User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


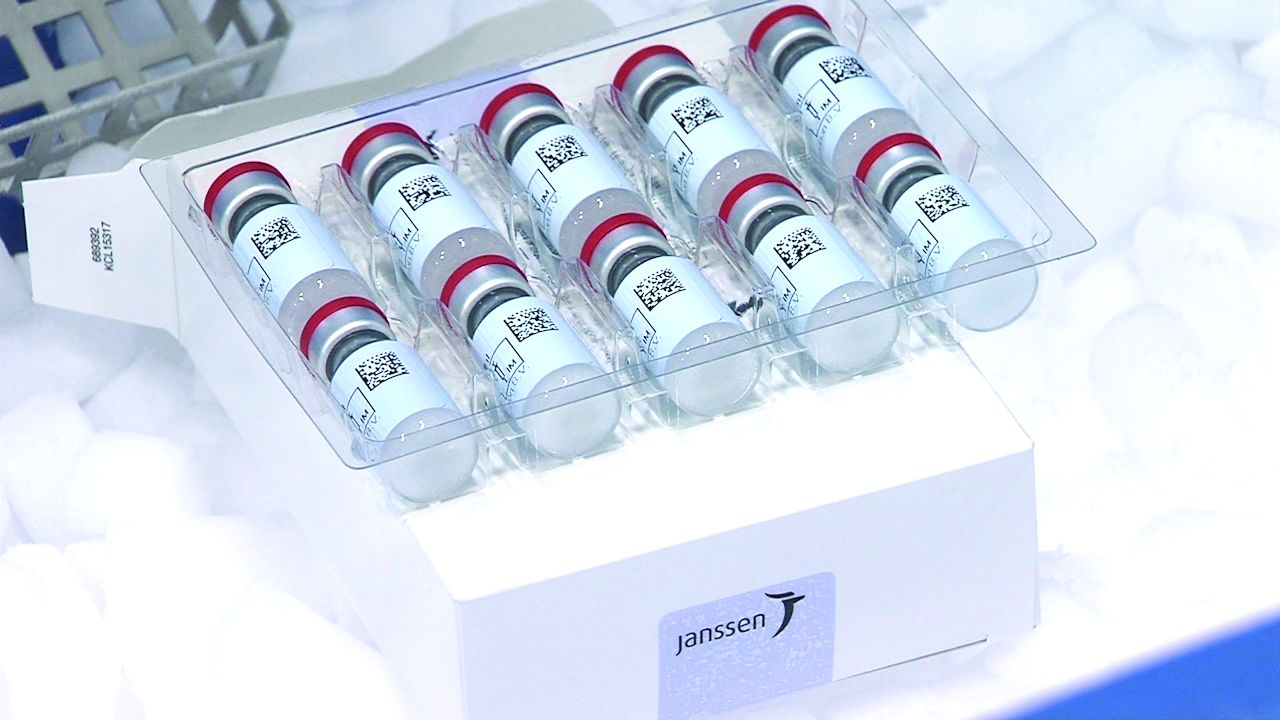
J&J COVID-19 vaccine wins unanimous backing of FDA panel
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is expected to quickly provide an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the vaccine following the recommendation by the panel. The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee voted 22-0 on this question: Based on the totality of scientific evidence available, do the benefits of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine outweigh its risks for use in individuals 18 years of age and older?
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine is expected to offer more convenient dosing and be easier to distribute than the two rival products already available in the United States. Janssen’s vaccine is intended to be given in a single dose. In December, the FDA granted EUAs for the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, which are each two-dose regimens.
Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine can be stored for at least 3 months at normal refrigerator temperatures of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Its shipping and storage fits into the existing medical supply infrastructure, the company said in its briefing materials for the FDA advisory committee meeting. In contrast, Pfizer’s vaccine is stored in ultracold freezers at temperatures between -80°C and -60°C (-112°F and -76°F), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Moderna’s vaccine may be stored in a freezer between -25°C and -15°C (-13°F and 5°F).
But FDA advisers focused more in their deliberations on concerns about Janssen’s vaccine, including emerging reports of allergic reactions.
The advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Johnson & Johnson’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. The company’s initial unveiling last month of key results for its vaccine caused an initial wave of disappointment, with its overall efficacy against moderate-to-severe COVID-19 28 days postvaccination first reported at about 66% globally. By contrast, results for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines suggest they have efficacy rates of 95% and 94%.
But in concluding, the advisers spoke of the Janssen vaccine as a much-needed tool to address the COVID-19 pandemic. The death toll in the United States attributed to the virus has reached 501,414, according to the World Health Organization.
“Despite the concerns that were raised during the discussion. I think what we have to keep in mind is that we’re still in the midst of this deadly pandemic,” said FDA adviser Archana Chatterjee, MD, PhD, from Rosalind Franklin University. “There is a shortage of vaccines that are currently authorized, and I think authorization of this vaccine will help meet the needs at the moment.”
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its advisers, but it often does so.
Anaphylaxis case
FDA advisers raised only a few questions for Johnson & Johnson and FDA staff ahead of their vote. The committee’s deliberations were less contentious and heated than had been during its December reviews of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. In those meetings, the panel voted 17-4, with one abstention, in favor of Pfizer’s vaccine and 20-0, with one abstention, on the Moderna vaccine.
“We are very comfortable now with the procedure, as well as the vaccines,” said Arnold Monto, MD, after the Feb. 26 vote on the Janssen vaccine. Dr. Monto, from the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor, has served as the chairman of the FDA panel through its review of all three COVID-19 vaccines.
Among the issues noted in the deliberations was the emergence of a concern about anaphylaxis with the vaccine.
This serious allergic reaction has been seen in people who have taken the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Before the week of the panel meeting, though, there had not been reports of anaphylaxis with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, said Macaya Douoguih, MD, MPH, head of clinical development and medical affairs for Janssen/ Johnson & Johnson’s vaccines division.
However, on February 24, Johnson & Johnson received preliminary reports about two cases of severe allergic reaction from an open-label study in South Africa, with one of these being anaphylaxis, Dr. Douoguih said. The company will continue to closely monitor for these events as outlined in their pharmacovigilance plan, Dr. Douoguih said.
Federal health officials have sought to make clinicians aware of the rare risk for anaphylaxis with COVID vaccines, while reminding the public that this reaction can be managed.
The FDA had Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC, give an update on postmarketing surveillance for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines as part of the review of the Johnson & Johnson application. Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues published a report in JAMA on February 14 that looked at an anaphylaxis case reported connected with COVID vaccines between December 14, 2020, and January 18, 2021.
The CDC identified 66 case reports received that met Brighton Collaboration case definition criteria for anaphylaxis (levels 1, 2, or 3): 47 following Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, for a reporting rate of 4.7 cases/million doses administered, and 19 following Moderna vaccine, for a reporting rate of 2.5 cases/million doses administered, Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues wrote.
The CDC has published materials to help clinicians prepare for the possibility of this rare event, Dr. Shimabukuro told the FDA advisers.
“The take-home message here is that these are rare events and anaphylaxis, although clinically serious, is treatable,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
At the conclusion of the meeting, FDA panelist Patrick Moore, MD, MPH, from the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania, stressed the need to convey to the public that the COVID vaccines appear so far to be safe. Many people earlier had doubts about how the FDA could both safely and quickly review the applications for EUAs for these products.
“As of February 26, things are looking good. That could change tomorrow,” Dr. Moore said. But “this whole EUA process does seem to have worked, despite my own personal concerns about it.”
No second-class vaccines
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine, known as Ad26.COV2.S, is composed of a recombinant, replication-incompetent human adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vector. It’s intended to encode a stabilized form of SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein. The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use a different mechanism. They rely on mRNA.
The FDA advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Janssen’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. They urged against people parsing study details too finely and seeking to pick and choose their shots.
“It’s important that people do not think that one vaccine is better than another,” said FDA adviser H. Cody Meissner, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston.
Dr. Monto agreed, noting that many people in the United States are still waiting for their turn to get COVID vaccines because of the limited early supply.
Trying to game the system to get one vaccine instead of another would not be wise. “In this environment, whatever you can get, get,” Dr. Monto said.
During an open public hearing, Sarah Christopherson, policy advocacy director of the National Women’s Health Network, said that press reports are fueling a damaging impression in the public that there are “first and second-class” vaccines.
“That has the potential to exacerbate existing mistrust” in vaccines, she said. “Public health authorities must address these perceptions head on.”
She urged against attempts to compare the Janssen vaccine to others, noting the potential effects of emerging variants of the virus.
“It’s difficult to make an apples-to-apples comparison between vaccines,” she said.
Johnson & Johnson’s efficacy results, which are lower than those of the mRNA vaccines, may be a reflection of the ways in which SARS-Co-V-2 is mutating and thus becoming more of a threat, according to the company. A key study of the new vaccine, involving about 44,000 people, coincided with the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, which were emerging in some of the countries where the pivotal COV3001 study was being conducted, the company said.
At least 14 days after vaccination, the Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine efficacy (95% confidence interval) was 72.0% (58.2, 81.7) in the United States, 68.1% (48.8, 80.7) in Brazil, and 64.0% (41.2, 78.7) in South Africa.
Weakened standards?
Several researchers called on the FDA to maintain a critical attitude when assessing Johnson & Johnson’s application for the EUA, warning of a potential for a permanent erosion of agency rules due to hasty action on COVID vaccines.
They raised concerns about the FDA demanding too little in terms of follow-up studies on COVID vaccines and with persisting murkiness resulting in attempts to determine how well these treatments work beyond the initial study period.
“I worry about FDA lowering its approval standards,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, from The BMJ and a faculty member at the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, during an open public hearing at the meeting.
“There’s a real urgency to stand back right now and look at the forest here, as well as the trees, and I urge the committee to consider the effects FDA decisions may have on the entire regulatory approval process,” Dr. Doshi said.
Dr. Doshi asked why Johnson & Johnson did not seek a standard full approval — a biologics license application (BLA) — instead of aiming for the lower bar of an EUA. The FDA already has allowed wide distribution of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines through EUAs. That removes the sense of urgency that FDA faced last year in his view.
The FDA’s June 2020 guidance on the development of COVID vaccines had asked drugmakers to plan on following participants in COVID vaccine trials for “ideally at least one to two years.” Yet people who got placebo in Moderna and Pfizer trials already are being vaccinated, Dr. Doshi said. And Johnson & Johnson said in its presentation to the FDA that if the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine were granted an EUA, the COV3001 study design would be amended to “facilitate cross-over of placebo participants in all participating countries to receive one dose of active study vaccine as fast as operationally feasible.”
“I’m nervous about the prospect of there never being a COVID vaccine that meets the FDA’s approval standard” for a BLA instead of the more limited EUA, Dr. Doshi said.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the FDA’s subsequent guidance tailored for EUAs for COVID vaccines “drastically shortened” the follow-up time to a median of 2 months. Dr. Zuckerman said that a crossover design would be “a reasonable compromise, but only if the placebo group has at least 6 months of data.” Dr. Zuckerman opened her remarks in the open public hearing by saying she had inherited Johnson & Johnson stock, so was speaking at the meeting against her own financial interest.
“As soon as a vaccine is authorized, we start losing the placebo group. If FDA lets that happen, that’s a huge loss for public health and a huge loss of information about how we can all stay safe,” Dr. Zuckerman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is expected to quickly provide an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the vaccine following the recommendation by the panel. The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee voted 22-0 on this question: Based on the totality of scientific evidence available, do the benefits of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine outweigh its risks for use in individuals 18 years of age and older?
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine is expected to offer more convenient dosing and be easier to distribute than the two rival products already available in the United States. Janssen’s vaccine is intended to be given in a single dose. In December, the FDA granted EUAs for the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, which are each two-dose regimens.
Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine can be stored for at least 3 months at normal refrigerator temperatures of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Its shipping and storage fits into the existing medical supply infrastructure, the company said in its briefing materials for the FDA advisory committee meeting. In contrast, Pfizer’s vaccine is stored in ultracold freezers at temperatures between -80°C and -60°C (-112°F and -76°F), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Moderna’s vaccine may be stored in a freezer between -25°C and -15°C (-13°F and 5°F).
But FDA advisers focused more in their deliberations on concerns about Janssen’s vaccine, including emerging reports of allergic reactions.
The advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Johnson & Johnson’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. The company’s initial unveiling last month of key results for its vaccine caused an initial wave of disappointment, with its overall efficacy against moderate-to-severe COVID-19 28 days postvaccination first reported at about 66% globally. By contrast, results for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines suggest they have efficacy rates of 95% and 94%.
But in concluding, the advisers spoke of the Janssen vaccine as a much-needed tool to address the COVID-19 pandemic. The death toll in the United States attributed to the virus has reached 501,414, according to the World Health Organization.
“Despite the concerns that were raised during the discussion. I think what we have to keep in mind is that we’re still in the midst of this deadly pandemic,” said FDA adviser Archana Chatterjee, MD, PhD, from Rosalind Franklin University. “There is a shortage of vaccines that are currently authorized, and I think authorization of this vaccine will help meet the needs at the moment.”
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its advisers, but it often does so.
Anaphylaxis case
FDA advisers raised only a few questions for Johnson & Johnson and FDA staff ahead of their vote. The committee’s deliberations were less contentious and heated than had been during its December reviews of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. In those meetings, the panel voted 17-4, with one abstention, in favor of Pfizer’s vaccine and 20-0, with one abstention, on the Moderna vaccine.
“We are very comfortable now with the procedure, as well as the vaccines,” said Arnold Monto, MD, after the Feb. 26 vote on the Janssen vaccine. Dr. Monto, from the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor, has served as the chairman of the FDA panel through its review of all three COVID-19 vaccines.
Among the issues noted in the deliberations was the emergence of a concern about anaphylaxis with the vaccine.
This serious allergic reaction has been seen in people who have taken the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Before the week of the panel meeting, though, there had not been reports of anaphylaxis with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, said Macaya Douoguih, MD, MPH, head of clinical development and medical affairs for Janssen/ Johnson & Johnson’s vaccines division.
However, on February 24, Johnson & Johnson received preliminary reports about two cases of severe allergic reaction from an open-label study in South Africa, with one of these being anaphylaxis, Dr. Douoguih said. The company will continue to closely monitor for these events as outlined in their pharmacovigilance plan, Dr. Douoguih said.
