User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
‘Doc, can I get a mask exemption?’
As more jurisdictions mandate facial coverings in public, questions have arisen about whether it’s safe for everyone – including those with lung disease – to wear masks.
To address these issues, Medscape spoke with the chief medical officer of the American Lung Association, Dr. Albert Rizzo.
The CDC recommendations on mask wearing say, “Cloth face coverings should not be placed on young children under age 2, anyone who has trouble breathing, or is unconscious, incapacitated, or otherwise unable to remove the mask without assistance.” Does this language suggest that there indeed is a subset of the adult population with lung disease who shouldn’t wear masks?
It makes sense to say that if it makes you uncomfortable to wear a mask because it affects your breathing, you should think twice about getting in a situation where you would have to wear a mask.
I’ve told many of my high-risk patients, “The best way to avoid getting COVID-19 is to stay home and stay away from sick people, especially if you feel that you are not going to be able to wear a mask or facial covering of some sort.”
The reason that some people have trouble with a mask is that they haven’t tried the right style of mask – by that I mean how tightly it fits and the material it’s made out of. Sometimes it really is just that people with lung disease don’t like to have anything covering their faces. Many of these patients feel better where there is air blowing across their faces – they will have a fan blowing even in the middle of winter because they feel more comfortable.
I won’t say it’s all in their heads, but sometimes it’s a matter of desensitizing themselves to wearing a mask. I liken it to people who have sleep apnea. We often have to desensitize them to wearing a mask for sleeping. We tell them to put it on while they are watching TV — don’t hook it up to anything yet, just get used to having something on your face.
I’ve told my patients the same thing about masks for COVID-19. Put on the mask, see how it feels. If you become uncomfortable breathing with it on, take it off, but maybe you can handle it for a half hour or 45 minutes. Find out how much time you have for a trip to the grocery store based on how comfortable you are wearing it at home.
It’s a matter of training the patient, giving them options of how to get comfortable with it, and then making them realize that they have to weigh the benefits and risks of wearing the mask and feeling out of breath versus going out in public and being potentially exposed to coronavirus. And the bottom line is, anybody who is wearing a mask and starts to feel uncomfortable, they can take the mask off.
You mentioned different types of masks. Is there a type of mask that is typically more breathable that clinicians can recommend to patients with lung disease?
First, I remind patients who think they will have trouble breathing with a mask on that they are choosing a mask not so much to protect themselves – that would take an N95 mask to filter out the virus. The mask is worn so that when they cough or drink or speak, they aren’t sending respiratory droplets out into the environment. Even when we speak, respiratory droplets can easily go out as far as 6 feet, or further with coughing or sneezing. With facial coverings, we try to keep those respiratory droplets from getting out and infecting others.
So when choosing a mask, you don’t have to worry as much about a tight-fitting mask. I recommend a loose-fitting mask that covers the nose and mouth and isn’t going to fall off but isn’t so tight around the ears and neck to make them feel uncomfortable. Even though it doesn’t really protect the wearer, it is cutting down on the ability to breathe in droplets – maybe not microscopic particles, but it’s better than nothing.
Is a face shield a reasonable alternative for someone who feels they can’t breathe with a mask on?
Yes. I’m surprised that face shields don’t get more attention. I’ve tried them out, and they are actually more comfortable than masks. They do impede the spilling out of droplets into the public, but they are not as close fitting to the face as a mask. If you want to protect others, the face shield should be adequate. It is not as good at preventing you from breathing in viral particles.
Some people have claimed that wearing a mask makes them hyperventilate and feel like they are going to pass out, or the mask causes them to become hypoxic. Are these valid concerns?
We get two questions about masks from patients who feel that they are short of breath or are worried about wearing a mask. One is whether their oxygen level is dropping. It’s usually not that. It’s usually because they feel that the mask is an impediment to getting air in. Their oxygen levels are stable.
The other question is whether the mask causes CO2 retention. For the mask to trap enough exhaled CO2 and for us to breathe enough of that CO2 back in to raise our CO2 level, it has to be a pretty tight-fitting mask. With the type of masks we are suggesting that people wear, that’s very unlikely to occur.
What can clinicians do to reassure patients with some type of lung disease that they can safely wear masks?
There are a few things they can do right in the office. Have them put the mask on for a few minutes and make sure they feel comfortable with it. With an oximeter, patients can see that their oxygen levels don’t change when they are breathing through the mask for a period of time.
You can’t really measure CO2 retention that easily, but most patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or pulmonary fibrosis don’t have an elevated CO2 at baseline. A little more education is helpful in those situations. In most cases, they aren’t going to retain enough CO2 to have problems wearing a mask.
Only a small percentage of patients with lung disease are CO2 retainers, and many of those patients are being seen by pulmonary specialists. Those are the patients you might want to be more cautious with, to make sure they aren’t wearing anything that is tight fitting or that makes them work harder to breathe. It’s not that the mask is causing CO2 retention, but the increased work of breathing may make it harder to exhale the CO2.
Does a mask interfere with supplemental oxygen in any way?
Supplemental oxygen is typically supplied through a nasal cannula, so 100% oxygen is still getting to the nasal passages and entrained down into the airway, so it shouldn’t be a problem.
Some of the resistance to wearing masks has come from people with asthma. Is it safe for patients with asthma to wear masks, or should these patients be exempt from wearing masks?
In general, the breathing of people with mild asthma, both young and old, should not be impeded by the wearing of facial coverings. The concerns about oxygen and carbon dioxide among patients with more severe lung disease should not play a role in asthma.
Since younger adults with COVID-19 seem to have fewer or no symptoms and may actually be carrying the virus unknowingly, this should be the main population who should wear masks to prevent transmission to others.
Exemptions for mask wearing for mild asthma should be discouraged and dealt with on a case-by-case basis if there is a particular concern for that individual.
How do you respond if a patient asks you for a formal medical exemption to wearing a mask?
We’ve been asked to do a lot of letter writing for patients around going back to work, as well as the issue of wearing masks. The discussion usually revolves around trying to avoid going somewhere where you would have to wear a mask if it makes you feel uncomfortable.
I do not recommend automatically exempting individuals from wearing masks, even many of my pulmonary patients. There needs to be an understanding by the patient regarding the purpose of the mask and the overall advice to stay out of situations where social distancing is not being practiced. If you can take the time to discuss options as mentioned above – mask styles, desensitization, etc – the patient usually understands and will try wearing a mask.
On a case-by-case basis, some individuals may need to be exempted, but I feel this is a small number. I prefer my high-risk (older, chronic disease, etc) patients do everything they can to avoid infection – handwashing, mask wearing, and socially distancing.
They should also realize that even with a note, it is not going to help if they are in the middle of the grocery store and someone confronts them about not wearing a mask. It may help as they enter a store that says “masks required” and they can show it to someone monitoring the door. But I’m not really sure in what situations having that note is going to be helpful if confrontations occur.
Patients are also asking how safe is it for them to go back to work and be out in public. I tell them, nothing is going to be 100% safe. Until we have an effective vaccine, we are all going to have to weigh the potential risks of going to an area where social distancing isn’t maintained, people aren’t wearing face masks, and you can’t wash your hands as much as you’d like to. That’s going to be a struggle for all of us to get back out into situations where people interact socially.
Albert A. Rizzo, MD, is chief medical officer for the American Lung Association, chief of the Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at the Christiana Care Health System in Newark, Delaware, and a member of Christiana Care Pulmonary Associates. He is board certified in internal medicine, pulmonary medicine, critical care medicine, and sleep medicine and is a clinical assistant professor of medicine at Thomas Jefferson University Medical School, Philadelphia.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As more jurisdictions mandate facial coverings in public, questions have arisen about whether it’s safe for everyone – including those with lung disease – to wear masks.
To address these issues, Medscape spoke with the chief medical officer of the American Lung Association, Dr. Albert Rizzo.
The CDC recommendations on mask wearing say, “Cloth face coverings should not be placed on young children under age 2, anyone who has trouble breathing, or is unconscious, incapacitated, or otherwise unable to remove the mask without assistance.” Does this language suggest that there indeed is a subset of the adult population with lung disease who shouldn’t wear masks?
It makes sense to say that if it makes you uncomfortable to wear a mask because it affects your breathing, you should think twice about getting in a situation where you would have to wear a mask.
I’ve told many of my high-risk patients, “The best way to avoid getting COVID-19 is to stay home and stay away from sick people, especially if you feel that you are not going to be able to wear a mask or facial covering of some sort.”
The reason that some people have trouble with a mask is that they haven’t tried the right style of mask – by that I mean how tightly it fits and the material it’s made out of. Sometimes it really is just that people with lung disease don’t like to have anything covering their faces. Many of these patients feel better where there is air blowing across their faces – they will have a fan blowing even in the middle of winter because they feel more comfortable.
I won’t say it’s all in their heads, but sometimes it’s a matter of desensitizing themselves to wearing a mask. I liken it to people who have sleep apnea. We often have to desensitize them to wearing a mask for sleeping. We tell them to put it on while they are watching TV — don’t hook it up to anything yet, just get used to having something on your face.
I’ve told my patients the same thing about masks for COVID-19. Put on the mask, see how it feels. If you become uncomfortable breathing with it on, take it off, but maybe you can handle it for a half hour or 45 minutes. Find out how much time you have for a trip to the grocery store based on how comfortable you are wearing it at home.
It’s a matter of training the patient, giving them options of how to get comfortable with it, and then making them realize that they have to weigh the benefits and risks of wearing the mask and feeling out of breath versus going out in public and being potentially exposed to coronavirus. And the bottom line is, anybody who is wearing a mask and starts to feel uncomfortable, they can take the mask off.
You mentioned different types of masks. Is there a type of mask that is typically more breathable that clinicians can recommend to patients with lung disease?
First, I remind patients who think they will have trouble breathing with a mask on that they are choosing a mask not so much to protect themselves – that would take an N95 mask to filter out the virus. The mask is worn so that when they cough or drink or speak, they aren’t sending respiratory droplets out into the environment. Even when we speak, respiratory droplets can easily go out as far as 6 feet, or further with coughing or sneezing. With facial coverings, we try to keep those respiratory droplets from getting out and infecting others.
So when choosing a mask, you don’t have to worry as much about a tight-fitting mask. I recommend a loose-fitting mask that covers the nose and mouth and isn’t going to fall off but isn’t so tight around the ears and neck to make them feel uncomfortable. Even though it doesn’t really protect the wearer, it is cutting down on the ability to breathe in droplets – maybe not microscopic particles, but it’s better than nothing.
Is a face shield a reasonable alternative for someone who feels they can’t breathe with a mask on?
Yes. I’m surprised that face shields don’t get more attention. I’ve tried them out, and they are actually more comfortable than masks. They do impede the spilling out of droplets into the public, but they are not as close fitting to the face as a mask. If you want to protect others, the face shield should be adequate. It is not as good at preventing you from breathing in viral particles.
Some people have claimed that wearing a mask makes them hyperventilate and feel like they are going to pass out, or the mask causes them to become hypoxic. Are these valid concerns?
We get two questions about masks from patients who feel that they are short of breath or are worried about wearing a mask. One is whether their oxygen level is dropping. It’s usually not that. It’s usually because they feel that the mask is an impediment to getting air in. Their oxygen levels are stable.
The other question is whether the mask causes CO2 retention. For the mask to trap enough exhaled CO2 and for us to breathe enough of that CO2 back in to raise our CO2 level, it has to be a pretty tight-fitting mask. With the type of masks we are suggesting that people wear, that’s very unlikely to occur.
What can clinicians do to reassure patients with some type of lung disease that they can safely wear masks?
There are a few things they can do right in the office. Have them put the mask on for a few minutes and make sure they feel comfortable with it. With an oximeter, patients can see that their oxygen levels don’t change when they are breathing through the mask for a period of time.
You can’t really measure CO2 retention that easily, but most patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or pulmonary fibrosis don’t have an elevated CO2 at baseline. A little more education is helpful in those situations. In most cases, they aren’t going to retain enough CO2 to have problems wearing a mask.
Only a small percentage of patients with lung disease are CO2 retainers, and many of those patients are being seen by pulmonary specialists. Those are the patients you might want to be more cautious with, to make sure they aren’t wearing anything that is tight fitting or that makes them work harder to breathe. It’s not that the mask is causing CO2 retention, but the increased work of breathing may make it harder to exhale the CO2.
Does a mask interfere with supplemental oxygen in any way?
Supplemental oxygen is typically supplied through a nasal cannula, so 100% oxygen is still getting to the nasal passages and entrained down into the airway, so it shouldn’t be a problem.
Some of the resistance to wearing masks has come from people with asthma. Is it safe for patients with asthma to wear masks, or should these patients be exempt from wearing masks?
In general, the breathing of people with mild asthma, both young and old, should not be impeded by the wearing of facial coverings. The concerns about oxygen and carbon dioxide among patients with more severe lung disease should not play a role in asthma.
Since younger adults with COVID-19 seem to have fewer or no symptoms and may actually be carrying the virus unknowingly, this should be the main population who should wear masks to prevent transmission to others.
Exemptions for mask wearing for mild asthma should be discouraged and dealt with on a case-by-case basis if there is a particular concern for that individual.
How do you respond if a patient asks you for a formal medical exemption to wearing a mask?
We’ve been asked to do a lot of letter writing for patients around going back to work, as well as the issue of wearing masks. The discussion usually revolves around trying to avoid going somewhere where you would have to wear a mask if it makes you feel uncomfortable.
I do not recommend automatically exempting individuals from wearing masks, even many of my pulmonary patients. There needs to be an understanding by the patient regarding the purpose of the mask and the overall advice to stay out of situations where social distancing is not being practiced. If you can take the time to discuss options as mentioned above – mask styles, desensitization, etc – the patient usually understands and will try wearing a mask.
On a case-by-case basis, some individuals may need to be exempted, but I feel this is a small number. I prefer my high-risk (older, chronic disease, etc) patients do everything they can to avoid infection – handwashing, mask wearing, and socially distancing.
They should also realize that even with a note, it is not going to help if they are in the middle of the grocery store and someone confronts them about not wearing a mask. It may help as they enter a store that says “masks required” and they can show it to someone monitoring the door. But I’m not really sure in what situations having that note is going to be helpful if confrontations occur.
Patients are also asking how safe is it for them to go back to work and be out in public. I tell them, nothing is going to be 100% safe. Until we have an effective vaccine, we are all going to have to weigh the potential risks of going to an area where social distancing isn’t maintained, people aren’t wearing face masks, and you can’t wash your hands as much as you’d like to. That’s going to be a struggle for all of us to get back out into situations where people interact socially.
Albert A. Rizzo, MD, is chief medical officer for the American Lung Association, chief of the Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at the Christiana Care Health System in Newark, Delaware, and a member of Christiana Care Pulmonary Associates. He is board certified in internal medicine, pulmonary medicine, critical care medicine, and sleep medicine and is a clinical assistant professor of medicine at Thomas Jefferson University Medical School, Philadelphia.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As more jurisdictions mandate facial coverings in public, questions have arisen about whether it’s safe for everyone – including those with lung disease – to wear masks.
To address these issues, Medscape spoke with the chief medical officer of the American Lung Association, Dr. Albert Rizzo.
The CDC recommendations on mask wearing say, “Cloth face coverings should not be placed on young children under age 2, anyone who has trouble breathing, or is unconscious, incapacitated, or otherwise unable to remove the mask without assistance.” Does this language suggest that there indeed is a subset of the adult population with lung disease who shouldn’t wear masks?
It makes sense to say that if it makes you uncomfortable to wear a mask because it affects your breathing, you should think twice about getting in a situation where you would have to wear a mask.
I’ve told many of my high-risk patients, “The best way to avoid getting COVID-19 is to stay home and stay away from sick people, especially if you feel that you are not going to be able to wear a mask or facial covering of some sort.”
The reason that some people have trouble with a mask is that they haven’t tried the right style of mask – by that I mean how tightly it fits and the material it’s made out of. Sometimes it really is just that people with lung disease don’t like to have anything covering their faces. Many of these patients feel better where there is air blowing across their faces – they will have a fan blowing even in the middle of winter because they feel more comfortable.
I won’t say it’s all in their heads, but sometimes it’s a matter of desensitizing themselves to wearing a mask. I liken it to people who have sleep apnea. We often have to desensitize them to wearing a mask for sleeping. We tell them to put it on while they are watching TV — don’t hook it up to anything yet, just get used to having something on your face.
I’ve told my patients the same thing about masks for COVID-19. Put on the mask, see how it feels. If you become uncomfortable breathing with it on, take it off, but maybe you can handle it for a half hour or 45 minutes. Find out how much time you have for a trip to the grocery store based on how comfortable you are wearing it at home.
It’s a matter of training the patient, giving them options of how to get comfortable with it, and then making them realize that they have to weigh the benefits and risks of wearing the mask and feeling out of breath versus going out in public and being potentially exposed to coronavirus. And the bottom line is, anybody who is wearing a mask and starts to feel uncomfortable, they can take the mask off.
You mentioned different types of masks. Is there a type of mask that is typically more breathable that clinicians can recommend to patients with lung disease?
First, I remind patients who think they will have trouble breathing with a mask on that they are choosing a mask not so much to protect themselves – that would take an N95 mask to filter out the virus. The mask is worn so that when they cough or drink or speak, they aren’t sending respiratory droplets out into the environment. Even when we speak, respiratory droplets can easily go out as far as 6 feet, or further with coughing or sneezing. With facial coverings, we try to keep those respiratory droplets from getting out and infecting others.
