User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Violent patient throws scalding oil on MD; other patient dangers
Ralph Newman, MD, got a taste of how dangerous medicine could be at age 10, when he witnessed a physician being shot by a patient.
“I was visiting a friend whose father was a psychiatrist,” Dr. Newman recalled. “We were playing in the living room when the doorbell rang. My friend went to the door and opened it. Then I heard a shot. I ran to the front hall and saw my friend’s father slumped at the bottom of the stairs. He had come down the stairs to see who was there. It was a patient armed with a shotgun.”
As a result of the shooting, a large portion of the psychiatrist’s intestines was removed. In spite of this traumatic incident, Dr. Newman went on to become a psychiatrist – who treated many violent prisoners. “I knew it was dangerous,” he said, “but I rationalized that I wouldn’t be attacked because I would be nicer.”
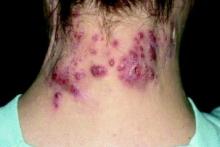
That attitude seemed to work until 2002, when a prisoner threw boiling oil on him. Dr. Newman was working at the Federal Medical Center Butner, a facility for prisoners in North Carolina. “A prisoner I had been treating was denied parole, based on my recommendation,” he said. “From then on, he was looking for a way to exact revenge.”
“One day I was sitting in the nursing station, typing up notes,” Dr. Newman said. “Two new nurses, who were also there, had forgotten to lock the door, and the prisoner noticed that. He heated up some baby oil in a microwave, which was available to prisoners at the time. Then he walked into the office, threw the oil on my back, and came at me with a sharp pencil.”
Dr. Newman said the nurses fled to an adjoining office, locked the door, and wouldn’t let him in. He went into another office and collapsed in exhaustion. He was saved by an inmate who came on the scene, fended off the attacker, and called for help.
“I was taken to the burn unit,” Dr. Newman recalled. “I had second- and third-degree burns on 9% of my body. It was extremely painful. It took me 45 days to recover enough to get back to work.” The two nurses were fired.
Doctors take threats by patients more seriously now
When orthopedic surgeon Preston Phillips, MD, was killed by a patient in Tulsa, Okla., on June 1, Jennifer M. Weiss, MD, recognized the potential danger to physicians.
“The news left me feeling very shaken,” said Dr. Weiss, a pediatric orthopedic surgeon at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, Los Angeles. “Every orthopedic surgeon I talked to about it felt shaken.”
Dr. Weiss said the impact of that event prompted her to take a patient’s abuse more seriously than she might have previously. “Before the killing, my colleagues and I might have swept the incident under the rug, but we reported it to the authorities,” she said.
“What happened was I told a parent of a school-aged child that the child wasn’t ready to go back to sports,” Dr. Weiss says. “This parent was incredibly triggered – screaming and making verbal threats. The parent was standing between me and the door, so I couldn’t get out.”
Coworkers down the hall heard the yelling and helped Dr. Weiss get out of the room. “The parent was escorted out of the building, and the incident was reported to our risk management team,” she said.
Shooters/killers vs. agitated patients
Patients who shoot to kill are very different from agitated patients seen by many doctors on a regular basis – particularly in emergency departments (EDs), psychiatric units, and pain clinics, said Scott Zeller, MD, a psychiatrist who is vice president of Acute Psychiatric Medicine at Vituity, a multistate physician partnership based in Emeryville, California.
“Agitated patients have trouble communicating their needs and can become physically and verbally aggressive,” Dr. Zeller said. He reports that there are 1.7 million such incidents a year in this country, but most of the incidents of verbal aggression can be kept from exploding into physical violence.
Shooters, however, are very hard to stop because they usually plan the action in advance, Dr. Zeller said. He recalled the 2017 murder of Todd Graham, MD, a friend from medical school. Dr. Graham, an orthopedic surgeon in South Bend, Ind., was gunned down by the husband of one of his patients after Dr. Graham declined to prescribe opioids for her.
Playing down the risk of violence
Doctors may play down the risk of violence, even after they have experienced it personally. “Patients can get angry and may make threatening comments,” Dr. Weiss said. “A lot of doctors just brush it off.”
Simple remarks can set off violence-prone patients, as happened to James P. Phillips, MD, director of disaster and operational medicine at George Washington University, Washington. He recalled asking a prisoner who was visiting his hospital to “lower the volume,” and the man exploded. “Even though he was handcuffed to the bed, he heaved an oxygen tank into a window,” Dr. Phillips said. “He said he would be coming back to kill me.”
Sometimes threats or other types of verbal abuse can be as destructive as physical violence. Diann Krywko, MD, an emergency physician at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) Health, Charleston, has had some tough assignments. She worked in EDs in Detroit and Flint, Mich., for a decade before coming to MUSC, where she serves as director of wellness, health, and resilience. One of the incidents that has bothered her the most involved a threat.
It happened when Dr. Krywko denied a patient’s request for narcotics. “She was very angry and said she’d come to my home and cut my children’s heads off,” Dr. Krywko said. “To this day, what she said horrifies me. I still see her smile as she said that.”
Dr. Krywko considered filing for a restraining order against the patient but didn’t because the patient could have learned her address. Dr. Phillips said fear of retaliation is one reason many doctors don’t report threats from patients. “The patient you report knows where you work and may come there to take revenge,” he said. “Also, you may have to continue caring for the person who punched you.”
Online threats also may cause a great deal of angst. Dr. Phillips said he received many online threats when was a medical analyst for CNN in 2020. “Someone sent my address to his Twitter followers, and they shared it with others, so now the whole world knows where I live,” he said. “I had to upgrade security at my home.”
How to deal with volatile patients
Being nice may not always work, but in many cases, it can keep a volatile situation from exploding, according to Dr. Krywko.
“When patients begin to show signs of agitation or are already there, we always try to verbally deescalate the situation, which involves listening,” Dr. Krywko said. “They want someone to hear them out.”
Doctors speak to patients from a position of authority, but Dr. Krywko advises that they should not be too blunt. “Don’t tell patients they’re wrong,” she said. “Even if they may be incorrect, they feel their viewpoint is valid. Encourage a dialogue with words like, ‘Tell me more,’ ” Dr. Krywko said.
Defending yourself
Doctors may have little warning of an impending attack because a patient’s mood can change quickly. This happened several years ago to Jennifer Casaletto, MD, an emergency physician in Charlotte, N.C.
“A man was brought into my ED by ambulance,” she said. “He seemed very calm for a long while, but then he became completely unhinged. A male nurse placed himself between the patient and others and was attacked. He got hurt but was able to continue working.”
Dr. Zeller said health care teams sometimes overreact when patients lash out. “The old-fashioned way to deal with an agitated patient is to call in the cavalry – everyone does a group takedown,” he said. “The patient is put in restraints and heavily sedated. This is not good for anybody. Not only is it likely to injure and traumatize the patient, it can also injure the care team.”
Many hospital EDs have security guards. “I feel safer when a hospital has armed security guards, but they need to be well trained,” Dr. Casaletto said. “Many small hospitals and freestanding EDs do not have security officers at all, or the guards are undertrained or told not to touch anybody.”
In many electronic health record systems, doctors can flag violent patients so future caregivers can be forewarned. However, Dr. Zeller advises against writing about patients’ violence or rudeness in the medical record, because patients can have access to it and might take revenge.
Rising violence from patients
“It feels like it has become much more dangerous to work in the ED,” said Hasan Gokal, MD, an emergency physician working in EDs at the Texas Medical Center. “Just last week, a woman pulled out a gun and fired it in an ED near Houston.”
The statistics back up Dr. Gokal’s assessment. Injuries caused by violent attacks against medical professionals grew by 67% from 2011 to 2018, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Those levels rose even more during the COVID-19 pandemic – the assault rate in hospitals rose 23% just in 2020.
Dr. Krywko said she had “a patient who said she wanted to hurt the next person who irritated her, and that happened to me. She jumped out of her bed swinging and punching, and I wasn’t ready for it. I yelled for help and the care team came.”
“The rise in violence has to do with a decline in respect for authority,” Dr. Phillips said. “Some people now believe doctors are lying to them about the need for COVID precautions because they are taking money from the vaccine companies. The pandemic has exacerbated violence in every way.”
Dr. Phillips said that a growing lack of resources had led to more anger among patients. “There are fewer nurses and reduced physician coverage,” he said. “That means longer wait times for patients, which increases patients’ frustrations.”
Dr. Weiss said patients have higher expectations. “In sports medicine, the expectations are incredible,” she said. “Parents want their kids to get back to playing as soon as possible.”
“Hospitals in particular are soft targets for violence,” Dr. Phillips said. “People know you can’t assault a flight attendant, because it’s a federal offense, but there is no such federal offense for violence against health care personnel.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ralph Newman, MD, got a taste of how dangerous medicine could be at age 10, when he witnessed a physician being shot by a patient.
“I was visiting a friend whose father was a psychiatrist,” Dr. Newman recalled. “We were playing in the living room when the doorbell rang. My friend went to the door and opened it. Then I heard a shot. I ran to the front hall and saw my friend’s father slumped at the bottom of the stairs. He had come down the stairs to see who was there. It was a patient armed with a shotgun.”
As a result of the shooting, a large portion of the psychiatrist’s intestines was removed. In spite of this traumatic incident, Dr. Newman went on to become a psychiatrist – who treated many violent prisoners. “I knew it was dangerous,” he said, “but I rationalized that I wouldn’t be attacked because I would be nicer.”
That attitude seemed to work until 2002, when a prisoner threw boiling oil on him. Dr. Newman was working at the Federal Medical Center Butner, a facility for prisoners in North Carolina. “A prisoner I had been treating was denied parole, based on my recommendation,” he said. “From then on, he was looking for a way to exact revenge.”
“One day I was sitting in the nursing station, typing up notes,” Dr. Newman said. “Two new nurses, who were also there, had forgotten to lock the door, and the prisoner noticed that. He heated up some baby oil in a microwave, which was available to prisoners at the time. Then he walked into the office, threw the oil on my back, and came at me with a sharp pencil.”
Dr. Newman said the nurses fled to an adjoining office, locked the door, and wouldn’t let him in. He went into another office and collapsed in exhaustion. He was saved by an inmate who came on the scene, fended off the attacker, and called for help.
“I was taken to the burn unit,” Dr. Newman recalled. “I had second- and third-degree burns on 9% of my body. It was extremely painful. It took me 45 days to recover enough to get back to work.” The two nurses were fired.
Doctors take threats by patients more seriously now
When orthopedic surgeon Preston Phillips, MD, was killed by a patient in Tulsa, Okla., on June 1, Jennifer M. Weiss, MD, recognized the potential danger to physicians.
“The news left me feeling very shaken,” said Dr. Weiss, a pediatric orthopedic surgeon at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, Los Angeles. “Every orthopedic surgeon I talked to about it felt shaken.”
Dr. Weiss said the impact of that event prompted her to take a patient’s abuse more seriously than she might have previously. “Before the killing, my colleagues and I might have swept the incident under the rug, but we reported it to the authorities,” she said.
“What happened was I told a parent of a school-aged child that the child wasn’t ready to go back to sports,” Dr. Weiss says. “This parent was incredibly triggered – screaming and making verbal threats. The parent was standing between me and the door, so I couldn’t get out.”
Coworkers down the hall heard the yelling and helped Dr. Weiss get out of the room. “The parent was escorted out of the building, and the incident was reported to our risk management team,” she said.
Shooters/killers vs. agitated patients
Patients who shoot to kill are very different from agitated patients seen by many doctors on a regular basis – particularly in emergency departments (EDs), psychiatric units, and pain clinics, said Scott Zeller, MD, a psychiatrist who is vice president of Acute Psychiatric Medicine at Vituity, a multistate physician partnership based in Emeryville, California.
“Agitated patients have trouble communicating their needs and can become physically and verbally aggressive,” Dr. Zeller said. He reports that there are 1.7 million such incidents a year in this country, but most of the incidents of verbal aggression can be kept from exploding into physical violence.
Shooters, however, are very hard to stop because they usually plan the action in advance, Dr. Zeller said. He recalled the 2017 murder of Todd Graham, MD, a friend from medical school. Dr. Graham, an orthopedic surgeon in South Bend, Ind., was gunned down by the husband of one of his patients after Dr. Graham declined to prescribe opioids for her.
Playing down the risk of violence
Doctors may play down the risk of violence, even after they have experienced it personally. “Patients can get angry and may make threatening comments,” Dr. Weiss said. “A lot of doctors just brush it off.”
Simple remarks can set off violence-prone patients, as happened to James P. Phillips, MD, director of disaster and operational medicine at George Washington University, Washington. He recalled asking a prisoner who was visiting his hospital to “lower the volume,” and the man exploded. “Even though he was handcuffed to the bed, he heaved an oxygen tank into a window,” Dr. Phillips said. “He said he would be coming back to kill me.”
Sometimes threats or other types of verbal abuse can be as destructive as physical violence. Diann Krywko, MD, an emergency physician at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) Health, Charleston, has had some tough assignments. She worked in EDs in Detroit and Flint, Mich., for a decade before coming to MUSC, where she serves as director of wellness, health, and resilience. One of the incidents that has bothered her the most involved a threat.
It happened when Dr. Krywko denied a patient’s request for narcotics. “She was very angry and said she’d come to my home and cut my children’s heads off,” Dr. Krywko said. “To this day, what she said horrifies me. I still see her smile as she said that.”
Dr. Krywko considered filing for a restraining order against the patient but didn’t because the patient could have learned her address. Dr. Phillips said fear of retaliation is one reason many doctors don’t report threats from patients. “The patient you report knows where you work and may come there to take revenge,” he said. “Also, you may have to continue caring for the person who punched you.”
Online threats also may cause a great deal of angst. Dr. Phillips said he received many online threats when was a medical analyst for CNN in 2020. “Someone sent my address to his Twitter followers, and they shared it with others, so now the whole world knows where I live,” he said. “I had to upgrade security at my home.”
How to deal with volatile patients
Being nice may not always work, but in many cases, it can keep a volatile situation from exploding, according to Dr. Krywko.
“When patients begin to show signs of agitation or are already there, we always try to verbally deescalate the situation, which involves listening,” Dr. Krywko said. “They want someone to hear them out.”
Doctors speak to patients from a position of authority, but Dr. Krywko advises that they should not be too blunt. “Don’t tell patients they’re wrong,” she said. “Even if they may be incorrect, they feel their viewpoint is valid. Encourage a dialogue with words like, ‘Tell me more,’ ” Dr. Krywko said.
Defending yourself
Doctors may have little warning of an impending attack because a patient’s mood can change quickly. This happened several years ago to Jennifer Casaletto, MD, an emergency physician in Charlotte, N.C.
“A man was brought into my ED by ambulance,” she said. “He seemed very calm for a long while, but then he became completely unhinged. A male nurse placed himself between the patient and others and was attacked. He got hurt but was able to continue working.”
Dr. Zeller said health care teams sometimes overreact when patients lash out. “The old-fashioned way to deal with an agitated patient is to call in the cavalry – everyone does a group takedown,” he said. “The patient is put in restraints and heavily sedated. This is not good for anybody. Not only is it likely to injure and traumatize the patient, it can also injure the care team.”
Many hospital EDs have security guards. “I feel safer when a hospital has armed security guards, but they need to be well trained,” Dr. Casaletto said. “Many small hospitals and freestanding EDs do not have security officers at all, or the guards are undertrained or told not to touch anybody.”
In many electronic health record systems, doctors can flag violent patients so future caregivers can be forewarned. However, Dr. Zeller advises against writing about patients’ violence or rudeness in the medical record, because patients can have access to it and might take revenge.
Rising violence from patients
“It feels like it has become much more dangerous to work in the ED,” said Hasan Gokal, MD, an emergency physician working in EDs at the Texas Medical Center. “Just last week, a woman pulled out a gun and fired it in an ED near Houston.”
The statistics back up Dr. Gokal’s assessment. Injuries caused by violent attacks against medical professionals grew by 67% from 2011 to 2018, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Those levels rose even more during the COVID-19 pandemic – the assault rate in hospitals rose 23% just in 2020.
Dr. Krywko said she had “a patient who said she wanted to hurt the next person who irritated her, and that happened to me. She jumped out of her bed swinging and punching, and I wasn’t ready for it. I yelled for help and the care team came.”
“The rise in violence has to do with a decline in respect for authority,” Dr. Phillips said. “Some people now believe doctors are lying to them about the need for COVID precautions because they are taking money from the vaccine companies. The pandemic has exacerbated violence in every way.”
Dr. Phillips said that a growing lack of resources had led to more anger among patients. “There are fewer nurses and reduced physician coverage,” he said. “That means longer wait times for patients, which increases patients’ frustrations.”
Dr. Weiss said patients have higher expectations. “In sports medicine, the expectations are incredible,” she said. “Parents want their kids to get back to playing as soon as possible.”
“Hospitals in particular are soft targets for violence,” Dr. Phillips said. “People know you can’t assault a flight attendant, because it’s a federal offense, but there is no such federal offense for violence against health care personnel.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ralph Newman, MD, got a taste of how dangerous medicine could be at age 10, when he witnessed a physician being shot by a patient.
“I was visiting a friend whose father was a psychiatrist,” Dr. Newman recalled. “We were playing in the living room when the doorbell rang. My friend went to the door and opened it. Then I heard a shot. I ran to the front hall and saw my friend’s father slumped at the bottom of the stairs. He had come down the stairs to see who was there. It was a patient armed with a shotgun.”
As a result of the shooting, a large portion of the psychiatrist’s intestines was removed. In spite of this traumatic incident, Dr. Newman went on to become a psychiatrist – who treated many violent prisoners. “I knew it was dangerous,” he said, “but I rationalized that I wouldn’t be attacked because I would be nicer.”
That attitude seemed to work until 2002, when a prisoner threw boiling oil on him. Dr. Newman was working at the Federal Medical Center Butner, a facility for prisoners in North Carolina. “A prisoner I had been treating was denied parole, based on my recommendation,” he said. “From then on, he was looking for a way to exact revenge.”
“One day I was sitting in the nursing station, typing up notes,” Dr. Newman said. “Two new nurses, who were also there, had forgotten to lock the door, and the prisoner noticed that. He heated up some baby oil in a microwave, which was available to prisoners at the time. Then he walked into the office, threw the oil on my back, and came at me with a sharp pencil.”
