User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
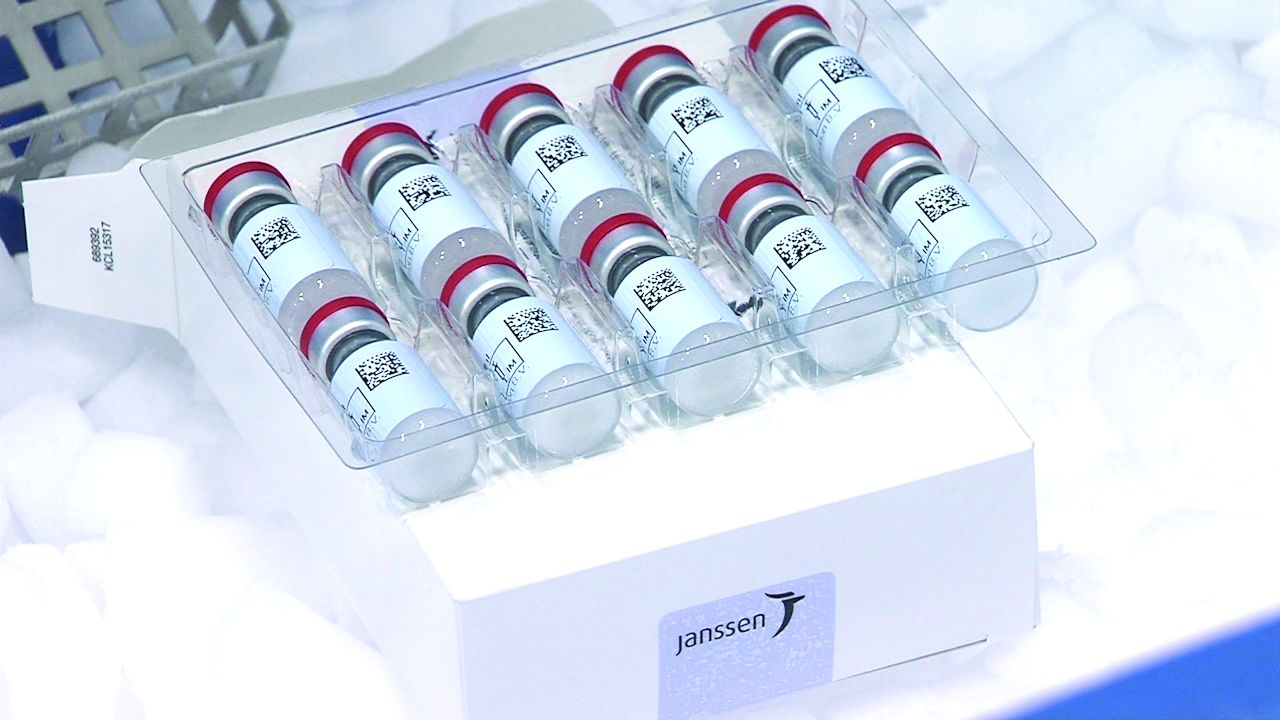
J&J COVID-19 vaccine wins unanimous backing of FDA panel
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is expected to quickly provide an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the vaccine following the recommendation by the panel. The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee voted 22-0 on this question: Based on the totality of scientific evidence available, do the benefits of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine outweigh its risks for use in individuals 18 years of age and older?
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine is expected to offer more convenient dosing and be easier to distribute than the two rival products already available in the United States. Janssen’s vaccine is intended to be given in a single dose. In December, the FDA granted EUAs for the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, which are each two-dose regimens.
Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine can be stored for at least 3 months at normal refrigerator temperatures of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Its shipping and storage fits into the existing medical supply infrastructure, the company said in its briefing materials for the FDA advisory committee meeting. In contrast, Pfizer’s vaccine is stored in ultracold freezers at temperatures between -80°C and -60°C (-112°F and -76°F), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Moderna’s vaccine may be stored in a freezer between -25°C and -15°C (-13°F and 5°F).
But FDA advisers focused more in their deliberations on concerns about Janssen’s vaccine, including emerging reports of allergic reactions.
The advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Johnson & Johnson’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. The company’s initial unveiling last month of key results for its vaccine caused an initial wave of disappointment, with its overall efficacy against moderate-to-severe COVID-19 28 days postvaccination first reported at about 66% globally. By contrast, results for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines suggest they have efficacy rates of 95% and 94%.
But in concluding, the advisers spoke of the Janssen vaccine as a much-needed tool to address the COVID-19 pandemic. The death toll in the United States attributed to the virus has reached 501,414, according to the World Health Organization.
“Despite the concerns that were raised during the discussion. I think what we have to keep in mind is that we’re still in the midst of this deadly pandemic,” said FDA adviser Archana Chatterjee, MD, PhD, from Rosalind Franklin University. “There is a shortage of vaccines that are currently authorized, and I think authorization of this vaccine will help meet the needs at the moment.”
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its advisers, but it often does so.
Anaphylaxis case
FDA advisers raised only a few questions for Johnson & Johnson and FDA staff ahead of their vote. The committee’s deliberations were less contentious and heated than had been during its December reviews of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. In those meetings, the panel voted 17-4, with one abstention, in favor of Pfizer’s vaccine and 20-0, with one abstention, on the Moderna vaccine.
“We are very comfortable now with the procedure, as well as the vaccines,” said Arnold Monto, MD, after the Feb. 26 vote on the Janssen vaccine. Dr. Monto, from the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor, has served as the chairman of the FDA panel through its review of all three COVID-19 vaccines.
Among the issues noted in the deliberations was the emergence of a concern about anaphylaxis with the vaccine.
This serious allergic reaction has been seen in people who have taken the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Before the week of the panel meeting, though, there had not been reports of anaphylaxis with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, said Macaya Douoguih, MD, MPH, head of clinical development and medical affairs for Janssen/ Johnson & Johnson’s vaccines division.
However, on February 24, Johnson & Johnson received preliminary reports about two cases of severe allergic reaction from an open-label study in South Africa, with one of these being anaphylaxis, Dr. Douoguih said. The company will continue to closely monitor for these events as outlined in their pharmacovigilance plan, Dr. Douoguih said.
Federal health officials have sought to make clinicians aware of the rare risk for anaphylaxis with COVID vaccines, while reminding the public that this reaction can be managed.
The FDA had Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC, give an update on postmarketing surveillance for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines as part of the review of the Johnson & Johnson application. Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues published a report in JAMA on February 14 that looked at an anaphylaxis case reported connected with COVID vaccines between December 14, 2020, and January 18, 2021.
The CDC identified 66 case reports received that met Brighton Collaboration case definition criteria for anaphylaxis (levels 1, 2, or 3): 47 following Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, for a reporting rate of 4.7 cases/million doses administered, and 19 following Moderna vaccine, for a reporting rate of 2.5 cases/million doses administered, Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues wrote.
The CDC has published materials to help clinicians prepare for the possibility of this rare event, Dr. Shimabukuro told the FDA advisers.
“The take-home message here is that these are rare events and anaphylaxis, although clinically serious, is treatable,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
At the conclusion of the meeting, FDA panelist Patrick Moore, MD, MPH, from the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania, stressed the need to convey to the public that the COVID vaccines appear so far to be safe. Many people earlier had doubts about how the FDA could both safely and quickly review the applications for EUAs for these products.
“As of February 26, things are looking good. That could change tomorrow,” Dr. Moore said. But “this whole EUA process does seem to have worked, despite my own personal concerns about it.”
No second-class vaccines
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine, known as Ad26.COV2.S, is composed of a recombinant, replication-incompetent human adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vector. It’s intended to encode a stabilized form of SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein. The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use a different mechanism. They rely on mRNA.
The FDA advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Janssen’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. They urged against people parsing study details too finely and seeking to pick and choose their shots.
“It’s important that people do not think that one vaccine is better than another,” said FDA adviser H. Cody Meissner, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston.
Dr. Monto agreed, noting that many people in the United States are still waiting for their turn to get COVID vaccines because of the limited early supply.
Trying to game the system to get one vaccine instead of another would not be wise. “In this environment, whatever you can get, get,” Dr. Monto said.
During an open public hearing, Sarah Christopherson, policy advocacy director of the National Women’s Health Network, said that press reports are fueling a damaging impression in the public that there are “first and second-class” vaccines.
“That has the potential to exacerbate existing mistrust” in vaccines, she said. “Public health authorities must address these perceptions head on.”
She urged against attempts to compare the Janssen vaccine to others, noting the potential effects of emerging variants of the virus.
“It’s difficult to make an apples-to-apples comparison between vaccines,” she said.
Johnson & Johnson’s efficacy results, which are lower than those of the mRNA vaccines, may be a reflection of the ways in which SARS-Co-V-2 is mutating and thus becoming more of a threat, according to the company. A key study of the new vaccine, involving about 44,000 people, coincided with the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, which were emerging in some of the countries where the pivotal COV3001 study was being conducted, the company said.
At least 14 days after vaccination, the Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine efficacy (95% confidence interval) was 72.0% (58.2, 81.7) in the United States, 68.1% (48.8, 80.7) in Brazil, and 64.0% (41.2, 78.7) in South Africa.
Weakened standards?
Several researchers called on the FDA to maintain a critical attitude when assessing Johnson & Johnson’s application for the EUA, warning of a potential for a permanent erosion of agency rules due to hasty action on COVID vaccines.
They raised concerns about the FDA demanding too little in terms of follow-up studies on COVID vaccines and with persisting murkiness resulting in attempts to determine how well these treatments work beyond the initial study period.
“I worry about FDA lowering its approval standards,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, from The BMJ and a faculty member at the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, during an open public hearing at the meeting.
“There’s a real urgency to stand back right now and look at the forest here, as well as the trees, and I urge the committee to consider the effects FDA decisions may have on the entire regulatory approval process,” Dr. Doshi said.
Dr. Doshi asked why Johnson & Johnson did not seek a standard full approval — a biologics license application (BLA) — instead of aiming for the lower bar of an EUA. The FDA already has allowed wide distribution of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines through EUAs. That removes the sense of urgency that FDA faced last year in his view.
The FDA’s June 2020 guidance on the development of COVID vaccines had asked drugmakers to plan on following participants in COVID vaccine trials for “ideally at least one to two years.” Yet people who got placebo in Moderna and Pfizer trials already are being vaccinated, Dr. Doshi said. And Johnson & Johnson said in its presentation to the FDA that if the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine were granted an EUA, the COV3001 study design would be amended to “facilitate cross-over of placebo participants in all participating countries to receive one dose of active study vaccine as fast as operationally feasible.”
“I’m nervous about the prospect of there never being a COVID vaccine that meets the FDA’s approval standard” for a BLA instead of the more limited EUA, Dr. Doshi said.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the FDA’s subsequent guidance tailored for EUAs for COVID vaccines “drastically shortened” the follow-up time to a median of 2 months. Dr. Zuckerman said that a crossover design would be “a reasonable compromise, but only if the placebo group has at least 6 months of data.” Dr. Zuckerman opened her remarks in the open public hearing by saying she had inherited Johnson & Johnson stock, so was speaking at the meeting against her own financial interest.
“As soon as a vaccine is authorized, we start losing the placebo group. If FDA lets that happen, that’s a huge loss for public health and a huge loss of information about how we can all stay safe,” Dr. Zuckerman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is expected to quickly provide an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the vaccine following the recommendation by the panel. The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee voted 22-0 on this question: Based on the totality of scientific evidence available, do the benefits of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine outweigh its risks for use in individuals 18 years of age and older?
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine is expected to offer more convenient dosing and be easier to distribute than the two rival products already available in the United States. Janssen’s vaccine is intended to be given in a single dose. In December, the FDA granted EUAs for the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, which are each two-dose regimens.
Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine can be stored for at least 3 months at normal refrigerator temperatures of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Its shipping and storage fits into the existing medical supply infrastructure, the company said in its briefing materials for the FDA advisory committee meeting. In contrast, Pfizer’s vaccine is stored in ultracold freezers at temperatures between -80°C and -60°C (-112°F and -76°F), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Moderna’s vaccine may be stored in a freezer between -25°C and -15°C (-13°F and 5°F).
But FDA advisers focused more in their deliberations on concerns about Janssen’s vaccine, including emerging reports of allergic reactions.
The advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Johnson & Johnson’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. The company’s initial unveiling last month of key results for its vaccine caused an initial wave of disappointment, with its overall efficacy against moderate-to-severe COVID-19 28 days postvaccination first reported at about 66% globally. By contrast, results for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines suggest they have efficacy rates of 95% and 94%.
But in concluding, the advisers spoke of the Janssen vaccine as a much-needed tool to address the COVID-19 pandemic. The death toll in the United States attributed to the virus has reached 501,414, according to the World Health Organization.
“Despite the concerns that were raised during the discussion. I think what we have to keep in mind is that we’re still in the midst of this deadly pandemic,” said FDA adviser Archana Chatterjee, MD, PhD, from Rosalind Franklin University. “There is a shortage of vaccines that are currently authorized, and I think authorization of this vaccine will help meet the needs at the moment.”
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its advisers, but it often does so.
Anaphylaxis case
FDA advisers raised only a few questions for Johnson & Johnson and FDA staff ahead of their vote. The committee’s deliberations were less contentious and heated than had been during its December reviews of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. In those meetings, the panel voted 17-4, with one abstention, in favor of Pfizer’s vaccine and 20-0, with one abstention, on the Moderna vaccine.
“We are very comfortable now with the procedure, as well as the vaccines,” said Arnold Monto, MD, after the Feb. 26 vote on the Janssen vaccine. Dr. Monto, from the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor, has served as the chairman of the FDA panel through its review of all three COVID-19 vaccines.
Among the issues noted in the deliberations was the emergence of a concern about anaphylaxis with the vaccine.
This serious allergic reaction has been seen in people who have taken the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Before the week of the panel meeting, though, there had not been reports of anaphylaxis with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, said Macaya Douoguih, MD, MPH, head of clinical development and medical affairs for Janssen/ Johnson & Johnson’s vaccines division.
However, on February 24, Johnson & Johnson received preliminary reports about two cases of severe allergic reaction from an open-label study in South Africa, with one of these being anaphylaxis, Dr. Douoguih said. The company will continue to closely monitor for these events as outlined in their pharmacovigilance plan, Dr. Douoguih said.
Federal health officials have sought to make clinicians aware of the rare risk for anaphylaxis with COVID vaccines, while reminding the public that this reaction can be managed.
The FDA had Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC, give an update on postmarketing surveillance for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines as part of the review of the Johnson & Johnson application. Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues published a report in JAMA on February 14 that looked at an anaphylaxis case reported connected with COVID vaccines between December 14, 2020, and January 18, 2021.
The CDC identified 66 case reports received that met Brighton Collaboration case definition criteria for anaphylaxis (levels 1, 2, or 3): 47 following Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, for a reporting rate of 4.7 cases/million doses administered, and 19 following Moderna vaccine, for a reporting rate of 2.5 cases/million doses administered, Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues wrote.
The CDC has published materials to help clinicians prepare for the possibility of this rare event, Dr. Shimabukuro told the FDA advisers.
“The take-home message here is that these are rare events and anaphylaxis, although clinically serious, is treatable,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
At the conclusion of the meeting, FDA panelist Patrick Moore, MD, MPH, from the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania, stressed the need to convey to the public that the COVID vaccines appear so far to be safe. Many people earlier had doubts about how the FDA could both safely and quickly review the applications for EUAs for these products.
“As of February 26, things are looking good. That could change tomorrow,” Dr. Moore said. But “this whole EUA process does seem to have worked, despite my own personal concerns about it.”
No second-class vaccines
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine, known as Ad26.COV2.S, is composed of a recombinant, replication-incompetent human adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vector. It’s intended to encode a stabilized form of SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein. The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use a different mechanism. They rely on mRNA.
The FDA advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Janssen’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. They urged against people parsing study details too finely and seeking to pick and choose their shots.
“It’s important that people do not think that one vaccine is better than another,” said FDA adviser H. Cody Meissner, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston.
Dr. Monto agreed, noting that many people in the United States are still waiting for their turn to get COVID vaccines because of the limited early supply.
Trying to game the system to get one vaccine instead of another would not be wise. “In this environment, whatever you can get, get,” Dr. Monto said.
During an open public hearing, Sarah Christopherson, policy advocacy director of the National Women’s Health Network, said that press reports are fueling a damaging impression in the public that there are “first and second-class” vaccines.
“That has the potential to exacerbate existing mistrust” in vaccines, she said. “Public health authorities must address these perceptions head on.”
She urged against attempts to compare the Janssen vaccine to others, noting the potential effects of emerging variants of the virus.
“It’s difficult to make an apples-to-apples comparison between vaccines,” she said.
Johnson & Johnson’s efficacy results, which are lower than those of the mRNA vaccines, may be a reflection of the ways in which SARS-Co-V-2 is mutating and thus becoming more of a threat, according to the company. A key study of the new vaccine, involving about 44,000 people, coincided with the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, which were emerging in some of the countries where the pivotal COV3001 study was being conducted, the company said.
At least 14 days after vaccination, the Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine efficacy (95% confidence interval) was 72.0% (58.2, 81.7) in the United States, 68.1% (48.8, 80.7) in Brazil, and 64.0% (41.2, 78.7) in South Africa.
Weakened standards?
Several researchers called on the FDA to maintain a critical attitude when assessing Johnson & Johnson’s application for the EUA, warning of a potential for a permanent erosion of agency rules due to hasty action on COVID vaccines.
They raised concerns about the FDA demanding too little in terms of follow-up studies on COVID vaccines and with persisting murkiness resulting in attempts to determine how well these treatments work beyond the initial study period.
“I worry about FDA lowering its approval standards,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, from The BMJ and a faculty member at the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, during an open public hearing at the meeting.
“There’s a real urgency to stand back right now and look at the forest here, as well as the trees, and I urge the committee to consider the effects FDA decisions may have on the entire regulatory approval process,” Dr. Doshi said.
Dr. Doshi asked why Johnson & Johnson did not seek a standard full approval — a biologics license application (BLA) — instead of aiming for the lower bar of an EUA. The FDA already has allowed wide distribution of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines through EUAs. That removes the sense of urgency that FDA faced last year in his view.
