User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with GI symptoms have worse outcomes
Patients with COVID-19 who experience gastrointestinal symptoms have overall worse in-hospital complications but less cardiomyopathy and mortality, according to a new study.
About 20% of COVID-19 patients experience gastrointestinal symptoms, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, which clinicians should consider when treating their hospitalized patients, wrote researchers led by Nikita Patil, MD, a hospitalist at Nash General Hospital–UNC Nash Healthcare in Rocky Mount, N.C., in Gastro Hep Advances.
“It’s important to know that certain complications are higher in people with GI symptoms,” she said in an interview. “Even without an increased risk of death, there are many problems that affect quality of life and lead to people not being able to do the things they were able to do before.”
Dr. Patil and colleagues analyzed the association of GI symptoms with adverse outcomes in 100,902 patients from the Cerner Real-World Data COVID-19 Database, which included hospital encounters and ED visits for COVID-19 between December 2019 to November 2020; the data were taken from EMRs at centers with which Cerner has a data use agreement. They also looked at factors associated with poor outcomes such as acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and ventilator requirement or oxygen dependence.
The average age of the patients was 52, and a higher proportion of patients with GI symptoms were 50 and older. Of those with GI symptoms, 54.5% were women. Overall, patients with GI symptoms were more likely to have higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores and have comorbidities such as acute liver failure, gastroesophageal reflux disease, GI malignancy, and inflammatory bowel disease.
The research team found that COVID-19 patients with GI symptoms were more likely to have acute respiratory distress syndrome (odds ratio, 1.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.29), sepsis (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.14-1.24), acute kidney injury (OR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.24-1.36), venous thromboembolism (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.22-1.52), and GI bleeding (OR 1.62; 95% CI, 1.47-1.79), as compared with COVID-19 patients without GI symptoms (P < .0001 for all comparisons). At the same time, those with GI symptoms were less likely to experience cardiomyopathy (OR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.99; P = .027), respiratory failure (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.88-0.95; P < .0001), or death (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.67-0.75; P < .0001).
GI bleed was the most common GI complication, found among 2% of all patients, and was more likely in patients with GI symptoms than in those without (3.5% vs. 1.6%). Intestinal ischemia, pancreatitis, acute liver injury, and intestinal pseudo-obstruction weren’t associated with GI symptoms.
Among the 19,915 patients with GI symptoms, older age, higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores, use of proton pump inhibitors, and use of H2 receptor antagonists were associated with higher mortality, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and ventilator or oxygen requirement. Men with GI symptoms also had a higher risk of mortality, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and sepsis.
In particular, proton pump inhibitor use was associated with more than twice the risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (OR, 2.19; 95% CI, 1.32-1.66; P < .0001). Similarly, H2 receptor antagonist use was associated with higher likelihood of death (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.57-2.02), as well as more than three times the risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (OR, 3.75; 95% CI, 3.29-4.28), more than twice the risk of sepsis (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 2.28-2.73), and nearly twice the risk of ventilator or oxygen dependence (OR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.68-2.30) (P < .0001 for all).
The findings could guide risk stratification, prognosis, and treatment decisions in COVID-19 patients with GI symptoms, as well as inform future research focused on risk mitigation and improvement of COVID-19 outcomes, Dr. Patil said.
“The protocols for COVID-19 treatment have changed over the past 2 years with blood thinners and steroids,” she said. “Although we likely can’t avoid anti-reflux medicines entirely, it’s something we need to be cognizant of and look out for in our hospitalized patients.”
One study limitation was its inclusion of only inpatient or ED encounters and, therefore, omission of those treated at home; this confers bias toward those with more aggressive disease, according to the authors.
The authors reported no grant support or funding sources for this study. One author declared grant support and consultant fees from several companies, including some medical and pharmaceutical companies, which were unrelated to this research. Dr. Patil reported no disclosures.
This article was updated Aug. 26, 2022.
Patients with COVID-19 who experience gastrointestinal symptoms have overall worse in-hospital complications but less cardiomyopathy and mortality, according to a new study.
About 20% of COVID-19 patients experience gastrointestinal symptoms, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, which clinicians should consider when treating their hospitalized patients, wrote researchers led by Nikita Patil, MD, a hospitalist at Nash General Hospital–UNC Nash Healthcare in Rocky Mount, N.C., in Gastro Hep Advances.
“It’s important to know that certain complications are higher in people with GI symptoms,” she said in an interview. “Even without an increased risk of death, there are many problems that affect quality of life and lead to people not being able to do the things they were able to do before.”
Dr. Patil and colleagues analyzed the association of GI symptoms with adverse outcomes in 100,902 patients from the Cerner Real-World Data COVID-19 Database, which included hospital encounters and ED visits for COVID-19 between December 2019 to November 2020; the data were taken from EMRs at centers with which Cerner has a data use agreement. They also looked at factors associated with poor outcomes such as acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and ventilator requirement or oxygen dependence.
The average age of the patients was 52, and a higher proportion of patients with GI symptoms were 50 and older. Of those with GI symptoms, 54.5% were women. Overall, patients with GI symptoms were more likely to have higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores and have comorbidities such as acute liver failure, gastroesophageal reflux disease, GI malignancy, and inflammatory bowel disease.
The research team found that COVID-19 patients with GI symptoms were more likely to have acute respiratory distress syndrome (odds ratio, 1.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.29), sepsis (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.14-1.24), acute kidney injury (OR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.24-1.36), venous thromboembolism (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.22-1.52), and GI bleeding (OR 1.62; 95% CI, 1.47-1.79), as compared with COVID-19 patients without GI symptoms (P < .0001 for all comparisons). At the same time, those with GI symptoms were less likely to experience cardiomyopathy (OR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.99; P = .027), respiratory failure (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.88-0.95; P < .0001), or death (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.67-0.75; P < .0001).
GI bleed was the most common GI complication, found among 2% of all patients, and was more likely in patients with GI symptoms than in those without (3.5% vs. 1.6%). Intestinal ischemia, pancreatitis, acute liver injury, and intestinal pseudo-obstruction weren’t associated with GI symptoms.
Among the 19,915 patients with GI symptoms, older age, higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores, use of proton pump inhibitors, and use of H2 receptor antagonists were associated with higher mortality, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and ventilator or oxygen requirement. Men with GI symptoms also had a higher risk of mortality, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and sepsis.
In particular, proton pump inhibitor use was associated with more than twice the risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (OR, 2.19; 95% CI, 1.32-1.66; P < .0001). Similarly, H2 receptor antagonist use was associated with higher likelihood of death (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.57-2.02), as well as more than three times the risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (OR, 3.75; 95% CI, 3.29-4.28), more than twice the risk of sepsis (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 2.28-2.73), and nearly twice the risk of ventilator or oxygen dependence (OR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.68-2.30) (P < .0001 for all).
The findings could guide risk stratification, prognosis, and treatment decisions in COVID-19 patients with GI symptoms, as well as inform future research focused on risk mitigation and improvement of COVID-19 outcomes, Dr. Patil said.
“The protocols for COVID-19 treatment have changed over the past 2 years with blood thinners and steroids,” she said. “Although we likely can’t avoid anti-reflux medicines entirely, it’s something we need to be cognizant of and look out for in our hospitalized patients.”
One study limitation was its inclusion of only inpatient or ED encounters and, therefore, omission of those treated at home; this confers bias toward those with more aggressive disease, according to the authors.
The authors reported no grant support or funding sources for this study. One author declared grant support and consultant fees from several companies, including some medical and pharmaceutical companies, which were unrelated to this research. Dr. Patil reported no disclosures.
This article was updated Aug. 26, 2022.
Patients with COVID-19 who experience gastrointestinal symptoms have overall worse in-hospital complications but less cardiomyopathy and mortality, according to a new study.
About 20% of COVID-19 patients experience gastrointestinal symptoms, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, which clinicians should consider when treating their hospitalized patients, wrote researchers led by Nikita Patil, MD, a hospitalist at Nash General Hospital–UNC Nash Healthcare in Rocky Mount, N.C., in Gastro Hep Advances.
“It’s important to know that certain complications are higher in people with GI symptoms,” she said in an interview. “Even without an increased risk of death, there are many problems that affect quality of life and lead to people not being able to do the things they were able to do before.”
Dr. Patil and colleagues analyzed the association of GI symptoms with adverse outcomes in 100,902 patients from the Cerner Real-World Data COVID-19 Database, which included hospital encounters and ED visits for COVID-19 between December 2019 to November 2020; the data were taken from EMRs at centers with which Cerner has a data use agreement. They also looked at factors associated with poor outcomes such as acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and ventilator requirement or oxygen dependence.
The average age of the patients was 52, and a higher proportion of patients with GI symptoms were 50 and older. Of those with GI symptoms, 54.5% were women. Overall, patients with GI symptoms were more likely to have higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores and have comorbidities such as acute liver failure, gastroesophageal reflux disease, GI malignancy, and inflammatory bowel disease.
The research team found that COVID-19 patients with GI symptoms were more likely to have acute respiratory distress syndrome (odds ratio, 1.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.29), sepsis (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.14-1.24), acute kidney injury (OR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.24-1.36), venous thromboembolism (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.22-1.52), and GI bleeding (OR 1.62; 95% CI, 1.47-1.79), as compared with COVID-19 patients without GI symptoms (P < .0001 for all comparisons). At the same time, those with GI symptoms were less likely to experience cardiomyopathy (OR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.99; P = .027), respiratory failure (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.88-0.95; P < .0001), or death (OR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.67-0.75; P < .0001).
GI bleed was the most common GI complication, found among 2% of all patients, and was more likely in patients with GI symptoms than in those without (3.5% vs. 1.6%). Intestinal ischemia, pancreatitis, acute liver injury, and intestinal pseudo-obstruction weren’t associated with GI symptoms.
Among the 19,915 patients with GI symptoms, older age, higher Charlson Comorbidity Index scores, use of proton pump inhibitors, and use of H2 receptor antagonists were associated with higher mortality, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and ventilator or oxygen requirement. Men with GI symptoms also had a higher risk of mortality, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and sepsis.
In particular, proton pump inhibitor use was associated with more than twice the risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (OR, 2.19; 95% CI, 1.32-1.66; P < .0001). Similarly, H2 receptor antagonist use was associated with higher likelihood of death (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.57-2.02), as well as more than three times the risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (OR, 3.75; 95% CI, 3.29-4.28), more than twice the risk of sepsis (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 2.28-2.73), and nearly twice the risk of ventilator or oxygen dependence (OR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.68-2.30) (P < .0001 for all).
The findings could guide risk stratification, prognosis, and treatment decisions in COVID-19 patients with GI symptoms, as well as inform future research focused on risk mitigation and improvement of COVID-19 outcomes, Dr. Patil said.
“The protocols for COVID-19 treatment have changed over the past 2 years with blood thinners and steroids,” she said. “Although we likely can’t avoid anti-reflux medicines entirely, it’s something we need to be cognizant of and look out for in our hospitalized patients.”
One study limitation was its inclusion of only inpatient or ED encounters and, therefore, omission of those treated at home; this confers bias toward those with more aggressive disease, according to the authors.
The authors reported no grant support or funding sources for this study. One author declared grant support and consultant fees from several companies, including some medical and pharmaceutical companies, which were unrelated to this research. Dr. Patil reported no disclosures.
This article was updated Aug. 26, 2022.
FROM GASTRO HEP ADVANCES
Preparing for back to school amid monkeypox outbreak and ever-changing COVID landscape
Unlike last school year, there are now vaccines available for all over the age of 6 months, and home rapid antigen tests are more readily available. Additionally, many have now been exposed either by infection or vaccination to the virus.
The CDC has removed the recommendations for maintaining cohorts in the K-12 population. This changing landscape along with differing levels of personal risk make it challenging to counsel families about what to expect in terms of COVID this year.
The best defense that we currently have against COVID is the vaccine. Although it seems that many are susceptible to the virus despite the vaccine, those who have been vaccinated are less susceptible to serious disease, including young children.
As older children may be heading to college, it is important
to encourage them to isolate when they have symptoms, even when they test negative for COVID as we would all like to avoid being sick in general.
Additionally, they should pay attention to the COVID risk level in their area and wear masks, particularly when indoors, as the levels increase. College students should have a plan for where they can isolate when not feeling well. If anyone does test positive for COVID, they should follow the most recent quarantine guidelines, including wearing a well fitted mask when they do begin returning to activities.
Monkeypox
We now have a new health concern for this school year.
Monkeypox has come onto the scene with information changing as rapidly as information previously did for COVID. With this virus, we must particularly counsel those heading away to college to be careful to limit their exposure to this disease.
Dormitories and other congregate settings are high-risk locations for the spread of monkeypox. Particularly, students headed to stay in dormitories should be counseled about avoiding:
- sexual activity with those with lesions consistent with monkeypox;
- sharing eating and drinking utensils; and
- sleeping in the same bed as or sharing bedding or towels with anyone with a diagnosis of or lesions consistent with monkeypox.
Additionally, as with prevention of all infections, it is important to frequently wash hands or use alcohol-based sanitizer before eating, and avoid touching the face after using the restroom.
Guidance for those eligible for vaccines against monkeypox seems to be quickly changing as well.
At the time of this article, CDC guidance recommends the vaccine against monkeypox for:
- those considered to be at high risk for it, including those identified by public health officials as a contact of someone with monkeypox;
- those who are aware that a sexual partner had a diagnosis of monkeypox within the past 2 weeks;
- those with multiple sex partners in the past 2 weeks in an area with known monkeypox; and
- those whose jobs may expose them to monkeypox.
Currently, the CDC recommends the vaccine JYNNEOS, a two-dose vaccine that reaches maximum protection after fourteen days. Ultimately, guidance is likely to continue to quickly change for both COVID-19 and Monkeypox throughout the fall. It is possible that new vaccinations will become available, and families and physicians alike will have many questions.
Primary care offices should ensure that someone is keeping up to date with the latest guidance to share with the office so that physicians may share accurate information with their patients.
Families should be counseled that we anticipate information about monkeypox, particularly related to vaccinations, to continue to change, as it has during all stages of the COVID pandemic.
As always, patients should be reminded to continue regular routine vaccinations, including the annual influenza vaccine.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Unlike last school year, there are now vaccines available for all over the age of 6 months, and home rapid antigen tests are more readily available. Additionally, many have now been exposed either by infection or vaccination to the virus.
The CDC has removed the recommendations for maintaining cohorts in the K-12 population. This changing landscape along with differing levels of personal risk make it challenging to counsel families about what to expect in terms of COVID this year.
The best defense that we currently have against COVID is the vaccine. Although it seems that many are susceptible to the virus despite the vaccine, those who have been vaccinated are less susceptible to serious disease, including young children.
As older children may be heading to college, it is important
to encourage them to isolate when they have symptoms, even when they test negative for COVID as we would all like to avoid being sick in general.
Additionally, they should pay attention to the COVID risk level in their area and wear masks, particularly when indoors, as the levels increase. College students should have a plan for where they can isolate when not feeling well. If anyone does test positive for COVID, they should follow the most recent quarantine guidelines, including wearing a well fitted mask when they do begin returning to activities.
Monkeypox
We now have a new health concern for this school year.
Monkeypox has come onto the scene with information changing as rapidly as information previously did for COVID. With this virus, we must particularly counsel those heading away to college to be careful to limit their exposure to this disease.
Dormitories and other congregate settings are high-risk locations for the spread of monkeypox. Particularly, students headed to stay in dormitories should be counseled about avoiding:
- sexual activity with those with lesions consistent with monkeypox;
- sharing eating and drinking utensils; and
- sleeping in the same bed as or sharing bedding or towels with anyone with a diagnosis of or lesions consistent with monkeypox.
Additionally, as with prevention of all infections, it is important to frequently wash hands or use alcohol-based sanitizer before eating, and avoid touching the face after using the restroom.
Guidance for those eligible for vaccines against monkeypox seems to be quickly changing as well.
At the time of this article, CDC guidance recommends the vaccine against monkeypox for:
- those considered to be at high risk for it, including those identified by public health officials as a contact of someone with monkeypox;
- those who are aware that a sexual partner had a diagnosis of monkeypox within the past 2 weeks;
- those with multiple sex partners in the past 2 weeks in an area with known monkeypox; and
- those whose jobs may expose them to monkeypox.
Currently, the CDC recommends the vaccine JYNNEOS, a two-dose vaccine that reaches maximum protection after fourteen days. Ultimately, guidance is likely to continue to quickly change for both COVID-19 and Monkeypox throughout the fall. It is possible that new vaccinations will become available, and families and physicians alike will have many questions.
Primary care offices should ensure that someone is keeping up to date with the latest guidance to share with the office so that physicians may share accurate information with their patients.
Families should be counseled that we anticipate information about monkeypox, particularly related to vaccinations, to continue to change, as it has during all stages of the COVID pandemic.
As always, patients should be reminded to continue regular routine vaccinations, including the annual influenza vaccine.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Unlike last school year, there are now vaccines available for all over the age of 6 months, and home rapid antigen tests are more readily available. Additionally, many have now been exposed either by infection or vaccination to the virus.
The CDC has removed the recommendations for maintaining cohorts in the K-12 population. This changing landscape along with differing levels of personal risk make it challenging to counsel families about what to expect in terms of COVID this year.
The best defense that we currently have against COVID is the vaccine. Although it seems that many are susceptible to the virus despite the vaccine, those who have been vaccinated are less susceptible to serious disease, including young children.
As older children may be heading to college, it is important
to encourage them to isolate when they have symptoms, even when they test negative for COVID as we would all like to avoid being sick in general.
Additionally, they should pay attention to the COVID risk level in their area and wear masks, particularly when indoors, as the levels increase. College students should have a plan for where they can isolate when not feeling well. If anyone does test positive for COVID, they should follow the most recent quarantine guidelines, including wearing a well fitted mask when they do begin returning to activities.
Monkeypox
We now have a new health concern for this school year.
Monkeypox has come onto the scene with information changing as rapidly as information previously did for COVID. With this virus, we must particularly counsel those heading away to college to be careful to limit their exposure to this disease.
Dormitories and other congregate settings are high-risk locations for the spread of monkeypox. Particularly, students headed to stay in dormitories should be counseled about avoiding:
- sexual activity with those with lesions consistent with monkeypox;
- sharing eating and drinking utensils; and
- sleeping in the same bed as or sharing bedding or towels with anyone with a diagnosis of or lesions consistent with monkeypox.
Additionally, as with prevention of all infections, it is important to frequently wash hands or use alcohol-based sanitizer before eating, and avoid touching the face after using the restroom.
Guidance for those eligible for vaccines against monkeypox seems to be quickly changing as well.
At the time of this article, CDC guidance recommends the vaccine against monkeypox for:
- those considered to be at high risk for it, including those identified by public health officials as a contact of someone with monkeypox;
- those who are aware that a sexual partner had a diagnosis of monkeypox within the past 2 weeks;
- those with multiple sex partners in the past 2 weeks in an area with known monkeypox; and
- those whose jobs may expose them to monkeypox.