Federal health officials have sought to make clinicians aware of the rare risk for anaphylaxis with COVID vaccines, while reminding the public that this reaction can be managed.
The FDA had Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC, give an update on postmarketing surveillance for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines as part of the review of the Johnson & Johnson application. Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues published a report in JAMA on February 14 that looked at an anaphylaxis case reported connected with COVID vaccines between December 14, 2020, and January 18, 2021.
The CDC identified 66 case reports received that met Brighton Collaboration case definition criteria for anaphylaxis (levels 1, 2, or 3): 47 following Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, for a reporting rate of 4.7 cases/million doses administered, and 19 following Moderna vaccine, for a reporting rate of 2.5 cases/million doses administered, Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues wrote.
The CDC has published materials to help clinicians prepare for the possibility of this rare event, Dr. Shimabukuro told the FDA advisers.
“The take-home message here is that these are rare events and anaphylaxis, although clinically serious, is treatable,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
At the conclusion of the meeting, FDA panelist Patrick Moore, MD, MPH, from the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania, stressed the need to convey to the public that the COVID vaccines appear so far to be safe. Many people earlier had doubts about how the FDA could both safely and quickly review the applications for EUAs for these products.
“As of February 26, things are looking good. That could change tomorrow,” Dr. Moore said. But “this whole EUA process does seem to have worked, despite my own personal concerns about it.”
No second-class vaccines
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine, known as Ad26.COV2.S, is composed of a recombinant, replication-incompetent human adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vector. It’s intended to encode a stabilized form of SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein. The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use a different mechanism. They rely on mRNA.
The FDA advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Janssen’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. They urged against people parsing study details too finely and seeking to pick and choose their shots.
“It’s important that people do not think that one vaccine is better than another,” said FDA adviser H. Cody Meissner, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston.
Dr. Monto agreed, noting that many people in the United States are still waiting for their turn to get COVID vaccines because of the limited early supply.
Trying to game the system to get one vaccine instead of another would not be wise. “In this environment, whatever you can get, get,” Dr. Monto said.
During an open public hearing, Sarah Christopherson, policy advocacy director of the National Women’s Health Network, said that press reports are fueling a damaging impression in the public that there are “first and second-class” vaccines.
“That has the potential to exacerbate existing mistrust” in vaccines, she said. “Public health authorities must address these perceptions head on.”
She urged against attempts to compare the Janssen vaccine to others, noting the potential effects of emerging variants of the virus.
“It’s difficult to make an apples-to-apples comparison between vaccines,” she said.
Johnson & Johnson’s efficacy results, which are lower than those of the mRNA vaccines, may be a reflection of the ways in which SARS-Co-V-2 is mutating and thus becoming more of a threat, according to the company. A key study of the new vaccine, involving about 44,000 people, coincided with the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, which were emerging in some of the countries where the pivotal COV3001 study was being conducted, the company said.
At least 14 days after vaccination, the Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine efficacy (95% confidence interval) was 72.0% (58.2, 81.7) in the United States, 68.1% (48.8, 80.7) in Brazil, and 64.0% (41.2, 78.7) in South Africa.
Weakened standards?
Several researchers called on the FDA to maintain a critical attitude when assessing Johnson & Johnson’s application for the EUA, warning of a potential for a permanent erosion of agency rules due to hasty action on COVID vaccines.
They raised concerns about the FDA demanding too little in terms of follow-up studies on COVID vaccines and with persisting murkiness resulting in attempts to determine how well these treatments work beyond the initial study period.
“I worry about FDA lowering its approval standards,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, from The BMJ and a faculty member at the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, during an open public hearing at the meeting.
“There’s a real urgency to stand back right now and look at the forest here, as well as the trees, and I urge the committee to consider the effects FDA decisions may have on the entire regulatory approval process,” Dr. Doshi said.
Dr. Doshi asked why Johnson & Johnson did not seek a standard full approval — a biologics license application (BLA) — instead of aiming for the lower bar of an EUA. The FDA already has allowed wide distribution of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines through EUAs. That removes the sense of urgency that FDA faced last year in his view.
The FDA’s June 2020 guidance on the development of COVID vaccines had asked drugmakers to plan on following participants in COVID vaccine trials for “ideally at least one to two years.” Yet people who got placebo in Moderna and Pfizer trials already are being vaccinated, Dr. Doshi said. And Johnson & Johnson said in its presentation to the FDA that if the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine were granted an EUA, the COV3001 study design would be amended to “facilitate cross-over of placebo participants in all participating countries to receive one dose of active study vaccine as fast as operationally feasible.”
“I’m nervous about the prospect of there never being a COVID vaccine that meets the FDA’s approval standard” for a BLA instead of the more limited EUA, Dr. Doshi said.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the FDA’s subsequent guidance tailored for EUAs for COVID vaccines “drastically shortened” the follow-up time to a median of 2 months. Dr. Zuckerman said that a crossover design would be “a reasonable compromise, but only if the placebo group has at least 6 months of data.” Dr. Zuckerman opened her remarks in the open public hearing by saying she had inherited Johnson & Johnson stock, so was speaking at the meeting against her own financial interest.
“As soon as a vaccine is authorized, we start losing the placebo group. If FDA lets that happen, that’s a huge loss for public health and a huge loss of information about how we can all stay safe,” Dr. Zuckerman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is expected to quickly provide an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the vaccine following the recommendation by the panel. The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee voted 22-0 on this question: Based on the totality of scientific evidence available, do the benefits of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine outweigh its risks for use in individuals 18 years of age and older?
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine is expected to offer more convenient dosing and be easier to distribute than the two rival products already available in the United States. Janssen’s vaccine is intended to be given in a single dose. In December, the FDA granted EUAs for the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, which are each two-dose regimens.
Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine can be stored for at least 3 months at normal refrigerator temperatures of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Its shipping and storage fits into the existing medical supply infrastructure, the company said in its briefing materials for the FDA advisory committee meeting. In contrast, Pfizer’s vaccine is stored in ultracold freezers at temperatures between -80°C and -60°C (-112°F and -76°F), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Moderna’s vaccine may be stored in a freezer between -25°C and -15°C (-13°F and 5°F).
But FDA advisers focused more in their deliberations on concerns about Janssen’s vaccine, including emerging reports of allergic reactions.
The advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Johnson & Johnson’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. The company’s initial unveiling last month of key results for its vaccine caused an initial wave of disappointment, with its overall efficacy against moderate-to-severe COVID-19 28 days postvaccination first reported at about 66% globally. By contrast, results for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines suggest they have efficacy rates of 95% and 94%.
But in concluding, the advisers spoke of the Janssen vaccine as a much-needed tool to address the COVID-19 pandemic. The death toll in the United States attributed to the virus has reached 501,414, according to the World Health Organization.
“Despite the concerns that were raised during the discussion. I think what we have to keep in mind is that we’re still in the midst of this deadly pandemic,” said FDA adviser Archana Chatterjee, MD, PhD, from Rosalind Franklin University. “There is a shortage of vaccines that are currently authorized, and I think authorization of this vaccine will help meet the needs at the moment.”
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its advisers, but it often does so.
Anaphylaxis case
FDA advisers raised only a few questions for Johnson & Johnson and FDA staff ahead of their vote. The committee’s deliberations were less contentious and heated than had been during its December reviews of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. In those meetings, the panel voted 17-4, with one abstention, in favor of Pfizer’s vaccine and 20-0, with one abstention, on the Moderna vaccine.
“We are very comfortable now with the procedure, as well as the vaccines,” said Arnold Monto, MD, after the Feb. 26 vote on the Janssen vaccine. Dr. Monto, from the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor, has served as the chairman of the FDA panel through its review of all three COVID-19 vaccines.
Among the issues noted in the deliberations was the emergence of a concern about anaphylaxis with the vaccine.
This serious allergic reaction has been seen in people who have taken the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Before the week of the panel meeting, though, there had not been reports of anaphylaxis with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, said Macaya Douoguih, MD, MPH, head of clinical development and medical affairs for Janssen/ Johnson & Johnson’s vaccines division.
However, on February 24, Johnson & Johnson received preliminary reports about two cases of severe allergic reaction from an open-label study in South Africa, with one of these being anaphylaxis, Dr. Douoguih said. The company will continue to closely monitor for these events as outlined in their pharmacovigilance plan, Dr. Douoguih said.
Federal health officials have sought to make clinicians aware of the rare risk for anaphylaxis with COVID vaccines, while reminding the public that this reaction can be managed.
The FDA had Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC, give an update on postmarketing surveillance for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines as part of the review of the Johnson & Johnson application. Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues published a report in JAMA on February 14 that looked at an anaphylaxis case reported connected with COVID vaccines between December 14, 2020, and January 18, 2021.
The CDC identified 66 case reports received that met Brighton Collaboration case definition criteria for anaphylaxis (levels 1, 2, or 3): 47 following Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, for a reporting rate of 4.7 cases/million doses administered, and 19 following Moderna vaccine, for a reporting rate of 2.5 cases/million doses administered, Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues wrote.
The CDC has published materials to help clinicians prepare for the possibility of this rare event, Dr. Shimabukuro told the FDA advisers.
“The take-home message here is that these are rare events and anaphylaxis, although clinically serious, is treatable,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
At the conclusion of the meeting, FDA panelist Patrick Moore, MD, MPH, from the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania, stressed the need to convey to the public that the COVID vaccines appear so far to be safe. Many people earlier had doubts about how the FDA could both safely and quickly review the applications for EUAs for these products.
“As of February 26, things are looking good. That could change tomorrow,” Dr. Moore said. But “this whole EUA process does seem to have worked, despite my own personal concerns about it.”
No second-class vaccines
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine, known as Ad26.COV2.S, is composed of a recombinant, replication-incompetent human adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vector. It’s intended to encode a stabilized form of SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein. The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use a different mechanism. They rely on mRNA.
The FDA advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Janssen’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. They urged against people parsing study details too finely and seeking to pick and choose their shots.
“It’s important that people do not think that one vaccine is better than another,” said FDA adviser H. Cody Meissner, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston.
Dr. Monto agreed, noting that many people in the United States are still waiting for their turn to get COVID vaccines because of the limited early supply.
Trying to game the system to get one vaccine instead of another would not be wise. “In this environment, whatever you can get, get,” Dr. Monto said.
During an open public hearing, Sarah Christopherson, policy advocacy director of the National Women’s Health Network, said that press reports are fueling a damaging impression in the public that there are “first and second-class” vaccines.
“That has the potential to exacerbate existing mistrust” in vaccines, she said. “Public health authorities must address these perceptions head on.”
She urged against attempts to compare the Janssen vaccine to others, noting the potential effects of emerging variants of the virus.
“It’s difficult to make an apples-to-apples comparison between vaccines,” she said.
Johnson & Johnson’s efficacy results, which are lower than those of the mRNA vaccines, may be a reflection of the ways in which SARS-Co-V-2 is mutating and thus becoming more of a threat, according to the company. A key study of the new vaccine, involving about 44,000 people, coincided with the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, which were emerging in some of the countries where the pivotal COV3001 study was being conducted, the company said.
At least 14 days after vaccination, the Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine efficacy (95% confidence interval) was 72.0% (58.2, 81.7) in the United States, 68.1% (48.8, 80.7) in Brazil, and 64.0% (41.2, 78.7) in South Africa.
Weakened standards?
Several researchers called on the FDA to maintain a critical attitude when assessing Johnson & Johnson’s application for the EUA, warning of a potential for a permanent erosion of agency rules due to hasty action on COVID vaccines.
They raised concerns about the FDA demanding too little in terms of follow-up studies on COVID vaccines and with persisting murkiness resulting in attempts to determine how well these treatments work beyond the initial study period.
“I worry about FDA lowering its approval standards,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, from The BMJ and a faculty member at the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, during an open public hearing at the meeting.
“There’s a real urgency to stand back right now and look at the forest here, as well as the trees, and I urge the committee to consider the effects FDA decisions may have on the entire regulatory approval process,” Dr. Doshi said.
Dr. Doshi asked why Johnson & Johnson did not seek a standard full approval — a biologics license application (BLA) — instead of aiming for the lower bar of an EUA. The FDA already has allowed wide distribution of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines through EUAs. That removes the sense of urgency that FDA faced last year in his view.
The FDA’s June 2020 guidance on the development of COVID vaccines had asked drugmakers to plan on following participants in COVID vaccine trials for “ideally at least one to two years.” Yet people who got placebo in Moderna and Pfizer trials already are being vaccinated, Dr. Doshi said. And Johnson & Johnson said in its presentation to the FDA that if the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine were granted an EUA, the COV3001 study design would be amended to “facilitate cross-over of placebo participants in all participating countries to receive one dose of active study vaccine as fast as operationally feasible.”
“I’m nervous about the prospect of there never being a COVID vaccine that meets the FDA’s approval standard” for a BLA instead of the more limited EUA, Dr. Doshi said.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the FDA’s subsequent guidance tailored for EUAs for COVID vaccines “drastically shortened” the follow-up time to a median of 2 months. Dr. Zuckerman said that a crossover design would be “a reasonable compromise, but only if the placebo group has at least 6 months of data.” Dr. Zuckerman opened her remarks in the open public hearing by saying she had inherited Johnson & Johnson stock, so was speaking at the meeting against her own financial interest.
“As soon as a vaccine is authorized, we start losing the placebo group. If FDA lets that happen, that’s a huge loss for public health and a huge loss of information about how we can all stay safe,” Dr. Zuckerman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PTSD prevalent in survivors of severe COVID-19
Posttraumatic stress disorder may occur in up to a third of patients who recover from severe COVID-19 infection, new research suggests.
A study of more than 300 patients who presented to the emergency department with the virus showed a 30.2% prevalence for PTSD 30-120 days after COVID recovery.
or having persistent medical symptoms after hospitalization.
Additional diagnoses, such as depressive and hypomanic episodes and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), were also present in some of the survivors.
“Previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with PTSD diagnoses in postillness stages, with meta-analytic findings indicating a prevalence of 32.2%,” write the investigators, led by Delfina Janiri, MD, department of psychiatry, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS, Rome.
However, data focused specifically on COVID-19 have been “piecemeal,” they add.
