User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Severe COVID-19 adds 20 years of cognitive aging: Study
adding that the impairment is “equivalent to losing 10 IQ points.”
In their study, published in eClinicalMedicine, a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London said there is growing evidence that COVID-19 can cause lasting cognitive and mental health problems. Patients report fatigue, “brain fog,” problems recalling words, sleep disturbances, anxiety, and even posttraumatic stress disorder months after infection.
The researchers analyzed data from 46 individuals who received critical care for COVID-19 at Addenbrooke’s Hospital between March and July 2020 (27 females, 19 males, mean age 51 years, 16 of whom had mechanical ventilation) and were recruited to the NIHR COVID-19 BioResource project.
At an average of 6 months after acute COVID-19 illness, the study participants underwent detailed computerized cognitive tests via the Cognitron platform, comprising eight tasks deployed on an iPad measuring mental function such as memory, attention, and reasoning. Also assessed were anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder via standard mood, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress scales – specifically the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), and the PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (PCL-5). Their data were compared against 460 controls – matched for age, sex, education, and first language – and the pattern of deficits across tasks was qualitatively compared with normal age-related decline and early-stage dementia.
Less accurate and slower response times
The authors highlighted how this was the first time a “rigorous assessment and comparison” had been carried out in relation to the after-effects of severe COVID-19.
“Cognitive impairment is common to a wide range of neurological disorders, including dementia, and even routine aging, but the patterns we saw – the cognitive ‘fingerprint’ of COVID-19 – was distinct from all of these,” said David Menon, MD, division of anesthesia at the University of Cambridge, England, and the study’s senior author.
The scientists found that COVID-19 survivors were less accurate and had slower response times than the control population, and added that survivors scored particularly poorly on verbal analogical reasoning and showed slower processing speeds.
Critically, the scale of the cognitive deficits correlated with acute illness severity, but not fatigue or mental health status at the time of cognitive assessment, said the authors.
Recovery ‘at best gradual’
The effects were strongest for those with more severe acute illness, and who required mechanical ventilation, said the authors, who found that acute illness severity was “better at predicting the cognitive deficits.”
The authors pointed out how these deficits were still detectable when patients were followed up 6 months later, and that, although patients’ scores and reaction times began to improve over time, any recovery was “at best gradual” and likely to be influenced by factors such as illness severity and its neurological or psychological impacts.
“We followed some patients up as late as 10 months after their acute infection, so were able to see a very slow improvement,” Dr. Menon said. He explained how, while this improvement was not statistically significant, it was “at least heading in the right direction.”
However, he warned it is very possible that some of these individuals “will never fully recover.”
The cognitive deficits observed may be due to several factors in combination, said the authors, including inadequate oxygen or blood supply to the brain, blockage of large or small blood vessels due to clotting, and microscopic bleeds. They highlighted how the most important mechanism, however, may be “damage caused by the body’s own inflammatory response and immune system.”
Adam Hampshire, PhD, of the department of brain sciences at Imperial College London, one of the study’s authors, described how around 40,000 people have been through intensive care with COVID-19 in England alone, with many more despite having been very sick not admitted to hospital. This means there is a “large number of people out there still experiencing problems with cognition many months later,” he said. “We urgently need to look at what can be done to help these people.”
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
adding that the impairment is “equivalent to losing 10 IQ points.”
In their study, published in eClinicalMedicine, a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London said there is growing evidence that COVID-19 can cause lasting cognitive and mental health problems. Patients report fatigue, “brain fog,” problems recalling words, sleep disturbances, anxiety, and even posttraumatic stress disorder months after infection.
The researchers analyzed data from 46 individuals who received critical care for COVID-19 at Addenbrooke’s Hospital between March and July 2020 (27 females, 19 males, mean age 51 years, 16 of whom had mechanical ventilation) and were recruited to the NIHR COVID-19 BioResource project.
At an average of 6 months after acute COVID-19 illness, the study participants underwent detailed computerized cognitive tests via the Cognitron platform, comprising eight tasks deployed on an iPad measuring mental function such as memory, attention, and reasoning. Also assessed were anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder via standard mood, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress scales – specifically the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), and the PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (PCL-5). Their data were compared against 460 controls – matched for age, sex, education, and first language – and the pattern of deficits across tasks was qualitatively compared with normal age-related decline and early-stage dementia.
Less accurate and slower response times
The authors highlighted how this was the first time a “rigorous assessment and comparison” had been carried out in relation to the after-effects of severe COVID-19.
“Cognitive impairment is common to a wide range of neurological disorders, including dementia, and even routine aging, but the patterns we saw – the cognitive ‘fingerprint’ of COVID-19 – was distinct from all of these,” said David Menon, MD, division of anesthesia at the University of Cambridge, England, and the study’s senior author.
The scientists found that COVID-19 survivors were less accurate and had slower response times than the control population, and added that survivors scored particularly poorly on verbal analogical reasoning and showed slower processing speeds.
Critically, the scale of the cognitive deficits correlated with acute illness severity, but not fatigue or mental health status at the time of cognitive assessment, said the authors.
Recovery ‘at best gradual’
The effects were strongest for those with more severe acute illness, and who required mechanical ventilation, said the authors, who found that acute illness severity was “better at predicting the cognitive deficits.”
The authors pointed out how these deficits were still detectable when patients were followed up 6 months later, and that, although patients’ scores and reaction times began to improve over time, any recovery was “at best gradual” and likely to be influenced by factors such as illness severity and its neurological or psychological impacts.
“We followed some patients up as late as 10 months after their acute infection, so were able to see a very slow improvement,” Dr. Menon said. He explained how, while this improvement was not statistically significant, it was “at least heading in the right direction.”
However, he warned it is very possible that some of these individuals “will never fully recover.”
The cognitive deficits observed may be due to several factors in combination, said the authors, including inadequate oxygen or blood supply to the brain, blockage of large or small blood vessels due to clotting, and microscopic bleeds. They highlighted how the most important mechanism, however, may be “damage caused by the body’s own inflammatory response and immune system.”
Adam Hampshire, PhD, of the department of brain sciences at Imperial College London, one of the study’s authors, described how around 40,000 people have been through intensive care with COVID-19 in England alone, with many more despite having been very sick not admitted to hospital. This means there is a “large number of people out there still experiencing problems with cognition many months later,” he said. “We urgently need to look at what can be done to help these people.”
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
adding that the impairment is “equivalent to losing 10 IQ points.”
In their study, published in eClinicalMedicine, a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London said there is growing evidence that COVID-19 can cause lasting cognitive and mental health problems. Patients report fatigue, “brain fog,” problems recalling words, sleep disturbances, anxiety, and even posttraumatic stress disorder months after infection.
The researchers analyzed data from 46 individuals who received critical care for COVID-19 at Addenbrooke’s Hospital between March and July 2020 (27 females, 19 males, mean age 51 years, 16 of whom had mechanical ventilation) and were recruited to the NIHR COVID-19 BioResource project.
At an average of 6 months after acute COVID-19 illness, the study participants underwent detailed computerized cognitive tests via the Cognitron platform, comprising eight tasks deployed on an iPad measuring mental function such as memory, attention, and reasoning. Also assessed were anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder via standard mood, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress scales – specifically the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7), the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), and the PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (PCL-5). Their data were compared against 460 controls – matched for age, sex, education, and first language – and the pattern of deficits across tasks was qualitatively compared with normal age-related decline and early-stage dementia.
Less accurate and slower response times
The authors highlighted how this was the first time a “rigorous assessment and comparison” had been carried out in relation to the after-effects of severe COVID-19.
“Cognitive impairment is common to a wide range of neurological disorders, including dementia, and even routine aging, but the patterns we saw – the cognitive ‘fingerprint’ of COVID-19 – was distinct from all of these,” said David Menon, MD, division of anesthesia at the University of Cambridge, England, and the study’s senior author.
The scientists found that COVID-19 survivors were less accurate and had slower response times than the control population, and added that survivors scored particularly poorly on verbal analogical reasoning and showed slower processing speeds.
Critically, the scale of the cognitive deficits correlated with acute illness severity, but not fatigue or mental health status at the time of cognitive assessment, said the authors.
Recovery ‘at best gradual’
The effects were strongest for those with more severe acute illness, and who required mechanical ventilation, said the authors, who found that acute illness severity was “better at predicting the cognitive deficits.”
The authors pointed out how these deficits were still detectable when patients were followed up 6 months later, and that, although patients’ scores and reaction times began to improve over time, any recovery was “at best gradual” and likely to be influenced by factors such as illness severity and its neurological or psychological impacts.
“We followed some patients up as late as 10 months after their acute infection, so were able to see a very slow improvement,” Dr. Menon said. He explained how, while this improvement was not statistically significant, it was “at least heading in the right direction.”
However, he warned it is very possible that some of these individuals “will never fully recover.”
The cognitive deficits observed may be due to several factors in combination, said the authors, including inadequate oxygen or blood supply to the brain, blockage of large or small blood vessels due to clotting, and microscopic bleeds. They highlighted how the most important mechanism, however, may be “damage caused by the body’s own inflammatory response and immune system.”
Adam Hampshire, PhD, of the department of brain sciences at Imperial College London, one of the study’s authors, described how around 40,000 people have been through intensive care with COVID-19 in England alone, with many more despite having been very sick not admitted to hospital. This means there is a “large number of people out there still experiencing problems with cognition many months later,” he said. “We urgently need to look at what can be done to help these people.”
A version of this article first appeared on Univadis.
FROM ECLINICAL MEDICINE
‘Embarrassing’: High-intensity statin uptake in ASCVD patients ‘terrible’
New research suggests physicians face a Herculean task to get Americans with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) to take high-intensity statins, despite multiple professional guidelines giving the therapy their highest level recommendation.
Results from more 600,000 commercially insured patients with established ASCVD showed:
- Only one in five patients (22.5%) were taking a high-intensity statin.
- 27.6% were taking a low- or moderate-intensity statin.
- One-half (49.9%) were not taking any statin.
“It’s embarrassing,” senior author Christopher B. Granger, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., told this news organization. “It should be embarrassing for anybody in health care that we do such a terrible job with something so simple and effective.”
The results were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Statins have been shown to reduce the risk for ASCVD events by about 30%, with an added 15% reduction with a high-intensity formulation. The class I recommendation for high-intensity statin use in ASCVD patients younger than 75 years in the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association cholesterol guidelines prompted a jump in prescriptions that plateaued by 2017.
A class II recommendation was added to the 2018 guideline update for high-intensity statins in adults older than 75 years with ASCVD. But underuse persists, despite falling prices with generic availability and initiatives to improve statin adoption, the authors noted.
“There are a lot of barriers for patients to statin use, including the misinformation on the Internet and elsewhere that statins have all kinds of side effects,” Dr. Granger said. “They have uncommon side effects, but when we look at it carefully, only about 10% of patients, even with statin intolerance, have true intolerance.”
Efforts are needed to better understand and address these barriers, particularly for younger and female patients, he noted.
In multivariate analyses, patients who were middle-aged (odds ratio, 2.66) or at least 75 years of age (OR, 2.09) were more than twice as likely as patients younger than 45 years to be on any statin.
Not surprisingly, women were 30% less likely than men to receive a statin (OR, 0.70), Dr. Granger said. A high Charlson comorbidity score (OR, 0.72) and peripheral artery disease (OR, 0.55) also reduced the odds of a statin prescription.
Among statin users, middle-aged (OR, 0.83) and older (OR, 0.44) patients were less likely to be on a high-intensity statin, as were women (OR, 0.68) and patients with peripheral artery disease (OR, 0.43).
Visiting a cardiologist in the previous 12 months, however, increased the odds a patient was on a high-intensity statin (OR, 1.21), as did the use of other LDL-cholesterol-lowering drugs (OR, 1.44).
“With no evidence of heterogeneity in efficacy by sex, ongoing work must not only address misperceptions and barriers to the prescription of high-intensity statins in women, but also further understand (and address) differences in tolerability, which may be related to sex-based variation in statin metabolism,” wrote the authors, led by Adam J. Nelson, MBBS, MBA, MPH, also from Duke.
The study involved 601,934 patients (mean age, 67.5 years) who had a diagnosis of ASCVD between Jan. 31, 2018, and an index date of Jan. 31, 2019, and were enrolled in the HealthCore Integrated Research Environment database.
Two-thirds (70.9%) of patients visited a cardiologist in the 12 months prior to the index date, and three-fourths (81.3%) visited a primary care provider.
Pharmacy claims for the 12 months after the index date showed 82.8% of high-intensity users at index achieved coverage for at least 75% of days. Those with the least adherence (< 50% of days covered) included younger patients, as well as those with chronic kidney disease or depression.
“We need implementation research. What are the tools and the methods that we can use to improve the proportion of patients who are having the life-saving benefits from statins?” Dr. Granger said.
He noted that the team has submitted a National Institutes of Health grant to try to use pharmacists, as a mechanism within the context of health systems and payer systems, to improve the appropriate use of statins in a randomized trial. “I think that’s a win.”
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, and Michael DeBakey VA Medical Center, Houston, and colleagues point out in a related editorial that the rates of statin usage in the study are “considerably lower” than in other contemporary studies, where about 80% and 50% of ASCVD patients are receiving statins and high-intensity statins, respectively.