The FDA’s June 2020 guidance on the development of COVID vaccines had asked drugmakers to plan on following participants in COVID vaccine trials for “ideally at least one to two years.” Yet people who got placebo in Moderna and Pfizer trials already are being vaccinated, Dr. Doshi said. And Johnson & Johnson said in its presentation to the FDA that if the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine were granted an EUA, the COV3001 study design would be amended to “facilitate cross-over of placebo participants in all participating countries to receive one dose of active study vaccine as fast as operationally feasible.”
“I’m nervous about the prospect of there never being a COVID vaccine that meets the FDA’s approval standard” for a BLA instead of the more limited EUA, Dr. Doshi said.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the FDA’s subsequent guidance tailored for EUAs for COVID vaccines “drastically shortened” the follow-up time to a median of 2 months. Dr. Zuckerman said that a crossover design would be “a reasonable compromise, but only if the placebo group has at least 6 months of data.” Dr. Zuckerman opened her remarks in the open public hearing by saying she had inherited Johnson & Johnson stock, so was speaking at the meeting against her own financial interest.
“As soon as a vaccine is authorized, we start losing the placebo group. If FDA lets that happen, that’s a huge loss for public health and a huge loss of information about how we can all stay safe,” Dr. Zuckerman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is expected to quickly provide an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the vaccine following the recommendation by the panel. The FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee voted 22-0 on this question: Based on the totality of scientific evidence available, do the benefits of the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine outweigh its risks for use in individuals 18 years of age and older?
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine is expected to offer more convenient dosing and be easier to distribute than the two rival products already available in the United States. Janssen’s vaccine is intended to be given in a single dose. In December, the FDA granted EUAs for the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines, which are each two-dose regimens.
Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine can be stored for at least 3 months at normal refrigerator temperatures of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Its shipping and storage fits into the existing medical supply infrastructure, the company said in its briefing materials for the FDA advisory committee meeting. In contrast, Pfizer’s vaccine is stored in ultracold freezers at temperatures between -80°C and -60°C (-112°F and -76°F), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Moderna’s vaccine may be stored in a freezer between -25°C and -15°C (-13°F and 5°F).
But FDA advisers focused more in their deliberations on concerns about Janssen’s vaccine, including emerging reports of allergic reactions.
The advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Johnson & Johnson’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. The company’s initial unveiling last month of key results for its vaccine caused an initial wave of disappointment, with its overall efficacy against moderate-to-severe COVID-19 28 days postvaccination first reported at about 66% globally. By contrast, results for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines suggest they have efficacy rates of 95% and 94%.
But in concluding, the advisers spoke of the Janssen vaccine as a much-needed tool to address the COVID-19 pandemic. The death toll in the United States attributed to the virus has reached 501,414, according to the World Health Organization.
“Despite the concerns that were raised during the discussion. I think what we have to keep in mind is that we’re still in the midst of this deadly pandemic,” said FDA adviser Archana Chatterjee, MD, PhD, from Rosalind Franklin University. “There is a shortage of vaccines that are currently authorized, and I think authorization of this vaccine will help meet the needs at the moment.”
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its advisers, but it often does so.
Anaphylaxis case
FDA advisers raised only a few questions for Johnson & Johnson and FDA staff ahead of their vote. The committee’s deliberations were less contentious and heated than had been during its December reviews of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. In those meetings, the panel voted 17-4, with one abstention, in favor of Pfizer’s vaccine and 20-0, with one abstention, on the Moderna vaccine.
“We are very comfortable now with the procedure, as well as the vaccines,” said Arnold Monto, MD, after the Feb. 26 vote on the Janssen vaccine. Dr. Monto, from the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor, has served as the chairman of the FDA panel through its review of all three COVID-19 vaccines.
Among the issues noted in the deliberations was the emergence of a concern about anaphylaxis with the vaccine.
This serious allergic reaction has been seen in people who have taken the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. Before the week of the panel meeting, though, there had not been reports of anaphylaxis with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, said Macaya Douoguih, MD, MPH, head of clinical development and medical affairs for Janssen/ Johnson & Johnson’s vaccines division.
However, on February 24, Johnson & Johnson received preliminary reports about two cases of severe allergic reaction from an open-label study in South Africa, with one of these being anaphylaxis, Dr. Douoguih said. The company will continue to closely monitor for these events as outlined in their pharmacovigilance plan, Dr. Douoguih said.
Federal health officials have sought to make clinicians aware of the rare risk for anaphylaxis with COVID vaccines, while reminding the public that this reaction can be managed.
The FDA had Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, from the CDC, give an update on postmarketing surveillance for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines as part of the review of the Johnson & Johnson application. Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues published a report in JAMA on February 14 that looked at an anaphylaxis case reported connected with COVID vaccines between December 14, 2020, and January 18, 2021.
The CDC identified 66 case reports received that met Brighton Collaboration case definition criteria for anaphylaxis (levels 1, 2, or 3): 47 following Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, for a reporting rate of 4.7 cases/million doses administered, and 19 following Moderna vaccine, for a reporting rate of 2.5 cases/million doses administered, Dr. Shimabukuro and CDC colleagues wrote.
The CDC has published materials to help clinicians prepare for the possibility of this rare event, Dr. Shimabukuro told the FDA advisers.
“The take-home message here is that these are rare events and anaphylaxis, although clinically serious, is treatable,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
At the conclusion of the meeting, FDA panelist Patrick Moore, MD, MPH, from the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania, stressed the need to convey to the public that the COVID vaccines appear so far to be safe. Many people earlier had doubts about how the FDA could both safely and quickly review the applications for EUAs for these products.
“As of February 26, things are looking good. That could change tomorrow,” Dr. Moore said. But “this whole EUA process does seem to have worked, despite my own personal concerns about it.”
No second-class vaccines
The Johnson & Johnson vaccine, known as Ad26.COV2.S, is composed of a recombinant, replication-incompetent human adenovirus type 26 (Ad26) vector. It’s intended to encode a stabilized form of SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein. The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use a different mechanism. They rely on mRNA.
The FDA advisers also discussed how patients might respond to the widely reported gap between Janssen’s topline efficacy rates compared with rivals. They urged against people parsing study details too finely and seeking to pick and choose their shots.
“It’s important that people do not think that one vaccine is better than another,” said FDA adviser H. Cody Meissner, MD, from Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston.
Dr. Monto agreed, noting that many people in the United States are still waiting for their turn to get COVID vaccines because of the limited early supply.
Trying to game the system to get one vaccine instead of another would not be wise. “In this environment, whatever you can get, get,” Dr. Monto said.
During an open public hearing, Sarah Christopherson, policy advocacy director of the National Women’s Health Network, said that press reports are fueling a damaging impression in the public that there are “first and second-class” vaccines.
“That has the potential to exacerbate existing mistrust” in vaccines, she said. “Public health authorities must address these perceptions head on.”
She urged against attempts to compare the Janssen vaccine to others, noting the potential effects of emerging variants of the virus.
“It’s difficult to make an apples-to-apples comparison between vaccines,” she said.
Johnson & Johnson’s efficacy results, which are lower than those of the mRNA vaccines, may be a reflection of the ways in which SARS-Co-V-2 is mutating and thus becoming more of a threat, according to the company. A key study of the new vaccine, involving about 44,000 people, coincided with the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, which were emerging in some of the countries where the pivotal COV3001 study was being conducted, the company said.
At least 14 days after vaccination, the Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine efficacy (95% confidence interval) was 72.0% (58.2, 81.7) in the United States, 68.1% (48.8, 80.7) in Brazil, and 64.0% (41.2, 78.7) in South Africa.
Weakened standards?
Several researchers called on the FDA to maintain a critical attitude when assessing Johnson & Johnson’s application for the EUA, warning of a potential for a permanent erosion of agency rules due to hasty action on COVID vaccines.
They raised concerns about the FDA demanding too little in terms of follow-up studies on COVID vaccines and with persisting murkiness resulting in attempts to determine how well these treatments work beyond the initial study period.
“I worry about FDA lowering its approval standards,” said Peter Doshi, PhD, from The BMJ and a faculty member at the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, during an open public hearing at the meeting.
“There’s a real urgency to stand back right now and look at the forest here, as well as the trees, and I urge the committee to consider the effects FDA decisions may have on the entire regulatory approval process,” Dr. Doshi said.
Dr. Doshi asked why Johnson & Johnson did not seek a standard full approval — a biologics license application (BLA) — instead of aiming for the lower bar of an EUA. The FDA already has allowed wide distribution of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines through EUAs. That removes the sense of urgency that FDA faced last year in his view.
The FDA’s June 2020 guidance on the development of COVID vaccines had asked drugmakers to plan on following participants in COVID vaccine trials for “ideally at least one to two years.” Yet people who got placebo in Moderna and Pfizer trials already are being vaccinated, Dr. Doshi said. And Johnson & Johnson said in its presentation to the FDA that if the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine were granted an EUA, the COV3001 study design would be amended to “facilitate cross-over of placebo participants in all participating countries to receive one dose of active study vaccine as fast as operationally feasible.”
“I’m nervous about the prospect of there never being a COVID vaccine that meets the FDA’s approval standard” for a BLA instead of the more limited EUA, Dr. Doshi said.
Diana Zuckerman, PhD, president of the nonprofit National Center for Health Research, noted that the FDA’s subsequent guidance tailored for EUAs for COVID vaccines “drastically shortened” the follow-up time to a median of 2 months. Dr. Zuckerman said that a crossover design would be “a reasonable compromise, but only if the placebo group has at least 6 months of data.” Dr. Zuckerman opened her remarks in the open public hearing by saying she had inherited Johnson & Johnson stock, so was speaking at the meeting against her own financial interest.
“As soon as a vaccine is authorized, we start losing the placebo group. If FDA lets that happen, that’s a huge loss for public health and a huge loss of information about how we can all stay safe,” Dr. Zuckerman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How to convince patients muscle pain isn’t a statin Achilles heel: StatinWISE
Another randomized trial, on the heels of the recently published SAMSON, has concluded – many would say confirmed – that .
Affected patients who sorely doubt that conclusion might possibly embrace statins, researchers say, if the new trial’s creative methodology could somehow be applied to them in clinical practice.
The recent SAMSON trial made waves in November 2020 by concluding, with some caveats, that about 90% of the burden of muscle symptoms reported by patients on statins may be attributable to a nocebo effect; that is, they are attributed to the drugs – perhaps because of negative expectations – but not actually caused by them.
The new trial, StatinWISE (Statin Web-based Investigation of Side Effects), triple the size but similar in design and conducted parallel to SAMSON, similarly saw no important differences in patient-reported muscle symptom prevalence or severity during administration of atorvastatin 20 mg/day or placebo, in withdrawal from the study because of such symptoms, or in patient quality of life.
The findings also support years of observational evidence that argues against a statin effect on muscle symptoms except in rare cases of confirmed myopathy, as well as results from randomized trials like ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE and GAUSS-3, in which significant muscle symptoms in “statin-intolerant” patients were unusual, note StatinWISE investigators in their report, published online Feb. 24 in BMJ, with lead author Emily Herrett, MSc, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“I’m hoping it can change minds a bit and reassure people. That was part of the reason we did it, to inform this debate about harms and benefits of statins,” principal investigator Liam Smeeth, MBChB, MSc, PhD, from the same institution, said during a virtual press conference on the trial conducted by the U.K. nonprofit Science Media Centre.
“In thinking through whether to take a statin or not, people can be reassured that these muscle symptoms are rare; they aren’t common. Aches and pains are common, but are not caused by statins,” said Dr. Smeeth, who is senior author on the trial publication.
Another goal of the 200-patient study, he said, was to explore whether patients who had experienced muscle symptoms on a statin but were willing to explore whether the statin was to blame could be convinced – depending on what they learned in the trial – to stay on the drugs.
It seemed to work; two-thirds of the participants who finished the study “decided that they would actually want to try starting statins again, which was quite amazing.”
But there was a “slight caveat,” Dr. Smeeth observed. “To join our trial, yes, you had to have had a bad experience with statins, but you probably had to be a little bit open to the idea of trying them again. So, I can’t claim that that two-thirds would apply to everybody in the population.”
Because StatinWISE entered only patients who had reported severe muscle symptoms on a statin but hadn’t showed significant enzymatic evidence of myopathy, all had either taken themselves off the statin or were “considering” it. And the study had excluded anyone with “persistent, generalized, unexplained muscle pain” regardless of any statin therapy.
“This was very deliberately a select group of people who had serious problems taking statins. This was not a random sample by any means,” Dr. Smeeth said.
“The patients in the study were willing to participate and take statins again,” suggesting they “may not be completely representative of all those who believe they experience side effects with statins, as anyone who refused to take statins ever again would not have been recruited,” observed Tim Chico, MBChB, MD, University of Sheffield (England) in a Science Media Centre press release on StatinWISE.
Still, even among this “supersaturated group of people” selected for having had muscle symptoms on statins, Dr. Smeeth said at the briefing, “in almost all cases, their pains and aches were no worse on statins than they were on placebo. We’re not saying that anyone is making up their aches and pains. These are real aches and pains. What we’re showing very clearly is that those aches and pains are no worse on statins than they are on placebo.”
Rechallenge is possible
Some people are more likely than others to experience adverse reactions to any drug, “and that’s true of statins,” Neil J. Stone, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization. But StatinWISE underscores that many patients with muscle symptoms on the drugs can be convinced to continue with them rather than stop them entirely.
“The study didn’t say that everybody who has symptoms on a statin is having a nocebo effect,” said Dr. Stone, vice chair for the multisociety 2018 Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol, who was not involved with StatinWISE.
“It simply said,” allowing for some caveats, “that a significant number of patients may have symptoms that don’t preclude them from being rechallenged with a statin again, once they understand what this nocebo effect is.”
And, Dr. Stone said, “it amplifies the 2018 guidelines, with their emphasis on the clinician-patient discussion before starting therapy,” by showing that statin-associated muscle pain isn’t necessarily caused by the drugs and isn’t a reason to stop them.
“That there is a second study confirming SAMSON is helpful, and the results are helpful because they say many of these patients, once they are shown the results, can be rechallenged and will then tolerate statins,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“They were able to get two-thirds of those completing the trial into long-term treatment, which I think is obviously very admirable and very important,” said Dr. Nissen, who was GAUSS-3 principal investigator but not associated with StatinWISE.
“I think it is important, however, that we not completely dismiss patients who complain of adverse effects. Because, in fact, there probably are some people who do have muscle-related symptoms,” he said. “But you know, to really call somebody statin intolerant, they really should fail three statins, which would be a very good standard.”
In his experience, said Patrick M. Moriarty, MD, who directs the Atherosclerosis & Lipoprotein-Apheresis Center at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, perhaps 80%-90% of patients who believe they are statin intolerant because of muscle symptoms are actually not statin intolerant at all.
“I think a massive amount of it is supratentorial,” Dr. Moriarty, who was not part of StatinWISE, told this news organization. It comes directly from “what they heard, what they read, or what they were told – and at their age, they’re going to have aches and pains.”
Value of the n-of-1 trial
Dr. Smeeth and colleagues framed StatinWISE in part as a test of a strategy for overcoming nocebo-based aversion to statins. One goal was to see whether these methods might be helpful in practice for convincing patients who want to reject statins because of muscle symptoms to give the drugs another chance.
In StatinWISE, patients were individually assigned to take atorvastatin or placebo in randomized order with multiple blinding during each of six successive 2-month periods, so that they were on one or the other agent half the time. They rated their symptoms at the end of each period.
So the trial in composite was, as the publication states, “a series of randomized, placebo-controlled n-of-1 trials.” SAMSON followed a similar scheme, except – as previously reported – it had specified 4 months of atorvastatin, 4 months of placebo, and 4 months with patients on neither statin nor placebo.
StatinWISE “provides a useful approach (the n = 1 study) that could be used in real life to help patients understand the cause of their own possible side effects, which could also be applied to medications other than statins,” Dr. Chico added in the Science Media Centre release.
“I often encounter people who have a firmly held view that statins cause muscle pains, even when they haven’t taken these medications themselves, and I hope that this study may help change this view and make them willing to try such an ‘experiment,’ ” he said.
Others aren’t sure an experiment resembling an n-of-1 trial would be practical or effective when conducted in routine practice.
More efficient and useful, Dr. Moriarty noted, would be for physicians to nurture a close relationship with patients, one that could help transform their negative feelings about statins into a willingness to accept the drugs. “This is a trust you have to build; these are human beings.”
He said getting the patient’s confidence is critical. “You have to explain the pluses and minuses of getting treatment, of the 30% reduction in cardiovascular events that occur with the statin. You don’t go ‘testing this and that.’ I think it’s more about getting them on board.”
No statin effect on muscle symptoms
Patients in StatinWISE were recruited from 50 primary care practices in England and Wales from December 2016 to April 2018, the report notes; their mean age was 69 years, and 58% were men. Of the 200 patients, 151 recorded muscle-symptom scores for at least one statin period and one placebo period, and so were included in the primary-endpoint assessment.
The mean muscle symptom score was lower on statin therapy than on placebo (1.68 vs. 2.57), but there was no significant difference in adjusted analysis (mean difference, –0.11 (95% confidence interval, –0.36 to 0.14; P = .40).
Statins showed no significant effect on development of muscle symptoms overall, it was reported, with an odds ratio of 1.11 (99% confidence interval, 0.62-1.99). Nor was there an effect on “muscle symptoms that could not be attributed to another cause,” (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.77-1.94).
Of the 80 withdrawals during the study for any reason, 43% occurred when the patient was on the statin, 49% when the patient was on placebo, and 9% after randomization but before either statin or placebo had been initiated. Of those, 33 were because of “intolerable muscle symptoms,” says the report. But withdrawal occurred about as often on statin therapy as off the drug – 9% and 7%, respectively – throughout the 1-year study.
“This study provides further evidence through the lived experience of individuals that muscle pains often attributed to statins are not due to the drug,” said Sir Nilesh J. Samani, MBChB, MD, medical director for the British Heart Foundation, as quoted in the Science Media Centre press release.
“The use of each patient as their own control in the trial provides a powerful way of distinguishing the effect of a statin from that of taking a pill,” he said. “The findings should give confidence to patients who may be concerned about taking statins.”
StatinWISE was funded by the National Institute for Health Research-Health Technology Program and sponsored by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. The authors declare that they have “no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.” Dr. Smeeth reports receiving grants from GlaxoSmithKline, and personal fees for advisory work from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Stone reports no industry relationships or other disclosures. Dr. Nissen reports that his center has received funding for clinical trials from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Cerenis, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Medtronic, MyoKardia, Novartis, Orexigen, Pfizer, Takeda, The Medicines Company, and Silence Therapeutics; that he is involved in these trials but receives no personal remuneration; and that he consults for many pharmaceutical companies but requires them to donate all honoraria or fees directly to charity so that he receives neither income nor a tax deduction. Dr. Chico had no conflicts. Dr. Moriarty declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Samani had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Another randomized trial, on the heels of the recently published SAMSON, has concluded – many would say confirmed – that .