Currently, the CDC recommends the vaccine JYNNEOS, a two-dose vaccine that reaches maximum protection after fourteen days. Ultimately, guidance is likely to continue to quickly change for both COVID-19 and Monkeypox throughout the fall. It is possible that new vaccinations will become available, and families and physicians alike will have many questions.
Primary care offices should ensure that someone is keeping up to date with the latest guidance to share with the office so that physicians may share accurate information with their patients.
Families should be counseled that we anticipate information about monkeypox, particularly related to vaccinations, to continue to change, as it has during all stages of the COVID pandemic.
As always, patients should be reminded to continue regular routine vaccinations, including the annual influenza vaccine.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Metformin fails as early COVID-19 treatment but shows potential
Neither metformin, ivermectin, or fluvoxamine had any impact on reducing disease severity, hospitalization, or death from COVID-19, according to results from more than 1,000 overweight or obese adult patients in the COVID-OUT randomized trial.
However, metformin showed some potential in a secondary analysis.
Early treatment to prevent severe disease remains a goal in managing the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, and biophysical modeling suggested that metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine may serve as antivirals to help reduce severe disease in COVID-19 patients, Carolyn T. Bramante, MD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues wrote.
“We started enrolling patients at the end of December 2020,” Dr. Bramante said in an interview. “At that time, even though vaccine data were coming out, we thought it was important to test early outpatient treatment with widely available safe medications with no interactions, because the virus would evolve and vaccine availability may be limited.”
In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers used a two-by-three factorial design to test the ability of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine to prevent severe COVID-19 infection in nonhospitalized adults aged 30-85 years. A total of 1,431 patients at six U.S. sites were enrolled within 3 days of a confirmed infection and less than 7 days after the start of symptoms, then randomized to one of six groups: metformin plus fluvoxamine; metformin plus ivermectin; metformin plus placebo; placebo plus fluvoxamine; placebo plus ivermectin; and placebo plus placebo.
A total of 1,323 patients were included in the primary analysis. The median age of the patients was 46 years, 56% were female (of whom 6% were pregnant), and all individuals met criteria for overweight or obesity. About half (52%) of the patients had been vaccinated against COVID-19.
The primary endpoint was a composite of hypoxemia, ED visit, hospitalization, or death. The analyses were adjusted for COVID-19 vaccination and other trial medications. Overall, the adjusted odds ratios of any primary event, compared with placebo, was 0.84 for metformin (P = .19), 1.05 for ivermectin (P = .78), and 0.94 for fluvoxamine (P = .75).
The researchers also conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of components of the primary endpoint. In this analysis, the aORs for an ED visit, hospitalization, or death was 0.58 for metformin, 1.39 for ivermectin, and 1.17 for fluvoxamine. The aORs for hospitalization or death were 0.47, 0.73, and 1.11 for metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine, respectively. No medication-related serious adverse events were reported with any of the drugs during the study period.
The possible benefit for prevention of severe COVID-19 with metformin was a prespecified secondary endpoint, and therefore not definitive until more research has been completed, the researchers said. Metformin has demonstrated anti-inflammatory actions in previous studies, and has shown protective effects against COVID-19 lung injury in animal studies.
Previous observational studies also have shown an association between metformin use and less severe COVID-19 in patients already taking metformin. “The proposed mechanisms of action against COVID-19 for metformin include anti-inflammatory and antiviral activity and the prevention of hyperglycemia during acute illness,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the population age range and focus on overweight and obese patients, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the disproportionately small percentage of Black and Latino patients and the potential lack of accuracy in identifying hypoxemia via home oxygen monitors.
However, the results demonstrate that none of the three repurposed drugs – metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine – prevented primary events or reduced symptom severity in COVID-19, compared with placebos, the researchers concluded.
“Metformin had several streams of evidence supporting its use: in vitro, in silico [computer modeled], observational, and in tissue. We were not surprised to see that it reduced emergency department visits, hospitalization, and death,” Dr. Bramante said in an interview.
The take-home message for clinicians is to continue to look to guideline committees for direction on COVID-19 treatments, but to continue to consider metformin along with other treatments, she said.
“All research should be replicated, whether the primary outcome is positive or negative,” Dr. Bramante emphasized. “In this case, when our positive outcome was negative and secondary outcome was positive, a confirmatory trial for metformin is particularly important.”
Ineffective drugs are inefficient use of resources
“The results of the COVID-OUT trial provide persuasive additional data that increase the confidence and degree of certainty that fluvoxamine and ivermectin are not effective in preventing progression to severe disease,” wrote Salim S. Abdool Karim, MB, and Nikita Devnarain, PhD, of the Centre for the AIDS Programme of Research in South Africa, Durban, in an accompanying editorial.
At the start of the study, in 2020, data on the use of the three drugs to prevent severe COVID-19 were “either unavailable or equivocal,” they said. Since then, accumulating data support the current study findings of the nonefficacy of ivermectin and fluvoxamine, and the World Health Organization has advised against their use for COVID-19, although the WHO has not provided guidance for the use of metformin.
The authors called on clinicians to stop using ivermectin and fluvoxamine to treat COVID-19 patients.
“With respect to clinical decisions about COVID-19 treatment, some drug choices, especially those that have negative [World Health Organization] recommendations, are clearly wrong,” they wrote. “In keeping with evidence-based medical practice, patients with COVID-19 must be treated with efficacious medications; they deserve nothing less.”
The study was supported by the Parsemus Foundation, Rainwater Charitable Foundation, Fast Grants, and UnitedHealth Group Foundation. The fluvoxamine placebo tablets were donated by Apotex Pharmaceuticals. The ivermectin placebo and active tablets were donated by Edenbridge Pharmaceuticals. Lead author Dr. Bramante was supported the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Abdool Karim serves as a member of the World Health Organization Science Council. Dr. Devnarain had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Neither metformin, ivermectin, or fluvoxamine had any impact on reducing disease severity, hospitalization, or death from COVID-19, according to results from more than 1,000 overweight or obese adult patients in the COVID-OUT randomized trial.
However, metformin showed some potential in a secondary analysis.
Early treatment to prevent severe disease remains a goal in managing the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, and biophysical modeling suggested that metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine may serve as antivirals to help reduce severe disease in COVID-19 patients, Carolyn T. Bramante, MD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues wrote.
“We started enrolling patients at the end of December 2020,” Dr. Bramante said in an interview. “At that time, even though vaccine data were coming out, we thought it was important to test early outpatient treatment with widely available safe medications with no interactions, because the virus would evolve and vaccine availability may be limited.”
In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers used a two-by-three factorial design to test the ability of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine to prevent severe COVID-19 infection in nonhospitalized adults aged 30-85 years. A total of 1,431 patients at six U.S. sites were enrolled within 3 days of a confirmed infection and less than 7 days after the start of symptoms, then randomized to one of six groups: metformin plus fluvoxamine; metformin plus ivermectin; metformin plus placebo; placebo plus fluvoxamine; placebo plus ivermectin; and placebo plus placebo.
A total of 1,323 patients were included in the primary analysis. The median age of the patients was 46 years, 56% were female (of whom 6% were pregnant), and all individuals met criteria for overweight or obesity. About half (52%) of the patients had been vaccinated against COVID-19.
The primary endpoint was a composite of hypoxemia, ED visit, hospitalization, or death. The analyses were adjusted for COVID-19 vaccination and other trial medications. Overall, the adjusted odds ratios of any primary event, compared with placebo, was 0.84 for metformin (P = .19), 1.05 for ivermectin (P = .78), and 0.94 for fluvoxamine (P = .75).
The researchers also conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of components of the primary endpoint. In this analysis, the aORs for an ED visit, hospitalization, or death was 0.58 for metformin, 1.39 for ivermectin, and 1.17 for fluvoxamine. The aORs for hospitalization or death were 0.47, 0.73, and 1.11 for metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine, respectively. No medication-related serious adverse events were reported with any of the drugs during the study period.
The possible benefit for prevention of severe COVID-19 with metformin was a prespecified secondary endpoint, and therefore not definitive until more research has been completed, the researchers said. Metformin has demonstrated anti-inflammatory actions in previous studies, and has shown protective effects against COVID-19 lung injury in animal studies.
Previous observational studies also have shown an association between metformin use and less severe COVID-19 in patients already taking metformin. “The proposed mechanisms of action against COVID-19 for metformin include anti-inflammatory and antiviral activity and the prevention of hyperglycemia during acute illness,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the population age range and focus on overweight and obese patients, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the disproportionately small percentage of Black and Latino patients and the potential lack of accuracy in identifying hypoxemia via home oxygen monitors.
However, the results demonstrate that none of the three repurposed drugs – metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine – prevented primary events or reduced symptom severity in COVID-19, compared with placebos, the researchers concluded.
“Metformin had several streams of evidence supporting its use: in vitro, in silico [computer modeled], observational, and in tissue. We were not surprised to see that it reduced emergency department visits, hospitalization, and death,” Dr. Bramante said in an interview.
The take-home message for clinicians is to continue to look to guideline committees for direction on COVID-19 treatments, but to continue to consider metformin along with other treatments, she said.
“All research should be replicated, whether the primary outcome is positive or negative,” Dr. Bramante emphasized. “In this case, when our positive outcome was negative and secondary outcome was positive, a confirmatory trial for metformin is particularly important.”
Ineffective drugs are inefficient use of resources
“The results of the COVID-OUT trial provide persuasive additional data that increase the confidence and degree of certainty that fluvoxamine and ivermectin are not effective in preventing progression to severe disease,” wrote Salim S. Abdool Karim, MB, and Nikita Devnarain, PhD, of the Centre for the AIDS Programme of Research in South Africa, Durban, in an accompanying editorial.
At the start of the study, in 2020, data on the use of the three drugs to prevent severe COVID-19 were “either unavailable or equivocal,” they said. Since then, accumulating data support the current study findings of the nonefficacy of ivermectin and fluvoxamine, and the World Health Organization has advised against their use for COVID-19, although the WHO has not provided guidance for the use of metformin.
The authors called on clinicians to stop using ivermectin and fluvoxamine to treat COVID-19 patients.
“With respect to clinical decisions about COVID-19 treatment, some drug choices, especially those that have negative [World Health Organization] recommendations, are clearly wrong,” they wrote. “In keeping with evidence-based medical practice, patients with COVID-19 must be treated with efficacious medications; they deserve nothing less.”
The study was supported by the Parsemus Foundation, Rainwater Charitable Foundation, Fast Grants, and UnitedHealth Group Foundation. The fluvoxamine placebo tablets were donated by Apotex Pharmaceuticals. The ivermectin placebo and active tablets were donated by Edenbridge Pharmaceuticals. Lead author Dr. Bramante was supported the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Abdool Karim serves as a member of the World Health Organization Science Council. Dr. Devnarain had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Neither metformin, ivermectin, or fluvoxamine had any impact on reducing disease severity, hospitalization, or death from COVID-19, according to results from more than 1,000 overweight or obese adult patients in the COVID-OUT randomized trial.
However, metformin showed some potential in a secondary analysis.
Early treatment to prevent severe disease remains a goal in managing the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, and biophysical modeling suggested that metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine may serve as antivirals to help reduce severe disease in COVID-19 patients, Carolyn T. Bramante, MD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues wrote.
“We started enrolling patients at the end of December 2020,” Dr. Bramante said in an interview. “At that time, even though vaccine data were coming out, we thought it was important to test early outpatient treatment with widely available safe medications with no interactions, because the virus would evolve and vaccine availability may be limited.”
In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers used a two-by-three factorial design to test the ability of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine to prevent severe COVID-19 infection in nonhospitalized adults aged 30-85 years. A total of 1,431 patients at six U.S. sites were enrolled within 3 days of a confirmed infection and less than 7 days after the start of symptoms, then randomized to one of six groups: metformin plus fluvoxamine; metformin plus ivermectin; metformin plus placebo; placebo plus fluvoxamine; placebo plus ivermectin; and placebo plus placebo.
A total of 1,323 patients were included in the primary analysis. The median age of the patients was 46 years, 56% were female (of whom 6% were pregnant), and all individuals met criteria for overweight or obesity. About half (52%) of the patients had been vaccinated against COVID-19.
The primary endpoint was a composite of hypoxemia, ED visit, hospitalization, or death. The analyses were adjusted for COVID-19 vaccination and other trial medications. Overall, the adjusted odds ratios of any primary event, compared with placebo, was 0.84 for metformin (P = .19), 1.05 for ivermectin (P = .78), and 0.94 for fluvoxamine (P = .75).
The researchers also conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of components of the primary endpoint. In this analysis, the aORs for an ED visit, hospitalization, or death was 0.58 for metformin, 1.39 for ivermectin, and 1.17 for fluvoxamine. The aORs for hospitalization or death were 0.47, 0.73, and 1.11 for metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine, respectively. No medication-related serious adverse events were reported with any of the drugs during the study period.
The possible benefit for prevention of severe COVID-19 with metformin was a prespecified secondary endpoint, and therefore not definitive until more research has been completed, the researchers said. Metformin has demonstrated anti-inflammatory actions in previous studies, and has shown protective effects against COVID-19 lung injury in animal studies.
Previous observational studies also have shown an association between metformin use and less severe COVID-19 in patients already taking metformin. “The proposed mechanisms of action against COVID-19 for metformin include anti-inflammatory and antiviral activity and the prevention of hyperglycemia during acute illness,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the population age range and focus on overweight and obese patients, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the disproportionately small percentage of Black and Latino patients and the potential lack of accuracy in identifying hypoxemia via home oxygen monitors.
However, the results demonstrate that none of the three repurposed drugs – metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine – prevented primary events or reduced symptom severity in COVID-19, compared with placebos, the researchers concluded.
“Metformin had several streams of evidence supporting its use: in vitro, in silico [computer modeled], observational, and in tissue. We were not surprised to see that it reduced emergency department visits, hospitalization, and death,” Dr. Bramante said in an interview.
The take-home message for clinicians is to continue to look to guideline committees for direction on COVID-19 treatments, but to continue to consider metformin along with other treatments, she said.
“All research should be replicated, whether the primary outcome is positive or negative,” Dr. Bramante emphasized. “In this case, when our positive outcome was negative and secondary outcome was positive, a confirmatory trial for metformin is particularly important.”
Ineffective drugs are inefficient use of resources
“The results of the COVID-OUT trial provide persuasive additional data that increase the confidence and degree of certainty that fluvoxamine and ivermectin are not effective in preventing progression to severe disease,” wrote Salim S. Abdool Karim, MB, and Nikita Devnarain, PhD, of the Centre for the AIDS Programme of Research in South Africa, Durban, in an accompanying editorial.
At the start of the study, in 2020, data on the use of the three drugs to prevent severe COVID-19 were “either unavailable or equivocal,” they said. Since then, accumulating data support the current study findings of the nonefficacy of ivermectin and fluvoxamine, and the World Health Organization has advised against their use for COVID-19, although the WHO has not provided guidance for the use of metformin.
The authors called on clinicians to stop using ivermectin and fluvoxamine to treat COVID-19 patients.
“With respect to clinical decisions about COVID-19 treatment, some drug choices, especially those that have negative [World Health Organization] recommendations, are clearly wrong,” they wrote. “In keeping with evidence-based medical practice, patients with COVID-19 must be treated with efficacious medications; they deserve nothing less.”
The study was supported by the Parsemus Foundation, Rainwater Charitable Foundation, Fast Grants, and UnitedHealth Group Foundation. The fluvoxamine placebo tablets were donated by Apotex Pharmaceuticals. The ivermectin placebo and active tablets were donated by Edenbridge Pharmaceuticals. Lead author Dr. Bramante was supported the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Abdool Karim serves as a member of the World Health Organization Science Council. Dr. Devnarain had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Pfizer seeks approval for updated COVID booster
Pfizer has sent an application to the Food and Drug Administration for emergency use authorization of its updated COVID-19 booster vaccine for the fall of 2022, the company announced on Aug. 22.
The vaccine, which is adapted for the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron variants, would be meant for ages 12 and older. If authorized by the FDA, the doses could ship as soon as September.
“Having rapidly scaled up production, we are positioned to immediately begin distribution of the bivalent Omicron BA.4/BA.5 boosters, if authorized, to help protect individuals and families as we prepare for potential fall and winter surges,” Albert Bourla, PhD, Pfizer’s chairman and CEO, said in the statement.
Earlier this year, the FDA ordered vaccine makers such as Pfizer and Moderna to update their shots to target BA.4 and BA.5, which are better at escaping immunity from earlier vaccines and previous infections.
The United States has a contract to buy 105 million of the Pfizer doses and 66 million of the Moderna doses, according to The Associated Press. Moderna is expected to file its FDA application soon as well.
The new shots target both the original spike protein on the coronavirus and the spike mutations carried by BA.4 and BA.5. For now, BA.5 is causing 89% of new infections in the United States, followed by BA.4.6 with 6.3% and BA.4 with 4.3%, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data.
There’s no way to tell if BA.5 will still be the dominant strain this winter or if new variant will replace it, the AP reported. But public health officials have supported the updated boosters as a way to target the most recent strains and increase immunity again.
On Aug. 15, Great Britain became the first country to authorize another one of Moderna’s updated vaccines, which adds protection against BA.1, or the original Omicron strain that became dominant in the winter of 2021-2022. European regulators are considering this shot, the AP reported, but the United States opted not to use this version since new Omicron variants have become dominant.
To approve the latest Pfizer shot, the FDA will rely on scientific testing of prior updates to the vaccine, rather than the newest boosters, to decide whether to fast-track the updated shots for fall, the AP reported. This method is like how flu vaccines are updated each year without large studies that take months.
Previously, Pfizer announced results from a study that found the earlier Omicron update significantly boosted antibodies capable of fighting the BA.1 variant and provided some protection against BA.4 and BA.5. The company’s latest FDA application contains that data and animal testing on the newest booster, the AP reported.
Pfizer will start a trial using the BA.4/BA.5 booster in coming weeks to get more data on how well the latest shot works. Moderna has begun a similar study.
The full results from these studies won’t be available before a fall booster campaign, which is why the FDA and public health officials have called for an updated shot to be ready for distribution in September.
“It’s clear that none of these vaccines are going to completely prevent infection,” Rachel Presti, MD, a researcher with the Moderna trial and an infectious diseases specialist at Washington University in St. Louis, told the AP.
But previous studies of variant booster candidates have shown that “you still get a broader immune response giving a variant booster than giving the same booster,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Pfizer has sent an application to the Food and Drug Administration for emergency use authorization of its updated COVID-19 booster vaccine for the fall of 2022, the company announced on Aug. 22.
The vaccine, which is adapted for the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron variants, would be meant for ages 12 and older. If authorized by the FDA, the doses could ship as soon as September.
“Having rapidly scaled up production, we are positioned to immediately begin distribution of the bivalent Omicron BA.4/BA.5 boosters, if authorized, to help protect individuals and families as we prepare for potential fall and winter surges,” Albert Bourla, PhD, Pfizer’s chairman and CEO, said in the statement.
