User login
Hidradenitis suppurativa packs mighty QOL impact
KAUAI, HAWAII – Anyone who has treated patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) recognizes that this can be a debilitating disease. Helping put that into fuller perspective, recent evidence has shown that the quality of life effects of moderate to severe HS are objectively worse than those of moderate to severe psoriasis, according to Iltefat H. Hamzavi, MD, president of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation and a dermatologist at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit.
He was lead author of a study in which he and his coinvestigators compared weighted averages of a variety of quality of life measures in patients with moderate to severe HS or psoriasis who participated in five AbbVie-sponsored randomized clinical trials of biologic agents (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Dec;77[6]:1038-46).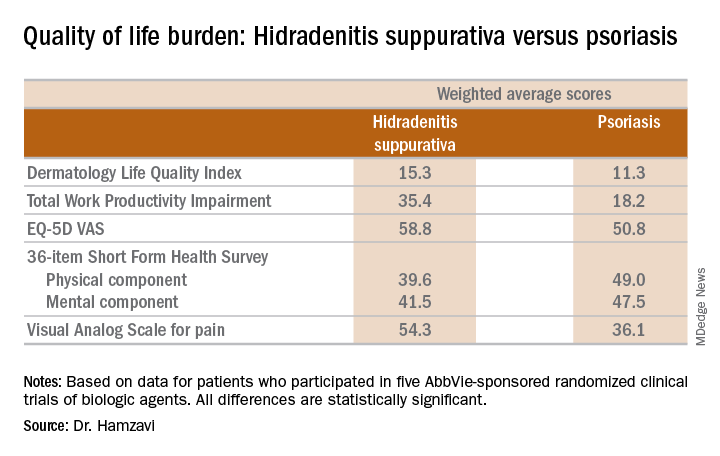
“The number of HS patients who experience downward drift – losing their job and their health insurance and ultimately being unable to move out of a lower socioeconomic group – is staggering,” the dermatologist said.
which underscores the importance of a psychiatric evaluation as part of routine care for patients with this dermatologic disease. “Suicide is much more common in the HS population than in almost any other dermatologic disease,” Dr. Hamzavi added.
He reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Incyte, and UCB.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – Anyone who has treated patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) recognizes that this can be a debilitating disease. Helping put that into fuller perspective, recent evidence has shown that the quality of life effects of moderate to severe HS are objectively worse than those of moderate to severe psoriasis, according to Iltefat H. Hamzavi, MD, president of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation and a dermatologist at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit.
He was lead author of a study in which he and his coinvestigators compared weighted averages of a variety of quality of life measures in patients with moderate to severe HS or psoriasis who participated in five AbbVie-sponsored randomized clinical trials of biologic agents (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Dec;77[6]:1038-46).
“The number of HS patients who experience downward drift – losing their job and their health insurance and ultimately being unable to move out of a lower socioeconomic group – is staggering,” the dermatologist said.
which underscores the importance of a psychiatric evaluation as part of routine care for patients with this dermatologic disease. “Suicide is much more common in the HS population than in almost any other dermatologic disease,” Dr. Hamzavi added.
He reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Incyte, and UCB.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – Anyone who has treated patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) recognizes that this can be a debilitating disease. Helping put that into fuller perspective, recent evidence has shown that the quality of life effects of moderate to severe HS are objectively worse than those of moderate to severe psoriasis, according to Iltefat H. Hamzavi, MD, president of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation and a dermatologist at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit.
He was lead author of a study in which he and his coinvestigators compared weighted averages of a variety of quality of life measures in patients with moderate to severe HS or psoriasis who participated in five AbbVie-sponsored randomized clinical trials of biologic agents (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Dec;77[6]:1038-46).
“The number of HS patients who experience downward drift – losing their job and their health insurance and ultimately being unable to move out of a lower socioeconomic group – is staggering,” the dermatologist said.
which underscores the importance of a psychiatric evaluation as part of routine care for patients with this dermatologic disease. “Suicide is much more common in the HS population than in almost any other dermatologic disease,” Dr. Hamzavi added.
He reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Incyte, and UCB.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Psoriasis duration reflects cardiovascular event risk
KAUAI, HAWAII – The recent report that the risk of a major adverse cardiovascular event increases by 1% more than in the general population for each additional year of psoriasis duration is sobering news for physicians who treat pediatric psoriasis.
“If I have a 16-year-old who has a 5-year history of psoriasis, what does that mean for when she’s 30 or 40? And should we be intervening more aggressively?” Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, asked at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“Even though there’s not a great deal of evidence, there’s some evidence to rationalize early screening in psoriasis,” according to Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
Psoriasis develops during childhood in almost one-third of patients.
The pediatric psoriasis screening guidelines describe a simple routine screening program and timeline for early identification of overweight or obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, anxiety, depression, substance abuse, inflammatory bowel disease, and quality of life issues, all of which are encountered with increased frequency in pediatric psoriasis patients. A fasting lipid panel is recommended in children aged 9-11 years with psoriasis and again at age 17-21 years.
“Don’t forget arthritis. For a kid with psoriasis, at every office visit, I ask about morning stiffness or limp. Those are probably the two most sensitive questions in screening for psoriatic arthritis,” according to Dr. Eichenfield.
It has been clear for some time that the skin is not the only organ affected by psoriatic inflammation. The study that quantified the relationship between psoriasis duration and cardiovascular risk – a 1% increase for each year of psoriasis – was a collaboration between investigators at the University of Copenhagen and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The two-part project included aortal imaging of 190 psoriasis patients using fludeoxyglucose F 18 PET/CT scan, which showed a strong relationship between duration of psoriasis and the degree of vascular inflammation. This was bolstered by a population-based study using Danish national registry data on 87,161 psoriasis patients and 4.2 million controls from the general Danish population (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Oct;77[4]:650-56.e3).
Dr. Eichenfield reported serving as a consultant to and/or recipient of research grants from more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – The recent report that the risk of a major adverse cardiovascular event increases by 1% more than in the general population for each additional year of psoriasis duration is sobering news for physicians who treat pediatric psoriasis.
“If I have a 16-year-old who has a 5-year history of psoriasis, what does that mean for when she’s 30 or 40? And should we be intervening more aggressively?” Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, asked at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“Even though there’s not a great deal of evidence, there’s some evidence to rationalize early screening in psoriasis,” according to Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
Psoriasis develops during childhood in almost one-third of patients.
The pediatric psoriasis screening guidelines describe a simple routine screening program and timeline for early identification of overweight or obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, anxiety, depression, substance abuse, inflammatory bowel disease, and quality of life issues, all of which are encountered with increased frequency in pediatric psoriasis patients. A fasting lipid panel is recommended in children aged 9-11 years with psoriasis and again at age 17-21 years.
“Don’t forget arthritis. For a kid with psoriasis, at every office visit, I ask about morning stiffness or limp. Those are probably the two most sensitive questions in screening for psoriatic arthritis,” according to Dr. Eichenfield.
It has been clear for some time that the skin is not the only organ affected by psoriatic inflammation. The study that quantified the relationship between psoriasis duration and cardiovascular risk – a 1% increase for each year of psoriasis – was a collaboration between investigators at the University of Copenhagen and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The two-part project included aortal imaging of 190 psoriasis patients using fludeoxyglucose F 18 PET/CT scan, which showed a strong relationship between duration of psoriasis and the degree of vascular inflammation. This was bolstered by a population-based study using Danish national registry data on 87,161 psoriasis patients and 4.2 million controls from the general Danish population (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Oct;77[4]:650-56.e3).
Dr. Eichenfield reported serving as a consultant to and/or recipient of research grants from more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – The recent report that the risk of a major adverse cardiovascular event increases by 1% more than in the general population for each additional year of psoriasis duration is sobering news for physicians who treat pediatric psoriasis.
“If I have a 16-year-old who has a 5-year history of psoriasis, what does that mean for when she’s 30 or 40? And should we be intervening more aggressively?” Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, asked at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“Even though there’s not a great deal of evidence, there’s some evidence to rationalize early screening in psoriasis,” according to Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
Psoriasis develops during childhood in almost one-third of patients.
The pediatric psoriasis screening guidelines describe a simple routine screening program and timeline for early identification of overweight or obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, anxiety, depression, substance abuse, inflammatory bowel disease, and quality of life issues, all of which are encountered with increased frequency in pediatric psoriasis patients. A fasting lipid panel is recommended in children aged 9-11 years with psoriasis and again at age 17-21 years.
“Don’t forget arthritis. For a kid with psoriasis, at every office visit, I ask about morning stiffness or limp. Those are probably the two most sensitive questions in screening for psoriatic arthritis,” according to Dr. Eichenfield.
It has been clear for some time that the skin is not the only organ affected by psoriatic inflammation. The study that quantified the relationship between psoriasis duration and cardiovascular risk – a 1% increase for each year of psoriasis – was a collaboration between investigators at the University of Copenhagen and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The two-part project included aortal imaging of 190 psoriasis patients using fludeoxyglucose F 18 PET/CT scan, which showed a strong relationship between duration of psoriasis and the degree of vascular inflammation. This was bolstered by a population-based study using Danish national registry data on 87,161 psoriasis patients and 4.2 million controls from the general Danish population (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Oct;77[4]:650-56.e3).
Dr. Eichenfield reported serving as a consultant to and/or recipient of research grants from more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Is PASI 100 the new benchmark in psoriasis?
KAUAI, HAWAII – I think we should just do away with PASI 90 [90% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score] and look at how well our drugs do against the metric of PASI 100. The whole ball of wax. Let’s just go for complete clearance,” Craig L. Leonardi, MD, declared in a provocative presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Skin Disease Education Foundation/Global Academy for Medical Education.
He advocates using number needed to treat (NNT) as a performance yardstick. He finds it helpful in translating sometimes-arcane clinical trial results into useful information to guide everyday practice. The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated with a drug or procedure in order to achieve one additional good outcome, compared with a control intervention or placebo. It’s the inverse of the absolute risk reduction. The lower the NNT, the better an intervention is performing.
He presented a chart that summarized the NNTs to achieve a PASI 100 response for various systemic agents commonly used in treating moderate to severe psoriasis. He obtained the data from Food and Drug Administration–regulated product labeling and phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Leonardi drew attention to the worst performers on the list: methotrexate, with an NNT of 25 to achieve a PASI 100 response, and etanercept, with an NNT of 23.3.
“Methotrexate is a drug that the insurance industry says we have to flow through on our way to biologic drugs. But if complete clearance is your goal, this is an exercise in futility. These patients will never, ever get to complete clearance – or it’s at least very unlikely. We shouldn’t be asked to go through methotrexate on our way to anything. We shouldn’t be asked to use methotrexate at all. We should be bypassing it. And some of us are working on this,” he said.
Ustekinumab and adalimumab are the current market leaders in biologic therapy for psoriasis, but they don’t stack up so well when viewed through the filter of PASI 100 response, with NNTs of 9.2 and 5.3, respectively.
“These market leaders may not be the most relevant drugs in the current era,” according to the dermatologist.
In contrast, the high-performance biologics – the interleukin-17 inhibitors secukinumab, ixekizumab, and brodalumab and the interleukin-23 antagonist guselkumab – have impressively low NNTs of 2.4-3.6 in order to achieve complete clearance.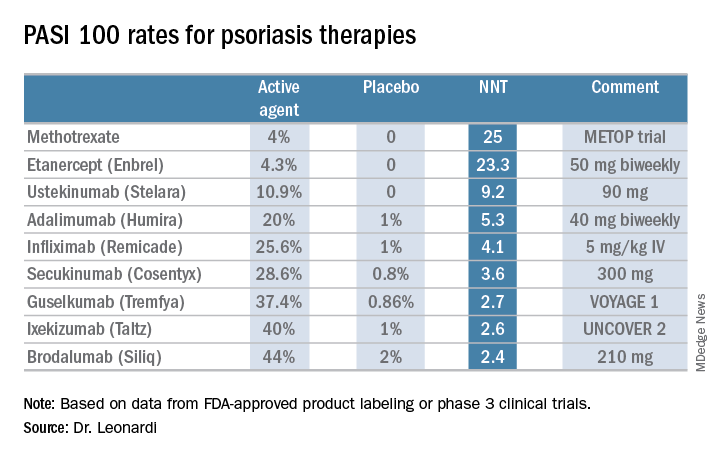
“But our IL-17 and IL-23 antagonists are markedly different from all other therapies, with NNTs of 1.3-1.1. With an NNT of 1.1, if you treated 11 patients with ixekizumab, 10 of them would achieve a PASI 75,” he explained.
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Leonardi commented. “Our first drug back in 2002 was alefacept, and that drug was a ‘twenty-one percenter’: 21% of patients achieved a PASI 75. And quite frankly, we thought that was rocking voodoo science back in the day. Well, we’re really out there now. This is utterly amazing data: a PASI 75 of 81.6% for secukinumab, 86% for brodalumab, 90% for ixekizumab, and 91.2% for guselkumab. This is why we’re publishing this stuff in the best medical journals, because these results are absolutely amazing. So many different medical specialties are interested in what we’re doing with these drugs.”
He reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Leo, Pfizer, Sandoz, and UCB and receiving research funding from 21 pharmaceutical companies.
The SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – I think we should just do away with PASI 90 [90% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score] and look at how well our drugs do against the metric of PASI 100. The whole ball of wax. Let’s just go for complete clearance,” Craig L. Leonardi, MD, declared in a provocative presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Skin Disease Education Foundation/Global Academy for Medical Education.
He advocates using number needed to treat (NNT) as a performance yardstick. He finds it helpful in translating sometimes-arcane clinical trial results into useful information to guide everyday practice. The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated with a drug or procedure in order to achieve one additional good outcome, compared with a control intervention or placebo. It’s the inverse of the absolute risk reduction. The lower the NNT, the better an intervention is performing.
He presented a chart that summarized the NNTs to achieve a PASI 100 response for various systemic agents commonly used in treating moderate to severe psoriasis. He obtained the data from Food and Drug Administration–regulated product labeling and phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Leonardi drew attention to the worst performers on the list: methotrexate, with an NNT of 25 to achieve a PASI 100 response, and etanercept, with an NNT of 23.3.
“Methotrexate is a drug that the insurance industry says we have to flow through on our way to biologic drugs. But if complete clearance is your goal, this is an exercise in futility. These patients will never, ever get to complete clearance – or it’s at least very unlikely. We shouldn’t be asked to go through methotrexate on our way to anything. We shouldn’t be asked to use methotrexate at all. We should be bypassing it. And some of us are working on this,” he said.
Ustekinumab and adalimumab are the current market leaders in biologic therapy for psoriasis, but they don’t stack up so well when viewed through the filter of PASI 100 response, with NNTs of 9.2 and 5.3, respectively.
“These market leaders may not be the most relevant drugs in the current era,” according to the dermatologist.