So when choosing a mask, you don’t have to worry as much about a tight-fitting mask. I recommend a loose-fitting mask that covers the nose and mouth and isn’t going to fall off but isn’t so tight around the ears and neck to make them feel uncomfortable. Even though it doesn’t really protect the wearer, it is cutting down on the ability to breathe in droplets – maybe not microscopic particles, but it’s better than nothing.
Is a face shield a reasonable alternative for someone who feels they can’t breathe with a mask on?
Yes. I’m surprised that face shields don’t get more attention. I’ve tried them out, and they are actually more comfortable than masks. They do impede the spilling out of droplets into the public, but they are not as close fitting to the face as a mask. If you want to protect others, the face shield should be adequate. It is not as good at preventing you from breathing in viral particles.
Some people have claimed that wearing a mask makes them hyperventilate and feel like they are going to pass out, or the mask causes them to become hypoxic. Are these valid concerns?
We get two questions about masks from patients who feel that they are short of breath or are worried about wearing a mask. One is whether their oxygen level is dropping. It’s usually not that. It’s usually because they feel that the mask is an impediment to getting air in. Their oxygen levels are stable.
The other question is whether the mask causes CO2 retention. For the mask to trap enough exhaled CO2 and for us to breathe enough of that CO2 back in to raise our CO2 level, it has to be a pretty tight-fitting mask. With the type of masks we are suggesting that people wear, that’s very unlikely to occur.
What can clinicians do to reassure patients with some type of lung disease that they can safely wear masks?
There are a few things they can do right in the office. Have them put the mask on for a few minutes and make sure they feel comfortable with it. With an oximeter, patients can see that their oxygen levels don’t change when they are breathing through the mask for a period of time.
You can’t really measure CO2 retention that easily, but most patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or pulmonary fibrosis don’t have an elevated CO2 at baseline. A little more education is helpful in those situations. In most cases, they aren’t going to retain enough CO2 to have problems wearing a mask.
Only a small percentage of patients with lung disease are CO2 retainers, and many of those patients are being seen by pulmonary specialists. Those are the patients you might want to be more cautious with, to make sure they aren’t wearing anything that is tight fitting or that makes them work harder to breathe. It’s not that the mask is causing CO2 retention, but the increased work of breathing may make it harder to exhale the CO2.
Does a mask interfere with supplemental oxygen in any way?
Supplemental oxygen is typically supplied through a nasal cannula, so 100% oxygen is still getting to the nasal passages and entrained down into the airway, so it shouldn’t be a problem.
Some of the resistance to wearing masks has come from people with asthma. Is it safe for patients with asthma to wear masks, or should these patients be exempt from wearing masks?
In general, the breathing of people with mild asthma, both young and old, should not be impeded by the wearing of facial coverings. The concerns about oxygen and carbon dioxide among patients with more severe lung disease should not play a role in asthma.
Since younger adults with COVID-19 seem to have fewer or no symptoms and may actually be carrying the virus unknowingly, this should be the main population who should wear masks to prevent transmission to others.
Exemptions for mask wearing for mild asthma should be discouraged and dealt with on a case-by-case basis if there is a particular concern for that individual.
How do you respond if a patient asks you for a formal medical exemption to wearing a mask?
We’ve been asked to do a lot of letter writing for patients around going back to work, as well as the issue of wearing masks. The discussion usually revolves around trying to avoid going somewhere where you would have to wear a mask if it makes you feel uncomfortable.
I do not recommend automatically exempting individuals from wearing masks, even many of my pulmonary patients. There needs to be an understanding by the patient regarding the purpose of the mask and the overall advice to stay out of situations where social distancing is not being practiced. If you can take the time to discuss options as mentioned above – mask styles, desensitization, etc – the patient usually understands and will try wearing a mask.
On a case-by-case basis, some individuals may need to be exempted, but I feel this is a small number. I prefer my high-risk (older, chronic disease, etc) patients do everything they can to avoid infection – handwashing, mask wearing, and socially distancing.
They should also realize that even with a note, it is not going to help if they are in the middle of the grocery store and someone confronts them about not wearing a mask. It may help as they enter a store that says “masks required” and they can show it to someone monitoring the door. But I’m not really sure in what situations having that note is going to be helpful if confrontations occur.
Patients are also asking how safe is it for them to go back to work and be out in public. I tell them, nothing is going to be 100% safe. Until we have an effective vaccine, we are all going to have to weigh the potential risks of going to an area where social distancing isn’t maintained, people aren’t wearing face masks, and you can’t wash your hands as much as you’d like to. That’s going to be a struggle for all of us to get back out into situations where people interact socially.
Albert A. Rizzo, MD, is chief medical officer for the American Lung Association, chief of the Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at the Christiana Care Health System in Newark, Delaware, and a member of Christiana Care Pulmonary Associates. He is board certified in internal medicine, pulmonary medicine, critical care medicine, and sleep medicine and is a clinical assistant professor of medicine at Thomas Jefferson University Medical School, Philadelphia.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How well trained is the class of COVID-19?
During a family medicine rotation at Oregon Health & Sciences University, Portland, third-year medical students are preparing for a patient visit. Only, instead of entering a clinic room, students sit down at a computer. The patient they’re virtually examining – a 42-year-old male cattle rancher with knee problems – is an actor.
He asks for an MRI. A student explains that kneecap pain calls for rehab rather than a scan. The patient pushes back. “It would ease my mind,” he says. “I really need to make sure I can keep the ranch running.” The student must now try to digitally maintain rapport while explaining why imaging isn’t necessary.
When COVID-19 hit, telehealth training and remote learning became major parts of medical education, seemingly overnight. Since the start of the pandemic, students have contended with canceled classes, missed rotations, and revised training timelines, even as the demand for new doctors grows ever more pressing.
Institutions have been forced to rethink how to best establish solid, long-term foundations to ensure that young doctors are adequately trained. “They may find themselves the only doctors to be practicing in a small town,” said Stephen G. Post, PhD, bioethicist and professor at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University. “They have to be ready.”
With limited hands-on access to patients, students must learn in ways most never have before. Medical schools are now test-driving a mix of new and reimagined teaching strategies that aim to produce doctors who will enter medicine just as prepared as their more seasoned peers.
Hands-off education
Soon after starting her pediatrics rotation in March, recent Stanford (Calif.) University graduate Paloma Marin-Nevarez, MD, heard that children were being admitted to her hospital for evaluation to rule out COVID-19. Dr. Marin-Nevarez was assigned to help care for them but never physically met any – an approach called “virtual rounding.”
In virtual rounding, a provider typically goes in, examines a patient, and uses a portable device such as an iPad to send video or take notes about the encounter. Students or others in another room then give input on the patient’s care. “It was bizarre doing rounds on patients I had not met yet, discussing their treatment plans in one of the team rooms,” Dr. Marin-Nevarez said. “There was something very eerie about passing that particular unit that said: ‘Do not enter,’ and never being able to go inside.”
Within weeks, the Association of American Medical Colleges advised medical schools to suspend any activities – including clinical rotations – that involved direct student contact with patients, even those who weren’t COVID-19 positive.
Many schools hope to have students back and participating in some degree of patient care at non–COVID-19 hospital wards as early as July 1, said Michael Gisondi, MD, vice chair of education at Stanford’s department of emergency medicine. Returning students must now adapt to a restricted training environment, often while scrambling to make up training time. “This is uncharted territory for medical schools. Elective cases are down, surgical cases are down. That’s potentially going to decrease exposure to training opportunities.”
When students come back, lectures are still likely to remain on hold at most schools, replaced by Zoom conferences and virtual presentations. That’s not completely new: A trend away from large, traditional classes predated the pandemic. In a 2017-2018 AAMC survey, one in four second-year medical students said they almost never went to in-person lectures. COVID-19 has accelerated this shift.
For faculty who have long emphasized hands-on, in-person learning, the shift presents “a whole pedagogical issue – you don’t necessarily know how to adjust your practices to an online format,” Dr. Gisondi said. Instructors have to be even more flexible in order to engage students. “Every week I ask the students: ‘What’s working? What’s not working?’ ” Dr. Gisondi said about his online classes. “We have to solicit feedback.”
Changes to lectures are the easy part, says Elisabeth Fassas, a second-year student at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County. Before the pandemic, she was taking a clinical medicine course that involved time in the hospital, something that helped link the academic with the practical. “You really get to see the stuff you’re learning being relevant: ‘Here’s a patient who has a cardiology problem,’ ” she said. “[Capturing] that piece of connection to what you’re working toward is going to be tricky, I think.”
Some students who graduated this past spring worry about that clinical time they lost. Many remain acutely conscious of specific knowledge gaps. “I did not get a ton of experience examining crying children or holding babies,” said Dr. Marin-Nevarez, who starts an emergency medicine residency this year. “I am going to have to be transparent with my future instructors and let them know I missed out because of the pandemic.”
Such knowledge gaps mean new doctors will have to make up ground, said Jeremiah Tao, MD, who trains ophthalmology residents at the University of California, Irvine. But Dr. Tao doesn’t see these setbacks as a major long-term problem. His residents are already starting to make up the patient hours they missed in the spring and are refining the skills that got short shrift earlier on. For eligibility, “most boards require a certain number of days of experience. But most of the message from our board is [that] they’re understanding, and they’re going to leave it to the program directors to declare someone competent.”
Robert Johnson, MD, dean of New Jersey Medical School, Newark, said short-term setbacks in training likely won’t translate into longer-term skill deficits. “What most schools have done is overprepare students. We’re sure they have acquired all the skills they need to practice.”
Closing the gaps
To fill existing knowledge gaps and prevent future deficits, institutions hope to strike a balance between keeping trainees safe and providing necessary on-site learning. In line with ongoing AAMC recommendations, which suggest schools curtail student involvement in direct patient care in areas with significant COVID-19 spread, virtual rounding will likely continue.
Many schools may use a hybrid approach, in which students take turns entering patient rooms to perform checkups or observations while other students and instructors watch a video broadcast. “It’s not that different from when I go into the room and supervise a trainee,” Dr. Gisondi said.
Some schools are going even further, transforming education in ways that reflect the demands of a COVID-19–era medical marketplace. Institutions such as Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and OHSU have invested in telemedicine training for years, but COVID-19 has given telehealth education an additional boost. These types of visits have surged dramatically, underscoring the importance of preparing new doctors to practice in a virtual setting – something that wasn’t common previously. In a 2019 survey, only about a quarter of sampled medical schools offered a telemedicine curriculum.
Simulated telehealth consults such as OHSU’s knee-pain scenario serve several purposes, says Ryan Palmer, EdD, associate dean of education at Northeast Ohio Universities, Rootstown. They virtually teach skills that students need – such as clearly explaining to patients why a care plan is called for – while allowing the trainees to practice forging an emotional connection with patients they are treating remotely.
“It’s less about how you use a specific system,” said Dr. Palmer, who developed OHSU’s TeleOSCE, a telehealth training system that has interested other schools. He sees this as an opportunity, inasmuch as telemedicine is likely to remain an important part of practice for the foreseeable future.
To that end, the AAMC recently hosted an online seminar to help faculty with telehealth instruction. But training such as this can only go so far, said Dr. Johnson. “There are techniques you do have to learn at the patient’s side.”
Dr. Johnson says that a traditional part of medical school at Rutgers has been having students spend time in general practitioners’ offices early on to see what the experience is like. “That’s going to be a problem – I expect many primary care practices will go out of business. Those types of shadowing experiences will probably go away. They may be replaced by experiences at larger clinics.”
Some learning in clinics may soon resume. Although fears about COVID-19 still loom large, Dr. Tao’s ophthalmology residents have started taking on something closer to a normal workload, thanks to patients returning for regular office visits. As people return to medical facilities in larger numbers, hospitals around the country have started separating patients with COVID-19 from others. Dr. Gisondi suggested that this means medical students may be able to circulate in non–COVID-19 wards, provided the institution has enough personal protective equipment. “The inpatient wards are really safe – there’s a low risk of transmission. That’s where core rotations occur.”
The road ahead
In settings where patients’ viral status remains uncertain, such as emergency wards and off-site clinics without rapid testing, in-person learning may be slower to resume. That’s where longer-term changes may come into play. Some schools are preparing digital learning platforms that have the potential to transform medical education.
For example, Haru Okuda, MD, an emergency medicine doctor and director of the Center for Advanced Medical Learning and Simulation at the University of South Florida, Tampa, is testing a new virtual-reality platform called Immertec. Dr. Okuda said that, unlike older teaching tools, the system is not a stale, static virtual environment that will become obsolete. Instead, it uses a live camera to visually teleport students into the space of a real clinic or operating room.
“Let’s say you have students learning gross anatomy, how to dissect the chest. You’d have a cadaver on the table, demonstrating anatomy. The student has a headset – you can see like you’re in the room.” The wraparound visual device allows students to watch surgical maneuvers close up or view additional input from devices such as laparoscopes.
Dr. Okuda acknowledges that educators don’t yet know whether this works as well as older, hands-on methods. As yet, no virtual reality system has touch-based sensors sophisticated enough to simulate even skills such as tying a basic surgical knot, Dr. Gisondi said. And immersive platforms are expensive, which means a gap may occur between schools that can afford them and those that can’t.
The long-term consequences of COVID-19 go beyond costs that institutions may have to bear. Some students are concerned that the pandemic is affecting their mental well-being in ways that may make training a tougher slog. A few students graduated early to serve on the COVID-19 front lines. Others, rather than planning trips to celebrate the gap between medical school and residency, watched from home as young doctors they knew worked under abusive and unsafe conditions.
“Many of us felt powerless, given what we saw happening around us,” said recent University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, graduate Marina Haque, MD. She thinks those feelings, along with the rigors of practicing medicine during a pandemic, may leave her and her colleagues more prone to burnout.
The pandemic has also had a galvanizing effect on students – some excited new doctors are eager to line up for duty on COVID-19 wards. But supervisors say they must weigh young doctors’ desire to serve against the possible risks. “You don’t want people who have a big future ahead of them rushing into these situations and getting severely ill,” said Dr. Post. “There is a balance.”
All these changes, temporary or lasting, have led many to question whether doctors who complete their training under the cloud of the pandemic will be more – or less – prepared than those who came before them. But it’s not really a question of better or worse, says Dr. Johnson, who stresses that medical education has always required flexibility.
“You come into medicine with a plan in mind, but things happen,” he said. He reflected on the HIV pandemic of the late 1980s and early 1990s that influenced his medical career. He hopes young doctors come through the COVID-19 crucible more seasoned, resilient, and confident in crisis situations. “This is a pivotal event in their lives, and it will shape many careers.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
During a family medicine rotation at Oregon Health & Sciences University, Portland, third-year medical students are preparing for a patient visit. Only, instead of entering a clinic room, students sit down at a computer. The patient they’re virtually examining – a 42-year-old male cattle rancher with knee problems – is an actor.
He asks for an MRI. A student explains that kneecap pain calls for rehab rather than a scan. The patient pushes back. “It would ease my mind,” he says. “I really need to make sure I can keep the ranch running.” The student must now try to digitally maintain rapport while explaining why imaging isn’t necessary.
When COVID-19 hit, telehealth training and remote learning became major parts of medical education, seemingly overnight. Since the start of the pandemic, students have contended with canceled classes, missed rotations, and revised training timelines, even as the demand for new doctors grows ever more pressing.
Institutions have been forced to rethink how to best establish solid, long-term foundations to ensure that young doctors are adequately trained. “They may find themselves the only doctors to be practicing in a small town,” said Stephen G. Post, PhD, bioethicist and professor at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University. “They have to be ready.”
With limited hands-on access to patients, students must learn in ways most never have before. Medical schools are now test-driving a mix of new and reimagined teaching strategies that aim to produce doctors who will enter medicine just as prepared as their more seasoned peers.
Hands-off education
Soon after starting her pediatrics rotation in March, recent Stanford (Calif.) University graduate Paloma Marin-Nevarez, MD, heard that children were being admitted to her hospital for evaluation to rule out COVID-19. Dr. Marin-Nevarez was assigned to help care for them but never physically met any – an approach called “virtual rounding.”
In virtual rounding, a provider typically goes in, examines a patient, and uses a portable device such as an iPad to send video or take notes about the encounter. Students or others in another room then give input on the patient’s care. “It was bizarre doing rounds on patients I had not met yet, discussing their treatment plans in one of the team rooms,” Dr. Marin-Nevarez said. “There was something very eerie about passing that particular unit that said: ‘Do not enter,’ and never being able to go inside.”
Within weeks, the Association of American Medical Colleges advised medical schools to suspend any activities – including clinical rotations – that involved direct student contact with patients, even those who weren’t COVID-19 positive.
Many schools hope to have students back and participating in some degree of patient care at non–COVID-19 hospital wards as early as July 1, said Michael Gisondi, MD, vice chair of education at Stanford’s department of emergency medicine. Returning students must now adapt to a restricted training environment, often while scrambling to make up training time. “This is uncharted territory for medical schools. Elective cases are down, surgical cases are down. That’s potentially going to decrease exposure to training opportunities.”
When students come back, lectures are still likely to remain on hold at most schools, replaced by Zoom conferences and virtual presentations. That’s not completely new: A trend away from large, traditional classes predated the pandemic. In a 2017-2018 AAMC survey, one in four second-year medical students said they almost never went to in-person lectures. COVID-19 has accelerated this shift.
For faculty who have long emphasized hands-on, in-person learning, the shift presents “a whole pedagogical issue – you don’t necessarily know how to adjust your practices to an online format,” Dr. Gisondi said. Instructors have to be even more flexible in order to engage students. “Every week I ask the students: ‘What’s working? What’s not working?’ ” Dr. Gisondi said about his online classes. “We have to solicit feedback.”
Changes to lectures are the easy part, says Elisabeth Fassas, a second-year student at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County. Before the pandemic, she was taking a clinical medicine course that involved time in the hospital, something that helped link the academic with the practical. “You really get to see the stuff you’re learning being relevant: ‘Here’s a patient who has a cardiology problem,’ ” she said. “[Capturing] that piece of connection to what you’re working toward is going to be tricky, I think.”
Some students who graduated this past spring worry about that clinical time they lost. Many remain acutely conscious of specific knowledge gaps. “I did not get a ton of experience examining crying children or holding babies,” said Dr. Marin-Nevarez, who starts an emergency medicine residency this year. “I am going to have to be transparent with my future instructors and let them know I missed out because of the pandemic.”
Such knowledge gaps mean new doctors will have to make up ground, said Jeremiah Tao, MD, who trains ophthalmology residents at the University of California, Irvine. But Dr. Tao doesn’t see these setbacks as a major long-term problem. His residents are already starting to make up the patient hours they missed in the spring and are refining the skills that got short shrift earlier on. For eligibility, “most boards require a certain number of days of experience. But most of the message from our board is [that] they’re understanding, and they’re going to leave it to the program directors to declare someone competent.”
Robert Johnson, MD, dean of New Jersey Medical School, Newark, said short-term setbacks in training likely won’t translate into longer-term skill deficits. “What most schools have done is overprepare students. We’re sure they have acquired all the skills they need to practice.”
Closing the gaps
To fill existing knowledge gaps and prevent future deficits, institutions hope to strike a balance between keeping trainees safe and providing necessary on-site learning. In line with ongoing AAMC recommendations, which suggest schools curtail student involvement in direct patient care in areas with significant COVID-19 spread, virtual rounding will likely continue.
Many schools may use a hybrid approach, in which students take turns entering patient rooms to perform checkups or observations while other students and instructors watch a video broadcast. “It’s not that different from when I go into the room and supervise a trainee,” Dr. Gisondi said.
Some schools are going even further, transforming education in ways that reflect the demands of a COVID-19–era medical marketplace. Institutions such as Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and OHSU have invested in telemedicine training for years, but COVID-19 has given telehealth education an additional boost. These types of visits have surged dramatically, underscoring the importance of preparing new doctors to practice in a virtual setting – something that wasn’t common previously. In a 2019 survey, only about a quarter of sampled medical schools offered a telemedicine curriculum.
Simulated telehealth consults such as OHSU’s knee-pain scenario serve several purposes, says Ryan Palmer, EdD, associate dean of education at Northeast Ohio Universities, Rootstown. They virtually teach skills that students need – such as clearly explaining to patients why a care plan is called for – while allowing the trainees to practice forging an emotional connection with patients they are treating remotely.
“It’s less about how you use a specific system,” said Dr. Palmer, who developed OHSU’s TeleOSCE, a telehealth training system that has interested other schools. He sees this as an opportunity, inasmuch as telemedicine is likely to remain an important part of practice for the foreseeable future.
To that end, the AAMC recently hosted an online seminar to help faculty with telehealth instruction. But training such as this can only go so far, said Dr. Johnson. “There are techniques you do have to learn at the patient’s side.”
Dr. Johnson says that a traditional part of medical school at Rutgers has been having students spend time in general practitioners’ offices early on to see what the experience is like. “That’s going to be a problem – I expect many primary care practices will go out of business. Those types of shadowing experiences will probably go away. They may be replaced by experiences at larger clinics.”
Some learning in clinics may soon resume. Although fears about COVID-19 still loom large, Dr. Tao’s ophthalmology residents have started taking on something closer to a normal workload, thanks to patients returning for regular office visits. As people return to medical facilities in larger numbers, hospitals around the country have started separating patients with COVID-19 from others. Dr. Gisondi suggested that this means medical students may be able to circulate in non–COVID-19 wards, provided the institution has enough personal protective equipment. “The inpatient wards are really safe – there’s a low risk of transmission. That’s where core rotations occur.”
The road ahead
In settings where patients’ viral status remains uncertain, such as emergency wards and off-site clinics without rapid testing, in-person learning may be slower to resume. That’s where longer-term changes may come into play. Some schools are preparing digital learning platforms that have the potential to transform medical education.
For example, Haru Okuda, MD, an emergency medicine doctor and director of the Center for Advanced Medical Learning and Simulation at the University of South Florida, Tampa, is testing a new virtual-reality platform called Immertec. Dr. Okuda said that, unlike older teaching tools, the system is not a stale, static virtual environment that will become obsolete. Instead, it uses a live camera to visually teleport students into the space of a real clinic or operating room.
“Let’s say you have students learning gross anatomy, how to dissect the chest. You’d have a cadaver on the table, demonstrating anatomy. The student has a headset – you can see like you’re in the room.” The wraparound visual device allows students to watch surgical maneuvers close up or view additional input from devices such as laparoscopes.
Dr. Okuda acknowledges that educators don’t yet know whether this works as well as older, hands-on methods. As yet, no virtual reality system has touch-based sensors sophisticated enough to simulate even skills such as tying a basic surgical knot, Dr. Gisondi said. And immersive platforms are expensive, which means a gap may occur between schools that can afford them and those that can’t.
The long-term consequences of COVID-19 go beyond costs that institutions may have to bear. Some students are concerned that the pandemic is affecting their mental well-being in ways that may make training a tougher slog. A few students graduated early to serve on the COVID-19 front lines. Others, rather than planning trips to celebrate the gap between medical school and residency, watched from home as young doctors they knew worked under abusive and unsafe conditions.
“Many of us felt powerless, given what we saw happening around us,” said recent University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, graduate Marina Haque, MD. She thinks those feelings, along with the rigors of practicing medicine during a pandemic, may leave her and her colleagues more prone to burnout.
The pandemic has also had a galvanizing effect on students – some excited new doctors are eager to line up for duty on COVID-19 wards. But supervisors say they must weigh young doctors’ desire to serve against the possible risks. “You don’t want people who have a big future ahead of them rushing into these situations and getting severely ill,” said Dr. Post. “There is a balance.”
All these changes, temporary or lasting, have led many to question whether doctors who complete their training under the cloud of the pandemic will be more – or less – prepared than those who came before them. But it’s not really a question of better or worse, says Dr. Johnson, who stresses that medical education has always required flexibility.
“You come into medicine with a plan in mind, but things happen,” he said. He reflected on the HIV pandemic of the late 1980s and early 1990s that influenced his medical career. He hopes young doctors come through the COVID-19 crucible more seasoned, resilient, and confident in crisis situations. “This is a pivotal event in their lives, and it will shape many careers.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
During a family medicine rotation at Oregon Health & Sciences University, Portland, third-year medical students are preparing for a patient visit. Only, instead of entering a clinic room, students sit down at a computer. The patient they’re virtually examining – a 42-year-old male cattle rancher with knee problems – is an actor.
He asks for an MRI. A student explains that kneecap pain calls for rehab rather than a scan. The patient pushes back. “It would ease my mind,” he says. “I really need to make sure I can keep the ranch running.” The student must now try to digitally maintain rapport while explaining why imaging isn’t necessary.
When COVID-19 hit, telehealth training and remote learning became major parts of medical education, seemingly overnight. Since the start of the pandemic, students have contended with canceled classes, missed rotations, and revised training timelines, even as the demand for new doctors grows ever more pressing.
Institutions have been forced to rethink how to best establish solid, long-term foundations to ensure that young doctors are adequately trained. “They may find themselves the only doctors to be practicing in a small town,” said Stephen G. Post, PhD, bioethicist and professor at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University. “They have to be ready.”
With limited hands-on access to patients, students must learn in ways most never have before. Medical schools are now test-driving a mix of new and reimagined teaching strategies that aim to produce doctors who will enter medicine just as prepared as their more seasoned peers.
Hands-off education
Soon after starting her pediatrics rotation in March, recent Stanford (Calif.) University graduate Paloma Marin-Nevarez, MD, heard that children were being admitted to her hospital for evaluation to rule out COVID-19. Dr. Marin-Nevarez was assigned to help care for them but never physically met any – an approach called “virtual rounding.”
In virtual rounding, a provider typically goes in, examines a patient, and uses a portable device such as an iPad to send video or take notes about the encounter. Students or others in another room then give input on the patient’s care. “It was bizarre doing rounds on patients I had not met yet, discussing their treatment plans in one of the team rooms,” Dr. Marin-Nevarez said. “There was something very eerie about passing that particular unit that said: ‘Do not enter,’ and never being able to go inside.”
Within weeks, the Association of American Medical Colleges advised medical schools to suspend any activities – including clinical rotations – that involved direct student contact with patients, even those who weren’t COVID-19 positive.
Many schools hope to have students back and participating in some degree of patient care at non–COVID-19 hospital wards as early as July 1, said Michael Gisondi, MD, vice chair of education at Stanford’s department of emergency medicine. Returning students must now adapt to a restricted training environment, often while scrambling to make up training time. “This is uncharted territory for medical schools. Elective cases are down, surgical cases are down. That’s potentially going to decrease exposure to training opportunities.”
When students come back, lectures are still likely to remain on hold at most schools, replaced by Zoom conferences and virtual presentations. That’s not completely new: A trend away from large, traditional classes predated the pandemic. In a 2017-2018 AAMC survey, one in four second-year medical students said they almost never went to in-person lectures. COVID-19 has accelerated this shift.
For faculty who have long emphasized hands-on, in-person learning, the shift presents “a whole pedagogical issue – you don’t necessarily know how to adjust your practices to an online format,” Dr. Gisondi said. Instructors have to be even more flexible in order to engage students. “Every week I ask the students: ‘What’s working? What’s not working?’ ” Dr. Gisondi said about his online classes. “We have to solicit feedback.”
Changes to lectures are the easy part, says Elisabeth Fassas, a second-year student at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County. Before the pandemic, she was taking a clinical medicine course that involved time in the hospital, something that helped link the academic with the practical. “You really get to see the stuff you’re learning being relevant: ‘Here’s a patient who has a cardiology problem,’ ” she said. “[Capturing] that piece of connection to what you’re working toward is going to be tricky, I think.”
Some students who graduated this past spring worry about that clinical time they lost. Many remain acutely conscious of specific knowledge gaps. “I did not get a ton of experience examining crying children or holding babies,” said Dr. Marin-Nevarez, who starts an emergency medicine residency this year. “I am going to have to be transparent with my future instructors and let them know I missed out because of the pandemic.”
Such knowledge gaps mean new doctors will have to make up ground, said Jeremiah Tao, MD, who trains ophthalmology residents at the University of California, Irvine. But Dr. Tao doesn’t see these setbacks as a major long-term problem. His residents are already starting to make up the patient hours they missed in the spring and are refining the skills that got short shrift earlier on. For eligibility, “most boards require a certain number of days of experience. But most of the message from our board is [that] they’re understanding, and they’re going to leave it to the program directors to declare someone competent.”
Robert Johnson, MD, dean of New Jersey Medical School, Newark, said short-term setbacks in training likely won’t translate into longer-term skill deficits. “What most schools have done is overprepare students. We’re sure they have acquired all the skills they need to practice.”
Closing the gaps
To fill existing knowledge gaps and prevent future deficits, institutions hope to strike a balance between keeping trainees safe and providing necessary on-site learning. In line with ongoing AAMC recommendations, which suggest schools curtail student involvement in direct patient care in areas with significant COVID-19 spread, virtual rounding will likely continue.
Many schools may use a hybrid approach, in which students take turns entering patient rooms to perform checkups or observations while other students and instructors watch a video broadcast. “It’s not that different from when I go into the room and supervise a trainee,” Dr. Gisondi said.
Some schools are going even further, transforming education in ways that reflect the demands of a COVID-19–era medical marketplace. Institutions such as Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, and OHSU have invested in telemedicine training for years, but COVID-19 has given telehealth education an additional boost. These types of visits have surged dramatically, underscoring the importance of preparing new doctors to practice in a virtual setting – something that wasn’t common previously. In a 2019 survey, only about a quarter of sampled medical schools offered a telemedicine curriculum.
Simulated telehealth consults such as OHSU’s knee-pain scenario serve several purposes, says Ryan Palmer, EdD, associate dean of education at Northeast Ohio Universities, Rootstown. They virtually teach skills that students need – such as clearly explaining to patients why a care plan is called for – while allowing the trainees to practice forging an emotional connection with patients they are treating remotely.
“It’s less about how you use a specific system,” said Dr. Palmer, who developed OHSU’s TeleOSCE, a telehealth training system that has interested other schools. He sees this as an opportunity, inasmuch as telemedicine is likely to remain an important part of practice for the foreseeable future.
To that end, the AAMC recently hosted an online seminar to help faculty with telehealth instruction. But training such as this can only go so far, said Dr. Johnson. “There are techniques you do have to learn at the patient’s side.”
Dr. Johnson says that a traditional part of medical school at Rutgers has been having students spend time in general practitioners’ offices early on to see what the experience is like. “That’s going to be a problem – I expect many primary care practices will go out of business. Those types of shadowing experiences will probably go away. They may be replaced by experiences at larger clinics.”
Some learning in clinics may soon resume. Although fears about COVID-19 still loom large, Dr. Tao’s ophthalmology residents have started taking on something closer to a normal workload, thanks to patients returning for regular office visits. As people return to medical facilities in larger numbers, hospitals around the country have started separating patients with COVID-19 from others. Dr. Gisondi suggested that this means medical students may be able to circulate in non–COVID-19 wards, provided the institution has enough personal protective equipment. “The inpatient wards are really safe – there’s a low risk of transmission. That’s where core rotations occur.”
The road ahead
In settings where patients’ viral status remains uncertain, such as emergency wards and off-site clinics without rapid testing, in-person learning may be slower to resume. That’s where longer-term changes may come into play. Some schools are preparing digital learning platforms that have the potential to transform medical education.
For example, Haru Okuda, MD, an emergency medicine doctor and director of the Center for Advanced Medical Learning and Simulation at the University of South Florida, Tampa, is testing a new virtual-reality platform called Immertec. Dr. Okuda said that, unlike older teaching tools, the system is not a stale, static virtual environment that will become obsolete. Instead, it uses a live camera to visually teleport students into the space of a real clinic or operating room.
“Let’s say you have students learning gross anatomy, how to dissect the chest. You’d have a cadaver on the table, demonstrating anatomy. The student has a headset – you can see like you’re in the room.” The wraparound visual device allows students to watch surgical maneuvers close up or view additional input from devices such as laparoscopes.
Dr. Okuda acknowledges that educators don’t yet know whether this works as well as older, hands-on methods. As yet, no virtual reality system has touch-based sensors sophisticated enough to simulate even skills such as tying a basic surgical knot, Dr. Gisondi said. And immersive platforms are expensive, which means a gap may occur between schools that can afford them and those that can’t.
The long-term consequences of COVID-19 go beyond costs that institutions may have to bear. Some students are concerned that the pandemic is affecting their mental well-being in ways that may make training a tougher slog. A few students graduated early to serve on the COVID-19 front lines. Others, rather than planning trips to celebrate the gap between medical school and residency, watched from home as young doctors they knew worked under abusive and unsafe conditions.
“Many of us felt powerless, given what we saw happening around us,” said recent University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, graduate Marina Haque, MD. She thinks those feelings, along with the rigors of practicing medicine during a pandemic, may leave her and her colleagues more prone to burnout.
The pandemic has also had a galvanizing effect on students – some excited new doctors are eager to line up for duty on COVID-19 wards. But supervisors say they must weigh young doctors’ desire to serve against the possible risks. “You don’t want people who have a big future ahead of them rushing into these situations and getting severely ill,” said Dr. Post. “There is a balance.”
All these changes, temporary or lasting, have led many to question whether doctors who complete their training under the cloud of the pandemic will be more – or less – prepared than those who came before them. But it’s not really a question of better or worse, says Dr. Johnson, who stresses that medical education has always required flexibility.
“You come into medicine with a plan in mind, but things happen,” he said. He reflected on the HIV pandemic of the late 1980s and early 1990s that influenced his medical career. He hopes young doctors come through the COVID-19 crucible more seasoned, resilient, and confident in crisis situations. “This is a pivotal event in their lives, and it will shape many careers.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
WHO plans to address airborne COVID-19 transmission
WHO will likely address airborne transmission of the virus after a commentary from almost 240 multidisciplinary scientists raised the alarm that virus particles could remain airborne longer that previously appreciated, particularly in poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
“Airborne route of infection transmission is significant, but so far completely undermined, and not recognized by the decision makers and bodies responsible for infection control,” lead commentary author Lidia Morawska, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
“This means that no control measures are taken to mitigate airborne transmission and, as a consequence, people are infected and can die,” said Morawska, director of the International Laboratory for Air Quality and Health at Queensland University of Technology in Brisbane, Australia. “We wanted to bring this to the attention of the world to prevent this from happening.”
The commentary was published July 6 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
WHO leaders defended their progress in announcing any changes regarding how COVID-19 can be transmitted during a virtual press briefing today. They have collaborated since April with some of the scientists who coauthored the commentary, for example, said Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO technical lead on COVID-19.
“We have been working on a scientific brief ... to consolidate knowledge around transmission,” she added.
One focus will be on how masks protect healthcare workers. “We are also looking at the possible role of airborne transmission in other settings,” Van Kerkhove said. “We will be releasing our brief in the coming days.”
“We acknowledge there is emerging evidence in this field,” Benedetta Allegranzi, MD, WHO technical lead on COVID-19, said during the briefing from Geneva. “Therefore, we believe we have to be open to this evidence and its implications.”
WHO participated in an international research meeting last week that addressed means for controlling modes of COVID-19 transmission, Allegranzi said. “Our group and others really highlighted importance of research on different modes of transmission, including droplets of different sizes and their relative importance,” she said. Another aim was determining the dose of the virus required for airborne transmission.
“These fields of research are really growing but not definitive. More evidence needs to be gathered and evaluated,” she explained.
In the meantime, Allegranzi said, “the possibility of airborne transmission in public settings – especially closed, poorly ventilated settings – cannot be ruled out.”
Morawska said the evidence already exists. “A continuous surprise is that it takes the world such a long time to accept this, while this has such solid scientific foundation.” As an example, she cited an April report she coauthored in the journal Environment International. She and colleagues call for “national authorities to acknowledge the reality that the virus spreads through air and recommend that adequate control measures be implemented to prevent further spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, in particularly removal of the virus-laden droplets from indoor air by ventilation.”
The take-home message from the commentary, Morawska said, is a call to action. The authors state there is a need “to provide sufficient and effective ventilation (supply clean outdoor air, minimize recirculating air) particularly in public buildings, workplace environments, schools, hospitals, and aged care homes.”
WHO Chief Scientist Soumya Swaminathan, MD, explained why the organization remains cautious about making premature pronouncements regarding airborne transmission. “Any guidance we put out has implications for billions of people around the world, so we want to be as careful as possible,” she said during the press briefing. “We have to consider the weight of the evidence.”
“We are constantly looking for information on how we can do better,” Swaminathan added. WHO officials are reviewing hundreds of scientific reports every day, she said, and not all are of good quality. For this reason, she and other scientists at WHO perform a “living systematic review” – updating the consensus of evidence on a weekly basis.
“This process on COVID-19 will, I am sure, continue for the weeks and months to come,” she added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WHO will likely address airborne transmission of the virus after a commentary from almost 240 multidisciplinary scientists raised the alarm that virus particles could remain airborne longer that previously appreciated, particularly in poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
“Airborne route of infection transmission is significant, but so far completely undermined, and not recognized by the decision makers and bodies responsible for infection control,” lead commentary author Lidia Morawska, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
“This means that no control measures are taken to mitigate airborne transmission and, as a consequence, people are infected and can die,” said Morawska, director of the International Laboratory for Air Quality and Health at Queensland University of Technology in Brisbane, Australia. “We wanted to bring this to the attention of the world to prevent this from happening.”
The commentary was published July 6 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
WHO leaders defended their progress in announcing any changes regarding how COVID-19 can be transmitted during a virtual press briefing today. They have collaborated since April with some of the scientists who coauthored the commentary, for example, said Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO technical lead on COVID-19.
“We have been working on a scientific brief ... to consolidate knowledge around transmission,” she added.
One focus will be on how masks protect healthcare workers. “We are also looking at the possible role of airborne transmission in other settings,” Van Kerkhove said. “We will be releasing our brief in the coming days.”
“We acknowledge there is emerging evidence in this field,” Benedetta Allegranzi, MD, WHO technical lead on COVID-19, said during the briefing from Geneva. “Therefore, we believe we have to be open to this evidence and its implications.”
WHO participated in an international research meeting last week that addressed means for controlling modes of COVID-19 transmission, Allegranzi said. “Our group and others really highlighted importance of research on different modes of transmission, including droplets of different sizes and their relative importance,” she said. Another aim was determining the dose of the virus required for airborne transmission.
“These fields of research are really growing but not definitive. More evidence needs to be gathered and evaluated,” she explained.
In the meantime, Allegranzi said, “the possibility of airborne transmission in public settings – especially closed, poorly ventilated settings – cannot be ruled out.”
Morawska said the evidence already exists. “A continuous surprise is that it takes the world such a long time to accept this, while this has such solid scientific foundation.” As an example, she cited an April report she coauthored in the journal Environment International. She and colleagues call for “national authorities to acknowledge the reality that the virus spreads through air and recommend that adequate control measures be implemented to prevent further spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, in particularly removal of the virus-laden droplets from indoor air by ventilation.”
The take-home message from the commentary, Morawska said, is a call to action. The authors state there is a need “to provide sufficient and effective ventilation (supply clean outdoor air, minimize recirculating air) particularly in public buildings, workplace environments, schools, hospitals, and aged care homes.”
WHO Chief Scientist Soumya Swaminathan, MD, explained why the organization remains cautious about making premature pronouncements regarding airborne transmission. “Any guidance we put out has implications for billions of people around the world, so we want to be as careful as possible,” she said during the press briefing. “We have to consider the weight of the evidence.”
“We are constantly looking for information on how we can do better,” Swaminathan added. WHO officials are reviewing hundreds of scientific reports every day, she said, and not all are of good quality. For this reason, she and other scientists at WHO perform a “living systematic review” – updating the consensus of evidence on a weekly basis.
“This process on COVID-19 will, I am sure, continue for the weeks and months to come,” she added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WHO will likely address airborne transmission of the virus after a commentary from almost 240 multidisciplinary scientists raised the alarm that virus particles could remain airborne longer that previously appreciated, particularly in poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
“Airborne route of infection transmission is significant, but so far completely undermined, and not recognized by the decision makers and bodies responsible for infection control,” lead commentary author Lidia Morawska, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
“This means that no control measures are taken to mitigate airborne transmission and, as a consequence, people are infected and can die,” said Morawska, director of the International Laboratory for Air Quality and Health at Queensland University of Technology in Brisbane, Australia. “We wanted to bring this to the attention of the world to prevent this from happening.”
The commentary was published July 6 in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
WHO leaders defended their progress in announcing any changes regarding how COVID-19 can be transmitted during a virtual press briefing today. They have collaborated since April with some of the scientists who coauthored the commentary, for example, said Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO technical lead on COVID-19.
“We have been working on a scientific brief ... to consolidate knowledge around transmission,” she added.
One focus will be on how masks protect healthcare workers. “We are also looking at the possible role of airborne transmission in other settings,” Van Kerkhove said. “We will be releasing our brief in the coming days.”
“We acknowledge there is emerging evidence in this field,” Benedetta Allegranzi, MD, WHO technical lead on COVID-19, said during the briefing from Geneva. “Therefore, we believe we have to be open to this evidence and its implications.”
WHO participated in an international research meeting last week that addressed means for controlling modes of COVID-19 transmission, Allegranzi said. “Our group and others really highlighted importance of research on different modes of transmission, including droplets of different sizes and their relative importance,” she said. Another aim was determining the dose of the virus required for airborne transmission.
“These fields of research are really growing but not definitive. More evidence needs to be gathered and evaluated,” she explained.
In the meantime, Allegranzi said, “the possibility of airborne transmission in public settings – especially closed, poorly ventilated settings – cannot be ruled out.”
Morawska said the evidence already exists. “A continuous surprise is that it takes the world such a long time to accept this, while this has such solid scientific foundation.” As an example, she cited an April report she coauthored in the journal Environment International. She and colleagues call for “national authorities to acknowledge the reality that the virus spreads through air and recommend that adequate control measures be implemented to prevent further spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, in particularly removal of the virus-laden droplets from indoor air by ventilation.”
The take-home message from the commentary, Morawska said, is a call to action. The authors state there is a need “to provide sufficient and effective ventilation (supply clean outdoor air, minimize recirculating air) particularly in public buildings, workplace environments, schools, hospitals, and aged care homes.”
WHO Chief Scientist Soumya Swaminathan, MD, explained why the organization remains cautious about making premature pronouncements regarding airborne transmission. “Any guidance we put out has implications for billions of people around the world, so we want to be as careful as possible,” she said during the press briefing. “We have to consider the weight of the evidence.”
“We are constantly looking for information on how we can do better,” Swaminathan added. WHO officials are reviewing hundreds of scientific reports every day, she said, and not all are of good quality. For this reason, she and other scientists at WHO perform a “living systematic review” – updating the consensus of evidence on a weekly basis.
“This process on COVID-19 will, I am sure, continue for the weeks and months to come,” she added.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Amid pandemic, Virginia hospital’s opioid overdoses up nearly 10-fold
Opioid overdoses have shot up by almost 10-fold at a Virginia ED since March, a new report finds. The report provides more evidence that the coronavirus pandemic is sparking a severe medical crisis among illicit drug users.
“Health care providers should closely monitor the number of overdoses coming into their hospitals and in the surrounding community during this time,” study lead author and postdoctoral research fellow Taylor Ochalek, PhD, said in an interview. “If they do notice an increasing trend of overdoses, they should spread awareness in the community to the general public, and offer resources and information for those that may be seeking help and/or may be at a high risk of overdosing.”
Dr. Ochalek presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence.
According to the report, opioid overdoses at the VCU Medical Center in Richmond, Va., grew from an average of six a month from February to December 2019 to 50, 57, and 63 in March, April, and May 2020. Of the 171 cases in the later time frame, the average age was 44 years, 72% were male, and 82% were African American.
“The steep increase in overdoses began primarily in March,” said Dr. Ochalek, of Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond. “This timing coincides with the Virginia governor’s state of emergency declaration, stay-at-home order, and closure of nonessential businesses order.”
The researchers did not provide details about the types of opioids used, the patient outcomes, or whether the patients tested positive for COVID-19. It’s unclear whether the pandemic directly spawned a higher number of overdoses, but there are growing signs of a stark nationwide trend.
“Nationwide, federal and local officials are reporting alarming spikes in drug overdoses – a hidden epidemic within the coronavirus pandemic,” the Washington Post reported on July 1, pointing to increases in Kentucky, Virginia, and the Chicago area.
Meanwhile, the federal Overdose Detection Mapping Application Program, which tracks overdoses nationwide, issued 191% more “spike alerts” in January to April 2020 than in the same time period in 2019. However, the spike alerts began to increase in January, weeks before the pandemic began to take hold.
The findings are consistent with trends in Houston, where overdose calls were up 31% in the first 3 months of 2020, compared with 2019, said psychologist James Bray, PhD, of the University of Texas, San Antonio, in an interview. More recent data suggest that the numbers are rising even higher, said Dr. Bray, who works with Houston first responders and has analyzed data.
Dr. Bray said.
Another potential factor is the disruption in the illicit drug supply chain because of limits on crossings at the southern border, said ED physician Scott Weiner, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. “As a result, opioids of extremely variable potency have infiltrated markets, and people using drugs may not be used to the new doses, especially if they are high-potency fentanyl analogues.”
Moving forward, Dr. Bray said, “people need continued access to treatment. Telehealth and other virtual services need to be provided so that people can continue to have access to treatment even during the pandemic.”
Dr. Weiner also emphasized the importance of treatment for patients who overdose on opioids. “In my previous work, we discovered that about 1 in 20 patients who are treated in an emergency department and survive would die within 1 year. That number will likely increase drastically during COVID,” he said. “When a patient presents after overdose, we must intervene aggressively with buprenorphine and other harm-reduction techniques to save these lives.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ochalek, Dr. Weiner, and Dr. Bray reported no relevant disclosures.
Opioid overdoses have shot up by almost 10-fold at a Virginia ED since March, a new report finds. The report provides more evidence that the coronavirus pandemic is sparking a severe medical crisis among illicit drug users.
“Health care providers should closely monitor the number of overdoses coming into their hospitals and in the surrounding community during this time,” study lead author and postdoctoral research fellow Taylor Ochalek, PhD, said in an interview. “If they do notice an increasing trend of overdoses, they should spread awareness in the community to the general public, and offer resources and information for those that may be seeking help and/or may be at a high risk of overdosing.”
Dr. Ochalek presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence.
According to the report, opioid overdoses at the VCU Medical Center in Richmond, Va., grew from an average of six a month from February to December 2019 to 50, 57, and 63 in March, April, and May 2020. Of the 171 cases in the later time frame, the average age was 44 years, 72% were male, and 82% were African American.
“The steep increase in overdoses began primarily in March,” said Dr. Ochalek, of Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond. “This timing coincides with the Virginia governor’s state of emergency declaration, stay-at-home order, and closure of nonessential businesses order.”
The researchers did not provide details about the types of opioids used, the patient outcomes, or whether the patients tested positive for COVID-19. It’s unclear whether the pandemic directly spawned a higher number of overdoses, but there are growing signs of a stark nationwide trend.
“Nationwide, federal and local officials are reporting alarming spikes in drug overdoses – a hidden epidemic within the coronavirus pandemic,” the Washington Post reported on July 1, pointing to increases in Kentucky, Virginia, and the Chicago area.
Meanwhile, the federal Overdose Detection Mapping Application Program, which tracks overdoses nationwide, issued 191% more “spike alerts” in January to April 2020 than in the same time period in 2019. However, the spike alerts began to increase in January, weeks before the pandemic began to take hold.
The findings are consistent with trends in Houston, where overdose calls were up 31% in the first 3 months of 2020, compared with 2019, said psychologist James Bray, PhD, of the University of Texas, San Antonio, in an interview. More recent data suggest that the numbers are rising even higher, said Dr. Bray, who works with Houston first responders and has analyzed data.
Dr. Bray said.
Another potential factor is the disruption in the illicit drug supply chain because of limits on crossings at the southern border, said ED physician Scott Weiner, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. “As a result, opioids of extremely variable potency have infiltrated markets, and people using drugs may not be used to the new doses, especially if they are high-potency fentanyl analogues.”
Moving forward, Dr. Bray said, “people need continued access to treatment. Telehealth and other virtual services need to be provided so that people can continue to have access to treatment even during the pandemic.”
Dr. Weiner also emphasized the importance of treatment for patients who overdose on opioids. “In my previous work, we discovered that about 1 in 20 patients who are treated in an emergency department and survive would die within 1 year. That number will likely increase drastically during COVID,” he said. “When a patient presents after overdose, we must intervene aggressively with buprenorphine and other harm-reduction techniques to save these lives.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ochalek, Dr. Weiner, and Dr. Bray reported no relevant disclosures.
Opioid overdoses have shot up by almost 10-fold at a Virginia ED since March, a new report finds. The report provides more evidence that the coronavirus pandemic is sparking a severe medical crisis among illicit drug users.
“Health care providers should closely monitor the number of overdoses coming into their hospitals and in the surrounding community during this time,” study lead author and postdoctoral research fellow Taylor Ochalek, PhD, said in an interview. “If they do notice an increasing trend of overdoses, they should spread awareness in the community to the general public, and offer resources and information for those that may be seeking help and/or may be at a high risk of overdosing.”
Dr. Ochalek presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence.
According to the report, opioid overdoses at the VCU Medical Center in Richmond, Va., grew from an average of six a month from February to December 2019 to 50, 57, and 63 in March, April, and May 2020. Of the 171 cases in the later time frame, the average age was 44 years, 72% were male, and 82% were African American.
“The steep increase in overdoses began primarily in March,” said Dr. Ochalek, of Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond. “This timing coincides with the Virginia governor’s state of emergency declaration, stay-at-home order, and closure of nonessential businesses order.”
The researchers did not provide details about the types of opioids used, the patient outcomes, or whether the patients tested positive for COVID-19. It’s unclear whether the pandemic directly spawned a higher number of overdoses, but there are growing signs of a stark nationwide trend.
“Nationwide, federal and local officials are reporting alarming spikes in drug overdoses – a hidden epidemic within the coronavirus pandemic,” the Washington Post reported on July 1, pointing to increases in Kentucky, Virginia, and the Chicago area.
Meanwhile, the federal Overdose Detection Mapping Application Program, which tracks overdoses nationwide, issued 191% more “spike alerts” in January to April 2020 than in the same time period in 2019. However, the spike alerts began to increase in January, weeks before the pandemic began to take hold.
The findings are consistent with trends in Houston, where overdose calls were up 31% in the first 3 months of 2020, compared with 2019, said psychologist James Bray, PhD, of the University of Texas, San Antonio, in an interview. More recent data suggest that the numbers are rising even higher, said Dr. Bray, who works with Houston first responders and has analyzed data.
Dr. Bray said.
Another potential factor is the disruption in the illicit drug supply chain because of limits on crossings at the southern border, said ED physician Scott Weiner, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. “As a result, opioids of extremely variable potency have infiltrated markets, and people using drugs may not be used to the new doses, especially if they are high-potency fentanyl analogues.”
Moving forward, Dr. Bray said, “people need continued access to treatment. Telehealth and other virtual services need to be provided so that people can continue to have access to treatment even during the pandemic.”
Dr. Weiner also emphasized the importance of treatment for patients who overdose on opioids. “In my previous work, we discovered that about 1 in 20 patients who are treated in an emergency department and survive would die within 1 year. That number will likely increase drastically during COVID,” he said. “When a patient presents after overdose, we must intervene aggressively with buprenorphine and other harm-reduction techniques to save these lives.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ochalek, Dr. Weiner, and Dr. Bray reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM CPDD 2020
Use of nonopioid pain meds is on the rise
Opioid and nonopioid prescription pain medications have taken different journeys since 2009, but they ended up in the same place in 2018, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.
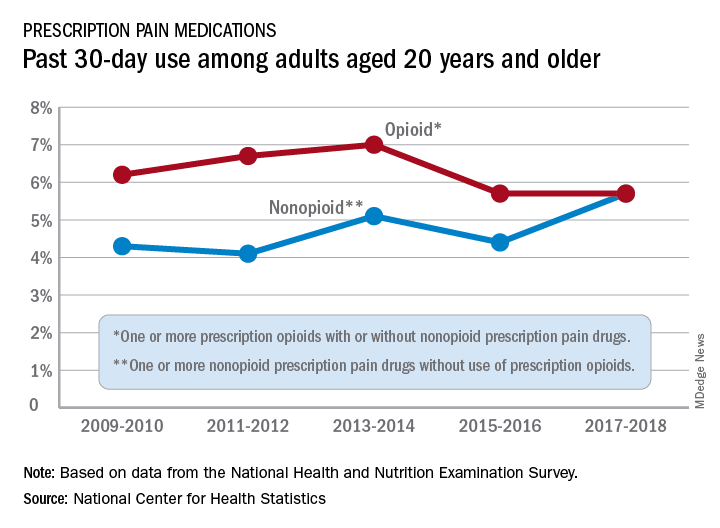
At least by one measure, anyway. Survey data from 2009 to 2010 show that 6.2% of adults aged 20 years and older had taken at least one prescription opioid in the last 30 days and 4.3% had used a prescription nonopioid without an opioid. By 2017-2018, past 30-day use of both drug groups was 5.7%, Craig M. Hales, MD, and associates said in an NCHS data brief.
“Opioids may be prescribed together with nonopioid pain medications, [but] nonpharmacologic and nonopioid-containing pharmacologic therapies are preferred for management of chronic pain,” the NCHS researchers noted.
as did the short-term increase in nonopioids from 2015-2016 to 2017-2018, but the 10-year trend for opioids was not significant, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Much of the analysis focused on 2015-2018, when 30-day use of any prescription pain medication was reported by 10.7% of adults aged 20 years and older, with use of opioids at 5.7% and nonopioids at 5.0%. For women, use of any pain drug was 12.6% (6.4% opioid, 6.2% nonopioid) from 2015 to 2018, compared with 8.7% for men (4.9%, 3.8%), Dr. Hales and associates reported.
Past 30-day use of both opioids and nonopioids over those 4 years was highest for non-Hispanic whites and lowest, by a significant margin for both drug groups, among non-Hispanic Asian adults, a pattern that held for both men and women, they said.
Opioid and nonopioid prescription pain medications have taken different journeys since 2009, but they ended up in the same place in 2018, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

At least by one measure, anyway. Survey data from 2009 to 2010 show that 6.2% of adults aged 20 years and older had taken at least one prescription opioid in the last 30 days and 4.3% had used a prescription nonopioid without an opioid. By 2017-2018, past 30-day use of both drug groups was 5.7%, Craig M. Hales, MD, and associates said in an NCHS data brief.
“Opioids may be prescribed together with nonopioid pain medications, [but] nonpharmacologic and nonopioid-containing pharmacologic therapies are preferred for management of chronic pain,” the NCHS researchers noted.
as did the short-term increase in nonopioids from 2015-2016 to 2017-2018, but the 10-year trend for opioids was not significant, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Much of the analysis focused on 2015-2018, when 30-day use of any prescription pain medication was reported by 10.7% of adults aged 20 years and older, with use of opioids at 5.7% and nonopioids at 5.0%. For women, use of any pain drug was 12.6% (6.4% opioid, 6.2% nonopioid) from 2015 to 2018, compared with 8.7% for men (4.9%, 3.8%), Dr. Hales and associates reported.
Past 30-day use of both opioids and nonopioids over those 4 years was highest for non-Hispanic whites and lowest, by a significant margin for both drug groups, among non-Hispanic Asian adults, a pattern that held for both men and women, they said.
Opioid and nonopioid prescription pain medications have taken different journeys since 2009, but they ended up in the same place in 2018, according to a recent report from the National Center for Health Statistics.

At least by one measure, anyway. Survey data from 2009 to 2010 show that 6.2% of adults aged 20 years and older had taken at least one prescription opioid in the last 30 days and 4.3% had used a prescription nonopioid without an opioid. By 2017-2018, past 30-day use of both drug groups was 5.7%, Craig M. Hales, MD, and associates said in an NCHS data brief.
“Opioids may be prescribed together with nonopioid pain medications, [but] nonpharmacologic and nonopioid-containing pharmacologic therapies are preferred for management of chronic pain,” the NCHS researchers noted.
as did the short-term increase in nonopioids from 2015-2016 to 2017-2018, but the 10-year trend for opioids was not significant, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Much of the analysis focused on 2015-2018, when 30-day use of any prescription pain medication was reported by 10.7% of adults aged 20 years and older, with use of opioids at 5.7% and nonopioids at 5.0%. For women, use of any pain drug was 12.6% (6.4% opioid, 6.2% nonopioid) from 2015 to 2018, compared with 8.7% for men (4.9%, 3.8%), Dr. Hales and associates reported.
Past 30-day use of both opioids and nonopioids over those 4 years was highest for non-Hispanic whites and lowest, by a significant margin for both drug groups, among non-Hispanic Asian adults, a pattern that held for both men and women, they said.
High percentage of stimulant use found in opioid ED cases
Nearly 40% of hundreds of opioid abusers at several emergency departments tested positive for stimulants, and they were more likely to be white than other users, a new study finds. Reflecting national trends, patients in the Midwest and West Coast regions were more likely to show signs of stimulant use.
Stimulant/opioid users were also “younger, with unstable housing, mostly unemployed, and reported high rates of recent incarcerations,” said substance use researcher and study lead author Marek Chawarski, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “They also reported higher rates of injection drug use during 1 month prior to the study admission and had higher rates of HCV infection. And higher proportions of amphetamine-type stimulant (ATS)–positive patients presented in the emergency departments (EDs) for an injury or with drug overdose.”
Dr. Chawarski, who presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence, said in an interview that the study is the first to analyze stimulant use in ED patients with opioid use disorder.
The researchers analyzed data for the period 2017-2019 from EDs in Baltimore, New York, Cincinnati, and Seattle. Out of 396 patients, 150 (38%) were positive for amphetamine-type stimulants.
Patients in the Midwest and West Coast were more likely to test positive (38%).
In general, stimulant use is higher in the Midwest and West Coast, said epidemiologist Brandon Marshall, PhD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., in an interview. “This is due to a number of supply-side, historical, and cultural reasons. New England, Appalachia, and large urban centers on the East Coast are the historical hot spots for opioid use, while states west of the Mississippi River have lower rates of opioid overdose, but a much higher prevalence of ATS use and stimulant-related morbidity and mortality.”
Those who showed signs of stimulant use were more likely to be white (69%) vs. the nonusers (46%), and were more likely to have unstable housing (67% vs. 49%).
Those who used stimulants also were more likely to be suffering from an overdose (23% vs. 13%) and to report injecting drugs in the last month (79% vs. 47%). More had unstable housing (67% vs. 49%, P < .05 for all comparisons).
Dr. Chawarski said there are many reasons why users might use more than one kind of drug. For example, they may take one drug to “alleviate problems created by the use of one substance with taking another substance and multiple other reasons,” he said. “Polysubstance use can exacerbate social and medical harms, including overdose risk. It can pose greater treatment challenges, both for the patients and treatment providers, and often is more difficult to overcome.”
Links between opioid and stimulant use are not new. Last year, a study of 2,244 opioid-related overdose deaths in Massachusetts from 2014 to 2015 found that 36% of patients also showed signs of stimulant use. “Persons older than 24 years, nonrural residents, those with comorbid mental illness, non-Hispanic black residents, and persons with recent homelessness were more likely than their counterparts to die with opioids and stimulants than opioids alone,” the researchers reported (Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019 Jul 1;200:59-63).
Dr. Marshall said the study findings are not surprising. However, he said, they do indicate “ongoing, intentional consumption of opioids. The trends and characteristics we are seeing here suggests a large population of persons who are intentionally using both stimulants and opioids, many of whom are also injecting.”
He added that the study sample is probably higher risk than the general population since they’re presenting to the emergency department, so the findings might not reflect the use of stimulants in the general opioid-misusing population.
Dr. Marshall added that “there have been several instances in modern U.S. history during which increases in stimulant use follow a rise in opioid use, so the pattern we are seeing isn’t entirely surprising.”
“What we don’t know,” he added, “is the extent to which overdoses involving both an opioid and a stimulant are due to fentanyl contamination of the methamphetamine supply or intentional concurrent use – e.g., ‘speedballing’ or ‘goof balling’ – or some other pattern of polysubstance use, such as using an opioid to come down off a methamphetamine high.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse funded the study. The study authors reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Marshall reported that he has collaborated frequently with two of the study coauthors.
Nearly 40% of hundreds of opioid abusers at several emergency departments tested positive for stimulants, and they were more likely to be white than other users, a new study finds. Reflecting national trends, patients in the Midwest and West Coast regions were more likely to show signs of stimulant use.
Stimulant/opioid users were also “younger, with unstable housing, mostly unemployed, and reported high rates of recent incarcerations,” said substance use researcher and study lead author Marek Chawarski, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “They also reported higher rates of injection drug use during 1 month prior to the study admission and had higher rates of HCV infection. And higher proportions of amphetamine-type stimulant (ATS)–positive patients presented in the emergency departments (EDs) for an injury or with drug overdose.”
Dr. Chawarski, who presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence, said in an interview that the study is the first to analyze stimulant use in ED patients with opioid use disorder.
The researchers analyzed data for the period 2017-2019 from EDs in Baltimore, New York, Cincinnati, and Seattle. Out of 396 patients, 150 (38%) were positive for amphetamine-type stimulants.
Patients in the Midwest and West Coast were more likely to test positive (38%).
In general, stimulant use is higher in the Midwest and West Coast, said epidemiologist Brandon Marshall, PhD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., in an interview. “This is due to a number of supply-side, historical, and cultural reasons. New England, Appalachia, and large urban centers on the East Coast are the historical hot spots for opioid use, while states west of the Mississippi River have lower rates of opioid overdose, but a much higher prevalence of ATS use and stimulant-related morbidity and mortality.”
Those who showed signs of stimulant use were more likely to be white (69%) vs. the nonusers (46%), and were more likely to have unstable housing (67% vs. 49%).
Those who used stimulants also were more likely to be suffering from an overdose (23% vs. 13%) and to report injecting drugs in the last month (79% vs. 47%). More had unstable housing (67% vs. 49%, P < .05 for all comparisons).
Dr. Chawarski said there are many reasons why users might use more than one kind of drug. For example, they may take one drug to “alleviate problems created by the use of one substance with taking another substance and multiple other reasons,” he said. “Polysubstance use can exacerbate social and medical harms, including overdose risk. It can pose greater treatment challenges, both for the patients and treatment providers, and often is more difficult to overcome.”
Links between opioid and stimulant use are not new. Last year, a study of 2,244 opioid-related overdose deaths in Massachusetts from 2014 to 2015 found that 36% of patients also showed signs of stimulant use. “Persons older than 24 years, nonrural residents, those with comorbid mental illness, non-Hispanic black residents, and persons with recent homelessness were more likely than their counterparts to die with opioids and stimulants than opioids alone,” the researchers reported (Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019 Jul 1;200:59-63).
Dr. Marshall said the study findings are not surprising. However, he said, they do indicate “ongoing, intentional consumption of opioids. The trends and characteristics we are seeing here suggests a large population of persons who are intentionally using both stimulants and opioids, many of whom are also injecting.”
He added that the study sample is probably higher risk than the general population since they’re presenting to the emergency department, so the findings might not reflect the use of stimulants in the general opioid-misusing population.
Dr. Marshall added that “there have been several instances in modern U.S. history during which increases in stimulant use follow a rise in opioid use, so the pattern we are seeing isn’t entirely surprising.”
“What we don’t know,” he added, “is the extent to which overdoses involving both an opioid and a stimulant are due to fentanyl contamination of the methamphetamine supply or intentional concurrent use – e.g., ‘speedballing’ or ‘goof balling’ – or some other pattern of polysubstance use, such as using an opioid to come down off a methamphetamine high.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse funded the study. The study authors reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Marshall reported that he has collaborated frequently with two of the study coauthors.
Nearly 40% of hundreds of opioid abusers at several emergency departments tested positive for stimulants, and they were more likely to be white than other users, a new study finds. Reflecting national trends, patients in the Midwest and West Coast regions were more likely to show signs of stimulant use.
Stimulant/opioid users were also “younger, with unstable housing, mostly unemployed, and reported high rates of recent incarcerations,” said substance use researcher and study lead author Marek Chawarski, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “They also reported higher rates of injection drug use during 1 month prior to the study admission and had higher rates of HCV infection. And higher proportions of amphetamine-type stimulant (ATS)–positive patients presented in the emergency departments (EDs) for an injury or with drug overdose.”
Dr. Chawarski, who presented the study findings at the virtual annual meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence, said in an interview that the study is the first to analyze stimulant use in ED patients with opioid use disorder.
The researchers analyzed data for the period 2017-2019 from EDs in Baltimore, New York, Cincinnati, and Seattle. Out of 396 patients, 150 (38%) were positive for amphetamine-type stimulants.
Patients in the Midwest and West Coast were more likely to test positive (38%).
In general, stimulant use is higher in the Midwest and West Coast, said epidemiologist Brandon Marshall, PhD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., in an interview. “This is due to a number of supply-side, historical, and cultural reasons. New England, Appalachia, and large urban centers on the East Coast are the historical hot spots for opioid use, while states west of the Mississippi River have lower rates of opioid overdose, but a much higher prevalence of ATS use and stimulant-related morbidity and mortality.”
Those who showed signs of stimulant use were more likely to be white (69%) vs. the nonusers (46%), and were more likely to have unstable housing (67% vs. 49%).
Those who used stimulants also were more likely to be suffering from an overdose (23% vs. 13%) and to report injecting drugs in the last month (79% vs. 47%). More had unstable housing (67% vs. 49%, P < .05 for all comparisons).
Dr. Chawarski said there are many reasons why users might use more than one kind of drug. For example, they may take one drug to “alleviate problems created by the use of one substance with taking another substance and multiple other reasons,” he said. “Polysubstance use can exacerbate social and medical harms, including overdose risk. It can pose greater treatment challenges, both for the patients and treatment providers, and often is more difficult to overcome.”
Links between opioid and stimulant use are not new. Last year, a study of 2,244 opioid-related overdose deaths in Massachusetts from 2014 to 2015 found that 36% of patients also showed signs of stimulant use. “Persons older than 24 years, nonrural residents, those with comorbid mental illness, non-Hispanic black residents, and persons with recent homelessness were more likely than their counterparts to die with opioids and stimulants than opioids alone,” the researchers reported (Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019 Jul 1;200:59-63).
Dr. Marshall said the study findings are not surprising. However, he said, they do indicate “ongoing, intentional consumption of opioids. The trends and characteristics we are seeing here suggests a large population of persons who are intentionally using both stimulants and opioids, many of whom are also injecting.”
He added that the study sample is probably higher risk than the general population since they’re presenting to the emergency department, so the findings might not reflect the use of stimulants in the general opioid-misusing population.
Dr. Marshall added that “there have been several instances in modern U.S. history during which increases in stimulant use follow a rise in opioid use, so the pattern we are seeing isn’t entirely surprising.”
“What we don’t know,” he added, “is the extent to which overdoses involving both an opioid and a stimulant are due to fentanyl contamination of the methamphetamine supply or intentional concurrent use – e.g., ‘speedballing’ or ‘goof balling’ – or some other pattern of polysubstance use, such as using an opioid to come down off a methamphetamine high.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse funded the study. The study authors reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Marshall reported that he has collaborated frequently with two of the study coauthors.
FROM CPDD 2020
Despite guidelines, children receive opioids and steroids for pneumonia and sinusitis
A significant percentage of children receive opioids and systemic corticosteroids for pneumonia and sinusitis despite guidelines, according to an analysis of 2016 Medicaid data from South Carolina.
Prescriptions for these drugs were more likely after visits to EDs than after ambulatory visits, researchers reported in Pediatrics.
“Each of the 828 opioid and 2,737 systemic steroid prescriptions in the data set represent a potentially inappropriate prescription,” wrote Karina G. Phang, MD, MPH, of Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., and colleagues. “These rates appear excessive given that the use of these medications is not supported by available research or recommended in national guidelines.”
To compare the frequency of opioid and corticosteroid prescriptions for children with pneumonia or sinusitis in ED and ambulatory care settings, the investigators studied 2016 South Carolina Medicaid claims, examining data for patients aged 5-18 years with pneumonia or sinusitis. They excluded children with chronic conditions and acute secondary diagnoses with potentially appropriate indications for steroids, such as asthma. They also excluded children seen at more than one type of clinical location or hospitalized within a week of the visit. Only the primary diagnosis of pneumonia or sinusitis during the first visit of the year for each patient was included.
The researchers included data from 31,838 children in the study, including 2,140 children with pneumonia and 29,698 with sinusitis.
Pneumonia was linked to an opioid prescription in 6% of ED visits (34 of 542) and 1.5% of ambulatory visits (24 of 1,590) (P ≤ .0001). Pneumonia was linked to a steroid prescription in 20% of ED visits (106 of 542) and 12% of ambulatory visits (196 of 1,590) (P ≤ .0001).
Sinusitis was linked to an opioid prescription in 7.5% of ED visits (202 of 2,705) and 2% of ambulatory visits (568 of 26,866) (P ≤ .0001). Sinusitis was linked to a steroid prescription in 19% of ED visits (510 of 2,705) and 7% of ambulatory visits (1,922 of 26,866) (P ≤ .0001).
In logistic regression analyses, ED visits for pneumonia or sinusitis were more than four times more likely to result in children receiving opioids, relative to ambulatory visits (adjusted odds ratio, 4.69 and 4.02, respectively). ED visits also were more likely to result in steroid prescriptions, with aORs of 1.67 for pneumonia and 3.05 for sinusitis.
“I was disappointed to read of these results, although not necessarily surprised,” Michael E. Pichichero, MD, a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital, said in an interview.
The data suggest that improved prescribing practices may be needed, “especially in the ED,” wrote Dr. Phang and colleagues. “Although more children who are acutely ill may be seen in the ED, national practice guidelines and research remain relevant for these patients.”
Repeated or prolonged courses of systemic corticosteroids put children at risk for adrenal suppression and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction. “Providers for children must also be aware of the trends in opioid abuse and diversion and must mitigate those risks while still providing adequate analgesia and symptom control,” they wrote.
The use of Medicaid data from 1 year in one state limits the generalizability of the findings. Nevertheless, the visits occurred “well after publication of relevant guidelines and after concerns of opioid prescribing had become widespread,” according to Dr. Phang and colleagues.
A post hoc evaluation identified one patient with a secondary diagnosis of fracture and 24 patients with a secondary diagnosis of pain, but none of these patients had received an opioid. “Thus, the small subset of patients who may have had secondary diagnoses that would warrant an opioid prescription would not have changed the overall results,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Phang KG et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 2. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3690.
A significant percentage of children receive opioids and systemic corticosteroids for pneumonia and sinusitis despite guidelines, according to an analysis of 2016 Medicaid data from South Carolina.
Prescriptions for these drugs were more likely after visits to EDs than after ambulatory visits, researchers reported in Pediatrics.
“Each of the 828 opioid and 2,737 systemic steroid prescriptions in the data set represent a potentially inappropriate prescription,” wrote Karina G. Phang, MD, MPH, of Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., and colleagues. “These rates appear excessive given that the use of these medications is not supported by available research or recommended in national guidelines.”
To compare the frequency of opioid and corticosteroid prescriptions for children with pneumonia or sinusitis in ED and ambulatory care settings, the investigators studied 2016 South Carolina Medicaid claims, examining data for patients aged 5-18 years with pneumonia or sinusitis. They excluded children with chronic conditions and acute secondary diagnoses with potentially appropriate indications for steroids, such as asthma. They also excluded children seen at more than one type of clinical location or hospitalized within a week of the visit. Only the primary diagnosis of pneumonia or sinusitis during the first visit of the year for each patient was included.
The researchers included data from 31,838 children in the study, including 2,140 children with pneumonia and 29,698 with sinusitis.
Pneumonia was linked to an opioid prescription in 6% of ED visits (34 of 542) and 1.5% of ambulatory visits (24 of 1,590) (P ≤ .0001). Pneumonia was linked to a steroid prescription in 20% of ED visits (106 of 542) and 12% of ambulatory visits (196 of 1,590) (P ≤ .0001).
Sinusitis was linked to an opioid prescription in 7.5% of ED visits (202 of 2,705) and 2% of ambulatory visits (568 of 26,866) (P ≤ .0001). Sinusitis was linked to a steroid prescription in 19% of ED visits (510 of 2,705) and 7% of ambulatory visits (1,922 of 26,866) (P ≤ .0001).
In logistic regression analyses, ED visits for pneumonia or sinusitis were more than four times more likely to result in children receiving opioids, relative to ambulatory visits (adjusted odds ratio, 4.69 and 4.02, respectively). ED visits also were more likely to result in steroid prescriptions, with aORs of 1.67 for pneumonia and 3.05 for sinusitis.
“I was disappointed to read of these results, although not necessarily surprised,” Michael E. Pichichero, MD, a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital, said in an interview.
The data suggest that improved prescribing practices may be needed, “especially in the ED,” wrote Dr. Phang and colleagues. “Although more children who are acutely ill may be seen in the ED, national practice guidelines and research remain relevant for these patients.”
Repeated or prolonged courses of systemic corticosteroids put children at risk for adrenal suppression and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction. “Providers for children must also be aware of the trends in opioid abuse and diversion and must mitigate those risks while still providing adequate analgesia and symptom control,” they wrote.
The use of Medicaid data from 1 year in one state limits the generalizability of the findings. Nevertheless, the visits occurred “well after publication of relevant guidelines and after concerns of opioid prescribing had become widespread,” according to Dr. Phang and colleagues.
A post hoc evaluation identified one patient with a secondary diagnosis of fracture and 24 patients with a secondary diagnosis of pain, but none of these patients had received an opioid. “Thus, the small subset of patients who may have had secondary diagnoses that would warrant an opioid prescription would not have changed the overall results,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Phang KG et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 2. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3690.
A significant percentage of children receive opioids and systemic corticosteroids for pneumonia and sinusitis despite guidelines, according to an analysis of 2016 Medicaid data from South Carolina.
Prescriptions for these drugs were more likely after visits to EDs than after ambulatory visits, researchers reported in Pediatrics.
“Each of the 828 opioid and 2,737 systemic steroid prescriptions in the data set represent a potentially inappropriate prescription,” wrote Karina G. Phang, MD, MPH, of Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., and colleagues. “These rates appear excessive given that the use of these medications is not supported by available research or recommended in national guidelines.”
To compare the frequency of opioid and corticosteroid prescriptions for children with pneumonia or sinusitis in ED and ambulatory care settings, the investigators studied 2016 South Carolina Medicaid claims, examining data for patients aged 5-18 years with pneumonia or sinusitis. They excluded children with chronic conditions and acute secondary diagnoses with potentially appropriate indications for steroids, such as asthma. They also excluded children seen at more than one type of clinical location or hospitalized within a week of the visit. Only the primary diagnosis of pneumonia or sinusitis during the first visit of the year for each patient was included.
The researchers included data from 31,838 children in the study, including 2,140 children with pneumonia and 29,698 with sinusitis.
Pneumonia was linked to an opioid prescription in 6% of ED visits (34 of 542) and 1.5% of ambulatory visits (24 of 1,590) (P ≤ .0001). Pneumonia was linked to a steroid prescription in 20% of ED visits (106 of 542) and 12% of ambulatory visits (196 of 1,590) (P ≤ .0001).
Sinusitis was linked to an opioid prescription in 7.5% of ED visits (202 of 2,705) and 2% of ambulatory visits (568 of 26,866) (P ≤ .0001). Sinusitis was linked to a steroid prescription in 19% of ED visits (510 of 2,705) and 7% of ambulatory visits (1,922 of 26,866) (P ≤ .0001).
In logistic regression analyses, ED visits for pneumonia or sinusitis were more than four times more likely to result in children receiving opioids, relative to ambulatory visits (adjusted odds ratio, 4.69 and 4.02, respectively). ED visits also were more likely to result in steroid prescriptions, with aORs of 1.67 for pneumonia and 3.05 for sinusitis.
“I was disappointed to read of these results, although not necessarily surprised,” Michael E. Pichichero, MD, a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital, said in an interview.
The data suggest that improved prescribing practices may be needed, “especially in the ED,” wrote Dr. Phang and colleagues. “Although more children who are acutely ill may be seen in the ED, national practice guidelines and research remain relevant for these patients.”
Repeated or prolonged courses of systemic corticosteroids put children at risk for adrenal suppression and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction. “Providers for children must also be aware of the trends in opioid abuse and diversion and must mitigate those risks while still providing adequate analgesia and symptom control,” they wrote.
The use of Medicaid data from 1 year in one state limits the generalizability of the findings. Nevertheless, the visits occurred “well after publication of relevant guidelines and after concerns of opioid prescribing had become widespread,” according to Dr. Phang and colleagues.
A post hoc evaluation identified one patient with a secondary diagnosis of fracture and 24 patients with a secondary diagnosis of pain, but none of these patients had received an opioid. “Thus, the small subset of patients who may have had secondary diagnoses that would warrant an opioid prescription would not have changed the overall results,” they wrote.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Phang KG et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 2. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3690.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Physician shortage grows in latest projections
Fifteen-year projections for the shortage of primary care and specialty physicians in the United States grew to between 54,000 and 139,000 in the latest annual report by the Association of American Medical Colleges.

Those estimates are up from last year’s projections of a shortfall of 46,900-121,900 by 2032.
The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections from 2018 to 2033, was the sixth annual study conducted for the AAMC by the Life Science division of global analytics firm IHS Markit.
This analysis, conducted in 2019, includes supply and demand scenarios but predates the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a telephone press briefing this morning, David J. Skorton, MD, AAMC’s president and CEO, told reporters that the pandemic has highlighted the acute effects of physician shortages.
“We’ve seen in stark detail how fragile and quickly overwhelmed America’s health care system truly is, and we’re nowhere near out of the woods with this public health emergency yet,” he said.
The persistent shortages mean people “will have ongoing difficulty accessing the care that they need, especially as we all age.”
Some of the biggest shortages will be seen in non–primary care specialists. Dr. Skorton notes that, during the pandemic, shortages of specialists in hospital settings, including critical care, emergency medicine, pulmonology, and infectious disease, are an urgent concern.
Population trends continue to be the biggest drivers of the shortage. Report authors found that by 2033, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.4% from 327 million to 361 million, with wide differences by age.
The under-18 population is expected to grow by 3.9%, whereas the numbers of those aged 65 and older is expected to balloon by 45.1% in that time, thus stoking demand for specialties focused on care for older Americans.
Physician age is also a large factor in the projections. More than two in five currently active physicians will be 65 or older in the next 10 years, according to the report. A wave of retirements will have a large impact on the supply of physicians.
The report explains that the projected shortages remain under predictable scenarios: an increase in the use of advanced practice nurses (APRNs) and physician assistants (PAs), more care in alternate settings such as retail clinics, and changes in payment and delivery.
According to the report, the supply of APRNs and PAs is on track to double over the next 15 years (with growth rates varying by APRN and PA specialty).
“At current rates of production, by 2033 APRN supply will grow by 276,000 [full-time equivalents (FTEs)] and PA supply by nearly 138,000 FTEs,” the report states.
However, authors acknowledge there is scant evidence on what effect these numbers will have on demand for physicians.
The report points out that if underserved communities were able to access health care in numbers similar to those without barriers imposed by where they live or what insurance they have, demand could rise beyond the projections in this report by an additional 74,000 to 145,000 physicians.
Stemming the shortages
The first step in addressing the shortage, Dr. Skorton said, is assuring a healthy physician pipeline to meet the demand for generations.
“One essential step that we believe Congress must take is to end the freeze that has been in place since 1997 that limits federal support for residency training of new physicians,” Skorton said.
He noted that AAMC supports the bipartisan Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act, introduced to Congress in 2019, which calls for an increase in Medicare support for 3000 new residency positions each year over the next 5 years.
However, additional steps are needed, including enabling advanced practice providers to play a greater role in increasing the health care workforce, Dr. Skorton said.
Pointing out some of the effects of physician shortages, Janis M. Orlowski, MD, chief health care officer for the AAMC, noted that high rates of maternal morbidity are partially linked to lack of adequate numbers of physicians in the United States, and a lack of behavioral health specialists has exacerbated effects of the opioid epidemic.
Shortages are already evident in the current pandemic, she added, saying, “Today we see governors calling for retired physicians or physicians from other states to come and help battle the pandemic within their states.”
The report explains that long-term effects on physician numbers from the pandemic likely will include workforce exits because of COVID-19 deaths, early retirements from burnout, or a shift in interest in certain specialties.
Karen Fisher, JD, chief public policy officer for AAMC, said telehealth will also play an important role in bridging gaps in access to care, and its importance has already been seen in this first wave of the pandemic.
She noted that temporary federal waivers have made it easier for those enrolled in Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program to receive telehealth services during the pandemic.
Expanding the access to telehealth permanently will be important in helping to fill gaps, Ms. Fisher said.
Dr. Skorton, Dr. Orlowski, and Ms. Fisher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Fifteen-year projections for the shortage of primary care and specialty physicians in the United States grew to between 54,000 and 139,000 in the latest annual report by the Association of American Medical Colleges.

Those estimates are up from last year’s projections of a shortfall of 46,900-121,900 by 2032.
The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections from 2018 to 2033, was the sixth annual study conducted for the AAMC by the Life Science division of global analytics firm IHS Markit.
This analysis, conducted in 2019, includes supply and demand scenarios but predates the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a telephone press briefing this morning, David J. Skorton, MD, AAMC’s president and CEO, told reporters that the pandemic has highlighted the acute effects of physician shortages.
“We’ve seen in stark detail how fragile and quickly overwhelmed America’s health care system truly is, and we’re nowhere near out of the woods with this public health emergency yet,” he said.
The persistent shortages mean people “will have ongoing difficulty accessing the care that they need, especially as we all age.”
Some of the biggest shortages will be seen in non–primary care specialists. Dr. Skorton notes that, during the pandemic, shortages of specialists in hospital settings, including critical care, emergency medicine, pulmonology, and infectious disease, are an urgent concern.
Population trends continue to be the biggest drivers of the shortage. Report authors found that by 2033, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.4% from 327 million to 361 million, with wide differences by age.
The under-18 population is expected to grow by 3.9%, whereas the numbers of those aged 65 and older is expected to balloon by 45.1% in that time, thus stoking demand for specialties focused on care for older Americans.
Physician age is also a large factor in the projections. More than two in five currently active physicians will be 65 or older in the next 10 years, according to the report. A wave of retirements will have a large impact on the supply of physicians.
The report explains that the projected shortages remain under predictable scenarios: an increase in the use of advanced practice nurses (APRNs) and physician assistants (PAs), more care in alternate settings such as retail clinics, and changes in payment and delivery.
According to the report, the supply of APRNs and PAs is on track to double over the next 15 years (with growth rates varying by APRN and PA specialty).
“At current rates of production, by 2033 APRN supply will grow by 276,000 [full-time equivalents (FTEs)] and PA supply by nearly 138,000 FTEs,” the report states.
However, authors acknowledge there is scant evidence on what effect these numbers will have on demand for physicians.
The report points out that if underserved communities were able to access health care in numbers similar to those without barriers imposed by where they live or what insurance they have, demand could rise beyond the projections in this report by an additional 74,000 to 145,000 physicians.
Stemming the shortages
The first step in addressing the shortage, Dr. Skorton said, is assuring a healthy physician pipeline to meet the demand for generations.
“One essential step that we believe Congress must take is to end the freeze that has been in place since 1997 that limits federal support for residency training of new physicians,” Skorton said.
He noted that AAMC supports the bipartisan Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act, introduced to Congress in 2019, which calls for an increase in Medicare support for 3000 new residency positions each year over the next 5 years.
However, additional steps are needed, including enabling advanced practice providers to play a greater role in increasing the health care workforce, Dr. Skorton said.
Pointing out some of the effects of physician shortages, Janis M. Orlowski, MD, chief health care officer for the AAMC, noted that high rates of maternal morbidity are partially linked to lack of adequate numbers of physicians in the United States, and a lack of behavioral health specialists has exacerbated effects of the opioid epidemic.
Shortages are already evident in the current pandemic, she added, saying, “Today we see governors calling for retired physicians or physicians from other states to come and help battle the pandemic within their states.”
The report explains that long-term effects on physician numbers from the pandemic likely will include workforce exits because of COVID-19 deaths, early retirements from burnout, or a shift in interest in certain specialties.
Karen Fisher, JD, chief public policy officer for AAMC, said telehealth will also play an important role in bridging gaps in access to care, and its importance has already been seen in this first wave of the pandemic.
She noted that temporary federal waivers have made it easier for those enrolled in Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program to receive telehealth services during the pandemic.
Expanding the access to telehealth permanently will be important in helping to fill gaps, Ms. Fisher said.
Dr. Skorton, Dr. Orlowski, and Ms. Fisher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Fifteen-year projections for the shortage of primary care and specialty physicians in the United States grew to between 54,000 and 139,000 in the latest annual report by the Association of American Medical Colleges.

Those estimates are up from last year’s projections of a shortfall of 46,900-121,900 by 2032.
The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections from 2018 to 2033, was the sixth annual study conducted for the AAMC by the Life Science division of global analytics firm IHS Markit.
This analysis, conducted in 2019, includes supply and demand scenarios but predates the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a telephone press briefing this morning, David J. Skorton, MD, AAMC’s president and CEO, told reporters that the pandemic has highlighted the acute effects of physician shortages.
“We’ve seen in stark detail how fragile and quickly overwhelmed America’s health care system truly is, and we’re nowhere near out of the woods with this public health emergency yet,” he said.
The persistent shortages mean people “will have ongoing difficulty accessing the care that they need, especially as we all age.”
Some of the biggest shortages will be seen in non–primary care specialists. Dr. Skorton notes that, during the pandemic, shortages of specialists in hospital settings, including critical care, emergency medicine, pulmonology, and infectious disease, are an urgent concern.
Population trends continue to be the biggest drivers of the shortage. Report authors found that by 2033, the U.S. population is expected to grow by 10.4% from 327 million to 361 million, with wide differences by age.
The under-18 population is expected to grow by 3.9%, whereas the numbers of those aged 65 and older is expected to balloon by 45.1% in that time, thus stoking demand for specialties focused on care for older Americans.
Physician age is also a large factor in the projections. More than two in five currently active physicians will be 65 or older in the next 10 years, according to the report. A wave of retirements will have a large impact on the supply of physicians.
The report explains that the projected shortages remain under predictable scenarios: an increase in the use of advanced practice nurses (APRNs) and physician assistants (PAs), more care in alternate settings such as retail clinics, and changes in payment and delivery.
According to the report, the supply of APRNs and PAs is on track to double over the next 15 years (with growth rates varying by APRN and PA specialty).
“At current rates of production, by 2033 APRN supply will grow by 276,000 [full-time equivalents (FTEs)] and PA supply by nearly 138,000 FTEs,” the report states.
However, authors acknowledge there is scant evidence on what effect these numbers will have on demand for physicians.
The report points out that if underserved communities were able to access health care in numbers similar to those without barriers imposed by where they live or what insurance they have, demand could rise beyond the projections in this report by an additional 74,000 to 145,000 physicians.
Stemming the shortages
The first step in addressing the shortage, Dr. Skorton said, is assuring a healthy physician pipeline to meet the demand for generations.
“One essential step that we believe Congress must take is to end the freeze that has been in place since 1997 that limits federal support for residency training of new physicians,” Skorton said.
He noted that AAMC supports the bipartisan Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act, introduced to Congress in 2019, which calls for an increase in Medicare support for 3000 new residency positions each year over the next 5 years.
However, additional steps are needed, including enabling advanced practice providers to play a greater role in increasing the health care workforce, Dr. Skorton said.
Pointing out some of the effects of physician shortages, Janis M. Orlowski, MD, chief health care officer for the AAMC, noted that high rates of maternal morbidity are partially linked to lack of adequate numbers of physicians in the United States, and a lack of behavioral health specialists has exacerbated effects of the opioid epidemic.
Shortages are already evident in the current pandemic, she added, saying, “Today we see governors calling for retired physicians or physicians from other states to come and help battle the pandemic within their states.”
The report explains that long-term effects on physician numbers from the pandemic likely will include workforce exits because of COVID-19 deaths, early retirements from burnout, or a shift in interest in certain specialties.
Karen Fisher, JD, chief public policy officer for AAMC, said telehealth will also play an important role in bridging gaps in access to care, and its importance has already been seen in this first wave of the pandemic.
She noted that temporary federal waivers have made it easier for those enrolled in Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program to receive telehealth services during the pandemic.
Expanding the access to telehealth permanently will be important in helping to fill gaps, Ms. Fisher said.
Dr. Skorton, Dr. Orlowski, and Ms. Fisher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnostic criteria may miss some MIS-C cases, experts say
New data from active surveillance of the severe inflammatory condition associated with COVID-19 in previously healthy children provide further insight into the prevalence and course of the rare syndrome, but experts are concerned that current diagnostic criteria may not capture the true scope of the problem.
In separate reports published online June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers from the New York State Department of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) describe the epidemiology and clinical features of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) on the basis of information derived from targeted surveillance programs in New York State and across the country.
For the New York study, Elizabeth M. Dufort, MD, from the New York Department of Health in Albany and colleagues analyzed MIS-C surveillance data from 106 hospitals across the state. Of 191 suspected MIS-C cases reported to the Department of Health from March 1 through May 10, 99 met the state’s interim case definition of the condition and were included in the analysis.
The incidence rate for MIS-C was two cases per 100,000 individuals younger than 21 years, whereas the incidence rate of confirmed COVID-19 cases in this age group was 322 per 100,000. Most cases occurred approximately 1 month after the state’s COVID-19 peak.
“Among our patients, predominantly from the New York Metropolitan Region, 40% were black and 36% were Hispanic. This may be a reflection of the well-documented elevated incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among black and Hispanic communities,” the authors report.
All children presented with fever or chills, and most had tachycardia (97%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (80%). Rash (60%), conjunctival infection (56%), hypotension (32%), and mucosal changes (27%) were reported. Among all of the children, levels of inflammatory markers were elevated, including levels of C-reactive protein (100%), D-dimer (91%), and troponin (71%). More than one third of the patients (36%) were diagnosed with myocarditis, and an additional 16% had clinical myocarditis.
Of the full cohort, 80% of the children required intensive care, 62% received vasopressor support, and two children died.
The high prevalence of cardiac dysfunction or depression, coagulopathy, gastrointestinal symptoms, mild respiratory symptoms, and indications for supplemental oxygen in patients with MIS-C stands in contrast to the clinical picture observed in most acute cases of COVID-19 in hospitalized children, the authors write.
“Although most children have mild or no illness from SARS-CoV-2 infection, MIS-C may follow Covid-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Recognition of the syndrome and early identification of children with MIS-C, including early monitoring of blood pressure and electrocardiographic and echocardiographic evaluation, could inform appropriate supportive care and other potential therapeutic options,” they continue.
The incidence of MIS-C among children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is unclear because children with COVID-19 often have mild or no symptoms and because children are not tested as frequently, the authors state. For this reason, “[i]t is crucial to establish surveillance for MIS-C cases, particularly in communities with higher levels of SARS-CoV-2 transmission.”
Important Differences From Kawasaki Disease
In a separate study, Leora R. Feldstein, MD, of the CDC, and colleagues report 186 cases of MIS-C collected through targeted surveillance of pediatric health centers in 26 US states from March 15 to May 20, 2020. As with the New York cohort, a disproportionate number of children in this cohort were black (25%) and Hispanic or Latino (31%).
Similar to the New York cohort, 80% of the children in this group required intensive care, 48% received vasoactive support, 20% required invasive mechanical ventilation, and four children died. Skin rashes, gastrointestinal symptoms, cardiovascular and hematologic effects, mucous changes, and elevations of inflammatory biomarkers were also similarly observed.
The researchers note that, although many of the features of MIS-C overlap with Kawasaki disease, there are some important differences, particularly with respect to the nature of cardiovascular involvement. “Approximately 5% of children with Kawasaki’s disease in the United States present with cardiovascular shock leading to vasopressor or inotropic support, as compared with 50% of the patients in our series,” the authors write.
In addition, coronary-artery aneurysms affect approximately one quarter of Kawasaki disease patients within 21 days of disease onset. “In our series, a maximum z score of 2.5 or higher in the left anterior descending or right coronary artery was reported in 8% of the patients overall and in 9% of patients with echocardiograms,” they report.
Additional differentiating features include patient age and race/ethnicity. Kawasaki disease occurs most commonly in children younger than 5 years. The median age in the multistate study was 8.3 years, and nearly half of the children in the New York cohort were in the 6- to 12-year age group. Further, Kawasaki disease is disproportionately prevalent in children of Asian descent.
Despite the differences, “until more is known about long-term cardiac sequelae of MIS-C, providers could consider following Kawasaki’s disease guidelines for follow-up, which recommend repeat echocardiographic imaging at 1 to 2 weeks.”
As was the case in the New York series, treatment in the multistate cohort most commonly included intravenous immunoglobulin and systemic glucocorticoids. Optimal management, however, will require a better understanding of the pathogenesis of MIS-C, Feldstein and colleagues write.
Questions Remain
With the accumulating data on this syndrome, the MIS-C picture seems to be getting incrementally clearer, but there is still much uncertainty, according to Michael Levin, FMedSci, PhD, from the Department of Infectious Disease, Imperial College London, United Kingdom.
“The recognition and description of new diseases often resemble the parable of the blind men and the elephant, with each declaring that the part of the beast they have touched fully defines it,” he writes in an accompanying editorial.
“As the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic has evolved, case reports have appeared describing children with unusual febrile illnesses that have features of Kawasaki’s disease, toxic shock syndrome, acute abdominal conditions, and encephalopathy, along with other reports of children with fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and multisystem involvement. It is now apparent that these reports were describing different clinical presentations of a new childhood inflammatory disorder.”
Although a consistent clinical picture is emerging, “[t]he published reports have used a variety of hastily developed case definitions based on the most severe cases, possibly missing less serious cases,” Levin writes. In particular, both the CDC and World Health Organization definitions require evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or exposure, which might contribute to underrecognition and underreporting because asymptomatic infections are common and antibody testing is not universally available.
“There is concern that children meeting current diagnostic criteria for MIS-C are the ‘tip of the iceberg,’ and a bigger problem may be lurking below the waterline,” Levin states. With approximately 1000 cases of the syndrome reported worldwide, “do we now have a clear picture of the new disorder, or as in the story of the blind men and the elephant, has only part of the beast been described?”
Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, who is a coauthor of the multistate report, agrees that there is still much to learn about MIS-C before the whole beast can be understood. In an interview with Medscape Medical News, she listed the following key questions that have yet to be answered:
- Why do some children get MIS-C and not others?
- What is the long-term outcome of children with MIS-C?
- How can we differentiate MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection in children with respiratory failure?
- Does MIS-C occur in young adults?
Randolph said her team is taking the best path forward toward answering these questions, including conducting a second study to identify risk factors for MIS-C and longer-term follow-up studies with the National Institutes of Health. “We are also getting consent to collect blood samples and look at other tests to help distinguish MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection,” she said. She encouraged heightened awareness among physicians who care for young adults to consider MIS-C in patients aged 21 years and older who present with similar signs and symptoms.
On the basis of the answers to these and additional questions, the case definitions for MIS-C may need refinement to capture the wider spectrum of illness, Levin writes in his editorial. “The challenges of this new condition will now be to understand its pathophysiological mechanisms, to develop diagnostics, and to define the best treatment.”
Kleinman has received grants from the Health Services Resources Administration outside the submitted work. Maddux has received grants from the NIH/NICHD and the Francis Family Foundation outside the submitted work. Randolph has received grants from Genentech and personal fees from La Jolla Pharma outside the submitted work and others from the CDC during the conduct of the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from active surveillance of the severe inflammatory condition associated with COVID-19 in previously healthy children provide further insight into the prevalence and course of the rare syndrome, but experts are concerned that current diagnostic criteria may not capture the true scope of the problem.
In separate reports published online June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers from the New York State Department of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) describe the epidemiology and clinical features of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) on the basis of information derived from targeted surveillance programs in New York State and across the country.
For the New York study, Elizabeth M. Dufort, MD, from the New York Department of Health in Albany and colleagues analyzed MIS-C surveillance data from 106 hospitals across the state. Of 191 suspected MIS-C cases reported to the Department of Health from March 1 through May 10, 99 met the state’s interim case definition of the condition and were included in the analysis.
The incidence rate for MIS-C was two cases per 100,000 individuals younger than 21 years, whereas the incidence rate of confirmed COVID-19 cases in this age group was 322 per 100,000. Most cases occurred approximately 1 month after the state’s COVID-19 peak.
“Among our patients, predominantly from the New York Metropolitan Region, 40% were black and 36% were Hispanic. This may be a reflection of the well-documented elevated incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among black and Hispanic communities,” the authors report.
All children presented with fever or chills, and most had tachycardia (97%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (80%). Rash (60%), conjunctival infection (56%), hypotension (32%), and mucosal changes (27%) were reported. Among all of the children, levels of inflammatory markers were elevated, including levels of C-reactive protein (100%), D-dimer (91%), and troponin (71%). More than one third of the patients (36%) were diagnosed with myocarditis, and an additional 16% had clinical myocarditis.
Of the full cohort, 80% of the children required intensive care, 62% received vasopressor support, and two children died.
The high prevalence of cardiac dysfunction or depression, coagulopathy, gastrointestinal symptoms, mild respiratory symptoms, and indications for supplemental oxygen in patients with MIS-C stands in contrast to the clinical picture observed in most acute cases of COVID-19 in hospitalized children, the authors write.
“Although most children have mild or no illness from SARS-CoV-2 infection, MIS-C may follow Covid-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Recognition of the syndrome and early identification of children with MIS-C, including early monitoring of blood pressure and electrocardiographic and echocardiographic evaluation, could inform appropriate supportive care and other potential therapeutic options,” they continue.
The incidence of MIS-C among children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is unclear because children with COVID-19 often have mild or no symptoms and because children are not tested as frequently, the authors state. For this reason, “[i]t is crucial to establish surveillance for MIS-C cases, particularly in communities with higher levels of SARS-CoV-2 transmission.”
Important Differences From Kawasaki Disease
In a separate study, Leora R. Feldstein, MD, of the CDC, and colleagues report 186 cases of MIS-C collected through targeted surveillance of pediatric health centers in 26 US states from March 15 to May 20, 2020. As with the New York cohort, a disproportionate number of children in this cohort were black (25%) and Hispanic or Latino (31%).
Similar to the New York cohort, 80% of the children in this group required intensive care, 48% received vasoactive support, 20% required invasive mechanical ventilation, and four children died. Skin rashes, gastrointestinal symptoms, cardiovascular and hematologic effects, mucous changes, and elevations of inflammatory biomarkers were also similarly observed.
The researchers note that, although many of the features of MIS-C overlap with Kawasaki disease, there are some important differences, particularly with respect to the nature of cardiovascular involvement. “Approximately 5% of children with Kawasaki’s disease in the United States present with cardiovascular shock leading to vasopressor or inotropic support, as compared with 50% of the patients in our series,” the authors write.
In addition, coronary-artery aneurysms affect approximately one quarter of Kawasaki disease patients within 21 days of disease onset. “In our series, a maximum z score of 2.5 or higher in the left anterior descending or right coronary artery was reported in 8% of the patients overall and in 9% of patients with echocardiograms,” they report.
Additional differentiating features include patient age and race/ethnicity. Kawasaki disease occurs most commonly in children younger than 5 years. The median age in the multistate study was 8.3 years, and nearly half of the children in the New York cohort were in the 6- to 12-year age group. Further, Kawasaki disease is disproportionately prevalent in children of Asian descent.
Despite the differences, “until more is known about long-term cardiac sequelae of MIS-C, providers could consider following Kawasaki’s disease guidelines for follow-up, which recommend repeat echocardiographic imaging at 1 to 2 weeks.”
As was the case in the New York series, treatment in the multistate cohort most commonly included intravenous immunoglobulin and systemic glucocorticoids. Optimal management, however, will require a better understanding of the pathogenesis of MIS-C, Feldstein and colleagues write.
Questions Remain
With the accumulating data on this syndrome, the MIS-C picture seems to be getting incrementally clearer, but there is still much uncertainty, according to Michael Levin, FMedSci, PhD, from the Department of Infectious Disease, Imperial College London, United Kingdom.
“The recognition and description of new diseases often resemble the parable of the blind men and the elephant, with each declaring that the part of the beast they have touched fully defines it,” he writes in an accompanying editorial.
“As the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic has evolved, case reports have appeared describing children with unusual febrile illnesses that have features of Kawasaki’s disease, toxic shock syndrome, acute abdominal conditions, and encephalopathy, along with other reports of children with fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and multisystem involvement. It is now apparent that these reports were describing different clinical presentations of a new childhood inflammatory disorder.”
Although a consistent clinical picture is emerging, “[t]he published reports have used a variety of hastily developed case definitions based on the most severe cases, possibly missing less serious cases,” Levin writes. In particular, both the CDC and World Health Organization definitions require evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or exposure, which might contribute to underrecognition and underreporting because asymptomatic infections are common and antibody testing is not universally available.
“There is concern that children meeting current diagnostic criteria for MIS-C are the ‘tip of the iceberg,’ and a bigger problem may be lurking below the waterline,” Levin states. With approximately 1000 cases of the syndrome reported worldwide, “do we now have a clear picture of the new disorder, or as in the story of the blind men and the elephant, has only part of the beast been described?”
Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, who is a coauthor of the multistate report, agrees that there is still much to learn about MIS-C before the whole beast can be understood. In an interview with Medscape Medical News, she listed the following key questions that have yet to be answered:
- Why do some children get MIS-C and not others?
- What is the long-term outcome of children with MIS-C?
- How can we differentiate MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection in children with respiratory failure?
- Does MIS-C occur in young adults?
Randolph said her team is taking the best path forward toward answering these questions, including conducting a second study to identify risk factors for MIS-C and longer-term follow-up studies with the National Institutes of Health. “We are also getting consent to collect blood samples and look at other tests to help distinguish MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection,” she said. She encouraged heightened awareness among physicians who care for young adults to consider MIS-C in patients aged 21 years and older who present with similar signs and symptoms.
On the basis of the answers to these and additional questions, the case definitions for MIS-C may need refinement to capture the wider spectrum of illness, Levin writes in his editorial. “The challenges of this new condition will now be to understand its pathophysiological mechanisms, to develop diagnostics, and to define the best treatment.”
Kleinman has received grants from the Health Services Resources Administration outside the submitted work. Maddux has received grants from the NIH/NICHD and the Francis Family Foundation outside the submitted work. Randolph has received grants from Genentech and personal fees from La Jolla Pharma outside the submitted work and others from the CDC during the conduct of the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from active surveillance of the severe inflammatory condition associated with COVID-19 in previously healthy children provide further insight into the prevalence and course of the rare syndrome, but experts are concerned that current diagnostic criteria may not capture the true scope of the problem.
In separate reports published online June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers from the New York State Department of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) describe the epidemiology and clinical features of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) on the basis of information derived from targeted surveillance programs in New York State and across the country.