Earlier this year, the FDA ordered vaccine makers such as Pfizer and Moderna to update their shots to target BA.4 and BA.5, which are better at escaping immunity from earlier vaccines and previous infections.
The United States has a contract to buy 105 million of the Pfizer doses and 66 million of the Moderna doses, according to The Associated Press. Moderna is expected to file its FDA application soon as well.
The new shots target both the original spike protein on the coronavirus and the spike mutations carried by BA.4 and BA.5. For now, BA.5 is causing 89% of new infections in the United States, followed by BA.4.6 with 6.3% and BA.4 with 4.3%, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data.
There’s no way to tell if BA.5 will still be the dominant strain this winter or if new variant will replace it, the AP reported. But public health officials have supported the updated boosters as a way to target the most recent strains and increase immunity again.
On Aug. 15, Great Britain became the first country to authorize another one of Moderna’s updated vaccines, which adds protection against BA.1, or the original Omicron strain that became dominant in the winter of 2021-2022. European regulators are considering this shot, the AP reported, but the United States opted not to use this version since new Omicron variants have become dominant.
To approve the latest Pfizer shot, the FDA will rely on scientific testing of prior updates to the vaccine, rather than the newest boosters, to decide whether to fast-track the updated shots for fall, the AP reported. This method is like how flu vaccines are updated each year without large studies that take months.
Previously, Pfizer announced results from a study that found the earlier Omicron update significantly boosted antibodies capable of fighting the BA.1 variant and provided some protection against BA.4 and BA.5. The company’s latest FDA application contains that data and animal testing on the newest booster, the AP reported.
Pfizer will start a trial using the BA.4/BA.5 booster in coming weeks to get more data on how well the latest shot works. Moderna has begun a similar study.
The full results from these studies won’t be available before a fall booster campaign, which is why the FDA and public health officials have called for an updated shot to be ready for distribution in September.
“It’s clear that none of these vaccines are going to completely prevent infection,” Rachel Presti, MD, a researcher with the Moderna trial and an infectious diseases specialist at Washington University in St. Louis, told the AP.
But previous studies of variant booster candidates have shown that “you still get a broader immune response giving a variant booster than giving the same booster,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Pfizer has sent an application to the Food and Drug Administration for emergency use authorization of its updated COVID-19 booster vaccine for the fall of 2022, the company announced on Aug. 22.
The vaccine, which is adapted for the BA.4 and BA.5 Omicron variants, would be meant for ages 12 and older. If authorized by the FDA, the doses could ship as soon as September.
“Having rapidly scaled up production, we are positioned to immediately begin distribution of the bivalent Omicron BA.4/BA.5 boosters, if authorized, to help protect individuals and families as we prepare for potential fall and winter surges,” Albert Bourla, PhD, Pfizer’s chairman and CEO, said in the statement.
Earlier this year, the FDA ordered vaccine makers such as Pfizer and Moderna to update their shots to target BA.4 and BA.5, which are better at escaping immunity from earlier vaccines and previous infections.
The United States has a contract to buy 105 million of the Pfizer doses and 66 million of the Moderna doses, according to The Associated Press. Moderna is expected to file its FDA application soon as well.
The new shots target both the original spike protein on the coronavirus and the spike mutations carried by BA.4 and BA.5. For now, BA.5 is causing 89% of new infections in the United States, followed by BA.4.6 with 6.3% and BA.4 with 4.3%, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data.
There’s no way to tell if BA.5 will still be the dominant strain this winter or if new variant will replace it, the AP reported. But public health officials have supported the updated boosters as a way to target the most recent strains and increase immunity again.
On Aug. 15, Great Britain became the first country to authorize another one of Moderna’s updated vaccines, which adds protection against BA.1, or the original Omicron strain that became dominant in the winter of 2021-2022. European regulators are considering this shot, the AP reported, but the United States opted not to use this version since new Omicron variants have become dominant.
To approve the latest Pfizer shot, the FDA will rely on scientific testing of prior updates to the vaccine, rather than the newest boosters, to decide whether to fast-track the updated shots for fall, the AP reported. This method is like how flu vaccines are updated each year without large studies that take months.
Previously, Pfizer announced results from a study that found the earlier Omicron update significantly boosted antibodies capable of fighting the BA.1 variant and provided some protection against BA.4 and BA.5. The company’s latest FDA application contains that data and animal testing on the newest booster, the AP reported.
Pfizer will start a trial using the BA.4/BA.5 booster in coming weeks to get more data on how well the latest shot works. Moderna has begun a similar study.
The full results from these studies won’t be available before a fall booster campaign, which is why the FDA and public health officials have called for an updated shot to be ready for distribution in September.
“It’s clear that none of these vaccines are going to completely prevent infection,” Rachel Presti, MD, a researcher with the Moderna trial and an infectious diseases specialist at Washington University in St. Louis, told the AP.
But previous studies of variant booster candidates have shown that “you still get a broader immune response giving a variant booster than giving the same booster,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: New cases fall again, ED rates rebound for some
The 7-day average percentage of ED visits with diagnosed COVID, which had reached a post-Omicron high of 3.5% in late July for those aged 12-15, began to fall and was down to 3.0% on Aug. 12. That trend reversed, however, and the rate was up to 3.6% on Aug. 19, the last date for which data are available from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.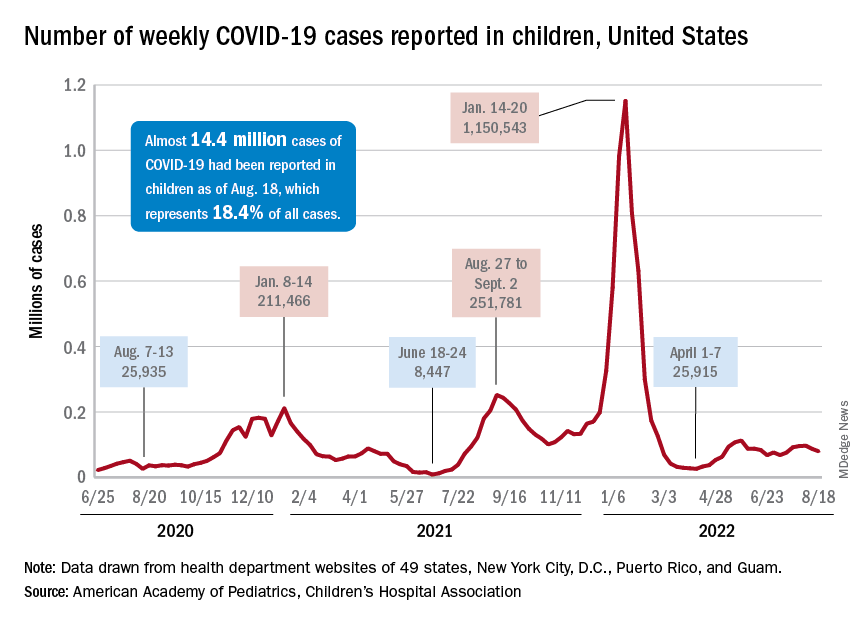
That change of COVID fortunes cannot yet be seen for all children. The 7-day average ED visit rate for those aged 0-11 years peaked at 6.8% during the last week of July and has continued to fall, dropping from 5.7% on Aug. 12 to 5.1% on Aug. 19. Children aged 16-17 years seem to be taking a middle path: Their ED-visit rate declined from late July into mid-August but held steady over the last week, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
There is a hint of the same trend regarding new admissions among children aged 0-17 years. The national rate, which had declined in recent weeks, ticked up from 0.42 to 0.43 new admissions per 100,000 population over the last week of available data, the CDC said.
Weekly cases fall below 80,000
New cases in general were down by 8.5% from the previous week, dropping from 87,902 for the week of Aug. 5-11 to 79,525 for Aug. 12-18. That marked the second straight week with fewer cases after a 4-week period that saw weekly totals increase from almost 68,000 to nearly 97,000, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP and CHA put the cumulative number of child COVID-19 cases at just under 14.4 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of cases among all ages. The CDC estimates that there have been almost 14.7 million cases in children aged 0-17 years, as well as 1,750 deaths, of which 14 were reported in the last week (Aug. 16-22).
The CDC age subgroups indicate that children aged 0-4 years have experienced fewer cases (2.9 million) than children aged 5-11 years (5.6 million cases) and 12-15 (3.0 million cases) but more deaths: 548 so far, versus 432 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 437 for 12- to 15-year-olds, the COVID Data Tracker shows. Those aged 0-4 make up 6% of the total U.S. population, compared with 8.7% and 5.1%, respectively, for the older children.
Most younger children still not vaccinated
Although it may not qualify as a big push to vaccinate children before the start of the new school year, first-time vaccinations did rise somewhat in late July and August for children aged 5-17 years. Among children younger than 5 years, though, initial doses of the vaccine fell during the second full week of August, especially in 2- to 4-year-olds, based on the CDC data.
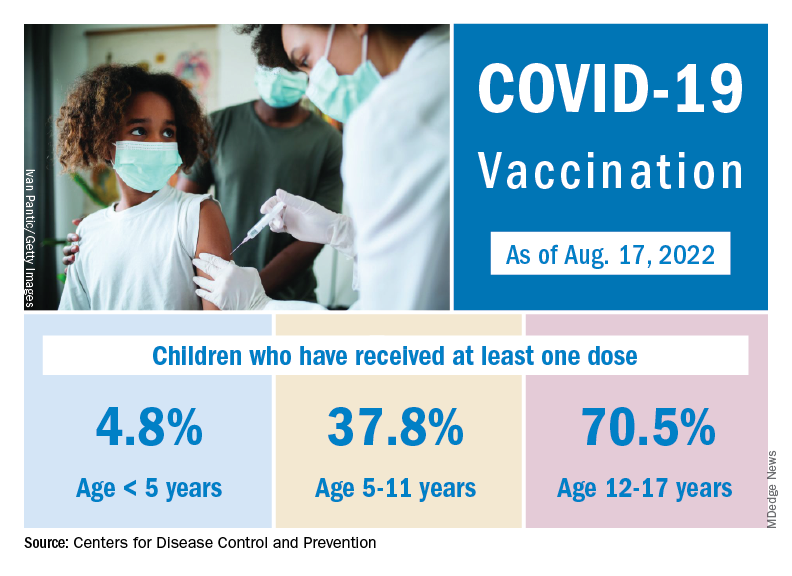
Through almost 2 months of vaccine eligibility, 4.8% of children under age 5 have received at least one dose and 0.9% are fully vaccinated as of Aug. 17. The current rates are 37.8% (one dose) and 30.4% (completed) for those aged 5-11 and 70.5% and 60.3% for 12- to 17-year-olds.
The 7-day average percentage of ED visits with diagnosed COVID, which had reached a post-Omicron high of 3.5% in late July for those aged 12-15, began to fall and was down to 3.0% on Aug. 12. That trend reversed, however, and the rate was up to 3.6% on Aug. 19, the last date for which data are available from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That change of COVID fortunes cannot yet be seen for all children. The 7-day average ED visit rate for those aged 0-11 years peaked at 6.8% during the last week of July and has continued to fall, dropping from 5.7% on Aug. 12 to 5.1% on Aug. 19. Children aged 16-17 years seem to be taking a middle path: Their ED-visit rate declined from late July into mid-August but held steady over the last week, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
There is a hint of the same trend regarding new admissions among children aged 0-17 years. The national rate, which had declined in recent weeks, ticked up from 0.42 to 0.43 new admissions per 100,000 population over the last week of available data, the CDC said.
Weekly cases fall below 80,000
New cases in general were down by 8.5% from the previous week, dropping from 87,902 for the week of Aug. 5-11 to 79,525 for Aug. 12-18. That marked the second straight week with fewer cases after a 4-week period that saw weekly totals increase from almost 68,000 to nearly 97,000, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP and CHA put the cumulative number of child COVID-19 cases at just under 14.4 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of cases among all ages. The CDC estimates that there have been almost 14.7 million cases in children aged 0-17 years, as well as 1,750 deaths, of which 14 were reported in the last week (Aug. 16-22).
The CDC age subgroups indicate that children aged 0-4 years have experienced fewer cases (2.9 million) than children aged 5-11 years (5.6 million cases) and 12-15 (3.0 million cases) but more deaths: 548 so far, versus 432 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 437 for 12- to 15-year-olds, the COVID Data Tracker shows. Those aged 0-4 make up 6% of the total U.S. population, compared with 8.7% and 5.1%, respectively, for the older children.
Most younger children still not vaccinated
Although it may not qualify as a big push to vaccinate children before the start of the new school year, first-time vaccinations did rise somewhat in late July and August for children aged 5-17 years. Among children younger than 5 years, though, initial doses of the vaccine fell during the second full week of August, especially in 2- to 4-year-olds, based on the CDC data.

Through almost 2 months of vaccine eligibility, 4.8% of children under age 5 have received at least one dose and 0.9% are fully vaccinated as of Aug. 17. The current rates are 37.8% (one dose) and 30.4% (completed) for those aged 5-11 and 70.5% and 60.3% for 12- to 17-year-olds.
The 7-day average percentage of ED visits with diagnosed COVID, which had reached a post-Omicron high of 3.5% in late July for those aged 12-15, began to fall and was down to 3.0% on Aug. 12. That trend reversed, however, and the rate was up to 3.6% on Aug. 19, the last date for which data are available from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That change of COVID fortunes cannot yet be seen for all children. The 7-day average ED visit rate for those aged 0-11 years peaked at 6.8% during the last week of July and has continued to fall, dropping from 5.7% on Aug. 12 to 5.1% on Aug. 19. Children aged 16-17 years seem to be taking a middle path: Their ED-visit rate declined from late July into mid-August but held steady over the last week, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
There is a hint of the same trend regarding new admissions among children aged 0-17 years. The national rate, which had declined in recent weeks, ticked up from 0.42 to 0.43 new admissions per 100,000 population over the last week of available data, the CDC said.
Weekly cases fall below 80,000
New cases in general were down by 8.5% from the previous week, dropping from 87,902 for the week of Aug. 5-11 to 79,525 for Aug. 12-18. That marked the second straight week with fewer cases after a 4-week period that saw weekly totals increase from almost 68,000 to nearly 97,000, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP and CHA put the cumulative number of child COVID-19 cases at just under 14.4 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of cases among all ages. The CDC estimates that there have been almost 14.7 million cases in children aged 0-17 years, as well as 1,750 deaths, of which 14 were reported in the last week (Aug. 16-22).
The CDC age subgroups indicate that children aged 0-4 years have experienced fewer cases (2.9 million) than children aged 5-11 years (5.6 million cases) and 12-15 (3.0 million cases) but more deaths: 548 so far, versus 432 for 5- to 11-year-olds and 437 for 12- to 15-year-olds, the COVID Data Tracker shows. Those aged 0-4 make up 6% of the total U.S. population, compared with 8.7% and 5.1%, respectively, for the older children.
Most younger children still not vaccinated
Although it may not qualify as a big push to vaccinate children before the start of the new school year, first-time vaccinations did rise somewhat in late July and August for children aged 5-17 years. Among children younger than 5 years, though, initial doses of the vaccine fell during the second full week of August, especially in 2- to 4-year-olds, based on the CDC data.

Through almost 2 months of vaccine eligibility, 4.8% of children under age 5 have received at least one dose and 0.9% are fully vaccinated as of Aug. 17. The current rates are 37.8% (one dose) and 30.4% (completed) for those aged 5-11 and 70.5% and 60.3% for 12- to 17-year-olds.
Regular physical activity may fight infection, illness from COVID: Study
New research suggests that regular physical activity can help lower the risk of COVID-19 infection and its severity, with a weekly tally of 150 minutes of moderate, or 75 minutes of vigorous, physical activity affording the best protection.
“, with potential benefits to reduce the risk of severe COVID-19,” say Antonio García-Hermoso, PhD, Public University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, and colleagues.
“Regular physical activity seemed to be related to a lower risk of COVID-19 infection, Dr. García-Hermoso said in an interview. “There is evidence that regular physical activity might contribute to a more effective immune response, providing enhanced protective immunity to infections, which could explain the relationship between exercise consistency with COVID-19 infection.”
Regular exercise may also help to boost the body’s anti-inflammatory responses, as well as cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, all of which may explain its beneficial effects on COVID-19 severity, the researchers say.
The study was published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Strong protection from COVID?
A growing body of evidence suggests that increased physical activity may modulate the course of COVID-19 infection and reduce the risk of poor outcomes. The new analysis is the first to systematically evaluate and pool data on the effect of regular physical activity on COVID-19 outcomes.
The findings are based on data from 16 studies with over 1.8 million adults (53% women, mean age 53 years).
Individuals who included regular physical activity in their weekly routine had an 11% lower risk for infection with SARS-CoV-2 (hazard ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-0.95), compared with inactive peers.
The physically active adults also had a 36% (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.54-0.76) lower risk of being hospitalized, a 44% (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.58-0.77) lower risk for severe COVID-19 illness, and a 43% (HR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.46-0.71) lower risk of dying from COVID-19 than their inactive peers.
The greatest protective effect occurs with achieving at least 500 metabolic equivalent of task (MET) minutes per week of physical activity – equivalent to 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 min of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week – with no added benefit beyond this level.
The researchers caution that the analysis included observational studies, differing study designs, subjective assessments of physical activity levels, and concerned only the Beta and Delta variants of SARS-CoV-2, not Omicron.
Despite these limitations, the researchers say their findings “may help guide physicians and health care policymakers in making recommendations and developing guidelines with respect to the degree of physical activity that can help reduce the risk of infectivity, hospitalization, severity, and mortality of COVID-19 at both the individual and the population level, especially in high-risk patients.”
Helpful, but not a panacea
Reached for comment, Sean Heffron, MD, a preventive cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health, New York, said the study “supports the well-established nonlinear association of increasing physical activity with adverse outcomes from a diverse array of diseases, including infectious diseases, such as COVID-19.”
The observation is not particularly surprising, he said.
“It is as I would suspect. They compiled data from a large number of studies published over the past several years that all had consistent findings,” Dr. Heffron said.
“The take-away from a public health standpoint is that being physically active improves health in myriad ways. That being said, it is not a panacea, so additional measures (masking, vaccinations, etc.) are important for everyone,” he said.
Also weighing in, Joseph Herrera, DO, chair of the department of rehabilitation for Mount Sinai Health System, New York, said, “If you are physically fit, your body is more resilient and better prepared to handle the stressors of COVID or any other disease process.”
For now, however, the question of whether physical fitness is actually protective against COVID remains unclear. “I’m just not sure right now,” Dr. Herrera said in an interview.
He said he has treated athletes in professional sports – including the National Football League and Major League Baseball – and some of them have had long COVID and have not returned to play. “These are athletes at the peak of fitness and their career.”
Nonetheless, Dr. Herrera said a good public health message in general is to stay fit or get fit.
“That’s something I preach all the time,” he told this news organization.
Dr. García-Hermoso agreed. “In contrast to the vast majority of drugs, exercise is free of adverse effects. It’s time to consider exercise as medicine. It’s never too late to start being physically active.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. García-Hermoso, Dr. Heffron, and Dr. Herrera have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research suggests that regular physical activity can help lower the risk of COVID-19 infection and its severity, with a weekly tally of 150 minutes of moderate, or 75 minutes of vigorous, physical activity affording the best protection.
