User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
Complete blood count scoring can predict COVID-19 severity
A scoring system based on 10 parameters in a complete blood count with differential within 3 days of hospital presentation predict those with COVID-19 who are most likely to progress to critical illness, new evidence shows.
Advantages include prognosis based on a common and inexpensive clinical measure, as well as automatic generation of the score along with CBC results, noted investigators in the observational study conducted throughout 11 European hospitals.
“COVID-19 comes along with specific alterations in circulating blood cells that can be detected by a routine hematology analyzer, especially when that hematology analyzer is also capable to recognize activated immune cells and early circulating blood cells, such as erythroblast and immature granulocytes,” senior author Andre van der Ven, MD, PhD, infectious diseases specialist and professor of international health at Radboud University Medical Center’s Center for Infectious Diseases in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
Furthermore, Dr. van der Ven said, “these specific changes are also seen in the early course of COVID-19 disease, and more in those that will develop serious disease compared to those with mild disease.”
The study was published online Dec. 21 in the journal eLife.
The study is “almost instinctively correct. It’s basically what clinicians do informally with complete blood count … looking at a combination of results to get the gestalt of what patients are going through,” Samuel Reichberg, MD, PhD, associate medical director of the Northwell Health Core Laboratory in Lake Success, N.Y., said in an interview.
“This is something that begs to be done for COVID-19. I’m surprised no one has done this before,” he added.
Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues created an algorithm based on 1,587 CBC assays from 923 adults. They also validated the scoring system in a second cohort of 217 CBC measurements in 202 people. The findings were concordant – the score accurately predicted the need for critical care within 14 days in 70.5% of the development cohort and 72% of the validation group.
The scoring system was superior to any of the 10 parameters alone. Over 14 days, the majority of those classified as noncritical within the first 3 days remained clinically stable, whereas the “clinical illness” group progressed. Clinical severity peaked on day 6.
Most previous COVID-19 prognosis research was geographically limited, carried a high risk for bias and/or did not validate the findings, Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues noted.
Early identification, early intervention
The aim of the score is “to assist with objective risk stratification to support patient management decision-making early on, and thus facilitate timely interventions, such as need for ICU or not, before symptoms of severe illness become clinically overt, with the intention to improve patient outcomes, and not to predict mortality,” the investigators noted.
Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues developed the score based on adults presenting from Feb. 21 to April 6, with outcomes followed until June 9. Median age of the 982 patients was 71 years and approximately two-thirds were men. They used a Sysmex Europe XN-1000 (Hamburg, Germany) hemocytometric analyzer in the study.
Only 7% of this cohort was not admitted to a hospital. Another 74% were admitted to a general ward and the remaining 19% were transferred directly to the ICU.
The scoring system includes parameters for neutrophils, monocytes, red blood cells and immature granulocytes, and when available, reticulocyte and iron bioavailability measures.
The researchers report significant differences over time in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio between the critical illness and noncritical groups (P < .001), for example. They also found significant differences in hemoglobin levels between cohorts after day 5.
The system generates a score from 0 to 28. Sensitivity for correctly predicting the need for critical care increased from 62% on day 1 to 93% on day 6.
A more objective assessment of risk
The study demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 infection is characterized by hemocytometric changes over time. These changes, reflected together in the prognostic score, could aid in the early identification of patients whose clinical course is more likely to deteriorate over time.
The findings also support other work that shows men are more likely to present to the hospital with COVID-19, and that older age and presence of comorbidities add to overall risk. “However,” the researchers noted, “not all young patients had a mild course, and not all old patients with comorbidities were critical.”
Therefore, the prognostic score can help identify patients at risk for severe progression outside other risk factors and “support individualized treatment decisions with objective data,” they added.
Dr. Reichberg called the concept of combining CBC parameters into one score “very valuable.” However, he added that incorporating an index into clinical practice “has historically been tricky.”
The results “probably have to be replicated,” Dr. Reichberg said.
He added that it is likely a CBC-based score will be combined with other measures. “I would like to see an index that combines all the tests we do [for COVID-19], including complete blood count.”
Dr. Van der Ven shared the next step in his research. “The algorithm should be installed on the hematology analyzers so the prognostic score will be automatically generated if a full blood count is asked for in a COVID-19 patient,” he said. “So implementation of score is the main focus now.”
Dr. van der Ven disclosed an ad hoc consultancy agreement with Sysmex Europe. Sysmex Europe provided the reagents in the study free of charge; no other funders were involved. Dr. Reichberg has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A scoring system based on 10 parameters in a complete blood count with differential within 3 days of hospital presentation predict those with COVID-19 who are most likely to progress to critical illness, new evidence shows.
Advantages include prognosis based on a common and inexpensive clinical measure, as well as automatic generation of the score along with CBC results, noted investigators in the observational study conducted throughout 11 European hospitals.
“COVID-19 comes along with specific alterations in circulating blood cells that can be detected by a routine hematology analyzer, especially when that hematology analyzer is also capable to recognize activated immune cells and early circulating blood cells, such as erythroblast and immature granulocytes,” senior author Andre van der Ven, MD, PhD, infectious diseases specialist and professor of international health at Radboud University Medical Center’s Center for Infectious Diseases in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
Furthermore, Dr. van der Ven said, “these specific changes are also seen in the early course of COVID-19 disease, and more in those that will develop serious disease compared to those with mild disease.”
The study was published online Dec. 21 in the journal eLife.
The study is “almost instinctively correct. It’s basically what clinicians do informally with complete blood count … looking at a combination of results to get the gestalt of what patients are going through,” Samuel Reichberg, MD, PhD, associate medical director of the Northwell Health Core Laboratory in Lake Success, N.Y., said in an interview.
“This is something that begs to be done for COVID-19. I’m surprised no one has done this before,” he added.
Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues created an algorithm based on 1,587 CBC assays from 923 adults. They also validated the scoring system in a second cohort of 217 CBC measurements in 202 people. The findings were concordant – the score accurately predicted the need for critical care within 14 days in 70.5% of the development cohort and 72% of the validation group.
The scoring system was superior to any of the 10 parameters alone. Over 14 days, the majority of those classified as noncritical within the first 3 days remained clinically stable, whereas the “clinical illness” group progressed. Clinical severity peaked on day 6.
Most previous COVID-19 prognosis research was geographically limited, carried a high risk for bias and/or did not validate the findings, Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues noted.
Early identification, early intervention
The aim of the score is “to assist with objective risk stratification to support patient management decision-making early on, and thus facilitate timely interventions, such as need for ICU or not, before symptoms of severe illness become clinically overt, with the intention to improve patient outcomes, and not to predict mortality,” the investigators noted.
Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues developed the score based on adults presenting from Feb. 21 to April 6, with outcomes followed until June 9. Median age of the 982 patients was 71 years and approximately two-thirds were men. They used a Sysmex Europe XN-1000 (Hamburg, Germany) hemocytometric analyzer in the study.
Only 7% of this cohort was not admitted to a hospital. Another 74% were admitted to a general ward and the remaining 19% were transferred directly to the ICU.
The scoring system includes parameters for neutrophils, monocytes, red blood cells and immature granulocytes, and when available, reticulocyte and iron bioavailability measures.
The researchers report significant differences over time in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio between the critical illness and noncritical groups (P < .001), for example. They also found significant differences in hemoglobin levels between cohorts after day 5.
The system generates a score from 0 to 28. Sensitivity for correctly predicting the need for critical care increased from 62% on day 1 to 93% on day 6.
A more objective assessment of risk
The study demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 infection is characterized by hemocytometric changes over time. These changes, reflected together in the prognostic score, could aid in the early identification of patients whose clinical course is more likely to deteriorate over time.
The findings also support other work that shows men are more likely to present to the hospital with COVID-19, and that older age and presence of comorbidities add to overall risk. “However,” the researchers noted, “not all young patients had a mild course, and not all old patients with comorbidities were critical.”
Therefore, the prognostic score can help identify patients at risk for severe progression outside other risk factors and “support individualized treatment decisions with objective data,” they added.
Dr. Reichberg called the concept of combining CBC parameters into one score “very valuable.” However, he added that incorporating an index into clinical practice “has historically been tricky.”
The results “probably have to be replicated,” Dr. Reichberg said.
He added that it is likely a CBC-based score will be combined with other measures. “I would like to see an index that combines all the tests we do [for COVID-19], including complete blood count.”
Dr. Van der Ven shared the next step in his research. “The algorithm should be installed on the hematology analyzers so the prognostic score will be automatically generated if a full blood count is asked for in a COVID-19 patient,” he said. “So implementation of score is the main focus now.”
Dr. van der Ven disclosed an ad hoc consultancy agreement with Sysmex Europe. Sysmex Europe provided the reagents in the study free of charge; no other funders were involved. Dr. Reichberg has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A scoring system based on 10 parameters in a complete blood count with differential within 3 days of hospital presentation predict those with COVID-19 who are most likely to progress to critical illness, new evidence shows.
Advantages include prognosis based on a common and inexpensive clinical measure, as well as automatic generation of the score along with CBC results, noted investigators in the observational study conducted throughout 11 European hospitals.
“COVID-19 comes along with specific alterations in circulating blood cells that can be detected by a routine hematology analyzer, especially when that hematology analyzer is also capable to recognize activated immune cells and early circulating blood cells, such as erythroblast and immature granulocytes,” senior author Andre van der Ven, MD, PhD, infectious diseases specialist and professor of international health at Radboud University Medical Center’s Center for Infectious Diseases in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
Furthermore, Dr. van der Ven said, “these specific changes are also seen in the early course of COVID-19 disease, and more in those that will develop serious disease compared to those with mild disease.”
The study was published online Dec. 21 in the journal eLife.
The study is “almost instinctively correct. It’s basically what clinicians do informally with complete blood count … looking at a combination of results to get the gestalt of what patients are going through,” Samuel Reichberg, MD, PhD, associate medical director of the Northwell Health Core Laboratory in Lake Success, N.Y., said in an interview.
“This is something that begs to be done for COVID-19. I’m surprised no one has done this before,” he added.
Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues created an algorithm based on 1,587 CBC assays from 923 adults. They also validated the scoring system in a second cohort of 217 CBC measurements in 202 people. The findings were concordant – the score accurately predicted the need for critical care within 14 days in 70.5% of the development cohort and 72% of the validation group.
The scoring system was superior to any of the 10 parameters alone. Over 14 days, the majority of those classified as noncritical within the first 3 days remained clinically stable, whereas the “clinical illness” group progressed. Clinical severity peaked on day 6.
Most previous COVID-19 prognosis research was geographically limited, carried a high risk for bias and/or did not validate the findings, Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues noted.
Early identification, early intervention
The aim of the score is “to assist with objective risk stratification to support patient management decision-making early on, and thus facilitate timely interventions, such as need for ICU or not, before symptoms of severe illness become clinically overt, with the intention to improve patient outcomes, and not to predict mortality,” the investigators noted.
Dr. Van der Ven and colleagues developed the score based on adults presenting from Feb. 21 to April 6, with outcomes followed until June 9. Median age of the 982 patients was 71 years and approximately two-thirds were men. They used a Sysmex Europe XN-1000 (Hamburg, Germany) hemocytometric analyzer in the study.
Only 7% of this cohort was not admitted to a hospital. Another 74% were admitted to a general ward and the remaining 19% were transferred directly to the ICU.
The scoring system includes parameters for neutrophils, monocytes, red blood cells and immature granulocytes, and when available, reticulocyte and iron bioavailability measures.
The researchers report significant differences over time in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio between the critical illness and noncritical groups (P < .001), for example. They also found significant differences in hemoglobin levels between cohorts after day 5.
The system generates a score from 0 to 28. Sensitivity for correctly predicting the need for critical care increased from 62% on day 1 to 93% on day 6.
A more objective assessment of risk
The study demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 infection is characterized by hemocytometric changes over time. These changes, reflected together in the prognostic score, could aid in the early identification of patients whose clinical course is more likely to deteriorate over time.
The findings also support other work that shows men are more likely to present to the hospital with COVID-19, and that older age and presence of comorbidities add to overall risk. “However,” the researchers noted, “not all young patients had a mild course, and not all old patients with comorbidities were critical.”
Therefore, the prognostic score can help identify patients at risk for severe progression outside other risk factors and “support individualized treatment decisions with objective data,” they added.
Dr. Reichberg called the concept of combining CBC parameters into one score “very valuable.” However, he added that incorporating an index into clinical practice “has historically been tricky.”
The results “probably have to be replicated,” Dr. Reichberg said.
He added that it is likely a CBC-based score will be combined with other measures. “I would like to see an index that combines all the tests we do [for COVID-19], including complete blood count.”
Dr. Van der Ven shared the next step in his research. “The algorithm should be installed on the hematology analyzers so the prognostic score will be automatically generated if a full blood count is asked for in a COVID-19 patient,” he said. “So implementation of score is the main focus now.”
Dr. van der Ven disclosed an ad hoc consultancy agreement with Sysmex Europe. Sysmex Europe provided the reagents in the study free of charge; no other funders were involved. Dr. Reichberg has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New pediatric cases down as U.S. tops 2 million children with COVID-19
The United States exceeded 2 million reported cases of COVID-19 in children just 6 weeks after recording its 1 millionth case, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
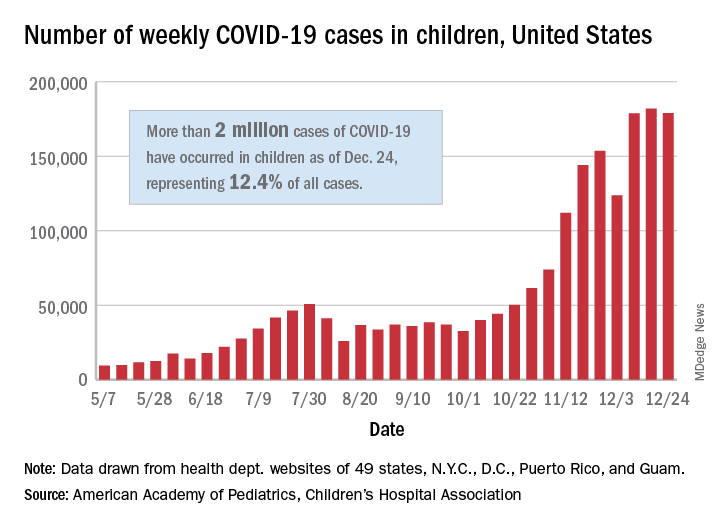
The total number of cases in children was 2,000,681 as of Dec. 24, which represents 12.4% of all cases reported by the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA stated Dec. 29.
The case count for just the latest week, 178,935, was actually down 1.7% from the 182,018 reported the week before, marking the second drop since the beginning of December. The first came during the week ending Dec. 3, when the number of cases dropped more than 19% from the previous week, based on data from the AAP/CHA report.
The cumulative national rate of coronavirus infection is now 2,658 cases per 100,000 children, and “13 states have reported more than 4,000 cases per 100,000,” the two groups said.
The highest rate for any state can be found in North Dakota, which has had 7,722 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children. Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children at 20.5%, and California has reported the most cases overall, 234,174, the report shows.
Data on testing, hospitalization, and mortality were not included in the Dec. 29 report because of the holiday but will be available in the next edition, scheduled for release on Jan. 5, 2021.
The United States exceeded 2 million reported cases of COVID-19 in children just 6 weeks after recording its 1 millionth case, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of cases in children was 2,000,681 as of Dec. 24, which represents 12.4% of all cases reported by the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA stated Dec. 29.
The case count for just the latest week, 178,935, was actually down 1.7% from the 182,018 reported the week before, marking the second drop since the beginning of December. The first came during the week ending Dec. 3, when the number of cases dropped more than 19% from the previous week, based on data from the AAP/CHA report.
The cumulative national rate of coronavirus infection is now 2,658 cases per 100,000 children, and “13 states have reported more than 4,000 cases per 100,000,” the two groups said.
The highest rate for any state can be found in North Dakota, which has had 7,722 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children. Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children at 20.5%, and California has reported the most cases overall, 234,174, the report shows.
Data on testing, hospitalization, and mortality were not included in the Dec. 29 report because of the holiday but will be available in the next edition, scheduled for release on Jan. 5, 2021.
The United States exceeded 2 million reported cases of COVID-19 in children just 6 weeks after recording its 1 millionth case, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of cases in children was 2,000,681 as of Dec. 24, which represents 12.4% of all cases reported by the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA stated Dec. 29.
The case count for just the latest week, 178,935, was actually down 1.7% from the 182,018 reported the week before, marking the second drop since the beginning of December. The first came during the week ending Dec. 3, when the number of cases dropped more than 19% from the previous week, based on data from the AAP/CHA report.
The cumulative national rate of coronavirus infection is now 2,658 cases per 100,000 children, and “13 states have reported more than 4,000 cases per 100,000,” the two groups said.
The highest rate for any state can be found in North Dakota, which has had 7,722 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children. Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children at 20.5%, and California has reported the most cases overall, 234,174, the report shows.
Data on testing, hospitalization, and mortality were not included in the Dec. 29 report because of the holiday but will be available in the next edition, scheduled for release on Jan. 5, 2021.
COVID-19 vaccines: Safe for immunocompromised patients?
Coronavirus vaccines have become a reality, as they are now being approved and authorized for use in a growing number of countries including the United States. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has just issued emergency authorization for the use of the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Pfizer and BioNTech. Close behind is the vaccine developed by Moderna, which has also applied to the FDA for emergency authorization.
The efficacy of a two-dose administration of the vaccine has been pegged at 95.0%, and the FDA has said that the 95% credible interval for the vaccine efficacy was 90.3%-97.6%. But as with many initial clinical trials, whether for drugs or vaccines, not all populations were represented in the trial cohort, including individuals who are immunocompromised. At the current time, it is largely unknown how safe or effective the vaccine may be in this large population, many of whom are at high risk for serious COVID-19 complications.
At a special session held during the recent annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Anthony Fauci, MD, the nation’s leading infectious disease expert, said that individuals with compromised immune systems, whether because of chemotherapy or a bone marrow transplant, should plan to be vaccinated when the opportunity arises.
In response to a question from ASH President Stephanie J. Lee, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, Dr. Fauci emphasized that, despite being excluded from clinical trials, this population should get vaccinated. “I think we should recommend that they get vaccinated,” he said. “I mean, it is clear that, if you are on immunosuppressive agents, history tells us that you’re not going to have as robust a response as if you had an intact immune system that was not being compromised. But some degree of immunity is better than no degree of immunity.”
That does seem to be the consensus among experts who spoke in interviews: that as long as these are not live attenuated vaccines, they hold no specific risk to an immunocompromised patient, other than any factors specific to the individual that could be a contraindication.
“Patients, family members, friends, and work contacts should be encouraged to receive the vaccine,” said William Stohl, MD, PhD, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “Clinicians should advise patients to obtain the vaccine sooner rather than later.”
Kevin C. Wang, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, agreed. “I am 100% with Dr. Fauci. Everyone should get the vaccine, even if it may not be as effective,” he said. “I would treat it exactly like the flu vaccines that we recommend folks get every year.”
Dr. Wang noted that he couldn’t think of any contraindications unless the immunosuppressed patients have a history of severe allergic reactions to prior vaccinations. “But I would even say patients with history of cancer, upon recommendation of their oncologists, are likely to be suitable candidates for the vaccine,” he added. “I would say clinicians should approach counseling the same way they counsel patients for the flu vaccine, and as far as I know, there are no concerns for systemic drugs commonly used in dermatology patients.”
However, guidance has not yet been issued from either the FDA or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention regarding the use of the vaccine in immunocompromised individuals. Given the lack of data, the FDA has said that “it will be something that providers will need to consider on an individual basis,” and that individuals should consult with physicians to weigh the potential benefits and potential risks.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has said that clinicians need more guidance on whether to use the vaccine in pregnant or breastfeeding women, the immunocompromised, or those who have a history of allergies. The CDC itself has not yet released its formal guidance on vaccine use.
COVID-19 vaccines
Vaccines typically require years of research and testing before reaching the clinic, but this year researchers embarked on a global effort to develop safe and effective coronavirus vaccines in record time. Both the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines have only a few months of phase 3 clinical trial data, so much remains unknown about them, including their duration of effect and any long-term safety signals. In addition to excluding immunocompromised individuals, the clinical trials did not include children or pregnant women, so data are lacking for several population subgroups.
But these will not be the only vaccines available, as the pipeline is already becoming crowded. U.S. clinical trial data from a vaccine jointly being developed by Oxford-AstraZeneca, could potentially be ready, along with a request for FDA emergency use authorization, by late January 2021.
In addition, China and Russia have released vaccines, and there are currently 61 vaccines being investigated in clinical trials and at least 85 preclinical products under active investigation.
