User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


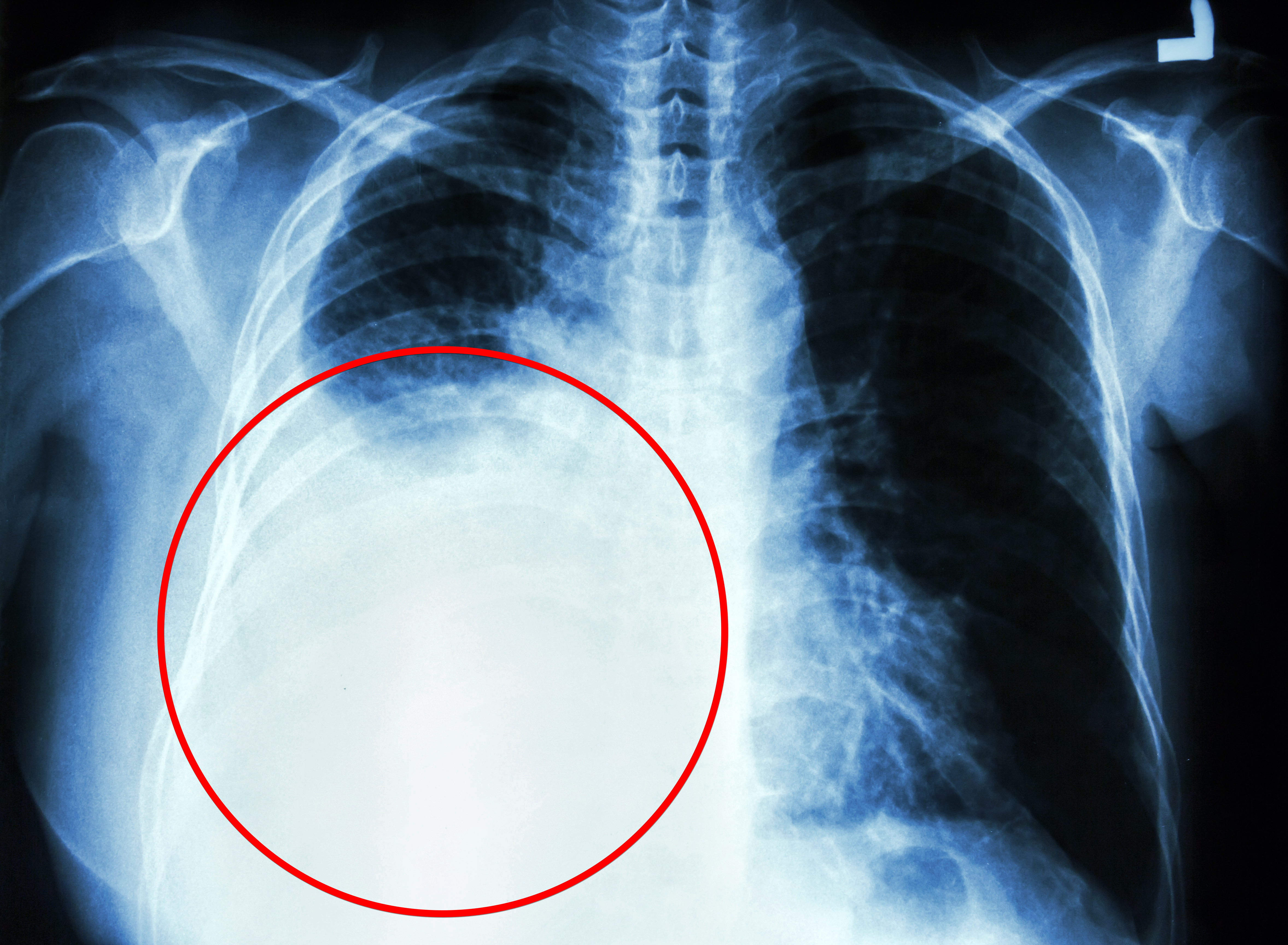
A ‘Fool’s Errand’? Picking a Winner for Treating Early-Stage NSCLC
For years, the default definitive treatment for patients with early-stage I non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been surgical resection, typically minimally invasive lobectomy with systematic lymph node dissection.
Guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and the European Society for Medical Oncology all list surgery (in particular, lobectomy) as the primary local therapy for fit, operable patients with stage I NSCLC.
More recently, however, stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), also called stereotactic ablative radiotherapy, has emerged as a definitive treatment option for stage I NSCLC, especially for older, less fit patients who are unsuitable or deemed high-risk for surgery.
“We see patients in our practice who cannot undergo surgery or who may not have adequate lung function to be able to tolerate surgery, and for these patients who are medically inoperable or surgically unresectable, radiation therapy may be a reasonable option,” Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, professor and lung cancer specialist, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
Given some encouraging data suggesting that SBRT could provide similar survival outcomes and be an alternative to surgery for operable disease, SBRT is also increasingly being considered in these early-stage patients. However, other evidence indicates that SBRT may be associated with higher rates of regional and distant recurrences and worse long-term survival, particularly in operable patients.
What may ultimately matter most is carefully selecting operable patients who undergo SBRT.
Aggarwal has encountered certain patients who are fit for surgery but would rather have radiation therapy. “This is an individual decision, and these patients are usually discussed at tumor board and in multidisciplinary discussions to really make sure that they’re making the right decision for themselves,” she explained.
The Pros and Cons of SBRT
SBRT is a nonsurgical approach in which precision high-dose radiation is delivered in just a few fractions — typically, 3, 5, or 8, depending on institutional protocols and tumor characteristics.
SBRT is performed on an outpatient basis, usually over 1-2 weeks, with most patients able to resume usual activities with minimal to no delay. Surgery, on the other hand, requires a hospital stay and takes most people about 2-6 weeks to return to regular activities. SBRT also avoids anesthesia and surgical incisions, both of which come with risks.
The data on SBRT in early-stage NSCLC are mixed. While some studies indicate that SBRT comes with promising survival outcomes, other research has reported worse survival and recurrence rates.
One potential reason for higher recurrence rates with SBRT is the lack of pathologic nodal staging, which only happens after surgery, as well as lower rates of nodal evaluation with endobronchial ultrasound or mediastinoscopy before surgery or SBRT. Without nodal assessments, clinicians may miss a more aggressive histology or more advanced nodal stage, which would go undertreated if patients received SBRT.
Latest Data in Large Cohort
A recent study published in Lung Cancer indicated that, when carefully selected, operable patients with early NSCLC have comparable survival with lobectomy or SBRT.
In the study, Dutch researchers took an in-depth look at survival and recurrence patterns in a retrospective cohort study of 2183 patients with clinical stage I NSCLC treated with minimally invasive lobectomy or SBRT. The study includes one of the largest cohorts to date, with robust data collection on baseline characteristics, comorbidities, tumor size, performance status, and follow-up.
Patients receiving SBRT were typically older (median age, 74 vs 67 years), had higher comorbidity burdens (Charlson index ≥ 5 in 57% of SBRT patients vs 23% of surgical patients), worse performance status, and lower lung function. To adjust for these differences, the researchers used propensity score weighting so the SBRT group’s baseline characteristics were comparable with those in the surgery group.
The surgery cohort had more invasive nodal evaluation: 21% underwent endobronchial ultrasound or mediastinoscopy vs only 12% in the SBRT group. The vast majority in both groups had PET-CT staging, reflecting modern imaging-based workups.
While 5-year local recurrence rates between the two groups were similar (13.1% for SBRT vs 12.1% for surgery), the 5-year regional recurrence rate was significantly higher after SBRT than lobectomy (18.1% vs 14.2%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.74), as was the distant metastasis rate (26.2% vs 20.2%; HR, 0.72).
Mortality at 30 days was higher after surgery than SBRT (1.0% vs 0.2%). And in the unadjusted analysis, 5-year overall survival was significantly better with lobectomy than SBRT (70.2% vs 40.3%).
However, when the analysis only included patients with similar baseline characteristics, overall survival was no longer significantly different in the two groups (HR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.65-1.20). Lung cancer–specific mortality was also not significantly different between the two treatments (HR, 1.08), but the study was underpowered to detect significant differences in this outcome on the basis of a relatively low number of deaths from NSCLC.
Still, even after comparing similar patients, recurrence-free survival was notably better with surgery (HR, 0.70), due to fewer regional recurrences and distant metastases. Overall, 13% of the surgical cohort had nodal upstaging at pathology, meaning that even in clinically “node-negative” stage I disease, a subset of patients had unsuspected nodal involvement.
Patients receiving SBRT did not have pathologic nodal staging, raising the possibility of occult micrometastases. The authors noted that the proportion of SBRT patients with occult lymph node metastases is likely at least equal to that in the surgery group, but these metastases would go undetected without pathologic assessment.
Missing potential occult micrometastases in the SBRT group likely contributed to higher regional recurrence rates over time. By improving nodal staging, more patients with occult lymph node metastases who would be undertreated with SBRT may be identified before treatment, the authors said.
What Do Experts Say?
So, is SBRT an option for patients with stage I NSCLC?
Opinions vary.
“If you got one shot for a cure, then you want to do the surgery because that’s what results in a cure,” said Raja Flores, MD, chairman of Thoracic Surgery, Mount Sinai Health System, New York City.
Flores noted that the survival rate with surgery is high in this population. “There’s really nothing out there that can compare,” he said.
In his view, surgery “remains the gold standard.” However, “radiation could be considered in nonsurgical candidates,” he said.
The most recent NCCN guidelines align with Flores’ take. The guidelines say that SBRT is indicated for stage IA-IIA (N0) NSCLC in patients who are deemed “medically inoperable, high surgical risk as determined by thoracic surgeon, and those who decline surgery after thoracic surgical consultation.”
Clifford G. Robinson, MD, agreed. “In the United States, we largely treat patients with SBRT who are medically inoperable or high-risk operable and a much smaller proportion who decline surgery,” said Robinson, professor of radiation oncology and chief of SBRT at Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis. “Many patients who are deemed operable are not offered SBRT.”
Still, for Robinson, determining which patients are best suited for surgery or SBRT remains unclear.
“Retrospective comparisons are fraught with problems because of confounding,” Robinson told this news organization. “That is, the healthier patients get surgery, and the less healthy ones get SBRT. No manner of fancy statistical manipulation can remove that fact.”
In fact, a recent meta-analysis found that the most significant variable predicting whether surgery or SBRT was superior in retrospective studies was whether the author was a surgeon or radiation oncologist.
Robinson noted that multiple randomized trials have attempted to randomize patients with medically operable early-stage NSCLC to surgery or SBRT and failed to accrue, largely due to patients’ “understandable unwillingness to be randomized between operative vs nonoperative interventions when most already prefer one or the other approach.”
Flores highlighted another point of caution about interpreting trial results: Not all early-stage NSCLC behaves similarly. “Some are slow-growing ‘turtles,’ and others are aggressive ‘rabbits’ — and the turtles are usually the ones that have been included in these radiotherapy trials, and that’s the danger,” he said.
While medical operability is the primary factor for deciding the treatment modality for early-stage NSCLC, there are other more subtle factors that can play into the decision.
These include prior surgery or radiotherapy to the chest, prior cancers, and social issues, such as the patient being a primary caregiver for another person and job insecurity, that might make recovery from surgery more challenging. And in rare instances, a patient may be medically fit to undergo surgery, but the cancer is technically challenging to resect due to anatomic issues or prior surgery to the chest, Robinson added.
A Winner?
Results from two ongoing, highly anticipated randomized trials expected in the next several years will hopefully provide additional insights and clarify ongoing uncertainties about the optimal treatment strategies for operable patients with stage I NSCLC.
STABLE-MATES is comparing outcomes after sublobar resection and SBRT in high-risk operable stage I NSCLC, and VALOR is evaluating outcomes after anatomic pulmonary resections and SBRT in patients with stage I NSCLC who have a long life expectancy and are fit enough to tolerate surgery.
But Robinson said his group believes that trying to decide on a winner is a “fool’s errand” and is instead running a pragmatic study across multiple academic and community centers around the United States and Canada where patients choose therapy based on their personal preferences and guidance from their physicians. The researchers will carefully track baseline comorbidity and frailty and assess serial quality-of-life changes over time.
“The goal is to create a calculator that a given patient might use in the future to determine what patients like them would have received, complete with expected outcomes and side effects,” Robinson said.
Robinson cautioned, however, that it “seems unlikely, given the existing literature, that one of the treatments will be truly ‘superior’ to the other one and lead to the ‘losing’ treatment fading away since both are excellent options with pros and cons.”
Aggarwal, Robinson, and Flores had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For years, the default definitive treatment for patients with early-stage I non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been surgical resection, typically minimally invasive lobectomy with systematic lymph node dissection.
Guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and the European Society for Medical Oncology all list surgery (in particular, lobectomy) as the primary local therapy for fit, operable patients with stage I NSCLC.
More recently, however, stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), also called stereotactic ablative radiotherapy, has emerged as a definitive treatment option for stage I NSCLC, especially for older, less fit patients who are unsuitable or deemed high-risk for surgery.
“We see patients in our practice who cannot undergo surgery or who may not have adequate lung function to be able to tolerate surgery, and for these patients who are medically inoperable or surgically unresectable, radiation therapy may be a reasonable option,” Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, professor and lung cancer specialist, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
Given some encouraging data suggesting that SBRT could provide similar survival outcomes and be an alternative to surgery for operable disease, SBRT is also increasingly being considered in these early-stage patients. However, other evidence indicates that SBRT may be associated with higher rates of regional and distant recurrences and worse long-term survival, particularly in operable patients.
What may ultimately matter most is carefully selecting operable patients who undergo SBRT.
Aggarwal has encountered certain patients who are fit for surgery but would rather have radiation therapy. “This is an individual decision, and these patients are usually discussed at tumor board and in multidisciplinary discussions to really make sure that they’re making the right decision for themselves,” she explained.
The Pros and Cons of SBRT
SBRT is a nonsurgical approach in which precision high-dose radiation is delivered in just a few fractions — typically, 3, 5, or 8, depending on institutional protocols and tumor characteristics.
SBRT is performed on an outpatient basis, usually over 1-2 weeks, with most patients able to resume usual activities with minimal to no delay. Surgery, on the other hand, requires a hospital stay and takes most people about 2-6 weeks to return to regular activities. SBRT also avoids anesthesia and surgical incisions, both of which come with risks.
The data on SBRT in early-stage NSCLC are mixed. While some studies indicate that SBRT comes with promising survival outcomes, other research has reported worse survival and recurrence rates.
One potential reason for higher recurrence rates with SBRT is the lack of pathologic nodal staging, which only happens after surgery, as well as lower rates of nodal evaluation with endobronchial ultrasound or mediastinoscopy before surgery or SBRT. Without nodal assessments, clinicians may miss a more aggressive histology or more advanced nodal stage, which would go undertreated if patients received SBRT.
Latest Data in Large Cohort
A recent study published in Lung Cancer indicated that, when carefully selected, operable patients with early NSCLC have comparable survival with lobectomy or SBRT.
In the study, Dutch researchers took an in-depth look at survival and recurrence patterns in a retrospective cohort study of 2183 patients with clinical stage I NSCLC treated with minimally invasive lobectomy or SBRT. The study includes one of the largest cohorts to date, with robust data collection on baseline characteristics, comorbidities, tumor size, performance status, and follow-up.
Patients receiving SBRT were typically older (median age, 74 vs 67 years), had higher comorbidity burdens (Charlson index ≥ 5 in 57% of SBRT patients vs 23% of surgical patients), worse performance status, and lower lung function. To adjust for these differences, the researchers used propensity score weighting so the SBRT group’s baseline characteristics were comparable with those in the surgery group.
The surgery cohort had more invasive nodal evaluation: 21% underwent endobronchial ultrasound or mediastinoscopy vs only 12% in the SBRT group. The vast majority in both groups had PET-CT staging, reflecting modern imaging-based workups.
While 5-year local recurrence rates between the two groups were similar (13.1% for SBRT vs 12.1% for surgery), the 5-year regional recurrence rate was significantly higher after SBRT than lobectomy (18.1% vs 14.2%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.74), as was the distant metastasis rate (26.2% vs 20.2%; HR, 0.72).
Mortality at 30 days was higher after surgery than SBRT (1.0% vs 0.2%). And in the unadjusted analysis, 5-year overall survival was significantly better with lobectomy than SBRT (70.2% vs 40.3%).
However, when the analysis only included patients with similar baseline characteristics, overall survival was no longer significantly different in the two groups (HR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.65-1.20). Lung cancer–specific mortality was also not significantly different between the two treatments (HR, 1.08), but the study was underpowered to detect significant differences in this outcome on the basis of a relatively low number of deaths from NSCLC.
Still, even after comparing similar patients, recurrence-free survival was notably better with surgery (HR, 0.70), due to fewer regional recurrences and distant metastases. Overall, 13% of the surgical cohort had nodal upstaging at pathology, meaning that even in clinically “node-negative” stage I disease, a subset of patients had unsuspected nodal involvement.
Patients receiving SBRT did not have pathologic nodal staging, raising the possibility of occult micrometastases. The authors noted that the proportion of SBRT patients with occult lymph node metastases is likely at least equal to that in the surgery group, but these metastases would go undetected without pathologic assessment.
Missing potential occult micrometastases in the SBRT group likely contributed to higher regional recurrence rates over time. By improving nodal staging, more patients with occult lymph node metastases who would be undertreated with SBRT may be identified before treatment, the authors said.
What Do Experts Say?
So, is SBRT an option for patients with stage I NSCLC?
Opinions vary.
“If you got one shot for a cure, then you want to do the surgery because that’s what results in a cure,” said Raja Flores, MD, chairman of Thoracic Surgery, Mount Sinai Health System, New York City.
Flores noted that the survival rate with surgery is high in this population. “There’s really nothing out there that can compare,” he said.
In his view, surgery “remains the gold standard.” However, “radiation could be considered in nonsurgical candidates,” he said.
The most recent NCCN guidelines align with Flores’ take. The guidelines say that SBRT is indicated for stage IA-IIA (N0) NSCLC in patients who are deemed “medically inoperable, high surgical risk as determined by thoracic surgeon, and those who decline surgery after thoracic surgical consultation.”
Clifford G. Robinson, MD, agreed. “In the United States, we largely treat patients with SBRT who are medically inoperable or high-risk operable and a much smaller proportion who decline surgery,” said Robinson, professor of radiation oncology and chief of SBRT at Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis. “Many patients who are deemed operable are not offered SBRT.”
Still, for Robinson, determining which patients are best suited for surgery or SBRT remains unclear.
“Retrospective comparisons are fraught with problems because of confounding,” Robinson told this news organization. “That is, the healthier patients get surgery, and the less healthy ones get SBRT. No manner of fancy statistical manipulation can remove that fact.”
In fact, a recent meta-analysis found that the most significant variable predicting whether surgery or SBRT was superior in retrospective studies was whether the author was a surgeon or radiation oncologist.
Robinson noted that multiple randomized trials have attempted to randomize patients with medically operable early-stage NSCLC to surgery or SBRT and failed to accrue, largely due to patients’ “understandable unwillingness to be randomized between operative vs nonoperative interventions when most already prefer one or the other approach.”
Flores highlighted another point of caution about interpreting trial results: Not all early-stage NSCLC behaves similarly. “Some are slow-growing ‘turtles,’ and others are aggressive ‘rabbits’ — and the turtles are usually the ones that have been included in these radiotherapy trials, and that’s the danger,” he said.
While medical operability is the primary factor for deciding the treatment modality for early-stage NSCLC, there are other more subtle factors that can play into the decision.
These include prior surgery or radiotherapy to the chest, prior cancers, and social issues, such as the patient being a primary caregiver for another person and job insecurity, that might make recovery from surgery more challenging. And in rare instances, a patient may be medically fit to undergo surgery, but the cancer is technically challenging to resect due to anatomic issues or prior surgery to the chest, Robinson added.
A Winner?
Results from two ongoing, highly anticipated randomized trials expected in the next several years will hopefully provide additional insights and clarify ongoing uncertainties about the optimal treatment strategies for operable patients with stage I NSCLC.
STABLE-MATES is comparing outcomes after sublobar resection and SBRT in high-risk operable stage I NSCLC, and VALOR is evaluating outcomes after anatomic pulmonary resections and SBRT in patients with stage I NSCLC who have a long life expectancy and are fit enough to tolerate surgery.
But Robinson said his group believes that trying to decide on a winner is a “fool’s errand” and is instead running a pragmatic study across multiple academic and community centers around the United States and Canada where patients choose therapy based on their personal preferences and guidance from their physicians. The researchers will carefully track baseline comorbidity and frailty and assess serial quality-of-life changes over time.
“The goal is to create a calculator that a given patient might use in the future to determine what patients like them would have received, complete with expected outcomes and side effects,” Robinson said.
Robinson cautioned, however, that it “seems unlikely, given the existing literature, that one of the treatments will be truly ‘superior’ to the other one and lead to the ‘losing’ treatment fading away since both are excellent options with pros and cons.”
Aggarwal, Robinson, and Flores had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For years, the default definitive treatment for patients with early-stage I non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been surgical resection, typically minimally invasive lobectomy with systematic lymph node dissection.
Guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and the European Society for Medical Oncology all list surgery (in particular, lobectomy) as the primary local therapy for fit, operable patients with stage I NSCLC.
More recently, however, stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), also called stereotactic ablative radiotherapy, has emerged as a definitive treatment option for stage I NSCLC, especially for older, less fit patients who are unsuitable or deemed high-risk for surgery.
“We see patients in our practice who cannot undergo surgery or who may not have adequate lung function to be able to tolerate surgery, and for these patients who are medically inoperable or surgically unresectable, radiation therapy may be a reasonable option,” Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, professor and lung cancer specialist, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
Given some encouraging data suggesting that SBRT could provide similar survival outcomes and be an alternative to surgery for operable disease, SBRT is also increasingly being considered in these early-stage patients. However, other evidence indicates that SBRT may be associated with higher rates of regional and distant recurrences and worse long-term survival, particularly in operable patients.
What may ultimately matter most is carefully selecting operable patients who undergo SBRT.
Aggarwal has encountered certain patients who are fit for surgery but would rather have radiation therapy. “This is an individual decision, and these patients are usually discussed at tumor board and in multidisciplinary discussions to really make sure that they’re making the right decision for themselves,” she explained.
The Pros and Cons of SBRT
SBRT is a nonsurgical approach in which precision high-dose radiation is delivered in just a few fractions — typically, 3, 5, or 8, depending on institutional protocols and tumor characteristics.
SBRT is performed on an outpatient basis, usually over 1-2 weeks, with most patients able to resume usual activities with minimal to no delay. Surgery, on the other hand, requires a hospital stay and takes most people about 2-6 weeks to return to regular activities. SBRT also avoids anesthesia and surgical incisions, both of which come with risks.
The data on SBRT in early-stage NSCLC are mixed. While some studies indicate that SBRT comes with promising survival outcomes, other research has reported worse survival and recurrence rates.
One potential reason for higher recurrence rates with SBRT is the lack of pathologic nodal staging, which only happens after surgery, as well as lower rates of nodal evaluation with endobronchial ultrasound or mediastinoscopy before surgery or SBRT. Without nodal assessments, clinicians may miss a more aggressive histology or more advanced nodal stage, which would go undertreated if patients received SBRT.
Latest Data in Large Cohort
A recent study published in Lung Cancer indicated that, when carefully selected, operable patients with early NSCLC have comparable survival with lobectomy or SBRT.
In the study, Dutch researchers took an in-depth look at survival and recurrence patterns in a retrospective cohort study of 2183 patients with clinical stage I NSCLC treated with minimally invasive lobectomy or SBRT. The study includes one of the largest cohorts to date, with robust data collection on baseline characteristics, comorbidities, tumor size, performance status, and follow-up.
Patients receiving SBRT were typically older (median age, 74 vs 67 years), had higher comorbidity burdens (Charlson index ≥ 5 in 57% of SBRT patients vs 23% of surgical patients), worse performance status, and lower lung function. To adjust for these differences, the researchers used propensity score weighting so the SBRT group’s baseline characteristics were comparable with those in the surgery group.
The surgery cohort had more invasive nodal evaluation: 21% underwent endobronchial ultrasound or mediastinoscopy vs only 12% in the SBRT group. The vast majority in both groups had PET-CT staging, reflecting modern imaging-based workups.
While 5-year local recurrence rates between the two groups were similar (13.1% for SBRT vs 12.1% for surgery), the 5-year regional recurrence rate was significantly higher after SBRT than lobectomy (18.1% vs 14.2%; hazard ratio [HR], 0.74), as was the distant metastasis rate (26.2% vs 20.2%; HR, 0.72).
Mortality at 30 days was higher after surgery than SBRT (1.0% vs 0.2%). And in the unadjusted analysis, 5-year overall survival was significantly better with lobectomy than SBRT (70.2% vs 40.3%).
However, when the analysis only included patients with similar baseline characteristics, overall survival was no longer significantly different in the two groups (HR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.65-1.20). Lung cancer–specific mortality was also not significantly different between the two treatments (HR, 1.08), but the study was underpowered to detect significant differences in this outcome on the basis of a relatively low number of deaths from NSCLC.
Still, even after comparing similar patients, recurrence-free survival was notably better with surgery (HR, 0.70), due to fewer regional recurrences and distant metastases. Overall, 13% of the surgical cohort had nodal upstaging at pathology, meaning that even in clinically “node-negative” stage I disease, a subset of patients had unsuspected nodal involvement.
Patients receiving SBRT did not have pathologic nodal staging, raising the possibility of occult micrometastases. The authors noted that the proportion of SBRT patients with occult lymph node metastases is likely at least equal to that in the surgery group, but these metastases would go undetected without pathologic assessment.
Missing potential occult micrometastases in the SBRT group likely contributed to higher regional recurrence rates over time. By improving nodal staging, more patients with occult lymph node metastases who would be undertreated with SBRT may be identified before treatment, the authors said.
What Do Experts Say?
So, is SBRT an option for patients with stage I NSCLC?
Opinions vary.
“If you got one shot for a cure, then you want to do the surgery because that’s what results in a cure,” said Raja Flores, MD, chairman of Thoracic Surgery, Mount Sinai Health System, New York City.
Flores noted that the survival rate with surgery is high in this population. “There’s really nothing out there that can compare,” he said.
In his view, surgery “remains the gold standard.” However, “radiation could be considered in nonsurgical candidates,” he said.
The most recent NCCN guidelines align with Flores’ take. The guidelines say that SBRT is indicated for stage IA-IIA (N0) NSCLC in patients who are deemed “medically inoperable, high surgical risk as determined by thoracic surgeon, and those who decline surgery after thoracic surgical consultation.”
Clifford G. Robinson, MD, agreed. “In the United States, we largely treat patients with SBRT who are medically inoperable or high-risk operable and a much smaller proportion who decline surgery,” said Robinson, professor of radiation oncology and chief of SBRT at Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis. “Many patients who are deemed operable are not offered SBRT.”
Still, for Robinson, determining which patients are best suited for surgery or SBRT remains unclear.
“Retrospective comparisons are fraught with problems because of confounding,” Robinson told this news organization. “That is, the healthier patients get surgery, and the less healthy ones get SBRT. No manner of fancy statistical manipulation can remove that fact.”
In fact, a recent meta-analysis found that the most significant variable predicting whether surgery or SBRT was superior in retrospective studies was whether the author was a surgeon or radiation oncologist.
Robinson noted that multiple randomized trials have attempted to randomize patients with medically operable early-stage NSCLC to surgery or SBRT and failed to accrue, largely due to patients’ “understandable unwillingness to be randomized between operative vs nonoperative interventions when most already prefer one or the other approach.”
Flores highlighted another point of caution about interpreting trial results: Not all early-stage NSCLC behaves similarly. “Some are slow-growing ‘turtles,’ and others are aggressive ‘rabbits’ — and the turtles are usually the ones that have been included in these radiotherapy trials, and that’s the danger,” he said.
While medical operability is the primary factor for deciding the treatment modality for early-stage NSCLC, there are other more subtle factors that can play into the decision.
These include prior surgery or radiotherapy to the chest, prior cancers, and social issues, such as the patient being a primary caregiver for another person and job insecurity, that might make recovery from surgery more challenging. And in rare instances, a patient may be medically fit to undergo surgery, but the cancer is technically challenging to resect due to anatomic issues or prior surgery to the chest, Robinson added.
A Winner?
Results from two ongoing, highly anticipated randomized trials expected in the next several years will hopefully provide additional insights and clarify ongoing uncertainties about the optimal treatment strategies for operable patients with stage I NSCLC.
STABLE-MATES is comparing outcomes after sublobar resection and SBRT in high-risk operable stage I NSCLC, and VALOR is evaluating outcomes after anatomic pulmonary resections and SBRT in patients with stage I NSCLC who have a long life expectancy and are fit enough to tolerate surgery.
But Robinson said his group believes that trying to decide on a winner is a “fool’s errand” and is instead running a pragmatic study across multiple academic and community centers around the United States and Canada where patients choose therapy based on their personal preferences and guidance from their physicians. The researchers will carefully track baseline comorbidity and frailty and assess serial quality-of-life changes over time.
“The goal is to create a calculator that a given patient might use in the future to determine what patients like them would have received, complete with expected outcomes and side effects,” Robinson said.
Robinson cautioned, however, that it “seems unlikely, given the existing literature, that one of the treatments will be truly ‘superior’ to the other one and lead to the ‘losing’ treatment fading away since both are excellent options with pros and cons.”
Aggarwal, Robinson, and Flores had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Approves Pluvicto for Earlier Use in PSMA-Positive Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has expanded the approval for lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan (Pluvicto, Novartis) to include adults with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), who have received androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) therapy and are considered appropriate to delay taxane-based chemotherapy.
The radioligand therapeutic agent was previously approved for the treatment of PSMA-positive mCRPC in patients who have already received ARPI therapy and taxane-based chemotherapy. Approval for the expanded indication was based on efficacy demonstrated in the randomized, open-label, phase 3 PSMAfore trial.
Treatment in 468 patients who progressed on one ARPI and who were deemed appropriate for delay of taxane-based chemotherapy was associated with improved radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) and overall survival (OS) vs a different ARPI.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan (7.4 GBq [200 mCi] every 6 weeks for six doses) or to receive a different ARPI, according to a statement from the FDA. Those who progressed on the new ARPI were allowed to cross over to the experimental therapy arm after progression, and 60% did so.
Median rPFS was 9.3 vs 5.6 months in the experimental and control arms, respectively (hazard ratio [HR], 0.41). Median OS durations were 24.5 and 23.1 months, respectively (HR, 0.91), but the difference in OS did not reach statistical significance.
Adverse reactions were consistent with the known safety profile of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan, which includes possible radiation exposure, myelosuppression, and renal toxicity.
The recommended dose, according to prescribing information, is 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) administered intravenously every 6 weeks for six doses or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
“The earlier indication for Pluvicto could really change our treatment paradigms for patients with mCRPC. It offers a targeted therapy that better delays disease progression compared to a second ARPI,” Michael Morris, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and the principal investigator of the study in the United States stated in a Novartis press release. “This approval is a significant step forward and should open the doorway to a therapy that has clear clinical advantages for the patient with mCRPC who has progressed on one ARPI and has not received chemotherapy.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has expanded the approval for lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan (Pluvicto, Novartis) to include adults with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), who have received androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) therapy and are considered appropriate to delay taxane-based chemotherapy.
The radioligand therapeutic agent was previously approved for the treatment of PSMA-positive mCRPC in patients who have already received ARPI therapy and taxane-based chemotherapy. Approval for the expanded indication was based on efficacy demonstrated in the randomized, open-label, phase 3 PSMAfore trial.
Treatment in 468 patients who progressed on one ARPI and who were deemed appropriate for delay of taxane-based chemotherapy was associated with improved radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) and overall survival (OS) vs a different ARPI.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan (7.4 GBq [200 mCi] every 6 weeks for six doses) or to receive a different ARPI, according to a statement from the FDA. Those who progressed on the new ARPI were allowed to cross over to the experimental therapy arm after progression, and 60% did so.
Median rPFS was 9.3 vs 5.6 months in the experimental and control arms, respectively (hazard ratio [HR], 0.41). Median OS durations were 24.5 and 23.1 months, respectively (HR, 0.91), but the difference in OS did not reach statistical significance.
Adverse reactions were consistent with the known safety profile of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan, which includes possible radiation exposure, myelosuppression, and renal toxicity.
The recommended dose, according to prescribing information, is 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) administered intravenously every 6 weeks for six doses or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
“The earlier indication for Pluvicto could really change our treatment paradigms for patients with mCRPC. It offers a targeted therapy that better delays disease progression compared to a second ARPI,” Michael Morris, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and the principal investigator of the study in the United States stated in a Novartis press release. “This approval is a significant step forward and should open the doorway to a therapy that has clear clinical advantages for the patient with mCRPC who has progressed on one ARPI and has not received chemotherapy.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has expanded the approval for lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan (Pluvicto, Novartis) to include adults with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), who have received androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) therapy and are considered appropriate to delay taxane-based chemotherapy.
The radioligand therapeutic agent was previously approved for the treatment of PSMA-positive mCRPC in patients who have already received ARPI therapy and taxane-based chemotherapy. Approval for the expanded indication was based on efficacy demonstrated in the randomized, open-label, phase 3 PSMAfore trial.
Treatment in 468 patients who progressed on one ARPI and who were deemed appropriate for delay of taxane-based chemotherapy was associated with improved radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) and overall survival (OS) vs a different ARPI.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan (7.4 GBq [200 mCi] every 6 weeks for six doses) or to receive a different ARPI, according to a statement from the FDA. Those who progressed on the new ARPI were allowed to cross over to the experimental therapy arm after progression, and 60% did so.