“, with potential benefits to reduce the risk of severe COVID-19,” say Antonio García-Hermoso, PhD, Public University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, and colleagues.
“Regular physical activity seemed to be related to a lower risk of COVID-19 infection, Dr. García-Hermoso said in an interview. “There is evidence that regular physical activity might contribute to a more effective immune response, providing enhanced protective immunity to infections, which could explain the relationship between exercise consistency with COVID-19 infection.”
Regular exercise may also help to boost the body’s anti-inflammatory responses, as well as cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, all of which may explain its beneficial effects on COVID-19 severity, the researchers say.
The study was published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Strong protection from COVID?
A growing body of evidence suggests that increased physical activity may modulate the course of COVID-19 infection and reduce the risk of poor outcomes. The new analysis is the first to systematically evaluate and pool data on the effect of regular physical activity on COVID-19 outcomes.
The findings are based on data from 16 studies with over 1.8 million adults (53% women, mean age 53 years).
Individuals who included regular physical activity in their weekly routine had an 11% lower risk for infection with SARS-CoV-2 (hazard ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-0.95), compared with inactive peers.
The physically active adults also had a 36% (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.54-0.76) lower risk of being hospitalized, a 44% (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.58-0.77) lower risk for severe COVID-19 illness, and a 43% (HR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.46-0.71) lower risk of dying from COVID-19 than their inactive peers.
The greatest protective effect occurs with achieving at least 500 metabolic equivalent of task (MET) minutes per week of physical activity – equivalent to 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 min of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week – with no added benefit beyond this level.
The researchers caution that the analysis included observational studies, differing study designs, subjective assessments of physical activity levels, and concerned only the Beta and Delta variants of SARS-CoV-2, not Omicron.
Despite these limitations, the researchers say their findings “may help guide physicians and health care policymakers in making recommendations and developing guidelines with respect to the degree of physical activity that can help reduce the risk of infectivity, hospitalization, severity, and mortality of COVID-19 at both the individual and the population level, especially in high-risk patients.”
Helpful, but not a panacea
Reached for comment, Sean Heffron, MD, a preventive cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health, New York, said the study “supports the well-established nonlinear association of increasing physical activity with adverse outcomes from a diverse array of diseases, including infectious diseases, such as COVID-19.”
The observation is not particularly surprising, he said.
“It is as I would suspect. They compiled data from a large number of studies published over the past several years that all had consistent findings,” Dr. Heffron said.
“The take-away from a public health standpoint is that being physically active improves health in myriad ways. That being said, it is not a panacea, so additional measures (masking, vaccinations, etc.) are important for everyone,” he said.
Also weighing in, Joseph Herrera, DO, chair of the department of rehabilitation for Mount Sinai Health System, New York, said, “If you are physically fit, your body is more resilient and better prepared to handle the stressors of COVID or any other disease process.”
For now, however, the question of whether physical fitness is actually protective against COVID remains unclear. “I’m just not sure right now,” Dr. Herrera said in an interview.
He said he has treated athletes in professional sports – including the National Football League and Major League Baseball – and some of them have had long COVID and have not returned to play. “These are athletes at the peak of fitness and their career.”
Nonetheless, Dr. Herrera said a good public health message in general is to stay fit or get fit.
“That’s something I preach all the time,” he told this news organization.
Dr. García-Hermoso agreed. “In contrast to the vast majority of drugs, exercise is free of adverse effects. It’s time to consider exercise as medicine. It’s never too late to start being physically active.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. García-Hermoso, Dr. Heffron, and Dr. Herrera have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research suggests that regular physical activity can help lower the risk of COVID-19 infection and its severity, with a weekly tally of 150 minutes of moderate, or 75 minutes of vigorous, physical activity affording the best protection.
“, with potential benefits to reduce the risk of severe COVID-19,” say Antonio García-Hermoso, PhD, Public University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, and colleagues.
“Regular physical activity seemed to be related to a lower risk of COVID-19 infection, Dr. García-Hermoso said in an interview. “There is evidence that regular physical activity might contribute to a more effective immune response, providing enhanced protective immunity to infections, which could explain the relationship between exercise consistency with COVID-19 infection.”
Regular exercise may also help to boost the body’s anti-inflammatory responses, as well as cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, all of which may explain its beneficial effects on COVID-19 severity, the researchers say.
The study was published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Strong protection from COVID?
A growing body of evidence suggests that increased physical activity may modulate the course of COVID-19 infection and reduce the risk of poor outcomes. The new analysis is the first to systematically evaluate and pool data on the effect of regular physical activity on COVID-19 outcomes.
The findings are based on data from 16 studies with over 1.8 million adults (53% women, mean age 53 years).
Individuals who included regular physical activity in their weekly routine had an 11% lower risk for infection with SARS-CoV-2 (hazard ratio, 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-0.95), compared with inactive peers.
The physically active adults also had a 36% (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.54-0.76) lower risk of being hospitalized, a 44% (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.58-0.77) lower risk for severe COVID-19 illness, and a 43% (HR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.46-0.71) lower risk of dying from COVID-19 than their inactive peers.
The greatest protective effect occurs with achieving at least 500 metabolic equivalent of task (MET) minutes per week of physical activity – equivalent to 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 min of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week – with no added benefit beyond this level.
The researchers caution that the analysis included observational studies, differing study designs, subjective assessments of physical activity levels, and concerned only the Beta and Delta variants of SARS-CoV-2, not Omicron.
Despite these limitations, the researchers say their findings “may help guide physicians and health care policymakers in making recommendations and developing guidelines with respect to the degree of physical activity that can help reduce the risk of infectivity, hospitalization, severity, and mortality of COVID-19 at both the individual and the population level, especially in high-risk patients.”
Helpful, but not a panacea
Reached for comment, Sean Heffron, MD, a preventive cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health, New York, said the study “supports the well-established nonlinear association of increasing physical activity with adverse outcomes from a diverse array of diseases, including infectious diseases, such as COVID-19.”
The observation is not particularly surprising, he said.
“It is as I would suspect. They compiled data from a large number of studies published over the past several years that all had consistent findings,” Dr. Heffron said.
“The take-away from a public health standpoint is that being physically active improves health in myriad ways. That being said, it is not a panacea, so additional measures (masking, vaccinations, etc.) are important for everyone,” he said.
Also weighing in, Joseph Herrera, DO, chair of the department of rehabilitation for Mount Sinai Health System, New York, said, “If you are physically fit, your body is more resilient and better prepared to handle the stressors of COVID or any other disease process.”
For now, however, the question of whether physical fitness is actually protective against COVID remains unclear. “I’m just not sure right now,” Dr. Herrera said in an interview.
He said he has treated athletes in professional sports – including the National Football League and Major League Baseball – and some of them have had long COVID and have not returned to play. “These are athletes at the peak of fitness and their career.”
Nonetheless, Dr. Herrera said a good public health message in general is to stay fit or get fit.
“That’s something I preach all the time,” he told this news organization.
Dr. García-Hermoso agreed. “In contrast to the vast majority of drugs, exercise is free of adverse effects. It’s time to consider exercise as medicine. It’s never too late to start being physically active.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. García-Hermoso, Dr. Heffron, and Dr. Herrera have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BRITISH JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE
Guidelines on GLP1RAs and continuous glucose monitors are among biggest news in diabetes
glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1RAs) and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology. I am hoping my discussion about these major advances in this edition of Highlights will be helpful to those caring for patients with diabetes.
Tirzepatide
The first GLP1RA, exenatide, was released in April 2005. Since then, numerous daily and weekly drugs of this class have been developed. We’ve learned they are effective glucose lowering drugs, and the weekly agents dulaglutide and semaglutide have shown impressive weight reduction properties as well as cardiovascular benefits.
Secondary outcomes have also shown renal benefits to these agents, and studies for primary renal efficacy are pending. Due to all of these properties, the GLP1RAs are recommended as the first injectable for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, prior to insulin initiation.1
The next generation of these agents are a combination of a GLP1RA and a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon secretion, delays gastric emptying, and has central effects inducing satiety.
We now understand that GIP is the main incretin hormone in those without diabetes, causative of most of the incretin effects. But the insulin response after GIP secretion in type 2 diabetes is strongly reduced. It is now appreciated that this poor effect of GIP can be reduced when used in combination with a GLP1RA. This combination incretin, called by some a “twincretin,” is the basis for the drug tirzepatide which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in May of 2022.
The data supporting this agent for both diabetes and obesity are impressive. For example, in a 40-week study with a baseline HbA1c of 8.0%, those randomized to tirzepatide at 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg had HbA1c reductions of 1.87%, 1.89%, and 2.07% respectively.2 Over 81% at all doses had HbA1c levels less than 6.5% at 40 weeks.
For the 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg doses, weight change from baseline was 7.9%, 9.3%, and 11.0% respectively. Like older GLP1RAs, gastrointestinal side effects were the main problem. For the three doses, 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, had to stop the drug, compared with the 3% who stopped taking the placebo. In another study, tirzepatide was noninferior or superior at all three doses compared with semaglutide 1 mg weekly.3
In a population without diabetes, with 40% of patients having prediabetes, weight loss percentages for the three doses were 15.0%, 19.5%, and 20.9% respectively.4 Discontinuation percentages due to side effects were 4%-7%. The exciting part is we now have a drug that approaches weight loss from bariatric surgery. The cardiovascular and renal outcome trials are now underway, but the enthusiasm for this drug is clear from the data.
Like other GLP1RAs, the key is to start low and go slowly. It is recommended to start tirzepatide at 2.5 mg four times a week, then increase to 5 mg. Due to gastrointestinal side effects, some patients will do better at the lower dose before increasing. For those switching from another GLP1RA, there are no data to guide us but, in my practice, I start those patients at 5 mg weekly.
Continuous glucose monitoring
Data continue to accumulate that this form of glycemic self-monitoring is effective to reduce HbA1c levels and minimize hypoglycemia in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The most important change to the 2022 American Diabetes Association (ADA) standards of care is recognizing CGM as level A evidence for those receiving basal insulin without mealtime insulin.5 There are four CGMs on the market, but most of the market uses the Dexcom G6 or the Libre 2. Both of these devices will be updated within the next few months to newer generation sensors.
While there are similarities and differences between the two devices, by late 2022 and early 2023 changes to both will reduce the dissimilarities.
The next generation Libre (Libre 3) will be continuous, and “scanning” will no longer be required. For those unable to get insurance to cover CGM, the Libre will continue to be more affordable than the Dexcom. Alerts will be present on both, but the Dexcom G7 will be approved for both the arm and the abdomen. The Dexcom also can communicate with several automated insulin delivery systems and data can be shared real-time with family members.
For clinicians just starting patients on this technology, my suggestion is to focus on one system so both the provider and staff can become familiar with it. It is key to review downloaded glucose metrics, in addition to the “ambulatory glucose profile,” a graphic overview of daily glycemia where patterns can be identified. It is also helpful to ask for assistance from endocrinologists who have experience with CGMs, in addition to the representatives of the companies.
COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes
From the beginning of the COVID 19 pandemic in 2020, it was clear that stress hyperglycemia and glucose dysregulation was an important observation for those infected. What was not known at the time is that for some, the hyperglycemia continued, and permanent diabetes ensued.
In one study of over 2.7 million U.S. veterans, men infected with COVID-19, but not women, were at a higher risk of new incident diabetes at 120 days after infection compared to no infection (odds ratio for men = 2.56).6
Another literature review using meta-analyses and cross-sectional studies concluded new-onset diabetes following COVID-19 infection can have a varied phenotype, with no risk factors, presenting from diabetic ketoacidosis to milder forms of diabetes.7
The current thought is that COVID-19 binds to the ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors which appear to be located on the beta-cells in the islet, resulting in insulin deficiency, in addition to the insulin resistance that seems to persist after the acute infection. Much more needs to be learned about this, but clinicians need to appreciate this appears to be a new form of diabetes and optimal treatments are not yet clear.
Dr. Hirsch is an endocrinologist, professor of medicine, and diabetes treatment and teaching chair at the University of Washington, Seattle. He has received research grant support from Dexcom and Insulet and has provided consulting to Abbott, Roche, Lifescan, and GWave. You can contact him at [email protected].
References
1. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S125-S143.
2. Rosenstock J et al. Efficacy and safety of a novel GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398:143-55.
3. Frias JP et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:503-15.
4. Jastreboff AM et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:205-16.
5. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes technology: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes–2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S97-S112.
6. Wander PL et al. The incidence of diabetes in 2,777,768 veterans with and without recent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Diabetes Care 2022;45:782-8.
7. Joshi SC and Pozzilli P. COVID-19 induced diabetes: A novel presentation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022 Aug 6;191:110034.
glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1RAs) and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology. I am hoping my discussion about these major advances in this edition of Highlights will be helpful to those caring for patients with diabetes.
Tirzepatide
The first GLP1RA, exenatide, was released in April 2005. Since then, numerous daily and weekly drugs of this class have been developed. We’ve learned they are effective glucose lowering drugs, and the weekly agents dulaglutide and semaglutide have shown impressive weight reduction properties as well as cardiovascular benefits.
Secondary outcomes have also shown renal benefits to these agents, and studies for primary renal efficacy are pending. Due to all of these properties, the GLP1RAs are recommended as the first injectable for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, prior to insulin initiation.1
The next generation of these agents are a combination of a GLP1RA and a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon secretion, delays gastric emptying, and has central effects inducing satiety.
We now understand that GIP is the main incretin hormone in those without diabetes, causative of most of the incretin effects. But the insulin response after GIP secretion in type 2 diabetes is strongly reduced. It is now appreciated that this poor effect of GIP can be reduced when used in combination with a GLP1RA. This combination incretin, called by some a “twincretin,” is the basis for the drug tirzepatide which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in May of 2022.
The data supporting this agent for both diabetes and obesity are impressive. For example, in a 40-week study with a baseline HbA1c of 8.0%, those randomized to tirzepatide at 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg had HbA1c reductions of 1.87%, 1.89%, and 2.07% respectively.2 Over 81% at all doses had HbA1c levels less than 6.5% at 40 weeks.
For the 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg doses, weight change from baseline was 7.9%, 9.3%, and 11.0% respectively. Like older GLP1RAs, gastrointestinal side effects were the main problem. For the three doses, 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, had to stop the drug, compared with the 3% who stopped taking the placebo. In another study, tirzepatide was noninferior or superior at all three doses compared with semaglutide 1 mg weekly.3
In a population without diabetes, with 40% of patients having prediabetes, weight loss percentages for the three doses were 15.0%, 19.5%, and 20.9% respectively.4 Discontinuation percentages due to side effects were 4%-7%. The exciting part is we now have a drug that approaches weight loss from bariatric surgery. The cardiovascular and renal outcome trials are now underway, but the enthusiasm for this drug is clear from the data.
Like other GLP1RAs, the key is to start low and go slowly. It is recommended to start tirzepatide at 2.5 mg four times a week, then increase to 5 mg. Due to gastrointestinal side effects, some patients will do better at the lower dose before increasing. For those switching from another GLP1RA, there are no data to guide us but, in my practice, I start those patients at 5 mg weekly.
Continuous glucose monitoring
Data continue to accumulate that this form of glycemic self-monitoring is effective to reduce HbA1c levels and minimize hypoglycemia in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The most important change to the 2022 American Diabetes Association (ADA) standards of care is recognizing CGM as level A evidence for those receiving basal insulin without mealtime insulin.5 There are four CGMs on the market, but most of the market uses the Dexcom G6 or the Libre 2. Both of these devices will be updated within the next few months to newer generation sensors.
While there are similarities and differences between the two devices, by late 2022 and early 2023 changes to both will reduce the dissimilarities.
The next generation Libre (Libre 3) will be continuous, and “scanning” will no longer be required. For those unable to get insurance to cover CGM, the Libre will continue to be more affordable than the Dexcom. Alerts will be present on both, but the Dexcom G7 will be approved for both the arm and the abdomen. The Dexcom also can communicate with several automated insulin delivery systems and data can be shared real-time with family members.
For clinicians just starting patients on this technology, my suggestion is to focus on one system so both the provider and staff can become familiar with it. It is key to review downloaded glucose metrics, in addition to the “ambulatory glucose profile,” a graphic overview of daily glycemia where patterns can be identified. It is also helpful to ask for assistance from endocrinologists who have experience with CGMs, in addition to the representatives of the companies.
COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes
From the beginning of the COVID 19 pandemic in 2020, it was clear that stress hyperglycemia and glucose dysregulation was an important observation for those infected. What was not known at the time is that for some, the hyperglycemia continued, and permanent diabetes ensued.
In one study of over 2.7 million U.S. veterans, men infected with COVID-19, but not women, were at a higher risk of new incident diabetes at 120 days after infection compared to no infection (odds ratio for men = 2.56).6
Another literature review using meta-analyses and cross-sectional studies concluded new-onset diabetes following COVID-19 infection can have a varied phenotype, with no risk factors, presenting from diabetic ketoacidosis to milder forms of diabetes.7
The current thought is that COVID-19 binds to the ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors which appear to be located on the beta-cells in the islet, resulting in insulin deficiency, in addition to the insulin resistance that seems to persist after the acute infection. Much more needs to be learned about this, but clinicians need to appreciate this appears to be a new form of diabetes and optimal treatments are not yet clear.
Dr. Hirsch is an endocrinologist, professor of medicine, and diabetes treatment and teaching chair at the University of Washington, Seattle. He has received research grant support from Dexcom and Insulet and has provided consulting to Abbott, Roche, Lifescan, and GWave. You can contact him at [email protected].
References
1. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S125-S143.
2. Rosenstock J et al. Efficacy and safety of a novel GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398:143-55.
3. Frias JP et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:503-15.
4. Jastreboff AM et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:205-16.
5. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes technology: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes–2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S97-S112.
6. Wander PL et al. The incidence of diabetes in 2,777,768 veterans with and without recent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Diabetes Care 2022;45:782-8.
7. Joshi SC and Pozzilli P. COVID-19 induced diabetes: A novel presentation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022 Aug 6;191:110034.
glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1RAs) and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology. I am hoping my discussion about these major advances in this edition of Highlights will be helpful to those caring for patients with diabetes.
Tirzepatide
The first GLP1RA, exenatide, was released in April 2005. Since then, numerous daily and weekly drugs of this class have been developed. We’ve learned they are effective glucose lowering drugs, and the weekly agents dulaglutide and semaglutide have shown impressive weight reduction properties as well as cardiovascular benefits.
Secondary outcomes have also shown renal benefits to these agents, and studies for primary renal efficacy are pending. Due to all of these properties, the GLP1RAs are recommended as the first injectable for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, prior to insulin initiation.1
The next generation of these agents are a combination of a GLP1RA and a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon secretion, delays gastric emptying, and has central effects inducing satiety.
