User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
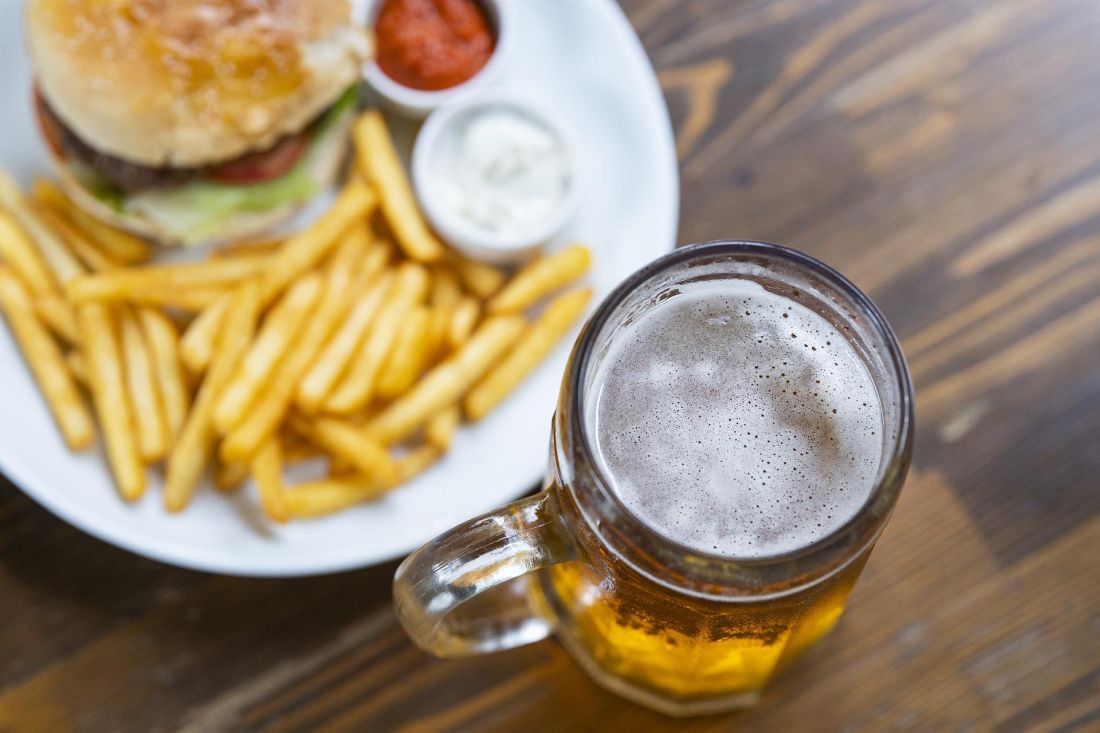
Microbiome’s new happy place: The beer gut
Your gut microbiome will thank you later
A healthy gut seems like the new catch-all to better overall health these days. Nutrition and diet culture has us drinking kombucha and ginger tea and coffee, but what if we told you that going to happy hour might also help?
In a recent double-blind study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 19 men were divided into two groups and asked to drink 11 ounces of alcoholic lager (5.2% by volume) or nonalcoholic lager with dinner for 4 weeks.
Beer? Yes. Beer.
We humans have trillions of microorganisms running rampant through our digestive tracts. When they’re happy, we have a lower chance of developing heart disease and diabetes. You know what else has millions of happy microorganisms from fermentation? Beer. It also has polyphenols that can help the body’s tissues fight cancers, as well as heart disease and inflammation. So beer is looking a little more healthy now, isn’t it?
In the study, the researchers found that both the alcoholic- and nonalcoholic-lager groups had a boost in bacterial diversity in the gut and higher fecal alkaline phosphatase levels, which showed improved intestinal health. They acknowledged, however, that the nonalcoholic route would be safer and healthier for overall health.
So add a lager to the list of gut-healthy foods that you should be consuming. It may give the phrase “beer gut” a whole new meaning.
We’ve lost our minds, but at least we know how fast they’re going
The phrase “quantum consciousness” sounds like something out of a particularly cheesy episode of Star Trek: “Oh no, Captain, the quantum consciousness has invaded our computer, and the only way to drive it out is to reverse the polarity of a focused tachyon beam.”
When it comes to understanding such basic existential issues as the origin of consciousness, however, quantum mechanics wasn’t off the table. The theory of the quantum origin of consciousness dates back to the 1990s (thanks in part to noted physician Roger Penrose), and goes something like this: There are microtubules within neurons in the brain that are small enough and isolated enough from the warm, wet, and chaotic brain environment where quantum effects can briefly come into play. We’re talking miniscule fractions of a second here, but still, long enough for quantum calculations to take place in the form of system wavefunction collapse, courtesy of gravity.
To plunge even deeper into the rabbit hole of quantum mechanics, the reason Schrödinger’s cat doesn’t occur in real life is wavefunction collapse; the more massive a quantum system is, the more likely it is to collapse into one state or another (alive or dead, in the cat’s case). The quantum origin of consciousness, or Orch OR theory, holds that human consciousness arises from electrical oscillations within the neuronal microtubules caused by the computations stemming from the collapse of small quantum systems.
That is an awful lot of overly simplified explanation, especially considering the study that just came out essentially disproved it. Oops. The research, published in Physics of Life Reviews, is pretty simple. The researchers went to a lab deep underground to avoid interference from cosmic rays, and sat around for months, observing a chunk of germanium for signs of spontaneous radiation, attributable to the same sort of wavefunction collapse that is supposedly occurring in our brains. They found nothing out of the ordinary, pretty definitively disproving most of Orch OR theory.
The researchers were unwilling to completely dismiss the idea (this is quantum mechanics, after all, uncertainty kind of goes with the territory), but it does seem like we’ll have to search elsewhere for sources of human consciousness. Personally, we’re big fans of the cymbal-playing monkey.
Missing links: A real fish story
Dear LOTME:
Ear’s a question that’s been keeping me up at night. Is the human middle ear the result of top-secret government experiments involving alien technology, Abraham Lincoln, and the Illuminati?
Restless in Roswell
Dear Restless:
The paleoanthropologic community has been sorting through this mystery for decades, and fossils discovered in China over the past 20 years finally provide a much less conspiratorially satisfying answer.
For some time now, experts in the field have believed that the bones of the human middle ear evolved from the spiracular gill of a fish. The spiracle is a small hole behind each eye that opens to the mouth in some fishes and was used to breathe air in the earliest, most primitive species. But how did we get from spiracle to ear?
The missing links come in the form of the cranial anatomy of Shuyu, a 438-million-year-old, fingernail-sized skull of a jawless fish, and the 419-million-year-old fossil of a completely preserved fish with gill filaments in the first branchial chamber.
“These fossils provided the first anatomical and fossil evidence for a vertebrate spiracle originating from fish gills,” senior author Gai Zhikun, PhD, of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, Beijing, said in a written statement.
In many ways, it seems, we are fish: “Many important structures of human beings can be traced back to our fish ancestors, such as our teeth, jaws, middle ears, etc,” added Zhu Min, PhD, also of the institute.
So, Restless, the next time you hear the soothing sounds of an angry mob storming the Capitol or you chew on a slab, slice, or chunk of mutant, laboratory-produced chicken in your favorite fast-food restaurant, be sure to thank Shuyu.
Can you lend me an ear?
If you thought locusts were only a nuisance, think again. They have their uses. If you take a locust’s ear and put it inside a robot, the robot will be able to hear and receive signals. Who knew?
Researchers from Tel Aviv University in Israel showed the robot’s hearing abilities by giving clap signals that told the robot what to do: One clap means go forward, two claps mean move back. What do you think the robot would do if it heard the clap break from Cha Cha Slide?
“Our task was to replace the robot’s electronic microphone with a dead insect’s ear, use the ear’s ability to detect the electrical signals from the environment, in this case vibrations in the air, and, using a special chip, convert the insect input to that of the robot,” Ben M. Maoz, PhD, said in a statement from the university.
And how does a dead locust ear work in a robot? Well, Dr. Maoz explained: “My laboratory has developed a special device – Ear-on-a-Chip – that allows the ear to be kept alive throughout the experiment by supplying oxygen and food to the organ while allowing the electrical signals to be taken out of the locust’s ear and amplified and transmitted to the robot.”
The research won’t stop at hearing, he said, as the other four senses also will be taken into consideration. This could help us sense dangers in the future, such as earthquakes or diseases. We said it before and we’ll say it again: We’re rooting for you, science!
Your gut microbiome will thank you later
A healthy gut seems like the new catch-all to better overall health these days. Nutrition and diet culture has us drinking kombucha and ginger tea and coffee, but what if we told you that going to happy hour might also help?
In a recent double-blind study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 19 men were divided into two groups and asked to drink 11 ounces of alcoholic lager (5.2% by volume) or nonalcoholic lager with dinner for 4 weeks.
Beer? Yes. Beer.
We humans have trillions of microorganisms running rampant through our digestive tracts. When they’re happy, we have a lower chance of developing heart disease and diabetes. You know what else has millions of happy microorganisms from fermentation? Beer. It also has polyphenols that can help the body’s tissues fight cancers, as well as heart disease and inflammation. So beer is looking a little more healthy now, isn’t it?
In the study, the researchers found that both the alcoholic- and nonalcoholic-lager groups had a boost in bacterial diversity in the gut and higher fecal alkaline phosphatase levels, which showed improved intestinal health. They acknowledged, however, that the nonalcoholic route would be safer and healthier for overall health.
So add a lager to the list of gut-healthy foods that you should be consuming. It may give the phrase “beer gut” a whole new meaning.
We’ve lost our minds, but at least we know how fast they’re going
The phrase “quantum consciousness” sounds like something out of a particularly cheesy episode of Star Trek: “Oh no, Captain, the quantum consciousness has invaded our computer, and the only way to drive it out is to reverse the polarity of a focused tachyon beam.”
When it comes to understanding such basic existential issues as the origin of consciousness, however, quantum mechanics wasn’t off the table. The theory of the quantum origin of consciousness dates back to the 1990s (thanks in part to noted physician Roger Penrose), and goes something like this: There are microtubules within neurons in the brain that are small enough and isolated enough from the warm, wet, and chaotic brain environment where quantum effects can briefly come into play. We’re talking miniscule fractions of a second here, but still, long enough for quantum calculations to take place in the form of system wavefunction collapse, courtesy of gravity.
To plunge even deeper into the rabbit hole of quantum mechanics, the reason Schrödinger’s cat doesn’t occur in real life is wavefunction collapse; the more massive a quantum system is, the more likely it is to collapse into one state or another (alive or dead, in the cat’s case). The quantum origin of consciousness, or Orch OR theory, holds that human consciousness arises from electrical oscillations within the neuronal microtubules caused by the computations stemming from the collapse of small quantum systems.
That is an awful lot of overly simplified explanation, especially considering the study that just came out essentially disproved it. Oops. The research, published in Physics of Life Reviews, is pretty simple. The researchers went to a lab deep underground to avoid interference from cosmic rays, and sat around for months, observing a chunk of germanium for signs of spontaneous radiation, attributable to the same sort of wavefunction collapse that is supposedly occurring in our brains. They found nothing out of the ordinary, pretty definitively disproving most of Orch OR theory.
The researchers were unwilling to completely dismiss the idea (this is quantum mechanics, after all, uncertainty kind of goes with the territory), but it does seem like we’ll have to search elsewhere for sources of human consciousness. Personally, we’re big fans of the cymbal-playing monkey.
Missing links: A real fish story
Dear LOTME:
Ear’s a question that’s been keeping me up at night. Is the human middle ear the result of top-secret government experiments involving alien technology, Abraham Lincoln, and the Illuminati?
Restless in Roswell
Dear Restless:
The paleoanthropologic community has been sorting through this mystery for decades, and fossils discovered in China over the past 20 years finally provide a much less conspiratorially satisfying answer.
For some time now, experts in the field have believed that the bones of the human middle ear evolved from the spiracular gill of a fish. The spiracle is a small hole behind each eye that opens to the mouth in some fishes and was used to breathe air in the earliest, most primitive species. But how did we get from spiracle to ear?
The missing links come in the form of the cranial anatomy of Shuyu, a 438-million-year-old, fingernail-sized skull of a jawless fish, and the 419-million-year-old fossil of a completely preserved fish with gill filaments in the first branchial chamber.
“These fossils provided the first anatomical and fossil evidence for a vertebrate spiracle originating from fish gills,” senior author Gai Zhikun, PhD, of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, Beijing, said in a written statement.
In many ways, it seems, we are fish: “Many important structures of human beings can be traced back to our fish ancestors, such as our teeth, jaws, middle ears, etc,” added Zhu Min, PhD, also of the institute.
So, Restless, the next time you hear the soothing sounds of an angry mob storming the Capitol or you chew on a slab, slice, or chunk of mutant, laboratory-produced chicken in your favorite fast-food restaurant, be sure to thank Shuyu.
Can you lend me an ear?
If you thought locusts were only a nuisance, think again. They have their uses. If you take a locust’s ear and put it inside a robot, the robot will be able to hear and receive signals. Who knew?
Researchers from Tel Aviv University in Israel showed the robot’s hearing abilities by giving clap signals that told the robot what to do: One clap means go forward, two claps mean move back. What do you think the robot would do if it heard the clap break from Cha Cha Slide?
“Our task was to replace the robot’s electronic microphone with a dead insect’s ear, use the ear’s ability to detect the electrical signals from the environment, in this case vibrations in the air, and, using a special chip, convert the insect input to that of the robot,” Ben M. Maoz, PhD, said in a statement from the university.
And how does a dead locust ear work in a robot? Well, Dr. Maoz explained: “My laboratory has developed a special device – Ear-on-a-Chip – that allows the ear to be kept alive throughout the experiment by supplying oxygen and food to the organ while allowing the electrical signals to be taken out of the locust’s ear and amplified and transmitted to the robot.”
The research won’t stop at hearing, he said, as the other four senses also will be taken into consideration. This could help us sense dangers in the future, such as earthquakes or diseases. We said it before and we’ll say it again: We’re rooting for you, science!
Your gut microbiome will thank you later
A healthy gut seems like the new catch-all to better overall health these days. Nutrition and diet culture has us drinking kombucha and ginger tea and coffee, but what if we told you that going to happy hour might also help?
In a recent double-blind study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 19 men were divided into two groups and asked to drink 11 ounces of alcoholic lager (5.2% by volume) or nonalcoholic lager with dinner for 4 weeks.
Beer? Yes. Beer.
We humans have trillions of microorganisms running rampant through our digestive tracts. When they’re happy, we have a lower chance of developing heart disease and diabetes. You know what else has millions of happy microorganisms from fermentation? Beer. It also has polyphenols that can help the body’s tissues fight cancers, as well as heart disease and inflammation. So beer is looking a little more healthy now, isn’t it?
In the study, the researchers found that both the alcoholic- and nonalcoholic-lager groups had a boost in bacterial diversity in the gut and higher fecal alkaline phosphatase levels, which showed improved intestinal health. They acknowledged, however, that the nonalcoholic route would be safer and healthier for overall health.
So add a lager to the list of gut-healthy foods that you should be consuming. It may give the phrase “beer gut” a whole new meaning.
We’ve lost our minds, but at least we know how fast they’re going
The phrase “quantum consciousness” sounds like something out of a particularly cheesy episode of Star Trek: “Oh no, Captain, the quantum consciousness has invaded our computer, and the only way to drive it out is to reverse the polarity of a focused tachyon beam.”
When it comes to understanding such basic existential issues as the origin of consciousness, however, quantum mechanics wasn’t off the table. The theory of the quantum origin of consciousness dates back to the 1990s (thanks in part to noted physician Roger Penrose), and goes something like this: There are microtubules within neurons in the brain that are small enough and isolated enough from the warm, wet, and chaotic brain environment where quantum effects can briefly come into play. We’re talking miniscule fractions of a second here, but still, long enough for quantum calculations to take place in the form of system wavefunction collapse, courtesy of gravity.
To plunge even deeper into the rabbit hole of quantum mechanics, the reason Schrödinger’s cat doesn’t occur in real life is wavefunction collapse; the more massive a quantum system is, the more likely it is to collapse into one state or another (alive or dead, in the cat’s case). The quantum origin of consciousness, or Orch OR theory, holds that human consciousness arises from electrical oscillations within the neuronal microtubules caused by the computations stemming from the collapse of small quantum systems.
That is an awful lot of overly simplified explanation, especially considering the study that just came out essentially disproved it. Oops. The research, published in Physics of Life Reviews, is pretty simple. The researchers went to a lab deep underground to avoid interference from cosmic rays, and sat around for months, observing a chunk of germanium for signs of spontaneous radiation, attributable to the same sort of wavefunction collapse that is supposedly occurring in our brains. They found nothing out of the ordinary, pretty definitively disproving most of Orch OR theory.
The researchers were unwilling to completely dismiss the idea (this is quantum mechanics, after all, uncertainty kind of goes with the territory), but it does seem like we’ll have to search elsewhere for sources of human consciousness. Personally, we’re big fans of the cymbal-playing monkey.
Missing links: A real fish story
Dear LOTME:
Ear’s a question that’s been keeping me up at night. Is the human middle ear the result of top-secret government experiments involving alien technology, Abraham Lincoln, and the Illuminati?
Restless in Roswell
Dear Restless:
The paleoanthropologic community has been sorting through this mystery for decades, and fossils discovered in China over the past 20 years finally provide a much less conspiratorially satisfying answer.
For some time now, experts in the field have believed that the bones of the human middle ear evolved from the spiracular gill of a fish. The spiracle is a small hole behind each eye that opens to the mouth in some fishes and was used to breathe air in the earliest, most primitive species. But how did we get from spiracle to ear?
The missing links come in the form of the cranial anatomy of Shuyu, a 438-million-year-old, fingernail-sized skull of a jawless fish, and the 419-million-year-old fossil of a completely preserved fish with gill filaments in the first branchial chamber.
“These fossils provided the first anatomical and fossil evidence for a vertebrate spiracle originating from fish gills,” senior author Gai Zhikun, PhD, of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, Beijing, said in a written statement.
In many ways, it seems, we are fish: “Many important structures of human beings can be traced back to our fish ancestors, such as our teeth, jaws, middle ears, etc,” added Zhu Min, PhD, also of the institute.
So, Restless, the next time you hear the soothing sounds of an angry mob storming the Capitol or you chew on a slab, slice, or chunk of mutant, laboratory-produced chicken in your favorite fast-food restaurant, be sure to thank Shuyu.
Can you lend me an ear?
If you thought locusts were only a nuisance, think again. They have their uses. If you take a locust’s ear and put it inside a robot, the robot will be able to hear and receive signals. Who knew?
Researchers from Tel Aviv University in Israel showed the robot’s hearing abilities by giving clap signals that told the robot what to do: One clap means go forward, two claps mean move back. What do you think the robot would do if it heard the clap break from Cha Cha Slide?
“Our task was to replace the robot’s electronic microphone with a dead insect’s ear, use the ear’s ability to detect the electrical signals from the environment, in this case vibrations in the air, and, using a special chip, convert the insect input to that of the robot,” Ben M. Maoz, PhD, said in a statement from the university.
And how does a dead locust ear work in a robot? Well, Dr. Maoz explained: “My laboratory has developed a special device – Ear-on-a-Chip – that allows the ear to be kept alive throughout the experiment by supplying oxygen and food to the organ while allowing the electrical signals to be taken out of the locust’s ear and amplified and transmitted to the robot.”
The research won’t stop at hearing, he said, as the other four senses also will be taken into consideration. This could help us sense dangers in the future, such as earthquakes or diseases. We said it before and we’ll say it again: We’re rooting for you, science!
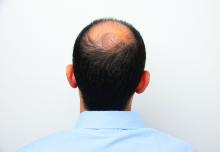
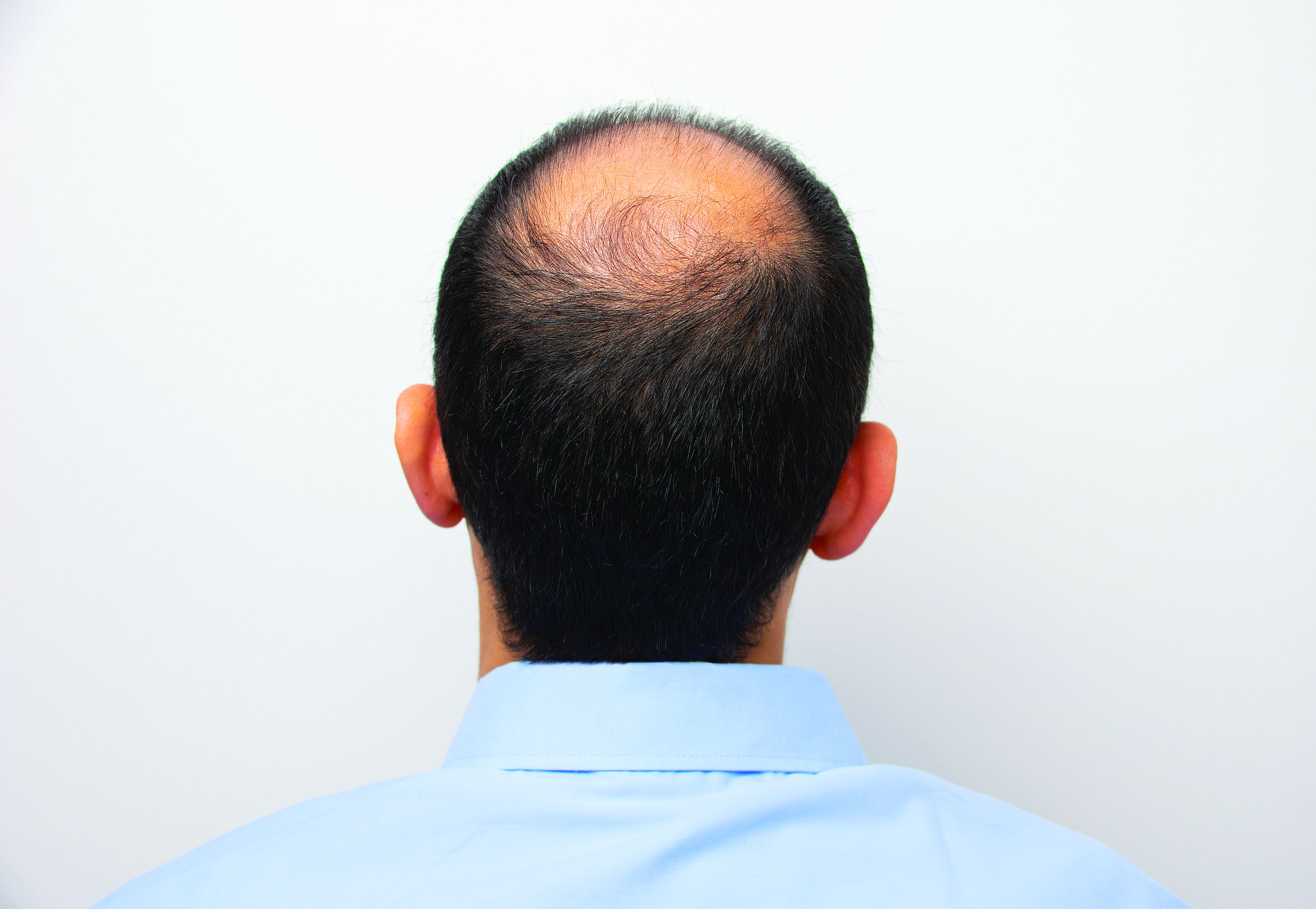
Hair disorder treatments are evolving
“No matter who the patient is, whether a child, adolescent, or adult, the key to figuring out hair disease is getting a good history,” Maria Hordinsky, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said at the Medscape Live Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
. She also urged physicians and other health care providers to use the electronic medical record and to be thorough in documenting information – noting nutrition, hair care habits, supplement use, and other details.
Lab tests should be selected based on that history, she said. For instance, low iron stores can be associated with hair shedding; and thyroid function studies might be needed.
Other highlights of her presentation included comments on different types of alopecia, and some new treatment approaches:
Androgenetic alopecia. In a meta-analysis and systematic review published in 2017, all treatments tested (2% and 5% minoxidil in men, 1 mg finasteride in men, 2% minoxidil in women, and low-level laser light therapy in men) were superior to placebo. Several photobiomodulation (PBM) devices (also known as low-level laser light) for home use have been cleared for androgenetic alopecia by the Food and Drug Administration; a clinician’s guide, published in 2018, provides information on these devices.
Hair and hormones. Combination therapy for female-pattern hair loss – low-dose minoxidil and spironolactone – is important to know about, she said, adding there are data from an observational pilot study supporting this treatment. Women should not become pregnant while on this treatment, Dr. Hordinsky cautioned.
PRP (platelet rich plasma). This treatment for hair loss can be costly, she cautioned, as it’s viewed as a cosmetic technique, “but it actually can work rather well.”
Hair regrowth measures. Traditionally, measures center on global assessment, the patient’s self-assessment, investigator assessment, and an independent photo review. Enter the dermatoscope. “We can now get pictures as a baseline. Patients can see, and also see the health of their scalp,” and if treatments make it look better or worse, she noted.
Alopecia areata (AA). Patients and families need to be made aware that this is an autoimmune disease that can recur, and if it does recur, the extent of hair loss is not predictable. According to Dr. Hordinsky, the most widely used tool to halt disease activity has been treatment with a corticosteroid (topical, intralesional, oral, or even intravenous corticosteroids).
Clinical trials and publications from 2018 to 2020 have triggered interest in off-label use and further studies of JAK inhibitors for treating AA, which include baricitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib. At the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March 2022, results of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 trial found that the JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib (50 mg or 20 mg daily, with or without a 200-mg loading dose), was efficacious in adults and adolescents with AA, compared with placebo, with no safety concerns noted. “This looks to be very, very promising,” she said, “and also very safe.” Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib also presented at the same meeting found it was superior to placebo for hair regrowth in adults with severe AA at 36 weeks. (On June 13, shortly after Dr. Hordinsky spoke at the meeting, the FDA approved baricitinib for treating AA in adults, making this the first systemic treatment to be approved for AA).
Research on topical JAK inhibitors for AA has been disappointing, Dr. Hordinsky said.
Alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis. For patients with both AA and AD, dupilumab may provide relief, she said. She referred to a recently published phase 2a trial in patients with AA (including some with both AA and AD), which found that Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores improved after 48 weeks of treatment, with higher response rates among those with baseline IgE levels of 200 IU/mL or higher. “If your patient has both, and their immunoglobulin-E level is greater than 200, then they may be a good candidate for dupilumab and both diseases may respond,” she said.
Scalp symptoms. It can be challenging when patients complain of itch, pain, or burning on the scalp, but have no obvious skin disease, Dr. Hordinsky said. Her tips: Some of these patients may be experiencing scalp symptoms secondary to a neuropathy; others may have mast cell degranulation, but for others, the basis of the symptoms may be unclear. Special nerve studies may be needed. For relief, a trial of antihistamines or topical or oral gabapentin may be needed, she said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). This condition, first described in postmenopausal women, is now reported in men and in younger women. While sunscreen has been suspected, there are no good data that have proven that link, she said. Cosmetics are also considered a possible culprit. For treatment, “the first thing we try to do is treat the inflammation,” Dr. Hordinsky said. Treatment options include topical high-potency corticosteroids, intralesional steroids, and topical nonsteroid anti-inflammatory creams (tier 1); hydroxychloroquine, low-dose antibiotics, and acitretin (tier 2); and cyclosporin and mycophenolate mofetil (tier 3).
In an observational study of mostly women with FFA, she noted, treatment with dutasteride was more effective than commonly used systemic treatments.
“Don’t forget to address the psychosocial needs of the hair loss patient,” Dr. Hordinsky advised. “Hair loss patients are very distressed, and you have to learn how to be fast and nimble and address those needs.” Working with a behavioral health specialist or therapist can help, she said.
She also recommended directing patients to appropriate organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, as well as conferences, such as the upcoming NAAF conference in Washington. “These organizations do give good information that should complement what you are doing.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Hordinsky reported no disclosures.
“No matter who the patient is, whether a child, adolescent, or adult, the key to figuring out hair disease is getting a good history,” Maria Hordinsky, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said at the Medscape Live Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
. She also urged physicians and other health care providers to use the electronic medical record and to be thorough in documenting information – noting nutrition, hair care habits, supplement use, and other details.
Lab tests should be selected based on that history, she said. For instance, low iron stores can be associated with hair shedding; and thyroid function studies might be needed.
Other highlights of her presentation included comments on different types of alopecia, and some new treatment approaches:
Androgenetic alopecia. In a meta-analysis and systematic review published in 2017, all treatments tested (2% and 5% minoxidil in men, 1 mg finasteride in men, 2% minoxidil in women, and low-level laser light therapy in men) were superior to placebo. Several photobiomodulation (PBM) devices (also known as low-level laser light) for home use have been cleared for androgenetic alopecia by the Food and Drug Administration; a clinician’s guide, published in 2018, provides information on these devices.
Hair and hormones. Combination therapy for female-pattern hair loss – low-dose minoxidil and spironolactone – is important to know about, she said, adding there are data from an observational pilot study supporting this treatment. Women should not become pregnant while on this treatment, Dr. Hordinsky cautioned.
PRP (platelet rich plasma). This treatment for hair loss can be costly, she cautioned, as it’s viewed as a cosmetic technique, “but it actually can work rather well.”
Hair regrowth measures. Traditionally, measures center on global assessment, the patient’s self-assessment, investigator assessment, and an independent photo review. Enter the dermatoscope. “We can now get pictures as a baseline. Patients can see, and also see the health of their scalp,” and if treatments make it look better or worse, she noted.
Alopecia areata (AA). Patients and families need to be made aware that this is an autoimmune disease that can recur, and if it does recur, the extent of hair loss is not predictable. According to Dr. Hordinsky, the most widely used tool to halt disease activity has been treatment with a corticosteroid (topical, intralesional, oral, or even intravenous corticosteroids).
Clinical trials and publications from 2018 to 2020 have triggered interest in off-label use and further studies of JAK inhibitors for treating AA, which include baricitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib. At the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March 2022, results of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 trial found that the JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib (50 mg or 20 mg daily, with or without a 200-mg loading dose), was efficacious in adults and adolescents with AA, compared with placebo, with no safety concerns noted. “This looks to be very, very promising,” she said, “and also very safe.” Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib also presented at the same meeting found it was superior to placebo for hair regrowth in adults with severe AA at 36 weeks. (On June 13, shortly after Dr. Hordinsky spoke at the meeting, the FDA approved baricitinib for treating AA in adults, making this the first systemic treatment to be approved for AA).
Research on topical JAK inhibitors for AA has been disappointing, Dr. Hordinsky said.
Alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis. For patients with both AA and AD, dupilumab may provide relief, she said. She referred to a recently published phase 2a trial in patients with AA (including some with both AA and AD), which found that Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores improved after 48 weeks of treatment, with higher response rates among those with baseline IgE levels of 200 IU/mL or higher. “If your patient has both, and their immunoglobulin-E level is greater than 200, then they may be a good candidate for dupilumab and both diseases may respond,” she said.
Scalp symptoms. It can be challenging when patients complain of itch, pain, or burning on the scalp, but have no obvious skin disease, Dr. Hordinsky said. Her tips: Some of these patients may be experiencing scalp symptoms secondary to a neuropathy; others may have mast cell degranulation, but for others, the basis of the symptoms may be unclear. Special nerve studies may be needed. For relief, a trial of antihistamines or topical or oral gabapentin may be needed, she said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). This condition, first described in postmenopausal women, is now reported in men and in younger women. While sunscreen has been suspected, there are no good data that have proven that link, she said. Cosmetics are also considered a possible culprit. For treatment, “the first thing we try to do is treat the inflammation,” Dr. Hordinsky said. Treatment options include topical high-potency corticosteroids, intralesional steroids, and topical nonsteroid anti-inflammatory creams (tier 1); hydroxychloroquine, low-dose antibiotics, and acitretin (tier 2); and cyclosporin and mycophenolate mofetil (tier 3).
In an observational study of mostly women with FFA, she noted, treatment with dutasteride was more effective than commonly used systemic treatments.
“Don’t forget to address the psychosocial needs of the hair loss patient,” Dr. Hordinsky advised. “Hair loss patients are very distressed, and you have to learn how to be fast and nimble and address those needs.” Working with a behavioral health specialist or therapist can help, she said.
She also recommended directing patients to appropriate organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, as well as conferences, such as the upcoming NAAF conference in Washington. “These organizations do give good information that should complement what you are doing.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Hordinsky reported no disclosures.
“No matter who the patient is, whether a child, adolescent, or adult, the key to figuring out hair disease is getting a good history,” Maria Hordinsky, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said at the Medscape Live Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
. She also urged physicians and other health care providers to use the electronic medical record and to be thorough in documenting information – noting nutrition, hair care habits, supplement use, and other details.
Lab tests should be selected based on that history, she said. For instance, low iron stores can be associated with hair shedding; and thyroid function studies might be needed.
Other highlights of her presentation included comments on different types of alopecia, and some new treatment approaches:
Androgenetic alopecia. In a meta-analysis and systematic review published in 2017, all treatments tested (2% and 5% minoxidil in men, 1 mg finasteride in men, 2% minoxidil in women, and low-level laser light therapy in men) were superior to placebo. Several photobiomodulation (PBM) devices (also known as low-level laser light) for home use have been cleared for androgenetic alopecia by the Food and Drug Administration; a clinician’s guide, published in 2018, provides information on these devices.
Hair and hormones. Combination therapy for female-pattern hair loss – low-dose minoxidil and spironolactone – is important to know about, she said, adding there are data from an observational pilot study supporting this treatment. Women should not become pregnant while on this treatment, Dr. Hordinsky cautioned.
PRP (platelet rich plasma). This treatment for hair loss can be costly, she cautioned, as it’s viewed as a cosmetic technique, “but it actually can work rather well.”
Hair regrowth measures. Traditionally, measures center on global assessment, the patient’s self-assessment, investigator assessment, and an independent photo review. Enter the dermatoscope. “We can now get pictures as a baseline. Patients can see, and also see the health of their scalp,” and if treatments make it look better or worse, she noted.
Alopecia areata (AA). Patients and families need to be made aware that this is an autoimmune disease that can recur, and if it does recur, the extent of hair loss is not predictable. According to Dr. Hordinsky, the most widely used tool to halt disease activity has been treatment with a corticosteroid (topical, intralesional, oral, or even intravenous corticosteroids).
Clinical trials and publications from 2018 to 2020 have triggered interest in off-label use and further studies of JAK inhibitors for treating AA, which include baricitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib. At the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March 2022, results of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 trial found that the JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib (50 mg or 20 mg daily, with or without a 200-mg loading dose), was efficacious in adults and adolescents with AA, compared with placebo, with no safety concerns noted. “This looks to be very, very promising,” she said, “and also very safe.” Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib also presented at the same meeting found it was superior to placebo for hair regrowth in adults with severe AA at 36 weeks. (On June 13, shortly after Dr. Hordinsky spoke at the meeting, the FDA approved baricitinib for treating AA in adults, making this the first systemic treatment to be approved for AA).
Research on topical JAK inhibitors for AA has been disappointing, Dr. Hordinsky said.
Alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis. For patients with both AA and AD, dupilumab may provide relief, she said. She referred to a recently published phase 2a trial in patients with AA (including some with both AA and AD), which found that Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores improved after 48 weeks of treatment, with higher response rates among those with baseline IgE levels of 200 IU/mL or higher. “If your patient has both, and their immunoglobulin-E level is greater than 200, then they may be a good candidate for dupilumab and both diseases may respond,” she said.
Scalp symptoms. It can be challenging when patients complain of itch, pain, or burning on the scalp, but have no obvious skin disease, Dr. Hordinsky said. Her tips: Some of these patients may be experiencing scalp symptoms secondary to a neuropathy; others may have mast cell degranulation, but for others, the basis of the symptoms may be unclear. Special nerve studies may be needed. For relief, a trial of antihistamines or topical or oral gabapentin may be needed, she said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). This condition, first described in postmenopausal women, is now reported in men and in younger women. While sunscreen has been suspected, there are no good data that have proven that link, she said. Cosmetics are also considered a possible culprit. For treatment, “the first thing we try to do is treat the inflammation,” Dr. Hordinsky said. Treatment options include topical high-potency corticosteroids, intralesional steroids, and topical nonsteroid anti-inflammatory creams (tier 1); hydroxychloroquine, low-dose antibiotics, and acitretin (tier 2); and cyclosporin and mycophenolate mofetil (tier 3).
In an observational study of mostly women with FFA, she noted, treatment with dutasteride was more effective than commonly used systemic treatments.
“Don’t forget to address the psychosocial needs of the hair loss patient,” Dr. Hordinsky advised. “Hair loss patients are very distressed, and you have to learn how to be fast and nimble and address those needs.” Working with a behavioral health specialist or therapist can help, she said.
She also recommended directing patients to appropriate organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, as well as conferences, such as the upcoming NAAF conference in Washington. “These organizations do give good information that should complement what you are doing.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Hordinsky reported no disclosures.
FROM MEDSCAPELIVE WOMEN’S & PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Bimekizumab calms psoriatic arthritis in phase 3 ‘BE’ trials
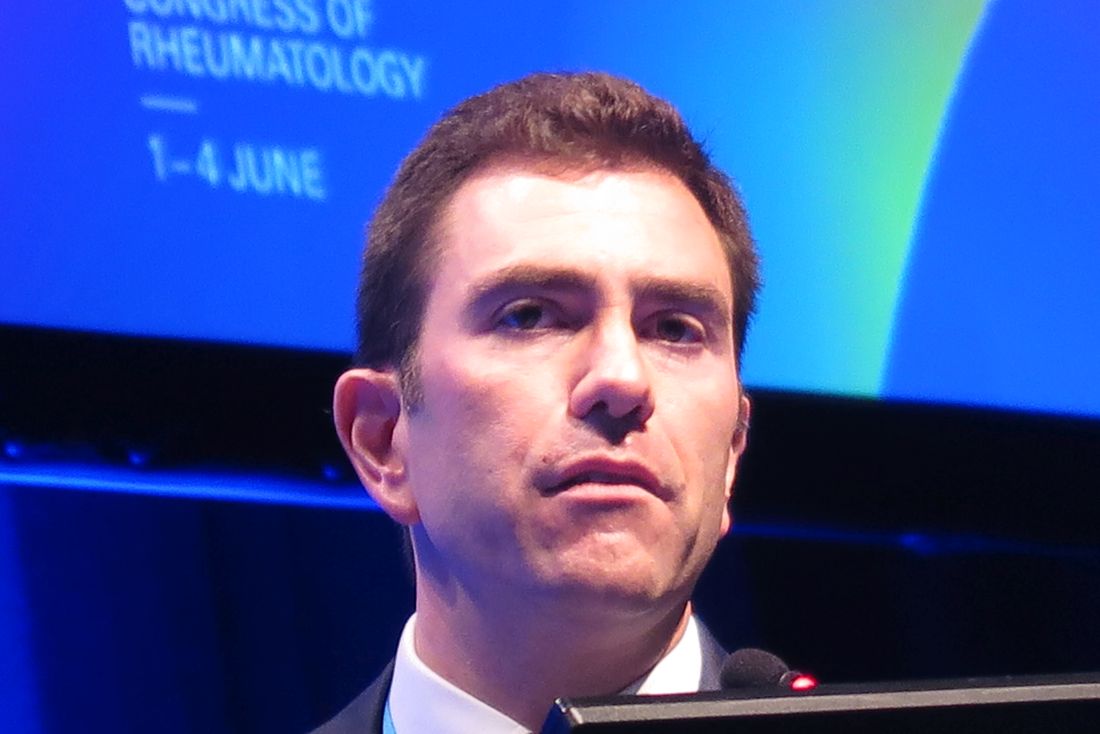
COPENHAGEN – For patients with active psoriatic arthritis for whom tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors failed to produce an adequate response, use of the dual interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx) was associated with significant improvement in joint, skin, and health-related quality-of-life parameters, compared with placebo, reported investigators in the phase 3, double-blind, randomized BE COMPLETE trial.
The primary endpoint, which was the percentage of patients who had 50% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR50) at 16 weeks, was achieved in 43.4% of patients assigned to receive bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks, compared with 6.8% among patients who received placebo, reported Joseph F. Merola, MD, a dermatologist and rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“The high-level and exciting take-home [message is] that BE COMPLETE did meet all primary and all ranked secondary endpoints at week 16,” he said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Also at the congress, Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, presented data from a second phase 3, double-blind, randomized trial called BE OPTIMAL that showed similar benefits for patients with psoriatic arthritis who had not previously received biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs.
“This is a new mode of action, inhibiting two cytokines simultaneously,” he said in a late-breaking oral abstract session.
As previously reported by this news organization, use of bimekizumab led to rapid reductions in signs and symptoms of radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in the phase 3 trial called BE MOBILE 2.
Bimekizumab is a monoclonal immunoglobulin G1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17A and IL-17F. It is approved in the European Union for treating adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
BE COMPLETE efficacy
Inclusion criteria comprised adult-onset psoriatic arthritis meeting Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) for at least 6 months; tender and swollen joint counts of at least 3/68; one or more active psoriatic lesions; and/or a documented history of psoriasis characterized by intolerance to one or two TNF inhibitors or failure of TNF inhibitors. Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive either bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks (n = 267) or placebo (n = 133) for 16 weeks.
Some participants are being followed in the extension BE VITAL study, which will evaluate response to treatment and long-term safety. Patients who do enroll in the extension study will be followed for safety for a period of 20 weeks after the last dose.
As noted before, the trial met its primary endpoint of a significant improvement over placebo in ACR50 (hazard ratio, 11.1; P < .001).
In addition, the trial met all ranked secondary endpoints, including the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index change from baseline, 90% improvement in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI90), Short-Form 36-Item Health Survey, and minimal disease activity (P < .001 for all comparisons).
Improvement with bimekizumab was rapid; curves began to separate from placebo by week 4, Dr. Merola said.
BE OPTIMAL efficacy
In this study, which had the same eligibility criteria as BE COMPLETE, patients were randomly assigned in a 2:3:1 ratio to receive 16 weeks of treatment with either placebo, bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks, or adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks as a reference treatment.
This trial also met its primary and ranked secondary endpoints, which were similar to those of BE COMPLETE but also included measures of pooled resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis and change from baseline in van der Heijde modified total Sharp score (P < .001 for all comparisons).
In all, 43.9% of patients who received bimekizumab and 45.7% who received adalimumab achieved ACR50 at week 16, compared with 10% of patients who received placebo. The difference between the placebo and bimekizumab groups was significant (P < .001).
Safety
More patients who received the two active agents in this trial had treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) in comparison with those in the placebo arm, but the incidence of serious TEAEs was less than 2% in each arm.
The most frequent events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, diarrhea, and hypertension.
Patients tolerated bimekizumab well, and there were no unexpected safety signals, Dr. McInnes said.
Clues to efficacy
In the question-and-answer session following Dr. McInnes’ presentation, Ronald Van Vollenhoven, MD, of the University of Amsterdam, said, “I have a question that is sort of generic in studies of psoriatic arthritis, so it does not only apply to this study, but the skin responses seem to be excellent – PASI90 sounds wonderful – but given that this is the case, is it reasonable to claim that the study is double-blinded in respect to the joints?”
Dr. McInnes replied that while he has considered this conundrum for many years in trials of drugs for psoriatic arthritis, “it doesn’t seem to be a major determinant of the outcome.”
The studies were supported by UCB Pharma. Dr. Merola and Dr. McInnes have consulted for UCB and other pharmaceutical companies that market drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Dr. Van Vollenhoven has received research support, has consulted for, and has spoken on behalf of UCB and other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COPENHAGEN – For patients with active psoriatic arthritis for whom tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors failed to produce an adequate response, use of the dual interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx) was associated with significant improvement in joint, skin, and health-related quality-of-life parameters, compared with placebo, reported investigators in the phase 3, double-blind, randomized BE COMPLETE trial.
The primary endpoint, which was the percentage of patients who had 50% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR50) at 16 weeks, was achieved in 43.4% of patients assigned to receive bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks, compared with 6.8% among patients who received placebo, reported Joseph F. Merola, MD, a dermatologist and rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“The high-level and exciting take-home [message is] that BE COMPLETE did meet all primary and all ranked secondary endpoints at week 16,” he said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Also at the congress, Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, presented data from a second phase 3, double-blind, randomized trial called BE OPTIMAL that showed similar benefits for patients with psoriatic arthritis who had not previously received biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs.
“This is a new mode of action, inhibiting two cytokines simultaneously,” he said in a late-breaking oral abstract session.
As previously reported by this news organization, use of bimekizumab led to rapid reductions in signs and symptoms of radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in the phase 3 trial called BE MOBILE 2.
Bimekizumab is a monoclonal immunoglobulin G1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17A and IL-17F. It is approved in the European Union for treating adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
BE COMPLETE efficacy
Inclusion criteria comprised adult-onset psoriatic arthritis meeting Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) for at least 6 months; tender and swollen joint counts of at least 3/68; one or more active psoriatic lesions; and/or a documented history of psoriasis characterized by intolerance to one or two TNF inhibitors or failure of TNF inhibitors. Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive either bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks (n = 267) or placebo (n = 133) for 16 weeks.
Some participants are being followed in the extension BE VITAL study, which will evaluate response to treatment and long-term safety. Patients who do enroll in the extension study will be followed for safety for a period of 20 weeks after the last dose.
As noted before, the trial met its primary endpoint of a significant improvement over placebo in ACR50 (hazard ratio, 11.1; P < .001).
In addition, the trial met all ranked secondary endpoints, including the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index change from baseline, 90% improvement in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI90), Short-Form 36-Item Health Survey, and minimal disease activity (P < .001 for all comparisons).
Improvement with bimekizumab was rapid; curves began to separate from placebo by week 4, Dr. Merola said.
BE OPTIMAL efficacy
In this study, which had the same eligibility criteria as BE COMPLETE, patients were randomly assigned in a 2:3:1 ratio to receive 16 weeks of treatment with either placebo, bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks, or adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks as a reference treatment.
This trial also met its primary and ranked secondary endpoints, which were similar to those of BE COMPLETE but also included measures of pooled resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis and change from baseline in van der Heijde modified total Sharp score (P < .001 for all comparisons).
In all, 43.9% of patients who received bimekizumab and 45.7% who received adalimumab achieved ACR50 at week 16, compared with 10% of patients who received placebo. The difference between the placebo and bimekizumab groups was significant (P < .001).
Safety
More patients who received the two active agents in this trial had treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) in comparison with those in the placebo arm, but the incidence of serious TEAEs was less than 2% in each arm.
The most frequent events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, diarrhea, and hypertension.
Patients tolerated bimekizumab well, and there were no unexpected safety signals, Dr. McInnes said.
Clues to efficacy
In the question-and-answer session following Dr. McInnes’ presentation, Ronald Van Vollenhoven, MD, of the University of Amsterdam, said, “I have a question that is sort of generic in studies of psoriatic arthritis, so it does not only apply to this study, but the skin responses seem to be excellent – PASI90 sounds wonderful – but given that this is the case, is it reasonable to claim that the study is double-blinded in respect to the joints?”
Dr. McInnes replied that while he has considered this conundrum for many years in trials of drugs for psoriatic arthritis, “it doesn’t seem to be a major determinant of the outcome.”
The studies were supported by UCB Pharma. Dr. Merola and Dr. McInnes have consulted for UCB and other pharmaceutical companies that market drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Dr. Van Vollenhoven has received research support, has consulted for, and has spoken on behalf of UCB and other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COPENHAGEN – For patients with active psoriatic arthritis for whom tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors failed to produce an adequate response, use of the dual interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx) was associated with significant improvement in joint, skin, and health-related quality-of-life parameters, compared with placebo, reported investigators in the phase 3, double-blind, randomized BE COMPLETE trial.
The primary endpoint, which was the percentage of patients who had 50% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR50) at 16 weeks, was achieved in 43.4% of patients assigned to receive bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks, compared with 6.8% among patients who received placebo, reported Joseph F. Merola, MD, a dermatologist and rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“The high-level and exciting take-home [message is] that BE COMPLETE did meet all primary and all ranked secondary endpoints at week 16,” he said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Also at the congress, Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, presented data from a second phase 3, double-blind, randomized trial called BE OPTIMAL that showed similar benefits for patients with psoriatic arthritis who had not previously received biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs.
“This is a new mode of action, inhibiting two cytokines simultaneously,” he said in a late-breaking oral abstract session.
As previously reported by this news organization, use of bimekizumab led to rapid reductions in signs and symptoms of radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in the phase 3 trial called BE MOBILE 2.
Bimekizumab is a monoclonal immunoglobulin G1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17A and IL-17F. It is approved in the European Union for treating adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
BE COMPLETE efficacy
Inclusion criteria comprised adult-onset psoriatic arthritis meeting Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) for at least 6 months; tender and swollen joint counts of at least 3/68; one or more active psoriatic lesions; and/or a documented history of psoriasis characterized by intolerance to one or two TNF inhibitors or failure of TNF inhibitors. Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive either bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks (n = 267) or placebo (n = 133) for 16 weeks.
Some participants are being followed in the extension BE VITAL study, which will evaluate response to treatment and long-term safety. Patients who do enroll in the extension study will be followed for safety for a period of 20 weeks after the last dose.
As noted before, the trial met its primary endpoint of a significant improvement over placebo in ACR50 (hazard ratio, 11.1; P < .001).
In addition, the trial met all ranked secondary endpoints, including the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index change from baseline, 90% improvement in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI90), Short-Form 36-Item Health Survey, and minimal disease activity (P < .001 for all comparisons).
Improvement with bimekizumab was rapid; curves began to separate from placebo by week 4, Dr. Merola said.
BE OPTIMAL efficacy
In this study, which had the same eligibility criteria as BE COMPLETE, patients were randomly assigned in a 2:3:1 ratio to receive 16 weeks of treatment with either placebo, bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks, or adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks as a reference treatment.
This trial also met its primary and ranked secondary endpoints, which were similar to those of BE COMPLETE but also included measures of pooled resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis and change from baseline in van der Heijde modified total Sharp score (P < .001 for all comparisons).
In all, 43.9% of patients who received bimekizumab and 45.7% who received adalimumab achieved ACR50 at week 16, compared with 10% of patients who received placebo. The difference between the placebo and bimekizumab groups was significant (P < .001).
Safety
More patients who received the two active agents in this trial had treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) in comparison with those in the placebo arm, but the incidence of serious TEAEs was less than 2% in each arm.
The most frequent events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, diarrhea, and hypertension.
Patients tolerated bimekizumab well, and there were no unexpected safety signals, Dr. McInnes said.
Clues to efficacy
In the question-and-answer session following Dr. McInnes’ presentation, Ronald Van Vollenhoven, MD, of the University of Amsterdam, said, “I have a question that is sort of generic in studies of psoriatic arthritis, so it does not only apply to this study, but the skin responses seem to be excellent – PASI90 sounds wonderful – but given that this is the case, is it reasonable to claim that the study is double-blinded in respect to the joints?”
Dr. McInnes replied that while he has considered this conundrum for many years in trials of drugs for psoriatic arthritis, “it doesn’t seem to be a major determinant of the outcome.”
The studies were supported by UCB Pharma. Dr. Merola and Dr. McInnes have consulted for UCB and other pharmaceutical companies that market drugs for psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Dr. Van Vollenhoven has received research support, has consulted for, and has spoken on behalf of UCB and other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT THE EULAR 2022 CONGRESS
Autoimmune disease linked to better late-stage breast cancer survival
CHICAGO – Comorbid autoimmune disease is associated with a greater chance of survival among women with stage IV breast cancer, according to a retrospective study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“It’s counterintuitive that, if you have two diseases instead of one, that you live longer, so then we had to scratch our heads a little bit and think about why these people are living longer,” said lead author Demitrios Dedousis, MD, University Hospitals, Case Medical Center, Cleveland.
Dr. Dedousis and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis of patients from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results–Medicare databases between 2007 and 2014 with breast cancer. The study included data from 137,324 patients diagnosed between 2007 and 2012, before the widespread use of immunotherapy. 27% of patients had an autoimmune disease, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (23%), psoriasis (2.4%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (1.1%).
When all patients were included in the analysis, those with autoimmune disorders had slightly longer survival times, but these weren’t clinically significant. A subanalysis found a greater difference in survival.
The association appears more pronounced in metastatic cancer. Patients with stage 4 breast cancer and autoimmune disease had a longer mean overall survival (36 months vs. 30 months; hazard ratio, 1.46; P < .0001. Cancer-specific survival: HR, 1.39; P < .0001). Patients with autoimmune disease and stage 1-3 breast cancer had lower overall survival (P < .0001, P < 0.0001, and P = 0.026 respectively), compared with patients without autoimmune disease.
“What we thought was happening is that the lack of increased survival in stages 1 through 3 was hiding the increase in survival among the stage IV patients when looking at the overall cohort,” Dr. Dedousis said.
The retrospective nature of the study makes it impossible to draw any firm conclusions about causation. It could be that patients who have already been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease are more vigilant about going to health checkups. “There are other possible explanations, but the one that’s most interesting to us is that their immune system is involved in fighting the cancer. Our study certainly didn’t prove that, but it’s suggesting that’s a possibility,” Dr. Dedousis said.
He and his coauthors anticipate conducting similar studies in other cancers to see if there are similar relationships. Some preliminary work has already suggested something similar in lung cancer. “I think demonstrating this in a few kinds of cancer goes part of the way towards showing that this is a real biological phenomenon,” he said.
Another research avenue is to examine the immune systems and pathology specimens in patients with both an autoimmune disease and cancer to see if there is a greater immune response within the tumor. If so, that could suggest new immunotherapy strategies.
Another possibility is to look at the specific immune pathways within “protective” autoimmune conditions. “For the sake of argument, if we find a particular autoimmune condition is improving survival across multiple kinds of cancers, we could look at those pathways that are specifically involved in that autoimmune condition. It might help us identify a target for drug development,” Dr. Dedousis said.
Asked why a potential benefit might be more apparent in late-stage disease, he suggested that, in early-stage breast cancer, surgery and other treatments may be so effective that the immune system’s role only rarely makes a difference. It could play a larger role in late-stage disease when there are less effective therapies. It could also be that the immune system doesn’t recognize the cancer until it has spread beyond the regional lymph nodes on its way to metastasizing.
According to the National Cancer Institute, 10%-30% of people with cancer also have an autoimmune disease.
Dr. Dedousis has no relevant financial disclosures.
CHICAGO – Comorbid autoimmune disease is associated with a greater chance of survival among women with stage IV breast cancer, according to a retrospective study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“It’s counterintuitive that, if you have two diseases instead of one, that you live longer, so then we had to scratch our heads a little bit and think about why these people are living longer,” said lead author Demitrios Dedousis, MD, University Hospitals, Case Medical Center, Cleveland.
Dr. Dedousis and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis of patients from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results–Medicare databases between 2007 and 2014 with breast cancer. The study included data from 137,324 patients diagnosed between 2007 and 2012, before the widespread use of immunotherapy. 27% of patients had an autoimmune disease, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (23%), psoriasis (2.4%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (1.1%).
When all patients were included in the analysis, those with autoimmune disorders had slightly longer survival times, but these weren’t clinically significant. A subanalysis found a greater difference in survival.
The association appears more pronounced in metastatic cancer. Patients with stage 4 breast cancer and autoimmune disease had a longer mean overall survival (36 months vs. 30 months; hazard ratio, 1.46; P < .0001. Cancer-specific survival: HR, 1.39; P < .0001). Patients with autoimmune disease and stage 1-3 breast cancer had lower overall survival (P < .0001, P < 0.0001, and P = 0.026 respectively), compared with patients without autoimmune disease.
“What we thought was happening is that the lack of increased survival in stages 1 through 3 was hiding the increase in survival among the stage IV patients when looking at the overall cohort,” Dr. Dedousis said.
The retrospective nature of the study makes it impossible to draw any firm conclusions about causation. It could be that patients who have already been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease are more vigilant about going to health checkups. “There are other possible explanations, but the one that’s most interesting to us is that their immune system is involved in fighting the cancer. Our study certainly didn’t prove that, but it’s suggesting that’s a possibility,” Dr. Dedousis said.
He and his coauthors anticipate conducting similar studies in other cancers to see if there are similar relationships. Some preliminary work has already suggested something similar in lung cancer. “I think demonstrating this in a few kinds of cancer goes part of the way towards showing that this is a real biological phenomenon,” he said.
Another research avenue is to examine the immune systems and pathology specimens in patients with both an autoimmune disease and cancer to see if there is a greater immune response within the tumor. If so, that could suggest new immunotherapy strategies.
Another possibility is to look at the specific immune pathways within “protective” autoimmune conditions. “For the sake of argument, if we find a particular autoimmune condition is improving survival across multiple kinds of cancers, we could look at those pathways that are specifically involved in that autoimmune condition. It might help us identify a target for drug development,” Dr. Dedousis said.
Asked why a potential benefit might be more apparent in late-stage disease, he suggested that, in early-stage breast cancer, surgery and other treatments may be so effective that the immune system’s role only rarely makes a difference. It could play a larger role in late-stage disease when there are less effective therapies. It could also be that the immune system doesn’t recognize the cancer until it has spread beyond the regional lymph nodes on its way to metastasizing.
According to the National Cancer Institute, 10%-30% of people with cancer also have an autoimmune disease.
Dr. Dedousis has no relevant financial disclosures.
CHICAGO – Comorbid autoimmune disease is associated with a greater chance of survival among women with stage IV breast cancer, according to a retrospective study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“It’s counterintuitive that, if you have two diseases instead of one, that you live longer, so then we had to scratch our heads a little bit and think about why these people are living longer,” said lead author Demitrios Dedousis, MD, University Hospitals, Case Medical Center, Cleveland.
Dr. Dedousis and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis of patients from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results–Medicare databases between 2007 and 2014 with breast cancer. The study included data from 137,324 patients diagnosed between 2007 and 2012, before the widespread use of immunotherapy. 27% of patients had an autoimmune disease, most commonly rheumatoid arthritis (23%), psoriasis (2.4%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (1.1%).
When all patients were included in the analysis, those with autoimmune disorders had slightly longer survival times, but these weren’t clinically significant. A subanalysis found a greater difference in survival.
The association appears more pronounced in metastatic cancer. Patients with stage 4 breast cancer and autoimmune disease had a longer mean overall survival (36 months vs. 30 months; hazard ratio, 1.46; P < .0001. Cancer-specific survival: HR, 1.39; P < .0001). Patients with autoimmune disease and stage 1-3 breast cancer had lower overall survival (P < .0001, P < 0.0001, and P = 0.026 respectively), compared with patients without autoimmune disease.
“What we thought was happening is that the lack of increased survival in stages 1 through 3 was hiding the increase in survival among the stage IV patients when looking at the overall cohort,” Dr. Dedousis said.
The retrospective nature of the study makes it impossible to draw any firm conclusions about causation. It could be that patients who have already been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease are more vigilant about going to health checkups. “There are other possible explanations, but the one that’s most interesting to us is that their immune system is involved in fighting the cancer. Our study certainly didn’t prove that, but it’s suggesting that’s a possibility,” Dr. Dedousis said.
He and his coauthors anticipate conducting similar studies in other cancers to see if there are similar relationships. Some preliminary work has already suggested something similar in lung cancer. “I think demonstrating this in a few kinds of cancer goes part of the way towards showing that this is a real biological phenomenon,” he said.
Another research avenue is to examine the immune systems and pathology specimens in patients with both an autoimmune disease and cancer to see if there is a greater immune response within the tumor. If so, that could suggest new immunotherapy strategies.
Another possibility is to look at the specific immune pathways within “protective” autoimmune conditions. “For the sake of argument, if we find a particular autoimmune condition is improving survival across multiple kinds of cancers, we could look at those pathways that are specifically involved in that autoimmune condition. It might help us identify a target for drug development,” Dr. Dedousis said.
Asked why a potential benefit might be more apparent in late-stage disease, he suggested that, in early-stage breast cancer, surgery and other treatments may be so effective that the immune system’s role only rarely makes a difference. It could play a larger role in late-stage disease when there are less effective therapies. It could also be that the immune system doesn’t recognize the cancer until it has spread beyond the regional lymph nodes on its way to metastasizing.
According to the National Cancer Institute, 10%-30% of people with cancer also have an autoimmune disease.
Dr. Dedousis has no relevant financial disclosures.
AT ASCO 2022
A fish tale? More on that seafood, melanoma study
A recent study linking the consumption of fish to melanoma had sushi eaters looking up the number of the nearest dermatologist. But experts said the findings had several important limitations and that no one should change their diet based on the results.
“It wouldn’t impact my fish consumption at all,” said Sancy Leachman, MD, PhD, who directs the melanoma program at Oregon Health & Science University’s Knight Cancer Institute in Portland. “Fish are part of a healthy diet,” particularly if it replaces less healthy proteins such as beef.
Even the authors of the study advised caution when interpreting the findings.
“I wouldn’t encourage anyone to change their fish consumption habits just because of this paper,” said study leader Eunyoung Cho, ScD, an epidemiologist at Brown University, Providence, R.I. “Fish is cardioprotective and is related to reduced risk of developing certain cancers too.”
Solid findings or fishing expedition?
The study quickly generated headlines and was the most viewed article of the journal Cancer Causes & Control within a day of its publication.
Dr. Cho, who is on the editorial board of the journal, analyzed the results of a study funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Association for the Advancement of Retired Persons that began in the 1990s and explored possible links between fish consumption and developing different forms of cancer.
Previous research from this project had shown eating fish was associated with an increased risk of melanoma – but no other type of cancer.
Dr. Cho speculated that the risk is due to contaminants, such as mercury and arsenic, in fish. But she was curious to see if she could find a connection between the amount of fish consumed and the risk of developing skin cancer.
At the beginning of the study people reported how much fish they had consumed over the previous year, which varied widely by person. Then researchers tracked participants for 15 years, recording who developed cancer and who did not.
Dietary recall can be difficult; people often say they can’t remember what they ate yesterday, much less 1 year ago. Still, dietitian Clare Collins, PhD, of the University of Newcastle (Australia), noted that previous research showed that the dietary recall tool for this study is reliable.
NIH researchers never checked to see how their diet changed over time, as this was a study meant to observe changes in health status starting from a baseline point. The researchers assumed that the level of fish intake recorded at the beginning of the study remained steady.
Of 491,000 people tracked in the study, 5,000 developed malignant melanoma and another 3,300 developed melanoma cells on the skin surface. People who ate the most fish – an average of almost 43 g, or about 1.5 ounces, per day – were 23% more likely to develop melanoma than the lightest fish eaters, who averaged 3 g per day.
That risk is modest, Dr. Leachman said, especially for people with red hair who, she said, are 400% more likely to get melanoma than others. “A 23% increase, in the whole scheme of things, is not nearly as important as not getting sunburned if you’re a redhead,” Dr. Leachman said.
And what about the sun? Sun exposure is the principal risk factor for developing melanoma, and the researchers didn’t account for that factor. People who developed melanoma during the study may simply have spent more time in tanning beds or on the beach – or perhaps fishing and then eating their catch.
Dr. Cho and colleagues tried to consider the effects of solar radiation by looking at average sun exposure times in the places where the participants in the study were living when the research began. Using that framework, variation in sun exposure made no difference to melanoma risk, but Dr. Leachman said the technique isn’t foolproof.
“They assumed that they were going to get a certain amount of ultraviolet light just based on where they lived. We don’t know how long they lived there or if they really had ultraviolet exposure or not,” Dr. Leachman said. Someone in presumably less sunny Pennsylvania could get more sun than someone in sun-drenched Arizona depending on their lifestyle and habits.
The kind of study Dr. Cho published cannot account for individual behaviors related to sun exposure, a limitation her team readily acknowledges. Nor does it include information about moles or hair color – important considerations for skin cancers. It may be that redheads with moles who barely ate any fish developed melanoma at higher rates than anyone else, but the data don’t allow for that kind of analysis.
Dr. Cho’s group found that canned tuna and any type of fish that wasn’t fried were associated with a higher risk of developing melanoma, as people reported eating more of those products. However, people who said they ate greater quantities of fried fish had a lower risk of melanoma, a counterintuitive finding that she said warrants further research.
Given that the study showed only a modest chance of developing melanoma regardless of fish intake, and left so many questions unanswered, what was the point?
Other journals declined to publish this paper, Dr. Cho acknowledged, but she defended the article as a step toward better understanding the health impact of environmental contaminants in fish.
Dr. Leachman agreed. “These kinds of studies are very important to do. They have large data sets, where you can start to see trends that may be important,” she said. “They can help you identify things that might be related. These experiments are hypothesis generating.”
“I already published an article showing that total mercury level is related to skin cancer, and we know very well that in the U.S. fish consumption is the major source of mercury contamination,” Dr. Cho said. “So, I naturally thought that fish consumption may be associated with increased risk of skin cancer too.” Dr. Cho said she believed the findings confirm that hypothesis.
Dr. Cho said the next step would be to measure blood levels of different contaminants such as mercury and arsenic in people with melanoma, to determine which toxin is the biggest driver of melanoma. She said she plans to seek funding for that research.
Meanwhile, pass the salmon – but go light on the salt.
Dr. Cho and Dr. Leachman reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Cho is on the editorial board of Cancer Causes & Control.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent study linking the consumption of fish to melanoma had sushi eaters looking up the number of the nearest dermatologist. But experts said the findings had several important limitations and that no one should change their diet based on the results.
“It wouldn’t impact my fish consumption at all,” said Sancy Leachman, MD, PhD, who directs the melanoma program at Oregon Health & Science University’s Knight Cancer Institute in Portland. “Fish are part of a healthy diet,” particularly if it replaces less healthy proteins such as beef.
Even the authors of the study advised caution when interpreting the findings.
“I wouldn’t encourage anyone to change their fish consumption habits just because of this paper,” said study leader Eunyoung Cho, ScD, an epidemiologist at Brown University, Providence, R.I. “Fish is cardioprotective and is related to reduced risk of developing certain cancers too.”
Solid findings or fishing expedition?
The study quickly generated headlines and was the most viewed article of the journal Cancer Causes & Control within a day of its publication.
Dr. Cho, who is on the editorial board of the journal, analyzed the results of a study funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Association for the Advancement of Retired Persons that began in the 1990s and explored possible links between fish consumption and developing different forms of cancer.
Previous research from this project had shown eating fish was associated with an increased risk of melanoma – but no other type of cancer.
Dr. Cho speculated that the risk is due to contaminants, such as mercury and arsenic, in fish. But she was curious to see if she could find a connection between the amount of fish consumed and the risk of developing skin cancer.
At the beginning of the study people reported how much fish they had consumed over the previous year, which varied widely by person. Then researchers tracked participants for 15 years, recording who developed cancer and who did not.
Dietary recall can be difficult; people often say they can’t remember what they ate yesterday, much less 1 year ago. Still, dietitian Clare Collins, PhD, of the University of Newcastle (Australia), noted that previous research showed that the dietary recall tool for this study is reliable.
NIH researchers never checked to see how their diet changed over time, as this was a study meant to observe changes in health status starting from a baseline point. The researchers assumed that the level of fish intake recorded at the beginning of the study remained steady.
Of 491,000 people tracked in the study, 5,000 developed malignant melanoma and another 3,300 developed melanoma cells on the skin surface. People who ate the most fish – an average of almost 43 g, or about 1.5 ounces, per day – were 23% more likely to develop melanoma than the lightest fish eaters, who averaged 3 g per day.
That risk is modest, Dr. Leachman said, especially for people with red hair who, she said, are 400% more likely to get melanoma than others. “A 23% increase, in the whole scheme of things, is not nearly as important as not getting sunburned if you’re a redhead,” Dr. Leachman said.
And what about the sun? Sun exposure is the principal risk factor for developing melanoma, and the researchers didn’t account for that factor. People who developed melanoma during the study may simply have spent more time in tanning beds or on the beach – or perhaps fishing and then eating their catch.
Dr. Cho and colleagues tried to consider the effects of solar radiation by looking at average sun exposure times in the places where the participants in the study were living when the research began. Using that framework, variation in sun exposure made no difference to melanoma risk, but Dr. Leachman said the technique isn’t foolproof.
“They assumed that they were going to get a certain amount of ultraviolet light just based on where they lived. We don’t know how long they lived there or if they really had ultraviolet exposure or not,” Dr. Leachman said. Someone in presumably less sunny Pennsylvania could get more sun than someone in sun-drenched Arizona depending on their lifestyle and habits.
The kind of study Dr. Cho published cannot account for individual behaviors related to sun exposure, a limitation her team readily acknowledges. Nor does it include information about moles or hair color – important considerations for skin cancers. It may be that redheads with moles who barely ate any fish developed melanoma at higher rates than anyone else, but the data don’t allow for that kind of analysis.
Dr. Cho’s group found that canned tuna and any type of fish that wasn’t fried were associated with a higher risk of developing melanoma, as people reported eating more of those products. However, people who said they ate greater quantities of fried fish had a lower risk of melanoma, a counterintuitive finding that she said warrants further research.
Given that the study showed only a modest chance of developing melanoma regardless of fish intake, and left so many questions unanswered, what was the point?
Other journals declined to publish this paper, Dr. Cho acknowledged, but she defended the article as a step toward better understanding the health impact of environmental contaminants in fish.
Dr. Leachman agreed. “These kinds of studies are very important to do. They have large data sets, where you can start to see trends that may be important,” she said. “They can help you identify things that might be related. These experiments are hypothesis generating.”
“I already published an article showing that total mercury level is related to skin cancer, and we know very well that in the U.S. fish consumption is the major source of mercury contamination,” Dr. Cho said. “So, I naturally thought that fish consumption may be associated with increased risk of skin cancer too.” Dr. Cho said she believed the findings confirm that hypothesis.
Dr. Cho said the next step would be to measure blood levels of different contaminants such as mercury and arsenic in people with melanoma, to determine which toxin is the biggest driver of melanoma. She said she plans to seek funding for that research.
Meanwhile, pass the salmon – but go light on the salt.
Dr. Cho and Dr. Leachman reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Cho is on the editorial board of Cancer Causes & Control.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent study linking the consumption of fish to melanoma had sushi eaters looking up the number of the nearest dermatologist. But experts said the findings had several important limitations and that no one should change their diet based on the results.
“It wouldn’t impact my fish consumption at all,” said Sancy Leachman, MD, PhD, who directs the melanoma program at Oregon Health & Science University’s Knight Cancer Institute in Portland. “Fish are part of a healthy diet,” particularly if it replaces less healthy proteins such as beef.
Even the authors of the study advised caution when interpreting the findings.
“I wouldn’t encourage anyone to change their fish consumption habits just because of this paper,” said study leader Eunyoung Cho, ScD, an epidemiologist at Brown University, Providence, R.I. “Fish is cardioprotective and is related to reduced risk of developing certain cancers too.”
Solid findings or fishing expedition?
The study quickly generated headlines and was the most viewed article of the journal Cancer Causes & Control within a day of its publication.
Dr. Cho, who is on the editorial board of the journal, analyzed the results of a study funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Association for the Advancement of Retired Persons that began in the 1990s and explored possible links between fish consumption and developing different forms of cancer.
Previous research from this project had shown eating fish was associated with an increased risk of melanoma – but no other type of cancer.
Dr. Cho speculated that the risk is due to contaminants, such as mercury and arsenic, in fish. But she was curious to see if she could find a connection between the amount of fish consumed and the risk of developing skin cancer.
At the beginning of the study people reported how much fish they had consumed over the previous year, which varied widely by person. Then researchers tracked participants for 15 years, recording who developed cancer and who did not.
Dietary recall can be difficult; people often say they can’t remember what they ate yesterday, much less 1 year ago. Still, dietitian Clare Collins, PhD, of the University of Newcastle (Australia), noted that previous research showed that the dietary recall tool for this study is reliable.
NIH researchers never checked to see how their diet changed over time, as this was a study meant to observe changes in health status starting from a baseline point. The researchers assumed that the level of fish intake recorded at the beginning of the study remained steady.
Of 491,000 people tracked in the study, 5,000 developed malignant melanoma and another 3,300 developed melanoma cells on the skin surface. People who ate the most fish – an average of almost 43 g, or about 1.5 ounces, per day – were 23% more likely to develop melanoma than the lightest fish eaters, who averaged 3 g per day.
That risk is modest, Dr. Leachman said, especially for people with red hair who, she said, are 400% more likely to get melanoma than others. “A 23% increase, in the whole scheme of things, is not nearly as important as not getting sunburned if you’re a redhead,” Dr. Leachman said.
And what about the sun? Sun exposure is the principal risk factor for developing melanoma, and the researchers didn’t account for that factor. People who developed melanoma during the study may simply have spent more time in tanning beds or on the beach – or perhaps fishing and then eating their catch.
Dr. Cho and colleagues tried to consider the effects of solar radiation by looking at average sun exposure times in the places where the participants in the study were living when the research began. Using that framework, variation in sun exposure made no difference to melanoma risk, but Dr. Leachman said the technique isn’t foolproof.
“They assumed that they were going to get a certain amount of ultraviolet light just based on where they lived. We don’t know how long they lived there or if they really had ultraviolet exposure or not,” Dr. Leachman said. Someone in presumably less sunny Pennsylvania could get more sun than someone in sun-drenched Arizona depending on their lifestyle and habits.
The kind of study Dr. Cho published cannot account for individual behaviors related to sun exposure, a limitation her team readily acknowledges. Nor does it include information about moles or hair color – important considerations for skin cancers. It may be that redheads with moles who barely ate any fish developed melanoma at higher rates than anyone else, but the data don’t allow for that kind of analysis.
Dr. Cho’s group found that canned tuna and any type of fish that wasn’t fried were associated with a higher risk of developing melanoma, as people reported eating more of those products. However, people who said they ate greater quantities of fried fish had a lower risk of melanoma, a counterintuitive finding that she said warrants further research.
Given that the study showed only a modest chance of developing melanoma regardless of fish intake, and left so many questions unanswered, what was the point?
Other journals declined to publish this paper, Dr. Cho acknowledged, but she defended the article as a step toward better understanding the health impact of environmental contaminants in fish.
Dr. Leachman agreed. “These kinds of studies are very important to do. They have large data sets, where you can start to see trends that may be important,” she said. “They can help you identify things that might be related. These experiments are hypothesis generating.”
“I already published an article showing that total mercury level is related to skin cancer, and we know very well that in the U.S. fish consumption is the major source of mercury contamination,” Dr. Cho said. “So, I naturally thought that fish consumption may be associated with increased risk of skin cancer too.” Dr. Cho said she believed the findings confirm that hypothesis.
Dr. Cho said the next step would be to measure blood levels of different contaminants such as mercury and arsenic in people with melanoma, to determine which toxin is the biggest driver of melanoma. She said she plans to seek funding for that research.
Meanwhile, pass the salmon – but go light on the salt.
Dr. Cho and Dr. Leachman reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Cho is on the editorial board of Cancer Causes & Control.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs first systemic treatment for alopecia areata
.
The disorder with the hallmark signs of patchy baldness affects more than 300,000 people in the United States each year. In patients with the autoimmune disorder, the body attacks its own hair follicles and hair falls out, often in clumps. In February, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA.
Baricitinib (Olumiant) is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which blocks the activity of one or more enzymes, interfering with the pathway that leads to inflammation.
The FDA reports the most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections, headache, acne, hyperlipidemia, increase of creatinine phosphokinase, urinary tract infection, elevated liver enzymes, inflammation of hair follicles, fatigue, lower respiratory tract infections, nausea, Candida infections, anemia, neutropenia, abdominal pain, herpes zoster (shingles), and weight gain. The labeling for baricitinib includes a boxed warning for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Evidence from two trials led to announcement
The decision came after review of the results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE AA-1 and BRAVE AA-2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT score) for more than 6 months.
Patients in these trials got either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36.
In BRAVE AA-1, 22% of the 184 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 35% of the 281 patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 5% of the 189 patients in the placebo group.
In BRAVE AA-2, 17% of the 156 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 32% of the 234 patients who received 4 mg achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 3% of the 156 patients in the placebo group.
The results were reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March.
Baricitinib was originally approved in 2018 as a treatment for adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blockers. It is also approved for treating COVID-19 in certain hospitalized adults.
Two other companies, Pfizer and Concert Pharmaceuticals, have JAK inhibitors in late-stage development for AA. The drugs are already on the market for treating rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. FDA approval is important for insurance coverage of the drugs, which have a list price of nearly $2,500 a month, according to The New York Times.
Until now, the only treatments for moderate to severe AA approved by the FDA have been intralesional steroid injections, contact sensitization, and systemic immunosuppressants, but they have demonstrated limited efficacy, are inconvenient for patients to take, and have been unsuitable for use long term.
“Today’s approval will help fulfill a significant unmet need for patients with severe alopecia areata,” Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release.
As Medscape reported last month, The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval of baricitinib for adults with severe AA.
AA received widespread international attention earlier this year at the Academy Awards ceremony, when actor Will Smith walked from the audience up onto the stage and slapped comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Mr. Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, about her shaved head. Mrs. Pinkett Smith has AA and has been public about her struggles with the disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The disorder with the hallmark signs of patchy baldness affects more than 300,000 people in the United States each year. In patients with the autoimmune disorder, the body attacks its own hair follicles and hair falls out, often in clumps. In February, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA.
Baricitinib (Olumiant) is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which blocks the activity of one or more enzymes, interfering with the pathway that leads to inflammation.
The FDA reports the most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections, headache, acne, hyperlipidemia, increase of creatinine phosphokinase, urinary tract infection, elevated liver enzymes, inflammation of hair follicles, fatigue, lower respiratory tract infections, nausea, Candida infections, anemia, neutropenia, abdominal pain, herpes zoster (shingles), and weight gain. The labeling for baricitinib includes a boxed warning for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Evidence from two trials led to announcement
The decision came after review of the results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE AA-1 and BRAVE AA-2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT score) for more than 6 months.
Patients in these trials got either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36.
In BRAVE AA-1, 22% of the 184 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 35% of the 281 patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 5% of the 189 patients in the placebo group.
In BRAVE AA-2, 17% of the 156 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 32% of the 234 patients who received 4 mg achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 3% of the 156 patients in the placebo group.
The results were reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March.
Baricitinib was originally approved in 2018 as a treatment for adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blockers. It is also approved for treating COVID-19 in certain hospitalized adults.
Two other companies, Pfizer and Concert Pharmaceuticals, have JAK inhibitors in late-stage development for AA. The drugs are already on the market for treating rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. FDA approval is important for insurance coverage of the drugs, which have a list price of nearly $2,500 a month, according to The New York Times.
Until now, the only treatments for moderate to severe AA approved by the FDA have been intralesional steroid injections, contact sensitization, and systemic immunosuppressants, but they have demonstrated limited efficacy, are inconvenient for patients to take, and have been unsuitable for use long term.
“Today’s approval will help fulfill a significant unmet need for patients with severe alopecia areata,” Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release.
As Medscape reported last month, The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval of baricitinib for adults with severe AA.
AA received widespread international attention earlier this year at the Academy Awards ceremony, when actor Will Smith walked from the audience up onto the stage and slapped comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Mr. Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, about her shaved head. Mrs. Pinkett Smith has AA and has been public about her struggles with the disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The disorder with the hallmark signs of patchy baldness affects more than 300,000 people in the United States each year. In patients with the autoimmune disorder, the body attacks its own hair follicles and hair falls out, often in clumps. In February, the FDA granted priority review for baricitinib in adults with severe AA.
Baricitinib (Olumiant) is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which blocks the activity of one or more enzymes, interfering with the pathway that leads to inflammation.
The FDA reports the most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections, headache, acne, hyperlipidemia, increase of creatinine phosphokinase, urinary tract infection, elevated liver enzymes, inflammation of hair follicles, fatigue, lower respiratory tract infections, nausea, Candida infections, anemia, neutropenia, abdominal pain, herpes zoster (shingles), and weight gain. The labeling for baricitinib includes a boxed warning for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Evidence from two trials led to announcement
The decision came after review of the results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (BRAVE AA-1 and BRAVE AA-2) with patients who had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT score) for more than 6 months.
Patients in these trials got either a placebo, 2 mg of baricitinib, or 4 mg of baricitinib every day. The primary endpoint for both trials was the proportion of patients who achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage at week 36.
In BRAVE AA-1, 22% of the 184 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 35% of the 281 patients who received 4 mg of baricitinib achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 5% of the 189 patients in the placebo group.
In BRAVE AA-2, 17% of the 156 patients who received 2 mg of baricitinib and 32% of the 234 patients who received 4 mg achieved at least 80% scalp hair coverage, compared with 3% of the 156 patients in the placebo group.
The results were reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March.
Baricitinib was originally approved in 2018 as a treatment for adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–blockers. It is also approved for treating COVID-19 in certain hospitalized adults.
Two other companies, Pfizer and Concert Pharmaceuticals, have JAK inhibitors in late-stage development for AA. The drugs are already on the market for treating rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. FDA approval is important for insurance coverage of the drugs, which have a list price of nearly $2,500 a month, according to The New York Times.
Until now, the only treatments for moderate to severe AA approved by the FDA have been intralesional steroid injections, contact sensitization, and systemic immunosuppressants, but they have demonstrated limited efficacy, are inconvenient for patients to take, and have been unsuitable for use long term.
“Today’s approval will help fulfill a significant unmet need for patients with severe alopecia areata,” Kendall Marcus, MD, director of the Division of Dermatology and Dentistry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the press release.
As Medscape reported last month, The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval of baricitinib for adults with severe AA.
AA received widespread international attention earlier this year at the Academy Awards ceremony, when actor Will Smith walked from the audience up onto the stage and slapped comedian Chris Rock in the face after he directed a joke at Mr. Smith’s wife, Jada Pinkett Smith, about her shaved head. Mrs. Pinkett Smith has AA and has been public about her struggles with the disease.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Surprising link between herpes zoster and dementia
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Current monkeypox outbreak marked by unconventional spread, clinical features
When Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, thinks back on what she learned about monkeypox during her training as a dermatologist and an infectious disease epidemiologist, it was widely considered a viral disease with rare outbreaks limited primarily to Central and Western Africa.
“Monkeypox is something we have traditionally only seen very rarely in the U.S.,” Dr. Freeman, director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “In the past, outbreaks in the U.S. have been related to international travel or import of exotic pets, which is very different than what we’re seeing as a global community now.”

Monkeypox virus belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, symptoms develop 5-21 days after infection and may include fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. Typically, within 1-3 days of the fever, a rash develops, followed by the formation of monkeypox lesions. These lesions progress from macules to papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs, before falling off. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
What makes the 2022 monkeypox outbreak different from others is clear evidence of community transmission. According to worldwide data from the CDC, as of June 9, 2022, there were 1,356 confirmed cases in 31 countries, including 44 cases in the United States. This means that person-to-person spread of the monkeypox virus is occurring among individuals who have not traveled outside of their own country.
“This is likely an underestimate, especially when we think about the U.S., which only has 44 confirmed cases at this time,” Dr. Freeman said. “However, at present, monkeypox cases have to be confirmed by the CDC, so there are a lot more suspected cases that are likely to be confirmed in the coming days. As with any outbreak, it’s a rapidly changing situation.”
A different clinical presentation
The clinical presentation of monkeypox cases in the current outbreak also differs from that of previous outbreaks. In the past, monkeypox rashes often morphed from a macule to a pustule and commonly affected the face, hands, feet, and trunk, with some patients harboring as many as 200 lesions at once. That pattern still occurs, but increasingly, the presentation is characterized by a more localized spread, especially in the genital region, which Dr. Freeman described as “unusual and not an area we traditionally thought of in the past as a focus for monkeypox.”
Also, affected individuals in the current outbreak may develop fewer lesions, sometimes between 1 and 5 instead of up to 200. “This doesn’t apply to everybody, but it is a bit of a different picture than what we’ve seen in case descriptions and photographs in the past from places like Central Africa,” she said. “What’s being reported out of case clusters from the United Kingdom and Spain is a mix, where some people are having more generalized involvement while others have more localized involvement.” Visual examples of the monkey pox rash can be found in photos from the United Kingdom, the country with the highest number of confirmed cases, on the CDC’s website, and in a report from Spain.
Clusters of monkeypox cases have been reported worldwide in men who have sex with men, “but this is not limited to a particular subgroup of people,” emphasizes Dr. Freeman, who is also a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force to Develop Monkeypox Content, which created an online resource for clinicians. “There are several mechanisms of spread, but direct contact with lesions or infected fluids is one,” she notes.
Moreover, If you have a patient with a new genital lesion and you’re not sure what it is, testing for monkeypox in addition to classic sexually transmitted infections like HSV or syphilis would be reasonable during the current outbreak situation.”
The 2022 monkeypox outbreak may pale in comparison to the spread of COVID-19 in terms of case numbers and societal impact, but dermatologists may be the first point of contact for a person infected with the monkeypox virus. “It’s important for dermatologists to be able to recognize monkeypox, because by recognizing cases, we can stop the outbreak,” Dr. Freeman said. “In theory, an infected person could show up in your clinic, regardless of where you practice in the U.S. But at the same time, it’s important not to panic. This is not COVID-19 all over again; this is different. Yes, it is an outbreak, but we already have a vaccine that works against monkeypox, and while one of the possible modes of transmission for monkeypox is respiratory, it’s much harder to transmit that way than SARS-CoV-2 – it requires closer and longer contact.”
Confirmation of a monkeypox virus infection is based on results of a PCR test based on swabs of a lesion. The AAD task force recommends contacting the local hospital epidemiologist, infection control personnel, and/or state health department about suspected cases, “as different locations will have different regulations on where to send the [PCR] test. If appropriate, the state health department will contact the CDC.”
According to the CDC, current recommendations for personal protective equipment for possible and confirmed monkeypox cases include gown, gloves, a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health-approved N-95 mask, and eye protection.
Topical antiviral an option
If the lesions in a patient with suspected monkeypox have turned into pustules while waiting for the PCR test results, one option is to prescribe 3%-5% topical cidofovir, according to Stephen K. Tyring, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology, microbiology & molecular genetics, and internal medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. “That’s the effective antiviral that is most available,” he said. Generic cidofovir is also now available.
Dr. Tyring recommends rapid referral of immunocompromised patients with suspected monkeypox to an infectious disease expert and/or consulting with the CDC. “The pediatric population also seems to be at somewhat more risk, as has been seen in sub-Saharan Africa,” said Dr. Tyring, who is one of the editors of the textbook Tropical Dermatology. “Also, by definition, pregnant women are at more risk because their immune systems aren’t up to par. You also want to make sure that if monkeypox is on a person’s skin that they don’t get it in their eyes, because they could lose their vision.” He added that sub-Saharan Africa has a monkeypox mortality of up to 10%, “which is something we don’t see in the U.S. or Europe. Those of us who grew up in the 20th century got routine smallpox vaccines, and we therefore probably have a degree of immunity to monkeypox. But for the past 40 years or so, unless you are in the military, you are not going to get a routine vaccine to prevent smallpox.”
Incubation period, appearance of lesions
Monkeypox has a long incubation period. According to Dr. Freeman, from the point of exposure to the development of symptomatic lesions is typically 7-14 days but can vary from 5-21 days. “It’s important for people to be aware that their exposure may have been in the more distant past, not just a few days ago” she said. “Identifying cases as quickly as possible gives us a window where we can vaccinate close contacts.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Tyring reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CDC guidance on vaccination before and after exposure to monkeypox can be found here . A general Q&A for health care professionals from the CDC can be found here.
When Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, thinks back on what she learned about monkeypox during her training as a dermatologist and an infectious disease epidemiologist, it was widely considered a viral disease with rare outbreaks limited primarily to Central and Western Africa.
“Monkeypox is something we have traditionally only seen very rarely in the U.S.,” Dr. Freeman, director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “In the past, outbreaks in the U.S. have been related to international travel or import of exotic pets, which is very different than what we’re seeing as a global community now.”

Monkeypox virus belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, symptoms develop 5-21 days after infection and may include fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. Typically, within 1-3 days of the fever, a rash develops, followed by the formation of monkeypox lesions. These lesions progress from macules to papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs, before falling off. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
What makes the 2022 monkeypox outbreak different from others is clear evidence of community transmission. According to worldwide data from the CDC, as of June 9, 2022, there were 1,356 confirmed cases in 31 countries, including 44 cases in the United States. This means that person-to-person spread of the monkeypox virus is occurring among individuals who have not traveled outside of their own country.
“This is likely an underestimate, especially when we think about the U.S., which only has 44 confirmed cases at this time,” Dr. Freeman said. “However, at present, monkeypox cases have to be confirmed by the CDC, so there are a lot more suspected cases that are likely to be confirmed in the coming days. As with any outbreak, it’s a rapidly changing situation.”
A different clinical presentation
The clinical presentation of monkeypox cases in the current outbreak also differs from that of previous outbreaks. In the past, monkeypox rashes often morphed from a macule to a pustule and commonly affected the face, hands, feet, and trunk, with some patients harboring as many as 200 lesions at once. That pattern still occurs, but increasingly, the presentation is characterized by a more localized spread, especially in the genital region, which Dr. Freeman described as “unusual and not an area we traditionally thought of in the past as a focus for monkeypox.”
Also, affected individuals in the current outbreak may develop fewer lesions, sometimes between 1 and 5 instead of up to 200. “This doesn’t apply to everybody, but it is a bit of a different picture than what we’ve seen in case descriptions and photographs in the past from places like Central Africa,” she said. “What’s being reported out of case clusters from the United Kingdom and Spain is a mix, where some people are having more generalized involvement while others have more localized involvement.” Visual examples of the monkey pox rash can be found in photos from the United Kingdom, the country with the highest number of confirmed cases, on the CDC’s website, and in a report from Spain.
Clusters of monkeypox cases have been reported worldwide in men who have sex with men, “but this is not limited to a particular subgroup of people,” emphasizes Dr. Freeman, who is also a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force to Develop Monkeypox Content, which created an online resource for clinicians. “There are several mechanisms of spread, but direct contact with lesions or infected fluids is one,” she notes.
Moreover, If you have a patient with a new genital lesion and you’re not sure what it is, testing for monkeypox in addition to classic sexually transmitted infections like HSV or syphilis would be reasonable during the current outbreak situation.”
The 2022 monkeypox outbreak may pale in comparison to the spread of COVID-19 in terms of case numbers and societal impact, but dermatologists may be the first point of contact for a person infected with the monkeypox virus. “It’s important for dermatologists to be able to recognize monkeypox, because by recognizing cases, we can stop the outbreak,” Dr. Freeman said. “In theory, an infected person could show up in your clinic, regardless of where you practice in the U.S. But at the same time, it’s important not to panic. This is not COVID-19 all over again; this is different. Yes, it is an outbreak, but we already have a vaccine that works against monkeypox, and while one of the possible modes of transmission for monkeypox is respiratory, it’s much harder to transmit that way than SARS-CoV-2 – it requires closer and longer contact.”
Confirmation of a monkeypox virus infection is based on results of a PCR test based on swabs of a lesion. The AAD task force recommends contacting the local hospital epidemiologist, infection control personnel, and/or state health department about suspected cases, “as different locations will have different regulations on where to send the [PCR] test. If appropriate, the state health department will contact the CDC.”
According to the CDC, current recommendations for personal protective equipment for possible and confirmed monkeypox cases include gown, gloves, a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health-approved N-95 mask, and eye protection.
Topical antiviral an option
If the lesions in a patient with suspected monkeypox have turned into pustules while waiting for the PCR test results, one option is to prescribe 3%-5% topical cidofovir, according to Stephen K. Tyring, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology, microbiology & molecular genetics, and internal medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. “That’s the effective antiviral that is most available,” he said. Generic cidofovir is also now available.
Dr. Tyring recommends rapid referral of immunocompromised patients with suspected monkeypox to an infectious disease expert and/or consulting with the CDC. “The pediatric population also seems to be at somewhat more risk, as has been seen in sub-Saharan Africa,” said Dr. Tyring, who is one of the editors of the textbook Tropical Dermatology. “Also, by definition, pregnant women are at more risk because their immune systems aren’t up to par. You also want to make sure that if monkeypox is on a person’s skin that they don’t get it in their eyes, because they could lose their vision.” He added that sub-Saharan Africa has a monkeypox mortality of up to 10%, “which is something we don’t see in the U.S. or Europe. Those of us who grew up in the 20th century got routine smallpox vaccines, and we therefore probably have a degree of immunity to monkeypox. But for the past 40 years or so, unless you are in the military, you are not going to get a routine vaccine to prevent smallpox.”
Incubation period, appearance of lesions
Monkeypox has a long incubation period. According to Dr. Freeman, from the point of exposure to the development of symptomatic lesions is typically 7-14 days but can vary from 5-21 days. “It’s important for people to be aware that their exposure may have been in the more distant past, not just a few days ago” she said. “Identifying cases as quickly as possible gives us a window where we can vaccinate close contacts.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Tyring reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CDC guidance on vaccination before and after exposure to monkeypox can be found here . A general Q&A for health care professionals from the CDC can be found here.
When Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, thinks back on what she learned about monkeypox during her training as a dermatologist and an infectious disease epidemiologist, it was widely considered a viral disease with rare outbreaks limited primarily to Central and Western Africa.
“Monkeypox is something we have traditionally only seen very rarely in the U.S.,” Dr. Freeman, director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “In the past, outbreaks in the U.S. have been related to international travel or import of exotic pets, which is very different than what we’re seeing as a global community now.”

Monkeypox virus belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, symptoms develop 5-21 days after infection and may include fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes. Typically, within 1-3 days of the fever, a rash develops, followed by the formation of monkeypox lesions. These lesions progress from macules to papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs, before falling off. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
What makes the 2022 monkeypox outbreak different from others is clear evidence of community transmission. According to worldwide data from the CDC, as of June 9, 2022, there were 1,356 confirmed cases in 31 countries, including 44 cases in the United States. This means that person-to-person spread of the monkeypox virus is occurring among individuals who have not traveled outside of their own country.
“This is likely an underestimate, especially when we think about the U.S., which only has 44 confirmed cases at this time,” Dr. Freeman said. “However, at present, monkeypox cases have to be confirmed by the CDC, so there are a lot more suspected cases that are likely to be confirmed in the coming days. As with any outbreak, it’s a rapidly changing situation.”
A different clinical presentation
The clinical presentation of monkeypox cases in the current outbreak also differs from that of previous outbreaks. In the past, monkeypox rashes often morphed from a macule to a pustule and commonly affected the face, hands, feet, and trunk, with some patients harboring as many as 200 lesions at once. That pattern still occurs, but increasingly, the presentation is characterized by a more localized spread, especially in the genital region, which Dr. Freeman described as “unusual and not an area we traditionally thought of in the past as a focus for monkeypox.”
Also, affected individuals in the current outbreak may develop fewer lesions, sometimes between 1 and 5 instead of up to 200. “This doesn’t apply to everybody, but it is a bit of a different picture than what we’ve seen in case descriptions and photographs in the past from places like Central Africa,” she said. “What’s being reported out of case clusters from the United Kingdom and Spain is a mix, where some people are having more generalized involvement while others have more localized involvement.” Visual examples of the monkey pox rash can be found in photos from the United Kingdom, the country with the highest number of confirmed cases, on the CDC’s website, and in a report from Spain.
Clusters of monkeypox cases have been reported worldwide in men who have sex with men, “but this is not limited to a particular subgroup of people,” emphasizes Dr. Freeman, who is also a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force to Develop Monkeypox Content, which created an online resource for clinicians. “There are several mechanisms of spread, but direct contact with lesions or infected fluids is one,” she notes.
Moreover, If you have a patient with a new genital lesion and you’re not sure what it is, testing for monkeypox in addition to classic sexually transmitted infections like HSV or syphilis would be reasonable during the current outbreak situation.”
The 2022 monkeypox outbreak may pale in comparison to the spread of COVID-19 in terms of case numbers and societal impact, but dermatologists may be the first point of contact for a person infected with the monkeypox virus. “It’s important for dermatologists to be able to recognize monkeypox, because by recognizing cases, we can stop the outbreak,” Dr. Freeman said. “In theory, an infected person could show up in your clinic, regardless of where you practice in the U.S. But at the same time, it’s important not to panic. This is not COVID-19 all over again; this is different. Yes, it is an outbreak, but we already have a vaccine that works against monkeypox, and while one of the possible modes of transmission for monkeypox is respiratory, it’s much harder to transmit that way than SARS-CoV-2 – it requires closer and longer contact.”
Confirmation of a monkeypox virus infection is based on results of a PCR test based on swabs of a lesion. The AAD task force recommends contacting the local hospital epidemiologist, infection control personnel, and/or state health department about suspected cases, “as different locations will have different regulations on where to send the [PCR] test. If appropriate, the state health department will contact the CDC.”
According to the CDC, current recommendations for personal protective equipment for possible and confirmed monkeypox cases include gown, gloves, a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health-approved N-95 mask, and eye protection.
Topical antiviral an option
If the lesions in a patient with suspected monkeypox have turned into pustules while waiting for the PCR test results, one option is to prescribe 3%-5% topical cidofovir, according to Stephen K. Tyring, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology, microbiology & molecular genetics, and internal medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. “That’s the effective antiviral that is most available,” he said. Generic cidofovir is also now available.
Dr. Tyring recommends rapid referral of immunocompromised patients with suspected monkeypox to an infectious disease expert and/or consulting with the CDC. “The pediatric population also seems to be at somewhat more risk, as has been seen in sub-Saharan Africa,” said Dr. Tyring, who is one of the editors of the textbook Tropical Dermatology. “Also, by definition, pregnant women are at more risk because their immune systems aren’t up to par. You also want to make sure that if monkeypox is on a person’s skin that they don’t get it in their eyes, because they could lose their vision.” He added that sub-Saharan Africa has a monkeypox mortality of up to 10%, “which is something we don’t see in the U.S. or Europe. Those of us who grew up in the 20th century got routine smallpox vaccines, and we therefore probably have a degree of immunity to monkeypox. But for the past 40 years or so, unless you are in the military, you are not going to get a routine vaccine to prevent smallpox.”
Incubation period, appearance of lesions
Monkeypox has a long incubation period. According to Dr. Freeman, from the point of exposure to the development of symptomatic lesions is typically 7-14 days but can vary from 5-21 days. “It’s important for people to be aware that their exposure may have been in the more distant past, not just a few days ago” she said. “Identifying cases as quickly as possible gives us a window where we can vaccinate close contacts.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Tyring reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CDC guidance on vaccination before and after exposure to monkeypox can be found here . A general Q&A for health care professionals from the CDC can be found here.
‘My malpractice insurance doubled!’ Why, when fewer patients are suing?
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA cautions against using OTC products to remove skin spots, moles
Those moles, skin tags, and liver spots should stay on your skin until you see a doctor, according to a new alert from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The alert warns against the use of over-the-counter products for removing moles, seborrheic keratoses (wart-like growths that are often brown), or skin tags, emphasizing that none are approved by the FDA for at-home use.
Dermatologists and the FDA say these products may lead to scarring and disfigurement.
Risks include “skin injuries, infection requiring antibiotics, scarring, and delayed skin cancer diagnosis and treatment,” according to the alert, which adds that the agency has received reports of people “who developed permanent skin injuries and infections after using products marketed as mole or skin tag removers. “
These products come in the form of gels, liquids, sticks, or ointments and commonly contain ingredients like salicylic acid, which are cytotoxic, or cell-killing. These chemicals are what make the products potentially dangerous, as each contains unregulated, and likely very high, amounts of these corrosive agents. Even products marketed as natural or organic have these same issues, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who notes that bloodroot is another ingredient found in these products.
Dr. Friedman explained that using these products without the supervision of a health care provider can create a chemical burn in the skin, leading to scarring. He’s treated patients for open wounds and infected ulcers caused by these products. “Over my career, I’ve seen many cases of patients coming in with self-inflicted harm due to using these quote, unquote, safe and natural products to remove benign, or even worse, potentially malignant neoplasms,” he told this news organization.
Another concern is that these spots on the skin are often the only sign of a serious issue – cancer. Early signs of melanoma, a type of skin cancer, include large, misshapen, or rapidly changing moles. Dr. Friedman said that if a patient uses one of these products on what is actually a cancerous mole, they will likely only remove the surface, and in turn, destroy the only sign of cancer – effectively killing the canary in the coal mine.
There’s a good chance that the root of the mole has been left intact under the skin surface, and as a result, the cancer has the potential to spread unnoticed. “If people aren’t going to a dermatologist to be properly diagnosed and properly managed, they’re going to cause more harm by thinking that they’ve taken care of a problem,” he said.
If you are concerned about any type of spot on your skin, a visit to the dermatologist will prove much simpler and safer for treating it than doing so at home. In the office, Dr. Friedman said, providers can use a range of highly studied techniques to remove skin lesions with minimal pain and scarring. From freezing, burning, snipping, or a quick moment under a scalpel, you’ll be healed in no time.
Anyone who has experienced an adverse event with one of these products and health care professionals should report cases to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Those moles, skin tags, and liver spots should stay on your skin until you see a doctor, according to a new alert from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The alert warns against the use of over-the-counter products for removing moles, seborrheic keratoses (wart-like growths that are often brown), or skin tags, emphasizing that none are approved by the FDA for at-home use.
Dermatologists and the FDA say these products may lead to scarring and disfigurement.
Risks include “skin injuries, infection requiring antibiotics, scarring, and delayed skin cancer diagnosis and treatment,” according to the alert, which adds that the agency has received reports of people “who developed permanent skin injuries and infections after using products marketed as mole or skin tag removers. “
These products come in the form of gels, liquids, sticks, or ointments and commonly contain ingredients like salicylic acid, which are cytotoxic, or cell-killing. These chemicals are what make the products potentially dangerous, as each contains unregulated, and likely very high, amounts of these corrosive agents. Even products marketed as natural or organic have these same issues, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who notes that bloodroot is another ingredient found in these products.
Dr. Friedman explained that using these products without the supervision of a health care provider can create a chemical burn in the skin, leading to scarring. He’s treated patients for open wounds and infected ulcers caused by these products. “Over my career, I’ve seen many cases of patients coming in with self-inflicted harm due to using these quote, unquote, safe and natural products to remove benign, or even worse, potentially malignant neoplasms,” he told this news organization.
Another concern is that these spots on the skin are often the only sign of a serious issue – cancer. Early signs of melanoma, a type of skin cancer, include large, misshapen, or rapidly changing moles. Dr. Friedman said that if a patient uses one of these products on what is actually a cancerous mole, they will likely only remove the surface, and in turn, destroy the only sign of cancer – effectively killing the canary in the coal mine.
There’s a good chance that the root of the mole has been left intact under the skin surface, and as a result, the cancer has the potential to spread unnoticed. “If people aren’t going to a dermatologist to be properly diagnosed and properly managed, they’re going to cause more harm by thinking that they’ve taken care of a problem,” he said.
If you are concerned about any type of spot on your skin, a visit to the dermatologist will prove much simpler and safer for treating it than doing so at home. In the office, Dr. Friedman said, providers can use a range of highly studied techniques to remove skin lesions with minimal pain and scarring. From freezing, burning, snipping, or a quick moment under a scalpel, you’ll be healed in no time.
Anyone who has experienced an adverse event with one of these products and health care professionals should report cases to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Those moles, skin tags, and liver spots should stay on your skin until you see a doctor, according to a new alert from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The alert warns against the use of over-the-counter products for removing moles, seborrheic keratoses (wart-like growths that are often brown), or skin tags, emphasizing that none are approved by the FDA for at-home use.
Dermatologists and the FDA say these products may lead to scarring and disfigurement.
Risks include “skin injuries, infection requiring antibiotics, scarring, and delayed skin cancer diagnosis and treatment,” according to the alert, which adds that the agency has received reports of people “who developed permanent skin injuries and infections after using products marketed as mole or skin tag removers. “
These products come in the form of gels, liquids, sticks, or ointments and commonly contain ingredients like salicylic acid, which are cytotoxic, or cell-killing. These chemicals are what make the products potentially dangerous, as each contains unregulated, and likely very high, amounts of these corrosive agents. Even products marketed as natural or organic have these same issues, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who notes that bloodroot is another ingredient found in these products.
Dr. Friedman explained that using these products without the supervision of a health care provider can create a chemical burn in the skin, leading to scarring. He’s treated patients for open wounds and infected ulcers caused by these products. “Over my career, I’ve seen many cases of patients coming in with self-inflicted harm due to using these quote, unquote, safe and natural products to remove benign, or even worse, potentially malignant neoplasms,” he told this news organization.
Another concern is that these spots on the skin are often the only sign of a serious issue – cancer. Early signs of melanoma, a type of skin cancer, include large, misshapen, or rapidly changing moles. Dr. Friedman said that if a patient uses one of these products on what is actually a cancerous mole, they will likely only remove the surface, and in turn, destroy the only sign of cancer – effectively killing the canary in the coal mine.
There’s a good chance that the root of the mole has been left intact under the skin surface, and as a result, the cancer has the potential to spread unnoticed. “If people aren’t going to a dermatologist to be properly diagnosed and properly managed, they’re going to cause more harm by thinking that they’ve taken care of a problem,” he said.
If you are concerned about any type of spot on your skin, a visit to the dermatologist will prove much simpler and safer for treating it than doing so at home. In the office, Dr. Friedman said, providers can use a range of highly studied techniques to remove skin lesions with minimal pain and scarring. From freezing, burning, snipping, or a quick moment under a scalpel, you’ll be healed in no time.
Anyone who has experienced an adverse event with one of these products and health care professionals should report cases to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting Program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.