Criteria for LANS
Broken down into core, standard, and advanced features
Core clinical features:
The patient must present with a slow, amnestic, predominant neurodegenerative syndrome — an insidious onset with gradual progression over 2 or more years — without another condition that better accounts for the clinical deficits.
Standard supportive features:
1. Older age at evaluation.
- Most patients are at least the age of 75 years. Older age increases the likelihood that the amnestic syndrome is caused by degeneration of the limbic system.
2. Mild clinical syndrome.
- A diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or mild amnestic dementia (ie, a score of ≤ 4 on the Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes [CDR-SB]) at the first visit.
3. Hippocampal atrophy out of proportion to syndrome severity.
- Hippocampal volume was smaller than expected on MRI, compared with the CDR-SB score.
4. Mildly impaired semantic memory.
Advanced supportive features:
1.Limbic hypometabolism and absence of neocortical degenerative pattern on fludeoxyglucose-18-PET imaging.
2. Low likelihood of significant neocortical tau pathology.
Dr. Jones and colleagues also classified a degree of certainty for LANS to use when making a diagnosis. Those with the highest likelihood meet all core, standard, and advanced features.
Patients with a high likelihood of having LANS meet core features, at least three standard features and one advanced feature; or meet core features, at least two standard features as well as two advanced features. Those with a moderate likelihood meet core features and at least three standard features or meet core features and at least two standard features and one advanced feature. Those with a low likelihood of LANS meet core features and two or fewer standard features.
To develop these criteria, the group screened 218 autopsied patients participating in databases for the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging and the multicenter Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. They conducted neuropathological assessments, reviewed MRI and PET scans of the brains, and studied fluid biomarkers from samples of cerebrospinal fluid.
In LANS, the neocortex exhibits normal function, Dr. Jones said. High-level language functions, visual spatial functions, and executive function are preserved, and the disease stays mild for many years. LANS is highly associated with LATE, for which no biomarkers are yet available.
The National Institute on Aging in May 2023 held a workshop on LATE, and a consensus group was formed to publish criteria to help with the diagnosis. Many LANS criteria likely will be in that publication as well, Dr. Jones said.
Several steps lay ahead to improve the definition of LANS, the authors wrote, including conducting prospective studies and developing clinical tools that are sensitive and specific to its cognitive features. The development of in vivo diagnostic markers of TDP-43 pathology is needed to embed LANS into a disease state driven by LATE-NC, according to Dr. Jones’ group. Because LANS is newly defined, clinical trials are needed to determine the best treatments.
Heterogeneous Dementia
“We are increasingly recognizing that the syndrome of dementia in older adults is heterogeneous,” said Sudha Seshadri, MD, DM, a behavioral neurologist and founding director of the Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative Diseases at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
LANS “is something that needs to be diagnosed early but also needs to be worked up in a nuanced manner, with assessment of the pattern of cognitive deficits, the pattern of brain shrinkage on MRI, and also how the disease progresses over, say, a year,” said Dr. Seshadri. “We need to have both some primary care physicians and geriatricians who are comfortable doing this kind of nuanced advising and others who may refer patients to behavioral neurologists, geriatricians, or psychiatrists who have that kind of expertise.”
About 10% of people presenting to dementia clinics potentially could fit the LANS definition, Dr. Seshadri said. Dr. Seshadri was not a coauthor of the classification article but sees patients in the clinic who fit this description.
“It may be that as we start more freely giving the diagnosis of a possible LANS, the proportion of people will go up,” Dr. Seshadri said.
Primary care physicians can use a variety of assessments to help diagnose dementias, she said. These include the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which takes about 10 minutes to administer, or an MRI to determine the level of hippocampal atrophy. Blood tests for p-tau 217 and other plasma tests can stratify risk and guide referrals to a neurologist. Clinicians also should look for reversible causes of memory complaints, such as deficiencies in vitamin B12, folate, or the thyroid hormone.
“There aren’t enough behavioral neurologists around to work up every single person who has memory problems,” Dr. Seshadri said. “We really need to partner on educating and learning from our primary care partners as to what challenges they face, advocating for them to be able to address that, and then sharing what we know, because what we know is an evolving thing.”
Other tools primary care clinicians can use in the initial evaluation of dementia include the General Practitioner Assessment of Cognition and the Mini-Cog, as part of annual Medicare wellness visits or in response to patient or caregiver concerns about memory, said Allison Kaplan, MD, a family physician at Desert Grove Family Medical in Gilbert, Arizona, who coauthored a point-of-care guide for the American Academy of Family Physicians. Each of these tests takes just 3-4 minutes to administer.
If a patient has a positive result on the Mini-Cog or similar test, they should return for further dementia evaluation using the MoCA, Mini-Mental State Examination, or Saint Louis University Mental Status examination, she said. Physicians also can order brain imaging and lab work, as Dr. Seshadri noted. Dementias often accompany some type of cardiovascular disease, which should be managed.