We now understand that GIP is the main incretin hormone in those without diabetes, causative of most of the incretin effects. But the insulin response after GIP secretion in type 2 diabetes is strongly reduced. It is now appreciated that this poor effect of GIP can be reduced when used in combination with a GLP1RA. This combination incretin, called by some a “twincretin,” is the basis for the drug tirzepatide which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in May of 2022.
The data supporting this agent for both diabetes and obesity are impressive. For example, in a 40-week study with a baseline HbA1c of 8.0%, those randomized to tirzepatide at 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg had HbA1c reductions of 1.87%, 1.89%, and 2.07% respectively.2 Over 81% at all doses had HbA1c levels less than 6.5% at 40 weeks.
For the 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg doses, weight change from baseline was 7.9%, 9.3%, and 11.0% respectively. Like older GLP1RAs, gastrointestinal side effects were the main problem. For the three doses, 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, had to stop the drug, compared with the 3% who stopped taking the placebo. In another study, tirzepatide was noninferior or superior at all three doses compared with semaglutide 1 mg weekly.3
In a population without diabetes, with 40% of patients having prediabetes, weight loss percentages for the three doses were 15.0%, 19.5%, and 20.9% respectively.4 Discontinuation percentages due to side effects were 4%-7%. The exciting part is we now have a drug that approaches weight loss from bariatric surgery. The cardiovascular and renal outcome trials are now underway, but the enthusiasm for this drug is clear from the data.
Like other GLP1RAs, the key is to start low and go slowly. It is recommended to start tirzepatide at 2.5 mg four times a week, then increase to 5 mg. Due to gastrointestinal side effects, some patients will do better at the lower dose before increasing. For those switching from another GLP1RA, there are no data to guide us but, in my practice, I start those patients at 5 mg weekly.
Continuous glucose monitoring
Data continue to accumulate that this form of glycemic self-monitoring is effective to reduce HbA1c levels and minimize hypoglycemia in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The most important change to the 2022 American Diabetes Association (ADA) standards of care is recognizing CGM as level A evidence for those receiving basal insulin without mealtime insulin.5 There are four CGMs on the market, but most of the market uses the Dexcom G6 or the Libre 2. Both of these devices will be updated within the next few months to newer generation sensors.
While there are similarities and differences between the two devices, by late 2022 and early 2023 changes to both will reduce the dissimilarities.
The next generation Libre (Libre 3) will be continuous, and “scanning” will no longer be required. For those unable to get insurance to cover CGM, the Libre will continue to be more affordable than the Dexcom. Alerts will be present on both, but the Dexcom G7 will be approved for both the arm and the abdomen. The Dexcom also can communicate with several automated insulin delivery systems and data can be shared real-time with family members.
For clinicians just starting patients on this technology, my suggestion is to focus on one system so both the provider and staff can become familiar with it. It is key to review downloaded glucose metrics, in addition to the “ambulatory glucose profile,” a graphic overview of daily glycemia where patterns can be identified. It is also helpful to ask for assistance from endocrinologists who have experience with CGMs, in addition to the representatives of the companies.
COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes
From the beginning of the COVID 19 pandemic in 2020, it was clear that stress hyperglycemia and glucose dysregulation was an important observation for those infected. What was not known at the time is that for some, the hyperglycemia continued, and permanent diabetes ensued.
In one study of over 2.7 million U.S. veterans, men infected with COVID-19, but not women, were at a higher risk of new incident diabetes at 120 days after infection compared to no infection (odds ratio for men = 2.56).6
Another literature review using meta-analyses and cross-sectional studies concluded new-onset diabetes following COVID-19 infection can have a varied phenotype, with no risk factors, presenting from diabetic ketoacidosis to milder forms of diabetes.7
The current thought is that COVID-19 binds to the ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors which appear to be located on the beta-cells in the islet, resulting in insulin deficiency, in addition to the insulin resistance that seems to persist after the acute infection. Much more needs to be learned about this, but clinicians need to appreciate this appears to be a new form of diabetes and optimal treatments are not yet clear.
Dr. Hirsch is an endocrinologist, professor of medicine, and diabetes treatment and teaching chair at the University of Washington, Seattle. He has received research grant support from Dexcom and Insulet and has provided consulting to Abbott, Roche, Lifescan, and GWave. You can contact him at [email protected].
References
1. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S125-S143.
2. Rosenstock J et al. Efficacy and safety of a novel GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398:143-55.
3. Frias JP et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:503-15.
4. Jastreboff AM et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:205-16.
5. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Diabetes technology: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes–2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S97-S112.
6. Wander PL et al. The incidence of diabetes in 2,777,768 veterans with and without recent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Diabetes Care 2022;45:782-8.
7. Joshi SC and Pozzilli P. COVID-19 induced diabetes: A novel presentation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022 Aug 6;191:110034.
Is it COVID or long COVID? Your organs may know
There’s little doubt long COVID is real. The federal government recognizes long COVID as a condition and said in two reports issued in August that one in five adult COVID-19 survivors have a health condition related to their illness.
COVID-19 can damage multiple organs in the body. Sometimes this damage leads to long COVID; sometimes other reasons are at play. Doctors are beginning to sort it out.
“COVID itself can actually cause prolonged illness, and we don’t really call that long COVID,” said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, a doctor at UCLA Health in Los Angeles. But if symptoms extend beyond 12 weeks, that puts patients in the realm of long COVID.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and can keep people from resuming their normal lives and jobs. Sometimes they last for months, according to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
Multiorgan damage
Lung scarring and other lung problems are common after COVID, said Leora Horwitz, MD, an internal medicine specialist at New York University. Even after a mild case, people can have breathing issues for months, a team at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, said in an online briefing. One study published in the journal Radiology found damage in people a full year after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Some people have persistent heart, kidney, liver, and nervous system problems after COVID-19. A study published in 2020 in JAMA Cardiology found 60% of people who had COVID-19 had ongoing signs of heart inflammation. Nearly a third of people hospitalized for COVID-19 get kidney damage that can become chronic, and some end up needing dialysis or a transplant, said C. John Sperati, MD, a kidney specialist at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
This might be, in part, because SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, directly infects the cells in many organs.
Nicole Bhave, MD, a cardiologist at University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor is concerned that COVID-19 appears to increase the risk of heart problems in some people.
“Some of the uptick may just be recognition bias, in that people with symptoms are seeking care,” she said. “But there’s definitely a biological basis by which COVID could tip people over into a new diagnosis of heart failure.”
Inflammation
Inflammation is probably a key part of the long-term effects of COVID-19.
Some people have a serious immune reaction to COVID-19 called a cytokine storm, said Nitra Aggarwal Gilotra, MD, a cardiologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine. This release of inflammation-causing molecules called cytokines is meant to attack the invading virus. But it can be so severe that it wreaks havoc on healthy tissues and organs and causes lasting damage – if patients even survive it.
In some people, inflammation can affect the heart, causing myocarditis. Myocarditis symptoms include chest pain, breathlessness, and heart palpitations. Though rare, it can be serious and can raise the risk of other heart problems, including heart failure, down the line.
Long COVID may also trigger an autoimmune condition, said Eline Luning Prak, MD, PhD, a pathologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Long COVID can share many hallmark symptoms with autoimmune diseases, including fatigue, widespread pain, memory problems, and mood disorders.
Blood clots
Studies have shown the overcharged inflammatory response to COVID-19 can cause blood clots. This sometimes overwhelming clotting was an early hallmark of COVID-19 infection, and when clots restrict blood flow in the brain, lungs, kidneys, or limbs, they can cause long-term damage. Some can be deadly. Researchers in Sweden found patients were at risk of deep vein thrombosis – a blood clot usually in the leg – up to 3 months after infection and at higher risk of a blood clot in the lung, called pulmonary embolism, for as long as 3 months.
Viral reservoirs
The virus itself may also linger in a patient’s body, causing continued symptoms and, potentially, new flare-ups. Zoe Swank, PhD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues reported in a preprint study that they found pieces of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the blood of most patients with long COVID symptoms they tested – some as long as a year after infection. The study has not yet been peer reviewed.
Another team found evidence of the virus in stool up to 7 months later, which suggests the virus hides out in the gut. Other early studies have found bits of viral RNA in the appendix, breast tissue, heart, eyes, and brain.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a risk factor for getting severe COVID-19, and multiple studies have shown people can get diabetes both while battling infection and afterward. One study of veterans, published in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, found COVID-19 survivors were about 40% more likely to get diabetes over the next year.
There are a few ways this might happen. Insulin-producing cells in the pancreas have SARS-CoV-2 receptors – a type of molecular doorway the coronavirus can attach to. Damage to these cells could make the body less able to produce insulin, which in turn can lead to diabetes. The virus could also disrupt the balance in the body or cause inflammation that leads to insulin resistance, which can develop into diabetes, Ziad Al-Aly, MD, of the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System, and colleagues wrote.
Nervous system issues
People who get COVID-19 are also more vulnerable to postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). This affects what’s known as the autonomic nervous system, which regulates blood circulation, and includes those things that happen in your body without your having to think about them, like breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. POTS can cause common long COVID neurologic symptoms, including headaches, fatigue, brain fog, insomnia, and problems thinking and concentrating. “This was a known condition prior to COVID, but it was incredibly rare,” said Dr. Viswanathan. “After COVID, I’ve seen it with increasing frequency.”
Long-term outlook
Lasting issues after COVID-19 are much more likely after a moderate or severe infection. Still, plenty of people are battling them even after a mild illness. “As for why, that’s the billion-dollar question,” said Dr. Horwitz. “It’s well known that viral infections can cause long-term dysregulation. Why that is, we really just don’t know.”
Whether it’s virus hiding out in the body, long-term organ damage, or an autoimmune reaction likely differs from person to person. “I’m believing, increasingly, that it’s a combination of all of these, just based on how different patients are responding to different medications,” said Dr. Viswanathan. “One patient will respond to something beautifully, and another patient won’t at all.”
But it’s clear a significant number of people are facing long-term health struggles because of COVID-19, which has infected at least 580 million people globally and 92 million – likely many more – in the United States, according to Johns Hopkins University.
Even a small increased risk of conditions like heart disease or diabetes translates to a huge number of people, Dr. Horwitz said. “If even 1% of people getting COVID have long-term symptoms, that’s a major public health crisis, because that’s 1% of pretty much everybody in the country.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
There’s little doubt long COVID is real. The federal government recognizes long COVID as a condition and said in two reports issued in August that one in five adult COVID-19 survivors have a health condition related to their illness.
COVID-19 can damage multiple organs in the body. Sometimes this damage leads to long COVID; sometimes other reasons are at play. Doctors are beginning to sort it out.
“COVID itself can actually cause prolonged illness, and we don’t really call that long COVID,” said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, a doctor at UCLA Health in Los Angeles. But if symptoms extend beyond 12 weeks, that puts patients in the realm of long COVID.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and can keep people from resuming their normal lives and jobs. Sometimes they last for months, according to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
Multiorgan damage
Lung scarring and other lung problems are common after COVID, said Leora Horwitz, MD, an internal medicine specialist at New York University. Even after a mild case, people can have breathing issues for months, a team at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, said in an online briefing. One study published in the journal Radiology found damage in people a full year after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Some people have persistent heart, kidney, liver, and nervous system problems after COVID-19. A study published in 2020 in JAMA Cardiology found 60% of people who had COVID-19 had ongoing signs of heart inflammation. Nearly a third of people hospitalized for COVID-19 get kidney damage that can become chronic, and some end up needing dialysis or a transplant, said C. John Sperati, MD, a kidney specialist at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
This might be, in part, because SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, directly infects the cells in many organs.
Nicole Bhave, MD, a cardiologist at University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor is concerned that COVID-19 appears to increase the risk of heart problems in some people.
“Some of the uptick may just be recognition bias, in that people with symptoms are seeking care,” she said. “But there’s definitely a biological basis by which COVID could tip people over into a new diagnosis of heart failure.”
Inflammation
Inflammation is probably a key part of the long-term effects of COVID-19.
Some people have a serious immune reaction to COVID-19 called a cytokine storm, said Nitra Aggarwal Gilotra, MD, a cardiologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine. This release of inflammation-causing molecules called cytokines is meant to attack the invading virus. But it can be so severe that it wreaks havoc on healthy tissues and organs and causes lasting damage – if patients even survive it.
In some people, inflammation can affect the heart, causing myocarditis. Myocarditis symptoms include chest pain, breathlessness, and heart palpitations. Though rare, it can be serious and can raise the risk of other heart problems, including heart failure, down the line.
Long COVID may also trigger an autoimmune condition, said Eline Luning Prak, MD, PhD, a pathologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Long COVID can share many hallmark symptoms with autoimmune diseases, including fatigue, widespread pain, memory problems, and mood disorders.
Blood clots
Studies have shown the overcharged inflammatory response to COVID-19 can cause blood clots. This sometimes overwhelming clotting was an early hallmark of COVID-19 infection, and when clots restrict blood flow in the brain, lungs, kidneys, or limbs, they can cause long-term damage. Some can be deadly. Researchers in Sweden found patients were at risk of deep vein thrombosis – a blood clot usually in the leg – up to 3 months after infection and at higher risk of a blood clot in the lung, called pulmonary embolism, for as long as 3 months.
Viral reservoirs
The virus itself may also linger in a patient’s body, causing continued symptoms and, potentially, new flare-ups. Zoe Swank, PhD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues reported in a preprint study that they found pieces of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the blood of most patients with long COVID symptoms they tested – some as long as a year after infection. The study has not yet been peer reviewed.
Another team found evidence of the virus in stool up to 7 months later, which suggests the virus hides out in the gut. Other early studies have found bits of viral RNA in the appendix, breast tissue, heart, eyes, and brain.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a risk factor for getting severe COVID-19, and multiple studies have shown people can get diabetes both while battling infection and afterward. One study of veterans, published in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, found COVID-19 survivors were about 40% more likely to get diabetes over the next year.
There are a few ways this might happen. Insulin-producing cells in the pancreas have SARS-CoV-2 receptors – a type of molecular doorway the coronavirus can attach to. Damage to these cells could make the body less able to produce insulin, which in turn can lead to diabetes. The virus could also disrupt the balance in the body or cause inflammation that leads to insulin resistance, which can develop into diabetes, Ziad Al-Aly, MD, of the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System, and colleagues wrote.
Nervous system issues
People who get COVID-19 are also more vulnerable to postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). This affects what’s known as the autonomic nervous system, which regulates blood circulation, and includes those things that happen in your body without your having to think about them, like breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. POTS can cause common long COVID neurologic symptoms, including headaches, fatigue, brain fog, insomnia, and problems thinking and concentrating. “This was a known condition prior to COVID, but it was incredibly rare,” said Dr. Viswanathan. “After COVID, I’ve seen it with increasing frequency.”
Long-term outlook
Lasting issues after COVID-19 are much more likely after a moderate or severe infection. Still, plenty of people are battling them even after a mild illness. “As for why, that’s the billion-dollar question,” said Dr. Horwitz. “It’s well known that viral infections can cause long-term dysregulation. Why that is, we really just don’t know.”
Whether it’s virus hiding out in the body, long-term organ damage, or an autoimmune reaction likely differs from person to person. “I’m believing, increasingly, that it’s a combination of all of these, just based on how different patients are responding to different medications,” said Dr. Viswanathan. “One patient will respond to something beautifully, and another patient won’t at all.”
But it’s clear a significant number of people are facing long-term health struggles because of COVID-19, which has infected at least 580 million people globally and 92 million – likely many more – in the United States, according to Johns Hopkins University.
Even a small increased risk of conditions like heart disease or diabetes translates to a huge number of people, Dr. Horwitz said. “If even 1% of people getting COVID have long-term symptoms, that’s a major public health crisis, because that’s 1% of pretty much everybody in the country.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
There’s little doubt long COVID is real. The federal government recognizes long COVID as a condition and said in two reports issued in August that one in five adult COVID-19 survivors have a health condition related to their illness.
COVID-19 can damage multiple organs in the body. Sometimes this damage leads to long COVID; sometimes other reasons are at play. Doctors are beginning to sort it out.
“COVID itself can actually cause prolonged illness, and we don’t really call that long COVID,” said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, a doctor at UCLA Health in Los Angeles. But if symptoms extend beyond 12 weeks, that puts patients in the realm of long COVID.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and can keep people from resuming their normal lives and jobs. Sometimes they last for months, according to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
Multiorgan damage
Lung scarring and other lung problems are common after COVID, said Leora Horwitz, MD, an internal medicine specialist at New York University. Even after a mild case, people can have breathing issues for months, a team at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, said in an online briefing. One study published in the journal Radiology found damage in people a full year after a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Some people have persistent heart, kidney, liver, and nervous system problems after COVID-19. A study published in 2020 in JAMA Cardiology found 60% of people who had COVID-19 had ongoing signs of heart inflammation. Nearly a third of people hospitalized for COVID-19 get kidney damage that can become chronic, and some end up needing dialysis or a transplant, said C. John Sperati, MD, a kidney specialist at Johns Hopkins Medicine.
This might be, in part, because SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, directly infects the cells in many organs.
Nicole Bhave, MD, a cardiologist at University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor is concerned that COVID-19 appears to increase the risk of heart problems in some people.
“Some of the uptick may just be recognition bias, in that people with symptoms are seeking care,” she said. “But there’s definitely a biological basis by which COVID could tip people over into a new diagnosis of heart failure.”
Inflammation
Inflammation is probably a key part of the long-term effects of COVID-19.
Some people have a serious immune reaction to COVID-19 called a cytokine storm, said Nitra Aggarwal Gilotra, MD, a cardiologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine. This release of inflammation-causing molecules called cytokines is meant to attack the invading virus. But it can be so severe that it wreaks havoc on healthy tissues and organs and causes lasting damage – if patients even survive it.
In some people, inflammation can affect the heart, causing myocarditis. Myocarditis symptoms include chest pain, breathlessness, and heart palpitations. Though rare, it can be serious and can raise the risk of other heart problems, including heart failure, down the line.
Long COVID may also trigger an autoimmune condition, said Eline Luning Prak, MD, PhD, a pathologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Long COVID can share many hallmark symptoms with autoimmune diseases, including fatigue, widespread pain, memory problems, and mood disorders.
Blood clots
Studies have shown the overcharged inflammatory response to COVID-19 can cause blood clots. This sometimes overwhelming clotting was an early hallmark of COVID-19 infection, and when clots restrict blood flow in the brain, lungs, kidneys, or limbs, they can cause long-term damage. Some can be deadly. Researchers in Sweden found patients were at risk of deep vein thrombosis – a blood clot usually in the leg – up to 3 months after infection and at higher risk of a blood clot in the lung, called pulmonary embolism, for as long as 3 months.
Viral reservoirs
The virus itself may also linger in a patient’s body, causing continued symptoms and, potentially, new flare-ups. Zoe Swank, PhD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues reported in a preprint study that they found pieces of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the blood of most patients with long COVID symptoms they tested – some as long as a year after infection. The study has not yet been peer reviewed.
