User login
The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management® is an independent, peer-reviewed journal offering evidence-based, practical information for improving the quality, safety, and value of health care.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Altering gut microbiome may reduce tumor-promoting effects of smoking
Altering the gut microbiome may reduce the tumor-promoting effects of cigarette smoking, based on a preclinical study.
Mice treated with microbiome-depleting antibiotics or genetically modified to lack an adaptive immune response did not show increased rates of cancer growth when exposed to cigarette smoke, reported lead author Prateek Sharma, MBBS, of the University of Miami, and colleagues.
Although previous research has shown that the gut microbiome plays a role in the progression of cancer and that smoking alters the gut microbiome, the collective effects of these changes have not been studied, the investigators wrote in an abstract released as part of the annual Digestive Disease Week, which was canceled because of COVID-19.
“There is information that smoking changes the gut microbiome ... but the impact of this change is not known,” Dr. Sharma said in a virtual press conference.
To learn more, the investigators first performed an experiment using wild-type mice. All mice were injected with a cancer cell line from the pancreas, colon, or bladder. Mice were then sorted into four groups, in which they were given microbiome-depleting antibiotics and exposed to smoke, given antibiotics alone, exposed to smoke alone, or left untreated and unexposed to serve as controls. Tumor size was then measured over the course of 2 months.
The experiment revealed that mice exposed to smoke but not treated with antibiotics had increased rates of tumor growth regardless of cancer type. But in mice treated with antibiotics, the tumor-promoting effects of smoke exposure were completely lost; the mice had rates of tumor growth even lower than controls.
This experiment was repeated with mice genetically engineered to lack an adaptive immune response. Regardless of smoke or antibiotic exposure, all mice had comparable rates of tumor growth.
Dr. Sharma offered a summary of the findings and their possible implications for human medicine.
“Cigarette smoking changes the gut microbiome, and this changed gut microbiome interacts with the immune system to affect cancer progression,” he said. “If we can target this changed microbiome with modulation strategies like antibiotics, probiotics, or administration of good bacteria, we can alter this process. And if the same results are found in human studies, it could go a long way to affect cancer outcomes in smokers.”
In addition to human studies, Dr. Sharma said that future research should aim to uncover the underlying mechanisms involved in this process, including the types of bacteria that play a role.
When asked if the study might lessen concerns about the negative impacts of smoking among cancer patients, Dr. Sharma suggested that, even if the findings do translate to humans, smoking would still carry significant health risks.
“Even if gut microbiome modulation strategies do work in these patients, it may help a little, but it’s not going to bring it down to the level of nonsmokers, so it’s no way an excuse to not fear or continue [smoking],” he said.
The study was funded by the Florida Department of Health. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
Altering the gut microbiome may reduce the tumor-promoting effects of cigarette smoking, based on a preclinical study.
Mice treated with microbiome-depleting antibiotics or genetically modified to lack an adaptive immune response did not show increased rates of cancer growth when exposed to cigarette smoke, reported lead author Prateek Sharma, MBBS, of the University of Miami, and colleagues.
Although previous research has shown that the gut microbiome plays a role in the progression of cancer and that smoking alters the gut microbiome, the collective effects of these changes have not been studied, the investigators wrote in an abstract released as part of the annual Digestive Disease Week, which was canceled because of COVID-19.
“There is information that smoking changes the gut microbiome ... but the impact of this change is not known,” Dr. Sharma said in a virtual press conference.
To learn more, the investigators first performed an experiment using wild-type mice. All mice were injected with a cancer cell line from the pancreas, colon, or bladder. Mice were then sorted into four groups, in which they were given microbiome-depleting antibiotics and exposed to smoke, given antibiotics alone, exposed to smoke alone, or left untreated and unexposed to serve as controls. Tumor size was then measured over the course of 2 months.
The experiment revealed that mice exposed to smoke but not treated with antibiotics had increased rates of tumor growth regardless of cancer type. But in mice treated with antibiotics, the tumor-promoting effects of smoke exposure were completely lost; the mice had rates of tumor growth even lower than controls.
This experiment was repeated with mice genetically engineered to lack an adaptive immune response. Regardless of smoke or antibiotic exposure, all mice had comparable rates of tumor growth.
Dr. Sharma offered a summary of the findings and their possible implications for human medicine.
“Cigarette smoking changes the gut microbiome, and this changed gut microbiome interacts with the immune system to affect cancer progression,” he said. “If we can target this changed microbiome with modulation strategies like antibiotics, probiotics, or administration of good bacteria, we can alter this process. And if the same results are found in human studies, it could go a long way to affect cancer outcomes in smokers.”
In addition to human studies, Dr. Sharma said that future research should aim to uncover the underlying mechanisms involved in this process, including the types of bacteria that play a role.
When asked if the study might lessen concerns about the negative impacts of smoking among cancer patients, Dr. Sharma suggested that, even if the findings do translate to humans, smoking would still carry significant health risks.
“Even if gut microbiome modulation strategies do work in these patients, it may help a little, but it’s not going to bring it down to the level of nonsmokers, so it’s no way an excuse to not fear or continue [smoking],” he said.
The study was funded by the Florida Department of Health. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
Altering the gut microbiome may reduce the tumor-promoting effects of cigarette smoking, based on a preclinical study.
Mice treated with microbiome-depleting antibiotics or genetically modified to lack an adaptive immune response did not show increased rates of cancer growth when exposed to cigarette smoke, reported lead author Prateek Sharma, MBBS, of the University of Miami, and colleagues.
Although previous research has shown that the gut microbiome plays a role in the progression of cancer and that smoking alters the gut microbiome, the collective effects of these changes have not been studied, the investigators wrote in an abstract released as part of the annual Digestive Disease Week, which was canceled because of COVID-19.
“There is information that smoking changes the gut microbiome ... but the impact of this change is not known,” Dr. Sharma said in a virtual press conference.
To learn more, the investigators first performed an experiment using wild-type mice. All mice were injected with a cancer cell line from the pancreas, colon, or bladder. Mice were then sorted into four groups, in which they were given microbiome-depleting antibiotics and exposed to smoke, given antibiotics alone, exposed to smoke alone, or left untreated and unexposed to serve as controls. Tumor size was then measured over the course of 2 months.
The experiment revealed that mice exposed to smoke but not treated with antibiotics had increased rates of tumor growth regardless of cancer type. But in mice treated with antibiotics, the tumor-promoting effects of smoke exposure were completely lost; the mice had rates of tumor growth even lower than controls.
This experiment was repeated with mice genetically engineered to lack an adaptive immune response. Regardless of smoke or antibiotic exposure, all mice had comparable rates of tumor growth.
Dr. Sharma offered a summary of the findings and their possible implications for human medicine.
“Cigarette smoking changes the gut microbiome, and this changed gut microbiome interacts with the immune system to affect cancer progression,” he said. “If we can target this changed microbiome with modulation strategies like antibiotics, probiotics, or administration of good bacteria, we can alter this process. And if the same results are found in human studies, it could go a long way to affect cancer outcomes in smokers.”
In addition to human studies, Dr. Sharma said that future research should aim to uncover the underlying mechanisms involved in this process, including the types of bacteria that play a role.
When asked if the study might lessen concerns about the negative impacts of smoking among cancer patients, Dr. Sharma suggested that, even if the findings do translate to humans, smoking would still carry significant health risks.
“Even if gut microbiome modulation strategies do work in these patients, it may help a little, but it’s not going to bring it down to the level of nonsmokers, so it’s no way an excuse to not fear or continue [smoking],” he said.
The study was funded by the Florida Department of Health. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM DDW 2020
Three months of COVID-19 may mean 80,000 missed cancer diagnoses
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.
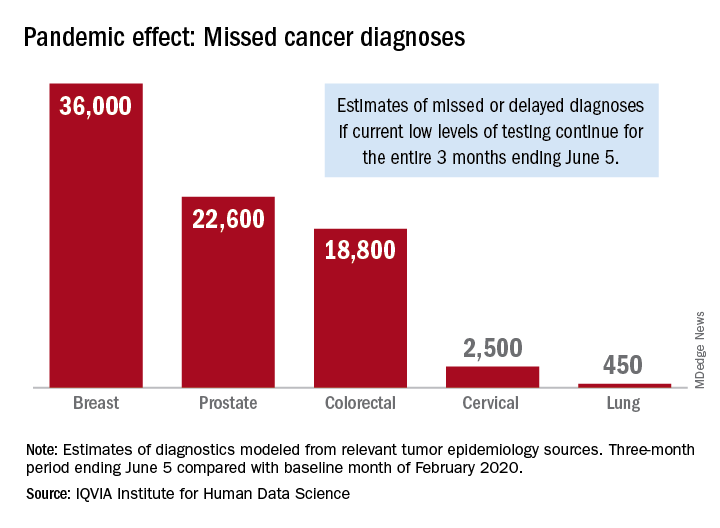
Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.

Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.

Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
Cancer screening, monitoring down during pandemic
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.