Even if a patient or family member doesn’t express concern about memory, physicians can look for certain signs during medical visits.
“Patients will keep asking the same question, or you notice they’re having difficulty taking care of themselves, especially independent activities of daily living, which could clue you in to a dementia diagnosis,” she said.
Dr. Jones ,Dr. Seshadri, and Dr. Kaplan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients experiencing memory problems often come to neurologist David Jones, MD, for second opinions. They repeat questions and sometimes misplace items. Their primary care clinician has suggested they may have Alzheimer’s disease or something else.
In many cases, Dr. Jones, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, performs a series of investigations and finds the patient instead has a different type of neurodegenerative syndrome, one that progresses slowly, seems limited chiefly to loss of memory, and which tests show affects only the limbic system.
The news of diagnosis can be reassuring to patients.
“Memory problems are not always Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Jones said. “It’s important to broaden the differential diagnosis and seek diagnostic clarity and precision for patients who experience problems with brain functioning later in life.”
Dr. Jones and colleagues recently published clinical criteria for what they call limbic-predominant amnestic neurodegenerative syndrome (LANS).
Various underlying etiologies are known to cause degeneration of the limbic system, the most frequent being a buildup of deposits of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) protein referred to as limbic-predominant, age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC). LATE-NC first involves the amygdala, followed by the hippocampus, and then the middle frontal gyrus, and is found in about 40% of autopsied brains in people over age of 85 years.
By contrast, amnestic syndromes originating from neocortical degeneration are largely caused by neuropathological changes from Alzheimer’s disease and often present with non-memory features.
Criteria for LANS
Broken down into core, standard, and advanced features
Core clinical features:
The patient must present with a slow, amnestic, predominant neurodegenerative syndrome — an insidious onset with gradual progression over 2 or more years — without another condition that better accounts for the clinical deficits.
Standard supportive features:
1. Older age at evaluation.
- Most patients are at least the age of 75 years. Older age increases the likelihood that the amnestic syndrome is caused by degeneration of the limbic system.
2. Mild clinical syndrome.
- A diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or mild amnestic dementia (ie, a score of ≤ 4 on the Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes [CDR-SB]) at the first visit.
3. Hippocampal atrophy out of proportion to syndrome severity.
- Hippocampal volume was smaller than expected on MRI, compared with the CDR-SB score.
4. Mildly impaired semantic memory.
Advanced supportive features:
1.Limbic hypometabolism and absence of neocortical degenerative pattern on fludeoxyglucose-18-PET imaging.
2. Low likelihood of significant neocortical tau pathology.
Dr. Jones and colleagues also classified a degree of certainty for LANS to use when making a diagnosis. Those with the highest likelihood meet all core, standard, and advanced features.
Patients with a high likelihood of having LANS meet core features, at least three standard features and one advanced feature; or meet core features, at least two standard features as well as two advanced features. Those with a moderate likelihood meet core features and at least three standard features or meet core features and at least two standard features and one advanced feature. Those with a low likelihood of LANS meet core features and two or fewer standard features.
To develop these criteria, the group screened 218 autopsied patients participating in databases for the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging and the multicenter Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. They conducted neuropathological assessments, reviewed MRI and PET scans of the brains, and studied fluid biomarkers from samples of cerebrospinal fluid.
In LANS, the neocortex exhibits normal function, Dr. Jones said. High-level language functions, visual spatial functions, and executive function are preserved, and the disease stays mild for many years. LANS is highly associated with LATE, for which no biomarkers are yet available.
The National Institute on Aging in May 2023 held a workshop on LATE, and a consensus group was formed to publish criteria to help with the diagnosis. Many LANS criteria likely will be in that publication as well, Dr. Jones said.
Several steps lay ahead to improve the definition of LANS, the authors wrote, including conducting prospective studies and developing clinical tools that are sensitive and specific to its cognitive features. The development of in vivo diagnostic markers of TDP-43 pathology is needed to embed LANS into a disease state driven by LATE-NC, according to Dr. Jones’ group. Because LANS is newly defined, clinical trials are needed to determine the best treatments.
Heterogeneous Dementia
“We are increasingly recognizing that the syndrome of dementia in older adults is heterogeneous,” said Sudha Seshadri, MD, DM, a behavioral neurologist and founding director of the Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative Diseases at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
LANS “is something that needs to be diagnosed early but also needs to be worked up in a nuanced manner, with assessment of the pattern of cognitive deficits, the pattern of brain shrinkage on MRI, and also how the disease progresses over, say, a year,” said Dr. Seshadri. “We need to have both some primary care physicians and geriatricians who are comfortable doing this kind of nuanced advising and others who may refer patients to behavioral neurologists, geriatricians, or psychiatrists who have that kind of expertise.”
About 10% of people presenting to dementia clinics potentially could fit the LANS definition, Dr. Seshadri said. Dr. Seshadri was not a coauthor of the classification article but sees patients in the clinic who fit this description.