Possible explanations are the use of rule-out codes, a short medication fill window from the index date, or issues with medication capture, they said. “Nevertheless, the findings are largely consistent with other work highlighting low use of statin therapy.”
The editorialists said social media, statin-related adverse effects, and therapeutic inertia are key drivers of non–guideline-concordant statin use. Possible solutions include improving guideline dissemination, leveraging team-based care, using smart clinical decision-support tools at the point of care, and identifying trustworthy and easily understood sources of information for patients.
“We can only hope that the fate of statin therapy is not repeated with sodium-glucose cotranspoerter-2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in another 30 years, or worse yet, that continued gaps in statin therapy use in patients with ASCVD persist 30 years from now,” Dr. Virani and colleagues concluded.
A sliver of optimism?
A research letter by Colantonio et al. in the same issue of JACC points to some positive steps, at least among patients having a myocardial infarction (MI). It reported that the percentage of patients who received a high-intensity statin as their first statin prescription 30 days after MI jumped from 30.7% in the first quarter of 2011 to 78.6% in the fourth quarter of 2019.
Similar increases were reported by race/ethnicity, despite statin use previously shown to be lower among non-Hispanic Black patients with ASCVD. In each calendar year, however, high-intensity statin therapy was lower among patients older than 75 years and among women.
Dr. Granger disclosed ties with Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, AKROS, Apple, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Food and Drug Administration, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic Foundation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Bayer, Boston Scientific, CeleCor Therapeutics, Correvio, Espero BioPharma, Medscape, Medtronic, Merck, National Institutes of Health, Novo Nordisk, Rhoshan Pharmaceuticals, and Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Virani disclosed ties with the Department of Veterans Affairs, the National Institutes of Health, the World Heart Federation, and the Jooma and Tahir Family, and the American College of Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research suggests physicians face a Herculean task to get Americans with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) to take high-intensity statins, despite multiple professional guidelines giving the therapy their highest level recommendation.
Results from more 600,000 commercially insured patients with established ASCVD showed:
- Only one in five patients (22.5%) were taking a high-intensity statin.
- 27.6% were taking a low- or moderate-intensity statin.
- One-half (49.9%) were not taking any statin.
“It’s embarrassing,” senior author Christopher B. Granger, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., told this news organization. “It should be embarrassing for anybody in health care that we do such a terrible job with something so simple and effective.”
The results were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Statins have been shown to reduce the risk for ASCVD events by about 30%, with an added 15% reduction with a high-intensity formulation. The class I recommendation for high-intensity statin use in ASCVD patients younger than 75 years in the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association cholesterol guidelines prompted a jump in prescriptions that plateaued by 2017.
A class II recommendation was added to the 2018 guideline update for high-intensity statins in adults older than 75 years with ASCVD. But underuse persists, despite falling prices with generic availability and initiatives to improve statin adoption, the authors noted.
“There are a lot of barriers for patients to statin use, including the misinformation on the Internet and elsewhere that statins have all kinds of side effects,” Dr. Granger said. “They have uncommon side effects, but when we look at it carefully, only about 10% of patients, even with statin intolerance, have true intolerance.”
Efforts are needed to better understand and address these barriers, particularly for younger and female patients, he noted.
In multivariate analyses, patients who were middle-aged (odds ratio, 2.66) or at least 75 years of age (OR, 2.09) were more than twice as likely as patients younger than 45 years to be on any statin.
Not surprisingly, women were 30% less likely than men to receive a statin (OR, 0.70), Dr. Granger said. A high Charlson comorbidity score (OR, 0.72) and peripheral artery disease (OR, 0.55) also reduced the odds of a statin prescription.
Among statin users, middle-aged (OR, 0.83) and older (OR, 0.44) patients were less likely to be on a high-intensity statin, as were women (OR, 0.68) and patients with peripheral artery disease (OR, 0.43).
Visiting a cardiologist in the previous 12 months, however, increased the odds a patient was on a high-intensity statin (OR, 1.21), as did the use of other LDL-cholesterol-lowering drugs (OR, 1.44).
“With no evidence of heterogeneity in efficacy by sex, ongoing work must not only address misperceptions and barriers to the prescription of high-intensity statins in women, but also further understand (and address) differences in tolerability, which may be related to sex-based variation in statin metabolism,” wrote the authors, led by Adam J. Nelson, MBBS, MBA, MPH, also from Duke.
The study involved 601,934 patients (mean age, 67.5 years) who had a diagnosis of ASCVD between Jan. 31, 2018, and an index date of Jan. 31, 2019, and were enrolled in the HealthCore Integrated Research Environment database.
Two-thirds (70.9%) of patients visited a cardiologist in the 12 months prior to the index date, and three-fourths (81.3%) visited a primary care provider.
Pharmacy claims for the 12 months after the index date showed 82.8% of high-intensity users at index achieved coverage for at least 75% of days. Those with the least adherence (< 50% of days covered) included younger patients, as well as those with chronic kidney disease or depression.
“We need implementation research. What are the tools and the methods that we can use to improve the proportion of patients who are having the life-saving benefits from statins?” Dr. Granger said.
He noted that the team has submitted a National Institutes of Health grant to try to use pharmacists, as a mechanism within the context of health systems and payer systems, to improve the appropriate use of statins in a randomized trial. “I think that’s a win.”
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, and Michael DeBakey VA Medical Center, Houston, and colleagues point out in a related editorial that the rates of statin usage in the study are “considerably lower” than in other contemporary studies, where about 80% and 50% of ASCVD patients are receiving statins and high-intensity statins, respectively.
Possible explanations are the use of rule-out codes, a short medication fill window from the index date, or issues with medication capture, they said. “Nevertheless, the findings are largely consistent with other work highlighting low use of statin therapy.”
The editorialists said social media, statin-related adverse effects, and therapeutic inertia are key drivers of non–guideline-concordant statin use. Possible solutions include improving guideline dissemination, leveraging team-based care, using smart clinical decision-support tools at the point of care, and identifying trustworthy and easily understood sources of information for patients.
“We can only hope that the fate of statin therapy is not repeated with sodium-glucose cotranspoerter-2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in another 30 years, or worse yet, that continued gaps in statin therapy use in patients with ASCVD persist 30 years from now,” Dr. Virani and colleagues concluded.
A sliver of optimism?
A research letter by Colantonio et al. in the same issue of JACC points to some positive steps, at least among patients having a myocardial infarction (MI). It reported that the percentage of patients who received a high-intensity statin as their first statin prescription 30 days after MI jumped from 30.7% in the first quarter of 2011 to 78.6% in the fourth quarter of 2019.
Similar increases were reported by race/ethnicity, despite statin use previously shown to be lower among non-Hispanic Black patients with ASCVD. In each calendar year, however, high-intensity statin therapy was lower among patients older than 75 years and among women.
Dr. Granger disclosed ties with Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, AKROS, Apple, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Food and Drug Administration, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic Foundation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Bayer, Boston Scientific, CeleCor Therapeutics, Correvio, Espero BioPharma, Medscape, Medtronic, Merck, National Institutes of Health, Novo Nordisk, Rhoshan Pharmaceuticals, and Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Virani disclosed ties with the Department of Veterans Affairs, the National Institutes of Health, the World Heart Federation, and the Jooma and Tahir Family, and the American College of Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research suggests physicians face a Herculean task to get Americans with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) to take high-intensity statins, despite multiple professional guidelines giving the therapy their highest level recommendation.
Results from more 600,000 commercially insured patients with established ASCVD showed:
- Only one in five patients (22.5%) were taking a high-intensity statin.
- 27.6% were taking a low- or moderate-intensity statin.
- One-half (49.9%) were not taking any statin.
“It’s embarrassing,” senior author Christopher B. Granger, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., told this news organization. “It should be embarrassing for anybody in health care that we do such a terrible job with something so simple and effective.”
The results were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Statins have been shown to reduce the risk for ASCVD events by about 30%, with an added 15% reduction with a high-intensity formulation. The class I recommendation for high-intensity statin use in ASCVD patients younger than 75 years in the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association cholesterol guidelines prompted a jump in prescriptions that plateaued by 2017.
A class II recommendation was added to the 2018 guideline update for high-intensity statins in adults older than 75 years with ASCVD. But underuse persists, despite falling prices with generic availability and initiatives to improve statin adoption, the authors noted.
“There are a lot of barriers for patients to statin use, including the misinformation on the Internet and elsewhere that statins have all kinds of side effects,” Dr. Granger said. “They have uncommon side effects, but when we look at it carefully, only about 10% of patients, even with statin intolerance, have true intolerance.”
Efforts are needed to better understand and address these barriers, particularly for younger and female patients, he noted.
In multivariate analyses, patients who were middle-aged (odds ratio, 2.66) or at least 75 years of age (OR, 2.09) were more than twice as likely as patients younger than 45 years to be on any statin.
Not surprisingly, women were 30% less likely than men to receive a statin (OR, 0.70), Dr. Granger said. A high Charlson comorbidity score (OR, 0.72) and peripheral artery disease (OR, 0.55) also reduced the odds of a statin prescription.
Among statin users, middle-aged (OR, 0.83) and older (OR, 0.44) patients were less likely to be on a high-intensity statin, as were women (OR, 0.68) and patients with peripheral artery disease (OR, 0.43).
Visiting a cardiologist in the previous 12 months, however, increased the odds a patient was on a high-intensity statin (OR, 1.21), as did the use of other LDL-cholesterol-lowering drugs (OR, 1.44).
“With no evidence of heterogeneity in efficacy by sex, ongoing work must not only address misperceptions and barriers to the prescription of high-intensity statins in women, but also further understand (and address) differences in tolerability, which may be related to sex-based variation in statin metabolism,” wrote the authors, led by Adam J. Nelson, MBBS, MBA, MPH, also from Duke.
The study involved 601,934 patients (mean age, 67.5 years) who had a diagnosis of ASCVD between Jan. 31, 2018, and an index date of Jan. 31, 2019, and were enrolled in the HealthCore Integrated Research Environment database.
Two-thirds (70.9%) of patients visited a cardiologist in the 12 months prior to the index date, and three-fourths (81.3%) visited a primary care provider.
Pharmacy claims for the 12 months after the index date showed 82.8% of high-intensity users at index achieved coverage for at least 75% of days. Those with the least adherence (< 50% of days covered) included younger patients, as well as those with chronic kidney disease or depression.
“We need implementation research. What are the tools and the methods that we can use to improve the proportion of patients who are having the life-saving benefits from statins?” Dr. Granger said.
He noted that the team has submitted a National Institutes of Health grant to try to use pharmacists, as a mechanism within the context of health systems and payer systems, to improve the appropriate use of statins in a randomized trial. “I think that’s a win.”
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, Baylor College of Medicine, and Michael DeBakey VA Medical Center, Houston, and colleagues point out in a related editorial that the rates of statin usage in the study are “considerably lower” than in other contemporary studies, where about 80% and 50% of ASCVD patients are receiving statins and high-intensity statins, respectively.
Possible explanations are the use of rule-out codes, a short medication fill window from the index date, or issues with medication capture, they said. “Nevertheless, the findings are largely consistent with other work highlighting low use of statin therapy.”
The editorialists said social media, statin-related adverse effects, and therapeutic inertia are key drivers of non–guideline-concordant statin use. Possible solutions include improving guideline dissemination, leveraging team-based care, using smart clinical decision-support tools at the point of care, and identifying trustworthy and easily understood sources of information for patients.
“We can only hope that the fate of statin therapy is not repeated with sodium-glucose cotranspoerter-2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in another 30 years, or worse yet, that continued gaps in statin therapy use in patients with ASCVD persist 30 years from now,” Dr. Virani and colleagues concluded.
A sliver of optimism?
A research letter by Colantonio et al. in the same issue of JACC points to some positive steps, at least among patients having a myocardial infarction (MI). It reported that the percentage of patients who received a high-intensity statin as their first statin prescription 30 days after MI jumped from 30.7% in the first quarter of 2011 to 78.6% in the fourth quarter of 2019.
Similar increases were reported by race/ethnicity, despite statin use previously shown to be lower among non-Hispanic Black patients with ASCVD. In each calendar year, however, high-intensity statin therapy was lower among patients older than 75 years and among women.
Dr. Granger disclosed ties with Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, AKROS, Apple, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Food and Drug Administration, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic Foundation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Bayer, Boston Scientific, CeleCor Therapeutics, Correvio, Espero BioPharma, Medscape, Medtronic, Merck, National Institutes of Health, Novo Nordisk, Rhoshan Pharmaceuticals, and Roche Diagnostics. Dr. Virani disclosed ties with the Department of Veterans Affairs, the National Institutes of Health, the World Heart Federation, and the Jooma and Tahir Family, and the American College of Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When it’s not long, but medium COVID?
Symptom timelines surrounding COVID infection tend to center on either the immediate 5-day quarantine protocols for acute infection or the long-COVID symptoms that can last a month or potentially far longer.
People may return to work or daily routines, but something is off: What had been simple exercise regimens become onerous. Everyday tasks take more effort.
Does this ill-defined subset point to a “medium COVID?”
Farha Ikramuddin, MD, MHA, a physiatrist and rehabilitation specialist at the University of Minnesota and M Health Fairview in Minneapolis, points out there is no definition or diagnostic code or shared official understanding of a middle category for COVID.
“But am I seeing that? Absolutely,” she said in an interview.
“I have seen patients who are younger, healthier, [and] with not so many comorbidities have either persistence of symptoms or reappearance after the initial infection is done,” she said.
Some patients report they had very low infection or were nonsymptomatic and returned to their normal health fairly quickly after infection. Then a week later they began experiencing fatigue, lost appetite, loss of smell, and feeling full after a few bites, Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Part of the trouble in categorizing the space between returning to normal after a week and having symptoms for months is that organizations can’t agree on a timeline for when symptoms warrant a “long-COVID” label.
For instance, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines it as 4 or more weeks after infection. The World Health Organization defines it as starting 3 months after COVID-19 symptom onset.
“I’m seeing ‘medium COVID’ – as one would call it – in younger and healthier patients. I’m also noticing that these symptoms are not severe enough to warrant stopping their job or changing their job schedules,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
They go back to work, she said, but start noticing something is off.
“I am seeing that.”
“I discharge at least two patients a week from my clinic because they have moved on and no longer have symptoms,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
In a story from Kaiser Health News published last month, WHYY health reporter Nina Feldman writes: “What I’ve come to think of as my ‘medium COVID’ affected my life. I couldn’t socialize much, drink, or stay up past 9:30 p.m. It took me 10 weeks to go for my first run – I’d been too afraid to try.”
She described a dinner with a friend after ending initial isolation protocols: “One glass of wine left me feeling like I’d had a whole bottle. I was bone-achingly exhausted but couldn’t sleep.”
Medical mystery
Dr. Ikramuddin notes the mechanism behind prolonged COVID-19 symptoms is still a medical mystery.
“In one scenario,” she said, “the question is being asked about whether the virus is staying dormant, similar to herpes zoster or HIV.”
“Right now, instead of getting more answers, we’re getting more questions,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Mouhib Naddour, MD, a pulmonary specialist with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, said he’s seeing that it’s taking some patients who have had COVID longer to recover than it would for other viral infections.
Some patients fall between those recovering within 2-3 weeks and patients having long COVID. Those patients in the gap could be lumped into a middle-range COVID, he told this news organization.
“We try to put things into tables and boxes but it is hard with this disease,” Dr. Naddour said.
He agrees there’s no medical definition for “medium” COVID, but he said the idea should bring hope for patients to know that, if their symptoms are persisting they don’t necessarily have long COVID – and their symptoms may still disappear.
“This is an illness that may take longer to completely recover from,” he said. “The majority of patients we’re seeing in this group could be healthy young patients who get COVID, then 2-3 weeks after they test negative, still have lingering symptoms.”
Common symptoms
Some commonly reported symptoms of those with enduring illness, which often overlap with other stages of COVID, are difficulty breathing, chest tightness, dry cough, chest pain, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and mood swings, Dr. Naddour said.
“We need to do an extensive assessment to make sure there’s no other problem causing these symptoms,” he said.
Still, there is no set timeline for the medium-COVID range, he noted, so checking in with a primary care physician is important for people experiencing symptoms.
It’s a continuum, not a category
Fernando Carnavali, MD, coordinator for Mount Sinai’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York, said he is not ready to recognize a separate category for a “medium” COVID.
He noted that science can’t even agree on a name for lasting post-COVID symptoms, whether it’s “long COVID” or “long-haul COVID,” “post-COVID syndrome” or “post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC ).” There’s no agreed-upon pathophysiology or biomarker.
“That creates these gaps of understanding on where we are,” Dr. Carnavali said in an interview.
He said he understands people’s need to categorize symptoms, but rather than a middle ground he sees a continuum.
It doesn’t mean what others may call COVID’s middle ground doesn’t exist, Dr. Carnavali said: “We are in the infancy of defining this. Trying to classify them may create more anxiety.”
The clinicians interviewed for this story report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Symptom timelines surrounding COVID infection tend to center on either the immediate 5-day quarantine protocols for acute infection or the long-COVID symptoms that can last a month or potentially far longer.
People may return to work or daily routines, but something is off: What had been simple exercise regimens become onerous. Everyday tasks take more effort.
Does this ill-defined subset point to a “medium COVID?”
Farha Ikramuddin, MD, MHA, a physiatrist and rehabilitation specialist at the University of Minnesota and M Health Fairview in Minneapolis, points out there is no definition or diagnostic code or shared official understanding of a middle category for COVID.
“But am I seeing that? Absolutely,” she said in an interview.
“I have seen patients who are younger, healthier, [and] with not so many comorbidities have either persistence of symptoms or reappearance after the initial infection is done,” she said.
Some patients report they had very low infection or were nonsymptomatic and returned to their normal health fairly quickly after infection. Then a week later they began experiencing fatigue, lost appetite, loss of smell, and feeling full after a few bites, Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Part of the trouble in categorizing the space between returning to normal after a week and having symptoms for months is that organizations can’t agree on a timeline for when symptoms warrant a “long-COVID” label.
For instance, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines it as 4 or more weeks after infection. The World Health Organization defines it as starting 3 months after COVID-19 symptom onset.
“I’m seeing ‘medium COVID’ – as one would call it – in younger and healthier patients. I’m also noticing that these symptoms are not severe enough to warrant stopping their job or changing their job schedules,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
They go back to work, she said, but start noticing something is off.
“I am seeing that.”
“I discharge at least two patients a week from my clinic because they have moved on and no longer have symptoms,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
In a story from Kaiser Health News published last month, WHYY health reporter Nina Feldman writes: “What I’ve come to think of as my ‘medium COVID’ affected my life. I couldn’t socialize much, drink, or stay up past 9:30 p.m. It took me 10 weeks to go for my first run – I’d been too afraid to try.”
She described a dinner with a friend after ending initial isolation protocols: “One glass of wine left me feeling like I’d had a whole bottle. I was bone-achingly exhausted but couldn’t sleep.”
Medical mystery
Dr. Ikramuddin notes the mechanism behind prolonged COVID-19 symptoms is still a medical mystery.
“In one scenario,” she said, “the question is being asked about whether the virus is staying dormant, similar to herpes zoster or HIV.”
“Right now, instead of getting more answers, we’re getting more questions,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Mouhib Naddour, MD, a pulmonary specialist with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, said he’s seeing that it’s taking some patients who have had COVID longer to recover than it would for other viral infections.
Some patients fall between those recovering within 2-3 weeks and patients having long COVID. Those patients in the gap could be lumped into a middle-range COVID, he told this news organization.
“We try to put things into tables and boxes but it is hard with this disease,” Dr. Naddour said.
He agrees there’s no medical definition for “medium” COVID, but he said the idea should bring hope for patients to know that, if their symptoms are persisting they don’t necessarily have long COVID – and their symptoms may still disappear.
“This is an illness that may take longer to completely recover from,” he said. “The majority of patients we’re seeing in this group could be healthy young patients who get COVID, then 2-3 weeks after they test negative, still have lingering symptoms.”
Common symptoms
Some commonly reported symptoms of those with enduring illness, which often overlap with other stages of COVID, are difficulty breathing, chest tightness, dry cough, chest pain, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and mood swings, Dr. Naddour said.
“We need to do an extensive assessment to make sure there’s no other problem causing these symptoms,” he said.
Still, there is no set timeline for the medium-COVID range, he noted, so checking in with a primary care physician is important for people experiencing symptoms.
It’s a continuum, not a category
Fernando Carnavali, MD, coordinator for Mount Sinai’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York, said he is not ready to recognize a separate category for a “medium” COVID.
He noted that science can’t even agree on a name for lasting post-COVID symptoms, whether it’s “long COVID” or “long-haul COVID,” “post-COVID syndrome” or “post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC ).” There’s no agreed-upon pathophysiology or biomarker.
“That creates these gaps of understanding on where we are,” Dr. Carnavali said in an interview.
He said he understands people’s need to categorize symptoms, but rather than a middle ground he sees a continuum.
It doesn’t mean what others may call COVID’s middle ground doesn’t exist, Dr. Carnavali said: “We are in the infancy of defining this. Trying to classify them may create more anxiety.”
The clinicians interviewed for this story report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Symptom timelines surrounding COVID infection tend to center on either the immediate 5-day quarantine protocols for acute infection or the long-COVID symptoms that can last a month or potentially far longer.
People may return to work or daily routines, but something is off: What had been simple exercise regimens become onerous. Everyday tasks take more effort.
Does this ill-defined subset point to a “medium COVID?”
Farha Ikramuddin, MD, MHA, a physiatrist and rehabilitation specialist at the University of Minnesota and M Health Fairview in Minneapolis, points out there is no definition or diagnostic code or shared official understanding of a middle category for COVID.
“But am I seeing that? Absolutely,” she said in an interview.
“I have seen patients who are younger, healthier, [and] with not so many comorbidities have either persistence of symptoms or reappearance after the initial infection is done,” she said.
Some patients report they had very low infection or were nonsymptomatic and returned to their normal health fairly quickly after infection. Then a week later they began experiencing fatigue, lost appetite, loss of smell, and feeling full after a few bites, Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Part of the trouble in categorizing the space between returning to normal after a week and having symptoms for months is that organizations can’t agree on a timeline for when symptoms warrant a “long-COVID” label.
For instance, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines it as 4 or more weeks after infection. The World Health Organization defines it as starting 3 months after COVID-19 symptom onset.
“I’m seeing ‘medium COVID’ – as one would call it – in younger and healthier patients. I’m also noticing that these symptoms are not severe enough to warrant stopping their job or changing their job schedules,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
They go back to work, she said, but start noticing something is off.
“I am seeing that.”
“I discharge at least two patients a week from my clinic because they have moved on and no longer have symptoms,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
In a story from Kaiser Health News published last month, WHYY health reporter Nina Feldman writes: “What I’ve come to think of as my ‘medium COVID’ affected my life. I couldn’t socialize much, drink, or stay up past 9:30 p.m. It took me 10 weeks to go for my first run – I’d been too afraid to try.”
She described a dinner with a friend after ending initial isolation protocols: “One glass of wine left me feeling like I’d had a whole bottle. I was bone-achingly exhausted but couldn’t sleep.”
Medical mystery
Dr. Ikramuddin notes the mechanism behind prolonged COVID-19 symptoms is still a medical mystery.
“In one scenario,” she said, “the question is being asked about whether the virus is staying dormant, similar to herpes zoster or HIV.”
“Right now, instead of getting more answers, we’re getting more questions,” Dr. Ikramuddin said.
Mouhib Naddour, MD, a pulmonary specialist with Sharp HealthCare in San Diego, said he’s seeing that it’s taking some patients who have had COVID longer to recover than it would for other viral infections.
Some patients fall between those recovering within 2-3 weeks and patients having long COVID. Those patients in the gap could be lumped into a middle-range COVID, he told this news organization.
“We try to put things into tables and boxes but it is hard with this disease,” Dr. Naddour said.
He agrees there’s no medical definition for “medium” COVID, but he said the idea should bring hope for patients to know that, if their symptoms are persisting they don’t necessarily have long COVID – and their symptoms may still disappear.
“This is an illness that may take longer to completely recover from,” he said. “The majority of patients we’re seeing in this group could be healthy young patients who get COVID, then 2-3 weeks after they test negative, still have lingering symptoms.”
Common symptoms
Some commonly reported symptoms of those with enduring illness, which often overlap with other stages of COVID, are difficulty breathing, chest tightness, dry cough, chest pain, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and mood swings, Dr. Naddour said.
“We need to do an extensive assessment to make sure there’s no other problem causing these symptoms,” he said.
Still, there is no set timeline for the medium-COVID range, he noted, so checking in with a primary care physician is important for people experiencing symptoms.
It’s a continuum, not a category
Fernando Carnavali, MD, coordinator for Mount Sinai’s Center for Post-COVID Care in New York, said he is not ready to recognize a separate category for a “medium” COVID.
He noted that science can’t even agree on a name for lasting post-COVID symptoms, whether it’s “long COVID” or “long-haul COVID,” “post-COVID syndrome” or “post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC ).” There’s no agreed-upon pathophysiology or biomarker.
“That creates these gaps of understanding on where we are,” Dr. Carnavali said in an interview.
He said he understands people’s need to categorize symptoms, but rather than a middle ground he sees a continuum.
It doesn’t mean what others may call COVID’s middle ground doesn’t exist, Dr. Carnavali said: “We are in the infancy of defining this. Trying to classify them may create more anxiety.”
The clinicians interviewed for this story report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data confirm risk of Guillain-Barré with J&J COVID shot
The Janssen vaccine (Ad26.COV2.S) is a replication-incompetent adenoviral vector vaccine.
The data show no increased risk of GBS with the Pfizer (BNT162b2) or Moderna (mRNA-1273) shots – both mRNA vaccines.
“Our findings support the current guidance from U.S. health officials that preferentially recommend use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines for primary and booster doses,” Nicola Klein, MD, PhD, with Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center, Oakland, Calif., told this news organization.
“Individuals who choose to receive Janssen/J&J COVID-19 vaccine should be informed of the potential safety risks, including GBS,” Dr. Klein said.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Eleven cases
Between mid-December 2020 and mid-November 2021, roughly 15.1 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine were administered to nearly 7.9 million adults in the United States.
This includes roughly 483,000 doses of the Janssen vaccine, 8.8 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine, and 5.8 million doses of the Moderna vaccine.
The researchers confirmed 11 cases of GBS after the Janssen vaccine.
The unadjusted incidence of GBS (per 100,000 person-years) was 32.4 in the first 21 days after the Janssen vaccine – substantially higher than the expected background rate of 1 to 2 cases per 100,000 person-years.
There were 36 confirmed cases of GBS after mRNA vaccines. The unadjusted incidence in the first 21 days after mRNA vaccination was 1.3 per 100,000 person-years, similar to the overall expected background rate.
In an adjusted head-to-head comparison, GBS incidence during the 21 days after receipt of the Janssen vaccine was 20.6 times higher than the GBS incidence during the 21 days after the Pfizer or Moderna mRNA vaccines, amounting to 15.5 excess cases per million Janssen vaccine recipients.
Most cases of GBS after the Janssen vaccine occurred during the 1- to 21-day risk interval, with the period of greatest risk in the 1-14 days after vaccination.
The findings of this analysis of surveillance data of COVID-19 vaccines are “consistent with an elevated risk of GBS after primary Ad26.COV2.S vaccination,” the authors wrote.
Novel presentation?
The researchers note that nearly all individuals who developed GBS after the Janssen vaccine had facial weakness or paralysis, in addition to weakness and decreased reflexes in the limbs, suggesting that the presentation of GBS after COVID-19 adenoviral vector vaccine may be novel.
“More research is needed to determine if the presentation of GBS after adenoviral vector vaccine differs from GBS after other exposures such as Campylobacter jejuni, and to investigate the mechanism for how adenoviral vector vaccines may cause GBS,” Dr. Klein and colleagues said.
“The Vaccine Safety Datalink continues to conduct safety surveillance for all COVID-19 vaccines, including monitoring for GBS and other serious health outcomes after vaccination,” Dr. Klein said in an interview.
This study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Klein reported receiving grants from Pfizer research support for a COVID vaccine clinical trial as well as other unrelated studies, grants from Merck, grants from GlaxoSmithKline, grants from Sanofi Pasteur, and grants from Protein Science (now Sanofi Pasteur) outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Janssen vaccine (Ad26.COV2.S) is a replication-incompetent adenoviral vector vaccine.
The data show no increased risk of GBS with the Pfizer (BNT162b2) or Moderna (mRNA-1273) shots – both mRNA vaccines.
“Our findings support the current guidance from U.S. health officials that preferentially recommend use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines for primary and booster doses,” Nicola Klein, MD, PhD, with Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center, Oakland, Calif., told this news organization.
“Individuals who choose to receive Janssen/J&J COVID-19 vaccine should be informed of the potential safety risks, including GBS,” Dr. Klein said.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Eleven cases
Between mid-December 2020 and mid-November 2021, roughly 15.1 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine were administered to nearly 7.9 million adults in the United States.
This includes roughly 483,000 doses of the Janssen vaccine, 8.8 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine, and 5.8 million doses of the Moderna vaccine.
The researchers confirmed 11 cases of GBS after the Janssen vaccine.
The unadjusted incidence of GBS (per 100,000 person-years) was 32.4 in the first 21 days after the Janssen vaccine – substantially higher than the expected background rate of 1 to 2 cases per 100,000 person-years.
There were 36 confirmed cases of GBS after mRNA vaccines. The unadjusted incidence in the first 21 days after mRNA vaccination was 1.3 per 100,000 person-years, similar to the overall expected background rate.
In an adjusted head-to-head comparison, GBS incidence during the 21 days after receipt of the Janssen vaccine was 20.6 times higher than the GBS incidence during the 21 days after the Pfizer or Moderna mRNA vaccines, amounting to 15.5 excess cases per million Janssen vaccine recipients.
Most cases of GBS after the Janssen vaccine occurred during the 1- to 21-day risk interval, with the period of greatest risk in the 1-14 days after vaccination.
The findings of this analysis of surveillance data of COVID-19 vaccines are “consistent with an elevated risk of GBS after primary Ad26.COV2.S vaccination,” the authors wrote.
Novel presentation?
The researchers note that nearly all individuals who developed GBS after the Janssen vaccine had facial weakness or paralysis, in addition to weakness and decreased reflexes in the limbs, suggesting that the presentation of GBS after COVID-19 adenoviral vector vaccine may be novel.
“More research is needed to determine if the presentation of GBS after adenoviral vector vaccine differs from GBS after other exposures such as Campylobacter jejuni, and to investigate the mechanism for how adenoviral vector vaccines may cause GBS,” Dr. Klein and colleagues said.
“The Vaccine Safety Datalink continues to conduct safety surveillance for all COVID-19 vaccines, including monitoring for GBS and other serious health outcomes after vaccination,” Dr. Klein said in an interview.
This study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Klein reported receiving grants from Pfizer research support for a COVID vaccine clinical trial as well as other unrelated studies, grants from Merck, grants from GlaxoSmithKline, grants from Sanofi Pasteur, and grants from Protein Science (now Sanofi Pasteur) outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Janssen vaccine (Ad26.COV2.S) is a replication-incompetent adenoviral vector vaccine.
The data show no increased risk of GBS with the Pfizer (BNT162b2) or Moderna (mRNA-1273) shots – both mRNA vaccines.
“Our findings support the current guidance from U.S. health officials that preferentially recommend use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines for primary and booster doses,” Nicola Klein, MD, PhD, with Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center, Oakland, Calif., told this news organization.
“Individuals who choose to receive Janssen/J&J COVID-19 vaccine should be informed of the potential safety risks, including GBS,” Dr. Klein said.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Eleven cases
Between mid-December 2020 and mid-November 2021, roughly 15.1 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine were administered to nearly 7.9 million adults in the United States.
This includes roughly 483,000 doses of the Janssen vaccine, 8.8 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine, and 5.8 million doses of the Moderna vaccine.
The researchers confirmed 11 cases of GBS after the Janssen vaccine.
The unadjusted incidence of GBS (per 100,000 person-years) was 32.4 in the first 21 days after the Janssen vaccine – substantially higher than the expected background rate of 1 to 2 cases per 100,000 person-years.
There were 36 confirmed cases of GBS after mRNA vaccines. The unadjusted incidence in the first 21 days after mRNA vaccination was 1.3 per 100,000 person-years, similar to the overall expected background rate.
In an adjusted head-to-head comparison, GBS incidence during the 21 days after receipt of the Janssen vaccine was 20.6 times higher than the GBS incidence during the 21 days after the Pfizer or Moderna mRNA vaccines, amounting to 15.5 excess cases per million Janssen vaccine recipients.
Most cases of GBS after the Janssen vaccine occurred during the 1- to 21-day risk interval, with the period of greatest risk in the 1-14 days after vaccination.
The findings of this analysis of surveillance data of COVID-19 vaccines are “consistent with an elevated risk of GBS after primary Ad26.COV2.S vaccination,” the authors wrote.
Novel presentation?
The researchers note that nearly all individuals who developed GBS after the Janssen vaccine had facial weakness or paralysis, in addition to weakness and decreased reflexes in the limbs, suggesting that the presentation of GBS after COVID-19 adenoviral vector vaccine may be novel.
“More research is needed to determine if the presentation of GBS after adenoviral vector vaccine differs from GBS after other exposures such as Campylobacter jejuni, and to investigate the mechanism for how adenoviral vector vaccines may cause GBS,” Dr. Klein and colleagues said.
“The Vaccine Safety Datalink continues to conduct safety surveillance for all COVID-19 vaccines, including monitoring for GBS and other serious health outcomes after vaccination,” Dr. Klein said in an interview.
This study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Klein reported receiving grants from Pfizer research support for a COVID vaccine clinical trial as well as other unrelated studies, grants from Merck, grants from GlaxoSmithKline, grants from Sanofi Pasteur, and grants from Protein Science (now Sanofi Pasteur) outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Children and COVID: New cases up for third straight week
Moderna submitted a request to the Food and Drug administration for emergency use authorization of its COVID-19 vaccine in children under the age of 6 years, according to this news organization, and Pfizer/BioNTech officially applied for authorization of a booster dose in children aged 5-11, the companies announced.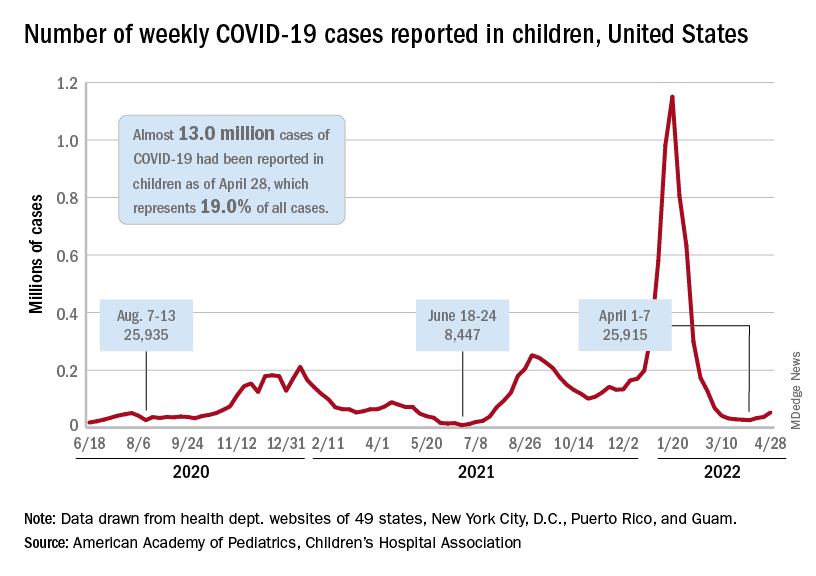
The FDA has tentatively scheduled meetings of its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee in June to consider the applications, saying that it “understands the urgency to authorize a vaccine for age groups who are not currently eligible for vaccination and will work diligently to complete our evaluation of the data. Should any of the submissions be completed in a timely manner and the data support a clear path forward following our evaluation, the FDA will act quickly” to convene the necessary meetings.
The need for greater access to vaccines seems to be increasing, as new pediatric COVID cases rose for the third consecutive week. April 22-28 saw over 53,000 new cases reported in children, up 43.5% from the previous week and up 105% since cases started rising again after dipping under 26,000 during the week of April 1-7, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Hospital admissions involving diagnosed COVID also ticked up over the latter half of April, although the most recent 7-day average (April 24-30) of 112 per day was lower than the 117 reported for the previous week (April 17-23), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, also noting that figures for the latest week “should be interpreted with caution.”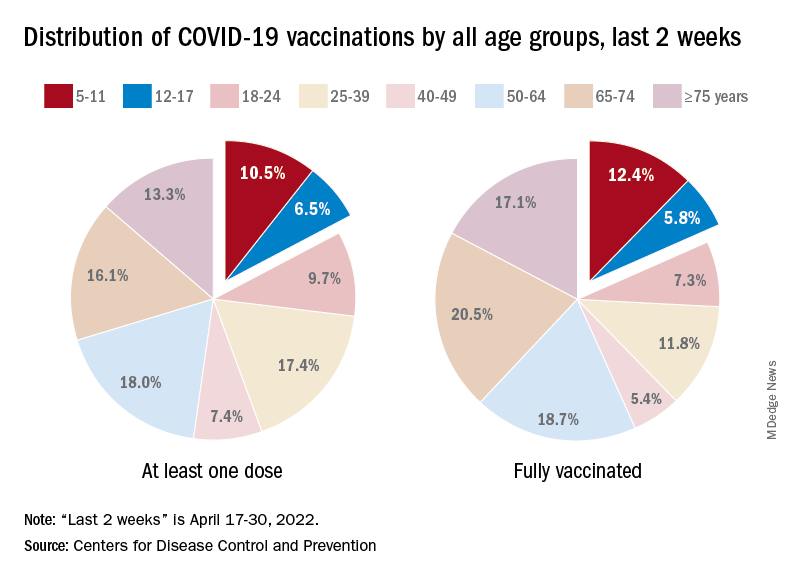
Vaccinations also were up slightly in children aged 5-11 years, with 52,000 receiving their first dose during the week of April 21-27, compared with 48,000 the week before. There was a slight dip, however, among 12- to 17-year-olds, who received 34,000 first doses during April 21-27, versus 35,000 the previous week, the AAP said in a separate report.
Cumulatively, almost 69% of all children aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and 59% are fully vaccinated. Those aged 5-11 are well short of those figures, with just over 35% having received at least one dose and 28.5% fully vaccinated, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A look at recent activity shows that children are not gaining on adults, who are much more likely to be vaccinated – full vaccination in those aged 50-64, for example, is 80%. During the 2 weeks from April 17-30, the 5- to 11-year-olds represented 10.5% of those who had initiated a first dose and 12.4% of those who gained full-vaccination status, both of which were well below the oldest age groups, the CDC reported.
Moderna submitted a request to the Food and Drug administration for emergency use authorization of its COVID-19 vaccine in children under the age of 6 years, according to this news organization, and Pfizer/BioNTech officially applied for authorization of a booster dose in children aged 5-11, the companies announced.
The FDA has tentatively scheduled meetings of its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee in June to consider the applications, saying that it “understands the urgency to authorize a vaccine for age groups who are not currently eligible for vaccination and will work diligently to complete our evaluation of the data. Should any of the submissions be completed in a timely manner and the data support a clear path forward following our evaluation, the FDA will act quickly” to convene the necessary meetings.
The need for greater access to vaccines seems to be increasing, as new pediatric COVID cases rose for the third consecutive week. April 22-28 saw over 53,000 new cases reported in children, up 43.5% from the previous week and up 105% since cases started rising again after dipping under 26,000 during the week of April 1-7, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Hospital admissions involving diagnosed COVID also ticked up over the latter half of April, although the most recent 7-day average (April 24-30) of 112 per day was lower than the 117 reported for the previous week (April 17-23), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, also noting that figures for the latest week “should be interpreted with caution.”
Vaccinations also were up slightly in children aged 5-11 years, with 52,000 receiving their first dose during the week of April 21-27, compared with 48,000 the week before. There was a slight dip, however, among 12- to 17-year-olds, who received 34,000 first doses during April 21-27, versus 35,000 the previous week, the AAP said in a separate report.
Cumulatively, almost 69% of all children aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and 59% are fully vaccinated. Those aged 5-11 are well short of those figures, with just over 35% having received at least one dose and 28.5% fully vaccinated, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A look at recent activity shows that children are not gaining on adults, who are much more likely to be vaccinated – full vaccination in those aged 50-64, for example, is 80%. During the 2 weeks from April 17-30, the 5- to 11-year-olds represented 10.5% of those who had initiated a first dose and 12.4% of those who gained full-vaccination status, both of which were well below the oldest age groups, the CDC reported.
Moderna submitted a request to the Food and Drug administration for emergency use authorization of its COVID-19 vaccine in children under the age of 6 years, according to this news organization, and Pfizer/BioNTech officially applied for authorization of a booster dose in children aged 5-11, the companies announced.
The FDA has tentatively scheduled meetings of its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee in June to consider the applications, saying that it “understands the urgency to authorize a vaccine for age groups who are not currently eligible for vaccination and will work diligently to complete our evaluation of the data. Should any of the submissions be completed in a timely manner and the data support a clear path forward following our evaluation, the FDA will act quickly” to convene the necessary meetings.
The need for greater access to vaccines seems to be increasing, as new pediatric COVID cases rose for the third consecutive week. April 22-28 saw over 53,000 new cases reported in children, up 43.5% from the previous week and up 105% since cases started rising again after dipping under 26,000 during the week of April 1-7, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Hospital admissions involving diagnosed COVID also ticked up over the latter half of April, although the most recent 7-day average (April 24-30) of 112 per day was lower than the 117 reported for the previous week (April 17-23), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, also noting that figures for the latest week “should be interpreted with caution.”
Vaccinations also were up slightly in children aged 5-11 years, with 52,000 receiving their first dose during the week of April 21-27, compared with 48,000 the week before. There was a slight dip, however, among 12- to 17-year-olds, who received 34,000 first doses during April 21-27, versus 35,000 the previous week, the AAP said in a separate report.
Cumulatively, almost 69% of all children aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine and 59% are fully vaccinated. Those aged 5-11 are well short of those figures, with just over 35% having received at least one dose and 28.5% fully vaccinated, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A look at recent activity shows that children are not gaining on adults, who are much more likely to be vaccinated – full vaccination in those aged 50-64, for example, is 80%. During the 2 weeks from April 17-30, the 5- to 11-year-olds represented 10.5% of those who had initiated a first dose and 12.4% of those who gained full-vaccination status, both of which were well below the oldest age groups, the CDC reported.
WHO, UNICEF warn about increased risk of measles outbreaks
The World Health Organization and United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund are warning about a heightened risk of measles spreading and triggering larger outbreaks in 2022.
Worldwide cases are up nearly 80% so far over 2021, the groups reported. More than 17,300 measles cases were reported worldwide in January and February, compared with 9,600 cases at the beginning of 2021.
In the last 12 months, there have been 21 “large and disruptive” measles outbreaks, particularly in Africa and the East Mediterranean region. The actual numbers are likely higher because of underreporting and disruptions to surveillance systems.
“Pandemic-related disruptions, increasing inequalities in access to vaccines, and the diversion of resources from routine immunization are leaving too many children without protection against measles and other vaccine-preventable diseases,” the organizations said.
As cities and countries relax COVID-19 restrictions, measles outbreaks are becoming more likely, they noted.
“It is encouraging that people in many communities are beginning to feel protected enough from COVID-19 to return to more social activities. But doing so in places where children are not receiving routine vaccination creates the perfect storm for the spread of a disease like measles,” Catherine Russell, executive director for UNICEF, said in the statement.
In the past year, the largest measles outbreaks have occurred in Somalia, Yemen, Nigeria, Afghanistan, and Ethiopia. The main reason for outbreaks is a lack measles vaccine coverage, the organizations said.
About 23 million children missed childhood vaccinations in 2020, the groups said. Childhood vaccination campaigns were hindered because of the COVID-19 pandemic and conflicts in Ukraine, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Afghanistan.
Overall, 57 campaigns targeting vaccine-preventable diseases across 43 countries that were scheduled to take place since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic are still postponed, the groups said, which could affect 203 million people. Among those, 19 are measles campaigns, which could put 73 million children at risk of measles because of missed vaccinations.
Vaccine coverage of 95% or higher with two doses of the measles vaccine can provide protection, according to the organizations. But the five countries that had the highest measles cases in the last year had first-dose coverage between 46% and 68%.
In the United States, measles vaccinations in kindergarten students dropped from about 95% to 93.9% for the 2020-2021 school year, according to CNN.
Vaccination coverage also dropped from 95% to 93.6% for diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, and varicella. Even though the decreases appear small, it means tens of thousands of children across the United States started school without their common childhood vaccinations, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
“We are concerned that missed routine vaccinations could leave children vulnerable to preventable diseases like measles and whooping cough, which are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children,” Shannon Stokley, DrPH, deputy director of the CDC’s immunization services division, told CNN.
The numbers show a “concerning decline in childhood immunizations that began in March 2020,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The World Health Organization and United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund are warning about a heightened risk of measles spreading and triggering larger outbreaks in 2022.
Worldwide cases are up nearly 80% so far over 2021, the groups reported. More than 17,300 measles cases were reported worldwide in January and February, compared with 9,600 cases at the beginning of 2021.
In the last 12 months, there have been 21 “large and disruptive” measles outbreaks, particularly in Africa and the East Mediterranean region. The actual numbers are likely higher because of underreporting and disruptions to surveillance systems.
“Pandemic-related disruptions, increasing inequalities in access to vaccines, and the diversion of resources from routine immunization are leaving too many children without protection against measles and other vaccine-preventable diseases,” the organizations said.
As cities and countries relax COVID-19 restrictions, measles outbreaks are becoming more likely, they noted.
“It is encouraging that people in many communities are beginning to feel protected enough from COVID-19 to return to more social activities. But doing so in places where children are not receiving routine vaccination creates the perfect storm for the spread of a disease like measles,” Catherine Russell, executive director for UNICEF, said in the statement.
In the past year, the largest measles outbreaks have occurred in Somalia, Yemen, Nigeria, Afghanistan, and Ethiopia. The main reason for outbreaks is a lack measles vaccine coverage, the organizations said.
About 23 million children missed childhood vaccinations in 2020, the groups said. Childhood vaccination campaigns were hindered because of the COVID-19 pandemic and conflicts in Ukraine, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Afghanistan.
Overall, 57 campaigns targeting vaccine-preventable diseases across 43 countries that were scheduled to take place since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic are still postponed, the groups said, which could affect 203 million people. Among those, 19 are measles campaigns, which could put 73 million children at risk of measles because of missed vaccinations.
Vaccine coverage of 95% or higher with two doses of the measles vaccine can provide protection, according to the organizations. But the five countries that had the highest measles cases in the last year had first-dose coverage between 46% and 68%.
In the United States, measles vaccinations in kindergarten students dropped from about 95% to 93.9% for the 2020-2021 school year, according to CNN.
Vaccination coverage also dropped from 95% to 93.6% for diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, and varicella. Even though the decreases appear small, it means tens of thousands of children across the United States started school without their common childhood vaccinations, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
“We are concerned that missed routine vaccinations could leave children vulnerable to preventable diseases like measles and whooping cough, which are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children,” Shannon Stokley, DrPH, deputy director of the CDC’s immunization services division, told CNN.
The numbers show a “concerning decline in childhood immunizations that began in March 2020,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The World Health Organization and United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund are warning about a heightened risk of measles spreading and triggering larger outbreaks in 2022.
Worldwide cases are up nearly 80% so far over 2021, the groups reported. More than 17,300 measles cases were reported worldwide in January and February, compared with 9,600 cases at the beginning of 2021.
In the last 12 months, there have been 21 “large and disruptive” measles outbreaks, particularly in Africa and the East Mediterranean region. The actual numbers are likely higher because of underreporting and disruptions to surveillance systems.
“Pandemic-related disruptions, increasing inequalities in access to vaccines, and the diversion of resources from routine immunization are leaving too many children without protection against measles and other vaccine-preventable diseases,” the organizations said.
As cities and countries relax COVID-19 restrictions, measles outbreaks are becoming more likely, they noted.
“It is encouraging that people in many communities are beginning to feel protected enough from COVID-19 to return to more social activities. But doing so in places where children are not receiving routine vaccination creates the perfect storm for the spread of a disease like measles,” Catherine Russell, executive director for UNICEF, said in the statement.
In the past year, the largest measles outbreaks have occurred in Somalia, Yemen, Nigeria, Afghanistan, and Ethiopia. The main reason for outbreaks is a lack measles vaccine coverage, the organizations said.
About 23 million children missed childhood vaccinations in 2020, the groups said. Childhood vaccination campaigns were hindered because of the COVID-19 pandemic and conflicts in Ukraine, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Afghanistan.
Overall, 57 campaigns targeting vaccine-preventable diseases across 43 countries that were scheduled to take place since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic are still postponed, the groups said, which could affect 203 million people. Among those, 19 are measles campaigns, which could put 73 million children at risk of measles because of missed vaccinations.
Vaccine coverage of 95% or higher with two doses of the measles vaccine can provide protection, according to the organizations. But the five countries that had the highest measles cases in the last year had first-dose coverage between 46% and 68%.
In the United States, measles vaccinations in kindergarten students dropped from about 95% to 93.9% for the 2020-2021 school year, according to CNN.
Vaccination coverage also dropped from 95% to 93.6% for diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, and varicella. Even though the decreases appear small, it means tens of thousands of children across the United States started school without their common childhood vaccinations, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
“We are concerned that missed routine vaccinations could leave children vulnerable to preventable diseases like measles and whooping cough, which are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children,” Shannon Stokley, DrPH, deputy director of the CDC’s immunization services division, told CNN.
The numbers show a “concerning decline in childhood immunizations that began in March 2020,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Nurses, med staff voice their heartache about California nurse suicide
The Santa Clara Police Department “thoroughly investigated” a report April 27 at Kaiser Permanente Santa Clara Medical Center that a male nurse in the emergency department died from a self-inflicted gunshot wound and ruled it a suicide, according to Wahid Kazem, assistant chief of police.
“This tragic event occurred in a closed room that is not used for patient care, adjacent to the emergency department. No other staff or patients were threatened,” according to Rakesh Chaudhary, MD, physician-in-chief of the medical center.
He added that the emergency department remained open for walk-in patients during the investigation, but ambulances were temporarily diverted to nearby hospitals. “The Santa Clara Police Department and our staff immediately took precautions to isolate the affected area and avoid impact to patient care.”
In terms of the effect on those closer to the victim, Dr. Chaudhary said, “Our hearts go out to the family, friends, and coworkers affected by this terrible loss. Our teams are on site providing emotional support and resources for staff.”
Neither the police nor the hospital released the victim’s name. “Out of respect for the privacy of our colleague and their family, we cannot provide any additional details,” Dr. Chaudhary said.
Among those who tweeted reactions to the news the past few days was someone who worked with the victim, according to the post: “My heart goes out to my coworker who thought he had no one to lean on and to my good friend who had to witness this tragedy. Love my ER fam.”
A male critical care RN tweeted: “My heart hurts for the nurse, his loved ones, and colleagues. Anyone working in ER understands the unique stress that we’ve been under. This is so tragic.”
While others cited the need for more mental health services to care for nurses, a psychiatrist on Twitter added, “Nurses are not OK and pizza and pats on the back aren’t going to fix it. This affects all of us.”
Mental health support was listed as a prime demand of striking workers recently at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care and Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital in Palo Alto, about a half hour away from Santa Clara Medical Center.
The nurses’ strike ended May 2 with an agreement between the health systems and the Committee for Recognition of Nursing Achievement union representing the nurses. The contract includes improvements to existing benefits supporting nurses’ health and well-being, according to a StanfordPackardVoice.com newsletter updating the negotiations.
Earlier this year, an intensive care unit RN from Stanford, Michael Odell, reportedly walked off his shift and was found dead 2 days later in San Francisco by the Alameda County Sheriff’s Office dive team. No foul play was suspected and the incident was believed to be a suicide.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Santa Clara Police Department “thoroughly investigated” a report April 27 at Kaiser Permanente Santa Clara Medical Center that a male nurse in the emergency department died from a self-inflicted gunshot wound and ruled it a suicide, according to Wahid Kazem, assistant chief of police.
“This tragic event occurred in a closed room that is not used for patient care, adjacent to the emergency department. No other staff or patients were threatened,” according to Rakesh Chaudhary, MD, physician-in-chief of the medical center.
He added that the emergency department remained open for walk-in patients during the investigation, but ambulances were temporarily diverted to nearby hospitals. “The Santa Clara Police Department and our staff immediately took precautions to isolate the affected area and avoid impact to patient care.”
In terms of the effect on those closer to the victim, Dr. Chaudhary said, “Our hearts go out to the family, friends, and coworkers affected by this terrible loss. Our teams are on site providing emotional support and resources for staff.”
Neither the police nor the hospital released the victim’s name. “Out of respect for the privacy of our colleague and their family, we cannot provide any additional details,” Dr. Chaudhary said.
Among those who tweeted reactions to the news the past few days was someone who worked with the victim, according to the post: “My heart goes out to my coworker who thought he had no one to lean on and to my good friend who had to witness this tragedy. Love my ER fam.”
A male critical care RN tweeted: “My heart hurts for the nurse, his loved ones, and colleagues. Anyone working in ER understands the unique stress that we’ve been under. This is so tragic.”
While others cited the need for more mental health services to care for nurses, a psychiatrist on Twitter added, “Nurses are not OK and pizza and pats on the back aren’t going to fix it. This affects all of us.”
Mental health support was listed as a prime demand of striking workers recently at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care and Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital in Palo Alto, about a half hour away from Santa Clara Medical Center.
The nurses’ strike ended May 2 with an agreement between the health systems and the Committee for Recognition of Nursing Achievement union representing the nurses. The contract includes improvements to existing benefits supporting nurses’ health and well-being, according to a StanfordPackardVoice.com newsletter updating the negotiations.
Earlier this year, an intensive care unit RN from Stanford, Michael Odell, reportedly walked off his shift and was found dead 2 days later in San Francisco by the Alameda County Sheriff’s Office dive team. No foul play was suspected and the incident was believed to be a suicide.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Santa Clara Police Department “thoroughly investigated” a report April 27 at Kaiser Permanente Santa Clara Medical Center that a male nurse in the emergency department died from a self-inflicted gunshot wound and ruled it a suicide, according to Wahid Kazem, assistant chief of police.
“This tragic event occurred in a closed room that is not used for patient care, adjacent to the emergency department. No other staff or patients were threatened,” according to Rakesh Chaudhary, MD, physician-in-chief of the medical center.
He added that the emergency department remained open for walk-in patients during the investigation, but ambulances were temporarily diverted to nearby hospitals. “The Santa Clara Police Department and our staff immediately took precautions to isolate the affected area and avoid impact to patient care.”
In terms of the effect on those closer to the victim, Dr. Chaudhary said, “Our hearts go out to the family, friends, and coworkers affected by this terrible loss. Our teams are on site providing emotional support and resources for staff.”
Neither the police nor the hospital released the victim’s name. “Out of respect for the privacy of our colleague and their family, we cannot provide any additional details,” Dr. Chaudhary said.
Among those who tweeted reactions to the news the past few days was someone who worked with the victim, according to the post: “My heart goes out to my coworker who thought he had no one to lean on and to my good friend who had to witness this tragedy. Love my ER fam.”
A male critical care RN tweeted: “My heart hurts for the nurse, his loved ones, and colleagues. Anyone working in ER understands the unique stress that we’ve been under. This is so tragic.”
While others cited the need for more mental health services to care for nurses, a psychiatrist on Twitter added, “Nurses are not OK and pizza and pats on the back aren’t going to fix it. This affects all of us.”
Mental health support was listed as a prime demand of striking workers recently at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care and Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital in Palo Alto, about a half hour away from Santa Clara Medical Center.
The nurses’ strike ended May 2 with an agreement between the health systems and the Committee for Recognition of Nursing Achievement union representing the nurses. The contract includes improvements to existing benefits supporting nurses’ health and well-being, according to a StanfordPackardVoice.com newsletter updating the negotiations.
Earlier this year, an intensive care unit RN from Stanford, Michael Odell, reportedly walked off his shift and was found dead 2 days later in San Francisco by the Alameda County Sheriff’s Office dive team. No foul play was suspected and the incident was believed to be a suicide.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Premature return to play after concussion has decreased
, according to a recent chart review. Rates of premature return to learn (RTL) are essentially unchanged, however.
“Delay in recovery is the major reason why it’s important not to RTL or RTP prematurely,” said James Carson, MD, associate professor of family and community medicine, University of Toronto.
“That delay in recovery only sets students further back in terms of the stress they get from being delayed with their schoolwork – they could lose their year in school, lose all their social contacts. So, there are a number of psychosocial issues that come into play if recovery is delayed, and that is what premature RTL and premature RTP will do – they delay the student’s recovery,” he emphasized.
The study was published in Canadian Family Physician.
Differences by sex
The study involved 241 students who had 258 distinct cases of SRC. The researchers defined premature RTP and RTL as chart records documenting the relapse, recurrence, or worsening of concussion symptoms that accompanied the patient’s RTP or RTL. Between 2011 and 2016, 26.7% of students had evidence of premature RTP, while 42.6% of them had evidence of premature RTL, the authors noted.
Compared with findings from an earlier survey of data from 2006 to 2011, the incidence of premature RTP dropped by 38.6% (P = .0003). In contrast, symptoms associated with premature RTL dropped by only 4.7% from the previous survey. This change was not statistically significant.
There was also a significant difference between males and females in the proportion of SRC cases with relapse of symptoms. Relapse occurred in 43.4% of female athletes with SRC versus 29.7% of male athletes with SRC (P = .023).
Female athletes also had significantly longer times before being cleared for RTP. The mean time was 74.5 days for females, compared with a mean of 42.3 days for male athletes (P < .001). “The median time to RTP clearance was nearly double [for female athletes] at 49 days versus 25 days [for male athletes],” wrote the authors.
The rate of premature RTL was also higher among secondary school students (48.8%), compared with 28% among elementary students and 42% among postsecondary students.
More concussions coming?
Before the first consensus conference, organized by the Concussion in Sport Group in 2001, management of concussion was based on rating and grading scales that had no medical evidence to support them, said Dr. Carson. After the consensus conference, it was recommended that physicians manage each concussion individually and, when it came to RTP, recommendations were based upon symptom resolution.
In contrast, there was nothing in the literature regarding how student athletes who sustain a concussion should RTL. Some schools made generous accommodations, and others none. This situation changed around 2011, when experts started publishing data about how better to accommodate student athletes who have a temporary disability for which schools need to introduce temporary accommodations to help them recover.
“Recommendations for RTP essentially had a 12-year head-start,” Dr. Carson emphasized, “and RTL had a much slower start.” Unfortunately, Dr. Carson foresees more athletes sustaining concussions as pandemic restrictions ease over the next few months. “As athletes RTP after the pandemic, they just will not be in game shape,” he said.
“In other words, athletes may not have the neuromuscular control to avoid these injuries as easily,” he added. Worse, athletes may not realize they are not quite ready to return to the expected level of participation so quickly. “I believe this scenario will lead to more concussions that will be difficult to manage in the context of an already strained health care system,” said Dr. Carson.
A limitation of the study was that it was difficult to assess whether all patients followed medical advice consistently.
“Very positive shifts”
Commenting on the findings, Nick Reed, PhD, Canada research chair in pediatric concussion and associate professor of occupational science and occupational therapy, University of Toronto, said that sports medicine physicians are seeing “very positive shifts” in concussion awareness and related behaviors such as providing education, support, and accommodations to students within the school environment. “More and more teachers are seeking education to learn what a concussion is and what to do to best support their students with concussion,” he said. Dr. Reed was not involved in the current study.
Indeed, this increasing awareness led to the development of a concussion education tool for teachers – SCHOOLFirst – although Dr. Reed did acknowledge that not all teachers have either the knowledge or the resources they need to optimally support their students with concussion. In the meantime, to reduce the risk of injury, Dr. Reed stressed that it is important for students to wear equipment appropriate for the game being played and to play by the rules.
“It is key to play sports in a way that is fair and respectful and not [engage] in behaviors with the intent of injuring an opponent,” he stressed. It is also important for athletes themselves to know the signs and symptoms of concussion and, if they think they have a concussion, to immediately stop playing, report how they are feeling to a coach, teacher, or parent, and to seek medical assessment to determine if they have a concussion or not.
“The key here is to focus on what the athlete can do after a concussion rather than what they can’t do,” Dr. Reed said. After even a few days of complete rest, students with a concussion can gradually introduce low levels of physical and cognitive activity that won’t make their symptoms worse. This activity can include going back to school with temporary accommodations in place, such as shorter school days and increased rest breaks. “When returning to school and to sport after a concussion, it is important to follow a stepwise and gradual return to activities so that you aren’t doing too much too fast,” Dr. Reed emphasized.
The study was conducted without external funding. Dr. Carson and Dr. Reed reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a recent chart review. Rates of premature return to learn (RTL) are essentially unchanged, however.
“Delay in recovery is the major reason why it’s important not to RTL or RTP prematurely,” said James Carson, MD, associate professor of family and community medicine, University of Toronto.
“That delay in recovery only sets students further back in terms of the stress they get from being delayed with their schoolwork – they could lose their year in school, lose all their social contacts. So, there are a number of psychosocial issues that come into play if recovery is delayed, and that is what premature RTL and premature RTP will do – they delay the student’s recovery,” he emphasized.
The study was published in Canadian Family Physician.
Differences by sex
The study involved 241 students who had 258 distinct cases of SRC. The researchers defined premature RTP and RTL as chart records documenting the relapse, recurrence, or worsening of concussion symptoms that accompanied the patient’s RTP or RTL. Between 2011 and 2016, 26.7% of students had evidence of premature RTP, while 42.6% of them had evidence of premature RTL, the authors noted.
Compared with findings from an earlier survey of data from 2006 to 2011, the incidence of premature RTP dropped by 38.6% (P = .0003). In contrast, symptoms associated with premature RTL dropped by only 4.7% from the previous survey. This change was not statistically significant.
There was also a significant difference between males and females in the proportion of SRC cases with relapse of symptoms. Relapse occurred in 43.4% of female athletes with SRC versus 29.7% of male athletes with SRC (P = .023).
Female athletes also had significantly longer times before being cleared for RTP. The mean time was 74.5 days for females, compared with a mean of 42.3 days for male athletes (P < .001). “The median time to RTP clearance was nearly double [for female athletes] at 49 days versus 25 days [for male athletes],” wrote the authors.
The rate of premature RTL was also higher among secondary school students (48.8%), compared with 28% among elementary students and 42% among postsecondary students.
More concussions coming?
Before the first consensus conference, organized by the Concussion in Sport Group in 2001, management of concussion was based on rating and grading scales that had no medical evidence to support them, said Dr. Carson. After the consensus conference, it was recommended that physicians manage each concussion individually and, when it came to RTP, recommendations were based upon symptom resolution.
In contrast, there was nothing in the literature regarding how student athletes who sustain a concussion should RTL. Some schools made generous accommodations, and others none. This situation changed around 2011, when experts started publishing data about how better to accommodate student athletes who have a temporary disability for which schools need to introduce temporary accommodations to help them recover.
“Recommendations for RTP essentially had a 12-year head-start,” Dr. Carson emphasized, “and RTL had a much slower start.” Unfortunately, Dr. Carson foresees more athletes sustaining concussions as pandemic restrictions ease over the next few months. “As athletes RTP after the pandemic, they just will not be in game shape,” he said.
“In other words, athletes may not have the neuromuscular control to avoid these injuries as easily,” he added. Worse, athletes may not realize they are not quite ready to return to the expected level of participation so quickly. “I believe this scenario will lead to more concussions that will be difficult to manage in the context of an already strained health care system,” said Dr. Carson.
A limitation of the study was that it was difficult to assess whether all patients followed medical advice consistently.
“Very positive shifts”
Commenting on the findings, Nick Reed, PhD, Canada research chair in pediatric concussion and associate professor of occupational science and occupational therapy, University of Toronto, said that sports medicine physicians are seeing “very positive shifts” in concussion awareness and related behaviors such as providing education, support, and accommodations to students within the school environment. “More and more teachers are seeking education to learn what a concussion is and what to do to best support their students with concussion,” he said. Dr. Reed was not involved in the current study.
Indeed, this increasing awareness led to the development of a concussion education tool for teachers – SCHOOLFirst – although Dr. Reed did acknowledge that not all teachers have either the knowledge or the resources they need to optimally support their students with concussion. In the meantime, to reduce the risk of injury, Dr. Reed stressed that it is important for students to wear equipment appropriate for the game being played and to play by the rules.
“It is key to play sports in a way that is fair and respectful and not [engage] in behaviors with the intent of injuring an opponent,” he stressed. It is also important for athletes themselves to know the signs and symptoms of concussion and, if they think they have a concussion, to immediately stop playing, report how they are feeling to a coach, teacher, or parent, and to seek medical assessment to determine if they have a concussion or not.
“The key here is to focus on what the athlete can do after a concussion rather than what they can’t do,” Dr. Reed said. After even a few days of complete rest, students with a concussion can gradually introduce low levels of physical and cognitive activity that won’t make their symptoms worse. This activity can include going back to school with temporary accommodations in place, such as shorter school days and increased rest breaks. “When returning to school and to sport after a concussion, it is important to follow a stepwise and gradual return to activities so that you aren’t doing too much too fast,” Dr. Reed emphasized.
The study was conducted without external funding. Dr. Carson and Dr. Reed reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a recent chart review. Rates of premature return to learn (RTL) are essentially unchanged, however.
“Delay in recovery is the major reason why it’s important not to RTL or RTP prematurely,” said James Carson, MD, associate professor of family and community medicine, University of Toronto.
“That delay in recovery only sets students further back in terms of the stress they get from being delayed with their schoolwork – they could lose their year in school, lose all their social contacts. So, there are a number of psychosocial issues that come into play if recovery is delayed, and that is what premature RTL and premature RTP will do – they delay the student’s recovery,” he emphasized.
The study was published in Canadian Family Physician.
Differences by sex
The study involved 241 students who had 258 distinct cases of SRC. The researchers defined premature RTP and RTL as chart records documenting the relapse, recurrence, or worsening of concussion symptoms that accompanied the patient’s RTP or RTL. Between 2011 and 2016, 26.7% of students had evidence of premature RTP, while 42.6% of them had evidence of premature RTL, the authors noted.
Compared with findings from an earlier survey of data from 2006 to 2011, the incidence of premature RTP dropped by 38.6% (P = .0003). In contrast, symptoms associated with premature RTL dropped by only 4.7% from the previous survey. This change was not statistically significant.
There was also a significant difference between males and females in the proportion of SRC cases with relapse of symptoms. Relapse occurred in 43.4% of female athletes with SRC versus 29.7% of male athletes with SRC (P = .023).
Female athletes also had significantly longer times before being cleared for RTP. The mean time was 74.5 days for females, compared with a mean of 42.3 days for male athletes (P < .001). “The median time to RTP clearance was nearly double [for female athletes] at 49 days versus 25 days [for male athletes],” wrote the authors.
The rate of premature RTL was also higher among secondary school students (48.8%), compared with 28% among elementary students and 42% among postsecondary students.
More concussions coming?
Before the first consensus conference, organized by the Concussion in Sport Group in 2001, management of concussion was based on rating and grading scales that had no medical evidence to support them, said Dr. Carson. After the consensus conference, it was recommended that physicians manage each concussion individually and, when it came to RTP, recommendations were based upon symptom resolution.
In contrast, there was nothing in the literature regarding how student athletes who sustain a concussion should RTL. Some schools made generous accommodations, and others none. This situation changed around 2011, when experts started publishing data about how better to accommodate student athletes who have a temporary disability for which schools need to introduce temporary accommodations to help them recover.
“Recommendations for RTP essentially had a 12-year head-start,” Dr. Carson emphasized, “and RTL had a much slower start.” Unfortunately, Dr. Carson foresees more athletes sustaining concussions as pandemic restrictions ease over the next few months. “As athletes RTP after the pandemic, they just will not be in game shape,” he said.
“In other words, athletes may not have the neuromuscular control to avoid these injuries as easily,” he added. Worse, athletes may not realize they are not quite ready to return to the expected level of participation so quickly. “I believe this scenario will lead to more concussions that will be difficult to manage in the context of an already strained health care system,” said Dr. Carson.
A limitation of the study was that it was difficult to assess whether all patients followed medical advice consistently.
“Very positive shifts”
Commenting on the findings, Nick Reed, PhD, Canada research chair in pediatric concussion and associate professor of occupational science and occupational therapy, University of Toronto, said that sports medicine physicians are seeing “very positive shifts” in concussion awareness and related behaviors such as providing education, support, and accommodations to students within the school environment. “More and more teachers are seeking education to learn what a concussion is and what to do to best support their students with concussion,” he said. Dr. Reed was not involved in the current study.
Indeed, this increasing awareness led to the development of a concussion education tool for teachers – SCHOOLFirst – although Dr. Reed did acknowledge that not all teachers have either the knowledge or the resources they need to optimally support their students with concussion. In the meantime, to reduce the risk of injury, Dr. Reed stressed that it is important for students to wear equipment appropriate for the game being played and to play by the rules.
“It is key to play sports in a way that is fair and respectful and not [engage] in behaviors with the intent of injuring an opponent,” he stressed. It is also important for athletes themselves to know the signs and symptoms of concussion and, if they think they have a concussion, to immediately stop playing, report how they are feeling to a coach, teacher, or parent, and to seek medical assessment to determine if they have a concussion or not.
“The key here is to focus on what the athlete can do after a concussion rather than what they can’t do,” Dr. Reed said. After even a few days of complete rest, students with a concussion can gradually introduce low levels of physical and cognitive activity that won’t make their symptoms worse. This activity can include going back to school with temporary accommodations in place, such as shorter school days and increased rest breaks. “When returning to school and to sport after a concussion, it is important to follow a stepwise and gradual return to activities so that you aren’t doing too much too fast,” Dr. Reed emphasized.
The study was conducted without external funding. Dr. Carson and Dr. Reed reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paxlovid doesn’t prevent infection in households, Pfizer says
Paxlovid works as a treatment for COVID-19 but not as a preventive measure, particularly if you’ve been exposed to the coronavirus through a household member who is infected, according to a new announcement from Pfizer.
In a clinical trial, the oral antiviral tablets were tested for postexposure prophylactic use, or tested for how well they prevented a coronavirus infection in people exposed to the virus. Paxlovid somewhat reduced the risk of infection, but the results weren’t statistically significant.
“We designed the clinical development program for Paxlovid to be comprehensive and ambitious with the aim of being able to help combat COVID-19 in a very broad population of patients,” Albert Bourla, PhD, Pfizer’s chairman and CEO, said in the announcement.
“While we are disappointed in the outcome of this particular study, these results do not impact the strong efficacy and safety data we’ve observed in our earlier trial for the treatment of COVID-19 patients at high risk of developing severe illness,” he said.
The trial included nearly 3,000 adults who were living with someone who recently tested positive for COVID-19 and had symptoms. The people in the trial, who tested negative and didn’t have symptoms, were given either Paxlovid twice daily for 5 or 10 days or a placebo. The study recruitment began in September 2021 and was completed during the peak of the Omicron wave.
Those who took the 5-day course of Paxlovid were found to be 32% less likely to become infected than the placebo group. Those who took the 10-day treatment had a 37% risk reduction. But the results weren’t statistically significant and may have been because of chance.
“Traditionally, it’s been difficult to use small-molecule antivirals for true prophylaxis because the biology of treating infection is different from the biology of preventing infection,” Daniel Barouch, MD, director of the Center for Virology and Vaccine Research at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, told STAT News.
He also noted that the Omicron variant could have played a role.
“That hyperinfectiousness probably makes it more difficult to prevent infections,” Dr. Barouch said.
The safety data was consistent with that of previous studies, Pfizer said, which found that the treatment was about 90% effective at preventing hospitalization or death in COVID-19 patients with a high risk of severe illness if the pills were taken for 5 days soon after symptoms started.
Paxlovid is approved or authorized for conditional or emergency use in more than 60 countries to treat high-risk COVID-19 patients, Pfizer said. In the United States, the drug is authorized for emergency use for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in those aged 12 and older who face high risks for severe disease, hospitalization, or death.
The full study data will be released in coming months and submitted to a peer-reviewed publication, the company said. More details are on the ClinicalTrials.gov website (NCT05047601).
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Paxlovid works as a treatment for COVID-19 but not as a preventive measure, particularly if you’ve been exposed to the coronavirus through a household member who is infected, according to a new announcement from Pfizer.
In a clinical trial, the oral antiviral tablets were tested for postexposure prophylactic use, or tested for how well they prevented a coronavirus infection in people exposed to the virus. Paxlovid somewhat reduced the risk of infection, but the results weren’t statistically significant.
“We designed the clinical development program for Paxlovid to be comprehensive and ambitious with the aim of being able to help combat COVID-19 in a very broad population of patients,” Albert Bourla, PhD, Pfizer’s chairman and CEO, said in the announcement.
“While we are disappointed in the outcome of this particular study, these results do not impact the strong efficacy and safety data we’ve observed in our earlier trial for the treatment of COVID-19 patients at high risk of developing severe illness,” he said.
The trial included nearly 3,000 adults who were living with someone who recently tested positive for COVID-19 and had symptoms. The people in the trial, who tested negative and didn’t have symptoms, were given either Paxlovid twice daily for 5 or 10 days or a placebo. The study recruitment began in September 2021 and was completed during the peak of the Omicron wave.
Those who took the 5-day course of Paxlovid were found to be 32% less likely to become infected than the placebo group. Those who took the 10-day treatment had a 37% risk reduction. But the results weren’t statistically significant and may have been because of chance.
“Traditionally, it’s been difficult to use small-molecule antivirals for true prophylaxis because the biology of treating infection is different from the biology of preventing infection,” Daniel Barouch, MD, director of the Center for Virology and Vaccine Research at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, told STAT News.
He also noted that the Omicron variant could have played a role.
“That hyperinfectiousness probably makes it more difficult to prevent infections,” Dr. Barouch said.
The safety data was consistent with that of previous studies, Pfizer said, which found that the treatment was about 90% effective at preventing hospitalization or death in COVID-19 patients with a high risk of severe illness if the pills were taken for 5 days soon after symptoms started.
Paxlovid is approved or authorized for conditional or emergency use in more than 60 countries to treat high-risk COVID-19 patients, Pfizer said. In the United States, the drug is authorized for emergency use for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in those aged 12 and older who face high risks for severe disease, hospitalization, or death.
The full study data will be released in coming months and submitted to a peer-reviewed publication, the company said. More details are on the ClinicalTrials.gov website (NCT05047601).
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Paxlovid works as a treatment for COVID-19 but not as a preventive measure, particularly if you’ve been exposed to the coronavirus through a household member who is infected, according to a new announcement from Pfizer.
In a clinical trial, the oral antiviral tablets were tested for postexposure prophylactic use, or tested for how well they prevented a coronavirus infection in people exposed to the virus. Paxlovid somewhat reduced the risk of infection, but the results weren’t statistically significant.
“We designed the clinical development program for Paxlovid to be comprehensive and ambitious with the aim of being able to help combat COVID-19 in a very broad population of patients,” Albert Bourla, PhD, Pfizer’s chairman and CEO, said in the announcement.
“While we are disappointed in the outcome of this particular study, these results do not impact the strong efficacy and safety data we’ve observed in our earlier trial for the treatment of COVID-19 patients at high risk of developing severe illness,” he said.
The trial included nearly 3,000 adults who were living with someone who recently tested positive for COVID-19 and had symptoms. The people in the trial, who tested negative and didn’t have symptoms, were given either Paxlovid twice daily for 5 or 10 days or a placebo. The study recruitment began in September 2021 and was completed during the peak of the Omicron wave.
Those who took the 5-day course of Paxlovid were found to be 32% less likely to become infected than the placebo group. Those who took the 10-day treatment had a 37% risk reduction. But the results weren’t statistically significant and may have been because of chance.
“Traditionally, it’s been difficult to use small-molecule antivirals for true prophylaxis because the biology of treating infection is different from the biology of preventing infection,” Daniel Barouch, MD, director of the Center for Virology and Vaccine Research at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, told STAT News.
He also noted that the Omicron variant could have played a role.
“That hyperinfectiousness probably makes it more difficult to prevent infections,” Dr. Barouch said.
The safety data was consistent with that of previous studies, Pfizer said, which found that the treatment was about 90% effective at preventing hospitalization or death in COVID-19 patients with a high risk of severe illness if the pills were taken for 5 days soon after symptoms started.
Paxlovid is approved or authorized for conditional or emergency use in more than 60 countries to treat high-risk COVID-19 patients, Pfizer said. In the United States, the drug is authorized for emergency use for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in those aged 12 and older who face high risks for severe disease, hospitalization, or death.
The full study data will be released in coming months and submitted to a peer-reviewed publication, the company said. More details are on the ClinicalTrials.gov website (NCT05047601).
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Higher ‘chemical restraint’ rates in Black psych patients in the ED
Black patients presenting with psychiatric disorders to hospital emergency departments across the United States have significantly higher rates of chemical restraint than their White counterparts, new research shows.
The investigators also found White patients were more likely to receive chemical sedation at hospitals with a higher proportion of Black patients – a finding that suggests hospital demographics influence practice patterns and that structural racism may be a root cause.
“There is a large disparity in the rates at which patients who presented to EDs nationally in the United States are restrained by race. You are 63% more likely, for the same set of chief complaints, to be chemically sedated if you are Black versus if you’re White,” senior investigator Ari Friedman, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine, and medical ethics and health policy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“The major mediator of that difference is the institution you are at – hospitals that primarily serve Black patients are more likely to chemically sedate their patients for these chief complaints – including White patients. So, it’s mediated by the practice pattern and environment,” Dr. Friedman added.
The study was published in the May issue of Annals of Epidemiology.
First large-scale study
Chemical sedation, also known as chemical restraint, is used to calm and help protect patients from harming themselves or others. Previous research on racial differences in the care of ED psychiatric patients with agitation suggests that there may be treatment disparities.
“Previous research from single institutions [has] shown that Black patients are more likely than White patients to be physically restrained, and this has been shown to be true among adult patients and pediatric patients,” lead author Utsha Khatri, MD, assistant professor of emergency medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine, New York, told this news organization.
Specifically, two single-institution studies within the last year revealed similar disparities, with higher rates of physical restraint for Black and Hispanic psychiatric patients in the ED. Another recent study showed an association with race, ethnicity, and pharmacological restraint use among pediatric patients presenting to the ED for mental health concerns.
“There has been work in psychiatry on disparities in this context, although there is less work in emergency departments,” said Dr. Friedman. “We looked across all U.S. EDs as opposed to within a single health system. The major trade-offs for us were that we weren’t able to observe restraint orders, which don’t find their way into national datasets, so we had to make some inferences based on the type of medications given.”
For the study the investigators analyzed data from 2008-2018 through the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Survey (NHAMCS) database. They examined the association of race and the administration of chemical sedation, with either an antipsychotic or ketamine, in ED visits for psychiatric disorders. These were any visit where the reason for the visit was “symptoms referable to psychological and mental disorders.”
Of the 76.2 million total ED visits evaluated, the researchers found that Black patients presenting with a psychiatric disorder were significantly more likely to receive chemical sedation with antipsychotics or ketamine than White patients presenting with the same conditions (5.3% vs. 3.0%; P < .01). This difference remained significant when accounting for admission or transfer to psychiatric facilities.
Combatting the forces of racism
When researchers accounted for the percent of hospital population that was Black, they found that patient race no longer affected the likelihood of chemical restraint.
“We found the key source of this racial disparity in use of chemical sedation is accounted for by the fact that hospitals that treat a higher proportion of Black patients tend to use more sedation,” said Dr. Khatri.
“Our findings suggest that patients who present to hospitals that serve a patient population that is 60% Black would have [a] roughly 1.8 times likelihood of getting chemically sedated, compared with a hospital that serves a population that is 10% Black,” she added.
“When a hospital has fewer resources, they often don’t have the staff or time to de-escalate a patient in distress and can have to resort to chemical sedation more quickly than a hospital with ample staff and resources,” said Dr. Friedman in a release.
Dr. Khatri added that the study highlights the need to combat the forces of racism by focusing not just on provider bias but by addressing the “underlying structural issues that lead to Black patients getting worse care based on where they live.”
“Hospitals have unequal distribution of resources and quality, largely patterned on the racial makeup of their patients. Dedicated training and funding for de-escalation techniques as well as sufficient staffing and availability of outpatient mental health care may help keep both patients and staff safe by reducing the use of physical restraint and chemical sedation in appropriate circumstances,” said Dr. Khatri.
Dr. Friedman noted that there will always be a need for restraint use to facilitate rapid medical evaluation and stabilization of patients, but “we want to make it as humane, thoughtful, and rare as possible, and to have a large armamentarium of alternative strategies that can be equitably applied across emergency departments.”
Need for widespread, systemic change
Commenting on the findings, Regina James, MD, the American Psychiatric Association’s chief of Diversity and Health Equity and deputy medical director, said the large-scale study confirms the widespread existence of racial and ethnic disparities in patients with psychiatric disorders.
“This study and previous studies, not only in psychiatry but in other areas of medicine, all bring to light that there continues to be evidence of racial and ethnic disparities in health care, and this is consistent across a range of illnesses and health care services,” said Dr. James.
“It’s important that as we think about the solution, we also think about the etiology of the problem and the layers that have contributed to it – understanding, embracing, and recognizing that these differences didn’t just come up de novo. It’s policies, practices, and behaviors that got us to this point, and it’s going to be policies, practices, and behaviors that are going to move us away from this point,” noted Dr. James.
She added that future research should focus on further understanding which factors exacerbate agitation among patients and what resources directed at the hospital level, including de-escalation training, nursing staff, and waiting room crowding, may be effective at reducing the use of chemical sedation when clinically appropriate.
The authors and Dr. James report no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Black patients presenting with psychiatric disorders to hospital emergency departments across the United States have significantly higher rates of chemical restraint than their White counterparts, new research shows.
The investigators also found White patients were more likely to receive chemical sedation at hospitals with a higher proportion of Black patients – a finding that suggests hospital demographics influence practice patterns and that structural racism may be a root cause.
“There is a large disparity in the rates at which patients who presented to EDs nationally in the United States are restrained by race. You are 63% more likely, for the same set of chief complaints, to be chemically sedated if you are Black versus if you’re White,” senior investigator Ari Friedman, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine, and medical ethics and health policy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“The major mediator of that difference is the institution you are at – hospitals that primarily serve Black patients are more likely to chemically sedate their patients for these chief complaints – including White patients. So, it’s mediated by the practice pattern and environment,” Dr. Friedman added.
The study was published in the May issue of Annals of Epidemiology.
First large-scale study
Chemical sedation, also known as chemical restraint, is used to calm and help protect patients from harming themselves or others. Previous research on racial differences in the care of ED psychiatric patients with agitation suggests that there may be treatment disparities.
“Previous research from single institutions [has] shown that Black patients are more likely than White patients to be physically restrained, and this has been shown to be true among adult patients and pediatric patients,” lead author Utsha Khatri, MD, assistant professor of emergency medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine, New York, told this news organization.
Specifically, two single-institution studies within the last year revealed similar disparities, with higher rates of physical restraint for Black and Hispanic psychiatric patients in the ED. Another recent study showed an association with race, ethnicity, and pharmacological restraint use among pediatric patients presenting to the ED for mental health concerns.
“There has been work in psychiatry on disparities in this context, although there is less work in emergency departments,” said Dr. Friedman. “We looked across all U.S. EDs as opposed to within a single health system. The major trade-offs for us were that we weren’t able to observe restraint orders, which don’t find their way into national datasets, so we had to make some inferences based on the type of medications given.”
For the study the investigators analyzed data from 2008-2018 through the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Survey (NHAMCS) database. They examined the association of race and the administration of chemical sedation, with either an antipsychotic or ketamine, in ED visits for psychiatric disorders. These were any visit where the reason for the visit was “symptoms referable to psychological and mental disorders.”
Of the 76.2 million total ED visits evaluated, the researchers found that Black patients presenting with a psychiatric disorder were significantly more likely to receive chemical sedation with antipsychotics or ketamine than White patients presenting with the same conditions (5.3% vs. 3.0%; P < .01). This difference remained significant when accounting for admission or transfer to psychiatric facilities.
Combatting the forces of racism
When researchers accounted for the percent of hospital population that was Black, they found that patient race no longer affected the likelihood of chemical restraint.
“We found the key source of this racial disparity in use of chemical sedation is accounted for by the fact that hospitals that treat a higher proportion of Black patients tend to use more sedation,” said Dr. Khatri.
“Our findings suggest that patients who present to hospitals that serve a patient population that is 60% Black would have [a] roughly 1.8 times likelihood of getting chemically sedated, compared with a hospital that serves a population that is 10% Black,” she added.
“When a hospital has fewer resources, they often don’t have the staff or time to de-escalate a patient in distress and can have to resort to chemical sedation more quickly than a hospital with ample staff and resources,” said Dr. Friedman in a release.
Dr. Khatri added that the study highlights the need to combat the forces of racism by focusing not just on provider bias but by addressing the “underlying structural issues that lead to Black patients getting worse care based on where they live.”
“Hospitals have unequal distribution of resources and quality, largely patterned on the racial makeup of their patients. Dedicated training and funding for de-escalation techniques as well as sufficient staffing and availability of outpatient mental health care may help keep both patients and staff safe by reducing the use of physical restraint and chemical sedation in appropriate circumstances,” said Dr. Khatri.
Dr. Friedman noted that there will always be a need for restraint use to facilitate rapid medical evaluation and stabilization of patients, but “we want to make it as humane, thoughtful, and rare as possible, and to have a large armamentarium of alternative strategies that can be equitably applied across emergency departments.”
Need for widespread, systemic change
Commenting on the findings, Regina James, MD, the American Psychiatric Association’s chief of Diversity and Health Equity and deputy medical director, said the large-scale study confirms the widespread existence of racial and ethnic disparities in patients with psychiatric disorders.
“This study and previous studies, not only in psychiatry but in other areas of medicine, all bring to light that there continues to be evidence of racial and ethnic disparities in health care, and this is consistent across a range of illnesses and health care services,” said Dr. James.
“It’s important that as we think about the solution, we also think about the etiology of the problem and the layers that have contributed to it – understanding, embracing, and recognizing that these differences didn’t just come up de novo. It’s policies, practices, and behaviors that got us to this point, and it’s going to be policies, practices, and behaviors that are going to move us away from this point,” noted Dr. James.
She added that future research should focus on further understanding which factors exacerbate agitation among patients and what resources directed at the hospital level, including de-escalation training, nursing staff, and waiting room crowding, may be effective at reducing the use of chemical sedation when clinically appropriate.
The authors and Dr. James report no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Black patients presenting with psychiatric disorders to hospital emergency departments across the United States have significantly higher rates of chemical restraint than their White counterparts, new research shows.
The investigators also found White patients were more likely to receive chemical sedation at hospitals with a higher proportion of Black patients – a finding that suggests hospital demographics influence practice patterns and that structural racism may be a root cause.
“There is a large disparity in the rates at which patients who presented to EDs nationally in the United States are restrained by race. You are 63% more likely, for the same set of chief complaints, to be chemically sedated if you are Black versus if you’re White,” senior investigator Ari Friedman, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine, and medical ethics and health policy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“The major mediator of that difference is the institution you are at – hospitals that primarily serve Black patients are more likely to chemically sedate their patients for these chief complaints – including White patients. So, it’s mediated by the practice pattern and environment,” Dr. Friedman added.
The study was published in the May issue of Annals of Epidemiology.
First large-scale study
Chemical sedation, also known as chemical restraint, is used to calm and help protect patients from harming themselves or others. Previous research on racial differences in the care of ED psychiatric patients with agitation suggests that there may be treatment disparities.
“Previous research from single institutions [has] shown that Black patients are more likely than White patients to be physically restrained, and this has been shown to be true among adult patients and pediatric patients,” lead author Utsha Khatri, MD, assistant professor of emergency medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine, New York, told this news organization.
Specifically, two single-institution studies within the last year revealed similar disparities, with higher rates of physical restraint for Black and Hispanic psychiatric patients in the ED. Another recent study showed an association with race, ethnicity, and pharmacological restraint use among pediatric patients presenting to the ED for mental health concerns.
“There has been work in psychiatry on disparities in this context, although there is less work in emergency departments,” said Dr. Friedman. “We looked across all U.S. EDs as opposed to within a single health system. The major trade-offs for us were that we weren’t able to observe restraint orders, which don’t find their way into national datasets, so we had to make some inferences based on the type of medications given.”
For the study the investigators analyzed data from 2008-2018 through the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Survey (NHAMCS) database. They examined the association of race and the administration of chemical sedation, with either an antipsychotic or ketamine, in ED visits for psychiatric disorders. These were any visit where the reason for the visit was “symptoms referable to psychological and mental disorders.”
Of the 76.2 million total ED visits evaluated, the researchers found that Black patients presenting with a psychiatric disorder were significantly more likely to receive chemical sedation with antipsychotics or ketamine than White patients presenting with the same conditions (5.3% vs. 3.0%; P < .01). This difference remained significant when accounting for admission or transfer to psychiatric facilities.
Combatting the forces of racism
When researchers accounted for the percent of hospital population that was Black, they found that patient race no longer affected the likelihood of chemical restraint.
“We found the key source of this racial disparity in use of chemical sedation is accounted for by the fact that hospitals that treat a higher proportion of Black patients tend to use more sedation,” said Dr. Khatri.
“Our findings suggest that patients who present to hospitals that serve a patient population that is 60% Black would have [a] roughly 1.8 times likelihood of getting chemically sedated, compared with a hospital that serves a population that is 10% Black,” she added.
“When a hospital has fewer resources, they often don’t have the staff or time to de-escalate a patient in distress and can have to resort to chemical sedation more quickly than a hospital with ample staff and resources,” said Dr. Friedman in a release.
Dr. Khatri added that the study highlights the need to combat the forces of racism by focusing not just on provider bias but by addressing the “underlying structural issues that lead to Black patients getting worse care based on where they live.”
“Hospitals have unequal distribution of resources and quality, largely patterned on the racial makeup of their patients. Dedicated training and funding for de-escalation techniques as well as sufficient staffing and availability of outpatient mental health care may help keep both patients and staff safe by reducing the use of physical restraint and chemical sedation in appropriate circumstances,” said Dr. Khatri.
Dr. Friedman noted that there will always be a need for restraint use to facilitate rapid medical evaluation and stabilization of patients, but “we want to make it as humane, thoughtful, and rare as possible, and to have a large armamentarium of alternative strategies that can be equitably applied across emergency departments.”
Need for widespread, systemic change
Commenting on the findings, Regina James, MD, the American Psychiatric Association’s chief of Diversity and Health Equity and deputy medical director, said the large-scale study confirms the widespread existence of racial and ethnic disparities in patients with psychiatric disorders.
“This study and previous studies, not only in psychiatry but in other areas of medicine, all bring to light that there continues to be evidence of racial and ethnic disparities in health care, and this is consistent across a range of illnesses and health care services,” said Dr. James.
“It’s important that as we think about the solution, we also think about the etiology of the problem and the layers that have contributed to it – understanding, embracing, and recognizing that these differences didn’t just come up de novo. It’s policies, practices, and behaviors that got us to this point, and it’s going to be policies, practices, and behaviors that are going to move us away from this point,” noted Dr. James.
She added that future research should focus on further understanding which factors exacerbate agitation among patients and what resources directed at the hospital level, including de-escalation training, nursing staff, and waiting room crowding, may be effective at reducing the use of chemical sedation when clinically appropriate.
The authors and Dr. James report no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.