Affected patients who sorely doubt that conclusion might possibly embrace statins, researchers say, if the new trial’s creative methodology could somehow be applied to them in clinical practice.
The recent SAMSON trial made waves in November 2020 by concluding, with some caveats, that about 90% of the burden of muscle symptoms reported by patients on statins may be attributable to a nocebo effect; that is, they are attributed to the drugs – perhaps because of negative expectations – but not actually caused by them.
The new trial, StatinWISE (Statin Web-based Investigation of Side Effects), triple the size but similar in design and conducted parallel to SAMSON, similarly saw no important differences in patient-reported muscle symptom prevalence or severity during administration of atorvastatin 20 mg/day or placebo, in withdrawal from the study because of such symptoms, or in patient quality of life.
The findings also support years of observational evidence that argues against a statin effect on muscle symptoms except in rare cases of confirmed myopathy, as well as results from randomized trials like ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE and GAUSS-3, in which significant muscle symptoms in “statin-intolerant” patients were unusual, note StatinWISE investigators in their report, published online Feb. 24 in BMJ, with lead author Emily Herrett, MSc, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“I’m hoping it can change minds a bit and reassure people. That was part of the reason we did it, to inform this debate about harms and benefits of statins,” principal investigator Liam Smeeth, MBChB, MSc, PhD, from the same institution, said during a virtual press conference on the trial conducted by the U.K. nonprofit Science Media Centre.
“In thinking through whether to take a statin or not, people can be reassured that these muscle symptoms are rare; they aren’t common. Aches and pains are common, but are not caused by statins,” said Dr. Smeeth, who is senior author on the trial publication.
Another goal of the 200-patient study, he said, was to explore whether patients who had experienced muscle symptoms on a statin but were willing to explore whether the statin was to blame could be convinced – depending on what they learned in the trial – to stay on the drugs.
It seemed to work; two-thirds of the participants who finished the study “decided that they would actually want to try starting statins again, which was quite amazing.”
But there was a “slight caveat,” Dr. Smeeth observed. “To join our trial, yes, you had to have had a bad experience with statins, but you probably had to be a little bit open to the idea of trying them again. So, I can’t claim that that two-thirds would apply to everybody in the population.”
Because StatinWISE entered only patients who had reported severe muscle symptoms on a statin but hadn’t showed significant enzymatic evidence of myopathy, all had either taken themselves off the statin or were “considering” it. And the study had excluded anyone with “persistent, generalized, unexplained muscle pain” regardless of any statin therapy.
“This was very deliberately a select group of people who had serious problems taking statins. This was not a random sample by any means,” Dr. Smeeth said.
“The patients in the study were willing to participate and take statins again,” suggesting they “may not be completely representative of all those who believe they experience side effects with statins, as anyone who refused to take statins ever again would not have been recruited,” observed Tim Chico, MBChB, MD, University of Sheffield (England) in a Science Media Centre press release on StatinWISE.
Still, even among this “supersaturated group of people” selected for having had muscle symptoms on statins, Dr. Smeeth said at the briefing, “in almost all cases, their pains and aches were no worse on statins than they were on placebo. We’re not saying that anyone is making up their aches and pains. These are real aches and pains. What we’re showing very clearly is that those aches and pains are no worse on statins than they are on placebo.”
Rechallenge is possible
Some people are more likely than others to experience adverse reactions to any drug, “and that’s true of statins,” Neil J. Stone, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization. But StatinWISE underscores that many patients with muscle symptoms on the drugs can be convinced to continue with them rather than stop them entirely.
“The study didn’t say that everybody who has symptoms on a statin is having a nocebo effect,” said Dr. Stone, vice chair for the multisociety 2018 Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol, who was not involved with StatinWISE.
“It simply said,” allowing for some caveats, “that a significant number of patients may have symptoms that don’t preclude them from being rechallenged with a statin again, once they understand what this nocebo effect is.”
And, Dr. Stone said, “it amplifies the 2018 guidelines, with their emphasis on the clinician-patient discussion before starting therapy,” by showing that statin-associated muscle pain isn’t necessarily caused by the drugs and isn’t a reason to stop them.
“That there is a second study confirming SAMSON is helpful, and the results are helpful because they say many of these patients, once they are shown the results, can be rechallenged and will then tolerate statins,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“They were able to get two-thirds of those completing the trial into long-term treatment, which I think is obviously very admirable and very important,” said Dr. Nissen, who was GAUSS-3 principal investigator but not associated with StatinWISE.
“I think it is important, however, that we not completely dismiss patients who complain of adverse effects. Because, in fact, there probably are some people who do have muscle-related symptoms,” he said. “But you know, to really call somebody statin intolerant, they really should fail three statins, which would be a very good standard.”
In his experience, said Patrick M. Moriarty, MD, who directs the Atherosclerosis & Lipoprotein-Apheresis Center at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, perhaps 80%-90% of patients who believe they are statin intolerant because of muscle symptoms are actually not statin intolerant at all.
“I think a massive amount of it is supratentorial,” Dr. Moriarty, who was not part of StatinWISE, told this news organization. It comes directly from “what they heard, what they read, or what they were told – and at their age, they’re going to have aches and pains.”
Value of the n-of-1 trial
Dr. Smeeth and colleagues framed StatinWISE in part as a test of a strategy for overcoming nocebo-based aversion to statins. One goal was to see whether these methods might be helpful in practice for convincing patients who want to reject statins because of muscle symptoms to give the drugs another chance.
In StatinWISE, patients were individually assigned to take atorvastatin or placebo in randomized order with multiple blinding during each of six successive 2-month periods, so that they were on one or the other agent half the time. They rated their symptoms at the end of each period.
So the trial in composite was, as the publication states, “a series of randomized, placebo-controlled n-of-1 trials.” SAMSON followed a similar scheme, except – as previously reported – it had specified 4 months of atorvastatin, 4 months of placebo, and 4 months with patients on neither statin nor placebo.
StatinWISE “provides a useful approach (the n = 1 study) that could be used in real life to help patients understand the cause of their own possible side effects, which could also be applied to medications other than statins,” Dr. Chico added in the Science Media Centre release.
“I often encounter people who have a firmly held view that statins cause muscle pains, even when they haven’t taken these medications themselves, and I hope that this study may help change this view and make them willing to try such an ‘experiment,’ ” he said.
Others aren’t sure an experiment resembling an n-of-1 trial would be practical or effective when conducted in routine practice.
More efficient and useful, Dr. Moriarty noted, would be for physicians to nurture a close relationship with patients, one that could help transform their negative feelings about statins into a willingness to accept the drugs. “This is a trust you have to build; these are human beings.”
He said getting the patient’s confidence is critical. “You have to explain the pluses and minuses of getting treatment, of the 30% reduction in cardiovascular events that occur with the statin. You don’t go ‘testing this and that.’ I think it’s more about getting them on board.”
No statin effect on muscle symptoms
Patients in StatinWISE were recruited from 50 primary care practices in England and Wales from December 2016 to April 2018, the report notes; their mean age was 69 years, and 58% were men. Of the 200 patients, 151 recorded muscle-symptom scores for at least one statin period and one placebo period, and so were included in the primary-endpoint assessment.
The mean muscle symptom score was lower on statin therapy than on placebo (1.68 vs. 2.57), but there was no significant difference in adjusted analysis (mean difference, –0.11 (95% confidence interval, –0.36 to 0.14; P = .40).
Statins showed no significant effect on development of muscle symptoms overall, it was reported, with an odds ratio of 1.11 (99% confidence interval, 0.62-1.99). Nor was there an effect on “muscle symptoms that could not be attributed to another cause,” (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.77-1.94).
Of the 80 withdrawals during the study for any reason, 43% occurred when the patient was on the statin, 49% when the patient was on placebo, and 9% after randomization but before either statin or placebo had been initiated. Of those, 33 were because of “intolerable muscle symptoms,” says the report. But withdrawal occurred about as often on statin therapy as off the drug – 9% and 7%, respectively – throughout the 1-year study.
“This study provides further evidence through the lived experience of individuals that muscle pains often attributed to statins are not due to the drug,” said Sir Nilesh J. Samani, MBChB, MD, medical director for the British Heart Foundation, as quoted in the Science Media Centre press release.
“The use of each patient as their own control in the trial provides a powerful way of distinguishing the effect of a statin from that of taking a pill,” he said. “The findings should give confidence to patients who may be concerned about taking statins.”
StatinWISE was funded by the National Institute for Health Research-Health Technology Program and sponsored by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. The authors declare that they have “no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.” Dr. Smeeth reports receiving grants from GlaxoSmithKline, and personal fees for advisory work from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Stone reports no industry relationships or other disclosures. Dr. Nissen reports that his center has received funding for clinical trials from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Cerenis, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Medtronic, MyoKardia, Novartis, Orexigen, Pfizer, Takeda, The Medicines Company, and Silence Therapeutics; that he is involved in these trials but receives no personal remuneration; and that he consults for many pharmaceutical companies but requires them to donate all honoraria or fees directly to charity so that he receives neither income nor a tax deduction. Dr. Chico had no conflicts. Dr. Moriarty declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Samani had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Another randomized trial, on the heels of the recently published SAMSON, has concluded – many would say confirmed – that .
Affected patients who sorely doubt that conclusion might possibly embrace statins, researchers say, if the new trial’s creative methodology could somehow be applied to them in clinical practice.
The recent SAMSON trial made waves in November 2020 by concluding, with some caveats, that about 90% of the burden of muscle symptoms reported by patients on statins may be attributable to a nocebo effect; that is, they are attributed to the drugs – perhaps because of negative expectations – but not actually caused by them.
The new trial, StatinWISE (Statin Web-based Investigation of Side Effects), triple the size but similar in design and conducted parallel to SAMSON, similarly saw no important differences in patient-reported muscle symptom prevalence or severity during administration of atorvastatin 20 mg/day or placebo, in withdrawal from the study because of such symptoms, or in patient quality of life.
The findings also support years of observational evidence that argues against a statin effect on muscle symptoms except in rare cases of confirmed myopathy, as well as results from randomized trials like ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE and GAUSS-3, in which significant muscle symptoms in “statin-intolerant” patients were unusual, note StatinWISE investigators in their report, published online Feb. 24 in BMJ, with lead author Emily Herrett, MSc, PhD, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“I’m hoping it can change minds a bit and reassure people. That was part of the reason we did it, to inform this debate about harms and benefits of statins,” principal investigator Liam Smeeth, MBChB, MSc, PhD, from the same institution, said during a virtual press conference on the trial conducted by the U.K. nonprofit Science Media Centre.
“In thinking through whether to take a statin or not, people can be reassured that these muscle symptoms are rare; they aren’t common. Aches and pains are common, but are not caused by statins,” said Dr. Smeeth, who is senior author on the trial publication.
Another goal of the 200-patient study, he said, was to explore whether patients who had experienced muscle symptoms on a statin but were willing to explore whether the statin was to blame could be convinced – depending on what they learned in the trial – to stay on the drugs.
It seemed to work; two-thirds of the participants who finished the study “decided that they would actually want to try starting statins again, which was quite amazing.”
But there was a “slight caveat,” Dr. Smeeth observed. “To join our trial, yes, you had to have had a bad experience with statins, but you probably had to be a little bit open to the idea of trying them again. So, I can’t claim that that two-thirds would apply to everybody in the population.”
Because StatinWISE entered only patients who had reported severe muscle symptoms on a statin but hadn’t showed significant enzymatic evidence of myopathy, all had either taken themselves off the statin or were “considering” it. And the study had excluded anyone with “persistent, generalized, unexplained muscle pain” regardless of any statin therapy.
“This was very deliberately a select group of people who had serious problems taking statins. This was not a random sample by any means,” Dr. Smeeth said.
“The patients in the study were willing to participate and take statins again,” suggesting they “may not be completely representative of all those who believe they experience side effects with statins, as anyone who refused to take statins ever again would not have been recruited,” observed Tim Chico, MBChB, MD, University of Sheffield (England) in a Science Media Centre press release on StatinWISE.
Still, even among this “supersaturated group of people” selected for having had muscle symptoms on statins, Dr. Smeeth said at the briefing, “in almost all cases, their pains and aches were no worse on statins than they were on placebo. We’re not saying that anyone is making up their aches and pains. These are real aches and pains. What we’re showing very clearly is that those aches and pains are no worse on statins than they are on placebo.”
Rechallenge is possible
Some people are more likely than others to experience adverse reactions to any drug, “and that’s true of statins,” Neil J. Stone, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, told this news organization. But StatinWISE underscores that many patients with muscle symptoms on the drugs can be convinced to continue with them rather than stop them entirely.
“The study didn’t say that everybody who has symptoms on a statin is having a nocebo effect,” said Dr. Stone, vice chair for the multisociety 2018 Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol, who was not involved with StatinWISE.
“It simply said,” allowing for some caveats, “that a significant number of patients may have symptoms that don’t preclude them from being rechallenged with a statin again, once they understand what this nocebo effect is.”
And, Dr. Stone said, “it amplifies the 2018 guidelines, with their emphasis on the clinician-patient discussion before starting therapy,” by showing that statin-associated muscle pain isn’t necessarily caused by the drugs and isn’t a reason to stop them.
“That there is a second study confirming SAMSON is helpful, and the results are helpful because they say many of these patients, once they are shown the results, can be rechallenged and will then tolerate statins,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“They were able to get two-thirds of those completing the trial into long-term treatment, which I think is obviously very admirable and very important,” said Dr. Nissen, who was GAUSS-3 principal investigator but not associated with StatinWISE.
“I think it is important, however, that we not completely dismiss patients who complain of adverse effects. Because, in fact, there probably are some people who do have muscle-related symptoms,” he said. “But you know, to really call somebody statin intolerant, they really should fail three statins, which would be a very good standard.”
In his experience, said Patrick M. Moriarty, MD, who directs the Atherosclerosis & Lipoprotein-Apheresis Center at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, perhaps 80%-90% of patients who believe they are statin intolerant because of muscle symptoms are actually not statin intolerant at all.
“I think a massive amount of it is supratentorial,” Dr. Moriarty, who was not part of StatinWISE, told this news organization. It comes directly from “what they heard, what they read, or what they were told – and at their age, they’re going to have aches and pains.”
Value of the n-of-1 trial
Dr. Smeeth and colleagues framed StatinWISE in part as a test of a strategy for overcoming nocebo-based aversion to statins. One goal was to see whether these methods might be helpful in practice for convincing patients who want to reject statins because of muscle symptoms to give the drugs another chance.
In StatinWISE, patients were individually assigned to take atorvastatin or placebo in randomized order with multiple blinding during each of six successive 2-month periods, so that they were on one or the other agent half the time. They rated their symptoms at the end of each period.
So the trial in composite was, as the publication states, “a series of randomized, placebo-controlled n-of-1 trials.” SAMSON followed a similar scheme, except – as previously reported – it had specified 4 months of atorvastatin, 4 months of placebo, and 4 months with patients on neither statin nor placebo.
StatinWISE “provides a useful approach (the n = 1 study) that could be used in real life to help patients understand the cause of their own possible side effects, which could also be applied to medications other than statins,” Dr. Chico added in the Science Media Centre release.
“I often encounter people who have a firmly held view that statins cause muscle pains, even when they haven’t taken these medications themselves, and I hope that this study may help change this view and make them willing to try such an ‘experiment,’ ” he said.
Others aren’t sure an experiment resembling an n-of-1 trial would be practical or effective when conducted in routine practice.
More efficient and useful, Dr. Moriarty noted, would be for physicians to nurture a close relationship with patients, one that could help transform their negative feelings about statins into a willingness to accept the drugs. “This is a trust you have to build; these are human beings.”
He said getting the patient’s confidence is critical. “You have to explain the pluses and minuses of getting treatment, of the 30% reduction in cardiovascular events that occur with the statin. You don’t go ‘testing this and that.’ I think it’s more about getting them on board.”
No statin effect on muscle symptoms
Patients in StatinWISE were recruited from 50 primary care practices in England and Wales from December 2016 to April 2018, the report notes; their mean age was 69 years, and 58% were men. Of the 200 patients, 151 recorded muscle-symptom scores for at least one statin period and one placebo period, and so were included in the primary-endpoint assessment.
The mean muscle symptom score was lower on statin therapy than on placebo (1.68 vs. 2.57), but there was no significant difference in adjusted analysis (mean difference, –0.11 (95% confidence interval, –0.36 to 0.14; P = .40).
Statins showed no significant effect on development of muscle symptoms overall, it was reported, with an odds ratio of 1.11 (99% confidence interval, 0.62-1.99). Nor was there an effect on “muscle symptoms that could not be attributed to another cause,” (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.77-1.94).
Of the 80 withdrawals during the study for any reason, 43% occurred when the patient was on the statin, 49% when the patient was on placebo, and 9% after randomization but before either statin or placebo had been initiated. Of those, 33 were because of “intolerable muscle symptoms,” says the report. But withdrawal occurred about as often on statin therapy as off the drug – 9% and 7%, respectively – throughout the 1-year study.
“This study provides further evidence through the lived experience of individuals that muscle pains often attributed to statins are not due to the drug,” said Sir Nilesh J. Samani, MBChB, MD, medical director for the British Heart Foundation, as quoted in the Science Media Centre press release.
“The use of each patient as their own control in the trial provides a powerful way of distinguishing the effect of a statin from that of taking a pill,” he said. “The findings should give confidence to patients who may be concerned about taking statins.”
StatinWISE was funded by the National Institute for Health Research-Health Technology Program and sponsored by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. The authors declare that they have “no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.” Dr. Smeeth reports receiving grants from GlaxoSmithKline, and personal fees for advisory work from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Stone reports no industry relationships or other disclosures. Dr. Nissen reports that his center has received funding for clinical trials from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Cerenis, Eli Lilly, Esperion, Medtronic, MyoKardia, Novartis, Orexigen, Pfizer, Takeda, The Medicines Company, and Silence Therapeutics; that he is involved in these trials but receives no personal remuneration; and that he consults for many pharmaceutical companies but requires them to donate all honoraria or fees directly to charity so that he receives neither income nor a tax deduction. Dr. Chico had no conflicts. Dr. Moriarty declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Samani had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocardial injury seen on MRI in 54% of recovered COVID-19 patients
About half of 148 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and elevated troponin levels had at least some evidence of myocardial injury on cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging 2 months later, a new study shows.
“Our results demonstrate that in this subset of patients surviving severe COVID-19 and with troponin elevation, ongoing localized myocardial inflammation, whilst less frequent than previously reported, remains present in a proportion of patients and may represent an emerging issue of clinical relevance,” wrote Marianna Fontana, MD, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues.
The cardiac abnormalities identified were classified as nonischemic (including “myocarditis-like” late gadolinium enhancement [LGE]) in 26% of the cohort; as related to ischemic heart disease (infarction or inducible ischemia) in 22%; and as dual pathology in 6%.
Left ventricular (LV) function was normal in 89% of the 148 patients. In the 17 patients (11%) with LV dysfunction, only four had an ejection fraction below 35%. Of the nine patients whose LV dysfunction was related to myocardial infarction, six had a known history of ischemic heart disease.
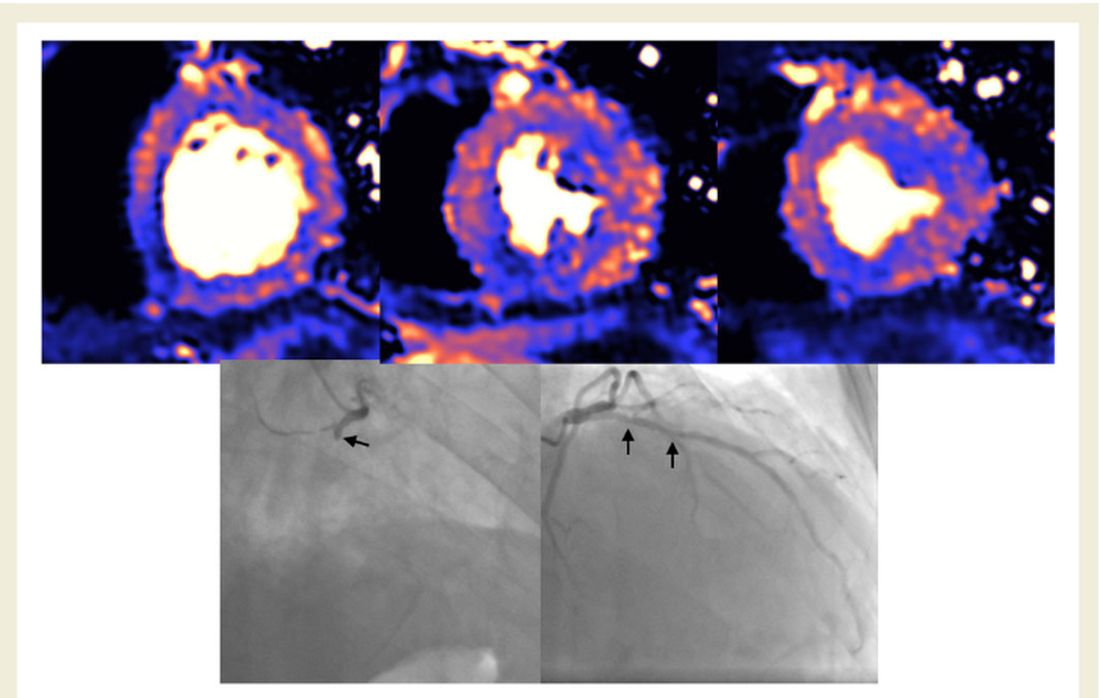
No patients with “myocarditis-pattern” LGE had regional wall motion abnormalities, and neither admission nor peak troponin values were predictive of the diagnosis of myocarditis.
The results were published online Feb. 18 in the European Heart Journal.
Glass half full
Taking a “glass half full” approach, co–senior author Graham D. Cole, MD, PhD, noted on Twitter that nearly half the patients had no major cardiac abnormalities on CMR just 2 months after a bout with troponin-positive COVID-19.
“We think this is important: Even in a group who had been very sick with raised troponin, it was common to find no evidence of heart damage,” said Dr. Cole, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust.
“We believe our data challenge the hypothesis that chronic inflammation, diffuse fibrosis, or long-term LV dysfunction is a dominant feature in those surviving COVID-19,” the investigators concluded in their report.
In an interview, Dr. Fontana explained further: “It has been reported in an early ‘pathfinder’ study that two-thirds of patients recovered from COVID-19 had CMR evidence of abnormal findings with a high incidence of elevated T1 and T2 in keeping with diffuse fibrosis and edema. Our findings with a larger, multicenter study and better controls show low rates of heart impairment and much less ongoing inflammation, which is reassuring.”
She also noted that the different patterns of injury suggest that different mechanisms are at play, including the possibility that “at least some of the found damage might have been preexisting, because people with heart damage are more likely to get severe disease.”
The investigators, including first author Tushar Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, also noted that myocarditis-like injury was limited to three or fewer myocardial segments in 88% of cases with no associated ventricular dysfunction, and that biventricular function was no different than in those without myocarditis.
“We use the word ‘myocarditis-like’ but we don’t have histology,” Dr. Fontana said. “Our group actually suspects a lot of this will be microvascular clotting (microangiopathic thrombosis). This is exciting, as newer anticoagulation strategies – for example, those being tried in RECOVERY – may have benefit.”
Aloke V. Finn, MD, of the CVPath Institute in Gaithersburg, Md., wishes researchers would stop using the term myocarditis altogether to describe clinical or imaging findings in COVID-19.
“MRI can’t diagnose myocarditis. It is a specific diagnosis that requires, ideally, histology, as the investigators acknowledged,” Dr. Finn said in an interview.
His group at CVPath recently published data showing pathologic evidence of myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection, as reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
“As a clinician, when I think of myocarditis, I look at the echo and an LV gram, and I see if there is a wall motion abnormality and troponin elevation, but with normal coronary arteries. And if all that is there, then I think about myocarditis in my differential diagnosis,” he said. “But in most of these cases, as the authors rightly point out, most patients did not have what is necessary to really entertain a diagnosis of myocarditis.”
He agreed with Dr. Fontana’s suggestion that what the CMR might be picking up in these survivors is microthrombi, as his group saw in their recent autopsy study.
“It’s very possible these findings are concordant with the recent autopsy studies done by my group and others in terms of detecting the presence of microthrombi, but we don’t know this for certain because no one has ever studied this entity before in the clinic and we don’t really know how microthrombi might appear on CMR.”
Largest study to date
The 148 participants (mean age, 64 years; 70% male) in the largest study to date to investigate convalescing COVID-19 patients who had elevated troponins – something identified early in the pandemic as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 – were treated at one of six hospitals in London.
Patients who had abnormal troponin levels were offered an MRI scan of the heart after discharge and were compared with those from a control group of patients who had not had COVID-19 and with 40 healthy volunteers.
Median length of stay was 9 days, and 32% of patients required ventilatory support in the intensive care unit.
Just over half the patients (57%) had hypertension, 7% had had a previous myocardial infarction, 34% had diabetes, 46% had hypercholesterolemia, and 24% were smokers. Mean body mass index was 28.5 kg/m2.
CMR follow-up was conducted a median of 68 days after confirmation of a COVID-19 diagnosis.
On Twitter, Dr. Cole noted that the findings are subject to both survivor bias and referral bias. “We didn’t scan frail patients where the clinician felt [CMR] was unlikely to inform management.”
The findings, said Dr. Fontana, “say nothing about what happens to people who are not hospitalized with COVID, or those who are hospitalized but without elevated troponin.”
What they do offer, particularly if replicated, is a way forward in identifying patients at higher or lower risk for long-term sequelae and inform strategies that could improve outcomes, she added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About half of 148 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and elevated troponin levels had at least some evidence of myocardial injury on cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging 2 months later, a new study shows.
“Our results demonstrate that in this subset of patients surviving severe COVID-19 and with troponin elevation, ongoing localized myocardial inflammation, whilst less frequent than previously reported, remains present in a proportion of patients and may represent an emerging issue of clinical relevance,” wrote Marianna Fontana, MD, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues.
The cardiac abnormalities identified were classified as nonischemic (including “myocarditis-like” late gadolinium enhancement [LGE]) in 26% of the cohort; as related to ischemic heart disease (infarction or inducible ischemia) in 22%; and as dual pathology in 6%.
Left ventricular (LV) function was normal in 89% of the 148 patients. In the 17 patients (11%) with LV dysfunction, only four had an ejection fraction below 35%. Of the nine patients whose LV dysfunction was related to myocardial infarction, six had a known history of ischemic heart disease.

No patients with “myocarditis-pattern” LGE had regional wall motion abnormalities, and neither admission nor peak troponin values were predictive of the diagnosis of myocarditis.
The results were published online Feb. 18 in the European Heart Journal.
Glass half full
Taking a “glass half full” approach, co–senior author Graham D. Cole, MD, PhD, noted on Twitter that nearly half the patients had no major cardiac abnormalities on CMR just 2 months after a bout with troponin-positive COVID-19.
“We think this is important: Even in a group who had been very sick with raised troponin, it was common to find no evidence of heart damage,” said Dr. Cole, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust.
“We believe our data challenge the hypothesis that chronic inflammation, diffuse fibrosis, or long-term LV dysfunction is a dominant feature in those surviving COVID-19,” the investigators concluded in their report.
In an interview, Dr. Fontana explained further: “It has been reported in an early ‘pathfinder’ study that two-thirds of patients recovered from COVID-19 had CMR evidence of abnormal findings with a high incidence of elevated T1 and T2 in keeping with diffuse fibrosis and edema. Our findings with a larger, multicenter study and better controls show low rates of heart impairment and much less ongoing inflammation, which is reassuring.”
She also noted that the different patterns of injury suggest that different mechanisms are at play, including the possibility that “at least some of the found damage might have been preexisting, because people with heart damage are more likely to get severe disease.”
The investigators, including first author Tushar Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, also noted that myocarditis-like injury was limited to three or fewer myocardial segments in 88% of cases with no associated ventricular dysfunction, and that biventricular function was no different than in those without myocarditis.
“We use the word ‘myocarditis-like’ but we don’t have histology,” Dr. Fontana said. “Our group actually suspects a lot of this will be microvascular clotting (microangiopathic thrombosis). This is exciting, as newer anticoagulation strategies – for example, those being tried in RECOVERY – may have benefit.”
Aloke V. Finn, MD, of the CVPath Institute in Gaithersburg, Md., wishes researchers would stop using the term myocarditis altogether to describe clinical or imaging findings in COVID-19.
“MRI can’t diagnose myocarditis. It is a specific diagnosis that requires, ideally, histology, as the investigators acknowledged,” Dr. Finn said in an interview.
His group at CVPath recently published data showing pathologic evidence of myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection, as reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
“As a clinician, when I think of myocarditis, I look at the echo and an LV gram, and I see if there is a wall motion abnormality and troponin elevation, but with normal coronary arteries. And if all that is there, then I think about myocarditis in my differential diagnosis,” he said. “But in most of these cases, as the authors rightly point out, most patients did not have what is necessary to really entertain a diagnosis of myocarditis.”
He agreed with Dr. Fontana’s suggestion that what the CMR might be picking up in these survivors is microthrombi, as his group saw in their recent autopsy study.
“It’s very possible these findings are concordant with the recent autopsy studies done by my group and others in terms of detecting the presence of microthrombi, but we don’t know this for certain because no one has ever studied this entity before in the clinic and we don’t really know how microthrombi might appear on CMR.”
Largest study to date
The 148 participants (mean age, 64 years; 70% male) in the largest study to date to investigate convalescing COVID-19 patients who had elevated troponins – something identified early in the pandemic as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 – were treated at one of six hospitals in London.
Patients who had abnormal troponin levels were offered an MRI scan of the heart after discharge and were compared with those from a control group of patients who had not had COVID-19 and with 40 healthy volunteers.
Median length of stay was 9 days, and 32% of patients required ventilatory support in the intensive care unit.
Just over half the patients (57%) had hypertension, 7% had had a previous myocardial infarction, 34% had diabetes, 46% had hypercholesterolemia, and 24% were smokers. Mean body mass index was 28.5 kg/m2.
CMR follow-up was conducted a median of 68 days after confirmation of a COVID-19 diagnosis.
On Twitter, Dr. Cole noted that the findings are subject to both survivor bias and referral bias. “We didn’t scan frail patients where the clinician felt [CMR] was unlikely to inform management.”
The findings, said Dr. Fontana, “say nothing about what happens to people who are not hospitalized with COVID, or those who are hospitalized but without elevated troponin.”
What they do offer, particularly if replicated, is a way forward in identifying patients at higher or lower risk for long-term sequelae and inform strategies that could improve outcomes, she added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About half of 148 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and elevated troponin levels had at least some evidence of myocardial injury on cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging 2 months later, a new study shows.
“Our results demonstrate that in this subset of patients surviving severe COVID-19 and with troponin elevation, ongoing localized myocardial inflammation, whilst less frequent than previously reported, remains present in a proportion of patients and may represent an emerging issue of clinical relevance,” wrote Marianna Fontana, MD, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues.
The cardiac abnormalities identified were classified as nonischemic (including “myocarditis-like” late gadolinium enhancement [LGE]) in 26% of the cohort; as related to ischemic heart disease (infarction or inducible ischemia) in 22%; and as dual pathology in 6%.
Left ventricular (LV) function was normal in 89% of the 148 patients. In the 17 patients (11%) with LV dysfunction, only four had an ejection fraction below 35%. Of the nine patients whose LV dysfunction was related to myocardial infarction, six had a known history of ischemic heart disease.

No patients with “myocarditis-pattern” LGE had regional wall motion abnormalities, and neither admission nor peak troponin values were predictive of the diagnosis of myocarditis.
The results were published online Feb. 18 in the European Heart Journal.
Glass half full
Taking a “glass half full” approach, co–senior author Graham D. Cole, MD, PhD, noted on Twitter that nearly half the patients had no major cardiac abnormalities on CMR just 2 months after a bout with troponin-positive COVID-19.
“We think this is important: Even in a group who had been very sick with raised troponin, it was common to find no evidence of heart damage,” said Dr. Cole, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust.
“We believe our data challenge the hypothesis that chronic inflammation, diffuse fibrosis, or long-term LV dysfunction is a dominant feature in those surviving COVID-19,” the investigators concluded in their report.
In an interview, Dr. Fontana explained further: “It has been reported in an early ‘pathfinder’ study that two-thirds of patients recovered from COVID-19 had CMR evidence of abnormal findings with a high incidence of elevated T1 and T2 in keeping with diffuse fibrosis and edema. Our findings with a larger, multicenter study and better controls show low rates of heart impairment and much less ongoing inflammation, which is reassuring.”
She also noted that the different patterns of injury suggest that different mechanisms are at play, including the possibility that “at least some of the found damage might have been preexisting, because people with heart damage are more likely to get severe disease.”
The investigators, including first author Tushar Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, of the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, also noted that myocarditis-like injury was limited to three or fewer myocardial segments in 88% of cases with no associated ventricular dysfunction, and that biventricular function was no different than in those without myocarditis.
“We use the word ‘myocarditis-like’ but we don’t have histology,” Dr. Fontana said. “Our group actually suspects a lot of this will be microvascular clotting (microangiopathic thrombosis). This is exciting, as newer anticoagulation strategies – for example, those being tried in RECOVERY – may have benefit.”
Aloke V. Finn, MD, of the CVPath Institute in Gaithersburg, Md., wishes researchers would stop using the term myocarditis altogether to describe clinical or imaging findings in COVID-19.
“MRI can’t diagnose myocarditis. It is a specific diagnosis that requires, ideally, histology, as the investigators acknowledged,” Dr. Finn said in an interview.
His group at CVPath recently published data showing pathologic evidence of myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection, as reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
“As a clinician, when I think of myocarditis, I look at the echo and an LV gram, and I see if there is a wall motion abnormality and troponin elevation, but with normal coronary arteries. And if all that is there, then I think about myocarditis in my differential diagnosis,” he said. “But in most of these cases, as the authors rightly point out, most patients did not have what is necessary to really entertain a diagnosis of myocarditis.”
He agreed with Dr. Fontana’s suggestion that what the CMR might be picking up in these survivors is microthrombi, as his group saw in their recent autopsy study.
“It’s very possible these findings are concordant with the recent autopsy studies done by my group and others in terms of detecting the presence of microthrombi, but we don’t know this for certain because no one has ever studied this entity before in the clinic and we don’t really know how microthrombi might appear on CMR.”
Largest study to date
The 148 participants (mean age, 64 years; 70% male) in the largest study to date to investigate convalescing COVID-19 patients who had elevated troponins – something identified early in the pandemic as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 – were treated at one of six hospitals in London.
Patients who had abnormal troponin levels were offered an MRI scan of the heart after discharge and were compared with those from a control group of patients who had not had COVID-19 and with 40 healthy volunteers.
Median length of stay was 9 days, and 32% of patients required ventilatory support in the intensive care unit.
Just over half the patients (57%) had hypertension, 7% had had a previous myocardial infarction, 34% had diabetes, 46% had hypercholesterolemia, and 24% were smokers. Mean body mass index was 28.5 kg/m2.
CMR follow-up was conducted a median of 68 days after confirmation of a COVID-19 diagnosis.
On Twitter, Dr. Cole noted that the findings are subject to both survivor bias and referral bias. “We didn’t scan frail patients where the clinician felt [CMR] was unlikely to inform management.”
The findings, said Dr. Fontana, “say nothing about what happens to people who are not hospitalized with COVID, or those who are hospitalized but without elevated troponin.”
What they do offer, particularly if replicated, is a way forward in identifying patients at higher or lower risk for long-term sequelae and inform strategies that could improve outcomes, she added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Janssen/J&J COVID-19 vaccine cuts transmission, new data show
The single-dose vaccine reduces the risk of asymptomatic transmission by 74% at 71 days, compared with placebo, according to documents released today by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“The decrease in asymptomatic transmission is very welcome news too in curbing the spread of the virus,” Phyllis Tien, MD, told this news organization.
“While the earlier press release reported that the vaccine was effective against preventing severe COVID-19 disease, as well as hospitalizations and death, this new data shows that the vaccine can also decrease transmission, which is very important on a public health level,” said Dr. Tien, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It is extremely important in terms of getting to herd immunity,” Paul Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic and infectious disease specialist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in an interview. “It means that this vaccine is likely preventing subsequent transmission after a single dose, which could have huge implications once we get the majority of folks vaccinated.”