“It may be that as we start more freely giving the diagnosis of a possible LANS, the proportion of people will go up,” Dr. Seshadri said.
Primary care physicians can use a variety of assessments to help diagnose dementias, she said. These include the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which takes about 10 minutes to administer, or an MRI to determine the level of hippocampal atrophy. Blood tests for p-tau 217 and other plasma tests can stratify risk and guide referrals to a neurologist. Clinicians also should look for reversible causes of memory complaints, such as deficiencies in vitamin B12, folate, or the thyroid hormone.
“There aren’t enough behavioral neurologists around to work up every single person who has memory problems,” Dr. Seshadri said. “We really need to partner on educating and learning from our primary care partners as to what challenges they face, advocating for them to be able to address that, and then sharing what we know, because what we know is an evolving thing.”
Other tools primary care clinicians can use in the initial evaluation of dementia include the General Practitioner Assessment of Cognition and the Mini-Cog, as part of annual Medicare wellness visits or in response to patient or caregiver concerns about memory, said Allison Kaplan, MD, a family physician at Desert Grove Family Medical in Gilbert, Arizona, who coauthored a point-of-care guide for the American Academy of Family Physicians. Each of these tests takes just 3-4 minutes to administer.
If a patient has a positive result on the Mini-Cog or similar test, they should return for further dementia evaluation using the MoCA, Mini-Mental State Examination, or Saint Louis University Mental Status examination, she said. Physicians also can order brain imaging and lab work, as Dr. Seshadri noted. Dementias often accompany some type of cardiovascular disease, which should be managed.
Even if a patient or family member doesn’t express concern about memory, physicians can look for certain signs during medical visits.
“Patients will keep asking the same question, or you notice they’re having difficulty taking care of themselves, especially independent activities of daily living, which could clue you in to a dementia diagnosis,” she said.
Dr. Jones ,Dr. Seshadri, and Dr. Kaplan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BRAIN COMMUNICATION
FDA Approves First Targeted Therapy for Gliomas With IDH Mutations
Specifically, the oral targeted inhibitor of IDH1 and IDH2 was approved for use after surgery in adults and children aged 12 years or older who have grade 2 astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation. According to the FDA, surgery includes biopsy, subtotal resection, or gross total resection.
Mutations in IDH1 are present in around 80% of grade 2 gliomas, whereas IDH2 mutations are more infrequent, occurring in about 4%.
Prior to the approval, which was based on progression-free survival (PFS) and safety findings from the pivotal phase 3 INDIGO trial, patients with this type of glioma had limited treatment options, said a Servier spokesperson.
The approval of vorasidenib marks “one of the biggest advances in low-grade glioma in more than two decades” and “will empower patients to take active control of their disease with a once-daily pill,” according to the spokesperson.
In the INDIGO trial, 331 patients were randomly assigned to receive 40 mg of vorasidenib once daily (n = 168) or placebo (n = 163). At a median follow-up of 14.2 months, the median PFS was more than twice as long among those who received vorasidenib vs placebo: 27.7 months vs 11.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] for disease progression or death, 0.39). The time to next intervention was also significantly longer with vorasidenib vs placebo (median not reached vs 17.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.26).
The 61% reduction in the risk for tumor progression or death observed in the trial represents “a significant sign of efficacy that has the potential to change the landscape in this disease,” first author Ingo K. Mellinghoff, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, told this news organization in 2023, when presenting the findings at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology conference. These findings were simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Glenn Lesser, MD, a discussant at the 2023 meeting, commented on the “striking” findings. The results are “statistically highly significant, and more importantly, they’re clinically very, very significant,” said Dr. Lesser, from Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Vorasidenib can also potentially delay the use of toxic chemotherapies and radiation for many years in patients with these tumors, Dr. Lesser added.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 22.8% of those who received vorasidenib and in 13.5% of those in the placebo group. Increased alanine aminotransferase levels of grade 3 or higher occurred in 9.6 vs 0% of patients in the groups, respectively.
The most common adverse reactions with vorasidenib, affecting at least 15% of treated patients, include fatigue, headache, COVID-19, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and seizure. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were increased alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as well as decreased neutrophils.
The recommended dose of vorasidenib for adults is 40 mg given orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In children aged 12 or older, the recommended dose is 40 mg given orally once daily for those weighing ≥ 40 kg, and 20 mg given orally once daily for those weighing < 40 kg.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the oral targeted inhibitor of IDH1 and IDH2 was approved for use after surgery in adults and children aged 12 years or older who have grade 2 astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation. According to the FDA, surgery includes biopsy, subtotal resection, or gross total resection.
Mutations in IDH1 are present in around 80% of grade 2 gliomas, whereas IDH2 mutations are more infrequent, occurring in about 4%.
Prior to the approval, which was based on progression-free survival (PFS) and safety findings from the pivotal phase 3 INDIGO trial, patients with this type of glioma had limited treatment options, said a Servier spokesperson.