The vaccine candidates are using both conventional and novel mechanisms of action to elicit an immune response in patients. Conventional methods include attenuated inactivated (killed) virus and recombinant viral protein vaccines to develop immunity. Novel approaches include replication-deficient, adenovirus vector-based vaccines that contain the viral protein, and mRNA-based vaccines, such as the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, that encode for a SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
“The special vaccine concern for immunocompromised individuals is introduction of a live virus,” Dr. Stohl said. “Neither the Moderna nor Pfizer vaccines are live viruses, so there should be no special contraindication for such individuals.”
Live vaccine should be avoided in immunocompromised patients, and currently, live SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are only being developed in India and Turkey.
It is not unusual for vaccine trials to begin with cohorts that exclude participants with various health conditions, including those who are immunocompromised. These groups are generally then evaluated in phase 4 trials, or postmarketing surveillance. While the precise number of immunosuppressed adults in the United States is not known, the numbers are believed to be rising because of increased life expectancy among immunosuppressed adults as a result of advances in treatment and new and wider indications for therapies that can affect the immune system.
According to data from the 2013 National Health Interview Survey, an estimated 2.7% of U.S. adults are immunosuppressed. This population covers a broad array of health conditions and medical specialties; people living with inflammatory or autoimmune conditions, such as inflammatory rheumatic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, lupus); inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis); psoriasis; multiple sclerosis; organ transplant recipients; patients undergoing chemotherapy; and life-long immunosuppression attributable to HIV infection.
As the vaccines begin to roll out and become available, how should clinicians advise their patients, in the absence of any clinical trial data?
Risk vs. benefit
Gilaad Kaplan, MD, MPH, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at the University of Calgary (Alta.), noted that the inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) community has dealt with tremendous anxiety during the pandemic because many are immunocompromised because of the medications they use to treat their disease.
“For example, many patients with IBD are on biologics like anti-TNF [tumor necrosis factor] therapies, which are also used in other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,” he said. “Understandably, individuals with IBD on immunosuppressive medications are concerned about the risk of severe complications due to COVID-19.”
The entire IBD community, along with the world, celebrated the announcement that multiple vaccines are protective against SARS-CoV-2, he noted. “Vaccines offer the potential to reduce the spread of COVID-19, allowing society to revert back to normalcy,” Dr. Kaplan said. “Moreover, for vulnerable populations, including those who are immunocompromised, vaccines offer the potential to directly protect them from the morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19.”
That said, even though the news of vaccines are extremely promising, some cautions must be raised regarding their use in immunocompromised populations, such as persons with IBD. “The current trials, to my knowledge, did not include immunocompromised individuals and thus, we can only extrapolate from what we know from other trials of different vaccines,” he explained. “We know from prior vaccines studies that the immune response following vaccination is less robust in those who are immunocompromised as compared to a healthy control population.”
Dr. Kaplan also pointed to recent reports of allergic reactions that have been reported in healthy individuals. “We don’t know whether side effects, like allergic reactions, may be different in unstudied populations,” he said. “Thus, the medical and scientific community should prioritize clinical studies of safety and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in immunocompromised populations.”
So, what does this mean for an individual with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who is immunocompromised? Dr. Kaplan explained that it is a balance between the potential harm of being infected with COVID-19 and the uncertainty of receiving a vaccine in an understudied population. For those who are highly susceptible to dying from COVID-19, such as an older adult with IBD, or someone who faces high exposure, such as a health care worker, the potential protection of the vaccine greatly outweighs the uncertainty.
“However, for individuals who are at otherwise lower risk – for example, young and able to work from home – then waiting a few extra months for postmarketing surveillance studies in immunocompromised populations may be a reasonable approach, as long as these individuals are taking great care to avoid infection,” he said.
No waiting needed
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, feels that the newly approved vaccine should be safe for most of his patients.
“Patients with psoriatic disease should get the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible based on eligibility as determined by the CDC and local public health officials,” he said. “It is not a live vaccine, and therefore patients on biologics or other immune-modulating or immune-suppressing treatment can receive it.”
However, the impact of psoriasis treatment on immune response to the mRNA-based vaccines is not known. Dr. Gelfand noted that, extrapolating from the vaccine literature, there is some evidence that methotrexate reduces response to the influenza vaccine. “However, the clinical significance of this finding is not clear,” he said. “Since the mRNA vaccine needs to be taken twice, a few weeks apart, I do not recommend interrupting or delaying treatment for psoriatic disease while undergoing vaccination for COVID-19.”
Given the reports of allergic reactions, he added that it is advisable for patients with a history of life-threatening allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis or who have been advised to carry an epinephrine autoinjector, to talk with their health care provider to determine if COVID-19 vaccination is medically appropriate.
The National Psoriasis Foundation has issued guidance on COVID-19, explained Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, pathology, and social sciences & health policy at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., who is also a member of the committee that is working on those guidelines and keeping them up to date. “We are in the process of updating the guidelines with information on COVID vaccines,” he said.
He agreed that there are no contraindications for psoriasis patients to receive the vaccine, regardless of whether they are on immunosuppressive treatment, even though definitive data are lacking. “Fortunately, there’s a lot of good data coming out of Italy that patients with psoriasis on biologics do not appear to be at increased risk of getting COVID or of having worse outcomes from COVID,” he said.
Patients are going to ask about the vaccines, and when counseling them, clinicians should discuss the available data, the residual uncertainty, and patients’ concerns should be considered, Dr. Feldman explained. “There may be some concern that steroids and cyclosporine would reduce the effectiveness of vaccines, but there is no concern that any of the drugs would cause increased risk from nonlive vaccines.”
He added that there is evidence that “patients on biologics who receive nonlive vaccines do develop antibody responses and are immunized.”
Boosting efficacy
Even prior to making their announcement, the American College of Rheumatology had said that they would endorse the vaccine for all patients, explained rheumatologist Brett Smith, DO, from Blount Memorial Physicians Group and East Tennessee Children’s Hospital, Alcoa. “The vaccine is safe for all patients, but the problem may be that it’s not as effective,” he said. “But we don’t know that because it hasn’t been tested.”
With other vaccines, biologic medicines are held for 2 weeks before and afterwards, to get the best response. “But some patients don’t want to stop the medication,” Dr. Smith said. “They are afraid that their symptoms will return.”
As for counseling patients as to whether they should receive this vaccine, he explained that he typically doesn’t try to sway patients one way or another until they are really high risk. “When I counsel, it really depends on the individual situation. And for this vaccine, we have to be open to the fact that many people have already made up their mind.”
There are a lot of questions regarding the vaccine. One is the short time frame of development. “Vaccines typically take 6-10 years to come on the market, and this one is now available after a 3-month study,” Dr. Smith said. “Some have already decided that it’s too new for them.”
The process is also new, and patients need to understand that it doesn’t contain an active virus and “you can’t catch coronavirus from it.”
Dr. Smith also explained that, because the vaccine may be less effective in a person using biologic therapies, there is currently no information available on repeat vaccination. “These are all unanswered questions,” he said. “If the antibodies wane in a short time, can we be revaccinated and in what time frame? We just don’t know that yet.”
Marcelo Bonomi, MD, a medical oncologist from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, explained that one way to ensure a more optimal response to the vaccine would be to wait until the patient has finished chemotherapy.* “The vaccine can be offered at that time, and in the meantime, they can take other steps to avoid infection,” he said. “If they are very immunosuppressed, it isn’t worth trying to give the vaccine.”
Cancer patients should be encouraged to stay as healthy as possible, and to wear masks and social distance. “It’s a comprehensive approach. Eat healthy, avoid alcohol and tobacco, and exercise. [These things] will help boost the immune system,” Dr. Bonomi said. “Family members should be encouraged to get vaccinated, which will help them avoid infection and exposing the patient.”
Jim Boonyaratanakornkit, MD, PhD, an infectious disease specialist who cares for cancer patients at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, agreed. “Giving a vaccine right after a transplant is a futile endeavor,” he said. “We need to wait 6 months to have an immune response.”
He pointed out there may be a continuing higher number of cases, with high levels peaking in Washington in February and March. “Close friends and family should be vaccinated if possible,” he said, “which will help interrupt transmission.”
The vaccines are using new platforms that are totally different, and there is no clear data as to how long the antibodies will persist. “We know that they last for at least 4 months,” said Dr. Boonyaratanakornkit. “We don’t know what level of antibody will protect them from COVID-19 infection. Current studies are being conducted, but we don’t have that information for anyone yet.”
*Correction, 1/7/21: An earlier version of this article misattributed quotes from Dr. Marcelo Bonomi.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
Coronavirus vaccines have become a reality, as they are now being approved and authorized for use in a growing number of countries including the United States. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has just issued emergency authorization for the use of the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Pfizer and BioNTech. Close behind is the vaccine developed by Moderna, which has also applied to the FDA for emergency authorization.
The efficacy of a two-dose administration of the vaccine has been pegged at 95.0%, and the FDA has said that the 95% credible interval for the vaccine efficacy was 90.3%-97.6%. But as with many initial clinical trials, whether for drugs or vaccines, not all populations were represented in the trial cohort, including individuals who are immunocompromised. At the current time, it is largely unknown how safe or effective the vaccine may be in this large population, many of whom are at high risk for serious COVID-19 complications.
At a special session held during the recent annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Anthony Fauci, MD, the nation’s leading infectious disease expert, said that individuals with compromised immune systems, whether because of chemotherapy or a bone marrow transplant, should plan to be vaccinated when the opportunity arises.
In response to a question from ASH President Stephanie J. Lee, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, Dr. Fauci emphasized that, despite being excluded from clinical trials, this population should get vaccinated. “I think we should recommend that they get vaccinated,” he said. “I mean, it is clear that, if you are on immunosuppressive agents, history tells us that you’re not going to have as robust a response as if you had an intact immune system that was not being compromised. But some degree of immunity is better than no degree of immunity.”
That does seem to be the consensus among experts who spoke in interviews: that as long as these are not live attenuated vaccines, they hold no specific risk to an immunocompromised patient, other than any factors specific to the individual that could be a contraindication.
“Patients, family members, friends, and work contacts should be encouraged to receive the vaccine,” said William Stohl, MD, PhD, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “Clinicians should advise patients to obtain the vaccine sooner rather than later.”
Kevin C. Wang, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, agreed. “I am 100% with Dr. Fauci. Everyone should get the vaccine, even if it may not be as effective,” he said. “I would treat it exactly like the flu vaccines that we recommend folks get every year.”
Dr. Wang noted that he couldn’t think of any contraindications unless the immunosuppressed patients have a history of severe allergic reactions to prior vaccinations. “But I would even say patients with history of cancer, upon recommendation of their oncologists, are likely to be suitable candidates for the vaccine,” he added. “I would say clinicians should approach counseling the same way they counsel patients for the flu vaccine, and as far as I know, there are no concerns for systemic drugs commonly used in dermatology patients.”
However, guidance has not yet been issued from either the FDA or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention regarding the use of the vaccine in immunocompromised individuals. Given the lack of data, the FDA has said that “it will be something that providers will need to consider on an individual basis,” and that individuals should consult with physicians to weigh the potential benefits and potential risks.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has said that clinicians need more guidance on whether to use the vaccine in pregnant or breastfeeding women, the immunocompromised, or those who have a history of allergies. The CDC itself has not yet released its formal guidance on vaccine use.
COVID-19 vaccines
Vaccines typically require years of research and testing before reaching the clinic, but this year researchers embarked on a global effort to develop safe and effective coronavirus vaccines in record time. Both the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines have only a few months of phase 3 clinical trial data, so much remains unknown about them, including their duration of effect and any long-term safety signals. In addition to excluding immunocompromised individuals, the clinical trials did not include children or pregnant women, so data are lacking for several population subgroups.
But these will not be the only vaccines available, as the pipeline is already becoming crowded. U.S. clinical trial data from a vaccine jointly being developed by Oxford-AstraZeneca, could potentially be ready, along with a request for FDA emergency use authorization, by late January 2021.
In addition, China and Russia have released vaccines, and there are currently 61 vaccines being investigated in clinical trials and at least 85 preclinical products under active investigation.
The vaccine candidates are using both conventional and novel mechanisms of action to elicit an immune response in patients. Conventional methods include attenuated inactivated (killed) virus and recombinant viral protein vaccines to develop immunity. Novel approaches include replication-deficient, adenovirus vector-based vaccines that contain the viral protein, and mRNA-based vaccines, such as the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, that encode for a SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
“The special vaccine concern for immunocompromised individuals is introduction of a live virus,” Dr. Stohl said. “Neither the Moderna nor Pfizer vaccines are live viruses, so there should be no special contraindication for such individuals.”
Live vaccine should be avoided in immunocompromised patients, and currently, live SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are only being developed in India and Turkey.
It is not unusual for vaccine trials to begin with cohorts that exclude participants with various health conditions, including those who are immunocompromised. These groups are generally then evaluated in phase 4 trials, or postmarketing surveillance. While the precise number of immunosuppressed adults in the United States is not known, the numbers are believed to be rising because of increased life expectancy among immunosuppressed adults as a result of advances in treatment and new and wider indications for therapies that can affect the immune system.
According to data from the 2013 National Health Interview Survey, an estimated 2.7% of U.S. adults are immunosuppressed. This population covers a broad array of health conditions and medical specialties; people living with inflammatory or autoimmune conditions, such as inflammatory rheumatic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, lupus); inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis); psoriasis; multiple sclerosis; organ transplant recipients; patients undergoing chemotherapy; and life-long immunosuppression attributable to HIV infection.
As the vaccines begin to roll out and become available, how should clinicians advise their patients, in the absence of any clinical trial data?
Risk vs. benefit
Gilaad Kaplan, MD, MPH, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at the University of Calgary (Alta.), noted that the inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) community has dealt with tremendous anxiety during the pandemic because many are immunocompromised because of the medications they use to treat their disease.
“For example, many patients with IBD are on biologics like anti-TNF [tumor necrosis factor] therapies, which are also used in other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,” he said. “Understandably, individuals with IBD on immunosuppressive medications are concerned about the risk of severe complications due to COVID-19.”
The entire IBD community, along with the world, celebrated the announcement that multiple vaccines are protective against SARS-CoV-2, he noted. “Vaccines offer the potential to reduce the spread of COVID-19, allowing society to revert back to normalcy,” Dr. Kaplan said. “Moreover, for vulnerable populations, including those who are immunocompromised, vaccines offer the potential to directly protect them from the morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19.”
That said, even though the news of vaccines are extremely promising, some cautions must be raised regarding their use in immunocompromised populations, such as persons with IBD. “The current trials, to my knowledge, did not include immunocompromised individuals and thus, we can only extrapolate from what we know from other trials of different vaccines,” he explained. “We know from prior vaccines studies that the immune response following vaccination is less robust in those who are immunocompromised as compared to a healthy control population.”
Dr. Kaplan also pointed to recent reports of allergic reactions that have been reported in healthy individuals. “We don’t know whether side effects, like allergic reactions, may be different in unstudied populations,” he said. “Thus, the medical and scientific community should prioritize clinical studies of safety and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in immunocompromised populations.”
So, what does this mean for an individual with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who is immunocompromised? Dr. Kaplan explained that it is a balance between the potential harm of being infected with COVID-19 and the uncertainty of receiving a vaccine in an understudied population. For those who are highly susceptible to dying from COVID-19, such as an older adult with IBD, or someone who faces high exposure, such as a health care worker, the potential protection of the vaccine greatly outweighs the uncertainty.
“However, for individuals who are at otherwise lower risk – for example, young and able to work from home – then waiting a few extra months for postmarketing surveillance studies in immunocompromised populations may be a reasonable approach, as long as these individuals are taking great care to avoid infection,” he said.
No waiting needed
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, feels that the newly approved vaccine should be safe for most of his patients.
“Patients with psoriatic disease should get the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible based on eligibility as determined by the CDC and local public health officials,” he said. “It is not a live vaccine, and therefore patients on biologics or other immune-modulating or immune-suppressing treatment can receive it.”
However, the impact of psoriasis treatment on immune response to the mRNA-based vaccines is not known. Dr. Gelfand noted that, extrapolating from the vaccine literature, there is some evidence that methotrexate reduces response to the influenza vaccine. “However, the clinical significance of this finding is not clear,” he said. “Since the mRNA vaccine needs to be taken twice, a few weeks apart, I do not recommend interrupting or delaying treatment for psoriatic disease while undergoing vaccination for COVID-19.”
Given the reports of allergic reactions, he added that it is advisable for patients with a history of life-threatening allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis or who have been advised to carry an epinephrine autoinjector, to talk with their health care provider to determine if COVID-19 vaccination is medically appropriate.
The National Psoriasis Foundation has issued guidance on COVID-19, explained Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, pathology, and social sciences & health policy at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., who is also a member of the committee that is working on those guidelines and keeping them up to date. “We are in the process of updating the guidelines with information on COVID vaccines,” he said.
He agreed that there are no contraindications for psoriasis patients to receive the vaccine, regardless of whether they are on immunosuppressive treatment, even though definitive data are lacking. “Fortunately, there’s a lot of good data coming out of Italy that patients with psoriasis on biologics do not appear to be at increased risk of getting COVID or of having worse outcomes from COVID,” he said.
Patients are going to ask about the vaccines, and when counseling them, clinicians should discuss the available data, the residual uncertainty, and patients’ concerns should be considered, Dr. Feldman explained. “There may be some concern that steroids and cyclosporine would reduce the effectiveness of vaccines, but there is no concern that any of the drugs would cause increased risk from nonlive vaccines.”
He added that there is evidence that “patients on biologics who receive nonlive vaccines do develop antibody responses and are immunized.”
Boosting efficacy
Even prior to making their announcement, the American College of Rheumatology had said that they would endorse the vaccine for all patients, explained rheumatologist Brett Smith, DO, from Blount Memorial Physicians Group and East Tennessee Children’s Hospital, Alcoa. “The vaccine is safe for all patients, but the problem may be that it’s not as effective,” he said. “But we don’t know that because it hasn’t been tested.”
With other vaccines, biologic medicines are held for 2 weeks before and afterwards, to get the best response. “But some patients don’t want to stop the medication,” Dr. Smith said. “They are afraid that their symptoms will return.”
As for counseling patients as to whether they should receive this vaccine, he explained that he typically doesn’t try to sway patients one way or another until they are really high risk. “When I counsel, it really depends on the individual situation. And for this vaccine, we have to be open to the fact that many people have already made up their mind.”
There are a lot of questions regarding the vaccine. One is the short time frame of development. “Vaccines typically take 6-10 years to come on the market, and this one is now available after a 3-month study,” Dr. Smith said. “Some have already decided that it’s too new for them.”
The process is also new, and patients need to understand that it doesn’t contain an active virus and “you can’t catch coronavirus from it.”
Dr. Smith also explained that, because the vaccine may be less effective in a person using biologic therapies, there is currently no information available on repeat vaccination. “These are all unanswered questions,” he said. “If the antibodies wane in a short time, can we be revaccinated and in what time frame? We just don’t know that yet.”
Marcelo Bonomi, MD, a medical oncologist from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, explained that one way to ensure a more optimal response to the vaccine would be to wait until the patient has finished chemotherapy.* “The vaccine can be offered at that time, and in the meantime, they can take other steps to avoid infection,” he said. “If they are very immunosuppressed, it isn’t worth trying to give the vaccine.”
Cancer patients should be encouraged to stay as healthy as possible, and to wear masks and social distance. “It’s a comprehensive approach. Eat healthy, avoid alcohol and tobacco, and exercise. [These things] will help boost the immune system,” Dr. Bonomi said. “Family members should be encouraged to get vaccinated, which will help them avoid infection and exposing the patient.”
Jim Boonyaratanakornkit, MD, PhD, an infectious disease specialist who cares for cancer patients at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, agreed. “Giving a vaccine right after a transplant is a futile endeavor,” he said. “We need to wait 6 months to have an immune response.”
He pointed out there may be a continuing higher number of cases, with high levels peaking in Washington in February and March. “Close friends and family should be vaccinated if possible,” he said, “which will help interrupt transmission.”
The vaccines are using new platforms that are totally different, and there is no clear data as to how long the antibodies will persist. “We know that they last for at least 4 months,” said Dr. Boonyaratanakornkit. “We don’t know what level of antibody will protect them from COVID-19 infection. Current studies are being conducted, but we don’t have that information for anyone yet.”
*Correction, 1/7/21: An earlier version of this article misattributed quotes from Dr. Marcelo Bonomi.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
Coronavirus vaccines have become a reality, as they are now being approved and authorized for use in a growing number of countries including the United States. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has just issued emergency authorization for the use of the COVID-19 vaccine produced by Pfizer and BioNTech. Close behind is the vaccine developed by Moderna, which has also applied to the FDA for emergency authorization.