In contrast, the high-performance biologics – the interleukin-17 inhibitors secukinumab, ixekizumab, and brodalumab and the interleukin-23 antagonist guselkumab – have impressively low NNTs of 2.4-3.6 in order to achieve complete clearance.
“But our IL-17 and IL-23 antagonists are markedly different from all other therapies, with NNTs of 1.3-1.1. With an NNT of 1.1, if you treated 11 patients with ixekizumab, 10 of them would achieve a PASI 75,” he explained.
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Leonardi commented. “Our first drug back in 2002 was alefacept, and that drug was a ‘twenty-one percenter’: 21% of patients achieved a PASI 75. And quite frankly, we thought that was rocking voodoo science back in the day. Well, we’re really out there now. This is utterly amazing data: a PASI 75 of 81.6% for secukinumab, 86% for brodalumab, 90% for ixekizumab, and 91.2% for guselkumab. This is why we’re publishing this stuff in the best medical journals, because these results are absolutely amazing. So many different medical specialties are interested in what we’re doing with these drugs.”
He reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Leo, Pfizer, Sandoz, and UCB and receiving research funding from 21 pharmaceutical companies.
The SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – I think we should just do away with PASI 90 [90% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score] and look at how well our drugs do against the metric of PASI 100. The whole ball of wax. Let’s just go for complete clearance,” Craig L. Leonardi, MD, declared in a provocative presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Skin Disease Education Foundation/Global Academy for Medical Education.
He advocates using number needed to treat (NNT) as a performance yardstick. He finds it helpful in translating sometimes-arcane clinical trial results into useful information to guide everyday practice. The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated with a drug or procedure in order to achieve one additional good outcome, compared with a control intervention or placebo. It’s the inverse of the absolute risk reduction. The lower the NNT, the better an intervention is performing.
He presented a chart that summarized the NNTs to achieve a PASI 100 response for various systemic agents commonly used in treating moderate to severe psoriasis. He obtained the data from Food and Drug Administration–regulated product labeling and phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Leonardi drew attention to the worst performers on the list: methotrexate, with an NNT of 25 to achieve a PASI 100 response, and etanercept, with an NNT of 23.3.
“Methotrexate is a drug that the insurance industry says we have to flow through on our way to biologic drugs. But if complete clearance is your goal, this is an exercise in futility. These patients will never, ever get to complete clearance – or it’s at least very unlikely. We shouldn’t be asked to go through methotrexate on our way to anything. We shouldn’t be asked to use methotrexate at all. We should be bypassing it. And some of us are working on this,” he said.
Ustekinumab and adalimumab are the current market leaders in biologic therapy for psoriasis, but they don’t stack up so well when viewed through the filter of PASI 100 response, with NNTs of 9.2 and 5.3, respectively.
“These market leaders may not be the most relevant drugs in the current era,” according to the dermatologist.
In contrast, the high-performance biologics – the interleukin-17 inhibitors secukinumab, ixekizumab, and brodalumab and the interleukin-23 antagonist guselkumab – have impressively low NNTs of 2.4-3.6 in order to achieve complete clearance.
“But our IL-17 and IL-23 antagonists are markedly different from all other therapies, with NNTs of 1.3-1.1. With an NNT of 1.1, if you treated 11 patients with ixekizumab, 10 of them would achieve a PASI 75,” he explained.
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Leonardi commented. “Our first drug back in 2002 was alefacept, and that drug was a ‘twenty-one percenter’: 21% of patients achieved a PASI 75. And quite frankly, we thought that was rocking voodoo science back in the day. Well, we’re really out there now. This is utterly amazing data: a PASI 75 of 81.6% for secukinumab, 86% for brodalumab, 90% for ixekizumab, and 91.2% for guselkumab. This is why we’re publishing this stuff in the best medical journals, because these results are absolutely amazing. So many different medical specialties are interested in what we’re doing with these drugs.”
He reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Leo, Pfizer, Sandoz, and UCB and receiving research funding from 21 pharmaceutical companies.
The SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
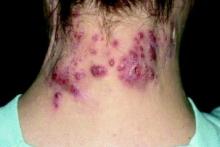
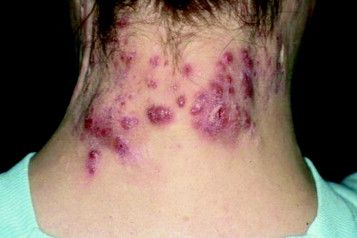
Surgical excision essential in severe hidradenitis suppurativa
KAUAI, HAWAII – Medical therapy alone is never sufficient in Hurley stage III hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), Iltefat H. Hamzavi, MD, observed at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“Even with the advances in biologics and antibiotic therapy, you still have to excise once you’re in full-blown Hurley stage III disease. Surgery has to be part of your protocol,” according to Dr. Hamzavi, a dermatologist at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, which runs one of the nation’s largest hidradenitis suppurativa clinics, with roughly 1,600 patients.
“Of course we’re biased. But until the data can set us free, you’re stuck with me,” the dermatologist quipped.
A core principle of the Henry Ford algorithm is this: “Medical therapy [for patients with advanced HS] stabilizes them and reduces their draining and pain, then you try to bring them back to a lower stage with surgical options,” he explained.
Although other HS staging systems exist, Dr. Hamzavi and his colleagues rely on the Hurley staging system to guide their treatment. Basically, Hurley stage I consists of follicular nodules and abscesses. When the nodules connect to form sinus tracts with scarring, that’s stage II. And if the sinus tracts interconnect throughout an entire area, that’s stage III.
Hurley stage I
First-line treatment of localized Hurley stage I disease at Henry Ford is a 10% topical benzoyl peroxide wash left on for 5 minutes before bathing, followed by postbathing topical clindamycin 1% lotion or solution applied to the nodules. If this maintenance regimen isn’t sufficient to prevent formation of new and worsening nodules, Dr. Hamzavi supplements it with up to three once-monthly 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser sessions aimed at follicular ablation. It’s a laser application he and his colleagues pioneered (Dermatol Surg. 2009 Aug;35[8]:1188-98). They subsequently documented the histopathologic basis of the procedure’s efficacy, which entails selective thermolysis of follicles, destruction of inflammatory lesions in the superficial to mid-dermis, followed by fibrosis and scarring (Arch Dermatol. 2011 Jan;147[1]:21-8).
In generalized Hurley stage I HS, the Henry Ford approach is to supplement the topical regimen and laser sessions with oral doxycycline at 100-150 mg daily for 1-6 months.
“The theory here is this is a dysbiotic event. The antibiotics reduce commensal bacteria, which ultimately reduces the reactive inflammatory response. But when you stop the antibiotics, the inflammatory response returns. So antibiotics can help stabilize the disease state but really can’t reverse the disease state. For that we have to turn to ablative treatment options: laser, surgery,” the dermatologist continued.
Hurley stage II
“At this point you’re looking at procedures,” according to Dr. Hamzavi. “Once you have sinus tracts it’s critical to remove them.”
The treatment backbone in stage II disease is 8-10 weeks of oral clindamycin and rifampin, both at 300 mg twice daily.
“This is one of the fundamental building blocks of HS clinics throughout the world,” he noted.
Clostridium difficile infection is exceedingly rare in HS patients on this regimen, for reasons still unclear.
If this dual-antibiotic regimen doesn’t dramatically reduce drainage and pain, he adds levofloxacin at 500 mg twice daily for up to 2 weeks in an effort to calm down unstable, decompensating disease.
Dapsone at 50-150 mg/day for up to 12 weeks is an additional option. It’s most useful in patients with nodules that are disproportionately painful, in Dr. Hamzavi’s experience.
Deroofing is a simple procedure that should be considered for all sinus tracts. It entails numbing the area with a ring block then introducing a curette or surgical probe into the sinus tract to open it up and get rid of the gelatinous material within. Dutch investigators have detailed the technique (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010 Sep;63[3]:475-80).
Tumor necrosis factor–inhibitor therapy has been a major advance in Hurley stage II and III disease. “It doesn’t work in everybody, but a lot of patients can be stabilized,” Dr. Hamzavi observed.
Efficacy has been amply demonstrated for adalimumab (Humira) and infliximab (Remicade). In Dr. Hamzavi’s experience infliximab works better, probably because it offers more dosing options.
Assuming medical therapy has resulted in disease stabilization, CO2 laser excision of sinus tracts under local anesthesia can then be employed as an office procedure to turn back the clock and return to an earlier stage of disease. Dermatologists at the Cleveland Clinic have described the technique in detail (Dermatol Surg. 2010 Feb;36[2]:208-13).
Hurley stage III
If biologic therapy doesn’t bring disease stabilization, the patient is likely headed for surgical excision using the CO2 laser. The Henry Ford team favors a specific regimen of surgical preparation using wide-spectrum antibiotics. The program begins with 6 weeks of IV ertapenem at 1 g/day delivered by a peripherally inserted central catheter managed by infectious disease colleagues.
“IV ertapenem is a drug you may not know much about. We find it works really well as a great way to bridge patients towards surgery,” the dermatologist explained.
The IV ertapenem is followed by 6 weeks of oral triple therapy with rifampin, moxifloxacin, and metronidazole then another 6 weeks of rifampin plus moxifloxacin. Next it’s surgical excision time.
Lifestyle modification
Lifestyle modification deserves to be a major priority in all HS patients, regardless of Hurley stage. Smoking cessation results in significantly greater likelihood of favorable response to first-line therapy. In obese patients, greater than 15% weight loss has been associated with significant reduction in disease severity. A sartorial shift to loose-fitting clothing can quiet down skin lesions through decreased friction and pressure. And proper utilization of warm compression will rapidly decrease acute lesional pain.
Dr. Hamzavi and his coinvestigators have described the Henry Ford Hospital treatment algorithm in a review of HS published in an open-access journal meant to serve as a resource for patients and physicians alike (F1000Res. 2017 Jul 28;6:1272. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11337.1. eCollection 2017).
He reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Incyte, and UCB.
The Global Academy for Medical Education/SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – Medical therapy alone is never sufficient in Hurley stage III hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), Iltefat H. Hamzavi, MD, observed at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“Even with the advances in biologics and antibiotic therapy, you still have to excise once you’re in full-blown Hurley stage III disease. Surgery has to be part of your protocol,” according to Dr. Hamzavi, a dermatologist at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, which runs one of the nation’s largest hidradenitis suppurativa clinics, with roughly 1,600 patients.
“Of course we’re biased. But until the data can set us free, you’re stuck with me,” the dermatologist quipped.
A core principle of the Henry Ford algorithm is this: “Medical therapy [for patients with advanced HS] stabilizes them and reduces their draining and pain, then you try to bring them back to a lower stage with surgical options,” he explained.
Although other HS staging systems exist, Dr. Hamzavi and his colleagues rely on the Hurley staging system to guide their treatment. Basically, Hurley stage I consists of follicular nodules and abscesses. When the nodules connect to form sinus tracts with scarring, that’s stage II. And if the sinus tracts interconnect throughout an entire area, that’s stage III.
Hurley stage I
First-line treatment of localized Hurley stage I disease at Henry Ford is a 10% topical benzoyl peroxide wash left on for 5 minutes before bathing, followed by postbathing topical clindamycin 1% lotion or solution applied to the nodules. If this maintenance regimen isn’t sufficient to prevent formation of new and worsening nodules, Dr. Hamzavi supplements it with up to three once-monthly 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser sessions aimed at follicular ablation. It’s a laser application he and his colleagues pioneered (Dermatol Surg. 2009 Aug;35[8]:1188-98). They subsequently documented the histopathologic basis of the procedure’s efficacy, which entails selective thermolysis of follicles, destruction of inflammatory lesions in the superficial to mid-dermis, followed by fibrosis and scarring (Arch Dermatol. 2011 Jan;147[1]:21-8).
In generalized Hurley stage I HS, the Henry Ford approach is to supplement the topical regimen and laser sessions with oral doxycycline at 100-150 mg daily for 1-6 months.
“The theory here is this is a dysbiotic event. The antibiotics reduce commensal bacteria, which ultimately reduces the reactive inflammatory response. But when you stop the antibiotics, the inflammatory response returns. So antibiotics can help stabilize the disease state but really can’t reverse the disease state. For that we have to turn to ablative treatment options: laser, surgery,” the dermatologist continued.
Hurley stage II
“At this point you’re looking at procedures,” according to Dr. Hamzavi. “Once you have sinus tracts it’s critical to remove them.”
The treatment backbone in stage II disease is 8-10 weeks of oral clindamycin and rifampin, both at 300 mg twice daily.
“This is one of the fundamental building blocks of HS clinics throughout the world,” he noted.
Clostridium difficile infection is exceedingly rare in HS patients on this regimen, for reasons still unclear.
If this dual-antibiotic regimen doesn’t dramatically reduce drainage and pain, he adds levofloxacin at 500 mg twice daily for up to 2 weeks in an effort to calm down unstable, decompensating disease.
Dapsone at 50-150 mg/day for up to 12 weeks is an additional option. It’s most useful in patients with nodules that are disproportionately painful, in Dr. Hamzavi’s experience.
Deroofing is a simple procedure that should be considered for all sinus tracts. It entails numbing the area with a ring block then introducing a curette or surgical probe into the sinus tract to open it up and get rid of the gelatinous material within. Dutch investigators have detailed the technique (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010 Sep;63[3]:475-80).
Tumor necrosis factor–inhibitor therapy has been a major advance in Hurley stage II and III disease. “It doesn’t work in everybody, but a lot of patients can be stabilized,” Dr. Hamzavi observed.
Efficacy has been amply demonstrated for adalimumab (Humira) and infliximab (Remicade). In Dr. Hamzavi’s experience infliximab works better, probably because it offers more dosing options.
Assuming medical therapy has resulted in disease stabilization, CO2 laser excision of sinus tracts under local anesthesia can then be employed as an office procedure to turn back the clock and return to an earlier stage of disease. Dermatologists at the Cleveland Clinic have described the technique in detail (Dermatol Surg. 2010 Feb;36[2]:208-13).
Hurley stage III
If biologic therapy doesn’t bring disease stabilization, the patient is likely headed for surgical excision using the CO2 laser. The Henry Ford team favors a specific regimen of surgical preparation using wide-spectrum antibiotics. The program begins with 6 weeks of IV ertapenem at 1 g/day delivered by a peripherally inserted central catheter managed by infectious disease colleagues.
“IV ertapenem is a drug you may not know much about. We find it works really well as a great way to bridge patients towards surgery,” the dermatologist explained.
The IV ertapenem is followed by 6 weeks of oral triple therapy with rifampin, moxifloxacin, and metronidazole then another 6 weeks of rifampin plus moxifloxacin. Next it’s surgical excision time.
Lifestyle modification
Lifestyle modification deserves to be a major priority in all HS patients, regardless of Hurley stage. Smoking cessation results in significantly greater likelihood of favorable response to first-line therapy. In obese patients, greater than 15% weight loss has been associated with significant reduction in disease severity. A sartorial shift to loose-fitting clothing can quiet down skin lesions through decreased friction and pressure. And proper utilization of warm compression will rapidly decrease acute lesional pain.