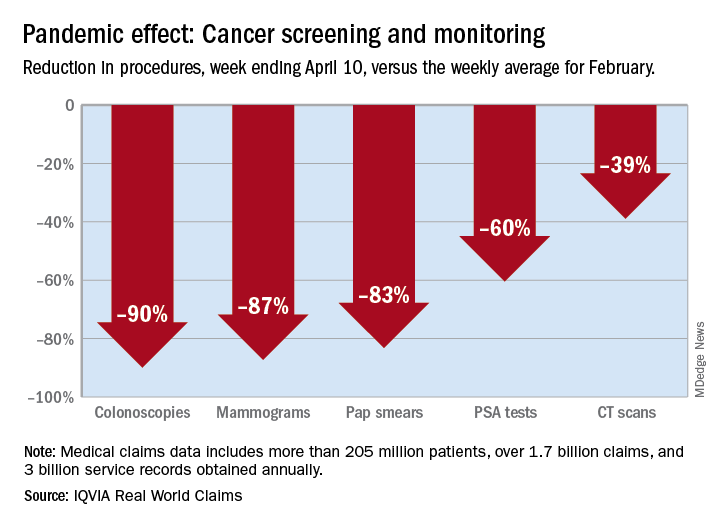
There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.

There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.

There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
FDA tightens requirements for COVID-19 antibody tests
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
Hydroxychloroquine-triggered QTc-interval prolongations mount in COVID-19 patients
The potential for serious arrhythmias from hydroxychloroquine treatment of COVID-19 patients received further documentation from a pair of studies released on May 1, casting further doubt on whether the uncertain benefit from this or related drugs to infected patients is worth the clear risks the agents pose.
A report from 90 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine at one Boston hospital during March-April 2020 identified a significantly prolonged, corrected QT (QTc) interval of at least 500 msec in 18 patients (20%), which included 10 patients whose QTc rose by at least 60 msec above baseline, and a total of 21 patients (23%) having a notable prolongation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1834). This series included one patient who developed torsades de pointes following treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, “which to our knowledge has yet to be reported elsewhere in the literature,” the report said.
The second report, from a single center in Lyon, France, included 40 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine during 2 weeks in late March, and found that 37 (93%) had some increase in the QTc interval, including 14 patients (36%) with an increase of at least 60 msec, and 7 patients (18%) whose QTc rose to at least 500 msec (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1787). However, none of the 40 patients in this series developed an identified ventricular arrhythmia. All patients in both studies received hydroxychloroquine for at least 1 day, and roughly half the patients in each series also received concurrent azithromycin, another drug that can prolong the QTc interval and that has been frequently used in combination with hydroxychloroquine as an unproven COVID-19 treatment cocktail.
These two reports, as well as prior report from Brazil on COVID-19 patients treated with chloroquine diphosphate (JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3[4]:e208857), “underscore the potential risk associated with widespread use of hydroxychloroquine and the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in ambulatory patients with known or suspected COVID-19. Understanding whether this risk is worth taking in the absence of evidence of therapeutic efficacy creates a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” wrote Robert O. Bonow, MD, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, and coauthors in an editorial that accompanied the two reports (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4;doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1782). The editorial cited two recently-begun prospective trials, ORCHID and RECOVERY, that are more systematically assessing the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine treatment in COVID-19 patients.
The findings lend further support to a Safety Communication from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on April 24 that reminded clinicians that the Emergency Use Authorization for hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 patients that the FDA issued on March 28 applied to only certain hospitalized patients or those enrolled in clinical trials. The Safety Communication also said that agency was aware of reports of adverse arrhythmia events when COVID-19 patients received these drugs outside a hospital setting as well as uninfected people who had received one of these drugs for preventing infection.
In addition, leaders of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Rhythm Society on April 10 issued a summary of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to treat COVID-19 patients, and noted that a way to minimized the risk from these drugs is to withhold them from patients with a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater at baseline (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). The summary also highlighted the need for regular ECG monitoring of COVID-19 patients who receive drugs that can prolong the QTc interval, and recommended withdrawing treatment from patients when their QTc exceeds the 500 msec threshold.
None of the authors of the two reports and editorial had relevant commercial disclosures.
The potential for serious arrhythmias from hydroxychloroquine treatment of COVID-19 patients received further documentation from a pair of studies released on May 1, casting further doubt on whether the uncertain benefit from this or related drugs to infected patients is worth the clear risks the agents pose.
A report from 90 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine at one Boston hospital during March-April 2020 identified a significantly prolonged, corrected QT (QTc) interval of at least 500 msec in 18 patients (20%), which included 10 patients whose QTc rose by at least 60 msec above baseline, and a total of 21 patients (23%) having a notable prolongation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1834). This series included one patient who developed torsades de pointes following treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, “which to our knowledge has yet to be reported elsewhere in the literature,” the report said.
The second report, from a single center in Lyon, France, included 40 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine during 2 weeks in late March, and found that 37 (93%) had some increase in the QTc interval, including 14 patients (36%) with an increase of at least 60 msec, and 7 patients (18%) whose QTc rose to at least 500 msec (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1787). However, none of the 40 patients in this series developed an identified ventricular arrhythmia. All patients in both studies received hydroxychloroquine for at least 1 day, and roughly half the patients in each series also received concurrent azithromycin, another drug that can prolong the QTc interval and that has been frequently used in combination with hydroxychloroquine as an unproven COVID-19 treatment cocktail.
These two reports, as well as prior report from Brazil on COVID-19 patients treated with chloroquine diphosphate (JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3[4]:e208857), “underscore the potential risk associated with widespread use of hydroxychloroquine and the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in ambulatory patients with known or suspected COVID-19. Understanding whether this risk is worth taking in the absence of evidence of therapeutic efficacy creates a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” wrote Robert O. Bonow, MD, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, and coauthors in an editorial that accompanied the two reports (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4;doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1782). The editorial cited two recently-begun prospective trials, ORCHID and RECOVERY, that are more systematically assessing the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine treatment in COVID-19 patients.
The findings lend further support to a Safety Communication from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on April 24 that reminded clinicians that the Emergency Use Authorization for hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 patients that the FDA issued on March 28 applied to only certain hospitalized patients or those enrolled in clinical trials. The Safety Communication also said that agency was aware of reports of adverse arrhythmia events when COVID-19 patients received these drugs outside a hospital setting as well as uninfected people who had received one of these drugs for preventing infection.
In addition, leaders of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Rhythm Society on April 10 issued a summary of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to treat COVID-19 patients, and noted that a way to minimized the risk from these drugs is to withhold them from patients with a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater at baseline (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). The summary also highlighted the need for regular ECG monitoring of COVID-19 patients who receive drugs that can prolong the QTc interval, and recommended withdrawing treatment from patients when their QTc exceeds the 500 msec threshold.
None of the authors of the two reports and editorial had relevant commercial disclosures.
The potential for serious arrhythmias from hydroxychloroquine treatment of COVID-19 patients received further documentation from a pair of studies released on May 1, casting further doubt on whether the uncertain benefit from this or related drugs to infected patients is worth the clear risks the agents pose.
A report from 90 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine at one Boston hospital during March-April 2020 identified a significantly prolonged, corrected QT (QTc) interval of at least 500 msec in 18 patients (20%), which included 10 patients whose QTc rose by at least 60 msec above baseline, and a total of 21 patients (23%) having a notable prolongation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1834). This series included one patient who developed torsades de pointes following treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, “which to our knowledge has yet to be reported elsewhere in the literature,” the report said.
The second report, from a single center in Lyon, France, included 40 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine during 2 weeks in late March, and found that 37 (93%) had some increase in the QTc interval, including 14 patients (36%) with an increase of at least 60 msec, and 7 patients (18%) whose QTc rose to at least 500 msec (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1787). However, none of the 40 patients in this series developed an identified ventricular arrhythmia. All patients in both studies received hydroxychloroquine for at least 1 day, and roughly half the patients in each series also received concurrent azithromycin, another drug that can prolong the QTc interval and that has been frequently used in combination with hydroxychloroquine as an unproven COVID-19 treatment cocktail.
These two reports, as well as prior report from Brazil on COVID-19 patients treated with chloroquine diphosphate (JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3[4]:e208857), “underscore the potential risk associated with widespread use of hydroxychloroquine and the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in ambulatory patients with known or suspected COVID-19. Understanding whether this risk is worth taking in the absence of evidence of therapeutic efficacy creates a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” wrote Robert O. Bonow, MD, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, and coauthors in an editorial that accompanied the two reports (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4;doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1782). The editorial cited two recently-begun prospective trials, ORCHID and RECOVERY, that are more systematically assessing the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine treatment in COVID-19 patients.
The findings lend further support to a Safety Communication from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on April 24 that reminded clinicians that the Emergency Use Authorization for hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 patients that the FDA issued on March 28 applied to only certain hospitalized patients or those enrolled in clinical trials. The Safety Communication also said that agency was aware of reports of adverse arrhythmia events when COVID-19 patients received these drugs outside a hospital setting as well as uninfected people who had received one of these drugs for preventing infection.
In addition, leaders of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Rhythm Society on April 10 issued a summary of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to treat COVID-19 patients, and noted that a way to minimized the risk from these drugs is to withhold them from patients with a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater at baseline (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). The summary also highlighted the need for regular ECG monitoring of COVID-19 patients who receive drugs that can prolong the QTc interval, and recommended withdrawing treatment from patients when their QTc exceeds the 500 msec threshold.
None of the authors of the two reports and editorial had relevant commercial disclosures.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
COVID-19: Social distancing with young children
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
COVID-19: To have and to hold ... in quarantine
Tips for marriage survival during a pandemic
Most married couples vowed to stay with their partners during sickness and health, but none of us vowed to remain trapped with our loved ones behind the same four walls, all day, every day, for an unknown period of time. We didn’t sign up for this! Some romantics may be titillated by the prospect, while more independent partners may panic at the mere thought of spending all day and night with their loved ones.
Because of the swift implementation of the lifestyle-altering restrictions, couples did not have ample time to mentally and physically prepare. A lack of preparation and loss of control heightens our emotions. It can make couples more susceptible to engage in unhealthy styles of communication and destructive behaviors that are harmful to their relationships.
There are psychological reasons that “absence makes the heart grow fonder.” Distance from your partner is not just a clever way to make your partner appreciate and desire you more. It is human nature to habituate to what is part of your daily life. For instance, when your partner is away from you while on a work trip, you may find the first night or two alone relaxing; but by day 3, you begin to miss your partner’s hugs and kisses, smell, and touch. And after many days apart, you may even miss the incessant nagging that secretly motivates you. Physical distance from our partners essentially gives us the ability to long for and appreciate each other. Our brains are wired to pay more attention to things that are novel and exciting and less interested in what is in our everyday lives.
Separation gives us the ability to miss our partners, while quarantine does the complete opposite.
To avoid contemplating how to murder one’s spouse before quarantine ends, partners can strengthen their relationships by using the strategies I’ve outlined below, which are loosely based on dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). These strategies can be useful for anyone – providers and patients alike – going through these struggles.
Dialectical behavior therapy was developed by psychologist Marsha Linehan PhD, to help regulate emotions for people diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. These skills help to identify thoughts and feelings, to accept one’s inner emotional world and outward behaviors. The idea is that, once you can recognize and accept, then change is possible. The “dialectic” in dialectical behavior therapy implies that one is attempting to find a balance between acceptance and change. All of us can benefit from these skills, especially emotionally volatile couples who are trapped together in quarantine.
Radically accept what is uncertain in your lives
Radical acceptance is a practice used in DBT in situations that are out of our control, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Radically accept that you and your partner are trapped in quarantine without attempting to place blame on our government, your spouse, your boss, and even yourself. Radical acceptance is exactly what the name implies. Accept your current situation for what it is and not what you hoped it to be.
Accept the unknown and unanswered questions such as when will this quarantine end? Will there be a summer camp? Will I get back to my office this summer? Will my children even return to school in the fall? The acceptance of what is out of your control will ultimately decrease your mental time spent worrying and obsessing about the uncertainties of your post-quarantine life and instead provide you more time to be present with your spouse.
Remain mindful during all communication with your spouse. To stay in the moment, you need to be aware of your bodily reactions to distress and notice when your heart rate increases, breathing becomes more shallow, stomach muscles tighten, and when your thoughts become more negative. Mindfulness skills enable us to use physiological changes in our body to become aware of our emotions. You can use your partner’s nonverbal body language and tone of voice to gauge that person’s emotional reactivity.
The practice of mindfulness leads to an increased emotional intelligence. The goal is to have enough self-awareness and emotional understanding of your partner and enough empathy to know when a conversation is becoming too emotionally charged and to let it go and back off. Mindfulness is not nagging your partner to remember to change the heating unit filters with a reminder of what happened years ago when this wasn’t done promptly – without first checking in to make sure your partner is emotionally ready for this type of conversation.
When we have strong emotions, we are using the more primitive parts of our brain that induce a fight or flight reaction. These emotional reactions overshadow the more advanced prefrontal region of our brain that stores our rational thoughts and reasoning skills, a concept identified by psychologist Daniel Goleman as “emotional hijacking.”
Use distress tolerance skills to deal with negative emotions
Distress tolerance is an individual’s ability to manage feelings in response to stress. Distress tolerance skills are aimed at helping one manage intense emotions without worsening a situation by engaging in behaviors that are destructive and may exacerbate the problem. The goal is to tolerate the stress while with your partner and not respond negatively or in a way that is harmful to the integrity of your relationship.
To prioritize your relationship, this may mean that you choose not to react negatively when your partner makes a passive-aggressive comment on how you spent your day during quarantine since you still have a pile of laundry on your bedroom floor and overflowing dishes in the kitchen sink. A high level of distress tolerance will enable you to not overreact or withdraw from your spouse when flooded with emotions of anger or sadness.
Distraction techniques are a type of distress tolerance skill. You can engage in activities that keep you distracted and require your full attention. When things get heated between you and your spouse during quarantine, try to obtain some distance from each other to cool down and engage in an activity that involves your full concentration.
Many of us have been surprised by our hidden talents that were discovered during the quarantine. Use the time away from your partner to distract yourself with your new passion for writing, baking, organizing, and even your newfound love of balloon artistry. Do an activity that engages your mind and provides you the necessary physical and mental time away from your partner to deescalate. You can always revisit the initial cause of the conflict when both you and your partner are not emotionally charged. You can also distract yourself with self-soothing tactics such as taking a warm bath or a reading good book. Perhaps distract yourself by giving back to others and spending time planning a drive-by surprise party for your sister’s birthday next month. It can be helpful to distract yourself by comparing yourself to others less fortunate than you or a time in your life when you and your partner were struggling much worse than now, to provide perspective. The goal is not to add to your distress but instead, provide yourself a sense of perspective.
Use interpersonal effectiveness skills to establish a healthy relationship
Be gentle in all your communications with your partner, think about your spouse’s perspective, show empathy and interest in what your partner has to say by your verbal communication or body language, such as maintaining eye contact, and offer recognitional cues, such as “uh-huh” and “oh, really.” Avoid communication that is at all invalidating. Never start a sentence with “YOU” while having heated conversations with your spouse; instead, use “I feel” statements. This type of communication avoids the blame game that gets many couples into trouble.
Instead, communicate how you feel while not necessarily blaming your spouse but rather expressing your emotions. This will ultimately lead to less defensive communication from your partner. Remember that not all communication is for the sole purpose of communicating. Much of the time, communication is used as an attempt for one partner to connect with the other partner. Couples may say that they have difficulty with communication when it is not the communication that is the issue but instead the underlying disconnect of the couple.
This disconnect usually manifests while couples are communicating, and therefore, can be misconstrued as solely a communication issue by the couple. When your partner asks you to stop staring at your phone during dinner, it is not necessarily that your spouse is attempting to control you or wants to engage in some deep conversation, but more likely a bid to try to connect with you. Your partner is attempting to tell you that he or she feels disconnected, misses you, and wants to reconnect.
Provide validation and acceptance to your partner
Focus on your partner’s strengths and accept the weaknesses. Accept that your partner is scattered, disorganized, and takes at least 20 minutes to find the phone and keys every morning. Remember that during your courtship days, you found your partner’s flighty attributes to be endearing. Do the same for your strengths and weaknesses.
Accept that the pandemic is unpredictable and that you may need to strengthen your ability to be flexible and more adaptable. This will ultimately lead to feeling less disappointment by your partner and more accepting of shortcomings. Acceptance of your imperfections will improve your sense of worth and confidence and lessen negative emotions, such as guilt, regret, and shame.
Accept the fact that, as similar as we all are, we use different methods to recharge ourselves. In contrast, your spouse needs alone time without distractions to reboot mentally and prepare for the following day. In the pre-pandemic world, if there were a mismatch in what a couple needed to feel rejuvenated, they could independently compensate and search for fulfillment outside of the home. Before stay-at-home orders were rolled out throughout the country, spouses had ample opportunities to spend time away from their partners at work, dinner with friends, or while squeezing in a 7 p.m. yoga sculpt class – barely getting home in time to kiss our children goodnight – with a few minutes to spare to engage in mundane conversation with our partners before our nighttime routine of TV commenced. Unfortunately, COVID-19 has made it very hard for couples to carve out that time for compensatory activities outside of the home.
Remember that you are a team
Remind yourself of the reason why you initially fell in love with your partner. Teammates do not keep score or compete with one another. They support each other when one player is not feeling well, and they make sacrifices for the betterment of the team.
Your marriage vows included “through sickness and health” and now should include “through quarantine.”