Another team found evidence of the virus in stool up to 7 months later, which suggests the virus hides out in the gut. Other early studies have found bits of viral RNA in the appendix, breast tissue, heart, eyes, and brain.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a risk factor for getting severe COVID-19, and multiple studies have shown people can get diabetes both while battling infection and afterward. One study of veterans, published in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, found COVID-19 survivors were about 40% more likely to get diabetes over the next year.
There are a few ways this might happen. Insulin-producing cells in the pancreas have SARS-CoV-2 receptors – a type of molecular doorway the coronavirus can attach to. Damage to these cells could make the body less able to produce insulin, which in turn can lead to diabetes. The virus could also disrupt the balance in the body or cause inflammation that leads to insulin resistance, which can develop into diabetes, Ziad Al-Aly, MD, of the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System, and colleagues wrote.
Nervous system issues
People who get COVID-19 are also more vulnerable to postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). This affects what’s known as the autonomic nervous system, which regulates blood circulation, and includes those things that happen in your body without your having to think about them, like breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. POTS can cause common long COVID neurologic symptoms, including headaches, fatigue, brain fog, insomnia, and problems thinking and concentrating. “This was a known condition prior to COVID, but it was incredibly rare,” said Dr. Viswanathan. “After COVID, I’ve seen it with increasing frequency.”
Long-term outlook
Lasting issues after COVID-19 are much more likely after a moderate or severe infection. Still, plenty of people are battling them even after a mild illness. “As for why, that’s the billion-dollar question,” said Dr. Horwitz. “It’s well known that viral infections can cause long-term dysregulation. Why that is, we really just don’t know.”
Whether it’s virus hiding out in the body, long-term organ damage, or an autoimmune reaction likely differs from person to person. “I’m believing, increasingly, that it’s a combination of all of these, just based on how different patients are responding to different medications,” said Dr. Viswanathan. “One patient will respond to something beautifully, and another patient won’t at all.”
But it’s clear a significant number of people are facing long-term health struggles because of COVID-19, which has infected at least 580 million people globally and 92 million – likely many more – in the United States, according to Johns Hopkins University.
Even a small increased risk of conditions like heart disease or diabetes translates to a huge number of people, Dr. Horwitz said. “If even 1% of people getting COVID have long-term symptoms, that’s a major public health crisis, because that’s 1% of pretty much everybody in the country.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with Omicron don’t know they’re infected
Most people with Omicron likely don’t know it.
That’s according to a study in JAMA Network Open, which says 56% of people who have the Omicron variant of the coronavirus are unaware of their infection.
And it has an upside and a downside, depending on how you look at it, according to Time magazine.
“It’s good news, in some ways, since ) in vaccinated people,” Time says. “The downside is that many people are likely spreading the virus unintentionally.”
The study looked at 210 hospital patients and employees in the Los Angeles area. More than half who tested positive didn’t know it – because they had no symptoms, or they assumed they merely had a cold or allergies.
“The findings support early data from around the world suggesting that throughout the pandemic, anywhere from 25% to 40% of SARS-CoV-2 infections have been asymptomatic, which presents challenges for public health officials trying to control the spread of the virus,” Time reports.
The study found that awareness of infection rose after at-home tests became available this year. About three-quarters of people in January and February didn’t know their status, for example.
“Findings of this study suggest that low rates of Omicron variant infection awareness may be a key contributor to rapid transmission of the virus within communities,” the authors wrote. “Given that unawareness of active infection precludes self-initiated interventions, such as testing and self-isolation, even modest levels of undiagnosed infection can contribute to substantial population-level transmission.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with Omicron likely don’t know it.
That’s according to a study in JAMA Network Open, which says 56% of people who have the Omicron variant of the coronavirus are unaware of their infection.
And it has an upside and a downside, depending on how you look at it, according to Time magazine.
“It’s good news, in some ways, since ) in vaccinated people,” Time says. “The downside is that many people are likely spreading the virus unintentionally.”
The study looked at 210 hospital patients and employees in the Los Angeles area. More than half who tested positive didn’t know it – because they had no symptoms, or they assumed they merely had a cold or allergies.
“The findings support early data from around the world suggesting that throughout the pandemic, anywhere from 25% to 40% of SARS-CoV-2 infections have been asymptomatic, which presents challenges for public health officials trying to control the spread of the virus,” Time reports.
The study found that awareness of infection rose after at-home tests became available this year. About three-quarters of people in January and February didn’t know their status, for example.
“Findings of this study suggest that low rates of Omicron variant infection awareness may be a key contributor to rapid transmission of the virus within communities,” the authors wrote. “Given that unawareness of active infection precludes self-initiated interventions, such as testing and self-isolation, even modest levels of undiagnosed infection can contribute to substantial population-level transmission.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with Omicron likely don’t know it.
That’s according to a study in JAMA Network Open, which says 56% of people who have the Omicron variant of the coronavirus are unaware of their infection.
And it has an upside and a downside, depending on how you look at it, according to Time magazine.
“It’s good news, in some ways, since ) in vaccinated people,” Time says. “The downside is that many people are likely spreading the virus unintentionally.”
The study looked at 210 hospital patients and employees in the Los Angeles area. More than half who tested positive didn’t know it – because they had no symptoms, or they assumed they merely had a cold or allergies.
“The findings support early data from around the world suggesting that throughout the pandemic, anywhere from 25% to 40% of SARS-CoV-2 infections have been asymptomatic, which presents challenges for public health officials trying to control the spread of the virus,” Time reports.
The study found that awareness of infection rose after at-home tests became available this year. About three-quarters of people in January and February didn’t know their status, for example.
“Findings of this study suggest that low rates of Omicron variant infection awareness may be a key contributor to rapid transmission of the virus within communities,” the authors wrote. “Given that unawareness of active infection precludes self-initiated interventions, such as testing and self-isolation, even modest levels of undiagnosed infection can contribute to substantial population-level transmission.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
‘Medical Methuselahs’: Treating the growing population of centenarians
For about the past year, Priya Goel, MD, can be seen cruising around the island of Manhattan as she makes her way between visits to some of New York City’s most treasured residents: a small but essential group of patients born before the Empire State Building scraped the sky and the old Yankee Stadium had become the House That Ruth Built.
– the oldest is a 108-year-old man – whom she visits monthly.
The gray wave
Dr. Goel’s charges are among America’s latest baby boom – babies born a century ago, that is.
Between 1980 and 2019, the share of American centenarians, those aged 100 and up, grew faster than the total population. In 2019, 100,322 persons in the United States were at least 100 years old – more than triple the 1980 figure of 32,194, according to the U.S. Administration on Aging. By 2060, experts predict, the U.S. centenarian population will reach nearly 600,000.
Although some of the ultra-aged live in nursing homes, many continue to live independently. They require both routine and acute medical care. So, what does it take to be a physician for a centenarian?
Dr. Goel, who is in her mid-30s and could well be the great-granddaughter of some of her patients, urged her colleagues not to stereotype patients on the basis of age.
“You have to consider their functional and cognitive abilities, their ability to understand disease processes and make decisions for themselves,” Dr. Goel said. “Age is just one factor in the grand scheme of things.”
Visiting patients in their homes provides her with insights into how well they’re doing, including the safety of their environments and the depth of their social networks.
New York City has its peculiar demands. Heal provides Dr. Goel with a driver who chauffeurs her to her patient visits. She takes notes between stops.
“The idea is to have these patients remain in an environment where they’re comfortable, in surroundings where they’ve grown up or lived for many years,” she said. “A lot of them are in elevator buildings and they are wheelchair-bound or bed-bound and they physically can’t leave.”
She said she gets a far different view of the patient than does an office-based physician.
“When you go into their home, it’s very personal. You’re seeing what their daily environment is like, what their diet is like. You can see their food on the counter. You can see the level of hygiene,” Dr. Goel said. “You get to see their social support. Are their kids involved? Are they hoarding? Stuff that they wouldn’t just necessarily disclose but on a visit you get to see going into the home. It’s an extra layer of understanding that patient.”
Dr. Goel contrasted home care from care in a nursing home, where the patients are seen daily. On the basis of her observations, she decides whether to see her patients every month or every 3 months.
She applies this strategy to everyone from age 60 to over 100.
Tracking a growing group
Since 1995, geriatrician Thomas Perls, MD, has directed the New England Centenarian Study at Boston University. The study, largely funded by the National Institute on Aging, has enrolled 2,599 centenarian persons and 700 of their offspring. At any given time in the study, about 10% of the centenarians are alive. The study has a high mortality rate.
The people in Dr. Perls’s study range in age, but they top out at 119, the third oldest person ever in the world. Most centenarians are women.
“When we first began the study in 1995, the prevalence of centenarians in the United States was about 1 per 10,000 in the population,” Perls told this news organization. “And now, that prevalence has doubled to 1 per 5,000.”
Even if no one has achieved the record of Methuselah, the Biblical patriarch who was purported to have lived to the age of 969, some people always have lived into their 90s and beyond. Dr. Perls attributed the increase in longevity to control at the turn of the 20th century of typhoid fever, diphtheria, and other infectious diseases with effective public health measures, including the availability of clean water and improvement in socioeconomic conditions.
“Infant mortality just plummeted. So, come around 1915, 1920, we were no longer losing a quarter of our population to these diseases. That meant a quarter more of the population could age into adulthood and middle age,” he said. “A certain component of that group was, therefore, able to continue to age to a very, very old age.”
Other advances, such as antibiotics and vaccinations in the 1960s; the availability in the 1970s of much better detection and effective treatment of high blood pressure; the recognition of the harms of smoking; and much more effective treatment of cardiovascular disease and cancer have allowed many people who would have otherwise died in their 70s and 80s to live much longer. “I think what this means is that there is a substantial proportion of the population that has the biology to get to 100,” Dr. Perls said.
Perls said the Latino population and Blacks have a better track record than Whites in reaching the 100-year milestone. “The average life expectancy might be lower in these populations because of socioeconomic factors, but if they are able to get to around their early 80s, compared to Whites, their ability to get to 100 is actually better,” he said.
Asians fare best when it comes to longevity. While around 1% of White women in the United States live to 100, 10% of Asian women in Hong Kong hit that mark.
“I think some of that is better environment and health habits in Hong Kong than in the United States,” Dr. Perls said. “I think another piece may be a genetic advantage in East Asians. We’re looking into that.”
Dr. Perls said he agreed with Dr. Goel that health care providers and the lay public should not make assumptions on the basis of age alone as to how a person is doing. “People can age so very differently from one another,” he said.
Up to about age 90, the vast majority of those differences are determined by our health behaviors, such as smoking, alcohol use, exercise, sleep, the effect of our diets on weight, and access to good health care, including regular screening for problems such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and cancer. “People who are able to do everything right generally add healthy years to their lives, while those who do not have shorter life expectancies and longer periods of chronic diseases,” Dr. Perls said.
Paying diligent attention to these behaviors over the long run can have a huge payoff.
Dr. Perls’s team has found that to live beyond age 90 and on into the early 100s, protective genes can play a strong role. These genes help slow aging and decrease one’s risk for aging-related diseases. Centenarians usually have a history of aging very slowly and greatly delaying aging-related diseases and disability toward the ends of their lives.
Centenarians are the antithesis of the misguided belief that the older you get, the sicker you get. Quite the opposite occurs. For Dr. Perls, “the older you get, the healthier you’ve been.”
MD bias against the elderly?
Care of elderly patients is becoming essential in the practice of primary care physicians – but not all of them enjoy the work.
To be effective, physicians who treat centenarians must get a better idea of the individual patient’s functional status and comorbidities. “You absolutely cannot make assumptions on age alone,” Dr. Perls said.
The so-called “normal” temperature, 98.6° F, can spell trouble for centenarians and other very old patients, warned Natalie Baker, DNP, CRNP, an associate professor of nursing at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and president of the 3,000-member Gerontological Advanced Practice Nurses Association.
“We have to be very cognizant of what we call a typical presentation of disease or illness and that a very subtle change in an older adult can signal a serious infection or illness,” Dr. Baker said. “If your patient has a high fever, that is a potential problem.”
The average temperature of an older adult is lower than the accepted 98.6° F, and their body’s response to an infection is slow to exhibit an increase in temperature, Dr. Baker said. “When treating centenarians, clinicians must be cognizant of other subtle signs of infection, such as decreased appetite or change in mentation,” she cautioned.
A decline in appetite or insomnia may be a subtle sign that these patients need to be evaluated, she added.
COVID-19 and centenarians
Three-quarters of the 1 million U.S. deaths from COVID-19 occurred in people aged 65 and older. However, Dr. Perls said centenarians may be a special subpopulation when it comes to COVID.
The Japanese Health Ministry, which follows the large centenarian population in that country, noted a marked jump in the number of centenarians during the pandemic – although the reasons for the increase aren’t clear.
Centenarians may be a bit different. Dr. Perls said some evidence suggests that the over-100 crowd may have better immune systems than younger people. “Part of the trick of getting to 100 is having a pretty good immune system,” he said.
Don’t mess with success
“There is no need at that point for us to try to alter their diet to what we think it might be,” Dr. Baker said. “There’s no need to start with diabetic education. They may tell you their secret is a shot of vodka every day. Why should we stop it at that age? Accept their lifestyles, because they’ve done something right to get to that age.”
Opinions differ on how to approach screening for centenarians.
Dr. Goel said guidelines for routine screening, such as colonoscopies, mammograms, and PAP smears, drop off for patients starting at 75. Dr. Perls said this strategy stems from the belief that people will die from other things first, so screening is no longer needed. Dr. Perls said he disagrees with this approach.
“Again, we can’t base our screening and health care decisions on age alone. If I have an independently functioning and robust 95-year-old man in my office, you can be sure I am going to continue recommending regular screening for colon cancer and other screenings that are normal for people who are 30 years younger,” he said.
Justin Zaghi, MD, chief medical officer at Heal, said screening patients in their late 90s and 100s for cancer generally doesn’t make sense except in some rare circumstances in which the cancer would be unlikely to be a cause of death. “However, if we are talking about screening for fall risks, hearing difficulties, poor vision, pain, and malnutrition, those screenings still absolutely make sense for patients in their late 90s and 100s,” Dr. Zaghi said.
One high-functioning 104-year-old patient of Dr. Perls underwent a total hip replacement for a hip fracture and is faring well. “Obviously, if she had end-stage dementia, we’d do everything to keep the person comfortable, or if they had medical problems that made surgery too high risk, then you don’t do it,” he said. “But if they’re otherwise, I would proceed.”
Avoid the ED
Dr. Goel said doctors should avoid sending patients to the emergency department, an often chaotic place that is especially unfriendly to centenarians and the very old. “Sometimes I’ve seen older patients who are being rushed to the ER, and I ask, What are the goals of care?” she said.
Clinicians caring for seniors should keep in mind that infections can cause seniors to appear confused – and this may lead the clinician to think the patient has dementia. Or, Dr. Goel said, a patient with dementia may suddenly experience much worse dementia.
“In either case, you want to make sure you’re not dealing with any underlying infection, like urinary tract infection, or pneumonia brewing, or skin infections,” she said. “Their skin is so much frailer. You want to make sure there are no bedsores.”
She has had patients whose children report that their usually placid centenarian parents are suddenly acting out. “We’ll do a urinary test and it definitely shows a urinary tract infection. You want to make sure you’re not missing out on something else before you attribute it to dementia,” she said.
Environmental changes, such as moving a patient to a new room in a hospital setting, can trigger an acute mental status change, such as delirium, she added. Helping older patients feel in control as much as possible is important.
“You want to make sure you’re orienting them to the time of day. Make sure they get up at the same time, go to bed at the same time, have clocks and calendars present – just making sure that they feel like they’re still in control of their body and their day,” she said.
Physicians should be aware of potential depression in these patients, whose experience of loss – an unavoidable consequence of outliving family and friends – can result in problems with sleep and diet, as well as a sense of social isolation.
Neal Flomenbaum, MD, professor and emergency physician-in-chief emeritus, New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York, said sometimes the best thing for these very elderly patients is to “get them in and out of ED as quickly as possible, and do what you can diagnostically.”
He noted that EDs have been making accommodations to serve the elderly, such as using LEDs that replicate outdoor lighting conditions, as well as providing seniors with separate rooms with glass doors to protect them from noise, separate air handlers to prevent infections, and adequate space for visitors.
These patients often are subject to trauma from falls.
“The bones don’t heal as well as in younger people, and treating their comorbidities is essential. Once they have trouble with one area and they’re lying in bed and can’t move much, they can get bedsores,” Dr. Flomenbaum said. “In the hospital, they are vulnerable to infections. So, you’re thinking of all of these things at the same time and how to treat them appropriately and then get them out of the hospital as soon as possible with whatever care that they need in their own homes if at all possible.”
“I always err on the side of less is more,” Dr. Goel said. “Obviously, if there is something – if they have a cough, they need an x-ray. That’s very basic. We want to take care of that. Give them the antibiotic if they need that. But rushing them in and out of the hospital doesn’t add to their quality of life.”
Dr. Flomenbaum, a pioneer in geriatric emergency medicine, says physicians need to be aware that centenarians and other very old patients don’t present the same way as younger adults.
He began to notice more than 20 years ago that every night, patients would turn up in his ED who were in their late 90s into their 100s. Some would come in with what their children identified as sudden-onset dementia – they didn’t know their own names and couldn’t identify their kids. They didn’t know the time or day. Dr. Flomenbaum said the children often asked whether their parents should enter a nursing home.
“And I’d say, ‘Not so fast. Well, let’s take a look at this.’ You don’t develop that kind of dementia overnight. It usually takes a while,” he said.
He said he ordered complete blood cell counts and oxygen saturation tests that frequently turned out to be abnormal. They didn’t have a fever, and infiltrates initially weren’t seen on chest x-rays.
With rehydration and supplemental oxygen, their symptoms started to improve, and it became obvious that the symptoms were not of dementia but of pneumonia, and that they required antibiotics, Dr. Flomenbaum said.
Dementia dilemma
Too often, on the basis of age, doctors assume patients have dementia or other cognitive impairments.
“What a shock and a surprise when doctors actually talk to folks and do a neurocognitive screen and find they’re just fine,” Dr. Perls said.
The decline in hearing and vision can lead to a misdiagnosis of cognitive impairment because the patients are not able to hear what you’re asking them. “It’s really important that the person can hear you – whether you use an amplifying device or they have hearing aids, that’s critical,” he said. “You just have to be a good doctor.”
Often the physical toll of aging exacerbates social difficulties. Poor hearing, for example, can accelerate cognitive impairment and cause people to interact less often, and less meaningfully, with their environment. For some, wearing hearing aids seems demeaning – until they hear what they’ve been missing.
“I get them to wear their hearing aids and, lo and behold, they’re a whole new person because they’re now able to take in their environment and interact with others,” Dr. Perls said.
Dr. Flomenbaum said alcohol abuse and drug reactions can cause delirium, which, unlike dementia, is potentially reversible. Yet many physicians cannot reliably differentiate between dementia and delirium, he added.
The geriatric specialists talk about the lessons they’ve learned and the gratification they get from caring for centenarians.