The approval of vorasidenib marks “one of the biggest advances in low-grade glioma in more than two decades” and “will empower patients to take active control of their disease with a once-daily pill,” according to the spokesperson.
In the INDIGO trial, 331 patients were randomly assigned to receive 40 mg of vorasidenib once daily (n = 168) or placebo (n = 163). At a median follow-up of 14.2 months, the median PFS was more than twice as long among those who received vorasidenib vs placebo: 27.7 months vs 11.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] for disease progression or death, 0.39). The time to next intervention was also significantly longer with vorasidenib vs placebo (median not reached vs 17.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.26).
The 61% reduction in the risk for tumor progression or death observed in the trial represents “a significant sign of efficacy that has the potential to change the landscape in this disease,” first author Ingo K. Mellinghoff, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, told this news organization in 2023, when presenting the findings at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology conference. These findings were simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Glenn Lesser, MD, a discussant at the 2023 meeting, commented on the “striking” findings. The results are “statistically highly significant, and more importantly, they’re clinically very, very significant,” said Dr. Lesser, from Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Vorasidenib can also potentially delay the use of toxic chemotherapies and radiation for many years in patients with these tumors, Dr. Lesser added.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 22.8% of those who received vorasidenib and in 13.5% of those in the placebo group. Increased alanine aminotransferase levels of grade 3 or higher occurred in 9.6 vs 0% of patients in the groups, respectively.
The most common adverse reactions with vorasidenib, affecting at least 15% of treated patients, include fatigue, headache, COVID-19, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and seizure. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were increased alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as well as decreased neutrophils.
The recommended dose of vorasidenib for adults is 40 mg given orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In children aged 12 or older, the recommended dose is 40 mg given orally once daily for those weighing ≥ 40 kg, and 20 mg given orally once daily for those weighing < 40 kg.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the oral targeted inhibitor of IDH1 and IDH2 was approved for use after surgery in adults and children aged 12 years or older who have grade 2 astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation. According to the FDA, surgery includes biopsy, subtotal resection, or gross total resection.
Mutations in IDH1 are present in around 80% of grade 2 gliomas, whereas IDH2 mutations are more infrequent, occurring in about 4%.
Prior to the approval, which was based on progression-free survival (PFS) and safety findings from the pivotal phase 3 INDIGO trial, patients with this type of glioma had limited treatment options, said a Servier spokesperson.
The approval of vorasidenib marks “one of the biggest advances in low-grade glioma in more than two decades” and “will empower patients to take active control of their disease with a once-daily pill,” according to the spokesperson.
In the INDIGO trial, 331 patients were randomly assigned to receive 40 mg of vorasidenib once daily (n = 168) or placebo (n = 163). At a median follow-up of 14.2 months, the median PFS was more than twice as long among those who received vorasidenib vs placebo: 27.7 months vs 11.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] for disease progression or death, 0.39). The time to next intervention was also significantly longer with vorasidenib vs placebo (median not reached vs 17.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.26).
The 61% reduction in the risk for tumor progression or death observed in the trial represents “a significant sign of efficacy that has the potential to change the landscape in this disease,” first author Ingo K. Mellinghoff, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, told this news organization in 2023, when presenting the findings at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology conference. These findings were simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Glenn Lesser, MD, a discussant at the 2023 meeting, commented on the “striking” findings. The results are “statistically highly significant, and more importantly, they’re clinically very, very significant,” said Dr. Lesser, from Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Vorasidenib can also potentially delay the use of toxic chemotherapies and radiation for many years in patients with these tumors, Dr. Lesser added.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 22.8% of those who received vorasidenib and in 13.5% of those in the placebo group. Increased alanine aminotransferase levels of grade 3 or higher occurred in 9.6 vs 0% of patients in the groups, respectively.
The most common adverse reactions with vorasidenib, affecting at least 15% of treated patients, include fatigue, headache, COVID-19, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and seizure. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were increased alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as well as decreased neutrophils.
The recommended dose of vorasidenib for adults is 40 mg given orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In children aged 12 or older, the recommended dose is 40 mg given orally once daily for those weighing ≥ 40 kg, and 20 mg given orally once daily for those weighing < 40 kg.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last Call for Alcohol? Probably Not
For most of my formative years in medicine it was taken as gospel that 1-2 drinks/day, particularly red wine, was good for you.
Today though, the pendulum has swung the other way (granted, that could change in a year).
Recent re-analysis of the data now suggests there’s no benefit to any amount of alcohol. Zero. Zip. Nada.
This certainly isn’t the first time in medicine this has happened. It’s amazing how many studies end up getting re-analyzed, and re-re-analyzed, years later, with different conclusions reached.
It makes you wonder how these things happen. Possible explanations include flawed methodologies that either weren’t recognized at the time, confirmation bias, a rush to publish, and, rarely, outright fraud.