For the New York study, Elizabeth M. Dufort, MD, from the New York Department of Health in Albany and colleagues analyzed MIS-C surveillance data from 106 hospitals across the state. Of 191 suspected MIS-C cases reported to the Department of Health from March 1 through May 10, 99 met the state’s interim case definition of the condition and were included in the analysis.
The incidence rate for MIS-C was two cases per 100,000 individuals younger than 21 years, whereas the incidence rate of confirmed COVID-19 cases in this age group was 322 per 100,000. Most cases occurred approximately 1 month after the state’s COVID-19 peak.
“Among our patients, predominantly from the New York Metropolitan Region, 40% were black and 36% were Hispanic. This may be a reflection of the well-documented elevated incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among black and Hispanic communities,” the authors report.
All children presented with fever or chills, and most had tachycardia (97%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (80%). Rash (60%), conjunctival infection (56%), hypotension (32%), and mucosal changes (27%) were reported. Among all of the children, levels of inflammatory markers were elevated, including levels of C-reactive protein (100%), D-dimer (91%), and troponin (71%). More than one third of the patients (36%) were diagnosed with myocarditis, and an additional 16% had clinical myocarditis.
Of the full cohort, 80% of the children required intensive care, 62% received vasopressor support, and two children died.
The high prevalence of cardiac dysfunction or depression, coagulopathy, gastrointestinal symptoms, mild respiratory symptoms, and indications for supplemental oxygen in patients with MIS-C stands in contrast to the clinical picture observed in most acute cases of COVID-19 in hospitalized children, the authors write.
“Although most children have mild or no illness from SARS-CoV-2 infection, MIS-C may follow Covid-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Recognition of the syndrome and early identification of children with MIS-C, including early monitoring of blood pressure and electrocardiographic and echocardiographic evaluation, could inform appropriate supportive care and other potential therapeutic options,” they continue.
The incidence of MIS-C among children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is unclear because children with COVID-19 often have mild or no symptoms and because children are not tested as frequently, the authors state. For this reason, “[i]t is crucial to establish surveillance for MIS-C cases, particularly in communities with higher levels of SARS-CoV-2 transmission.”
Important Differences From Kawasaki Disease
In a separate study, Leora R. Feldstein, MD, of the CDC, and colleagues report 186 cases of MIS-C collected through targeted surveillance of pediatric health centers in 26 US states from March 15 to May 20, 2020. As with the New York cohort, a disproportionate number of children in this cohort were black (25%) and Hispanic or Latino (31%).
Similar to the New York cohort, 80% of the children in this group required intensive care, 48% received vasoactive support, 20% required invasive mechanical ventilation, and four children died. Skin rashes, gastrointestinal symptoms, cardiovascular and hematologic effects, mucous changes, and elevations of inflammatory biomarkers were also similarly observed.
The researchers note that, although many of the features of MIS-C overlap with Kawasaki disease, there are some important differences, particularly with respect to the nature of cardiovascular involvement. “Approximately 5% of children with Kawasaki’s disease in the United States present with cardiovascular shock leading to vasopressor or inotropic support, as compared with 50% of the patients in our series,” the authors write.
In addition, coronary-artery aneurysms affect approximately one quarter of Kawasaki disease patients within 21 days of disease onset. “In our series, a maximum z score of 2.5 or higher in the left anterior descending or right coronary artery was reported in 8% of the patients overall and in 9% of patients with echocardiograms,” they report.
Additional differentiating features include patient age and race/ethnicity. Kawasaki disease occurs most commonly in children younger than 5 years. The median age in the multistate study was 8.3 years, and nearly half of the children in the New York cohort were in the 6- to 12-year age group. Further, Kawasaki disease is disproportionately prevalent in children of Asian descent.
Despite the differences, “until more is known about long-term cardiac sequelae of MIS-C, providers could consider following Kawasaki’s disease guidelines for follow-up, which recommend repeat echocardiographic imaging at 1 to 2 weeks.”
As was the case in the New York series, treatment in the multistate cohort most commonly included intravenous immunoglobulin and systemic glucocorticoids. Optimal management, however, will require a better understanding of the pathogenesis of MIS-C, Feldstein and colleagues write.
Questions Remain
With the accumulating data on this syndrome, the MIS-C picture seems to be getting incrementally clearer, but there is still much uncertainty, according to Michael Levin, FMedSci, PhD, from the Department of Infectious Disease, Imperial College London, United Kingdom.
“The recognition and description of new diseases often resemble the parable of the blind men and the elephant, with each declaring that the part of the beast they have touched fully defines it,” he writes in an accompanying editorial.
“As the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic has evolved, case reports have appeared describing children with unusual febrile illnesses that have features of Kawasaki’s disease, toxic shock syndrome, acute abdominal conditions, and encephalopathy, along with other reports of children with fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and multisystem involvement. It is now apparent that these reports were describing different clinical presentations of a new childhood inflammatory disorder.”
Although a consistent clinical picture is emerging, “[t]he published reports have used a variety of hastily developed case definitions based on the most severe cases, possibly missing less serious cases,” Levin writes. In particular, both the CDC and World Health Organization definitions require evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection or exposure, which might contribute to underrecognition and underreporting because asymptomatic infections are common and antibody testing is not universally available.
“There is concern that children meeting current diagnostic criteria for MIS-C are the ‘tip of the iceberg,’ and a bigger problem may be lurking below the waterline,” Levin states. With approximately 1000 cases of the syndrome reported worldwide, “do we now have a clear picture of the new disorder, or as in the story of the blind men and the elephant, has only part of the beast been described?”
Adrienne Randolph, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, who is a coauthor of the multistate report, agrees that there is still much to learn about MIS-C before the whole beast can be understood. In an interview with Medscape Medical News, she listed the following key questions that have yet to be answered:
- Why do some children get MIS-C and not others?
- What is the long-term outcome of children with MIS-C?
- How can we differentiate MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection in children with respiratory failure?
- Does MIS-C occur in young adults?
Randolph said her team is taking the best path forward toward answering these questions, including conducting a second study to identify risk factors for MIS-C and longer-term follow-up studies with the National Institutes of Health. “We are also getting consent to collect blood samples and look at other tests to help distinguish MIS-C from acute COVID-19 infection,” she said. She encouraged heightened awareness among physicians who care for young adults to consider MIS-C in patients aged 21 years and older who present with similar signs and symptoms.
On the basis of the answers to these and additional questions, the case definitions for MIS-C may need refinement to capture the wider spectrum of illness, Levin writes in his editorial. “The challenges of this new condition will now be to understand its pathophysiological mechanisms, to develop diagnostics, and to define the best treatment.”
Kleinman has received grants from the Health Services Resources Administration outside the submitted work. Maddux has received grants from the NIH/NICHD and the Francis Family Foundation outside the submitted work. Randolph has received grants from Genentech and personal fees from La Jolla Pharma outside the submitted work and others from the CDC during the conduct of the study.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Captopril questioned for diabetes patients in COVID-19 setting
Captopril appears to be associated with a higher rate of pulmonary adverse reactions in patients with diabetes than that of other ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and therefore may not be the best choice for patients with diabetes and COVID-19, a new study suggests.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Pharmacists Association.
The authors, led by Emma G. Stafford, PharmD, University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Pharmacy, note that diabetes seems to confer a higher risk of adverse outcomes in COVID-19 infection and there is conflicting data on the contribution of ACE inhibitors and ARBs, commonly used medications in diabetes, on the mortality and morbidity of COVID-19.
“In light of the recent COVID-19 outbreak, more research is needed to understand the effects that diabetes (and its medications) may have on the respiratory system and how that could affect the management of diseases such as COVID-19,” they say.
“Although ACE inhibitors and ARBs are generally considered to have similar adverse event profiles, evaluation of postmarketing adverse events may shed light on minute differences that could have important clinical impacts,” they add.
For the current study, the researchers analyzed data from multiple publicly available data sources on adverse drug reactions in patients with diabetes taking ACE inhibitors or ARBs. The data included all adverse drug events (ADEs) reported nationally to the US Food and Drug Administration and internationally to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA).
Results showed that captopril, the first ACE inhibitor approved back in 1981, has a higher incidence of pulmonary ADEs in patients with diabetes as compared with other ACE-inhibitor drugs (P = .005) as well as a statistically significant difference in pulmonary events compared with ARBs (P = .012).
“These analyses suggest that pharmacists and clinicians will need to consider the specific medication’s adverse event profile, particularly captopril, on how it may affect infections and other acute disease states that alter pulmonary function, such as COVID-19,” the authors conclude.
They say that the high incidence of pulmonary adverse drug effects with captopril “highlights the fact that the drugs belonging in one class are not identical and that its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics can affect the patients’ health especially during acute processes like COVID-19.”
“This is especially important as current observational studies of COVID-19 patients tend to group drugs within a class and are not analyzing the potential differences within each class,” they add.
They note that ACE inhibitors can be broadly classified into 3 structural classes: sulfhydryl-, dicarboxyl-, and phosphorous- containing molecules. Notably, captopril is the only currently available ACE inhibitor belonging to the sulfhydryl-containing class and may explain the higher incidence of adverse drug effects observed, they comment.
“Health care providers have been left with many questions when treating patients with COVID-19, including how ACE inhibitors or ARBs may affect their clinical course. Results from this study may be helpful when prescribing or continuing ACE inhibitors or ARBs for patients with diabetes and infections or illnesses that may affect pulmonary function, such as COVID-19,” they conclude.
Questioning safety in COVID-19 an “overreach”
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Michael A. Weber, MD, professor of medicine at State University of New York, said he thought the current article appears to overreach in questioning captopril’s safety in the COVID-19 setting.
“Captopril was the first ACE inhibitor available for clinical use. In early prescribing its dosage was not well understood and it might have been administered in excessive amounts,” Weber notes.
“There were some renal and other adverse effects reported that at first were attributed to the fact that captopril, unlike any other popular ACE inhibitors, contained a sulfhydryl (SH) group in its molecule,” he said. “It is not clear whether this feature could be responsible for the increased pulmonary side effects and potential danger to COVID-19 patients now reported with captopril in this new pharmacy article.”
But he adds: “The article contains no evidence that the effect of captopril or any other ACE inhibitor on the pulmonary ACE-2 enzyme has a deleterious effect on outcomes of COVID-19 disease. In any case, captopril — which should be prescribed in a twice-daily dose — is not frequently prescribed these days since newer ACE inhibitors are effective with just once-daily dosing.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Captopril appears to be associated with a higher rate of pulmonary adverse reactions in patients with diabetes than that of other ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and therefore may not be the best choice for patients with diabetes and COVID-19, a new study suggests.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Pharmacists Association.
The authors, led by Emma G. Stafford, PharmD, University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Pharmacy, note that diabetes seems to confer a higher risk of adverse outcomes in COVID-19 infection and there is conflicting data on the contribution of ACE inhibitors and ARBs, commonly used medications in diabetes, on the mortality and morbidity of COVID-19.
“In light of the recent COVID-19 outbreak, more research is needed to understand the effects that diabetes (and its medications) may have on the respiratory system and how that could affect the management of diseases such as COVID-19,” they say.
“Although ACE inhibitors and ARBs are generally considered to have similar adverse event profiles, evaluation of postmarketing adverse events may shed light on minute differences that could have important clinical impacts,” they add.
For the current study, the researchers analyzed data from multiple publicly available data sources on adverse drug reactions in patients with diabetes taking ACE inhibitors or ARBs. The data included all adverse drug events (ADEs) reported nationally to the US Food and Drug Administration and internationally to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA).
Results showed that captopril, the first ACE inhibitor approved back in 1981, has a higher incidence of pulmonary ADEs in patients with diabetes as compared with other ACE-inhibitor drugs (P = .005) as well as a statistically significant difference in pulmonary events compared with ARBs (P = .012).
“These analyses suggest that pharmacists and clinicians will need to consider the specific medication’s adverse event profile, particularly captopril, on how it may affect infections and other acute disease states that alter pulmonary function, such as COVID-19,” the authors conclude.
They say that the high incidence of pulmonary adverse drug effects with captopril “highlights the fact that the drugs belonging in one class are not identical and that its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics can affect the patients’ health especially during acute processes like COVID-19.”
“This is especially important as current observational studies of COVID-19 patients tend to group drugs within a class and are not analyzing the potential differences within each class,” they add.
They note that ACE inhibitors can be broadly classified into 3 structural classes: sulfhydryl-, dicarboxyl-, and phosphorous- containing molecules. Notably, captopril is the only currently available ACE inhibitor belonging to the sulfhydryl-containing class and may explain the higher incidence of adverse drug effects observed, they comment.
“Health care providers have been left with many questions when treating patients with COVID-19, including how ACE inhibitors or ARBs may affect their clinical course. Results from this study may be helpful when prescribing or continuing ACE inhibitors or ARBs for patients with diabetes and infections or illnesses that may affect pulmonary function, such as COVID-19,” they conclude.
Questioning safety in COVID-19 an “overreach”
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Michael A. Weber, MD, professor of medicine at State University of New York, said he thought the current article appears to overreach in questioning captopril’s safety in the COVID-19 setting.
“Captopril was the first ACE inhibitor available for clinical use. In early prescribing its dosage was not well understood and it might have been administered in excessive amounts,” Weber notes.
“There were some renal and other adverse effects reported that at first were attributed to the fact that captopril, unlike any other popular ACE inhibitors, contained a sulfhydryl (SH) group in its molecule,” he said. “It is not clear whether this feature could be responsible for the increased pulmonary side effects and potential danger to COVID-19 patients now reported with captopril in this new pharmacy article.”
But he adds: “The article contains no evidence that the effect of captopril or any other ACE inhibitor on the pulmonary ACE-2 enzyme has a deleterious effect on outcomes of COVID-19 disease. In any case, captopril — which should be prescribed in a twice-daily dose — is not frequently prescribed these days since newer ACE inhibitors are effective with just once-daily dosing.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Captopril appears to be associated with a higher rate of pulmonary adverse reactions in patients with diabetes than that of other ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and therefore may not be the best choice for patients with diabetes and COVID-19, a new study suggests.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Pharmacists Association.
The authors, led by Emma G. Stafford, PharmD, University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Pharmacy, note that diabetes seems to confer a higher risk of adverse outcomes in COVID-19 infection and there is conflicting data on the contribution of ACE inhibitors and ARBs, commonly used medications in diabetes, on the mortality and morbidity of COVID-19.
“In light of the recent COVID-19 outbreak, more research is needed to understand the effects that diabetes (and its medications) may have on the respiratory system and how that could affect the management of diseases such as COVID-19,” they say.
“Although ACE inhibitors and ARBs are generally considered to have similar adverse event profiles, evaluation of postmarketing adverse events may shed light on minute differences that could have important clinical impacts,” they add.
For the current study, the researchers analyzed data from multiple publicly available data sources on adverse drug reactions in patients with diabetes taking ACE inhibitors or ARBs. The data included all adverse drug events (ADEs) reported nationally to the US Food and Drug Administration and internationally to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA).
Results showed that captopril, the first ACE inhibitor approved back in 1981, has a higher incidence of pulmonary ADEs in patients with diabetes as compared with other ACE-inhibitor drugs (P = .005) as well as a statistically significant difference in pulmonary events compared with ARBs (P = .012).
“These analyses suggest that pharmacists and clinicians will need to consider the specific medication’s adverse event profile, particularly captopril, on how it may affect infections and other acute disease states that alter pulmonary function, such as COVID-19,” the authors conclude.
They say that the high incidence of pulmonary adverse drug effects with captopril “highlights the fact that the drugs belonging in one class are not identical and that its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics can affect the patients’ health especially during acute processes like COVID-19.”
“This is especially important as current observational studies of COVID-19 patients tend to group drugs within a class and are not analyzing the potential differences within each class,” they add.
They note that ACE inhibitors can be broadly classified into 3 structural classes: sulfhydryl-, dicarboxyl-, and phosphorous- containing molecules. Notably, captopril is the only currently available ACE inhibitor belonging to the sulfhydryl-containing class and may explain the higher incidence of adverse drug effects observed, they comment.
“Health care providers have been left with many questions when treating patients with COVID-19, including how ACE inhibitors or ARBs may affect their clinical course. Results from this study may be helpful when prescribing or continuing ACE inhibitors or ARBs for patients with diabetes and infections or illnesses that may affect pulmonary function, such as COVID-19,” they conclude.
Questioning safety in COVID-19 an “overreach”
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Michael A. Weber, MD, professor of medicine at State University of New York, said he thought the current article appears to overreach in questioning captopril’s safety in the COVID-19 setting.
“Captopril was the first ACE inhibitor available for clinical use. In early prescribing its dosage was not well understood and it might have been administered in excessive amounts,” Weber notes.
“There were some renal and other adverse effects reported that at first were attributed to the fact that captopril, unlike any other popular ACE inhibitors, contained a sulfhydryl (SH) group in its molecule,” he said. “It is not clear whether this feature could be responsible for the increased pulmonary side effects and potential danger to COVID-19 patients now reported with captopril in this new pharmacy article.”
But he adds: “The article contains no evidence that the effect of captopril or any other ACE inhibitor on the pulmonary ACE-2 enzyme has a deleterious effect on outcomes of COVID-19 disease. In any case, captopril — which should be prescribed in a twice-daily dose — is not frequently prescribed these days since newer ACE inhibitors are effective with just once-daily dosing.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.