“I have come to realize the importance of family, of having a close circle, whether that’s through friends or neighbors,” Dr. Goel said. “This work is very rewarding because, if it wasn’t for homebound organizations, how would these people get care or get access to care?”
For Dr. Baker, a joy of the job is hearing centenarians share their life stories.
“I love to hear their stories about how they’ve overcome adversity, living through the depression and living through different wars,” she said. “I love talking to veterans, and I think that oftentimes, we do not value our older adults in our society as we should. Sometimes they are dismissed because they move slowly or are hard to communicate with due to hearing deficits. But they are, I think, a very important part of our lives.”
‘They’ve already won’
Most centenarians readily offer the secrets to their longevity. Aline Jacobsohn, of Boca Raton, Fla., is no different.
Ms. Jacobsohn, who will be 101 in October, thinks a diet of small portions of fish, vegetables, and fruit, which she has followed since her husband Leo died in 1982, has helped keep her healthy. She eats lots of salmon and herring and is a fan of spinach sautéed with olive oil. “The only thing I don’t eat is meat,” the trim and active Ms. Jacobsohn said in a recent interview over Zoom.
Her other secret: “Doctors. I like to stay away from them as much as possible.”
Shari Rosenbaum, MD, Jacobsohn’s internist, doesn’t dismiss that approach. She uses a version of it when managing her three centenarian patients, the oldest of whom is 103.
“Let them smoke! Let them drink! They’re happy. It’s not causing harm. Let them eat cake! They’ve already won,” said Dr. Rosenbaum, who is affiliated with Boca Raton–based MDVIP, a national membership-based network of 1,100 primary care physicians serving 368,000 patients. Of those, nearly 460 are centenarians.
“You’re not preventing those problems in this population,” she said. “They’re here to enjoy every moment that they have, and they might as well.”
Dr. Rosenbaum sees a divergence in her patients – those who will reach very old age, and those who won’t – starting in their 60s.
“The centenarians don’t have medical problems,” she said. “They don’t get cancer. They don’t get diabetes. Some of them take good care of themselves. Some don’t take such good care of themselves. But they are all optimists. They all see the glass half full. They all participate in life. They all have excellent support systems. They have good genes, a positive attitude toward life, and a strong social network.”
Ms. Jacobsohn – whose surname at the time was Bakst – grew up in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, during the rise of the Nazi regime. The family fled to Columbia in 1938, where she met and eventually married her husband, Leo, who ran a business importing clocks and watches in Cali.
In 1989, the Jacobsohns and their three children moved to south Florida to escape the dangers of kidnappings and ransoms posed by the drug cartels.
Ms. Jacobsohn agreed that she appears to have longevity genes – “good stock,” she calls it. “My mother died 23 days before she was 100. My grandmother lived till 99, almost 100,” she said.
Two years ago, she donated her car to a charity and stopped driving in the interest of her own safety and that of other drivers and pedestrians.
Ms. Jacobsohn has a strong support system. Two of her children live nearby and visit her nearly every day. A live-in companion helps her with the activities of daily life, including preparing meals.
Ms. Jacobsohn plays bridge regularly, and well. “I’m sorry to say that I’m a very good bridge player,” she said, frankly. “How is it possible that I’ve played bridge so well and then I don’t remember what I had for lunch yesterday?”
She reads, mainly a diet of history but occasionally novels, too. “They have to be engaging,” she said.
The loss of loved ones is an inevitable part of very old age. Her husband of 47 years died of emphysema, and one of her sons died in his 70s of prostate cancer.
She knows well the fate that awaits us all and accepts it philosophically.
“It’s a very normal thing that people die. You don’t live forever. So, whenever it comes, it’s okay. Enough is enough. Dayenu,” she said, using the Hebrew word for, “It would have been enough” – a favorite in the Passover Seder celebrating the ancient Jews’ liberation from slavery in Egypt.
Ms. Jacobsohn sang the song and then took a reporter on a Zoom tour of her tidy home and her large flower garden featuring Cattleya orchids from Colombia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For about the past year, Priya Goel, MD, can be seen cruising around the island of Manhattan as she makes her way between visits to some of New York City’s most treasured residents: a small but essential group of patients born before the Empire State Building scraped the sky and the old Yankee Stadium had become the House That Ruth Built.
– the oldest is a 108-year-old man – whom she visits monthly.
The gray wave
Dr. Goel’s charges are among America’s latest baby boom – babies born a century ago, that is.
Between 1980 and 2019, the share of American centenarians, those aged 100 and up, grew faster than the total population. In 2019, 100,322 persons in the United States were at least 100 years old – more than triple the 1980 figure of 32,194, according to the U.S. Administration on Aging. By 2060, experts predict, the U.S. centenarian population will reach nearly 600,000.
Although some of the ultra-aged live in nursing homes, many continue to live independently. They require both routine and acute medical care. So, what does it take to be a physician for a centenarian?
Dr. Goel, who is in her mid-30s and could well be the great-granddaughter of some of her patients, urged her colleagues not to stereotype patients on the basis of age.
“You have to consider their functional and cognitive abilities, their ability to understand disease processes and make decisions for themselves,” Dr. Goel said. “Age is just one factor in the grand scheme of things.”
Visiting patients in their homes provides her with insights into how well they’re doing, including the safety of their environments and the depth of their social networks.
New York City has its peculiar demands. Heal provides Dr. Goel with a driver who chauffeurs her to her patient visits. She takes notes between stops.
“The idea is to have these patients remain in an environment where they’re comfortable, in surroundings where they’ve grown up or lived for many years,” she said. “A lot of them are in elevator buildings and they are wheelchair-bound or bed-bound and they physically can’t leave.”
She said she gets a far different view of the patient than does an office-based physician.
“When you go into their home, it’s very personal. You’re seeing what their daily environment is like, what their diet is like. You can see their food on the counter. You can see the level of hygiene,” Dr. Goel said. “You get to see their social support. Are their kids involved? Are they hoarding? Stuff that they wouldn’t just necessarily disclose but on a visit you get to see going into the home. It’s an extra layer of understanding that patient.”
Dr. Goel contrasted home care from care in a nursing home, where the patients are seen daily. On the basis of her observations, she decides whether to see her patients every month or every 3 months.
She applies this strategy to everyone from age 60 to over 100.
Tracking a growing group
Since 1995, geriatrician Thomas Perls, MD, has directed the New England Centenarian Study at Boston University. The study, largely funded by the National Institute on Aging, has enrolled 2,599 centenarian persons and 700 of their offspring. At any given time in the study, about 10% of the centenarians are alive. The study has a high mortality rate.
The people in Dr. Perls’s study range in age, but they top out at 119, the third oldest person ever in the world. Most centenarians are women.
“When we first began the study in 1995, the prevalence of centenarians in the United States was about 1 per 10,000 in the population,” Perls told this news organization. “And now, that prevalence has doubled to 1 per 5,000.”
Even if no one has achieved the record of Methuselah, the Biblical patriarch who was purported to have lived to the age of 969, some people always have lived into their 90s and beyond. Dr. Perls attributed the increase in longevity to control at the turn of the 20th century of typhoid fever, diphtheria, and other infectious diseases with effective public health measures, including the availability of clean water and improvement in socioeconomic conditions.
“Infant mortality just plummeted. So, come around 1915, 1920, we were no longer losing a quarter of our population to these diseases. That meant a quarter more of the population could age into adulthood and middle age,” he said. “A certain component of that group was, therefore, able to continue to age to a very, very old age.”
Other advances, such as antibiotics and vaccinations in the 1960s; the availability in the 1970s of much better detection and effective treatment of high blood pressure; the recognition of the harms of smoking; and much more effective treatment of cardiovascular disease and cancer have allowed many people who would have otherwise died in their 70s and 80s to live much longer. “I think what this means is that there is a substantial proportion of the population that has the biology to get to 100,” Dr. Perls said.
Perls said the Latino population and Blacks have a better track record than Whites in reaching the 100-year milestone. “The average life expectancy might be lower in these populations because of socioeconomic factors, but if they are able to get to around their early 80s, compared to Whites, their ability to get to 100 is actually better,” he said.
Asians fare best when it comes to longevity. While around 1% of White women in the United States live to 100, 10% of Asian women in Hong Kong hit that mark.
“I think some of that is better environment and health habits in Hong Kong than in the United States,” Dr. Perls said. “I think another piece may be a genetic advantage in East Asians. We’re looking into that.”
Dr. Perls said he agreed with Dr. Goel that health care providers and the lay public should not make assumptions on the basis of age alone as to how a person is doing. “People can age so very differently from one another,” he said.
Up to about age 90, the vast majority of those differences are determined by our health behaviors, such as smoking, alcohol use, exercise, sleep, the effect of our diets on weight, and access to good health care, including regular screening for problems such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and cancer. “People who are able to do everything right generally add healthy years to their lives, while those who do not have shorter life expectancies and longer periods of chronic diseases,” Dr. Perls said.
Paying diligent attention to these behaviors over the long run can have a huge payoff.
Dr. Perls’s team has found that to live beyond age 90 and on into the early 100s, protective genes can play a strong role. These genes help slow aging and decrease one’s risk for aging-related diseases. Centenarians usually have a history of aging very slowly and greatly delaying aging-related diseases and disability toward the ends of their lives.
Centenarians are the antithesis of the misguided belief that the older you get, the sicker you get. Quite the opposite occurs. For Dr. Perls, “the older you get, the healthier you’ve been.”
MD bias against the elderly?
Care of elderly patients is becoming essential in the practice of primary care physicians – but not all of them enjoy the work.
To be effective, physicians who treat centenarians must get a better idea of the individual patient’s functional status and comorbidities. “You absolutely cannot make assumptions on age alone,” Dr. Perls said.
The so-called “normal” temperature, 98.6° F, can spell trouble for centenarians and other very old patients, warned Natalie Baker, DNP, CRNP, an associate professor of nursing at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and president of the 3,000-member Gerontological Advanced Practice Nurses Association.
“We have to be very cognizant of what we call a typical presentation of disease or illness and that a very subtle change in an older adult can signal a serious infection or illness,” Dr. Baker said. “If your patient has a high fever, that is a potential problem.”
The average temperature of an older adult is lower than the accepted 98.6° F, and their body’s response to an infection is slow to exhibit an increase in temperature, Dr. Baker said. “When treating centenarians, clinicians must be cognizant of other subtle signs of infection, such as decreased appetite or change in mentation,” she cautioned.
A decline in appetite or insomnia may be a subtle sign that these patients need to be evaluated, she added.
COVID-19 and centenarians
Three-quarters of the 1 million U.S. deaths from COVID-19 occurred in people aged 65 and older. However, Dr. Perls said centenarians may be a special subpopulation when it comes to COVID.
The Japanese Health Ministry, which follows the large centenarian population in that country, noted a marked jump in the number of centenarians during the pandemic – although the reasons for the increase aren’t clear.
Centenarians may be a bit different. Dr. Perls said some evidence suggests that the over-100 crowd may have better immune systems than younger people. “Part of the trick of getting to 100 is having a pretty good immune system,” he said.
Don’t mess with success
“There is no need at that point for us to try to alter their diet to what we think it might be,” Dr. Baker said. “There’s no need to start with diabetic education. They may tell you their secret is a shot of vodka every day. Why should we stop it at that age? Accept their lifestyles, because they’ve done something right to get to that age.”
Opinions differ on how to approach screening for centenarians.
Dr. Goel said guidelines for routine screening, such as colonoscopies, mammograms, and PAP smears, drop off for patients starting at 75. Dr. Perls said this strategy stems from the belief that people will die from other things first, so screening is no longer needed. Dr. Perls said he disagrees with this approach.
“Again, we can’t base our screening and health care decisions on age alone. If I have an independently functioning and robust 95-year-old man in my office, you can be sure I am going to continue recommending regular screening for colon cancer and other screenings that are normal for people who are 30 years younger,” he said.
Justin Zaghi, MD, chief medical officer at Heal, said screening patients in their late 90s and 100s for cancer generally doesn’t make sense except in some rare circumstances in which the cancer would be unlikely to be a cause of death. “However, if we are talking about screening for fall risks, hearing difficulties, poor vision, pain, and malnutrition, those screenings still absolutely make sense for patients in their late 90s and 100s,” Dr. Zaghi said.
One high-functioning 104-year-old patient of Dr. Perls underwent a total hip replacement for a hip fracture and is faring well. “Obviously, if she had end-stage dementia, we’d do everything to keep the person comfortable, or if they had medical problems that made surgery too high risk, then you don’t do it,” he said. “But if they’re otherwise, I would proceed.”
Avoid the ED
Dr. Goel said doctors should avoid sending patients to the emergency department, an often chaotic place that is especially unfriendly to centenarians and the very old. “Sometimes I’ve seen older patients who are being rushed to the ER, and I ask, What are the goals of care?” she said.
Clinicians caring for seniors should keep in mind that infections can cause seniors to appear confused – and this may lead the clinician to think the patient has dementia. Or, Dr. Goel said, a patient with dementia may suddenly experience much worse dementia.
“In either case, you want to make sure you’re not dealing with any underlying infection, like urinary tract infection, or pneumonia brewing, or skin infections,” she said. “Their skin is so much frailer. You want to make sure there are no bedsores.”
She has had patients whose children report that their usually placid centenarian parents are suddenly acting out. “We’ll do a urinary test and it definitely shows a urinary tract infection. You want to make sure you’re not missing out on something else before you attribute it to dementia,” she said.
Environmental changes, such as moving a patient to a new room in a hospital setting, can trigger an acute mental status change, such as delirium, she added. Helping older patients feel in control as much as possible is important.
“You want to make sure you’re orienting them to the time of day. Make sure they get up at the same time, go to bed at the same time, have clocks and calendars present – just making sure that they feel like they’re still in control of their body and their day,” she said.
Physicians should be aware of potential depression in these patients, whose experience of loss – an unavoidable consequence of outliving family and friends – can result in problems with sleep and diet, as well as a sense of social isolation.
Neal Flomenbaum, MD, professor and emergency physician-in-chief emeritus, New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York, said sometimes the best thing for these very elderly patients is to “get them in and out of ED as quickly as possible, and do what you can diagnostically.”
He noted that EDs have been making accommodations to serve the elderly, such as using LEDs that replicate outdoor lighting conditions, as well as providing seniors with separate rooms with glass doors to protect them from noise, separate air handlers to prevent infections, and adequate space for visitors.
These patients often are subject to trauma from falls.
“The bones don’t heal as well as in younger people, and treating their comorbidities is essential. Once they have trouble with one area and they’re lying in bed and can’t move much, they can get bedsores,” Dr. Flomenbaum said. “In the hospital, they are vulnerable to infections. So, you’re thinking of all of these things at the same time and how to treat them appropriately and then get them out of the hospital as soon as possible with whatever care that they need in their own homes if at all possible.”
“I always err on the side of less is more,” Dr. Goel said. “Obviously, if there is something – if they have a cough, they need an x-ray. That’s very basic. We want to take care of that. Give them the antibiotic if they need that. But rushing them in and out of the hospital doesn’t add to their quality of life.”
Dr. Flomenbaum, a pioneer in geriatric emergency medicine, says physicians need to be aware that centenarians and other very old patients don’t present the same way as younger adults.
He began to notice more than 20 years ago that every night, patients would turn up in his ED who were in their late 90s into their 100s. Some would come in with what their children identified as sudden-onset dementia – they didn’t know their own names and couldn’t identify their kids. They didn’t know the time or day. Dr. Flomenbaum said the children often asked whether their parents should enter a nursing home.
“And I’d say, ‘Not so fast. Well, let’s take a look at this.’ You don’t develop that kind of dementia overnight. It usually takes a while,” he said.
He said he ordered complete blood cell counts and oxygen saturation tests that frequently turned out to be abnormal. They didn’t have a fever, and infiltrates initially weren’t seen on chest x-rays.
With rehydration and supplemental oxygen, their symptoms started to improve, and it became obvious that the symptoms were not of dementia but of pneumonia, and that they required antibiotics, Dr. Flomenbaum said.
Dementia dilemma
Too often, on the basis of age, doctors assume patients have dementia or other cognitive impairments.
“What a shock and a surprise when doctors actually talk to folks and do a neurocognitive screen and find they’re just fine,” Dr. Perls said.
The decline in hearing and vision can lead to a misdiagnosis of cognitive impairment because the patients are not able to hear what you’re asking them. “It’s really important that the person can hear you – whether you use an amplifying device or they have hearing aids, that’s critical,” he said. “You just have to be a good doctor.”
Often the physical toll of aging exacerbates social difficulties. Poor hearing, for example, can accelerate cognitive impairment and cause people to interact less often, and less meaningfully, with their environment. For some, wearing hearing aids seems demeaning – until they hear what they’ve been missing.
“I get them to wear their hearing aids and, lo and behold, they’re a whole new person because they’re now able to take in their environment and interact with others,” Dr. Perls said.
Dr. Flomenbaum said alcohol abuse and drug reactions can cause delirium, which, unlike dementia, is potentially reversible. Yet many physicians cannot reliably differentiate between dementia and delirium, he added.
The geriatric specialists talk about the lessons they’ve learned and the gratification they get from caring for centenarians.
“I have come to realize the importance of family, of having a close circle, whether that’s through friends or neighbors,” Dr. Goel said. “This work is very rewarding because, if it wasn’t for homebound organizations, how would these people get care or get access to care?”
For Dr. Baker, a joy of the job is hearing centenarians share their life stories.
“I love to hear their stories about how they’ve overcome adversity, living through the depression and living through different wars,” she said. “I love talking to veterans, and I think that oftentimes, we do not value our older adults in our society as we should. Sometimes they are dismissed because they move slowly or are hard to communicate with due to hearing deficits. But they are, I think, a very important part of our lives.”
‘They’ve already won’
Most centenarians readily offer the secrets to their longevity. Aline Jacobsohn, of Boca Raton, Fla., is no different.
Ms. Jacobsohn, who will be 101 in October, thinks a diet of small portions of fish, vegetables, and fruit, which she has followed since her husband Leo died in 1982, has helped keep her healthy. She eats lots of salmon and herring and is a fan of spinach sautéed with olive oil. “The only thing I don’t eat is meat,” the trim and active Ms. Jacobsohn said in a recent interview over Zoom.
Her other secret: “Doctors. I like to stay away from them as much as possible.”
Shari Rosenbaum, MD, Jacobsohn’s internist, doesn’t dismiss that approach. She uses a version of it when managing her three centenarian patients, the oldest of whom is 103.
“Let them smoke! Let them drink! They’re happy. It’s not causing harm. Let them eat cake! They’ve already won,” said Dr. Rosenbaum, who is affiliated with Boca Raton–based MDVIP, a national membership-based network of 1,100 primary care physicians serving 368,000 patients. Of those, nearly 460 are centenarians.
“You’re not preventing those problems in this population,” she said. “They’re here to enjoy every moment that they have, and they might as well.”
Dr. Rosenbaum sees a divergence in her patients – those who will reach very old age, and those who won’t – starting in their 60s.