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
Tips for marriage survival during a pandemic
Tips for marriage survival during a pandemic
Most married couples vowed to stay with their partners during sickness and health, but none of us vowed to remain trapped with our loved ones behind the same four walls, all day, every day, for an unknown period of time. We didn’t sign up for this! Some romantics may be titillated by the prospect, while more independent partners may panic at the mere thought of spending all day and night with their loved ones.
Because of the swift implementation of the lifestyle-altering restrictions, couples did not have ample time to mentally and physically prepare. A lack of preparation and loss of control heightens our emotions. It can make couples more susceptible to engage in unhealthy styles of communication and destructive behaviors that are harmful to their relationships.
There are psychological reasons that “absence makes the heart grow fonder.” Distance from your partner is not just a clever way to make your partner appreciate and desire you more. It is human nature to habituate to what is part of your daily life. For instance, when your partner is away from you while on a work trip, you may find the first night or two alone relaxing; but by day 3, you begin to miss your partner’s hugs and kisses, smell, and touch. And after many days apart, you may even miss the incessant nagging that secretly motivates you. Physical distance from our partners essentially gives us the ability to long for and appreciate each other. Our brains are wired to pay more attention to things that are novel and exciting and less interested in what is in our everyday lives.
Separation gives us the ability to miss our partners, while quarantine does the complete opposite.
To avoid contemplating how to murder one’s spouse before quarantine ends, partners can strengthen their relationships by using the strategies I’ve outlined below, which are loosely based on dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). These strategies can be useful for anyone – providers and patients alike – going through these struggles.
Dialectical behavior therapy was developed by psychologist Marsha Linehan PhD, to help regulate emotions for people diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. These skills help to identify thoughts and feelings, to accept one’s inner emotional world and outward behaviors. The idea is that, once you can recognize and accept, then change is possible. The “dialectic” in dialectical behavior therapy implies that one is attempting to find a balance between acceptance and change. All of us can benefit from these skills, especially emotionally volatile couples who are trapped together in quarantine.
Radically accept what is uncertain in your lives
Radical acceptance is a practice used in DBT in situations that are out of our control, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Radically accept that you and your partner are trapped in quarantine without attempting to place blame on our government, your spouse, your boss, and even yourself. Radical acceptance is exactly what the name implies. Accept your current situation for what it is and not what you hoped it to be.
Accept the unknown and unanswered questions such as when will this quarantine end? Will there be a summer camp? Will I get back to my office this summer? Will my children even return to school in the fall? The acceptance of what is out of your control will ultimately decrease your mental time spent worrying and obsessing about the uncertainties of your post-quarantine life and instead provide you more time to be present with your spouse.
Remain mindful during all communication with your spouse. To stay in the moment, you need to be aware of your bodily reactions to distress and notice when your heart rate increases, breathing becomes more shallow, stomach muscles tighten, and when your thoughts become more negative. Mindfulness skills enable us to use physiological changes in our body to become aware of our emotions. You can use your partner’s nonverbal body language and tone of voice to gauge that person’s emotional reactivity.
The practice of mindfulness leads to an increased emotional intelligence. The goal is to have enough self-awareness and emotional understanding of your partner and enough empathy to know when a conversation is becoming too emotionally charged and to let it go and back off. Mindfulness is not nagging your partner to remember to change the heating unit filters with a reminder of what happened years ago when this wasn’t done promptly – without first checking in to make sure your partner is emotionally ready for this type of conversation.
When we have strong emotions, we are using the more primitive parts of our brain that induce a fight or flight reaction. These emotional reactions overshadow the more advanced prefrontal region of our brain that stores our rational thoughts and reasoning skills, a concept identified by psychologist Daniel Goleman as “emotional hijacking.”
Use distress tolerance skills to deal with negative emotions
Distress tolerance is an individual’s ability to manage feelings in response to stress. Distress tolerance skills are aimed at helping one manage intense emotions without worsening a situation by engaging in behaviors that are destructive and may exacerbate the problem. The goal is to tolerate the stress while with your partner and not respond negatively or in a way that is harmful to the integrity of your relationship.
To prioritize your relationship, this may mean that you choose not to react negatively when your partner makes a passive-aggressive comment on how you spent your day during quarantine since you still have a pile of laundry on your bedroom floor and overflowing dishes in the kitchen sink. A high level of distress tolerance will enable you to not overreact or withdraw from your spouse when flooded with emotions of anger or sadness.
Distraction techniques are a type of distress tolerance skill. You can engage in activities that keep you distracted and require your full attention. When things get heated between you and your spouse during quarantine, try to obtain some distance from each other to cool down and engage in an activity that involves your full concentration.
Many of us have been surprised by our hidden talents that were discovered during the quarantine. Use the time away from your partner to distract yourself with your new passion for writing, baking, organizing, and even your newfound love of balloon artistry. Do an activity that engages your mind and provides you the necessary physical and mental time away from your partner to deescalate. You can always revisit the initial cause of the conflict when both you and your partner are not emotionally charged. You can also distract yourself with self-soothing tactics such as taking a warm bath or a reading good book. Perhaps distract yourself by giving back to others and spending time planning a drive-by surprise party for your sister’s birthday next month. It can be helpful to distract yourself by comparing yourself to others less fortunate than you or a time in your life when you and your partner were struggling much worse than now, to provide perspective. The goal is not to add to your distress but instead, provide yourself a sense of perspective.
Use interpersonal effectiveness skills to establish a healthy relationship
Be gentle in all your communications with your partner, think about your spouse’s perspective, show empathy and interest in what your partner has to say by your verbal communication or body language, such as maintaining eye contact, and offer recognitional cues, such as “uh-huh” and “oh, really.” Avoid communication that is at all invalidating. Never start a sentence with “YOU” while having heated conversations with your spouse; instead, use “I feel” statements. This type of communication avoids the blame game that gets many couples into trouble.
Instead, communicate how you feel while not necessarily blaming your spouse but rather expressing your emotions. This will ultimately lead to less defensive communication from your partner. Remember that not all communication is for the sole purpose of communicating. Much of the time, communication is used as an attempt for one partner to connect with the other partner. Couples may say that they have difficulty with communication when it is not the communication that is the issue but instead the underlying disconnect of the couple.
This disconnect usually manifests while couples are communicating, and therefore, can be misconstrued as solely a communication issue by the couple. When your partner asks you to stop staring at your phone during dinner, it is not necessarily that your spouse is attempting to control you or wants to engage in some deep conversation, but more likely a bid to try to connect with you. Your partner is attempting to tell you that he or she feels disconnected, misses you, and wants to reconnect.
Provide validation and acceptance to your partner
Focus on your partner’s strengths and accept the weaknesses. Accept that your partner is scattered, disorganized, and takes at least 20 minutes to find the phone and keys every morning. Remember that during your courtship days, you found your partner’s flighty attributes to be endearing. Do the same for your strengths and weaknesses.
Accept that the pandemic is unpredictable and that you may need to strengthen your ability to be flexible and more adaptable. This will ultimately lead to feeling less disappointment by your partner and more accepting of shortcomings. Acceptance of your imperfections will improve your sense of worth and confidence and lessen negative emotions, such as guilt, regret, and shame.
Accept the fact that, as similar as we all are, we use different methods to recharge ourselves. In contrast, your spouse needs alone time without distractions to reboot mentally and prepare for the following day. In the pre-pandemic world, if there were a mismatch in what a couple needed to feel rejuvenated, they could independently compensate and search for fulfillment outside of the home. Before stay-at-home orders were rolled out throughout the country, spouses had ample opportunities to spend time away from their partners at work, dinner with friends, or while squeezing in a 7 p.m. yoga sculpt class – barely getting home in time to kiss our children goodnight – with a few minutes to spare to engage in mundane conversation with our partners before our nighttime routine of TV commenced. Unfortunately, COVID-19 has made it very hard for couples to carve out that time for compensatory activities outside of the home.
Remember that you are a team
Remind yourself of the reason why you initially fell in love with your partner. Teammates do not keep score or compete with one another. They support each other when one player is not feeling well, and they make sacrifices for the betterment of the team.
Your marriage vows included “through sickness and health” and now should include “through quarantine.”
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
Most married couples vowed to stay with their partners during sickness and health, but none of us vowed to remain trapped with our loved ones behind the same four walls, all day, every day, for an unknown period of time. We didn’t sign up for this! Some romantics may be titillated by the prospect, while more independent partners may panic at the mere thought of spending all day and night with their loved ones.
Because of the swift implementation of the lifestyle-altering restrictions, couples did not have ample time to mentally and physically prepare. A lack of preparation and loss of control heightens our emotions. It can make couples more susceptible to engage in unhealthy styles of communication and destructive behaviors that are harmful to their relationships.
There are psychological reasons that “absence makes the heart grow fonder.” Distance from your partner is not just a clever way to make your partner appreciate and desire you more. It is human nature to habituate to what is part of your daily life. For instance, when your partner is away from you while on a work trip, you may find the first night or two alone relaxing; but by day 3, you begin to miss your partner’s hugs and kisses, smell, and touch. And after many days apart, you may even miss the incessant nagging that secretly motivates you. Physical distance from our partners essentially gives us the ability to long for and appreciate each other. Our brains are wired to pay more attention to things that are novel and exciting and less interested in what is in our everyday lives.