All of them, except for the last, are understandable. We all make mistakes. We’re all susceptible to the same statistical and psychological biases. Isn’t that part of the reason we do the peer-review process, so more than one pair of eyes can look for errors?
So, basically, no amount of alcohol is good for you.
Do I really think this is going to change anything? Hell no.
A huge amount of our culture revolves around alcohol. I’m not much of a drinker, but have no desire to give up my 2-3 beers per month, either. Just shopping in the store you see T-shirts, kitchen towels, gift bags, etc., that say things like “wine is just fruit salad” or “1 tequila, 2, tequila, 3 tequila, floor.”
The archaeological record suggests we began making alcoholic beverages 13,000 years ago. That’s a long time, and a pretty hard cultural habit to break. For comparison, tobacco has only been used for 3000 years.
In one of our strangest moments, America launched a 13-year experiment in prohibition, which failed miserably. Think about that. One hundred years ago, in 1924, you couldn’t legally buy alcohol anywhere in the United States. You had to break the law to get a drink, which most people did. Even then it was dangerous —in order to keep industrial ethanol from being sold to the public it was denatured with various toxins. As a result several thousand Americans died from their routine nightcap — with the government’s blessing.
Basically, alcohol isn’t going away. Not now, probably not ever.
There may be some out there who will alter their drinking habits based on the study, but I doubt it. I just don’t see too many people having a glass solely for the same reason they might take Lipitor or a multivitamin.
But I have no issue with correcting the original data. In medicine, and life in general, finding out what works is just as important as learning what doesn’t.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
For most of my formative years in medicine it was taken as gospel that 1-2 drinks/day, particularly red wine, was good for you.
Today though, the pendulum has swung the other way (granted, that could change in a year).
Recent re-analysis of the data now suggests there’s no benefit to any amount of alcohol. Zero. Zip. Nada.
This certainly isn’t the first time in medicine this has happened. It’s amazing how many studies end up getting re-analyzed, and re-re-analyzed, years later, with different conclusions reached.
It makes you wonder how these things happen. Possible explanations include flawed methodologies that either weren’t recognized at the time, confirmation bias, a rush to publish, and, rarely, outright fraud.
All of them, except for the last, are understandable. We all make mistakes. We’re all susceptible to the same statistical and psychological biases. Isn’t that part of the reason we do the peer-review process, so more than one pair of eyes can look for errors?
So, basically, no amount of alcohol is good for you.
Do I really think this is going to change anything? Hell no.
A huge amount of our culture revolves around alcohol. I’m not much of a drinker, but have no desire to give up my 2-3 beers per month, either. Just shopping in the store you see T-shirts, kitchen towels, gift bags, etc., that say things like “wine is just fruit salad” or “1 tequila, 2, tequila, 3 tequila, floor.”
The archaeological record suggests we began making alcoholic beverages 13,000 years ago. That’s a long time, and a pretty hard cultural habit to break. For comparison, tobacco has only been used for 3000 years.
In one of our strangest moments, America launched a 13-year experiment in prohibition, which failed miserably. Think about that. One hundred years ago, in 1924, you couldn’t legally buy alcohol anywhere in the United States. You had to break the law to get a drink, which most people did. Even then it was dangerous —in order to keep industrial ethanol from being sold to the public it was denatured with various toxins. As a result several thousand Americans died from their routine nightcap — with the government’s blessing.
Basically, alcohol isn’t going away. Not now, probably not ever.
There may be some out there who will alter their drinking habits based on the study, but I doubt it. I just don’t see too many people having a glass solely for the same reason they might take Lipitor or a multivitamin.
But I have no issue with correcting the original data. In medicine, and life in general, finding out what works is just as important as learning what doesn’t.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
For most of my formative years in medicine it was taken as gospel that 1-2 drinks/day, particularly red wine, was good for you.
Today though, the pendulum has swung the other way (granted, that could change in a year).
Recent re-analysis of the data now suggests there’s no benefit to any amount of alcohol. Zero. Zip. Nada.
This certainly isn’t the first time in medicine this has happened. It’s amazing how many studies end up getting re-analyzed, and re-re-analyzed, years later, with different conclusions reached.
It makes you wonder how these things happen. Possible explanations include flawed methodologies that either weren’t recognized at the time, confirmation bias, a rush to publish, and, rarely, outright fraud.
All of them, except for the last, are understandable. We all make mistakes. We’re all susceptible to the same statistical and psychological biases. Isn’t that part of the reason we do the peer-review process, so more than one pair of eyes can look for errors?
So, basically, no amount of alcohol is good for you.
Do I really think this is going to change anything? Hell no.
A huge amount of our culture revolves around alcohol. I’m not much of a drinker, but have no desire to give up my 2-3 beers per month, either. Just shopping in the store you see T-shirts, kitchen towels, gift bags, etc., that say things like “wine is just fruit salad” or “1 tequila, 2, tequila, 3 tequila, floor.”
The archaeological record suggests we began making alcoholic beverages 13,000 years ago. That’s a long time, and a pretty hard cultural habit to break. For comparison, tobacco has only been used for 3000 years.
In one of our strangest moments, America launched a 13-year experiment in prohibition, which failed miserably. Think about that. One hundred years ago, in 1924, you couldn’t legally buy alcohol anywhere in the United States. You had to break the law to get a drink, which most people did. Even then it was dangerous —in order to keep industrial ethanol from being sold to the public it was denatured with various toxins. As a result several thousand Americans died from their routine nightcap — with the government’s blessing.
Basically, alcohol isn’t going away. Not now, probably not ever.
There may be some out there who will alter their drinking habits based on the study, but I doubt it. I just don’t see too many people having a glass solely for the same reason they might take Lipitor or a multivitamin.
But I have no issue with correcting the original data. In medicine, and life in general, finding out what works is just as important as learning what doesn’t.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
NODDI and DTI in Remote Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
, according to authors of a recent study. In particular, they said, using neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) to monitor long-term mTBI impact on brain regions related to cognitive and emotional processing can help clinicians assess recovery, predict progression, and optimize treatment.
“Currently,” said co-senior study author Ping-Hong Yeh, PhD, “there is a lack of minimally invasive, quantitative diagnostic biomarkers for monitoring progression or recovery after mild TBI. However, mild TBI can be quite disabling, with many patients reporting symptoms months or even years after injury. This is the most difficult part to diagnose.” Dr. Yeh is a researcher at the National Intrepid Center of Excellence (NICoE) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland.
The NICoE, a Department of Defense organization and the senior member of Defense Intrepid Network for Traumatic Brain Injury and Brain Health, is among several centers charged with improving support for injured service members’ recovery, rehabilitation, and reintegration into their communities. The overarching goal, said Dr. Yeh, is to enable community neurologists to refer service members and veterans to these centers for treatment and advanced imaging when needed.
Invisible Wounds
Limitations of conventional MRI and CT make it tough to discern which patients with mTBI will return to baseline functioning, and which will develop long-term complications. Addressing the silent or invisible wounds of mTBI will require improved diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic tools, he said.
For their study, published in JAMA Network Open, Dr. Yeh and colleagues compared diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and NODDI data from 65 male service members with remote (more than 2 years old) mTBI against scans of 33 noninjured controls matched for age, sex, and active-duty status.
“Although DTI is very sensitive in detecting microstructural changes in mild TBI,” he said, “it is not specific to the underlying pathophysiological changes.”
Conversely, NODDI uses biophysical modeling of intracellular diffusion, extracellular diffusion, and free water to help physicians to understand subtle pathophysiological changes with greater sensitivity and specificity than does DTI. “This will allow us to correlate symptoms with brain structural changes, making the invisible wound visible.”
In the study, the greatest differences between injured and control patients appeared in the following NODDI metrics (P <.001 in all analyses):
- Intracellular volume fraction (ICVF) of the right corticospinal tract (CST)
- Orientation dispersion index (ODI) of the left posterior thalamic radiation (PTR)
- ODI of the left uncinate fasciculus (UNC)
Regarding patient-reported neurobehavioral symptoms, Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory cognitive subscores were associated with fractional anisotropy of the left UNC. In addition, PTSD Checklist–Civilian version total scores and avoidance subscores corresponded, respectively, with isotropic volume fraction (ISOVF) of the genu of corpus callosum and with ODI of the left fornix and stria terminalis.
Next Steps
Presently, Dr. Yeh said, conventional MRI and CT usually cannot differentiate between axonal injury, axonal inflammation (which develops during the chronic phase of mTBI), and demyelination. “But newer biophysical modeling, such as NODDI, will allow us to tell the difference.” Along with providing prognostic information, he said, such technology can guide appropriate treatment, such as anti-inflammatory agents for chronic inflammation.
Most community neurologists refer patients with persistent mTBI symptoms in the absence of red flags using CT and conventional MRI for advanced neuroimaging, said Dr. Yeh. But because few community neurologists are familiar with NODDI, he said, broadening its reach will require educating these providers. Additional steps that Dr. Yeh said could occur over the next decade or more include boosting advanced dMRI sensitivity levels through improved hardware, software, and diagnostic tools.
“We need to make these techniques clinically feasible,” he added. Currently, protocols that allow advanced dMRI scans in about 10 minutes can be achievable.
The investments required to implement advanced dMRI techniques will be substantial. A state-of-the-art 3T MRI scanner that can support NODDI and DTI can easily cost $1 million, said Dr. Yeh. Factor in additional equipment options and construction costs, he added, and the total price tag can easily exceed $2 million. But rather than replacing all existing MRI systems, said Dr. Yeh, AI one day may help translate high-gradient capability even to widely used lower-field MRI scanners operating at 0.5T.