Dr. Hamzavi and his coinvestigators have described the Henry Ford Hospital treatment algorithm in a review of HS published in an open-access journal meant to serve as a resource for patients and physicians alike (F1000Res. 2017 Jul 28;6:1272. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11337.1. eCollection 2017).
He reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Incyte, and UCB.
The Global Academy for Medical Education/SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – Medical therapy alone is never sufficient in Hurley stage III hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), Iltefat H. Hamzavi, MD, observed at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“Even with the advances in biologics and antibiotic therapy, you still have to excise once you’re in full-blown Hurley stage III disease. Surgery has to be part of your protocol,” according to Dr. Hamzavi, a dermatologist at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, which runs one of the nation’s largest hidradenitis suppurativa clinics, with roughly 1,600 patients.
“Of course we’re biased. But until the data can set us free, you’re stuck with me,” the dermatologist quipped.
A core principle of the Henry Ford algorithm is this: “Medical therapy [for patients with advanced HS] stabilizes them and reduces their draining and pain, then you try to bring them back to a lower stage with surgical options,” he explained.
Although other HS staging systems exist, Dr. Hamzavi and his colleagues rely on the Hurley staging system to guide their treatment. Basically, Hurley stage I consists of follicular nodules and abscesses. When the nodules connect to form sinus tracts with scarring, that’s stage II. And if the sinus tracts interconnect throughout an entire area, that’s stage III.
Hurley stage I
First-line treatment of localized Hurley stage I disease at Henry Ford is a 10% topical benzoyl peroxide wash left on for 5 minutes before bathing, followed by postbathing topical clindamycin 1% lotion or solution applied to the nodules. If this maintenance regimen isn’t sufficient to prevent formation of new and worsening nodules, Dr. Hamzavi supplements it with up to three once-monthly 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser sessions aimed at follicular ablation. It’s a laser application he and his colleagues pioneered (Dermatol Surg. 2009 Aug;35[8]:1188-98). They subsequently documented the histopathologic basis of the procedure’s efficacy, which entails selective thermolysis of follicles, destruction of inflammatory lesions in the superficial to mid-dermis, followed by fibrosis and scarring (Arch Dermatol. 2011 Jan;147[1]:21-8).
In generalized Hurley stage I HS, the Henry Ford approach is to supplement the topical regimen and laser sessions with oral doxycycline at 100-150 mg daily for 1-6 months.
“The theory here is this is a dysbiotic event. The antibiotics reduce commensal bacteria, which ultimately reduces the reactive inflammatory response. But when you stop the antibiotics, the inflammatory response returns. So antibiotics can help stabilize the disease state but really can’t reverse the disease state. For that we have to turn to ablative treatment options: laser, surgery,” the dermatologist continued.
Hurley stage II
“At this point you’re looking at procedures,” according to Dr. Hamzavi. “Once you have sinus tracts it’s critical to remove them.”
The treatment backbone in stage II disease is 8-10 weeks of oral clindamycin and rifampin, both at 300 mg twice daily.
“This is one of the fundamental building blocks of HS clinics throughout the world,” he noted.
Clostridium difficile infection is exceedingly rare in HS patients on this regimen, for reasons still unclear.
If this dual-antibiotic regimen doesn’t dramatically reduce drainage and pain, he adds levofloxacin at 500 mg twice daily for up to 2 weeks in an effort to calm down unstable, decompensating disease.
Dapsone at 50-150 mg/day for up to 12 weeks is an additional option. It’s most useful in patients with nodules that are disproportionately painful, in Dr. Hamzavi’s experience.
Deroofing is a simple procedure that should be considered for all sinus tracts. It entails numbing the area with a ring block then introducing a curette or surgical probe into the sinus tract to open it up and get rid of the gelatinous material within. Dutch investigators have detailed the technique (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010 Sep;63[3]:475-80).
Tumor necrosis factor–inhibitor therapy has been a major advance in Hurley stage II and III disease. “It doesn’t work in everybody, but a lot of patients can be stabilized,” Dr. Hamzavi observed.
Efficacy has been amply demonstrated for adalimumab (Humira) and infliximab (Remicade). In Dr. Hamzavi’s experience infliximab works better, probably because it offers more dosing options.
Assuming medical therapy has resulted in disease stabilization, CO2 laser excision of sinus tracts under local anesthesia can then be employed as an office procedure to turn back the clock and return to an earlier stage of disease. Dermatologists at the Cleveland Clinic have described the technique in detail (Dermatol Surg. 2010 Feb;36[2]:208-13).
Hurley stage III
If biologic therapy doesn’t bring disease stabilization, the patient is likely headed for surgical excision using the CO2 laser. The Henry Ford team favors a specific regimen of surgical preparation using wide-spectrum antibiotics. The program begins with 6 weeks of IV ertapenem at 1 g/day delivered by a peripherally inserted central catheter managed by infectious disease colleagues.
“IV ertapenem is a drug you may not know much about. We find it works really well as a great way to bridge patients towards surgery,” the dermatologist explained.
The IV ertapenem is followed by 6 weeks of oral triple therapy with rifampin, moxifloxacin, and metronidazole then another 6 weeks of rifampin plus moxifloxacin. Next it’s surgical excision time.
Lifestyle modification
Lifestyle modification deserves to be a major priority in all HS patients, regardless of Hurley stage. Smoking cessation results in significantly greater likelihood of favorable response to first-line therapy. In obese patients, greater than 15% weight loss has been associated with significant reduction in disease severity. A sartorial shift to loose-fitting clothing can quiet down skin lesions through decreased friction and pressure. And proper utilization of warm compression will rapidly decrease acute lesional pain.
Dr. Hamzavi and his coinvestigators have described the Henry Ford Hospital treatment algorithm in a review of HS published in an open-access journal meant to serve as a resource for patients and physicians alike (F1000Res. 2017 Jul 28;6:1272. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11337.1. eCollection 2017).
He reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Incyte, and UCB.
The Global Academy for Medical Education/SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
How to avoid severe diarrhea from apremilast
KAUAI, HAWAII – Physicians have become much more cognizant of severe diarrhea and nausea as potential side effects of apremilast since the Food and Drug Administration–approved change in the warnings and precautions section of the drug’s labeling in June 2017. Jashin J. Wu, MD, director of the psoriasis clinic at Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center, has a tip for avoiding these problems: Delay up-titrating.
“In my opinion, that may be too quick of an up-titration. I tell patients that, if they feel the GI issues are still a problem for them on day 6, they should take 30 mg just once a day for the first 1-2 months. After that we’ll see how they’re doing, and if they feel they can make the jump to twice a day, then they can go for it. Of course, I also tell them that maybe their psoriasis will not clear as well as if they’d been on apremilast twice a day right from day 6, but if they’re able to tolerate it and can continue to take it, they can improve while they’re on it,” the dermatologist said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
Dr. Wu presented an update on recent developments regarding the newest oral drugs for psoriasis and one of the oldest: apremilast and methotrexate, respectively.
Apremilast
The revised warning label highlighting the risks of severe diarrhea and nausea associated with the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor says that most such events have occurred within the first few weeks of therapy. The guidance also notes that patients who reduced the dosage or discontinued treatment outright generally improved rapidly.
“I see this in a lot of my patients. They have to go to the bathroom pretty often. It’s actually unusual for me for a patient not to have any GI issues at all,” according to Dr. Wu.
He shared a number of other fresh insights into apremilast’s safety and efficacy derived from recent studies.
Efficacy appears to increase at least out to 1 year
A report from the phase 3b, randomized, placebo-controlled, 250-patient LIBERATE trial showed that the week 16 PASI 75 response rate was 39.8% with apremilast, 48.2% with etanercept (Enbrel), and 11.9% with placebo. After week 16, everyone switched to apremilast. The PASI 75 rate in patients on apremilast all along climbed from 39.8% at week 16 to 52.7% at week 52. That result was in the same ballpark as the 57% rate in those switched from etanercept to apremilast and the 53.4% PASI 75 rate at week 52 in patients switched from placebo to apremilast (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Mar;31[3]:507-17).
“It was interesting to see that, as the study continued on for 1 year, the PASI 75 rate continued to improve. That’s worth noting: In general, I tell patients you have to be on a drug for about 3 months before we’re going to say if it worked or not, and that’s true even with drugs for other conditions, like doxycycline for acne. But this study seems to indicate that you have much better improvement at the 1-year point, and that’s not so much true for the biologics,” the dermatologist observed.
Safety to 3 years looks reassuringly good: 3-year follow-up of the 1,184-patient, phase 3, randomized, controlled ESTEEM 1 and 2 trials provided by far the longest look to date at apremilast’s safety. There were no surprises, no serious opportunistic infections, and no significant changes in laboratory values (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77[2]:310-17.e1).
Of note, 21.9% of patients on apremilast lost more than 5% of their baseline body weight. Most of the weight loss occurred during year 1 of treatment and mostly in patients with a higher baseline body mass index.
“It seems like apremilast is definitely a good option if patients can tolerate the GI upset,” Dr. Wu said.
Apremilast can safely and effectively be combined with other psoriasis therapies: Dermatologists at the University of Toronto reported on a retrospective analysis of 81 biologic-naive psoriasis patients treated with apremilast in combination with methotrexate, acitretin (Soriatane), cyclosporine, narrowband UVB, etanercept, infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira), and/or ustekinumab (Stelara). Of these patients, 81% achieved a PASI 75 response at week 12 (J Cutan Med Surg. 2016 Jul;20[4]:313-6).
“That’s pretty good. It’s certainly better than apremilast by itself. So if you can get the payer to cover a combination of apremilast and something else, it may help get to PASI 75,” Dr. Wu noted.
Session chair Craig L. Leonardi, MD, said he hasn’t had any luck in going that route.
“The insurance industry just won’t give me apremilast in combination with a biologic drug. Even though it makes complete sense to use it in place of methotrexate with a biologic, I just can’t get it,” according to Dr. Leonardi, a dermatologist at Saint Louis University.
“I don’t have those limitations at Kaiser,” according to Dr. Wu. “I personally have only used apremilast and methotrexate and apremilast and acitretin in combination. I just want to be kind to Kaiser and not give two branded medications to a patient, but I certainly think it’s a feasible option.”
Methotrexate
A simple response prediction rule: Kenneth B. Gordon, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee, and his coinvestigators at AbbVie developed a methotrexate response/nonresponse prediction rule using data on 110 participants in the phase 3 CHAMPION trial. Then they validated the rule in the phase 3 M10-255 trial. They found that a PASI 25 response to methotrexate at week 4 was associated with an 8.9-fold increased likelihood of a week-16 PASI 75 response. Patients with a predicted response probability of less than 30% were asked to discontinue the drug; their week 16 PASI 75 rate was only 21.1%, compared with a 65.8% response rate in patients with a prediction rating (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Dec;77[6]:1030-7).
“Four weeks of methotrexate may be sufficient to determine the long-term response. It may not be necessary to put them on the drug for 3 months,” Dr. Wu commented.
Subcutaneous methotrexate: European investigators demonstrated that an intensified dosing schedule of subcutaneous methotrexate was safe and effective for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in the 52-week, phase 3, randomized, 16-center, double-blind, 120-patient, placebo-controlled METOP study.
The intensified subcutaneous regimen consisted of 17.5 mg/week initially, escalated to 22.5 mg/week after 8 weeks if a patient hadn’t achieved at least a PASI 50 response at that point. The primary outcome, the PASI 75 response at week 16, was 41% in the subcutaneous methotrexate group and 10% in controls, with a maximum PASI 75 rate of 51% seen beginning at week 24. The week 4 and 8 PASI 50 rates were 50% and 58%, respectively, with methotrexate versus 3% and 17% in placebo-treated controls. The subcutaneous regimen was generally well tolerated, with no serious infections or malignancies arising during 52 weeks (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:528-37).
Dr. Wu reported receiving research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Regeneron.
The Global Academy for Medical Education/SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – Physicians have become much more cognizant of severe diarrhea and nausea as potential side effects of apremilast since the Food and Drug Administration–approved change in the warnings and precautions section of the drug’s labeling in June 2017. Jashin J. Wu, MD, director of the psoriasis clinic at Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center, has a tip for avoiding these problems: Delay up-titrating.
“In my opinion, that may be too quick of an up-titration. I tell patients that, if they feel the GI issues are still a problem for them on day 6, they should take 30 mg just once a day for the first 1-2 months. After that we’ll see how they’re doing, and if they feel they can make the jump to twice a day, then they can go for it. Of course, I also tell them that maybe their psoriasis will not clear as well as if they’d been on apremilast twice a day right from day 6, but if they’re able to tolerate it and can continue to take it, they can improve while they’re on it,” the dermatologist said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
Dr. Wu presented an update on recent developments regarding the newest oral drugs for psoriasis and one of the oldest: apremilast and methotrexate, respectively.
Apremilast
The revised warning label highlighting the risks of severe diarrhea and nausea associated with the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor says that most such events have occurred within the first few weeks of therapy. The guidance also notes that patients who reduced the dosage or discontinued treatment outright generally improved rapidly.
“I see this in a lot of my patients. They have to go to the bathroom pretty often. It’s actually unusual for me for a patient not to have any GI issues at all,” according to Dr. Wu.
He shared a number of other fresh insights into apremilast’s safety and efficacy derived from recent studies.
Efficacy appears to increase at least out to 1 year
A report from the phase 3b, randomized, placebo-controlled, 250-patient LIBERATE trial showed that the week 16 PASI 75 response rate was 39.8% with apremilast, 48.2% with etanercept (Enbrel), and 11.9% with placebo. After week 16, everyone switched to apremilast. The PASI 75 rate in patients on apremilast all along climbed from 39.8% at week 16 to 52.7% at week 52. That result was in the same ballpark as the 57% rate in those switched from etanercept to apremilast and the 53.4% PASI 75 rate at week 52 in patients switched from placebo to apremilast (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Mar;31[3]:507-17).
“It was interesting to see that, as the study continued on for 1 year, the PASI 75 rate continued to improve. That’s worth noting: In general, I tell patients you have to be on a drug for about 3 months before we’re going to say if it worked or not, and that’s true even with drugs for other conditions, like doxycycline for acne. But this study seems to indicate that you have much better improvement at the 1-year point, and that’s not so much true for the biologics,” the dermatologist observed.
Safety to 3 years looks reassuringly good: 3-year follow-up of the 1,184-patient, phase 3, randomized, controlled ESTEEM 1 and 2 trials provided by far the longest look to date at apremilast’s safety. There were no surprises, no serious opportunistic infections, and no significant changes in laboratory values (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77[2]:310-17.e1).
Of note, 21.9% of patients on apremilast lost more than 5% of their baseline body weight. Most of the weight loss occurred during year 1 of treatment and mostly in patients with a higher baseline body mass index.
“It seems like apremilast is definitely a good option if patients can tolerate the GI upset,” Dr. Wu said.
Apremilast can safely and effectively be combined with other psoriasis therapies: Dermatologists at the University of Toronto reported on a retrospective analysis of 81 biologic-naive psoriasis patients treated with apremilast in combination with methotrexate, acitretin (Soriatane), cyclosporine, narrowband UVB, etanercept, infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira), and/or ustekinumab (Stelara). Of these patients, 81% achieved a PASI 75 response at week 12 (J Cutan Med Surg. 2016 Jul;20[4]:313-6).
“That’s pretty good. It’s certainly better than apremilast by itself. So if you can get the payer to cover a combination of apremilast and something else, it may help get to PASI 75,” Dr. Wu noted.
Session chair Craig L. Leonardi, MD, said he hasn’t had any luck in going that route.
“The insurance industry just won’t give me apremilast in combination with a biologic drug. Even though it makes complete sense to use it in place of methotrexate with a biologic, I just can’t get it,” according to Dr. Leonardi, a dermatologist at Saint Louis University.
“I don’t have those limitations at Kaiser,” according to Dr. Wu. “I personally have only used apremilast and methotrexate and apremilast and acitretin in combination. I just want to be kind to Kaiser and not give two branded medications to a patient, but I certainly think it’s a feasible option.”
Methotrexate
A simple response prediction rule: Kenneth B. Gordon, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee, and his coinvestigators at AbbVie developed a methotrexate response/nonresponse prediction rule using data on 110 participants in the phase 3 CHAMPION trial. Then they validated the rule in the phase 3 M10-255 trial. They found that a PASI 25 response to methotrexate at week 4 was associated with an 8.9-fold increased likelihood of a week-16 PASI 75 response. Patients with a predicted response probability of less than 30% were asked to discontinue the drug; their week 16 PASI 75 rate was only 21.1%, compared with a 65.8% response rate in patients with a prediction rating (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Dec;77[6]:1030-7).
“Four weeks of methotrexate may be sufficient to determine the long-term response. It may not be necessary to put them on the drug for 3 months,” Dr. Wu commented.
Subcutaneous methotrexate: European investigators demonstrated that an intensified dosing schedule of subcutaneous methotrexate was safe and effective for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in the 52-week, phase 3, randomized, 16-center, double-blind, 120-patient, placebo-controlled METOP study.
The intensified subcutaneous regimen consisted of 17.5 mg/week initially, escalated to 22.5 mg/week after 8 weeks if a patient hadn’t achieved at least a PASI 50 response at that point. The primary outcome, the PASI 75 response at week 16, was 41% in the subcutaneous methotrexate group and 10% in controls, with a maximum PASI 75 rate of 51% seen beginning at week 24. The week 4 and 8 PASI 50 rates were 50% and 58%, respectively, with methotrexate versus 3% and 17% in placebo-treated controls. The subcutaneous regimen was generally well tolerated, with no serious infections or malignancies arising during 52 weeks (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:528-37).
Dr. Wu reported receiving research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Regeneron.
The Global Academy for Medical Education/SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
KAUAI, HAWAII – Physicians have become much more cognizant of severe diarrhea and nausea as potential side effects of apremilast since the Food and Drug Administration–approved change in the warnings and precautions section of the drug’s labeling in June 2017. Jashin J. Wu, MD, director of the psoriasis clinic at Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center, has a tip for avoiding these problems: Delay up-titrating.
“In my opinion, that may be too quick of an up-titration. I tell patients that, if they feel the GI issues are still a problem for them on day 6, they should take 30 mg just once a day for the first 1-2 months. After that we’ll see how they’re doing, and if they feel they can make the jump to twice a day, then they can go for it. Of course, I also tell them that maybe their psoriasis will not clear as well as if they’d been on apremilast twice a day right from day 6, but if they’re able to tolerate it and can continue to take it, they can improve while they’re on it,” the dermatologist said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
Dr. Wu presented an update on recent developments regarding the newest oral drugs for psoriasis and one of the oldest: apremilast and methotrexate, respectively.
Apremilast
The revised warning label highlighting the risks of severe diarrhea and nausea associated with the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor says that most such events have occurred within the first few weeks of therapy. The guidance also notes that patients who reduced the dosage or discontinued treatment outright generally improved rapidly.
“I see this in a lot of my patients. They have to go to the bathroom pretty often. It’s actually unusual for me for a patient not to have any GI issues at all,” according to Dr. Wu.
He shared a number of other fresh insights into apremilast’s safety and efficacy derived from recent studies.
Efficacy appears to increase at least out to 1 year
A report from the phase 3b, randomized, placebo-controlled, 250-patient LIBERATE trial showed that the week 16 PASI 75 response rate was 39.8% with apremilast, 48.2% with etanercept (Enbrel), and 11.9% with placebo. After week 16, everyone switched to apremilast. The PASI 75 rate in patients on apremilast all along climbed from 39.8% at week 16 to 52.7% at week 52. That result was in the same ballpark as the 57% rate in those switched from etanercept to apremilast and the 53.4% PASI 75 rate at week 52 in patients switched from placebo to apremilast (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Mar;31[3]:507-17).
“It was interesting to see that, as the study continued on for 1 year, the PASI 75 rate continued to improve. That’s worth noting: In general, I tell patients you have to be on a drug for about 3 months before we’re going to say if it worked or not, and that’s true even with drugs for other conditions, like doxycycline for acne. But this study seems to indicate that you have much better improvement at the 1-year point, and that’s not so much true for the biologics,” the dermatologist observed.
Safety to 3 years looks reassuringly good: 3-year follow-up of the 1,184-patient, phase 3, randomized, controlled ESTEEM 1 and 2 trials provided by far the longest look to date at apremilast’s safety. There were no surprises, no serious opportunistic infections, and no significant changes in laboratory values (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77[2]:310-17.e1).
Of note, 21.9% of patients on apremilast lost more than 5% of their baseline body weight. Most of the weight loss occurred during year 1 of treatment and mostly in patients with a higher baseline body mass index.
“It seems like apremilast is definitely a good option if patients can tolerate the GI upset,” Dr. Wu said.
Apremilast can safely and effectively be combined with other psoriasis therapies: Dermatologists at the University of Toronto reported on a retrospective analysis of 81 biologic-naive psoriasis patients treated with apremilast in combination with methotrexate, acitretin (Soriatane), cyclosporine, narrowband UVB, etanercept, infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira), and/or ustekinumab (Stelara). Of these patients, 81% achieved a PASI 75 response at week 12 (J Cutan Med Surg. 2016 Jul;20[4]:313-6).
“That’s pretty good. It’s certainly better than apremilast by itself. So if you can get the payer to cover a combination of apremilast and something else, it may help get to PASI 75,” Dr. Wu noted.
Session chair Craig L. Leonardi, MD, said he hasn’t had any luck in going that route.
“The insurance industry just won’t give me apremilast in combination with a biologic drug. Even though it makes complete sense to use it in place of methotrexate with a biologic, I just can’t get it,” according to Dr. Leonardi, a dermatologist at Saint Louis University.
“I don’t have those limitations at Kaiser,” according to Dr. Wu. “I personally have only used apremilast and methotrexate and apremilast and acitretin in combination. I just want to be kind to Kaiser and not give two branded medications to a patient, but I certainly think it’s a feasible option.”
Methotrexate
A simple response prediction rule: Kenneth B. Gordon, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee, and his coinvestigators at AbbVie developed a methotrexate response/nonresponse prediction rule using data on 110 participants in the phase 3 CHAMPION trial. Then they validated the rule in the phase 3 M10-255 trial. They found that a PASI 25 response to methotrexate at week 4 was associated with an 8.9-fold increased likelihood of a week-16 PASI 75 response. Patients with a predicted response probability of less than 30% were asked to discontinue the drug; their week 16 PASI 75 rate was only 21.1%, compared with a 65.8% response rate in patients with a prediction rating (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Dec;77[6]:1030-7).
“Four weeks of methotrexate may be sufficient to determine the long-term response. It may not be necessary to put them on the drug for 3 months,” Dr. Wu commented.
Subcutaneous methotrexate: European investigators demonstrated that an intensified dosing schedule of subcutaneous methotrexate was safe and effective for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in the 52-week, phase 3, randomized, 16-center, double-blind, 120-patient, placebo-controlled METOP study.
The intensified subcutaneous regimen consisted of 17.5 mg/week initially, escalated to 22.5 mg/week after 8 weeks if a patient hadn’t achieved at least a PASI 50 response at that point. The primary outcome, the PASI 75 response at week 16, was 41% in the subcutaneous methotrexate group and 10% in controls, with a maximum PASI 75 rate of 51% seen beginning at week 24. The week 4 and 8 PASI 50 rates were 50% and 58%, respectively, with methotrexate versus 3% and 17% in placebo-treated controls. The subcutaneous regimen was generally well tolerated, with no serious infections or malignancies arising during 52 weeks (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:528-37).
Dr. Wu reported receiving research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Regeneron.
The Global Academy for Medical Education/SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
New PsA questionnaire fails to beat existing early screening methods
A new screening tool for detecting early psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis that combined the “most discriminative questions” from several other questionnaires performed as well as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST) for detecting the disease.
“The CONTEST questionnaire was developed using the best performing items from three other screening questionnaires in the hope that it would perform better than its originators,” Laura Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the Nuffield Department of Orthopaedics, Rheumatology and Musculoskeletal Sciences at the University of Oxford, England, and her coauthors wrote in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. “In development this was partly correct but the current study does not support this – statistically there was no difference between PEST and CONTEST in terms of ability to detect psoriatic arthritis [PsA] in patients with psoriasis.”
The researchers found 27 patients (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12.3%-21.7%) with previously undiagnosed PsA, 71 with a different musculoskeletal disease, and 61 without musculoskeletal disease. Patients with PsA tended to be male, older, with “worse functional ability,” a similar age at onset of psoriasis, and had similar skin and nail disease severity. The sensitivity for PEST was 0.60 (95% CI, 0.42-0.78) and the specificity was 0.76 (95% CI, 0.69-0.83), while for CONTEST, the sensitivity was 0.53 (95% CI, 0.34-0.72) and the specificity was 0.71 (95% CI, 0.63-0.79). The area under the receiver operating curve confidence intervals for both screening tools were similar, with PEST having an AUC of 0.72 (95% CI, 0.61-0.84) and CONTEST having an AUC of 0.66 (95% CI, 0.54-0.77).
“The relative simplicity of the PEST questionnaire has raised concerns that the tool is not able to detect pure axial forms of the disease,” Dr. Coates and her colleagues wrote. “The CONTEST questionnaire includes items specific to back and neck pain, and so it was hoped it would better detect this subgroup. In this study this is not the case, although the numbers were small and imaging of the spine was not part of the study.”
AbbVie supported this study with an educational grant. The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre. Some of the authors reported potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Coates L et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 26. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14971.
A new screening tool for detecting early psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis that combined the “most discriminative questions” from several other questionnaires performed as well as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST) for detecting the disease.
“The CONTEST questionnaire was developed using the best performing items from three other screening questionnaires in the hope that it would perform better than its originators,” Laura Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the Nuffield Department of Orthopaedics, Rheumatology and Musculoskeletal Sciences at the University of Oxford, England, and her coauthors wrote in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. “In development this was partly correct but the current study does not support this – statistically there was no difference between PEST and CONTEST in terms of ability to detect psoriatic arthritis [PsA] in patients with psoriasis.”
The researchers found 27 patients (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12.3%-21.7%) with previously undiagnosed PsA, 71 with a different musculoskeletal disease, and 61 without musculoskeletal disease. Patients with PsA tended to be male, older, with “worse functional ability,” a similar age at onset of psoriasis, and had similar skin and nail disease severity. The sensitivity for PEST was 0.60 (95% CI, 0.42-0.78) and the specificity was 0.76 (95% CI, 0.69-0.83), while for CONTEST, the sensitivity was 0.53 (95% CI, 0.34-0.72) and the specificity was 0.71 (95% CI, 0.63-0.79). The area under the receiver operating curve confidence intervals for both screening tools were similar, with PEST having an AUC of 0.72 (95% CI, 0.61-0.84) and CONTEST having an AUC of 0.66 (95% CI, 0.54-0.77).
“The relative simplicity of the PEST questionnaire has raised concerns that the tool is not able to detect pure axial forms of the disease,” Dr. Coates and her colleagues wrote. “The CONTEST questionnaire includes items specific to back and neck pain, and so it was hoped it would better detect this subgroup. In this study this is not the case, although the numbers were small and imaging of the spine was not part of the study.”
AbbVie supported this study with an educational grant. The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre. Some of the authors reported potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Coates L et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 26. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14971.
A new screening tool for detecting early psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis that combined the “most discriminative questions” from several other questionnaires performed as well as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST) for detecting the disease.
“The CONTEST questionnaire was developed using the best performing items from three other screening questionnaires in the hope that it would perform better than its originators,” Laura Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the Nuffield Department of Orthopaedics, Rheumatology and Musculoskeletal Sciences at the University of Oxford, England, and her coauthors wrote in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. “In development this was partly correct but the current study does not support this – statistically there was no difference between PEST and CONTEST in terms of ability to detect psoriatic arthritis [PsA] in patients with psoriasis.”
The researchers found 27 patients (17%; 95% confidence interval, 12.3%-21.7%) with previously undiagnosed PsA, 71 with a different musculoskeletal disease, and 61 without musculoskeletal disease. Patients with PsA tended to be male, older, with “worse functional ability,” a similar age at onset of psoriasis, and had similar skin and nail disease severity. The sensitivity for PEST was 0.60 (95% CI, 0.42-0.78) and the specificity was 0.76 (95% CI, 0.69-0.83), while for CONTEST, the sensitivity was 0.53 (95% CI, 0.34-0.72) and the specificity was 0.71 (95% CI, 0.63-0.79). The area under the receiver operating curve confidence intervals for both screening tools were similar, with PEST having an AUC of 0.72 (95% CI, 0.61-0.84) and CONTEST having an AUC of 0.66 (95% CI, 0.54-0.77).
“The relative simplicity of the PEST questionnaire has raised concerns that the tool is not able to detect pure axial forms of the disease,” Dr. Coates and her colleagues wrote. “The CONTEST questionnaire includes items specific to back and neck pain, and so it was hoped it would better detect this subgroup. In this study this is not the case, although the numbers were small and imaging of the spine was not part of the study.”
AbbVie supported this study with an educational grant. The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre. Some of the authors reported potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Coates L et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 26. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14971.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE EUROPEAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY
Key clinical point: The CONTEST screening tool detected psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis patients as accurately as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool.
Major finding: The sensitivity and specificity of CONTEST was 0.53 and 0.71, respectively, while PEST had a sensitivity of 0.60 and specificity of 0.76.
Study details: An observational, cross-sectional study of 159 psoriasis patients at four secondary care dermatology centers in the United Kingdom from November 2013 to March 2017.
Disclosures: AbbVie supported this study with an educational grant. The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre. Some of the authors reported potential conflicts of interest.
Source: Coates L et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 26. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14971.
AbbVie, Samsung Bioepis settle suits with delayed U.S. entry for adalimumab biosimilar
A new adalimumab biosimilar will become available in the European Union later this year, but a court settlement will keep Samsung Bioepis’ competitor off U.S. shelves until 2023.
Under the settlement, AbbVie, which manufactures adalimumab (Humira), will grant Bioepis and its partner, Biogen, a nonexclusive license to the intellectual property relating to the antibody. Bioepis’ version, dubbed SB5 (Imraldi), will enter global markets in a staggered fashion, according to an AbbVie press statement. In most countries in the European Union, the license period will begin on Oct. 16, 2018. In the United States, Samsung Bioepis’ license period will begin on June 30, 2023, according to the Abbvie statement.
Biogen and Bioepis hailed the settlement as a victory, but Imraldi won’t be the first Humira biosimilar to break into the U.S. market. Last September, AbbVie settled a similar suit with Amgen, granting patent licenses for the global use and sale of its anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha antibody, Amgevita/Amjevita. Amgen expects to launch Amgevita in Europe on Oct. 16, 2018, and Amjevita in the United States on Jan. 31, 2023. Samsung Bioepis’ U.S. license date will not be accelerated upon Amgen’s entry.
Ian Henshaw, Biogen’s global head of biosimilars, said the deal further strengthens the company’s European biosimilars reach.
“Biogen is a leader in the emerging field of biosimilars through Samsung Bioepis, our joint venture with Samsung BioLogics,” Mr. Henshaw said in a press statement. “Biogen already markets two biosimilars in Europe and the planned introduction of Imraldi on Oct. 16 could potentially expand patient choice by offering physicians more options to meet the needs of patients while delivering significant savings to healthcare systems.”
AbbVie focused on the settlement as a global recognition of its leadership role in developing the anti-TNF-alpha antibody.
“The Samsung Bioepis settlement reflects the strength and breadth of AbbVie’s intellectual property,” Laura Schumacher, the company’s general counsel, said in the Abbvie statement. “We continue to believe biosimilars will play an important role in our healthcare system, but we also believe it is important to protect our investment in innovation. This agreement accomplishes both objectives.”
Samsung Bioepis will pay royalties to AbbVie for licensing its adalimumab patents once its biosimilar product is launched. As is the case with the prior Amgen resolution, AbbVie will not make any payments to Samsung Bioepis. “All litigation pending between the parties, as well as all litigation with Samsung Bioepis’ European partner, Biogen, will be dismissed. The precise terms of the agreements are confidential,” the Abbvie statement said.
The settlement brings to a closing a flurry of lawsuits Samsung Bioepis filed against AbbVie in 2017.
A new adalimumab biosimilar will become available in the European Union later this year, but a court settlement will keep Samsung Bioepis’ competitor off U.S. shelves until 2023.
Under the settlement, AbbVie, which manufactures adalimumab (Humira), will grant Bioepis and its partner, Biogen, a nonexclusive license to the intellectual property relating to the antibody. Bioepis’ version, dubbed SB5 (Imraldi), will enter global markets in a staggered fashion, according to an AbbVie press statement. In most countries in the European Union, the license period will begin on Oct. 16, 2018. In the United States, Samsung Bioepis’ license period will begin on June 30, 2023, according to the Abbvie statement.
Biogen and Bioepis hailed the settlement as a victory, but Imraldi won’t be the first Humira biosimilar to break into the U.S. market. Last September, AbbVie settled a similar suit with Amgen, granting patent licenses for the global use and sale of its anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha antibody, Amgevita/Amjevita. Amgen expects to launch Amgevita in Europe on Oct. 16, 2018, and Amjevita in the United States on Jan. 31, 2023. Samsung Bioepis’ U.S. license date will not be accelerated upon Amgen’s entry.
Ian Henshaw, Biogen’s global head of biosimilars, said the deal further strengthens the company’s European biosimilars reach.
“Biogen is a leader in the emerging field of biosimilars through Samsung Bioepis, our joint venture with Samsung BioLogics,” Mr. Henshaw said in a press statement. “Biogen already markets two biosimilars in Europe and the planned introduction of Imraldi on Oct. 16 could potentially expand patient choice by offering physicians more options to meet the needs of patients while delivering significant savings to healthcare systems.”
AbbVie focused on the settlement as a global recognition of its leadership role in developing the anti-TNF-alpha antibody.
“The Samsung Bioepis settlement reflects the strength and breadth of AbbVie’s intellectual property,” Laura Schumacher, the company’s general counsel, said in the Abbvie statement. “We continue to believe biosimilars will play an important role in our healthcare system, but we also believe it is important to protect our investment in innovation. This agreement accomplishes both objectives.”
Samsung Bioepis will pay royalties to AbbVie for licensing its adalimumab patents once its biosimilar product is launched. As is the case with the prior Amgen resolution, AbbVie will not make any payments to Samsung Bioepis. “All litigation pending between the parties, as well as all litigation with Samsung Bioepis’ European partner, Biogen, will be dismissed. The precise terms of the agreements are confidential,” the Abbvie statement said.
The settlement brings to a closing a flurry of lawsuits Samsung Bioepis filed against AbbVie in 2017.
A new adalimumab biosimilar will become available in the European Union later this year, but a court settlement will keep Samsung Bioepis’ competitor off U.S. shelves until 2023.
Under the settlement, AbbVie, which manufactures adalimumab (Humira), will grant Bioepis and its partner, Biogen, a nonexclusive license to the intellectual property relating to the antibody. Bioepis’ version, dubbed SB5 (Imraldi), will enter global markets in a staggered fashion, according to an AbbVie press statement. In most countries in the European Union, the license period will begin on Oct. 16, 2018. In the United States, Samsung Bioepis’ license period will begin on June 30, 2023, according to the Abbvie statement.
Biogen and Bioepis hailed the settlement as a victory, but Imraldi won’t be the first Humira biosimilar to break into the U.S. market. Last September, AbbVie settled a similar suit with Amgen, granting patent licenses for the global use and sale of its anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha antibody, Amgevita/Amjevita. Amgen expects to launch Amgevita in Europe on Oct. 16, 2018, and Amjevita in the United States on Jan. 31, 2023. Samsung Bioepis’ U.S. license date will not be accelerated upon Amgen’s entry.
Ian Henshaw, Biogen’s global head of biosimilars, said the deal further strengthens the company’s European biosimilars reach.
“Biogen is a leader in the emerging field of biosimilars through Samsung Bioepis, our joint venture with Samsung BioLogics,” Mr. Henshaw said in a press statement. “Biogen already markets two biosimilars in Europe and the planned introduction of Imraldi on Oct. 16 could potentially expand patient choice by offering physicians more options to meet the needs of patients while delivering significant savings to healthcare systems.”
AbbVie focused on the settlement as a global recognition of its leadership role in developing the anti-TNF-alpha antibody.
“The Samsung Bioepis settlement reflects the strength and breadth of AbbVie’s intellectual property,” Laura Schumacher, the company’s general counsel, said in the Abbvie statement. “We continue to believe biosimilars will play an important role in our healthcare system, but we also believe it is important to protect our investment in innovation. This agreement accomplishes both objectives.”
Samsung Bioepis will pay royalties to AbbVie for licensing its adalimumab patents once its biosimilar product is launched. As is the case with the prior Amgen resolution, AbbVie will not make any payments to Samsung Bioepis. “All litigation pending between the parties, as well as all litigation with Samsung Bioepis’ European partner, Biogen, will be dismissed. The precise terms of the agreements are confidential,” the Abbvie statement said.
The settlement brings to a closing a flurry of lawsuits Samsung Bioepis filed against AbbVie in 2017.
Dramatic improvements reported after surgery for hidradenitis suppurativa
A retrospective German study found that the majority of , with many saying they no longer suffered from everyday impairment from the disease.
“We were able to show that surgical therapy resulted in convincing improvement of life quality and long-term results for HS that are at least as effective as biologicals,” the researchers wrote. The study was published online in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Lukas Kofler, MD, and associates from the department of dermatology at Eberhard Karls University’s University Medical Center, Tübingen, Germany, surveyed 910 of the facility’s patients who had undergone wide local excision for HS from 2006 to 2015. Surgery was “designed to reach into clinically disease-free subcutaneous fatty tissue,” followed by second intention healing, they wrote.
A total of 255 patients answered the survey, a response rate of 28%. There were 103 men and 152 women with a median age of 38 years (range, 14-66 years); 75% reported prior “nicotine abuse.” Almost half had been treated previously, most often with systemic antibiotics in 68%. The mean follow-up time was 57 months (range, 19-127 months);
All cases were Hurley grade III. Just over three-quarters of the patients described disease-related limitations in private life prior to surgery as “very strong” or “strong,” and 95% reported that their day-to-day life was impaired. Sixty percent said the disease impaired their work life (another 8% were not employed).
After surgery, 27% experienced postoperative complications, including minor bleeding, infection, and limited mobility; 65% experienced pain but 38% of the patients required analgesics postoperatively.
After surgery, 80% were satisfied or very satisfied with the results, and more than two-thirds were satisfied with the cosmetic results. Just over half said their private life was not impaired by the disease at all, compared with 3% who said so before surgery. After surgery, 20% reported being strongly or very strongly impaired, compared with 77% before surgery.
Nearly 70% reported that HS recurred after surgery, but 62% of those with recurrences said the disease was not as severe as before surgery.
“Surgery represents an important treatment option by itself but should also be part of combined therapeutic strategies, especially in severe disease stages. However, consistent approaches combining systemic and surgical treatments have not been established yet,” the authors noted.
The study had no funding source. The authors had no conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kofler L et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 23. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14892.
A retrospective German study found that the majority of , with many saying they no longer suffered from everyday impairment from the disease.
“We were able to show that surgical therapy resulted in convincing improvement of life quality and long-term results for HS that are at least as effective as biologicals,” the researchers wrote. The study was published online in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Lukas Kofler, MD, and associates from the department of dermatology at Eberhard Karls University’s University Medical Center, Tübingen, Germany, surveyed 910 of the facility’s patients who had undergone wide local excision for HS from 2006 to 2015. Surgery was “designed to reach into clinically disease-free subcutaneous fatty tissue,” followed by second intention healing, they wrote.
A total of 255 patients answered the survey, a response rate of 28%. There were 103 men and 152 women with a median age of 38 years (range, 14-66 years); 75% reported prior “nicotine abuse.” Almost half had been treated previously, most often with systemic antibiotics in 68%. The mean follow-up time was 57 months (range, 19-127 months);
All cases were Hurley grade III. Just over three-quarters of the patients described disease-related limitations in private life prior to surgery as “very strong” or “strong,” and 95% reported that their day-to-day life was impaired. Sixty percent said the disease impaired their work life (another 8% were not employed).
After surgery, 27% experienced postoperative complications, including minor bleeding, infection, and limited mobility; 65% experienced pain but 38% of the patients required analgesics postoperatively.
After surgery, 80% were satisfied or very satisfied with the results, and more than two-thirds were satisfied with the cosmetic results. Just over half said their private life was not impaired by the disease at all, compared with 3% who said so before surgery. After surgery, 20% reported being strongly or very strongly impaired, compared with 77% before surgery.
Nearly 70% reported that HS recurred after surgery, but 62% of those with recurrences said the disease was not as severe as before surgery.
“Surgery represents an important treatment option by itself but should also be part of combined therapeutic strategies, especially in severe disease stages. However, consistent approaches combining systemic and surgical treatments have not been established yet,” the authors noted.
The study had no funding source. The authors had no conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kofler L et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 23. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14892.
A retrospective German study found that the majority of , with many saying they no longer suffered from everyday impairment from the disease.
“We were able to show that surgical therapy resulted in convincing improvement of life quality and long-term results for HS that are at least as effective as biologicals,” the researchers wrote. The study was published online in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Lukas Kofler, MD, and associates from the department of dermatology at Eberhard Karls University’s University Medical Center, Tübingen, Germany, surveyed 910 of the facility’s patients who had undergone wide local excision for HS from 2006 to 2015. Surgery was “designed to reach into clinically disease-free subcutaneous fatty tissue,” followed by second intention healing, they wrote.
A total of 255 patients answered the survey, a response rate of 28%. There were 103 men and 152 women with a median age of 38 years (range, 14-66 years); 75% reported prior “nicotine abuse.” Almost half had been treated previously, most often with systemic antibiotics in 68%. The mean follow-up time was 57 months (range, 19-127 months);
All cases were Hurley grade III. Just over three-quarters of the patients described disease-related limitations in private life prior to surgery as “very strong” or “strong,” and 95% reported that their day-to-day life was impaired. Sixty percent said the disease impaired their work life (another 8% were not employed).
After surgery, 27% experienced postoperative complications, including minor bleeding, infection, and limited mobility; 65% experienced pain but 38% of the patients required analgesics postoperatively.
After surgery, 80% were satisfied or very satisfied with the results, and more than two-thirds were satisfied with the cosmetic results. Just over half said their private life was not impaired by the disease at all, compared with 3% who said so before surgery. After surgery, 20% reported being strongly or very strongly impaired, compared with 77% before surgery.
Nearly 70% reported that HS recurred after surgery, but 62% of those with recurrences said the disease was not as severe as before surgery.
“Surgery represents an important treatment option by itself but should also be part of combined therapeutic strategies, especially in severe disease stages. However, consistent approaches combining systemic and surgical treatments have not been established yet,” the authors noted.
The study had no funding source. The authors had no conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Kofler L et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 23. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14892.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE EUROPEAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY.
Key clinical point: Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) report dramatic improvement after radical surgery.
Major finding: The percentage reporting strong or very strong impairment of private life fell from 77% before surgery to 20% afterward.
Study details: A retrospective survey of 255 patients who had undergone surgery for HS (Hurley stage III).
Disclosures: The study had no funding source. The authors had no conflicts to disclose.
Source: Kofler L et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Mar 23. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14892.
A Case of Pustular Psoriasis of Pregnancy With Positive Maternal-Fetal Outcomes
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy (PPP), also known as impetigo herpetiformis, is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder of pregnancy wherein lesions typically appear in the third trimester and resolve after delivery; however, lesions may persist through the postpartum period. Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy may be considered a fifth dermatosis of pregnancy, alongside the classic dermatoses of atopic eruption of pregnancy, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, pemphigoid gestationis, and pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.1
As PPP is a rare disease, its effects on maternal-fetal health outcomes and management remain to be elucidated. Though maternal mortality is rare in PPP, it is a unique dermatosis of pregnancy because it may be associated with severe systemic maternal symptoms.2 Fetal morbidity and mortality are less predictable in PPP, with reported cases of stillbirth, fetal anomalies, and neonatal death thought to be due largely to placental insufficiency, even with control of symptoms.1,3 Given the risk of serious harm to the fetus, reporting of cases and discussion of PPP management is critical.
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 29-year-old G2P1 woman at 32 weeks’ gestation presented to our emergency department with a 1-week history of a pruritic, burning rash that started on the thighs then spread diffusely. She denied any similar rash in her prior pregnancy. She was not currently taking any medications except for prenatal vitamins and denied any systemic symptoms. The patient’s obstetrician initiated treatment with methylprednisolone 50 mg once daily for the rash 3 days prior to the current presentation, which had not seemed to help. On physical examination, edematous pink plaques studded with 1- to 2-mm collarettes of scaling and sparse 1-mm pustules involving the arms, chest, abdomen, back, groin, buttocks, and legs were noted. The plaques on the back and inner thighs had a peripheral rim of desquamative scaling. There were pink macules on the palms, and superficial desquamation was noted on the lips. The oral mucosa was otherwise spared (Figure 1).
Biopsy specimens from the left arm revealed discrete subcorneal pustules with mild acanthosis of the epidermis with spongiosis (Figure 2). The papillary dermis showed a sparse infiltrate of neutrophils with many marginated neutrophils within vessels. Direct immunofluorescence was negative for human IgG, IgA, IgM, complement component 3, and fibrinogen. Laboratory workup revealed leukocytosis of 21.5×109/L (reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L) with neutrophilic predominance of 73.6% (reference range, 56%), an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 40 mm/h (reference range, 0–20 mm/h), and a mild hypocalcemia of 8.6 mg/dL (reference range, 8.2–10.2 mg/dL). The patient was started on methylprednisone 40 mg once daily with a plan to taper the dose by 8 mg every 5 days.
At 35 weeks’ gestation, the patient continued to report pruritus and burning in the areas where the rash had developed. The morphology of the rash had changed considerably, as she now had prominent, annular, pink plaques with central clearing, trailing scaling, and a border of subtle pustules on the legs. There also were rings of desquamative scaling on the palms. During follow-up at 37 weeks’ gestation, the back, chest, and abdomen were improved from the initial presentation, and annular pink plaques with central clearing were noted on the legs (Figure 3). Given the clinical and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of PPP was made. It was recommended that she undergo increased fetal surveillance with close obstetric follow-up. Weekly office visits with obstetrics and twice-weekly Doppler ultrasounds and fetal nonstress tests were deemed appropriate management. The patient was scheduled for induction at 39 weeks’ gestation given the risk for potential harm to the fetus. She was maintained on low-dose methylprednisolone 4 mg once daily for the duration of the pregnancy. The patient continued to have gradual improvement of the rash at the low treatment dose.
Following induction at 39 weeks’ gestation, the patient vaginally delivered a healthy, 6-lb male neonate at an outside hospital. She reported that the burning sensation improved within hours of delivery, and systemic steroids were stopped after delivery. At a follow-up visit 3 weeks postpartum, considerable improvement of the rash was noted with no evidence of pustules. Fading pink patches with a superficial scaling were noted on the back, chest, abdomen, arms, legs (Figure 4), and fingertips. The patient was counseled that PPP could recur in subsequent pregnancies and that she should be aware of the potential risks to the fetus.
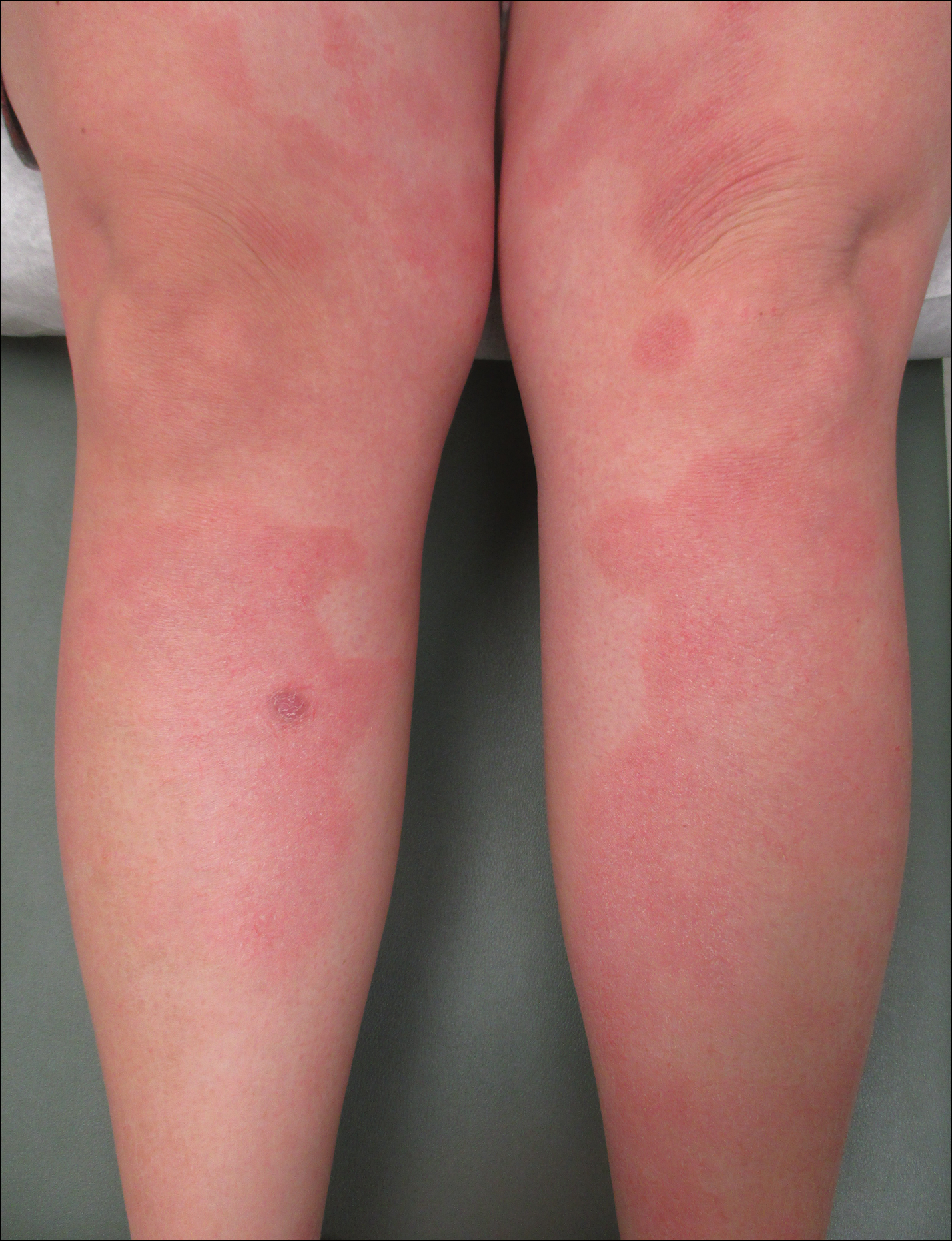
Comment
In our patient, the diagnosis of PPP was supported by the presence of erythematous, coalescent plaques with small pustules at the margins and central erosions as well as the histologic findings of subcorneal pustules with mild acanthosis of the epidermis with spongiosis and a sparse neutrophilic infiltrate into the dermis.
The typical presentation of PPP is characterized by lesions that initially develop in skin folds with centrifugal spread.3 The lesions usually begin as erythematous plaques with a pustular ring with a central erosion. The face, palms, and soles of the feet typically are spared with occasional involvement of oral and esophageal mucosae. Biopsy findings typically include spongiform pustules with neutrophil invasion into the epidermis. Typical laboratory findings include electrolyte derangements with elevated ESR and leukocytosis.1
Diagnosis of PPP is critical given the potential for associated fetal morbidity and mortality.4 Anticipatory guidance for the patient also is necessary, as PPP can recur with subsequent pregnancies or even use of oral contraceptive pills (OCPs). Notably, a patient with recurrences of PPP with each of 9 pregnancies also experienced a recurrence when taking a combination estrogen/progesterone OCP, but not with an estrogen-only diethylstilbestrol OCP.5 Although the pathophysiology is not entirely understood, the development of PPP is thought to be related to the hormonal changes that occur in the third trimester, most notably due to elevated progesterone levels.2 The presence of progesterone in OCPs and recurrences associated with their use supports this altered hormonal state, contributing to the underlying pathophysiology of PPP.
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy can occur in women without any personal or family history of psoriasis, and as such, it is unclear whether PPP is a separate entity or a hormonally induced variation of generalized pustular psoriasis. Recent evidence included reports of women with PPP who had a mutation in the IL-36 receptor antagonist, leading to a relative abundance of IL-36 inflammatory cytokines.6
The mainstay of treatment for PPP is oral corticosteroids. Cases of PPP that are unresponsive to systemic steroids have been documented, requiring treatment with cyclosporine.9 Antitumor necrosis factors also have been used safely during pregnancy.10 Narrowband UVB phototherapy also has been proposed as a treatment alternative for patients who do not respond to oral corticosteroids.11
Conclusion
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy is a rare dermatosis of pregnancy that, unlike most other common dermatoses of pregnancy, is associated with adverse fetal outcomes. Diagnosis and management of PPP are critical to ensure the best care and outcomes for the patient and fetus and for a successful delivery of a healthy neonate. Our patient with PPP presented with involvement of the body, palms, and oral mucosa in the absence of systemic symptoms. Close follow-up and comanagement with the patient’s obstetrician ensured safe outcomes for the patient and the neonate.
- Lehrhoff S, Pomeranz MK. Specific dermatoses of pregnancy and their treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:274-284.
- Kar S, Krishnan A, Shivkumar PV. Pregnancy and skin [published online August 28, 2012]. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2012;62:268-275.
- Kondo RN, Araújo FM, Pereira AM, et al. Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy (impetigo herpetiformis)—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 suppl 1):186-189.
- Oumeish OY, Parish JL. Impetigo herpetiformis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:101-104.
- Oumeish OY, Farraj SE, Bataineh AS. Some aspects of impetigo herpetiformis. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:103-105.
- Sugiura K, Oiso N, Iinuma S, et al. IL36RN mutations underlie impetigo herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2472-2474.
- Sugiura K. The genetic background of generalized pustular psoriasis: IL36RN mutations and CARD14 gain-of-function variants [published online March 5, 2014]. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;74:187-192.
- Li X, Chen M, Fu X, et al. Mutation analysis of the IL36RN gene in Chinese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis with/without psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;76:132-138.
- Hazarika D. Generalized pustular psoriasis of pregnancy successfully treated with cyclosporine. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:638.
- Puig L, Barco D, Alomar A. Treatment of psoriasis with anti-TNF drugs during pregnancy: case report and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2010;220:71-76.
- Bozdag K, Ozturk S, Ermete M. A case of recurrent impetigo herpetiformis treated with systemic corticosteroids and narrowband UVB [published online January 20, 2012]. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2012;31:67-69.
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy (PPP), also known as impetigo herpetiformis, is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder of pregnancy wherein lesions typically appear in the third trimester and resolve after delivery; however, lesions may persist through the postpartum period. Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy may be considered a fifth dermatosis of pregnancy, alongside the classic dermatoses of atopic eruption of pregnancy, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, pemphigoid gestationis, and pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.1
As PPP is a rare disease, its effects on maternal-fetal health outcomes and management remain to be elucidated. Though maternal mortality is rare in PPP, it is a unique dermatosis of pregnancy because it may be associated with severe systemic maternal symptoms.2 Fetal morbidity and mortality are less predictable in PPP, with reported cases of stillbirth, fetal anomalies, and neonatal death thought to be due largely to placental insufficiency, even with control of symptoms.1,3 Given the risk of serious harm to the fetus, reporting of cases and discussion of PPP management is critical.
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 29-year-old G2P1 woman at 32 weeks’ gestation presented to our emergency department with a 1-week history of a pruritic, burning rash that started on the thighs then spread diffusely. She denied any similar rash in her prior pregnancy. She was not currently taking any medications except for prenatal vitamins and denied any systemic symptoms. The patient’s obstetrician initiated treatment with methylprednisolone 50 mg once daily for the rash 3 days prior to the current presentation, which had not seemed to help. On physical examination, edematous pink plaques studded with 1- to 2-mm collarettes of scaling and sparse 1-mm pustules involving the arms, chest, abdomen, back, groin, buttocks, and legs were noted. The plaques on the back and inner thighs had a peripheral rim of desquamative scaling. There were pink macules on the palms, and superficial desquamation was noted on the lips. The oral mucosa was otherwise spared (Figure 1).

Biopsy specimens from the left arm revealed discrete subcorneal pustules with mild acanthosis of the epidermis with spongiosis (Figure 2). The papillary dermis showed a sparse infiltrate of neutrophils with many marginated neutrophils within vessels. Direct immunofluorescence was negative for human IgG, IgA, IgM, complement component 3, and fibrinogen. Laboratory workup revealed leukocytosis of 21.5×109/L (reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L) with neutrophilic predominance of 73.6% (reference range, 56%), an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 40 mm/h (reference range, 0–20 mm/h), and a mild hypocalcemia of 8.6 mg/dL (reference range, 8.2–10.2 mg/dL). The patient was started on methylprednisone 40 mg once daily with a plan to taper the dose by 8 mg every 5 days.

At 35 weeks’ gestation, the patient continued to report pruritus and burning in the areas where the rash had developed. The morphology of the rash had changed considerably, as she now had prominent, annular, pink plaques with central clearing, trailing scaling, and a border of subtle pustules on the legs. There also were rings of desquamative scaling on the palms. During follow-up at 37 weeks’ gestation, the back, chest, and abdomen were improved from the initial presentation, and annular pink plaques with central clearing were noted on the legs (Figure 3). Given the clinical and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of PPP was made. It was recommended that she undergo increased fetal surveillance with close obstetric follow-up. Weekly office visits with obstetrics and twice-weekly Doppler ultrasounds and fetal nonstress tests were deemed appropriate management. The patient was scheduled for induction at 39 weeks’ gestation given the risk for potential harm to the fetus. She was maintained on low-dose methylprednisolone 4 mg once daily for the duration of the pregnancy. The patient continued to have gradual improvement of the rash at the low treatment dose.

Following induction at 39 weeks’ gestation, the patient vaginally delivered a healthy, 6-lb male neonate at an outside hospital. She reported that the burning sensation improved within hours of delivery, and systemic steroids were stopped after delivery. At a follow-up visit 3 weeks postpartum, considerable improvement of the rash was noted with no evidence of pustules. Fading pink patches with a superficial scaling were noted on the back, chest, abdomen, arms, legs (Figure 4), and fingertips. The patient was counseled that PPP could recur in subsequent pregnancies and that she should be aware of the potential risks to the fetus.

Comment
In our patient, the diagnosis of PPP was supported by the presence of erythematous, coalescent plaques with small pustules at the margins and central erosions as well as the histologic findings of subcorneal pustules with mild acanthosis of the epidermis with spongiosis and a sparse neutrophilic infiltrate into the dermis.
The typical presentation of PPP is characterized by lesions that initially develop in skin folds with centrifugal spread.3 The lesions usually begin as erythematous plaques with a pustular ring with a central erosion. The face, palms, and soles of the feet typically are spared with occasional involvement of oral and esophageal mucosae. Biopsy findings typically include spongiform pustules with neutrophil invasion into the epidermis. Typical laboratory findings include electrolyte derangements with elevated ESR and leukocytosis.1
Diagnosis of PPP is critical given the potential for associated fetal morbidity and mortality.4 Anticipatory guidance for the patient also is necessary, as PPP can recur with subsequent pregnancies or even use of oral contraceptive pills (OCPs). Notably, a patient with recurrences of PPP with each of 9 pregnancies also experienced a recurrence when taking a combination estrogen/progesterone OCP, but not with an estrogen-only diethylstilbestrol OCP.5 Although the pathophysiology is not entirely understood, the development of PPP is thought to be related to the hormonal changes that occur in the third trimester, most notably due to elevated progesterone levels.2 The presence of progesterone in OCPs and recurrences associated with their use supports this altered hormonal state, contributing to the underlying pathophysiology of PPP.
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy can occur in women without any personal or family history of psoriasis, and as such, it is unclear whether PPP is a separate entity or a hormonally induced variation of generalized pustular psoriasis. Recent evidence included reports of women with PPP who had a mutation in the IL-36 receptor antagonist, leading to a relative abundance of IL-36 inflammatory cytokines.6
The mainstay of treatment for PPP is oral corticosteroids. Cases of PPP that are unresponsive to systemic steroids have been documented, requiring treatment with cyclosporine.9 Antitumor necrosis factors also have been used safely during pregnancy.10 Narrowband UVB phototherapy also has been proposed as a treatment alternative for patients who do not respond to oral corticosteroids.11
Conclusion
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy is a rare dermatosis of pregnancy that, unlike most other common dermatoses of pregnancy, is associated with adverse fetal outcomes. Diagnosis and management of PPP are critical to ensure the best care and outcomes for the patient and fetus and for a successful delivery of a healthy neonate. Our patient with PPP presented with involvement of the body, palms, and oral mucosa in the absence of systemic symptoms. Close follow-up and comanagement with the patient’s obstetrician ensured safe outcomes for the patient and the neonate.
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy (PPP), also known as impetigo herpetiformis, is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder of pregnancy wherein lesions typically appear in the third trimester and resolve after delivery; however, lesions may persist through the postpartum period. Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy may be considered a fifth dermatosis of pregnancy, alongside the classic dermatoses of atopic eruption of pregnancy, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, pemphigoid gestationis, and pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.1
As PPP is a rare disease, its effects on maternal-fetal health outcomes and management remain to be elucidated. Though maternal mortality is rare in PPP, it is a unique dermatosis of pregnancy because it may be associated with severe systemic maternal symptoms.2 Fetal morbidity and mortality are less predictable in PPP, with reported cases of stillbirth, fetal anomalies, and neonatal death thought to be due largely to placental insufficiency, even with control of symptoms.1,3 Given the risk of serious harm to the fetus, reporting of cases and discussion of PPP management is critical.
Case Report
An otherwise healthy 29-year-old G2P1 woman at 32 weeks’ gestation presented to our emergency department with a 1-week history of a pruritic, burning rash that started on the thighs then spread diffusely. She denied any similar rash in her prior pregnancy. She was not currently taking any medications except for prenatal vitamins and denied any systemic symptoms. The patient’s obstetrician initiated treatment with methylprednisolone 50 mg once daily for the rash 3 days prior to the current presentation, which had not seemed to help. On physical examination, edematous pink plaques studded with 1- to 2-mm collarettes of scaling and sparse 1-mm pustules involving the arms, chest, abdomen, back, groin, buttocks, and legs were noted. The plaques on the back and inner thighs had a peripheral rim of desquamative scaling. There were pink macules on the palms, and superficial desquamation was noted on the lips. The oral mucosa was otherwise spared (Figure 1).

Biopsy specimens from the left arm revealed discrete subcorneal pustules with mild acanthosis of the epidermis with spongiosis (Figure 2). The papillary dermis showed a sparse infiltrate of neutrophils with many marginated neutrophils within vessels. Direct immunofluorescence was negative for human IgG, IgA, IgM, complement component 3, and fibrinogen. Laboratory workup revealed leukocytosis of 21.5×109/L (reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L) with neutrophilic predominance of 73.6% (reference range, 56%), an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 40 mm/h (reference range, 0–20 mm/h), and a mild hypocalcemia of 8.6 mg/dL (reference range, 8.2–10.2 mg/dL). The patient was started on methylprednisone 40 mg once daily with a plan to taper the dose by 8 mg every 5 days.

At 35 weeks’ gestation, the patient continued to report pruritus and burning in the areas where the rash had developed. The morphology of the rash had changed considerably, as she now had prominent, annular, pink plaques with central clearing, trailing scaling, and a border of subtle pustules on the legs. There also were rings of desquamative scaling on the palms. During follow-up at 37 weeks’ gestation, the back, chest, and abdomen were improved from the initial presentation, and annular pink plaques with central clearing were noted on the legs (Figure 3). Given the clinical and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of PPP was made. It was recommended that she undergo increased fetal surveillance with close obstetric follow-up. Weekly office visits with obstetrics and twice-weekly Doppler ultrasounds and fetal nonstress tests were deemed appropriate management. The patient was scheduled for induction at 39 weeks’ gestation given the risk for potential harm to the fetus. She was maintained on low-dose methylprednisolone 4 mg once daily for the duration of the pregnancy. The patient continued to have gradual improvement of the rash at the low treatment dose.

Following induction at 39 weeks’ gestation, the patient vaginally delivered a healthy, 6-lb male neonate at an outside hospital. She reported that the burning sensation improved within hours of delivery, and systemic steroids were stopped after delivery. At a follow-up visit 3 weeks postpartum, considerable improvement of the rash was noted with no evidence of pustules. Fading pink patches with a superficial scaling were noted on the back, chest, abdomen, arms, legs (Figure 4), and fingertips. The patient was counseled that PPP could recur in subsequent pregnancies and that she should be aware of the potential risks to the fetus.

Comment
In our patient, the diagnosis of PPP was supported by the presence of erythematous, coalescent plaques with small pustules at the margins and central erosions as well as the histologic findings of subcorneal pustules with mild acanthosis of the epidermis with spongiosis and a sparse neutrophilic infiltrate into the dermis.
The typical presentation of PPP is characterized by lesions that initially develop in skin folds with centrifugal spread.3 The lesions usually begin as erythematous plaques with a pustular ring with a central erosion. The face, palms, and soles of the feet typically are spared with occasional involvement of oral and esophageal mucosae. Biopsy findings typically include spongiform pustules with neutrophil invasion into the epidermis. Typical laboratory findings include electrolyte derangements with elevated ESR and leukocytosis.1
Diagnosis of PPP is critical given the potential for associated fetal morbidity and mortality.4 Anticipatory guidance for the patient also is necessary, as PPP can recur with subsequent pregnancies or even use of oral contraceptive pills (OCPs). Notably, a patient with recurrences of PPP with each of 9 pregnancies also experienced a recurrence when taking a combination estrogen/progesterone OCP, but not with an estrogen-only diethylstilbestrol OCP.5 Although the pathophysiology is not entirely understood, the development of PPP is thought to be related to the hormonal changes that occur in the third trimester, most notably due to elevated progesterone levels.2 The presence of progesterone in OCPs and recurrences associated with their use supports this altered hormonal state, contributing to the underlying pathophysiology of PPP.
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy can occur in women without any personal or family history of psoriasis, and as such, it is unclear whether PPP is a separate entity or a hormonally induced variation of generalized pustular psoriasis. Recent evidence included reports of women with PPP who had a mutation in the IL-36 receptor antagonist, leading to a relative abundance of IL-36 inflammatory cytokines.6
The mainstay of treatment for PPP is oral corticosteroids. Cases of PPP that are unresponsive to systemic steroids have been documented, requiring treatment with cyclosporine.9 Antitumor necrosis factors also have been used safely during pregnancy.10 Narrowband UVB phototherapy also has been proposed as a treatment alternative for patients who do not respond to oral corticosteroids.11
Conclusion
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy is a rare dermatosis of pregnancy that, unlike most other common dermatoses of pregnancy, is associated with adverse fetal outcomes. Diagnosis and management of PPP are critical to ensure the best care and outcomes for the patient and fetus and for a successful delivery of a healthy neonate. Our patient with PPP presented with involvement of the body, palms, and oral mucosa in the absence of systemic symptoms. Close follow-up and comanagement with the patient’s obstetrician ensured safe outcomes for the patient and the neonate.
- Lehrhoff S, Pomeranz MK. Specific dermatoses of pregnancy and their treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:274-284.
- Kar S, Krishnan A, Shivkumar PV. Pregnancy and skin [published online August 28, 2012]. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2012;62:268-275.
- Kondo RN, Araújo FM, Pereira AM, et al. Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy (impetigo herpetiformis)—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 suppl 1):186-189.
- Oumeish OY, Parish JL. Impetigo herpetiformis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:101-104.
- Oumeish OY, Farraj SE, Bataineh AS. Some aspects of impetigo herpetiformis. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:103-105.
- Sugiura K, Oiso N, Iinuma S, et al. IL36RN mutations underlie impetigo herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2472-2474.
- Sugiura K. The genetic background of generalized pustular psoriasis: IL36RN mutations and CARD14 gain-of-function variants [published online March 5, 2014]. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;74:187-192.
- Li X, Chen M, Fu X, et al. Mutation analysis of the IL36RN gene in Chinese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis with/without psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;76:132-138.
- Hazarika D. Generalized pustular psoriasis of pregnancy successfully treated with cyclosporine. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:638.
- Puig L, Barco D, Alomar A. Treatment of psoriasis with anti-TNF drugs during pregnancy: case report and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2010;220:71-76.
- Bozdag K, Ozturk S, Ermete M. A case of recurrent impetigo herpetiformis treated with systemic corticosteroids and narrowband UVB [published online January 20, 2012]. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2012;31:67-69.
- Lehrhoff S, Pomeranz MK. Specific dermatoses of pregnancy and their treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:274-284.
- Kar S, Krishnan A, Shivkumar PV. Pregnancy and skin [published online August 28, 2012]. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2012;62:268-275.
- Kondo RN, Araújo FM, Pereira AM, et al. Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy (impetigo herpetiformis)—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 suppl 1):186-189.
- Oumeish OY, Parish JL. Impetigo herpetiformis. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:101-104.
- Oumeish OY, Farraj SE, Bataineh AS. Some aspects of impetigo herpetiformis. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:103-105.
- Sugiura K, Oiso N, Iinuma S, et al. IL36RN mutations underlie impetigo herpetiformis. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2472-2474.
- Sugiura K. The genetic background of generalized pustular psoriasis: IL36RN mutations and CARD14 gain-of-function variants [published online March 5, 2014]. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;74:187-192.
- Li X, Chen M, Fu X, et al. Mutation analysis of the IL36RN gene in Chinese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis with/without psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;76:132-138.
- Hazarika D. Generalized pustular psoriasis of pregnancy successfully treated with cyclosporine. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:638.
- Puig L, Barco D, Alomar A. Treatment of psoriasis with anti-TNF drugs during pregnancy: case report and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2010;220:71-76.
- Bozdag K, Ozturk S, Ermete M. A case of recurrent impetigo herpetiformis treated with systemic corticosteroids and narrowband UVB [published online January 20, 2012]. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2012;31:67-69.
Practice Points
- Given its association with maternal and fetal morbidity/mortality, it is important for physicians to have a high suspicion for pustular psoriasis of pregnancy (PPP) in pregnant women with widespread cutaneous eruptions.
- Oral corticosteroids and close involvement of obstetric care is the mainstay of treatment for PPP.
Study using U.K. data quantifies infection risk associated with psoriasis
Psoriasis was linked to increased risk of serious infection, with more severe disease associated with increased infection risk, in a study that used electronic medical records of patients in the United Kingdom.
The most common serious infections were lower respiratory tract, skin and soft tissue, and upper respiratory tract infections; and the most common opportunistic infection was tuberculosis, reported Junko Takeshita, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and her coauthors.
They identified 199,700 psoriasis patients and 954,315 healthy patients from THIN (the Health Improvement Network), a medical records database in the United Kingdom. Of the psoriasis patients, 187,258 had mild disease and 12,442 had moderate to severe disease; almost 70% of patients with moderate to severe disease were treated with methotrexate.
Adjusted hazard ratios for serious infection were 1.21 (95% confidence interval, 1.18-1.23) for psoriasis patients overall, 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.21) for those with mild psoriasis, and 1.63 (95% CI, 1.52-1.75) for those with moderate to severe psoriasis, Dr. Takeshita and her coauthors wrote in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Among all psoriasis patients, the attributable risk of serious infection was 16.2 per 10,000 person-years, compared with 14.4 per 10,000 person-years among those with mild psoriasis, and 49.5 per 10,000 person-years, among those with moderate to severe disease.
The investigators also analyzed data from a nested cohort – the iHOPE (Incident Health Outcomes and Psoriasis Events) study – of 8,569 psoriasis patients, with mild (less than 3% of body surface area involvement) or moderate to severe disease (3% or greater BSA), and 83,540 matched patients without psoriasis.
The adjusted HR for serious infection was 1.21 (95% CI, 1.09-1.35) for all psoriasis patients, 1.16 (95% CI, 0.99-1.35) for those with mild disease, and 1.27 (95% CI, 1.10-1.47) for those with moderate to severe disease. When patients who had received immunosuppressive treatment were excluded from the analysis, hazard ratios were similar among the different psoriasis groups, at 1.18 for all psoriasis patients (95% CI, 1.05-1.32), 1.15 among those with mild disease (95% CI, 0.99-1.34), and 1.21 for those with moderate to severe disease (95% CI, 1.03-1.42).
“Importantly, the risk of serious infection was observed to be similar in both the full THIN and iHOPE cohorts with the exception of the moderate to severe psoriasis subgroup among whom the risk of serious infection was attenuated but still significantly elevated in the iHOPE versus full THIN cohort,” they observed.
In the THIN cohort, the most common opportunistic infection “by far” was tuberculosis, with incidence rates of 1.05, 0.94, and 3.00 per 10,000 person-years among all psoriasis patients, patients with mild disease, and patients with moderate to severe disease, respectively, compared with 1.15 for those without psoriasis.
Patients with moderate to severe disease had an increased risk of opportunistic infection (HR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.06-2.34), but rates were similar among those with mild disease and those without psoriasis, Dr. Takeshita and her colleagues reported. But the opportunistic infection risk was “substantially attenuated” when patients who had received immunosuppressive treatment were excluded (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.44-3.12).
Patients with moderate to severe disease also had the greatest risk of herpes zoster (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.06-1.30). While the increased risk of herpes zoster was smaller in patients with mild psoriasis, it was still significant (HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.10). Again, when exclusion of patients who had received immunosuppressive therapies, the risk for herpes zoster associated with moderate to severe psoriasis no longer was elevated (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.76-1.23).
“Our findings suggest that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of serious infection, and more severe psoriasis, whether defined by treatment pattern or by BSA involvement, is a predictor of greater serious infection risk,” the authors wrote. Clinicians should ensure that patients, especially those with severe disease and those who receive immunosuppressive treatment, are vaccinated against influenza and pneumonia, and “should also consider herpes zoster vaccination with the new nonlive vaccine.”
“Future studies will be important to further characterize the risk of various infections among patients with psoriasis, compare the risk of infection associated with psoriasis to that of other chronic diseases, and delineate the pathophysiologic mechanisms that contribute to the increased risk of infections associated with psoriasis and its therapies,” they concluded.
The study was funded by an unrestricted Pfizer grant. Dr. Takeshita has received a research grant (to the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania) from Pfizer for unrelated work payment for continuing medical education work related to psoriasis supported indirectly by Eli Lilly and Novartis. Other authors’ disclosures included servings as a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, Coherus, and other pharmaceutical companies.
[email protected]
SOURCE: Takeshita J et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Mar 2. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.01.039.
Psoriasis was linked to increased risk of serious infection, with more severe disease associated with increased infection risk, in a study that used electronic medical records of patients in the United Kingdom.
The most common serious infections were lower respiratory tract, skin and soft tissue, and upper respiratory tract infections; and the most common opportunistic infection was tuberculosis, reported Junko Takeshita, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and her coauthors.
They identified 199,700 psoriasis patients and 954,315 healthy patients from THIN (the Health Improvement Network), a medical records database in the United Kingdom. Of the psoriasis patients, 187,258 had mild disease and 12,442 had moderate to severe disease; almost 70% of patients with moderate to severe disease were treated with methotrexate.
Adjusted hazard ratios for serious infection were 1.21 (95% confidence interval, 1.18-1.23) for psoriasis patients overall, 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.21) for those with mild psoriasis, and 1.63 (95% CI, 1.52-1.75) for those with moderate to severe psoriasis, Dr. Takeshita and her coauthors wrote in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Among all psoriasis patients, the attributable risk of serious infection was 16.2 per 10,000 person-years, compared with 14.4 per 10,000 person-years among those with mild psoriasis, and 49.5 per 10,000 person-years, among those with moderate to severe disease.
The investigators also analyzed data from a nested cohort – the iHOPE (Incident Health Outcomes and Psoriasis Events) study – of 8,569 psoriasis patients, with mild (less than 3% of body surface area involvement) or moderate to severe disease (3% or greater BSA), and 83,540 matched patients without psoriasis.
The adjusted HR for serious infection was 1.21 (95% CI, 1.09-1.35) for all psoriasis patients, 1.16 (95% CI, 0.99-1.35) for those with mild disease, and 1.27 (95% CI, 1.10-1.47) for those with moderate to severe disease. When patients who had received immunosuppressive treatment were excluded from the analysis, hazard ratios were similar among the different psoriasis groups, at 1.18 for all psoriasis patients (95% CI, 1.05-1.32), 1.15 among those with mild disease (95% CI, 0.99-1.34), and 1.21 for those with moderate to severe disease (95% CI, 1.03-1.42).
“Importantly, the risk of serious infection was observed to be similar in both the full THIN and iHOPE cohorts with the exception of the moderate to severe psoriasis subgroup among whom the risk of serious infection was attenuated but still significantly elevated in the iHOPE versus full THIN cohort,” they observed.
In the THIN cohort, the most common opportunistic infection “by far” was tuberculosis, with incidence rates of 1.05, 0.94, and 3.00 per 10,000 person-years among all psoriasis patients, patients with mild disease, and patients with moderate to severe disease, respectively, compared with 1.15 for those without psoriasis.
Patients with moderate to severe disease had an increased risk of opportunistic infection (HR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.06-2.34), but rates were similar among those with mild disease and those without psoriasis, Dr. Takeshita and her colleagues reported. But the opportunistic infection risk was “substantially attenuated” when patients who had received immunosuppressive treatment were excluded (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.44-3.12).
Patients with moderate to severe disease also had the greatest risk of herpes zoster (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.06-1.30). While the increased risk of herpes zoster was smaller in patients with mild psoriasis, it was still significant (HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.10). Again, when exclusion of patients who had received immunosuppressive therapies, the risk for herpes zoster associated with moderate to severe psoriasis no longer was elevated (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.76-1.23).
“Our findings suggest that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of serious infection, and more severe psoriasis, whether defined by treatment pattern or by BSA involvement, is a predictor of greater serious infection risk,” the authors wrote. Clinicians should ensure that patients, especially those with severe disease and those who receive immunosuppressive treatment, are vaccinated against influenza and pneumonia, and “should also consider herpes zoster vaccination with the new nonlive vaccine.”
“Future studies will be important to further characterize the risk of various infections among patients with psoriasis, compare the risk of infection associated with psoriasis to that of other chronic diseases, and delineate the pathophysiologic mechanisms that contribute to the increased risk of infections associated with psoriasis and its therapies,” they concluded.
The study was funded by an unrestricted Pfizer grant. Dr. Takeshita has received a research grant (to the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania) from Pfizer for unrelated work payment for continuing medical education work related to psoriasis supported indirectly by Eli Lilly and Novartis. Other authors’ disclosures included servings as a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, Coherus, and other pharmaceutical companies.
[email protected]
SOURCE: Takeshita J et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Mar 2. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.01.039.
Psoriasis was linked to increased risk of serious infection, with more severe disease associated with increased infection risk, in a study that used electronic medical records of patients in the United Kingdom.
The most common serious infections were lower respiratory tract, skin and soft tissue, and upper respiratory tract infections; and the most common opportunistic infection was tuberculosis, reported Junko Takeshita, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and her coauthors.
They identified 199,700 psoriasis patients and 954,315 healthy patients from THIN (the Health Improvement Network), a medical records database in the United Kingdom. Of the psoriasis patients, 187,258 had mild disease and 12,442 had moderate to severe disease; almost 70% of patients with moderate to severe disease were treated with methotrexate.
Adjusted hazard ratios for serious infection were 1.21 (95% confidence interval, 1.18-1.23) for psoriasis patients overall, 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.21) for those with mild psoriasis, and 1.63 (95% CI, 1.52-1.75) for those with moderate to severe psoriasis, Dr. Takeshita and her coauthors wrote in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Among all psoriasis patients, the attributable risk of serious infection was 16.2 per 10,000 person-years, compared with 14.4 per 10,000 person-years among those with mild psoriasis, and 49.5 per 10,000 person-years, among those with moderate to severe disease.
The investigators also analyzed data from a nested cohort – the iHOPE (Incident Health Outcomes and Psoriasis Events) study – of 8,569 psoriasis patients, with mild (less than 3% of body surface area involvement) or moderate to severe disease (3% or greater BSA), and 83,540 matched patients without psoriasis.
The adjusted HR for serious infection was 1.21 (95% CI, 1.09-1.35) for all psoriasis patients, 1.16 (95% CI, 0.99-1.35) for those with mild disease, and 1.27 (95% CI, 1.10-1.47) for those with moderate to severe disease. When patients who had received immunosuppressive treatment were excluded from the analysis, hazard ratios were similar among the different psoriasis groups, at 1.18 for all psoriasis patients (95% CI, 1.05-1.32), 1.15 among those with mild disease (95% CI, 0.99-1.34), and 1.21 for those with moderate to severe disease (95% CI, 1.03-1.42).
“Importantly, the risk of serious infection was observed to be similar in both the full THIN and iHOPE cohorts with the exception of the moderate to severe psoriasis subgroup among whom the risk of serious infection was attenuated but still significantly elevated in the iHOPE versus full THIN cohort,” they observed.
In the THIN cohort, the most common opportunistic infection “by far” was tuberculosis, with incidence rates of 1.05, 0.94, and 3.00 per 10,000 person-years among all psoriasis patients, patients with mild disease, and patients with moderate to severe disease, respectively, compared with 1.15 for those without psoriasis.
Patients with moderate to severe disease had an increased risk of opportunistic infection (HR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.06-2.34), but rates were similar among those with mild disease and those without psoriasis, Dr. Takeshita and her colleagues reported. But the opportunistic infection risk was “substantially attenuated” when patients who had received immunosuppressive treatment were excluded (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.44-3.12).
Patients with moderate to severe disease also had the greatest risk of herpes zoster (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.06-1.30). While the increased risk of herpes zoster was smaller in patients with mild psoriasis, it was still significant (HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.10). Again, when exclusion of patients who had received immunosuppressive therapies, the risk for herpes zoster associated with moderate to severe psoriasis no longer was elevated (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.76-1.23).
“Our findings suggest that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of serious infection, and more severe psoriasis, whether defined by treatment pattern or by BSA involvement, is a predictor of greater serious infection risk,” the authors wrote. Clinicians should ensure that patients, especially those with severe disease and those who receive immunosuppressive treatment, are vaccinated against influenza and pneumonia, and “should also consider herpes zoster vaccination with the new nonlive vaccine.”
“Future studies will be important to further characterize the risk of various infections among patients with psoriasis, compare the risk of infection associated with psoriasis to that of other chronic diseases, and delineate the pathophysiologic mechanisms that contribute to the increased risk of infections associated with psoriasis and its therapies,” they concluded.
The study was funded by an unrestricted Pfizer grant. Dr. Takeshita has received a research grant (to the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania) from Pfizer for unrelated work payment for continuing medical education work related to psoriasis supported indirectly by Eli Lilly and Novartis. Other authors’ disclosures included servings as a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, Coherus, and other pharmaceutical companies.
[email protected]
SOURCE: Takeshita J et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Mar 2. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.01.039.
Key clinical point: Psoriasis is linked to risk of serious infection, with increased risk in more severe disease.
Major finding: Hazard ratios for serious infection were 1.21 (95% CI, 1.18-1.23) for psoriasis overall, 1.18 (95% CI, 1.16-1.21) for mild psoriasis, and 1.63 (95% CI, 1.52-1.75) for moderate to severe psoriasis.
Study details: The evaluation included data on 199,700 patients with psoriasis and 954,315 patients without psoriasis in a U.K. electronic medical records database.
Disclosures: The study was funded by an unrestricted Pfizer grant. Dr. Takeshita has received a research grant (to the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania) from Pfizer for unrelated work payment for continuing medical education work related to psoriasis supported indirectly by Eli Lilly and Novartis. Other authors’ disclosures included servings as a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, Coherus, and other pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Takeshita J et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Mar 2. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.01.039.
mainbar
Psoriasis was linked to increased risk of serious infection, with more severe disease associated with increased infection risk, in a study that used electronic medical records of patients in the United Kingdom.
The most common serious infections were lower respiratory tract, skin and soft tissue, and upper respiratory tract infections; and the most common opportunistic infection was tuberculosis, reported Junko Takeshita, MD, PhD, of the departments of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and her coauthors.
Adjusted hazard ratios for serious infection were 1.21 (95% confidence interval, 1.18-1.23) for psoriasis patients overall, 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.21) for those with mild psoriasis, and 1.63 (95% CI, 1.52-1.75) for those with moderate to severe psoriasis, Dr. Takeshita and her coauthors wrote in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Among all psoriasis patients, the attributable risk of serious infection was 16.2 per 10,000 person-years, compared with 14.4 per 10,000 person-years among those with mild psoriasis, and 49.5 per 10,000 person-years, among those with moderate to severe disease.
The investigators also analyzed data from a nested cohort – the iHOPE (Incident Health Outcomes and Psoriasis Events) study – of 8,569 psoriasis patients, with mild (less than 3% of body surface area involvement) or moderate to severe disease (3% or greater BSA), and 83,540 matched patients without psoriasis. The adjusted HR for serious infection was 1.21 (95% CI, 1.09-1.35) for all psoriasis patients, 1.16 (95% CI, 0.99-1.35) for those with mild disease, and 1.27 (95% CI, 1.10-1.47) for those with moderate to severe disease. When patients who had received immunosuppressive treatment were excluded from the analysis, hazard ratios were similar among the different psoriasis groups, at 1.18 for all psoriasis patients (95% CI, 1.05-1.32), 1.15 among those with mild disease (95% CI, 0.99-1.34), and 1.21 for those with moderate to severe disease (95% CI, 1.03-1.42).
“Importantly, the risk of serious infection was observed to be similar in both the full THIN and iHOPE cohorts with the exception of the moderate to severe psoriasis subgroup among whom the risk of serious infection was attenuated but still significantly elevated in the iHOPE versus full THIN cohort,” they observed.
In the THIN cohort, the most common opportunistic infection “by far” was tuberculosis, with incidence rates of 1.05, 0.94, and 3.00 per 10,000 person-years among all psoriasis patients, patients with mild disease, and patients with moderate to severe disease, respectively, compared with 1.15 for those without psoriasis.
Patients with moderate to severe disease had an increased risk of opportunistic infection (HR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.06-2.34), but rates were similar among those with mild disease and those without psoriasis, Dr. Takeshita and her colleagues reported. But the opportunistic infection risk was “substantially attenuated” when patients who had received immunosuppressive treatment were excluded (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.44-3.12).
Patients with moderate to severe disease also had the greatest risk of herpes zoster (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.06-1.30). While the increased risk of herpes zoster was smaller in patients with mild psoriasis, it was still significant (HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.05-1.10). Again, when exclusion of patients who had received immunosuppressive therapies, the risk for herpes zoster associated with moderate to severe psoriasis no longer was elevated (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.76-1.23).
“Our findings suggest that psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of serious infection, and more severe psoriasis, whether defined by treatment pattern or by BSA involvement, is a predictor of greater serious infection risk,” the authors wrote. Clinicians should ensure that patients, especially those with severe disease and those who receive immunosuppressive treatment, are vaccinated against influenza and pneumonia, and “should also consider herpes zoster vaccination with the new nonlive vaccine.”
“Future studies will be important to further characterize the risk of various infections among patients with psoriasis, compare the risk of infection associated with psoriasis to that of other chronic diseases, and delineate the pathophysiologic mechanisms that contribute to the increased risk of infections associated with psoriasis and its therapies,” they concluded.
The study was funded by an unrestricted Pfizer grant. Dr. Takeshita has received a research grant (to the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania) from Pfizer for unrelated work payment for continuing medical education work related to psoriasis supported indirectly by Eli Lilly and Novartis. Other authors’ disclosures included servings as a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, Coherus, and other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Takeshita J et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Mar 2. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.01.039.