Separation gives us the ability to miss our partners, while quarantine does the complete opposite.
To avoid contemplating how to murder one’s spouse before quarantine ends, partners can strengthen their relationships by using the strategies I’ve outlined below, which are loosely based on dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). These strategies can be useful for anyone – providers and patients alike – going through these struggles.
Dialectical behavior therapy was developed by psychologist Marsha Linehan PhD, to help regulate emotions for people diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. These skills help to identify thoughts and feelings, to accept one’s inner emotional world and outward behaviors. The idea is that, once you can recognize and accept, then change is possible. The “dialectic” in dialectical behavior therapy implies that one is attempting to find a balance between acceptance and change. All of us can benefit from these skills, especially emotionally volatile couples who are trapped together in quarantine.
Radically accept what is uncertain in your lives
Radical acceptance is a practice used in DBT in situations that are out of our control, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Radically accept that you and your partner are trapped in quarantine without attempting to place blame on our government, your spouse, your boss, and even yourself. Radical acceptance is exactly what the name implies. Accept your current situation for what it is and not what you hoped it to be.
Accept the unknown and unanswered questions such as when will this quarantine end? Will there be a summer camp? Will I get back to my office this summer? Will my children even return to school in the fall? The acceptance of what is out of your control will ultimately decrease your mental time spent worrying and obsessing about the uncertainties of your post-quarantine life and instead provide you more time to be present with your spouse.
Remain mindful during all communication with your spouse. To stay in the moment, you need to be aware of your bodily reactions to distress and notice when your heart rate increases, breathing becomes more shallow, stomach muscles tighten, and when your thoughts become more negative. Mindfulness skills enable us to use physiological changes in our body to become aware of our emotions. You can use your partner’s nonverbal body language and tone of voice to gauge that person’s emotional reactivity.
The practice of mindfulness leads to an increased emotional intelligence. The goal is to have enough self-awareness and emotional understanding of your partner and enough empathy to know when a conversation is becoming too emotionally charged and to let it go and back off. Mindfulness is not nagging your partner to remember to change the heating unit filters with a reminder of what happened years ago when this wasn’t done promptly – without first checking in to make sure your partner is emotionally ready for this type of conversation.
When we have strong emotions, we are using the more primitive parts of our brain that induce a fight or flight reaction. These emotional reactions overshadow the more advanced prefrontal region of our brain that stores our rational thoughts and reasoning skills, a concept identified by psychologist Daniel Goleman as “emotional hijacking.”
Use distress tolerance skills to deal with negative emotions
Distress tolerance is an individual’s ability to manage feelings in response to stress. Distress tolerance skills are aimed at helping one manage intense emotions without worsening a situation by engaging in behaviors that are destructive and may exacerbate the problem. The goal is to tolerate the stress while with your partner and not respond negatively or in a way that is harmful to the integrity of your relationship.
To prioritize your relationship, this may mean that you choose not to react negatively when your partner makes a passive-aggressive comment on how you spent your day during quarantine since you still have a pile of laundry on your bedroom floor and overflowing dishes in the kitchen sink. A high level of distress tolerance will enable you to not overreact or withdraw from your spouse when flooded with emotions of anger or sadness.
Distraction techniques are a type of distress tolerance skill. You can engage in activities that keep you distracted and require your full attention. When things get heated between you and your spouse during quarantine, try to obtain some distance from each other to cool down and engage in an activity that involves your full concentration.
Many of us have been surprised by our hidden talents that were discovered during the quarantine. Use the time away from your partner to distract yourself with your new passion for writing, baking, organizing, and even your newfound love of balloon artistry. Do an activity that engages your mind and provides you the necessary physical and mental time away from your partner to deescalate. You can always revisit the initial cause of the conflict when both you and your partner are not emotionally charged. You can also distract yourself with self-soothing tactics such as taking a warm bath or a reading good book. Perhaps distract yourself by giving back to others and spending time planning a drive-by surprise party for your sister’s birthday next month. It can be helpful to distract yourself by comparing yourself to others less fortunate than you or a time in your life when you and your partner were struggling much worse than now, to provide perspective. The goal is not to add to your distress but instead, provide yourself a sense of perspective.
Use interpersonal effectiveness skills to establish a healthy relationship
Be gentle in all your communications with your partner, think about your spouse’s perspective, show empathy and interest in what your partner has to say by your verbal communication or body language, such as maintaining eye contact, and offer recognitional cues, such as “uh-huh” and “oh, really.” Avoid communication that is at all invalidating. Never start a sentence with “YOU” while having heated conversations with your spouse; instead, use “I feel” statements. This type of communication avoids the blame game that gets many couples into trouble.
Instead, communicate how you feel while not necessarily blaming your spouse but rather expressing your emotions. This will ultimately lead to less defensive communication from your partner. Remember that not all communication is for the sole purpose of communicating. Much of the time, communication is used as an attempt for one partner to connect with the other partner. Couples may say that they have difficulty with communication when it is not the communication that is the issue but instead the underlying disconnect of the couple.
This disconnect usually manifests while couples are communicating, and therefore, can be misconstrued as solely a communication issue by the couple. When your partner asks you to stop staring at your phone during dinner, it is not necessarily that your spouse is attempting to control you or wants to engage in some deep conversation, but more likely a bid to try to connect with you. Your partner is attempting to tell you that he or she feels disconnected, misses you, and wants to reconnect.
Provide validation and acceptance to your partner
Focus on your partner’s strengths and accept the weaknesses. Accept that your partner is scattered, disorganized, and takes at least 20 minutes to find the phone and keys every morning. Remember that during your courtship days, you found your partner’s flighty attributes to be endearing. Do the same for your strengths and weaknesses.
Accept that the pandemic is unpredictable and that you may need to strengthen your ability to be flexible and more adaptable. This will ultimately lead to feeling less disappointment by your partner and more accepting of shortcomings. Acceptance of your imperfections will improve your sense of worth and confidence and lessen negative emotions, such as guilt, regret, and shame.
Accept the fact that, as similar as we all are, we use different methods to recharge ourselves. In contrast, your spouse needs alone time without distractions to reboot mentally and prepare for the following day. In the pre-pandemic world, if there were a mismatch in what a couple needed to feel rejuvenated, they could independently compensate and search for fulfillment outside of the home. Before stay-at-home orders were rolled out throughout the country, spouses had ample opportunities to spend time away from their partners at work, dinner with friends, or while squeezing in a 7 p.m. yoga sculpt class – barely getting home in time to kiss our children goodnight – with a few minutes to spare to engage in mundane conversation with our partners before our nighttime routine of TV commenced. Unfortunately, COVID-19 has made it very hard for couples to carve out that time for compensatory activities outside of the home.
Remember that you are a team
Remind yourself of the reason why you initially fell in love with your partner. Teammates do not keep score or compete with one another. They support each other when one player is not feeling well, and they make sacrifices for the betterment of the team.
Your marriage vows included “through sickness and health” and now should include “through quarantine.”
Dr. Abraham is a psychiatrist in private practice in Philadelphia. She has no disclosures.
FDA authorizes emergency use of remdesivir for COVID-19
The investigational antiviral drug, manufactured by Gilead Sciences Inc., was shown in a preliminary analysis of a National Institutes of Health (NIH) clinical trial to shorten recovery time in some patients, according to information presented during a White House press conference earlier this week. However, the results of the trial have not been published and little is known about how safe and effective it is in treating people in the hospital with COVID-19.
The emergency use authorization (EUA) designation means remdesivir can be distributed in the United States and administered intravenously by healthcare providers, as appropriate to treat severe disease. Those with severe disease, the FDA said in a press release, are patients with low blood oxygen levels or those who need oxygen therapy or more intensive support such as a mechanical ventilator.
“There’s tremendous interest among all parties to identify and arm ourselves with medicines to combat COVID-19, and through our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA is working around-the-clock and using every tool at our disposal to speed these efforts,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
The FDA writes, “Based on evaluation of the emergency use authorization criteria and the scientific evidence available, it was determined that it is reasonable to believe that remdesivir may be effective in treating COVID-19, and that, given there are no adequate, approved, or available alternative treatments, the known and potential benefits to treat this serious or life-threatening virus currently outweigh the known and potential risks of the drug’s use.”
The drug must be administered intravenously and the optimal dosing and duration are not yet known, the company said in a press release issued May 1.
In addition, Gilead advises that infusion-related reactions and liver transaminase elevations have been seen in patients treated with the drug.
“If signs and symptoms of a clinically significant infusion reaction occur, immediately discontinue administration of remdesivir and initiate appropriate treatment. Patients should have appropriate clinical and laboratory monitoring to aid in early detection of any potential adverse events. Monitor renal and hepatic function prior to initiating and daily during therapy with remdesivir; additionally monitor serum chemistries and hematology daily during therapy,” the company said.