Dr. Newman said the nurses fled to an adjoining office, locked the door, and wouldn’t let him in. He went into another office and collapsed in exhaustion. He was saved by an inmate who came on the scene, fended off the attacker, and called for help.
“I was taken to the burn unit,” Dr. Newman recalled. “I had second- and third-degree burns on 9% of my body. It was extremely painful. It took me 45 days to recover enough to get back to work.” The two nurses were fired.
Doctors take threats by patients more seriously now
When orthopedic surgeon Preston Phillips, MD, was killed by a patient in Tulsa, Okla., on June 1, Jennifer M. Weiss, MD, recognized the potential danger to physicians.
“The news left me feeling very shaken,” said Dr. Weiss, a pediatric orthopedic surgeon at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, Los Angeles. “Every orthopedic surgeon I talked to about it felt shaken.”
Dr. Weiss said the impact of that event prompted her to take a patient’s abuse more seriously than she might have previously. “Before the killing, my colleagues and I might have swept the incident under the rug, but we reported it to the authorities,” she said.
“What happened was I told a parent of a school-aged child that the child wasn’t ready to go back to sports,” Dr. Weiss says. “This parent was incredibly triggered – screaming and making verbal threats. The parent was standing between me and the door, so I couldn’t get out.”
Coworkers down the hall heard the yelling and helped Dr. Weiss get out of the room. “The parent was escorted out of the building, and the incident was reported to our risk management team,” she said.
Shooters/killers vs. agitated patients
Patients who shoot to kill are very different from agitated patients seen by many doctors on a regular basis – particularly in emergency departments (EDs), psychiatric units, and pain clinics, said Scott Zeller, MD, a psychiatrist who is vice president of Acute Psychiatric Medicine at Vituity, a multistate physician partnership based in Emeryville, California.
“Agitated patients have trouble communicating their needs and can become physically and verbally aggressive,” Dr. Zeller said. He reports that there are 1.7 million such incidents a year in this country, but most of the incidents of verbal aggression can be kept from exploding into physical violence.
Shooters, however, are very hard to stop because they usually plan the action in advance, Dr. Zeller said. He recalled the 2017 murder of Todd Graham, MD, a friend from medical school. Dr. Graham, an orthopedic surgeon in South Bend, Ind., was gunned down by the husband of one of his patients after Dr. Graham declined to prescribe opioids for her.
Playing down the risk of violence
Doctors may play down the risk of violence, even after they have experienced it personally. “Patients can get angry and may make threatening comments,” Dr. Weiss said. “A lot of doctors just brush it off.”
Simple remarks can set off violence-prone patients, as happened to James P. Phillips, MD, director of disaster and operational medicine at George Washington University, Washington. He recalled asking a prisoner who was visiting his hospital to “lower the volume,” and the man exploded. “Even though he was handcuffed to the bed, he heaved an oxygen tank into a window,” Dr. Phillips said. “He said he would be coming back to kill me.”
Sometimes threats or other types of verbal abuse can be as destructive as physical violence. Diann Krywko, MD, an emergency physician at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) Health, Charleston, has had some tough assignments. She worked in EDs in Detroit and Flint, Mich., for a decade before coming to MUSC, where she serves as director of wellness, health, and resilience. One of the incidents that has bothered her the most involved a threat.
It happened when Dr. Krywko denied a patient’s request for narcotics. “She was very angry and said she’d come to my home and cut my children’s heads off,” Dr. Krywko said. “To this day, what she said horrifies me. I still see her smile as she said that.”
Dr. Krywko considered filing for a restraining order against the patient but didn’t because the patient could have learned her address. Dr. Phillips said fear of retaliation is one reason many doctors don’t report threats from patients. “The patient you report knows where you work and may come there to take revenge,” he said. “Also, you may have to continue caring for the person who punched you.”
Online threats also may cause a great deal of angst. Dr. Phillips said he received many online threats when was a medical analyst for CNN in 2020. “Someone sent my address to his Twitter followers, and they shared it with others, so now the whole world knows where I live,” he said. “I had to upgrade security at my home.”
How to deal with volatile patients
Being nice may not always work, but in many cases, it can keep a volatile situation from exploding, according to Dr. Krywko.
“When patients begin to show signs of agitation or are already there, we always try to verbally deescalate the situation, which involves listening,” Dr. Krywko said. “They want someone to hear them out.”
Doctors speak to patients from a position of authority, but Dr. Krywko advises that they should not be too blunt. “Don’t tell patients they’re wrong,” she said. “Even if they may be incorrect, they feel their viewpoint is valid. Encourage a dialogue with words like, ‘Tell me more,’ ” Dr. Krywko said.
Defending yourself
Doctors may have little warning of an impending attack because a patient’s mood can change quickly. This happened several years ago to Jennifer Casaletto, MD, an emergency physician in Charlotte, N.C.
“A man was brought into my ED by ambulance,” she said. “He seemed very calm for a long while, but then he became completely unhinged. A male nurse placed himself between the patient and others and was attacked. He got hurt but was able to continue working.”
Dr. Zeller said health care teams sometimes overreact when patients lash out. “The old-fashioned way to deal with an agitated patient is to call in the cavalry – everyone does a group takedown,” he said. “The patient is put in restraints and heavily sedated. This is not good for anybody. Not only is it likely to injure and traumatize the patient, it can also injure the care team.”
Many hospital EDs have security guards. “I feel safer when a hospital has armed security guards, but they need to be well trained,” Dr. Casaletto said. “Many small hospitals and freestanding EDs do not have security officers at all, or the guards are undertrained or told not to touch anybody.”
In many electronic health record systems, doctors can flag violent patients so future caregivers can be forewarned. However, Dr. Zeller advises against writing about patients’ violence or rudeness in the medical record, because patients can have access to it and might take revenge.
Rising violence from patients
“It feels like it has become much more dangerous to work in the ED,” said Hasan Gokal, MD, an emergency physician working in EDs at the Texas Medical Center. “Just last week, a woman pulled out a gun and fired it in an ED near Houston.”
The statistics back up Dr. Gokal’s assessment. Injuries caused by violent attacks against medical professionals grew by 67% from 2011 to 2018, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Those levels rose even more during the COVID-19 pandemic – the assault rate in hospitals rose 23% just in 2020.
Dr. Krywko said she had “a patient who said she wanted to hurt the next person who irritated her, and that happened to me. She jumped out of her bed swinging and punching, and I wasn’t ready for it. I yelled for help and the care team came.”
“The rise in violence has to do with a decline in respect for authority,” Dr. Phillips said. “Some people now believe doctors are lying to them about the need for COVID precautions because they are taking money from the vaccine companies. The pandemic has exacerbated violence in every way.”
Dr. Phillips said that a growing lack of resources had led to more anger among patients. “There are fewer nurses and reduced physician coverage,” he said. “That means longer wait times for patients, which increases patients’ frustrations.”
Dr. Weiss said patients have higher expectations. “In sports medicine, the expectations are incredible,” she said. “Parents want their kids to get back to playing as soon as possible.”
“Hospitals in particular are soft targets for violence,” Dr. Phillips said. “People know you can’t assault a flight attendant, because it’s a federal offense, but there is no such federal offense for violence against health care personnel.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ten steps for clinicians to avoid being racist: The Francis commitment
As a Black man who grew up in this country, I can tell you first-hand what it does to you. The scars never go away, and your status is always in question, no matter your title or uniforms of respect. Eventually it wears you down.
I was born into poverty and the segregation of southwest Louisiana. I experienced the dehumanization intended for me: separate drinking fountains and poor foundational education. I was lucky to attend a historically Black college or university (Southern University, Baton Rouge, La.), that gave me my bearings. I then went to some of the very best, predominantly White institutions.
When I looked for a job after training, there were few integrated medical groups, so I started my own. It included practitioners who were White, Black, Jewish, Asian, Middle Eastern, Muslim, Christian, etc. We cross covered and treated patients from every corner of the globe.
In medicine, we treat human beings with disease. The disease should be the only difference that sets us apart. There is absolutely no place for racism.
It is difficult to be called a racist, and I have met only a handful of people in health care whom I would label as such. But racism is structural and institutionalized so that it is often hidden.
One way to overcome this is to make every effort possible to get to know people as individuals. Only then can we see that there are few real differences between us. I would often seek out a colleague from a different culture or race to have lunch with so I could learn more about them.
We all strive for the same things – validation, happiness, love, family, and a future. We all grieve over the same things.
What some caregivers may not realize is that, just as clinicians have been trained to recognize subtle signs and symptoms of disease, minorities can recognize racism immediately during a medical encounter. Our past experiences make us skilled at picking up a lack of eye contact or body language and tone of voice that are dismissive and disrespectful.
A patient who has felt racism may still return for care because of insurance coverage limitations, location, or a lack of alternatives. But trust and loyalty will never develop on the part of this patient, and empathy will be absent on the part of their caregiver.
To counter this in my own practice, I developed the Francis Commitment to avoid any hint of racism or bias toward my patients.
I commit to the following:
1. I see you.
2. I hear you.
3. I accept who you are.
4. I will try to understand how you must feel (empathy).
5. Treating you is very important to me.
6. I would like to gain your trust that I will do my very best to make you better.
7. I value you as a human being and will treat you as if you are family.
8. I care about what happens to you.
9. I want us to work together to fight this disease.
10. I am grateful that you chose me as your caregiver.
The INOVA health care system where I work has undertaken an initiative called What Matters Most to better understand the needs of every patient. We are currently working on a strategy of patient personalization to not only learn about their medical needs but also to discover who they are as a person. We incorporate Social Determinants of Health in our dealings with patients. We also have participated in a program called “A Long Talk”, where we learned that those of us who remain silent when we see or hear racism are responsible for its persistence and growth.
But we must do more. Racism will propagate if we live in silos surrounded by people whose ideas reflect our own. As long as we have nondiversified board rooms, departments, and staff, the problem will persist.
A lot of the biases that we unconsciously carry in our heads and hearts have no basis in reality and were placed there without our permission by parents, society, and friends. But we can replace these divisive thoughts and impulses.
What’s in your heart can only be known and controlled by you. How tolerant we are of racism is up to us: Do you call out racism; do you challenge any inkling of racism from friends or acquaintances; do you put pressure on institutions where you work to diversify in recruiting and hiring?
Think of all the advances in medicine that were achieved by people from different cultures and races. Racism has no place in what we have all devoted our lives to do – take care of our fellow humans.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a Black man who grew up in this country, I can tell you first-hand what it does to you. The scars never go away, and your status is always in question, no matter your title or uniforms of respect. Eventually it wears you down.
I was born into poverty and the segregation of southwest Louisiana. I experienced the dehumanization intended for me: separate drinking fountains and poor foundational education. I was lucky to attend a historically Black college or university (Southern University, Baton Rouge, La.), that gave me my bearings. I then went to some of the very best, predominantly White institutions.
When I looked for a job after training, there were few integrated medical groups, so I started my own. It included practitioners who were White, Black, Jewish, Asian, Middle Eastern, Muslim, Christian, etc. We cross covered and treated patients from every corner of the globe.
In medicine, we treat human beings with disease. The disease should be the only difference that sets us apart. There is absolutely no place for racism.
It is difficult to be called a racist, and I have met only a handful of people in health care whom I would label as such. But racism is structural and institutionalized so that it is often hidden.
One way to overcome this is to make every effort possible to get to know people as individuals. Only then can we see that there are few real differences between us. I would often seek out a colleague from a different culture or race to have lunch with so I could learn more about them.
We all strive for the same things – validation, happiness, love, family, and a future. We all grieve over the same things.
What some caregivers may not realize is that, just as clinicians have been trained to recognize subtle signs and symptoms of disease, minorities can recognize racism immediately during a medical encounter. Our past experiences make us skilled at picking up a lack of eye contact or body language and tone of voice that are dismissive and disrespectful.
A patient who has felt racism may still return for care because of insurance coverage limitations, location, or a lack of alternatives. But trust and loyalty will never develop on the part of this patient, and empathy will be absent on the part of their caregiver.
To counter this in my own practice, I developed the Francis Commitment to avoid any hint of racism or bias toward my patients.
I commit to the following:
1. I see you.
2. I hear you.
3. I accept who you are.
4. I will try to understand how you must feel (empathy).
5. Treating you is very important to me.
6. I would like to gain your trust that I will do my very best to make you better.
7. I value you as a human being and will treat you as if you are family.
8. I care about what happens to you.
9. I want us to work together to fight this disease.
10. I am grateful that you chose me as your caregiver.
The INOVA health care system where I work has undertaken an initiative called What Matters Most to better understand the needs of every patient. We are currently working on a strategy of patient personalization to not only learn about their medical needs but also to discover who they are as a person. We incorporate Social Determinants of Health in our dealings with patients. We also have participated in a program called “A Long Talk”, where we learned that those of us who remain silent when we see or hear racism are responsible for its persistence and growth.
But we must do more. Racism will propagate if we live in silos surrounded by people whose ideas reflect our own. As long as we have nondiversified board rooms, departments, and staff, the problem will persist.
A lot of the biases that we unconsciously carry in our heads and hearts have no basis in reality and were placed there without our permission by parents, society, and friends. But we can replace these divisive thoughts and impulses.
What’s in your heart can only be known and controlled by you. How tolerant we are of racism is up to us: Do you call out racism; do you challenge any inkling of racism from friends or acquaintances; do you put pressure on institutions where you work to diversify in recruiting and hiring?
Think of all the advances in medicine that were achieved by people from different cultures and races. Racism has no place in what we have all devoted our lives to do – take care of our fellow humans.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a Black man who grew up in this country, I can tell you first-hand what it does to you. The scars never go away, and your status is always in question, no matter your title or uniforms of respect. Eventually it wears you down.
I was born into poverty and the segregation of southwest Louisiana. I experienced the dehumanization intended for me: separate drinking fountains and poor foundational education. I was lucky to attend a historically Black college or university (Southern University, Baton Rouge, La.), that gave me my bearings. I then went to some of the very best, predominantly White institutions.
When I looked for a job after training, there were few integrated medical groups, so I started my own. It included practitioners who were White, Black, Jewish, Asian, Middle Eastern, Muslim, Christian, etc. We cross covered and treated patients from every corner of the globe.
In medicine, we treat human beings with disease. The disease should be the only difference that sets us apart. There is absolutely no place for racism.
It is difficult to be called a racist, and I have met only a handful of people in health care whom I would label as such. But racism is structural and institutionalized so that it is often hidden.
One way to overcome this is to make every effort possible to get to know people as individuals. Only then can we see that there are few real differences between us. I would often seek out a colleague from a different culture or race to have lunch with so I could learn more about them.
We all strive for the same things – validation, happiness, love, family, and a future. We all grieve over the same things.
What some caregivers may not realize is that, just as clinicians have been trained to recognize subtle signs and symptoms of disease, minorities can recognize racism immediately during a medical encounter. Our past experiences make us skilled at picking up a lack of eye contact or body language and tone of voice that are dismissive and disrespectful.
A patient who has felt racism may still return for care because of insurance coverage limitations, location, or a lack of alternatives. But trust and loyalty will never develop on the part of this patient, and empathy will be absent on the part of their caregiver.
To counter this in my own practice, I developed the Francis Commitment to avoid any hint of racism or bias toward my patients.
I commit to the following:
1. I see you.
2. I hear you.
3. I accept who you are.
4. I will try to understand how you must feel (empathy).
5. Treating you is very important to me.
6. I would like to gain your trust that I will do my very best to make you better.
7. I value you as a human being and will treat you as if you are family.
8. I care about what happens to you.
9. I want us to work together to fight this disease.
10. I am grateful that you chose me as your caregiver.
The INOVA health care system where I work has undertaken an initiative called What Matters Most to better understand the needs of every patient. We are currently working on a strategy of patient personalization to not only learn about their medical needs but also to discover who they are as a person. We incorporate Social Determinants of Health in our dealings with patients. We also have participated in a program called “A Long Talk”, where we learned that those of us who remain silent when we see or hear racism are responsible for its persistence and growth.
But we must do more. Racism will propagate if we live in silos surrounded by people whose ideas reflect our own. As long as we have nondiversified board rooms, departments, and staff, the problem will persist.
A lot of the biases that we unconsciously carry in our heads and hearts have no basis in reality and were placed there without our permission by parents, society, and friends. But we can replace these divisive thoughts and impulses.
What’s in your heart can only be known and controlled by you. How tolerant we are of racism is up to us: Do you call out racism; do you challenge any inkling of racism from friends or acquaintances; do you put pressure on institutions where you work to diversify in recruiting and hiring?
Think of all the advances in medicine that were achieved by people from different cultures and races. Racism has no place in what we have all devoted our lives to do – take care of our fellow humans.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderate drinking shows more benefit for older vs. younger adults
The health risks and benefits of moderate alcohol consumption are complex and remain a hot topic of debate. The data suggest that small amounts of alcohol may reduce the risk of certain health outcomes over time, but increase the risk of others, wrote Dana Bryazka, MS, a researcher at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues, in a paper published in the Lancet.
“The amount of alcohol that minimizes health loss is likely to depend on the distribution of underlying causes of disease burden in a given population. Since this distribution varies widely by geography, age, sex, and time, the level of alcohol consumption associated with the lowest risk to health would depend on the age structure and disease composition of that population,” the researchers wrote.
“We estimate that 1.78 million people worldwide died due to alcohol use in 2020,” Ms. Bryazka said in an interview. “It is important that alcohol consumption guidelines and policies are updated to minimize this harm, particularly in the populations at greatest risk,” she said.
“Existing alcohol consumption guidelines frequently vary by sex, with higher consumption thresholds set for males compared to females. Interestingly, with the currently available data we do not see evidence that risk of alcohol use varies by sex,” she noted.
Methods and results
In the study, the researchers conducted a systematic analysis of burden-weighted dose-response relative risk curves across 22 health outcomes. They used disease rates from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2020 for the years 1990-2020 for 21 regions, including 204 countries and territories. The data were analyzed by 5-year age group, sex, and year for individuals aged 15-95 years and older. The researchers estimated the theoretical minimum risk exposure level (TMREL) and nondrinker equivalent (NDE), meaning the amount of alcohol at which the health risk equals that of a nondrinker.
One standard drink was defined as 10 g of pure alcohol, equivalent to a small glass of red wine (100 mL or 3.4 fluid ounces) at 13% alcohol by volume, a can or bottle of beer (375 mL or 12 fluid ounces) at 3.5% alcohol by volume, or a shot of whiskey or other spirits (30 mL or 1.0 fluid ounces) at 40% alcohol by volume.