The FDA cautioned that the numbers of participants included in the study are relatively small and need to be verified. However, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine might not be the only product offering this advantage. Early data suggest that the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine also decreases transmission, providing further evidence that the protection offered by immunization goes beyond the individual.
The new analyses were provided by the FDA in advance of its review of the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The agency plans to fully address the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine at its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee Meeting on Friday, including evaluating its safety and efficacy.
The agency’s decision on whether or not to grant emergency use authorization (EUA) to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine could come as early as Friday evening or Saturday.
In addition to the newly released data, officials are likely to discuss phase 3 data, released Jan. 29, that reveal an 85% efficacy for the vaccine against severe COVID-19 illness globally, including data from South America, South Africa, and the United States. When the analysis was restricted to data from U.S. participants, the trial showed a 73% efficacy against moderate to severe COVID-19.
If and when the FDA grants an EUA, it remains unclear how much of the new vaccine will be immediately available. Initially, Johnson & Johnson predicted 18 million doses would be ready by the end of February, but others stated the figure will be closer to 2-4 million. The manufacturer’s contract with the U.S. government stipulates production of 100-million doses by the end of June.
Dr. Tien received support from Johnson & Johnson to conduct the J&J COVID-19 vaccine trial in the SF VA HealthCare System. Dr. Goepfert has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The single-dose vaccine reduces the risk of asymptomatic transmission by 74% at 71 days, compared with placebo, according to documents released today by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“The decrease in asymptomatic transmission is very welcome news too in curbing the spread of the virus,” Phyllis Tien, MD, told this news organization.
“While the earlier press release reported that the vaccine was effective against preventing severe COVID-19 disease, as well as hospitalizations and death, this new data shows that the vaccine can also decrease transmission, which is very important on a public health level,” said Dr. Tien, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It is extremely important in terms of getting to herd immunity,” Paul Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic and infectious disease specialist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in an interview. “It means that this vaccine is likely preventing subsequent transmission after a single dose, which could have huge implications once we get the majority of folks vaccinated.”
The FDA cautioned that the numbers of participants included in the study are relatively small and need to be verified. However, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine might not be the only product offering this advantage. Early data suggest that the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine also decreases transmission, providing further evidence that the protection offered by immunization goes beyond the individual.
The new analyses were provided by the FDA in advance of its review of the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The agency plans to fully address the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine at its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee Meeting on Friday, including evaluating its safety and efficacy.
The agency’s decision on whether or not to grant emergency use authorization (EUA) to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine could come as early as Friday evening or Saturday.
In addition to the newly released data, officials are likely to discuss phase 3 data, released Jan. 29, that reveal an 85% efficacy for the vaccine against severe COVID-19 illness globally, including data from South America, South Africa, and the United States. When the analysis was restricted to data from U.S. participants, the trial showed a 73% efficacy against moderate to severe COVID-19.
If and when the FDA grants an EUA, it remains unclear how much of the new vaccine will be immediately available. Initially, Johnson & Johnson predicted 18 million doses would be ready by the end of February, but others stated the figure will be closer to 2-4 million. The manufacturer’s contract with the U.S. government stipulates production of 100-million doses by the end of June.
Dr. Tien received support from Johnson & Johnson to conduct the J&J COVID-19 vaccine trial in the SF VA HealthCare System. Dr. Goepfert has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The single-dose vaccine reduces the risk of asymptomatic transmission by 74% at 71 days, compared with placebo, according to documents released today by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
“The decrease in asymptomatic transmission is very welcome news too in curbing the spread of the virus,” Phyllis Tien, MD, told this news organization.
“While the earlier press release reported that the vaccine was effective against preventing severe COVID-19 disease, as well as hospitalizations and death, this new data shows that the vaccine can also decrease transmission, which is very important on a public health level,” said Dr. Tien, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It is extremely important in terms of getting to herd immunity,” Paul Goepfert, MD, director of the Alabama Vaccine Research Clinic and infectious disease specialist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, said in an interview. “It means that this vaccine is likely preventing subsequent transmission after a single dose, which could have huge implications once we get the majority of folks vaccinated.”
The FDA cautioned that the numbers of participants included in the study are relatively small and need to be verified. However, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine might not be the only product offering this advantage. Early data suggest that the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine also decreases transmission, providing further evidence that the protection offered by immunization goes beyond the individual.
The new analyses were provided by the FDA in advance of its review of the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The agency plans to fully address the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine at its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee Meeting on Friday, including evaluating its safety and efficacy.
The agency’s decision on whether or not to grant emergency use authorization (EUA) to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine could come as early as Friday evening or Saturday.
In addition to the newly released data, officials are likely to discuss phase 3 data, released Jan. 29, that reveal an 85% efficacy for the vaccine against severe COVID-19 illness globally, including data from South America, South Africa, and the United States. When the analysis was restricted to data from U.S. participants, the trial showed a 73% efficacy against moderate to severe COVID-19.
If and when the FDA grants an EUA, it remains unclear how much of the new vaccine will be immediately available. Initially, Johnson & Johnson predicted 18 million doses would be ready by the end of February, but others stated the figure will be closer to 2-4 million. The manufacturer’s contract with the U.S. government stipulates production of 100-million doses by the end of June.
Dr. Tien received support from Johnson & Johnson to conduct the J&J COVID-19 vaccine trial in the SF VA HealthCare System. Dr. Goepfert has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New cases of child COVID-19 drop for fifth straight week
The fifth consecutive week with a decline has the number of new COVID-19 cases in children at its lowest level since late October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
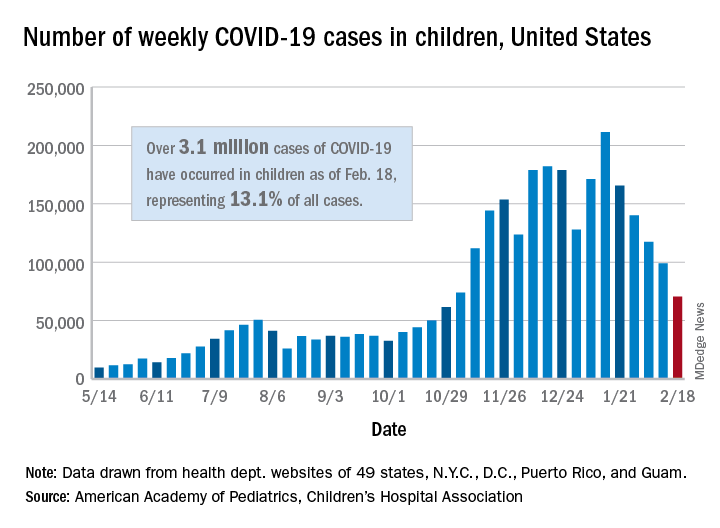
, when 61,000 cases were reported, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children is now just over 3.1 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all ages in the United States, based on data gathered from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
More children in California (439,000) have been infected than in any other state, while Illinois (176,000), Florida (145,000), Tennessee (137,000), Arizona (127,000), Ohio (121,000), and Pennsylvania (111,000) are the only other states with more than 100,000 cases, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Proportionally, the children of Wyoming have been hardest hit: Pediatric cases represent 19.4% of all cases in the state. The other four states with proportions of 18% or more are Alaska, Vermont, South Carolina, and Tennessee. Cumulative rates, however, tell a somewhat different story, as North Dakota leads with just over 8,500 cases per 100,000 children, followed by Tennessee (7,700 per 100,000) and Rhode Island (7,000 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children, which had not been following the trend of fewer new cases over the last few weeks, dropped below double digits for the first time in a month. The six deaths that occurred during the week of Feb. 12-18 bring the total to 247 since the start of the pandemic in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, according to the report.
The fifth consecutive week with a decline has the number of new COVID-19 cases in children at its lowest level since late October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

, when 61,000 cases were reported, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children is now just over 3.1 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all ages in the United States, based on data gathered from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
More children in California (439,000) have been infected than in any other state, while Illinois (176,000), Florida (145,000), Tennessee (137,000), Arizona (127,000), Ohio (121,000), and Pennsylvania (111,000) are the only other states with more than 100,000 cases, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Proportionally, the children of Wyoming have been hardest hit: Pediatric cases represent 19.4% of all cases in the state. The other four states with proportions of 18% or more are Alaska, Vermont, South Carolina, and Tennessee. Cumulative rates, however, tell a somewhat different story, as North Dakota leads with just over 8,500 cases per 100,000 children, followed by Tennessee (7,700 per 100,000) and Rhode Island (7,000 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children, which had not been following the trend of fewer new cases over the last few weeks, dropped below double digits for the first time in a month. The six deaths that occurred during the week of Feb. 12-18 bring the total to 247 since the start of the pandemic in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, according to the report.
The fifth consecutive week with a decline has the number of new COVID-19 cases in children at its lowest level since late October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

, when 61,000 cases were reported, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children is now just over 3.1 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all ages in the United States, based on data gathered from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
More children in California (439,000) have been infected than in any other state, while Illinois (176,000), Florida (145,000), Tennessee (137,000), Arizona (127,000), Ohio (121,000), and Pennsylvania (111,000) are the only other states with more than 100,000 cases, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Proportionally, the children of Wyoming have been hardest hit: Pediatric cases represent 19.4% of all cases in the state. The other four states with proportions of 18% or more are Alaska, Vermont, South Carolina, and Tennessee. Cumulative rates, however, tell a somewhat different story, as North Dakota leads with just over 8,500 cases per 100,000 children, followed by Tennessee (7,700 per 100,000) and Rhode Island (7,000 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children, which had not been following the trend of fewer new cases over the last few weeks, dropped below double digits for the first time in a month. The six deaths that occurred during the week of Feb. 12-18 bring the total to 247 since the start of the pandemic in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, according to the report.
Variants spur new FDA guidance on COVID vaccines, tests, drugs
The United States is currently facing three main variant threats, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom; B.1.351 from South Africa; and the P.1 variant, which originated in Brazil.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said on a telephone press briefing call Feb. 22 that the FDA has already been communicating with individual manufacturers as they assess the variants’ effect on their products, but these guidelines are issued for the sake of transparency and to welcome scientific input.
Tailoring may be necessary
Dr. Woodcock emphasized that, “at this time, available data suggest the FDA-authorized vaccines are effective in protecting circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2.” However, in the event the strains start to show resistance, it may be necessary to tailor the vaccine to the variant.
In that case, effectiveness of a modified vaccine should be determined by data from clinical immunogenicity studies, which would compare a recipient’s immune response with virus variants induced by the modified vaccine against the immune response to the authorized vaccine, the guidance states.
Manufacturers should also study the vaccine in both nonvaccinated people and people fully vaccinated with the authorized vaccine, according to the guidance.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said on the call that the clinical immunogenicity data is needed to understand, for instance, whether a new vaccine strain is able to cover the new and old strain or whether it just covers the new strain. Information is also needed to understand whether the modified vaccine, when given to someone fully vaccinated, will still promote a positive response without introducing safety concerns.
Further discussions will be necessary to decide whether future modified vaccines may be authorized without the need for clinical studies.
Variants and testing
The FDA’s updated guidance for test developers, Policy for Evaluating Impact of Viral Mutations on COVID-19 Tests, includes information that test performance can be influenced by the sequence of the variant, prevalence of the variant in the population, or design of the test. For example, molecular tests designed to detect multiple SARS-CoV-2 genetic targets are less susceptible to genetic variants than tests designed to detect a single genetic target.
The FDA already issued a safety alert on Jan. 8 to caution that genetic mutations to the virus in a patient sample can potentially change the performance of a diagnostic test. The FDA identified three tests that had been granted emergency-use authorization (EUA) that are known to be affected.
However, Dr. Woodcock said on the call, “at this time the impact does not appear to be significant.”
Updated guidance for therapeutics
The FDA has issued new guidance on the effect of variants on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“The FDA is aware that some of the monoclonal antibodies that have been authorized are less active against some of the SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged,” the FDA noted in its press release. “This guidance provides recommendations on efficient approaches to the generation of ... manufacturing and controls data that could potentially support an EUA for monoclonal antibody products that may be effective against emerging variants.”
While the FDA is monitoring the effects of variants, manufacturers bear a lot of the responsibility as well.
The FDA added: “With these guidances, the FDA is encouraging developers of drugs or biological products targeting SARS-CoV-2 to continuously monitor genomic databases for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and evaluate phenotypically any specific variants in the product target that are becoming prevalent or could potentially impact its activity.”
Dr.Woodcock added that “we urge all Americans to continue to get tested, get their vaccines when available, and follow important heath measures such as handwashing, masking, and social distancing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States is currently facing three main variant threats, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom; B.1.351 from South Africa; and the P.1 variant, which originated in Brazil.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said on a telephone press briefing call Feb. 22 that the FDA has already been communicating with individual manufacturers as they assess the variants’ effect on their products, but these guidelines are issued for the sake of transparency and to welcome scientific input.
Tailoring may be necessary
Dr. Woodcock emphasized that, “at this time, available data suggest the FDA-authorized vaccines are effective in protecting circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2.” However, in the event the strains start to show resistance, it may be necessary to tailor the vaccine to the variant.
In that case, effectiveness of a modified vaccine should be determined by data from clinical immunogenicity studies, which would compare a recipient’s immune response with virus variants induced by the modified vaccine against the immune response to the authorized vaccine, the guidance states.
Manufacturers should also study the vaccine in both nonvaccinated people and people fully vaccinated with the authorized vaccine, according to the guidance.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said on the call that the clinical immunogenicity data is needed to understand, for instance, whether a new vaccine strain is able to cover the new and old strain or whether it just covers the new strain. Information is also needed to understand whether the modified vaccine, when given to someone fully vaccinated, will still promote a positive response without introducing safety concerns.
Further discussions will be necessary to decide whether future modified vaccines may be authorized without the need for clinical studies.
Variants and testing
The FDA’s updated guidance for test developers, Policy for Evaluating Impact of Viral Mutations on COVID-19 Tests, includes information that test performance can be influenced by the sequence of the variant, prevalence of the variant in the population, or design of the test. For example, molecular tests designed to detect multiple SARS-CoV-2 genetic targets are less susceptible to genetic variants than tests designed to detect a single genetic target.
The FDA already issued a safety alert on Jan. 8 to caution that genetic mutations to the virus in a patient sample can potentially change the performance of a diagnostic test. The FDA identified three tests that had been granted emergency-use authorization (EUA) that are known to be affected.
However, Dr. Woodcock said on the call, “at this time the impact does not appear to be significant.”
Updated guidance for therapeutics
The FDA has issued new guidance on the effect of variants on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“The FDA is aware that some of the monoclonal antibodies that have been authorized are less active against some of the SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged,” the FDA noted in its press release. “This guidance provides recommendations on efficient approaches to the generation of ... manufacturing and controls data that could potentially support an EUA for monoclonal antibody products that may be effective against emerging variants.”
While the FDA is monitoring the effects of variants, manufacturers bear a lot of the responsibility as well.
The FDA added: “With these guidances, the FDA is encouraging developers of drugs or biological products targeting SARS-CoV-2 to continuously monitor genomic databases for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and evaluate phenotypically any specific variants in the product target that are becoming prevalent or could potentially impact its activity.”
Dr.Woodcock added that “we urge all Americans to continue to get tested, get their vaccines when available, and follow important heath measures such as handwashing, masking, and social distancing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States is currently facing three main variant threats, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom; B.1.351 from South Africa; and the P.1 variant, which originated in Brazil.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said on a telephone press briefing call Feb. 22 that the FDA has already been communicating with individual manufacturers as they assess the variants’ effect on their products, but these guidelines are issued for the sake of transparency and to welcome scientific input.
Tailoring may be necessary
Dr. Woodcock emphasized that, “at this time, available data suggest the FDA-authorized vaccines are effective in protecting circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2.” However, in the event the strains start to show resistance, it may be necessary to tailor the vaccine to the variant.
In that case, effectiveness of a modified vaccine should be determined by data from clinical immunogenicity studies, which would compare a recipient’s immune response with virus variants induced by the modified vaccine against the immune response to the authorized vaccine, the guidance states.
Manufacturers should also study the vaccine in both nonvaccinated people and people fully vaccinated with the authorized vaccine, according to the guidance.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said on the call that the clinical immunogenicity data is needed to understand, for instance, whether a new vaccine strain is able to cover the new and old strain or whether it just covers the new strain. Information is also needed to understand whether the modified vaccine, when given to someone fully vaccinated, will still promote a positive response without introducing safety concerns.
Further discussions will be necessary to decide whether future modified vaccines may be authorized without the need for clinical studies.
Variants and testing
The FDA’s updated guidance for test developers, Policy for Evaluating Impact of Viral Mutations on COVID-19 Tests, includes information that test performance can be influenced by the sequence of the variant, prevalence of the variant in the population, or design of the test. For example, molecular tests designed to detect multiple SARS-CoV-2 genetic targets are less susceptible to genetic variants than tests designed to detect a single genetic target.
The FDA already issued a safety alert on Jan. 8 to caution that genetic mutations to the virus in a patient sample can potentially change the performance of a diagnostic test. The FDA identified three tests that had been granted emergency-use authorization (EUA) that are known to be affected.
However, Dr. Woodcock said on the call, “at this time the impact does not appear to be significant.”
Updated guidance for therapeutics
The FDA has issued new guidance on the effect of variants on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“The FDA is aware that some of the monoclonal antibodies that have been authorized are less active against some of the SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged,” the FDA noted in its press release. “This guidance provides recommendations on efficient approaches to the generation of ... manufacturing and controls data that could potentially support an EUA for monoclonal antibody products that may be effective against emerging variants.”
While the FDA is monitoring the effects of variants, manufacturers bear a lot of the responsibility as well.
The FDA added: “With these guidances, the FDA is encouraging developers of drugs or biological products targeting SARS-CoV-2 to continuously monitor genomic databases for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and evaluate phenotypically any specific variants in the product target that are becoming prevalent or could potentially impact its activity.”
Dr.Woodcock added that “we urge all Americans to continue to get tested, get their vaccines when available, and follow important heath measures such as handwashing, masking, and social distancing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pandemic puts patients with psoriatic disease off seeking medical help
More than half of respondents to a recent survey looking at how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected people with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) said that they had avoided seeking medical care in person with a doctor or at a hospital.
Moreover, around a quarter had their appointment with a rheumatologist canceled, rescheduled, or conducted virtually. Another 1 in 10 had their treatment plan disrupted, and 6% had to change or stop treatment entirely.
The mental health impact of living with these conditions during the pandemic was also notable, said Rachael Manion, the executive director of the Canadian Association of Psoriasis Patients (CAPP), which conducted the survey in collaboration with the Canadian Psoriasis Network (CPN) and Unmasking Psoriasis.
“It’s important to know that there have been a lot of different impacts of the pandemic on people living with psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Mental health in particular has had a really big hit as a result,” she said at the Canadian Arthritis Research Conference: Research with Impact.
“About half of the people who responded to our survey noted that their mental health was ‘worse’ or ‘much worse’ during the pandemic,” she said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the Arthritis Society, the Canadian Rheumatology Association, and Canada’s Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis. Anxiety and feelings of isolation were reported by a respective 57% and 58% of respondents, and 40% reported depression.
“We can compare that to our earlier information around depression,” Ms. Manion said, which showed that, prior to the pandemic, 24% of people with psoriasis and 23% of those with PsA had said they experienced depression.
“What I found alarming looking at these results was that about a third of people were experiencing despair. Now that’s a really big, scary, overwhelming emotion that has a lot of burden on your mental health,” Ms. Manion said.
Despite the substantial effects on mental health, only 29% of respondents said they had been able to access mental health services during the pandemic.
To look at the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the psoriasis and PsA community in Canada, three patient advocacy groups – CAPP, CPN, and Unmasking Psoriasis – codeveloped a survey to look at the disease experience before and after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey was performed once, with 830 respondents providing information on their lives with psoriasis or PsA in the months before the start of the pandemic and at the time they were surveyed in September and October 2020.
Most of the survey respondents lived in Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, or Alberta, although other provinces or territories were represented. Almost all respondents (96%) had psoriasis, and 60% also had PsA.
Pre-COVID, nearly half (49%) of patients said that they had not been seen by a rheumatologist, and 39% had not seen a dermatologist for treatment. Asked why, 56% and 27%, respectively, had not been referred, 9% and 15% said they had no specialist located nearby, and 7% and 10% stated that the wait list was too long.
“This tells us that there’s a lot more work that can be done and a lot more education of general practitioners and family medicine professionals about the benefits and the value of specialized care for psoriatic arthritis,” Ms. Manion suggested.
Before the pandemic, joint pain was occurring in 88% of patients, stiffness in 71%, and joint swelling in 67%. Disease flares or sudden periods of worsening occurred on a daily basis for 17%, and around one in five (21%) experienced multiple flares every month.
Prepandemic data also highlighted the negative impact that living with psoriasis or PsA has on people’s ability to sleep, interactions and intimacy with others, and on their school or work lives.
During the pandemic, around a quarter (26%) of respondents said they had worse or much worse access to employment, as well as its benefits such as a stable income (24%). A minority of respondent also described worse access to prescription medication (15%) and over-the-counter medication (13%).
“There are all kinds of things going on for patients in our community: changes to their work, changes to their drug coverage, their ability to sleep and sleep well, their mental health, and their ability to access care and treatments as part of their disease management,” Ms. Manion said.
Her final message to health care professionals was: “I just want to encourage you to continue to check in with your patients about what their experiences have been during the pandemic, and to really consider those impacts as you’re working with them to manage their disease.”
The survey received funding support from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, LEO Pharma, and Novartis.
More than half of respondents to a recent survey looking at how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected people with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) said that they had avoided seeking medical care in person with a doctor or at a hospital.
Moreover, around a quarter had their appointment with a rheumatologist canceled, rescheduled, or conducted virtually. Another 1 in 10 had their treatment plan disrupted, and 6% had to change or stop treatment entirely.
The mental health impact of living with these conditions during the pandemic was also notable, said Rachael Manion, the executive director of the Canadian Association of Psoriasis Patients (CAPP), which conducted the survey in collaboration with the Canadian Psoriasis Network (CPN) and Unmasking Psoriasis.
“It’s important to know that there have been a lot of different impacts of the pandemic on people living with psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Mental health in particular has had a really big hit as a result,” she said at the Canadian Arthritis Research Conference: Research with Impact.
“About half of the people who responded to our survey noted that their mental health was ‘worse’ or ‘much worse’ during the pandemic,” she said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the Arthritis Society, the Canadian Rheumatology Association, and Canada’s Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis. Anxiety and feelings of isolation were reported by a respective 57% and 58% of respondents, and 40% reported depression.
“We can compare that to our earlier information around depression,” Ms. Manion said, which showed that, prior to the pandemic, 24% of people with psoriasis and 23% of those with PsA had said they experienced depression.
“What I found alarming looking at these results was that about a third of people were experiencing despair. Now that’s a really big, scary, overwhelming emotion that has a lot of burden on your mental health,” Ms. Manion said.
Despite the substantial effects on mental health, only 29% of respondents said they had been able to access mental health services during the pandemic.
To look at the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the psoriasis and PsA community in Canada, three patient advocacy groups – CAPP, CPN, and Unmasking Psoriasis – codeveloped a survey to look at the disease experience before and after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey was performed once, with 830 respondents providing information on their lives with psoriasis or PsA in the months before the start of the pandemic and at the time they were surveyed in September and October 2020.
Most of the survey respondents lived in Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, or Alberta, although other provinces or territories were represented. Almost all respondents (96%) had psoriasis, and 60% also had PsA.
Pre-COVID, nearly half (49%) of patients said that they had not been seen by a rheumatologist, and 39% had not seen a dermatologist for treatment. Asked why, 56% and 27%, respectively, had not been referred, 9% and 15% said they had no specialist located nearby, and 7% and 10% stated that the wait list was too long.
“This tells us that there’s a lot more work that can be done and a lot more education of general practitioners and family medicine professionals about the benefits and the value of specialized care for psoriatic arthritis,” Ms. Manion suggested.
Before the pandemic, joint pain was occurring in 88% of patients, stiffness in 71%, and joint swelling in 67%. Disease flares or sudden periods of worsening occurred on a daily basis for 17%, and around one in five (21%) experienced multiple flares every month.
Prepandemic data also highlighted the negative impact that living with psoriasis or PsA has on people’s ability to sleep, interactions and intimacy with others, and on their school or work lives.
During the pandemic, around a quarter (26%) of respondents said they had worse or much worse access to employment, as well as its benefits such as a stable income (24%). A minority of respondent also described worse access to prescription medication (15%) and over-the-counter medication (13%).
“There are all kinds of things going on for patients in our community: changes to their work, changes to their drug coverage, their ability to sleep and sleep well, their mental health, and their ability to access care and treatments as part of their disease management,” Ms. Manion said.
Her final message to health care professionals was: “I just want to encourage you to continue to check in with your patients about what their experiences have been during the pandemic, and to really consider those impacts as you’re working with them to manage their disease.”
The survey received funding support from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, LEO Pharma, and Novartis.
More than half of respondents to a recent survey looking at how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected people with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) said that they had avoided seeking medical care in person with a doctor or at a hospital.
Moreover, around a quarter had their appointment with a rheumatologist canceled, rescheduled, or conducted virtually. Another 1 in 10 had their treatment plan disrupted, and 6% had to change or stop treatment entirely.
The mental health impact of living with these conditions during the pandemic was also notable, said Rachael Manion, the executive director of the Canadian Association of Psoriasis Patients (CAPP), which conducted the survey in collaboration with the Canadian Psoriasis Network (CPN) and Unmasking Psoriasis.
“It’s important to know that there have been a lot of different impacts of the pandemic on people living with psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Mental health in particular has had a really big hit as a result,” she said at the Canadian Arthritis Research Conference: Research with Impact.
“About half of the people who responded to our survey noted that their mental health was ‘worse’ or ‘much worse’ during the pandemic,” she said at the meeting, which was sponsored by the Arthritis Society, the Canadian Rheumatology Association, and Canada’s Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis. Anxiety and feelings of isolation were reported by a respective 57% and 58% of respondents, and 40% reported depression.
“We can compare that to our earlier information around depression,” Ms. Manion said, which showed that, prior to the pandemic, 24% of people with psoriasis and 23% of those with PsA had said they experienced depression.
“What I found alarming looking at these results was that about a third of people were experiencing despair. Now that’s a really big, scary, overwhelming emotion that has a lot of burden on your mental health,” Ms. Manion said.
Despite the substantial effects on mental health, only 29% of respondents said they had been able to access mental health services during the pandemic.
To look at the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the psoriasis and PsA community in Canada, three patient advocacy groups – CAPP, CPN, and Unmasking Psoriasis – codeveloped a survey to look at the disease experience before and after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey was performed once, with 830 respondents providing information on their lives with psoriasis or PsA in the months before the start of the pandemic and at the time they were surveyed in September and October 2020.
Most of the survey respondents lived in Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, or Alberta, although other provinces or territories were represented. Almost all respondents (96%) had psoriasis, and 60% also had PsA.
Pre-COVID, nearly half (49%) of patients said that they had not been seen by a rheumatologist, and 39% had not seen a dermatologist for treatment. Asked why, 56% and 27%, respectively, had not been referred, 9% and 15% said they had no specialist located nearby, and 7% and 10% stated that the wait list was too long.
“This tells us that there’s a lot more work that can be done and a lot more education of general practitioners and family medicine professionals about the benefits and the value of specialized care for psoriatic arthritis,” Ms. Manion suggested.
Before the pandemic, joint pain was occurring in 88% of patients, stiffness in 71%, and joint swelling in 67%. Disease flares or sudden periods of worsening occurred on a daily basis for 17%, and around one in five (21%) experienced multiple flares every month.
Prepandemic data also highlighted the negative impact that living with psoriasis or PsA has on people’s ability to sleep, interactions and intimacy with others, and on their school or work lives.
During the pandemic, around a quarter (26%) of respondents said they had worse or much worse access to employment, as well as its benefits such as a stable income (24%). A minority of respondent also described worse access to prescription medication (15%) and over-the-counter medication (13%).
“There are all kinds of things going on for patients in our community: changes to their work, changes to their drug coverage, their ability to sleep and sleep well, their mental health, and their ability to access care and treatments as part of their disease management,” Ms. Manion said.
Her final message to health care professionals was: “I just want to encourage you to continue to check in with your patients about what their experiences have been during the pandemic, and to really consider those impacts as you’re working with them to manage their disease.”
The survey received funding support from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, LEO Pharma, and Novartis.
FROM CARC 2021
New light cast on type 2 MI aims to sharpen diagnosis, therapy
The hospital and postdischarge course of patients diagnosed with type 2 myocardial infarction, triggered when myocardial oxygen demand outstrips supply, differs in telling ways from those with the more common atherothrombotic type 1 MI, suggests a new registry analysis that aims to lift a cloud of confusion surrounding their management.
The observational study of more than 250,000 patients with either form of MI, said to be the largest of its kind, points to widespread unfamiliarity with distinctions between the two, and the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of misclassification. It suggests, in particular, that type 2 MI may be grossly underdiagnosed and undertreated.
The minority of patients with type 2 MI were more likely female and to have heart failure (HF), renal disease, valve disease, or atrial fibrillation, and less likely to have a lipid disorder, compared with those with type 1 MI. They were one-fifth as likely to be referred for coronary angiography and 20 times less likely to undergo revascularization.
Indeed, only about 2% of the type 2 cohort ultimately underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass surgery (CABG). Yet the analysis suggests that cardiovascular risk climbs regardless of MI type and that in patients with type 2 MI, coronary revascularization might well cut the risk of death in half over the short term.
There were also disparities in clinical outcomes in the analysis, based on data from the final 3 months of 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database, which reportedly documents almost 60% of hospitalizations in the United States.
For example, those with type 1 or type 2 MI – as characterized in the then-current third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction and today’s UDMI-4 – were comparably at risk for both 30-day all-cause readmission and HF readmission. But type 2 patients were less likely to die in the hospital or be readmitted within 30 days for recurrent MI.
Revascularization uncertainty
Importantly, the study’s 3-month observation period immediately followed the debut of a code specifically for type 2 MI in the ICD-10-CM system.
Type 2 accounted for about 15% of MIs during that period, the percentage climbing sharply from the first to the third month. That suggests clinicians were still getting used to the code during the early weeks, “undercoding” for type-2 MI at first but less so after some experience, Cian P. McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“I can imagine that as people become more aware of the coding, using it more often, the proportion of type 2 MI relative to the total MI cases will probably be much higher,” said McCarthy, lead author on the study published online Feb. 15, 2021, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
What had been understood about type 2 MI came largely from single-center studies, he said. This “first national study of type-2 MI in the United States” sought to determine whether such findings are hospital specific or “representative of what people are doing nationally.”
The new analysis largely confirms that patients with type 2 MI are typically burdened with multiple comorbidities, Dr. McCarthy said, but also suggests that type 2 often was, and likely still is, incorrectly classified as type 1. So, it was “surprising” that they were rarely referred for angiography. “Only 1 in 50 received revascularization.”
Those diagnosed with type-2 MI were far less likely to receive coronary angiography (10.9% vs. 57.3%), PCI (1.7% vs. 38.5%), or CABG (0.4% vs. 7.8%) (P < .001 for all three differences), the report noted.
That, Dr. McCarthy said, “clearly shows that clinicians are uncertain about whether revascularization is beneficial” in type 2 MI.
Coding not in sync with UDMI
If there is confusion in practice about differentiating type 2 from type 1 MI, it likely has multiple sources, and one may be inconsistencies in how the UDMI and relevant ICD codes are applied in practice.
For example, the coding mandate is always to classify ST-segment elevation MI and non-STEMI as type 1, yet UDMI-4 itself states that a type 2 MI may be either STEMI or non-STEMI, noted Dr. McCarthy, as well as an editorial accompanying the report.
“It also can be difficult at times to distinguish type 2 MI from the diagnosis of myocardial injury,” both of which are partly defined by elevated cardiac troponin (cTn), adds the editorial, from Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
Crucially, but potentially sometimes overlooked, a diagnosis of infarction requires evidence of ischemia along with the biomarker elevation, whereas myocardial injury is defined by raised cTn without evidence of ischemia. Yet there is no ICD-10-CM code for “nonischemic myocardial injury,” Dr. Thygesen and Dr. Jaffe observed.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” they wrote. “Unfortunately, although some have advocated using this code for myocardial injury, it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading” and thus worsen the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
In the current study, 84.6% of the cohort were classified with type 1 MI, 14.8% with type 2, and 0.6% with both types. Of those with type 1 MI, 22.1% had STEMI, 76.4% had non-STEMI with the remainder “unspecified.”
“I think the introduction of ICD codes for type-2 MI is helpful in that we can study type 2 MI more broadly, across institutions, and try and get a better sense of its outcomes and how these patients are treated,” Dr. McCarthy said. But the coding system’s deficiencies may often lead to misclassification of patients. Especially, patients with type 2 STEMI may be miscoded as having type-1 STEMI, and those with only myocardial injury may be miscoded as having type 2 MI.
Most type 2 MI is a complication
A profile of patients with type 2 MI may be helpful for making distinctions. The analysis showed that, compared with patients with type 1 MI, they were slightly but significantly older and more likely to have clinical depression, alcohol or other substance abuse disorder, and to be female. They also had more heart failure (27.9% vs. 10.9%), kidney disease (35.7% vs. 25.7%), atrial fibrillation (31% vs. 21%), and anemia (26% vs. 18.9%) (P < .001 for all differences).
Type 2 patients were less likely to have CV risk factors usually associated with plaque instability and atherothrombosis, including a history of smoking, dyslipidemia, MI, PCI, or CABG (P < .001 for all differences), the group noted.
Of the 37,765 patients with type 2 MI, 91% received the diagnosis as secondary to another condition, including sepsis in 24.5%, hypertension in 16.9%, arrhythmias in 6.1%, respiratory failure in 4.3%, and pneumonia in 2.8% of cases.
In multivariate analyses, patients with type 2 MI, compared with type 1, showed lower risks of in-hospital death and readmission for MI within 30 days. Their 30-day risks of readmission from any cause and from MI were similar.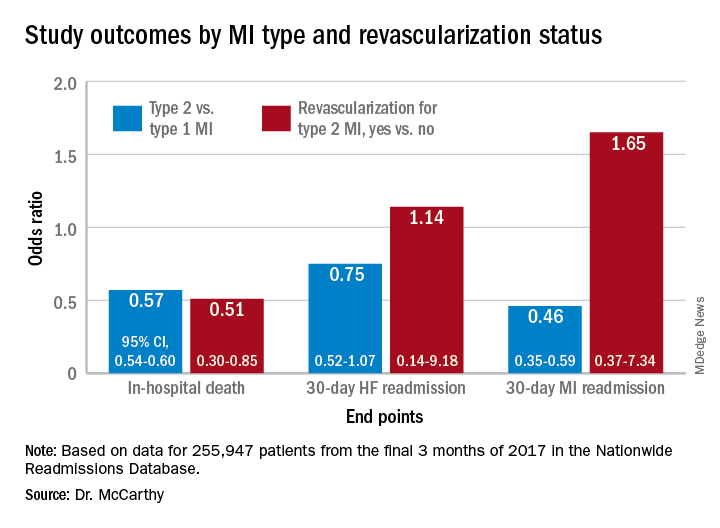
In-hospital mortality was lower for patients with type 2 MI who underwent revascularization, compared with those who did not, “but they were a very select, small proportion of the patient group. I would say there are probably unmeasured confounders,” Dr. McCarthy said.
“There’s a real kind of equipoise, so I think we desperately need a trial to guide us on whether revascularization is beneficial.”
Dr. McCarthy has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Thygesen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jaffe disclosed serving as a consultant for Abbott, Roche, Siemens, Beckman-Coulter, Radiometer, ET Healthcare, Sphingotec, Brava, Quidel, Amgen, Novartis, and Medscape for educational activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The hospital and postdischarge course of patients diagnosed with type 2 myocardial infarction, triggered when myocardial oxygen demand outstrips supply, differs in telling ways from those with the more common atherothrombotic type 1 MI, suggests a new registry analysis that aims to lift a cloud of confusion surrounding their management.
The observational study of more than 250,000 patients with either form of MI, said to be the largest of its kind, points to widespread unfamiliarity with distinctions between the two, and the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of misclassification. It suggests, in particular, that type 2 MI may be grossly underdiagnosed and undertreated.
The minority of patients with type 2 MI were more likely female and to have heart failure (HF), renal disease, valve disease, or atrial fibrillation, and less likely to have a lipid disorder, compared with those with type 1 MI. They were one-fifth as likely to be referred for coronary angiography and 20 times less likely to undergo revascularization.