The efficacy of a two-dose administration of the vaccine has been pegged at 95.0%, and the FDA has said that the 95% credible interval for the vaccine efficacy was 90.3%-97.6%. But as with many initial clinical trials, whether for drugs or vaccines, not all populations were represented in the trial cohort, including individuals who are immunocompromised. At the current time, it is largely unknown how safe or effective the vaccine may be in this large population, many of whom are at high risk for serious COVID-19 complications.
At a special session held during the recent annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Anthony Fauci, MD, the nation’s leading infectious disease expert, said that individuals with compromised immune systems, whether because of chemotherapy or a bone marrow transplant, should plan to be vaccinated when the opportunity arises.
In response to a question from ASH President Stephanie J. Lee, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, Dr. Fauci emphasized that, despite being excluded from clinical trials, this population should get vaccinated. “I think we should recommend that they get vaccinated,” he said. “I mean, it is clear that, if you are on immunosuppressive agents, history tells us that you’re not going to have as robust a response as if you had an intact immune system that was not being compromised. But some degree of immunity is better than no degree of immunity.”
That does seem to be the consensus among experts who spoke in interviews: that as long as these are not live attenuated vaccines, they hold no specific risk to an immunocompromised patient, other than any factors specific to the individual that could be a contraindication.
“Patients, family members, friends, and work contacts should be encouraged to receive the vaccine,” said William Stohl, MD, PhD, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “Clinicians should advise patients to obtain the vaccine sooner rather than later.”
Kevin C. Wang, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, agreed. “I am 100% with Dr. Fauci. Everyone should get the vaccine, even if it may not be as effective,” he said. “I would treat it exactly like the flu vaccines that we recommend folks get every year.”
Dr. Wang noted that he couldn’t think of any contraindications unless the immunosuppressed patients have a history of severe allergic reactions to prior vaccinations. “But I would even say patients with history of cancer, upon recommendation of their oncologists, are likely to be suitable candidates for the vaccine,” he added. “I would say clinicians should approach counseling the same way they counsel patients for the flu vaccine, and as far as I know, there are no concerns for systemic drugs commonly used in dermatology patients.”
However, guidance has not yet been issued from either the FDA or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention regarding the use of the vaccine in immunocompromised individuals. Given the lack of data, the FDA has said that “it will be something that providers will need to consider on an individual basis,” and that individuals should consult with physicians to weigh the potential benefits and potential risks.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has said that clinicians need more guidance on whether to use the vaccine in pregnant or breastfeeding women, the immunocompromised, or those who have a history of allergies. The CDC itself has not yet released its formal guidance on vaccine use.
COVID-19 vaccines
Vaccines typically require years of research and testing before reaching the clinic, but this year researchers embarked on a global effort to develop safe and effective coronavirus vaccines in record time. Both the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines have only a few months of phase 3 clinical trial data, so much remains unknown about them, including their duration of effect and any long-term safety signals. In addition to excluding immunocompromised individuals, the clinical trials did not include children or pregnant women, so data are lacking for several population subgroups.
But these will not be the only vaccines available, as the pipeline is already becoming crowded. U.S. clinical trial data from a vaccine jointly being developed by Oxford-AstraZeneca, could potentially be ready, along with a request for FDA emergency use authorization, by late January 2021.
In addition, China and Russia have released vaccines, and there are currently 61 vaccines being investigated in clinical trials and at least 85 preclinical products under active investigation.
The vaccine candidates are using both conventional and novel mechanisms of action to elicit an immune response in patients. Conventional methods include attenuated inactivated (killed) virus and recombinant viral protein vaccines to develop immunity. Novel approaches include replication-deficient, adenovirus vector-based vaccines that contain the viral protein, and mRNA-based vaccines, such as the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, that encode for a SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
“The special vaccine concern for immunocompromised individuals is introduction of a live virus,” Dr. Stohl said. “Neither the Moderna nor Pfizer vaccines are live viruses, so there should be no special contraindication for such individuals.”
Live vaccine should be avoided in immunocompromised patients, and currently, live SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are only being developed in India and Turkey.
It is not unusual for vaccine trials to begin with cohorts that exclude participants with various health conditions, including those who are immunocompromised. These groups are generally then evaluated in phase 4 trials, or postmarketing surveillance. While the precise number of immunosuppressed adults in the United States is not known, the numbers are believed to be rising because of increased life expectancy among immunosuppressed adults as a result of advances in treatment and new and wider indications for therapies that can affect the immune system.
According to data from the 2013 National Health Interview Survey, an estimated 2.7% of U.S. adults are immunosuppressed. This population covers a broad array of health conditions and medical specialties; people living with inflammatory or autoimmune conditions, such as inflammatory rheumatic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, lupus); inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis); psoriasis; multiple sclerosis; organ transplant recipients; patients undergoing chemotherapy; and life-long immunosuppression attributable to HIV infection.
As the vaccines begin to roll out and become available, how should clinicians advise their patients, in the absence of any clinical trial data?
Risk vs. benefit
Gilaad Kaplan, MD, MPH, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at the University of Calgary (Alta.), noted that the inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) community has dealt with tremendous anxiety during the pandemic because many are immunocompromised because of the medications they use to treat their disease.
“For example, many patients with IBD are on biologics like anti-TNF [tumor necrosis factor] therapies, which are also used in other immune-mediated inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,” he said. “Understandably, individuals with IBD on immunosuppressive medications are concerned about the risk of severe complications due to COVID-19.”
The entire IBD community, along with the world, celebrated the announcement that multiple vaccines are protective against SARS-CoV-2, he noted. “Vaccines offer the potential to reduce the spread of COVID-19, allowing society to revert back to normalcy,” Dr. Kaplan said. “Moreover, for vulnerable populations, including those who are immunocompromised, vaccines offer the potential to directly protect them from the morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19.”
That said, even though the news of vaccines are extremely promising, some cautions must be raised regarding their use in immunocompromised populations, such as persons with IBD. “The current trials, to my knowledge, did not include immunocompromised individuals and thus, we can only extrapolate from what we know from other trials of different vaccines,” he explained. “We know from prior vaccines studies that the immune response following vaccination is less robust in those who are immunocompromised as compared to a healthy control population.”
Dr. Kaplan also pointed to recent reports of allergic reactions that have been reported in healthy individuals. “We don’t know whether side effects, like allergic reactions, may be different in unstudied populations,” he said. “Thus, the medical and scientific community should prioritize clinical studies of safety and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in immunocompromised populations.”
So, what does this mean for an individual with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who is immunocompromised? Dr. Kaplan explained that it is a balance between the potential harm of being infected with COVID-19 and the uncertainty of receiving a vaccine in an understudied population. For those who are highly susceptible to dying from COVID-19, such as an older adult with IBD, or someone who faces high exposure, such as a health care worker, the potential protection of the vaccine greatly outweighs the uncertainty.
“However, for individuals who are at otherwise lower risk – for example, young and able to work from home – then waiting a few extra months for postmarketing surveillance studies in immunocompromised populations may be a reasonable approach, as long as these individuals are taking great care to avoid infection,” he said.
No waiting needed
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, feels that the newly approved vaccine should be safe for most of his patients.
“Patients with psoriatic disease should get the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible based on eligibility as determined by the CDC and local public health officials,” he said. “It is not a live vaccine, and therefore patients on biologics or other immune-modulating or immune-suppressing treatment can receive it.”
However, the impact of psoriasis treatment on immune response to the mRNA-based vaccines is not known. Dr. Gelfand noted that, extrapolating from the vaccine literature, there is some evidence that methotrexate reduces response to the influenza vaccine. “However, the clinical significance of this finding is not clear,” he said. “Since the mRNA vaccine needs to be taken twice, a few weeks apart, I do not recommend interrupting or delaying treatment for psoriatic disease while undergoing vaccination for COVID-19.”
Given the reports of allergic reactions, he added that it is advisable for patients with a history of life-threatening allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis or who have been advised to carry an epinephrine autoinjector, to talk with their health care provider to determine if COVID-19 vaccination is medically appropriate.
The National Psoriasis Foundation has issued guidance on COVID-19, explained Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, pathology, and social sciences & health policy at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., who is also a member of the committee that is working on those guidelines and keeping them up to date. “We are in the process of updating the guidelines with information on COVID vaccines,” he said.
He agreed that there are no contraindications for psoriasis patients to receive the vaccine, regardless of whether they are on immunosuppressive treatment, even though definitive data are lacking. “Fortunately, there’s a lot of good data coming out of Italy that patients with psoriasis on biologics do not appear to be at increased risk of getting COVID or of having worse outcomes from COVID,” he said.
Patients are going to ask about the vaccines, and when counseling them, clinicians should discuss the available data, the residual uncertainty, and patients’ concerns should be considered, Dr. Feldman explained. “There may be some concern that steroids and cyclosporine would reduce the effectiveness of vaccines, but there is no concern that any of the drugs would cause increased risk from nonlive vaccines.”
He added that there is evidence that “patients on biologics who receive nonlive vaccines do develop antibody responses and are immunized.”
Boosting efficacy
Even prior to making their announcement, the American College of Rheumatology had said that they would endorse the vaccine for all patients, explained rheumatologist Brett Smith, DO, from Blount Memorial Physicians Group and East Tennessee Children’s Hospital, Alcoa. “The vaccine is safe for all patients, but the problem may be that it’s not as effective,” he said. “But we don’t know that because it hasn’t been tested.”
With other vaccines, biologic medicines are held for 2 weeks before and afterwards, to get the best response. “But some patients don’t want to stop the medication,” Dr. Smith said. “They are afraid that their symptoms will return.”
As for counseling patients as to whether they should receive this vaccine, he explained that he typically doesn’t try to sway patients one way or another until they are really high risk. “When I counsel, it really depends on the individual situation. And for this vaccine, we have to be open to the fact that many people have already made up their mind.”
There are a lot of questions regarding the vaccine. One is the short time frame of development. “Vaccines typically take 6-10 years to come on the market, and this one is now available after a 3-month study,” Dr. Smith said. “Some have already decided that it’s too new for them.”
The process is also new, and patients need to understand that it doesn’t contain an active virus and “you can’t catch coronavirus from it.”
Dr. Smith also explained that, because the vaccine may be less effective in a person using biologic therapies, there is currently no information available on repeat vaccination. “These are all unanswered questions,” he said. “If the antibodies wane in a short time, can we be revaccinated and in what time frame? We just don’t know that yet.”
Marcelo Bonomi, MD, a medical oncologist from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, explained that one way to ensure a more optimal response to the vaccine would be to wait until the patient has finished chemotherapy.* “The vaccine can be offered at that time, and in the meantime, they can take other steps to avoid infection,” he said. “If they are very immunosuppressed, it isn’t worth trying to give the vaccine.”
Cancer patients should be encouraged to stay as healthy as possible, and to wear masks and social distance. “It’s a comprehensive approach. Eat healthy, avoid alcohol and tobacco, and exercise. [These things] will help boost the immune system,” Dr. Bonomi said. “Family members should be encouraged to get vaccinated, which will help them avoid infection and exposing the patient.”
Jim Boonyaratanakornkit, MD, PhD, an infectious disease specialist who cares for cancer patients at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, agreed. “Giving a vaccine right after a transplant is a futile endeavor,” he said. “We need to wait 6 months to have an immune response.”
He pointed out there may be a continuing higher number of cases, with high levels peaking in Washington in February and March. “Close friends and family should be vaccinated if possible,” he said, “which will help interrupt transmission.”
The vaccines are using new platforms that are totally different, and there is no clear data as to how long the antibodies will persist. “We know that they last for at least 4 months,” said Dr. Boonyaratanakornkit. “We don’t know what level of antibody will protect them from COVID-19 infection. Current studies are being conducted, but we don’t have that information for anyone yet.”
*Correction, 1/7/21: An earlier version of this article misattributed quotes from Dr. Marcelo Bonomi.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
Patients with cancer a ‘high priority’ for COVID-19 vaccine, says AACR task force
“The available evidence supports the conclusion that patients with cancer, in particular with hematologic malignancies, should be considered among the high-risk groups for priority COVID-19 vaccination,” according to the AACR’s COVID-19 and Cancer Task Force.
A review of literature suggested that COVID-19 fatality rates for patients with cancer were double that of individuals without cancer, the team noted. The higher mortality rates still trended upward, even after adjusting for confounders including age, sex, and comorbidities, indicating that there is a greater risk for severe disease and COVID-19–related mortality.
The new AACR position paper was published online Dec. 19 in Cancer Discovery.
“We conclude that patients with an active cancer should be considered for priority access to COVID-19 vaccination, along other particularly vulnerable populations with risk factors for adverse outcomes with COVID-19,” the team wrote.
However, the authors noted that “it is unclear whether this recommendation should be applicable to patients with a past diagnosis of cancer, as cancer survivors can be considered having the same risk as other persons with matched age and other risk factors.
“Given that there are nearly 17 million people living with a history of cancer in the United States alone, it is critical to understand whether these individuals are at a higher risk to contract SARS-COV-2 and to experience severe outcomes from COVID-19,” they added.
Allocation of initial doses
There has already been much discussion on the allocation of the initial doses of COVID-19 vaccines that have become available in the United States. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended that the first wave of vaccinations, described as phase 1a, should be administered to health care workers (about 21 million people) and residents of long-term care facilities (about 3 million).
The next priority group, phase 1b, should consist of frontline essential workers, a group of about 30 million, and adults aged 75 years or older, a group of about 21 million. When overlap between the groups is taken into account, phase 1b covers about 49 million people, according to the CDC.
Finally, phase 1c, the third priority group, would include adults aged 65-74 years (a group of about 32 million), adults aged 16-64 years with high-risk medical conditions (a group of about 110 million), and essential workers who did not qualify for inclusion in phase 1b (a group of about 57 million). With the overlap, Phase 1c would cover about 129 million people.
The AACR task force, led by Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, Los Angeles, noted in their position paper that their recommendation is consistent with ACIP’s guidelines. Those guidelines concluded that patients with cancer are at a higher risk for severe COVID-19, and should be one of the groups considered for early COVID-19 vaccination.
Questions remain
Approached for independent comment, Cardinale Smith, MD, PhD, chief quality officer for cancer services for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York, agreed with the AACR task force. “I share that they should be high priority,” she said, “But we don’t know that the efficacy will the same.”
Dr. Smith noted that the impact of cancer therapy on patient immune systems is more related to the type of treatment they’re receiving, and B- and T-cell responses. “But regardless, they should be getting the vaccine, and we just need to follow the guidelines.”
The AACR task force noted that information thus far is quite limited as to the effects of COVID-19 vaccination in patients with cancer. In the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 COVID vaccine trial, of 43,540 participants, only 3.7% were reported to have cancer. Other large COVID-19 vaccine trials will provide further follow-up information on the effectiveness of the vaccines in patients receiving different cancer treatments, they wrote, but for now, there is “currently not enough data to evaluate the interactions between active oncologic therapy with the ability to induce protective immunity” to COVID-19 with vaccination.
In a recent interview, Nora Disis, MD, a medical oncologist and director of both the Institute of Translational Health Sciences and the Cancer Vaccine Institute, University of Washington, Seattle, also discussed vaccinating cancer patients.
She pointed out that even though there are data suggesting that cancer patients are at higher risk, “they are a bit murky, in part because cancer patients are a heterogeneous group.”
“For example, there are data suggesting that lung and blood cancer patients fare worse,” said Dr. Disis, who is also editor in chief of JAMA Oncology. “There is also a suggestion that, like in the general population, COVID risk in cancer patients remains driven by comorbidities.”
She also pointed out the likelihood that individualized risk factors, including the type of cancer therapy, site of disease, and comorbidities, “will shape individual choices about vaccination among cancer patients.”
It is also reasonable to expect that patients with cancer will respond to the vaccines, even though historically some believed that they would be unable to mount an immune response. “Data on other viral vaccines have shown otherwise,” said Dr. Disis. “For example, there has been a long history of studies of flu vaccination in cancer patients, and in general, those vaccines confer protection.”
Several of the authors of the AACR position paper, including Dr. Ribas, reported relationships with industry as detailed in the paper. Dr. Smith has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The available evidence supports the conclusion that patients with cancer, in particular with hematologic malignancies, should be considered among the high-risk groups for priority COVID-19 vaccination,” according to the AACR’s COVID-19 and Cancer Task Force.
A review of literature suggested that COVID-19 fatality rates for patients with cancer were double that of individuals without cancer, the team noted. The higher mortality rates still trended upward, even after adjusting for confounders including age, sex, and comorbidities, indicating that there is a greater risk for severe disease and COVID-19–related mortality.
The new AACR position paper was published online Dec. 19 in Cancer Discovery.
“We conclude that patients with an active cancer should be considered for priority access to COVID-19 vaccination, along other particularly vulnerable populations with risk factors for adverse outcomes with COVID-19,” the team wrote.
However, the authors noted that “it is unclear whether this recommendation should be applicable to patients with a past diagnosis of cancer, as cancer survivors can be considered having the same risk as other persons with matched age and other risk factors.
“Given that there are nearly 17 million people living with a history of cancer in the United States alone, it is critical to understand whether these individuals are at a higher risk to contract SARS-COV-2 and to experience severe outcomes from COVID-19,” they added.
Allocation of initial doses
There has already been much discussion on the allocation of the initial doses of COVID-19 vaccines that have become available in the United States. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended that the first wave of vaccinations, described as phase 1a, should be administered to health care workers (about 21 million people) and residents of long-term care facilities (about 3 million).
The next priority group, phase 1b, should consist of frontline essential workers, a group of about 30 million, and adults aged 75 years or older, a group of about 21 million. When overlap between the groups is taken into account, phase 1b covers about 49 million people, according to the CDC.
Finally, phase 1c, the third priority group, would include adults aged 65-74 years (a group of about 32 million), adults aged 16-64 years with high-risk medical conditions (a group of about 110 million), and essential workers who did not qualify for inclusion in phase 1b (a group of about 57 million). With the overlap, Phase 1c would cover about 129 million people.
The AACR task force, led by Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, Los Angeles, noted in their position paper that their recommendation is consistent with ACIP’s guidelines. Those guidelines concluded that patients with cancer are at a higher risk for severe COVID-19, and should be one of the groups considered for early COVID-19 vaccination.
Questions remain
Approached for independent comment, Cardinale Smith, MD, PhD, chief quality officer for cancer services for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York, agreed with the AACR task force. “I share that they should be high priority,” she said, “But we don’t know that the efficacy will the same.”
Dr. Smith noted that the impact of cancer therapy on patient immune systems is more related to the type of treatment they’re receiving, and B- and T-cell responses. “But regardless, they should be getting the vaccine, and we just need to follow the guidelines.”
The AACR task force noted that information thus far is quite limited as to the effects of COVID-19 vaccination in patients with cancer. In the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 COVID vaccine trial, of 43,540 participants, only 3.7% were reported to have cancer. Other large COVID-19 vaccine trials will provide further follow-up information on the effectiveness of the vaccines in patients receiving different cancer treatments, they wrote, but for now, there is “currently not enough data to evaluate the interactions between active oncologic therapy with the ability to induce protective immunity” to COVID-19 with vaccination.
In a recent interview, Nora Disis, MD, a medical oncologist and director of both the Institute of Translational Health Sciences and the Cancer Vaccine Institute, University of Washington, Seattle, also discussed vaccinating cancer patients.
She pointed out that even though there are data suggesting that cancer patients are at higher risk, “they are a bit murky, in part because cancer patients are a heterogeneous group.”
“For example, there are data suggesting that lung and blood cancer patients fare worse,” said Dr. Disis, who is also editor in chief of JAMA Oncology. “There is also a suggestion that, like in the general population, COVID risk in cancer patients remains driven by comorbidities.”
She also pointed out the likelihood that individualized risk factors, including the type of cancer therapy, site of disease, and comorbidities, “will shape individual choices about vaccination among cancer patients.”
It is also reasonable to expect that patients with cancer will respond to the vaccines, even though historically some believed that they would be unable to mount an immune response. “Data on other viral vaccines have shown otherwise,” said Dr. Disis. “For example, there has been a long history of studies of flu vaccination in cancer patients, and in general, those vaccines confer protection.”
Several of the authors of the AACR position paper, including Dr. Ribas, reported relationships with industry as detailed in the paper. Dr. Smith has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The available evidence supports the conclusion that patients with cancer, in particular with hematologic malignancies, should be considered among the high-risk groups for priority COVID-19 vaccination,” according to the AACR’s COVID-19 and Cancer Task Force.
A review of literature suggested that COVID-19 fatality rates for patients with cancer were double that of individuals without cancer, the team noted. The higher mortality rates still trended upward, even after adjusting for confounders including age, sex, and comorbidities, indicating that there is a greater risk for severe disease and COVID-19–related mortality.
The new AACR position paper was published online Dec. 19 in Cancer Discovery.
“We conclude that patients with an active cancer should be considered for priority access to COVID-19 vaccination, along other particularly vulnerable populations with risk factors for adverse outcomes with COVID-19,” the team wrote.
However, the authors noted that “it is unclear whether this recommendation should be applicable to patients with a past diagnosis of cancer, as cancer survivors can be considered having the same risk as other persons with matched age and other risk factors.
“Given that there are nearly 17 million people living with a history of cancer in the United States alone, it is critical to understand whether these individuals are at a higher risk to contract SARS-COV-2 and to experience severe outcomes from COVID-19,” they added.
Allocation of initial doses
There has already been much discussion on the allocation of the initial doses of COVID-19 vaccines that have become available in the United States. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended that the first wave of vaccinations, described as phase 1a, should be administered to health care workers (about 21 million people) and residents of long-term care facilities (about 3 million).
The next priority group, phase 1b, should consist of frontline essential workers, a group of about 30 million, and adults aged 75 years or older, a group of about 21 million. When overlap between the groups is taken into account, phase 1b covers about 49 million people, according to the CDC.
Finally, phase 1c, the third priority group, would include adults aged 65-74 years (a group of about 32 million), adults aged 16-64 years with high-risk medical conditions (a group of about 110 million), and essential workers who did not qualify for inclusion in phase 1b (a group of about 57 million). With the overlap, Phase 1c would cover about 129 million people.
The AACR task force, led by Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, Los Angeles, noted in their position paper that their recommendation is consistent with ACIP’s guidelines. Those guidelines concluded that patients with cancer are at a higher risk for severe COVID-19, and should be one of the groups considered for early COVID-19 vaccination.
Questions remain
Approached for independent comment, Cardinale Smith, MD, PhD, chief quality officer for cancer services for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York, agreed with the AACR task force. “I share that they should be high priority,” she said, “But we don’t know that the efficacy will the same.”
Dr. Smith noted that the impact of cancer therapy on patient immune systems is more related to the type of treatment they’re receiving, and B- and T-cell responses. “But regardless, they should be getting the vaccine, and we just need to follow the guidelines.”
The AACR task force noted that information thus far is quite limited as to the effects of COVID-19 vaccination in patients with cancer. In the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 COVID vaccine trial, of 43,540 participants, only 3.7% were reported to have cancer. Other large COVID-19 vaccine trials will provide further follow-up information on the effectiveness of the vaccines in patients receiving different cancer treatments, they wrote, but for now, there is “currently not enough data to evaluate the interactions between active oncologic therapy with the ability to induce protective immunity” to COVID-19 with vaccination.
In a recent interview, Nora Disis, MD, a medical oncologist and director of both the Institute of Translational Health Sciences and the Cancer Vaccine Institute, University of Washington, Seattle, also discussed vaccinating cancer patients.
She pointed out that even though there are data suggesting that cancer patients are at higher risk, “they are a bit murky, in part because cancer patients are a heterogeneous group.”
“For example, there are data suggesting that lung and blood cancer patients fare worse,” said Dr. Disis, who is also editor in chief of JAMA Oncology. “There is also a suggestion that, like in the general population, COVID risk in cancer patients remains driven by comorbidities.”
She also pointed out the likelihood that individualized risk factors, including the type of cancer therapy, site of disease, and comorbidities, “will shape individual choices about vaccination among cancer patients.”
It is also reasonable to expect that patients with cancer will respond to the vaccines, even though historically some believed that they would be unable to mount an immune response. “Data on other viral vaccines have shown otherwise,” said Dr. Disis. “For example, there has been a long history of studies of flu vaccination in cancer patients, and in general, those vaccines confer protection.”
Several of the authors of the AACR position paper, including Dr. Ribas, reported relationships with industry as detailed in the paper. Dr. Smith has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
2.1 Million COVID Vaccine Doses Given in U.S.
The U.S. has distributed more than 11.4 million doses of the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, and more than 2.1 million of those had been given to people as of December 28, according to the CDC.
The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker showed the updated numbers as of 9 a.m. on that day. The distribution total is based on the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System, and the administered total is based on reports from state and local public health departments, as well as updates from five federal agencies: the Bureau of Prisons, Veterans Administration, Department of Defense, Department of State, and Indian Health Services.
Health care providers report to public health agencies up to 72 hours after the vaccine is given, and public health agencies report to the CDC after that, so there may be a lag in the data. The CDC’s numbers will be updated on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays.
“A large difference between the number of doses distributed and the number of doses administered is expected at this point in the COVID vaccination program due to several factors,” the CDC says.
Delays could occur due to the reporting of doses given, how states and local vaccine sites are managing vaccines, and the pending launch of vaccination through the federal Pharmacy Partnership for Long-Term Care Program.
“Numbers reported on other websites may differ from what is posted on CDC’s website because CDC’s overall numbers are validated through a data submission process with each jurisdiction,” the CDC says.
On Dec. 26, the agency’s tally showed that 9.5 million doses had been distributed and 1.9 million had been given, according to Reuters.
Public health officials and health care workers have begun to voice their concerns about the delay in giving the vaccines.
“We certainly are not at the numbers that we wanted to be at the end of December,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told CNNDec. 29.
Operation Warp Speed had planned for 20 million people to be vaccinated by the end of the year. Fauci said he hopes that number will be achieved next month.
“I believe that as we get into January, we are going to see an increase in the momentum,” he said.
Shipment delays have affected other priority groups as well. The New York Police Department anticipated a rollout Dec. 29, but it’s now been delayed since the department hasn’t received enough Moderna doses to start giving the shots, according to the New York Daily News.
“We’ve made numerous attempts to get updated information, and when we get further word on its availability, we will immediately keep our members appraised of the new date and the method of distribution,” Paul DiGiacomo, president of the Detectives’ Endowment Association, wrote in a memo to members on Dec. 28.
“Every detective squad has been crushed with [COVID-19],” he told the newspaper. “Within the last couple of weeks, we’ve had at least two detectives hospitalized.”
President-elect Joe Biden will receive a briefing from his COVID-19 advisory team, provide a general update on the pandemic, and describe his own plan for vaccinating people quickly during an address Dec. 29, a transition official told Axios. Biden has pledged to administer 100 million vaccine doses in his first 100 days in office.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMd.
The U.S. has distributed more than 11.4 million doses of the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, and more than 2.1 million of those had been given to people as of December 28, according to the CDC.
The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker showed the updated numbers as of 9 a.m. on that day. The distribution total is based on the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System, and the administered total is based on reports from state and local public health departments, as well as updates from five federal agencies: the Bureau of Prisons, Veterans Administration, Department of Defense, Department of State, and Indian Health Services.
Health care providers report to public health agencies up to 72 hours after the vaccine is given, and public health agencies report to the CDC after that, so there may be a lag in the data. The CDC’s numbers will be updated on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays.
“A large difference between the number of doses distributed and the number of doses administered is expected at this point in the COVID vaccination program due to several factors,” the CDC says.
Delays could occur due to the reporting of doses given, how states and local vaccine sites are managing vaccines, and the pending launch of vaccination through the federal Pharmacy Partnership for Long-Term Care Program.
“Numbers reported on other websites may differ from what is posted on CDC’s website because CDC’s overall numbers are validated through a data submission process with each jurisdiction,” the CDC says.
On Dec. 26, the agency’s tally showed that 9.5 million doses had been distributed and 1.9 million had been given, according to Reuters.
Public health officials and health care workers have begun to voice their concerns about the delay in giving the vaccines.
“We certainly are not at the numbers that we wanted to be at the end of December,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told CNNDec. 29.
Operation Warp Speed had planned for 20 million people to be vaccinated by the end of the year. Fauci said he hopes that number will be achieved next month.
“I believe that as we get into January, we are going to see an increase in the momentum,” he said.
Shipment delays have affected other priority groups as well. The New York Police Department anticipated a rollout Dec. 29, but it’s now been delayed since the department hasn’t received enough Moderna doses to start giving the shots, according to the New York Daily News.
“We’ve made numerous attempts to get updated information, and when we get further word on its availability, we will immediately keep our members appraised of the new date and the method of distribution,” Paul DiGiacomo, president of the Detectives’ Endowment Association, wrote in a memo to members on Dec. 28.
“Every detective squad has been crushed with [COVID-19],” he told the newspaper. “Within the last couple of weeks, we’ve had at least two detectives hospitalized.”
President-elect Joe Biden will receive a briefing from his COVID-19 advisory team, provide a general update on the pandemic, and describe his own plan for vaccinating people quickly during an address Dec. 29, a transition official told Axios. Biden has pledged to administer 100 million vaccine doses in his first 100 days in office.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMd.
The U.S. has distributed more than 11.4 million doses of the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, and more than 2.1 million of those had been given to people as of December 28, according to the CDC.
The CDC’s COVID Data Tracker showed the updated numbers as of 9 a.m. on that day. The distribution total is based on the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System, and the administered total is based on reports from state and local public health departments, as well as updates from five federal agencies: the Bureau of Prisons, Veterans Administration, Department of Defense, Department of State, and Indian Health Services.
Health care providers report to public health agencies up to 72 hours after the vaccine is given, and public health agencies report to the CDC after that, so there may be a lag in the data. The CDC’s numbers will be updated on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays.
“A large difference between the number of doses distributed and the number of doses administered is expected at this point in the COVID vaccination program due to several factors,” the CDC says.
Delays could occur due to the reporting of doses given, how states and local vaccine sites are managing vaccines, and the pending launch of vaccination through the federal Pharmacy Partnership for Long-Term Care Program.
“Numbers reported on other websites may differ from what is posted on CDC’s website because CDC’s overall numbers are validated through a data submission process with each jurisdiction,” the CDC says.
On Dec. 26, the agency’s tally showed that 9.5 million doses had been distributed and 1.9 million had been given, according to Reuters.
Public health officials and health care workers have begun to voice their concerns about the delay in giving the vaccines.
“We certainly are not at the numbers that we wanted to be at the end of December,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told CNNDec. 29.
Operation Warp Speed had planned for 20 million people to be vaccinated by the end of the year. Fauci said he hopes that number will be achieved next month.
“I believe that as we get into January, we are going to see an increase in the momentum,” he said.
Shipment delays have affected other priority groups as well. The New York Police Department anticipated a rollout Dec. 29, but it’s now been delayed since the department hasn’t received enough Moderna doses to start giving the shots, according to the New York Daily News.
“We’ve made numerous attempts to get updated information, and when we get further word on its availability, we will immediately keep our members appraised of the new date and the method of distribution,” Paul DiGiacomo, president of the Detectives’ Endowment Association, wrote in a memo to members on Dec. 28.
“Every detective squad has been crushed with [COVID-19],” he told the newspaper. “Within the last couple of weeks, we’ve had at least two detectives hospitalized.”
President-elect Joe Biden will receive a briefing from his COVID-19 advisory team, provide a general update on the pandemic, and describe his own plan for vaccinating people quickly during an address Dec. 29, a transition official told Axios. Biden has pledged to administer 100 million vaccine doses in his first 100 days in office.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMd.
CDC issues COVID-19 vaccine guidance for underlying conditions
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has issued updated guidance for people with underlying medical conditions who are considering getting the coronavirus vaccine.
“Adults of any age with certain underlying medical conditions are at increased risk for severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19,” the CDC said in the guidance, posted on Dec. 26. “mRNA COVID-19 vaccines may be administered to people with underlying medical conditions provided they have not had a severe allergic reaction to any of the ingredients in the vaccine.”
Both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use mRNA, or messenger RNA.
The CDC guidance had specific information for people with HIV, weakened immune systems, and autoimmune conditions such as Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and Bell’s palsy who are thinking of getting the vaccine.
People with HIV and weakened immune systems “may receive a COVID-19 vaccine. However, they should be aware of the limited safety data,” the CDC said.
There’s no information available yet about the safety of the vaccines for people with weakened immune systems. People with HIV were included in clinical trials, but “safety data specific to this group are not yet available at this time,” the CDC said.
Cases of Bell’s palsy, a temporary facial paralysis, were reported in people receiving the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines in clinical trials, the Food and Drug Administration said Dec. 17.
But the new CDC guidance said that the FDA “does not consider these to be above the rate expected in the general population. They have not concluded these cases were caused by vaccination. Therefore, persons who have previously had Bell’s palsy may receive an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.”
Researchers have determined the vaccines are safe for people with GBS, a rare autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks nerves just as they leave the spinal cord, the CDC said.
“To date, no cases of GBS have been reported following vaccination among participants in the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine clinical trials,” the CDC guidance said. “With few exceptions, the independent Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices general best practice guidelines for immunization do not include a history of GBS as a precaution to vaccination with other vaccines.”
For months, the CDC and other health authorities have said that people with certain medical conditions are at an increased risk of developing severe cases of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has issued updated guidance for people with underlying medical conditions who are considering getting the coronavirus vaccine.
“Adults of any age with certain underlying medical conditions are at increased risk for severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19,” the CDC said in the guidance, posted on Dec. 26. “mRNA COVID-19 vaccines may be administered to people with underlying medical conditions provided they have not had a severe allergic reaction to any of the ingredients in the vaccine.”
Both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use mRNA, or messenger RNA.
The CDC guidance had specific information for people with HIV, weakened immune systems, and autoimmune conditions such as Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and Bell’s palsy who are thinking of getting the vaccine.
People with HIV and weakened immune systems “may receive a COVID-19 vaccine. However, they should be aware of the limited safety data,” the CDC said.
There’s no information available yet about the safety of the vaccines for people with weakened immune systems. People with HIV were included in clinical trials, but “safety data specific to this group are not yet available at this time,” the CDC said.
Cases of Bell’s palsy, a temporary facial paralysis, were reported in people receiving the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines in clinical trials, the Food and Drug Administration said Dec. 17.
But the new CDC guidance said that the FDA “does not consider these to be above the rate expected in the general population. They have not concluded these cases were caused by vaccination. Therefore, persons who have previously had Bell’s palsy may receive an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.”
Researchers have determined the vaccines are safe for people with GBS, a rare autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks nerves just as they leave the spinal cord, the CDC said.
“To date, no cases of GBS have been reported following vaccination among participants in the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine clinical trials,” the CDC guidance said. “With few exceptions, the independent Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices general best practice guidelines for immunization do not include a history of GBS as a precaution to vaccination with other vaccines.”
For months, the CDC and other health authorities have said that people with certain medical conditions are at an increased risk of developing severe cases of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has issued updated guidance for people with underlying medical conditions who are considering getting the coronavirus vaccine.
“Adults of any age with certain underlying medical conditions are at increased risk for severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19,” the CDC said in the guidance, posted on Dec. 26. “mRNA COVID-19 vaccines may be administered to people with underlying medical conditions provided they have not had a severe allergic reaction to any of the ingredients in the vaccine.”
Both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use mRNA, or messenger RNA.
The CDC guidance had specific information for people with HIV, weakened immune systems, and autoimmune conditions such as Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and Bell’s palsy who are thinking of getting the vaccine.
People with HIV and weakened immune systems “may receive a COVID-19 vaccine. However, they should be aware of the limited safety data,” the CDC said.
There’s no information available yet about the safety of the vaccines for people with weakened immune systems. People with HIV were included in clinical trials, but “safety data specific to this group are not yet available at this time,” the CDC said.
Cases of Bell’s palsy, a temporary facial paralysis, were reported in people receiving the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines in clinical trials, the Food and Drug Administration said Dec. 17.
But the new CDC guidance said that the FDA “does not consider these to be above the rate expected in the general population. They have not concluded these cases were caused by vaccination. Therefore, persons who have previously had Bell’s palsy may receive an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.”
Researchers have determined the vaccines are safe for people with GBS, a rare autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks nerves just as they leave the spinal cord, the CDC said.
“To date, no cases of GBS have been reported following vaccination among participants in the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine clinical trials,” the CDC guidance said. “With few exceptions, the independent Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices general best practice guidelines for immunization do not include a history of GBS as a precaution to vaccination with other vaccines.”
For months, the CDC and other health authorities have said that people with certain medical conditions are at an increased risk of developing severe cases of COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Reducing COVID-19 opioid deaths
Editor's Note: Due to updated statistics from the CDC, the online version of this article has been modified from the version that appears in the printed edition of the January 2021 issue of Current Psychiatry.
Individuals with mental health and substance use disorders (SUDs) are particularly susceptible to negative effects of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The collision of the COVID-19 pandemic and the drug overdose epidemic has highlighted the urgent need for physicians, policymakers, and health care professionals to optimize care for individuals with SUDs because they may be particularly vulnerable to the effects of the virus due to compromised respiratory and immune function, and poor social support.1 In this commentary, we highlight the challenges of the drug overdose epidemic, and recommend strategies to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic among patients with SUDs.
A crisis exacerbated by COVID-19
The current drug overdose epidemic has become an American public health nightmare. According to preliminary data released by the CDC on December 17, 2020, there were more than 81,000 drug overdose deaths in the United States in the 12 months ending May 2020.2,3 This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period. The CDC also noted that while overdose deaths were already increasing in the months preceding the COVID-19 pandemic, the latest numbers suggest an acceleration of overdose deaths during the pandemic.
What is causing this significant loss of life? Prescription opioids and illegal opioids such as heroin and illicitly manufactured fentanyl are the main agents associated with overdose deaths. These opioids were responsible for 61% (28,647) of drug overdose deaths in the United States in 2014.4 In 2015, the opioid overdose death rate increased by 15.6%.5
The increase in the number of opioid overdose deaths in part coincides with a sharp increase in the availability and use of heroin. Heroin overdose deaths have more than tripled since 2010, but heroin is not the only opiate involved. Fentanyl, a synthetic, short-acting opioid that is approved for managing pain in patients with advanced cancers, is 50 times more potent than heroin. The abuse of prescribed fentanyl has been accelerating over the past decade, as is the use of illicitly produced fentanyl. Evidence from US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) seizure records shows heroin is being adulterated with illicit fentanyl to enhance the potency of the heroin.6,7 Mixing illicit fentanyl with heroin may be contributing to the recent increase in heroin overdose fatalities. According to the CDC, overdose deaths related to synthetic opioids increased 38.4% from the 12-month period leading up to June 2019 compared with the 12-month period leading up to May 2020.2,3 Postmortem studies of individuals who died from a heroin overdose have frequently found the presence of fentanyl along with heroin.8 Overdose deaths involving heroin may be occurring because individuals may be unknowingly using heroin adulterated with fentanyl.9 In addition, carfentanil, a powerful new synthetic fentanyl, has been recently identified in heroin mixtures. Carfentanil is 10,000 times stronger than morphine. Even in miniscule amounts, carfentanil can suppress breathing to the degree that multiple doses of naloxone are needed to restore respirations.
Initial studies indicate that the COVID-19 pandemic has been exacerbating this situation. Wainwright et al10 conducted an analysis of urine drug test results of patients with SUDs from 4 months before and 4 months after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, 2020. Compared with before COVID-19, the proportion of specimens testing positive since COVID-19 increased from 3.80% to 7.32% for fentanyl and from 1.29% to 2.09% for heroin.10
A similar drug testing study found that during the pandemic, the proportion of positive results (positivity) increased by 35% for non-prescribed fentanyl and 44% for heroin.11 Positivity for non-prescribed fentanyl increased significantly among patients who tested positive for other drugs, including by 89% for amphetamines; 48% for benzodiazepines; 34% for cocaine; and 39% for opiates (P < .1 for all).11
In a review of electronic medical records, Ochalek et al12 found that the number of nonfatal opioid overdoses in an emergency department in Virginia increased from 102 in March-June 2019 to 227 in March-June 2020. In an issue brief published on October 31, 2020, the American Medical Association reported increase in opioid and other drug-related overdoses in more than 40 states during the COVID-19 pandemic.13
Continue to: Strategies for intervention...
Strategies for intervention
A multi-dimensional approach is needed to protect the public from this growing opioid overdose epidemic. To address this challenging task, we recommend several strategies:
Enhance access to virtual treatment
Even when in-person treatment cannot take place due to COVID-19-related restrictions, it is vital that services are accessible to patients with SUDs during this pandemic. Examples of virtual treatment include:
- Telehealth for medication-assisted treatment (MAT) using buprenorphine (recently updated guidance from the US DEA and Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration [SAMHSA] allows this method of prescribing)
- Teletherapy to prevent relapse
- Remote drug screens by sending saliva or urine kits to patients' homes, visiting patients to collect fluid samples, or asking patients to come to a "drive-through" facility to provide samples
- Virtual (online) Alcoholics Anonymous, Narcotics Anonymous, SMART Recovery, and similar meetings to provide support in the absence of in-person meetings.
The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) offers guidance to treatment programs to focus on infection control and mitigation. The Table14 summarizes the ASAM recommendations for office-based opioid treatment during COVID-19.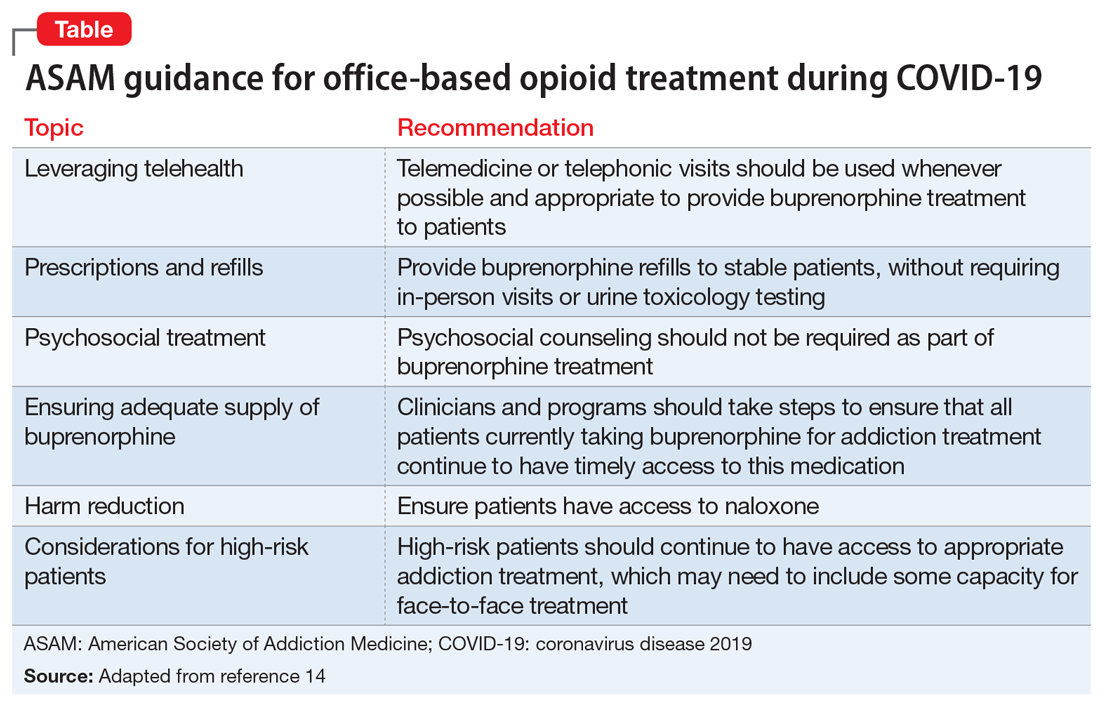
Expand access to treatment
This includes access to MAT (such as buprenorphine/naloxone, methadone, naltrexone, and depot naltrexone) and, equally important, to psychosocial treatment, counseling, and/or recovery services. Recent legislative changes have increased the number of patients that a qualified physician can treat with buprenorphine/naloxone from 100 to 275, and allowed physician extenders to prescribe buprenorphine/naloxone in office-based settings. A recent population-based, retrospective Canadian study showed that opioid agonist treatment decreased the risk of mortality among opioid users, and the protective effects of this treatment increased as fentanyl and other synthetic opioids became common in the illicit drug supply.15 However, because of the shortage of psychiatrists and addiction medicine specialists in several regions of the United States, access to treatment is extremely limited and often inadequate. This constitutes a major public health crisis and contributes to our inability to intervene effectively in the opioid epidemic. Telepsychiatry programs can bring needed services to underserved areas, but they need additional support and development. Further, involving other specialties is paramount for treating this epidemic. Integrating MAT in primary care settings can improve access to treatment. Harm-reduction approaches, such as syringe exchange programs, can play an important role in reducing the adverse consequences associated with heroin use and establish health care relationships with at-risk individuals. Syringe exchange programs can also reduce the rate of infections associated with IV drug use, such as human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus.
Continue to: Increase education on naloxone...
Increase education on naloxone
Naloxone is a safe and effective opioid antagonist used to treat opioid overdoses. Timely access to naloxone is of the essence when treating opioid-related overdoses. Many states have enacted laws allowing health care professionals, law enforcement officers, and patients and relatives to obtain naloxone without a physician's prescription. It appears this approach may be yielding results. For example, the North Carolina Harm Reduction Coalition distributed >101,000 free overdose rescue kits that included naloxone and recorded 13,392 confirmed cases of overdose rescue with naloxone from 2013 to 2019.16
Divert patients with SUDs from the criminal justice system to treatment
We need to develop programs to divert patients with SUDs from the criminal justice system, which is focused on punishment, to interventions that focus on treatment. Data indicates high recidivism rates for incarcerated individuals with SUDs who do not have access to treatment after they are released. Recognizing this, communities are developing programs that divert low-level offenders from the criminal justice system into treatment. For instance, in Seattle, the Law Enforcement Assisted Diversion is a pilot program developed to divert low-level drug and prostitution offenders into community-based treatment and support services. This helps provide housing, health care, job training, treatment, and mental health support. Innovative programs are needed to provide SUD treatment in the rehabilitation programs of correctional facilities and ensure case managers and discharge planners can transition participants to community treatment programs upon their release.
Develop early identification and prevention programs
These programs should focus on individuals at high risk, such as patients with comorbid SUDs and psychiatric disorders, those with chronic pain, and at-risk children whose parents abuse opiates. Traditional addiction treatment programs typically do not address patients with complex conditions or special populations, such as adolescents or pregnant women with substance use issues. Evidence-based approaches such as Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT), Integrated Dual Diagnosis Treatment (IDDT), and prevention approaches that target students in middle schools and high schools need to be more widely available.
Improve education on opioid prescribing
Responsible opioid prescribing for clinicians should include education about the regular use of prescription drug monitoring programs, urine drug screening, avoiding co-prescription of opioids with sedative-hypnotic medications, and better linkage with addiction treatment.
Treat comorbid psychiatric conditions
It is critical to both identify and effectively treat underlying affective, anxiety, and psychotic disorders in patients with SUDs. Anxiety, depression, and emotional dysregulation often contribute to worsening substance abuse, abuse of prescription drugs, diversion of prescribed drugs, and an increased risk of overdoses and suicides. Effective treatment of comorbid psychiatric conditions also may reduce relapses.
Increase research on causes and treatments
Through research, we must expand our knowledge to better understand the factors that contribute to this epidemic and develop better treatments. These efforts may allow for the development of prevention mechanisms. For example, a recent study found that the continued use of opioid medications after an overdose was associated with a high risk of a repeated overdosecall out material?.17 At the end of a 2-year observation, 17% (confidence interval [CI]: 14% to 20%) of patients receiving a high daily dosage of a prescribed opioid had a repeat overdose compared with 15% (CI: 10% to 21%) of those receiving a moderate dosage, 9% (CI: 6% to 14%) of those receiving a low dosage, and 8% (CI: 6% to 11%) of those receiving no opioids.17 Of the patients who overdosed on prescribed opiates, 30% switched to a new prescriber after their overdose, many of whom may not have been aware of the previous overdose. From a public health perspective, it would make sense for prescribers to know of prior opioid and/or benzodiazepine overdoses. This could be reported by emergency department clinicians, law enforcement, and hospitals into a prescription drug monitoring program, which is readily available to prescribers in most states.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Scott Proescholdbell, MPH, Injury and Violence Prevention Branch, Chronic Disease and Injury Section, Division of Public Health, North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services, for his assistance.
Bottom Line
The collision of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and the drug overdose epidemic has highlighted the urgent need for health care professionals to optimize care for individuals with substance use disorders. Suggested interventions include enhancing access to medication-assisted treatment and virtual treatment, improving education about naloxone and safe opioid prescribing practices, and diverting at-risk patients from the criminal justice system to interventions that focus on treatment.
1. Volkow ND. Collision of the COVID-19 and addiction epidemics. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173(1):61-62.
2.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overdose deaths accelerating during COVID-19. Accessed December 23, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2020/p1218-overdose-deaths-covid-19.html
3.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Health Statistics Vital Statistics Rapid Release. Provisional drug overdose death counts. Accessed December 30, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/drug-overdose-data.htm
4.Rudd RA, Aleshire N, Zibbell JE, et al. Increases in drug and opioid overdose deaths -- United States, 2000-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;64(50-51):1378-1382.
5.Rudd RA, Seth P, David F, et al. Increases in drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths -- United States, 2010-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(50-51):1445-1452.
6.US Drug Enforcement Administration. DEA issues nationwide alert on fentanyl as threat to health and public safety. Published March 19, 2015. Accessed October 28, 2020. http://www.dea.gov/divisions/hq/2015/hq031815.shtml
7.Gladden RM, Martinez P, Seth P. Fentanyl law enforcement submissions and increases in synthetic opioid-involved overdose deaths - 27 states, 2013-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(33):837-843.
8.Algren DA, Monteilh CP, Punja M, et al. Fentanyl-associated fatalities among illicit drug users in Wayne County, Michigan (July 2005-May 2006). J Med Toxicol. 2013;9(1):106-115.
9.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Increases in fentanyl drug confiscations and fentanyl-related overdose fatalities. HAN Health Advisory. Published October 26, 2015. Accessed October 28, 2020. http://emergency.cdc.gov/han/han00384.asp
10.Wainwright JJ, Mikre M, Whitley P, et al. Analysis of drug test results before and after the us declaration of a national emergency concerning the COVID-19 outbreak. JAMA. 2020;324(16):1674-1677.
11.Niles JK, Gudin J, Radliff J, et al. The opioid epidemic within the COVID-19 pandemic: drug testing in 2020 [published online October 8, 2020]. Population Health Management. doi: 10.1089/pop.2020.0230
12.Ochalek TA, Cumpston KL, Wills BK, et al. Nonfatal opioid overdoses at an urban emergency department during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA. 2020;324(16):1673-1674.
13.American Medical Association. Issue brief: reports of increases in opioid- and other drug-related overdose and other concerns during COVID pandemic. Published October 31, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2020. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2020-11/issue-brief-increases-in-opioid-related-overdose.pdf
14.American Society of Addiction Medicine. Caring for patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: ASAM COVID-19 Task Force recommendations. Accessed October 30, 2020. https://www.asam.org/docs/default-source/covid-19/medication-formulation-and-dosage-guidance-(1).pdf
15.Pearce LA, Min JE, Piske M, et al. Opioid agonist treatment and risk of mortality during opioid overdose public health emergency: population based retrospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;368:m772. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m772
16.North Carolina Harm Reduction Coalition. NCHRC'S community-based overdose prevention project. Accessed March 29, 2020. http://www.nchrc.org/programs-and-services
17.Larochelle MR, Liebschutz JM, Zhang F, et al. Opioid prescribing after nonfatal overdose and association with repeated overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(1):1-9.
Editor's Note: Due to updated statistics from the CDC, the online version of this article has been modified from the version that appears in the printed edition of the January 2021 issue of Current Psychiatry.
Individuals with mental health and substance use disorders (SUDs) are particularly susceptible to negative effects of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The collision of the COVID-19 pandemic and the drug overdose epidemic has highlighted the urgent need for physicians, policymakers, and health care professionals to optimize care for individuals with SUDs because they may be particularly vulnerable to the effects of the virus due to compromised respiratory and immune function, and poor social support.1 In this commentary, we highlight the challenges of the drug overdose epidemic, and recommend strategies to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic among patients with SUDs.
A crisis exacerbated by COVID-19
The current drug overdose epidemic has become an American public health nightmare. According to preliminary data released by the CDC on December 17, 2020, there were more than 81,000 drug overdose deaths in the United States in the 12 months ending May 2020.2,3 This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period. The CDC also noted that while overdose deaths were already increasing in the months preceding the COVID-19 pandemic, the latest numbers suggest an acceleration of overdose deaths during the pandemic.
What is causing this significant loss of life? Prescription opioids and illegal opioids such as heroin and illicitly manufactured fentanyl are the main agents associated with overdose deaths. These opioids were responsible for 61% (28,647) of drug overdose deaths in the United States in 2014.4 In 2015, the opioid overdose death rate increased by 15.6%.5
The increase in the number of opioid overdose deaths in part coincides with a sharp increase in the availability and use of heroin. Heroin overdose deaths have more than tripled since 2010, but heroin is not the only opiate involved. Fentanyl, a synthetic, short-acting opioid that is approved for managing pain in patients with advanced cancers, is 50 times more potent than heroin. The abuse of prescribed fentanyl has been accelerating over the past decade, as is the use of illicitly produced fentanyl. Evidence from US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) seizure records shows heroin is being adulterated with illicit fentanyl to enhance the potency of the heroin.6,7 Mixing illicit fentanyl with heroin may be contributing to the recent increase in heroin overdose fatalities. According to the CDC, overdose deaths related to synthetic opioids increased 38.4% from the 12-month period leading up to June 2019 compared with the 12-month period leading up to May 2020.2,3 Postmortem studies of individuals who died from a heroin overdose have frequently found the presence of fentanyl along with heroin.8 Overdose deaths involving heroin may be occurring because individuals may be unknowingly using heroin adulterated with fentanyl.9 In addition, carfentanil, a powerful new synthetic fentanyl, has been recently identified in heroin mixtures. Carfentanil is 10,000 times stronger than morphine. Even in miniscule amounts, carfentanil can suppress breathing to the degree that multiple doses of naloxone are needed to restore respirations.
Initial studies indicate that the COVID-19 pandemic has been exacerbating this situation. Wainwright et al10 conducted an analysis of urine drug test results of patients with SUDs from 4 months before and 4 months after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, 2020. Compared with before COVID-19, the proportion of specimens testing positive since COVID-19 increased from 3.80% to 7.32% for fentanyl and from 1.29% to 2.09% for heroin.10
A similar drug testing study found that during the pandemic, the proportion of positive results (positivity) increased by 35% for non-prescribed fentanyl and 44% for heroin.11 Positivity for non-prescribed fentanyl increased significantly among patients who tested positive for other drugs, including by 89% for amphetamines; 48% for benzodiazepines; 34% for cocaine; and 39% for opiates (P < .1 for all).11
In a review of electronic medical records, Ochalek et al12 found that the number of nonfatal opioid overdoses in an emergency department in Virginia increased from 102 in March-June 2019 to 227 in March-June 2020. In an issue brief published on October 31, 2020, the American Medical Association reported increase in opioid and other drug-related overdoses in more than 40 states during the COVID-19 pandemic.13
Continue to: Strategies for intervention...
Strategies for intervention
A multi-dimensional approach is needed to protect the public from this growing opioid overdose epidemic. To address this challenging task, we recommend several strategies:
Enhance access to virtual treatment
Even when in-person treatment cannot take place due to COVID-19-related restrictions, it is vital that services are accessible to patients with SUDs during this pandemic. Examples of virtual treatment include:
- Telehealth for medication-assisted treatment (MAT) using buprenorphine (recently updated guidance from the US DEA and Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration [SAMHSA] allows this method of prescribing)
- Teletherapy to prevent relapse
- Remote drug screens by sending saliva or urine kits to patients' homes, visiting patients to collect fluid samples, or asking patients to come to a "drive-through" facility to provide samples
- Virtual (online) Alcoholics Anonymous, Narcotics Anonymous, SMART Recovery, and similar meetings to provide support in the absence of in-person meetings.
The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) offers guidance to treatment programs to focus on infection control and mitigation. The Table14 summarizes the ASAM recommendations for office-based opioid treatment during COVID-19.
Expand access to treatment
This includes access to MAT (such as buprenorphine/naloxone, methadone, naltrexone, and depot naltrexone) and, equally important, to psychosocial treatment, counseling, and/or recovery services. Recent legislative changes have increased the number of patients that a qualified physician can treat with buprenorphine/naloxone from 100 to 275, and allowed physician extenders to prescribe buprenorphine/naloxone in office-based settings. A recent population-based, retrospective Canadian study showed that opioid agonist treatment decreased the risk of mortality among opioid users, and the protective effects of this treatment increased as fentanyl and other synthetic opioids became common in the illicit drug supply.15 However, because of the shortage of psychiatrists and addiction medicine specialists in several regions of the United States, access to treatment is extremely limited and often inadequate. This constitutes a major public health crisis and contributes to our inability to intervene effectively in the opioid epidemic. Telepsychiatry programs can bring needed services to underserved areas, but they need additional support and development. Further, involving other specialties is paramount for treating this epidemic. Integrating MAT in primary care settings can improve access to treatment. Harm-reduction approaches, such as syringe exchange programs, can play an important role in reducing the adverse consequences associated with heroin use and establish health care relationships with at-risk individuals. Syringe exchange programs can also reduce the rate of infections associated with IV drug use, such as human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus.
Continue to: Increase education on naloxone...
Increase education on naloxone
Naloxone is a safe and effective opioid antagonist used to treat opioid overdoses. Timely access to naloxone is of the essence when treating opioid-related overdoses. Many states have enacted laws allowing health care professionals, law enforcement officers, and patients and relatives to obtain naloxone without a physician's prescription. It appears this approach may be yielding results. For example, the North Carolina Harm Reduction Coalition distributed >101,000 free overdose rescue kits that included naloxone and recorded 13,392 confirmed cases of overdose rescue with naloxone from 2013 to 2019.16
Divert patients with SUDs from the criminal justice system to treatment
We need to develop programs to divert patients with SUDs from the criminal justice system, which is focused on punishment, to interventions that focus on treatment. Data indicates high recidivism rates for incarcerated individuals with SUDs who do not have access to treatment after they are released. Recognizing this, communities are developing programs that divert low-level offenders from the criminal justice system into treatment. For instance, in Seattle, the Law Enforcement Assisted Diversion is a pilot program developed to divert low-level drug and prostitution offenders into community-based treatment and support services. This helps provide housing, health care, job training, treatment, and mental health support. Innovative programs are needed to provide SUD treatment in the rehabilitation programs of correctional facilities and ensure case managers and discharge planners can transition participants to community treatment programs upon their release.
Develop early identification and prevention programs
These programs should focus on individuals at high risk, such as patients with comorbid SUDs and psychiatric disorders, those with chronic pain, and at-risk children whose parents abuse opiates. Traditional addiction treatment programs typically do not address patients with complex conditions or special populations, such as adolescents or pregnant women with substance use issues. Evidence-based approaches such as Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT), Integrated Dual Diagnosis Treatment (IDDT), and prevention approaches that target students in middle schools and high schools need to be more widely available.
Improve education on opioid prescribing
Responsible opioid prescribing for clinicians should include education about the regular use of prescription drug monitoring programs, urine drug screening, avoiding co-prescription of opioids with sedative-hypnotic medications, and better linkage with addiction treatment.
Treat comorbid psychiatric conditions
It is critical to both identify and effectively treat underlying affective, anxiety, and psychotic disorders in patients with SUDs. Anxiety, depression, and emotional dysregulation often contribute to worsening substance abuse, abuse of prescription drugs, diversion of prescribed drugs, and an increased risk of overdoses and suicides. Effective treatment of comorbid psychiatric conditions also may reduce relapses.
Increase research on causes and treatments
Through research, we must expand our knowledge to better understand the factors that contribute to this epidemic and develop better treatments. These efforts may allow for the development of prevention mechanisms. For example, a recent study found that the continued use of opioid medications after an overdose was associated with a high risk of a repeated overdosecall out material?.17 At the end of a 2-year observation, 17% (confidence interval [CI]: 14% to 20%) of patients receiving a high daily dosage of a prescribed opioid had a repeat overdose compared with 15% (CI: 10% to 21%) of those receiving a moderate dosage, 9% (CI: 6% to 14%) of those receiving a low dosage, and 8% (CI: 6% to 11%) of those receiving no opioids.17 Of the patients who overdosed on prescribed opiates, 30% switched to a new prescriber after their overdose, many of whom may not have been aware of the previous overdose. From a public health perspective, it would make sense for prescribers to know of prior opioid and/or benzodiazepine overdoses. This could be reported by emergency department clinicians, law enforcement, and hospitals into a prescription drug monitoring program, which is readily available to prescribers in most states.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Scott Proescholdbell, MPH, Injury and Violence Prevention Branch, Chronic Disease and Injury Section, Division of Public Health, North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services, for his assistance.
Bottom Line
The collision of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and the drug overdose epidemic has highlighted the urgent need for health care professionals to optimize care for individuals with substance use disorders. Suggested interventions include enhancing access to medication-assisted treatment and virtual treatment, improving education about naloxone and safe opioid prescribing practices, and diverting at-risk patients from the criminal justice system to interventions that focus on treatment.
Editor's Note: Due to updated statistics from the CDC, the online version of this article has been modified from the version that appears in the printed edition of the January 2021 issue of Current Psychiatry.
Individuals with mental health and substance use disorders (SUDs) are particularly susceptible to negative effects of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The collision of the COVID-19 pandemic and the drug overdose epidemic has highlighted the urgent need for physicians, policymakers, and health care professionals to optimize care for individuals with SUDs because they may be particularly vulnerable to the effects of the virus due to compromised respiratory and immune function, and poor social support.1 In this commentary, we highlight the challenges of the drug overdose epidemic, and recommend strategies to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic among patients with SUDs.
A crisis exacerbated by COVID-19
The current drug overdose epidemic has become an American public health nightmare. According to preliminary data released by the CDC on December 17, 2020, there were more than 81,000 drug overdose deaths in the United States in the 12 months ending May 2020.2,3 This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period. The CDC also noted that while overdose deaths were already increasing in the months preceding the COVID-19 pandemic, the latest numbers suggest an acceleration of overdose deaths during the pandemic.
What is causing this significant loss of life? Prescription opioids and illegal opioids such as heroin and illicitly manufactured fentanyl are the main agents associated with overdose deaths. These opioids were responsible for 61% (28,647) of drug overdose deaths in the United States in 2014.4 In 2015, the opioid overdose death rate increased by 15.6%.5
The increase in the number of opioid overdose deaths in part coincides with a sharp increase in the availability and use of heroin. Heroin overdose deaths have more than tripled since 2010, but heroin is not the only opiate involved. Fentanyl, a synthetic, short-acting opioid that is approved for managing pain in patients with advanced cancers, is 50 times more potent than heroin. The abuse of prescribed fentanyl has been accelerating over the past decade, as is the use of illicitly produced fentanyl. Evidence from US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) seizure records shows heroin is being adulterated with illicit fentanyl to enhance the potency of the heroin.6,7 Mixing illicit fentanyl with heroin may be contributing to the recent increase in heroin overdose fatalities. According to the CDC, overdose deaths related to synthetic opioids increased 38.4% from the 12-month period leading up to June 2019 compared with the 12-month period leading up to May 2020.2,3 Postmortem studies of individuals who died from a heroin overdose have frequently found the presence of fentanyl along with heroin.8 Overdose deaths involving heroin may be occurring because individuals may be unknowingly using heroin adulterated with fentanyl.9 In addition, carfentanil, a powerful new synthetic fentanyl, has been recently identified in heroin mixtures. Carfentanil is 10,000 times stronger than morphine. Even in miniscule amounts, carfentanil can suppress breathing to the degree that multiple doses of naloxone are needed to restore respirations.
Initial studies indicate that the COVID-19 pandemic has been exacerbating this situation. Wainwright et al10 conducted an analysis of urine drug test results of patients with SUDs from 4 months before and 4 months after COVID-19 was declared a national emergency on March 13, 2020. Compared with before COVID-19, the proportion of specimens testing positive since COVID-19 increased from 3.80% to 7.32% for fentanyl and from 1.29% to 2.09% for heroin.10
A similar drug testing study found that during the pandemic, the proportion of positive results (positivity) increased by 35% for non-prescribed fentanyl and 44% for heroin.11 Positivity for non-prescribed fentanyl increased significantly among patients who tested positive for other drugs, including by 89% for amphetamines; 48% for benzodiazepines; 34% for cocaine; and 39% for opiates (P < .1 for all).11
In a review of electronic medical records, Ochalek et al12 found that the number of nonfatal opioid overdoses in an emergency department in Virginia increased from 102 in March-June 2019 to 227 in March-June 2020. In an issue brief published on October 31, 2020, the American Medical Association reported increase in opioid and other drug-related overdoses in more than 40 states during the COVID-19 pandemic.13
Continue to: Strategies for intervention...
Strategies for intervention
A multi-dimensional approach is needed to protect the public from this growing opioid overdose epidemic. To address this challenging task, we recommend several strategies:
Enhance access to virtual treatment
Even when in-person treatment cannot take place due to COVID-19-related restrictions, it is vital that services are accessible to patients with SUDs during this pandemic. Examples of virtual treatment include:
- Telehealth for medication-assisted treatment (MAT) using buprenorphine (recently updated guidance from the US DEA and Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration [SAMHSA] allows this method of prescribing)
- Teletherapy to prevent relapse
- Remote drug screens by sending saliva or urine kits to patients' homes, visiting patients to collect fluid samples, or asking patients to come to a "drive-through" facility to provide samples
- Virtual (online) Alcoholics Anonymous, Narcotics Anonymous, SMART Recovery, and similar meetings to provide support in the absence of in-person meetings.
The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) offers guidance to treatment programs to focus on infection control and mitigation. The Table14 summarizes the ASAM recommendations for office-based opioid treatment during COVID-19.
Expand access to treatment
This includes access to MAT (such as buprenorphine/naloxone, methadone, naltrexone, and depot naltrexone) and, equally important, to psychosocial treatment, counseling, and/or recovery services. Recent legislative changes have increased the number of patients that a qualified physician can treat with buprenorphine/naloxone from 100 to 275, and allowed physician extenders to prescribe buprenorphine/naloxone in office-based settings. A recent population-based, retrospective Canadian study showed that opioid agonist treatment decreased the risk of mortality among opioid users, and the protective effects of this treatment increased as fentanyl and other synthetic opioids became common in the illicit drug supply.15 However, because of the shortage of psychiatrists and addiction medicine specialists in several regions of the United States, access to treatment is extremely limited and often inadequate. This constitutes a major public health crisis and contributes to our inability to intervene effectively in the opioid epidemic. Telepsychiatry programs can bring needed services to underserved areas, but they need additional support and development. Further, involving other specialties is paramount for treating this epidemic. Integrating MAT in primary care settings can improve access to treatment. Harm-reduction approaches, such as syringe exchange programs, can play an important role in reducing the adverse consequences associated with heroin use and establish health care relationships with at-risk individuals. Syringe exchange programs can also reduce the rate of infections associated with IV drug use, such as human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus.
Continue to: Increase education on naloxone...
Increase education on naloxone
Naloxone is a safe and effective opioid antagonist used to treat opioid overdoses. Timely access to naloxone is of the essence when treating opioid-related overdoses. Many states have enacted laws allowing health care professionals, law enforcement officers, and patients and relatives to obtain naloxone without a physician's prescription. It appears this approach may be yielding results. For example, the North Carolina Harm Reduction Coalition distributed >101,000 free overdose rescue kits that included naloxone and recorded 13,392 confirmed cases of overdose rescue with naloxone from 2013 to 2019.16
Divert patients with SUDs from the criminal justice system to treatment
We need to develop programs to divert patients with SUDs from the criminal justice system, which is focused on punishment, to interventions that focus on treatment. Data indicates high recidivism rates for incarcerated individuals with SUDs who do not have access to treatment after they are released. Recognizing this, communities are developing programs that divert low-level offenders from the criminal justice system into treatment. For instance, in Seattle, the Law Enforcement Assisted Diversion is a pilot program developed to divert low-level drug and prostitution offenders into community-based treatment and support services. This helps provide housing, health care, job training, treatment, and mental health support. Innovative programs are needed to provide SUD treatment in the rehabilitation programs of correctional facilities and ensure case managers and discharge planners can transition participants to community treatment programs upon their release.
Develop early identification and prevention programs
These programs should focus on individuals at high risk, such as patients with comorbid SUDs and psychiatric disorders, those with chronic pain, and at-risk children whose parents abuse opiates. Traditional addiction treatment programs typically do not address patients with complex conditions or special populations, such as adolescents or pregnant women with substance use issues. Evidence-based approaches such as Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT), Integrated Dual Diagnosis Treatment (IDDT), and prevention approaches that target students in middle schools and high schools need to be more widely available.
Improve education on opioid prescribing
Responsible opioid prescribing for clinicians should include education about the regular use of prescription drug monitoring programs, urine drug screening, avoiding co-prescription of opioids with sedative-hypnotic medications, and better linkage with addiction treatment.
Treat comorbid psychiatric conditions
It is critical to both identify and effectively treat underlying affective, anxiety, and psychotic disorders in patients with SUDs. Anxiety, depression, and emotional dysregulation often contribute to worsening substance abuse, abuse of prescription drugs, diversion of prescribed drugs, and an increased risk of overdoses and suicides. Effective treatment of comorbid psychiatric conditions also may reduce relapses.
Increase research on causes and treatments
Through research, we must expand our knowledge to better understand the factors that contribute to this epidemic and develop better treatments. These efforts may allow for the development of prevention mechanisms. For example, a recent study found that the continued use of opioid medications after an overdose was associated with a high risk of a repeated overdosecall out material?.17 At the end of a 2-year observation, 17% (confidence interval [CI]: 14% to 20%) of patients receiving a high daily dosage of a prescribed opioid had a repeat overdose compared with 15% (CI: 10% to 21%) of those receiving a moderate dosage, 9% (CI: 6% to 14%) of those receiving a low dosage, and 8% (CI: 6% to 11%) of those receiving no opioids.17 Of the patients who overdosed on prescribed opiates, 30% switched to a new prescriber after their overdose, many of whom may not have been aware of the previous overdose. From a public health perspective, it would make sense for prescribers to know of prior opioid and/or benzodiazepine overdoses. This could be reported by emergency department clinicians, law enforcement, and hospitals into a prescription drug monitoring program, which is readily available to prescribers in most states.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Scott Proescholdbell, MPH, Injury and Violence Prevention Branch, Chronic Disease and Injury Section, Division of Public Health, North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services, for his assistance.
Bottom Line
The collision of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and the drug overdose epidemic has highlighted the urgent need for health care professionals to optimize care for individuals with substance use disorders. Suggested interventions include enhancing access to medication-assisted treatment and virtual treatment, improving education about naloxone and safe opioid prescribing practices, and diverting at-risk patients from the criminal justice system to interventions that focus on treatment.
1. Volkow ND. Collision of the COVID-19 and addiction epidemics. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173(1):61-62.
2.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overdose deaths accelerating during COVID-19. Accessed December 23, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2020/p1218-overdose-deaths-covid-19.html
3.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Health Statistics Vital Statistics Rapid Release. Provisional drug overdose death counts. Accessed December 30, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/drug-overdose-data.htm
4.Rudd RA, Aleshire N, Zibbell JE, et al. Increases in drug and opioid overdose deaths -- United States, 2000-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;64(50-51):1378-1382.
5.Rudd RA, Seth P, David F, et al. Increases in drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths -- United States, 2010-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(50-51):1445-1452.
6.US Drug Enforcement Administration. DEA issues nationwide alert on fentanyl as threat to health and public safety. Published March 19, 2015. Accessed October 28, 2020. http://www.dea.gov/divisions/hq/2015/hq031815.shtml
7.Gladden RM, Martinez P, Seth P. Fentanyl law enforcement submissions and increases in synthetic opioid-involved overdose deaths - 27 states, 2013-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(33):837-843.
8.Algren DA, Monteilh CP, Punja M, et al. Fentanyl-associated fatalities among illicit drug users in Wayne County, Michigan (July 2005-May 2006). J Med Toxicol. 2013;9(1):106-115.
9.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Increases in fentanyl drug confiscations and fentanyl-related overdose fatalities. HAN Health Advisory. Published October 26, 2015. Accessed October 28, 2020. http://emergency.cdc.gov/han/han00384.asp
10.Wainwright JJ, Mikre M, Whitley P, et al. Analysis of drug test results before and after the us declaration of a national emergency concerning the COVID-19 outbreak. JAMA. 2020;324(16):1674-1677.
11.Niles JK, Gudin J, Radliff J, et al. The opioid epidemic within the COVID-19 pandemic: drug testing in 2020 [published online October 8, 2020]. Population Health Management. doi: 10.1089/pop.2020.0230
12.Ochalek TA, Cumpston KL, Wills BK, et al. Nonfatal opioid overdoses at an urban emergency department during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA. 2020;324(16):1673-1674.
13.American Medical Association. Issue brief: reports of increases in opioid- and other drug-related overdose and other concerns during COVID pandemic. Published October 31, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2020. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2020-11/issue-brief-increases-in-opioid-related-overdose.pdf
14.American Society of Addiction Medicine. Caring for patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: ASAM COVID-19 Task Force recommendations. Accessed October 30, 2020. https://www.asam.org/docs/default-source/covid-19/medication-formulation-and-dosage-guidance-(1).pdf
15.Pearce LA, Min JE, Piske M, et al. Opioid agonist treatment and risk of mortality during opioid overdose public health emergency: population based retrospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;368:m772. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m772
16.North Carolina Harm Reduction Coalition. NCHRC'S community-based overdose prevention project. Accessed March 29, 2020. http://www.nchrc.org/programs-and-services
17.Larochelle MR, Liebschutz JM, Zhang F, et al. Opioid prescribing after nonfatal overdose and association with repeated overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(1):1-9.
1. Volkow ND. Collision of the COVID-19 and addiction epidemics. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173(1):61-62.
2.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overdose deaths accelerating during COVID-19. Accessed December 23, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2020/p1218-overdose-deaths-covid-19.html
3.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Health Statistics Vital Statistics Rapid Release. Provisional drug overdose death counts. Accessed December 30, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/drug-overdose-data.htm
4.Rudd RA, Aleshire N, Zibbell JE, et al. Increases in drug and opioid overdose deaths -- United States, 2000-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;64(50-51):1378-1382.
5.Rudd RA, Seth P, David F, et al. Increases in drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths -- United States, 2010-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(50-51):1445-1452.
6.US Drug Enforcement Administration. DEA issues nationwide alert on fentanyl as threat to health and public safety. Published March 19, 2015. Accessed October 28, 2020. http://www.dea.gov/divisions/hq/2015/hq031815.shtml
7.Gladden RM, Martinez P, Seth P. Fentanyl law enforcement submissions and increases in synthetic opioid-involved overdose deaths - 27 states, 2013-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(33):837-843.
8.Algren DA, Monteilh CP, Punja M, et al. Fentanyl-associated fatalities among illicit drug users in Wayne County, Michigan (July 2005-May 2006). J Med Toxicol. 2013;9(1):106-115.
9.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Increases in fentanyl drug confiscations and fentanyl-related overdose fatalities. HAN Health Advisory. Published October 26, 2015. Accessed October 28, 2020. http://emergency.cdc.gov/han/han00384.asp
10.Wainwright JJ, Mikre M, Whitley P, et al. Analysis of drug test results before and after the us declaration of a national emergency concerning the COVID-19 outbreak. JAMA. 2020;324(16):1674-1677.
11.Niles JK, Gudin J, Radliff J, et al. The opioid epidemic within the COVID-19 pandemic: drug testing in 2020 [published online October 8, 2020]. Population Health Management. doi: 10.1089/pop.2020.0230
12.Ochalek TA, Cumpston KL, Wills BK, et al. Nonfatal opioid overdoses at an urban emergency department during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA. 2020;324(16):1673-1674.
13.American Medical Association. Issue brief: reports of increases in opioid- and other drug-related overdose and other concerns during COVID pandemic. Published October 31, 2020. Accessed November 9, 2020. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2020-11/issue-brief-increases-in-opioid-related-overdose.pdf
14.American Society of Addiction Medicine. Caring for patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: ASAM COVID-19 Task Force recommendations. Accessed October 30, 2020. https://www.asam.org/docs/default-source/covid-19/medication-formulation-and-dosage-guidance-(1).pdf
15.Pearce LA, Min JE, Piske M, et al. Opioid agonist treatment and risk of mortality during opioid overdose public health emergency: population based retrospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;368:m772. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m772
16.North Carolina Harm Reduction Coalition. NCHRC'S community-based overdose prevention project. Accessed March 29, 2020. http://www.nchrc.org/programs-and-services
17.Larochelle MR, Liebschutz JM, Zhang F, et al. Opioid prescribing after nonfatal overdose and association with repeated overdose: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(1):1-9.
Cancer treatment delays are deadly: 5- and 10-year data
The COVID-19 pandemic has meant delays in cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment — and a new study shows just how deadly delaying cancer treatment can be.
The study found evidence that longer time to starting treatment after diagnosis was generally associated with higher mortality across several common cancers, most notably for colon and early-stage lung cancer.
“There is a limit to how long we can safely defer treatment for cancer therapies, pandemic or not, which may be shorter than we think,” lead author Eugene Cone, MD, Combined Harvard Program in Urologic Oncology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“When you consider that cancer screening may have been delayed during the pandemic, which would further increase the period between developing a disease and getting therapy, timely treatment for cancer has never been more important,” Cone added.
The study was published online December 14 in JAMA Network Open.
The sooner the better
Using the National Cancer Database, Cone and colleagues identified roughly 2.24 million patients diagnosed with nonmetastatic breast (52%), prostate (38%), colon (4%) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC, 6%) between 2004 and 2015. Treatment and outcome data were analyzed from January to March 2020.
The time-to-treatment initiation (TTI) – the interval between cancer diagnosis and receipt of curative-intent therapy – was categorized as 8 to 60 days (reference), 61 to 120 days, 121 to 180 days, and 181 to 365 days. Median TTI was 32 days for breast, 79 days for prostate, 41 days for NSCLC, and 26 days for colon cancer.
All four cancers benefitted to some degree from a short interval between diagnosis and therapy, the researchers found.
Across all four cancers, increasing TTI was generally associated with higher predicted mortality at 5 and 10 years, although the degree varied by cancer type and stage. The most pronounced association between increasing TTI and mortality was observed for colon and lung cancer.
For example, for stage III colon cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 38.9% and 54%, respectively, with TTI of 61 to 120 days, and increased to 47.8% and 63.8%, respectively, with TTI of 181 to 365 days.
Each additional 60-day delay was associated with a 3.2% to 6% increase in 5-year mortality for stage III colon cancer and a 0.9% to 4.6% increase for stage I colon cancer, with a longer 10-year time horizon showing larger effect sizes with increasing TTI.
For stage I NSCLC, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 47.4% and 72.6%, respectively, with TTI of 61 to 120 days compared with 47.6% and 72.8%, respectively, with TTI of 181 to 365 days.
For stage I NSCLC, there was a 4% to 6.2% absolute increase in 5-year mortality for increased TTI groups compared with the 8- to 60-day reference group, with larger effect sizes on 10-year mortality. The data precluded conclusions about stage II NSCLC.
“For prostate cancer, deferral of treatment by even a few months was associated with a significant impact on mortality,” Cone told Medscape Medical News.
For high-risk prostate cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 12.8% and 31.2%, respectively, with TTI of 61-120 days increasing to 14.1% and 33.8%, respectively with TTI at 181-365 days.
For intermediate-risk prostate cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 7.4% and 20.4% with TTI of 61-120 days vs 8.3% and 22.6% with TTI at 181-365 days.
The data show all-cause mortality differences of 2.2% at 5 years and 4.6% at 10 years between high-risk prostate cancer patients who were treated expeditiously vs those waiting 4 to 6 months and differences of 0.9% at 5 years and 2.4% at 10 years for similar intermediate-risk patients.
No surprises
Turning to breast cancer, increased TTI was associated with the most negative survival effects for stage II and III breast cancer.
For stage II breast cancer, for example, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 17.7% and 30.5%, respectively, with TTI of 61-120 days vs 21.7% and 36.5% with TTI at 181-365 days.
Even for stage I breast cancer patients, there were significant differences in all-cause mortality with delayed definitive therapy, although the effect size is clinically small, the researchers report.
Patients with stage IA or IB breast cancer who were not treated until 61 to 120 days after diagnosis had 1.3% and 2.3% increased mortality at 5 years and 10 years, respectively, and those waiting longer suffered even greater increases in mortality. “As such, our analysis underscores the importance of timely definitive treatment, even for stage I breast cancer,” the authors write.
Charles Shapiro, MD, director of translational breast cancer research for the Mount Sinai Health System, New York City, was not surprised by the data.
The observation that delays in initiating cancer treatment are associated with worse survival is “not new, as delays in primary surgical treatments and chemotherapy for early-stage disease is an adverse prognostic factor for clinical outcomes,” Shapiro told Medscape Medical News.
“The bottom line is primary surgery and the start of chemotherapy should probably occur as soon as clinically feasible,” said Shapiro, who was not involved in the study.
The authors of an accompanying editorial agree.
This study supports avoiding unnecessary treatment delays and prioritizing timely cancer care, even during the COVID-19 pandemic, write Laura Van Metre Baum, MD, Division of Hematology and Oncology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
They note, however, that primary care, “the most important conduit for cancer screening and initial evaluation of new symptoms, has been the hardest hit economically and the most subject to profound disruption and restructuring during the current COVID-19 pandemic.
“In many centers, cancer care delivery has been disrupted and nonstandard therapies offered in an effort to minimize exposure of this high-risk group to the virus. The implications in appropriately balancing the urgency of cancer care and the threat of COVID-19 exposure in the pandemic are more complex,” the editorialists conclude.
Cone, Shapiro, and Van Metre Baum have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This work won first prize in the Commission on Cancer 2020 Cancer Research Paper Competition and was virtually presented at the Commission on Cancer Plenary Session on October 30, 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic has meant delays in cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment — and a new study shows just how deadly delaying cancer treatment can be.
The study found evidence that longer time to starting treatment after diagnosis was generally associated with higher mortality across several common cancers, most notably for colon and early-stage lung cancer.
“There is a limit to how long we can safely defer treatment for cancer therapies, pandemic or not, which may be shorter than we think,” lead author Eugene Cone, MD, Combined Harvard Program in Urologic Oncology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“When you consider that cancer screening may have been delayed during the pandemic, which would further increase the period between developing a disease and getting therapy, timely treatment for cancer has never been more important,” Cone added.
The study was published online December 14 in JAMA Network Open.
The sooner the better
Using the National Cancer Database, Cone and colleagues identified roughly 2.24 million patients diagnosed with nonmetastatic breast (52%), prostate (38%), colon (4%) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC, 6%) between 2004 and 2015. Treatment and outcome data were analyzed from January to March 2020.
The time-to-treatment initiation (TTI) – the interval between cancer diagnosis and receipt of curative-intent therapy – was categorized as 8 to 60 days (reference), 61 to 120 days, 121 to 180 days, and 181 to 365 days. Median TTI was 32 days for breast, 79 days for prostate, 41 days for NSCLC, and 26 days for colon cancer.
All four cancers benefitted to some degree from a short interval between diagnosis and therapy, the researchers found.
Across all four cancers, increasing TTI was generally associated with higher predicted mortality at 5 and 10 years, although the degree varied by cancer type and stage. The most pronounced association between increasing TTI and mortality was observed for colon and lung cancer.
For example, for stage III colon cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 38.9% and 54%, respectively, with TTI of 61 to 120 days, and increased to 47.8% and 63.8%, respectively, with TTI of 181 to 365 days.
Each additional 60-day delay was associated with a 3.2% to 6% increase in 5-year mortality for stage III colon cancer and a 0.9% to 4.6% increase for stage I colon cancer, with a longer 10-year time horizon showing larger effect sizes with increasing TTI.
For stage I NSCLC, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 47.4% and 72.6%, respectively, with TTI of 61 to 120 days compared with 47.6% and 72.8%, respectively, with TTI of 181 to 365 days.
For stage I NSCLC, there was a 4% to 6.2% absolute increase in 5-year mortality for increased TTI groups compared with the 8- to 60-day reference group, with larger effect sizes on 10-year mortality. The data precluded conclusions about stage II NSCLC.
“For prostate cancer, deferral of treatment by even a few months was associated with a significant impact on mortality,” Cone told Medscape Medical News.
For high-risk prostate cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 12.8% and 31.2%, respectively, with TTI of 61-120 days increasing to 14.1% and 33.8%, respectively with TTI at 181-365 days.
For intermediate-risk prostate cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 7.4% and 20.4% with TTI of 61-120 days vs 8.3% and 22.6% with TTI at 181-365 days.
The data show all-cause mortality differences of 2.2% at 5 years and 4.6% at 10 years between high-risk prostate cancer patients who were treated expeditiously vs those waiting 4 to 6 months and differences of 0.9% at 5 years and 2.4% at 10 years for similar intermediate-risk patients.
No surprises
Turning to breast cancer, increased TTI was associated with the most negative survival effects for stage II and III breast cancer.
For stage II breast cancer, for example, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 17.7% and 30.5%, respectively, with TTI of 61-120 days vs 21.7% and 36.5% with TTI at 181-365 days.
Even for stage I breast cancer patients, there were significant differences in all-cause mortality with delayed definitive therapy, although the effect size is clinically small, the researchers report.
Patients with stage IA or IB breast cancer who were not treated until 61 to 120 days after diagnosis had 1.3% and 2.3% increased mortality at 5 years and 10 years, respectively, and those waiting longer suffered even greater increases in mortality. “As such, our analysis underscores the importance of timely definitive treatment, even for stage I breast cancer,” the authors write.
Charles Shapiro, MD, director of translational breast cancer research for the Mount Sinai Health System, New York City, was not surprised by the data.
The observation that delays in initiating cancer treatment are associated with worse survival is “not new, as delays in primary surgical treatments and chemotherapy for early-stage disease is an adverse prognostic factor for clinical outcomes,” Shapiro told Medscape Medical News.
“The bottom line is primary surgery and the start of chemotherapy should probably occur as soon as clinically feasible,” said Shapiro, who was not involved in the study.
The authors of an accompanying editorial agree.
This study supports avoiding unnecessary treatment delays and prioritizing timely cancer care, even during the COVID-19 pandemic, write Laura Van Metre Baum, MD, Division of Hematology and Oncology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
They note, however, that primary care, “the most important conduit for cancer screening and initial evaluation of new symptoms, has been the hardest hit economically and the most subject to profound disruption and restructuring during the current COVID-19 pandemic.
“In many centers, cancer care delivery has been disrupted and nonstandard therapies offered in an effort to minimize exposure of this high-risk group to the virus. The implications in appropriately balancing the urgency of cancer care and the threat of COVID-19 exposure in the pandemic are more complex,” the editorialists conclude.
Cone, Shapiro, and Van Metre Baum have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This work won first prize in the Commission on Cancer 2020 Cancer Research Paper Competition and was virtually presented at the Commission on Cancer Plenary Session on October 30, 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic has meant delays in cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment — and a new study shows just how deadly delaying cancer treatment can be.
The study found evidence that longer time to starting treatment after diagnosis was generally associated with higher mortality across several common cancers, most notably for colon and early-stage lung cancer.
“There is a limit to how long we can safely defer treatment for cancer therapies, pandemic or not, which may be shorter than we think,” lead author Eugene Cone, MD, Combined Harvard Program in Urologic Oncology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, told Medscape Medical News.
“When you consider that cancer screening may have been delayed during the pandemic, which would further increase the period between developing a disease and getting therapy, timely treatment for cancer has never been more important,” Cone added.
The study was published online December 14 in JAMA Network Open.
The sooner the better
Using the National Cancer Database, Cone and colleagues identified roughly 2.24 million patients diagnosed with nonmetastatic breast (52%), prostate (38%), colon (4%) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC, 6%) between 2004 and 2015. Treatment and outcome data were analyzed from January to March 2020.
The time-to-treatment initiation (TTI) – the interval between cancer diagnosis and receipt of curative-intent therapy – was categorized as 8 to 60 days (reference), 61 to 120 days, 121 to 180 days, and 181 to 365 days. Median TTI was 32 days for breast, 79 days for prostate, 41 days for NSCLC, and 26 days for colon cancer.
All four cancers benefitted to some degree from a short interval between diagnosis and therapy, the researchers found.
Across all four cancers, increasing TTI was generally associated with higher predicted mortality at 5 and 10 years, although the degree varied by cancer type and stage. The most pronounced association between increasing TTI and mortality was observed for colon and lung cancer.
For example, for stage III colon cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 38.9% and 54%, respectively, with TTI of 61 to 120 days, and increased to 47.8% and 63.8%, respectively, with TTI of 181 to 365 days.
Each additional 60-day delay was associated with a 3.2% to 6% increase in 5-year mortality for stage III colon cancer and a 0.9% to 4.6% increase for stage I colon cancer, with a longer 10-year time horizon showing larger effect sizes with increasing TTI.
For stage I NSCLC, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 47.4% and 72.6%, respectively, with TTI of 61 to 120 days compared with 47.6% and 72.8%, respectively, with TTI of 181 to 365 days.
For stage I NSCLC, there was a 4% to 6.2% absolute increase in 5-year mortality for increased TTI groups compared with the 8- to 60-day reference group, with larger effect sizes on 10-year mortality. The data precluded conclusions about stage II NSCLC.
“For prostate cancer, deferral of treatment by even a few months was associated with a significant impact on mortality,” Cone told Medscape Medical News.
For high-risk prostate cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 12.8% and 31.2%, respectively, with TTI of 61-120 days increasing to 14.1% and 33.8%, respectively with TTI at 181-365 days.
For intermediate-risk prostate cancer, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 7.4% and 20.4% with TTI of 61-120 days vs 8.3% and 22.6% with TTI at 181-365 days.
The data show all-cause mortality differences of 2.2% at 5 years and 4.6% at 10 years between high-risk prostate cancer patients who were treated expeditiously vs those waiting 4 to 6 months and differences of 0.9% at 5 years and 2.4% at 10 years for similar intermediate-risk patients.
No surprises
Turning to breast cancer, increased TTI was associated with the most negative survival effects for stage II and III breast cancer.
For stage II breast cancer, for example, 5- and 10-year predicted mortality was 17.7% and 30.5%, respectively, with TTI of 61-120 days vs 21.7% and 36.5% with TTI at 181-365 days.
Even for stage I breast cancer patients, there were significant differences in all-cause mortality with delayed definitive therapy, although the effect size is clinically small, the researchers report.
Patients with stage IA or IB breast cancer who were not treated until 61 to 120 days after diagnosis had 1.3% and 2.3% increased mortality at 5 years and 10 years, respectively, and those waiting longer suffered even greater increases in mortality. “As such, our analysis underscores the importance of timely definitive treatment, even for stage I breast cancer,” the authors write.
Charles Shapiro, MD, director of translational breast cancer research for the Mount Sinai Health System, New York City, was not surprised by the data.
The observation that delays in initiating cancer treatment are associated with worse survival is “not new, as delays in primary surgical treatments and chemotherapy for early-stage disease is an adverse prognostic factor for clinical outcomes,” Shapiro told Medscape Medical News.
“The bottom line is primary surgery and the start of chemotherapy should probably occur as soon as clinically feasible,” said Shapiro, who was not involved in the study.
The authors of an accompanying editorial agree.
This study supports avoiding unnecessary treatment delays and prioritizing timely cancer care, even during the COVID-19 pandemic, write Laura Van Metre Baum, MD, Division of Hematology and Oncology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
They note, however, that primary care, “the most important conduit for cancer screening and initial evaluation of new symptoms, has been the hardest hit economically and the most subject to profound disruption and restructuring during the current COVID-19 pandemic.
“In many centers, cancer care delivery has been disrupted and nonstandard therapies offered in an effort to minimize exposure of this high-risk group to the virus. The implications in appropriately balancing the urgency of cancer care and the threat of COVID-19 exposure in the pandemic are more complex,” the editorialists conclude.
Cone, Shapiro, and Van Metre Baum have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. This work won first prize in the Commission on Cancer 2020 Cancer Research Paper Competition and was virtually presented at the Commission on Cancer Plenary Session on October 30, 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scant risk for SARS-CoV-2 from hospital air
Everywhere they look within hospitals, researchers find RNA from SARS-CoV-2 in the air. But viable viruses typically are found only close to patients, according to a review of published studies.
The finding supports recommendations to use surgical masks in most parts of the hospital, reserving respirators (such as N95 or FFP2) for aerosol-generating procedures on patients’ respiratory tracts, said Gabriel Birgand, PhD, an infectious disease researcher at Imperial College London.
“When the virus is spreading a lot in the community, it’s probably more likely for you to be contaminated in your friends’ areas or in your building than in your work area, where you are well equipped and compliant with all the measures,” he said in an interview. “So it’s pretty good news.”
The systematic review by Dr. Birgand and colleagues was published in JAMA Network Open.
Recommended precautions to protect health care workers from SARS-CoV-2 infections remain controversial. Most authorities believe droplets are the primary route of transmission, which would mean surgical masks may be sufficient protection. But some research has suggested transmission by aerosols as well, making N95 respirators seem necessary. There is even disagreement about the definitions of the words “aerosol” and “droplet.”
To better understand where traces of the virus can be found in the air in hospitals, Dr. Birgand and colleagues analyzed all the studies they could find on the subject in English.
They identified 24 articles with original data. All of the studies used reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests to identify SARS-CoV-2 RNA. In five studies, attempts were also made to culture viable viruses. Three studies assessed the particle size relative to RNA concentration or viral titer.
Of 893 air samples across the 24 studies, 52.7% were taken from areas close to patients, 26.5% were taken in clinical areas, 13.7% in staff areas, 4.7% in public areas, and 2.4% in toilets or bathrooms.
Among those studies that quantified RNA, the median interquartile range of concentrations varied from 1.0 x 103 copies/m3 in clinical areas to 9.7 x 103 copies/m3 in toilets or bathrooms.
One study found an RNA concentration of 2.0 x 103 copies for particle sizes >4 mcm and 1.3 x 103 copies/m3 for particle sizes ≤4 mcm, both in patients’ rooms.
Three studies included viral cultures; of those, two resulted in positive cultures, both in a non-ICU setting. In one study, 3 of 39 samples were positive, and in the other, 4 of 4 were positive. Viral cultures in toilets, clinical areas, staff areas, and public areas were negative.
One of these studies assessed viral concentration and found that the median interquartile range was 4.8 tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50)/m3 for particles <1 mcm, 4.27 TCID50/m3 for particles 1-4 mcm, and 1.82 TCID50/m3 for particles >4 mcm.
Although viable viruses weren’t found in staff areas, the presence of viral RNA in places such as dining rooms and meeting rooms raises a concern, Dr. Birgand said.
“All of these staff areas are probably playing an important role in contamination,” he said. “It’s pretty easy to see when you are dining, you are not wearing a face mask, and it’s associated with a strong risk when there is a strong dissemination of the virus in the community.”
Studies on contact tracing among health care workers have also identified meeting rooms and dining rooms as the second most common source of infection after community contact, he said.
In general, the findings of the review correspond to epidemiologic studies, said Angela Rasmussen, PhD, a virologist with the Georgetown University Center for Global Health Science and Security, Washington, who was not involved in the review. “Absent aerosol-generating procedures, health care workers are largely not getting infected when they take droplet precautions.”
One reason may be that patients shed the most infectious viruses a couple of days before and after symptoms begin. By the time they’re hospitalized, they’re less likely to be contagious but may continue to shed viral RNA.
“We don’t really know the basis for the persistence of RNA being produced long after people have been infected and have recovered from the acute infection,” she said, “but it has been observed quite frequently.”
Although the virus cannot remain viable for very long in the air, remnants may still be detected in the form of RNA, Dr. Rasmussen said. In addition, hospitals often do a good job of ventilation.
She pointed out that it can be difficult to cultivate viruses in air samples because of contaminants such as bacteria and fungi. “That’s one of the limitations of a study like this. You’re not really sure if it’s because there’s no viable virus there or because you just aren’t able to collect samples that would allow you to determine that.”
Dr. Birgand and colleagues acknowledged other limitations. The studies they reviewed used different approaches to sampling. Different procedures may have been underway in the rooms being sampled, and factors such as temperature and humidity could have affected the results. In addition, the studies used different cycle thresholds for PCR positivity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Everywhere they look within hospitals, researchers find RNA from SARS-CoV-2 in the air. But viable viruses typically are found only close to patients, according to a review of published studies.
The finding supports recommendations to use surgical masks in most parts of the hospital, reserving respirators (such as N95 or FFP2) for aerosol-generating procedures on patients’ respiratory tracts, said Gabriel Birgand, PhD, an infectious disease researcher at Imperial College London.
“When the virus is spreading a lot in the community, it’s probably more likely for you to be contaminated in your friends’ areas or in your building than in your work area, where you are well equipped and compliant with all the measures,” he said in an interview. “So it’s pretty good news.”
The systematic review by Dr. Birgand and colleagues was published in JAMA Network Open.
Recommended precautions to protect health care workers from SARS-CoV-2 infections remain controversial. Most authorities believe droplets are the primary route of transmission, which would mean surgical masks may be sufficient protection. But some research has suggested transmission by aerosols as well, making N95 respirators seem necessary. There is even disagreement about the definitions of the words “aerosol” and “droplet.”
To better understand where traces of the virus can be found in the air in hospitals, Dr. Birgand and colleagues analyzed all the studies they could find on the subject in English.
They identified 24 articles with original data. All of the studies used reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests to identify SARS-CoV-2 RNA. In five studies, attempts were also made to culture viable viruses. Three studies assessed the particle size relative to RNA concentration or viral titer.
Of 893 air samples across the 24 studies, 52.7% were taken from areas close to patients, 26.5% were taken in clinical areas, 13.7% in staff areas, 4.7% in public areas, and 2.4% in toilets or bathrooms.
Among those studies that quantified RNA, the median interquartile range of concentrations varied from 1.0 x 103 copies/m3 in clinical areas to 9.7 x 103 copies/m3 in toilets or bathrooms.
One study found an RNA concentration of 2.0 x 103 copies for particle sizes >4 mcm and 1.3 x 103 copies/m3 for particle sizes ≤4 mcm, both in patients’ rooms.
Three studies included viral cultures; of those, two resulted in positive cultures, both in a non-ICU setting. In one study, 3 of 39 samples were positive, and in the other, 4 of 4 were positive. Viral cultures in toilets, clinical areas, staff areas, and public areas were negative.
One of these studies assessed viral concentration and found that the median interquartile range was 4.8 tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50)/m3 for particles <1 mcm, 4.27 TCID50/m3 for particles 1-4 mcm, and 1.82 TCID50/m3 for particles >4 mcm.
Although viable viruses weren’t found in staff areas, the presence of viral RNA in places such as dining rooms and meeting rooms raises a concern, Dr. Birgand said.
“All of these staff areas are probably playing an important role in contamination,” he said. “It’s pretty easy to see when you are dining, you are not wearing a face mask, and it’s associated with a strong risk when there is a strong dissemination of the virus in the community.”
Studies on contact tracing among health care workers have also identified meeting rooms and dining rooms as the second most common source of infection after community contact, he said.
In general, the findings of the review correspond to epidemiologic studies, said Angela Rasmussen, PhD, a virologist with the Georgetown University Center for Global Health Science and Security, Washington, who was not involved in the review. “Absent aerosol-generating procedures, health care workers are largely not getting infected when they take droplet precautions.”
One reason may be that patients shed the most infectious viruses a couple of days before and after symptoms begin. By the time they’re hospitalized, they’re less likely to be contagious but may continue to shed viral RNA.
“We don’t really know the basis for the persistence of RNA being produced long after people have been infected and have recovered from the acute infection,” she said, “but it has been observed quite frequently.”
Although the virus cannot remain viable for very long in the air, remnants may still be detected in the form of RNA, Dr. Rasmussen said. In addition, hospitals often do a good job of ventilation.
She pointed out that it can be difficult to cultivate viruses in air samples because of contaminants such as bacteria and fungi. “That’s one of the limitations of a study like this. You’re not really sure if it’s because there’s no viable virus there or because you just aren’t able to collect samples that would allow you to determine that.”
Dr. Birgand and colleagues acknowledged other limitations. The studies they reviewed used different approaches to sampling. Different procedures may have been underway in the rooms being sampled, and factors such as temperature and humidity could have affected the results. In addition, the studies used different cycle thresholds for PCR positivity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Everywhere they look within hospitals, researchers find RNA from SARS-CoV-2 in the air. But viable viruses typically are found only close to patients, according to a review of published studies.
The finding supports recommendations to use surgical masks in most parts of the hospital, reserving respirators (such as N95 or FFP2) for aerosol-generating procedures on patients’ respiratory tracts, said Gabriel Birgand, PhD, an infectious disease researcher at Imperial College London.
“When the virus is spreading a lot in the community, it’s probably more likely for you to be contaminated in your friends’ areas or in your building than in your work area, where you are well equipped and compliant with all the measures,” he said in an interview. “So it’s pretty good news.”
The systematic review by Dr. Birgand and colleagues was published in JAMA Network Open.
Recommended precautions to protect health care workers from SARS-CoV-2 infections remain controversial. Most authorities believe droplets are the primary route of transmission, which would mean surgical masks may be sufficient protection. But some research has suggested transmission by aerosols as well, making N95 respirators seem necessary. There is even disagreement about the definitions of the words “aerosol” and “droplet.”
To better understand where traces of the virus can be found in the air in hospitals, Dr. Birgand and colleagues analyzed all the studies they could find on the subject in English.
They identified 24 articles with original data. All of the studies used reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests to identify SARS-CoV-2 RNA. In five studies, attempts were also made to culture viable viruses. Three studies assessed the particle size relative to RNA concentration or viral titer.
Of 893 air samples across the 24 studies, 52.7% were taken from areas close to patients, 26.5% were taken in clinical areas, 13.7% in staff areas, 4.7% in public areas, and 2.4% in toilets or bathrooms.
Among those studies that quantified RNA, the median interquartile range of concentrations varied from 1.0 x 103 copies/m3 in clinical areas to 9.7 x 103 copies/m3 in toilets or bathrooms.
One study found an RNA concentration of 2.0 x 103 copies for particle sizes >4 mcm and 1.3 x 103 copies/m3 for particle sizes ≤4 mcm, both in patients’ rooms.
Three studies included viral cultures; of those, two resulted in positive cultures, both in a non-ICU setting. In one study, 3 of 39 samples were positive, and in the other, 4 of 4 were positive. Viral cultures in toilets, clinical areas, staff areas, and public areas were negative.
One of these studies assessed viral concentration and found that the median interquartile range was 4.8 tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50)/m3 for particles <1 mcm, 4.27 TCID50/m3 for particles 1-4 mcm, and 1.82 TCID50/m3 for particles >4 mcm.
Although viable viruses weren’t found in staff areas, the presence of viral RNA in places such as dining rooms and meeting rooms raises a concern, Dr. Birgand said.
“All of these staff areas are probably playing an important role in contamination,” he said. “It’s pretty easy to see when you are dining, you are not wearing a face mask, and it’s associated with a strong risk when there is a strong dissemination of the virus in the community.”
Studies on contact tracing among health care workers have also identified meeting rooms and dining rooms as the second most common source of infection after community contact, he said.
In general, the findings of the review correspond to epidemiologic studies, said Angela Rasmussen, PhD, a virologist with the Georgetown University Center for Global Health Science and Security, Washington, who was not involved in the review. “Absent aerosol-generating procedures, health care workers are largely not getting infected when they take droplet precautions.”
One reason may be that patients shed the most infectious viruses a couple of days before and after symptoms begin. By the time they’re hospitalized, they’re less likely to be contagious but may continue to shed viral RNA.
“We don’t really know the basis for the persistence of RNA being produced long after people have been infected and have recovered from the acute infection,” she said, “but it has been observed quite frequently.”
Although the virus cannot remain viable for very long in the air, remnants may still be detected in the form of RNA, Dr. Rasmussen said. In addition, hospitals often do a good job of ventilation.
She pointed out that it can be difficult to cultivate viruses in air samples because of contaminants such as bacteria and fungi. “That’s one of the limitations of a study like this. You’re not really sure if it’s because there’s no viable virus there or because you just aren’t able to collect samples that would allow you to determine that.”
Dr. Birgand and colleagues acknowledged other limitations. The studies they reviewed used different approaches to sampling. Different procedures may have been underway in the rooms being sampled, and factors such as temperature and humidity could have affected the results. In addition, the studies used different cycle thresholds for PCR positivity.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New resilience center targets traumatized health care workers
A physician assistant participating in a virtual workshop began to cry, confessing that she felt overwhelmed with guilt because New Yorkers were hailing her as a frontline hero in the pandemic. That was when Joe Ciavarro knew he was in the right place.
“She was saying all the things I could not verbalize because I, too, didn’t feel like I deserved all this praise and thousands of people cheering for us every evening when people were losing jobs, didn’t have money for food, and their loved ones were dying without family at their side,” says Mr. Ciavarro, a PA at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York.
Mr. Ciavarro, who also manages 170 other PAs on two of Mount Sinai’s campuses in Manhattan, has been on the front lines since COVID-19 first hit; he lost a colleague and friend to suicide in September.
The mental anguish from his job prompted him to sign up for the resilience workshop offered by Mount Sinai’s Center for Stress, Resilience, and Personal Growth. The center – the first of its kind in North America – was launched in June to help health care workers like him cope with the intense psychological pressures they were facing. The weekly workshops became a safe place where Mr. Ciavarro and other staff members could share their darkest fears and learn ways to help them deal with their situation.
“It’s been grueling but we learned how to take care of ourselves so we can take care of our patients,” said Mr. Ciavarro. “This has become like a guided group therapy session on ways to manage and develop resilience. And I feel like my emotions are validated, knowing that others feel the same way.”
Caring for their own
Medical professionals treating patients with COVID-19 are in similar predicaments, and the psychological fallout is enormous: They’re exhausted by the seemingly never-ending patient load and staffing shortages, and haunted by fears for their own safety and that of their families. Studies in China, Canada, and Italy have revealed that a significant number of doctors and nurses in the early days of the pandemic experienced high levels of distress, depression, anxiety, nightmares, and insomnia.
after witnessing the deaths of so many patients who were alone, without family.
But the resilience workshop that Mr. Ciavarro attended offers some hope and is part of a multifaceted program that aims to be a model for other institutions and communities. The Mount Sinai health system already had some programs in place, including centers for 9/11 responders, for spirituality and health, and a wellness program to aid burned-out doctors. But the leadership at Mount Sinai, which includes psychiatrist Dennis Charney, MD, dean of the medical school and a leading expert on PTSD, knew early in the pandemic that emotional and psychological distress would plague health care workers, according to Deborah Marin, MD, director of the new center.
“We decided to quickly put in place a program that we could do virtually, with workshops and apps, that would give access to several services above and beyond what was already going on,” says Dr. Marin, a professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who also directs their center for spirituality and health.
The key components include a comprehensive screening tool that helps doctors at the center identify which potential participants are most at risk. Participants build personal inventories that detail the intensity of work-related exposures, personal or family stressors that have arisen because of the pandemic, or any mental health conditions or substance abuse problems that may make staff members more vulnerable.
The weekly workshops led by trained staff are designed to give participants the tools to foster resilience and process their experiences. Online apps provide feedback on their progress and engage them with video and other resources around meditation, relaxation, and resilience techniques.
In addition, all 40,000 members of the Mount Sinai staff are eligible for up to 14 one-on-one sessions with psychologists and psychiatrists who specialize in treating trauma.
“That’s highly unusual – to offer this at no cost to everyone,” said Dr. Marin. “We also have a treatment service that is specifically focused on behavioral health care, so people can learn better coping strategies, and we also have social workers to provide coaching.”
While the center doesn’t have specific numbers on how many nurses, physicians, and other staff have participated in treatment, they have trained over 70 peer leaders for their five workshops that home in on the most important factors of resilience.
“We’ve gotten enthusiastic responses from PAs and nurses,” said Craig Katz, MD, an expert in disaster psychiatry at Mount Sinai and a workshop moderator. Physicians have been slower to get on board. “Doctors are a tough nut to crack – it’s largely a culture where they may burn out but don’t want to talk about it. And asking for help is a hard transition for physicians to make.”
How to protect in midst of trauma
In formulating the program’s platform, Mount Sinai experts drew upon their extensive experience aiding 9/11 responders at the World Trade Center (WTC), as well as their system-wide wellness program that aids demoralized and burned-out physicians. While the reach of the pandemic is much broader than 9/11, experts see some commonalities in conditions that emerge after traumatic events, and they also discovered what can help.
“We learned from our WTC experience about what are protective factors – what are the social supports that buffer against depression, anxiety, and PTSD,” said Jonathan DePierro, PhD, clinical director of CSRPG and a psychologist at the Mount Sinai WTC Mental Health Program. “We also learned that people who have more prolonged exposures are at greater risk of developing mental health difficulties.”
The program itself reflects these lessons – and that’s why it’s open to all employees, not just medical professionals. Housekeepers, security staffers, even construction workers are also dealing with their lives being in danger. “That wasn’t in their job description,” said Dr. DePierro. “These people tend to have fewer social and economic resources, make less money and have fewer structural supports, which makes them even more vulnerable.”
Dr. Charney’s strategies on building resilience became a bible of sorts for the workshops, according to Dr. Katz, who authored the training curriculum. Sessions deal with how to build up reservoirs of realistic optimism, keep gratitude journals, find spiritual meaning in their lives, maintain physical wellness and create networks of social support. The workshops are meant to help participants create action plans, to reach out for support in their social networks, and keep the focus on the positives.
The goal is to give demoralized health care workers a renewed sense of competence. “The resilience workshop is a launching point to get people to show up and talk,” said Dr. Katz. “And if we do that, we’ve accomplished a lot just getting people in the door.”
The center will also have a research component to identify what works and what doesn’t so their platform can provide a template for other institutions; Dr. Marin said they’ve gotten inquiries about the program from major hospital systems in Michigan and California. They’ll also conduct longitudinal research to determine what lingering problems persist among healthcare workers over time.
Since the center opened its virtual doors, the curriculum has also been altered in response to feedback from the support staff, many of whom live in the community that surrounds Mount Sinai in northern Manhattan, which is largely lower-income Latinx and Black individuals. Workshop materials have been translated into Spanish and now feature people who reflect a more diverse set of experiences.
“Many of our employees and the population we serve identify as non-White so we’ve been doing outreach with a lot of the local unions,” said Dr. Marin. “Our next step is to take what we’re doing and work with local community organizations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A physician assistant participating in a virtual workshop began to cry, confessing that she felt overwhelmed with guilt because New Yorkers were hailing her as a frontline hero in the pandemic. That was when Joe Ciavarro knew he was in the right place.
“She was saying all the things I could not verbalize because I, too, didn’t feel like I deserved all this praise and thousands of people cheering for us every evening when people were losing jobs, didn’t have money for food, and their loved ones were dying without family at their side,” says Mr. Ciavarro, a PA at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York.
Mr. Ciavarro, who also manages 170 other PAs on two of Mount Sinai’s campuses in Manhattan, has been on the front lines since COVID-19 first hit; he lost a colleague and friend to suicide in September.
The mental anguish from his job prompted him to sign up for the resilience workshop offered by Mount Sinai’s Center for Stress, Resilience, and Personal Growth. The center – the first of its kind in North America – was launched in June to help health care workers like him cope with the intense psychological pressures they were facing. The weekly workshops became a safe place where Mr. Ciavarro and other staff members could share their darkest fears and learn ways to help them deal with their situation.
“It’s been grueling but we learned how to take care of ourselves so we can take care of our patients,” said Mr. Ciavarro. “This has become like a guided group therapy session on ways to manage and develop resilience. And I feel like my emotions are validated, knowing that others feel the same way.”
Caring for their own
Medical professionals treating patients with COVID-19 are in similar predicaments, and the psychological fallout is enormous: They’re exhausted by the seemingly never-ending patient load and staffing shortages, and haunted by fears for their own safety and that of their families. Studies in China, Canada, and Italy have revealed that a significant number of doctors and nurses in the early days of the pandemic experienced high levels of distress, depression, anxiety, nightmares, and insomnia.
after witnessing the deaths of so many patients who were alone, without family.
But the resilience workshop that Mr. Ciavarro attended offers some hope and is part of a multifaceted program that aims to be a model for other institutions and communities. The Mount Sinai health system already had some programs in place, including centers for 9/11 responders, for spirituality and health, and a wellness program to aid burned-out doctors. But the leadership at Mount Sinai, which includes psychiatrist Dennis Charney, MD, dean of the medical school and a leading expert on PTSD, knew early in the pandemic that emotional and psychological distress would plague health care workers, according to Deborah Marin, MD, director of the new center.
“We decided to quickly put in place a program that we could do virtually, with workshops and apps, that would give access to several services above and beyond what was already going on,” says Dr. Marin, a professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who also directs their center for spirituality and health.
The key components include a comprehensive screening tool that helps doctors at the center identify which potential participants are most at risk. Participants build personal inventories that detail the intensity of work-related exposures, personal or family stressors that have arisen because of the pandemic, or any mental health conditions or substance abuse problems that may make staff members more vulnerable.
The weekly workshops led by trained staff are designed to give participants the tools to foster resilience and process their experiences. Online apps provide feedback on their progress and engage them with video and other resources around meditation, relaxation, and resilience techniques.
In addition, all 40,000 members of the Mount Sinai staff are eligible for up to 14 one-on-one sessions with psychologists and psychiatrists who specialize in treating trauma.
“That’s highly unusual – to offer this at no cost to everyone,” said Dr. Marin. “We also have a treatment service that is specifically focused on behavioral health care, so people can learn better coping strategies, and we also have social workers to provide coaching.”
While the center doesn’t have specific numbers on how many nurses, physicians, and other staff have participated in treatment, they have trained over 70 peer leaders for their five workshops that home in on the most important factors of resilience.
“We’ve gotten enthusiastic responses from PAs and nurses,” said Craig Katz, MD, an expert in disaster psychiatry at Mount Sinai and a workshop moderator. Physicians have been slower to get on board. “Doctors are a tough nut to crack – it’s largely a culture where they may burn out but don’t want to talk about it. And asking for help is a hard transition for physicians to make.”
How to protect in midst of trauma
In formulating the program’s platform, Mount Sinai experts drew upon their extensive experience aiding 9/11 responders at the World Trade Center (WTC), as well as their system-wide wellness program that aids demoralized and burned-out physicians. While the reach of the pandemic is much broader than 9/11, experts see some commonalities in conditions that emerge after traumatic events, and they also discovered what can help.
“We learned from our WTC experience about what are protective factors – what are the social supports that buffer against depression, anxiety, and PTSD,” said Jonathan DePierro, PhD, clinical director of CSRPG and a psychologist at the Mount Sinai WTC Mental Health Program. “We also learned that people who have more prolonged exposures are at greater risk of developing mental health difficulties.”
The program itself reflects these lessons – and that’s why it’s open to all employees, not just medical professionals. Housekeepers, security staffers, even construction workers are also dealing with their lives being in danger. “That wasn’t in their job description,” said Dr. DePierro. “These people tend to have fewer social and economic resources, make less money and have fewer structural supports, which makes them even more vulnerable.”
Dr. Charney’s strategies on building resilience became a bible of sorts for the workshops, according to Dr. Katz, who authored the training curriculum. Sessions deal with how to build up reservoirs of realistic optimism, keep gratitude journals, find spiritual meaning in their lives, maintain physical wellness and create networks of social support. The workshops are meant to help participants create action plans, to reach out for support in their social networks, and keep the focus on the positives.
The goal is to give demoralized health care workers a renewed sense of competence. “The resilience workshop is a launching point to get people to show up and talk,” said Dr. Katz. “And if we do that, we’ve accomplished a lot just getting people in the door.”
The center will also have a research component to identify what works and what doesn’t so their platform can provide a template for other institutions; Dr. Marin said they’ve gotten inquiries about the program from major hospital systems in Michigan and California. They’ll also conduct longitudinal research to determine what lingering problems persist among healthcare workers over time.
Since the center opened its virtual doors, the curriculum has also been altered in response to feedback from the support staff, many of whom live in the community that surrounds Mount Sinai in northern Manhattan, which is largely lower-income Latinx and Black individuals. Workshop materials have been translated into Spanish and now feature people who reflect a more diverse set of experiences.
“Many of our employees and the population we serve identify as non-White so we’ve been doing outreach with a lot of the local unions,” said Dr. Marin. “Our next step is to take what we’re doing and work with local community organizations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A physician assistant participating in a virtual workshop began to cry, confessing that she felt overwhelmed with guilt because New Yorkers were hailing her as a frontline hero in the pandemic. That was when Joe Ciavarro knew he was in the right place.
“She was saying all the things I could not verbalize because I, too, didn’t feel like I deserved all this praise and thousands of people cheering for us every evening when people were losing jobs, didn’t have money for food, and their loved ones were dying without family at their side,” says Mr. Ciavarro, a PA at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York.
Mr. Ciavarro, who also manages 170 other PAs on two of Mount Sinai’s campuses in Manhattan, has been on the front lines since COVID-19 first hit; he lost a colleague and friend to suicide in September.
The mental anguish from his job prompted him to sign up for the resilience workshop offered by Mount Sinai’s Center for Stress, Resilience, and Personal Growth. The center – the first of its kind in North America – was launched in June to help health care workers like him cope with the intense psychological pressures they were facing. The weekly workshops became a safe place where Mr. Ciavarro and other staff members could share their darkest fears and learn ways to help them deal with their situation.
“It’s been grueling but we learned how to take care of ourselves so we can take care of our patients,” said Mr. Ciavarro. “This has become like a guided group therapy session on ways to manage and develop resilience. And I feel like my emotions are validated, knowing that others feel the same way.”
Caring for their own
Medical professionals treating patients with COVID-19 are in similar predicaments, and the psychological fallout is enormous: They’re exhausted by the seemingly never-ending patient load and staffing shortages, and haunted by fears for their own safety and that of their families. Studies in China, Canada, and Italy have revealed that a significant number of doctors and nurses in the early days of the pandemic experienced high levels of distress, depression, anxiety, nightmares, and insomnia.
after witnessing the deaths of so many patients who were alone, without family.
But the resilience workshop that Mr. Ciavarro attended offers some hope and is part of a multifaceted program that aims to be a model for other institutions and communities. The Mount Sinai health system already had some programs in place, including centers for 9/11 responders, for spirituality and health, and a wellness program to aid burned-out doctors. But the leadership at Mount Sinai, which includes psychiatrist Dennis Charney, MD, dean of the medical school and a leading expert on PTSD, knew early in the pandemic that emotional and psychological distress would plague health care workers, according to Deborah Marin, MD, director of the new center.
“We decided to quickly put in place a program that we could do virtually, with workshops and apps, that would give access to several services above and beyond what was already going on,” says Dr. Marin, a professor of psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who also directs their center for spirituality and health.
The key components include a comprehensive screening tool that helps doctors at the center identify which potential participants are most at risk. Participants build personal inventories that detail the intensity of work-related exposures, personal or family stressors that have arisen because of the pandemic, or any mental health conditions or substance abuse problems that may make staff members more vulnerable.
The weekly workshops led by trained staff are designed to give participants the tools to foster resilience and process their experiences. Online apps provide feedback on their progress and engage them with video and other resources around meditation, relaxation, and resilience techniques.
In addition, all 40,000 members of the Mount Sinai staff are eligible for up to 14 one-on-one sessions with psychologists and psychiatrists who specialize in treating trauma.
“That’s highly unusual – to offer this at no cost to everyone,” said Dr. Marin. “We also have a treatment service that is specifically focused on behavioral health care, so people can learn better coping strategies, and we also have social workers to provide coaching.”
While the center doesn’t have specific numbers on how many nurses, physicians, and other staff have participated in treatment, they have trained over 70 peer leaders for their five workshops that home in on the most important factors of resilience.
“We’ve gotten enthusiastic responses from PAs and nurses,” said Craig Katz, MD, an expert in disaster psychiatry at Mount Sinai and a workshop moderator. Physicians have been slower to get on board. “Doctors are a tough nut to crack – it’s largely a culture where they may burn out but don’t want to talk about it. And asking for help is a hard transition for physicians to make.”
How to protect in midst of trauma
In formulating the program’s platform, Mount Sinai experts drew upon their extensive experience aiding 9/11 responders at the World Trade Center (WTC), as well as their system-wide wellness program that aids demoralized and burned-out physicians. While the reach of the pandemic is much broader than 9/11, experts see some commonalities in conditions that emerge after traumatic events, and they also discovered what can help.
“We learned from our WTC experience about what are protective factors – what are the social supports that buffer against depression, anxiety, and PTSD,” said Jonathan DePierro, PhD, clinical director of CSRPG and a psychologist at the Mount Sinai WTC Mental Health Program. “We also learned that people who have more prolonged exposures are at greater risk of developing mental health difficulties.”
The program itself reflects these lessons – and that’s why it’s open to all employees, not just medical professionals. Housekeepers, security staffers, even construction workers are also dealing with their lives being in danger. “That wasn’t in their job description,” said Dr. DePierro. “These people tend to have fewer social and economic resources, make less money and have fewer structural supports, which makes them even more vulnerable.”
Dr. Charney’s strategies on building resilience became a bible of sorts for the workshops, according to Dr. Katz, who authored the training curriculum. Sessions deal with how to build up reservoirs of realistic optimism, keep gratitude journals, find spiritual meaning in their lives, maintain physical wellness and create networks of social support. The workshops are meant to help participants create action plans, to reach out for support in their social networks, and keep the focus on the positives.
The goal is to give demoralized health care workers a renewed sense of competence. “The resilience workshop is a launching point to get people to show up and talk,” said Dr. Katz. “And if we do that, we’ve accomplished a lot just getting people in the door.”
The center will also have a research component to identify what works and what doesn’t so their platform can provide a template for other institutions; Dr. Marin said they’ve gotten inquiries about the program from major hospital systems in Michigan and California. They’ll also conduct longitudinal research to determine what lingering problems persist among healthcare workers over time.
Since the center opened its virtual doors, the curriculum has also been altered in response to feedback from the support staff, many of whom live in the community that surrounds Mount Sinai in northern Manhattan, which is largely lower-income Latinx and Black individuals. Workshop materials have been translated into Spanish and now feature people who reflect a more diverse set of experiences.
“Many of our employees and the population we serve identify as non-White so we’ve been doing outreach with a lot of the local unions,” said Dr. Marin. “Our next step is to take what we’re doing and work with local community organizations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.