Overall, the TMREL was low regardless of age, sex, time, or geography, and varied from 0 to 1.87 standard drinks per day. However, it was lowest for males aged 15-39 years (0.136 drinks per day) and only slightly higher for females aged 15-39 (0.273), representing 1-2 tenths of a standard drink.
For adults aged 40 and older without any underlying health conditions, drinking a small amount of alcohol may provide some benefits, such as reducing the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, the researchers noted. In general, for individuals aged 40-64 years, TMRELs ranged from about half a standard drink per day (0.527 drinks for males and 0.562 standard drinks per day for females) to almost two standard drinks (1.69 standard drinks per day for males and 1.82 for females). For those older than 65 years, the TMRELs represented just over 3 standard drinks per day (3.19 for males and 3.51 for females). For individuals aged 40 years and older, the distribution of disease burden varied by region, but was J-shaped across all regions, the researchers noted.
The researchers also found that those individuals consuming harmful amounts of alcohol were most likely to be aged 15-39 (59.1%) and male (76.9%).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and lack of data on drinking patterns, such as binge drinking, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the lack of data reflecting patterns of alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, and exclusion of outcomes often associated with alcohol use, such as depression, anxiety, and dementia, that might reduce estimates of TMREL and NDE.
However, the results add to the ongoing discussion of the relationship between moderate alcohol consumption and health, the researchers said.
“The findings of this study support the development of tailored guidelines and recommendations on alcohol consumption by age and across regions and highlight that existing low consumption thresholds are too high for younger populations in all regions,” they concluded.
Consider individual factors when counseling patients
The takeaway message for primary care is that alcohol consumed in moderation can reduce the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, Ms. Bryazka noted. “However, it also increases the risk of many cancers, intentional and unintentional injuries, and infectious diseases like tuberculosis,” she said. “Of these health outcomes, young people are most likely to experience injuries, and as a result, we find that there are significant health risks associated with consuming alcohol for young people. Among older individuals, the relative proportions of these outcomes vary by geography, and so do the risks associated with consuming alcohol,” she explained.
“Importantly, our analysis was conducted at the population level; when evaluating risk at the individual level, it is also important to consider other factors such as the presence of comorbidities and interactions between alcohol and medications,” she emphasized.
Health and alcohol interaction is complicated
“These findings seemingly contradict a previous [Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study] estimate published in The Lancet, which emphasized that any alcohol use, regardless of amount, leads to health loss across populations,” wrote Robyn Burton, PhD, and Nick Sheron, MD, both of King’s College, London, in an accompanying comment.
However, the novel methods of weighting relative risk curves according to levels of underlying disease drive the difference in results, along with disaggregated estimates by age, sex, and region, they said.
“Across most geographical regions in this latest analysis, injuries accounted for most alcohol-related harm in younger age groups. This led to a minimum risk level of zero, or very close to zero, among individuals aged 15-39 years across all geographical regions,” which is lower than the level for older adults because of the shift in alcohol-related disease burden towards cardiovascular disease and cancers, they said. “This highlights the need to consider existing rates of disease in a population when trying to determine the total harm posed by alcohol,” the commentators wrote.
In an additional commentary, Tony Rao, MD, a visiting clinical research fellow in psychiatry at King’s College, London, noted that “the elephant in the room with this study is the interpretation of risk based on outcomes for cardiovascular disease – particularly in older people. We know that any purported health benefits from alcohol on the heart and circulation are balanced out by the increased risk from other conditions such as cancer, liver disease, and mental disorders such as depression and dementia,” Dr. Rao said. “If we are to simply draw the conclusion that older people should continue or start drinking small amounts because it protects against diseases affecting heart and circulation – which still remains controversial – other lifestyle changes or the use of drugs targeted at individual cardiovascular disorders seem like a less harmful way of improving health and wellbeing.”
Data can guide clinical practice
No previous study has examined the effect of the theoretical minimum risk of alcohol consumption by geography, age, sex, and time in the context of background disease rates, said Noel Deep, MD, in an interview.
“This study enabled the researchers to quantify the proportion of the population that consumed alcohol in amounts that exceeded the thresholds by location, age, sex, and year, and this can serve as a guide in our efforts to target the control of alcohol intake by individuals,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc. He also serves as chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
The first take-home message for clinicians is that even low levels of alcohol consumption can have deleterious effects on the health of patients, and patients should be advised accordingly based on the prevalence of diseases in that community and geographic area, Dr. Deep said. “Secondly, clinicians should also consider the risk of alcohol consumption on all forms of health impacts in a given population rather than just focusing on alcohol-related health conditions,” he added.
“This study provides us with the data to tailor our efforts in educating the clinicians and the public about the relationship between alcohol consumption and disease outcomes based on the observed disease rates in each population,” Dr. Deep explained. “The data should provide another reason for physicians to advise their younger patients, especially the younger males, to avoid or minimize alcohol use,” he said. The data also can help clinicians formulate public health messaging and community education to reduce harmful alcohol use, he added.
As for additional research, Dr. Deep said he would like to see data on the difference in the health-related effects of alcohol in binge-drinkers vs. those who regularly consume alcohol on a daily basis. “It would probably also be helpful to figure out what type of alcohol is being studied and the quality of the alcohol,” he said.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Ms. Bryazka and colleagues had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Burton disclosed serving as a consultant to the World Health Organization European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Dr. Sheron had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Internal Medicine News.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
The health risks and benefits of moderate alcohol consumption are complex and remain a hot topic of debate. The data suggest that small amounts of alcohol may reduce the risk of certain health outcomes over time, but increase the risk of others, wrote Dana Bryazka, MS, a researcher at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues, in a paper published in the Lancet.
“The amount of alcohol that minimizes health loss is likely to depend on the distribution of underlying causes of disease burden in a given population. Since this distribution varies widely by geography, age, sex, and time, the level of alcohol consumption associated with the lowest risk to health would depend on the age structure and disease composition of that population,” the researchers wrote.
“We estimate that 1.78 million people worldwide died due to alcohol use in 2020,” Ms. Bryazka said in an interview. “It is important that alcohol consumption guidelines and policies are updated to minimize this harm, particularly in the populations at greatest risk,” she said.
“Existing alcohol consumption guidelines frequently vary by sex, with higher consumption thresholds set for males compared to females. Interestingly, with the currently available data we do not see evidence that risk of alcohol use varies by sex,” she noted.
Methods and results
In the study, the researchers conducted a systematic analysis of burden-weighted dose-response relative risk curves across 22 health outcomes. They used disease rates from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2020 for the years 1990-2020 for 21 regions, including 204 countries and territories. The data were analyzed by 5-year age group, sex, and year for individuals aged 15-95 years and older. The researchers estimated the theoretical minimum risk exposure level (TMREL) and nondrinker equivalent (NDE), meaning the amount of alcohol at which the health risk equals that of a nondrinker.
One standard drink was defined as 10 g of pure alcohol, equivalent to a small glass of red wine (100 mL or 3.4 fluid ounces) at 13% alcohol by volume, a can or bottle of beer (375 mL or 12 fluid ounces) at 3.5% alcohol by volume, or a shot of whiskey or other spirits (30 mL or 1.0 fluid ounces) at 40% alcohol by volume.
Overall, the TMREL was low regardless of age, sex, time, or geography, and varied from 0 to 1.87 standard drinks per day. However, it was lowest for males aged 15-39 years (0.136 drinks per day) and only slightly higher for females aged 15-39 (0.273), representing 1-2 tenths of a standard drink.
For adults aged 40 and older without any underlying health conditions, drinking a small amount of alcohol may provide some benefits, such as reducing the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, the researchers noted. In general, for individuals aged 40-64 years, TMRELs ranged from about half a standard drink per day (0.527 drinks for males and 0.562 standard drinks per day for females) to almost two standard drinks (1.69 standard drinks per day for males and 1.82 for females). For those older than 65 years, the TMRELs represented just over 3 standard drinks per day (3.19 for males and 3.51 for females). For individuals aged 40 years and older, the distribution of disease burden varied by region, but was J-shaped across all regions, the researchers noted.
The researchers also found that those individuals consuming harmful amounts of alcohol were most likely to be aged 15-39 (59.1%) and male (76.9%).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and lack of data on drinking patterns, such as binge drinking, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the lack of data reflecting patterns of alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, and exclusion of outcomes often associated with alcohol use, such as depression, anxiety, and dementia, that might reduce estimates of TMREL and NDE.
However, the results add to the ongoing discussion of the relationship between moderate alcohol consumption and health, the researchers said.
“The findings of this study support the development of tailored guidelines and recommendations on alcohol consumption by age and across regions and highlight that existing low consumption thresholds are too high for younger populations in all regions,” they concluded.
Consider individual factors when counseling patients
The takeaway message for primary care is that alcohol consumed in moderation can reduce the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, Ms. Bryazka noted. “However, it also increases the risk of many cancers, intentional and unintentional injuries, and infectious diseases like tuberculosis,” she said. “Of these health outcomes, young people are most likely to experience injuries, and as a result, we find that there are significant health risks associated with consuming alcohol for young people. Among older individuals, the relative proportions of these outcomes vary by geography, and so do the risks associated with consuming alcohol,” she explained.
“Importantly, our analysis was conducted at the population level; when evaluating risk at the individual level, it is also important to consider other factors such as the presence of comorbidities and interactions between alcohol and medications,” she emphasized.
Health and alcohol interaction is complicated
“These findings seemingly contradict a previous [Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study] estimate published in The Lancet, which emphasized that any alcohol use, regardless of amount, leads to health loss across populations,” wrote Robyn Burton, PhD, and Nick Sheron, MD, both of King’s College, London, in an accompanying comment.
However, the novel methods of weighting relative risk curves according to levels of underlying disease drive the difference in results, along with disaggregated estimates by age, sex, and region, they said.
“Across most geographical regions in this latest analysis, injuries accounted for most alcohol-related harm in younger age groups. This led to a minimum risk level of zero, or very close to zero, among individuals aged 15-39 years across all geographical regions,” which is lower than the level for older adults because of the shift in alcohol-related disease burden towards cardiovascular disease and cancers, they said. “This highlights the need to consider existing rates of disease in a population when trying to determine the total harm posed by alcohol,” the commentators wrote.
In an additional commentary, Tony Rao, MD, a visiting clinical research fellow in psychiatry at King’s College, London, noted that “the elephant in the room with this study is the interpretation of risk based on outcomes for cardiovascular disease – particularly in older people. We know that any purported health benefits from alcohol on the heart and circulation are balanced out by the increased risk from other conditions such as cancer, liver disease, and mental disorders such as depression and dementia,” Dr. Rao said. “If we are to simply draw the conclusion that older people should continue or start drinking small amounts because it protects against diseases affecting heart and circulation – which still remains controversial – other lifestyle changes or the use of drugs targeted at individual cardiovascular disorders seem like a less harmful way of improving health and wellbeing.”
Data can guide clinical practice
No previous study has examined the effect of the theoretical minimum risk of alcohol consumption by geography, age, sex, and time in the context of background disease rates, said Noel Deep, MD, in an interview.
“This study enabled the researchers to quantify the proportion of the population that consumed alcohol in amounts that exceeded the thresholds by location, age, sex, and year, and this can serve as a guide in our efforts to target the control of alcohol intake by individuals,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc. He also serves as chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
The first take-home message for clinicians is that even low levels of alcohol consumption can have deleterious effects on the health of patients, and patients should be advised accordingly based on the prevalence of diseases in that community and geographic area, Dr. Deep said. “Secondly, clinicians should also consider the risk of alcohol consumption on all forms of health impacts in a given population rather than just focusing on alcohol-related health conditions,” he added.
“This study provides us with the data to tailor our efforts in educating the clinicians and the public about the relationship between alcohol consumption and disease outcomes based on the observed disease rates in each population,” Dr. Deep explained. “The data should provide another reason for physicians to advise their younger patients, especially the younger males, to avoid or minimize alcohol use,” he said. The data also can help clinicians formulate public health messaging and community education to reduce harmful alcohol use, he added.
As for additional research, Dr. Deep said he would like to see data on the difference in the health-related effects of alcohol in binge-drinkers vs. those who regularly consume alcohol on a daily basis. “It would probably also be helpful to figure out what type of alcohol is being studied and the quality of the alcohol,” he said.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Ms. Bryazka and colleagues had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Burton disclosed serving as a consultant to the World Health Organization European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Dr. Sheron had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Internal Medicine News.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
The health risks and benefits of moderate alcohol consumption are complex and remain a hot topic of debate. The data suggest that small amounts of alcohol may reduce the risk of certain health outcomes over time, but increase the risk of others, wrote Dana Bryazka, MS, a researcher at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues, in a paper published in the Lancet.
“The amount of alcohol that minimizes health loss is likely to depend on the distribution of underlying causes of disease burden in a given population. Since this distribution varies widely by geography, age, sex, and time, the level of alcohol consumption associated with the lowest risk to health would depend on the age structure and disease composition of that population,” the researchers wrote.
“We estimate that 1.78 million people worldwide died due to alcohol use in 2020,” Ms. Bryazka said in an interview. “It is important that alcohol consumption guidelines and policies are updated to minimize this harm, particularly in the populations at greatest risk,” she said.
“Existing alcohol consumption guidelines frequently vary by sex, with higher consumption thresholds set for males compared to females. Interestingly, with the currently available data we do not see evidence that risk of alcohol use varies by sex,” she noted.
Methods and results
In the study, the researchers conducted a systematic analysis of burden-weighted dose-response relative risk curves across 22 health outcomes. They used disease rates from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2020 for the years 1990-2020 for 21 regions, including 204 countries and territories. The data were analyzed by 5-year age group, sex, and year for individuals aged 15-95 years and older. The researchers estimated the theoretical minimum risk exposure level (TMREL) and nondrinker equivalent (NDE), meaning the amount of alcohol at which the health risk equals that of a nondrinker.
One standard drink was defined as 10 g of pure alcohol, equivalent to a small glass of red wine (100 mL or 3.4 fluid ounces) at 13% alcohol by volume, a can or bottle of beer (375 mL or 12 fluid ounces) at 3.5% alcohol by volume, or a shot of whiskey or other spirits (30 mL or 1.0 fluid ounces) at 40% alcohol by volume.
Overall, the TMREL was low regardless of age, sex, time, or geography, and varied from 0 to 1.87 standard drinks per day. However, it was lowest for males aged 15-39 years (0.136 drinks per day) and only slightly higher for females aged 15-39 (0.273), representing 1-2 tenths of a standard drink.
For adults aged 40 and older without any underlying health conditions, drinking a small amount of alcohol may provide some benefits, such as reducing the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, the researchers noted. In general, for individuals aged 40-64 years, TMRELs ranged from about half a standard drink per day (0.527 drinks for males and 0.562 standard drinks per day for females) to almost two standard drinks (1.69 standard drinks per day for males and 1.82 for females). For those older than 65 years, the TMRELs represented just over 3 standard drinks per day (3.19 for males and 3.51 for females). For individuals aged 40 years and older, the distribution of disease burden varied by region, but was J-shaped across all regions, the researchers noted.
The researchers also found that those individuals consuming harmful amounts of alcohol were most likely to be aged 15-39 (59.1%) and male (76.9%).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and lack of data on drinking patterns, such as binge drinking, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the lack of data reflecting patterns of alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, and exclusion of outcomes often associated with alcohol use, such as depression, anxiety, and dementia, that might reduce estimates of TMREL and NDE.
However, the results add to the ongoing discussion of the relationship between moderate alcohol consumption and health, the researchers said.
“The findings of this study support the development of tailored guidelines and recommendations on alcohol consumption by age and across regions and highlight that existing low consumption thresholds are too high for younger populations in all regions,” they concluded.
Consider individual factors when counseling patients
The takeaway message for primary care is that alcohol consumed in moderation can reduce the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, Ms. Bryazka noted. “However, it also increases the risk of many cancers, intentional and unintentional injuries, and infectious diseases like tuberculosis,” she said. “Of these health outcomes, young people are most likely to experience injuries, and as a result, we find that there are significant health risks associated with consuming alcohol for young people. Among older individuals, the relative proportions of these outcomes vary by geography, and so do the risks associated with consuming alcohol,” she explained.
“Importantly, our analysis was conducted at the population level; when evaluating risk at the individual level, it is also important to consider other factors such as the presence of comorbidities and interactions between alcohol and medications,” she emphasized.
Health and alcohol interaction is complicated
“These findings seemingly contradict a previous [Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study] estimate published in The Lancet, which emphasized that any alcohol use, regardless of amount, leads to health loss across populations,” wrote Robyn Burton, PhD, and Nick Sheron, MD, both of King’s College, London, in an accompanying comment.
However, the novel methods of weighting relative risk curves according to levels of underlying disease drive the difference in results, along with disaggregated estimates by age, sex, and region, they said.
“Across most geographical regions in this latest analysis, injuries accounted for most alcohol-related harm in younger age groups. This led to a minimum risk level of zero, or very close to zero, among individuals aged 15-39 years across all geographical regions,” which is lower than the level for older adults because of the shift in alcohol-related disease burden towards cardiovascular disease and cancers, they said. “This highlights the need to consider existing rates of disease in a population when trying to determine the total harm posed by alcohol,” the commentators wrote.
In an additional commentary, Tony Rao, MD, a visiting clinical research fellow in psychiatry at King’s College, London, noted that “the elephant in the room with this study is the interpretation of risk based on outcomes for cardiovascular disease – particularly in older people. We know that any purported health benefits from alcohol on the heart and circulation are balanced out by the increased risk from other conditions such as cancer, liver disease, and mental disorders such as depression and dementia,” Dr. Rao said. “If we are to simply draw the conclusion that older people should continue or start drinking small amounts because it protects against diseases affecting heart and circulation – which still remains controversial – other lifestyle changes or the use of drugs targeted at individual cardiovascular disorders seem like a less harmful way of improving health and wellbeing.”
Data can guide clinical practice
No previous study has examined the effect of the theoretical minimum risk of alcohol consumption by geography, age, sex, and time in the context of background disease rates, said Noel Deep, MD, in an interview.
“This study enabled the researchers to quantify the proportion of the population that consumed alcohol in amounts that exceeded the thresholds by location, age, sex, and year, and this can serve as a guide in our efforts to target the control of alcohol intake by individuals,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc. He also serves as chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
The first take-home message for clinicians is that even low levels of alcohol consumption can have deleterious effects on the health of patients, and patients should be advised accordingly based on the prevalence of diseases in that community and geographic area, Dr. Deep said. “Secondly, clinicians should also consider the risk of alcohol consumption on all forms of health impacts in a given population rather than just focusing on alcohol-related health conditions,” he added.
“This study provides us with the data to tailor our efforts in educating the clinicians and the public about the relationship between alcohol consumption and disease outcomes based on the observed disease rates in each population,” Dr. Deep explained. “The data should provide another reason for physicians to advise their younger patients, especially the younger males, to avoid or minimize alcohol use,” he said. The data also can help clinicians formulate public health messaging and community education to reduce harmful alcohol use, he added.
As for additional research, Dr. Deep said he would like to see data on the difference in the health-related effects of alcohol in binge-drinkers vs. those who regularly consume alcohol on a daily basis. “It would probably also be helpful to figure out what type of alcohol is being studied and the quality of the alcohol,” he said.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Ms. Bryazka and colleagues had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Burton disclosed serving as a consultant to the World Health Organization European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Dr. Sheron had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Internal Medicine News.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
FROM THE LANCET
Bevacizumab first matches aflibercept for diabetic macular edema
A cost-saving, stepwise approach to treating diabetic macular edema was as effective and at least as safe as what’s been the standard approach, which jumps straight to the costlier treatment, in a head-to-head, multicenter, U.S. randomized trial of the two regimens that included 312 eyes in 270 adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
The findings validate a treatment regimen for diabetic macular edema that’s already common in U.S. practice based on requirements by many health insurance providers because of the money it saves.
The step-therapy approach studied involves starting off-label treatment with the relatively inexpensive agent bevacizumab (Avastin), followed by a switch to the much pricier aflibercept (Eylea) when patients don’t adequately respond, following a prespecified algorithm that applies four criteria to determine when patients need to change agents.
These new findings build on a 2016 study that compared aflibercept monotherapy with bevacizumab monotherapy and showed that after 2 years of treatment aflibercept produced clearly better outcomes.
The new trial findings “are particularly relevant given the increasing frequency of insurers mandating step therapy with bevacizumab before the use of other drugs” such as aflibercept, noted Chirag D. Jhaveri, MD, and colleagues in the study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Opportunity for ‘substantial cost reductions’
Jhaveri, a retina surgeon in Austin, Texas, and associates note that, based on Medicare reimbursement rates of $1,830 for a single dose of aflibercept and $70 for one dose of bevacizumab, starting treatment with bevacizumab could produce “substantial cost reductions for the health care system.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial agree. Step therapy that starts with bevacizumab would probably result in “substantial” cost savings, and the findings document “similar outcomes” from the two tested regimens based on improvements in visual acuity and changes in the thickness measurement of the central retina during the 2-year trial, write David C. Musch, PhD, and Emily Y. Chew, MD.
Dr. Musch, a professor and ophthalmology epidemiologist at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, and Dr. Chew, director of the Division of Epidemiology and Clinical Applications at the National Eye Institute in Bethesda, Md., also laud the “rigorous” study for its design and conduct that was “beyond reproach,” and for producing evidence that “applies well to clinical practice.”
The only potential drawback to the step-therapy approach, they write, is that people with diabetes often have “numerous coexisting conditions that make it more difficult for them to adhere to frequent follow-up visits,” a key element of the tested step-care protocol, which mandated follow-up visits every 4 weeks during the first year and every 4-16 weeks during the second year.
312 eyes of 270 patients
The new trial, organized by the DRCR Retinal Network and the Jaeb Center for Health Research in Tampa, Fla., ran at 54 U.S. sites from December 2017 to November 2019. The study randomized 158 eyes in 137 patients to aflibercept monotherapy, and 154 eyes in 133 patients to the step-care regimen (both eyes were treated in several patients in each group, with each eye receiving a different regimen). Participants were around 60 years old, 48% were women, and 95% had type 2 diabetes.
To be eligible for enrollment, patients had at least one eye with a best-corrected visual-acuity letter score of 24-69 on an Electronic Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study chart (ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating better visual acuity), which corresponds to Snellen chart values of 20/320-20/50, readings that encompass most patients with diabetic macular edema, noted study authors Adam R. Glassman and Jennifer K. Sun, MD, in an interview.
“Very few patients with diabetic macular edema have vision due to this alone that is worse than 20/320, which meets criteria for legal blindness,” said Dr. Glassman, who is executive director of the Jaeb Center for Health Research, and Dr. Sun, who is chief of the center for clinical eye research and trials at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston and chair of the DRCR Retinal Network.
The primary outcome was time-averaged change in visual-acuity letter score from baseline to 2 years, which improved by an average of 15.0 letters in the aflibercept monotherapy group and an average of 14.0 letters in the step-therapy group, an adjusted difference of 0.8 letters, which was not significant. An improvement from baseline of at least 15 letters occurred in 53% of the eyes in the aflibercept monotherapy group and in 58% of those who had step therapy, and 77% of eyes in both groups had improvements of at least 10 letters.
Central retinal thickness dropped from baseline by an average of 192 mcm with aflibercept monotherapy and 198 mcm with step therapy. The average number of total treatments (by intravitreous injection) was 14.6 in the aflibercept monotherapy group and 16.1 in the step-therapy group. After the first 24 weeks of the study, 39% of eyes in the step-therapy group had switched from bevacizumab to aflibercept injections; after 1 year, 60% of eyes had switched; and by study end, after 2 years, 70% had changed.
The bevacizumab-first group also showed at least comparable if not better safety, with similar rates of prespecified ocular events in both groups, but with a significantly lower rate of serious systemic adverse events, which occurred in 52% of the eyes treated with aflibercept only and 36% of eyes that began treatment on bevacizumab. Serious systemic adverse events occurred in 43% of patients who had two eyes treated as part of the trial.
‘Bevacizumab first was noninferior’
The team that designed the trial opted for a superiority design rather than a noninferiority trial and powered the study based on the presumption that aflibercept monotherapy would prove superior, said Dr. Glassman and Dr. Sun. “We feel that the clinical interpretation of these results will be similar to the interpretation if we had conducted a noninferiority study, and we found that bevacizumab first was noninferior to aflibercept monotherapy,” they maintained in an interview.
Dr. Glassman and Dr. Sun said they and their coauthors are now analyzing the results to try to find patient characteristics that could identify eyes most likely to respond to the bevacizumab-first approach. “It would be clinically valuable” to use the results to identify characteristics that could help guide clinicians’ treatment approach and enhance patient counseling, they said.
The study received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Genentech, Novartis, and Regenxbio. Dr. Glassman has reported receiving grants from Genentech and Regeneron. Dr. Sun has reported receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Biotech, KalVista, Optovue, and Physical Sciences, grants and travel support from Novartis and Novo Nordisk, travel support from Merck, writing support from Genentech, and equipment supplied by Adaptive Sensory and Boston Micromachines. Dr. Musch and Dr. Chew have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A cost-saving, stepwise approach to treating diabetic macular edema was as effective and at least as safe as what’s been the standard approach, which jumps straight to the costlier treatment, in a head-to-head, multicenter, U.S. randomized trial of the two regimens that included 312 eyes in 270 adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
The findings validate a treatment regimen for diabetic macular edema that’s already common in U.S. practice based on requirements by many health insurance providers because of the money it saves.
The step-therapy approach studied involves starting off-label treatment with the relatively inexpensive agent bevacizumab (Avastin), followed by a switch to the much pricier aflibercept (Eylea) when patients don’t adequately respond, following a prespecified algorithm that applies four criteria to determine when patients need to change agents.
These new findings build on a 2016 study that compared aflibercept monotherapy with bevacizumab monotherapy and showed that after 2 years of treatment aflibercept produced clearly better outcomes.
The new trial findings “are particularly relevant given the increasing frequency of insurers mandating step therapy with bevacizumab before the use of other drugs” such as aflibercept, noted Chirag D. Jhaveri, MD, and colleagues in the study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Opportunity for ‘substantial cost reductions’
Jhaveri, a retina surgeon in Austin, Texas, and associates note that, based on Medicare reimbursement rates of $1,830 for a single dose of aflibercept and $70 for one dose of bevacizumab, starting treatment with bevacizumab could produce “substantial cost reductions for the health care system.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial agree. Step therapy that starts with bevacizumab would probably result in “substantial” cost savings, and the findings document “similar outcomes” from the two tested regimens based on improvements in visual acuity and changes in the thickness measurement of the central retina during the 2-year trial, write David C. Musch, PhD, and Emily Y. Chew, MD.
Dr. Musch, a professor and ophthalmology epidemiologist at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, and Dr. Chew, director of the Division of Epidemiology and Clinical Applications at the National Eye Institute in Bethesda, Md., also laud the “rigorous” study for its design and conduct that was “beyond reproach,” and for producing evidence that “applies well to clinical practice.”
The only potential drawback to the step-therapy approach, they write, is that people with diabetes often have “numerous coexisting conditions that make it more difficult for them to adhere to frequent follow-up visits,” a key element of the tested step-care protocol, which mandated follow-up visits every 4 weeks during the first year and every 4-16 weeks during the second year.
312 eyes of 270 patients
The new trial, organized by the DRCR Retinal Network and the Jaeb Center for Health Research in Tampa, Fla., ran at 54 U.S. sites from December 2017 to November 2019. The study randomized 158 eyes in 137 patients to aflibercept monotherapy, and 154 eyes in 133 patients to the step-care regimen (both eyes were treated in several patients in each group, with each eye receiving a different regimen). Participants were around 60 years old, 48% were women, and 95% had type 2 diabetes.
To be eligible for enrollment, patients had at least one eye with a best-corrected visual-acuity letter score of 24-69 on an Electronic Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study chart (ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating better visual acuity), which corresponds to Snellen chart values of 20/320-20/50, readings that encompass most patients with diabetic macular edema, noted study authors Adam R. Glassman and Jennifer K. Sun, MD, in an interview.
“Very few patients with diabetic macular edema have vision due to this alone that is worse than 20/320, which meets criteria for legal blindness,” said Dr. Glassman, who is executive director of the Jaeb Center for Health Research, and Dr. Sun, who is chief of the center for clinical eye research and trials at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston and chair of the DRCR Retinal Network.
The primary outcome was time-averaged change in visual-acuity letter score from baseline to 2 years, which improved by an average of 15.0 letters in the aflibercept monotherapy group and an average of 14.0 letters in the step-therapy group, an adjusted difference of 0.8 letters, which was not significant. An improvement from baseline of at least 15 letters occurred in 53% of the eyes in the aflibercept monotherapy group and in 58% of those who had step therapy, and 77% of eyes in both groups had improvements of at least 10 letters.
Central retinal thickness dropped from baseline by an average of 192 mcm with aflibercept monotherapy and 198 mcm with step therapy. The average number of total treatments (by intravitreous injection) was 14.6 in the aflibercept monotherapy group and 16.1 in the step-therapy group. After the first 24 weeks of the study, 39% of eyes in the step-therapy group had switched from bevacizumab to aflibercept injections; after 1 year, 60% of eyes had switched; and by study end, after 2 years, 70% had changed.
The bevacizumab-first group also showed at least comparable if not better safety, with similar rates of prespecified ocular events in both groups, but with a significantly lower rate of serious systemic adverse events, which occurred in 52% of the eyes treated with aflibercept only and 36% of eyes that began treatment on bevacizumab. Serious systemic adverse events occurred in 43% of patients who had two eyes treated as part of the trial.
‘Bevacizumab first was noninferior’
The team that designed the trial opted for a superiority design rather than a noninferiority trial and powered the study based on the presumption that aflibercept monotherapy would prove superior, said Dr. Glassman and Dr. Sun. “We feel that the clinical interpretation of these results will be similar to the interpretation if we had conducted a noninferiority study, and we found that bevacizumab first was noninferior to aflibercept monotherapy,” they maintained in an interview.
Dr. Glassman and Dr. Sun said they and their coauthors are now analyzing the results to try to find patient characteristics that could identify eyes most likely to respond to the bevacizumab-first approach. “It would be clinically valuable” to use the results to identify characteristics that could help guide clinicians’ treatment approach and enhance patient counseling, they said.
The study received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Genentech, Novartis, and Regenxbio. Dr. Glassman has reported receiving grants from Genentech and Regeneron. Dr. Sun has reported receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Biotech, KalVista, Optovue, and Physical Sciences, grants and travel support from Novartis and Novo Nordisk, travel support from Merck, writing support from Genentech, and equipment supplied by Adaptive Sensory and Boston Micromachines. Dr. Musch and Dr. Chew have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A cost-saving, stepwise approach to treating diabetic macular edema was as effective and at least as safe as what’s been the standard approach, which jumps straight to the costlier treatment, in a head-to-head, multicenter, U.S. randomized trial of the two regimens that included 312 eyes in 270 adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
The findings validate a treatment regimen for diabetic macular edema that’s already common in U.S. practice based on requirements by many health insurance providers because of the money it saves.
The step-therapy approach studied involves starting off-label treatment with the relatively inexpensive agent bevacizumab (Avastin), followed by a switch to the much pricier aflibercept (Eylea) when patients don’t adequately respond, following a prespecified algorithm that applies four criteria to determine when patients need to change agents.
These new findings build on a 2016 study that compared aflibercept monotherapy with bevacizumab monotherapy and showed that after 2 years of treatment aflibercept produced clearly better outcomes.
The new trial findings “are particularly relevant given the increasing frequency of insurers mandating step therapy with bevacizumab before the use of other drugs” such as aflibercept, noted Chirag D. Jhaveri, MD, and colleagues in the study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Opportunity for ‘substantial cost reductions’
Jhaveri, a retina surgeon in Austin, Texas, and associates note that, based on Medicare reimbursement rates of $1,830 for a single dose of aflibercept and $70 for one dose of bevacizumab, starting treatment with bevacizumab could produce “substantial cost reductions for the health care system.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial agree. Step therapy that starts with bevacizumab would probably result in “substantial” cost savings, and the findings document “similar outcomes” from the two tested regimens based on improvements in visual acuity and changes in the thickness measurement of the central retina during the 2-year trial, write David C. Musch, PhD, and Emily Y. Chew, MD.
Dr. Musch, a professor and ophthalmology epidemiologist at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, and Dr. Chew, director of the Division of Epidemiology and Clinical Applications at the National Eye Institute in Bethesda, Md., also laud the “rigorous” study for its design and conduct that was “beyond reproach,” and for producing evidence that “applies well to clinical practice.”
The only potential drawback to the step-therapy approach, they write, is that people with diabetes often have “numerous coexisting conditions that make it more difficult for them to adhere to frequent follow-up visits,” a key element of the tested step-care protocol, which mandated follow-up visits every 4 weeks during the first year and every 4-16 weeks during the second year.
312 eyes of 270 patients
The new trial, organized by the DRCR Retinal Network and the Jaeb Center for Health Research in Tampa, Fla., ran at 54 U.S. sites from December 2017 to November 2019. The study randomized 158 eyes in 137 patients to aflibercept monotherapy, and 154 eyes in 133 patients to the step-care regimen (both eyes were treated in several patients in each group, with each eye receiving a different regimen). Participants were around 60 years old, 48% were women, and 95% had type 2 diabetes.
To be eligible for enrollment, patients had at least one eye with a best-corrected visual-acuity letter score of 24-69 on an Electronic Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study chart (ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating better visual acuity), which corresponds to Snellen chart values of 20/320-20/50, readings that encompass most patients with diabetic macular edema, noted study authors Adam R. Glassman and Jennifer K. Sun, MD, in an interview.
“Very few patients with diabetic macular edema have vision due to this alone that is worse than 20/320, which meets criteria for legal blindness,” said Dr. Glassman, who is executive director of the Jaeb Center for Health Research, and Dr. Sun, who is chief of the center for clinical eye research and trials at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston and chair of the DRCR Retinal Network.
The primary outcome was time-averaged change in visual-acuity letter score from baseline to 2 years, which improved by an average of 15.0 letters in the aflibercept monotherapy group and an average of 14.0 letters in the step-therapy group, an adjusted difference of 0.8 letters, which was not significant. An improvement from baseline of at least 15 letters occurred in 53% of the eyes in the aflibercept monotherapy group and in 58% of those who had step therapy, and 77% of eyes in both groups had improvements of at least 10 letters.
Central retinal thickness dropped from baseline by an average of 192 mcm with aflibercept monotherapy and 198 mcm with step therapy. The average number of total treatments (by intravitreous injection) was 14.6 in the aflibercept monotherapy group and 16.1 in the step-therapy group. After the first 24 weeks of the study, 39% of eyes in the step-therapy group had switched from bevacizumab to aflibercept injections; after 1 year, 60% of eyes had switched; and by study end, after 2 years, 70% had changed.
The bevacizumab-first group also showed at least comparable if not better safety, with similar rates of prespecified ocular events in both groups, but with a significantly lower rate of serious systemic adverse events, which occurred in 52% of the eyes treated with aflibercept only and 36% of eyes that began treatment on bevacizumab. Serious systemic adverse events occurred in 43% of patients who had two eyes treated as part of the trial.
‘Bevacizumab first was noninferior’
The team that designed the trial opted for a superiority design rather than a noninferiority trial and powered the study based on the presumption that aflibercept monotherapy would prove superior, said Dr. Glassman and Dr. Sun. “We feel that the clinical interpretation of these results will be similar to the interpretation if we had conducted a noninferiority study, and we found that bevacizumab first was noninferior to aflibercept monotherapy,” they maintained in an interview.
Dr. Glassman and Dr. Sun said they and their coauthors are now analyzing the results to try to find patient characteristics that could identify eyes most likely to respond to the bevacizumab-first approach. “It would be clinically valuable” to use the results to identify characteristics that could help guide clinicians’ treatment approach and enhance patient counseling, they said.
The study received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Genentech, Novartis, and Regenxbio. Dr. Glassman has reported receiving grants from Genentech and Regeneron. Dr. Sun has reported receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Biotech, KalVista, Optovue, and Physical Sciences, grants and travel support from Novartis and Novo Nordisk, travel support from Merck, writing support from Genentech, and equipment supplied by Adaptive Sensory and Boston Micromachines. Dr. Musch and Dr. Chew have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
People really can get ‘hangry’ when hungry
The notion that people get ‘hangry’ – irritable and short-tempered when they’re hungry – is such an established part of modern folklore that the word has even been added to the Oxford English Dictionary. Although experimental studies in the past have shown that low blood glucose levels increase impulsivity, anger, and aggression, there has been little solid evidence that this translates to real-life settings.
Now new research has confirmed that the phenomenon does really exist in everyday life. The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, is the first to investigate how hunger affects people’s emotions on a day-to-day level. Lead author Viren Swami, professor of social psychology at Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge, England, said: “Many of us are aware that being hungry can influence our emotions, but surprisingly little scientific research has focused on being ‘hangry’.”
He and coauthors from Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences in Krems an der Donau, Austria, recruited 64 participants from Central Europe who completed a 21-day experience sampling phase, in which they were prompted to report their feelings on a smartphone app five times a day. At each prompt, they reported their levels of hunger, anger, irritability, pleasure, and arousal on a visual analog scale.
Participants were on average 29.9 years old (range = 18-60), predominantly (81.3%) women, and had a mean body mass index of 23.8 kg/m2 (range 15.8-36.5 kg/m2).
Anger was rated on a 5-point scale but the team explained that the effects of hunger are unlikely to be unique to anger per se, so they also asked about experiences of irritability and, in order to obtain a more holistic view of emotionality, also about pleasure and arousal, as indexed using Russell’s affect grid.
They also asked about eating behaviors over the previous 3 weeks, including frequency of main meals, snacking behavior, healthy eating, feeling hungry, and sense of satiety, and about dietary behaviors including restrictive eating, emotionally induced eating, and externally determined eating behavior.
Analysis of the resulting total of 9,142 responses showed that higher levels of self-reported hunger were associated with greater feelings of anger and irritability, and with lower levels of pleasure. These findings remained significant after accounting for participants’ sex, age, body mass index, dietary behaviors, and trait anger. However, associations with arousal were not significant.
The authors commented that the use of the app allowed data collection to take place in subjects’ everyday environments, such as their workplace and at home. “These results provide evidence that everyday levels of hunger are associated with negative emotionality and supports the notion of being ‘hangry.’ ”
‘Substantial’ effects
“The effects were substantial,” the team said, “even after taking into account demographic factors” such as age and sex, body mass index, dietary behavior, and individual personality traits. Hunger was associated with 37% of the variance in irritability, 34% of the variance in anger, and 38% of the variance in pleasure recorded by the participants.
The research also showed that the negative emotions – irritability, anger, and unpleasantness – were caused by both day-to-day fluctuations in hunger and residual levels of hunger measured by averages over the 3-week period.
The authors said their findings “suggest that the experience of being hangry is real, insofar as hunger was associated with greater anger and irritability, and lower pleasure, in our sample over a period of 3 weeks.
“These results may have important implications for understanding everyday experiences of emotions, and may also assist practitioners to more effectively ensure productive individual behaviors and interpersonal relationships (for example, by ensuring that no one goes hungry).”
Although the majority of participants (55%) said they paid attention to hunger pangs, only 23% said that they knew when they were full and then stopped eating, whereas 63% said they could tell when they were full but sometimes continued to eat. Few (4.7%) people said they could not tell when they were full and therefore oriented their eating based on the size of the meal, but 9% described frequent overeating because of not feeling satiated, and 13% stated they ate when they were stressed, upset, angry, or bored.
Professor Swami said: “Ours is the first study to examine being ‘hangry’ outside of a lab. By following people in their day-to-day lives, we found that hunger was related to levels of anger, irritability, and pleasure.
“Although our study doesn’t present ways to mitigate negative hunger-induced emotions, research suggests that being able to label an emotion can help people to regulate it, such as by recognizing that we feel angry simply because we are hungry. Therefore, greater awareness of being ‘hangry’ could reduce the likelihood that hunger results in negative emotions and behaviors in individuals.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
The notion that people get ‘hangry’ – irritable and short-tempered when they’re hungry – is such an established part of modern folklore that the word has even been added to the Oxford English Dictionary. Although experimental studies in the past have shown that low blood glucose levels increase impulsivity, anger, and aggression, there has been little solid evidence that this translates to real-life settings.
Now new research has confirmed that the phenomenon does really exist in everyday life. The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, is the first to investigate how hunger affects people’s emotions on a day-to-day level. Lead author Viren Swami, professor of social psychology at Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge, England, said: “Many of us are aware that being hungry can influence our emotions, but surprisingly little scientific research has focused on being ‘hangry’.”
He and coauthors from Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences in Krems an der Donau, Austria, recruited 64 participants from Central Europe who completed a 21-day experience sampling phase, in which they were prompted to report their feelings on a smartphone app five times a day. At each prompt, they reported their levels of hunger, anger, irritability, pleasure, and arousal on a visual analog scale.
Participants were on average 29.9 years old (range = 18-60), predominantly (81.3%) women, and had a mean body mass index of 23.8 kg/m2 (range 15.8-36.5 kg/m2).
Anger was rated on a 5-point scale but the team explained that the effects of hunger are unlikely to be unique to anger per se, so they also asked about experiences of irritability and, in order to obtain a more holistic view of emotionality, also about pleasure and arousal, as indexed using Russell’s affect grid.
They also asked about eating behaviors over the previous 3 weeks, including frequency of main meals, snacking behavior, healthy eating, feeling hungry, and sense of satiety, and about dietary behaviors including restrictive eating, emotionally induced eating, and externally determined eating behavior.
Analysis of the resulting total of 9,142 responses showed that higher levels of self-reported hunger were associated with greater feelings of anger and irritability, and with lower levels of pleasure. These findings remained significant after accounting for participants’ sex, age, body mass index, dietary behaviors, and trait anger. However, associations with arousal were not significant.
The authors commented that the use of the app allowed data collection to take place in subjects’ everyday environments, such as their workplace and at home. “These results provide evidence that everyday levels of hunger are associated with negative emotionality and supports the notion of being ‘hangry.’ ”
‘Substantial’ effects
“The effects were substantial,” the team said, “even after taking into account demographic factors” such as age and sex, body mass index, dietary behavior, and individual personality traits. Hunger was associated with 37% of the variance in irritability, 34% of the variance in anger, and 38% of the variance in pleasure recorded by the participants.
The research also showed that the negative emotions – irritability, anger, and unpleasantness – were caused by both day-to-day fluctuations in hunger and residual levels of hunger measured by averages over the 3-week period.
The authors said their findings “suggest that the experience of being hangry is real, insofar as hunger was associated with greater anger and irritability, and lower pleasure, in our sample over a period of 3 weeks.
“These results may have important implications for understanding everyday experiences of emotions, and may also assist practitioners to more effectively ensure productive individual behaviors and interpersonal relationships (for example, by ensuring that no one goes hungry).”
Although the majority of participants (55%) said they paid attention to hunger pangs, only 23% said that they knew when they were full and then stopped eating, whereas 63% said they could tell when they were full but sometimes continued to eat. Few (4.7%) people said they could not tell when they were full and therefore oriented their eating based on the size of the meal, but 9% described frequent overeating because of not feeling satiated, and 13% stated they ate when they were stressed, upset, angry, or bored.
Professor Swami said: “Ours is the first study to examine being ‘hangry’ outside of a lab. By following people in their day-to-day lives, we found that hunger was related to levels of anger, irritability, and pleasure.
“Although our study doesn’t present ways to mitigate negative hunger-induced emotions, research suggests that being able to label an emotion can help people to regulate it, such as by recognizing that we feel angry simply because we are hungry. Therefore, greater awareness of being ‘hangry’ could reduce the likelihood that hunger results in negative emotions and behaviors in individuals.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
The notion that people get ‘hangry’ – irritable and short-tempered when they’re hungry – is such an established part of modern folklore that the word has even been added to the Oxford English Dictionary. Although experimental studies in the past have shown that low blood glucose levels increase impulsivity, anger, and aggression, there has been little solid evidence that this translates to real-life settings.
Now new research has confirmed that the phenomenon does really exist in everyday life. The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, is the first to investigate how hunger affects people’s emotions on a day-to-day level. Lead author Viren Swami, professor of social psychology at Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge, England, said: “Many of us are aware that being hungry can influence our emotions, but surprisingly little scientific research has focused on being ‘hangry’.”
He and coauthors from Karl Landsteiner University of Health Sciences in Krems an der Donau, Austria, recruited 64 participants from Central Europe who completed a 21-day experience sampling phase, in which they were prompted to report their feelings on a smartphone app five times a day. At each prompt, they reported their levels of hunger, anger, irritability, pleasure, and arousal on a visual analog scale.
Participants were on average 29.9 years old (range = 18-60), predominantly (81.3%) women, and had a mean body mass index of 23.8 kg/m2 (range 15.8-36.5 kg/m2).
Anger was rated on a 5-point scale but the team explained that the effects of hunger are unlikely to be unique to anger per se, so they also asked about experiences of irritability and, in order to obtain a more holistic view of emotionality, also about pleasure and arousal, as indexed using Russell’s affect grid.
They also asked about eating behaviors over the previous 3 weeks, including frequency of main meals, snacking behavior, healthy eating, feeling hungry, and sense of satiety, and about dietary behaviors including restrictive eating, emotionally induced eating, and externally determined eating behavior.
Analysis of the resulting total of 9,142 responses showed that higher levels of self-reported hunger were associated with greater feelings of anger and irritability, and with lower levels of pleasure. These findings remained significant after accounting for participants’ sex, age, body mass index, dietary behaviors, and trait anger. However, associations with arousal were not significant.
The authors commented that the use of the app allowed data collection to take place in subjects’ everyday environments, such as their workplace and at home. “These results provide evidence that everyday levels of hunger are associated with negative emotionality and supports the notion of being ‘hangry.’ ”
‘Substantial’ effects
“The effects were substantial,” the team said, “even after taking into account demographic factors” such as age and sex, body mass index, dietary behavior, and individual personality traits. Hunger was associated with 37% of the variance in irritability, 34% of the variance in anger, and 38% of the variance in pleasure recorded by the participants.
The research also showed that the negative emotions – irritability, anger, and unpleasantness – were caused by both day-to-day fluctuations in hunger and residual levels of hunger measured by averages over the 3-week period.
The authors said their findings “suggest that the experience of being hangry is real, insofar as hunger was associated with greater anger and irritability, and lower pleasure, in our sample over a period of 3 weeks.
“These results may have important implications for understanding everyday experiences of emotions, and may also assist practitioners to more effectively ensure productive individual behaviors and interpersonal relationships (for example, by ensuring that no one goes hungry).”
Although the majority of participants (55%) said they paid attention to hunger pangs, only 23% said that they knew when they were full and then stopped eating, whereas 63% said they could tell when they were full but sometimes continued to eat. Few (4.7%) people said they could not tell when they were full and therefore oriented their eating based on the size of the meal, but 9% described frequent overeating because of not feeling satiated, and 13% stated they ate when they were stressed, upset, angry, or bored.
Professor Swami said: “Ours is the first study to examine being ‘hangry’ outside of a lab. By following people in their day-to-day lives, we found that hunger was related to levels of anger, irritability, and pleasure.
“Although our study doesn’t present ways to mitigate negative hunger-induced emotions, research suggests that being able to label an emotion can help people to regulate it, such as by recognizing that we feel angry simply because we are hungry. Therefore, greater awareness of being ‘hangry’ could reduce the likelihood that hunger results in negative emotions and behaviors in individuals.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
FROM PLOS ONE
Some have heavier periods after COVID vaccine
Many women who got a COVID-19 vaccine have reported heavier bleeding during their periods since they had the shots.
A team of researchers investigated the trend and set out to find out who among the vaccinated were more likely to experience the menstruation changes.
The researchers were led by Katharine M.N. Lee, PhD, MS, of the division of public health sciences at Washington University in St. Louis. Their findings were published ahead of print in Science Advances.
The investigators analyzed more than 139,000 responses from an online survey from both currently and formerly menstruating women.
They found that, among people who have regular periods, about the same percentage had heavier bleeding after they got a COVID vaccine as had no change in bleeding after the vaccine (44% vs. 42%, respectively).
“A much smaller portion had lighter periods,” they write.
The phenomenon has been difficult to study because questions about changes in menstruation are not a standard part of vaccine trials.
Date of last period is often tracked in clinical trials to make sure a participant is not pregnant, but the questions about periods often stop there.
Additionally, periods are different for everyone and can be influenced by all sorts of environmental factors, so making associations regarding exposures is problematic.
No changes found to fertility
The authors emphasized that, generally, changes to menstrual bleeding are not uncommon nor dangerous. They also emphasized that the changes in bleeding don’t mean changes to fertility.
The uterine reproductive system is flexible when the body is under stress, they note.
“We know that running a marathon may influence hormone concentrations in the short term while not rendering that person infertile,” the authors write.
However, they acknowledge that investigating these reports is critical in building trust in medicine.
This report includes information that hasn’t been available through the clinical trial follow-up process.
For instance, the authors write, “To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to examine breakthrough bleeding after vaccination in either pre- or postmenopausal people.”
Reports of changes to periods after vaccination started emerging in 2021. But without data, reports were largely dismissed, fueling criticism from those waging campaigns against COVID vaccines.
Dr. Lee and colleagues gathered data from those who responded to the online survey and detailed some trends.
People who were bleeding more heavily after vaccination were more likely to be older, Hispanic, had vaccine side effects of fever and fatigue, had been pregnant at some point, or had given birth.
People with regular periods who had endometriosis, prolonged bleeding during their periods, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or fibroids were also more likely to have increased bleeding after a COVID vaccine.
Breakthrough bleeding
For people who don’t menstruate, but have not reached menopause, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in women who had been pregnant and/or had given birth.
Among respondents who were postmenopausal, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in younger people and/or those who are Hispanic.
More than a third of the respondents (39%) who use gender-affirming hormones that eliminate menstruation reported breakthrough bleeding after vaccination.
The majority of premenopausal people on long-acting, reversible contraception (71%) and the majority of postmenopausal respondents (66%) had breakthrough bleeding as well.
The authors note that you can’t compare the percentages who report these experiences in the survey with the incidence of those who would experience changes in menstrual bleeding in the general population.
The nature of the online survey means it may be naturally biased because the people who responded may be more often those who noted some change in their own menstrual experiences, particularly if that involved discomfort, pain, or fear.
Researchers also acknowledge that Black, Indigenous, Latinx, and other respondents of color are underrepresented in this research and that represents a limitation in the work.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, was not involved with Dr. Lee and associates’ study but has also studied the relationship between COVID vaccines and menstruation.
Her team’s study found that COVID vaccination is associated with a small change in time between periods but not length of periods.
She said about the work by Dr. Lee and colleagues, “This work really elevates the voices of the public and what they’re experiencing.”
The association makes sense, Dr. Edelman says, in that the reproductive system and the immune system talk to each other and inflammation in the immune system is going to be noticed by the system governing periods.
Lack of data on the relationship between exposures and menstruation didn’t start with COVID. “There has been a signal in the population before with other vaccines that’s been dismissed,” she said.
Tracking menstruation information in clinical trials can help physicians counsel women on what may be coming with any vaccine and alleviate fears and vaccine hesitancy, Dr. Edelman explained. It can also help vaccine developers know what to include in information about their product.
“When you are counseled about what to expect, it’s not as scary. That provides trust in the system,” she said. She likened it to original lack of data on whether COVID-19 vaccines would affect pregnancy.
“We have great science now that COVID vaccine does not affect fertility and [vaccine] does not impact pregnancy.”
Another important aspect of this paper is that it included subgroups not studied before regarding menstruation and breakthrough bleeding, such as those taking gender-affirming hormones, she added.
Menstruation has been often overlooked as important in clinical trial exposures but Dr. Edelman hopes this recent attention and question will escalate and prompt more research.
“I’m hoping with the immense outpouring from the public about how important this is, that future studies will look at this a little bit better,” she says.
She said when the National Institutes of Health opened up funding for trials on COVID-19 vaccines and menstruation, researchers got flooded with requests from women to share their stories.
“As a researcher – I’ve been doing research for over 20 years – that’s not something that usually happens. I would love to have that happen for every research project.”
The authors and Dr. Edelman declare that they have no competing interests. This research was supported in part by the University of Illinois Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Illinois Interdisciplinary Health Sciences Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Siteman Cancer Center.
Many women who got a COVID-19 vaccine have reported heavier bleeding during their periods since they had the shots.
A team of researchers investigated the trend and set out to find out who among the vaccinated were more likely to experience the menstruation changes.
The researchers were led by Katharine M.N. Lee, PhD, MS, of the division of public health sciences at Washington University in St. Louis. Their findings were published ahead of print in Science Advances.
The investigators analyzed more than 139,000 responses from an online survey from both currently and formerly menstruating women.
They found that, among people who have regular periods, about the same percentage had heavier bleeding after they got a COVID vaccine as had no change in bleeding after the vaccine (44% vs. 42%, respectively).
“A much smaller portion had lighter periods,” they write.
The phenomenon has been difficult to study because questions about changes in menstruation are not a standard part of vaccine trials.
Date of last period is often tracked in clinical trials to make sure a participant is not pregnant, but the questions about periods often stop there.
Additionally, periods are different for everyone and can be influenced by all sorts of environmental factors, so making associations regarding exposures is problematic.
No changes found to fertility
The authors emphasized that, generally, changes to menstrual bleeding are not uncommon nor dangerous. They also emphasized that the changes in bleeding don’t mean changes to fertility.
The uterine reproductive system is flexible when the body is under stress, they note.
“We know that running a marathon may influence hormone concentrations in the short term while not rendering that person infertile,” the authors write.
However, they acknowledge that investigating these reports is critical in building trust in medicine.
This report includes information that hasn’t been available through the clinical trial follow-up process.
For instance, the authors write, “To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to examine breakthrough bleeding after vaccination in either pre- or postmenopausal people.”
Reports of changes to periods after vaccination started emerging in 2021. But without data, reports were largely dismissed, fueling criticism from those waging campaigns against COVID vaccines.
Dr. Lee and colleagues gathered data from those who responded to the online survey and detailed some trends.
People who were bleeding more heavily after vaccination were more likely to be older, Hispanic, had vaccine side effects of fever and fatigue, had been pregnant at some point, or had given birth.
People with regular periods who had endometriosis, prolonged bleeding during their periods, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or fibroids were also more likely to have increased bleeding after a COVID vaccine.
Breakthrough bleeding
For people who don’t menstruate, but have not reached menopause, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in women who had been pregnant and/or had given birth.
Among respondents who were postmenopausal, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in younger people and/or those who are Hispanic.
More than a third of the respondents (39%) who use gender-affirming hormones that eliminate menstruation reported breakthrough bleeding after vaccination.
The majority of premenopausal people on long-acting, reversible contraception (71%) and the majority of postmenopausal respondents (66%) had breakthrough bleeding as well.
The authors note that you can’t compare the percentages who report these experiences in the survey with the incidence of those who would experience changes in menstrual bleeding in the general population.
The nature of the online survey means it may be naturally biased because the people who responded may be more often those who noted some change in their own menstrual experiences, particularly if that involved discomfort, pain, or fear.
Researchers also acknowledge that Black, Indigenous, Latinx, and other respondents of color are underrepresented in this research and that represents a limitation in the work.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, was not involved with Dr. Lee and associates’ study but has also studied the relationship between COVID vaccines and menstruation.
Her team’s study found that COVID vaccination is associated with a small change in time between periods but not length of periods.
She said about the work by Dr. Lee and colleagues, “This work really elevates the voices of the public and what they’re experiencing.”
The association makes sense, Dr. Edelman says, in that the reproductive system and the immune system talk to each other and inflammation in the immune system is going to be noticed by the system governing periods.
Lack of data on the relationship between exposures and menstruation didn’t start with COVID. “There has been a signal in the population before with other vaccines that’s been dismissed,” she said.
Tracking menstruation information in clinical trials can help physicians counsel women on what may be coming with any vaccine and alleviate fears and vaccine hesitancy, Dr. Edelman explained. It can also help vaccine developers know what to include in information about their product.
“When you are counseled about what to expect, it’s not as scary. That provides trust in the system,” she said. She likened it to original lack of data on whether COVID-19 vaccines would affect pregnancy.
“We have great science now that COVID vaccine does not affect fertility and [vaccine] does not impact pregnancy.”
Another important aspect of this paper is that it included subgroups not studied before regarding menstruation and breakthrough bleeding, such as those taking gender-affirming hormones, she added.
Menstruation has been often overlooked as important in clinical trial exposures but Dr. Edelman hopes this recent attention and question will escalate and prompt more research.
“I’m hoping with the immense outpouring from the public about how important this is, that future studies will look at this a little bit better,” she says.
She said when the National Institutes of Health opened up funding for trials on COVID-19 vaccines and menstruation, researchers got flooded with requests from women to share their stories.
“As a researcher – I’ve been doing research for over 20 years – that’s not something that usually happens. I would love to have that happen for every research project.”
The authors and Dr. Edelman declare that they have no competing interests. This research was supported in part by the University of Illinois Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Illinois Interdisciplinary Health Sciences Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Siteman Cancer Center.
Many women who got a COVID-19 vaccine have reported heavier bleeding during their periods since they had the shots.
A team of researchers investigated the trend and set out to find out who among the vaccinated were more likely to experience the menstruation changes.
The researchers were led by Katharine M.N. Lee, PhD, MS, of the division of public health sciences at Washington University in St. Louis. Their findings were published ahead of print in Science Advances.
The investigators analyzed more than 139,000 responses from an online survey from both currently and formerly menstruating women.
They found that, among people who have regular periods, about the same percentage had heavier bleeding after they got a COVID vaccine as had no change in bleeding after the vaccine (44% vs. 42%, respectively).
“A much smaller portion had lighter periods,” they write.
The phenomenon has been difficult to study because questions about changes in menstruation are not a standard part of vaccine trials.
Date of last period is often tracked in clinical trials to make sure a participant is not pregnant, but the questions about periods often stop there.
Additionally, periods are different for everyone and can be influenced by all sorts of environmental factors, so making associations regarding exposures is problematic.
No changes found to fertility
The authors emphasized that, generally, changes to menstrual bleeding are not uncommon nor dangerous. They also emphasized that the changes in bleeding don’t mean changes to fertility.
The uterine reproductive system is flexible when the body is under stress, they note.
“We know that running a marathon may influence hormone concentrations in the short term while not rendering that person infertile,” the authors write.
However, they acknowledge that investigating these reports is critical in building trust in medicine.
This report includes information that hasn’t been available through the clinical trial follow-up process.
For instance, the authors write, “To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to examine breakthrough bleeding after vaccination in either pre- or postmenopausal people.”
Reports of changes to periods after vaccination started emerging in 2021. But without data, reports were largely dismissed, fueling criticism from those waging campaigns against COVID vaccines.
Dr. Lee and colleagues gathered data from those who responded to the online survey and detailed some trends.
People who were bleeding more heavily after vaccination were more likely to be older, Hispanic, had vaccine side effects of fever and fatigue, had been pregnant at some point, or had given birth.
People with regular periods who had endometriosis, prolonged bleeding during their periods, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or fibroids were also more likely to have increased bleeding after a COVID vaccine.
Breakthrough bleeding
For people who don’t menstruate, but have not reached menopause, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in women who had been pregnant and/or had given birth.
Among respondents who were postmenopausal, breakthrough bleeding happened more often in younger people and/or those who are Hispanic.
More than a third of the respondents (39%) who use gender-affirming hormones that eliminate menstruation reported breakthrough bleeding after vaccination.
The majority of premenopausal people on long-acting, reversible contraception (71%) and the majority of postmenopausal respondents (66%) had breakthrough bleeding as well.
The authors note that you can’t compare the percentages who report these experiences in the survey with the incidence of those who would experience changes in menstrual bleeding in the general population.
The nature of the online survey means it may be naturally biased because the people who responded may be more often those who noted some change in their own menstrual experiences, particularly if that involved discomfort, pain, or fear.
Researchers also acknowledge that Black, Indigenous, Latinx, and other respondents of color are underrepresented in this research and that represents a limitation in the work.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, with the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, was not involved with Dr. Lee and associates’ study but has also studied the relationship between COVID vaccines and menstruation.
Her team’s study found that COVID vaccination is associated with a small change in time between periods but not length of periods.
She said about the work by Dr. Lee and colleagues, “This work really elevates the voices of the public and what they’re experiencing.”
The association makes sense, Dr. Edelman says, in that the reproductive system and the immune system talk to each other and inflammation in the immune system is going to be noticed by the system governing periods.
Lack of data on the relationship between exposures and menstruation didn’t start with COVID. “There has been a signal in the population before with other vaccines that’s been dismissed,” she said.
Tracking menstruation information in clinical trials can help physicians counsel women on what may be coming with any vaccine and alleviate fears and vaccine hesitancy, Dr. Edelman explained. It can also help vaccine developers know what to include in information about their product.
“When you are counseled about what to expect, it’s not as scary. That provides trust in the system,” she said. She likened it to original lack of data on whether COVID-19 vaccines would affect pregnancy.
“We have great science now that COVID vaccine does not affect fertility and [vaccine] does not impact pregnancy.”
Another important aspect of this paper is that it included subgroups not studied before regarding menstruation and breakthrough bleeding, such as those taking gender-affirming hormones, she added.
Menstruation has been often overlooked as important in clinical trial exposures but Dr. Edelman hopes this recent attention and question will escalate and prompt more research.
“I’m hoping with the immense outpouring from the public about how important this is, that future studies will look at this a little bit better,” she says.
She said when the National Institutes of Health opened up funding for trials on COVID-19 vaccines and menstruation, researchers got flooded with requests from women to share their stories.
“As a researcher – I’ve been doing research for over 20 years – that’s not something that usually happens. I would love to have that happen for every research project.”
The authors and Dr. Edelman declare that they have no competing interests. This research was supported in part by the University of Illinois Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Illinois Interdisciplinary Health Sciences Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital, and the Siteman Cancer Center.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
Two congressmen targeting ‘gender transition’ physicians
Two GOP congressmen have introduced legislation aimed at holding doctors who perform gender transition procedures on minors liable for their actions, says a story reported on KATV.com, among other news sites.
The two GOP lawmakers – Rep. Jim Banks (IN) and Sen. Tom Cotton (AR) – introduced the Protecting Minors from Medical Malpractice Act in their respective chambers.
If passed, the House and Senate bills would make doctors liable for any gender transition surgery on a minor that results in injury, whether physical, psychological, emotional, or physiological. Minors who believe they’ve been harmed would have up to 30 years from when they turn 18 to file a claim.
The House proposal would also strip federal funding from states that require health care professionals to provide gender transition procedures, including puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and gender reassignment surgeries.
A companion House bill, also sponsored by Banks, targets another issue related to gender transitioning for minors: parental consent.
If passed, the Empower Parents to Protect Their Kids Act of 2022 would deny federal funding to any elementary and secondary schools that initiate a minor’s gender transition without first securing parental consent. (Last October, Sen. Cotton released a similar bill in the Senate.)
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two GOP congressmen have introduced legislation aimed at holding doctors who perform gender transition procedures on minors liable for their actions, says a story reported on KATV.com, among other news sites.
The two GOP lawmakers – Rep. Jim Banks (IN) and Sen. Tom Cotton (AR) – introduced the Protecting Minors from Medical Malpractice Act in their respective chambers.
If passed, the House and Senate bills would make doctors liable for any gender transition surgery on a minor that results in injury, whether physical, psychological, emotional, or physiological. Minors who believe they’ve been harmed would have up to 30 years from when they turn 18 to file a claim.
The House proposal would also strip federal funding from states that require health care professionals to provide gender transition procedures, including puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and gender reassignment surgeries.
A companion House bill, also sponsored by Banks, targets another issue related to gender transitioning for minors: parental consent.
If passed, the Empower Parents to Protect Their Kids Act of 2022 would deny federal funding to any elementary and secondary schools that initiate a minor’s gender transition without first securing parental consent. (Last October, Sen. Cotton released a similar bill in the Senate.)
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two GOP congressmen have introduced legislation aimed at holding doctors who perform gender transition procedures on minors liable for their actions, says a story reported on KATV.com, among other news sites.
The two GOP lawmakers – Rep. Jim Banks (IN) and Sen. Tom Cotton (AR) – introduced the Protecting Minors from Medical Malpractice Act in their respective chambers.
If passed, the House and Senate bills would make doctors liable for any gender transition surgery on a minor that results in injury, whether physical, psychological, emotional, or physiological. Minors who believe they’ve been harmed would have up to 30 years from when they turn 18 to file a claim.
The House proposal would also strip federal funding from states that require health care professionals to provide gender transition procedures, including puberty blockers, cross-sex hormones, and gender reassignment surgeries.
A companion House bill, also sponsored by Banks, targets another issue related to gender transitioning for minors: parental consent.
If passed, the Empower Parents to Protect Their Kids Act of 2022 would deny federal funding to any elementary and secondary schools that initiate a minor’s gender transition without first securing parental consent. (Last October, Sen. Cotton released a similar bill in the Senate.)
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Reliance on any information provided in this article is solely at your own risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Don’t wait for a cyberattack; know what coverage you have now
Barbara L. McAneny, MD, CEO of New Mexico Oncology Hematology Consultants, experienced a data breach about 10 years ago, when a laptop was stolen from her large practice.
She and the other physicians were upset and worried that the individual would attempt to log in to the computer system and hack their patients’ private health information.
Dr. McAneny was also worried that the practice would have to pay a hefty fine to the government for having unsecured private health information on a laptop. She could have paid from $50,000 to more than $1.9 million for lost and stolen devices (although that didn’t happen).
Dr. McAneny had a standard cyber liability benefit in her med-mal policy that covered up to $50,000 of the data breach costs. That covered the legal advice The Doctors Company provided about state and federal reporting requirements when a data breach occurs and the costs the practice incurred from mailing letters to all of its patients notifying them of the data breach, says Dr. McAneny.
“The data breach taught me a lot. Our practice spent a lot of money on increasing our internal controls, cybersecurity, and monitoring. Our IT department started testing our computer firewalls periodically, and that’s how we discovered that cybercriminals were attempting to break into our computer system at least 100 times daily,” says Dr. McAneny.
That discovery changed how she thought about insurance. “I decided the med-mal benefit wasn’t enough. I bought the best cybersecurity policy we could afford to protect against future breaches, especially malware or ransomware attacks.”
Her practice also had to make its electronic health records (EHRs) more secure to comply with the Department of Health & Human Services Office of Civil Rights standards for protected health information. The cost of increased security wasn’t covered by her cyber benefit.
Cyberattacks increasing in health care
Despite having comprehensive coverage, Dr. McAneny worries that the cybercriminals are a step ahead of the cybersecurity experts and her practice will eventually have another data breach.
“The policy only covers things that we know about today. As we upgrade our defenses, criminals are finding new ways to breach firewalls and work around our defenses,” she says.
So far this year, nearly 200 medical groups have reported cyberattacks involving 500 or more of their patients’ medical records to the federal government.
EHRs are valuable targets to cybercriminals because of the protected health information they contain. Cybercriminals grab information such as Social Security numbers, dates of birth, medical procedures and results, and in some cases billing and financial information and sell it on the dark web.
They typically bundle the information and sell it to other criminals who later use it for various kinds of fraud and extortion such as banking and credit fraud, health care fraud, identity theft, and ransom extortion.
What do most doctors have?
The vast majority (82%) of doctors polled by the Medical Group Management Association last year said they had cyber insurance, compared with 54% in 2018.
For those who answered “yes,” many said they have coverage through their malpractice insurance carrier.
David Zetter, president of Zetter HealthCare Management Consultants, recommends that physicians speak with their malpractice carrier to determine what coverage they have, if any, within their malpractice policy.
A typical cybersecurity benefit is limited to what is needed to fix and resolve the hacking incident, says Raj Shah, senior regulatory attorney and policyholder advisor at MagMutual, which insures medical practices for malpractice and cyber liability.
That usually covers investigating the cause of the breach and the extent of the damage, legal advice about federal and state reporting requirements, whether to pay a ransom, and a public relations professional to handle patient communication, says Mr. Shah.
The benefit doesn’t cover lost patient revenue when practices have to shut down their operations, the cost of replacing damaged computers, or the ransom payment, he says.
Mr. Zetter advises doctors to consider buying cybersecurity coverage. “I recommend that they speak with an insurance broker who is experienced with cybersecurity policies sold to health care professionals to determine what type of coverage and how much coverage they may need. Their malpractice carrier may also be able to provide some answers,” says Mr. Zetter.
The physician will need to be able to answer questions about their network and how many staff they have and may need to involve their IT vendor too, he adds.
How does comprehensive coverage compare?
Ransomware attacks continue to be one of the most frequent types of attacks, and the amount criminals are demanding has risen significantly. The median ransom payment was $5,000 in the fourth quarter of 2018, compared with over $300,000 during the fourth quarter of 2021.
Cybercriminals now engage in “double extortion” – demanding a ransom payment to hand over the code that will unlock their encrypted data – and then another ransom payment to not post patients’ sensitive medical information they copied onto the dark web.
Comprehensive cybersecurity insurance will cover “double extortion” payments, legal costs that may arise from defending against patient lawsuits, and the costs of meeting federal and state privacy requirements, including notifying patients of the data breach and regulatory investigations, says Michael Carr, head of risk engineering for North America for Coalition, a cyber insurance firm.
Cyber insurers also contract with vendors who sell bitcoin, which is the currency cybercriminals typically demand for ransom payments, and work with ransom negotiators.
For example, once Coalition decided to pay the ransom on behalf of a health care client, it negotiated the ransom demand down by nearly 75% from $750,000 to $200,000, and proceeded to help the company restore all of its data.
The costs to respond to the incident, to recover lost data, and to pay the extortion, together with the lost business income resulting from the incident, were covered by Coalition’s cyber insurance policy.
Other clients have had their funds retrieved before a fraudulent wire transfer was completed. “Medical practices have vendors they pay regularly. A cybercriminal may compromise your email or take over a bank account and then impersonate a vendor asking to be paid for services they didn’t provide,” says Mr. Carr.
How much coverage do you need? Cost?
Dr. McAneny has increased her cybersecurity coverage every year. “It’s expensive, but I think it’s worth it. But you can never buy enough protection due to the coverage limits.”
She worries that the costs could exceed the limits if a ransomware attack disrupts her practice for days, weeks, or longer, or if the Office for Civil Rights fines her practice $10,000 per patient chart – the practice has 100,000 health records. “That can run several millions of dollars and ruin a practice,” she says.
Health systems and hospitals need massive amounts of coverage, which often runs from $20 million to $30 million, says Mr. Shah. However, practices insured through MagMutual have lower coverage limits that range from $1 million to $5 million, he says.
“A large practice does not necessarily need more than $1,000,000 in coverage if they have limited loss in this area and strong internal processes and controls. Most large practices also have a dedicated information security director, which reduces their risk, so they may be comfortable with $1,000,000 in coverage,” says Mr. Shah.
Premiums are based on the number of patient health records per practice, which translates into higher premiums for larger practices.
Other factors that come into play include the underlying coverage, risk controls the practice has implemented, and its claims history, says Mr. Shah.
However, the cost for cyber liability insurance has increased, and practices can expect to pay higher premiums and deductibles. For example, a practice that paid $10,000 in premiums for a new policy last year will have to pay $20,000 this year, says Dan Hanson, senior vice president of management liability and client experience at Marsh & McLennon Agency, a risk management firm that sells cyber insurance policies.
“We saw 71% of our self-insured clients experience higher deductibles over last year due to increased claim activity and the lack of capacity in the market. The carriers are saying they will set limits, but you are going to pay a lot more, and you are going to participate more in losses through the higher deductibles,” says Mr. Hanson.
Are you eligible?
Cyber insurance companies have a vested interest in avoiding claims. With increasing cyberattacks and larger payouts, many insurers are requiring practices to implement some defensive measures before they insure them. Some insurers, such as Coalition, say they may still insure small practices for comprehensive coverage, but it may impact the pricing or what’s covered, says Mr. Carr.
Here are some of the security measures that cyber insurers are looking for:
- Multifactorial authentication (MFA) requires an extra layer of security to access the system. For example, when logging into your organization’s EHR platform, instead of just using a username and password to access the platform, MFA would require you to input an additional unique login credential before you can access the EHR. A secondary login credential may include security questions, a one-time PIN, or biometrics.
- Removing a terminated employee’s login credentials quickly from the computer system. “One of the most damaging and expensive types of attacks are by disgruntled employees who still have their login credentials and take revenge by logging back into the system and planting malware,” says Mr. Shah.
- Automatic system updates (patches). “Phishing email compromises usually result from a failure to fix vulnerabilities. When a system needs to restart, it should be set to automatically update any potential security loopholes within programs or products,” says Mr. Carr. The firewall settings should also be updated.
- Prior hacking incidents: Are the attackers out of your system? Once criminals hack into the system, your practice is vulnerable to repeat attacks. “If a cyberattack is not completely addressed, threat actors will maintain access to or a presence on the compromised network. In general, we will work with the insured to ensure that the initial point of compromise has been addressed and that any threat actor presence in the network has been removed,” says Mr. Carr.
When doctors compare cybersecurity policies, experts recommend avoiding companies that may offer lower prices but lack a proven track record of handling claims and do not offer resources that can detect a threat, such as ongoing network monitoring and employee training with simulated exercises.
“Practices tend to think, ‘It won’t happen to me.’ Every practice needs to take this seriously,” says Dr. McAneny.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Barbara L. McAneny, MD, CEO of New Mexico Oncology Hematology Consultants, experienced a data breach about 10 years ago, when a laptop was stolen from her large practice.
She and the other physicians were upset and worried that the individual would attempt to log in to the computer system and hack their patients’ private health information.
Dr. McAneny was also worried that the practice would have to pay a hefty fine to the government for having unsecured private health information on a laptop. She could have paid from $50,000 to more than $1.9 million for lost and stolen devices (although that didn’t happen).
Dr. McAneny had a standard cyber liability benefit in her med-mal policy that covered up to $50,000 of the data breach costs. That covered the legal advice The Doctors Company provided about state and federal reporting requirements when a data breach occurs and the costs the practice incurred from mailing letters to all of its patients notifying them of the data breach, says Dr. McAneny.
“The data breach taught me a lot. Our practice spent a lot of money on increasing our internal controls, cybersecurity, and monitoring. Our IT department started testing our computer firewalls periodically, and that’s how we discovered that cybercriminals were attempting to break into our computer system at least 100 times daily,” says Dr. McAneny.
That discovery changed how she thought about insurance. “I decided the med-mal benefit wasn’t enough. I bought the best cybersecurity policy we could afford to protect against future breaches, especially malware or ransomware attacks.”
Her practice also had to make its electronic health records (EHRs) more secure to comply with the Department of Health & Human Services Office of Civil Rights standards for protected health information. The cost of increased security wasn’t covered by her cyber benefit.
Cyberattacks increasing in health care
Despite having comprehensive coverage, Dr. McAneny worries that the cybercriminals are a step ahead of the cybersecurity experts and her practice will eventually have another data breach.
“The policy only covers things that we know about today. As we upgrade our defenses, criminals are finding new ways to breach firewalls and work around our defenses,” she says.
So far this year, nearly 200 medical groups have reported cyberattacks involving 500 or more of their patients’ medical records to the federal government.
EHRs are valuable targets to cybercriminals because of the protected health information they contain. Cybercriminals grab information such as Social Security numbers, dates of birth, medical procedures and results, and in some cases billing and financial information and sell it on the dark web.
They typically bundle the information and sell it to other criminals who later use it for various kinds of fraud and extortion such as banking and credit fraud, health care fraud, identity theft, and ransom extortion.
What do most doctors have?
The vast majority (82%) of doctors polled by the Medical Group Management Association last year said they had cyber insurance, compared with 54% in 2018.
For those who answered “yes,” many said they have coverage through their malpractice insurance carrier.
David Zetter, president of Zetter HealthCare Management Consultants, recommends that physicians speak with their malpractice carrier to determine what coverage they have, if any, within their malpractice policy.
A typical cybersecurity benefit is limited to what is needed to fix and resolve the hacking incident, says Raj Shah, senior regulatory attorney and policyholder advisor at MagMutual, which insures medical practices for malpractice and cyber liability.
That usually covers investigating the cause of the breach and the extent of the damage, legal advice about federal and state reporting requirements, whether to pay a ransom, and a public relations professional to handle patient communication, says Mr. Shah.
The benefit doesn’t cover lost patient revenue when practices have to shut down their operations, the cost of replacing damaged computers, or the ransom payment, he says.
Mr. Zetter advises doctors to consider buying cybersecurity coverage. “I recommend that they speak with an insurance broker who is experienced with cybersecurity policies sold to health care professionals to determine what type of coverage and how much coverage they may need. Their malpractice carrier may also be able to provide some answers,” says Mr. Zetter.
The physician will need to be able to answer questions about their network and how many staff they have and may need to involve their IT vendor too, he adds.
How does comprehensive coverage compare?
Ransomware attacks continue to be one of the most frequent types of attacks, and the amount criminals are demanding has risen significantly. The median ransom payment was $5,000 in the fourth quarter of 2018, compared with over $300,000 during the fourth quarter of 2021.
Cybercriminals now engage in “double extortion” – demanding a ransom payment to hand over the code that will unlock their encrypted data – and then another ransom payment to not post patients’ sensitive medical information they copied onto the dark web.
Comprehensive cybersecurity insurance will cover “double extortion” payments, legal costs that may arise from defending against patient lawsuits, and the costs of meeting federal and state privacy requirements, including notifying patients of the data breach and regulatory investigations, says Michael Carr, head of risk engineering for North America for Coalition, a cyber insurance firm.
Cyber insurers also contract with vendors who sell bitcoin, which is the currency cybercriminals typically demand for ransom payments, and work with ransom negotiators.
For example, once Coalition decided to pay the ransom on behalf of a health care client, it negotiated the ransom demand down by nearly 75% from $750,000 to $200,000, and proceeded to help the company restore all of its data.
The costs to respond to the incident, to recover lost data, and to pay the extortion, together with the lost business income resulting from the incident, were covered by Coalition’s cyber insurance policy.
Other clients have had their funds retrieved before a fraudulent wire transfer was completed. “Medical practices have vendors they pay regularly. A cybercriminal may compromise your email or take over a bank account and then impersonate a vendor asking to be paid for services they didn’t provide,” says Mr. Carr.
How much coverage do you need? Cost?
Dr. McAneny has increased her cybersecurity coverage every year. “It’s expensive, but I think it’s worth it. But you can never buy enough protection due to the coverage limits.”
She worries that the costs could exceed the limits if a ransomware attack disrupts her practice for days, weeks, or longer, or if the Office for Civil Rights fines her practice $10,000 per patient chart – the practice has 100,000 health records. “That can run several millions of dollars and ruin a practice,” she says.
Health systems and hospitals need massive amounts of coverage, which often runs from $20 million to $30 million, says Mr. Shah. However, practices insured through MagMutual have lower coverage limits that range from $1 million to $5 million, he says.
“A large practice does not necessarily need more than $1,000,000 in coverage if they have limited loss in this area and strong internal processes and controls. Most large practices also have a dedicated information security director, which reduces their risk, so they may be comfortable with $1,000,000 in coverage,” says Mr. Shah.
Premiums are based on the number of patient health records per practice, which translates into higher premiums for larger practices.
Other factors that come into play include the underlying coverage, risk controls the practice has implemented, and its claims history, says Mr. Shah.
However, the cost for cyber liability insurance has increased, and practices can expect to pay higher premiums and deductibles. For example, a practice that paid $10,000 in premiums for a new policy last year will have to pay $20,000 this year, says Dan Hanson, senior vice president of management liability and client experience at Marsh & McLennon Agency, a risk management firm that sells cyber insurance policies.
“We saw 71% of our self-insured clients experience higher deductibles over last year due to increased claim activity and the lack of capacity in the market. The carriers are saying they will set limits, but you are going to pay a lot more, and you are going to participate more in losses through the higher deductibles,” says Mr. Hanson.
Are you eligible?
Cyber insurance companies have a vested interest in avoiding claims. With increasing cyberattacks and larger payouts, many insurers are requiring practices to implement some defensive measures before they insure them. Some insurers, such as Coalition, say they may still insure small practices for comprehensive coverage, but it may impact the pricing or what’s covered, says Mr. Carr.
Here are some of the security measures that cyber insurers are looking for:
- Multifactorial authentication (MFA) requires an extra layer of security to access the system. For example, when logging into your organization’s EHR platform, instead of just using a username and password to access the platform, MFA would require you to input an additional unique login credential before you can access the EHR. A secondary login credential may include security questions, a one-time PIN, or biometrics.
- Removing a terminated employee’s login credentials quickly from the computer system. “One of the most damaging and expensive types of attacks are by disgruntled employees who still have their login credentials and take revenge by logging back into the system and planting malware,” says Mr. Shah.
- Automatic system updates (patches). “Phishing email compromises usually result from a failure to fix vulnerabilities. When a system needs to restart, it should be set to automatically update any potential security loopholes within programs or products,” says Mr. Carr. The firewall settings should also be updated.
- Prior hacking incidents: Are the attackers out of your system? Once criminals hack into the system, your practice is vulnerable to repeat attacks. “If a cyberattack is not completely addressed, threat actors will maintain access to or a presence on the compromised network. In general, we will work with the insured to ensure that the initial point of compromise has been addressed and that any threat actor presence in the network has been removed,” says Mr. Carr.
When doctors compare cybersecurity policies, experts recommend avoiding companies that may offer lower prices but lack a proven track record of handling claims and do not offer resources that can detect a threat, such as ongoing network monitoring and employee training with simulated exercises.
“Practices tend to think, ‘It won’t happen to me.’ Every practice needs to take this seriously,” says Dr. McAneny.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Barbara L. McAneny, MD, CEO of New Mexico Oncology Hematology Consultants, experienced a data breach about 10 years ago, when a laptop was stolen from her large practice.
She and the other physicians were upset and worried that the individual would attempt to log in to the computer system and hack their patients’ private health information.
Dr. McAneny was also worried that the practice would have to pay a hefty fine to the government for having unsecured private health information on a laptop. She could have paid from $50,000 to more than $1.9 million for lost and stolen devices (although that didn’t happen).
Dr. McAneny had a standard cyber liability benefit in her med-mal policy that covered up to $50,000 of the data breach costs. That covered the legal advice The Doctors Company provided about state and federal reporting requirements when a data breach occurs and the costs the practice incurred from mailing letters to all of its patients notifying them of the data breach, says Dr. McAneny.
“The data breach taught me a lot. Our practice spent a lot of money on increasing our internal controls, cybersecurity, and monitoring. Our IT department started testing our computer firewalls periodically, and that’s how we discovered that cybercriminals were attempting to break into our computer system at least 100 times daily,” says Dr. McAneny.
That discovery changed how she thought about insurance. “I decided the med-mal benefit wasn’t enough. I bought the best cybersecurity policy we could afford to protect against future breaches, especially malware or ransomware attacks.”
Her practice also had to make its electronic health records (EHRs) more secure to comply with the Department of Health & Human Services Office of Civil Rights standards for protected health information. The cost of increased security wasn’t covered by her cyber benefit.
Cyberattacks increasing in health care
Despite having comprehensive coverage, Dr. McAneny worries that the cybercriminals are a step ahead of the cybersecurity experts and her practice will eventually have another data breach.
“The policy only covers things that we know about today. As we upgrade our defenses, criminals are finding new ways to breach firewalls and work around our defenses,” she says.
So far this year, nearly 200 medical groups have reported cyberattacks involving 500 or more of their patients’ medical records to the federal government.
EHRs are valuable targets to cybercriminals because of the protected health information they contain. Cybercriminals grab information such as Social Security numbers, dates of birth, medical procedures and results, and in some cases billing and financial information and sell it on the dark web.
They typically bundle the information and sell it to other criminals who later use it for various kinds of fraud and extortion such as banking and credit fraud, health care fraud, identity theft, and ransom extortion.
What do most doctors have?
The vast majority (82%) of doctors polled by the Medical Group Management Association last year said they had cyber insurance, compared with 54% in 2018.
For those who answered “yes,” many said they have coverage through their malpractice insurance carrier.
David Zetter, president of Zetter HealthCare Management Consultants, recommends that physicians speak with their malpractice carrier to determine what coverage they have, if any, within their malpractice policy.
A typical cybersecurity benefit is limited to what is needed to fix and resolve the hacking incident, says Raj Shah, senior regulatory attorney and policyholder advisor at MagMutual, which insures medical practices for malpractice and cyber liability.
That usually covers investigating the cause of the breach and the extent of the damage, legal advice about federal and state reporting requirements, whether to pay a ransom, and a public relations professional to handle patient communication, says Mr. Shah.
The benefit doesn’t cover lost patient revenue when practices have to shut down their operations, the cost of replacing damaged computers, or the ransom payment, he says.
Mr. Zetter advises doctors to consider buying cybersecurity coverage. “I recommend that they speak with an insurance broker who is experienced with cybersecurity policies sold to health care professionals to determine what type of coverage and how much coverage they may need. Their malpractice carrier may also be able to provide some answers,” says Mr. Zetter.
The physician will need to be able to answer questions about their network and how many staff they have and may need to involve their IT vendor too, he adds.
How does comprehensive coverage compare?
Ransomware attacks continue to be one of the most frequent types of attacks, and the amount criminals are demanding has risen significantly. The median ransom payment was $5,000 in the fourth quarter of 2018, compared with over $300,000 during the fourth quarter of 2021.
Cybercriminals now engage in “double extortion” – demanding a ransom payment to hand over the code that will unlock their encrypted data – and then another ransom payment to not post patients’ sensitive medical information they copied onto the dark web.
Comprehensive cybersecurity insurance will cover “double extortion” payments, legal costs that may arise from defending against patient lawsuits, and the costs of meeting federal and state privacy requirements, including notifying patients of the data breach and regulatory investigations, says Michael Carr, head of risk engineering for North America for Coalition, a cyber insurance firm.
Cyber insurers also contract with vendors who sell bitcoin, which is the currency cybercriminals typically demand for ransom payments, and work with ransom negotiators.
For example, once Coalition decided to pay the ransom on behalf of a health care client, it negotiated the ransom demand down by nearly 75% from $750,000 to $200,000, and proceeded to help the company restore all of its data.
The costs to respond to the incident, to recover lost data, and to pay the extortion, together with the lost business income resulting from the incident, were covered by Coalition’s cyber insurance policy.
Other clients have had their funds retrieved before a fraudulent wire transfer was completed. “Medical practices have vendors they pay regularly. A cybercriminal may compromise your email or take over a bank account and then impersonate a vendor asking to be paid for services they didn’t provide,” says Mr. Carr.
How much coverage do you need? Cost?
Dr. McAneny has increased her cybersecurity coverage every year. “It’s expensive, but I think it’s worth it. But you can never buy enough protection due to the coverage limits.”
She worries that the costs could exceed the limits if a ransomware attack disrupts her practice for days, weeks, or longer, or if the Office for Civil Rights fines her practice $10,000 per patient chart – the practice has 100,000 health records. “That can run several millions of dollars and ruin a practice,” she says.
Health systems and hospitals need massive amounts of coverage, which often runs from $20 million to $30 million, says Mr. Shah. However, practices insured through MagMutual have lower coverage limits that range from $1 million to $5 million, he says.
“A large practice does not necessarily need more than $1,000,000 in coverage if they have limited loss in this area and strong internal processes and controls. Most large practices also have a dedicated information security director, which reduces their risk, so they may be comfortable with $1,000,000 in coverage,” says Mr. Shah.
Premiums are based on the number of patient health records per practice, which translates into higher premiums for larger practices.
Other factors that come into play include the underlying coverage, risk controls the practice has implemented, and its claims history, says Mr. Shah.
However, the cost for cyber liability insurance has increased, and practices can expect to pay higher premiums and deductibles. For example, a practice that paid $10,000 in premiums for a new policy last year will have to pay $20,000 this year, says Dan Hanson, senior vice president of management liability and client experience at Marsh & McLennon Agency, a risk management firm that sells cyber insurance policies.
“We saw 71% of our self-insured clients experience higher deductibles over last year due to increased claim activity and the lack of capacity in the market. The carriers are saying they will set limits, but you are going to pay a lot more, and you are going to participate more in losses through the higher deductibles,” says Mr. Hanson.
Are you eligible?
Cyber insurance companies have a vested interest in avoiding claims. With increasing cyberattacks and larger payouts, many insurers are requiring practices to implement some defensive measures before they insure them. Some insurers, such as Coalition, say they may still insure small practices for comprehensive coverage, but it may impact the pricing or what’s covered, says Mr. Carr.
Here are some of the security measures that cyber insurers are looking for:
- Multifactorial authentication (MFA) requires an extra layer of security to access the system. For example, when logging into your organization’s EHR platform, instead of just using a username and password to access the platform, MFA would require you to input an additional unique login credential before you can access the EHR. A secondary login credential may include security questions, a one-time PIN, or biometrics.
- Removing a terminated employee’s login credentials quickly from the computer system. “One of the most damaging and expensive types of attacks are by disgruntled employees who still have their login credentials and take revenge by logging back into the system and planting malware,” says Mr. Shah.
- Automatic system updates (patches). “Phishing email compromises usually result from a failure to fix vulnerabilities. When a system needs to restart, it should be set to automatically update any potential security loopholes within programs or products,” says Mr. Carr. The firewall settings should also be updated.
- Prior hacking incidents: Are the attackers out of your system? Once criminals hack into the system, your practice is vulnerable to repeat attacks. “If a cyberattack is not completely addressed, threat actors will maintain access to or a presence on the compromised network. In general, we will work with the insured to ensure that the initial point of compromise has been addressed and that any threat actor presence in the network has been removed,” says Mr. Carr.
When doctors compare cybersecurity policies, experts recommend avoiding companies that may offer lower prices but lack a proven track record of handling claims and do not offer resources that can detect a threat, such as ongoing network monitoring and employee training with simulated exercises.
“Practices tend to think, ‘It won’t happen to me.’ Every practice needs to take this seriously,” says Dr. McAneny.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study eyes characteristics of pediatric patients with hidradenitis suppurativa
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
AT SPD 2022
Shift schedule today could worsen that stroke tomorrow
Body clocks and the shifting risks of stroke
Health care professionals, we’re sure, are no strangers to rotating shifts. And, as practitioners of the shiftly arts, you should know new research shows that working those kinds of hours can have lasting effects on your health. And it’s all based on your sleep-wake cycle.
In a study published in Neurobiology of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms, investigators at Texas A&M University looked at the effects of working these kinds of shifts for a long period of time and then returning to a regular 24-hour cycle later in life. The study piggybacks on a previous study, which showed that rats on shift schedules had more severe stroke outcomes than those who were on a 24-hour cycle.
The current study demonstrates that working rotating shifts does have a lasting effect, by way of messing with the sleep-wake cycle. Based on the research, the rats that performed those kinds of shifts never got back to a normal schedule. When strokes occurred, outcomes were much worse, and the females had a higher mortality rate and more severe functional deficits than the males.
Now for the “good” news: Even if you’re among those who haven’t worked a rotating shift, you may not be safe either.
People who have regular working hours have a tendency to take work home and stay up late, especially with so many moving to a remote-work model. And if you’re staying up late on the weekends you’re producing what lead author David J. Earnest, PhD, called “social jet lag,” which messes with your circadian rhythm to wind you down for sleep. All of these things can lead to the same kind of effects that working rotating shifts has on your health, he said in a written statement.
How do you combat this? Dr. Earnest recommended creating a sleep schedule and setting regular mealtimes. Also ease up on high-fat foods, drinking, and smoking. The connection between your brain and gut also could play a part in how severe a stroke can be.
So continue to work hard, but not too hard.
Got 3 minutes? You got time for culture
Much like a Krabby Patty, art is good for your soul. Seriously, staring at a 500-year-old painting may not seem like much, but research has proven time and again that going to a museum and looking at paintings by long-dead artists you probably know better as pizza-eating superhero turtles improves mood, stress, and well-being.
A couple of years ago, however, museums and art galleries ran into a big virus-shaped problem. You may have heard of it. All of a sudden it became a very bad idea for people to gather together in one building and huddle around the Mona Lisa, which, by the way, is a lot smaller in person than you might expect. But, rather than sit around with a bunch of priceless art for an indeterminate amount of time, museums brought their exhibits to the Internet so that people from all over the world could see great works from their couches.
This is absolutely a good thing for public access, but do these virtual art exhibits provide the same health benefits as going to a museum in person? That’s what a group of European researchers aimed to find out, and in a study published in Frontiers of Psychology, that’s exactly what they found.
Their directive to the 84 study participants was simple: Take a well-being survey, engage with either of a pair of online exhibits (a Monet painting and a display of Japanese culinary traditions) for just 3 minutes, then take another well-being assessment. The results were quite clear: Even just a couple of minutes of viewing art online improved all the well-being categories on the survey, such as lowering anxiety, negative mood, and loneliness, as well as increasing subjective well-being. Also, the more beautiful or meaningful a person found the art, the more their mood and well-being improved.
The researchers noted that these results could help access in places where access to art is limited, such as waiting rooms, hospitals, and rural areas. Let’s just hope it sticks to that, and that big businesses don’t take notice. Just imagine them plastering ads with classic Renaissance artworks. After all, art makes you feel good, and you know what else feels good on a hot summer day? An ice-cold Coca-Cola! By the way, we’re taking offers, advertising agencies. The LOTME staff can absolutely be bought.
Appetite for etymology
Today on “It’s a Thing,” we examine various states of hunger and what they should be called. Our first guest is that historically hungry royal person, King Henry VIII of England. Your majesty, have you ever been “hangry?”
KH8: First, let me thank you for inviting me on the show, Maurice. I’m a huge fan. A recent study done in the United Kingdom and Austria showed that “hunger is associated with greater levels of anger and irritability, as well as lower levels of pleasure,” according to a Eurekalert statement. So, yes, I have been “hangry.”
Maurice: Now to our next guest. Martha Stewart, can you add anything about that study?
Martha: Happy to, Maurice. The 64 participants used a smartphone app to record their hunger levels and emotional states five times a day for 21 days. It’s the first time that “hanger” was studied outside a lab, and it showed that hunger “was associated with 37% of the variance in irritability, 34% of the variance in anger, and 38% of the variance in pleasure recorded by the participants,” the investigators said in that statement.
Maurice: It’s official, then. Hangry is a thing, and we don’t need to put it in quotes anymore. Now let’s meet our third and final guest, Betty Crocker. Betty, I’m told you have a study to plug.
Betty: That’s right, Mo. Researchers at Tel Aviv University looked at survey data from almost 3,000 men and women and found that men ate 17% more food during the warmer months (March to September) than they did the rest of the year. Among women, however, caloric intake did not change.
KH8: I saw that study. Didn’t they put 27 people out in the sun and then take blood samples?
Betty: Indeed they did, Hank. After 25 minutes of sun exposure, the 13 men felt hungrier than before, but the 14 women did not. The men also had higher levels of ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating hormone, than the women.
Maurice: To sum all this up, then, we’ve got angry and hungry officially combining to make hangry, and now it looks like the sun is causing hunger in men, which makes them … sungry?
Martha: It’s a thing.
Chicken cutlets with a side of COVID
You stopped at the drive through at McDonald’s on the way home from work, and while you’re looking for something sweet in the refrigerator for dessert, you see that chicken breast that expires today.
Freezing meat that’s about to expire might be your go-to so it doesn’t go to waste, but it’s been found that SARS-CoV-2 can live in meat that’s been in the refrigerator or freezer for more than a month.
Researchers exposed chicken, beef, pork, and salmon to surrogate viruses that are similar to COVID but not as harmful and stored them in freezers at –4° F and in the refrigerator at 39.2° F. “We even found that the viruses could be cultured after [being frozen for] that length of time,” lead author Emily Bailey, PhD, of Campbell University in Buies Creek, N.C., said in Study Finds.
The team began its research after hearing of COVID-19 outbreaks where there were no reports of community transmission, such as in Southeast Asia. Tracing eventually led to packaged meats as the culprits in those cases. SARS-CoV-2 is able to replicate in the gut, as well as the respiratory tract, so it could affect the gut before respiratory symptoms start. It is crucial to ensure cross contamination doesn’t occur, and inadequate sanitation prior to packaging needs to be addressed, the investigators said.
Honestly, we didn’t think anything could survive in a freezer for that long, but SARS-CoV-2 is a fighter.
Body clocks and the shifting risks of stroke
Health care professionals, we’re sure, are no strangers to rotating shifts. And, as practitioners of the shiftly arts, you should know new research shows that working those kinds of hours can have lasting effects on your health. And it’s all based on your sleep-wake cycle.
In a study published in Neurobiology of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms, investigators at Texas A&M University looked at the effects of working these kinds of shifts for a long period of time and then returning to a regular 24-hour cycle later in life. The study piggybacks on a previous study, which showed that rats on shift schedules had more severe stroke outcomes than those who were on a 24-hour cycle.
The current study demonstrates that working rotating shifts does have a lasting effect, by way of messing with the sleep-wake cycle. Based on the research, the rats that performed those kinds of shifts never got back to a normal schedule. When strokes occurred, outcomes were much worse, and the females had a higher mortality rate and more severe functional deficits than the males.
Now for the “good” news: Even if you’re among those who haven’t worked a rotating shift, you may not be safe either.
People who have regular working hours have a tendency to take work home and stay up late, especially with so many moving to a remote-work model. And if you’re staying up late on the weekends you’re producing what lead author David J. Earnest, PhD, called “social jet lag,” which messes with your circadian rhythm to wind you down for sleep. All of these things can lead to the same kind of effects that working rotating shifts has on your health, he said in a written statement.
How do you combat this? Dr. Earnest recommended creating a sleep schedule and setting regular mealtimes. Also ease up on high-fat foods, drinking, and smoking. The connection between your brain and gut also could play a part in how severe a stroke can be.
So continue to work hard, but not too hard.
Got 3 minutes? You got time for culture
Much like a Krabby Patty, art is good for your soul. Seriously, staring at a 500-year-old painting may not seem like much, but research has proven time and again that going to a museum and looking at paintings by long-dead artists you probably know better as pizza-eating superhero turtles improves mood, stress, and well-being.
A couple of years ago, however, museums and art galleries ran into a big virus-shaped problem. You may have heard of it. All of a sudden it became a very bad idea for people to gather together in one building and huddle around the Mona Lisa, which, by the way, is a lot smaller in person than you might expect. But, rather than sit around with a bunch of priceless art for an indeterminate amount of time, museums brought their exhibits to the Internet so that people from all over the world could see great works from their couches.
This is absolutely a good thing for public access, but do these virtual art exhibits provide the same health benefits as going to a museum in person? That’s what a group of European researchers aimed to find out, and in a study published in Frontiers of Psychology, that’s exactly what they found.
Their directive to the 84 study participants was simple: Take a well-being survey, engage with either of a pair of online exhibits (a Monet painting and a display of Japanese culinary traditions) for just 3 minutes, then take another well-being assessment. The results were quite clear: Even just a couple of minutes of viewing art online improved all the well-being categories on the survey, such as lowering anxiety, negative mood, and loneliness, as well as increasing subjective well-being. Also, the more beautiful or meaningful a person found the art, the more their mood and well-being improved.
The researchers noted that these results could help access in places where access to art is limited, such as waiting rooms, hospitals, and rural areas. Let’s just hope it sticks to that, and that big businesses don’t take notice. Just imagine them plastering ads with classic Renaissance artworks. After all, art makes you feel good, and you know what else feels good on a hot summer day? An ice-cold Coca-Cola! By the way, we’re taking offers, advertising agencies. The LOTME staff can absolutely be bought.
Appetite for etymology
Today on “It’s a Thing,” we examine various states of hunger and what they should be called. Our first guest is that historically hungry royal person, King Henry VIII of England. Your majesty, have you ever been “hangry?”
KH8: First, let me thank you for inviting me on the show, Maurice. I’m a huge fan. A recent study done in the United Kingdom and Austria showed that “hunger is associated with greater levels of anger and irritability, as well as lower levels of pleasure,” according to a Eurekalert statement. So, yes, I have been “hangry.”
Maurice: Now to our next guest. Martha Stewart, can you add anything about that study?
Martha: Happy to, Maurice. The 64 participants used a smartphone app to record their hunger levels and emotional states five times a day for 21 days. It’s the first time that “hanger” was studied outside a lab, and it showed that hunger “was associated with 37% of the variance in irritability, 34% of the variance in anger, and 38% of the variance in pleasure recorded by the participants,” the investigators said in that statement.
Maurice: It’s official, then. Hangry is a thing, and we don’t need to put it in quotes anymore. Now let’s meet our third and final guest, Betty Crocker. Betty, I’m told you have a study to plug.
Betty: That’s right, Mo. Researchers at Tel Aviv University looked at survey data from almost 3,000 men and women and found that men ate 17% more food during the warmer months (March to September) than they did the rest of the year. Among women, however, caloric intake did not change.
KH8: I saw that study. Didn’t they put 27 people out in the sun and then take blood samples?
Betty: Indeed they did, Hank. After 25 minutes of sun exposure, the 13 men felt hungrier than before, but the 14 women did not. The men also had higher levels of ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating hormone, than the women.
Maurice: To sum all this up, then, we’ve got angry and hungry officially combining to make hangry, and now it looks like the sun is causing hunger in men, which makes them … sungry?
Martha: It’s a thing.
Chicken cutlets with a side of COVID
You stopped at the drive through at McDonald’s on the way home from work, and while you’re looking for something sweet in the refrigerator for dessert, you see that chicken breast that expires today.
Freezing meat that’s about to expire might be your go-to so it doesn’t go to waste, but it’s been found that SARS-CoV-2 can live in meat that’s been in the refrigerator or freezer for more than a month.
Researchers exposed chicken, beef, pork, and salmon to surrogate viruses that are similar to COVID but not as harmful and stored them in freezers at –4° F and in the refrigerator at 39.2° F. “We even found that the viruses could be cultured after [being frozen for] that length of time,” lead author Emily Bailey, PhD, of Campbell University in Buies Creek, N.C., said in Study Finds.
The team began its research after hearing of COVID-19 outbreaks where there were no reports of community transmission, such as in Southeast Asia. Tracing eventually led to packaged meats as the culprits in those cases. SARS-CoV-2 is able to replicate in the gut, as well as the respiratory tract, so it could affect the gut before respiratory symptoms start. It is crucial to ensure cross contamination doesn’t occur, and inadequate sanitation prior to packaging needs to be addressed, the investigators said.
Honestly, we didn’t think anything could survive in a freezer for that long, but SARS-CoV-2 is a fighter.
Body clocks and the shifting risks of stroke
Health care professionals, we’re sure, are no strangers to rotating shifts. And, as practitioners of the shiftly arts, you should know new research shows that working those kinds of hours can have lasting effects on your health. And it’s all based on your sleep-wake cycle.
In a study published in Neurobiology of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms, investigators at Texas A&M University looked at the effects of working these kinds of shifts for a long period of time and then returning to a regular 24-hour cycle later in life. The study piggybacks on a previous study, which showed that rats on shift schedules had more severe stroke outcomes than those who were on a 24-hour cycle.
The current study demonstrates that working rotating shifts does have a lasting effect, by way of messing with the sleep-wake cycle. Based on the research, the rats that performed those kinds of shifts never got back to a normal schedule. When strokes occurred, outcomes were much worse, and the females had a higher mortality rate and more severe functional deficits than the males.
Now for the “good” news: Even if you’re among those who haven’t worked a rotating shift, you may not be safe either.
People who have regular working hours have a tendency to take work home and stay up late, especially with so many moving to a remote-work model. And if you’re staying up late on the weekends you’re producing what lead author David J. Earnest, PhD, called “social jet lag,” which messes with your circadian rhythm to wind you down for sleep. All of these things can lead to the same kind of effects that working rotating shifts has on your health, he said in a written statement.
How do you combat this? Dr. Earnest recommended creating a sleep schedule and setting regular mealtimes. Also ease up on high-fat foods, drinking, and smoking. The connection between your brain and gut also could play a part in how severe a stroke can be.
So continue to work hard, but not too hard.
Got 3 minutes? You got time for culture
Much like a Krabby Patty, art is good for your soul. Seriously, staring at a 500-year-old painting may not seem like much, but research has proven time and again that going to a museum and looking at paintings by long-dead artists you probably know better as pizza-eating superhero turtles improves mood, stress, and well-being.
A couple of years ago, however, museums and art galleries ran into a big virus-shaped problem. You may have heard of it. All of a sudden it became a very bad idea for people to gather together in one building and huddle around the Mona Lisa, which, by the way, is a lot smaller in person than you might expect. But, rather than sit around with a bunch of priceless art for an indeterminate amount of time, museums brought their exhibits to the Internet so that people from all over the world could see great works from their couches.
This is absolutely a good thing for public access, but do these virtual art exhibits provide the same health benefits as going to a museum in person? That’s what a group of European researchers aimed to find out, and in a study published in Frontiers of Psychology, that’s exactly what they found.
Their directive to the 84 study participants was simple: Take a well-being survey, engage with either of a pair of online exhibits (a Monet painting and a display of Japanese culinary traditions) for just 3 minutes, then take another well-being assessment. The results were quite clear: Even just a couple of minutes of viewing art online improved all the well-being categories on the survey, such as lowering anxiety, negative mood, and loneliness, as well as increasing subjective well-being. Also, the more beautiful or meaningful a person found the art, the more their mood and well-being improved.
The researchers noted that these results could help access in places where access to art is limited, such as waiting rooms, hospitals, and rural areas. Let’s just hope it sticks to that, and that big businesses don’t take notice. Just imagine them plastering ads with classic Renaissance artworks. After all, art makes you feel good, and you know what else feels good on a hot summer day? An ice-cold Coca-Cola! By the way, we’re taking offers, advertising agencies. The LOTME staff can absolutely be bought.
Appetite for etymology
Today on “It’s a Thing,” we examine various states of hunger and what they should be called. Our first guest is that historically hungry royal person, King Henry VIII of England. Your majesty, have you ever been “hangry?”
KH8: First, let me thank you for inviting me on the show, Maurice. I’m a huge fan. A recent study done in the United Kingdom and Austria showed that “hunger is associated with greater levels of anger and irritability, as well as lower levels of pleasure,” according to a Eurekalert statement. So, yes, I have been “hangry.”
Maurice: Now to our next guest. Martha Stewart, can you add anything about that study?
Martha: Happy to, Maurice. The 64 participants used a smartphone app to record their hunger levels and emotional states five times a day for 21 days. It’s the first time that “hanger” was studied outside a lab, and it showed that hunger “was associated with 37% of the variance in irritability, 34% of the variance in anger, and 38% of the variance in pleasure recorded by the participants,” the investigators said in that statement.
Maurice: It’s official, then. Hangry is a thing, and we don’t need to put it in quotes anymore. Now let’s meet our third and final guest, Betty Crocker. Betty, I’m told you have a study to plug.
Betty: That’s right, Mo. Researchers at Tel Aviv University looked at survey data from almost 3,000 men and women and found that men ate 17% more food during the warmer months (March to September) than they did the rest of the year. Among women, however, caloric intake did not change.
KH8: I saw that study. Didn’t they put 27 people out in the sun and then take blood samples?
Betty: Indeed they did, Hank. After 25 minutes of sun exposure, the 13 men felt hungrier than before, but the 14 women did not. The men also had higher levels of ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating hormone, than the women.
Maurice: To sum all this up, then, we’ve got angry and hungry officially combining to make hangry, and now it looks like the sun is causing hunger in men, which makes them … sungry?
Martha: It’s a thing.
Chicken cutlets with a side of COVID
You stopped at the drive through at McDonald’s on the way home from work, and while you’re looking for something sweet in the refrigerator for dessert, you see that chicken breast that expires today.
Freezing meat that’s about to expire might be your go-to so it doesn’t go to waste, but it’s been found that SARS-CoV-2 can live in meat that’s been in the refrigerator or freezer for more than a month.
Researchers exposed chicken, beef, pork, and salmon to surrogate viruses that are similar to COVID but not as harmful and stored them in freezers at –4° F and in the refrigerator at 39.2° F. “We even found that the viruses could be cultured after [being frozen for] that length of time,” lead author Emily Bailey, PhD, of Campbell University in Buies Creek, N.C., said in Study Finds.
The team began its research after hearing of COVID-19 outbreaks where there were no reports of community transmission, such as in Southeast Asia. Tracing eventually led to packaged meats as the culprits in those cases. SARS-CoV-2 is able to replicate in the gut, as well as the respiratory tract, so it could affect the gut before respiratory symptoms start. It is crucial to ensure cross contamination doesn’t occur, and inadequate sanitation prior to packaging needs to be addressed, the investigators said.
Honestly, we didn’t think anything could survive in a freezer for that long, but SARS-CoV-2 is a fighter.