Before granting the emergency use authorization, the FDA had allowed for study of the drug in clinical trials, as well as expanded access use for individual patients and through a multipatient expanded access program coordinated by Gilead.
“The EUA will be effective until the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of drugs and biologics for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is terminated and may be revised or revoked if it is determined the EUA no longer meets the statutory criteria for issuance,” the FDA said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigational antiviral drug, manufactured by Gilead Sciences Inc., was shown in a preliminary analysis of a National Institutes of Health (NIH) clinical trial to shorten recovery time in some patients, according to information presented during a White House press conference earlier this week. However, the results of the trial have not been published and little is known about how safe and effective it is in treating people in the hospital with COVID-19.
The emergency use authorization (EUA) designation means remdesivir can be distributed in the United States and administered intravenously by healthcare providers, as appropriate to treat severe disease. Those with severe disease, the FDA said in a press release, are patients with low blood oxygen levels or those who need oxygen therapy or more intensive support such as a mechanical ventilator.
“There’s tremendous interest among all parties to identify and arm ourselves with medicines to combat COVID-19, and through our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA is working around-the-clock and using every tool at our disposal to speed these efforts,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
The FDA writes, “Based on evaluation of the emergency use authorization criteria and the scientific evidence available, it was determined that it is reasonable to believe that remdesivir may be effective in treating COVID-19, and that, given there are no adequate, approved, or available alternative treatments, the known and potential benefits to treat this serious or life-threatening virus currently outweigh the known and potential risks of the drug’s use.”
The drug must be administered intravenously and the optimal dosing and duration are not yet known, the company said in a press release issued May 1.
In addition, Gilead advises that infusion-related reactions and liver transaminase elevations have been seen in patients treated with the drug.
“If signs and symptoms of a clinically significant infusion reaction occur, immediately discontinue administration of remdesivir and initiate appropriate treatment. Patients should have appropriate clinical and laboratory monitoring to aid in early detection of any potential adverse events. Monitor renal and hepatic function prior to initiating and daily during therapy with remdesivir; additionally monitor serum chemistries and hematology daily during therapy,” the company said.
Before granting the emergency use authorization, the FDA had allowed for study of the drug in clinical trials, as well as expanded access use for individual patients and through a multipatient expanded access program coordinated by Gilead.
“The EUA will be effective until the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of drugs and biologics for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is terminated and may be revised or revoked if it is determined the EUA no longer meets the statutory criteria for issuance,” the FDA said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigational antiviral drug, manufactured by Gilead Sciences Inc., was shown in a preliminary analysis of a National Institutes of Health (NIH) clinical trial to shorten recovery time in some patients, according to information presented during a White House press conference earlier this week. However, the results of the trial have not been published and little is known about how safe and effective it is in treating people in the hospital with COVID-19.
The emergency use authorization (EUA) designation means remdesivir can be distributed in the United States and administered intravenously by healthcare providers, as appropriate to treat severe disease. Those with severe disease, the FDA said in a press release, are patients with low blood oxygen levels or those who need oxygen therapy or more intensive support such as a mechanical ventilator.
“There’s tremendous interest among all parties to identify and arm ourselves with medicines to combat COVID-19, and through our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA is working around-the-clock and using every tool at our disposal to speed these efforts,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a statement.
The FDA writes, “Based on evaluation of the emergency use authorization criteria and the scientific evidence available, it was determined that it is reasonable to believe that remdesivir may be effective in treating COVID-19, and that, given there are no adequate, approved, or available alternative treatments, the known and potential benefits to treat this serious or life-threatening virus currently outweigh the known and potential risks of the drug’s use.”
The drug must be administered intravenously and the optimal dosing and duration are not yet known, the company said in a press release issued May 1.
In addition, Gilead advises that infusion-related reactions and liver transaminase elevations have been seen in patients treated with the drug.
“If signs and symptoms of a clinically significant infusion reaction occur, immediately discontinue administration of remdesivir and initiate appropriate treatment. Patients should have appropriate clinical and laboratory monitoring to aid in early detection of any potential adverse events. Monitor renal and hepatic function prior to initiating and daily during therapy with remdesivir; additionally monitor serum chemistries and hematology daily during therapy,” the company said.
Before granting the emergency use authorization, the FDA had allowed for study of the drug in clinical trials, as well as expanded access use for individual patients and through a multipatient expanded access program coordinated by Gilead.
“The EUA will be effective until the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of drugs and biologics for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is terminated and may be revised or revoked if it is determined the EUA no longer meets the statutory criteria for issuance,” the FDA said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Biologics better solo than with methotrexate in psoriatic arthritis
Ustekinumab or a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) are better used alone than with methotrexate in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis suggest the results of PsABio (A Study on Assessment of STELARA and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibitor Therapies in Participants With Psoriatic Arthritis), a large, ongoing, prospective observational study.
The percentages of patients achieving multiple psoriatic arthritis disease activity outcome measures at 6 months were higher if biologic monotherapy was used rather than a biologic in combination with methotrexate.
For example, minimal disease activity (MDA) was achieved by 27.5% of patients taking ustekinumab as monotherapy and by 32.1% of those taking a TNFi alone. When methotrexate was used in combination, the respective percentages of patients achieving MDA were 23.7% and 27.8%.
A similar pattern was seen for very-low disease activity (VLDA), with 9.8% of patients in the ustekinumab monotherapy arm and 12% of those in the TNFi monotherapy arm achieving this target, compared with 5.7% and 5.4% when these drugs were combined with methotrexate.
MDA is defined as meeting five or more cutoffs for seven domains of disease activity, and VLDA for all seven: 0-1 tender joints, 0-1 swollen joints, Psoriasis Area Severity Index 1 or less or body surface area involved 3% or less, 0-1 tender entheseal points, Health Assessment Questionnaire score of 0.5 or less, patient global disease activity visual analog scale score of 20 or lower, and patient pain visual analog scale score of 15 or lower.
Other outcome measures used that showed no advantage of adding methotrexate to these biologics were the Clinical Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis low disease activity and remission scores, the patient acceptable symptoms rate of the 12-item Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease Questionnaire, and improvement in skin involvement.
“Patients were no more likely to achieve lower disease activity or a remission target having received methotrexate than they did just on the biologic drug on its own,” Stefan Siebert, MBBCh, PhD, one of the PsABio investigators, said in an interview.
Dr. Siebert, who is clinical senior lecturer in inflammation and rheumatology at the University of Glasgow (Scotland), was scheduled to present the findings at the British Society for Rheumatology annual conference. The meeting was canceled because of the ongoing COVID-19 crisis. Abstracts and ePosters from the meeting have since been released in a supplement to Rheumatology and via the BSR’s conference app.
First data for ustekinumab
“There certainly doesn’t appear to be any added benefit from using methotrexate on a group level in patients getting ustekinumab and TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Siebert said. “We’ve looked at everything,” he emphasized, and “none of the single domains or composite measures were improved by the addition of methotrexate. I think we knew that for TNF inhibitors, but the key thing is we’ve never known that for ustekinumab, and this is the first study to show that.”
Indeed, the findings match up with those from the SEAM-PsA (Etanercept and Methotrexate in Subjects with Psoriatic Arthritis) study in which patients who were treated with the TNFi etanercept as monotherapy did much better than those given the TNFi in combination with methotrexate or methotrexate alone. While not a randomized trial, PsABio now shows that the same is true for ustekinumab.
Obviously, there are some clear differences between a clinical trial and an observational study such as PsABio. For one thing, there was no randomization and patients taking methotrexate were presumably doing so for good reason, Dr. Siebert said. Secondly, there was no methotrexate-only arm.
PsABio recruited patients who were starting treatment with either ustekinumab or a new TNFi as first-, second-, or third-line biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic therapy (DMARD). “These are all people starting on a biologic, so they’ve already got severe disease and have failed methotrexate on some level. So everything we’ve done is biologic without methotrexate or biologic with methotrexate,” Dr. Siebert explained. Patients may not have been taking methotrexate for a variety of reasons, such as inefficacy or side effects, so PsABio “doesn’t tell us anything about methotrexate on its own.”
Time to rethink ingrained methotrexate use
The rationale for using methotrexate in combination with biologics in psoriatic arthritis comes from its long-standing use in rheumatoid arthritis. Much of what is advocated in guidelines comes from experience in RA, Dr. Siebert said.
“In rheumatoid arthritis, we know that the TNF inhibitors work much better if you use methotrexate, that’s a given,” he noted. “We’ve been trained that you have to have methotrexate to have a biologic. However, PsABio, together with other studies, show that you don’t have to, and you should have a good reason to add methotrexate.”
Individual patients may still benefit from methotrexate use, but the decision to treat all patients the same is not supported by the current evidence. “It’s good that it shows that, actually, once you get someone on a decent biologic, it’s working: It’s doing what it ‘says on the tin’ for a lot of patients. I really think that is the key message, here, that you don’t have to; this reassures clinicians and actually makes them think ‘should this patient be on methotrexate?’ ” Dr. Siebert said.
The PsABio study was funded by Janssen. Dr. Siebert has acted as a consultant to and received research funding from Janssen, UCB, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Celgene. He has also acted as a consultant for AbbVie and received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Siebert S et al. Rheumatology. 2020;59(Suppl 2). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa110.023, Abstract O24.
Ustekinumab or a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) are better used alone than with methotrexate in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis suggest the results of PsABio (A Study on Assessment of STELARA and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibitor Therapies in Participants With Psoriatic Arthritis), a large, ongoing, prospective observational study.
The percentages of patients achieving multiple psoriatic arthritis disease activity outcome measures at 6 months were higher if biologic monotherapy was used rather than a biologic in combination with methotrexate.
For example, minimal disease activity (MDA) was achieved by 27.5% of patients taking ustekinumab as monotherapy and by 32.1% of those taking a TNFi alone. When methotrexate was used in combination, the respective percentages of patients achieving MDA were 23.7% and 27.8%.
A similar pattern was seen for very-low disease activity (VLDA), with 9.8% of patients in the ustekinumab monotherapy arm and 12% of those in the TNFi monotherapy arm achieving this target, compared with 5.7% and 5.4% when these drugs were combined with methotrexate.
MDA is defined as meeting five or more cutoffs for seven domains of disease activity, and VLDA for all seven: 0-1 tender joints, 0-1 swollen joints, Psoriasis Area Severity Index 1 or less or body surface area involved 3% or less, 0-1 tender entheseal points, Health Assessment Questionnaire score of 0.5 or less, patient global disease activity visual analog scale score of 20 or lower, and patient pain visual analog scale score of 15 or lower.
Other outcome measures used that showed no advantage of adding methotrexate to these biologics were the Clinical Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis low disease activity and remission scores, the patient acceptable symptoms rate of the 12-item Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease Questionnaire, and improvement in skin involvement.
“Patients were no more likely to achieve lower disease activity or a remission target having received methotrexate than they did just on the biologic drug on its own,” Stefan Siebert, MBBCh, PhD, one of the PsABio investigators, said in an interview.
Dr. Siebert, who is clinical senior lecturer in inflammation and rheumatology at the University of Glasgow (Scotland), was scheduled to present the findings at the British Society for Rheumatology annual conference. The meeting was canceled because of the ongoing COVID-19 crisis. Abstracts and ePosters from the meeting have since been released in a supplement to Rheumatology and via the BSR’s conference app.
First data for ustekinumab
“There certainly doesn’t appear to be any added benefit from using methotrexate on a group level in patients getting ustekinumab and TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Siebert said. “We’ve looked at everything,” he emphasized, and “none of the single domains or composite measures were improved by the addition of methotrexate. I think we knew that for TNF inhibitors, but the key thing is we’ve never known that for ustekinumab, and this is the first study to show that.”
Indeed, the findings match up with those from the SEAM-PsA (Etanercept and Methotrexate in Subjects with Psoriatic Arthritis) study in which patients who were treated with the TNFi etanercept as monotherapy did much better than those given the TNFi in combination with methotrexate or methotrexate alone. While not a randomized trial, PsABio now shows that the same is true for ustekinumab.
Obviously, there are some clear differences between a clinical trial and an observational study such as PsABio. For one thing, there was no randomization and patients taking methotrexate were presumably doing so for good reason, Dr. Siebert said. Secondly, there was no methotrexate-only arm.
PsABio recruited patients who were starting treatment with either ustekinumab or a new TNFi as first-, second-, or third-line biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic therapy (DMARD). “These are all people starting on a biologic, so they’ve already got severe disease and have failed methotrexate on some level. So everything we’ve done is biologic without methotrexate or biologic with methotrexate,” Dr. Siebert explained. Patients may not have been taking methotrexate for a variety of reasons, such as inefficacy or side effects, so PsABio “doesn’t tell us anything about methotrexate on its own.”
Time to rethink ingrained methotrexate use
The rationale for using methotrexate in combination with biologics in psoriatic arthritis comes from its long-standing use in rheumatoid arthritis. Much of what is advocated in guidelines comes from experience in RA, Dr. Siebert said.
“In rheumatoid arthritis, we know that the TNF inhibitors work much better if you use methotrexate, that’s a given,” he noted. “We’ve been trained that you have to have methotrexate to have a biologic. However, PsABio, together with other studies, show that you don’t have to, and you should have a good reason to add methotrexate.”
Individual patients may still benefit from methotrexate use, but the decision to treat all patients the same is not supported by the current evidence. “It’s good that it shows that, actually, once you get someone on a decent biologic, it’s working: It’s doing what it ‘says on the tin’ for a lot of patients. I really think that is the key message, here, that you don’t have to; this reassures clinicians and actually makes them think ‘should this patient be on methotrexate?’ ” Dr. Siebert said.
The PsABio study was funded by Janssen. Dr. Siebert has acted as a consultant to and received research funding from Janssen, UCB, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Celgene. He has also acted as a consultant for AbbVie and received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Siebert S et al. Rheumatology. 2020;59(Suppl 2). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa110.023, Abstract O24.
Ustekinumab or a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) are better used alone than with methotrexate in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis suggest the results of PsABio (A Study on Assessment of STELARA and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibitor Therapies in Participants With Psoriatic Arthritis), a large, ongoing, prospective observational study.
The percentages of patients achieving multiple psoriatic arthritis disease activity outcome measures at 6 months were higher if biologic monotherapy was used rather than a biologic in combination with methotrexate.
For example, minimal disease activity (MDA) was achieved by 27.5% of patients taking ustekinumab as monotherapy and by 32.1% of those taking a TNFi alone. When methotrexate was used in combination, the respective percentages of patients achieving MDA were 23.7% and 27.8%.
A similar pattern was seen for very-low disease activity (VLDA), with 9.8% of patients in the ustekinumab monotherapy arm and 12% of those in the TNFi monotherapy arm achieving this target, compared with 5.7% and 5.4% when these drugs were combined with methotrexate.
MDA is defined as meeting five or more cutoffs for seven domains of disease activity, and VLDA for all seven: 0-1 tender joints, 0-1 swollen joints, Psoriasis Area Severity Index 1 or less or body surface area involved 3% or less, 0-1 tender entheseal points, Health Assessment Questionnaire score of 0.5 or less, patient global disease activity visual analog scale score of 20 or lower, and patient pain visual analog scale score of 15 or lower.
Other outcome measures used that showed no advantage of adding methotrexate to these biologics were the Clinical Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis low disease activity and remission scores, the patient acceptable symptoms rate of the 12-item Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease Questionnaire, and improvement in skin involvement.
“Patients were no more likely to achieve lower disease activity or a remission target having received methotrexate than they did just on the biologic drug on its own,” Stefan Siebert, MBBCh, PhD, one of the PsABio investigators, said in an interview.
Dr. Siebert, who is clinical senior lecturer in inflammation and rheumatology at the University of Glasgow (Scotland), was scheduled to present the findings at the British Society for Rheumatology annual conference. The meeting was canceled because of the ongoing COVID-19 crisis. Abstracts and ePosters from the meeting have since been released in a supplement to Rheumatology and via the BSR’s conference app.
First data for ustekinumab
“There certainly doesn’t appear to be any added benefit from using methotrexate on a group level in patients getting ustekinumab and TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Siebert said. “We’ve looked at everything,” he emphasized, and “none of the single domains or composite measures were improved by the addition of methotrexate. I think we knew that for TNF inhibitors, but the key thing is we’ve never known that for ustekinumab, and this is the first study to show that.”
Indeed, the findings match up with those from the SEAM-PsA (Etanercept and Methotrexate in Subjects with Psoriatic Arthritis) study in which patients who were treated with the TNFi etanercept as monotherapy did much better than those given the TNFi in combination with methotrexate or methotrexate alone. While not a randomized trial, PsABio now shows that the same is true for ustekinumab.
Obviously, there are some clear differences between a clinical trial and an observational study such as PsABio. For one thing, there was no randomization and patients taking methotrexate were presumably doing so for good reason, Dr. Siebert said. Secondly, there was no methotrexate-only arm.
PsABio recruited patients who were starting treatment with either ustekinumab or a new TNFi as first-, second-, or third-line biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic therapy (DMARD). “These are all people starting on a biologic, so they’ve already got severe disease and have failed methotrexate on some level. So everything we’ve done is biologic without methotrexate or biologic with methotrexate,” Dr. Siebert explained. Patients may not have been taking methotrexate for a variety of reasons, such as inefficacy or side effects, so PsABio “doesn’t tell us anything about methotrexate on its own.”
Time to rethink ingrained methotrexate use
The rationale for using methotrexate in combination with biologics in psoriatic arthritis comes from its long-standing use in rheumatoid arthritis. Much of what is advocated in guidelines comes from experience in RA, Dr. Siebert said.
“In rheumatoid arthritis, we know that the TNF inhibitors work much better if you use methotrexate, that’s a given,” he noted. “We’ve been trained that you have to have methotrexate to have a biologic. However, PsABio, together with other studies, show that you don’t have to, and you should have a good reason to add methotrexate.”
Individual patients may still benefit from methotrexate use, but the decision to treat all patients the same is not supported by the current evidence. “It’s good that it shows that, actually, once you get someone on a decent biologic, it’s working: It’s doing what it ‘says on the tin’ for a lot of patients. I really think that is the key message, here, that you don’t have to; this reassures clinicians and actually makes them think ‘should this patient be on methotrexate?’ ” Dr. Siebert said.
The PsABio study was funded by Janssen. Dr. Siebert has acted as a consultant to and received research funding from Janssen, UCB, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Celgene. He has also acted as a consultant for AbbVie and received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Siebert S et al. Rheumatology. 2020;59(Suppl 2). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa110.023, Abstract O24.
FROM BSR 2020
CMS hikes telephone visit payments during pandemic
Physicians who are conducting telephone visits during the COVID-19 pandemic will be paid at a higher rate, more closely aligning the rates with payments for face-to-face visits.
On April 30, officials at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced the temporary telephone visit rate change and expanded the scope of services that are eligible telephone visits to include many behavioral health and patient education services.
Rates for telephone visits will jump from $14-$41 per visit to about $46-$110. The pay increase is retroactive to March 1, 2020.
The move was welcomed by the American College of Physicians, but the organization said more needs to be done in order help maintain the financial stability of physician practices.
“ACP has repeatedly requested this change from CMS as the country has been dealing with the COVID-19 national emergency, and we are heartened that they have heard our concerns,” ACP President Jacqueline Fincher, MD, said in a statement. “More still needs to be done to ensure that physician practices are able to remain operational and care for their patients, but this change in payment policy addresses one of the biggest issues facing physicians as they struggle to make up for lost revenue and provide appropriate care to patients.”
CMS also is expanding payment availability for audio-only telemedicine services by waiving the video requirement for certain evaluation and management services. The move is aimed at reaching Medicare beneficiaries who may not have access to video technology or choose not to use it.
“This is a major victory for medicine that will enable physicians to care for their patients, especially their elderly patients with chronic conditions who may not have access to audio-visual technology or high-speed Internet,” Patrice Harris, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a statement. “This change will help patients address their health challenges that existed before COVID-19.”
Shawn Martin, senior vice president at the American Academy of Family Physicians, said his group is pleased to see CMS roll out this change and noted that it is especially important for patients with underlying health conditions. “This is the only connectivity they may have with a health care system for their ongoing health care needs.”
Samuel Jones, MD, chair of the Health Affairs Committee at the American College of Cardiology, highlighted the expansion and coverage of audio-only telemedicine appointments as a huge plus for patient access.*
“There was a huge hunger to say, ‘Can we just have improvement in the reimbursement for telephone, which is providing a good service, our patients our asking for it,’ and we were able to get that,” Dr. Jones said in an interview. “It really was, I think, a good thing for patient care.”
Dr. Jones also suggested that the temporary policy be extended after the COVID-19 crisis is over.
“Telemedicine is here to stay,” he said. “But if all of these relaxations suddenly go away with a snap of the finger, or if the reimbursement [is lowered], if all that changes as soon as this emergency declaration is over, we are going to have a hard time.”
The pay increase for telephone services was part of a broader package of increased regulatory flexibility CMS rolled out, including expanding the types of providers who can order a COVID-19 test.
*Correction, 5/5/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated Dr. Samuel Jones' affiliation. He is the chair of the Health Affairs Committee at the American College of Cardiology.
Physicians who are conducting telephone visits during the COVID-19 pandemic will be paid at a higher rate, more closely aligning the rates with payments for face-to-face visits.
On April 30, officials at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced the temporary telephone visit rate change and expanded the scope of services that are eligible telephone visits to include many behavioral health and patient education services.
Rates for telephone visits will jump from $14-$41 per visit to about $46-$110. The pay increase is retroactive to March 1, 2020.
The move was welcomed by the American College of Physicians, but the organization said more needs to be done in order help maintain the financial stability of physician practices.
“ACP has repeatedly requested this change from CMS as the country has been dealing with the COVID-19 national emergency, and we are heartened that they have heard our concerns,” ACP President Jacqueline Fincher, MD, said in a statement. “More still needs to be done to ensure that physician practices are able to remain operational and care for their patients, but this change in payment policy addresses one of the biggest issues facing physicians as they struggle to make up for lost revenue and provide appropriate care to patients.”
CMS also is expanding payment availability for audio-only telemedicine services by waiving the video requirement for certain evaluation and management services. The move is aimed at reaching Medicare beneficiaries who may not have access to video technology or choose not to use it.
“This is a major victory for medicine that will enable physicians to care for their patients, especially their elderly patients with chronic conditions who may not have access to audio-visual technology or high-speed Internet,” Patrice Harris, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a statement. “This change will help patients address their health challenges that existed before COVID-19.”
Shawn Martin, senior vice president at the American Academy of Family Physicians, said his group is pleased to see CMS roll out this change and noted that it is especially important for patients with underlying health conditions. “This is the only connectivity they may have with a health care system for their ongoing health care needs.”
Samuel Jones, MD, chair of the Health Affairs Committee at the American College of Cardiology, highlighted the expansion and coverage of audio-only telemedicine appointments as a huge plus for patient access.*
“There was a huge hunger to say, ‘Can we just have improvement in the reimbursement for telephone, which is providing a good service, our patients our asking for it,’ and we were able to get that,” Dr. Jones said in an interview. “It really was, I think, a good thing for patient care.”
Dr. Jones also suggested that the temporary policy be extended after the COVID-19 crisis is over.
“Telemedicine is here to stay,” he said. “But if all of these relaxations suddenly go away with a snap of the finger, or if the reimbursement [is lowered], if all that changes as soon as this emergency declaration is over, we are going to have a hard time.”
The pay increase for telephone services was part of a broader package of increased regulatory flexibility CMS rolled out, including expanding the types of providers who can order a COVID-19 test.
*Correction, 5/5/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated Dr. Samuel Jones' affiliation. He is the chair of the Health Affairs Committee at the American College of Cardiology.
Physicians who are conducting telephone visits during the COVID-19 pandemic will be paid at a higher rate, more closely aligning the rates with payments for face-to-face visits.
On April 30, officials at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced the temporary telephone visit rate change and expanded the scope of services that are eligible telephone visits to include many behavioral health and patient education services.
Rates for telephone visits will jump from $14-$41 per visit to about $46-$110. The pay increase is retroactive to March 1, 2020.
The move was welcomed by the American College of Physicians, but the organization said more needs to be done in order help maintain the financial stability of physician practices.
“ACP has repeatedly requested this change from CMS as the country has been dealing with the COVID-19 national emergency, and we are heartened that they have heard our concerns,” ACP President Jacqueline Fincher, MD, said in a statement. “More still needs to be done to ensure that physician practices are able to remain operational and care for their patients, but this change in payment policy addresses one of the biggest issues facing physicians as they struggle to make up for lost revenue and provide appropriate care to patients.”
CMS also is expanding payment availability for audio-only telemedicine services by waiving the video requirement for certain evaluation and management services. The move is aimed at reaching Medicare beneficiaries who may not have access to video technology or choose not to use it.
“This is a major victory for medicine that will enable physicians to care for their patients, especially their elderly patients with chronic conditions who may not have access to audio-visual technology or high-speed Internet,” Patrice Harris, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a statement. “This change will help patients address their health challenges that existed before COVID-19.”
Shawn Martin, senior vice president at the American Academy of Family Physicians, said his group is pleased to see CMS roll out this change and noted that it is especially important for patients with underlying health conditions. “This is the only connectivity they may have with a health care system for their ongoing health care needs.”
Samuel Jones, MD, chair of the Health Affairs Committee at the American College of Cardiology, highlighted the expansion and coverage of audio-only telemedicine appointments as a huge plus for patient access.*
“There was a huge hunger to say, ‘Can we just have improvement in the reimbursement for telephone, which is providing a good service, our patients our asking for it,’ and we were able to get that,” Dr. Jones said in an interview. “It really was, I think, a good thing for patient care.”
Dr. Jones also suggested that the temporary policy be extended after the COVID-19 crisis is over.
“Telemedicine is here to stay,” he said. “But if all of these relaxations suddenly go away with a snap of the finger, or if the reimbursement [is lowered], if all that changes as soon as this emergency declaration is over, we are going to have a hard time.”
The pay increase for telephone services was part of a broader package of increased regulatory flexibility CMS rolled out, including expanding the types of providers who can order a COVID-19 test.
*Correction, 5/5/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated Dr. Samuel Jones' affiliation. He is the chair of the Health Affairs Committee at the American College of Cardiology.









