User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Abdominal fat linked to lower brain volume in midlife
In a large study of healthy middle-aged adults, greater visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat on abdominal MRI predicted brain atrophy on imaging, especially in women.
“The study shows that excess fat is bad for the brain and worse in women, including in Alzheimer’s disease risk regions,” lead author Cyrus Raji, MD, PhD, with the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University, St. Louis, Mo., said in an interview.
The study was published online in the journal Aging and Disease
Modifiable risk factor
Multiple studies have suggested a connection between body fat accumulation and increased dementia risk. But few have examined the relationship between types of fat (visceral and subcutaneous) and brain volume.
For the new study, 10,000 healthy adults aged 20-80 years (mean age, 52.9 years; 53% men) underwent a short whole-body MRI protocol. Regression analyses of abdominal fat types and normalized brain volumes were evaluated, controlling for age and sex.
The research team found that higher amounts of both visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat predicted lower total gray and white matter volume, as well as lower volume in the hippocampus, frontal cortex, and temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes.
“The findings are quite dramatic,” Dr. Raji told this news organization. “Overall, we found that both subcutaneous and visceral fat has similar levels of negative relationships with brain volumes.”
Women had a higher burden of brain atrophy with increased visceral fat than men. However, it’s difficult to place the sex differences in context because of the lack of prior work specifically investigating visceral fat, brain volume loss, and sex differences, the researchers caution.
They also note that while statistically significant relationships were observed between visceral fat levels and gray matter volume changes, their effect sizes were generally small.
“Thus, the statistical significance of this work is influenced by the large sample size and less so by large effect size in any given set of regions,” the investigators write.
Other limitations include the cross-sectional nature of the study, which precludes conclusions about causality. The analysis also did not account for other lifestyle factors such as physical activity, diet, and genetic variables.
The researchers call for further investigation “to better elucidate underlying mechanisms and discover possible interventions targeting abdominal fat reduction as a strategy to maintain brain health.”
‘Helpful addition to the literature’
In a comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, noted that “previous studies have linked obesity with cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia. Rather than using BMI as a proxy for body fat, the current study examined visceral and subcutaneous fat directly using imaging techniques.”
Dr. Sexton, who was not associated with this study, said the finding that increased body fat was associated with reduced brain volumes suggests “a possible mechanism to explain the previously reported associations between obesity and cognition.”
“Though some degree of atrophy and brain shrinkage is common with old age, awareness of this association is important because reduced brain volume may be associated with problems with thinking, memory, and performing everyday tasks, and because rates of obesity continue to rise in the United States, along with obesity-related conditions including heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer,” she added.
“While a helpful addition to the literature, the study does have important limitations. As an observational study, it cannot establish whether higher levels of body fat directly causes reduced brain volumes,” Dr. Sexton cautioned.
In addition, the study did not take into account important related factors like physical activity and diet, which may influence any relationship between body fat and brain volumes, she noted. “Overall, it is not just one factor that is important to consider when considering risk for cognitive decline and dementia, but multiple factors.
“Obesity and the location of body fat must be considered in combination with one’s total lived experience and habits, including physical activity, education, head injury, sleep, mental health, and the health of your heart/cardiovascular system and other key bodily systems,” Dr. Sexton said.
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as U.S. POINTER to see whether combining physical activity, healthy nutrition, social and intellectual challenges, and improved self-management of medical conditions can protect cognitive function in older adults who are at increased risk for cognitive decline.
This work was supported in part by Providence St. Joseph Health in Seattle; Saint John’s Health Center Foundation; Pacific Neuroscience Institute and Foundation; Will and Cary Singleton; and the McLoughlin family. Dr. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Voxelwise, Neurevolution, Pacific Neuroscience Institute Foundation, and Icometrix. Dr. Sexton reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a large study of healthy middle-aged adults, greater visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat on abdominal MRI predicted brain atrophy on imaging, especially in women.
“The study shows that excess fat is bad for the brain and worse in women, including in Alzheimer’s disease risk regions,” lead author Cyrus Raji, MD, PhD, with the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University, St. Louis, Mo., said in an interview.
The study was published online in the journal Aging and Disease
Modifiable risk factor
Multiple studies have suggested a connection between body fat accumulation and increased dementia risk. But few have examined the relationship between types of fat (visceral and subcutaneous) and brain volume.
For the new study, 10,000 healthy adults aged 20-80 years (mean age, 52.9 years; 53% men) underwent a short whole-body MRI protocol. Regression analyses of abdominal fat types and normalized brain volumes were evaluated, controlling for age and sex.
The research team found that higher amounts of both visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat predicted lower total gray and white matter volume, as well as lower volume in the hippocampus, frontal cortex, and temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes.
“The findings are quite dramatic,” Dr. Raji told this news organization. “Overall, we found that both subcutaneous and visceral fat has similar levels of negative relationships with brain volumes.”
Women had a higher burden of brain atrophy with increased visceral fat than men. However, it’s difficult to place the sex differences in context because of the lack of prior work specifically investigating visceral fat, brain volume loss, and sex differences, the researchers caution.
They also note that while statistically significant relationships were observed between visceral fat levels and gray matter volume changes, their effect sizes were generally small.
“Thus, the statistical significance of this work is influenced by the large sample size and less so by large effect size in any given set of regions,” the investigators write.
Other limitations include the cross-sectional nature of the study, which precludes conclusions about causality. The analysis also did not account for other lifestyle factors such as physical activity, diet, and genetic variables.
The researchers call for further investigation “to better elucidate underlying mechanisms and discover possible interventions targeting abdominal fat reduction as a strategy to maintain brain health.”
‘Helpful addition to the literature’
In a comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, noted that “previous studies have linked obesity with cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia. Rather than using BMI as a proxy for body fat, the current study examined visceral and subcutaneous fat directly using imaging techniques.”
Dr. Sexton, who was not associated with this study, said the finding that increased body fat was associated with reduced brain volumes suggests “a possible mechanism to explain the previously reported associations between obesity and cognition.”
“Though some degree of atrophy and brain shrinkage is common with old age, awareness of this association is important because reduced brain volume may be associated with problems with thinking, memory, and performing everyday tasks, and because rates of obesity continue to rise in the United States, along with obesity-related conditions including heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer,” she added.
“While a helpful addition to the literature, the study does have important limitations. As an observational study, it cannot establish whether higher levels of body fat directly causes reduced brain volumes,” Dr. Sexton cautioned.
In addition, the study did not take into account important related factors like physical activity and diet, which may influence any relationship between body fat and brain volumes, she noted. “Overall, it is not just one factor that is important to consider when considering risk for cognitive decline and dementia, but multiple factors.
“Obesity and the location of body fat must be considered in combination with one’s total lived experience and habits, including physical activity, education, head injury, sleep, mental health, and the health of your heart/cardiovascular system and other key bodily systems,” Dr. Sexton said.