Indeed, only about 2% of the type 2 cohort ultimately underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass surgery (CABG). Yet the analysis suggests that cardiovascular risk climbs regardless of MI type and that in patients with type 2 MI, coronary revascularization might well cut the risk of death in half over the short term.
There were also disparities in clinical outcomes in the analysis, based on data from the final 3 months of 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database, which reportedly documents almost 60% of hospitalizations in the United States.
For example, those with type 1 or type 2 MI – as characterized in the then-current third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction and today’s UDMI-4 – were comparably at risk for both 30-day all-cause readmission and HF readmission. But type 2 patients were less likely to die in the hospital or be readmitted within 30 days for recurrent MI.
Revascularization uncertainty
Importantly, the study’s 3-month observation period immediately followed the debut of a code specifically for type 2 MI in the ICD-10-CM system.
Type 2 accounted for about 15% of MIs during that period, the percentage climbing sharply from the first to the third month. That suggests clinicians were still getting used to the code during the early weeks, “undercoding” for type-2 MI at first but less so after some experience, Cian P. McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“I can imagine that as people become more aware of the coding, using it more often, the proportion of type 2 MI relative to the total MI cases will probably be much higher,” said McCarthy, lead author on the study published online Feb. 15, 2021, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
What had been understood about type 2 MI came largely from single-center studies, he said. This “first national study of type-2 MI in the United States” sought to determine whether such findings are hospital specific or “representative of what people are doing nationally.”
The new analysis largely confirms that patients with type 2 MI are typically burdened with multiple comorbidities, Dr. McCarthy said, but also suggests that type 2 often was, and likely still is, incorrectly classified as type 1. So, it was “surprising” that they were rarely referred for angiography. “Only 1 in 50 received revascularization.”
Those diagnosed with type-2 MI were far less likely to receive coronary angiography (10.9% vs. 57.3%), PCI (1.7% vs. 38.5%), or CABG (0.4% vs. 7.8%) (P < .001 for all three differences), the report noted.
That, Dr. McCarthy said, “clearly shows that clinicians are uncertain about whether revascularization is beneficial” in type 2 MI.
Coding not in sync with UDMI
If there is confusion in practice about differentiating type 2 from type 1 MI, it likely has multiple sources, and one may be inconsistencies in how the UDMI and relevant ICD codes are applied in practice.
For example, the coding mandate is always to classify ST-segment elevation MI and non-STEMI as type 1, yet UDMI-4 itself states that a type 2 MI may be either STEMI or non-STEMI, noted Dr. McCarthy, as well as an editorial accompanying the report.
“It also can be difficult at times to distinguish type 2 MI from the diagnosis of myocardial injury,” both of which are partly defined by elevated cardiac troponin (cTn), adds the editorial, from Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
Crucially, but potentially sometimes overlooked, a diagnosis of infarction requires evidence of ischemia along with the biomarker elevation, whereas myocardial injury is defined by raised cTn without evidence of ischemia. Yet there is no ICD-10-CM code for “nonischemic myocardial injury,” Dr. Thygesen and Dr. Jaffe observed.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” they wrote. “Unfortunately, although some have advocated using this code for myocardial injury, it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading” and thus worsen the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
In the current study, 84.6% of the cohort were classified with type 1 MI, 14.8% with type 2, and 0.6% with both types. Of those with type 1 MI, 22.1% had STEMI, 76.4% had non-STEMI with the remainder “unspecified.”
“I think the introduction of ICD codes for type-2 MI is helpful in that we can study type 2 MI more broadly, across institutions, and try and get a better sense of its outcomes and how these patients are treated,” Dr. McCarthy said. But the coding system’s deficiencies may often lead to misclassification of patients. Especially, patients with type 2 STEMI may be miscoded as having type-1 STEMI, and those with only myocardial injury may be miscoded as having type 2 MI.
Most type 2 MI is a complication
A profile of patients with type 2 MI may be helpful for making distinctions. The analysis showed that, compared with patients with type 1 MI, they were slightly but significantly older and more likely to have clinical depression, alcohol or other substance abuse disorder, and to be female. They also had more heart failure (27.9% vs. 10.9%), kidney disease (35.7% vs. 25.7%), atrial fibrillation (31% vs. 21%), and anemia (26% vs. 18.9%) (P < .001 for all differences).
Type 2 patients were less likely to have CV risk factors usually associated with plaque instability and atherothrombosis, including a history of smoking, dyslipidemia, MI, PCI, or CABG (P < .001 for all differences), the group noted.
Of the 37,765 patients with type 2 MI, 91% received the diagnosis as secondary to another condition, including sepsis in 24.5%, hypertension in 16.9%, arrhythmias in 6.1%, respiratory failure in 4.3%, and pneumonia in 2.8% of cases.
In multivariate analyses, patients with type 2 MI, compared with type 1, showed lower risks of in-hospital death and readmission for MI within 30 days. Their 30-day risks of readmission from any cause and from MI were similar.
In-hospital mortality was lower for patients with type 2 MI who underwent revascularization, compared with those who did not, “but they were a very select, small proportion of the patient group. I would say there are probably unmeasured confounders,” Dr. McCarthy said.
“There’s a real kind of equipoise, so I think we desperately need a trial to guide us on whether revascularization is beneficial.”
Dr. McCarthy has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Thygesen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jaffe disclosed serving as a consultant for Abbott, Roche, Siemens, Beckman-Coulter, Radiometer, ET Healthcare, Sphingotec, Brava, Quidel, Amgen, Novartis, and Medscape for educational activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The hospital and postdischarge course of patients diagnosed with type 2 myocardial infarction, triggered when myocardial oxygen demand outstrips supply, differs in telling ways from those with the more common atherothrombotic type 1 MI, suggests a new registry analysis that aims to lift a cloud of confusion surrounding their management.
The observational study of more than 250,000 patients with either form of MI, said to be the largest of its kind, points to widespread unfamiliarity with distinctions between the two, and the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of misclassification. It suggests, in particular, that type 2 MI may be grossly underdiagnosed and undertreated.
The minority of patients with type 2 MI were more likely female and to have heart failure (HF), renal disease, valve disease, or atrial fibrillation, and less likely to have a lipid disorder, compared with those with type 1 MI. They were one-fifth as likely to be referred for coronary angiography and 20 times less likely to undergo revascularization.
Indeed, only about 2% of the type 2 cohort ultimately underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass surgery (CABG). Yet the analysis suggests that cardiovascular risk climbs regardless of MI type and that in patients with type 2 MI, coronary revascularization might well cut the risk of death in half over the short term.
There were also disparities in clinical outcomes in the analysis, based on data from the final 3 months of 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database, which reportedly documents almost 60% of hospitalizations in the United States.
For example, those with type 1 or type 2 MI – as characterized in the then-current third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction and today’s UDMI-4 – were comparably at risk for both 30-day all-cause readmission and HF readmission. But type 2 patients were less likely to die in the hospital or be readmitted within 30 days for recurrent MI.
Revascularization uncertainty
Importantly, the study’s 3-month observation period immediately followed the debut of a code specifically for type 2 MI in the ICD-10-CM system.
Type 2 accounted for about 15% of MIs during that period, the percentage climbing sharply from the first to the third month. That suggests clinicians were still getting used to the code during the early weeks, “undercoding” for type-2 MI at first but less so after some experience, Cian P. McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“I can imagine that as people become more aware of the coding, using it more often, the proportion of type 2 MI relative to the total MI cases will probably be much higher,” said McCarthy, lead author on the study published online Feb. 15, 2021, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
What had been understood about type 2 MI came largely from single-center studies, he said. This “first national study of type-2 MI in the United States” sought to determine whether such findings are hospital specific or “representative of what people are doing nationally.”
The new analysis largely confirms that patients with type 2 MI are typically burdened with multiple comorbidities, Dr. McCarthy said, but also suggests that type 2 often was, and likely still is, incorrectly classified as type 1. So, it was “surprising” that they were rarely referred for angiography. “Only 1 in 50 received revascularization.”
Those diagnosed with type-2 MI were far less likely to receive coronary angiography (10.9% vs. 57.3%), PCI (1.7% vs. 38.5%), or CABG (0.4% vs. 7.8%) (P < .001 for all three differences), the report noted.
That, Dr. McCarthy said, “clearly shows that clinicians are uncertain about whether revascularization is beneficial” in type 2 MI.
Coding not in sync with UDMI
If there is confusion in practice about differentiating type 2 from type 1 MI, it likely has multiple sources, and one may be inconsistencies in how the UDMI and relevant ICD codes are applied in practice.
For example, the coding mandate is always to classify ST-segment elevation MI and non-STEMI as type 1, yet UDMI-4 itself states that a type 2 MI may be either STEMI or non-STEMI, noted Dr. McCarthy, as well as an editorial accompanying the report.
“It also can be difficult at times to distinguish type 2 MI from the diagnosis of myocardial injury,” both of which are partly defined by elevated cardiac troponin (cTn), adds the editorial, from Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
Crucially, but potentially sometimes overlooked, a diagnosis of infarction requires evidence of ischemia along with the biomarker elevation, whereas myocardial injury is defined by raised cTn without evidence of ischemia. Yet there is no ICD-10-CM code for “nonischemic myocardial injury,” Dr. Thygesen and Dr. Jaffe observed.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” they wrote. “Unfortunately, although some have advocated using this code for myocardial injury, it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading” and thus worsen the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
In the current study, 84.6% of the cohort were classified with type 1 MI, 14.8% with type 2, and 0.6% with both types. Of those with type 1 MI, 22.1% had STEMI, 76.4% had non-STEMI with the remainder “unspecified.”
“I think the introduction of ICD codes for type-2 MI is helpful in that we can study type 2 MI more broadly, across institutions, and try and get a better sense of its outcomes and how these patients are treated,” Dr. McCarthy said. But the coding system’s deficiencies may often lead to misclassification of patients. Especially, patients with type 2 STEMI may be miscoded as having type-1 STEMI, and those with only myocardial injury may be miscoded as having type 2 MI.
Most type 2 MI is a complication
A profile of patients with type 2 MI may be helpful for making distinctions. The analysis showed that, compared with patients with type 1 MI, they were slightly but significantly older and more likely to have clinical depression, alcohol or other substance abuse disorder, and to be female. They also had more heart failure (27.9% vs. 10.9%), kidney disease (35.7% vs. 25.7%), atrial fibrillation (31% vs. 21%), and anemia (26% vs. 18.9%) (P < .001 for all differences).
Type 2 patients were less likely to have CV risk factors usually associated with plaque instability and atherothrombosis, including a history of smoking, dyslipidemia, MI, PCI, or CABG (P < .001 for all differences), the group noted.
Of the 37,765 patients with type 2 MI, 91% received the diagnosis as secondary to another condition, including sepsis in 24.5%, hypertension in 16.9%, arrhythmias in 6.1%, respiratory failure in 4.3%, and pneumonia in 2.8% of cases.
In multivariate analyses, patients with type 2 MI, compared with type 1, showed lower risks of in-hospital death and readmission for MI within 30 days. Their 30-day risks of readmission from any cause and from MI were similar.
In-hospital mortality was lower for patients with type 2 MI who underwent revascularization, compared with those who did not, “but they were a very select, small proportion of the patient group. I would say there are probably unmeasured confounders,” Dr. McCarthy said.
“There’s a real kind of equipoise, so I think we desperately need a trial to guide us on whether revascularization is beneficial.”
Dr. McCarthy has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Thygesen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jaffe disclosed serving as a consultant for Abbott, Roche, Siemens, Beckman-Coulter, Radiometer, ET Healthcare, Sphingotec, Brava, Quidel, Amgen, Novartis, and Medscape for educational activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Organ transplant patient dies after receiving COVID-19–infected lungs
Doctors say a woman in Michigan contracted COVID-19 and died last fall 2 months after receiving a tainted double-lung transplant from a donor who turned out to harbor the virus that causes the disease – despite showing no signs of illness and initially testing negative.
Officials at the University of Michigan Medical School suggested it may be the first proven case of COVID-19 in the U.S. in which the virus was transmitted via an organ transplant. A surgeon who handled the donor lungs was also infected with the virus and fell ill but later recovered.
The incident appears to be isolated – the only confirmed case among nearly 40,000 transplants in 2020. But it has led to calls for more thorough testing of lung transplant donors, with samples taken from deep within the donor lungs as well as the nose and throat, said Dr. Daniel Kaul, director of Michigan Medicine’s transplant infectious disease service.
“We would absolutely not have used the lungs if we’d had a positive COVID-19 test,” said Dr. Kaul, who coauthored a report about the case in the American Journal of Transplantation.
The virus was transmitted when lungs from a woman from the Upper Midwest, who died after suffering a severe brain injury in a car accident, were transplanted into a woman with chronic obstructive lung disease at University Hospital in Ann Arbor. The nose and throat samples routinely collected from both organ donors and recipients tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes covid.
“All the screening that we normally do and are able to do, we did,” Dr. Kaul said.
Three days after the operation, however, the recipient spiked a fever; her blood pressure fell and her breathing became labored. Imaging showed signs of lung infection.
As her condition worsened, the patient developed septic shock and heart function problems. Doctors decided to test for SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Kaul said. Samples from her new lungs came back positive.
Suspicious about the origin of the infection, doctors returned to samples from the transplant donor. A molecular test of a swab from the donor’s nose and throat, taken 48 hours after her lungs were procured, had been negative for SARS-Cov-2. The donor’s family told doctors she had no history of recent travel or COVID-19 symptoms and no known exposure to anyone with the disease.
But doctors had kept a sample of fluid washed from deep within the donor lungs. When they tested that fluid, it was positive for the virus. Four days after the transplant, the surgeon who handled the donor lungs and performed the surgery tested positive, too. Genetic screening revealed that the transplant recipient and the surgeon had been infected by the donor. Ten other members of the transplant team tested negative for the virus.
The transplant recipient deteriorated rapidly, developing multisystem organ failure. Doctors tried known treatments for COVID-19, including remdesivir, a newly approved drug, and convalescent blood plasma from people previously infected with the disease. Eventually, she was placed on the last-resort option of ECMO, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, to no avail. Life support was withdrawn, and she died 61 days after the transplant.
Dr. Kaul called the incident “a tragic case.”
While the Michigan case marks the first confirmed incident in the U.S. of transmission through a transplant, others have been suspected. A recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report reviewed eight possible cases of what’s known as donor-derived infection that occurred last spring, but concluded the most likely source of transmission of the COVID-19 virus in those cases was in a community or health care setting.
Before this incident, it was not clear whether the COVID-19 virus could be transmitted through solid organ transplants, though it’s well documented with other respiratory viruses. Donor transmission of H1N1 2009 pandemic influenza has been detected almost exclusively in lung transplant recipients, Dr. Kaul noted.
While it’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 can be transmitted through infected lungs, it remains uncertain whether other organs affected by COVID-19 – hearts, livers and kidneys, for instance – can transmit the virus, too.
“It seems for non-lung donors that it may be very difficult to transmit COVID-19, even if the donor has COVID-19,” Dr. Kaul said.
Organ donors have been tested routinely for SARS-CoV-2 during the pandemic, though it’s not required by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, or OPTN, which oversees transplants in the U.S. But the Michigan case underscores the need for more extensive sampling before transplant, especially in areas with high rates of covid transmission, Dr. Kaul said.
When it comes to lungs, that means making sure to test samples from the donor’s lower respiratory tract, as well as from the nose and throat. Obtaining and testing such samples from donors can be difficult to carry out in a timely fashion. There’s also the risk of introducing infection into the donated lungs, Dr. Kaul said.
Because no organs other than lungs were used, the Michigan case doesn’t provide insight into testing protocols for other organs.
Overall, viral transmissions from organ donors to recipients remain rare, occurring in fewer than 1% of transplant recipients, research shows. The medical risks facing ailing patients who reject a donor organ are generally far higher, said Dr. David Klassen, chief medical officer with the United Network for Organ Sharing, the federal contractor that runs the OPTN.
“The risks of turning down transplants are catastrophic,” he said. “I don’t think patients should be afraid of the transplant process.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Doctors say a woman in Michigan contracted COVID-19 and died last fall 2 months after receiving a tainted double-lung transplant from a donor who turned out to harbor the virus that causes the disease – despite showing no signs of illness and initially testing negative.
Officials at the University of Michigan Medical School suggested it may be the first proven case of COVID-19 in the U.S. in which the virus was transmitted via an organ transplant. A surgeon who handled the donor lungs was also infected with the virus and fell ill but later recovered.
The incident appears to be isolated – the only confirmed case among nearly 40,000 transplants in 2020. But it has led to calls for more thorough testing of lung transplant donors, with samples taken from deep within the donor lungs as well as the nose and throat, said Dr. Daniel Kaul, director of Michigan Medicine’s transplant infectious disease service.
“We would absolutely not have used the lungs if we’d had a positive COVID-19 test,” said Dr. Kaul, who coauthored a report about the case in the American Journal of Transplantation.
The virus was transmitted when lungs from a woman from the Upper Midwest, who died after suffering a severe brain injury in a car accident, were transplanted into a woman with chronic obstructive lung disease at University Hospital in Ann Arbor. The nose and throat samples routinely collected from both organ donors and recipients tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes covid.
“All the screening that we normally do and are able to do, we did,” Dr. Kaul said.
Three days after the operation, however, the recipient spiked a fever; her blood pressure fell and her breathing became labored. Imaging showed signs of lung infection.
As her condition worsened, the patient developed septic shock and heart function problems. Doctors decided to test for SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Kaul said. Samples from her new lungs came back positive.
Suspicious about the origin of the infection, doctors returned to samples from the transplant donor. A molecular test of a swab from the donor’s nose and throat, taken 48 hours after her lungs were procured, had been negative for SARS-Cov-2. The donor’s family told doctors she had no history of recent travel or COVID-19 symptoms and no known exposure to anyone with the disease.
But doctors had kept a sample of fluid washed from deep within the donor lungs. When they tested that fluid, it was positive for the virus. Four days after the transplant, the surgeon who handled the donor lungs and performed the surgery tested positive, too. Genetic screening revealed that the transplant recipient and the surgeon had been infected by the donor. Ten other members of the transplant team tested negative for the virus.
The transplant recipient deteriorated rapidly, developing multisystem organ failure. Doctors tried known treatments for COVID-19, including remdesivir, a newly approved drug, and convalescent blood plasma from people previously infected with the disease. Eventually, she was placed on the last-resort option of ECMO, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, to no avail. Life support was withdrawn, and she died 61 days after the transplant.
Dr. Kaul called the incident “a tragic case.”
While the Michigan case marks the first confirmed incident in the U.S. of transmission through a transplant, others have been suspected. A recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report reviewed eight possible cases of what’s known as donor-derived infection that occurred last spring, but concluded the most likely source of transmission of the COVID-19 virus in those cases was in a community or health care setting.
Before this incident, it was not clear whether the COVID-19 virus could be transmitted through solid organ transplants, though it’s well documented with other respiratory viruses. Donor transmission of H1N1 2009 pandemic influenza has been detected almost exclusively in lung transplant recipients, Dr. Kaul noted.
While it’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 can be transmitted through infected lungs, it remains uncertain whether other organs affected by COVID-19 – hearts, livers and kidneys, for instance – can transmit the virus, too.
“It seems for non-lung donors that it may be very difficult to transmit COVID-19, even if the donor has COVID-19,” Dr. Kaul said.
Organ donors have been tested routinely for SARS-CoV-2 during the pandemic, though it’s not required by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, or OPTN, which oversees transplants in the U.S. But the Michigan case underscores the need for more extensive sampling before transplant, especially in areas with high rates of covid transmission, Dr. Kaul said.
When it comes to lungs, that means making sure to test samples from the donor’s lower respiratory tract, as well as from the nose and throat. Obtaining and testing such samples from donors can be difficult to carry out in a timely fashion. There’s also the risk of introducing infection into the donated lungs, Dr. Kaul said.
Because no organs other than lungs were used, the Michigan case doesn’t provide insight into testing protocols for other organs.
Overall, viral transmissions from organ donors to recipients remain rare, occurring in fewer than 1% of transplant recipients, research shows. The medical risks facing ailing patients who reject a donor organ are generally far higher, said Dr. David Klassen, chief medical officer with the United Network for Organ Sharing, the federal contractor that runs the OPTN.
“The risks of turning down transplants are catastrophic,” he said. “I don’t think patients should be afraid of the transplant process.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Doctors say a woman in Michigan contracted COVID-19 and died last fall 2 months after receiving a tainted double-lung transplant from a donor who turned out to harbor the virus that causes the disease – despite showing no signs of illness and initially testing negative.
Officials at the University of Michigan Medical School suggested it may be the first proven case of COVID-19 in the U.S. in which the virus was transmitted via an organ transplant. A surgeon who handled the donor lungs was also infected with the virus and fell ill but later recovered.
The incident appears to be isolated – the only confirmed case among nearly 40,000 transplants in 2020. But it has led to calls for more thorough testing of lung transplant donors, with samples taken from deep within the donor lungs as well as the nose and throat, said Dr. Daniel Kaul, director of Michigan Medicine’s transplant infectious disease service.
“We would absolutely not have used the lungs if we’d had a positive COVID-19 test,” said Dr. Kaul, who coauthored a report about the case in the American Journal of Transplantation.
The virus was transmitted when lungs from a woman from the Upper Midwest, who died after suffering a severe brain injury in a car accident, were transplanted into a woman with chronic obstructive lung disease at University Hospital in Ann Arbor. The nose and throat samples routinely collected from both organ donors and recipients tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes covid.
“All the screening that we normally do and are able to do, we did,” Dr. Kaul said.
Three days after the operation, however, the recipient spiked a fever; her blood pressure fell and her breathing became labored. Imaging showed signs of lung infection.
As her condition worsened, the patient developed septic shock and heart function problems. Doctors decided to test for SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Kaul said. Samples from her new lungs came back positive.
Suspicious about the origin of the infection, doctors returned to samples from the transplant donor. A molecular test of a swab from the donor’s nose and throat, taken 48 hours after her lungs were procured, had been negative for SARS-Cov-2. The donor’s family told doctors she had no history of recent travel or COVID-19 symptoms and no known exposure to anyone with the disease.
But doctors had kept a sample of fluid washed from deep within the donor lungs. When they tested that fluid, it was positive for the virus. Four days after the transplant, the surgeon who handled the donor lungs and performed the surgery tested positive, too. Genetic screening revealed that the transplant recipient and the surgeon had been infected by the donor. Ten other members of the transplant team tested negative for the virus.
The transplant recipient deteriorated rapidly, developing multisystem organ failure. Doctors tried known treatments for COVID-19, including remdesivir, a newly approved drug, and convalescent blood plasma from people previously infected with the disease. Eventually, she was placed on the last-resort option of ECMO, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, to no avail. Life support was withdrawn, and she died 61 days after the transplant.
Dr. Kaul called the incident “a tragic case.”
While the Michigan case marks the first confirmed incident in the U.S. of transmission through a transplant, others have been suspected. A recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report reviewed eight possible cases of what’s known as donor-derived infection that occurred last spring, but concluded the most likely source of transmission of the COVID-19 virus in those cases was in a community or health care setting.
Before this incident, it was not clear whether the COVID-19 virus could be transmitted through solid organ transplants, though it’s well documented with other respiratory viruses. Donor transmission of H1N1 2009 pandemic influenza has been detected almost exclusively in lung transplant recipients, Dr. Kaul noted.
While it’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 can be transmitted through infected lungs, it remains uncertain whether other organs affected by COVID-19 – hearts, livers and kidneys, for instance – can transmit the virus, too.
“It seems for non-lung donors that it may be very difficult to transmit COVID-19, even if the donor has COVID-19,” Dr. Kaul said.
Organ donors have been tested routinely for SARS-CoV-2 during the pandemic, though it’s not required by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, or OPTN, which oversees transplants in the U.S. But the Michigan case underscores the need for more extensive sampling before transplant, especially in areas with high rates of covid transmission, Dr. Kaul said.
When it comes to lungs, that means making sure to test samples from the donor’s lower respiratory tract, as well as from the nose and throat. Obtaining and testing such samples from donors can be difficult to carry out in a timely fashion. There’s also the risk of introducing infection into the donated lungs, Dr. Kaul said.
Because no organs other than lungs were used, the Michigan case doesn’t provide insight into testing protocols for other organs.
Overall, viral transmissions from organ donors to recipients remain rare, occurring in fewer than 1% of transplant recipients, research shows. The medical risks facing ailing patients who reject a donor organ are generally far higher, said Dr. David Klassen, chief medical officer with the United Network for Organ Sharing, the federal contractor that runs the OPTN.
“The risks of turning down transplants are catastrophic,” he said. “I don’t think patients should be afraid of the transplant process.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
More from DAPA-HF: Dapagliflozin quickly reduces heart failure events
Dapagliflozin’s benefits in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction appeared quickly after treatment began, and patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within the prior year got the biggest boost from the drug, according to secondary analyses of the more than 4,700-patient DAPA-HF trial.
Dapagliflozin’s significant reduction of the incidence of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure became apparent in DAPA-HF within 28 days after patients started treatment, by which time those on the study drug had a 49% cut in this combined endpoint, compared with patients on placebo, David D. Berg, MD, and associates said in a recent report published in JAMA Cardiology.
Their analyses also showed that the absolute reduction linked with dapagliflozin treatment for this primary endpoint of the study (which classified worsening heart failure as either hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent visit because of heart failure that required intravenous therapy) was greatest, 10% during 2 years of follow-up, among the roughly one-quarter of enrolled patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within 12 months of entering the study. Patients previously hospitalized for heart failure more than 12 months before they entered DAPA-HF had a 4% absolute cut in their primary-outcome events during the trial, and those who had never been hospitalized for heart failure had a 2% absolute benefit, compared with placebo, during 2 years of follow-up.
These findings were consistent with the timing of benefits for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in recent studies of two other drugs from the same class, the sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitors, including empagliflozin (Jardiance, which inhibits SGLT-2) in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial, and sotagliflozin (Zynquista, which inhibits both SGLT1 and -2) in the SOLOIST-WHF trial, noted Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, and Clyde W. Yancy, MD, in an editor’s note that accompanied the new report.
The new findings show “the opportunity to expeditiously implement this remarkable class of therapy for HFrEF is now compelling and deserves disruptive efforts to ensure comprehensive treatment and the best patient outcomes,” wrote Dr. Fonarow, a professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Yancy, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
But despite these new findings, their exact meaning remains unclear in terms of when to start dapagliflozin (or a different drug from the same class), compared with the other drug classes that have proven highly effective in patients with HFrEF, and exactly how long after hospitalization for heart failure dapagliflozin can safely and effectively begin.
Data needed on starting an SGLT inhibitor soon after hospitalization in patients without diabetes
“DAPA-HF showed that, in patients with or without diabetes, an SGLT2 inhibitor reduced the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with stable HFrEF. SOLOIST-WHF looked strictly at patients with diabetes, and showed that a combined SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor could reduce the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with recently decompensated heart failure,” Dr. Berg, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted in an interview. “What we don’t have is a trial focused exclusively on enrolling patients while hospitalized with acute heart failure, irrespective of whether they have diabetes, and testing the immediate clinical efficacy and safety of starting an SGLT2 inhibitor. That is what we are testing with the ongoing DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68 trial.”
In addition, updated recommendations from the American College of Cardiology on initiating drug therapy in patients newly diagnosed with HFrEF that appeared in early 2021 promoted a sequence that starts most patients on sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) and a beta-blocker, followed by a diuretic (when needed), a mineralocorticoid receptor agonist, and then an SGLT inhibitor. The recommendations note that starting a patient on all these drug classes could take 3-6 months.
“There are intense debates about the optimal sequence for introducing these therapies, and I don’t think we have solid data to suggest that one sequence is clearly better than another,” noted Dr. Berg. “A one-size-fits-all approach probably doesn’t make sense. For example, each of these therapies has a different set of effects on heart rate and blood pressure, and each has a unique side effect profile, so clinicians will often need to tailor the treatment approach to the patient. And, of course, cost is an important consideration. Although the optimal time to start an SGLT2 inhibitor remains uncertain, the results of our analysis suggest that waiting may result in preventable adverse heart failure events.”
DAPA-HF randomized 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV at 410 sites in 20 countries. The incidence of the primary, combined endpoint fell by 26% with dapagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, during a median 18-month follow-up. Among the study cohort 27% of patients had been hospitalized for heart failure within a year of their entry, 20% had been hospitalized for heart failure more than 1 year before entry, and 53% had no history of a hospitalization for heart failure.
DAPA-HF was sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Berg has received research support through his institution from AstraZeneca. Dr. Fonarow has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from numerous other companies. Dr. Yancy’s spouse works for Abbott Laboratories.
Dapagliflozin’s benefits in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction appeared quickly after treatment began, and patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within the prior year got the biggest boost from the drug, according to secondary analyses of the more than 4,700-patient DAPA-HF trial.
Dapagliflozin’s significant reduction of the incidence of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure became apparent in DAPA-HF within 28 days after patients started treatment, by which time those on the study drug had a 49% cut in this combined endpoint, compared with patients on placebo, David D. Berg, MD, and associates said in a recent report published in JAMA Cardiology.
Their analyses also showed that the absolute reduction linked with dapagliflozin treatment for this primary endpoint of the study (which classified worsening heart failure as either hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent visit because of heart failure that required intravenous therapy) was greatest, 10% during 2 years of follow-up, among the roughly one-quarter of enrolled patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within 12 months of entering the study. Patients previously hospitalized for heart failure more than 12 months before they entered DAPA-HF had a 4% absolute cut in their primary-outcome events during the trial, and those who had never been hospitalized for heart failure had a 2% absolute benefit, compared with placebo, during 2 years of follow-up.
These findings were consistent with the timing of benefits for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in recent studies of two other drugs from the same class, the sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitors, including empagliflozin (Jardiance, which inhibits SGLT-2) in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial, and sotagliflozin (Zynquista, which inhibits both SGLT1 and -2) in the SOLOIST-WHF trial, noted Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, and Clyde W. Yancy, MD, in an editor’s note that accompanied the new report.
The new findings show “the opportunity to expeditiously implement this remarkable class of therapy for HFrEF is now compelling and deserves disruptive efforts to ensure comprehensive treatment and the best patient outcomes,” wrote Dr. Fonarow, a professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Yancy, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
But despite these new findings, their exact meaning remains unclear in terms of when to start dapagliflozin (or a different drug from the same class), compared with the other drug classes that have proven highly effective in patients with HFrEF, and exactly how long after hospitalization for heart failure dapagliflozin can safely and effectively begin.
Data needed on starting an SGLT inhibitor soon after hospitalization in patients without diabetes
“DAPA-HF showed that, in patients with or without diabetes, an SGLT2 inhibitor reduced the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with stable HFrEF. SOLOIST-WHF looked strictly at patients with diabetes, and showed that a combined SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor could reduce the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with recently decompensated heart failure,” Dr. Berg, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted in an interview. “What we don’t have is a trial focused exclusively on enrolling patients while hospitalized with acute heart failure, irrespective of whether they have diabetes, and testing the immediate clinical efficacy and safety of starting an SGLT2 inhibitor. That is what we are testing with the ongoing DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68 trial.”
In addition, updated recommendations from the American College of Cardiology on initiating drug therapy in patients newly diagnosed with HFrEF that appeared in early 2021 promoted a sequence that starts most patients on sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) and a beta-blocker, followed by a diuretic (when needed), a mineralocorticoid receptor agonist, and then an SGLT inhibitor. The recommendations note that starting a patient on all these drug classes could take 3-6 months.
“There are intense debates about the optimal sequence for introducing these therapies, and I don’t think we have solid data to suggest that one sequence is clearly better than another,” noted Dr. Berg. “A one-size-fits-all approach probably doesn’t make sense. For example, each of these therapies has a different set of effects on heart rate and blood pressure, and each has a unique side effect profile, so clinicians will often need to tailor the treatment approach to the patient. And, of course, cost is an important consideration. Although the optimal time to start an SGLT2 inhibitor remains uncertain, the results of our analysis suggest that waiting may result in preventable adverse heart failure events.”
DAPA-HF randomized 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV at 410 sites in 20 countries. The incidence of the primary, combined endpoint fell by 26% with dapagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, during a median 18-month follow-up. Among the study cohort 27% of patients had been hospitalized for heart failure within a year of their entry, 20% had been hospitalized for heart failure more than 1 year before entry, and 53% had no history of a hospitalization for heart failure.
DAPA-HF was sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Berg has received research support through his institution from AstraZeneca. Dr. Fonarow has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from numerous other companies. Dr. Yancy’s spouse works for Abbott Laboratories.
Dapagliflozin’s benefits in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction appeared quickly after treatment began, and patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within the prior year got the biggest boost from the drug, according to secondary analyses of the more than 4,700-patient DAPA-HF trial.
Dapagliflozin’s significant reduction of the incidence of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure became apparent in DAPA-HF within 28 days after patients started treatment, by which time those on the study drug had a 49% cut in this combined endpoint, compared with patients on placebo, David D. Berg, MD, and associates said in a recent report published in JAMA Cardiology.
Their analyses also showed that the absolute reduction linked with dapagliflozin treatment for this primary endpoint of the study (which classified worsening heart failure as either hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent visit because of heart failure that required intravenous therapy) was greatest, 10% during 2 years of follow-up, among the roughly one-quarter of enrolled patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within 12 months of entering the study. Patients previously hospitalized for heart failure more than 12 months before they entered DAPA-HF had a 4% absolute cut in their primary-outcome events during the trial, and those who had never been hospitalized for heart failure had a 2% absolute benefit, compared with placebo, during 2 years of follow-up.
These findings were consistent with the timing of benefits for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in recent studies of two other drugs from the same class, the sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitors, including empagliflozin (Jardiance, which inhibits SGLT-2) in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial, and sotagliflozin (Zynquista, which inhibits both SGLT1 and -2) in the SOLOIST-WHF trial, noted Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, and Clyde W. Yancy, MD, in an editor’s note that accompanied the new report.
The new findings show “the opportunity to expeditiously implement this remarkable class of therapy for HFrEF is now compelling and deserves disruptive efforts to ensure comprehensive treatment and the best patient outcomes,” wrote Dr. Fonarow, a professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Yancy, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
But despite these new findings, their exact meaning remains unclear in terms of when to start dapagliflozin (or a different drug from the same class), compared with the other drug classes that have proven highly effective in patients with HFrEF, and exactly how long after hospitalization for heart failure dapagliflozin can safely and effectively begin.
Data needed on starting an SGLT inhibitor soon after hospitalization in patients without diabetes
“DAPA-HF showed that, in patients with or without diabetes, an SGLT2 inhibitor reduced the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with stable HFrEF. SOLOIST-WHF looked strictly at patients with diabetes, and showed that a combined SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor could reduce the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with recently decompensated heart failure,” Dr. Berg, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted in an interview. “What we don’t have is a trial focused exclusively on enrolling patients while hospitalized with acute heart failure, irrespective of whether they have diabetes, and testing the immediate clinical efficacy and safety of starting an SGLT2 inhibitor. That is what we are testing with the ongoing DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68 trial.”
In addition, updated recommendations from the American College of Cardiology on initiating drug therapy in patients newly diagnosed with HFrEF that appeared in early 2021 promoted a sequence that starts most patients on sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) and a beta-blocker, followed by a diuretic (when needed), a mineralocorticoid receptor agonist, and then an SGLT inhibitor. The recommendations note that starting a patient on all these drug classes could take 3-6 months.
“There are intense debates about the optimal sequence for introducing these therapies, and I don’t think we have solid data to suggest that one sequence is clearly better than another,” noted Dr. Berg. “A one-size-fits-all approach probably doesn’t make sense. For example, each of these therapies has a different set of effects on heart rate and blood pressure, and each has a unique side effect profile, so clinicians will often need to tailor the treatment approach to the patient. And, of course, cost is an important consideration. Although the optimal time to start an SGLT2 inhibitor remains uncertain, the results of our analysis suggest that waiting may result in preventable adverse heart failure events.”
DAPA-HF randomized 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV at 410 sites in 20 countries. The incidence of the primary, combined endpoint fell by 26% with dapagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, during a median 18-month follow-up. Among the study cohort 27% of patients had been hospitalized for heart failure within a year of their entry, 20% had been hospitalized for heart failure more than 1 year before entry, and 53% had no history of a hospitalization for heart failure.
DAPA-HF was sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Berg has received research support through his institution from AstraZeneca. Dr. Fonarow has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from numerous other companies. Dr. Yancy’s spouse works for Abbott Laboratories.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY