User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Do new Alzheimer’s drugs get us closer to solving the Alzheimer’s disease riddle?
Two antiamyloid drugs were recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating early-stage Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In trials of both lecanemab (Leqembi) and donanemab, a long-held neuropharmacologic dream was realized: Most amyloid plaques – the primary pathologic marker for AD – were eliminated from the brains of patients with late pre-AD or early AD.
Implications for the amyloid hypothesis
The reduction of amyloid plaques has been argued by many scientists and clinical authorities to be the likely pharmacologic solution for AD. These trials are appropriately viewed as a test of the hypothesis that amyloid bodies are a primary cause of the neurobehavioral symptoms we call AD.
In parallel with that striking reduction in amyloid bodies, drug-treated patients had an initially slower progression of neurobehavioral decline than did placebo-treated control patients. That slowing in symptom progression was accompanied by a modest but statistically significant difference in neurobehavioral ability. After several months in treatment, the rate of decline again paralleled that recorded in the control group. The sustained difference of about a half point on cognitive assessment scores separating treatment and control participants was well short of the 1.5-point difference typically considered clinically significant.
A small number of unexpected and unexplained deaths occurred in the treatment groups. Brain swelling and/or micro-hemorrhages were seen in 20%-30% of treated individuals. Significant brain shrinkage was recorded. These adverse findings are indicative of drug-induced trauma in the target organ for these drugs (i.e., the brain) and were the basis for a boxed warning label for drug usage. Antiamyloid drug treatment was not effective in patients who had higher initial numbers of amyloid plaques, indicating that these drugs would not measurably help the majority of AD patients, who are at more advanced disease stages.
These drugs do not appear to be an “answer” for AD. A modest delay in progression does not mean that we’re on a path to a “cure.” Treatment cost estimates are high – more than $80,000 per year. With requisite PET exams and high copays, patient accessibility issues will be daunting.
Of note, To the contrary, they add strong support for the counterargument that the emergence of amyloid plaques is an effect and not a fundamental cause of that progressive loss of neurologic function that we ultimately define as “Alzheimer’s disease.”
Time to switch gears
The more obvious path to winning the battle against this human scourge is prevention. A recent analysis published in The Lancet argued that about 40% of AD and other dementias are potentially preventable. I disagree. I believe that 80%-90% of prospective cases can be substantially delayed or prevented. Studies have shown that progression to AD or other dementias is driven primarily by the progressive deterioration of organic brain health, expressed by the loss of what psychologists have termed “cognitive reserve.” Cognitive reserve is resilience arising from active brain usage, akin to physical resilience attributable to a physically active life. Scientific studies have shown us that an individual’s cognitive resilience (reserve) is a greater predictor of risk for dementia than are amyloid plaques – indeed, greater than any combination of pathologic markers in dementia patients.
Building up cognitive reserve
It’s increasingly clear to this observer that cognitive reserve is synonymous with organic brain health. The primary factors that underlie cognitive reserve are processing speed in the brain, executive control, response withholding, memory acquisition, reasoning, and attention abilities. Faster, more accurate brains are necessarily more physically optimized. They necessarily sustain brain system connectivity. They are necessarily healthier. Such brains bear a relatively low risk of developing AD or other dementias, just as physically healthier bodies bear a lower risk of being prematurely banished to semi-permanent residence in an easy chair or a bed.
Brain health can be sustained by deploying inexpensive, self-administered, app-based assessments of neurologic performance limits, which inform patients and their medical teams about general brain health status. These assessments can help doctors guide their patients to adopt more intelligent brain-healthy lifestyles, or direct them to the “brain gym” to progressively exercise their brains in ways that contribute to rapid, potentially large-scale, rejuvenating improvements in physical and functional brain health.
Randomized controlled trials incorporating different combinations of physical exercise, diet, and cognitive training have recorded significant improvements in physical and functional neurologic status, indicating substantially advanced brain health. Consistent moderate-to-intense physical exercise, brain- and heart-healthy eating habits, and, particularly, computerized brain training have repeatedly been shown to improve cognitive function and physically rejuvenate the brain. With cognitive training in the right forms, improvements in processing speed and other measures manifest improving brain health and greater safety.
In the National Institutes of Health–funded ACTIVE study with more than 2,800 older adults, just 10-18 hours of a specific speed of processing training (now part of BrainHQ, a program that I was involved in developing) reduced the probability of a progression to dementia over the following 10 years by 29%, and by 48% in those who did the most training.
This approach is several orders of magnitude less expensive than the pricey new AD drugs. It presents less serious issues of accessibility and has no side effects. It delivers far more powerful therapeutic benefits in older normal and at-risk populations.
Sustained wellness supporting prevention is the far more sensible medical way forward to save people from AD and other dementias – at a far lower medical and societal cost.
Dr. Merzenich is professor emeritus, department of neuroscience, University of California, San Francisco. He reported conflicts of interest with Posit Science, Stronger Brains, and the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two antiamyloid drugs were recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating early-stage Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In trials of both lecanemab (Leqembi) and donanemab, a long-held neuropharmacologic dream was realized: Most amyloid plaques – the primary pathologic marker for AD – were eliminated from the brains of patients with late pre-AD or early AD.
Implications for the amyloid hypothesis
The reduction of amyloid plaques has been argued by many scientists and clinical authorities to be the likely pharmacologic solution for AD. These trials are appropriately viewed as a test of the hypothesis that amyloid bodies are a primary cause of the neurobehavioral symptoms we call AD.
In parallel with that striking reduction in amyloid bodies, drug-treated patients had an initially slower progression of neurobehavioral decline than did placebo-treated control patients. That slowing in symptom progression was accompanied by a modest but statistically significant difference in neurobehavioral ability. After several months in treatment, the rate of decline again paralleled that recorded in the control group. The sustained difference of about a half point on cognitive assessment scores separating treatment and control participants was well short of the 1.5-point difference typically considered clinically significant.
A small number of unexpected and unexplained deaths occurred in the treatment groups. Brain swelling and/or micro-hemorrhages were seen in 20%-30% of treated individuals. Significant brain shrinkage was recorded. These adverse findings are indicative of drug-induced trauma in the target organ for these drugs (i.e., the brain) and were the basis for a boxed warning label for drug usage. Antiamyloid drug treatment was not effective in patients who had higher initial numbers of amyloid plaques, indicating that these drugs would not measurably help the majority of AD patients, who are at more advanced disease stages.
These drugs do not appear to be an “answer” for AD. A modest delay in progression does not mean that we’re on a path to a “cure.” Treatment cost estimates are high – more than $80,000 per year. With requisite PET exams and high copays, patient accessibility issues will be daunting.
Of note, To the contrary, they add strong support for the counterargument that the emergence of amyloid plaques is an effect and not a fundamental cause of that progressive loss of neurologic function that we ultimately define as “Alzheimer’s disease.”
Time to switch gears
The more obvious path to winning the battle against this human scourge is prevention. A recent analysis published in The Lancet argued that about 40% of AD and other dementias are potentially preventable. I disagree. I believe that 80%-90% of prospective cases can be substantially delayed or prevented. Studies have shown that progression to AD or other dementias is driven primarily by the progressive deterioration of organic brain health, expressed by the loss of what psychologists have termed “cognitive reserve.” Cognitive reserve is resilience arising from active brain usage, akin to physical resilience attributable to a physically active life. Scientific studies have shown us that an individual’s cognitive resilience (reserve) is a greater predictor of risk for dementia than are amyloid plaques – indeed, greater than any combination of pathologic markers in dementia patients.
Building up cognitive reserve
It’s increasingly clear to this observer that cognitive reserve is synonymous with organic brain health. The primary factors that underlie cognitive reserve are processing speed in the brain, executive control, response withholding, memory acquisition, reasoning, and attention abilities. Faster, more accurate brains are necessarily more physically optimized. They necessarily sustain brain system connectivity. They are necessarily healthier. Such brains bear a relatively low risk of developing AD or other dementias, just as physically healthier bodies bear a lower risk of being prematurely banished to semi-permanent residence in an easy chair or a bed.
Brain health can be sustained by deploying inexpensive, self-administered, app-based assessments of neurologic performance limits, which inform patients and their medical teams about general brain health status. These assessments can help doctors guide their patients to adopt more intelligent brain-healthy lifestyles, or direct them to the “brain gym” to progressively exercise their brains in ways that contribute to rapid, potentially large-scale, rejuvenating improvements in physical and functional brain health.
Randomized controlled trials incorporating different combinations of physical exercise, diet, and cognitive training have recorded significant improvements in physical and functional neurologic status, indicating substantially advanced brain health. Consistent moderate-to-intense physical exercise, brain- and heart-healthy eating habits, and, particularly, computerized brain training have repeatedly been shown to improve cognitive function and physically rejuvenate the brain. With cognitive training in the right forms, improvements in processing speed and other measures manifest improving brain health and greater safety.
In the National Institutes of Health–funded ACTIVE study with more than 2,800 older adults, just 10-18 hours of a specific speed of processing training (now part of BrainHQ, a program that I was involved in developing) reduced the probability of a progression to dementia over the following 10 years by 29%, and by 48% in those who did the most training.
This approach is several orders of magnitude less expensive than the pricey new AD drugs. It presents less serious issues of accessibility and has no side effects. It delivers far more powerful therapeutic benefits in older normal and at-risk populations.
Sustained wellness supporting prevention is the far more sensible medical way forward to save people from AD and other dementias – at a far lower medical and societal cost.
Dr. Merzenich is professor emeritus, department of neuroscience, University of California, San Francisco. He reported conflicts of interest with Posit Science, Stronger Brains, and the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two antiamyloid drugs were recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating early-stage Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In trials of both lecanemab (Leqembi) and donanemab, a long-held neuropharmacologic dream was realized: Most amyloid plaques – the primary pathologic marker for AD – were eliminated from the brains of patients with late pre-AD or early AD.
Implications for the amyloid hypothesis
The reduction of amyloid plaques has been argued by many scientists and clinical authorities to be the likely pharmacologic solution for AD. These trials are appropriately viewed as a test of the hypothesis that amyloid bodies are a primary cause of the neurobehavioral symptoms we call AD.
In parallel with that striking reduction in amyloid bodies, drug-treated patients had an initially slower progression of neurobehavioral decline than did placebo-treated control patients. That slowing in symptom progression was accompanied by a modest but statistically significant difference in neurobehavioral ability. After several months in treatment, the rate of decline again paralleled that recorded in the control group. The sustained difference of about a half point on cognitive assessment scores separating treatment and control participants was well short of the 1.5-point difference typically considered clinically significant.
A small number of unexpected and unexplained deaths occurred in the treatment groups. Brain swelling and/or micro-hemorrhages were seen in 20%-30% of treated individuals. Significant brain shrinkage was recorded. These adverse findings are indicative of drug-induced trauma in the target organ for these drugs (i.e., the brain) and were the basis for a boxed warning label for drug usage. Antiamyloid drug treatment was not effective in patients who had higher initial numbers of amyloid plaques, indicating that these drugs would not measurably help the majority of AD patients, who are at more advanced disease stages.
These drugs do not appear to be an “answer” for AD. A modest delay in progression does not mean that we’re on a path to a “cure.” Treatment cost estimates are high – more than $80,000 per year. With requisite PET exams and high copays, patient accessibility issues will be daunting.
Of note, To the contrary, they add strong support for the counterargument that the emergence of amyloid plaques is an effect and not a fundamental cause of that progressive loss of neurologic function that we ultimately define as “Alzheimer’s disease.”
Time to switch gears
The more obvious path to winning the battle against this human scourge is prevention. A recent analysis published in The Lancet argued that about 40% of AD and other dementias are potentially preventable. I disagree. I believe that 80%-90% of prospective cases can be substantially delayed or prevented. Studies have shown that progression to AD or other dementias is driven primarily by the progressive deterioration of organic brain health, expressed by the loss of what psychologists have termed “cognitive reserve.” Cognitive reserve is resilience arising from active brain usage, akin to physical resilience attributable to a physically active life. Scientific studies have shown us that an individual’s cognitive resilience (reserve) is a greater predictor of risk for dementia than are amyloid plaques – indeed, greater than any combination of pathologic markers in dementia patients.
Building up cognitive reserve
It’s increasingly clear to this observer that cognitive reserve is synonymous with organic brain health. The primary factors that underlie cognitive reserve are processing speed in the brain, executive control, response withholding, memory acquisition, reasoning, and attention abilities. Faster, more accurate brains are necessarily more physically optimized. They necessarily sustain brain system connectivity. They are necessarily healthier. Such brains bear a relatively low risk of developing AD or other dementias, just as physically healthier bodies bear a lower risk of being prematurely banished to semi-permanent residence in an easy chair or a bed.
Brain health can be sustained by deploying inexpensive, self-administered, app-based assessments of neurologic performance limits, which inform patients and their medical teams about general brain health status. These assessments can help doctors guide their patients to adopt more intelligent brain-healthy lifestyles, or direct them to the “brain gym” to progressively exercise their brains in ways that contribute to rapid, potentially large-scale, rejuvenating improvements in physical and functional brain health.
Randomized controlled trials incorporating different combinations of physical exercise, diet, and cognitive training have recorded significant improvements in physical and functional neurologic status, indicating substantially advanced brain health. Consistent moderate-to-intense physical exercise, brain- and heart-healthy eating habits, and, particularly, computerized brain training have repeatedly been shown to improve cognitive function and physically rejuvenate the brain. With cognitive training in the right forms, improvements in processing speed and other measures manifest improving brain health and greater safety.
In the National Institutes of Health–funded ACTIVE study with more than 2,800 older adults, just 10-18 hours of a specific speed of processing training (now part of BrainHQ, a program that I was involved in developing) reduced the probability of a progression to dementia over the following 10 years by 29%, and by 48% in those who did the most training.
This approach is several orders of magnitude less expensive than the pricey new AD drugs. It presents less serious issues of accessibility and has no side effects. It delivers far more powerful therapeutic benefits in older normal and at-risk populations.
Sustained wellness supporting prevention is the far more sensible medical way forward to save people from AD and other dementias – at a far lower medical and societal cost.
Dr. Merzenich is professor emeritus, department of neuroscience, University of California, San Francisco. He reported conflicts of interest with Posit Science, Stronger Brains, and the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents’ acute care use for eating disorders has risen
In a repeated cross-sectional study that examined population-based data from January 2017 through August 2022, ED visits increased by 121% above expected levels, and hospital admissions increased by 54% above expected among patients aged 10-17 years during the pandemic.
“We are hoping this study continues to heighten awareness of the importance of eating disorders, and also to bolster support for eating disorder programs so that we can adequately care for patients and address the increasing demand for treatment and services,” lead author Alene Toulany, MD, adolescent medicine specialist and researcher at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, told this news organization.
The study was published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
‘A pressing concern’
The researchers used linked health administrative databases that included all patients in Ontario who were eligible for the Ontario Health Insurance Plan, which is publicly funded. They compared observed and expected rates of ED visits and hospitalizations for eating disorders between a prepandemic period (Jan. 1, 2017, to Feb. 29, 2020) and a pandemic period (Mar. 1, 2020, to Aug. 31, 2022). The researchers examined the following four age categories: adolescents (aged 10-17 years), young adults (aged 18-26 years), adults (aged 27-40 years), and older adults (aged 41-105 years).
Among adolescents, the observed rate of ED visits during the 30 pandemic months studied was 7.38 per 100,000 population, compared with 3.33 per 100,000 before the pandemic (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 2.21).
The rate of ED visits among young adults increased by 13% above the expected rate. It reached 2.79 per 100,000, compared with 2.46 per 100,000 in the prepandemic period (IRR, 1.13).
Among older adults, ED visits increased from 0.11 per 100,000 in the prepandemic period to 0.14 per 100,000 in the pandemic period (IRR, 1.15). The rate of ED visits among adults remained approximately the same.
The rate of hospital admissions among adolescents increased by 54% above the expected rate during the pandemic. The observed rate of hospital admissions before the pandemic was 5.74 per 100,000, vs. 8.82 per 100,000 during the pandemic (IRR, 1.54). Hospital admissions remained stable or decreased for the other age groups.
“Eating disorders have increased globally in children and adolescents during COVID,” said Dr. Toulany. “There are a number of risk factors contributing to this pandemic rise, including isolation, more time on social media, decreased access to care (as many in-person services were not available due to the pandemic), as well as fear of getting infected. All of these could contribute to an increased risk of developing an eating disorder or of making an existing one worse.”
Regardless of the cause, more investment in eating disorders research and eating disorder programs for adolescents and adults is needed, she said.
“The pandemic served as a catalyst, because it started to shed light on the prevalence of eating disorders, especially in young people. But it’s very important that we recognize that this has been a long-standing issue and a pressing concern that has been consistently overlooked and underfunded,” said Dr. Toulany.
Surging eating disorders
Commenting on the findings, Victor Fornari, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Zucker Hillside Hospital/Northwell Health in Glen Oaks, N.Y., said, “Our experience in the United States parallels what is described in this Canadian paper. This was a surge of eating disorders the likes of which I had not experienced in my career.” Dr. Fornari did not participate in the current study.
“I’ve been here for over 40 years, and the average number of our inpatients in our eating disorder program has been three to five and about a dozen patients in our day clinic at any one time. But in the spring of 2020, we surged to 20 inpatients and over 20 day patients,” Dr. Fornari said.
“We can speculate as to the reasons for this,” he continued. “Kids were isolated. School was closed. They spent more time on social media and the Internet. Their sports activities were curtailed. There was anxiety because the guidance that we were all offered to prevent contagion was increasing people’s anxiety about safety and danger. So, I think we saw dramatic rises in eating disorders in the same way we saw dramatic rises in anxiety and depression in adolescents, as well.”
Dr. Fornari cited social media as an important contributing factor to eating disorders, especially among vulnerable teenagers. “Many of these vulnerable kids are looking at pictures of people who are very thin and comparing themselves, feeling inadequate, feeling sad. Social media is one of the reasons why the rates of psychopathology amongst teens has skyrocketed in the last decade. The surgeon general recently said we should delay access to social media until age 16 because the younger kids are impressionable and vulnerable. I think there is wisdom there, but it is very hard to actually put into practice.”
Worsening mental health
“I thought this was very relevant research and an important contribution to our understanding of eating disorders during pandemic times,” said Simon Sherry, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia. “It also dovetails with my own experience as a practitioner.” Dr. Sherry was not involved in the research.
The pandemic has been difficult for people with disordered eating for many reasons, Dr. Sherry said. “There was a massive disruption or ‘loss of normal’ around food. Restaurants closed, grocery shopping was disrupted, scarcity of food occurred, hoarding of food occurred. That meant that eating was difficult for all of us, but especially for individuals who were rigid and controlling around the consumption of food. In this COVID era, you would need flexibility and acceptance around eating, but if you had a narrow range of preferred foods and preferred shopping locations, no doubt the pandemic made this a lot worse.”
Certain forms of disordered eating would be much more likely during the pandemic, Dr. Sherry noted. “For example, binge eating is often triggered by psychological, social, and environmental events,” and those triggers were abundant at the beginning of the pandemic. Boredom, anxiety, depression, stress, loneliness, confinement, and isolation are among the triggers. “COVID-19-related stress was and is very fertile ground for the growth of emotional eating, binge eating, or turning to food to cope. Eating disorders tend to fester amid silence and isolation and inactivity, and that was very much our experience during the lockdown phase of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Sherry agrees with the need for more funding for eating disorders research. “We know in Canada that eating disorders are a very important and deadly issue that is chronically underfunded. We are not funding disordered eating in proportion to its prevalence or in proportion to the amount of harm and destruction it creates for individuals, their family members, and our society at large. The authors are absolutely correct to advocate for care in proportion to the prevalence and the damage associated with eating disorders,” he said.
The study was supported by ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health, the Ministry of Long-Term Care, and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR). Dr. Toulany, Dr. Fornari, and Dr. Sherry reported no relevant financial relationships. One study author reported receiving personal fees from the BMJ Group’s Archives of Diseases in Childhood and grants from CIHR, the Ontario Ministry of Health, the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, and the Hospital for Sick Children. A second author reported funding from CIHR.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a repeated cross-sectional study that examined population-based data from January 2017 through August 2022, ED visits increased by 121% above expected levels, and hospital admissions increased by 54% above expected among patients aged 10-17 years during the pandemic.
“We are hoping this study continues to heighten awareness of the importance of eating disorders, and also to bolster support for eating disorder programs so that we can adequately care for patients and address the increasing demand for treatment and services,” lead author Alene Toulany, MD, adolescent medicine specialist and researcher at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, told this news organization.
The study was published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
‘A pressing concern’
The researchers used linked health administrative databases that included all patients in Ontario who were eligible for the Ontario Health Insurance Plan, which is publicly funded. They compared observed and expected rates of ED visits and hospitalizations for eating disorders between a prepandemic period (Jan. 1, 2017, to Feb. 29, 2020) and a pandemic period (Mar. 1, 2020, to Aug. 31, 2022). The researchers examined the following four age categories: adolescents (aged 10-17 years), young adults (aged 18-26 years), adults (aged 27-40 years), and older adults (aged 41-105 years).
Among adolescents, the observed rate of ED visits during the 30 pandemic months studied was 7.38 per 100,000 population, compared with 3.33 per 100,000 before the pandemic (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 2.21).
The rate of ED visits among young adults increased by 13% above the expected rate. It reached 2.79 per 100,000, compared with 2.46 per 100,000 in the prepandemic period (IRR, 1.13).
Among older adults, ED visits increased from 0.11 per 100,000 in the prepandemic period to 0.14 per 100,000 in the pandemic period (IRR, 1.15). The rate of ED visits among adults remained approximately the same.
The rate of hospital admissions among adolescents increased by 54% above the expected rate during the pandemic. The observed rate of hospital admissions before the pandemic was 5.74 per 100,000, vs. 8.82 per 100,000 during the pandemic (IRR, 1.54). Hospital admissions remained stable or decreased for the other age groups.
“Eating disorders have increased globally in children and adolescents during COVID,” said Dr. Toulany. “There are a number of risk factors contributing to this pandemic rise, including isolation, more time on social media, decreased access to care (as many in-person services were not available due to the pandemic), as well as fear of getting infected. All of these could contribute to an increased risk of developing an eating disorder or of making an existing one worse.”
Regardless of the cause, more investment in eating disorders research and eating disorder programs for adolescents and adults is needed, she said.
“The pandemic served as a catalyst, because it started to shed light on the prevalence of eating disorders, especially in young people. But it’s very important that we recognize that this has been a long-standing issue and a pressing concern that has been consistently overlooked and underfunded,” said Dr. Toulany.
Surging eating disorders
Commenting on the findings, Victor Fornari, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Zucker Hillside Hospital/Northwell Health in Glen Oaks, N.Y., said, “Our experience in the United States parallels what is described in this Canadian paper. This was a surge of eating disorders the likes of which I had not experienced in my career.” Dr. Fornari did not participate in the current study.
“I’ve been here for over 40 years, and the average number of our inpatients in our eating disorder program has been three to five and about a dozen patients in our day clinic at any one time. But in the spring of 2020, we surged to 20 inpatients and over 20 day patients,” Dr. Fornari said.
“We can speculate as to the reasons for this,” he continued. “Kids were isolated. School was closed. They spent more time on social media and the Internet. Their sports activities were curtailed. There was anxiety because the guidance that we were all offered to prevent contagion was increasing people’s anxiety about safety and danger. So, I think we saw dramatic rises in eating disorders in the same way we saw dramatic rises in anxiety and depression in adolescents, as well.”
Dr. Fornari cited social media as an important contributing factor to eating disorders, especially among vulnerable teenagers. “Many of these vulnerable kids are looking at pictures of people who are very thin and comparing themselves, feeling inadequate, feeling sad. Social media is one of the reasons why the rates of psychopathology amongst teens has skyrocketed in the last decade. The surgeon general recently said we should delay access to social media until age 16 because the younger kids are impressionable and vulnerable. I think there is wisdom there, but it is very hard to actually put into practice.”
Worsening mental health
“I thought this was very relevant research and an important contribution to our understanding of eating disorders during pandemic times,” said Simon Sherry, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia. “It also dovetails with my own experience as a practitioner.” Dr. Sherry was not involved in the research.
The pandemic has been difficult for people with disordered eating for many reasons, Dr. Sherry said. “There was a massive disruption or ‘loss of normal’ around food. Restaurants closed, grocery shopping was disrupted, scarcity of food occurred, hoarding of food occurred. That meant that eating was difficult for all of us, but especially for individuals who were rigid and controlling around the consumption of food. In this COVID era, you would need flexibility and acceptance around eating, but if you had a narrow range of preferred foods and preferred shopping locations, no doubt the pandemic made this a lot worse.”
Certain forms of disordered eating would be much more likely during the pandemic, Dr. Sherry noted. “For example, binge eating is often triggered by psychological, social, and environmental events,” and those triggers were abundant at the beginning of the pandemic. Boredom, anxiety, depression, stress, loneliness, confinement, and isolation are among the triggers. “COVID-19-related stress was and is very fertile ground for the growth of emotional eating, binge eating, or turning to food to cope. Eating disorders tend to fester amid silence and isolation and inactivity, and that was very much our experience during the lockdown phase of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Sherry agrees with the need for more funding for eating disorders research. “We know in Canada that eating disorders are a very important and deadly issue that is chronically underfunded. We are not funding disordered eating in proportion to its prevalence or in proportion to the amount of harm and destruction it creates for individuals, their family members, and our society at large. The authors are absolutely correct to advocate for care in proportion to the prevalence and the damage associated with eating disorders,” he said.
The study was supported by ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health, the Ministry of Long-Term Care, and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR). Dr. Toulany, Dr. Fornari, and Dr. Sherry reported no relevant financial relationships. One study author reported receiving personal fees from the BMJ Group’s Archives of Diseases in Childhood and grants from CIHR, the Ontario Ministry of Health, the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, and the Hospital for Sick Children. A second author reported funding from CIHR.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a repeated cross-sectional study that examined population-based data from January 2017 through August 2022, ED visits increased by 121% above expected levels, and hospital admissions increased by 54% above expected among patients aged 10-17 years during the pandemic.
“We are hoping this study continues to heighten awareness of the importance of eating disorders, and also to bolster support for eating disorder programs so that we can adequately care for patients and address the increasing demand for treatment and services,” lead author Alene Toulany, MD, adolescent medicine specialist and researcher at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, told this news organization.
The study was published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
‘A pressing concern’
The researchers used linked health administrative databases that included all patients in Ontario who were eligible for the Ontario Health Insurance Plan, which is publicly funded. They compared observed and expected rates of ED visits and hospitalizations for eating disorders between a prepandemic period (Jan. 1, 2017, to Feb. 29, 2020) and a pandemic period (Mar. 1, 2020, to Aug. 31, 2022). The researchers examined the following four age categories: adolescents (aged 10-17 years), young adults (aged 18-26 years), adults (aged 27-40 years), and older adults (aged 41-105 years).
Among adolescents, the observed rate of ED visits during the 30 pandemic months studied was 7.38 per 100,000 population, compared with 3.33 per 100,000 before the pandemic (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 2.21).
The rate of ED visits among young adults increased by 13% above the expected rate. It reached 2.79 per 100,000, compared with 2.46 per 100,000 in the prepandemic period (IRR, 1.13).
Among older adults, ED visits increased from 0.11 per 100,000 in the prepandemic period to 0.14 per 100,000 in the pandemic period (IRR, 1.15). The rate of ED visits among adults remained approximately the same.
The rate of hospital admissions among adolescents increased by 54% above the expected rate during the pandemic. The observed rate of hospital admissions before the pandemic was 5.74 per 100,000, vs. 8.82 per 100,000 during the pandemic (IRR, 1.54). Hospital admissions remained stable or decreased for the other age groups.
“Eating disorders have increased globally in children and adolescents during COVID,” said Dr. Toulany. “There are a number of risk factors contributing to this pandemic rise, including isolation, more time on social media, decreased access to care (as many in-person services were not available due to the pandemic), as well as fear of getting infected. All of these could contribute to an increased risk of developing an eating disorder or of making an existing one worse.”
Regardless of the cause, more investment in eating disorders research and eating disorder programs for adolescents and adults is needed, she said.
“The pandemic served as a catalyst, because it started to shed light on the prevalence of eating disorders, especially in young people. But it’s very important that we recognize that this has been a long-standing issue and a pressing concern that has been consistently overlooked and underfunded,” said Dr. Toulany.
Surging eating disorders
Commenting on the findings, Victor Fornari, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Zucker Hillside Hospital/Northwell Health in Glen Oaks, N.Y., said, “Our experience in the United States parallels what is described in this Canadian paper. This was a surge of eating disorders the likes of which I had not experienced in my career.” Dr. Fornari did not participate in the current study.
“I’ve been here for over 40 years, and the average number of our inpatients in our eating disorder program has been three to five and about a dozen patients in our day clinic at any one time. But in the spring of 2020, we surged to 20 inpatients and over 20 day patients,” Dr. Fornari said.
“We can speculate as to the reasons for this,” he continued. “Kids were isolated. School was closed. They spent more time on social media and the Internet. Their sports activities were curtailed. There was anxiety because the guidance that we were all offered to prevent contagion was increasing people’s anxiety about safety and danger. So, I think we saw dramatic rises in eating disorders in the same way we saw dramatic rises in anxiety and depression in adolescents, as well.”
Dr. Fornari cited social media as an important contributing factor to eating disorders, especially among vulnerable teenagers. “Many of these vulnerable kids are looking at pictures of people who are very thin and comparing themselves, feeling inadequate, feeling sad. Social media is one of the reasons why the rates of psychopathology amongst teens has skyrocketed in the last decade. The surgeon general recently said we should delay access to social media until age 16 because the younger kids are impressionable and vulnerable. I think there is wisdom there, but it is very hard to actually put into practice.”
Worsening mental health
“I thought this was very relevant research and an important contribution to our understanding of eating disorders during pandemic times,” said Simon Sherry, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia. “It also dovetails with my own experience as a practitioner.” Dr. Sherry was not involved in the research.
The pandemic has been difficult for people with disordered eating for many reasons, Dr. Sherry said. “There was a massive disruption or ‘loss of normal’ around food. Restaurants closed, grocery shopping was disrupted, scarcity of food occurred, hoarding of food occurred. That meant that eating was difficult for all of us, but especially for individuals who were rigid and controlling around the consumption of food. In this COVID era, you would need flexibility and acceptance around eating, but if you had a narrow range of preferred foods and preferred shopping locations, no doubt the pandemic made this a lot worse.”
Certain forms of disordered eating would be much more likely during the pandemic, Dr. Sherry noted. “For example, binge eating is often triggered by psychological, social, and environmental events,” and those triggers were abundant at the beginning of the pandemic. Boredom, anxiety, depression, stress, loneliness, confinement, and isolation are among the triggers. “COVID-19-related stress was and is very fertile ground for the growth of emotional eating, binge eating, or turning to food to cope. Eating disorders tend to fester amid silence and isolation and inactivity, and that was very much our experience during the lockdown phase of the pandemic,” he said.
Dr. Sherry agrees with the need for more funding for eating disorders research. “We know in Canada that eating disorders are a very important and deadly issue that is chronically underfunded. We are not funding disordered eating in proportion to its prevalence or in proportion to the amount of harm and destruction it creates for individuals, their family members, and our society at large. The authors are absolutely correct to advocate for care in proportion to the prevalence and the damage associated with eating disorders,” he said.
The study was supported by ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health, the Ministry of Long-Term Care, and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR). Dr. Toulany, Dr. Fornari, and Dr. Sherry reported no relevant financial relationships. One study author reported receiving personal fees from the BMJ Group’s Archives of Diseases in Childhood and grants from CIHR, the Ontario Ministry of Health, the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, and the Hospital for Sick Children. A second author reported funding from CIHR.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNAL
New insight into genetic link between schizophrenia and CVD
TOPLINE:
There is an extensive genetic overlap between schizophrenia and smoking, but there are also schizophrenia genes that may protect against obesity, illustrating the bidirectional effects of shared loci across cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, results of new research suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers obtained what they call an “unprecedentedly large” set of GWAS samples, including schizophrenia (53,386 patients and 77,258 controls) and various CVD risk factors.
- They used analytic approaches to identify genetic links between schizophrenia and CVD risk factors, including bivariate causal mixture model (MiXeR), which estimates the number of shared genetic variants between pairs of phenotypes, and conditional and conjunctional false discovery rate (condFDR and conjFDR), to identify specific genetic loci; these approaches can identify genetic overlap regardless of the effect directions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Using MiXeR, the study showed that several genetic variants underlying schizophrenia also influence CVD phenotypes, particularly risk factors of smoking and BMI.
- A total of 825 distinct loci were jointly associated with schizophrenia and CVD phenotypes at conjFDR < .05.
- Most of the loci shared with smoking were in line with positive genetic correlations; the authors noted individuals with schizophrenia are more nicotine dependent than the general population, and they experience greater reinforcing effects of nicotine and worse withdrawal symptoms during abstinence than the general population.
- The overlapping loci with BMI had effect directions consistent with negative genetic correlations, suggesting people with schizophrenia are genetically predisposed to lower BMI; this is in line with evidence of low BMI being a risk factor for schizophrenia, although obesity is more common in people with schizophrenia.
- There was a pattern of mixed effect directions among loci jointly associated with schizophrenia and lipids, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, waist-to-hip ratio, and coronary artery disease, which may reflect variation in genetic susceptibility to CVD across subgroups of schizophrenia.
IN PRACTICE:
The new results “shed light” on biological pathways associated with comorbidity between CVD and schizophrenia, said the authors, adding future work could provide insights into mechanisms underlying the comorbidity and could facilitate development of antipsychotics with lower metabolic side effects, which could help prevent comorbid CVD, “thereby helping to mitigate a major clinical and health care problem.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Linn Rødevand, PhD, Norwegian Center for Mental Disorders Research, Division of Mental Health and Addiction, Institute of Clinical Medicine, Oslo University Hospital, University of Oslo, and colleagues. It was published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS:
Methods used in the study are limited by uncertainties in translating genetic loci to causal variants, which restricts the biological interpretation of the shared genetic variants. Among other methodological limitations are that discrepancies between the linkage disequilibrium structure of the samples used for the GWAS and that of the reference panel may have biased estimates underlying MiXeR.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the Research Council of Norway, Norwegian Health Association, South-East Norway Regional Health Authority, and the European Union. Dr. Rødevand reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
There is an extensive genetic overlap between schizophrenia and smoking, but there are also schizophrenia genes that may protect against obesity, illustrating the bidirectional effects of shared loci across cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, results of new research suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers obtained what they call an “unprecedentedly large” set of GWAS samples, including schizophrenia (53,386 patients and 77,258 controls) and various CVD risk factors.
- They used analytic approaches to identify genetic links between schizophrenia and CVD risk factors, including bivariate causal mixture model (MiXeR), which estimates the number of shared genetic variants between pairs of phenotypes, and conditional and conjunctional false discovery rate (condFDR and conjFDR), to identify specific genetic loci; these approaches can identify genetic overlap regardless of the effect directions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Using MiXeR, the study showed that several genetic variants underlying schizophrenia also influence CVD phenotypes, particularly risk factors of smoking and BMI.
- A total of 825 distinct loci were jointly associated with schizophrenia and CVD phenotypes at conjFDR < .05.
- Most of the loci shared with smoking were in line with positive genetic correlations; the authors noted individuals with schizophrenia are more nicotine dependent than the general population, and they experience greater reinforcing effects of nicotine and worse withdrawal symptoms during abstinence than the general population.
- The overlapping loci with BMI had effect directions consistent with negative genetic correlations, suggesting people with schizophrenia are genetically predisposed to lower BMI; this is in line with evidence of low BMI being a risk factor for schizophrenia, although obesity is more common in people with schizophrenia.
- There was a pattern of mixed effect directions among loci jointly associated with schizophrenia and lipids, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, waist-to-hip ratio, and coronary artery disease, which may reflect variation in genetic susceptibility to CVD across subgroups of schizophrenia.
IN PRACTICE:
The new results “shed light” on biological pathways associated with comorbidity between CVD and schizophrenia, said the authors, adding future work could provide insights into mechanisms underlying the comorbidity and could facilitate development of antipsychotics with lower metabolic side effects, which could help prevent comorbid CVD, “thereby helping to mitigate a major clinical and health care problem.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Linn Rødevand, PhD, Norwegian Center for Mental Disorders Research, Division of Mental Health and Addiction, Institute of Clinical Medicine, Oslo University Hospital, University of Oslo, and colleagues. It was published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS:
Methods used in the study are limited by uncertainties in translating genetic loci to causal variants, which restricts the biological interpretation of the shared genetic variants. Among other methodological limitations are that discrepancies between the linkage disequilibrium structure of the samples used for the GWAS and that of the reference panel may have biased estimates underlying MiXeR.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the Research Council of Norway, Norwegian Health Association, South-East Norway Regional Health Authority, and the European Union. Dr. Rødevand reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
There is an extensive genetic overlap between schizophrenia and smoking, but there are also schizophrenia genes that may protect against obesity, illustrating the bidirectional effects of shared loci across cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, results of new research suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers obtained what they call an “unprecedentedly large” set of GWAS samples, including schizophrenia (53,386 patients and 77,258 controls) and various CVD risk factors.
- They used analytic approaches to identify genetic links between schizophrenia and CVD risk factors, including bivariate causal mixture model (MiXeR), which estimates the number of shared genetic variants between pairs of phenotypes, and conditional and conjunctional false discovery rate (condFDR and conjFDR), to identify specific genetic loci; these approaches can identify genetic overlap regardless of the effect directions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Using MiXeR, the study showed that several genetic variants underlying schizophrenia also influence CVD phenotypes, particularly risk factors of smoking and BMI.
- A total of 825 distinct loci were jointly associated with schizophrenia and CVD phenotypes at conjFDR < .05.
- Most of the loci shared with smoking were in line with positive genetic correlations; the authors noted individuals with schizophrenia are more nicotine dependent than the general population, and they experience greater reinforcing effects of nicotine and worse withdrawal symptoms during abstinence than the general population.
- The overlapping loci with BMI had effect directions consistent with negative genetic correlations, suggesting people with schizophrenia are genetically predisposed to lower BMI; this is in line with evidence of low BMI being a risk factor for schizophrenia, although obesity is more common in people with schizophrenia.
- There was a pattern of mixed effect directions among loci jointly associated with schizophrenia and lipids, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, waist-to-hip ratio, and coronary artery disease, which may reflect variation in genetic susceptibility to CVD across subgroups of schizophrenia.
IN PRACTICE:
The new results “shed light” on biological pathways associated with comorbidity between CVD and schizophrenia, said the authors, adding future work could provide insights into mechanisms underlying the comorbidity and could facilitate development of antipsychotics with lower metabolic side effects, which could help prevent comorbid CVD, “thereby helping to mitigate a major clinical and health care problem.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Linn Rødevand, PhD, Norwegian Center for Mental Disorders Research, Division of Mental Health and Addiction, Institute of Clinical Medicine, Oslo University Hospital, University of Oslo, and colleagues. It was published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS:
Methods used in the study are limited by uncertainties in translating genetic loci to causal variants, which restricts the biological interpretation of the shared genetic variants. Among other methodological limitations are that discrepancies between the linkage disequilibrium structure of the samples used for the GWAS and that of the reference panel may have biased estimates underlying MiXeR.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the Research Council of Norway, Norwegian Health Association, South-East Norway Regional Health Authority, and the European Union. Dr. Rødevand reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY
Training more doctors should be our first priority, says ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, the Supreme Court of the United States struck down the use of affirmative action in admissions to colleges, universities, medical schools, and nursing schools. This has led to an enormous amount of worry and concern, particularly in medical school admissions in the world I’m in, where people start to say that diversity matters. Diversity is important.
I know many deans of medical schools immediately sent out messages of reassurance to their students, saying New York University or Stanford or Harvard or Minnesota or Case Western is still deeply concerned about diversity, and we’re going to do what we can to preserve attention to diversity.
I’ve served on admissions at a number of schools over the years for med school. I understand – and have been told – that diversity is important, and according to the Supreme Court, not explicitly by race. There are obviously many variables to take into account when trying to keep diversity at the forefront of admissions.
At the schools I’ve been at, including Columbia, NYU, University of Pittsburgh, University of Minnesota, and University of Pennsylvania, there are plenty of qualified students. Happily, we’ve always been engaged in some effort to try and whittle down the class to the size that we can manage and accept, and many qualified students don’t get admitted.
The first order of business for me is not to worry about how to maintain diversity. It’s to recognize that we need more doctors, nurses, and mental health care providers. I will, in a second, say a few words about diversity and where it fits into admissions, but I want to make the point clearly that what we should be doing is trying to expand the pool of students who are going to become doctors, nurses, mental health care providers, and social workers.
There are too many early retirements. We don’t have the person power we need to manage the health care challenges of an aging population. Let’s not get lost in arguing about what characteristics ought to get you into the finest medical schools. Let’s realize that we have to expand the number of schools we have.
We better be working pretty hard to expand our physician assistant programs, to make sure that we give full authority to qualified dentists and nurses who can help deliver some clinical care. We need more folks. That’s really where the battle ought to be: How do we get that done and how do we get it done quickly, not arguing about who’s in, who’s out, and why.
That said, diversity to me has never meant just race. I’m always interested in gender orientation, disability, and geographic input. Sometimes in decisions that you’re looking at, when I have students in front of me, they tell me they play a musical instrument or about the obstacles they had to overcome to get to medical school. Some of them will say they were involved in 4-H and did rodeo in high school or junior high school, which makes them a diverse potential student with characteristics that maybe some others don’t bring.
I’m not against diversity. I think having a rich set of experiences in any class – medicine, nursing, whatever it’s going to be – is beneficial to the students. They learn from each other. It is sometimes said that it’s also good for patients. I’m a little less excited about that, because I think our training goal should be to make every medical student and nursing student qualified to treat anybody.
I don’t think that, just because you’re Latinx or gay, that’s going to make a gay patient feel better. I think we should teach our students how to give care to everybody that they encounter. They shouldn’t have to match up characteristics to feel like they’re going to get quality care. That isn’t the right reason.
When you have a diverse set of providers, they can call that out and be on the alert for it, and that’s very important.
I also believe that we should think widely and broadly about diversity. Maybe race is out, but certainly other experiences related to income, background, struggle that got you to the point where you’re applying to medical school, motivation, the kinds of experiences you might have had caring for an elderly person, dealing with a disability or learning disability, and trying to overcome, let’s say, going to school in a poor area with not such a wonderful school, really help in terms of forming professionalism, empathy, and a caring point of view.
To me, the main goal is to expand our workforce. The secondary goal is to stay diverse, because we get better providers when we do so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, the Supreme Court of the United States struck down the use of affirmative action in admissions to colleges, universities, medical schools, and nursing schools. This has led to an enormous amount of worry and concern, particularly in medical school admissions in the world I’m in, where people start to say that diversity matters. Diversity is important.
I know many deans of medical schools immediately sent out messages of reassurance to their students, saying New York University or Stanford or Harvard or Minnesota or Case Western is still deeply concerned about diversity, and we’re going to do what we can to preserve attention to diversity.
I’ve served on admissions at a number of schools over the years for med school. I understand – and have been told – that diversity is important, and according to the Supreme Court, not explicitly by race. There are obviously many variables to take into account when trying to keep diversity at the forefront of admissions.
At the schools I’ve been at, including Columbia, NYU, University of Pittsburgh, University of Minnesota, and University of Pennsylvania, there are plenty of qualified students. Happily, we’ve always been engaged in some effort to try and whittle down the class to the size that we can manage and accept, and many qualified students don’t get admitted.
The first order of business for me is not to worry about how to maintain diversity. It’s to recognize that we need more doctors, nurses, and mental health care providers. I will, in a second, say a few words about diversity and where it fits into admissions, but I want to make the point clearly that what we should be doing is trying to expand the pool of students who are going to become doctors, nurses, mental health care providers, and social workers.
There are too many early retirements. We don’t have the person power we need to manage the health care challenges of an aging population. Let’s not get lost in arguing about what characteristics ought to get you into the finest medical schools. Let’s realize that we have to expand the number of schools we have.
We better be working pretty hard to expand our physician assistant programs, to make sure that we give full authority to qualified dentists and nurses who can help deliver some clinical care. We need more folks. That’s really where the battle ought to be: How do we get that done and how do we get it done quickly, not arguing about who’s in, who’s out, and why.
That said, diversity to me has never meant just race. I’m always interested in gender orientation, disability, and geographic input. Sometimes in decisions that you’re looking at, when I have students in front of me, they tell me they play a musical instrument or about the obstacles they had to overcome to get to medical school. Some of them will say they were involved in 4-H and did rodeo in high school or junior high school, which makes them a diverse potential student with characteristics that maybe some others don’t bring.
I’m not against diversity. I think having a rich set of experiences in any class – medicine, nursing, whatever it’s going to be – is beneficial to the students. They learn from each other. It is sometimes said that it’s also good for patients. I’m a little less excited about that, because I think our training goal should be to make every medical student and nursing student qualified to treat anybody.
I don’t think that, just because you’re Latinx or gay, that’s going to make a gay patient feel better. I think we should teach our students how to give care to everybody that they encounter. They shouldn’t have to match up characteristics to feel like they’re going to get quality care. That isn’t the right reason.
When you have a diverse set of providers, they can call that out and be on the alert for it, and that’s very important.
I also believe that we should think widely and broadly about diversity. Maybe race is out, but certainly other experiences related to income, background, struggle that got you to the point where you’re applying to medical school, motivation, the kinds of experiences you might have had caring for an elderly person, dealing with a disability or learning disability, and trying to overcome, let’s say, going to school in a poor area with not such a wonderful school, really help in terms of forming professionalism, empathy, and a caring point of view.
To me, the main goal is to expand our workforce. The secondary goal is to stay diverse, because we get better providers when we do so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, the Supreme Court of the United States struck down the use of affirmative action in admissions to colleges, universities, medical schools, and nursing schools. This has led to an enormous amount of worry and concern, particularly in medical school admissions in the world I’m in, where people start to say that diversity matters. Diversity is important.
I know many deans of medical schools immediately sent out messages of reassurance to their students, saying New York University or Stanford or Harvard or Minnesota or Case Western is still deeply concerned about diversity, and we’re going to do what we can to preserve attention to diversity.
I’ve served on admissions at a number of schools over the years for med school. I understand – and have been told – that diversity is important, and according to the Supreme Court, not explicitly by race. There are obviously many variables to take into account when trying to keep diversity at the forefront of admissions.
At the schools I’ve been at, including Columbia, NYU, University of Pittsburgh, University of Minnesota, and University of Pennsylvania, there are plenty of qualified students. Happily, we’ve always been engaged in some effort to try and whittle down the class to the size that we can manage and accept, and many qualified students don’t get admitted.
The first order of business for me is not to worry about how to maintain diversity. It’s to recognize that we need more doctors, nurses, and mental health care providers. I will, in a second, say a few words about diversity and where it fits into admissions, but I want to make the point clearly that what we should be doing is trying to expand the pool of students who are going to become doctors, nurses, mental health care providers, and social workers.
There are too many early retirements. We don’t have the person power we need to manage the health care challenges of an aging population. Let’s not get lost in arguing about what characteristics ought to get you into the finest medical schools. Let’s realize that we have to expand the number of schools we have.
We better be working pretty hard to expand our physician assistant programs, to make sure that we give full authority to qualified dentists and nurses who can help deliver some clinical care. We need more folks. That’s really where the battle ought to be: How do we get that done and how do we get it done quickly, not arguing about who’s in, who’s out, and why.
That said, diversity to me has never meant just race. I’m always interested in gender orientation, disability, and geographic input. Sometimes in decisions that you’re looking at, when I have students in front of me, they tell me they play a musical instrument or about the obstacles they had to overcome to get to medical school. Some of them will say they were involved in 4-H and did rodeo in high school or junior high school, which makes them a diverse potential student with characteristics that maybe some others don’t bring.
I’m not against diversity. I think having a rich set of experiences in any class – medicine, nursing, whatever it’s going to be – is beneficial to the students. They learn from each other. It is sometimes said that it’s also good for patients. I’m a little less excited about that, because I think our training goal should be to make every medical student and nursing student qualified to treat anybody.
I don’t think that, just because you’re Latinx or gay, that’s going to make a gay patient feel better. I think we should teach our students how to give care to everybody that they encounter. They shouldn’t have to match up characteristics to feel like they’re going to get quality care. That isn’t the right reason.
When you have a diverse set of providers, they can call that out and be on the alert for it, and that’s very important.
I also believe that we should think widely and broadly about diversity. Maybe race is out, but certainly other experiences related to income, background, struggle that got you to the point where you’re applying to medical school, motivation, the kinds of experiences you might have had caring for an elderly person, dealing with a disability or learning disability, and trying to overcome, let’s say, going to school in a poor area with not such a wonderful school, really help in terms of forming professionalism, empathy, and a caring point of view.
To me, the main goal is to expand our workforce. The secondary goal is to stay diverse, because we get better providers when we do so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Loneliness tied to increased risk for Parkinson’s disease
TOPLINE:
Loneliness is associated with a higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease (PD) across demographic groups and independent of other risk factors, data from nearly 500,000 U.K. adults suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Loneliness is associated with illness and death, including higher risk of neurodegenerative diseases, but no study has examined whether the association between loneliness and detrimental outcomes extends to PD.
- The current analysis included 491,603 U.K. Biobank participants (mean age, 56; 54% women) without a diagnosis of PD at baseline.
- Loneliness was assessed by a single question at baseline and incident PD was ascertained via health records over 15 years.
- Researchers assessed whether the association between loneliness and PD was moderated by age, sex, or genetic risk and whether the association was accounted for by sociodemographic factors; behavioral, mental, physical, or social factors; or genetic risk.
TAKEAWAY:
- Roughly 19% of the cohort reported being lonely. Compared with those who were not lonely, those who did report being lonely were slightly younger and were more likely to be women. They also had fewer resources, more health risk behaviors (current smoker and physically inactive), and worse physical and mental health.
- Over 15+ years of follow-up, 2,822 participants developed PD (incidence rate: 47 per 100,000 person-years). Compared with those who did not develop PD, those who did were older and more likely to be male, former smokers, have higher BMI and PD polygenetic risk score, and to have diabetes, hypertension, myocardial infarction or stroke, anxiety, or depression.
- In the primary analysis, individuals who reported being lonely had a higher risk for PD (hazard ratio, 1.37) – an association that remained after accounting for demographic and socioeconomic status, social isolation, PD polygenetic risk score, smoking, physical activity, BMI, diabetes, hypertension, stroke, myocardial infarction, depression, and having ever seen a psychiatrist (fully adjusted HR, 1.25).
- The association between loneliness and incident PD was not moderated by sex, age, or polygenetic risk score.
- Contrary to expectations for a prodromal syndrome, loneliness was not associated with incident PD in the first 5 years after baseline but was associated with PD risk in the subsequent 10 years of follow-up (HR, 1.32).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings complement other evidence that loneliness is a psychosocial determinant of health associated with increased risk of morbidity and mortality [and] supports recent calls for the protective and healing effects of personally meaningful social connection,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Antonio Terracciano, PhD, of Florida State University College of Medicine, Tallahassee, was published online in JAMA Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
This observational study could not determine causality or whether reverse causality could explain the association. Loneliness was assessed by a single yes/no question. PD diagnosis relied on hospital admission and death records and may have missed early PD diagnoses.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health and National Institute on Aging. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Loneliness is associated with a higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease (PD) across demographic groups and independent of other risk factors, data from nearly 500,000 U.K. adults suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Loneliness is associated with illness and death, including higher risk of neurodegenerative diseases, but no study has examined whether the association between loneliness and detrimental outcomes extends to PD.
- The current analysis included 491,603 U.K. Biobank participants (mean age, 56; 54% women) without a diagnosis of PD at baseline.
- Loneliness was assessed by a single question at baseline and incident PD was ascertained via health records over 15 years.
- Researchers assessed whether the association between loneliness and PD was moderated by age, sex, or genetic risk and whether the association was accounted for by sociodemographic factors; behavioral, mental, physical, or social factors; or genetic risk.
TAKEAWAY:
- Roughly 19% of the cohort reported being lonely. Compared with those who were not lonely, those who did report being lonely were slightly younger and were more likely to be women. They also had fewer resources, more health risk behaviors (current smoker and physically inactive), and worse physical and mental health.
- Over 15+ years of follow-up, 2,822 participants developed PD (incidence rate: 47 per 100,000 person-years). Compared with those who did not develop PD, those who did were older and more likely to be male, former smokers, have higher BMI and PD polygenetic risk score, and to have diabetes, hypertension, myocardial infarction or stroke, anxiety, or depression.
- In the primary analysis, individuals who reported being lonely had a higher risk for PD (hazard ratio, 1.37) – an association that remained after accounting for demographic and socioeconomic status, social isolation, PD polygenetic risk score, smoking, physical activity, BMI, diabetes, hypertension, stroke, myocardial infarction, depression, and having ever seen a psychiatrist (fully adjusted HR, 1.25).
- The association between loneliness and incident PD was not moderated by sex, age, or polygenetic risk score.
- Contrary to expectations for a prodromal syndrome, loneliness was not associated with incident PD in the first 5 years after baseline but was associated with PD risk in the subsequent 10 years of follow-up (HR, 1.32).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings complement other evidence that loneliness is a psychosocial determinant of health associated with increased risk of morbidity and mortality [and] supports recent calls for the protective and healing effects of personally meaningful social connection,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Antonio Terracciano, PhD, of Florida State University College of Medicine, Tallahassee, was published online in JAMA Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
This observational study could not determine causality or whether reverse causality could explain the association. Loneliness was assessed by a single yes/no question. PD diagnosis relied on hospital admission and death records and may have missed early PD diagnoses.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health and National Institute on Aging. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Loneliness is associated with a higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease (PD) across demographic groups and independent of other risk factors, data from nearly 500,000 U.K. adults suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Loneliness is associated with illness and death, including higher risk of neurodegenerative diseases, but no study has examined whether the association between loneliness and detrimental outcomes extends to PD.
- The current analysis included 491,603 U.K. Biobank participants (mean age, 56; 54% women) without a diagnosis of PD at baseline.
- Loneliness was assessed by a single question at baseline and incident PD was ascertained via health records over 15 years.
- Researchers assessed whether the association between loneliness and PD was moderated by age, sex, or genetic risk and whether the association was accounted for by sociodemographic factors; behavioral, mental, physical, or social factors; or genetic risk.
TAKEAWAY:
- Roughly 19% of the cohort reported being lonely. Compared with those who were not lonely, those who did report being lonely were slightly younger and were more likely to be women. They also had fewer resources, more health risk behaviors (current smoker and physically inactive), and worse physical and mental health.
- Over 15+ years of follow-up, 2,822 participants developed PD (incidence rate: 47 per 100,000 person-years). Compared with those who did not develop PD, those who did were older and more likely to be male, former smokers, have higher BMI and PD polygenetic risk score, and to have diabetes, hypertension, myocardial infarction or stroke, anxiety, or depression.
- In the primary analysis, individuals who reported being lonely had a higher risk for PD (hazard ratio, 1.37) – an association that remained after accounting for demographic and socioeconomic status, social isolation, PD polygenetic risk score, smoking, physical activity, BMI, diabetes, hypertension, stroke, myocardial infarction, depression, and having ever seen a psychiatrist (fully adjusted HR, 1.25).
- The association between loneliness and incident PD was not moderated by sex, age, or polygenetic risk score.
- Contrary to expectations for a prodromal syndrome, loneliness was not associated with incident PD in the first 5 years after baseline but was associated with PD risk in the subsequent 10 years of follow-up (HR, 1.32).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings complement other evidence that loneliness is a psychosocial determinant of health associated with increased risk of morbidity and mortality [and] supports recent calls for the protective and healing effects of personally meaningful social connection,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Antonio Terracciano, PhD, of Florida State University College of Medicine, Tallahassee, was published online in JAMA Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
This observational study could not determine causality or whether reverse causality could explain the association. Loneliness was assessed by a single yes/no question. PD diagnosis relied on hospital admission and death records and may have missed early PD diagnoses.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by the National Institutes of Health and National Institute on Aging. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The surprising link between loneliness and Parkinson’s disease
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
On May 3, 2023, Surgeon General Vivek Murthy issued an advisory raising an alarm about what he called an “epidemic of loneliness” in the United States.
Now, I am not saying that Vivek Murthy read my book, “How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t” – released in January and available in bookstores now – where, in chapter 11, I call attention to the problem of loneliness and its relationship to the exponential rise in deaths of despair. But Vivek, if you did, let me know. I could use the publicity.
No, of course the idea that loneliness is a public health issue is not new, but I’m glad to see it finally getting attention. At this point, studies have linked loneliness to heart disease, stroke, dementia, and premature death.
The UK Biobank is really a treasure trove of data for epidemiologists. I must see three to four studies a week coming out of this mega-dataset. This one, appearing in JAMA Neurology, caught my eye for its focus specifically on loneliness as a risk factor – something I’m hoping to see more of in the future.
The study examines data from just under 500,000 individuals in the United Kingdom who answered a survey including the question “Do you often feel lonely?” between 2006 and 2010; 18.4% of people answered yes. Individuals’ electronic health record data were then monitored over time to see who would get a new diagnosis code consistent with Parkinson’s disease. Through 2021, 2822 people did – that’s just over half a percent.
So, now we do the statistics thing. Of the nonlonely folks, 2,273 went on to develop Parkinson’s disease. Of those who said they often feel lonely, 549 people did. The raw numbers here, to be honest, aren’t that compelling. Lonely people had an absolute risk for Parkinson’s disease about 0.03% higher than that of nonlonely people. Put another way, you’d need to take over 3,000 lonely souls and make them not lonely to prevent 1 case of Parkinson’s disease.
Still, the costs of loneliness are not measured exclusively in Parkinson’s disease, and I would argue that the real risks here come from other sources: alcohol abuse, drug abuse, and suicide. Nevertheless, the weak but significant association with Parkinson’s disease reminds us that loneliness is a neurologic phenomenon. There is something about social connection that affects our brain in a way that is not just spiritual; it is actually biological.
Of course, people who say they are often lonely are different in other ways from people who report not being lonely. Lonely people, in this dataset, were younger, more likely to be female, less likely to have a college degree, in worse physical health, and engaged in more high-risk health behaviors like smoking.
The authors adjusted for all of these factors and found that, on the relative scale, lonely people were still about 20%-30% more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease.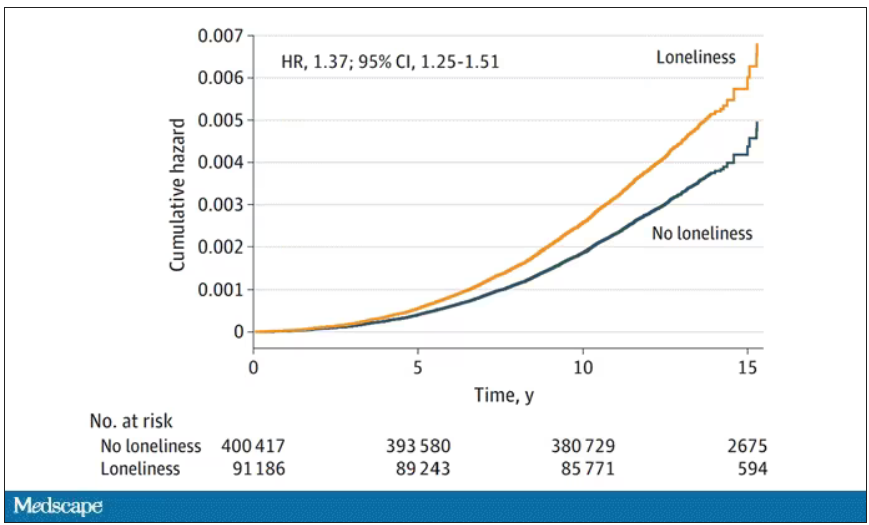
So, what do we do about this? There is no pill for loneliness, and God help us if there ever is. Recognizing the problem is a good start. But there are some policy things we can do to reduce loneliness. We can invest in public spaces that bring people together – parks, museums, libraries – and public transportation. We can deal with tech companies that are so optimized at capturing our attention that we cease to engage with other humans. And, individually, we can just reach out a bit more. We’ve spent the past few pandemic years with our attention focused sharply inward. It’s time to look out again.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
On May 3, 2023, Surgeon General Vivek Murthy issued an advisory raising an alarm about what he called an “epidemic of loneliness” in the United States.
Now, I am not saying that Vivek Murthy read my book, “How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t” – released in January and available in bookstores now – where, in chapter 11, I call attention to the problem of loneliness and its relationship to the exponential rise in deaths of despair. But Vivek, if you did, let me know. I could use the publicity.
No, of course the idea that loneliness is a public health issue is not new, but I’m glad to see it finally getting attention. At this point, studies have linked loneliness to heart disease, stroke, dementia, and premature death.
The UK Biobank is really a treasure trove of data for epidemiologists. I must see three to four studies a week coming out of this mega-dataset. This one, appearing in JAMA Neurology, caught my eye for its focus specifically on loneliness as a risk factor – something I’m hoping to see more of in the future.
The study examines data from just under 500,000 individuals in the United Kingdom who answered a survey including the question “Do you often feel lonely?” between 2006 and 2010; 18.4% of people answered yes. Individuals’ electronic health record data were then monitored over time to see who would get a new diagnosis code consistent with Parkinson’s disease. Through 2021, 2822 people did – that’s just over half a percent.
So, now we do the statistics thing. Of the nonlonely folks, 2,273 went on to develop Parkinson’s disease. Of those who said they often feel lonely, 549 people did. The raw numbers here, to be honest, aren’t that compelling. Lonely people had an absolute risk for Parkinson’s disease about 0.03% higher than that of nonlonely people. Put another way, you’d need to take over 3,000 lonely souls and make them not lonely to prevent 1 case of Parkinson’s disease.
Still, the costs of loneliness are not measured exclusively in Parkinson’s disease, and I would argue that the real risks here come from other sources: alcohol abuse, drug abuse, and suicide. Nevertheless, the weak but significant association with Parkinson’s disease reminds us that loneliness is a neurologic phenomenon. There is something about social connection that affects our brain in a way that is not just spiritual; it is actually biological.
Of course, people who say they are often lonely are different in other ways from people who report not being lonely. Lonely people, in this dataset, were younger, more likely to be female, less likely to have a college degree, in worse physical health, and engaged in more high-risk health behaviors like smoking.
The authors adjusted for all of these factors and found that, on the relative scale, lonely people were still about 20%-30% more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease.
So, what do we do about this? There is no pill for loneliness, and God help us if there ever is. Recognizing the problem is a good start. But there are some policy things we can do to reduce loneliness. We can invest in public spaces that bring people together – parks, museums, libraries – and public transportation. We can deal with tech companies that are so optimized at capturing our attention that we cease to engage with other humans. And, individually, we can just reach out a bit more. We’ve spent the past few pandemic years with our attention focused sharply inward. It’s time to look out again.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
On May 3, 2023, Surgeon General Vivek Murthy issued an advisory raising an alarm about what he called an “epidemic of loneliness” in the United States.
Now, I am not saying that Vivek Murthy read my book, “How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t” – released in January and available in bookstores now – where, in chapter 11, I call attention to the problem of loneliness and its relationship to the exponential rise in deaths of despair. But Vivek, if you did, let me know. I could use the publicity.
No, of course the idea that loneliness is a public health issue is not new, but I’m glad to see it finally getting attention. At this point, studies have linked loneliness to heart disease, stroke, dementia, and premature death.
The UK Biobank is really a treasure trove of data for epidemiologists. I must see three to four studies a week coming out of this mega-dataset. This one, appearing in JAMA Neurology, caught my eye for its focus specifically on loneliness as a risk factor – something I’m hoping to see more of in the future.
The study examines data from just under 500,000 individuals in the United Kingdom who answered a survey including the question “Do you often feel lonely?” between 2006 and 2010; 18.4% of people answered yes. Individuals’ electronic health record data were then monitored over time to see who would get a new diagnosis code consistent with Parkinson’s disease. Through 2021, 2822 people did – that’s just over half a percent.
So, now we do the statistics thing. Of the nonlonely folks, 2,273 went on to develop Parkinson’s disease. Of those who said they often feel lonely, 549 people did. The raw numbers here, to be honest, aren’t that compelling. Lonely people had an absolute risk for Parkinson’s disease about 0.03% higher than that of nonlonely people. Put another way, you’d need to take over 3,000 lonely souls and make them not lonely to prevent 1 case of Parkinson’s disease.
Still, the costs of loneliness are not measured exclusively in Parkinson’s disease, and I would argue that the real risks here come from other sources: alcohol abuse, drug abuse, and suicide. Nevertheless, the weak but significant association with Parkinson’s disease reminds us that loneliness is a neurologic phenomenon. There is something about social connection that affects our brain in a way that is not just spiritual; it is actually biological.
Of course, people who say they are often lonely are different in other ways from people who report not being lonely. Lonely people, in this dataset, were younger, more likely to be female, less likely to have a college degree, in worse physical health, and engaged in more high-risk health behaviors like smoking.
The authors adjusted for all of these factors and found that, on the relative scale, lonely people were still about 20%-30% more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease.
So, what do we do about this? There is no pill for loneliness, and God help us if there ever is. Recognizing the problem is a good start. But there are some policy things we can do to reduce loneliness. We can invest in public spaces that bring people together – parks, museums, libraries – and public transportation. We can deal with tech companies that are so optimized at capturing our attention that we cease to engage with other humans. And, individually, we can just reach out a bit more. We’ve spent the past few pandemic years with our attention focused sharply inward. It’s time to look out again.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From scrubs to screens: Growing your patient base with social media
With physicians under increasing pressure to see more patients in shorter office visits, developing a social media presence may offer valuable opportunities to connect with patients, explain procedures, combat misinformation, talk through a published article, and even share a joke or meme.
But there are caveats for doctors posting on social media platforms. This news organization spoke to four doctors who successfully use social media.
Use social media for the right reasons
While you’re under no obligation to build a social media presence, if you’re going to do it, be sure your intentions are solid, said Don S. Dizon, MD, professor of medicine and professor of surgery at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Dizon, as @DoctorDon, has 44,700 TikTok followers and uses the platform to answer cancer-related questions.
“It should be your altruism that motivates you to post,” said Dr. Dizon, who is also associate director of community outreach and engagement at the Legorreta Cancer Center in Providence, R.I., and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital. “What we can do for society at large is to provide our input into issues, add informed opinions where there’s controversy, and address misinformation.”
If you don’t know where to start, consider seeking a digital mentor to talk through your options.
“You may never meet this person, but you should choose them if you like their style, their content, their delivery, and their perspective,” Dr. Dizon said. “Find another doctor out there on social media whom you feel you can emulate. Take your time, too. Soon enough, you’ll develop your own style and your own online persona.”
Post clear, accurate information
If you want to be lighthearted on social media, that’s your choice. But Jennifer Trachtenberg, a pediatrician with nearly 7,000 Instagram followers in New York who posts as @askdrjen, prefers to offer vaccine scheduling tips, alert parents about COVID-19 rates, and offer advice on cold and flu prevention.
“Right now, I’m mainly doing this to educate patients and make them aware of topics that I think are important and that I see my patients needing more information on,” she said. “We have to be clear: People take what we say seriously. So, while it’s important to be relatable, it’s even more important to share evidence-based information.”
Many patients get their information on social media
While patients once came to the doctor armed with information sourced via “Doctor Google,” today, just as many patients use social media to learn about their condition or the medications they’re taking.
Unfortunately, a recent Ohio State University, Columbus, study found that the majority of gynecologic cancer advice on TikTok, for example, was either misleading or inaccurate.
“This misinformation should be a motivator for physicians to explore the social media space,” Dr. Dizon said. “Our voices need to be on there.”
Break down barriers – and make connections
Mike Natter, MD, an endocrinologist in New York, has type 1 diabetes. This informs his work – and his life – and he’s passionate about sharing it with his 117,000 followers as @mike.natter on Instagram.
“A lot of type 1s follow me, so there’s an advocacy component to what I do,” he said. “I enjoy being able to raise awareness and keep people up to date on the newest research and treatment.”
But that’s not all: Dr. Natter is also an artist who went to art school before he went to medical school, and his account is rife with his cartoons and illustrations about everything from valvular disease to diabetic ketoacidosis.
“I found that I was drawing a lot of my notes in medical school,” he said. “When I drew my notes, I did quite well, and I think that using art and illustration is a great tool. It breaks down barriers and makes health information all the more accessible to everyone.”
Share your expertise as a doctor – and a person
As a mom and pediatrician, Krupa Playforth, MD, who practices in Vienna, Va., knows that what she posts carries weight. So, whether she’s writing about backpack safety tips, choking hazards, or separation anxiety, her followers can rest assured that she’s posting responsibly.
“Pediatricians often underestimate how smart parents are,” said Dr. Playforth, who has three kids, ages 8, 5, and 2, and has 137,000 followers on @thepediatricianmom, her Instagram account. “Their anxiety comes from an understandable place, which is why I see my role as that of a parent and pediatrician who can translate the knowledge pediatricians have into something parents can understand.”
Dr. Playforth, who jumped on social media during COVID-19 and experienced a positive response in her local community, said being on social media is imperative if you’re a pediatrician.
“This is the future of pediatric medicine in particular,” she said. “A lot of pediatricians don’t want to embrace social media, but I think that’s a mistake. After all, while parents think pediatricians have all the answers, when we think of our own children, most doctors are like other parents – we can’t think objectively about our kids. It’s helpful for me to share that and to help parents feel less alone.”
If you’re not yet using social media to the best of your physician abilities, you might take a shot at becoming widely recognizable. Pick a preferred platform, answer common patient questions, dispel medical myths, provide pertinent information, and let your personality shine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With physicians under increasing pressure to see more patients in shorter office visits, developing a social media presence may offer valuable opportunities to connect with patients, explain procedures, combat misinformation, talk through a published article, and even share a joke or meme.
But there are caveats for doctors posting on social media platforms. This news organization spoke to four doctors who successfully use social media.
Use social media for the right reasons
While you’re under no obligation to build a social media presence, if you’re going to do it, be sure your intentions are solid, said Don S. Dizon, MD, professor of medicine and professor of surgery at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Dizon, as @DoctorDon, has 44,700 TikTok followers and uses the platform to answer cancer-related questions.
“It should be your altruism that motivates you to post,” said Dr. Dizon, who is also associate director of community outreach and engagement at the Legorreta Cancer Center in Providence, R.I., and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital. “What we can do for society at large is to provide our input into issues, add informed opinions where there’s controversy, and address misinformation.”
If you don’t know where to start, consider seeking a digital mentor to talk through your options.
“You may never meet this person, but you should choose them if you like their style, their content, their delivery, and their perspective,” Dr. Dizon said. “Find another doctor out there on social media whom you feel you can emulate. Take your time, too. Soon enough, you’ll develop your own style and your own online persona.”
Post clear, accurate information
If you want to be lighthearted on social media, that’s your choice. But Jennifer Trachtenberg, a pediatrician with nearly 7,000 Instagram followers in New York who posts as @askdrjen, prefers to offer vaccine scheduling tips, alert parents about COVID-19 rates, and offer advice on cold and flu prevention.
“Right now, I’m mainly doing this to educate patients and make them aware of topics that I think are important and that I see my patients needing more information on,” she said. “We have to be clear: People take what we say seriously. So, while it’s important to be relatable, it’s even more important to share evidence-based information.”
Many patients get their information on social media
While patients once came to the doctor armed with information sourced via “Doctor Google,” today, just as many patients use social media to learn about their condition or the medications they’re taking.
Unfortunately, a recent Ohio State University, Columbus, study found that the majority of gynecologic cancer advice on TikTok, for example, was either misleading or inaccurate.
“This misinformation should be a motivator for physicians to explore the social media space,” Dr. Dizon said. “Our voices need to be on there.”
Break down barriers – and make connections
Mike Natter, MD, an endocrinologist in New York, has type 1 diabetes. This informs his work – and his life – and he’s passionate about sharing it with his 117,000 followers as @mike.natter on Instagram.
“A lot of type 1s follow me, so there’s an advocacy component to what I do,” he said. “I enjoy being able to raise awareness and keep people up to date on the newest research and treatment.”
But that’s not all: Dr. Natter is also an artist who went to art school before he went to medical school, and his account is rife with his cartoons and illustrations about everything from valvular disease to diabetic ketoacidosis.
“I found that I was drawing a lot of my notes in medical school,” he said. “When I drew my notes, I did quite well, and I think that using art and illustration is a great tool. It breaks down barriers and makes health information all the more accessible to everyone.”
Share your expertise as a doctor – and a person
As a mom and pediatrician, Krupa Playforth, MD, who practices in Vienna, Va., knows that what she posts carries weight. So, whether she’s writing about backpack safety tips, choking hazards, or separation anxiety, her followers can rest assured that she’s posting responsibly.
“Pediatricians often underestimate how smart parents are,” said Dr. Playforth, who has three kids, ages 8, 5, and 2, and has 137,000 followers on @thepediatricianmom, her Instagram account. “Their anxiety comes from an understandable place, which is why I see my role as that of a parent and pediatrician who can translate the knowledge pediatricians have into something parents can understand.”
Dr. Playforth, who jumped on social media during COVID-19 and experienced a positive response in her local community, said being on social media is imperative if you’re a pediatrician.
“This is the future of pediatric medicine in particular,” she said. “A lot of pediatricians don’t want to embrace social media, but I think that’s a mistake. After all, while parents think pediatricians have all the answers, when we think of our own children, most doctors are like other parents – we can’t think objectively about our kids. It’s helpful for me to share that and to help parents feel less alone.”
If you’re not yet using social media to the best of your physician abilities, you might take a shot at becoming widely recognizable. Pick a preferred platform, answer common patient questions, dispel medical myths, provide pertinent information, and let your personality shine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With physicians under increasing pressure to see more patients in shorter office visits, developing a social media presence may offer valuable opportunities to connect with patients, explain procedures, combat misinformation, talk through a published article, and even share a joke or meme.
But there are caveats for doctors posting on social media platforms. This news organization spoke to four doctors who successfully use social media.
Use social media for the right reasons
While you’re under no obligation to build a social media presence, if you’re going to do it, be sure your intentions are solid, said Don S. Dizon, MD, professor of medicine and professor of surgery at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Dizon, as @DoctorDon, has 44,700 TikTok followers and uses the platform to answer cancer-related questions.
“It should be your altruism that motivates you to post,” said Dr. Dizon, who is also associate director of community outreach and engagement at the Legorreta Cancer Center in Providence, R.I., and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital. “What we can do for society at large is to provide our input into issues, add informed opinions where there’s controversy, and address misinformation.”
If you don’t know where to start, consider seeking a digital mentor to talk through your options.
“You may never meet this person, but you should choose them if you like their style, their content, their delivery, and their perspective,” Dr. Dizon said. “Find another doctor out there on social media whom you feel you can emulate. Take your time, too. Soon enough, you’ll develop your own style and your own online persona.”
Post clear, accurate information
If you want to be lighthearted on social media, that’s your choice. But Jennifer Trachtenberg, a pediatrician with nearly 7,000 Instagram followers in New York who posts as @askdrjen, prefers to offer vaccine scheduling tips, alert parents about COVID-19 rates, and offer advice on cold and flu prevention.
“Right now, I’m mainly doing this to educate patients and make them aware of topics that I think are important and that I see my patients needing more information on,” she said. “We have to be clear: People take what we say seriously. So, while it’s important to be relatable, it’s even more important to share evidence-based information.”
Many patients get their information on social media
While patients once came to the doctor armed with information sourced via “Doctor Google,” today, just as many patients use social media to learn about their condition or the medications they’re taking.
Unfortunately, a recent Ohio State University, Columbus, study found that the majority of gynecologic cancer advice on TikTok, for example, was either misleading or inaccurate.
“This misinformation should be a motivator for physicians to explore the social media space,” Dr. Dizon said. “Our voices need to be on there.”
Break down barriers – and make connections
Mike Natter, MD, an endocrinologist in New York, has type 1 diabetes. This informs his work – and his life – and he’s passionate about sharing it with his 117,000 followers as @mike.natter on Instagram.
“A lot of type 1s follow me, so there’s an advocacy component to what I do,” he said. “I enjoy being able to raise awareness and keep people up to date on the newest research and treatment.”
But that’s not all: Dr. Natter is also an artist who went to art school before he went to medical school, and his account is rife with his cartoons and illustrations about everything from valvular disease to diabetic ketoacidosis.
“I found that I was drawing a lot of my notes in medical school,” he said. “When I drew my notes, I did quite well, and I think that using art and illustration is a great tool. It breaks down barriers and makes health information all the more accessible to everyone.”
Share your expertise as a doctor – and a person
As a mom and pediatrician, Krupa Playforth, MD, who practices in Vienna, Va., knows that what she posts carries weight. So, whether she’s writing about backpack safety tips, choking hazards, or separation anxiety, her followers can rest assured that she’s posting responsibly.
“Pediatricians often underestimate how smart parents are,” said Dr. Playforth, who has three kids, ages 8, 5, and 2, and has 137,000 followers on @thepediatricianmom, her Instagram account. “Their anxiety comes from an understandable place, which is why I see my role as that of a parent and pediatrician who can translate the knowledge pediatricians have into something parents can understand.”
Dr. Playforth, who jumped on social media during COVID-19 and experienced a positive response in her local community, said being on social media is imperative if you’re a pediatrician.
“This is the future of pediatric medicine in particular,” she said. “A lot of pediatricians don’t want to embrace social media, but I think that’s a mistake. After all, while parents think pediatricians have all the answers, when we think of our own children, most doctors are like other parents – we can’t think objectively about our kids. It’s helpful for me to share that and to help parents feel less alone.”
If you’re not yet using social media to the best of your physician abilities, you might take a shot at becoming widely recognizable. Pick a preferred platform, answer common patient questions, dispel medical myths, provide pertinent information, and let your personality shine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CBT effectively treats sexual concerns in menopausal women
PHILADELPHIA – . Four CBT sessions specifically focused on sexual concerns resulted in decreased sexual distress and concern, reduced depressive and menopausal symptoms, and increased sexual desire and functioning, as well as improved body image and relationship satisfaction.
An estimated 68%-87% of perimenopausal and postmenopausal women report sexual concerns, Sheryl Green, PhD, CPsych, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University and a psychologist at St. Joseph’s Healthcare’s Women’s Health Concerns Clinic, both in Hamilton, Ont., told attendees at the meeting.
“Sexual concerns over the menopausal transition are not just physical, but they’re also psychological and emotional,” Dr. Green said. “Three common challenges include decreased sexual desire, a reduction in physical arousal and ability to achieve an orgasm, and sexual pain and discomfort during intercourse.”
The reasons for these concerns are multifactorial, she said. Decreased sexual desire can stem from stress, medical problems, their relationship with their partner, or other causes. A woman’s difficulty with reduced physical arousal or ability to have an orgasm can result from changes in hormone levels and vaginal changes, such as vaginal atrophy, which can also contribute to the sexual pain or discomfort reported by 17%-45% of postmenopausal women.
Two pharmacologic treatments exist for sexual concerns: oral flibanserin (Addyi) and injectable bremelanotide (Vyleesi). But many women may be unable or unwilling to take medication for their concerns. Previous research from Lori Brotto has found cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness interventions to effectively improve sexual functioning in women treated for gynecologic cancer and in women without a history of cancer.
“Sexual function needs to be understood from a bio-psychosocial model, looking at the biologic factors, the psychological factors, the sociocultural factors, and the interpersonal factors,” Sheryl Kingsberg, PhD, a professor of psychiatry and reproductive biology at Case Western Reserve University and a psychologist at University Hospitals in Cleveland, said in an interview.
“They can all overlap, and the clinician can ask a few pointed questions that help identify what the source of the problem is,” said Dr. Kingsberg, who was not involved in this study. She noted that the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health has an algorithm that can help in determining the source of the problems.
“Sometimes it’s going to be a biologic condition for which pharmacologic options are nice, but even if it is primarily pharmacologic, psychotherapy is always useful,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “Once the problem is there, even if it’s biologically based, then you have all the things in terms of the cognitive distortion, anxiety,” and other issues that a cognitive behavioral approach can help address. “And access is now much wider because of telehealth,” she added.
‘Psychology of menopause’
The study led by Dr. Green focused on peri- and postmenopausal women, with an average age of 50, who were experiencing primary sexual concerns based on a score of at least 26 on the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). Among the 20 women recruited for the study, 6 had already been prescribed hormone therapy for sexual concerns.
All reported decreased sexual desire, 17 reported decreased sexual arousal, 14 had body image dissatisfaction related to sexual concerns, and 6 reported urogenital problems. Nine of the women were in full remission from major depressive disorder, one had post-traumatic stress syndrome, and one had subclinical generalized anxiety disorder.
After spending 4 weeks on a wait list as self-control group for the study, the 15 women who completed the trial underwent four individual CBT sessions focusing on sexual concerns. The first session focused on psychoeducation and thought monitoring, and the second focused on cognitive distortions, cognitive strategies, and unhelpful beliefs or expectations related to sexual concerns. The third session looked at the role of problematic behaviors and behavioral experiments, and the fourth focused on continuation of strategies, long-term goals, and maintaining gains.
The participants completed eight measures at baseline, after the 4 weeks on the wait list, and after the four CBT sessions to assess the following:
- Sexual satisfaction, distress, and desire, using the FSFI, the Female Sexual Distress Scale-Revised (FSDS-R), and the Female Sexual Desire Questionnaire (FSDQ).
- Menopause symptoms, using the Greene Climacteric Scale (GCS).
- Body image, using the Dresden Body Image Questionnaire (DBIQ).
- Relationship satisfaction, using the Couples Satisfaction Index (CSI).
- Depression, using the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II).
- Anxiety, using the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A).
The women did not experience any significant changes while on the wait list except a slight decrease on the FSDQ concern subscale. Following the CBT sessions, however, the women experienced a significant decrease in sexual distress and concern as well as an increase in sexual dyadic desire and sexual functioning (P = .003 for FSFI, P = .002 for FSDS-R, and P = .003 for FSDQ).
Participants also experienced a decrease in depression (P < .0001) and menopausal symptoms (P = .001) and an increase in body-image satisfaction (P = .018) and relationship satisfaction (P = .0011) after the CBT sessions. The researchers assessed participants’ satisfaction with the Client Satisfaction Questionnaire after the CBT sessions and reported some of the qualitative findings.
“The treatment program was able to assist me with recognizing that some of my sexual concerns were normal, emotional as well as physical and hormonal, and provided me the ability to delve more deeply into the psychology of menopause and how to work through symptoms and concerns in more manageable pieces,” one participant wrote. Another found helpful the “homework exercises of recognizing a thought/feeling/emotion surrounding how I feel about myself/body and working through. More positive thought pattern/restructuring a response the most helpful.”
The main complaint about the program was that it was too short, with women wanting more sessions to help continue their progress.
Not an ‘either-or’ approach
Dr. Kingsberg said ISSWSH has a variety of sexual medicine practitioners, including providers who can provide CBT for sexual concerns, and the American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors and Therapists has a referral directory.
“Keeping in mind the bio-psychosocial model, sometimes psychotherapy is going to be a really effective treatment for sexual concerns,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “Sometimes the pharmacologic option is going to be a really effective treatment for some concerns, and sometimes the combination is going to have a really nice treatment effect. So it’s not a one-size-fits-all, and it doesn’t have to be an either-or.”
The sexual concerns of women still do not get adequately addressed in medical schools and residencies, Dr. Kingsberg said, which is distinctly different from how male sexual concerns are addressed in health care.
“Erectile dysfunction is kind of in the norm, and women are still a little hesitant to bring up their sexual concerns,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “They don’t know if it’s appropriate and they’re hoping that their clinician will ask.”
One way clinicians can do that is with a global question for all their patients: “Most of my patients have sexual questions or concerns; what concerns do you have?”
“They don’t have to go through a checklist of 10 things,” Dr. Kingsberg said. If the patient does not bring anything up, providers can then ask a single follow up question: “Do you have any concerns with desire, arousal, orgasm, or pain?” That question, Dr. Kingsberg said, covers the four main areas of concern.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Green reported no disclosures. Dr. Kingsberg has consulted for or served on the advisory board for Alloy, Astellas, Bayer, Dare Bioscience, Freya, Reunion Neuroscience, Materna Medical, Madorra, Palatin, Pfizer, ReJoy, Sprout, Strategic Science Technologies, and MsMedicine.
PHILADELPHIA – . Four CBT sessions specifically focused on sexual concerns resulted in decreased sexual distress and concern, reduced depressive and menopausal symptoms, and increased sexual desire and functioning, as well as improved body image and relationship satisfaction.
An estimated 68%-87% of perimenopausal and postmenopausal women report sexual concerns, Sheryl Green, PhD, CPsych, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University and a psychologist at St. Joseph’s Healthcare’s Women’s Health Concerns Clinic, both in Hamilton, Ont., told attendees at the meeting.
“Sexual concerns over the menopausal transition are not just physical, but they’re also psychological and emotional,” Dr. Green said. “Three common challenges include decreased sexual desire, a reduction in physical arousal and ability to achieve an orgasm, and sexual pain and discomfort during intercourse.”
The reasons for these concerns are multifactorial, she said. Decreased sexual desire can stem from stress, medical problems, their relationship with their partner, or other causes. A woman’s difficulty with reduced physical arousal or ability to have an orgasm can result from changes in hormone levels and vaginal changes, such as vaginal atrophy, which can also contribute to the sexual pain or discomfort reported by 17%-45% of postmenopausal women.
Two pharmacologic treatments exist for sexual concerns: oral flibanserin (Addyi) and injectable bremelanotide (Vyleesi). But many women may be unable or unwilling to take medication for their concerns. Previous research from Lori Brotto has found cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness interventions to effectively improve sexual functioning in women treated for gynecologic cancer and in women without a history of cancer.
“Sexual function needs to be understood from a bio-psychosocial model, looking at the biologic factors, the psychological factors, the sociocultural factors, and the interpersonal factors,” Sheryl Kingsberg, PhD, a professor of psychiatry and reproductive biology at Case Western Reserve University and a psychologist at University Hospitals in Cleveland, said in an interview.
“They can all overlap, and the clinician can ask a few pointed questions that help identify what the source of the problem is,” said Dr. Kingsberg, who was not involved in this study. She noted that the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health has an algorithm that can help in determining the source of the problems.
“Sometimes it’s going to be a biologic condition for which pharmacologic options are nice, but even if it is primarily pharmacologic, psychotherapy is always useful,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “Once the problem is there, even if it’s biologically based, then you have all the things in terms of the cognitive distortion, anxiety,” and other issues that a cognitive behavioral approach can help address. “And access is now much wider because of telehealth,” she added.
‘Psychology of menopause’
The study led by Dr. Green focused on peri- and postmenopausal women, with an average age of 50, who were experiencing primary sexual concerns based on a score of at least 26 on the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). Among the 20 women recruited for the study, 6 had already been prescribed hormone therapy for sexual concerns.
All reported decreased sexual desire, 17 reported decreased sexual arousal, 14 had body image dissatisfaction related to sexual concerns, and 6 reported urogenital problems. Nine of the women were in full remission from major depressive disorder, one had post-traumatic stress syndrome, and one had subclinical generalized anxiety disorder.
After spending 4 weeks on a wait list as self-control group for the study, the 15 women who completed the trial underwent four individual CBT sessions focusing on sexual concerns. The first session focused on psychoeducation and thought monitoring, and the second focused on cognitive distortions, cognitive strategies, and unhelpful beliefs or expectations related to sexual concerns. The third session looked at the role of problematic behaviors and behavioral experiments, and the fourth focused on continuation of strategies, long-term goals, and maintaining gains.
The participants completed eight measures at baseline, after the 4 weeks on the wait list, and after the four CBT sessions to assess the following:
- Sexual satisfaction, distress, and desire, using the FSFI, the Female Sexual Distress Scale-Revised (FSDS-R), and the Female Sexual Desire Questionnaire (FSDQ).
- Menopause symptoms, using the Greene Climacteric Scale (GCS).
- Body image, using the Dresden Body Image Questionnaire (DBIQ).
- Relationship satisfaction, using the Couples Satisfaction Index (CSI).
- Depression, using the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II).
- Anxiety, using the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A).
The women did not experience any significant changes while on the wait list except a slight decrease on the FSDQ concern subscale. Following the CBT sessions, however, the women experienced a significant decrease in sexual distress and concern as well as an increase in sexual dyadic desire and sexual functioning (P = .003 for FSFI, P = .002 for FSDS-R, and P = .003 for FSDQ).
Participants also experienced a decrease in depression (P < .0001) and menopausal symptoms (P = .001) and an increase in body-image satisfaction (P = .018) and relationship satisfaction (P = .0011) after the CBT sessions. The researchers assessed participants’ satisfaction with the Client Satisfaction Questionnaire after the CBT sessions and reported some of the qualitative findings.
“The treatment program was able to assist me with recognizing that some of my sexual concerns were normal, emotional as well as physical and hormonal, and provided me the ability to delve more deeply into the psychology of menopause and how to work through symptoms and concerns in more manageable pieces,” one participant wrote. Another found helpful the “homework exercises of recognizing a thought/feeling/emotion surrounding how I feel about myself/body and working through. More positive thought pattern/restructuring a response the most helpful.”
The main complaint about the program was that it was too short, with women wanting more sessions to help continue their progress.
Not an ‘either-or’ approach
Dr. Kingsberg said ISSWSH has a variety of sexual medicine practitioners, including providers who can provide CBT for sexual concerns, and the American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors and Therapists has a referral directory.
“Keeping in mind the bio-psychosocial model, sometimes psychotherapy is going to be a really effective treatment for sexual concerns,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “Sometimes the pharmacologic option is going to be a really effective treatment for some concerns, and sometimes the combination is going to have a really nice treatment effect. So it’s not a one-size-fits-all, and it doesn’t have to be an either-or.”
The sexual concerns of women still do not get adequately addressed in medical schools and residencies, Dr. Kingsberg said, which is distinctly different from how male sexual concerns are addressed in health care.
“Erectile dysfunction is kind of in the norm, and women are still a little hesitant to bring up their sexual concerns,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “They don’t know if it’s appropriate and they’re hoping that their clinician will ask.”
One way clinicians can do that is with a global question for all their patients: “Most of my patients have sexual questions or concerns; what concerns do you have?”
“They don’t have to go through a checklist of 10 things,” Dr. Kingsberg said. If the patient does not bring anything up, providers can then ask a single follow up question: “Do you have any concerns with desire, arousal, orgasm, or pain?” That question, Dr. Kingsberg said, covers the four main areas of concern.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Green reported no disclosures. Dr. Kingsberg has consulted for or served on the advisory board for Alloy, Astellas, Bayer, Dare Bioscience, Freya, Reunion Neuroscience, Materna Medical, Madorra, Palatin, Pfizer, ReJoy, Sprout, Strategic Science Technologies, and MsMedicine.
PHILADELPHIA – . Four CBT sessions specifically focused on sexual concerns resulted in decreased sexual distress and concern, reduced depressive and menopausal symptoms, and increased sexual desire and functioning, as well as improved body image and relationship satisfaction.
An estimated 68%-87% of perimenopausal and postmenopausal women report sexual concerns, Sheryl Green, PhD, CPsych, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University and a psychologist at St. Joseph’s Healthcare’s Women’s Health Concerns Clinic, both in Hamilton, Ont., told attendees at the meeting.
“Sexual concerns over the menopausal transition are not just physical, but they’re also psychological and emotional,” Dr. Green said. “Three common challenges include decreased sexual desire, a reduction in physical arousal and ability to achieve an orgasm, and sexual pain and discomfort during intercourse.”
The reasons for these concerns are multifactorial, she said. Decreased sexual desire can stem from stress, medical problems, their relationship with their partner, or other causes. A woman’s difficulty with reduced physical arousal or ability to have an orgasm can result from changes in hormone levels and vaginal changes, such as vaginal atrophy, which can also contribute to the sexual pain or discomfort reported by 17%-45% of postmenopausal women.
Two pharmacologic treatments exist for sexual concerns: oral flibanserin (Addyi) and injectable bremelanotide (Vyleesi). But many women may be unable or unwilling to take medication for their concerns. Previous research from Lori Brotto has found cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness interventions to effectively improve sexual functioning in women treated for gynecologic cancer and in women without a history of cancer.
“Sexual function needs to be understood from a bio-psychosocial model, looking at the biologic factors, the psychological factors, the sociocultural factors, and the interpersonal factors,” Sheryl Kingsberg, PhD, a professor of psychiatry and reproductive biology at Case Western Reserve University and a psychologist at University Hospitals in Cleveland, said in an interview.
“They can all overlap, and the clinician can ask a few pointed questions that help identify what the source of the problem is,” said Dr. Kingsberg, who was not involved in this study. She noted that the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health has an algorithm that can help in determining the source of the problems.
“Sometimes it’s going to be a biologic condition for which pharmacologic options are nice, but even if it is primarily pharmacologic, psychotherapy is always useful,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “Once the problem is there, even if it’s biologically based, then you have all the things in terms of the cognitive distortion, anxiety,” and other issues that a cognitive behavioral approach can help address. “And access is now much wider because of telehealth,” she added.
‘Psychology of menopause’
The study led by Dr. Green focused on peri- and postmenopausal women, with an average age of 50, who were experiencing primary sexual concerns based on a score of at least 26 on the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). Among the 20 women recruited for the study, 6 had already been prescribed hormone therapy for sexual concerns.
All reported decreased sexual desire, 17 reported decreased sexual arousal, 14 had body image dissatisfaction related to sexual concerns, and 6 reported urogenital problems. Nine of the women were in full remission from major depressive disorder, one had post-traumatic stress syndrome, and one had subclinical generalized anxiety disorder.
After spending 4 weeks on a wait list as self-control group for the study, the 15 women who completed the trial underwent four individual CBT sessions focusing on sexual concerns. The first session focused on psychoeducation and thought monitoring, and the second focused on cognitive distortions, cognitive strategies, and unhelpful beliefs or expectations related to sexual concerns. The third session looked at the role of problematic behaviors and behavioral experiments, and the fourth focused on continuation of strategies, long-term goals, and maintaining gains.
The participants completed eight measures at baseline, after the 4 weeks on the wait list, and after the four CBT sessions to assess the following:
- Sexual satisfaction, distress, and desire, using the FSFI, the Female Sexual Distress Scale-Revised (FSDS-R), and the Female Sexual Desire Questionnaire (FSDQ).
- Menopause symptoms, using the Greene Climacteric Scale (GCS).
- Body image, using the Dresden Body Image Questionnaire (DBIQ).
- Relationship satisfaction, using the Couples Satisfaction Index (CSI).
- Depression, using the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II).
- Anxiety, using the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A).
The women did not experience any significant changes while on the wait list except a slight decrease on the FSDQ concern subscale. Following the CBT sessions, however, the women experienced a significant decrease in sexual distress and concern as well as an increase in sexual dyadic desire and sexual functioning (P = .003 for FSFI, P = .002 for FSDS-R, and P = .003 for FSDQ).
Participants also experienced a decrease in depression (P < .0001) and menopausal symptoms (P = .001) and an increase in body-image satisfaction (P = .018) and relationship satisfaction (P = .0011) after the CBT sessions. The researchers assessed participants’ satisfaction with the Client Satisfaction Questionnaire after the CBT sessions and reported some of the qualitative findings.
“The treatment program was able to assist me with recognizing that some of my sexual concerns were normal, emotional as well as physical and hormonal, and provided me the ability to delve more deeply into the psychology of menopause and how to work through symptoms and concerns in more manageable pieces,” one participant wrote. Another found helpful the “homework exercises of recognizing a thought/feeling/emotion surrounding how I feel about myself/body and working through. More positive thought pattern/restructuring a response the most helpful.”
The main complaint about the program was that it was too short, with women wanting more sessions to help continue their progress.
Not an ‘either-or’ approach
Dr. Kingsberg said ISSWSH has a variety of sexual medicine practitioners, including providers who can provide CBT for sexual concerns, and the American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors and Therapists has a referral directory.
“Keeping in mind the bio-psychosocial model, sometimes psychotherapy is going to be a really effective treatment for sexual concerns,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “Sometimes the pharmacologic option is going to be a really effective treatment for some concerns, and sometimes the combination is going to have a really nice treatment effect. So it’s not a one-size-fits-all, and it doesn’t have to be an either-or.”
The sexual concerns of women still do not get adequately addressed in medical schools and residencies, Dr. Kingsberg said, which is distinctly different from how male sexual concerns are addressed in health care.
“Erectile dysfunction is kind of in the norm, and women are still a little hesitant to bring up their sexual concerns,” Dr. Kingsberg said. “They don’t know if it’s appropriate and they’re hoping that their clinician will ask.”
One way clinicians can do that is with a global question for all their patients: “Most of my patients have sexual questions or concerns; what concerns do you have?”
“They don’t have to go through a checklist of 10 things,” Dr. Kingsberg said. If the patient does not bring anything up, providers can then ask a single follow up question: “Do you have any concerns with desire, arousal, orgasm, or pain?” That question, Dr. Kingsberg said, covers the four main areas of concern.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Green reported no disclosures. Dr. Kingsberg has consulted for or served on the advisory board for Alloy, Astellas, Bayer, Dare Bioscience, Freya, Reunion Neuroscience, Materna Medical, Madorra, Palatin, Pfizer, ReJoy, Sprout, Strategic Science Technologies, and MsMedicine.
AT NAMS 2023
CBT linked to reduced pain, less catastrophizing in fibromyalgia
TOPLINE:
In patients with fibromyalgia, cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) can reduce pain through its effect on pain-related catastrophizing, which involves intensified cognitive and emotional responses to things like intrusive thoughts, a new study suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 98 female patients with fibromyalgia (FM), mean age about 42 years, who underwent a baseline neuroimaging assessment and were randomly assigned to CBT (where patients learned to identify negative thoughts and use cognitive restructuring to diminish pain-related distress) or a matched educational intervention (where patients learned about fibromyalgia and chronic pain); both groups had eight weekly individual 60- to 75-minute visits.
- The primary outcome was the pain interference subscale of the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI); secondary outcomes included the BPI pain severity subscale, the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire–Revised (FIQR), and the Pain Catastrophizing Scale (PCS), which includes subscales of rumination, magnification, and helplessness.
- Researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)-adapted task to investigate the neural circuitry supporting pain catastrophizing.
TAKEAWAY:
- After controlling for baseline values, BPI pain interference scores were significantly reduced, with a larger reduction in the CBT group, compared with the education group (P = .03), which was also the case for FIQR scores (P = .05) and pain catastrophizing (P = .04).
- There were larger reductions in pain-related symptomatology in the CBT group, but they did not reach statistical significance.
- Following CBT treatment, the study showed reduced connectivity between regions of the brain associated with self-awareness, pain, and emotional processing.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “highlight the important role of targeting pain catastrophizing with psychotherapy, particularly for patients reporting high levels of catastrophizing cognitions” write the authors, adding that altered network connectivity identified by the study “may emerge as a valuable biomarker of catastrophizing-related cognitive and affective processes.”
SOURCE:
The study was carried out by Jeungchan Lee, PhD, department of radiology, center for biomedical imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and the Discovery Center for Recovery from Chronic Pain, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues. It was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Findings were limited to female participants. CBT for chronic pain includes different therapeutic modules, and the study can’t draw definitive conclusions regarding which CBT skills were most beneficial to patients in reducing catastrophizing. Baseline symptom severity was higher for the CBT group, which may complicate interpretation of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health: National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the National Center for Research Resources. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with fibromyalgia, cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) can reduce pain through its effect on pain-related catastrophizing, which involves intensified cognitive and emotional responses to things like intrusive thoughts, a new study suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 98 female patients with fibromyalgia (FM), mean age about 42 years, who underwent a baseline neuroimaging assessment and were randomly assigned to CBT (where patients learned to identify negative thoughts and use cognitive restructuring to diminish pain-related distress) or a matched educational intervention (where patients learned about fibromyalgia and chronic pain); both groups had eight weekly individual 60- to 75-minute visits.
- The primary outcome was the pain interference subscale of the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI); secondary outcomes included the BPI pain severity subscale, the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire–Revised (FIQR), and the Pain Catastrophizing Scale (PCS), which includes subscales of rumination, magnification, and helplessness.
- Researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)-adapted task to investigate the neural circuitry supporting pain catastrophizing.
TAKEAWAY:
- After controlling for baseline values, BPI pain interference scores were significantly reduced, with a larger reduction in the CBT group, compared with the education group (P = .03), which was also the case for FIQR scores (P = .05) and pain catastrophizing (P = .04).
- There were larger reductions in pain-related symptomatology in the CBT group, but they did not reach statistical significance.
- Following CBT treatment, the study showed reduced connectivity between regions of the brain associated with self-awareness, pain, and emotional processing.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “highlight the important role of targeting pain catastrophizing with psychotherapy, particularly for patients reporting high levels of catastrophizing cognitions” write the authors, adding that altered network connectivity identified by the study “may emerge as a valuable biomarker of catastrophizing-related cognitive and affective processes.”
SOURCE:
The study was carried out by Jeungchan Lee, PhD, department of radiology, center for biomedical imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and the Discovery Center for Recovery from Chronic Pain, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues. It was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Findings were limited to female participants. CBT for chronic pain includes different therapeutic modules, and the study can’t draw definitive conclusions regarding which CBT skills were most beneficial to patients in reducing catastrophizing. Baseline symptom severity was higher for the CBT group, which may complicate interpretation of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health: National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the National Center for Research Resources. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with fibromyalgia, cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) can reduce pain through its effect on pain-related catastrophizing, which involves intensified cognitive and emotional responses to things like intrusive thoughts, a new study suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 98 female patients with fibromyalgia (FM), mean age about 42 years, who underwent a baseline neuroimaging assessment and were randomly assigned to CBT (where patients learned to identify negative thoughts and use cognitive restructuring to diminish pain-related distress) or a matched educational intervention (where patients learned about fibromyalgia and chronic pain); both groups had eight weekly individual 60- to 75-minute visits.
- The primary outcome was the pain interference subscale of the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI); secondary outcomes included the BPI pain severity subscale, the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire–Revised (FIQR), and the Pain Catastrophizing Scale (PCS), which includes subscales of rumination, magnification, and helplessness.
- Researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)-adapted task to investigate the neural circuitry supporting pain catastrophizing.
TAKEAWAY:
- After controlling for baseline values, BPI pain interference scores were significantly reduced, with a larger reduction in the CBT group, compared with the education group (P = .03), which was also the case for FIQR scores (P = .05) and pain catastrophizing (P = .04).
- There were larger reductions in pain-related symptomatology in the CBT group, but they did not reach statistical significance.
- Following CBT treatment, the study showed reduced connectivity between regions of the brain associated with self-awareness, pain, and emotional processing.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “highlight the important role of targeting pain catastrophizing with psychotherapy, particularly for patients reporting high levels of catastrophizing cognitions” write the authors, adding that altered network connectivity identified by the study “may emerge as a valuable biomarker of catastrophizing-related cognitive and affective processes.”
SOURCE:
The study was carried out by Jeungchan Lee, PhD, department of radiology, center for biomedical imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and the Discovery Center for Recovery from Chronic Pain, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues. It was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Findings were limited to female participants. CBT for chronic pain includes different therapeutic modules, and the study can’t draw definitive conclusions regarding which CBT skills were most beneficial to patients in reducing catastrophizing. Baseline symptom severity was higher for the CBT group, which may complicate interpretation of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health: National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the National Center for Research Resources. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What’s right and wrong for doctors on social media
She went by the name “Dr. Roxy” on social media and became something of a sensation on TikTok, where she livestreamed her patients’ operations. Ultimately, however, plastic surgeon Katharine Roxanne Grawe, MD, lost her medical license based partly on her “life-altering, reckless treatment,” heightened by her social media fame. In July, the Ohio state medical board permanently revoked Dr. Grawe’s license after twice reprimanding her for her failure to meet the standard of care. The board also determined that, by livestreaming procedures, she placed her patients in danger of immediate and serious harm.
Although most doctors don’t use social media to the degree that Dr. Grawe did, using the various platforms – from X (formerly Twitter) to Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok – can be a slippery slope. Medscape’s Physician Behavior Report 2023 revealed that doctors have seen their share of unprofessional or offensive social media use from their peers. Nearly 7 in 10 said it is unethical for a doctor to act rudely, offensively, or unprofessionally on social media, even if their medical practice isn’t mentioned. As one physician put it: “Professional is not a 9-to-5 descriptor.”
“There’s still a stigma attached,” said Liudmila Schafer, MD, an oncologist with The Doctor Connect, a career consulting firm. “Physicians face a tougher challenge due to societal expectations of perfection, with greater consequences for mistakes. We’re under constant ‘observation’ from peers, employers, and patients.”
Beverly Hills plastic surgeon Jay Calvert, MD, says he holds firm boundaries with how he uses social media. “I do comedy on the side, but it’s not acceptable for me as a doctor to share that on social media,” he said. “People want doctors who are professional, and I’m always concerned about how I present myself.”
Dr. Calvert said it is fairly easy to spot doctors who cross the line with social media. “You have to hold yourself back when posting. Doing things like dancing in the OR are out of whack with the profession.”
According to Dr. Schafer, a definite line to avoid crossing is offering medical advice or guidance on social media. “You also can’t discuss confidential practice details, respond to unfamiliar contacts, or discuss institutional policies without permission,” she said. “It’s important to add disclaimers if a personal scientific opinion is shared without reference [or] research or with unchecked sources.”
Navigating the many social media sites
Each social media platform has its pros and cons. Doctors need to determine why to use them and what the payback of each might be. Dr. Schafer uses multiple sites, including LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, X, Threads, YouTube, and, to a lesser degree, Clubhouse. How and what she posts on each varies. “I use them almost 95% professionally,” she said. “It’s challenging to meet and engage in person, so that is where social media helps.”
Stephen Pribut, MD, a Washington-based podiatrist, likes to use X as an information source. He follows pretty simple rules when it comes to what he tweets and shares on various sites: “I stay away from politics and religion,” he said. “I also avoid controversial topics online, such as vaccines.”
Joseph Daibes, DO, who specializes in cardiovascular medicine at New Jersey Heart and Vein, Clifton, said he has changed how he uses social media. “Initially, I was a passive consumer, but as I recognized the importance of accurate medical information online, I became more active in weighing in responsibly, occasionally sharing studies, debunking myths, and engaging in meaningful conversations,” he said. “Social media can get dangerous, so we have a duty to use it responsibly, and I cannot stress that enough.”
For plastic surgeons like Dr. Calvert, the visual platforms such as Instagram can prove invaluable for marketing purposes. “I’ve been using Instagram since 2012, and it’s been my most positive experience,” he said. “I don’t generate business from it, but I use it to back up my qualifications as a surgeon.”
Potential patients like to scroll through posts by plastic surgeons to learn what their finished product looks like, Dr. Calvert said. In many cases, plastic surgeons hire social media experts to cultivate their content. “I’ve hired and fired social media managers over the years, ultimately deciding I should develop my own content,” he said. “I want people to see the same doctor on social media that they will see in the office. I like an authentic presentation, not glitzy.”
Social media gone wrong
Dr. Calvert said that in the world of plastic surgery, some doctors use social media to present “before and after” compilations that in his opinion aren’t necessarily fully authentic, and this rubs him wrong. “There’s a bit of ‘cheating’ in some of these posts, using filters, making the ‘befores’ particularly bad, and other tricks,” he said.
Dr. Daibes has also seen his share of social media misuse: ”Red flags include oversharing personal indulgences, engaging in online spats, or making unfounded medical claims,” he said. “It’s essential to remember our role as educators and advocates, and to present ourselves in a way that upholds the dignity of our profession.”
At the end of the day, social media can have positive uses for physicians, and it is clearly here to stay. The onus for responsible use ultimately falls to the physicians using it.
Dr. Daibes emphasizes the fact that a doctor’s words carry weight – perhaps more so than those of other professionals. “The added scrutiny is good because it keeps us accountable; it’s crucial that our information is accurate,” he said. “The downside is that the scrutiny can be stifling at times and lead to self-censorship, even on nonmedical matters.”
Physicians have suggested eight guidelines for doctors to follow when using social media:
- Remember that you represent your profession, even if posting on personal accounts.
- Never post from the operating room, the emergency department, or any sort of medical space.
- If you’re employed, before you post, check with your employer to see whether they have any rules or guidance surrounding social media.
- Never use social media to badmouth colleagues, hospitals, or other healthcare organizations.
- Never use social media to dispense medical advice.
- Steer clear of the obvious hot-button issues, like religion and politics.
- Always protect patient privacy when posting.
- Be careful with how and whom you engage on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
She went by the name “Dr. Roxy” on social media and became something of a sensation on TikTok, where she livestreamed her patients’ operations. Ultimately, however, plastic surgeon Katharine Roxanne Grawe, MD, lost her medical license based partly on her “life-altering, reckless treatment,” heightened by her social media fame. In July, the Ohio state medical board permanently revoked Dr. Grawe’s license after twice reprimanding her for her failure to meet the standard of care. The board also determined that, by livestreaming procedures, she placed her patients in danger of immediate and serious harm.
Although most doctors don’t use social media to the degree that Dr. Grawe did, using the various platforms – from X (formerly Twitter) to Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok – can be a slippery slope. Medscape’s Physician Behavior Report 2023 revealed that doctors have seen their share of unprofessional or offensive social media use from their peers. Nearly 7 in 10 said it is unethical for a doctor to act rudely, offensively, or unprofessionally on social media, even if their medical practice isn’t mentioned. As one physician put it: “Professional is not a 9-to-5 descriptor.”
“There’s still a stigma attached,” said Liudmila Schafer, MD, an oncologist with The Doctor Connect, a career consulting firm. “Physicians face a tougher challenge due to societal expectations of perfection, with greater consequences for mistakes. We’re under constant ‘observation’ from peers, employers, and patients.”
Beverly Hills plastic surgeon Jay Calvert, MD, says he holds firm boundaries with how he uses social media. “I do comedy on the side, but it’s not acceptable for me as a doctor to share that on social media,” he said. “People want doctors who are professional, and I’m always concerned about how I present myself.”
Dr. Calvert said it is fairly easy to spot doctors who cross the line with social media. “You have to hold yourself back when posting. Doing things like dancing in the OR are out of whack with the profession.”
According to Dr. Schafer, a definite line to avoid crossing is offering medical advice or guidance on social media. “You also can’t discuss confidential practice details, respond to unfamiliar contacts, or discuss institutional policies without permission,” she said. “It’s important to add disclaimers if a personal scientific opinion is shared without reference [or] research or with unchecked sources.”
Navigating the many social media sites
Each social media platform has its pros and cons. Doctors need to determine why to use them and what the payback of each might be. Dr. Schafer uses multiple sites, including LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, X, Threads, YouTube, and, to a lesser degree, Clubhouse. How and what she posts on each varies. “I use them almost 95% professionally,” she said. “It’s challenging to meet and engage in person, so that is where social media helps.”
Stephen Pribut, MD, a Washington-based podiatrist, likes to use X as an information source. He follows pretty simple rules when it comes to what he tweets and shares on various sites: “I stay away from politics and religion,” he said. “I also avoid controversial topics online, such as vaccines.”
Joseph Daibes, DO, who specializes in cardiovascular medicine at New Jersey Heart and Vein, Clifton, said he has changed how he uses social media. “Initially, I was a passive consumer, but as I recognized the importance of accurate medical information online, I became more active in weighing in responsibly, occasionally sharing studies, debunking myths, and engaging in meaningful conversations,” he said. “Social media can get dangerous, so we have a duty to use it responsibly, and I cannot stress that enough.”
For plastic surgeons like Dr. Calvert, the visual platforms such as Instagram can prove invaluable for marketing purposes. “I’ve been using Instagram since 2012, and it’s been my most positive experience,” he said. “I don’t generate business from it, but I use it to back up my qualifications as a surgeon.”
Potential patients like to scroll through posts by plastic surgeons to learn what their finished product looks like, Dr. Calvert said. In many cases, plastic surgeons hire social media experts to cultivate their content. “I’ve hired and fired social media managers over the years, ultimately deciding I should develop my own content,” he said. “I want people to see the same doctor on social media that they will see in the office. I like an authentic presentation, not glitzy.”
Social media gone wrong
Dr. Calvert said that in the world of plastic surgery, some doctors use social media to present “before and after” compilations that in his opinion aren’t necessarily fully authentic, and this rubs him wrong. “There’s a bit of ‘cheating’ in some of these posts, using filters, making the ‘befores’ particularly bad, and other tricks,” he said.
Dr. Daibes has also seen his share of social media misuse: ”Red flags include oversharing personal indulgences, engaging in online spats, or making unfounded medical claims,” he said. “It’s essential to remember our role as educators and advocates, and to present ourselves in a way that upholds the dignity of our profession.”
At the end of the day, social media can have positive uses for physicians, and it is clearly here to stay. The onus for responsible use ultimately falls to the physicians using it.
Dr. Daibes emphasizes the fact that a doctor’s words carry weight – perhaps more so than those of other professionals. “The added scrutiny is good because it keeps us accountable; it’s crucial that our information is accurate,” he said. “The downside is that the scrutiny can be stifling at times and lead to self-censorship, even on nonmedical matters.”
Physicians have suggested eight guidelines for doctors to follow when using social media:
- Remember that you represent your profession, even if posting on personal accounts.
- Never post from the operating room, the emergency department, or any sort of medical space.
- If you’re employed, before you post, check with your employer to see whether they have any rules or guidance surrounding social media.
- Never use social media to badmouth colleagues, hospitals, or other healthcare organizations.
- Never use social media to dispense medical advice.
- Steer clear of the obvious hot-button issues, like religion and politics.
- Always protect patient privacy when posting.
- Be careful with how and whom you engage on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
She went by the name “Dr. Roxy” on social media and became something of a sensation on TikTok, where she livestreamed her patients’ operations. Ultimately, however, plastic surgeon Katharine Roxanne Grawe, MD, lost her medical license based partly on her “life-altering, reckless treatment,” heightened by her social media fame. In July, the Ohio state medical board permanently revoked Dr. Grawe’s license after twice reprimanding her for her failure to meet the standard of care. The board also determined that, by livestreaming procedures, she placed her patients in danger of immediate and serious harm.
Although most doctors don’t use social media to the degree that Dr. Grawe did, using the various platforms – from X (formerly Twitter) to Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok – can be a slippery slope. Medscape’s Physician Behavior Report 2023 revealed that doctors have seen their share of unprofessional or offensive social media use from their peers. Nearly 7 in 10 said it is unethical for a doctor to act rudely, offensively, or unprofessionally on social media, even if their medical practice isn’t mentioned. As one physician put it: “Professional is not a 9-to-5 descriptor.”
“There’s still a stigma attached,” said Liudmila Schafer, MD, an oncologist with The Doctor Connect, a career consulting firm. “Physicians face a tougher challenge due to societal expectations of perfection, with greater consequences for mistakes. We’re under constant ‘observation’ from peers, employers, and patients.”
Beverly Hills plastic surgeon Jay Calvert, MD, says he holds firm boundaries with how he uses social media. “I do comedy on the side, but it’s not acceptable for me as a doctor to share that on social media,” he said. “People want doctors who are professional, and I’m always concerned about how I present myself.”
Dr. Calvert said it is fairly easy to spot doctors who cross the line with social media. “You have to hold yourself back when posting. Doing things like dancing in the OR are out of whack with the profession.”
According to Dr. Schafer, a definite line to avoid crossing is offering medical advice or guidance on social media. “You also can’t discuss confidential practice details, respond to unfamiliar contacts, or discuss institutional policies without permission,” she said. “It’s important to add disclaimers if a personal scientific opinion is shared without reference [or] research or with unchecked sources.”
Navigating the many social media sites
Each social media platform has its pros and cons. Doctors need to determine why to use them and what the payback of each might be. Dr. Schafer uses multiple sites, including LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, X, Threads, YouTube, and, to a lesser degree, Clubhouse. How and what she posts on each varies. “I use them almost 95% professionally,” she said. “It’s challenging to meet and engage in person, so that is where social media helps.”
Stephen Pribut, MD, a Washington-based podiatrist, likes to use X as an information source. He follows pretty simple rules when it comes to what he tweets and shares on various sites: “I stay away from politics and religion,” he said. “I also avoid controversial topics online, such as vaccines.”
Joseph Daibes, DO, who specializes in cardiovascular medicine at New Jersey Heart and Vein, Clifton, said he has changed how he uses social media. “Initially, I was a passive consumer, but as I recognized the importance of accurate medical information online, I became more active in weighing in responsibly, occasionally sharing studies, debunking myths, and engaging in meaningful conversations,” he said. “Social media can get dangerous, so we have a duty to use it responsibly, and I cannot stress that enough.”
For plastic surgeons like Dr. Calvert, the visual platforms such as Instagram can prove invaluable for marketing purposes. “I’ve been using Instagram since 2012, and it’s been my most positive experience,” he said. “I don’t generate business from it, but I use it to back up my qualifications as a surgeon.”
Potential patients like to scroll through posts by plastic surgeons to learn what their finished product looks like, Dr. Calvert said. In many cases, plastic surgeons hire social media experts to cultivate their content. “I’ve hired and fired social media managers over the years, ultimately deciding I should develop my own content,” he said. “I want people to see the same doctor on social media that they will see in the office. I like an authentic presentation, not glitzy.”
Social media gone wrong
Dr. Calvert said that in the world of plastic surgery, some doctors use social media to present “before and after” compilations that in his opinion aren’t necessarily fully authentic, and this rubs him wrong. “There’s a bit of ‘cheating’ in some of these posts, using filters, making the ‘befores’ particularly bad, and other tricks,” he said.
Dr. Daibes has also seen his share of social media misuse: ”Red flags include oversharing personal indulgences, engaging in online spats, or making unfounded medical claims,” he said. “It’s essential to remember our role as educators and advocates, and to present ourselves in a way that upholds the dignity of our profession.”
At the end of the day, social media can have positive uses for physicians, and it is clearly here to stay. The onus for responsible use ultimately falls to the physicians using it.
Dr. Daibes emphasizes the fact that a doctor’s words carry weight – perhaps more so than those of other professionals. “The added scrutiny is good because it keeps us accountable; it’s crucial that our information is accurate,” he said. “The downside is that the scrutiny can be stifling at times and lead to self-censorship, even on nonmedical matters.”
Physicians have suggested eight guidelines for doctors to follow when using social media:
- Remember that you represent your profession, even if posting on personal accounts.
- Never post from the operating room, the emergency department, or any sort of medical space.
- If you’re employed, before you post, check with your employer to see whether they have any rules or guidance surrounding social media.
- Never use social media to badmouth colleagues, hospitals, or other healthcare organizations.
- Never use social media to dispense medical advice.
- Steer clear of the obvious hot-button issues, like religion and politics.
- Always protect patient privacy when posting.
- Be careful with how and whom you engage on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