Median rPFS was 9.3 vs 5.6 months in the experimental and control arms, respectively (hazard ratio [HR], 0.41). Median OS durations were 24.5 and 23.1 months, respectively (HR, 0.91), but the difference in OS did not reach statistical significance.
Adverse reactions were consistent with the known safety profile of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan, which includes possible radiation exposure, myelosuppression, and renal toxicity.
The recommended dose, according to prescribing information, is 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) administered intravenously every 6 weeks for six doses or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
“The earlier indication for Pluvicto could really change our treatment paradigms for patients with mCRPC. It offers a targeted therapy that better delays disease progression compared to a second ARPI,” Michael Morris, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and the principal investigator of the study in the United States stated in a Novartis press release. “This approval is a significant step forward and should open the doorway to a therapy that has clear clinical advantages for the patient with mCRPC who has progressed on one ARPI and has not received chemotherapy.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Gives Clinical Edge to Transperineal Prostate Biopsies
In the largest head-to-head randomized trial of its kind, UK researchers found transperineal prostate biopsies using local anesthesia (LATP) superior to the transrectal approach in detecting clinically significant cancers.
The TRANSLATE study, with more than 1100 patients, found LATP identified 5.7% more cases of clinically significant prostate cancer, defined as Grade Group 2 or higher, than biopsies using transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS).
Previous research comparing the two techniques has focused mainly on rates of infection rather than cancer detection, said Richard Bryant, PhD, a consultant urologist at Nuffield Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Oxford in Oxford, England, who led the trial.
“We decided that the most important thing to look at is the detection rate of clinically significant prostate cancer, because that is why the man is having the biopsy in the first place, rather than to avoid infection, although avoiding infection is of course also important,” Bryant said.
Bryant presented the findings at the 2025 annual congress of the European Association of Urology and his group published the results in The Lancet Oncology.
The TRANSLATE trial was powered to identify a difference in the rate of cancer detection but not factors such as pain and sepsis. Hospitalization after biopsies served as a proxy for sepsis.
Men in the trial were nearly twice as likely to report LATP to be problematic immediately after the procedure than those who underwent transrectal biopsies. These issues included pain, discomfort, and embarrassment.
Two of the 562 men in the LATP group were hospitalized within 35 days of the procedure compared with nine of the 564 in the TRUS group. Bryant said this trend favored LATP, but the difference did not reach statistical significance.
The data on infection and other secondary outcomes were encouraging, but not conclusive, Bryant’s group reported.
Richard Szabo, MD, a prostate biopsy researcher at University of California Irvine, said the reduction in post-biopsy sepsis has been “an additional major advantage” of transperineal over transrectal prostate biopsy.
Almost 90% of men who received LATP had the biopsies without antibiotics — a “bonus,” Bryant said.
Antibiotic stewardship is a major factor in research and policies regarding biopsies in Europe. Transperineal biopsies avoid the rectum and pass needles through the perineum between the anus and the testicles, reducing risk for infection.
Jim Hu, MD, a urologic oncology researcher at Weill Cornell in New York City and the principal investigator on the 2024 PREVENT trial, said three of four randomized trials reported in the past year, including PREVENT and TRANSLATE, have found transperineal biopsies resulted in fewer infections than the transrectal method.
European guidelines call transperineal biopsy the preferred approach based on infection concerns, whereas guidance from the American Urological Association gives equal weight to transperineal and transrectal biopsies.
Badar Mian, MD, a urologist at Albany Med Health System in Albany, New York, said the field should “shift our focus from picking a winner to instead focus on whether prostate biopsy procedures are safe and effective. Patients should be reassured that, while there are trade-offs, both procedures can be performed safely and with a high degree of accuracy.”
The UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Research funded TRANSLATE. Bryant received support from BXTAccelyon to attend biopsy training provided by Guys’ Hospital, in London, England.
Howard Wolinsky is a Chicago-based freelance writer.
A version of this article appeared at Medscape.com.
In the largest head-to-head randomized trial of its kind, UK researchers found transperineal prostate biopsies using local anesthesia (LATP) superior to the transrectal approach in detecting clinically significant cancers.
The TRANSLATE study, with more than 1100 patients, found LATP identified 5.7% more cases of clinically significant prostate cancer, defined as Grade Group 2 or higher, than biopsies using transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS).
Previous research comparing the two techniques has focused mainly on rates of infection rather than cancer detection, said Richard Bryant, PhD, a consultant urologist at Nuffield Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Oxford in Oxford, England, who led the trial.
“We decided that the most important thing to look at is the detection rate of clinically significant prostate cancer, because that is why the man is having the biopsy in the first place, rather than to avoid infection, although avoiding infection is of course also important,” Bryant said.
Bryant presented the findings at the 2025 annual congress of the European Association of Urology and his group published the results in The Lancet Oncology.
The TRANSLATE trial was powered to identify a difference in the rate of cancer detection but not factors such as pain and sepsis. Hospitalization after biopsies served as a proxy for sepsis.
Men in the trial were nearly twice as likely to report LATP to be problematic immediately after the procedure than those who underwent transrectal biopsies. These issues included pain, discomfort, and embarrassment.
Two of the 562 men in the LATP group were hospitalized within 35 days of the procedure compared with nine of the 564 in the TRUS group. Bryant said this trend favored LATP, but the difference did not reach statistical significance.
The data on infection and other secondary outcomes were encouraging, but not conclusive, Bryant’s group reported.
Richard Szabo, MD, a prostate biopsy researcher at University of California Irvine, said the reduction in post-biopsy sepsis has been “an additional major advantage” of transperineal over transrectal prostate biopsy.
Almost 90% of men who received LATP had the biopsies without antibiotics — a “bonus,” Bryant said.
Antibiotic stewardship is a major factor in research and policies regarding biopsies in Europe. Transperineal biopsies avoid the rectum and pass needles through the perineum between the anus and the testicles, reducing risk for infection.
Jim Hu, MD, a urologic oncology researcher at Weill Cornell in New York City and the principal investigator on the 2024 PREVENT trial, said three of four randomized trials reported in the past year, including PREVENT and TRANSLATE, have found transperineal biopsies resulted in fewer infections than the transrectal method.
European guidelines call transperineal biopsy the preferred approach based on infection concerns, whereas guidance from the American Urological Association gives equal weight to transperineal and transrectal biopsies.
Badar Mian, MD, a urologist at Albany Med Health System in Albany, New York, said the field should “shift our focus from picking a winner to instead focus on whether prostate biopsy procedures are safe and effective. Patients should be reassured that, while there are trade-offs, both procedures can be performed safely and with a high degree of accuracy.”
The UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Research funded TRANSLATE. Bryant received support from BXTAccelyon to attend biopsy training provided by Guys’ Hospital, in London, England.
Howard Wolinsky is a Chicago-based freelance writer.
A version of this article appeared at Medscape.com.
In the largest head-to-head randomized trial of its kind, UK researchers found transperineal prostate biopsies using local anesthesia (LATP) superior to the transrectal approach in detecting clinically significant cancers.
The TRANSLATE study, with more than 1100 patients, found LATP identified 5.7% more cases of clinically significant prostate cancer, defined as Grade Group 2 or higher, than biopsies using transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS).
Previous research comparing the two techniques has focused mainly on rates of infection rather than cancer detection, said Richard Bryant, PhD, a consultant urologist at Nuffield Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Oxford in Oxford, England, who led the trial.
“We decided that the most important thing to look at is the detection rate of clinically significant prostate cancer, because that is why the man is having the biopsy in the first place, rather than to avoid infection, although avoiding infection is of course also important,” Bryant said.
Bryant presented the findings at the 2025 annual congress of the European Association of Urology and his group published the results in The Lancet Oncology.
The TRANSLATE trial was powered to identify a difference in the rate of cancer detection but not factors such as pain and sepsis. Hospitalization after biopsies served as a proxy for sepsis.
Men in the trial were nearly twice as likely to report LATP to be problematic immediately after the procedure than those who underwent transrectal biopsies. These issues included pain, discomfort, and embarrassment.
Two of the 562 men in the LATP group were hospitalized within 35 days of the procedure compared with nine of the 564 in the TRUS group. Bryant said this trend favored LATP, but the difference did not reach statistical significance.
The data on infection and other secondary outcomes were encouraging, but not conclusive, Bryant’s group reported.
Richard Szabo, MD, a prostate biopsy researcher at University of California Irvine, said the reduction in post-biopsy sepsis has been “an additional major advantage” of transperineal over transrectal prostate biopsy.
Almost 90% of men who received LATP had the biopsies without antibiotics — a “bonus,” Bryant said.
Antibiotic stewardship is a major factor in research and policies regarding biopsies in Europe. Transperineal biopsies avoid the rectum and pass needles through the perineum between the anus and the testicles, reducing risk for infection.
Jim Hu, MD, a urologic oncology researcher at Weill Cornell in New York City and the principal investigator on the 2024 PREVENT trial, said three of four randomized trials reported in the past year, including PREVENT and TRANSLATE, have found transperineal biopsies resulted in fewer infections than the transrectal method.
European guidelines call transperineal biopsy the preferred approach based on infection concerns, whereas guidance from the American Urological Association gives equal weight to transperineal and transrectal biopsies.
Badar Mian, MD, a urologist at Albany Med Health System in Albany, New York, said the field should “shift our focus from picking a winner to instead focus on whether prostate biopsy procedures are safe and effective. Patients should be reassured that, while there are trade-offs, both procedures can be performed safely and with a high degree of accuracy.”
The UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Research funded TRANSLATE. Bryant received support from BXTAccelyon to attend biopsy training provided by Guys’ Hospital, in London, England.
Howard Wolinsky is a Chicago-based freelance writer.
A version of this article appeared at Medscape.com.
A Better Biopsy for Prostate Cancer?
Micro-ultrasound–guided biopsies were found for the first time to be “noninferior” to MRI-guided procedures, according to new research presented at the 2025 annual congress of the European Association of Urology.
The OPTIMUM study found 4.5% more clinically significant cancers among men who underwent micro-ultrasound–guided biopsies of the prostate than in those scanned using MRI.
“The take-home message is that men being worked up for an elevated PSA [prostate-specific antigen] or an abnormal digital rectal examination who are at increased risk of prostate cancer may safely undergo a micro-ultrasound–guided biopsy rather than an MRI-guided biopsy,” said Adam Kinnaird, MD, PhD, the Frank and Carla Sojonky Chair in Prostate Cancer Research at the University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, and principal investigator of the study.
Micro-ultrasound can image to as small as 70 μm, ie, the width of a human hair.
OPTIMUM was an international, open-label, randomized, noninferiority trial in 20 centers in eight countries of men with clinical suspicion of prostate cancer, elevated PSAs, abnormal digital rectal exams, or a combination of these risk factors. None of the men previously had undergone biopsies.
The study had three arms to which men were assigned randomly: Micro-ultrasound–guided biopsy (n = 121); biopsies guided by micro-ultrasound and fusion MRI (n = 226), and MRI plus conventional ultrasound–guided biopsy (n = 331).
Subjects had a median age of 65 years and a median PSA level of 6.9 ng/mL; 83% self-identified as White individuals.
“Micro-ultrasound was found to be no worse than MRI at the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. We don’t show it is equivalent. We don’t show it better. We show it is not worse,” Kinnaird said.
The study, funded by Exact Imaging, which makes the ExactVu micro-ultrasound platform, appeared simultaneously in JAMA.
Laurence Klotz, MD, the Sunnybrook Chair of Prostate Cancer Research at the University of Toronto Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, and senior researcher on the OPTIMUM trial, said as the incidence of prostate cancer rises globally, micro-ultrasound may be of particular value in low-income and middle-income countries where MRI is not widely available.
“It’s extremely appealing in places that can’t offer MRI to everyone, but I think it also will have a role going forward in regions where there is no problem about getting access to MRI,” Klotz told Medscape Medical News.
This group is next studying the financial aspects of the technology, he added.
Gerald Andriole, MD, then urology chief at Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, Missouri, designed the original studies of the ExactVu system, which the US Food and Drug Administration approved in 2017.
Andriole, now chief medical officer of Prostatype Genomics, said MRIs are costly, subjective, and uncomfortable for many patients, due to claustrophobia and obesity, requiring complicated co-registration procedures to perform an accurate targeted biopsy into the most worrisome regions of the prostate. “Proceeding directly to a micro-ultrasound study avoids these impediments to discovering whether the patient has clinically significant cancer,” he said.
Micro-ultrasound testing involves a single visit to a urologist whereas MRI requires two trips for the patient — one to the urologist and the other to a radiologist, Klotz said. “It’s one-stop shopping,” he said. “So, the patient has his micro-ultrasound. If there’s a target found, he then does the targeted biopsy.”
Klotz said micro-ultrasound helps patients avoid the expense and health risks of gadolinium in contrast with MRIs.
“I don’t think micro-ultrasound is going to replace MRIs,” he said. “I think they’re somewhat complementary. You get cases where they’re visible on MRI and not visible on micro-ultrasound and vice versa.”
The researchers received a grant from Exact Imaging.
A version of this article appeared at Medscape.com.
Howard Wolinsky is a Chicago-based freelance writer.
Micro-ultrasound–guided biopsies were found for the first time to be “noninferior” to MRI-guided procedures, according to new research presented at the 2025 annual congress of the European Association of Urology.
The OPTIMUM study found 4.5% more clinically significant cancers among men who underwent micro-ultrasound–guided biopsies of the prostate than in those scanned using MRI.
“The take-home message is that men being worked up for an elevated PSA [prostate-specific antigen] or an abnormal digital rectal examination who are at increased risk of prostate cancer may safely undergo a micro-ultrasound–guided biopsy rather than an MRI-guided biopsy,” said Adam Kinnaird, MD, PhD, the Frank and Carla Sojonky Chair in Prostate Cancer Research at the University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, and principal investigator of the study.
Micro-ultrasound can image to as small as 70 μm, ie, the width of a human hair.
OPTIMUM was an international, open-label, randomized, noninferiority trial in 20 centers in eight countries of men with clinical suspicion of prostate cancer, elevated PSAs, abnormal digital rectal exams, or a combination of these risk factors. None of the men previously had undergone biopsies.
The study had three arms to which men were assigned randomly: Micro-ultrasound–guided biopsy (n = 121); biopsies guided by micro-ultrasound and fusion MRI (n = 226), and MRI plus conventional ultrasound–guided biopsy (n = 331).
Subjects had a median age of 65 years and a median PSA level of 6.9 ng/mL; 83% self-identified as White individuals.
“Micro-ultrasound was found to be no worse than MRI at the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. We don’t show it is equivalent. We don’t show it better. We show it is not worse,” Kinnaird said.
The study, funded by Exact Imaging, which makes the ExactVu micro-ultrasound platform, appeared simultaneously in JAMA.
Laurence Klotz, MD, the Sunnybrook Chair of Prostate Cancer Research at the University of Toronto Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, and senior researcher on the OPTIMUM trial, said as the incidence of prostate cancer rises globally, micro-ultrasound may be of particular value in low-income and middle-income countries where MRI is not widely available.
“It’s extremely appealing in places that can’t offer MRI to everyone, but I think it also will have a role going forward in regions where there is no problem about getting access to MRI,” Klotz told Medscape Medical News.
This group is next studying the financial aspects of the technology, he added.
Gerald Andriole, MD, then urology chief at Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, Missouri, designed the original studies of the ExactVu system, which the US Food and Drug Administration approved in 2017.
Andriole, now chief medical officer of Prostatype Genomics, said MRIs are costly, subjective, and uncomfortable for many patients, due to claustrophobia and obesity, requiring complicated co-registration procedures to perform an accurate targeted biopsy into the most worrisome regions of the prostate. “Proceeding directly to a micro-ultrasound study avoids these impediments to discovering whether the patient has clinically significant cancer,” he said.
Micro-ultrasound testing involves a single visit to a urologist whereas MRI requires two trips for the patient — one to the urologist and the other to a radiologist, Klotz said. “It’s one-stop shopping,” he said. “So, the patient has his micro-ultrasound. If there’s a target found, he then does the targeted biopsy.”
Klotz said micro-ultrasound helps patients avoid the expense and health risks of gadolinium in contrast with MRIs.
“I don’t think micro-ultrasound is going to replace MRIs,” he said. “I think they’re somewhat complementary. You get cases where they’re visible on MRI and not visible on micro-ultrasound and vice versa.”
The researchers received a grant from Exact Imaging.
A version of this article appeared at Medscape.com.
Howard Wolinsky is a Chicago-based freelance writer.
Micro-ultrasound–guided biopsies were found for the first time to be “noninferior” to MRI-guided procedures, according to new research presented at the 2025 annual congress of the European Association of Urology.
The OPTIMUM study found 4.5% more clinically significant cancers among men who underwent micro-ultrasound–guided biopsies of the prostate than in those scanned using MRI.
“The take-home message is that men being worked up for an elevated PSA [prostate-specific antigen] or an abnormal digital rectal examination who are at increased risk of prostate cancer may safely undergo a micro-ultrasound–guided biopsy rather than an MRI-guided biopsy,” said Adam Kinnaird, MD, PhD, the Frank and Carla Sojonky Chair in Prostate Cancer Research at the University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, and principal investigator of the study.
Micro-ultrasound can image to as small as 70 μm, ie, the width of a human hair.
OPTIMUM was an international, open-label, randomized, noninferiority trial in 20 centers in eight countries of men with clinical suspicion of prostate cancer, elevated PSAs, abnormal digital rectal exams, or a combination of these risk factors. None of the men previously had undergone biopsies.
The study had three arms to which men were assigned randomly: Micro-ultrasound–guided biopsy (n = 121); biopsies guided by micro-ultrasound and fusion MRI (n = 226), and MRI plus conventional ultrasound–guided biopsy (n = 331).
Subjects had a median age of 65 years and a median PSA level of 6.9 ng/mL; 83% self-identified as White individuals.
“Micro-ultrasound was found to be no worse than MRI at the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. We don’t show it is equivalent. We don’t show it better. We show it is not worse,” Kinnaird said.
The study, funded by Exact Imaging, which makes the ExactVu micro-ultrasound platform, appeared simultaneously in JAMA.
Laurence Klotz, MD, the Sunnybrook Chair of Prostate Cancer Research at the University of Toronto Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, and senior researcher on the OPTIMUM trial, said as the incidence of prostate cancer rises globally, micro-ultrasound may be of particular value in low-income and middle-income countries where MRI is not widely available.
“It’s extremely appealing in places that can’t offer MRI to everyone, but I think it also will have a role going forward in regions where there is no problem about getting access to MRI,” Klotz told Medscape Medical News.
This group is next studying the financial aspects of the technology, he added.
Gerald Andriole, MD, then urology chief at Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, Missouri, designed the original studies of the ExactVu system, which the US Food and Drug Administration approved in 2017.
Andriole, now chief medical officer of Prostatype Genomics, said MRIs are costly, subjective, and uncomfortable for many patients, due to claustrophobia and obesity, requiring complicated co-registration procedures to perform an accurate targeted biopsy into the most worrisome regions of the prostate. “Proceeding directly to a micro-ultrasound study avoids these impediments to discovering whether the patient has clinically significant cancer,” he said.
Micro-ultrasound testing involves a single visit to a urologist whereas MRI requires two trips for the patient — one to the urologist and the other to a radiologist, Klotz said. “It’s one-stop shopping,” he said. “So, the patient has his micro-ultrasound. If there’s a target found, he then does the targeted biopsy.”
Klotz said micro-ultrasound helps patients avoid the expense and health risks of gadolinium in contrast with MRIs.
“I don’t think micro-ultrasound is going to replace MRIs,” he said. “I think they’re somewhat complementary. You get cases where they’re visible on MRI and not visible on micro-ultrasound and vice versa.”
The researchers received a grant from Exact Imaging.
A version of this article appeared at Medscape.com.
Howard Wolinsky is a Chicago-based freelance writer.
Inadequate Grading of Intraductal Carcinoma of the Prostate
BOSTON — Solid intraductal carcinoma of the prostate (IDC-P) is associated with significantly worse outcomes compared with conventional Gleason grade 5 prostate cancers and is more commonly present in metastatic than nonmetastatic cancers, according to two studies presented this week at the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology (USCAP) 2025 Annual Meeting.
“Our findings suggest that solid IDC-P is more aggressive than Gleason grade 5 conventional prostate adenocarcinoma or cribriform IDC-P,” and it may therefore be better not to consider it as a grade 5 pattern, said first author of one of the studies, Hangchuan Shi, MD, PhD, of the University of Rochester Medical Center, in Rochester, New York.
Although IDC-P — reported in about 20% of men with prostate cancer — is known to be associated with poorer response to treatment, there is a debate over whether to grade the entity with Gleason scoring or not.
The International Society of Urological Pathology recommends incorporating IDC-P into the Gleason score, while the Genitourinary Pathology Society does not.
To evaluate the prognostic significance of solid IDC-P compared with Gleason grade 5 conventional prostate cancer, Shi and his colleagues identified 115 cases in the surgical pathology database at the University of Rochester Medical Center between 2008 and 2015 involving Gleason grade 5 conventional prostatic adenocarcinoma as a primary, secondary, or tertiary pattern, as well as cribriform IDC-P.
The researchers excluded cases showing comedonecrosis within IDC-P, due to the potential for worse outcomes.
Of the grade 5 conventional prostate cancer cases with cribriform carcinoma, 28 (24.3%) had solid nest pattern IDC-P. Patients with and without solid IDC-P had a matching mean age of about 64 years, and their mean preoperative PSA was about 12.27 ng/mL.
Adjuvant therapy prior to recurrence was significantly more common in those who had solid IDC-P (60.7% vs 34.5%; P = .016).
Compared with the conventional prostate cancer cases, those with solid IDC-P had a significantly higher incidence of lymph node metastasis (P = .014) and had larger estimated tumor volume (P = .011).
There were no significant differences in other clinicopathologic features, such as preoperative prostate-specific antigen, grade group, pT stage, and surgical margin status.
After adjustment for key factors in a multivariable analysis, solid IDC-P was significantly associated with poorer recurrence-free survival (P = .007), and poorer cancer-specific survival (P = .004).
Finally, solid IDC-P was an independent predictor of recurrence (hazard ratio [HR] 1.960; P = .031), whereas other measures, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA), cancer grade, pT, lymph node metastasis, surgical and tumor volume were not significant factors.
“We found the solid IDC-P patients had almost two-times the risk of recurrence compared with the patients without solid IDC-P in our study,” Shi said.
The findings underscore the importance of accurately identifying IDC-P, senior author Hiroshi Miyamoto, MD, PhD, director of Genitourinary Pathology at School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York, told Medscape Medical News.
“It may be difficult for some pathologists, especially those who have no specific training in genitourinary pathology, to adequately recognize” this form of cancer, he said.
Although it is recognized as an aggressive form of prostate cancer, “based on our studies, we believe that it is inadequate to grade IDC-P” as a Gleason grade 5 cancer, Miyamoto added.
IDC More Common in Metastases
Poorer outcomes associated with IDC-P were further described in a post hoc sub-analysis of the phase 3, prospective PATRON clinical trial that is evaluating prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET-CT–guided intensification of therapy.
In the multicenter trial, 825 patients were stratified into three cohorts: High-risk patients receiving radiation therapy (45%), high-risk patients receiving salvage radiation therapy post-radical prostatectomy (47%), and those receiving a radical prostatectomy (8%).
The patients in all three cohorts were randomized 1:1 to receive imaging with or without PSMA PET-CT.
IDC-P and/or cribriform carcinoma were present among 342 patients in the PSMA PET-CT group including 48% of high-risk patients receiving radiotherapy, 42% of high-risk patients receiving salvage radiation therapy post-radical prostatectomy, and 40% of those receiving a radical prostatectomy.
IDC-P was reported in 64% of cases with metastases detected by PSMA PET-CT compared with just 36% of cases without metastasis (P = .008), with the ratios being similar in each individual patient cohort.
Of note, the association between the presence of IDC-P and metastases was not observed when IDC-P and cribriform carcinoma were combined — IDC-P and/or cribriform carcinoma was detected in 54% of cases with PSMA PET-CT–detectable metastasis and in 46% of cases without metastasis (P = .362).
The first author Dominique Trudel, MD, PhD, of the Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, said the findings add to understanding of IDC-P’s relationship with poorer outcomes.
“As pathologists, we know that IDC is associated with poor outcomes and that men with IDC who are treated with standard therapies do benefit from them, but they never benefit as much as men without IDC,” she told Medscape Medical News.
As the study is ongoing, “in approximately 4-5 years, we will know how much of a difference IDC-P makes in outcomes after treatment,” Trudel noted.
The take-home message from the collective research should be that “IDC-P matters,” she said.
“I think that if your patient has IDC-P and [cribriform carcinoma], it is worth at least asking someone from an academic center to see what the treatment options are. We know that some radiation oncologists are increasing doses for IDC-P. It is empiric, but they’re doing it,” she explained.
The authors had no disclosures to report.
The article first appeared in Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Solid intraductal carcinoma of the prostate (IDC-P) is associated with significantly worse outcomes compared with conventional Gleason grade 5 prostate cancers and is more commonly present in metastatic than nonmetastatic cancers, according to two studies presented this week at the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology (USCAP) 2025 Annual Meeting.
“Our findings suggest that solid IDC-P is more aggressive than Gleason grade 5 conventional prostate adenocarcinoma or cribriform IDC-P,” and it may therefore be better not to consider it as a grade 5 pattern, said first author of one of the studies, Hangchuan Shi, MD, PhD, of the University of Rochester Medical Center, in Rochester, New York.
Although IDC-P — reported in about 20% of men with prostate cancer — is known to be associated with poorer response to treatment, there is a debate over whether to grade the entity with Gleason scoring or not.
The International Society of Urological Pathology recommends incorporating IDC-P into the Gleason score, while the Genitourinary Pathology Society does not.
To evaluate the prognostic significance of solid IDC-P compared with Gleason grade 5 conventional prostate cancer, Shi and his colleagues identified 115 cases in the surgical pathology database at the University of Rochester Medical Center between 2008 and 2015 involving Gleason grade 5 conventional prostatic adenocarcinoma as a primary, secondary, or tertiary pattern, as well as cribriform IDC-P.
The researchers excluded cases showing comedonecrosis within IDC-P, due to the potential for worse outcomes.
Of the grade 5 conventional prostate cancer cases with cribriform carcinoma, 28 (24.3%) had solid nest pattern IDC-P. Patients with and without solid IDC-P had a matching mean age of about 64 years, and their mean preoperative PSA was about 12.27 ng/mL.
Adjuvant therapy prior to recurrence was significantly more common in those who had solid IDC-P (60.7% vs 34.5%; P = .016).
Compared with the conventional prostate cancer cases, those with solid IDC-P had a significantly higher incidence of lymph node metastasis (P = .014) and had larger estimated tumor volume (P = .011).
There were no significant differences in other clinicopathologic features, such as preoperative prostate-specific antigen, grade group, pT stage, and surgical margin status.
After adjustment for key factors in a multivariable analysis, solid IDC-P was significantly associated with poorer recurrence-free survival (P = .007), and poorer cancer-specific survival (P = .004).
Finally, solid IDC-P was an independent predictor of recurrence (hazard ratio [HR] 1.960; P = .031), whereas other measures, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA), cancer grade, pT, lymph node metastasis, surgical and tumor volume were not significant factors.
“We found the solid IDC-P patients had almost two-times the risk of recurrence compared with the patients without solid IDC-P in our study,” Shi said.
The findings underscore the importance of accurately identifying IDC-P, senior author Hiroshi Miyamoto, MD, PhD, director of Genitourinary Pathology at School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York, told Medscape Medical News.
“It may be difficult for some pathologists, especially those who have no specific training in genitourinary pathology, to adequately recognize” this form of cancer, he said.
Although it is recognized as an aggressive form of prostate cancer, “based on our studies, we believe that it is inadequate to grade IDC-P” as a Gleason grade 5 cancer, Miyamoto added.
IDC More Common in Metastases
Poorer outcomes associated with IDC-P were further described in a post hoc sub-analysis of the phase 3, prospective PATRON clinical trial that is evaluating prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET-CT–guided intensification of therapy.
In the multicenter trial, 825 patients were stratified into three cohorts: High-risk patients receiving radiation therapy (45%), high-risk patients receiving salvage radiation therapy post-radical prostatectomy (47%), and those receiving a radical prostatectomy (8%).
The patients in all three cohorts were randomized 1:1 to receive imaging with or without PSMA PET-CT.
IDC-P and/or cribriform carcinoma were present among 342 patients in the PSMA PET-CT group including 48% of high-risk patients receiving radiotherapy, 42% of high-risk patients receiving salvage radiation therapy post-radical prostatectomy, and 40% of those receiving a radical prostatectomy.
IDC-P was reported in 64% of cases with metastases detected by PSMA PET-CT compared with just 36% of cases without metastasis (P = .008), with the ratios being similar in each individual patient cohort.
Of note, the association between the presence of IDC-P and metastases was not observed when IDC-P and cribriform carcinoma were combined — IDC-P and/or cribriform carcinoma was detected in 54% of cases with PSMA PET-CT–detectable metastasis and in 46% of cases without metastasis (P = .362).
The first author Dominique Trudel, MD, PhD, of the Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, said the findings add to understanding of IDC-P’s relationship with poorer outcomes.
“As pathologists, we know that IDC is associated with poor outcomes and that men with IDC who are treated with standard therapies do benefit from them, but they never benefit as much as men without IDC,” she told Medscape Medical News.
As the study is ongoing, “in approximately 4-5 years, we will know how much of a difference IDC-P makes in outcomes after treatment,” Trudel noted.
The take-home message from the collective research should be that “IDC-P matters,” she said.
“I think that if your patient has IDC-P and [cribriform carcinoma], it is worth at least asking someone from an academic center to see what the treatment options are. We know that some radiation oncologists are increasing doses for IDC-P. It is empiric, but they’re doing it,” she explained.
The authors had no disclosures to report.
The article first appeared in Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Solid intraductal carcinoma of the prostate (IDC-P) is associated with significantly worse outcomes compared with conventional Gleason grade 5 prostate cancers and is more commonly present in metastatic than nonmetastatic cancers, according to two studies presented this week at the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology (USCAP) 2025 Annual Meeting.
“Our findings suggest that solid IDC-P is more aggressive than Gleason grade 5 conventional prostate adenocarcinoma or cribriform IDC-P,” and it may therefore be better not to consider it as a grade 5 pattern, said first author of one of the studies, Hangchuan Shi, MD, PhD, of the University of Rochester Medical Center, in Rochester, New York.
Although IDC-P — reported in about 20% of men with prostate cancer — is known to be associated with poorer response to treatment, there is a debate over whether to grade the entity with Gleason scoring or not.
The International Society of Urological Pathology recommends incorporating IDC-P into the Gleason score, while the Genitourinary Pathology Society does not.
To evaluate the prognostic significance of solid IDC-P compared with Gleason grade 5 conventional prostate cancer, Shi and his colleagues identified 115 cases in the surgical pathology database at the University of Rochester Medical Center between 2008 and 2015 involving Gleason grade 5 conventional prostatic adenocarcinoma as a primary, secondary, or tertiary pattern, as well as cribriform IDC-P.
The researchers excluded cases showing comedonecrosis within IDC-P, due to the potential for worse outcomes.
Of the grade 5 conventional prostate cancer cases with cribriform carcinoma, 28 (24.3%) had solid nest pattern IDC-P. Patients with and without solid IDC-P had a matching mean age of about 64 years, and their mean preoperative PSA was about 12.27 ng/mL.
Adjuvant therapy prior to recurrence was significantly more common in those who had solid IDC-P (60.7% vs 34.5%; P = .016).
Compared with the conventional prostate cancer cases, those with solid IDC-P had a significantly higher incidence of lymph node metastasis (P = .014) and had larger estimated tumor volume (P = .011).
There were no significant differences in other clinicopathologic features, such as preoperative prostate-specific antigen, grade group, pT stage, and surgical margin status.
After adjustment for key factors in a multivariable analysis, solid IDC-P was significantly associated with poorer recurrence-free survival (P = .007), and poorer cancer-specific survival (P = .004).
Finally, solid IDC-P was an independent predictor of recurrence (hazard ratio [HR] 1.960; P = .031), whereas other measures, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA), cancer grade, pT, lymph node metastasis, surgical and tumor volume were not significant factors.
“We found the solid IDC-P patients had almost two-times the risk of recurrence compared with the patients without solid IDC-P in our study,” Shi said.
The findings underscore the importance of accurately identifying IDC-P, senior author Hiroshi Miyamoto, MD, PhD, director of Genitourinary Pathology at School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York, told Medscape Medical News.
“It may be difficult for some pathologists, especially those who have no specific training in genitourinary pathology, to adequately recognize” this form of cancer, he said.
Although it is recognized as an aggressive form of prostate cancer, “based on our studies, we believe that it is inadequate to grade IDC-P” as a Gleason grade 5 cancer, Miyamoto added.
IDC More Common in Metastases
Poorer outcomes associated with IDC-P were further described in a post hoc sub-analysis of the phase 3, prospective PATRON clinical trial that is evaluating prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET-CT–guided intensification of therapy.
In the multicenter trial, 825 patients were stratified into three cohorts: High-risk patients receiving radiation therapy (45%), high-risk patients receiving salvage radiation therapy post-radical prostatectomy (47%), and those receiving a radical prostatectomy (8%).
The patients in all three cohorts were randomized 1:1 to receive imaging with or without PSMA PET-CT.
IDC-P and/or cribriform carcinoma were present among 342 patients in the PSMA PET-CT group including 48% of high-risk patients receiving radiotherapy, 42% of high-risk patients receiving salvage radiation therapy post-radical prostatectomy, and 40% of those receiving a radical prostatectomy.
IDC-P was reported in 64% of cases with metastases detected by PSMA PET-CT compared with just 36% of cases without metastasis (P = .008), with the ratios being similar in each individual patient cohort.
Of note, the association between the presence of IDC-P and metastases was not observed when IDC-P and cribriform carcinoma were combined — IDC-P and/or cribriform carcinoma was detected in 54% of cases with PSMA PET-CT–detectable metastasis and in 46% of cases without metastasis (P = .362).
The first author Dominique Trudel, MD, PhD, of the Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, said the findings add to understanding of IDC-P’s relationship with poorer outcomes.
“As pathologists, we know that IDC is associated with poor outcomes and that men with IDC who are treated with standard therapies do benefit from them, but they never benefit as much as men without IDC,” she told Medscape Medical News.
As the study is ongoing, “in approximately 4-5 years, we will know how much of a difference IDC-P makes in outcomes after treatment,” Trudel noted.
The take-home message from the collective research should be that “IDC-P matters,” she said.
“I think that if your patient has IDC-P and [cribriform carcinoma], it is worth at least asking someone from an academic center to see what the treatment options are. We know that some radiation oncologists are increasing doses for IDC-P. It is empiric, but they’re doing it,” she explained.
The authors had no disclosures to report.
The article first appeared in Medscape.com.
VA Shake-up Disrupts Mental Health Services for Some US Veterans
SAN FRANCISCO (Reuters) — Joey Cortez, who served 24 years in the US Air Force, had been waiting since August to see a mental health specialist from the Department of Veterans’ Affairs, when he experienced a fresh jolt of anxiety.
Cortez was fired last month from his human resources job at the agency - one of about 2400 employees who lost their jobs at Veterans’ Affairs (VA) in the first wave of President Donald Trump’s efforts to shrink the federal workforce.
“Once the firings happened and I was terminated, I started having panic attacks to the point where I black out,” Cortez, who suffers from post-traumatic stress disorder, told Reuters. The layoff is also making it harder to maintain his sobriety, as a recovering alcoholic.
“Not a day has gone by since I was fired that I haven’t thought about picking up a bottle,” said Cortez.
After losing his job, Cortez asked the VA to expedite his wait for a therapist and was told there was no record of his request, he said. After a month of calls to the agency, he got an appointment for this August, one year after he started the process. Then the VA offered him an appointment next week because another patient had canceled.
The VA provides health care to 9.31 million US veterans at hundreds of medical centers, clinics, and nursing homes across the country.
It also faces complex problems.
“The VA has bloat. There are redundancies. There are places where we have questioned the administration of care and asked, does it need to be the way it is?” Pat Murray, the legislative director for the Veterans of Foreign Wars, which represents Americans who have fought overseas, said in an interview.
The Trump administration plans additional cuts to the VA of more than 80,000 personnel, according to an internal memo obtained by Reuters. The agency has also announced it is phasing out telework.
Reuters spoke to nine current and former VA employees in California, Oregon, Texas, and the Washington D.C. area who said the changes were further disrupting some mental health services and fueling anxieties among those who provide and rely on them.
The VA employees — who include six mental health professionals and three people in leadership positions — described cancellations of some in-person and telehealth appointments; confusion over staffing of a crisis hot-line; and professionals conducting telehealth visits in makeshift meeting rooms inside VA buildings.
They spoke on the condition of anonymity, because they were not authorized to speak with the media.
STAFFING SHORTAGES
A former employee at the VA’s Office of Inspector General, who is also a veteran, said any future large-scale staffing cuts would likely worsen shortages and impact the quality of care.
“There’s no way to take a scalpel and do it appropriately that quickly,” he said.
VA spokesperson Peter Kasperowicz told Reuters mental health professionals, such as psychologists and social workers, were not included in February’s staffing cuts, and the agency is working to recruit mental health providers and improve wait times.
He did not specify how many support staff for these providers had been affected.
Last week, two federal judges ordered the VA and other federal agencies to reinstate thousands of fired probationary workers. Cortez’s pay was reinstated but he was told not to return to work.
The Veterans Health Administration, the branch of the VA that provides healthcare, has experienced severe staffing shortages since 2015, especially among mental health professionals, according to an OIG report last year.
Veterans often benefit from specialized services to treat anxiety, trauma, depression and substance abuse. The proportion of veterans receiving mental health services rose to 31% in 2022 from 20% in 2007, according to the VA. Suicide among veterans is twice the rate of Americans overall.
The VFW’s Murray said his organization supports a thorough review of the VA’s mental health services, but it needs to be done carefully, “not with a chainsaw.”
‘THE MOOD IS SO LOW’
In recent years, the agency had encouraged remote work to help expand access to telehealth services and reduce wait times, especially in rural areas where recruiting providers is difficult.
The VA’s Kasperowicz said that, while providers will need to return to VA facilities, veterans will be able to access telehealth appointments.
He did not directly address questions about why mental health providers needed to return to the office.
“The VA will make accommodations as needed to ensure employees have enough space to work and will always ensure that Veterans’ access to benefits and services remains uninterrupted as employees return to in-person work,” Kasperowicz said.
In the last few weeks, demand for services among veterans who are VA employees has also risen, one of the mental health professionals, a social worker, told Reuters. A quarter of VA employees are veterans.
The social worker said he is meeting with two to three VA employees a week who are seeking access to mental health care, citing stress and the fear that they will lose their jobs.
“People are calling out sick. People are ill with stress and worry. The mood is so low.”
A mental health supervisor in California described scrambling to cover the caseload of a remote worker who had to cancel appointments with more than a dozen veterans, because she could not access a VA facility.
VA employees in the Washington area and in Oregon said mental health professionals were unsure if they were allowed to answer calls from the VA’s crisis hot-line if they were not physically in an office, because they had been instructed not to conduct work outside of a facility.
“People are nervous to be on-call,” said a supervisor of mental health providers in the Washington area. “The system is under a lot of duress.”
The VA told Reuters that crisis line workers are exempt from the return-to-office policy, and that staff continue to respond quickly to nearly 3000 calls daily.
Therapists returning to the office are struggling to find private meeting rooms at some VA facilities, according to four of the mental health professionals interviewed by Reuters.
They described medical and mental health professionals converting closets and conference rooms into offices to comply with the mandate to conduct telehealth visits from VA facilities. They expressed concerns that the crowded rooms could violate patient privacy rights.
“We are scrambling to find space,” said a provider in California. “Veterans are going without until we can find spaces for these providers.”
Reuters was unable to independently verify the accounts of overcrowding. Kasperowicz said the agency’s “policy is to bring as many employees back to the office as space permits.”
(Reporting by Robin Respaut in San Francisco; additional reporting by Julia Harte in New York and Gabriella Borter in D.C.; Editing by Michele Gershberg and Suzanne Goldenberg)
SAN FRANCISCO (Reuters) — Joey Cortez, who served 24 years in the US Air Force, had been waiting since August to see a mental health specialist from the Department of Veterans’ Affairs, when he experienced a fresh jolt of anxiety.
Cortez was fired last month from his human resources job at the agency - one of about 2400 employees who lost their jobs at Veterans’ Affairs (VA) in the first wave of President Donald Trump’s efforts to shrink the federal workforce.
“Once the firings happened and I was terminated, I started having panic attacks to the point where I black out,” Cortez, who suffers from post-traumatic stress disorder, told Reuters. The layoff is also making it harder to maintain his sobriety, as a recovering alcoholic.
“Not a day has gone by since I was fired that I haven’t thought about picking up a bottle,” said Cortez.
After losing his job, Cortez asked the VA to expedite his wait for a therapist and was told there was no record of his request, he said. After a month of calls to the agency, he got an appointment for this August, one year after he started the process. Then the VA offered him an appointment next week because another patient had canceled.
The VA provides health care to 9.31 million US veterans at hundreds of medical centers, clinics, and nursing homes across the country.
It also faces complex problems.
“The VA has bloat. There are redundancies. There are places where we have questioned the administration of care and asked, does it need to be the way it is?” Pat Murray, the legislative director for the Veterans of Foreign Wars, which represents Americans who have fought overseas, said in an interview.
The Trump administration plans additional cuts to the VA of more than 80,000 personnel, according to an internal memo obtained by Reuters. The agency has also announced it is phasing out telework.
Reuters spoke to nine current and former VA employees in California, Oregon, Texas, and the Washington D.C. area who said the changes were further disrupting some mental health services and fueling anxieties among those who provide and rely on them.
The VA employees — who include six mental health professionals and three people in leadership positions — described cancellations of some in-person and telehealth appointments; confusion over staffing of a crisis hot-line; and professionals conducting telehealth visits in makeshift meeting rooms inside VA buildings.
They spoke on the condition of anonymity, because they were not authorized to speak with the media.
STAFFING SHORTAGES
A former employee at the VA’s Office of Inspector General, who is also a veteran, said any future large-scale staffing cuts would likely worsen shortages and impact the quality of care.
“There’s no way to take a scalpel and do it appropriately that quickly,” he said.
VA spokesperson Peter Kasperowicz told Reuters mental health professionals, such as psychologists and social workers, were not included in February’s staffing cuts, and the agency is working to recruit mental health providers and improve wait times.
He did not specify how many support staff for these providers had been affected.
Last week, two federal judges ordered the VA and other federal agencies to reinstate thousands of fired probationary workers. Cortez’s pay was reinstated but he was told not to return to work.
The Veterans Health Administration, the branch of the VA that provides healthcare, has experienced severe staffing shortages since 2015, especially among mental health professionals, according to an OIG report last year.
Veterans often benefit from specialized services to treat anxiety, trauma, depression and substance abuse. The proportion of veterans receiving mental health services rose to 31% in 2022 from 20% in 2007, according to the VA. Suicide among veterans is twice the rate of Americans overall.
The VFW’s Murray said his organization supports a thorough review of the VA’s mental health services, but it needs to be done carefully, “not with a chainsaw.”
‘THE MOOD IS SO LOW’
In recent years, the agency had encouraged remote work to help expand access to telehealth services and reduce wait times, especially in rural areas where recruiting providers is difficult.
The VA’s Kasperowicz said that, while providers will need to return to VA facilities, veterans will be able to access telehealth appointments.
He did not directly address questions about why mental health providers needed to return to the office.
“The VA will make accommodations as needed to ensure employees have enough space to work and will always ensure that Veterans’ access to benefits and services remains uninterrupted as employees return to in-person work,” Kasperowicz said.
In the last few weeks, demand for services among veterans who are VA employees has also risen, one of the mental health professionals, a social worker, told Reuters. A quarter of VA employees are veterans.
The social worker said he is meeting with two to three VA employees a week who are seeking access to mental health care, citing stress and the fear that they will lose their jobs.
“People are calling out sick. People are ill with stress and worry. The mood is so low.”
A mental health supervisor in California described scrambling to cover the caseload of a remote worker who had to cancel appointments with more than a dozen veterans, because she could not access a VA facility.
VA employees in the Washington area and in Oregon said mental health professionals were unsure if they were allowed to answer calls from the VA’s crisis hot-line if they were not physically in an office, because they had been instructed not to conduct work outside of a facility.
“People are nervous to be on-call,” said a supervisor of mental health providers in the Washington area. “The system is under a lot of duress.”
The VA told Reuters that crisis line workers are exempt from the return-to-office policy, and that staff continue to respond quickly to nearly 3000 calls daily.
Therapists returning to the office are struggling to find private meeting rooms at some VA facilities, according to four of the mental health professionals interviewed by Reuters.
They described medical and mental health professionals converting closets and conference rooms into offices to comply with the mandate to conduct telehealth visits from VA facilities. They expressed concerns that the crowded rooms could violate patient privacy rights.
“We are scrambling to find space,” said a provider in California. “Veterans are going without until we can find spaces for these providers.”
Reuters was unable to independently verify the accounts of overcrowding. Kasperowicz said the agency’s “policy is to bring as many employees back to the office as space permits.”
(Reporting by Robin Respaut in San Francisco; additional reporting by Julia Harte in New York and Gabriella Borter in D.C.; Editing by Michele Gershberg and Suzanne Goldenberg)
SAN FRANCISCO (Reuters) — Joey Cortez, who served 24 years in the US Air Force, had been waiting since August to see a mental health specialist from the Department of Veterans’ Affairs, when he experienced a fresh jolt of anxiety.
Cortez was fired last month from his human resources job at the agency - one of about 2400 employees who lost their jobs at Veterans’ Affairs (VA) in the first wave of President Donald Trump’s efforts to shrink the federal workforce.
“Once the firings happened and I was terminated, I started having panic attacks to the point where I black out,” Cortez, who suffers from post-traumatic stress disorder, told Reuters. The layoff is also making it harder to maintain his sobriety, as a recovering alcoholic.
“Not a day has gone by since I was fired that I haven’t thought about picking up a bottle,” said Cortez.
After losing his job, Cortez asked the VA to expedite his wait for a therapist and was told there was no record of his request, he said. After a month of calls to the agency, he got an appointment for this August, one year after he started the process. Then the VA offered him an appointment next week because another patient had canceled.
The VA provides health care to 9.31 million US veterans at hundreds of medical centers, clinics, and nursing homes across the country.
It also faces complex problems.
“The VA has bloat. There are redundancies. There are places where we have questioned the administration of care and asked, does it need to be the way it is?” Pat Murray, the legislative director for the Veterans of Foreign Wars, which represents Americans who have fought overseas, said in an interview.
The Trump administration plans additional cuts to the VA of more than 80,000 personnel, according to an internal memo obtained by Reuters. The agency has also announced it is phasing out telework.
Reuters spoke to nine current and former VA employees in California, Oregon, Texas, and the Washington D.C. area who said the changes were further disrupting some mental health services and fueling anxieties among those who provide and rely on them.
The VA employees — who include six mental health professionals and three people in leadership positions — described cancellations of some in-person and telehealth appointments; confusion over staffing of a crisis hot-line; and professionals conducting telehealth visits in makeshift meeting rooms inside VA buildings.
They spoke on the condition of anonymity, because they were not authorized to speak with the media.
STAFFING SHORTAGES
A former employee at the VA’s Office of Inspector General, who is also a veteran, said any future large-scale staffing cuts would likely worsen shortages and impact the quality of care.
“There’s no way to take a scalpel and do it appropriately that quickly,” he said.
VA spokesperson Peter Kasperowicz told Reuters mental health professionals, such as psychologists and social workers, were not included in February’s staffing cuts, and the agency is working to recruit mental health providers and improve wait times.
He did not specify how many support staff for these providers had been affected.
Last week, two federal judges ordered the VA and other federal agencies to reinstate thousands of fired probationary workers. Cortez’s pay was reinstated but he was told not to return to work.
The Veterans Health Administration, the branch of the VA that provides healthcare, has experienced severe staffing shortages since 2015, especially among mental health professionals, according to an OIG report last year.
Veterans often benefit from specialized services to treat anxiety, trauma, depression and substance abuse. The proportion of veterans receiving mental health services rose to 31% in 2022 from 20% in 2007, according to the VA. Suicide among veterans is twice the rate of Americans overall.
The VFW’s Murray said his organization supports a thorough review of the VA’s mental health services, but it needs to be done carefully, “not with a chainsaw.”
‘THE MOOD IS SO LOW’
In recent years, the agency had encouraged remote work to help expand access to telehealth services and reduce wait times, especially in rural areas where recruiting providers is difficult.
The VA’s Kasperowicz said that, while providers will need to return to VA facilities, veterans will be able to access telehealth appointments.
He did not directly address questions about why mental health providers needed to return to the office.
“The VA will make accommodations as needed to ensure employees have enough space to work and will always ensure that Veterans’ access to benefits and services remains uninterrupted as employees return to in-person work,” Kasperowicz said.
In the last few weeks, demand for services among veterans who are VA employees has also risen, one of the mental health professionals, a social worker, told Reuters. A quarter of VA employees are veterans.
The social worker said he is meeting with two to three VA employees a week who are seeking access to mental health care, citing stress and the fear that they will lose their jobs.
“People are calling out sick. People are ill with stress and worry. The mood is so low.”
A mental health supervisor in California described scrambling to cover the caseload of a remote worker who had to cancel appointments with more than a dozen veterans, because she could not access a VA facility.
VA employees in the Washington area and in Oregon said mental health professionals were unsure if they were allowed to answer calls from the VA’s crisis hot-line if they were not physically in an office, because they had been instructed not to conduct work outside of a facility.
“People are nervous to be on-call,” said a supervisor of mental health providers in the Washington area. “The system is under a lot of duress.”
The VA told Reuters that crisis line workers are exempt from the return-to-office policy, and that staff continue to respond quickly to nearly 3000 calls daily.
Therapists returning to the office are struggling to find private meeting rooms at some VA facilities, according to four of the mental health professionals interviewed by Reuters.
They described medical and mental health professionals converting closets and conference rooms into offices to comply with the mandate to conduct telehealth visits from VA facilities. They expressed concerns that the crowded rooms could violate patient privacy rights.
“We are scrambling to find space,” said a provider in California. “Veterans are going without until we can find spaces for these providers.”
Reuters was unable to independently verify the accounts of overcrowding. Kasperowicz said the agency’s “policy is to bring as many employees back to the office as space permits.”
(Reporting by Robin Respaut in San Francisco; additional reporting by Julia Harte in New York and Gabriella Borter in D.C.; Editing by Michele Gershberg and Suzanne Goldenberg)
Do Patients With Intermediate-Risk Cervical Cancer Need Adjuvant Chemotherapy?
New findings on radiation plus adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with intermediate-risk cervical cancer seem to spell the end for the dual therapy in this group.
Results from a phase 3 clinical trial of 316 women who’d had radical hysterectomies found that adjuvant chemotherapy as treatment for their early-stage, intermediate-risk cervical carcinoma did not improve outcomes but did increase toxicity. The results were the inverse of the study’s intention.
The NRG-GOG 0263 (NCT01101451) study failed to reach its endpoint of improving recurrence-free survival through the addition of cisplatin chemotherapy, confirming instead that cisplatin chemotherapy given adjuvantly with radiotherapy is not a superior alternative in this cohort. The results were presented during a plenary session of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancers in Seattle, Washington.
The current standard of care in this cohort is for radiotherapy alone, although the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines place adjuvant chemotherapy in category 2B recommendations.
“Perhaps the NCCN guidelines will have to change what it says here,” Andrew Berchuck, MD, chief of gynecologic oncology and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization. Berchuck was not involved in the clinical trial.
The National Cancer Institute lists adjuvant chemotherapy first in its guidelines for this group.
Another study published online this month in JAMA Oncology concluded that morbidity in these patients could be reduced if the use of chemoradiotherapy were de-escalated.
This population-based cohort study of 1116 women, conducted by Núria Agustí Garcia, MD, postdoctoral fellow at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and colleagues, found no significant overall survival benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in intermediate-risk cervical cancer, and that when it was given, patients tended to have larger tumors and nonsquamous cell history.
The 5-year survival rate in patients who received chemoradiotherapy was 87%, compared with an 87% 5-year survival rate in those who received radiotherapy alone (hazard ratio = 0.85; 95% CI, 0.59-1.23; P =.38).
If the standard of care in this cohort is radiation only, and outcomes are not better in adjuvant treatment, then why is there a controversy at all, and why are some investigators such as Agustí Garcia attempting to clarify adjuvant treatment’s effects?
Experts say it’s because of the history of adjuvant chemotherapy in more advanced cervical cancer and the extrapolations clinicians made when treating patients with intermediate risk.
What Is the History of Adjuvant Treatment in Cervical Cancer?
Concomitant therapies in intermediate-risk cervical cancer began in the late 1990s, at a time when it was found effective in more advanced disease, according to Berchuck, who also was not involved in the population study.
“Say back then, you had a stage IIIb cervical cancer. With external radiation alone, followed by brachytherapy internally, the cure rate for something like that would have been maybe 50 or 60%,” Berchuck said in an interview. “Adding cisplatin improved the cure rate by about 15%.”
That cisplatin improved survival rates in advanced disease, led to using it in less advanced cases, according to Berchuck. “The idea here was that if the pathology report indicated a larger tumor involving the lymphatics, the risk of recurrence went up to about 20%, so by adding chemo to postsurgical radiotherapy, you could improve things more than with just radiation alone,” Berchuck said.
Studies of adjuvant chemotherapy in advanced cervical cancers confused the matter, according to Agustí Garcia.
“The theoretical benefit of adding chemotherapy to radiotherapy for patients with intermediate-risk cervical cancer has been extrapolated from studies on locally advanced or high-risk cases, for example, those with parametrial or lymph node metastases,” Agustí Garcia said in an interview.
“However, before its implementation, there was no solid evidence supporting this approach in intermediate-risk patients,” she said. “The oncologic behavior of this subgroup may differ, and in the absence of parametrial or lymph node metastasis, chemotherapy may not be necessary.”
Do Both Studies Suggest That Radiotherapy Has Become More Effective Recently?
“Probably. Modern radiation techniques, such as IMRT [intensity-modulated radiation therapy] and IGRT [image-guided radiation therapy] are more effective than historical techniques,” said Amer Karam, MD, a clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California. Karam was not involved in either study mentioned previously.
Agustí Garcia said that while it’s true radiotherapy techniques have improved, these advancements primarily impact morbidity rather than survival outcomes.
“The lack of survival benefit from concomitant chemotherapy in intermediate-risk patients suggests that such benefit may never have existed in this subgroup,” she said.
What Explains Why Overall Survival Did Not Significantly Differ Between Patients Who Received Radiotherapy Alone and Those Who Received Chemoradiotherapy?
For Karam, there is a question as to whether chemosensitization mechanisms in radiation therapy, such as reactive oxygen species, inhibition of DNA repair, modulating tumor microenvironment, and cell cycle arrest — all used to induce apoptosis — are as efficacious as once thought.
“Also, systemic chemosensitization may not be as effective at controlling systemic disease beyond the pelvis and radiation field,” he said.
“Radiation is extremely effective in cervical cancer,” said Berchuck. “When you’re giving radiation in a situation like this where there is none, to only microscopic disease, it makes sense that radiation could be effective by itself.”
Why in the JAMA Oncology Study Were Larger Tumor Size and Nonsquamous Histology Associated With the Use of Chemoradiotherapy?
All experts agreed this is likely because this subgroup of patients with larger tumors is typically seen as being at higher risk for recurrence. This might be due to what Karam called an “unfavorable histology” and certain tumor characteristics, including depth of invasion.
Yet Agustí Garcia said, in her study, even after propensity score matching, adjuvant chemotherapy did not demonstrate any survival benefit in this subgroup.
“The importance of performing propensity score matching in our analysis was to ensure that populations with comparable baseline recurrence and death risks were being evaluated fairly,” she told this news organization.
Do These Findings Change Clinical Practice for Intermediate-Risk Cervical Cancer Treatment?
For Karam, the new evidence in intermediate-risk cervical cancer confirms rather than changes clinical practice. “The standard of care was radiation therapy alone, which is now confirmed, based on the results of GOG 263,” Karam said. “The standard of care for these patients will remain the same.”
Agustí Garcia said her study results can help “refine” clinical practice.
“The results suggest that adjuvant therapy could be safely de-escalated in intermediate-risk cervical cancer,” Agustí Garcia said.
“We should avoid chemotherapy when there is no evidence-based benefit, reserving its use for locally advanced or high-risk cases, refining clinical guidelines to ensure treatment recommendations are based on higher-quality evidence, thereby standardizing care and reducing overtreatment,” she continued. “Current guidelines lack consensus and rely on lower-quality evidence.”
Agustí Garcia reported grants from Fundación Alfonso Martín Escudero. Berchuck has no disclosures. Karam reported royalties from UpToDate and that he is a speaker for AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New findings on radiation plus adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with intermediate-risk cervical cancer seem to spell the end for the dual therapy in this group.
Results from a phase 3 clinical trial of 316 women who’d had radical hysterectomies found that adjuvant chemotherapy as treatment for their early-stage, intermediate-risk cervical carcinoma did not improve outcomes but did increase toxicity. The results were the inverse of the study’s intention.
The NRG-GOG 0263 (NCT01101451) study failed to reach its endpoint of improving recurrence-free survival through the addition of cisplatin chemotherapy, confirming instead that cisplatin chemotherapy given adjuvantly with radiotherapy is not a superior alternative in this cohort. The results were presented during a plenary session of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancers in Seattle, Washington.
The current standard of care in this cohort is for radiotherapy alone, although the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines place adjuvant chemotherapy in category 2B recommendations.
“Perhaps the NCCN guidelines will have to change what it says here,” Andrew Berchuck, MD, chief of gynecologic oncology and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization. Berchuck was not involved in the clinical trial.
The National Cancer Institute lists adjuvant chemotherapy first in its guidelines for this group.
Another study published online this month in JAMA Oncology concluded that morbidity in these patients could be reduced if the use of chemoradiotherapy were de-escalated.
This population-based cohort study of 1116 women, conducted by Núria Agustí Garcia, MD, postdoctoral fellow at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and colleagues, found no significant overall survival benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in intermediate-risk cervical cancer, and that when it was given, patients tended to have larger tumors and nonsquamous cell history.
The 5-year survival rate in patients who received chemoradiotherapy was 87%, compared with an 87% 5-year survival rate in those who received radiotherapy alone (hazard ratio = 0.85; 95% CI, 0.59-1.23; P =.38).
If the standard of care in this cohort is radiation only, and outcomes are not better in adjuvant treatment, then why is there a controversy at all, and why are some investigators such as Agustí Garcia attempting to clarify adjuvant treatment’s effects?
Experts say it’s because of the history of adjuvant chemotherapy in more advanced cervical cancer and the extrapolations clinicians made when treating patients with intermediate risk.
What Is the History of Adjuvant Treatment in Cervical Cancer?
Concomitant therapies in intermediate-risk cervical cancer began in the late 1990s, at a time when it was found effective in more advanced disease, according to Berchuck, who also was not involved in the population study.
“Say back then, you had a stage IIIb cervical cancer. With external radiation alone, followed by brachytherapy internally, the cure rate for something like that would have been maybe 50 or 60%,” Berchuck said in an interview. “Adding cisplatin improved the cure rate by about 15%.”
That cisplatin improved survival rates in advanced disease, led to using it in less advanced cases, according to Berchuck. “The idea here was that if the pathology report indicated a larger tumor involving the lymphatics, the risk of recurrence went up to about 20%, so by adding chemo to postsurgical radiotherapy, you could improve things more than with just radiation alone,” Berchuck said.
Studies of adjuvant chemotherapy in advanced cervical cancers confused the matter, according to Agustí Garcia.
“The theoretical benefit of adding chemotherapy to radiotherapy for patients with intermediate-risk cervical cancer has been extrapolated from studies on locally advanced or high-risk cases, for example, those with parametrial or lymph node metastases,” Agustí Garcia said in an interview.
“However, before its implementation, there was no solid evidence supporting this approach in intermediate-risk patients,” she said. “The oncologic behavior of this subgroup may differ, and in the absence of parametrial or lymph node metastasis, chemotherapy may not be necessary.”
Do Both Studies Suggest That Radiotherapy Has Become More Effective Recently?
“Probably. Modern radiation techniques, such as IMRT [intensity-modulated radiation therapy] and IGRT [image-guided radiation therapy] are more effective than historical techniques,” said Amer Karam, MD, a clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California. Karam was not involved in either study mentioned previously.
Agustí Garcia said that while it’s true radiotherapy techniques have improved, these advancements primarily impact morbidity rather than survival outcomes.
“The lack of survival benefit from concomitant chemotherapy in intermediate-risk patients suggests that such benefit may never have existed in this subgroup,” she said.
What Explains Why Overall Survival Did Not Significantly Differ Between Patients Who Received Radiotherapy Alone and Those Who Received Chemoradiotherapy?
For Karam, there is a question as to whether chemosensitization mechanisms in radiation therapy, such as reactive oxygen species, inhibition of DNA repair, modulating tumor microenvironment, and cell cycle arrest — all used to induce apoptosis — are as efficacious as once thought.
“Also, systemic chemosensitization may not be as effective at controlling systemic disease beyond the pelvis and radiation field,” he said.
“Radiation is extremely effective in cervical cancer,” said Berchuck. “When you’re giving radiation in a situation like this where there is none, to only microscopic disease, it makes sense that radiation could be effective by itself.”
Why in the JAMA Oncology Study Were Larger Tumor Size and Nonsquamous Histology Associated With the Use of Chemoradiotherapy?
All experts agreed this is likely because this subgroup of patients with larger tumors is typically seen as being at higher risk for recurrence. This might be due to what Karam called an “unfavorable histology” and certain tumor characteristics, including depth of invasion.
Yet Agustí Garcia said, in her study, even after propensity score matching, adjuvant chemotherapy did not demonstrate any survival benefit in this subgroup.
“The importance of performing propensity score matching in our analysis was to ensure that populations with comparable baseline recurrence and death risks were being evaluated fairly,” she told this news organization.
Do These Findings Change Clinical Practice for Intermediate-Risk Cervical Cancer Treatment?
For Karam, the new evidence in intermediate-risk cervical cancer confirms rather than changes clinical practice. “The standard of care was radiation therapy alone, which is now confirmed, based on the results of GOG 263,” Karam said. “The standard of care for these patients will remain the same.”
Agustí Garcia said her study results can help “refine” clinical practice.
“The results suggest that adjuvant therapy could be safely de-escalated in intermediate-risk cervical cancer,” Agustí Garcia said.
“We should avoid chemotherapy when there is no evidence-based benefit, reserving its use for locally advanced or high-risk cases, refining clinical guidelines to ensure treatment recommendations are based on higher-quality evidence, thereby standardizing care and reducing overtreatment,” she continued. “Current guidelines lack consensus and rely on lower-quality evidence.”
Agustí Garcia reported grants from Fundación Alfonso Martín Escudero. Berchuck has no disclosures. Karam reported royalties from UpToDate and that he is a speaker for AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New findings on radiation plus adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with intermediate-risk cervical cancer seem to spell the end for the dual therapy in this group.
Results from a phase 3 clinical trial of 316 women who’d had radical hysterectomies found that adjuvant chemotherapy as treatment for their early-stage, intermediate-risk cervical carcinoma did not improve outcomes but did increase toxicity. The results were the inverse of the study’s intention.
The NRG-GOG 0263 (NCT01101451) study failed to reach its endpoint of improving recurrence-free survival through the addition of cisplatin chemotherapy, confirming instead that cisplatin chemotherapy given adjuvantly with radiotherapy is not a superior alternative in this cohort. The results were presented during a plenary session of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancers in Seattle, Washington.
The current standard of care in this cohort is for radiotherapy alone, although the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines place adjuvant chemotherapy in category 2B recommendations.
“Perhaps the NCCN guidelines will have to change what it says here,” Andrew Berchuck, MD, chief of gynecologic oncology and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization. Berchuck was not involved in the clinical trial.
The National Cancer Institute lists adjuvant chemotherapy first in its guidelines for this group.
Another study published online this month in JAMA Oncology concluded that morbidity in these patients could be reduced if the use of chemoradiotherapy were de-escalated.
This population-based cohort study of 1116 women, conducted by Núria Agustí Garcia, MD, postdoctoral fellow at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and colleagues, found no significant overall survival benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in intermediate-risk cervical cancer, and that when it was given, patients tended to have larger tumors and nonsquamous cell history.
The 5-year survival rate in patients who received chemoradiotherapy was 87%, compared with an 87% 5-year survival rate in those who received radiotherapy alone (hazard ratio = 0.85; 95% CI, 0.59-1.23; P =.38).
If the standard of care in this cohort is radiation only, and outcomes are not better in adjuvant treatment, then why is there a controversy at all, and why are some investigators such as Agustí Garcia attempting to clarify adjuvant treatment’s effects?
Experts say it’s because of the history of adjuvant chemotherapy in more advanced cervical cancer and the extrapolations clinicians made when treating patients with intermediate risk.
What Is the History of Adjuvant Treatment in Cervical Cancer?
Concomitant therapies in intermediate-risk cervical cancer began in the late 1990s, at a time when it was found effective in more advanced disease, according to Berchuck, who also was not involved in the population study.
“Say back then, you had a stage IIIb cervical cancer. With external radiation alone, followed by brachytherapy internally, the cure rate for something like that would have been maybe 50 or 60%,” Berchuck said in an interview. “Adding cisplatin improved the cure rate by about 15%.”
That cisplatin improved survival rates in advanced disease, led to using it in less advanced cases, according to Berchuck. “The idea here was that if the pathology report indicated a larger tumor involving the lymphatics, the risk of recurrence went up to about 20%, so by adding chemo to postsurgical radiotherapy, you could improve things more than with just radiation alone,” Berchuck said.
Studies of adjuvant chemotherapy in advanced cervical cancers confused the matter, according to Agustí Garcia.
“The theoretical benefit of adding chemotherapy to radiotherapy for patients with intermediate-risk cervical cancer has been extrapolated from studies on locally advanced or high-risk cases, for example, those with parametrial or lymph node metastases,” Agustí Garcia said in an interview.
“However, before its implementation, there was no solid evidence supporting this approach in intermediate-risk patients,” she said. “The oncologic behavior of this subgroup may differ, and in the absence of parametrial or lymph node metastasis, chemotherapy may not be necessary.”
Do Both Studies Suggest That Radiotherapy Has Become More Effective Recently?
“Probably. Modern radiation techniques, such as IMRT [intensity-modulated radiation therapy] and IGRT [image-guided radiation therapy] are more effective than historical techniques,” said Amer Karam, MD, a clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California. Karam was not involved in either study mentioned previously.
Agustí Garcia said that while it’s true radiotherapy techniques have improved, these advancements primarily impact morbidity rather than survival outcomes.
“The lack of survival benefit from concomitant chemotherapy in intermediate-risk patients suggests that such benefit may never have existed in this subgroup,” she said.
What Explains Why Overall Survival Did Not Significantly Differ Between Patients Who Received Radiotherapy Alone and Those Who Received Chemoradiotherapy?
For Karam, there is a question as to whether chemosensitization mechanisms in radiation therapy, such as reactive oxygen species, inhibition of DNA repair, modulating tumor microenvironment, and cell cycle arrest — all used to induce apoptosis — are as efficacious as once thought.
“Also, systemic chemosensitization may not be as effective at controlling systemic disease beyond the pelvis and radiation field,” he said.
“Radiation is extremely effective in cervical cancer,” said Berchuck. “When you’re giving radiation in a situation like this where there is none, to only microscopic disease, it makes sense that radiation could be effective by itself.”
Why in the JAMA Oncology Study Were Larger Tumor Size and Nonsquamous Histology Associated With the Use of Chemoradiotherapy?
All experts agreed this is likely because this subgroup of patients with larger tumors is typically seen as being at higher risk for recurrence. This might be due to what Karam called an “unfavorable histology” and certain tumor characteristics, including depth of invasion.
Yet Agustí Garcia said, in her study, even after propensity score matching, adjuvant chemotherapy did not demonstrate any survival benefit in this subgroup.
“The importance of performing propensity score matching in our analysis was to ensure that populations with comparable baseline recurrence and death risks were being evaluated fairly,” she told this news organization.
Do These Findings Change Clinical Practice for Intermediate-Risk Cervical Cancer Treatment?
For Karam, the new evidence in intermediate-risk cervical cancer confirms rather than changes clinical practice. “The standard of care was radiation therapy alone, which is now confirmed, based on the results of GOG 263,” Karam said. “The standard of care for these patients will remain the same.”
Agustí Garcia said her study results can help “refine” clinical practice.
“The results suggest that adjuvant therapy could be safely de-escalated in intermediate-risk cervical cancer,” Agustí Garcia said.
“We should avoid chemotherapy when there is no evidence-based benefit, reserving its use for locally advanced or high-risk cases, refining clinical guidelines to ensure treatment recommendations are based on higher-quality evidence, thereby standardizing care and reducing overtreatment,” she continued. “Current guidelines lack consensus and rely on lower-quality evidence.”
Agustí Garcia reported grants from Fundación Alfonso Martín Escudero. Berchuck has no disclosures. Karam reported royalties from UpToDate and that he is a speaker for AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Adjuvant Immunotherapy Boost Survival Outcomes in Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer?
TOPLINE:
Adjuvant therapy with camrelizumab significantly improved 3-year event-free survival in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma compared with observation, according to findings from the phase 3 DIPPER trial.
METHODOLOGY:
- About 20%-30% of patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma experience disease relapse after definitive chemoradiotherapy. Camrelizumab plus chemotherapy can improve progression-free survival in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma, but its effectiveness as adjuvant therapy in locoregionally advanced disease remains unclear.
- Researchers conducted the randomized phase 3 DIPPER trial at 11 centers in China, enrolling 450 patients with T4N1M0 or T1-4N2-3M0 nasopharyngeal carcinoma who had completed induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
- Participants were randomly assigned to receive either adjuvant camrelizumab (200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks for 12 cycles; n = 226) or observation (n = 224). The median follow-up duration was 39 months.
- The primary endpoint was event-free survival, defined as freedom from distant metastasis, locoregional relapse, or death due to any cause; secondary endpoints included distant metastasis–free survival, locoregional relapse–free survival, overall survival, and safety.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients who received camrelizumab had a higher 3-year event-free survival rate than those who underwent observation (86.9% vs 77.3%; stratified hazard ratio [HR], 0.56; P = .01).
- The 3-year distant metastasis–free survival was also higher in the camrelizumab group (92.4% vs 84.5%; stratified HR, 0.54; P = .04).
- Patients in the camrelizumab group had higher locoregional relapse–free survival at 3 years than those in the observation group (92.8% vs 87.0%; stratified HR, 0.53; P = .046). However, the difference in overall survival between the groups was not significant.
- The safety analysis included 426 patients; 97.1% of those who received camrelizumab experienced at least one adverse event of any grade, the most common being reactive capillary endothelial proliferation compared with 85.5% of those in the observation group. Further, 11.2% of patients taking camrelizumab reported grade 3 or 4 events, including leukopenia and neutropenia compared with 3% in the observation group.
IN PRACTICE:
“The DIPPER trial demonstrated that adjuvant camrelizumab following induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy significantly improved event-free survival by 9.6% with a favorable safety profile in patients with locoregionally advanced [nasopharyngeal carcinoma],” the authors wrote.
“If survival is eventually proven to be improved with induction chemoimmunotherapy, can we begin asking about de-escalation of chemoradiotherapy” for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma? “This question is exceptionally important, given the significant long-term consequences of radiotherapy on survivors,” the author of an accompanying editorial wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ye-Lin Liang, MD, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, and was published online in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included patients from an endemic region where nasopharyngeal carcinoma is predominantly linked to Epstein-Barr virus infection, potentially affecting the generalizability of the findings to nonendemic populations. The open-label design may have introduced bias. Additionally, combined positive scores for programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) were unavailable for some patients, potentially affecting the analysis of the correlation between PD-L1 expression and clinical outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Guangzhou Municipal Health Commission, Key Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, Overseas Expertise Introduction Project for Discipline Innovation, and Cancer Innovative Research Program of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adjuvant therapy with camrelizumab significantly improved 3-year event-free survival in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma compared with observation, according to findings from the phase 3 DIPPER trial.
METHODOLOGY:
- About 20%-30% of patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma experience disease relapse after definitive chemoradiotherapy. Camrelizumab plus chemotherapy can improve progression-free survival in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma, but its effectiveness as adjuvant therapy in locoregionally advanced disease remains unclear.
- Researchers conducted the randomized phase 3 DIPPER trial at 11 centers in China, enrolling 450 patients with T4N1M0 or T1-4N2-3M0 nasopharyngeal carcinoma who had completed induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
- Participants were randomly assigned to receive either adjuvant camrelizumab (200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks for 12 cycles; n = 226) or observation (n = 224). The median follow-up duration was 39 months.
- The primary endpoint was event-free survival, defined as freedom from distant metastasis, locoregional relapse, or death due to any cause; secondary endpoints included distant metastasis–free survival, locoregional relapse–free survival, overall survival, and safety.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients who received camrelizumab had a higher 3-year event-free survival rate than those who underwent observation (86.9% vs 77.3%; stratified hazard ratio [HR], 0.56; P = .01).
- The 3-year distant metastasis–free survival was also higher in the camrelizumab group (92.4% vs 84.5%; stratified HR, 0.54; P = .04).
- Patients in the camrelizumab group had higher locoregional relapse–free survival at 3 years than those in the observation group (92.8% vs 87.0%; stratified HR, 0.53; P = .046). However, the difference in overall survival between the groups was not significant.
- The safety analysis included 426 patients; 97.1% of those who received camrelizumab experienced at least one adverse event of any grade, the most common being reactive capillary endothelial proliferation compared with 85.5% of those in the observation group. Further, 11.2% of patients taking camrelizumab reported grade 3 or 4 events, including leukopenia and neutropenia compared with 3% in the observation group.
IN PRACTICE:
“The DIPPER trial demonstrated that adjuvant camrelizumab following induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy significantly improved event-free survival by 9.6% with a favorable safety profile in patients with locoregionally advanced [nasopharyngeal carcinoma],” the authors wrote.
“If survival is eventually proven to be improved with induction chemoimmunotherapy, can we begin asking about de-escalation of chemoradiotherapy” for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma? “This question is exceptionally important, given the significant long-term consequences of radiotherapy on survivors,” the author of an accompanying editorial wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ye-Lin Liang, MD, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, and was published online in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included patients from an endemic region where nasopharyngeal carcinoma is predominantly linked to Epstein-Barr virus infection, potentially affecting the generalizability of the findings to nonendemic populations. The open-label design may have introduced bias. Additionally, combined positive scores for programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) were unavailable for some patients, potentially affecting the analysis of the correlation between PD-L1 expression and clinical outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Guangzhou Municipal Health Commission, Key Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, Overseas Expertise Introduction Project for Discipline Innovation, and Cancer Innovative Research Program of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adjuvant therapy with camrelizumab significantly improved 3-year event-free survival in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma compared with observation, according to findings from the phase 3 DIPPER trial.
METHODOLOGY:
- About 20%-30% of patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma experience disease relapse after definitive chemoradiotherapy. Camrelizumab plus chemotherapy can improve progression-free survival in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma, but its effectiveness as adjuvant therapy in locoregionally advanced disease remains unclear.
- Researchers conducted the randomized phase 3 DIPPER trial at 11 centers in China, enrolling 450 patients with T4N1M0 or T1-4N2-3M0 nasopharyngeal carcinoma who had completed induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
- Participants were randomly assigned to receive either adjuvant camrelizumab (200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks for 12 cycles; n = 226) or observation (n = 224). The median follow-up duration was 39 months.
- The primary endpoint was event-free survival, defined as freedom from distant metastasis, locoregional relapse, or death due to any cause; secondary endpoints included distant metastasis–free survival, locoregional relapse–free survival, overall survival, and safety.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients who received camrelizumab had a higher 3-year event-free survival rate than those who underwent observation (86.9% vs 77.3%; stratified hazard ratio [HR], 0.56; P = .01).
- The 3-year distant metastasis–free survival was also higher in the camrelizumab group (92.4% vs 84.5%; stratified HR, 0.54; P = .04).
- Patients in the camrelizumab group had higher locoregional relapse–free survival at 3 years than those in the observation group (92.8% vs 87.0%; stratified HR, 0.53; P = .046). However, the difference in overall survival between the groups was not significant.
- The safety analysis included 426 patients; 97.1% of those who received camrelizumab experienced at least one adverse event of any grade, the most common being reactive capillary endothelial proliferation compared with 85.5% of those in the observation group. Further, 11.2% of patients taking camrelizumab reported grade 3 or 4 events, including leukopenia and neutropenia compared with 3% in the observation group.
IN PRACTICE:
“The DIPPER trial demonstrated that adjuvant camrelizumab following induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy significantly improved event-free survival by 9.6% with a favorable safety profile in patients with locoregionally advanced [nasopharyngeal carcinoma],” the authors wrote.
“If survival is eventually proven to be improved with induction chemoimmunotherapy, can we begin asking about de-escalation of chemoradiotherapy” for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma? “This question is exceptionally important, given the significant long-term consequences of radiotherapy on survivors,” the author of an accompanying editorial wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ye-Lin Liang, MD, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, and was published online in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included patients from an endemic region where nasopharyngeal carcinoma is predominantly linked to Epstein-Barr virus infection, potentially affecting the generalizability of the findings to nonendemic populations. The open-label design may have introduced bias. Additionally, combined positive scores for programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) were unavailable for some patients, potentially affecting the analysis of the correlation between PD-L1 expression and clinical outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Guangzhou Municipal Health Commission, Key Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, Overseas Expertise Introduction Project for Discipline Innovation, and Cancer Innovative Research Program of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
OK to Skip Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection in Cervical Cancer?
Results from the PHENIX-I trial support skipping pelvic lymphadenectomy in women with early cervical cancer who have a negative sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Omitting pelvic lymphadenectomy in these patients “did not compromise disease-free survival and potentially [led to] improved overall survival,” reported lead investigator Jihong Liu, MD, gynecologic oncologist, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China.
Forgoing the additional procedure also decreased the incidence of retroperitoneal lymph node recurrence and adverse events and demonstrated superior surgical outcomes including shorter operative duration, reduced blood loss, and a lower morbidity.
Liu reported the PHENIX-I results at this year’s Society of Gynecologic Oncology Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancers (SGO) 2025.
Pelvic lymphadenectomy has been part of standard care for early-stage cervical cancer for over a century, even though the incidence of lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer is relatively low. Overtreatment and increased morbidity have been notable drawbacks of the procedure.
It may be possible to forgo pelvic lymphadenectomy in early-stage cervical cancer when sentinel lymph node biopsy findings are negative, but evidence from randomized controlled trials are lacking, Liu explained.
The PHENIX-I trial prospectively assessed survival outcomes among patients who received pelvic lymphadenectomy and those who did not. More specifically, all patients underwent sentinel lymph node biopsy and patients with negative lymph nodes were then intraoperatively randomized (1:1) to undergo pelvic lymphadenectomy (417 patients) or not (416 patients).
The multicenter, randomized controlled trial involved patients undergoing radical hysterectomy for stage IA1 (lymphovascular invasion), IA2, IB1, IB2 or IIA1 cervical cancer with tumor size not exceeding 3 cm.
“The only difference between the two groups was that patients in the experimental arm did not have pelvic lymphadenectomy,” Liu said.
Liu and colleagues reported that 23 patients (2.8%) had a positive lymph node on postoperative pathology examination. The rate of false-negative sentinel lymph node biopsy was < 1%. About half the patients in both groups received postoperative adjuvant therapy, and there was no significant between-group difference in the rates and time to initiate adjuvant therapy.
Overall, about 3.85% of patients (n = 16) in the biopsy-only group had a recurrence compared with 6.24% (n = 26) in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group at a median follow-up of 50 months.
But no patients in the biopsy-only group had a recurrence in the retroperitoneal lymph nodes compared with 9 patients in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group.
The 3-year disease-free survival (primary endpoint) rates were similar between the two groups — 96.8% in the biopsy-only group and 94.5% in the lymphadenectomy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.61; P = .12). However, the 3-year overall survival was significantly higher in biopsy-only group — 100% vs 97.8% in the lymphadenectomy group (HR, 0.21; P = .007). Overall, three patients (19%) in the biopsy-only group died from cervical cancer vs 14 (54%) in the lymphadenectomy group.
As for surgical complications, pelvic lymphadenectomy was associated with a higher incidence of pain (5.8% vs 1.7%), lymphocyst (22.1% vs 8.4%), and lymphedema (10.1% vs 2.4%), as well as longer operating time and more blood loss.
Offering perspective on PHENIX-I, discussant Premal Thaker, MD, noted that this is the first randomized trial to report on the use of sentinel lymph node biopsy alone vs biopsy plus pelvic lymphadenectomy after radical hysterectomy.
Key takeaways are the “equivalent” 3-year disease-free outcomes but “lower” overall survival in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group as well as more adverse events, said Thaker, gynecologic oncologist and surgeon, Siteman Cancer Center, Washington University, St Louis.
Although quality of life data was not presented in the trial, patients who skipped pelvic lymphadenectomy had fewer adverse events, “which is very important for our patients,” Thaker added.
This study had no commercial funding. Liu and Thaker had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results from the PHENIX-I trial support skipping pelvic lymphadenectomy in women with early cervical cancer who have a negative sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Omitting pelvic lymphadenectomy in these patients “did not compromise disease-free survival and potentially [led to] improved overall survival,” reported lead investigator Jihong Liu, MD, gynecologic oncologist, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China.
Forgoing the additional procedure also decreased the incidence of retroperitoneal lymph node recurrence and adverse events and demonstrated superior surgical outcomes including shorter operative duration, reduced blood loss, and a lower morbidity.
Liu reported the PHENIX-I results at this year’s Society of Gynecologic Oncology Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancers (SGO) 2025.
Pelvic lymphadenectomy has been part of standard care for early-stage cervical cancer for over a century, even though the incidence of lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer is relatively low. Overtreatment and increased morbidity have been notable drawbacks of the procedure.
It may be possible to forgo pelvic lymphadenectomy in early-stage cervical cancer when sentinel lymph node biopsy findings are negative, but evidence from randomized controlled trials are lacking, Liu explained.
The PHENIX-I trial prospectively assessed survival outcomes among patients who received pelvic lymphadenectomy and those who did not. More specifically, all patients underwent sentinel lymph node biopsy and patients with negative lymph nodes were then intraoperatively randomized (1:1) to undergo pelvic lymphadenectomy (417 patients) or not (416 patients).
The multicenter, randomized controlled trial involved patients undergoing radical hysterectomy for stage IA1 (lymphovascular invasion), IA2, IB1, IB2 or IIA1 cervical cancer with tumor size not exceeding 3 cm.
“The only difference between the two groups was that patients in the experimental arm did not have pelvic lymphadenectomy,” Liu said.
Liu and colleagues reported that 23 patients (2.8%) had a positive lymph node on postoperative pathology examination. The rate of false-negative sentinel lymph node biopsy was < 1%. About half the patients in both groups received postoperative adjuvant therapy, and there was no significant between-group difference in the rates and time to initiate adjuvant therapy.
Overall, about 3.85% of patients (n = 16) in the biopsy-only group had a recurrence compared with 6.24% (n = 26) in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group at a median follow-up of 50 months.
But no patients in the biopsy-only group had a recurrence in the retroperitoneal lymph nodes compared with 9 patients in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group.
The 3-year disease-free survival (primary endpoint) rates were similar between the two groups — 96.8% in the biopsy-only group and 94.5% in the lymphadenectomy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.61; P = .12). However, the 3-year overall survival was significantly higher in biopsy-only group — 100% vs 97.8% in the lymphadenectomy group (HR, 0.21; P = .007). Overall, three patients (19%) in the biopsy-only group died from cervical cancer vs 14 (54%) in the lymphadenectomy group.
As for surgical complications, pelvic lymphadenectomy was associated with a higher incidence of pain (5.8% vs 1.7%), lymphocyst (22.1% vs 8.4%), and lymphedema (10.1% vs 2.4%), as well as longer operating time and more blood loss.
Offering perspective on PHENIX-I, discussant Premal Thaker, MD, noted that this is the first randomized trial to report on the use of sentinel lymph node biopsy alone vs biopsy plus pelvic lymphadenectomy after radical hysterectomy.
Key takeaways are the “equivalent” 3-year disease-free outcomes but “lower” overall survival in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group as well as more adverse events, said Thaker, gynecologic oncologist and surgeon, Siteman Cancer Center, Washington University, St Louis.
Although quality of life data was not presented in the trial, patients who skipped pelvic lymphadenectomy had fewer adverse events, “which is very important for our patients,” Thaker added.
This study had no commercial funding. Liu and Thaker had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results from the PHENIX-I trial support skipping pelvic lymphadenectomy in women with early cervical cancer who have a negative sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Omitting pelvic lymphadenectomy in these patients “did not compromise disease-free survival and potentially [led to] improved overall survival,” reported lead investigator Jihong Liu, MD, gynecologic oncologist, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China.
Forgoing the additional procedure also decreased the incidence of retroperitoneal lymph node recurrence and adverse events and demonstrated superior surgical outcomes including shorter operative duration, reduced blood loss, and a lower morbidity.
Liu reported the PHENIX-I results at this year’s Society of Gynecologic Oncology Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancers (SGO) 2025.
Pelvic lymphadenectomy has been part of standard care for early-stage cervical cancer for over a century, even though the incidence of lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer is relatively low. Overtreatment and increased morbidity have been notable drawbacks of the procedure.
It may be possible to forgo pelvic lymphadenectomy in early-stage cervical cancer when sentinel lymph node biopsy findings are negative, but evidence from randomized controlled trials are lacking, Liu explained.
The PHENIX-I trial prospectively assessed survival outcomes among patients who received pelvic lymphadenectomy and those who did not. More specifically, all patients underwent sentinel lymph node biopsy and patients with negative lymph nodes were then intraoperatively randomized (1:1) to undergo pelvic lymphadenectomy (417 patients) or not (416 patients).
The multicenter, randomized controlled trial involved patients undergoing radical hysterectomy for stage IA1 (lymphovascular invasion), IA2, IB1, IB2 or IIA1 cervical cancer with tumor size not exceeding 3 cm.
“The only difference between the two groups was that patients in the experimental arm did not have pelvic lymphadenectomy,” Liu said.
Liu and colleagues reported that 23 patients (2.8%) had a positive lymph node on postoperative pathology examination. The rate of false-negative sentinel lymph node biopsy was < 1%. About half the patients in both groups received postoperative adjuvant therapy, and there was no significant between-group difference in the rates and time to initiate adjuvant therapy.
Overall, about 3.85% of patients (n = 16) in the biopsy-only group had a recurrence compared with 6.24% (n = 26) in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group at a median follow-up of 50 months.
But no patients in the biopsy-only group had a recurrence in the retroperitoneal lymph nodes compared with 9 patients in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group.
The 3-year disease-free survival (primary endpoint) rates were similar between the two groups — 96.8% in the biopsy-only group and 94.5% in the lymphadenectomy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.61; P = .12). However, the 3-year overall survival was significantly higher in biopsy-only group — 100% vs 97.8% in the lymphadenectomy group (HR, 0.21; P = .007). Overall, three patients (19%) in the biopsy-only group died from cervical cancer vs 14 (54%) in the lymphadenectomy group.
As for surgical complications, pelvic lymphadenectomy was associated with a higher incidence of pain (5.8% vs 1.7%), lymphocyst (22.1% vs 8.4%), and lymphedema (10.1% vs 2.4%), as well as longer operating time and more blood loss.
Offering perspective on PHENIX-I, discussant Premal Thaker, MD, noted that this is the first randomized trial to report on the use of sentinel lymph node biopsy alone vs biopsy plus pelvic lymphadenectomy after radical hysterectomy.
Key takeaways are the “equivalent” 3-year disease-free outcomes but “lower” overall survival in the pelvic lymphadenectomy group as well as more adverse events, said Thaker, gynecologic oncologist and surgeon, Siteman Cancer Center, Washington University, St Louis.
Although quality of life data was not presented in the trial, patients who skipped pelvic lymphadenectomy had fewer adverse events, “which is very important for our patients,” Thaker added.
This study had no commercial funding. Liu and Thaker had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SGO 2025
3D Total Body Photography Shown to Decrease Biopsies, Improve Dx of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers
ORLANDO, Fla. — A study of automated three-dimensional total-body photography (3D TBP) found that it improved “hit” rates of positive malignant biopsies and reduced unnecessary biopsies of skin lesions but left unanswered questions about the practicality of its widespread use and cost-effectiveness.
“We did observe improved biopsy practices and outcomes,” said Jordan Phillipps, MD, a dermatology resident at Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida, who reported the results of the study during a late-breaker session at the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) 2025 Annual Meeting.
“We observed reduced unnecessary biopsies, which was driven by benign and premalignant, particularly actinic keratosis, lesions,” Phillipps said. “We observed improved malignancy detection, which was profoundly driven by nonmelanoma skin cancers.”
Study Design and Results
The retrospective study included 410 adult patients who had at least two sessions with the Vectra WB360 3D TBP imaging system at a dedicated 3D imaging clinic at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota Patient eligibility for the 3D clinic requires a previous melanoma diagnosis. All study participants also underwent dermoscopy, Phillipps said. Their average age was 51.6 years, and 53% were women.
The study accounted for 5981 total patient encounters, including 1150 dedicated Vectra imaging sessions, Phillipps said. In this group, 3006 biopsies were performed, of which 56% were benign, 32% were malignant, and 12% were premalignant. The study also separately evaluated lesion type, focusing on keratinocytic and pigmented lesions.
Most of the keratinocytic lesions were nonmelanoma skin cancers, he said, whereas the pigmented lesions were mostly benign.
“The intervention did significantly reduce biopsies per encounter by 35%, and this was driven by benign lesions and premalignant lesions, particularly actinic keratosis lesions,” Phillipps said.
Previous studies of automated TBP have been hampered by small study populations, he said, and this is one of the largest studies of the Vectra WB360 device. “Nonmelanoma skin cancers are underreported,” Phillipps said, noting that most studies focus on melanoma and pigmented lesions. “Our aim was to assess the effect of Vectra implementation on biopsy practice and outcomes,” he explained.
For malignant lesions, the investigators observed an improvement in malignancy detection, a modest 1.6% increase in hit rates of positive malignant biopsies, and a modest 1.3% decrease in the number needed to biopsy, he said.
A subgroup analysis of pigmented and keratinocytic lesions demonstrated that improved malignancy detection is “profoundly driven by nonmelanoma skin cancers” of 71% per biopsy, Phillipps said, along with “sizable” increases in the hit rate (+17%) and a reduction in the number of biopsies (–14%).
Melanoma detection decreased by 62% per biopsy. Phillipps said the reduction was probably because of the study methodology, specifically the eligibility requirement of having had a previous melanoma diagnosis. “These patients typically develop only one primary melanoma,” Phillipps said. To test this, the investigators compared melanoma hit rates with a matched, unexposed cohort that did not have Vectra imaging. They found that the hit rates were similar. “So this was reassuring that we weren’t missing any melanomas,” Phillipps said.
The results also showed improved efficacy for detecting severely dysplastic nevi, for which the hit rate increased by 16% and the number needed to biopsy decreased by 13%. “Actinic keratoses lesions were biopsied less,” he said, noting a 50% decrease. Both benign keratinocytic lesions, predominantly seborrheic keratosis and benign lichenoid keratosis, and benign pigmented (benign nevi) lesions were biopsied less.
Limitations and Questions
The highly selective nature of the patient population was a limitation of the study, Phillipps noted, along with financial and logistical challenges that impede the generalizability of the findings. Overall, he said, the study emphasized that 3D TBP is effective in skin cancer screening and diagnosis, notably beyond pigmented lesions.
Kristina Callis Duffin, MD, MS, chair of dermatology at The University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, called the findings “exciting” but noted that the study did not compare results to the gold standard of clinician-performed skin screenings. “That absolutely would be the important way to do it, through a randomized trial,” she said, “but that’s a hard study to do.”
The cost-effectiveness of total-body imaging also needs to be evaluated, Duffin said. “You really have to look at a number of factors in terms of protection compared to a human gold standard, the rates of biopsies,” she said. “There are a lot of things to unpack; that cost-effectiveness has to be balanced with a more accurate diagnosis and reduction of morbidity with multiple biopsies.”
Phillipps reported no relevant financial relationships. Duffin disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Alumis, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, FIDE, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, Fla. — A study of automated three-dimensional total-body photography (3D TBP) found that it improved “hit” rates of positive malignant biopsies and reduced unnecessary biopsies of skin lesions but left unanswered questions about the practicality of its widespread use and cost-effectiveness.
“We did observe improved biopsy practices and outcomes,” said Jordan Phillipps, MD, a dermatology resident at Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida, who reported the results of the study during a late-breaker session at the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) 2025 Annual Meeting.
“We observed reduced unnecessary biopsies, which was driven by benign and premalignant, particularly actinic keratosis, lesions,” Phillipps said. “We observed improved malignancy detection, which was profoundly driven by nonmelanoma skin cancers.”
Study Design and Results
The retrospective study included 410 adult patients who had at least two sessions with the Vectra WB360 3D TBP imaging system at a dedicated 3D imaging clinic at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota Patient eligibility for the 3D clinic requires a previous melanoma diagnosis. All study participants also underwent dermoscopy, Phillipps said. Their average age was 51.6 years, and 53% were women.
The study accounted for 5981 total patient encounters, including 1150 dedicated Vectra imaging sessions, Phillipps said. In this group, 3006 biopsies were performed, of which 56% were benign, 32% were malignant, and 12% were premalignant. The study also separately evaluated lesion type, focusing on keratinocytic and pigmented lesions.
Most of the keratinocytic lesions were nonmelanoma skin cancers, he said, whereas the pigmented lesions were mostly benign.
“The intervention did significantly reduce biopsies per encounter by 35%, and this was driven by benign lesions and premalignant lesions, particularly actinic keratosis lesions,” Phillipps said.
Previous studies of automated TBP have been hampered by small study populations, he said, and this is one of the largest studies of the Vectra WB360 device. “Nonmelanoma skin cancers are underreported,” Phillipps said, noting that most studies focus on melanoma and pigmented lesions. “Our aim was to assess the effect of Vectra implementation on biopsy practice and outcomes,” he explained.
For malignant lesions, the investigators observed an improvement in malignancy detection, a modest 1.6% increase in hit rates of positive malignant biopsies, and a modest 1.3% decrease in the number needed to biopsy, he said.
A subgroup analysis of pigmented and keratinocytic lesions demonstrated that improved malignancy detection is “profoundly driven by nonmelanoma skin cancers” of 71% per biopsy, Phillipps said, along with “sizable” increases in the hit rate (+17%) and a reduction in the number of biopsies (–14%).
Melanoma detection decreased by 62% per biopsy. Phillipps said the reduction was probably because of the study methodology, specifically the eligibility requirement of having had a previous melanoma diagnosis. “These patients typically develop only one primary melanoma,” Phillipps said. To test this, the investigators compared melanoma hit rates with a matched, unexposed cohort that did not have Vectra imaging. They found that the hit rates were similar. “So this was reassuring that we weren’t missing any melanomas,” Phillipps said.
The results also showed improved efficacy for detecting severely dysplastic nevi, for which the hit rate increased by 16% and the number needed to biopsy decreased by 13%. “Actinic keratoses lesions were biopsied less,” he said, noting a 50% decrease. Both benign keratinocytic lesions, predominantly seborrheic keratosis and benign lichenoid keratosis, and benign pigmented (benign nevi) lesions were biopsied less.
Limitations and Questions
The highly selective nature of the patient population was a limitation of the study, Phillipps noted, along with financial and logistical challenges that impede the generalizability of the findings. Overall, he said, the study emphasized that 3D TBP is effective in skin cancer screening and diagnosis, notably beyond pigmented lesions.
Kristina Callis Duffin, MD, MS, chair of dermatology at The University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, called the findings “exciting” but noted that the study did not compare results to the gold standard of clinician-performed skin screenings. “That absolutely would be the important way to do it, through a randomized trial,” she said, “but that’s a hard study to do.”
The cost-effectiveness of total-body imaging also needs to be evaluated, Duffin said. “You really have to look at a number of factors in terms of protection compared to a human gold standard, the rates of biopsies,” she said. “There are a lot of things to unpack; that cost-effectiveness has to be balanced with a more accurate diagnosis and reduction of morbidity with multiple biopsies.”
Phillipps reported no relevant financial relationships. Duffin disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Alumis, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, FIDE, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, Fla. — A study of automated three-dimensional total-body photography (3D TBP) found that it improved “hit” rates of positive malignant biopsies and reduced unnecessary biopsies of skin lesions but left unanswered questions about the practicality of its widespread use and cost-effectiveness.
“We did observe improved biopsy practices and outcomes,” said Jordan Phillipps, MD, a dermatology resident at Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida, who reported the results of the study during a late-breaker session at the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) 2025 Annual Meeting.
“We observed reduced unnecessary biopsies, which was driven by benign and premalignant, particularly actinic keratosis, lesions,” Phillipps said. “We observed improved malignancy detection, which was profoundly driven by nonmelanoma skin cancers.”
Study Design and Results
The retrospective study included 410 adult patients who had at least two sessions with the Vectra WB360 3D TBP imaging system at a dedicated 3D imaging clinic at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota Patient eligibility for the 3D clinic requires a previous melanoma diagnosis. All study participants also underwent dermoscopy, Phillipps said. Their average age was 51.6 years, and 53% were women.
The study accounted for 5981 total patient encounters, including 1150 dedicated Vectra imaging sessions, Phillipps said. In this group, 3006 biopsies were performed, of which 56% were benign, 32% were malignant, and 12% were premalignant. The study also separately evaluated lesion type, focusing on keratinocytic and pigmented lesions.
Most of the keratinocytic lesions were nonmelanoma skin cancers, he said, whereas the pigmented lesions were mostly benign.
“The intervention did significantly reduce biopsies per encounter by 35%, and this was driven by benign lesions and premalignant lesions, particularly actinic keratosis lesions,” Phillipps said.
Previous studies of automated TBP have been hampered by small study populations, he said, and this is one of the largest studies of the Vectra WB360 device. “Nonmelanoma skin cancers are underreported,” Phillipps said, noting that most studies focus on melanoma and pigmented lesions. “Our aim was to assess the effect of Vectra implementation on biopsy practice and outcomes,” he explained.
For malignant lesions, the investigators observed an improvement in malignancy detection, a modest 1.6% increase in hit rates of positive malignant biopsies, and a modest 1.3% decrease in the number needed to biopsy, he said.
A subgroup analysis of pigmented and keratinocytic lesions demonstrated that improved malignancy detection is “profoundly driven by nonmelanoma skin cancers” of 71% per biopsy, Phillipps said, along with “sizable” increases in the hit rate (+17%) and a reduction in the number of biopsies (–14%).
Melanoma detection decreased by 62% per biopsy. Phillipps said the reduction was probably because of the study methodology, specifically the eligibility requirement of having had a previous melanoma diagnosis. “These patients typically develop only one primary melanoma,” Phillipps said. To test this, the investigators compared melanoma hit rates with a matched, unexposed cohort that did not have Vectra imaging. They found that the hit rates were similar. “So this was reassuring that we weren’t missing any melanomas,” Phillipps said.
The results also showed improved efficacy for detecting severely dysplastic nevi, for which the hit rate increased by 16% and the number needed to biopsy decreased by 13%. “Actinic keratoses lesions were biopsied less,” he said, noting a 50% decrease. Both benign keratinocytic lesions, predominantly seborrheic keratosis and benign lichenoid keratosis, and benign pigmented (benign nevi) lesions were biopsied less.
Limitations and Questions
The highly selective nature of the patient population was a limitation of the study, Phillipps noted, along with financial and logistical challenges that impede the generalizability of the findings. Overall, he said, the study emphasized that 3D TBP is effective in skin cancer screening and diagnosis, notably beyond pigmented lesions.
Kristina Callis Duffin, MD, MS, chair of dermatology at The University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, called the findings “exciting” but noted that the study did not compare results to the gold standard of clinician-performed skin screenings. “That absolutely would be the important way to do it, through a randomized trial,” she said, “but that’s a hard study to do.”
The cost-effectiveness of total-body imaging also needs to be evaluated, Duffin said. “You really have to look at a number of factors in terms of protection compared to a human gold standard, the rates of biopsies,” she said. “There are a lot of things to unpack; that cost-effectiveness has to be balanced with a more accurate diagnosis and reduction of morbidity with multiple biopsies.”
Phillipps reported no relevant financial relationships. Duffin disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Alumis, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, FIDE, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2025