“The centenarians don’t have medical problems,” she said. “They don’t get cancer. They don’t get diabetes. Some of them take good care of themselves. Some don’t take such good care of themselves. But they are all optimists. They all see the glass half full. They all participate in life. They all have excellent support systems. They have good genes, a positive attitude toward life, and a strong social network.”
Ms. Jacobsohn – whose surname at the time was Bakst – grew up in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, during the rise of the Nazi regime. The family fled to Columbia in 1938, where she met and eventually married her husband, Leo, who ran a business importing clocks and watches in Cali.
In 1989, the Jacobsohns and their three children moved to south Florida to escape the dangers of kidnappings and ransoms posed by the drug cartels.
Ms. Jacobsohn agreed that she appears to have longevity genes – “good stock,” she calls it. “My mother died 23 days before she was 100. My grandmother lived till 99, almost 100,” she said.
Two years ago, she donated her car to a charity and stopped driving in the interest of her own safety and that of other drivers and pedestrians.
Ms. Jacobsohn has a strong support system. Two of her children live nearby and visit her nearly every day. A live-in companion helps her with the activities of daily life, including preparing meals.
Ms. Jacobsohn plays bridge regularly, and well. “I’m sorry to say that I’m a very good bridge player,” she said, frankly. “How is it possible that I’ve played bridge so well and then I don’t remember what I had for lunch yesterday?”
She reads, mainly a diet of history but occasionally novels, too. “They have to be engaging,” she said.
The loss of loved ones is an inevitable part of very old age. Her husband of 47 years died of emphysema, and one of her sons died in his 70s of prostate cancer.
She knows well the fate that awaits us all and accepts it philosophically.
“It’s a very normal thing that people die. You don’t live forever. So, whenever it comes, it’s okay. Enough is enough. Dayenu,” she said, using the Hebrew word for, “It would have been enough” – a favorite in the Passover Seder celebrating the ancient Jews’ liberation from slavery in Egypt.
Ms. Jacobsohn sang the song and then took a reporter on a Zoom tour of her tidy home and her large flower garden featuring Cattleya orchids from Colombia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For about the past year, Priya Goel, MD, can be seen cruising around the island of Manhattan as she makes her way between visits to some of New York City’s most treasured residents: a small but essential group of patients born before the Empire State Building scraped the sky and the old Yankee Stadium had become the House That Ruth Built.
– the oldest is a 108-year-old man – whom she visits monthly.
The gray wave
Dr. Goel’s charges are among America’s latest baby boom – babies born a century ago, that is.
Between 1980 and 2019, the share of American centenarians, those aged 100 and up, grew faster than the total population. In 2019, 100,322 persons in the United States were at least 100 years old – more than triple the 1980 figure of 32,194, according to the U.S. Administration on Aging. By 2060, experts predict, the U.S. centenarian population will reach nearly 600,000.
Although some of the ultra-aged live in nursing homes, many continue to live independently. They require both routine and acute medical care. So, what does it take to be a physician for a centenarian?
Dr. Goel, who is in her mid-30s and could well be the great-granddaughter of some of her patients, urged her colleagues not to stereotype patients on the basis of age.
“You have to consider their functional and cognitive abilities, their ability to understand disease processes and make decisions for themselves,” Dr. Goel said. “Age is just one factor in the grand scheme of things.”
Visiting patients in their homes provides her with insights into how well they’re doing, including the safety of their environments and the depth of their social networks.
New York City has its peculiar demands. Heal provides Dr. Goel with a driver who chauffeurs her to her patient visits. She takes notes between stops.
“The idea is to have these patients remain in an environment where they’re comfortable, in surroundings where they’ve grown up or lived for many years,” she said. “A lot of them are in elevator buildings and they are wheelchair-bound or bed-bound and they physically can’t leave.”
She said she gets a far different view of the patient than does an office-based physician.
“When you go into their home, it’s very personal. You’re seeing what their daily environment is like, what their diet is like. You can see their food on the counter. You can see the level of hygiene,” Dr. Goel said. “You get to see their social support. Are their kids involved? Are they hoarding? Stuff that they wouldn’t just necessarily disclose but on a visit you get to see going into the home. It’s an extra layer of understanding that patient.”
Dr. Goel contrasted home care from care in a nursing home, where the patients are seen daily. On the basis of her observations, she decides whether to see her patients every month or every 3 months.
She applies this strategy to everyone from age 60 to over 100.
Tracking a growing group
Since 1995, geriatrician Thomas Perls, MD, has directed the New England Centenarian Study at Boston University. The study, largely funded by the National Institute on Aging, has enrolled 2,599 centenarian persons and 700 of their offspring. At any given time in the study, about 10% of the centenarians are alive. The study has a high mortality rate.
The people in Dr. Perls’s study range in age, but they top out at 119, the third oldest person ever in the world. Most centenarians are women.
“When we first began the study in 1995, the prevalence of centenarians in the United States was about 1 per 10,000 in the population,” Perls told this news organization. “And now, that prevalence has doubled to 1 per 5,000.”
Even if no one has achieved the record of Methuselah, the Biblical patriarch who was purported to have lived to the age of 969, some people always have lived into their 90s and beyond. Dr. Perls attributed the increase in longevity to control at the turn of the 20th century of typhoid fever, diphtheria, and other infectious diseases with effective public health measures, including the availability of clean water and improvement in socioeconomic conditions.
“Infant mortality just plummeted. So, come around 1915, 1920, we were no longer losing a quarter of our population to these diseases. That meant a quarter more of the population could age into adulthood and middle age,” he said. “A certain component of that group was, therefore, able to continue to age to a very, very old age.”
Other advances, such as antibiotics and vaccinations in the 1960s; the availability in the 1970s of much better detection and effective treatment of high blood pressure; the recognition of the harms of smoking; and much more effective treatment of cardiovascular disease and cancer have allowed many people who would have otherwise died in their 70s and 80s to live much longer. “I think what this means is that there is a substantial proportion of the population that has the biology to get to 100,” Dr. Perls said.
Perls said the Latino population and Blacks have a better track record than Whites in reaching the 100-year milestone. “The average life expectancy might be lower in these populations because of socioeconomic factors, but if they are able to get to around their early 80s, compared to Whites, their ability to get to 100 is actually better,” he said.
Asians fare best when it comes to longevity. While around 1% of White women in the United States live to 100, 10% of Asian women in Hong Kong hit that mark.
“I think some of that is better environment and health habits in Hong Kong than in the United States,” Dr. Perls said. “I think another piece may be a genetic advantage in East Asians. We’re looking into that.”
Dr. Perls said he agreed with Dr. Goel that health care providers and the lay public should not make assumptions on the basis of age alone as to how a person is doing. “People can age so very differently from one another,” he said.
Up to about age 90, the vast majority of those differences are determined by our health behaviors, such as smoking, alcohol use, exercise, sleep, the effect of our diets on weight, and access to good health care, including regular screening for problems such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and cancer. “People who are able to do everything right generally add healthy years to their lives, while those who do not have shorter life expectancies and longer periods of chronic diseases,” Dr. Perls said.
Paying diligent attention to these behaviors over the long run can have a huge payoff.
Dr. Perls’s team has found that to live beyond age 90 and on into the early 100s, protective genes can play a strong role. These genes help slow aging and decrease one’s risk for aging-related diseases. Centenarians usually have a history of aging very slowly and greatly delaying aging-related diseases and disability toward the ends of their lives.
Centenarians are the antithesis of the misguided belief that the older you get, the sicker you get. Quite the opposite occurs. For Dr. Perls, “the older you get, the healthier you’ve been.”
MD bias against the elderly?
Care of elderly patients is becoming essential in the practice of primary care physicians – but not all of them enjoy the work.
To be effective, physicians who treat centenarians must get a better idea of the individual patient’s functional status and comorbidities. “You absolutely cannot make assumptions on age alone,” Dr. Perls said.
The so-called “normal” temperature, 98.6° F, can spell trouble for centenarians and other very old patients, warned Natalie Baker, DNP, CRNP, an associate professor of nursing at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and president of the 3,000-member Gerontological Advanced Practice Nurses Association.
“We have to be very cognizant of what we call a typical presentation of disease or illness and that a very subtle change in an older adult can signal a serious infection or illness,” Dr. Baker said. “If your patient has a high fever, that is a potential problem.”
The average temperature of an older adult is lower than the accepted 98.6° F, and their body’s response to an infection is slow to exhibit an increase in temperature, Dr. Baker said. “When treating centenarians, clinicians must be cognizant of other subtle signs of infection, such as decreased appetite or change in mentation,” she cautioned.
A decline in appetite or insomnia may be a subtle sign that these patients need to be evaluated, she added.
COVID-19 and centenarians
Three-quarters of the 1 million U.S. deaths from COVID-19 occurred in people aged 65 and older. However, Dr. Perls said centenarians may be a special subpopulation when it comes to COVID.
The Japanese Health Ministry, which follows the large centenarian population in that country, noted a marked jump in the number of centenarians during the pandemic – although the reasons for the increase aren’t clear.
Centenarians may be a bit different. Dr. Perls said some evidence suggests that the over-100 crowd may have better immune systems than younger people. “Part of the trick of getting to 100 is having a pretty good immune system,” he said.
Don’t mess with success
“There is no need at that point for us to try to alter their diet to what we think it might be,” Dr. Baker said. “There’s no need to start with diabetic education. They may tell you their secret is a shot of vodka every day. Why should we stop it at that age? Accept their lifestyles, because they’ve done something right to get to that age.”
Opinions differ on how to approach screening for centenarians.
Dr. Goel said guidelines for routine screening, such as colonoscopies, mammograms, and PAP smears, drop off for patients starting at 75. Dr. Perls said this strategy stems from the belief that people will die from other things first, so screening is no longer needed. Dr. Perls said he disagrees with this approach.
“Again, we can’t base our screening and health care decisions on age alone. If I have an independently functioning and robust 95-year-old man in my office, you can be sure I am going to continue recommending regular screening for colon cancer and other screenings that are normal for people who are 30 years younger,” he said.
Justin Zaghi, MD, chief medical officer at Heal, said screening patients in their late 90s and 100s for cancer generally doesn’t make sense except in some rare circumstances in which the cancer would be unlikely to be a cause of death. “However, if we are talking about screening for fall risks, hearing difficulties, poor vision, pain, and malnutrition, those screenings still absolutely make sense for patients in their late 90s and 100s,” Dr. Zaghi said.
One high-functioning 104-year-old patient of Dr. Perls underwent a total hip replacement for a hip fracture and is faring well. “Obviously, if she had end-stage dementia, we’d do everything to keep the person comfortable, or if they had medical problems that made surgery too high risk, then you don’t do it,” he said. “But if they’re otherwise, I would proceed.”
Avoid the ED
Dr. Goel said doctors should avoid sending patients to the emergency department, an often chaotic place that is especially unfriendly to centenarians and the very old. “Sometimes I’ve seen older patients who are being rushed to the ER, and I ask, What are the goals of care?” she said.
Clinicians caring for seniors should keep in mind that infections can cause seniors to appear confused – and this may lead the clinician to think the patient has dementia. Or, Dr. Goel said, a patient with dementia may suddenly experience much worse dementia.
“In either case, you want to make sure you’re not dealing with any underlying infection, like urinary tract infection, or pneumonia brewing, or skin infections,” she said. “Their skin is so much frailer. You want to make sure there are no bedsores.”
She has had patients whose children report that their usually placid centenarian parents are suddenly acting out. “We’ll do a urinary test and it definitely shows a urinary tract infection. You want to make sure you’re not missing out on something else before you attribute it to dementia,” she said.
Environmental changes, such as moving a patient to a new room in a hospital setting, can trigger an acute mental status change, such as delirium, she added. Helping older patients feel in control as much as possible is important.
“You want to make sure you’re orienting them to the time of day. Make sure they get up at the same time, go to bed at the same time, have clocks and calendars present – just making sure that they feel like they’re still in control of their body and their day,” she said.
Physicians should be aware of potential depression in these patients, whose experience of loss – an unavoidable consequence of outliving family and friends – can result in problems with sleep and diet, as well as a sense of social isolation.
Neal Flomenbaum, MD, professor and emergency physician-in-chief emeritus, New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York, said sometimes the best thing for these very elderly patients is to “get them in and out of ED as quickly as possible, and do what you can diagnostically.”
He noted that EDs have been making accommodations to serve the elderly, such as using LEDs that replicate outdoor lighting conditions, as well as providing seniors with separate rooms with glass doors to protect them from noise, separate air handlers to prevent infections, and adequate space for visitors.
These patients often are subject to trauma from falls.
“The bones don’t heal as well as in younger people, and treating their comorbidities is essential. Once they have trouble with one area and they’re lying in bed and can’t move much, they can get bedsores,” Dr. Flomenbaum said. “In the hospital, they are vulnerable to infections. So, you’re thinking of all of these things at the same time and how to treat them appropriately and then get them out of the hospital as soon as possible with whatever care that they need in their own homes if at all possible.”
“I always err on the side of less is more,” Dr. Goel said. “Obviously, if there is something – if they have a cough, they need an x-ray. That’s very basic. We want to take care of that. Give them the antibiotic if they need that. But rushing them in and out of the hospital doesn’t add to their quality of life.”
Dr. Flomenbaum, a pioneer in geriatric emergency medicine, says physicians need to be aware that centenarians and other very old patients don’t present the same way as younger adults.
He began to notice more than 20 years ago that every night, patients would turn up in his ED who were in their late 90s into their 100s. Some would come in with what their children identified as sudden-onset dementia – they didn’t know their own names and couldn’t identify their kids. They didn’t know the time or day. Dr. Flomenbaum said the children often asked whether their parents should enter a nursing home.
“And I’d say, ‘Not so fast. Well, let’s take a look at this.’ You don’t develop that kind of dementia overnight. It usually takes a while,” he said.
He said he ordered complete blood cell counts and oxygen saturation tests that frequently turned out to be abnormal. They didn’t have a fever, and infiltrates initially weren’t seen on chest x-rays.
With rehydration and supplemental oxygen, their symptoms started to improve, and it became obvious that the symptoms were not of dementia but of pneumonia, and that they required antibiotics, Dr. Flomenbaum said.
Dementia dilemma
Too often, on the basis of age, doctors assume patients have dementia or other cognitive impairments.
“What a shock and a surprise when doctors actually talk to folks and do a neurocognitive screen and find they’re just fine,” Dr. Perls said.
The decline in hearing and vision can lead to a misdiagnosis of cognitive impairment because the patients are not able to hear what you’re asking them. “It’s really important that the person can hear you – whether you use an amplifying device or they have hearing aids, that’s critical,” he said. “You just have to be a good doctor.”
Often the physical toll of aging exacerbates social difficulties. Poor hearing, for example, can accelerate cognitive impairment and cause people to interact less often, and less meaningfully, with their environment. For some, wearing hearing aids seems demeaning – until they hear what they’ve been missing.
“I get them to wear their hearing aids and, lo and behold, they’re a whole new person because they’re now able to take in their environment and interact with others,” Dr. Perls said.
Dr. Flomenbaum said alcohol abuse and drug reactions can cause delirium, which, unlike dementia, is potentially reversible. Yet many physicians cannot reliably differentiate between dementia and delirium, he added.
The geriatric specialists talk about the lessons they’ve learned and the gratification they get from caring for centenarians.
“I have come to realize the importance of family, of having a close circle, whether that’s through friends or neighbors,” Dr. Goel said. “This work is very rewarding because, if it wasn’t for homebound organizations, how would these people get care or get access to care?”
For Dr. Baker, a joy of the job is hearing centenarians share their life stories.
“I love to hear their stories about how they’ve overcome adversity, living through the depression and living through different wars,” she said. “I love talking to veterans, and I think that oftentimes, we do not value our older adults in our society as we should. Sometimes they are dismissed because they move slowly or are hard to communicate with due to hearing deficits. But they are, I think, a very important part of our lives.”
‘They’ve already won’
Most centenarians readily offer the secrets to their longevity. Aline Jacobsohn, of Boca Raton, Fla., is no different.
Ms. Jacobsohn, who will be 101 in October, thinks a diet of small portions of fish, vegetables, and fruit, which she has followed since her husband Leo died in 1982, has helped keep her healthy. She eats lots of salmon and herring and is a fan of spinach sautéed with olive oil. “The only thing I don’t eat is meat,” the trim and active Ms. Jacobsohn said in a recent interview over Zoom.
Her other secret: “Doctors. I like to stay away from them as much as possible.”
Shari Rosenbaum, MD, Jacobsohn’s internist, doesn’t dismiss that approach. She uses a version of it when managing her three centenarian patients, the oldest of whom is 103.
“Let them smoke! Let them drink! They’re happy. It’s not causing harm. Let them eat cake! They’ve already won,” said Dr. Rosenbaum, who is affiliated with Boca Raton–based MDVIP, a national membership-based network of 1,100 primary care physicians serving 368,000 patients. Of those, nearly 460 are centenarians.
“You’re not preventing those problems in this population,” she said. “They’re here to enjoy every moment that they have, and they might as well.”
Dr. Rosenbaum sees a divergence in her patients – those who will reach very old age, and those who won’t – starting in their 60s.
“The centenarians don’t have medical problems,” she said. “They don’t get cancer. They don’t get diabetes. Some of them take good care of themselves. Some don’t take such good care of themselves. But they are all optimists. They all see the glass half full. They all participate in life. They all have excellent support systems. They have good genes, a positive attitude toward life, and a strong social network.”
Ms. Jacobsohn – whose surname at the time was Bakst – grew up in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, during the rise of the Nazi regime. The family fled to Columbia in 1938, where she met and eventually married her husband, Leo, who ran a business importing clocks and watches in Cali.
In 1989, the Jacobsohns and their three children moved to south Florida to escape the dangers of kidnappings and ransoms posed by the drug cartels.
Ms. Jacobsohn agreed that she appears to have longevity genes – “good stock,” she calls it. “My mother died 23 days before she was 100. My grandmother lived till 99, almost 100,” she said.
Two years ago, she donated her car to a charity and stopped driving in the interest of her own safety and that of other drivers and pedestrians.
Ms. Jacobsohn has a strong support system. Two of her children live nearby and visit her nearly every day. A live-in companion helps her with the activities of daily life, including preparing meals.
Ms. Jacobsohn plays bridge regularly, and well. “I’m sorry to say that I’m a very good bridge player,” she said, frankly. “How is it possible that I’ve played bridge so well and then I don’t remember what I had for lunch yesterday?”
She reads, mainly a diet of history but occasionally novels, too. “They have to be engaging,” she said.
The loss of loved ones is an inevitable part of very old age. Her husband of 47 years died of emphysema, and one of her sons died in his 70s of prostate cancer.
She knows well the fate that awaits us all and accepts it philosophically.
“It’s a very normal thing that people die. You don’t live forever. So, whenever it comes, it’s okay. Enough is enough. Dayenu,” she said, using the Hebrew word for, “It would have been enough” – a favorite in the Passover Seder celebrating the ancient Jews’ liberation from slavery in Egypt.
Ms. Jacobsohn sang the song and then took a reporter on a Zoom tour of her tidy home and her large flower garden featuring Cattleya orchids from Colombia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.