The findings were published online Feb. 18 in a research letter in JAMA Psychiatry.
A traumatic event
From April to October 2020, the researchers assessed 381 consecutive patients (100% white; 56.4% men; mean age, 55.3 years) who presented to the ED and subsequently participated in a health check at the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli.
The mean length of stay for the 309 patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 was 18.4 days.
Results showed that 115 participants (30.2%) had PTSD, based on DSM-5 criteria, and 55.7% of the women had the disorder. Additional diagnoses found in the full patient population included:
- Depressive episodes (17.3%).
- GAD (7%).
- Hypomanic episodes (0.7%).
- Psychotic disorders (0.2%).
Patients with PTSD had higher rates than those without PTSD of a previous history of psychiatric disorders (34.8% vs. 20.7%; P = .003) and of delirium or agitation during hospitalization, as assessed with the Confusion Assessment Method (16.5% vs. 6.4%; P = .002).
In addition, 62.6% of those with PTSD had three or more persistent COVID-19 symptoms vs. 37.2% of their counterparts without PTSD (P < .001).
After logistic regression analyses, significant factors associated with a PTSD diagnosis were persistent medical symptoms (P = .002), delirium or agitation (P = .02), and being female (P = .02).
The investigators note that their results are “in line” with findings reported in research examining other traumatic events. This includes about 30% of Hurricane Katrina survivors who experienced PTSD, as did around 25% of survivors of the 2011 “Great Japan Earthquake and Tsunami.”
Study limitations cited include the “relatively small” size of the patient population, that it focused on only one participating center, and that it didn’t include a control group of non-COVID patients who reported to the ED.
“Further longitudinal studies are needed to tailor therapeutic interventions and prevention strategies,” the researchers write.
Dr. Janiri and four of the five other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The other author, Gabriele Sani, MD, reported having received personal fees from Angelini Spa, Janssen, and Lundbeck outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Posttraumatic stress disorder may occur in up to a third of patients who recover from severe COVID-19 infection, new research suggests.
A study of more than 300 patients who presented to the emergency department with the virus showed a 30.2% prevalence for PTSD 30-120 days after COVID recovery.
or having persistent medical symptoms after hospitalization.
Additional diagnoses, such as depressive and hypomanic episodes and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), were also present in some of the survivors.
“Previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with PTSD diagnoses in postillness stages, with meta-analytic findings indicating a prevalence of 32.2%,” write the investigators, led by Delfina Janiri, MD, department of psychiatry, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS, Rome.
However, data focused specifically on COVID-19 have been “piecemeal,” they add.
The findings were published online Feb. 18 in a research letter in JAMA Psychiatry.
A traumatic event
From April to October 2020, the researchers assessed 381 consecutive patients (100% white; 56.4% men; mean age, 55.3 years) who presented to the ED and subsequently participated in a health check at the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli.
The mean length of stay for the 309 patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 was 18.4 days.
Results showed that 115 participants (30.2%) had PTSD, based on DSM-5 criteria, and 55.7% of the women had the disorder. Additional diagnoses found in the full patient population included:
- Depressive episodes (17.3%).
- GAD (7%).
- Hypomanic episodes (0.7%).
- Psychotic disorders (0.2%).
Patients with PTSD had higher rates than those without PTSD of a previous history of psychiatric disorders (34.8% vs. 20.7%; P = .003) and of delirium or agitation during hospitalization, as assessed with the Confusion Assessment Method (16.5% vs. 6.4%; P = .002).
In addition, 62.6% of those with PTSD had three or more persistent COVID-19 symptoms vs. 37.2% of their counterparts without PTSD (P < .001).
After logistic regression analyses, significant factors associated with a PTSD diagnosis were persistent medical symptoms (P = .002), delirium or agitation (P = .02), and being female (P = .02).
The investigators note that their results are “in line” with findings reported in research examining other traumatic events. This includes about 30% of Hurricane Katrina survivors who experienced PTSD, as did around 25% of survivors of the 2011 “Great Japan Earthquake and Tsunami.”
Study limitations cited include the “relatively small” size of the patient population, that it focused on only one participating center, and that it didn’t include a control group of non-COVID patients who reported to the ED.
“Further longitudinal studies are needed to tailor therapeutic interventions and prevention strategies,” the researchers write.
Dr. Janiri and four of the five other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The other author, Gabriele Sani, MD, reported having received personal fees from Angelini Spa, Janssen, and Lundbeck outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Posttraumatic stress disorder may occur in up to a third of patients who recover from severe COVID-19 infection, new research suggests.
A study of more than 300 patients who presented to the emergency department with the virus showed a 30.2% prevalence for PTSD 30-120 days after COVID recovery.
or having persistent medical symptoms after hospitalization.
Additional diagnoses, such as depressive and hypomanic episodes and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), were also present in some of the survivors.
“Previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with PTSD diagnoses in postillness stages, with meta-analytic findings indicating a prevalence of 32.2%,” write the investigators, led by Delfina Janiri, MD, department of psychiatry, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS, Rome.
However, data focused specifically on COVID-19 have been “piecemeal,” they add.
The findings were published online Feb. 18 in a research letter in JAMA Psychiatry.
A traumatic event
From April to October 2020, the researchers assessed 381 consecutive patients (100% white; 56.4% men; mean age, 55.3 years) who presented to the ED and subsequently participated in a health check at the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli.
The mean length of stay for the 309 patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 was 18.4 days.
Results showed that 115 participants (30.2%) had PTSD, based on DSM-5 criteria, and 55.7% of the women had the disorder. Additional diagnoses found in the full patient population included:
- Depressive episodes (17.3%).
- GAD (7%).
- Hypomanic episodes (0.7%).
- Psychotic disorders (0.2%).
Patients with PTSD had higher rates than those without PTSD of a previous history of psychiatric disorders (34.8% vs. 20.7%; P = .003) and of delirium or agitation during hospitalization, as assessed with the Confusion Assessment Method (16.5% vs. 6.4%; P = .002).
In addition, 62.6% of those with PTSD had three or more persistent COVID-19 symptoms vs. 37.2% of their counterparts without PTSD (P < .001).
After logistic regression analyses, significant factors associated with a PTSD diagnosis were persistent medical symptoms (P = .002), delirium or agitation (P = .02), and being female (P = .02).
The investigators note that their results are “in line” with findings reported in research examining other traumatic events. This includes about 30% of Hurricane Katrina survivors who experienced PTSD, as did around 25% of survivors of the 2011 “Great Japan Earthquake and Tsunami.”
Study limitations cited include the “relatively small” size of the patient population, that it focused on only one participating center, and that it didn’t include a control group of non-COVID patients who reported to the ED.
“Further longitudinal studies are needed to tailor therapeutic interventions and prevention strategies,” the researchers write.
Dr. Janiri and four of the five other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The other author, Gabriele Sani, MD, reported having received personal fees from Angelini Spa, Janssen, and Lundbeck outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seeking the next generation of antibiotics
Crispr drugs can be effective
Globally, some 700,000 people die from antibiotic-resistant infections ever year; by 2050, that number could be 10 million, according to the United Nations. To find new ways to fight pathogenic microorganisms, scientists are looking to Crispr, the gene-editing tool, according to the New York Times.
“Crispr is a specialized region of DNA that creates what amount to genetic scissors – enzymes that allow the cell (or a scientist) to precisely edit other DNA or its sister molecule, RNA…Crispr was originally discovered in bacteria, where it helps keep track of past injury. When a virus attacks, the bacterium stores small chunks of the viral genome within its own DNA. This helps the bacterium recognize viral infections when they occur again. Then, using Crispr-associated enzymes, it can disarm the virus and prevent the infection from spreading…today researchers are looking to Crispr to edit bacteria and viruses that infect humans and create new treatments.”
In a recent study, researchers successfully used a Crispr-associated enzyme called Cas9 to eliminate a species of Salmonella. They programmed the Cas9 to view the bacterium as the enemy and forced Salmonella to make lethal cuts to its own genome.
Some companies are now exploring Crispr-based antibiotics that might be delivered through viruses engineered so that they cannot reproduce or cause infections themselves, to name just one approach.
“Now researchers face the challenge of demonstrating that Crispr antibacterial and antiviral drugs are effective in living animals and in humans, not just in the lab, and that they will be cheaper than conventional therapies.”
Reference
1. Sheikh K. Is Crispr the Next Antibiotic? The New York Times. Oct 28, 2019.
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/28/health/crispr-genetics-antibiotic-resistance.html. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.
Crispr drugs can be effective
Crispr drugs can be effective
Globally, some 700,000 people die from antibiotic-resistant infections ever year; by 2050, that number could be 10 million, according to the United Nations. To find new ways to fight pathogenic microorganisms, scientists are looking to Crispr, the gene-editing tool, according to the New York Times.
“Crispr is a specialized region of DNA that creates what amount to genetic scissors – enzymes that allow the cell (or a scientist) to precisely edit other DNA or its sister molecule, RNA…Crispr was originally discovered in bacteria, where it helps keep track of past injury. When a virus attacks, the bacterium stores small chunks of the viral genome within its own DNA. This helps the bacterium recognize viral infections when they occur again. Then, using Crispr-associated enzymes, it can disarm the virus and prevent the infection from spreading…today researchers are looking to Crispr to edit bacteria and viruses that infect humans and create new treatments.”
In a recent study, researchers successfully used a Crispr-associated enzyme called Cas9 to eliminate a species of Salmonella. They programmed the Cas9 to view the bacterium as the enemy and forced Salmonella to make lethal cuts to its own genome.
Some companies are now exploring Crispr-based antibiotics that might be delivered through viruses engineered so that they cannot reproduce or cause infections themselves, to name just one approach.
“Now researchers face the challenge of demonstrating that Crispr antibacterial and antiviral drugs are effective in living animals and in humans, not just in the lab, and that they will be cheaper than conventional therapies.”
Reference
1. Sheikh K. Is Crispr the Next Antibiotic? The New York Times. Oct 28, 2019.
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/28/health/crispr-genetics-antibiotic-resistance.html. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.
Globally, some 700,000 people die from antibiotic-resistant infections ever year; by 2050, that number could be 10 million, according to the United Nations. To find new ways to fight pathogenic microorganisms, scientists are looking to Crispr, the gene-editing tool, according to the New York Times.
“Crispr is a specialized region of DNA that creates what amount to genetic scissors – enzymes that allow the cell (or a scientist) to precisely edit other DNA or its sister molecule, RNA…Crispr was originally discovered in bacteria, where it helps keep track of past injury. When a virus attacks, the bacterium stores small chunks of the viral genome within its own DNA. This helps the bacterium recognize viral infections when they occur again. Then, using Crispr-associated enzymes, it can disarm the virus and prevent the infection from spreading…today researchers are looking to Crispr to edit bacteria and viruses that infect humans and create new treatments.”
In a recent study, researchers successfully used a Crispr-associated enzyme called Cas9 to eliminate a species of Salmonella. They programmed the Cas9 to view the bacterium as the enemy and forced Salmonella to make lethal cuts to its own genome.
Some companies are now exploring Crispr-based antibiotics that might be delivered through viruses engineered so that they cannot reproduce or cause infections themselves, to name just one approach.
“Now researchers face the challenge of demonstrating that Crispr antibacterial and antiviral drugs are effective in living animals and in humans, not just in the lab, and that they will be cheaper than conventional therapies.”
Reference
1. Sheikh K. Is Crispr the Next Antibiotic? The New York Times. Oct 28, 2019.
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/28/health/crispr-genetics-antibiotic-resistance.html. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.
New-onset arrhythmias low in COVID-19 and flu
Among 3,970 patients treated during the early months of the pandemic, new onset AF/AFL was seen in 4%, matching the 4% incidence found in a historic cohort of patients hospitalized with influenza.
On the other hand, mortality was similarly high in both groups of patients studied with AF/AFL, showing a 77% increased risk of death in COVID-19 and a 78% increased risk in influenza, a team from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York reported.
“We saw new onset Afib and flutter in a minority of patients and it was associated with much higher mortality, but the point is that this increase is basically the same as what you see in influenza, which we feel is an indication that this is more of a generalized response to the inflammatory milieu of such a severe viral illness, as opposed to something specific to COVID,” Vivek Y. Reddy, MD, said in the report, published online Feb. 25 in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
“Here we see, with a similar respiratory virus used as controls, that the results are exactly what I would have expected to see, which is that where there is a lot of inflammation, we see Afib,” said John Mandrola, MD, of Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky., who was not involved with the study.
“We need more studies like this one because we know SARS-CoV-2 is a bad virus that may have important effects on the heart, but all the of research done so far has been problematic because it didn’t include controls.”
Atrial arrhythmias in COVID and flu
Dr. Reddy and coinvestigators performed a retrospective analysis of a large cohort of patients admitted with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 during Feb. 4-April 22, 2020, to one of five hospitals within the Mount Sinai Health System.
Their comparator arm included 1,420 patients with confirmed influenza A or B hospitalized between Jan. 1, 2017, and Jan. 1, 2020. For both cohorts, automated electronic record abstraction was used and all patient data were de-identified prior to analysis. In the COVID-19 cohort, a manual review of 1,110 charts was also performed.
Compared with those who did not develop AF/AFL, COVID-19 patients with newly detected AF/AFL and COVID-19 were older (74 vs. 66 years; P < .01) and had higher levels of inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, and higher troponin and D-dimer levels (all P < .01).
Overall, including those with a history of atrial arrhythmias, 10% of patients with hospitalized COVID-19 (13% in the manual review) and 12% of those with influenza had AF/AFL detected during their hospitalization.
Mortality at 30 days was higher in COVID-19 patients with AF/AFL compared to those without (46% vs. 26%; P < .01), as were the rates of intubation (27% vs. 15%; relative risk, 1.8; P < .01), and stroke (1.6% vs. 0.6%, RR, 2.7; P = .05).
Despite having more comorbidities, in-hospital mortality was significantly lower in the influenza cohort overall, compared to the COVID-19 cohort (9% vs. 29%; P < .01), reflecting the higher case fatality rate in COVID-19, Dr. Reddy, director of cardiac arrhythmia services at Mount Sinai Hospital, said in an interview.
But as with COVID-19, those influenza patients who had in-hospital AF/AFL were more likely to require intubation (14% vs. 7%; P = .004) or die (16% vs. 10%; P = .003).
“The data are not perfect and there are always limitations when doing an observational study using historic controls, but my guess would be that if we looked at other databases and other populations hospitalized for severe illness, we’d likely see something similar because when the body is inflamed, you’re more likely to see Afib,” said Dr. Mandrola.
Dr. Reddy concurred, noting that they considered comparing other populations to COVID-19 patients, including those with “just generalized severe illness,” but in the end felt there were many similarities between influenza and COVID-19, even though mortality in the latter is higher.
“It would be interesting for people to look at other illnesses and see if they find the same thing,” he said.
Dr. Reddy reported having no disclosures relevant to COVID-19. Dr. Mandrola is chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.com. He reported having no relevant disclosures. MDedge is a member of the Medscape Professional Network.
Among 3,970 patients treated during the early months of the pandemic, new onset AF/AFL was seen in 4%, matching the 4% incidence found in a historic cohort of patients hospitalized with influenza.
On the other hand, mortality was similarly high in both groups of patients studied with AF/AFL, showing a 77% increased risk of death in COVID-19 and a 78% increased risk in influenza, a team from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York reported.
“We saw new onset Afib and flutter in a minority of patients and it was associated with much higher mortality, but the point is that this increase is basically the same as what you see in influenza, which we feel is an indication that this is more of a generalized response to the inflammatory milieu of such a severe viral illness, as opposed to something specific to COVID,” Vivek Y. Reddy, MD, said in the report, published online Feb. 25 in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
“Here we see, with a similar respiratory virus used as controls, that the results are exactly what I would have expected to see, which is that where there is a lot of inflammation, we see Afib,” said John Mandrola, MD, of Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky., who was not involved with the study.
“We need more studies like this one because we know SARS-CoV-2 is a bad virus that may have important effects on the heart, but all the of research done so far has been problematic because it didn’t include controls.”
Atrial arrhythmias in COVID and flu
Dr. Reddy and coinvestigators performed a retrospective analysis of a large cohort of patients admitted with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 during Feb. 4-April 22, 2020, to one of five hospitals within the Mount Sinai Health System.
Their comparator arm included 1,420 patients with confirmed influenza A or B hospitalized between Jan. 1, 2017, and Jan. 1, 2020. For both cohorts, automated electronic record abstraction was used and all patient data were de-identified prior to analysis. In the COVID-19 cohort, a manual review of 1,110 charts was also performed.
Compared with those who did not develop AF/AFL, COVID-19 patients with newly detected AF/AFL and COVID-19 were older (74 vs. 66 years; P < .01) and had higher levels of inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, and higher troponin and D-dimer levels (all P < .01).
Overall, including those with a history of atrial arrhythmias, 10% of patients with hospitalized COVID-19 (13% in the manual review) and 12% of those with influenza had AF/AFL detected during their hospitalization.
Mortality at 30 days was higher in COVID-19 patients with AF/AFL compared to those without (46% vs. 26%; P < .01), as were the rates of intubation (27% vs. 15%; relative risk, 1.8; P < .01), and stroke (1.6% vs. 0.6%, RR, 2.7; P = .05).
Despite having more comorbidities, in-hospital mortality was significantly lower in the influenza cohort overall, compared to the COVID-19 cohort (9% vs. 29%; P < .01), reflecting the higher case fatality rate in COVID-19, Dr. Reddy, director of cardiac arrhythmia services at Mount Sinai Hospital, said in an interview.
But as with COVID-19, those influenza patients who had in-hospital AF/AFL were more likely to require intubation (14% vs. 7%; P = .004) or die (16% vs. 10%; P = .003).
“The data are not perfect and there are always limitations when doing an observational study using historic controls, but my guess would be that if we looked at other databases and other populations hospitalized for severe illness, we’d likely see something similar because when the body is inflamed, you’re more likely to see Afib,” said Dr. Mandrola.
Dr. Reddy concurred, noting that they considered comparing other populations to COVID-19 patients, including those with “just generalized severe illness,” but in the end felt there were many similarities between influenza and COVID-19, even though mortality in the latter is higher.
“It would be interesting for people to look at other illnesses and see if they find the same thing,” he said.
Dr. Reddy reported having no disclosures relevant to COVID-19. Dr. Mandrola is chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.com. He reported having no relevant disclosures. MDedge is a member of the Medscape Professional Network.
Among 3,970 patients treated during the early months of the pandemic, new onset AF/AFL was seen in 4%, matching the 4% incidence found in a historic cohort of patients hospitalized with influenza.
On the other hand, mortality was similarly high in both groups of patients studied with AF/AFL, showing a 77% increased risk of death in COVID-19 and a 78% increased risk in influenza, a team from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York reported.
“We saw new onset Afib and flutter in a minority of patients and it was associated with much higher mortality, but the point is that this increase is basically the same as what you see in influenza, which we feel is an indication that this is more of a generalized response to the inflammatory milieu of such a severe viral illness, as opposed to something specific to COVID,” Vivek Y. Reddy, MD, said in the report, published online Feb. 25 in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
“Here we see, with a similar respiratory virus used as controls, that the results are exactly what I would have expected to see, which is that where there is a lot of inflammation, we see Afib,” said John Mandrola, MD, of Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky., who was not involved with the study.
“We need more studies like this one because we know SARS-CoV-2 is a bad virus that may have important effects on the heart, but all the of research done so far has been problematic because it didn’t include controls.”
Atrial arrhythmias in COVID and flu
Dr. Reddy and coinvestigators performed a retrospective analysis of a large cohort of patients admitted with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 during Feb. 4-April 22, 2020, to one of five hospitals within the Mount Sinai Health System.
Their comparator arm included 1,420 patients with confirmed influenza A or B hospitalized between Jan. 1, 2017, and Jan. 1, 2020. For both cohorts, automated electronic record abstraction was used and all patient data were de-identified prior to analysis. In the COVID-19 cohort, a manual review of 1,110 charts was also performed.
Compared with those who did not develop AF/AFL, COVID-19 patients with newly detected AF/AFL and COVID-19 were older (74 vs. 66 years; P < .01) and had higher levels of inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, and higher troponin and D-dimer levels (all P < .01).
Overall, including those with a history of atrial arrhythmias, 10% of patients with hospitalized COVID-19 (13% in the manual review) and 12% of those with influenza had AF/AFL detected during their hospitalization.
Mortality at 30 days was higher in COVID-19 patients with AF/AFL compared to those without (46% vs. 26%; P < .01), as were the rates of intubation (27% vs. 15%; relative risk, 1.8; P < .01), and stroke (1.6% vs. 0.6%, RR, 2.7; P = .05).
Despite having more comorbidities, in-hospital mortality was significantly lower in the influenza cohort overall, compared to the COVID-19 cohort (9% vs. 29%; P < .01), reflecting the higher case fatality rate in COVID-19, Dr. Reddy, director of cardiac arrhythmia services at Mount Sinai Hospital, said in an interview.
But as with COVID-19, those influenza patients who had in-hospital AF/AFL were more likely to require intubation (14% vs. 7%; P = .004) or die (16% vs. 10%; P = .003).
“The data are not perfect and there are always limitations when doing an observational study using historic controls, but my guess would be that if we looked at other databases and other populations hospitalized for severe illness, we’d likely see something similar because when the body is inflamed, you’re more likely to see Afib,” said Dr. Mandrola.
Dr. Reddy concurred, noting that they considered comparing other populations to COVID-19 patients, including those with “just generalized severe illness,” but in the end felt there were many similarities between influenza and COVID-19, even though mortality in the latter is higher.
“It would be interesting for people to look at other illnesses and see if they find the same thing,” he said.
Dr. Reddy reported having no disclosures relevant to COVID-19. Dr. Mandrola is chief cardiology correspondent for Medscape.com. He reported having no relevant disclosures. MDedge is a member of the Medscape Professional Network.
FROM JACC: CLINICAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
Variant found in NYC, Northeast
, according to CNN.
The variant, called B.1.526, has appeared in diverse neighborhoods in New York City and is “scattered in the Northeast,” the researchers said.
“We observed a steady increase in the detection rate from late December to mid-February, with an alarming rise to 12.7% in the past two weeks,” researchers from Columbia University Medical Center wrote in a report, which was published as a preprint Feb. 25.
On Feb. 22, the team released another preprint about the B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants first identified in the United Kingdom and South Africa, respectively, which also mentions the B.1.526 variant in the U.S. Neither report has been peer reviewed.
Viruses mutate often, and several coronavirus variants have been identified and followed during the pandemic. Not all mutations are significant or are necessarily more contagious or dangerous. Researchers have been tracking the B.1.526 variant in the U.S. to find out if there are significant mutations that could be a cause for concern.
In the most recent preprints, the variant appears to have the same mutation found in B.1.351, called E484K, which may allow the virus to evade vaccines and the body’s natural immune response. The E484K mutation has shown up in at least 59 lines of the coronavirus, the research team said. That means the virus is evolving independently across the country and world, which could give the virus an advantage.
“A concern is that it might be beginning to overtake other strains, just like the U.K. and South African variants,” David Ho, MD, the lead study author and director of the Aaron Diamond AIDS Research Center at Columbia, told CNN.
“However, we don’t have enough data to firm up this point now,” he said.
In a separate preprint posted Feb. 23, a research team at the California Institute of Technology developed a software tool that noticed the rise of B.1.526 in the New York region. The preprint hasn’t yet been peer reviewed.
“It appears that the frequency of lineage B.1.526 has increased rapidly in New York,” they wrote.
Both teams also reported on another variant, called B.1.427/B.1.429, which appears to be increasing in California. The variant could be more contagious and cause more severe disease, they said, but the research is still in the early stages.
Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, have tested virus samples from recent outbreaks in California and also found that the variant is becoming more common. The variant didn’t appear in samples from September but was in half of the samples by late January. It has a different pattern of mutations than other variants, and one called L452R may affect the spike protein on the virus and allow it attach to cells more easily.
“Our data shows that this is likely the key mutation that makes this variant more infectious,” Charles Chiu, MD, associate director of the clinical microbiology lab at UCSF, told CNN.
The team also noticed that patients with a B.1.427/B.1.429 infection had more severe COVID-19 cases and needed more oxygen, CNN reported. The team plans to post a preprint once public health officials in San Francisco review the report.
Right now, the CDC provides public data for three variants: B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1, which was first identified in Brazil. The U.S. has reported 1,881 B.1.1.7 cases across 45 states, 46 B.1.351 cases in 14 states, and five P.1 cases in four states, according to a CDC tally as of Feb. 23.
At the moment, lab officials aren’t able to tell patients or doctors whether someone has been infected by a variant, according to Kaiser Health News. High-level labs conduct genomic sequencing on samples and aren’t able to communicate information back to individual people.
But the Association of Public Health Laboratories and public health officials in several states are pushing for federal authorization of a test that could sequence the full genome and notify doctors. The test could be available in coming weeks, the news outlet reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to CNN.
The variant, called B.1.526, has appeared in diverse neighborhoods in New York City and is “scattered in the Northeast,” the researchers said.
“We observed a steady increase in the detection rate from late December to mid-February, with an alarming rise to 12.7% in the past two weeks,” researchers from Columbia University Medical Center wrote in a report, which was published as a preprint Feb. 25.
On Feb. 22, the team released another preprint about the B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants first identified in the United Kingdom and South Africa, respectively, which also mentions the B.1.526 variant in the U.S. Neither report has been peer reviewed.
Viruses mutate often, and several coronavirus variants have been identified and followed during the pandemic. Not all mutations are significant or are necessarily more contagious or dangerous. Researchers have been tracking the B.1.526 variant in the U.S. to find out if there are significant mutations that could be a cause for concern.
In the most recent preprints, the variant appears to have the same mutation found in B.1.351, called E484K, which may allow the virus to evade vaccines and the body’s natural immune response. The E484K mutation has shown up in at least 59 lines of the coronavirus, the research team said. That means the virus is evolving independently across the country and world, which could give the virus an advantage.
“A concern is that it might be beginning to overtake other strains, just like the U.K. and South African variants,” David Ho, MD, the lead study author and director of the Aaron Diamond AIDS Research Center at Columbia, told CNN.
“However, we don’t have enough data to firm up this point now,” he said.
In a separate preprint posted Feb. 23, a research team at the California Institute of Technology developed a software tool that noticed the rise of B.1.526 in the New York region. The preprint hasn’t yet been peer reviewed.
“It appears that the frequency of lineage B.1.526 has increased rapidly in New York,” they wrote.
Both teams also reported on another variant, called B.1.427/B.1.429, which appears to be increasing in California. The variant could be more contagious and cause more severe disease, they said, but the research is still in the early stages.
Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, have tested virus samples from recent outbreaks in California and also found that the variant is becoming more common. The variant didn’t appear in samples from September but was in half of the samples by late January. It has a different pattern of mutations than other variants, and one called L452R may affect the spike protein on the virus and allow it attach to cells more easily.
“Our data shows that this is likely the key mutation that makes this variant more infectious,” Charles Chiu, MD, associate director of the clinical microbiology lab at UCSF, told CNN.
The team also noticed that patients with a B.1.427/B.1.429 infection had more severe COVID-19 cases and needed more oxygen, CNN reported. The team plans to post a preprint once public health officials in San Francisco review the report.
Right now, the CDC provides public data for three variants: B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1, which was first identified in Brazil. The U.S. has reported 1,881 B.1.1.7 cases across 45 states, 46 B.1.351 cases in 14 states, and five P.1 cases in four states, according to a CDC tally as of Feb. 23.
At the moment, lab officials aren’t able to tell patients or doctors whether someone has been infected by a variant, according to Kaiser Health News. High-level labs conduct genomic sequencing on samples and aren’t able to communicate information back to individual people.
But the Association of Public Health Laboratories and public health officials in several states are pushing for federal authorization of a test that could sequence the full genome and notify doctors. The test could be available in coming weeks, the news outlet reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to CNN.
The variant, called B.1.526, has appeared in diverse neighborhoods in New York City and is “scattered in the Northeast,” the researchers said.
“We observed a steady increase in the detection rate from late December to mid-February, with an alarming rise to 12.7% in the past two weeks,” researchers from Columbia University Medical Center wrote in a report, which was published as a preprint Feb. 25.
On Feb. 22, the team released another preprint about the B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants first identified in the United Kingdom and South Africa, respectively, which also mentions the B.1.526 variant in the U.S. Neither report has been peer reviewed.
Viruses mutate often, and several coronavirus variants have been identified and followed during the pandemic. Not all mutations are significant or are necessarily more contagious or dangerous. Researchers have been tracking the B.1.526 variant in the U.S. to find out if there are significant mutations that could be a cause for concern.
In the most recent preprints, the variant appears to have the same mutation found in B.1.351, called E484K, which may allow the virus to evade vaccines and the body’s natural immune response. The E484K mutation has shown up in at least 59 lines of the coronavirus, the research team said. That means the virus is evolving independently across the country and world, which could give the virus an advantage.
“A concern is that it might be beginning to overtake other strains, just like the U.K. and South African variants,” David Ho, MD, the lead study author and director of the Aaron Diamond AIDS Research Center at Columbia, told CNN.
“However, we don’t have enough data to firm up this point now,” he said.
In a separate preprint posted Feb. 23, a research team at the California Institute of Technology developed a software tool that noticed the rise of B.1.526 in the New York region. The preprint hasn’t yet been peer reviewed.
“It appears that the frequency of lineage B.1.526 has increased rapidly in New York,” they wrote.
Both teams also reported on another variant, called B.1.427/B.1.429, which appears to be increasing in California. The variant could be more contagious and cause more severe disease, they said, but the research is still in the early stages.
Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, have tested virus samples from recent outbreaks in California and also found that the variant is becoming more common. The variant didn’t appear in samples from September but was in half of the samples by late January. It has a different pattern of mutations than other variants, and one called L452R may affect the spike protein on the virus and allow it attach to cells more easily.
“Our data shows that this is likely the key mutation that makes this variant more infectious,” Charles Chiu, MD, associate director of the clinical microbiology lab at UCSF, told CNN.
The team also noticed that patients with a B.1.427/B.1.429 infection had more severe COVID-19 cases and needed more oxygen, CNN reported. The team plans to post a preprint once public health officials in San Francisco review the report.
Right now, the CDC provides public data for three variants: B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1, which was first identified in Brazil. The U.S. has reported 1,881 B.1.1.7 cases across 45 states, 46 B.1.351 cases in 14 states, and five P.1 cases in four states, according to a CDC tally as of Feb. 23.
At the moment, lab officials aren’t able to tell patients or doctors whether someone has been infected by a variant, according to Kaiser Health News. High-level labs conduct genomic sequencing on samples and aren’t able to communicate information back to individual people.
But the Association of Public Health Laboratories and public health officials in several states are pushing for federal authorization of a test that could sequence the full genome and notify doctors. The test could be available in coming weeks, the news outlet reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Myocardial injury seen on MRI in 54% of recovered COVID-19 patients
About half of 148 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and elevated troponin levels had at least some evidence of myocardial injury on cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging 2 months later, a new study shows.
“Our results demonstrate that in this subset of patients surviving severe COVID-19 and with troponin elevation, ongoing localized myocardial inflammation, whilst less frequent than previously reported, remains present in a proportion of patients and may represent an emerging issue of clinical relevance,” wrote Marianna Fontana, MD, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues.
The cardiac abnormalities identified were classified as nonischemic (including “myocarditis-like” late gadolinium enhancement [LGE]) in 26% of the cohort; as related to ischemic heart disease (infarction or inducible ischemia) in 22%; and as dual pathology in 6%.
Left ventricular (LV) function was normal in 89% of the 148 patients. In the 17 patients (11%) with LV dysfunction, only four had an ejection fraction below 35%. Of the nine patients whose LV dysfunction was related to myocardial infarction, six had a known history of ischemic heart disease.
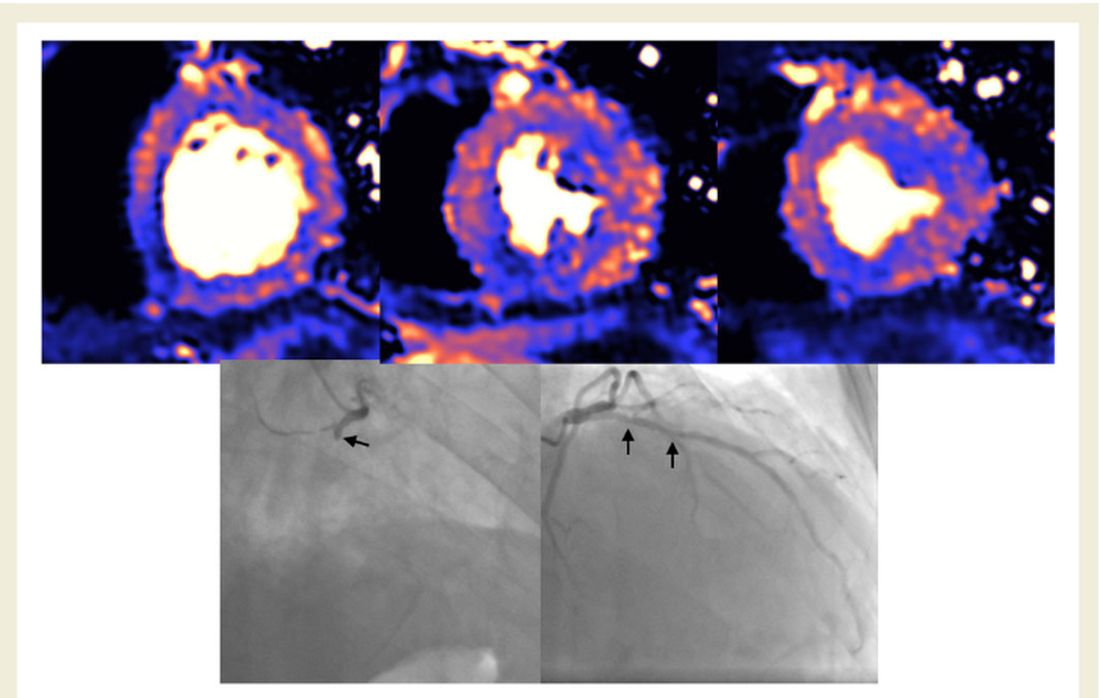
No patients with “myocarditis-pattern” LGE had regional wall motion abnormalities, and neither admission nor peak troponin values were predictive of the diagnosis of myocarditis.
The results were published online Feb. 18 in the European Heart Journal.
Glass half full
Taking a “glass half full” approach, co–senior author Graham D. Cole, MD, PhD, noted on Twitter that nearly half the patients had no major cardiac abnormalities on CMR just 2 months after a bout with troponin-positive COVID-19.
“We think this is important: Even in a group who had been very sick with raised troponin, it was common to find no evidence of heart damage,” said Dr. Cole, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust.
“We believe our data challenge the hypothesis that chronic inflammation, diffuse fibrosis, or long-term LV dysfunction is a dominant feature in those surviving COVID-19,” the investigators concluded in their report.
In an interview, Dr. Fontana explained further: “It has been reported in an early ‘pathfinder’ study that two-thirds of patients recovered from COVID-19 had CMR evidence of abnormal findings with a high incidence of elevated T1 and T2 in keeping with diffuse fibrosis and edema. Our findings with a larger, multicenter study and better controls show low rates of heart impairment and much less ongoing inflammation, which is reassuring.”
She also noted that the different patterns of injury suggest that different mechanisms are at play, including the possibility that “at least some of the found damage might have been preexisting, because people with heart damage are more likely to get severe disease.”
The investigators, including first author Tushar Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, also noted that myocarditis-like injury was limited to three or fewer myocardial segments in 88% of cases with no associated ventricular dysfunction, and that biventricular function was no different than in those without myocarditis.
“We use the word ‘myocarditis-like’ but we don’t have histology,” Dr. Fontana said. “Our group actually suspects a lot of this will be microvascular clotting (microangiopathic thrombosis). This is exciting, as newer anticoagulation strategies – for example, those being tried in RECOVERY – may have benefit.”
Aloke V. Finn, MD, of the CVPath Institute in Gaithersburg, Md., wishes researchers would stop using the term myocarditis altogether to describe clinical or imaging findings in COVID-19.
“MRI can’t diagnose myocarditis. It is a specific diagnosis that requires, ideally, histology, as the investigators acknowledged,” Dr. Finn said in an interview.
His group at CVPath recently published data showing pathologic evidence of myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection, as reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
“As a clinician, when I think of myocarditis, I look at the echo and an LV gram, and I see if there is a wall motion abnormality and troponin elevation, but with normal coronary arteries. And if all that is there, then I think about myocarditis in my differential diagnosis,” he said. “But in most of these cases, as the authors rightly point out, most patients did not have what is necessary to really entertain a diagnosis of myocarditis.”
He agreed with Dr. Fontana’s suggestion that what the CMR might be picking up in these survivors is microthrombi, as his group saw in their recent autopsy study.
“It’s very possible these findings are concordant with the recent autopsy studies done by my group and others in terms of detecting the presence of microthrombi, but we don’t know this for certain because no one has ever studied this entity before in the clinic and we don’t really know how microthrombi might appear on CMR.”
Largest study to date
The 148 participants (mean age, 64 years; 70% male) in the largest study to date to investigate convalescing COVID-19 patients who had elevated troponins – something identified early in the pandemic as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 – were treated at one of six hospitals in London.
Patients who had abnormal troponin levels were offered an MRI scan of the heart after discharge and were compared with those from a control group of patients who had not had COVID-19 and with 40 healthy volunteers.
Median length of stay was 9 days, and 32% of patients required ventilatory support in the intensive care unit.
Just over half the patients (57%) had hypertension, 7% had had a previous myocardial infarction, 34% had diabetes, 46% had hypercholesterolemia, and 24% were smokers. Mean body mass index was 28.5 kg/m2.
CMR follow-up was conducted a median of 68 days after confirmation of a COVID-19 diagnosis.
On Twitter, Dr. Cole noted that the findings are subject to both survivor bias and referral bias. “We didn’t scan frail patients where the clinician felt [CMR] was unlikely to inform management.”
The findings, said Dr. Fontana, “say nothing about what happens to people who are not hospitalized with COVID, or those who are hospitalized but without elevated troponin.”
What they do offer, particularly if replicated, is a way forward in identifying patients at higher or lower risk for long-term sequelae and inform strategies that could improve outcomes, she added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About half of 148 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and elevated troponin levels had at least some evidence of myocardial injury on cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging 2 months later, a new study shows.
“Our results demonstrate that in this subset of patients surviving severe COVID-19 and with troponin elevation, ongoing localized myocardial inflammation, whilst less frequent than previously reported, remains present in a proportion of patients and may represent an emerging issue of clinical relevance,” wrote Marianna Fontana, MD, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues.
The cardiac abnormalities identified were classified as nonischemic (including “myocarditis-like” late gadolinium enhancement [LGE]) in 26% of the cohort; as related to ischemic heart disease (infarction or inducible ischemia) in 22%; and as dual pathology in 6%.
Left ventricular (LV) function was normal in 89% of the 148 patients. In the 17 patients (11%) with LV dysfunction, only four had an ejection fraction below 35%. Of the nine patients whose LV dysfunction was related to myocardial infarction, six had a known history of ischemic heart disease.

No patients with “myocarditis-pattern” LGE had regional wall motion abnormalities, and neither admission nor peak troponin values were predictive of the diagnosis of myocarditis.
The results were published online Feb. 18 in the European Heart Journal.
Glass half full
Taking a “glass half full” approach, co–senior author Graham D. Cole, MD, PhD, noted on Twitter that nearly half the patients had no major cardiac abnormalities on CMR just 2 months after a bout with troponin-positive COVID-19.
“We think this is important: Even in a group who had been very sick with raised troponin, it was common to find no evidence of heart damage,” said Dr. Cole, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust.
“We believe our data challenge the hypothesis that chronic inflammation, diffuse fibrosis, or long-term LV dysfunction is a dominant feature in those surviving COVID-19,” the investigators concluded in their report.
In an interview, Dr. Fontana explained further: “It has been reported in an early ‘pathfinder’ study that two-thirds of patients recovered from COVID-19 had CMR evidence of abnormal findings with a high incidence of elevated T1 and T2 in keeping with diffuse fibrosis and edema. Our findings with a larger, multicenter study and better controls show low rates of heart impairment and much less ongoing inflammation, which is reassuring.”
She also noted that the different patterns of injury suggest that different mechanisms are at play, including the possibility that “at least some of the found damage might have been preexisting, because people with heart damage are more likely to get severe disease.”
The investigators, including first author Tushar Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, also noted that myocarditis-like injury was limited to three or fewer myocardial segments in 88% of cases with no associated ventricular dysfunction, and that biventricular function was no different than in those without myocarditis.
“We use the word ‘myocarditis-like’ but we don’t have histology,” Dr. Fontana said. “Our group actually suspects a lot of this will be microvascular clotting (microangiopathic thrombosis). This is exciting, as newer anticoagulation strategies – for example, those being tried in RECOVERY – may have benefit.”
Aloke V. Finn, MD, of the CVPath Institute in Gaithersburg, Md., wishes researchers would stop using the term myocarditis altogether to describe clinical or imaging findings in COVID-19.
“MRI can’t diagnose myocarditis. It is a specific diagnosis that requires, ideally, histology, as the investigators acknowledged,” Dr. Finn said in an interview.
His group at CVPath recently published data showing pathologic evidence of myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection, as reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
“As a clinician, when I think of myocarditis, I look at the echo and an LV gram, and I see if there is a wall motion abnormality and troponin elevation, but with normal coronary arteries. And if all that is there, then I think about myocarditis in my differential diagnosis,” he said. “But in most of these cases, as the authors rightly point out, most patients did not have what is necessary to really entertain a diagnosis of myocarditis.”
He agreed with Dr. Fontana’s suggestion that what the CMR might be picking up in these survivors is microthrombi, as his group saw in their recent autopsy study.
“It’s very possible these findings are concordant with the recent autopsy studies done by my group and others in terms of detecting the presence of microthrombi, but we don’t know this for certain because no one has ever studied this entity before in the clinic and we don’t really know how microthrombi might appear on CMR.”
Largest study to date
The 148 participants (mean age, 64 years; 70% male) in the largest study to date to investigate convalescing COVID-19 patients who had elevated troponins – something identified early in the pandemic as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 – were treated at one of six hospitals in London.
Patients who had abnormal troponin levels were offered an MRI scan of the heart after discharge and were compared with those from a control group of patients who had not had COVID-19 and with 40 healthy volunteers.
Median length of stay was 9 days, and 32% of patients required ventilatory support in the intensive care unit.
Just over half the patients (57%) had hypertension, 7% had had a previous myocardial infarction, 34% had diabetes, 46% had hypercholesterolemia, and 24% were smokers. Mean body mass index was 28.5 kg/m2.
CMR follow-up was conducted a median of 68 days after confirmation of a COVID-19 diagnosis.
On Twitter, Dr. Cole noted that the findings are subject to both survivor bias and referral bias. “We didn’t scan frail patients where the clinician felt [CMR] was unlikely to inform management.”
The findings, said Dr. Fontana, “say nothing about what happens to people who are not hospitalized with COVID, or those who are hospitalized but without elevated troponin.”
What they do offer, particularly if replicated, is a way forward in identifying patients at higher or lower risk for long-term sequelae and inform strategies that could improve outcomes, she added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About half of 148 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and elevated troponin levels had at least some evidence of myocardial injury on cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging 2 months later, a new study shows.
“Our results demonstrate that in this subset of patients surviving severe COVID-19 and with troponin elevation, ongoing localized myocardial inflammation, whilst less frequent than previously reported, remains present in a proportion of patients and may represent an emerging issue of clinical relevance,” wrote Marianna Fontana, MD, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues.
The cardiac abnormalities identified were classified as nonischemic (including “myocarditis-like” late gadolinium enhancement [LGE]) in 26% of the cohort; as related to ischemic heart disease (infarction or inducible ischemia) in 22%; and as dual pathology in 6%.
Left ventricular (LV) function was normal in 89% of the 148 patients. In the 17 patients (11%) with LV dysfunction, only four had an ejection fraction below 35%. Of the nine patients whose LV dysfunction was related to myocardial infarction, six had a known history of ischemic heart disease.

No patients with “myocarditis-pattern” LGE had regional wall motion abnormalities, and neither admission nor peak troponin values were predictive of the diagnosis of myocarditis.
The results were published online Feb. 18 in the European Heart Journal.
Glass half full
Taking a “glass half full” approach, co–senior author Graham D. Cole, MD, PhD, noted on Twitter that nearly half the patients had no major cardiac abnormalities on CMR just 2 months after a bout with troponin-positive COVID-19.
“We think this is important: Even in a group who had been very sick with raised troponin, it was common to find no evidence of heart damage,” said Dr. Cole, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust.
“We believe our data challenge the hypothesis that chronic inflammation, diffuse fibrosis, or long-term LV dysfunction is a dominant feature in those surviving COVID-19,” the investigators concluded in their report.
In an interview, Dr. Fontana explained further: “It has been reported in an early ‘pathfinder’ study that two-thirds of patients recovered from COVID-19 had CMR evidence of abnormal findings with a high incidence of elevated T1 and T2 in keeping with diffuse fibrosis and edema. Our findings with a larger, multicenter study and better controls show low rates of heart impairment and much less ongoing inflammation, which is reassuring.”
She also noted that the different patterns of injury suggest that different mechanisms are at play, including the possibility that “at least some of the found damage might have been preexisting, because people with heart damage are more likely to get severe disease.”
The investigators, including first author Tushar Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, also noted that myocarditis-like injury was limited to three or fewer myocardial segments in 88% of cases with no associated ventricular dysfunction, and that biventricular function was no different than in those without myocarditis.
“We use the word ‘myocarditis-like’ but we don’t have histology,” Dr. Fontana said. “Our group actually suspects a lot of this will be microvascular clotting (microangiopathic thrombosis). This is exciting, as newer anticoagulation strategies – for example, those being tried in RECOVERY – may have benefit.”
Aloke V. Finn, MD, of the CVPath Institute in Gaithersburg, Md., wishes researchers would stop using the term myocarditis altogether to describe clinical or imaging findings in COVID-19.
“MRI can’t diagnose myocarditis. It is a specific diagnosis that requires, ideally, histology, as the investigators acknowledged,” Dr. Finn said in an interview.
His group at CVPath recently published data showing pathologic evidence of myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection, as reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
“As a clinician, when I think of myocarditis, I look at the echo and an LV gram, and I see if there is a wall motion abnormality and troponin elevation, but with normal coronary arteries. And if all that is there, then I think about myocarditis in my differential diagnosis,” he said. “But in most of these cases, as the authors rightly point out, most patients did not have what is necessary to really entertain a diagnosis of myocarditis.”
He agreed with Dr. Fontana’s suggestion that what the CMR might be picking up in these survivors is microthrombi, as his group saw in their recent autopsy study.
“It’s very possible these findings are concordant with the recent autopsy studies done by my group and others in terms of detecting the presence of microthrombi, but we don’t know this for certain because no one has ever studied this entity before in the clinic and we don’t really know how microthrombi might appear on CMR.”
Largest study to date
The 148 participants (mean age, 64 years; 70% male) in the largest study to date to investigate convalescing COVID-19 patients who had elevated troponins – something identified early in the pandemic as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 – were treated at one of six hospitals in London.
Patients who had abnormal troponin levels were offered an MRI scan of the heart after discharge and were compared with those from a control group of patients who had not had COVID-19 and with 40 healthy volunteers.
Median length of stay was 9 days, and 32% of patients required ventilatory support in the intensive care unit.
Just over half the patients (57%) had hypertension, 7% had had a previous myocardial infarction, 34% had diabetes, 46% had hypercholesterolemia, and 24% were smokers. Mean body mass index was 28.5 kg/m2.
CMR follow-up was conducted a median of 68 days after confirmation of a COVID-19 diagnosis.
On Twitter, Dr. Cole noted that the findings are subject to both survivor bias and referral bias. “We didn’t scan frail patients where the clinician felt [CMR] was unlikely to inform management.”
The findings, said Dr. Fontana, “say nothing about what happens to people who are not hospitalized with COVID, or those who are hospitalized but without elevated troponin.”
What they do offer, particularly if replicated, is a way forward in identifying patients at higher or lower risk for long-term sequelae and inform strategies that could improve outcomes, she added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Innovation requires experimentation
A call for more health care trials
Successful innovation requires experimentation, according to a recent editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety – that’s why health systems should engage in more experimenting, more systematically, to improve health care.
“Most health systems implement interventions without testing them against other designs,” said co-author Mitesh S. Patel, MD, MBA, MS, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “This means that good ideas are often not spread (because we don’t know how impactful they are) and bad ones persist (because we don’t realize they don’t work).”
Dr. Patel, who is director of the Penn Medicine Nudge Unit at the Perelman Center for Advanced Medicine, encourages health systems and clinicians to implement new interventions in testable ways such as through a randomized trial, so that we can learn what works and why. A more systematic approach could help to expand programs that work and improve workflow and patient care.
“First, we must embed research teams within health systems in order to create the capacity for this kind of work. Expertise is required to identify a promising intervention, design the conceptual approach, conduct the technical implementation and rigorously evaluate the trial. These teams are also able to design interventions within the context of existing workflows in order to ensure that successful projects can be quickly scaled and that ineffective initiatives can be seamlessly terminated.” the authors wrote.
“Second, we must take advantage of existing data systems. The field of health care is ripe with detailed and reliable administrative data and electronic medical record data. These data offer the potential to do high-quality, low-cost, rapid trials. Third, we must measure a wide range of meaningful outcomes. We should examine the effect of interventions on health care costs, health care utilization and health outcomes.”
Next steps could be focused on thinking about the key priority areas and how can experiments be used to generate new knowledge on what works and what does not. “Luckily, the complex world of health care provides endless opportunities for rapid-cycle, randomized trials that target health care costs and outcomes,” Dr. Patel said.
Reference
1. Oakes AH, Patel MS. A nudge towards increased experimentation to more rapidly improve healthcare. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:179-181. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009948. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.
A call for more health care trials
A call for more health care trials
Successful innovation requires experimentation, according to a recent editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety – that’s why health systems should engage in more experimenting, more systematically, to improve health care.
“Most health systems implement interventions without testing them against other designs,” said co-author Mitesh S. Patel, MD, MBA, MS, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “This means that good ideas are often not spread (because we don’t know how impactful they are) and bad ones persist (because we don’t realize they don’t work).”
Dr. Patel, who is director of the Penn Medicine Nudge Unit at the Perelman Center for Advanced Medicine, encourages health systems and clinicians to implement new interventions in testable ways such as through a randomized trial, so that we can learn what works and why. A more systematic approach could help to expand programs that work and improve workflow and patient care.
“First, we must embed research teams within health systems in order to create the capacity for this kind of work. Expertise is required to identify a promising intervention, design the conceptual approach, conduct the technical implementation and rigorously evaluate the trial. These teams are also able to design interventions within the context of existing workflows in order to ensure that successful projects can be quickly scaled and that ineffective initiatives can be seamlessly terminated.” the authors wrote.
“Second, we must take advantage of existing data systems. The field of health care is ripe with detailed and reliable administrative data and electronic medical record data. These data offer the potential to do high-quality, low-cost, rapid trials. Third, we must measure a wide range of meaningful outcomes. We should examine the effect of interventions on health care costs, health care utilization and health outcomes.”
Next steps could be focused on thinking about the key priority areas and how can experiments be used to generate new knowledge on what works and what does not. “Luckily, the complex world of health care provides endless opportunities for rapid-cycle, randomized trials that target health care costs and outcomes,” Dr. Patel said.
Reference
1. Oakes AH, Patel MS. A nudge towards increased experimentation to more rapidly improve healthcare. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:179-181. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009948. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.
Successful innovation requires experimentation, according to a recent editorial in BMJ Quality & Safety – that’s why health systems should engage in more experimenting, more systematically, to improve health care.
“Most health systems implement interventions without testing them against other designs,” said co-author Mitesh S. Patel, MD, MBA, MS, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “This means that good ideas are often not spread (because we don’t know how impactful they are) and bad ones persist (because we don’t realize they don’t work).”
Dr. Patel, who is director of the Penn Medicine Nudge Unit at the Perelman Center for Advanced Medicine, encourages health systems and clinicians to implement new interventions in testable ways such as through a randomized trial, so that we can learn what works and why. A more systematic approach could help to expand programs that work and improve workflow and patient care.
“First, we must embed research teams within health systems in order to create the capacity for this kind of work. Expertise is required to identify a promising intervention, design the conceptual approach, conduct the technical implementation and rigorously evaluate the trial. These teams are also able to design interventions within the context of existing workflows in order to ensure that successful projects can be quickly scaled and that ineffective initiatives can be seamlessly terminated.” the authors wrote.
“Second, we must take advantage of existing data systems. The field of health care is ripe with detailed and reliable administrative data and electronic medical record data. These data offer the potential to do high-quality, low-cost, rapid trials. Third, we must measure a wide range of meaningful outcomes. We should examine the effect of interventions on health care costs, health care utilization and health outcomes.”
Next steps could be focused on thinking about the key priority areas and how can experiments be used to generate new knowledge on what works and what does not. “Luckily, the complex world of health care provides endless opportunities for rapid-cycle, randomized trials that target health care costs and outcomes,” Dr. Patel said.
Reference
1. Oakes AH, Patel MS. A nudge towards increased experimentation to more rapidly improve healthcare. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:179-181. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009948. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.
Janssen/J&J COVID-19 vaccine cuts transmission, new data show
The single-dose vaccine reduces the risk of asymptomatic transmission by 74% at 71 days, compared with placebo, according to documents released today by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“The decrease in asymptomatic transmission is very welcome news too in curbing the spread of the virus,” Phyllis Tien, MD, told this news organization.
“While the earlier press release reported that the vaccine was effective against preventing severe COVID-19 disease, as well as hospitalizations and death, this new data shows that the vaccine can also decrease transmission, which is very important on a public health level,” said Dr. Tien, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It is extremely important in terms of getting to herd immunity,” Paul Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic and infectious disease specialist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in an interview. “It means that this vaccine is likely preventing subsequent transmission after a single dose, which could have huge implications once we get the majority of folks vaccinated.”
The FDA cautioned that the numbers of participants included in the study are relatively small and need to be verified. However, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine might not be the only product offering this advantage. Early data suggest that the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine also decreases transmission, providing further evidence that the protection offered by immunization goes beyond the individual.
The new analyses were provided by the FDA in advance of its review of the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The agency plans to fully address the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine at its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee Meeting on Friday, including evaluating its safety and efficacy.
The agency’s decision on whether or not to grant emergency use authorization (EUA) to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine could come as early as Friday evening or Saturday.
In addition to the newly released data, officials are likely to discuss phase 3 data, released Jan. 29, that reveal an 85% efficacy for the vaccine against severe COVID-19 illness globally, including data from South America, South Africa, and the United States. When the analysis was restricted to data from U.S. participants, the trial showed a 73% efficacy against moderate to severe COVID-19.
If and when the FDA grants an EUA, it remains unclear how much of the new vaccine will be immediately available. Initially, Johnson & Johnson predicted 18 million doses would be ready by the end of February, but others stated the figure will be closer to 2-4 million. The manufacturer’s contract with the U.S. government stipulates production of 100-million doses by the end of June.
Dr. Tien received support from Johnson & Johnson to conduct the J&J COVID-19 vaccine trial in the SF VA HealthCare System. Dr. Goepfert has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The single-dose vaccine reduces the risk of asymptomatic transmission by 74% at 71 days, compared with placebo, according to documents released today by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“The decrease in asymptomatic transmission is very welcome news too in curbing the spread of the virus,” Phyllis Tien, MD, told this news organization.
“While the earlier press release reported that the vaccine was effective against preventing severe COVID-19 disease, as well as hospitalizations and death, this new data shows that the vaccine can also decrease transmission, which is very important on a public health level,” said Dr. Tien, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It is extremely important in terms of getting to herd immunity,” Paul Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic and infectious disease specialist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in an interview. “It means that this vaccine is likely preventing subsequent transmission after a single dose, which could have huge implications once we get the majority of folks vaccinated.”
The FDA cautioned that the numbers of participants included in the study are relatively small and need to be verified. However, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine might not be the only product offering this advantage. Early data suggest that the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine also decreases transmission, providing further evidence that the protection offered by immunization goes beyond the individual.
The new analyses were provided by the FDA in advance of its review of the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The agency plans to fully address the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine at its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee Meeting on Friday, including evaluating its safety and efficacy.
The agency’s decision on whether or not to grant emergency use authorization (EUA) to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine could come as early as Friday evening or Saturday.
In addition to the newly released data, officials are likely to discuss phase 3 data, released Jan. 29, that reveal an 85% efficacy for the vaccine against severe COVID-19 illness globally, including data from South America, South Africa, and the United States. When the analysis was restricted to data from U.S. participants, the trial showed a 73% efficacy against moderate to severe COVID-19.
If and when the FDA grants an EUA, it remains unclear how much of the new vaccine will be immediately available. Initially, Johnson & Johnson predicted 18 million doses would be ready by the end of February, but others stated the figure will be closer to 2-4 million. The manufacturer’s contract with the U.S. government stipulates production of 100-million doses by the end of June.
Dr. Tien received support from Johnson & Johnson to conduct the J&J COVID-19 vaccine trial in the SF VA HealthCare System. Dr. Goepfert has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The single-dose vaccine reduces the risk of asymptomatic transmission by 74% at 71 days, compared with placebo, according to documents released today by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“The decrease in asymptomatic transmission is very welcome news too in curbing the spread of the virus,” Phyllis Tien, MD, told this news organization.
“While the earlier press release reported that the vaccine was effective against preventing severe COVID-19 disease, as well as hospitalizations and death, this new data shows that the vaccine can also decrease transmission, which is very important on a public health level,” said Dr. Tien, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It is extremely important in terms of getting to herd immunity,” Paul Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic and infectious disease specialist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in an interview. “It means that this vaccine is likely preventing subsequent transmission after a single dose, which could have huge implications once we get the majority of folks vaccinated.”
The FDA cautioned that the numbers of participants included in the study are relatively small and need to be verified. However, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine might not be the only product offering this advantage. Early data suggest that the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine also decreases transmission, providing further evidence that the protection offered by immunization goes beyond the individual.
The new analyses were provided by the FDA in advance of its review of the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The agency plans to fully address the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine at its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee Meeting on Friday, including evaluating its safety and efficacy.
The agency’s decision on whether or not to grant emergency use authorization (EUA) to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine could come as early as Friday evening or Saturday.
In addition to the newly released data, officials are likely to discuss phase 3 data, released Jan. 29, that reveal an 85% efficacy for the vaccine against severe COVID-19 illness globally, including data from South America, South Africa, and the United States. When the analysis was restricted to data from U.S. participants, the trial showed a 73% efficacy against moderate to severe COVID-19.
If and when the FDA grants an EUA, it remains unclear how much of the new vaccine will be immediately available. Initially, Johnson & Johnson predicted 18 million doses would be ready by the end of February, but others stated the figure will be closer to 2-4 million. The manufacturer’s contract with the U.S. government stipulates production of 100-million doses by the end of June.
Dr. Tien received support from Johnson & Johnson to conduct the J&J COVID-19 vaccine trial in the SF VA HealthCare System. Dr. Goepfert has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Loss of smell lingers post COVID-19
The findings illustrate that olfactory problems are common not only during the acute COVID-19 phase but also “in the long run” and that these problems should be “taken into consideration” when following up these patients, study investigator Johannes Frasnelli, MD, professor, department of anatomy, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, said in an interview.
Loss of the sense of smell can affect quality of life because it affects eating and drinking, and may even be dangerous, said Dr. Frasnelli. “If your sense of smell is impaired, you may unknowingly eat spoiled food, or you may not smell smoke or gas in your home,” he said. In addition, Dr. Frasnelli noted that an impaired sense of smell is associated with higher rates of depression. The findings will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology in April.
‘Striking’ finding
Research shows that about 60% of patients with COVID-19 lose their sense of smell to some degree during the acute phase of the disease. “But we wanted to go further and look at the longer-term effects of loss of smell and taste,” said Dr. Frasnelli.
The analysis included 813 health care workers in the province of Quebec. For all the patients, SARS-CoV-2 infection was confirmed through testing with a nasopharyngeal viral swab.
Participants completed a 64-item online questionnaire that asked about three senses: olfactory; gustatory, which includes tastes such as sweet, sour, bitter, salty, savory and umami; and trigeminal, which includes sensations such as spiciness of hot peppers and “coolness” of mint.
They were asked to rate these on a scale of 0 (no perception) to 10 (very strong perception) before the infection, during the infection, and currently. They were also asked about other symptoms, including fatigue.
Most respondents had been infected in the first wave of the virus in March and April of 2020 and responded to the questionnaire an average of 5 months later.
The vast majority of respondents (84.1%) were women, which Dr. Frasnelli said was not surprising because women predominate in the health care field.
The analysis showed that average smell ratings were 8.98 before infection, 2.85 during the acute phase, and 7.41 when respondents answered the questionnaire. The sense of taste was less affected and recovered faster than did the sense of smell. Results for taste were 9.20 before infection, 3.59 during the acute phase, and 8.05 after COVID-19.
Among 580 respondents who indicated a compromised sense of smell during the acute phase, the average smell rating when answering the questionnaire was 6.89, compared to 9.03 before the infection. More than half (51.2%) reported not regaining full olfactory function.
The fact that the sense of smell had not returned to normal for half the participants so long after being infected is “novel and quite striking,” said Dr. Frasnelli.
However, he noted, this doesn’t necessarily mean all those with a compromised sense of smell “have huge problems.” In some cases, he said, the problem “is more subtle.”
Not a CNS problem?
Respondents also completed a chemosensory dysfunction home test (CD-HT). They were asked to prepare common household food items, such as peanut butter, sugar, salt, and vinegar, in a particular way – for example, to add sugar or salt to water – and provide feedback on how they smell and taste.
For this CD-HT analysis, 18.4% of respondents reported having persistent loss of smell. This, Dr. Frasnelli said, adds to evidence from self-reported responses and suggests that in some cases, the problem is more than senses not returning to normal.
“From the questionnaires, roughly 50% said their sense of smell is still not back to normal, and when we look at the CD home test, we see that almost 20% of subjects indeed have pretty strong impairment of their sense of smell,” he said.
The results showed no sex differences, although Dr. Frasnelli noted that most of the sample were women. “It’s tricky to look at the data with regard to sex because it’s a bit skewed,” he said.
Male respondents were older than female participants, but there was no difference in impairment between age groups. Dr. Frasnelli said this was “quite interesting,” inasmuch as older people usually lose some sense of smell.
The researchers have not yet examined whether the results differ by type of health care worker.
They also have not examined in detail whether infection severity affects the risk for extended olfactory impairment. Although some research suggests that the problem with smell is more common in less severe cases, Dr. Frasnelli noted this could be because loss of smell is not a huge problem for patients battling grave health problems.
As for other symptoms, many respondents reported lingering fatigue; some reported debilitating fatigue, said Dr. Frasnelli. However, he cautioned that this is difficult to interpret, because the participants were health care workers, many of whom returned to work during the pandemic and perhaps had not fully rested.
He also noted that he and his colleagues have not “made the link” between impaired smell and the degree of fatigue.
The COVID-19 virus appears to attack supporting sustentacular cells in the olfactory epithelium, not nerve cells.
“Right now, it seems that the smell problem is not a central nervous system problem but a peripheral problem,” said Dr. Frasnelli. “But we don’t know for sure; it may be that the virus somehow gets into the brain and some symptoms are caused by the effects of the infection on the brain.”
The researchers will extend their research with another questionnaire to assess senses 10-12 months after COVID-19.
Limitations of the study include the subjective nature of the smell and taste ratings and the single time point at which data were collected.
Confirmatory findings
Commenting on the research in an interview, Thomas Hummel, MD, professor, smell and taste clinic, department of otorhinolaryngology, Technische Universität Dresden (Germany), said the new results regarding loss of smell after COVID-19 are “very congruent” with what he and his colleagues have observed.
Research shows that up to one in five of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 experience olfactory loss. “While the numbers may vary a bit from study to study or lab to lab, I think 5% to 20% of post–COVID-19 patients exhibit long-term olfactory loss,” Dr. Hummel said.
His group has observed that “many more are not back to normal,” which conforms with what Dr. Frasnelli’s study reveals, said Dr. Hummel.
Also commenting on the research, Kenneth L. Tyler, MD, professor of neurology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a fellow of the American Academy of Neurology, said the study was relatively large and the results “interesting.”
Although it “provides more evidence there’s a subset of patients with symptoms even well past the acute phase” of COVID-19, the results are “mostly confirmatory” and include “nothing super surprising,” Dr. Tyler said in an interview.
However, the investigators did attempt to make the study “a little more quantitative” and “to confirm the self-reporting with their validated CD home test,” he said.
Dr. Tyler wondered how representative the sample was and whether the study drew more participants with impaired senses. “If I had a loss of smell or taste, maybe I would be more likely to respond to such a survey,” he said.
He also noted the difficulty of separating loss of smell from loss of taste.
“If you lose your sense of smell, things don’t taste right, so it can be confounding as to how to separate out those two,” he noted.
The study was supported by the Foundation of the Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières and the Province of Quebec. Dr. Frasnelli has received royalties from Styriabooks in Austria for a book on olfaction published in 2019 and has received honoraria for speaking engagements. Dr. Hummel and Dr. Tyler have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The findings illustrate that olfactory problems are common not only during the acute COVID-19 phase but also “in the long run” and that these problems should be “taken into consideration” when following up these patients, study investigator Johannes Frasnelli, MD, professor, department of anatomy, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, said in an interview.
Loss of the sense of smell can affect quality of life because it affects eating and drinking, and may even be dangerous, said Dr. Frasnelli. “If your sense of smell is impaired, you may unknowingly eat spoiled food, or you may not smell smoke or gas in your home,” he said. In addition, Dr. Frasnelli noted that an impaired sense of smell is associated with higher rates of depression. The findings will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology in April.
‘Striking’ finding
Research shows that about 60% of patients with COVID-19 lose their sense of smell to some degree during the acute phase of the disease. “But we wanted to go further and look at the longer-term effects of loss of smell and taste,” said Dr. Frasnelli.
The analysis included 813 health care workers in the province of Quebec. For all the patients, SARS-CoV-2 infection was confirmed through testing with a nasopharyngeal viral swab.
Participants completed a 64-item online questionnaire that asked about three senses: olfactory; gustatory, which includes tastes such as sweet, sour, bitter, salty, savory and umami; and trigeminal, which includes sensations such as spiciness of hot peppers and “coolness” of mint.
They were asked to rate these on a scale of 0 (no perception) to 10 (very strong perception) before the infection, during the infection, and currently. They were also asked about other symptoms, including fatigue.
Most respondents had been infected in the first wave of the virus in March and April of 2020 and responded to the questionnaire an average of 5 months later.
The vast majority of respondents (84.1%) were women, which Dr. Frasnelli said was not surprising because women predominate in the health care field.
The analysis showed that average smell ratings were 8.98 before infection, 2.85 during the acute phase, and 7.41 when respondents answered the questionnaire. The sense of taste was less affected and recovered faster than did the sense of smell. Results for taste were 9.20 before infection, 3.59 during the acute phase, and 8.05 after COVID-19.
Among 580 respondents who indicated a compromised sense of smell during the acute phase, the average smell rating when answering the questionnaire was 6.89, compared to 9.03 before the infection. More than half (51.2%) reported not regaining full olfactory function.
The fact that the sense of smell had not returned to normal for half the participants so long after being infected is “novel and quite striking,” said Dr. Frasnelli.
However, he noted, this doesn’t necessarily mean all those with a compromised sense of smell “have huge problems.” In some cases, he said, the problem “is more subtle.”
Not a CNS problem?
Respondents also completed a chemosensory dysfunction home test (CD-HT). They were asked to prepare common household food items, such as peanut butter, sugar, salt, and vinegar, in a particular way – for example, to add sugar or salt to water – and provide feedback on how they smell and taste.
For this CD-HT analysis, 18.4% of respondents reported having persistent loss of smell. This, Dr. Frasnelli said, adds to evidence from self-reported responses and suggests that in some cases, the problem is more than senses not returning to normal.
“From the questionnaires, roughly 50% said their sense of smell is still not back to normal, and when we look at the CD home test, we see that almost 20% of subjects indeed have pretty strong impairment of their sense of smell,” he said.
The results showed no sex differences, although Dr. Frasnelli noted that most of the sample were women. “It’s tricky to look at the data with regard to sex because it’s a bit skewed,” he said.
Male respondents were older than female participants, but there was no difference in impairment between age groups. Dr. Frasnelli said this was “quite interesting,” inasmuch as older people usually lose some sense of smell.
The researchers have not yet examined whether the results differ by type of health care worker.
They also have not examined in detail whether infection severity affects the risk for extended olfactory impairment. Although some research suggests that the problem with smell is more common in less severe cases, Dr. Frasnelli noted this could be because loss of smell is not a huge problem for patients battling grave health problems.
As for other symptoms, many respondents reported lingering fatigue; some reported debilitating fatigue, said Dr. Frasnelli. However, he cautioned that this is difficult to interpret, because the participants were health care workers, many of whom returned to work during the pandemic and perhaps had not fully rested.
He also noted that he and his colleagues have not “made the link” between impaired smell and the degree of fatigue.
The COVID-19 virus appears to attack supporting sustentacular cells in the olfactory epithelium, not nerve cells.
“Right now, it seems that the smell problem is not a central nervous system problem but a peripheral problem,” said Dr. Frasnelli. “But we don’t know for sure; it may be that the virus somehow gets into the brain and some symptoms are caused by the effects of the infection on the brain.”
The researchers will extend their research with another questionnaire to assess senses 10-12 months after COVID-19.
Limitations of the study include the subjective nature of the smell and taste ratings and the single time point at which data were collected.
Confirmatory findings
Commenting on the research in an interview, Thomas Hummel, MD, professor, smell and taste clinic, department of otorhinolaryngology, Technische Universität Dresden (Germany), said the new results regarding loss of smell after COVID-19 are “very congruent” with what he and his colleagues have observed.
Research shows that up to one in five of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 experience olfactory loss. “While the numbers may vary a bit from study to study or lab to lab, I think 5% to 20% of post–COVID-19 patients exhibit long-term olfactory loss,” Dr. Hummel said.
His group has observed that “many more are not back to normal,” which conforms with what Dr. Frasnelli’s study reveals, said Dr. Hummel.
Also commenting on the research, Kenneth L. Tyler, MD, professor of neurology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a fellow of the American Academy of Neurology, said the study was relatively large and the results “interesting.”
Although it “provides more evidence there’s a subset of patients with symptoms even well past the acute phase” of COVID-19, the results are “mostly confirmatory” and include “nothing super surprising,” Dr. Tyler said in an interview.
However, the investigators did attempt to make the study “a little more quantitative” and “to confirm the self-reporting with their validated CD home test,” he said.
Dr. Tyler wondered how representative the sample was and whether the study drew more participants with impaired senses. “If I had a loss of smell or taste, maybe I would be more likely to respond to such a survey,” he said.
He also noted the difficulty of separating loss of smell from loss of taste.
“If you lose your sense of smell, things don’t taste right, so it can be confounding as to how to separate out those two,” he noted.
The study was supported by the Foundation of the Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières and the Province of Quebec. Dr. Frasnelli has received royalties from Styriabooks in Austria for a book on olfaction published in 2019 and has received honoraria for speaking engagements. Dr. Hummel and Dr. Tyler have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The findings illustrate that olfactory problems are common not only during the acute COVID-19 phase but also “in the long run” and that these problems should be “taken into consideration” when following up these patients, study investigator Johannes Frasnelli, MD, professor, department of anatomy, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, said in an interview.
Loss of the sense of smell can affect quality of life because it affects eating and drinking, and may even be dangerous, said Dr. Frasnelli. “If your sense of smell is impaired, you may unknowingly eat spoiled food, or you may not smell smoke or gas in your home,” he said. In addition, Dr. Frasnelli noted that an impaired sense of smell is associated with higher rates of depression. The findings will be presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology in April.
‘Striking’ finding
Research shows that about 60% of patients with COVID-19 lose their sense of smell to some degree during the acute phase of the disease. “But we wanted to go further and look at the longer-term effects of loss of smell and taste,” said Dr. Frasnelli.
The analysis included 813 health care workers in the province of Quebec. For all the patients, SARS-CoV-2 infection was confirmed through testing with a nasopharyngeal viral swab.
Participants completed a 64-item online questionnaire that asked about three senses: olfactory; gustatory, which includes tastes such as sweet, sour, bitter, salty, savory and umami; and trigeminal, which includes sensations such as spiciness of hot peppers and “coolness” of mint.
They were asked to rate these on a scale of 0 (no perception) to 10 (very strong perception) before the infection, during the infection, and currently. They were also asked about other symptoms, including fatigue.
Most respondents had been infected in the first wave of the virus in March and April of 2020 and responded to the questionnaire an average of 5 months later.
The vast majority of respondents (84.1%) were women, which Dr. Frasnelli said was not surprising because women predominate in the health care field.
The analysis showed that average smell ratings were 8.98 before infection, 2.85 during the acute phase, and 7.41 when respondents answered the questionnaire. The sense of taste was less affected and recovered faster than did the sense of smell. Results for taste were 9.20 before infection, 3.59 during the acute phase, and 8.05 after COVID-19.
Among 580 respondents who indicated a compromised sense of smell during the acute phase, the average smell rating when answering the questionnaire was 6.89, compared to 9.03 before the infection. More than half (51.2%) reported not regaining full olfactory function.
The fact that the sense of smell had not returned to normal for half the participants so long after being infected is “novel and quite striking,” said Dr. Frasnelli.
However, he noted, this doesn’t necessarily mean all those with a compromised sense of smell “have huge problems.” In some cases, he said, the problem “is more subtle.”
Not a CNS problem?
Respondents also completed a chemosensory dysfunction home test (CD-HT). They were asked to prepare common household food items, such as peanut butter, sugar, salt, and vinegar, in a particular way – for example, to add sugar or salt to water – and provide feedback on how they smell and taste.
For this CD-HT analysis, 18.4% of respondents reported having persistent loss of smell. This, Dr. Frasnelli said, adds to evidence from self-reported responses and suggests that in some cases, the problem is more than senses not returning to normal.
“From the questionnaires, roughly 50% said their sense of smell is still not back to normal, and when we look at the CD home test, we see that almost 20% of subjects indeed have pretty strong impairment of their sense of smell,” he said.
The results showed no sex differences, although Dr. Frasnelli noted that most of the sample were women. “It’s tricky to look at the data with regard to sex because it’s a bit skewed,” he said.
Male respondents were older than female participants, but there was no difference in impairment between age groups. Dr. Frasnelli said this was “quite interesting,” inasmuch as older people usually lose some sense of smell.
The researchers have not yet examined whether the results differ by type of health care worker.
They also have not examined in detail whether infection severity affects the risk for extended olfactory impairment. Although some research suggests that the problem with smell is more common in less severe cases, Dr. Frasnelli noted this could be because loss of smell is not a huge problem for patients battling grave health problems.
As for other symptoms, many respondents reported lingering fatigue; some reported debilitating fatigue, said Dr. Frasnelli. However, he cautioned that this is difficult to interpret, because the participants were health care workers, many of whom returned to work during the pandemic and perhaps had not fully rested.
He also noted that he and his colleagues have not “made the link” between impaired smell and the degree of fatigue.
The COVID-19 virus appears to attack supporting sustentacular cells in the olfactory epithelium, not nerve cells.
“Right now, it seems that the smell problem is not a central nervous system problem but a peripheral problem,” said Dr. Frasnelli. “But we don’t know for sure; it may be that the virus somehow gets into the brain and some symptoms are caused by the effects of the infection on the brain.”
The researchers will extend their research with another questionnaire to assess senses 10-12 months after COVID-19.
Limitations of the study include the subjective nature of the smell and taste ratings and the single time point at which data were collected.
Confirmatory findings
Commenting on the research in an interview, Thomas Hummel, MD, professor, smell and taste clinic, department of otorhinolaryngology, Technische Universität Dresden (Germany), said the new results regarding loss of smell after COVID-19 are “very congruent” with what he and his colleagues have observed.
Research shows that up to one in five of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 experience olfactory loss. “While the numbers may vary a bit from study to study or lab to lab, I think 5% to 20% of post–COVID-19 patients exhibit long-term olfactory loss,” Dr. Hummel said.
His group has observed that “many more are not back to normal,” which conforms with what Dr. Frasnelli’s study reveals, said Dr. Hummel.
Also commenting on the research, Kenneth L. Tyler, MD, professor of neurology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a fellow of the American Academy of Neurology, said the study was relatively large and the results “interesting.”
Although it “provides more evidence there’s a subset of patients with symptoms even well past the acute phase” of COVID-19, the results are “mostly confirmatory” and include “nothing super surprising,” Dr. Tyler said in an interview.
However, the investigators did attempt to make the study “a little more quantitative” and “to confirm the self-reporting with their validated CD home test,” he said.
Dr. Tyler wondered how representative the sample was and whether the study drew more participants with impaired senses. “If I had a loss of smell or taste, maybe I would be more likely to respond to such a survey,” he said.
He also noted the difficulty of separating loss of smell from loss of taste.
“If you lose your sense of smell, things don’t taste right, so it can be confounding as to how to separate out those two,” he noted.
The study was supported by the Foundation of the Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières and the Province of Quebec. Dr. Frasnelli has received royalties from Styriabooks in Austria for a book on olfaction published in 2019 and has received honoraria for speaking engagements. Dr. Hummel and Dr. Tyler have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SHM Converge: New format, fresh content
While we all long for a traditional in-person meeting “like the good old days”, there are some significant advantages to a virtual meeting like Converge.
The most significant advantage is the ability to review more content than ever before, as we offer a combination of live and recorded “on-demand” sessions. This allows for incredible flexibility in garnering “top-shelf” content from hospital medicine experts around the country, without having to choose from competing sessions. We are especially looking forward to new sessions this year focused on COVID-19; diversity, equity, and inclusion; and resilience.
The Converge conference will still be offering networking sessions throughout – even in the virtual conference environment. We consider networking a vital and endearing part of the value equation for SHM members. For example, we now can participate in several Special Interest Forums, since many of us have several niche interests and want to take advantage of more than one of these networking opportunities. We also carefully preserved the signature “Update in Hospital Medicine” session, as well as the scientific abstract poster reception and the Best of Research and Innovation sessions. These are long-term favorites at the annual conference and lend themselves well to virtual transformation. Some of the workshops and special sessions have exclusive audience engagement and are not offered on demand, so signing up early for these sessions is highly recommended.
SHM remains the professional home for hospitalists, and we rely on the annual conference to keep us all informed on current and forward-thinking clinical practice, practice management, leadership, academics, research, and other topics. This is one of many examples of how SHM has been able to pivot to meet the needs of hospitalists throughout the pandemic. Not only have we successfully converted “traditional” meetings into virtual meetings, but we have been able to curate and deliver content faster and more seamlessly than ever before.
Whether via The Hospitalist, the Journal of Hospital Medicine, the SHM website, or our other educational platforms, SHM has remained committed to being the single “source of truth” for all things hospital medicine. Within the tumultuous political landscape of the past year, the SHM advocacy team has been more active and engaged than ever, in advocating for a myriad of hospitalist-related legislative changes. These are just a few of the ways SHM continues to add value to hospitalist members every day.
Although we will certainly miss seeing each other in person, we are confident that the SHM team will meet and exceed expectations on content delivery and will take advantage of the virtual format to improve content access. We look forward to “seeing” you at SHM Converge this year and hope you take advantage of the enhanced delivery and access to an array of amazing content!
Dr. Scheurer is president of the Society of Hospital Medicine. She is a hospitalist and chief quality officer, MUSC Health System, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
While we all long for a traditional in-person meeting “like the good old days”, there are some significant advantages to a virtual meeting like Converge.
The most significant advantage is the ability to review more content than ever before, as we offer a combination of live and recorded “on-demand” sessions. This allows for incredible flexibility in garnering “top-shelf” content from hospital medicine experts around the country, without having to choose from competing sessions. We are especially looking forward to new sessions this year focused on COVID-19; diversity, equity, and inclusion; and resilience.
The Converge conference will still be offering networking sessions throughout – even in the virtual conference environment. We consider networking a vital and endearing part of the value equation for SHM members. For example, we now can participate in several Special Interest Forums, since many of us have several niche interests and want to take advantage of more than one of these networking opportunities. We also carefully preserved the signature “Update in Hospital Medicine” session, as well as the scientific abstract poster reception and the Best of Research and Innovation sessions. These are long-term favorites at the annual conference and lend themselves well to virtual transformation. Some of the workshops and special sessions have exclusive audience engagement and are not offered on demand, so signing up early for these sessions is highly recommended.
SHM remains the professional home for hospitalists, and we rely on the annual conference to keep us all informed on current and forward-thinking clinical practice, practice management, leadership, academics, research, and other topics. This is one of many examples of how SHM has been able to pivot to meet the needs of hospitalists throughout the pandemic. Not only have we successfully converted “traditional” meetings into virtual meetings, but we have been able to curate and deliver content faster and more seamlessly than ever before.
Whether via The Hospitalist, the Journal of Hospital Medicine, the SHM website, or our other educational platforms, SHM has remained committed to being the single “source of truth” for all things hospital medicine. Within the tumultuous political landscape of the past year, the SHM advocacy team has been more active and engaged than ever, in advocating for a myriad of hospitalist-related legislative changes. These are just a few of the ways SHM continues to add value to hospitalist members every day.
Although we will certainly miss seeing each other in person, we are confident that the SHM team will meet and exceed expectations on content delivery and will take advantage of the virtual format to improve content access. We look forward to “seeing” you at SHM Converge this year and hope you take advantage of the enhanced delivery and access to an array of amazing content!
Dr. Scheurer is president of the Society of Hospital Medicine. She is a hospitalist and chief quality officer, MUSC Health System, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
While we all long for a traditional in-person meeting “like the good old days”, there are some significant advantages to a virtual meeting like Converge.
The most significant advantage is the ability to review more content than ever before, as we offer a combination of live and recorded “on-demand” sessions. This allows for incredible flexibility in garnering “top-shelf” content from hospital medicine experts around the country, without having to choose from competing sessions. We are especially looking forward to new sessions this year focused on COVID-19; diversity, equity, and inclusion; and resilience.
The Converge conference will still be offering networking sessions throughout – even in the virtual conference environment. We consider networking a vital and endearing part of the value equation for SHM members. For example, we now can participate in several Special Interest Forums, since many of us have several niche interests and want to take advantage of more than one of these networking opportunities. We also carefully preserved the signature “Update in Hospital Medicine” session, as well as the scientific abstract poster reception and the Best of Research and Innovation sessions. These are long-term favorites at the annual conference and lend themselves well to virtual transformation. Some of the workshops and special sessions have exclusive audience engagement and are not offered on demand, so signing up early for these sessions is highly recommended.
SHM remains the professional home for hospitalists, and we rely on the annual conference to keep us all informed on current and forward-thinking clinical practice, practice management, leadership, academics, research, and other topics. This is one of many examples of how SHM has been able to pivot to meet the needs of hospitalists throughout the pandemic. Not only have we successfully converted “traditional” meetings into virtual meetings, but we have been able to curate and deliver content faster and more seamlessly than ever before.
Whether via The Hospitalist, the Journal of Hospital Medicine, the SHM website, or our other educational platforms, SHM has remained committed to being the single “source of truth” for all things hospital medicine. Within the tumultuous political landscape of the past year, the SHM advocacy team has been more active and engaged than ever, in advocating for a myriad of hospitalist-related legislative changes. These are just a few of the ways SHM continues to add value to hospitalist members every day.
Although we will certainly miss seeing each other in person, we are confident that the SHM team will meet and exceed expectations on content delivery and will take advantage of the virtual format to improve content access. We look forward to “seeing” you at SHM Converge this year and hope you take advantage of the enhanced delivery and access to an array of amazing content!
Dr. Scheurer is president of the Society of Hospital Medicine. She is a hospitalist and chief quality officer, MUSC Health System, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.