Streamlining systems that incorporate disparate scanners with different acquisition parameters will require standardized data acquisition and sharing parameters. Along with helping to evaluate new techniques as they become available, data harmonization and sharing can facilitate a shift from research comparisons between large groups to comparing a single patient against many others — a move that Dr. Yeh said must occur for advanced dMRI techniques to achieve clinical relevance.
In addition, experts will need to revise clinical guidelines for use of new technologies as their availability grows. “Improper use of these techniques will not only increase health costs, but also probably result in adverse health results.” Such guidelines could be very useful in evaluating the suitability and quality of referrals for diagnostic images, Dr. Yeh said.
Dr. Yeh reports no relevant financial interests. The project was partially funded by the US Army Medical Research and Materiel Command.
, according to authors of a recent study. In particular, they said, using neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) to monitor long-term mTBI impact on brain regions related to cognitive and emotional processing can help clinicians assess recovery, predict progression, and optimize treatment.
“Currently,” said co-senior study author Ping-Hong Yeh, PhD, “there is a lack of minimally invasive, quantitative diagnostic biomarkers for monitoring progression or recovery after mild TBI. However, mild TBI can be quite disabling, with many patients reporting symptoms months or even years after injury. This is the most difficult part to diagnose.” Dr. Yeh is a researcher at the National Intrepid Center of Excellence (NICoE) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland.
The NICoE, a Department of Defense organization and the senior member of Defense Intrepid Network for Traumatic Brain Injury and Brain Health, is among several centers charged with improving support for injured service members’ recovery, rehabilitation, and reintegration into their communities. The overarching goal, said Dr. Yeh, is to enable community neurologists to refer service members and veterans to these centers for treatment and advanced imaging when needed.
Invisible Wounds
Limitations of conventional MRI and CT make it tough to discern which patients with mTBI will return to baseline functioning, and which will develop long-term complications. Addressing the silent or invisible wounds of mTBI will require improved diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic tools, he said.
For their study, published in JAMA Network Open, Dr. Yeh and colleagues compared diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and NODDI data from 65 male service members with remote (more than 2 years old) mTBI against scans of 33 noninjured controls matched for age, sex, and active-duty status.
“Although DTI is very sensitive in detecting microstructural changes in mild TBI,” he said, “it is not specific to the underlying pathophysiological changes.”
Conversely, NODDI uses biophysical modeling of intracellular diffusion, extracellular diffusion, and free water to help physicians to understand subtle pathophysiological changes with greater sensitivity and specificity than does DTI. “This will allow us to correlate symptoms with brain structural changes, making the invisible wound visible.”
In the study, the greatest differences between injured and control patients appeared in the following NODDI metrics (P <.001 in all analyses):
- Intracellular volume fraction (ICVF) of the right corticospinal tract (CST)
- Orientation dispersion index (ODI) of the left posterior thalamic radiation (PTR)
- ODI of the left uncinate fasciculus (UNC)
Regarding patient-reported neurobehavioral symptoms, Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory cognitive subscores were associated with fractional anisotropy of the left UNC. In addition, PTSD Checklist–Civilian version total scores and avoidance subscores corresponded, respectively, with isotropic volume fraction (ISOVF) of the genu of corpus callosum and with ODI of the left fornix and stria terminalis.
Next Steps
Presently, Dr. Yeh said, conventional MRI and CT usually cannot differentiate between axonal injury, axonal inflammation (which develops during the chronic phase of mTBI), and demyelination. “But newer biophysical modeling, such as NODDI, will allow us to tell the difference.” Along with providing prognostic information, he said, such technology can guide appropriate treatment, such as anti-inflammatory agents for chronic inflammation.
Most community neurologists refer patients with persistent mTBI symptoms in the absence of red flags using CT and conventional MRI for advanced neuroimaging, said Dr. Yeh. But because few community neurologists are familiar with NODDI, he said, broadening its reach will require educating these providers. Additional steps that Dr. Yeh said could occur over the next decade or more include boosting advanced dMRI sensitivity levels through improved hardware, software, and diagnostic tools.
“We need to make these techniques clinically feasible,” he added. Currently, protocols that allow advanced dMRI scans in about 10 minutes can be achievable.
The investments required to implement advanced dMRI techniques will be substantial. A state-of-the-art 3T MRI scanner that can support NODDI and DTI can easily cost $1 million, said Dr. Yeh. Factor in additional equipment options and construction costs, he added, and the total price tag can easily exceed $2 million. But rather than replacing all existing MRI systems, said Dr. Yeh, AI one day may help translate high-gradient capability even to widely used lower-field MRI scanners operating at 0.5T.
Streamlining systems that incorporate disparate scanners with different acquisition parameters will require standardized data acquisition and sharing parameters. Along with helping to evaluate new techniques as they become available, data harmonization and sharing can facilitate a shift from research comparisons between large groups to comparing a single patient against many others — a move that Dr. Yeh said must occur for advanced dMRI techniques to achieve clinical relevance.
In addition, experts will need to revise clinical guidelines for use of new technologies as their availability grows. “Improper use of these techniques will not only increase health costs, but also probably result in adverse health results.” Such guidelines could be very useful in evaluating the suitability and quality of referrals for diagnostic images, Dr. Yeh said.
Dr. Yeh reports no relevant financial interests. The project was partially funded by the US Army Medical Research and Materiel Command.
, according to authors of a recent study. In particular, they said, using neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) to monitor long-term mTBI impact on brain regions related to cognitive and emotional processing can help clinicians assess recovery, predict progression, and optimize treatment.
“Currently,” said co-senior study author Ping-Hong Yeh, PhD, “there is a lack of minimally invasive, quantitative diagnostic biomarkers for monitoring progression or recovery after mild TBI. However, mild TBI can be quite disabling, with many patients reporting symptoms months or even years after injury. This is the most difficult part to diagnose.” Dr. Yeh is a researcher at the National Intrepid Center of Excellence (NICoE) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland.
The NICoE, a Department of Defense organization and the senior member of Defense Intrepid Network for Traumatic Brain Injury and Brain Health, is among several centers charged with improving support for injured service members’ recovery, rehabilitation, and reintegration into their communities. The overarching goal, said Dr. Yeh, is to enable community neurologists to refer service members and veterans to these centers for treatment and advanced imaging when needed.
Invisible Wounds
Limitations of conventional MRI and CT make it tough to discern which patients with mTBI will return to baseline functioning, and which will develop long-term complications. Addressing the silent or invisible wounds of mTBI will require improved diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic tools, he said.
For their study, published in JAMA Network Open, Dr. Yeh and colleagues compared diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and NODDI data from 65 male service members with remote (more than 2 years old) mTBI against scans of 33 noninjured controls matched for age, sex, and active-duty status.
“Although DTI is very sensitive in detecting microstructural changes in mild TBI,” he said, “it is not specific to the underlying pathophysiological changes.”
Conversely, NODDI uses biophysical modeling of intracellular diffusion, extracellular diffusion, and free water to help physicians to understand subtle pathophysiological changes with greater sensitivity and specificity than does DTI. “This will allow us to correlate symptoms with brain structural changes, making the invisible wound visible.”
In the study, the greatest differences between injured and control patients appeared in the following NODDI metrics (P <.001 in all analyses):
- Intracellular volume fraction (ICVF) of the right corticospinal tract (CST)
- Orientation dispersion index (ODI) of the left posterior thalamic radiation (PTR)
- ODI of the left uncinate fasciculus (UNC)
Regarding patient-reported neurobehavioral symptoms, Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory cognitive subscores were associated with fractional anisotropy of the left UNC. In addition, PTSD Checklist–Civilian version total scores and avoidance subscores corresponded, respectively, with isotropic volume fraction (ISOVF) of the genu of corpus callosum and with ODI of the left fornix and stria terminalis.
Next Steps
Presently, Dr. Yeh said, conventional MRI and CT usually cannot differentiate between axonal injury, axonal inflammation (which develops during the chronic phase of mTBI), and demyelination. “But newer biophysical modeling, such as NODDI, will allow us to tell the difference.” Along with providing prognostic information, he said, such technology can guide appropriate treatment, such as anti-inflammatory agents for chronic inflammation.
Most community neurologists refer patients with persistent mTBI symptoms in the absence of red flags using CT and conventional MRI for advanced neuroimaging, said Dr. Yeh. But because few community neurologists are familiar with NODDI, he said, broadening its reach will require educating these providers. Additional steps that Dr. Yeh said could occur over the next decade or more include boosting advanced dMRI sensitivity levels through improved hardware, software, and diagnostic tools.
“We need to make these techniques clinically feasible,” he added. Currently, protocols that allow advanced dMRI scans in about 10 minutes can be achievable.
The investments required to implement advanced dMRI techniques will be substantial. A state-of-the-art 3T MRI scanner that can support NODDI and DTI can easily cost $1 million, said Dr. Yeh. Factor in additional equipment options and construction costs, he added, and the total price tag can easily exceed $2 million. But rather than replacing all existing MRI systems, said Dr. Yeh, AI one day may help translate high-gradient capability even to widely used lower-field MRI scanners operating at 0.5T.
Streamlining systems that incorporate disparate scanners with different acquisition parameters will require standardized data acquisition and sharing parameters. Along with helping to evaluate new techniques as they become available, data harmonization and sharing can facilitate a shift from research comparisons between large groups to comparing a single patient against many others — a move that Dr. Yeh said must occur for advanced dMRI techniques to achieve clinical relevance.
In addition, experts will need to revise clinical guidelines for use of new technologies as their availability grows. “Improper use of these techniques will not only increase health costs, but also probably result in adverse health results.” Such guidelines could be very useful in evaluating the suitability and quality of referrals for diagnostic images, Dr. Yeh said.
Dr. Yeh reports no relevant financial interests. The project was partially funded by the US Army Medical Research and Materiel Command.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN