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as U.S. POINTER to see whether combining physical activity, healthy nutrition, social and intellectual challenges, and improved self-management of medical conditions can protect cognitive function in older adults who are at increased risk for cognitive decline.
This work was supported in part by Providence St. Joseph Health in Seattle; Saint John’s Health Center Foundation; Pacific Neuroscience Institute and Foundation; Will and Cary Singleton; and the McLoughlin family. Dr. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Voxelwise, Neurevolution, Pacific Neuroscience Institute Foundation, and Icometrix. Dr. Sexton reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a large study of healthy middle-aged adults, greater visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat on abdominal MRI predicted brain atrophy on imaging, especially in women.
“The study shows that excess fat is bad for the brain and worse in women, including in Alzheimer’s disease risk regions,” lead author Cyrus Raji, MD, PhD, with the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University, St. Louis, Mo., said in an interview.
The study was published online in the journal Aging and Disease
Modifiable risk factor
Multiple studies have suggested a connection between body fat accumulation and increased dementia risk. But few have examined the relationship between types of fat (visceral and subcutaneous) and brain volume.
For the new study, 10,000 healthy adults aged 20-80 years (mean age, 52.9 years; 53% men) underwent a short whole-body MRI protocol. Regression analyses of abdominal fat types and normalized brain volumes were evaluated, controlling for age and sex.
The research team found that higher amounts of both visceral and subcutaneous abdominal fat predicted lower total gray and white matter volume, as well as lower volume in the hippocampus, frontal cortex, and temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes.
“The findings are quite dramatic,” Dr. Raji told this news organization. “Overall, we found that both subcutaneous and visceral fat has similar levels of negative relationships with brain volumes.”
Women had a higher burden of brain atrophy with increased visceral fat than men. However, it’s difficult to place the sex differences in context because of the lack of prior work specifically investigating visceral fat, brain volume loss, and sex differences, the researchers caution.
They also note that while statistically significant relationships were observed between visceral fat levels and gray matter volume changes, their effect sizes were generally small.
“Thus, the statistical significance of this work is influenced by the large sample size and less so by large effect size in any given set of regions,” the investigators write.
Other limitations include the cross-sectional nature of the study, which precludes conclusions about causality. The analysis also did not account for other lifestyle factors such as physical activity, diet, and genetic variables.
The researchers call for further investigation “to better elucidate underlying mechanisms and discover possible interventions targeting abdominal fat reduction as a strategy to maintain brain health.”
‘Helpful addition to the literature’
In a comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, noted that “previous studies have linked obesity with cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia. Rather than using BMI as a proxy for body fat, the current study examined visceral and subcutaneous fat directly using imaging techniques.”
Dr. Sexton, who was not associated with this study, said the finding that increased body fat was associated with reduced brain volumes suggests “a possible mechanism to explain the previously reported associations between obesity and cognition.”
“Though some degree of atrophy and brain shrinkage is common with old age, awareness of this association is important because reduced brain volume may be associated with problems with thinking, memory, and performing everyday tasks, and because rates of obesity continue to rise in the United States, along with obesity-related conditions including heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer,” she added.
“While a helpful addition to the literature, the study does have important limitations. As an observational study, it cannot establish whether higher levels of body fat directly causes reduced brain volumes,” Dr. Sexton cautioned.
In addition, the study did not take into account important related factors like physical activity and diet, which may influence any relationship between body fat and brain volumes, she noted. “Overall, it is not just one factor that is important to consider when considering risk for cognitive decline and dementia, but multiple factors.
“Obesity and the location of body fat must be considered in combination with one’s total lived experience and habits, including physical activity, education, head injury, sleep, mental health, and the health of your heart/cardiovascular system and other key bodily systems,” Dr. Sexton said.
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as U.S. POINTER to see whether combining physical activity, healthy nutrition, social and intellectual challenges, and improved self-management of medical conditions can protect cognitive function in older adults who are at increased risk for cognitive decline.
This work was supported in part by Providence St. Joseph Health in Seattle; Saint John’s Health Center Foundation; Pacific Neuroscience Institute and Foundation; Will and Cary Singleton; and the McLoughlin family. Dr. Raji is a consultant for Brainreader, Apollo Health, Voxelwise, Neurevolution, Pacific Neuroscience Institute Foundation, and Icometrix. Dr. Sexton reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AGING AND DISEASES
Domestic violence in health care is real and underreported
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.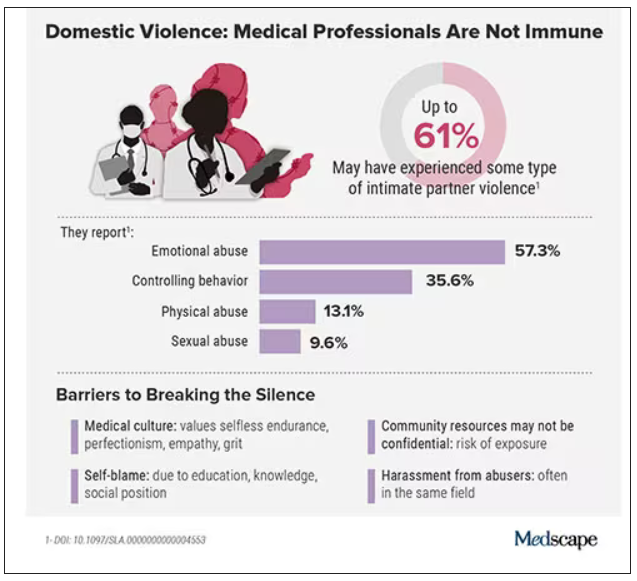
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in five doctors with long COVID can no longer work: Survey
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Resident creates AI alternative to U.S. News med school ranking
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Q&A: What to know about the new BA 2.86 COVID variant
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA to step up oversight of cosmetics, assess ‘forever chemicals’
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PTSD: Written exposure therapy matches prolonged exposure therapy
Investigators also found that participants randomly assigned to receive WET were significantly less likely to drop out of treatment than those receiving PE.
Written exposure therapy involves writing about thoughts and feelings during a specific traumatic event during five supervised, 30-minute sessions and discussing the writing process with the therapist supervising the sessions.
In the latter sessions, the participant talks about how the event affected them.
“Clinicians should consider using WET in their practices as some clients would prefer a shorter treatment approach, and it may be the only option for some clients – for instance, those who have limited time for therapy and may not be able to do a longer treatment,” study investigator Denise Sloan, PhD, said in an interview.
She also noted that WET is covered by insurance and that “most providers I know indicate that they list it as CBT [cognitive-behavioral therapy] code to insurance companies.”
Sloan is senior clinician investigator of the National Center for PTSD at VA Boston Healthcare System and professor of psychiatry at Boston University.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
High attrition rates
The disadvantage to the three major types of therapy used most often to treat PTSD in veterans – eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, cognitive processing therapy (CPT), and PE – are the dropout rates, that range from 18% to as high as 50%.
Prior studies have shown that WET is briefer and just as effective as CPT, but investigators noted that it had never been tested against PE in a randomized clinical trial.
To find out how the two types of therapy compare, Dr. Sloan and associates randomized 178 veterans with PTSD from three VA centers – Boston; Charleston, S.C.; and Madison, Wisc. – to receive either WET or PE.
PE consisted of 8-15 90-minute therapy sessions during which participants imagine the most distressing aspect of their traumatic memory, and between sessions, they confront the people, places, or situations they have been avoiding because of the trauma.
The investigators used the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 at baseline to screen participants at high risk for suicide, comorbid substance use disorder, and unstable bipolar disorder, who were excluded from the study.
At baseline, 10, 20, and 30 weeks after the first treatment session, the investigators measured the severity of each patient’s PTSD symptoms with the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5, which has a range of 0 (no PTSD symptoms) to 80 (most severe PTSD symptoms).
Of the 178 veterans, 134 were men, and their mean age was 45 years. The majority (63%) was White, while 21% were Black.
The researchers found that study participants were not significantly more likely to meet PTSD diagnostic criteria in the WET or PE conditions at any assessment.
WET briefer, better retention
Investigators noted the largest difference in PTSD scores in favor of WET at the 10-month assessment: The mean score for those receiving WET was 27.7, and the mean score for those receiving PE was 30.1 (odds ratio, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.35-1.46).
Among those who finished treatment, the mean number of treatment sessions was 12.5 for PE and 6 for WET.
Participants assigned to receive PE were significantly more likely to drop out of the study prematurely; 32 (35.6%) dropped out, compared with 11 (12.5%) participants assigned to WET.
Notably, of the 32 participants who dropped out of PE, 30 did so by session 7, so the increased dropout in PE was not related to the greater number of sessions, the investigators noted.
They added that findings could have been limited by stressors related to the global COVID-19 pandemic, which was taking place during the treatment, and the fact that all of the participants were veterans, which could limit the generalizability of the findings.
In an editorial, Charles Taylor, PhD, and Murray Stein, MD, MPH, both from the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, wrote that “WET achieved comparable reductions in PTSD symptoms through fewer sessions, shorter duration sessions, less therapist involvement, and no explicit prescription of homework.
“These findings should galvanize the psychotherapy field to design parsimonious treatments from the start, systematically testing the effects of different dose parameters,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the VA. Dr. Sloan reported receiving royalty payments for the published Written Exposure Therapy manual from the American Psychological Association outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators also found that participants randomly assigned to receive WET were significantly less likely to drop out of treatment than those receiving PE.
Written exposure therapy involves writing about thoughts and feelings during a specific traumatic event during five supervised, 30-minute sessions and discussing the writing process with the therapist supervising the sessions.
In the latter sessions, the participant talks about how the event affected them.
“Clinicians should consider using WET in their practices as some clients would prefer a shorter treatment approach, and it may be the only option for some clients – for instance, those who have limited time for therapy and may not be able to do a longer treatment,” study investigator Denise Sloan, PhD, said in an interview.
She also noted that WET is covered by insurance and that “most providers I know indicate that they list it as CBT [cognitive-behavioral therapy] code to insurance companies.”
Sloan is senior clinician investigator of the National Center for PTSD at VA Boston Healthcare System and professor of psychiatry at Boston University.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
High attrition rates
The disadvantage to the three major types of therapy used most often to treat PTSD in veterans – eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, cognitive processing therapy (CPT), and PE – are the dropout rates, that range from 18% to as high as 50%.
Prior studies have shown that WET is briefer and just as effective as CPT, but investigators noted that it had never been tested against PE in a randomized clinical trial.
To find out how the two types of therapy compare, Dr. Sloan and associates randomized 178 veterans with PTSD from three VA centers – Boston; Charleston, S.C.; and Madison, Wisc. – to receive either WET or PE.
PE consisted of 8-15 90-minute therapy sessions during which participants imagine the most distressing aspect of their traumatic memory, and between sessions, they confront the people, places, or situations they have been avoiding because of the trauma.
The investigators used the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 at baseline to screen participants at high risk for suicide, comorbid substance use disorder, and unstable bipolar disorder, who were excluded from the study.
At baseline, 10, 20, and 30 weeks after the first treatment session, the investigators measured the severity of each patient’s PTSD symptoms with the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5, which has a range of 0 (no PTSD symptoms) to 80 (most severe PTSD symptoms).
Of the 178 veterans, 134 were men, and their mean age was 45 years. The majority (63%) was White, while 21% were Black.
The researchers found that study participants were not significantly more likely to meet PTSD diagnostic criteria in the WET or PE conditions at any assessment.
WET briefer, better retention
Investigators noted the largest difference in PTSD scores in favor of WET at the 10-month assessment: The mean score for those receiving WET was 27.7, and the mean score for those receiving PE was 30.1 (odds ratio, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.35-1.46).
Among those who finished treatment, the mean number of treatment sessions was 12.5 for PE and 6 for WET.
Participants assigned to receive PE were significantly more likely to drop out of the study prematurely; 32 (35.6%) dropped out, compared with 11 (12.5%) participants assigned to WET.
Notably, of the 32 participants who dropped out of PE, 30 did so by session 7, so the increased dropout in PE was not related to the greater number of sessions, the investigators noted.
They added that findings could have been limited by stressors related to the global COVID-19 pandemic, which was taking place during the treatment, and the fact that all of the participants were veterans, which could limit the generalizability of the findings.
In an editorial, Charles Taylor, PhD, and Murray Stein, MD, MPH, both from the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, wrote that “WET achieved comparable reductions in PTSD symptoms through fewer sessions, shorter duration sessions, less therapist involvement, and no explicit prescription of homework.
“These findings should galvanize the psychotherapy field to design parsimonious treatments from the start, systematically testing the effects of different dose parameters,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the VA. Dr. Sloan reported receiving royalty payments for the published Written Exposure Therapy manual from the American Psychological Association outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators also found that participants randomly assigned to receive WET were significantly less likely to drop out of treatment than those receiving PE.
Written exposure therapy involves writing about thoughts and feelings during a specific traumatic event during five supervised, 30-minute sessions and discussing the writing process with the therapist supervising the sessions.
In the latter sessions, the participant talks about how the event affected them.
“Clinicians should consider using WET in their practices as some clients would prefer a shorter treatment approach, and it may be the only option for some clients – for instance, those who have limited time for therapy and may not be able to do a longer treatment,” study investigator Denise Sloan, PhD, said in an interview.
She also noted that WET is covered by insurance and that “most providers I know indicate that they list it as CBT [cognitive-behavioral therapy] code to insurance companies.”
Sloan is senior clinician investigator of the National Center for PTSD at VA Boston Healthcare System and professor of psychiatry at Boston University.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
High attrition rates
The disadvantage to the three major types of therapy used most often to treat PTSD in veterans – eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, cognitive processing therapy (CPT), and PE – are the dropout rates, that range from 18% to as high as 50%.
Prior studies have shown that WET is briefer and just as effective as CPT, but investigators noted that it had never been tested against PE in a randomized clinical trial.
To find out how the two types of therapy compare, Dr. Sloan and associates randomized 178 veterans with PTSD from three VA centers – Boston; Charleston, S.C.; and Madison, Wisc. – to receive either WET or PE.
PE consisted of 8-15 90-minute therapy sessions during which participants imagine the most distressing aspect of their traumatic memory, and between sessions, they confront the people, places, or situations they have been avoiding because of the trauma.
The investigators used the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 at baseline to screen participants at high risk for suicide, comorbid substance use disorder, and unstable bipolar disorder, who were excluded from the study.
At baseline, 10, 20, and 30 weeks after the first treatment session, the investigators measured the severity of each patient’s PTSD symptoms with the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5, which has a range of 0 (no PTSD symptoms) to 80 (most severe PTSD symptoms).
Of the 178 veterans, 134 were men, and their mean age was 45 years. The majority (63%) was White, while 21% were Black.
The researchers found that study participants were not significantly more likely to meet PTSD diagnostic criteria in the WET or PE conditions at any assessment.
WET briefer, better retention
Investigators noted the largest difference in PTSD scores in favor of WET at the 10-month assessment: The mean score for those receiving WET was 27.7, and the mean score for those receiving PE was 30.1 (odds ratio, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.35-1.46).
Among those who finished treatment, the mean number of treatment sessions was 12.5 for PE and 6 for WET.
Participants assigned to receive PE were significantly more likely to drop out of the study prematurely; 32 (35.6%) dropped out, compared with 11 (12.5%) participants assigned to WET.
Notably, of the 32 participants who dropped out of PE, 30 did so by session 7, so the increased dropout in PE was not related to the greater number of sessions, the investigators noted.
They added that findings could have been limited by stressors related to the global COVID-19 pandemic, which was taking place during the treatment, and the fact that all of the participants were veterans, which could limit the generalizability of the findings.
In an editorial, Charles Taylor, PhD, and Murray Stein, MD, MPH, both from the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, wrote that “WET achieved comparable reductions in PTSD symptoms through fewer sessions, shorter duration sessions, less therapist involvement, and no explicit prescription of homework.
“These findings should galvanize the psychotherapy field to design parsimonious treatments from the start, systematically testing the effects of different dose parameters,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the VA. Dr. Sloan reported receiving royalty payments for the published Written Exposure Therapy manual from the American Psychological Association outside the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
CTE common among young athletes in largest brain donor study
Analysis of brain tissue from athletes who were exposed to RHIs and died before the age of 30 revealed neuropathological evidence of shrinkage of the brain and microscopic changes that indicate a breach of the blood-brain barrier. The case series also identified the first known American female athlete with CTE.
Nearly all of those with CTE had a mild form of the disease and 71% played only at the amateur level in youth, high school, or college sports.
“A lot of people think CTE is a result of high-level, professional play such as football, ice hockey, and boxing, but it can affect amateur athletes and can affect people at a young age,” lead author Ann McKee, MD, professor of neurology and pathology and director of the Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Center at Boston University, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A rare look
Brain donation at younger ages is rare, so most of what is known about CTE comes from studies in older athletes.
“We’ve always known that young people could develop this disease early after just amateur high school, youth, and college exposure, but this is the largest study of donor brains at this age,” Dr. McKee said.
The case series included 152 brains of athletes who played contact sports, experienced RHIs, and died before age 30. The tissues are part of the Understanding Neurologic Injury and Traumatic Encephalopathy (UNITE) Brain Bank and were donated between February 2008 and September 2022.
Researchers reviewed the donors’ medical records and conducted retrospective interviews with the donors’ next of kin to assess cognitive symptoms, mood disturbances, and neurobehavioral issues.
Donors died between the ages of 13 and 29 years, 92.8% were male and 73% were White. In 57.2% of the cases, suicide was the cause of death, with no difference between those with or without CTE.
CTE was neuropathologically diagnosed in 41.4% of athletes, using diagnostic criteria developed by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
More than 95% had mild CTE. Diagnosis was associated with older age (mean difference, 3.92 years; P < .001) and significantly more years of exposure to contact sports (11.6 vs. 8.8 years).
Among those with CTE, 71.4% played amateur sports, including football (60.9%), soccer (17.2%), hockey (7.8%), and wrestling (7%).
The cohort includes the first known American female athlete with CTE. Recruiting female brain donors has always been a challenge, Dr. McKee said. In this study, females comprised about 7% of the entire cohort and tended to be younger and play fewer years of a sport, compared with their male counterparts. All of that could lower their risk for CTE, Dr. McKee said.
“We don’t have enough brain donations to make any comments about differences between the genders, but we’ve always known that women can develop CTE,” she said. “It’s been reported after domestic violence and in an autistic woman who was a headbanger, so it was just a matter of time before we found our first case.”
Early stage of CTE?
Neuropathological analysis revealed neuronal p-tau aggregates in all CTE cases, a hallmark of the disease.
Young athletes with CTE had significantly more ventricular dilatation, suggesting atrophy or shrinkage of the brain, and more cavum septum pellucidum.
“I was surprised that even at this very young age group we could see structural changes to the gross pathology,” Dr. McKee said.
Investigators also found evidence of perivascular macrophages in the deep white matter, a microscopic change that correlated with CTE and years of play and indicates a breach of the blood-brain barrier that could allow pro-inflammatory molecules to enter the brain, setting up a neuroinflammatory response.
“Neuroinflammation is a very early change after repetitive head impacts, as well as in CTE,” Dr. McKee said. “This may be one of the mechanisms by which the inflammation starts, meaning microvascular injury might be an integral part of the pathogenesis of CTE.”
A message for clinicians
All athletes had symptoms of mood and neurobehavioral dysfunction common in people with RHIs. There were no significant differences in those clinical symptoms based on CTE diagnosis, which is likely related to the retrospective nature of the clinical evaluations, Dr. McKee said.
While the study leaves many questions about CTE in younger athletes unanswered, there is a message for clinicians and for patients in the findings, she said.
For clinicians, it’s important to note that “this young population of amateur athletes can be very symptomatic, and in all likelihood, a lot of these symptoms are reversible with proper care and management,” Dr. McKee said.
“For individual athletes, it’s important to note that 58% of this cohort did not have CTE, so just because you have these symptoms is not an indication that you have a neurodegenerative disease,” she added.
The study was funded by Andlinger Foundation, the National Football League, Mac Parkman Foundation, National Operating Committee on Standards for Athletic Equipment, and the Nick and Lynn Buoniconti Foundation, World Wrestling Entertainment, Alzheimer’s Association, National Institutes of Health, Concussion Legacy Foundation, U.S. Department of Defense and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Dr. McKee is a member of the Mackey-White Health and Safety Committee of the National Football League Players Association and reported receiving grants from the NIH and Department of Veteran Affairs and other funding from the Buoniconti Foundation and Mac Parkman Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Analysis of brain tissue from athletes who were exposed to RHIs and died before the age of 30 revealed neuropathological evidence of shrinkage of the brain and microscopic changes that indicate a breach of the blood-brain barrier. The case series also identified the first known American female athlete with CTE.
Nearly all of those with CTE had a mild form of the disease and 71% played only at the amateur level in youth, high school, or college sports.
“A lot of people think CTE is a result of high-level, professional play such as football, ice hockey, and boxing, but it can affect amateur athletes and can affect people at a young age,” lead author Ann McKee, MD, professor of neurology and pathology and director of the Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Center at Boston University, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A rare look
Brain donation at younger ages is rare, so most of what is known about CTE comes from studies in older athletes.
“We’ve always known that young people could develop this disease early after just amateur high school, youth, and college exposure, but this is the largest study of donor brains at this age,” Dr. McKee said.
The case series included 152 brains of athletes who played contact sports, experienced RHIs, and died before age 30. The tissues are part of the Understanding Neurologic Injury and Traumatic Encephalopathy (UNITE) Brain Bank and were donated between February 2008 and September 2022.
Researchers reviewed the donors’ medical records and conducted retrospective interviews with the donors’ next of kin to assess cognitive symptoms, mood disturbances, and neurobehavioral issues.
Donors died between the ages of 13 and 29 years, 92.8% were male and 73% were White. In 57.2% of the cases, suicide was the cause of death, with no difference between those with or without CTE.
CTE was neuropathologically diagnosed in 41.4% of athletes, using diagnostic criteria developed by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
More than 95% had mild CTE. Diagnosis was associated with older age (mean difference, 3.92 years; P < .001) and significantly more years of exposure to contact sports (11.6 vs. 8.8 years).
Among those with CTE, 71.4% played amateur sports, including football (60.9%), soccer (17.2%), hockey (7.8%), and wrestling (7%).
The cohort includes the first known American female athlete with CTE. Recruiting female brain donors has always been a challenge, Dr. McKee said. In this study, females comprised about 7% of the entire cohort and tended to be younger and play fewer years of a sport, compared with their male counterparts. All of that could lower their risk for CTE, Dr. McKee said.
“We don’t have enough brain donations to make any comments about differences between the genders, but we’ve always known that women can develop CTE,” she said. “It’s been reported after domestic violence and in an autistic woman who was a headbanger, so it was just a matter of time before we found our first case.”
Early stage of CTE?
Neuropathological analysis revealed neuronal p-tau aggregates in all CTE cases, a hallmark of the disease.
Young athletes with CTE had significantly more ventricular dilatation, suggesting atrophy or shrinkage of the brain, and more cavum septum pellucidum.
“I was surprised that even at this very young age group we could see structural changes to the gross pathology,” Dr. McKee said.
Investigators also found evidence of perivascular macrophages in the deep white matter, a microscopic change that correlated with CTE and years of play and indicates a breach of the blood-brain barrier that could allow pro-inflammatory molecules to enter the brain, setting up a neuroinflammatory response.
“Neuroinflammation is a very early change after repetitive head impacts, as well as in CTE,” Dr. McKee said. “This may be one of the mechanisms by which the inflammation starts, meaning microvascular injury might be an integral part of the pathogenesis of CTE.”
A message for clinicians
All athletes had symptoms of mood and neurobehavioral dysfunction common in people with RHIs. There were no significant differences in those clinical symptoms based on CTE diagnosis, which is likely related to the retrospective nature of the clinical evaluations, Dr. McKee said.
While the study leaves many questions about CTE in younger athletes unanswered, there is a message for clinicians and for patients in the findings, she said.
For clinicians, it’s important to note that “this young population of amateur athletes can be very symptomatic, and in all likelihood, a lot of these symptoms are reversible with proper care and management,” Dr. McKee said.
“For individual athletes, it’s important to note that 58% of this cohort did not have CTE, so just because you have these symptoms is not an indication that you have a neurodegenerative disease,” she added.
The study was funded by Andlinger Foundation, the National Football League, Mac Parkman Foundation, National Operating Committee on Standards for Athletic Equipment, and the Nick and Lynn Buoniconti Foundation, World Wrestling Entertainment, Alzheimer’s Association, National Institutes of Health, Concussion Legacy Foundation, U.S. Department of Defense and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Dr. McKee is a member of the Mackey-White Health and Safety Committee of the National Football League Players Association and reported receiving grants from the NIH and Department of Veteran Affairs and other funding from the Buoniconti Foundation and Mac Parkman Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Analysis of brain tissue from athletes who were exposed to RHIs and died before the age of 30 revealed neuropathological evidence of shrinkage of the brain and microscopic changes that indicate a breach of the blood-brain barrier. The case series also identified the first known American female athlete with CTE.
Nearly all of those with CTE had a mild form of the disease and 71% played only at the amateur level in youth, high school, or college sports.
“A lot of people think CTE is a result of high-level, professional play such as football, ice hockey, and boxing, but it can affect amateur athletes and can affect people at a young age,” lead author Ann McKee, MD, professor of neurology and pathology and director of the Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Center at Boston University, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A rare look
Brain donation at younger ages is rare, so most of what is known about CTE comes from studies in older athletes.
“We’ve always known that young people could develop this disease early after just amateur high school, youth, and college exposure, but this is the largest study of donor brains at this age,” Dr. McKee said.
The case series included 152 brains of athletes who played contact sports, experienced RHIs, and died before age 30. The tissues are part of the Understanding Neurologic Injury and Traumatic Encephalopathy (UNITE) Brain Bank and were donated between February 2008 and September 2022.
Researchers reviewed the donors’ medical records and conducted retrospective interviews with the donors’ next of kin to assess cognitive symptoms, mood disturbances, and neurobehavioral issues.
Donors died between the ages of 13 and 29 years, 92.8% were male and 73% were White. In 57.2% of the cases, suicide was the cause of death, with no difference between those with or without CTE.
CTE was neuropathologically diagnosed in 41.4% of athletes, using diagnostic criteria developed by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
More than 95% had mild CTE. Diagnosis was associated with older age (mean difference, 3.92 years; P < .001) and significantly more years of exposure to contact sports (11.6 vs. 8.8 years).
Among those with CTE, 71.4% played amateur sports, including football (60.9%), soccer (17.2%), hockey (7.8%), and wrestling (7%).
The cohort includes the first known American female athlete with CTE. Recruiting female brain donors has always been a challenge, Dr. McKee said. In this study, females comprised about 7% of the entire cohort and tended to be younger and play fewer years of a sport, compared with their male counterparts. All of that could lower their risk for CTE, Dr. McKee said.
“We don’t have enough brain donations to make any comments about differences between the genders, but we’ve always known that women can develop CTE,” she said. “It’s been reported after domestic violence and in an autistic woman who was a headbanger, so it was just a matter of time before we found our first case.”
Early stage of CTE?
Neuropathological analysis revealed neuronal p-tau aggregates in all CTE cases, a hallmark of the disease.
Young athletes with CTE had significantly more ventricular dilatation, suggesting atrophy or shrinkage of the brain, and more cavum septum pellucidum.
“I was surprised that even at this very young age group we could see structural changes to the gross pathology,” Dr. McKee said.
Investigators also found evidence of perivascular macrophages in the deep white matter, a microscopic change that correlated with CTE and years of play and indicates a breach of the blood-brain barrier that could allow pro-inflammatory molecules to enter the brain, setting up a neuroinflammatory response.
“Neuroinflammation is a very early change after repetitive head impacts, as well as in CTE,” Dr. McKee said. “This may be one of the mechanisms by which the inflammation starts, meaning microvascular injury might be an integral part of the pathogenesis of CTE.”
A message for clinicians
All athletes had symptoms of mood and neurobehavioral dysfunction common in people with RHIs. There were no significant differences in those clinical symptoms based on CTE diagnosis, which is likely related to the retrospective nature of the clinical evaluations, Dr. McKee said.
While the study leaves many questions about CTE in younger athletes unanswered, there is a message for clinicians and for patients in the findings, she said.
For clinicians, it’s important to note that “this young population of amateur athletes can be very symptomatic, and in all likelihood, a lot of these symptoms are reversible with proper care and management,” Dr. McKee said.
“For individual athletes, it’s important to note that 58% of this cohort did not have CTE, so just because you have these symptoms is not an indication that you have a neurodegenerative disease,” she added.
The study was funded by Andlinger Foundation, the National Football League, Mac Parkman Foundation, National Operating Committee on Standards for Athletic Equipment, and the Nick and Lynn Buoniconti Foundation, World Wrestling Entertainment, Alzheimer’s Association, National Institutes of Health, Concussion Legacy Foundation, U.S. Department of Defense and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Dr. McKee is a member of the Mackey-White Health and Safety Committee of the National Football League Players Association and reported receiving grants from the NIH and Department of Veteran Affairs and other funding from the Buoniconti Foundation and Mac Parkman Foundation during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Both too much and not enough sleep raises T2D risk
TOPLINE:
suggests an analysis of a Dutch study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data on 5,561 participants aged 40–75 years from The Maastricht Study who completed the baseline survey between November 2010 and January 2018 and had full data available were included.
- Sleep duration was assessed as the in-bed time in minutes, using a median of 7 nights’ data from an activPAL3 (PAL Technologies) accelerometer, which is worn on the thigh.
- Glucose metabolism was determined via an oral glucose tolerance test and categorized as prediabetes or type 2 diabetes in line with World Health Organization diagnostic criteria.
- The association between sleep duration and type 2 diabetes was assessed on multivariate logistic regression analysis, taking into account a range of potential confounding factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- The mean age of the participants was 60.1 years, and there was an even split between men and women. In all, 832 had prediabetes and 1,341 type 2 diabetes, and the mean sleep duration was 8.3 hours.
- The results indicated there was a U-shaped relationship between sleep duration and type 2 diabetes, so that both long and short sleep durations increased the risk.
- In the fully adjusted model, a sleep duration of 5 hours was associated with an odds ratio for type 2 diabetes versus 8 hours sleep of 2.9. For a sleep duration of 12 hours, the odds ratio was 1.8.
- The association between sleep duration and diabetes was not significant.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “support the idea that sleep duration could be a relevant risk factor for type 2 diabetes independent of lifestyle risk factors, including diet, physical activity, smoking behavior, and alcohol consumption,” wrote the authors.
“These findings underpin the importance of promoting healthy sleep habits to avoid sleep deprivation,” they added.
STUDY DETAILS:
The research was led by Jeroen D. Albers, MSc, department of social medicine, Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, and published in Sleep Health. It is an analysis of The Maastricht Study.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its cross-sectional nature, particularly because there are “plausible causal paths between sleep duration and type 2 in both directions,” the authors note. The accelerometer used in the study also cannot reliably distinguish between waking and sleeping time in bed, with the potential for misclassification. Daytime naps were also not included, and long-term changes sleep patterns were not measured. In addition, it was not possible to control for some potential confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The Maastricht Study was supported by the European Regional Development Fund via OP-Zuid, the Province of Limburg, the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs, Stichting De Weijerhorst, the Pearl String Initiative Diabetes, the School for Cardiovascular Diseases, the School for Public Health and Primary Care, the School for Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism, Stichting Annadal, Health Foundation Limburg, and unrestricted grants from Janssen-Cilag, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi Aventis Netherlands. One author declares a relationship with Novo Nordisk outside the submitted work. No other relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
suggests an analysis of a Dutch study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data on 5,561 participants aged 40–75 years from The Maastricht Study who completed the baseline survey between November 2010 and January 2018 and had full data available were included.
- Sleep duration was assessed as the in-bed time in minutes, using a median of 7 nights’ data from an activPAL3 (PAL Technologies) accelerometer, which is worn on the thigh.
- Glucose metabolism was determined via an oral glucose tolerance test and categorized as prediabetes or type 2 diabetes in line with World Health Organization diagnostic criteria.
- The association between sleep duration and type 2 diabetes was assessed on multivariate logistic regression analysis, taking into account a range of potential confounding factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- The mean age of the participants was 60.1 years, and there was an even split between men and women. In all, 832 had prediabetes and 1,341 type 2 diabetes, and the mean sleep duration was 8.3 hours.
- The results indicated there was a U-shaped relationship between sleep duration and type 2 diabetes, so that both long and short sleep durations increased the risk.
- In the fully adjusted model, a sleep duration of 5 hours was associated with an odds ratio for type 2 diabetes versus 8 hours sleep of 2.9. For a sleep duration of 12 hours, the odds ratio was 1.8.
- The association between sleep duration and diabetes was not significant.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “support the idea that sleep duration could be a relevant risk factor for type 2 diabetes independent of lifestyle risk factors, including diet, physical activity, smoking behavior, and alcohol consumption,” wrote the authors.
“These findings underpin the importance of promoting healthy sleep habits to avoid sleep deprivation,” they added.
STUDY DETAILS:
The research was led by Jeroen D. Albers, MSc, department of social medicine, Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, and published in Sleep Health. It is an analysis of The Maastricht Study.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its cross-sectional nature, particularly because there are “plausible causal paths between sleep duration and type 2 in both directions,” the authors note. The accelerometer used in the study also cannot reliably distinguish between waking and sleeping time in bed, with the potential for misclassification. Daytime naps were also not included, and long-term changes sleep patterns were not measured. In addition, it was not possible to control for some potential confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The Maastricht Study was supported by the European Regional Development Fund via OP-Zuid, the Province of Limburg, the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs, Stichting De Weijerhorst, the Pearl String Initiative Diabetes, the School for Cardiovascular Diseases, the School for Public Health and Primary Care, the School for Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism, Stichting Annadal, Health Foundation Limburg, and unrestricted grants from Janssen-Cilag, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi Aventis Netherlands. One author declares a relationship with Novo Nordisk outside the submitted work. No other relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
suggests an analysis of a Dutch study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data on 5,561 participants aged 40–75 years from The Maastricht Study who completed the baseline survey between November 2010 and January 2018 and had full data available were included.
- Sleep duration was assessed as the in-bed time in minutes, using a median of 7 nights’ data from an activPAL3 (PAL Technologies) accelerometer, which is worn on the thigh.
- Glucose metabolism was determined via an oral glucose tolerance test and categorized as prediabetes or type 2 diabetes in line with World Health Organization diagnostic criteria.
- The association between sleep duration and type 2 diabetes was assessed on multivariate logistic regression analysis, taking into account a range of potential confounding factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- The mean age of the participants was 60.1 years, and there was an even split between men and women. In all, 832 had prediabetes and 1,341 type 2 diabetes, and the mean sleep duration was 8.3 hours.
- The results indicated there was a U-shaped relationship between sleep duration and type 2 diabetes, so that both long and short sleep durations increased the risk.
- In the fully adjusted model, a sleep duration of 5 hours was associated with an odds ratio for type 2 diabetes versus 8 hours sleep of 2.9. For a sleep duration of 12 hours, the odds ratio was 1.8.
- The association between sleep duration and diabetes was not significant.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “support the idea that sleep duration could be a relevant risk factor for type 2 diabetes independent of lifestyle risk factors, including diet, physical activity, smoking behavior, and alcohol consumption,” wrote the authors.
“These findings underpin the importance of promoting healthy sleep habits to avoid sleep deprivation,” they added.
STUDY DETAILS:
The research was led by Jeroen D. Albers, MSc, department of social medicine, Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, and published in Sleep Health. It is an analysis of The Maastricht Study.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its cross-sectional nature, particularly because there are “plausible causal paths between sleep duration and type 2 in both directions,” the authors note. The accelerometer used in the study also cannot reliably distinguish between waking and sleeping time in bed, with the potential for misclassification. Daytime naps were also not included, and long-term changes sleep patterns were not measured. In addition, it was not possible to control for some potential confounding factors.
DISCLOSURES:
The Maastricht Study was supported by the European Regional Development Fund via OP-Zuid, the Province of Limburg, the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs, Stichting De Weijerhorst, the Pearl String Initiative Diabetes, the School for Cardiovascular Diseases, the School for Public Health and Primary Care, the School for Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism, Stichting Annadal, Health Foundation Limburg, and unrestricted grants from Janssen-Cilag, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi Aventis Netherlands. One author declares a relationship with Novo Nordisk outside the submitted work. No other relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SLEEP HEALTH
Cruel summer for medical students and Taylor Swift fans
Most medical students won’t see Taylor Swift perform her hit song “Cruel Summer,” but they will spend thousands of dollars on ERAS as they prepare for the 2024 residency match. Medical students applying for residency tend to be as stressed out as Swifties trying to score concert tickets. Aside from the expenses of residency applications, students also face an increasingly complex application process: a match algorithm many of them do not understand and major changes to the application process that most learn about right before the application cycle begins.
I have gone through two matches myself, one for internal medicine and one for neurology, and I have also guided students through the process for almost a decade as a dean of student affairs at a medical school. Every summer, the application process is filled with numerous changes, often with little, if any, warning for the students. One year, for example, a specialty required additional essays tailored to each program. Though this requirement may have helped programs discern which students are most enthusiastic about their programs, it also disadvantaged students working on busier rotations, strapped for time to write as many as 70 additional essays in a matter of weeks.
Other recent changes have included “signaling” programs, selecting preferred regions, and preinterview recordings for some specialties. In 2023, students cannot include more than 10 activities on their ERAS application. I have spoken to students at numerous medical schools concerned about the difficulty of selecting 10 activities out of dozens of meaningful pursuits throughout their journeys; this challenge is particularly acute for students who had other careers before entering medical school.
The stress continues to mount even after residency applications have been submitted. Students often feel tied to their phones because offers for residency interviews roll in day and night by email, and if they wait more than a few hours to respond, they’re often moved to a waiting list for their preferred interview date. One year, while we were rounding on patients, a student stepped away to schedule an interview; while doing so, he missed out on managing a patient who developed a neurologic emergency. Thankfully, many but not all specialties have put rules in place to allow students more time to think through interview offers. Having more time to think, even if it’s just 48 hours, may decrease stress, limit the negative impacts on medical education, and promote informed decisions during interview season.
To be sure, most changes are being made in an effort to improve the experience of the students and programs. But as with anything, the result has been a mix of good and bad. The transition to virtual interviews allowed students to apply more broadly to programs without worrying about travel costs. The move also benefits students with disabilities who face accessibility and other challenges with traveling. However, virtual interviews came with several downsides, including but not limited to an increased number of applications submitted (recall that this was also a benefit), interview hoarding, and challenges of connecting personally via virtual platform. Despite the virtual format, applicants increasingly are doing in-person second looks, which some worry may give those applicants an additional advantage over applicants who do not have the time or financial resources to travel for a second look. Despite these shortcomings, it is important that virtual interviews remain an option for those applicants who need it.
Another change, which has been extensively debated in medical education in recent years, was the switch to pass/fail on the USMLE Step 1 exam. Though this move decreased the stress students experienced in the first 2 years of medical school, it has resulted in a new challenge as many residency programs put more emphasis on USMLE Step 2. Many medical students feel they do not have a good gauge of their competitiveness until a few weeks before they submit their application, particularly those applicants attending medical schools that do not provide them with information regarding their class standing until right before they submit their applications.
By the time Swift’s Eras Tour ends in the summer of 2024, medical students will already have matched and started their residency programs. At the same time, a new batch of students will be entering the next year’s match. Though the number of anticipated changes may not reach the level of seismic activity caused by the Swifties at her Seattle concert, many medical students fear that the changes may be just like tectonic plates shifting the match process away from its original purpose: to provide an orderly and fair mechanism for matching the preferences of applicants for U.S. residency positions with the preferences of residency program directors.
Dr. Etienne is with WMCHealth Good Samaritan Hospital, New York, and New York Medical College. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most medical students won’t see Taylor Swift perform her hit song “Cruel Summer,” but they will spend thousands of dollars on ERAS as they prepare for the 2024 residency match. Medical students applying for residency tend to be as stressed out as Swifties trying to score concert tickets. Aside from the expenses of residency applications, students also face an increasingly complex application process: a match algorithm many of them do not understand and major changes to the application process that most learn about right before the application cycle begins.
I have gone through two matches myself, one for internal medicine and one for neurology, and I have also guided students through the process for almost a decade as a dean of student affairs at a medical school. Every summer, the application process is filled with numerous changes, often with little, if any, warning for the students. One year, for example, a specialty required additional essays tailored to each program. Though this requirement may have helped programs discern which students are most enthusiastic about their programs, it also disadvantaged students working on busier rotations, strapped for time to write as many as 70 additional essays in a matter of weeks.
Other recent changes have included “signaling” programs, selecting preferred regions, and preinterview recordings for some specialties. In 2023, students cannot include more than 10 activities on their ERAS application. I have spoken to students at numerous medical schools concerned about the difficulty of selecting 10 activities out of dozens of meaningful pursuits throughout their journeys; this challenge is particularly acute for students who had other careers before entering medical school.
The stress continues to mount even after residency applications have been submitted. Students often feel tied to their phones because offers for residency interviews roll in day and night by email, and if they wait more than a few hours to respond, they’re often moved to a waiting list for their preferred interview date. One year, while we were rounding on patients, a student stepped away to schedule an interview; while doing so, he missed out on managing a patient who developed a neurologic emergency. Thankfully, many but not all specialties have put rules in place to allow students more time to think through interview offers. Having more time to think, even if it’s just 48 hours, may decrease stress, limit the negative impacts on medical education, and promote informed decisions during interview season.
To be sure, most changes are being made in an effort to improve the experience of the students and programs. But as with anything, the result has been a mix of good and bad. The transition to virtual interviews allowed students to apply more broadly to programs without worrying about travel costs. The move also benefits students with disabilities who face accessibility and other challenges with traveling. However, virtual interviews came with several downsides, including but not limited to an increased number of applications submitted (recall that this was also a benefit), interview hoarding, and challenges of connecting personally via virtual platform. Despite the virtual format, applicants increasingly are doing in-person second looks, which some worry may give those applicants an additional advantage over applicants who do not have the time or financial resources to travel for a second look. Despite these shortcomings, it is important that virtual interviews remain an option for those applicants who need it.
Another change, which has been extensively debated in medical education in recent years, was the switch to pass/fail on the USMLE Step 1 exam. Though this move decreased the stress students experienced in the first 2 years of medical school, it has resulted in a new challenge as many residency programs put more emphasis on USMLE Step 2. Many medical students feel they do not have a good gauge of their competitiveness until a few weeks before they submit their application, particularly those applicants attending medical schools that do not provide them with information regarding their class standing until right before they submit their applications.
By the time Swift’s Eras Tour ends in the summer of 2024, medical students will already have matched and started their residency programs. At the same time, a new batch of students will be entering the next year’s match. Though the number of anticipated changes may not reach the level of seismic activity caused by the Swifties at her Seattle concert, many medical students fear that the changes may be just like tectonic plates shifting the match process away from its original purpose: to provide an orderly and fair mechanism for matching the preferences of applicants for U.S. residency positions with the preferences of residency program directors.
Dr. Etienne is with WMCHealth Good Samaritan Hospital, New York, and New York Medical College. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most medical students won’t see Taylor Swift perform her hit song “Cruel Summer,” but they will spend thousands of dollars on ERAS as they prepare for the 2024 residency match. Medical students applying for residency tend to be as stressed out as Swifties trying to score concert tickets. Aside from the expenses of residency applications, students also face an increasingly complex application process: a match algorithm many of them do not understand and major changes to the application process that most learn about right before the application cycle begins.
I have gone through two matches myself, one for internal medicine and one for neurology, and I have also guided students through the process for almost a decade as a dean of student affairs at a medical school. Every summer, the application process is filled with numerous changes, often with little, if any, warning for the students. One year, for example, a specialty required additional essays tailored to each program. Though this requirement may have helped programs discern which students are most enthusiastic about their programs, it also disadvantaged students working on busier rotations, strapped for time to write as many as 70 additional essays in a matter of weeks.
Other recent changes have included “signaling” programs, selecting preferred regions, and preinterview recordings for some specialties. In 2023, students cannot include more than 10 activities on their ERAS application. I have spoken to students at numerous medical schools concerned about the difficulty of selecting 10 activities out of dozens of meaningful pursuits throughout their journeys; this challenge is particularly acute for students who had other careers before entering medical school.
The stress continues to mount even after residency applications have been submitted. Students often feel tied to their phones because offers for residency interviews roll in day and night by email, and if they wait more than a few hours to respond, they’re often moved to a waiting list for their preferred interview date. One year, while we were rounding on patients, a student stepped away to schedule an interview; while doing so, he missed out on managing a patient who developed a neurologic emergency. Thankfully, many but not all specialties have put rules in place to allow students more time to think through interview offers. Having more time to think, even if it’s just 48 hours, may decrease stress, limit the negative impacts on medical education, and promote informed decisions during interview season.
To be sure, most changes are being made in an effort to improve the experience of the students and programs. But as with anything, the result has been a mix of good and bad. The transition to virtual interviews allowed students to apply more broadly to programs without worrying about travel costs. The move also benefits students with disabilities who face accessibility and other challenges with traveling. However, virtual interviews came with several downsides, including but not limited to an increased number of applications submitted (recall that this was also a benefit), interview hoarding, and challenges of connecting personally via virtual platform. Despite the virtual format, applicants increasingly are doing in-person second looks, which some worry may give those applicants an additional advantage over applicants who do not have the time or financial resources to travel for a second look. Despite these shortcomings, it is important that virtual interviews remain an option for those applicants who need it.
Another change, which has been extensively debated in medical education in recent years, was the switch to pass/fail on the USMLE Step 1 exam. Though this move decreased the stress students experienced in the first 2 years of medical school, it has resulted in a new challenge as many residency programs put more emphasis on USMLE Step 2. Many medical students feel they do not have a good gauge of their competitiveness until a few weeks before they submit their application, particularly those applicants attending medical schools that do not provide them with information regarding their class standing until right before they submit their applications.
By the time Swift’s Eras Tour ends in the summer of 2024, medical students will already have matched and started their residency programs. At the same time, a new batch of students will be entering the next year’s match. Though the number of anticipated changes may not reach the level of seismic activity caused by the Swifties at her Seattle concert, many medical students fear that the changes may be just like tectonic plates shifting the match process away from its original purpose: to provide an orderly and fair mechanism for matching the preferences of applicants for U.S. residency positions with the preferences of residency program directors.
Dr. Etienne is with WMCHealth Good Samaritan Hospital, New York, and New York Medical College. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.



